Patents
Literature
67results about "Logic circuits using dielectric elements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
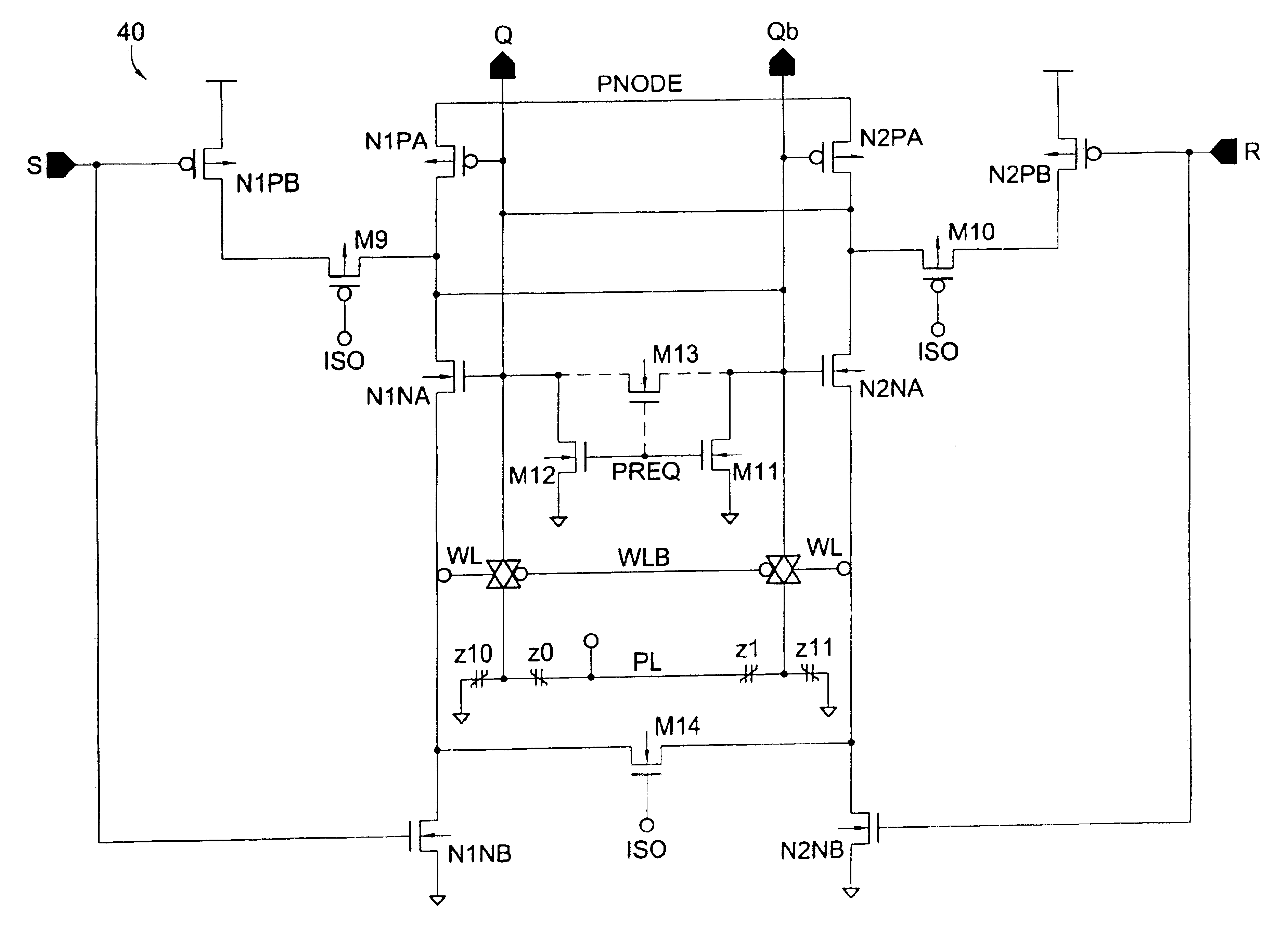
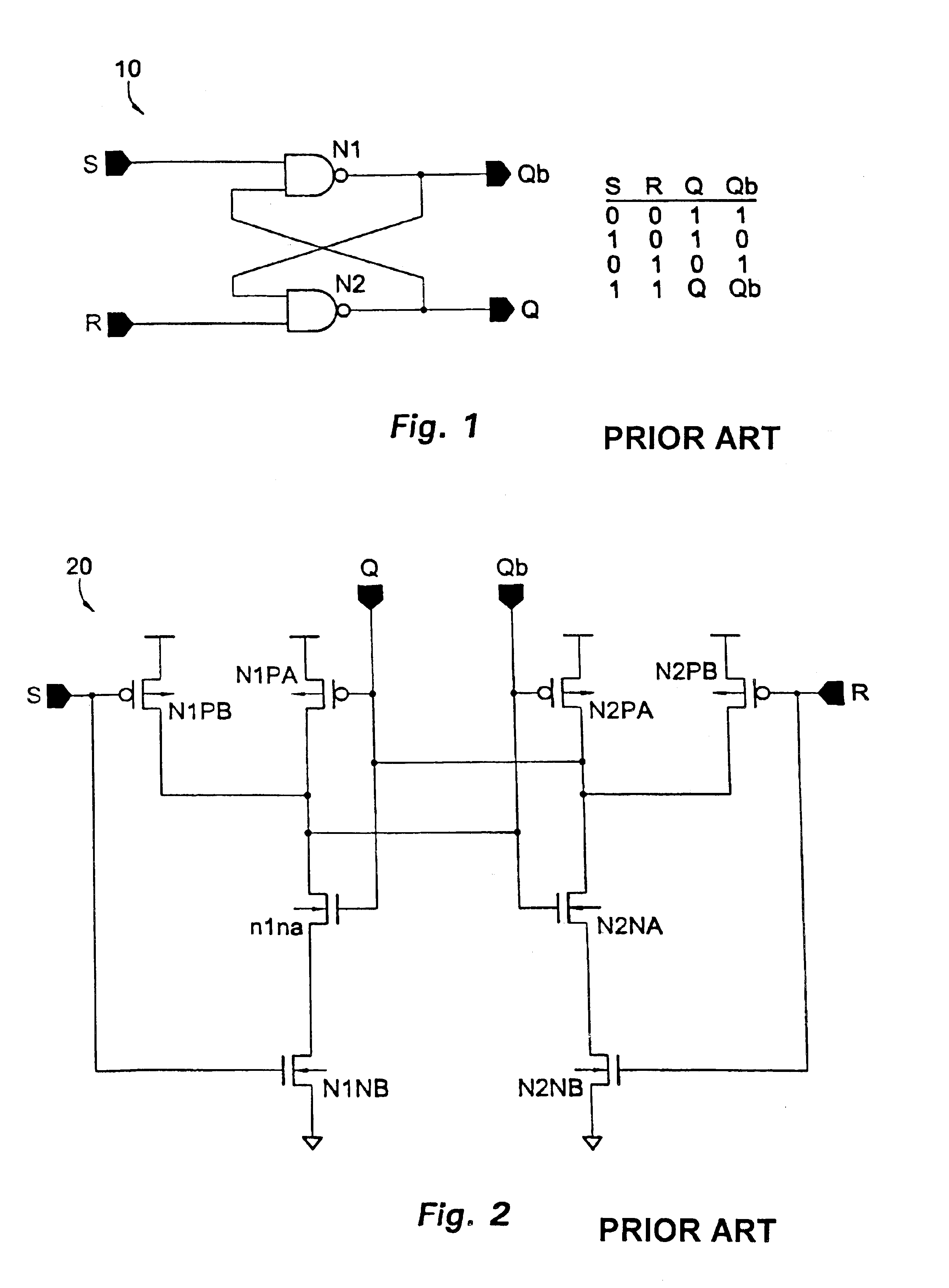
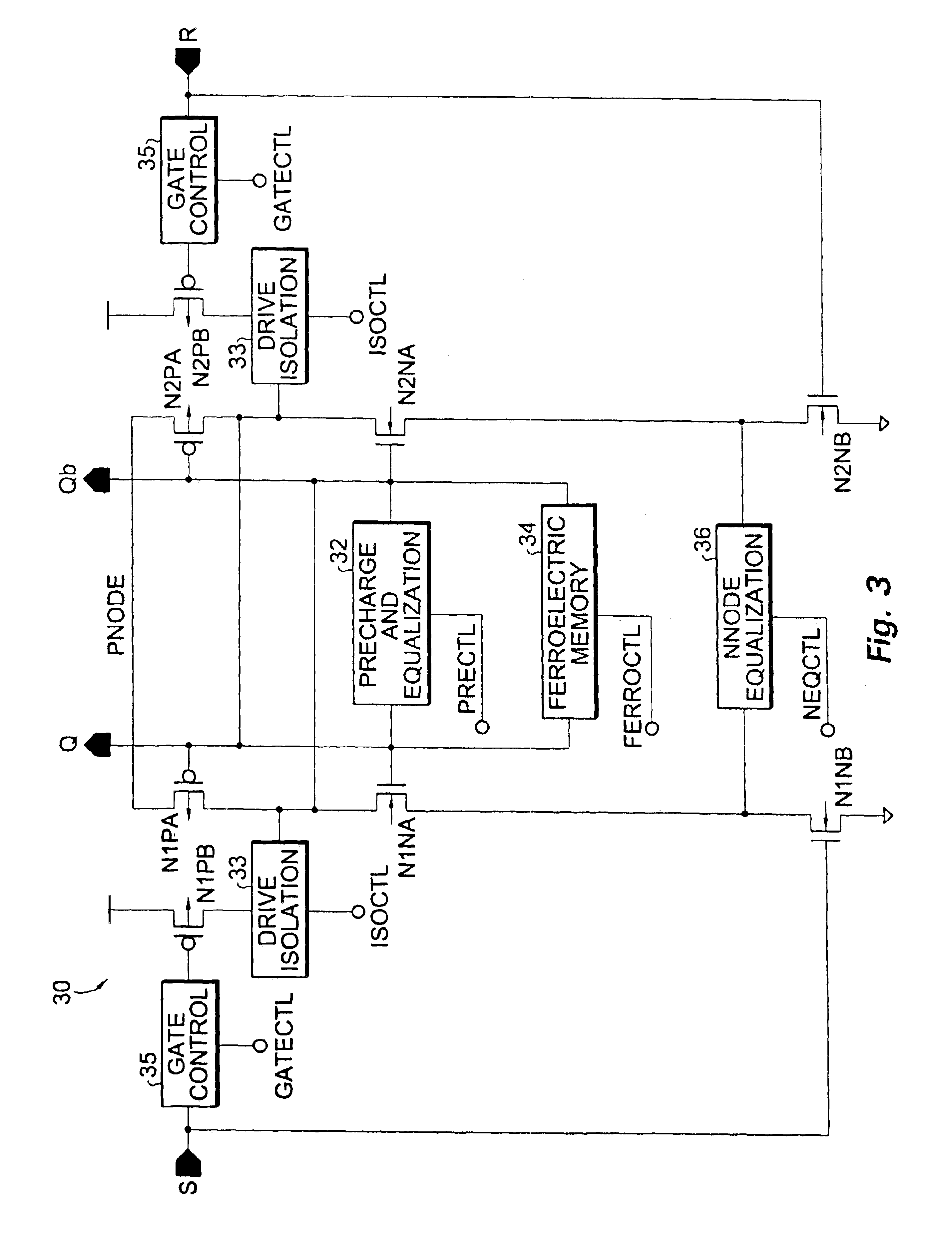
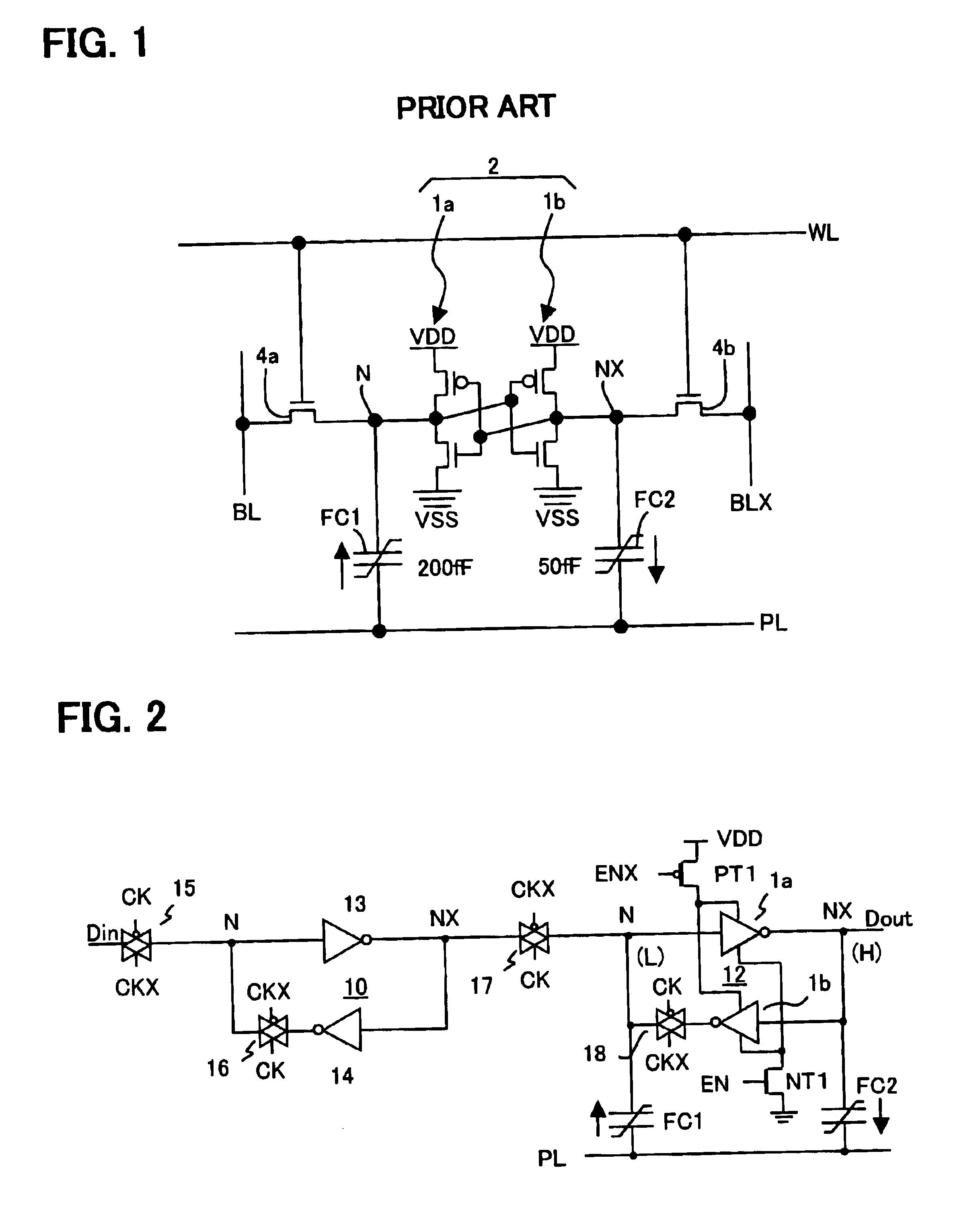
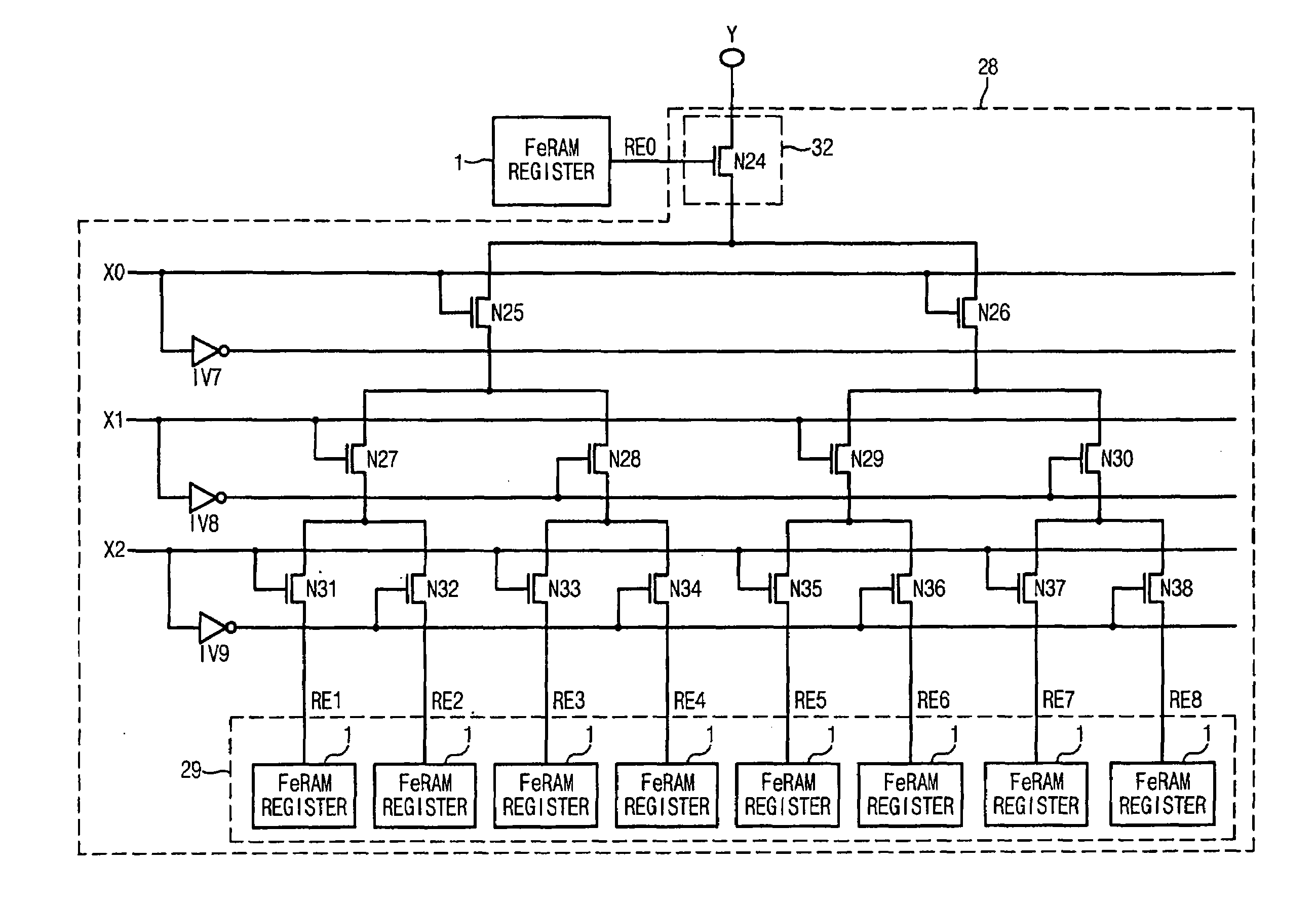
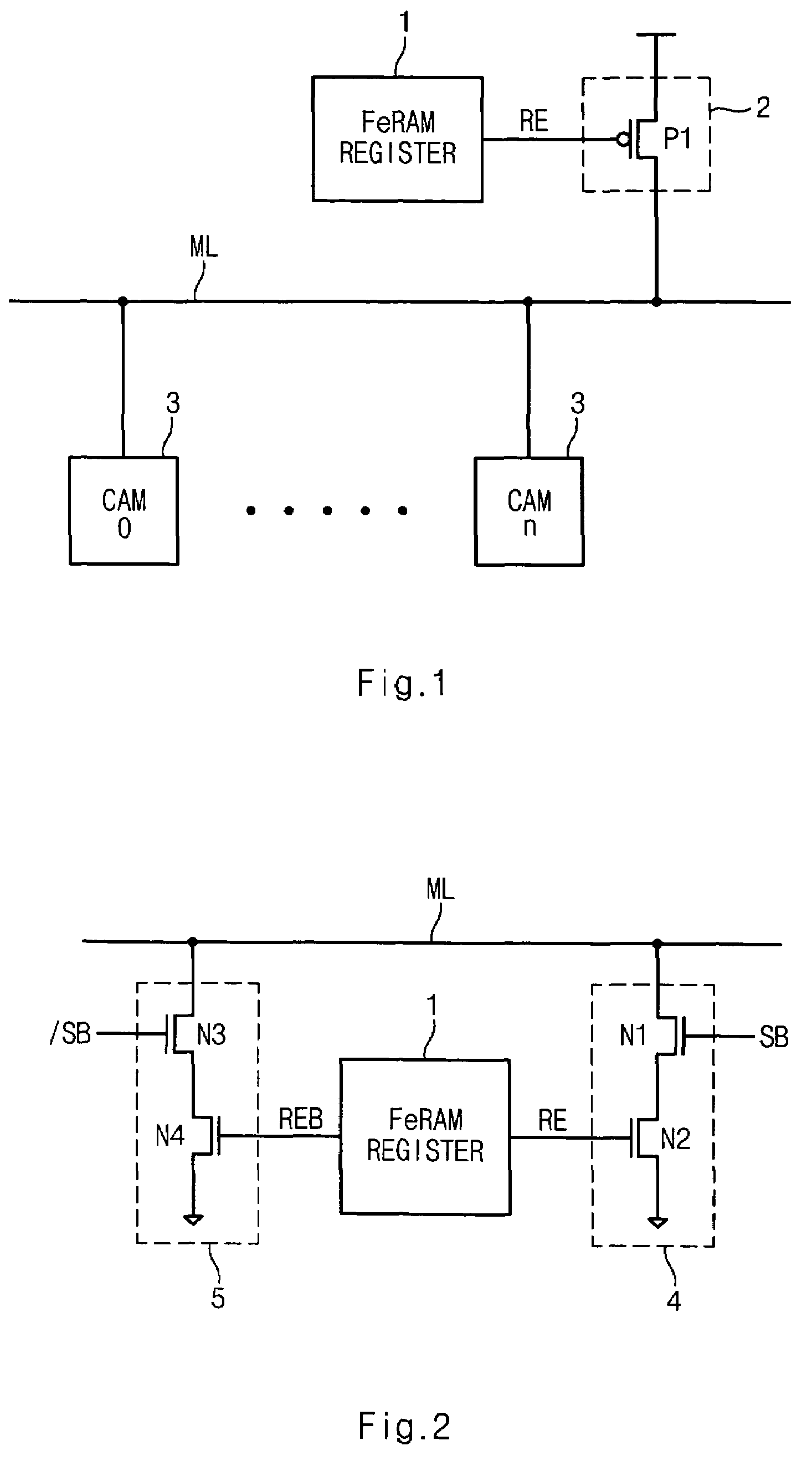
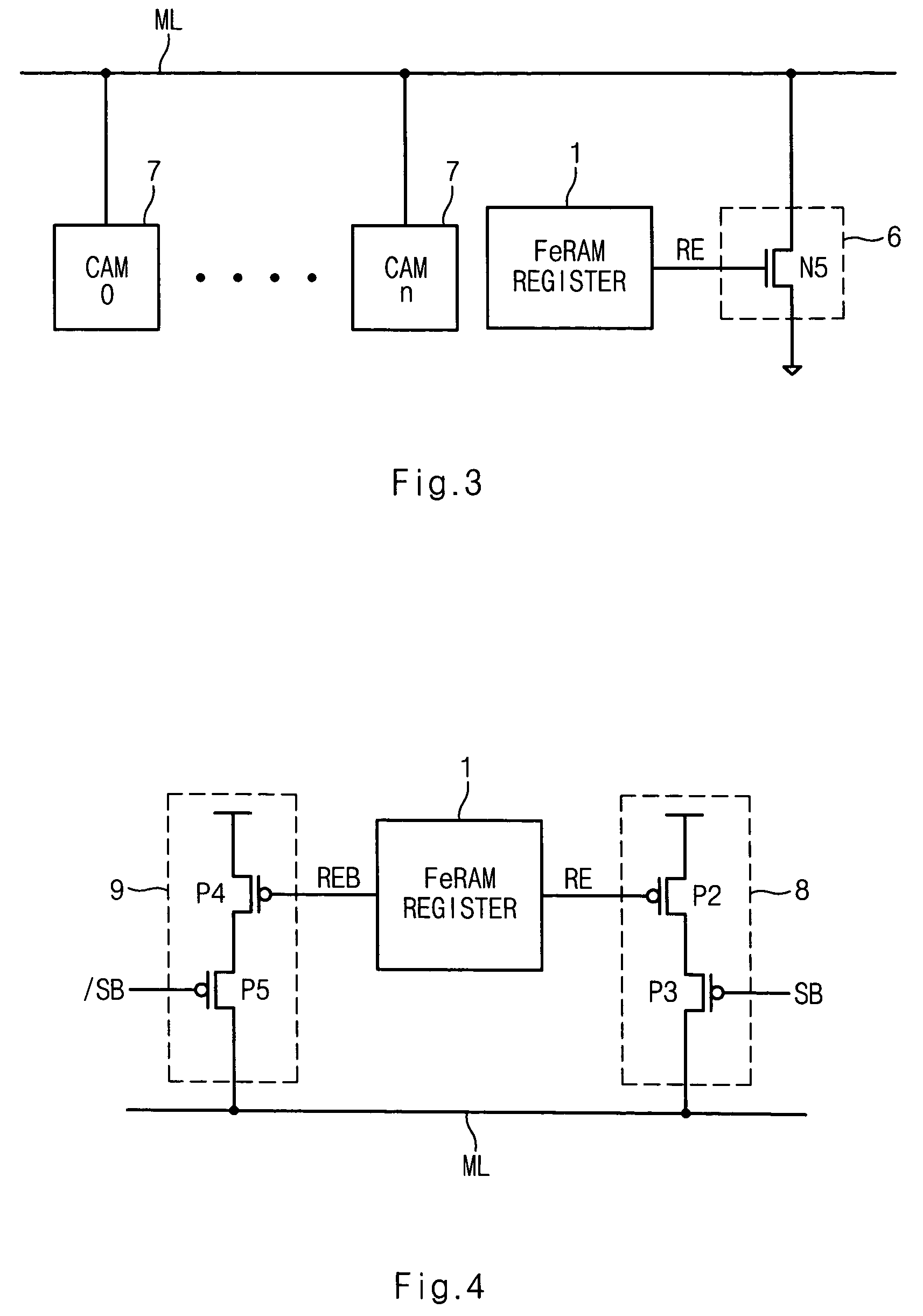
Ferroelectric non-volatile logic elements
InactiveUS6894549B2Easy translationImprove performanceTransistorPulse generation by non-linear magnetic/dielectric devicesShift registerAudio power amplifier
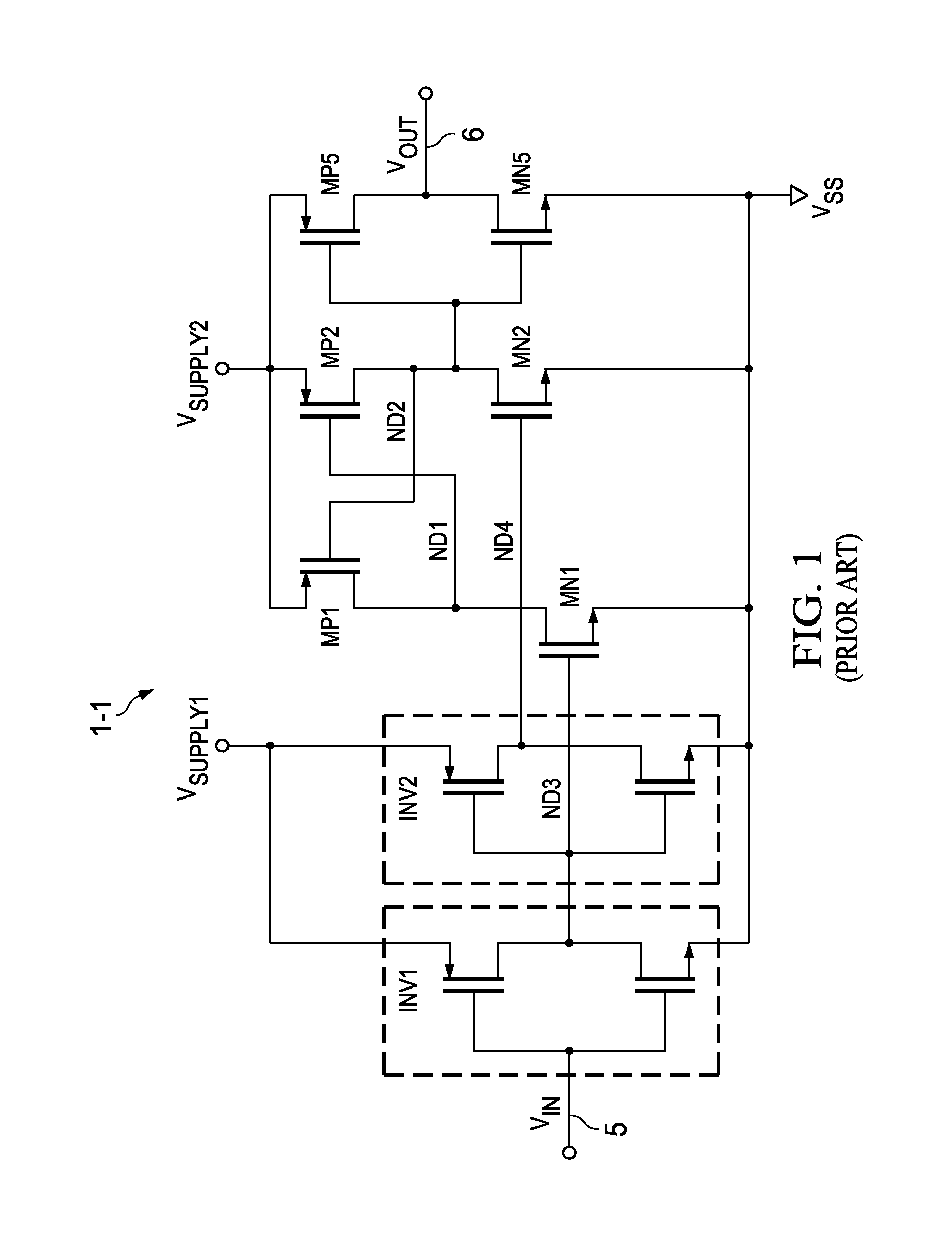
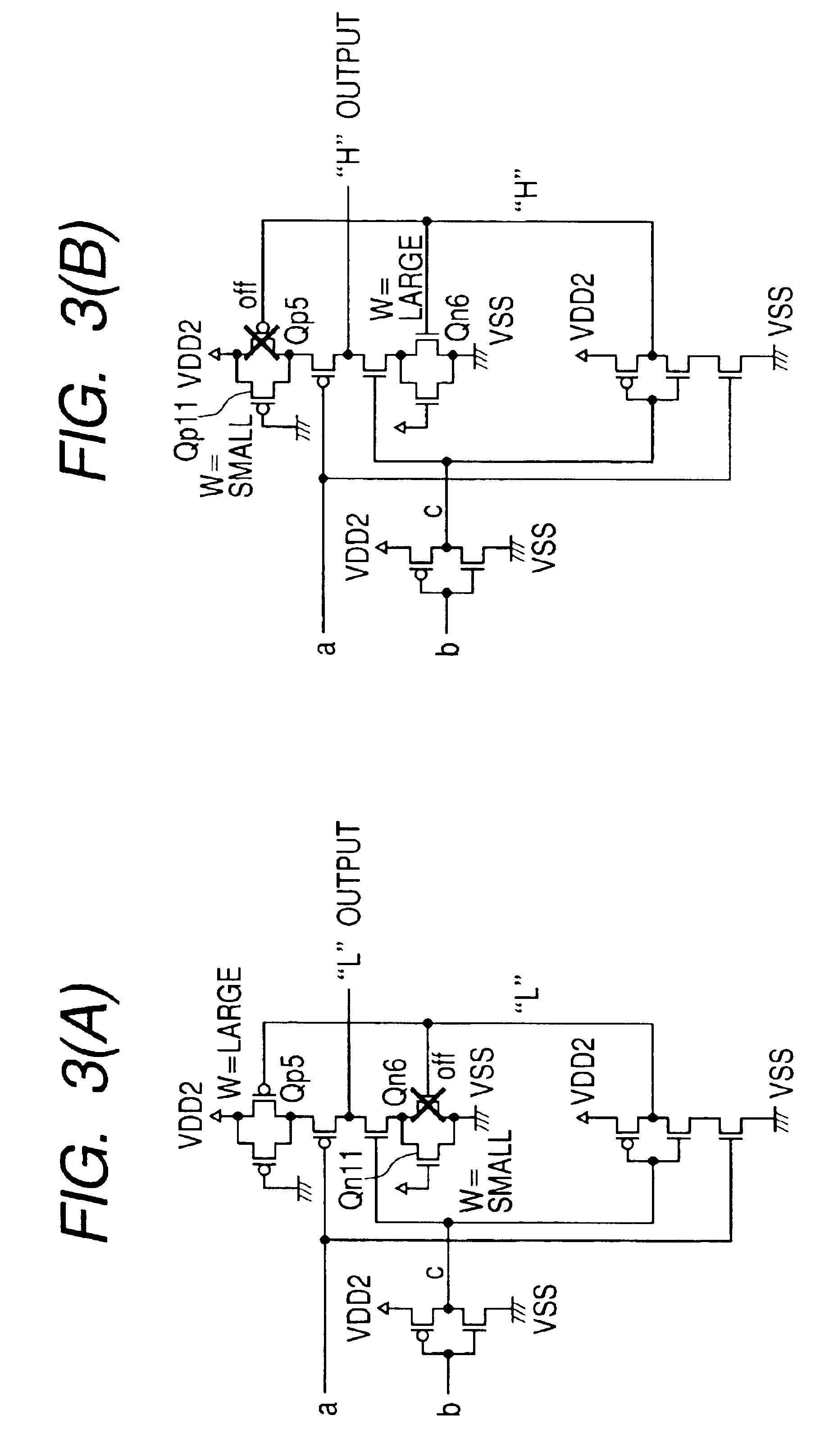
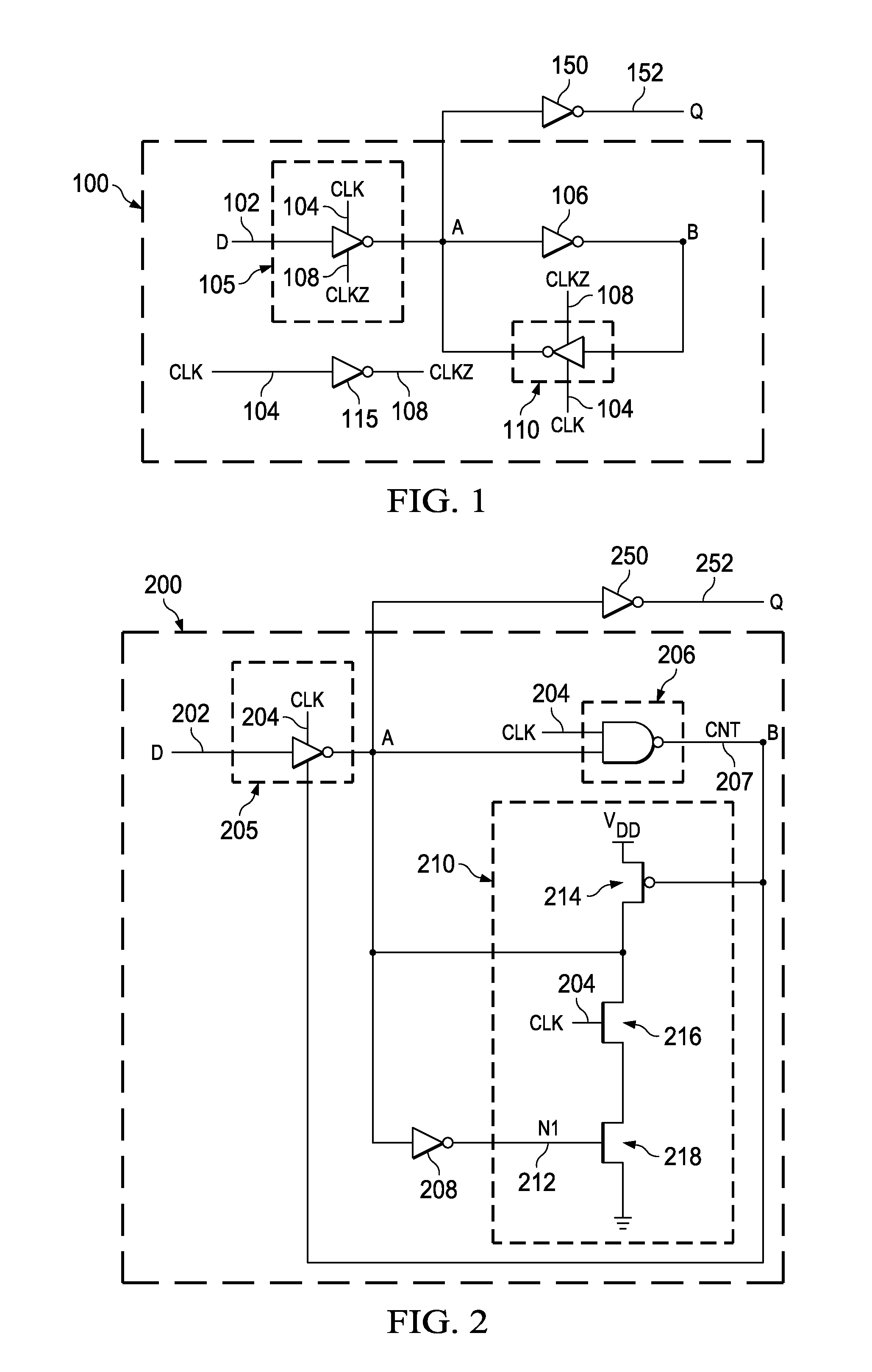
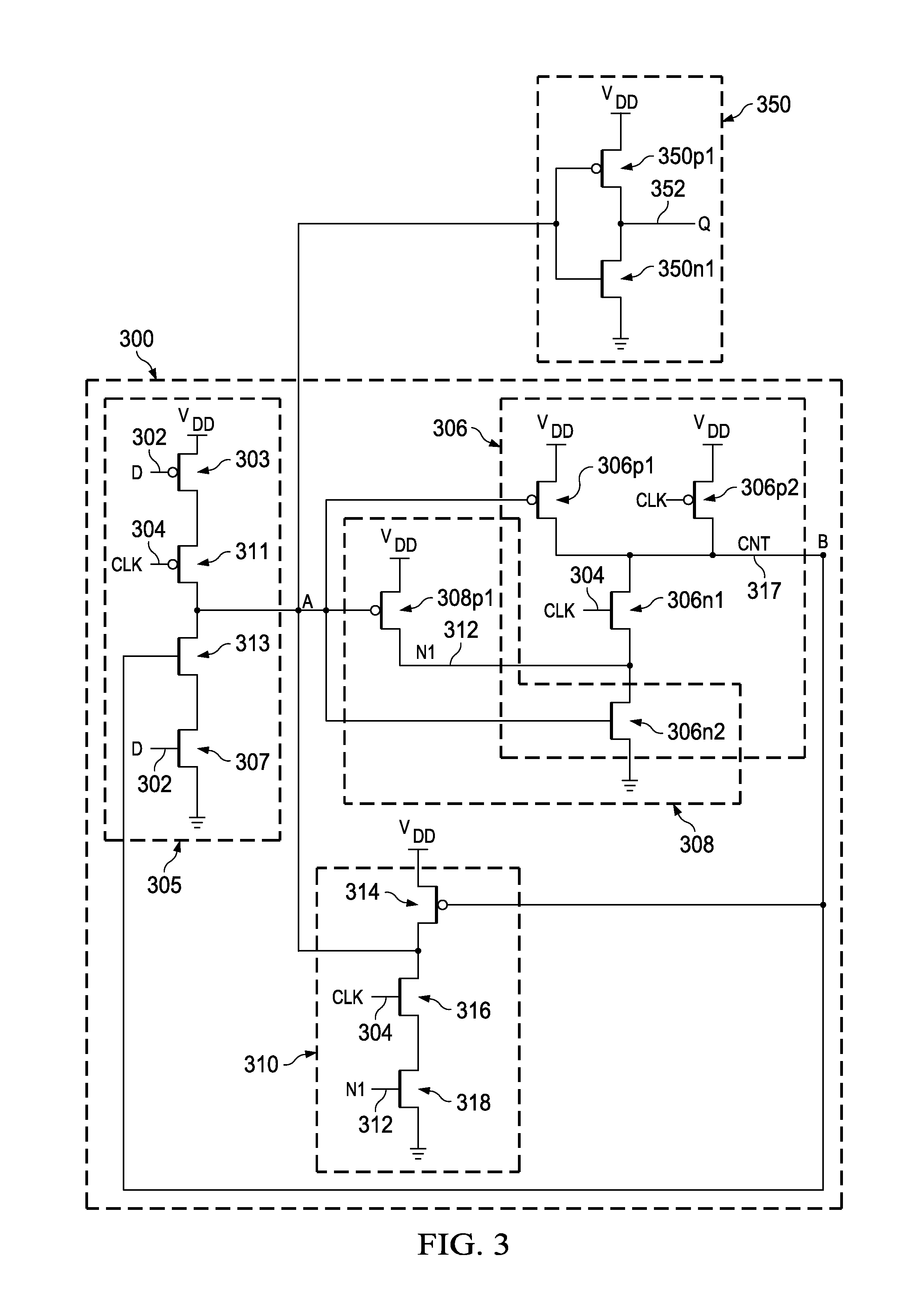
Various logic elements such as SR flip-flops, JK flip-flops, D-type flip-flops, master-slave flip-flops, parallel and serial shift registers, and the like are converted into non-volatile logic elements capable of retaining a current output logic state even though external power is removed or interrupted through the strategic addition of ferroelectric capacitors and supporting circuitry. In each case, the building blocks of a cross-coupled sense amplifier are identified within the logic element and the basic cell is modified and / or optimized for sensing performance.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
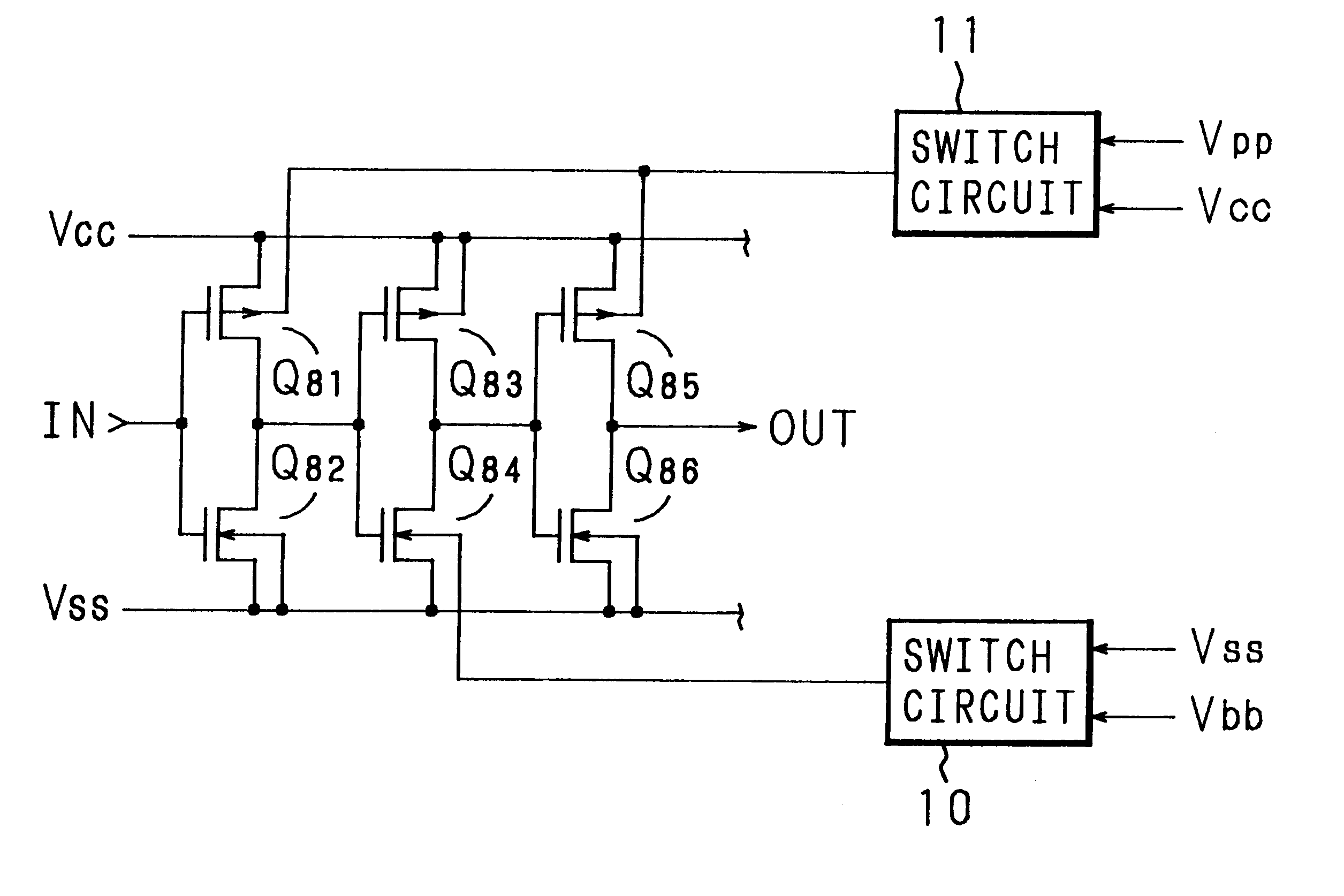
Switched backgate bias for FET
InactiveUS6232793B1Reliability increasing modificationsPower reduction by control/clock signalHemt circuitsEngineering
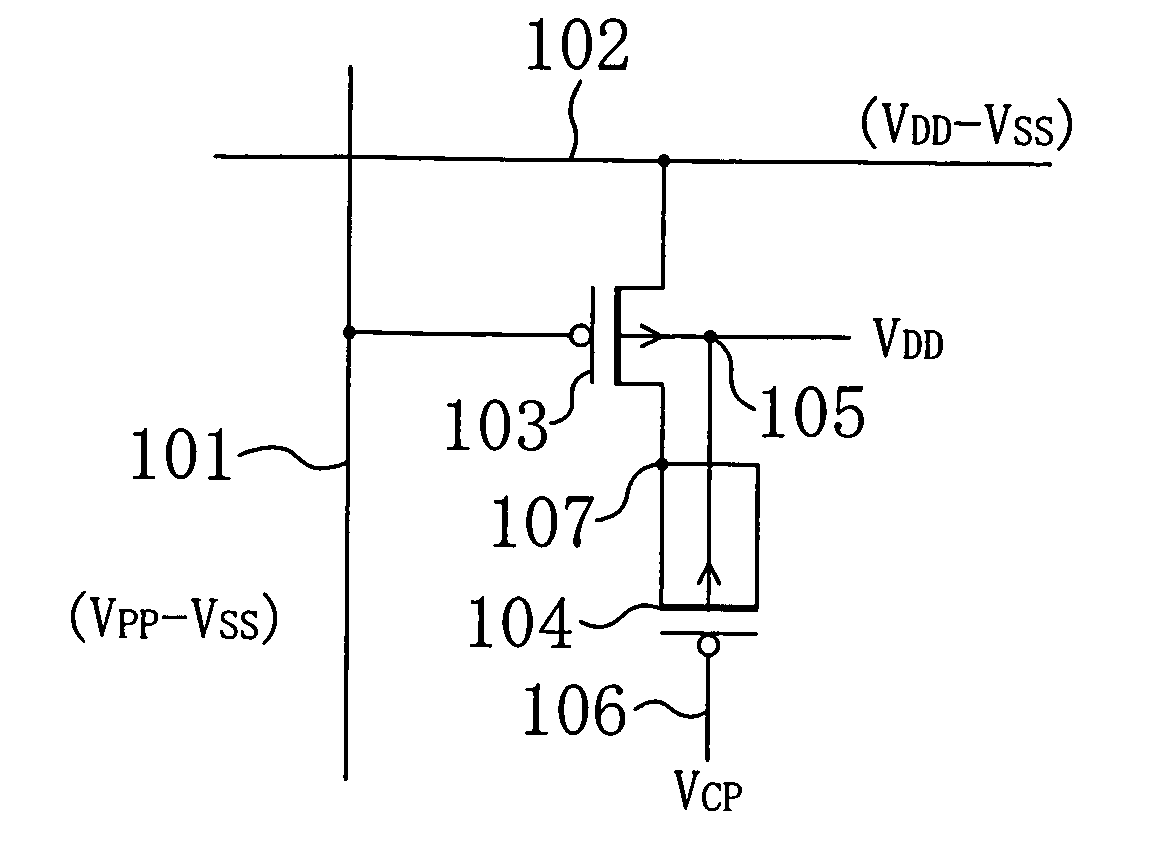
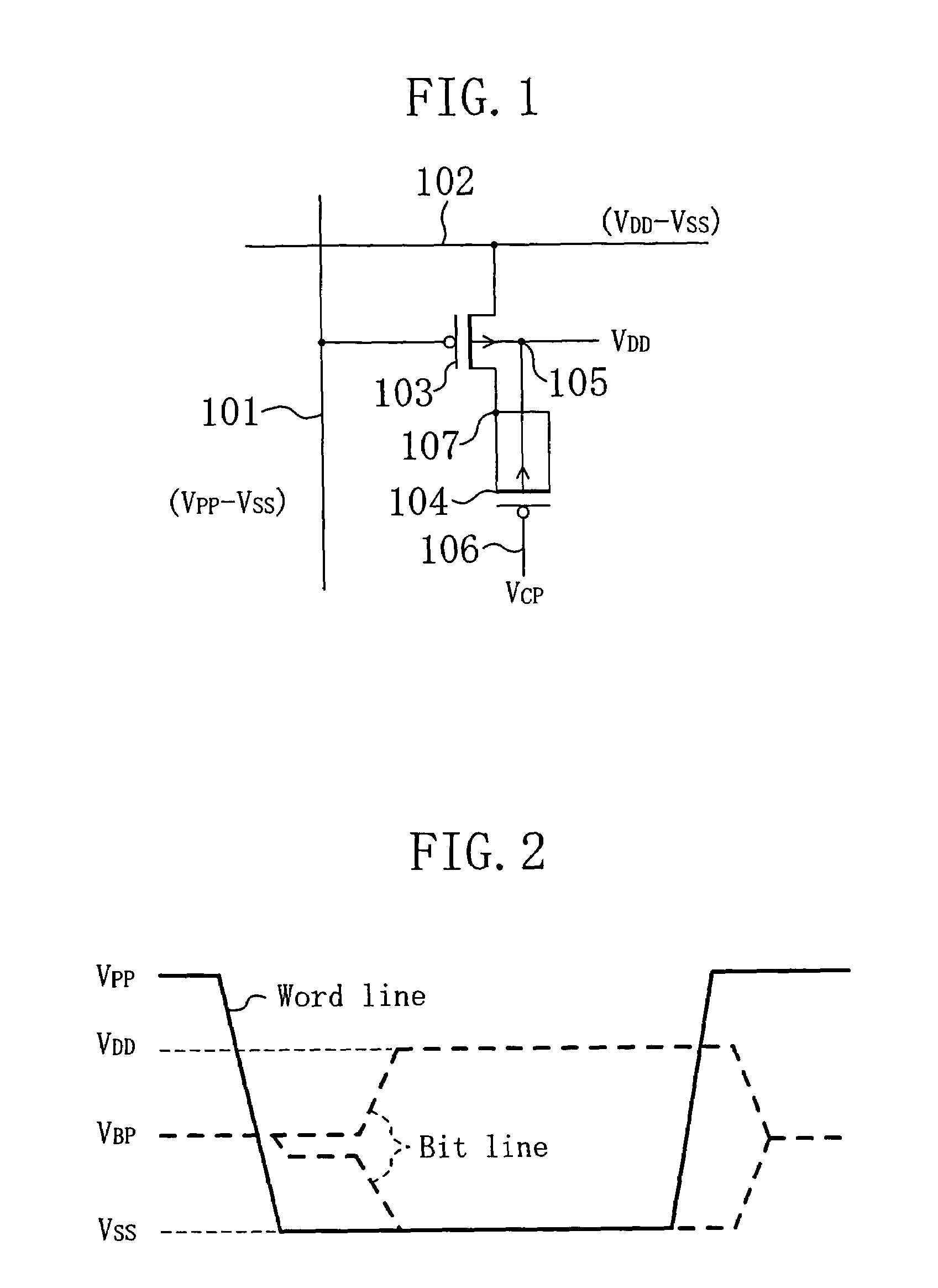
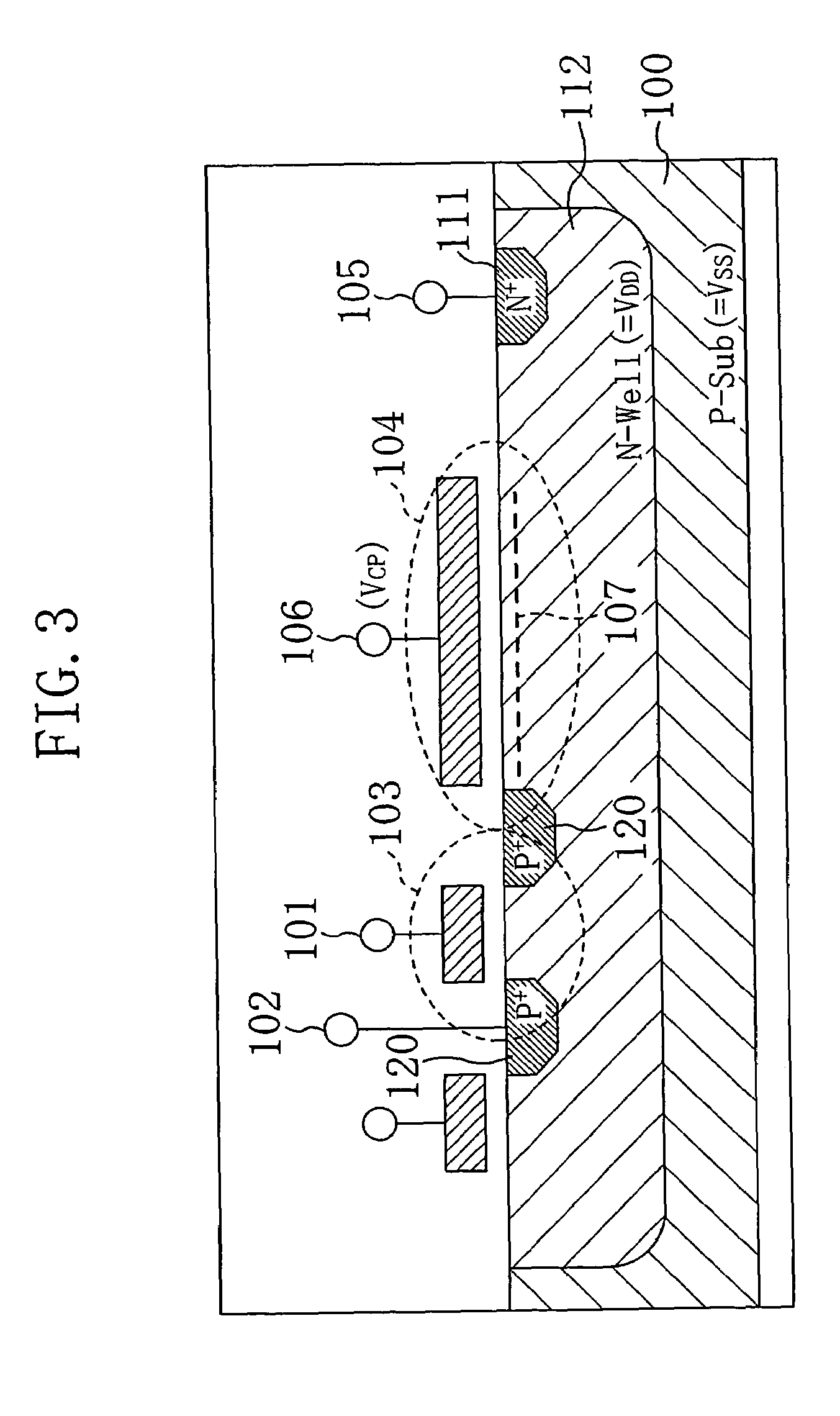
A semiconductor circuit or a MOS-DRAM wherein converting means is provided that converts substrate potential or body bias potential between two values for MOS-FETs in a logic circuit, memory cells, and operating circuit of the MOS-DRAM, thereby raising the threshold voltage of the MOS-FETs when in the standby state and lowering it when in active state. The converting means includes a level shift circuit and a switch circuit. The substrate potential or body bias potential is controlled only of the MOS-FETs which are nonconducting in the standby state; this configuration achieves a reduction in power consumption associated with the potential switching. Furthermore, in a structure where MOS-FETs of the same conductivity type are formed adjacent to each other, MOS-FETs of SOI structure are preferable for better results.