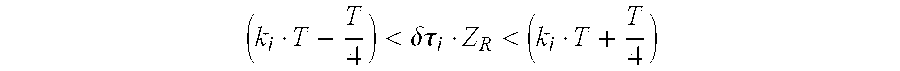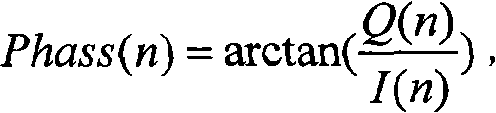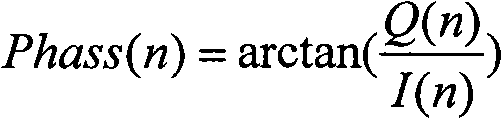Patents
Literature
228 results about "Bit time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
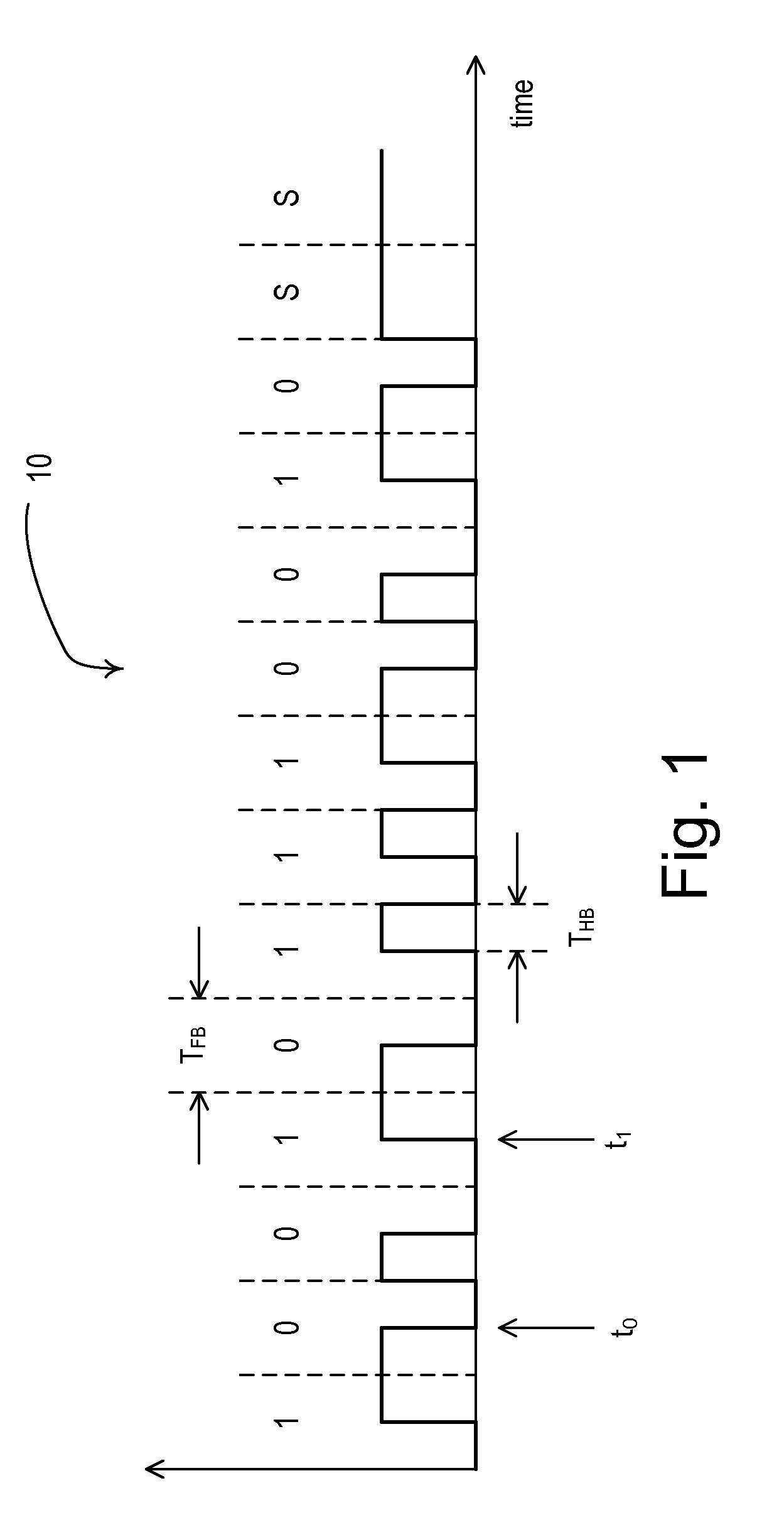
Bit time is a concept in computer networking. It is defined as the time it takes for one bit to be ejected from a Network Interface Card (NIC) operating at some predefined standard speed, such as 10 Mbit/s. The time is measured between the time the logical link control layer 2 sublayer receives the instruction from the operating system until the bit actually leaves the NIC. The bit time has nothing to do with the time it takes for a bit to travel on the network medium, but has to do with the internals of the NIC.
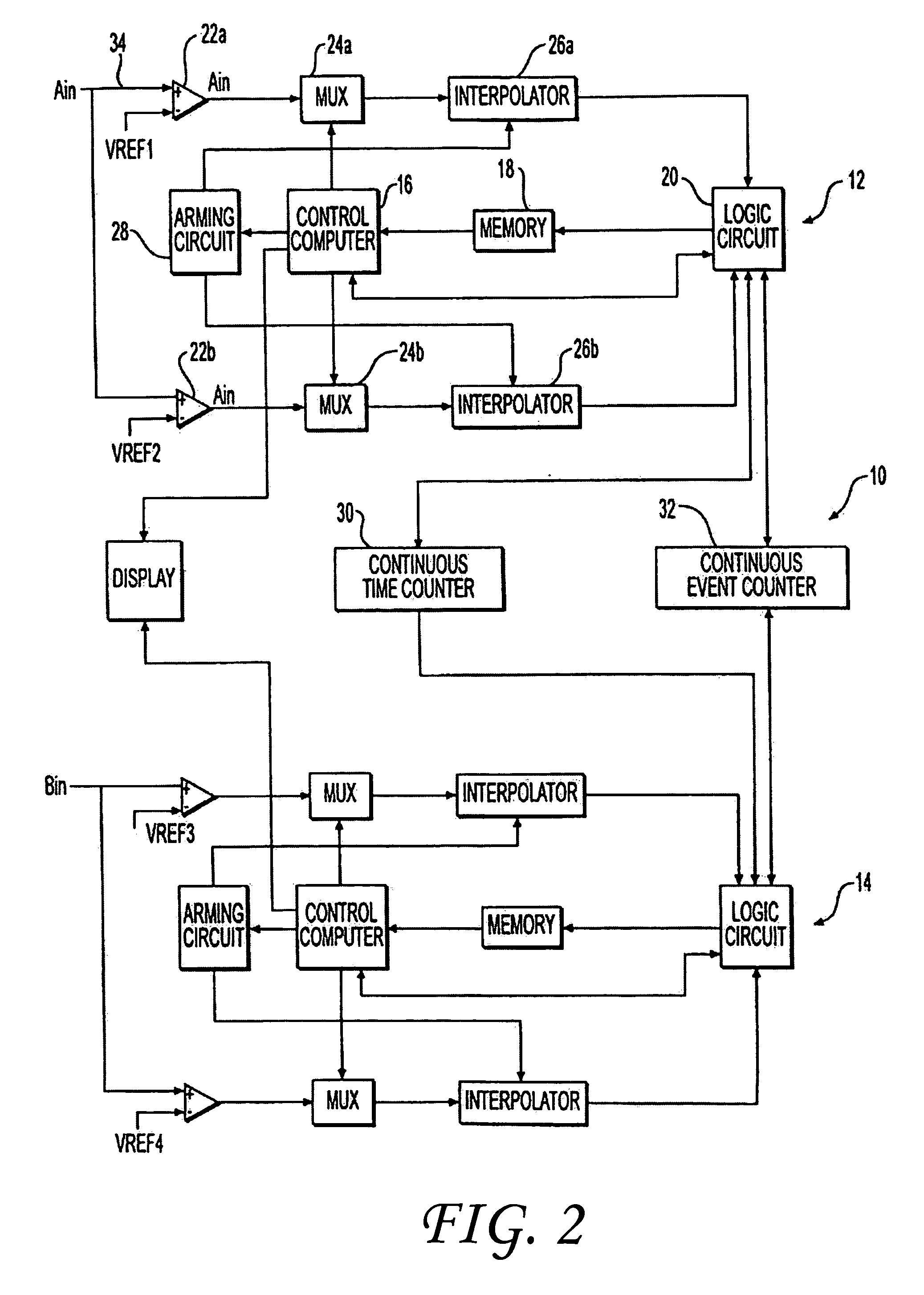
Spare block management of non-volatile memories
ActiveUS8040744B2Memory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesBit timeNon-volatile memory
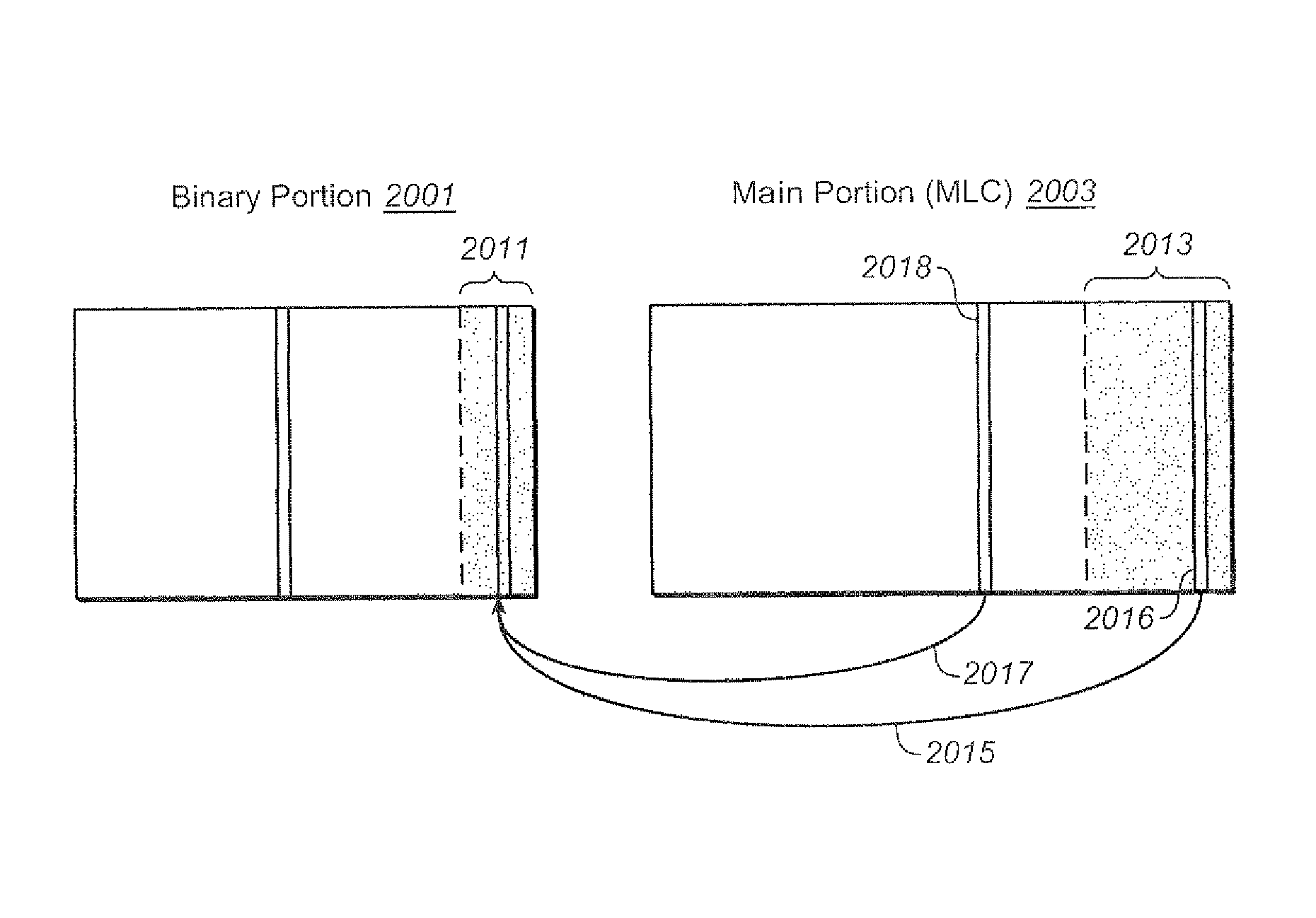
Techniques for the management of spare blocks in re-programmable non-volatile memory system, such as a flash EEPROM system, are presented. In one set of techniques, for a memory partitioned into two sections (for example a binary section and a multi-state section), where blocks of one section are more prone to error, spare blocks can be transferred from the more error prone partition to the less error prone partition. In another set of techniques for a memory partitioned into two sections, blocks which fail in the more error prone partition are transferred to serve as spare blocks in the other partition. In a complementary set of techniques, a 1-bit time stamp is maintained for free blocks to determine whether the block has been written recently. Other techniques allow for spare blocks to be managed by way of a logical to physical conversion table by assigning them logical addresses that exceed the logical address space of which a host is aware.