Patents
Literature
216 results about "Coupling noise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
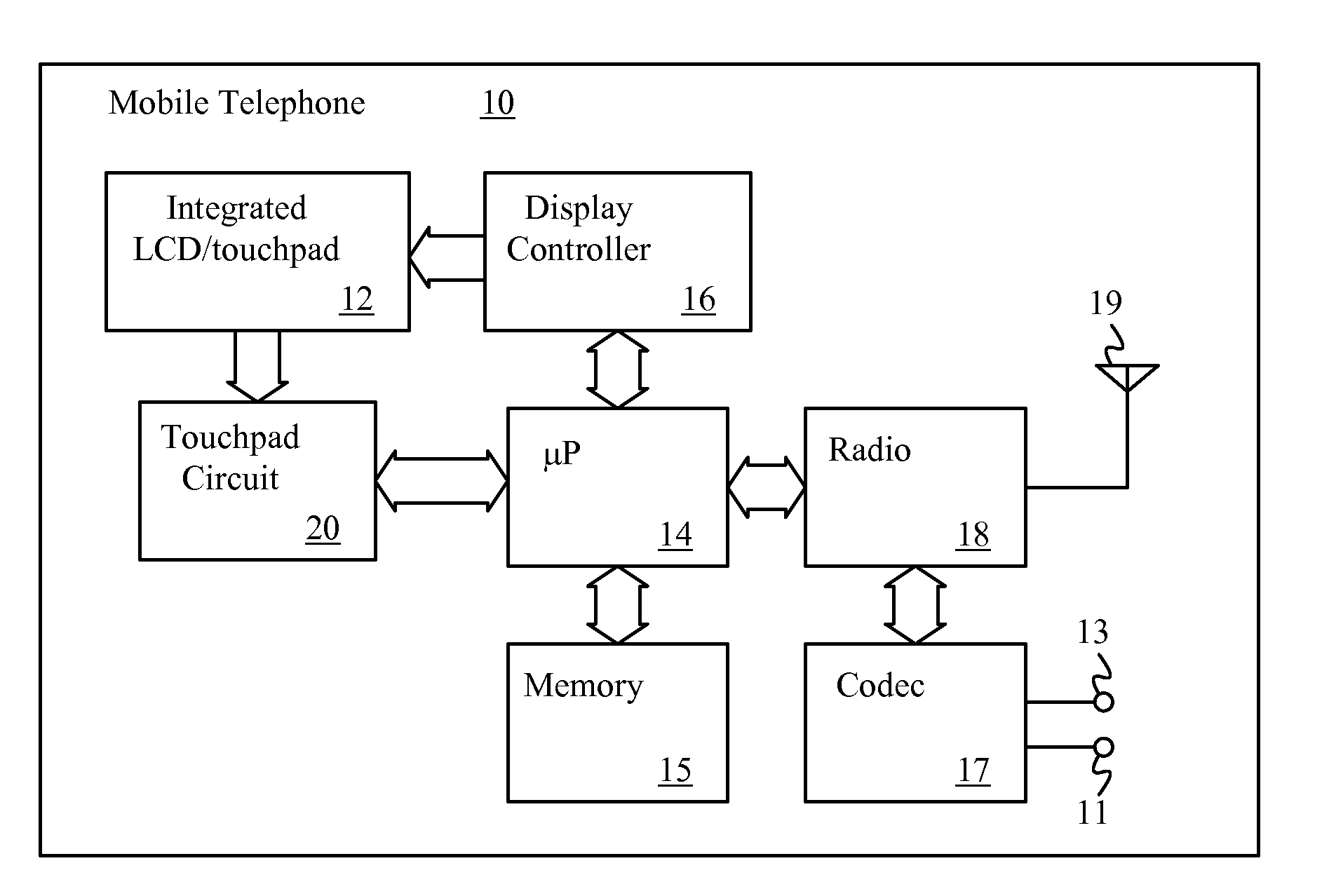
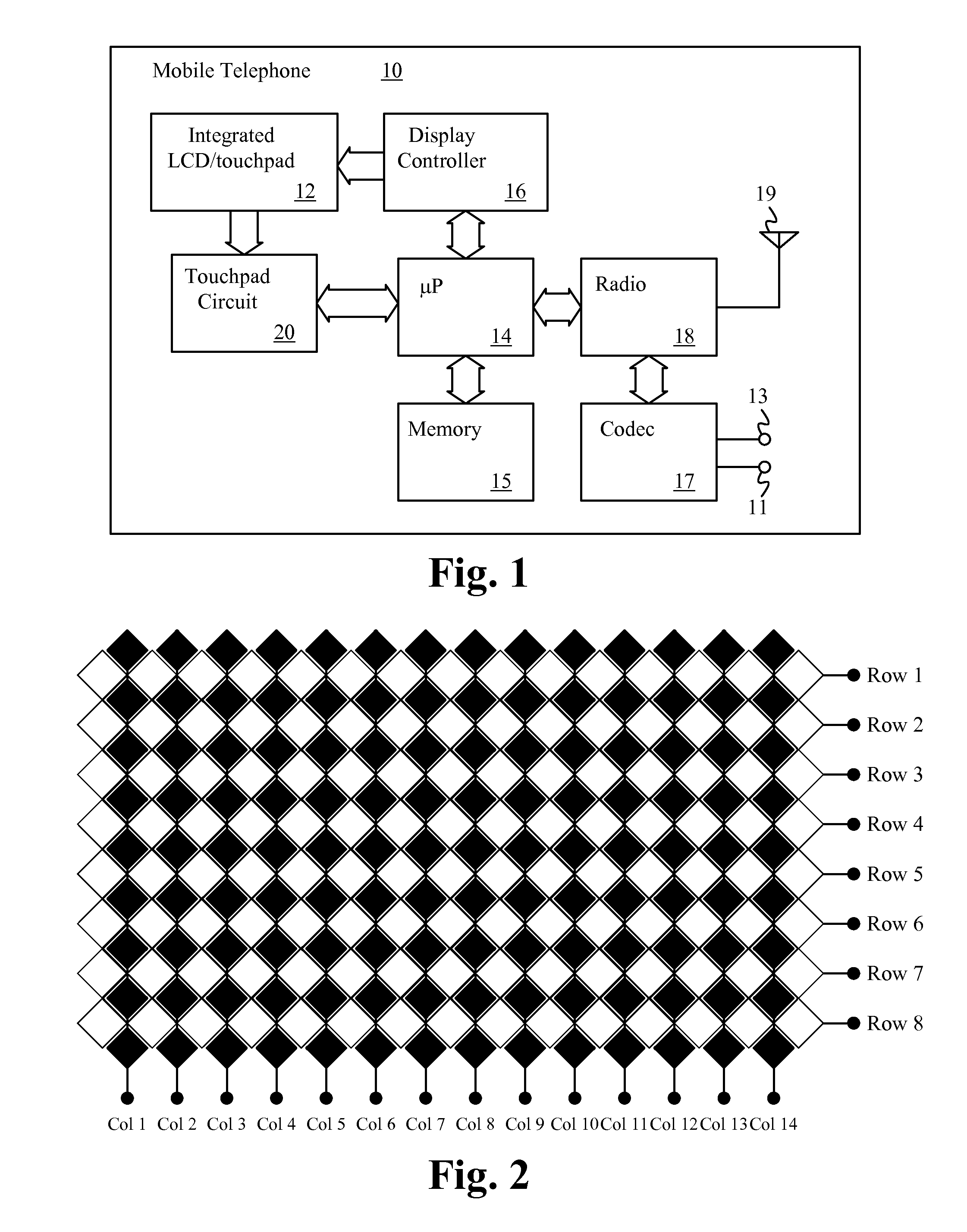
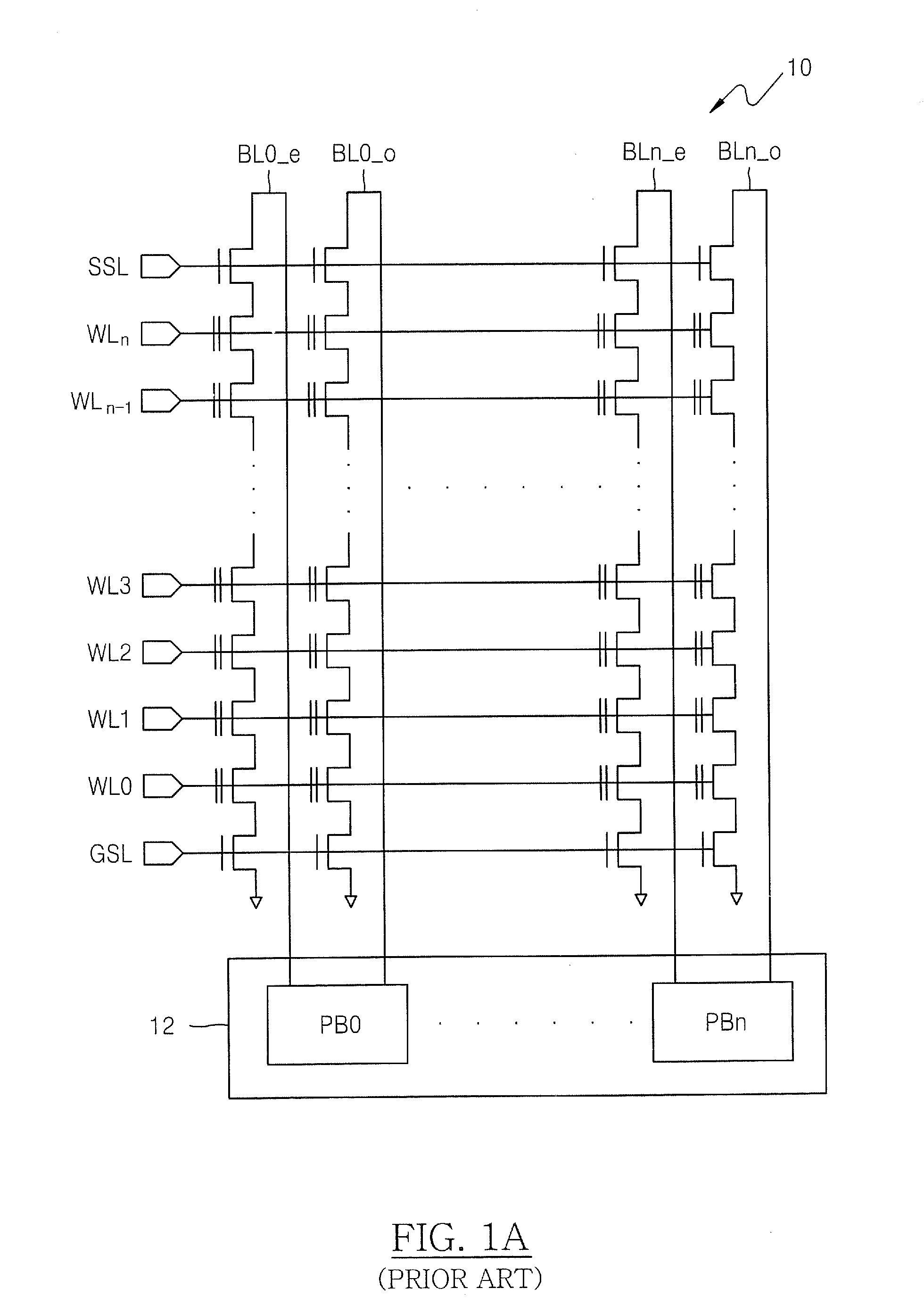
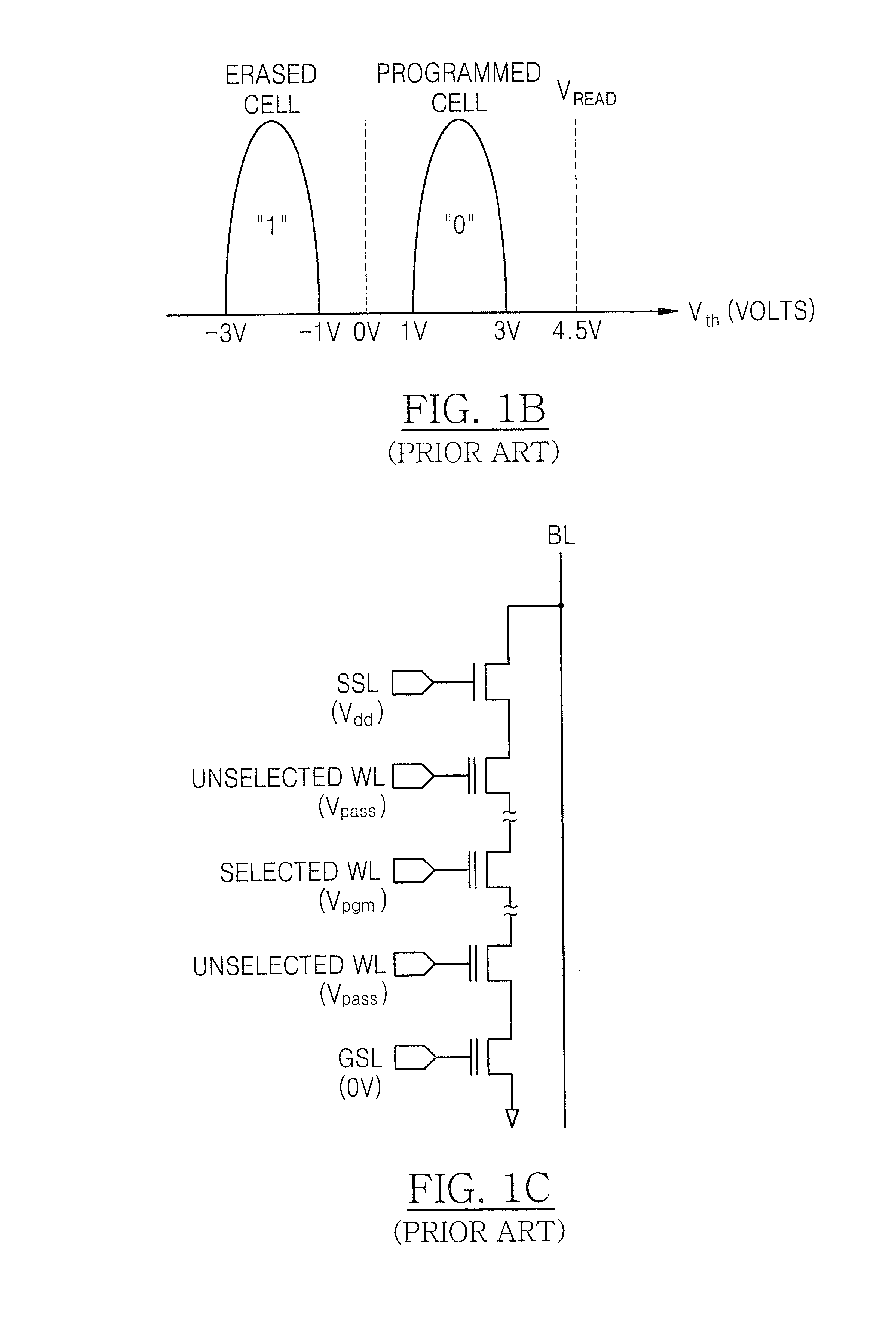
LCDS with integrated touch panels
InactiveUS20080129898A1Avoid failureEliminating coupling noiseNon-linear opticsInput/output processes for data processingEngineeringTouch panel
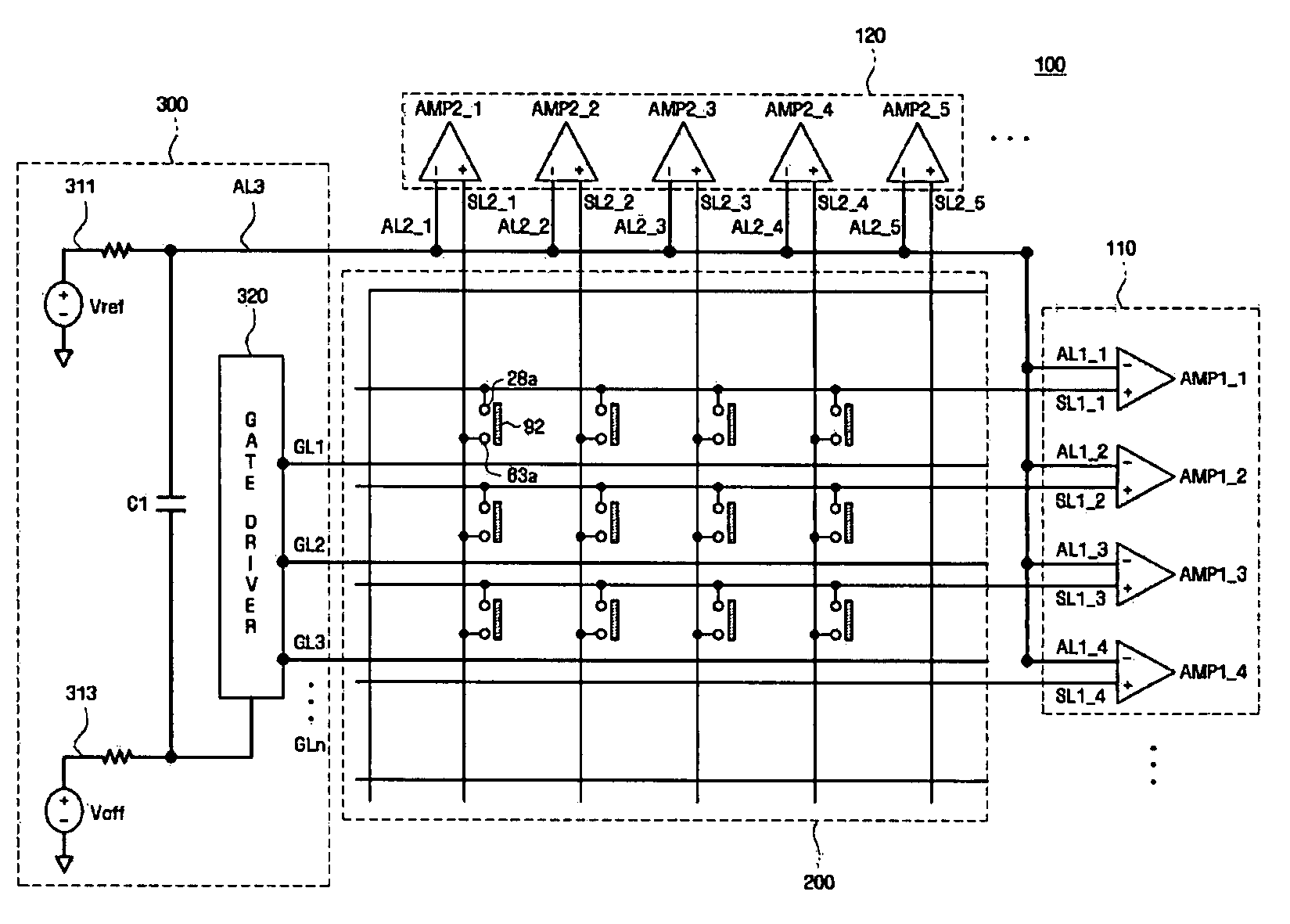
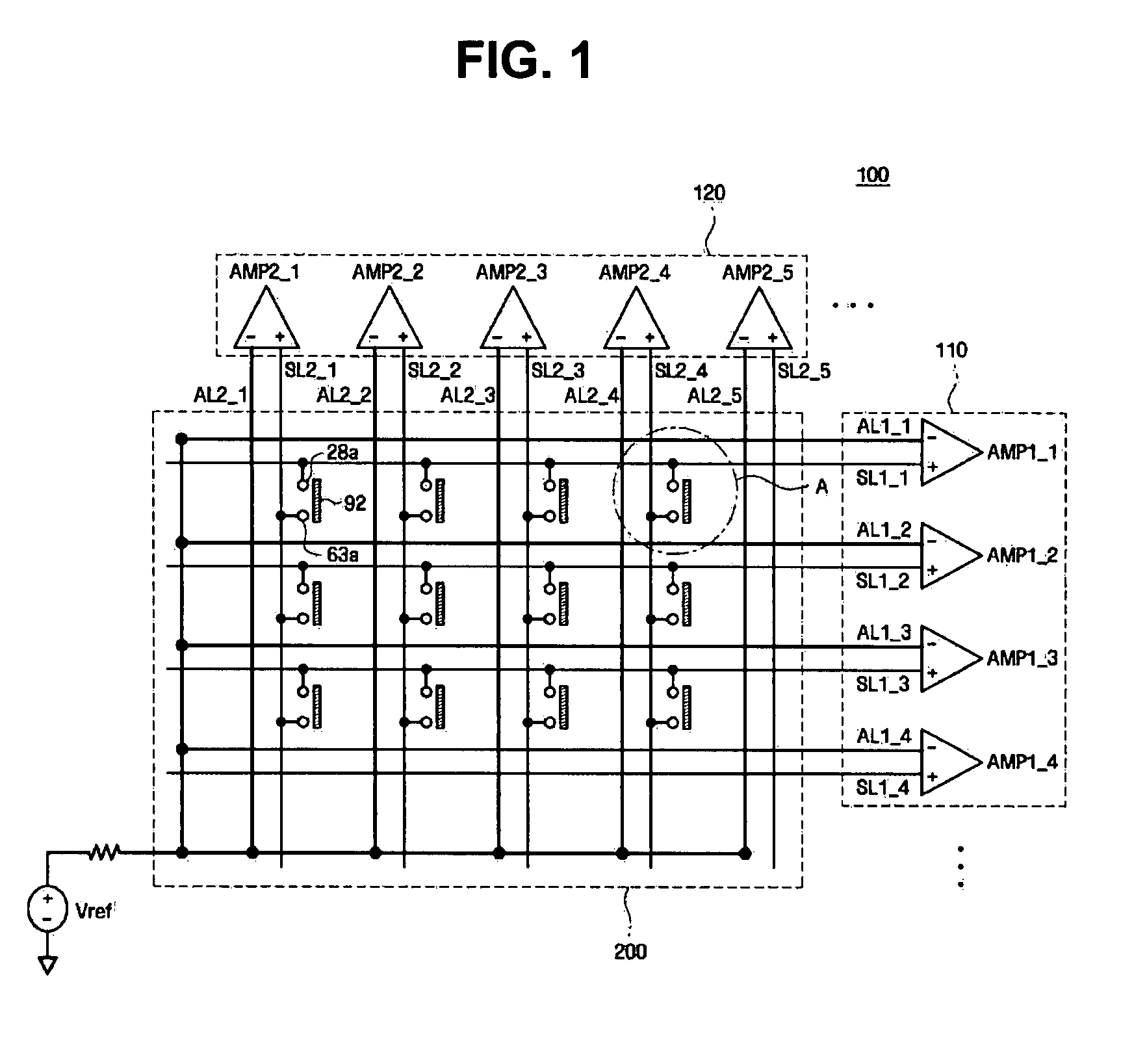
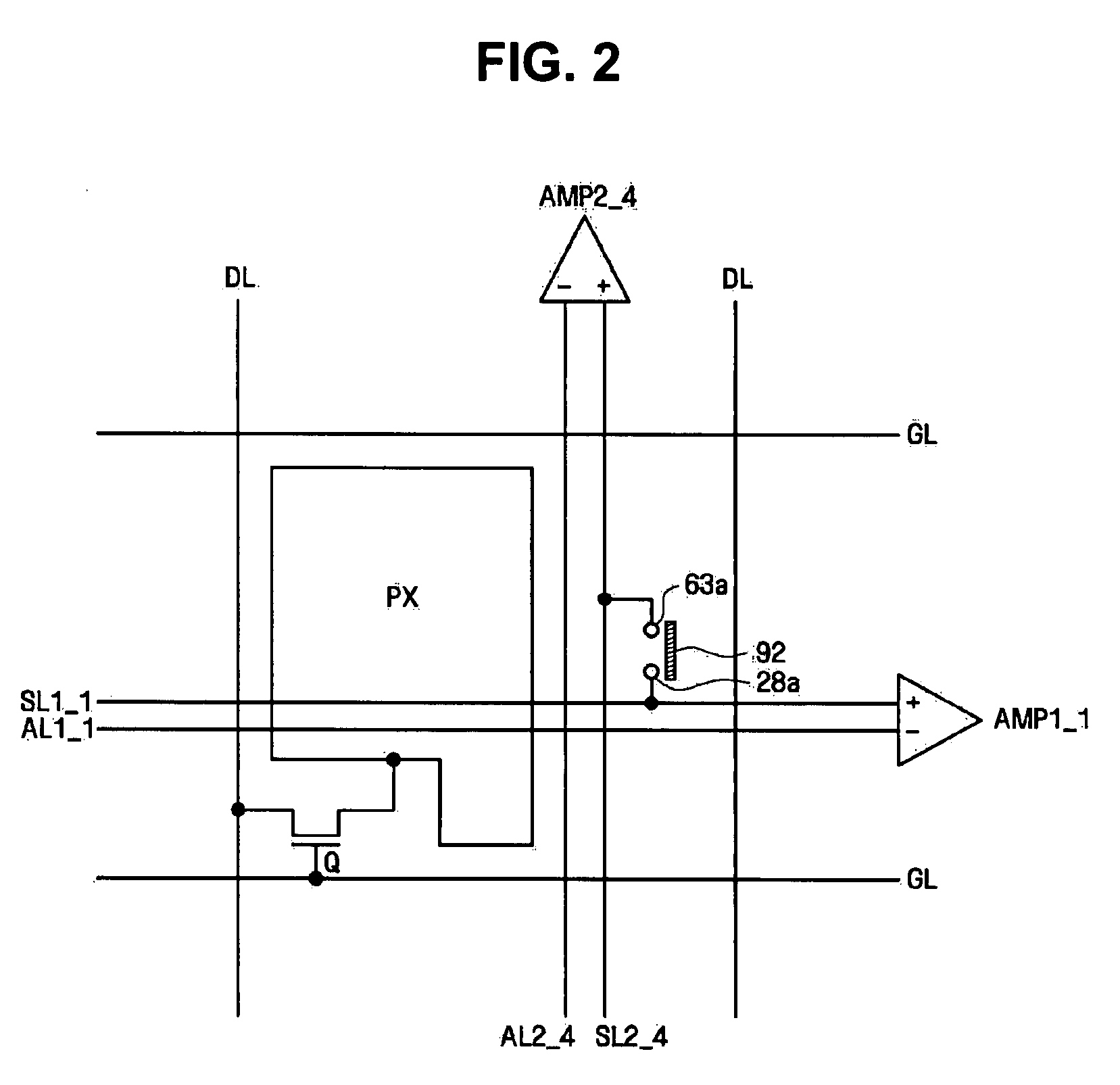
An LCD with an integrated touch panel that prevents sensor malfunction by eliminating coupling noises includes an insulating substrate, a plurality of gate lines formed on the insulating substrate so as to extend in a first direction, a plurality of data lines formed in a second direction so as to intersect the plurality of gate lines, a plurality of thin film transistors (TFTs), each formed at an area defined by the gate lines and the data lines, a plurality of sensor lines formed in the same directions as the gate lines and the data lines, and a plurality of dummy lines formed in the same directions as the sensor lines.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Local self-boost inhibit scheme with shielded word line
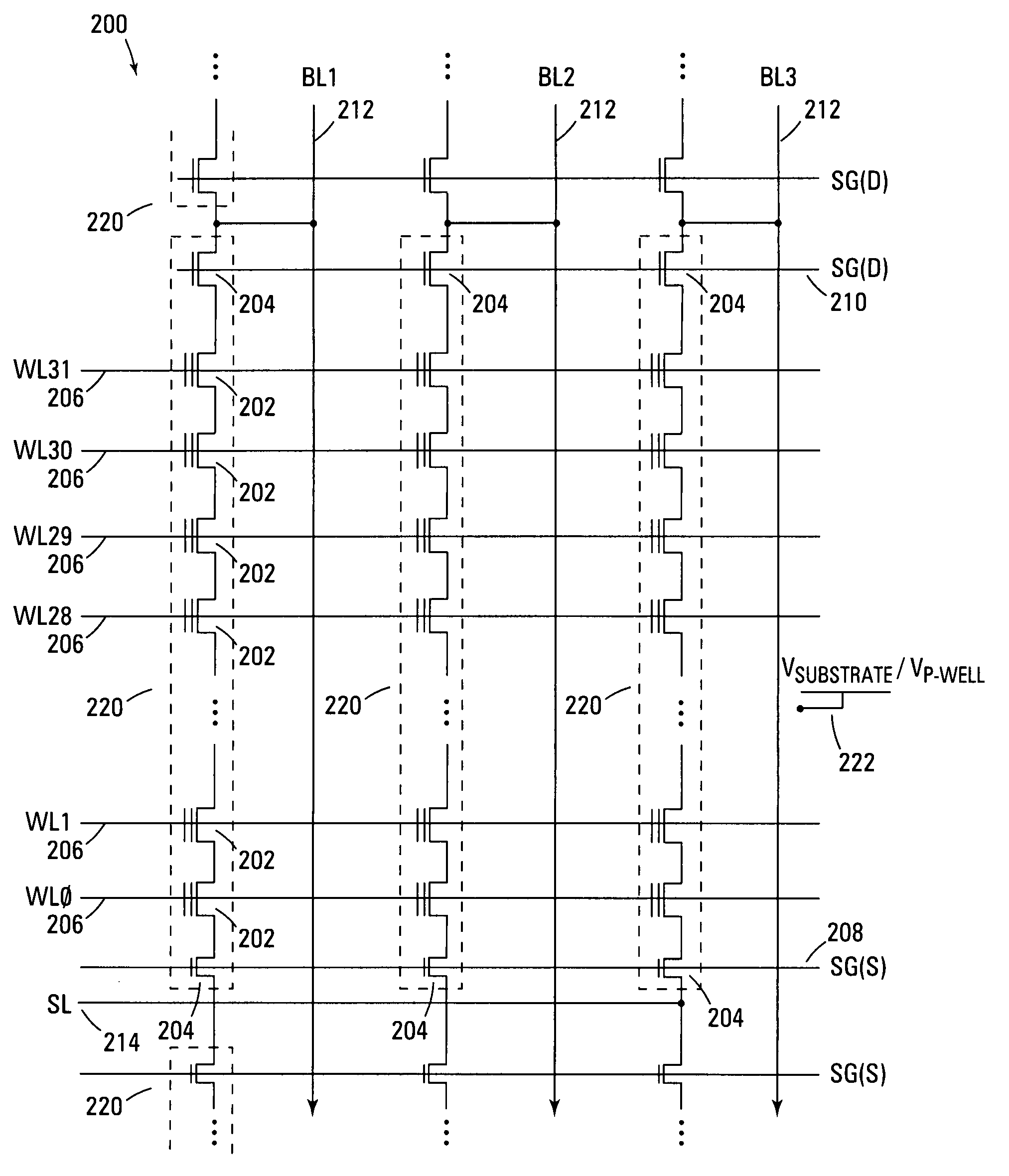
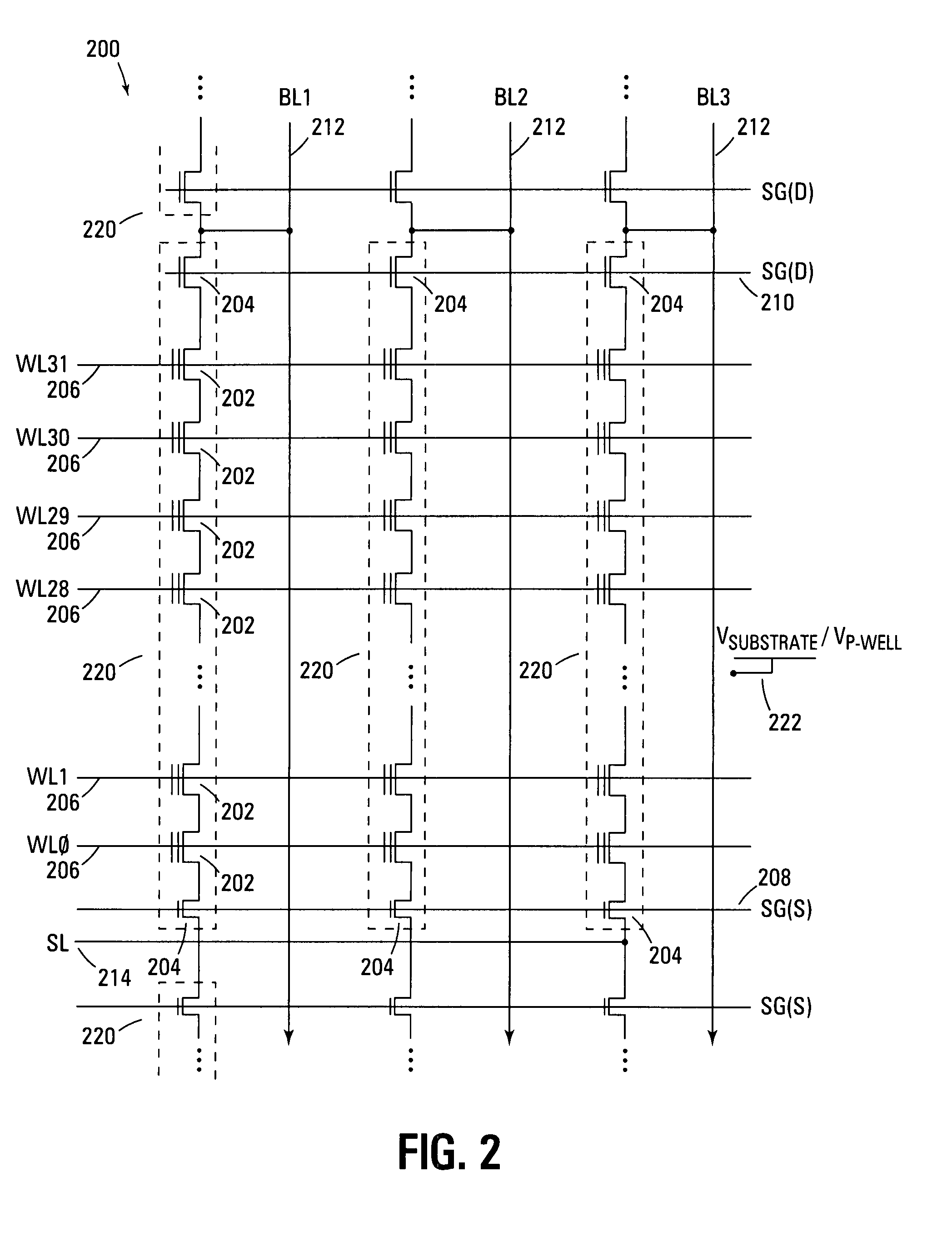
A NAND architecture non-volatile memory device and programming process is described that reduces the effects of word line to word line voltage coupling by utilizing sets of two or more adjacent word lines and applying the same voltage to each in array access operations. This allows each word line of the set or pair to shield the other from word line to word line capacitive voltage coupling. In NAND memory string embodiments the various cells of strings of non-volatile memory cells are programmed utilizing modified or unmodified drain-side self boost, source-side self boost, local self boost, and virtual ground programming processes that utilize two or more “blocking” memory cells on either the source line side and drain line side of a selected memory cell. The paired blocking cells shield each other during programming to reduce coupled noise, to prevent charge leakage from the boosted channel of the selected memory cell.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
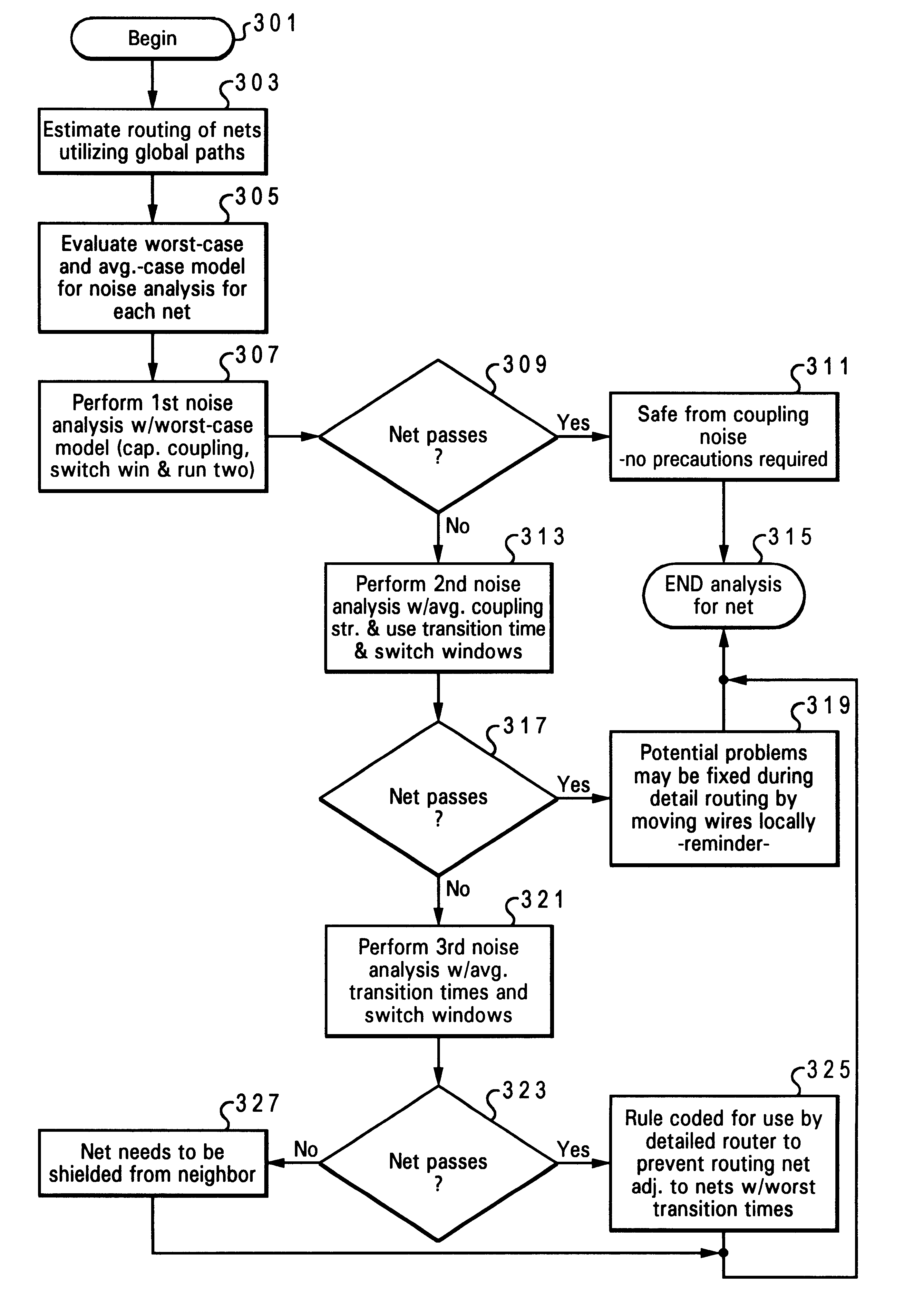
Coupled noise estimation and avoidance of noise-failure using global routing information