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
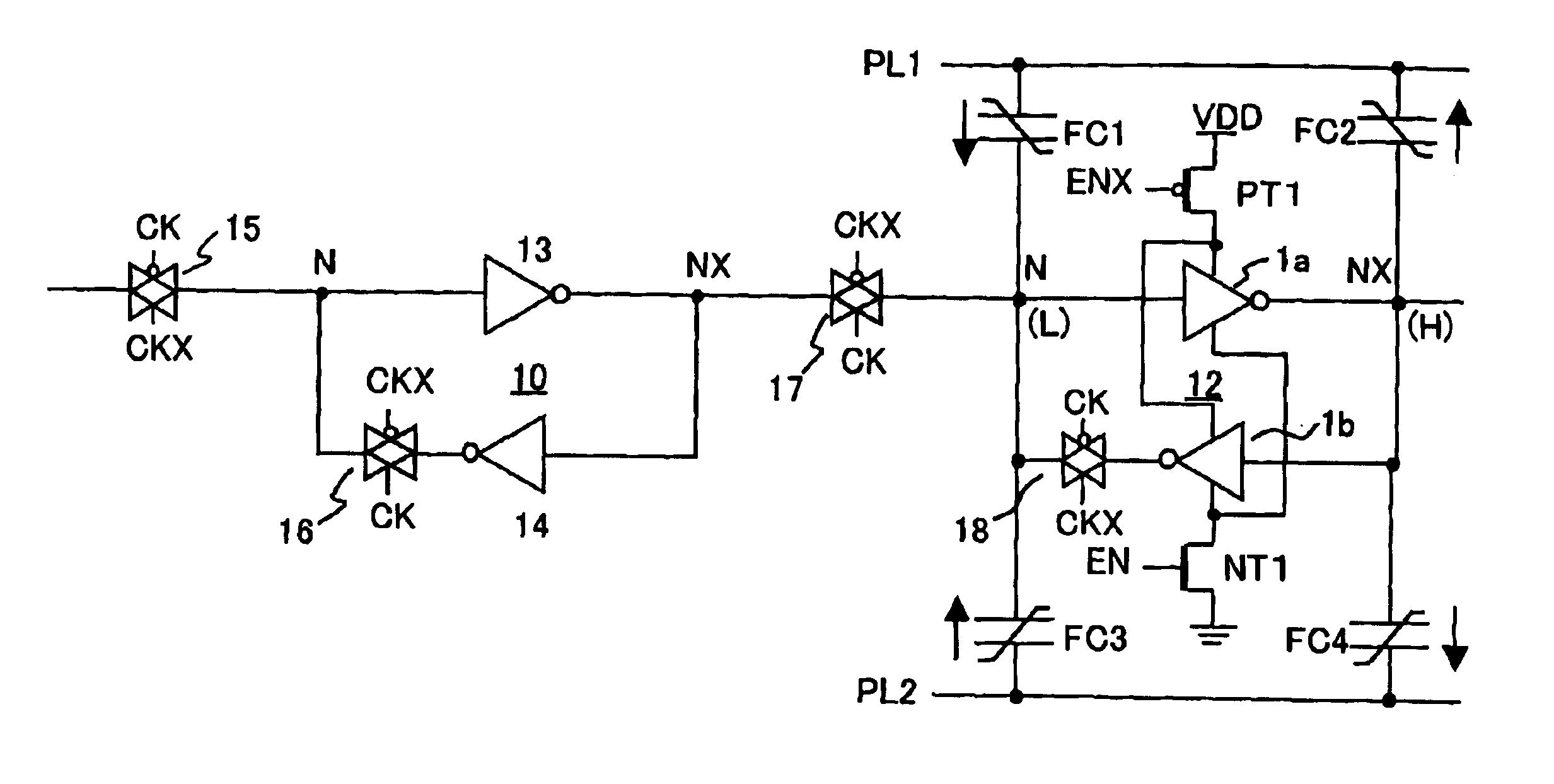
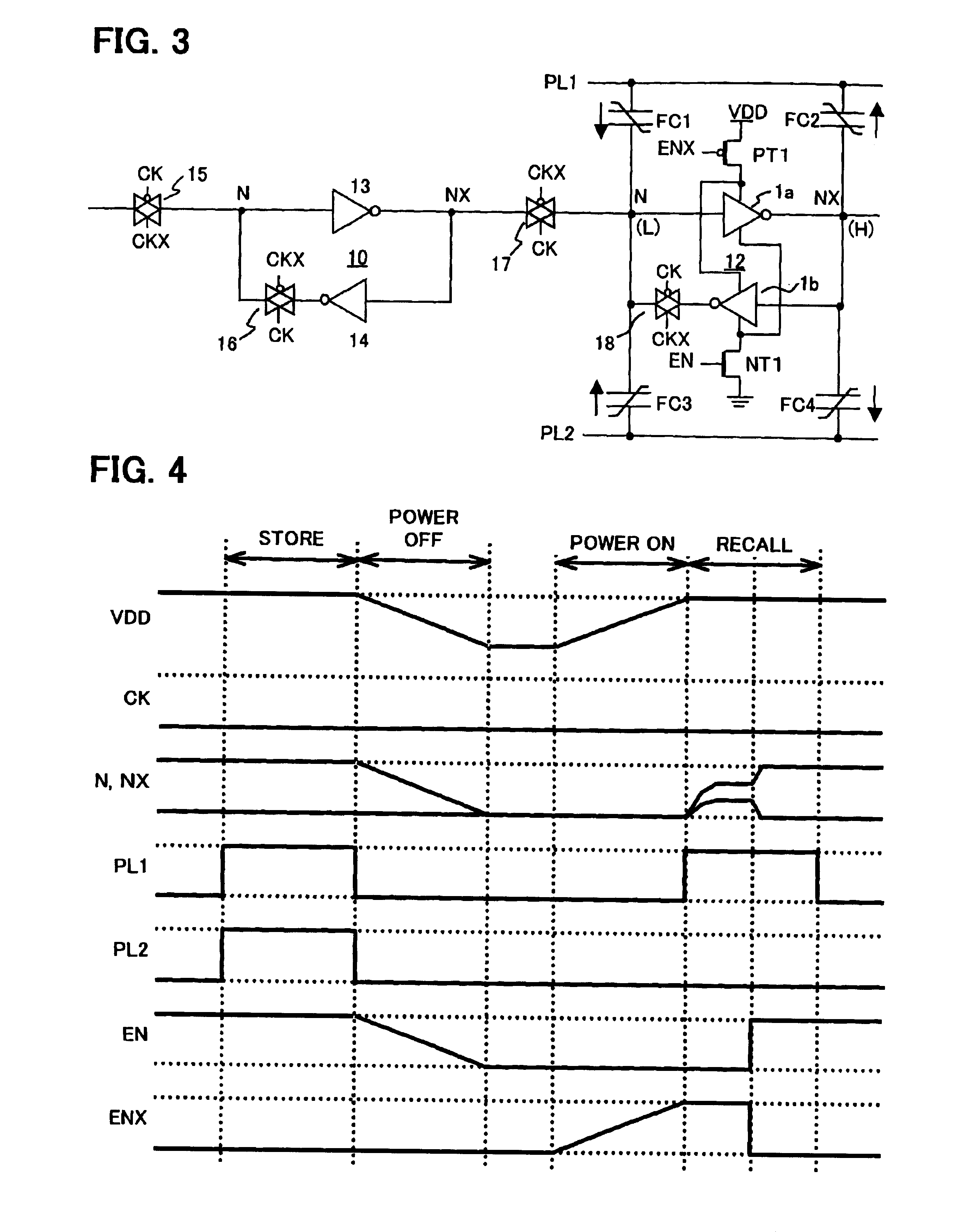
Non-volatile latch circuit and a driving method thereof
ActiveUS6845032B2High voltageSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesThreshold voltageFerroelectric capacitor
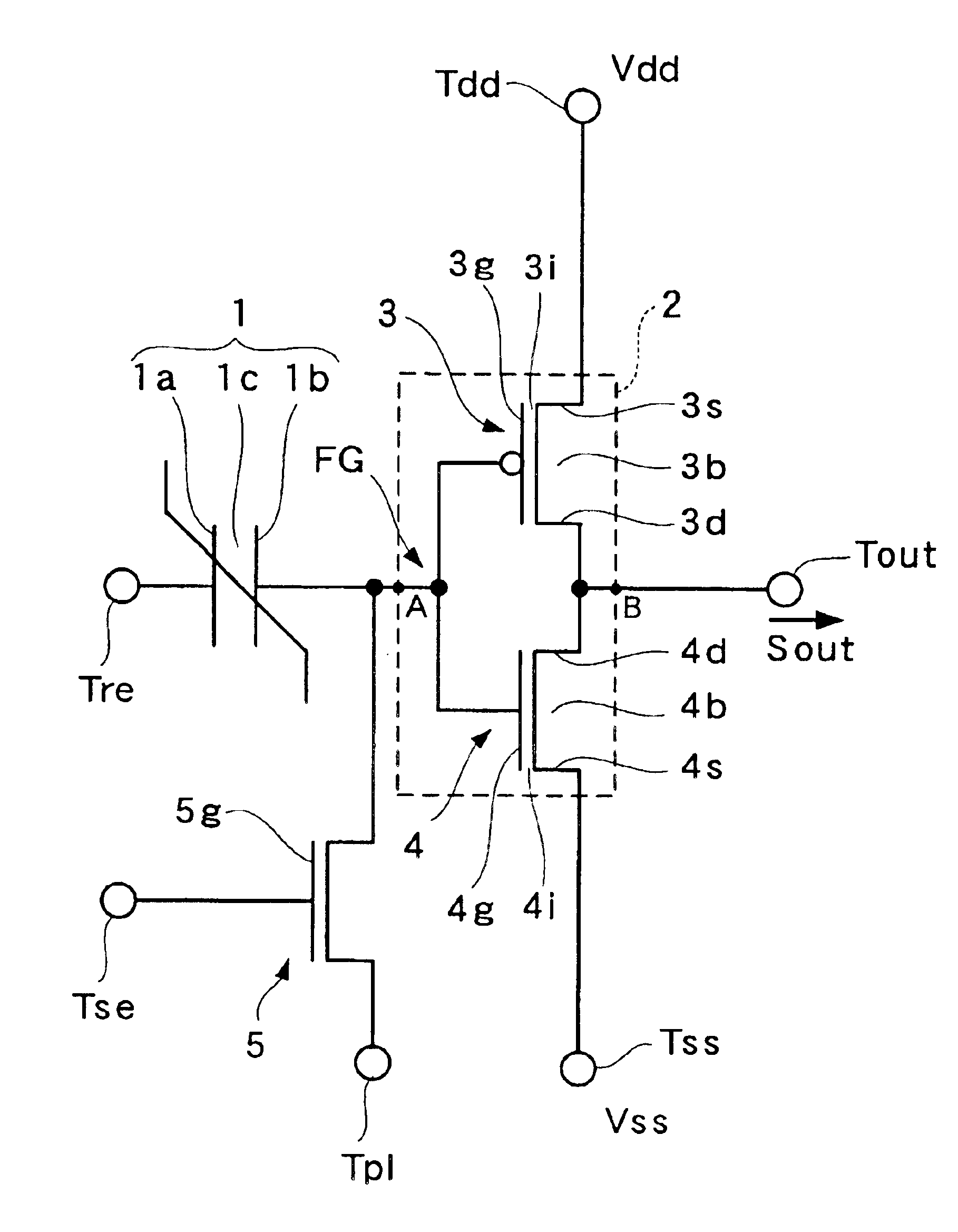
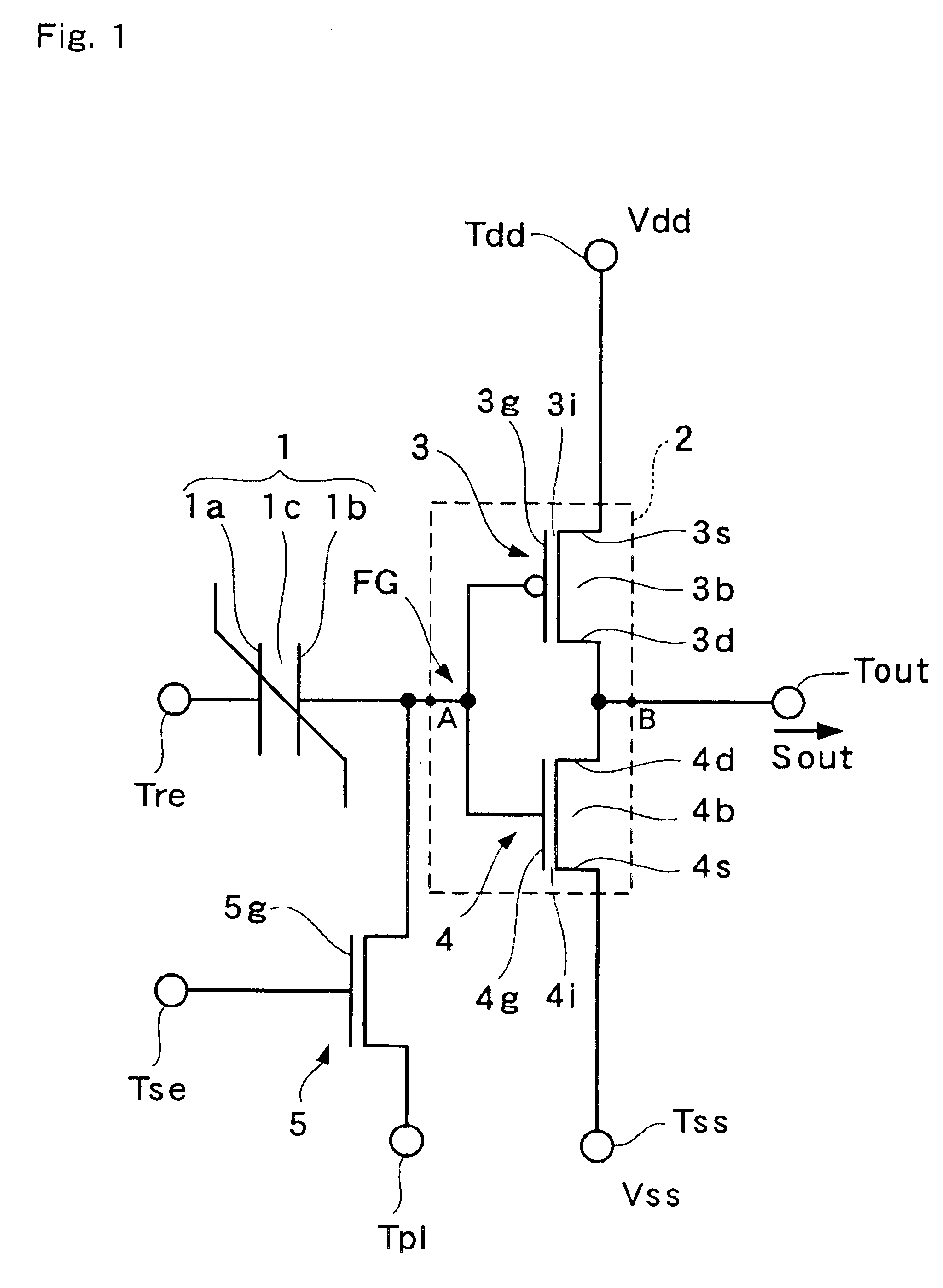
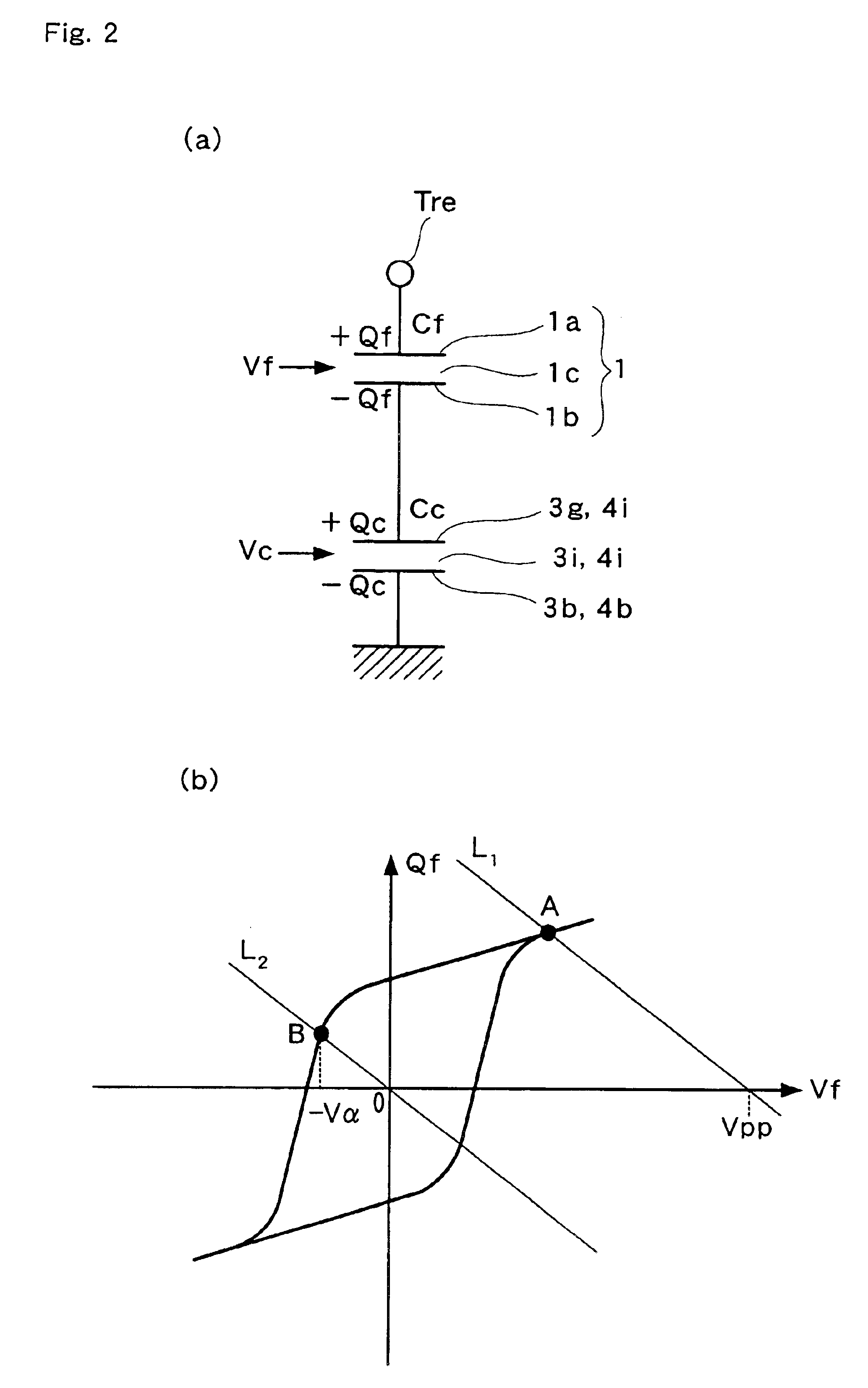
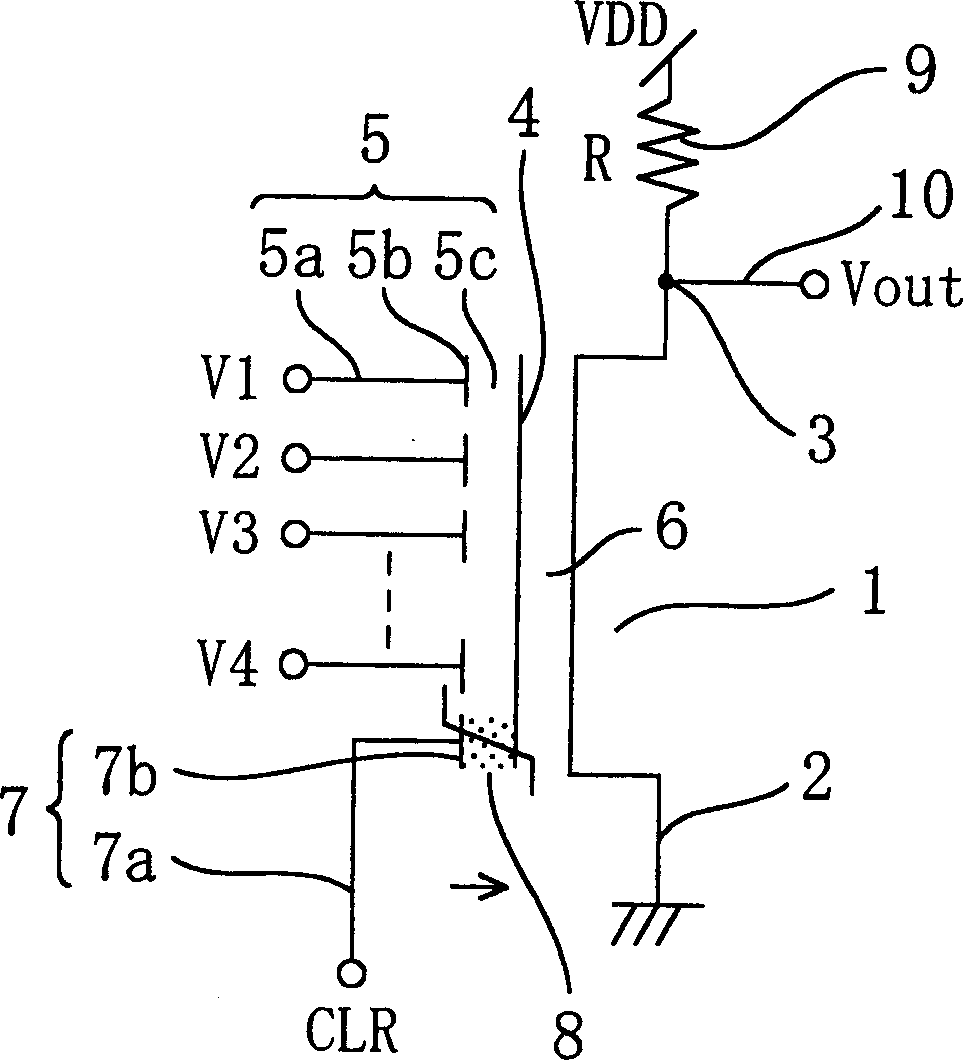
Non-volatile latch circuit 10 of the present invention comprises ferroelectric capacitor 1 provided with a first electrode 1a, second electrode 1b, and ferroelectric film 1c that lies between these electrodes; reset terminal Tre that is connected to first electrode 1a and a CMOS inverter element 2 that is connected to second electrode 1b of ferroelectric capacitor 1; voltage switching terminal Tpl that applies a voltage to second electrode 1b; switching element 5 that is connected between second electrode 1b and second input terminal Tpl and switches a voltage applied to second electrode 1b; and set terminal Tse that applies a voltage for switching on or off switching element 5, wherein the voltage generated in second electrode 1b caused by polarization retained by ferroelectric film 1c is higher than the threshold voltage Vtn of NMISFET 4 of CMOS inverter element 2.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Voltage generating circuit, voltage generating device and semiconductor device using the same, and driving method thereof
ActiveUS20040183508A1Stable maintenanceElectronic switchingApparatus without intermediate ac conversionSemiconductorFerroelectric capacitor
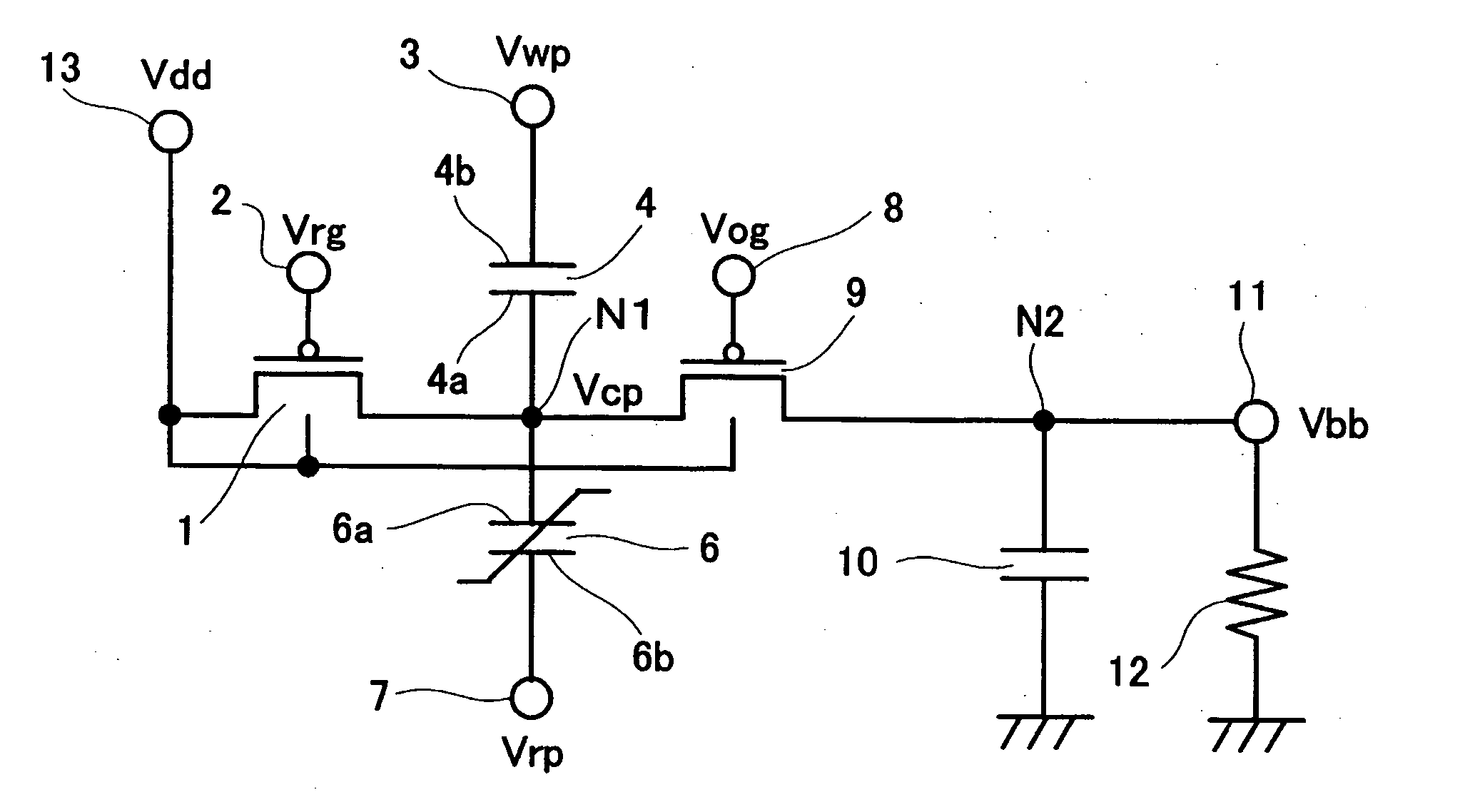
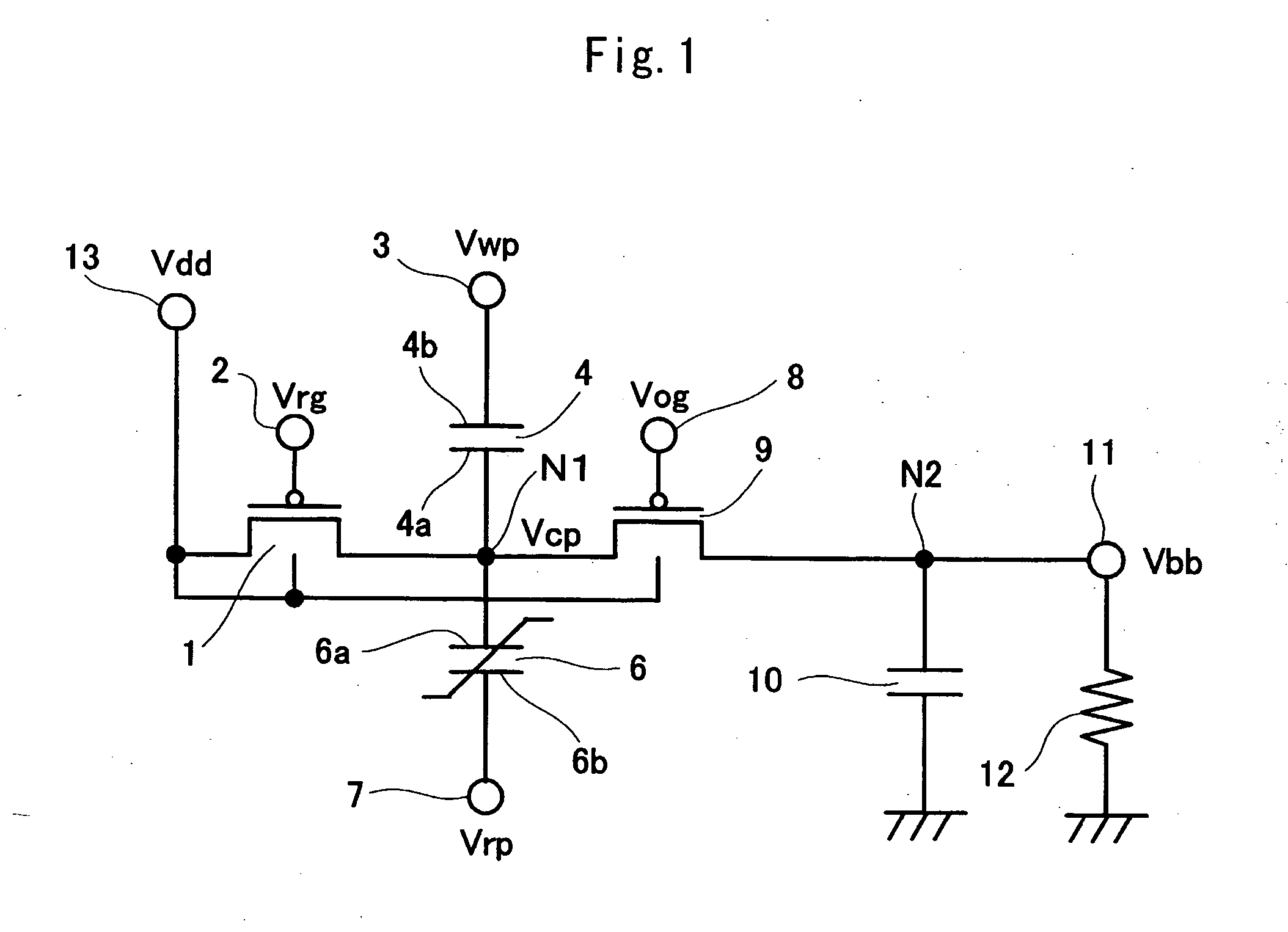
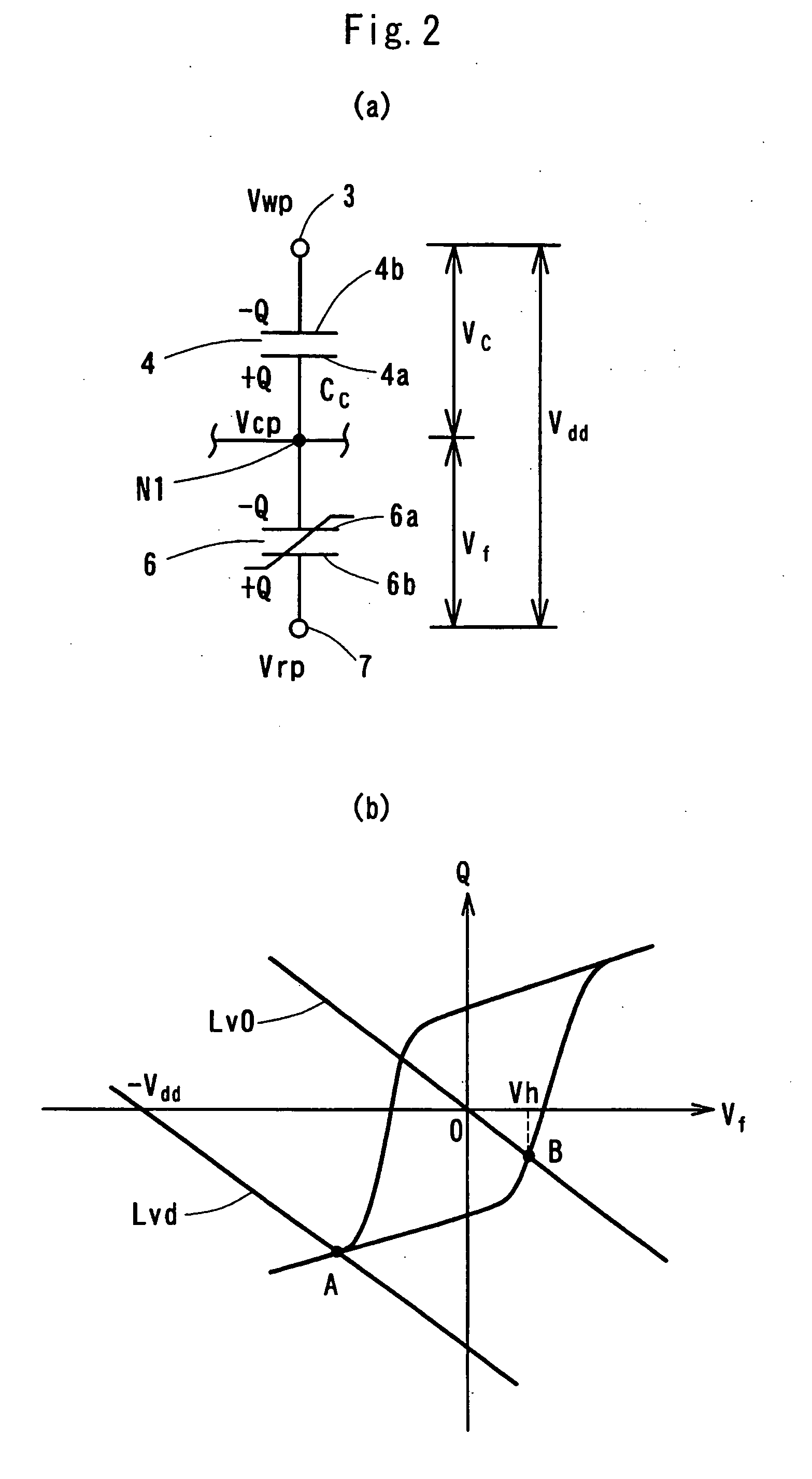
