Patents
Literature
14559 results about "Non-volatile memory" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
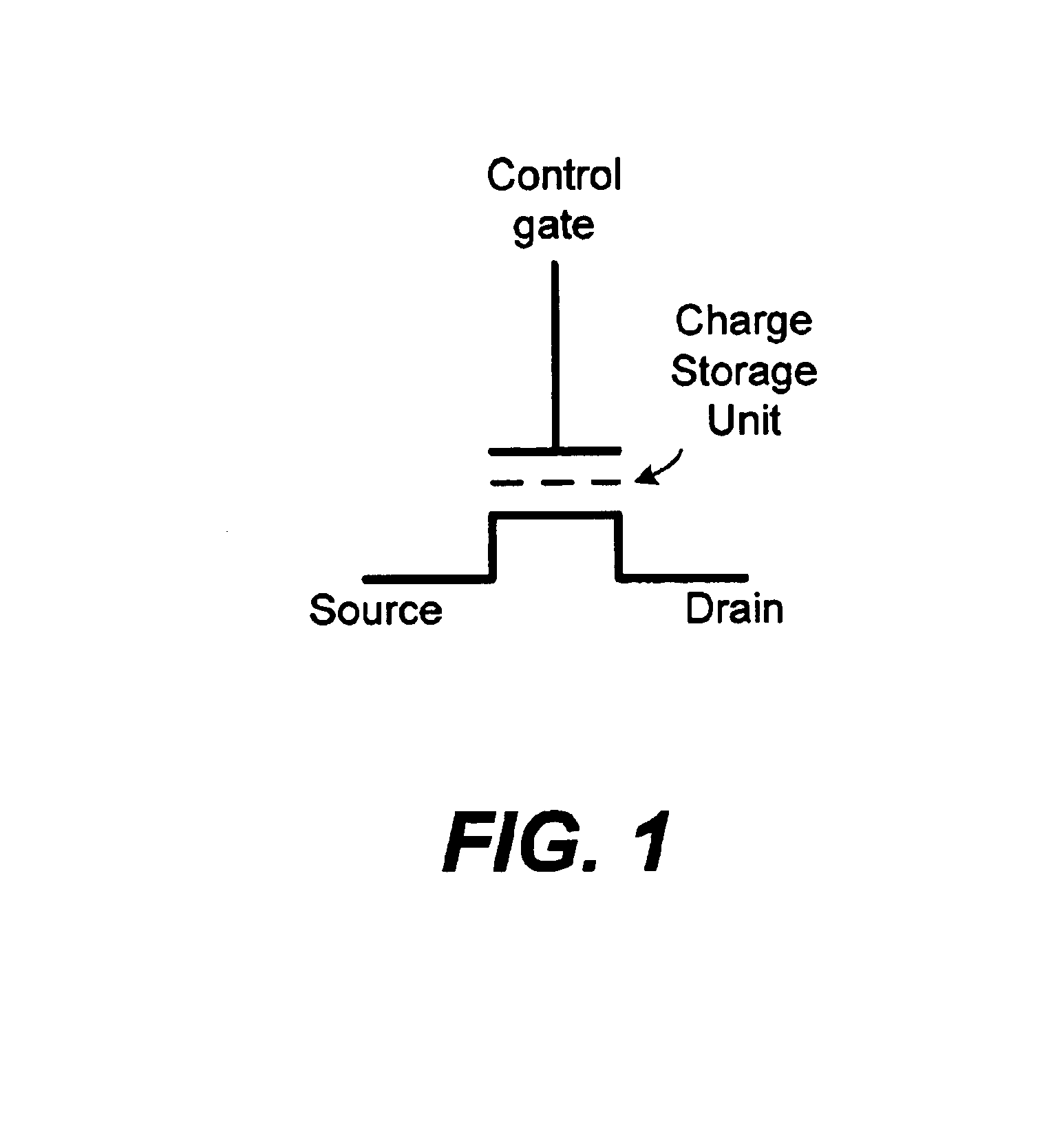
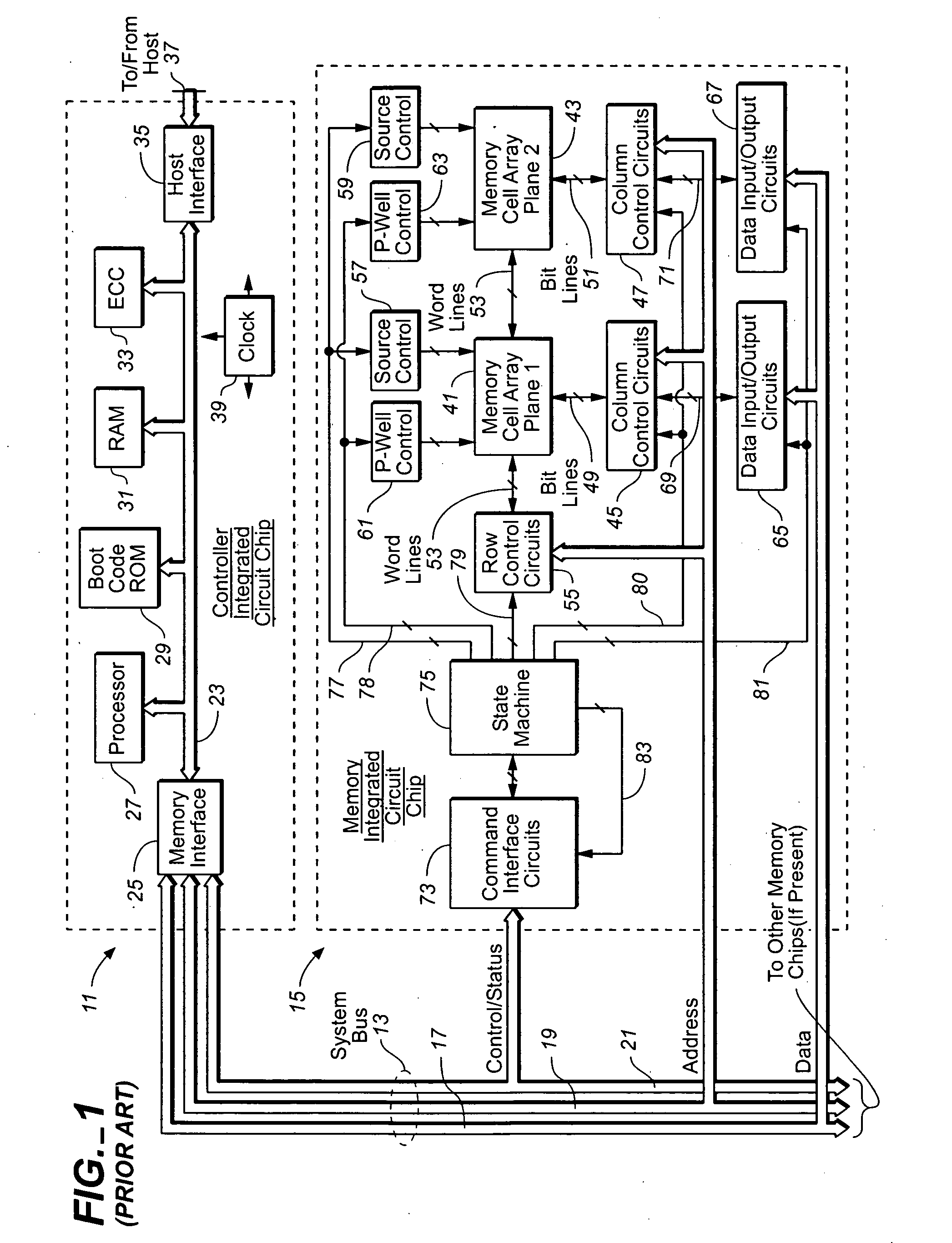
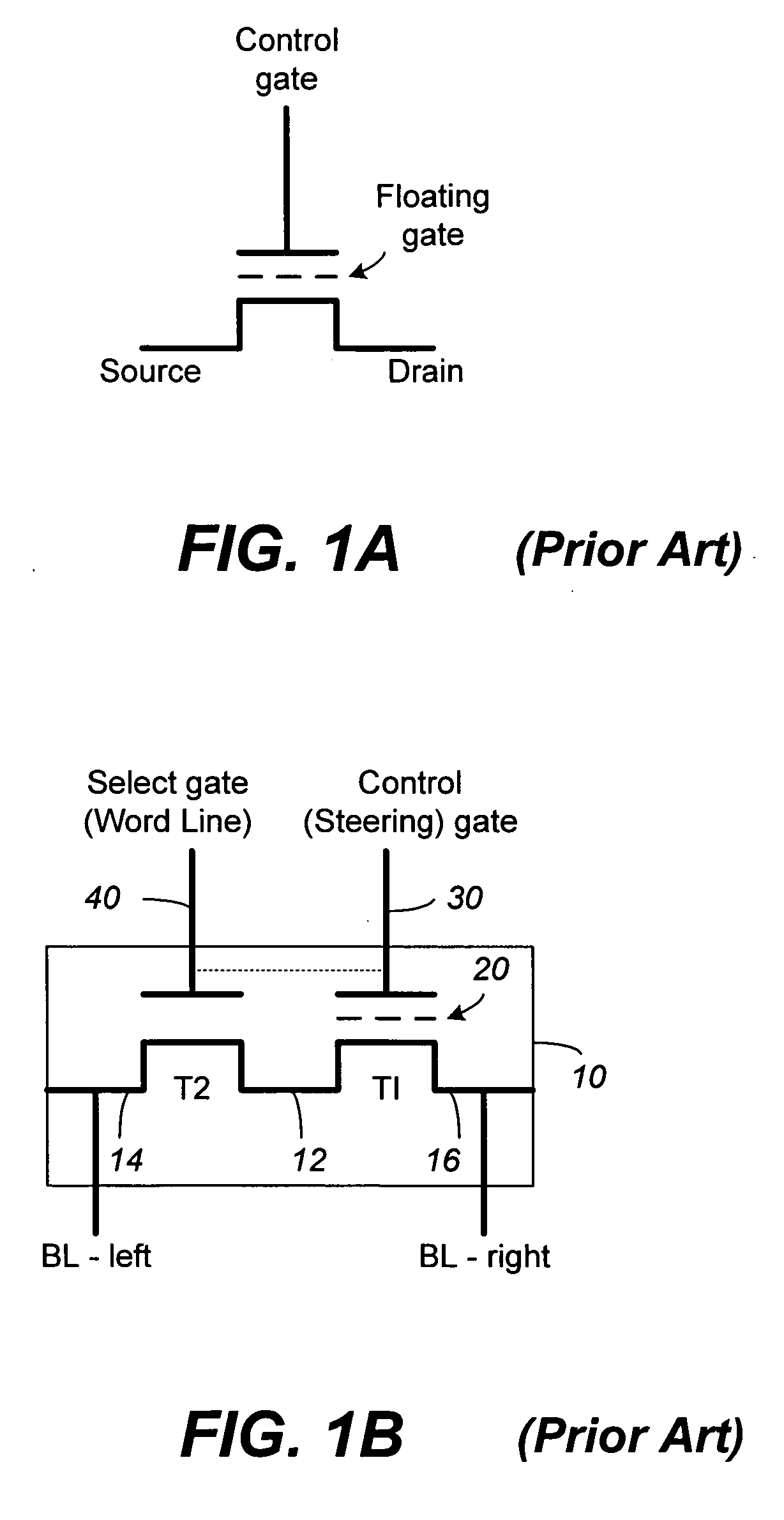
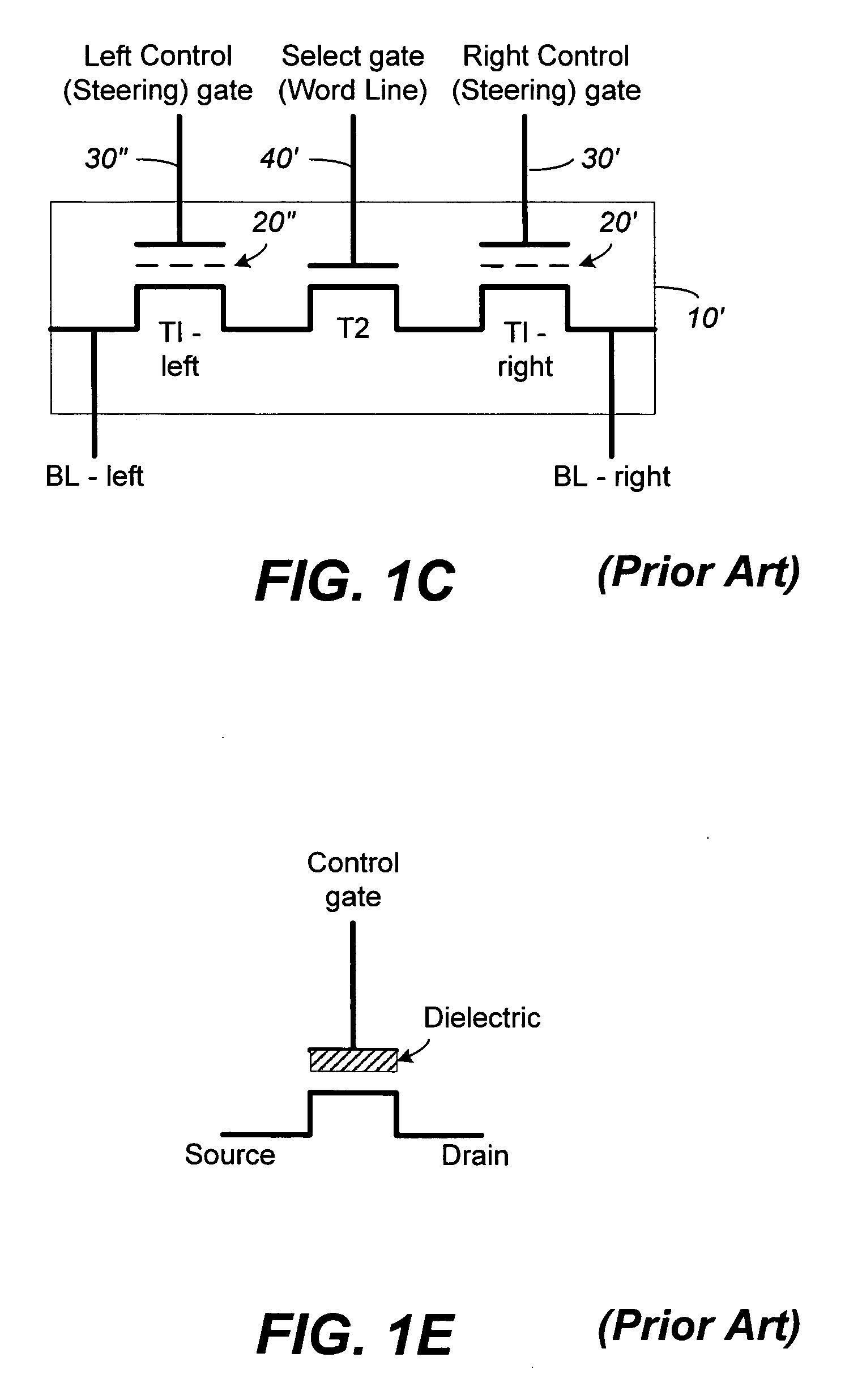
Non-volatile memory (NVM) or non-volatile storage is a type of computer memory that can retrieve stored information even after having been power cycled. In contrast, volatile memory needs constant power in order to retain data. Examples of non-volatile memory include flash memory, read-only memory (ROM), ferroelectric RAM, most types of magnetic computer storage devices (e.g. hard disk drives, floppy disks, and magnetic tape), optical discs, and early computer storage methods such as paper tape and punched cards.
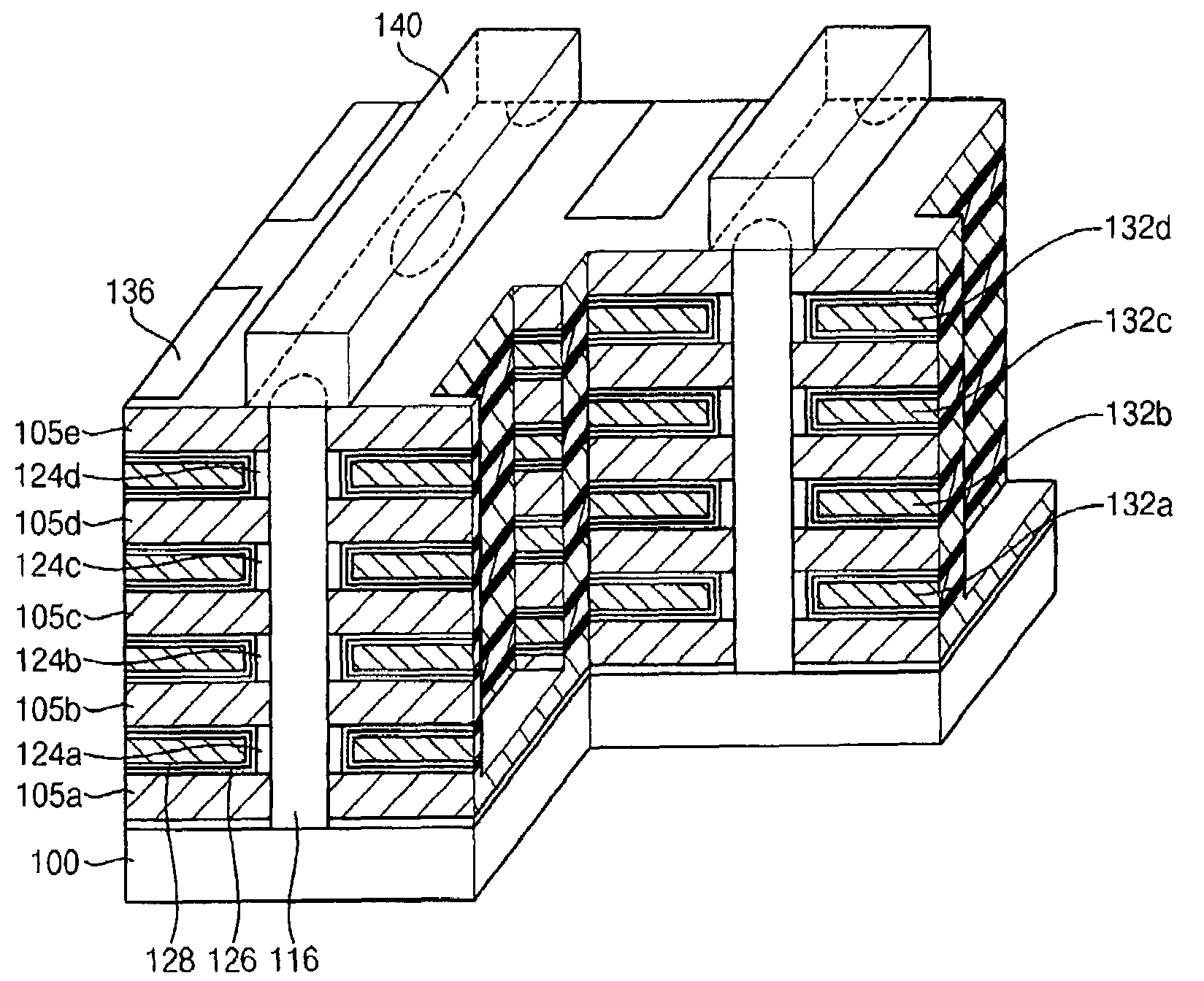
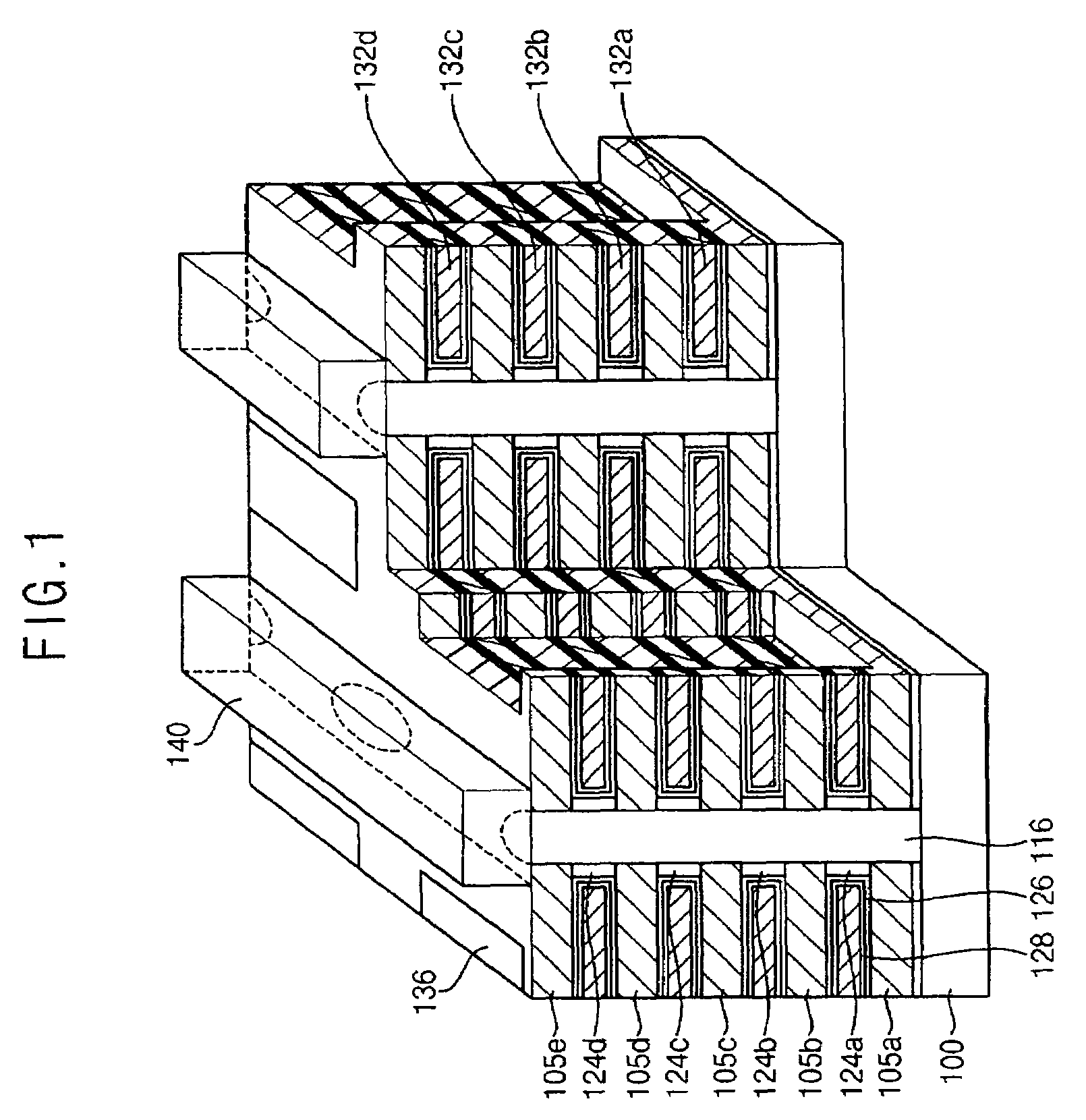
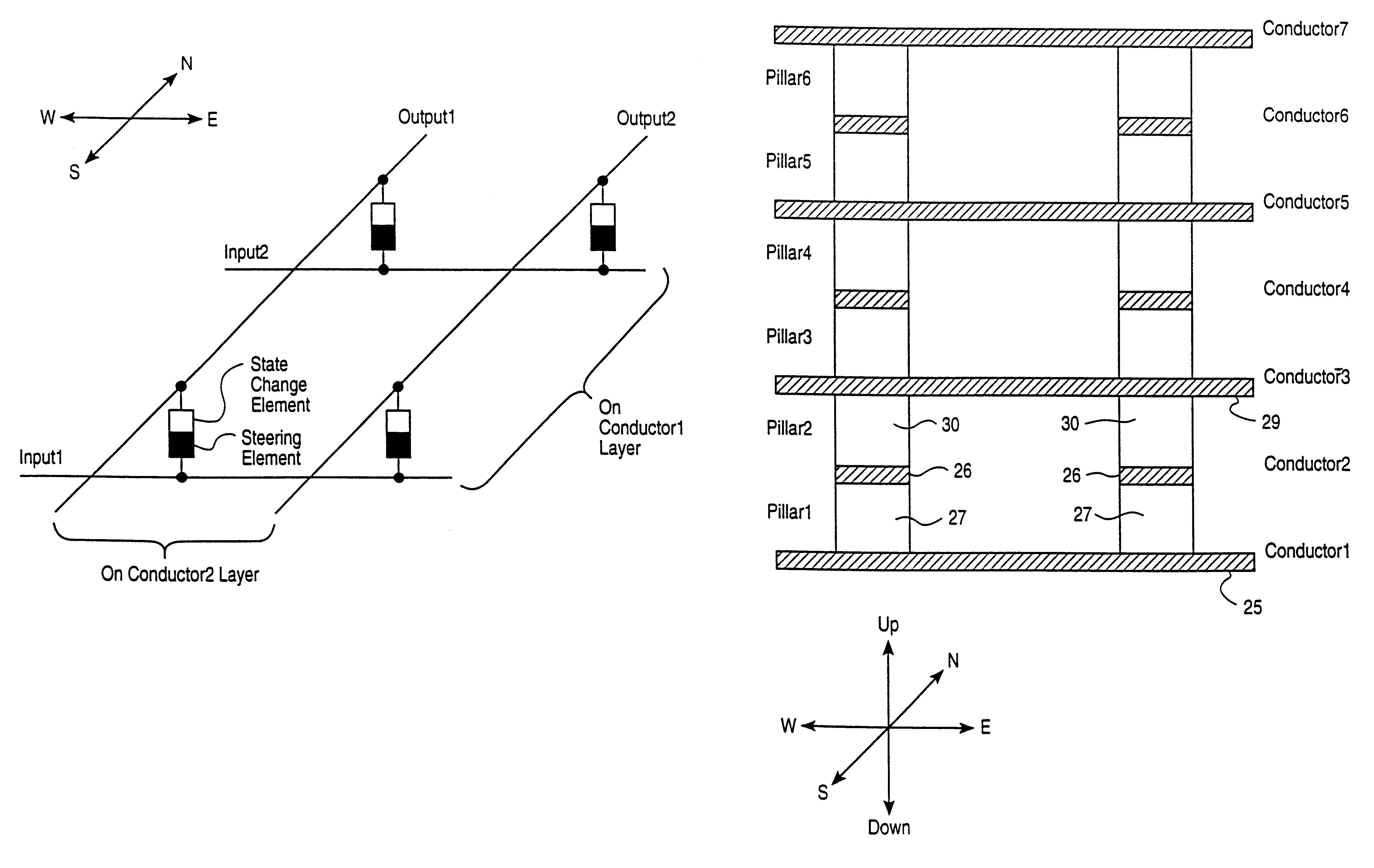
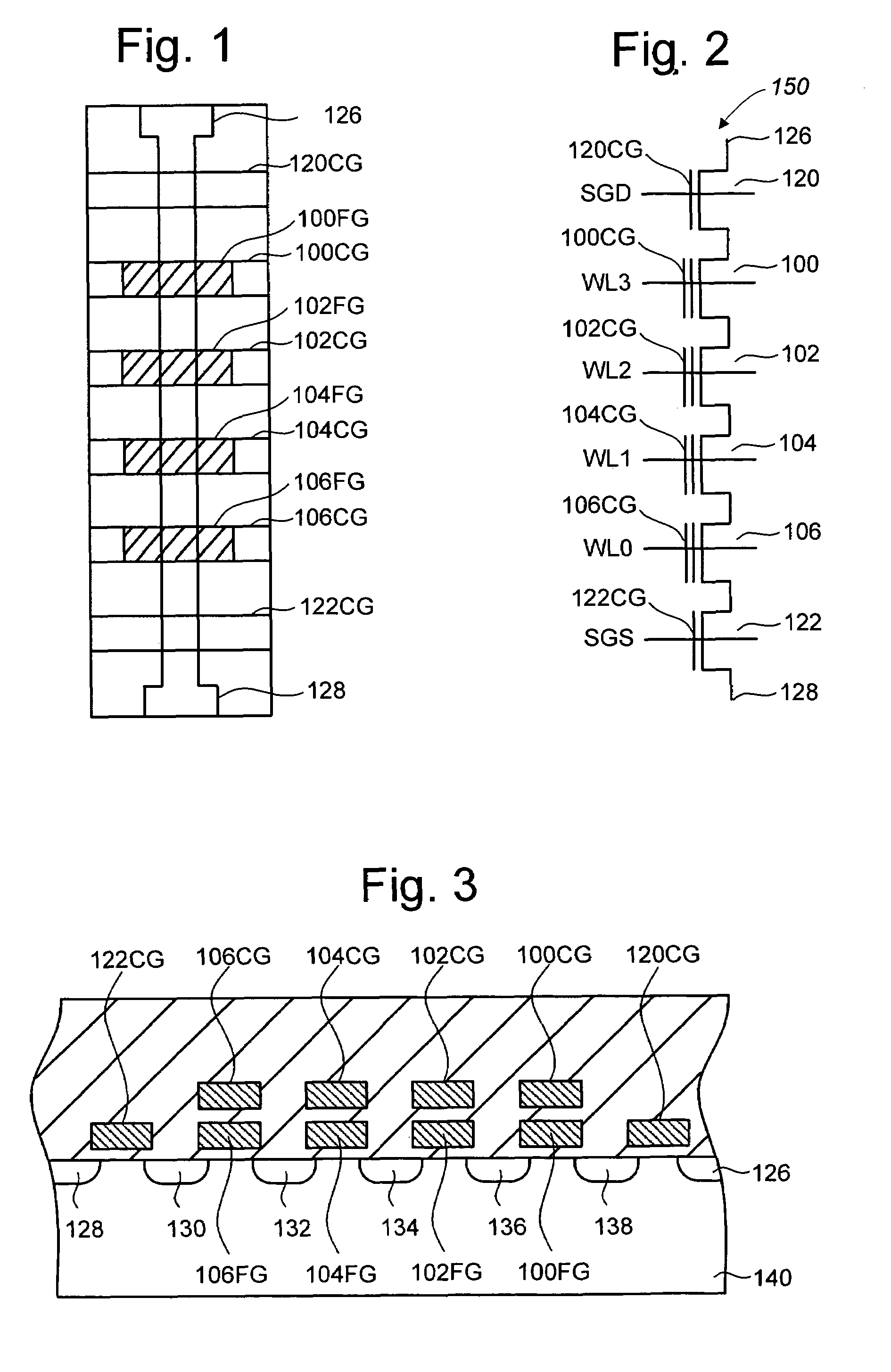
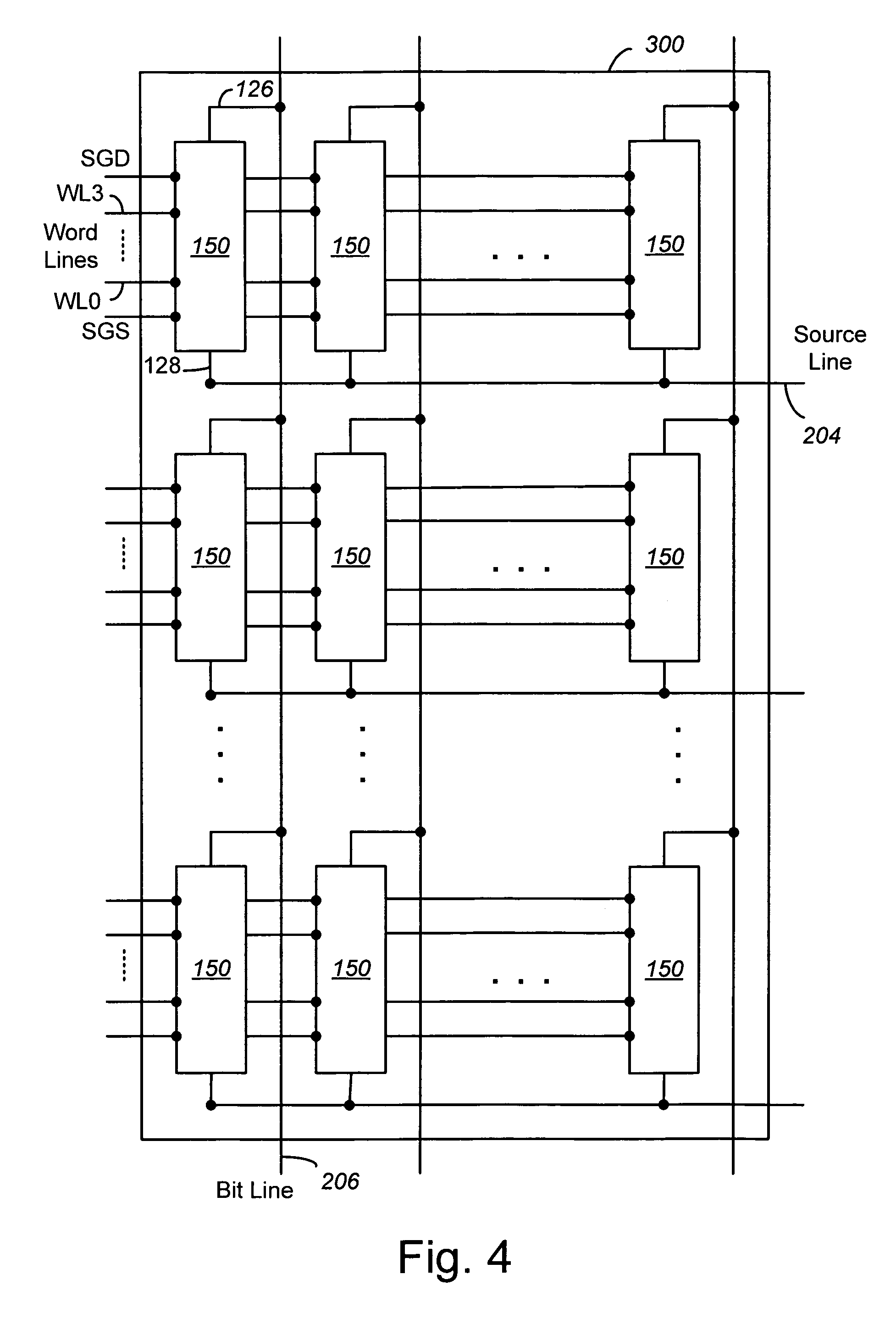
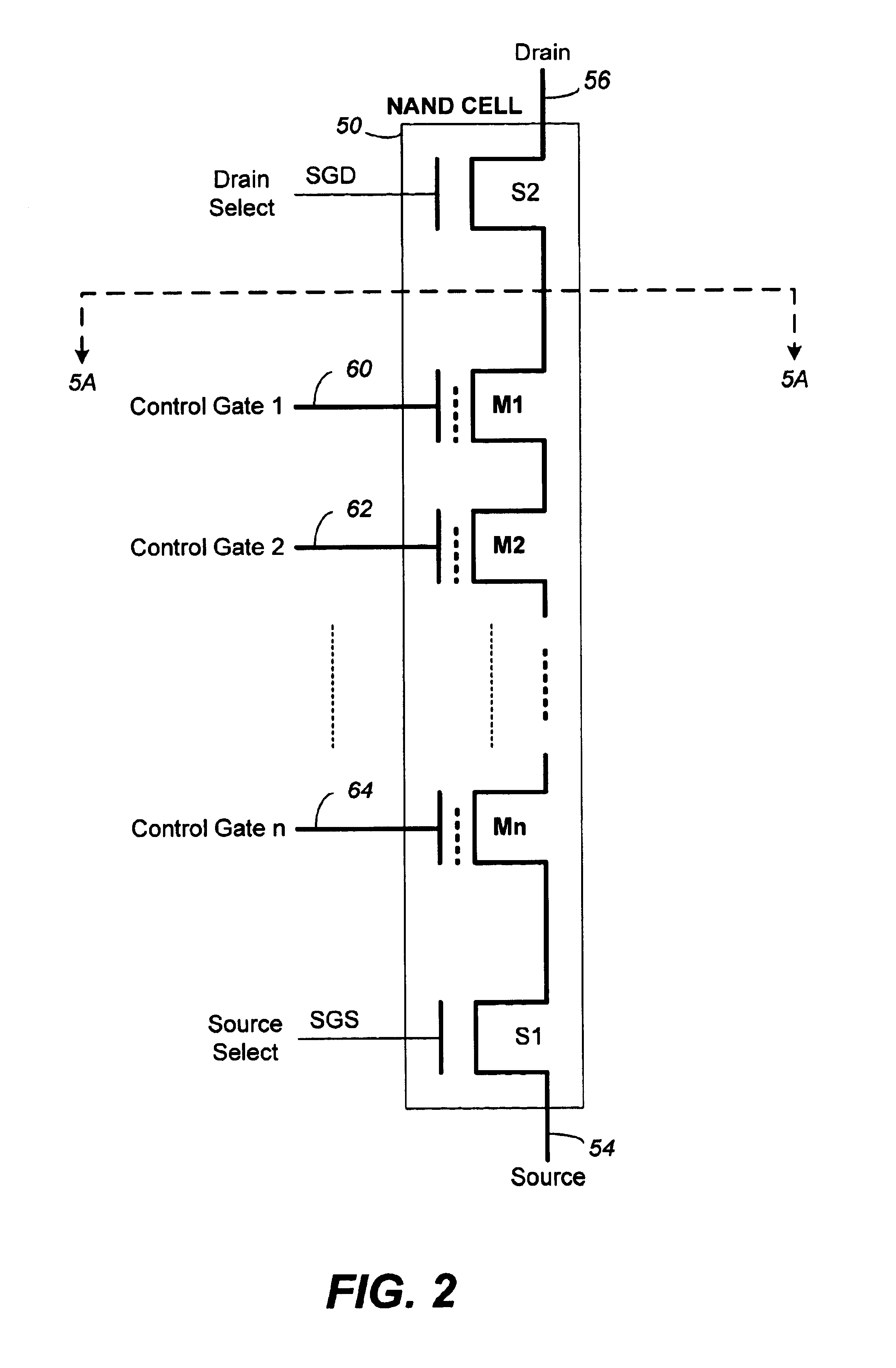
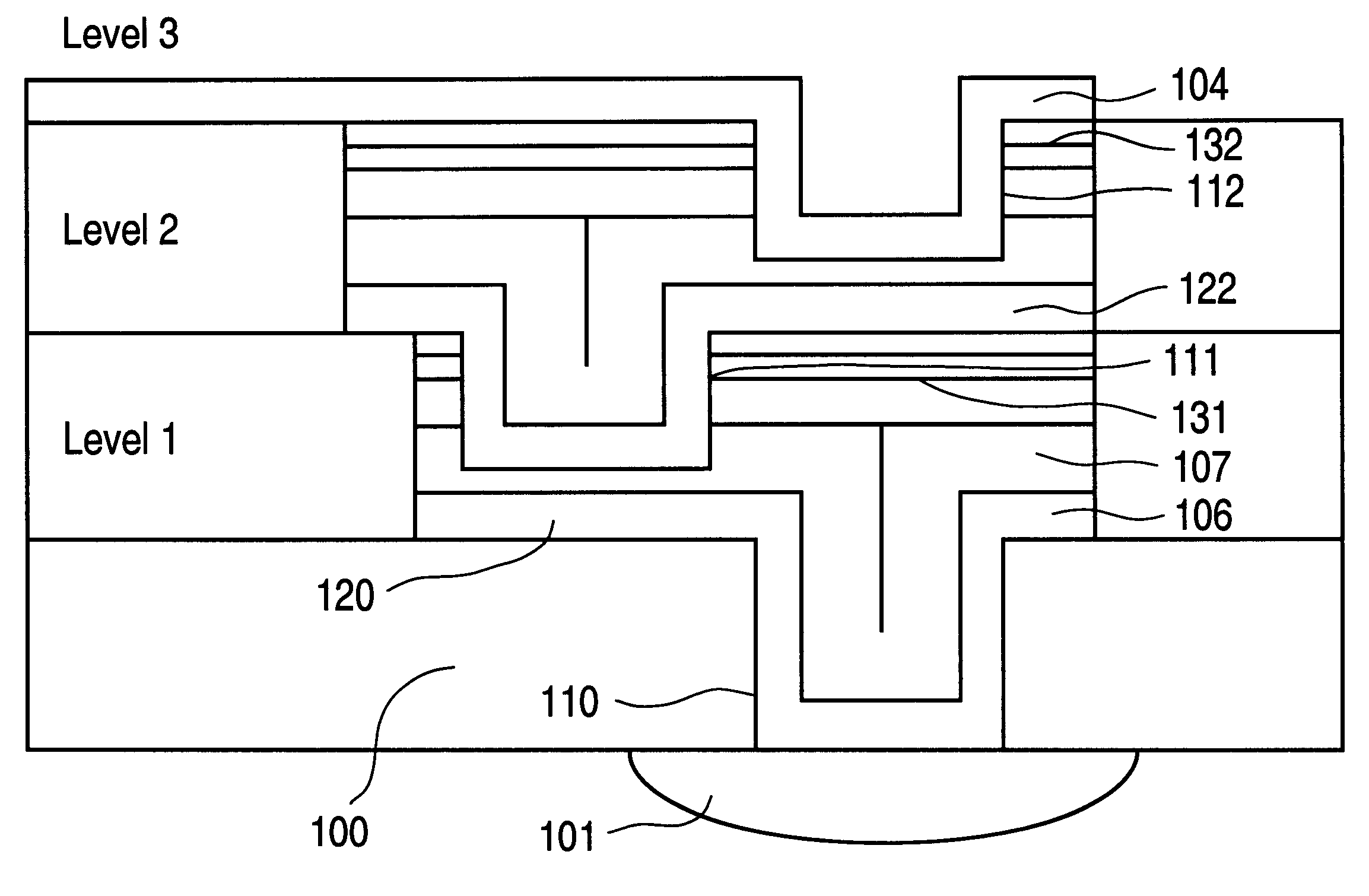
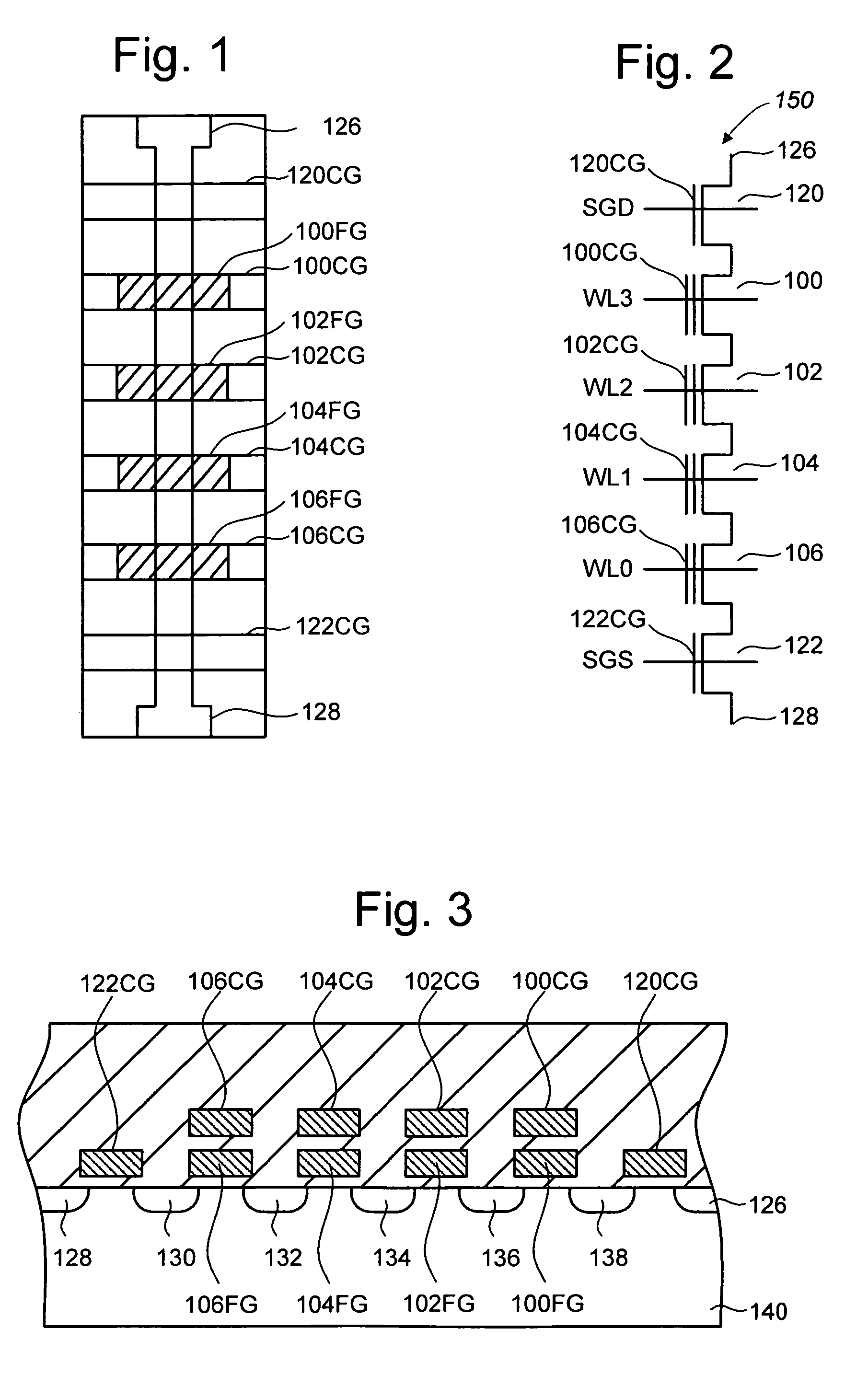
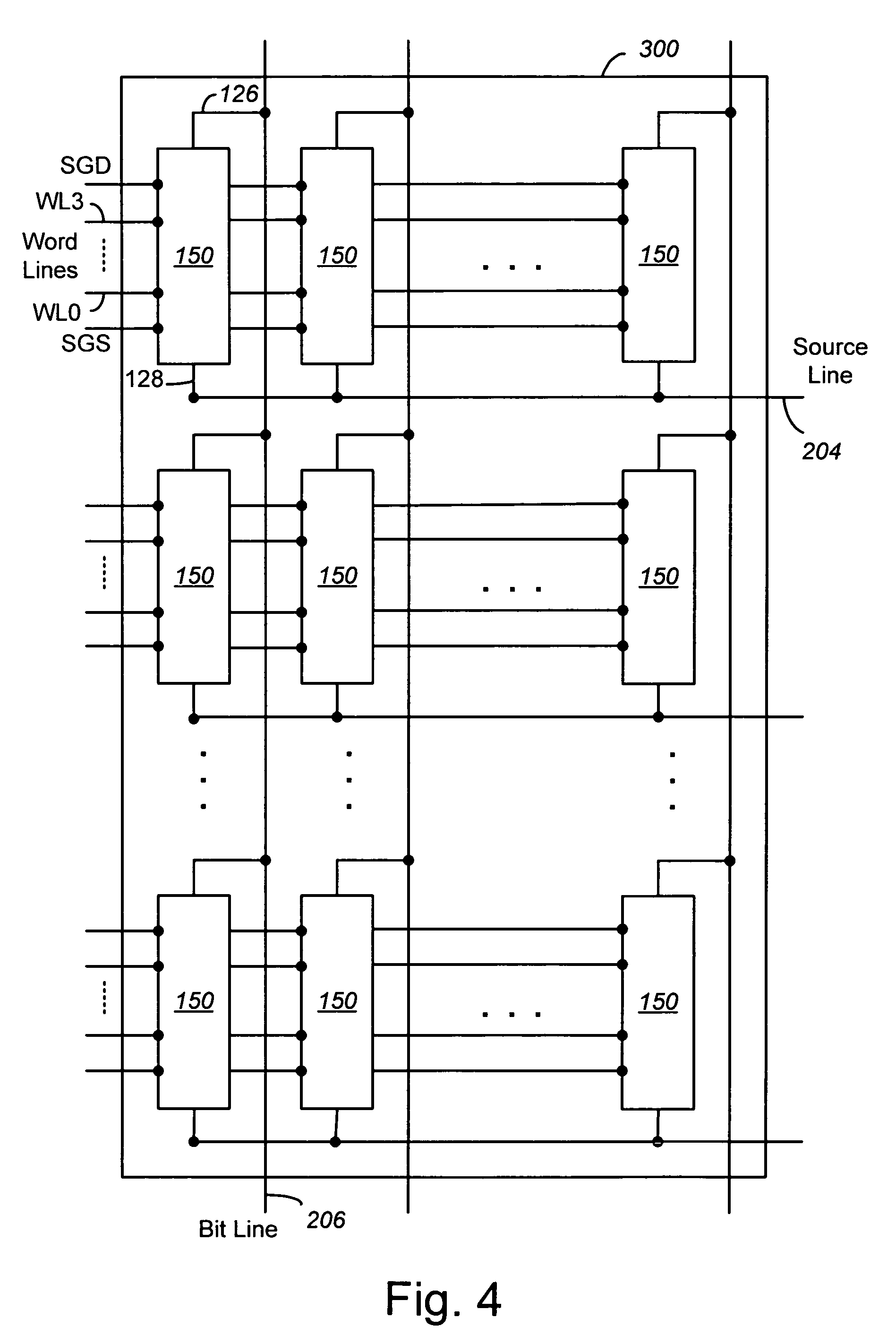
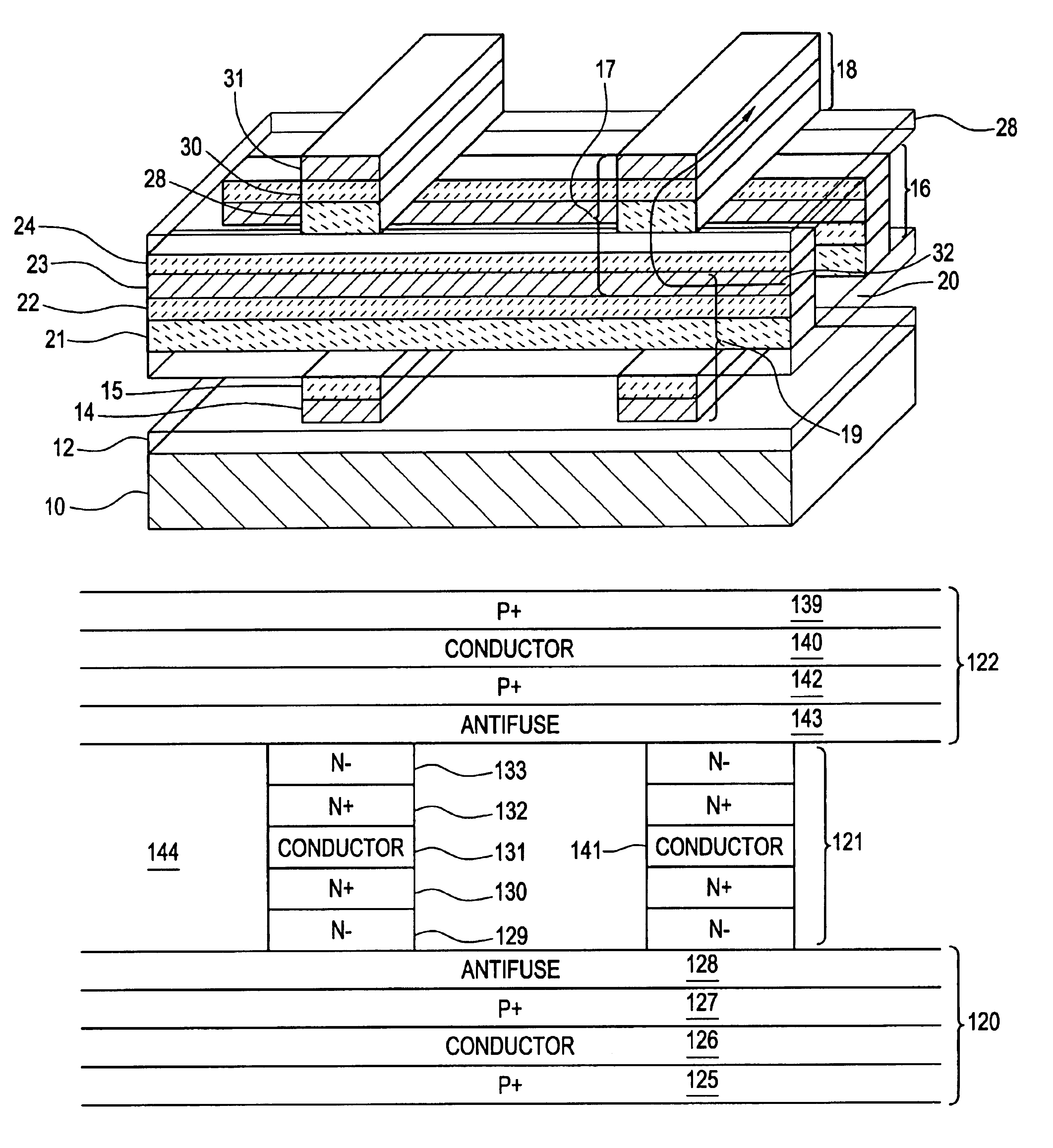
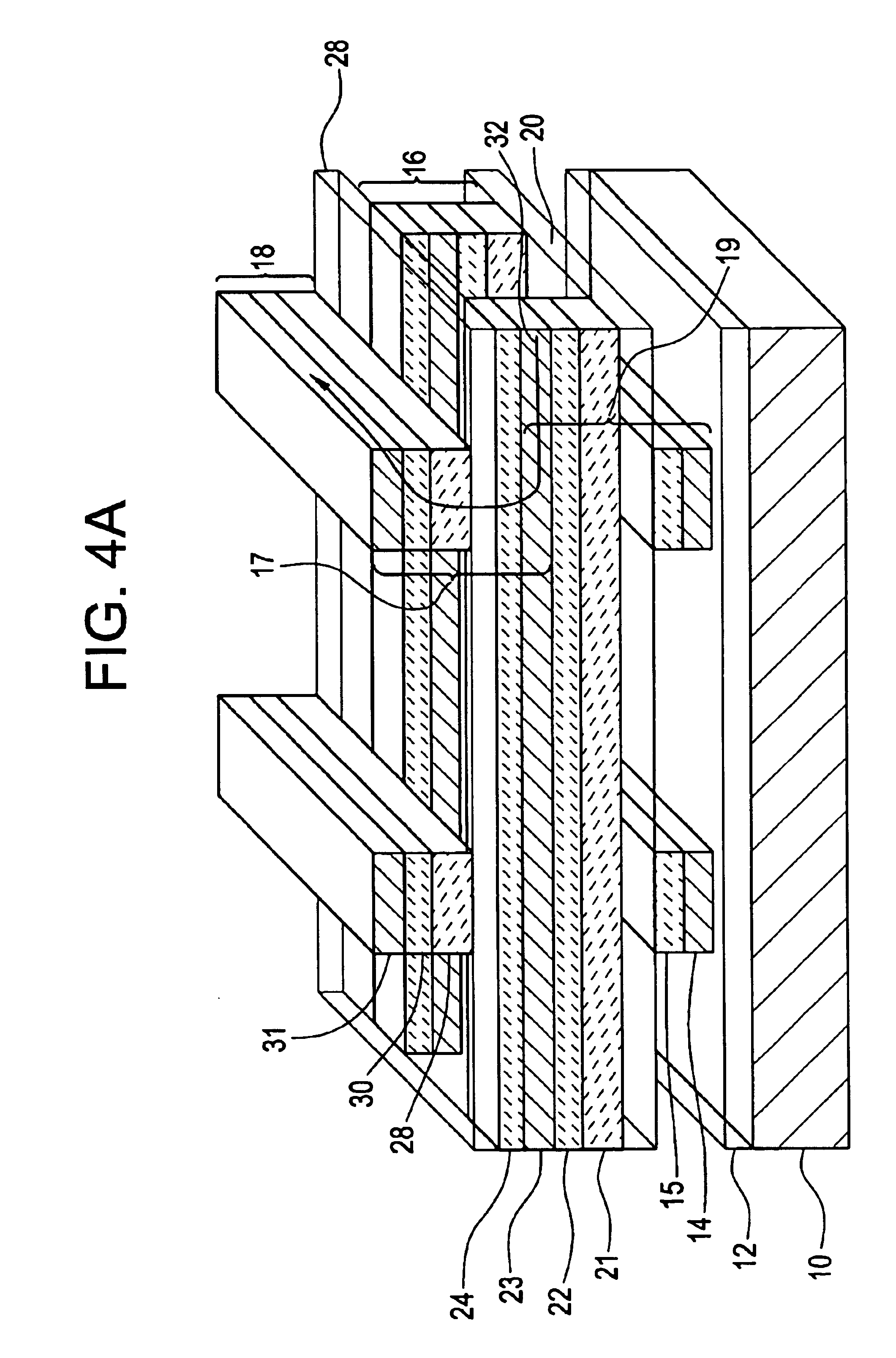
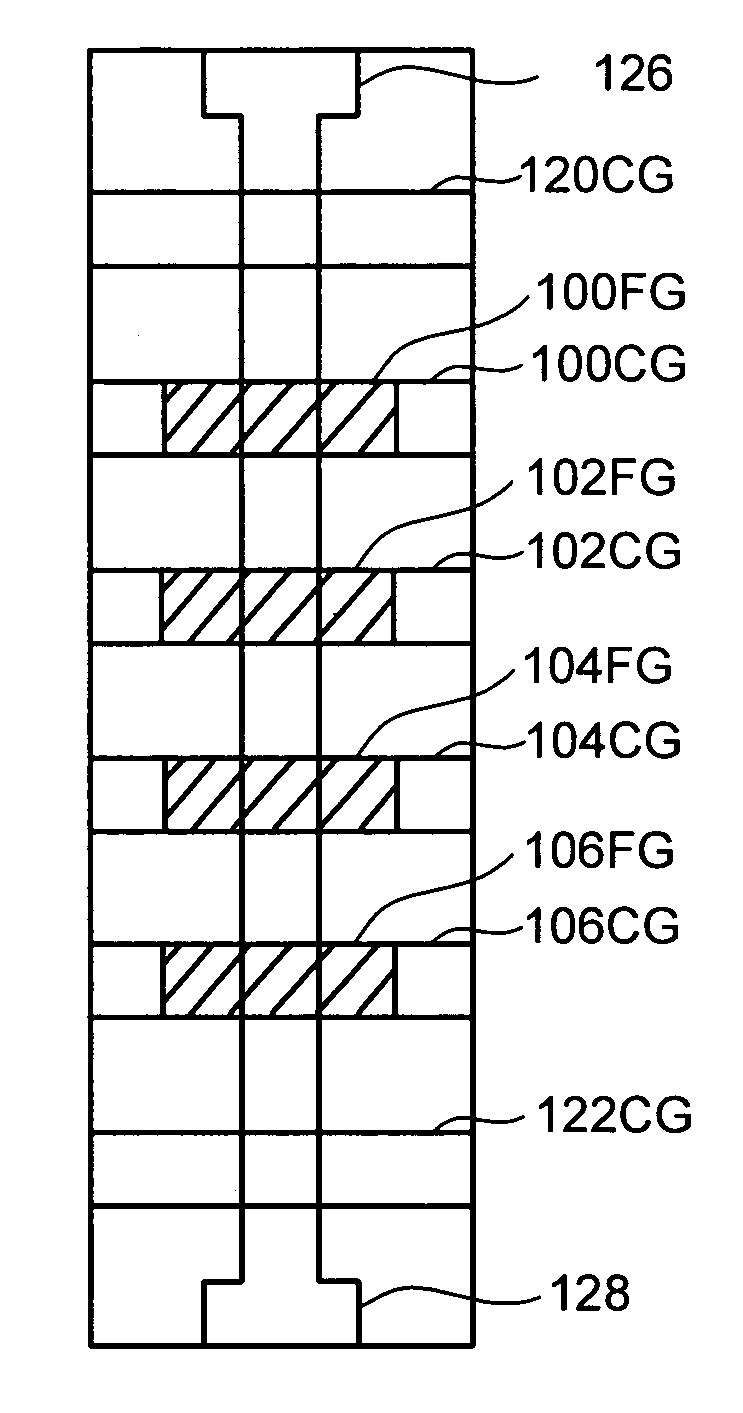
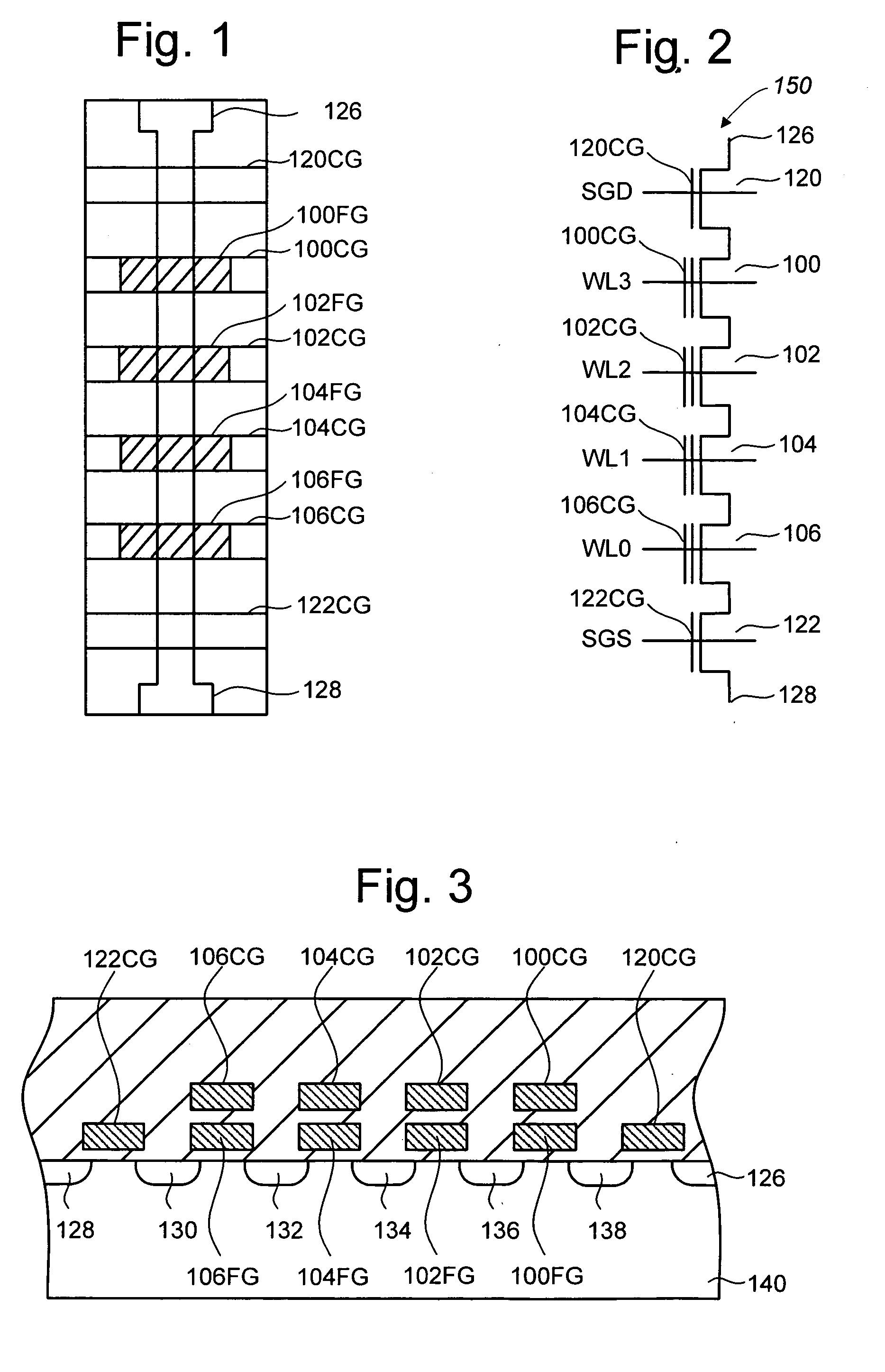