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
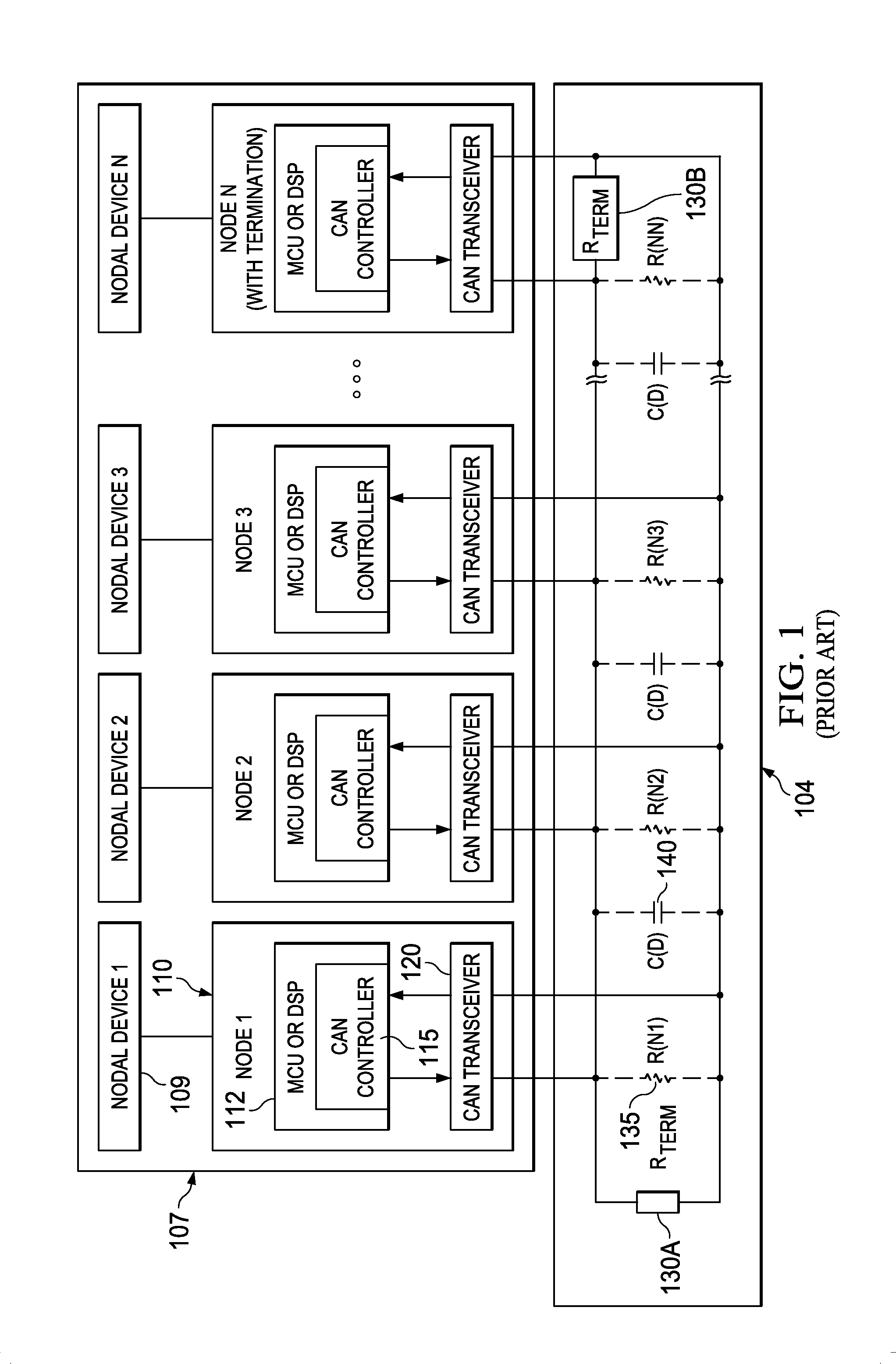
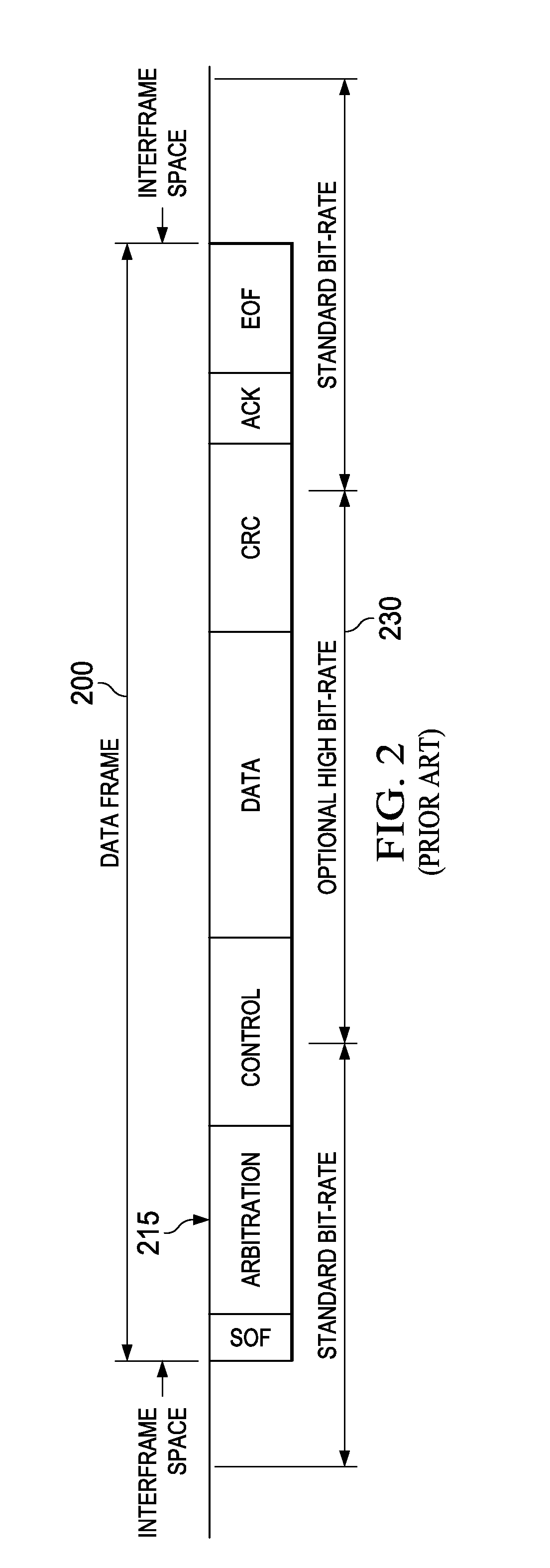
Can bus edge timing control apparatus, systems and methods
ActiveUS20140156893A1Easy dischargeSacrificing integrityData switching networksElectric digital data processingArea networkEngineering
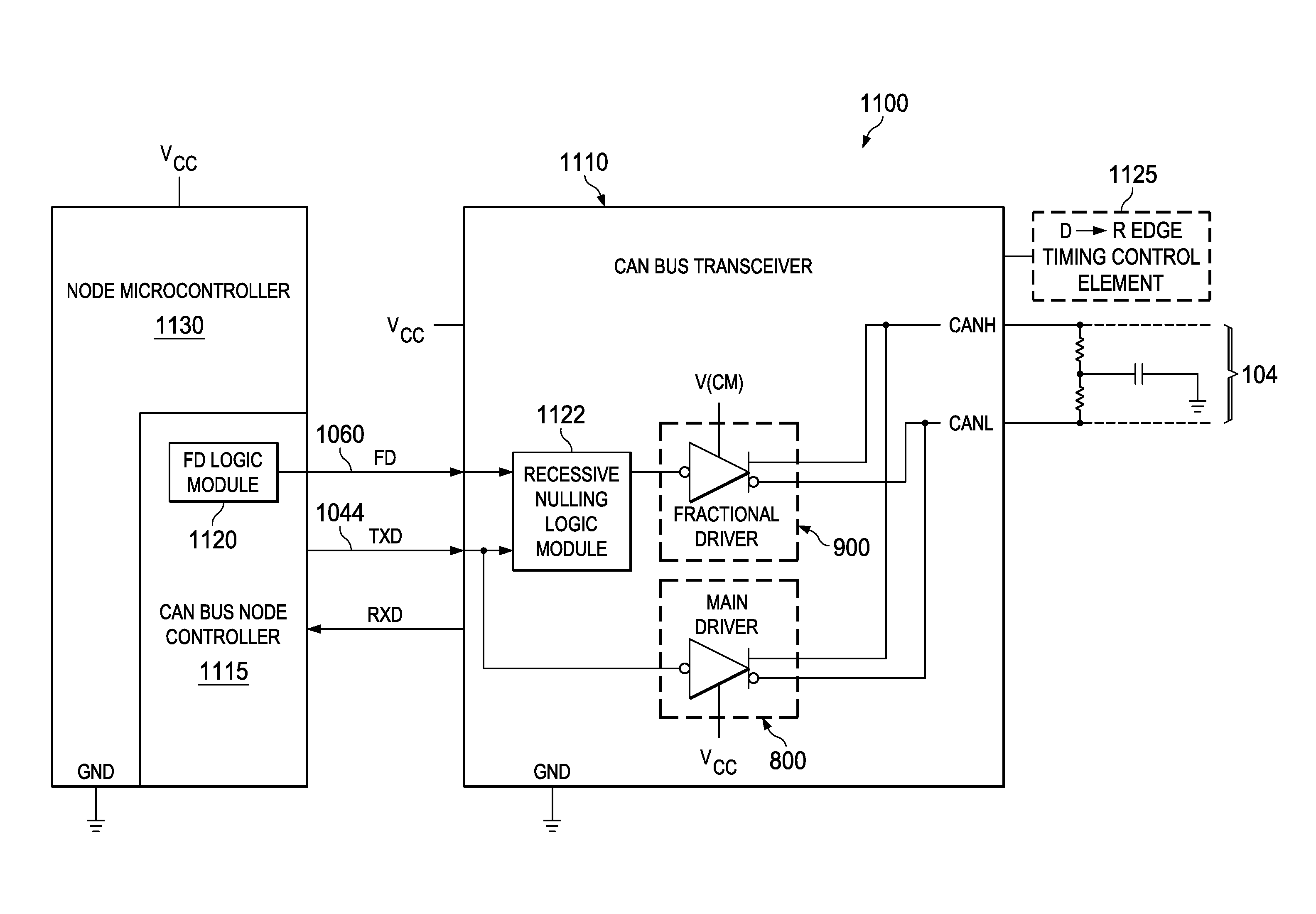
Structures and methods herein insert one or more parallel “recessive nulling” driver impedances across a controller area network (CAN) bus starting at the time of a dominant-to-recessive data bit transition and extending for a selected recessive nulling time period. Doing so increases a rate of decay of a CAN bus dominant-to-recessive differential signal waveform, permits a shortened recessive bit time period, and allows for increased CAN bus bandwidth. Various modes of operation are applicable to various CAN bus node topologies. Recessive nulling may be applied to only the beginning portion of a recessive bit following a dominant bit (“LRN mode”) or to the entire recessive bit time (“HRN mode”). And, some embodiments may apply LRN operations to some recessive CAN frame bits and HRN operations to others.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
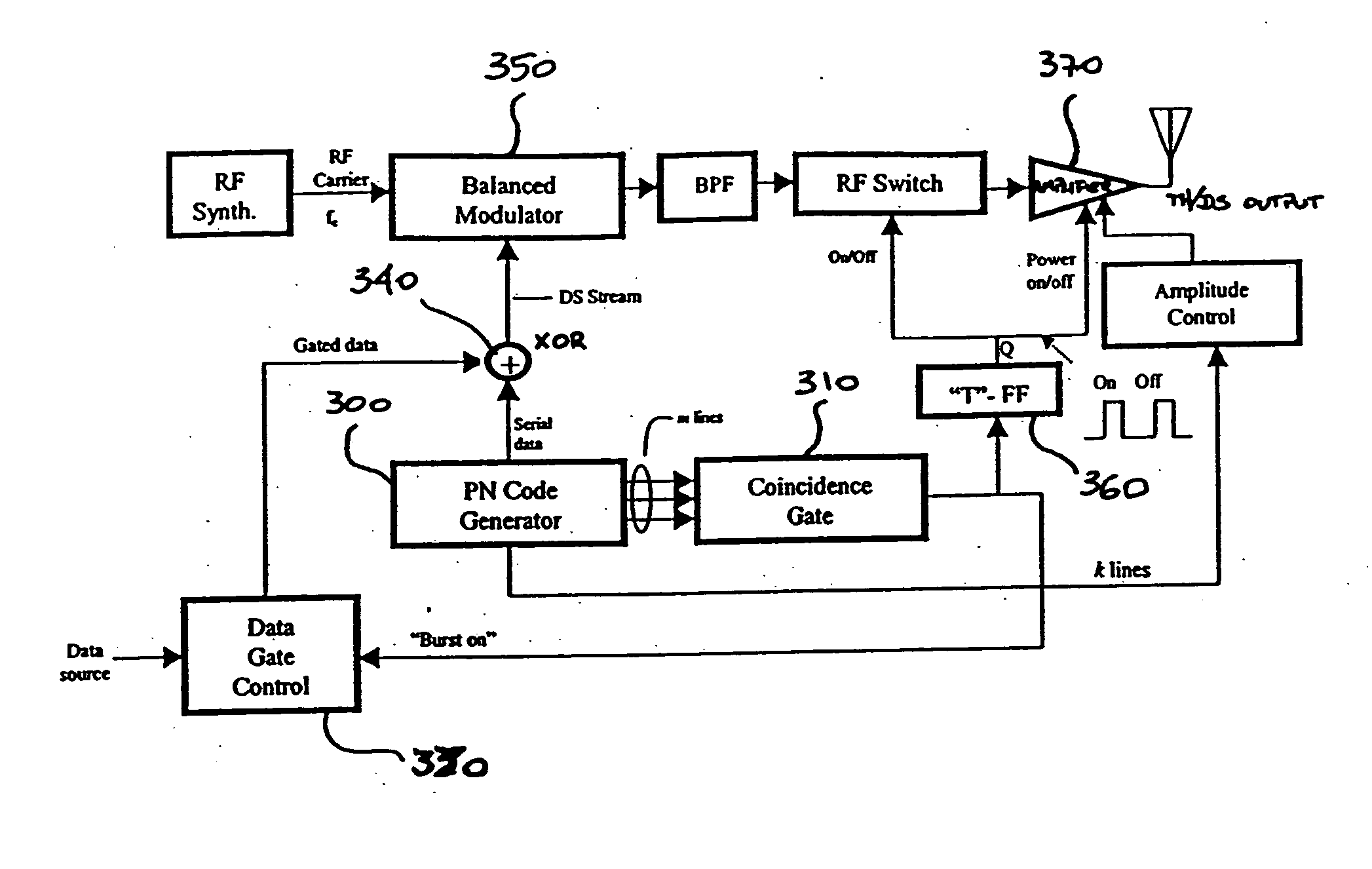
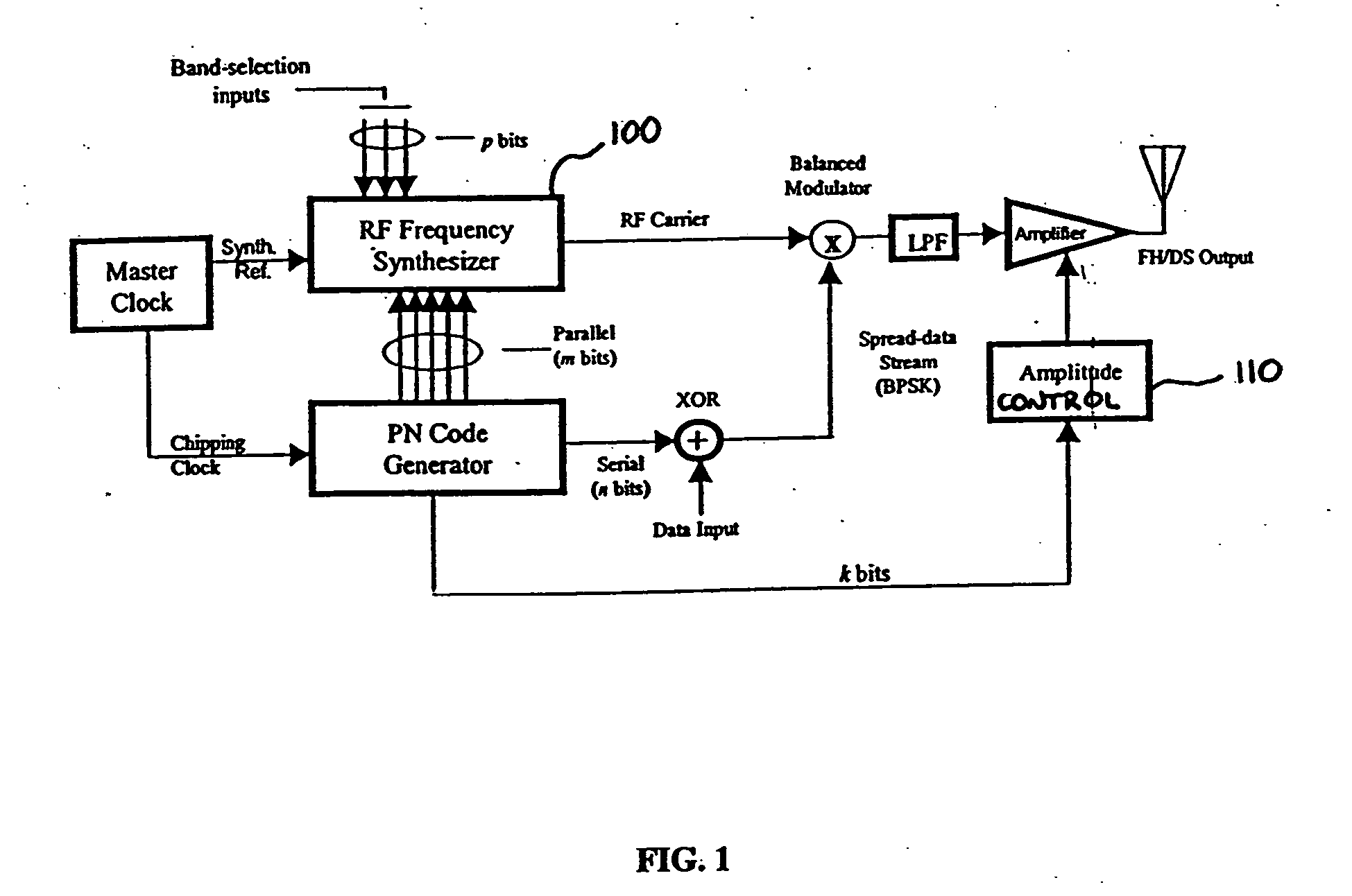
Hybrid spread spectrum radio system
InactiveUS20050141594A1Superior multiple-access performanceGood varietyTransmissionFrequency synthesizerEngineering
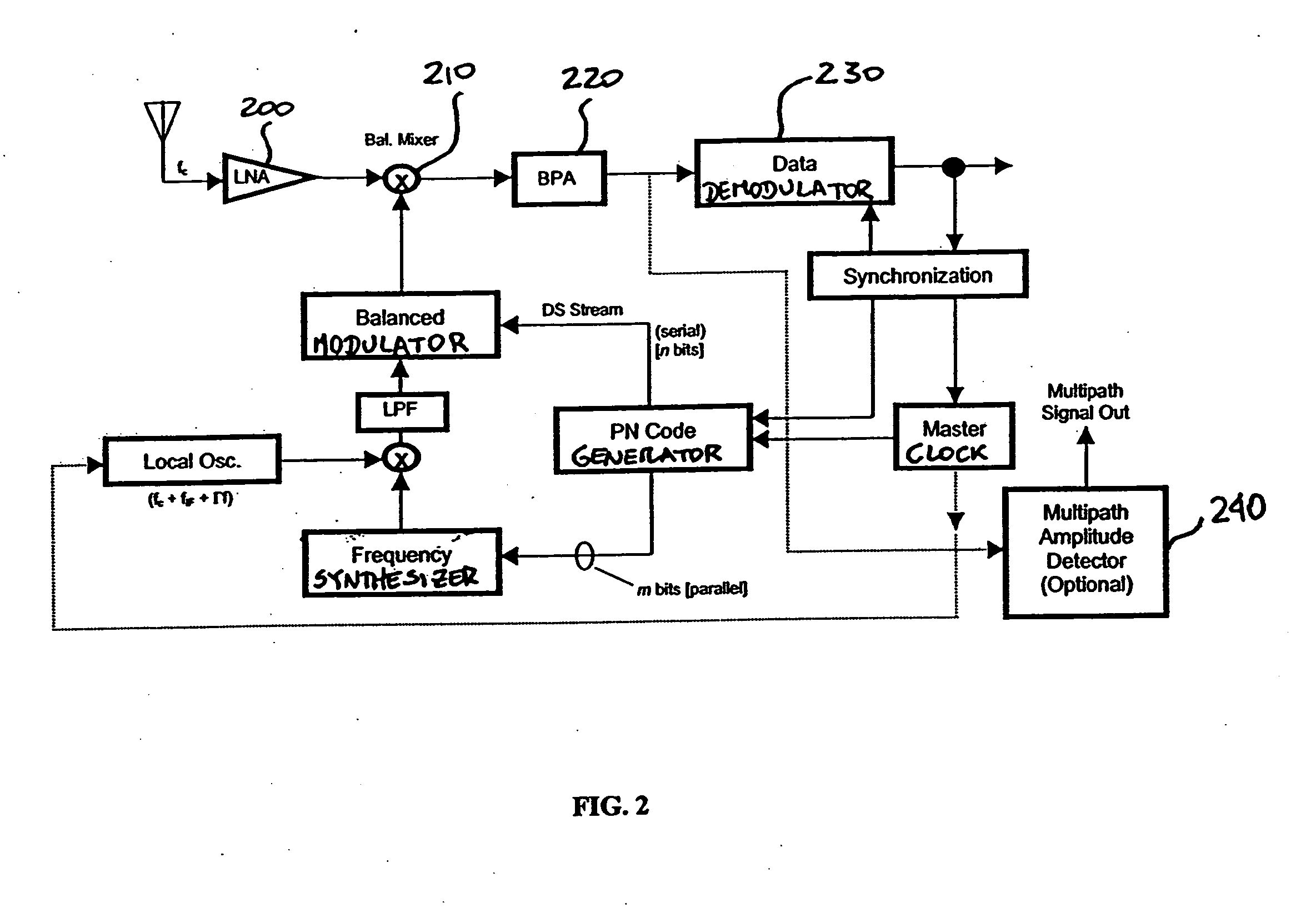
