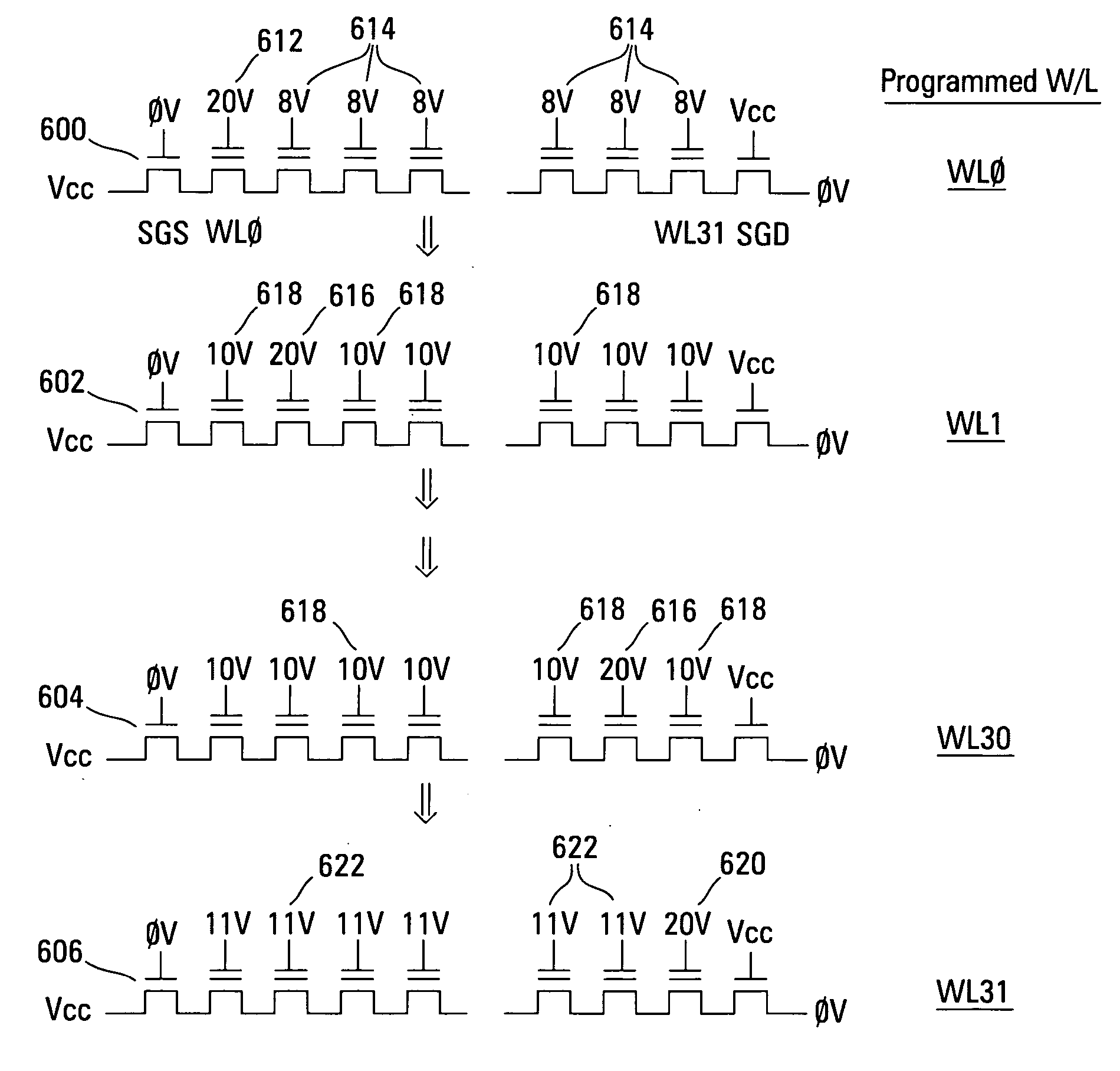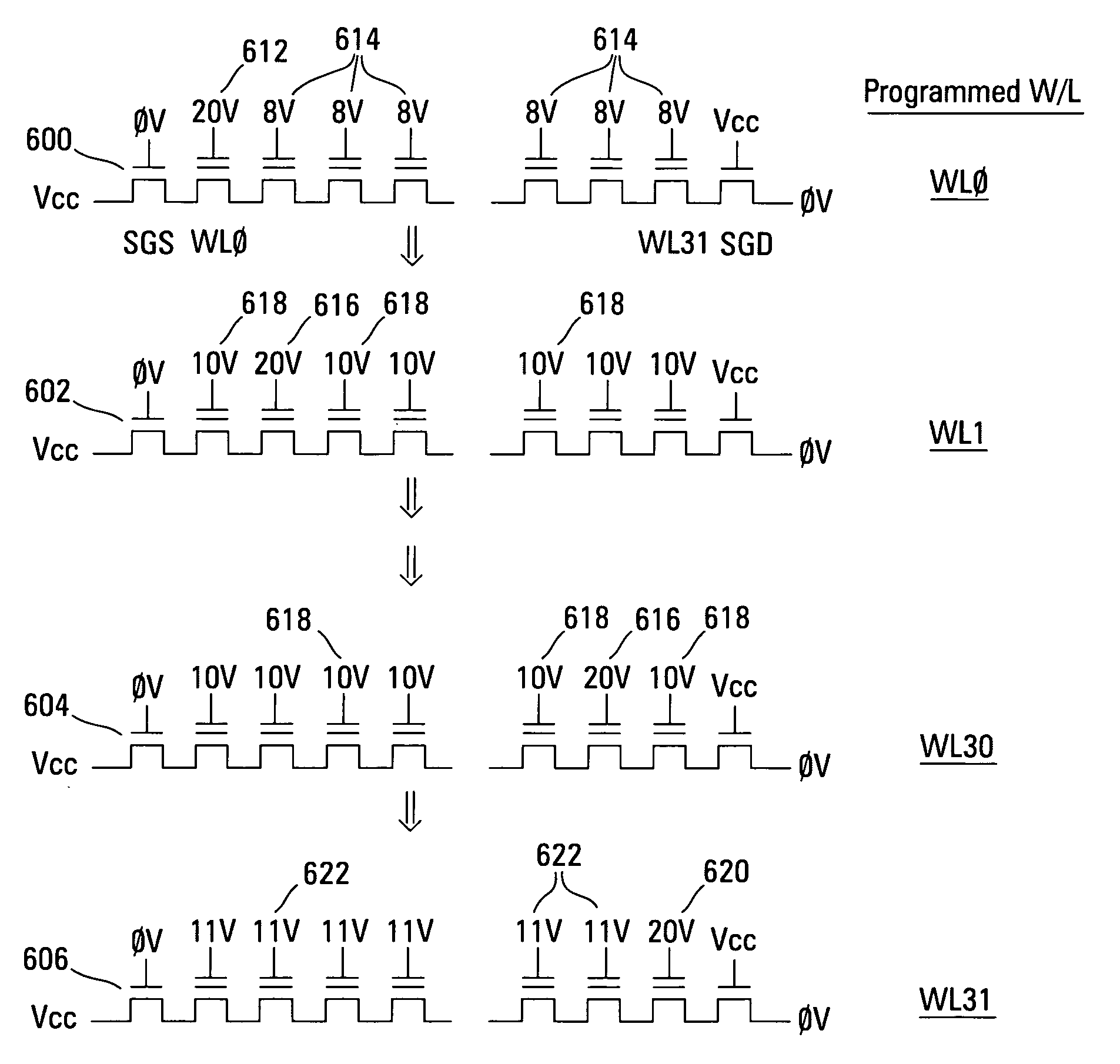Patents
Literature
2874 results about "EEPROM" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
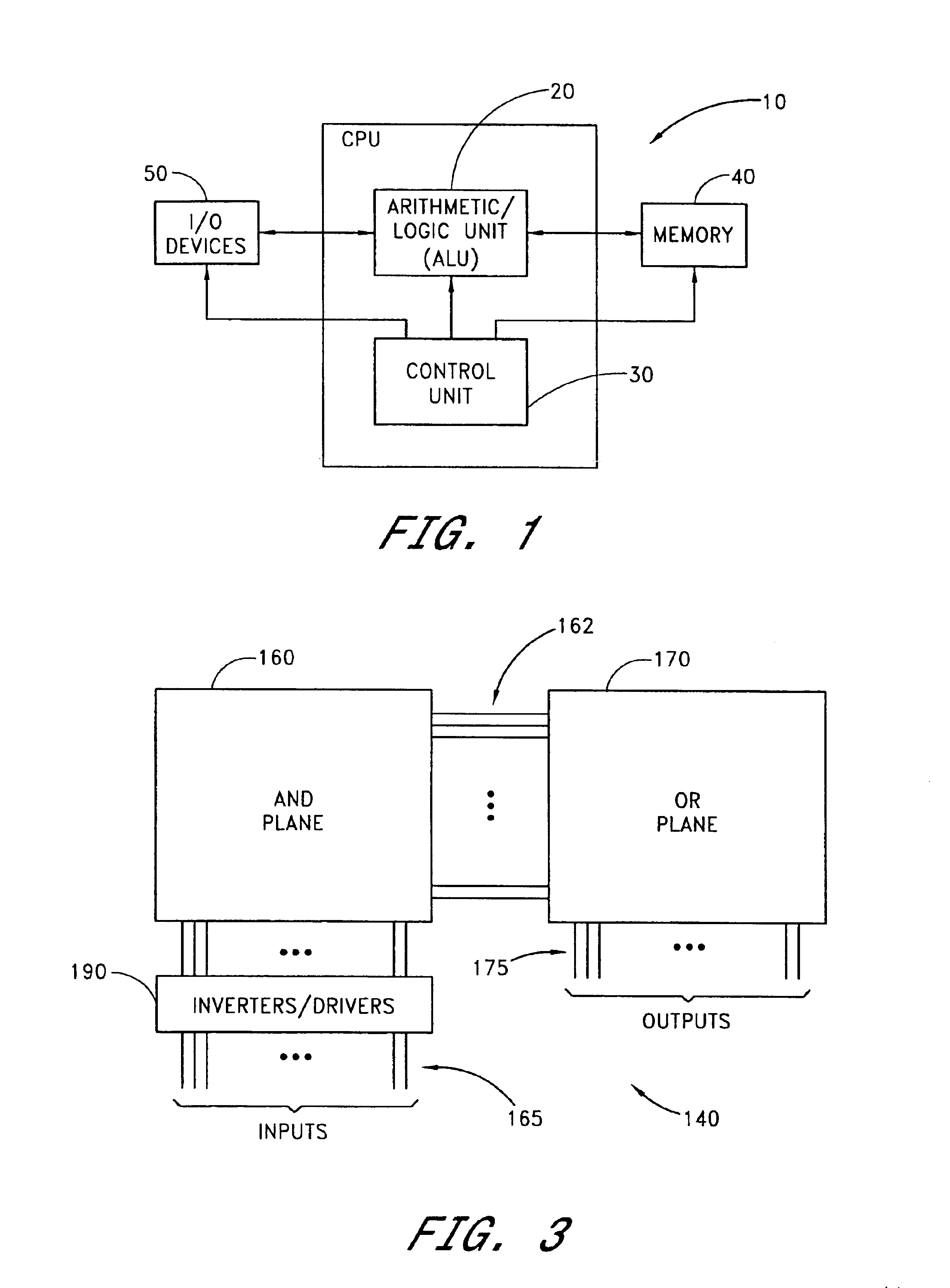
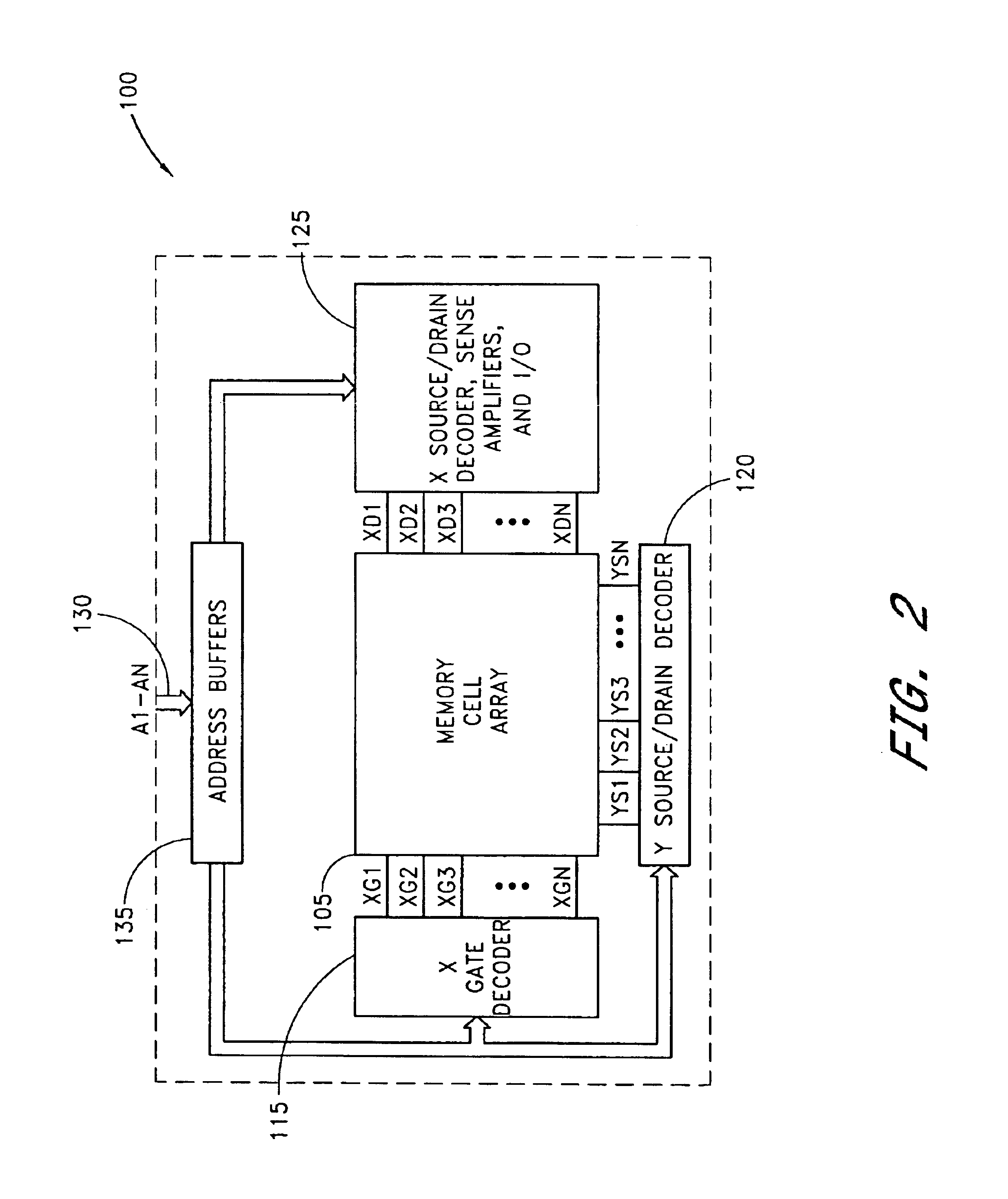
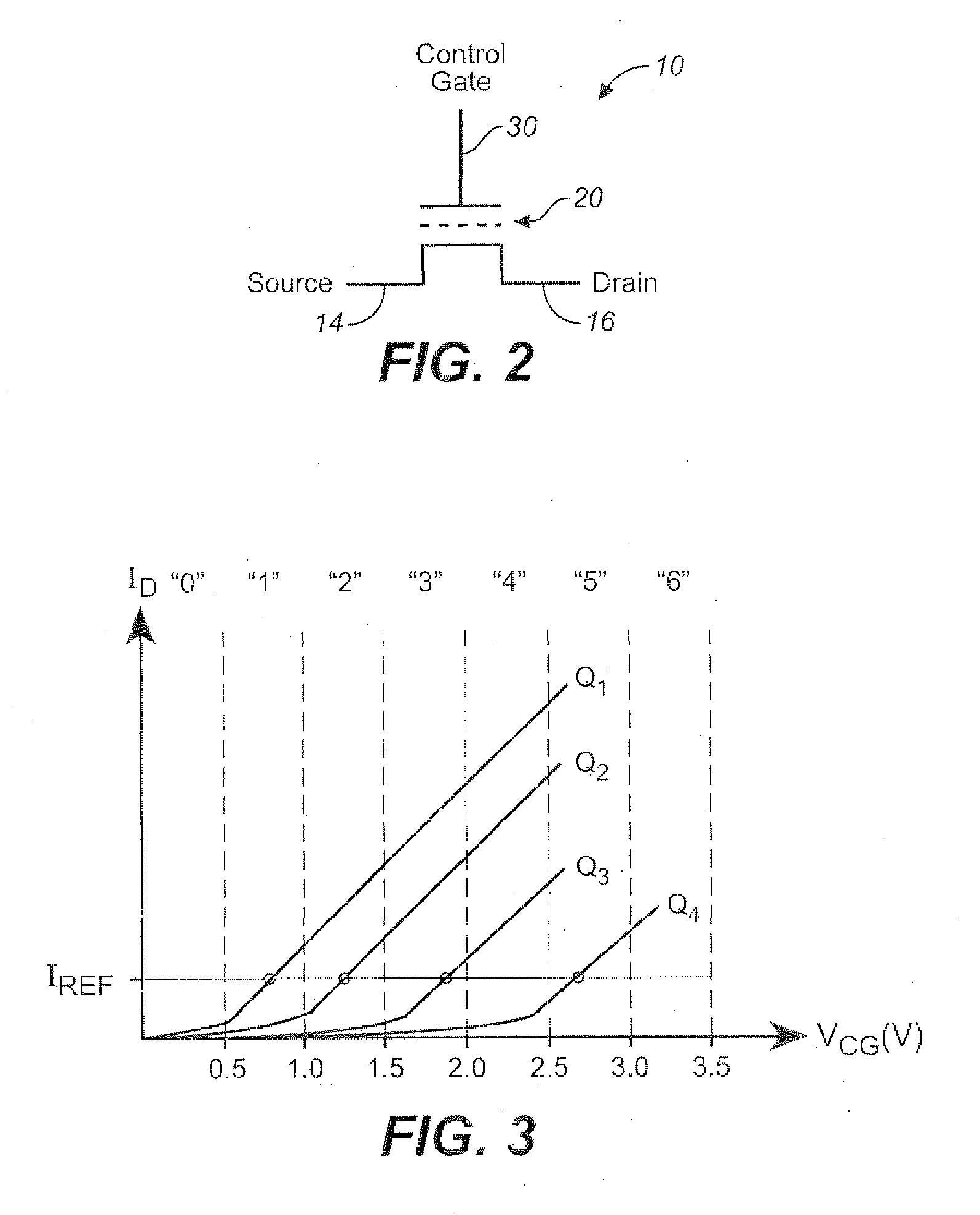
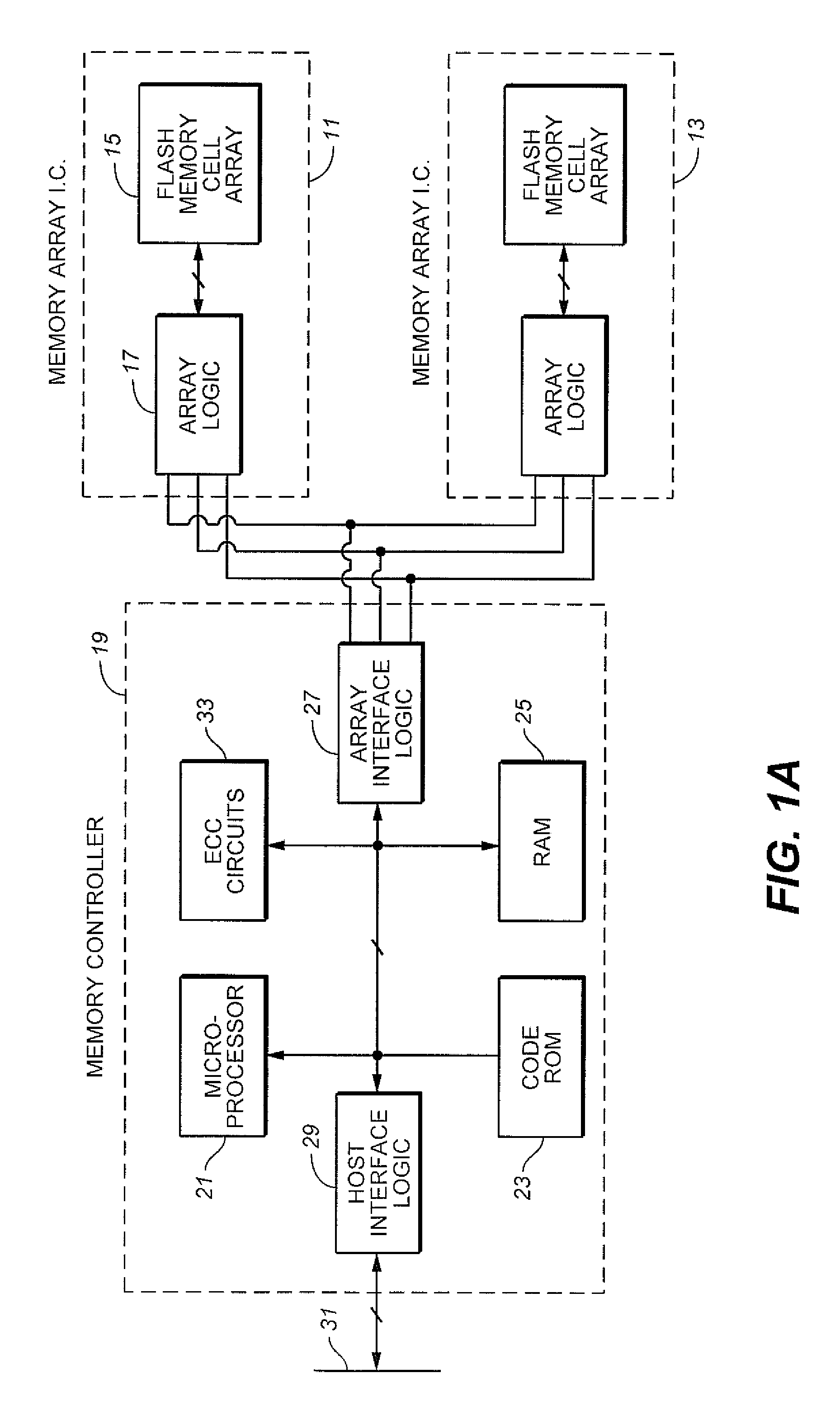
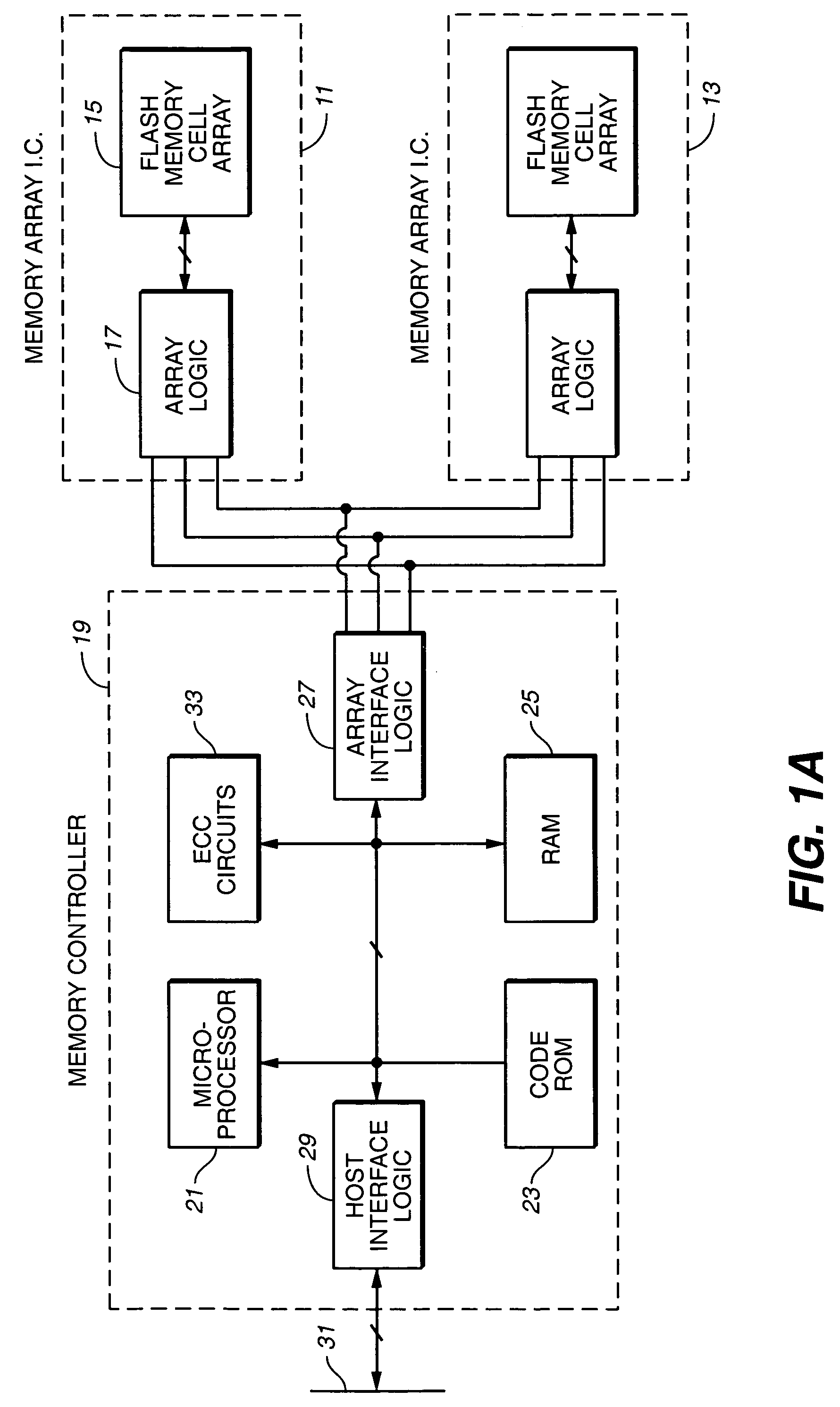
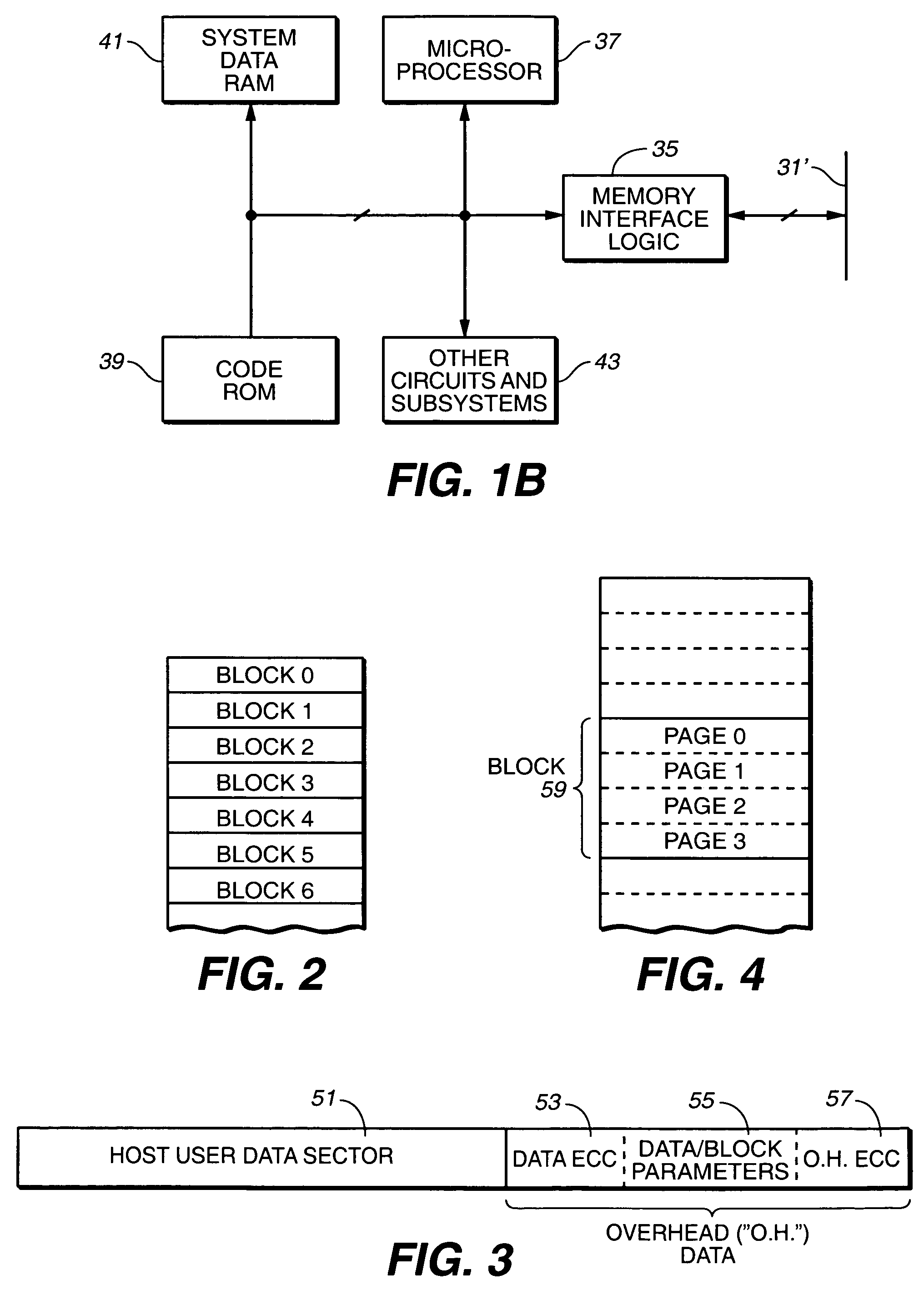
EEPROM (also E²PROM) stands for electrically erasable programmable read-only memory and is a type of non-volatile memory used in computers, integrated in microcontrollers for smart cards and remote keyless systems, and other electronic devices to store relatively small amounts of data but allowing individual bytes to be erased and reprogrammed.