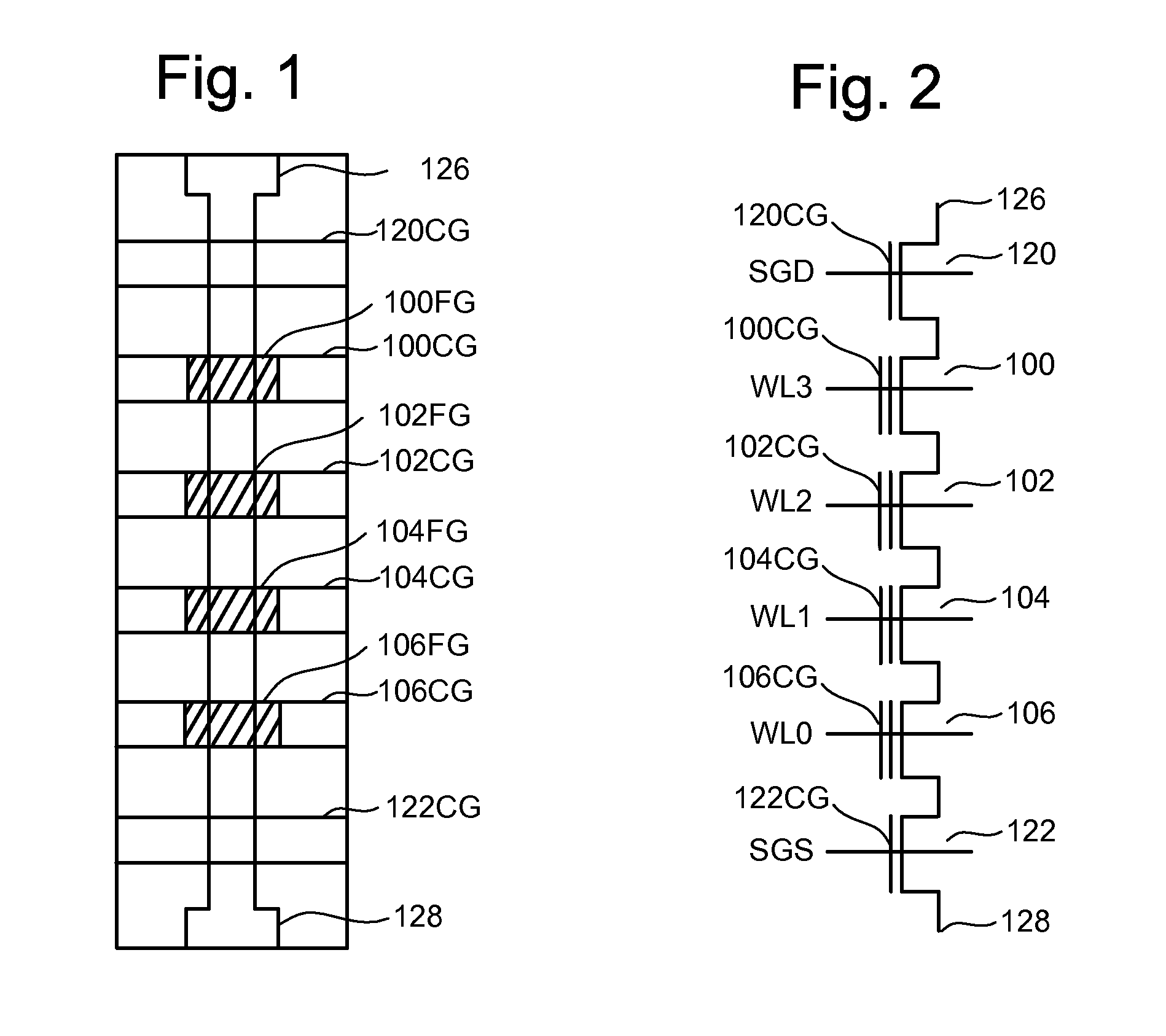
Vertically stacked field programmable nonvolatile memory and method of fabrication
A very high density field programmable memory is disclosed. An array is formed vertically above a substrate using several layers, each layer of which includes vertically fabricated memory cells. The cell in an N level array may be formed with N+1 masking steps plus masking steps needed for contacts. Maximum use of self alignment techniques minimizes photolithographic limitations. In one embodiment the peripheral circuits are formed in a silicon substrate and an N level array is fabricated above the substrate.