A voltage generating circuit comprising a capacitor (4), a ferroelectric capacitor (6) serially connected to the capacitor (4), an output terminal (11), a capacitor (10) which grounds the output terminal (11), a supply voltage supplying terminal (13), a switch (1) which connects the supply voltage supplying terminal (13) and the connecting node (N1) of the two capacitors (4, 6), and a switch (9) which connects the connecting node (N1) and output terminal (11); wherein during a first period, with the two switches (1) and (9) placed in the OFF state, a terminal (3) is grounded and a terminal (7) is provided with a supply voltage; wherein during a second period, the terminal (3) is provided with the supply voltage and the switch (9) is placed in the ON state; wherein during a third period, the switch (9) is placed in the OFF state, the switch (1) is placed in the ON state, and the terminal (7) is grounded; wherein during a fourth period, the terminal (7) is provided with the supply voltage; and wherein thereafter the first through fourth periods are repeated.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Logical operation circuit and logical operation device
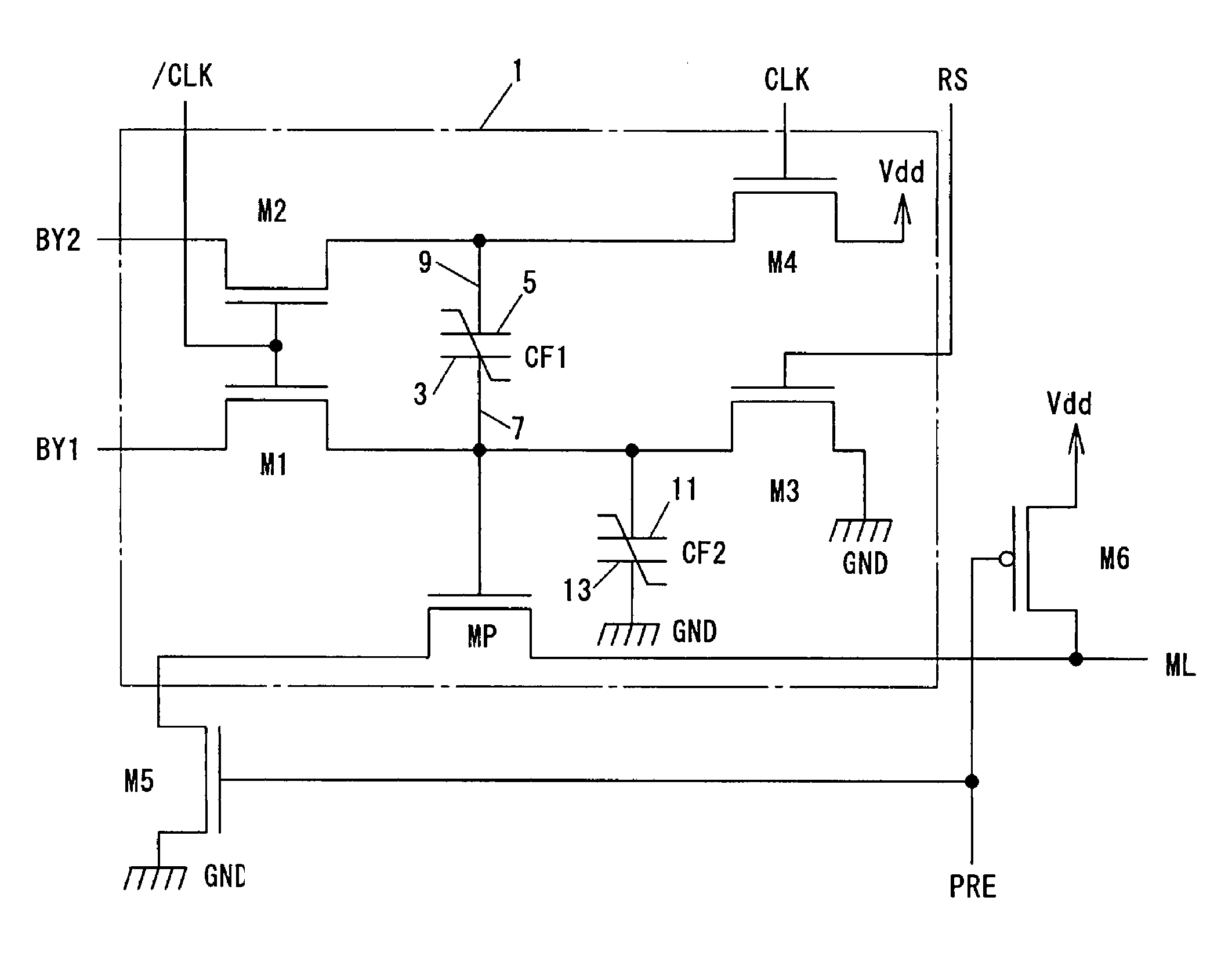
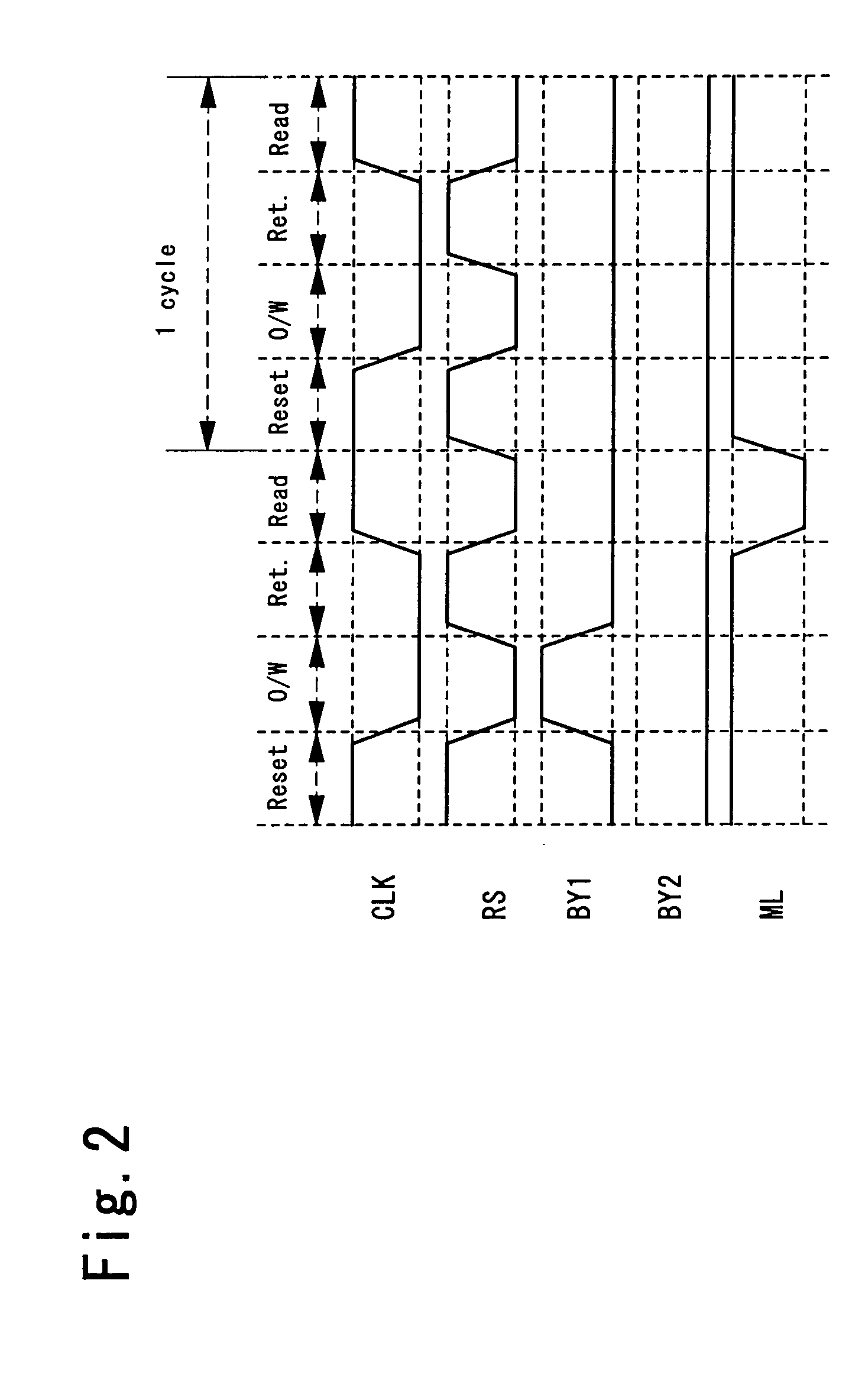
InactiveUS7428565B2Logic circuits characterised by logic functionSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsPotential differenceHemt circuits
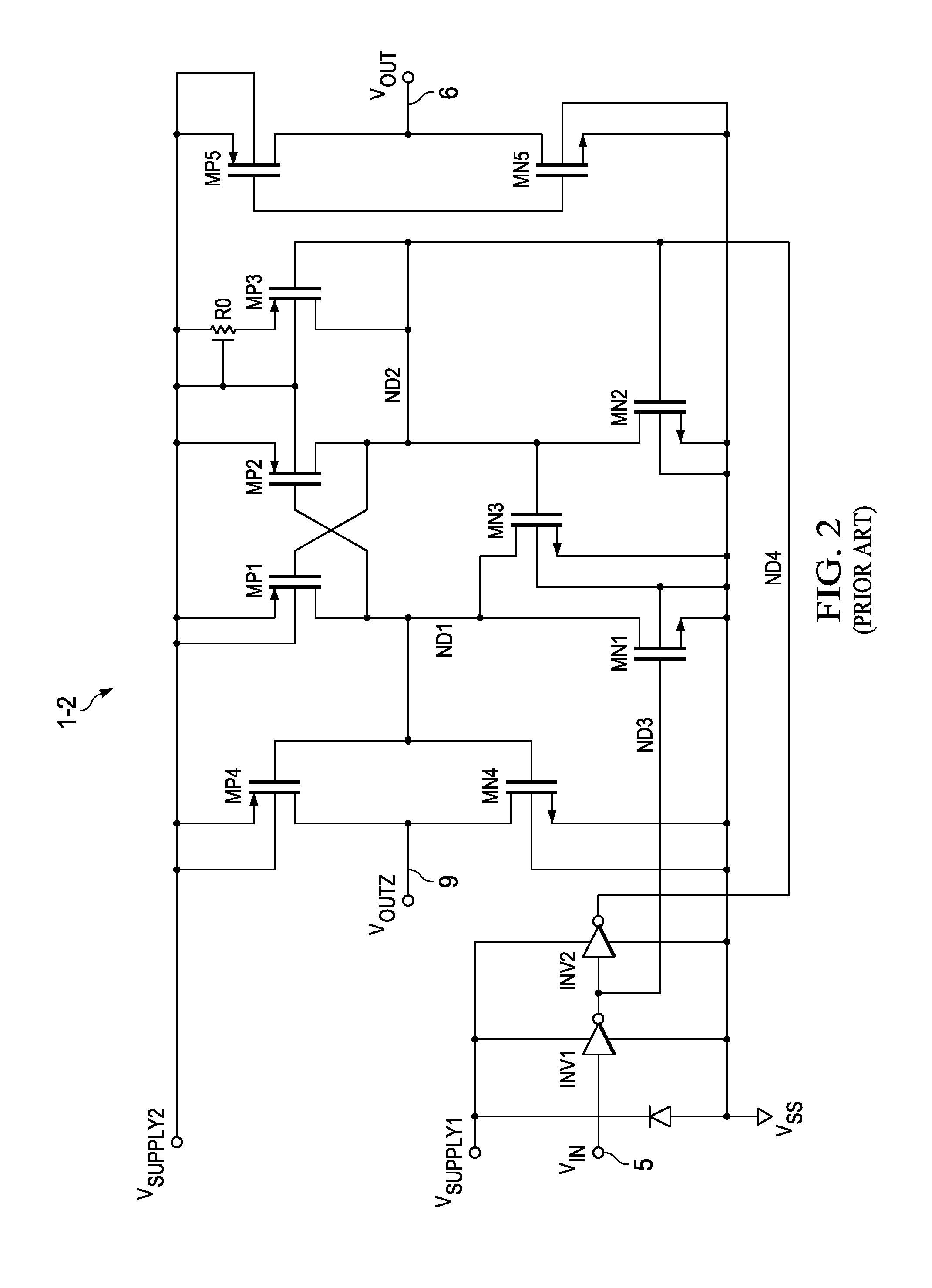
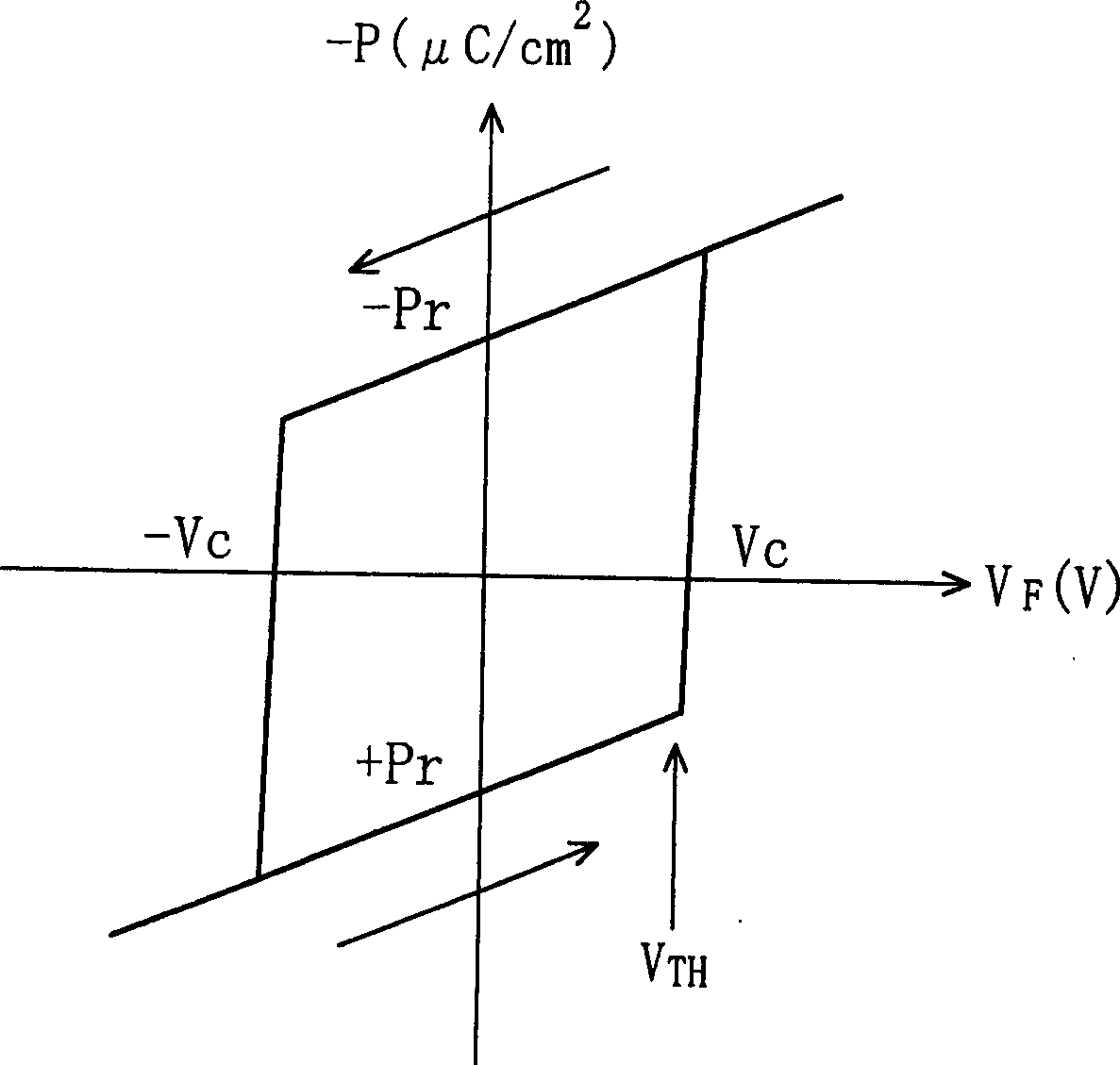
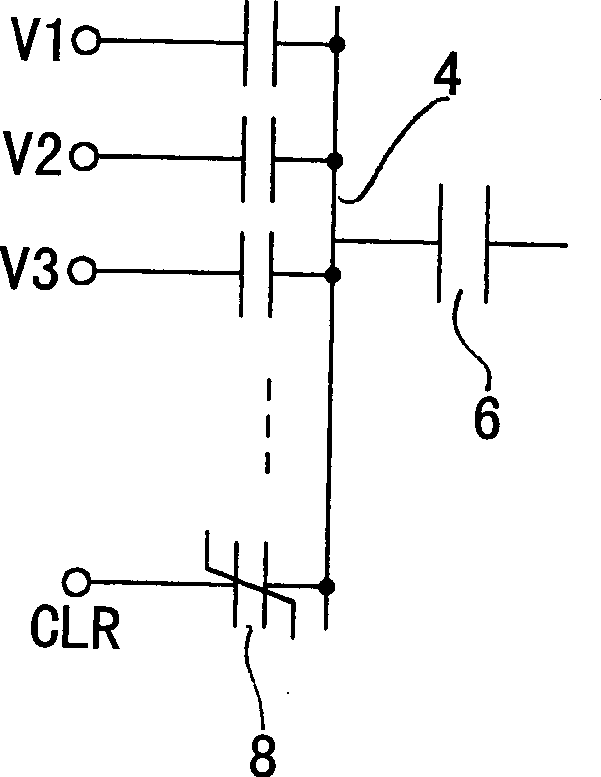
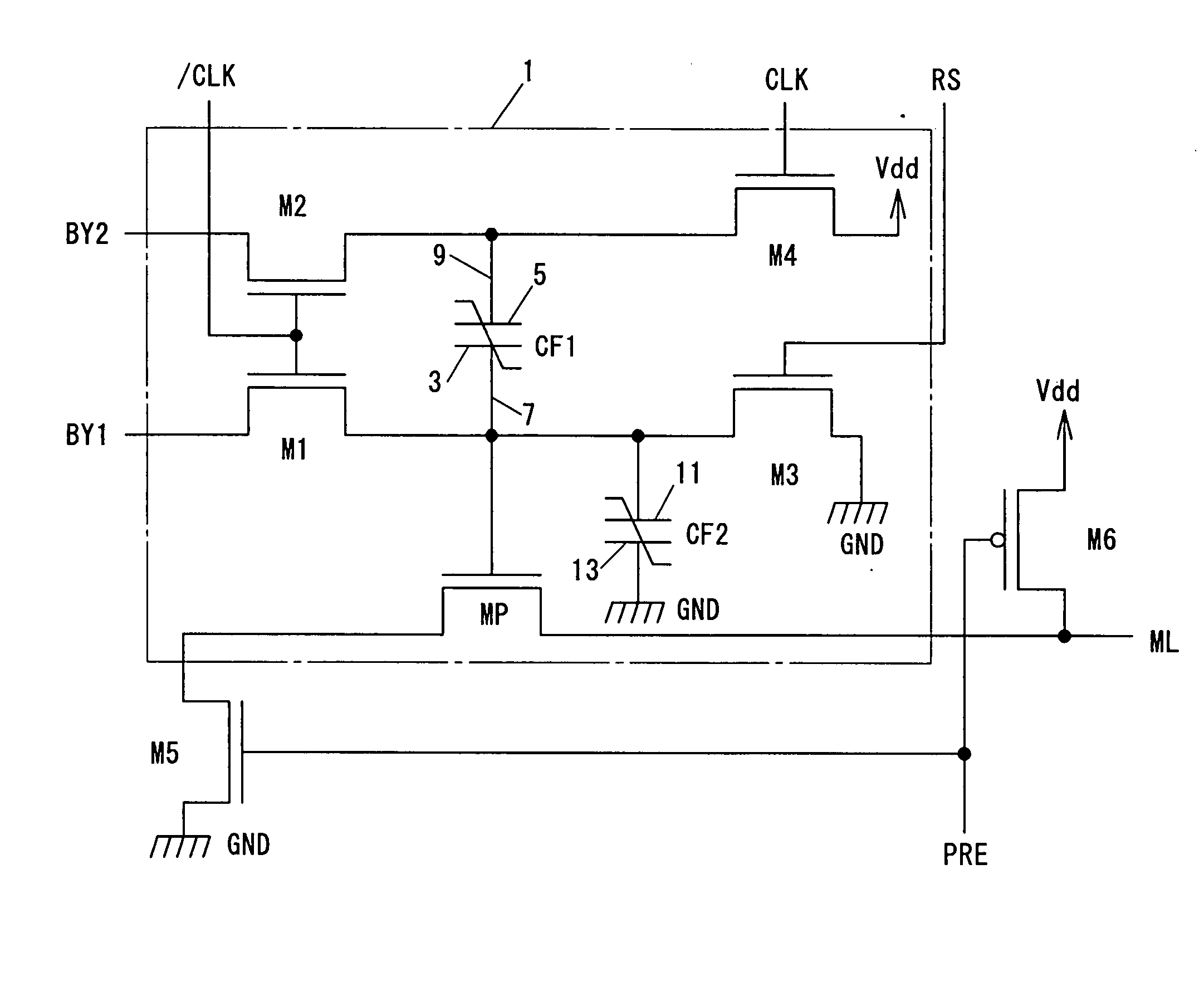
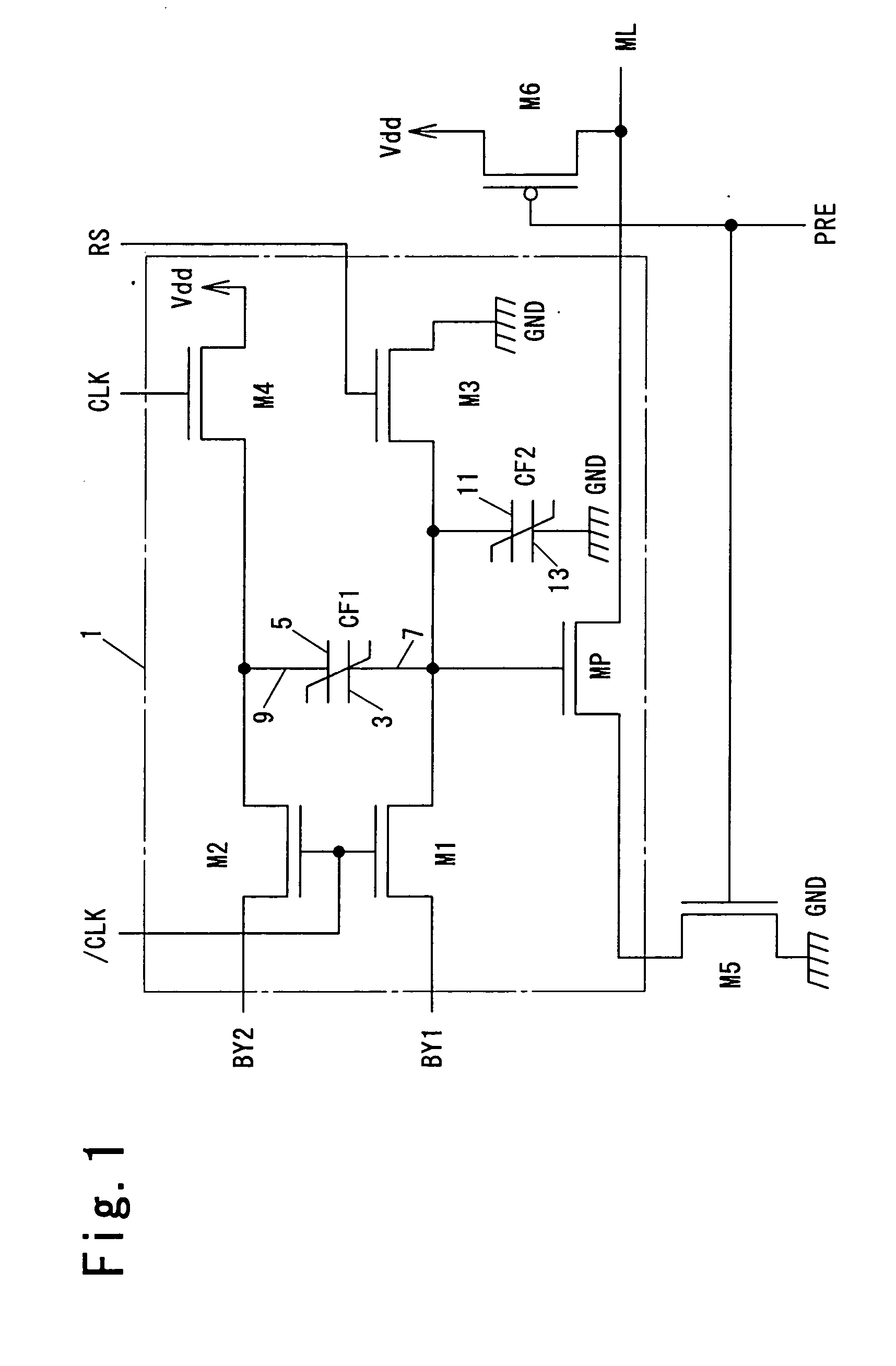
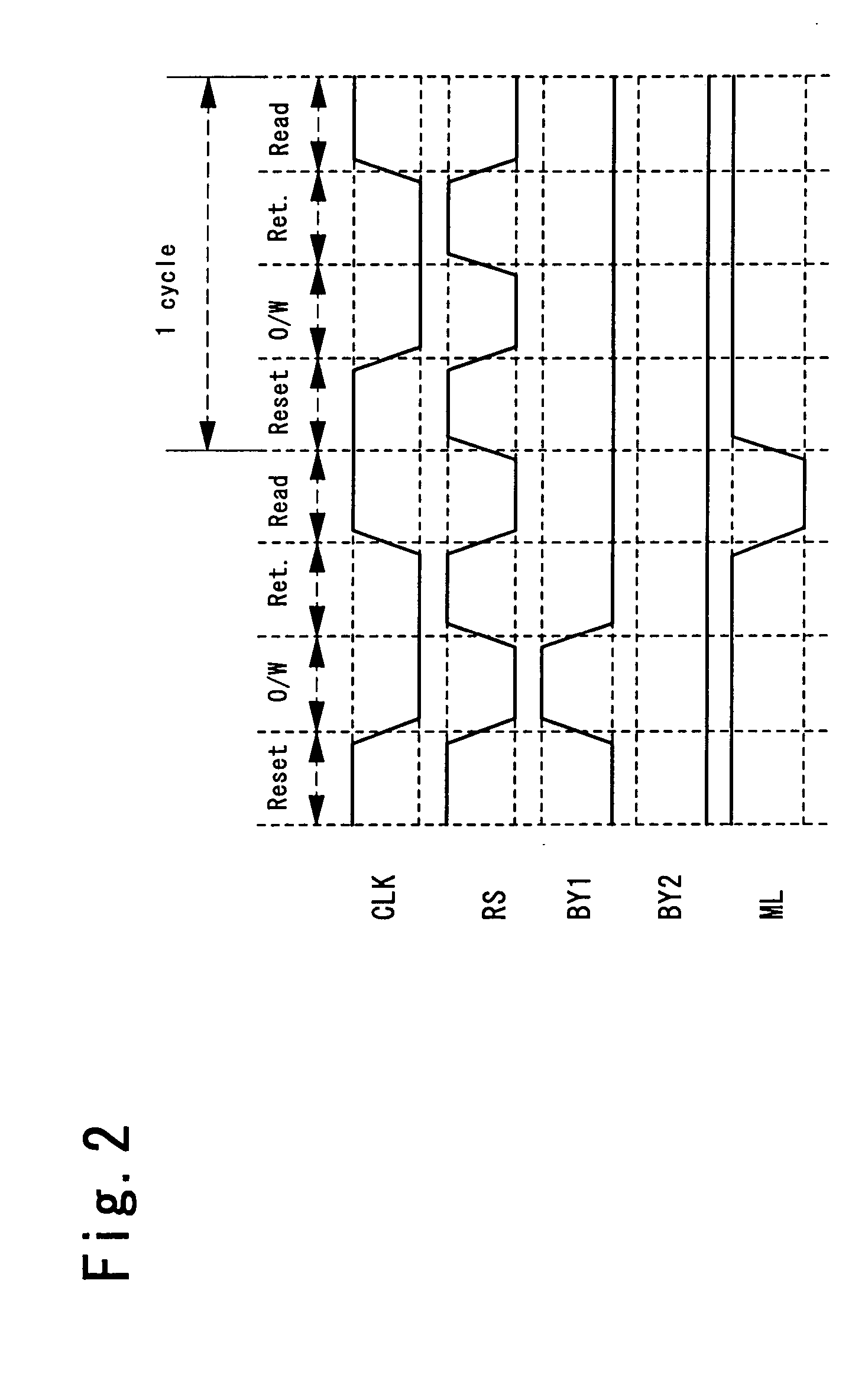
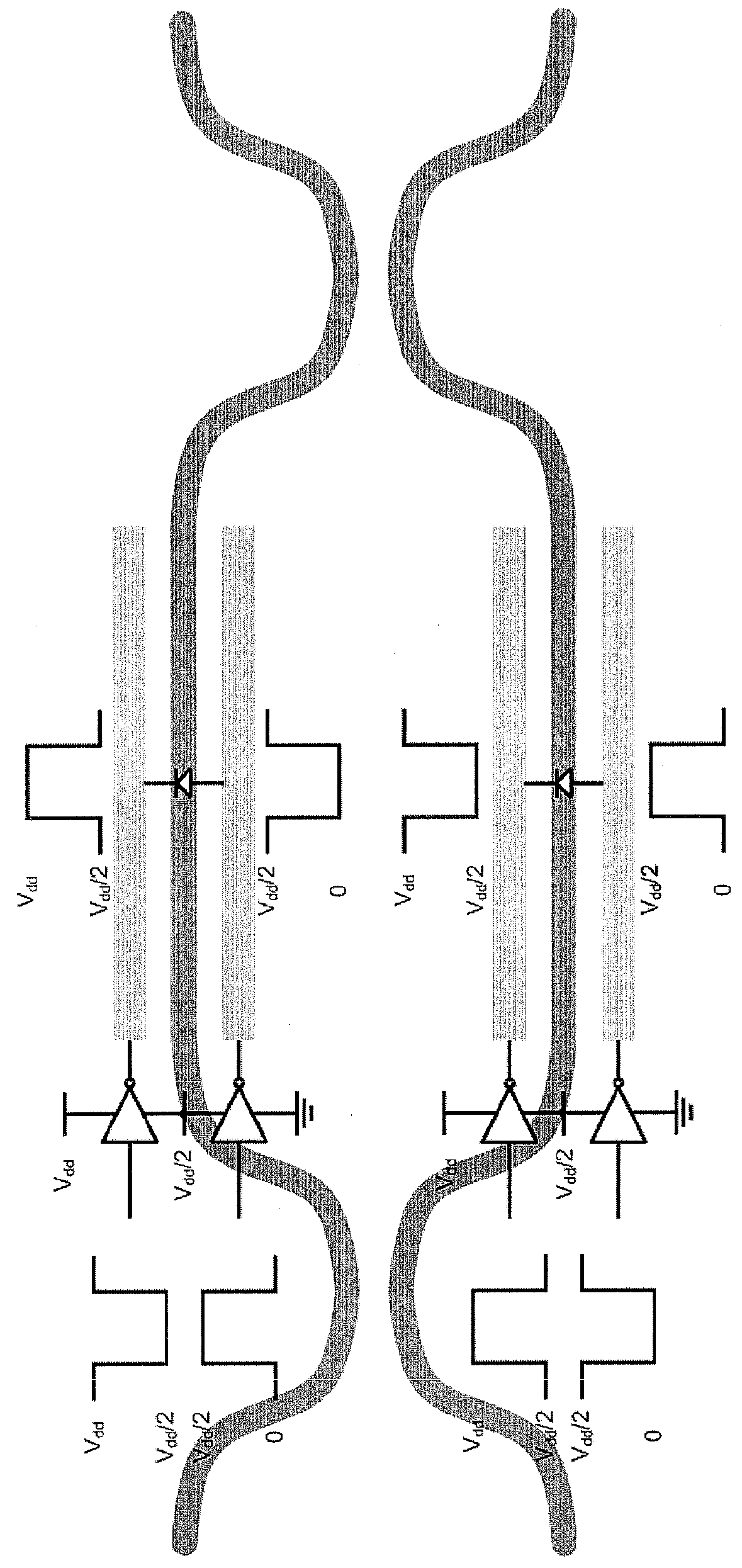
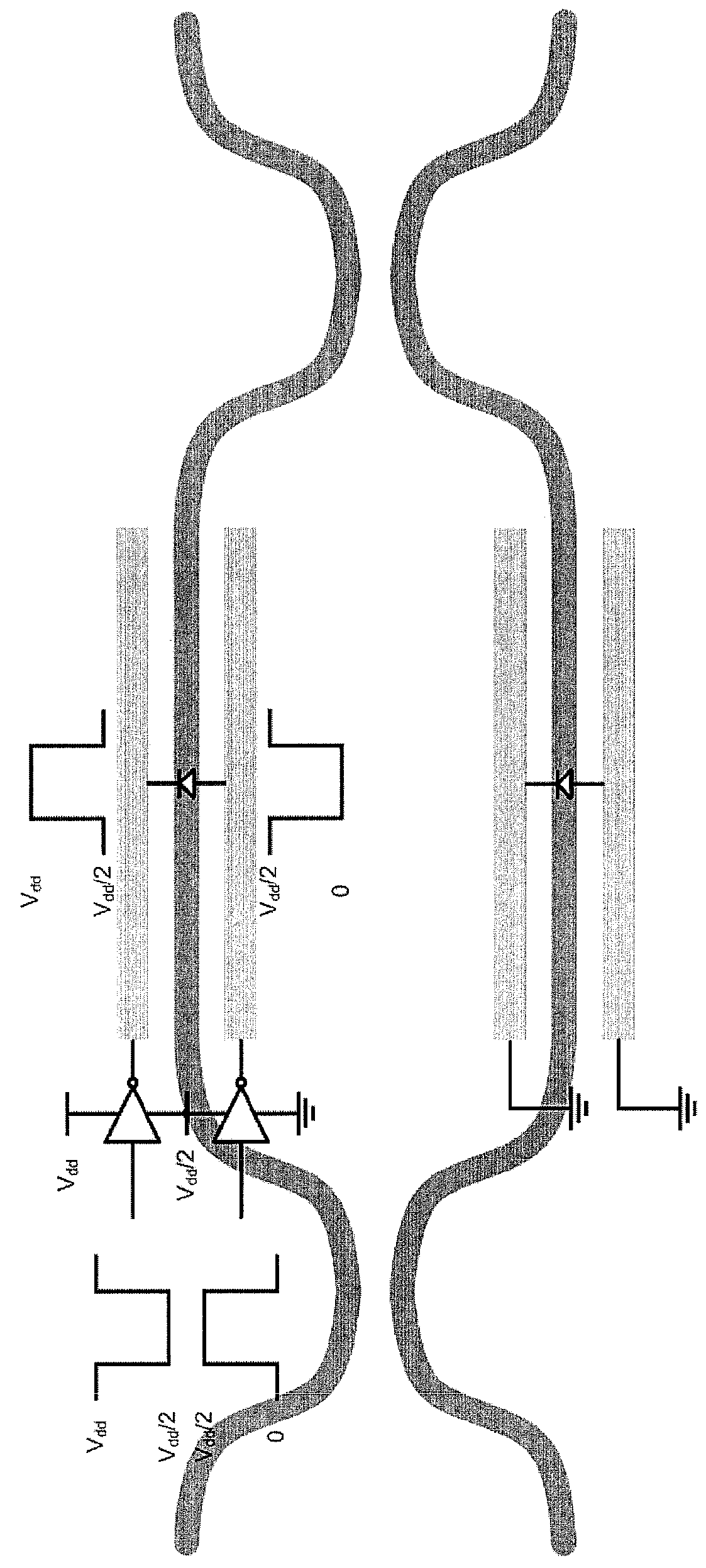
To provide a logical operation circuit and a logical operation device which can performs a logical operation using a ferroelectric capacitor. The area ratio between the ferroelectric capacitors CF1 and CF2 are set such that the potential difference Vdef between voltages Va1 and Va0 is as large as possible, and a transistor MP has a threshold voltage Vth which is about ½·(Va0+Va1). Thus, the ON / OFF operation margin of the transistor MP can be significantly large. As a result, a reading process can be performed at a high speed without using an amplifying circuit such as a sense amplifier. Also, the logical operation circuit and the logical operation device can be highly integrated with ease since no sense amplifier is used.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
