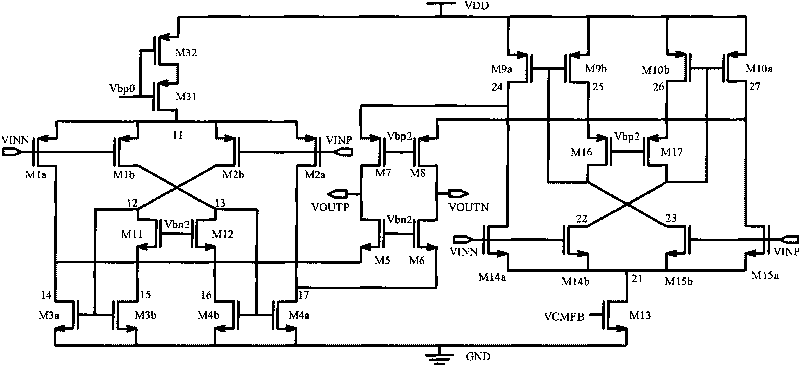
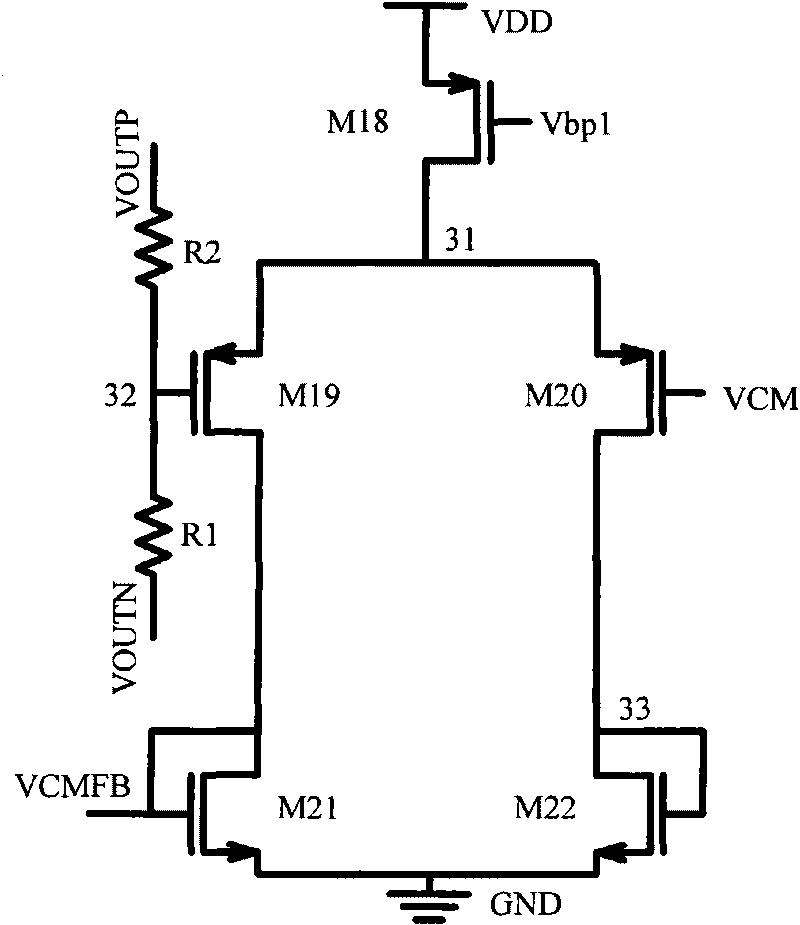
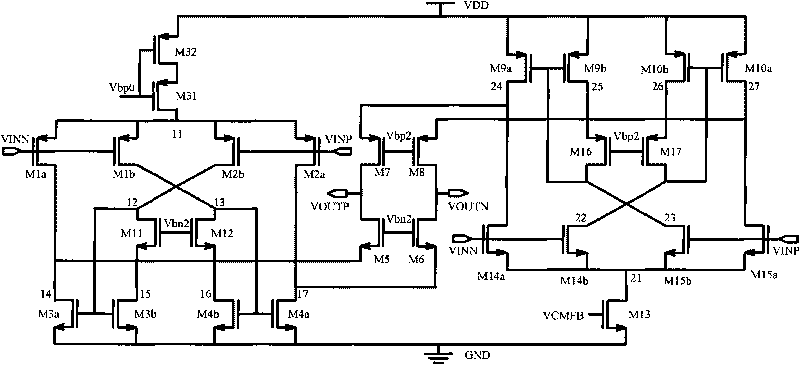
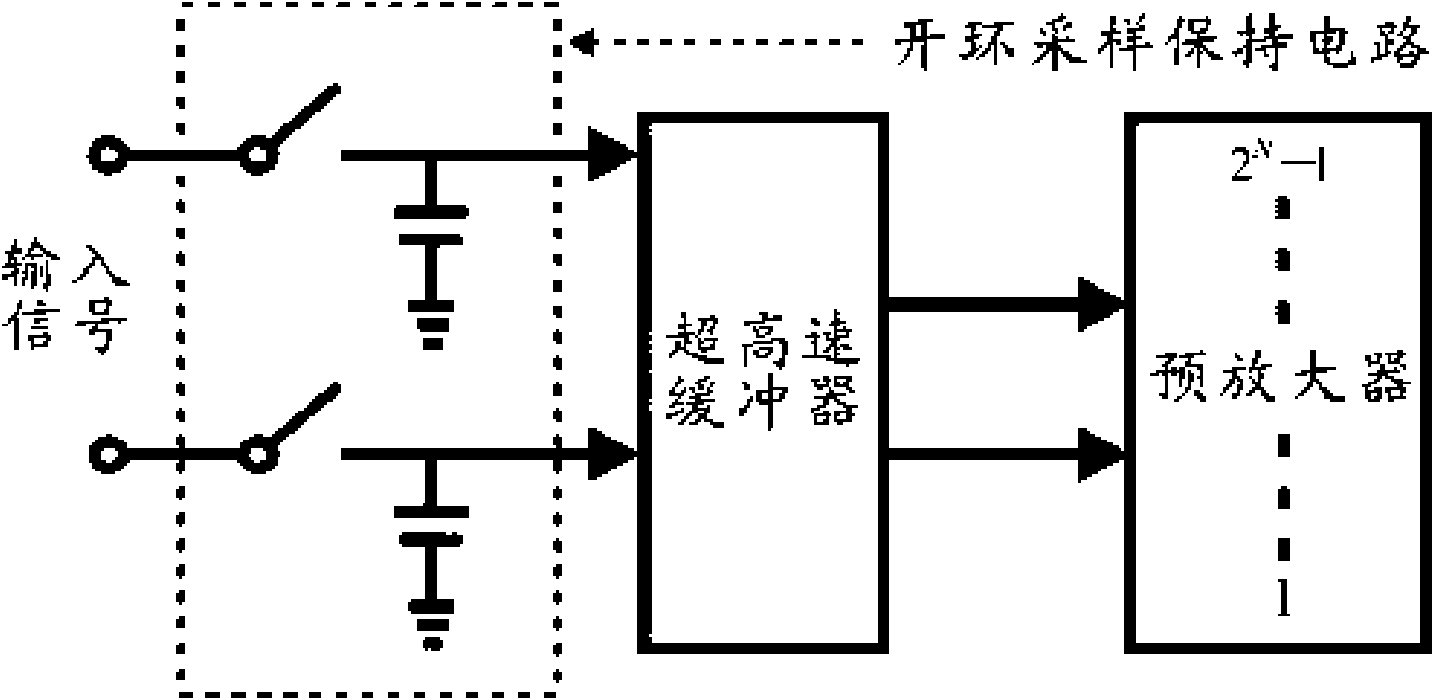
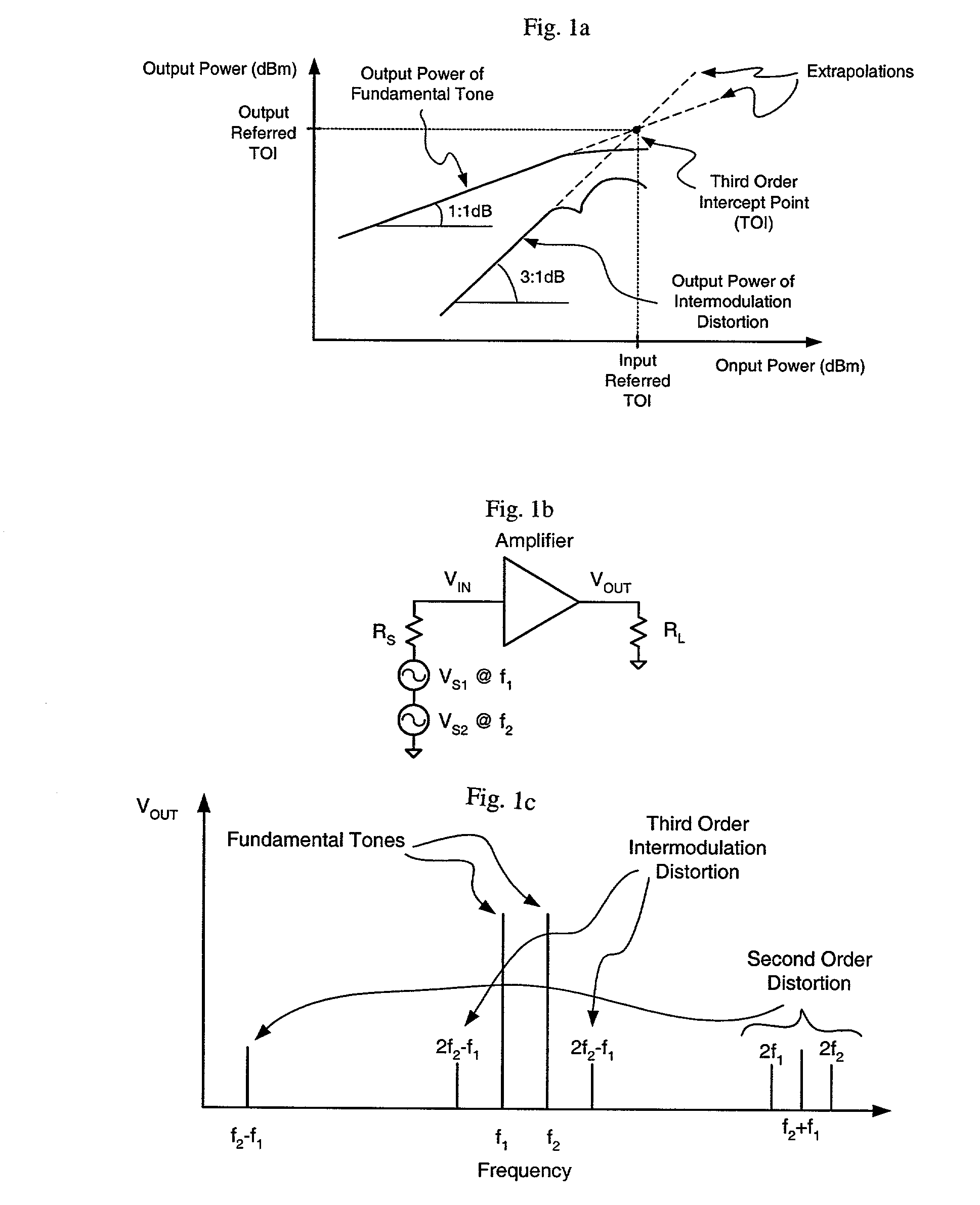
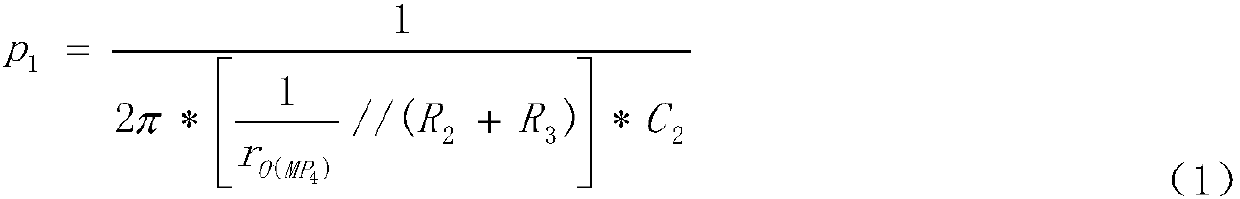Patents
Literature
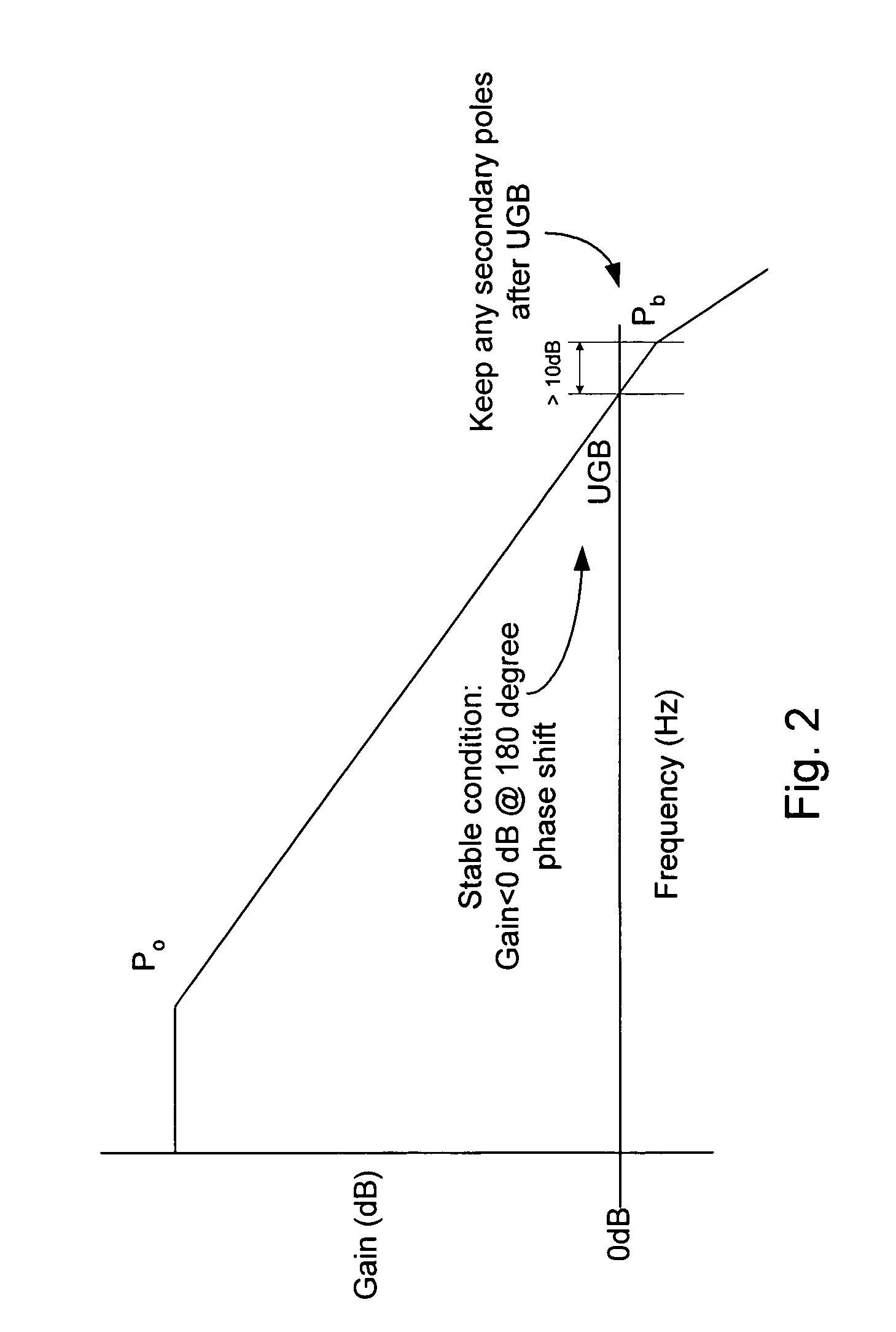
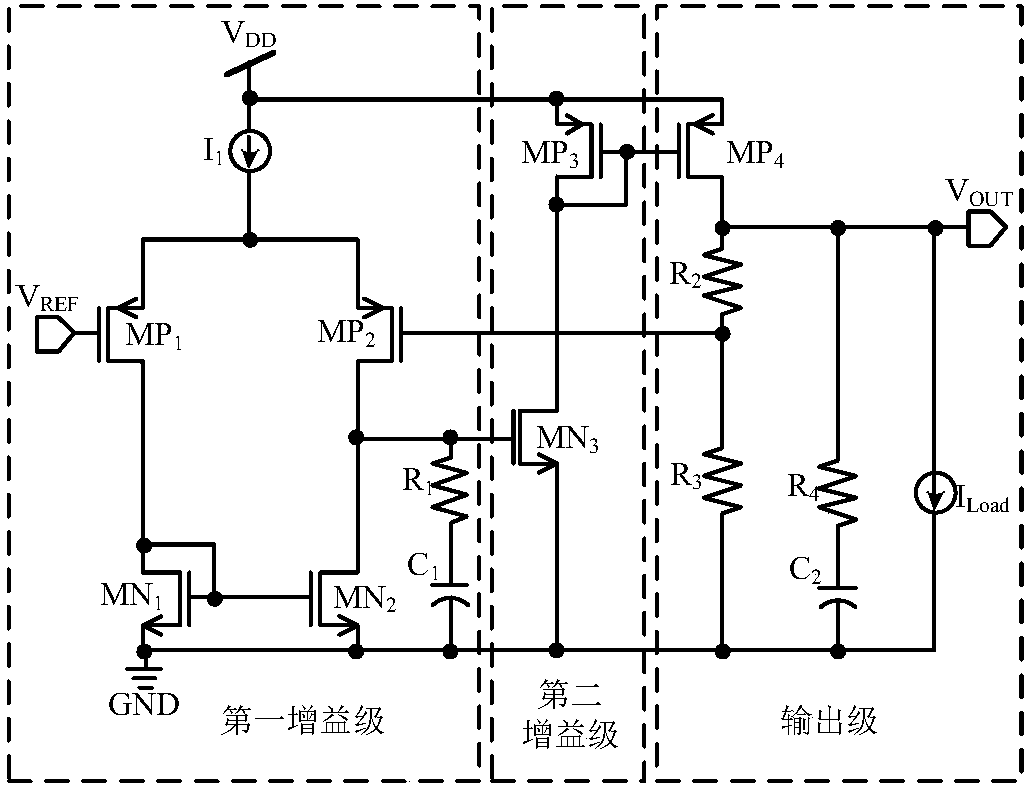
234 results about "Unity gain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
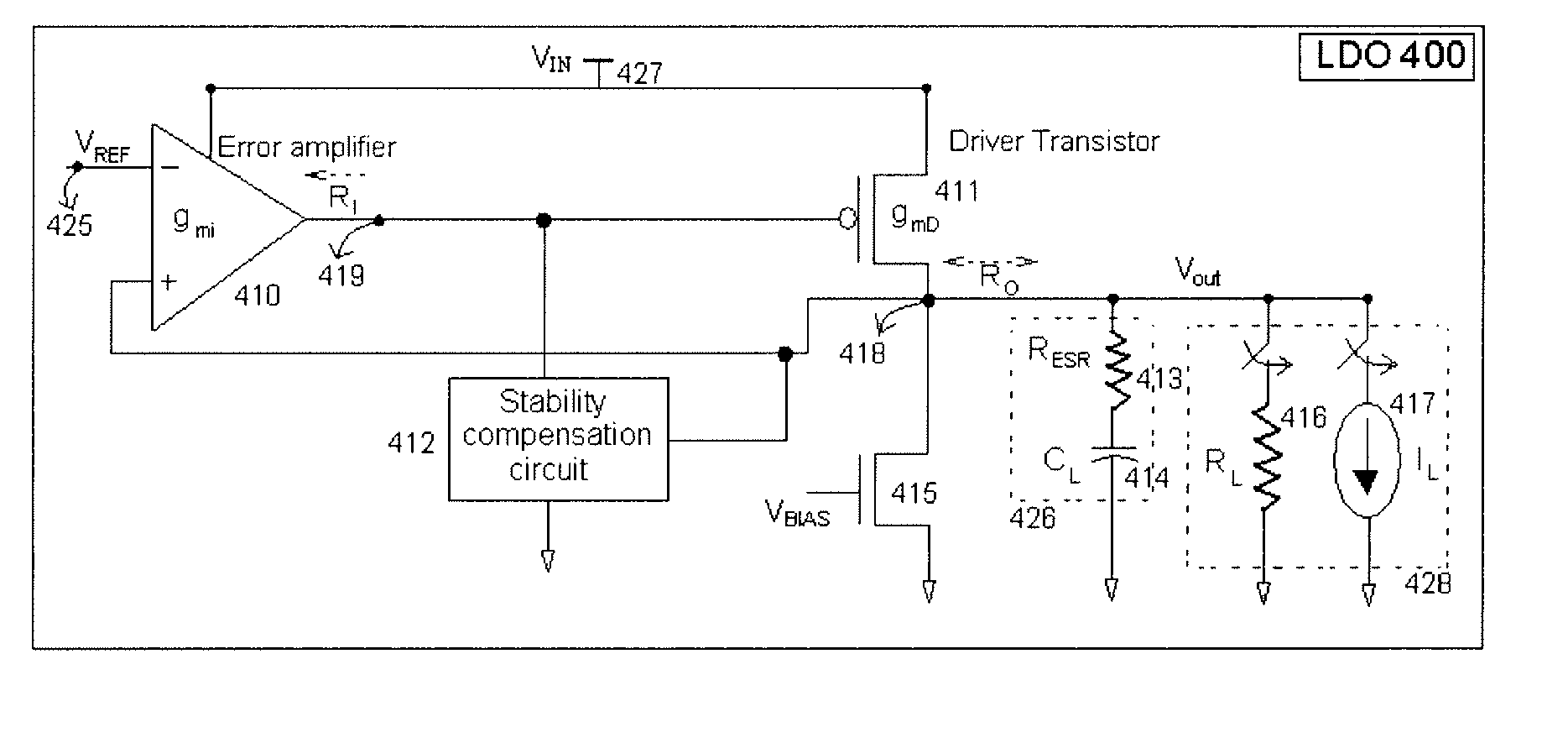
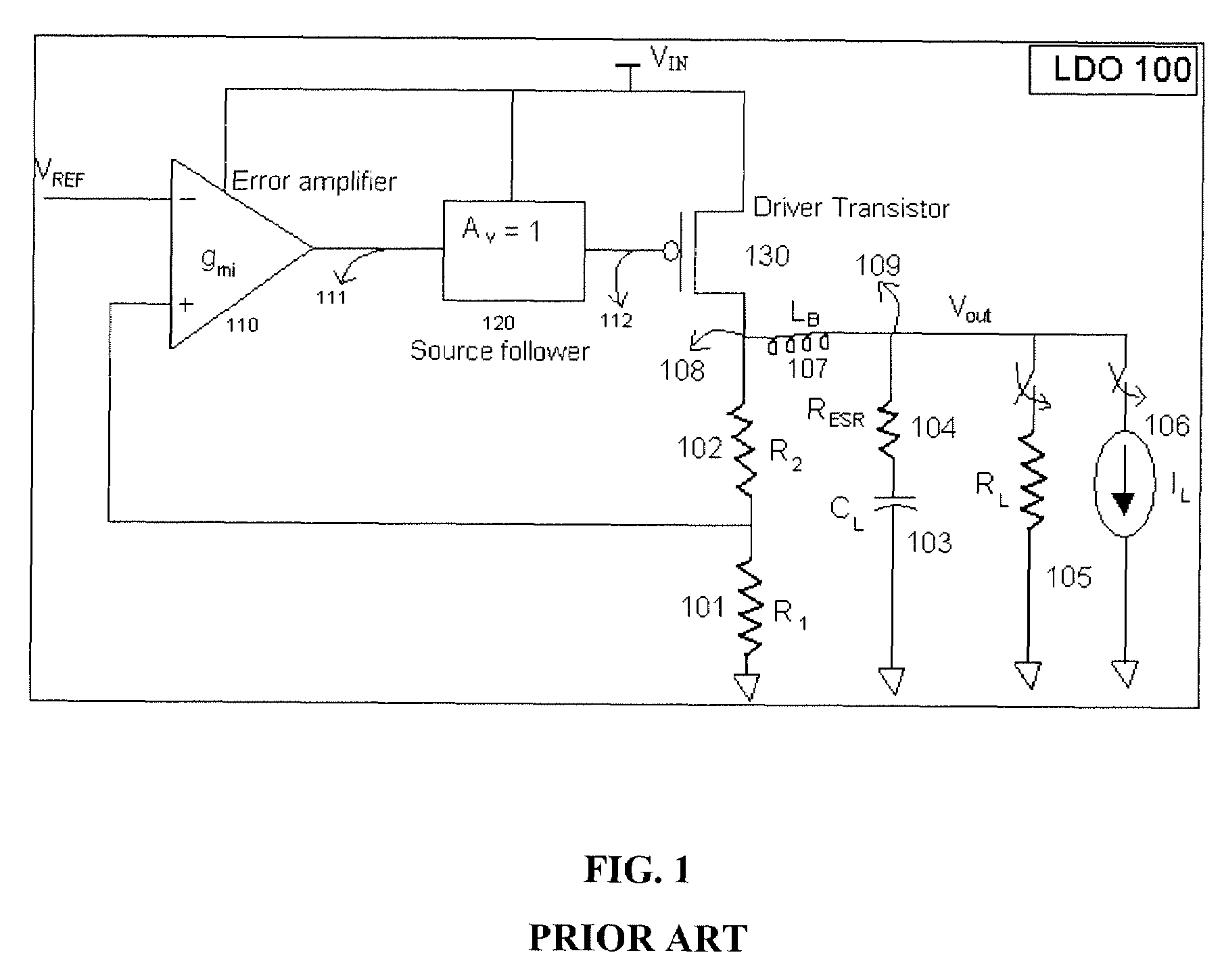
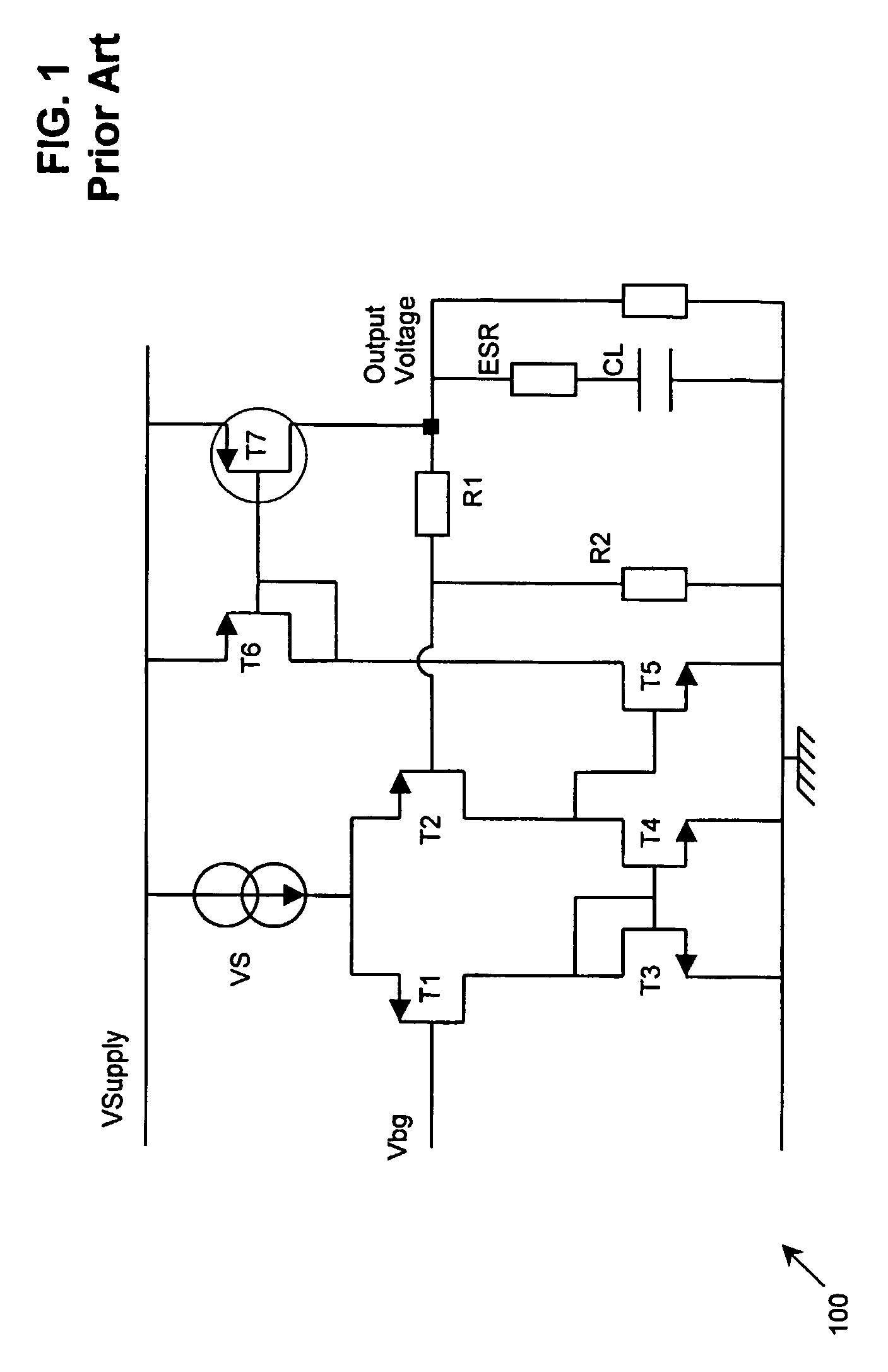
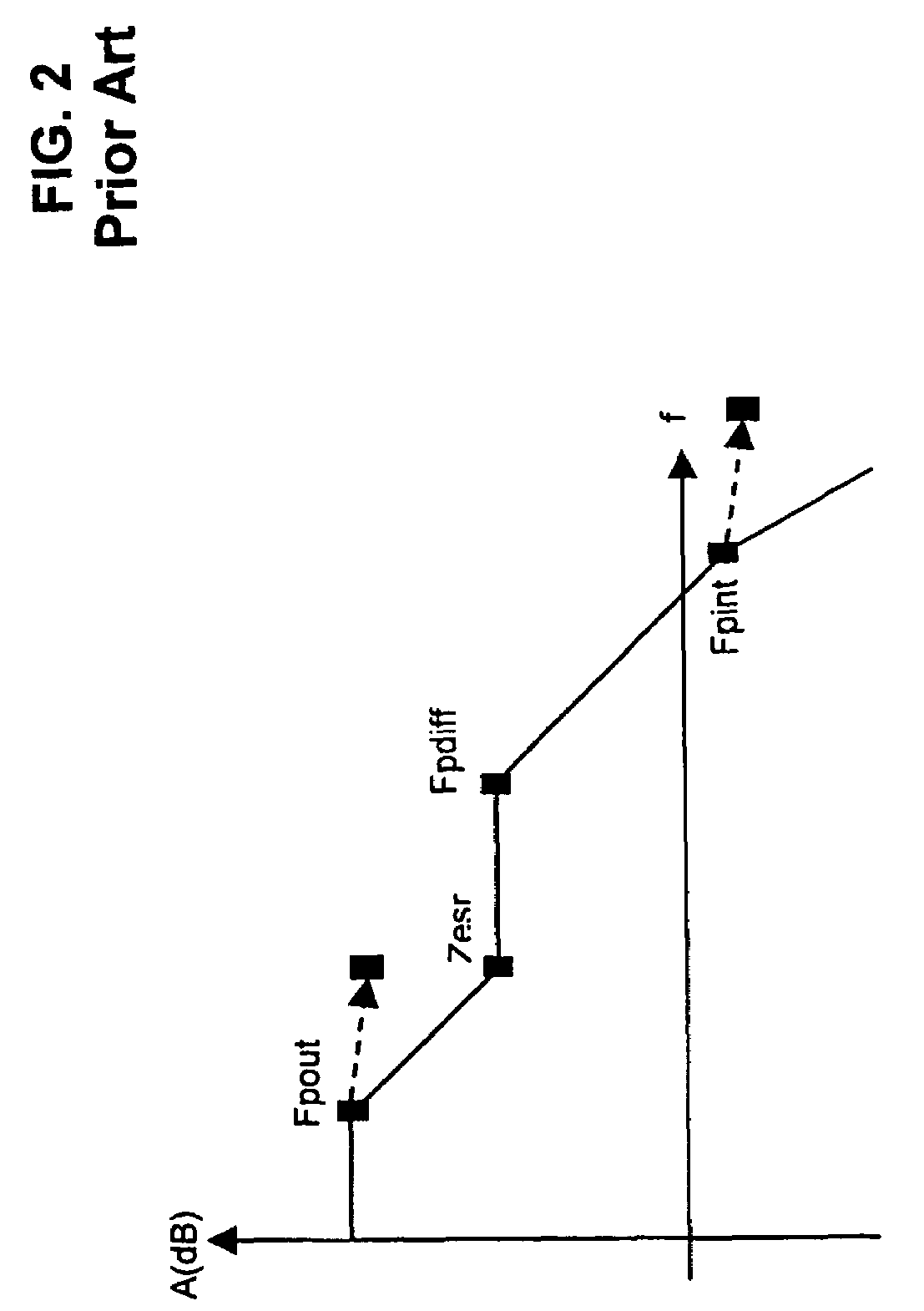
Low dropout regulator
InactiveUS20070159146A1Good phase marginMinimize power consumptionElectric variable regulationLow loadEngineering
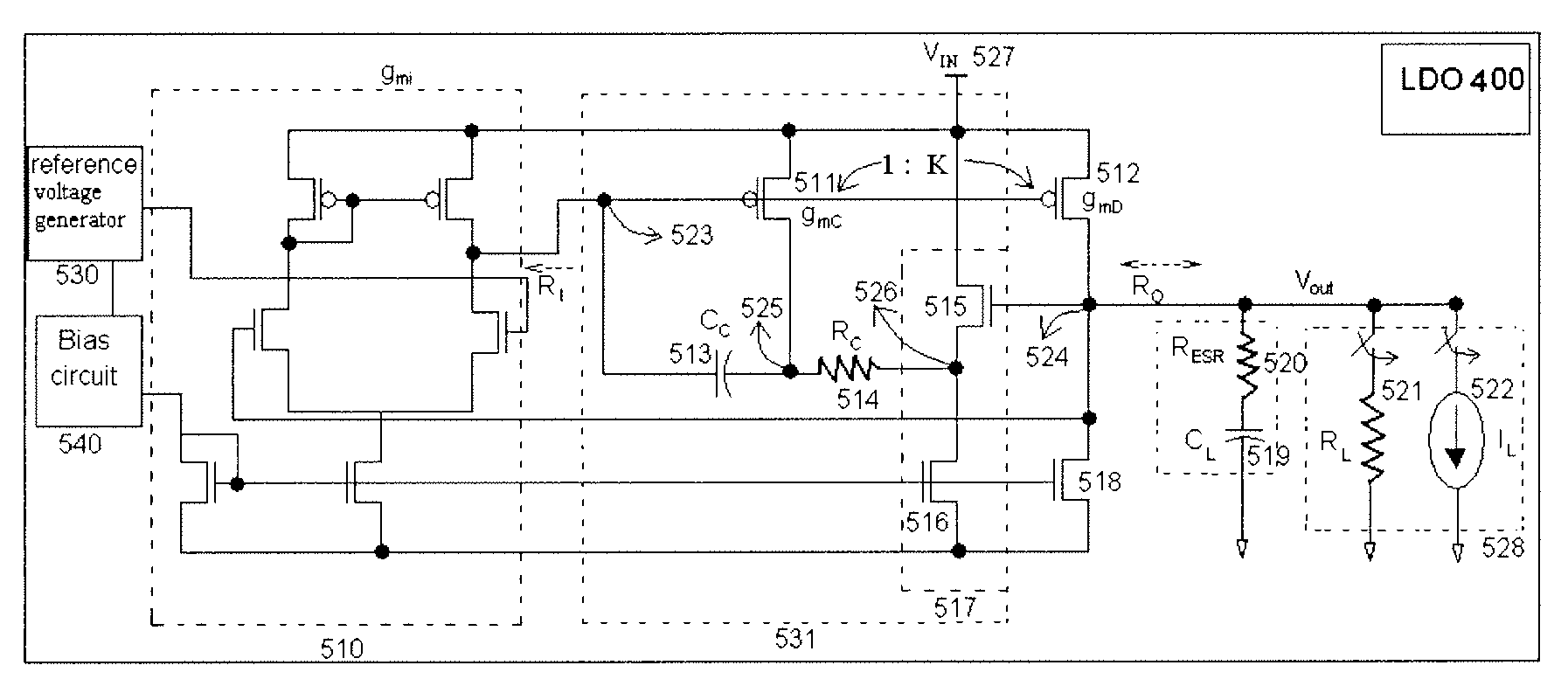
The present invention provides a low dropout (LDO) regulator with a stability compensation circuit. A “zero frequency” tracking as well as “non-dominant parasitic poles' frequency reshaping” are performed to achieve a good phase margin for the LDO by means of the compensation circuit. In this compensation method neither a large load capacitor nor its equivalent series resistance is needed to stabilize a regulator. LDO regulators, in system on chip application, having load capacitors in the range of few nano-Farads to few hundreds of nano-Farads can be efficiently compensated with this compensation method. A dominant pole for the regulator is realized at an internal node and the second pole at an output node of the regulator is tracked with a variable capacitor generated zero over a range of load current to cancel the effect of each other. A third pole of the system is pushed out above the unity gain frequency of the open loop transfer function with the help of the frequency compensation circuit. The compensation technique is very effective in realizing a low power, low-load-capacitor LDO desirable for system on chip applications.
