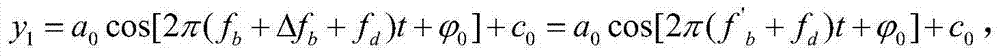Patents
Literature
437 results about "Zero frequency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
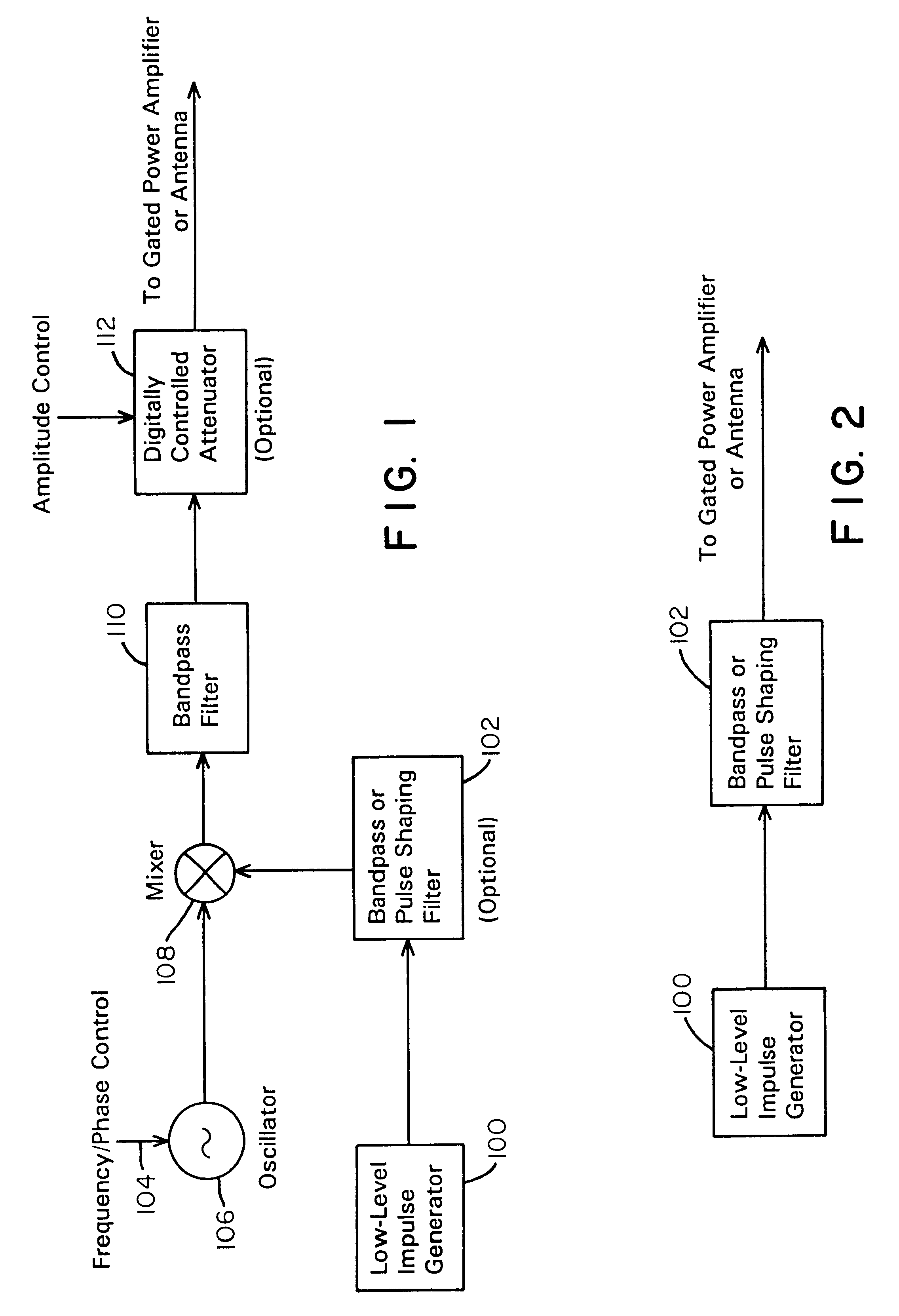
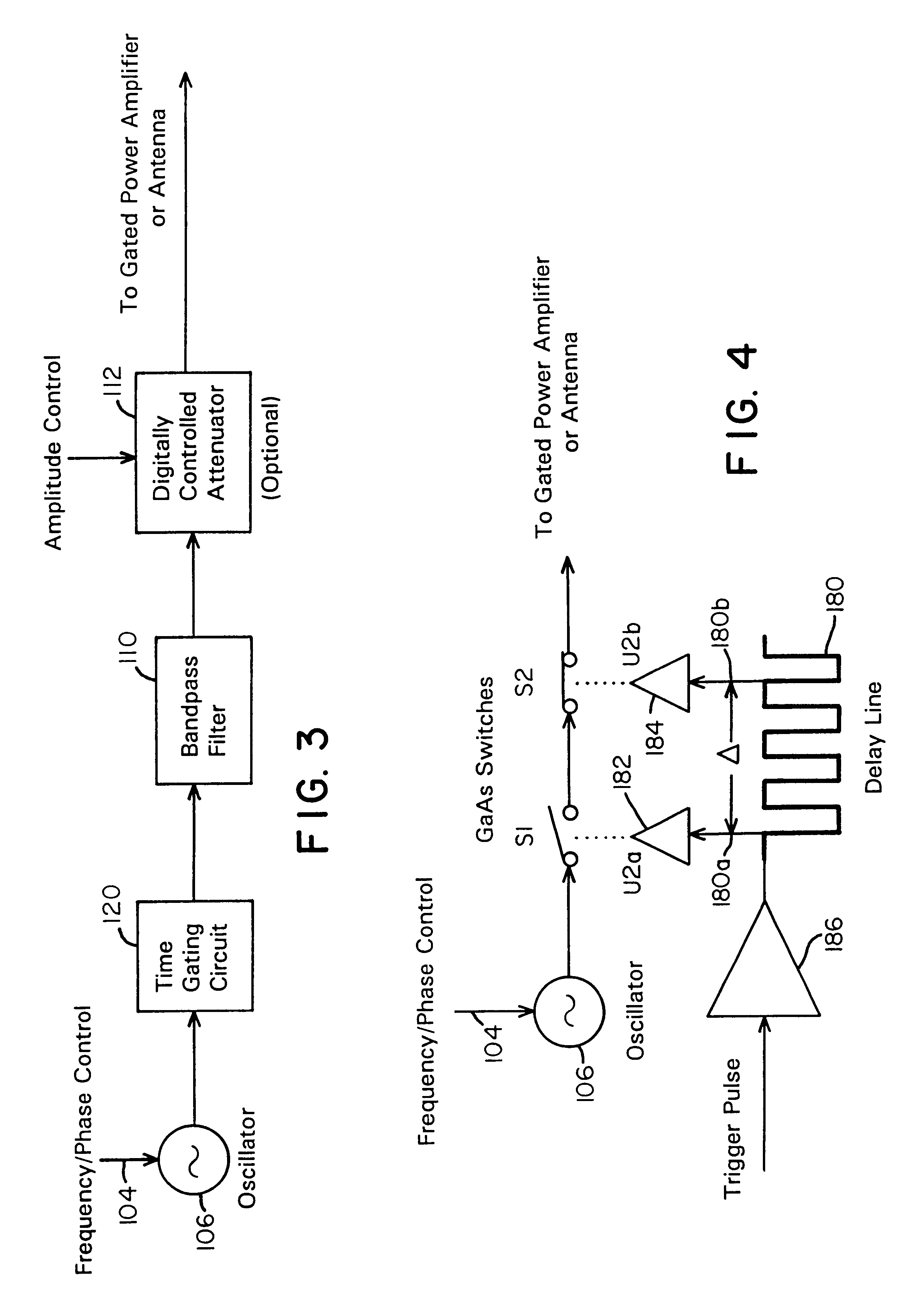
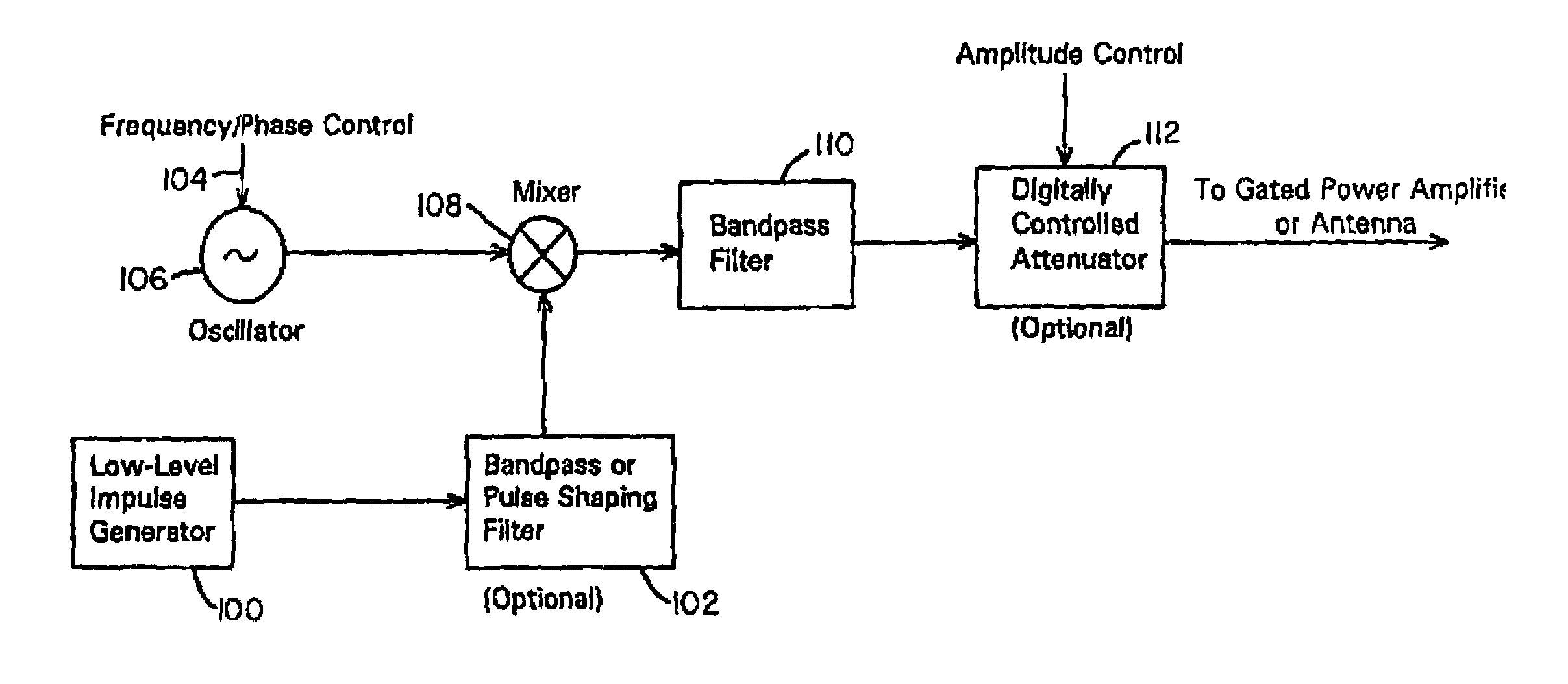
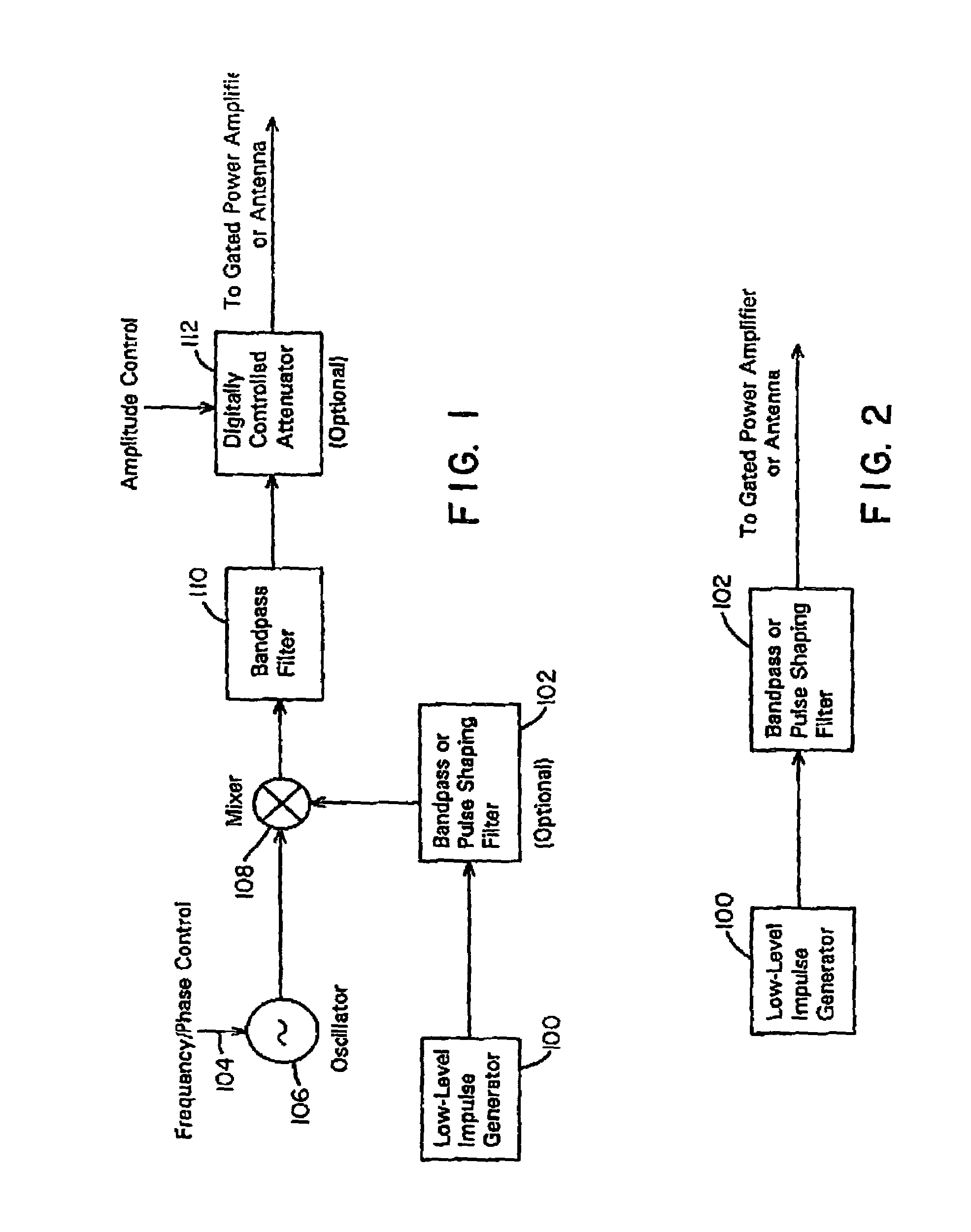
Waveform adaptive ultra-wideband transmitter
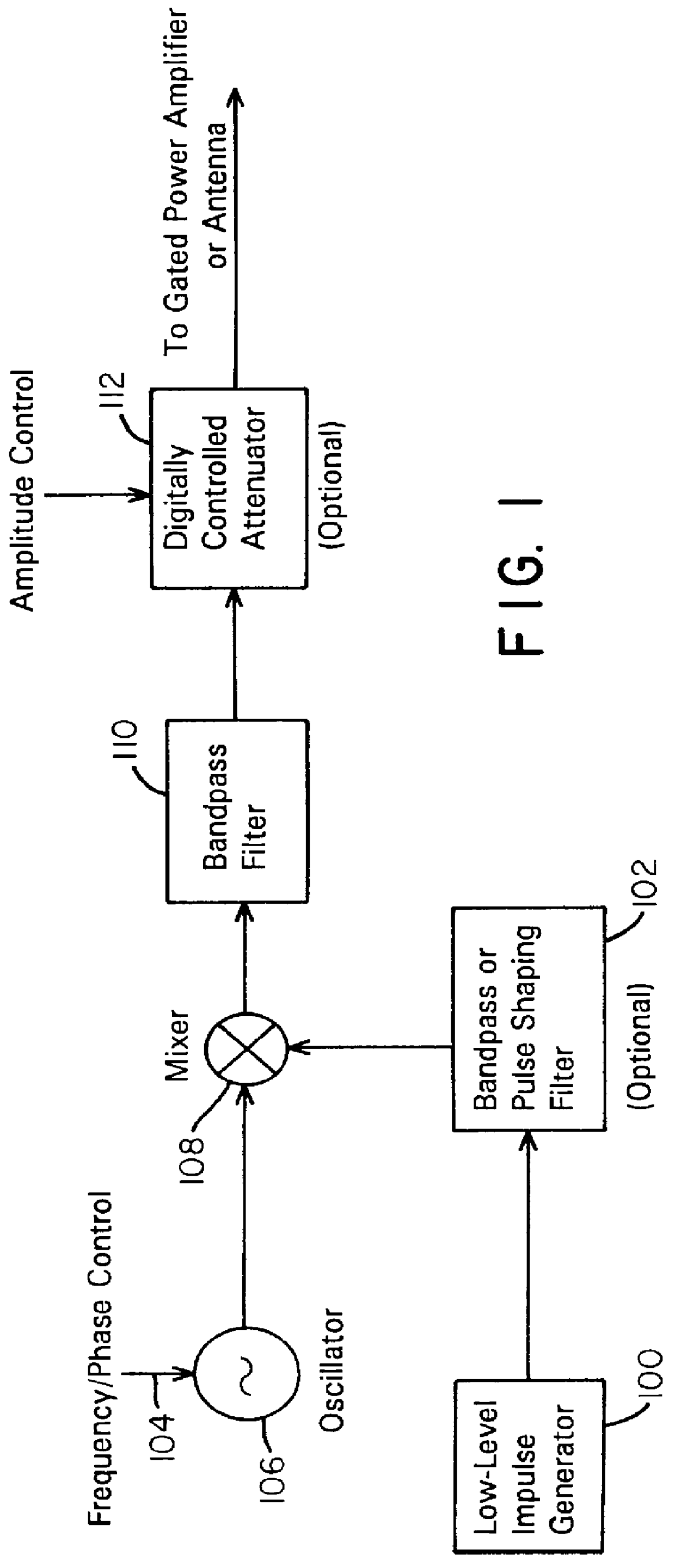
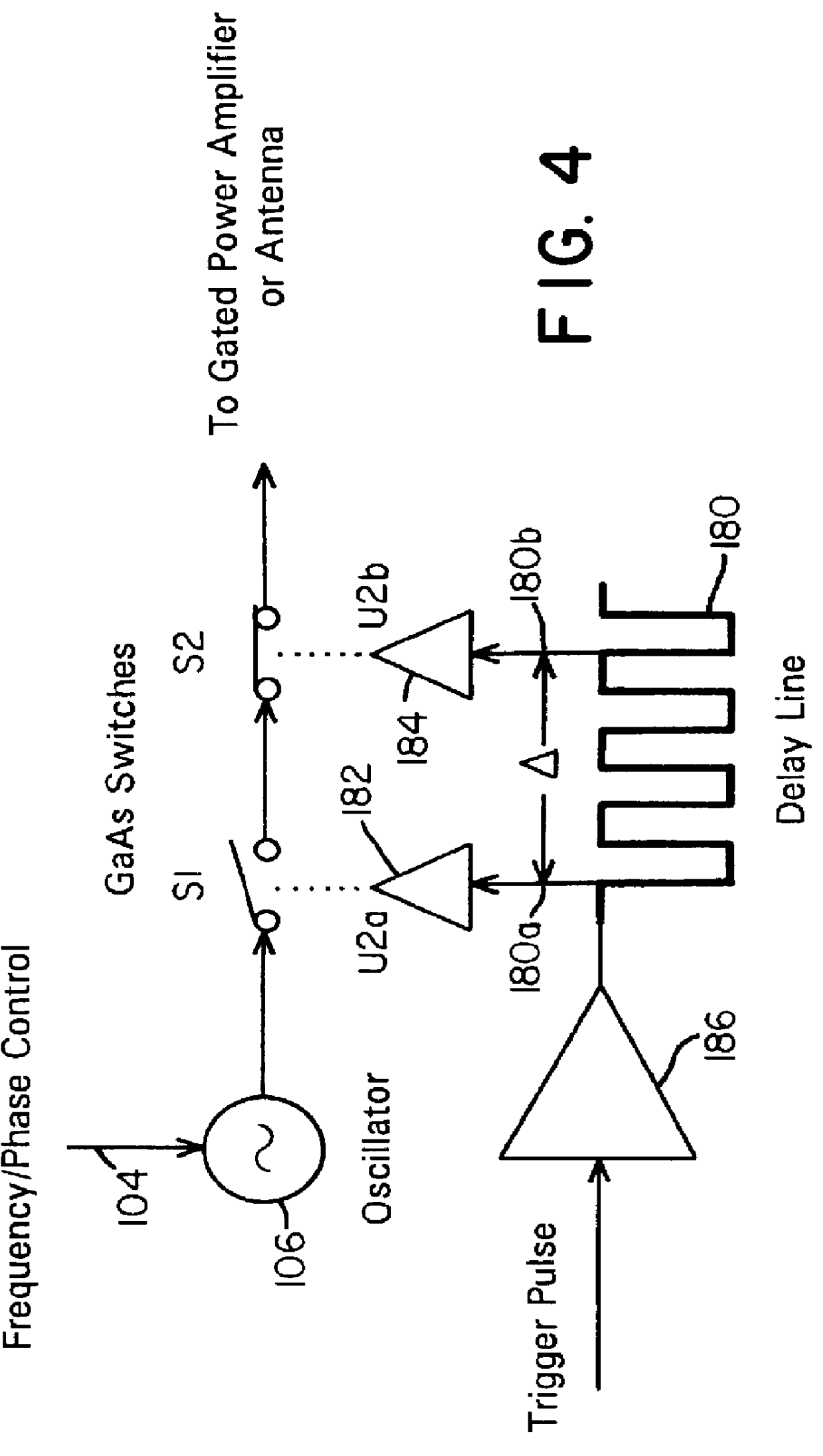
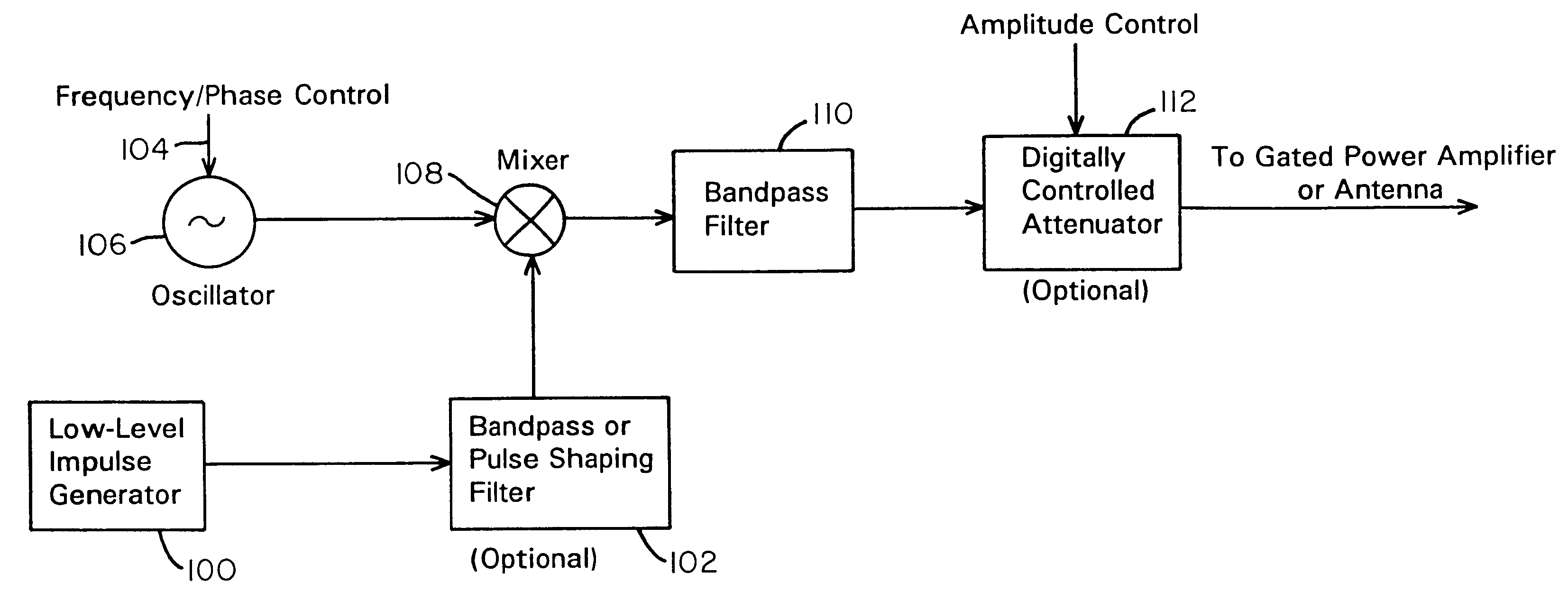
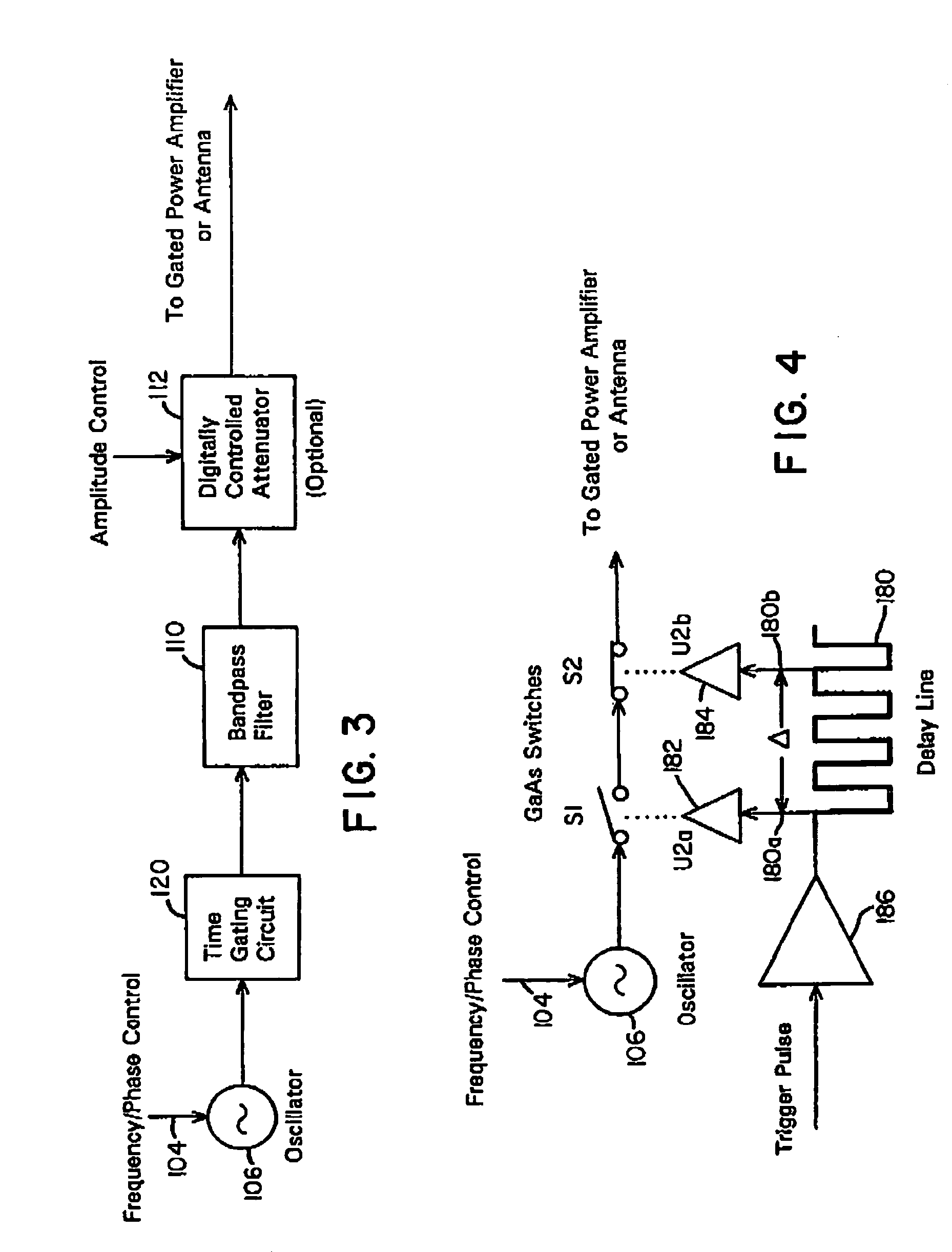
A waveform adaptive transmitter that conditions and / or modulates the phase, frequency, bandwidth, amplitude and / or attenuation of ultra-wideband (UWB) pulses. The transmitter confines or band-limits UWB signals within spectral limits for use in communication, positioning, and / or radar applications. One embodiment comprises a low-level UWB source (e.g., an impulse generator or time-gated oscillator (fixed or voltage-controlled)), a waveform adapter (e.g., digital or analog filter, pulse shaper, and / or voltage variable attenuator), a power amplifier, and an antenna to radiate a band-limited and / or modulated UWB or wideband signals. In a special case where the oscillator has zero frequency and outputs a DC bias, a low-level impulse generator impulse-excites a bandpass filter to produce an UWB signal having an adjustable center frequency and desired bandwidth based on a characteristic of the filter. In another embodiment, a low-level impulse signal is approximated by a time-gated continuous-wave oscillator to produce an extremely wide bandwidth pulse with deterministic center frequency and bandwidth characteristics. The UWB signal may be modulated to carry multi-megabit per second digital data, or may be used in object detection or for ranging applications. Activation of the power amplifier may be time-gated in cadence with the UWB source thereby to reduce inter-pulse power consumption. The UWB transmitter is capable of extremely high pulse repetition frequencies (PRFs) and data rates in the hundreds of megabits per second or more, frequency agility on a pulse-to-pulse basis allowing frequency hopping if desired, and extensibility from below HF to millimeter wave frequencies.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
Ultra wideband data transmission system and method
InactiveUS6690741B1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsAngle modulationBandpass filteringExtensibility
A data-modulated ultra wideband transmitter that modulates the phase, frequency, bandwidth, amplitude and / or attenuation of ultra-wideband (UWB) pulses. The transmitter confines or band-limits UWB signals within spectral limits for use in communication, positioning, and / or radar applications. One embodiment comprises a low-level UWB source (e.g., an impulse generator or time-gated oscillator (fixed or voltage-controlled)), a waveform adapter (e.g., digital or analog filter, pulse shaper, and / or voltage variable attenuator), a power amplifier, and an antenna to radiate a band-limited and / or modulated UWB or wideband signals. In a special case where the oscillator has zero frequency and outputs a DC bias, a low-level impulse generator impulse-excites a bandpass filter to produce an UWB signal having an adjustable center frequency and desired bandwidth based on a characteristic of the filter. In another embodiment, a low-level impulse signal is approximated by a time-gated continuous-wave oscillator to produce an extremely wide bandwidth pulse with deterministic center frequency and bandwidth characteristics. The UWB signal may be modulated to carry multi-megabit per second digital data, or may be used in object detection or for ranging applications. Activation of the power amplifier may be time-gated in cadence with the UWB source thereby to reduce inter-pulse power consumption. The UWB transmitter is capable of extremely high pulse repetition frequencies (PRFs) and data rates in the hundreds of megabits per second or more, frequency agility on a pulse-to-pulse basis allowing frequency hopping if desired, and extensibility from below HF to millimeter wave frequencies.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