Systems and methods are described for hybrid spread spectrum radio systems. A method includes modulating a signal by utilizing a subset of bits from a pseudo-random code generator to control an amplification circuit that provides a gain to the signal. Another method includes: modulating a signal by utilizing a subset of bits from a pseudo-random code generator to control a fast hopping frequency synthesizer; and fast frequency hopping the signal with the fast hopping frequency synthesizer, wherein multiple frequency hops occur within a single data-bit time.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
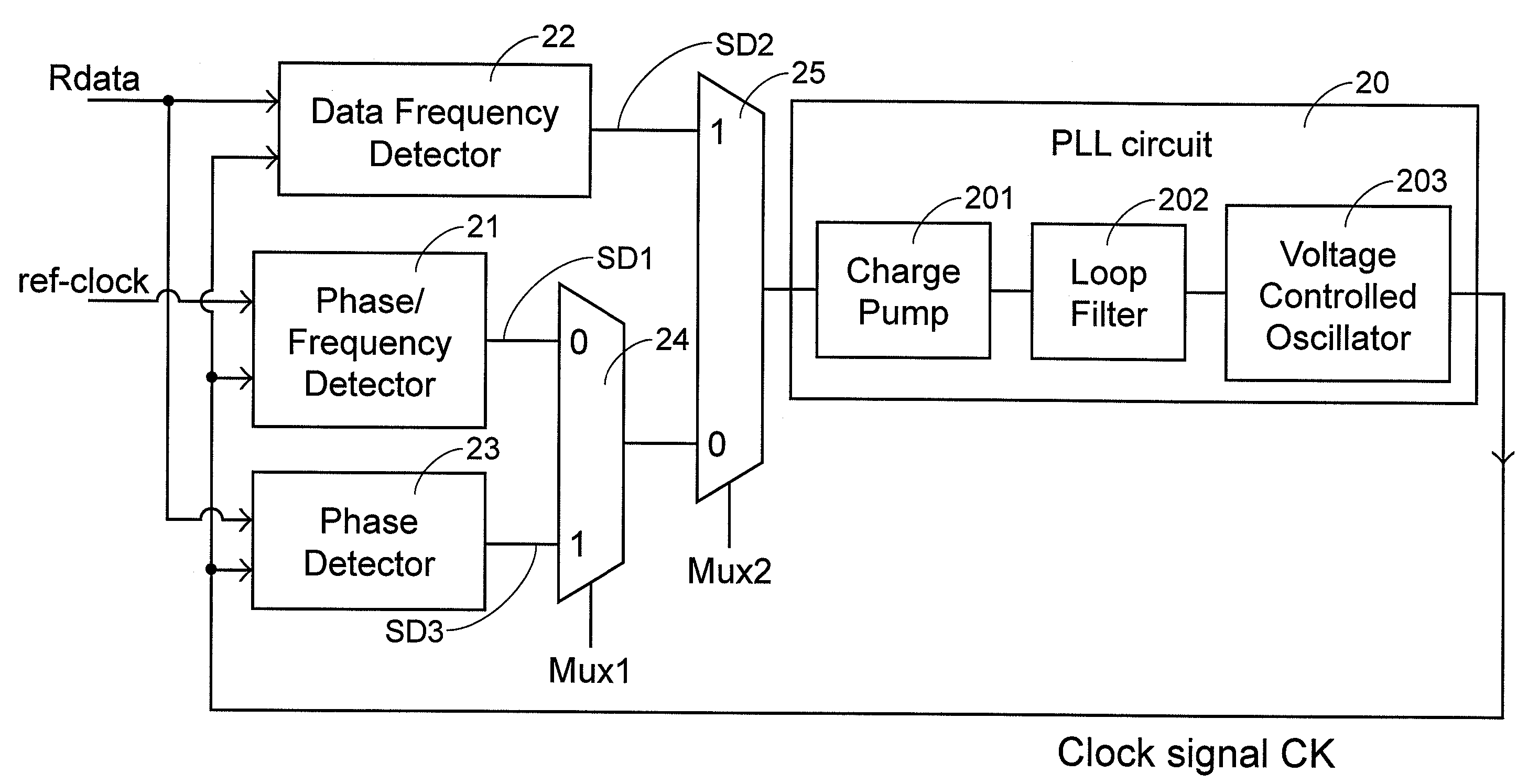
Clock-signal adjusting method and device
ActiveUS20070041485A1Pulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionClock rateWave shape
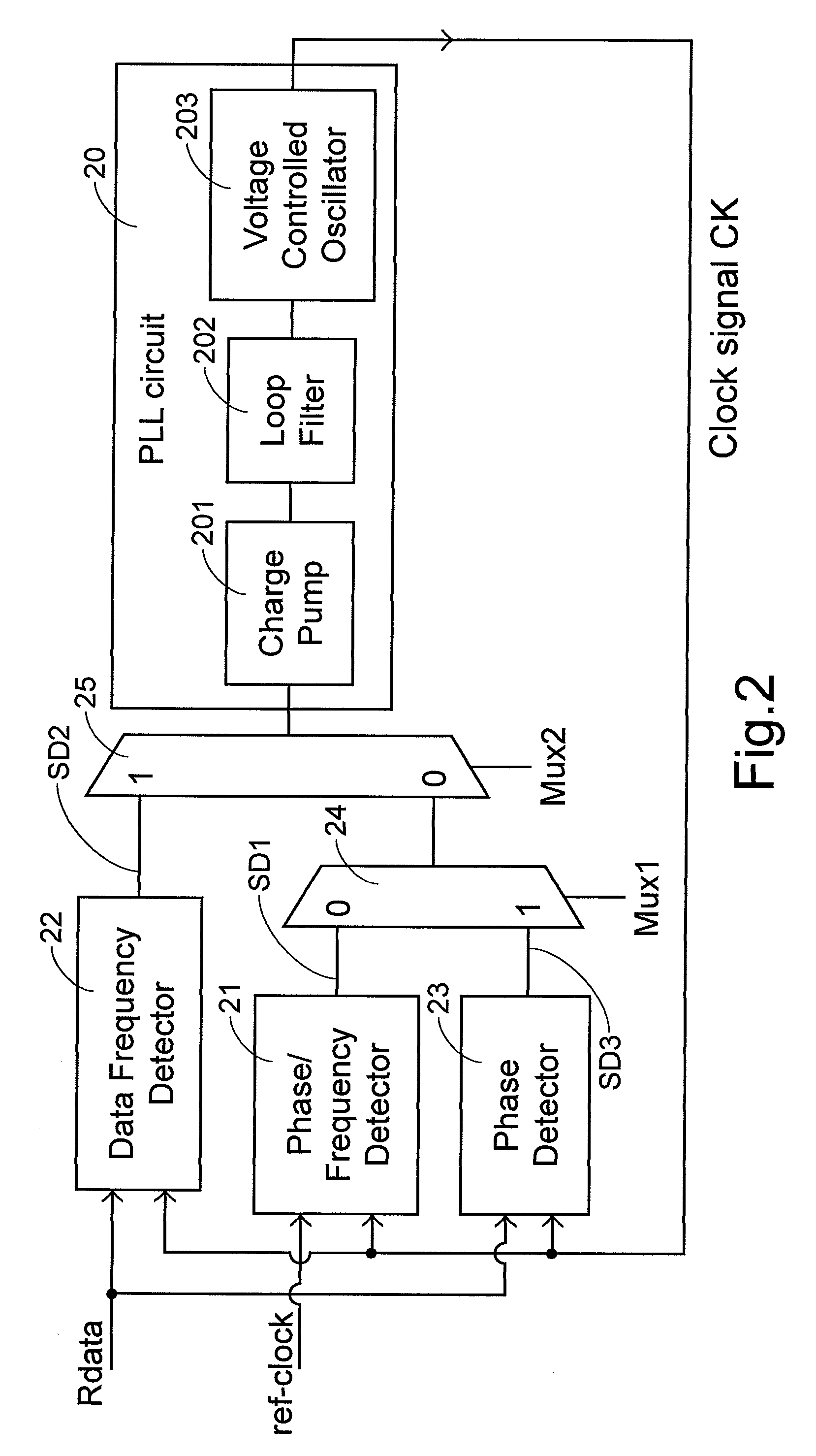
A clock-signal adjusting method and device is used for adjusting a frequency of a clock signal according to a frequency of an input data. The input data is sampled with a sampling frequency m times of the clock frequency to obtain a data transition waveform indicating data transition timing distribution. A unitary bit time of the input data is divided into m zones. A frequency relationship between the clock signal and the input data is determined according to a shift of the data transition waveform relative to the zones. The frequency of the clock signal is adjusted according to the frequency relationship.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
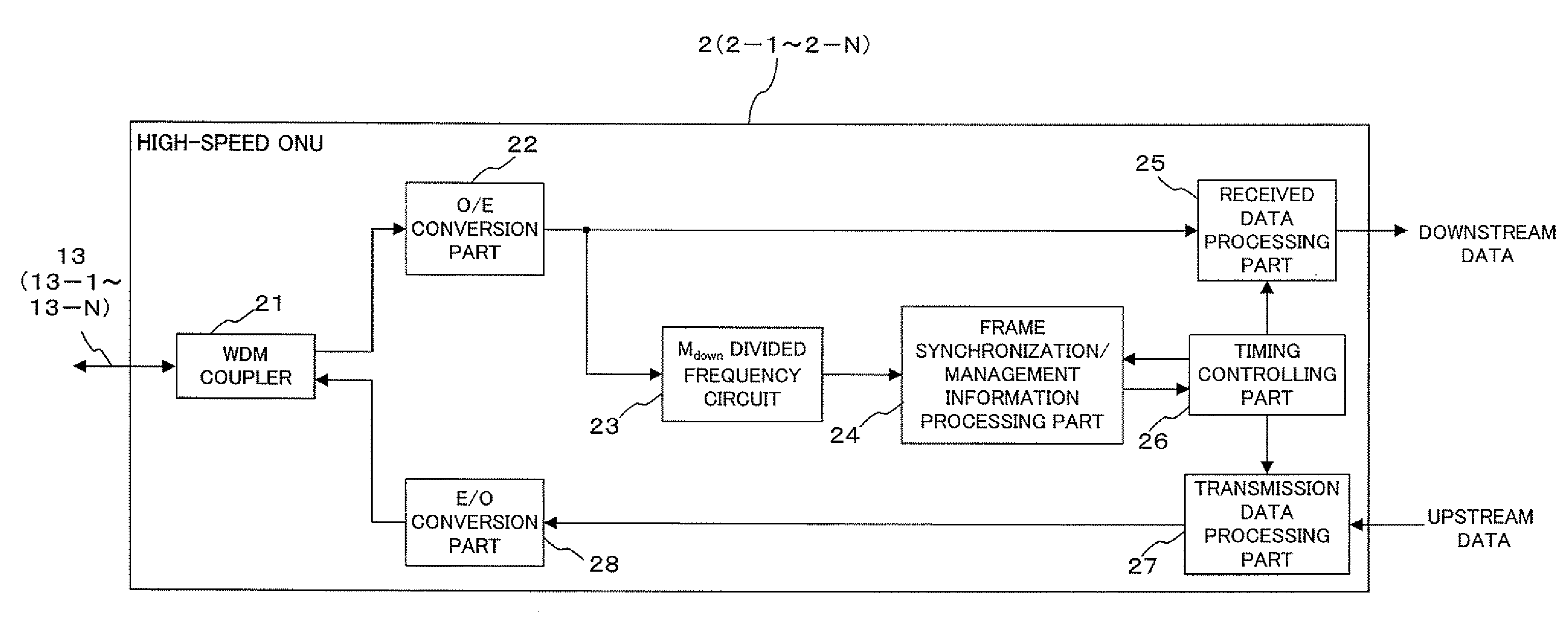
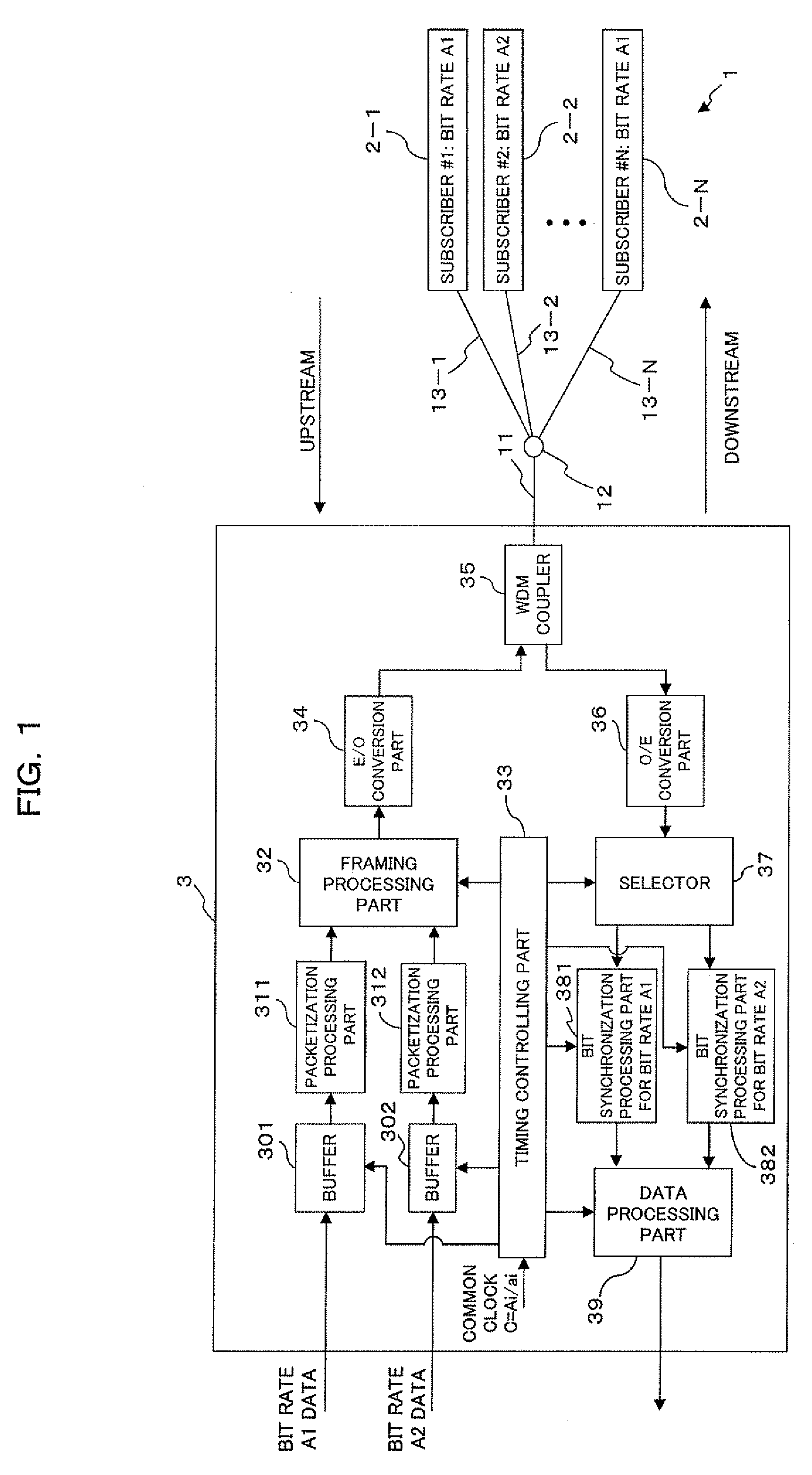
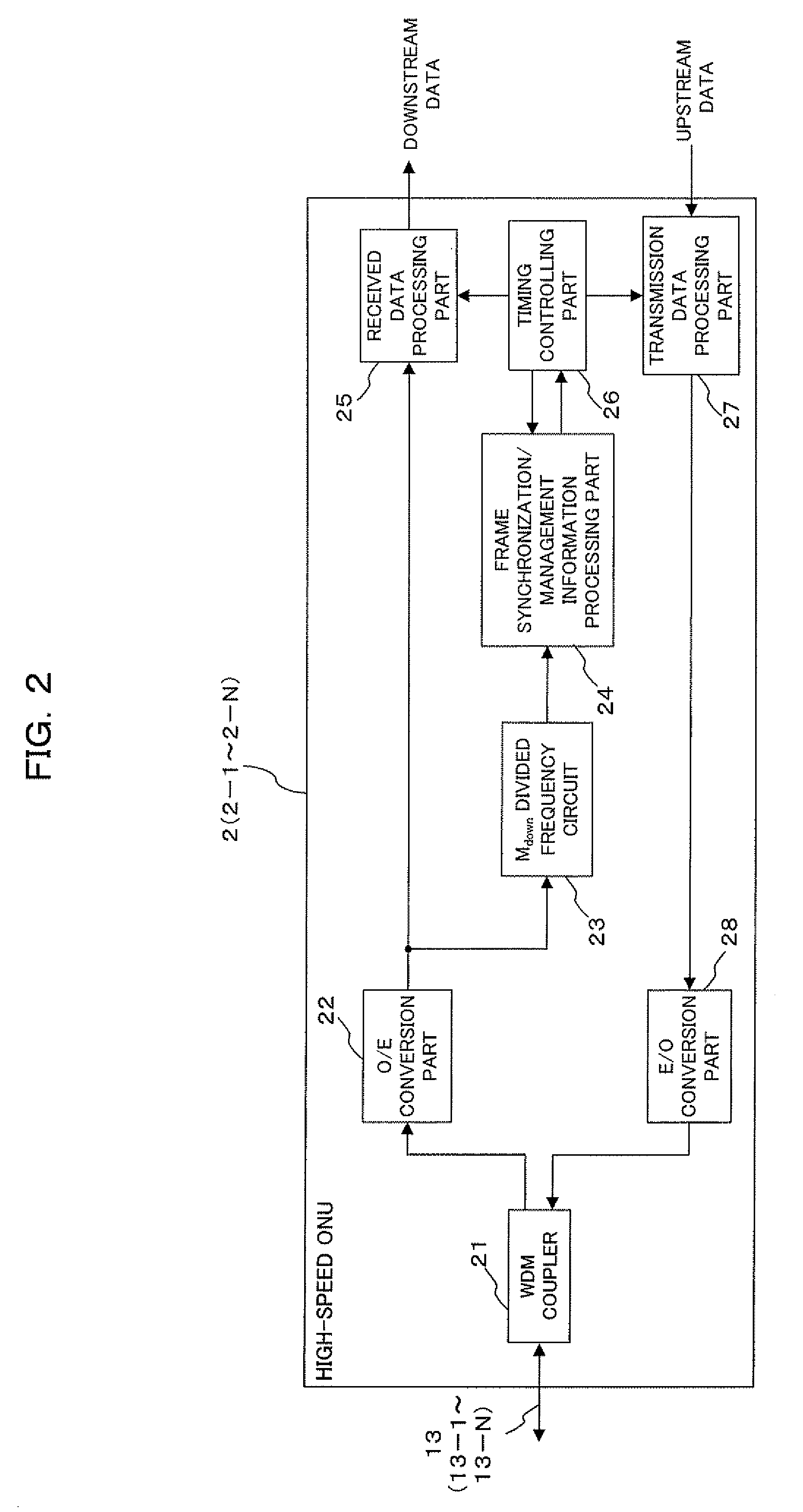
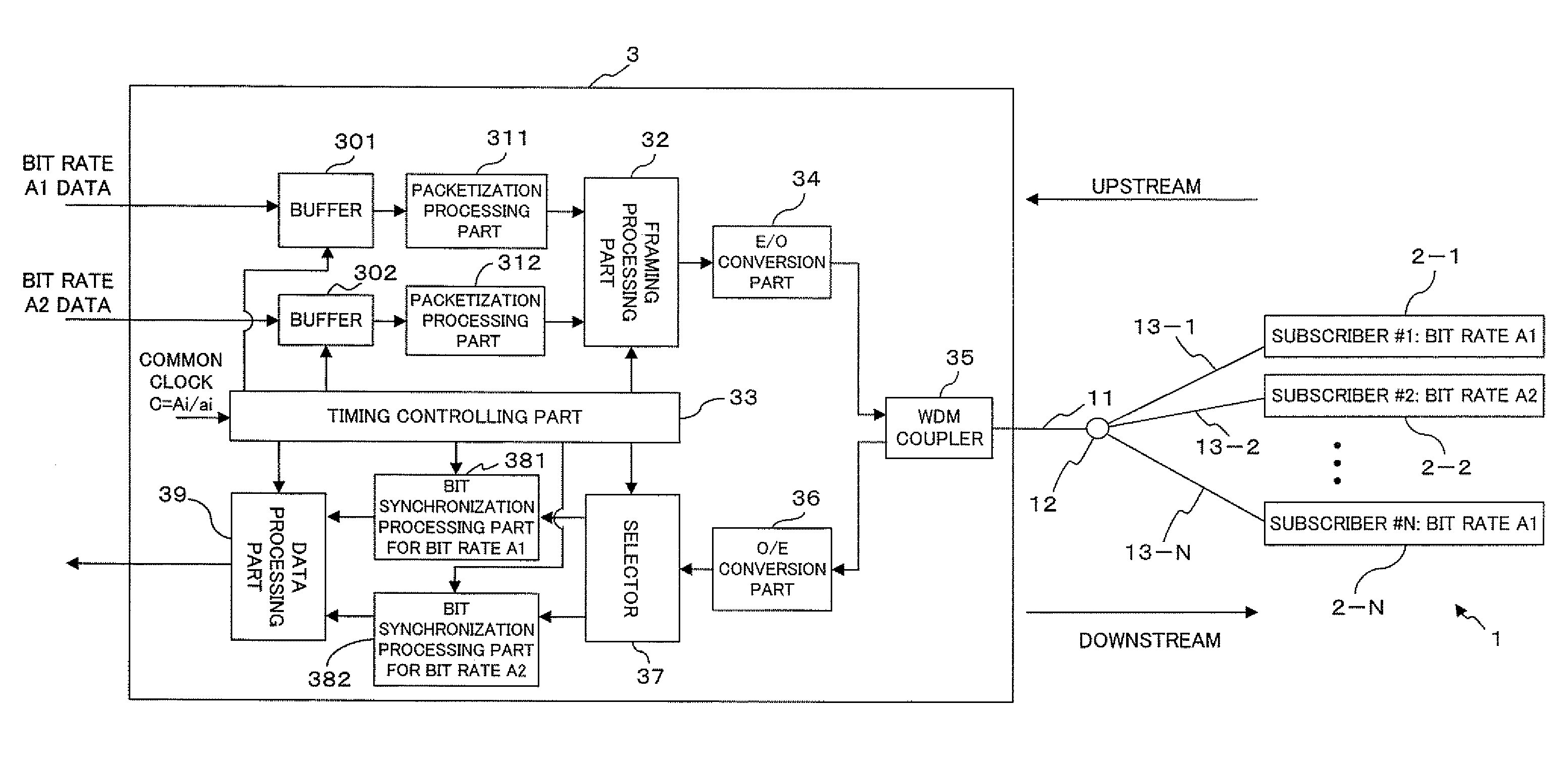
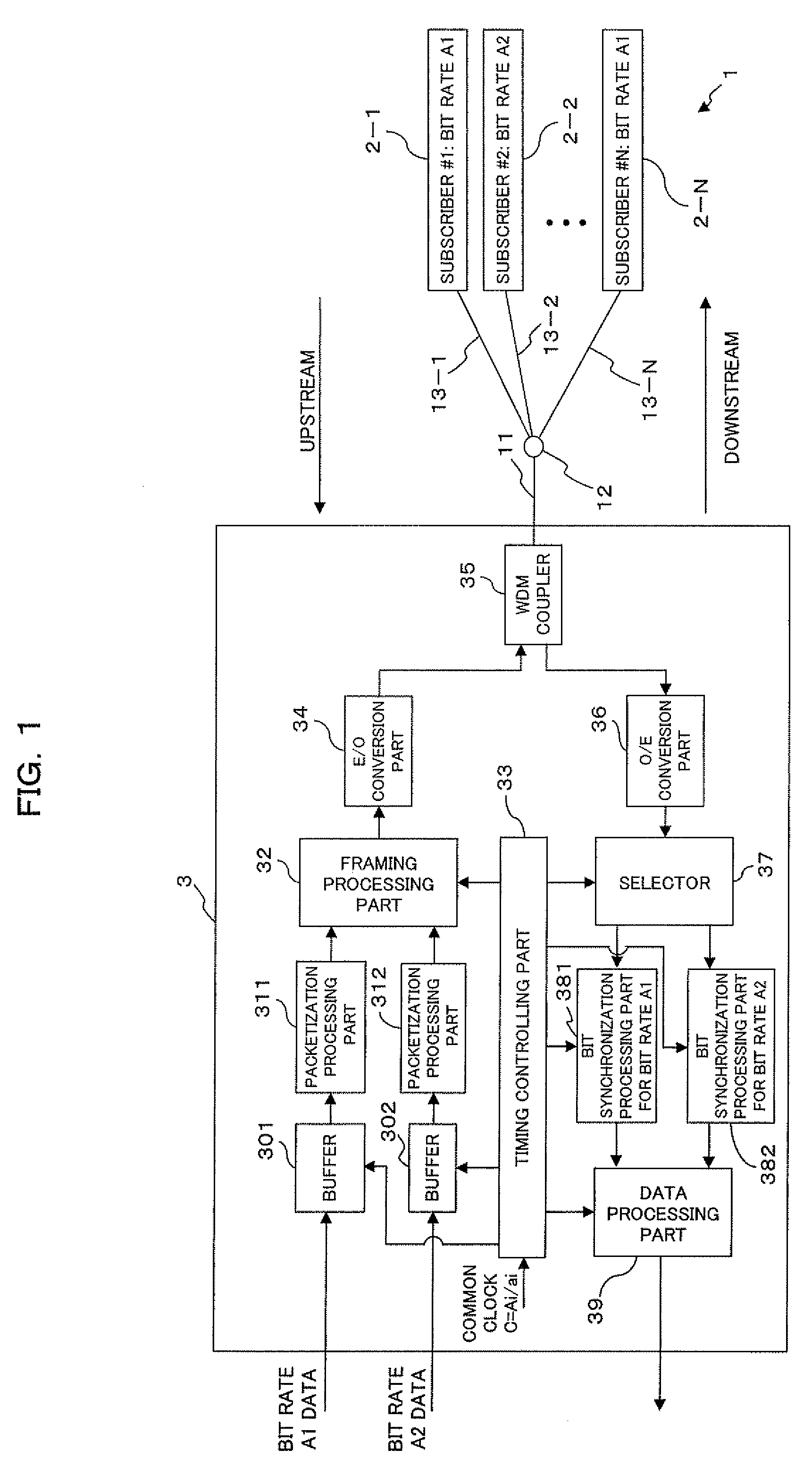
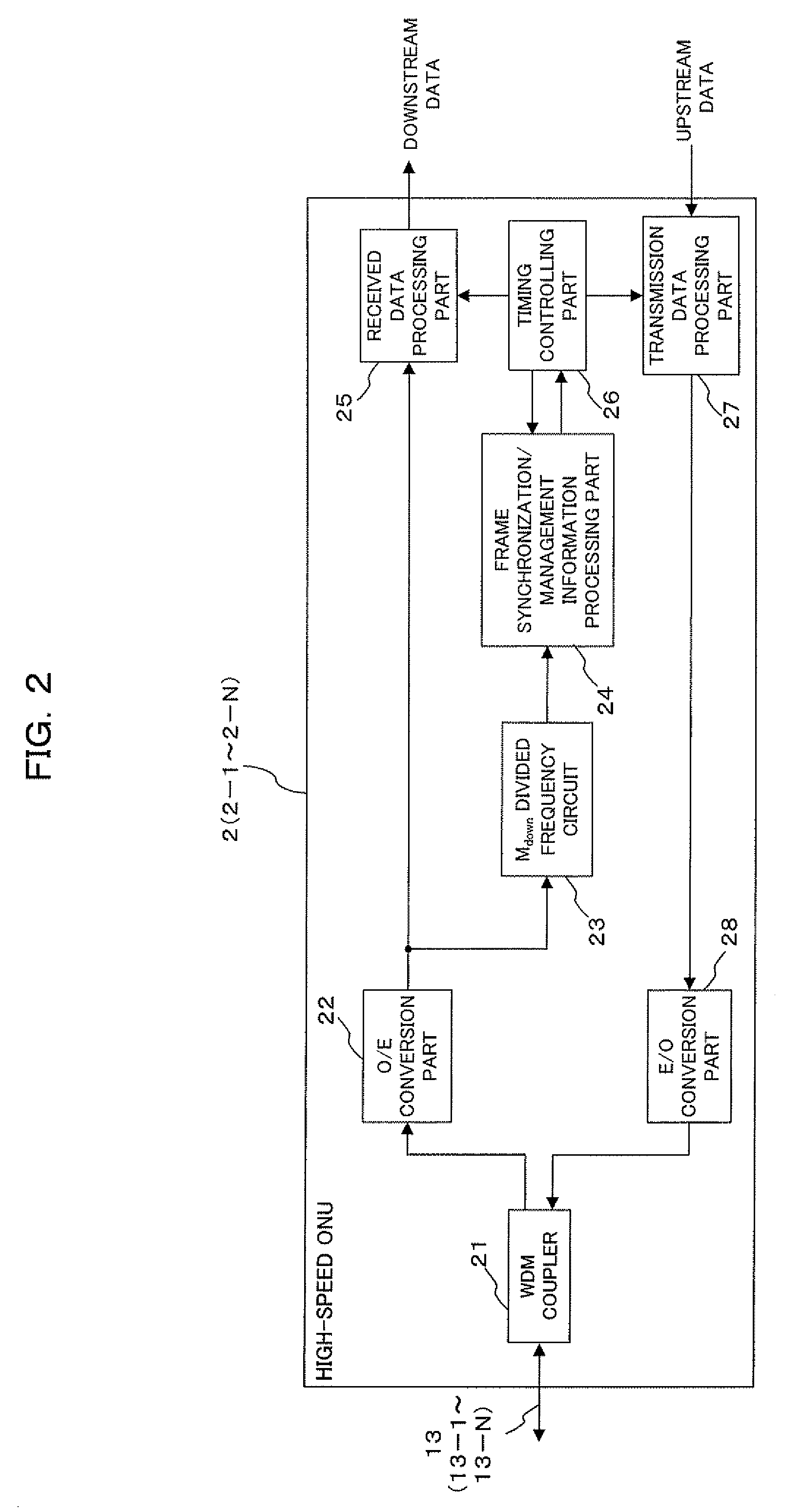