Owner:ST ERICSSON SA
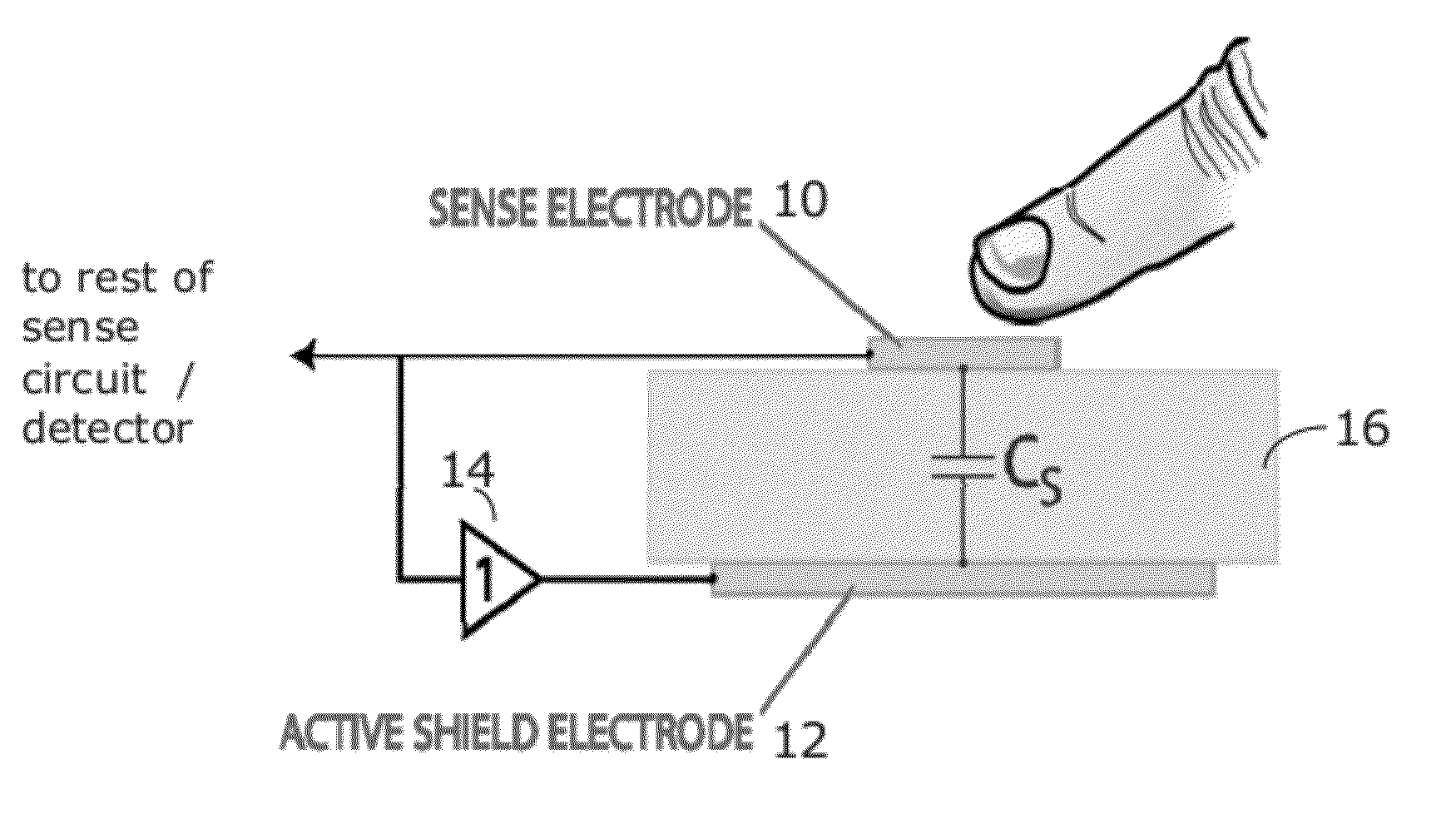
Capacitive sensor with active shield electrode
InactiveUS20120074961A1Reduce manufacturing costHigh sensitivityResistance/reactance/impedenceElectronic switchingAudio power amplifierCapacitive sensing
A capacitive sensor having an active shield electrode driven by a unity gain amplifier. Various arrangements using multiplexors or switch arrays may allow single shield with multiple sense electrodes.
Owner:KOPIN CORPORATION
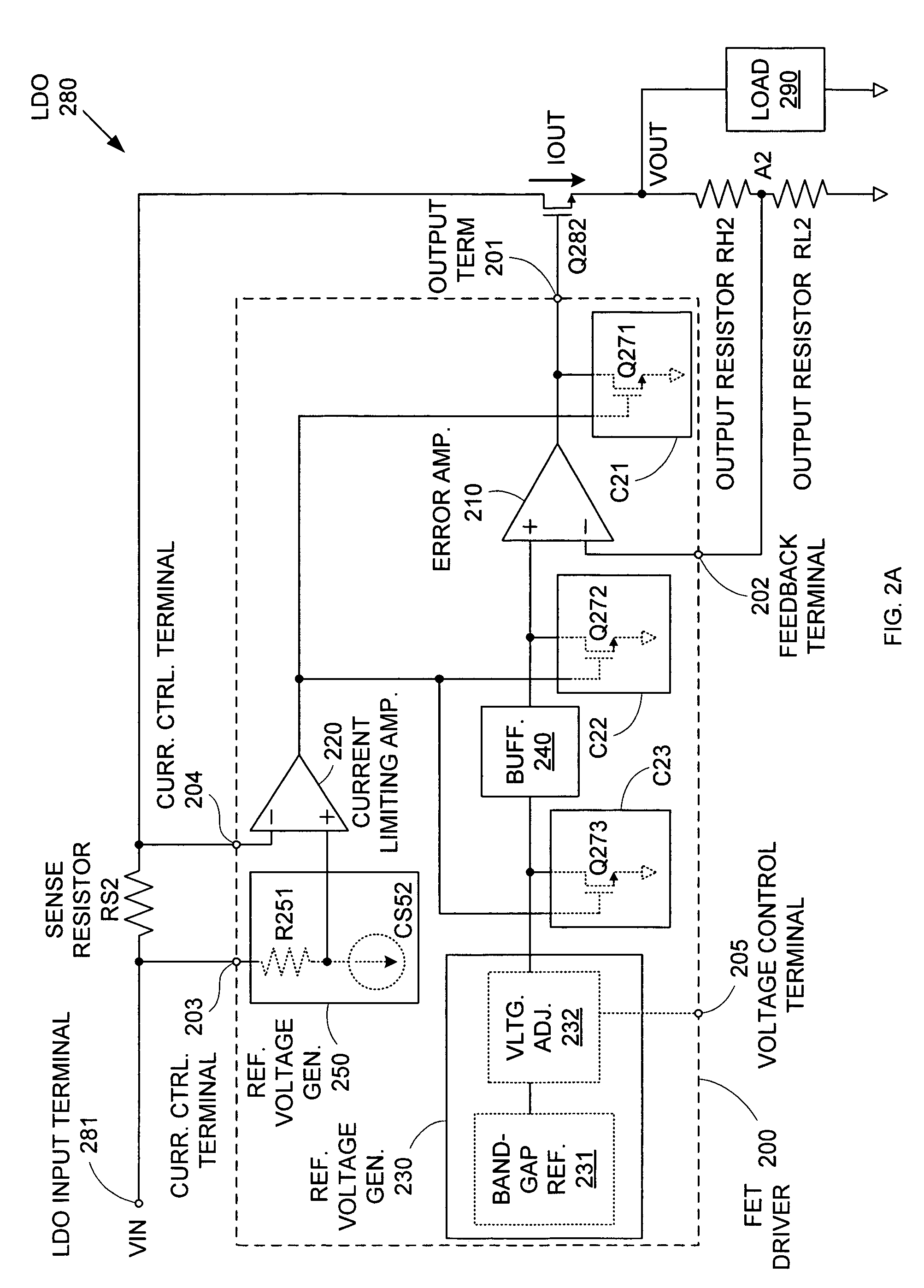
Current-limiting circuitry
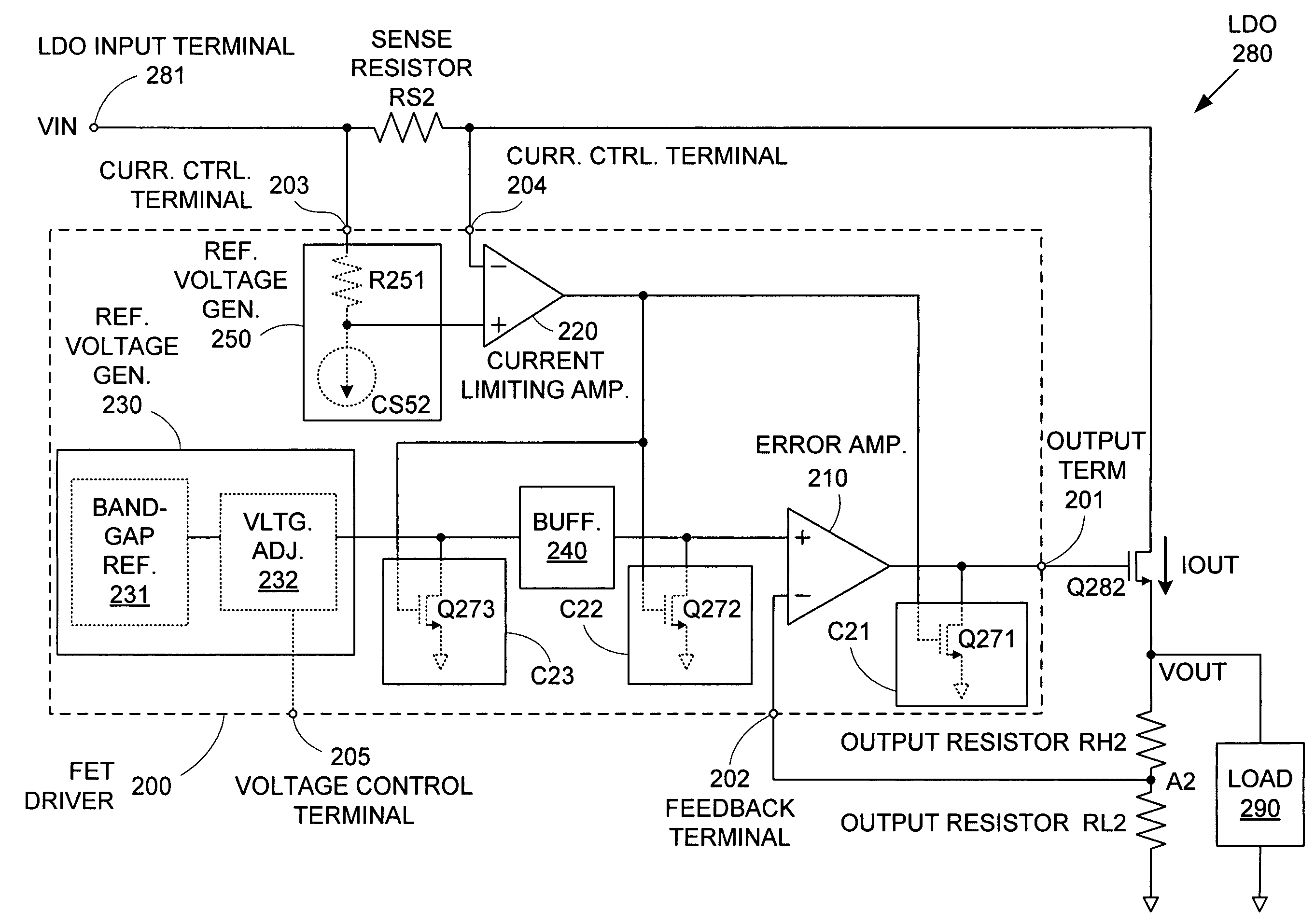
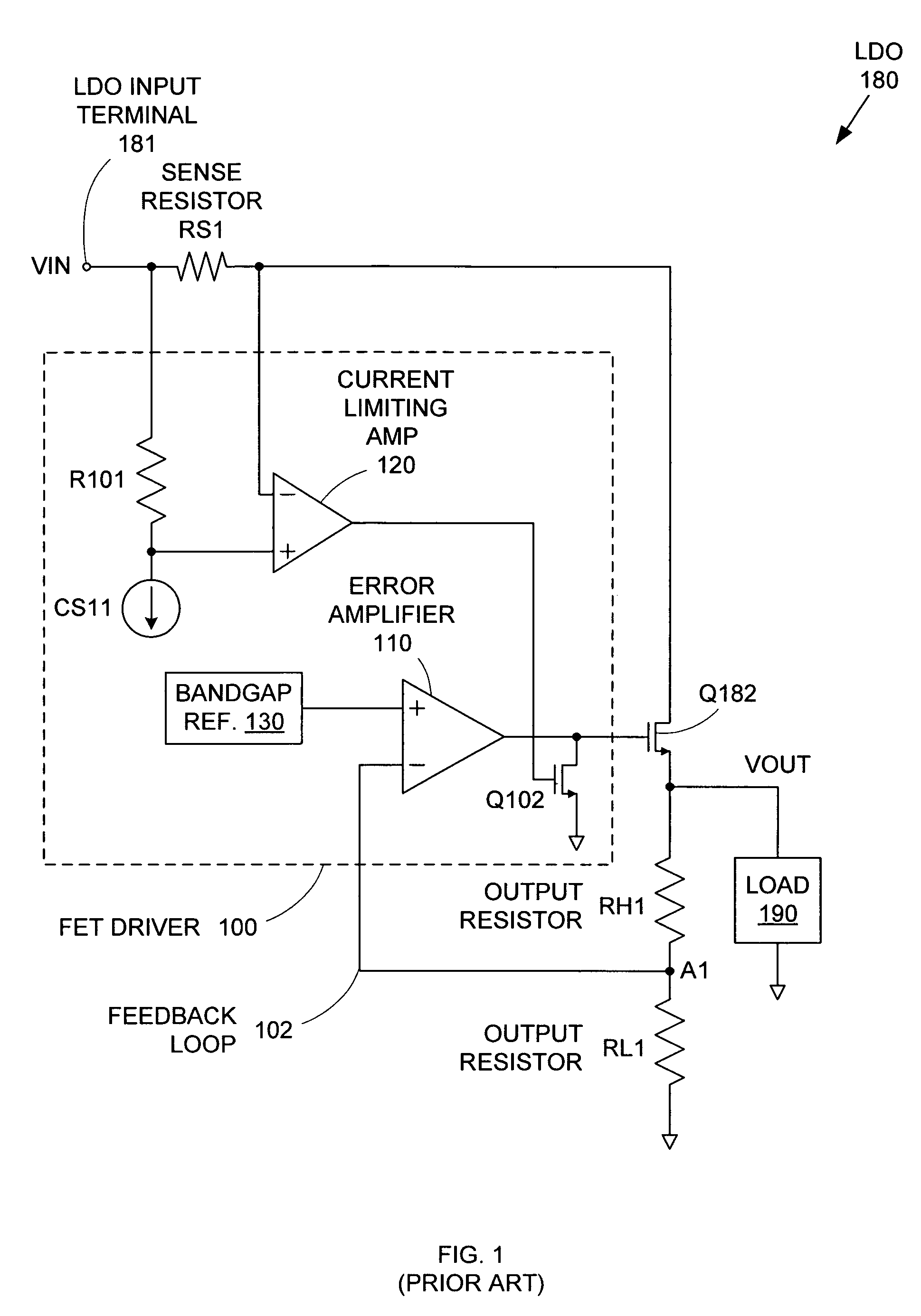
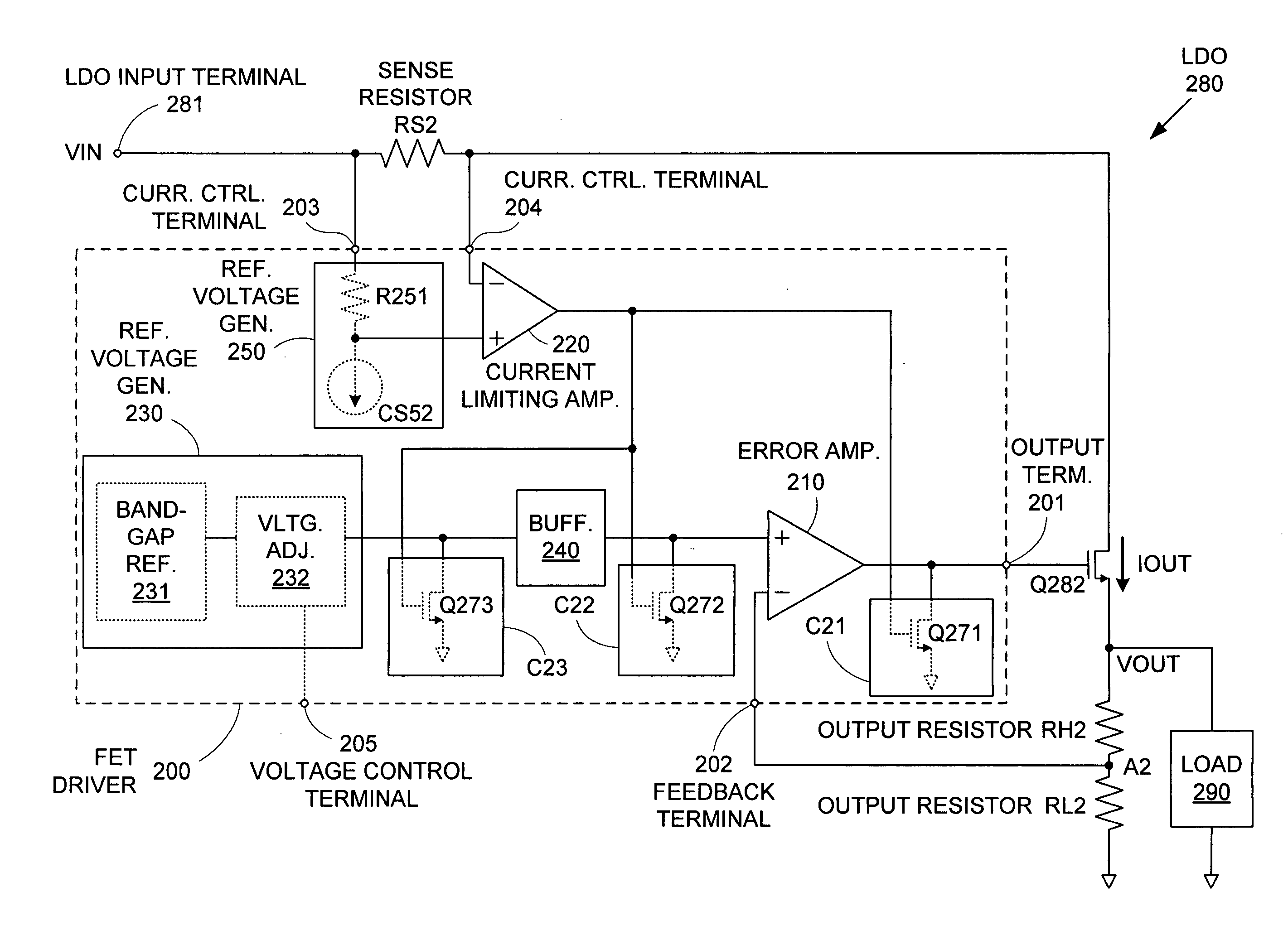
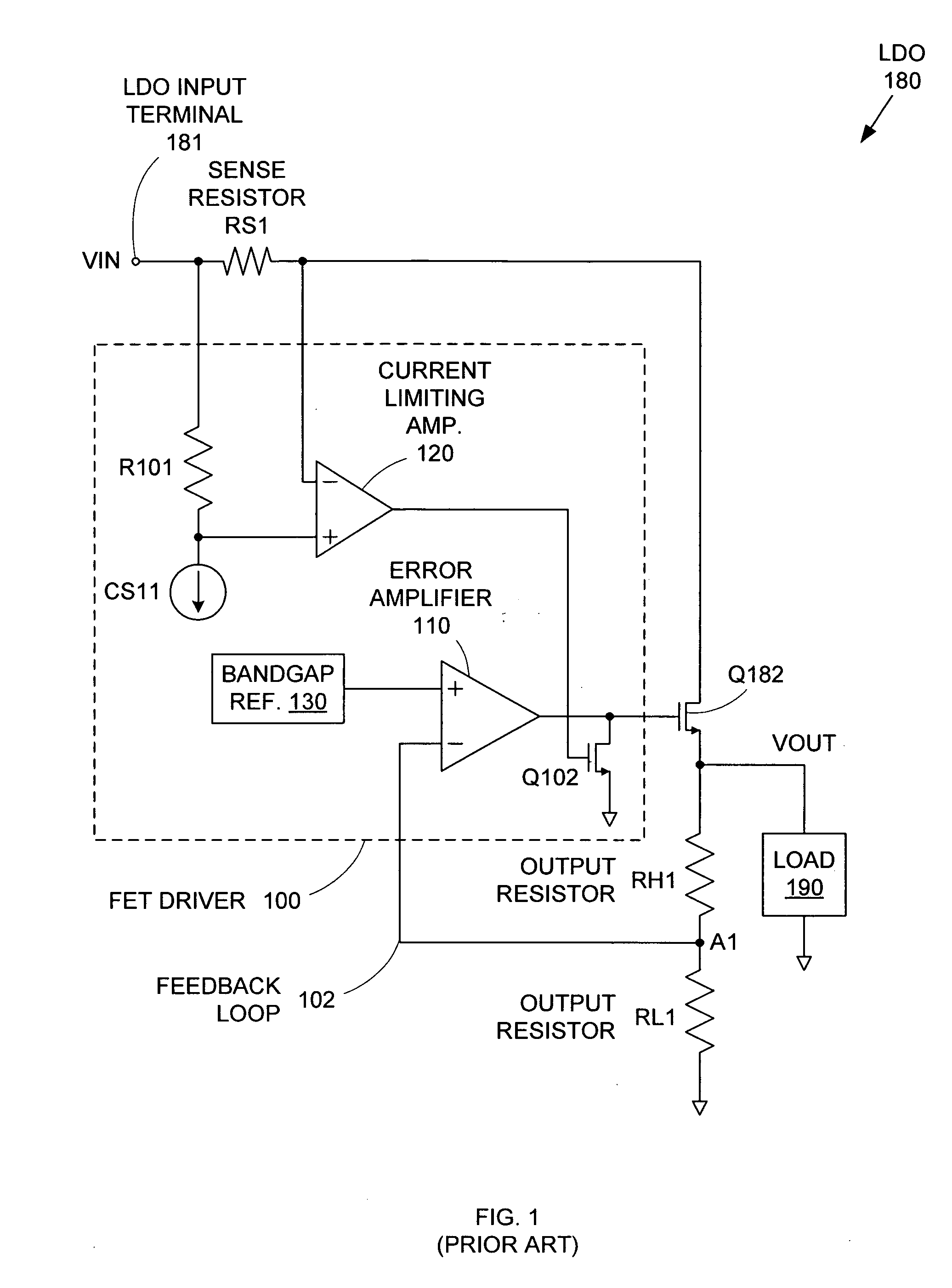
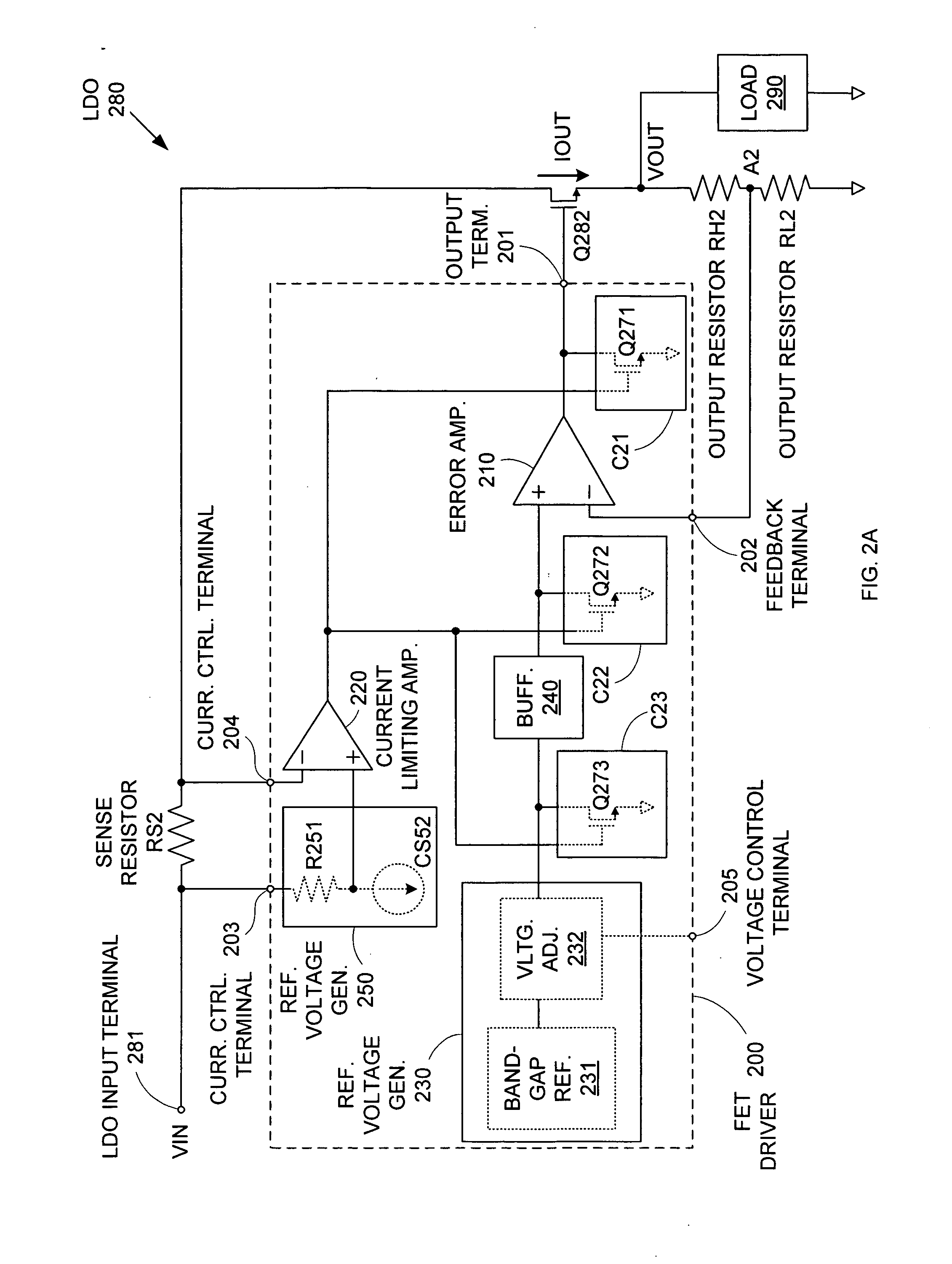
ActiveUS7015680B2Preventing excessive current flow through the FETReduce voltagePower supply linesElectric variable regulationDriver circuitAudio power amplifier
Owner:MICREL
Broad output current scope low pressure difference linear manostat
InactiveCN101339443AIncreased unity-gain bandwidthImprove stabilityLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsDifferential amplifiersCapacitanceCurrent range
A low dropout linear voltage regulator with wide output current range and low pressure difference, comprises an error amplifier in the folding common source and common gate structure, a buffer circuit, a driving element, a feedback circuit, a load capacitance equivalent series resistance compensating circuit and a multistage Miller compensation circuit, wherein the buffer circuit changes the low frequency pole into a medium frequency pole and a high frequency pole; the large load capacitance of the load capacitance equivalent series resistance compensating circuit pushes the main pole to the low frequency, causing the gain crossover point to push inwards, and generating a medium frequency zero point for counteracting the medium frequency pole connected serially with the equivalent series resistance; the stride multilevel Miller compensation circuit generates a medium high frequency pole and a medium high frequency zero point slightly smaller than the medium high frequency pole for advancing the phase margin, thereby not only adding the unity gain bandwidth, but also saving considerable chip area. When the output current has a large change range, the structure provided by the invention generates wider unity gain bandwidth, provides the phase margin of greater than 85 degrees, ensures the stability of the system and advances the low pressure difference linear voltage stabilization performance.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Systems and methods for interference-suppression with directional sensing patterns
InactiveUS20060115103A1Reduce varianceReduce the differencePiezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesMicrophonesEngineeringHearing perception
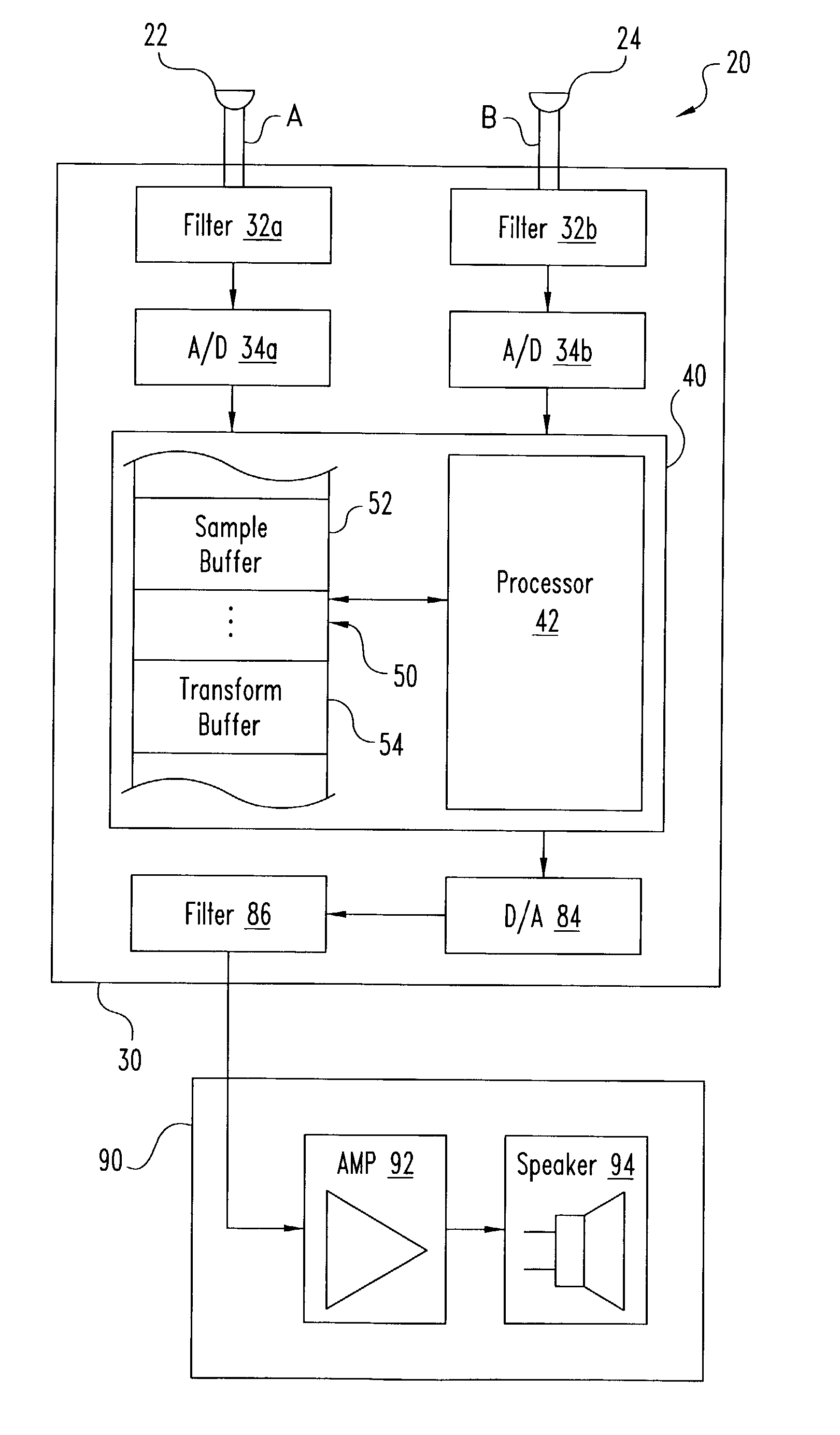
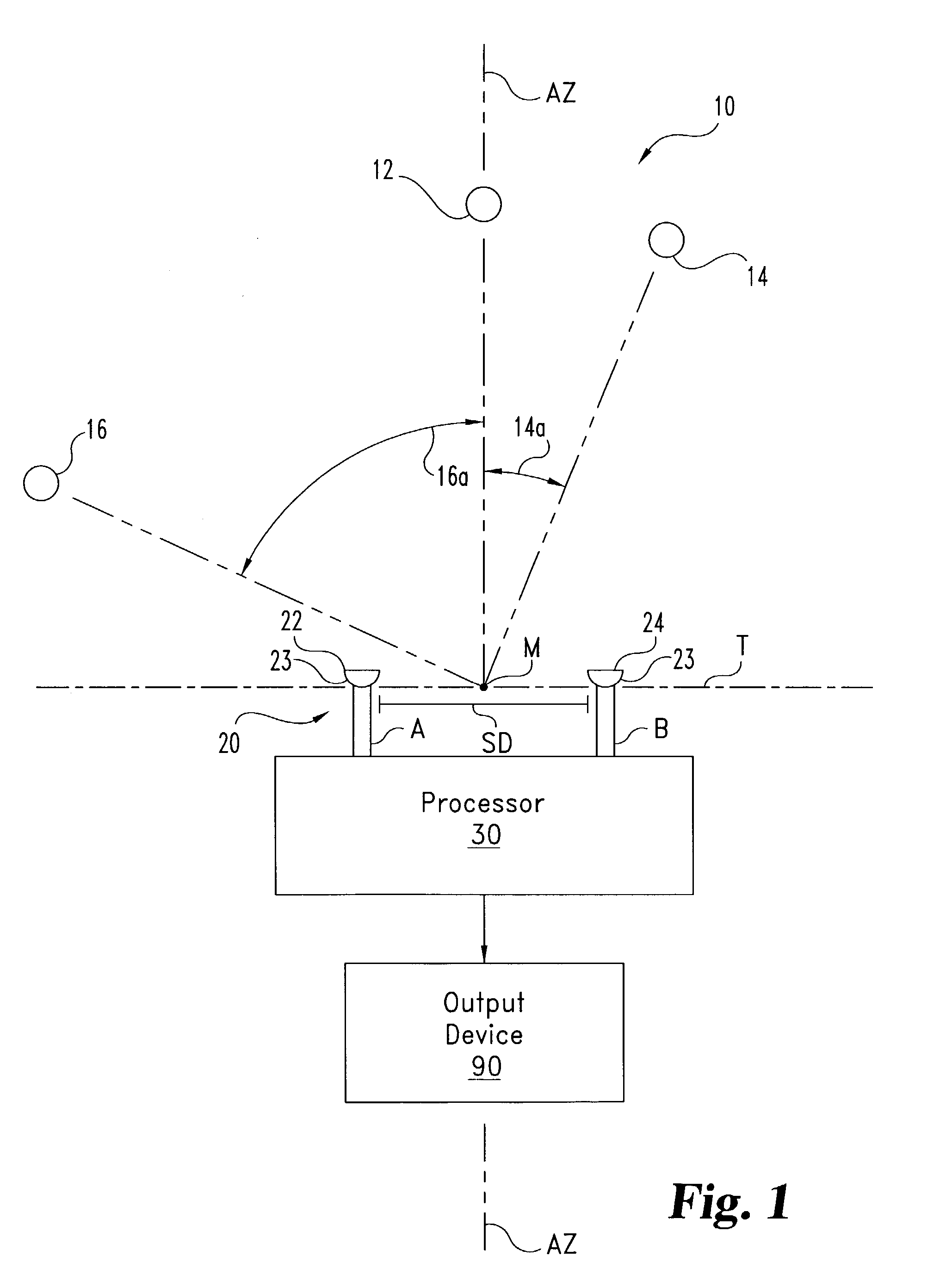
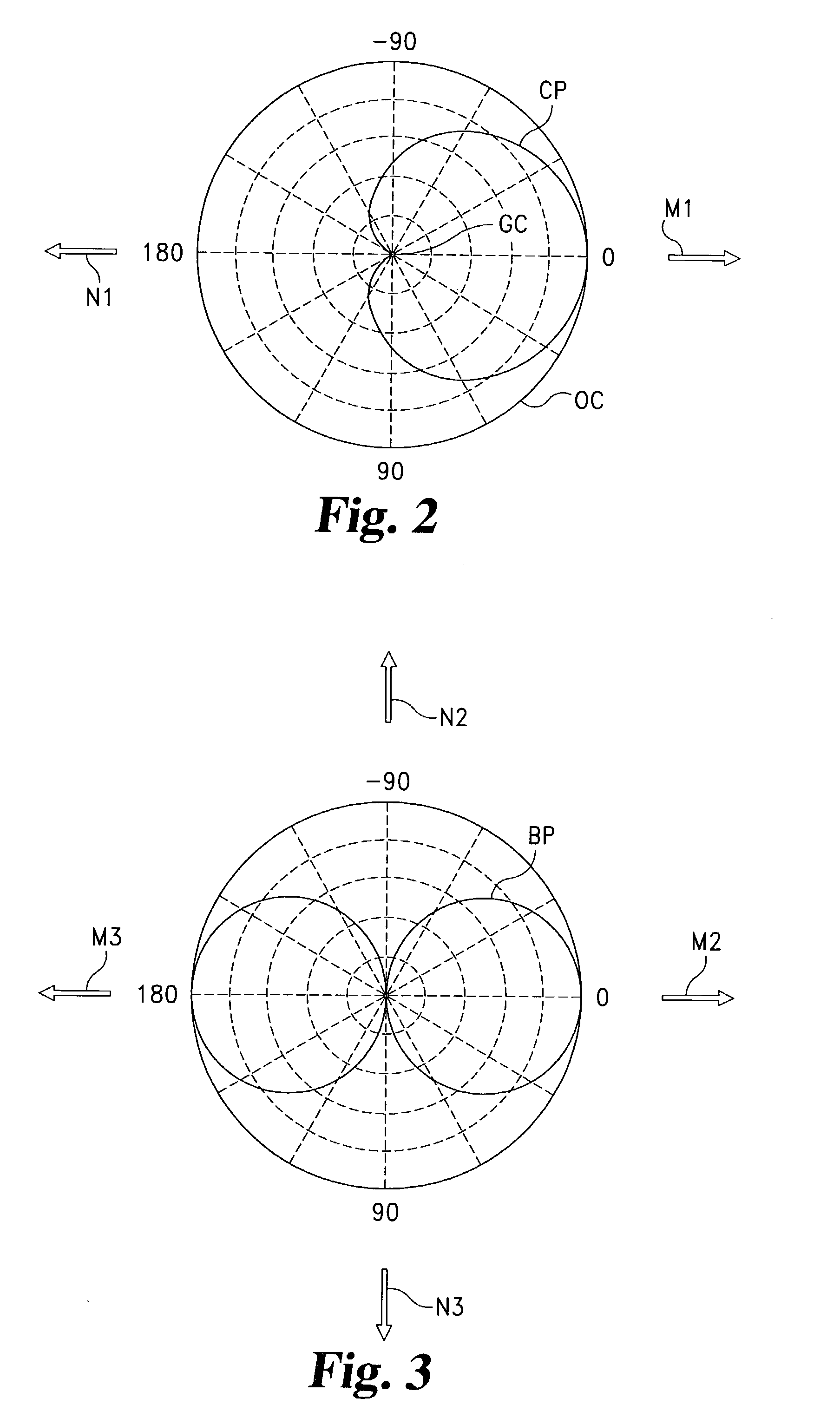
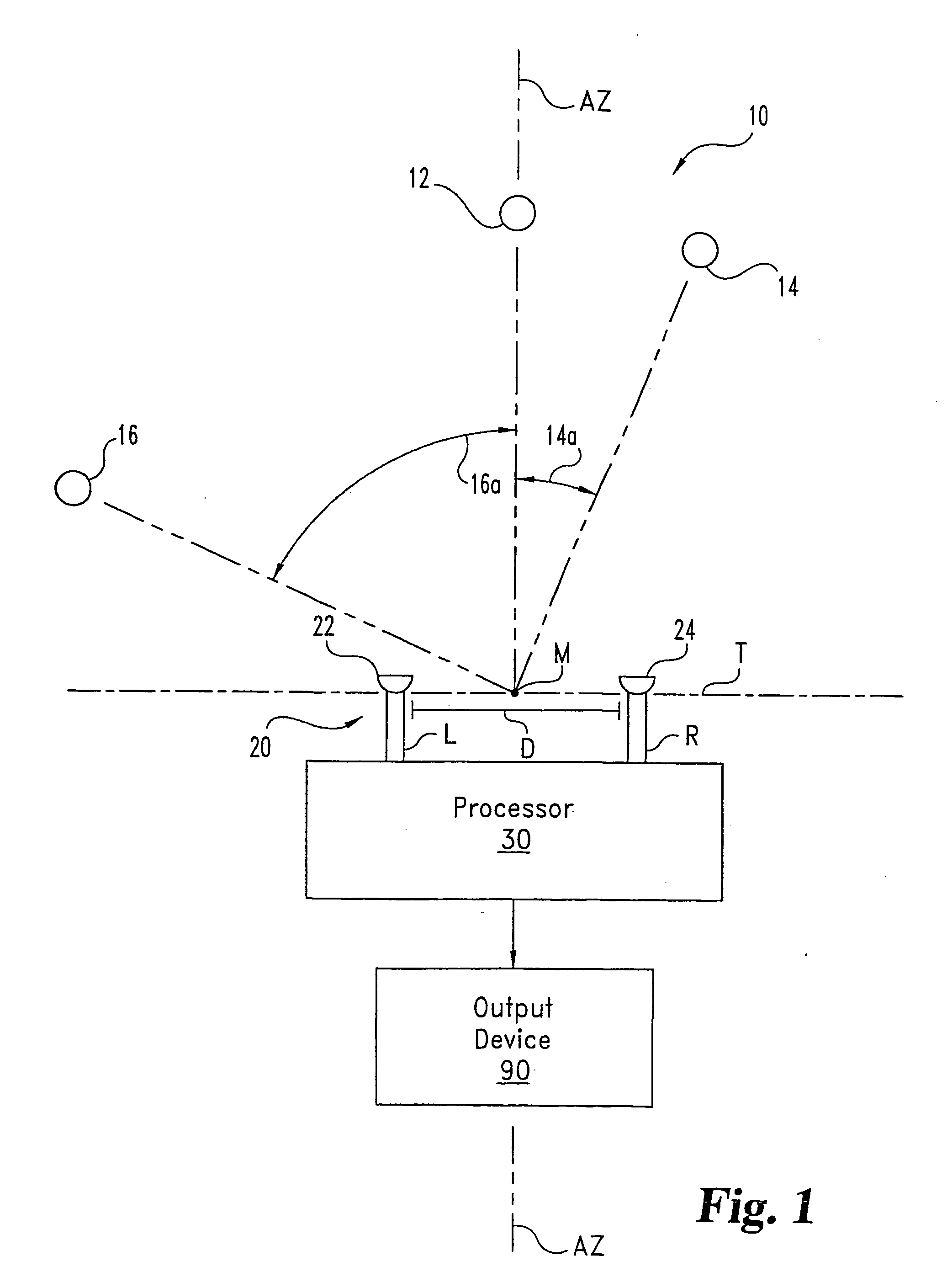
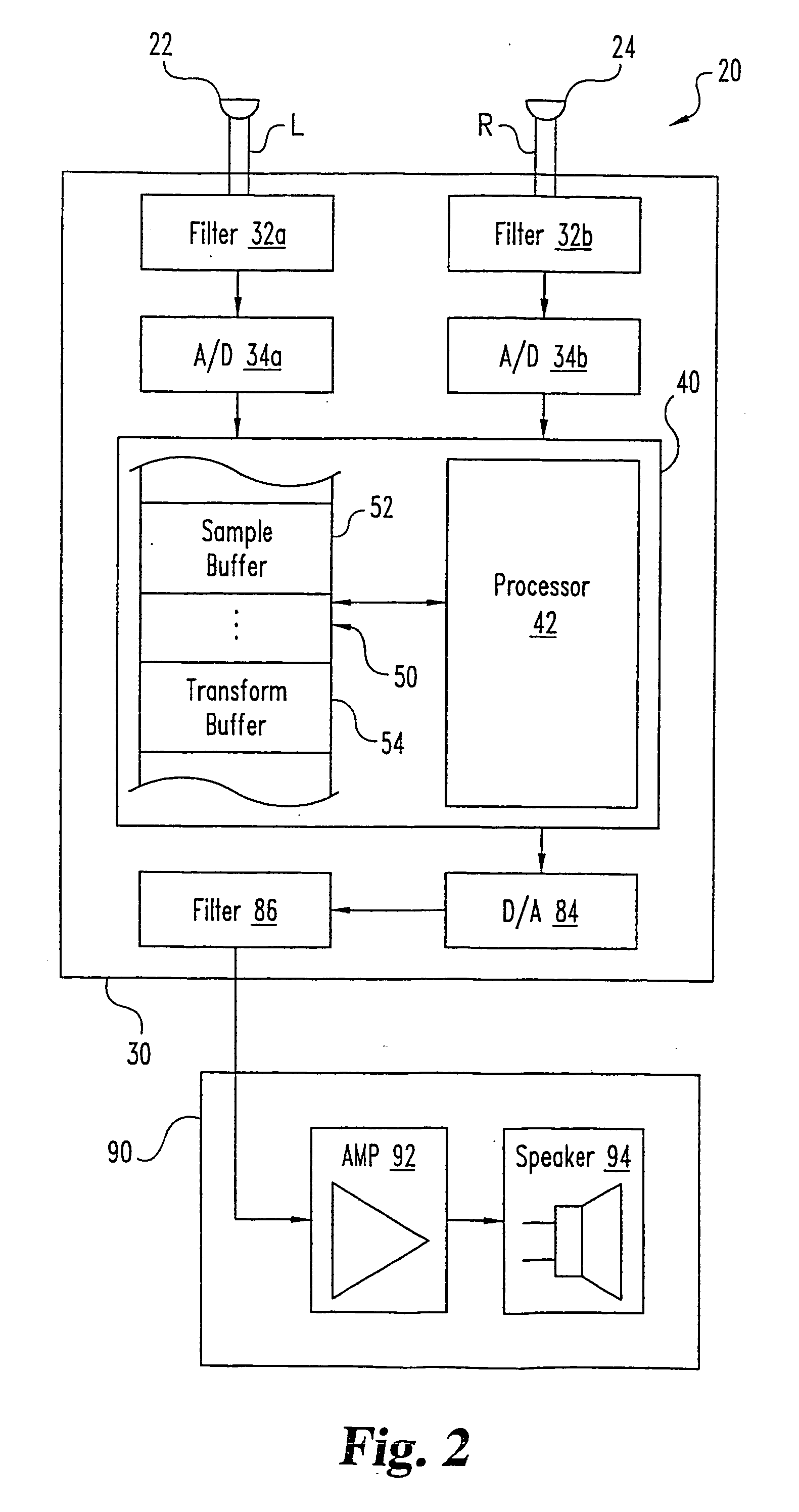