Apparatus and method for altering generator functions in an ultrasonic surgical system
InactiveUS6908472B2Avoid mistakesNew system functionalityIncision instrumentsDiagnosticsDriving currentElectricity
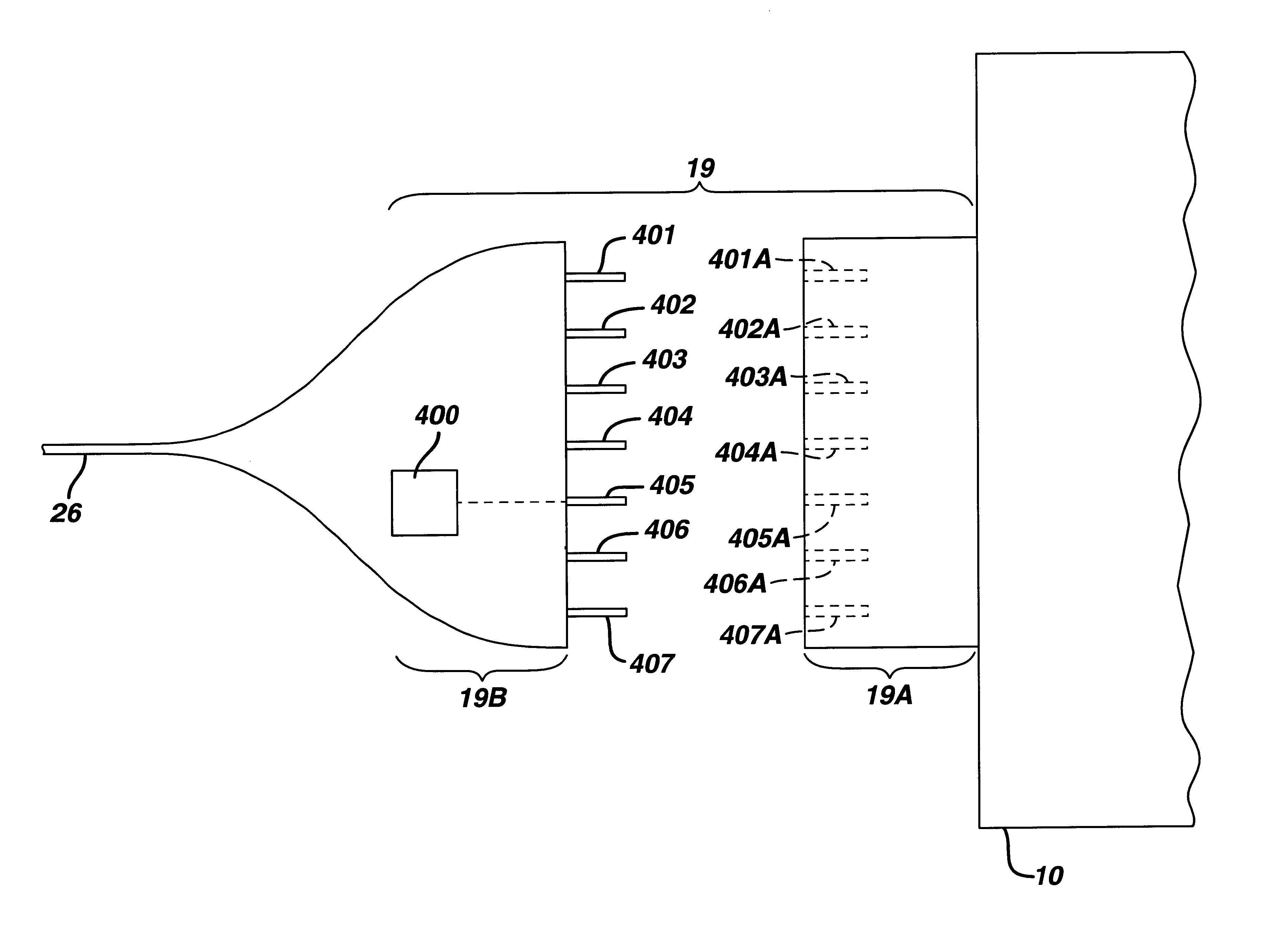
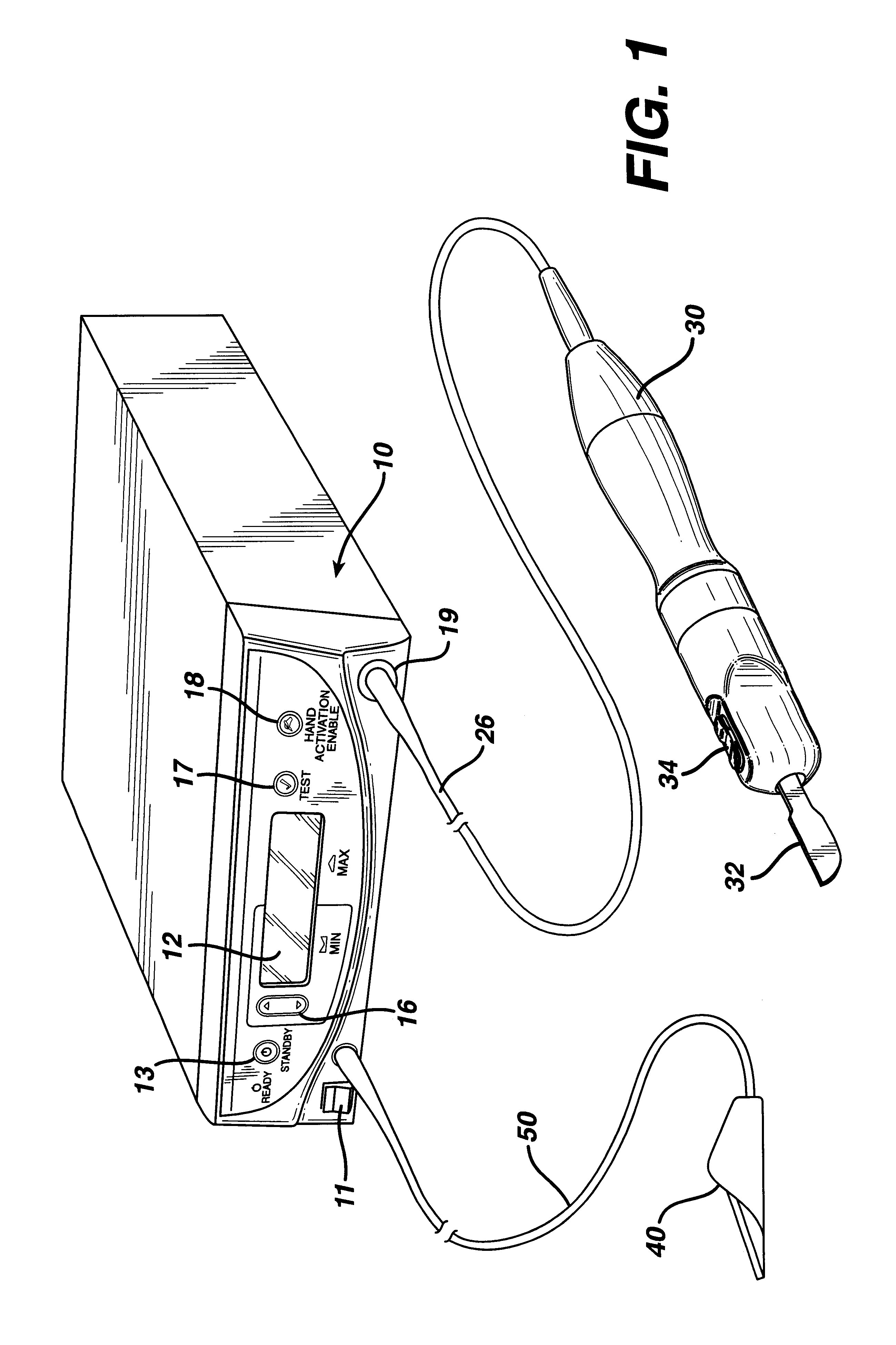
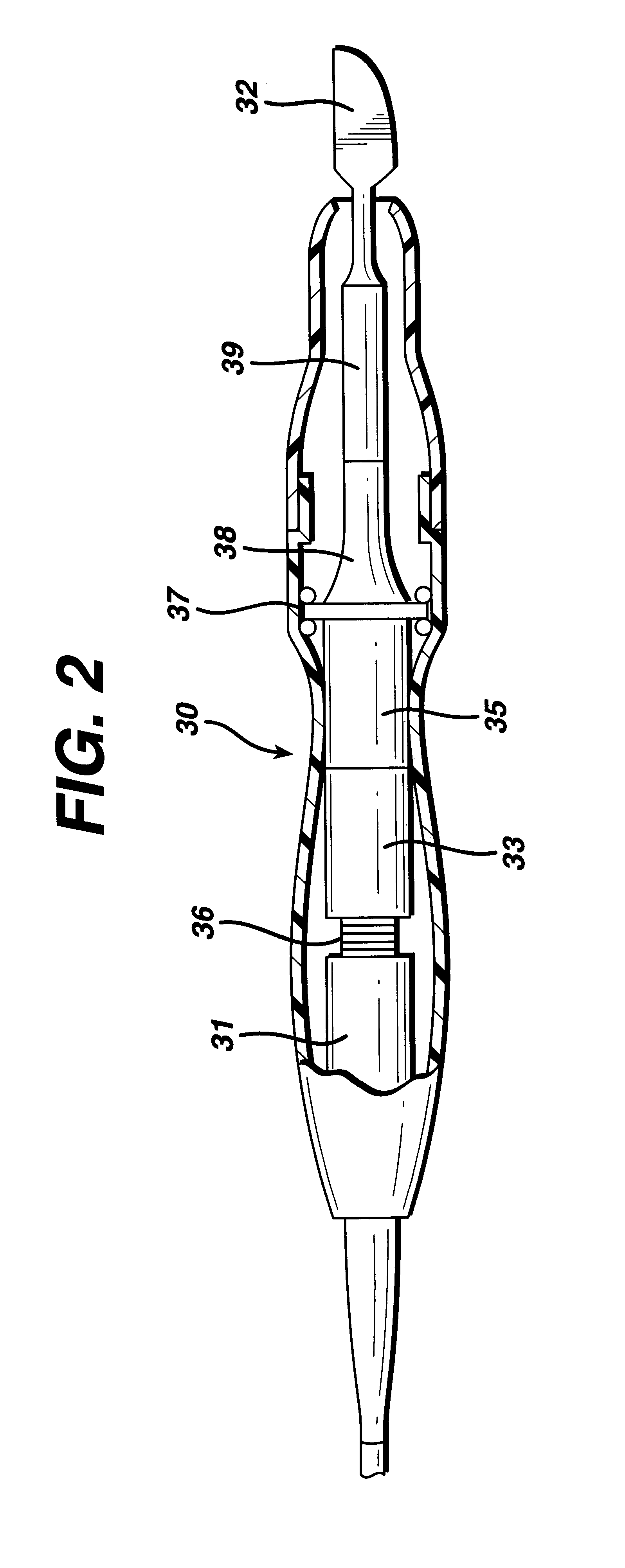
The present invention provides a system for implementing surgical procedures which includes an ultrasonic surgical hand piece having an end-effector, a console having a digital signal processor (DSP) for controlling the hand piece, an electrical connection connecting the hand piece and the console, and a memory, such as an EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory), disposed in the electrical connection. The console sends a drive current to drive the hand piece which imparts ultrasonic longitudinal movement to the blade. The console reads the memory and authenticates the hand piece for use with the console if particular or proprietary data are present in the memory. Moreover, to prevent errors in operating the hand piece, the memory can store certain diagnostic information which the console can utilize in determining whether the operation of the hand piece should be handicapped or disabled. Furthermore, the memory can be used to reprogram the console, if needed.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
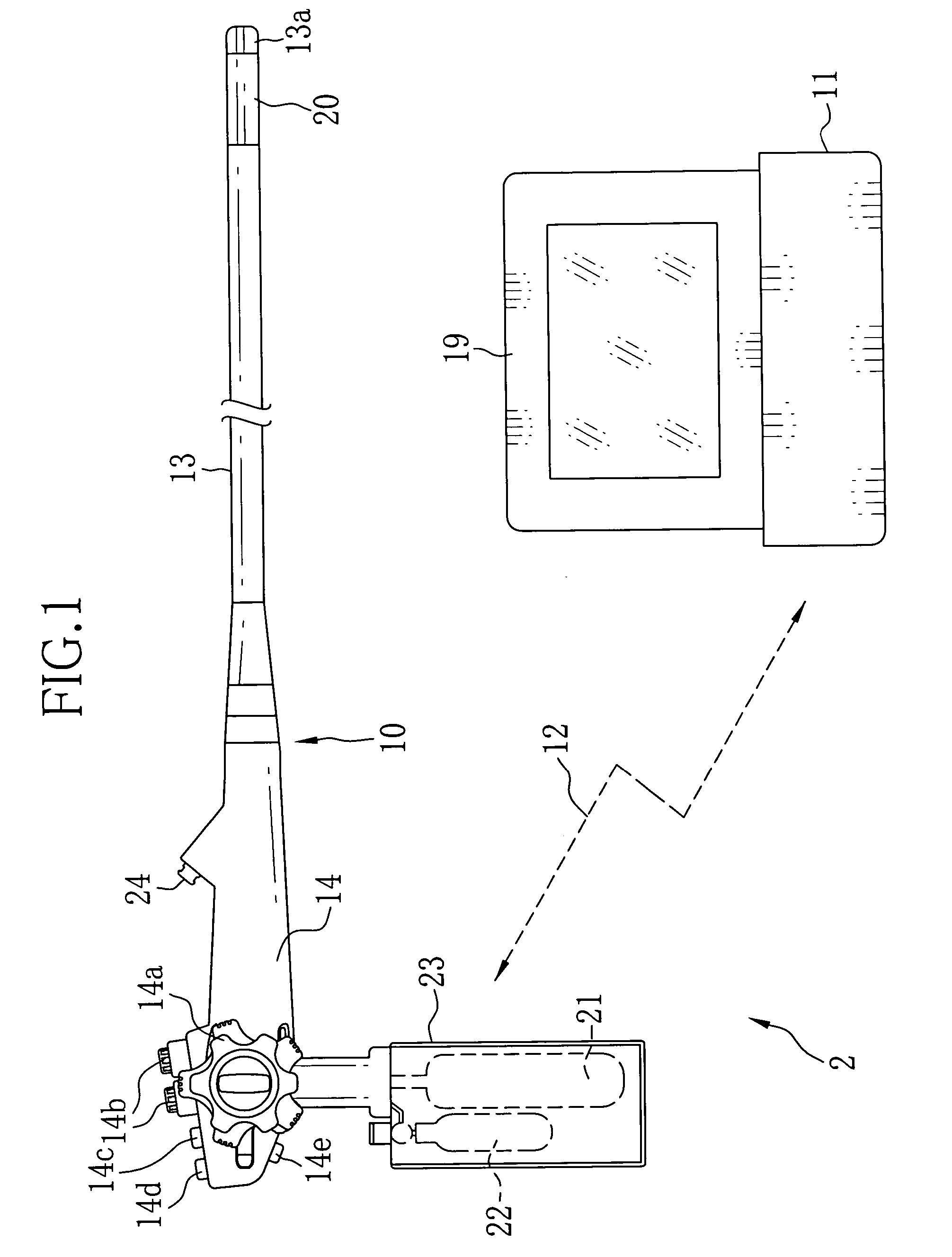
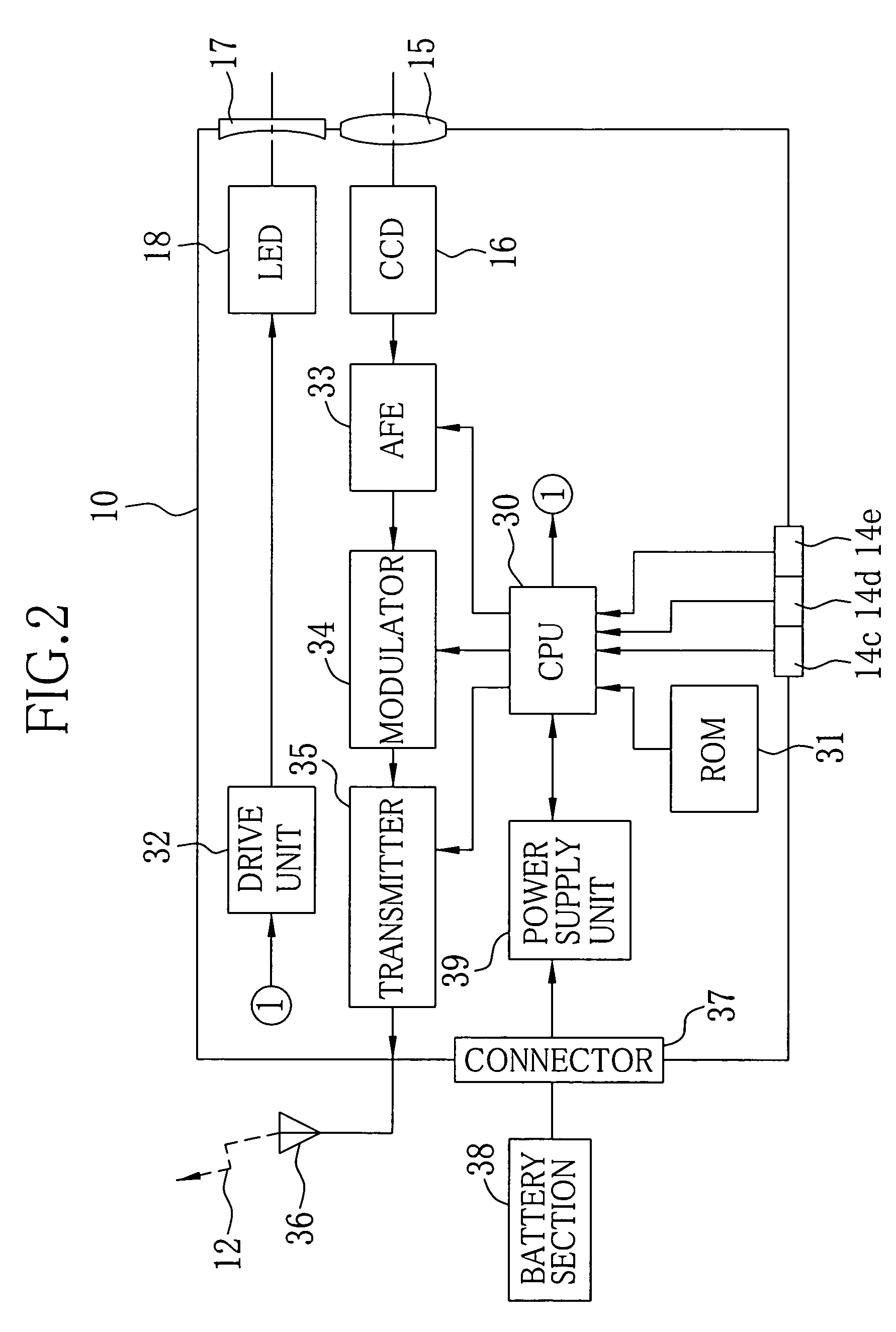
Electronic endoscope battery section
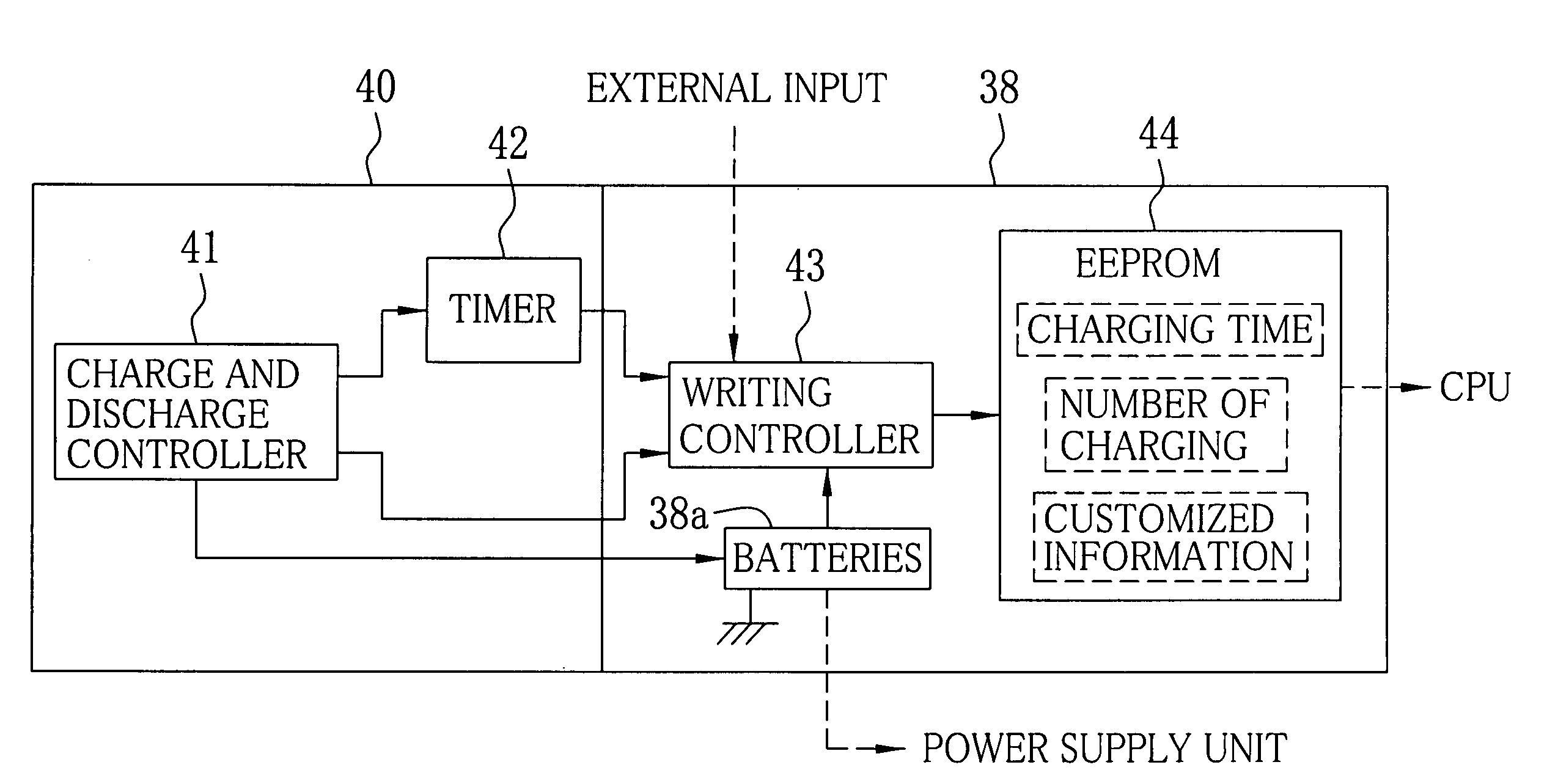
A battery section of an electronic endoscope is provided with an EEPROM. The EEPROM stores charging time and the number of charging of batteries, necessary for calculating remaining power of the batteries, and customized information for assigning functions to first, second and third switches of an operation section. A remaining-power calculator calculates the remaining power of the batteries based on a relation between discharge voltage and discharge time of the batteries as well as on the charging time and the number of charging of the batteries read out from the EEPROM. A function assignment circuit assigns the functions to the first, second and third switches in accordance with the customized information read out from the EEPROM.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
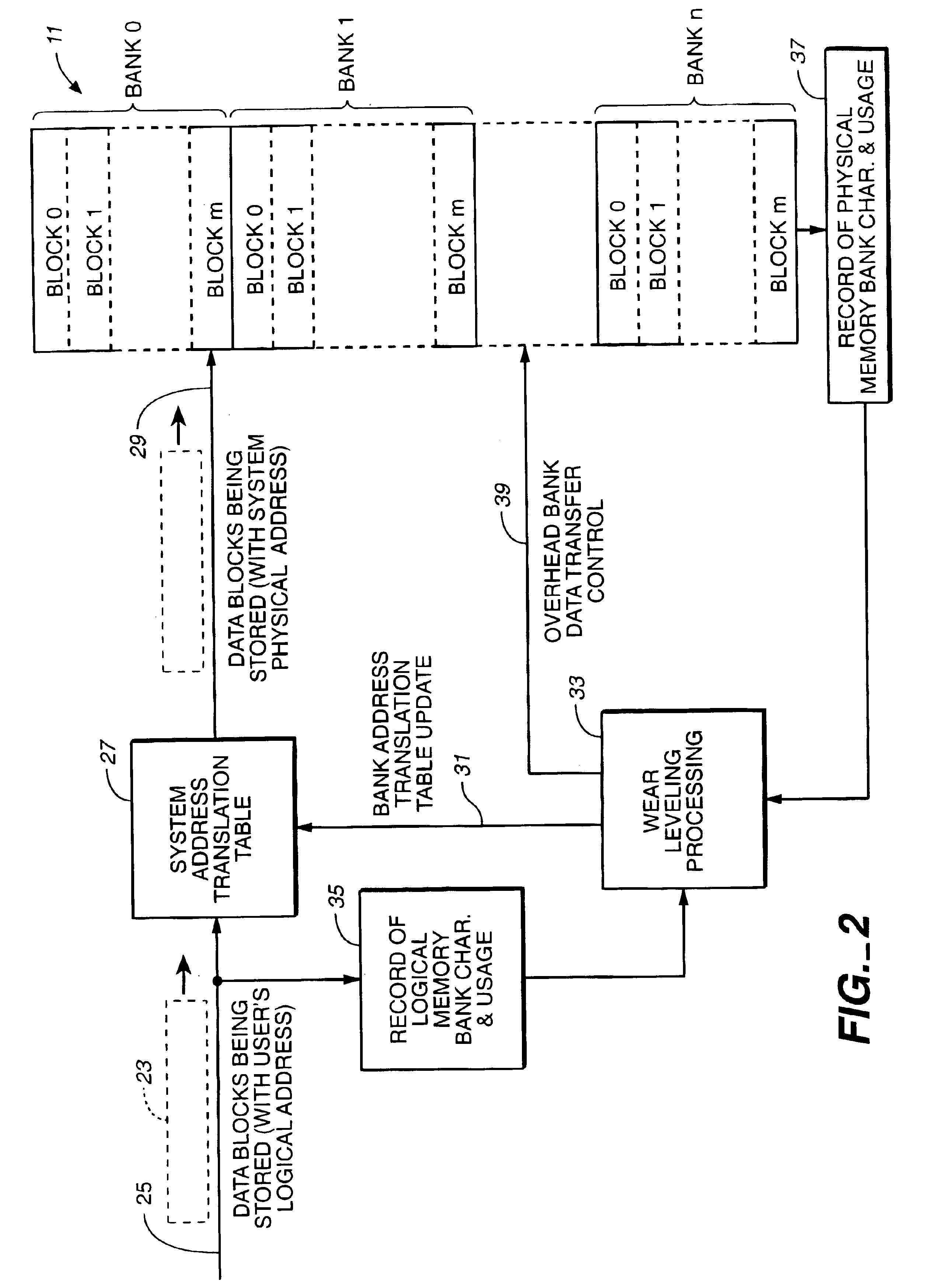
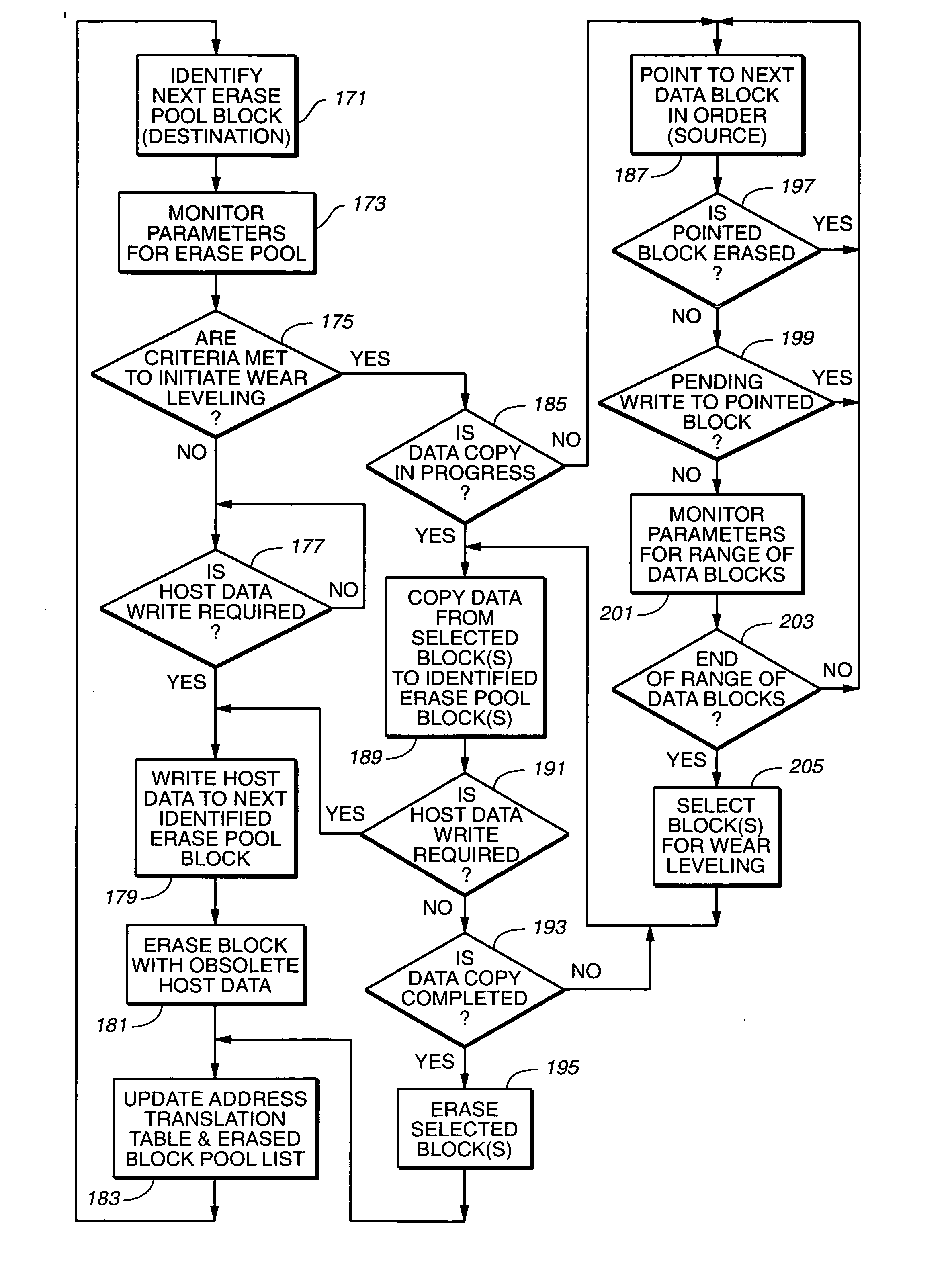
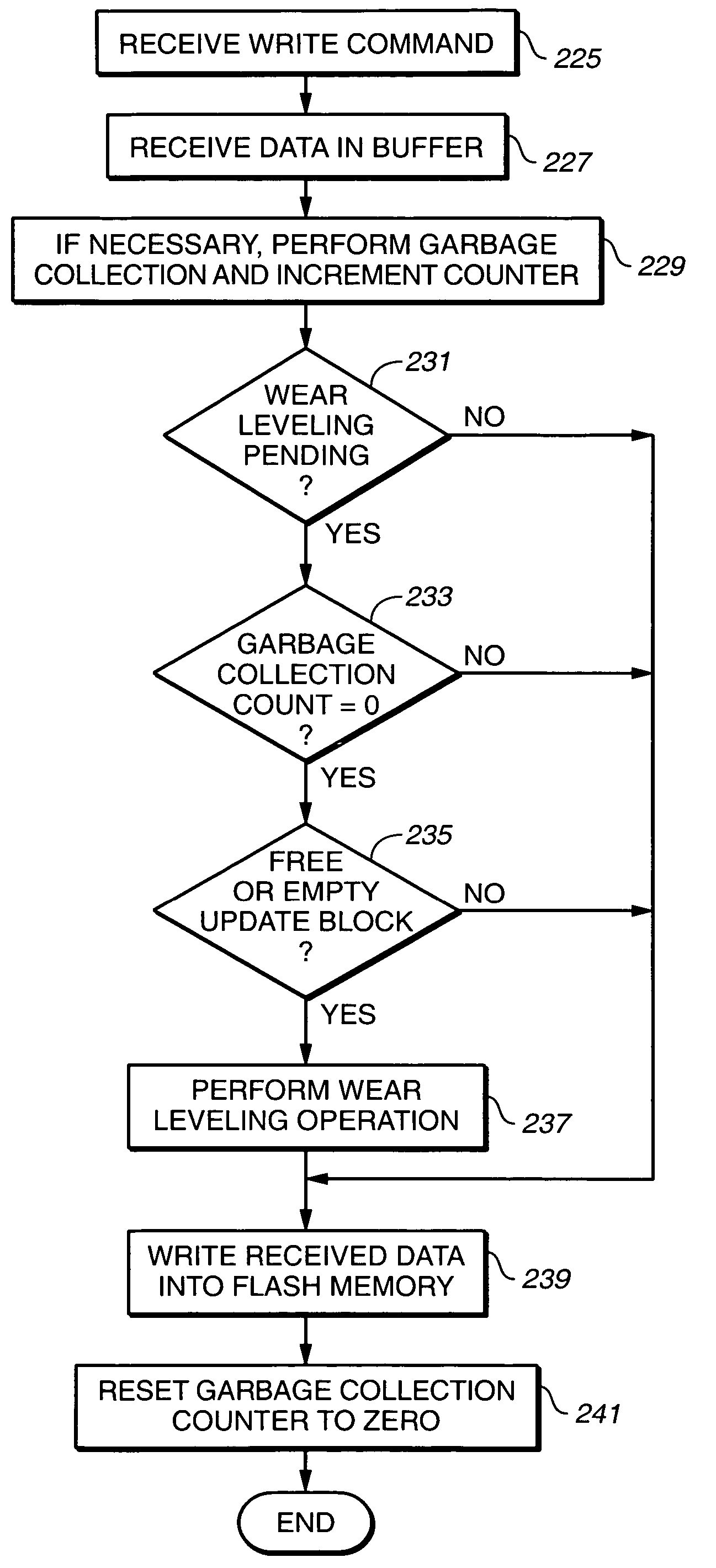
Wear leveling techniques for flash EEPROM systems
InactiveUS6850443B2Avoid uneven wearExtended service lifeMemory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesElectricityProgrammable read-only memory
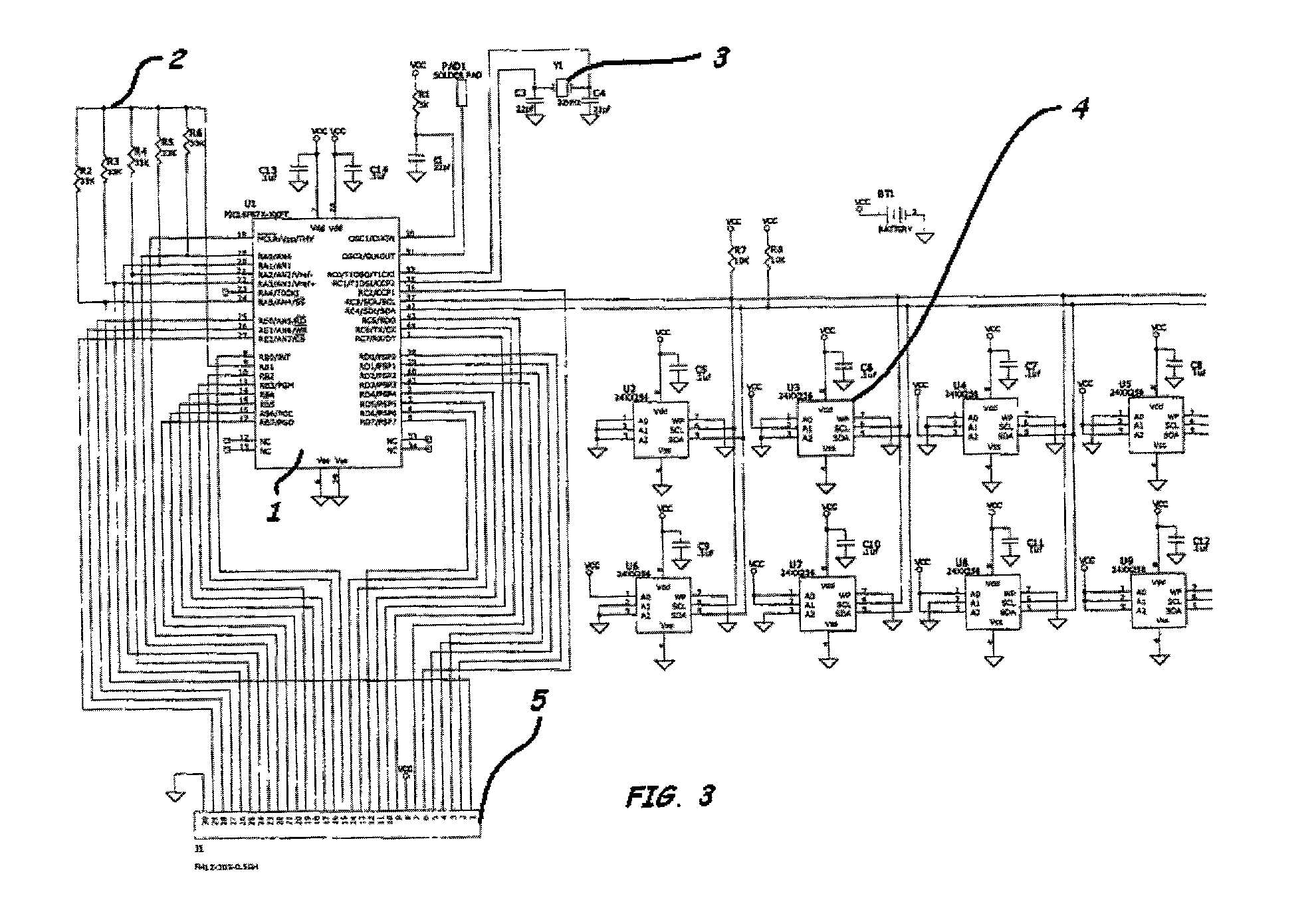
A mass storage system made of flash electrically erasable and programmable read only memory (“EEPROM”) cells organized into blocks, the blocks in turn being grouped into memory banks, is managed to even out the numbers of erase and rewrite cycles experienced by the memory banks in order to extend the service lifetime of the memory system. Since this type of memory cell becomes unusable after a finite number of erase and rewrite cycles, although in the tens of thousands of cycles, uneven use of the memory banks is avoided so that the entire memory does not become inoperative because one of its banks has reached its end of life while others of the banks are little used. Relative use of the memory banks is monitored and, in response to detection of uneven use, have their physical addresses periodically swapped for each other in order to even out their use over the lifetime of the memory.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Dram-like nvm memory array and sense amplifier design for high temperature and high endurance operation
InactiveUS20110267883A1Improve threshold voltage sensing marginLarge silicon areaRead-only memoriesDigital storageBit lineAudio power amplifier
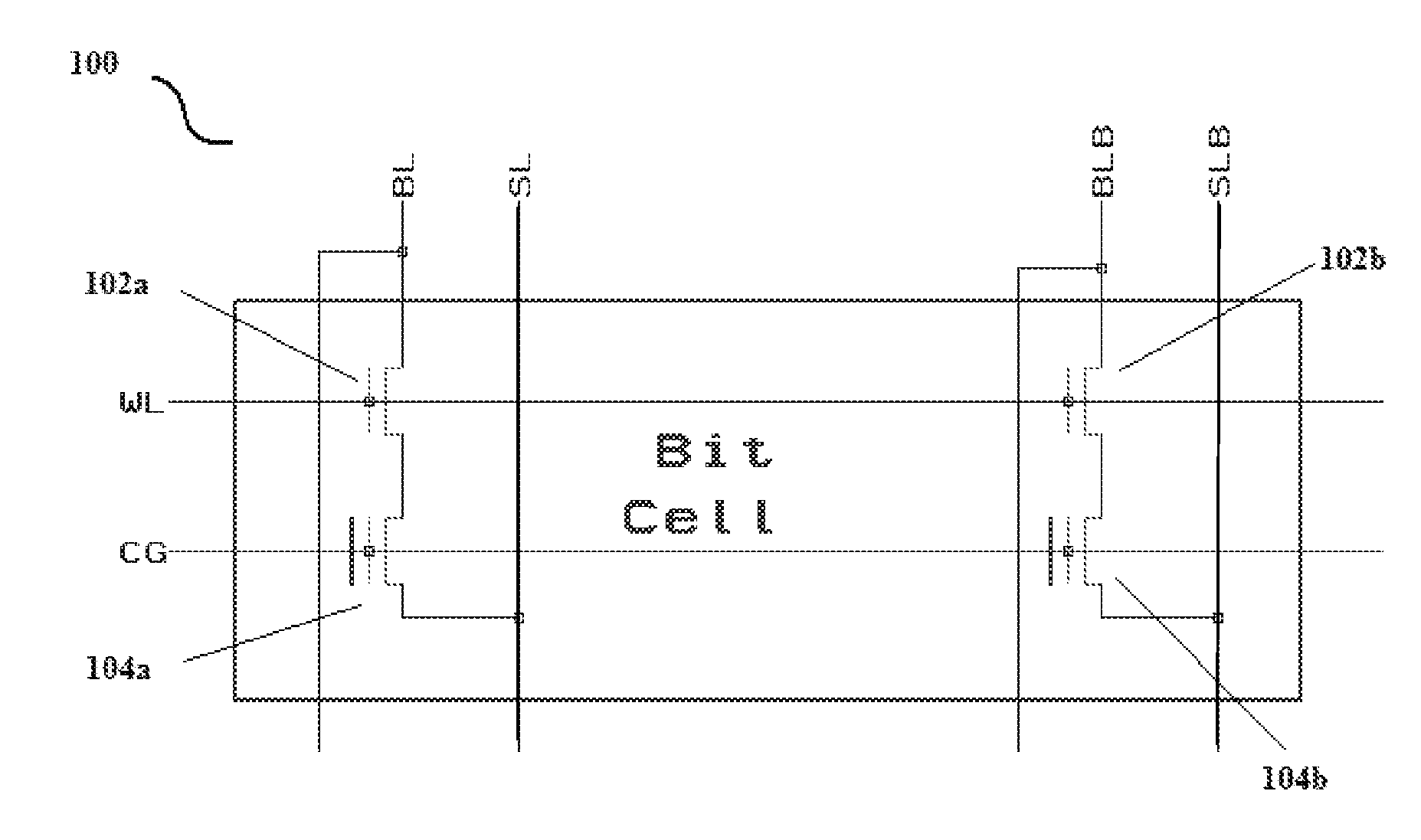