Multiple bit rate optical communication method, optical network unit and optical line terminal
InactiveUS20080056721A1Improve matchReducing cost of manpowerTime-division optical multiplex systemsTime-division multiplexOptical communicationOptical network unit
The present invention is a method of transmitting data of different bit rates in a simple manner and, if positive minimal multiples whose multiple operation values on the bit time lengths 1 / Ai for a plurality of communication bit rates Ai become common are minimal multiples ai respectively, an optical line terminal constitutes a time division multiplex signal composed of a first data area having a bit rate Ai / ai and including frame synchronization information and a second data area in which packets addressed to each optical network unit of the bit rate Ai are time division multiplexed, and transmits the time division multiplex signal to a plurality of optical network units via a branching / multiplexing means.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
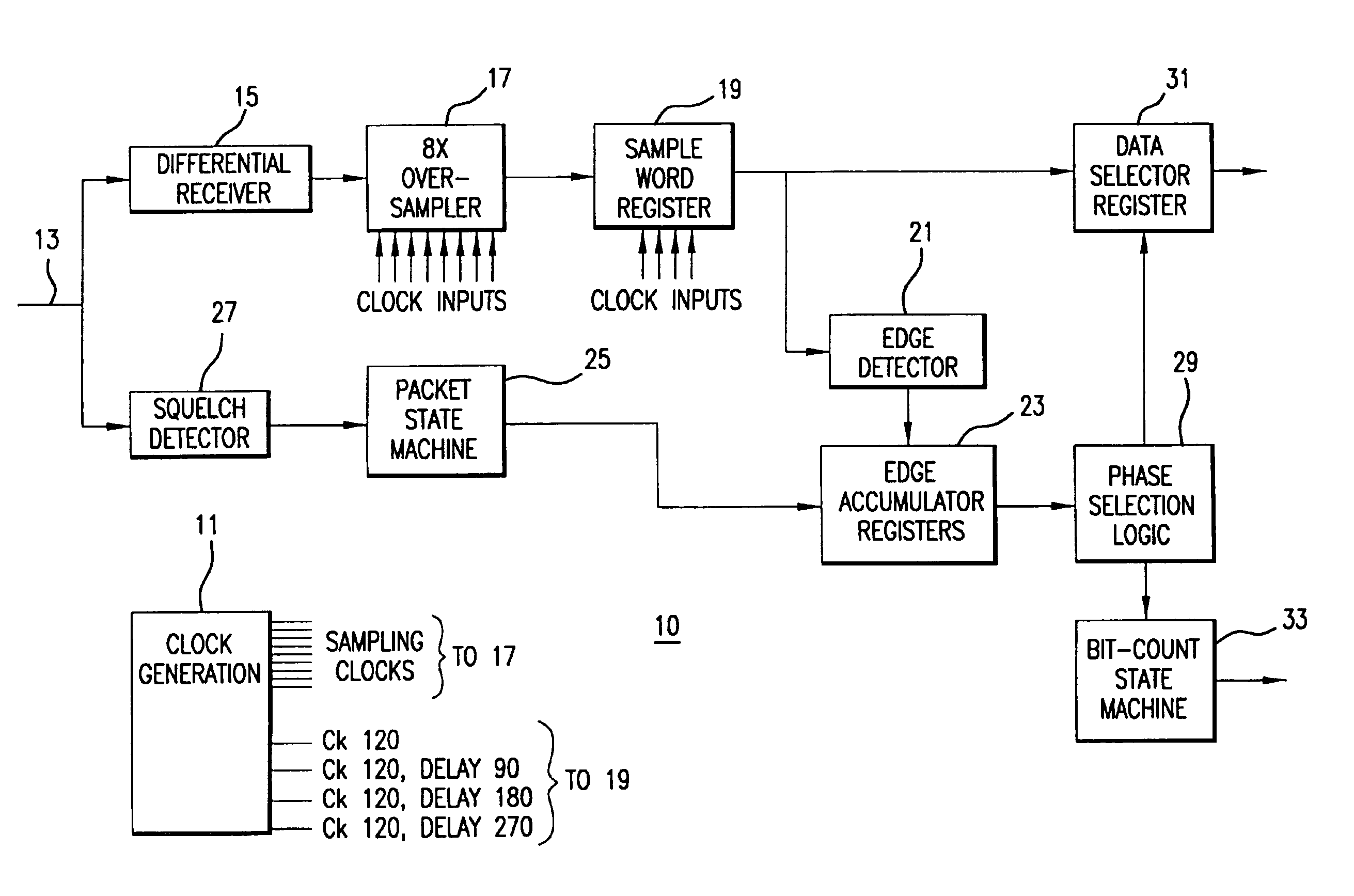
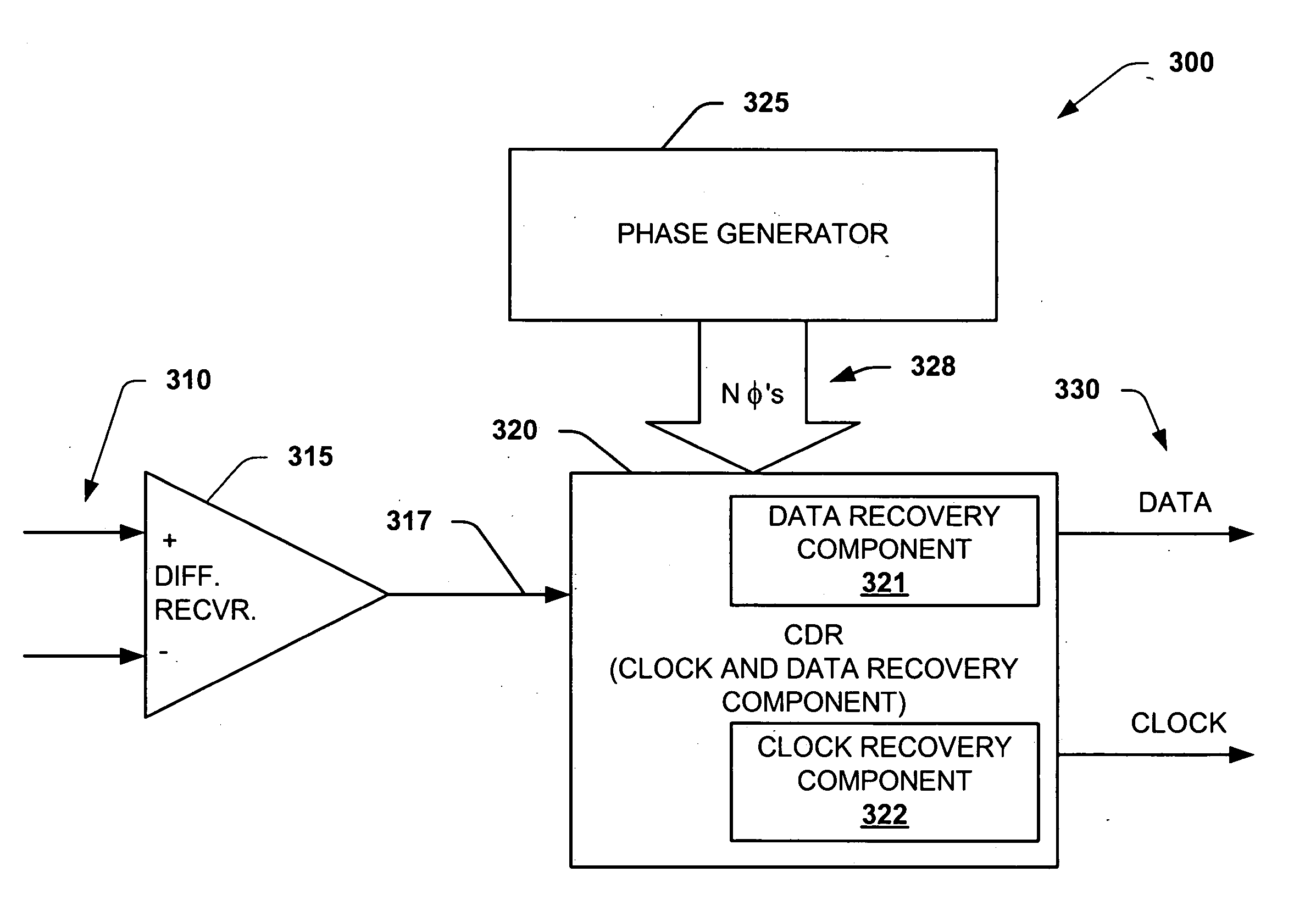
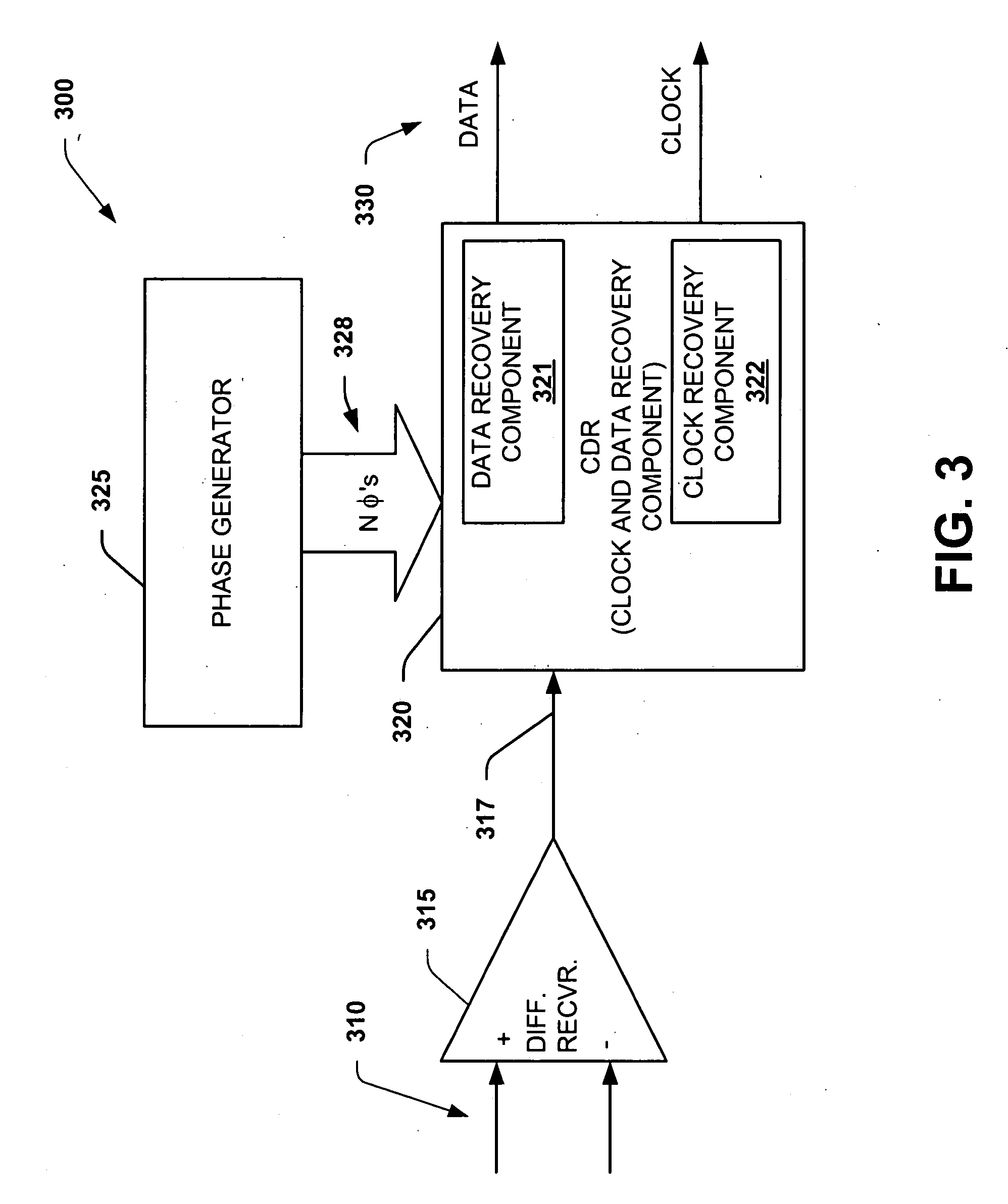
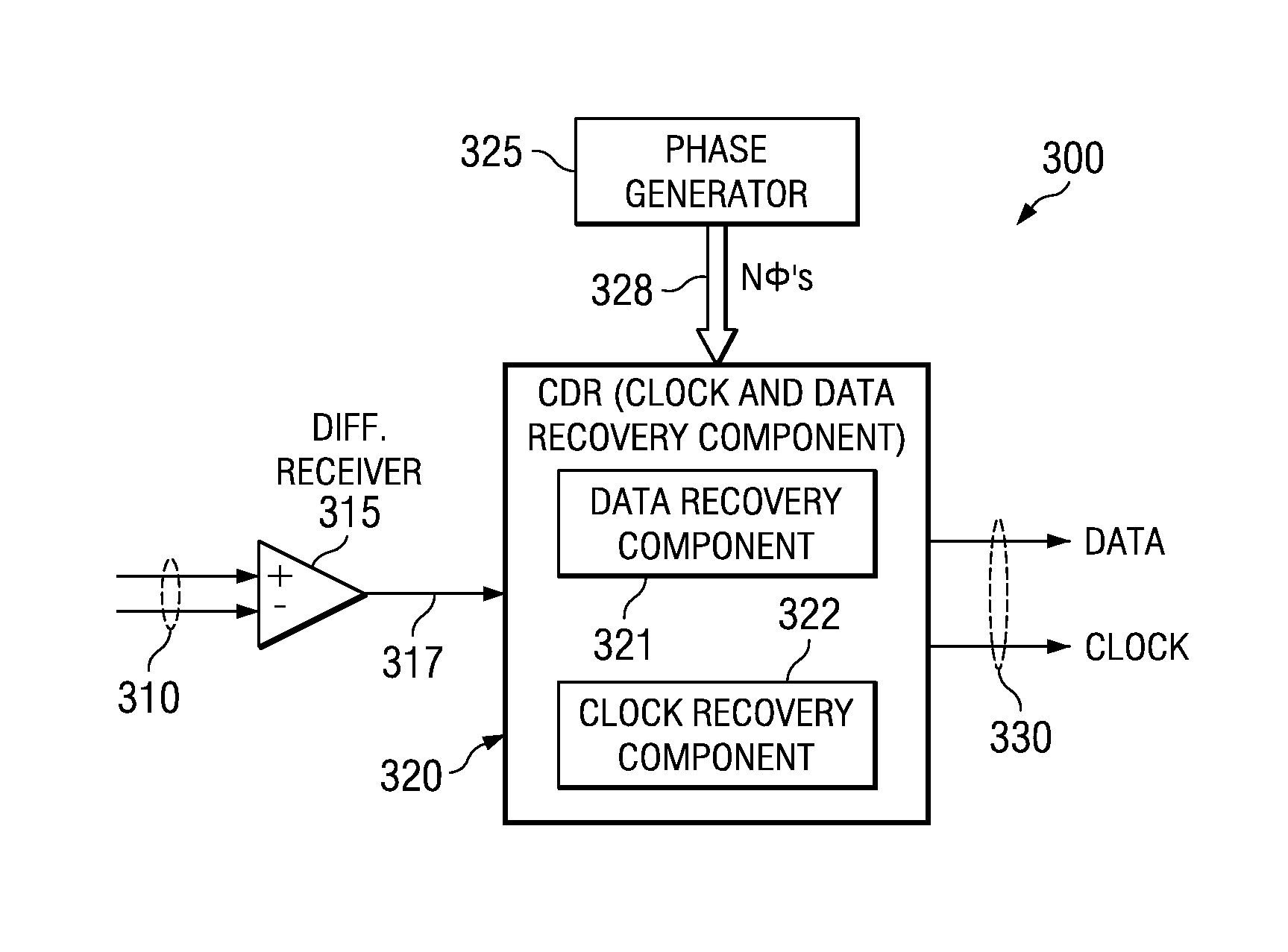
Data recovery method and apparatus
InactiveUS6907096B1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionRecovery methodClock rate
In order to recover phase information, data transmitted at a first frequency is over-sampled using a clock at a second frequency, n times per bit time to obtain n samples. The n samples are used to detect the transitions between two logic levels in said transmitted data which are stored in groups of m sets of said n edge results which are, in turn output at a clock frequency which is the second frequency divided by m, for further processing.