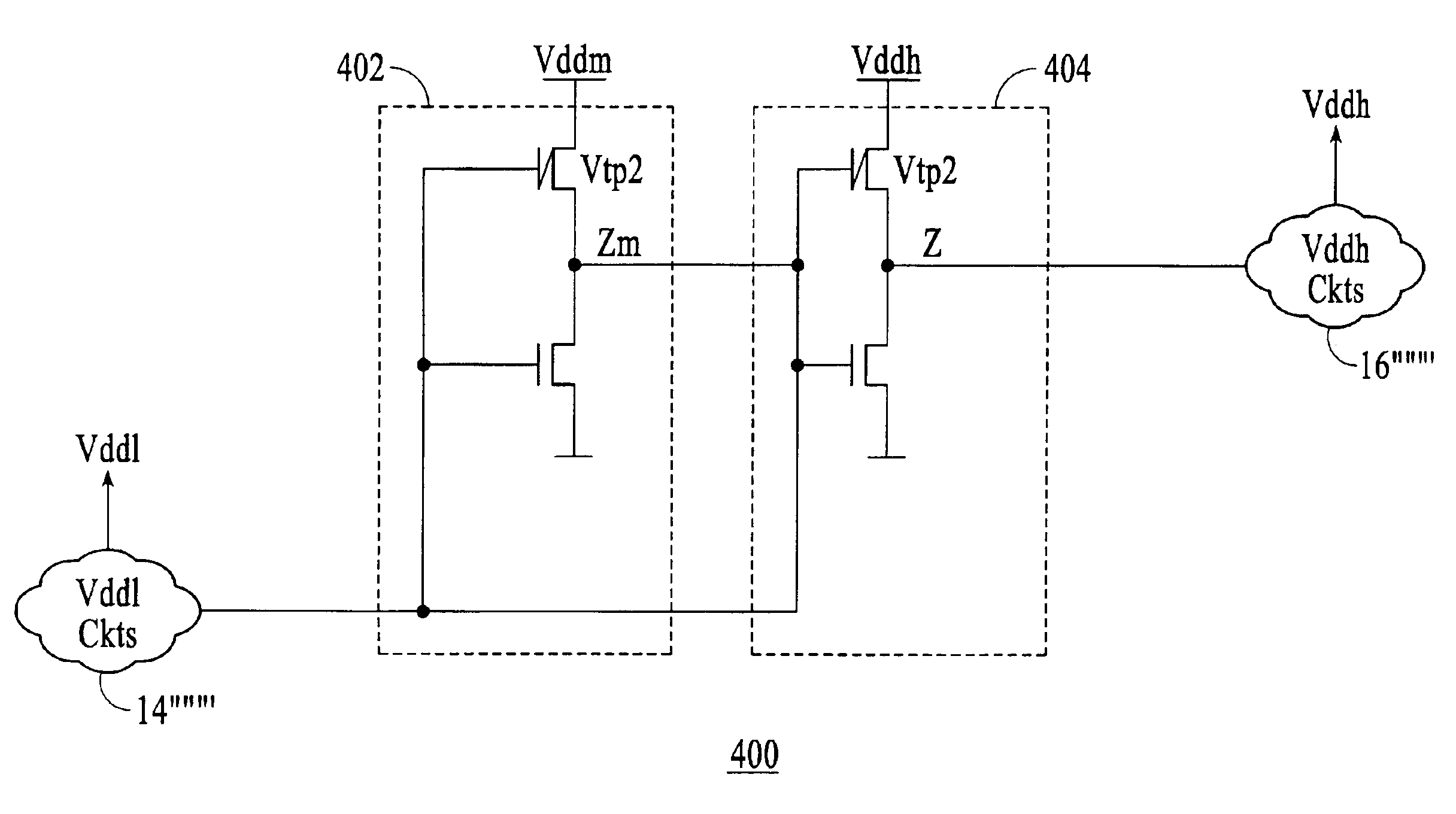
Supply-state-enabled level shifter interface circuit and method
ActiveUS9257973B1Avoid it happening againInhibit currentLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsElectric pulse generatorLevel shiftingNormal level
An enable circuit receives an input enable signal that is referenced to a first voltage and generates a level-shifted output enable signal referenced to a second voltage. Bias control circuitry prevents shoot-through currents during ramping of the first voltage and from causing indeterminate logic levels of the level-shifted output enable signal. An enabled level-shifting circuit receives an input logic signal that is referenced to the first voltage and generates a level-shifted output logic signal referenced to the second voltage. Enable circuitry operates in response to the level-shifted output enable signal to enable normal level-shifting operation while the first and second voltages are at normal operating levels and prevents shoot-through currents in the enabled level-shifting circuit from causing indeterminate levels of the level-shifted output logic signal.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
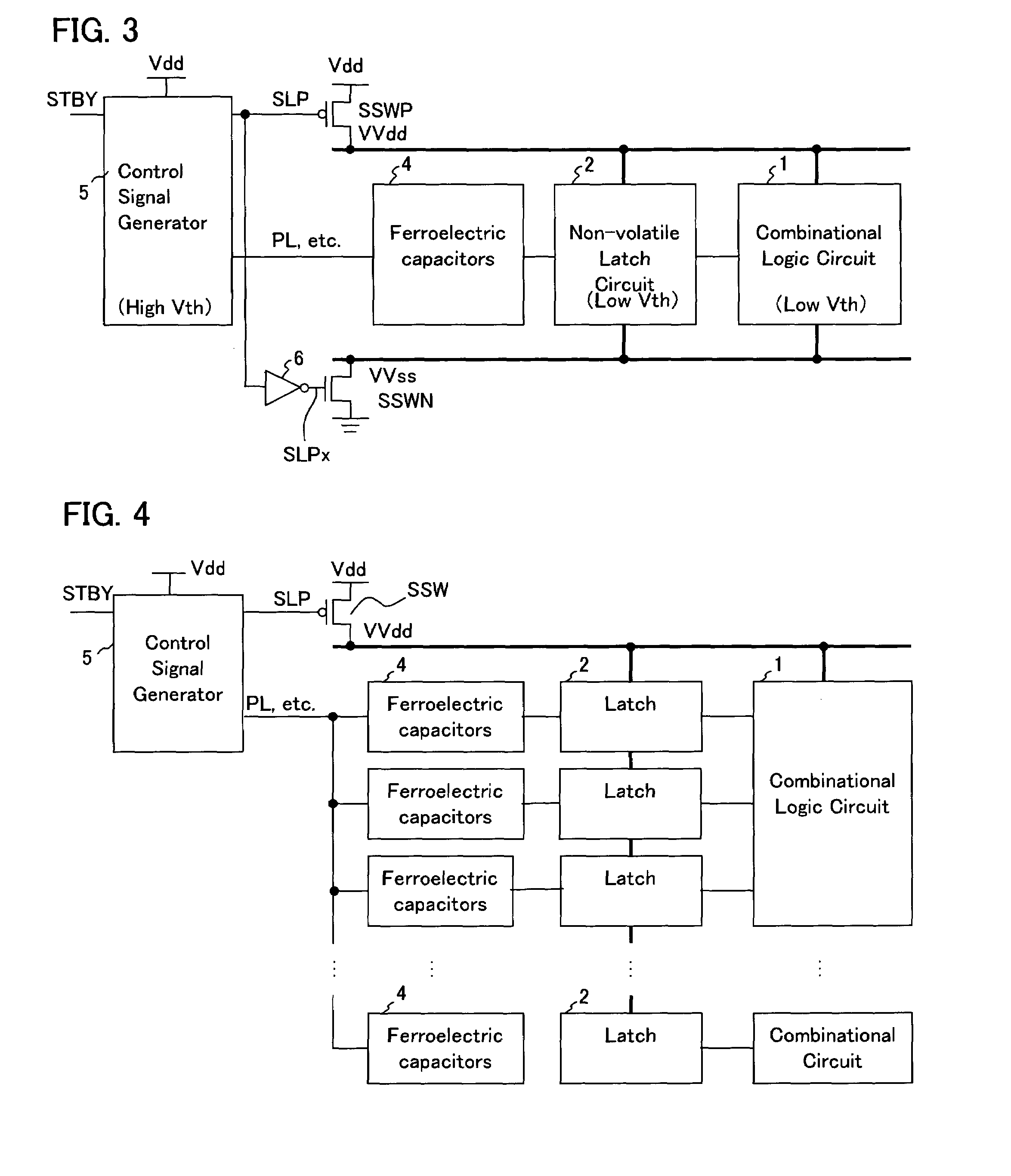
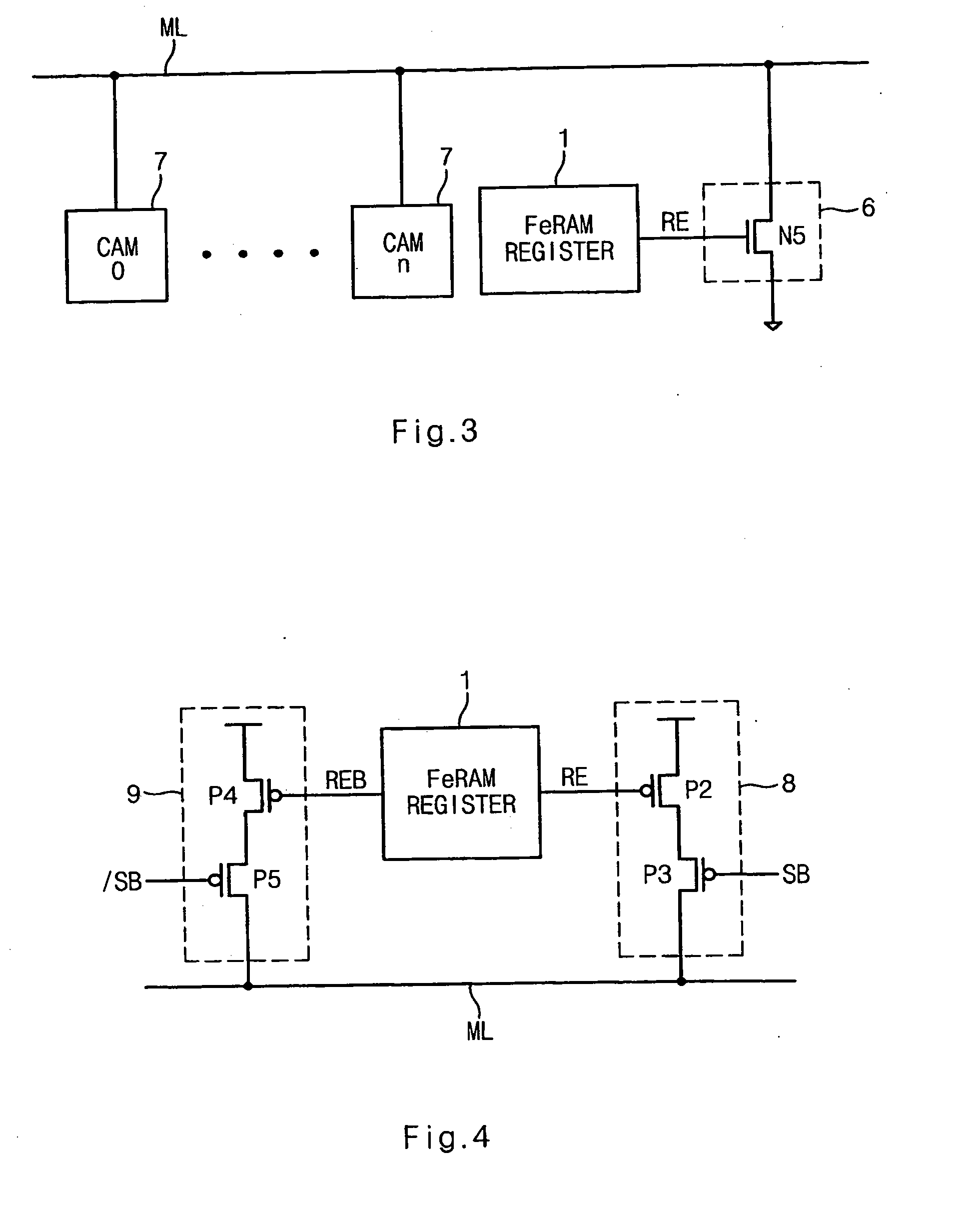
Multi-threshold-voltage integrated circuit having a non-volatile data storage circuit
ActiveUS7080270B2High precisionIncrease the differenceVolume/mass flow measurementSolid-state devicesControl signalEngineering
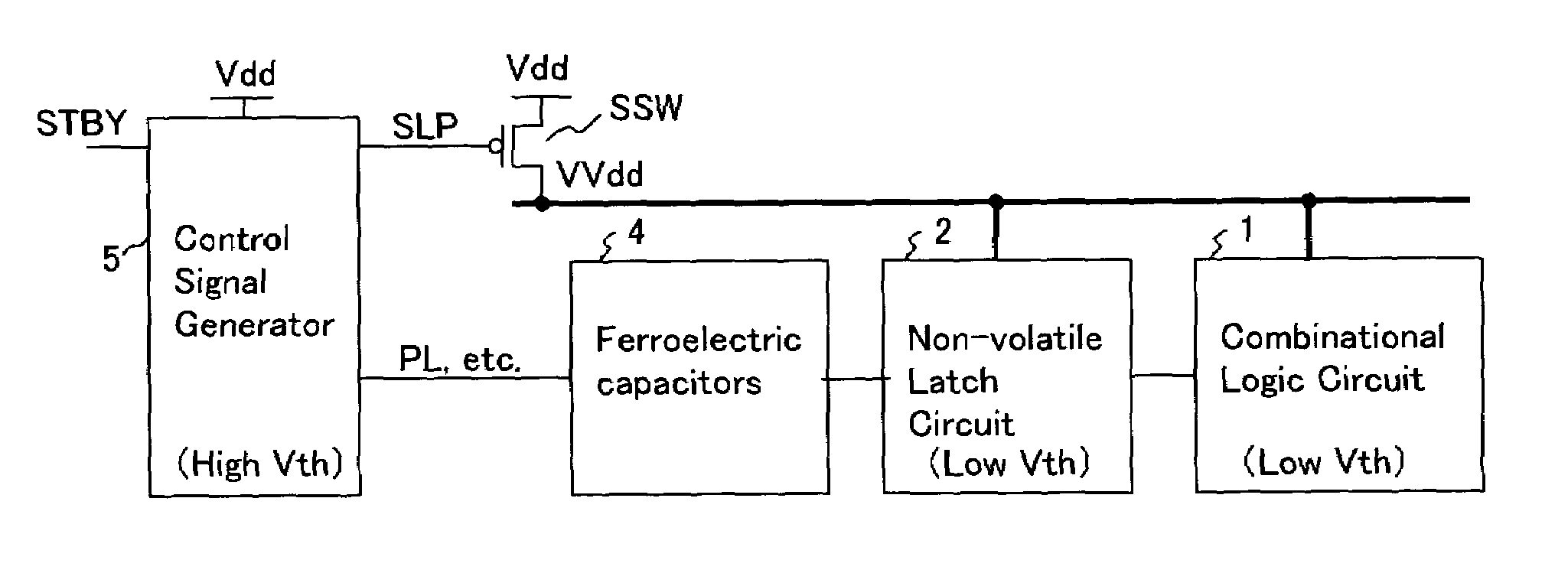
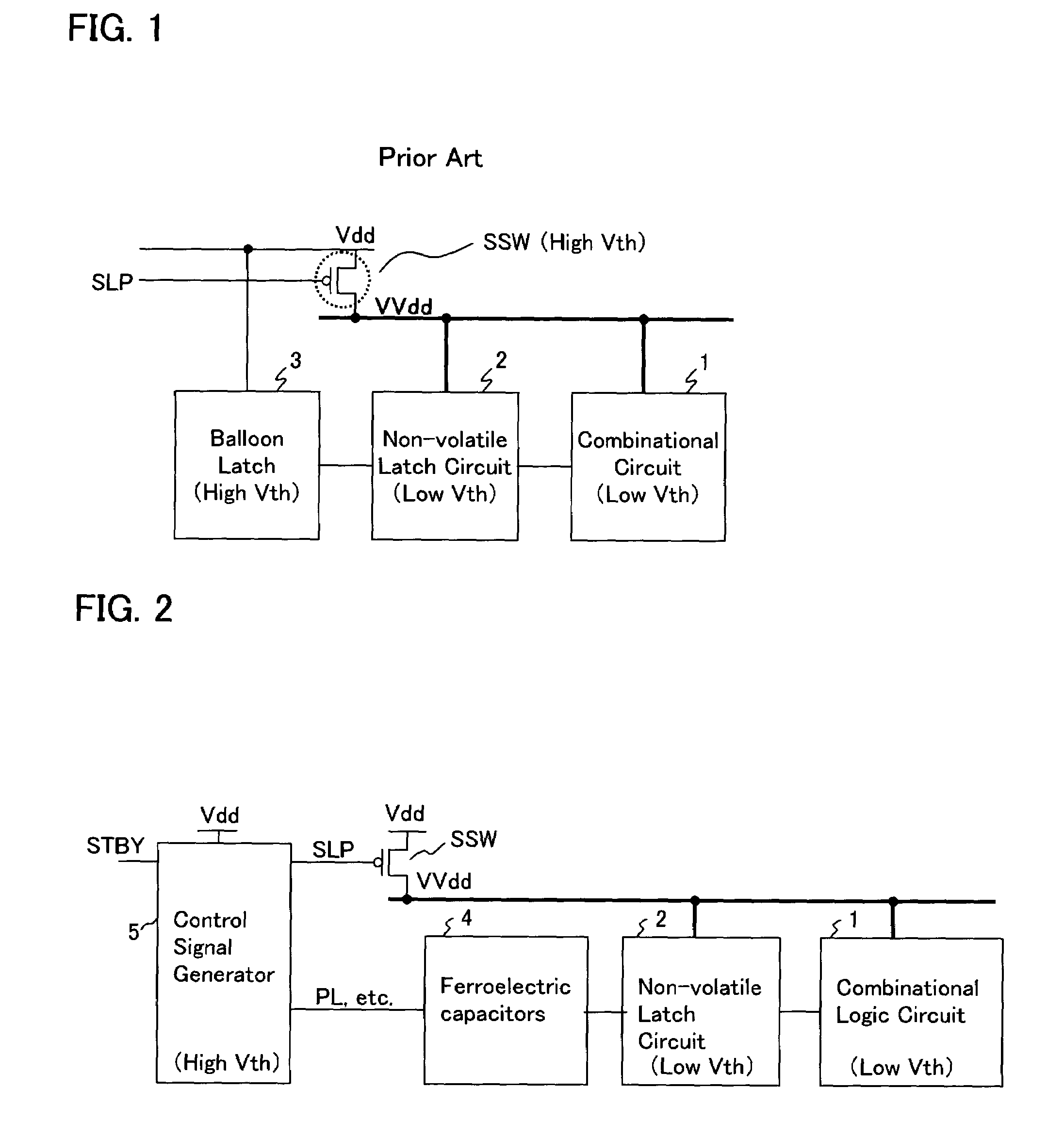
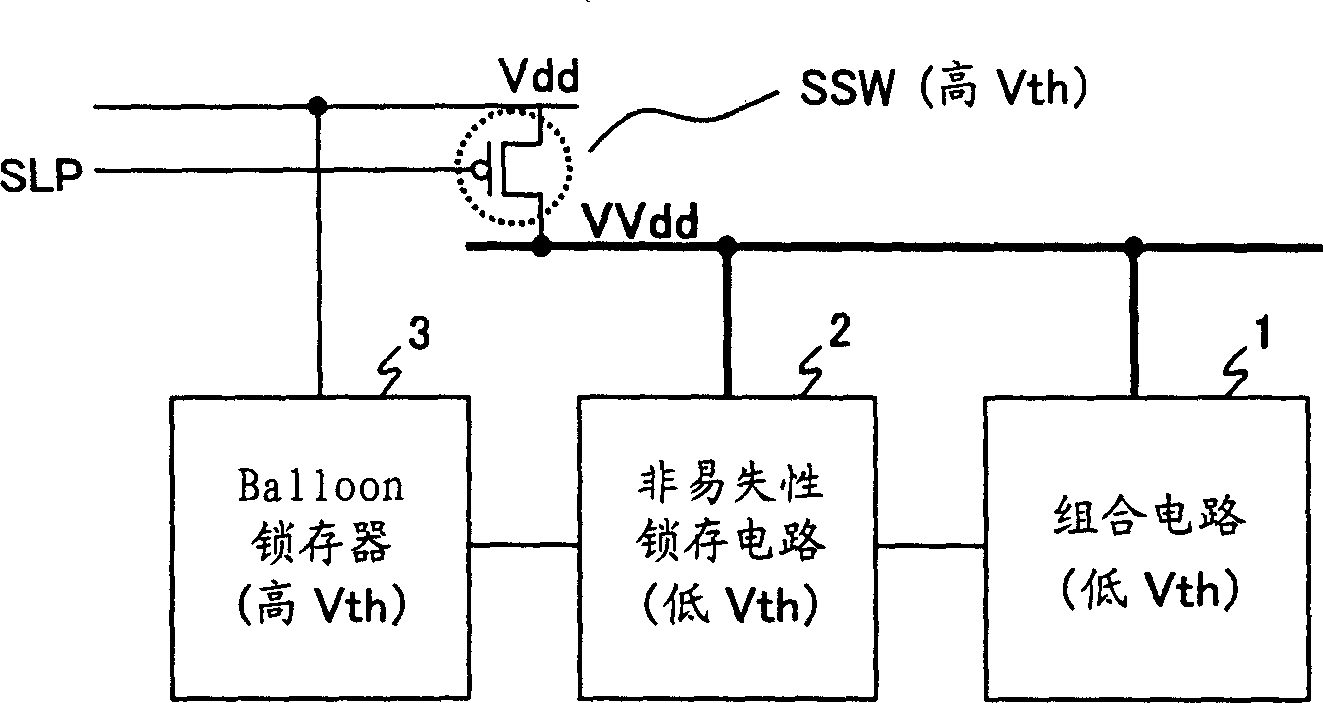
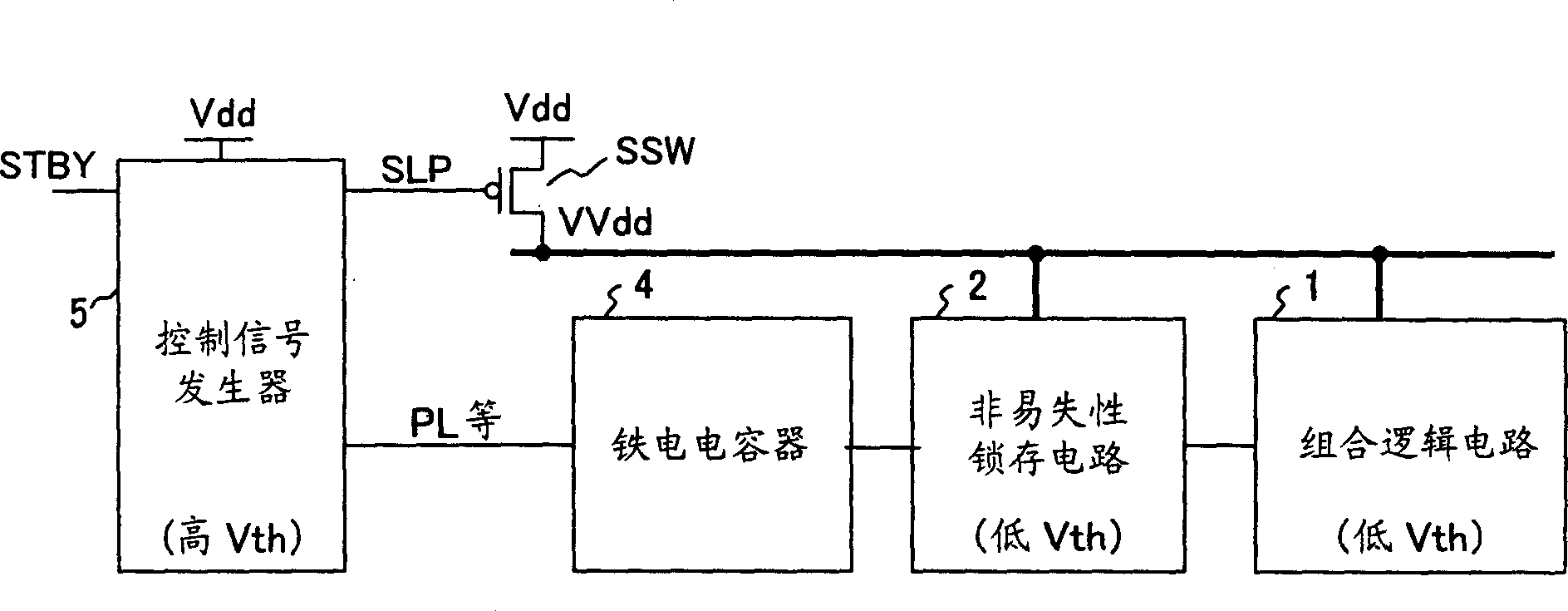
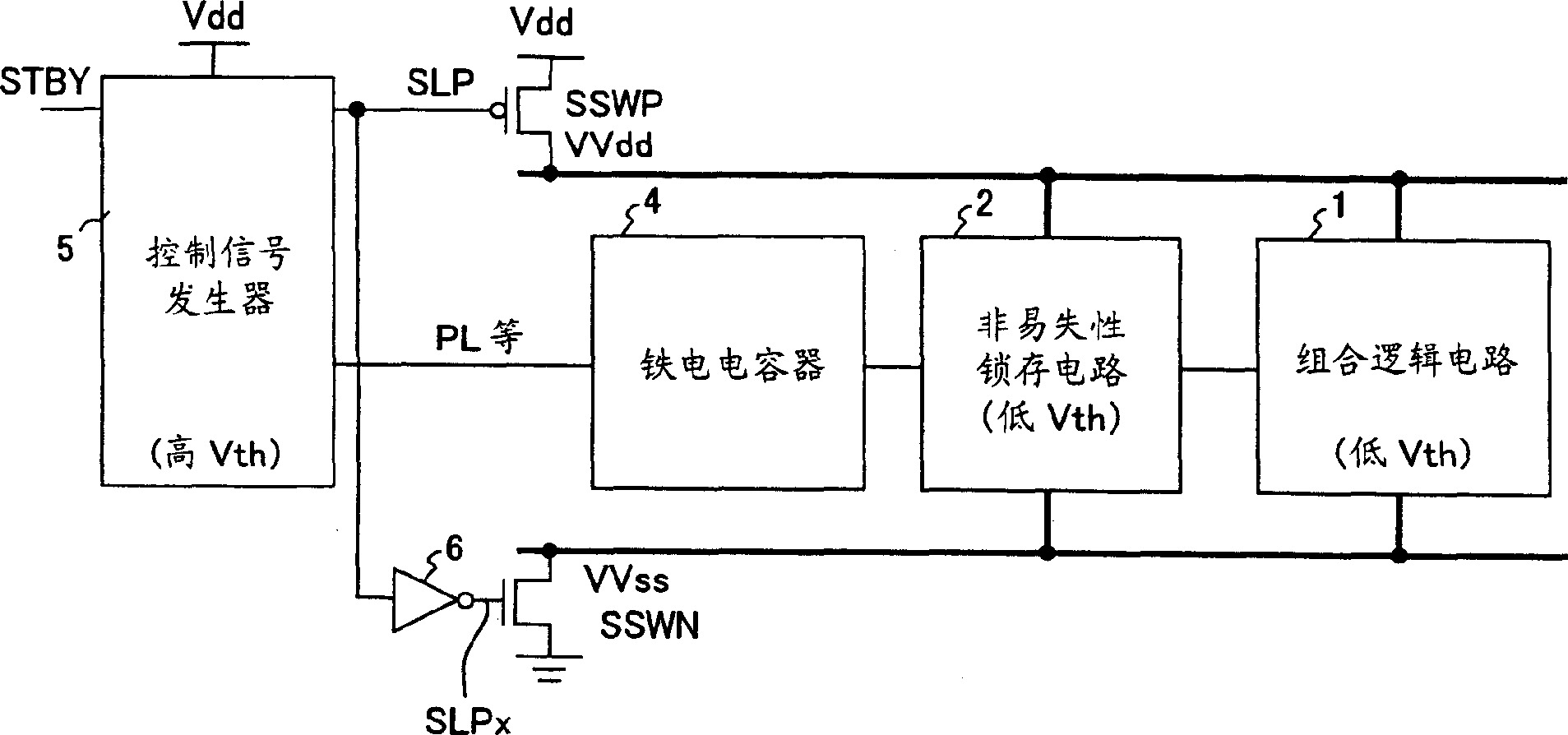
An integrated circuit has a sleep switch, provided between a first power line and a second power line, which is constituted by a transistor of a first threshold voltage, and which becomes non-conducting in a sleep mode, and further has a latch circuit, connected to the second power line, which is constituted by a transistor of a second threshold voltage which is lower than the first threshold voltage, and