Owner:RHOMBUS
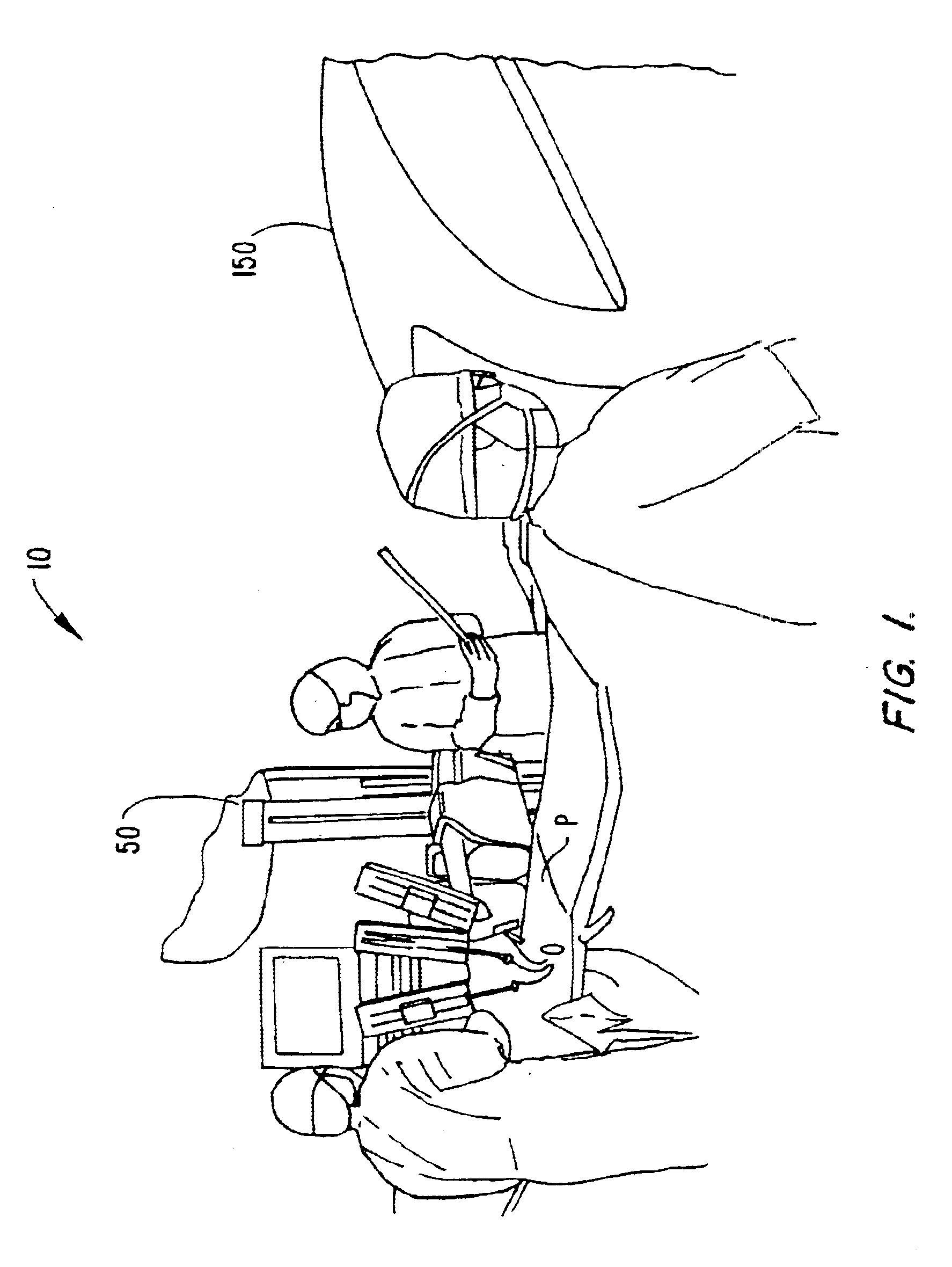
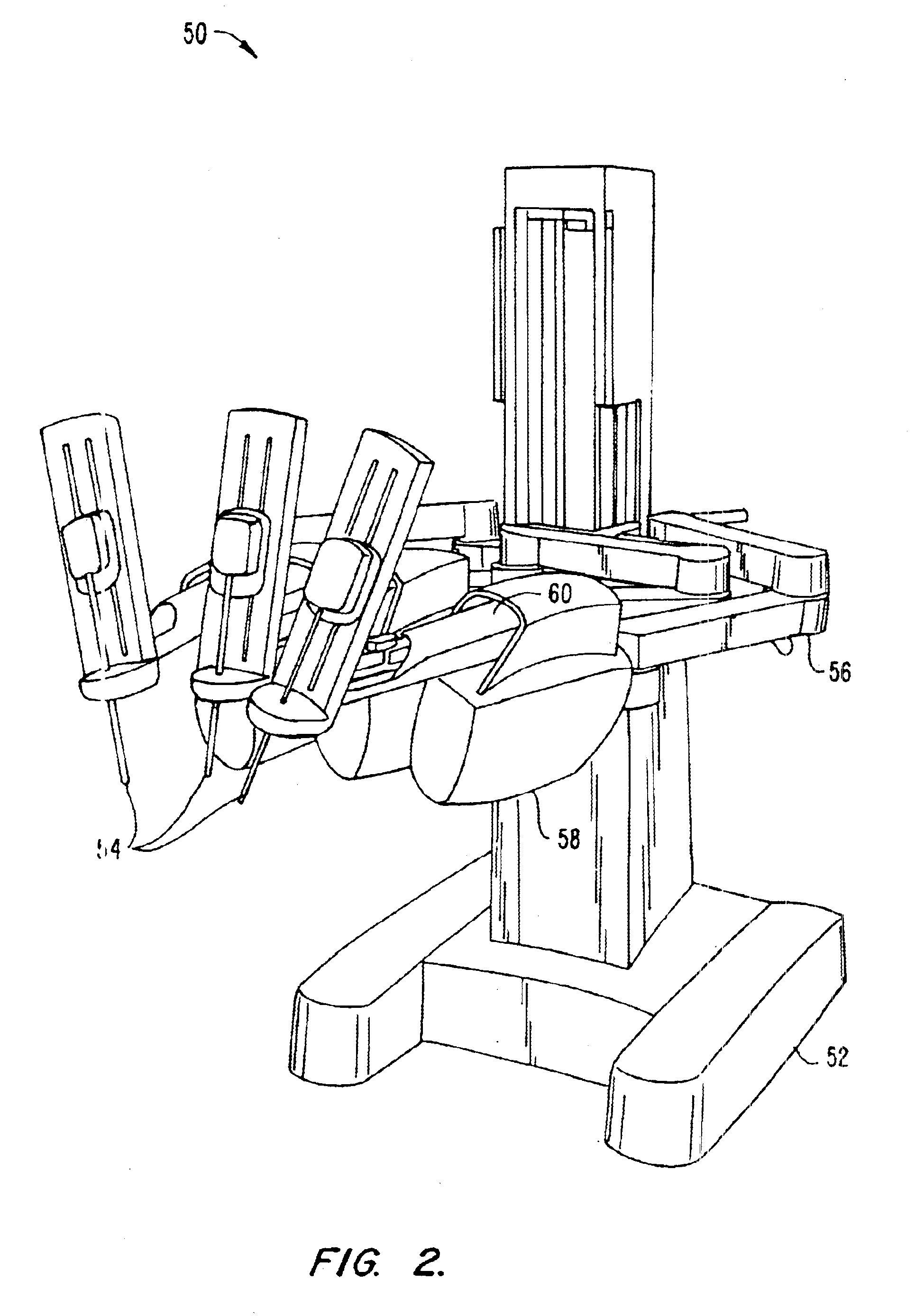
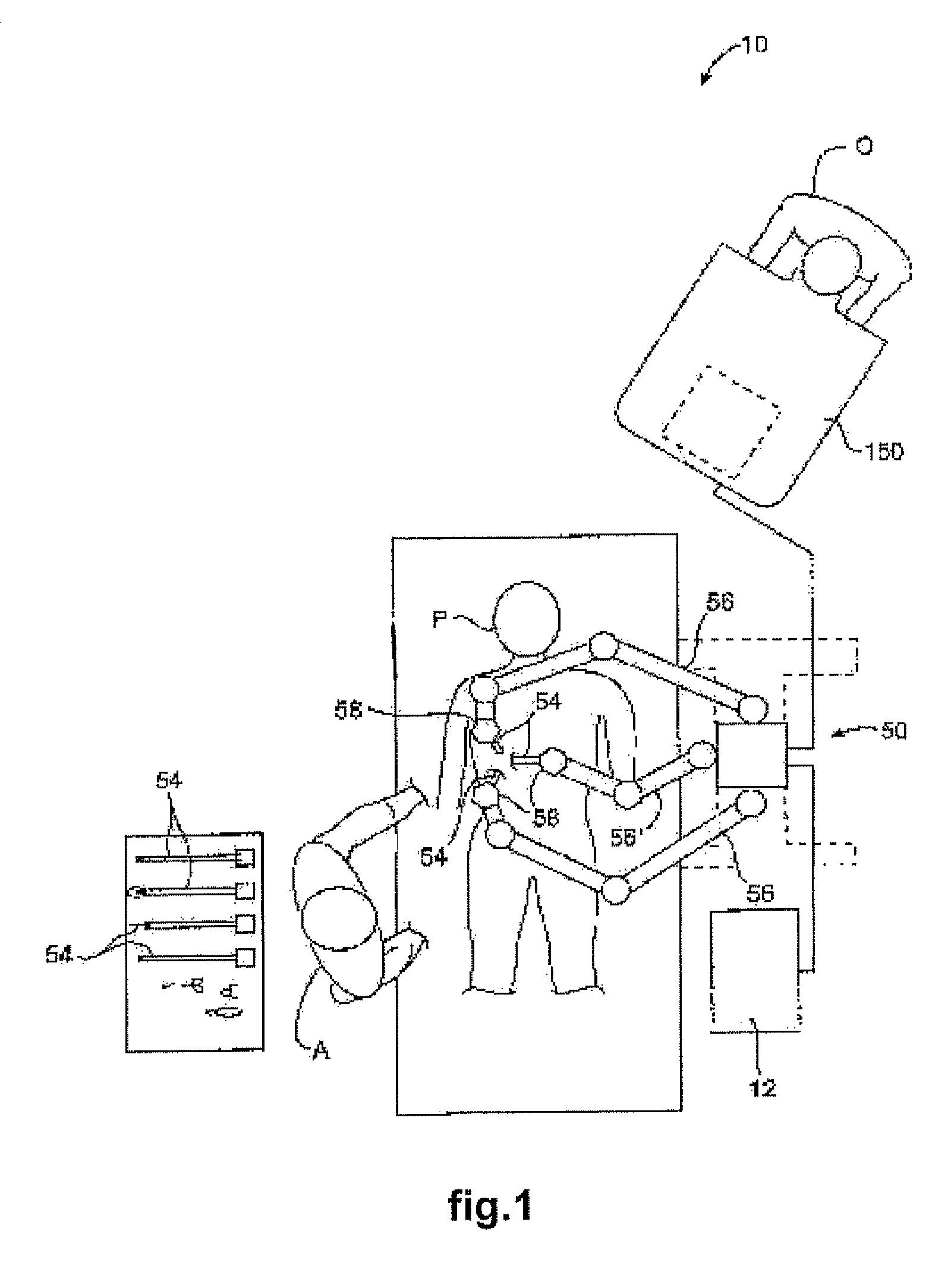
Surgical robotic tools, data architecture, and use
Robotic surgical tools, systems, and methods for preparing for and performing robotic surgery include a memory mounted on the tool. The memory can perform a number of functions when the tool is loaded on the tool manipulator: first, the memory can provide a signal verifying that the tool is compatible with that particular robotic system. Secondly, the tool memory may identify the tool-type to the robotic system so that the robotic system can reconfigure its programming. Thirdly, the memory of the tool may indicate tool-specific information, including measured calibration offsets indicating misalignment of the tool drive system, tool life data, or the like. This information may be stored in a read only memory (ROM), or in a nonvolatile memory which can be written to only a single time. The invention further provides improved engagement structures for coupling robotic surgical tools with manipulator structures.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
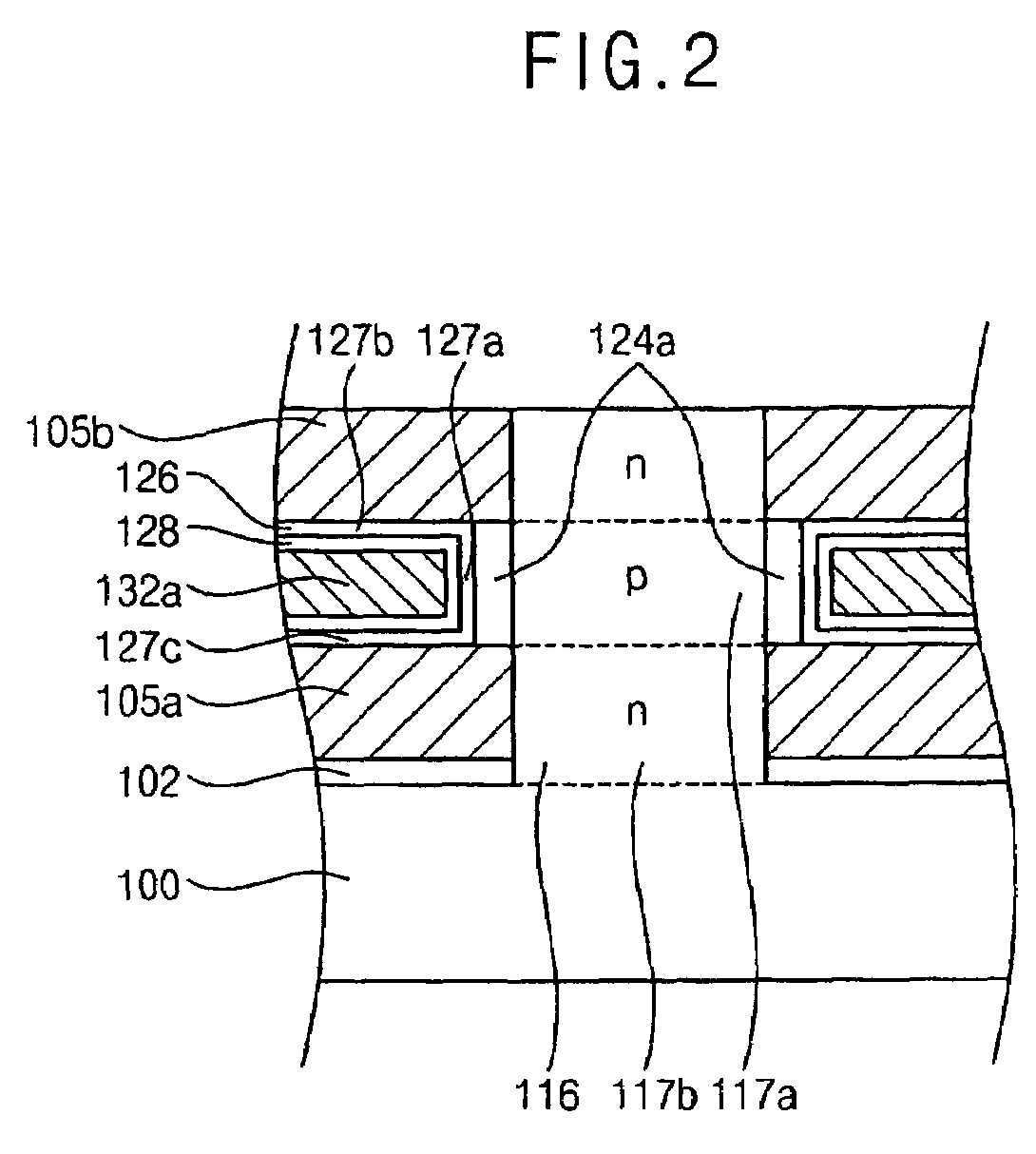
Vertical-type non-volatile memory devices
ActiveUS7679133B2Reduce the possibilityReduce in quantityTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductor materialsDevice material
In a semiconductor device, and a method of manufacturing thereof, the device includes a substrate of single-crystal semiconductor material extending in a horizontal direction and a plurality of interlayer dielectric layers on the substrate. A plurality of gate patterns are provided, each gate pattern being between a neighboring lower interlayer dielectric layer and a neighboring upper interlayer dielectric layer. A vertical channel of single-crystal semiconductor material extends in a vertical direction through the plurality of interlayer dielectric layers and the plurality of gate patterns, a gate insulating layer being between each gate pattern and the vertical channel that insulates the gate pattern from the vertical channel.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
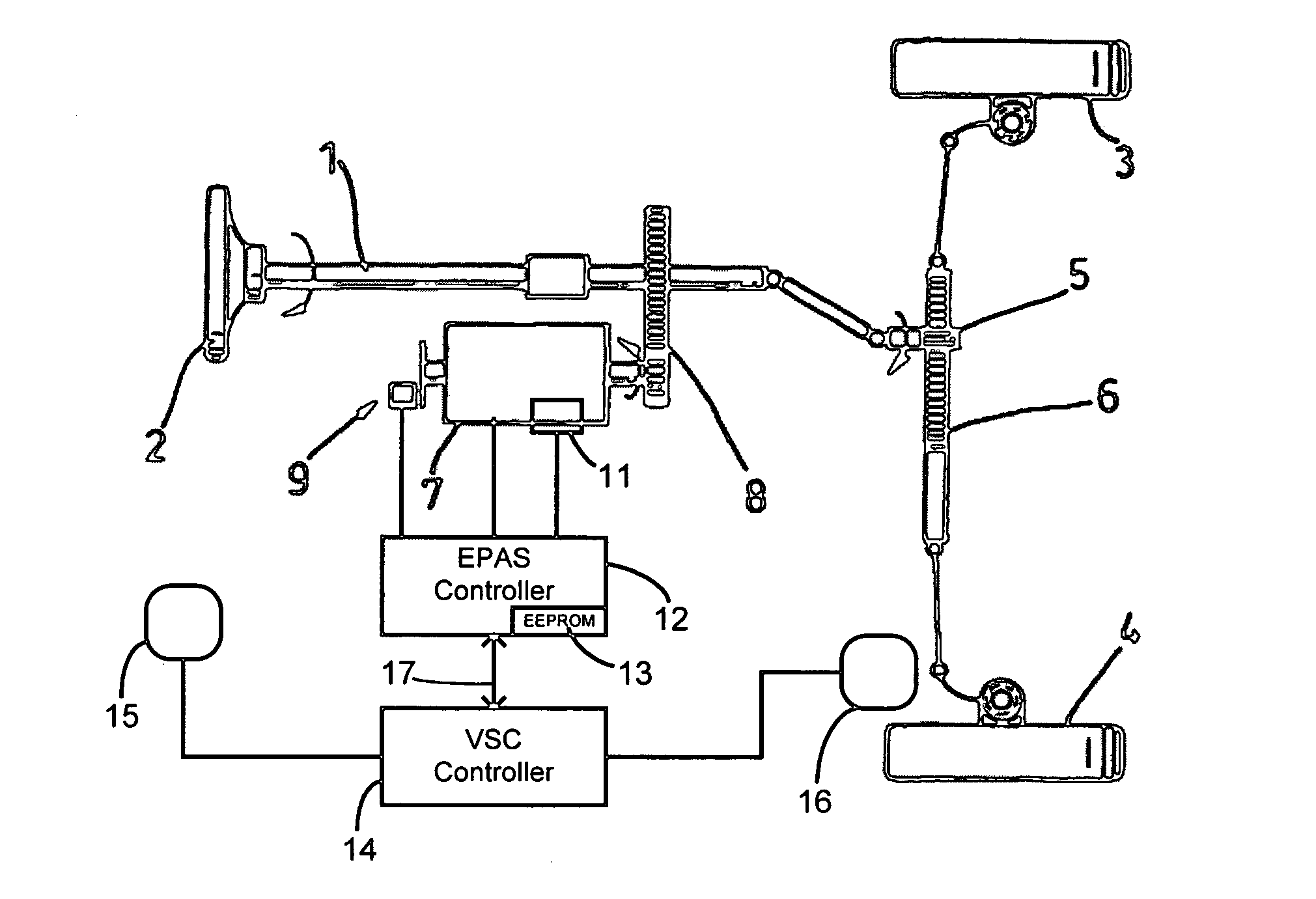
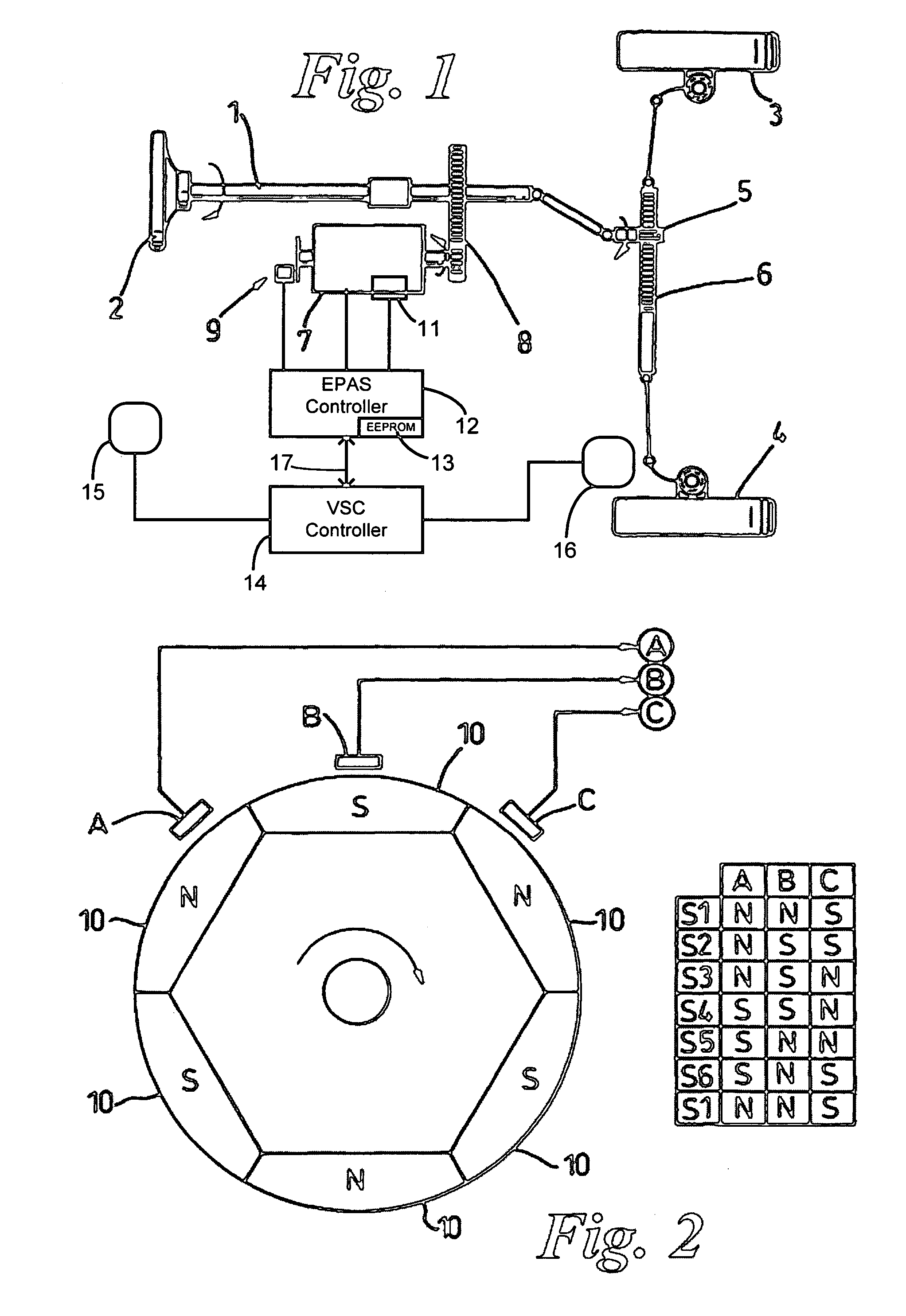
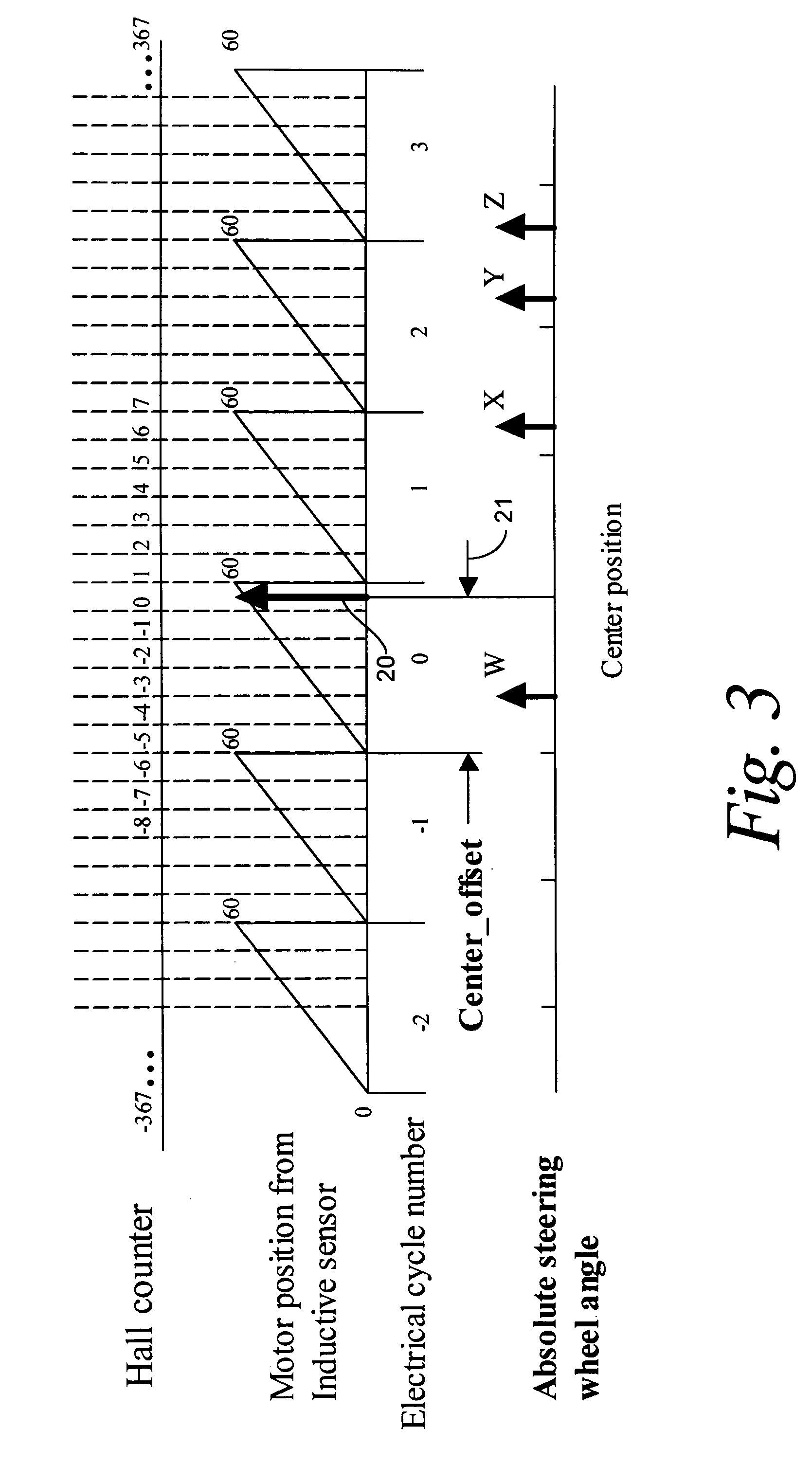
Recovery of calibrated center steering position after loss of battery power
ActiveUS7295907B2Accurate absolute steering angleAvoid the needDigital data processing detailsOptical signallingElectric power steeringSteering angle
The steering angle of a vehicle is monitored using position sensors of an electric motor of an electric power assisted steering (EPAS) system. A position of the electric motor corresponding to the straight-ahead, center position of the steering system is stored in non-volatile memory during a steering calibration procedure, such as an end-of-line calibration in a vehicle assembly plant. Following power loss due to a dead battery, a steering angle zeroing procedure performed in a vehicle stability control (VSC) system generates a center position with enough accuracy to be within one electrical cycle of the motor. The pre-stored electric motor position is then used to determine the electrical cycle where the center position was located, and accurate monitoring of steering angle is resumed.