Owner:INTEL CORP
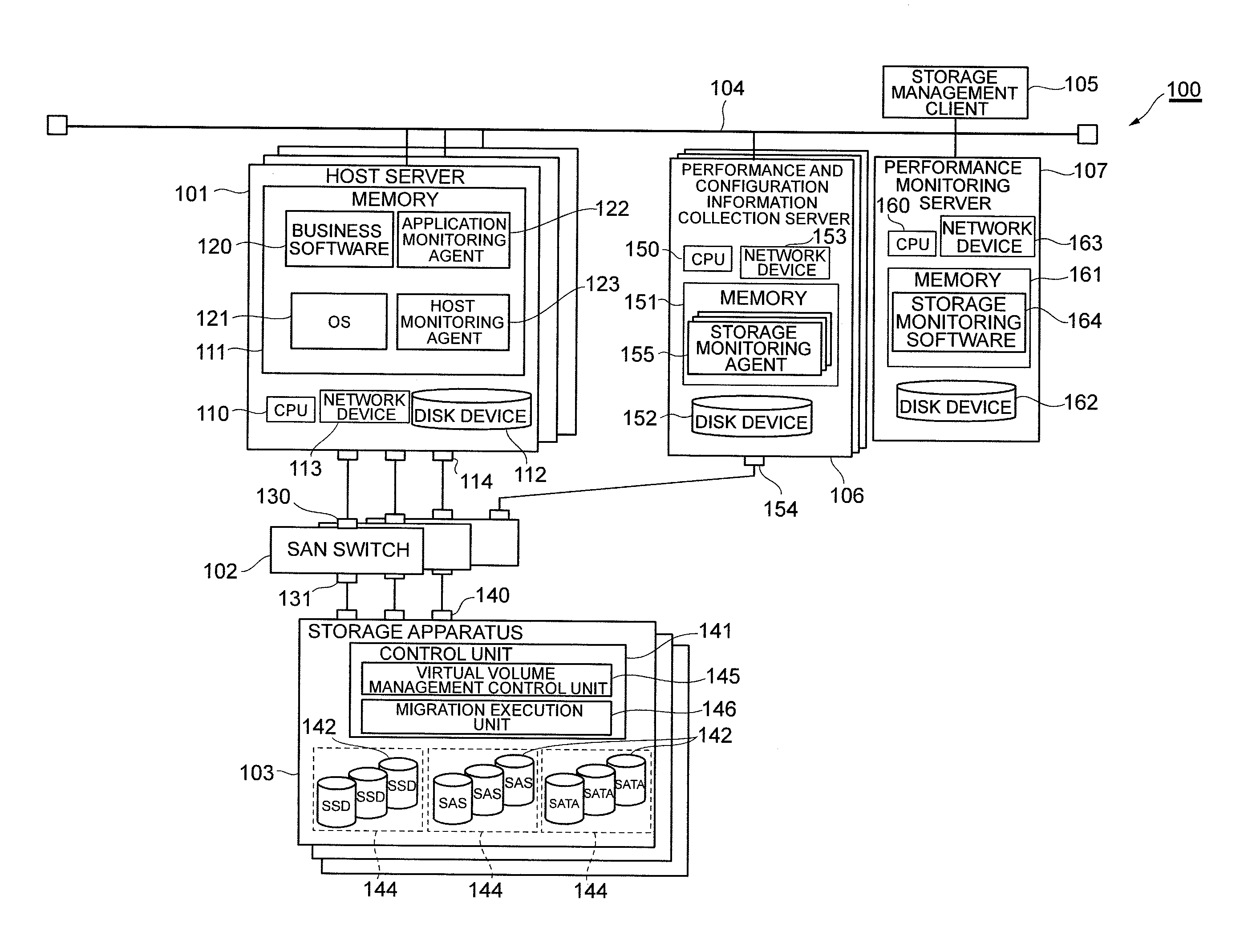
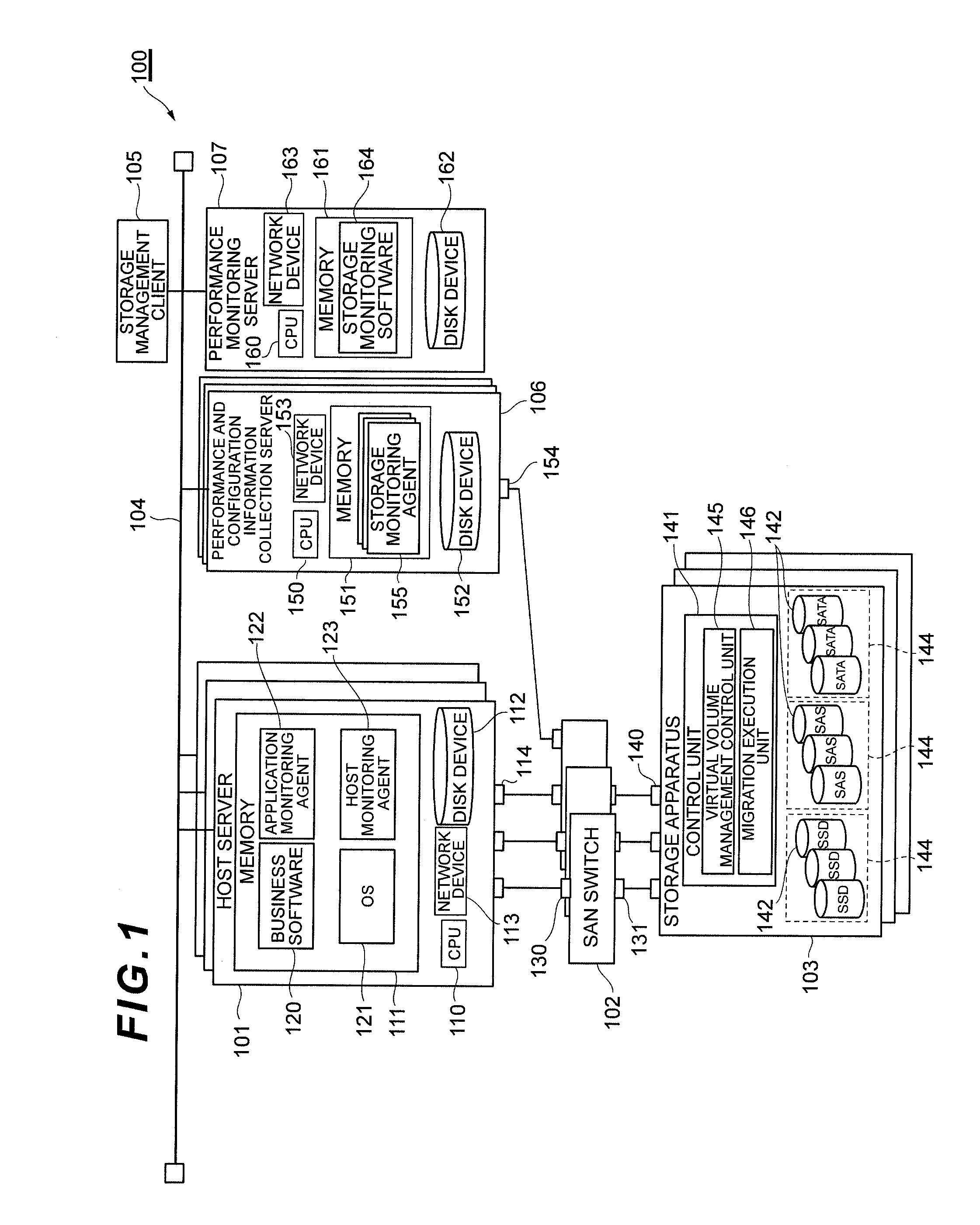
Management method and management apparatus
InactiveUS20110246740A1Maximizing response rateImprove responsivenessMemory adressing/allocation/relocationInput/output processes for data processingOperating systemPool
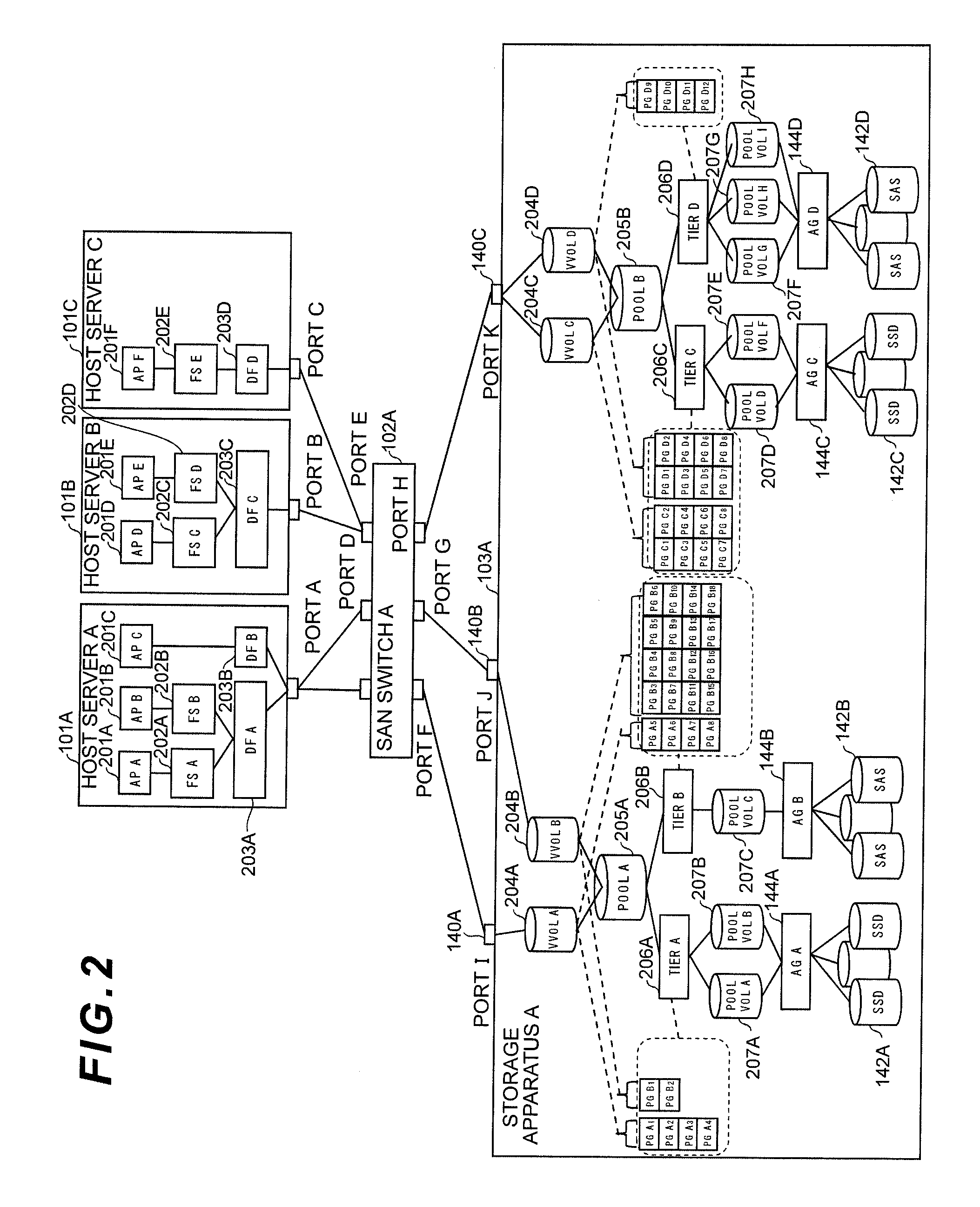
A management method and management apparatus that can prevent deterioration of response performance of an entire system is suggested.A management method and apparatus for managing a storage apparatus to which a hierarchical pool configuration technique is applied is designed to: select a migration-candidate virtual volume(s) from among virtual volumes to which a page(s) is allocated from a pool constituted from a storage tier(s) whose number of accesses per unit time has reached a performance threshold and whose used capacity has not reached a capacity threshold; select a pool(s) from which a page(s) is allocated to the virtual volume, as a migration source pool; also select a pool(s) constituted from a storage tier whose number of accesses per unit time has not reached the performance threshold, as a migration destination pool; decide a migration candidate pair(s) by combining the migration-candidate virtual volume(s) with the migration destination pool(s); calculate response performance of the entire system before and after migration respectively; and decide a migration candidate pair which is a migration object, based on the calculation result.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
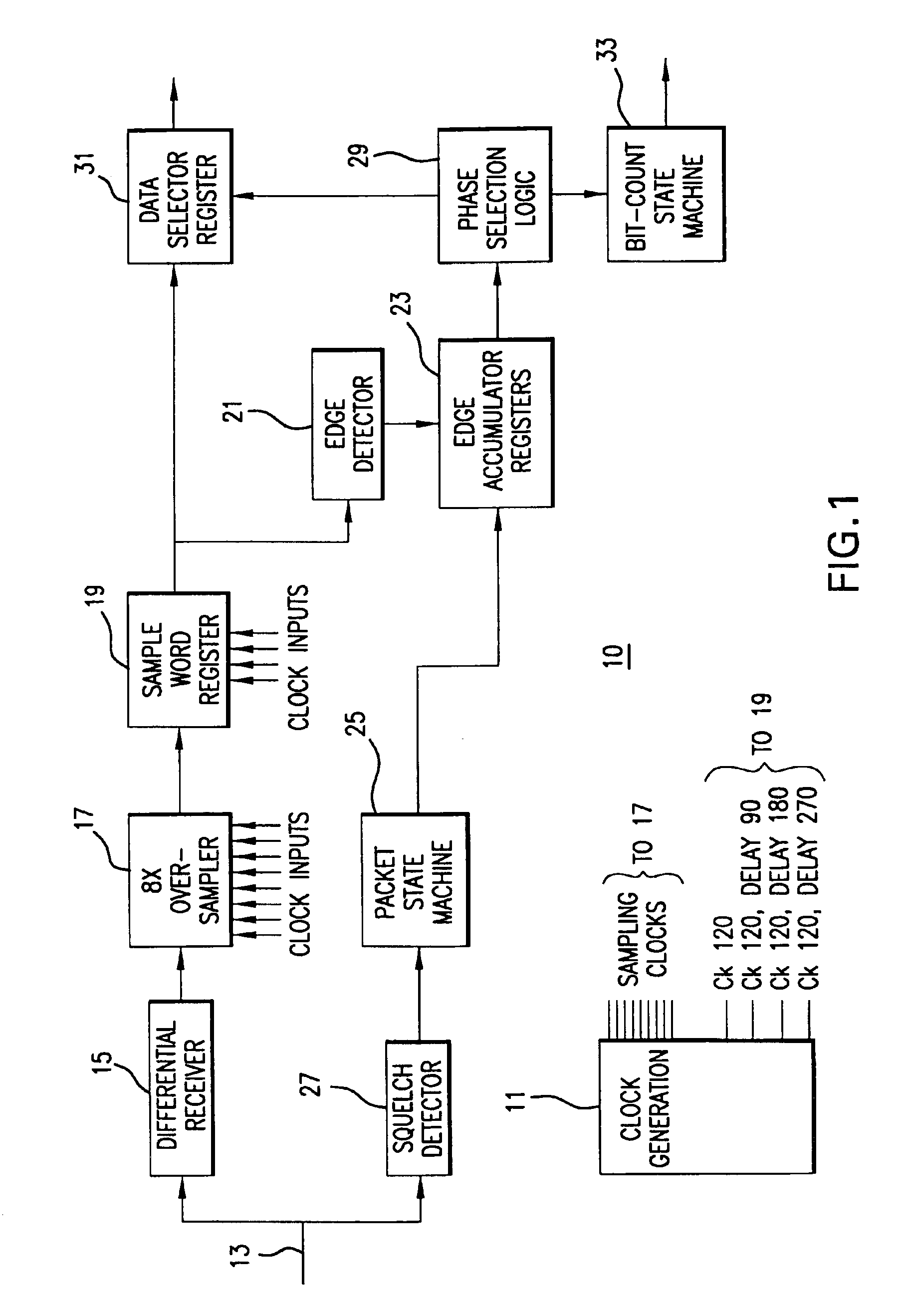
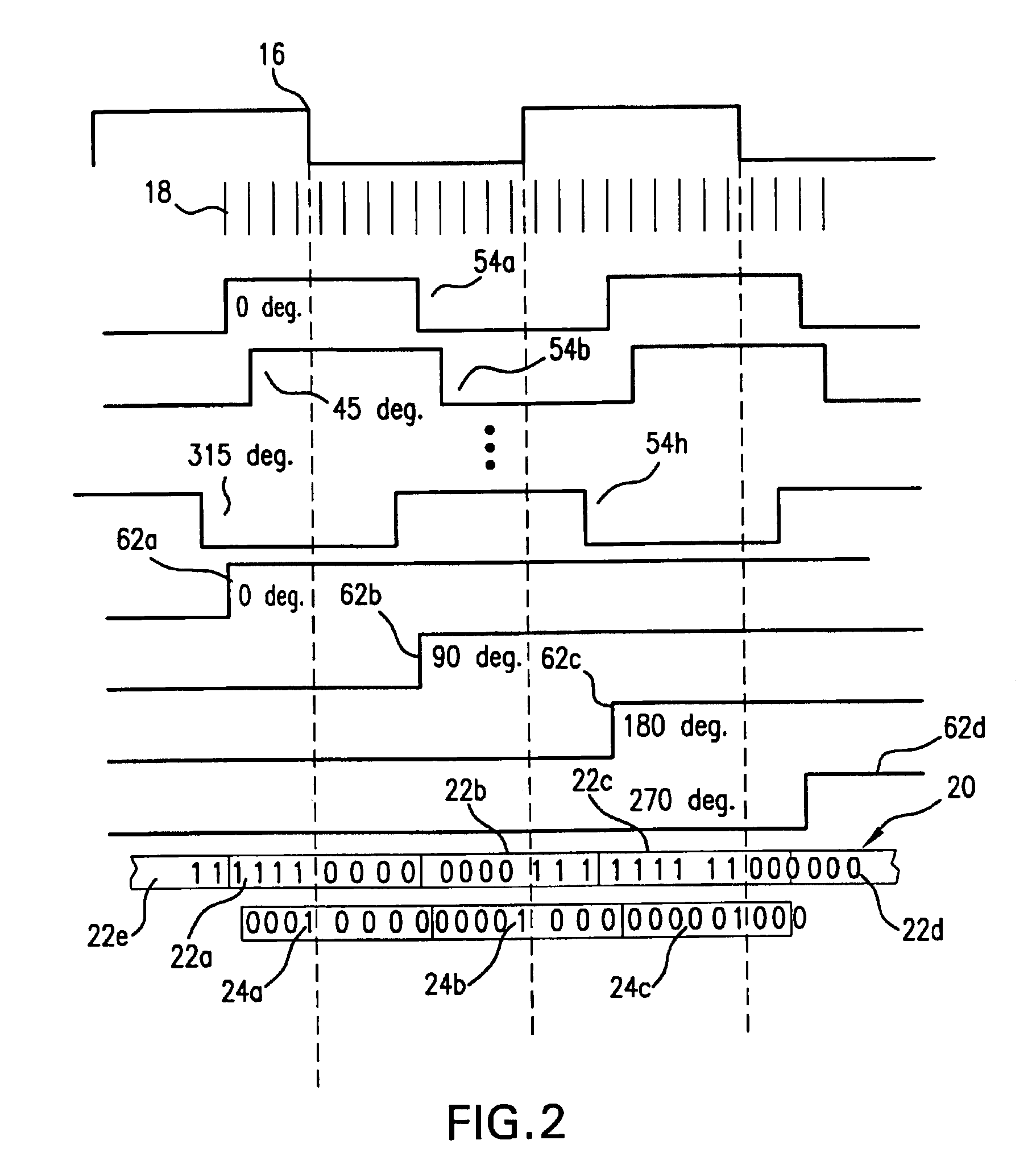
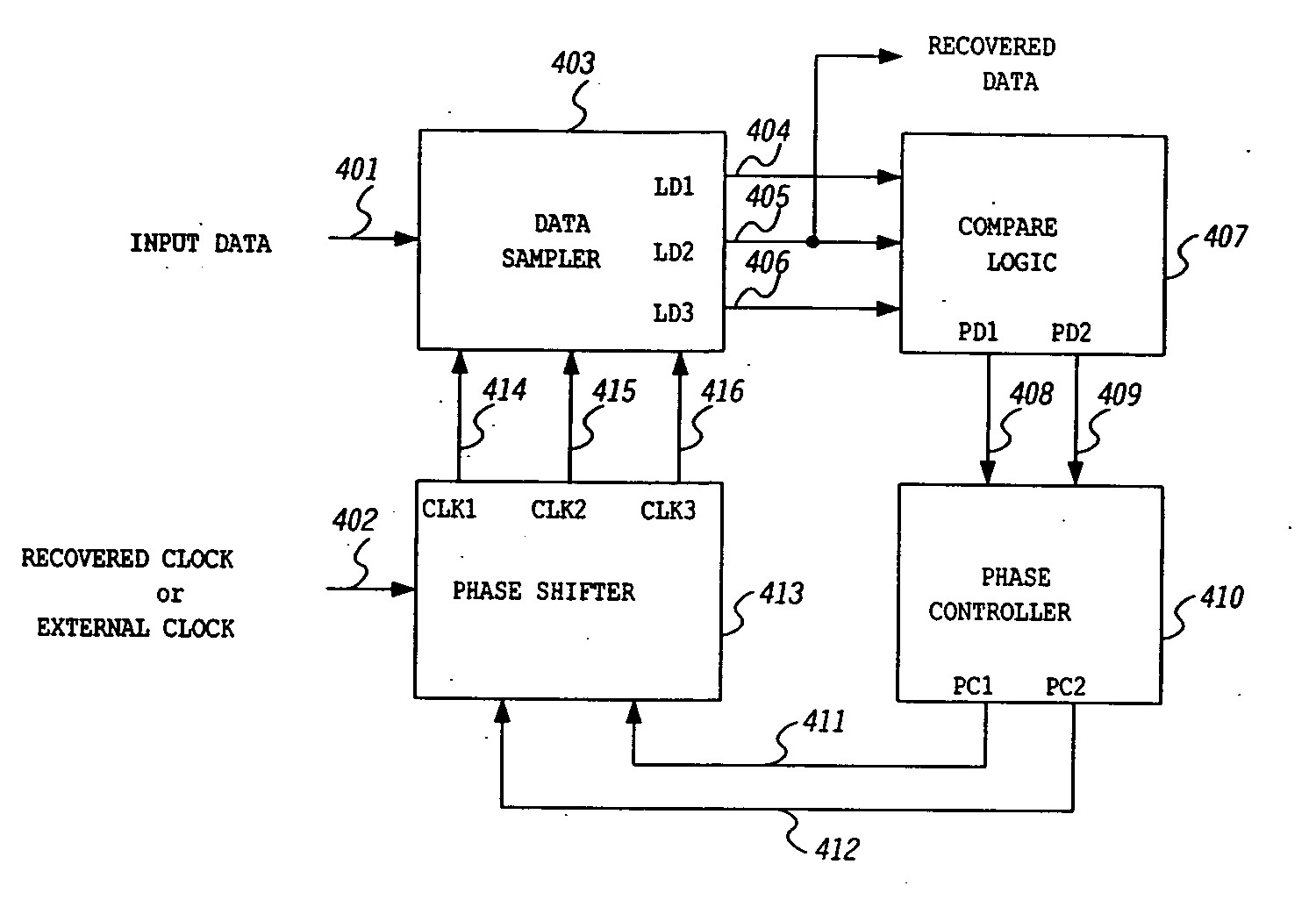
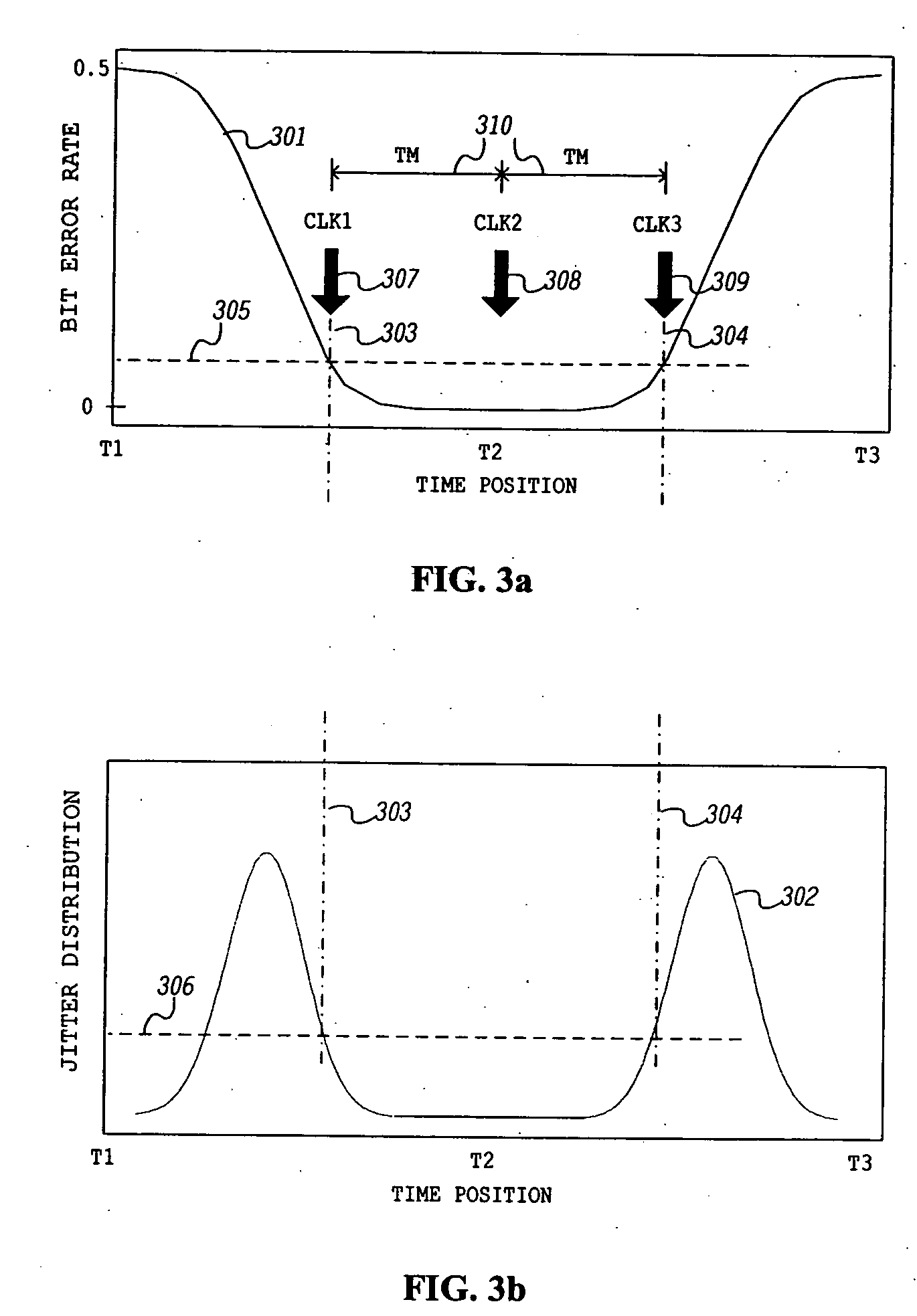
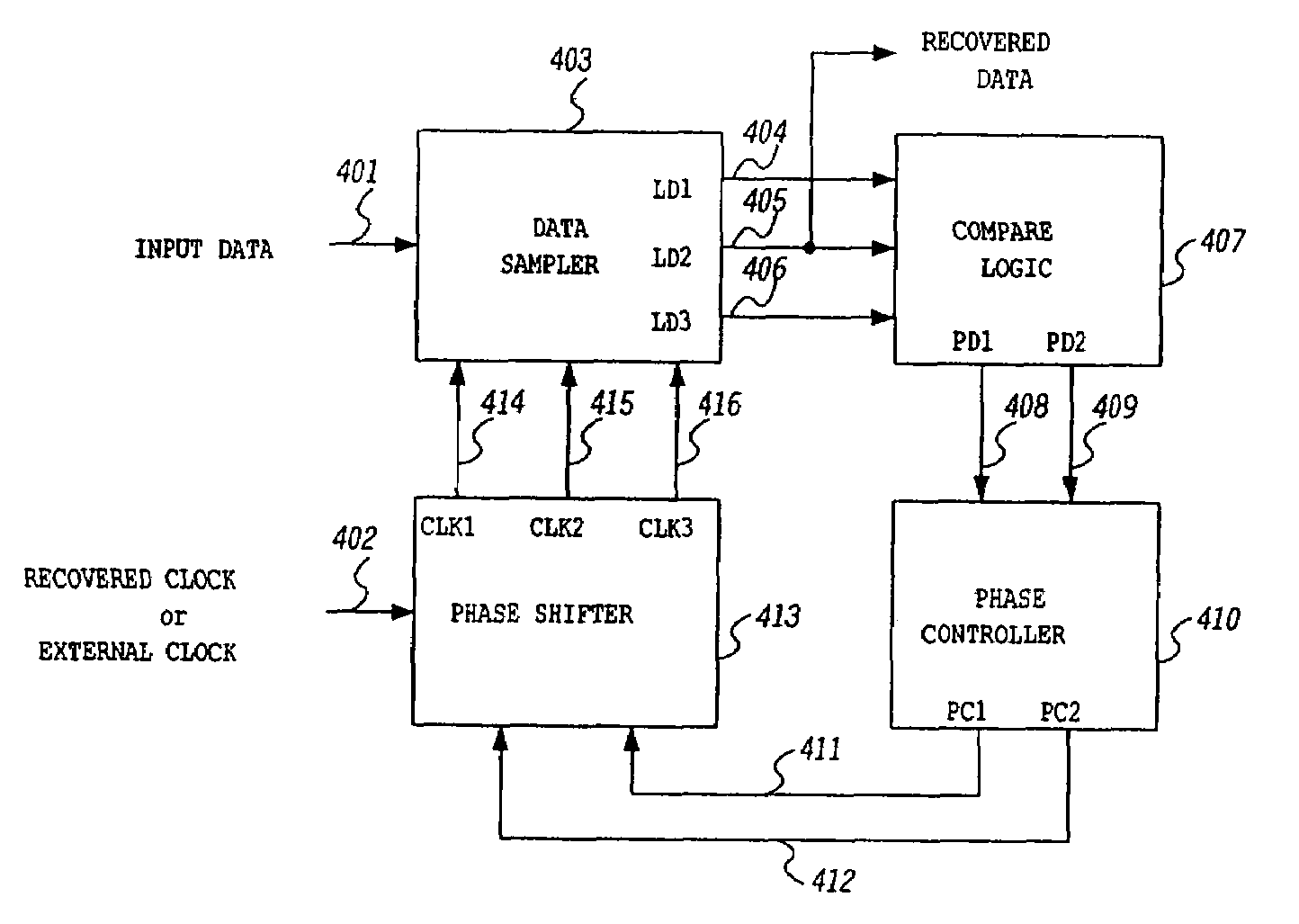
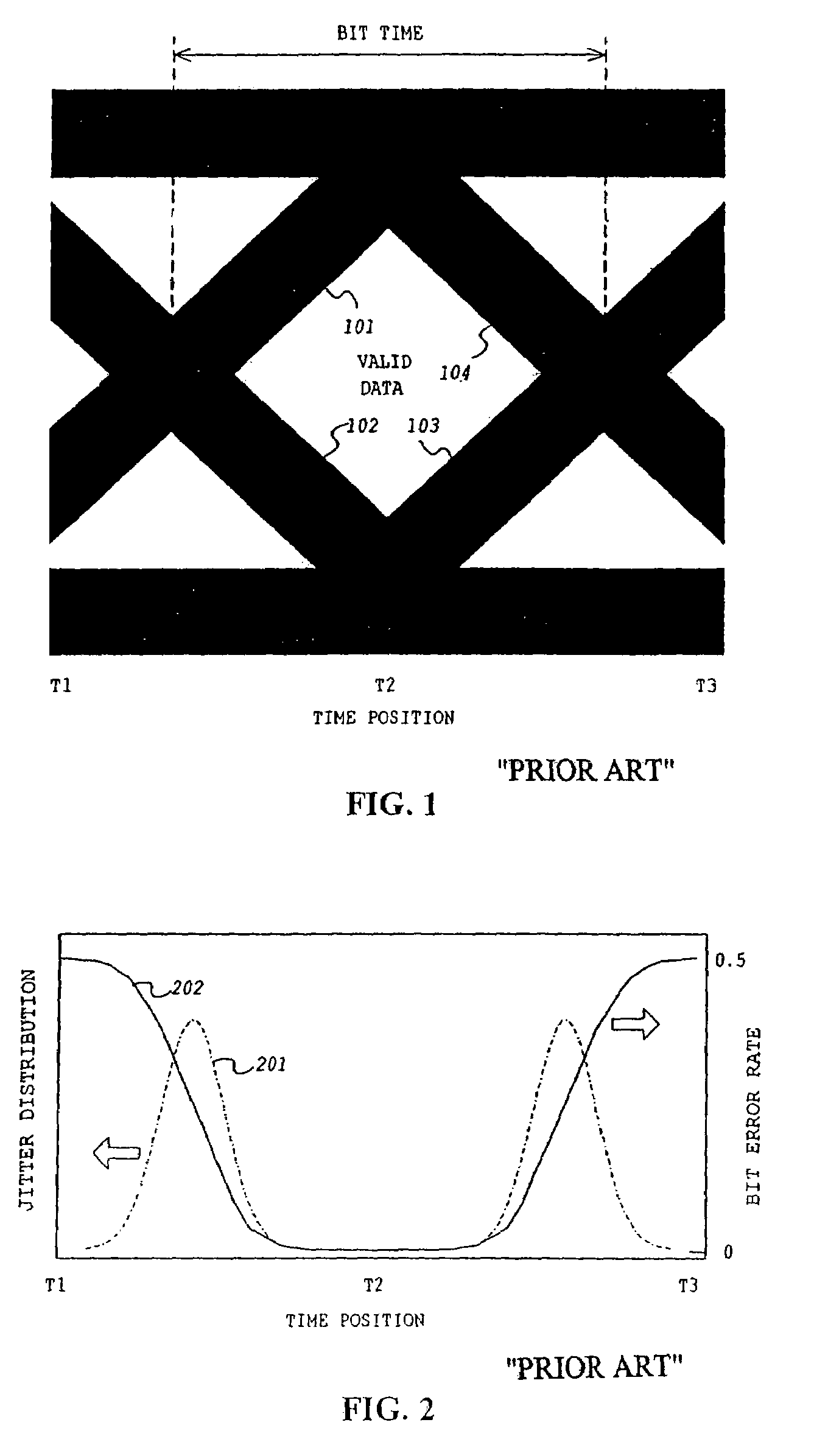
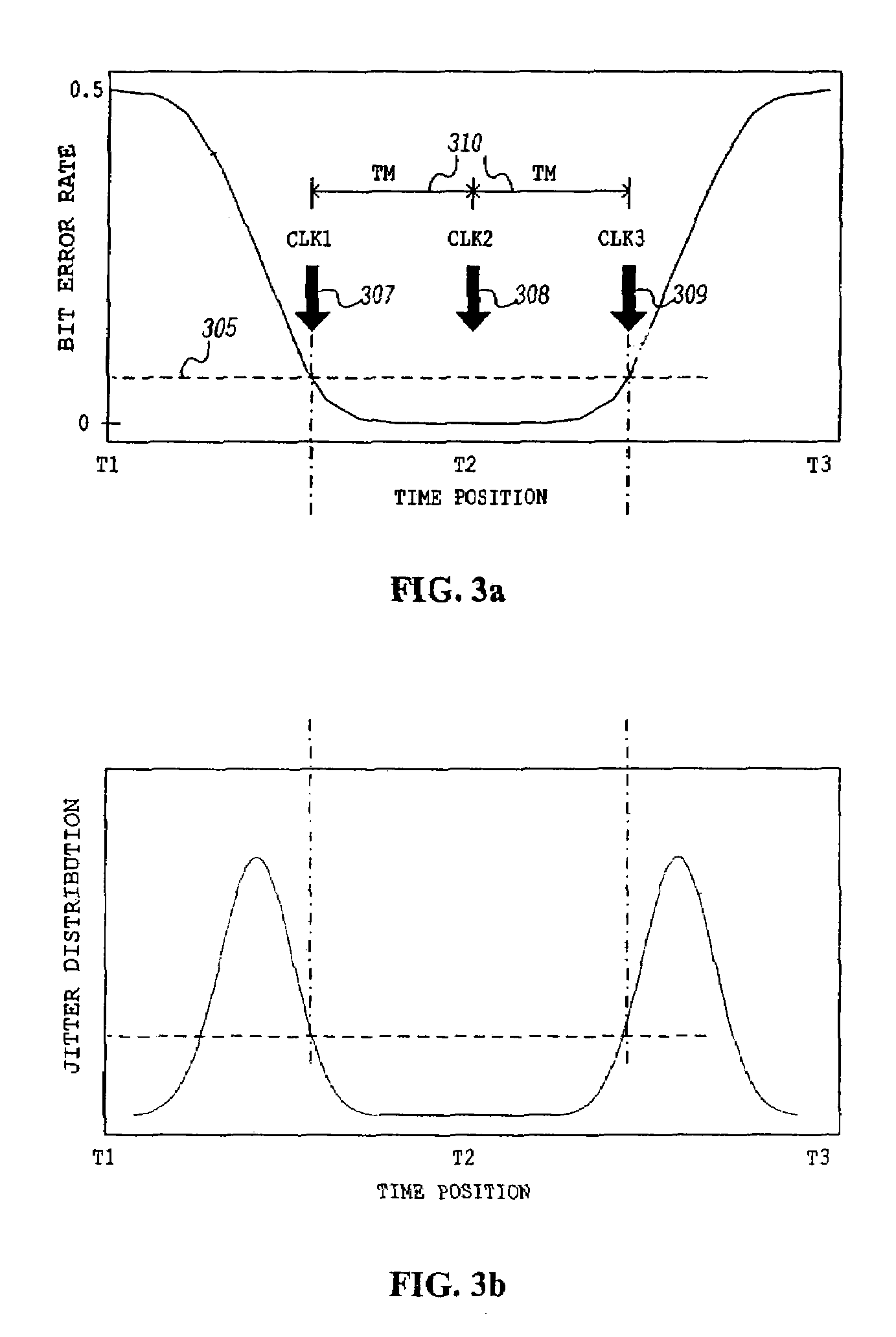
Data recovery using data eye tracking
A data recovery system for a serial digital data link includes a data sampler, compare logic, a phase controller, and a phase shifter. The data sampler samples input data three times in a bit time which time is determined by clock pulses generated by the phase shifter, and recovers digital data according to a predetermined decision criterion. Data sampling phases are split so as to track the data eye. The compare logic compares the output of the data sampler according to a predetermined method. Phase controller uses the output of the compare logic and generates