System (10) is disclosed including an acoustic sensor array (20) coupled to processor (42). System (10) processes inputs from array (20) to extract a desired acoustic signal through the suppression of interfering signals. The extraction / suppression is performed by modifying the array (20) inputs in the frequency domain with weights selected to minimize variance of the resulting output signal while maintaining unity gain of signals received in the direction of the desired acoustic signal. System (10) may be utilized in hearing, cochlear implants, speech recognition, voice input devices, surveillance devices, hands-free telephony devices, remote telepresence or teleconferencing, wireless acoustic sensor arrays, and other applications.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
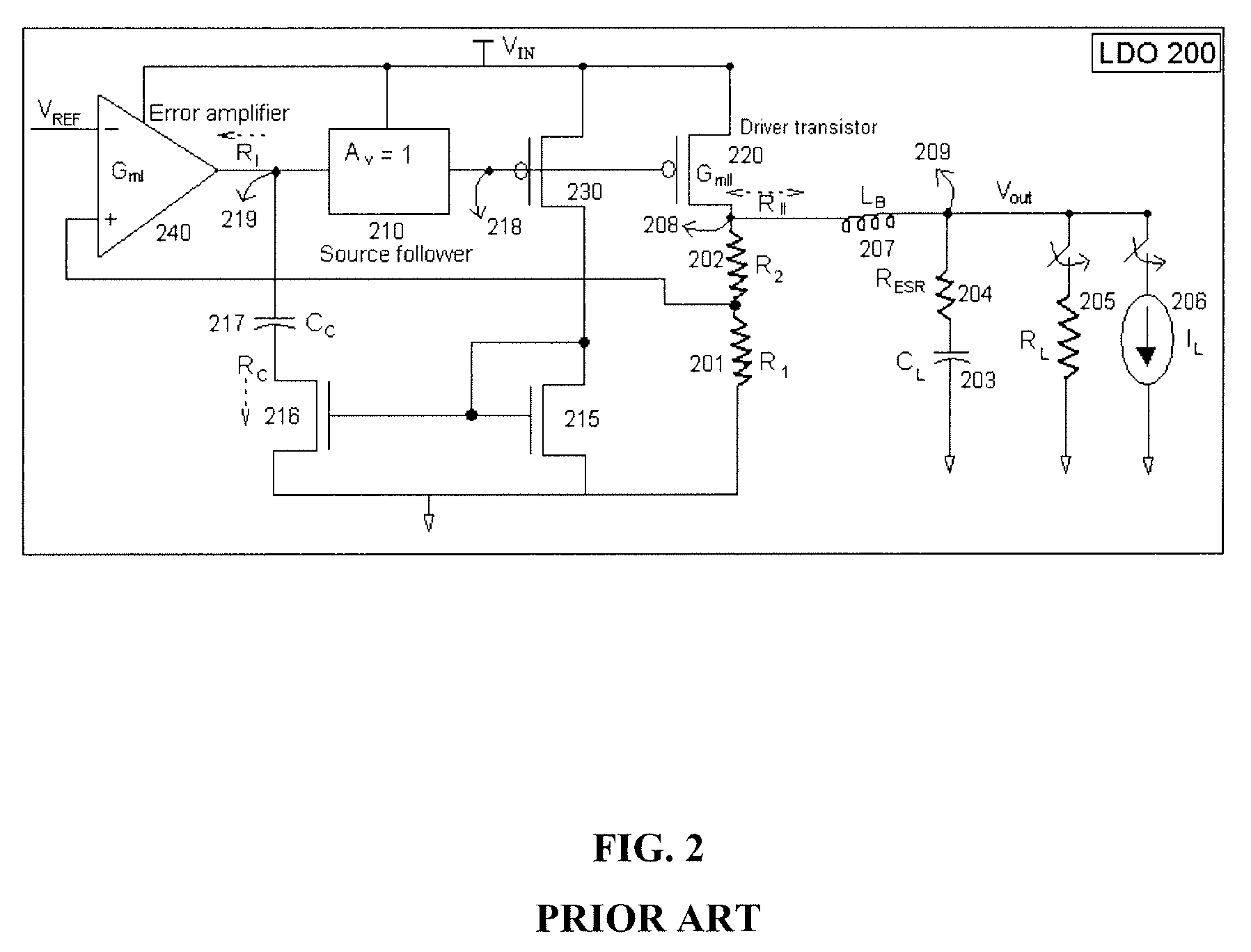
Low dropout regulator with stability compensation
InactiveUS7589507B2Good phase marginMinimize power consumptionElectric variable regulationLow loadEngineering
The present invention provides a low dropout (LDO) regulator with a stability compensation circuit. A “zero frequency” tracking as well as “non-dominant parasitic poles' frequency reshaping” are performed to achieve a good phase margin for the LDO by means of the compensation circuit. In this compensation method neither a large load capacitor nor its equivalent series resistance is needed to stabilize a regulator. LDO regulators, in system on chip application, having load capacitors in the range of few nano-Farads to few hundreds of nano-Farads can be efficiently compensated with this compensation method. A dominant pole for the regulator is realized at an internal node and the second pole at an output node of the regulator is tracked with a variable capacitor generated zero over a range of load current to cancel the effect of each other. A third pole of the system is pushed out above the unity gain frequency of the open loop transfer function with the help of the frequency compensation circuit. The compensation technique is very effective in realizing a low power, low-load-capacitor LDO desirable for system on chip applications.
Owner:ST ERICSSON SA
Cell balancing circuit
A cell balancing circuit monitors the voltage between serially connected cells and compares it to a reference voltage. From that comparison, the cell balancing circuit sources or sinks current into a midpoint node between rechargeable cells to keep the cells balanced during the charging process. In one preferred embodiment, the cell balancing circuit includes an op-amp, connected in a unity gain configuration. A voltage divider establishes a reference voltage equal to the average of the two cell voltages. The op-amp compares this average to the measured voltage at the midpoint node. When the average voltage exceeds the voltage at the midpoint node, the op-amp sources current into the midpoint node. When the average voltage falls below the voltage at the midpoint node, the op-amp sinks current from the midpoint node. By sourcing or sinking current, the cell balancing circuit allows the lesser charged cell to catch up with the more fully charged cell.