Owner:TRW AUTOMOTIVE US LLC
Vertically stacked field programmable nonvolatile memory and method of fabrication
A very high density field programmable memory is disclosed. An array is formed vertically above a substrate using several layers, each layer of which includes vertically fabricated memory cells. The cell in an N level array may be formed with N+1 masking steps plus masking steps needed for contacts. Maximum use of self alignment techniques minimizes photolithographic limitations. In one embodiment the peripheral circuits are formed in a silicon substrate and an N level array is fabricated above the substrate.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
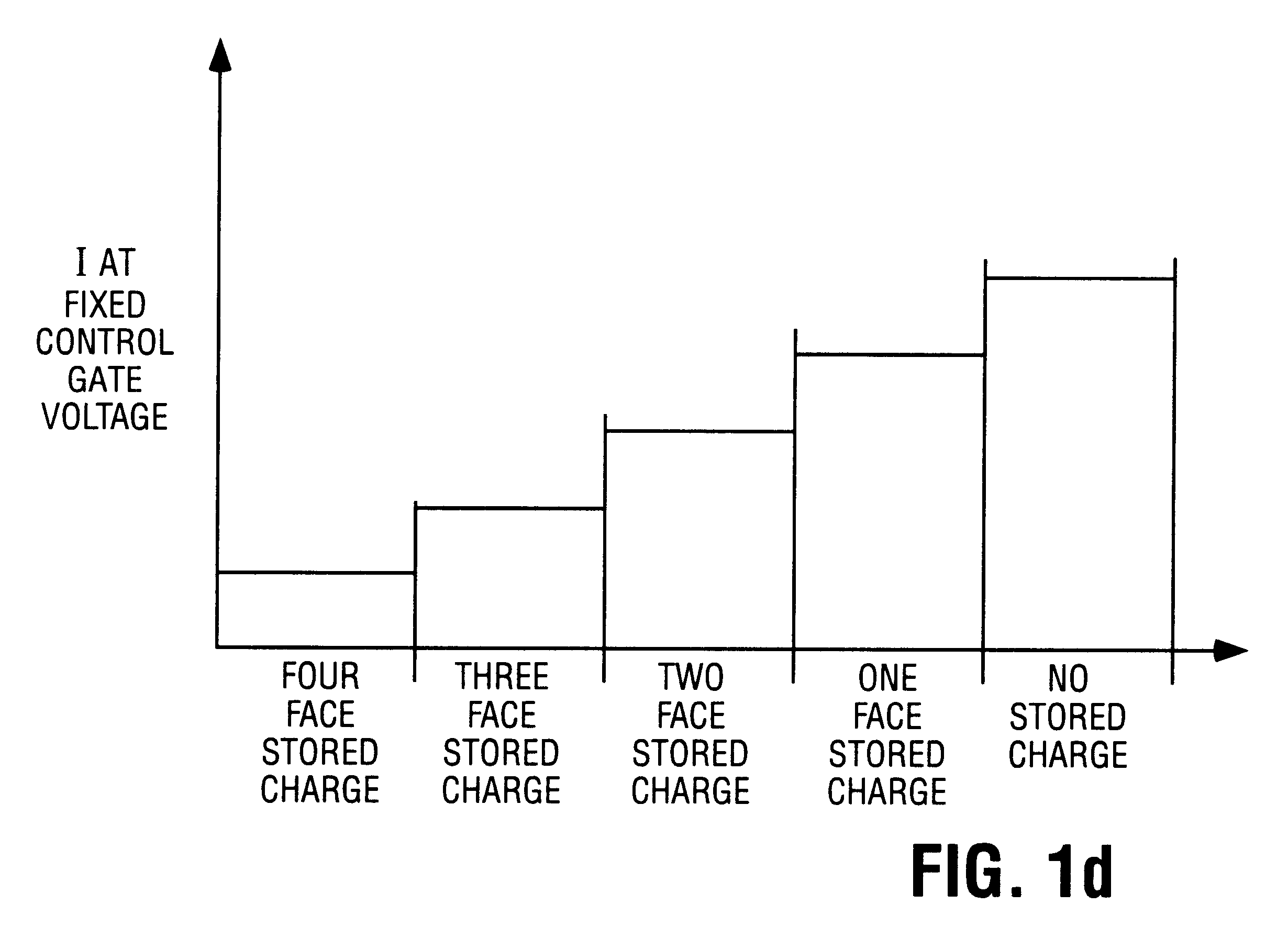
Compensating for coupling during read operations of non-volatile memory
Shifts in the apparent charge stored on a floating gate (or other charge storing element) of a non-volatile memory cell can occur because of the coupling of an electric field based on the charge stored in adjacent floating gates (or other adjacent charge storing elements). The problem occurs most pronouncedly between sets of adjacent memory cells that have been programmed at different times. To compensate for this coupling, the read process for a given memory cell will take into account the programmed state of an adjacent memory cell.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
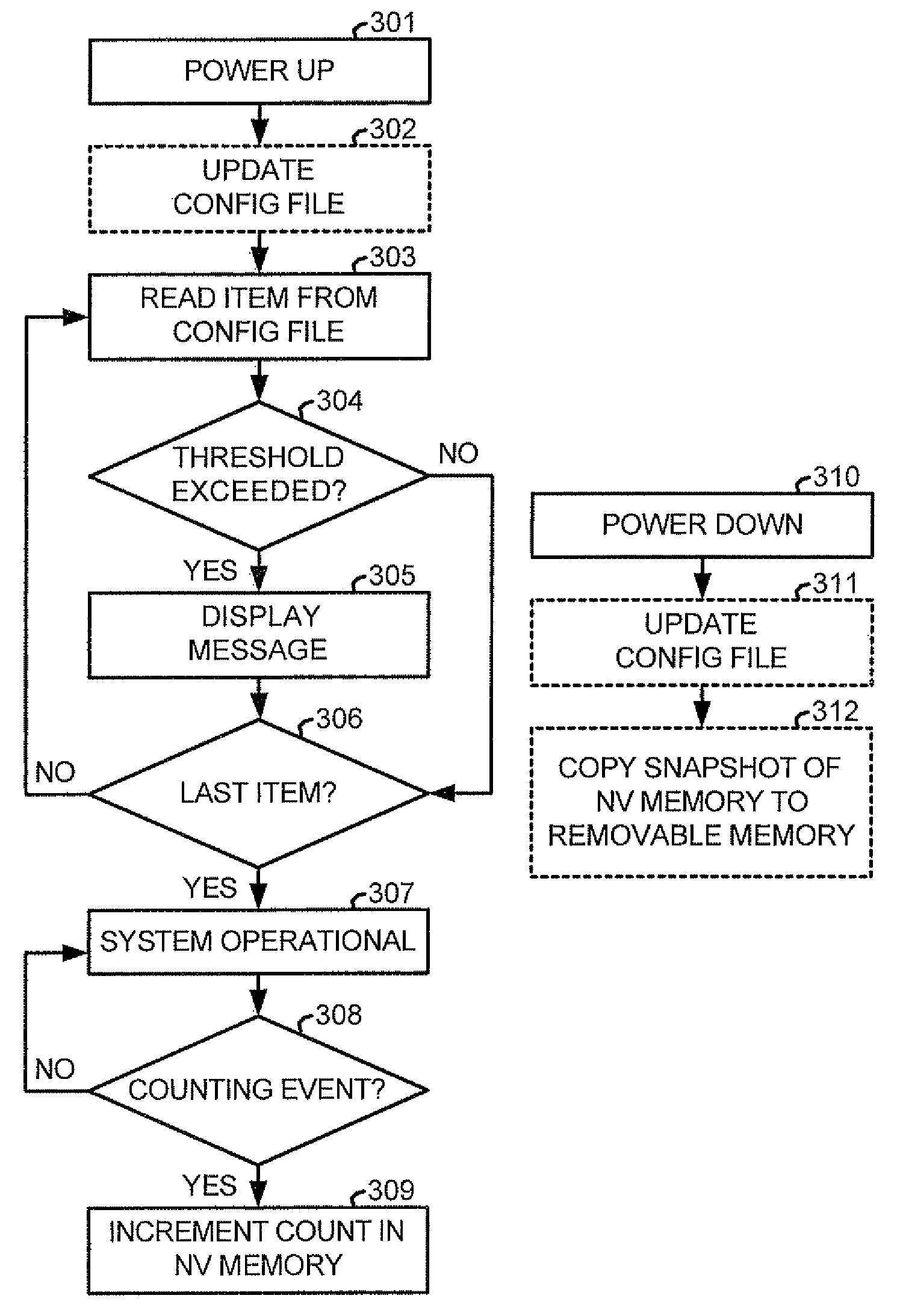
Method for tracking and reporting usage events to determine when preventive maintenance is due for a medical robotic system
A medical robotic system comprises a number of components that may be monitored to determine their preventive maintenance needs by recording usage-related information for the monitored components into associated non-volatile memories. When usage of the component exceeds a specified usage threshold, the system displays a warning message on its display screen to have preventive maintenance performed for the component. If the usage continues without such maintenance and exceeds a higher usage threshold, the system displays an error message on its display screen and the system transitions into an error state during which medical procedures are not allowed to be performed. The usage-related information may also be communicated to a remote computer which gathers and processes usage-related information from a number of medical robotic systems to estimate resource requirements for timely performing preventive maintenance on the medical robotic systems, and anticipated service revenues from such maintenance.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
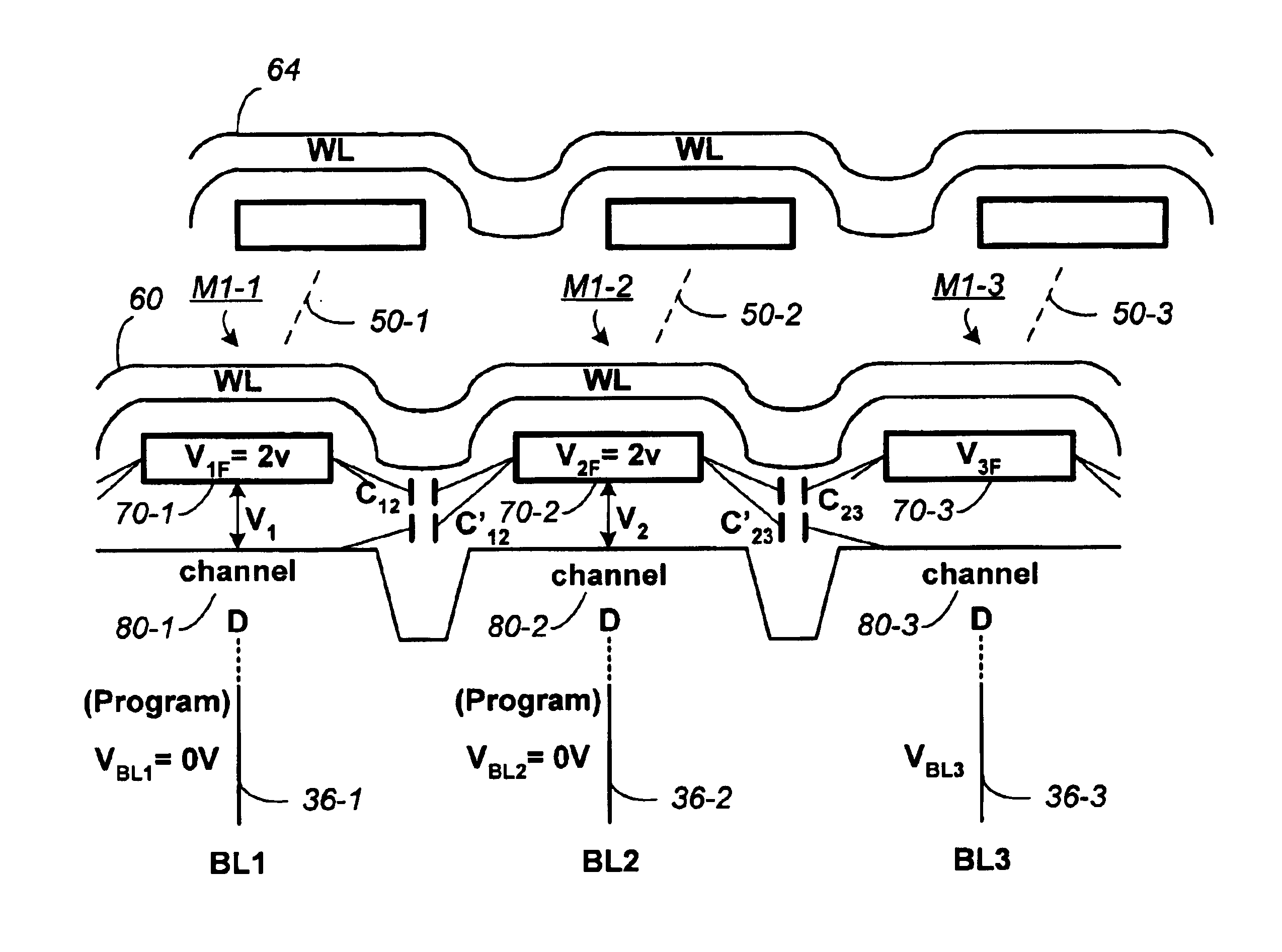
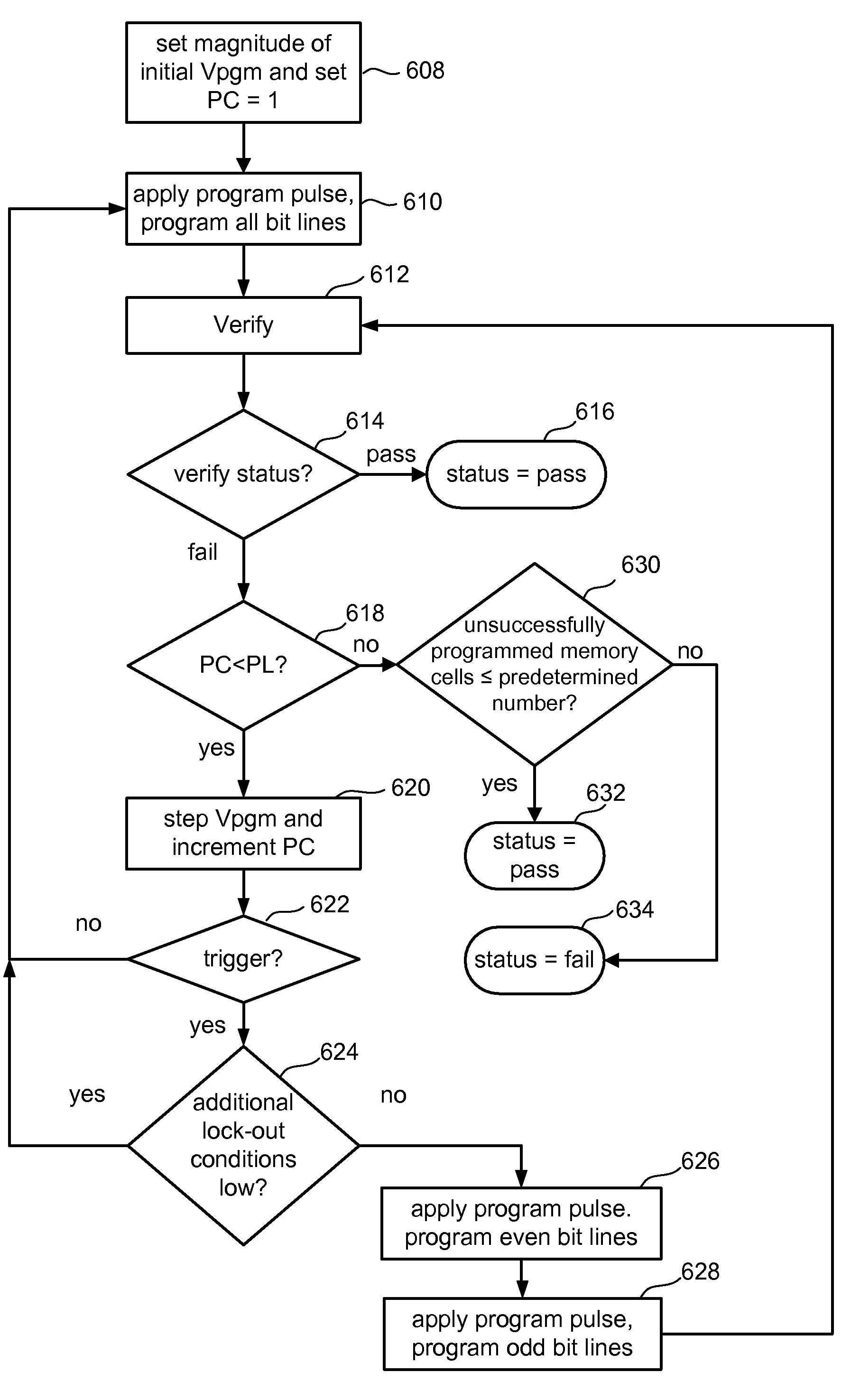
Variable programming of non-volatile memory
ActiveUS7020017B2Improve data retentionDecreased program disturbRead-only memoriesDigital storageReading levelNon-volatile memory
Systems and methods in accordance with various embodiments can provide for reduced program disturb in non-volatile semiconductor memory. In one embodiment, select memory cells such as those connected to a last word line of a NAND string are programmed using one or more program verify levels or voltages that are different than a corresponding level used to program other cells or word lines. One exemplary embodiment includes using a lower threshold voltage verify level for select physical states when programming the last word line to be programmed for a string during a program operation. Another embodiment includes applying a lower program voltage to program memory cells of the last word line to select physical states. Additional read levels are established for reading the states programmed using lower verify levels in some exemplary implementations. A second program voltage step size that is larger than a nominal step size is used in one embodiment when programming select memory cells or word lines, such as the last word line to be programmed for a NAND string.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Source side self boosting technique for non-volatile memory
InactiveUS6859397B2Improve performanceMinimize program disturbRead-only memoriesDigital storagePre-chargeProgramming process
A non-volatile semiconductor memory system (or other type of memory system) is programmed in a manner that avoids program disturb. In one embodiment that includes a flash memory system using a NAND architecture, program disturb is avoided by increasing the channel potential of the source side of the NAND string during the programming process. One exemplar implementation includes applying a voltage (e.g. Vdd) to the source contact and turning on the source side select transistor for the NAND sting corresponding to the cell being inhibited. Another implementation includes applying a pre-charging voltage to the unselected word lines of the NAND string corresponding to the cell being inhibited prior to applying the program voltage.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
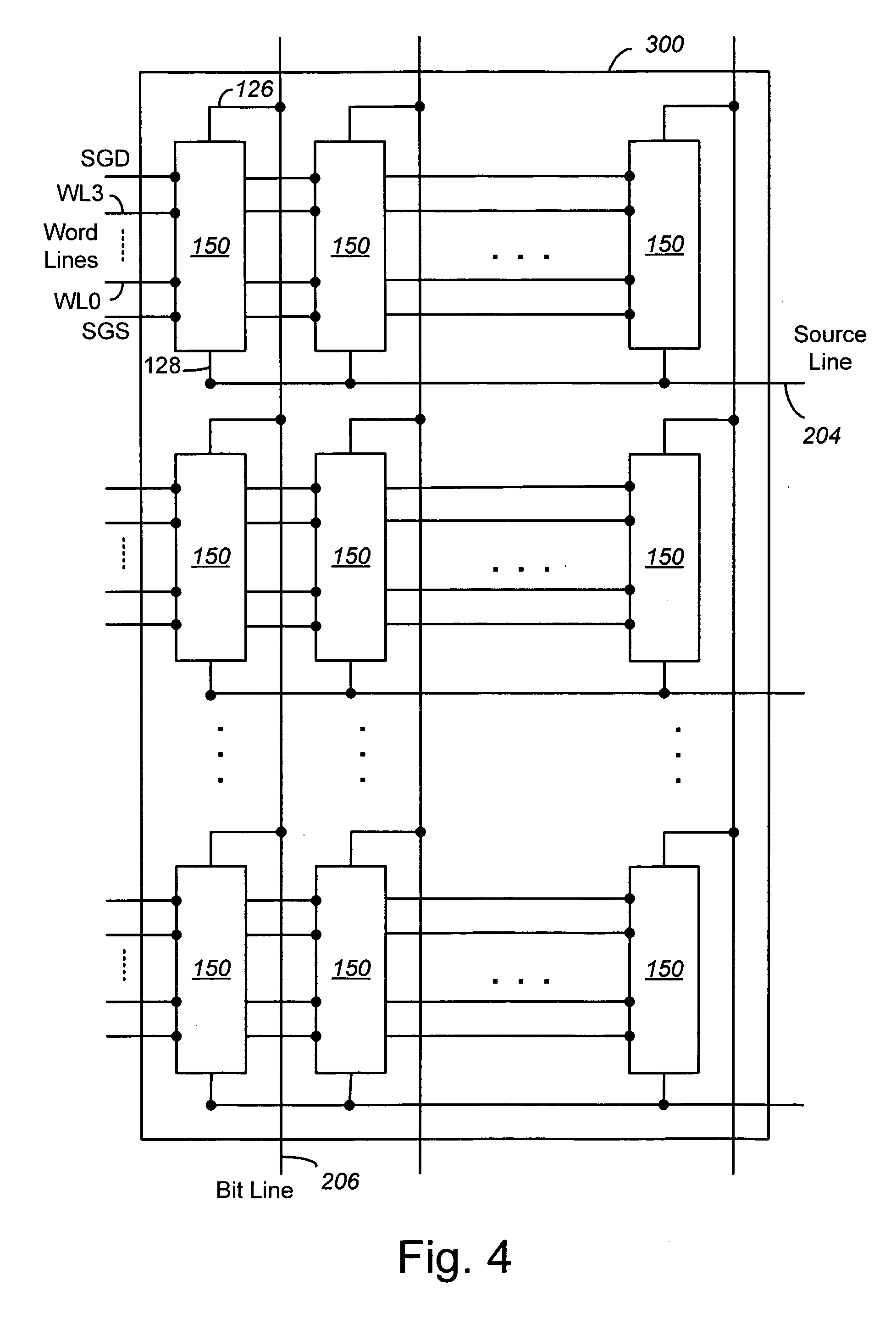
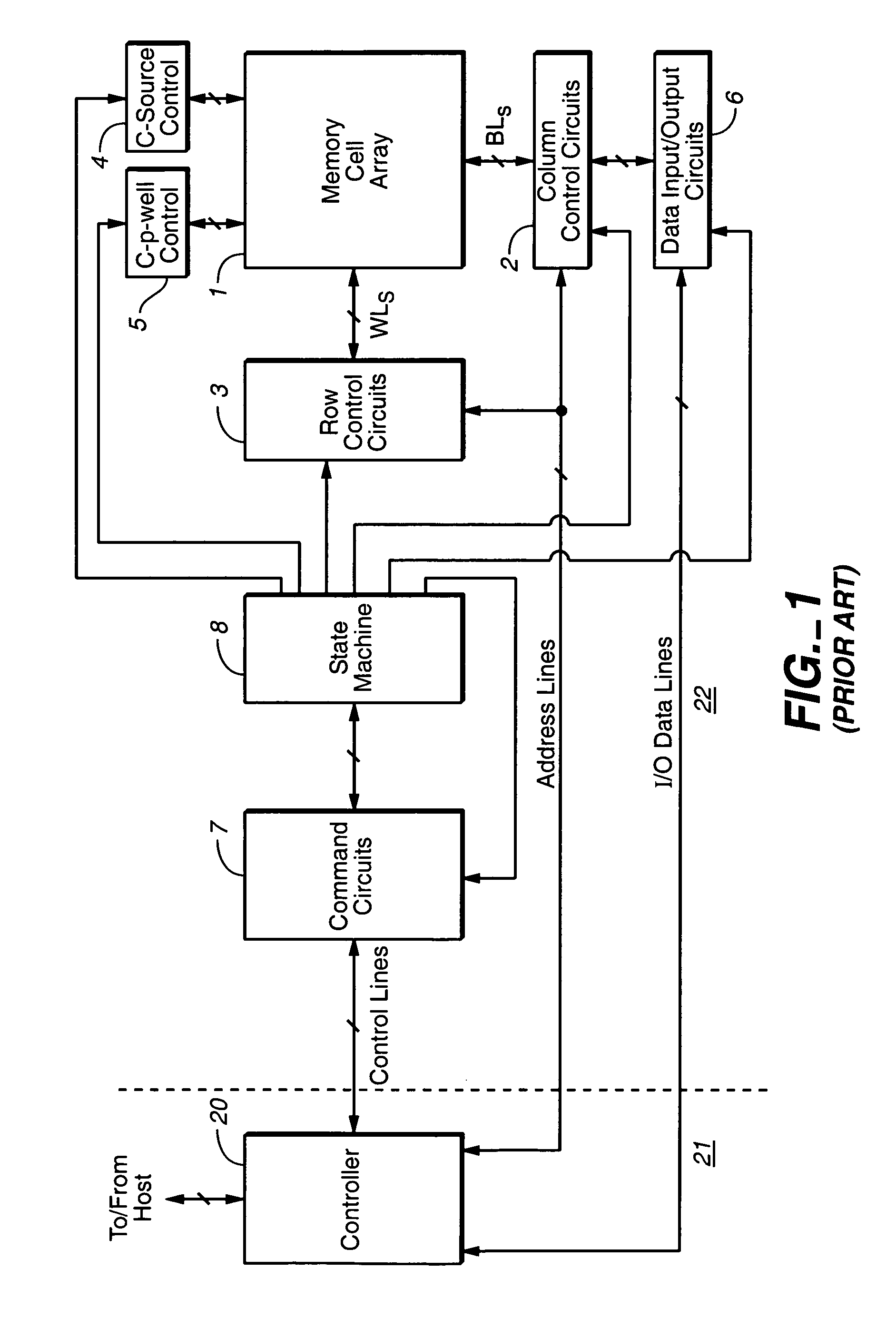
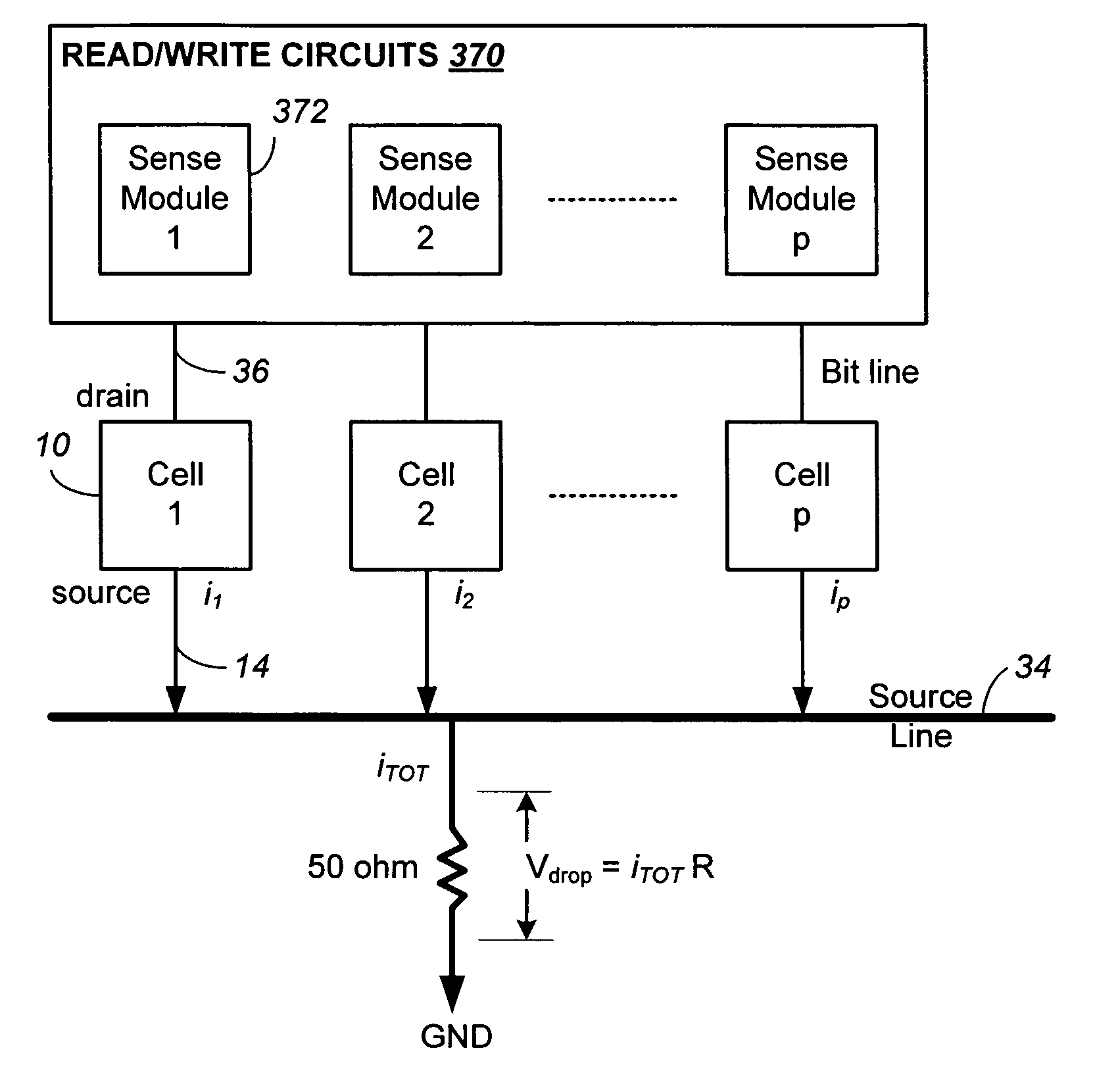
Non-volatile memory and method with shared processing for an aggregate of read/write circuits
InactiveUS20060140007A1Maximum versatilityMinimal componentRead-only memoriesDigital storageAudio power amplifierAssociative processor