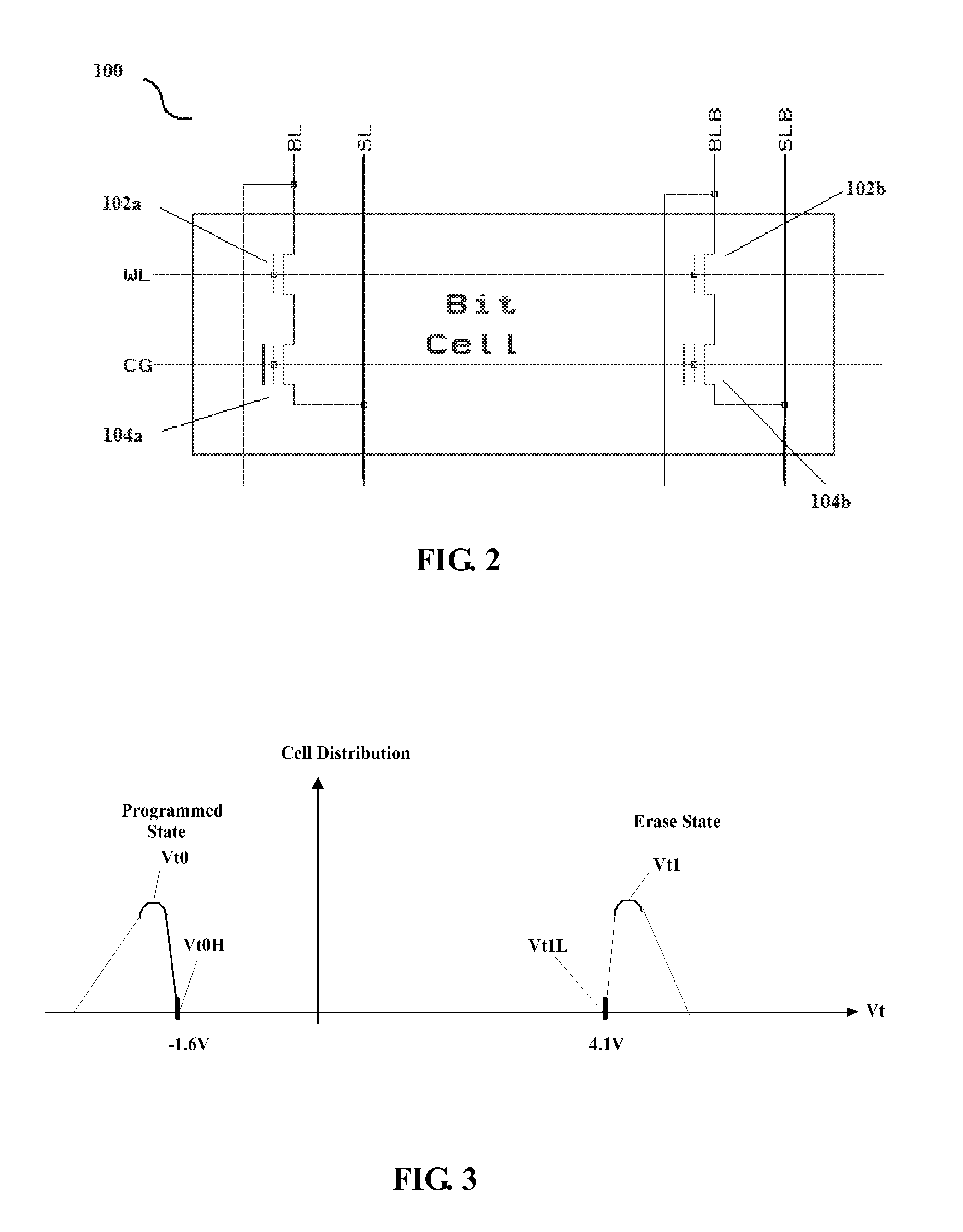
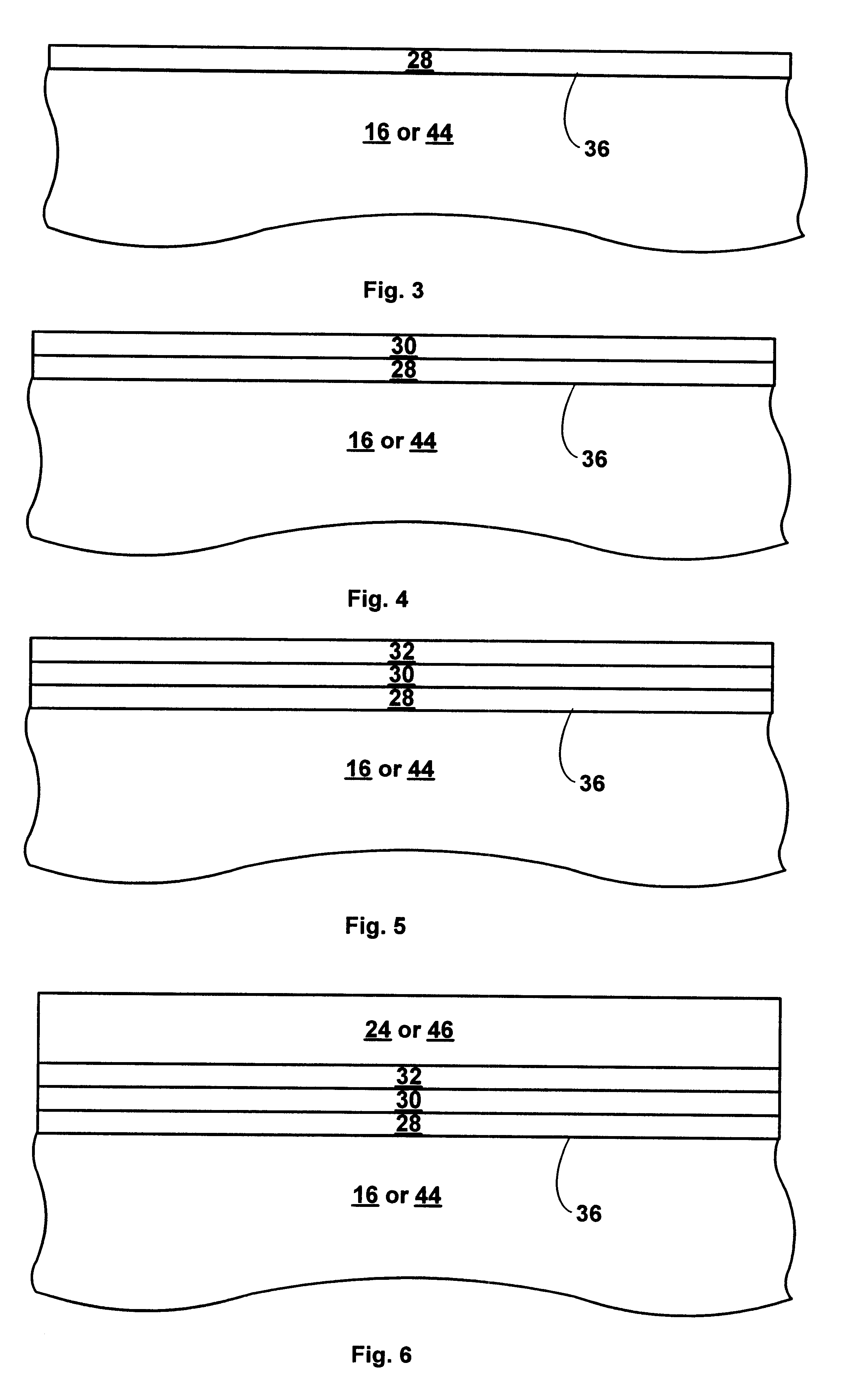
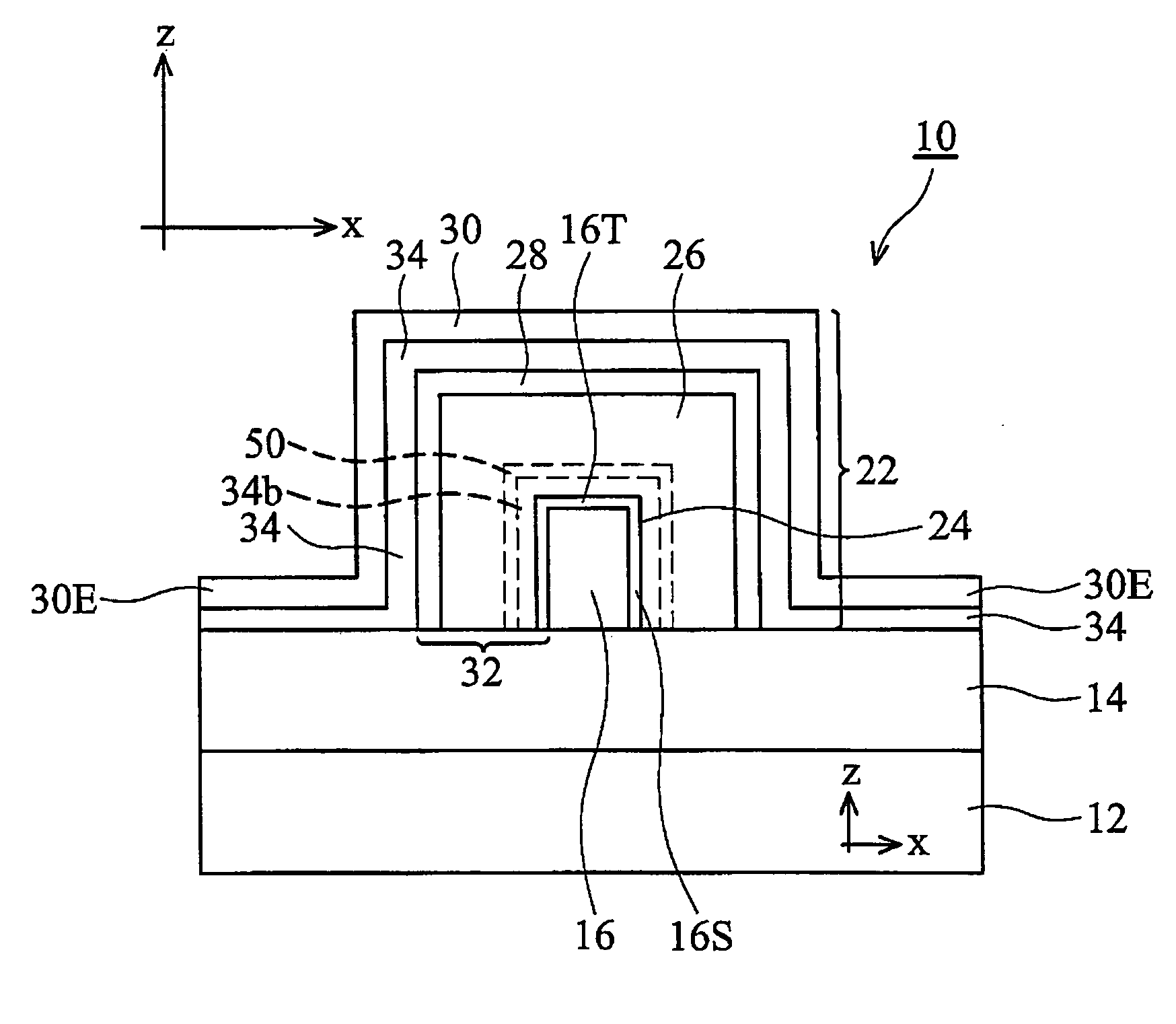
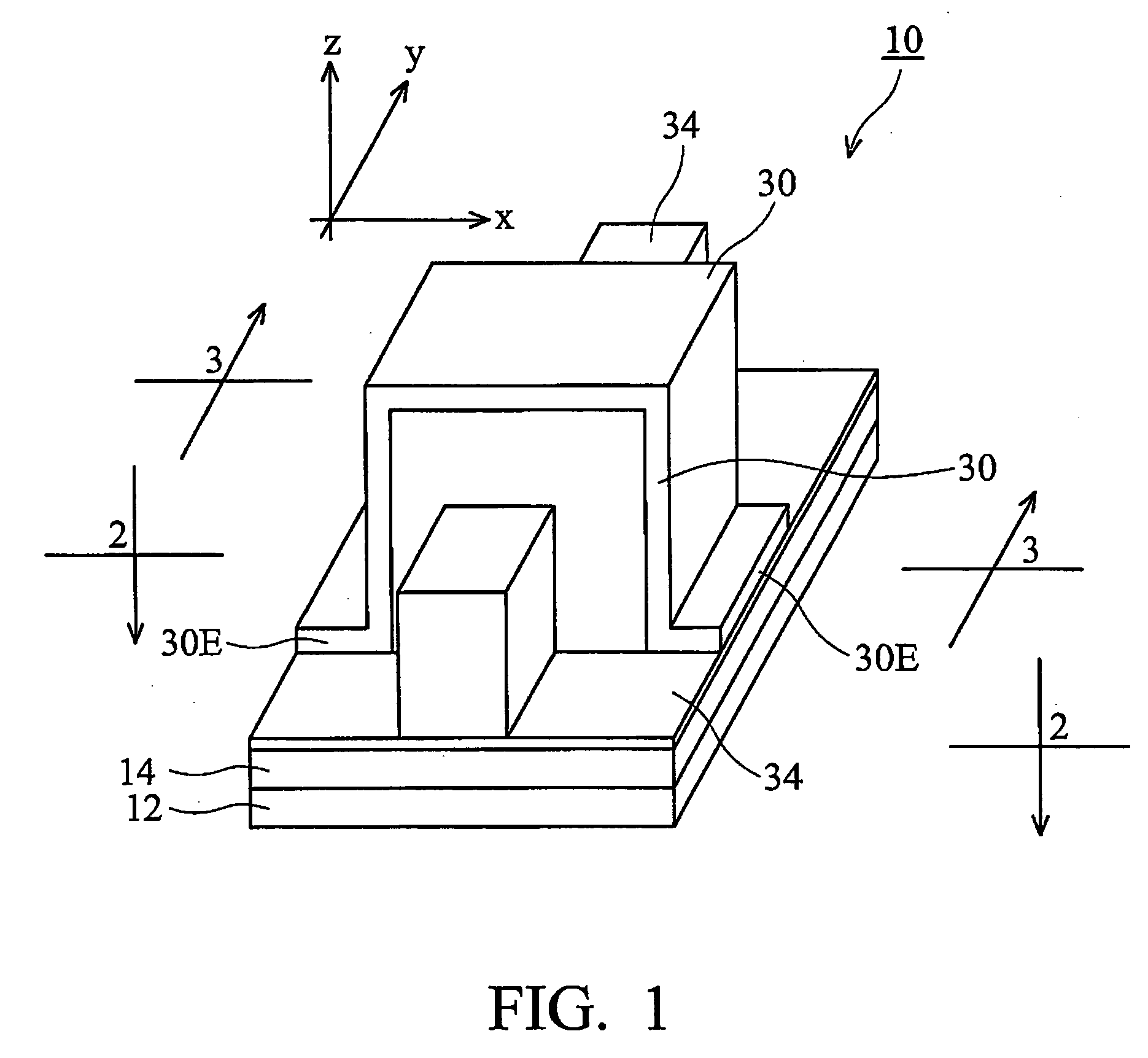
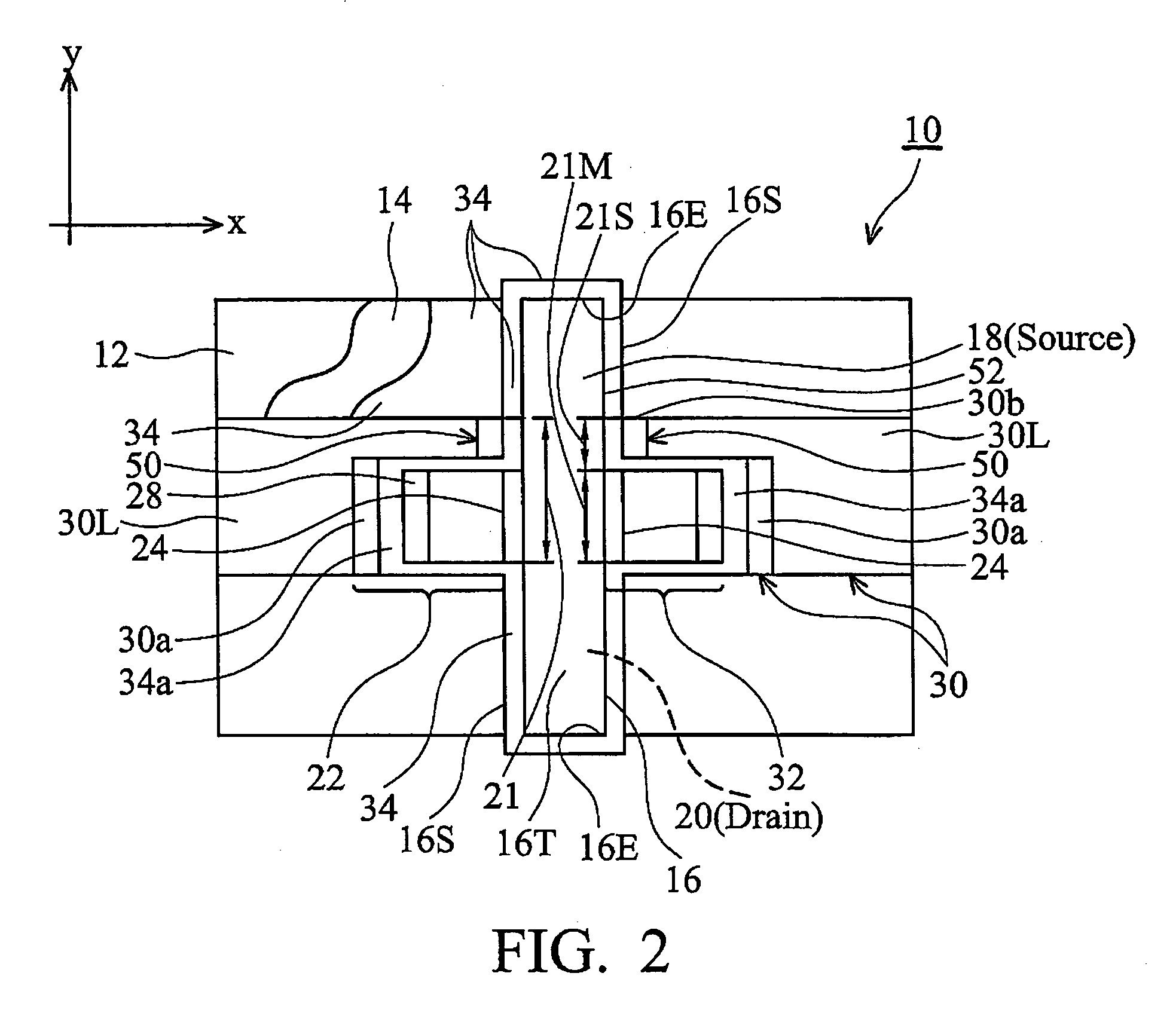
A DRAM-like non-volatile memory array includes a cell array of non-volatile cell units with a DRAM-like cross-coupled latch-type sense amplifier. Each non-volatile cell unit has two non-volatile cell devices with respective bit lines and source lines running in parallel and laid out perpendicular to the word line associated with the non-volatile cell unit. The two non-volatile cell devices are programmed with erased and programmed threshold voltages as a pair for storing a single bit of binary data. The two bit lines of each non-volatile cell unit are coupled through a Y-decoder and a latch device to the two respective inputs of the latch-type sense amplifier which provides a large sensing margin for the cell array to operate properly even with a narrowed threshold voltage gap. Each non-volatile cell device may be a 2 T FLOTOX-based EEPROM cell, a 2 T flash cell, 11 T flash cell or a 1.5 T split-gate flash cell.
Owner:APLUS FLASH TECH
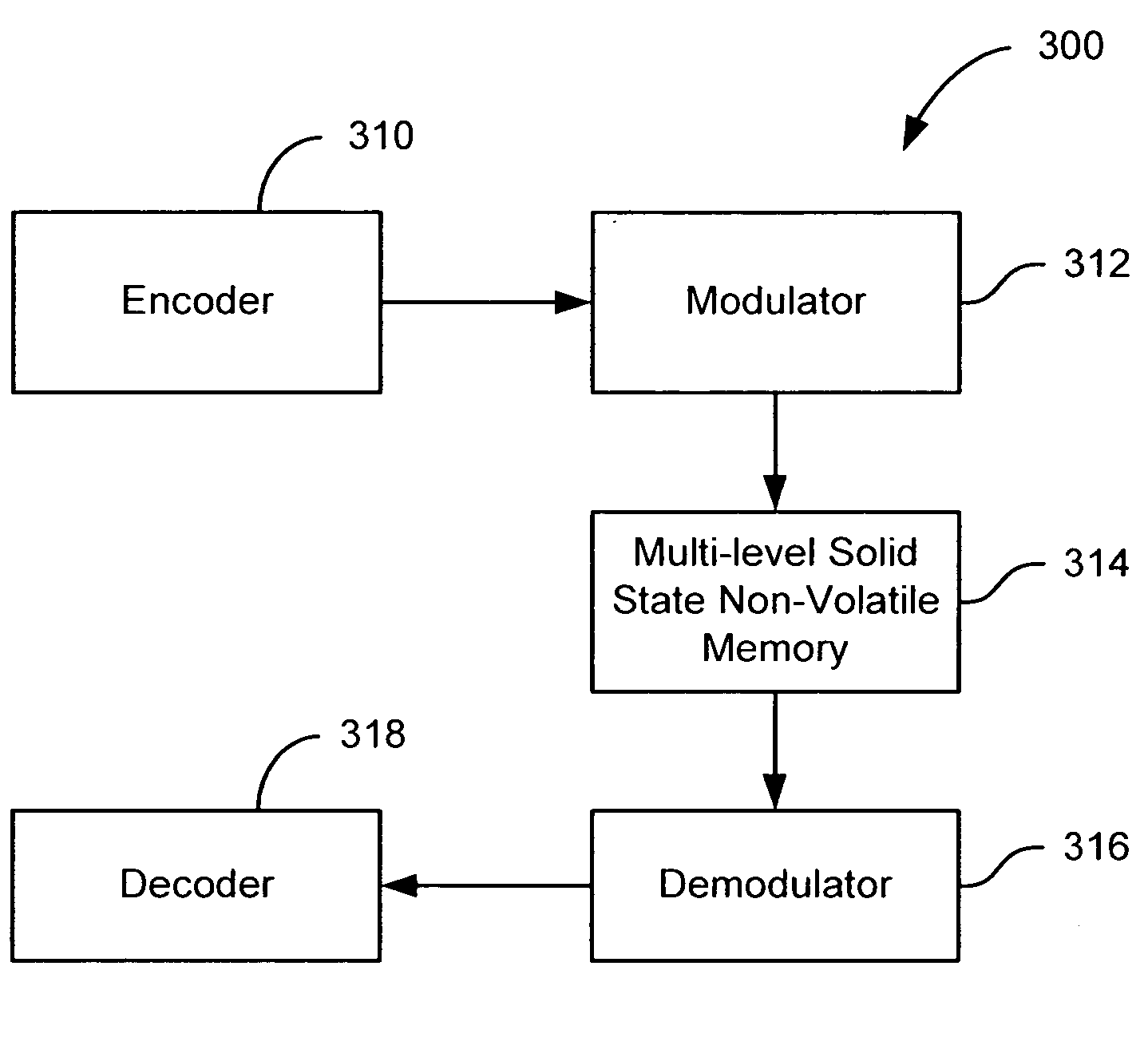
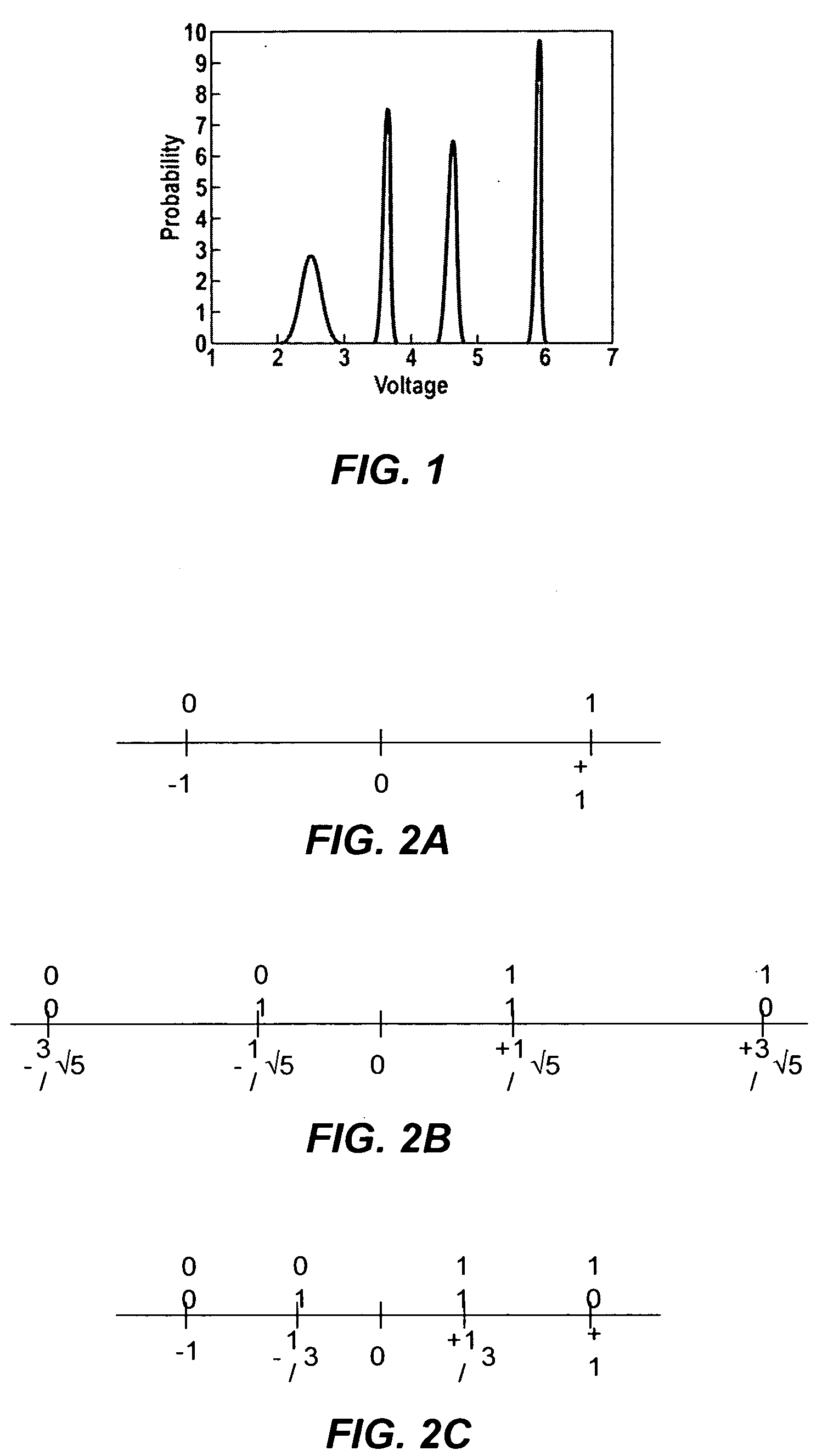
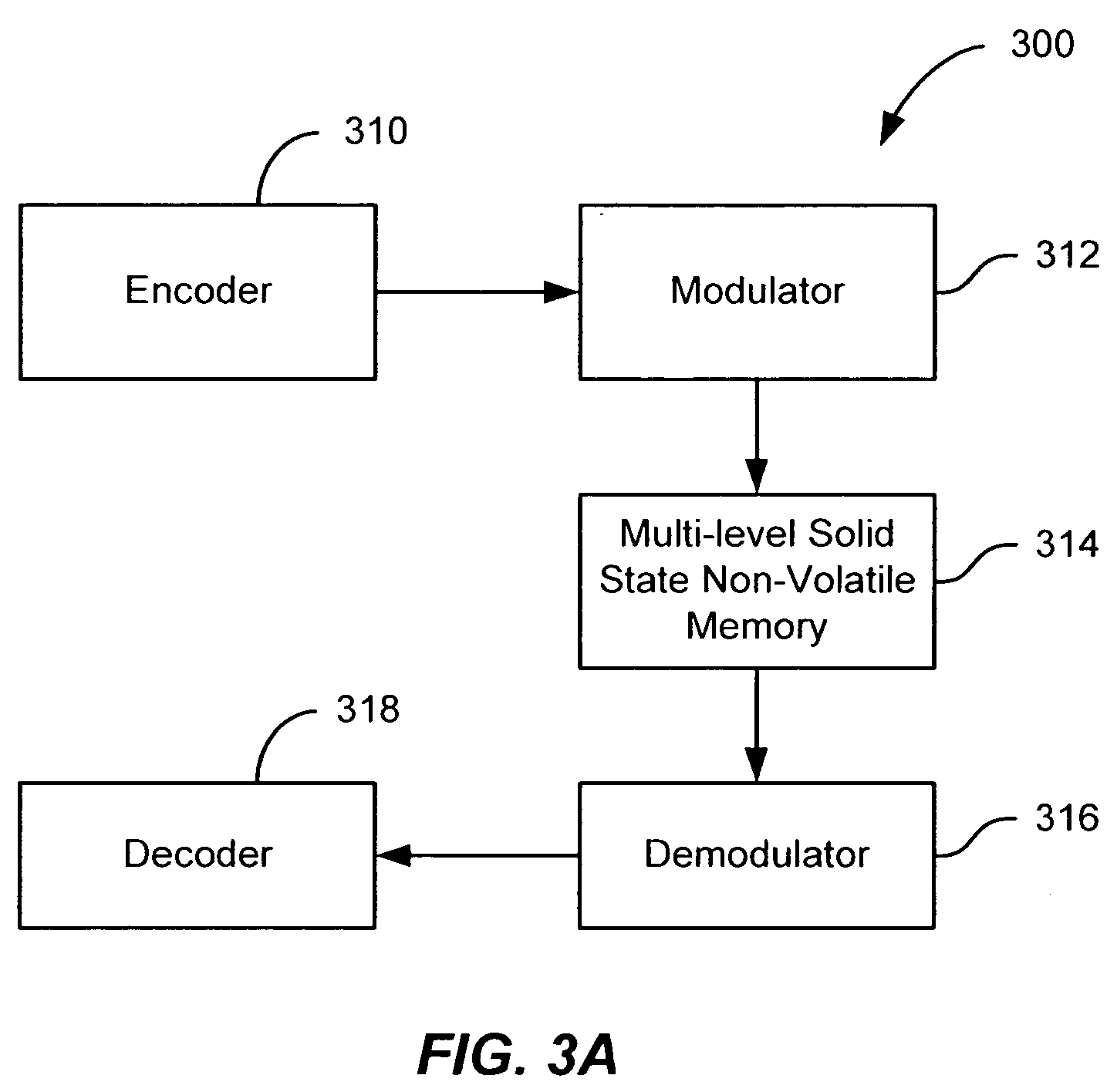
Flash memory with coding and signal processing
A solid state non-volatile memory unit includes, in part, an encoder, a multi-level solid state non-volatile memory array adapted to store data encoded by the encoder, and a decoder adapted to decode the data retrieved from the memory array. The memory array may be a flash EEPROM array. The memory unit optionally includes a modulator and a demodulator. The data modulated by the modulator is stored in the memory array. The demodulator demodulates the modulated data retrieved from the memory array.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Floating gate transistor with horizontal gate layers stacked next to vertical body
Vertical body transistors with adjacent horizontal gate layers are used to form a memory array in a high density flash electrically erasable and programmable read only memory (EEPROM) or a logic array in a high density field programmable logic array (FPLA). The transistor is a field-effect transistor (FET) having an electrically isolated (floating) gate that controls electrical conduction between source regions and drain regions. If a particular floating gate is charged with stored electrons, then the transistor will not turn on and will provide an indication of the stored data at this location in the memory array within the EEPROM or will act as the absence of a transistor at this location in the logic array within the FPLA. The memory array or the logic array includes densely packed cells, each cell having a semiconductor pillar providing shared source and drain regions for two vertical body transistors that have control gates overlaying floating gates distributed on opposing sides of the semiconductor pillar. Both bulk semiconductor and silicon-on-insulator embodiments are provided. If a floating gate transistor is used to store a single bit of data or to represent a logic function, an area of only 2F<2 >is needed per respective bit of data or bit of logic, where F is the minimum lithographic feature size.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Instrumented insole
A combination of sensors, including solid-state gyros and force-sensitive resistors, are mounted in an insole suitable for insertion into a shoe. Data from the sensors is recorded by an in situ Programmable Interface Controller (PIC), logged into on-board EEPROM / Flash memory and relayed to a base station computer via a miniature telemetry transmitter triggered by RFID tagging. Software then uses this data to compute the cadence and ankle power of the subject, as well as other parameters, in order to analyze and assess the gait and activity of the subject.