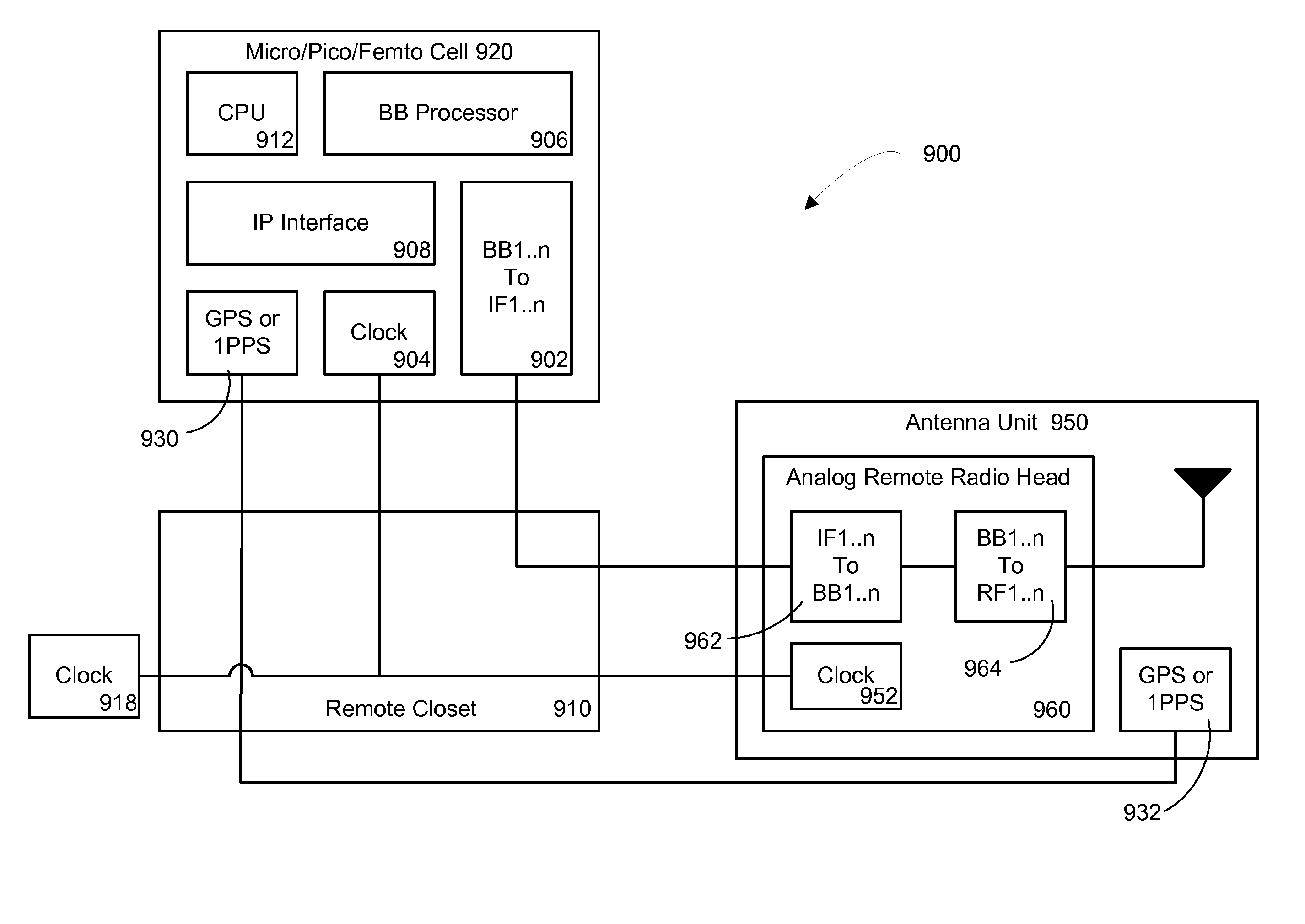
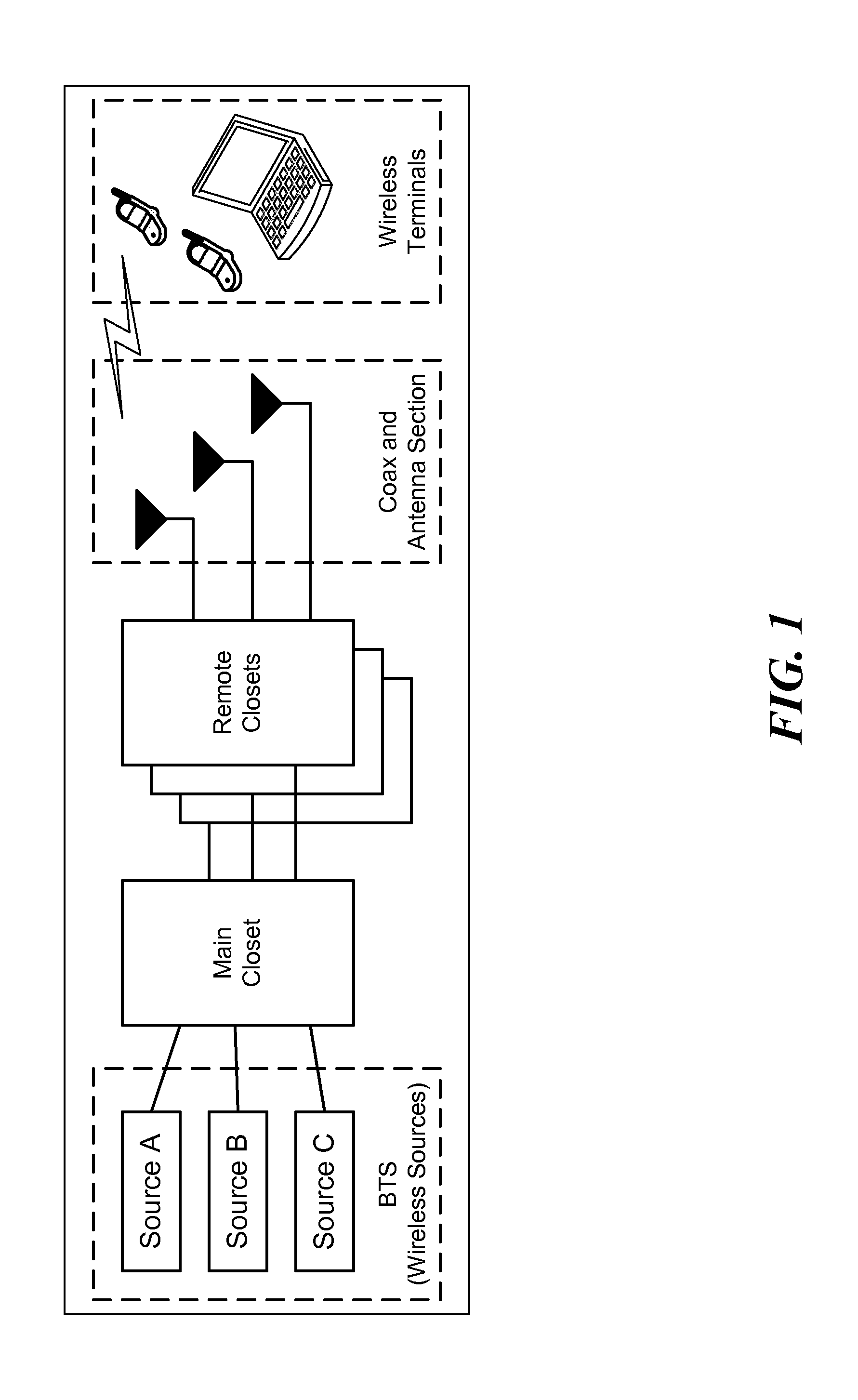
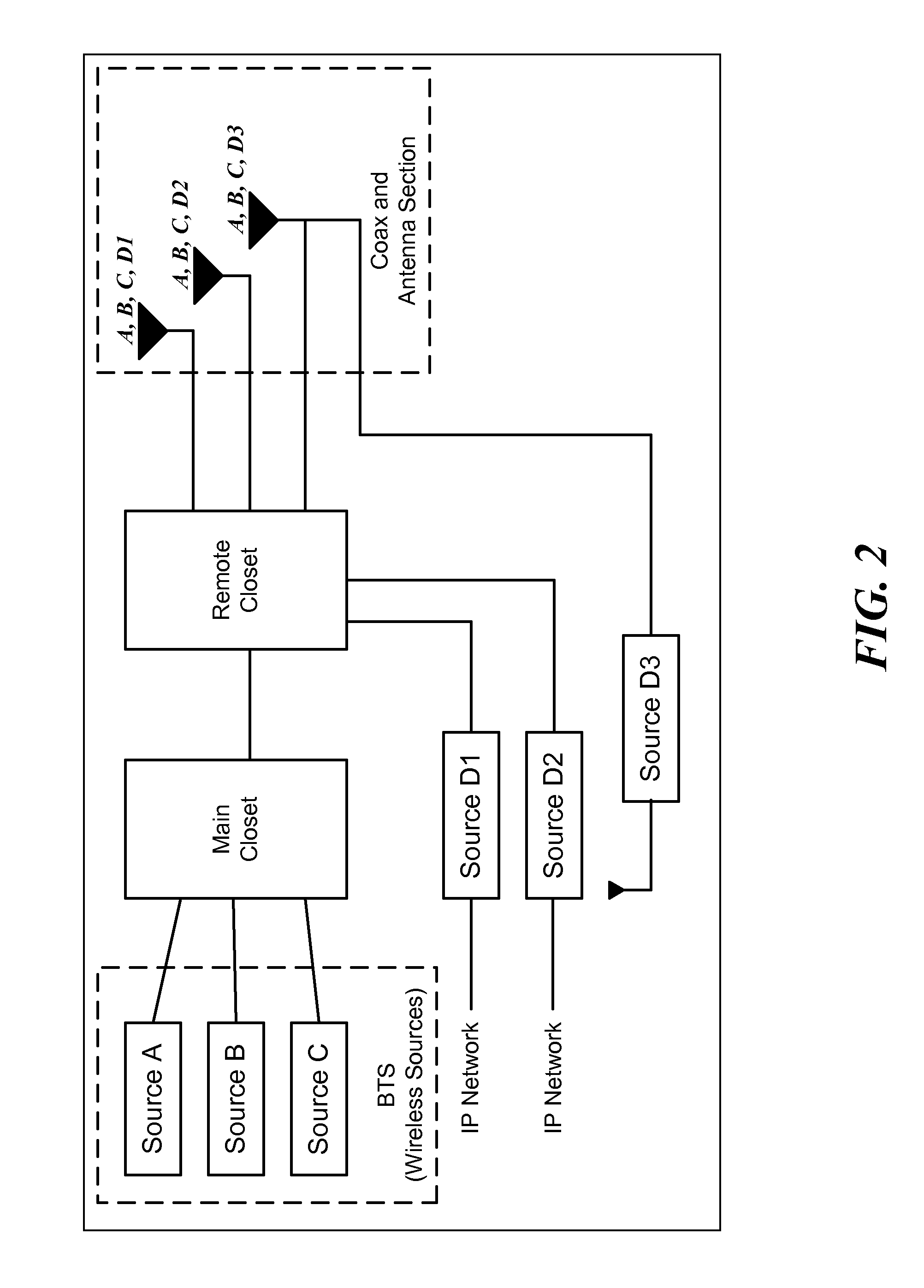
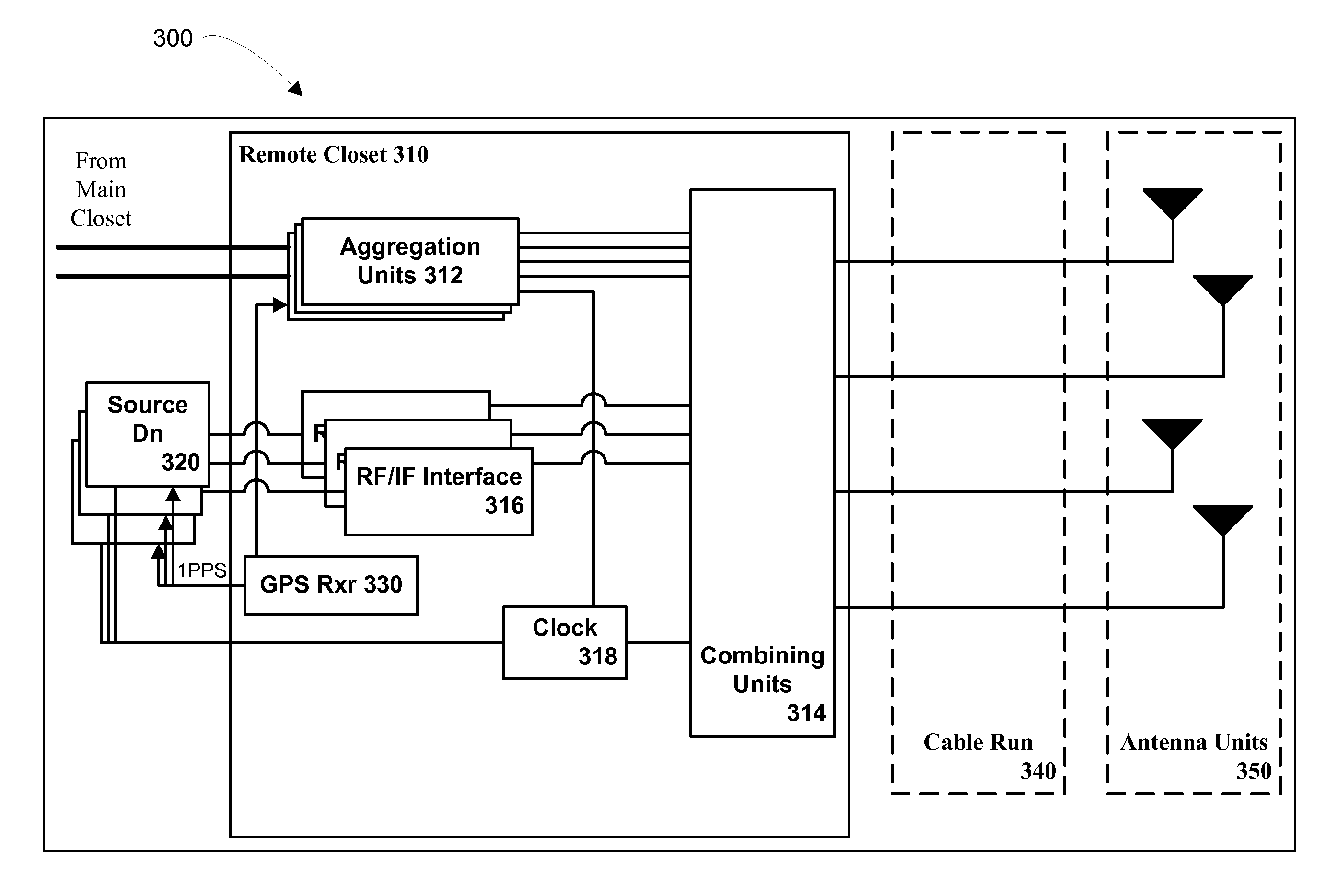
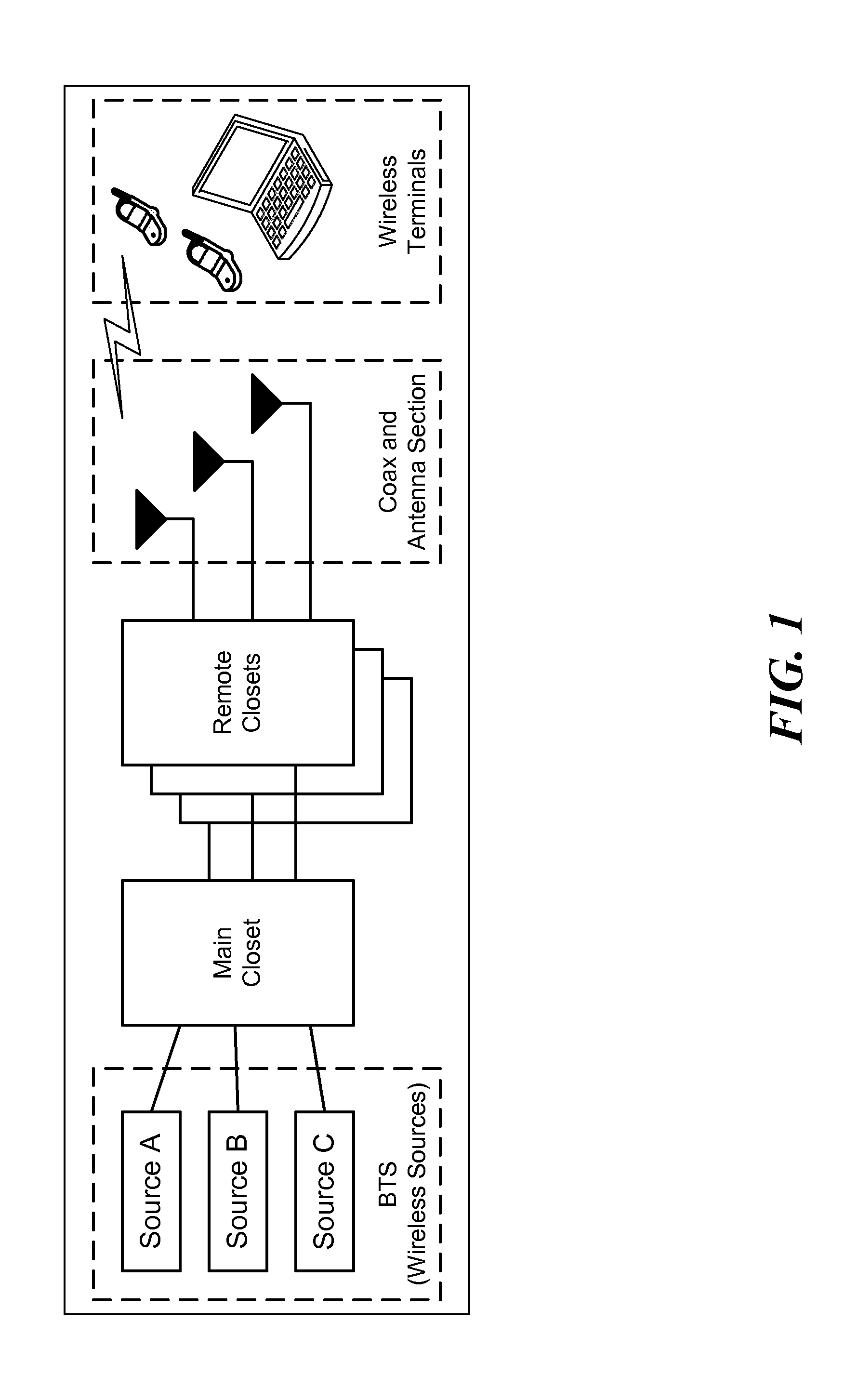
Multiple Data Services Over a Distributed Antenna System
InactiveUS20100093391A1Avoid spendingReduce energy costsSite diversityNetwork traffic/resource managementDistributed antenna systemGps receiver
The invention is directed to a method and system for supporting multiple time division duplexed (TDD) based wireless services or frequency division duplexed (FDD) wireless services on a Distributed Antenna System (DAS). A DAS can support a many wireless services, including voice and data services using the same physical equipment. TDD based services use a common clock signal to synchronize the components of the DAS for transmission and reception of TDD signals. In accordance with the invention, the DAS can include a GPS receiver which can extract a timing signal (such as a 1 pps signal) from a GPS signal and distribute the timing signal to any and all components of the DAS to enable synchronization of the components for transmitting and receiving TDD signals. The GPS receiver can be part of the interface that connects a TDD based service to the DAS or separate component of the DAS. In accordance with the invention, the DAS can distribute a reference clock signal to all of the components of the DAS in order to maintain zero frequency shift while manipulating with the carrier frequencies of the various wireless services carried by the DAS. In addition, and in accordance with the invention, two analog architectures for better integration between the services sources (BTS) and the DAS are disclosed.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM WIRELESS
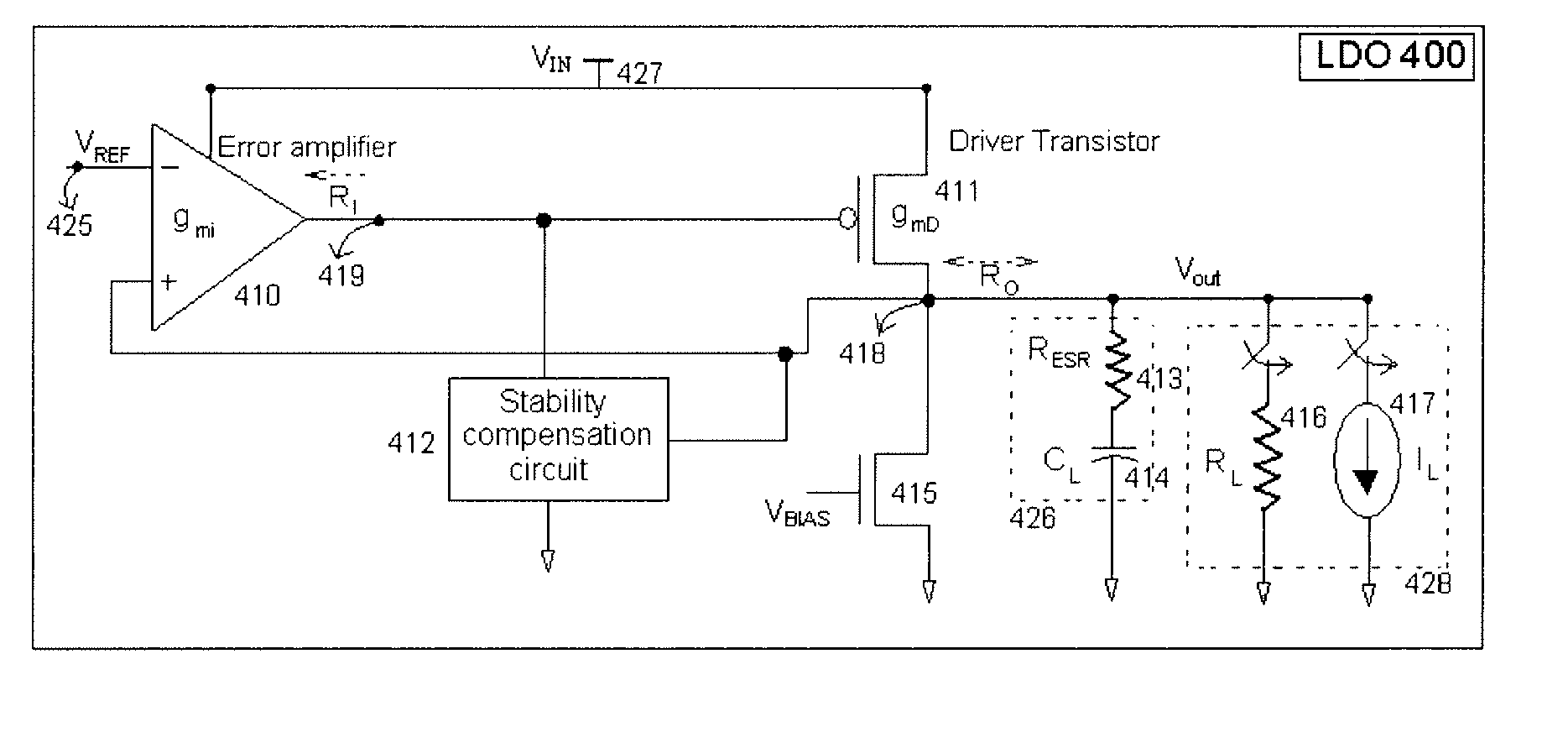
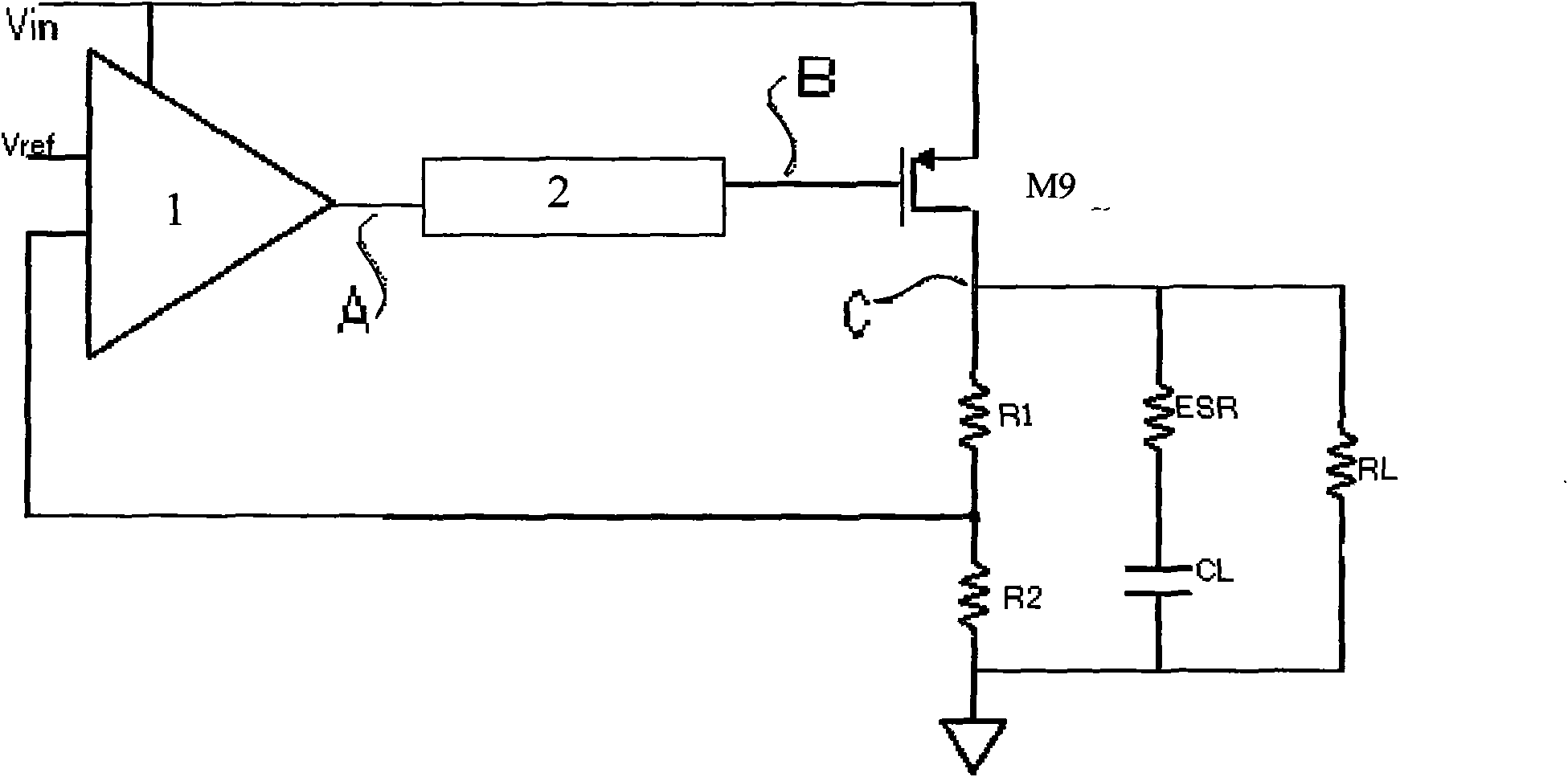
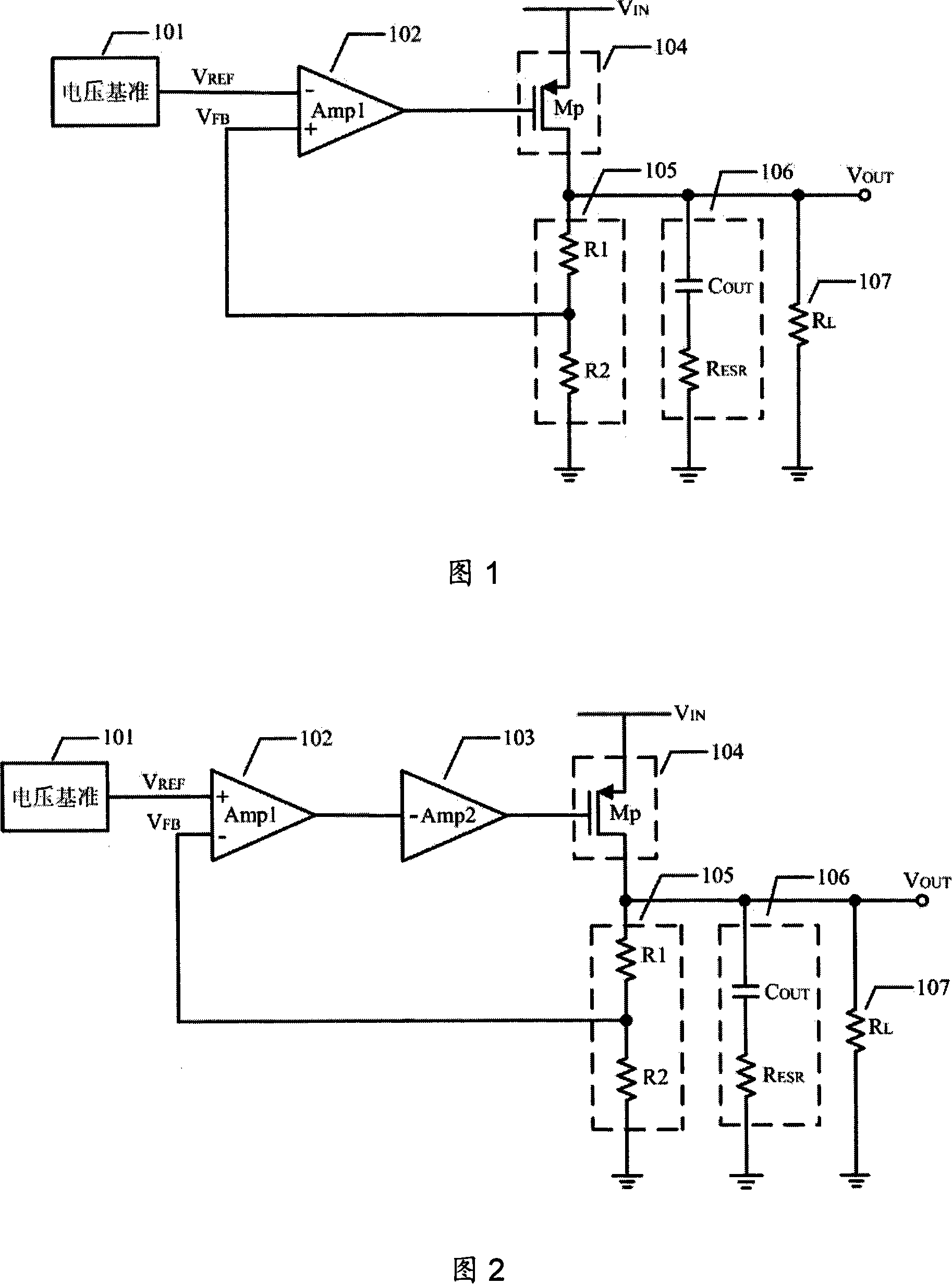
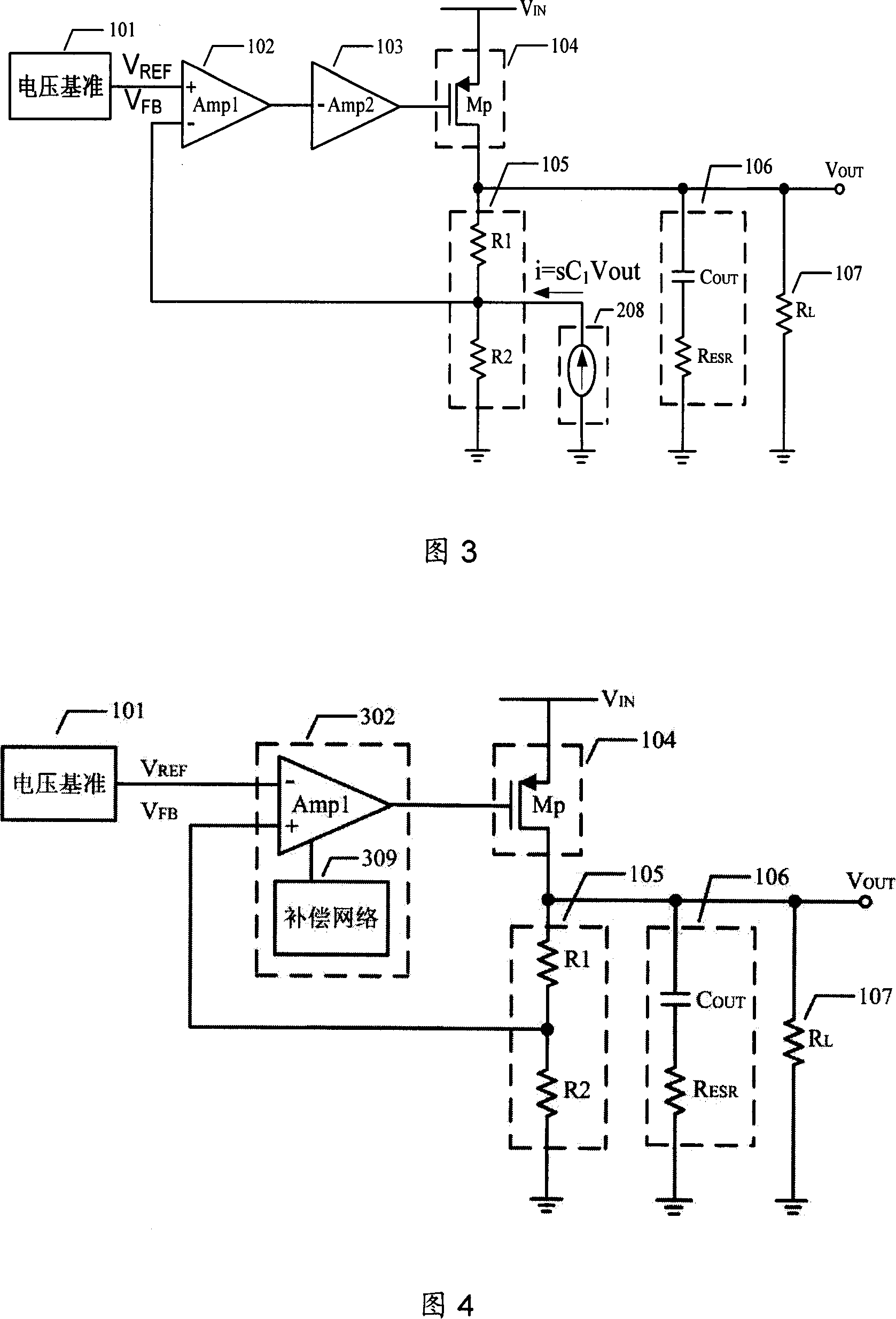
Low dropout regulator
InactiveUS20070159146A1Good phase marginMinimize power consumptionElectric variable regulationLow loadEngineering
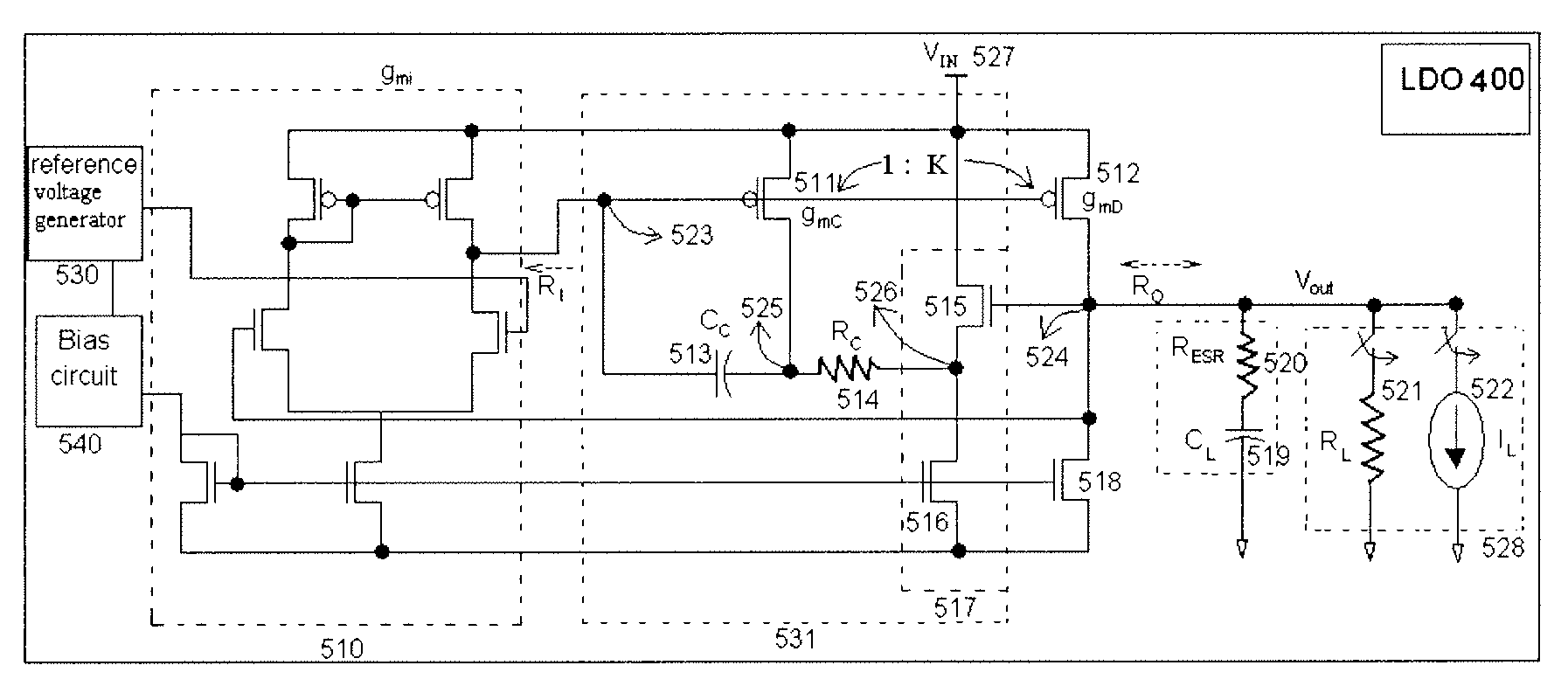
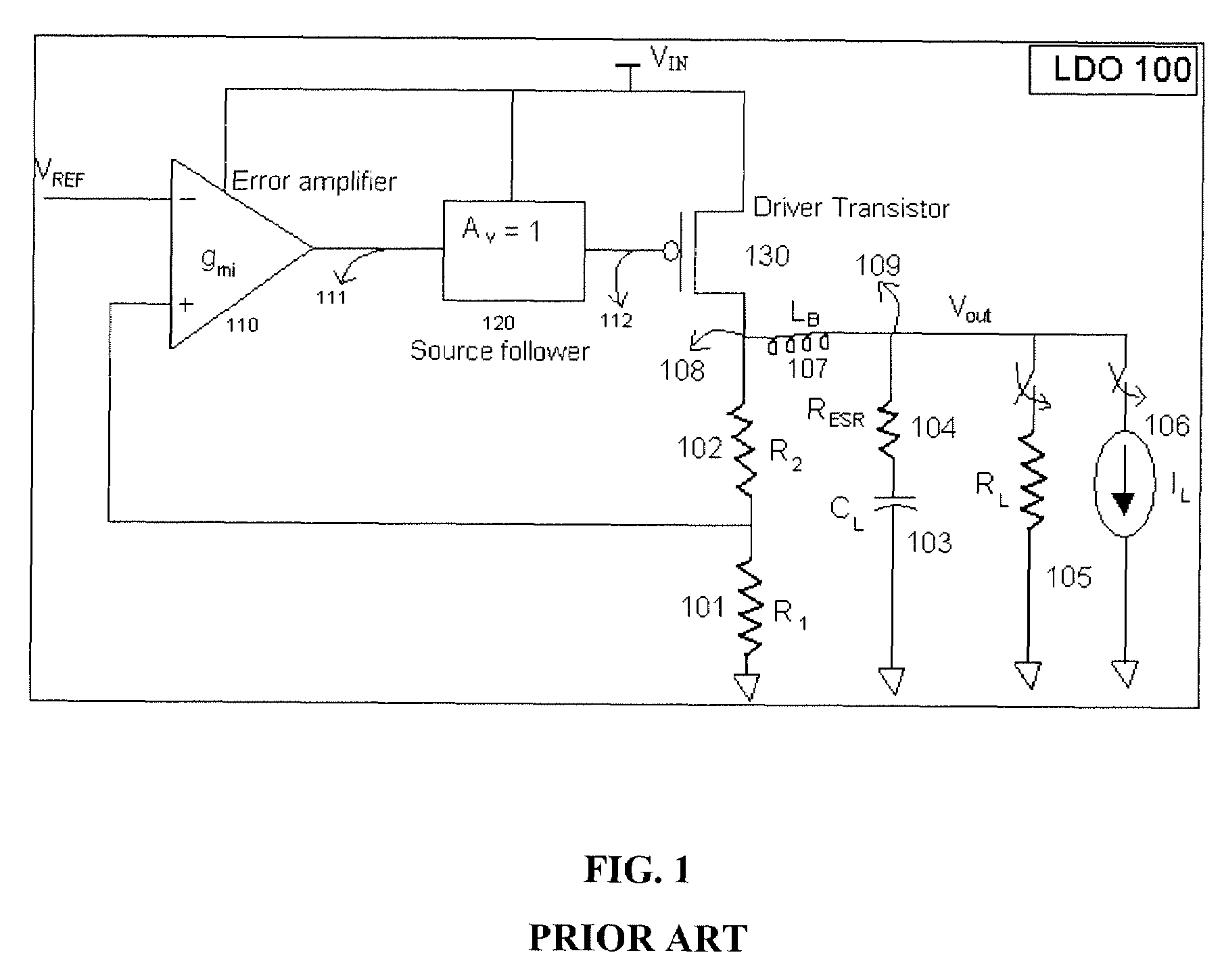
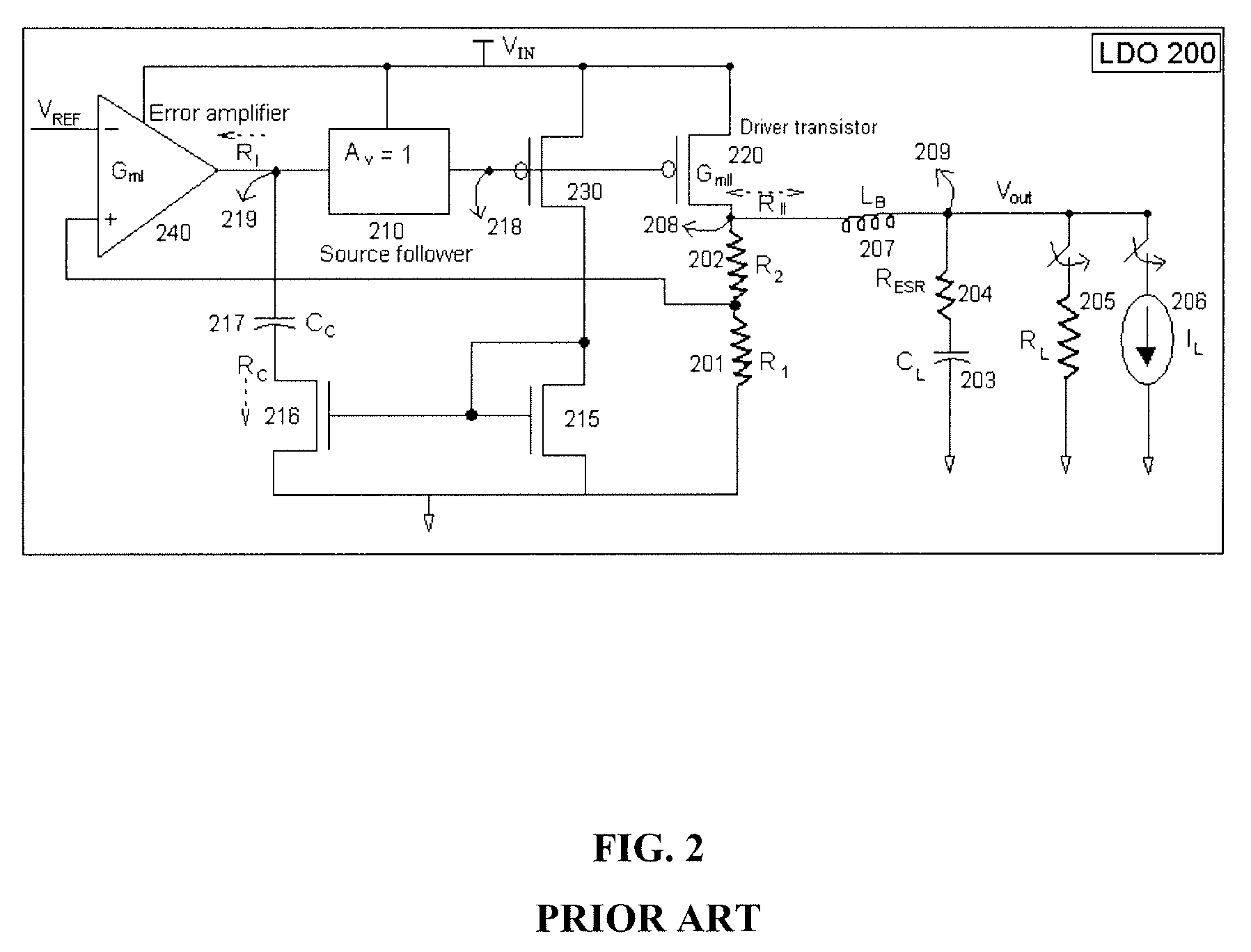
The present invention provides a low dropout (LDO) regulator with a stability compensation circuit. A “zero frequency” tracking as well as “non-dominant parasitic poles' frequency reshaping” are performed to achieve a good phase margin for the LDO by means of the compensation circuit. In this compensation method neither a large load capacitor nor its equivalent series resistance is needed to stabilize a regulator. LDO regulators, in system on chip application, having load capacitors in the range of few nano-Farads to few hundreds of nano-Farads can be efficiently compensated with this compensation method. A dominant pole for the regulator is realized at an internal node and the second pole at an output node of the regulator is tracked with a variable capacitor generated zero over a range of load current to cancel the effect of each other. A third pole of the system is pushed out above the unity gain frequency of the open loop transfer function with the help of the frequency compensation circuit. The compensation technique is very effective in realizing a low power, low-load-capacitor LDO desirable for system on chip applications.