a ferroelectric capacitor for storing data held in the latch circuit in accordance with the polarization direction of a ferroelectric film thereof. The integrated circuit also comprises a control signal generating circuit which, when returning to an active mode from the sleep mode, generates a plate signal for driving a terminal of the ferroelectric capacitor to generate a voltage in the latch circuit in accordance with the polarization direction, and generates a sleep signal for causing the sleep switch to conduct to thereby activate the latch circuit following the driving of the ferroelectric capacitor.
Owner:FUJITSU SEMICON LTD
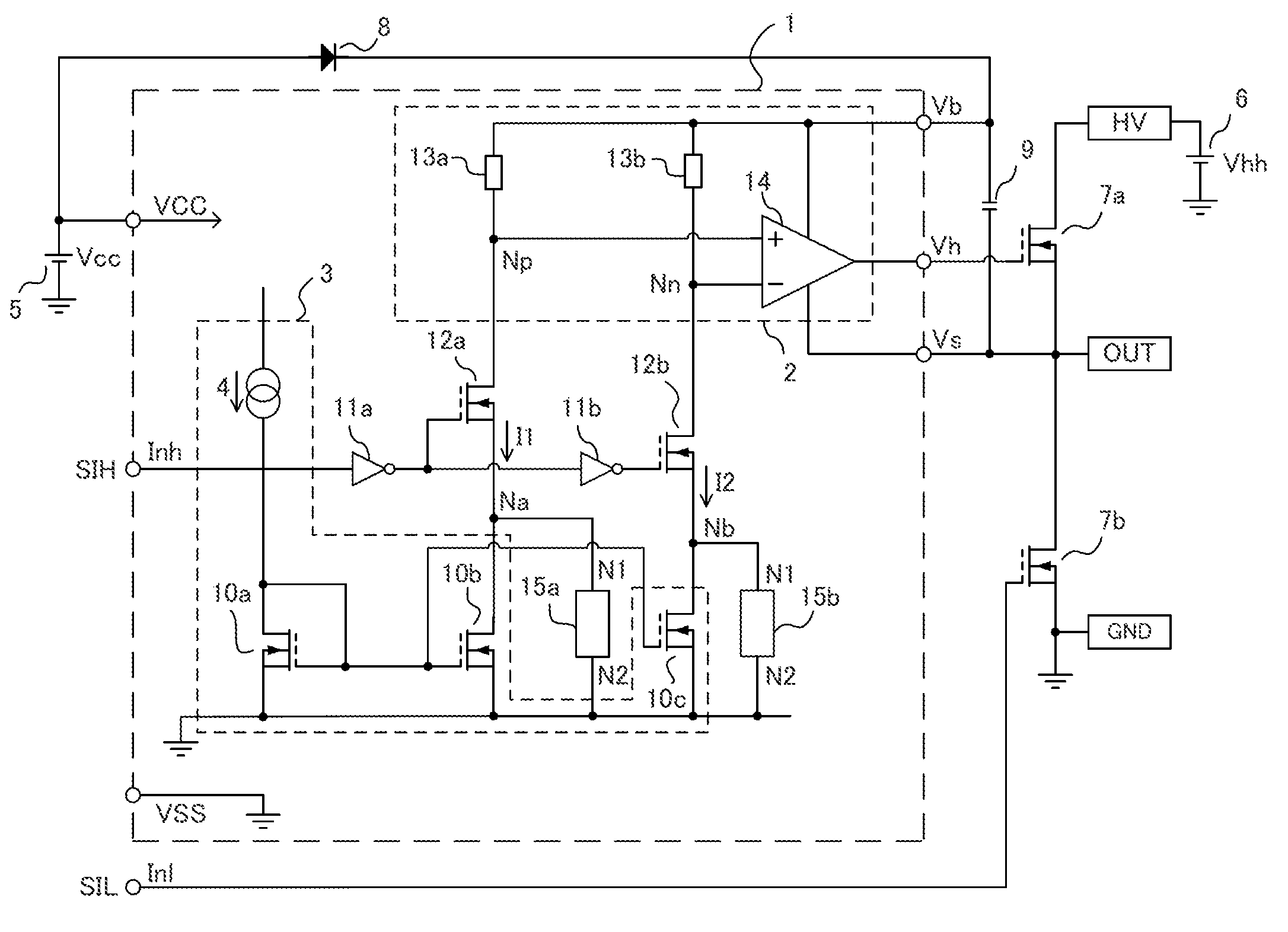
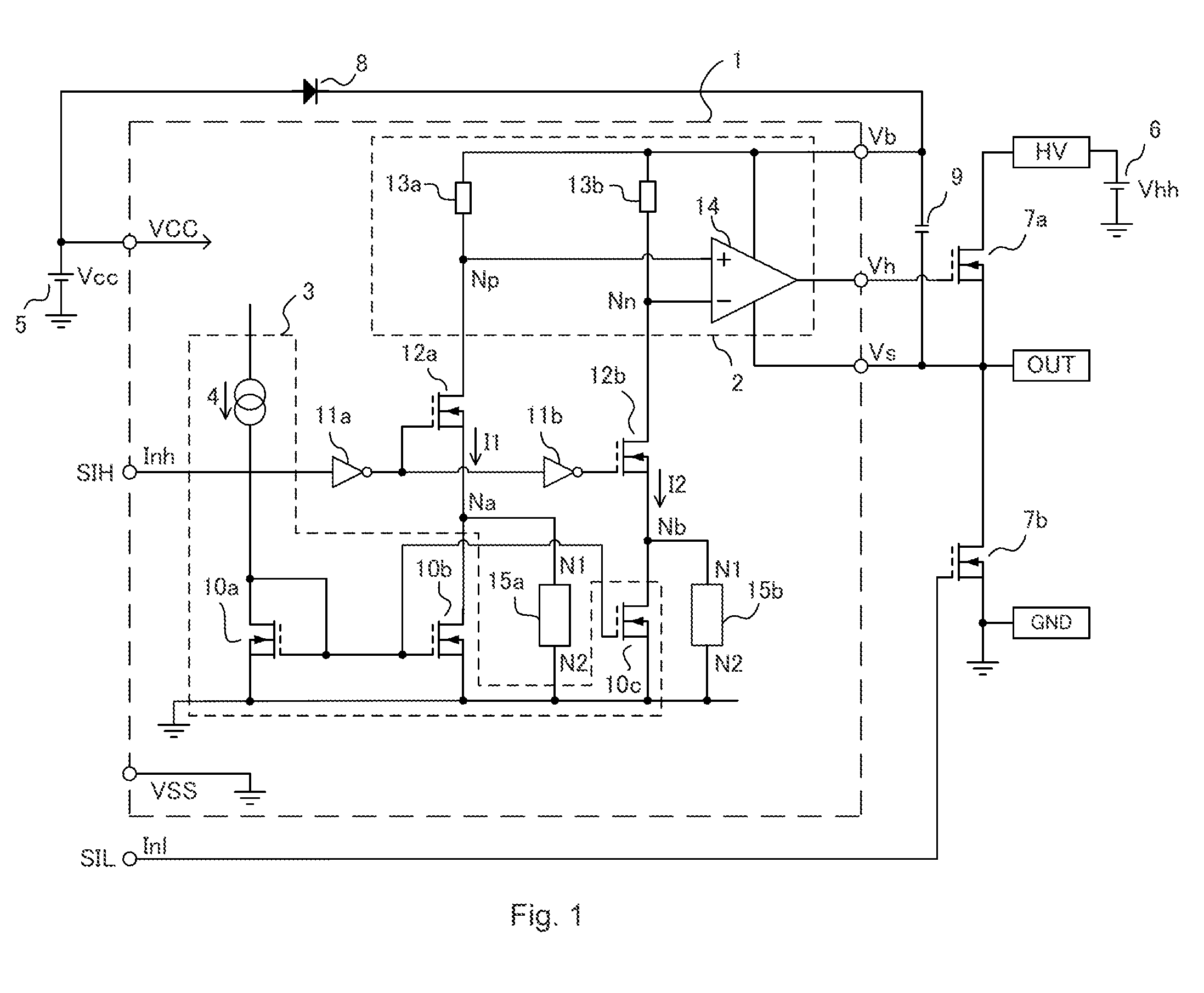
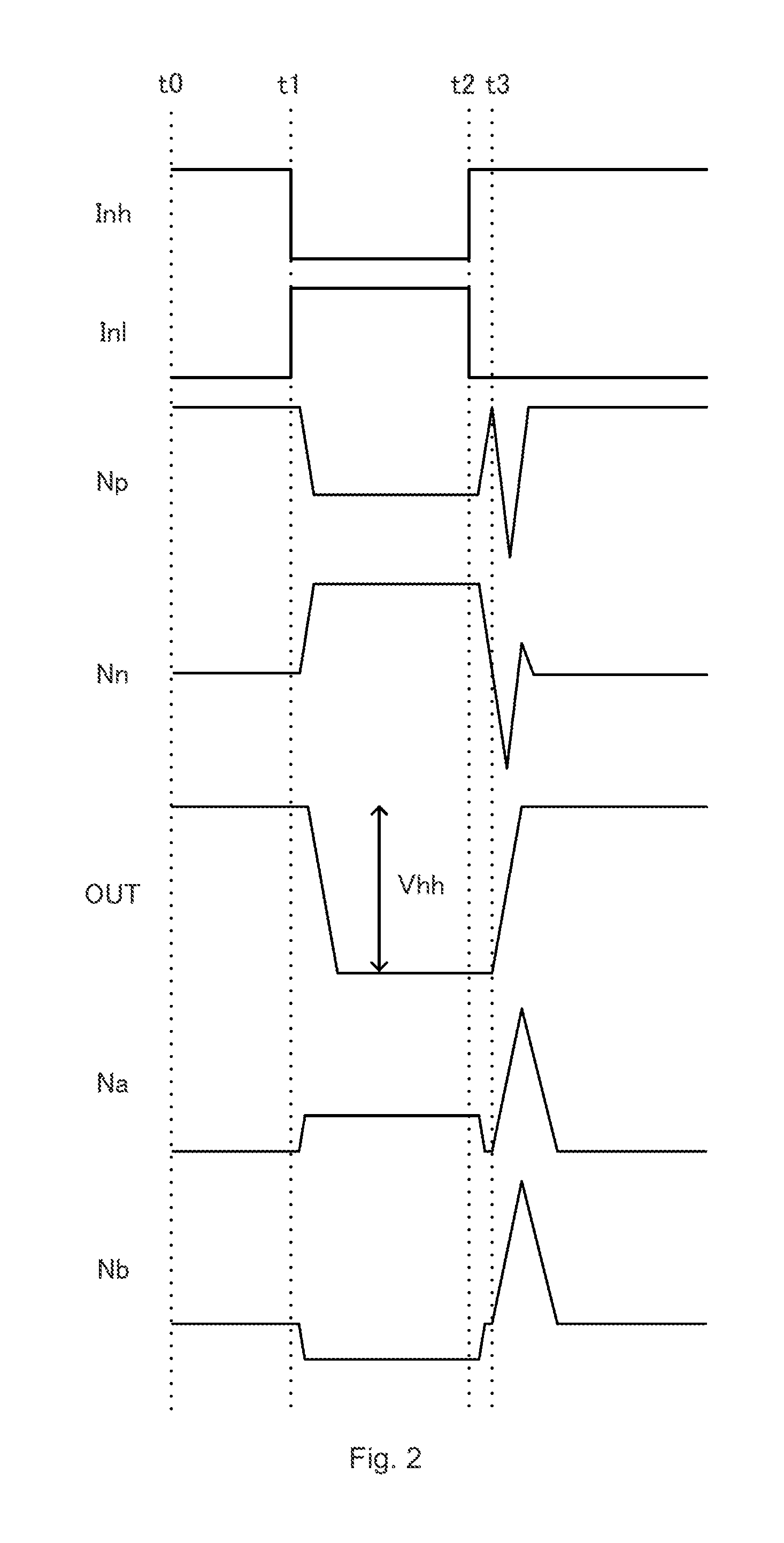
Level shift circuit
ActiveUS9264022B2Avoid circuit damageAvoid misuseLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsElectric pulse generatorLoad circuitPower flow
Provided is a high-reliability level shift circuit not prone to faulty operation due to noise. A level shift circuit 1 is provided with: first and second current control elements 12a and 12b into control terminals of which a reverse-phase input signal and an in-phase input signal are input, respectively; first and second load circuits 13a and 13b which are connected at one end to a high-side power source terminal Vb and at the other end to each of first terminals of the first and second current control elements 12a and 12b; a comparator 14 in which a pair of differential input terminals Np and Nn are connected separately to each of the first terminals of the first and second current control elements 12a and 12b; a current generating circuit 3 in which first and second current output terminals Na and Nb are connected to second terminals of the first and second current control elements 12a and 12b, and which separately generates a current which flows through the respective first and second current control elements 12a and 12b; and voltage suppressing circuits 15a and 15b which are connected separately or commonly to the first and second current output terminals Na and Nb, respectively, and suppress voltage from rising in the first and second current output terminals Na and Nb, respectively.