Owner:CATHOLIC UNIV OF AMERICA
Cyclic flash memory wear leveling
InactiveUS7441067B2Speed up the processShorten the counting processMemory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesNon-volatile memoryWear leveling
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Spare Block Management of Non-Volatile Memories
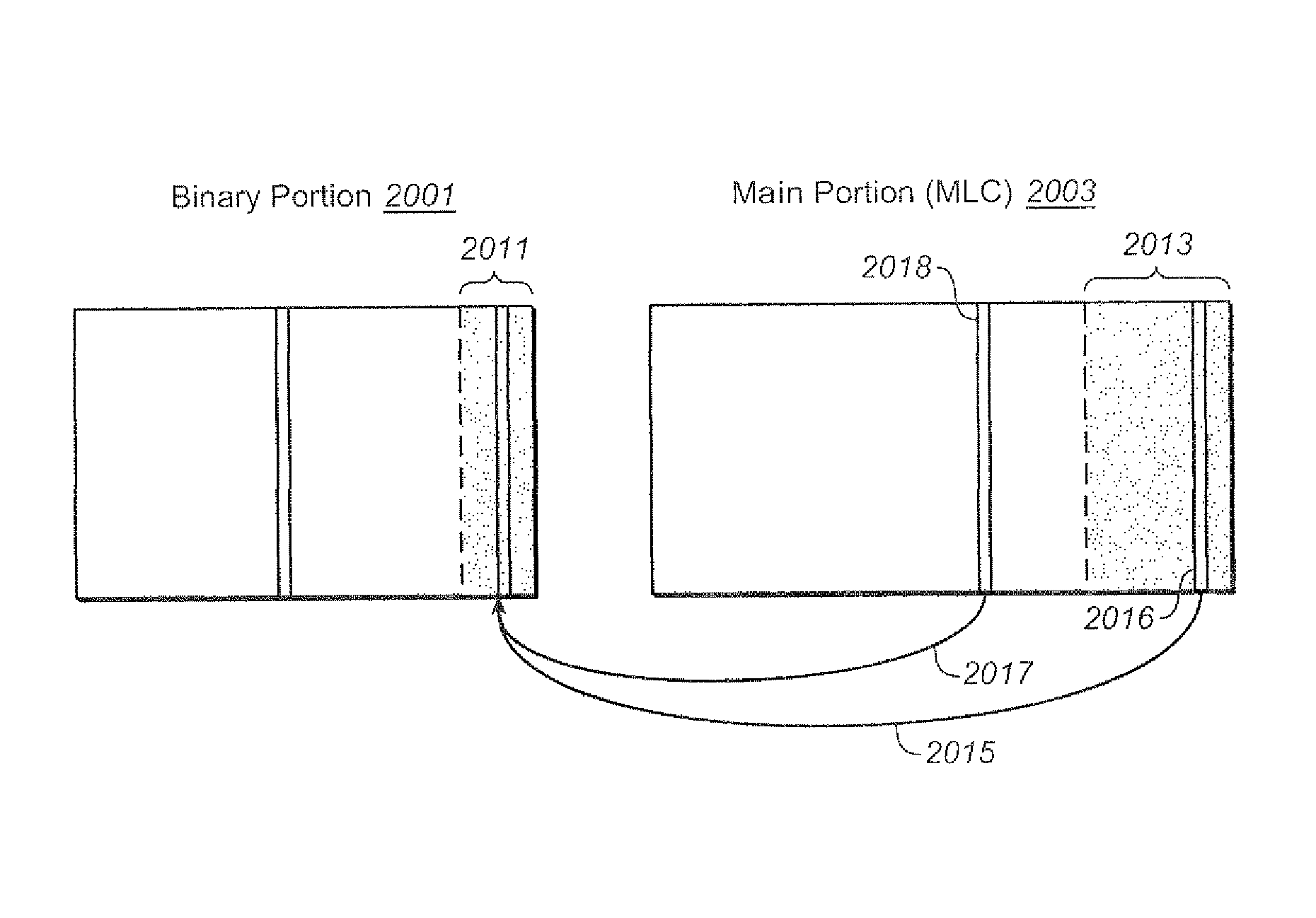
ActiveUS20100172179A1Improve staminaMemory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesNon-volatile memoryLogical address
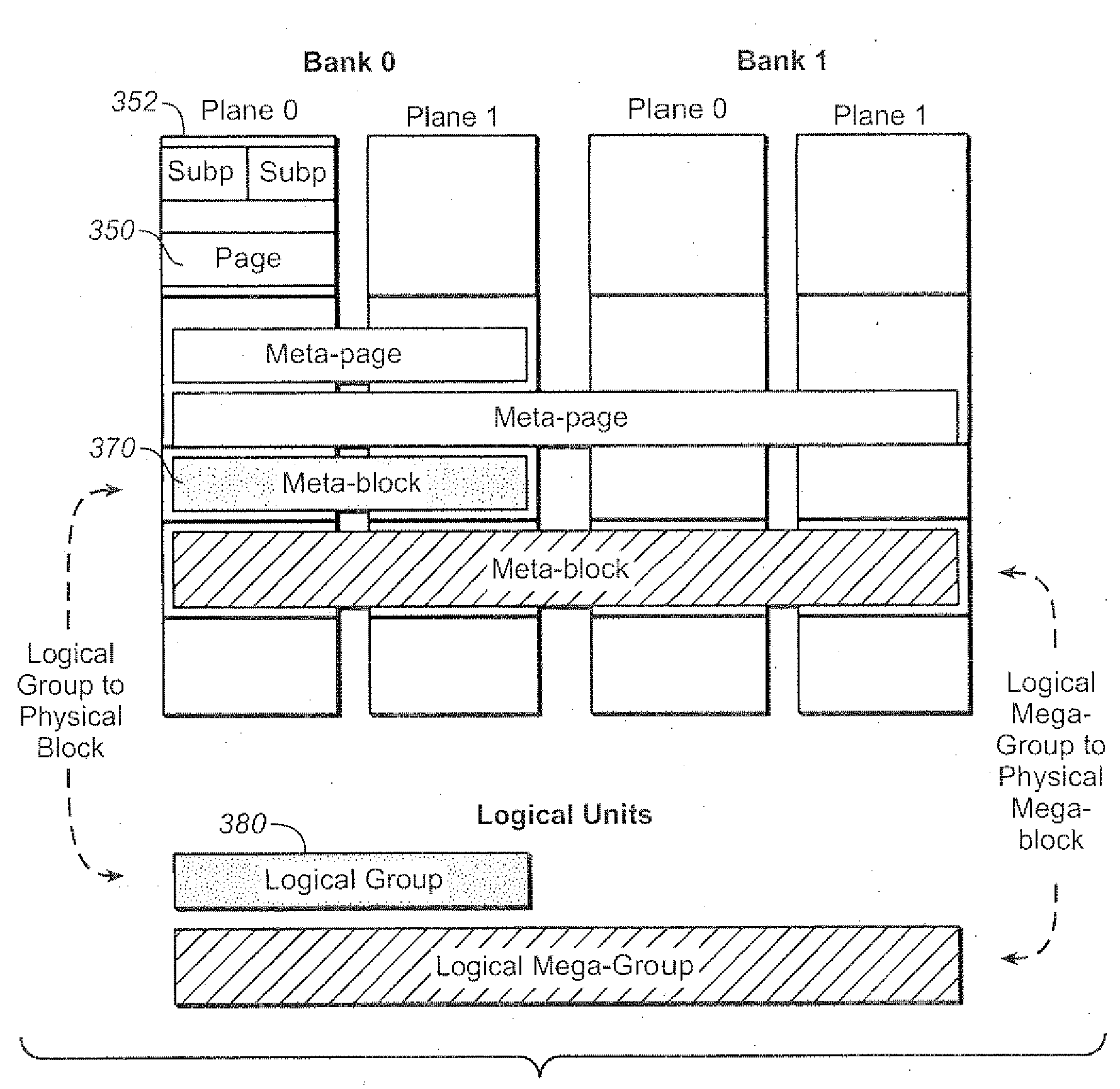
Techniques for the management of spare blocks in re-programmable non-volatile memory system, such as a flash EEPROM system, are presented. In one set of techniques, for a memory partitioned into two sections (for example a binary section and a multi-state section), where blocks of one section are more prone to error, spare blocks can be transferred from the more error prone partition to the less error prone partition. In another set of techniques for a memory partitioned into two sections, blocks which fail in the more error prone partition are transferred to serve as spare blocks in the other partition. In a complementary set of techniques, a 1-bit time stamp is maintained for free blocks to determine whether the block has been written recently. Other techniques allow for spare blocks to be managed by way of a logical to physical conversion table by assigning them logical addresses that exceed the logical address space of which a host is aware.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Wear Leveling for Non-Volatile Memories: Maintenance of Experience Count and Passive Techniques
InactiveUS20100174845A1Shorten the counting processMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData managementCounting sort
Wear leveling techniques for re-programmable non-volatile memory systems, such as a flash EEPROM system, are described. One set of techniques uses “passive” arrangements, where, when a blocks are selected for writing, blocks with relatively low experience count are selected. This can be done by ordering the list of available free blocks based on experience count, with the “coldest” blocks placed at the front of the list, or by searching the free blocks to find a block that is “cold enough”. In another, complementary set of techniques, usable for more standard wear leveling operations as well as for “passive” techniques and other applications where the experience count is needed, the experience count of a block or meta-block is maintained as a block's attribute along its address in the data management structures, such as address tables.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
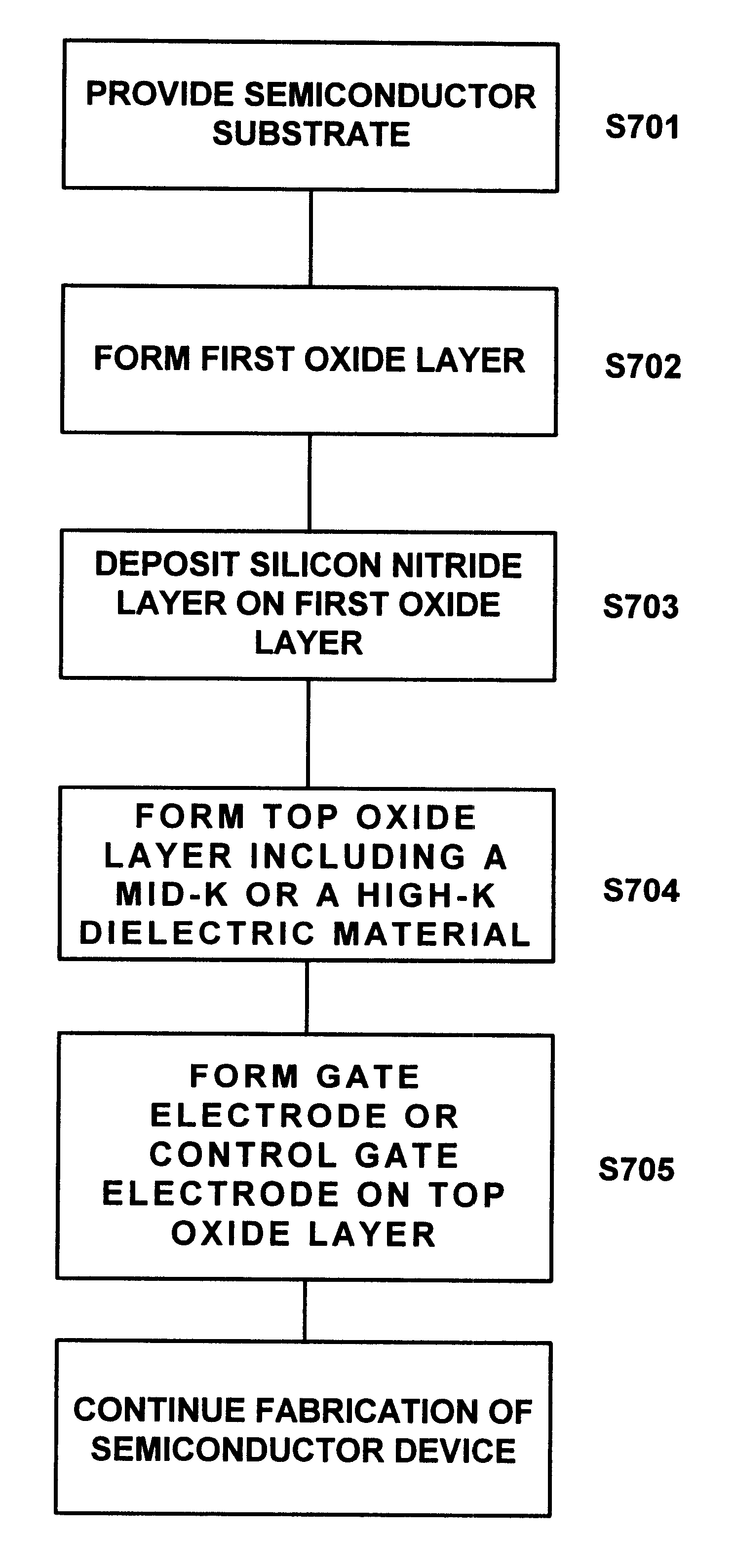
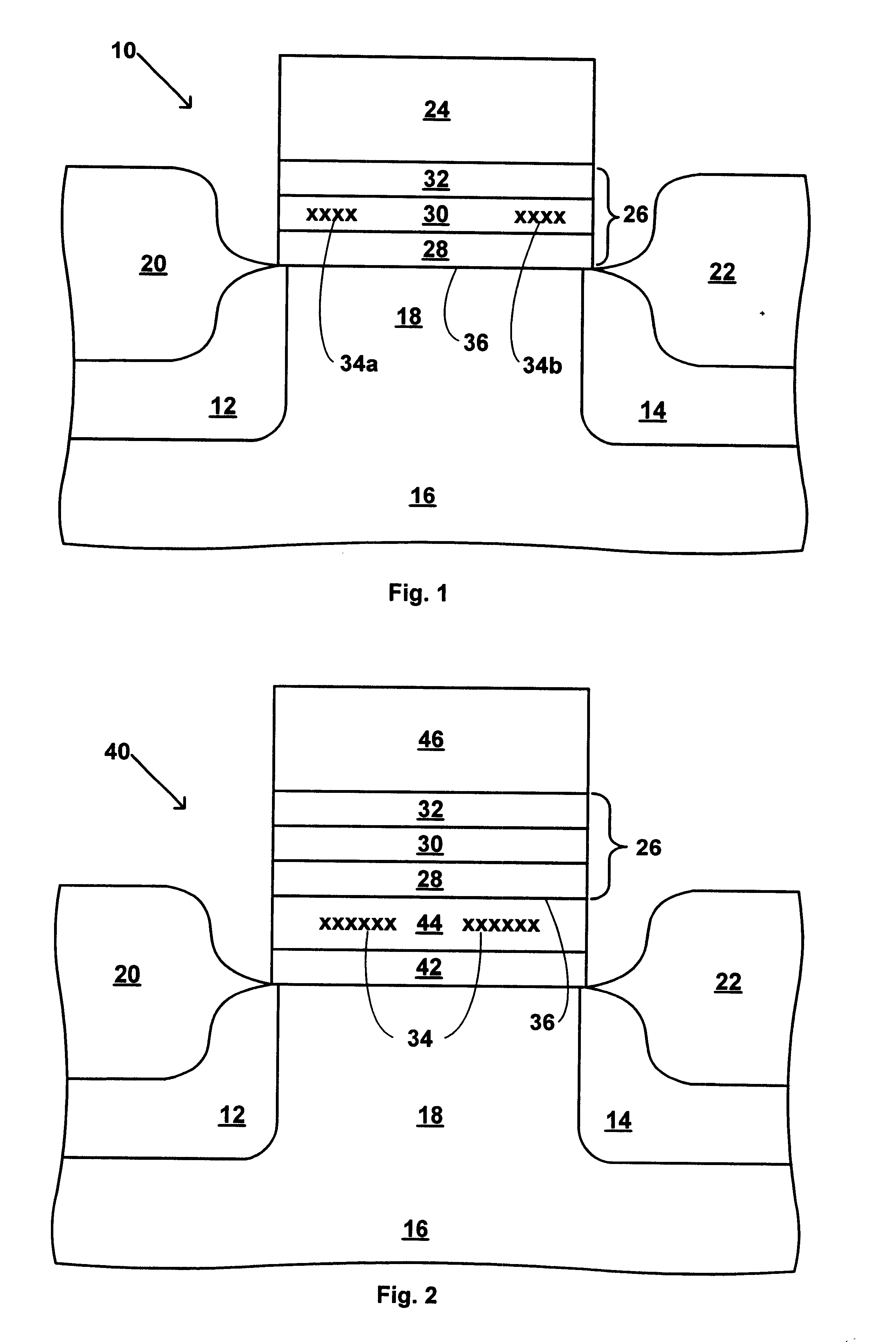
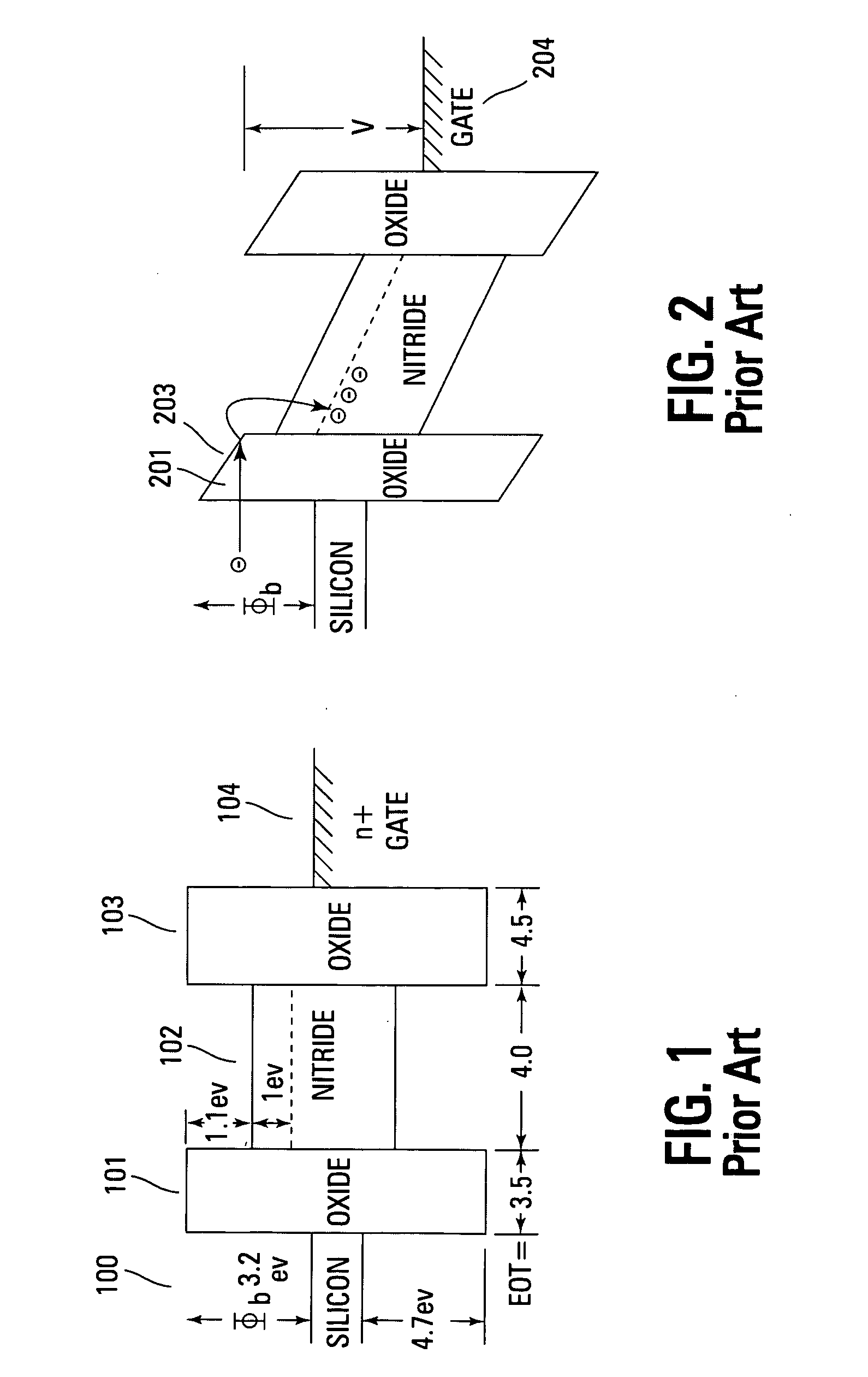
Use of high-K dielectric material in modified ONO structure for semiconductor devices
InactiveUS6642573B1Reduced dimensionSacrificing charge trapping abilityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricSemiconductor
A process for fabrication of a semiconductor device including a modified ONO structure, comprising forming the modified ONO structure by providing a semiconductor substrate; forming a first dielectric material layer on the semiconductor substrate; depositing a silicon nitride layer on the first dielectric material layer; and forming a top dielectric material layer, wherein at least one of the bottom dielectric material layer and the top dielectric material layer comprise a mid-K or a high-K dielectric material. The semiconductor device may be, e.g., a SONOS two-bit EEPROM device or a floating gate flash device including the modified ONO structure.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
FinFET split gate EEPROM structure and method of its fabrication
A FinFET split gate EEPROM structure includes a semiconductor substrate and an elongated semiconductor fin extending above the substrate. A control gate straddles the fin, the fin's sides and a first drain-proximate portion of a channel between a source and drain in the fin. The control gate includes a tunnel layer and a floating electrode over which are a first insulative stratum and a first conductive stratum. A select gate straddles the fin and its sides and a second, source-promixate portion of the channel. The select gate includes a second insulative stratum and a second conductive stratum. The insulative strata are portions of a continuous insulative layer covering the substrate and the fin. The conductive strata are electrically continuous portions of a continuous conductive layer formed on the insulative layer.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Cyclic flash memory wear leveling