Owner:ST ERICSSON SA
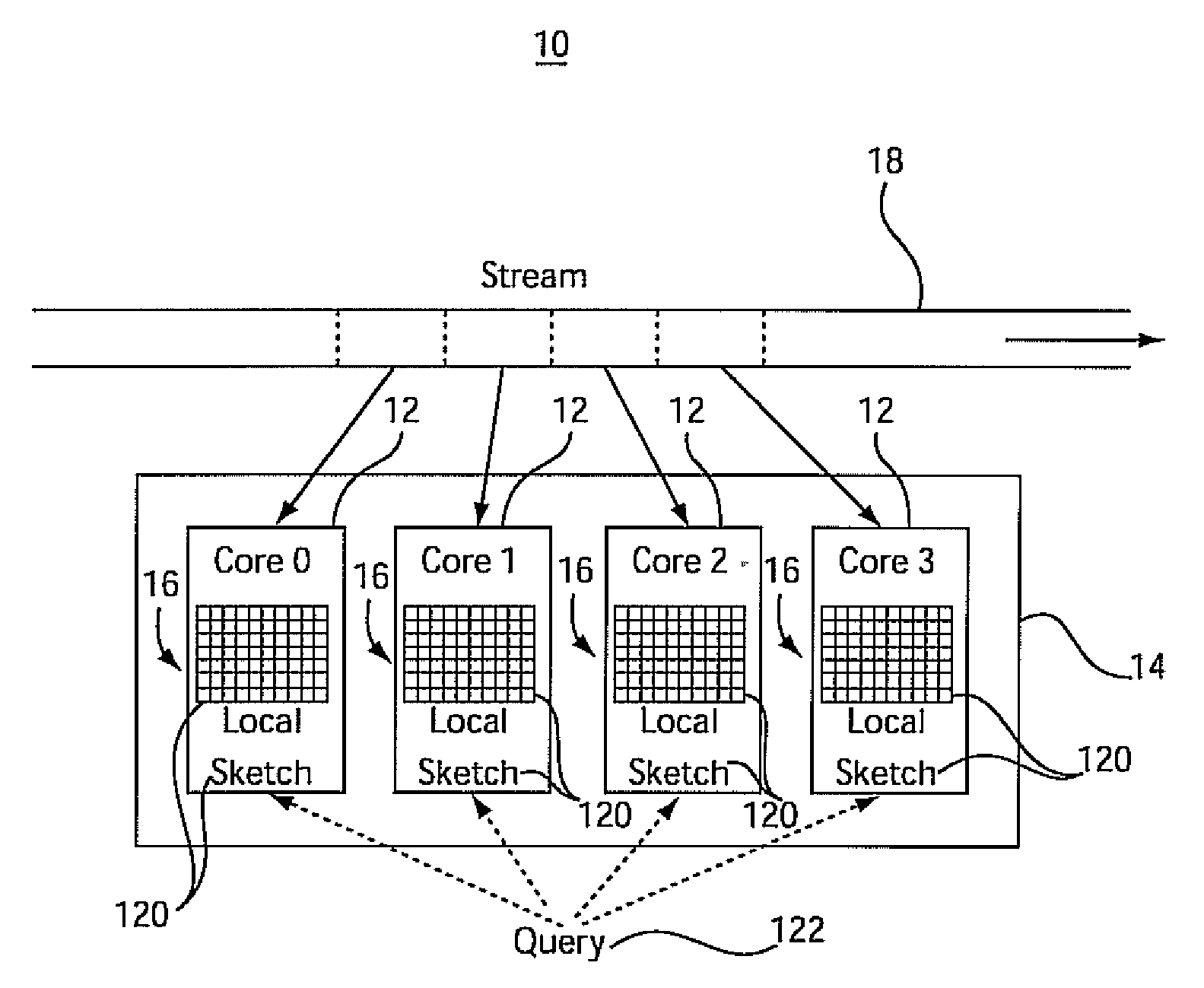
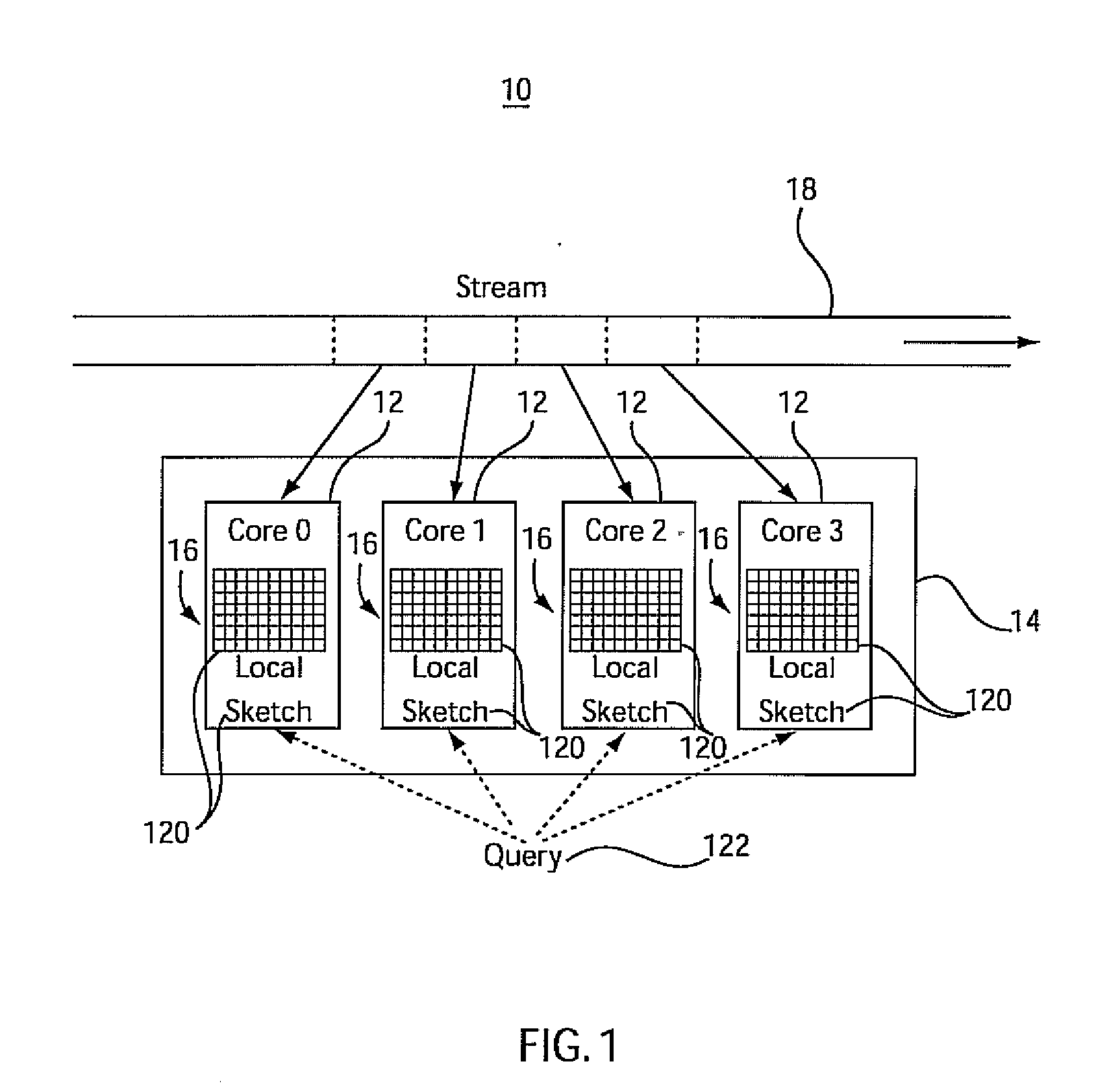
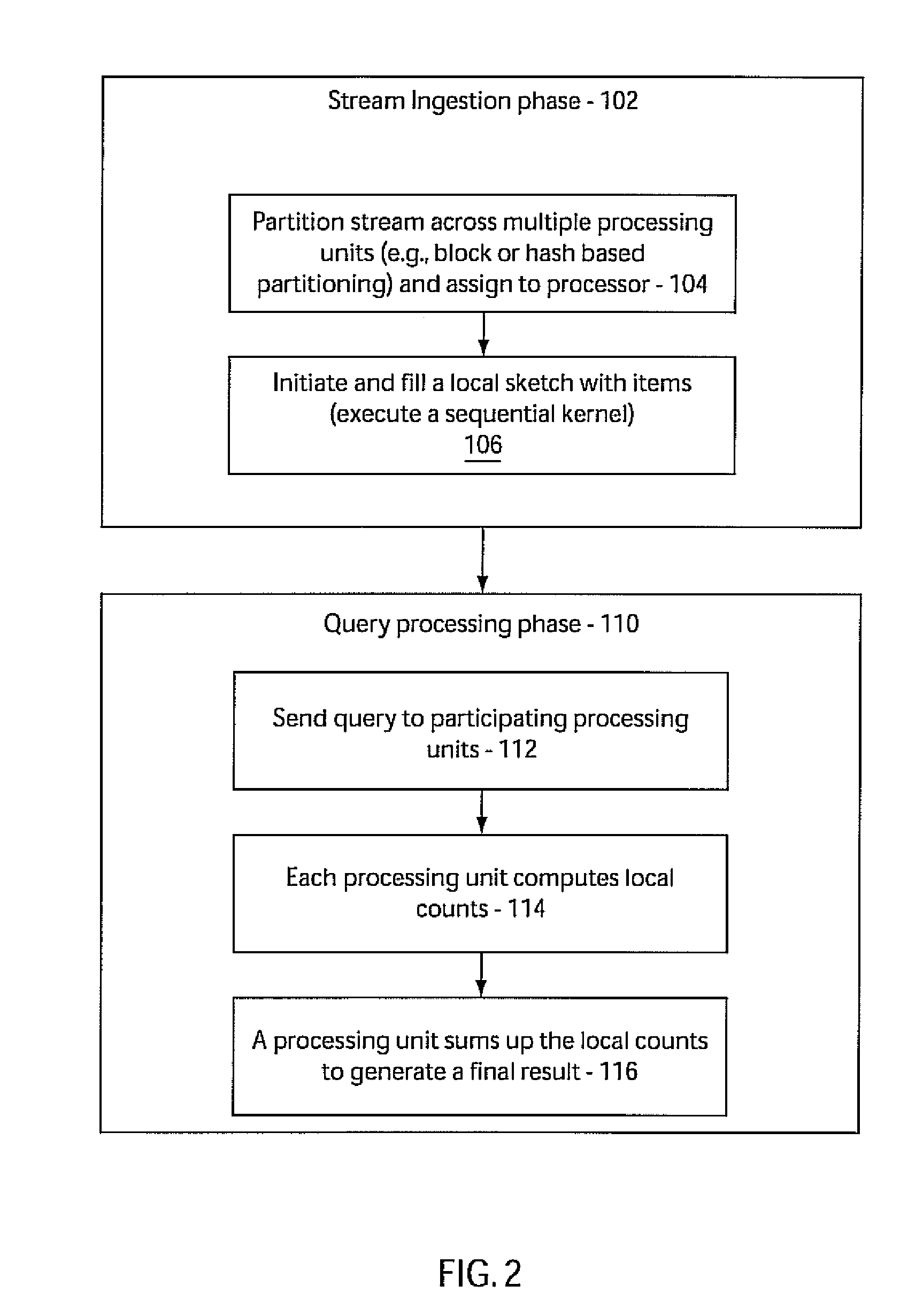
System and method for analyzing streams and counting stream items on multi-core processors
InactiveUS20090031175A1Improve computing powerImprove performanceProgram control using stored programsError detection/correctionMulti-core processorZero frequency
Systems and methods for parallel stream item counting are disclosed. A data stream is partitioned into portions and the portions are assigned to a plurality of processing cores. A sequential kernel is executed at each processing core to compute a local count for items in an assigned portion of the data stream for that processing core. The counts are aggregated for all the processing cores to determine a final count for the items in the data stream. A frequency-aware counting method (FCM) for data streams includes dynamically capturing relative frequency phases of items from a data stream and placing the items in a sketch structure using a plurality of hash functions where a number of hash functions is based on the frequency phase of the item. A zero-frequency table is provided to reduce errors due to absent items.
Owner:IBM CORP
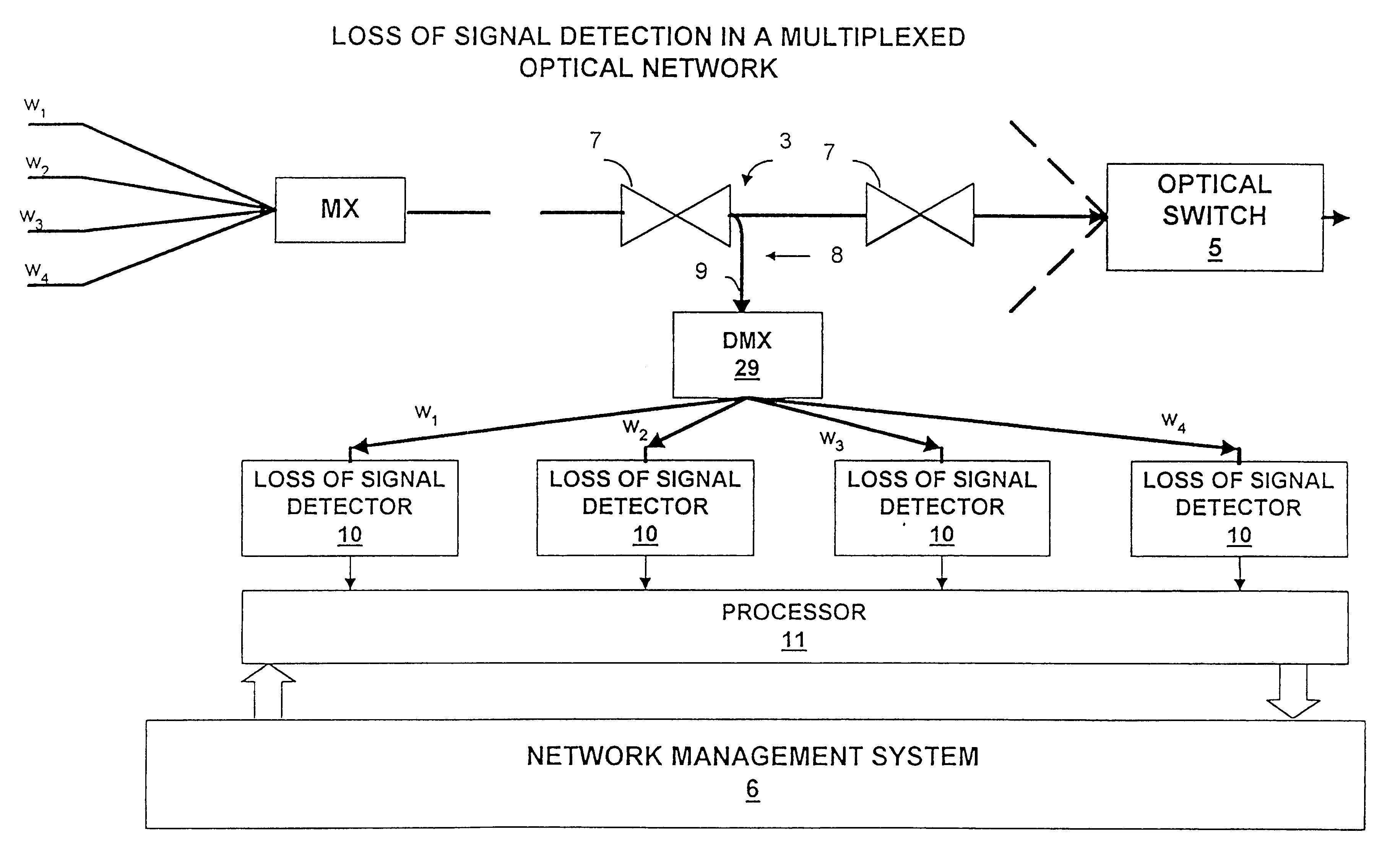
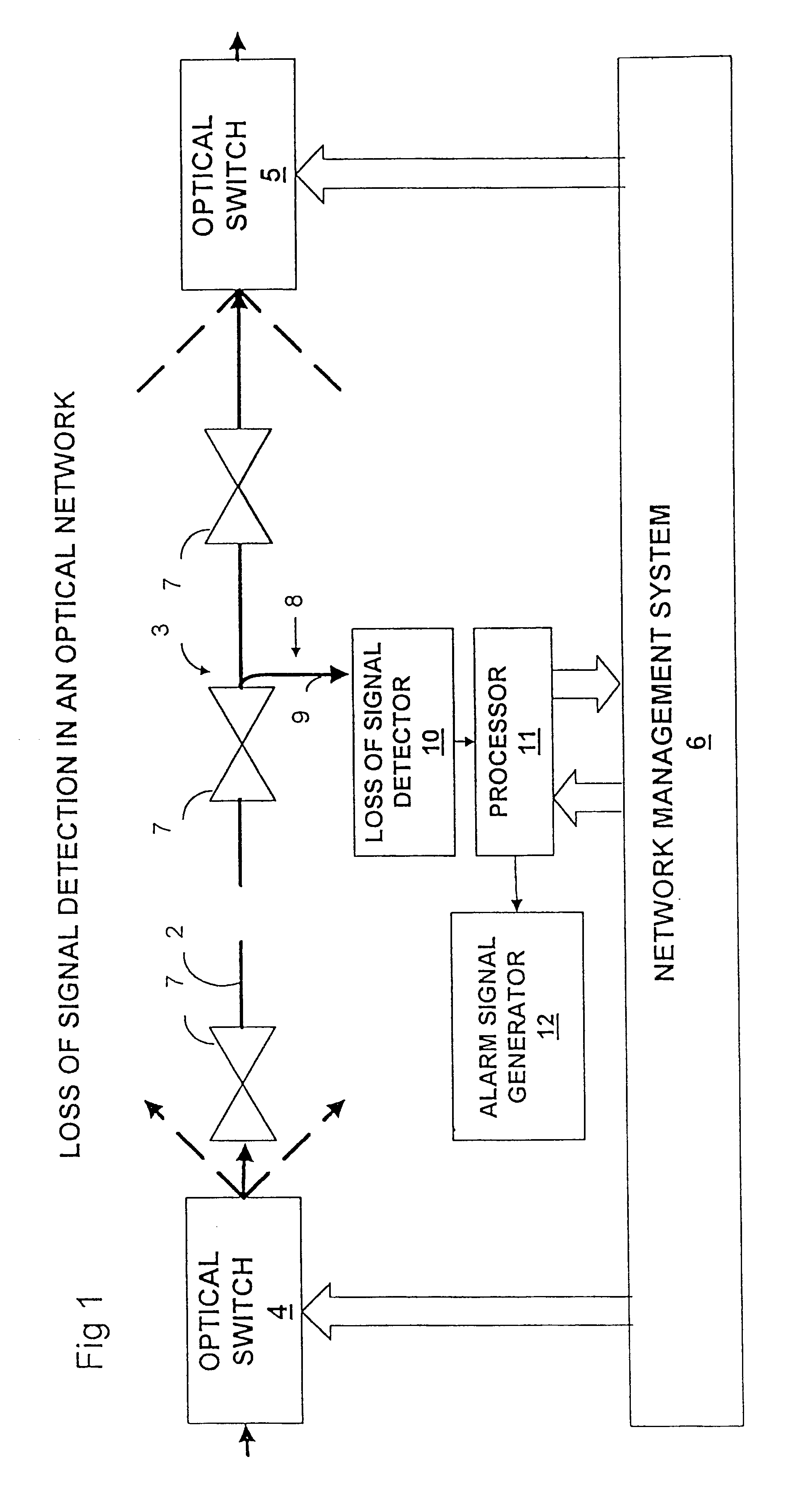
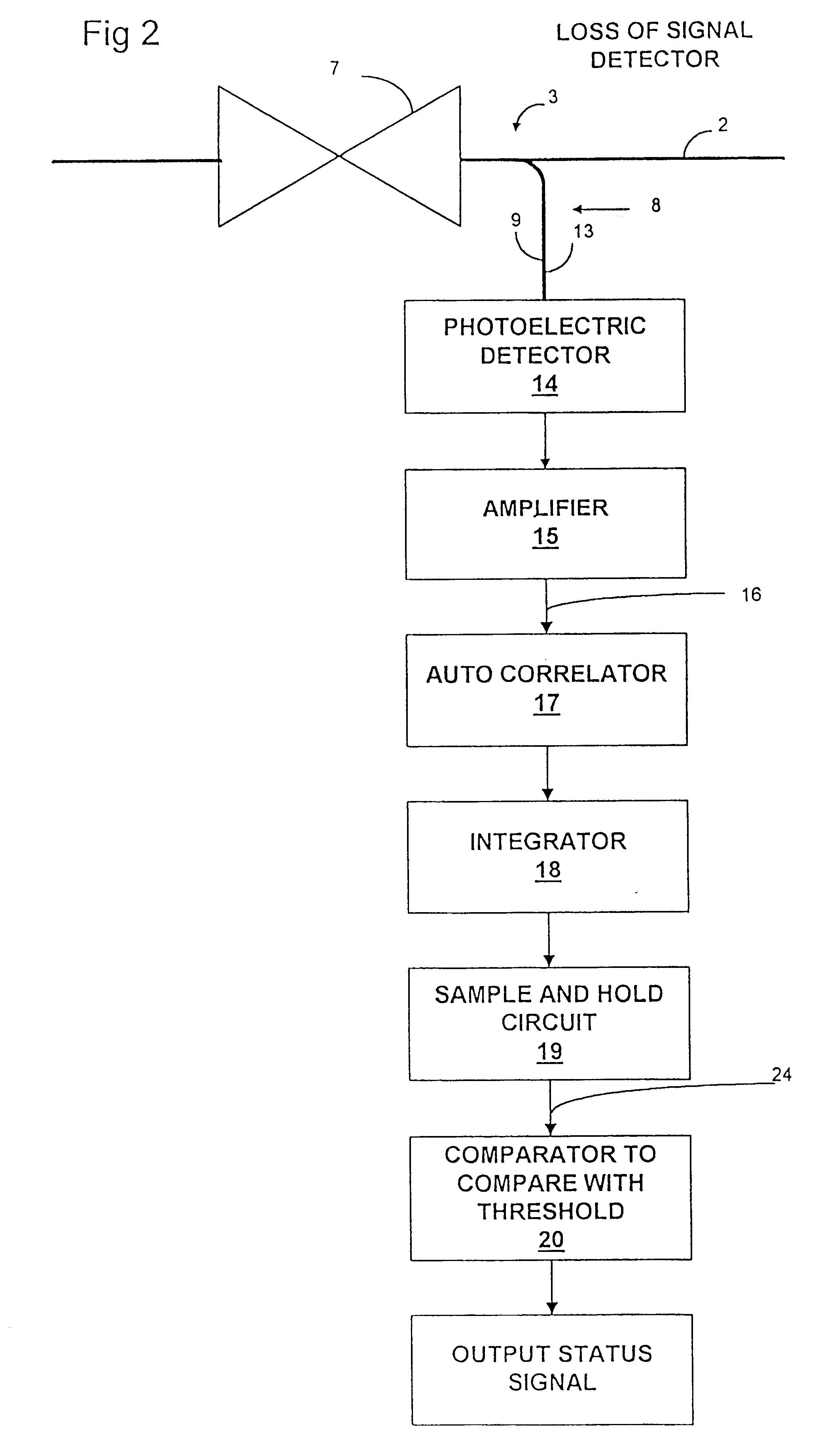
Optical network loss-of-signal detection
Loss of optical signal is detected in a synchronous communications system by detecting features of a monitor signal occurring at a detection frequency corresponding to the frame rate. Since the frame rate is substantially less than the bit rate, monitoring and detection can be performed at a lower bandwidth than the bit rate. An auto-correlation circuit utilises delays which are an integral multiple of the frame rate and produces a detection value which is compared with a threshold value. Alternatively, detection may be based on a power measurement of a band pass filtered monitor signal by setting the lower bandwidth limit above zero frequency and normalizing the measurement of power relative to an average power measurement. A loss of signal may then be detected by a change in power measurement relative to a threshold and can be used for asynchronous systems as well as synchronous systems. Loss of signal detection may be utilised to control an optical switch to re-route optical signals and generate alarm signals. The use of such detection in all optical networks avoids the requirement for electronic processing at the bit rate as a means of detection of loss of signal.
Owner:CIENA
Ultra-wideband receiver and transmitter
InactiveUS7209523B1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsPulse demodulatorExtensibilityBandpass filtering
A waveform-adaptive ultra-wideband (UWB) transmitter and noise-tracking UWB receiver for use in communications, object detection and radar applications. In one embodiment, the output of an oscillator is gated by a low-level impulse generator either directly or through an optional filter. In a special case of that embodiment wherein the oscillator is zero frequency and outputs a DC bias, a low-level impulse generator impulse-excites a bandpass filter to produce an UWB signal having an adjustable center frequency and desired bandwidth based on a characteristic of the filter. In another embodiment, the low-level impulse signal is approximated by a time-gated continuous-wave oscillator to produce an extremely wide bandwidth pulse with deterministic center frequency and bandwidth characteristics. The low-level impulse signal can be generated digitally. The UWB signal may be modulated to carry data, or may be used in object detection or ranging applications. The power amplifier may be gated to provide a power-efficient UWB transmitter. The UWB transmitter exhibits well defined and controllable spectral characteristics. The UWB transmitter is capable of extremely high pulse repetition frequencies (PRFs) and data rates in the hundreds of megabits per second or more, frequency agility on a pulse-to-pulse basis allowing frequency hopping if desired, and extensibility from below HF to millimeter wave frequencies.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
Low dropout regulator with stability compensation
InactiveUS7589507B2Good phase marginMinimize power consumptionElectric variable regulationLow loadEngineering
The present invention provides a low dropout (LDO) regulator with a stability compensation circuit. A “zero frequency” tracking as well as “non-dominant parasitic poles' frequency reshaping” are performed to achieve a good phase margin for the LDO by means of the compensation circuit. In this compensation method neither a large load capacitor nor its equivalent series resistance is needed to stabilize a regulator. LDO regulators, in system on chip application, having load capacitors in the range of few nano-Farads to few hundreds of nano-Farads can be efficiently compensated with this compensation method. A dominant pole for the regulator is realized at an internal node and the second pole at an output node of the regulator is tracked with a variable capacitor generated zero over a range of load current to cancel the effect of each other. A third pole of the system is pushed out above the unity gain frequency of the open loop transfer function with the help of the frequency compensation circuit. The compensation technique is very effective in realizing a low power, low-load-capacitor LDO desirable for system on chip applications.