phase control signals. These signals are set so as to control the sampling times of the data sampler and to attain near optimally recovered data stream. The phase shifter uses the phase control signals and makes three different phase clocks from input clock. The input clock can be an external clock, or can be recovered from the external clock or input data stream.
Owner:SUPER INTERCONNECT TECH
Broadcast router having a serial digital audio data stream decoder
InactiveUS7747447B2Broadcast information characterisationTime-division multiplexData streamDigital Audio Tape
A bi-phase decoder suitable for use in a broadcast router and an associated method for extracting subframes of digital audio data from a stream of digital audio data. Logical circuitry within the bi-phase decoder extracts subframes of the digital audio data by constructing a transition window from an estimated bit time, sampling the stream of digital audio data using a fast clock and applying the sampled stream of digital audio data to the transition window to identify transitions indicative of preambles of the subframes of digital audio data.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
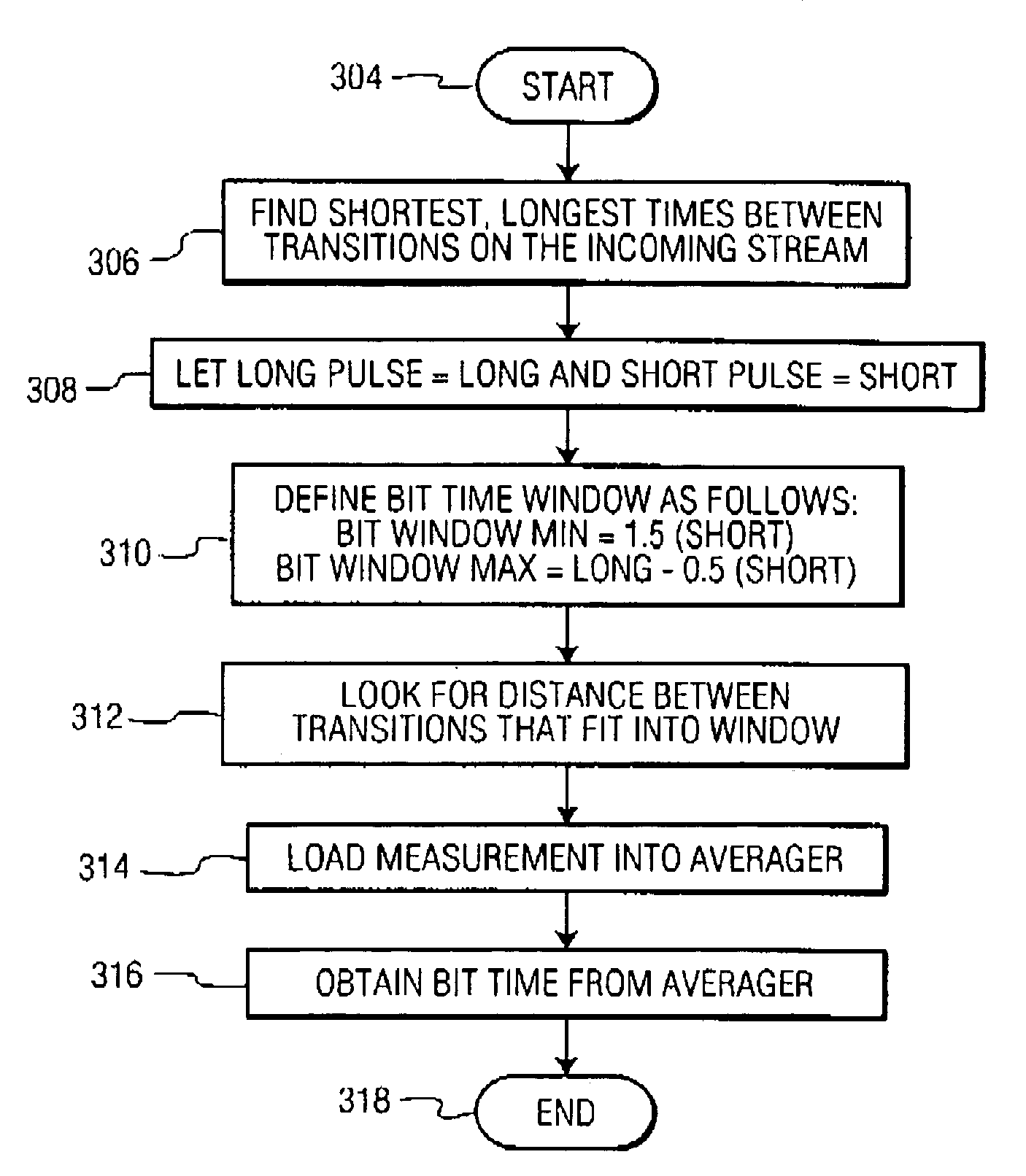
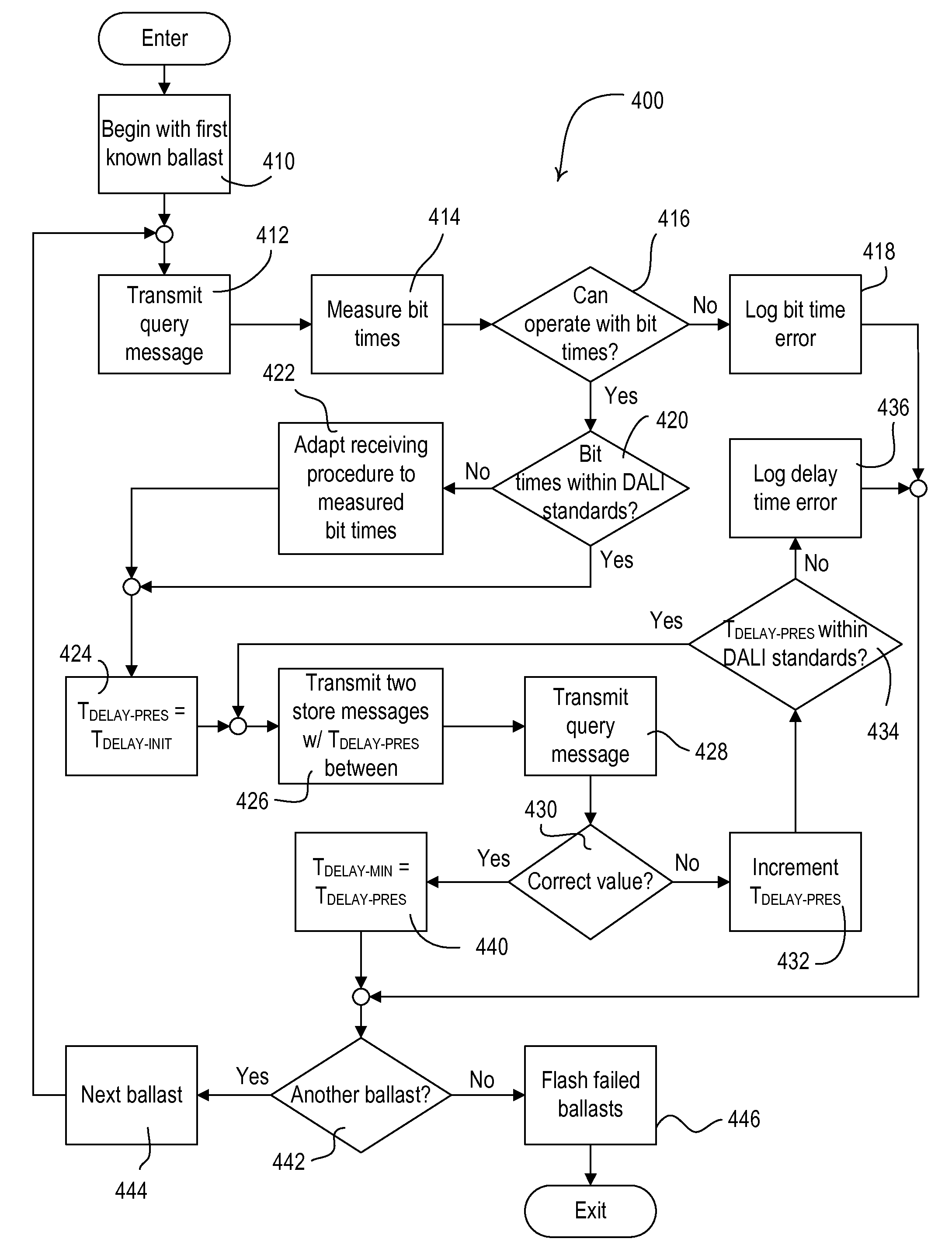
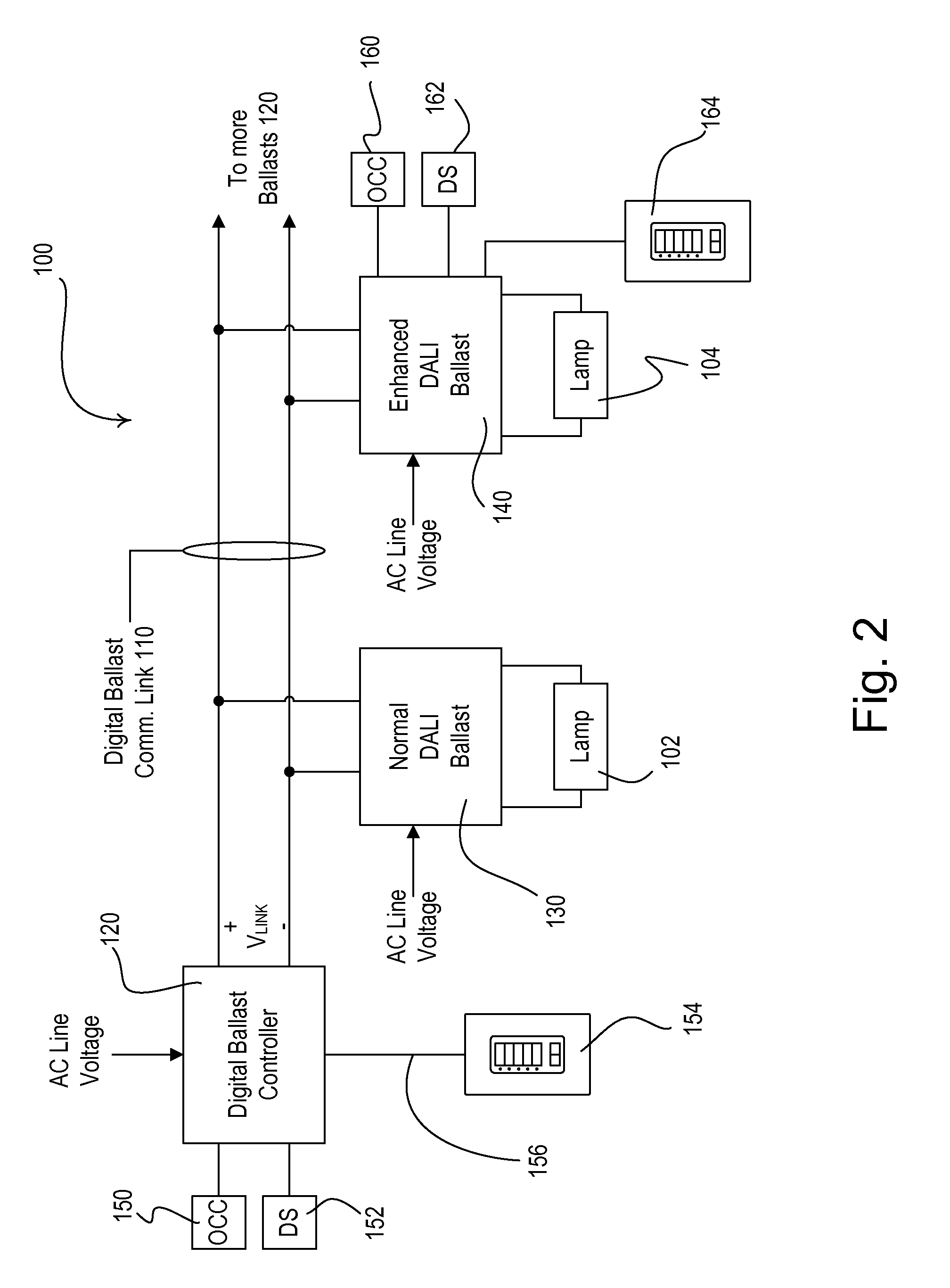
Method of Confirming that a Control Device Complies with a Predefined Protocol Standard
ActiveUS20100238047A1Electric signal transmission systemsElectrical apparatusTelecommunications linkDelayed time
A control device, such as a digital ballast controller, is adapted to be coupled to an electronic ballast, such as a DALI ballast, via a communication link, and is operable to determine whether the ballast is operating within the specifications of a predefined protocol standard, e.g., the DALI standard. For example, the control device may measure the bit times of a digital message received from the ballast and to determine if the bit times fall within the limits set by the standard. The control device may also determine the minimum delay time required between two digital messages received by the ballast and determine if the minimum delay time falls within the limit set by the standard. The control device may adapt its normal operation (e.g., how digital messages are received and transmitted) or may provide feedback (e.g., by flashing a lamp) in response to determining that the ballast is operating outside of the specifications of the standard.