Owner:SHARP KK
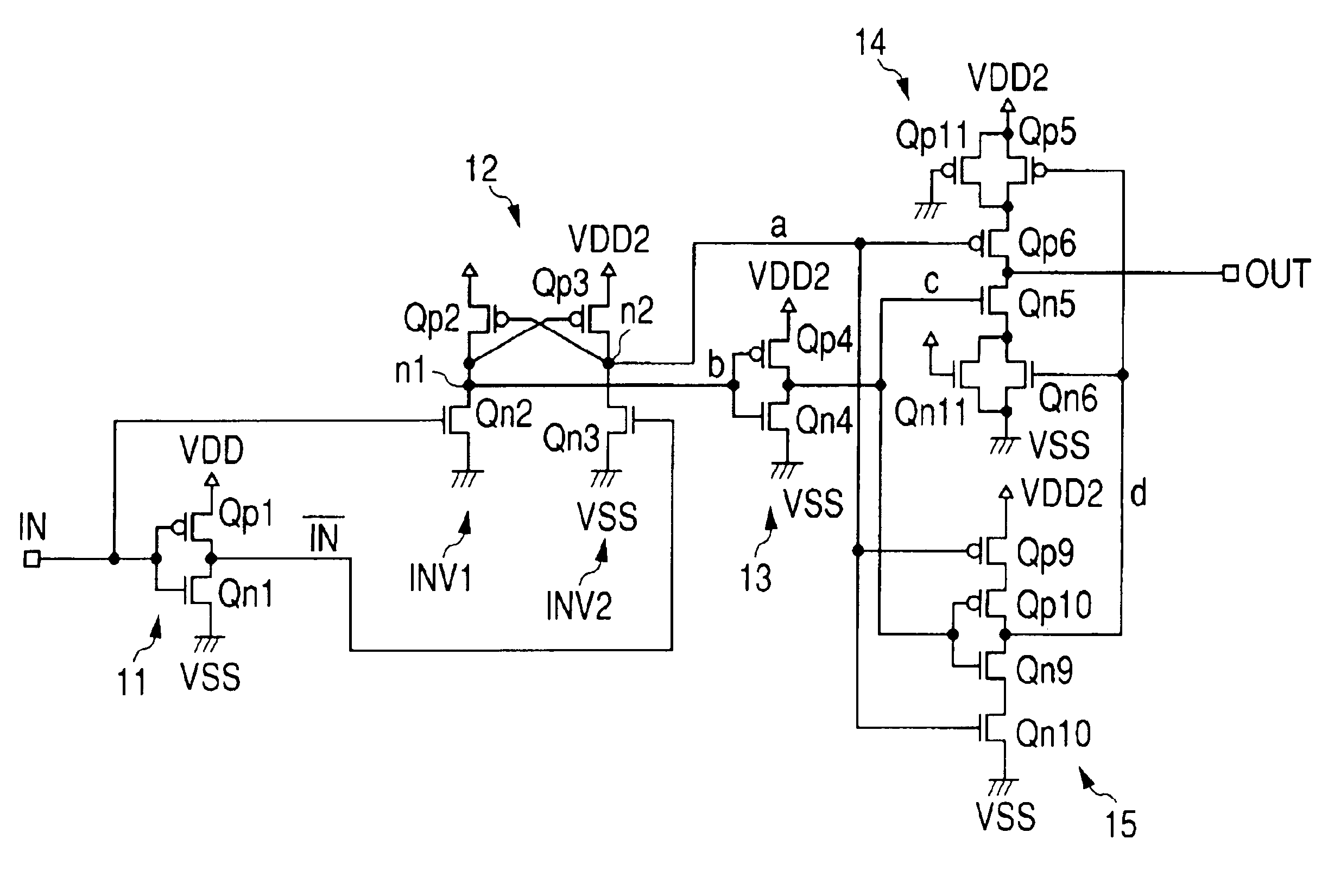
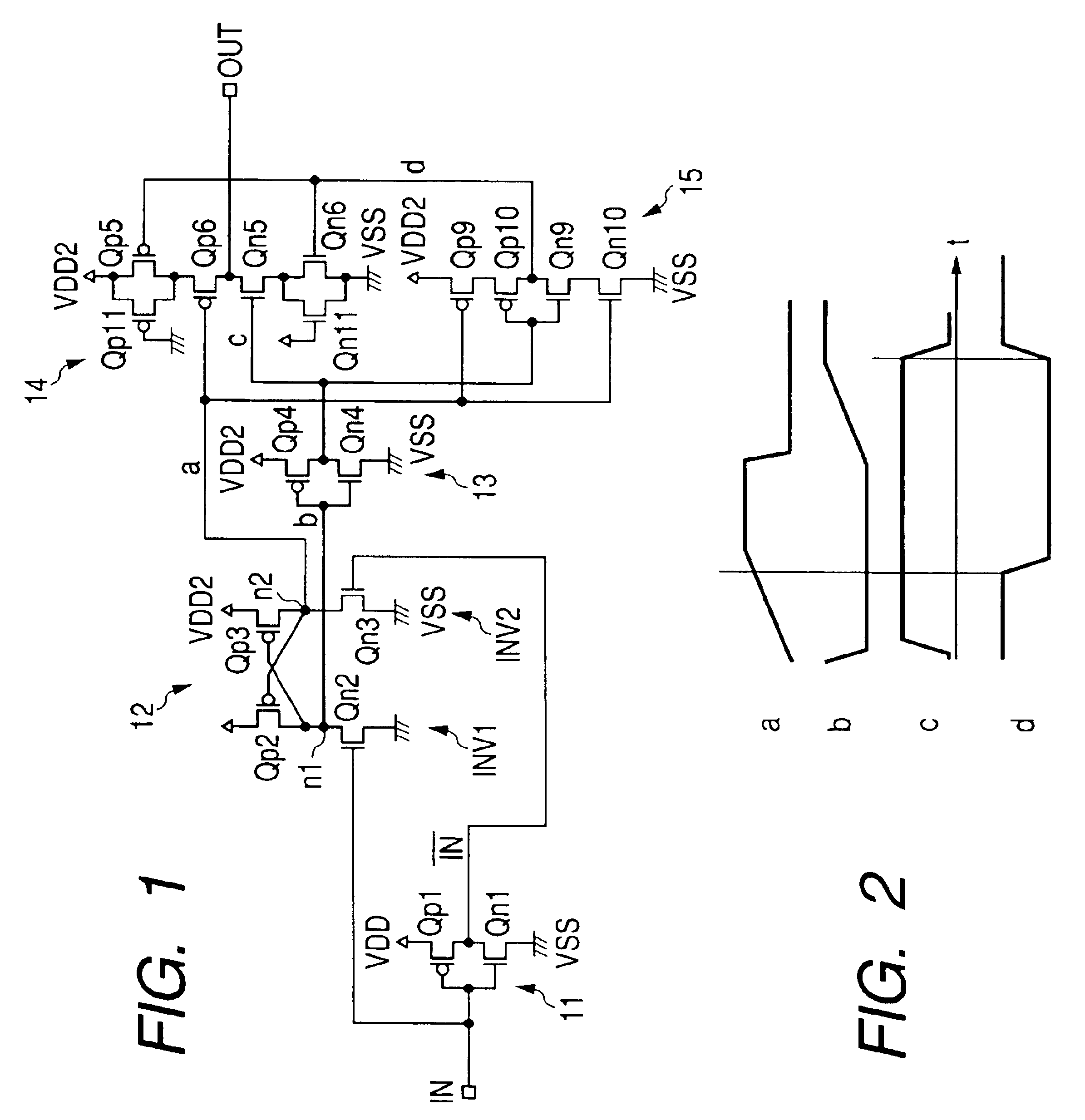
Buffer based on source electrode follower
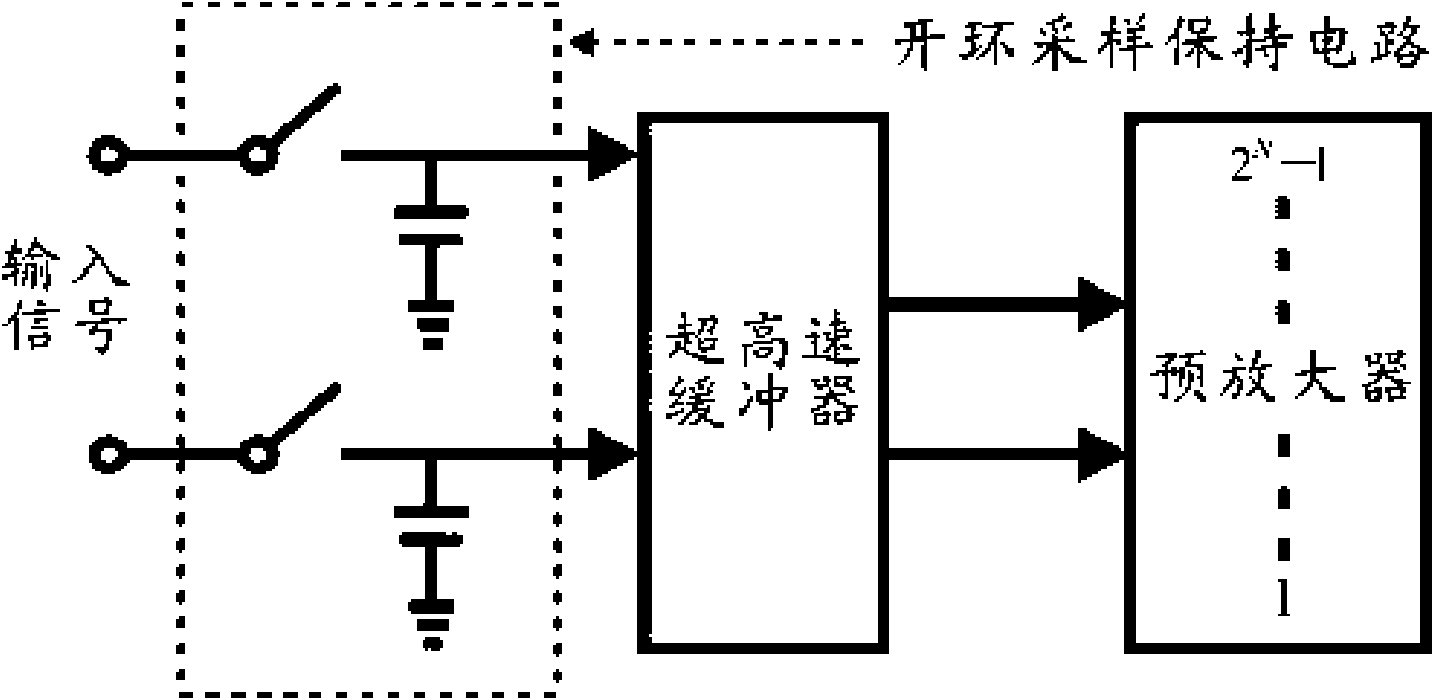
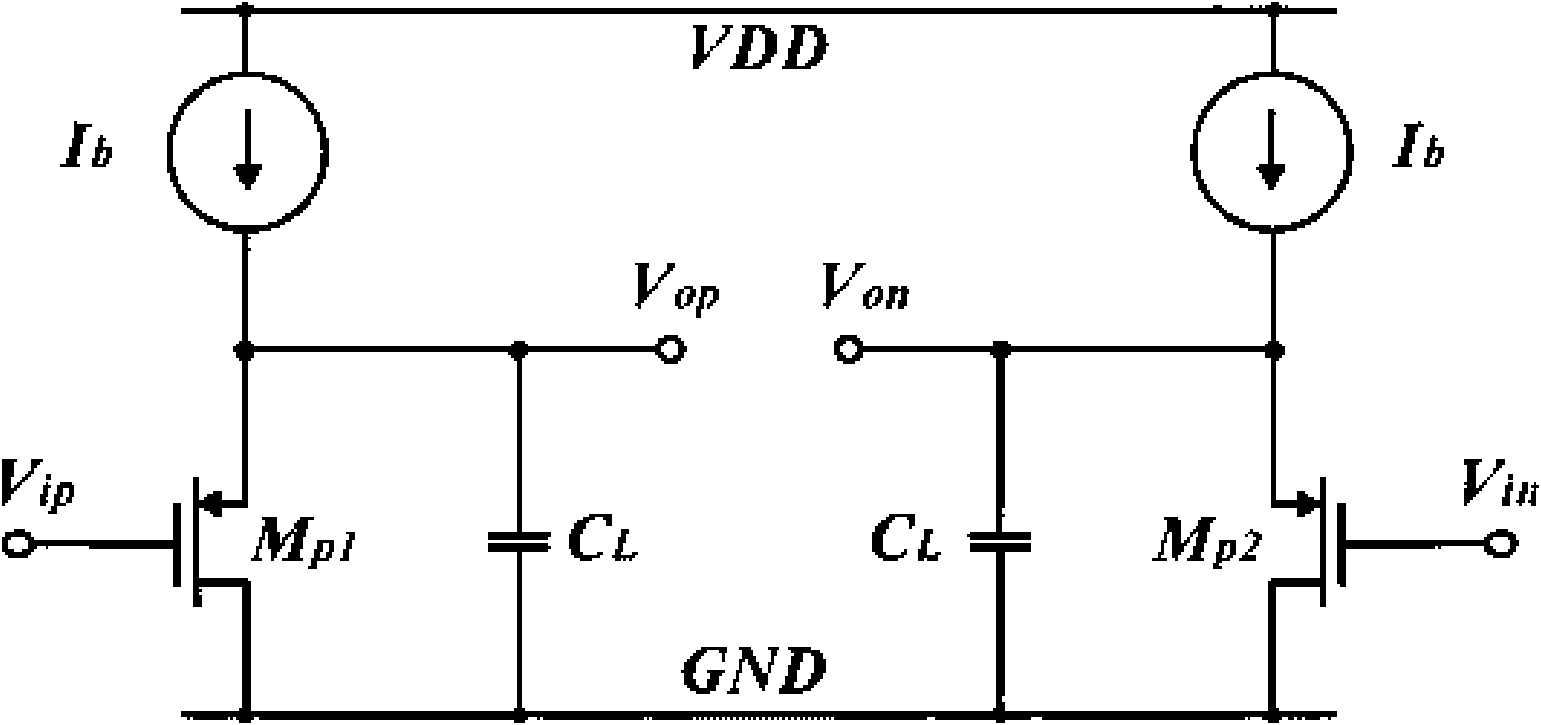
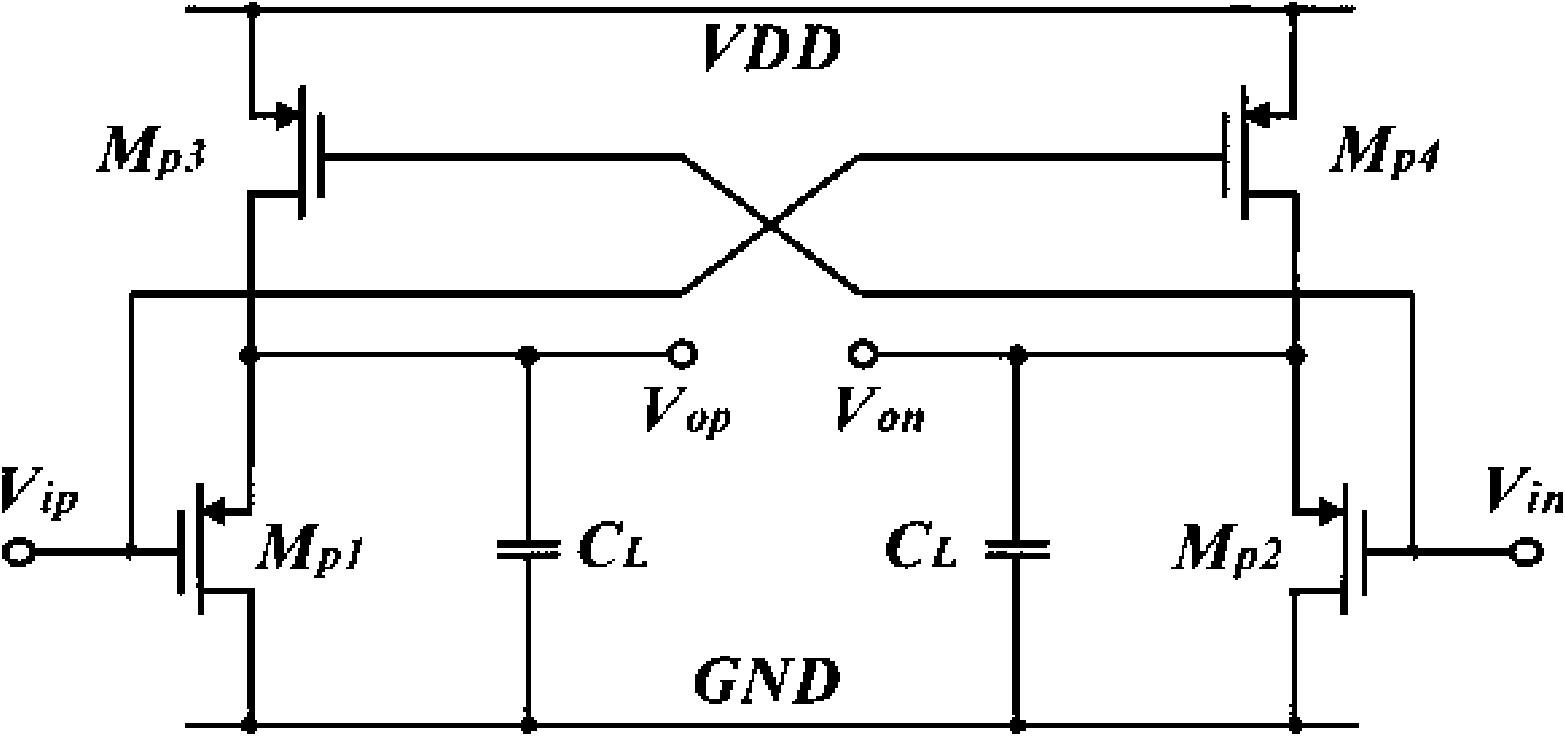
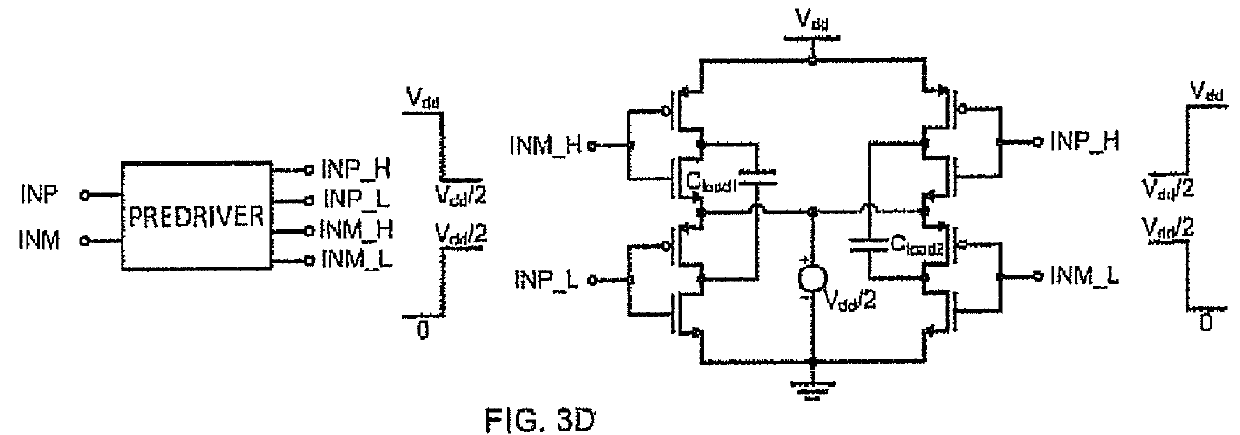
InactiveCN101594139AAchieving a unity-gain buffered outputAmplifiers with impedence circuitsLogic circuits using dielectric elementsCapacitanceEngineering
The invention discloses a buffer based on a source electrode follower and belongs to the technical field of analog integrated circuit design. The buffer comprises a pseudo differential input level, a cross coupling common source level, a current source and a capacitance load, wherein the pseudo differential input level is used for receiving a difference input signal; the cross coupling common source level is connected with the pseudo differential input level, used for forming negative resistance and offsetting output resistance of the buffer; the current source is connected with the pseudo differential input level and used for providing branch current of the buffer; and the capacitance load is connected with the pseudo differential input level and used as output load of the buffer. The negative resistance is formed by the cross coupling common source level, so that the buffer offsets the output resistance of the high-speed buffer and realizes unity-gain buffering output. The buffer based on the source electrode follower realizes ultra-high speed, the unity-gain buffering output and high dynamic characteristics by theoretical analysis and simulation verification.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
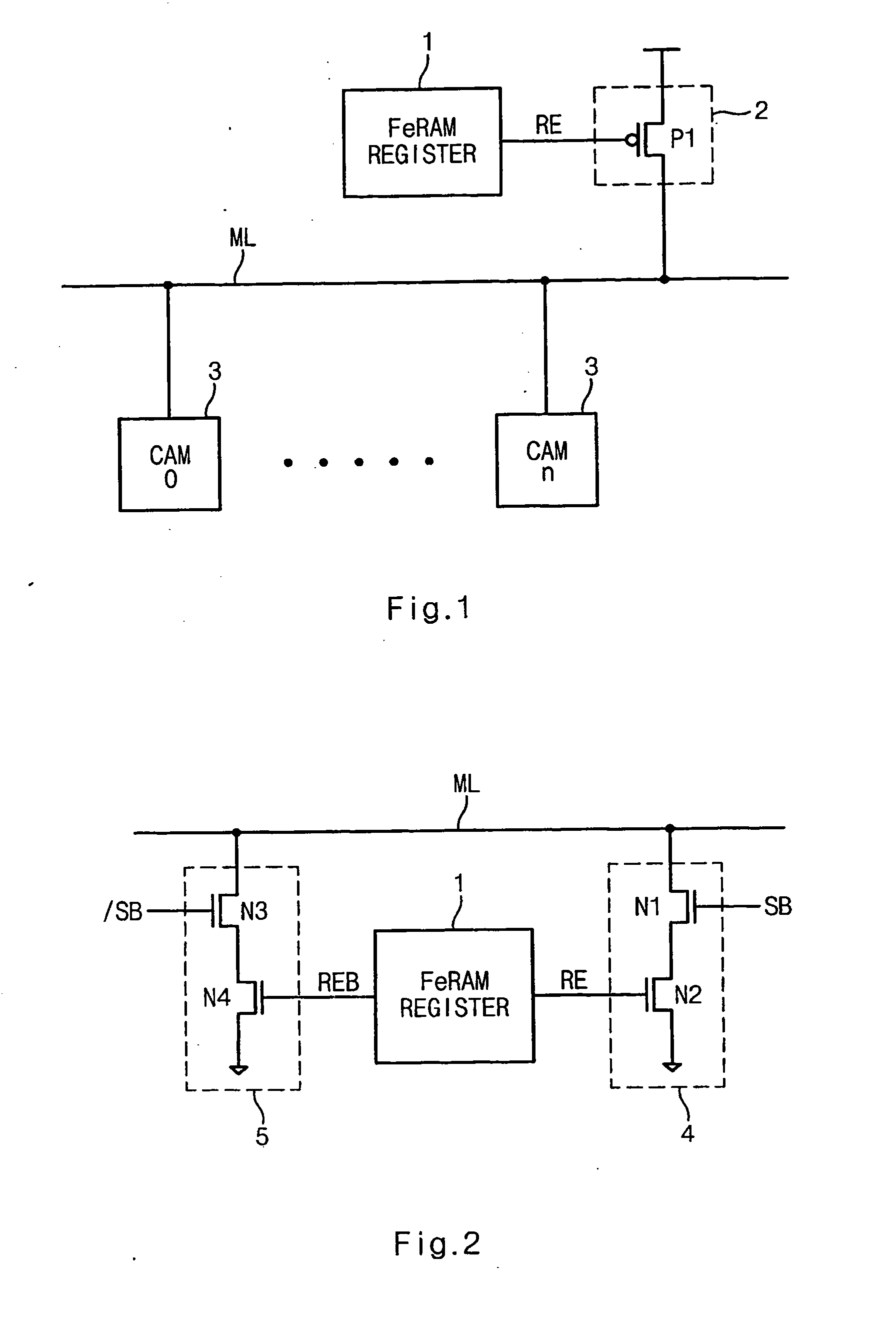
Nonvolatile data storage circuit using ferroelectric capacitors
InactiveUS6934178B2Avoid dataReduce coupling noiseSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFerroelectric capacitorCoupling noise
A nonvolatile data storage circuit has a data holding circuit having a storage node, and a plurality of ferroelectric capacitors one electrodes of which are connected to the storage node. In this nonvolatile data storage circuit, in store operations to write data from the data holding circuit to the ferroelectric capacitors, the timing of at least the rising or the falling of plate signals supplied to the other electrodes of the plurality of ferroelectric capacitors, is made different. During store operation, the timing of the plate signals applied to the plurality of ferroelectric capacitors connected to the storage node is shifted, so that coupling noise between the ferroelectric capacitors is dispersed and can be reduced, and data inversion of the data holding circuit can be prevented.
Owner:FUJITSU SEMICON LTD
Level shift circuit and semiconductor integrated circuit
A level conversion circuit is composed of a level shift circuit for supplying a level-converted signal in the same phase as the input signal and a signal in the reverse phase thereto and a follow-up circuit responsive to the earlier of the output signals of the level shift circuit for generating an output signal, wherein the follow-up circuit consists of an inverter circuit in which two p-channel type MOS transistors and two n-channel type MOS transistors are connected in series between a first voltage terminal and a second voltage terminal, of which one pair is used as input transistors and the remaining pair of transistors are subjected to feedback based on the output signal of the level shift circuit to be quickly responsive to the next variation.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP +1
Integrated circuit with nonvoltile data memory circuit
An integrated circuit has a sleep switch, provided between a first power line and a second power line, which is constituted by a transistor of a first threshold voltage, and which becomes non-conducting in a sleep mode, and further has a latch circuit, connected to the second power line, which is constituted by a transistor of a second threshold voltage which is lower than the first threshold voltage, and a ferroelectric capacitor for storing data held in the latch circuit in accordance with the polarization direction of a ferroelectric film thereof. The integrated circuit also comprises a control signal generating circuit which, when returning to an active mode from the sleep mode, generates a plate signal for driving a terminal of the ferroelectric capacitor to generate a voltage in the latch circuit in accordance with the polarization direction, and generates a sleep signal for causing the sleep switch to conduct to thereby activate the latch circuit following the driving of the ferroelectric capacitor.
Owner:FUJITSU SEMICON LTD
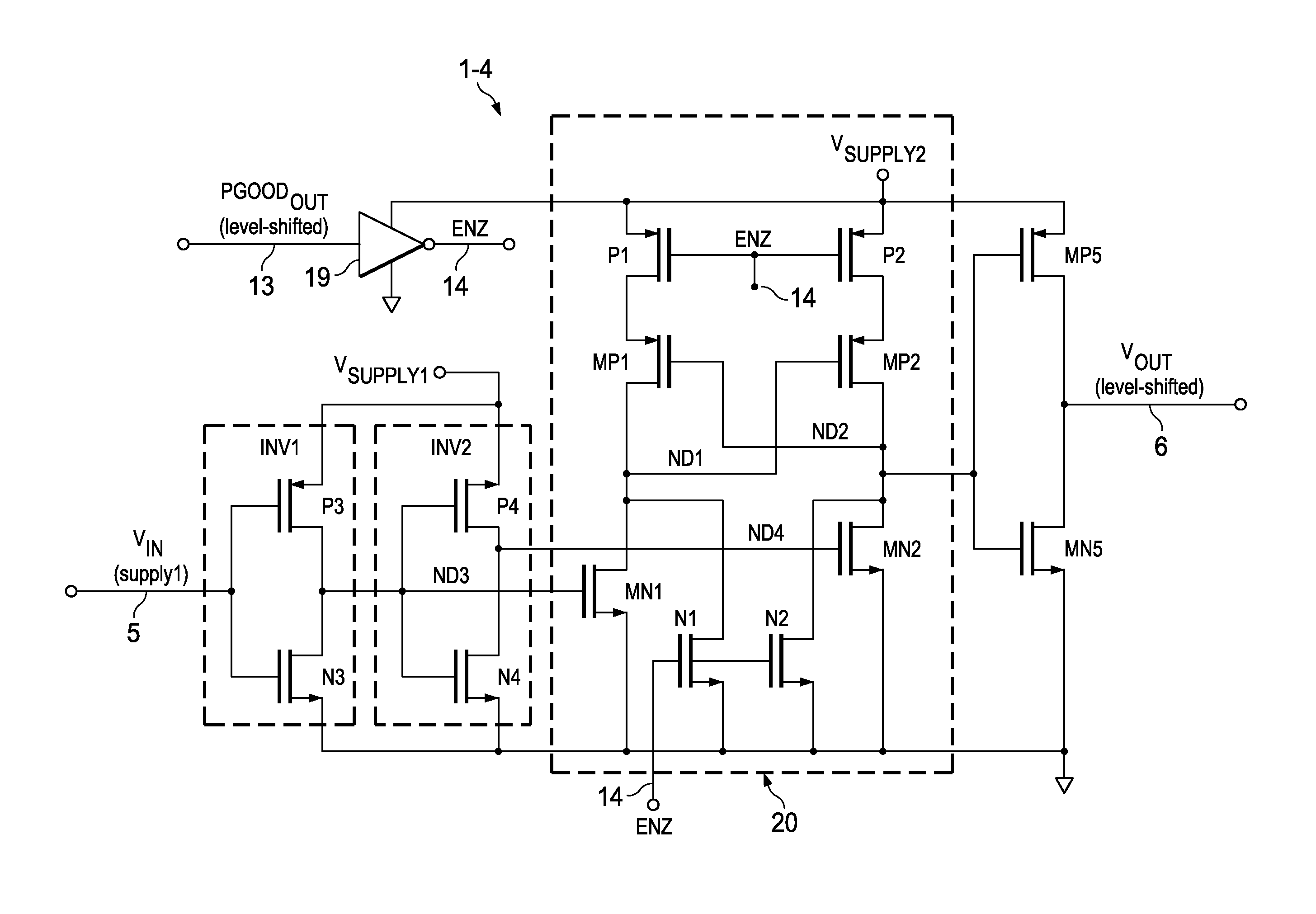
Interface circuit
ActiveUS20150381180A1Reduce power consumptionIncrease speedInput/output impedence modificationPulse automatic controlVoltage amplitudeCMOS
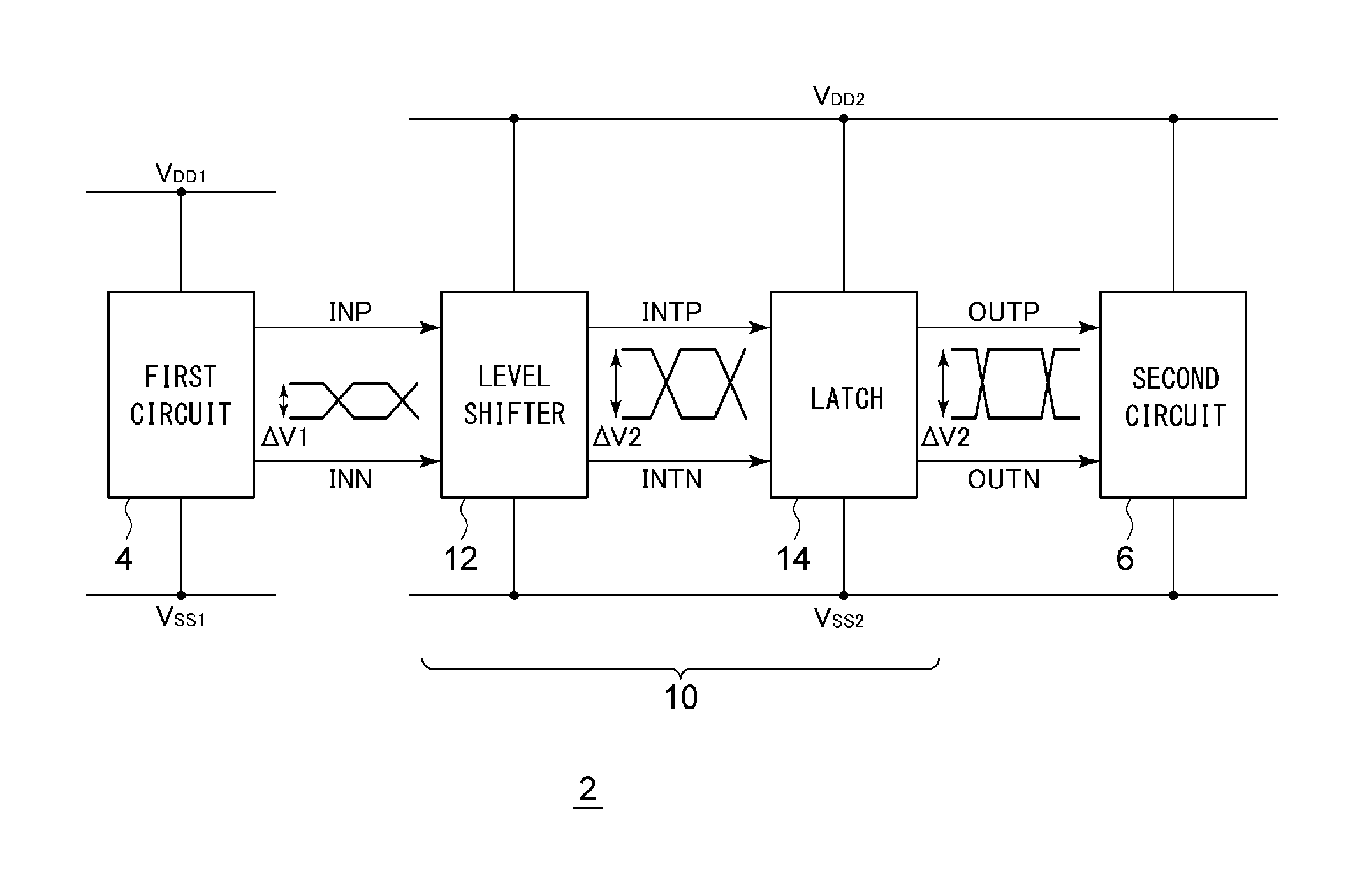