Owner:ST ERICSSON SA
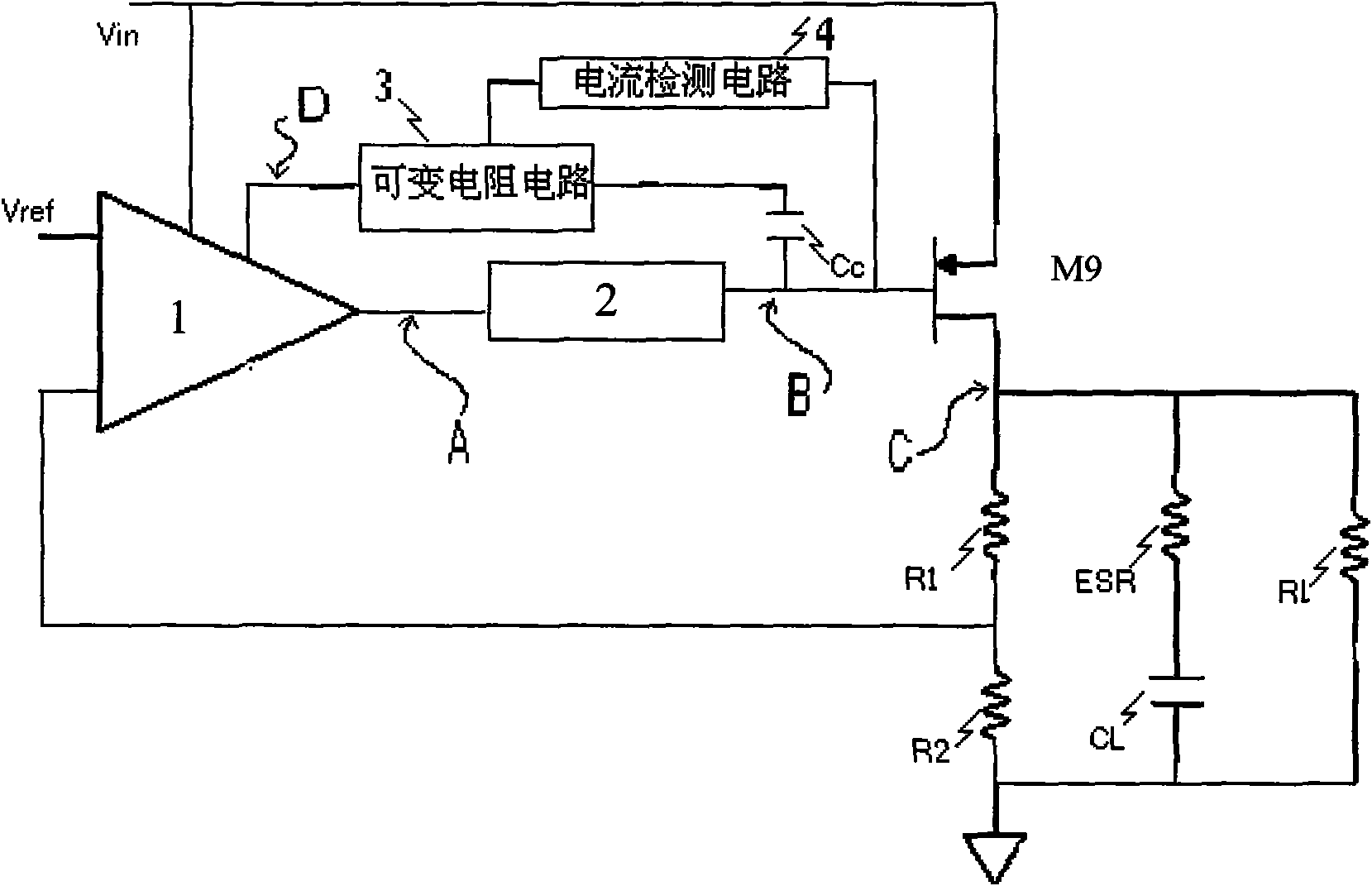
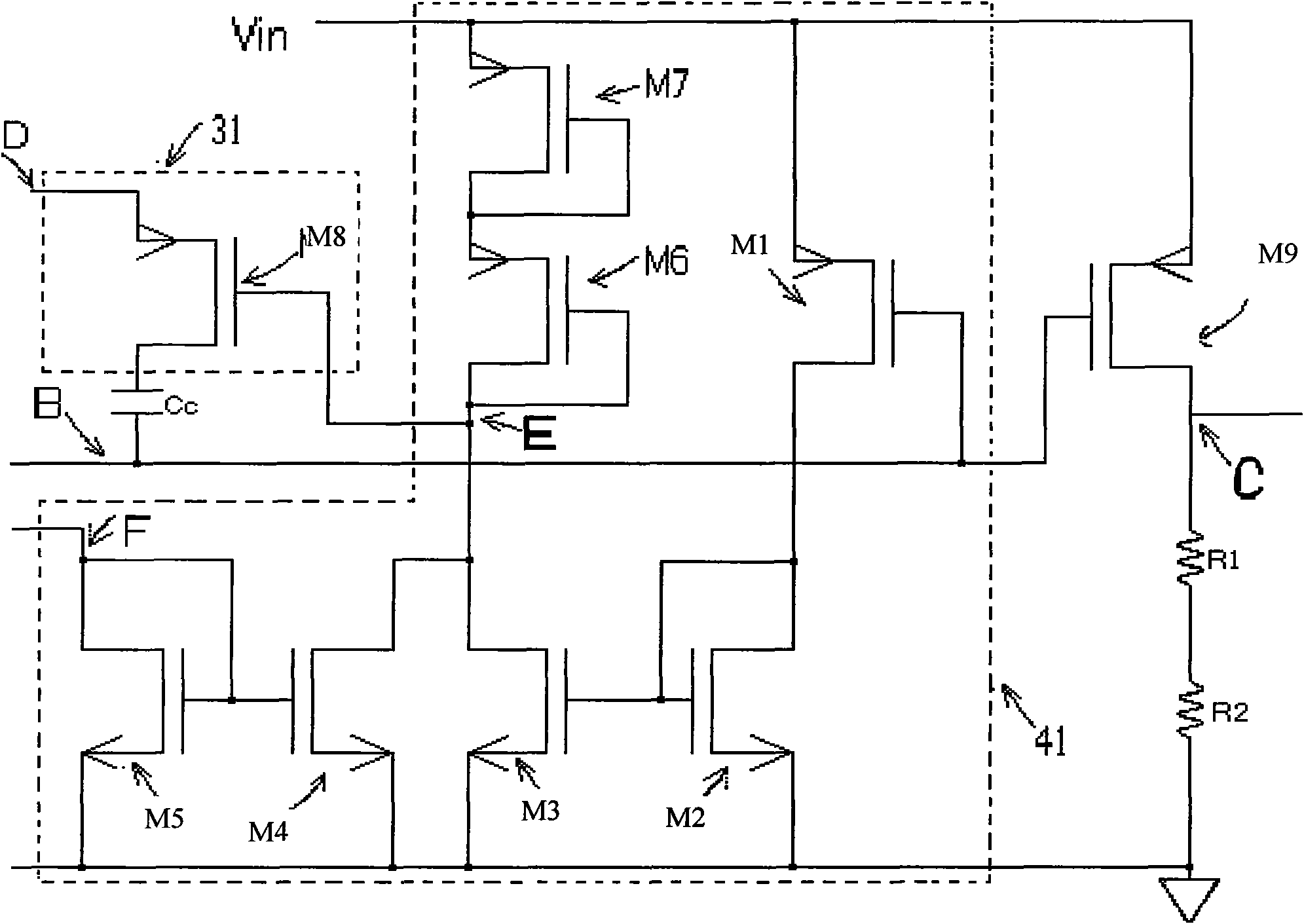
Self-adaption zero-frequency compensation circuit in low-voltage difference linear voltage regulator
ActiveCN101957628ALower resistanceFix stability issuesElectric variable regulationCapacitanceLow voltage
The invention relates to a self-adaption zero-frequency compensation circuit in a low-voltage difference linear voltage regulator. The output end of a transconductance amplifier is connected with a voltage regulation pipe by a voltage bumper, a current detection circuit is connected with the voltage bumper and the common end of the voltage regulation pipe, and the other end is connected with a variable-resistance circuit connected with the compensation end of the transconductance amplifier. In the invention, when a load is higher and current is lower, the current detection circuit can detect the load and the current and the load and the current act on the variable-resistance circuit at the moment to ensure that the resistance is enlarged, and the zero position is also relatively lower; on the contrary, when the load is reduced and the current is enlarged, the resistance value of the variable-resistance circuit is reduced, and the zero position is higher. Therefore, the self-adaption zero can change along with the change of a pole so that the compensation circuit takes the effect of compensation and effectively ensures the stable state of system operation. The compensation circuit successfully solves the problem of poor stability of a low-voltage difference linear voltage regulator so that a load capacitance equivalent series resistance is not really important to the influence on system stability, transient response and ripple waves.
Owner:江西芯世达微电子有限公司
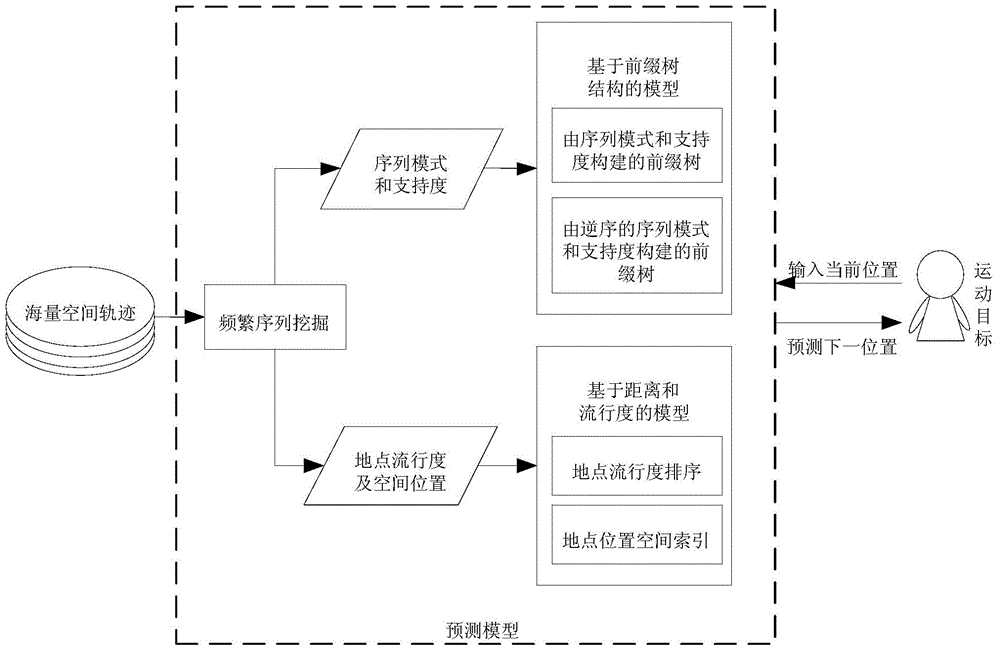
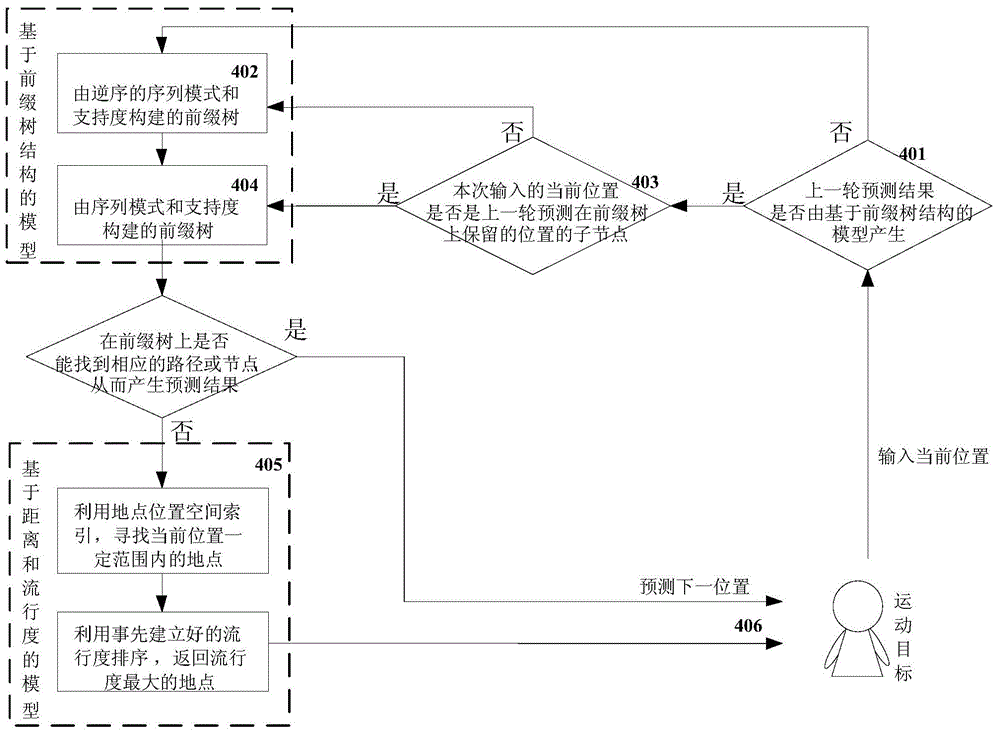
On-line position prediction method based on mass of space trajectory excavation
ActiveCN104462190AImprove accuracySpecial data processing applicationsGeographic siteComputation complexity
The invention relates to an on-line position prediction method based on mass of space trajectory excavation and belongs to the field of space trajectory excavation. The method comprises the steps of firstly, excavating frequent sequential patterns from the mass of space trajectory excavation, secondly, using the sequence patterns to establish a model based on a prefix tree structure, thirdly, establishing a model based on distance and popularity to solve the zero frequency problem, and finally, using the established predication models to predict the next position of a moving target according to the current trajectory information of the moving target. The accuracy of the prediction method is improved greatly compared with the existing methods, the calculation complexity is low, real-time prediction can be carried out on the position of the moving target, only the position information of the moving target is needed, and therefore the on-line position prediction method based on mass of space trajectory excavation can be widely applied to the fields such as intelligent traffic and services based on geographic positions.
Owner:THE 28TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP
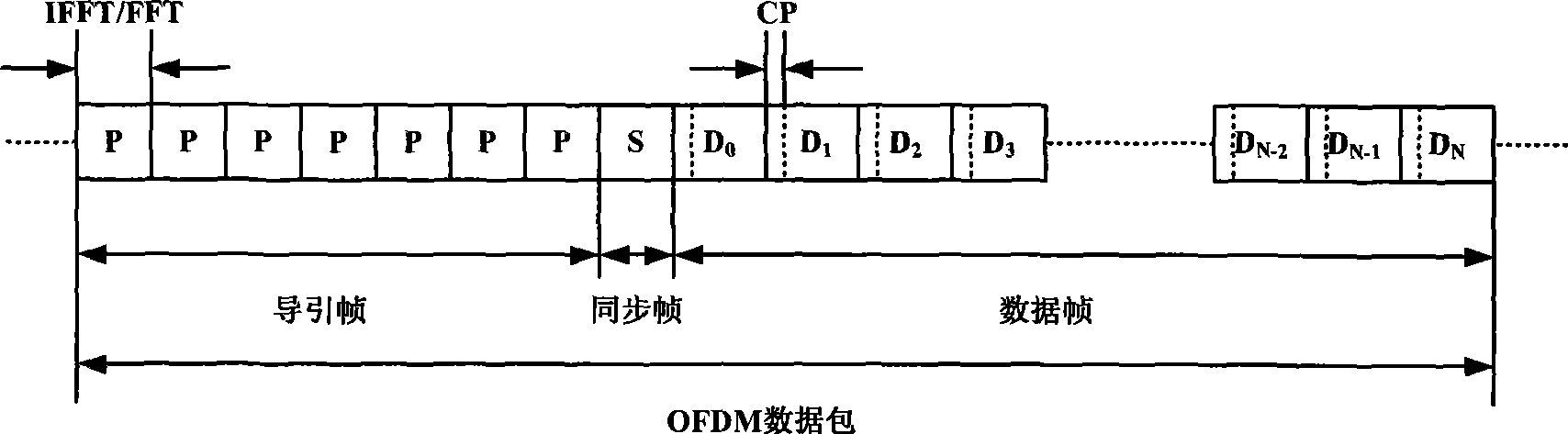
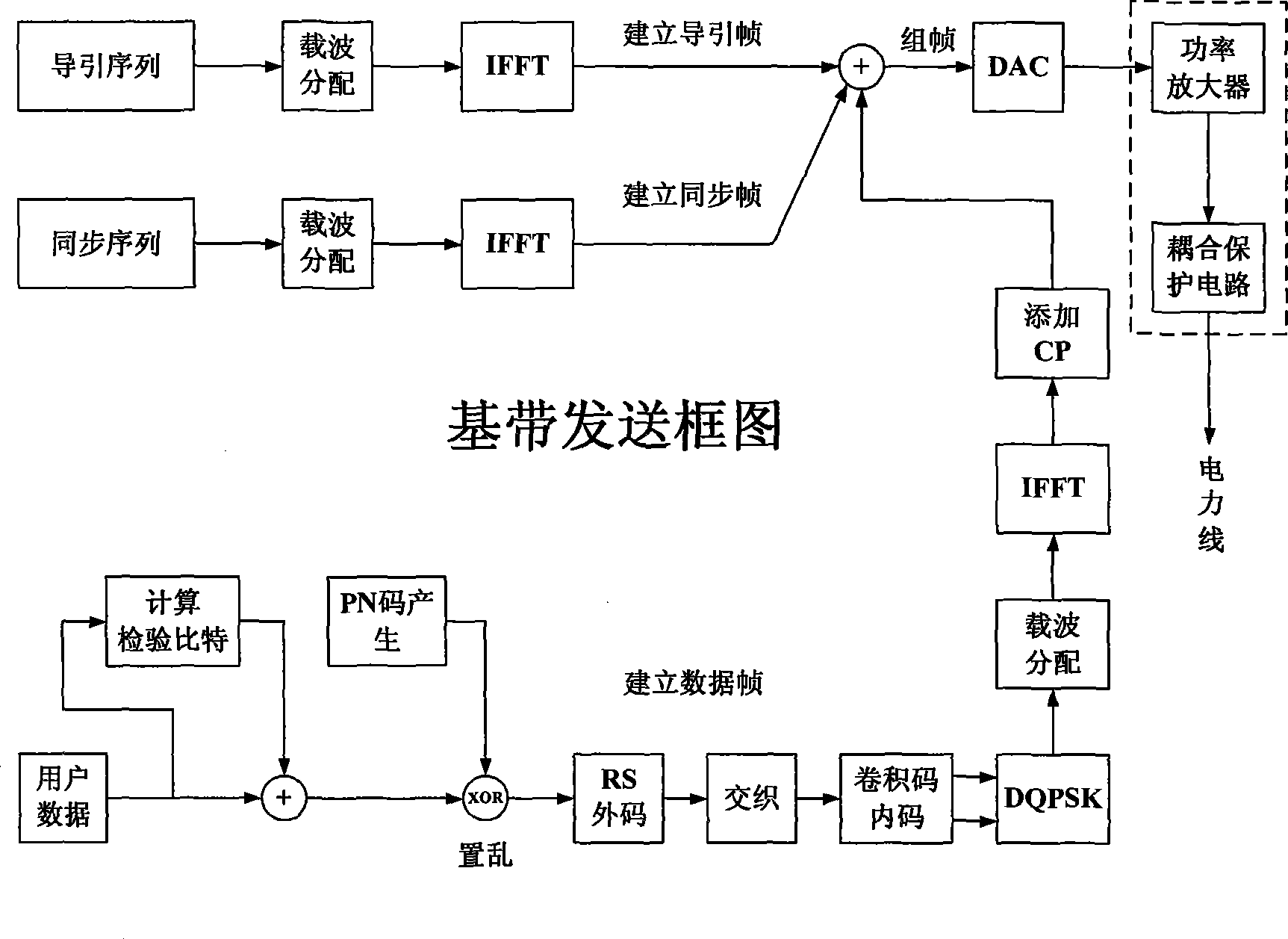
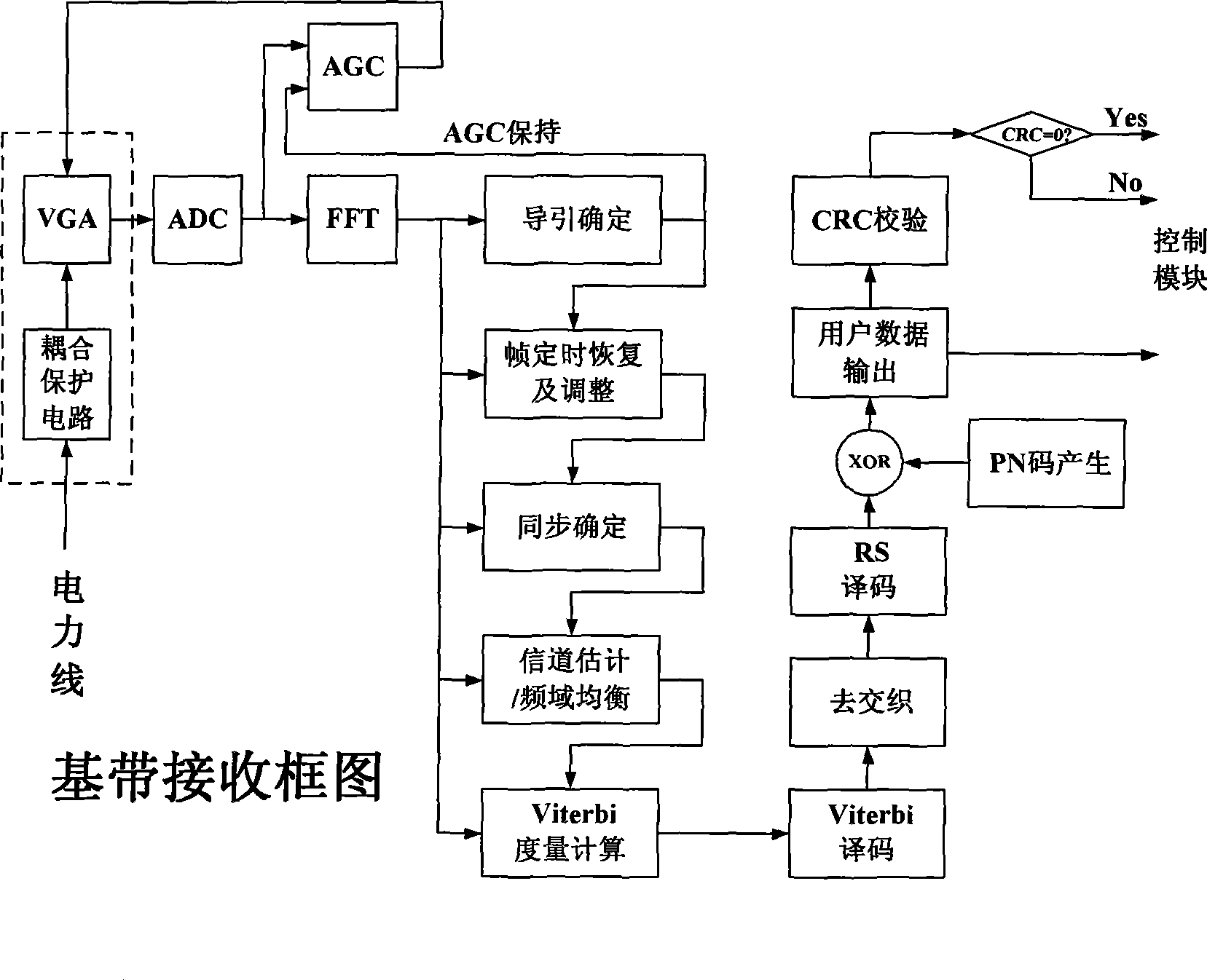
Zero frequency conversion and adaptive frequency selecting power line carrier data transmission method
The invention discloses a data transmission method of a carrier wave of a power line, with frequency conversion and adaptive frequency selection. Communication band can be flexibly divided into a plurality of subcarriers through the arrangement of IFFT points and a sampling rate. When the carrier wave is distributed before the conversion of the IFFT, modulation data is just distributed on the subcarriers of 40 kHz to 500 kHz, and data on the other subcarriers is zero, thereby ensuring that the actual applied frequency range is 40 kHz to 500 kHz, without the need of the frequency spectrum displacement. A local end can figure out the channel condition of each subcarrier through the method of receiving a known signal sent by an opposite end, chooses the subcarrier which has the good channel condition to send a signal, and abandons the subscriber which has the channel condition. The invention can directly modulate the signal on the needed transmission band and carrier frequency, thereby reducing realization complexity and choosing the transmission band of the signal in an adaptive manner.
Owner:STATE GRID ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
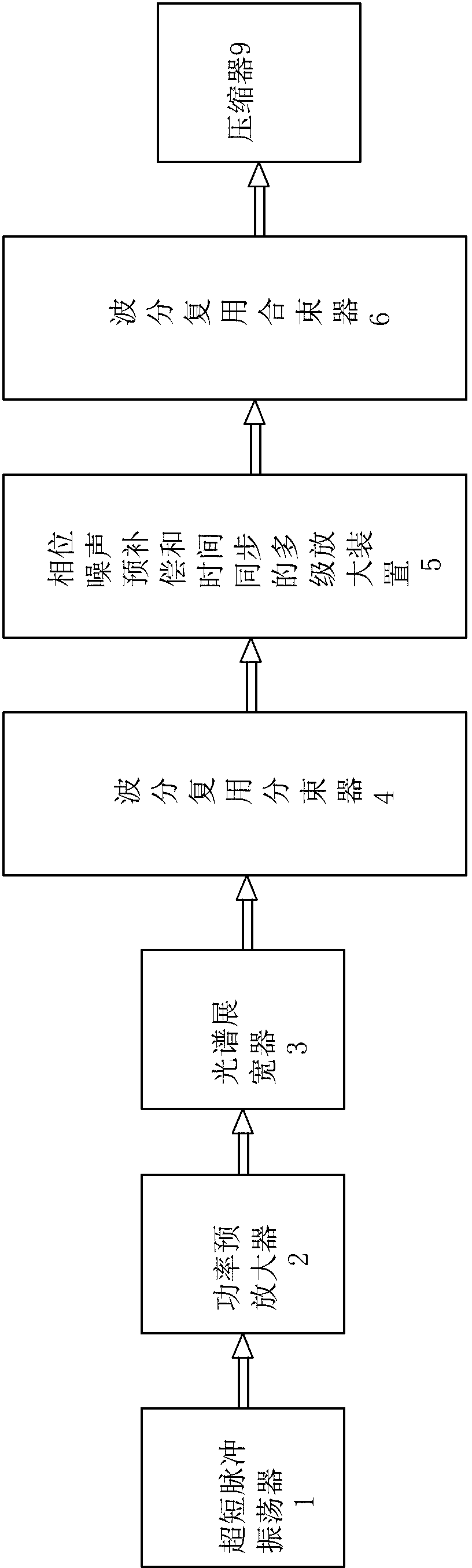
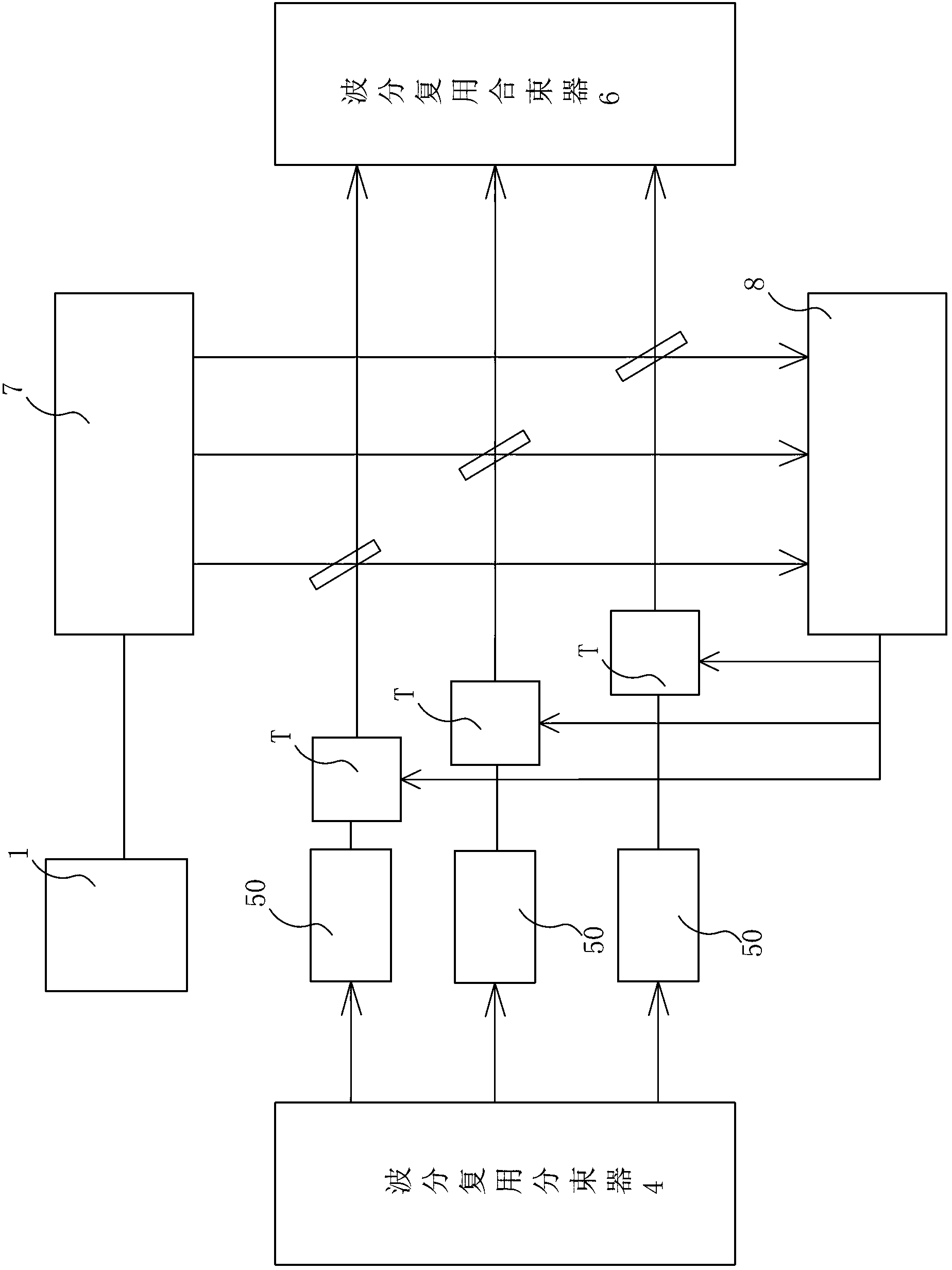
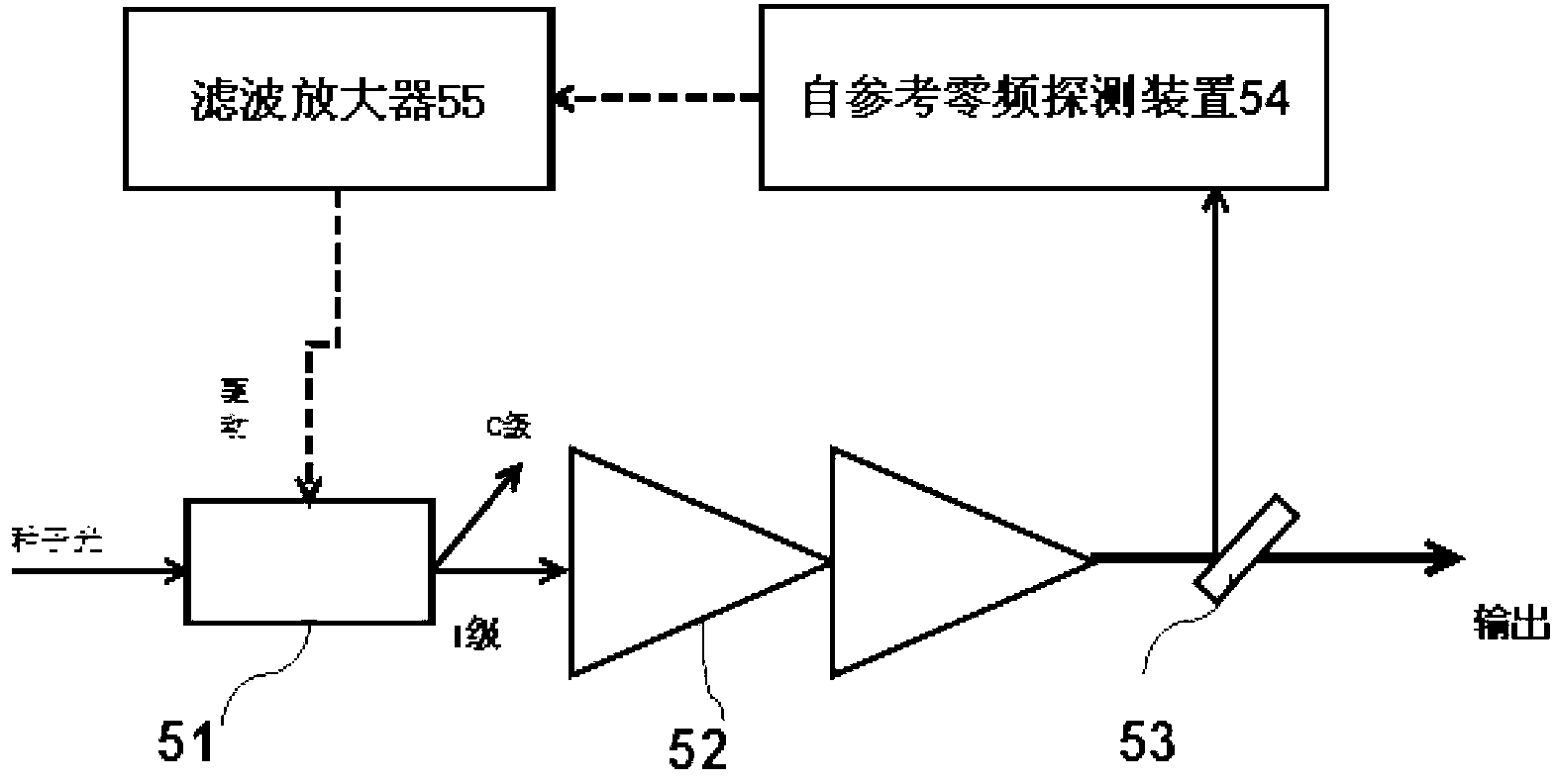
Novel method for realizing spectral combination amplification based on frequency division multiplexing technology
ActiveCN103022877AAddressing Gain Narrowing EffectsIncrease powerLaser detailsFrequency spectrumAcousto-optics
The invention discloses a novel method for realizing spectral combination amplification based on the frequency division multiplexing technology, which comprises the following steps of: (a), pre-amplifying and broadening laser pulse generated by an ultra-short pulse oscillator; (b), segmenting the frequency spectrum of a super-continuous broad-band spectrum into multiplex optical pulses with different central wavelengths; (c), amplifying each optical pulse, outputting a part of amplified seed light to a self-reference zero-frequency detection device by using a splitting slice, and taking a beat frequency signal output by the self-reference zero-frequency detection device as the driving frequency of an acousto-optic frequency shifter after filtering and amplifying; (d), coherently synthesizing amplification pulses output by various multi-stage optical fibre amplifiers through a wavelength division multiplexing beam combiner; and (e), carrying out dispersion compensation and pulse width compression of coherently synthesized pulses by using a compressor so as to obtain ultra-short pulse output with high peak power. According to the invention, the frequency division multiplexing technology and the coherent synthesizing technology are organically combined; therefore, the pulse synchronization problem and the spectrum coherent problem in the ultra-short pulse optical fibre laser coherent synthesizing process are solved.