InactiveUS20060106972A1Enhance wear leveling processShorten the counting processMemory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesStorage cellNon-volatile memory
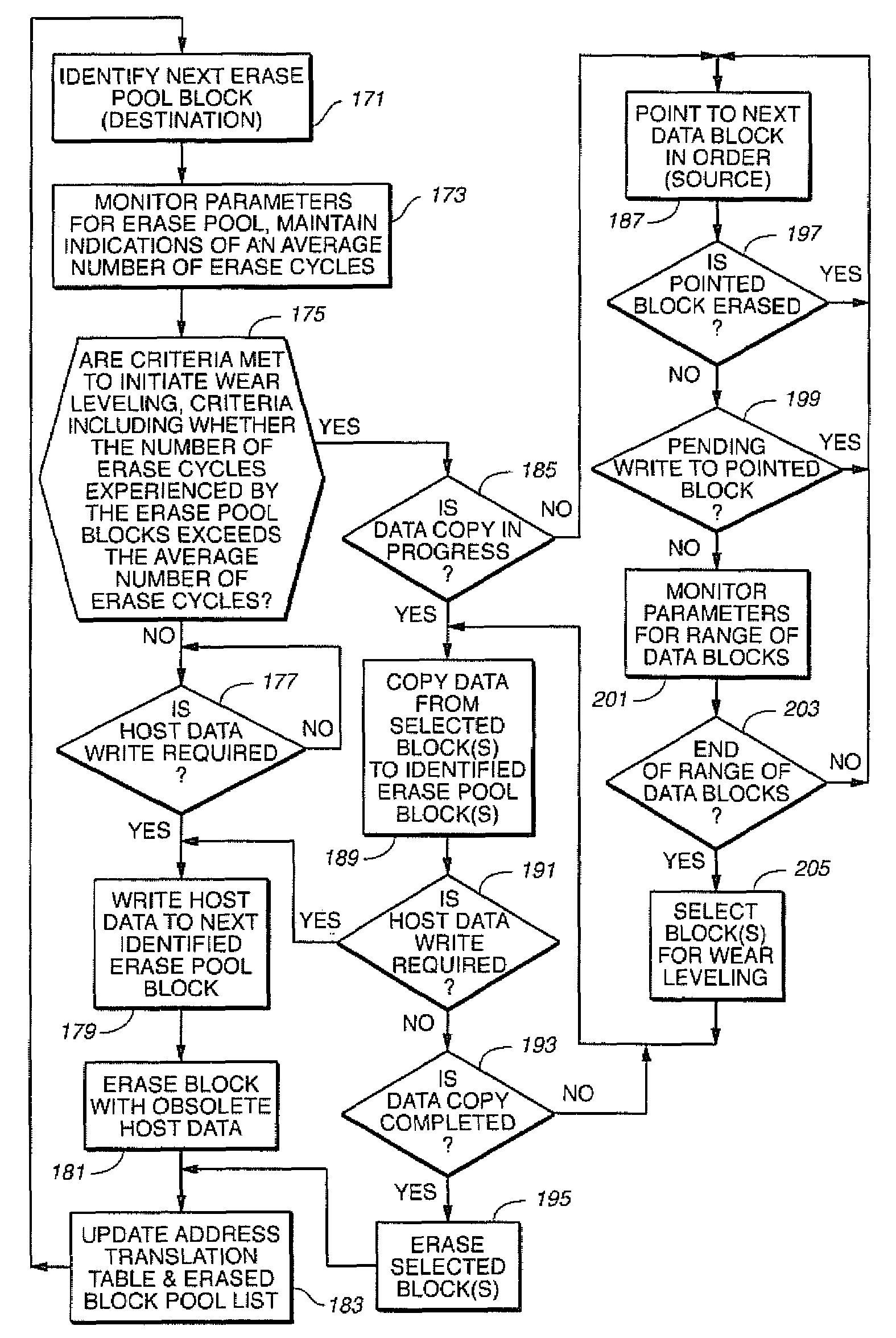
A re-programmable non-volatile memory system, such as a flash EEPROM system, having its memory cells grouped into blocks of cells that are simultaneously erasable is operated in a manner to level out the wear of the individual blocks through repetitive erasing and re-programming. This may be accomplished without use of counts of the number of times the individual blocks experience erase and re-programming but such counts can optionally aid in carrying out the wear leveling process. Individual active physical blocks are chosen to be exchanged with those of an erased block pool in a predefined order.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
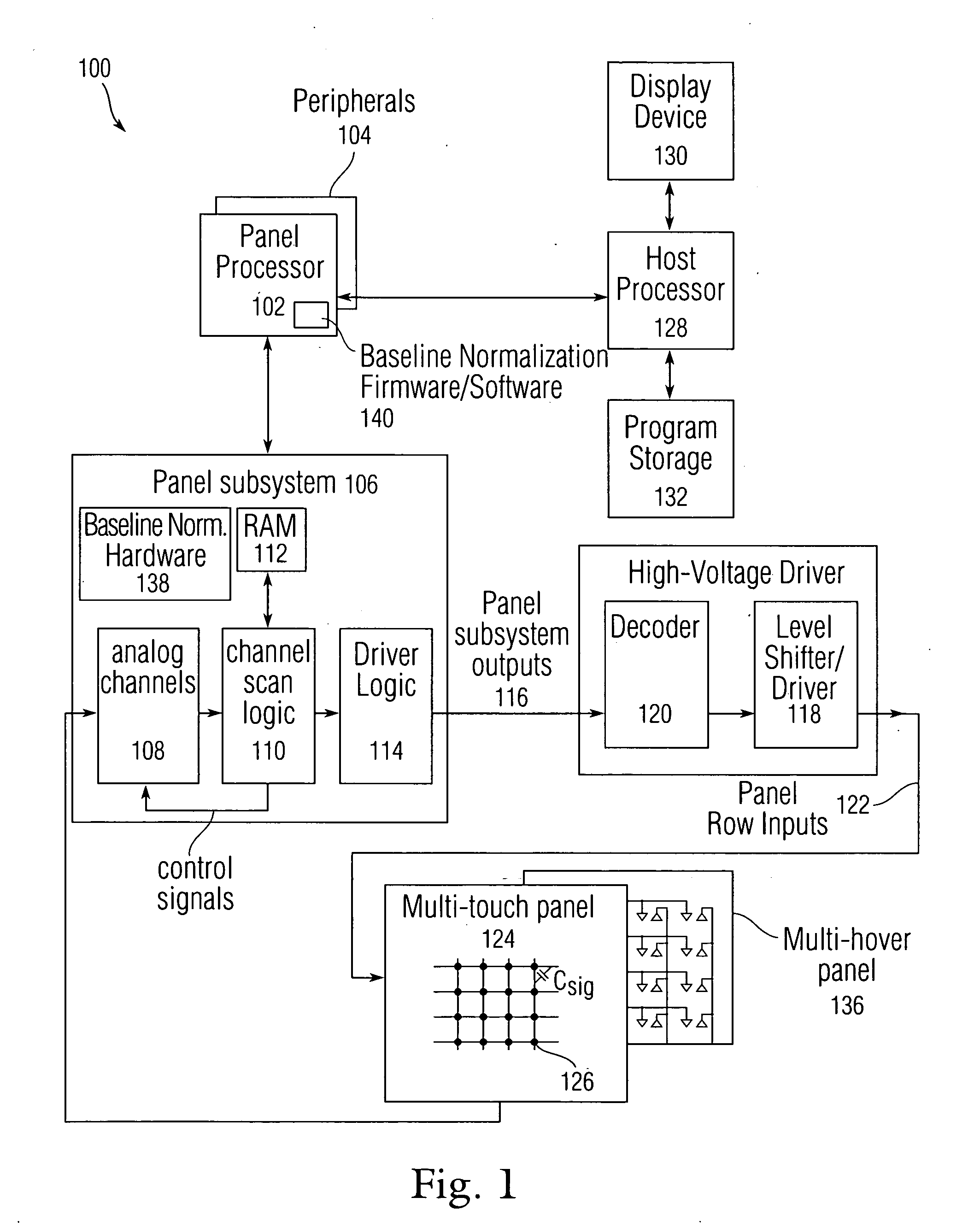
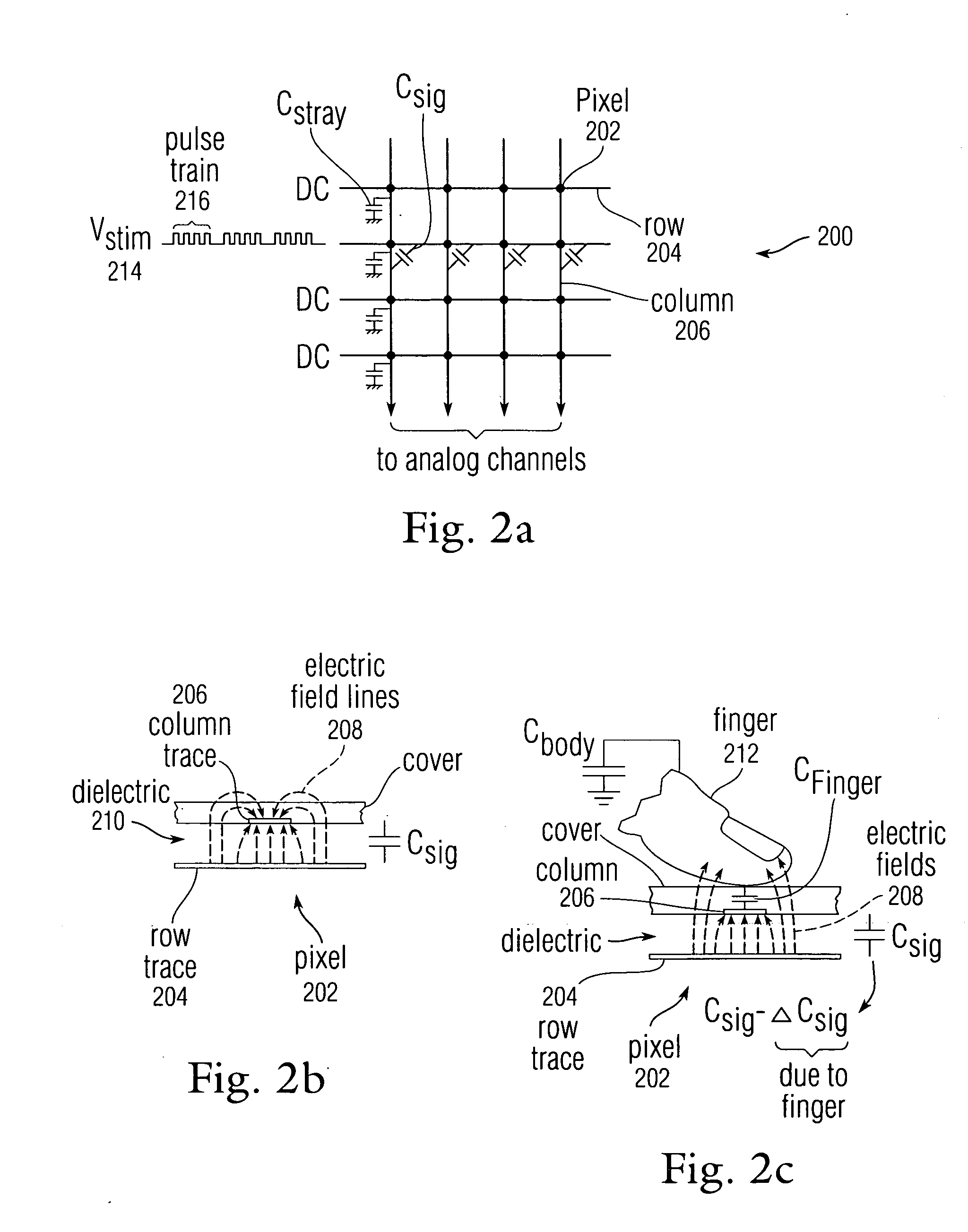
Storing baseline information in EEPROM
ActiveUS20080158174A1Easy to detectEliminate captureInput/output processes for data processingStandardizationReal-time computing
Owner:APPLE INC
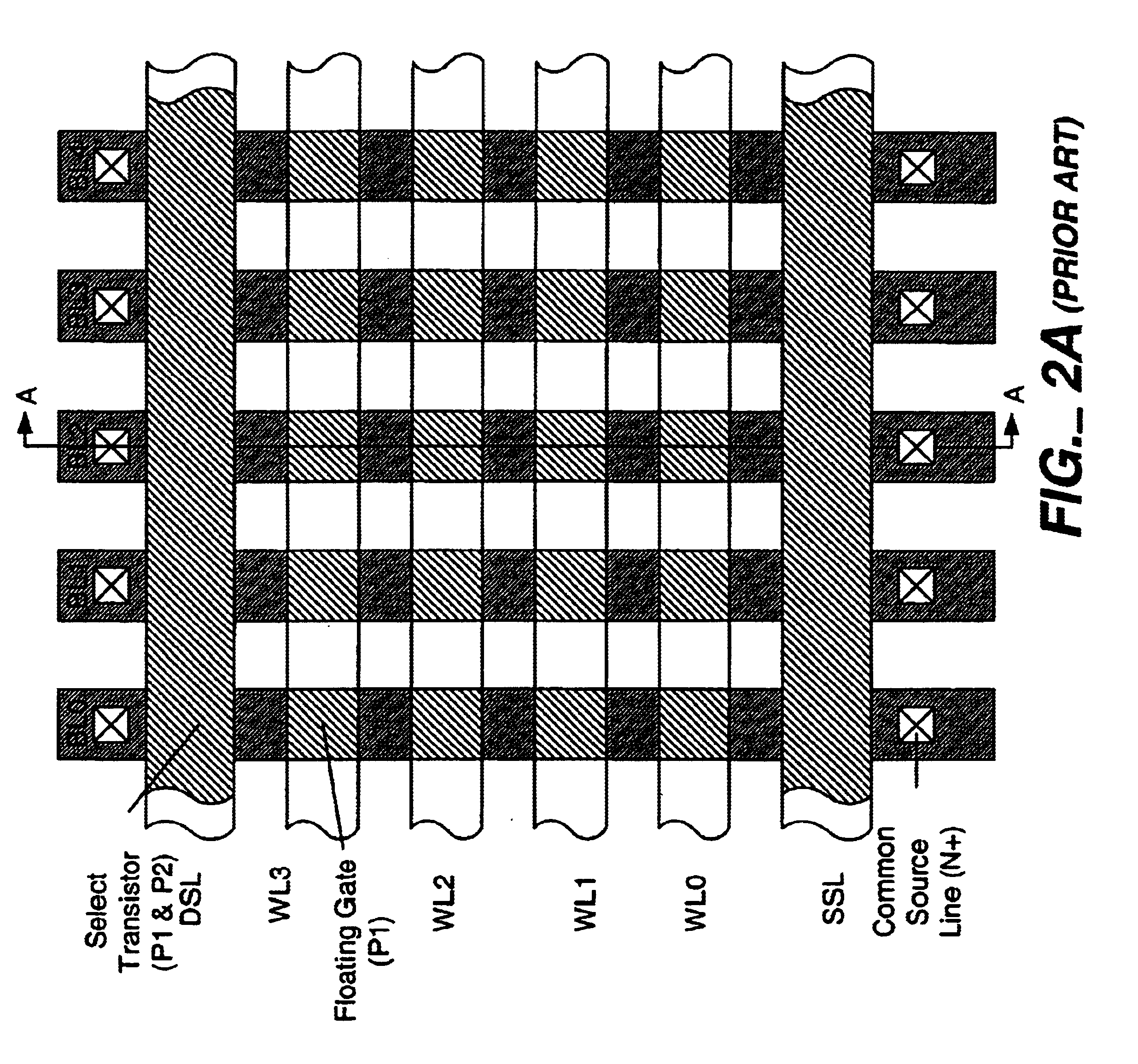
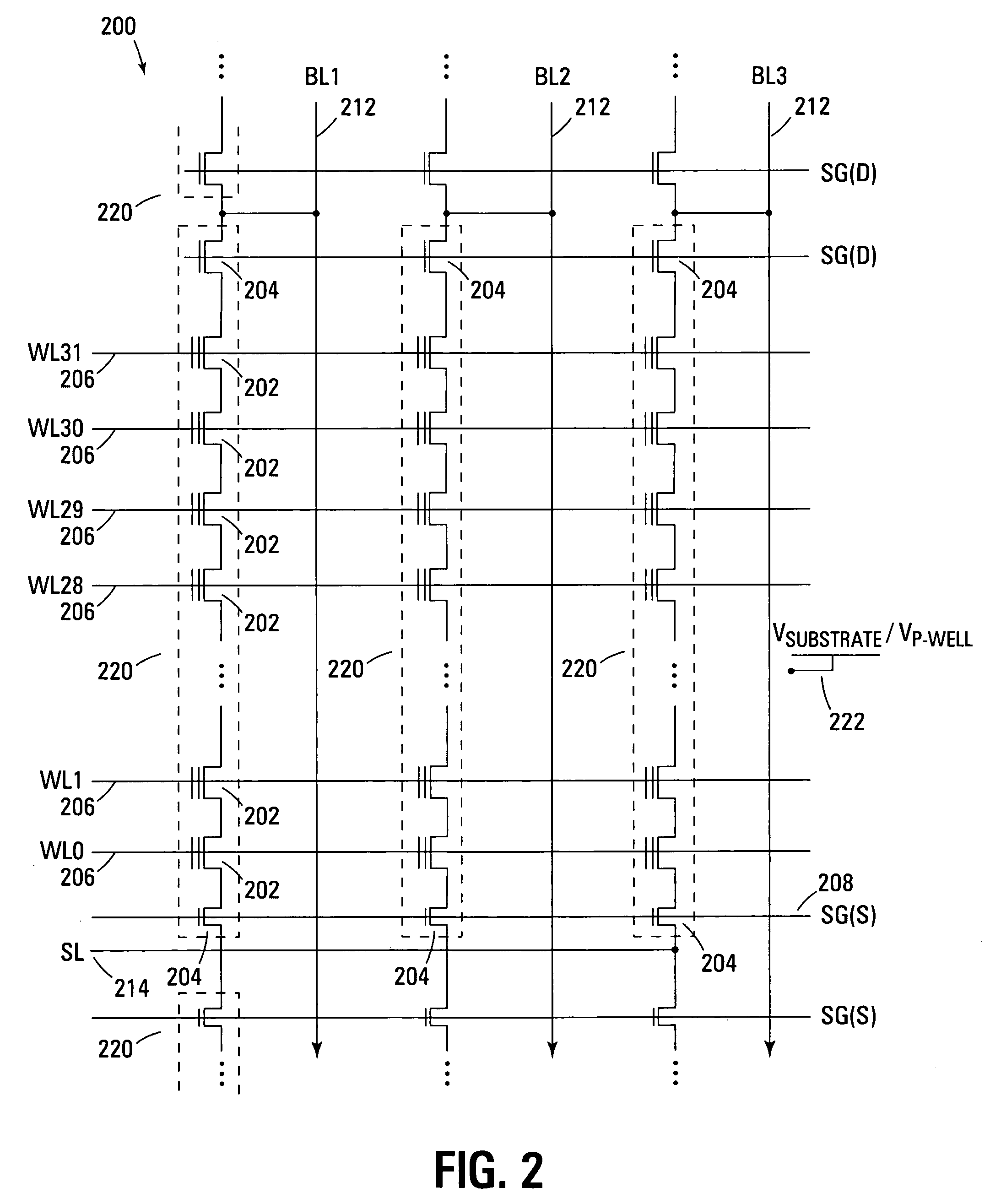
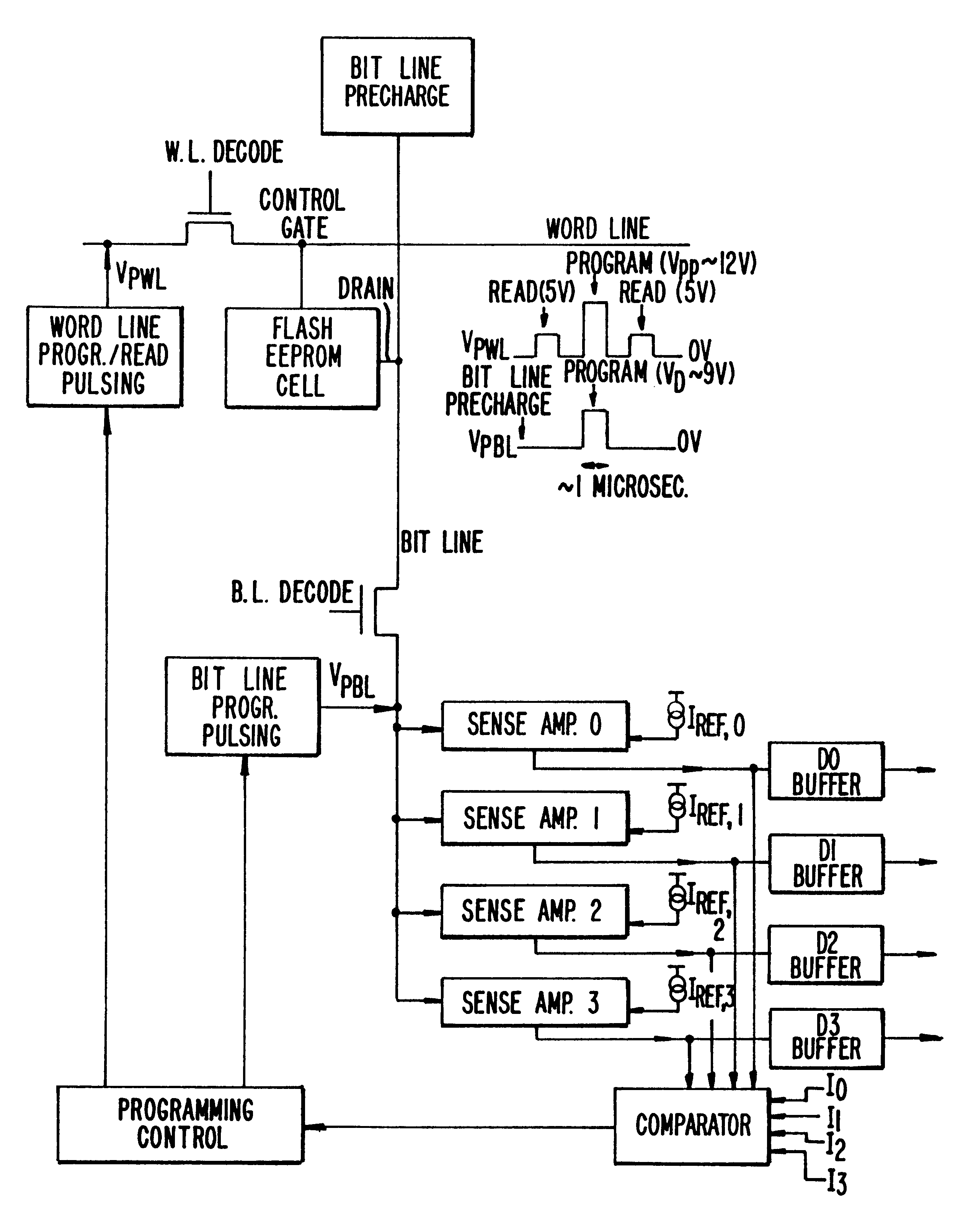
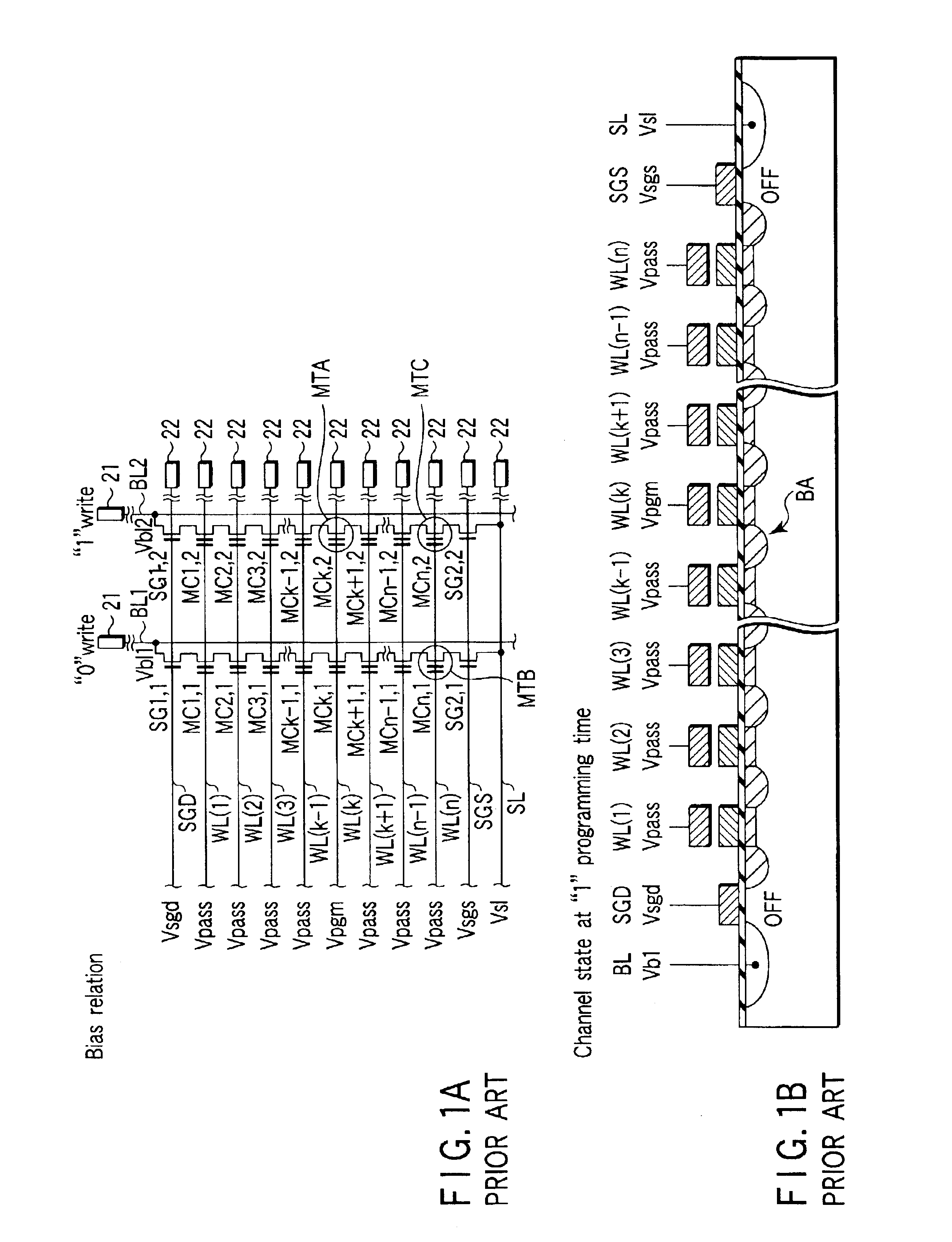
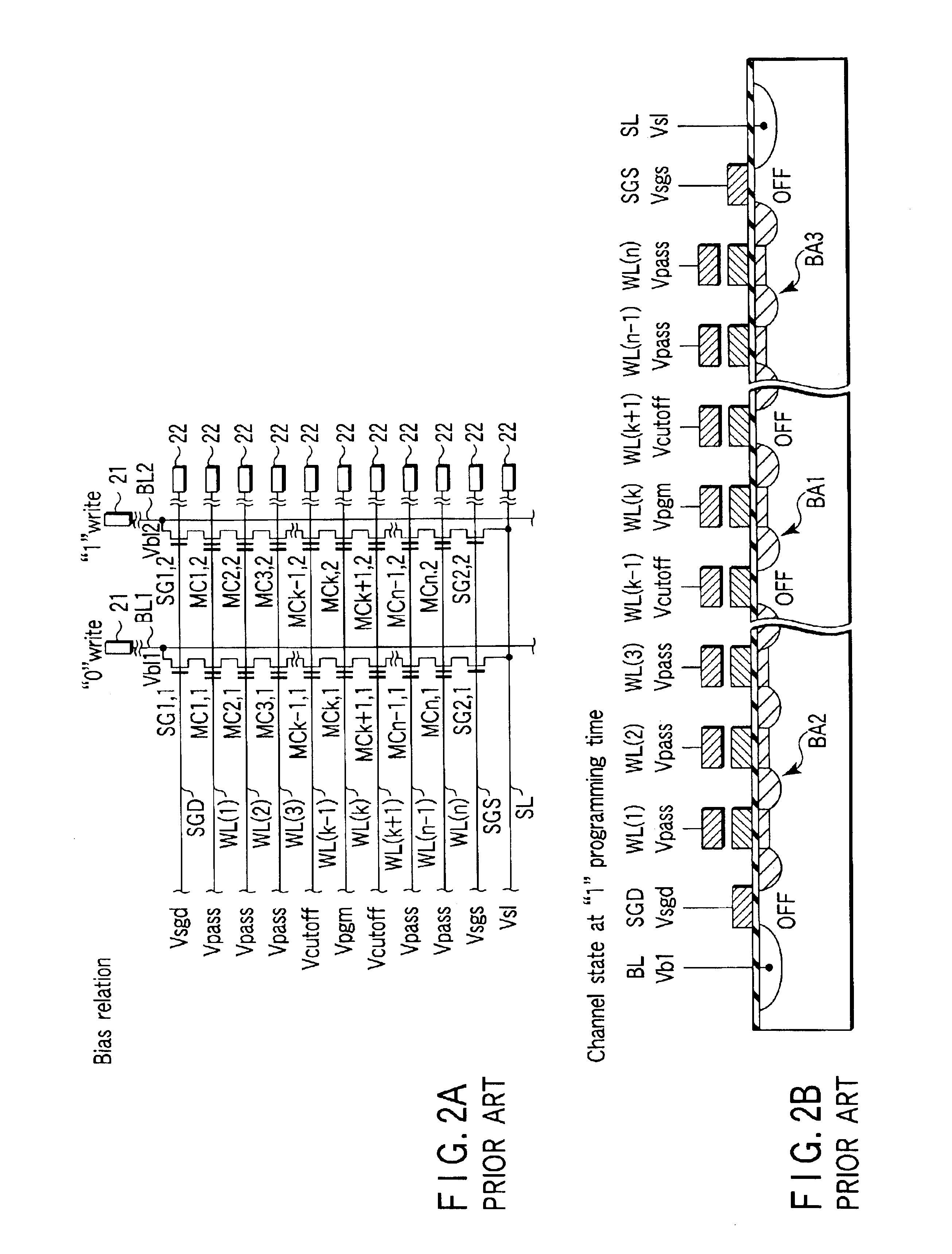
Programming method for NAND EEPROM
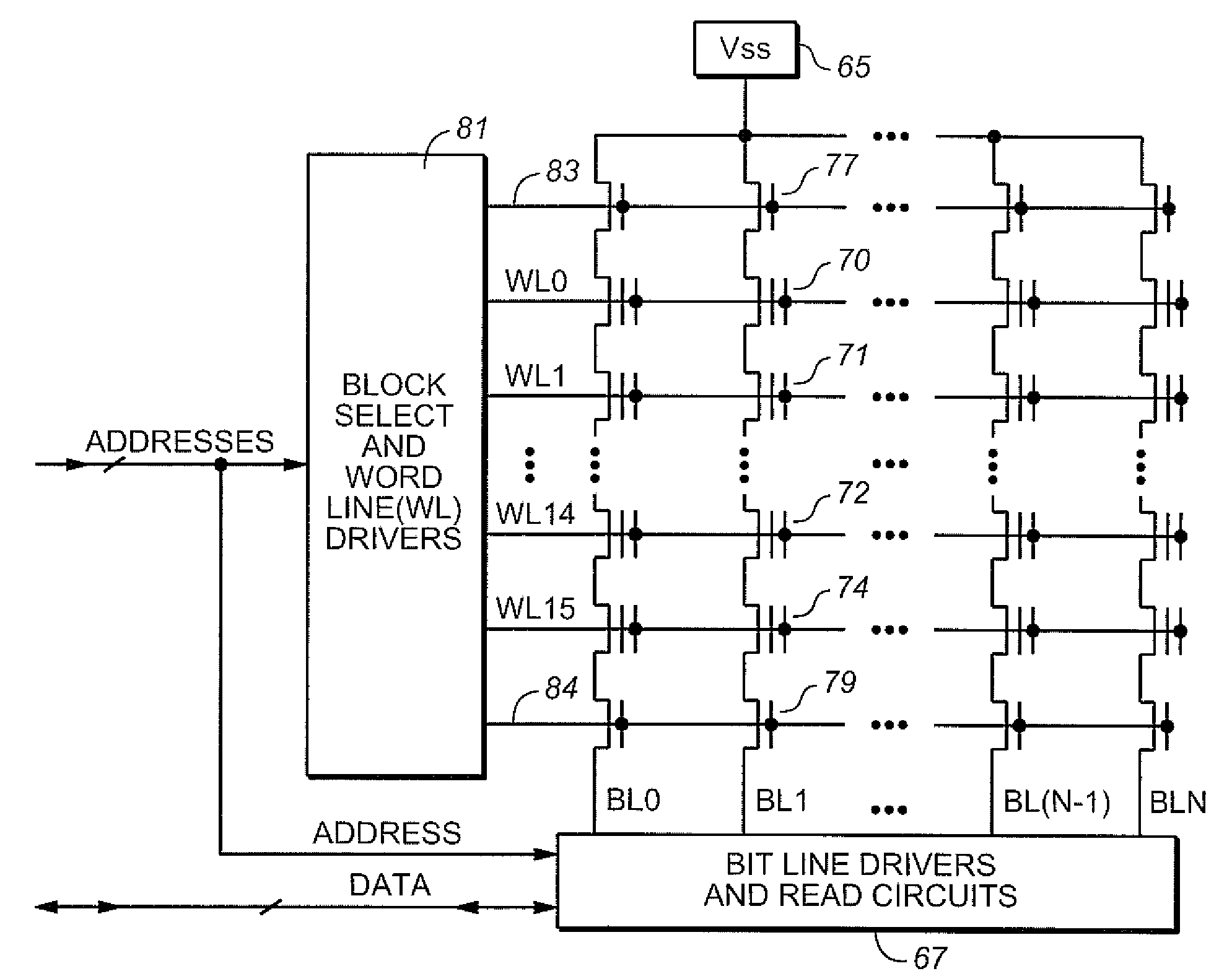
A NAND architecture non-volatile memory device and programming process is described that programs the various cells of strings of non-volatile memory cells by the application of differing word line pass voltages (Vpass) to the unselected word lines of the memory cell string or array during an programming cycle. In one embodiment of the present invention, the differing word line pass voltages (Vpass) are utilized depending on the placement of the memory cell in the NAND memory cell string. In another embodiment of the present invention, the differing word line pass voltages (Vpass) are utilized to compensate for faster and slower programming word lines / memory cells.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
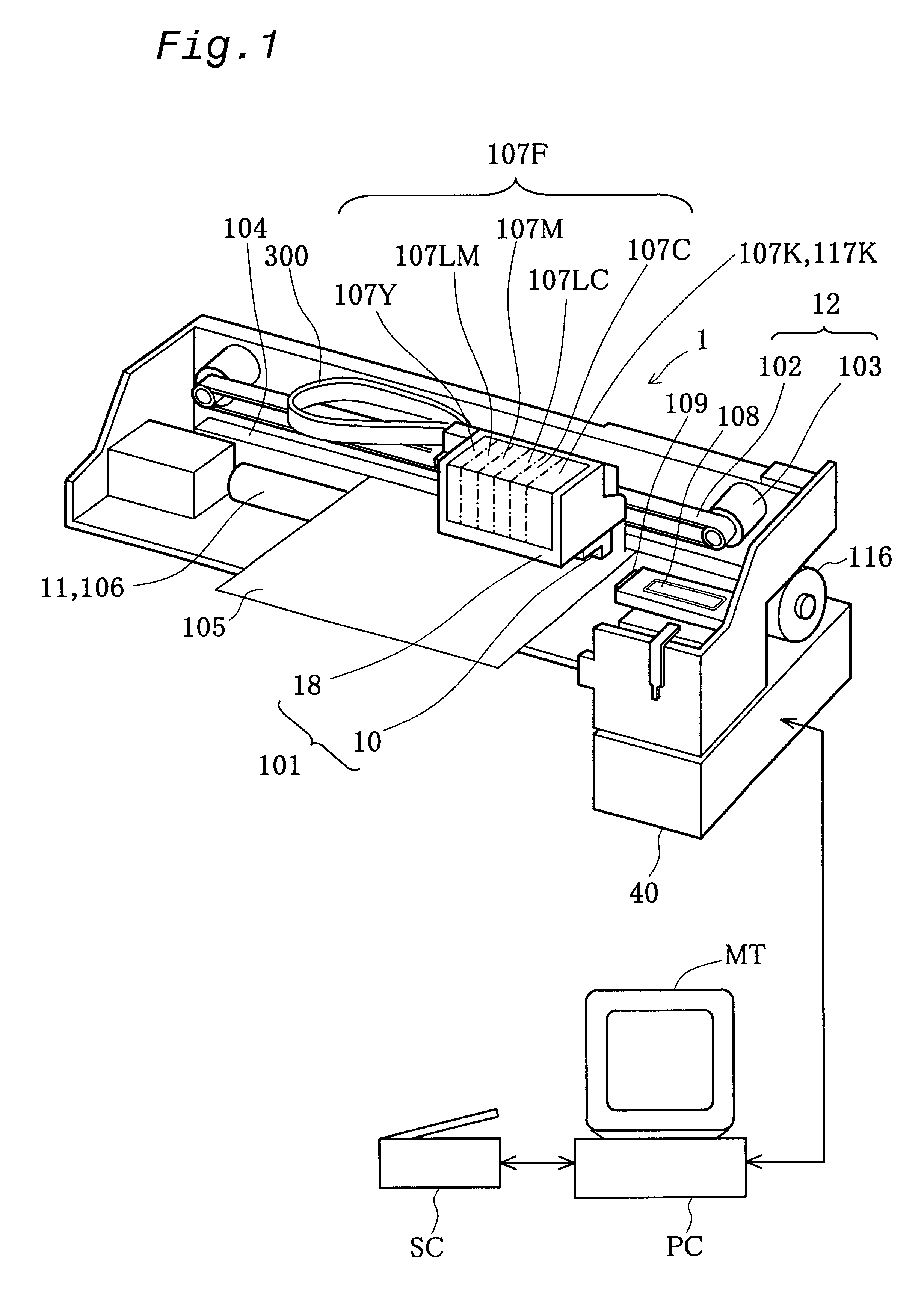
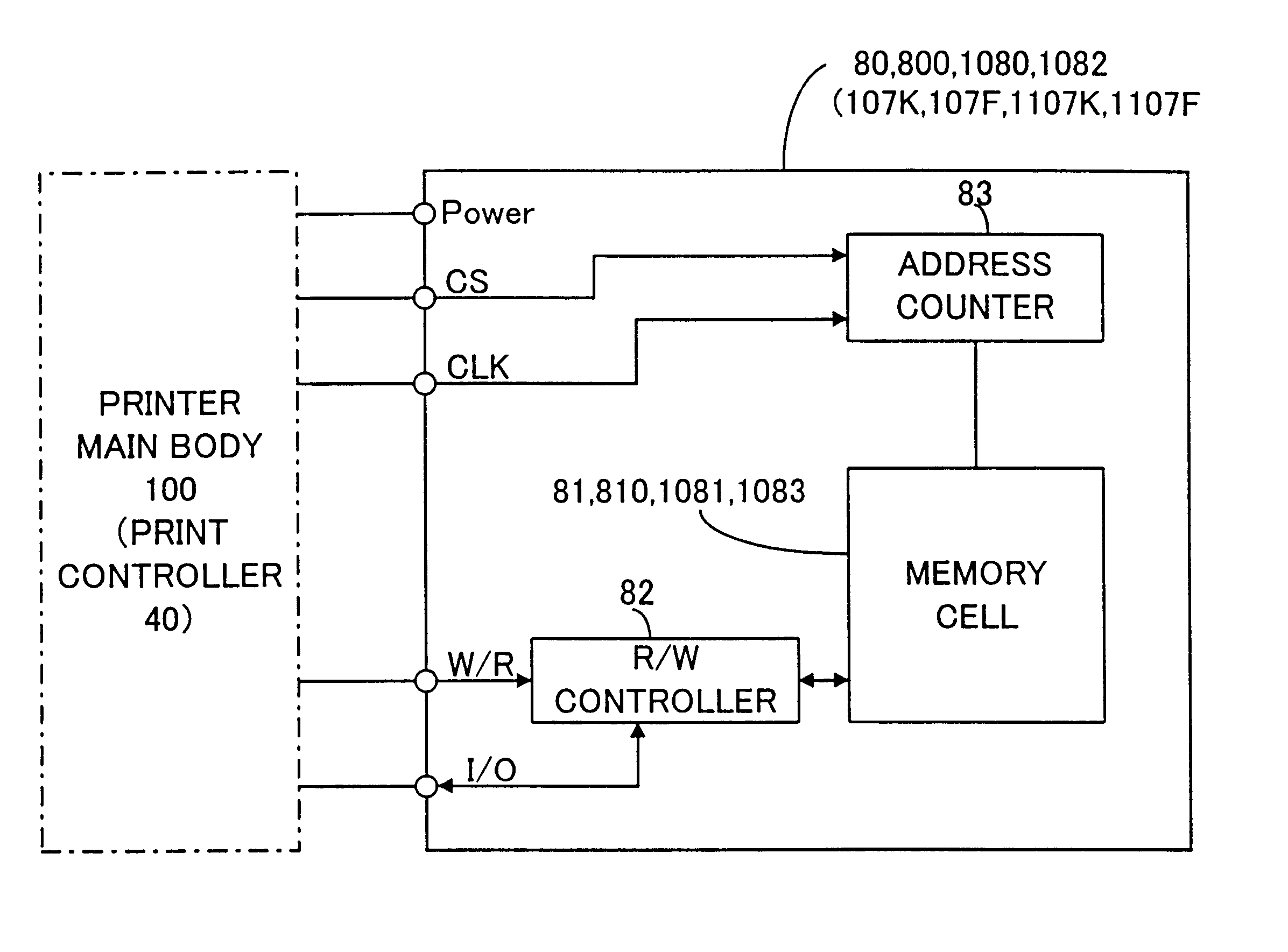
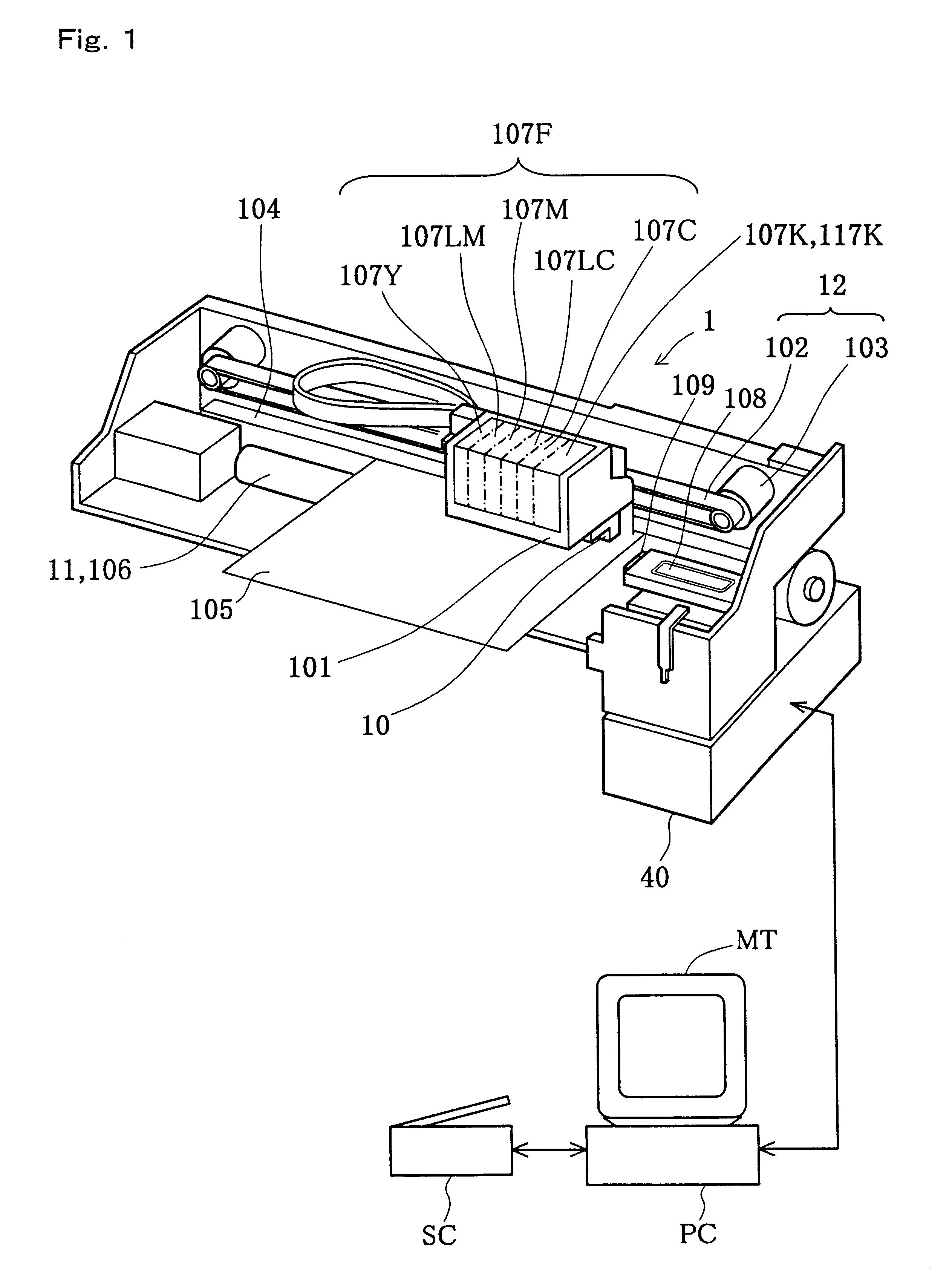
Printer and ink cartridge attached thereto
InactiveUS6631967B1Low costExtra processingRecording apparatusPower drive mechanismsComputer printingEngineering
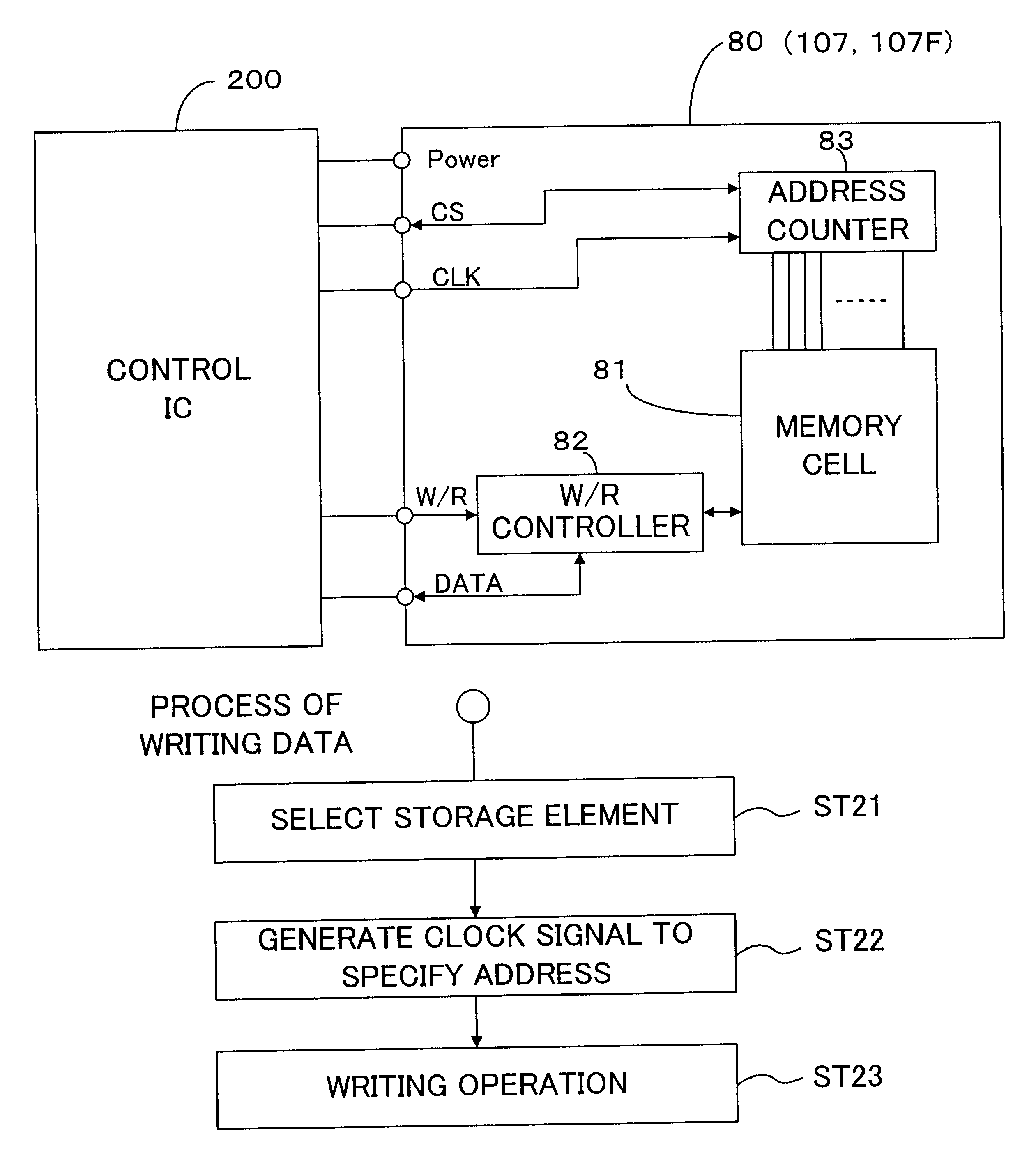
In a printer of the present invention, an EEPROM that carries out sequential access and has a relatively small storage capacity is applied for storage elements mounted on both black and color ink cartridges, which are detachably attached to the printer. Pieces of information relating to each ink cartridge, for example, pieces of information on remaining quantities of respective inks in the ink cartridge, are stored in the storage element of the ink cartridge. A format of addressing adopted in the storage elements of the ink cartridges Is different from that adopted in an EEPROM incorporated in a printer main body of the printer. A control IC provided in the printer accordingly converts the storage format of addressing, before writing the information into the storage elements of the ink cartridges. In the printer, a RAM is mounted with the control IC on a carriage, and the pieces of information to be written Into the storage elements of the ink cartridges are temporarily registered in the RAM. The pieces of information are then written into the respective storage elements of the black and color ink cartridges, for example, at a timing of a powe-off operation. The signal lines and the memory used in the course of writing the information into the storage elements are identical with the signal lines, through which print data are transmitted to a print head mounted on the carriage of the printer, and the memory, in which the print data are stored. The arrangement of the present invention reduces the manufacturing cost of the ink cartridge and also enables size reduction of the whole printer.< / PTEXT>
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Method for patching ROM instructions in an electronic embedded system including at least a further memory portion
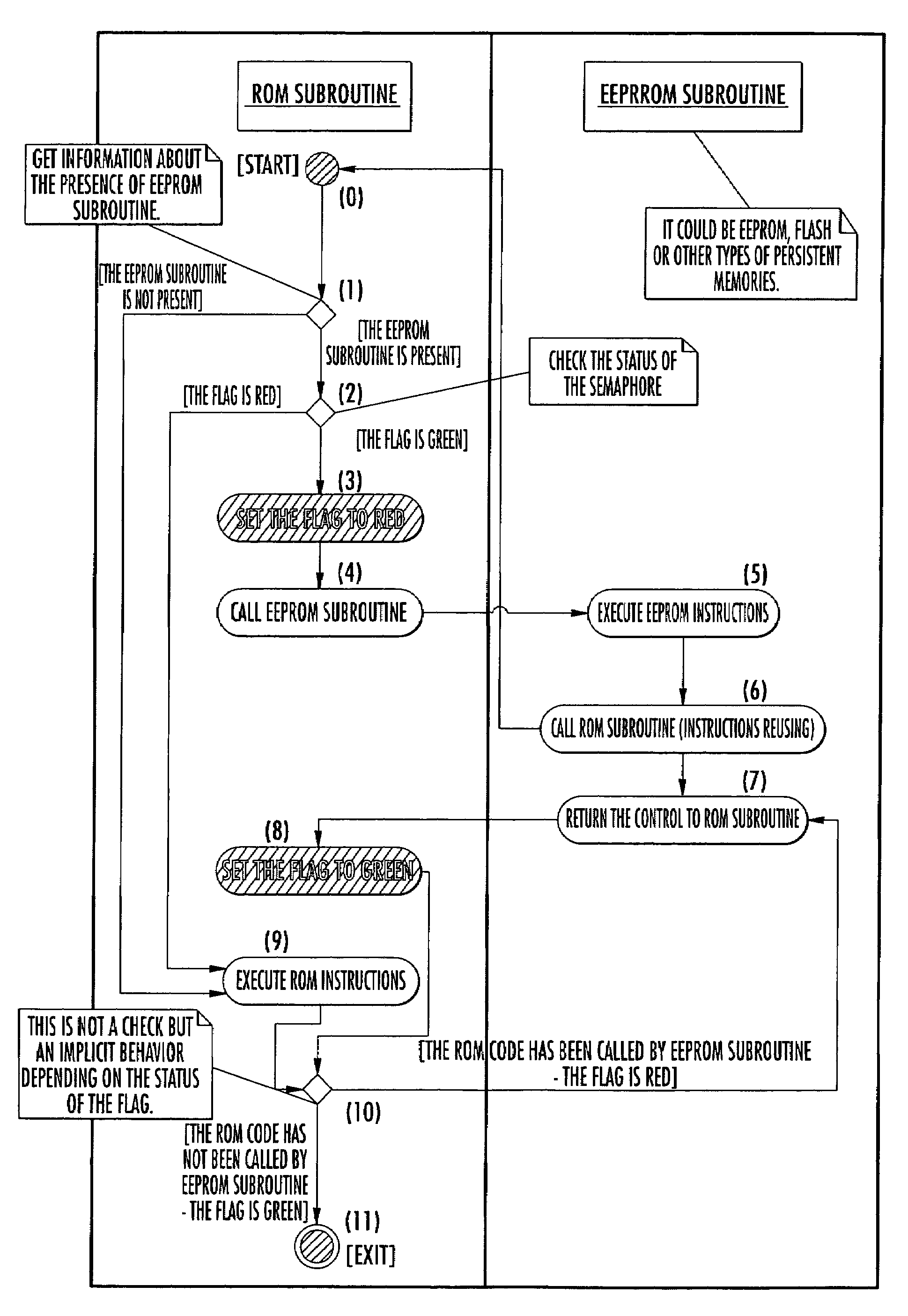
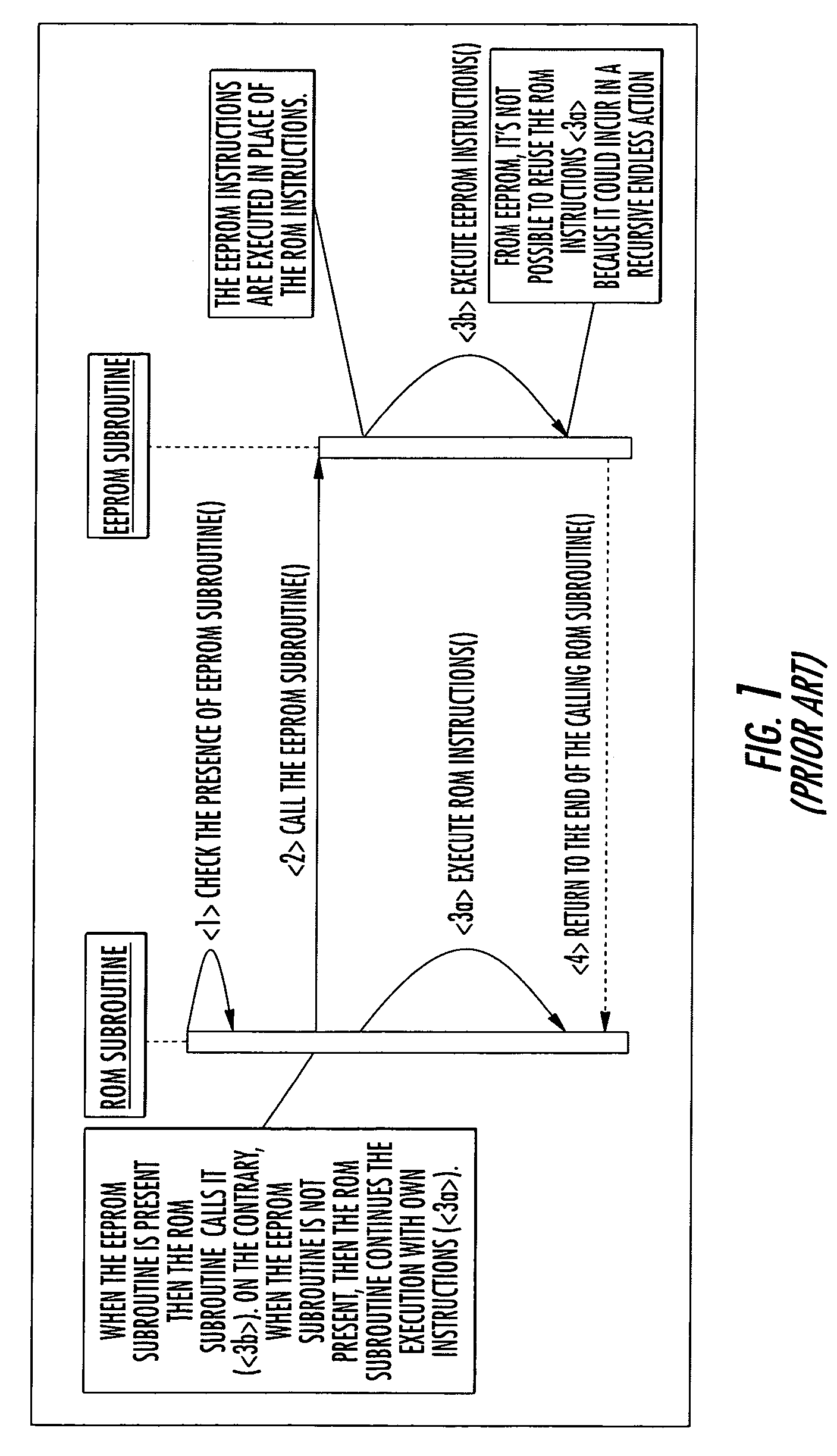
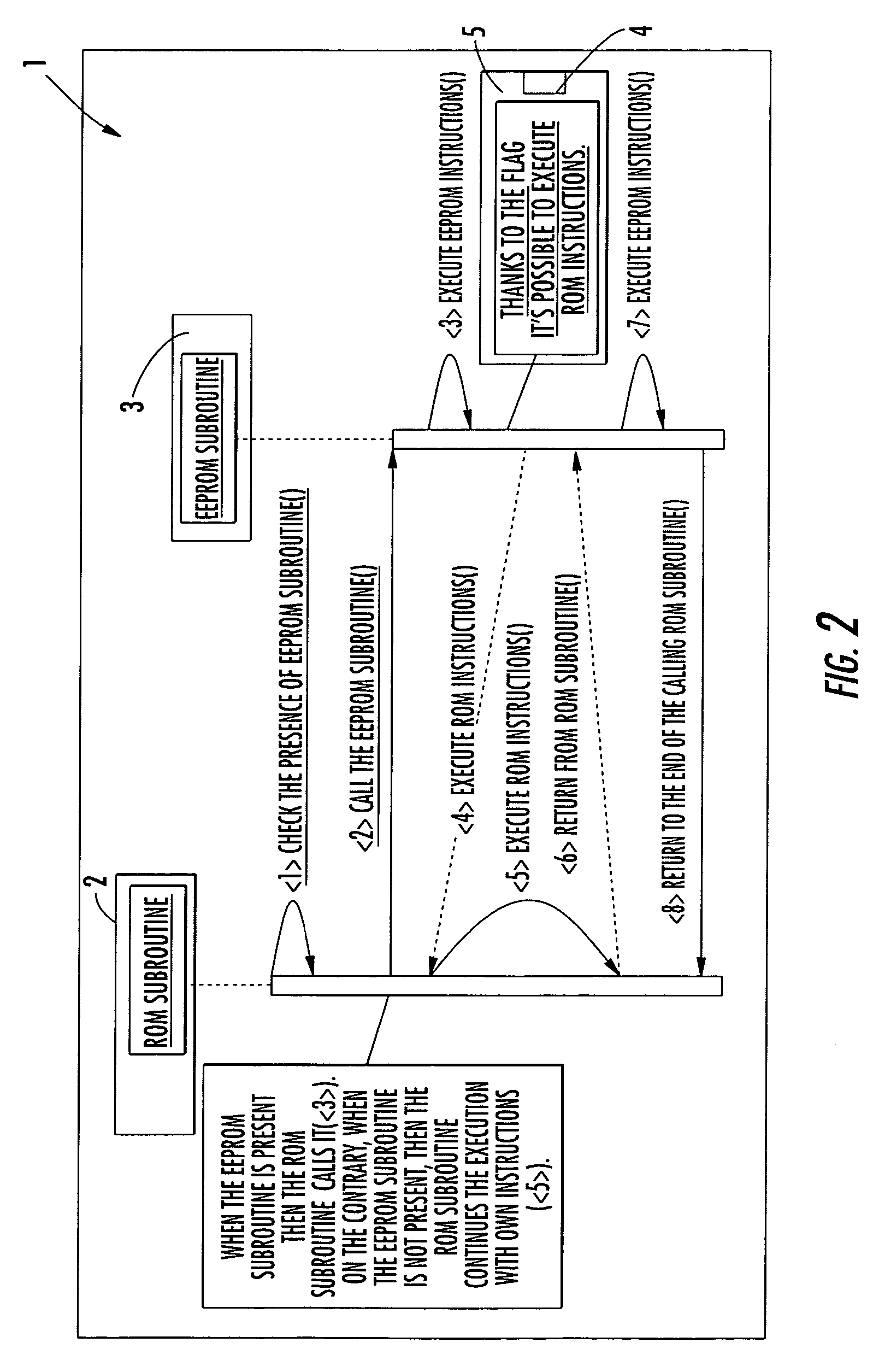
A mechanism for patching read only memory (ROM) instructions in an embedded system is provided. The embedded system includes non-volatile memory such as a ROM, a RAM and an EEPROM. In one configuration, the ROM contains application modules (subroutines) that are subordinate to a flag status. The flag status indicates to the subroutine whether to execute the ROM instructions in the ROM or the extended instructions in the EEPROM. The instructions in the EEPROM may be used to patch or to extend the behaviors masked in the ROM instructions. The extended instructions in the EEPROM may reuse the ROM instructions in the ROM without resulting in recursive actions.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS INT NV