An interface circuit receives an input signal IN having a first voltage amplitude from a first circuit, and outputs an output signal OUT having a second voltage amplitude to a second circuit. A level shifter comprises a first CMOS inverter and a second CMOS inverter which are cross-coupled, and a current limiting circuit that limits a current that flows through the first CMOS inverter and the second CMOS inverter, and converts the input signal IN into an intermediate signal INT which is a differential signal. A latch circuit receives the intermediate signal INT from the level shifter, and switches its state according to the positive signal and the negative signal of the intermediate signal INT.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
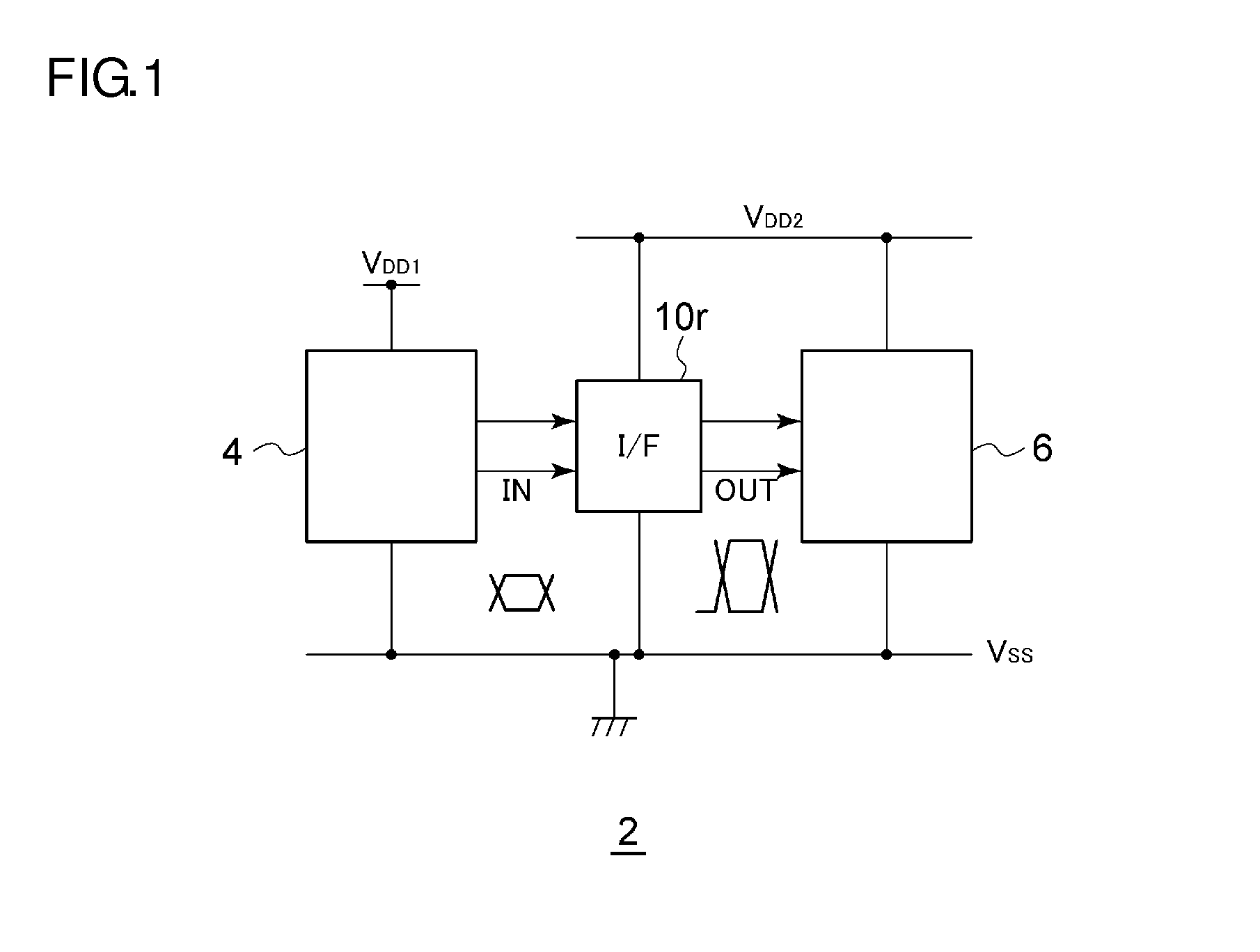
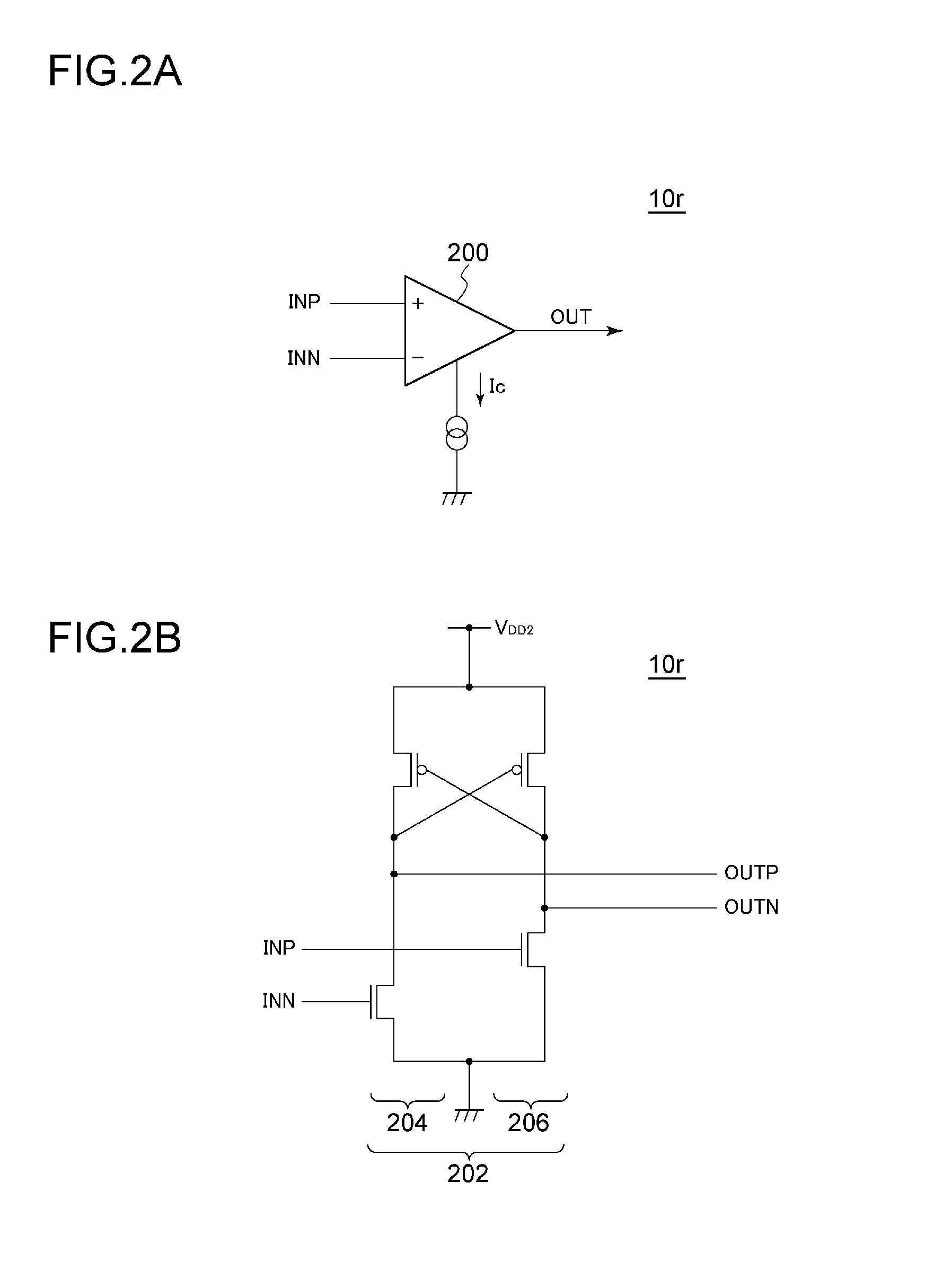
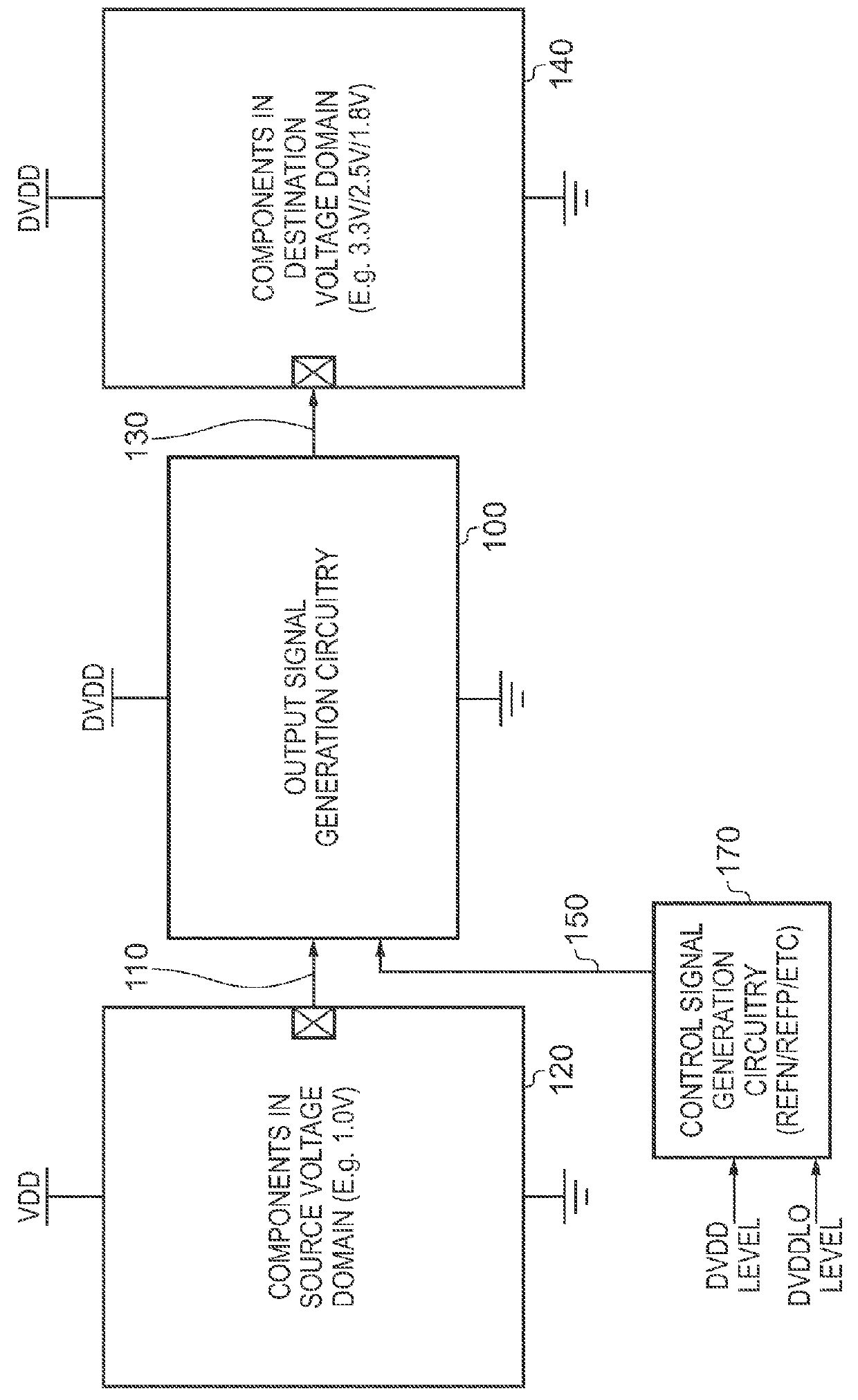
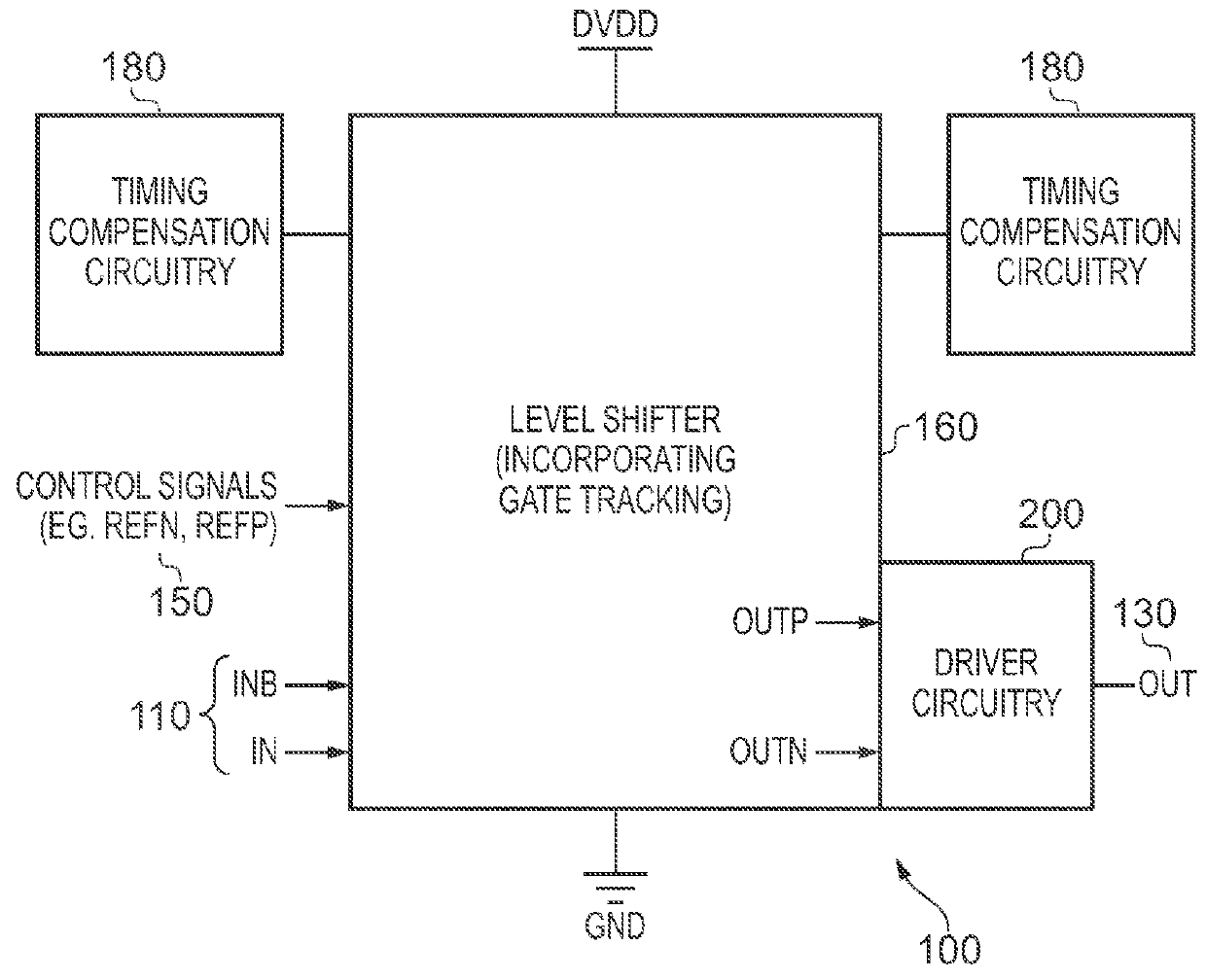
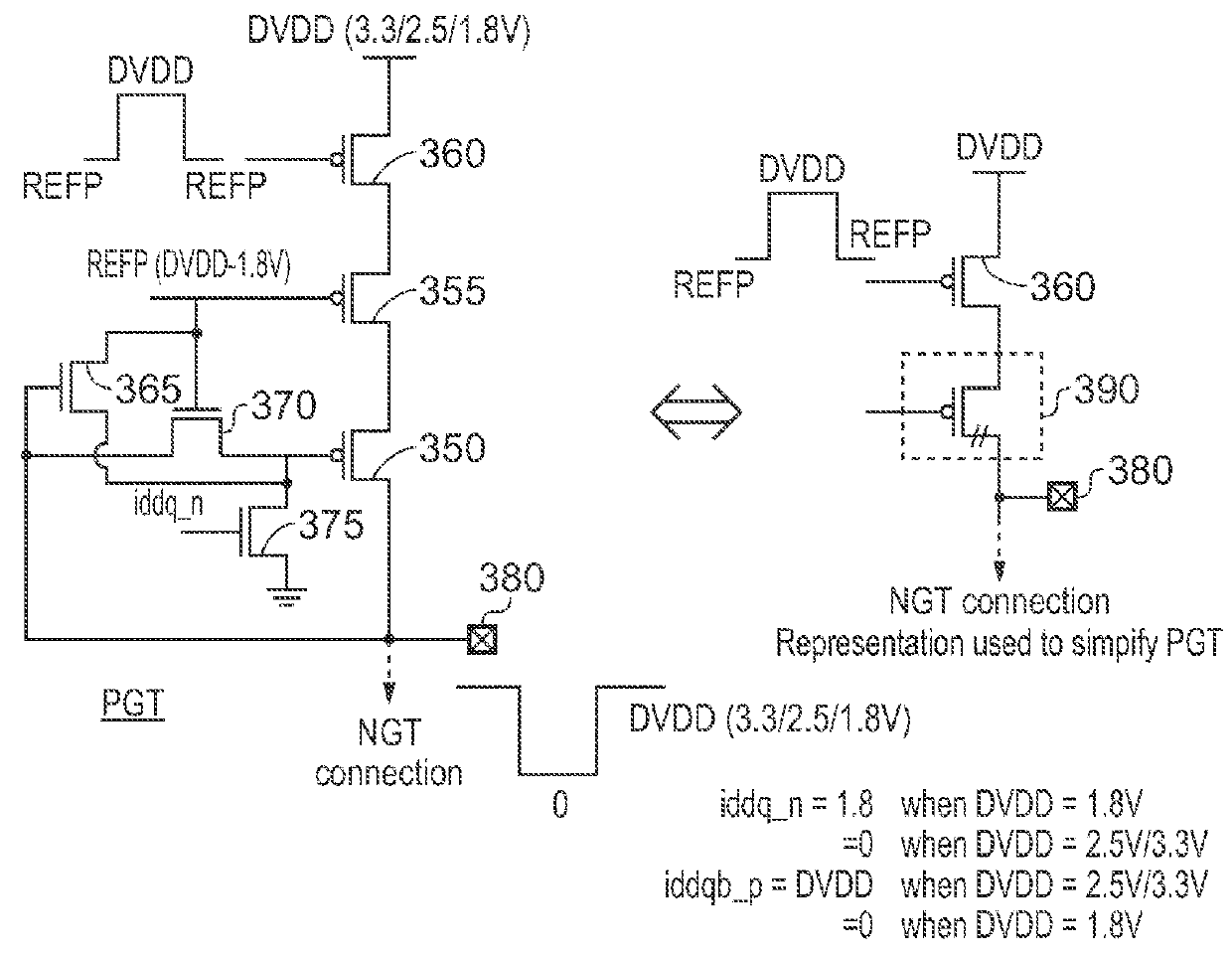
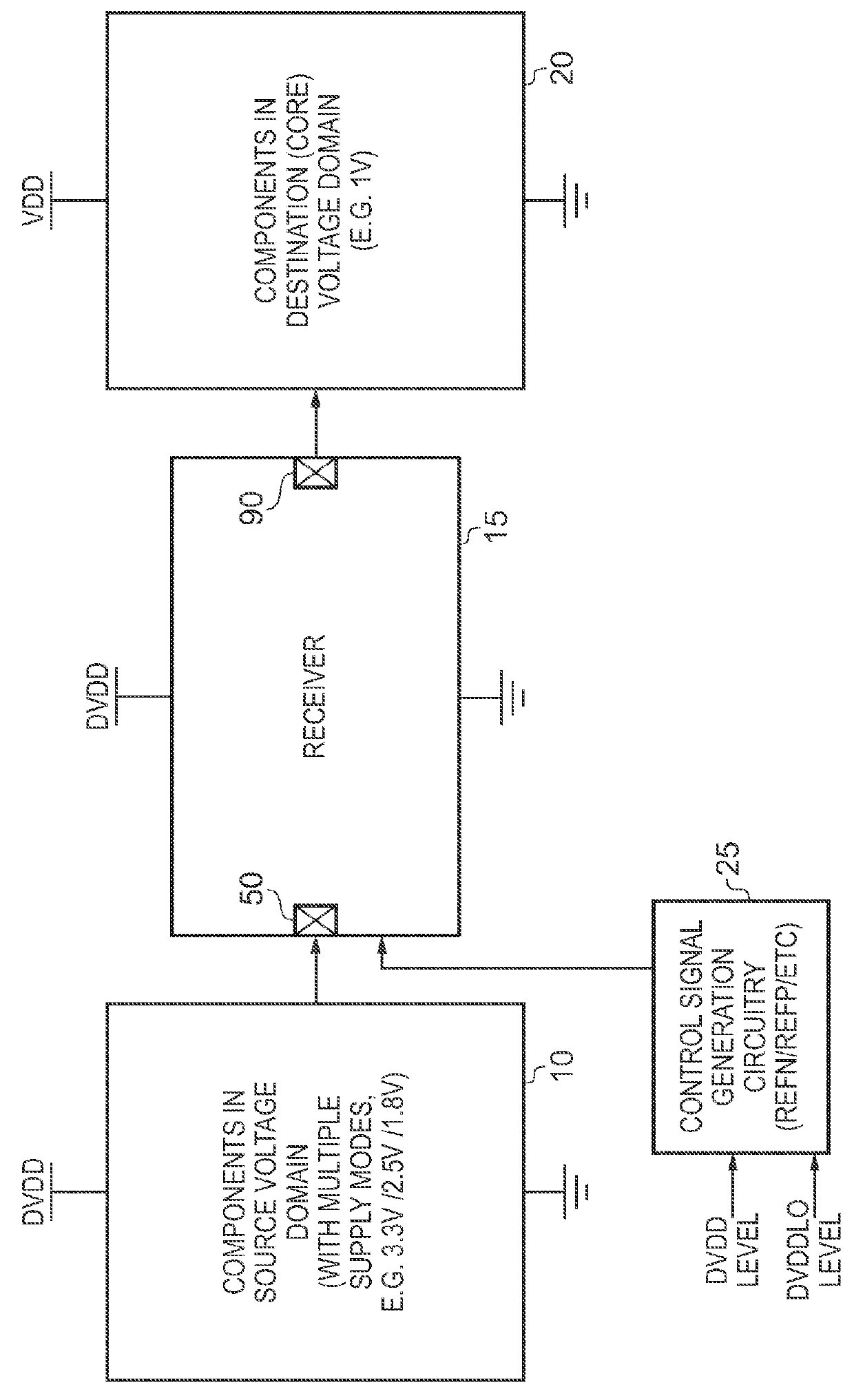
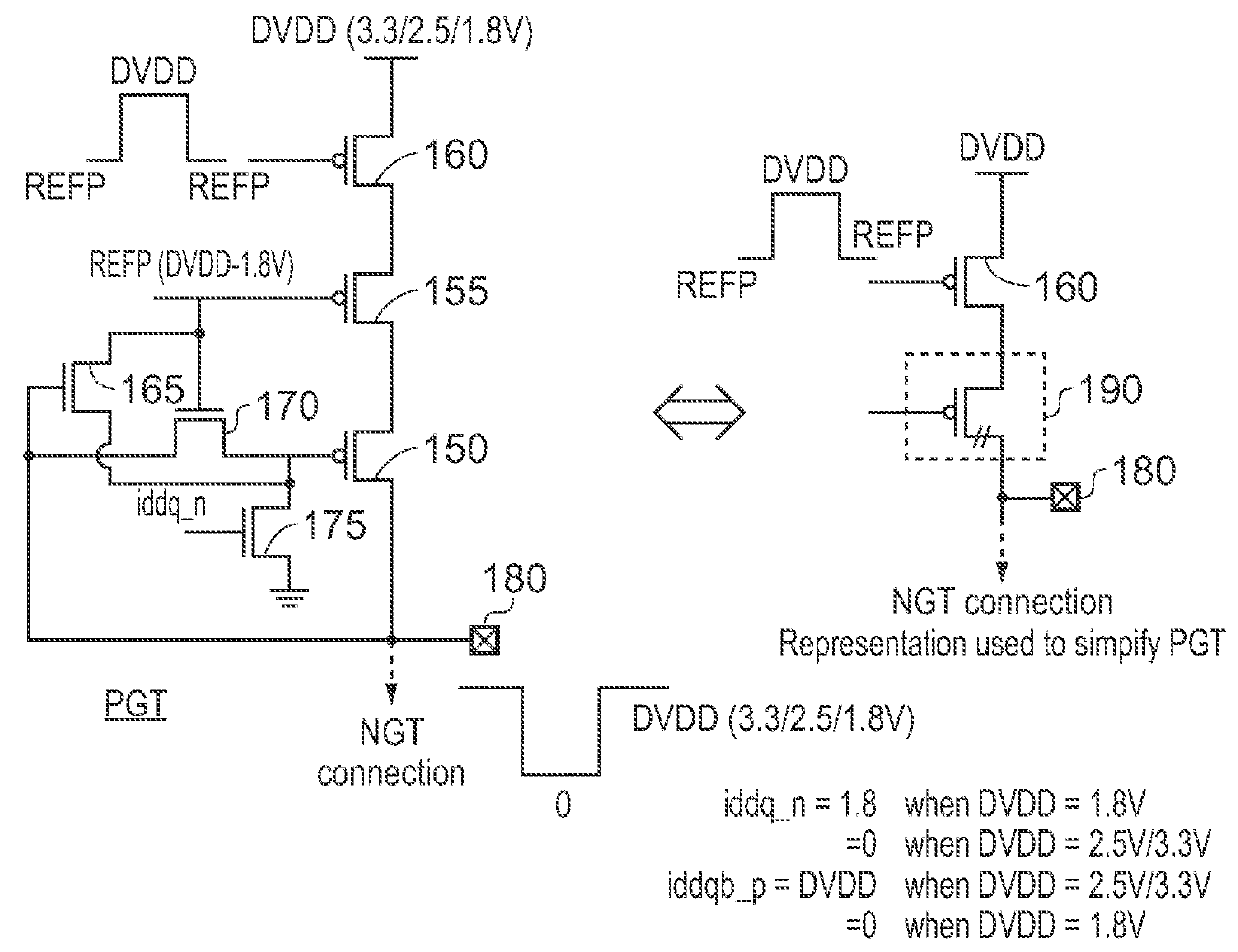
Output Signal Generation Circuitry for Converting an Input Signal From a Source Voltage Domain Into an Output Signal for a Destination Voltage Domain
ActiveUS20160036441A1Power reduction in field effect transistorsLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsLevel shiftingVoltage drop
Owner:ARM LTD
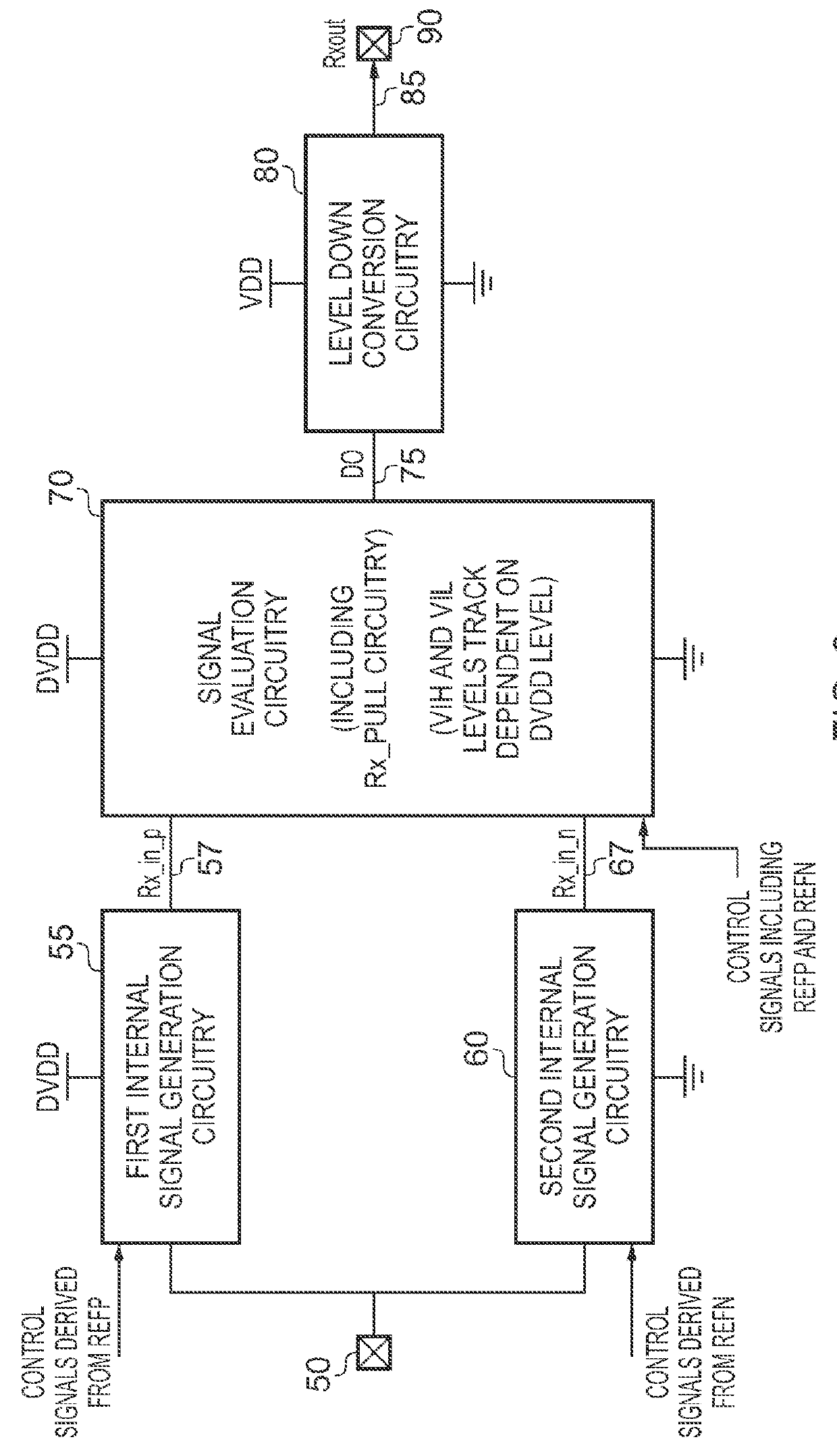
Receiver Circuitry and Method for Converting an Input Signal From a Source Voltage Domain Into an Output Signal for a Destination Voltage Domain
ActiveUS20160036445A1Reduce marginIncrease marginLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsReliability increase in field effect transistorsLow voltageVoltage range
The present invention provides a receiver circuit and method for receiving an input signal from a source voltage domain and converting the input signal into an output signal for a destination voltage domain. The source voltage domain operates from a supply voltage that exceeds a stressing threshold of components within the receiver circuitry, and the receiver circuitry is configured to operate from the supply voltage of the source voltage domain. The receiver circuitry comprises first internal signal generation circuitry configured to convert the input signal into a first internal signal in a first voltage range, and second internal signal generation circuitry configured to convert the input signal into a second internal signal in a second voltage range. Signal evaluation circuitry establishes a logic high voltage threshold and a logic low voltage threshold dependent on the supply voltage, and employs the first and second internal signals in order to detect based on the logic high voltage threshold and logic low voltage threshold when the input signal transitions between a logic low level and a logic high level (in either direction). Output generation circuitry then generates the output signal in dependence on the detection performed by the signal evaluation circuitry. The first voltage range and the second voltage range are such that the first internal signal and second internal signal will not exceed the stressing threshold of components in the signal evaluation circuitry. The receiver circuitry is able to reliably detect transitions in the input signal in situations where the supply voltage of the source voltage domain exceeds the stressing threshold of the receiver's components, but without overstress of the receiver's components.
Owner:ARM LTD
Nonvolatile programmable logic circuit
ActiveUS20090058460A1Reduce power consumptionReduce areaLogic circuits characterised by logic functionDigital storageField-programmable gate arrayLogic circuitry
A nonvolatile programmable logic circuit using a ferroelectric memory performs a nonvolatile memory function and an operation function without additional memory devices, thereby reducing power consumption. Also, a nonvolatile ferroelectric memory is applied to a FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array), thereby preventing leakage of internal data and reducing the area of a chip.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Level translator circuit for power supply disablement
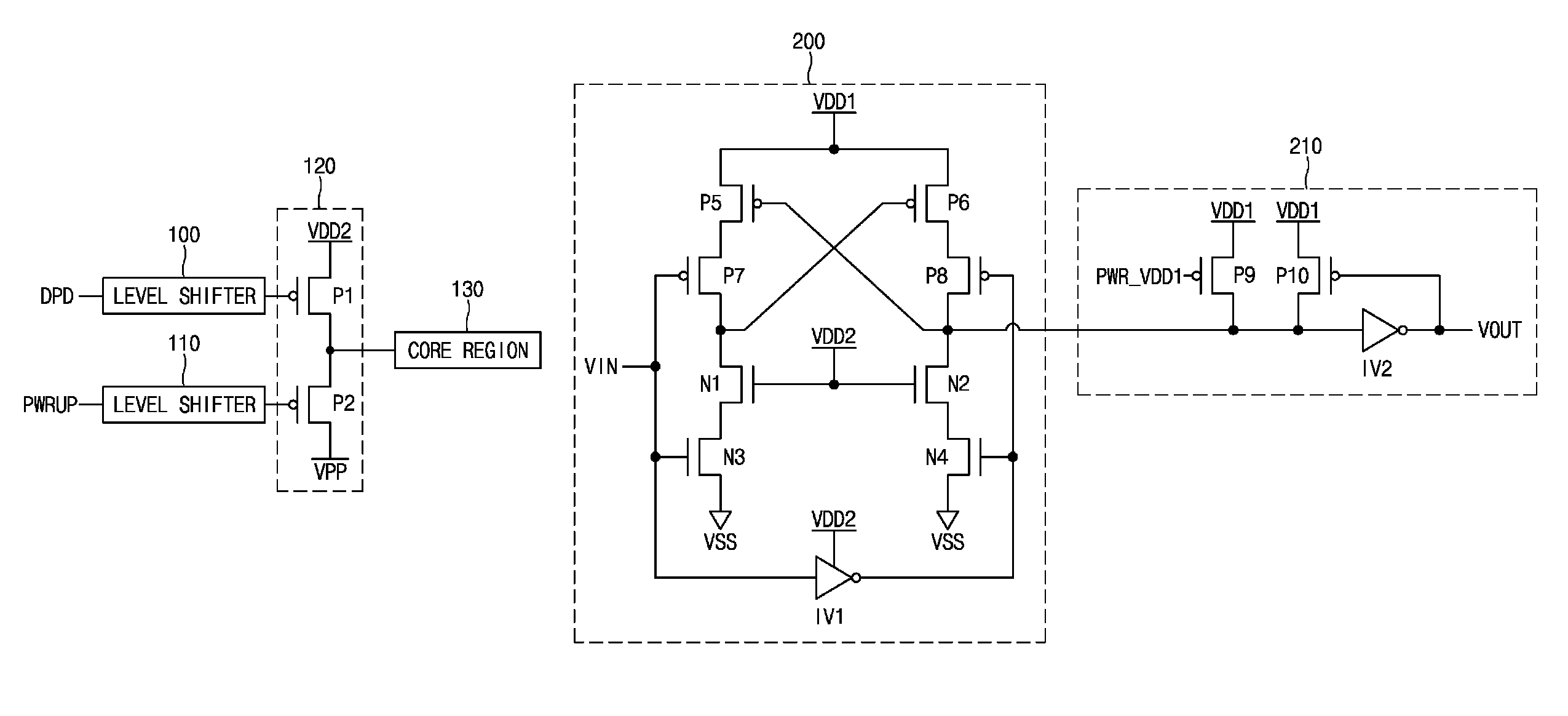
InactiveUS6861873B2Leakage current can be minimizedPulse automatic controlElectric pulse generatorPower inverterDrain current
A level translator circuit for use between a transmitting voltage potential circuit and a receiving voltage potential circuit is disclosed. The translator circuit comprises a logic element coupled between the transmitting circuit and the receiving circuit for translating the voltage level. The logic element includes a device which has a threshold voltage of such a level that leakage current will be minimized when the transmitting voltage potential circuit's power supply is disabled. In one embodiment, the logic element comprises a multistage inverter wherein a first stage comprises an intermediate power supply. The intermediate power supply allows for the threshold voltage to be lower. Accordingly, a level translation circuit is provided that operates effectively even when one of the voltage potential circuits is turned off. In addition, leakage current is minimized for two distinct power supplies by providing a high threshold voltage device within the level translator of the circuit to ensure that an appropriate logical level is provided at the output of the circuit.