Owner:广东华快光子科技有限公司 +1
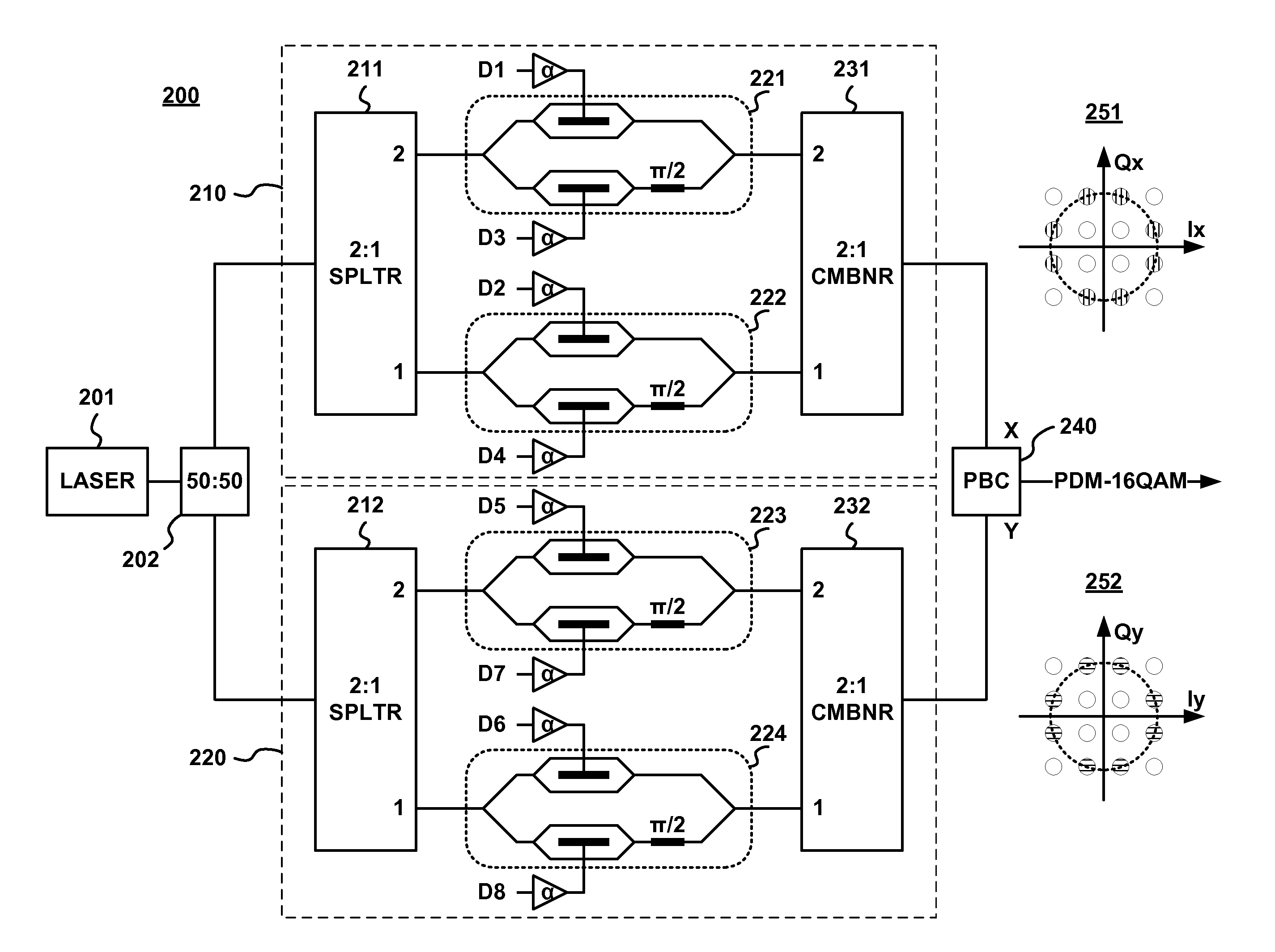
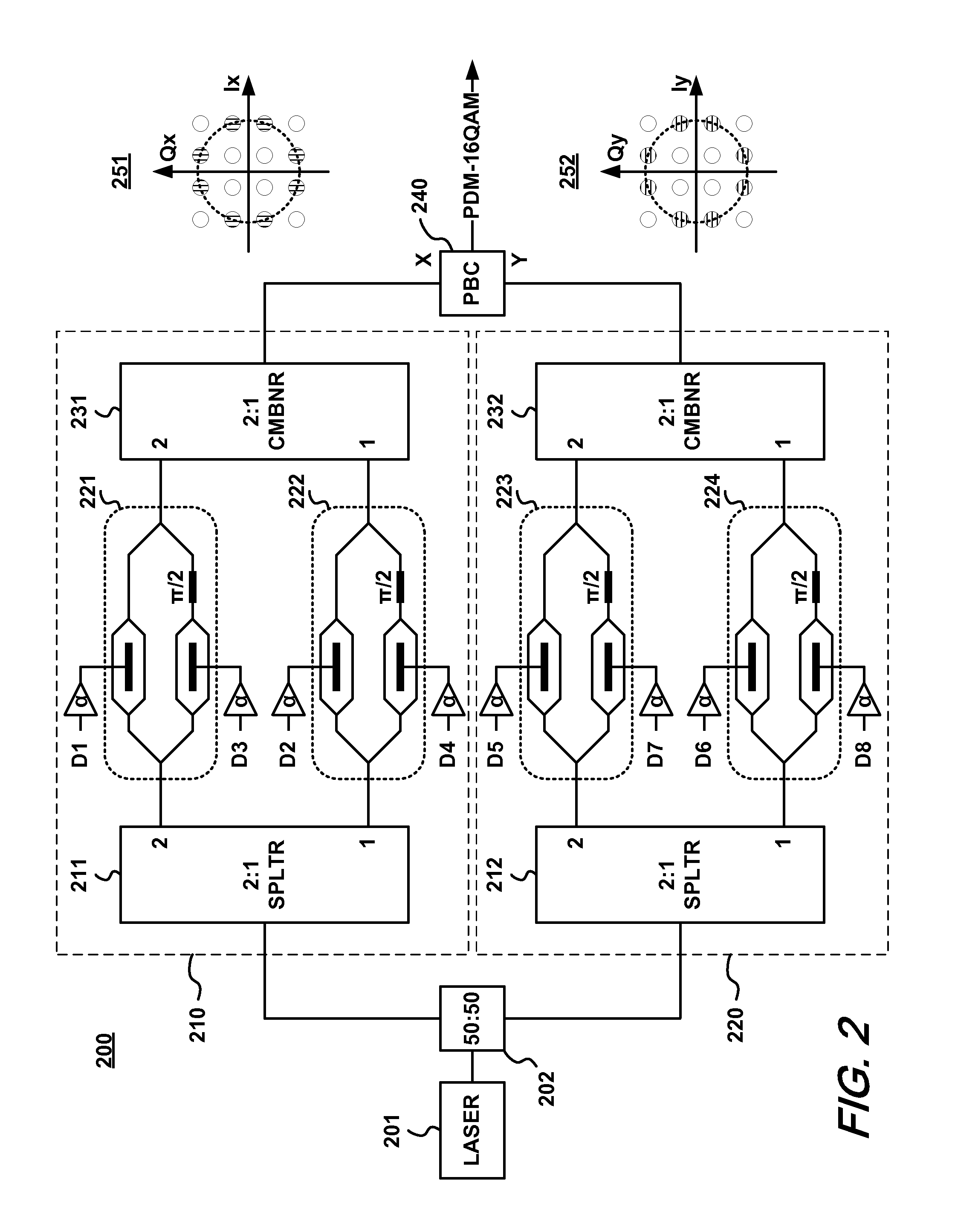
Method and apparatus for transmitting high-level qam optical signals with binary drive signals
ActiveUS20130170841A1Accurate and reliable channel estimationMinimizes fiber nonlinearity impairmentElectromagnetic transmittersTime domainConstant power
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
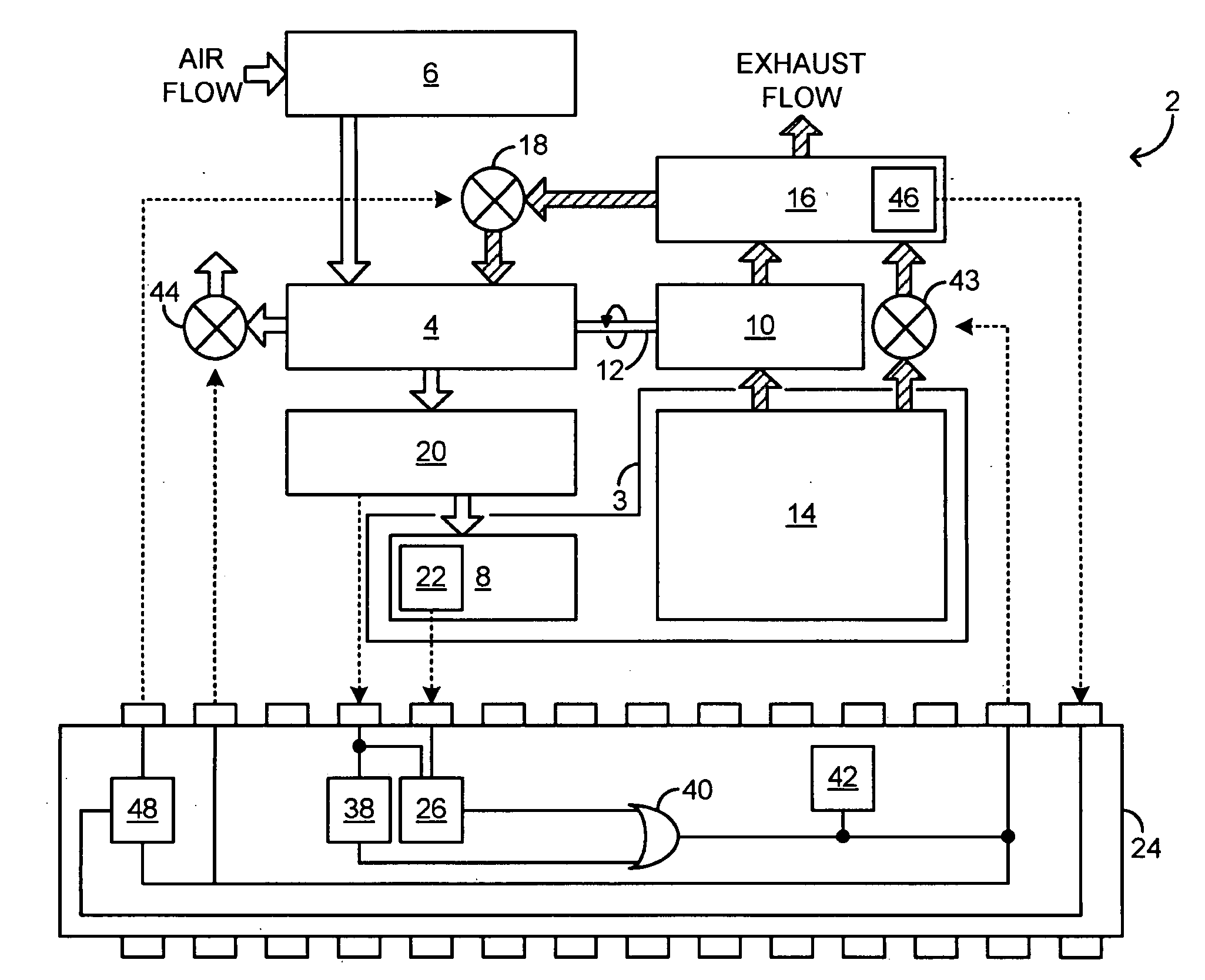
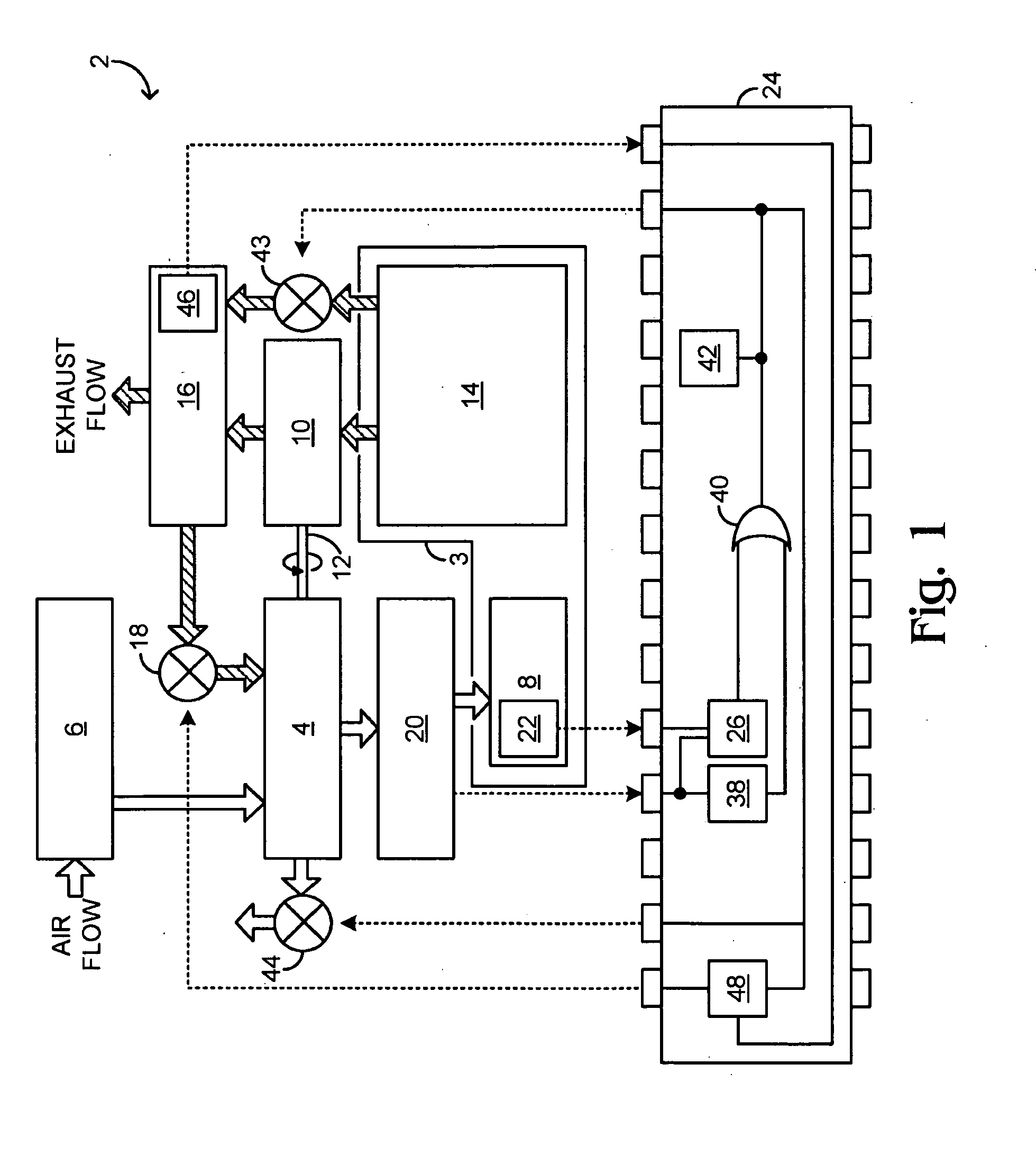
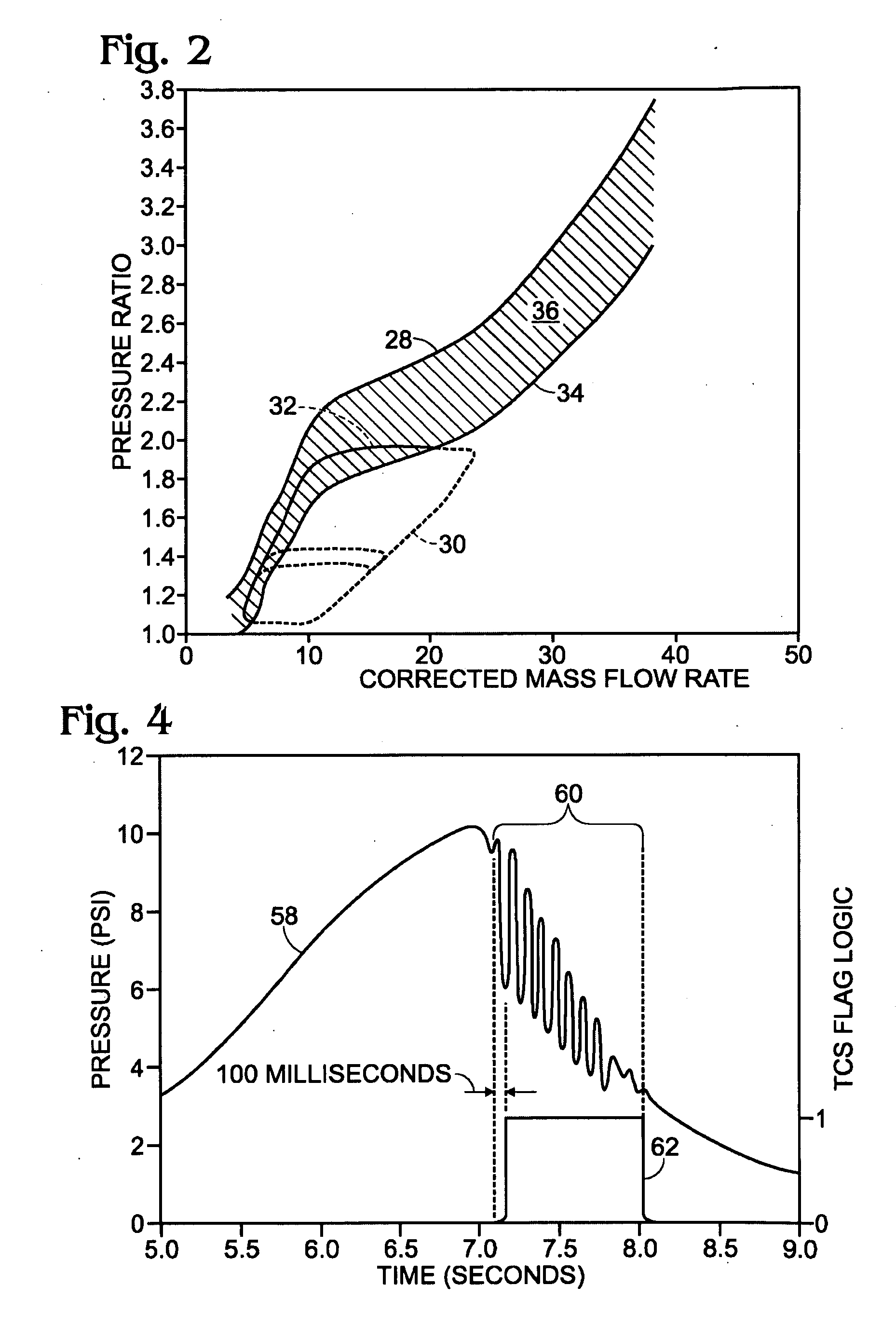
Transient compressor surge response for a turbocharged engine
ActiveUS20090293477A1High power outputQuality improvementElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesMobile vehicleTurbocharger
A method for responding to an existing or incipient surge condition of a turbocharger coupled to an engine of a motor vehicle is provided. The method comprises receiving a signal responsive to an operating condition of the turbocharger and adjusting one or more operating parameters of the motor vehicle when a power of the signal, integrated over a pre-selected range of non-zero frequencies, exceeds a pre-selected threshold. Other embodiments provide related systems for responding to an existing or incipient surge condition of a turbocharger.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
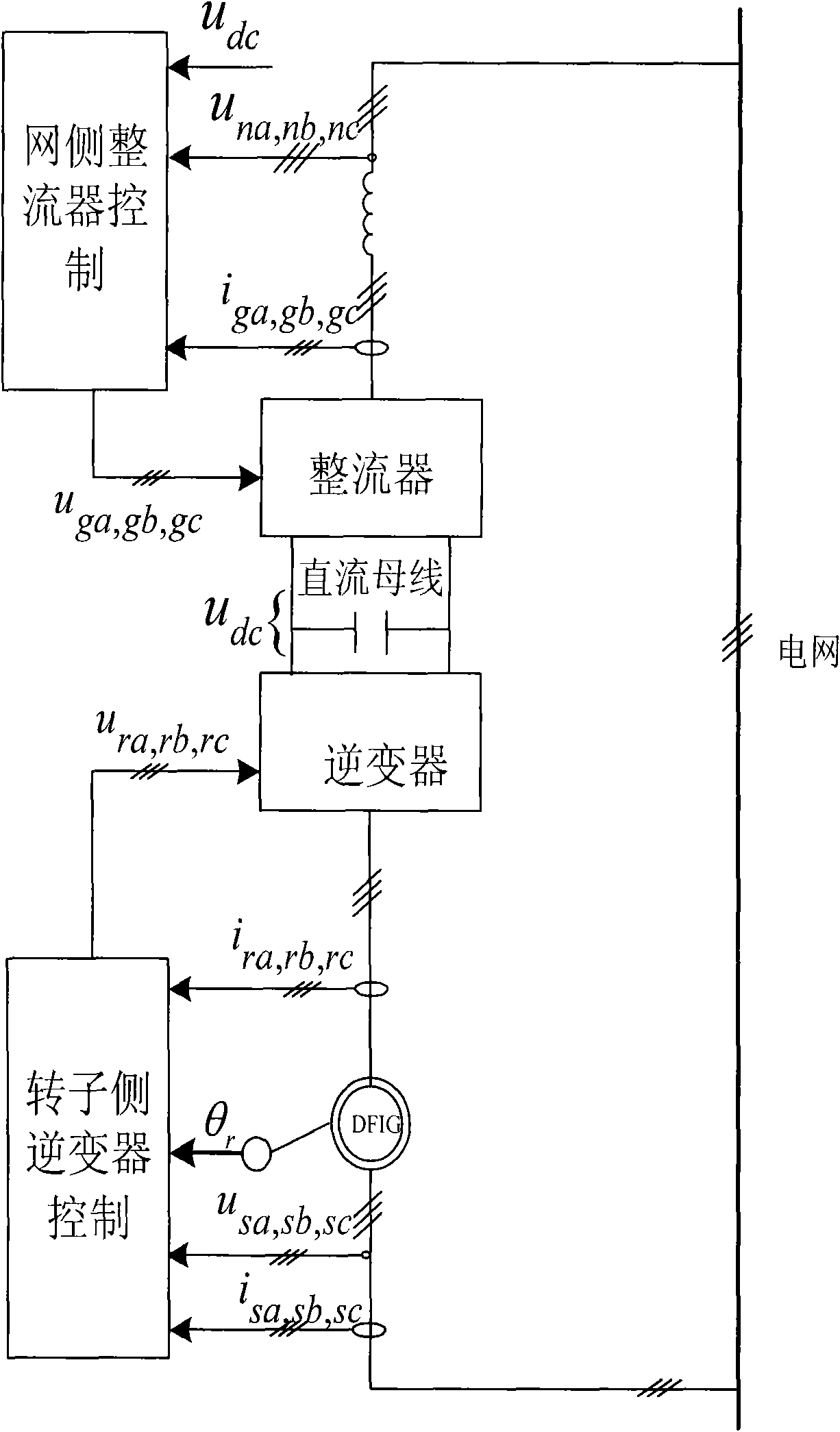
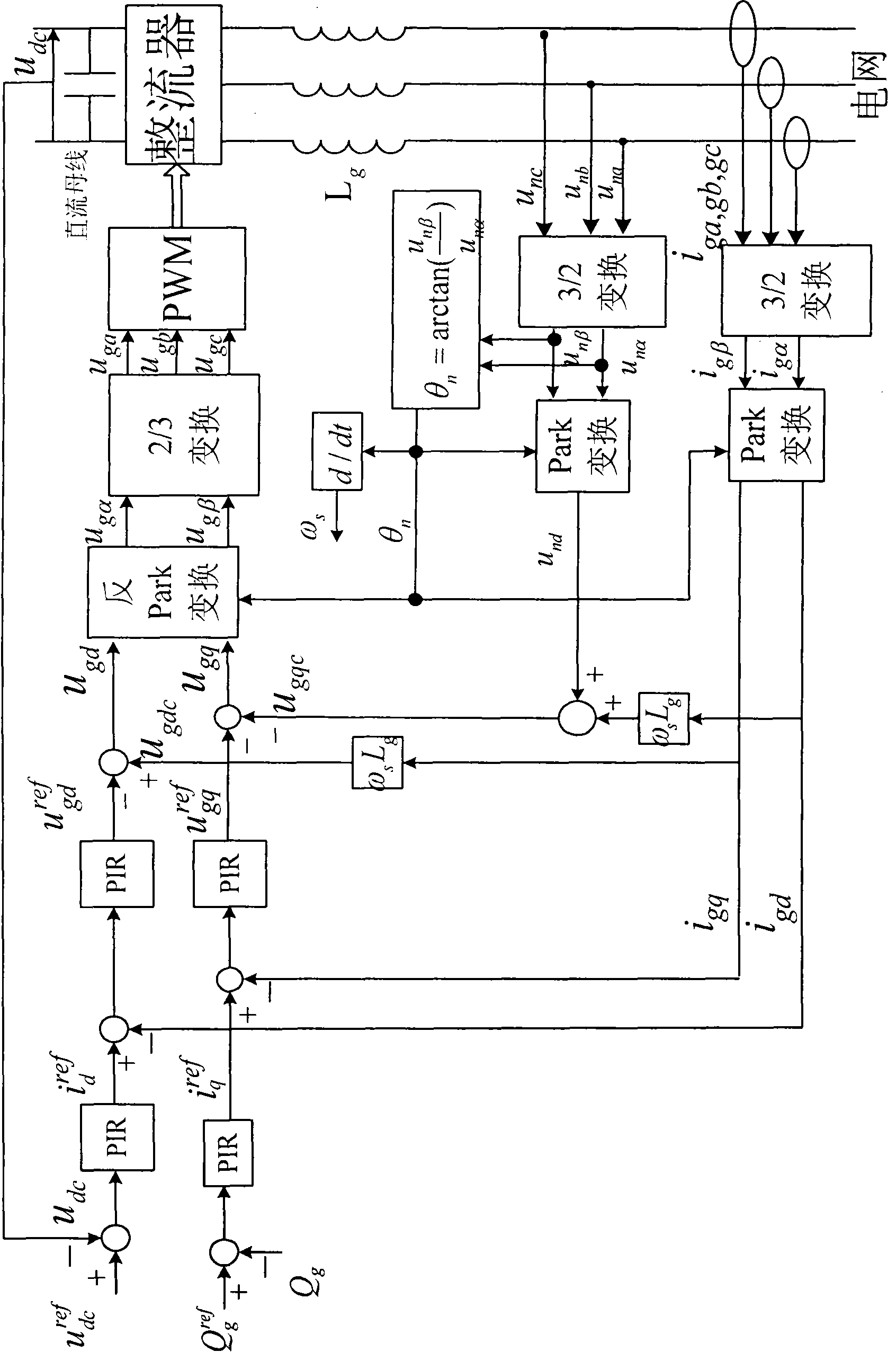
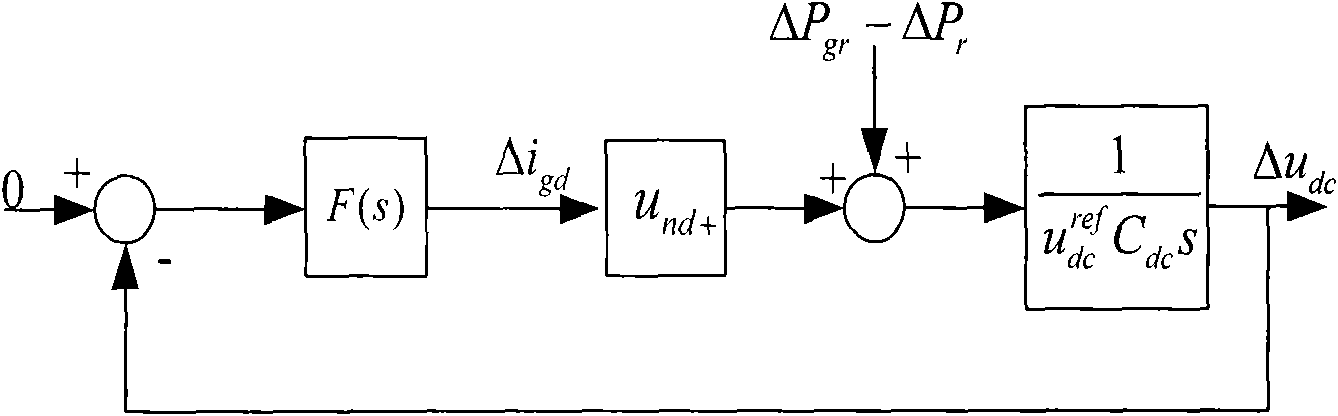
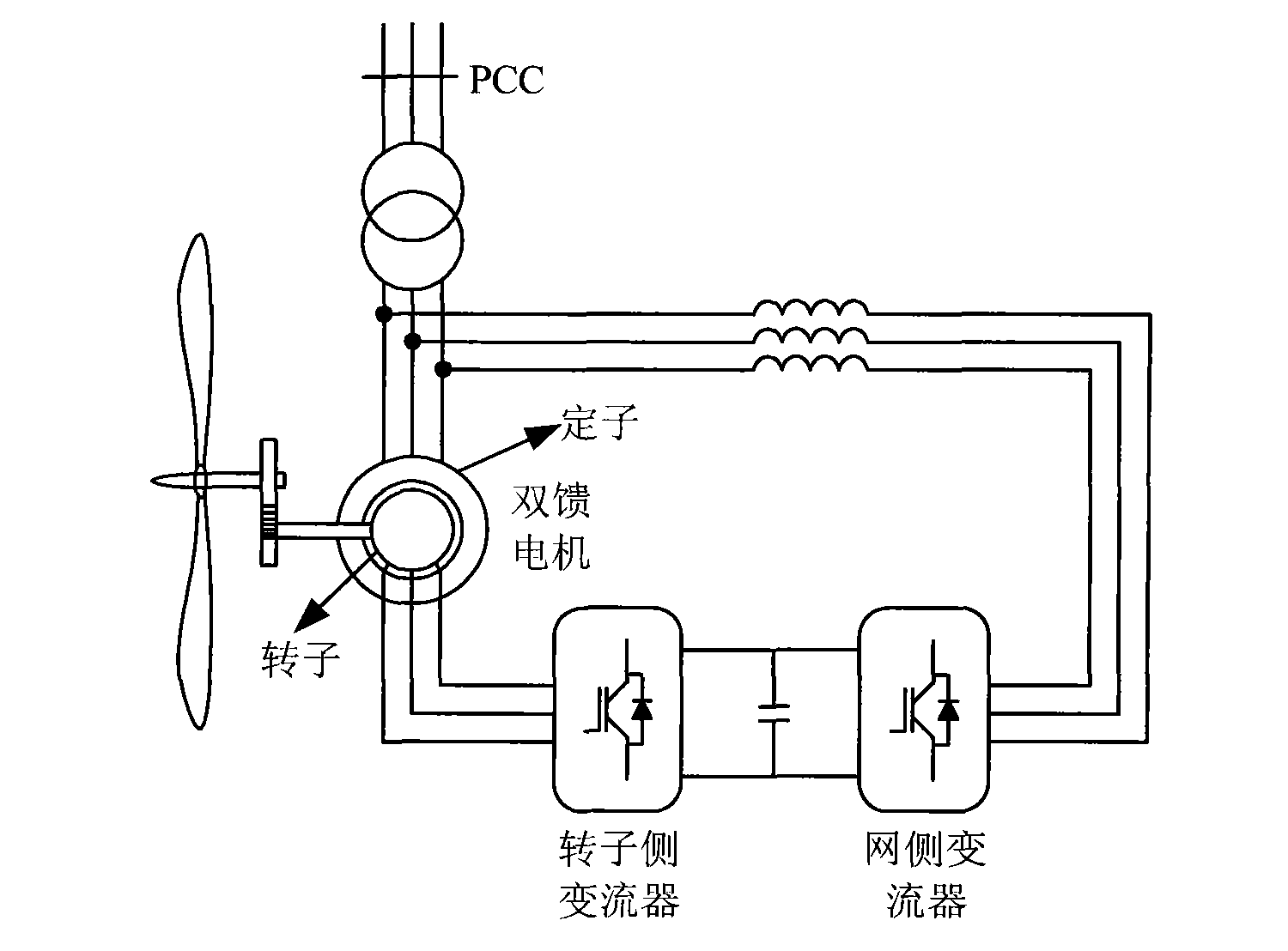
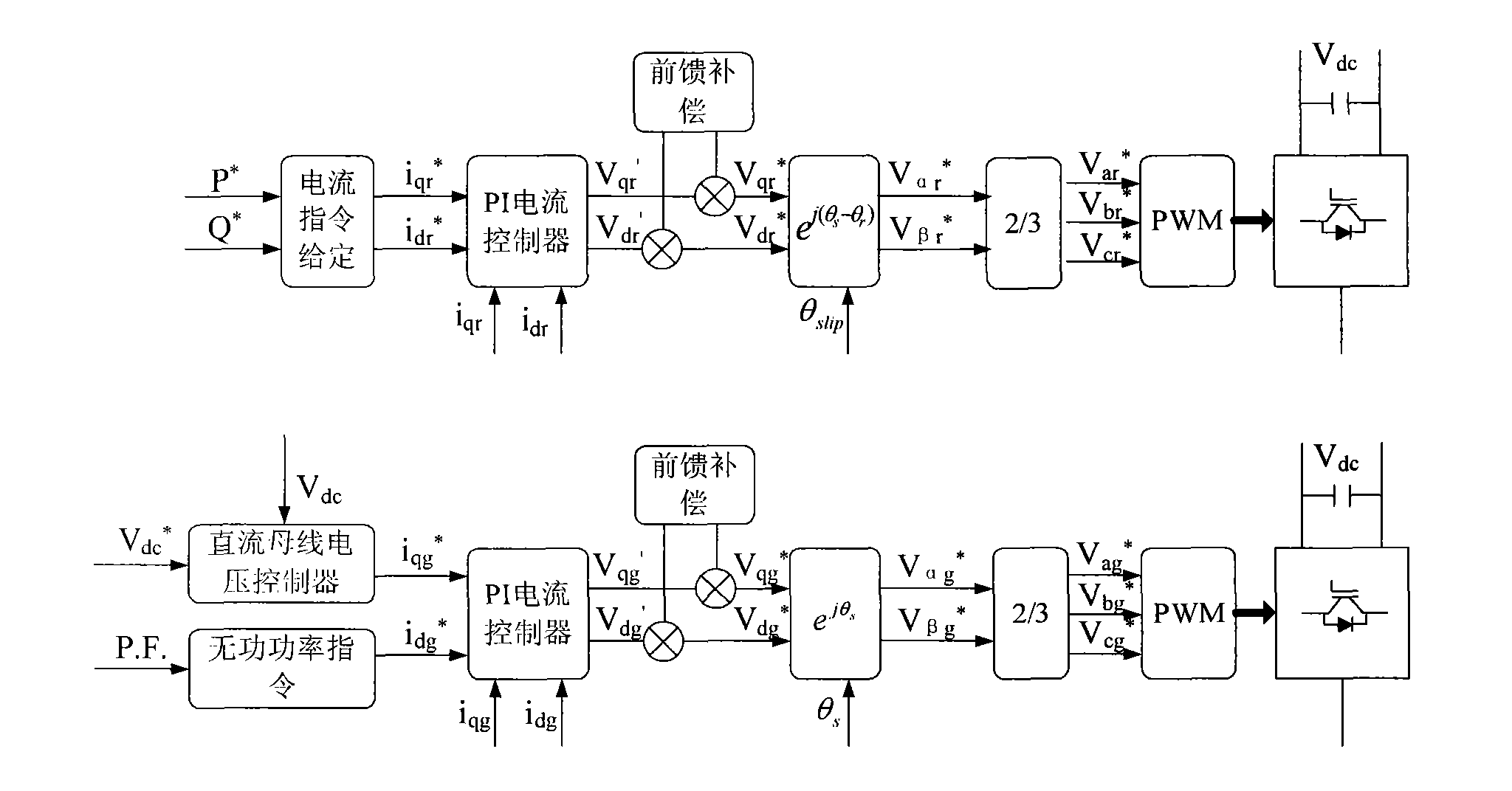
Control method of net-side rectifier of double-fed asynchronous wind power generator under unbalanced network voltage
InactiveCN101557190ASuppression of doubling AC volumeReduce the effects of harmonicsElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsUltrasound attenuationHarmonic
A control method of a net-side rectifier of a double-fed asynchronous wind power generator designed by the invention can realize zero steady-state error tracking of zero frequency and frequency-doubled component in an input signal of a forward channel as well as the complete attenuation of zero frequency and frequency-doubled interference by changing a traditional PI adjustor to a PIR adjustor and setting a set frequency Omega[c] in the PIR adjustor to a double synchronous rotation angular speed Omega[s], thus relieving the influence caused by harmonic generated due to unbalanced network voltage. Only through the replacement of the adjustor, the method realizes the control over the net-side rectifier of the generator under the condition of unbalanced network voltage, is simple in modification and obvious in effect, does not relate to the design of complicated parts and is easy for implementation.