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
Method and structure for improving the linearity of MOS switches
InactiveUS6897701B2Improve dynamic rangeEliminate the effects ofTransistorPulse automatic controlCapacitanceLinearity
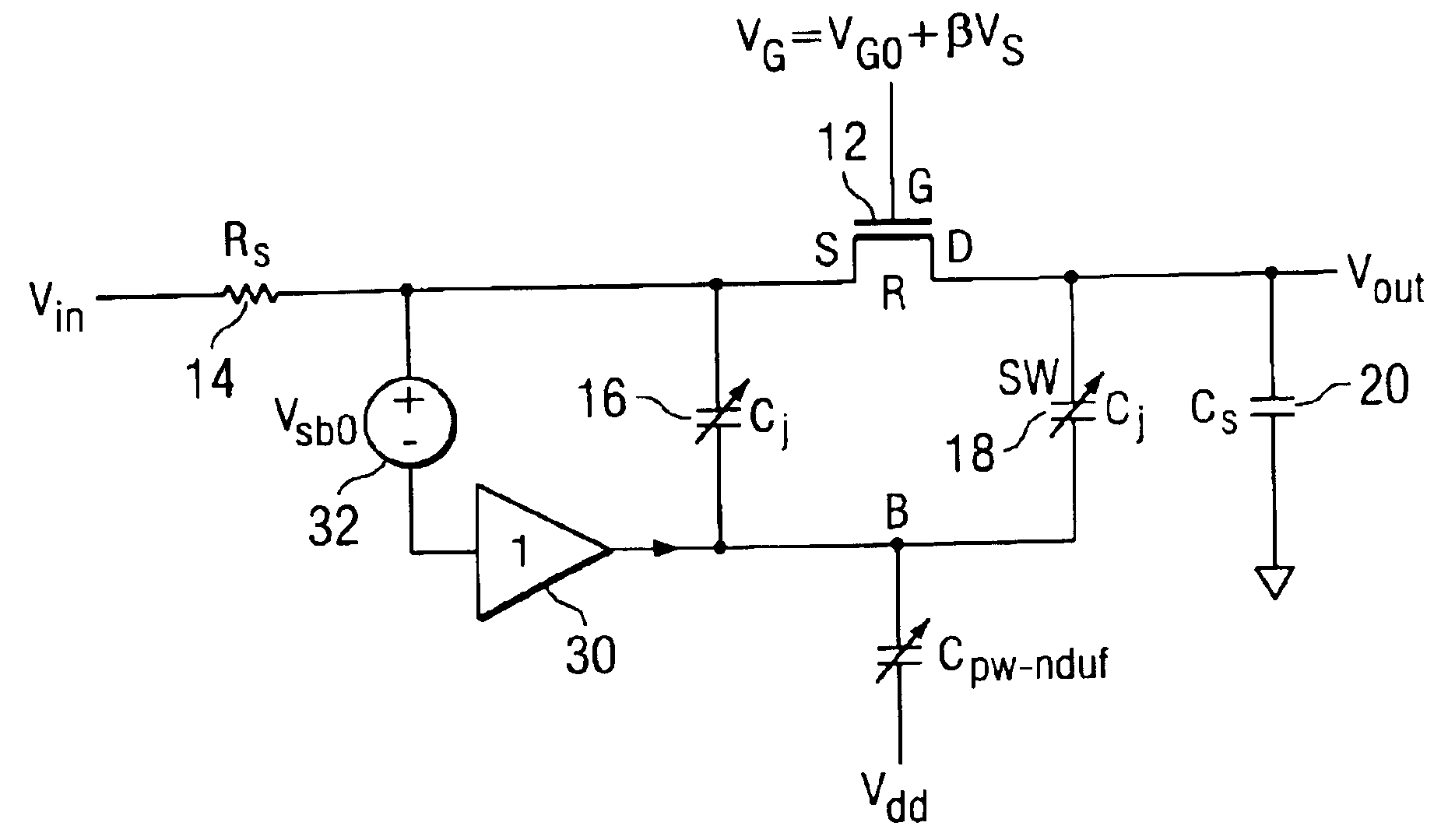
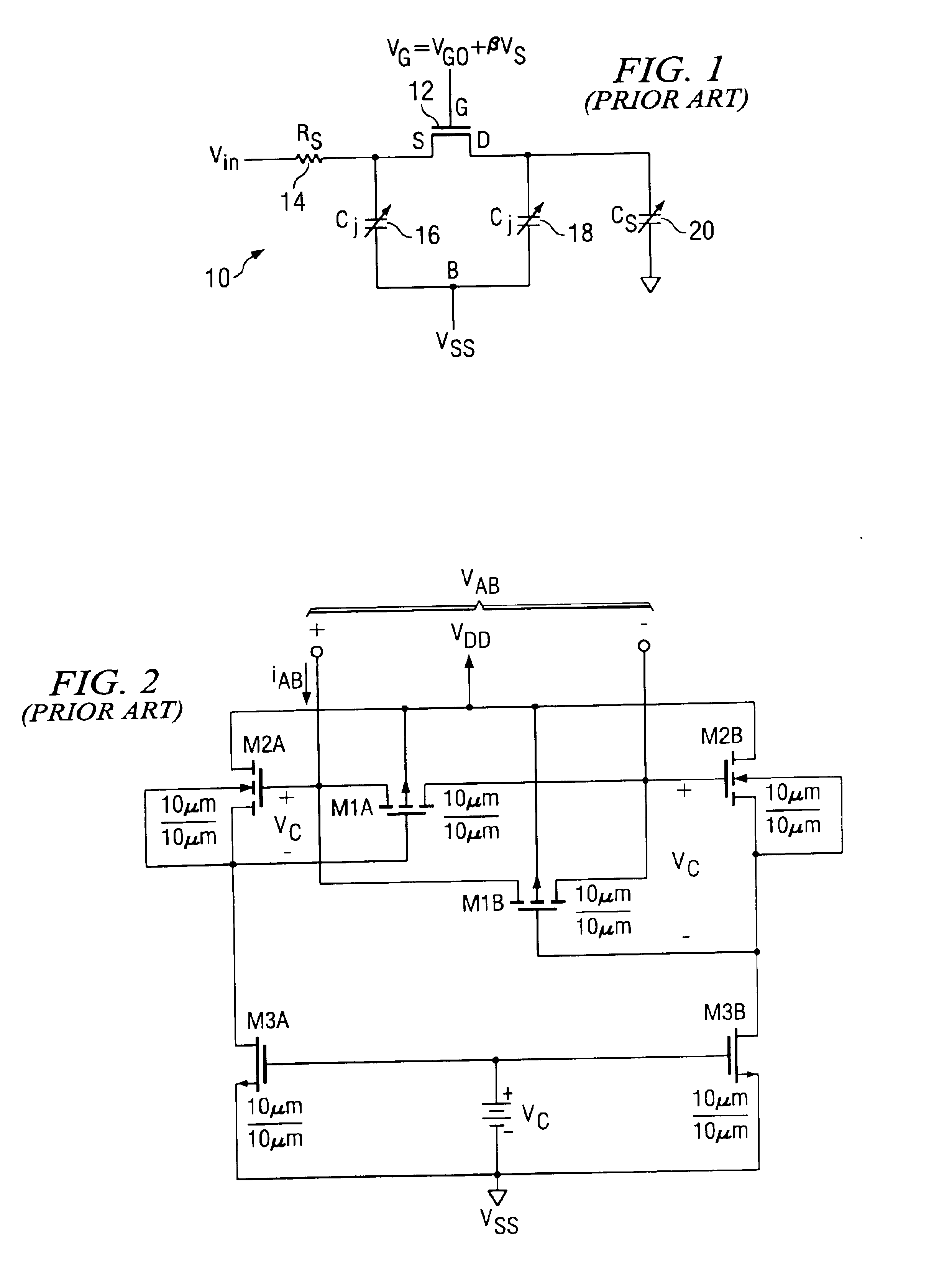
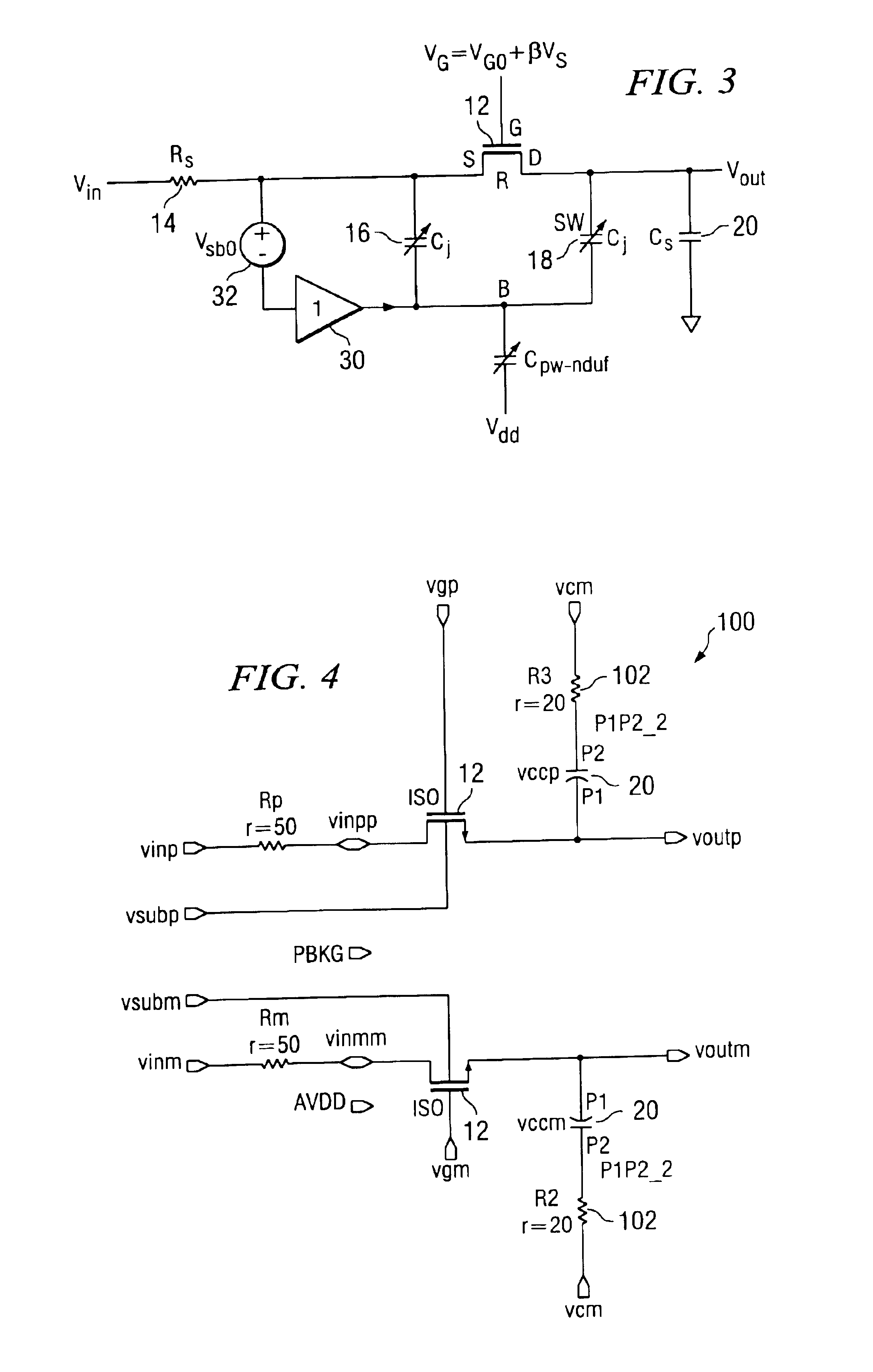
A technique is provided to linearize a MOS switch on-resistance and the nonlinear junction capacitance. The technique linearizes the sampling switch by using a buffer having substantially unity gain with proper DC shift to drive an isolated bulk terminal of the MOS well to improve the spurious free dynamic range (SFDR). In this way, the 2nd-order effect such as nonlinear body effect (VT(VSB)) and nonlinear junction capacitance (Cj(VSB)) can be substantially removed.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Current-limiting circuitry
ActiveUS20050275394A1Preventing excessive current flow through the FETReduce voltagePower supply linesElectric variable regulationDriver circuitCurrent limiting
A field effect transistor (FET) driver circuit includes an error amplifier for providing a FET control signal and a current limiting amplifier for preventing excessive current flow through the FET. The current limiting amplifier generates an overcurrent signal when an excessive current is detected. In response to the overcurrent signal, a voltage control circuit adjusts the voltage at the output of the error amplifier to turn off the FET. Meanwhile, a pulldown circuit at an input of the error amplifier adjusts the voltage provided to that input to cause the error amplifier to provide an output voltage that also tends to turn off the FET. If a buffer is present at that input to the error amplifier, a second pulldown circuit is placed at the input to the buffer to maintain a stable unity gain across the buffer.
Owner:MICREL
Cascode fully integrated low-dropout linear voltage regulator circuit
ActiveCN105005351AHigh loop gainImproved load transient response performanceElectric variable regulationCapacitanceLow load
The invention discloses a cascode fully integrated low-dropout linear voltage regulator circuit. According to the invention, a ascode current source is introduced to replace a conventional single transistor current source in a Cascoded Flipped Voltage Follower-Low-dropout (CAFVF-LDO) circuit, which increases the loop gain of the CAFVF-LDO circuit under heavy load condition; at the same time based on the structure features of the Cascode Current Source (CCS), a cascode compensation technology is introduced. Compared with the conventional CAFVF-LDO, the circuit of the invention, by means of a very small on chip compensation capacitor, realizes stable operation under a much lower load current, and a cascode compensation capacitor also expands the Unity-Gain-Frequency (UGF) of the LDO circuit under heavy load condition, and further improves load transient response of the circuit. The cascode fully integrated low-dropout linear voltage regulator circuit can be widely applied to the field of integrated circuits.
Owner:拓尔微电子股份有限公司
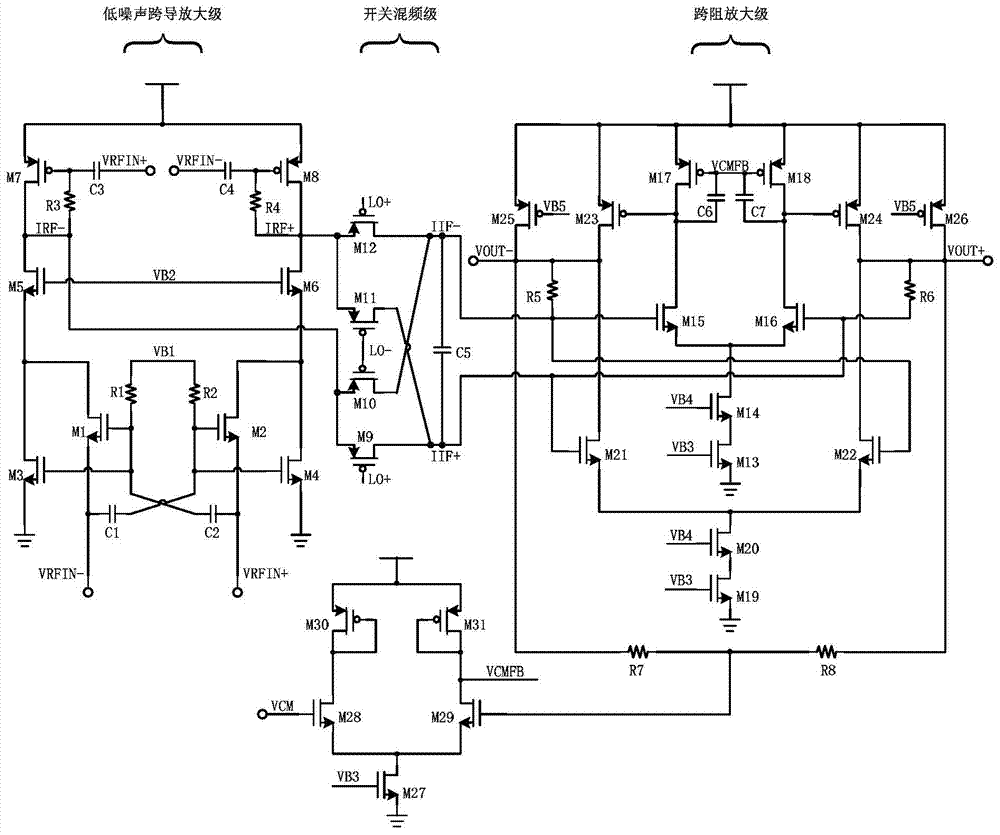
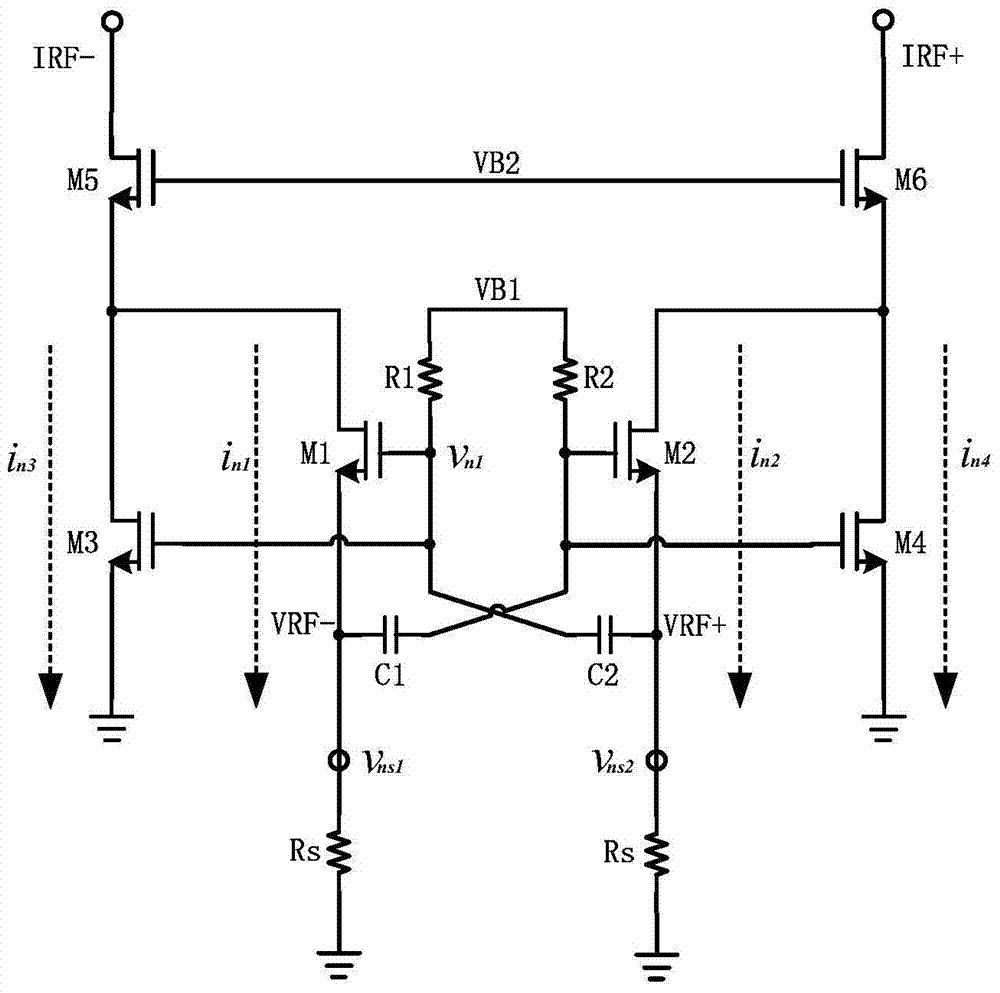
Low-noise passive frequency mixer
InactiveCN103490731AImprove Noise PerformanceReduce noiseTransmissionMulti-frequency-changing modulation transferenceLow noiseIntermediate frequency
The invention discloses a low-noise passive frequency mixer. The low-noise passive frequency mixer comprises a low-noise transconductance amplifier stage, a switch frequency mixing stage and a transimpedance amplifier stage. The low-noise transconductance amplifier stage mainly adopts a cross coupling master-slave noise cancellation technology, a main transconductance conduit adopts a cross coupled structure to double an equivalent transconductance value, an appropriate transconductance value is provided through the main transconductance conduit and the noise of the main transconductance conduit is lowered through a master-slave structure; the switch frequency mixing stage is used for modulating and filtering radiofrequency currents output from the low-noise transconductance amplifier stage and outputting intermediate frequency currents; the transimpedance amplifier stage consists of a full-differential operational transconductance amplifier and a load resistor; the operational transconductance amplifier is based on a feed-forward compensation technology, and a consequent pole point in a transfer function of the amplifier is offset by a zero point introduced to a feed-forward stage of the operational transconductance amplifier, so that a large unity-gain bandwidth is achieved; the load resistor is used for converting the intermediate frequency currents into intermediate frequency voltage signals which are then output, by virtue of a voltage-current negative-feedback connection way. The low-noise passive frequency mixer has the characteristics of low noise, high gain and low power consumption.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
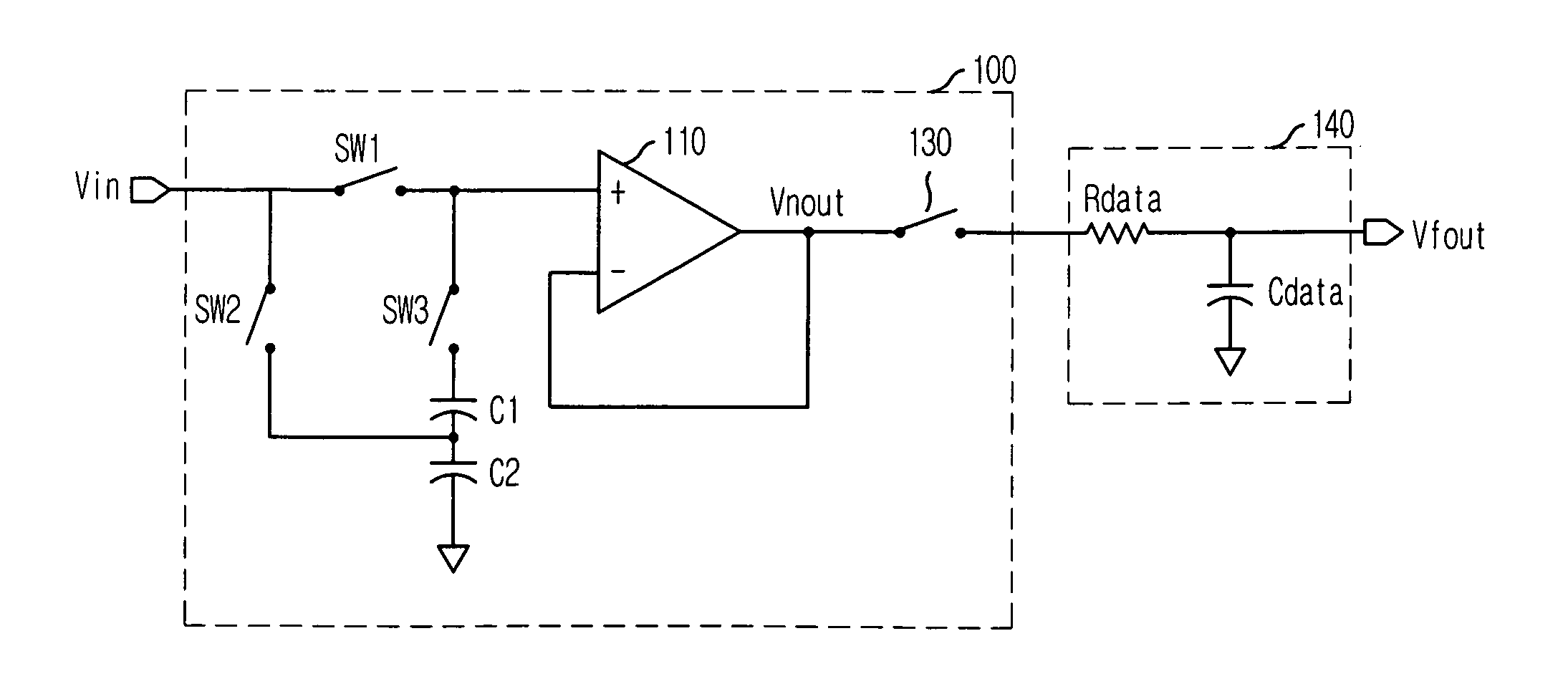
Liquid crystal on silicon (LCOS) display driving system and the method thereof
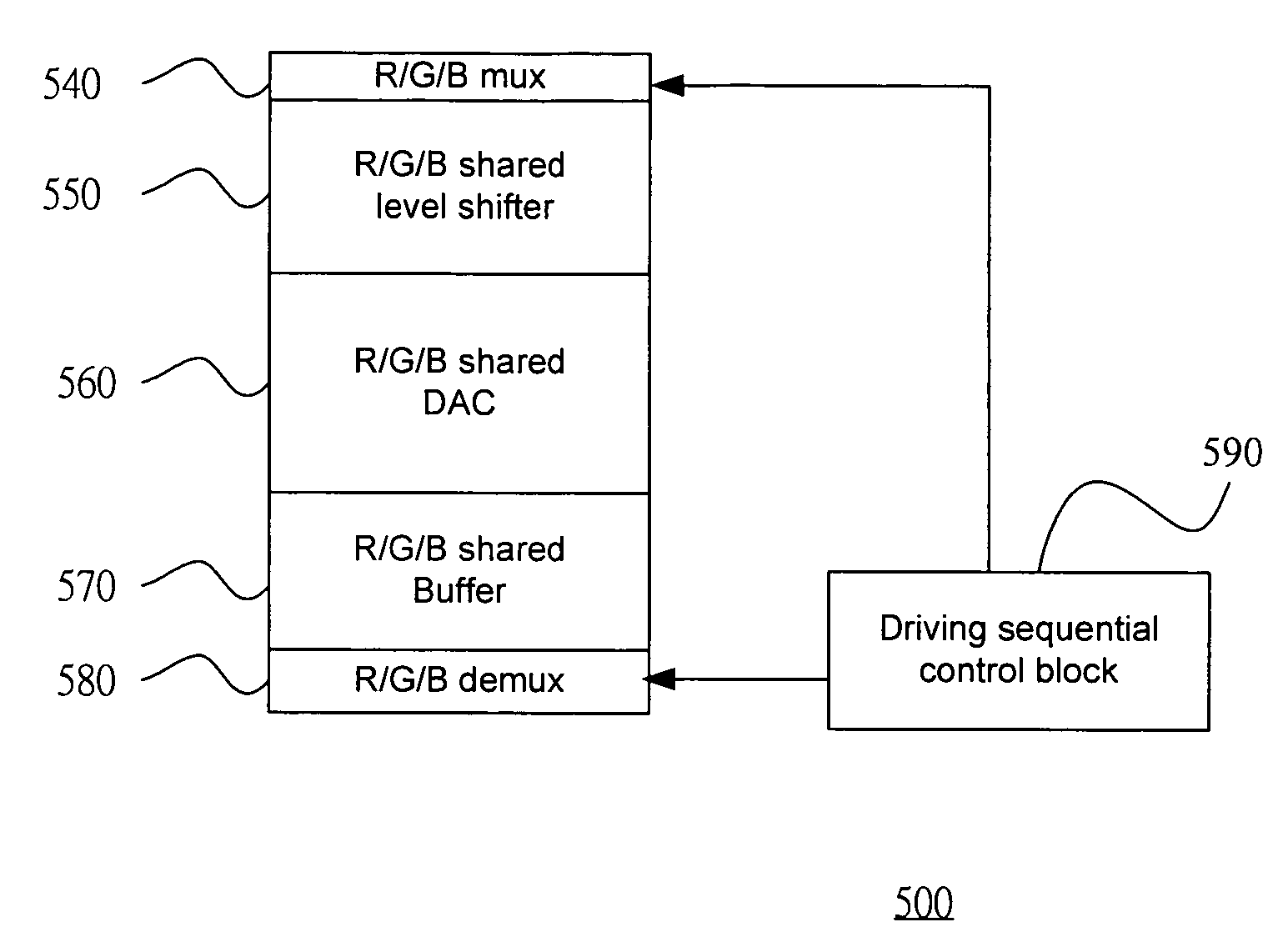
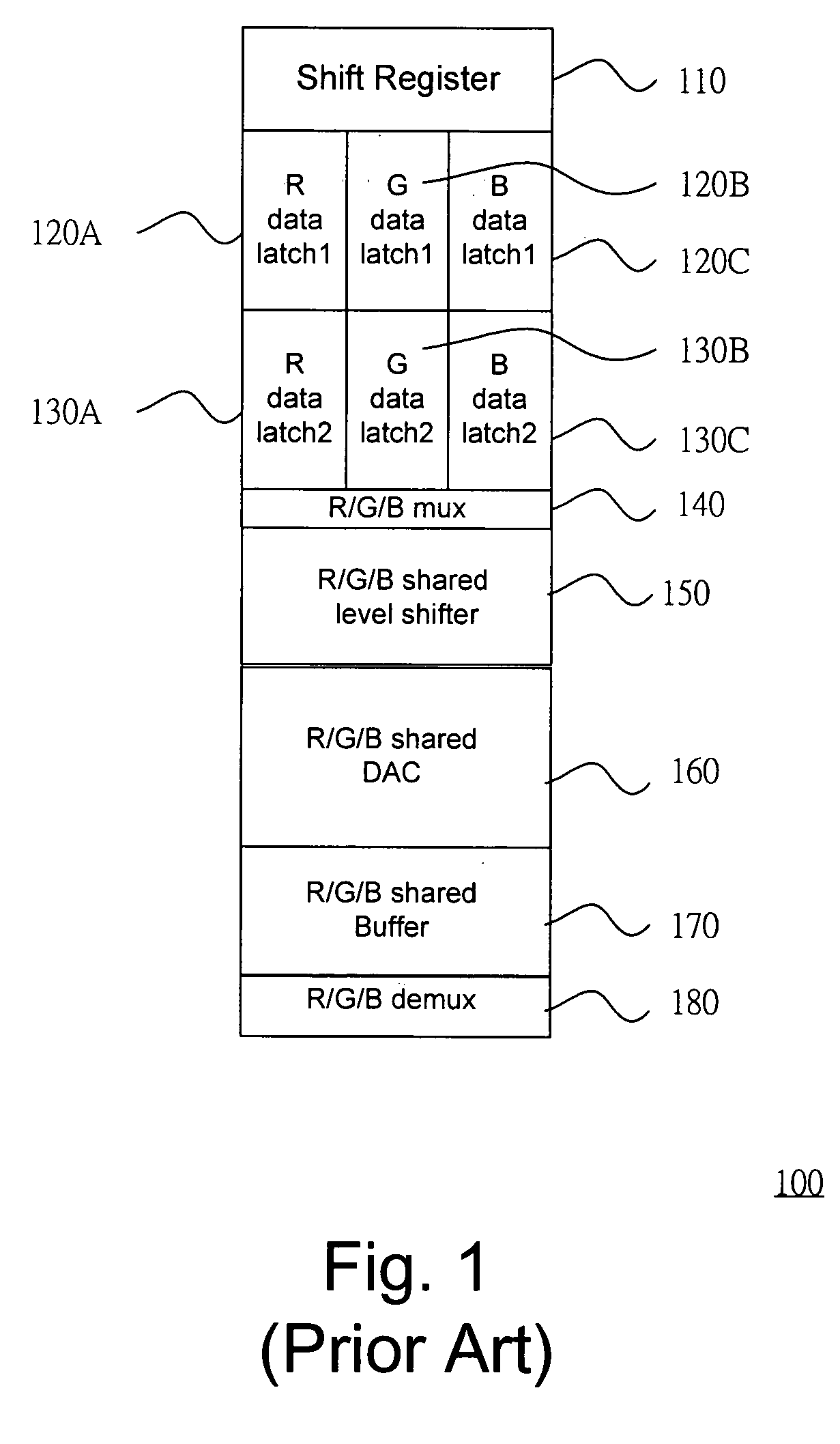
ActiveUS20060176256A1Minimize coupling effectMinimize impactTelevision system detailsStatic indicating devicesMultiplexingDigital analog converter
The present invention relates to a LCOS display driving system. The driving sequential control block generates a control code representing a loading sequence of the R, G, and B data for pixels in one of scan lines. The multiplexer multiplexes the R, G, and B data from latches according the control code. The shared level shifter shifts the level of the R, G, and B data from the multiplexer. The digital analog converts converting the R, G, and B data to a corresponding analog R, G, and B data voltage. The shared unity-gain buffer stores the analog R, G, and B data voltage from the shared digital analog converter. The demultiplexer demultiplexes the analog R, G, and B data voltage according the control code.