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
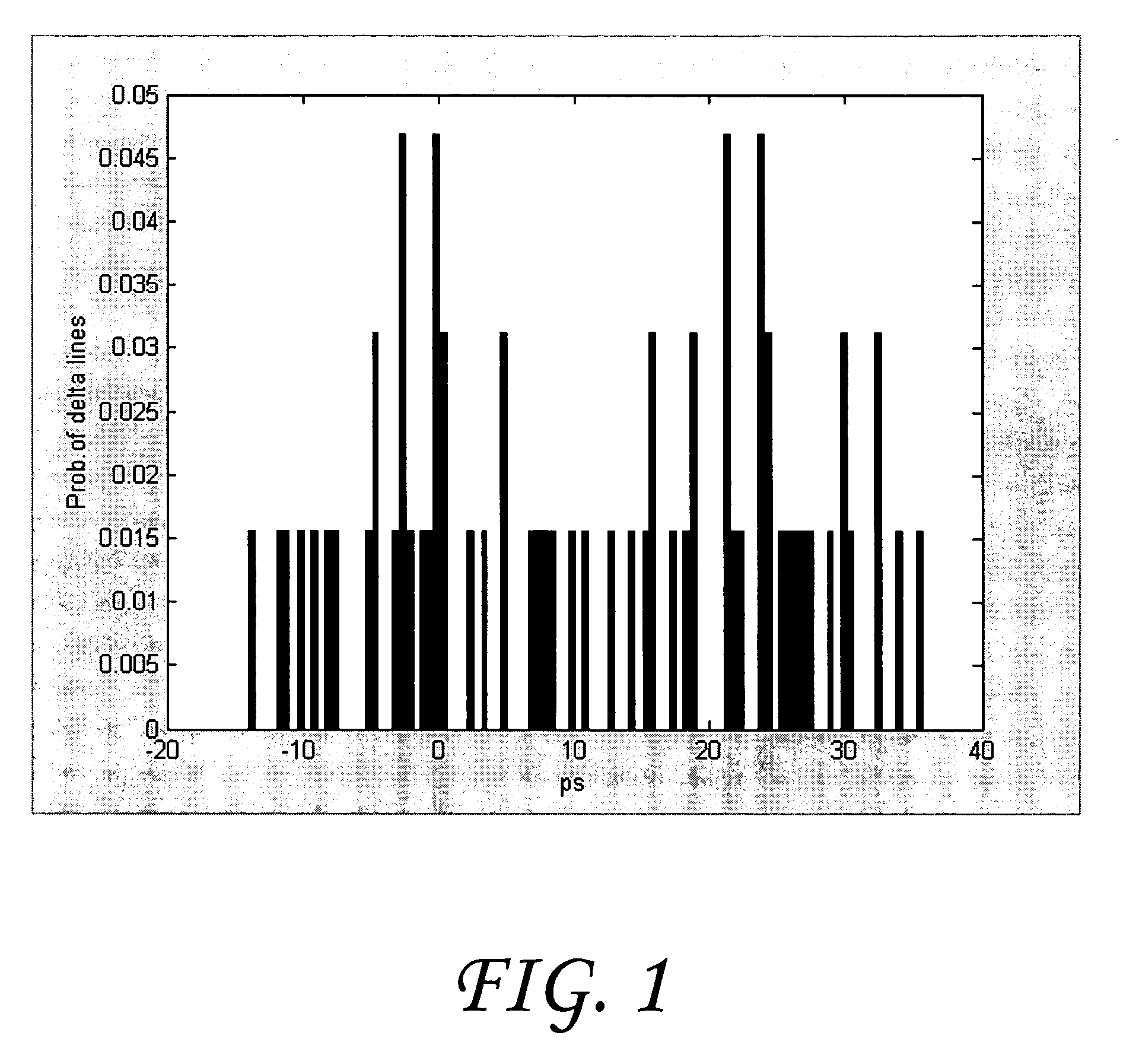
System and method of obtaining data-dependent jitter (DDJ) estimates from measured signal data
InactiveUS7203610B2Enhanced low frequencyImprove the measurement effectNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementVoltage-current phase angleDuty cycle distortionData signal
Methods for estimating data-dependent jitter (DDJ) from measured samples of a transmitted data signal include a first exemplary step of obtaining a plurality of measurements (e.g., time tags and event counts for selected pulse widths in the data signal). Such measurements may be obtained at predetermined intervals within a transmitted signal or may be obtained at randomly selected intervals, and should yield measurements for each data pulse in a repeating data pattern. An average unit interval value representative of the average bit time of the transmitted signal is determined. Time interval error estimates representative of the timing deviation from each signal edge's measured value relative to its ideal value (determined in part from the calculated average unit interval value) are also determined, as well as a classification for each measured signal edge relative to a corresponding data pulse in the repeating data pattern. DDJ delta lines are then calculated for signal edges of each pulse width in the transmitted data pattern, from which peak-to-peak DDJ values and / or estimates of duty-cycle-distortion (DCD) can be determined.
Owner:GUIDE TECH
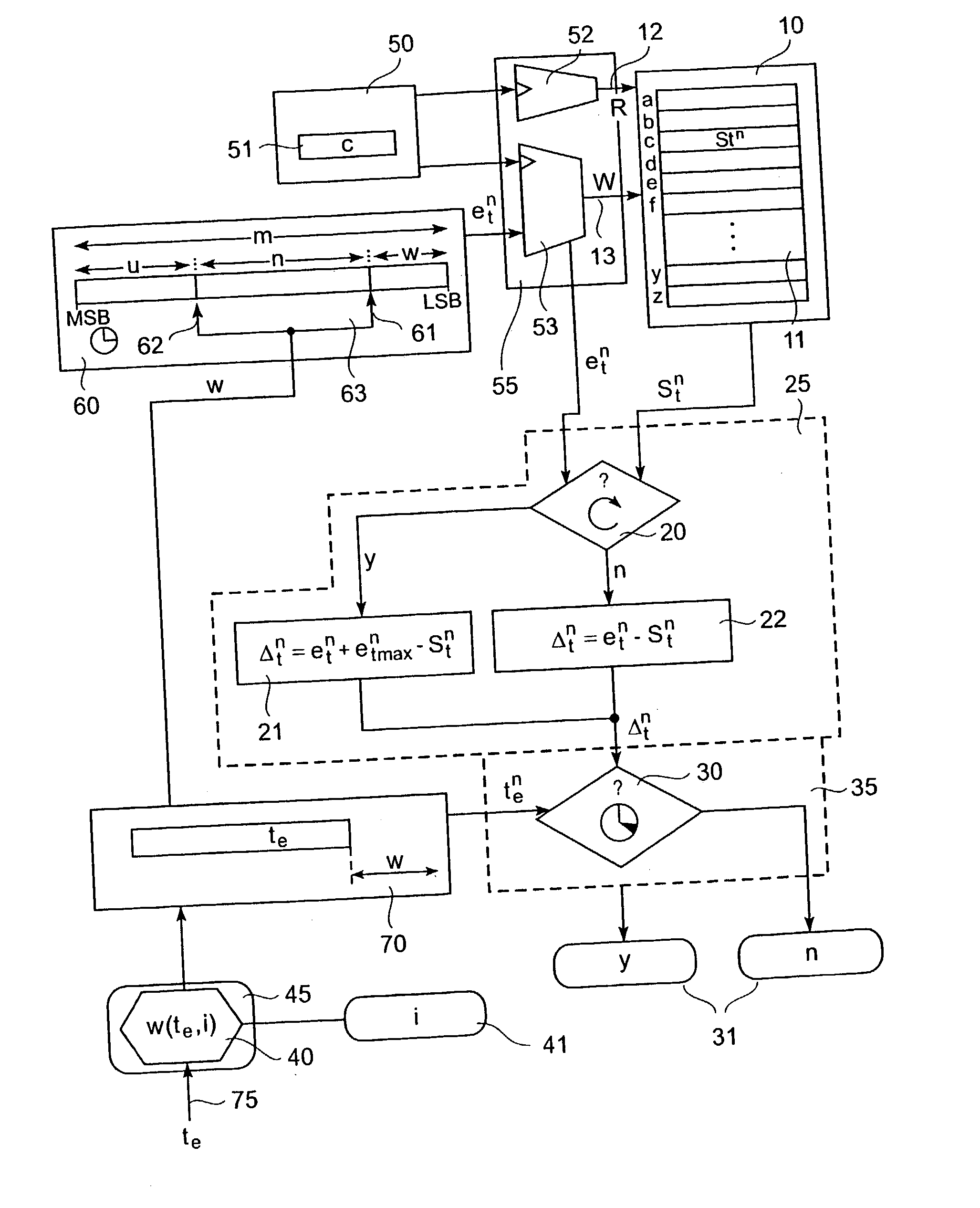
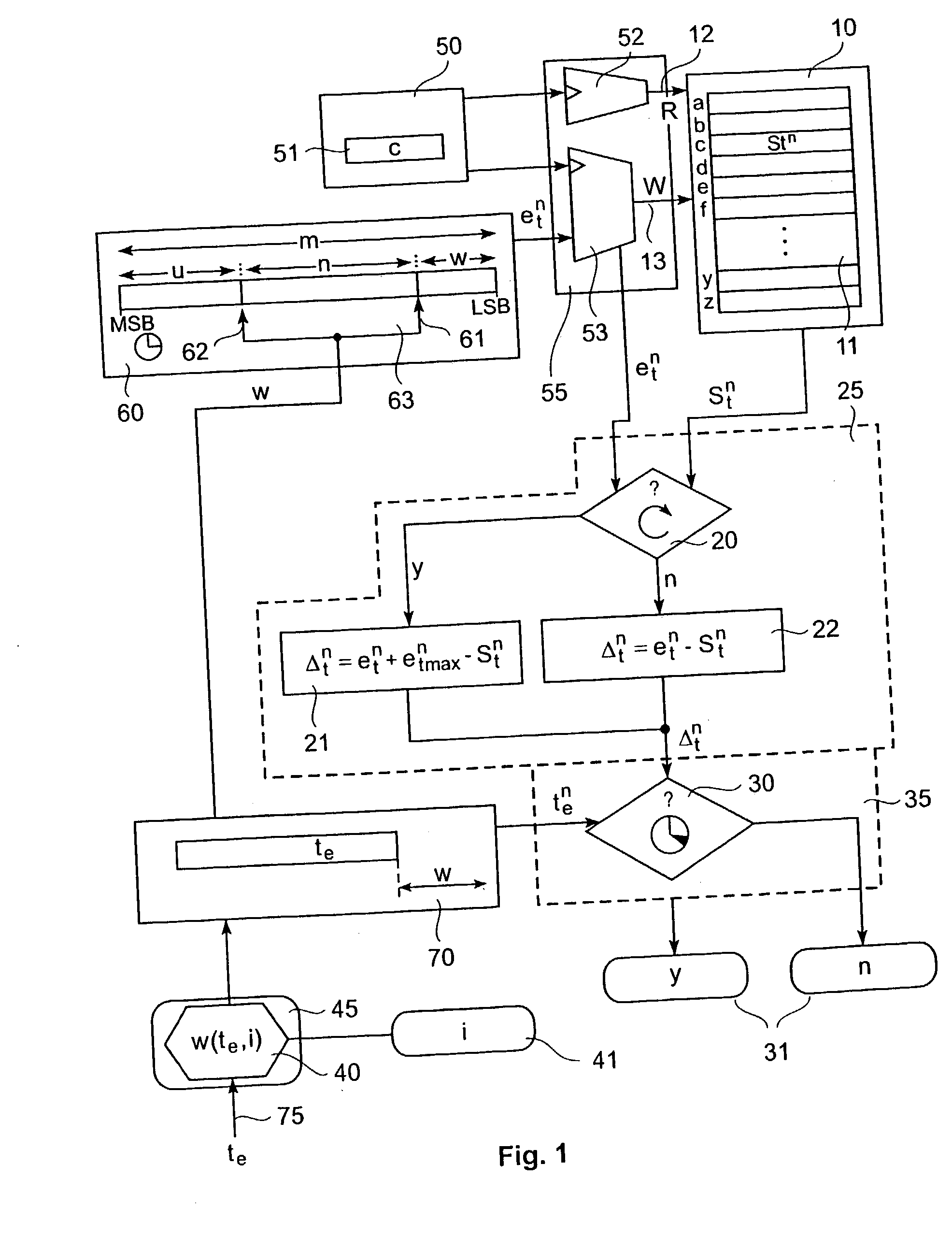
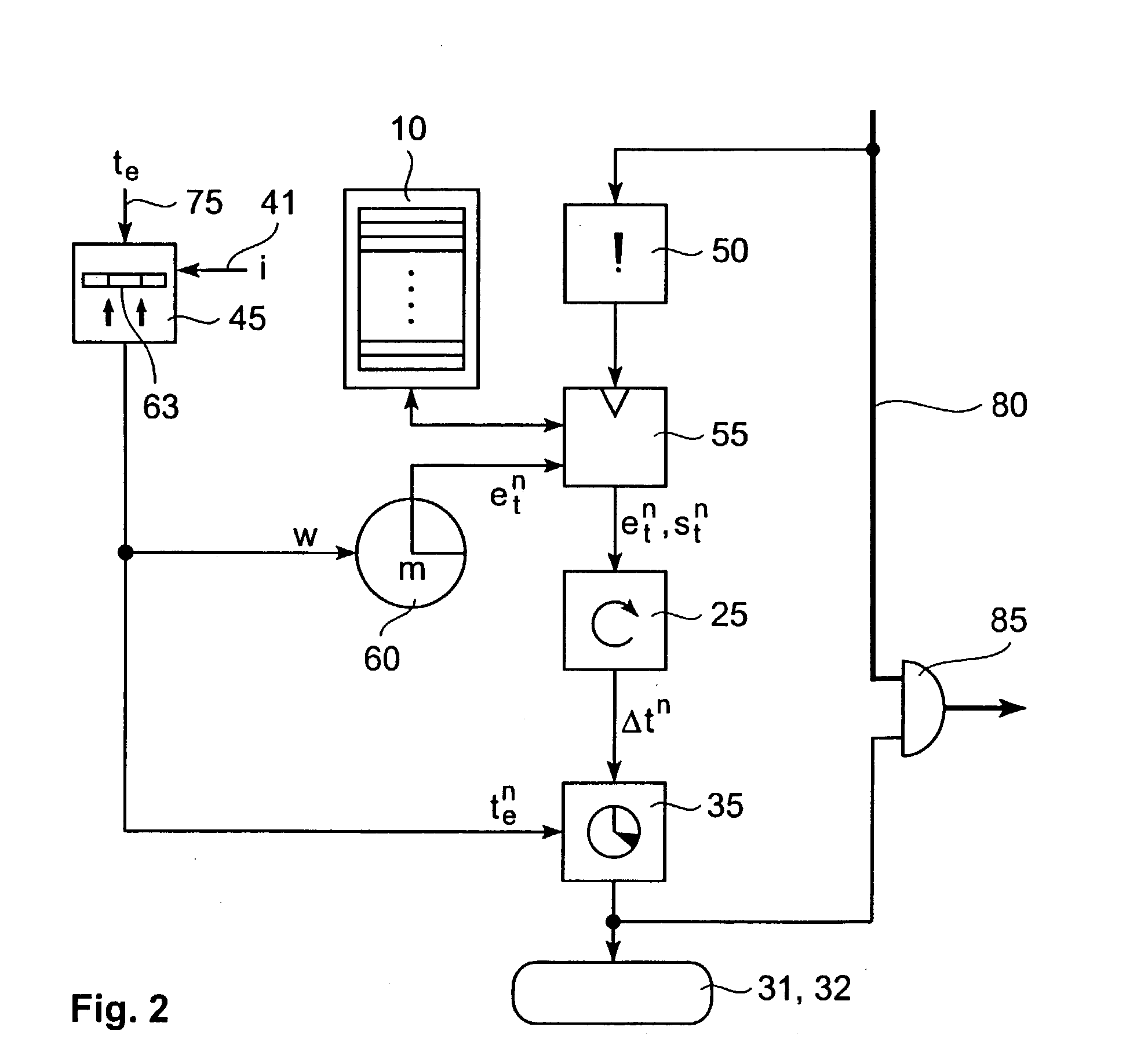
Timeout determination method and apparatus
InactiveUS20030202482A1More freedom in system designError preventionTransmission systemsComputer scienceTime difference
A method (and apparatus) for determining, in a system including an m-bit time counter, whether an event-occurrence time lies after a predetermined timeout-value, includes reading out of a time-stamp memory a stored time-stamp value, determining the time-difference between the time-stamp value and the event-occurrence time, and determining whether the time-difference is larger than the predetermined timeout-value. The event-occurrence time is represented by a subset of the bits of the m-bit time counter, the subset being determined by a plurality of parameters including any two of a lower bit-position, an upper bit-position, and a subset width. The lower bit-position is dependent on the predetermined timeout-value.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