Disclosed is a method for pre-design estimation of coupling noise and avoidance of coupling noise failures in interconnects. An initial routing of a plurality of nets is estimated utilizing global paths. Then, the worst-case and average-case models for various parameters of each net are evaluated. With these models, a noise analysis is completed by which a determination is made whether coupling noise of any one of the nets is above a threshold level for noise-induced failure (i.e., a noise-failure threshold). When it is determined that the estimated coupling noise of a net falls below the noise-failure threshold, a response mechanism is triggered for later implementation during detailed routing of the nets to prevent the coupling noise from reaching the noise-failure threshold.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
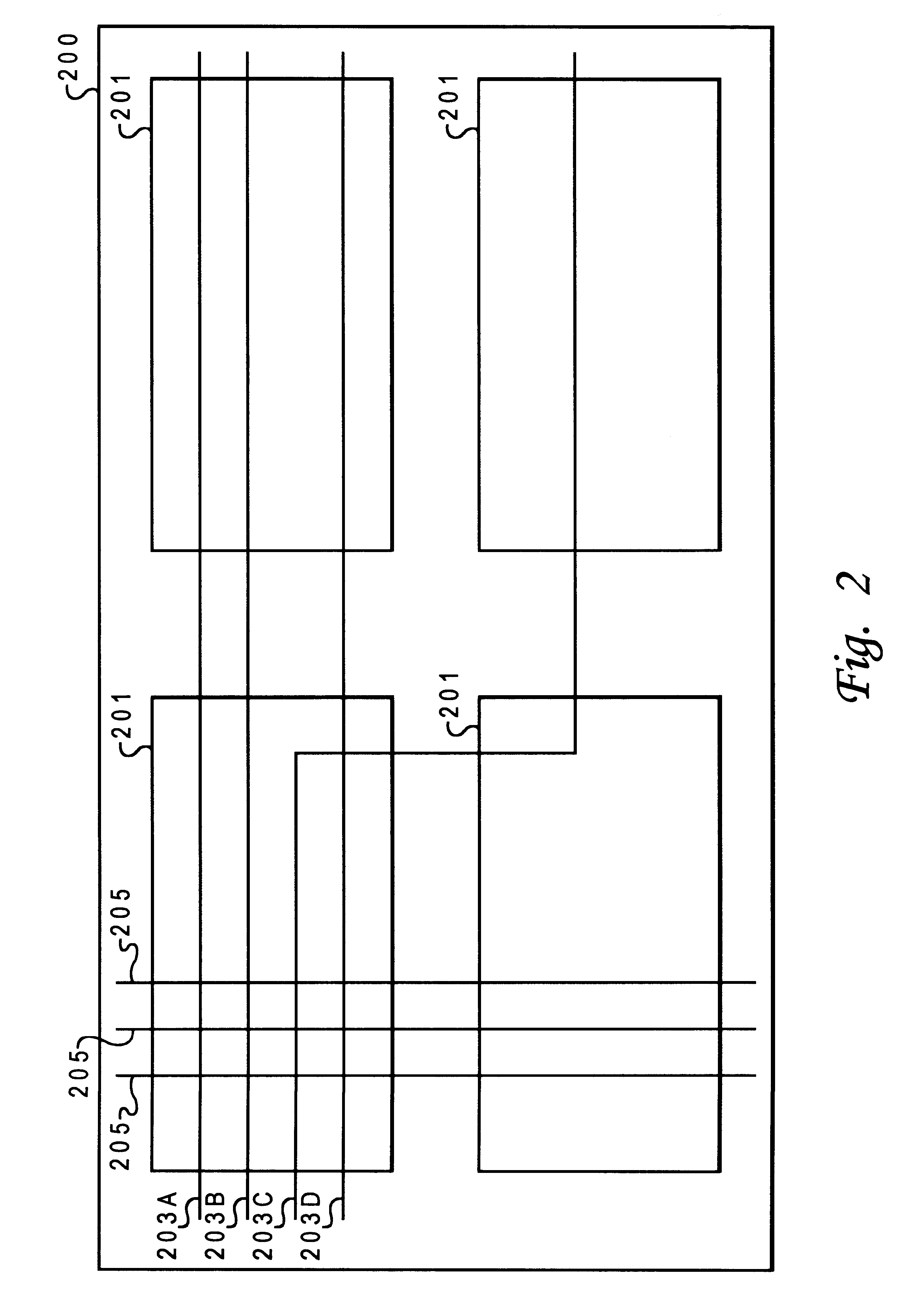
Coupled noise estimation method for on-chip interconnects
InactiveUS6029117AMeasuring interference from external sourcesComputer aided designCapacitanceEstimation methods
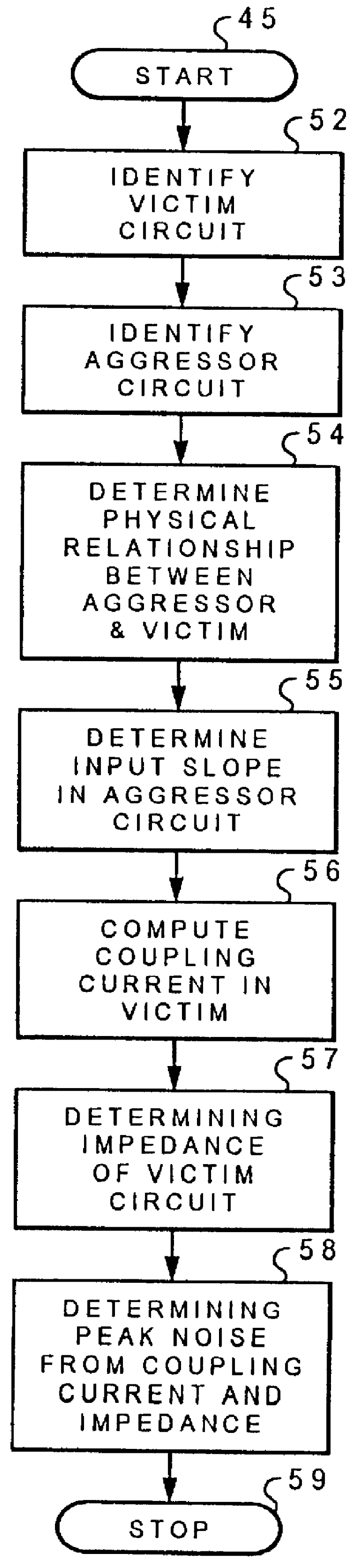
An efficient method for identifying potential noise failures in an integrated circuit design by predicting peak noise within a victim circuit of an integrated circuit. Initially, a victim circuit within an integrated circuit is located. An aggressor circuit within the integrated circuit is located which has a physical relationship with the victim circuit, normally proximity. The slope of a signal within the aggressor circuit is analyzed and the coupling currents induced in the victim circuit by the aggressor circuit are computed. The input slope of the aggressor circuit and the physical relationship between the victim circuit and the aggressor circuit are utilized to determine a peak current induced into the victim circuit utilizing modelled coupling capacitance. The peak current and the equivalent impedance of the victim circuit can be utilized to determine peak noise. Noise failures on integrated circuits can be avoided by detecting peak noise which is above acceptable levels.
Owner:IBM CORP
Shift register unit, gate drive circuit and display device
ActiveCN104078017ASimple structureLow costStatic indicating devicesDigital storageShift registerCapacitance
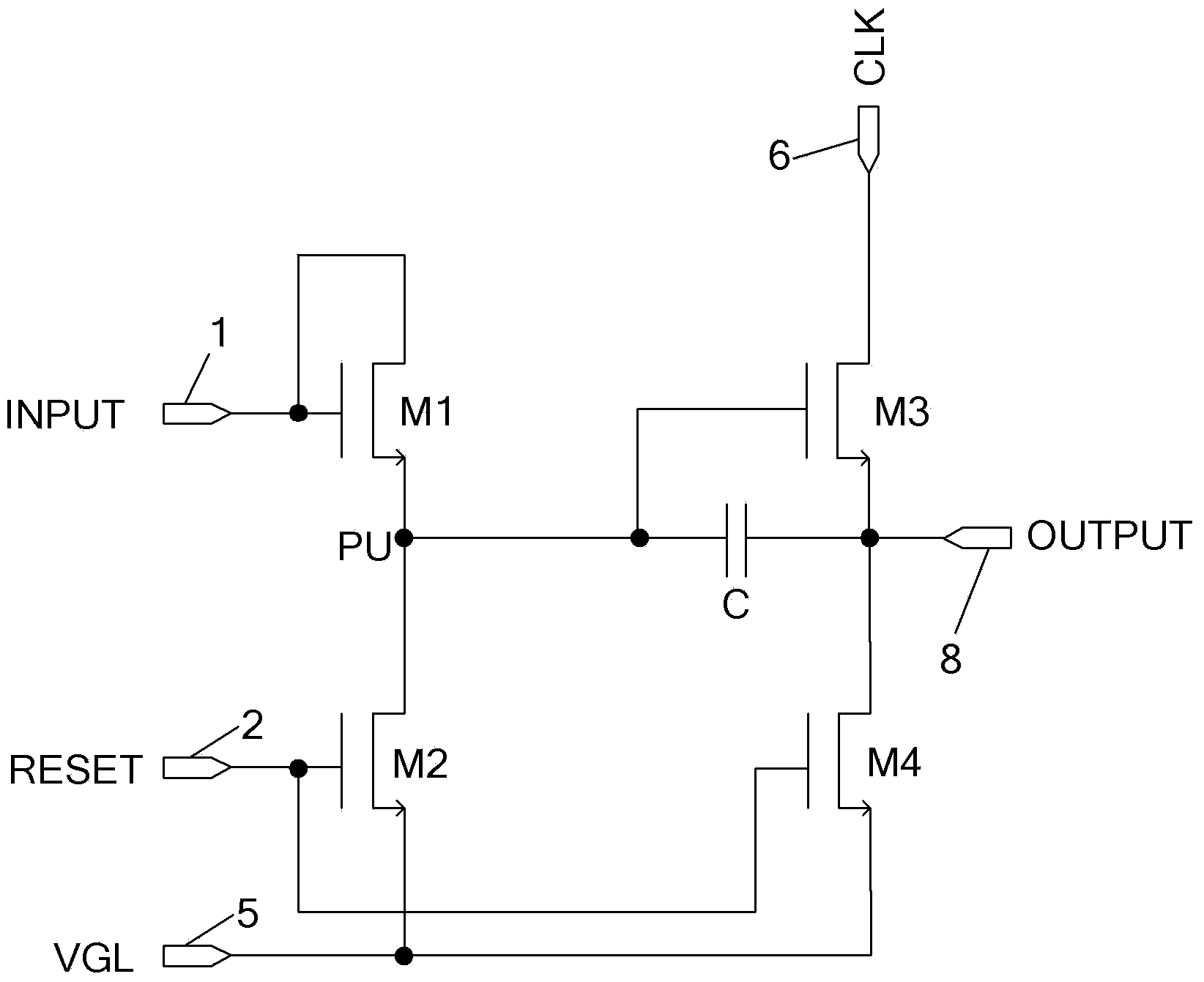
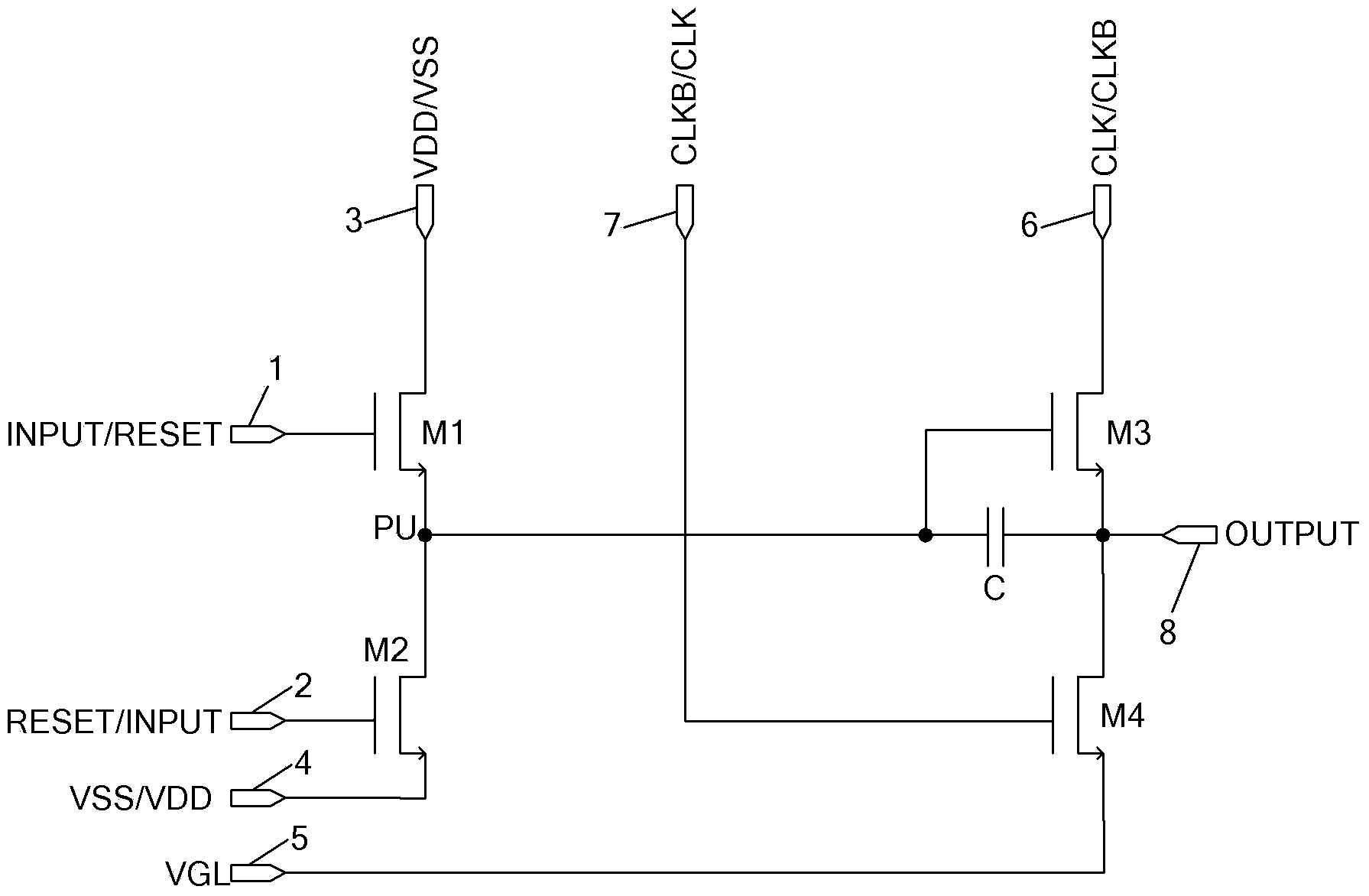
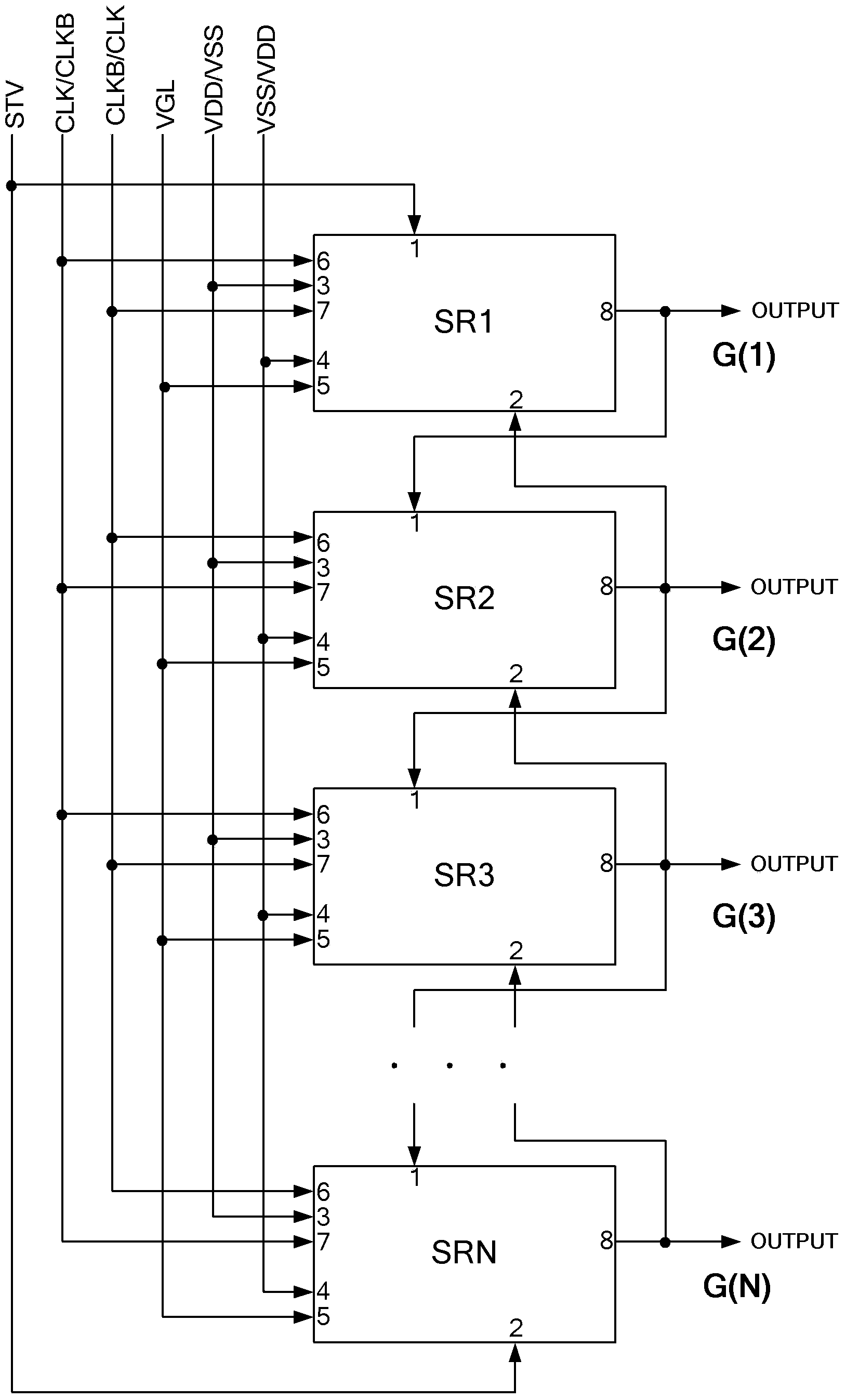
The invention discloses a bidirectional scanning gate drive circuit and a shift register unit of the bidirectional scanning gate drive circuit. The shift register unit comprises a first input end (1), a second input end (2), a first clock end (6) and an output end (8). A shift trigger signal and a reset signal are connected into the first input end (1) and the second input end (2) respectively. When forward shift and backward shift are switched, the signals connected into the first input end (1) and the second input end (2) are switched; a clock signal is connected into the first clock end (6), and the clock signal is used for providing drive level for the output end (8). The circuit of the shift register unit can be composed of at least four transistors and one capacitor. The circuit of the shift register unit is simple in structure, and the problem of coupled noise voltage caused by the clock signal can be solved.