Owner:HIMAX TECH LTD
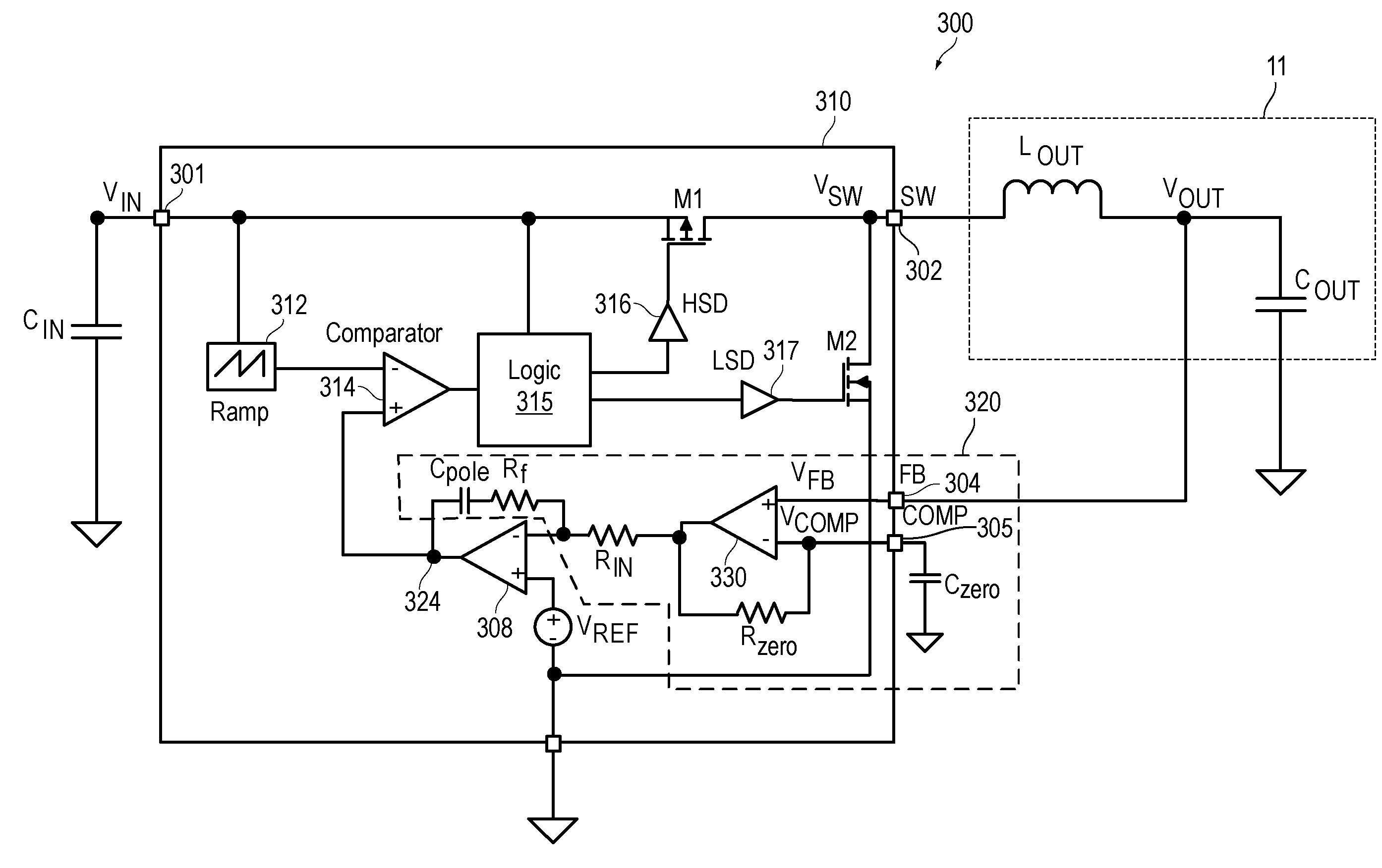
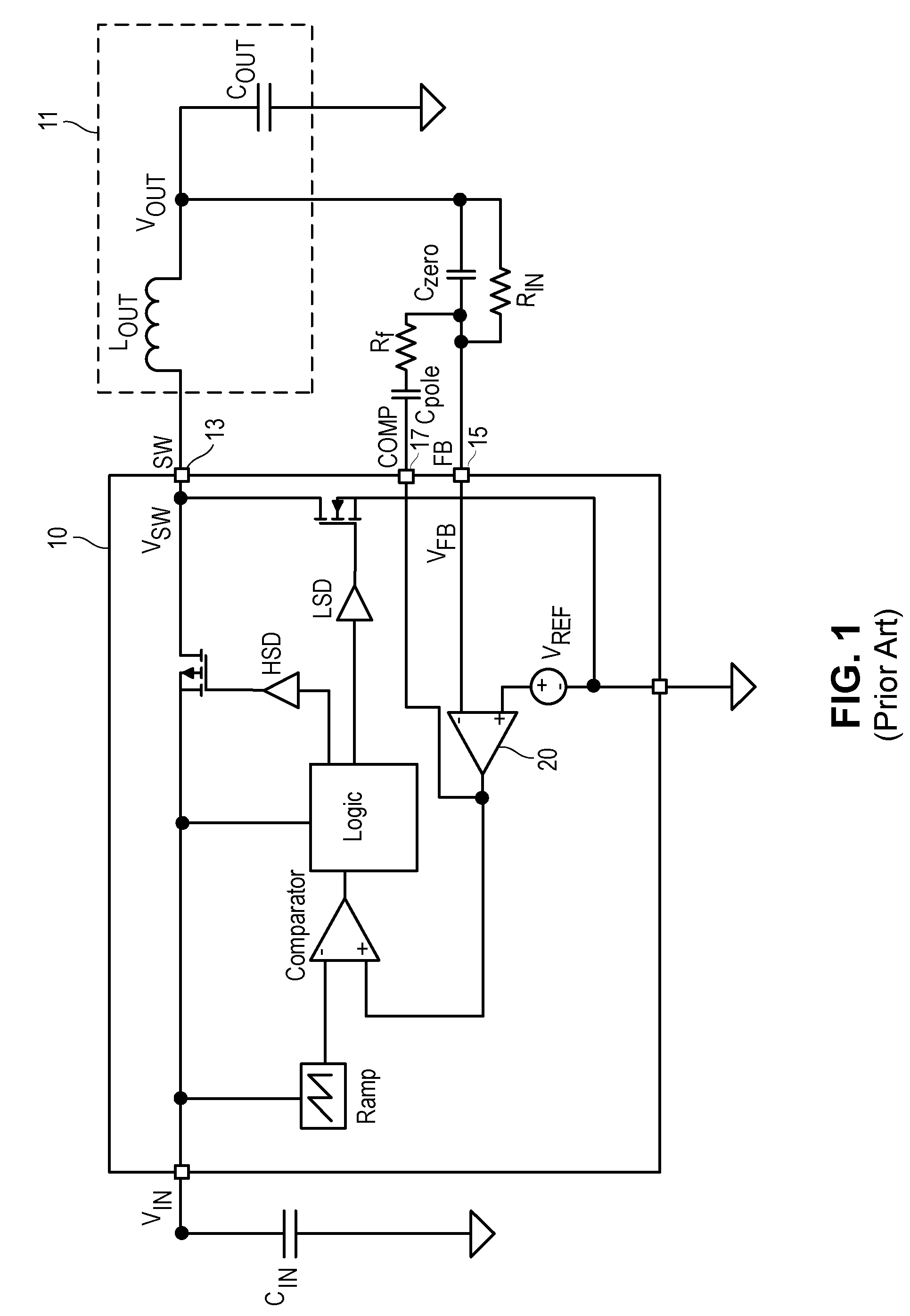
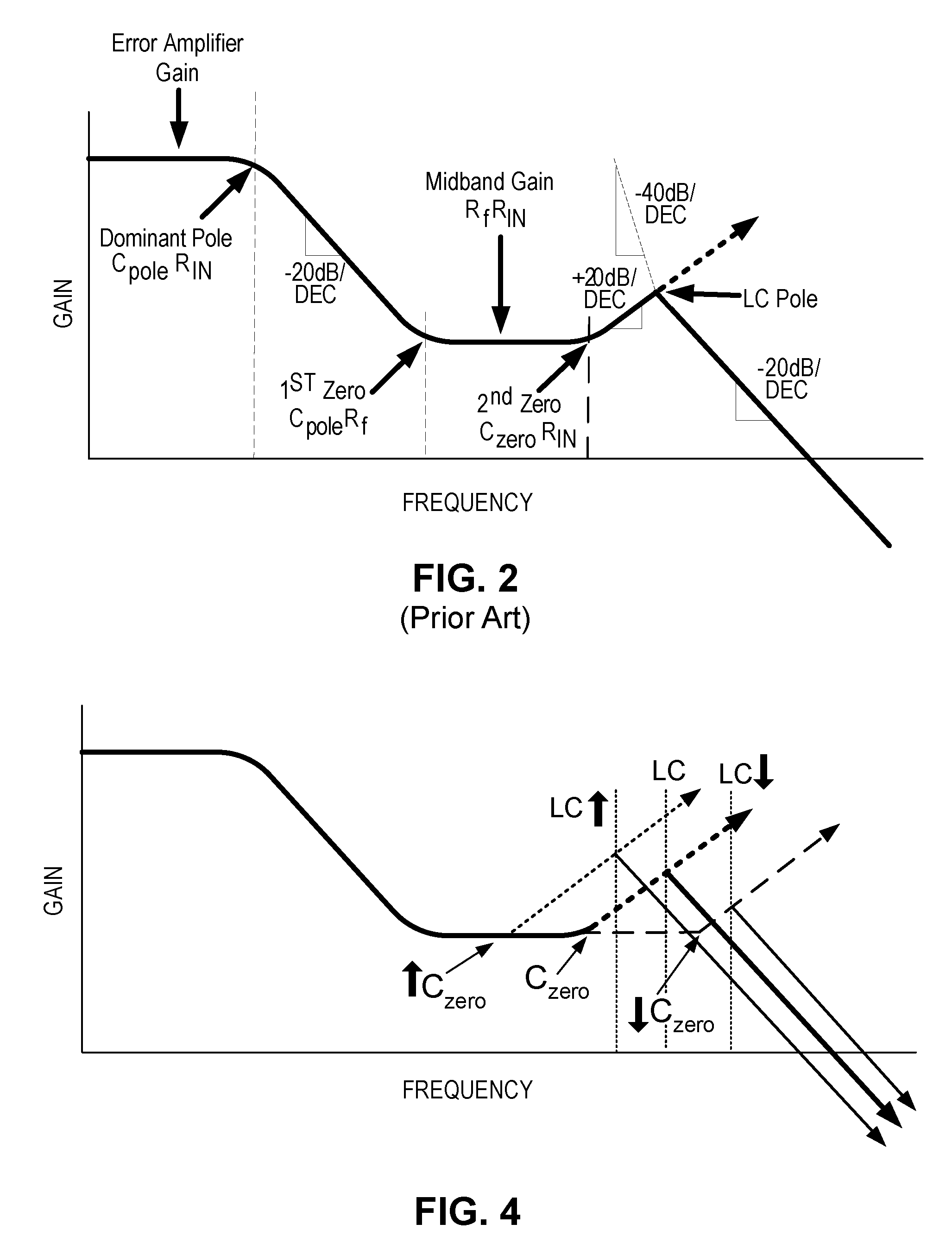
Frequency compensation scheme for a switching regulator using external zero
ActiveUS7170264B1Simple for the user to implementZero compensationDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationFrequency compensationAudio power amplifier
A compensation circuit in a monolithic switching regulator controller being incorporated in a closed loop feedback system of a switching regulator includes an amplifier configured in a unity gain feedback configuration with a first resistor and including a non-inverting input terminal receiving the feedback voltage and an inverting input terminal coupled to a first terminal of the switching regulator controller. The compensation circuit further includes a first capacitor and a third resistor connected in series between an input terminal and an output terminal of an error amplifier of the switching regulator controller. The first capacitor and the third resistor introduce a first zero in the closed loop feedback system. When a second capacitor is coupled to the first terminal of the switching regulator controller, a second zero is introduced in the closed loop feedback system. The second capacitor is an off-chip capacitor formed external to the monolithic switching regulator controller.
Owner:MICREL
Driving circuit for liquid crystal display device
ActiveUS20060238477A1Simple control structureStatic indicating devicesCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
A driving circuit for Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) device includes a unity-gain operation amplifier (OP amp), three switches, and two capacitors. The unity-gain OP amp buffers and carries a signal voltage on a transmission line. The first switch switches a connection between a noninverting terminal of the unity-gain OP amp and an input line of the signal voltage. One end of the second switch is connected to the input line of the signal voltage. One end of the third switch is connected to the noninverting terminal of the unity-gain OP amp. The first capacitor is connected between the other end of the third switch and the other end of the second switch. The second capacitor is connected between the other end of the first capacitor and the ground voltage terminal.
Owner:MAGNACHIP SEMICONDUCTOR LTD
Systems and methods for interference-suppression with directional sensing patterns
InactiveUS7076072B2Reduce the differenceReduce variancePiezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesMicrophonesSensor arrayEngineering
System (10) is disclosed including an acoustic sensor array (20) coupled to processor (42). System (10) processes inputs from array (20) to extract a desired acoustic signal through the suppression of interfering signals. The extraction / suppression is performed by modifying the array (20) inputs in the frequency domain with weights selected to minimize variance of the resulting output signal while maintaining unity gain of signals received in the direction of the desired acoustic signal. System (10) may be utilized in hearing, cochlear implants, speech recognition, voice input devices, surveillance devices, hands-free telephony devices, remote telepresence or teleconferencing, wireless acoustic sensor arrays, and other applications.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
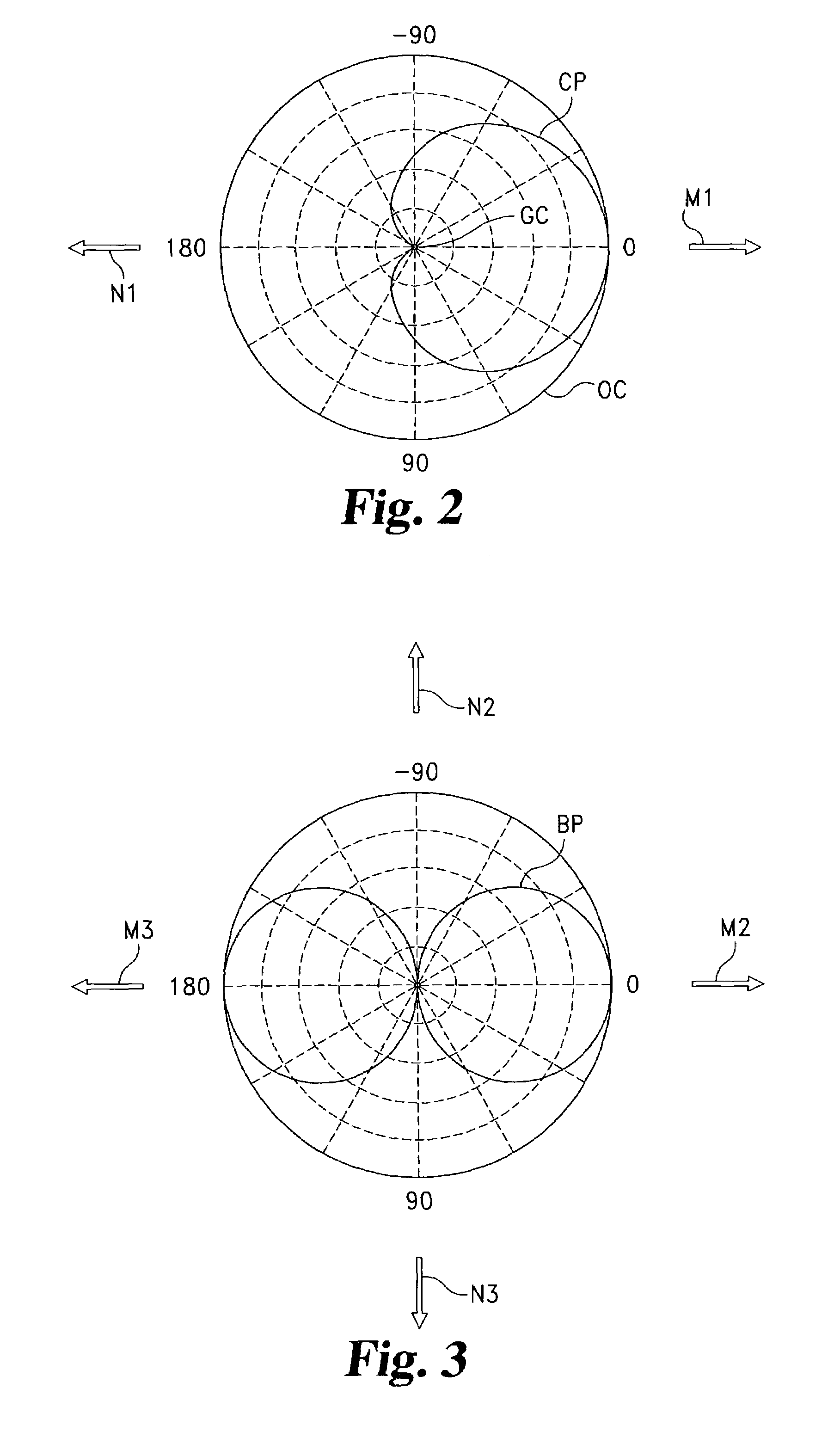
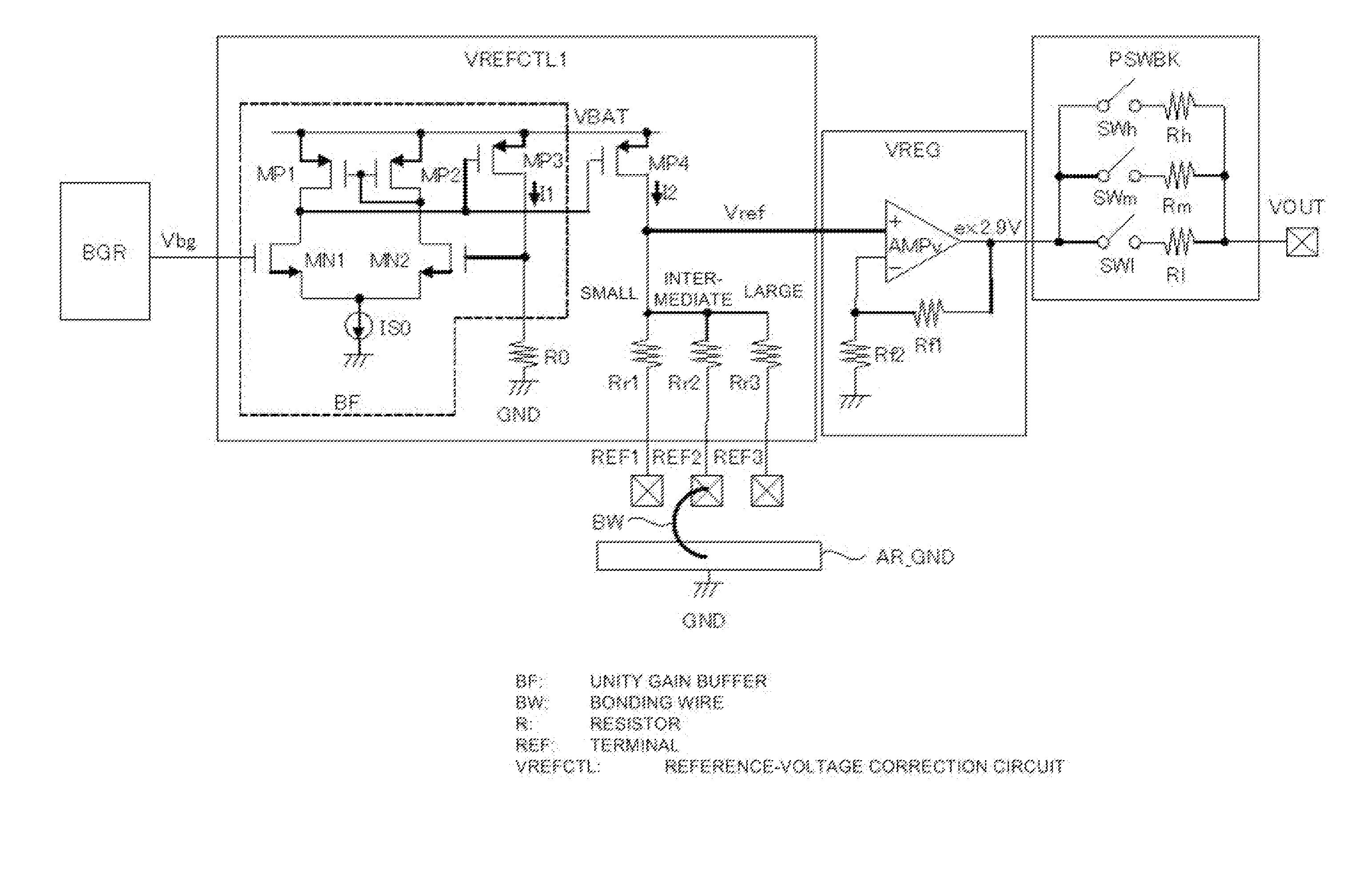
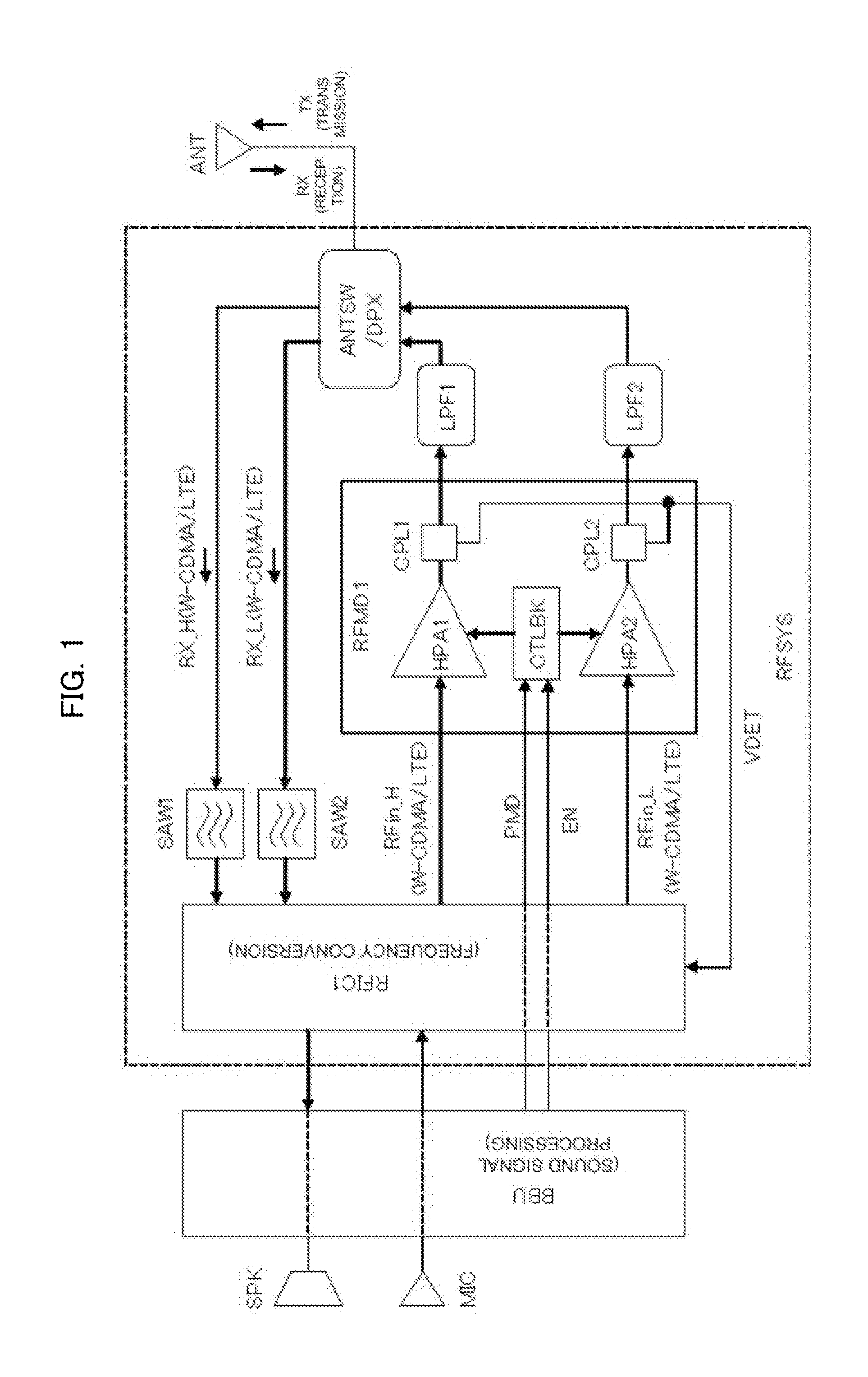
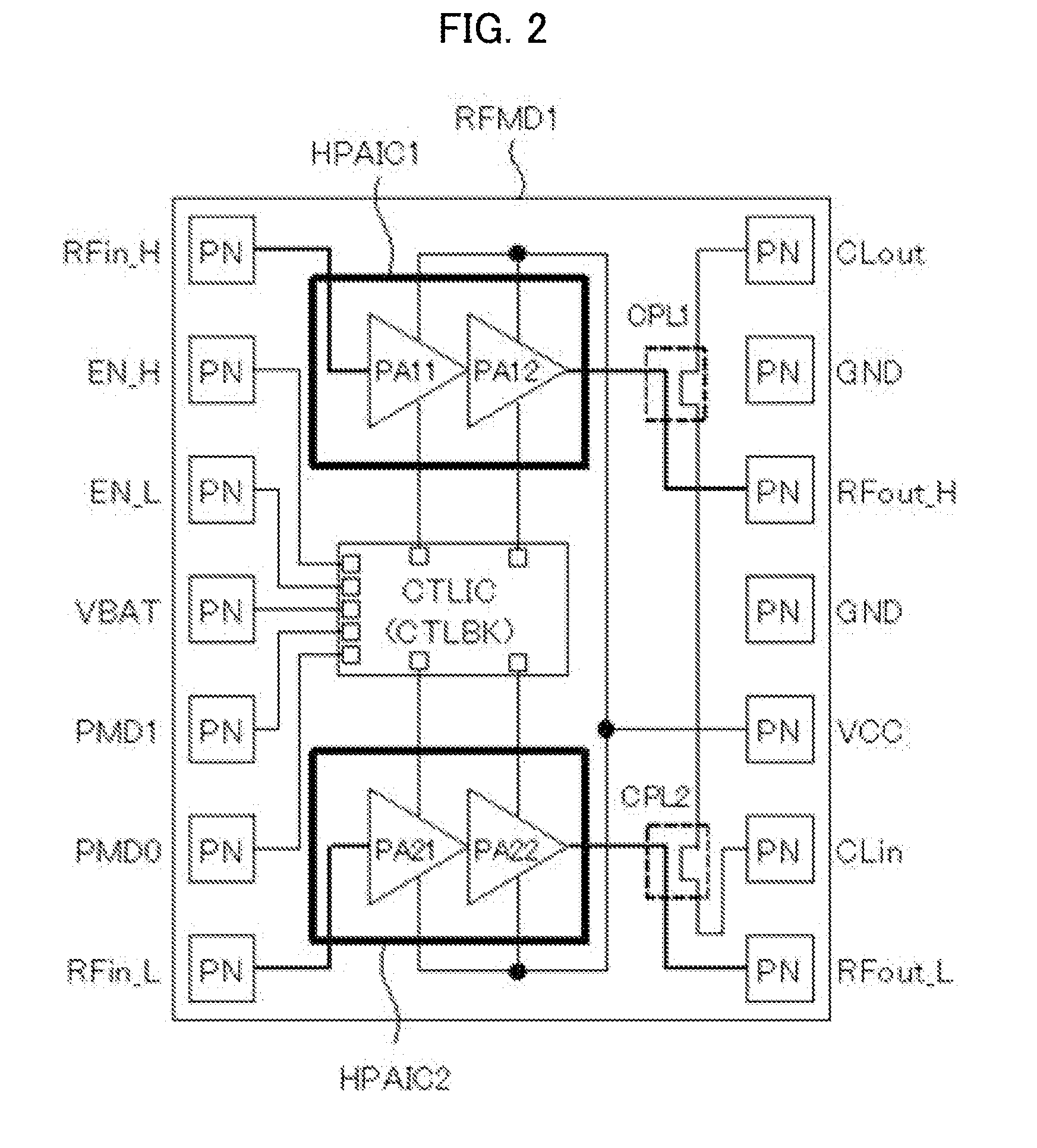
Semiconductor integrated circuit device and high-frequency power amplifier module
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
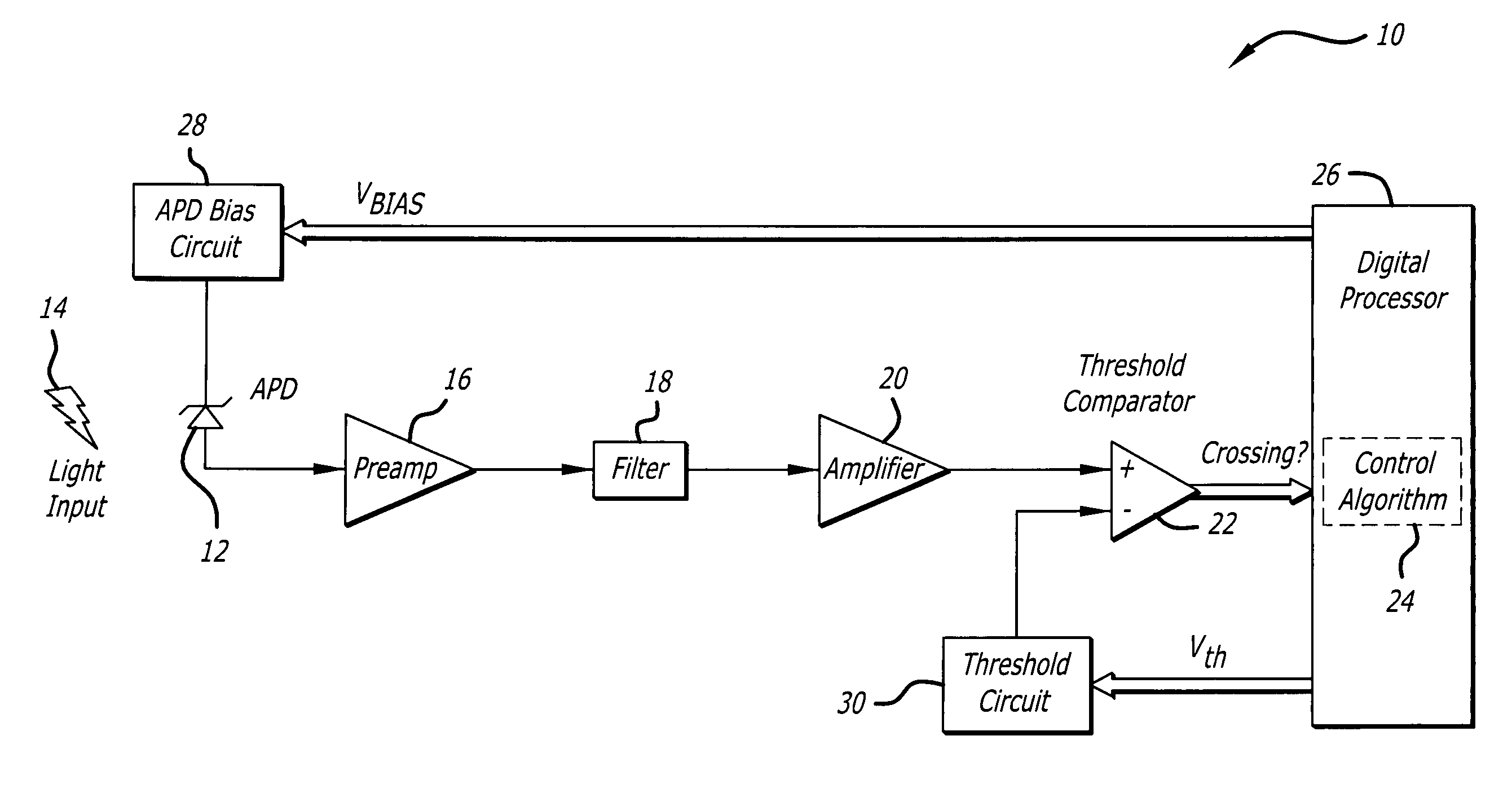
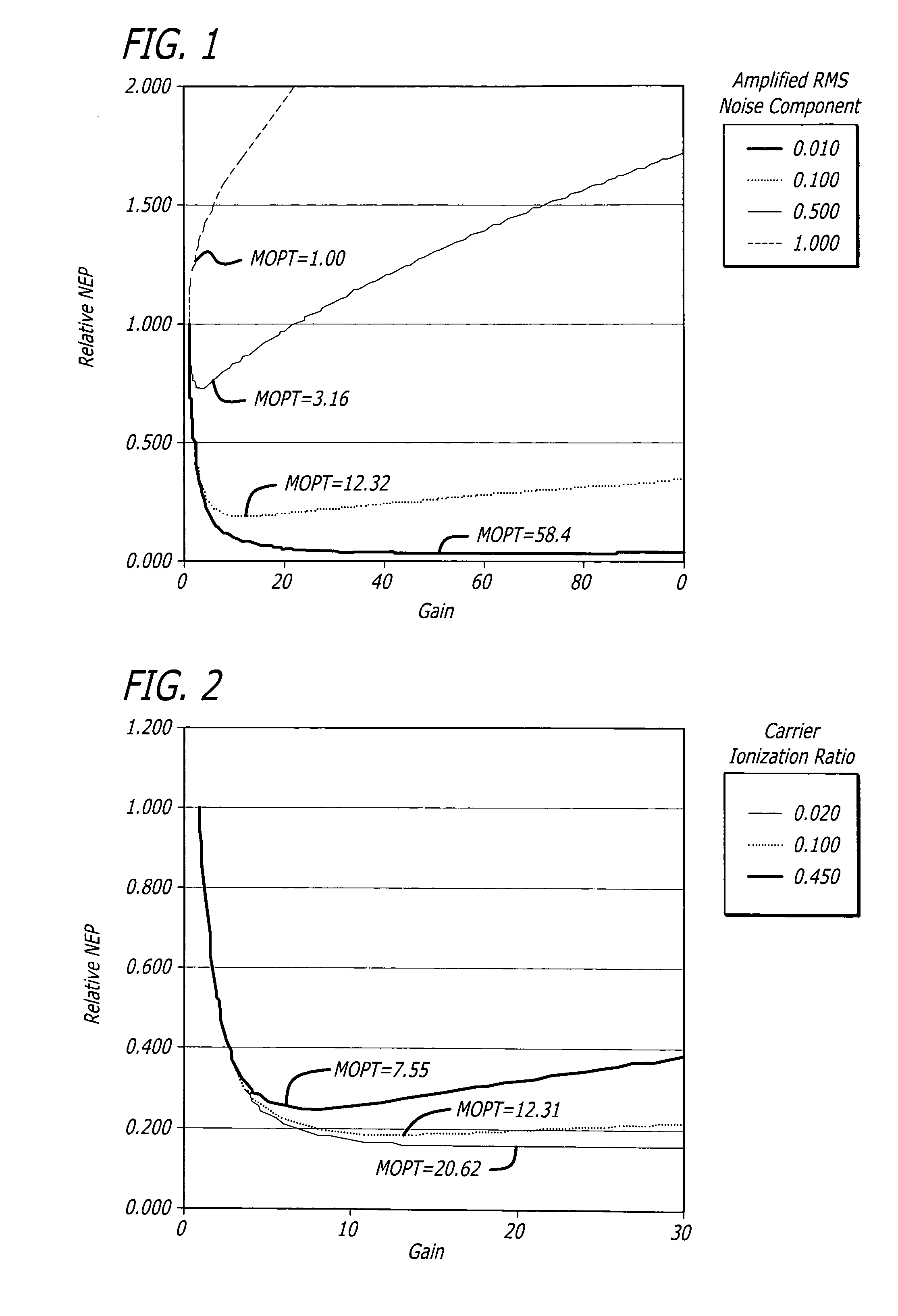
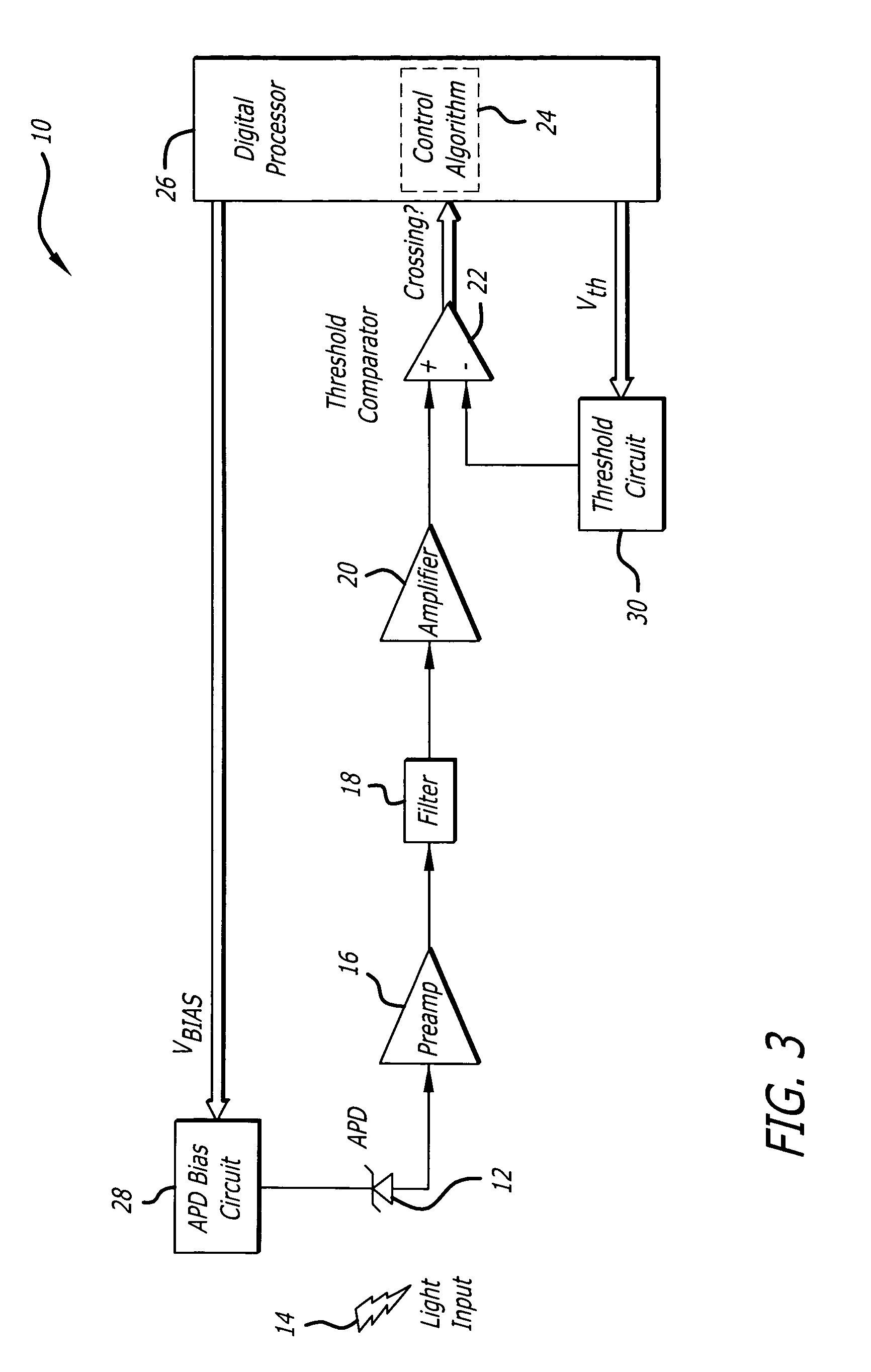
Automatic avalanche photodiode bias setting system based on unity-gain noise measurement
ActiveUS20080017785A1Material analysis by optical meansPhotoelectric discharge tubesEngineeringAvalanche photodiode
A system for setting the bias of a device. The novel bias setting system includes a first system for determining a ratio between noise at an operating gain of the device and noise at a reference gain of the device, and a second system for adjusting the bias until that ratio is equal to a predetermined factor Z. The reference gain is the unity gain or reach-through gain of the device. In an illustrative embodiment, the first system is adapted to measure the noise at operating gain by determining an operating gain threshold, and measure the noise at the reference gain by determining a reference gain threshold. The second system then adjusts the bias until the ratio of the operating gain threshold to the reference gain threshold is equal to the predetermined factor Z.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Interference suppression techniques
System (10) is disclosed including an acoustic sensor array (20) coupled to processor (42). System (10) processes inputs from array (20) to extract a desired acoustic signal through the suppression of interfering signals. The extraction / suppression is performed by modifying the array (20) inputs in the frequency domain with weights selected to minimize variance of the resulting output signal while maintaining unity gain of signals received in the direction of the desired acoustic signal. System (10) may be utilized in hearing aids, voice input devices, surveillance devices, and other applications.