A non-volatile memory device capable of reading and writing a large number of memory cells with multiple read / write circuits in parallel has an architecture that reduces redundancy in the multiple read / write circuits to a minimum. The multiple read / write circuits are organized into a bank of similar stacks of components. Redundant circuits such as a processor for processing data among stacks each associated with multiple memory cells are factored out. The processor is implemented with an input logic, a latch and an output logic. The input logic can transform the data received from either the sense amplifier or the data latches. The output logic further processes the transformed data to send to either the sense amplifier or the data latches or to a controller. This provides an infrastructure with maximum versatility and a minimum of components for sophisticated processing of the data sensed and the data to be input or output.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
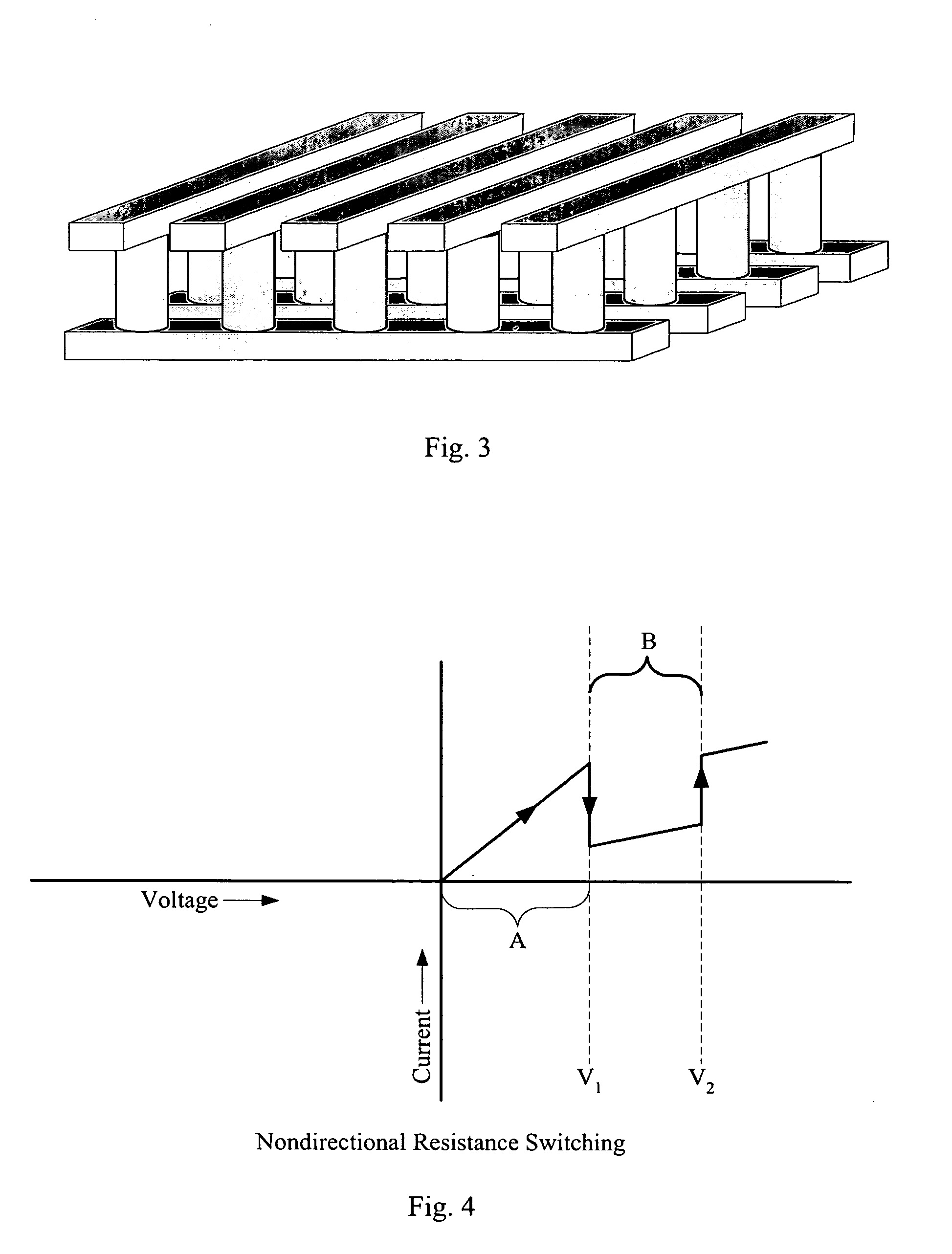
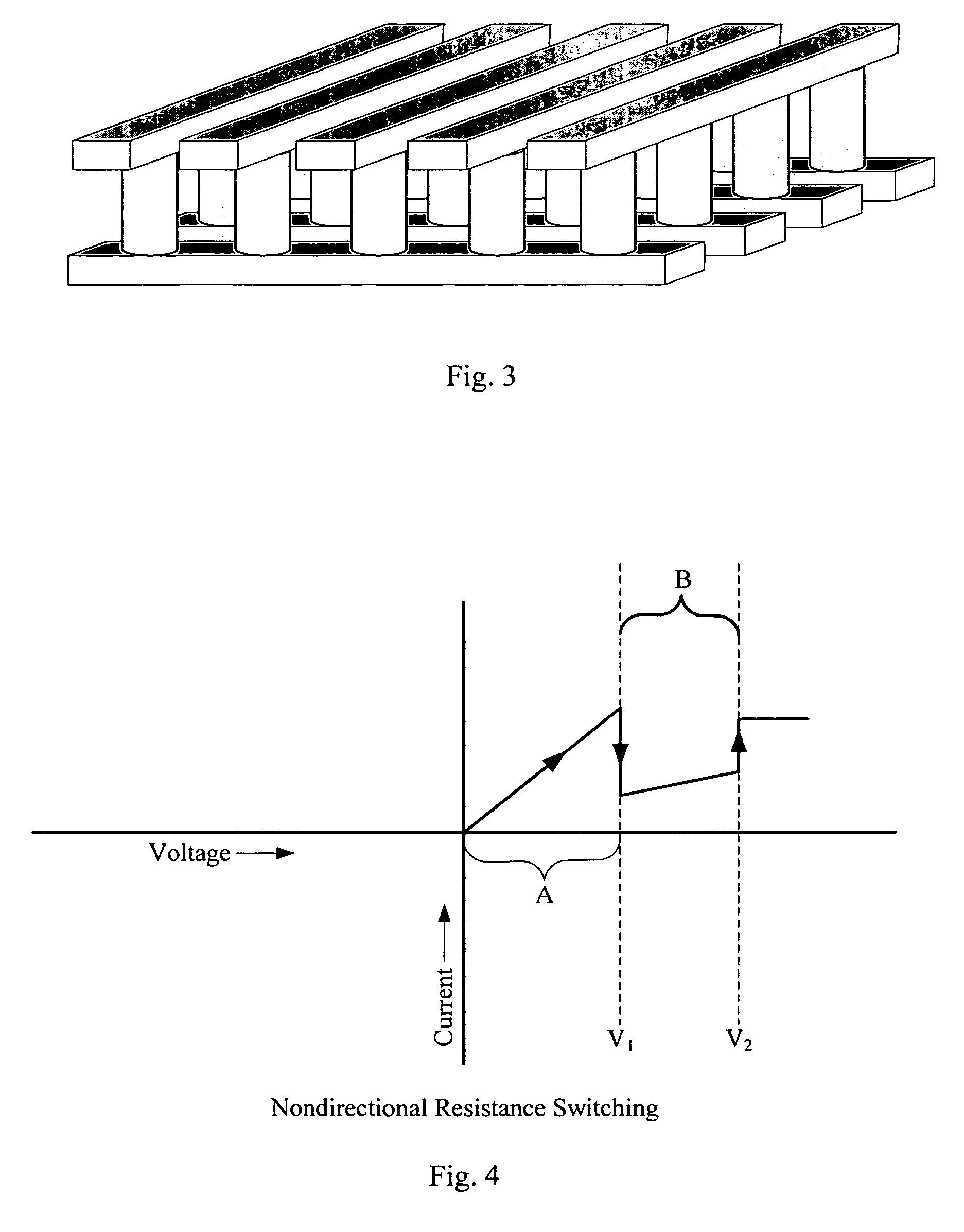
Rewriteable memory cell comprising a diode and a resistance-switching material
In a novel rewriteable nonvolatile memory cell formed above a substrate, a diode is paired with a reversible resistance-switching material, preferably a metal oxide or nitride such as, for example, NiO, Nb2O5, TiO2, HfO2, Al2O3, MgOx, CrO2, VO, BN, and AlN. In preferred embodiments, the diode is formed as a vertical pillar disposed between conductors. Multiple memory levels can be stacked to form a monolithic three dimensional memory array. In some embodiments, the diode comprises germanium or a germanium alloy, which can be deposited and crystallized at relatively low temperatures, allowing use of aluminum or copper in the conductors.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Non-volatile memory and method with bit line compensation dependent on neighboring operating modes
ActiveUS6956770B2Large capacityImprove performanceRead-only memoriesDigital storageBit lineHigh density
When programming a contiguous page of memory storage units, every time a memory storage unit has reached its targeted state and is program-inhibited or locked out from further programming, it creates a perturbation on an adjacent memory storage unit still under programming. The present invention provides as part of a programming circuit and method in which an offset to the perturbation is added to the adjacent memory storage unit still under programming. The offset is added as voltage offset to a bit line of a storage unit under programming. The voltage offset is a predetermined function of whether none or one or both of its neighbors are in a mode that creates perturbation, such as in a program inhibit mode. In this way, an error inherent in programming in parallel high-density memory storage units is eliminated or minimized.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Vertically stacked field programmable nonvolatile memory and method of fabrication
A very high density field programmable memory is disclosed. An array is formed vertically above a substrate using several layers, each layer of which includes vertically fabricated memory cells. The cell in an N level array may be formed with N+1 masking steps plus masking steps needed for contacts. Maximum use of self alignment techniques minimizes photolithographic limitations. In one embodiment the peripheral circuits are formed in a silicon substrate and an N level array is fabricated above the substrate.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Read operation for non-volatile storage that includes compensation for coupling
Shifts in the apparent charge stored on a floating gate (or other charge storing element) of a non-volatile memory cell can occur because of the coupling of an electric field based on the charge stored in adjacent floating gates (or other adjacent charge storing elements). The problem occurs most pronouncedly between sets of adjacent memory cells that have been programmed at different times. To compensate for this coupling, the read process for a given memory cell will take into account the programmed state of an adjacent memory cell.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
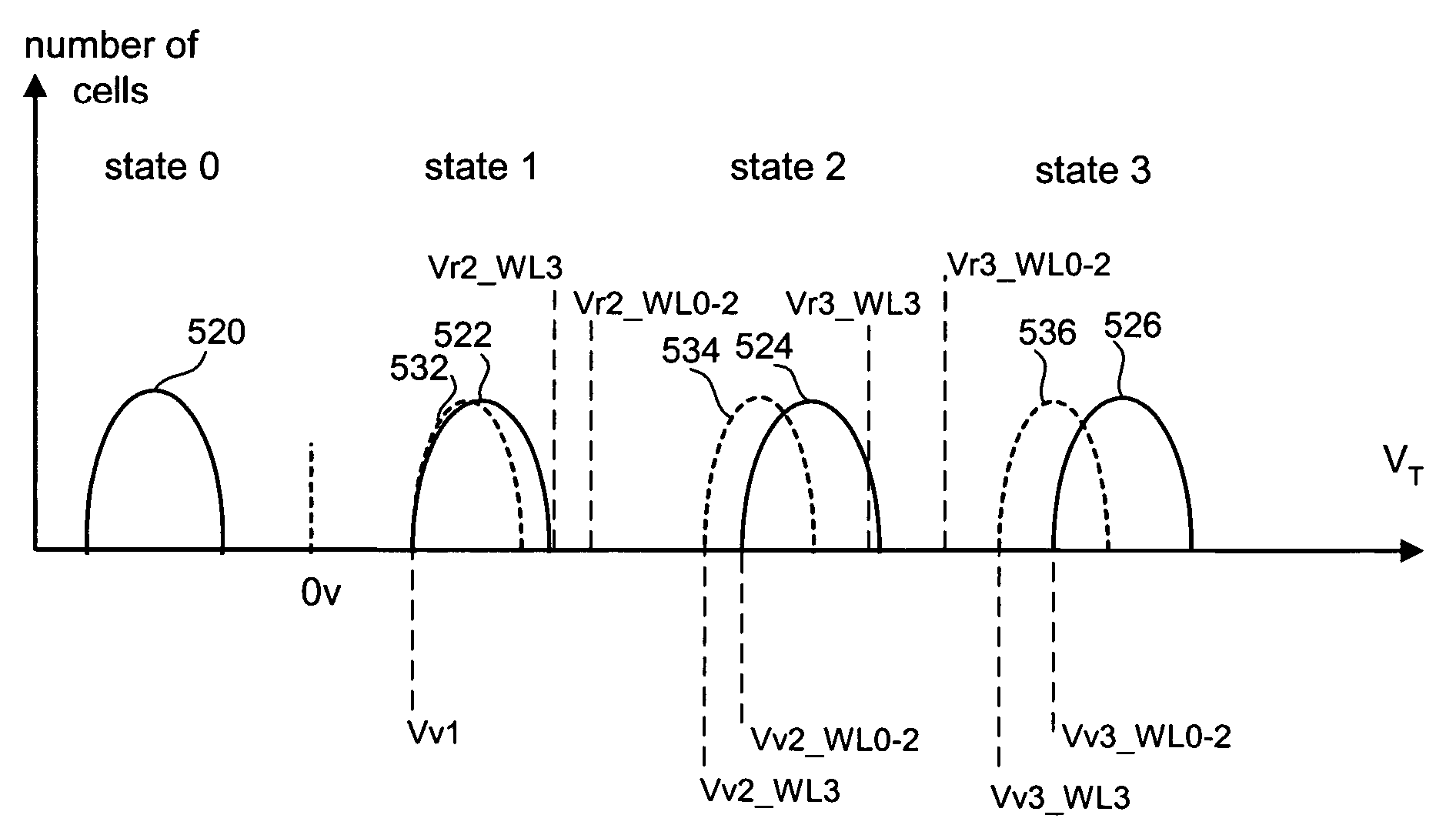
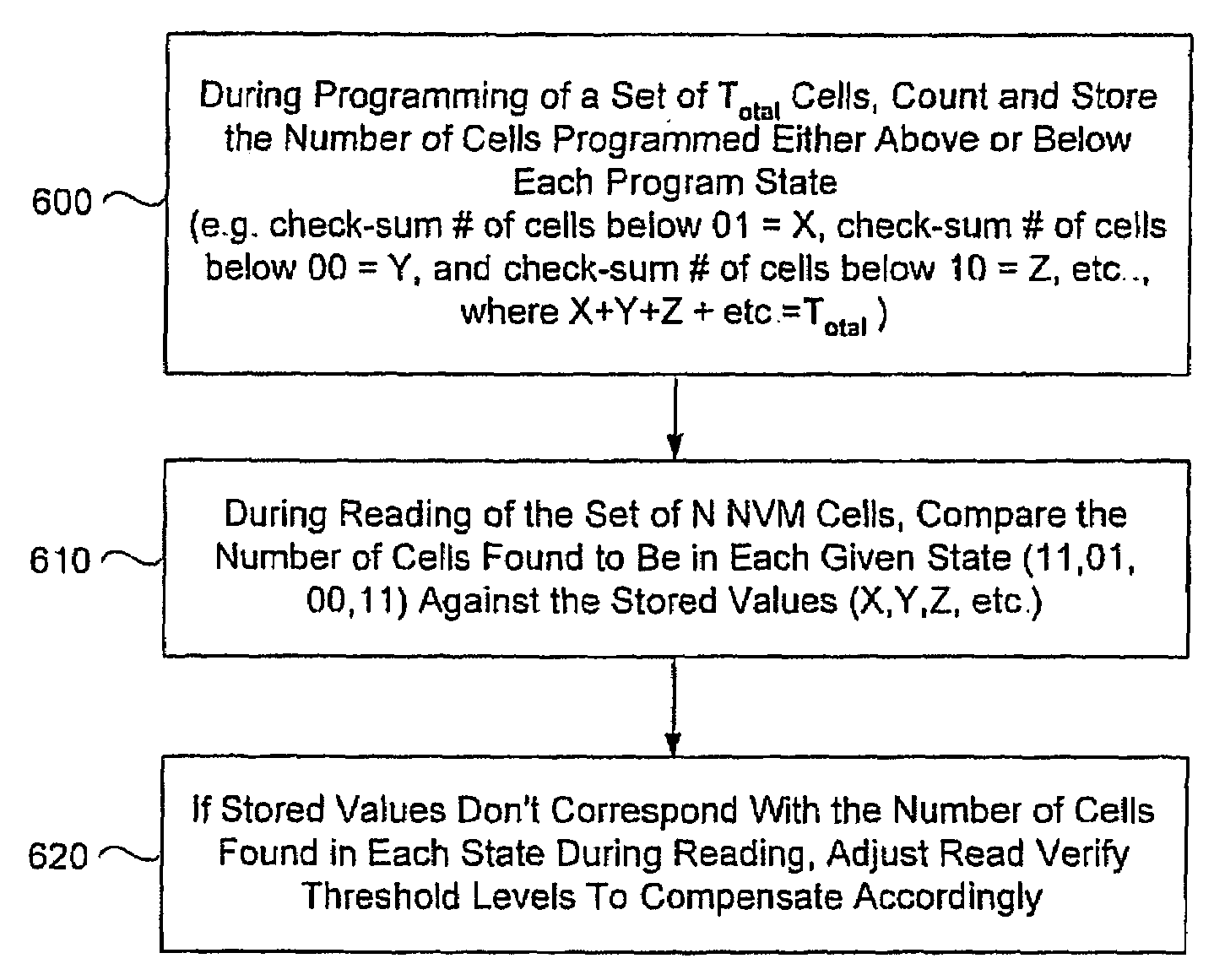
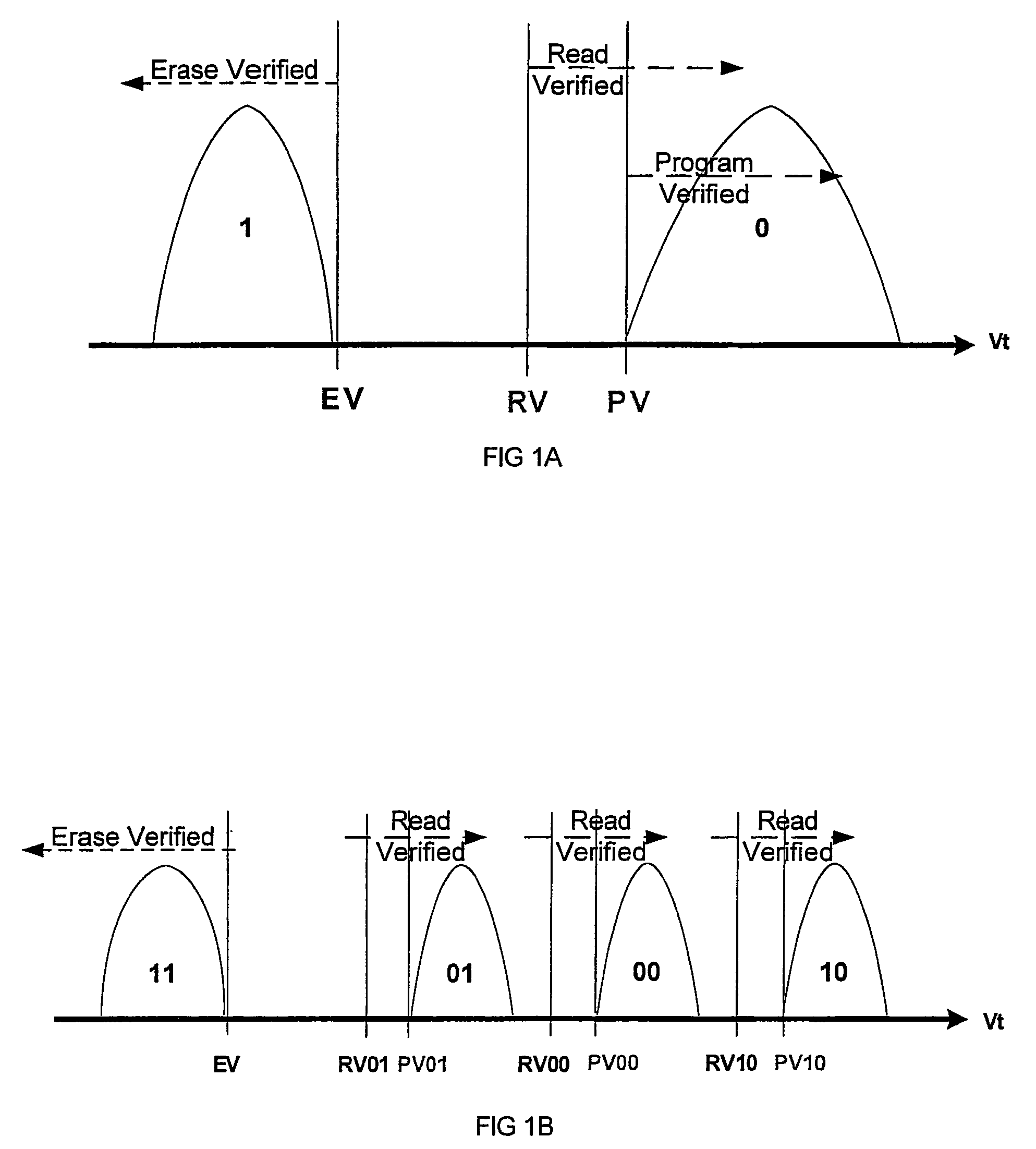
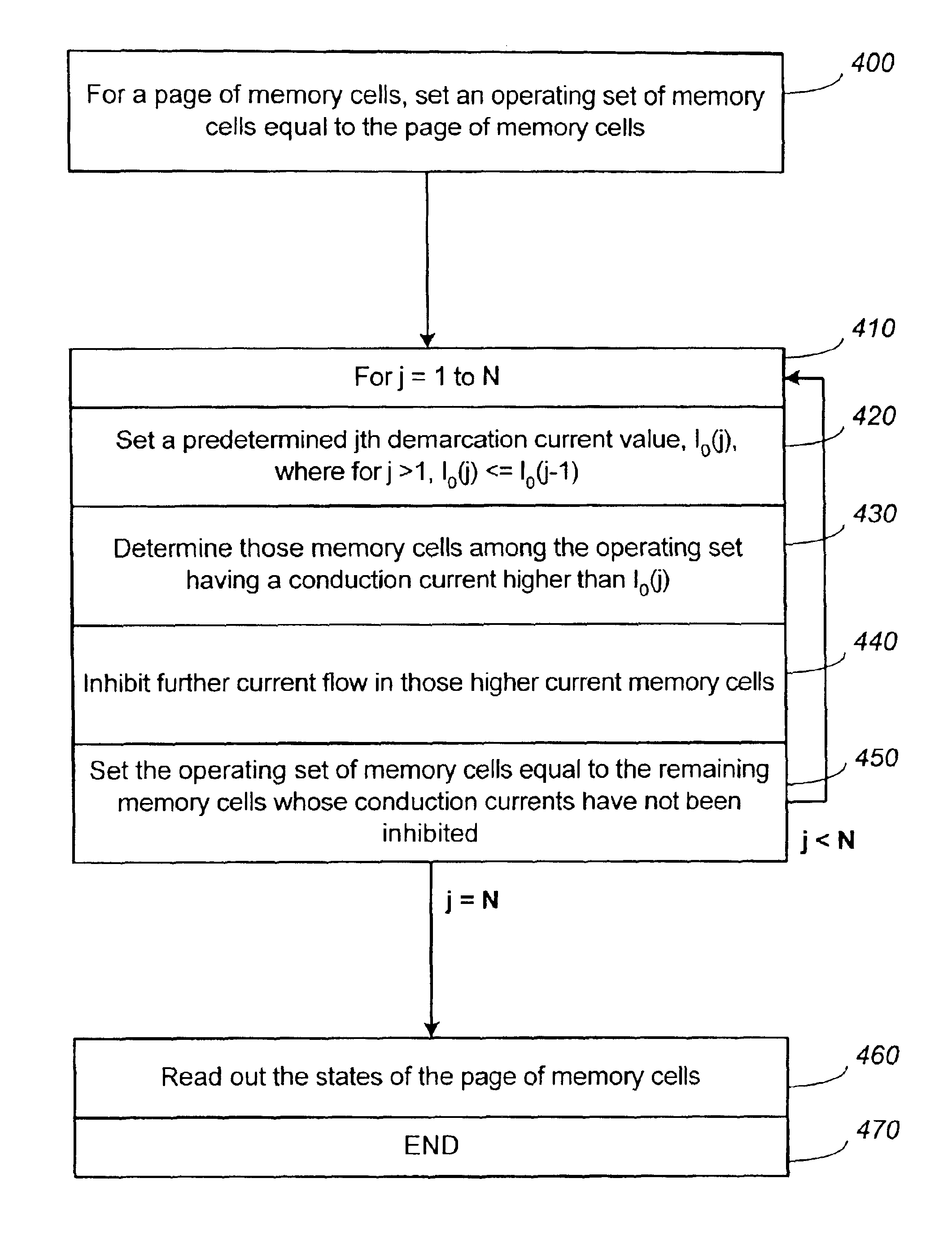
Method circuit and system for read error detection in a non-volatile memory array
The present invention is a method, circuit and system for determining a reference voltage to be used in reading cells programmed to a given program state. Some embodiments of the present invention relate to a system, method and circuit for establishing a set of operating reference cells to be used in operating (e.g. reading) cells in a NVM block or array. As part of the present invention, at least a subset of cells of the NVM block or array may be read and the number of cells found at a given state associated with the array may be compared to one or more check sum values obtained during programming of the at least a subset of cells. A Read Verify threshold reference voltage associated with the given program state or associated with an adjacent state may be adjusted based on the result of the comparison.