Owner:HEFEI BOE OPTOELECTRONICS TECH +1
Display device including touch panel device, and coupling-noise eliminating method
InactiveUS20110057890A1Remove noiseEliminate couplingInput/output processes for data processingDisplay deviceTouchpad
A display device includes; a touch panel device including; a touch panel and a touch controller connected to the touch panel, the touch controller including; a sampling unit which samples a sensing output signal input thereto from the touch panel to generate a sampled signal, and an analog / digital converter which converts the sampled signal to generate contact information, and a display panel device including; a display panel, a gate driver which applies a gate signal to the display panel, and a data driver which applies a data voltage to the display panel, wherein the sampling unit samples a portion of the sensing output signal which does not include a coupling noise.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
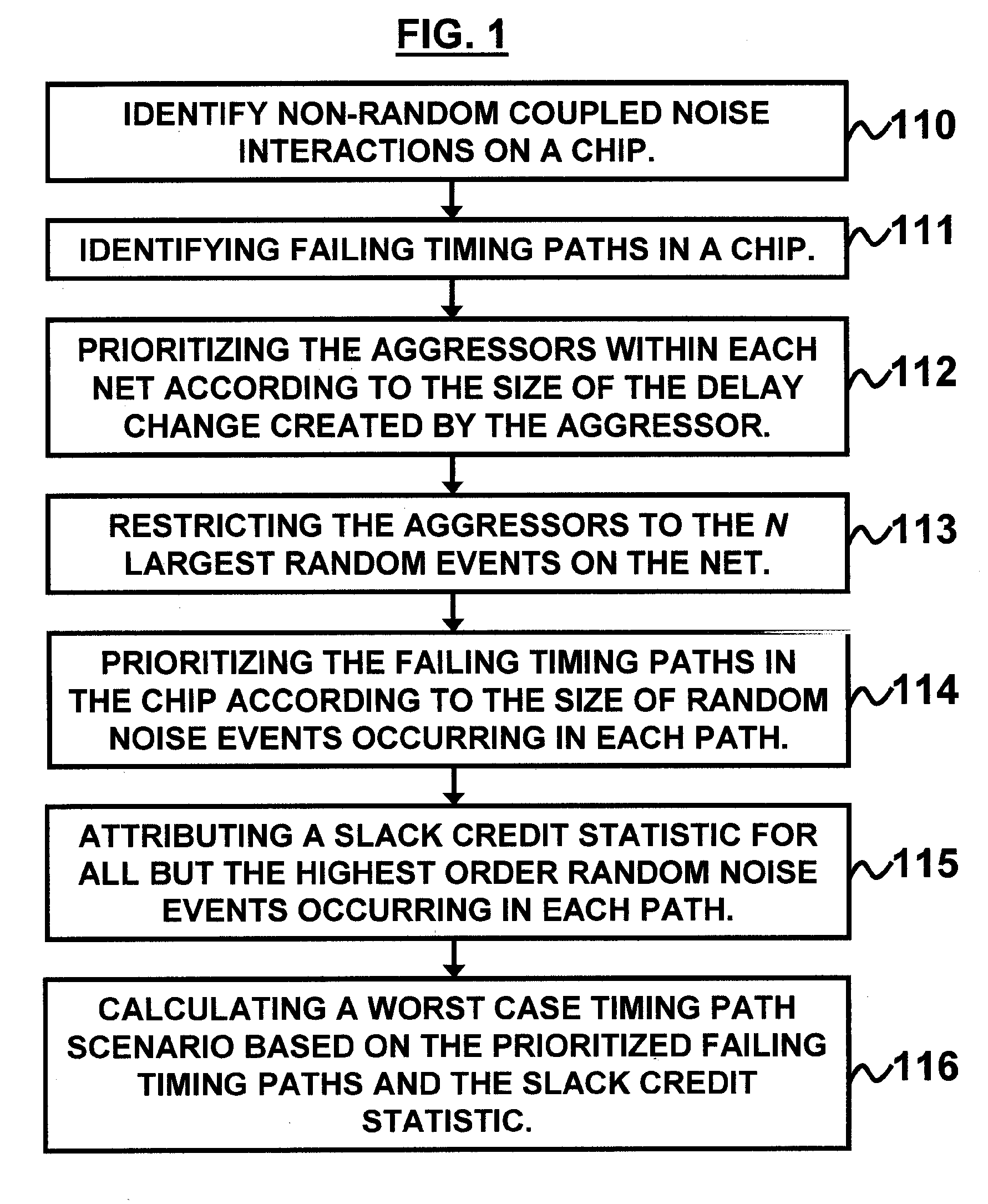
Priortizing of nets for coupled noise analysis
InactiveUS20060248485A1Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationRandom noiseComputer science
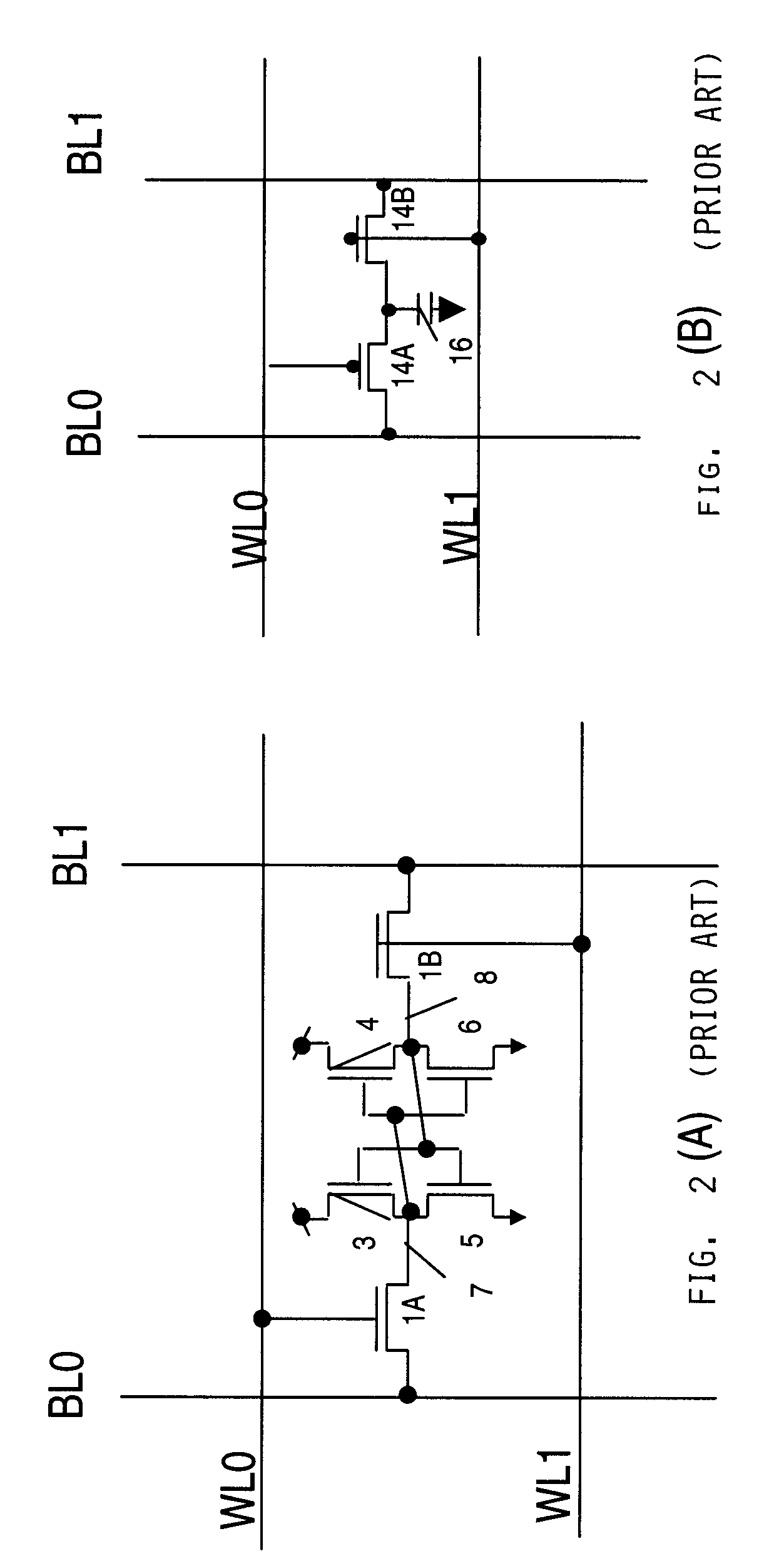
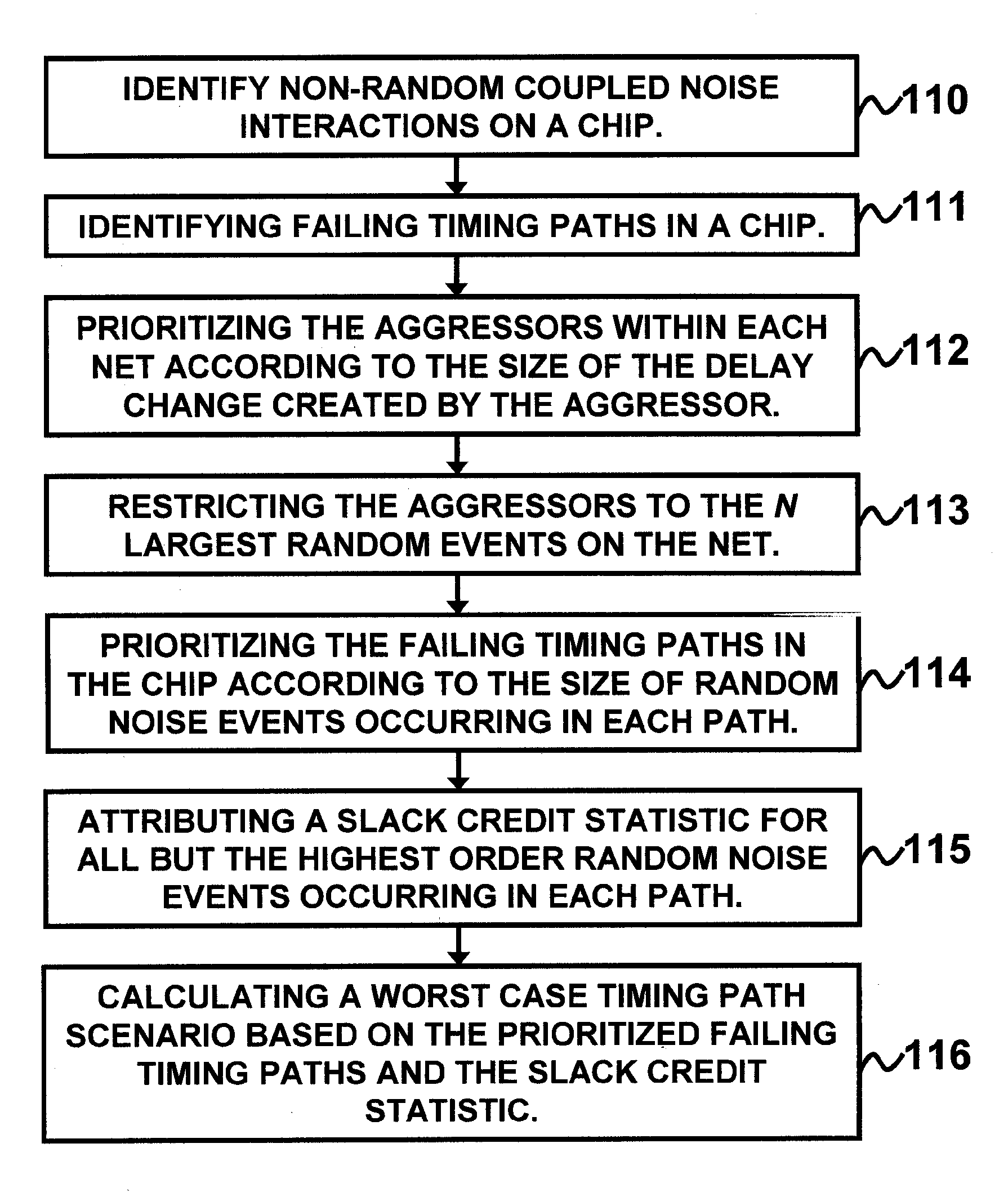
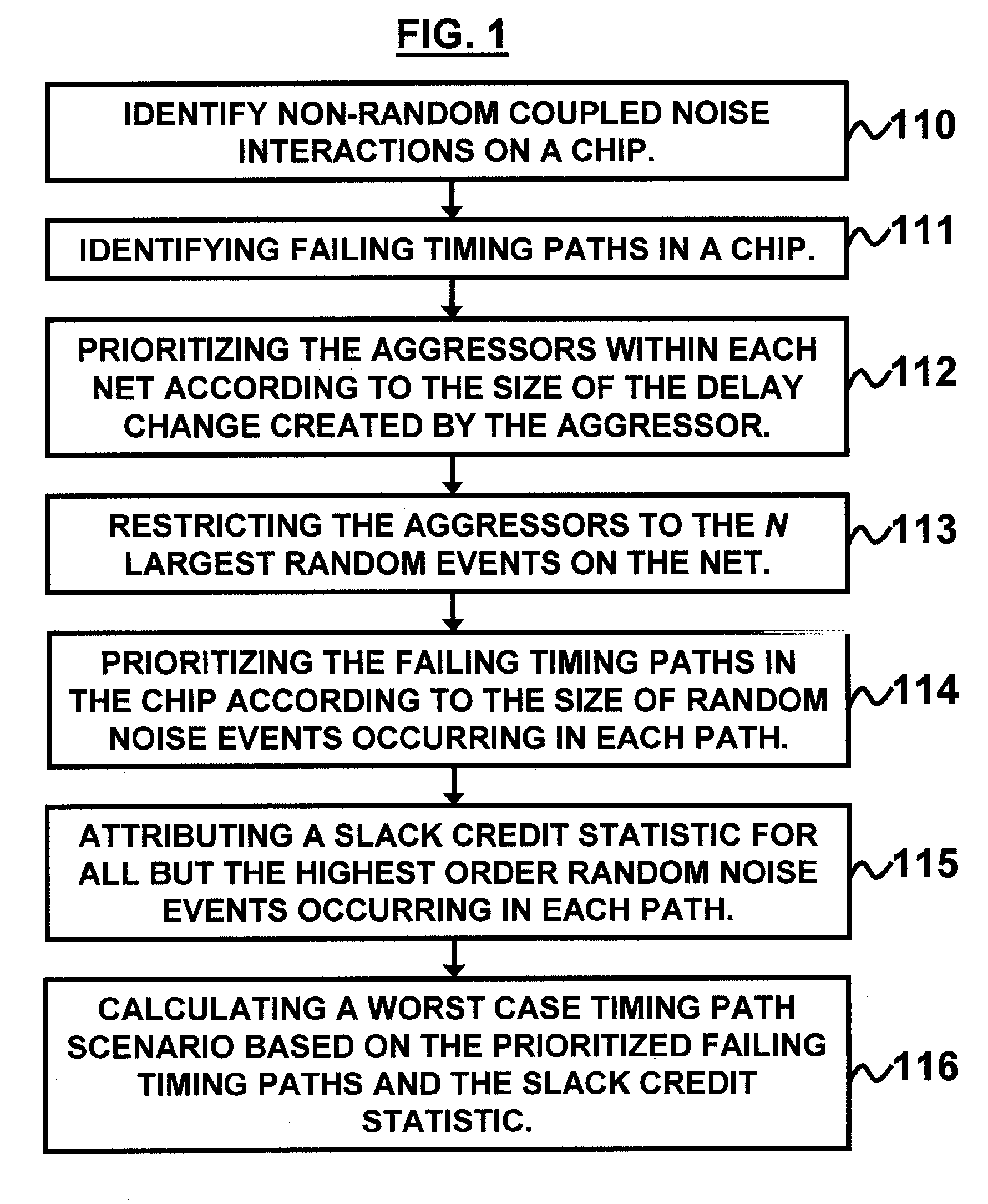
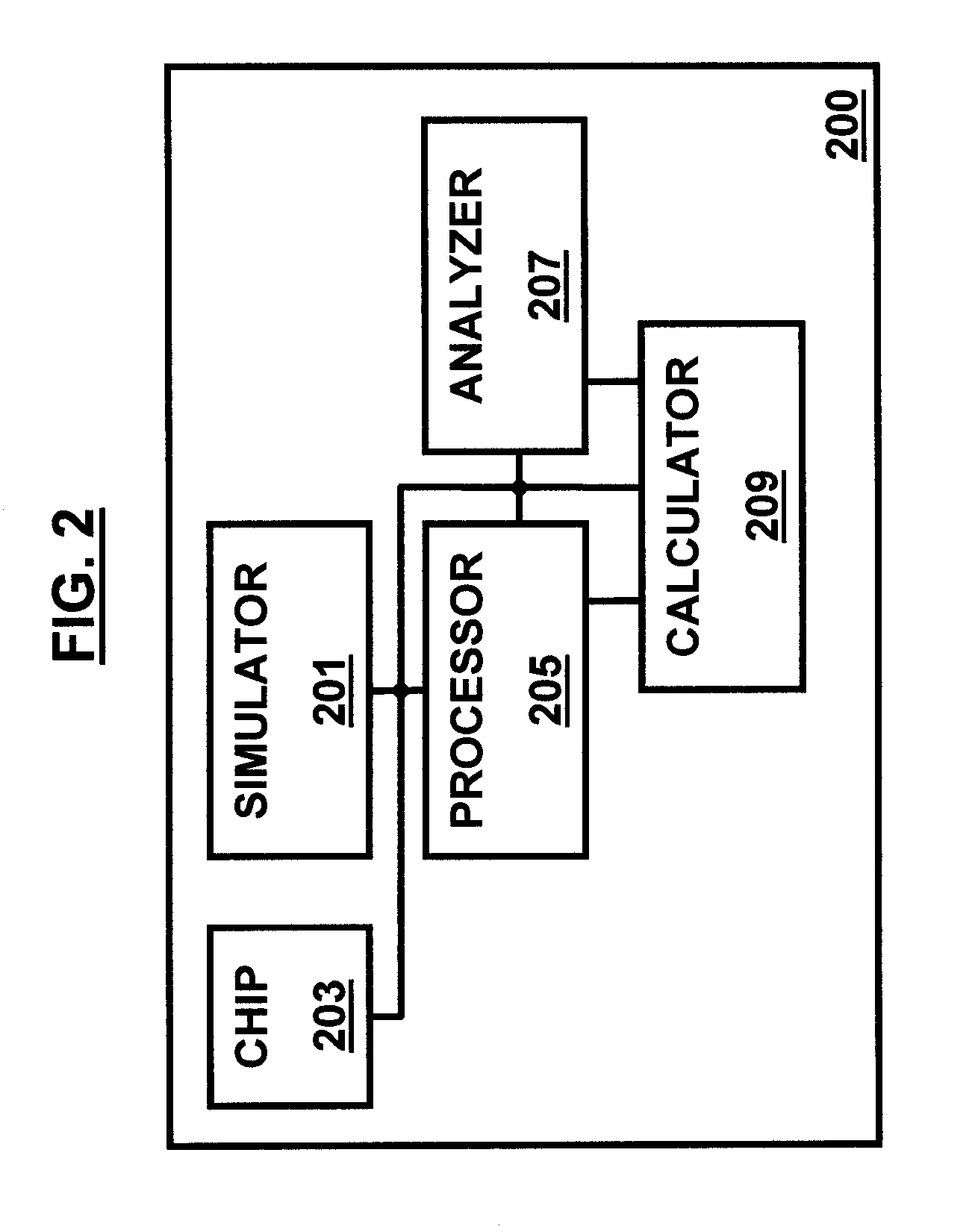
A system and method of performing microelectronic chip timing analysis, wherein the method comprises identifying failing timing paths in a chip; prioritizing the failing timing paths in the chip according to a size of random noise events occurring in each timing path; attributing a slack credit statistic for all but highest order random noise events occurring in each timing path; and calculating a worst case timing path scenario based on the prioritized failing timing paths and the slack credit statistic. Preferably, the random noise events comprise non-clock events. Moreover, the random noise events may comprise victim / aggressor net groups belonging to different regularity groups. Preferably, the size of random noise events comprises coupled noise delta delays due to the random noise events occurring in the chip.
Owner:IBM CORP
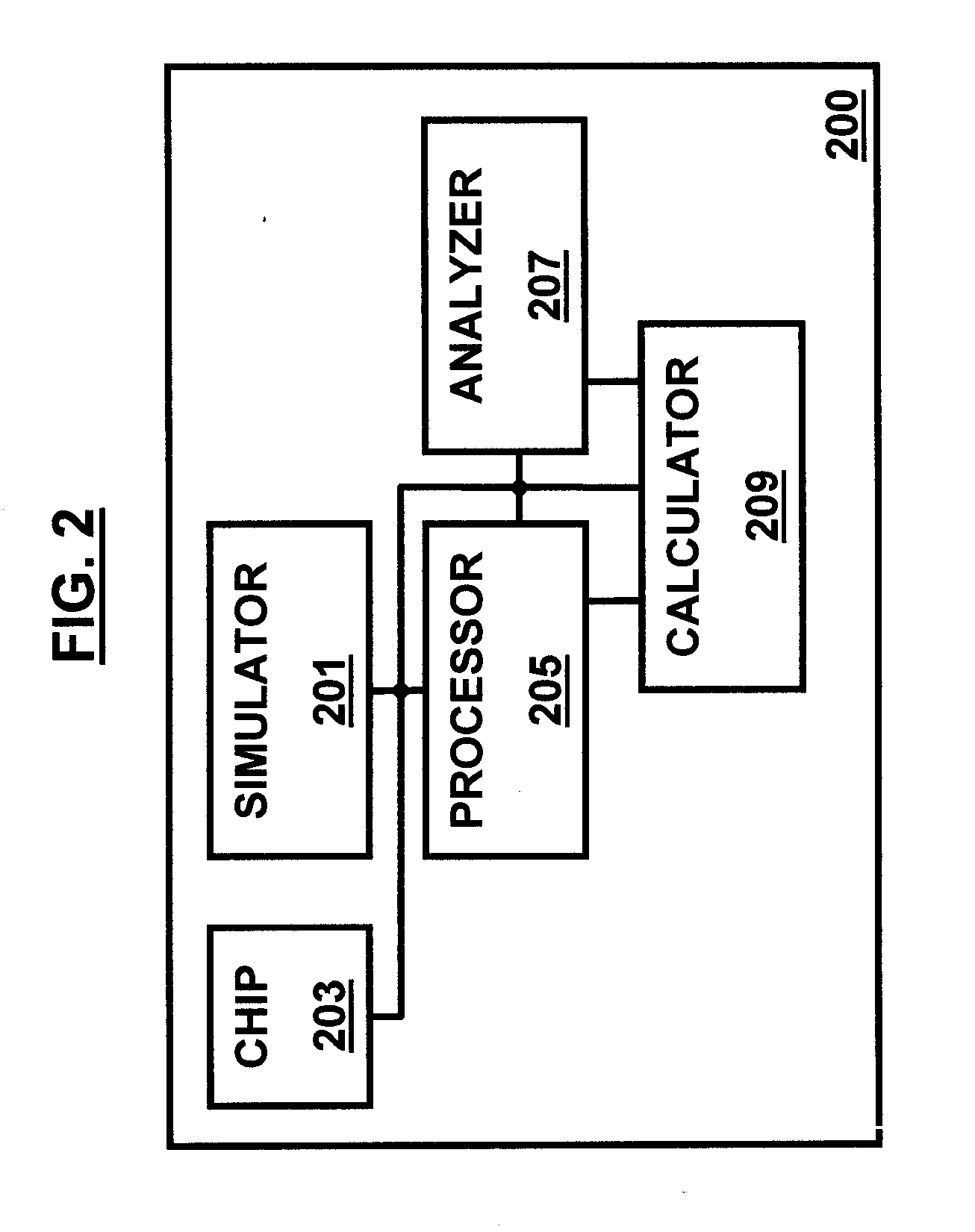
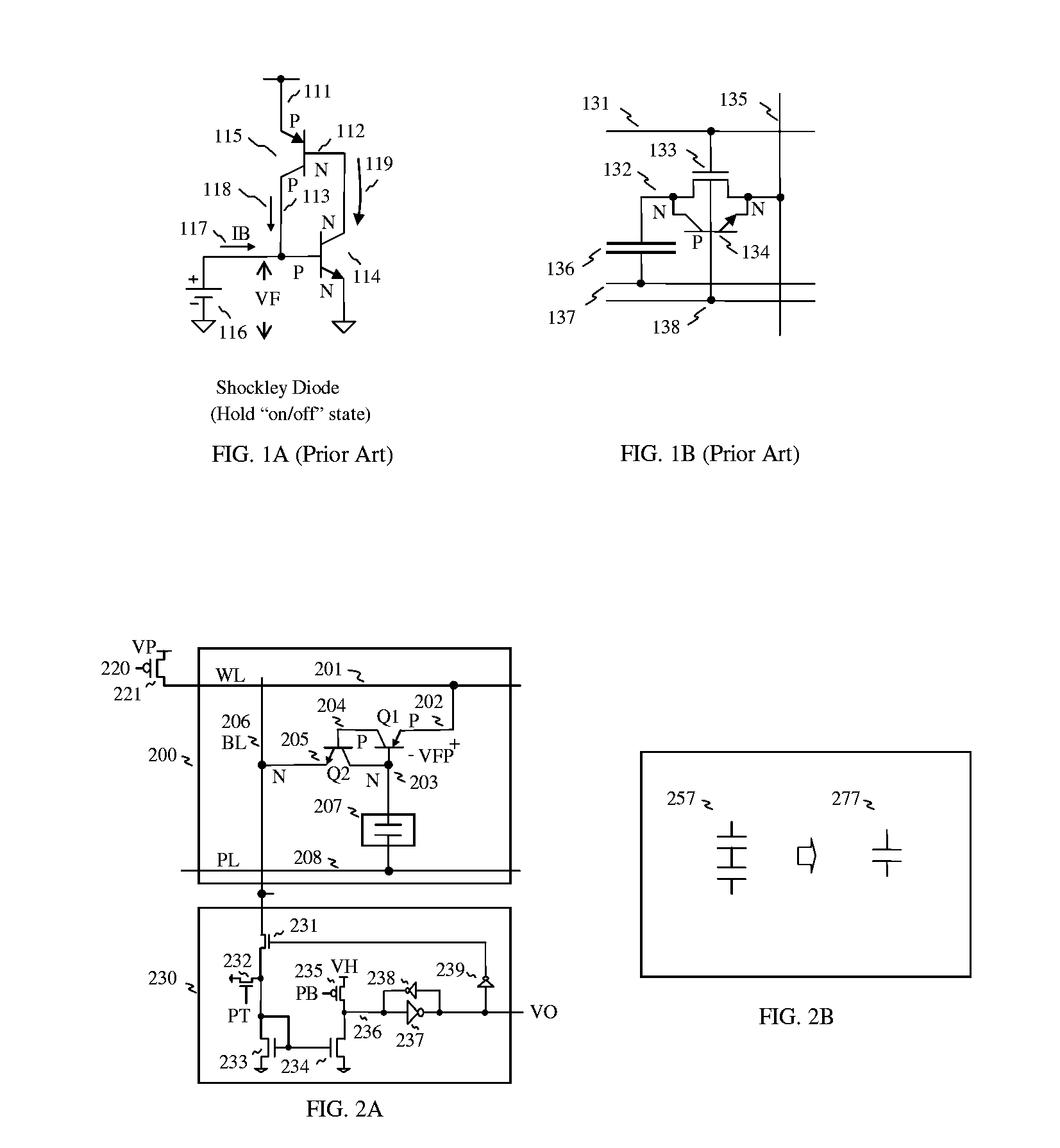
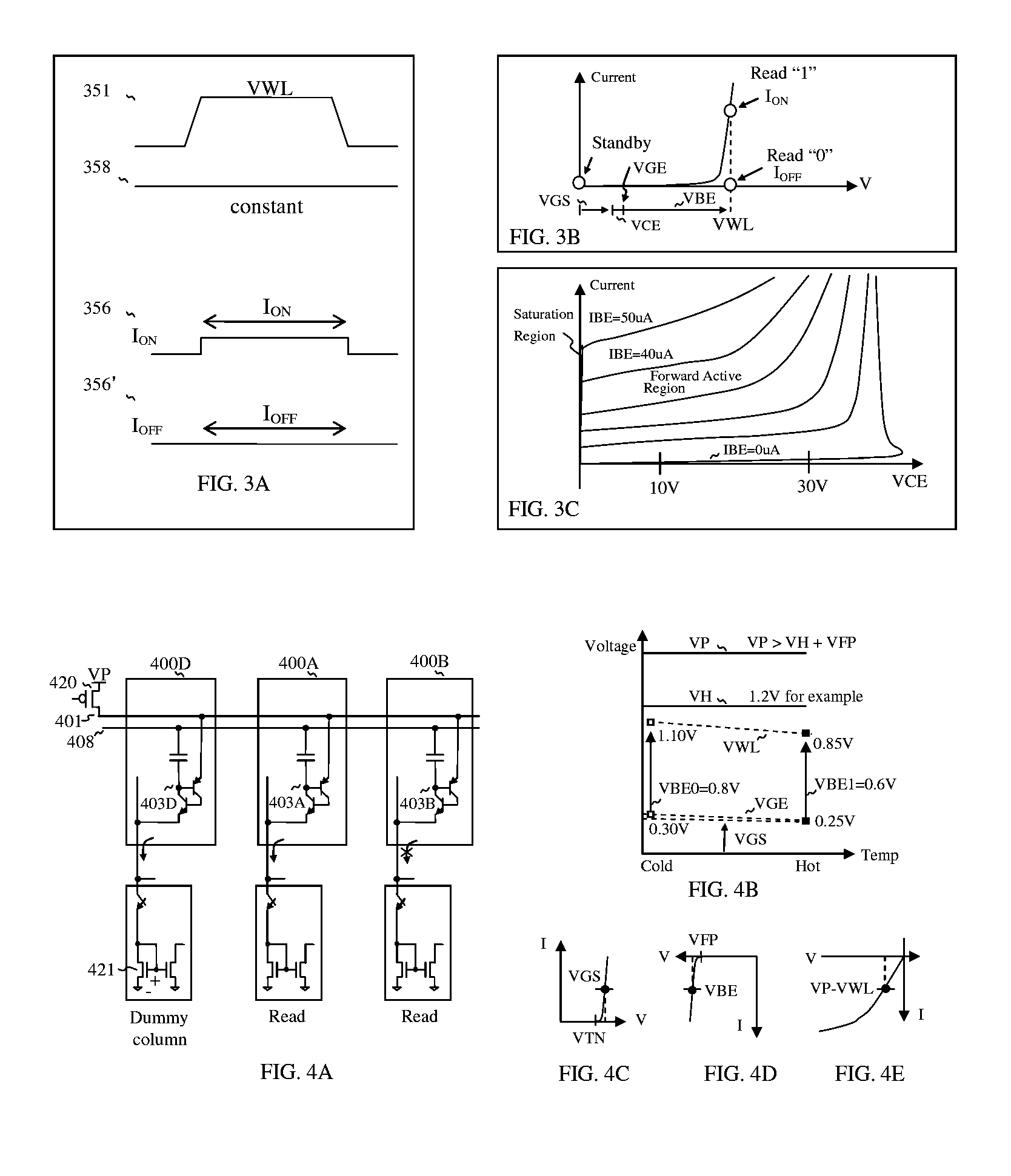
Stacked capacitor memory
InactiveUS20070183191A1Reduce chip areaLess complicated to fabricateSolid-state devicesDiodeEngineeringMulti port
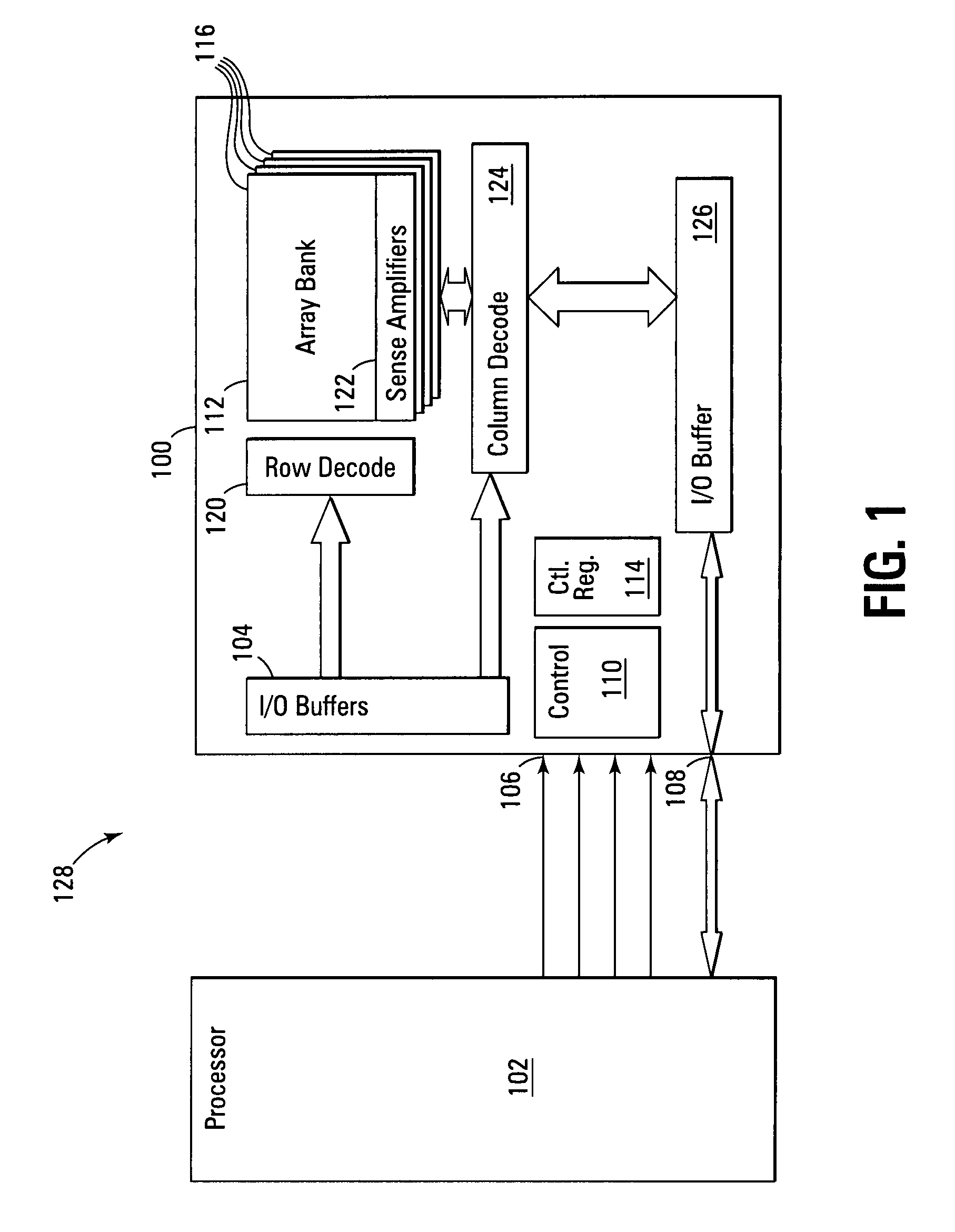
Stacked capacitor memory is realized, wherein a capacitor stores data and a diode serves as an access device instead of MOS transistor, the first terminal is connected to a word line, the second terminal is connected to the first electrode of the capacitor which serves as a storage node while the second electrode is connected to a plate line, the third terminal is floating, and the fourth terminal is connected to a bit line. When write, the storage node is charged or not, depending on the conducting state of the diode which is controlled by the bit line. When read, the diode also serves as a sense amplifier to detect whether the storage node is forward bias or not, and it sends binary data to a latch device wherein includes a current mirror and a feedback loop which cuts off the current path after latching, thus it reduces active current, minimizes data pattern sensitivity, and also rejects coupling noise. And dummy rows and columns generate replica delay signals which guarantee timing margin and reduce cycle time. And its applications are extended to single port, multi port and content addressable memory. In addition, the memory cells are formed in between the routing layers, which memory cells can be stacked over the transistor or another capacitor memory cell.