Owner:JONES DOUGLAS +9
Efficient low dropout linear regulator
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
LDO circuit with dynamic compensation and rapid transient response
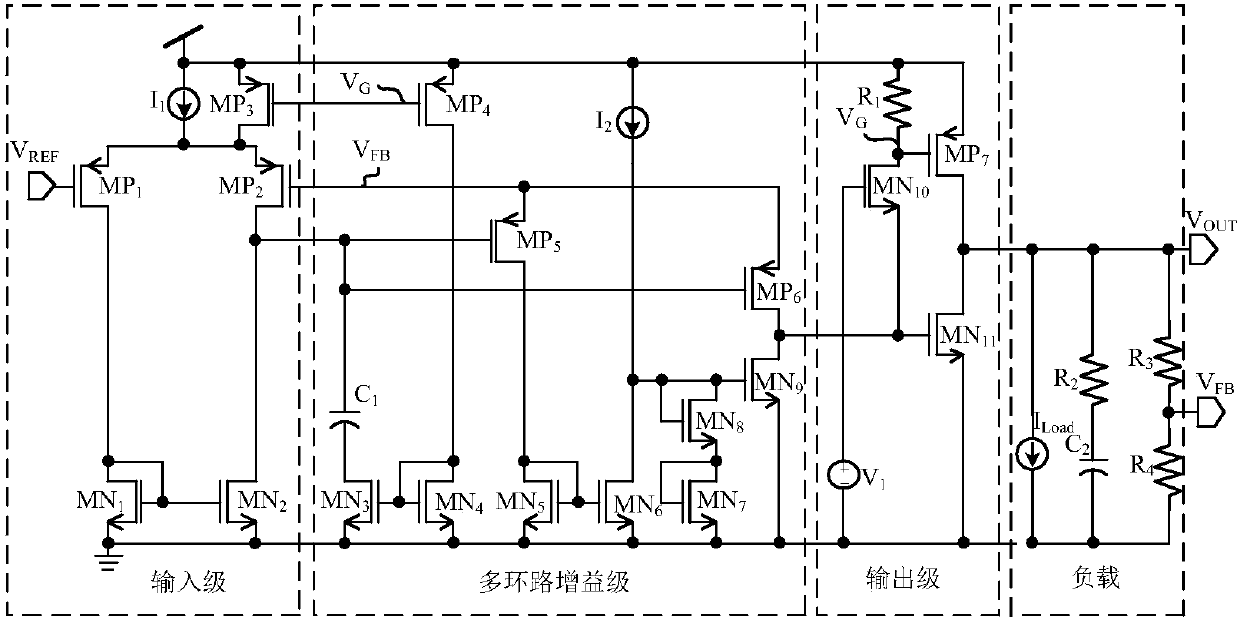
ActiveCN107797599AGuaranteed stabilityImprove power supply rejection ratioElectric variable regulationEngineeringHeavy load
The embodiment of the invention relates to the technical field of analog integrated circuits, in particular to an LDO circuit with dynamic compensation and rapid transient response. The circuit comprises an input stage, a multi-loop gain stage, an output stage and a load stage. By introducing the dynamic bias mode, gain of the input stage, C1 in the multi-loop gain stage and a pole-zero doublet introduced by an MOS resistor RMN3 working in a deep linear region are related to load current ILoad, and the stability of loops within the whole load range is ensured. Meanwhile, due to the dynamic bias mode, the unity-gain bandwidth of the input stage becomes larger, and the power supply rejection ratio of the circuit is increased. In addition, MP6 and MN11 adopted in the multi-loop gain stage, sothat discharging of charges on an output cavity can be accelerated, and the circuit response speed during hopping from heavy load to light load is increased. Due to the MN9, discharging of charges ona power tube MP7 grid stray capacitor can be accelerated, and the response speed of the circuit during hopping from light load to heavy load is increased.
Owner:58TH RES INST OF CETC
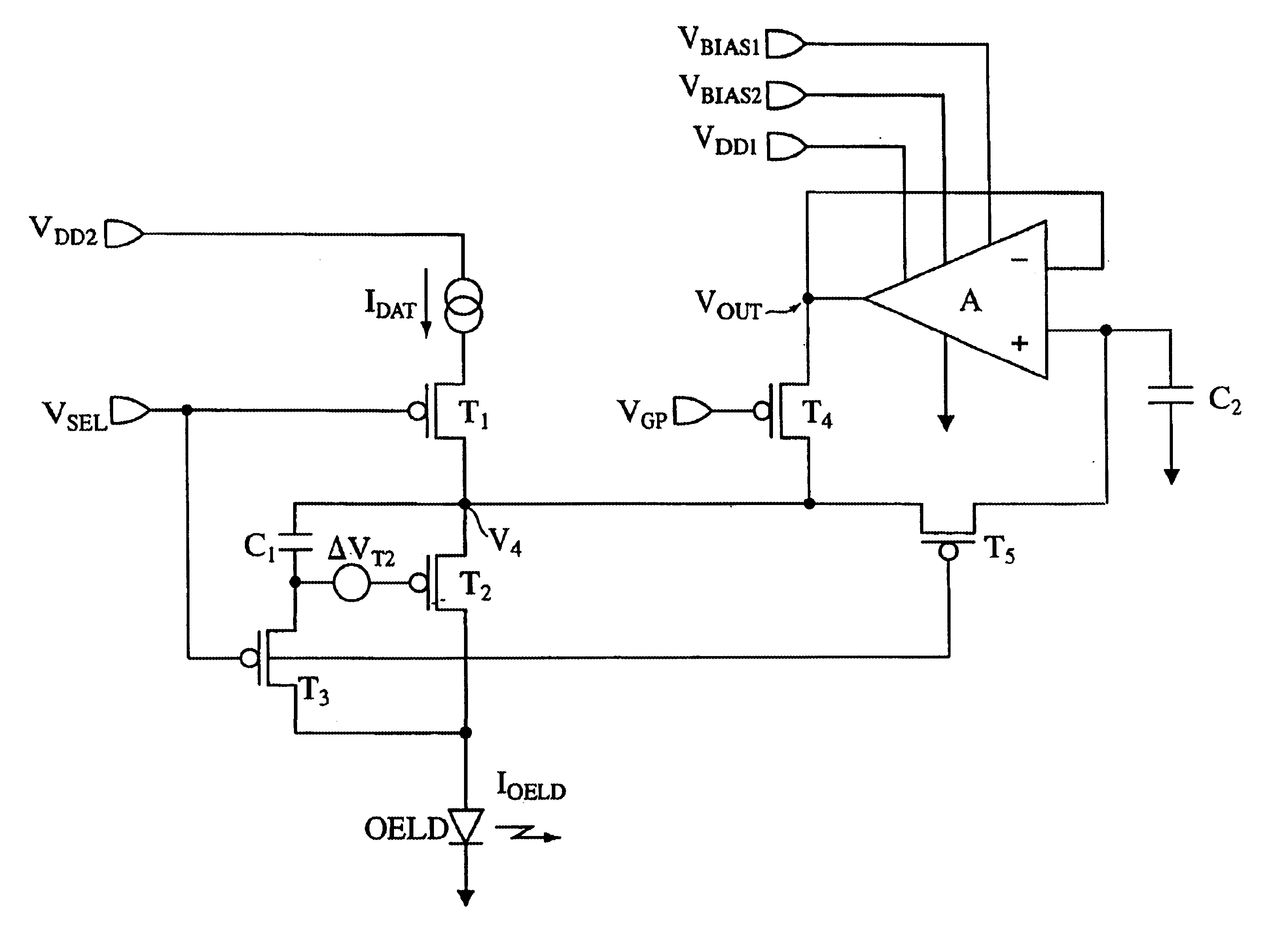
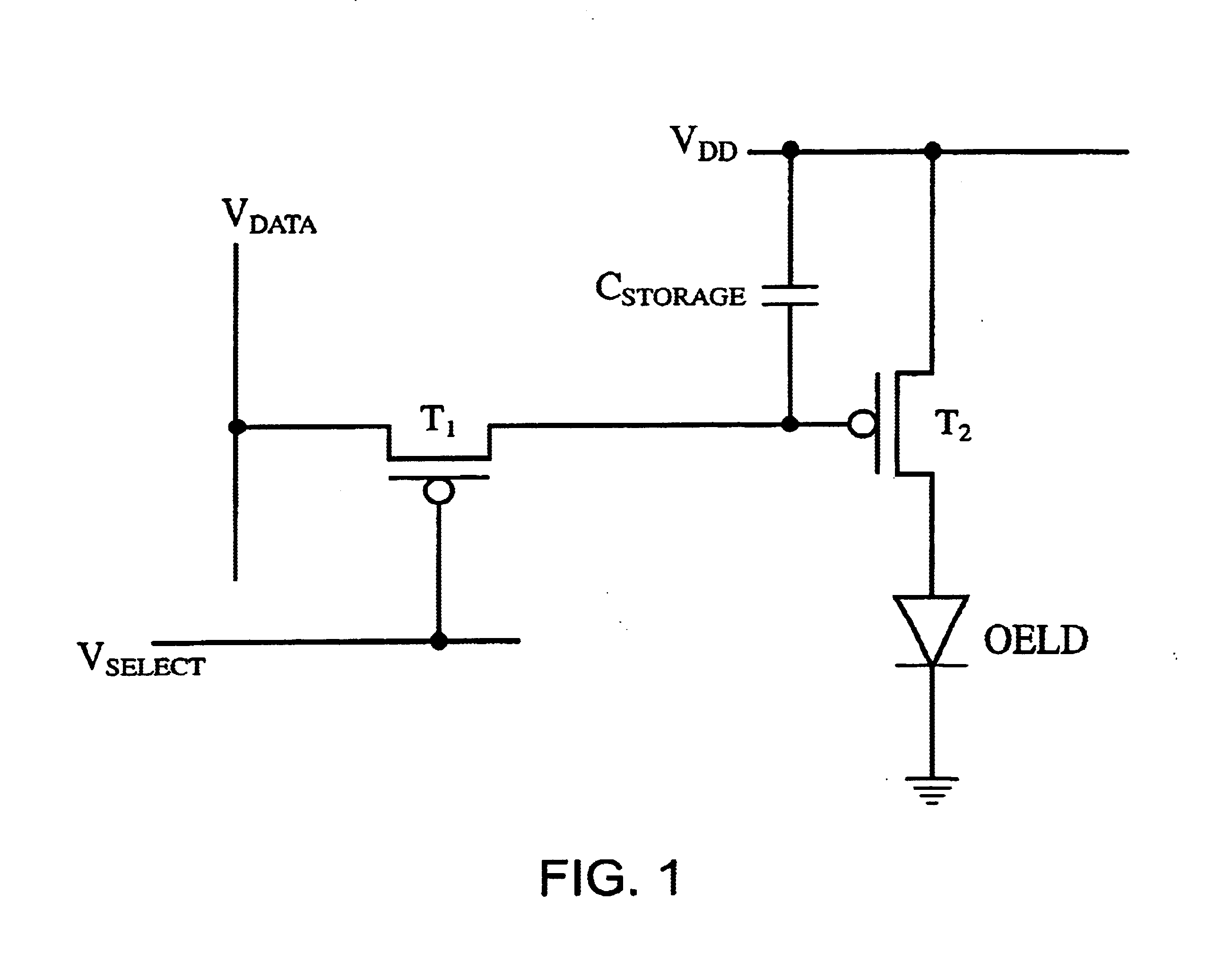
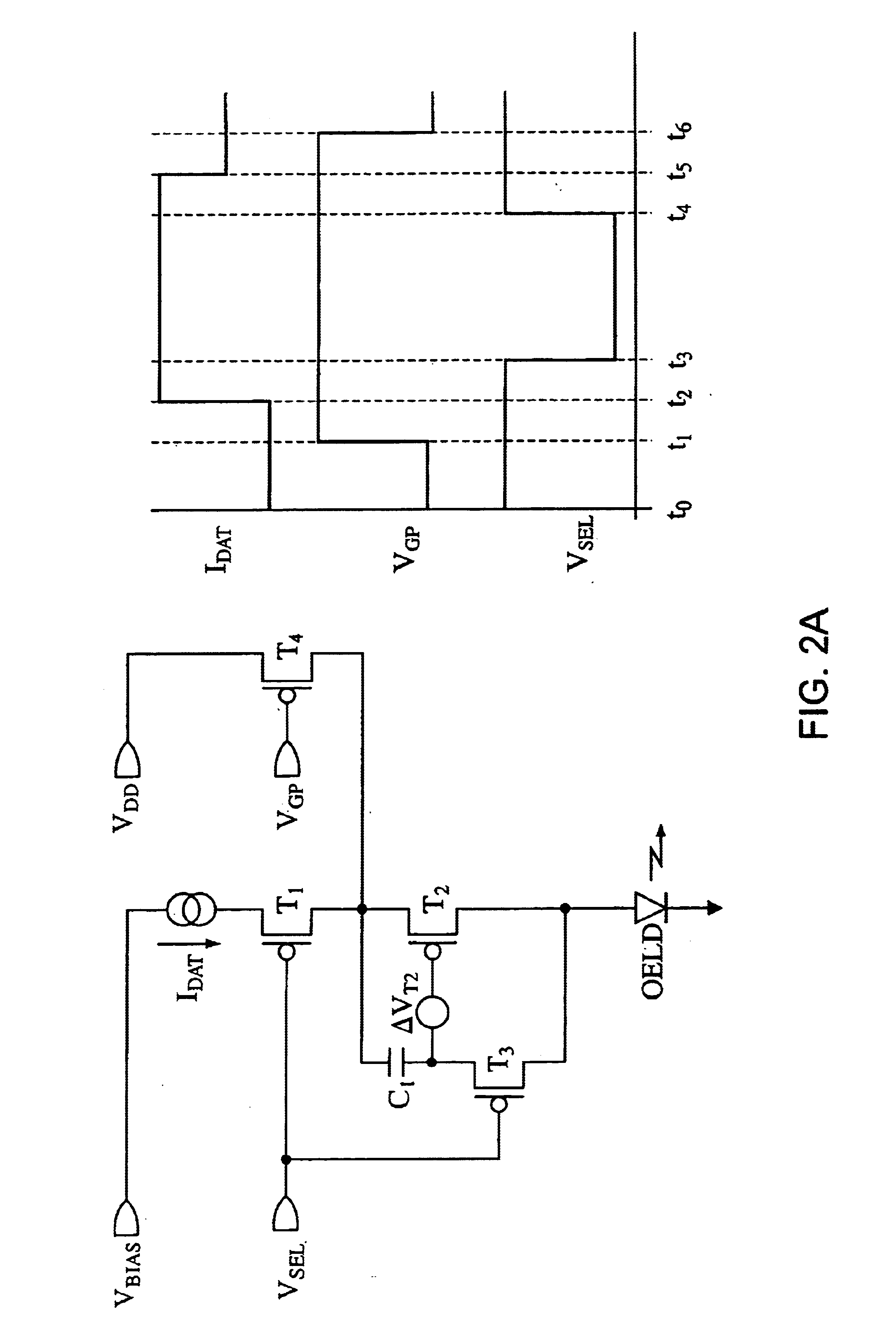
Organic electroluminescent device compensated pixel driver circuit
A compensated pixel driver circuit for an organic electroluminescent device, wherein the circuit comprises a unity gain buffer which is preferably implemented as an operational amplifier. The circuit provides a unity gain sample and hold function, thereby compensating the current supply to the electroluminescent element by providing a self adjusting load.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
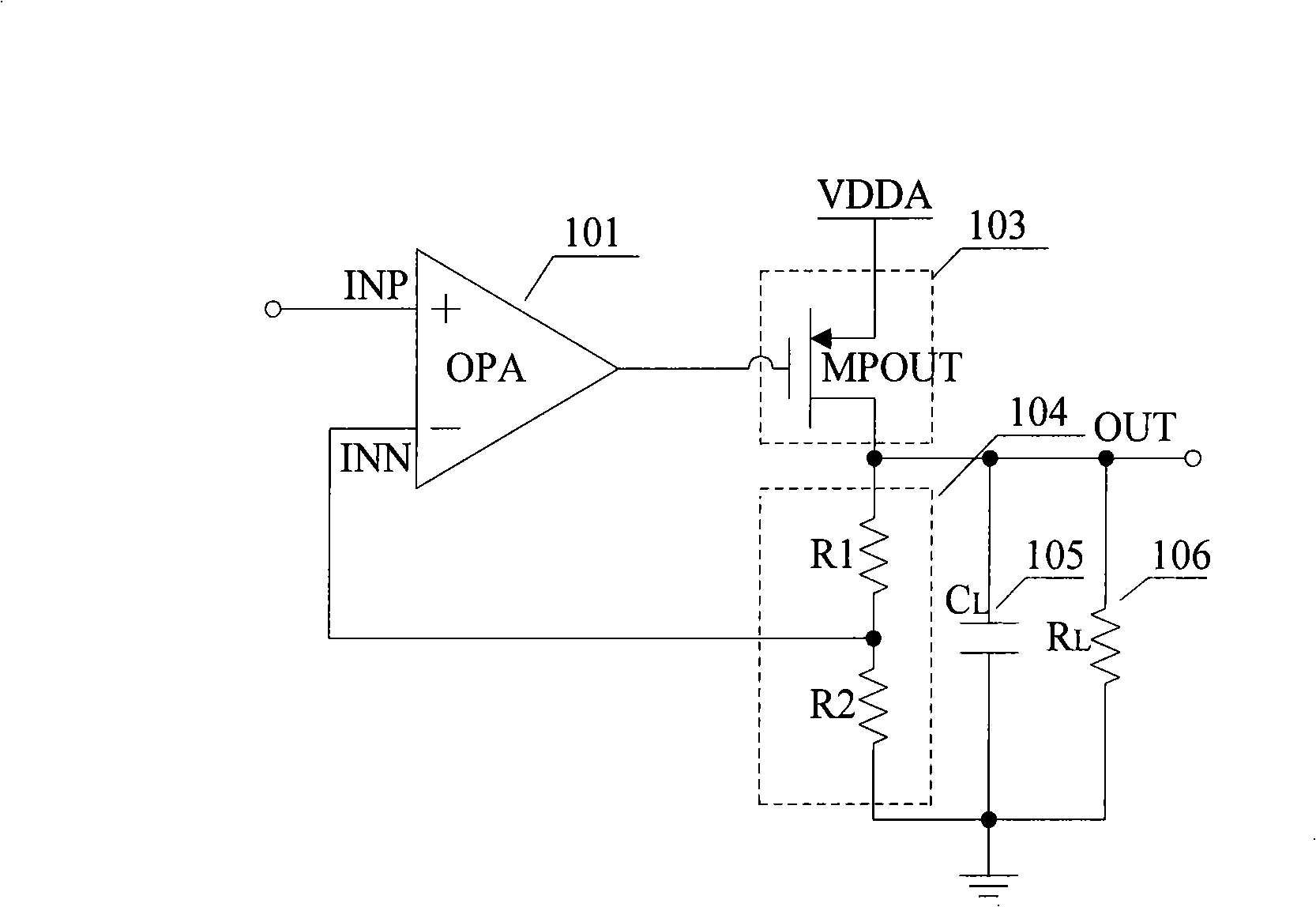
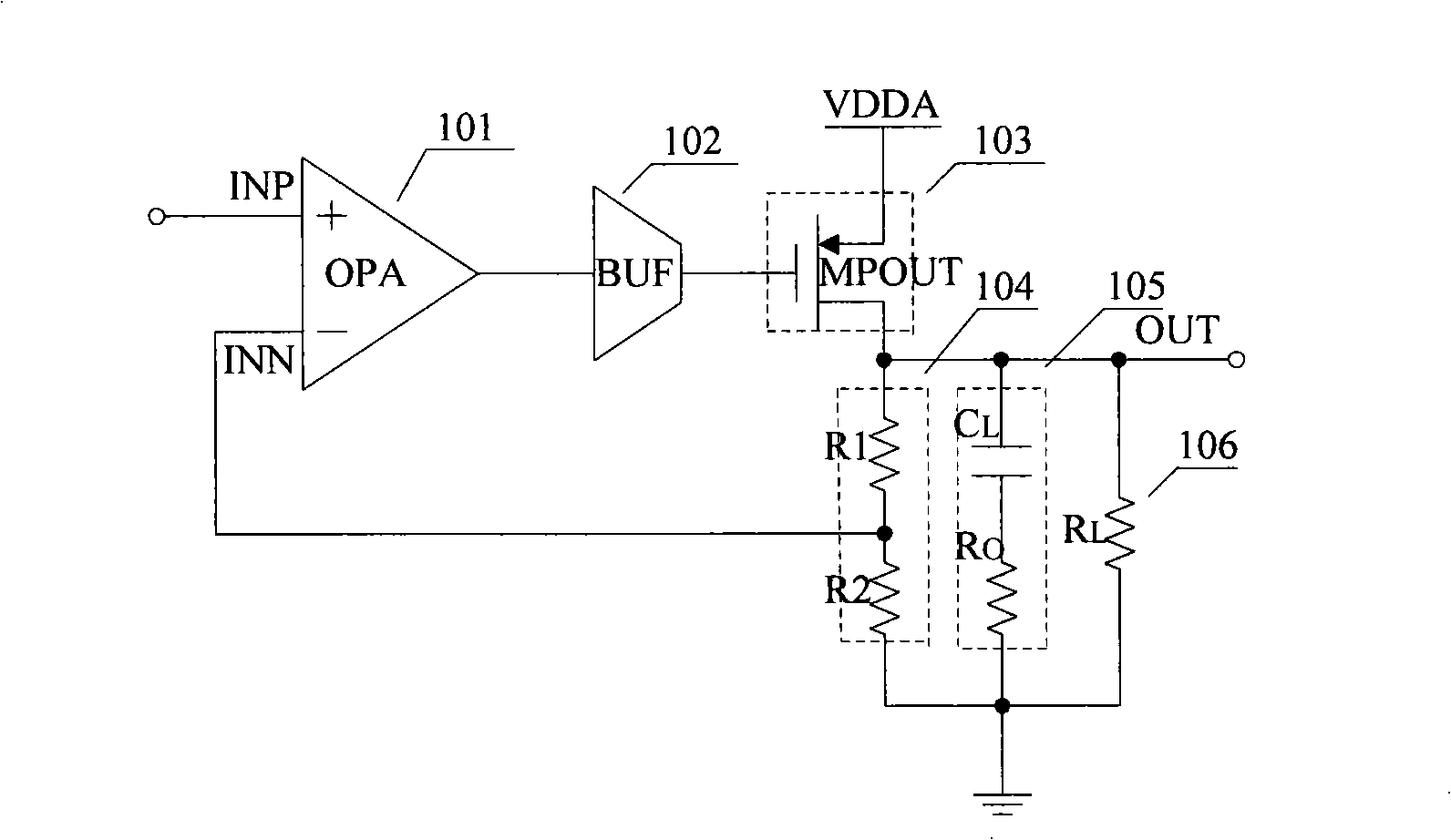
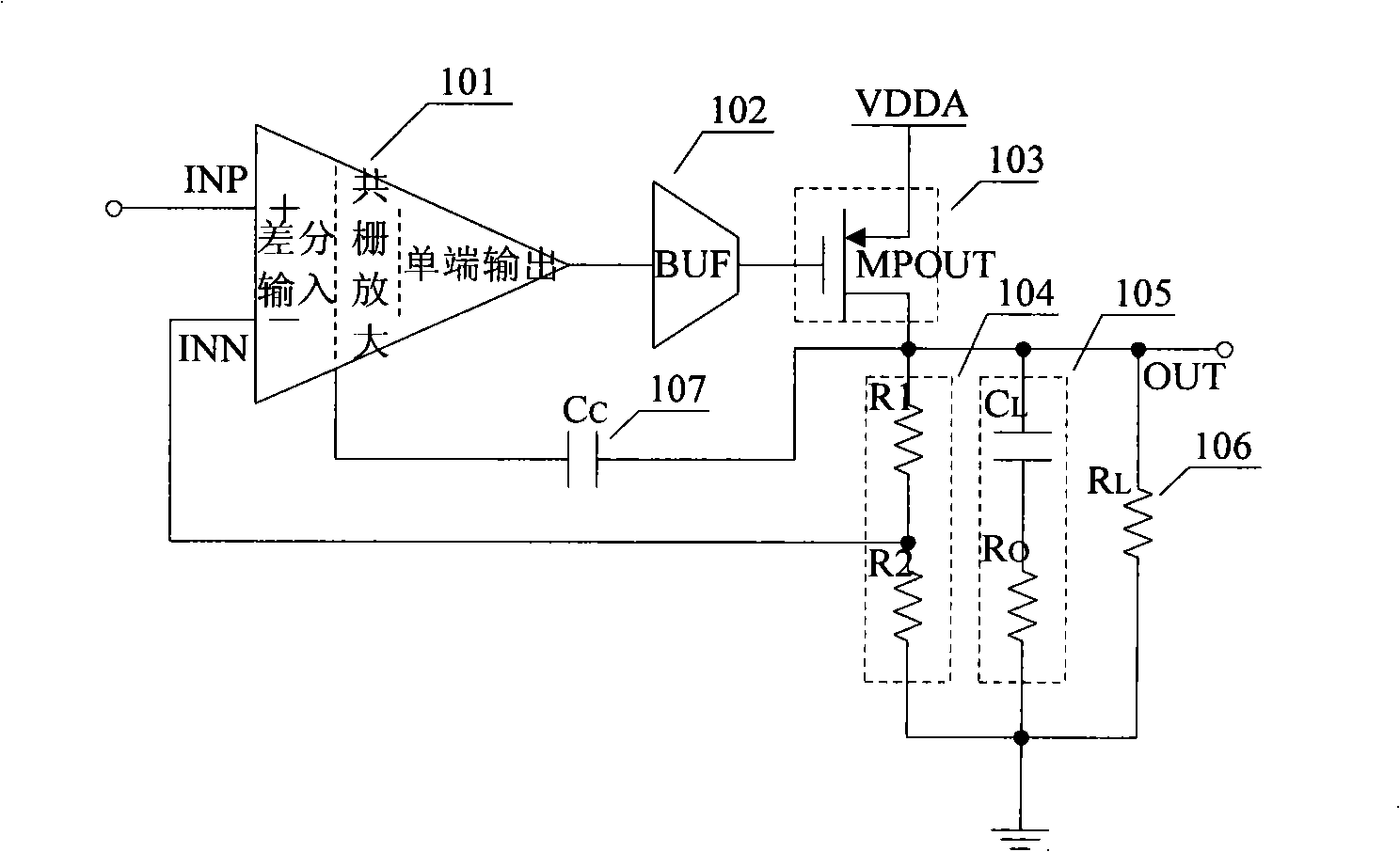
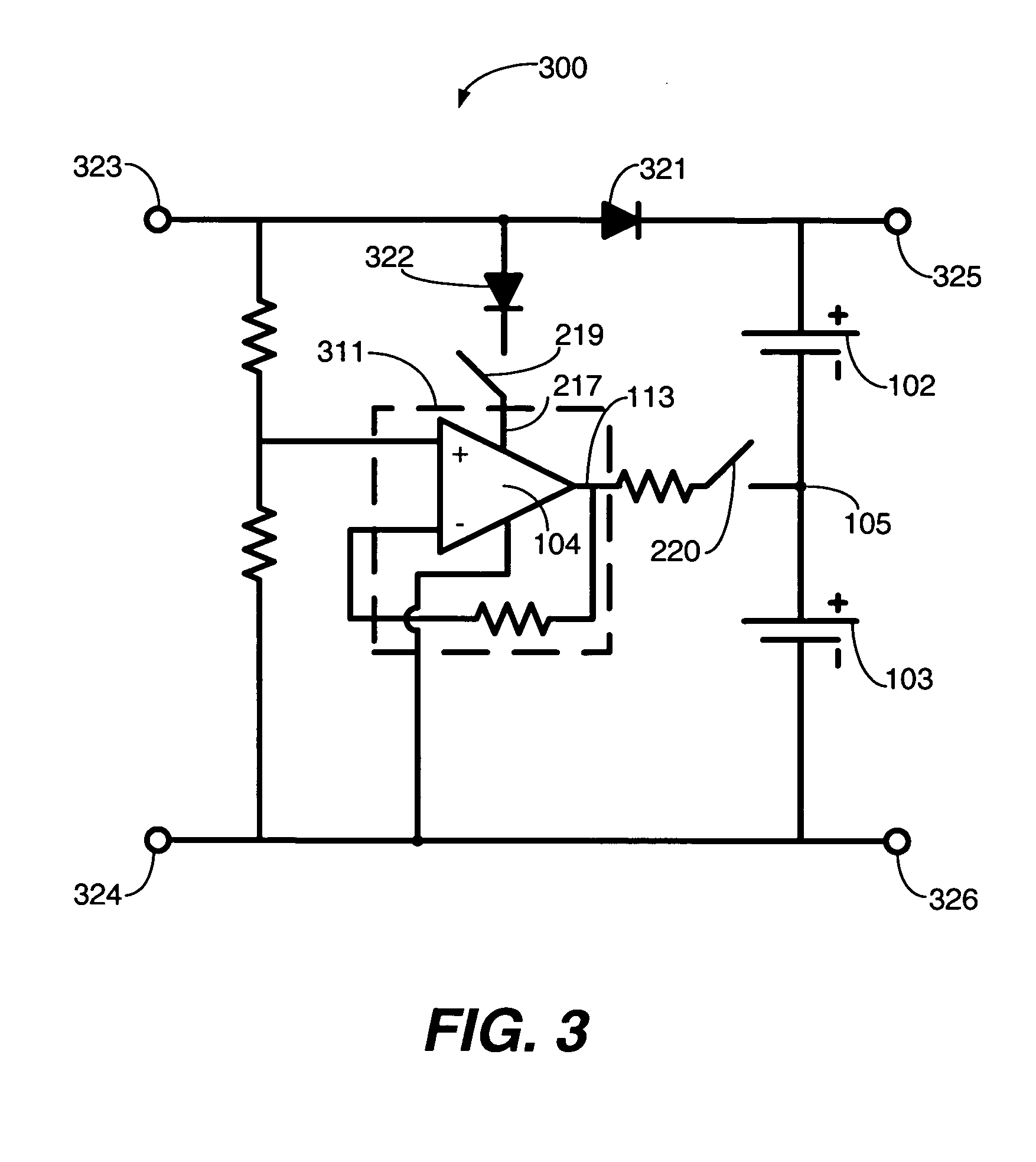
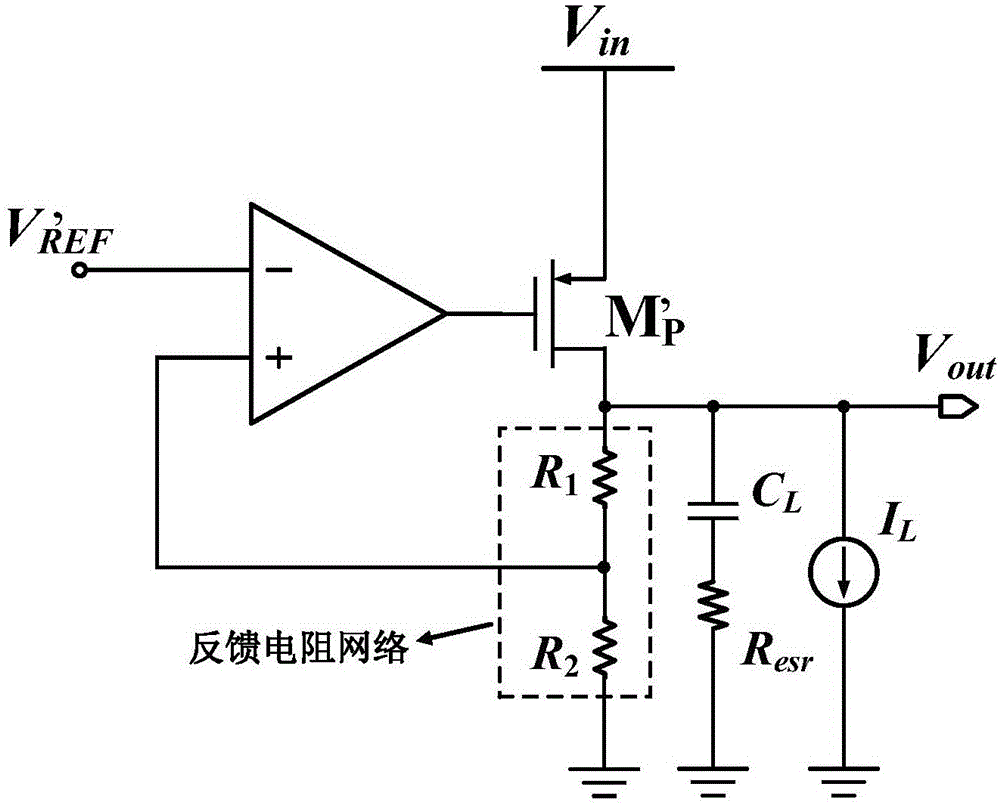
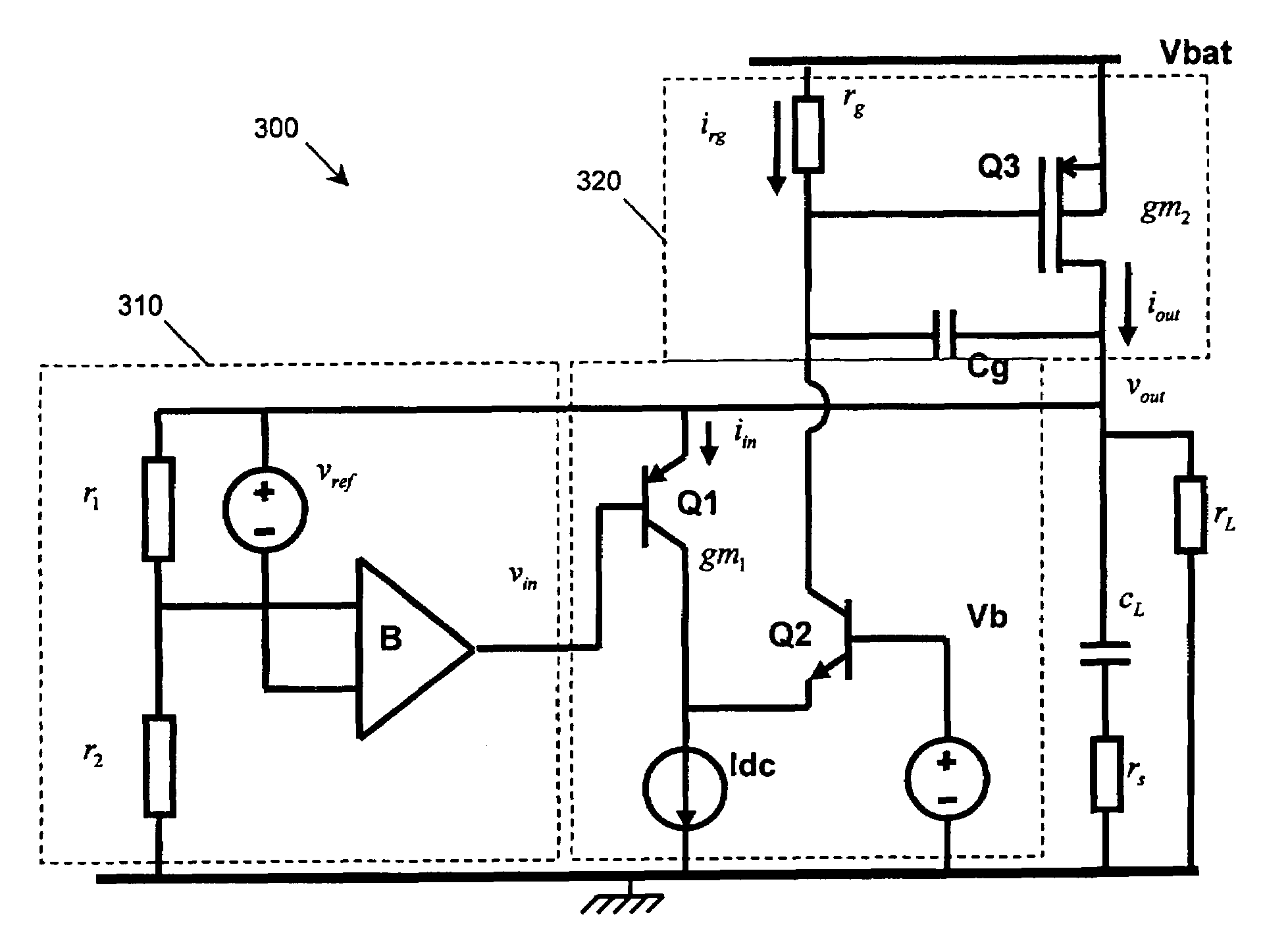
Low drop-out voltage regulator and method
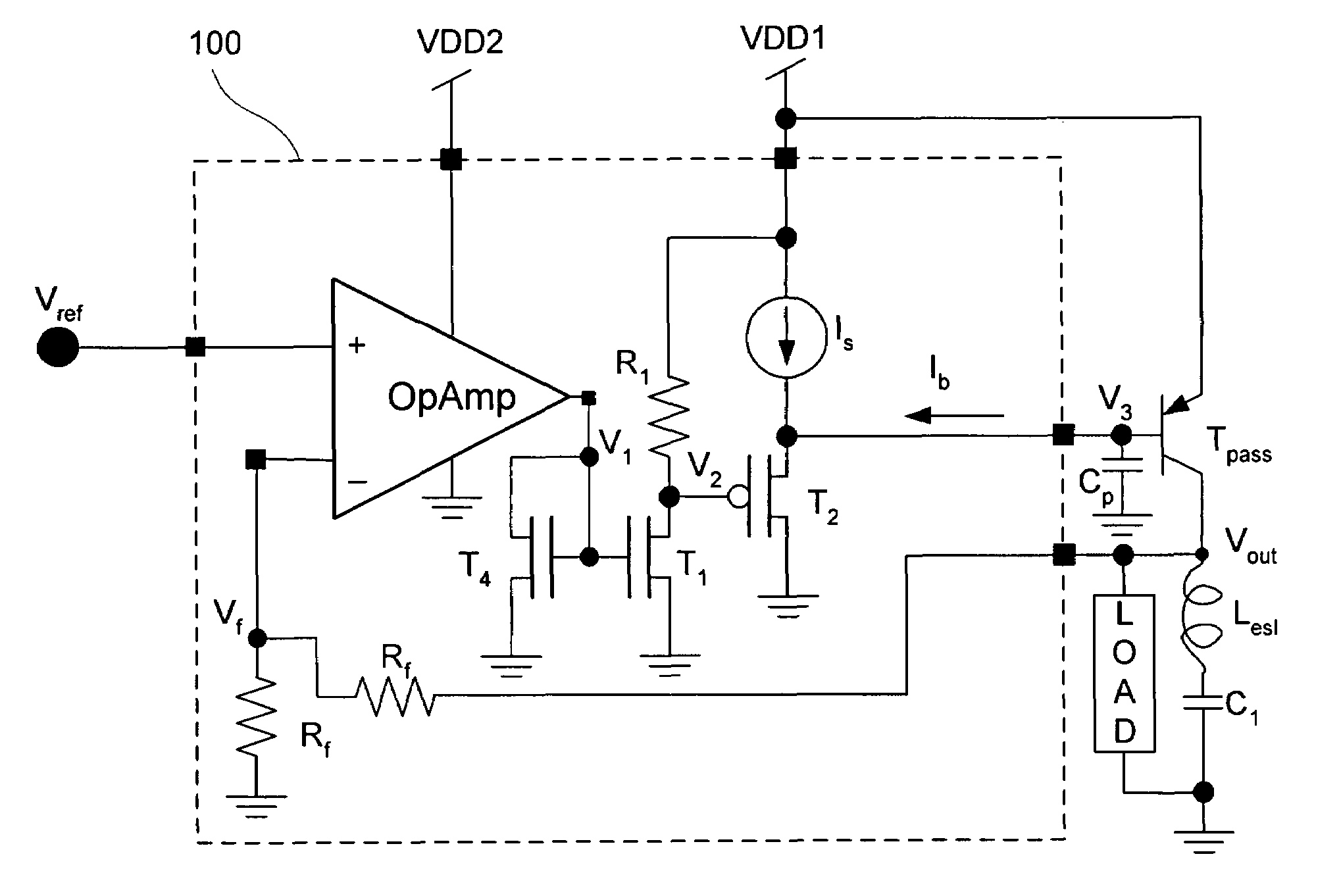
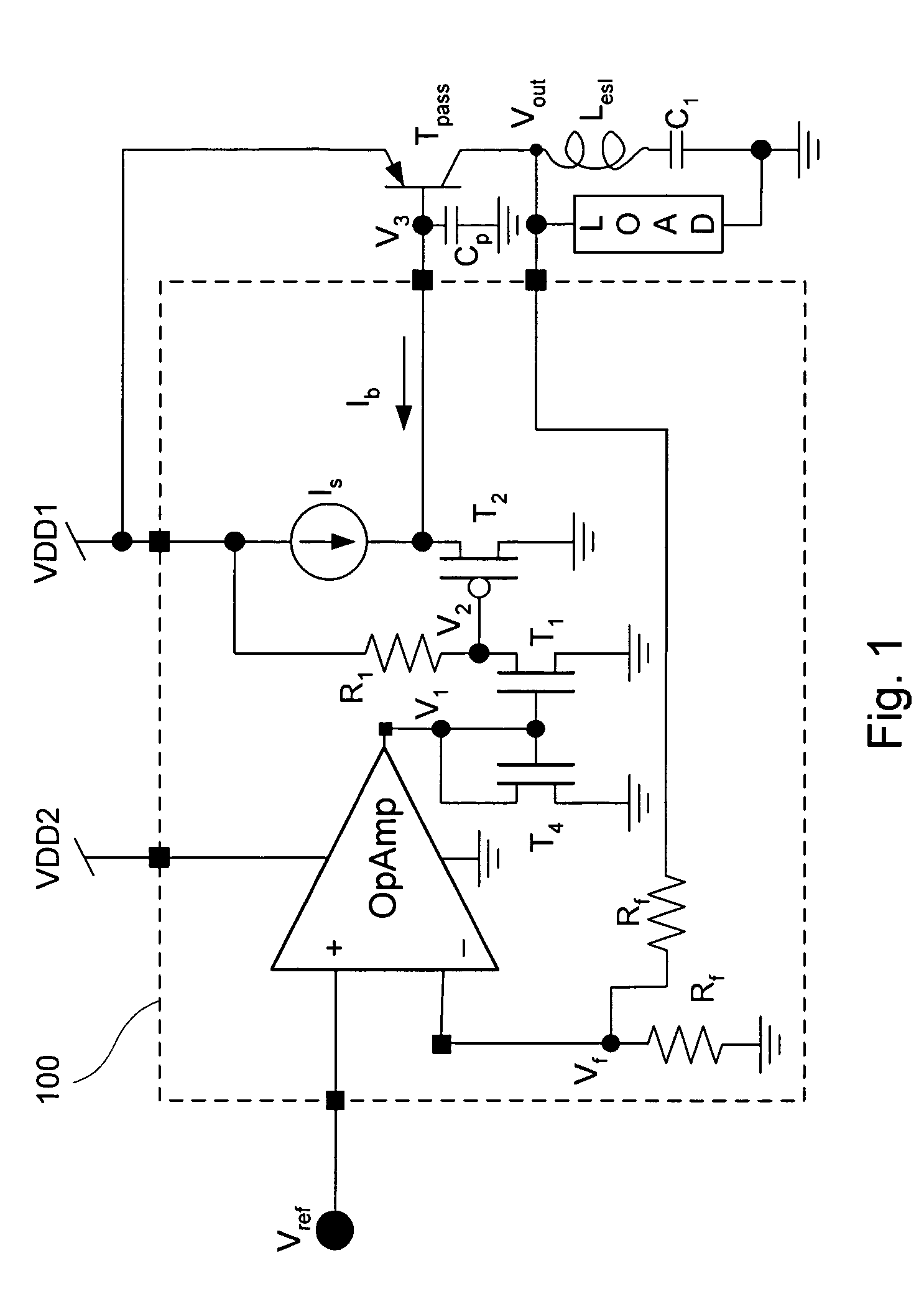