Owner:IMB
Semiconductor device and high side circuit drive method
ActiveUS20140292392A1Suppression delayReduce power lossTransistorPulse automatic controlEngineeringHigh pressure
Aspects of the invention can include a pulse generating means that outputs a set signal and reset signal for driving the high potential side switching element is such that, while either one of the set signal or reset signal is in an on-state as a main pulse signal for putting the high potential side switching element into a conductive state or non-conductive state, the other signal is turned on a certain time after the rise of the main pulse signal, thereby generating a condition in which the set signal and reset signal are both in an on-state.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
A voltage level shifter
InactiveCN101944905AElectric pulse generatorLogic circuits using dielectric elementsSignal transitionPass transistor logic
A voltage level shifter is provided for receiving an input signal from an input voltage domain and converting said signal to a shifted signal in a shifted voltage domain. The voltage level shifter has an input, switching circuitry, a pass transistor and an output. The switching circuitry is configured to isolate an output of said pass transistor from said supply voltage rail when said input voltage domain corresponds to a logical zero.
Owner:ARM LTD
Low power consumption logic cell
ActiveUS20170179954A1Capacitance varyPower reduction in field effect transistorsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionCapacitanceElectrical battery
The invention relates to a logic cell for an integrated circuit including at least one first variable-capacitance capacitor having first and second main electrodes separated by an insulating region, and a third control electrode capable of receiving a control voltage referenced to a reference node of the cell to vary the capacitance between the first and second main electrodes, the third electrode being coupled to a node of application of a first logic input signal of the cell, and the first and second electrodes being respectively coupled to a node of application of a cell power supply voltage and to a node for supplying a logic output signal of the cell.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Integrated clock gating cell using a low area and a low power latch
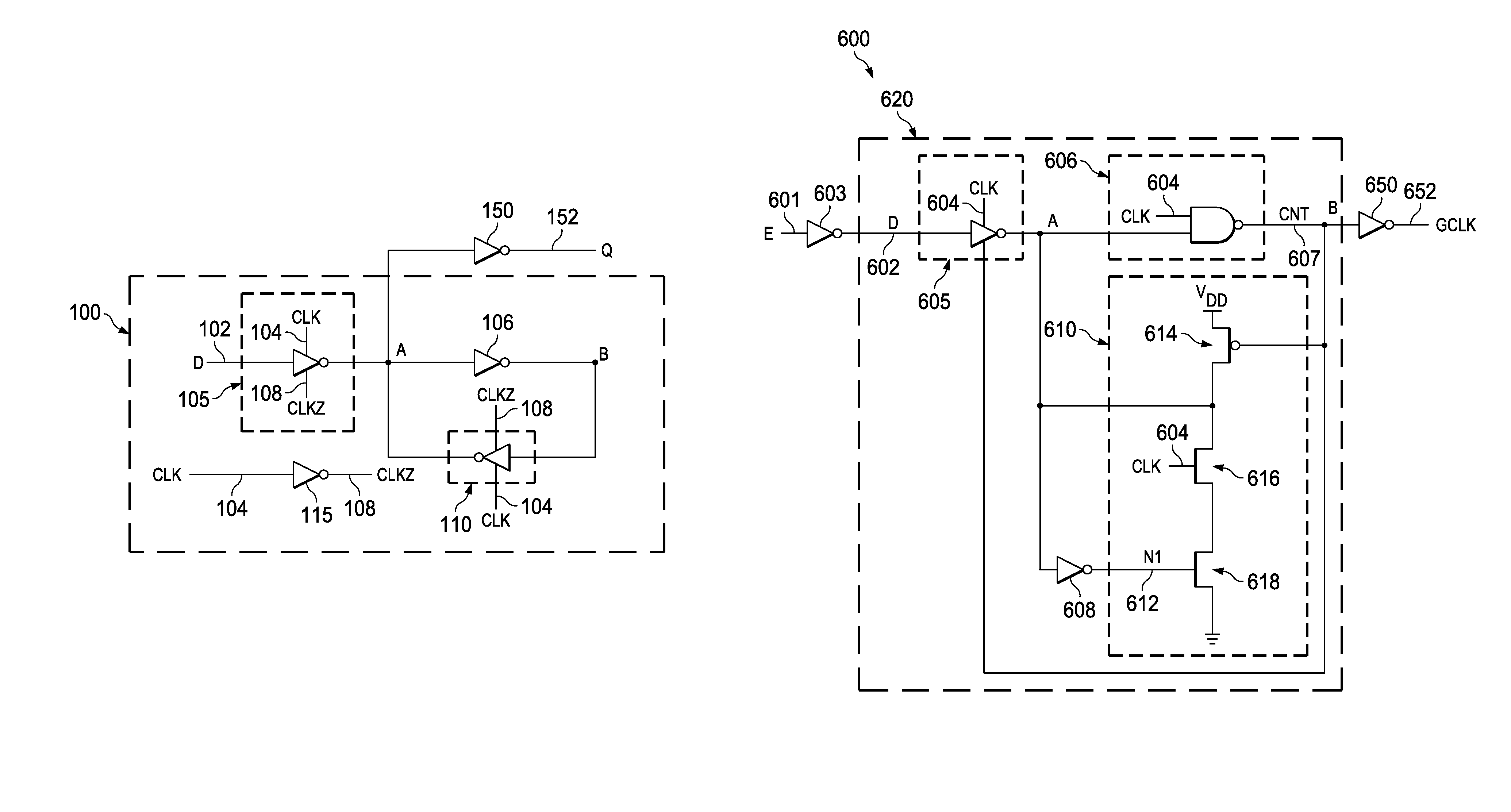
ActiveUS9246489B1Power reduction in field effect transistorsPower reduction by control/clock signalControl signalInverter
The disclosure provides an ICG (integrated clock gating) cell that utilizes a low area and a low power latch. The ICG cell includes a first logic gate that receives an enable signal and generates a latch input. A latch is coupled to the first logic gate and receives the latch input and a clock input. The latch includes a tri-state inverter and an inverting logic gate. The tri-state inverter is activated by a control signal generated by the inverting logic gate. A second logic gate receives the control signal and generates a gated clock.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Semiconductor device
In an electric potential generating device, a source of an N type MIS transistor is mutually connected to that of a P type MIS transistor and also connected to an output terminal. A drain of an N type MIS transistor 54 is connected to a power supply voltage supply portion for supplying power supply voltage VDD, and a drain of the P type MIS transistor is connected to a ground. In addition, a substrate potential of the N type MIS transistor is a ground voltage VSS, and that of a P type MIS transistor 56 is the power supply voltage VDD. Thus, it is constituted as a source follower circuit for taking output out of the source. It is possible, by utilizing this electric potential generating device, to obtain a logic transformation circuit for stably switching between NOR operation and NAND operation.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
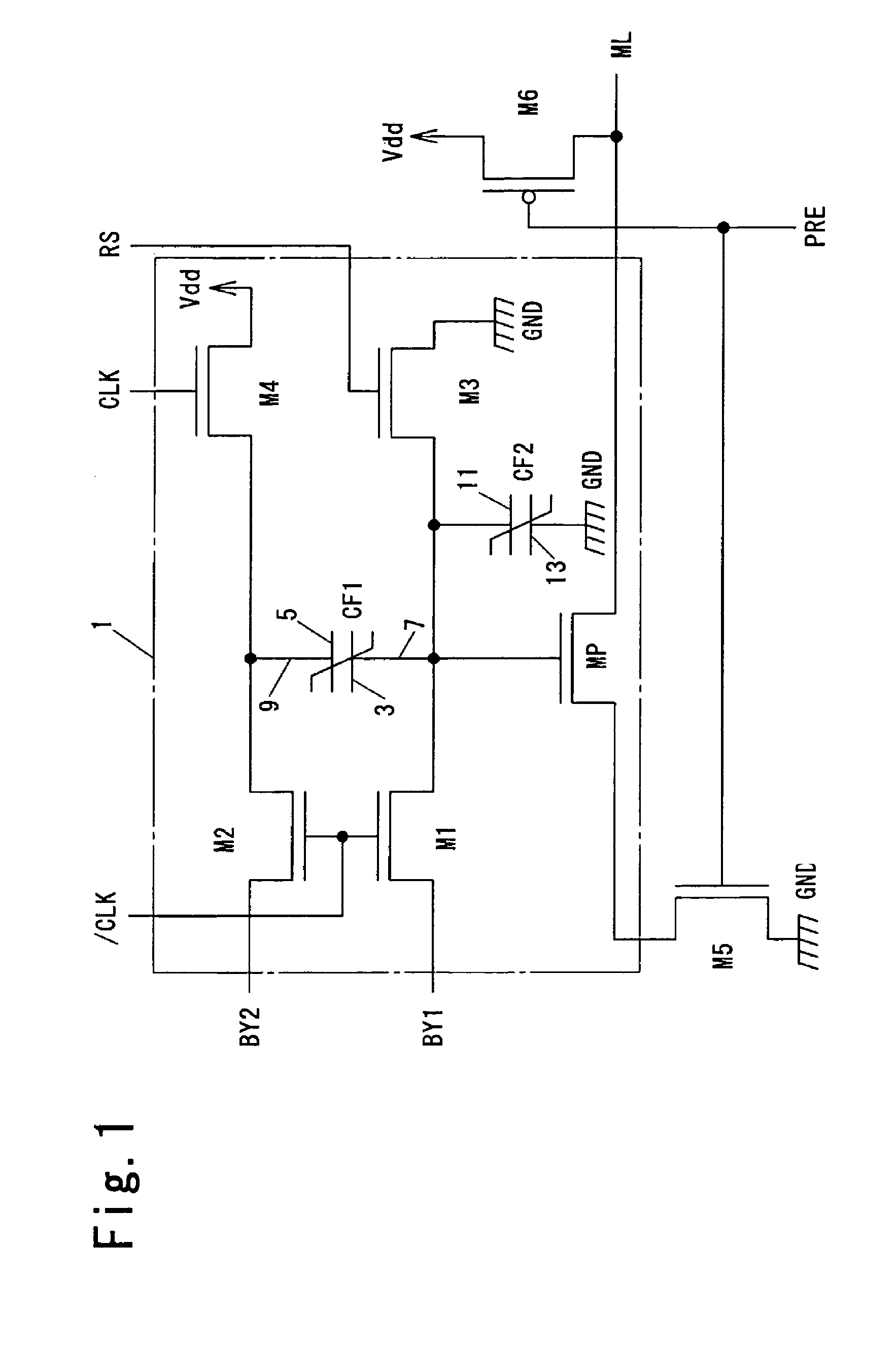
Logical operation circuit and logical operation device
InactiveUS20050017757A1Reduce voltageLogic circuits characterised by logic functionSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsAudio power amplifierPotential difference
To provide a logical operation circuit and a logical operation device which can performs a logical operation using a ferroelectric capacitor. The area ratio between the ferroelectric capacitors CF1 and CF2 are set such that the potential difference Vdef between voltages Va1 and Va0 is as large as possible, and a transistor MP has a threshold voltage Vth which is about 1 / 2 ·(Va0+Va1). Thus, the ON / OFF operation margin of the transistor MP can be significantly large. As a result, a reading process can be performed at a high speed without using an amplifying circuit such as a sense amplifier. Also, the logical operation circuit and the logical operation device can be highly integrated with ease since no sense amplifier is used.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Semiconductor device having level shift circuit
ActiveUS20150002206A1Pulse automatic controlLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsPower semiconductor deviceEngineering
Disclosed herein is a device includes; a level conversion circuit coupled to first and third power supply lines, receiving a first signal and an inverted signal of the first signal each having an amplitude between first and second potentials, and output ting a second signal having an amplitude between first and third potentials; a delay circuit coupled to the first and second power supply lines, and output ting a third signal delayed from the first signal; and an output circuit including first and second transistors coupled in series between the first and third power supply lines, the first transistor having a control electrode supplied with the second signal, and the second transistor having a control electrode supplied with the third signal.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Nonvolatile programmable logic circuit
ActiveUS7428160B2Reduce power consumptionReduce areaLogic circuits characterised by logic functionDigital storageField-programmable gate arrayLogic circuitry
A nonvolatile programmable logic circuit using a ferroelectric memory performs a nonvolatile memory function and an operation function without additional memory devices, thereby reducing power consumption. Also, a nonvolatile ferroelectric memory is applied to a FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array), thereby preventing leakage of internal data and reducing the area of a chip.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Electro-optical modulator interface
ActiveUS9229250B2Low costLow techLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsNon-linear opticsCapacitanceCMOS
A relatively high-speed, high-efficiency CMOS two branch driver core that may operate under relatively low supply voltage may include thin oxide CMOS transistors configured to generate rail-to-rail output swings larger than twice a supply voltage and without exceeding safe operating area limits. Each of the two branches may include two stacked CMOS inverter pairs configured to drive a respective load capacitance coupled between respective CMOS inverter outputs, in phase opposition to the other branch. A pre-driver circuit input with a differential modulating signal may output two synchronous differential voltage drive signals of a swing of half of the supply voltage and DC-shifted by half of the supply voltage with respect to each other and that may be applied to the respective CMOS inverter inputs of the two branches.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS INT NV
Power control device
ActiveUS9236859B1Logic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsElectronic switchingElectricityEngineering
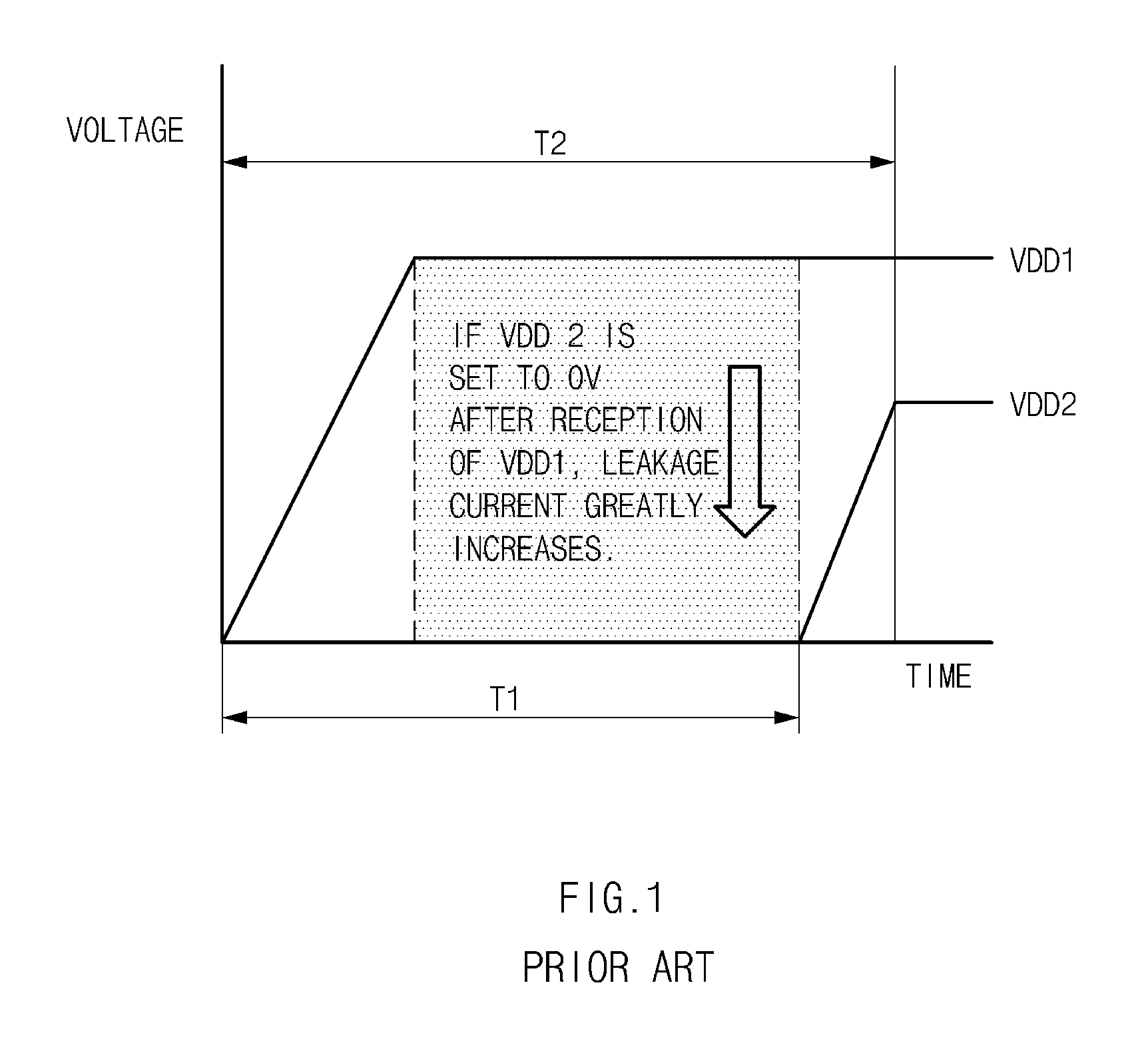
A power control device may include a first power-supply voltage source configured to generate a first power-supply voltage, and a second power-supply voltage source configured to generate a second power-supply voltage having a voltage level different from that of the first power-supply voltage. The power control device may include a power driver configured to provide an internal power source in response to the second power-supply voltage, irrespective of the first power-supply voltage source and the second power-supply voltage source, during an initial power-up period.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
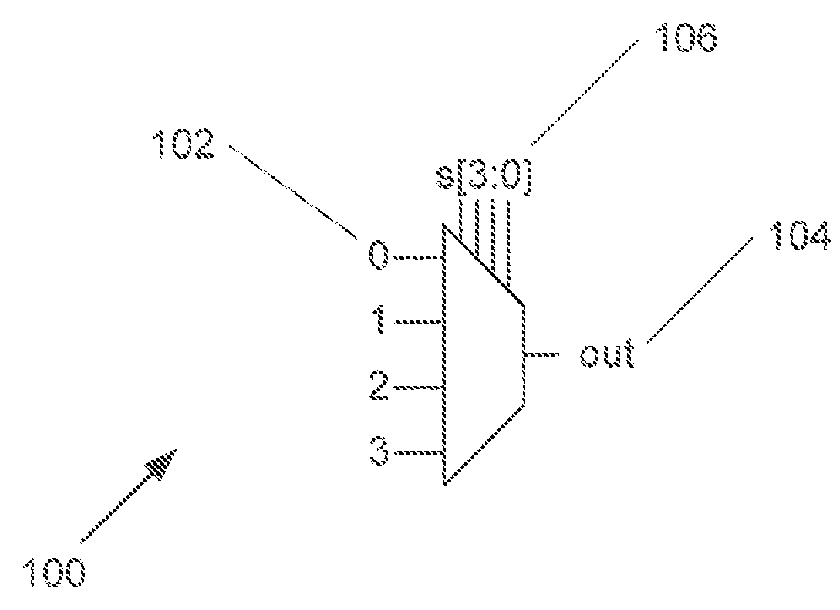
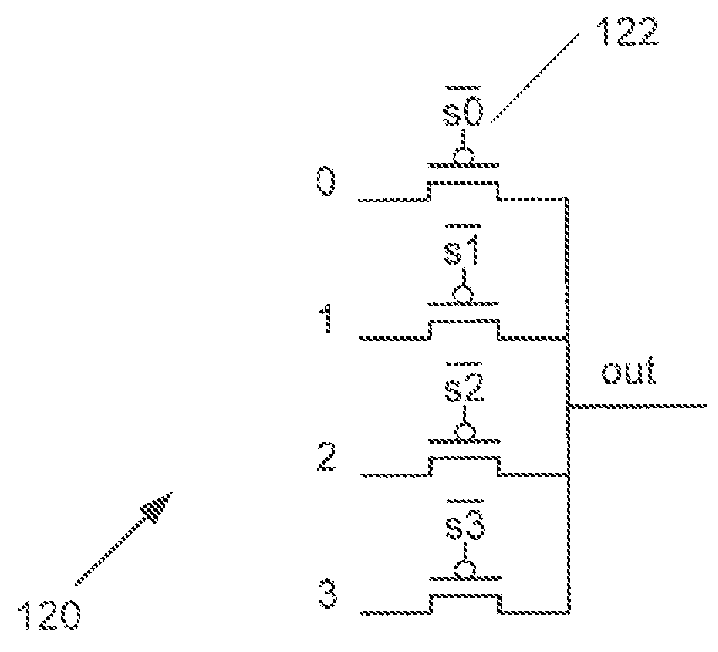
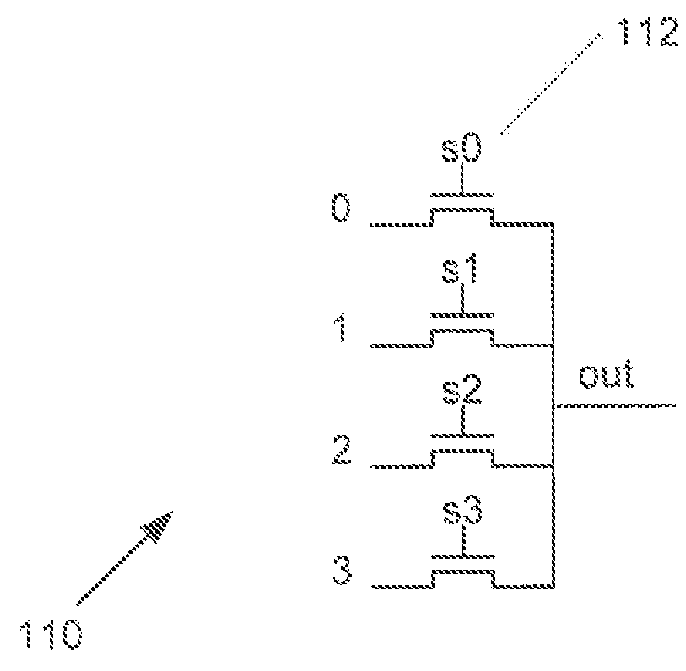
Fine-Grained Power Gating in FPGA Interconnects
ActiveUS20160036428A1Power reduction by control/clock signalLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsMultiplexerEngineering
Systems and methods for power gating in logic and / or computing circuitry in accordance with embodiments of the inventions are disclosed. In one embodiment, a multiplexer for fine-grain power gating includes a first supply voltage and a second supply voltage, a plurality of inputs, a plurality of selection inputs, a selection circuitry configured to select one of the plurality of inputs, where one of the plurality of inputs is the first supply voltage and one of the selection inputs is a power gating enable input, an output inverter stage including a PMOS transistor and an NMOS transistor, where at least one input to the inverter stage is provided to the gates of the PMOS and NMOS transistors and selection of the power gating enable signal applies the first supply voltage to the gate of the PMOS transistor and places the PMOS transistor in a cutoff mode of operation.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
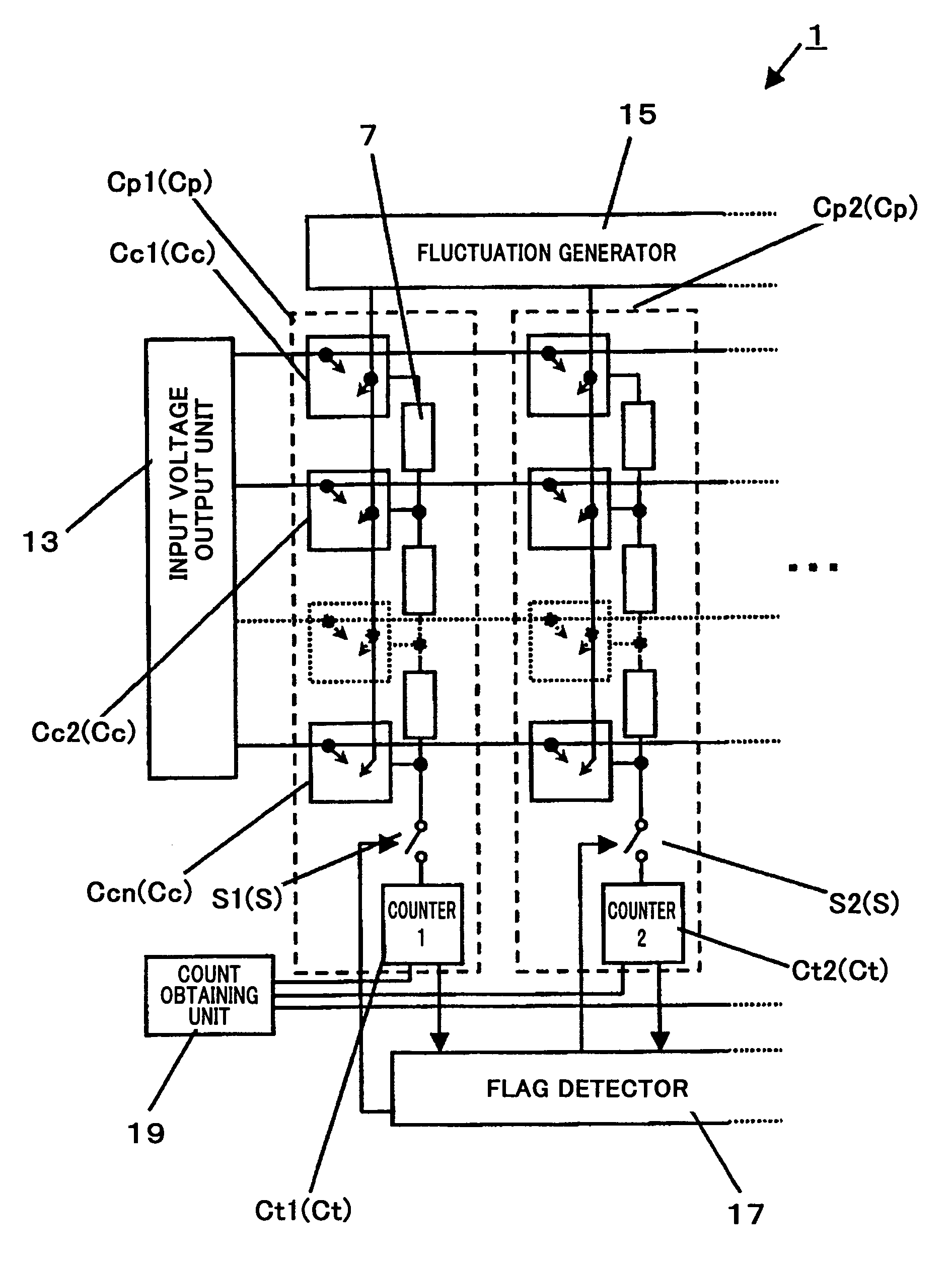
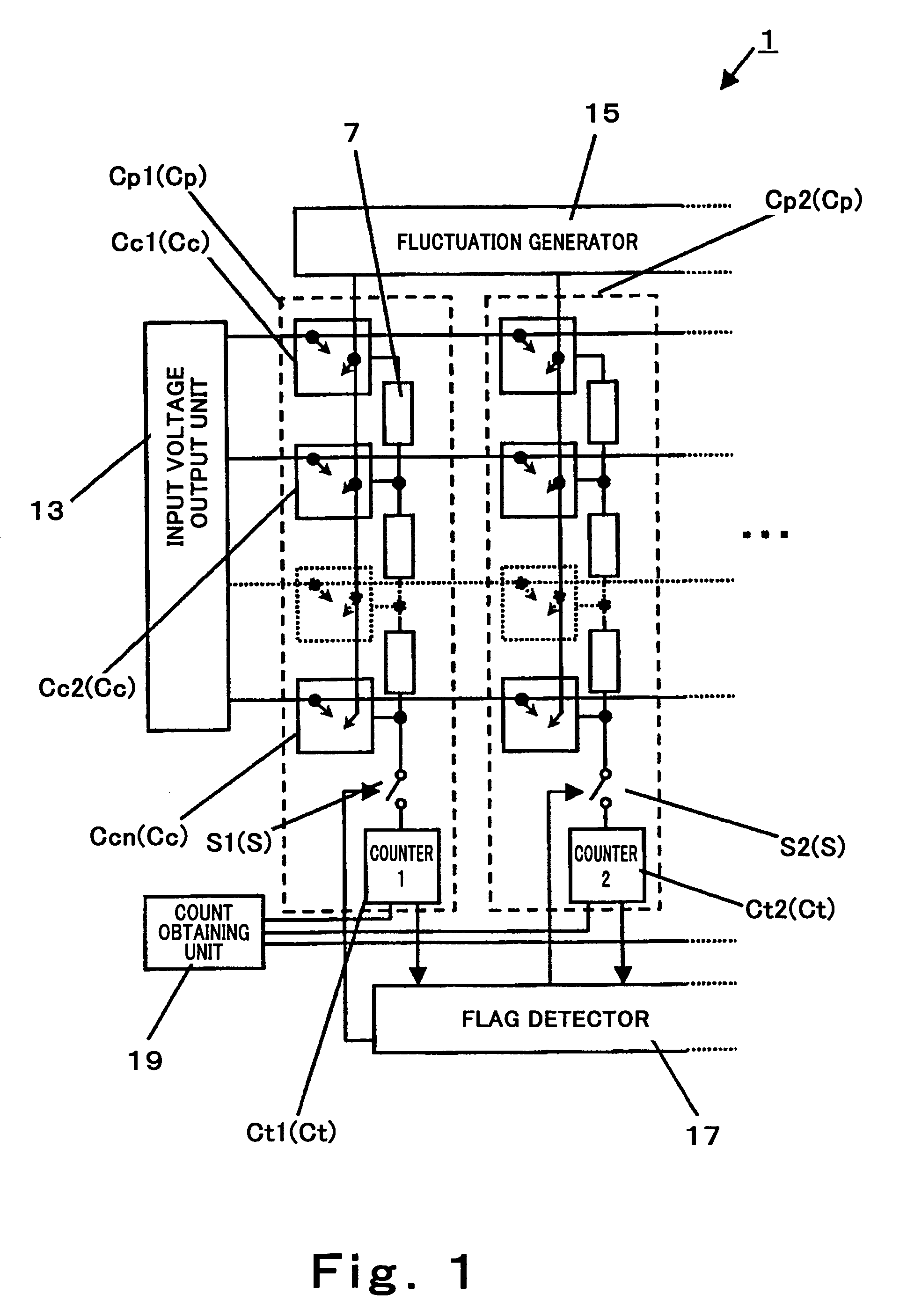
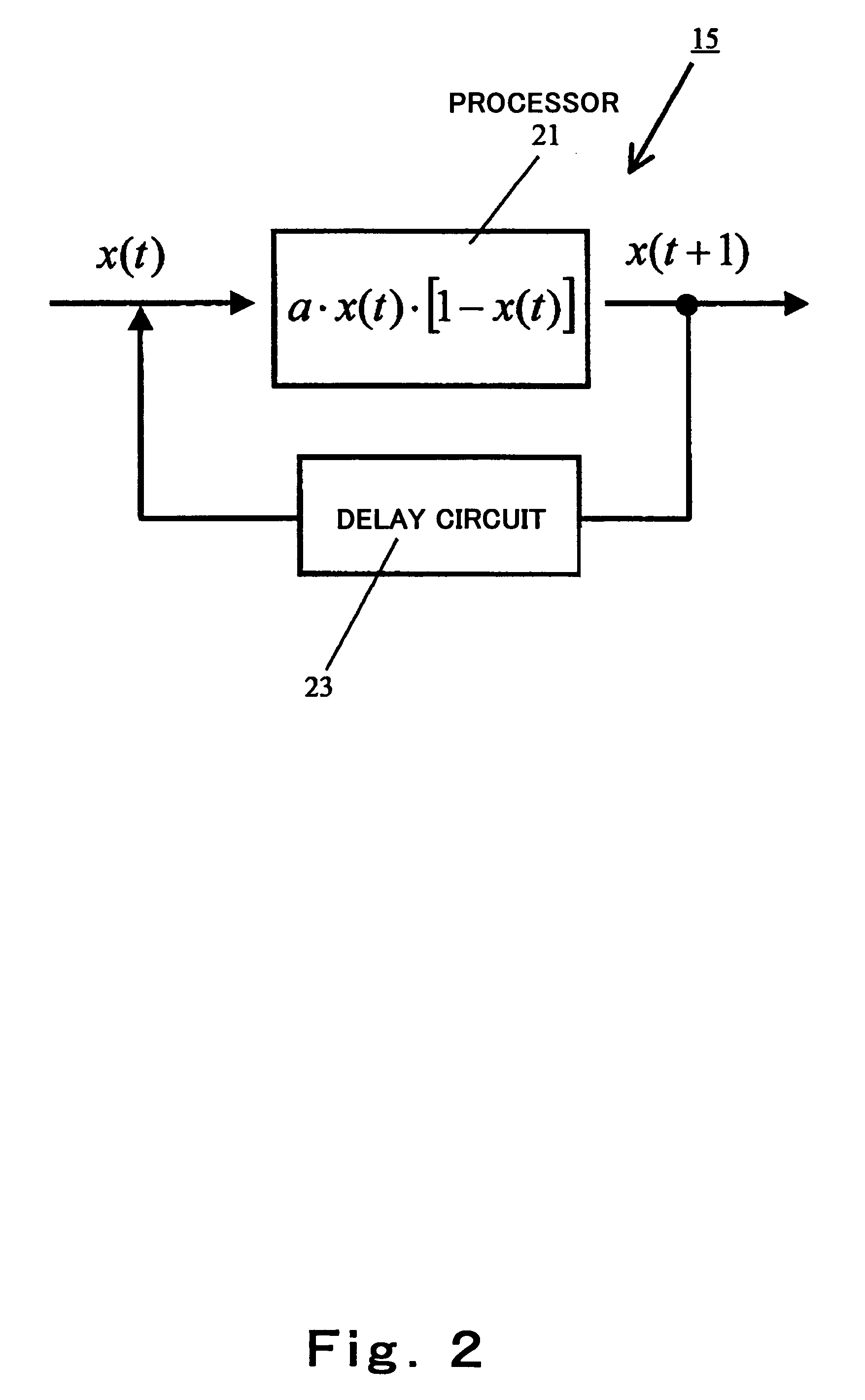
Stochastic processor, driving method thereof, and recognition process device using the same
ActiveUS7493353B2Easy to judgeManhattan distanceLogic circuits characterised by logic functionProbabilistic networksEngineeringImpulse detection
A stochastic processor of the present invention includes a fluctuation generator configured to output an analog quantity having a fluctuation, a fluctuation difference calculation means configured to output fluctuation difference data with an output of the fluctuation generator added to analog difference between two data, a thresholding unit configured to perform thresholding on an output of the fluctuation difference calculation means to thereby generate a pulse, and a pulse detection means configured to detect the pulse output from the thresholding unit.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Popular searches
Electric pulse generator details Logic circuit coupling/interface arrangements Semiconductor devices Electric variable regulation Space heating and ventilation control systems Heat exchange apparatus Computation using denominational number representation Voltage/current interference elimination Power supply for data processing Logic circuits using elementary logic circuit components
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com