Flash memory cell arrays having dual control gates per memory cell charge storage element
InactiveUS6888755B2Increase coupling areaImprove the coupling ratioTransistorSolid-state devicesCapacitanceImage resolution
A flash NAND type EEPROM system with individual ones of an array of charge storage elements, such as floating gates, being capacitively coupled with at least two control gate lines. The control gate lines are preferably positioned between floating gates to be coupled with sidewalls of floating gates. The memory cell coupling ratio is desirably increased, as a result. Both control gate lines on opposite sides of a selected row of floating gates are usually raised to the same voltage while the second control gate lines coupled to unselected rows of floating gates immediately adjacent and on opposite sides of the selected row are kept low. The control gate lines can also be capacitively coupled with the substrate in order to selectively raise its voltage in the region of selected floating gates. The length of the floating gates and the thicknesses of the control gate lines can be made less than the minimum resolution element of the process by forming an etch mask of spacers.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
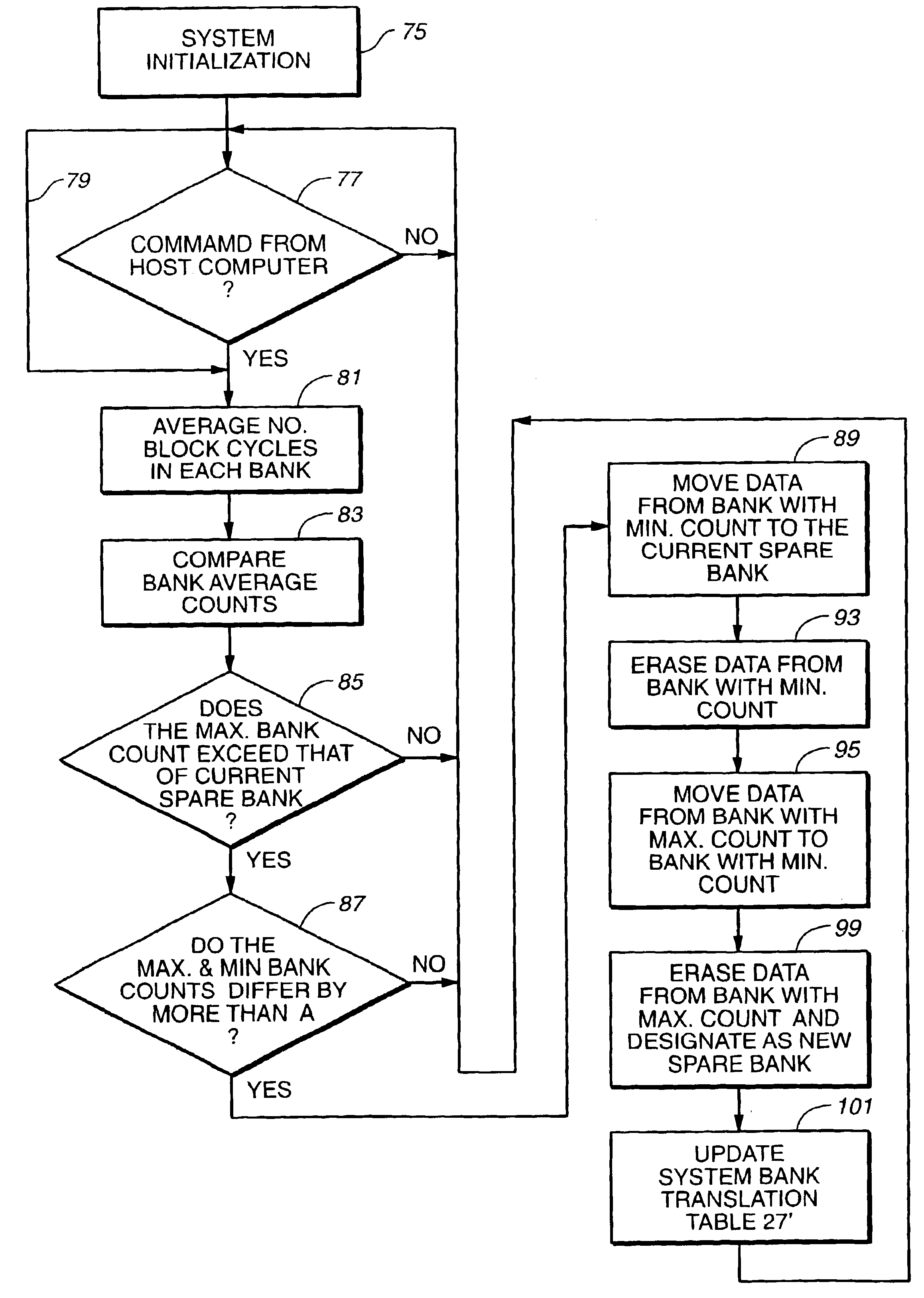
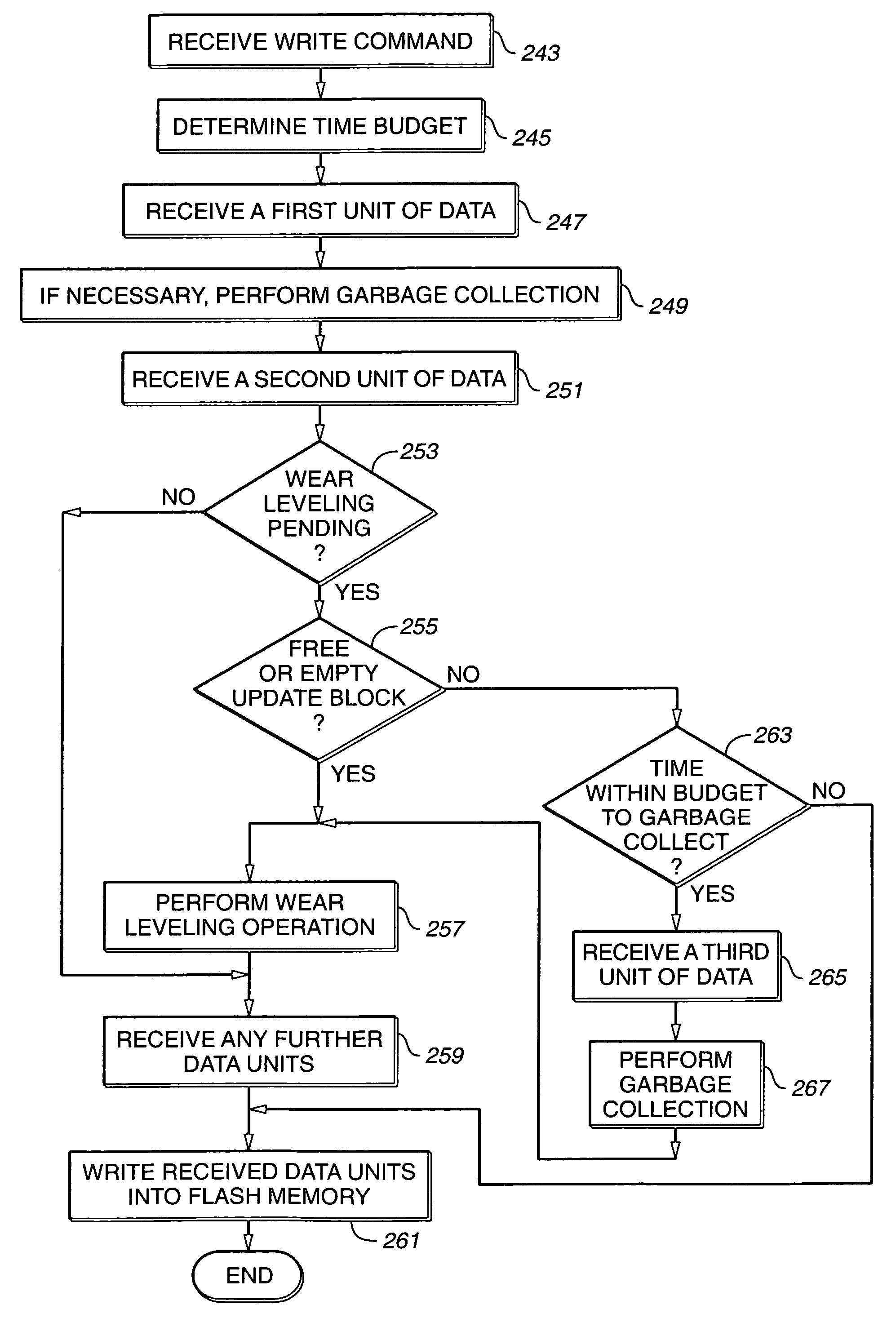
Scheduling of housekeeping operations in flash memory systems
InactiveUS20060161724A1Improved performance characteristicsMaximum countMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory systemsSystems managementNon-volatile memory
A re-programmable non-volatile memory system, such as a flash EEPROM system, having its memory cells grouped into blocks of cells that are simultaneously erasable is operated to perform memory system housekeeping operations in the foreground during execution of a host command, wherein the housekeeping operations are unrelated to execution of the host command. Both one or more such housekeeping operations and execution of the host command are performed within a time budget established for executing that particular command. One such command is to write data being received to the memory. One such housekeeping operation is to level out the wear of the individual blocks that accumulates through repetitive erasing and re-programming.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Band engineered nano-crystal non-volatile memory device utilizing enhanced gate injection
ActiveUS20070045718A1Increased device feature scalingEfficient erasureTransistorNanoinformaticsCharge retentionNon symmetric
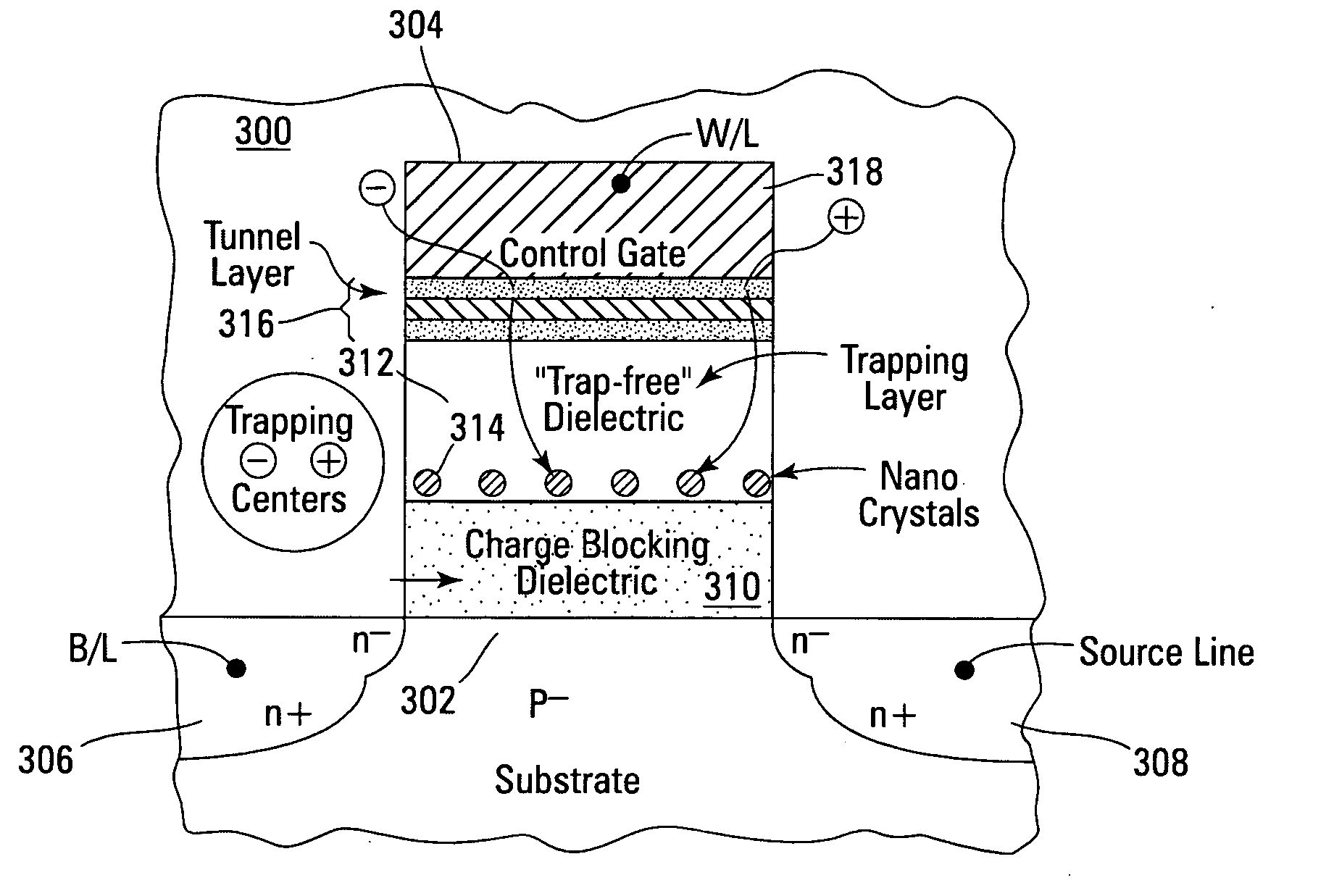
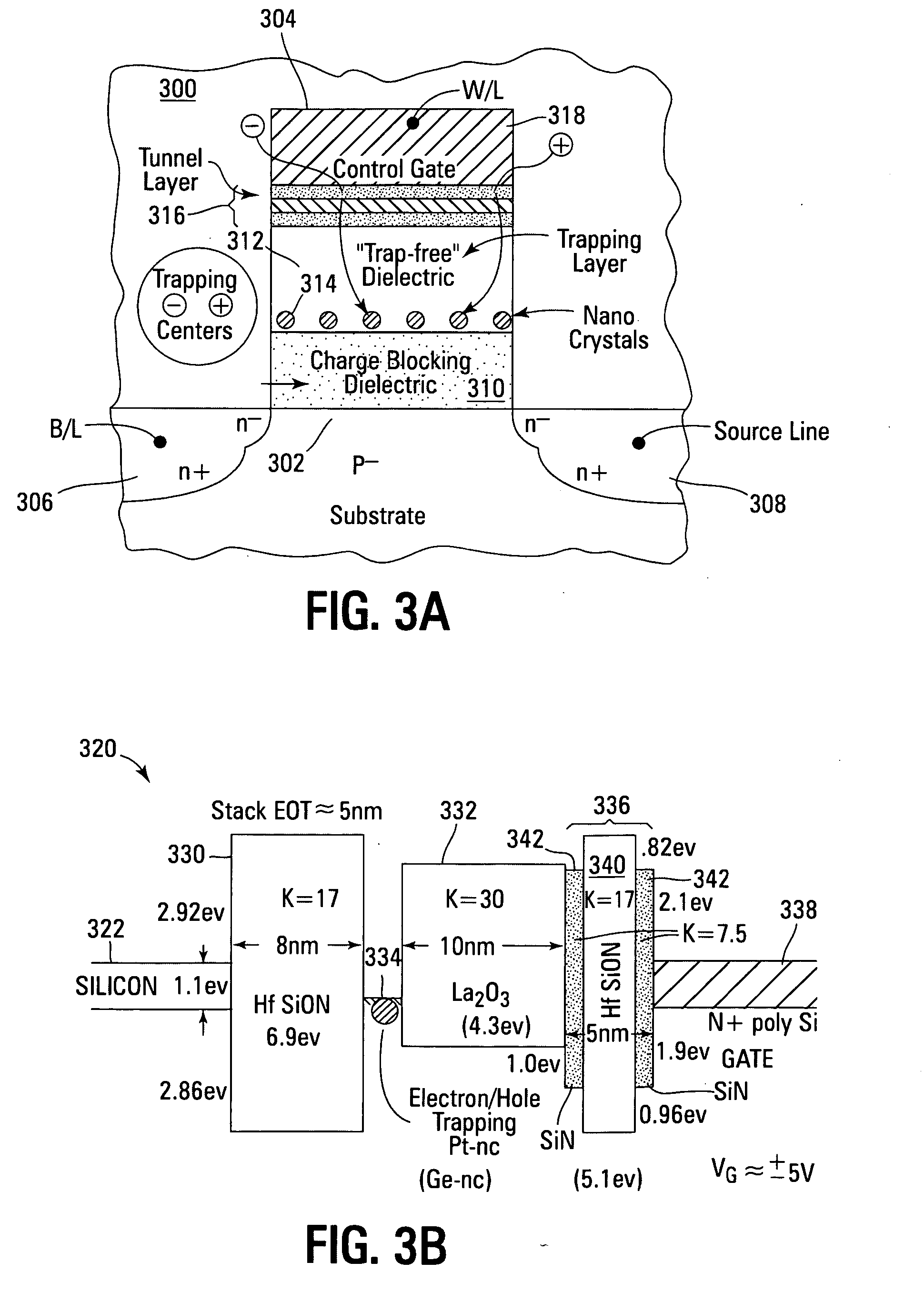
Non-volatile memory devices and arrays are described that utilize reverse mode non-volatile memory cells that have band engineered gate-stacks and nano-crystal charge trapping in EEPROM and block erasable memory devices, such as Flash memory devices. Embodiments of the present invention allow a reverse mode gate-insulator stack memory cell that utilizes the control gate for programming and erasure through a band engineered crested tunnel barrier. Charge retention is enhanced by utilization of high work function nano-crystals in a non-conductive trapping layer and a high K dielectric charge blocking layer. The band-gap engineered gate-stack with symmetric or asymmetric crested barrier tunnel layers of the non-volatile memory cells of embodiments of the present invention allow for low voltage tunneling programming and erase with electrons and holes, while maintaining high charge blocking barriers and deep carrier trapping sites for good charge retention.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Spare block management of non-volatile memories
ActiveUS8040744B2Memory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesBit timeNon-volatile memory
Techniques for the management of spare blocks in re-programmable non-volatile memory system, such as a flash EEPROM system, are presented. In one set of techniques, for a memory partitioned into two sections (for example a binary section and a multi-state section), where blocks of one section are more prone to error, spare blocks can be transferred from the more error prone partition to the less error prone partition. In another set of techniques for a memory partitioned into two sections, blocks which fail in the more error prone partition are transferred to serve as spare blocks in the other partition. In a complementary set of techniques, a 1-bit time stamp is maintained for free blocks to determine whether the block has been written recently. Other techniques allow for spare blocks to be managed by way of a logical to physical conversion table by assigning them logical addresses that exceed the logical address space of which a host is aware.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