Owner:KIM JUHAN
Integrated circuit
InactiveUS6982477B2Decrease electromagnetic coupling noise noiseReduce noiseTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectromagnetic couplingLine width
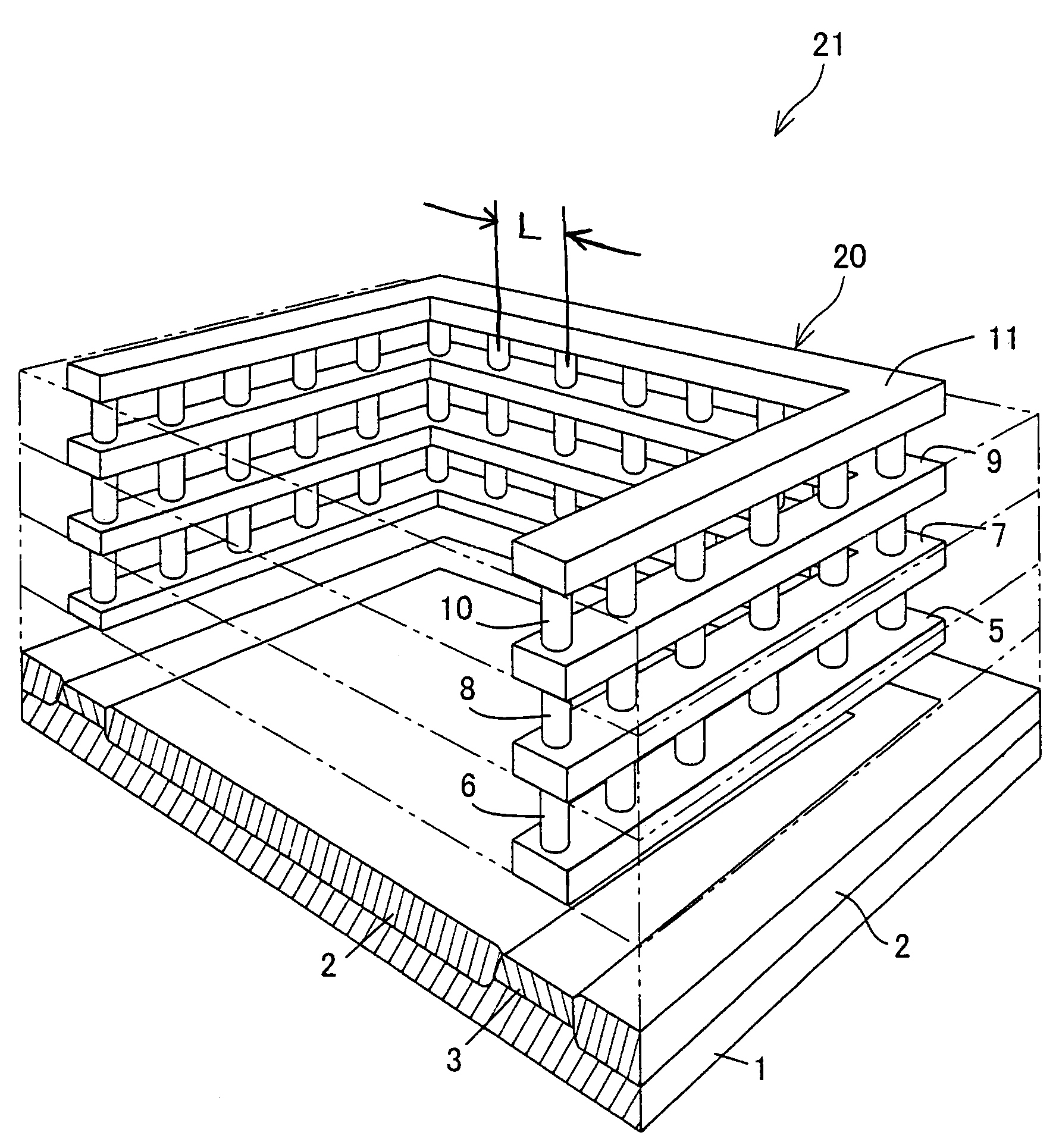
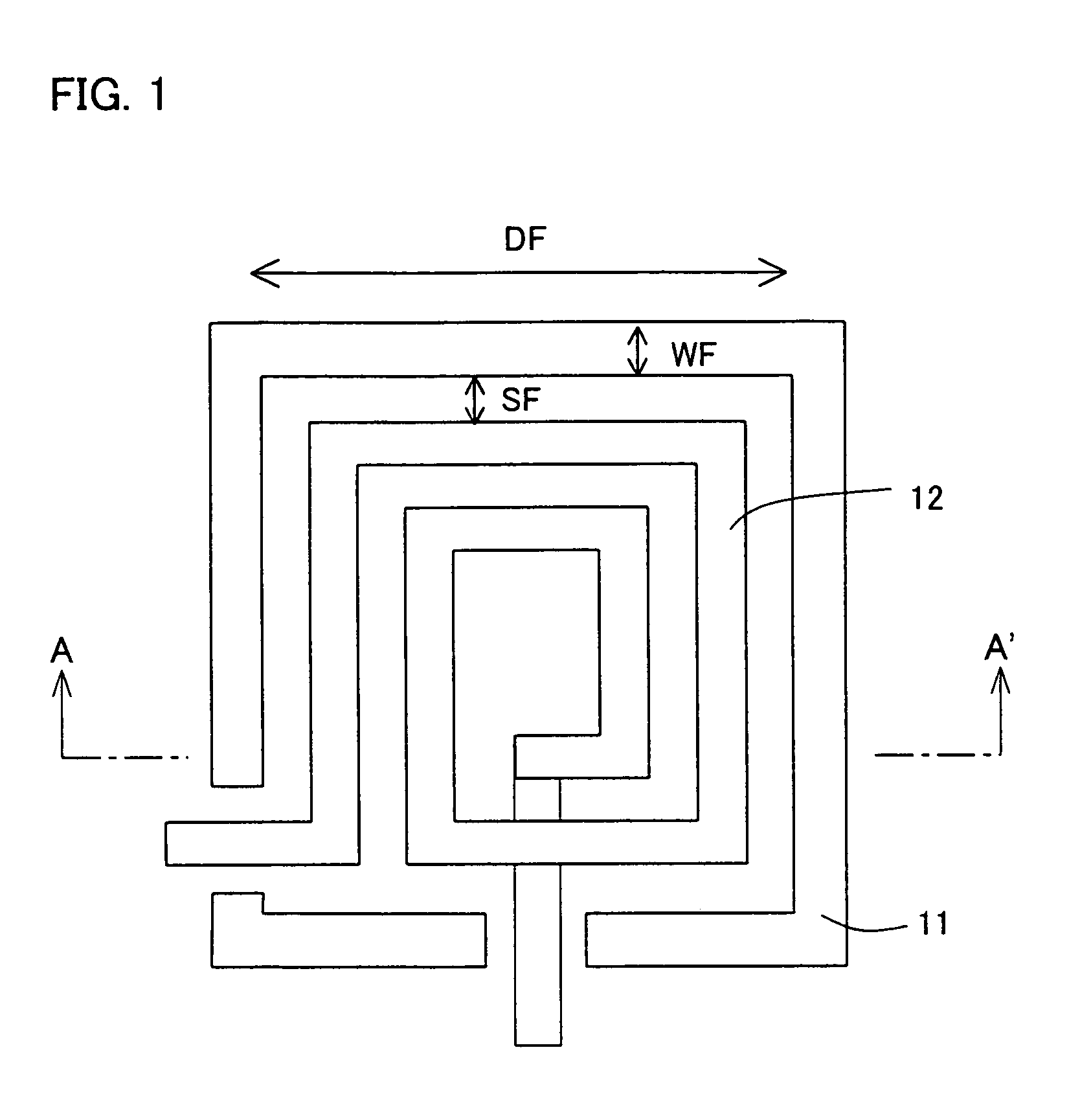
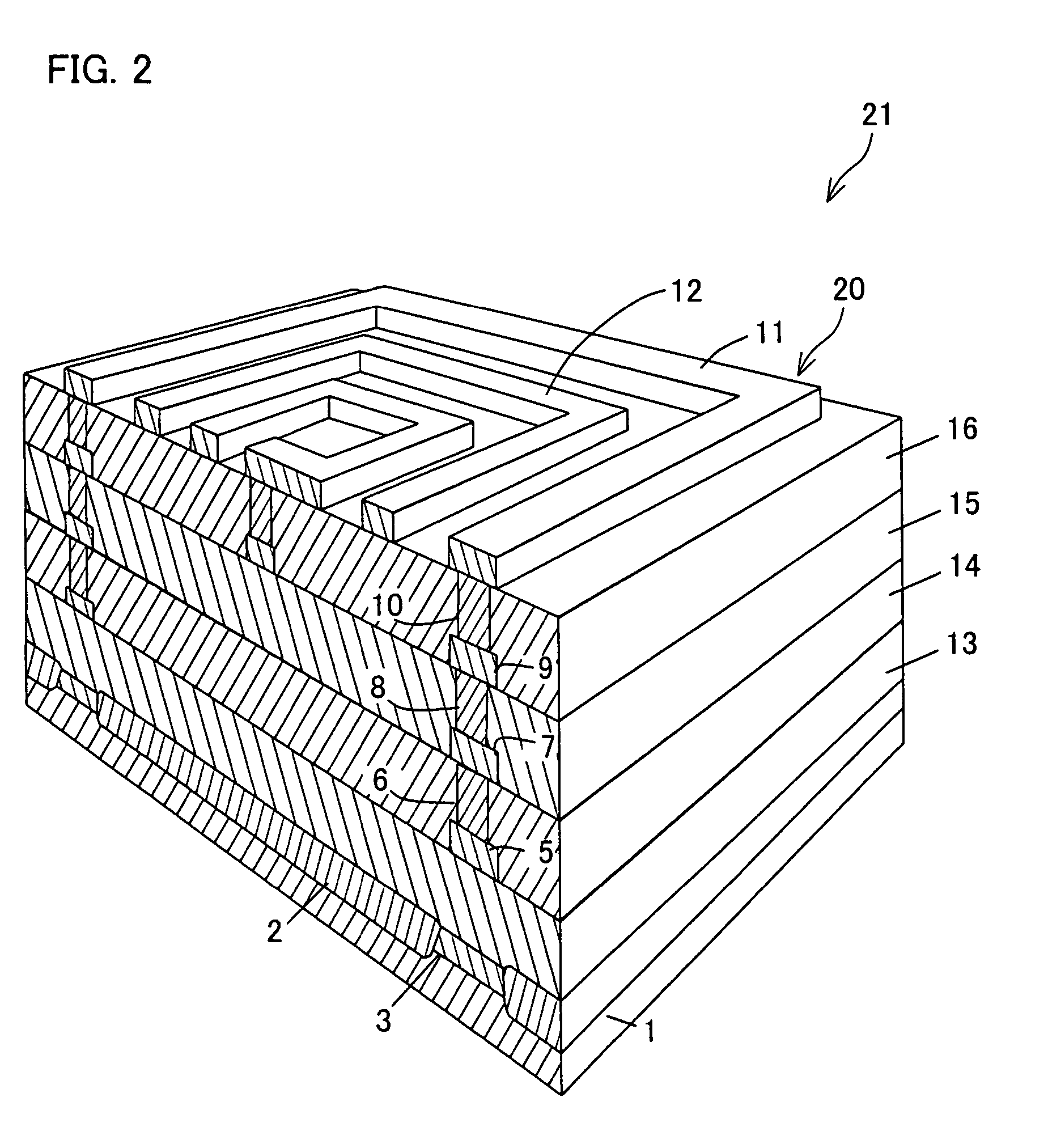
A lamination of metal wire layers forms an electromagnetic isolation structure. The metal wire layers are connected with each other by vias, so that a metal fence having a laminated structure is formed. The metal fence is provided so as to surround an element (e.g. a spiral inductor) that generates an electromagnetic field in an integrated circuit. The metal wire satisfies d≦λ / 8, WF≧5δ, and L≦λ / 20, where δ is a skin depth of an electromagnetic wave, c is a velocity of light, f is an operating frequency of the integrated circuit, d is a lateral-direction size of a metal-fence region, WF is a surrounding-line width of the metal fence, L is an interval between the vias, and λ=c / f is a wavelength of a signal. With this arrangement, it is possible to decrease electromagnetic coupling noises and coupling noises caused via the substrate.
Owner:SHARP KK
Electronic device with noise-cancelling force sensor
An electronic device may have a housing in which components such as a display are mounted. A strain gauge may be mounted on a layer of the display such as a cover layer or may be mounted on a portion of the housing or other support structure. The layer of material on which the strain gauge is mounted may be configured to flex in response to pressure applied by a finger of a user. The strain gauge may serve as a button for the electronic device or may form part of other input circuitry. A differential amplifier and analog-to-digital converter circuit may be used to gather and process strain gauge signals. The strain gauge may be formed form variable resistor structures that make up part of a bridge circuit that is coupled to the differential amplifier. The bridge circuit may be configured to reduce the impact of capacitively coupled noise.
Owner:APPLE INC
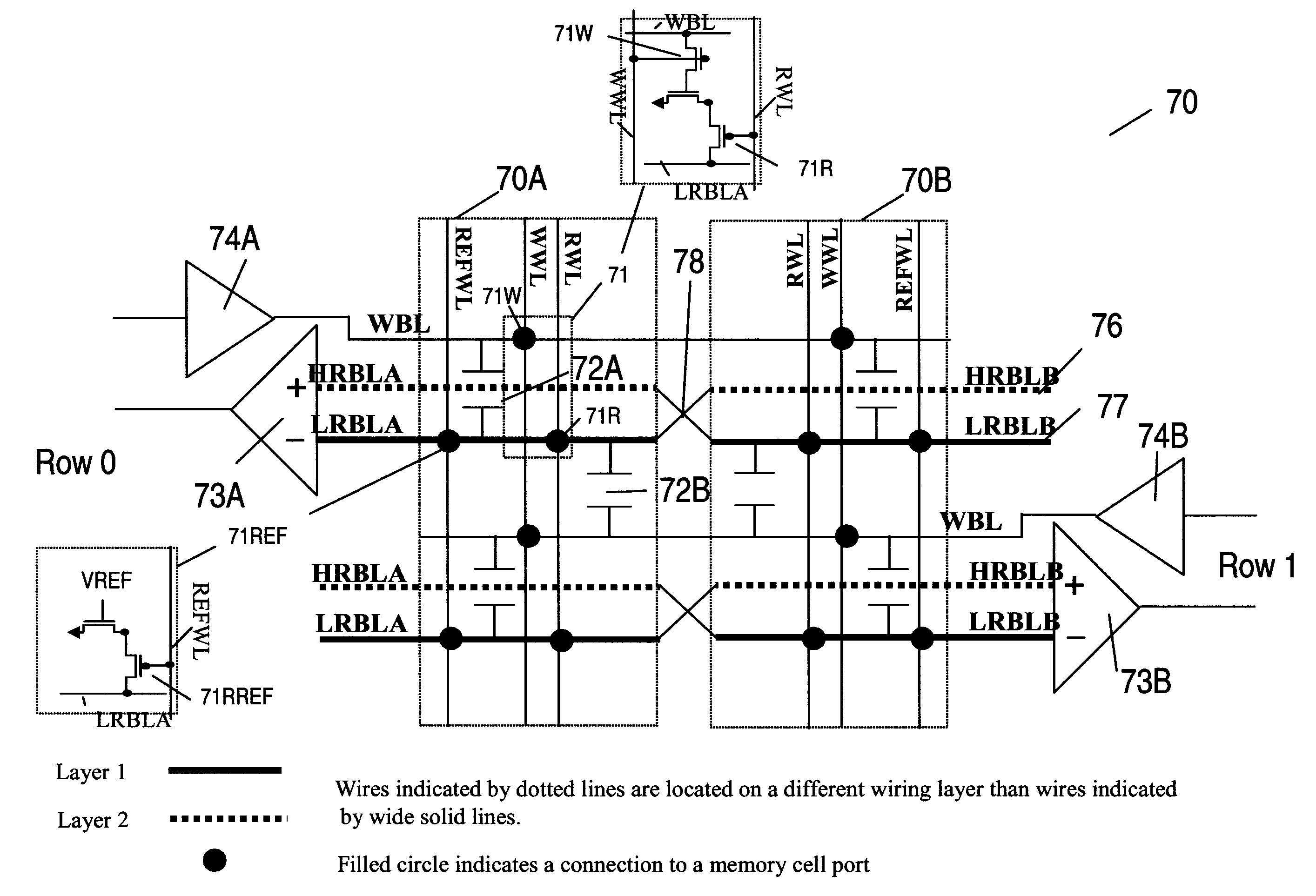
Multi-port memory architecture
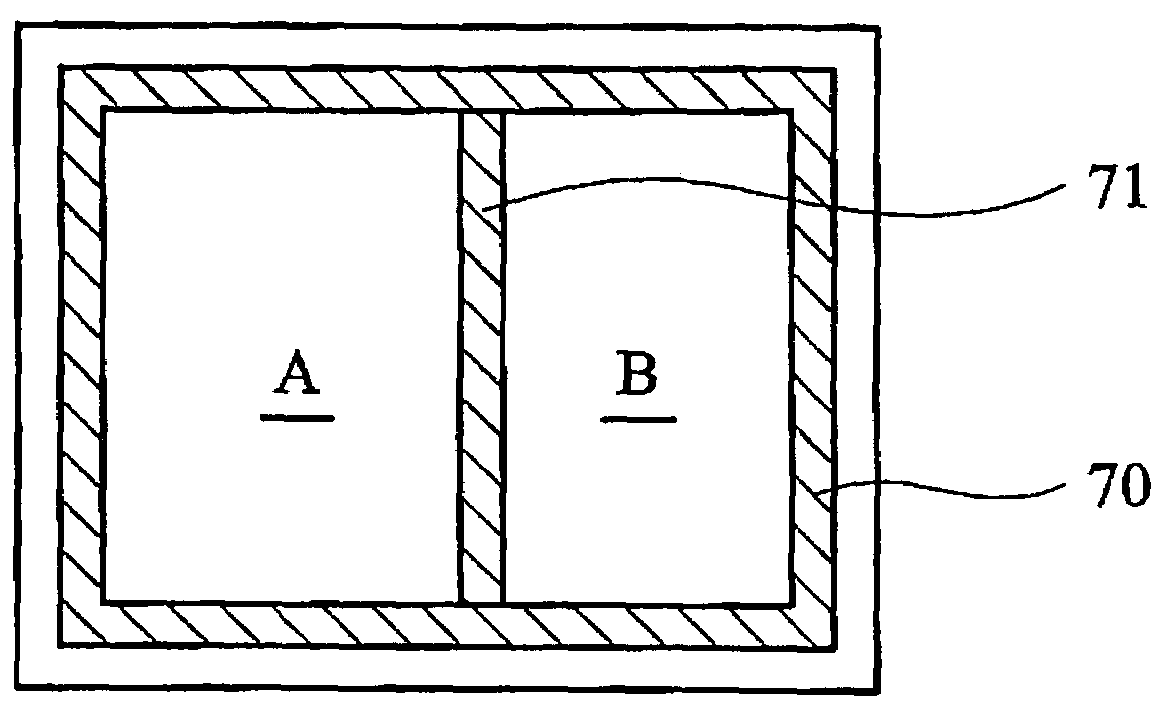
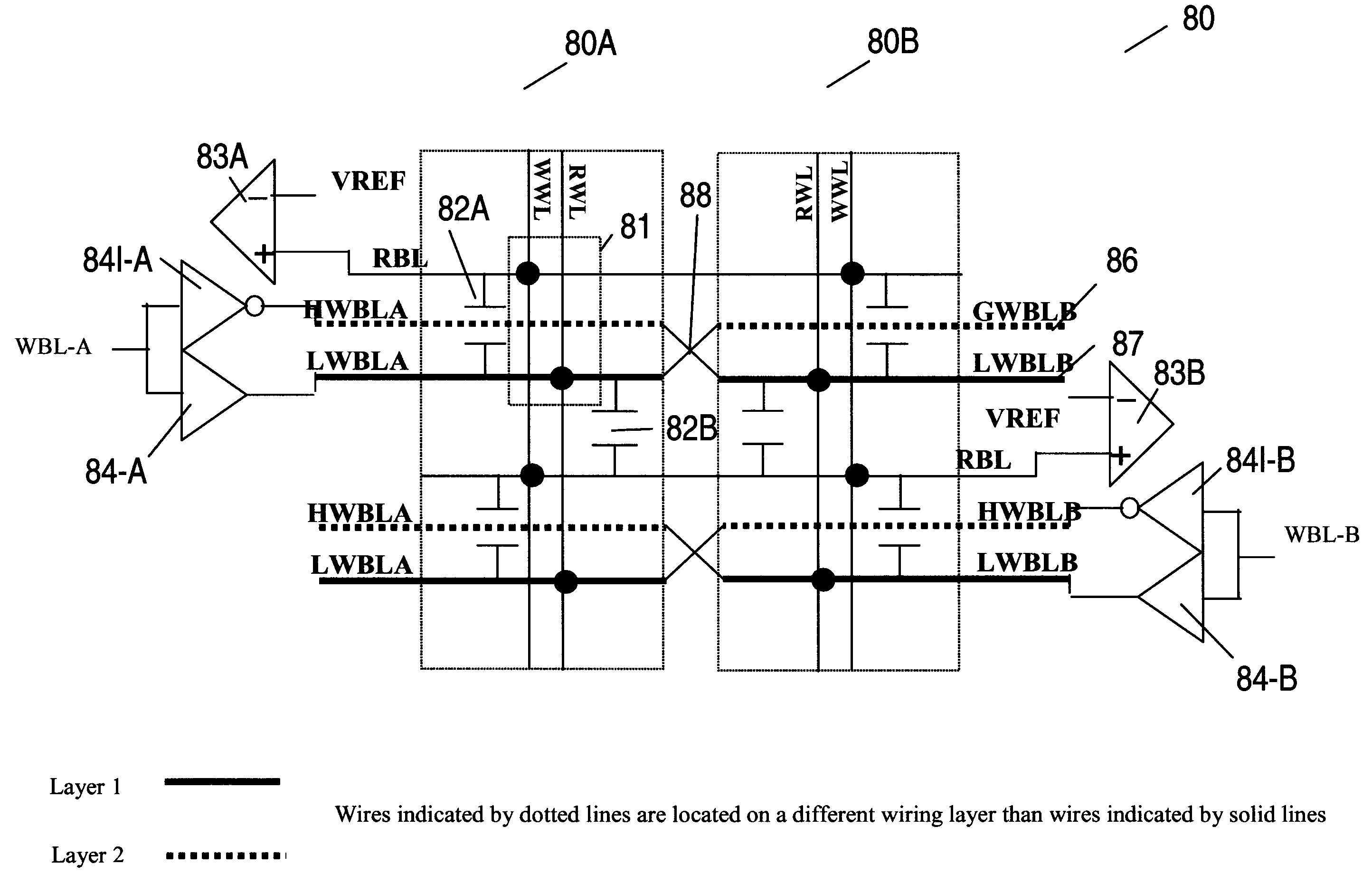
A multi-port memory architecture utilizing an open bitline configuration for the read bitline is described. The memory is sub-divided into two arrays (A and B) consisting of memory gain cells arranged in a matrix formation, the cells having two general ports or separate read and write ports to enable simultaneous a read and write operation. Each memory array includes a reference wordline coupled to reference cells. When the reference cell is accessed, the read bitline (RBL) discharges to a level at half the value taken by a cell storing a 0 or 1. Each pair of RBLB in the same column of the two arrays is coupled to a differential sense amplifier, and each write bitline (WBL) in the two arrays is linked to write drivers WBLs in the two arrays are driven to the same voltage and at the same slew rate. The WBL swing in each array creates coupling noise by the bitline-to-bitline capacitors. For a given sense amplifier and its associated RBLs, the coupling creates an identical coupling noise on RBLA and RBLB that are positioned in the two arrays A and B. This common mode noise is rejected by the differential sense amplifier. Thus, a read sense amplifier can accurately discriminate between the signal by activating the cell by way of RWL, and the reference cell by way of REFWL.
Owner:TWITTER INC
Prioritizing of nets for coupled noise analysis
InactiveUS7181711B2Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationRandom noiseComputer science
A system and method of performing microelectronic chip timing analysis, wherein the method comprises identifying failing timing paths in a chip; prioritizing the failing timing paths in the chip according to a size of random noise events occurring in each timing path; attributing a slack credit statistic for all but highest order random noise events occurring in each timing path; and calculating a worst case timing path scenario based on the prioritized failing timing paths and the slack credit statistic. Preferably, the random noise events comprise non-clock events. Moreover, the random noise events may comprise victim / aggressor net groups belonging to different regularity groups. Preferably, the size of random noise events comprises coupled noise delta delays due to the random noise events occurring in the chip.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
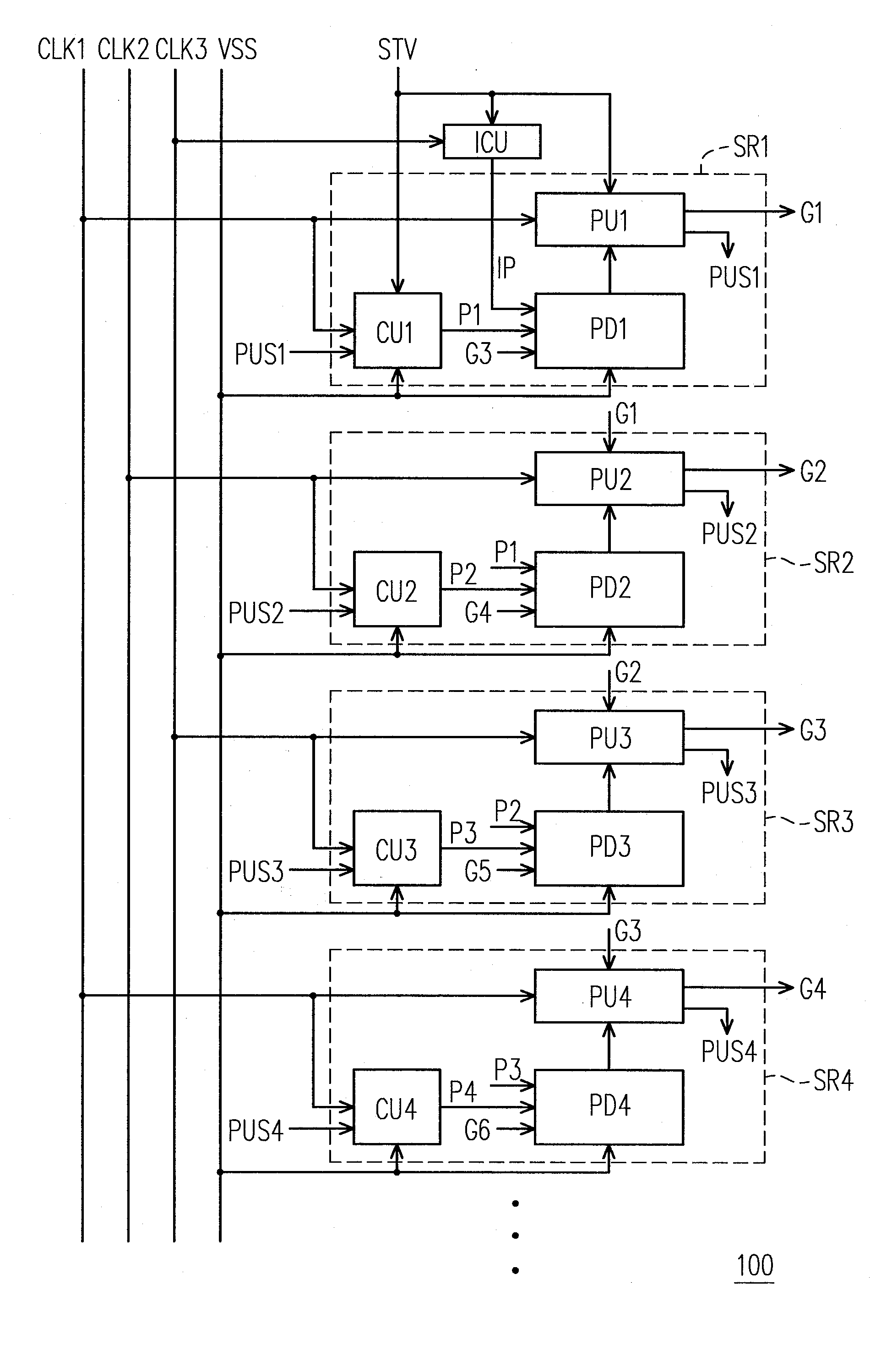
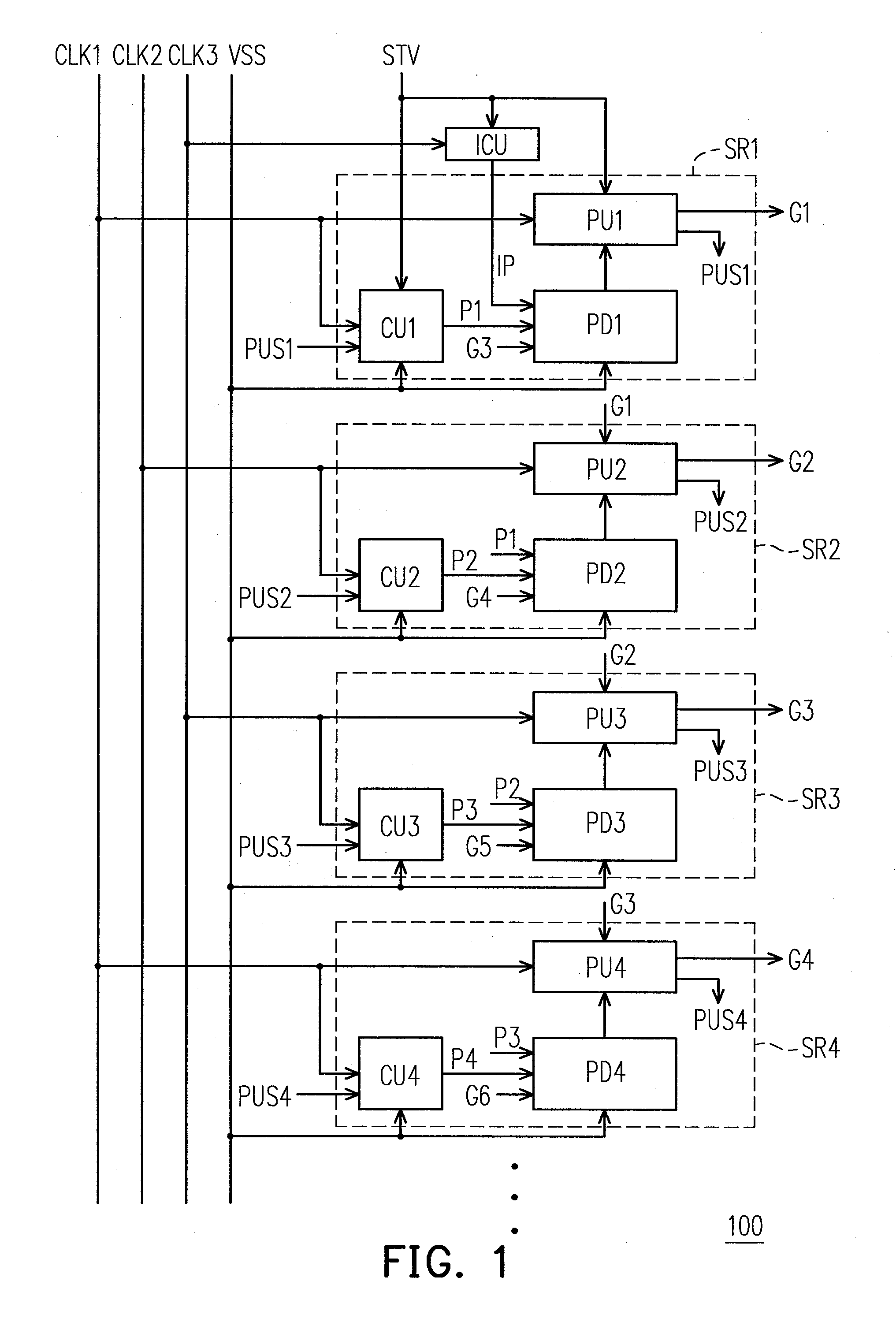
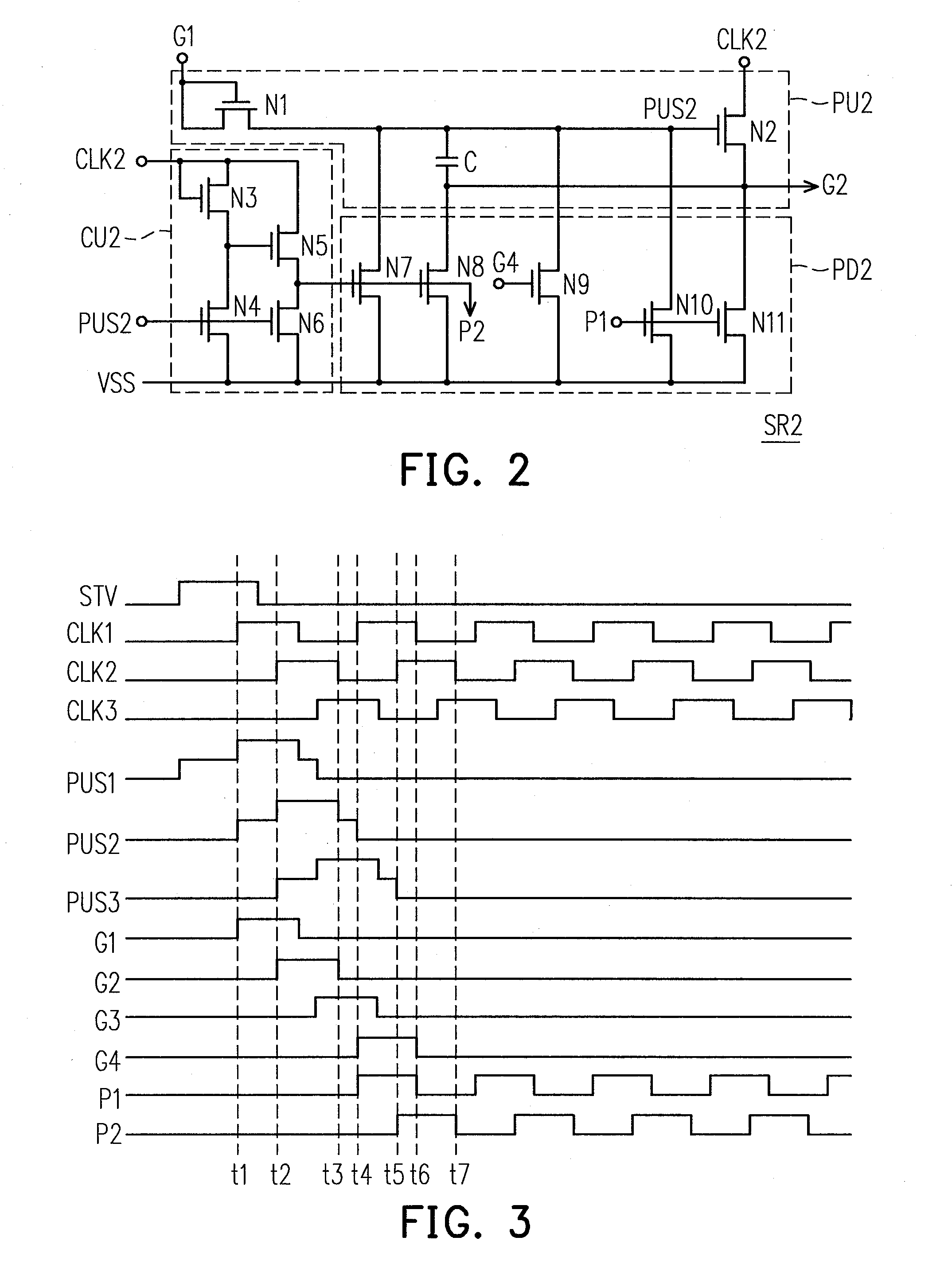
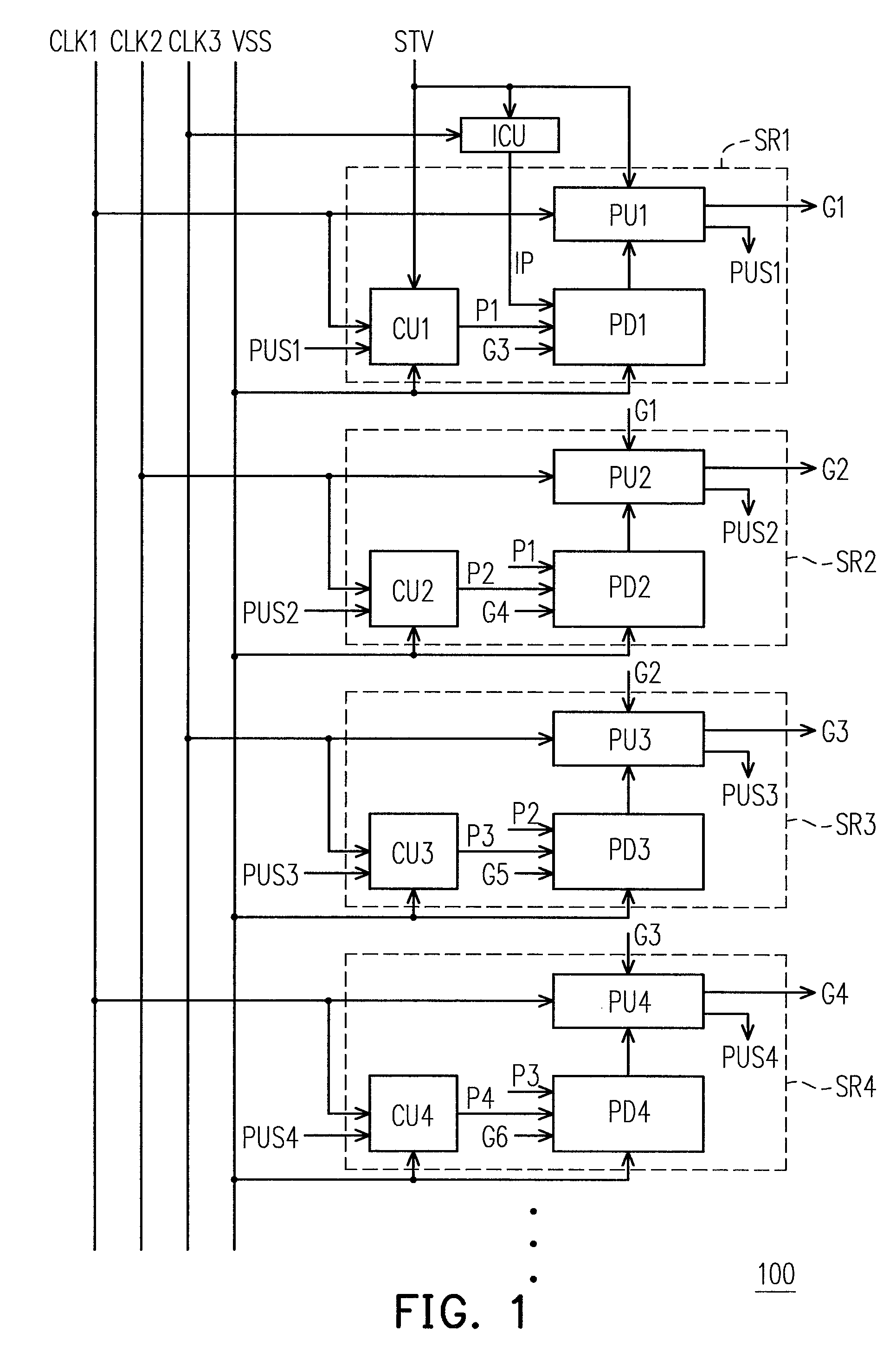
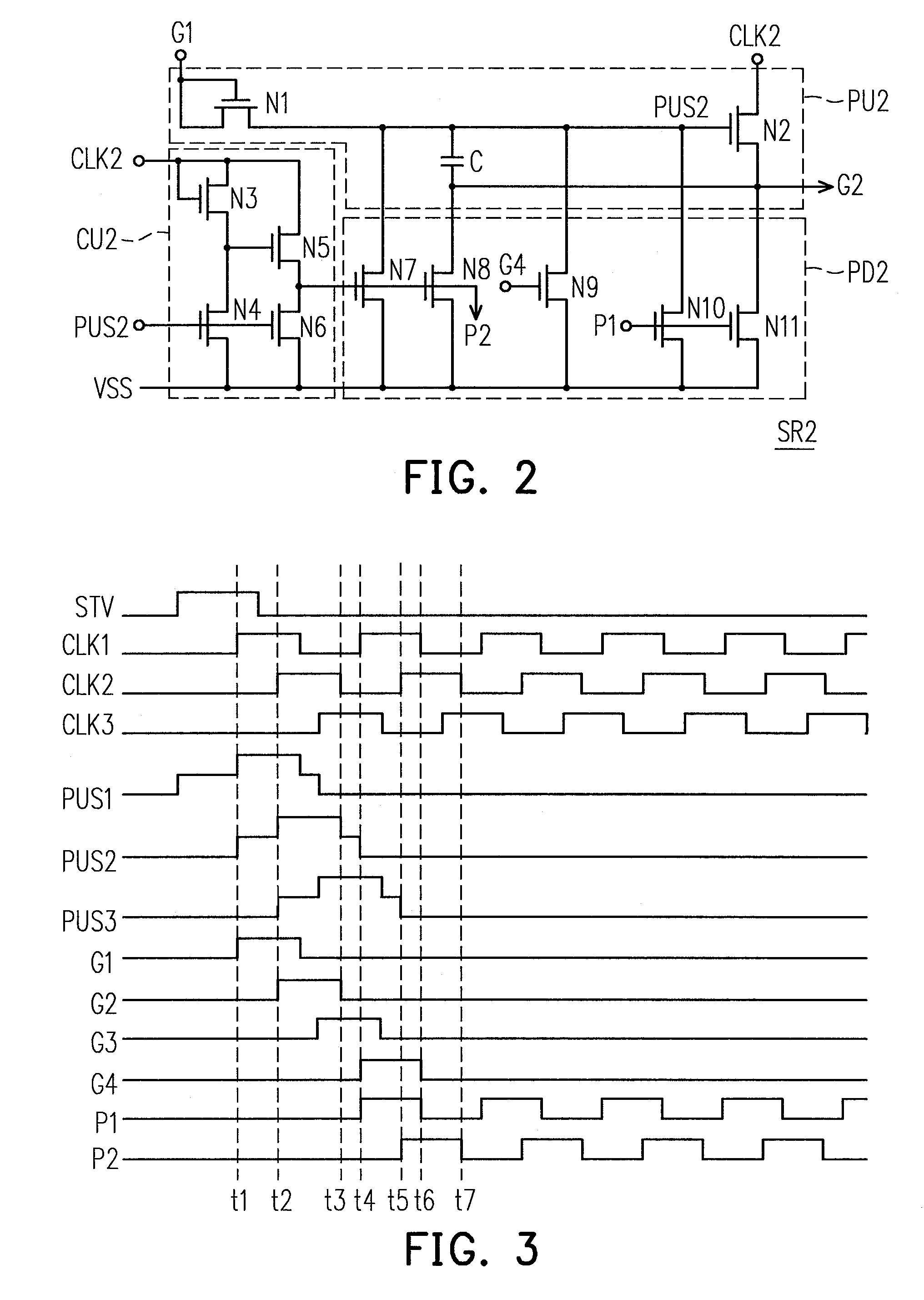