Owner:SPANSION ISRAEL
Vertical memory device structures
Vertically oriented semiconductor memory cells are added to a separately fabricated substrate that includes electrical devices and / or interconnect. The plurality of vertically oriented semiconductor memory cells are physically separated from each other, and are not disposed within the same semiconductor body. The plurality of vertically oriented semiconductor memory cells can be added to the separately fabricated substrate as a thin layer including several doped semiconductor regions which, subsequent to attachment, are etched to produce individual doped stack structures, which are then supplied with various dielectric coatings, gate electrodes, and contacts by means of further processing operations. Alternatively, the plurality of vertically oriented semiconductor memory cells may be completely fabricated prior to attachment. DRAMs, SRAMs, non-volatile memories, and combinations of memory types can be provided.
Owner:BESANG
Nonvolatile memory on SOI and compound semiconductor substrates and method of fabrication
A nonvolatile memory array is provided. The array includes an array of nonvolatile memory devices, at least one driver circuit, and a substrate. The at least one driver circuit is not located in a bulk monocrystalline silicon substrate. The at least one driver circuit may be located in a silicon on insulator substrate or in a compound semiconductor substrate.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Non-volatile memory and method with reduced neighboring field errors
InactiveUS6987693B2Large capacityImprove performanceRead-only memoriesDigital storageNon-volatile memoryParallel programing
A memory device and a method thereof allow programming and sensing a plurality of memory cells in parallel in order to minimize errors caused by coupling from fields of neighboring cells and to improve performance. The memory device and method have the plurality of memory cells linked by the same word line and a read / write circuit is coupled to each memory cells in a contiguous manner. Thus, a memory cell and its neighbors are programmed together and the field environment for each memory cell relative to its neighbors during programming and subsequent reading is less varying. This improves performance and reduces errors caused by coupling from fields of neighboring cells, as compared to conventional architectures and methods in which cells on even columns are programmed independently of cells in odd columns.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Nonvolatile memory cell comprising a diode and a resistance-switching material
In a novel nonvolatile memory cell formed above a substrate, a diode is paired with a reversible resistance-switching material, preferably a metal oxide or nitride such as, for example, NixOy, NbxOy, TixOy, HFxOy, AlxOy, MgxOy, CoxOy, CrxOy, VxOy, ZnxOy, ZrxOy, BxNy, and AlxNy. In preferred embodiments, the diode is formed as a vertical pillar disposed between conductors. Multiple memory levels can be stacked to form a monolithic three dimensional memory array. In some embodiments, the diode comprises germanium or a germanium alloy, which can be deposited and crystallized at relatively low temperatures, allowing use of aluminum or copper in the conductors. The memory cell of the present invention can be used as a rewriteable memory cell or a one-time-programmable memory cell, and can store two or more data states.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Compensating for coupling during read operations on non-volatile memory
Shifts in the apparent charge stored on a floating gate (or other charge storing element) of a non-volatile memory cell can occur because of the coupling of an electric field based on the charge stored in adjacent floating gates (or other adjacent charge storing elements). The problem occurs most pronouncedly between sets of adjacent memory cells that have been programmed at different times. To compensate for this coupling, the read process for a given memory cell will take into account the programmed state of an adjacent memory cell.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Handpiece with electrode and non-volatile memory
InactiveUS7115123B2Assist in treatmentElectrotherapyPneumatic massageSkin surfaceNon-volatile memory
An apparatus for cooling a skin surface includes an RF device that has an RF electrode with dielectric and conductive portions. The RF device is configured to be coupled to an RF energy source. A cooling member is coupled to the RF device. A memory is coupled to the RF device. The memory is configured to store information to facilitate operation of at least one of the RF electrode, the cooling member, and the RF energy source.
Owner:THERMAGE INC
Reducing the impact of interference during programming
ActiveUS7869273B2Reduce the impact of interferenceRead-only memoriesDigital storageParallel computingNon-volatile memory
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
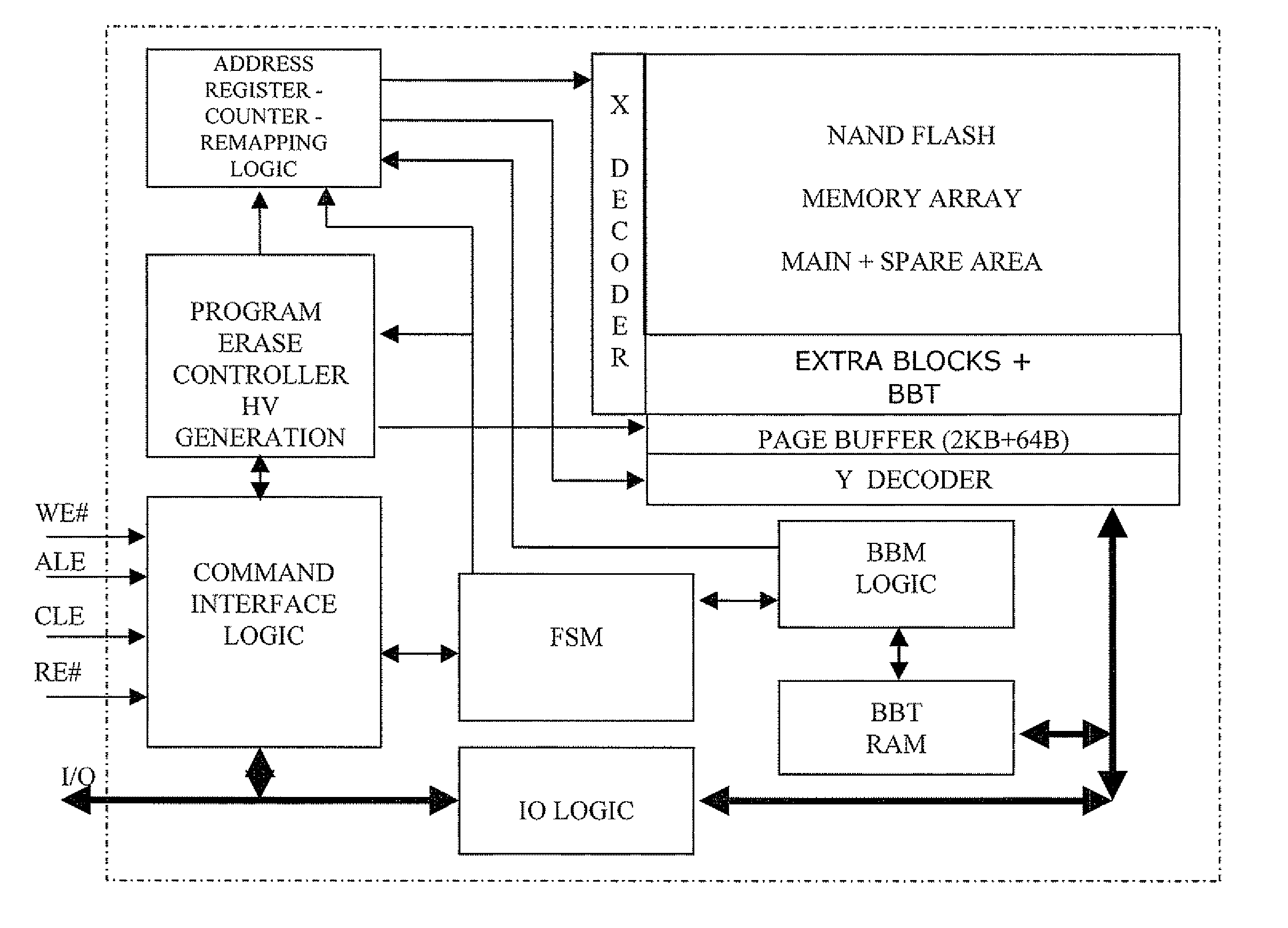
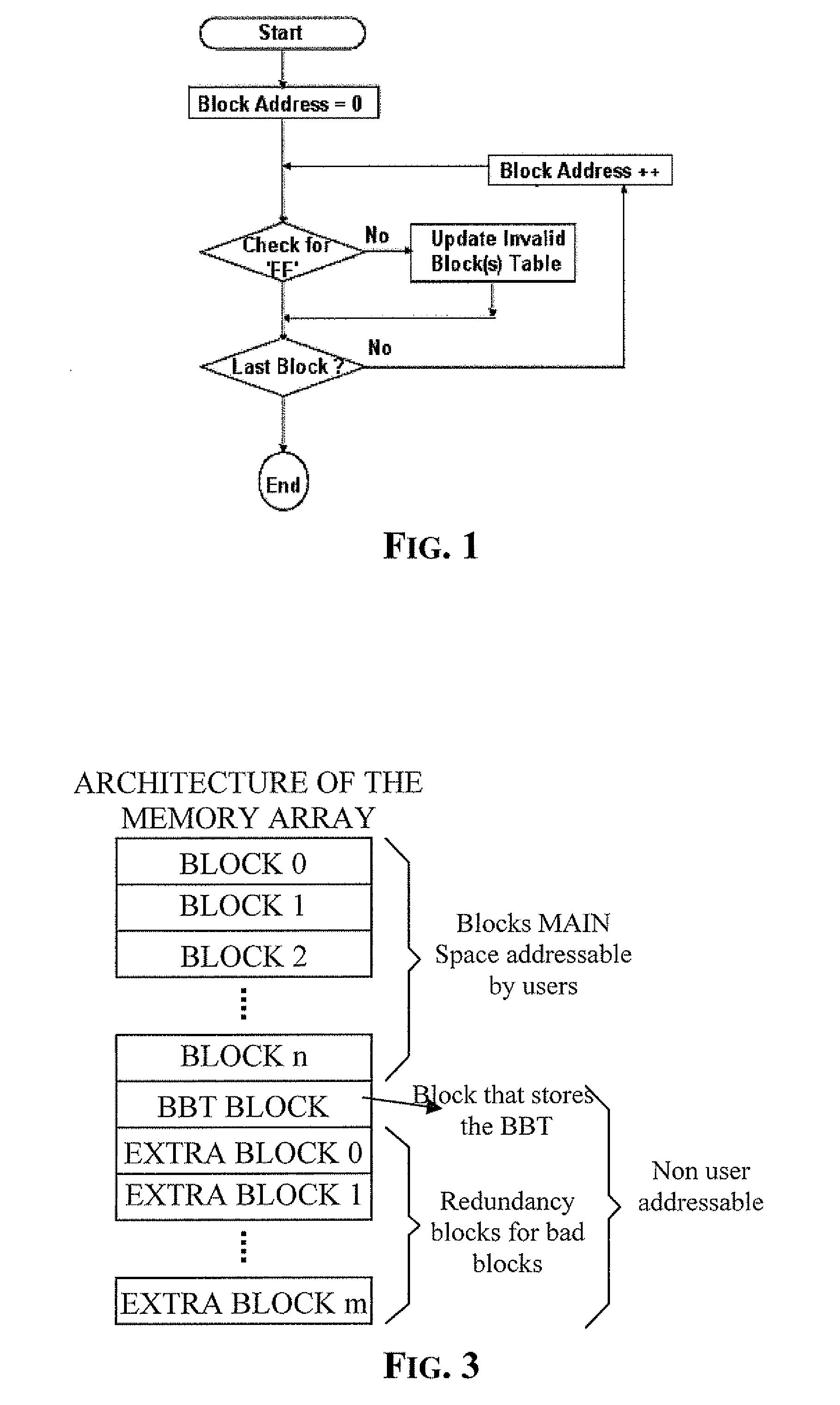
Method of managing fails in a non-volatile memory device and relative memory device
ActiveUS20070109856A1Easy to implementLow costRead-only memoriesDigital storageElectricityWorking life
A method of managing fails in a non-volatile memory device including an array of cells grouped in blocks of data storage cells includes defining in the array a first subset of user addressable blocks of cells, and a second subset of redundancy blocks of cells. Each block including at least one failed cell in the first subset is located during a test on wafer of the non-volatile memory device. Each block is marked as bad, and a bad block address table of respective codes is stored in a non-volatile memory buffer. At power-on, the bad block address table is copied from the non-volatile memory buffer to the random access memory. A block of memory cells of the first subset is verified as bad by looking up the bad block address table, and if a block is bad, then remapping access to a corresponding block of redundancy cells. A third subset of non-user addressable blocks of cells is defined in the array for storing the bad block address table of respective codes in an addressable page of cells of a block of the third subset. Each page of the third subset is associated to a corresponding redundancy block. If during the working life of the memory device a block of cells previously judged good in a test phase becomes failed, each block is marked as bad and the stored table in the random access memory is updated.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Non-volatile memory storage system
InactiveUS20100125695A1Speed up data transferCost-effective structureMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRAIDComputer science
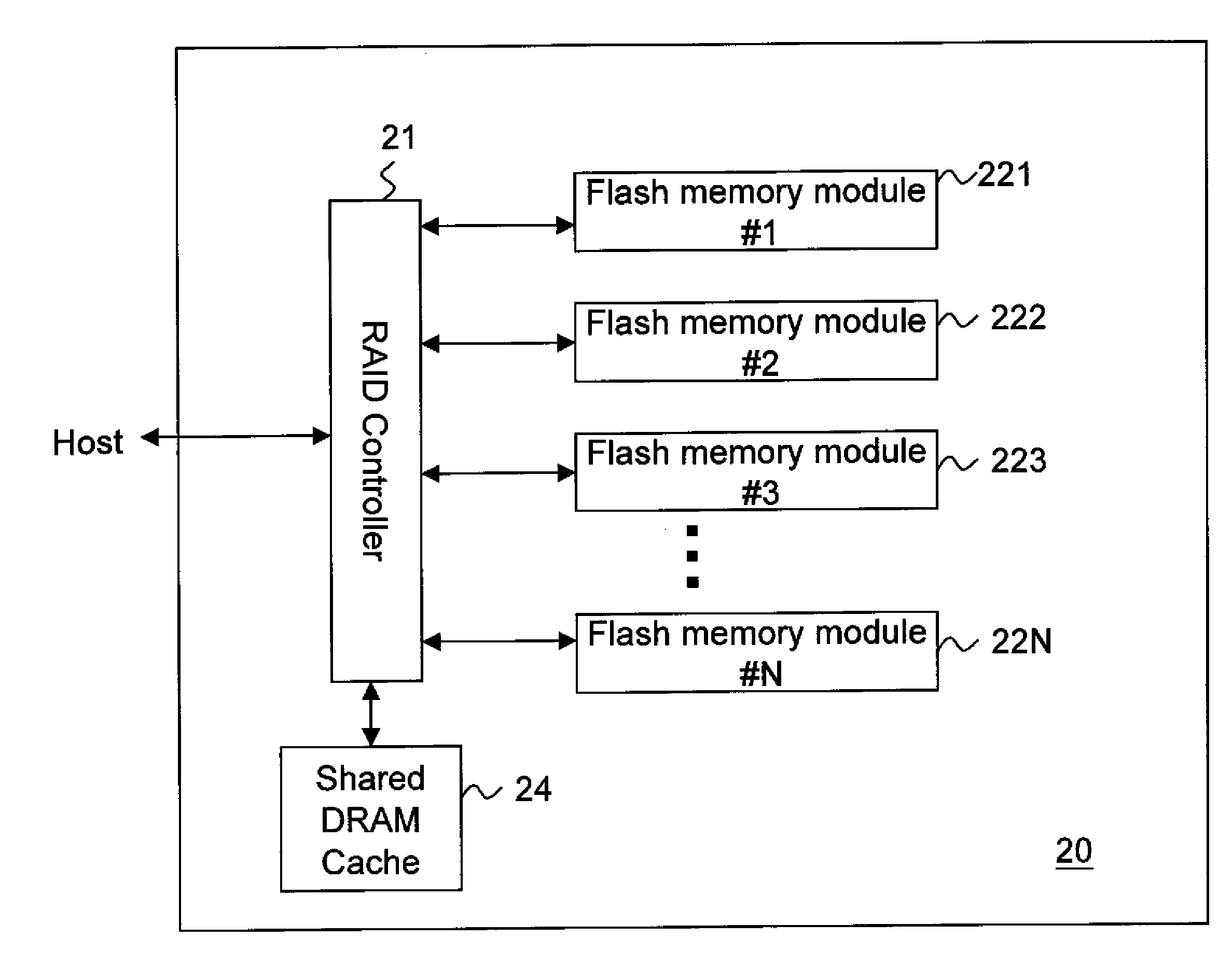
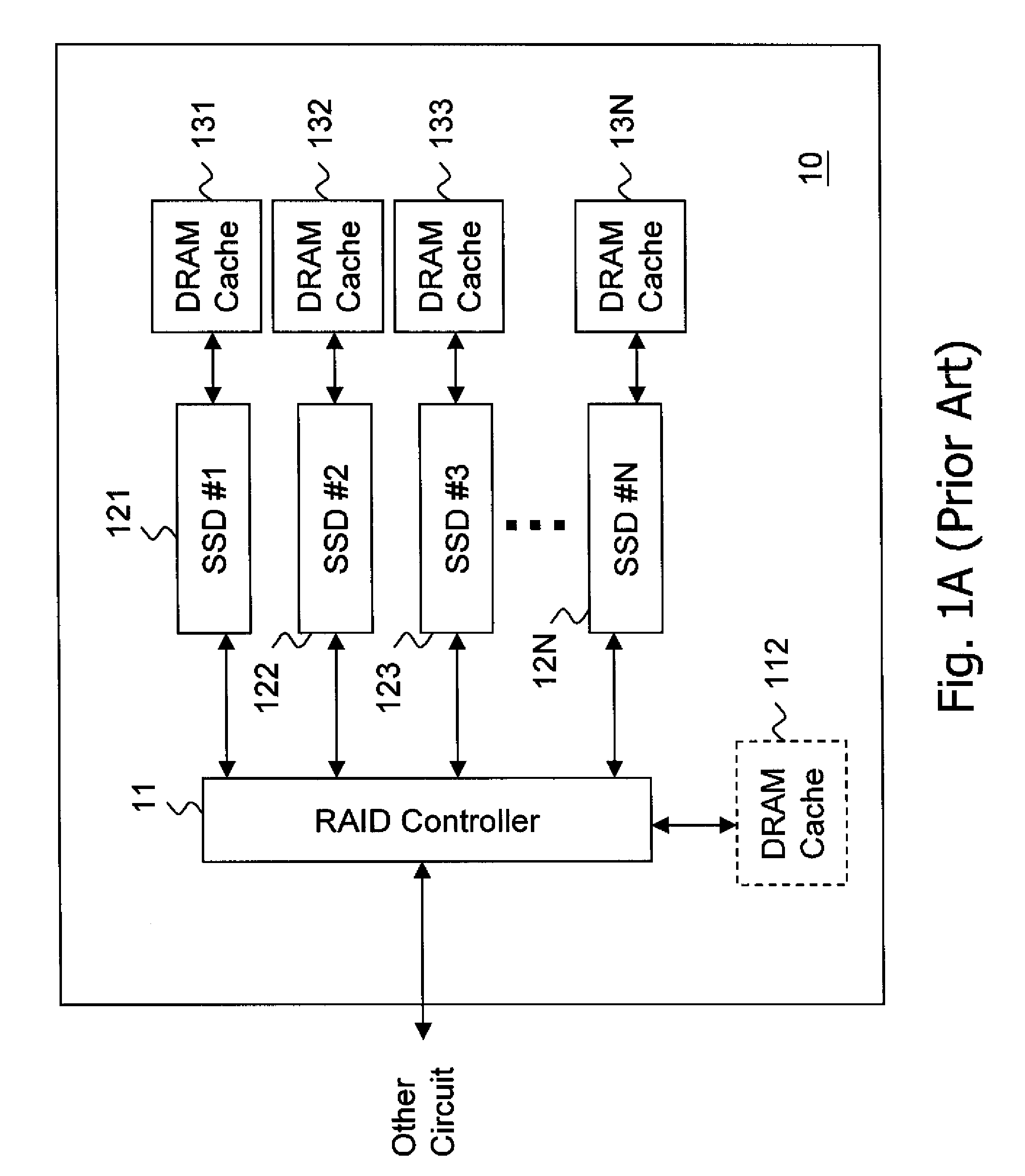
The present invention discloses a flash memory storage system, comprising at least one RAID controller; a plurality of flash memory cards electrically connected with the RAID controller; and a cache memory electrically connected with the RAID controller and shared by the RAID controller and the flash memory cards. The cache memory efficiently enhances the system performance. The storage system may comprise more RAID controllers to construct a nested RAID architecture.