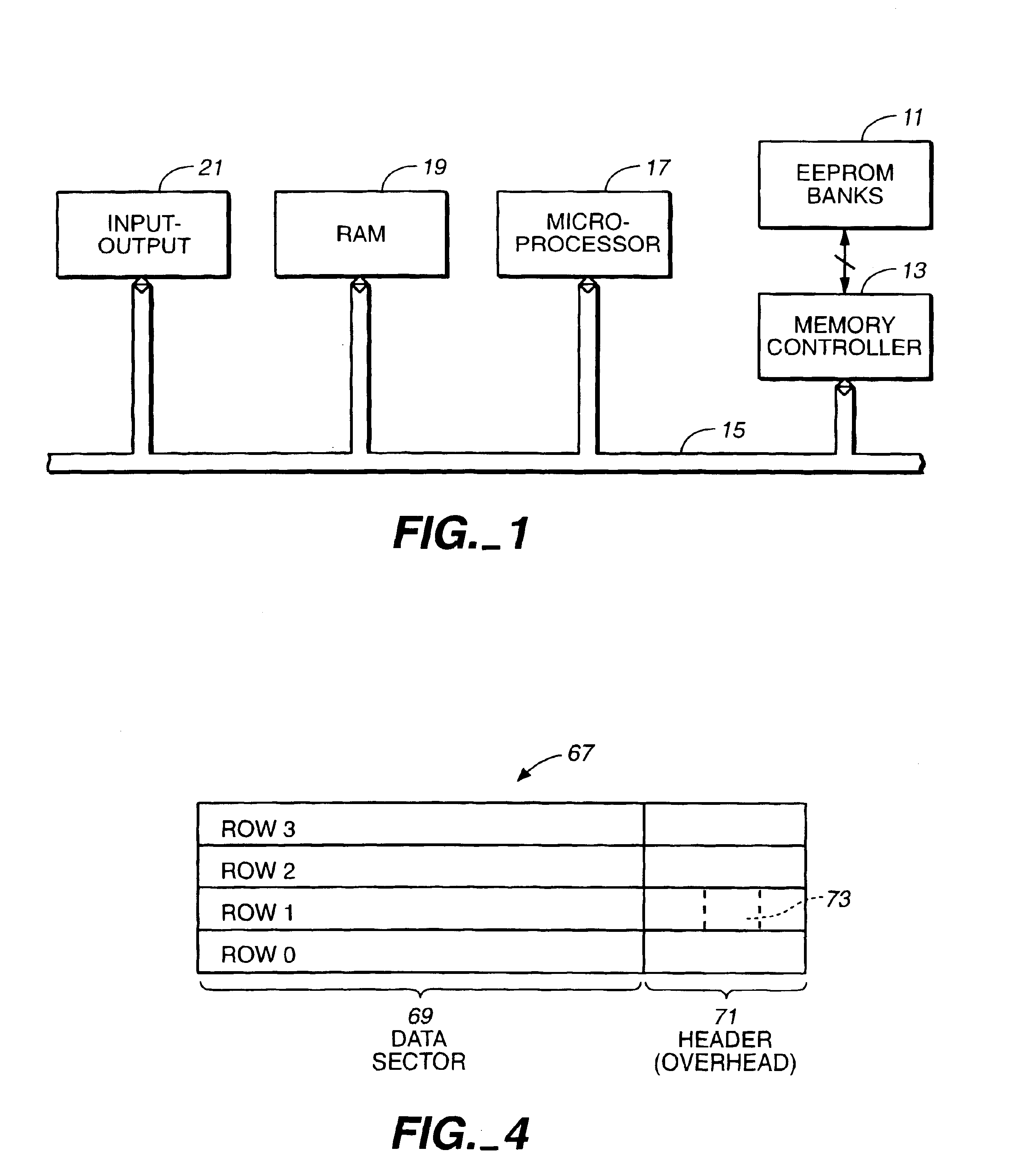
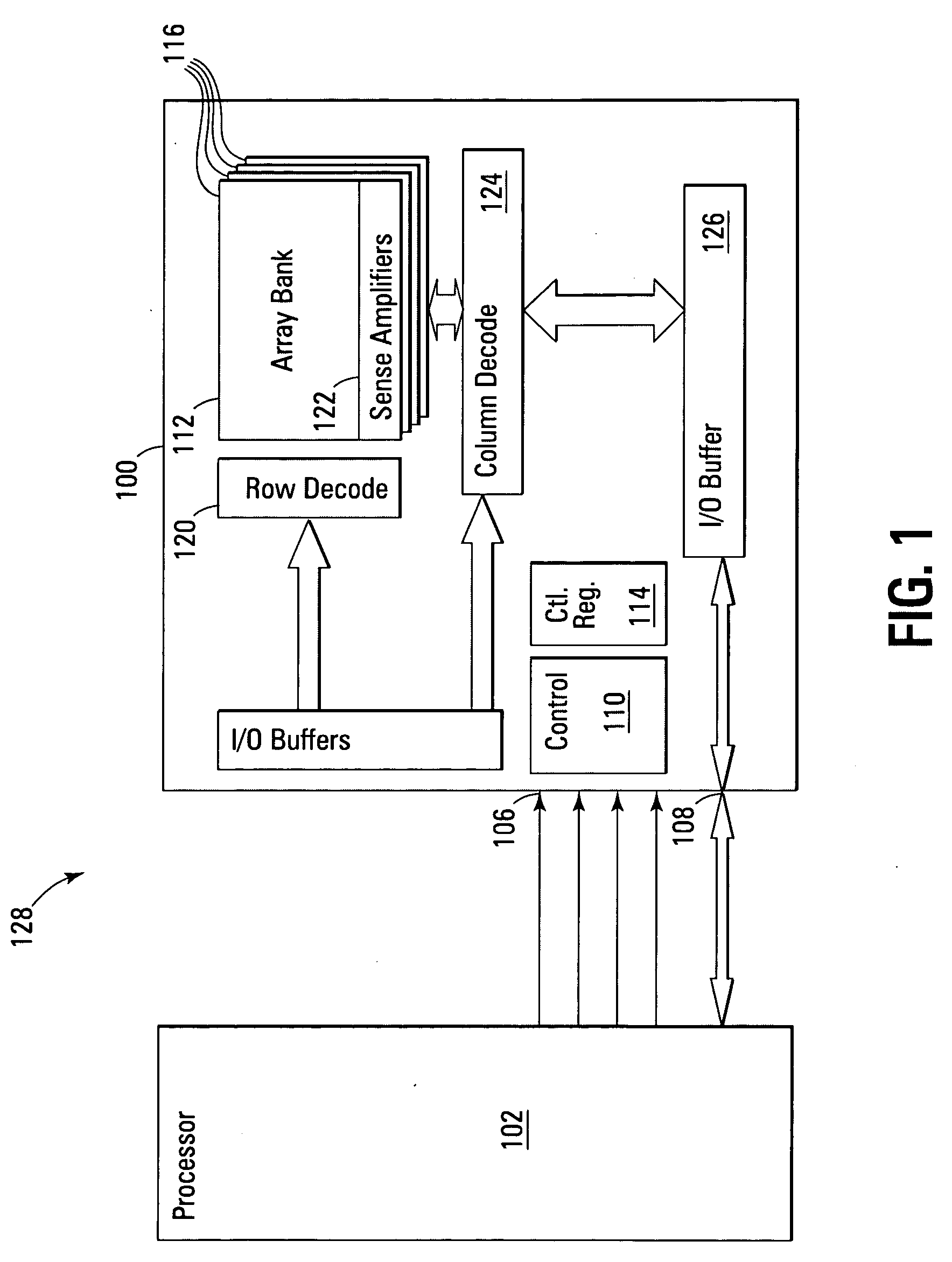
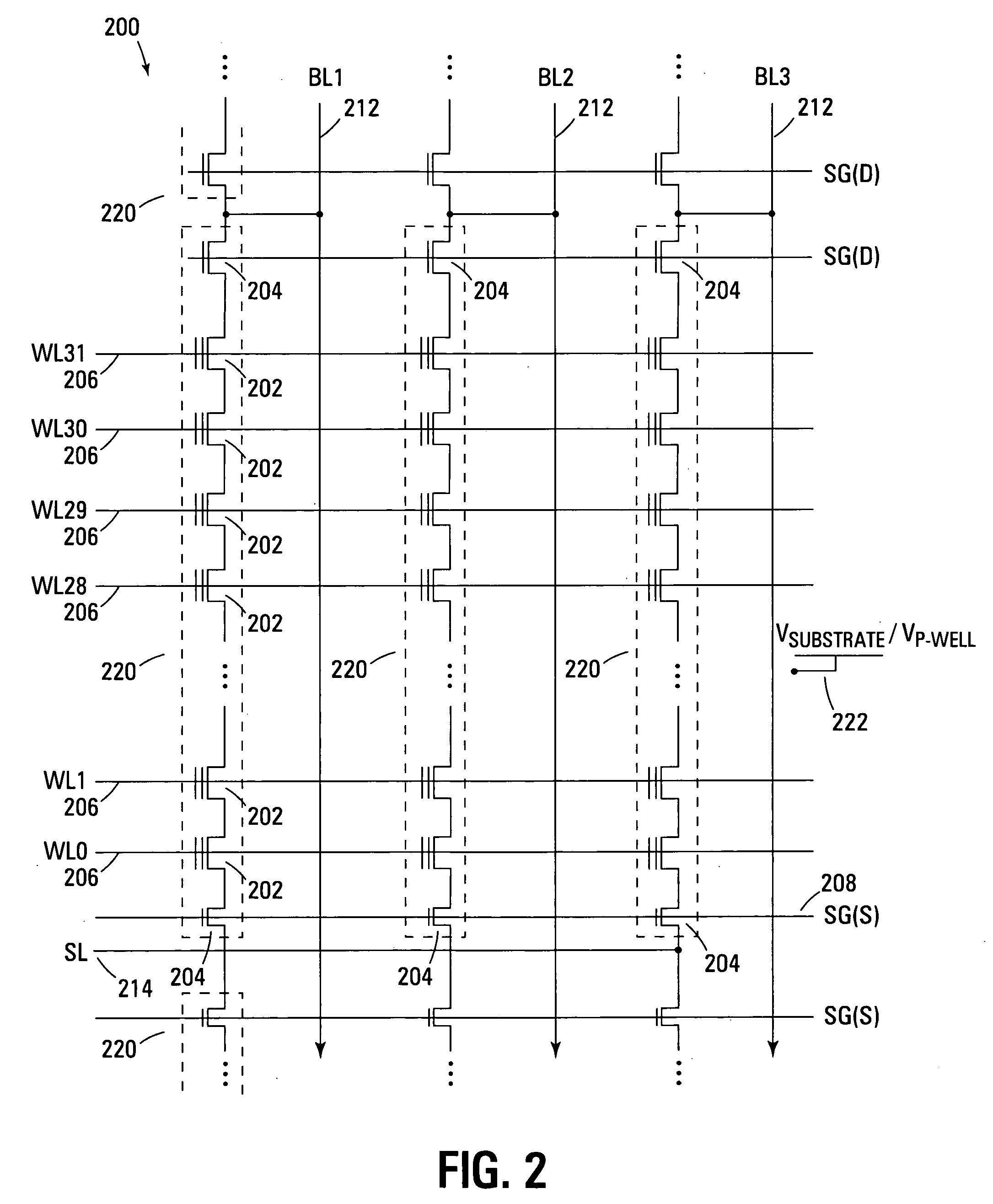
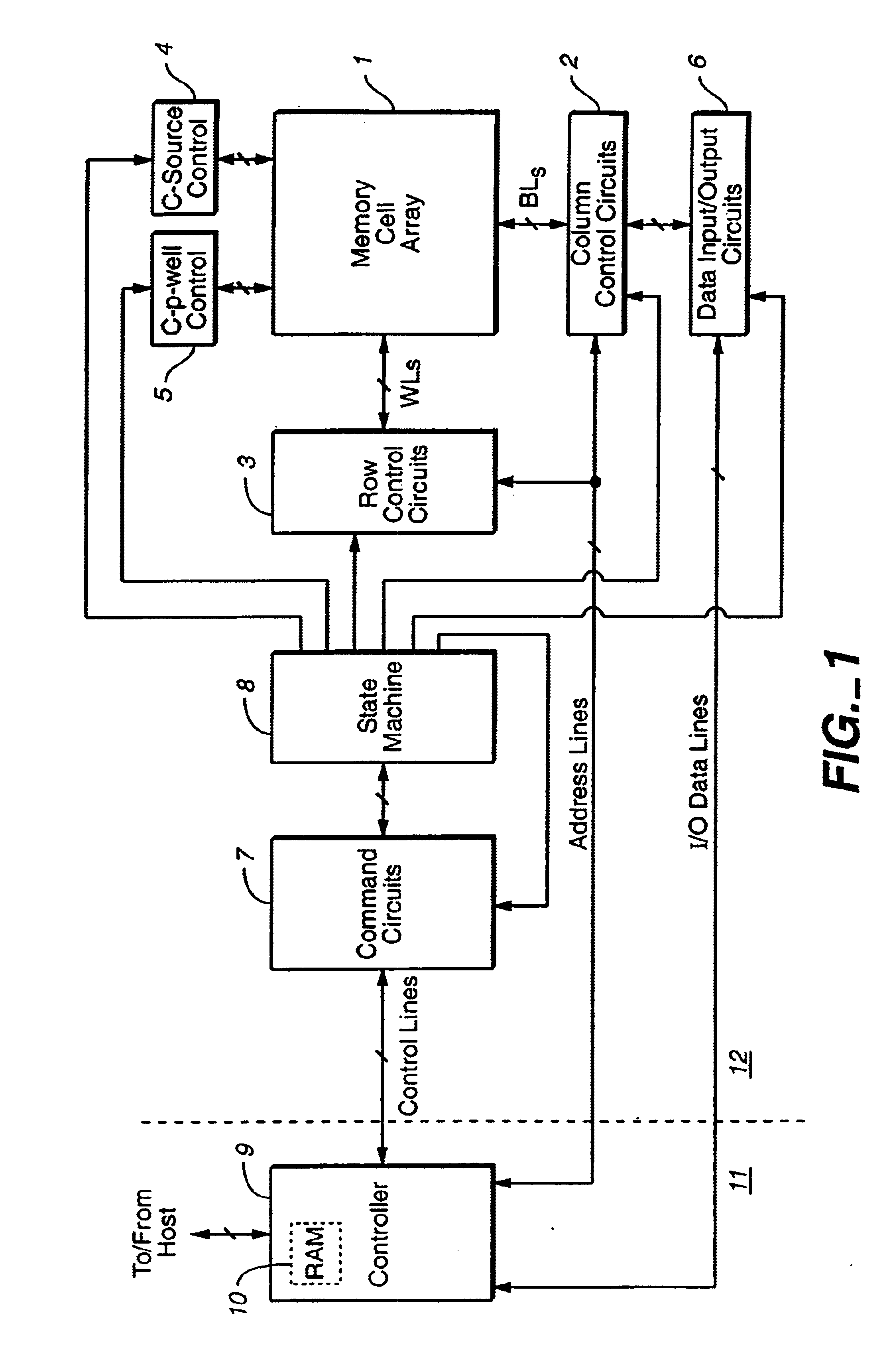
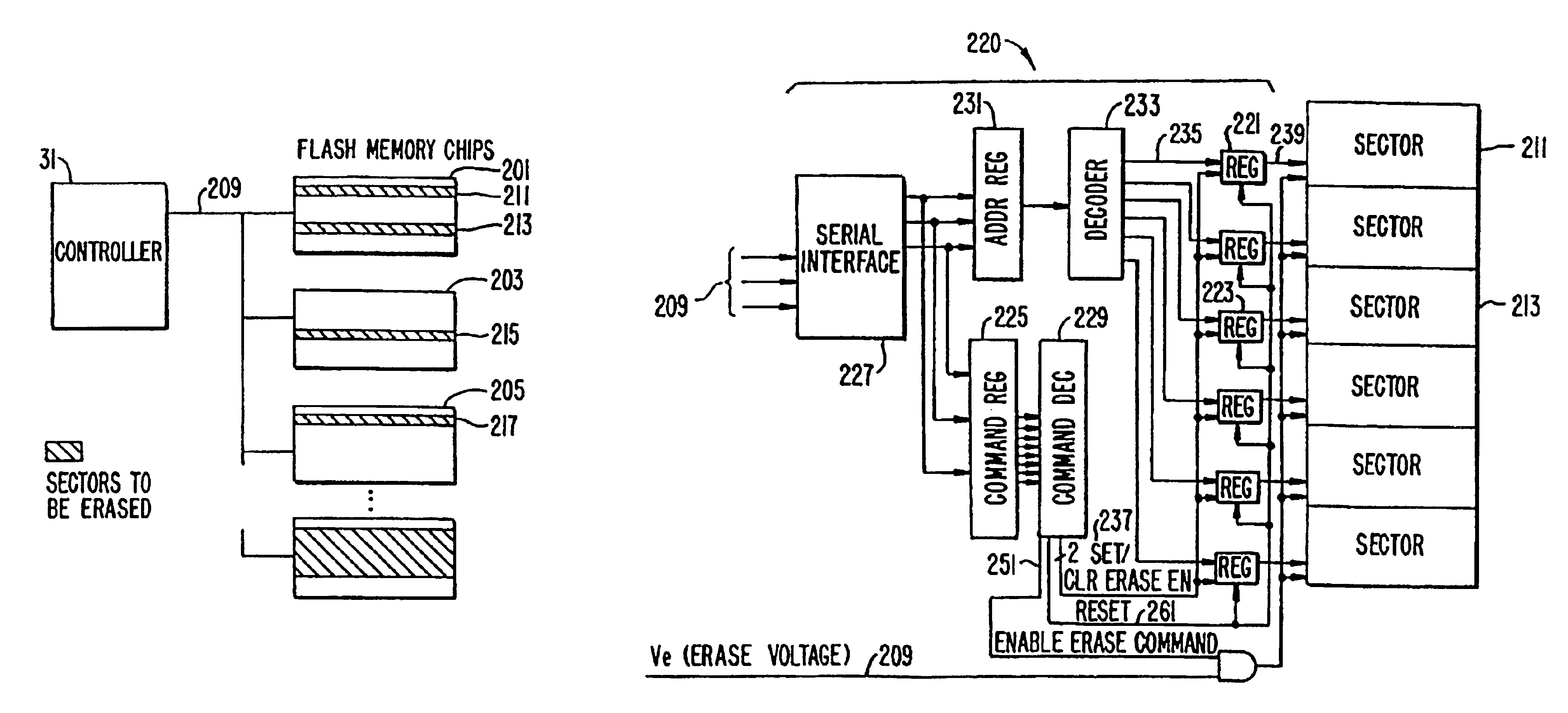
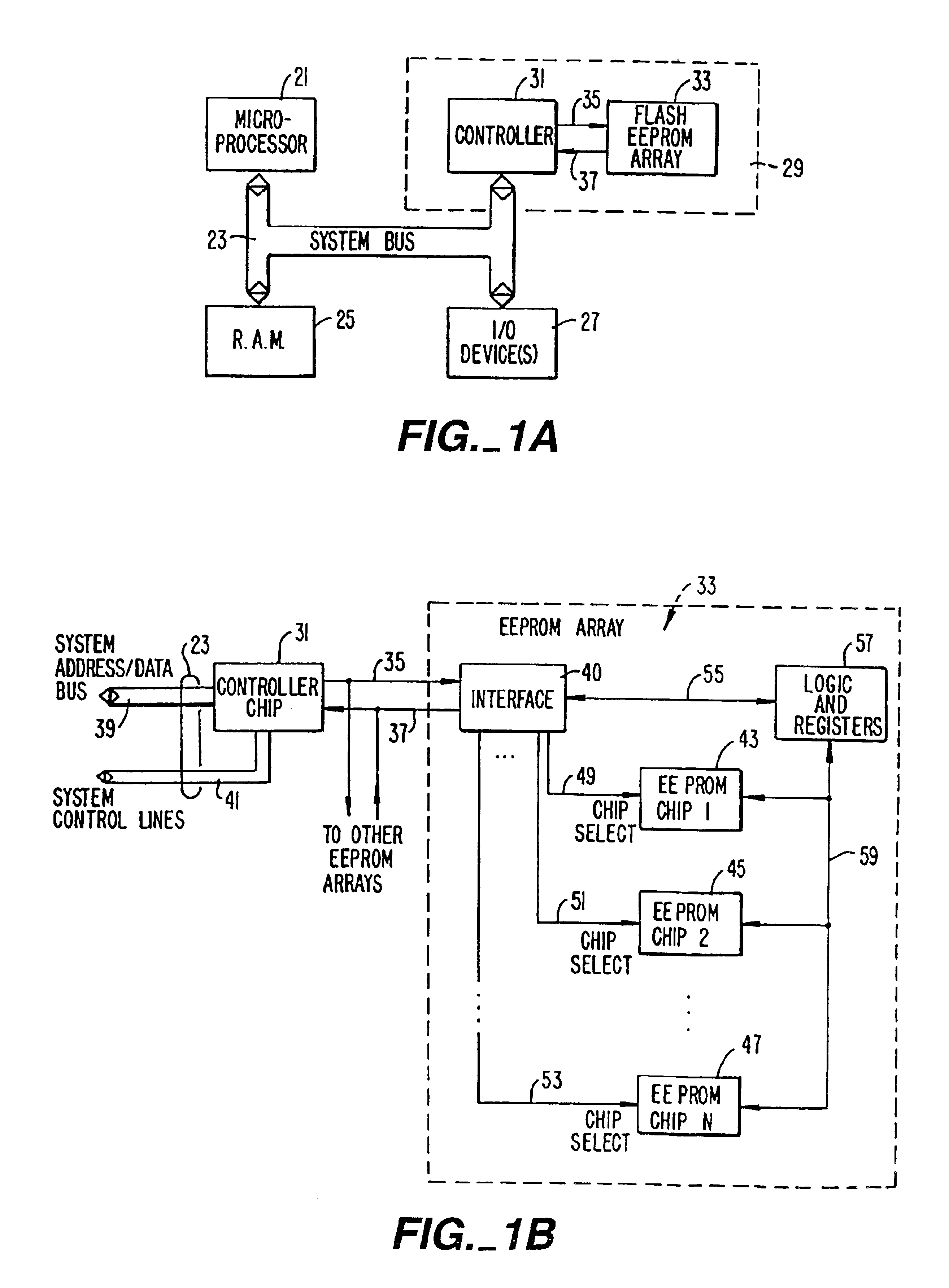
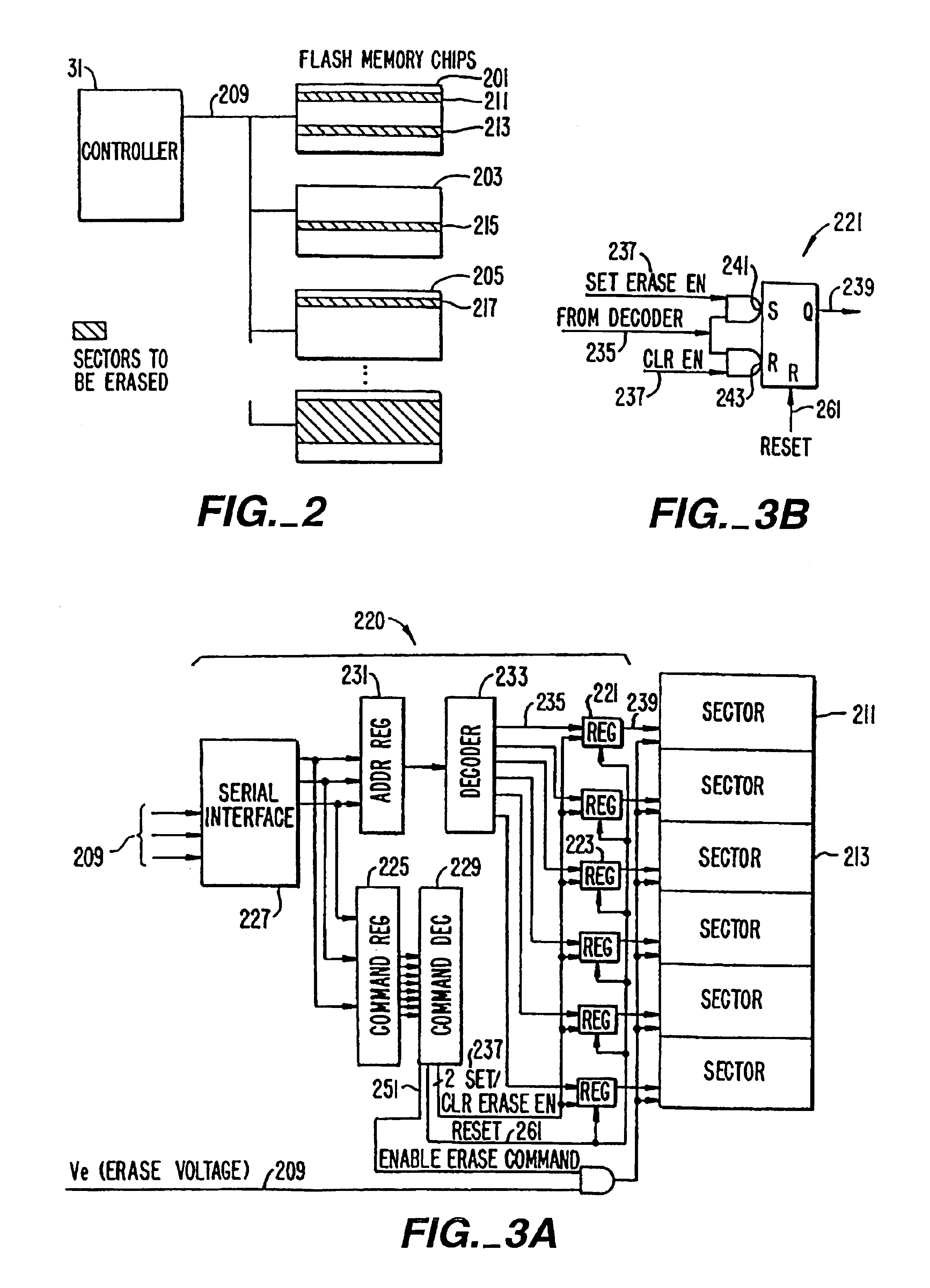
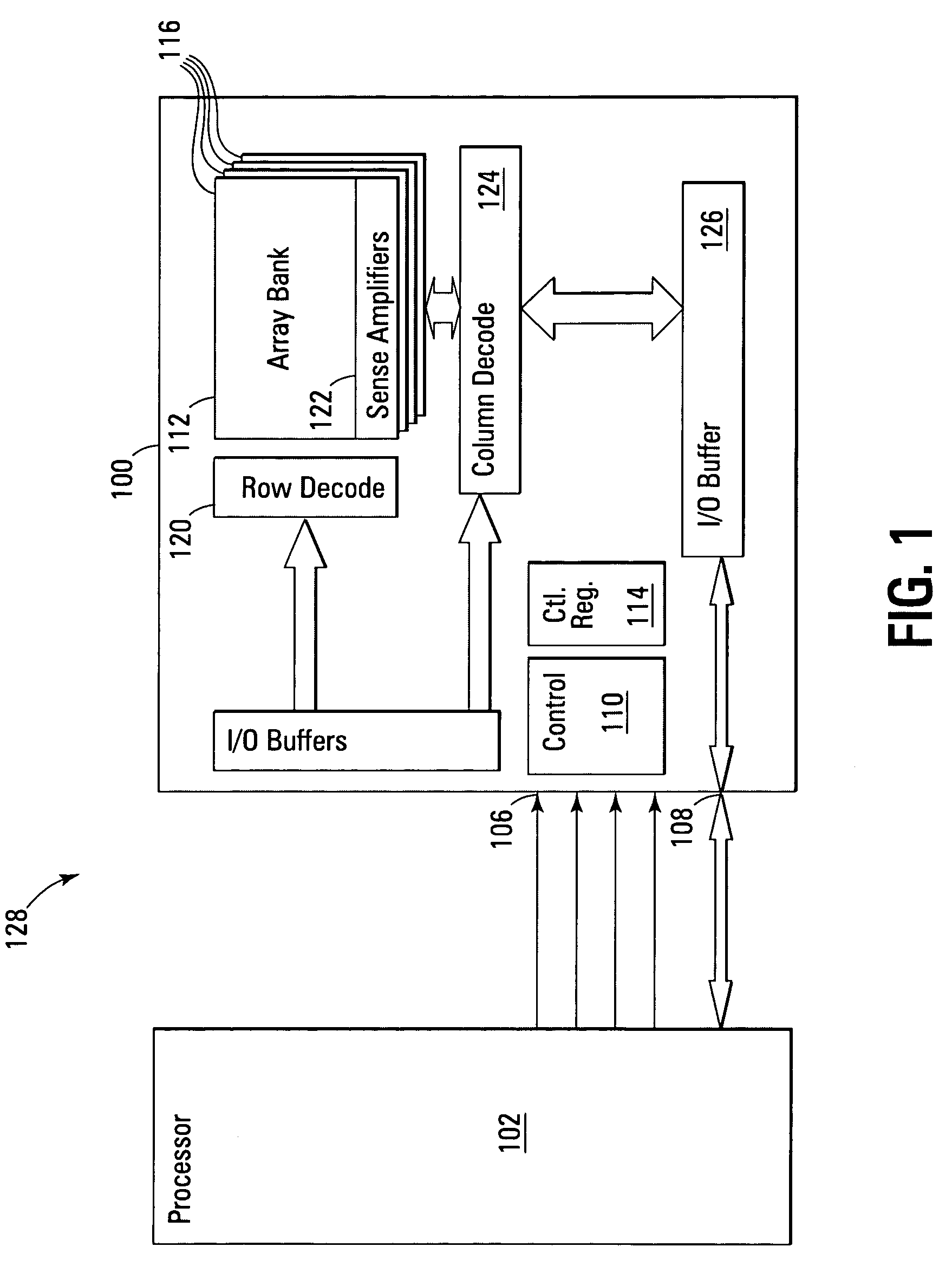
Flash EEprom system
InactiveUS6914846B2Minimize the numberAnti agingMemory architecture accessing/allocationTransistorMemory chipControl circuit
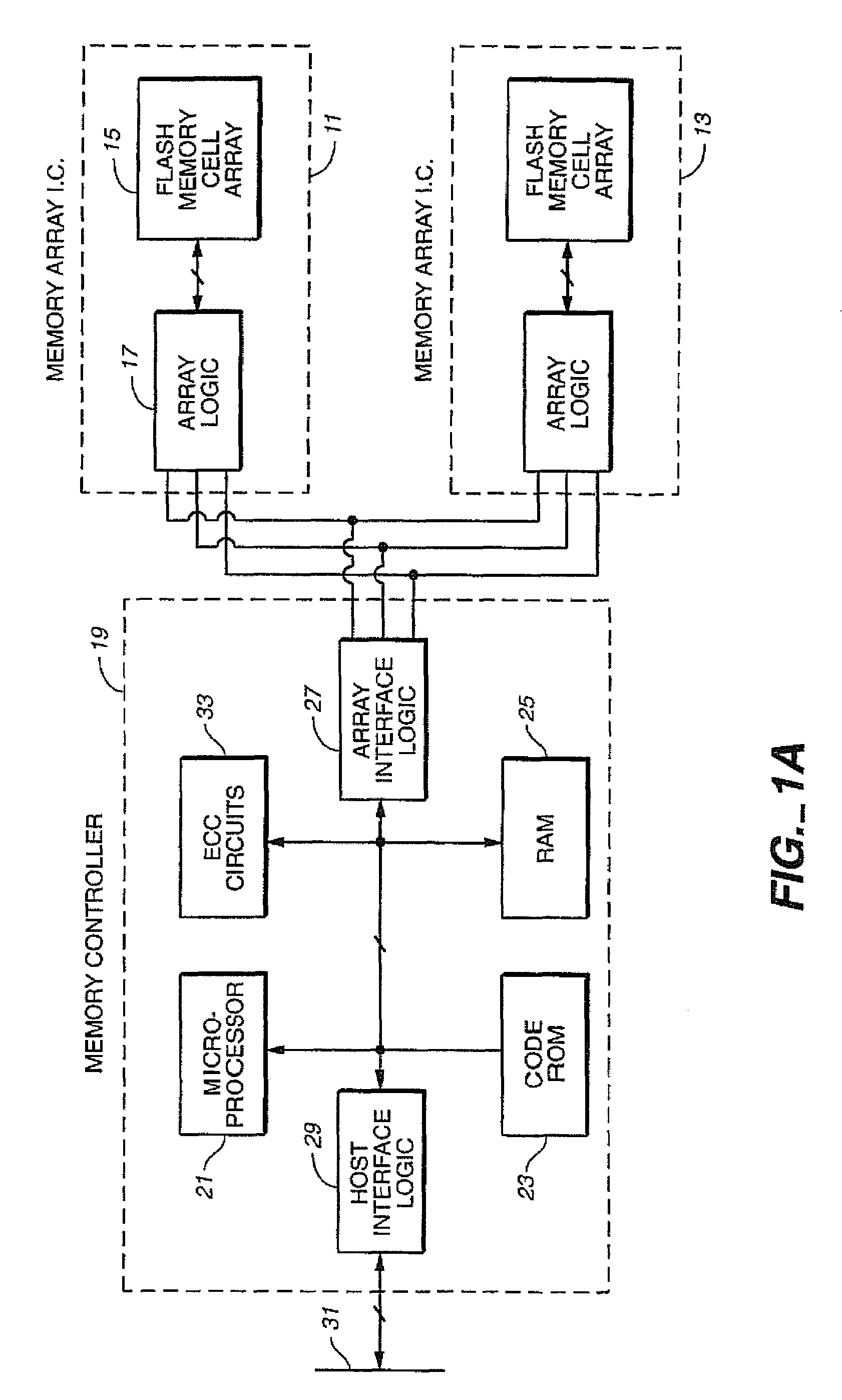
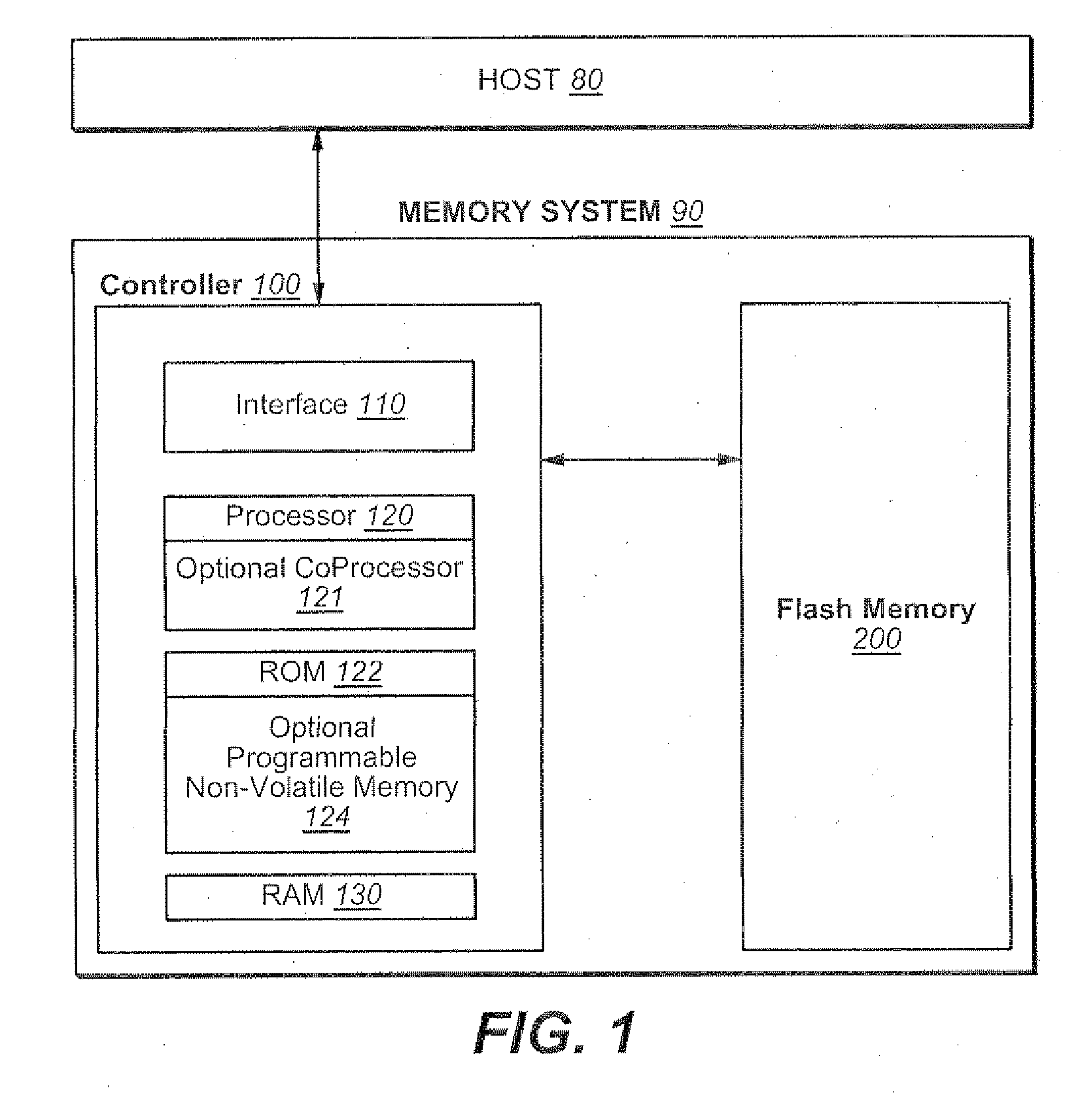
A system of Flash EEprom memory chips with controlling circuits serves as non-volatile memory such as that provided by magnetic disk drives. Improvements include selective multiple sector erase, in which any combinations of Flash sectors may be erased together. Selective sectors among the selected combination may also be de-selected during the erase operation. Another improvement is the ability to remap and replace defective cells with substitute cells. The remapping is performed automatically as soon as a defective cell is detected. When the number of defects in a Flash sector becomes large, the whole sector is remapped. Yet another improvement is the use of a write cache to reduce the number of writes to the Flash EEprom memory, thereby minimizing the stress to the device from undergoing too many write / erase cycling.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
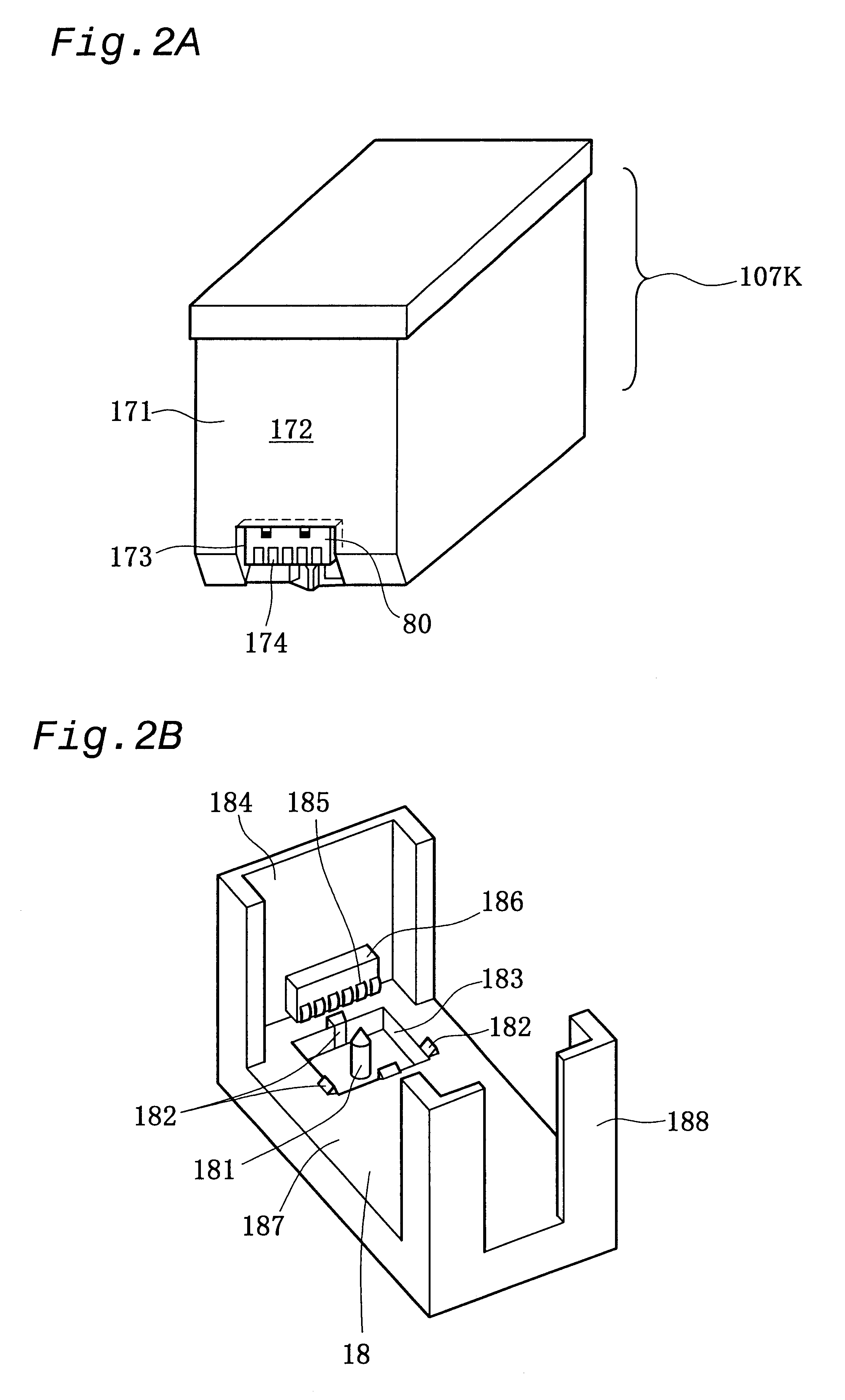
Ink cartridge and printer using the same
InactiveUS6565198B2Low costStored quickly and securelyOther printing apparatusManufacturing cost reductionInk printer
In an ink jet printer of the present invention, in order to reduce the manufacturing cost, an inexpensive EEPROM enabling only sequential accesses is applied for storage elements incorporated in a black ink cartridge and a color ink cartridge. The data array of a memory cell included in each of the storage elements mounted on the ink cartridges is determined in such a manner that a second storage area, in which rewritable data, for example, data on remaining quantities of inks in the ink cartridge, are stored, is accessed prior to a first storage area, in which read only data are stored. This configuration enables the rewritable data to be securely written into the second storage area even after a power-off operation. The second storage area has two memory divisions allocated to each ink, that is, a first ink remaining quantity memory division and a second ink remaining quantity memory division. Latest data on the remaining quantity of each ink is alternately written into these two memory divisions. Alternatively, the latest data on the remaining quantity of each ink is written into these two memory divisions in a duplicated manner. Each ink remaining quantity memory division has a write complete flag to determine whether or not a writing operation has been completed normally in the ink remaining quantity memory division. This arrangement enables the remaining quantities of the respective inks to be monitored accurately and continuously.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
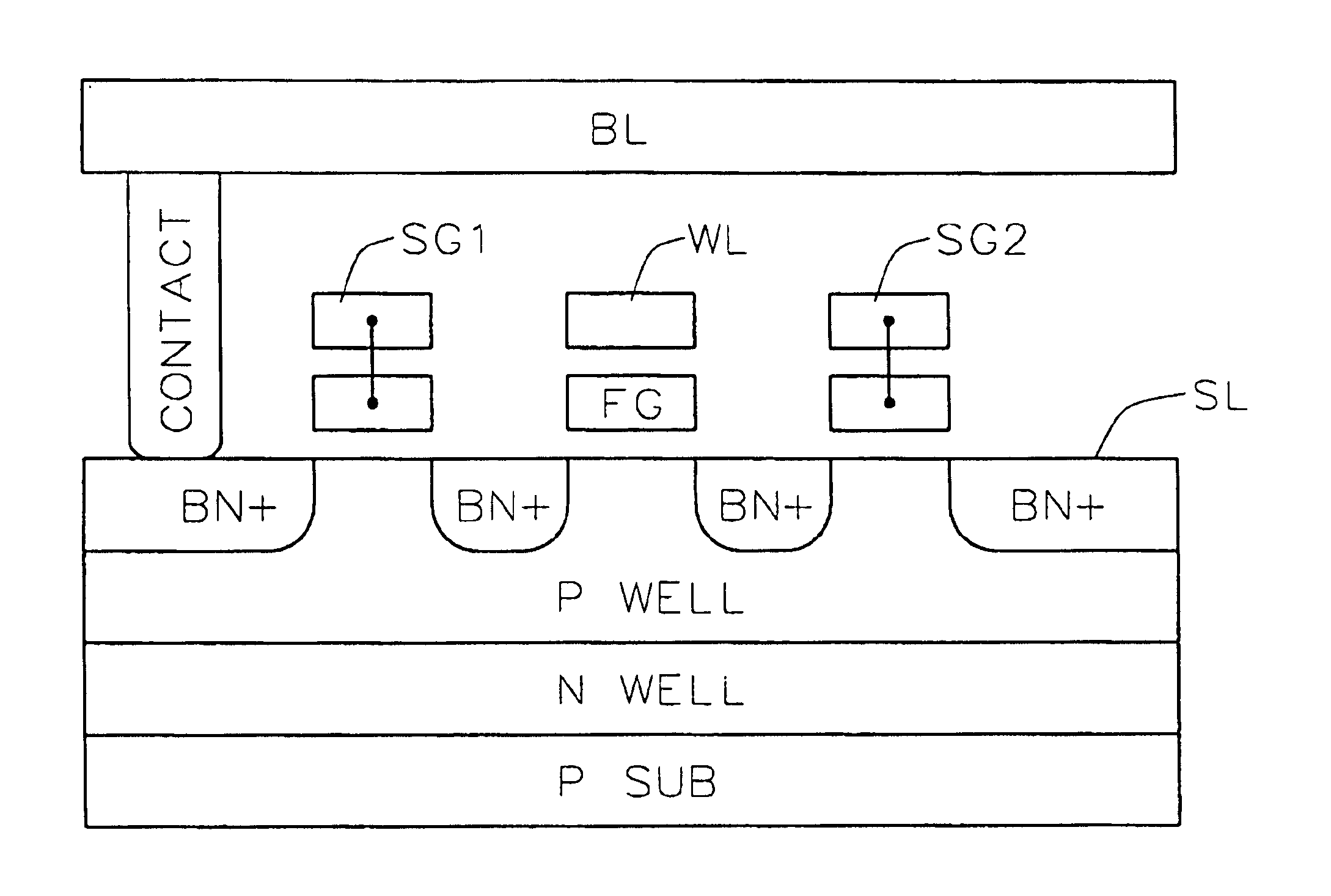
Monolithic, combo nonvolatile memory allowing byte, page and block write with no disturb and divided-well in the cell array using a unified cell structure and technology with a new scheme of decoder and layout
InactiveUS6862223B1Eliminate area-consuming divided triple-wellSuperior combo, monolithic, nonvolatile memorySolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesUnit structureByte
A novel FLASH-based EEPROM cell, decoder, and layout scheme are disclosed to eliminate the area-consuming divided triple-well in cell array and allows byte-erase and byte-program for high P / E cycles. Furthermore, the process-compatible FLASH cell for EEPROM part can be integrated with FLASH and ROM parts so that a superior combo, monolithic, nonvolatile memory is achieved. Unlike all previous arts, the novel combo nonvolatile memory of the present invention of ROM, EEPROM and FLASH or combination of any two is made of one unified, fully compatible, highly-scalable BN+cell and unified process. In addition, its cell operation schemes have zero array overhead and zero disturbance during P / E operations. The novel combo nonvolatile memory is designed to meet the need in those markets requiring flexible write size in units of bytes, pages and blocks at a lower cost.