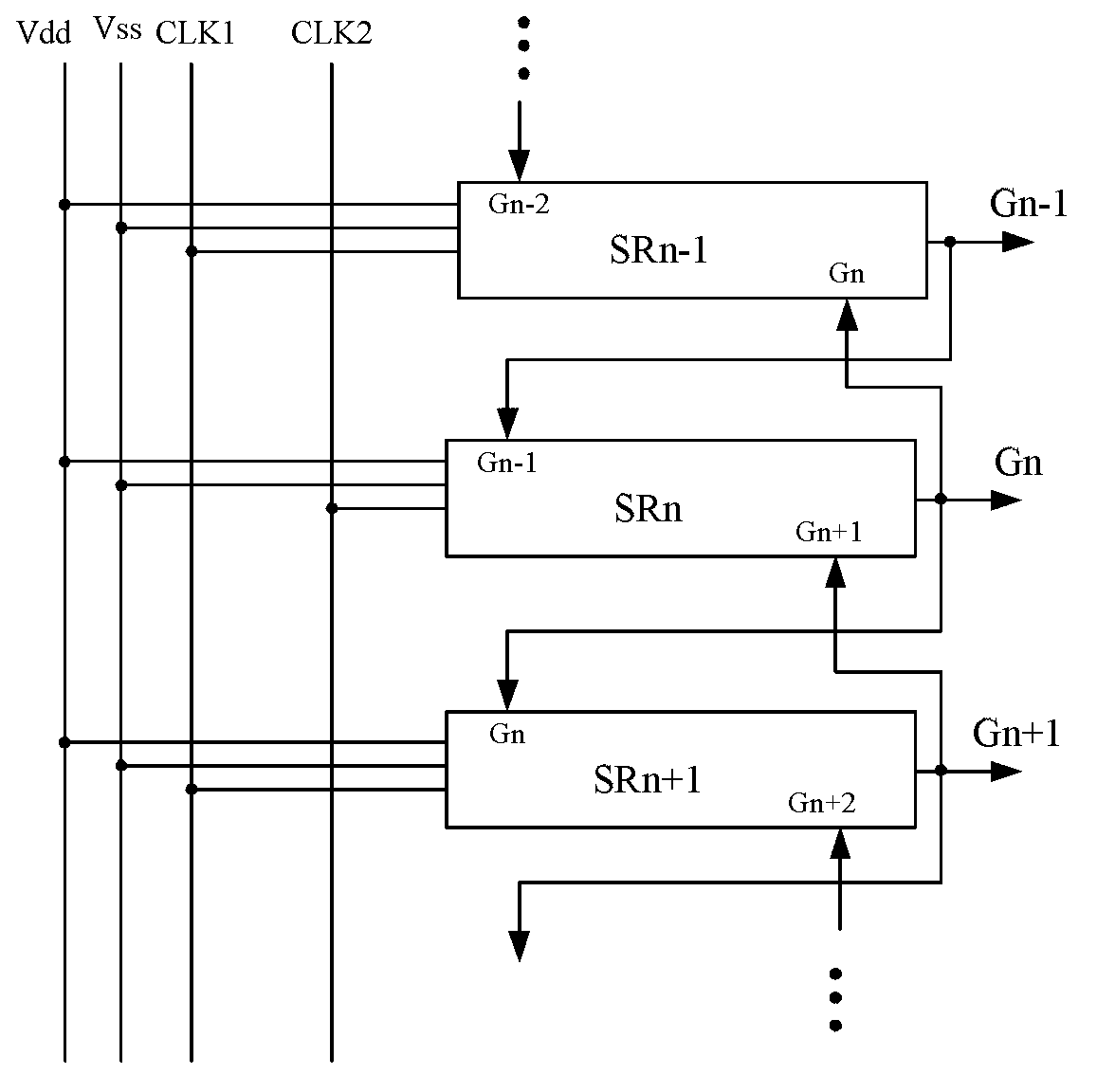
Shift register apparatus
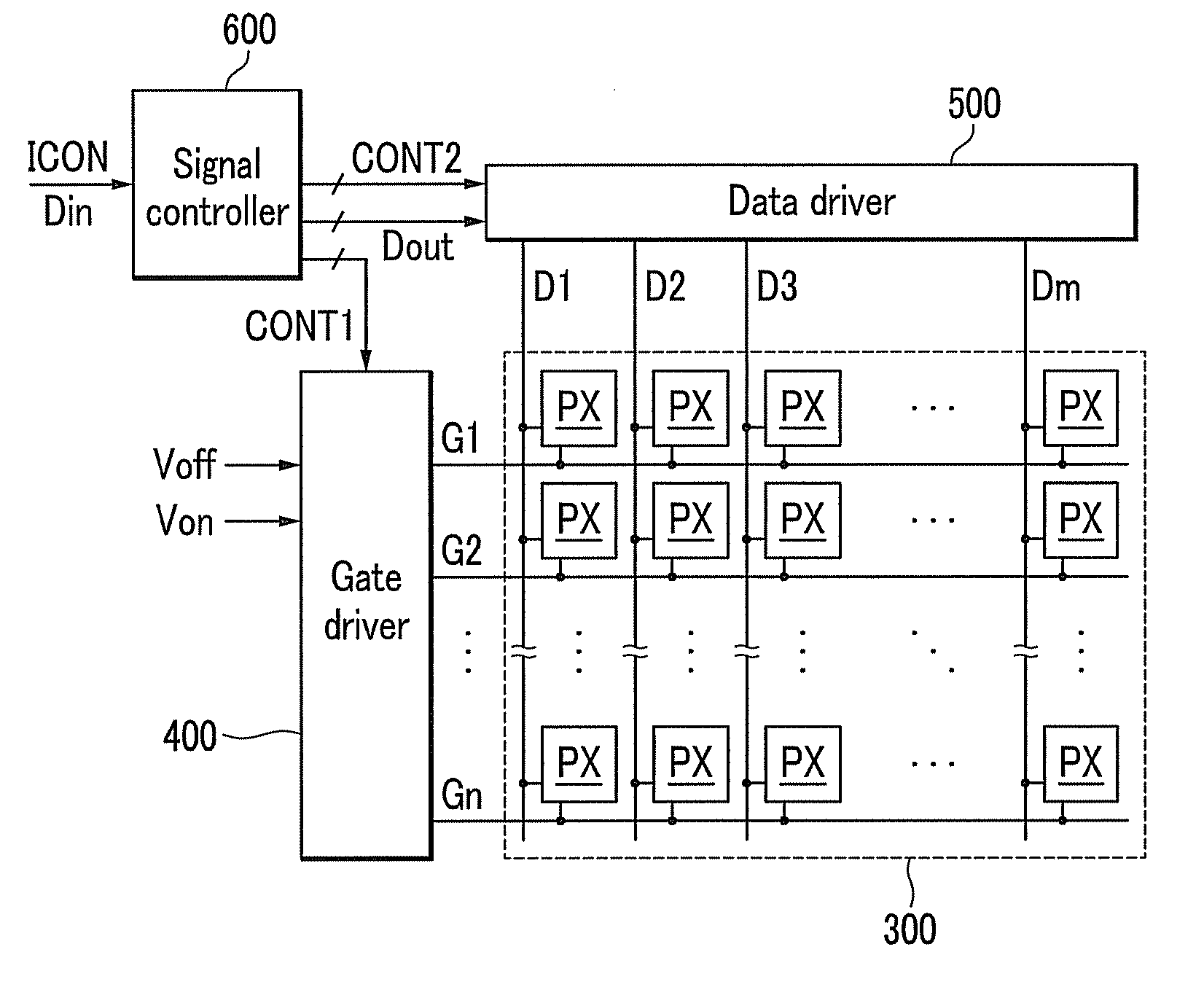
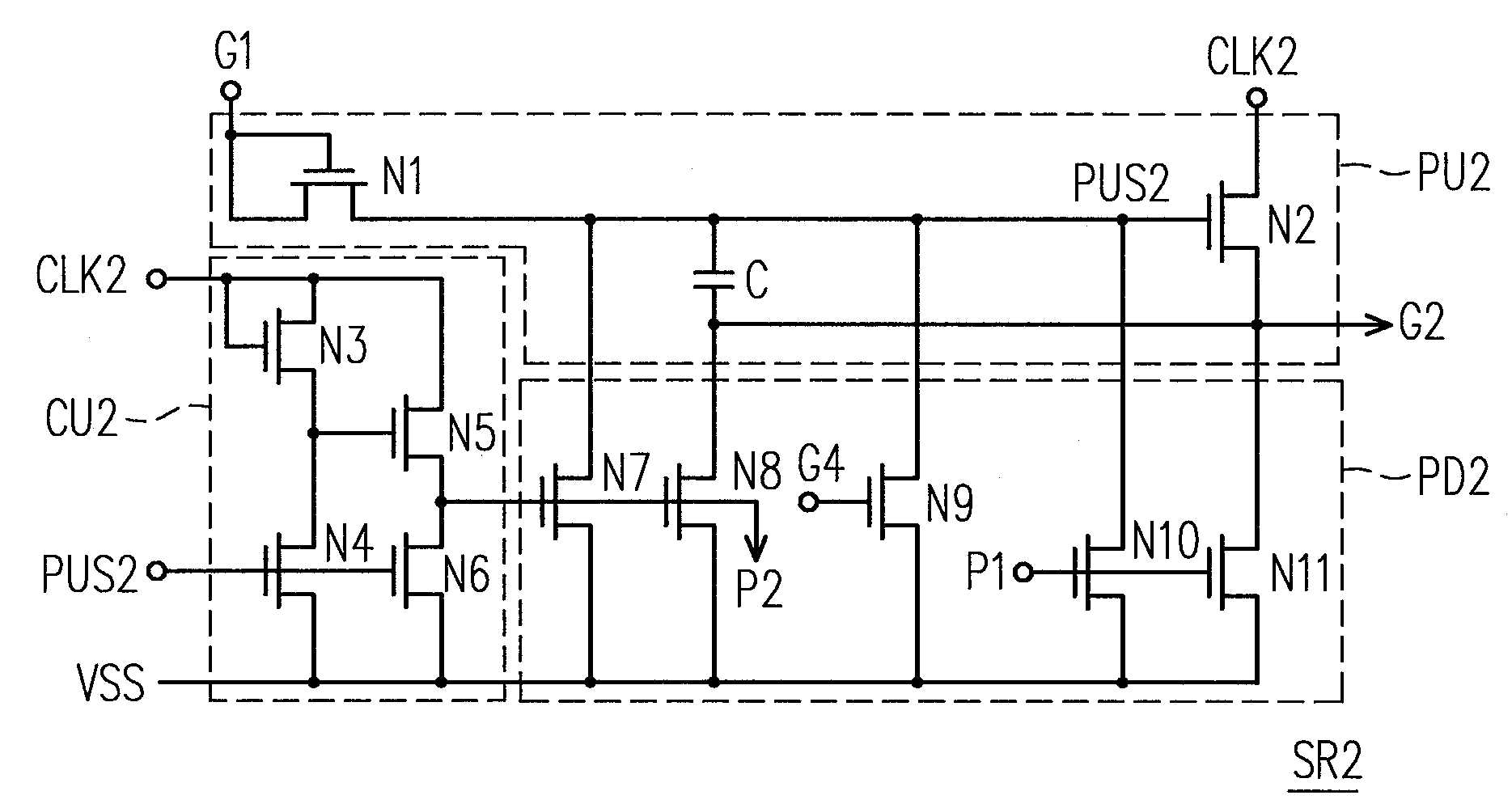
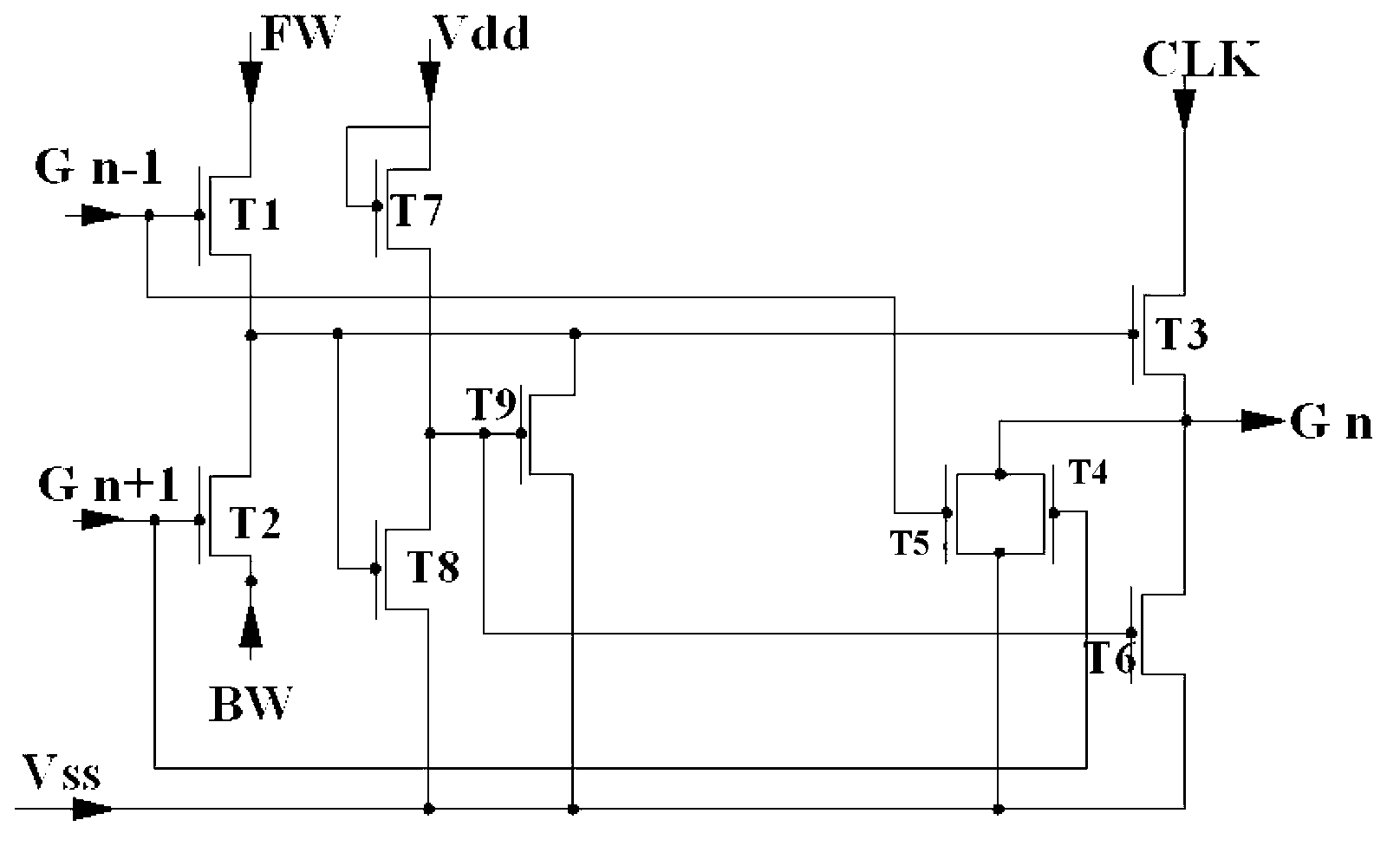
ActiveUS20100134234A1Prevent coupling noiseImprove output performanceDigital storageProtective switch operating/release mechanismsVoltage regulationCoupling noise
A shift register apparatus is provided. The pull-down unit of each of the shift registers in the shift register apparatus is controlled by itself, previous, and next two shift registers to enhance the ability of pull-down and voltage regulating. Therefore, the circuit structure of each of the shift registers does not need to be designed a large compensation capacitor therein to substantially restrain the coupling noise effect caused by the clock signal, and thus permitting that each of the shift registers can be collocated with a small compensation capacitor to enhance the output capability thereof.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Bionic coupling noise elimination noise reduction spiral tougue
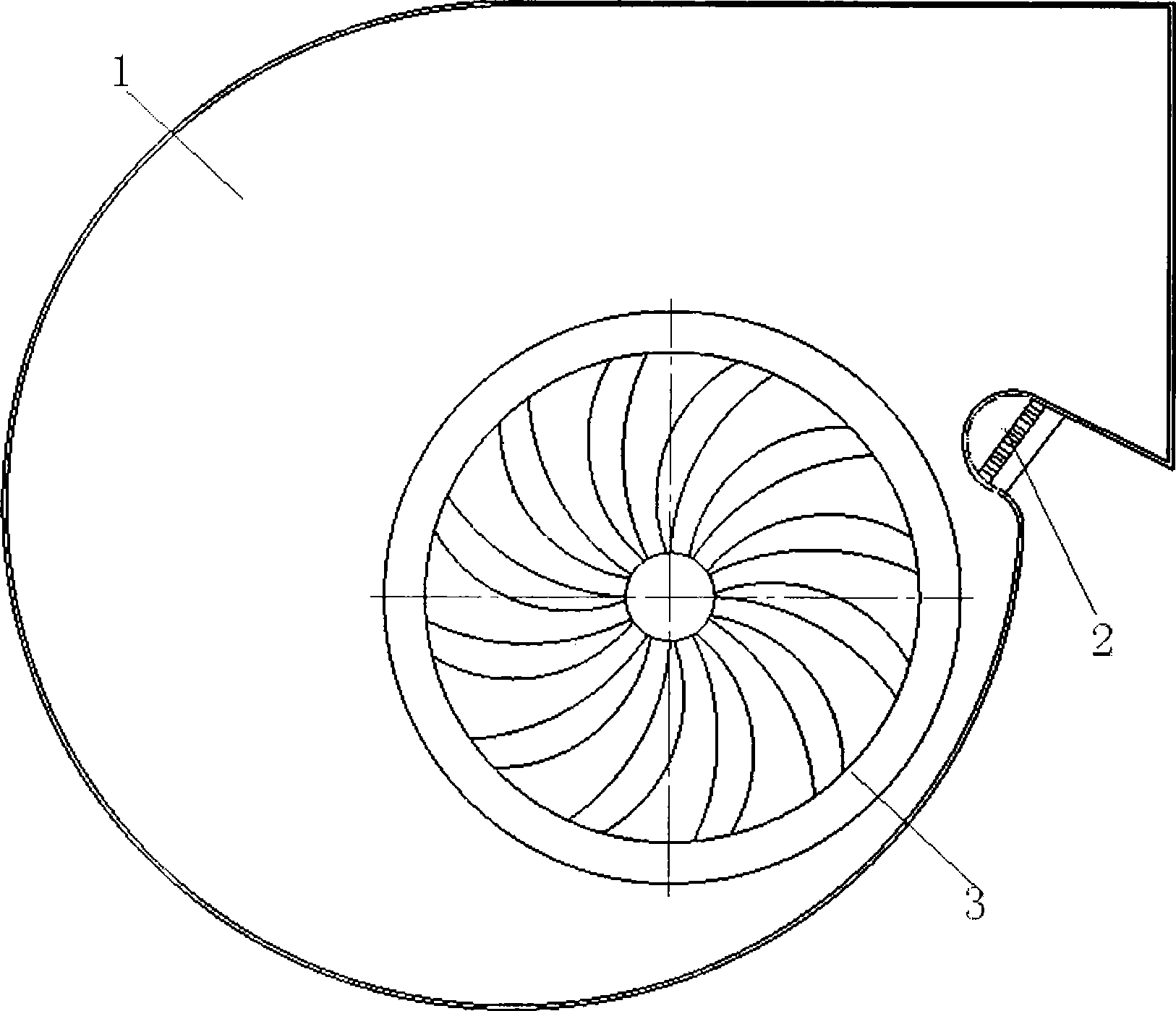
InactiveCN101509506AEasy to processReduced eddy current sheddingPump componentsPumpsNoise controlLow noise
The invention relates to a bionic coupling noise elimination volute tongue controlled by the aerodynamic noise of a centrifugal fan. The bionic coupling noise elimination volute tongue is arranged at a volute mouth of a volute casing. The bionic coupling noise elimination wolute tongue comprises a bionic coupling noise elimination volute tongue micro-gap ply, a bionic coupling noise elimination volute tongue micro-punch ply and an air chamber backing plate. A bionic coupling noise elimination volute tongue thin cavity layer is arranged between the bionic coupling noise elimination volute tongue micro-punch ply and the air chamber backing plate which is connected with the volute casing in a rivet welding way. The bionic coupling noise elimination volute tongue is simply processed and has the effects of sound absorption and noise reduction and rectification and noise reduction without needing changing the outline of the original fan volute casing. When air current flows through the surface of the bionic coupling noise elimination volute tongue, the bionic micro-gap ply contacted with the air current has the function of rectification and reducing the surface eddy shedding of the volute tongue. Experiments proves that the rotating speed of the fan selects the rotating speed of the working condition which is 1800r / min, for the original fan with higher noise lever, the noise can be reduced about by 3-5db (A), the noise reduction rate is 5%, for the original fan with lower noise lever, the noise can be reduced by 2-3db (A), and the noise reduction rate is 4.5%.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Use of random sampling technique to reduce finger-coupled noise
ActiveUS20110261008A1Electronic switchingInput/output processes for data processingSensor arrayComputer science
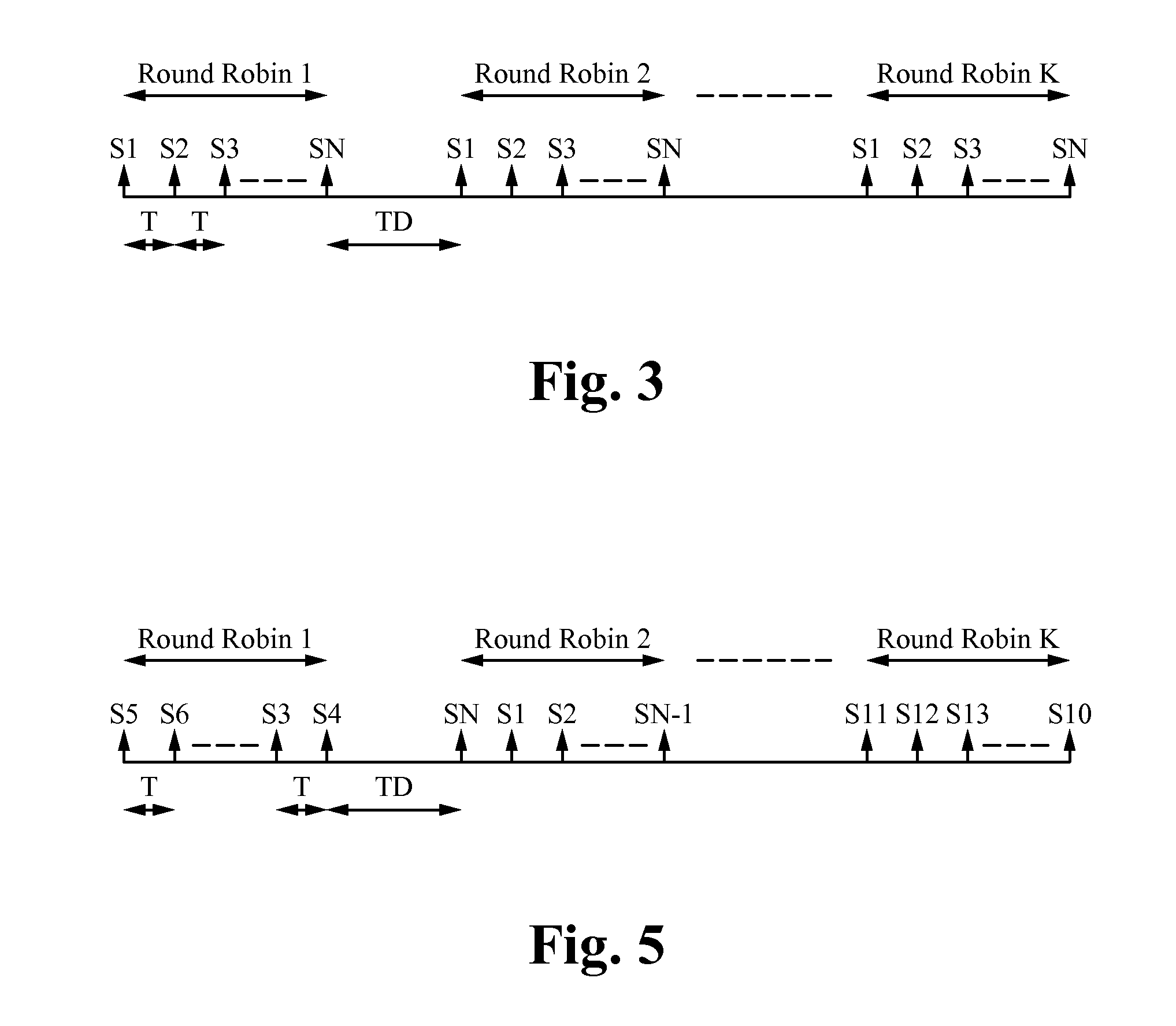
Random sampling techniques include techniques for reducing or eliminating errors in the output of capacitive sensor arrays such as touch panels. The channels of the touch panel are periodically sampled to determine the presence of one or more touch events. Each channel is individually sampled in a round robin fashion, referred to as a sampling cycle. During each sampling cycle, all channels are sampled once. Multiple sampling cycles are performed such that each channel is sampled multiple times. Random sampling techniques are used to sample each of the channels. One random sampling technique randomizes a starting channel in each sampling cycle. Another random sampling technique randomizes the selection of all channels in each sampling cycle. Yet another random sampling technique randomizes the sampling cycle delay period between each sampling cycle. Still another random sampling technique randomizes the channel delay period between sampling each channel.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
High frequency semiconductor integrated circuit device, wireless electric unit and wireless communication system
InactiveUS7132900B2Output levelImprove detection levelMultiple-port networksSolid-state devicesAudio power amplifierCommunications system
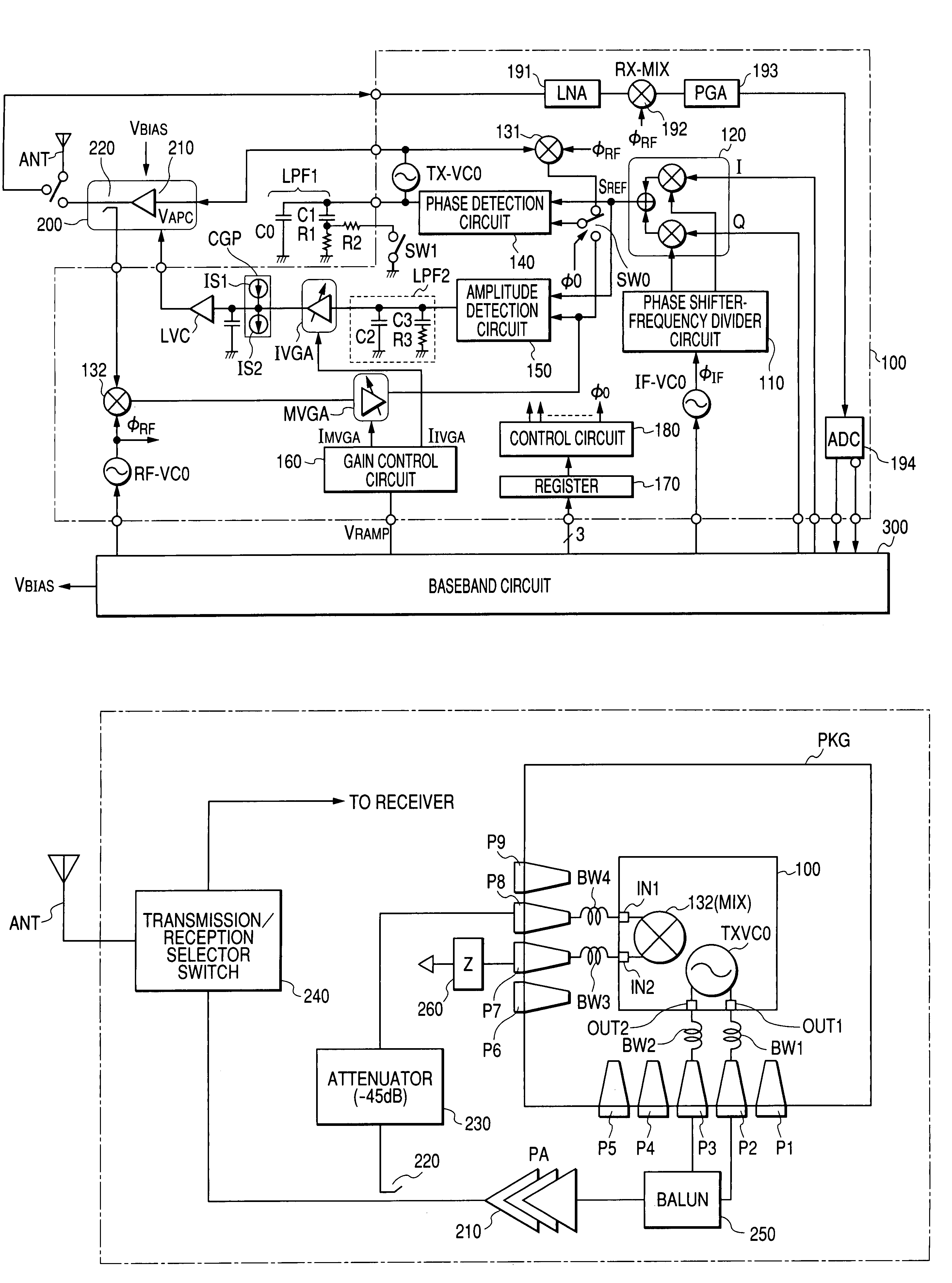
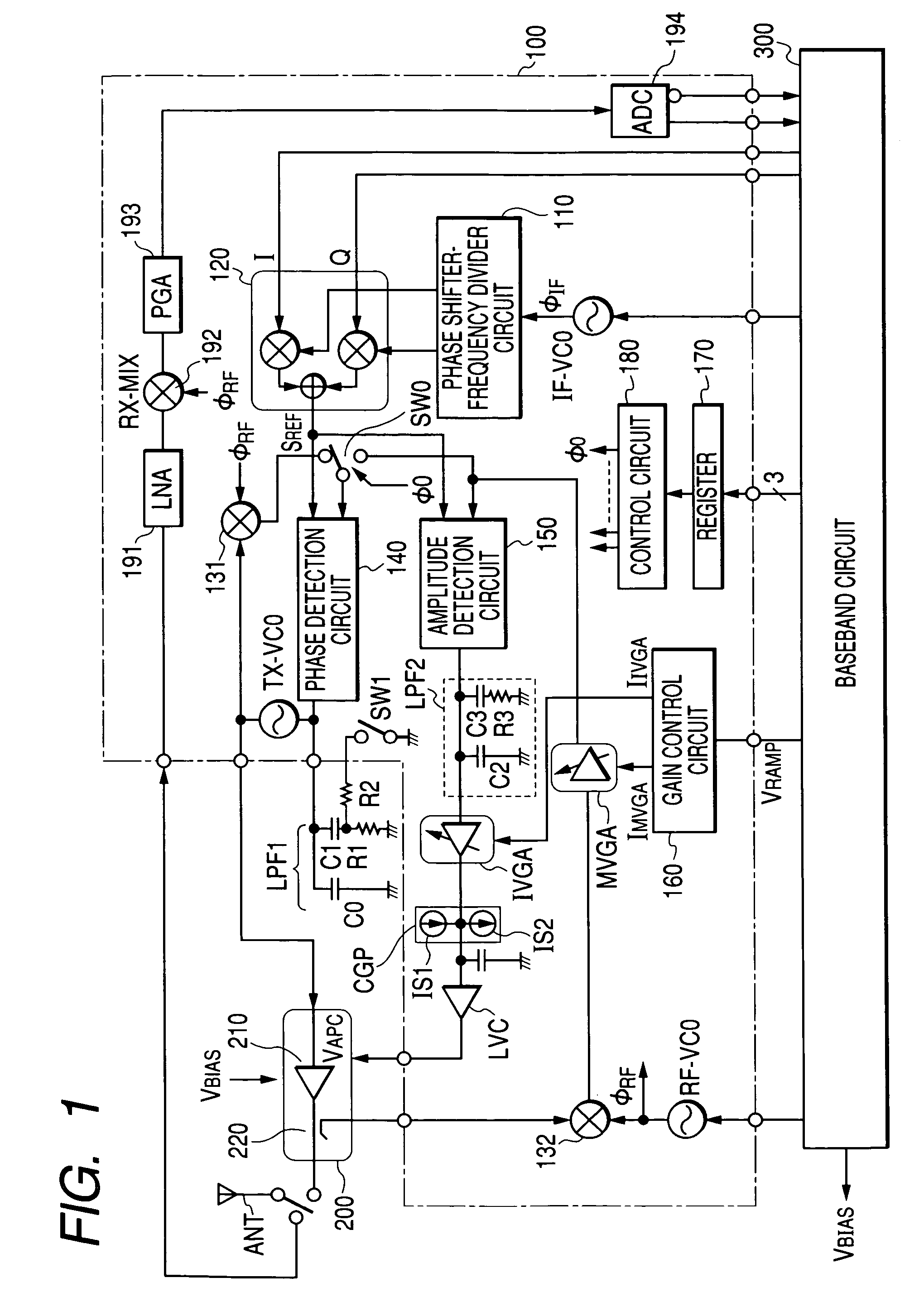
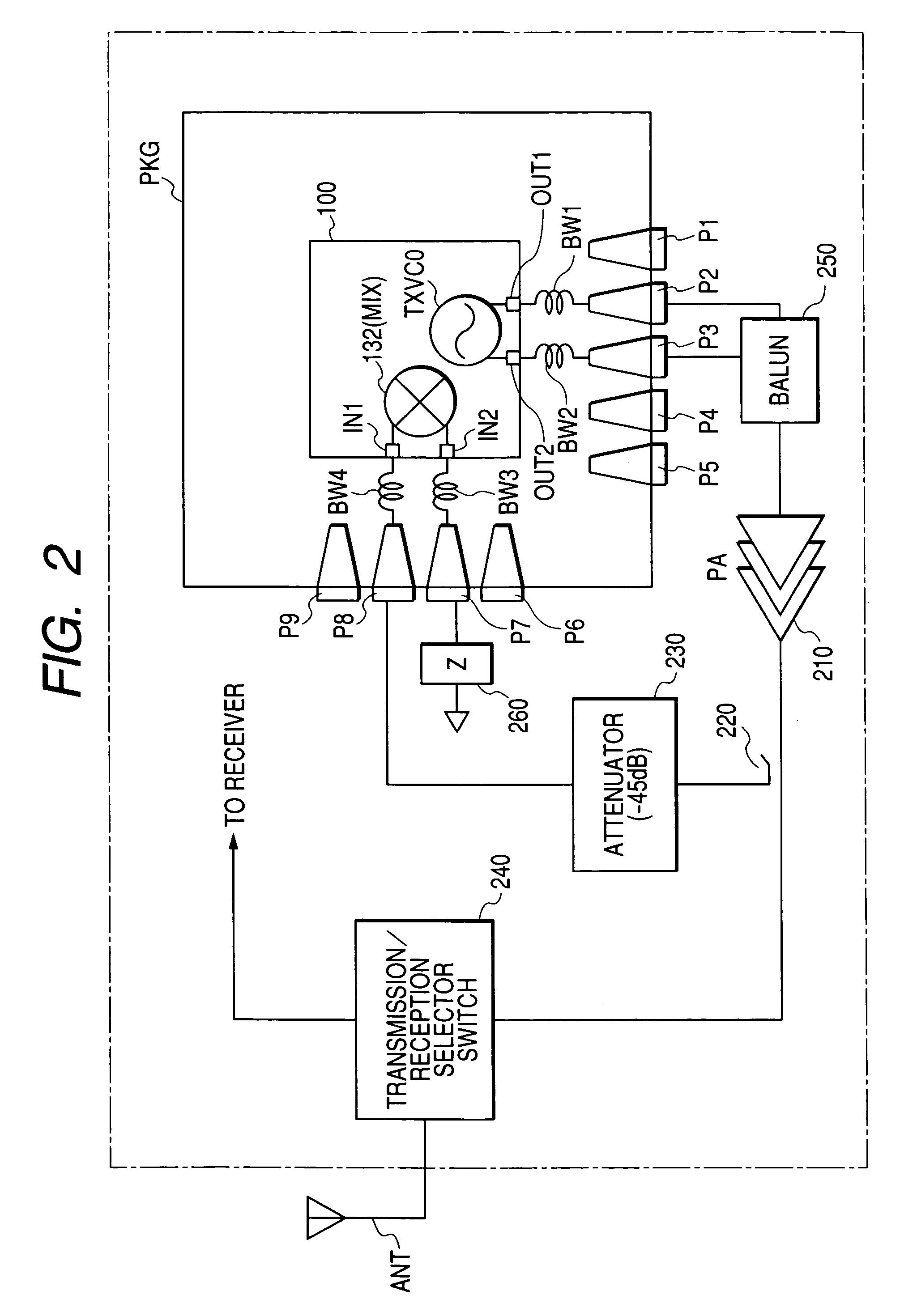