A low drop-out voltage regulator (300) and method comprising: a differential transistor arrangement (Q1–Q2) for receiving a reference voltage and in dependence thereon producing a regulatred output voltage; an output stage (Q3) for coupling to a load; and a control loop (310) coupled to the differential transistor arrangement for providing a dominant pole. Since a load capacitance is not used for dominant pole, stability of operation may be obtained with a lower load capacitance. The output stage is preferably a closed-loop unity gain amplifier providing a low impedance output. This provides the following advantages: 1—The output capacitor can be dramatically reduced or removed (a low dominant pole, allows the regulator to worth with 0nF output capacitor). 2—internal power consumption can be reduced, improving regulator efficiency. 3—Low output impedance is provided, with very low DC output resistance. 4—The load capacitor can have zero ESR (equivalent serial resistance).
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
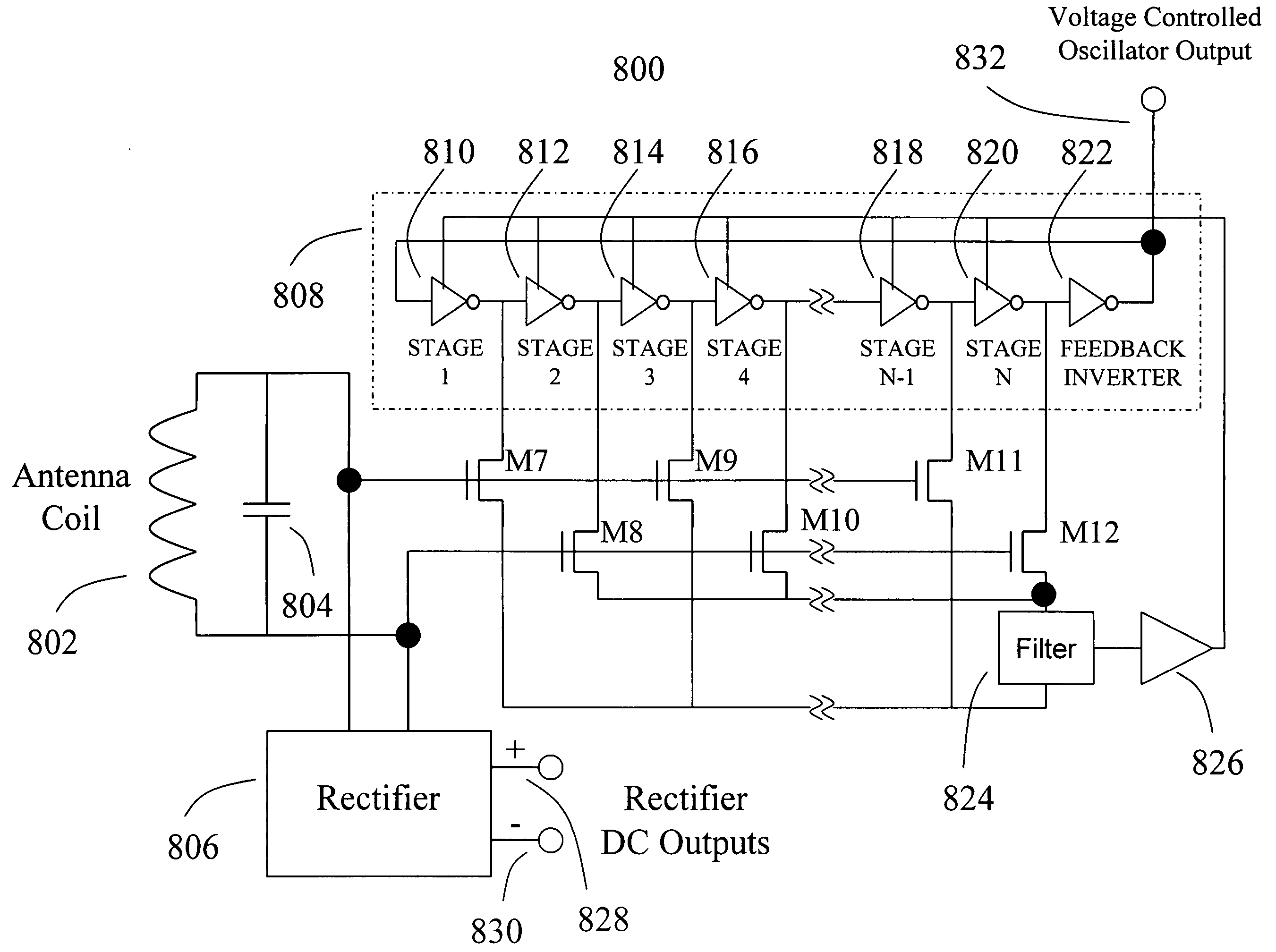
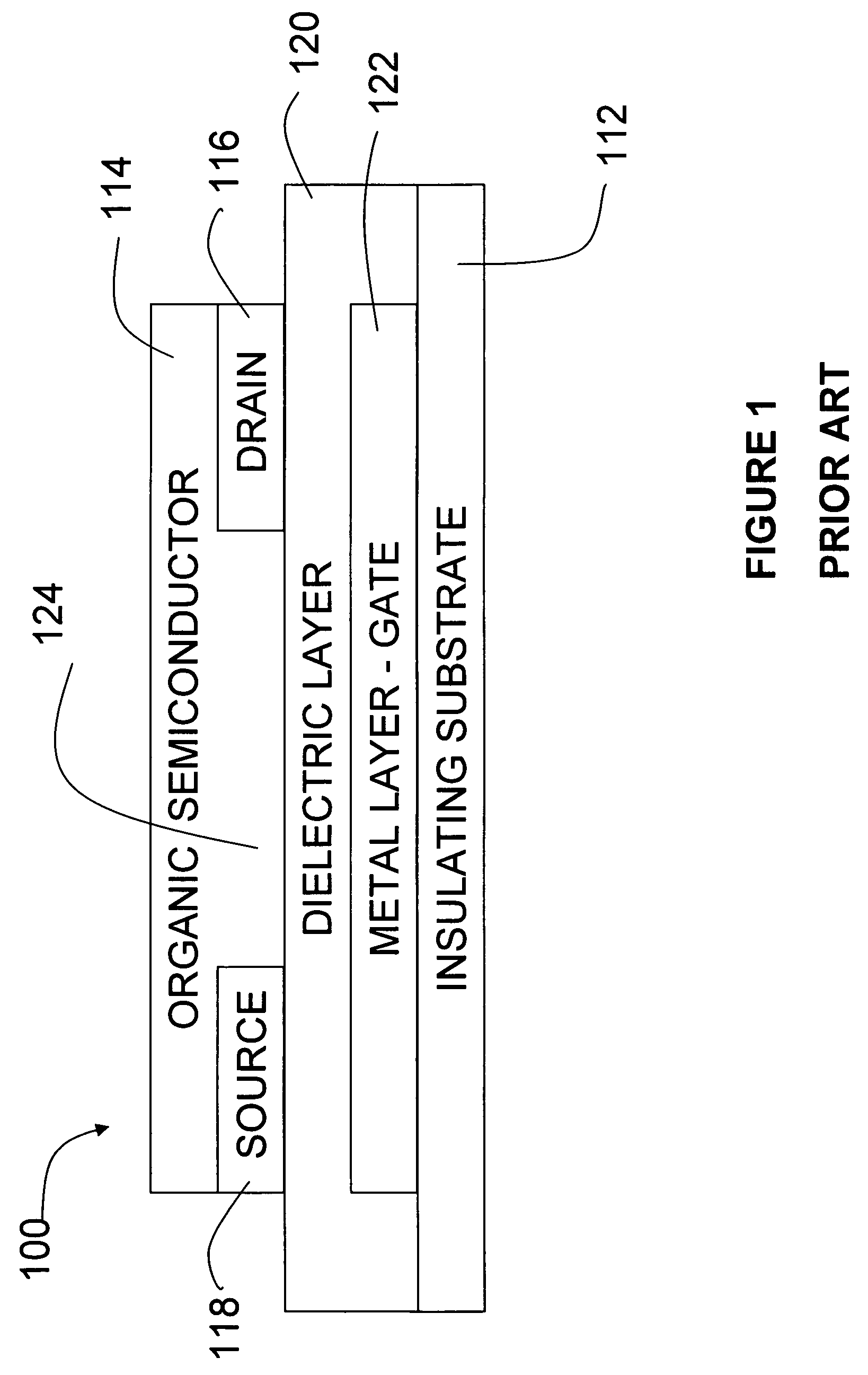
Non-quasistatic phase lock loop frequency divider circuit
ActiveUS20050156641A1Reduce output frequencyThe implementation process is simplePulse automatic controlPulse generation by logic circuitsCapacitancePhysics
A non-quasistatic MOS frequency divider circuit uses a phase lock loop configuration including an antenna coil to induce a differential input signal, an antenna resonating capacitor, a rectifier, a voltage controlled ring oscillator, a phase detector and a loop filter. All transistors used are organic MOS devices of PMOS, NMOS or both PMOS and NMOS varieties. The voltage-controlled oscillator includes a multiple delay stage ring oscillator. The phase detector includes transistors connected as sampling switches to sample the individual oscillator stage voltages into the loop filter. The sampling transistors have gates connected to the coil. The loop filter provides a substantially direct current to a loop amplifier and then to the voltage controlled oscillator delay control input. This configuration results in the voltage controlled oscillator frequency being synchronous to—and at a sub-multiple of the antenna signal frequency. The sampling transistor gates are all connected to the coil and thereby become part of the capacitance of the radio frequency parallel resonant network. The transistor gates are then efficiently switched at the rate of the radio frequency signal with no delay relative to the coil voltage. Operation of the phase detector organic transistors is based on non-quasistatic behavior of the transistor. Non-quasistatic operation results in phase detection at a frequency much higher than the quasistatic limit of transistor unity gain bandwidth.