Owner:北京清能华福风电技术有限公司
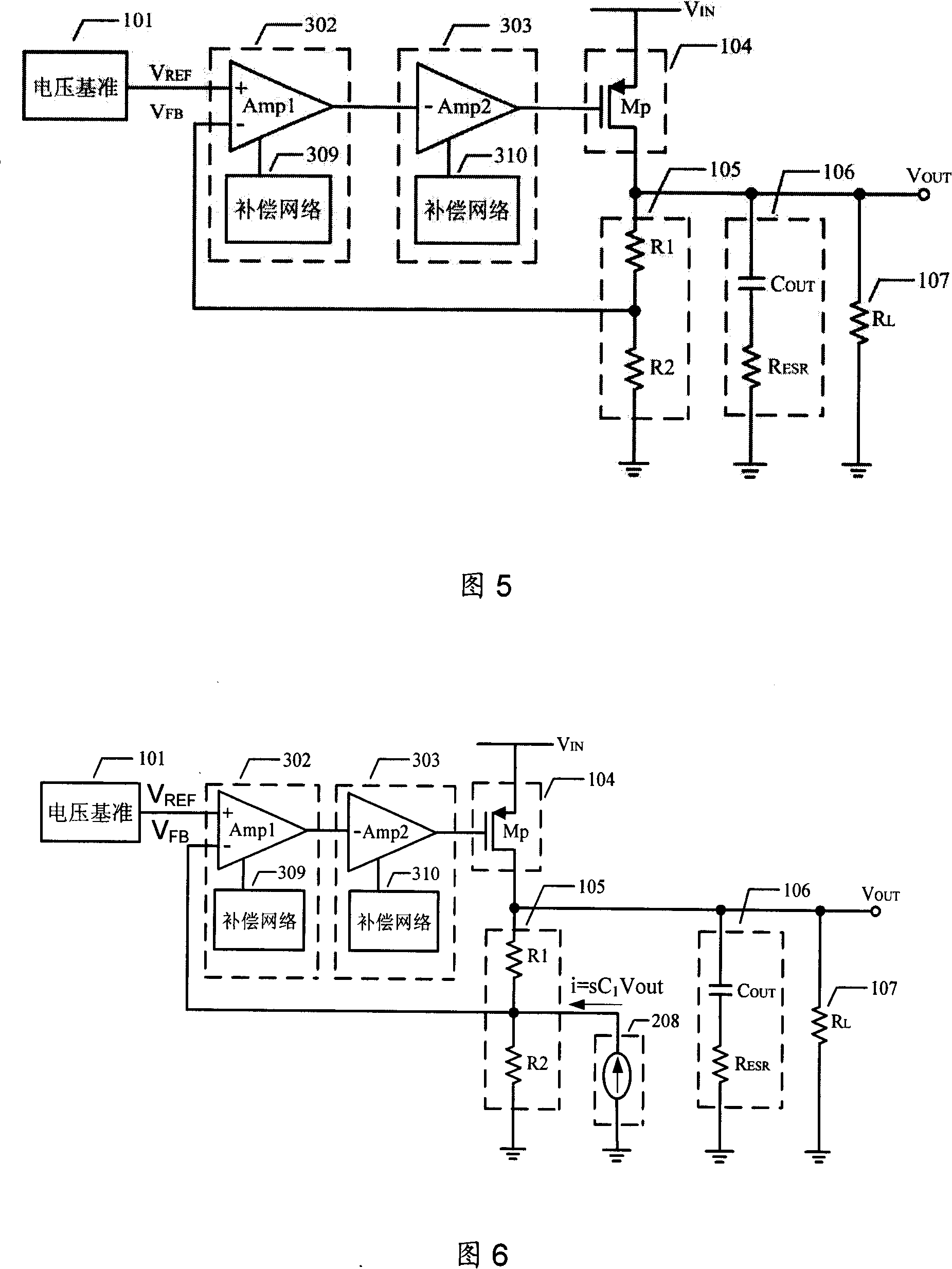
Low pressure difference linearity voltage stabilizer for enhancing performance by amplifier embedded compensation network
InactiveCN101140478AImprove performanceIncrease phase marginElectric variable regulationCapacitanceLinear regulator
A low voltage differential linear regulator utilizes an embedded compensation network in an amplifier to improve performance, which embeds a compensation network composed of resistances and capacitances into an amplifier to increase one or a plurality of pole-zero pairs with their pole-zero frequency lower than pole frequency in a transfer function of a feedback loop without changing static operating point of the amplifier and increasing static current. Frequency of the pole-zero pairs can be accurately confirmed to enhance stability of the feedback loop of the low voltage differential linear regulator, expand loop unit gain bandwidth and increase phase margin and DC and low-frequency gain of the loop, thus enhancing performance of the low voltage differential linear regulator.
Owner:BEIJING MXTRONICS CORP +2
Synthesis method for an active polyphase filter
InactiveUS7098731B1Improve the level ofOscillations generatorsTransmissionElectrical conductorSynthesis methods
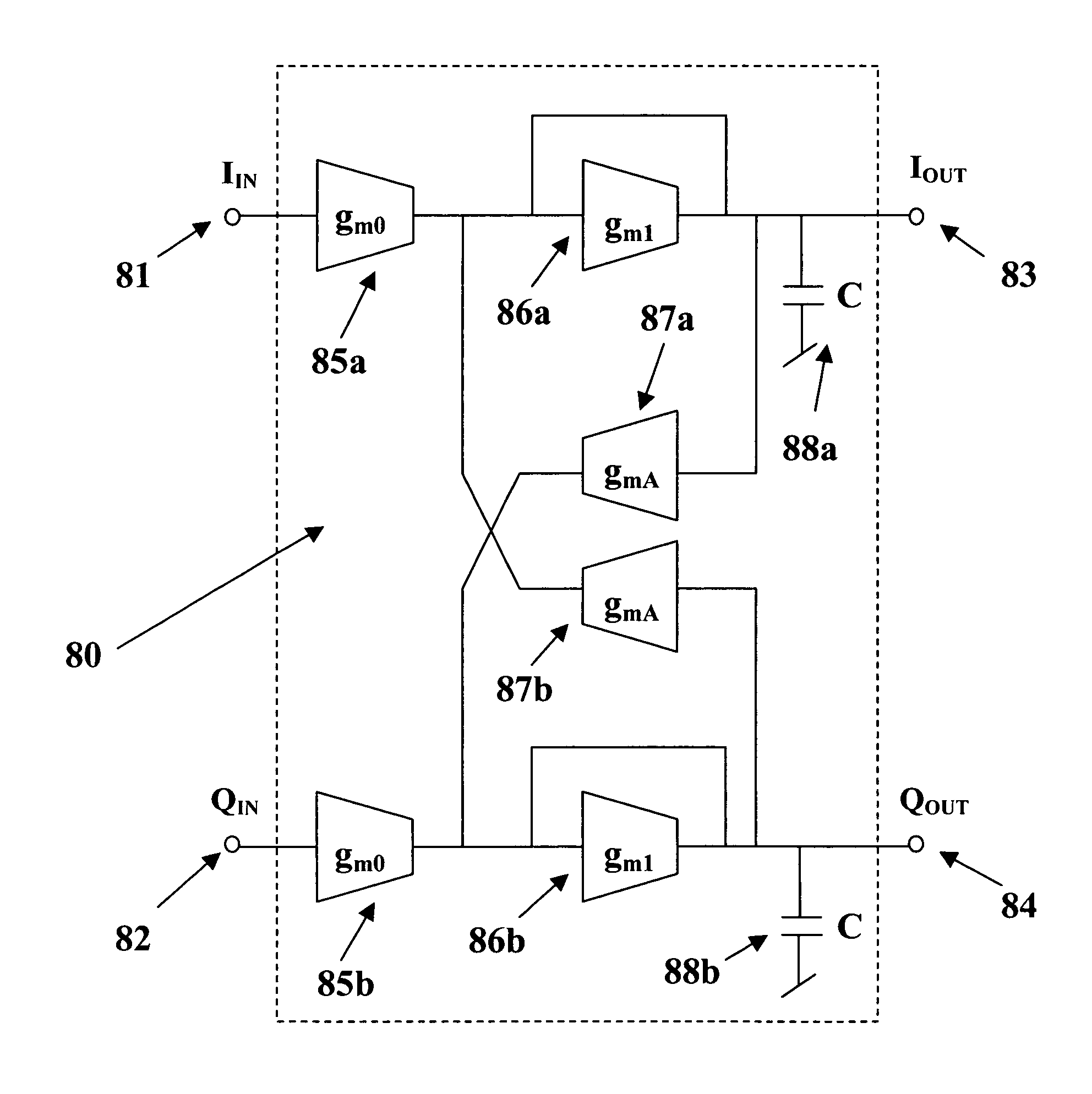
A fully-integrated continuous-time active complex bandpass IF filter that may contain transmission zeros yielding much sharper roll-off than that of an all-pole filter is implemented using transconductors and capacitors only. Each of the filter second-Order sections realizes a pair of complex poles and a may realize a double imaginary axis zero. Since the transconductors are electronically tunable the positions of filter zeros and poles are adjustable using an automatic tuning system. In each filter section the value of different transconductors are modified to separately change the pole frequency, its Q-factor and the zero frequency. Each pole and zero are separately tuned, which achieves a higher level of tuning accuracy than in case where all poles and zeros were adjusted simultaneously.
Owner:WYSZYNSKI ADAM S
Traceable calibration method and calibration device for dynamic characteristic of big pressure sensor
InactiveCN101358894AEffective protectionWide frequency band coverageFluid pressure measurementForce/torque/work measurement apparatus calibration/testingUltra short pulseTransducer
The invention relates to a method of the dynamic characteristic traceability calibration of a high-pressure transducer, and calibration equipment, belonging to the technical field of pressure transducer. The method is as follows: exerting a static pressure on a high-pressure transducer to be calibrated, for realizing a frequency area to be zero frequency traceability calibration; on the basis, exerting an ultra-short pulse motivating pressure, testing the frequency responding characteristic of the high-pressure transducer through a test or a metrologic instrument. The method has the advantages that the method uses a common hydraulic pressure calibration method to realize the dynamic characteristic traceability calibration of the high-pressure transducer; because of adopting a pre-exerting static pressure processing method, the reversed pressure received by the transducer to be tested is reduced, thus effectively protecting the expensive transducer, and the frequency service range of the calibration method is 0-1MHz; the pressure value is as high as 800MPa, the calibration method is advanced, has the creative thought, is worthy of being popularized and learned; the adopted calibration equipment has simple structure, low cost, safe calibration process, no damage to the transducer, high calibration pressure value and wide frequency service range which can cover the zero frequency for traceability calibration, and the calibration equipment is worthy of being adopted and popularized.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
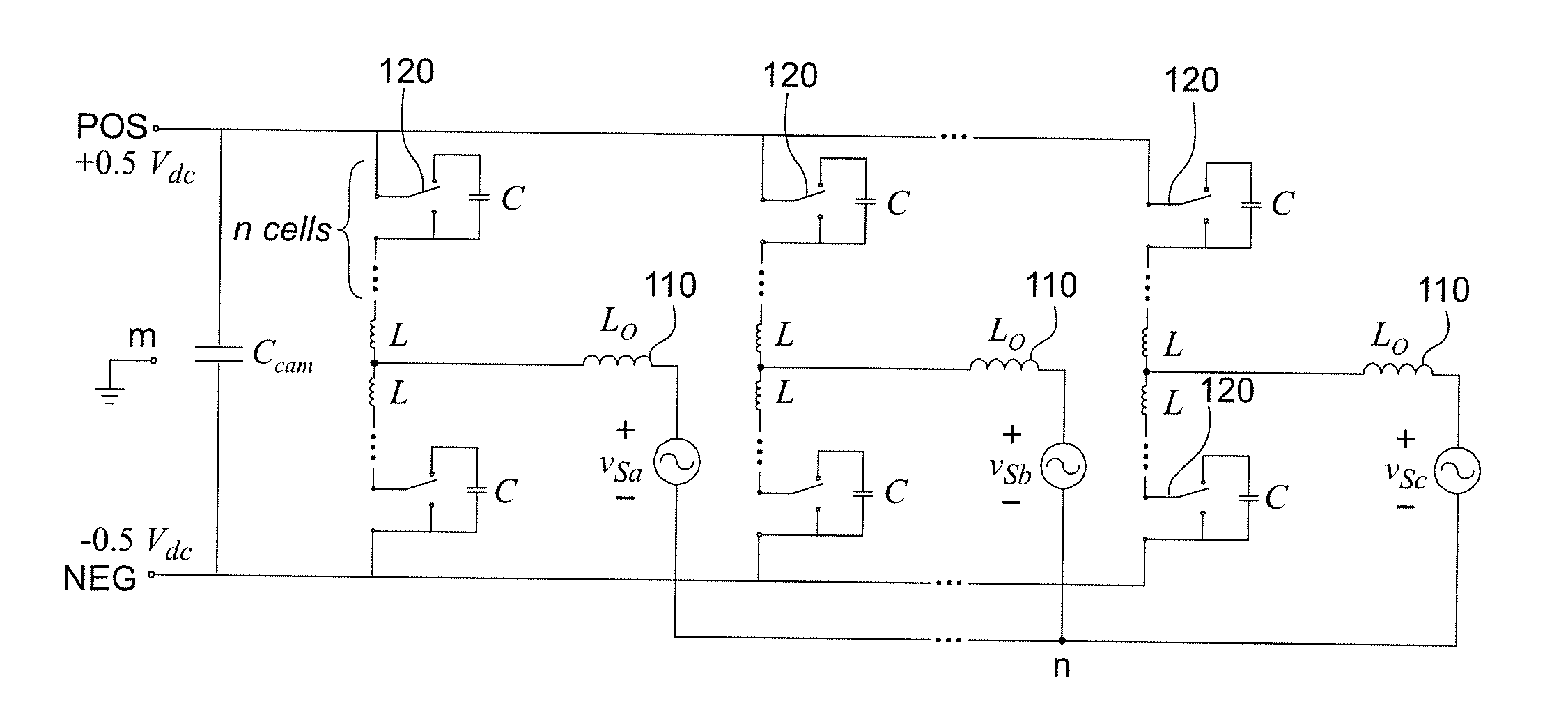
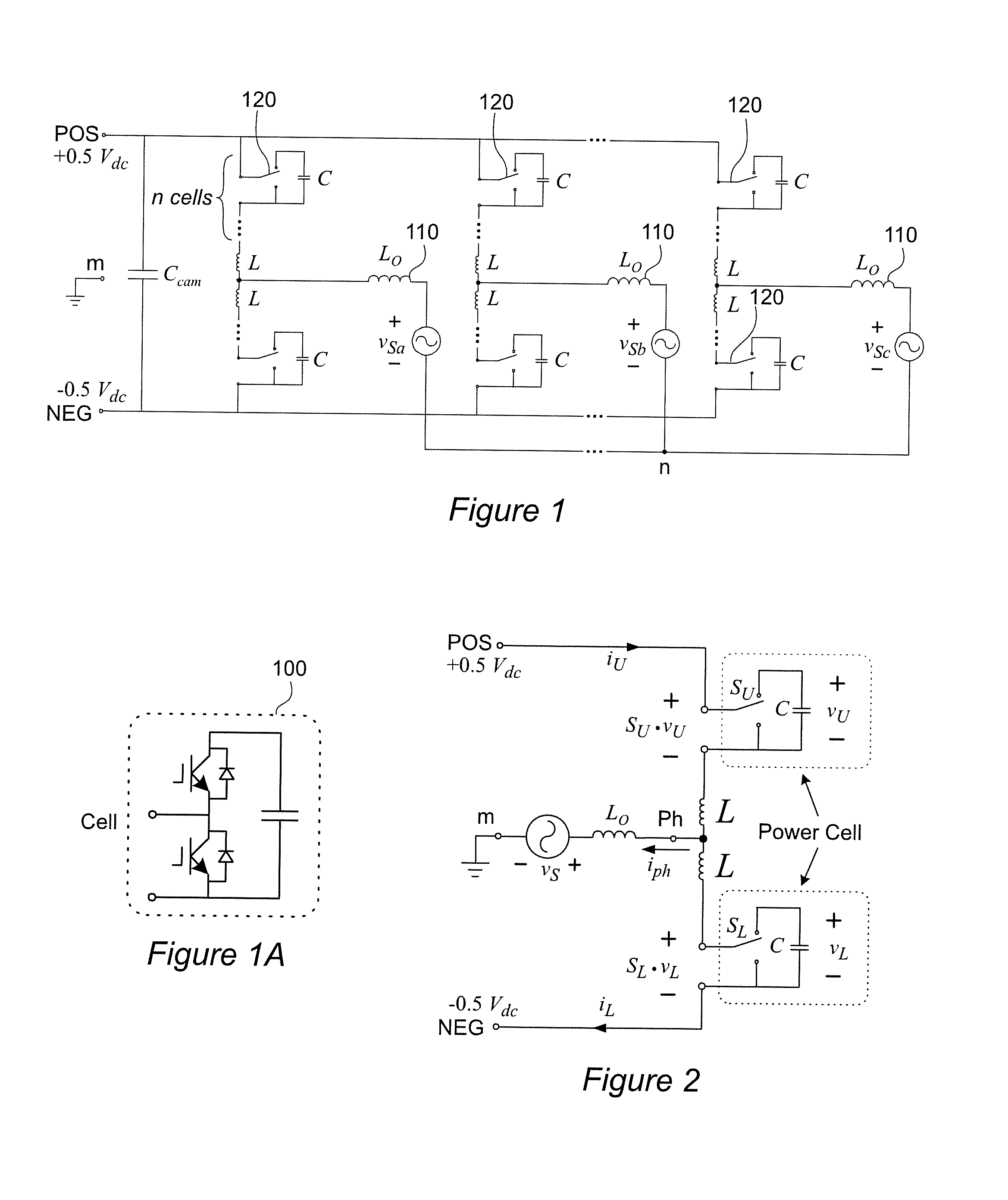
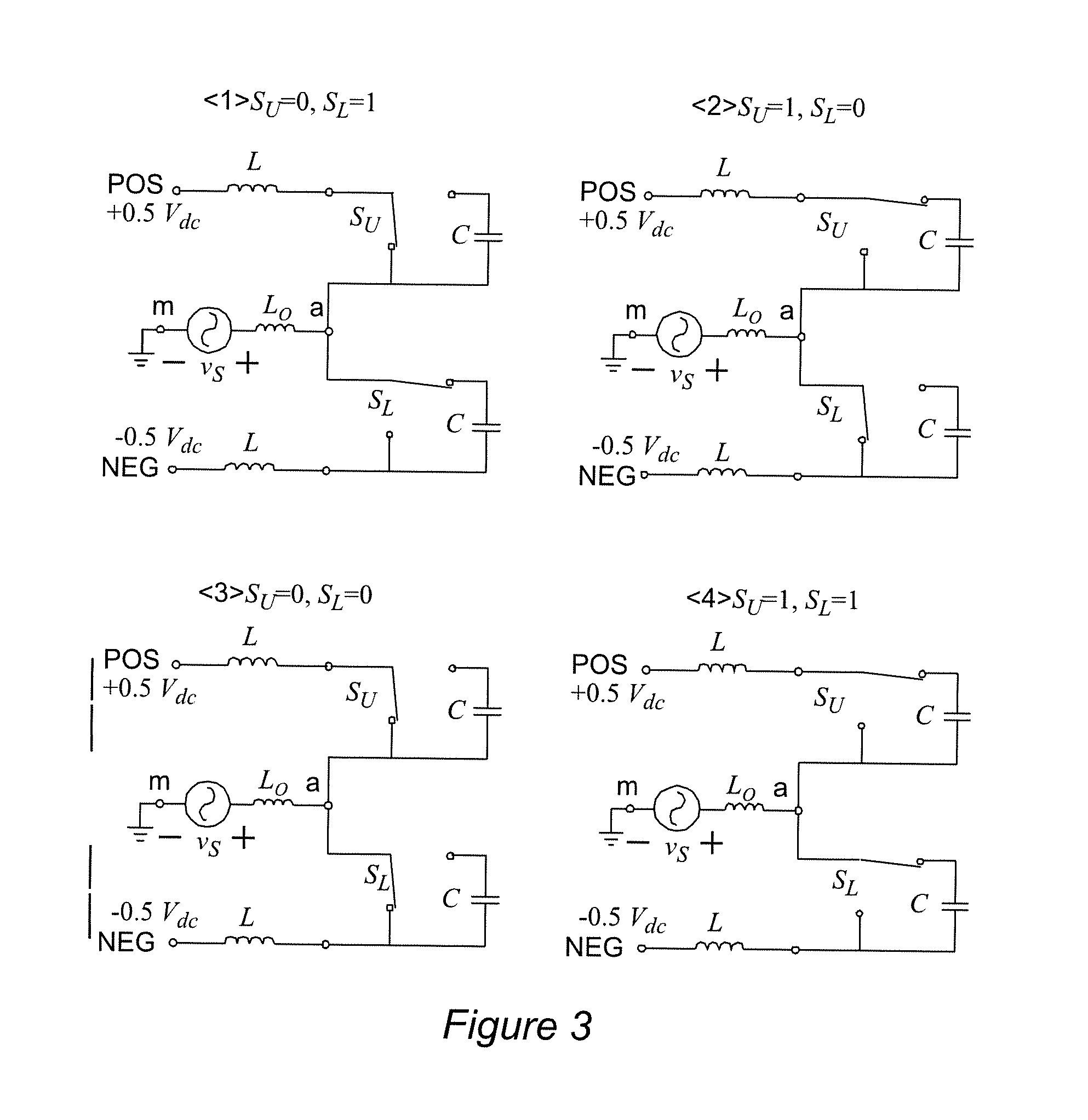
Power-Cell Switching-Cycle Capacitor Voltage Control for Modular Multi-Level Converters
ActiveUS20150207434A1Reduced capacitor valueReduce size requirementsAc-dc conversionSwitching cycleWave shape
In a modular multi-level power converter, additional switching states are interleaved between main switching states that control output voltage or waveform. The additional switching states provide current from a DC-link to charge capacitors in respective modules or cells to an offset voltage from which the capacitor voltages are controlled toward a reference voltage during each switching cycle rather than being allowed to build up over a period of an output waveform of variable line frequency, possibly including zero frequency. Since the switching cycle is much shorter than the duration of a line frequency cycle and the capacitor voltages are balanced during each switching cycle, output voltage ripple can be limited as desired with a capacitor of much smaller value and size than would otherwise be required.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
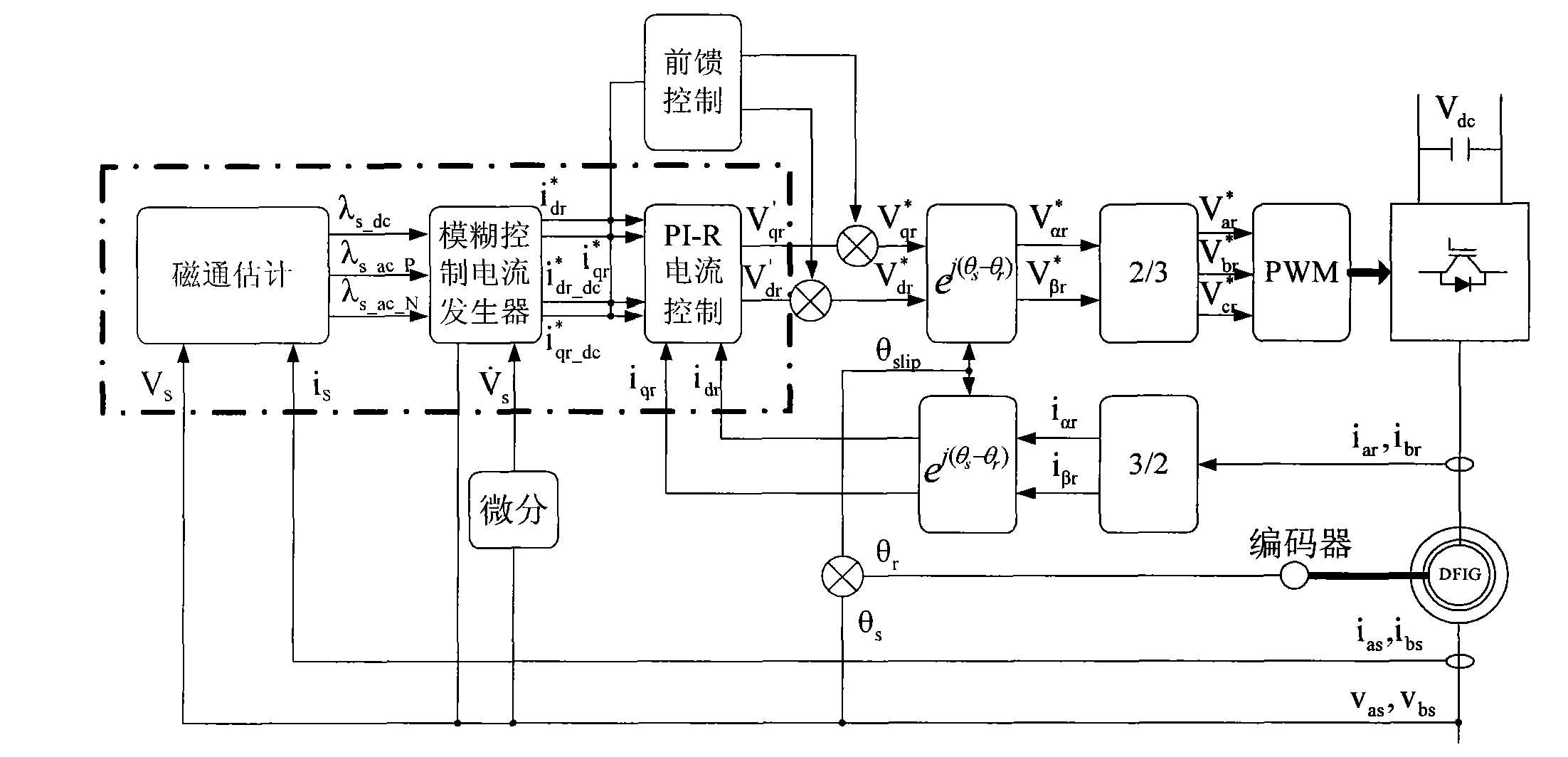
Low-voltage traversing control method for double-fed wind power generation system
InactiveCN102097816AImprove performanceLow costSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsWind energy generationDouble-timeLow voltage
The invention discloses a low-voltage traversing control method for a double-fed wind power generation system. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) detecting zero frequency transient flux component of a motor; 2) when the motor has zero frequency transient flux component outburst, controlling a rotor current transformer and a network current transformer, and attenuating the zero frequency transient flux components of the current transformers; and 3) controlling torque current and power grid reactive compensation current to inhibit the growth of harmful voltage and prevent the formation of harmful current. The method can really realize the elimination of the transient flux caused by sudden decline and sudden rise of a stator voltage and inhibit negative sequence current so as to avoid offline of the fan power generation system at the same time of protecting the rotor current transformer and the network current transformer; meanwhile, by the method, double times ultrahigh dangerous voltage of rotor induction caused by zero frequency transient flux superposition when the voltage is recovered can be prevented, and power grid-friendly intelligent low-voltage traversing is realized.