If a transmission oscillator is incorporated into a communication semiconductor integrated circuit, such as high a frequency IC, constituting a wireless communication system, a problem arises. The accuracy of control of the output power of a power amplifier is degraded. This degradation in accuracy is caused by coupling noise between the output pins of the transmission oscillator and an input pin for detection signals (feedback signals) associated with the output level of the power amplifier or crosstalk. To prevent this, a transmission oscillator of differential output configuration is incorporated into a high frequency IC and an impedance equivalent to the impedance connected with a regular output terminal or a dummy external terminal for outputting transmit signals in opposite phase is provided.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
Design structure for coupling noise prevention
ActiveUS7615841B2Avoid noiseCross talkSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor structureSemiconductor chip
A semiconductor structure for preventing coupling noise in integrated circuits and a method of forming the same are provided. The semiconductor structure includes a signal-grounded seal ring. The seal ring includes a plurality of metal lines, each in a respective metal layer and surrounding a circuit region of the semiconductor chip, a plurality of vias connecting respective metal lines, and a plurality of dielectric layers isolating each metal layer from any other metal layers. The seal ring may further include additional seal rings formed inside or outside the seal ring. The semiconductor structure may include laser fuses and protective rings. The protective rings are preferably signal grounded. Cross talk between sub circuits in a chip can be reduced by forming a seal ring extension between the sub circuits.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Shift register apparatus
ActiveUS7778379B2Avoid noiseImprove output performanceDigital storageProtective switch operating/release mechanismsShift registerVoltage regulation
A shift register apparatus is provided. The pull-down unit of each of the shift registers in the shift register apparatus is controlled by itself, previous, and next two shift registers to enhance the ability of pull-down and voltage regulating. Therefore, the circuit structure of each of the shift registers does not need to be designed a large compensation capacitor therein to substantially restrain the coupling noise effect caused by the clock signal, and thus permitting that each of the shift registers can be collocated with a small compensation capacitor to enhance the output capability thereof.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
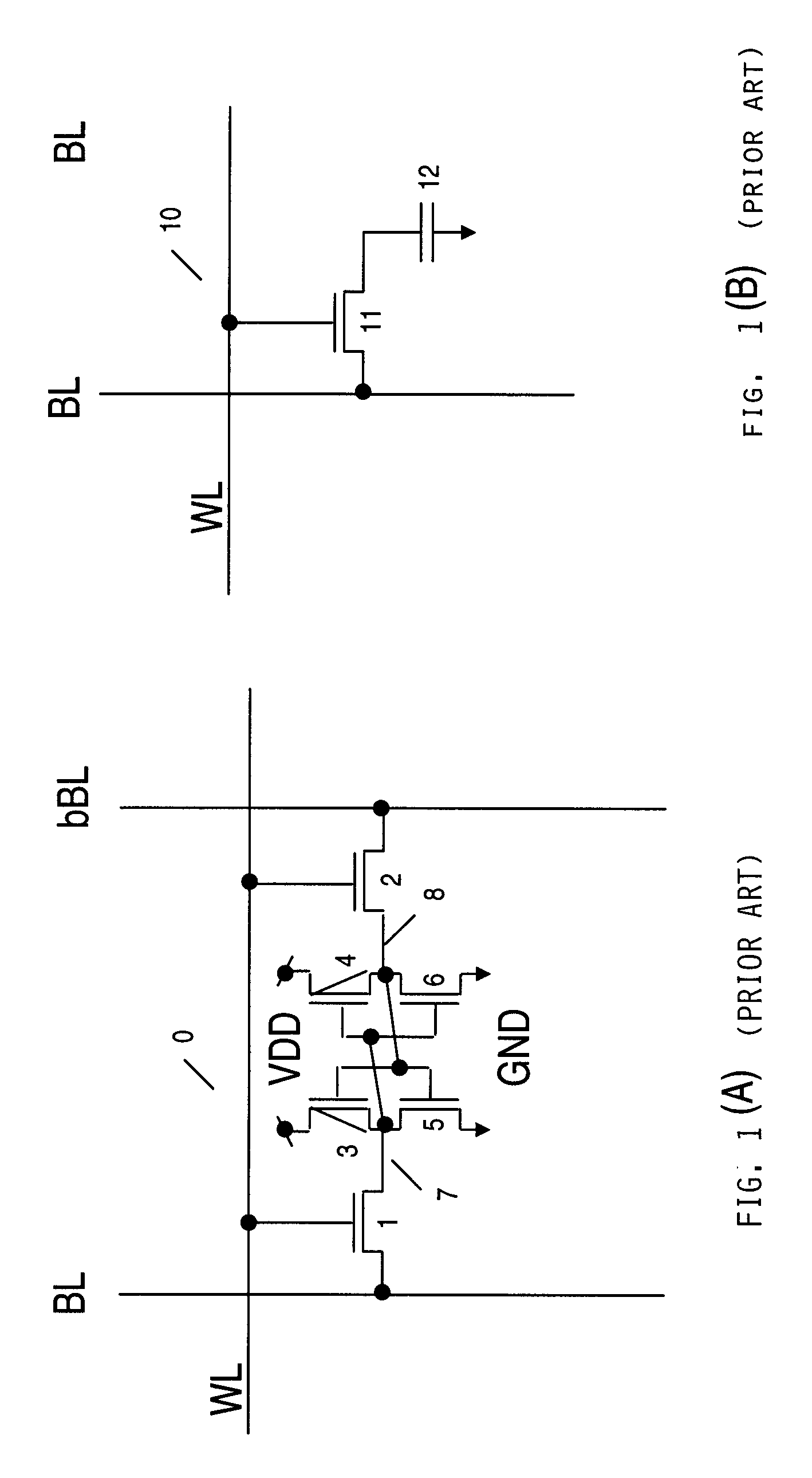
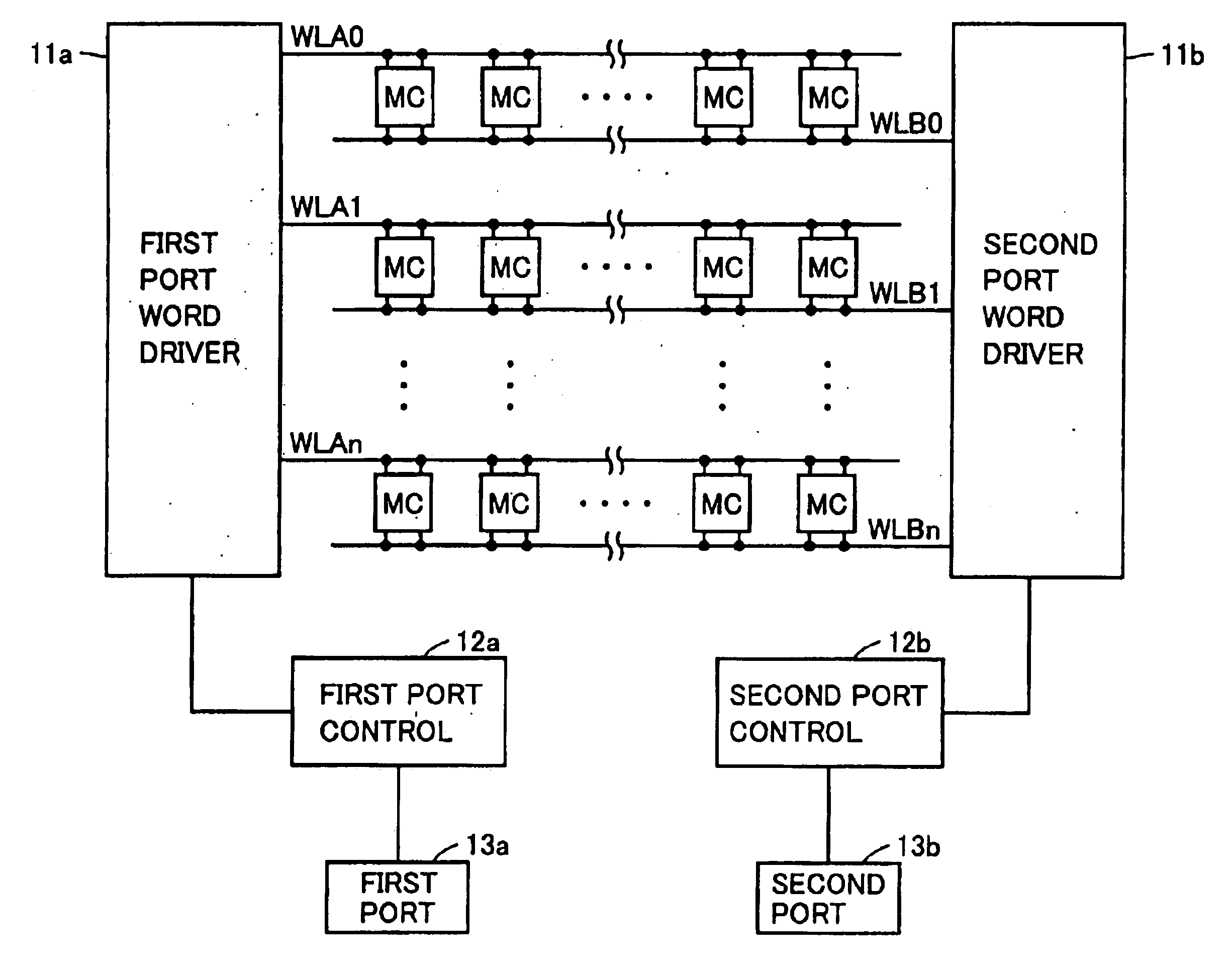
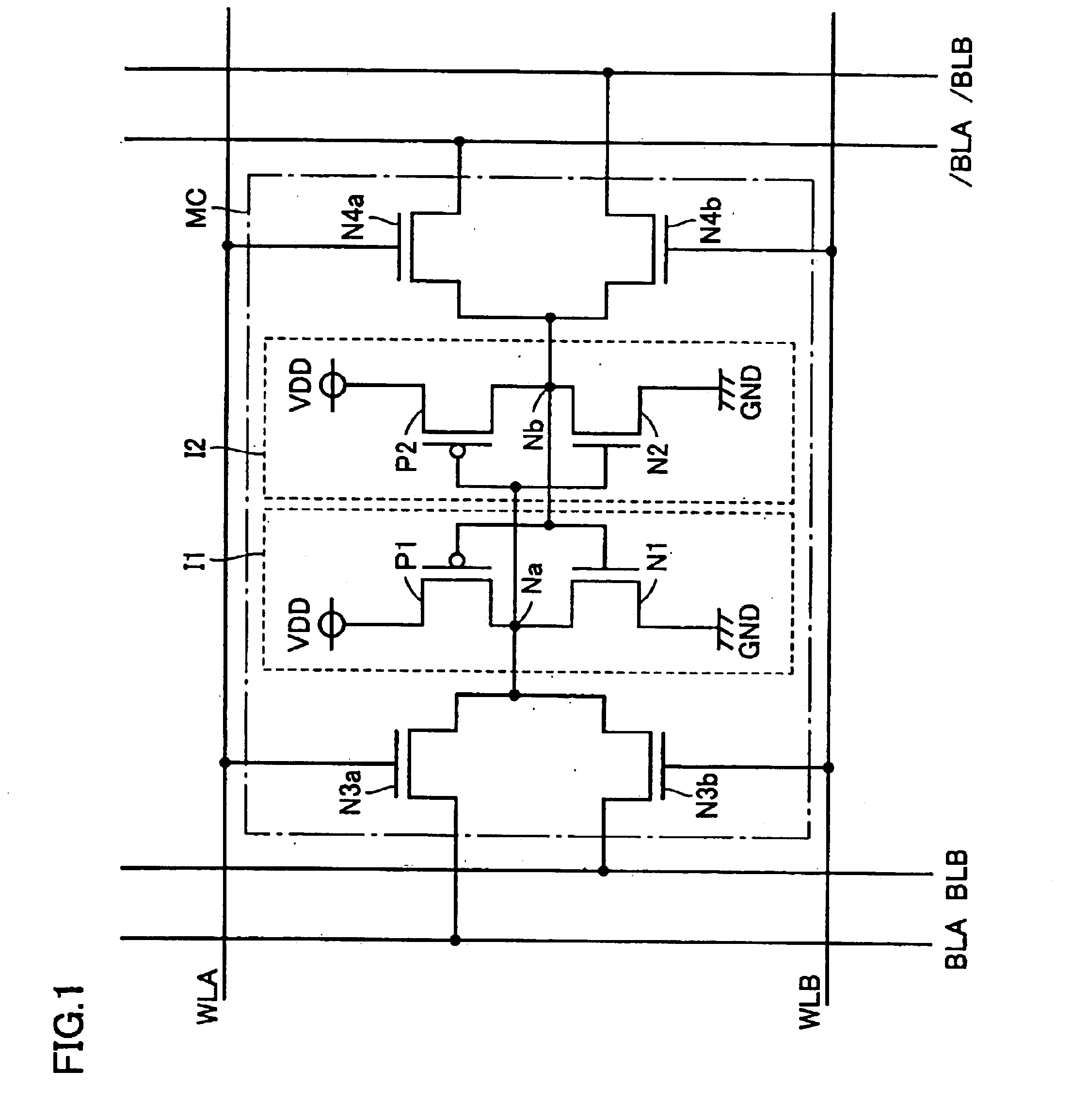
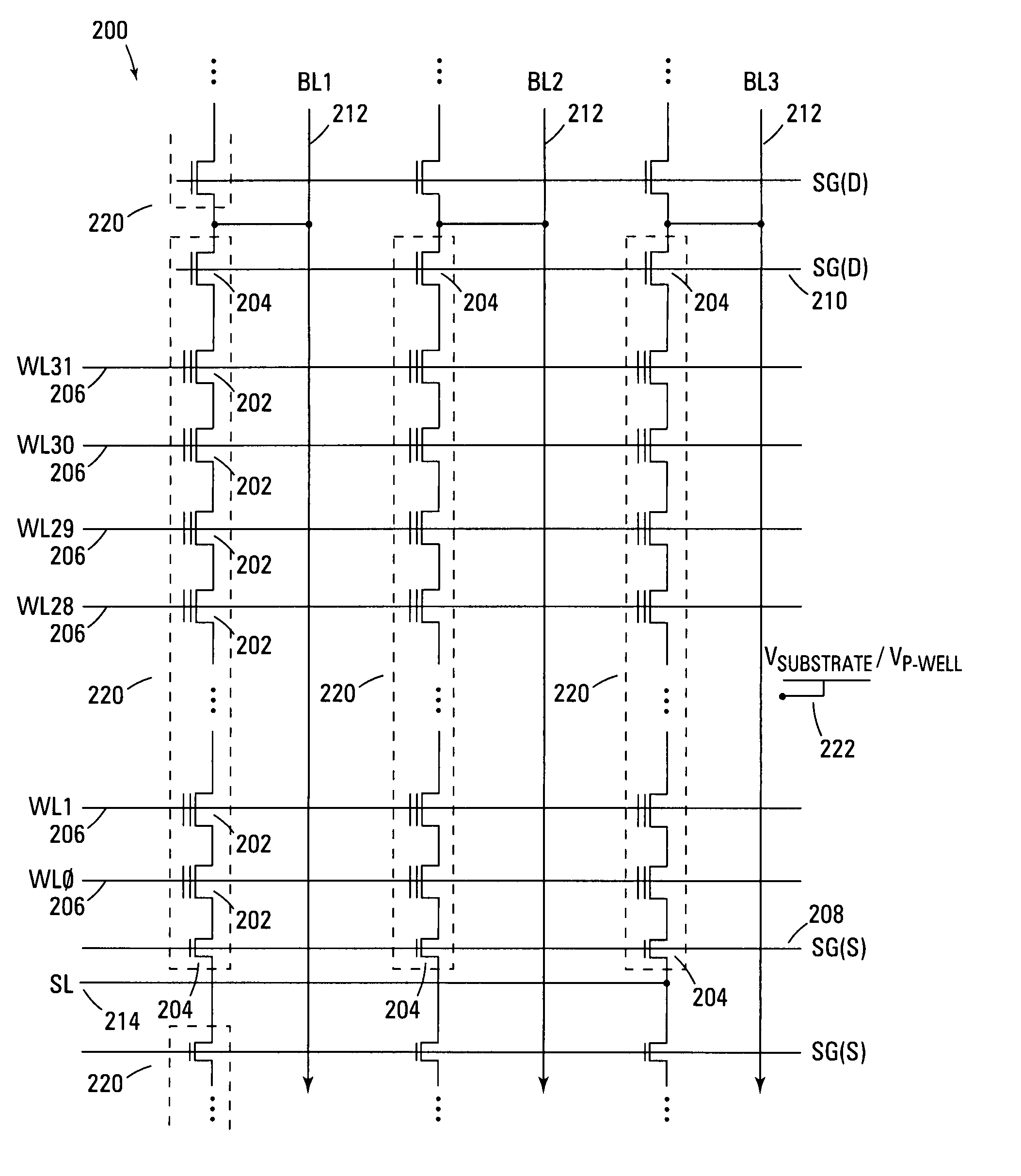
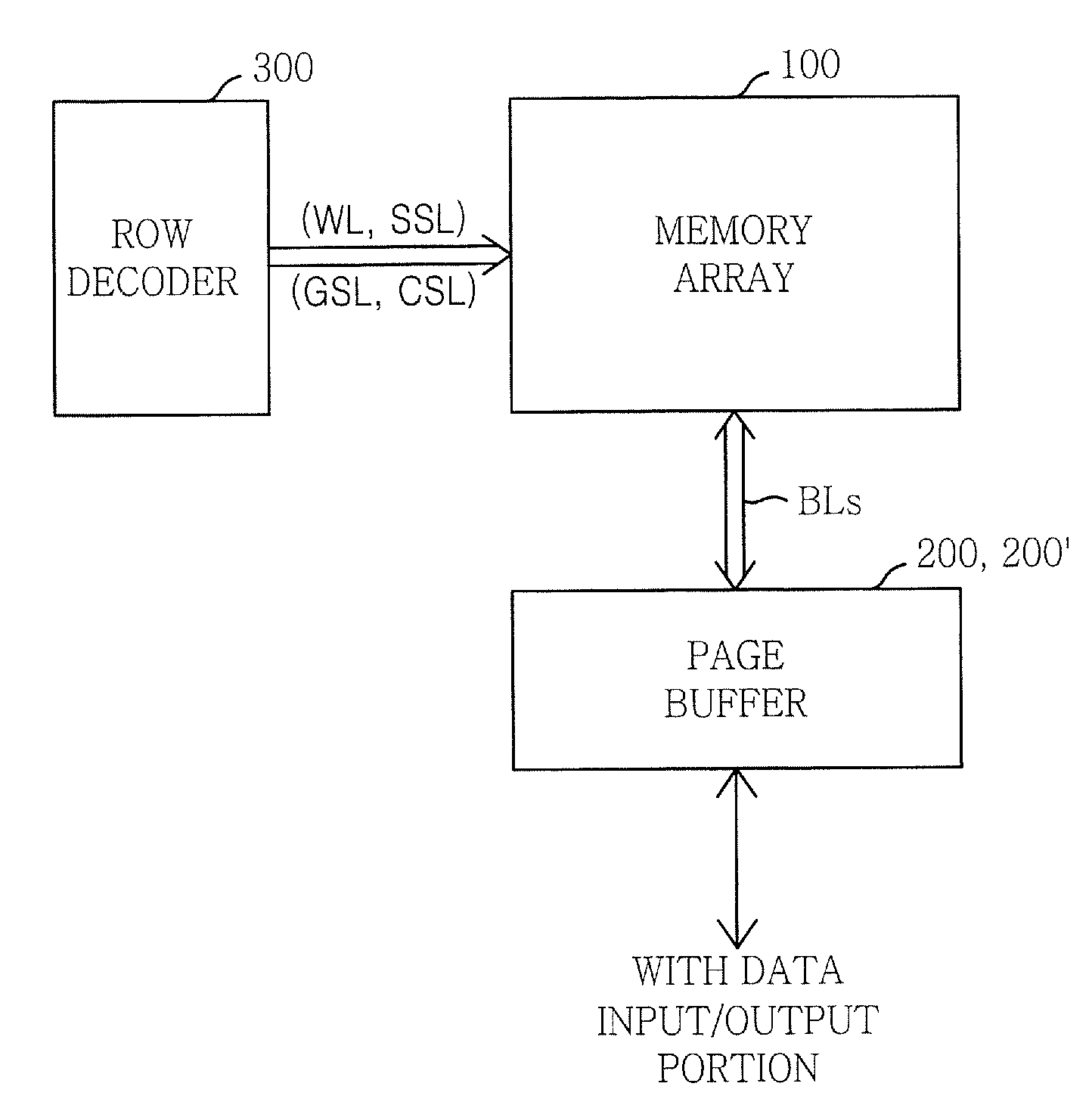
Reduction of capacitive effects in a semiconductor memory device
ActiveUS6917560B2Reduce coupling noiseIncrease the areaTransistorSolid-state devicesCapacitanceCapacitive effect
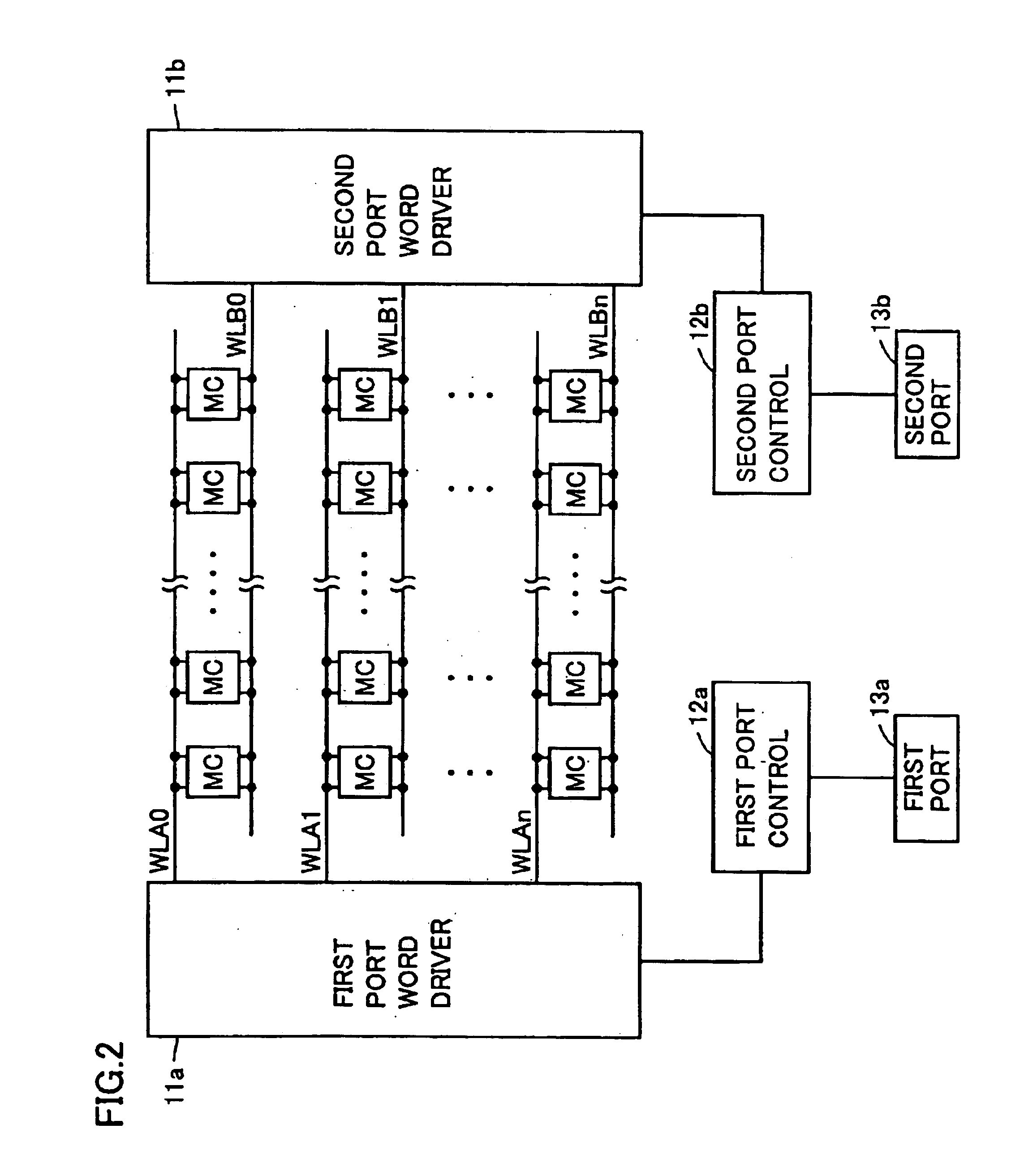
A semiconductor memory device having a multiport memory includes a plurality of memory cells MC arranged in columns and rows, a plurality of first word lines WLA0-WLAn connected to a first port 13a, and a plurality of second word lines WLB0-WLBn connected to a second port 13b. Each of a plurality of first word lines WLA0-WLAn and each of a plurality of second word lines WLB0-WLBn are arranged alternately in a planar layout. A semiconductor memory device is thus obtained that allows a coupling noise between interconnections to be reduced without an increase in memory cell area.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Multi-port memory architecture
A multi-port memory architecture utilizing an open bitline configuration for the read bitline is described. The memory is sub-divided into two arrays (A and B) consisting of memory gain cells arranged in a matrix formation, the cells having two general ports or separate read and write ports to enable simultaneous a read and write operation. Each memory array includes a reference wordline coupled to reference cells. When the reference cell is accessed, the read bitline (RBL) discharges to a level at half the value taken by a cell storing a 0 or 1. Each pair of RBLB in the same column of the two arrays is coupled to a differential sense amplifier, and each write bitline (WBL) in the two arrays is linked to write drivers WBLs in the two arrays are driven to the same voltage and at the same slew rate. The WBL swing in each array creates coupling noise by the bitline-to-bitline capacitors. For a given sense amplifier and its associated RBLs, the coupling creates an identical coupling noise on RBLA and RBLB that are positioned in the two arrays A and B. This common mode noise is rejected by the differential sense amplifier. Thus, a read sense amplifier can accurately discriminate between the signal by activating the cell by way of RWL, and the reference cell by way of REFWL.