Owner:GULA CONSULTING LLC
Method and apparatus for compensating an amplifier
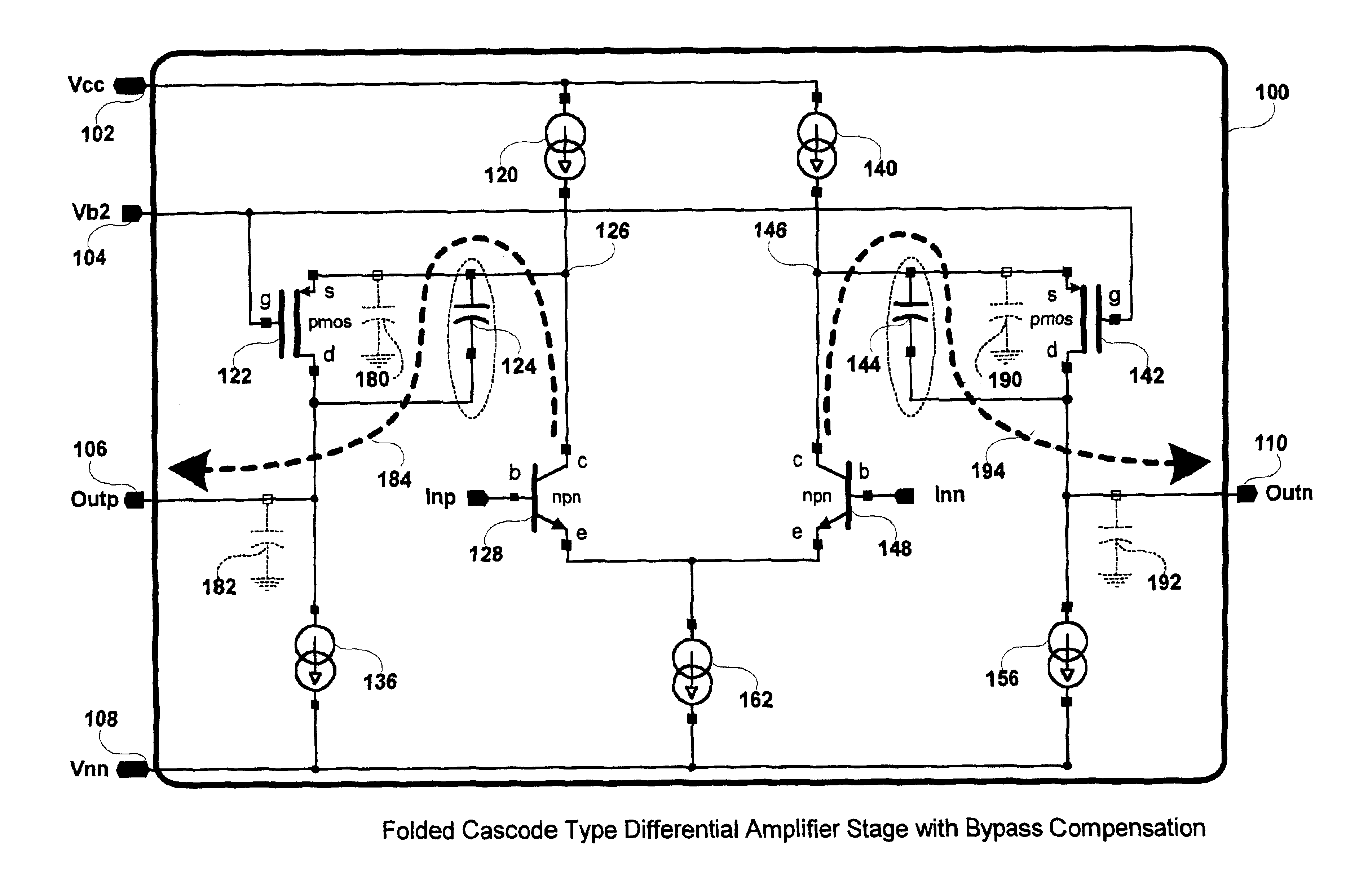
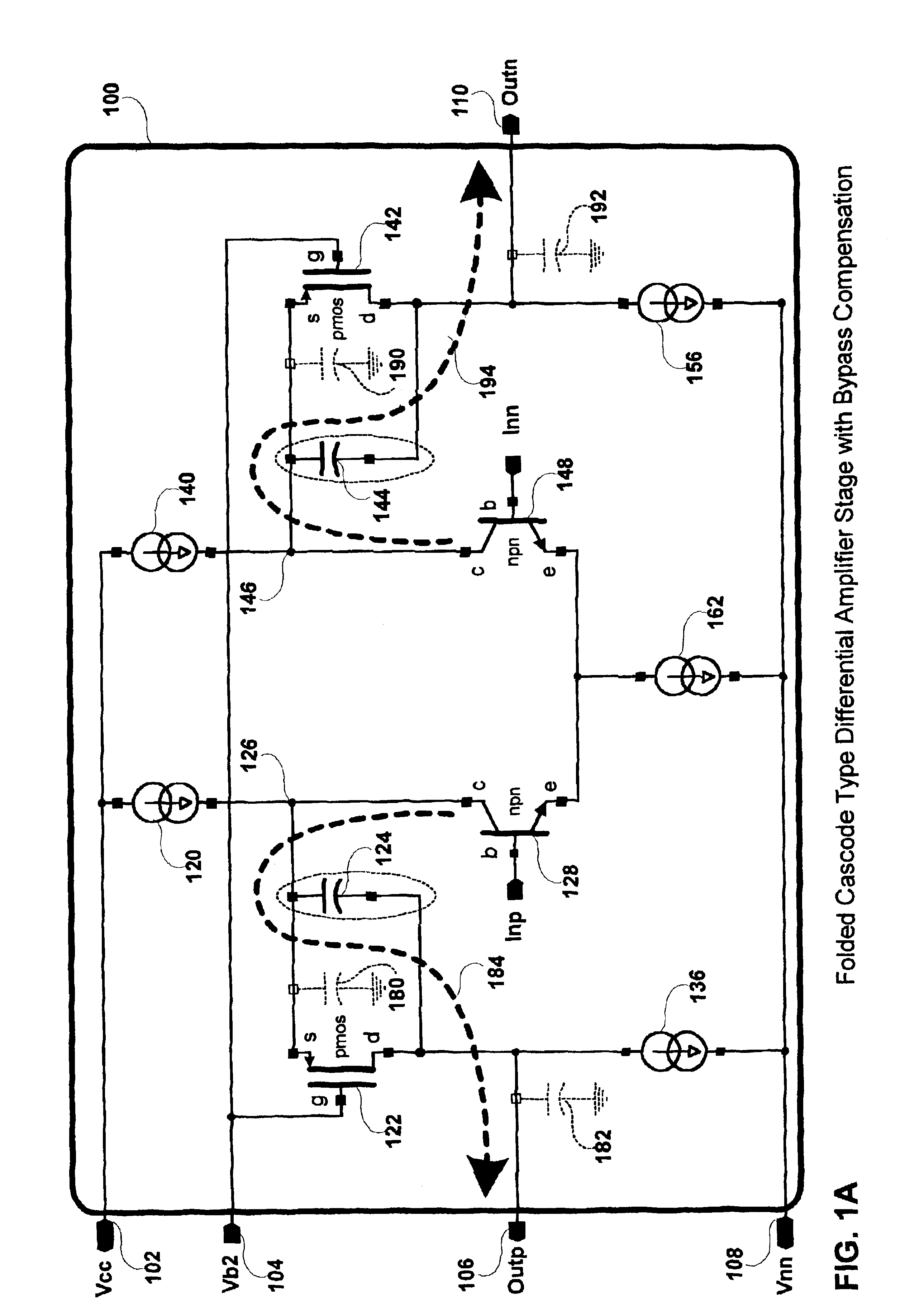
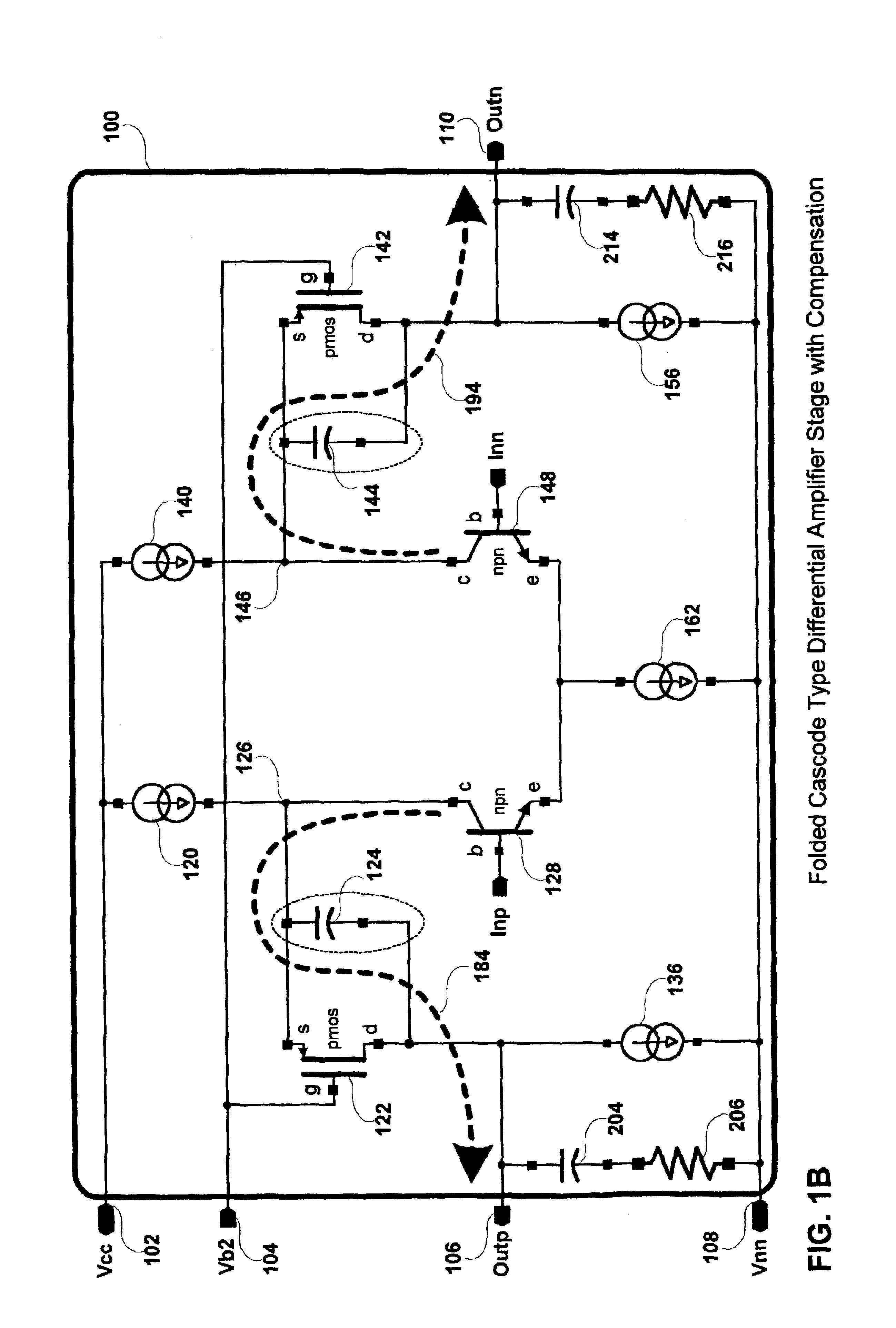
InactiveUS6924701B1Increased unity-gain bandwidthDifferential amplifiersAmplifier detailsAudio power amplifierCascode
A method and apparatus for compensating an amplifier is disclosed which significantly improves the unity gain bandwidth of the amplifier. In an embodiment of the invention the amplifier includes at least one compensated pair of cascode coupled transistors including: an input transistor, a cascode transistor, and a bypass element. The input transistor exhibits a first transition frequency. The cascode transistor is cascode coupled to the input transistor. The cascode transistor exhibits a second transition frequency less than or equal to the first transition frequency of the input transistor. The bypass element couples across a corresponding current interface of the cascode transistor to substantially bypass the cascode transistor at a pole frequency thereof.
Owner:IKANOS COMMUNICATIONS
Complementary input circularly folding operational transconductance amplifier
InactiveCN101741328ADifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesAudio power amplifierEngineering
The invention relates to a complementary input circularly folding operational transconductance amplifier, belongs to the technical field of operational amplifiers, and is characterized in that: the unity gain bandwidth of the operational transconductance amplifier is increased through the complementary input of P-type transistors (M1a, M1b, M2a and M2b) and N-type transistors (M14a, M14b, M15a and M15b) and through the adoption of the circularly folding operational transconductance amplifier. A circuit has the advantages of high unity gain bandwidth and low power consumption and accords with the research and development direction of an integrated circuit.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Buffer based on source electrode follower
InactiveCN101594139AAchieving a unity-gain buffered outputAmplifiers with impedence circuitsLogic circuits using dielectric elementsCapacitanceEngineering
The invention discloses a buffer based on a source electrode follower and belongs to the technical field of analog integrated circuit design. The buffer comprises a pseudo differential input level, a cross coupling common source level, a current source and a capacitance load, wherein the pseudo differential input level is used for receiving a difference input signal; the cross coupling common source level is connected with the pseudo differential input level, used for forming negative resistance and offsetting output resistance of the buffer; the current source is connected with the pseudo differential input level and used for providing branch current of the buffer; and the capacitance load is connected with the pseudo differential input level and used as output load of the buffer. The negative resistance is formed by the cross coupling common source level, so that the buffer offsets the output resistance of the high-speed buffer and realizes unity-gain buffering output. The buffer based on the source electrode follower realizes ultra-high speed, the unity-gain buffering output and high dynamic characteristics by theoretical analysis and simulation verification.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Circuit for linearizing electronic devices
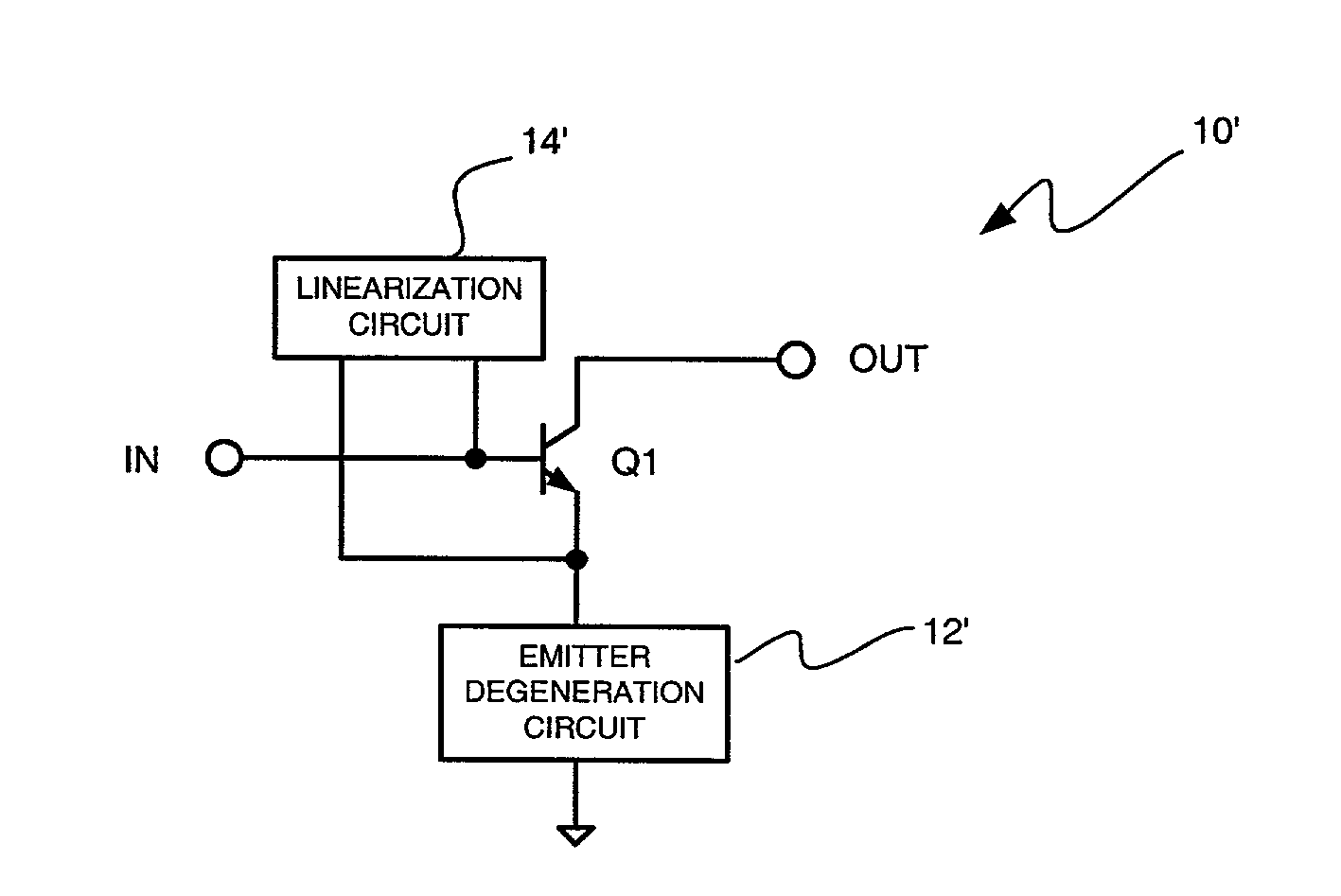
InactiveUS20020067205A1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsInductorLinearity
A radio frequency amplifier with improved linearity and minimal third-order distortion. The amplifier includes a first transistor having first, second and third terminals with the first terminal being an input terminal and the second terminal being the output terminal and the third terminal being a common terminal. A linearization circuit is included having first and second terminals. The first terminal is connected to the common terminal of the transistor and the second terminal is connected to the input terminal of the transistor. In a specific embodiment, the linearization circuit is implemented as a unity gain buffer with an input terminal connected to the common terminal of the transistor and an output terminal connected to the input terminal of the transistor. In accordance with the inventive teachings, the buffer has a low gain and high output impedance at first frequency (f1) of a first signal applied to the circuit and a second frequency (f2) of a second signal applied to the circuit and a unity gain and low output impedance a difference between the first and second frequencies. In another specific embodiment, the inductor is inserted between the output of the unity gain buffer and the input terminal of the transistor. In alternative embodiments, circuitry is shown for providing a direct current offset at the input of the transistor. As another alternative, the linearization circuit consists of series inductor and capacitor connected between the common and input terminals of the transistor. In yet another embodiment, the linearization circuit consists of the first and the second series inductor and capacitor circuits. The first series LC circuit is connected between the common terminal of the transistor and ground and the second series LC circuit is connected between the input terminal of the transistor and ground.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
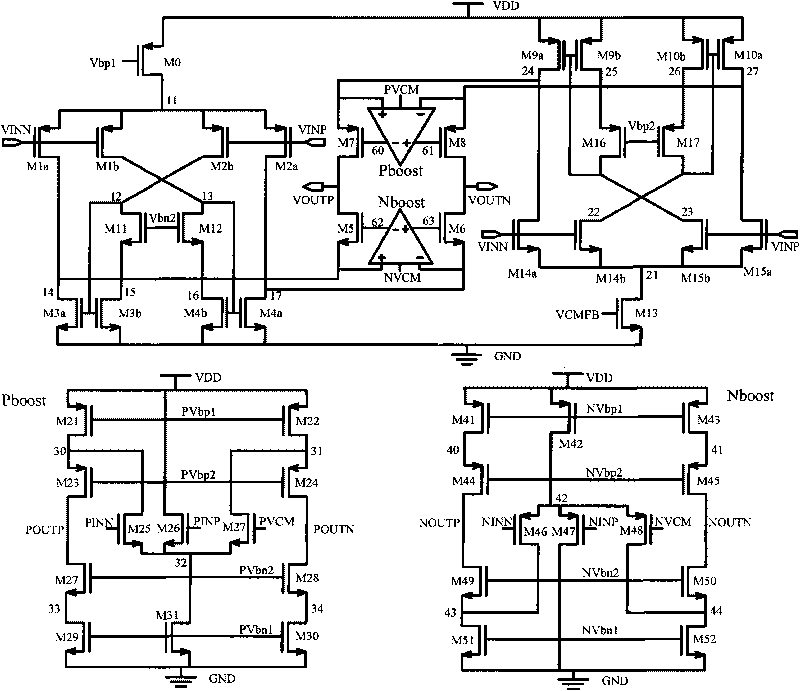
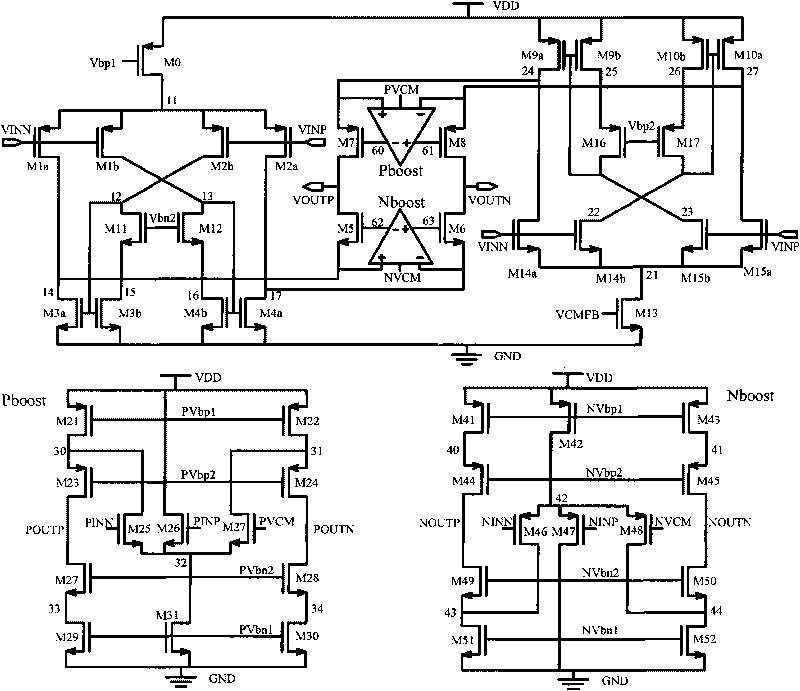
Complementary input circularly folding gain bootstrap operational transconductance amplifier
ActiveCN101741329ADifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesAudio power amplifierCascode
The invention relates to a complementary input circularly folding gain bootstrap operational transconductance amplifier, belongs to the technical field of operational amplifiers, and is characterized by comprising a complementary input circularly folding differential input circuit and a cascode bootstrap circuit, wherein the cascode bootstrap circuit comprises auxiliary operational amplifiers Nboost and Pboost; and the auxiliary operational amplifier Pboost is a folding operational transconductance amplifier consisting of N-type input transistors. Due to the adoption of a structure combining complementary input circularly folding transconductance with the cascode bootstrap circuit, a gain bootstrap operational amplifier with high unity gain bandwidth is obtained so as to greatly improve the working speed of the bootstrap operational amplifier.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Readout circuit bias structure
ActiveCN102494781AReduce complexityImprove general performanceAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsAudio power amplifierEngineering
The invention discloses a readout circuit bias structure, which comprises a first MOS (metal oxide semiconductor) transistor, a second MOS (metal oxide semiconductor) transistor, a reference resistor, a thermistor, operational amplifiers, a temperature compensation resistor, a third MOS (metal oxide semiconductor) transistor and a fourth MOS (metal oxide semiconductor) transistor, wherein one endof the temperature compensation resistor is connected between the first MOS transistor and the second MOS transistor, the other end of the temperature compensation resistor is connected between the third MOS transistor and the fourth MOS transistor and connected with a substrate of the third MOS transistor, an in-phase input end of the third operational amplifier is connected between the first MOS transistor and the second MOS transistor, and an anti-phase input end of the third operational amplifier is connected with an output end of the third operational amplifier to form a unity-gain buffer. Besides, the unity-gain buffer is connected to an inverted input end of the fourth operational amplifier through the resistor, and an integrating capacitor is used for integration and voltage output.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
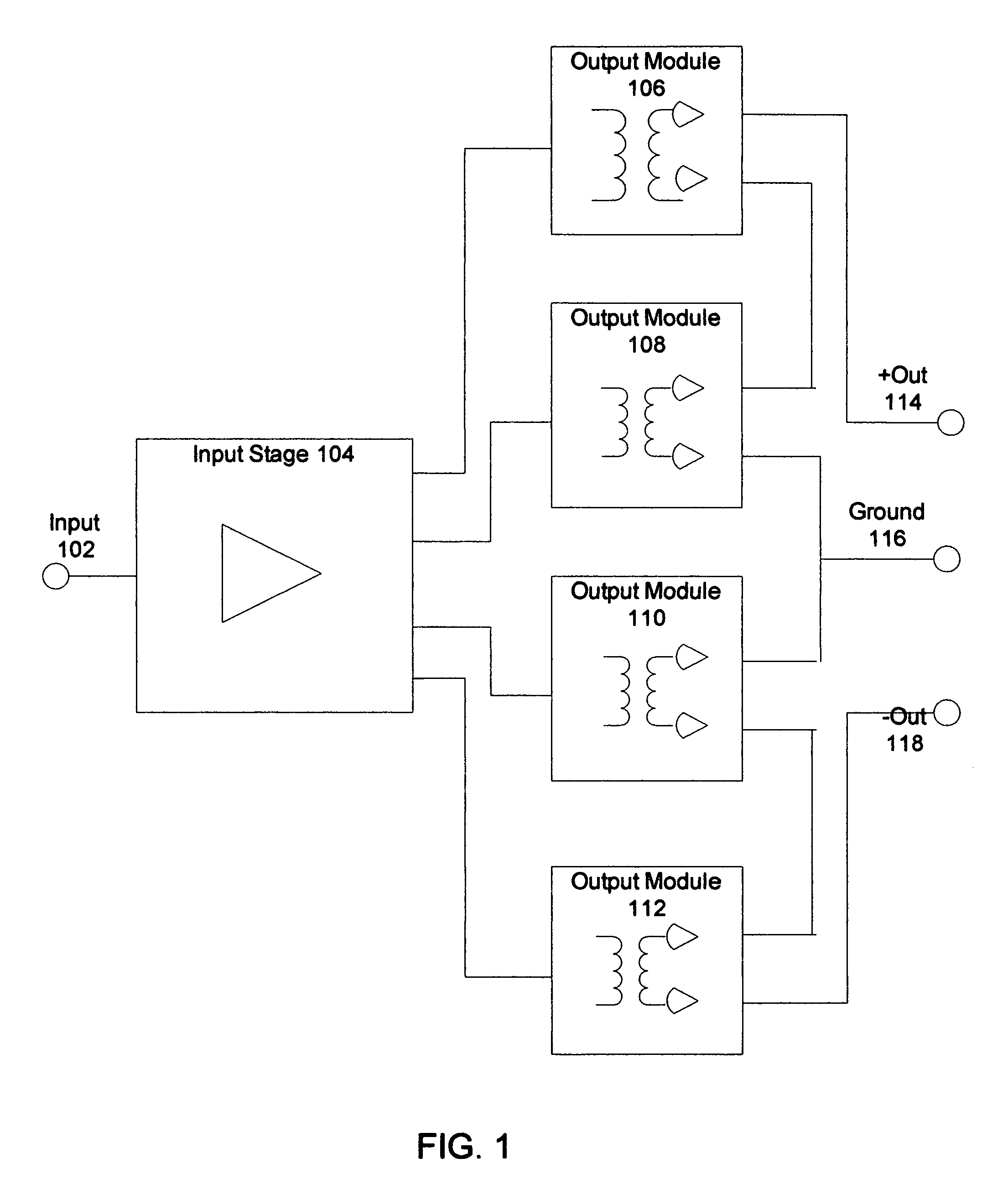
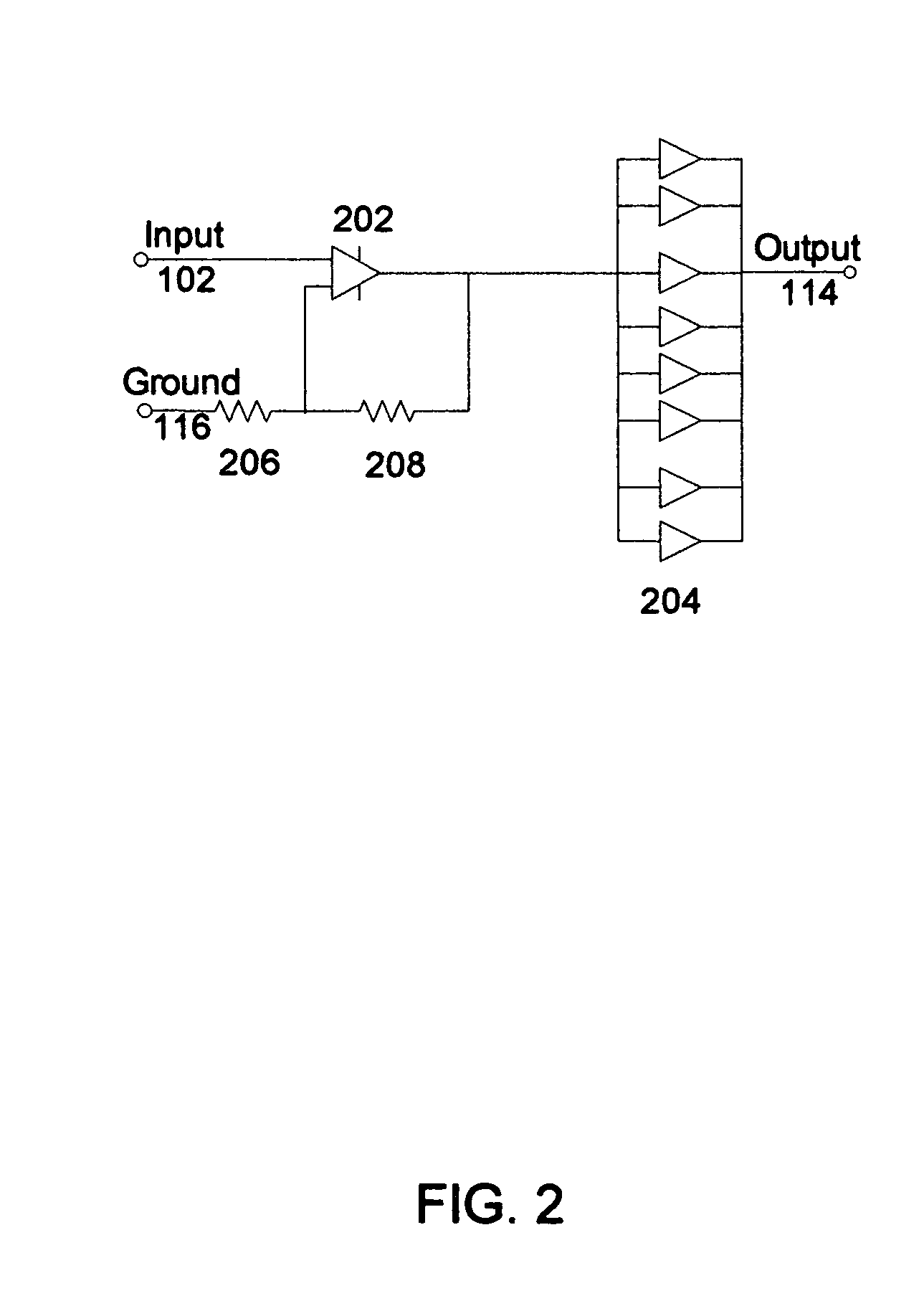
High voltage, high current, and high accuracy amplifier
A method and system to use voltage isolated and floating differential output amplifiers wired in series and parallel to achieve arbitrary output drive voltage and current for the applications load. A second embodiment uses multiple matched voltage-isolated and floating differential output amplifiers in a single chassis to enable selection between a multi-channel amplifier and a high current and / or high voltage mono amplifier. A third embodiment uses a step-up transformer and paralleled unity-gain buffer amplifiers, on input and / or output stages, to produce a zero feedback, high performance, high drive amplifier. A fourth embodiment uses a high voltage unity-gain driver amplifier to bias a unity-gain buffer amplifier and its power supply to achieve an ultra low distortion high voltage buffer amplifier. A fifth embodiment uses multiple voltage-isolated and linearized devices to enable dynamically modifiable, Class A, Class B, and Class AB topologies of predetermined voltage and current performance. A sixth embodiment corrects an output by linearizing one or more devices in a circuit by utilizing a linearization module (e.g., including one or more digital lookup tables, an error simulation circuit, or an equivalent) to linearize at least one parameter of at least one device in the circuit.
Owner:HOOVER D ROBERT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com