Owner:徐隆亚 +2
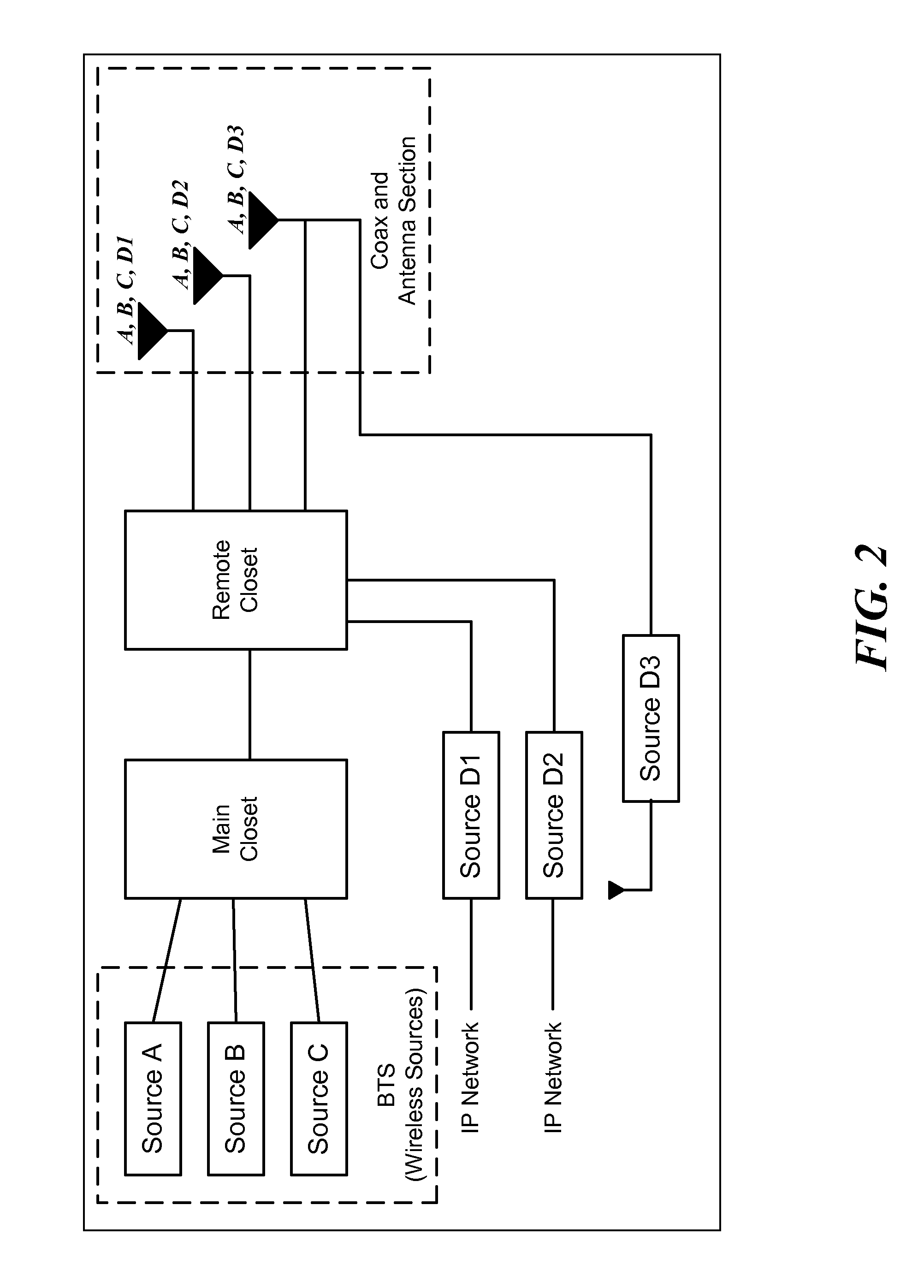
Multiple data services over a distributed antenna system
InactiveUS8195224B2Avoid spendingReduce energy costsSite diversityNetwork traffic/resource managementDistributed antenna systemGps receiver
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM WIRELESS
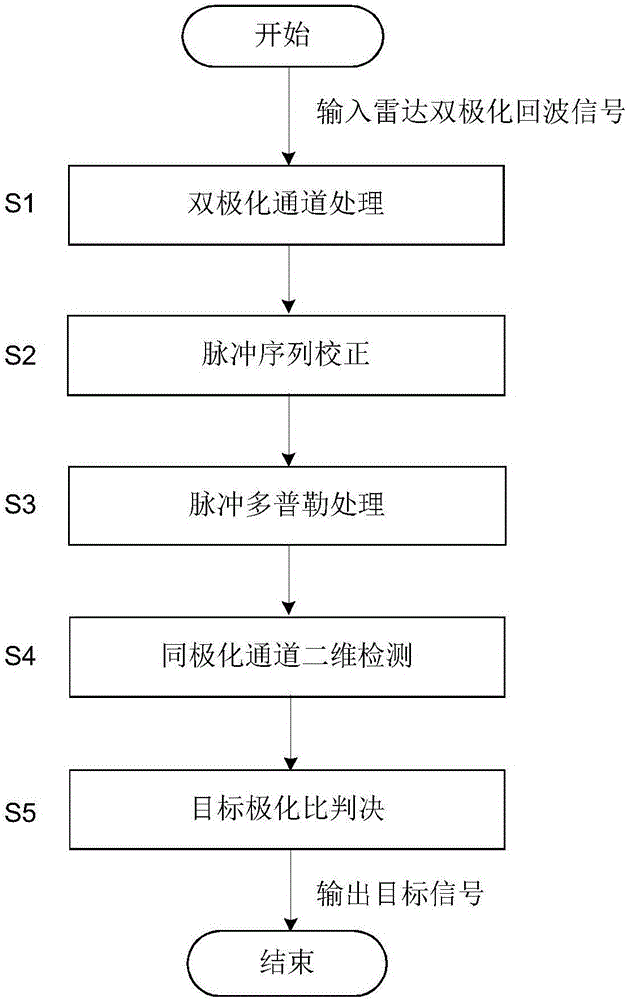
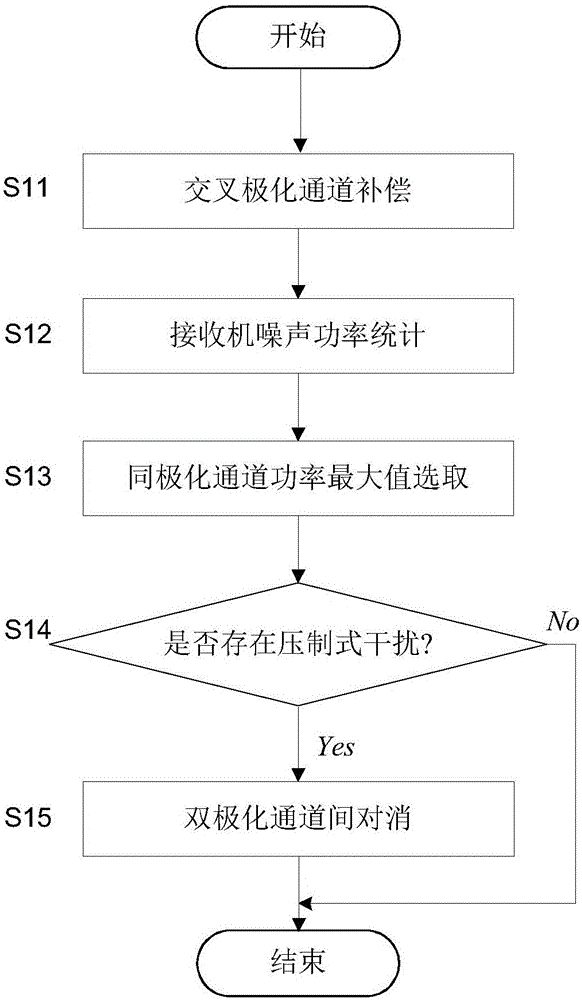
Pulse Doppler radar polarization anti-jamming method
ActiveCN106125053ASuppress interferenceImprove the probability of correct detection of the targetWave based measurement systemsAnti jammingFrequency spectrum
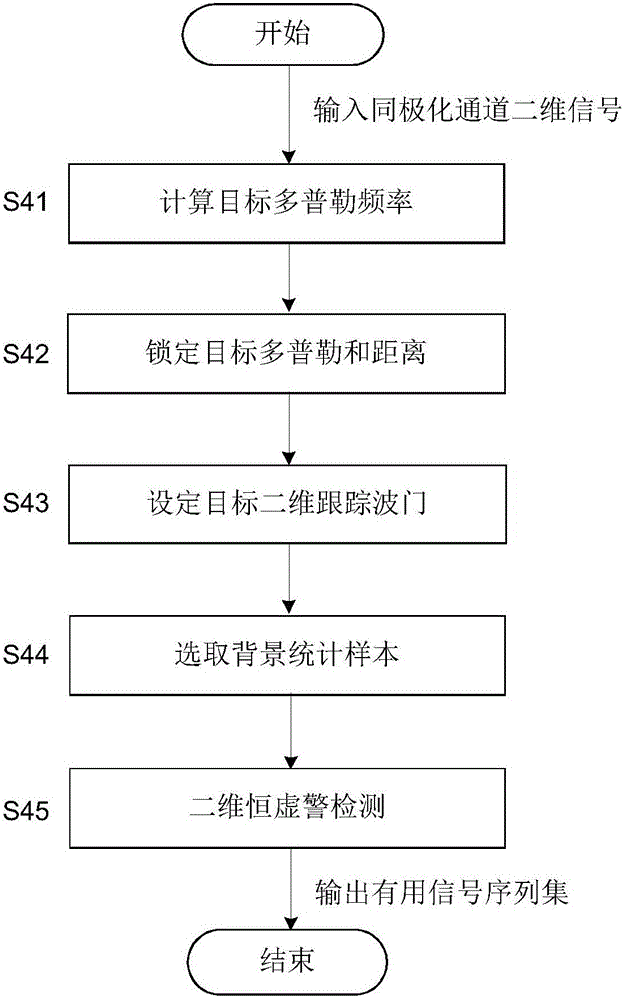
The present invention provides a pulse Doppler radar polarization anti-jamming method under a complicated interference environment. By utilizing the method of the present invention, the inhibition capability aiming at various interference, such as chaffs, active suppression, cheat, etc., can be improved substantially, and the targets can be detected effectively. The method is realized by the following technical scheme of inputting a radar dual polarization echo signal, determining whether the active suppression-type interference exists, when the suppression-type interference exists, carrying out the polarization cancellation; then calculating the target signal walking time between the front and back pulses, and carrying out the range walking correction on a pulse sequence; and then carrying out the phase-coherent accumulation on a dual polarization channel, shifting the zero to a frequency spectrum center in a frequency shift manner, identifying the channel number of a target in a Doppler-range two-dimensional matrix, setting a two dimensional tracking gate of the target, and carrying out the two dimensional constant false alarm detection in the tracking gate; finally, carrying out the target polarization ratio detection determination, and outputting a signal passing the detection determination as a target signal after the interference inhibition, thereby improving the correct detection probability of the target.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
System and method for compressing and decompressing images
InactiveUS6282322B1Optimization parametersPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionPattern recognitionImage compression
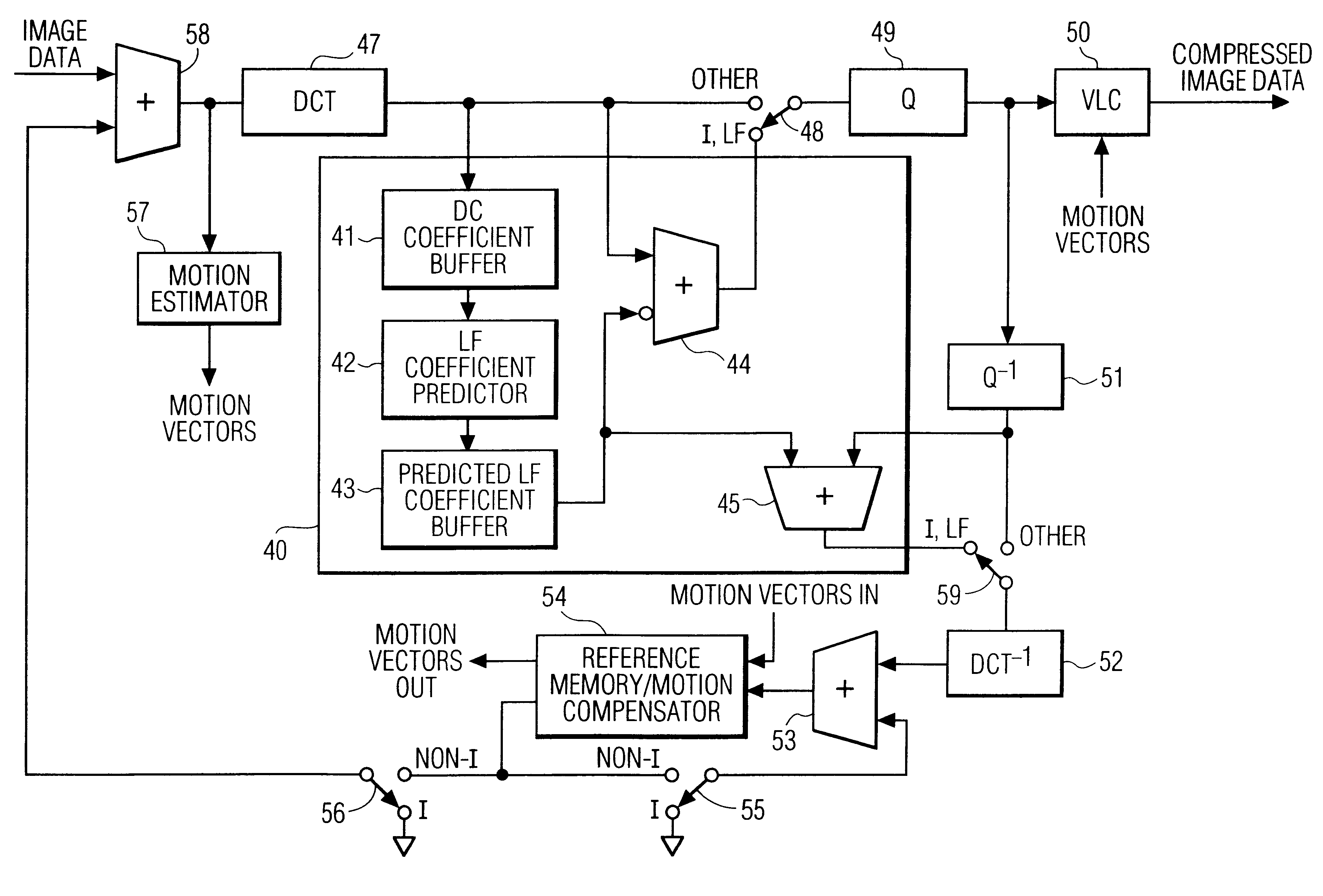
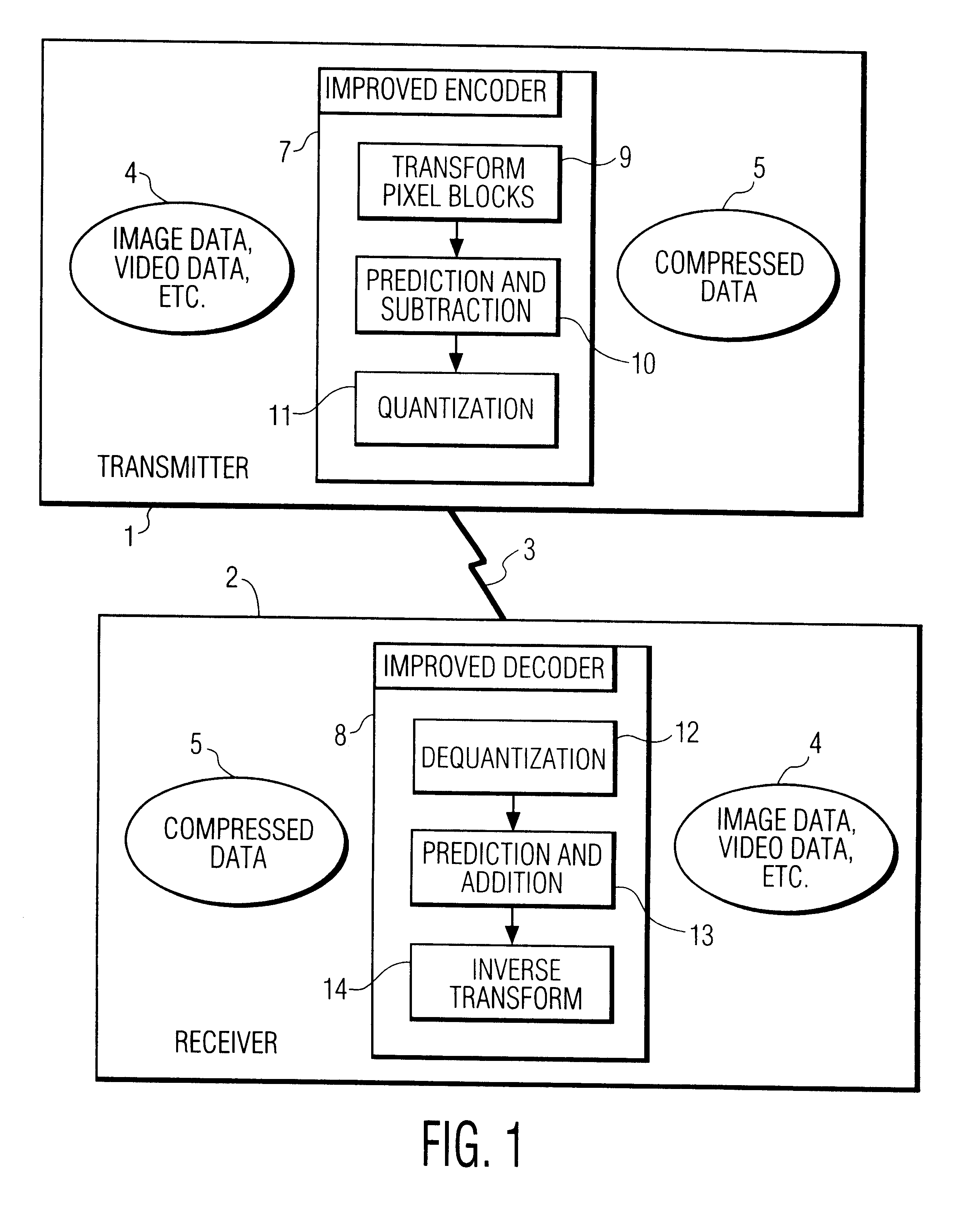
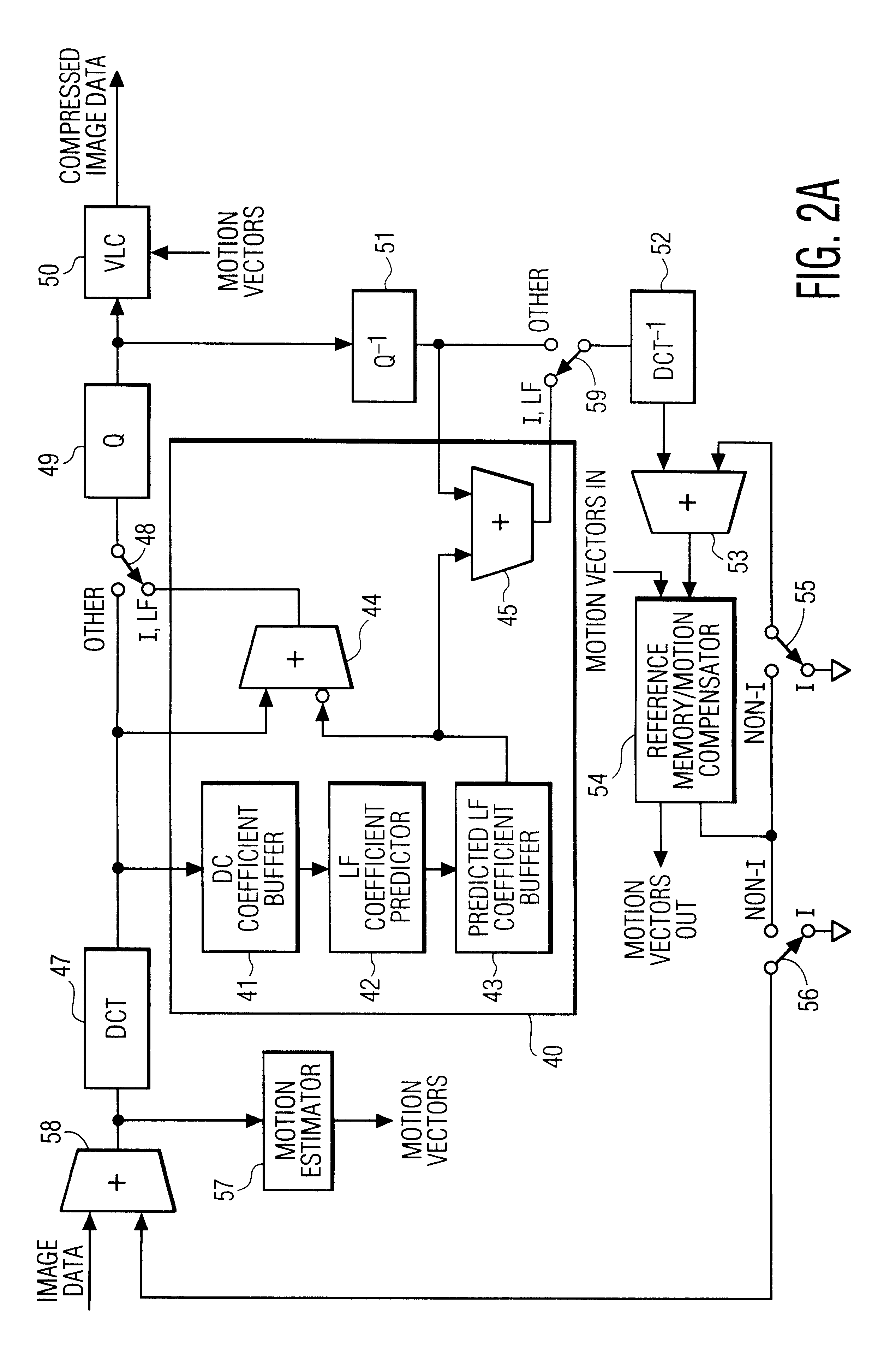
This invention relates to systems and methods for increasing image compression. The systems and methods are improvements applicable to encoder / decoders which compress images by, inter alia, transforming non-overlapping independent blocks of pixels into a frequency domain and then quantizing the resulting frequency domain coefficients. The invention achieves increased compression by predicting low frequency coefficients of a block from, preferably, the average intensities, or zero frequency coefficients, of the block and its adjacent blocks. In an encoder, the low frequency coefficients are predicted, are then subtracted from the actual transform coefficients, and the difference coefficients are transmitted to a decoder. In the decoder, the low frequency coefficients are again predicted, are added to the received difference coefficients, and the resulting actual transform coefficients are used to reconstruct an image.
Owner:UNILOC 2017 LLC
Text-based fuzzy search
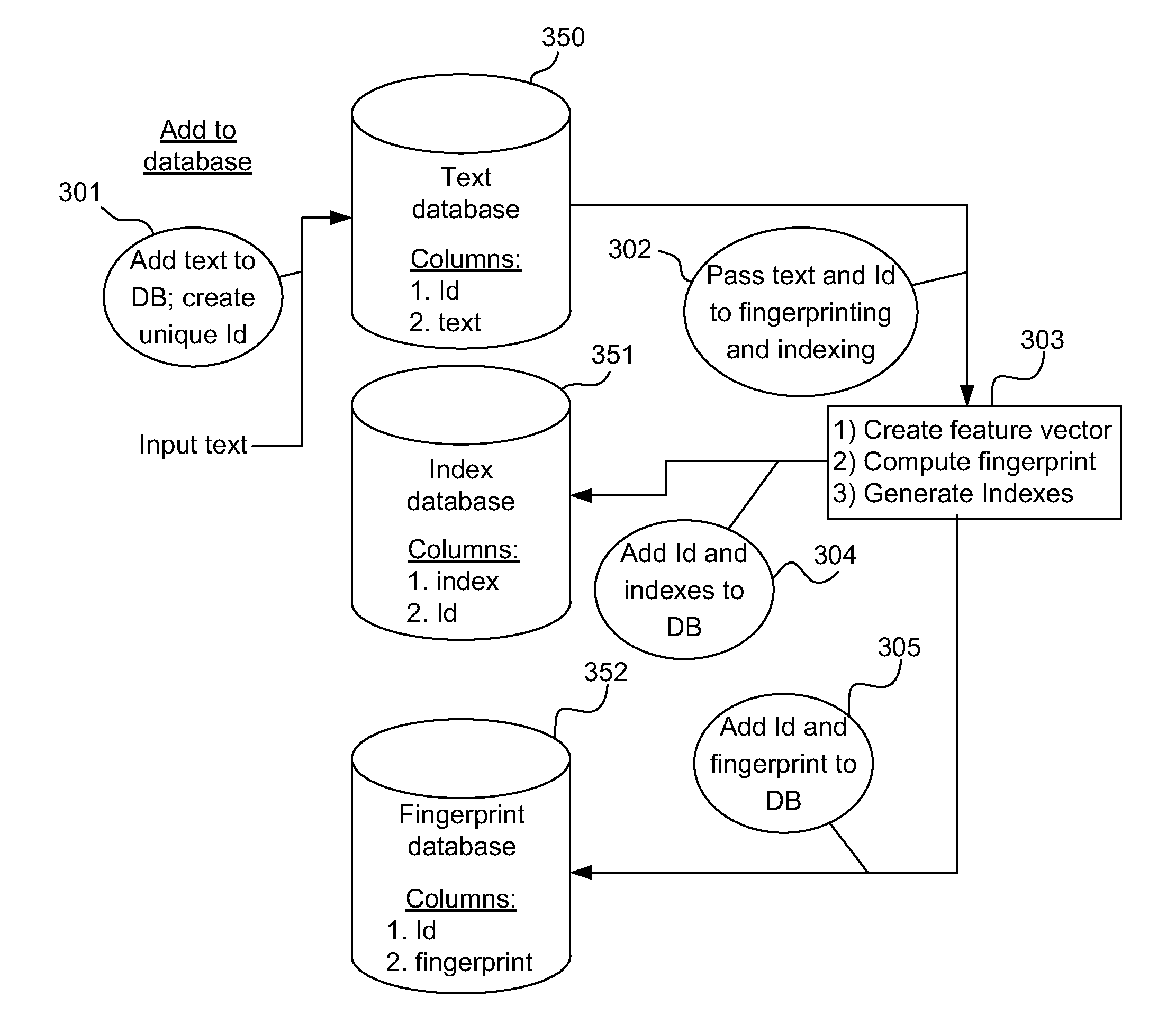
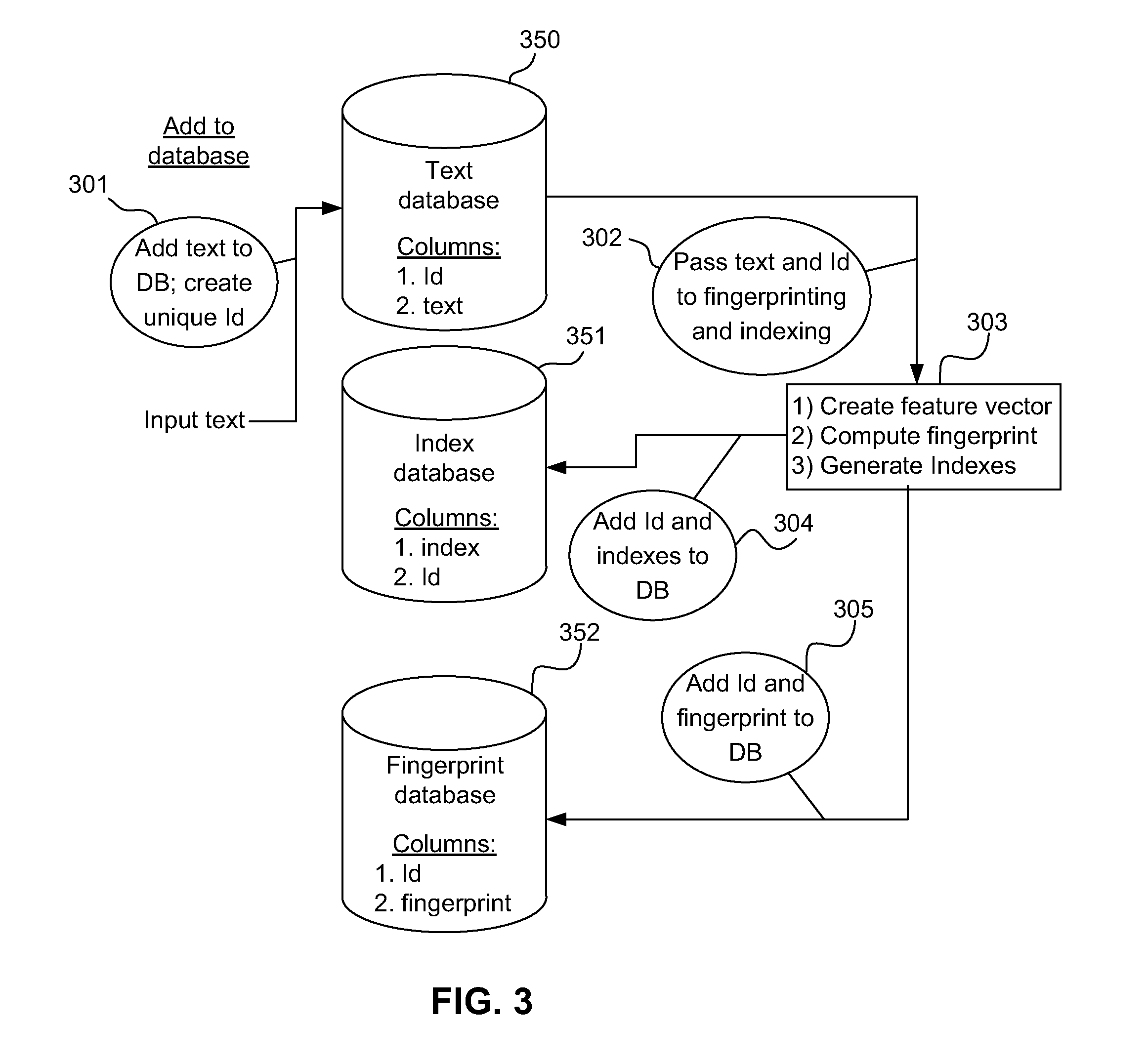
ActiveUS20120303663A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsFeature vectorFrequency of occurrence
An input feature vector is computed from an input text record, the input feature vector comprising one or more features, each feature including a subsequence of characters and a frequency of occurrence of the associated subsequence. A input fingerprint is generated out of the input feature vector by choosing one or more features with non-zero frequencies and alphabetizing the features chosen. One or more input indices are generated by alphabetizing features in the input fingerprint and concatenating features occurring in subsequent locations of the input fingerprint. The input text record is matched against a target text record if (1) one or more of the input indices match a target index corresponding to the target text record and (2) the corresponding input fingerprint matches a target fingerprint corresponding to the target text record. The target text record is outputted as a search result if it matches the input text record.
Owner:ROVI TECH CORP
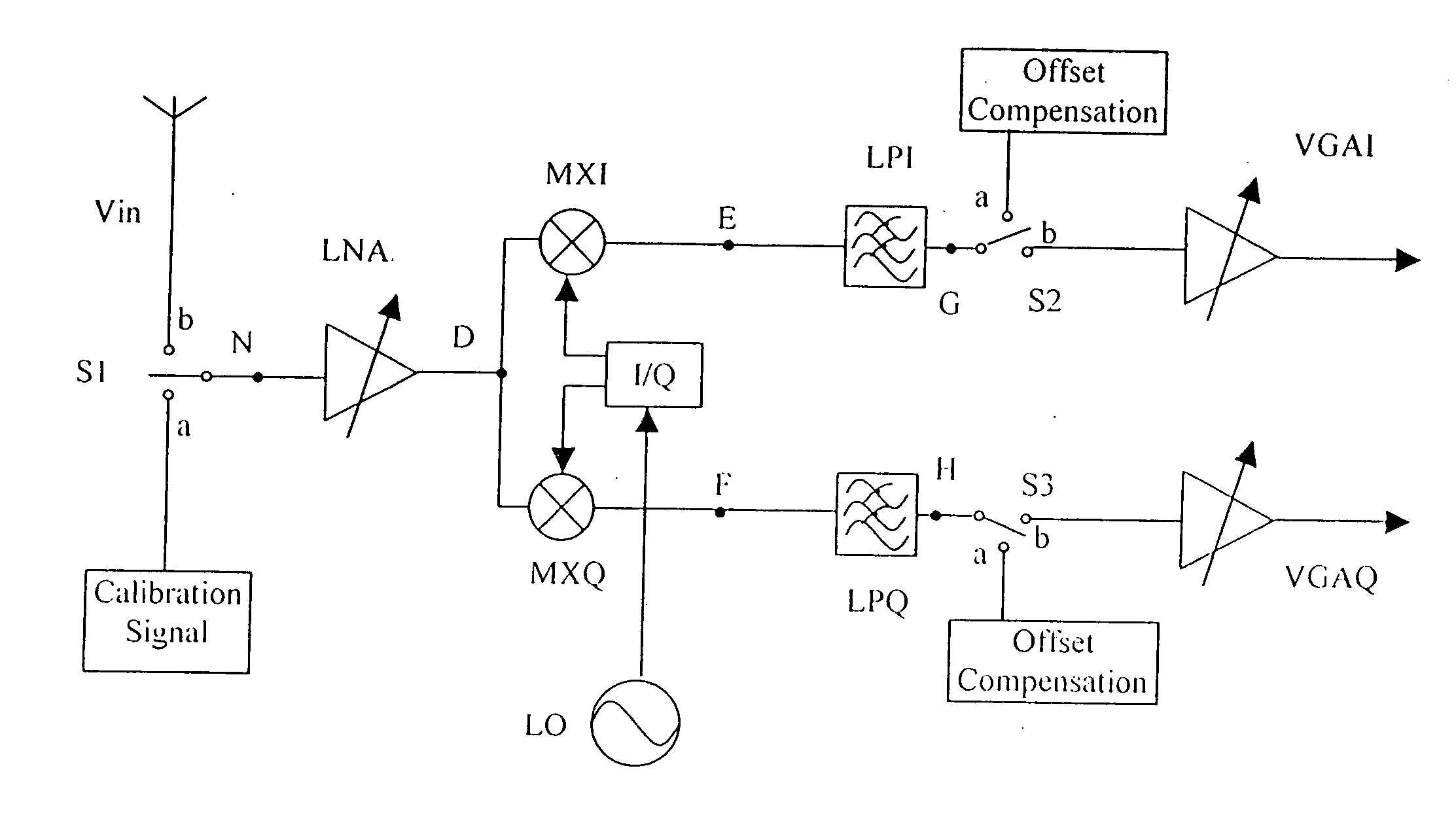
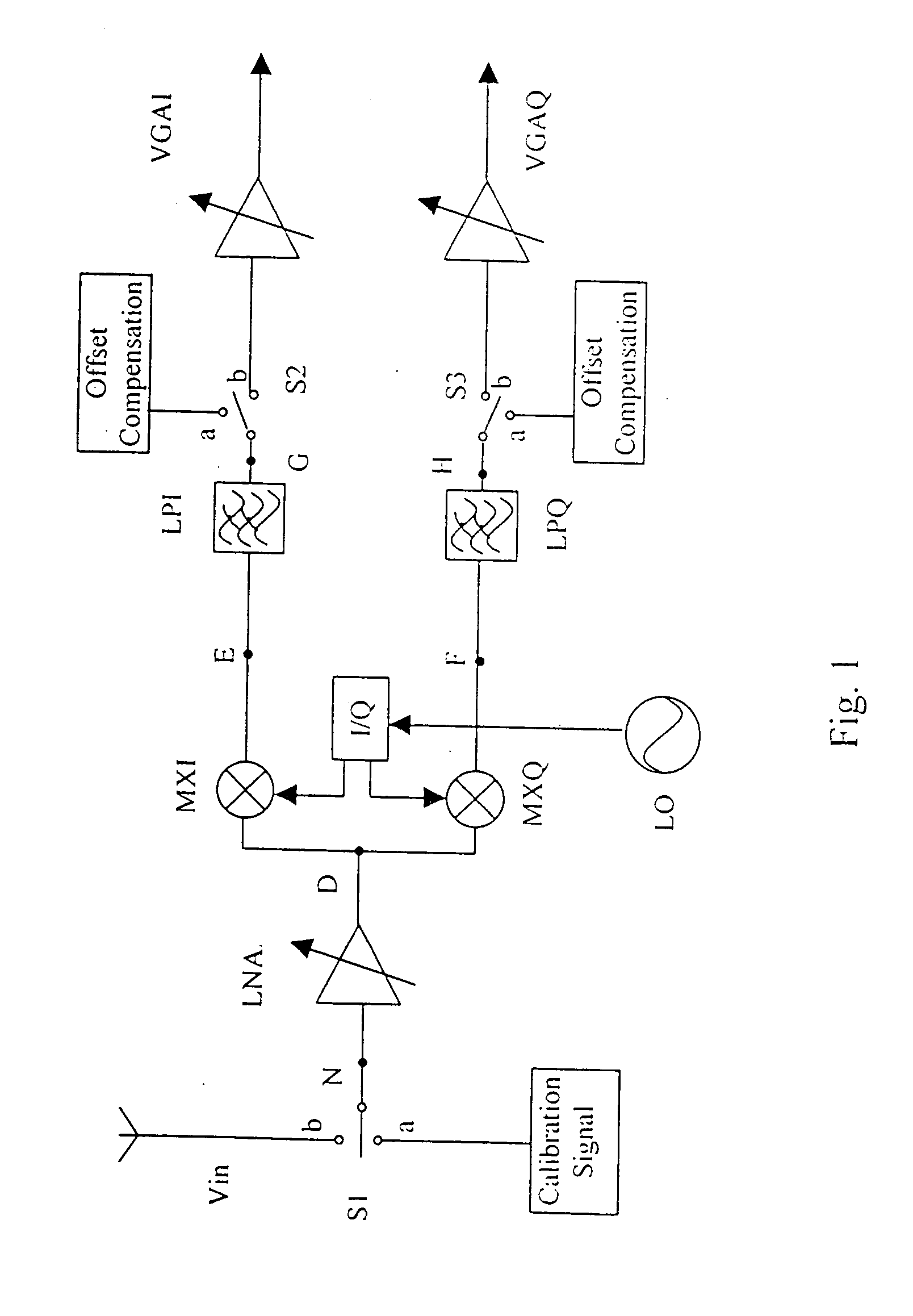
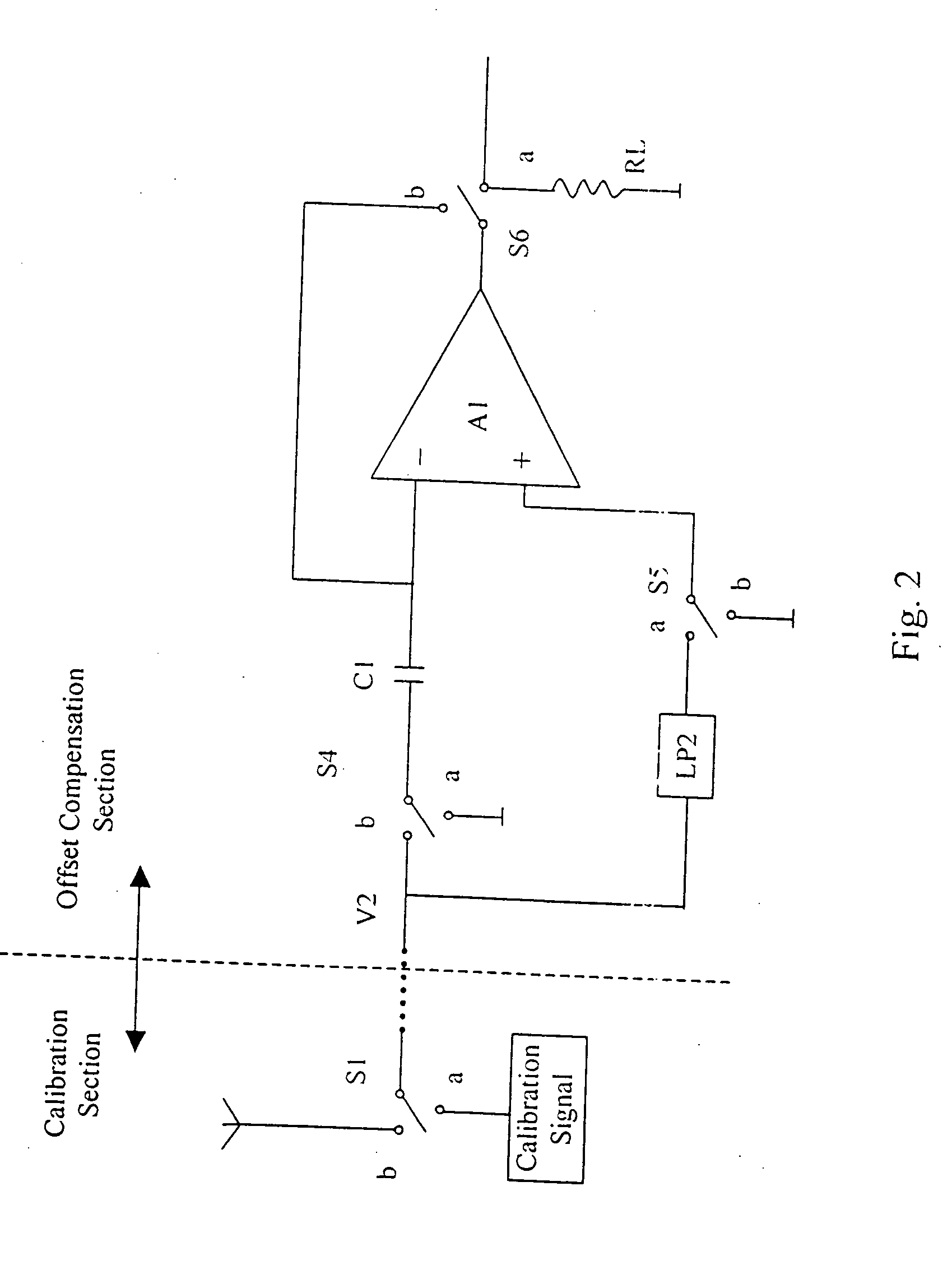
DC offset and 1/f noise compensation of a direct conversion receiver
InactiveUS20050221781A1Minimize noisePulse automatic controlTransmission monitoringIntermediate frequencyDirect-conversion receiver
In a direct conversion receiver with zero-frequency intermediate frequency (IF) signal, the DC offset and 1 / f noise of the IF signal is compensated by means of double-sampling. The first period of the doubling-sampling is a calibration phase, which stores the DC offset and the 1 / f noise. The second period is a signal flow phase during which the stored DC offset and 1 / f noise is connected in opposition with the IF signal to cancel the DC offset and 1 / f noise.