Owner:NANOSTAR CORP
Dram-like nvm memory array and sense amplifier design for high temperature and high endurance operation
InactiveUS20110267883A1Improve threshold voltage sensing marginLarge silicon areaRead-only memoriesDigital storageBit lineAudio power amplifier
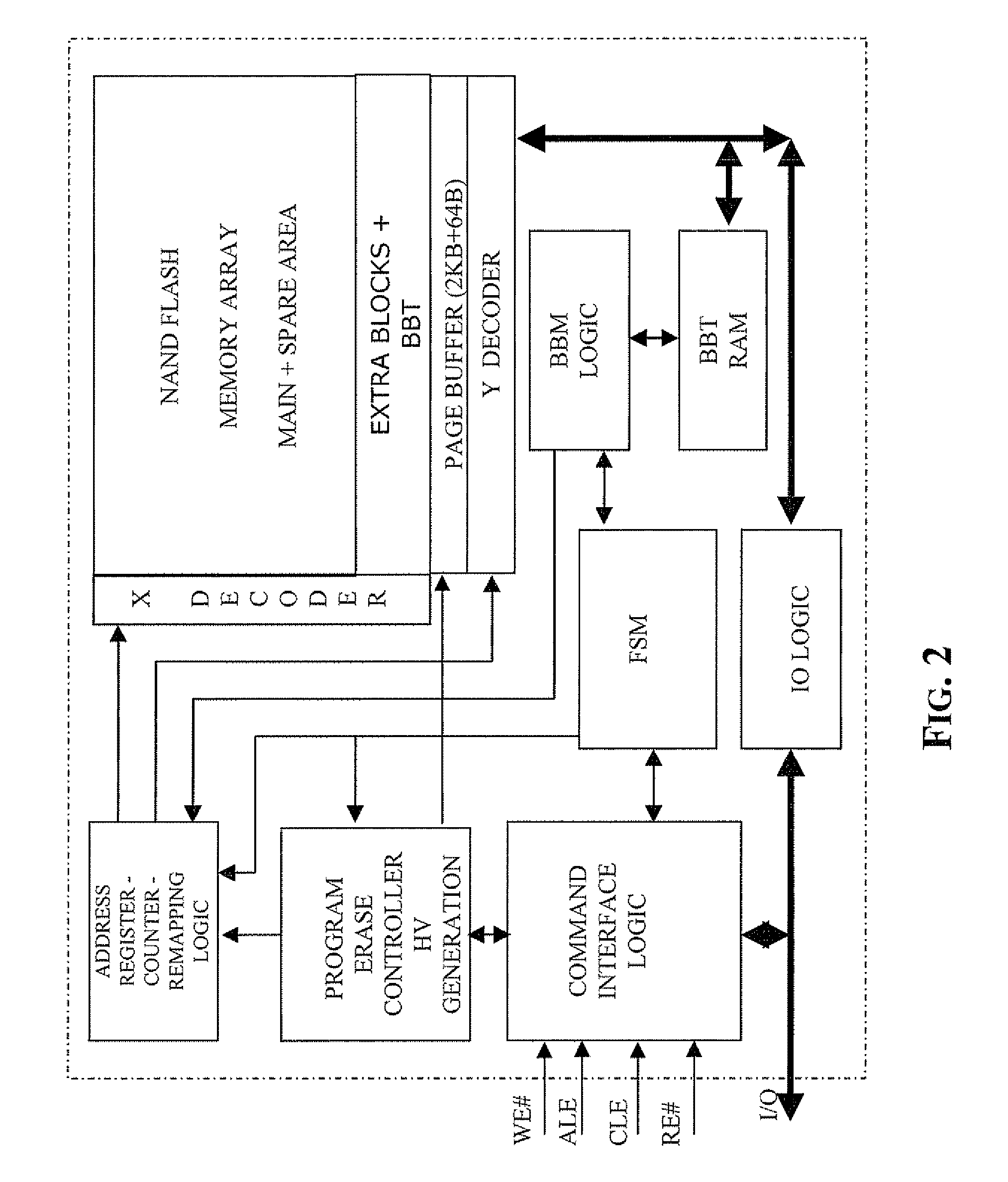
A DRAM-like non-volatile memory array includes a cell array of non-volatile cell units with a DRAM-like cross-coupled latch-type sense amplifier. Each non-volatile cell unit has two non-volatile cell devices with respective bit lines and source lines running in parallel and laid out perpendicular to the word line associated with the non-volatile cell unit. The two non-volatile cell devices are programmed with erased and programmed threshold voltages as a pair for storing a single bit of binary data. The two bit lines of each non-volatile cell unit are coupled through a Y-decoder and a latch device to the two respective inputs of the latch-type sense amplifier which provides a large sensing margin for the cell array to operate properly even with a narrowed threshold voltage gap. Each non-volatile cell device may be a 2 T FLOTOX-based EEPROM cell, a 2 T flash cell, 11 T flash cell or a 1.5 T split-gate flash cell.
Owner:APLUS FLASH TECH
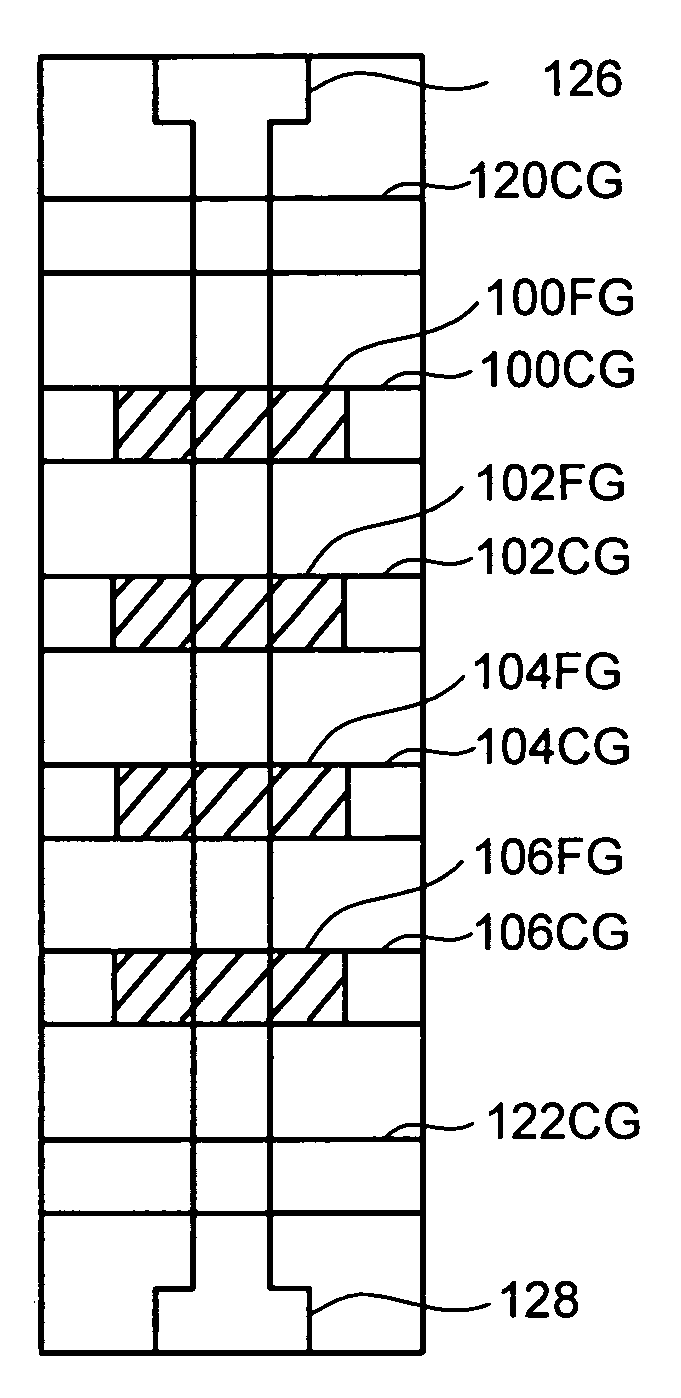
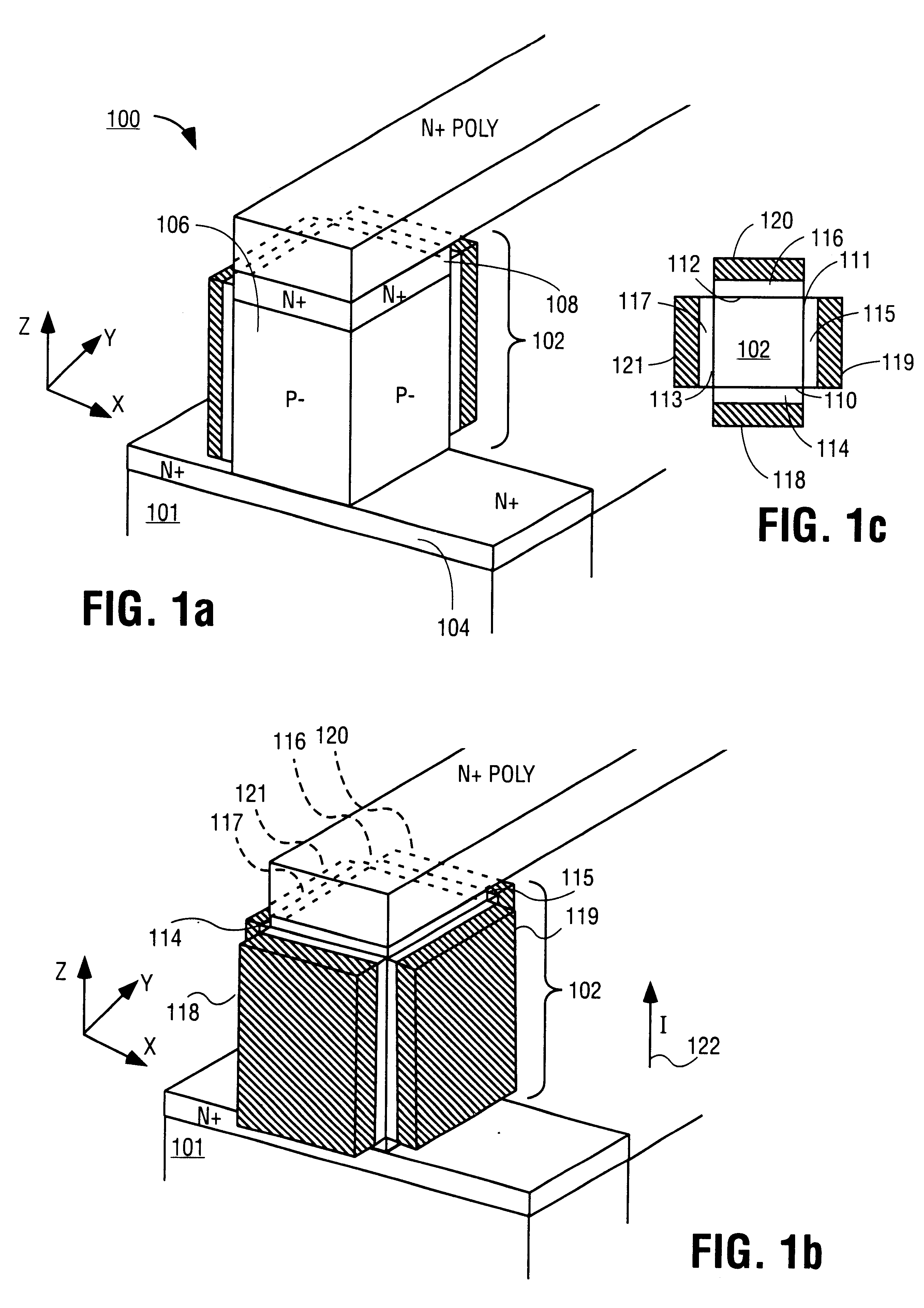
Multigate semiconductor device with vertical channel current and method of fabrication
The present invention is a multibit nonvolatile memory and its method of fabrication. According to the present invention a silicon channel body having a first and second channel surface is formed. A charge storage medium is formed adjacent to the first channel surface and a second charge storage medium is formed adjacent to the second channel surface. A first control gate is formed adjacent to the first charge storage medium adjacent to the first channel surface and a second control gate is formed adjacent to the second charge storage medium adjacent to the second surface.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
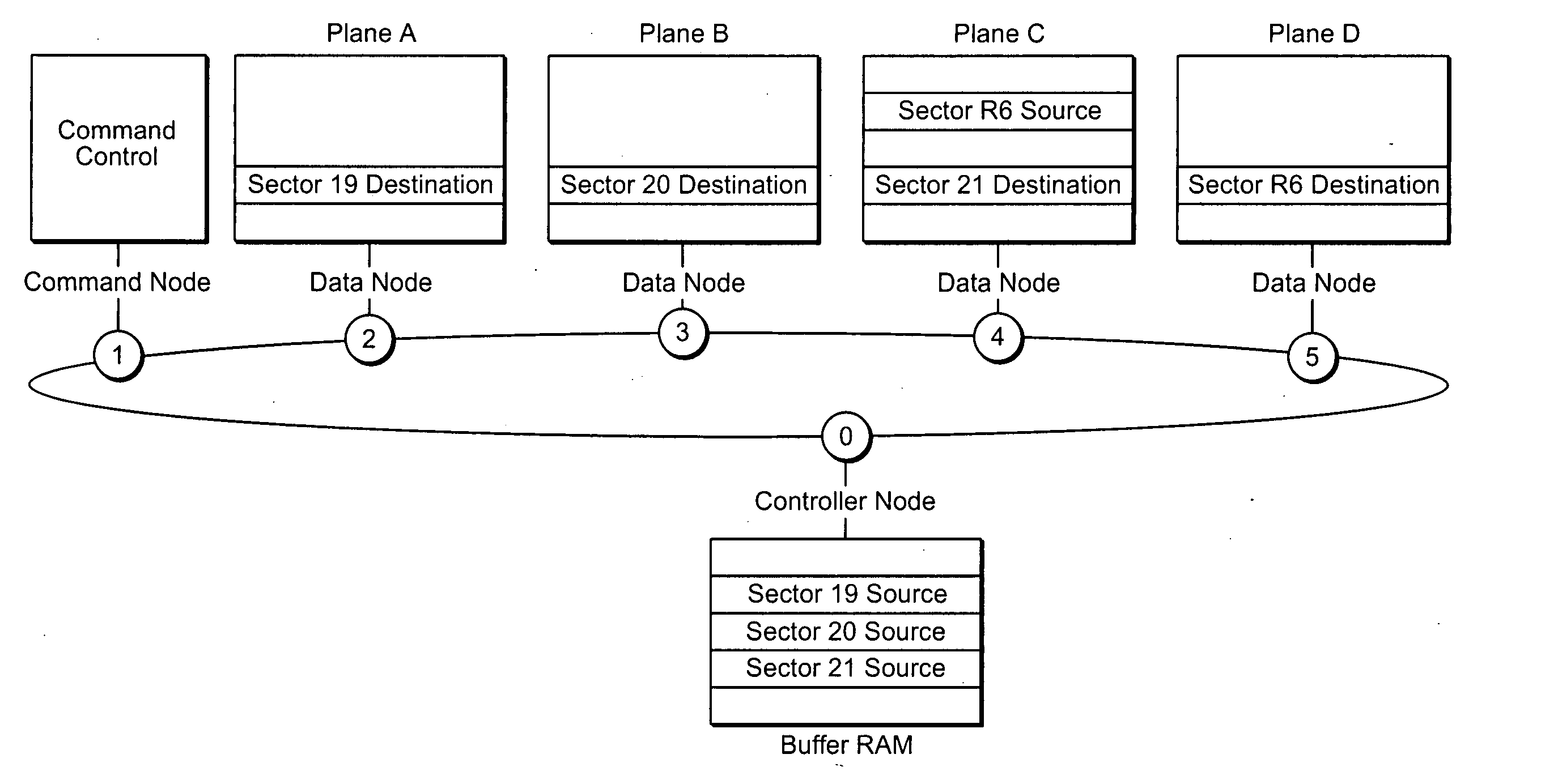
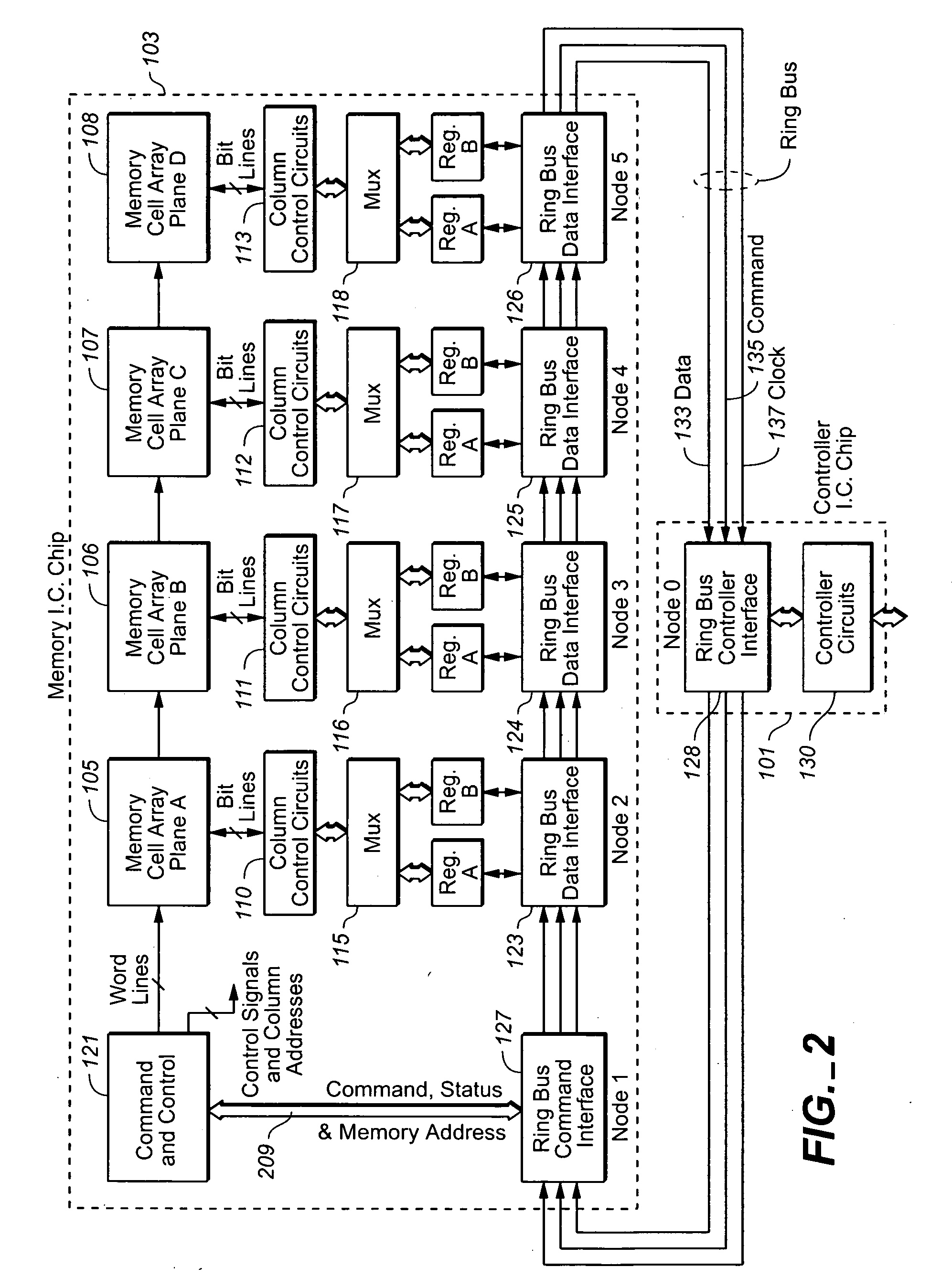
Ring bus structure and its use in flash memory systems
ActiveUS20060031593A1Easy to checkIncrease flexibilityMultiple digital computer combinationsElectric digital data processingSystem controllerNon-volatile memory
A system and integrated circuit chips used in the system utilize a bus in the form of a ring to interconnect nodes of individual components for transfer of data and commands therebetween. An example system described is a memory having one or more re-programmable non-volatile memory cell arrays connected to each other and to a system controller by a ring bus.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Compensating for coupling during programming
Shifts in the apparent charge stored on a floating gate (or other charge storing element) of a non-volatile memory cell can occur because of the coupling of an electric field based on the charge stored in adjacent floating gates (or other adjacent charge storing elements). To compensate for this coupling, the read or programming process for a given memory cell can take into account the programmed state of an adjacent memory cell. To determine whether compensation is needed, a process can be performed that includes sensing information about the programmed state of an adjacent memory cell (e.g., on an adjacent bit line or other location).
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
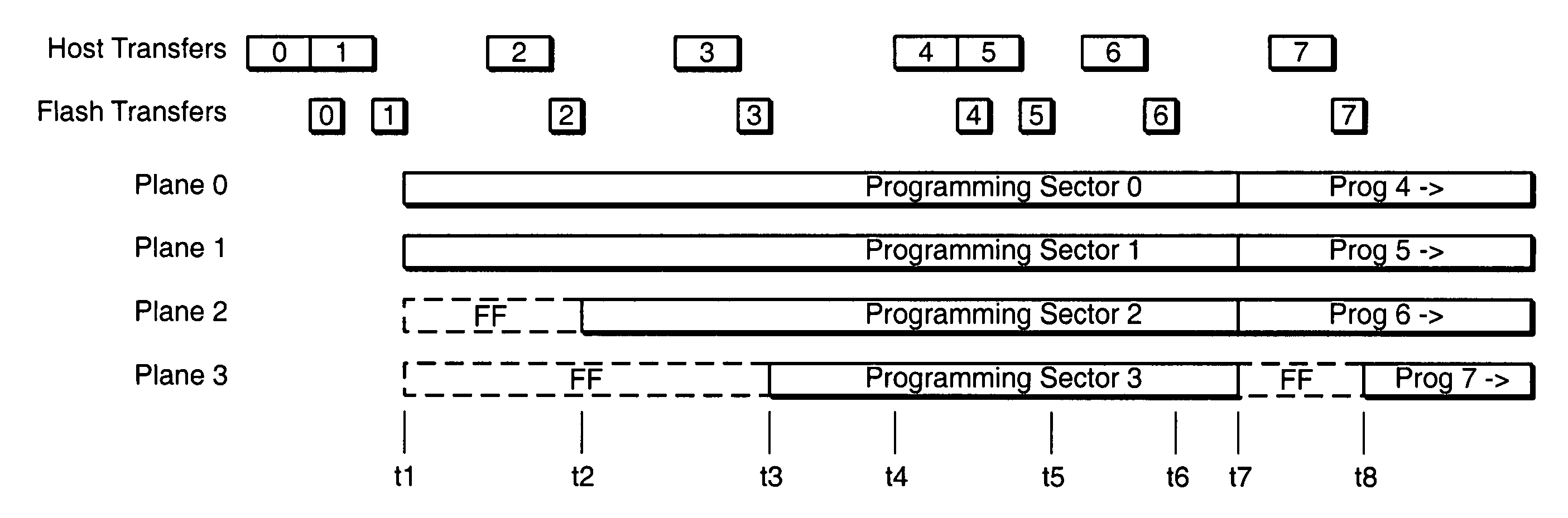
Pipelined programming of non-volatile memories using early data
ActiveUS20060126390A1Improve performanceRead-only memoriesDigital storageFull dataProgramming process
The present invention presents techniques whereby a memory system interrupts a programming process and restarts it including additional data. More specifically, when a memory system programs data into a group of cells together as programming unit, programming can begin with less than the full data content which the group can hold. In one embodiment, the present invention allows overlapped programming of upper and lower data pages, where once the memory begins programming the lower logical data page, if data is received for the upper page assigned to the same physical page, programming is interrupted and recommenced with the concurrent programming of both the upper and the loser pages. In a complimentary embodiment, when a page contains multiple sectors of data, programming of the physical page can begin when one or more, but less than all, of the sectors forming the corresponding logical page have been received, stopped and restarted to include additional sectors of the page.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Reference sense amplifier for non-volatile memory
InactiveUS20060158947A1Large capacityImprove performanceRead-only memoriesDigital storageAudio power amplifierReference current
One or more sense amplifiers for sensing the conduction current of non-volatile memory is controlled by signals that are timed by a reference sense amplifier having similar characteristics and operating conditions. In one aspect, a sensing period is determined by when the reference sense amplifier sensing a reference current detects an expected state. In another aspect, an integration period for an amplified output is determined by when the reference sense amplifier outputs an expected state. When these determined timings are used to control the one or more sense amplifiers, environment and systemic variations are tracked.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com