Owner:CALLAHAN CELLULAR L L C
Programming method for NAND EEPROM
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
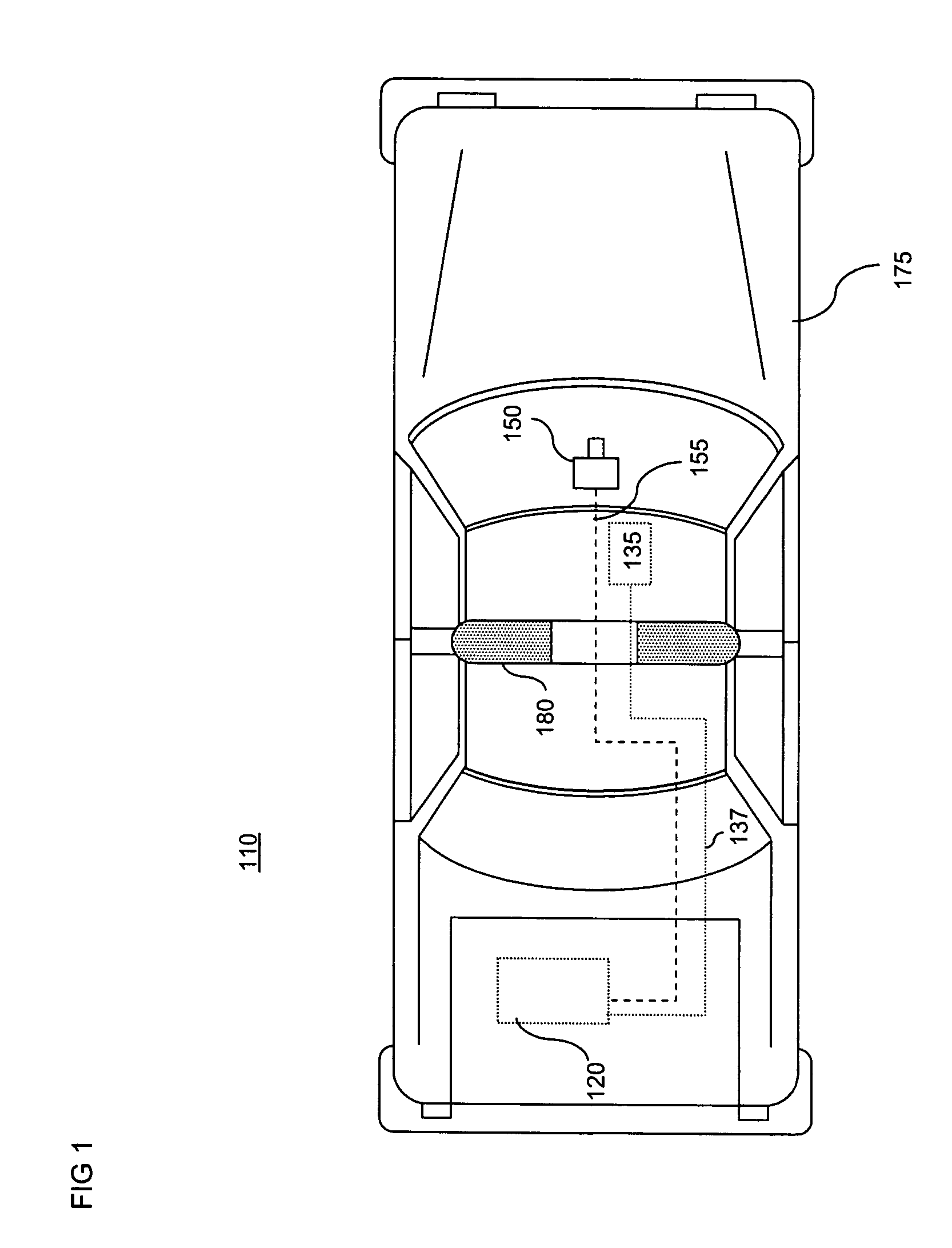
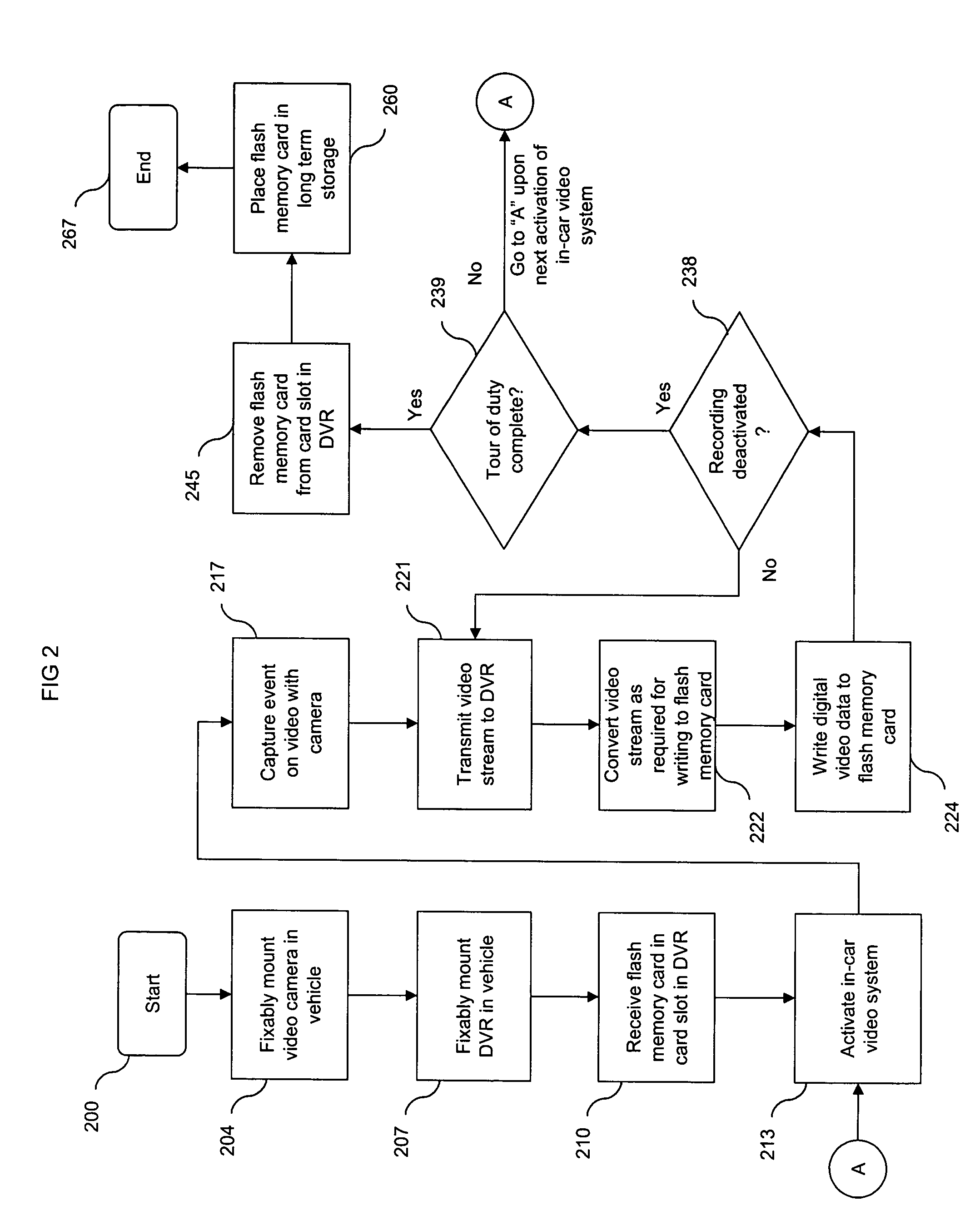
In-car video system using flash memory as a recording medium
InactiveUS20050088521A1Enhanced system packagingInherently reliableAnti-theft devicesColor television detailsDigital videoProgrammable read-only memory
An inventive system and method is provided by an in-car video system that uses a type of electrically erasable programmable read-only memory known as flash memory to store video of an incident or event. In an illustrative embodiment of the invention, a digital video recorder and video camera are fixably mounted in a vehicle such as a police cruiser. An event of interest is captured by a camera and the resulting video stream is converted into a form that writable to a flash memory. The video recorder writes the video to flash memory to thereby store a record of the event on the flash memory as a storage medium.
Owner:L 3 COMM MOBILE VISION
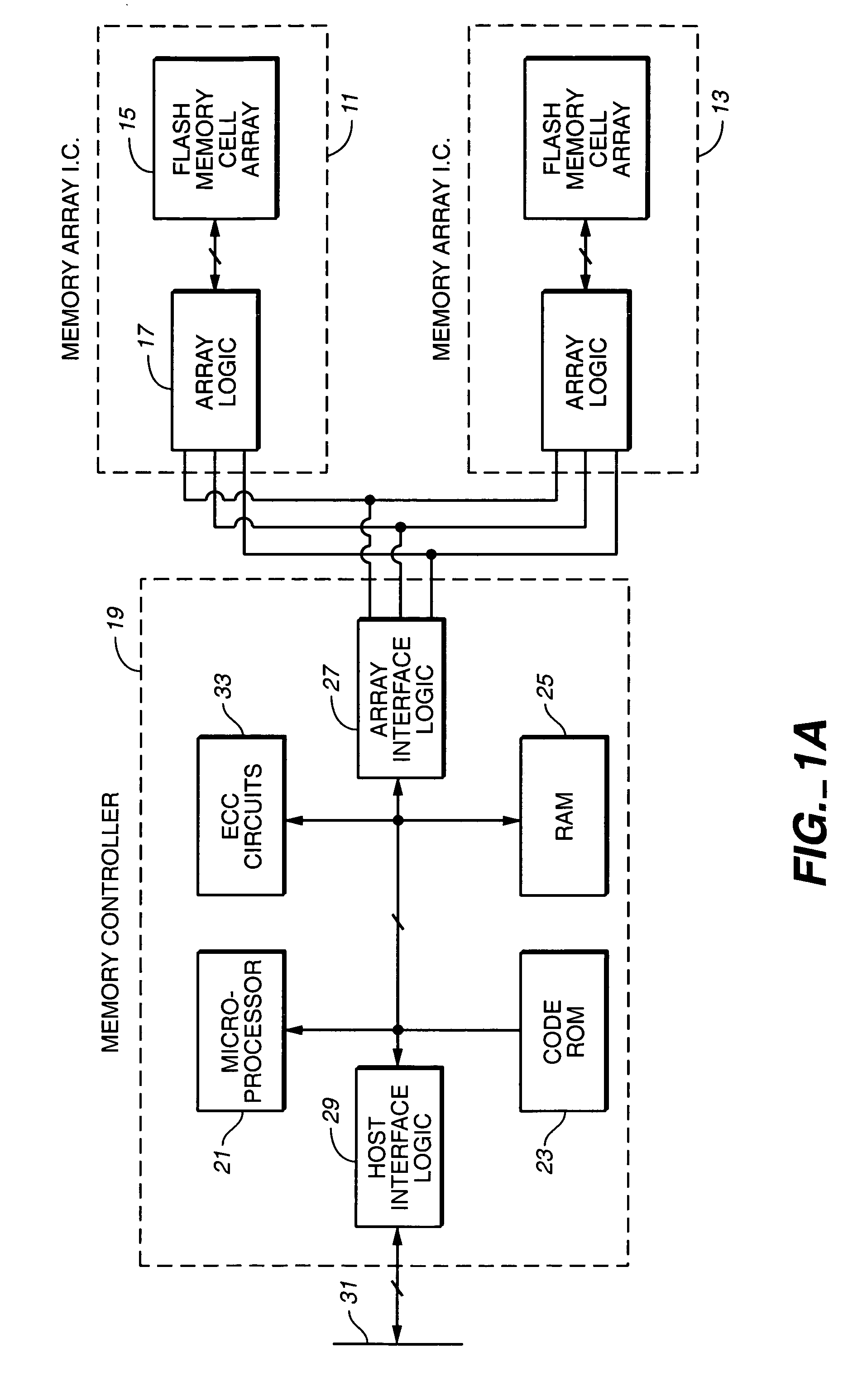
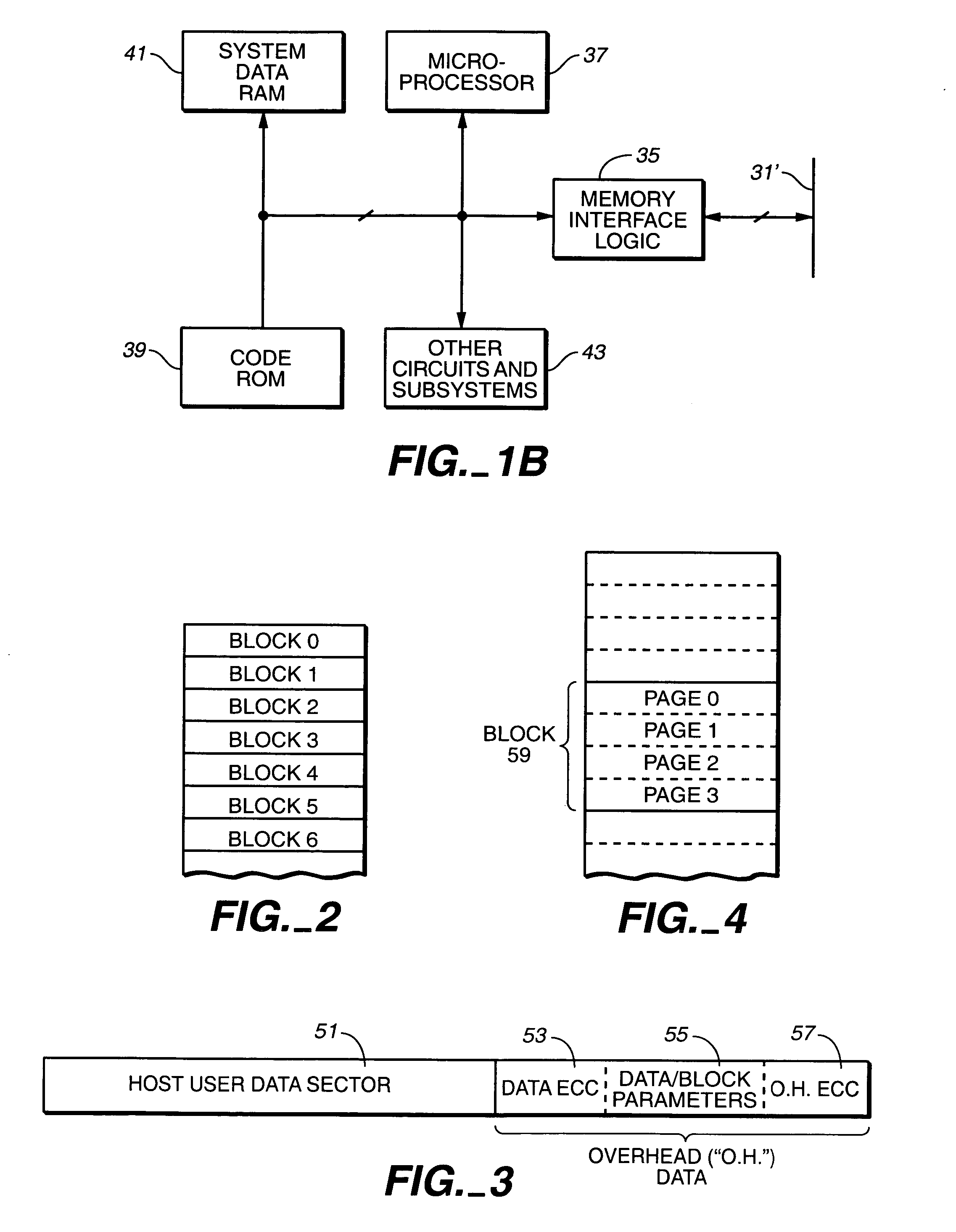
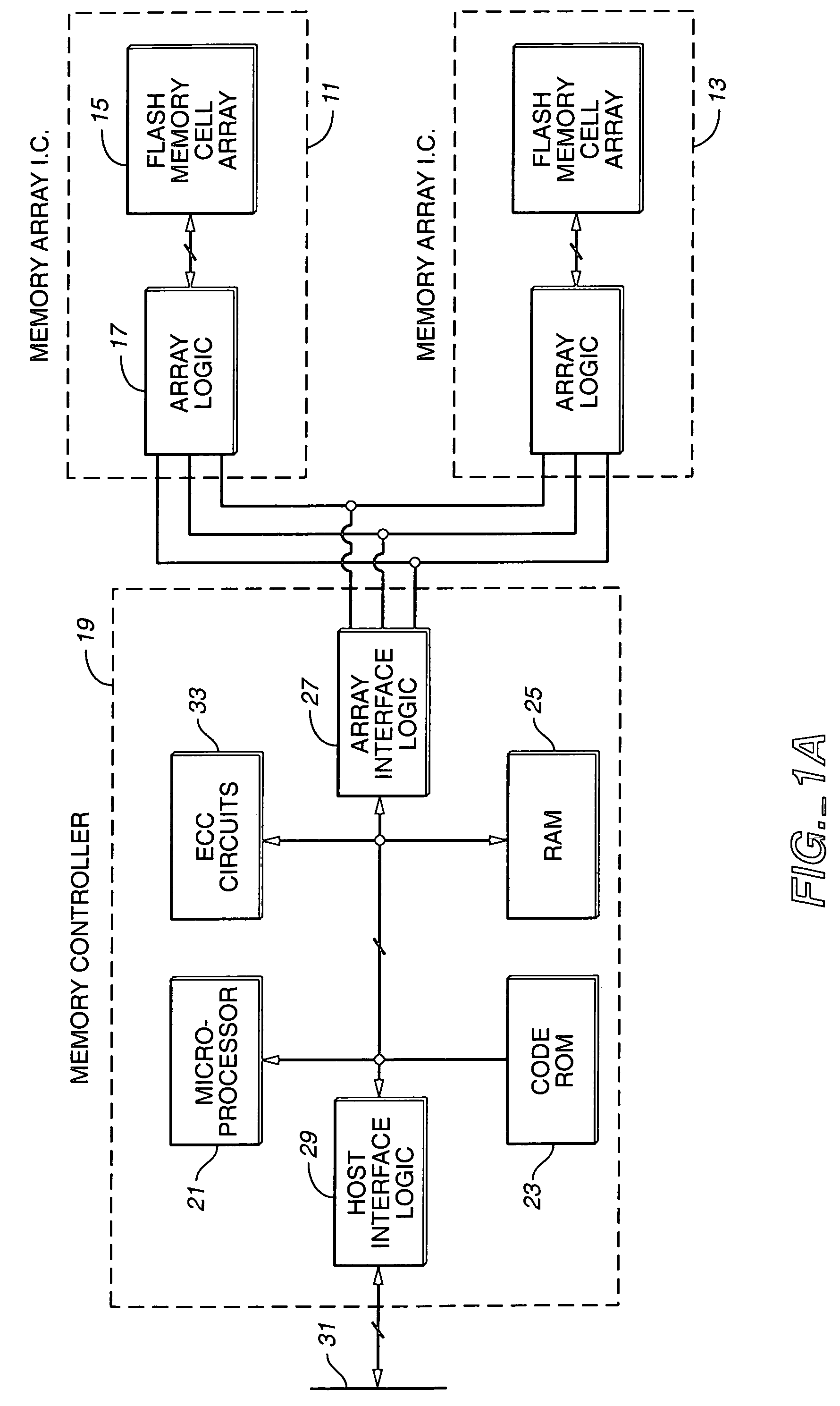
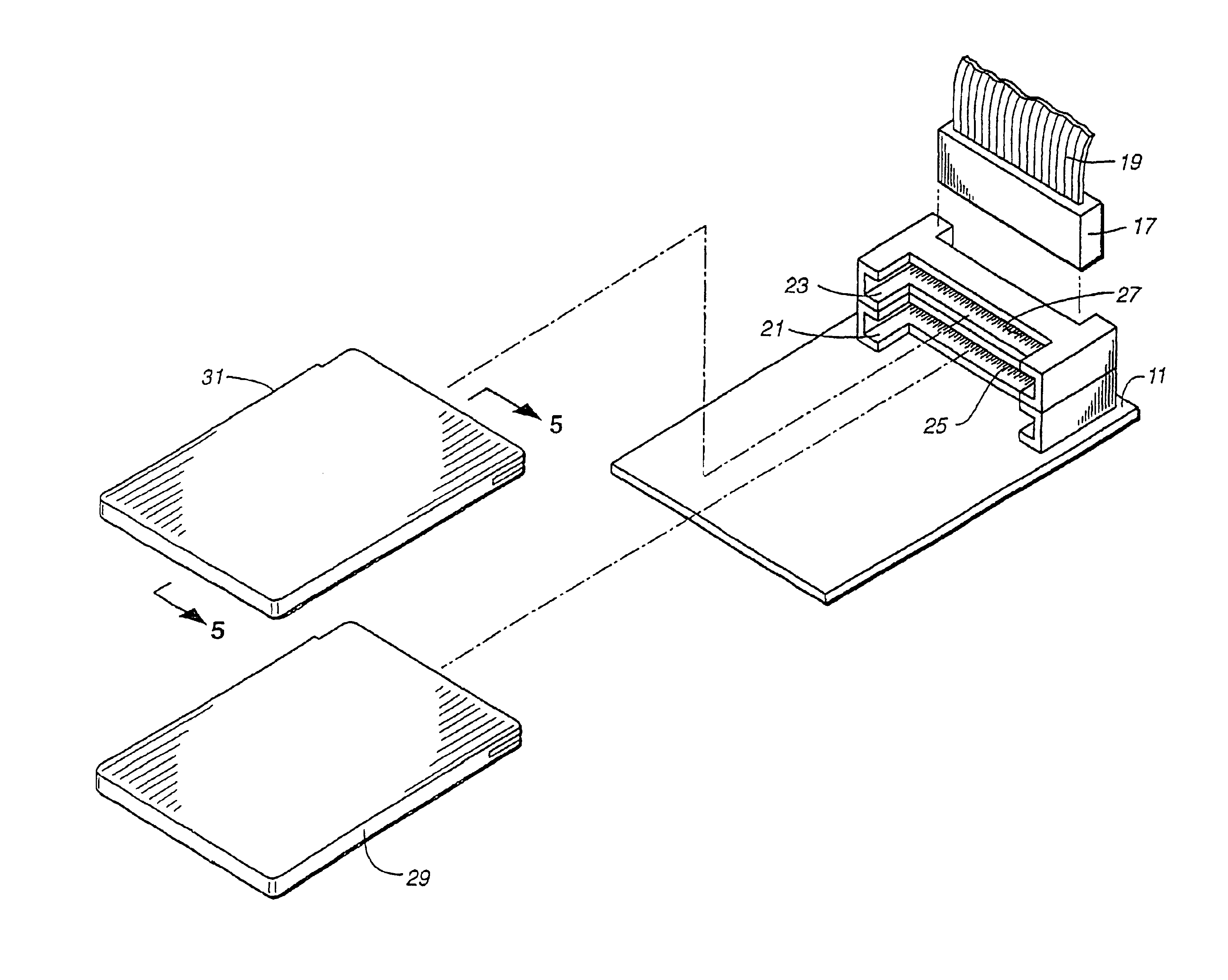
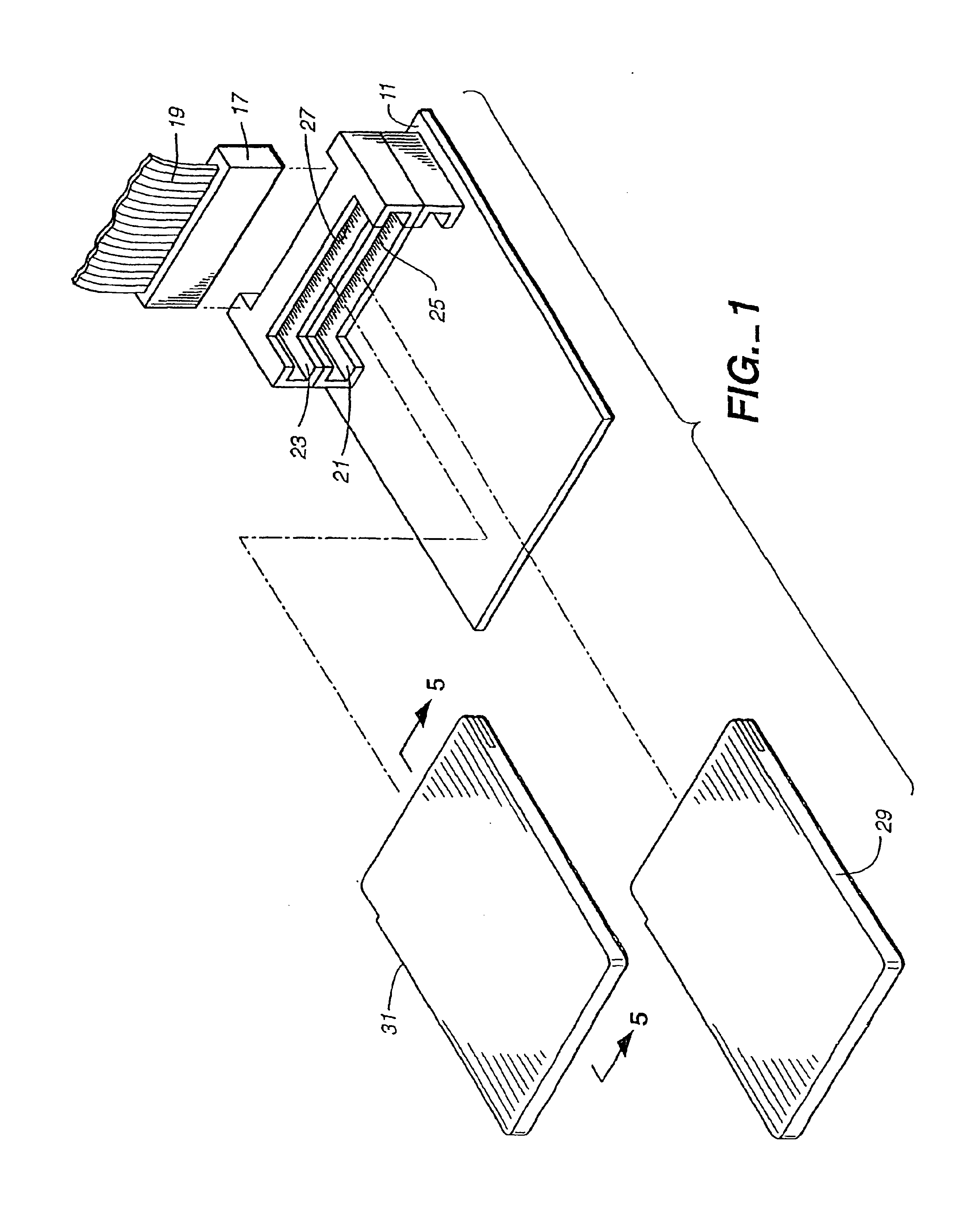
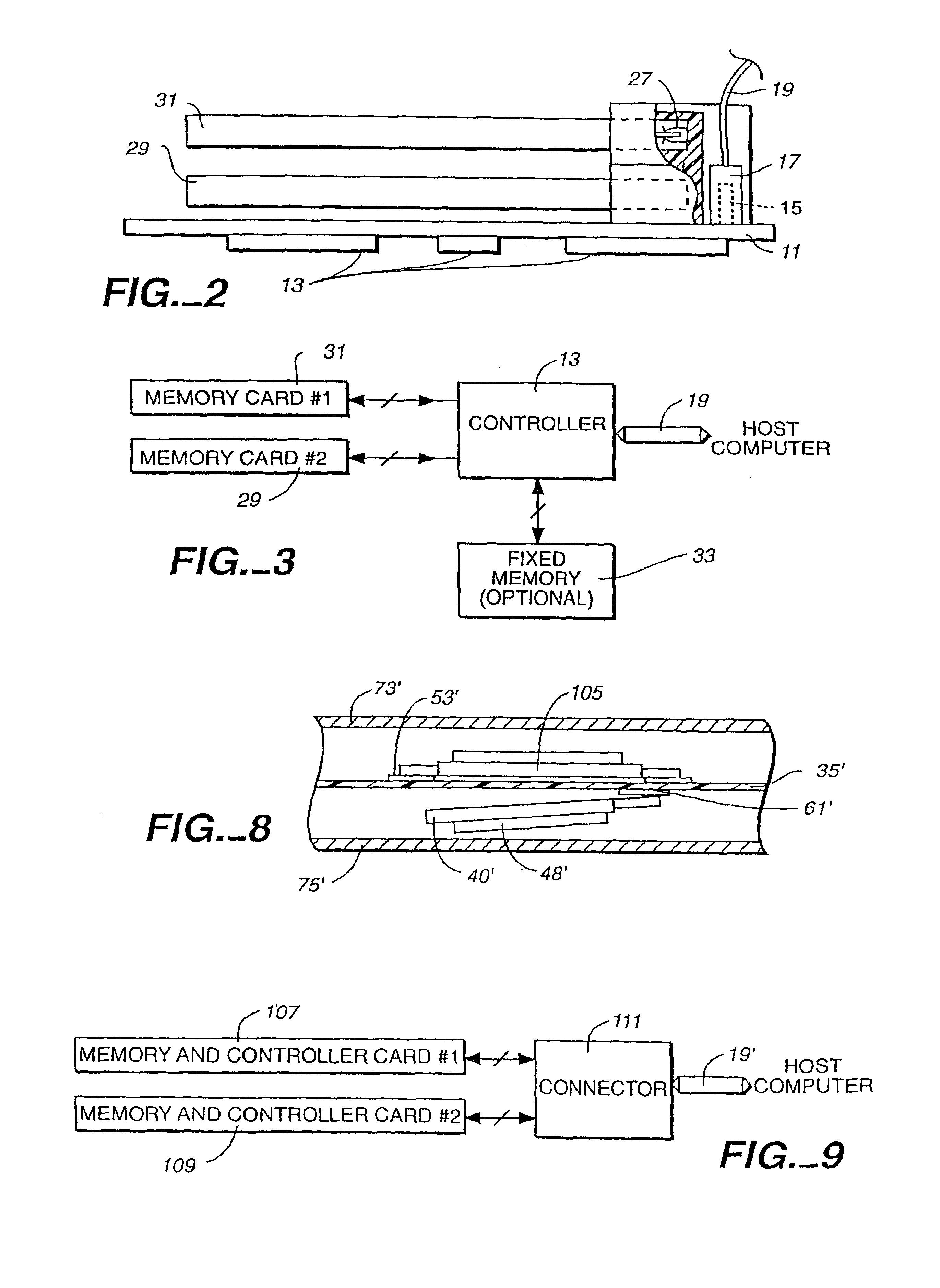
Computer memory cards using flash EEPROM integrated circuit chips and memory-controller systems
InactiveUS6947332B2Easy to useInput/output to record carriersPrinted circuit aspectsElectronic systemsComputerized system
A very small computer memory card is densely packed with a large number of flash EEPROM integrated circuit chips. A computer memory system provides for the ability to removably connect one or more of such cards with a common controller circuit that interfaces between the memory cards and a standard computer system bus. Alternately, each card can be provided with the necessary controller circuitry and thus is connectable directly to the computer system bus. An electronic system is described for a memory system and its controller within a single memory card. In a preferred physical arrangement, the cards utilize a main circuit board with a plurality of sub-boards attached thereto on both sides, each sub-board carrying several integrated circuit chips.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Highly compact EPROM and flash EEPROM devices
Structures, methods of manufacturing and methods of use of electrically programmable read only memories (EPROM) and flash electrically erasable and programmable read only memories (EEPROM) include split channel and other cell configurations. An arrangement of elements and cooperative processes of manufacture provide self-alignment of the elements. An intelligent programming technique allows each memory cell to store more than the usual one bit of information. An intelligent erase algorithm prolongs the useful life of the memory cells. Use of these various features provides a memory having a very high storage density and a long life, making it particularly useful as a solid state memory in place of magnetic disk storage devices in computer systems.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
NAND type flash EEPROM in which sequential programming process is performed by using different intermediate voltages
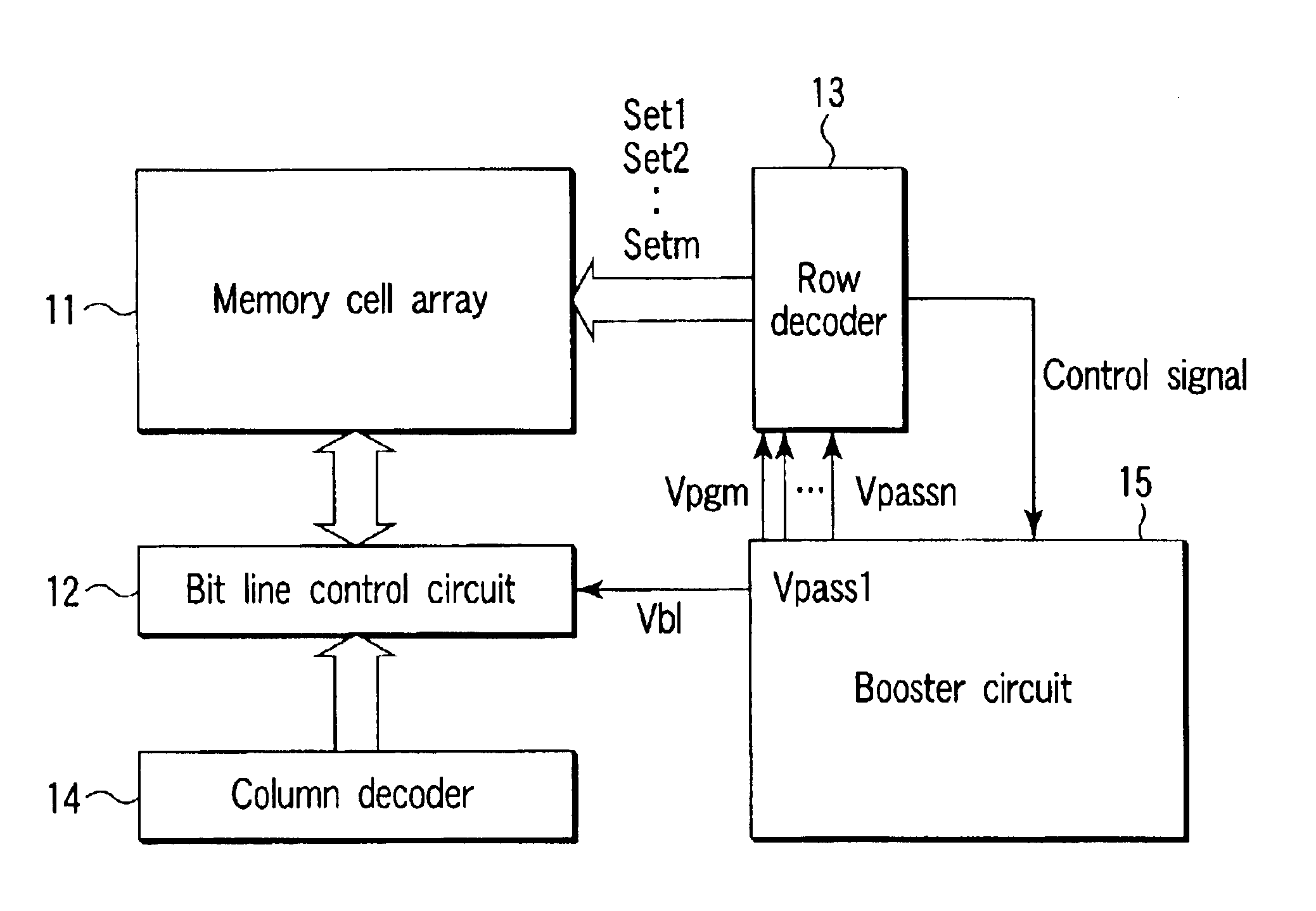
A nonvolatile semiconductor memory device includes a NAND memory cell array, booster circuit, row decoder, bit line control circuit and column decoder. In the device, the magnitude of intermediate voltage applied to the control gates of memory transistors from the booster circuit via the row decoder is changed according to the position of a selected control gate line when data is sequentially programmed into the memory transistors in the memory cell array. Alternatively, a plurality of different intermediate voltages are applied when data is simultaneously programmed into memory transistors connected to the selected control gate line.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Scheduling of housekeeping operations in flash memory systems
ActiveUS7315917B2Memory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesSystems managementNon-volatile memory
A re-programmable non-volatile memory system, such as a flash EEPROM system, having its memory cells grouped into blocks of cells that are simultaneously erasable is operated to perform memory system housekeeping operations in the foreground during execution of a host command, wherein the housekeeping operations are unrelated to execution of the host command. Both one or more such housekeeping operations and execution of the host command are performed within a time budget established for executing that particular command. One such command is to write data being received to the memory. One such housekeeping operation is to level out the wear of the individual blocks that accumulates through repetitive erasing and re-programming.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com