Owner:TWITTER INC
Data transmitting system
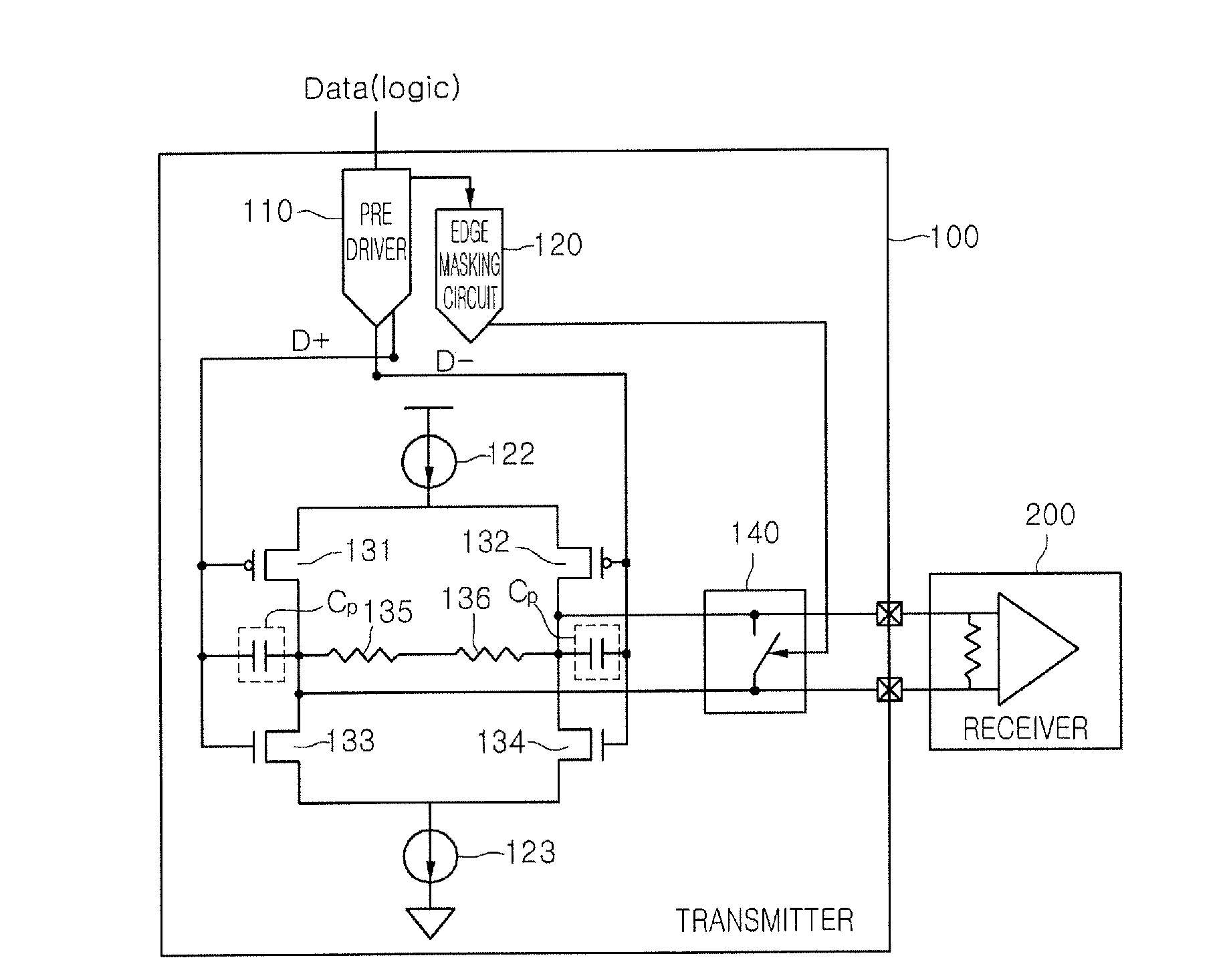
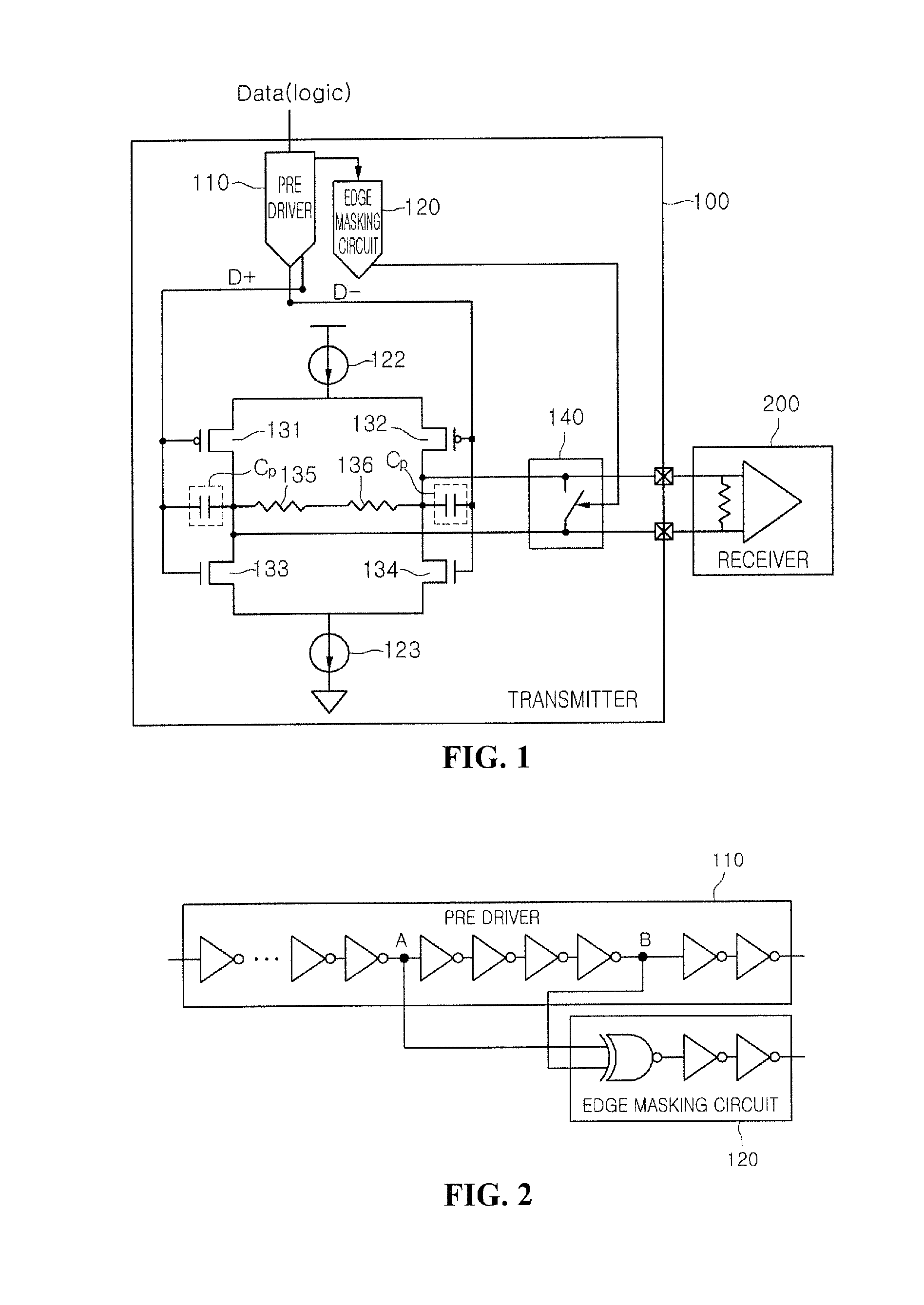
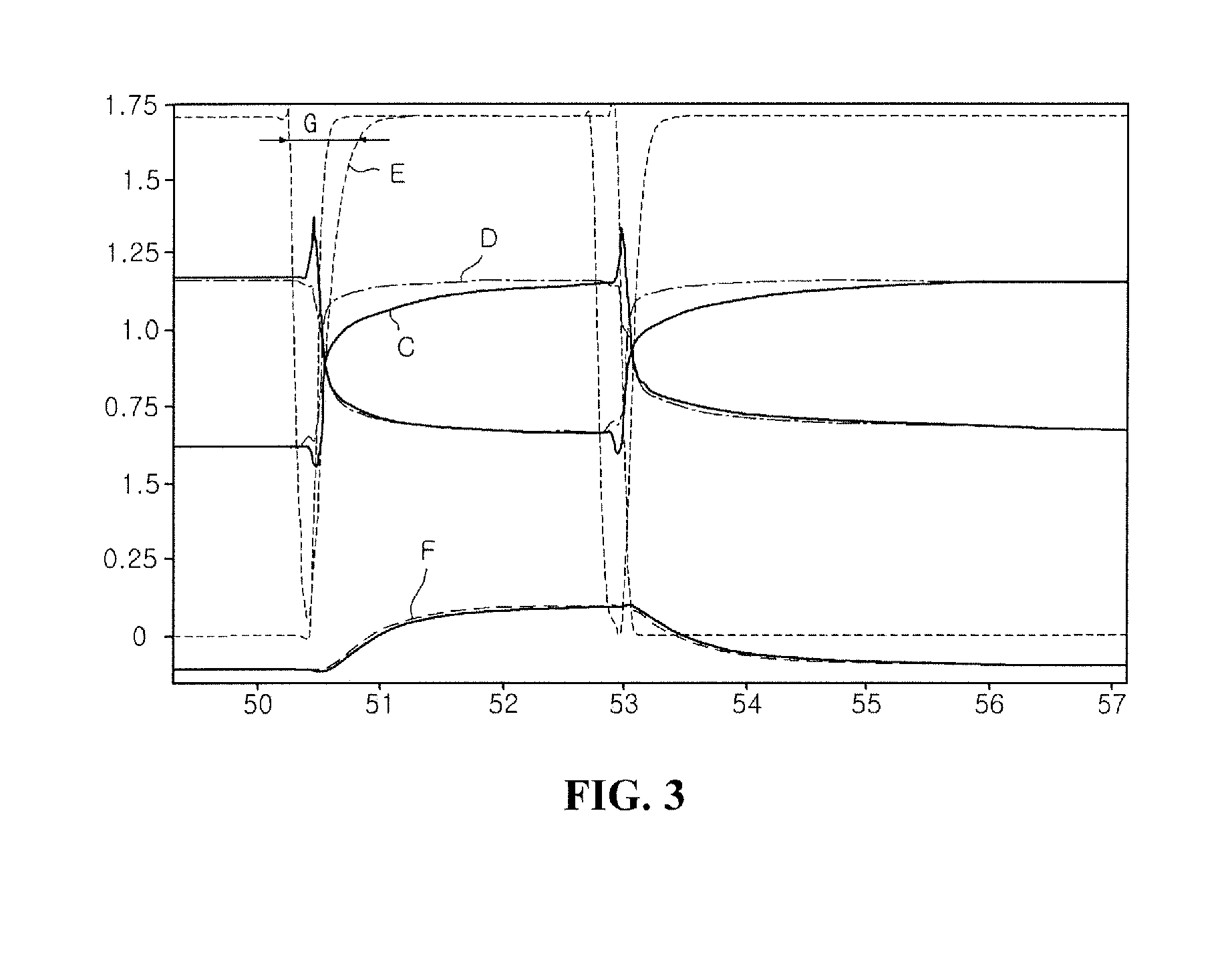
InactiveUS20100124298A1Short transition timeAvoid volatilityDigital storageSecret communicationEngineeringTransmitter
A data transmitting system is provided that includes a transmitter that suppresses coupling noise by being operated using a differential voltage driving scheme at the time of transmitting data and being operated using a common voltage driving scheme by equalizing potential of a pair of transmission lines during a transition interval; and a receiver that is connected to the transmitter through the pair of transmission lines and recovers the data by sensing the voltage difference in signals of the pair of transmission lines.
Owner:DONGBU HITEK CO LTD
Local self-boost inhibit scheme with shielded word line
A NAND architecture non-volatile memory device and programming process is described that reduces the effects of word line to word line voltage coupling by utilizing sets of two or more adjacent word lines and applying the same voltage to each in array access operations. This allows each word line of the set or pair to shield the other from word line to word line capacitive voltage coupling. In NAND memory string embodiments the various cells of strings of non-volatile memory cells are programmed utilizing modified or unmodified drain-side self boost, source-side self boost, local self boost, and virtual ground programming processes that utilize two or more “blocking” memory cells on either the source line side and drain line side of a selected memory cell. The paired blocking cells shield each other during programming to reduce coupled noise, to prevent charge leakage from the boosted channel of the selected memory cell.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Shifting register, working method of shifting register, grid electrode driving device and display device
ActiveCN103021318AStable jobExtended service lifeStatic indicating devicesDigital storageShift registerDisplay device
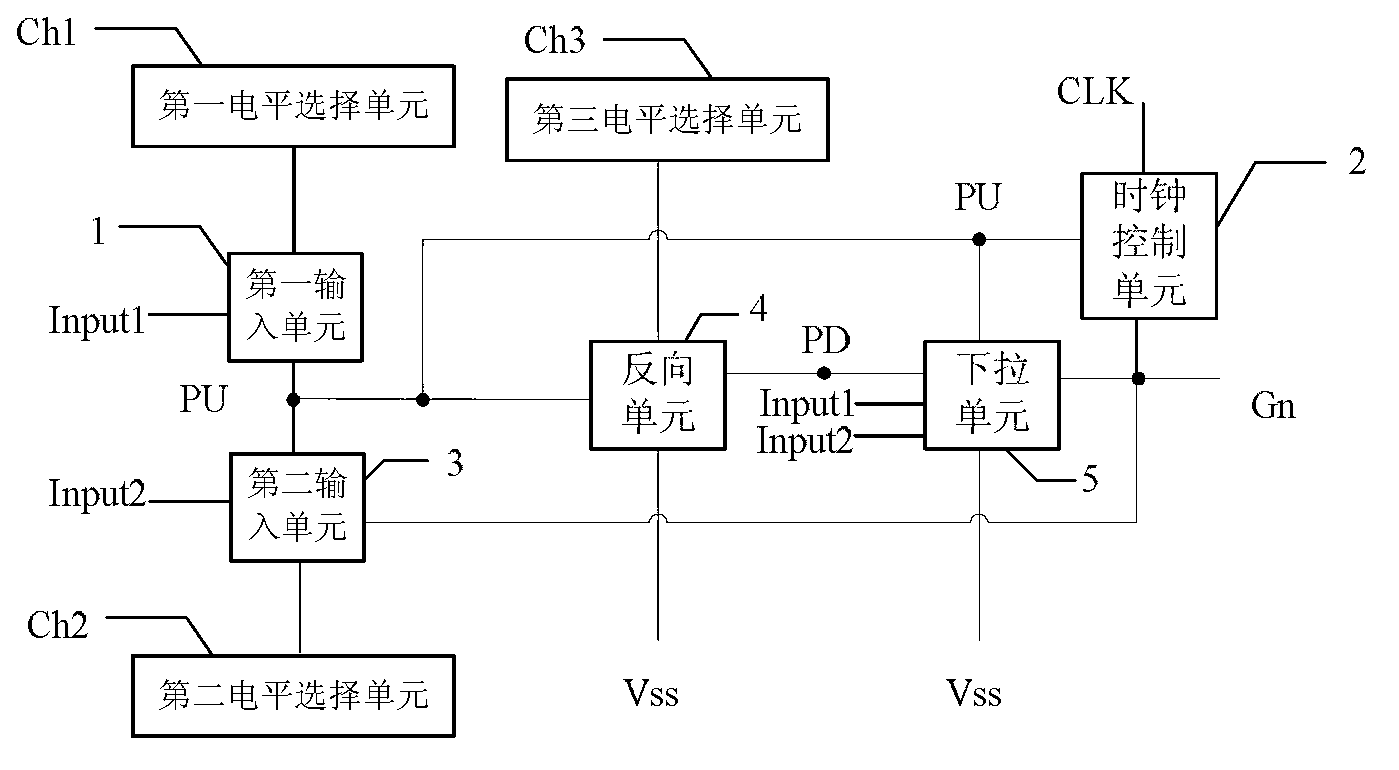
The embodiment of the invention discloses a shifting register, a working method of the shifting register, a grid electrode driving device and a display device, relates to the technical field of displaying, and aims at effectively eliminating voltage coupling noise generated by clock signals at an output end of the shifting register. The shifting register comprises a first input unit, a clock control unit, a second input unit, a reverse unit, a pull-down unit, a first electrical level selection unit, a second electrical level selection unit and a third electrical level selection unit. The first input unit is respectively connected with a first input signal, a first electrical level selection unit and the second input unit, wherein a node where the first input unit and the second input unit are connected is a pull up node, and the first input unit is used for controlling electric potential of the pull up node. The shifting register, the working method of the shifting register, the grid electrode driving device and the display device can be used in various display devices.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Non-Volatile Memory Devices that Utilize Mirror-Image Programming Techniques to Inhibit Program Coupling Noise and Methods of Programming Same
ActiveUS20070195597A1Improve reliability of data storedReduce coupling noiseRead-only memoriesDigital storageMirror imageComputer science
Non-volatile memory devices have improved data storage reliability resulting from mirror-image programming techniques that operate to reduce coupling noise between adjacent memory cells within a memory array. The adjacent memory cells include a first pair of memory cells and a second pair of memory cells. A program control circuit is provided to support mirror-image programming of the first and second pairs of memory cells when the two pairs of memory cells are storing the same 3-bit data.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Low power sensing scheme for the semiconductor memory
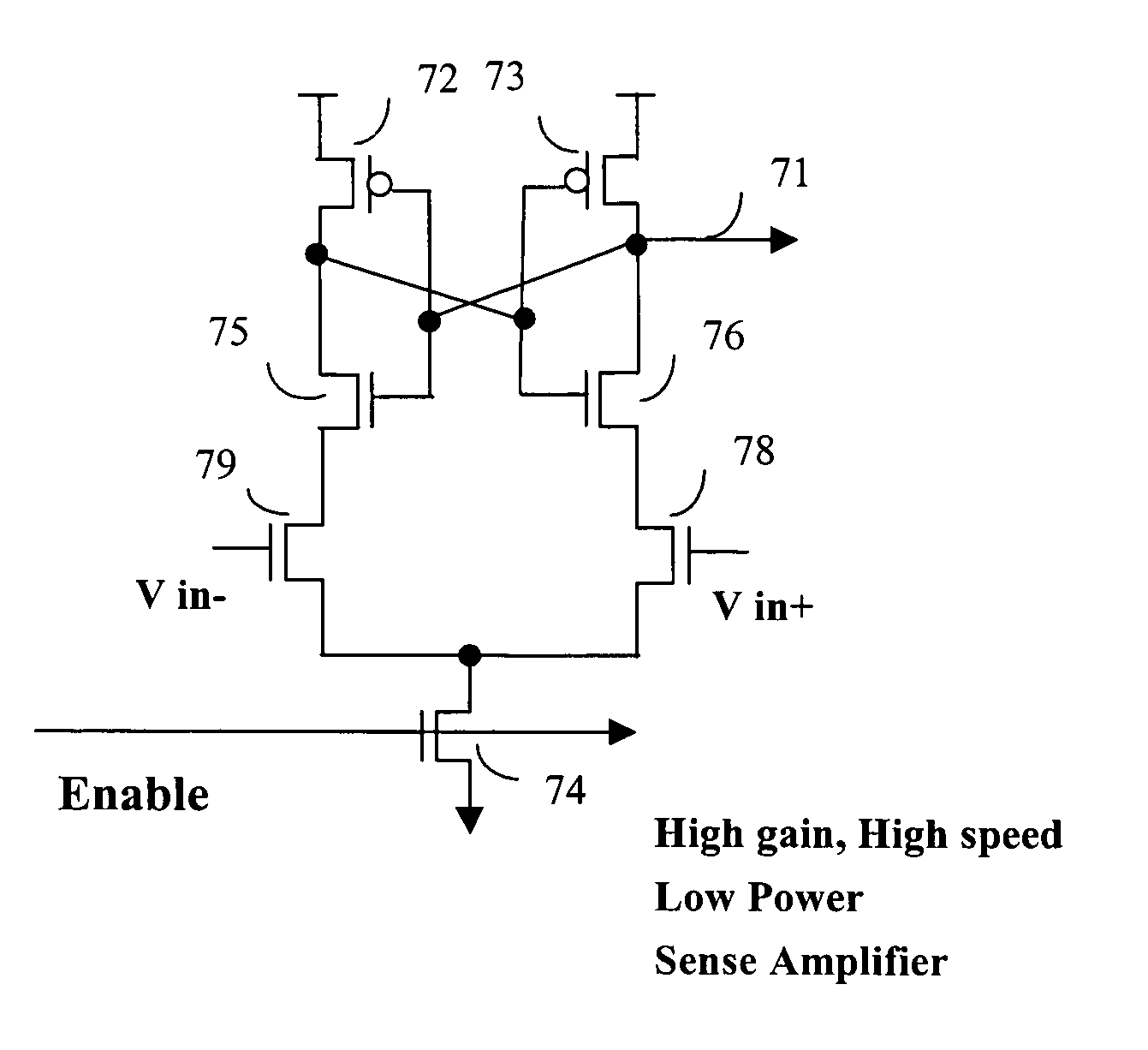
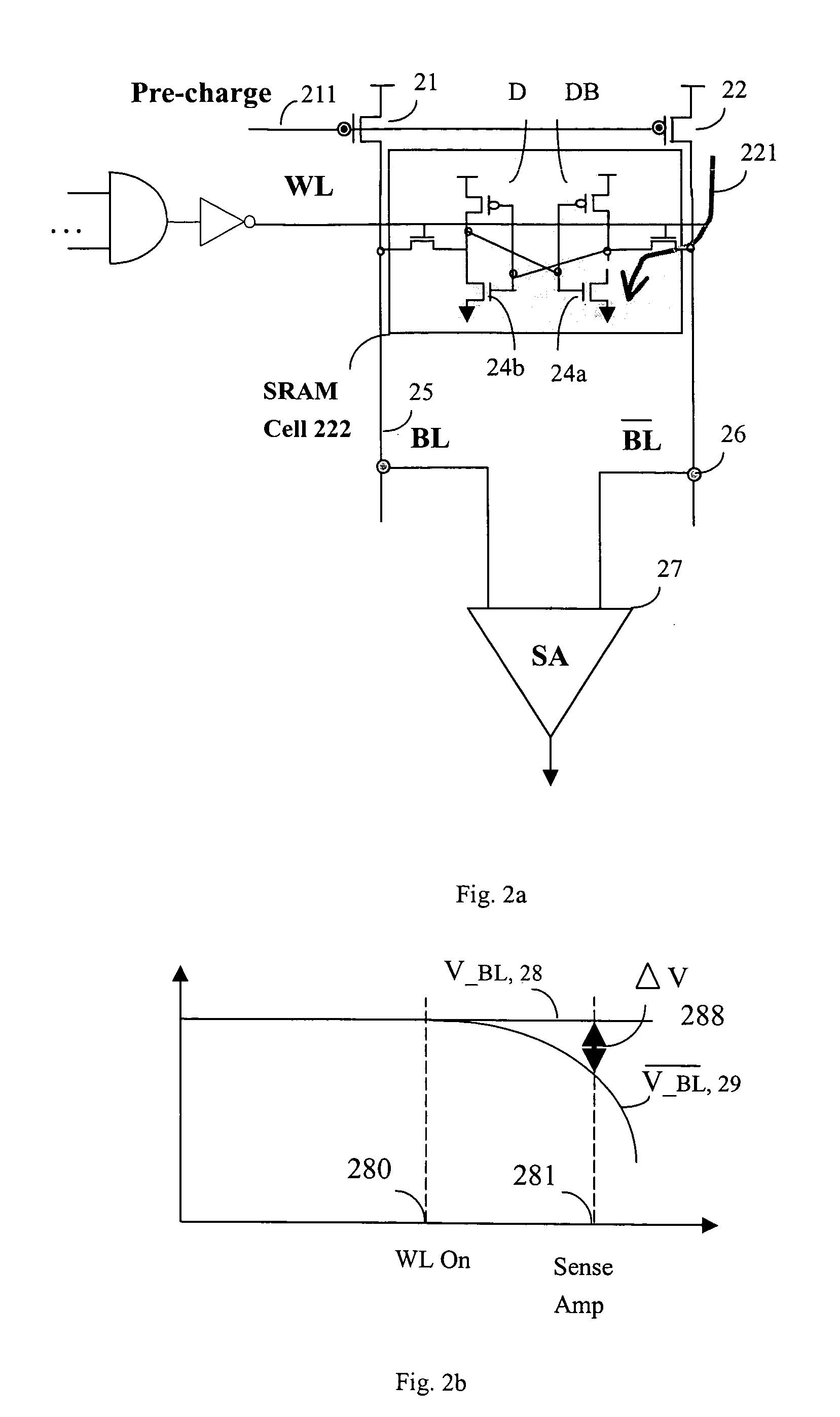
InactiveUS20050117424A1Reduce noiseReduces power/ground bouncingDigital storageBit lineAudio power amplifier
The present invention provides a sensing scheme for semiconductor memory. N-type devices coupling between ground and a bit line and a bit line-bar of memory cells quickly discharge a bit line and a bit line-bar during non-accessing mode. During data accessing mode, one P-type device of an SRAM memory cell pulls up bit line or bit line-bar node slowly to minimize the inductive coupling noise and VDD, Ground bouncing, hence allows smaller amount of differential voltage input to the sense amplifier and results in lower power consumption. A self-timer counts the needed time and sends a signal to enable the current driven sense amplifier and to pull down the word line to avoid further pulling up the bit line or bit line-bar voltage and to reduce the power dissipation. A delay device coupling between the self-timer and bit line and bit line-bar avoids overlapping of pull-down and word line and reduces power leakage.