Owner:MARYLAND SEMICON
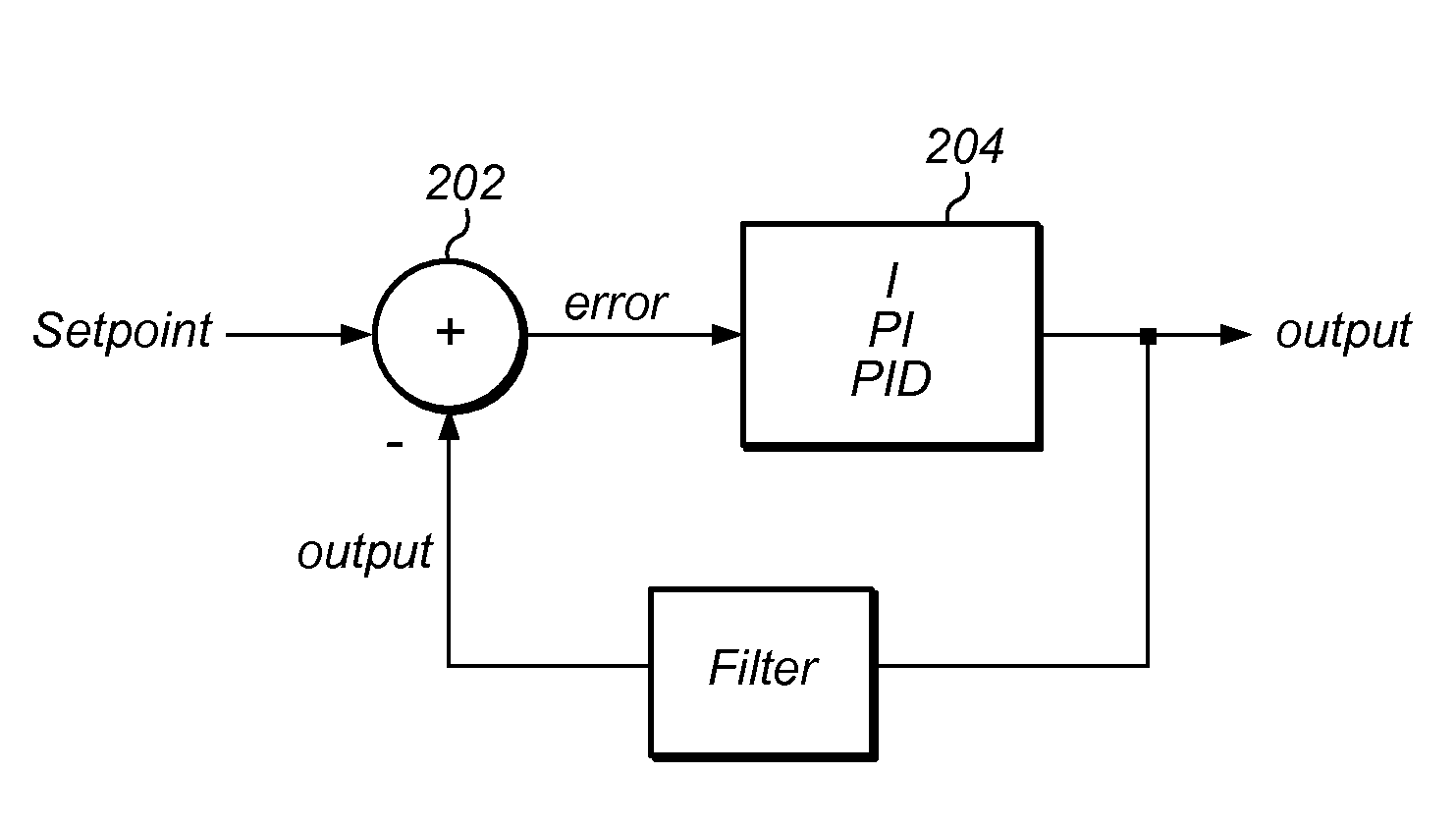
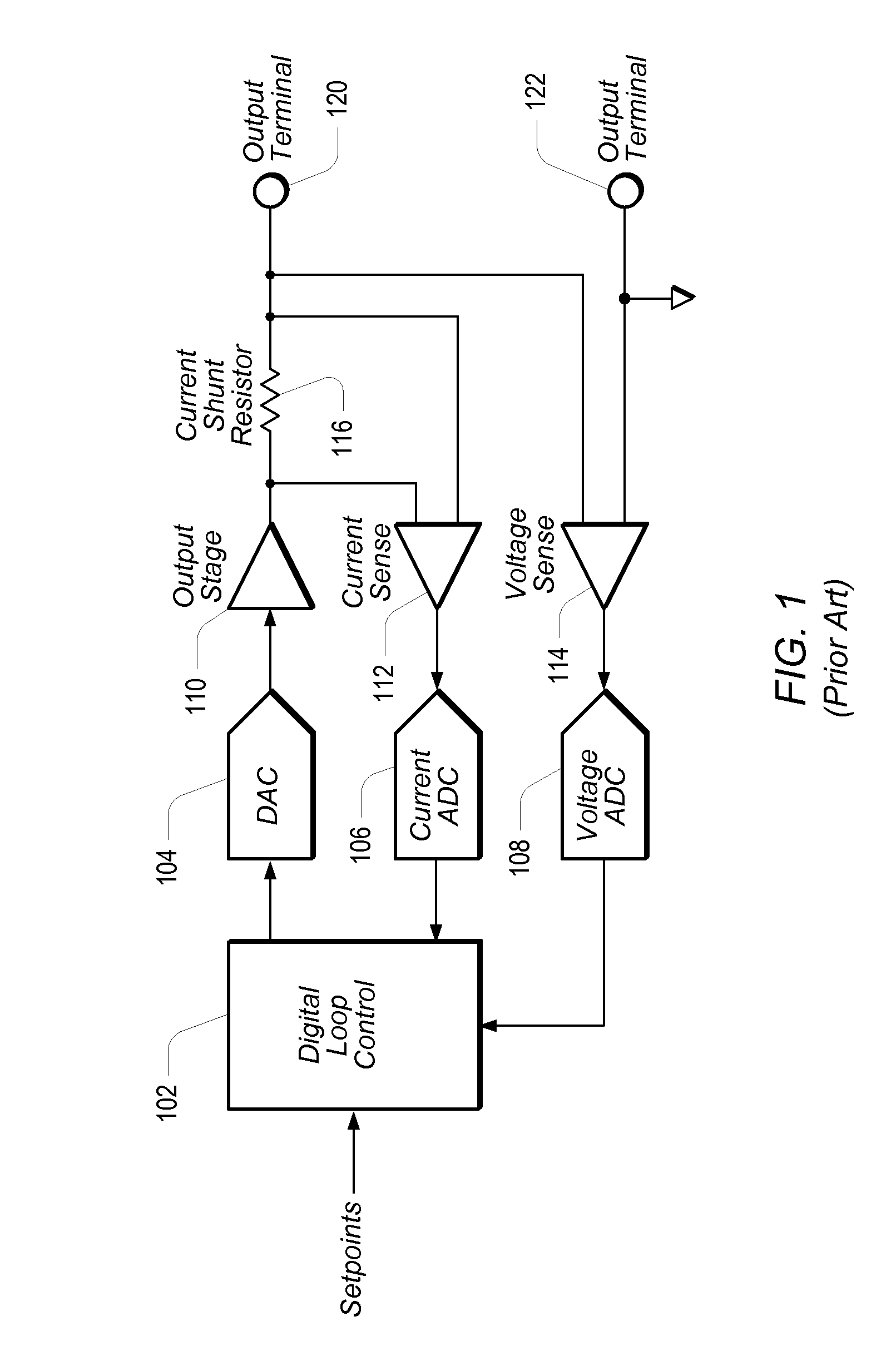
Compensation Methods for Digital Source-Measure-Units (SMUs)
ActiveUS20120306517A1Increase flexibilityConvenient and accurateFault location by increasing destruction at faultEngineeringZero frequency
A source-measure unit (SMU) may be implemented with respective digital control loops for output voltage and output current. The output voltage and output current may be measured with dedicated ADCs (analog-to-digital converters). The readings obtained by the ADCs may be compared to a setpoint, which may be set in a digital loop controller. The digital loop controller may be used to produce an output to drive a DAC (digital-to-analog converter) until the output voltage and / or output current and / or a function thereof reach the respective desired levels. The digital loop controller may implement respective integrating functions for the respective digital control loops, and may also implement a compensation function featuring pole-zero pairs to stabilize the respective current / voltage outputs. Coefficients of the compensation function may be calculated based on user programmable parameters corresponding to the gain bandwidth product, compensation frequency, and ratio of the added pole-zero frequencies.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
Method and system thereof for signal demodulation of heterodyne laser
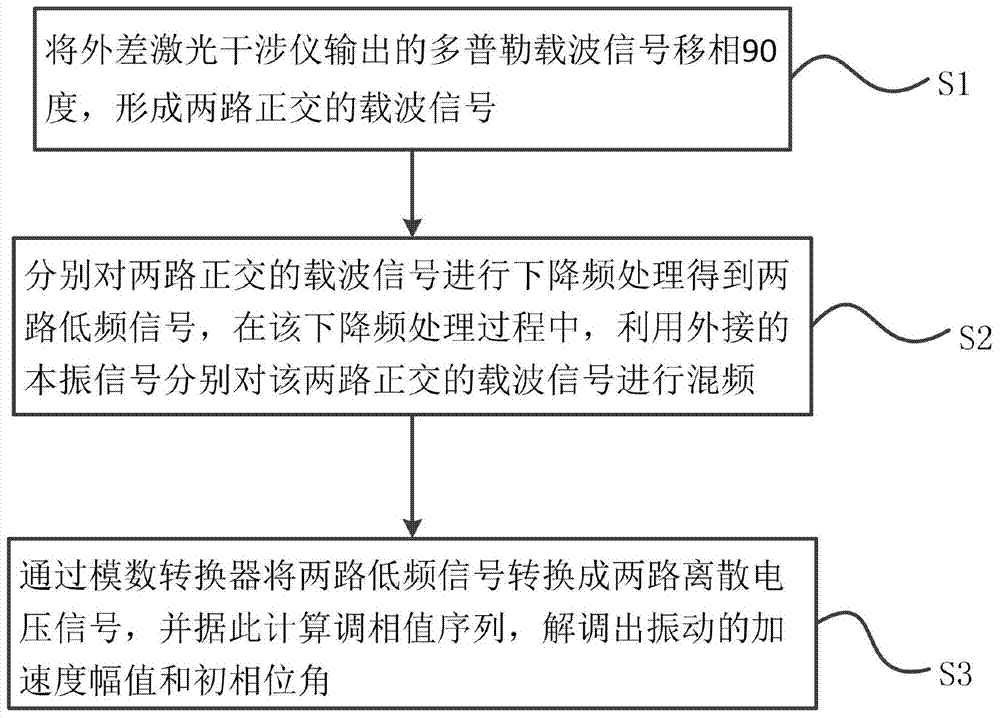
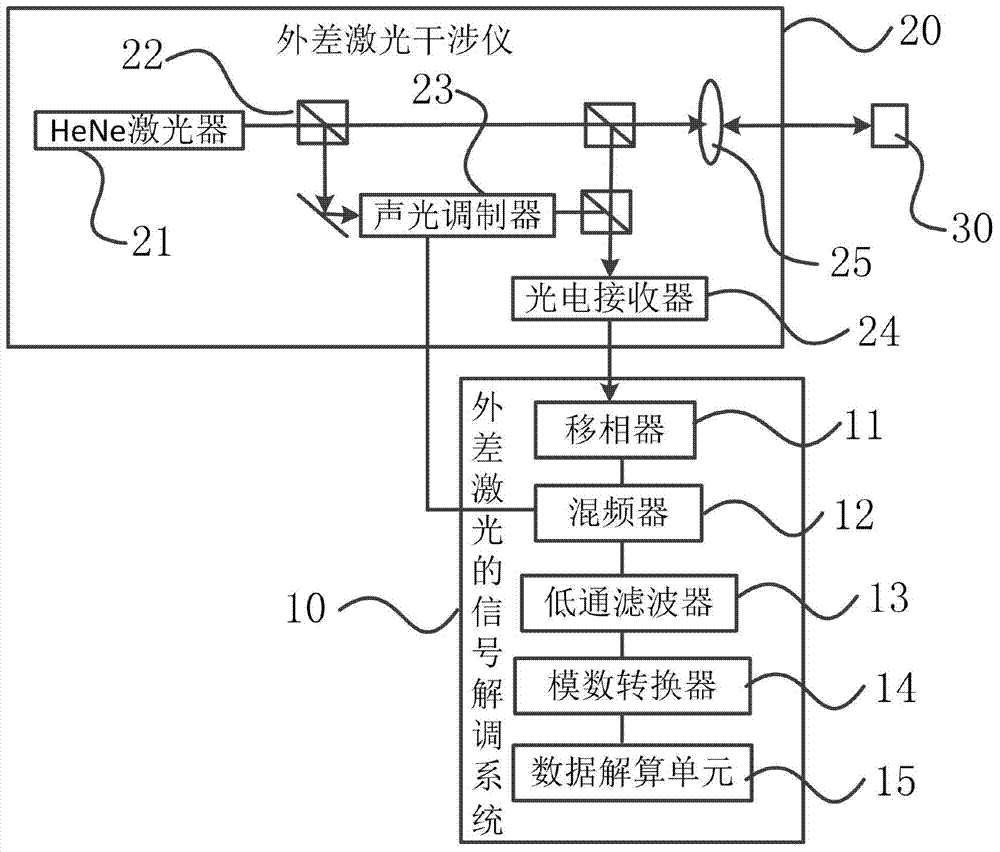
ActiveCN104501940AReduce difficultyFrequency of low vibration measurementsSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansCarrier signalZero frequency
The invention provides a method and a system thereof for signal demodulation of heterodyne laser. The method comprises the following steps of performing 90-degree phase shifting on a Doppler carrier signal outputted by a heterodyne laser interferometer to form two paths of orthogonal carrier signals; respectively performing frequency dropping processing on the two paths of orthogonal carrier signals to obtain two paths of low-frequency signals, wherein during frequency dropping processing, the two paths of orthogonal carrier signals are subject to frequency mixing by an external local oscillation signal; converting the two paths of low-frequency signals into two paths of discrete voltage signals by an analog to digital converter, calculating a phase modulation value sequence, and demodulating the acceleration amplitude and the initial phase angle of oscillation. The method has the advantages that the requirement of data collecting speed is greatly decreased, the problem of huge data and difficult solving in the data solving are reduced, the low-frequency vibration is measured by the heterodyne laser interferometer, the same-clock method is adopted in the zero frequency change process, the influence of interference on the measuring result by the outside environment is avoided, and the measuring stability and measuring accuracy are improved.
Owner:NAT INST OF METROLOGY CHINA
Rapid broadband frequency domain beamforming method based on acoustic vector sensor uniform linear array
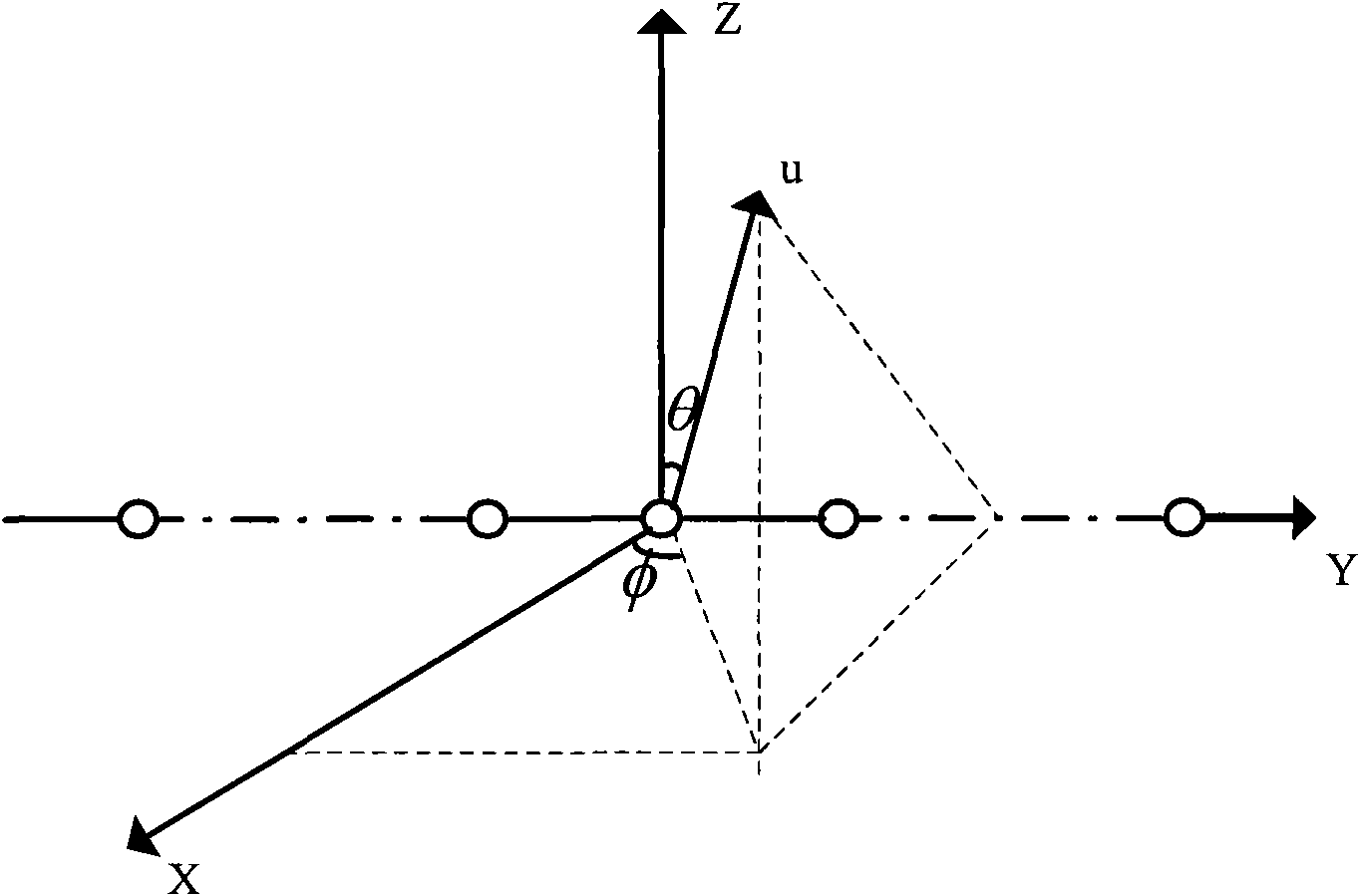
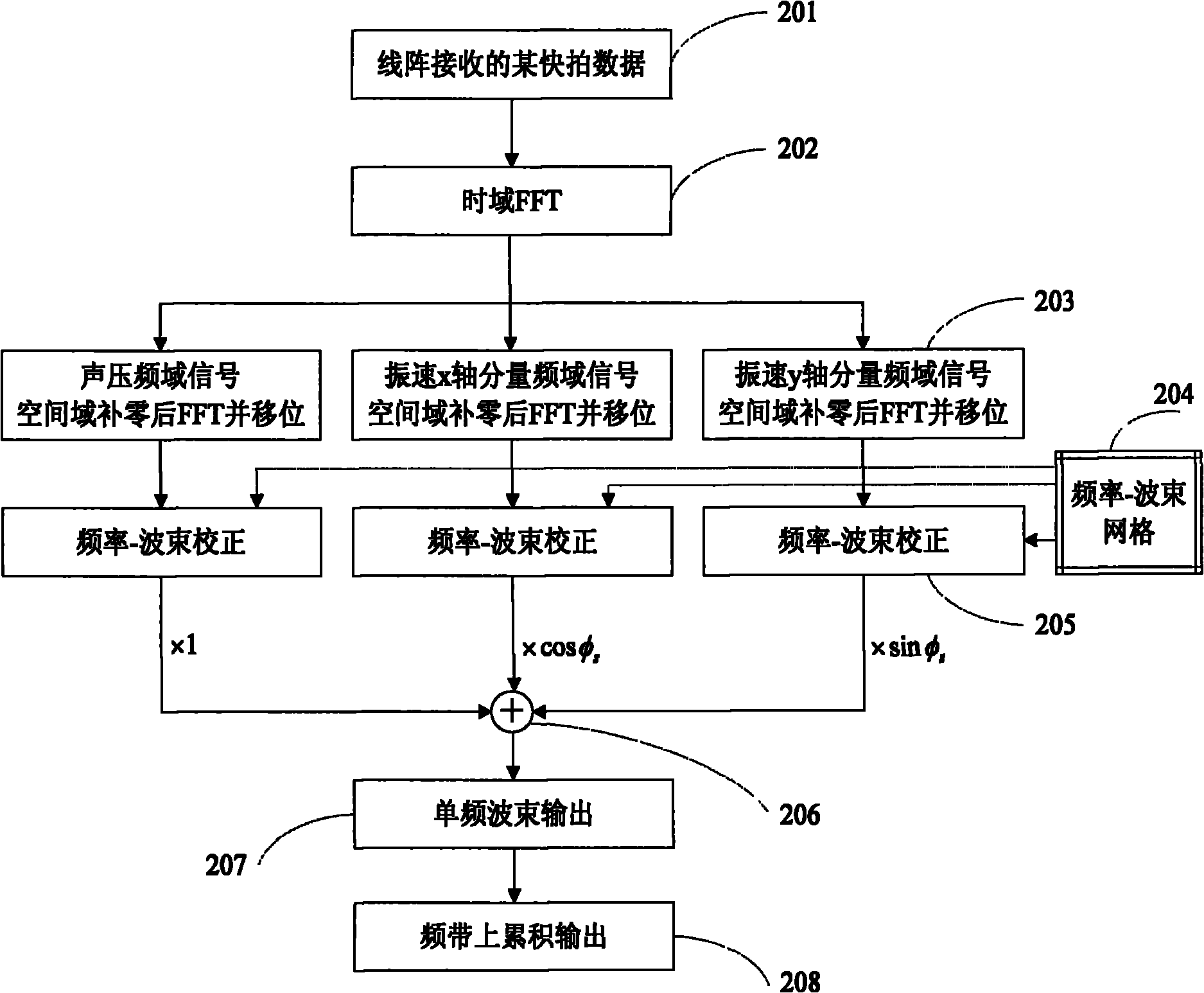
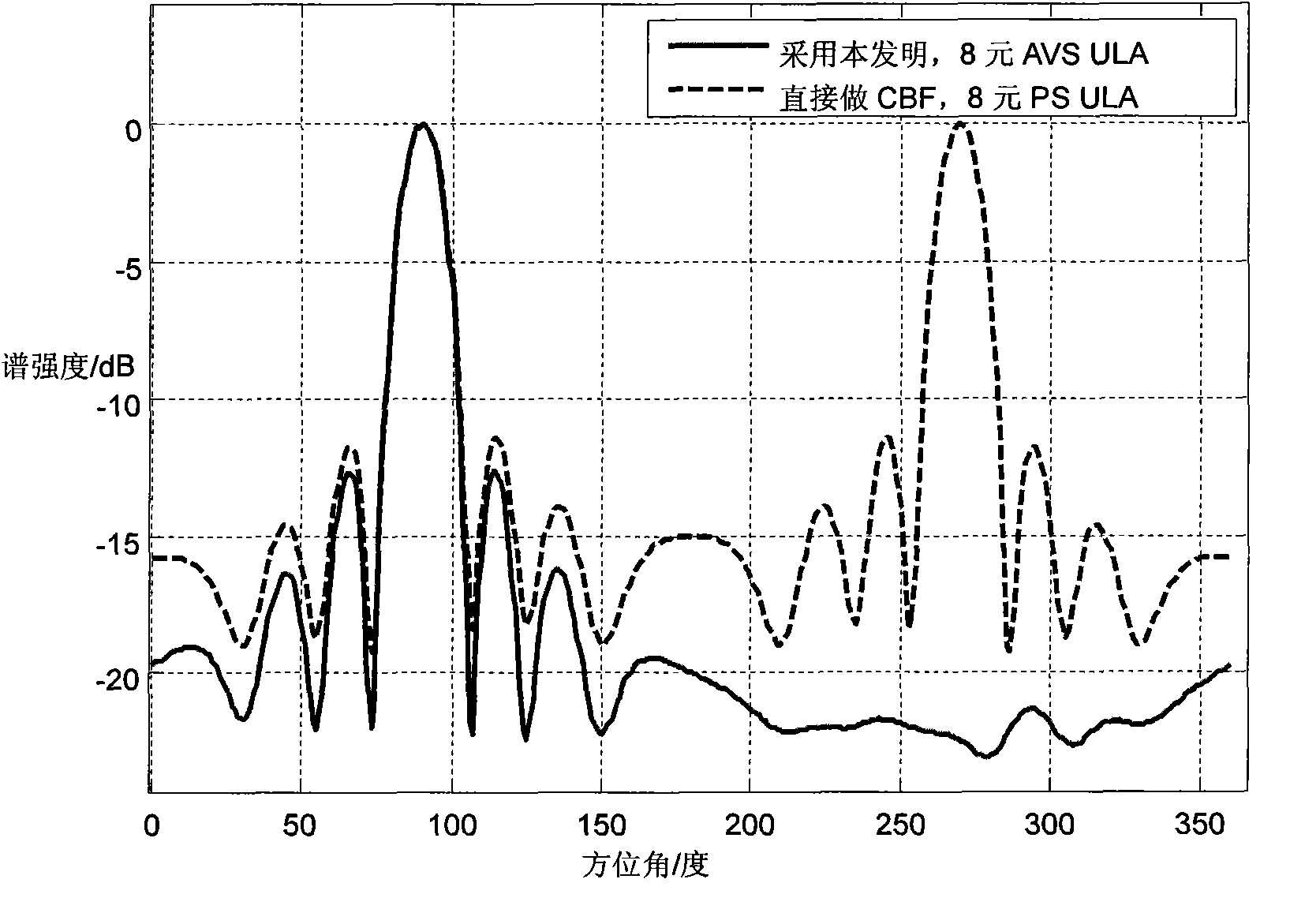
InactiveCN102043145AEasy to detectImprove robustnessWave based measurement systemsFourier transform on finite groupsArray element
The invention relates to a rapid broadband frequency domain beamforming method based on an acoustic vector sensor uniform linear array. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, receiving spatial signals through the acoustic vector sensor uniform linear array to obtain time domain signals of all array elements, wherein the time domain signals comprise time domain acoustic pressure signals and time domain vibration velocity signals, and performing Fourier transform on snapshot data needed to be processed so as to obtain a corresponding frequency domain signal; secondly, performing zero fill on the acoustic pressure signals and the vibration velocity signals of all the array elements in a space domain according to a frequency band range needed to be processed, performing fast Fourier transform (FFT) on the signals in the space domain, and transferring a zero frequency component of the transform result to a spectrum center; thirdly, performing alignment correction and corresponding linear addition on beam and space domain Fourier results at each frequency point of bandwidth needed to be processed according to a frequency-beam grid corresponding to the acoustic pressure signals and the vibration velocity signals so as to obtain beamforming results of different frequency points; and finally, synthesizing beamforming results of different frequencies to obtain power output of a linear array spatially.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Unsmooth dynamic compensation method for ultralow-frequency horizontal vibration table guide rail
ActiveCN103822703ALittle impact on accuracyReduced precision requirementsSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementCalibration resultEngineering
The invention discloses an unsmooth dynamic compensation method for an ultralow-frequency horizontal vibration table guide rail. The unsmooth dynamic compensation method comprises the following steps: measuring unsmooth dynamic characteristics of the ultralow-frequency horizontal vibration table guide rail and output uori t of a calibrated acceleration sensor in real time by taking a horizontal direction as reference; constructing a guide rail unsmoothness dynamic compensation system, and removing a gravitational acceleration component in the output of the calibrated sensor generated by pitching of a sliding table from the original output of the calibrated sensor in real time in the vibration calibration process; calibrating a calibrated acceleration sensor by adopting the compensated output ucomt of the calibrated sensor, calculating to obtain a compensated amplitude-frequency curve, and finishing vibration calibration of the calibrated sensor. The unsmooth dynamic compensation method has the advantages that the calibration result deviation of the acceleration sensor with zero frequency response caused by guide rail unsmoothness based on the ultralow-frequency horizontal vibration table can be compensated in real time in the vibration calibration process, so that the precision of ultralow-frequency vibration calibration is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Random bit sequence generator
A random-bit sequence generator includes a biasing circuit, a source of a noisy voltage signal biased by the biasing circuit, an amplification stage generating an amplified signal representative of the sole non-zero-frequency (AC) component of the noisy voltage signal and an output stage electrically in cascade to the amplification stage that generates a random bit sequence in function of the amplified signal. The generator also filters the undesired low-frequency disturbance components because the amplification stage comprises an input low-pass filter that feeds the zero- (DC) component of the noisy voltage signal to one of the inputs of a differential amplifier, to another input of which is fed the non-filtered noisy voltage signal.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com