Owner:TAIWAN IMAGINGTEK
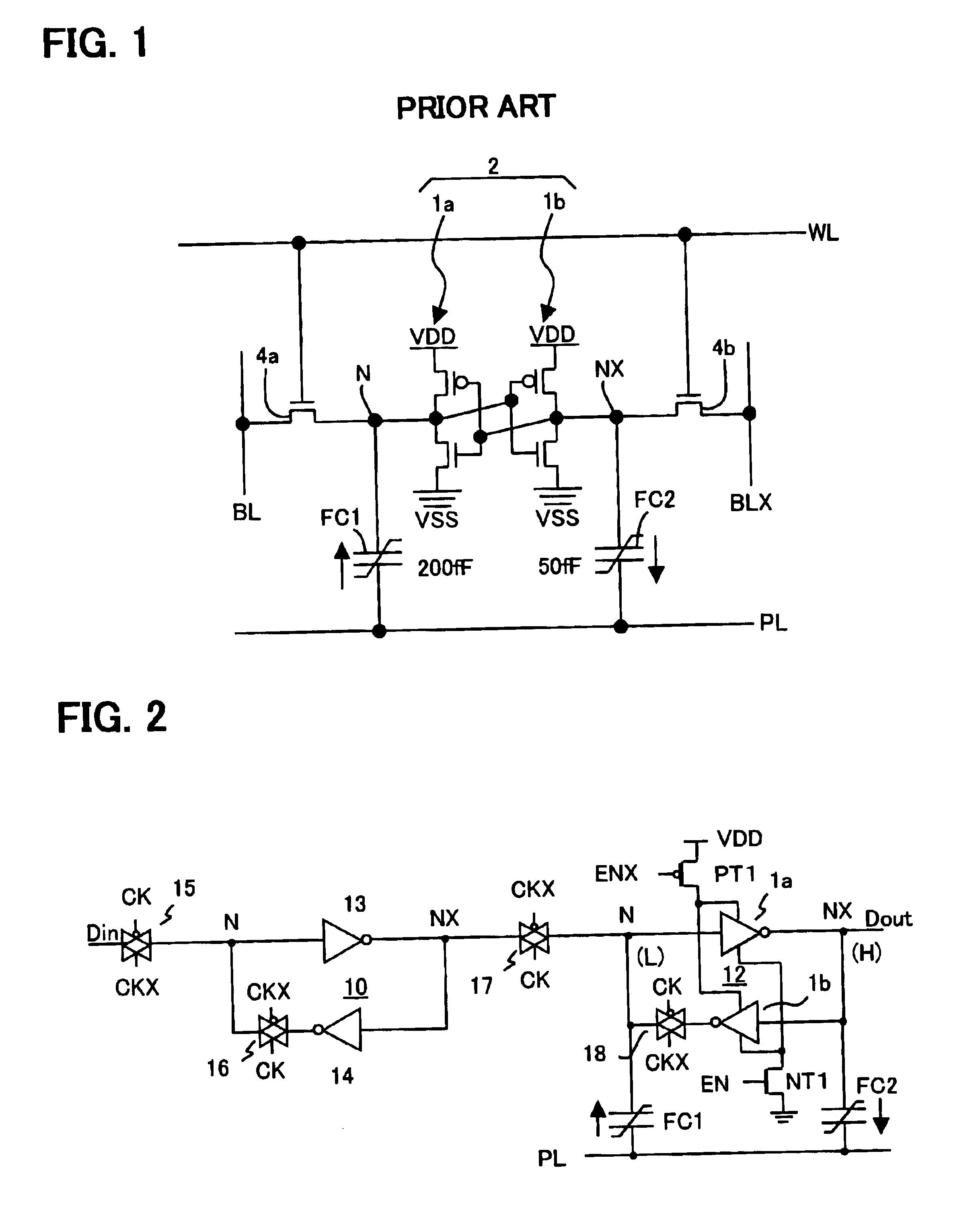
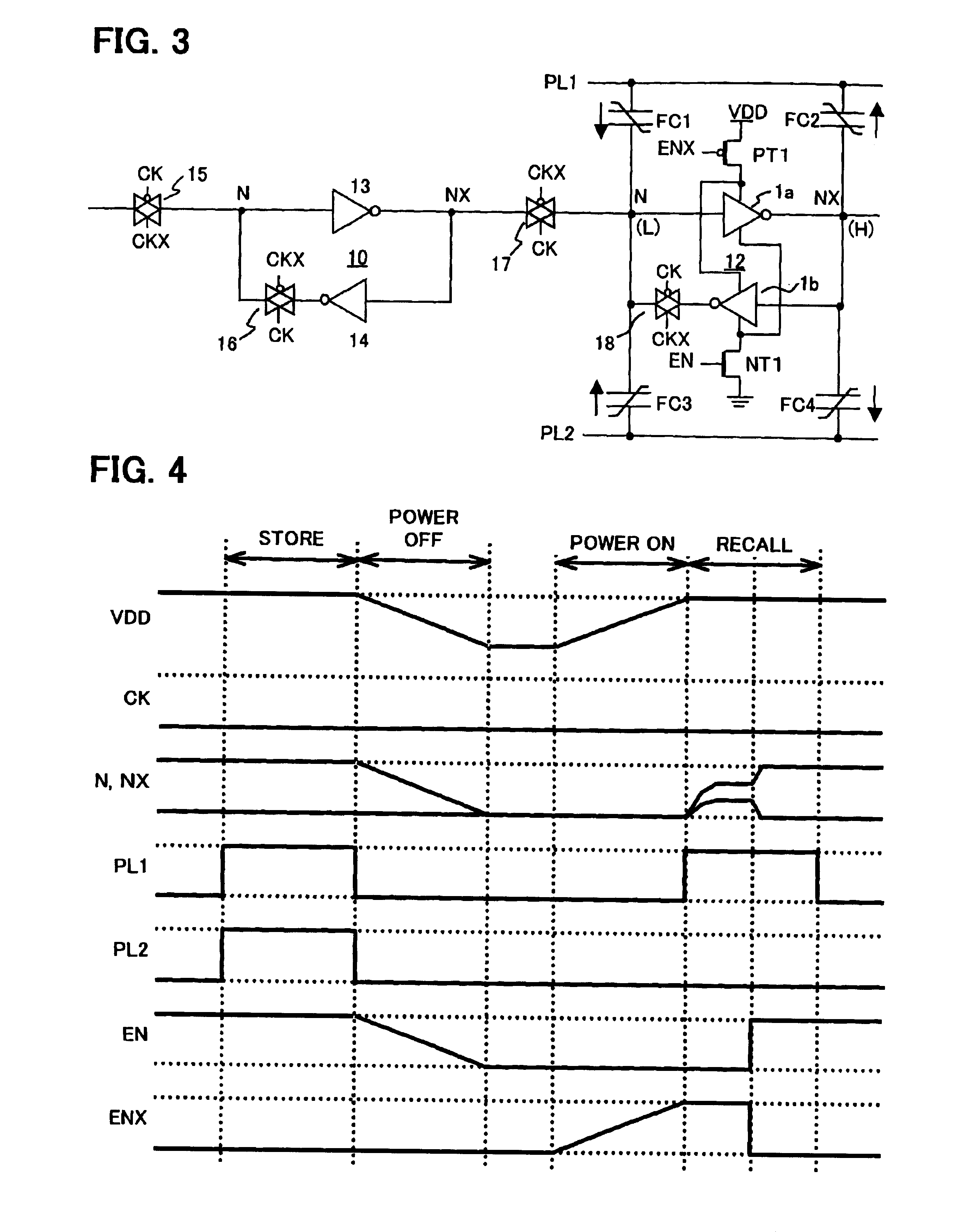
Nonvolatile data storage circuit using ferroelectric capacitors
InactiveUS6934178B2Avoid dataReduce coupling noiseSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFerroelectric capacitorCoupling noise
A nonvolatile data storage circuit has a data holding circuit having a storage node, and a plurality of ferroelectric capacitors one electrodes of which are connected to the storage node. In this nonvolatile data storage circuit, in store operations to write data from the data holding circuit to the ferroelectric capacitors, the timing of at least the rising or the falling of plate signals supplied to the other electrodes of the plurality of ferroelectric capacitors, is made different. During store operation, the timing of the plate signals applied to the plurality of ferroelectric capacitors connected to the storage node is shifted, so that coupling noise between the ferroelectric capacitors is dispersed and can be reduced, and data inversion of the data holding circuit can be prevented.
Owner:FUJITSU SEMICON LTD
Printed circuit board having shield structure of signal transmission line
InactiveUS20060119448A1Reduce the possibilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCross-talk/noise/interference reductionSemiconductor packagePrinted circuit board
A printed circuit board for a high-speed semiconductor package uses bonding wires as a shield structure, e.g., to shield an open portion of signal transmission lines, and thereby reduce the likelihood of coupling noises, e.g., between signal transmission lines.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Write head driver circuit and method for writing to a memory disk
InactiveUS20030090828A1Filamentary/web carriers operation controlH-bridge head driver circuitCapacitanceControl signal
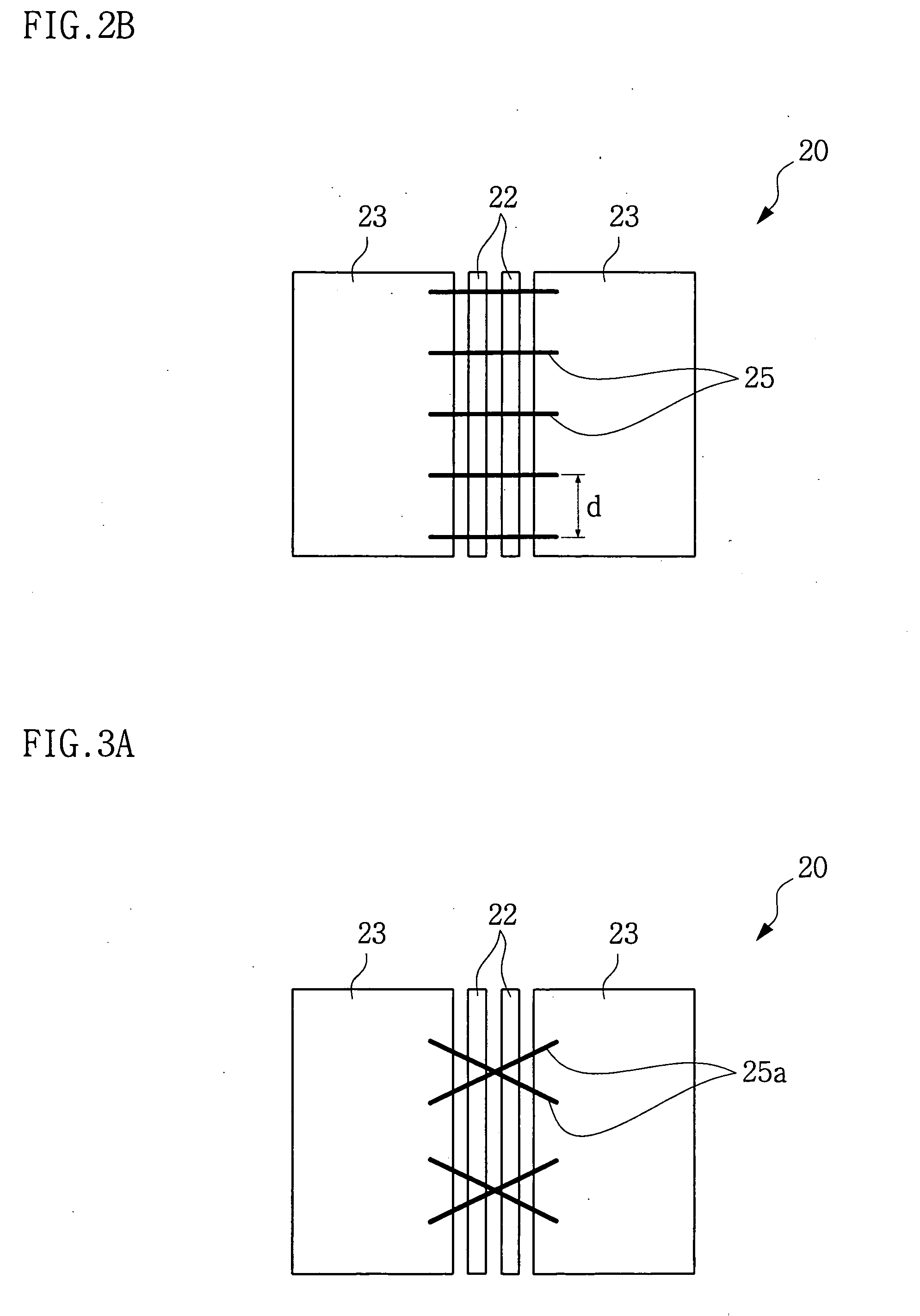
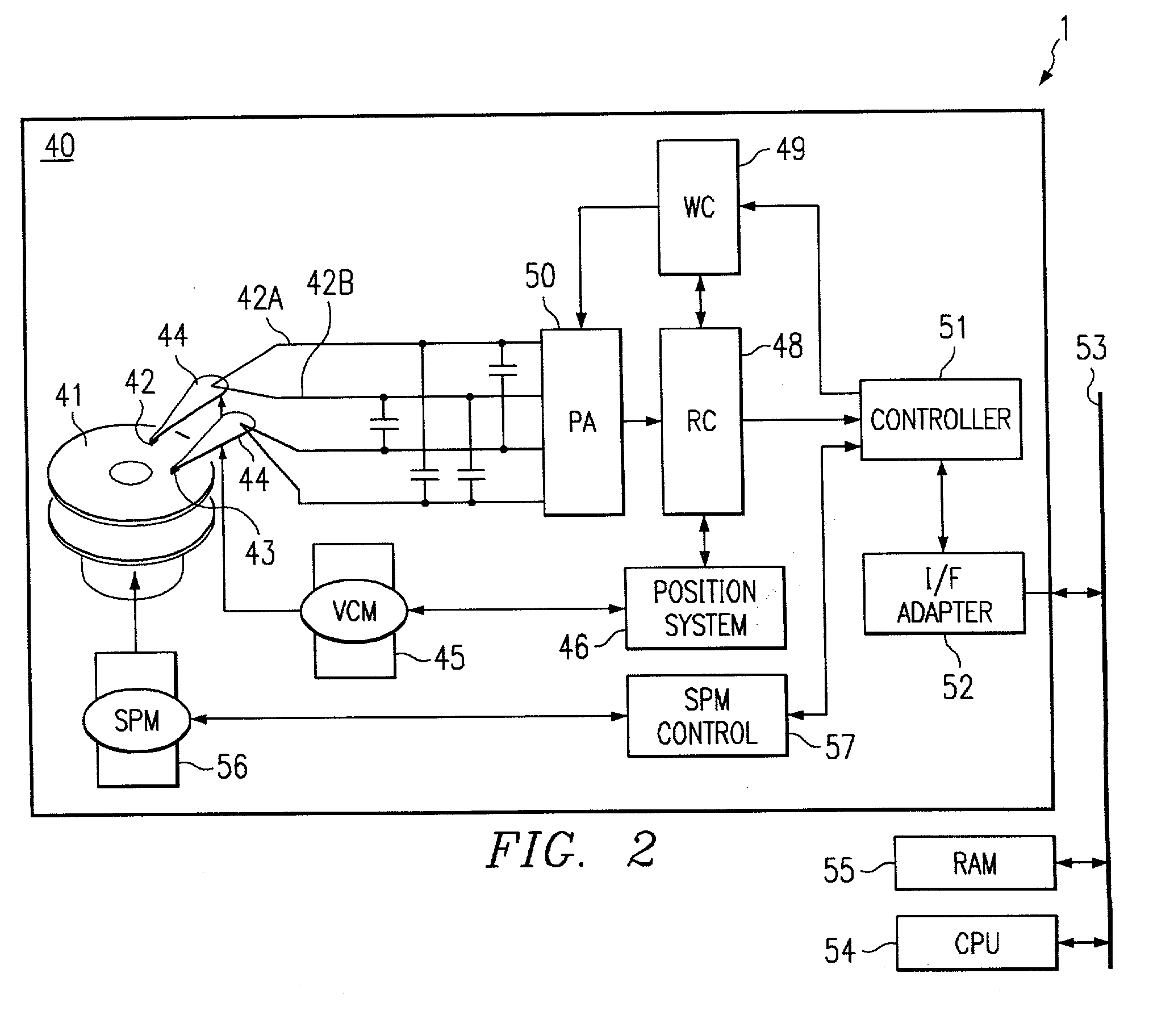
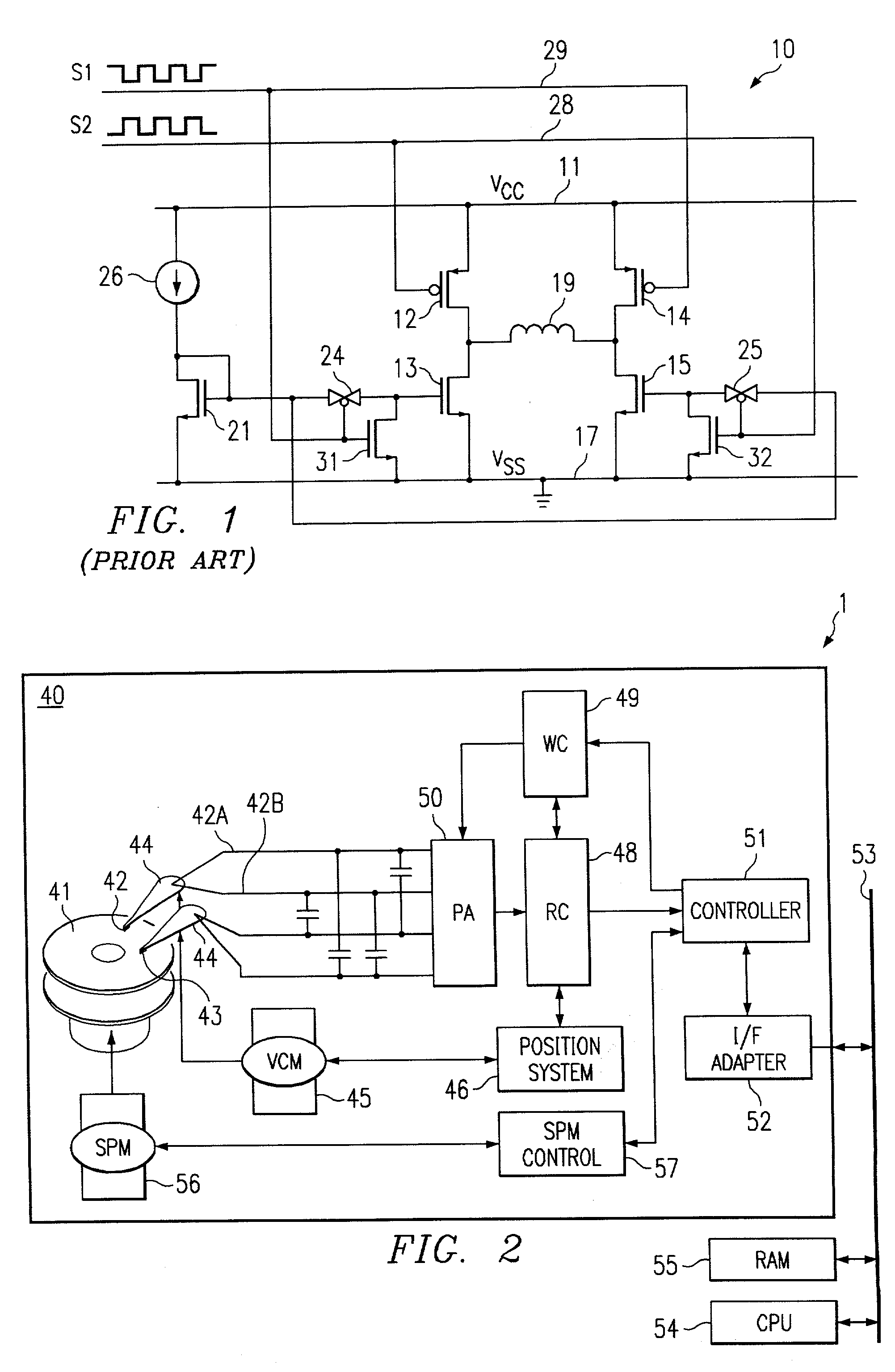
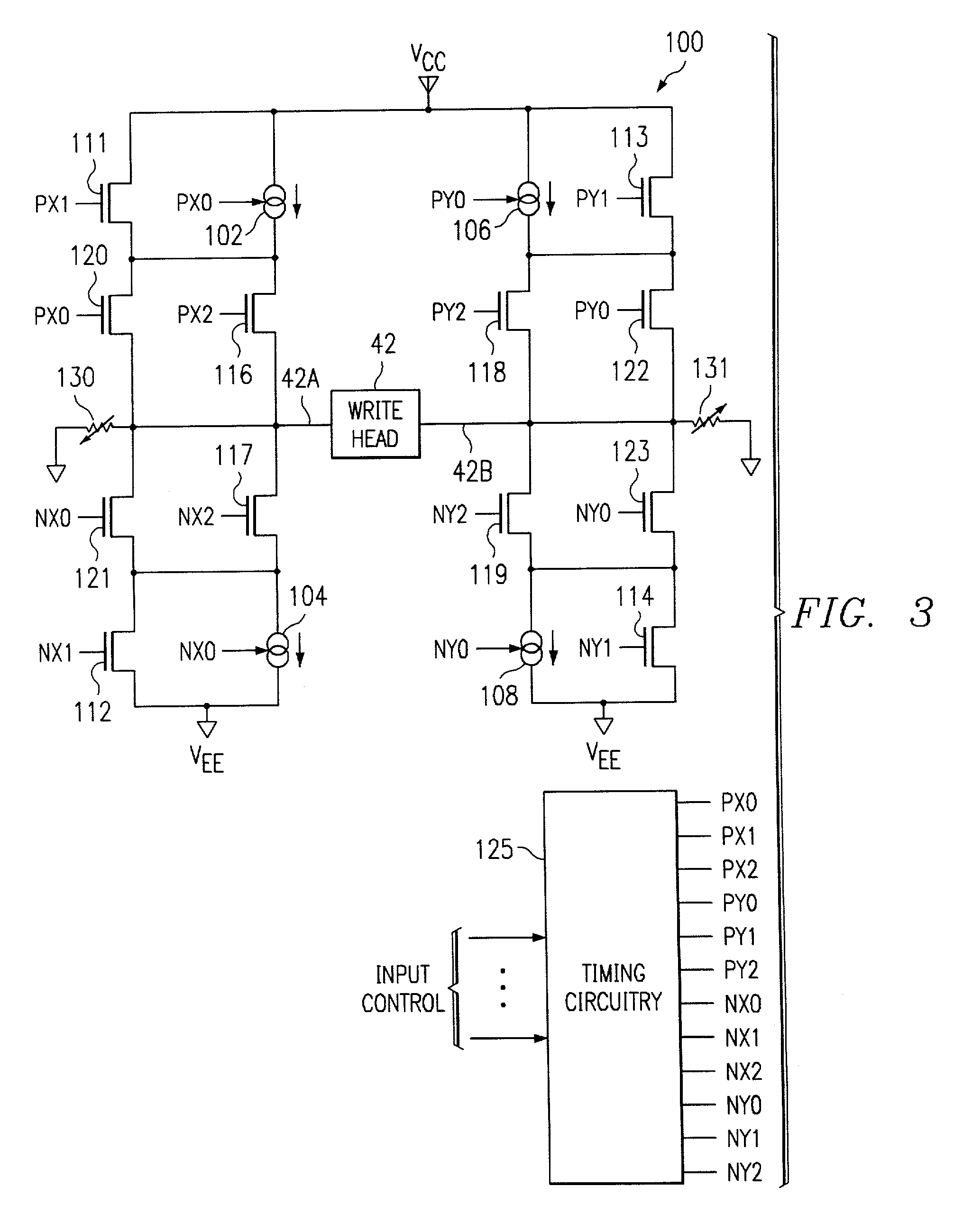
A circuit and method are disclosed for relatively rapidly causing the current flowing through a write head to transition between steady states without generating an appreciable amount of capacitively-coupled noise. Embodiments of the present invention generally provide drive voltage signals to the write head that have no common mode voltage levels during transitions between steady state current levels in the write head. In other words, the drive voltage signals applied to the write head are substantially entirely differential during write head current transitions. In an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, a driver circuit includes switching circuitry connected between the terminals of the write head and reference voltage supplies, such as positive and negative voltage supplies. The driver circuit further includes timing circuitry that generates control signals for controlling the switching circuitry.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
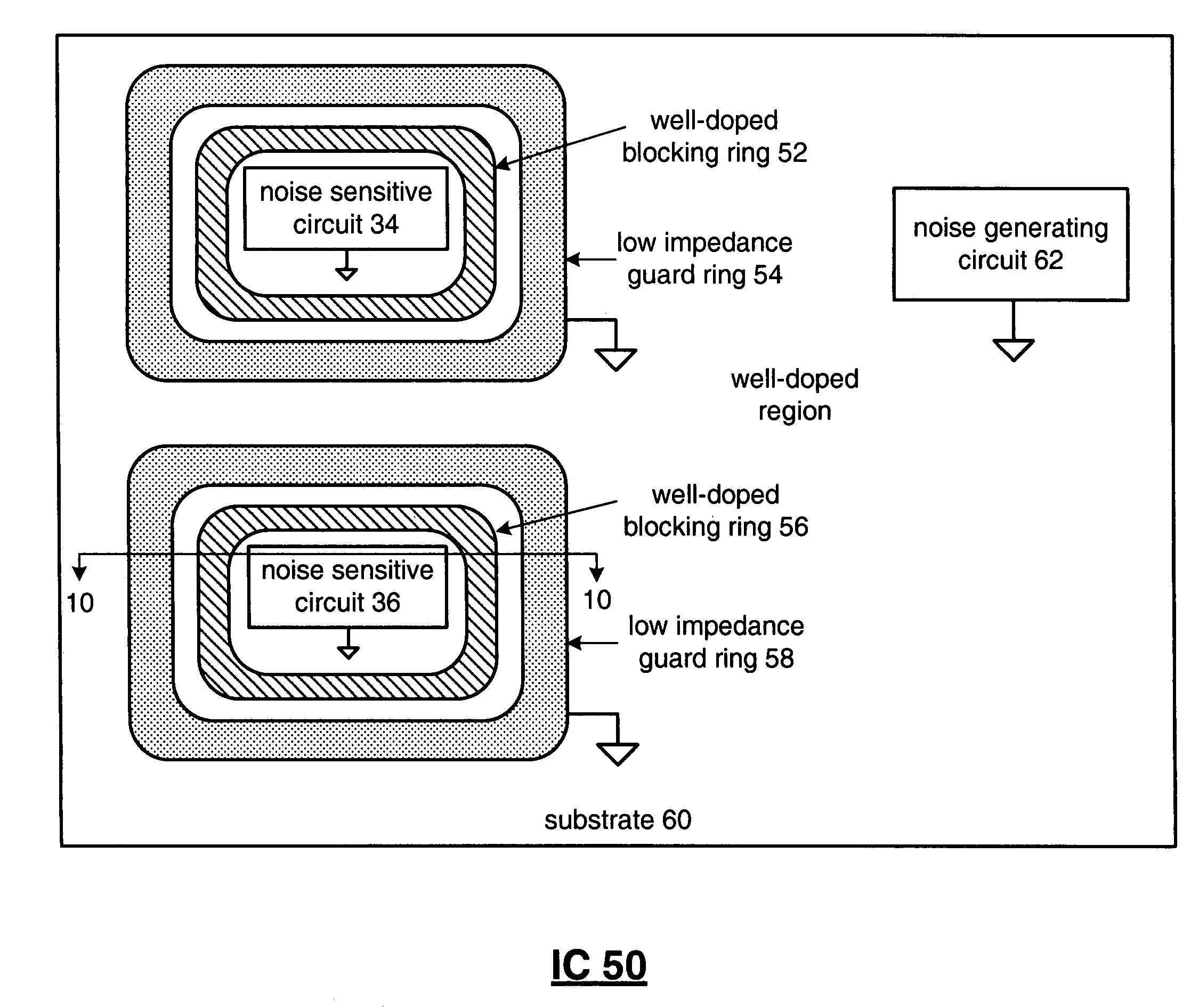
Substrate coupled noise isolation for integrated circuits
ActiveUS7541652B1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPhotonic integrated circuitNoise isolation
An integrated circuit includes a substrate, a noise sensitive circuit, and a first low impedance guard ring. The substrate includes a well-doped blocking ring that at least partially surrounds the noise sensitive circuit. The noise sensitive circuit is fabricated on the substrate. The first low impedance guard ring is fabricated on the substrate to at least partially surround the well-doped blocking ring, wherein the first low impedance guard ring is operably coupled to a first circuit ground, wherein impedance of the first low impedance guard ring is substantially less than impedance of the well-doped blocking ring.
Owner:XILINX INC
Scaling method of foundation microwave radiometer
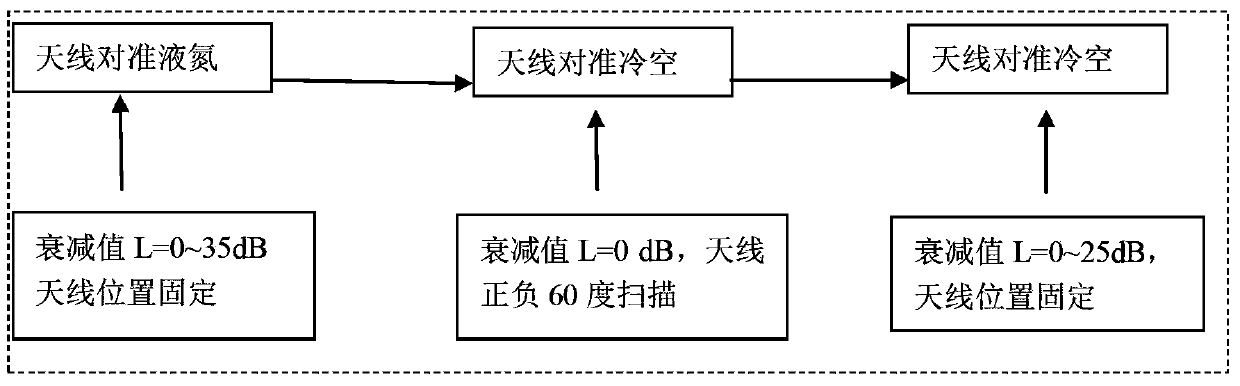
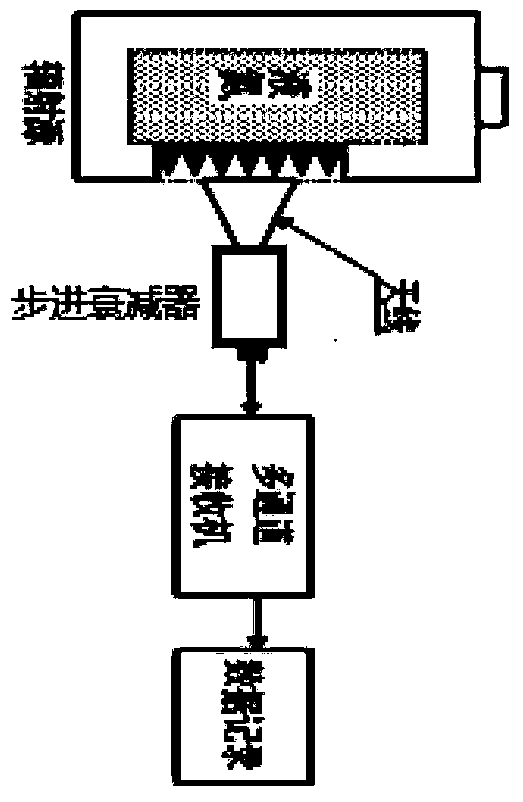
InactiveCN104181511AImprove inversion accuracyReduce calibration errorRadio wave reradiation/reflectionICT adaptationCold airData matching
The invention relates to a scaling method of a foundation microwave radiometer. The scaling method comprises: obtaining voltage values output through each channel in different attenuation values, calculating corresponding equivalent brightness temperature values through attenuation values, calculating system non-linear factors and noise source injection noises according to corresponding relation between each equivalent brightness temperature value and the output voltage of each channel, and completing preliminary scaling; according to sounding profile data matching with time and place, establishing a corresponding relation of atmosphere optics thickness and atmosphere quality, substituting scaling parameters, obtaining a scaling relation curve, determining the scaling parameters according to the scaling relation curve; observing cold air and cold air coupling noises at each attenuation value, obtaining voltage values output through each channel at different attenuation values and fitting the attenuation values and the voltage values; calculating the equivalent noise temperature when an antenna aligns with the cold air through the relation of the attenuation values and the output voltage values of the attenuator, and determining the brightness temperature values corresponding to the cold air observed by the foundation microwave radiometer in different time and places.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com