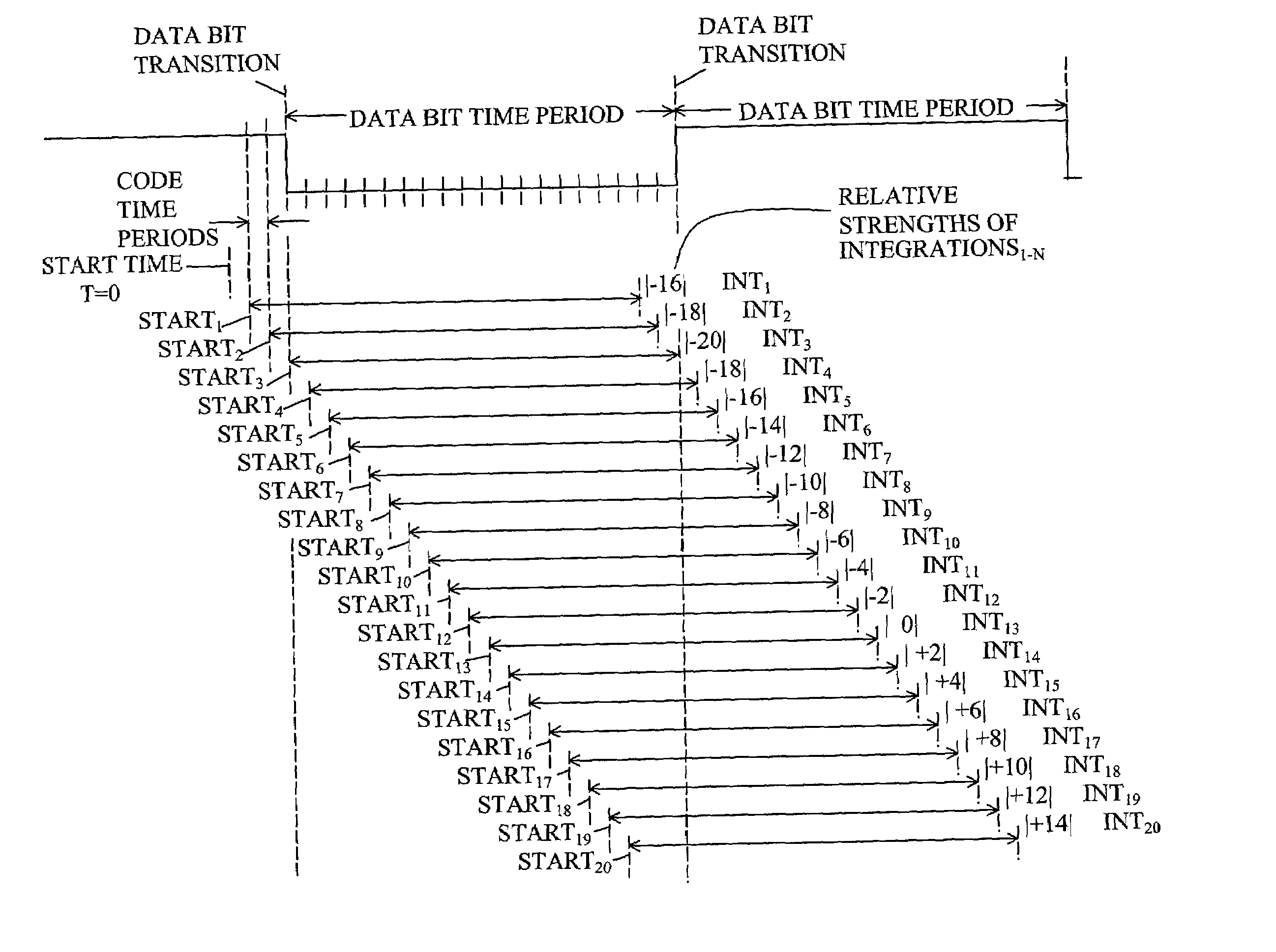
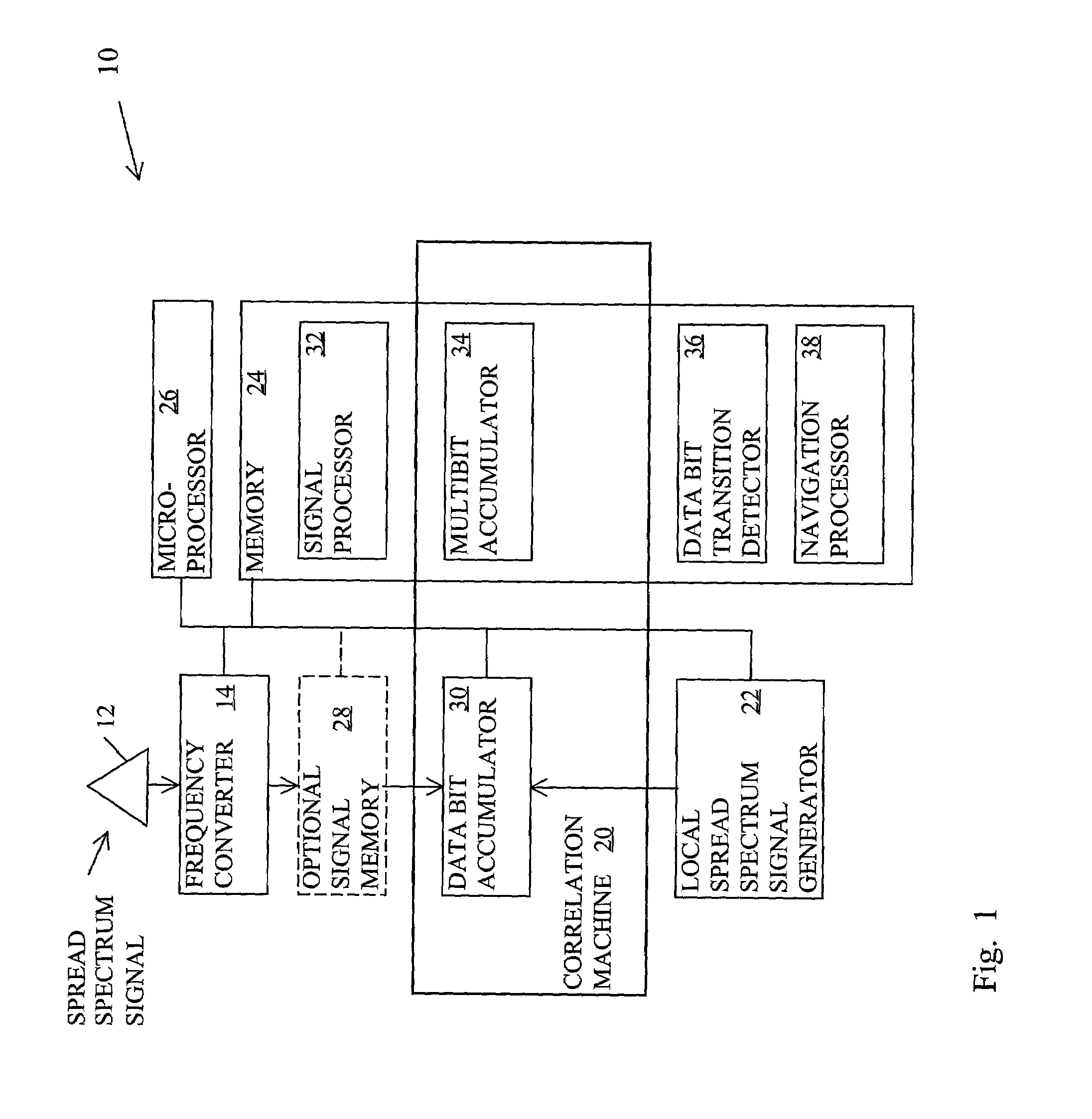
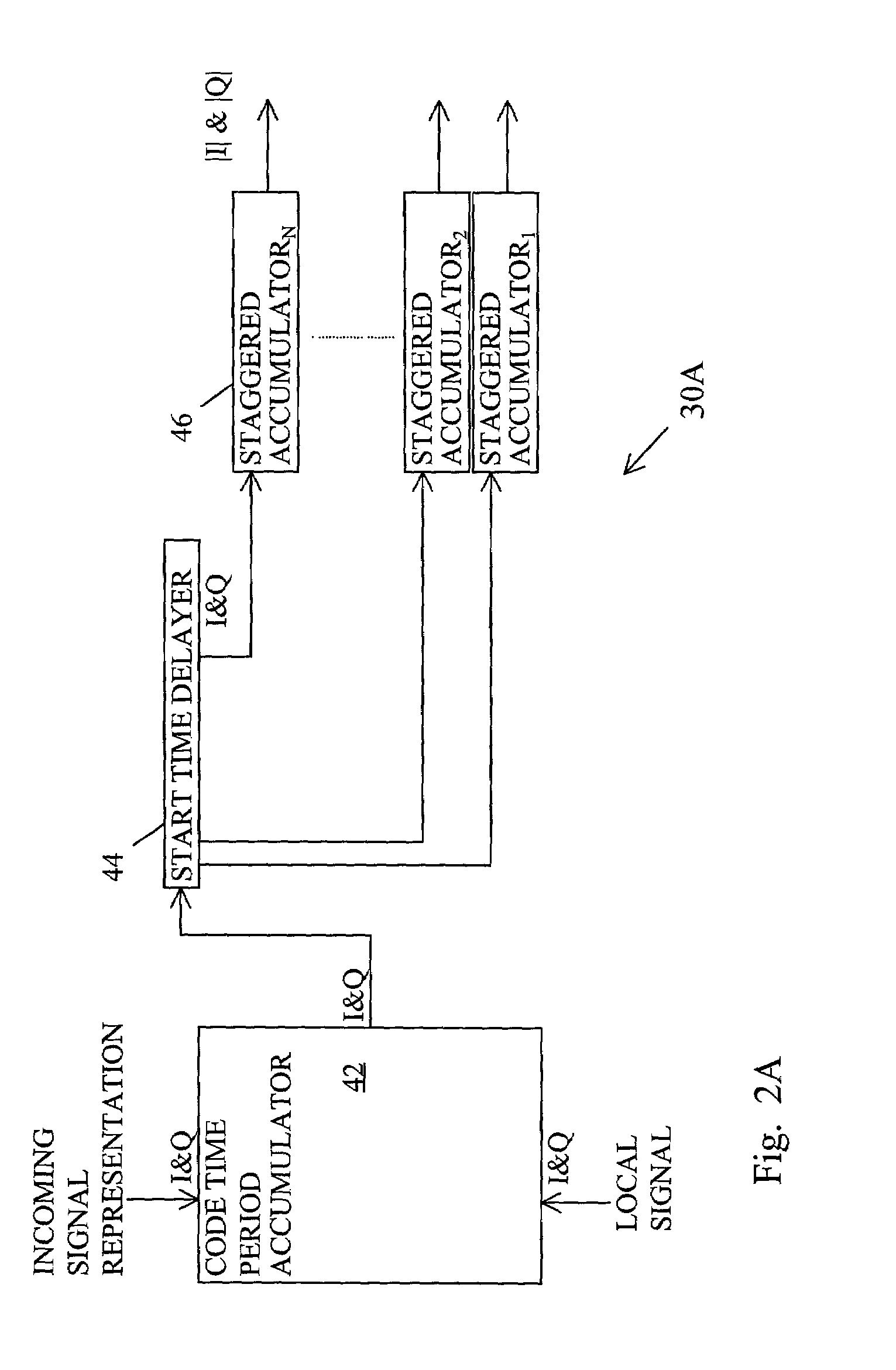
Method for determining data bit transitions for a low level spread spectrum signal
Apparatus and methods for determining the timing of the data bit transitions. “N” assumptions of data bit transitions are used for determining N integrations of an incoming spread signal for data bit time periods where N is the data bit time period divided by the code time period. In a first variation, the N assumptions use N start times separated by code time periods. In a second variation, the N assumptions use N sign inversion times separated by code time periods. In either variation the unsigned values of the N integrations, respectively, may be combined for several data bit time periods. The assumed transition timing that results in the strongest of the N integrations is indicative of the timing of the data bit transitions.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
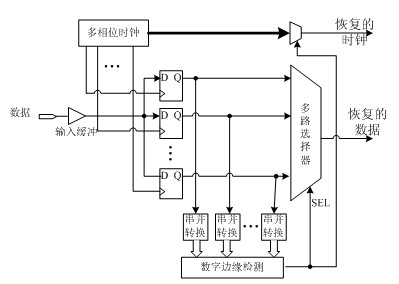
Elastic interface de-skew mechanism
InactiveUS20060184817A1Need be addressError detection/correctionData resettingComputer scienceBit time
A mechanism for de-skewing and aligning data bits sent between two chips on an elastic interface. On the receiving end of an elastic interface, the eye of each data bit within a clock / data group is delayed by less than a bit time to align the eyes with the nearest clock edge of a received clock signal. In addition to aligning the eyes of the individual data bits with the nearest clock edge, IAP patterns are used to determine the amount of further delay needed to line up the individual data beats from each data bit. If the data beats for the data bits are not aligned, all but the slowest data beat are delayed to align the data beats for all bits. The additional delay is achieved using sample latches that result in a delayed signal with less jitter. As a result of having less jitter, the received, de-skewed, and aligned clock / data group can be forwarded to the operative portion of the receiving chip at an increased frequency.
Owner:IBM CORP
Ask demodulation device and wireless device using the same
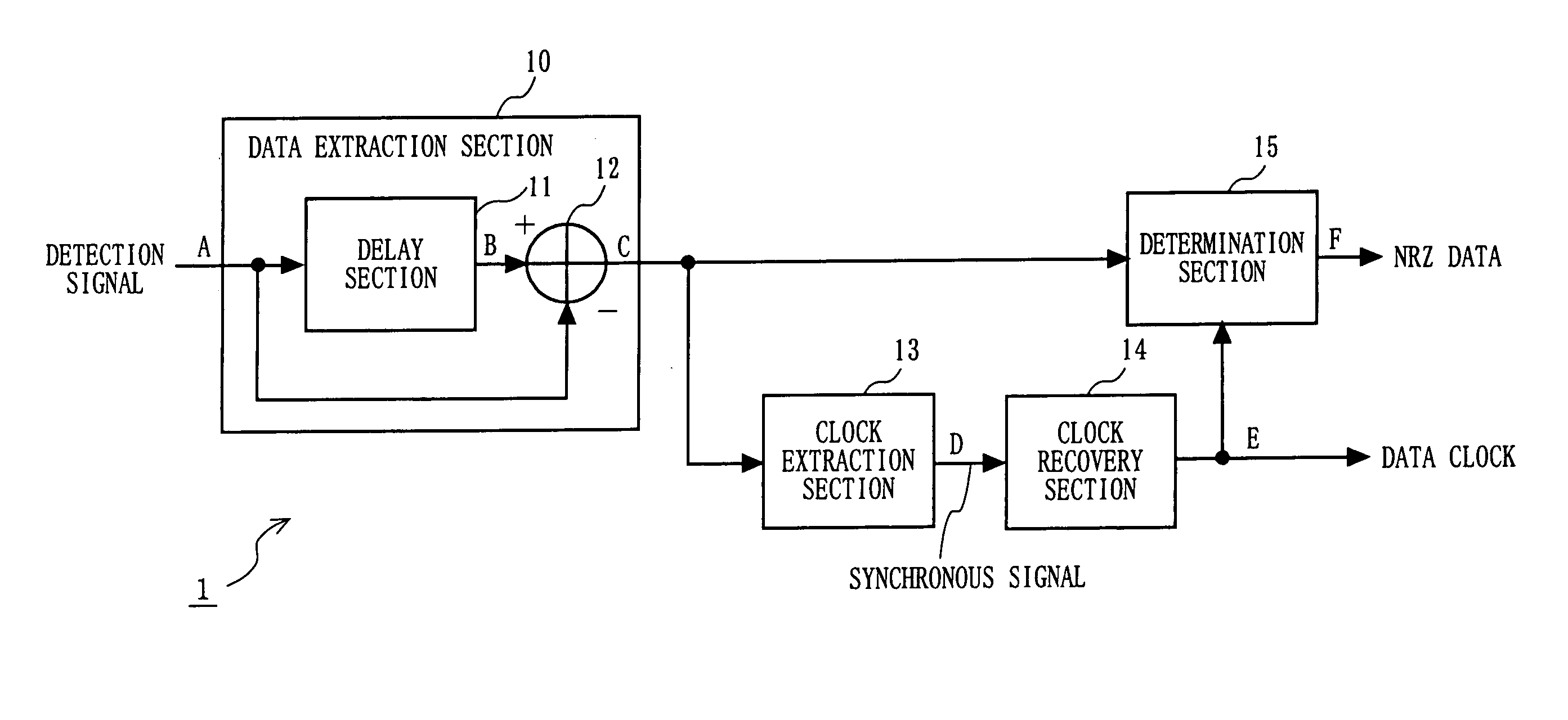
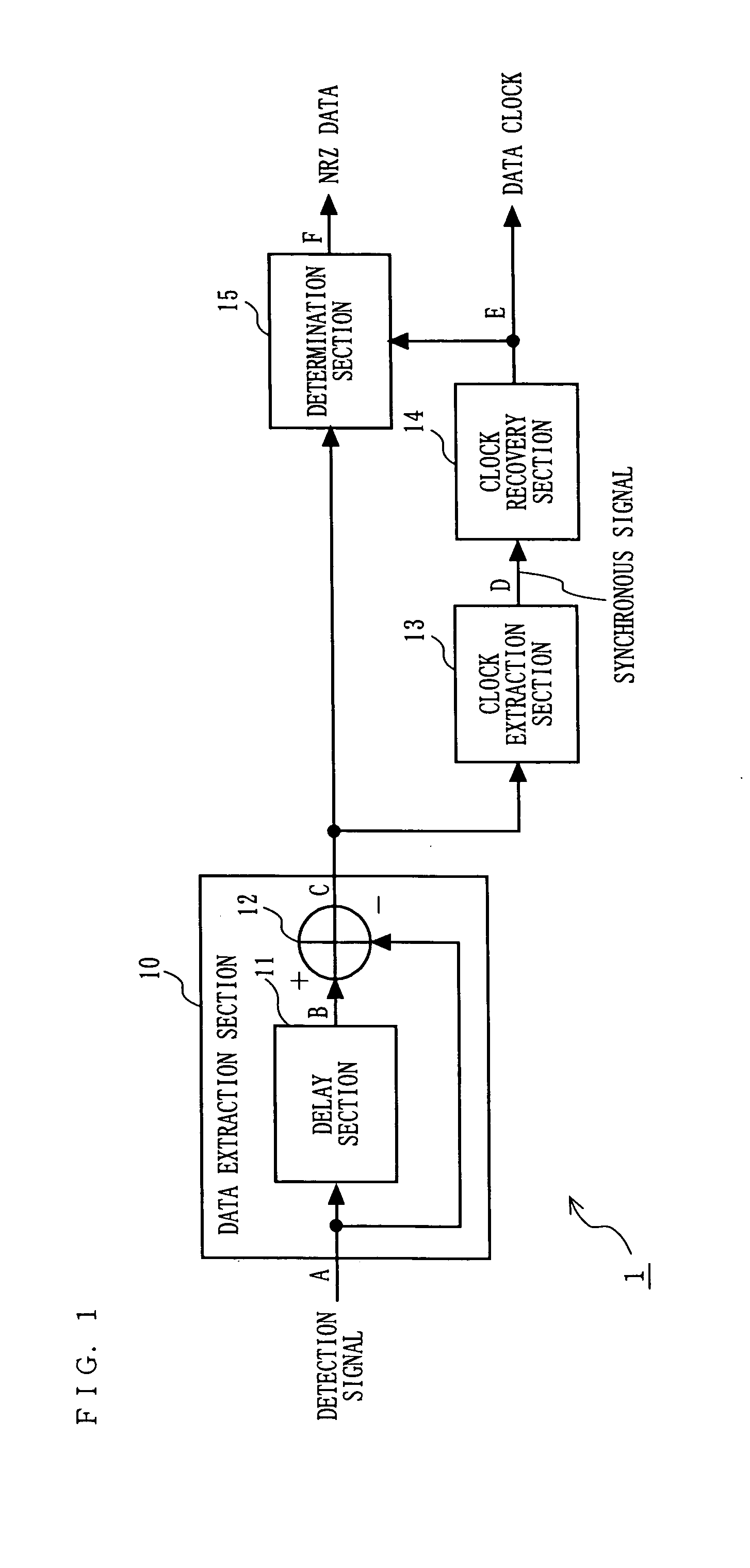
ActiveUS20050094745A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioExcellent bit error rate characteristicAmplitude demodulation by homodyne/synchrodyne circuitsIndividual digits conversionClock recoveryDemodulation
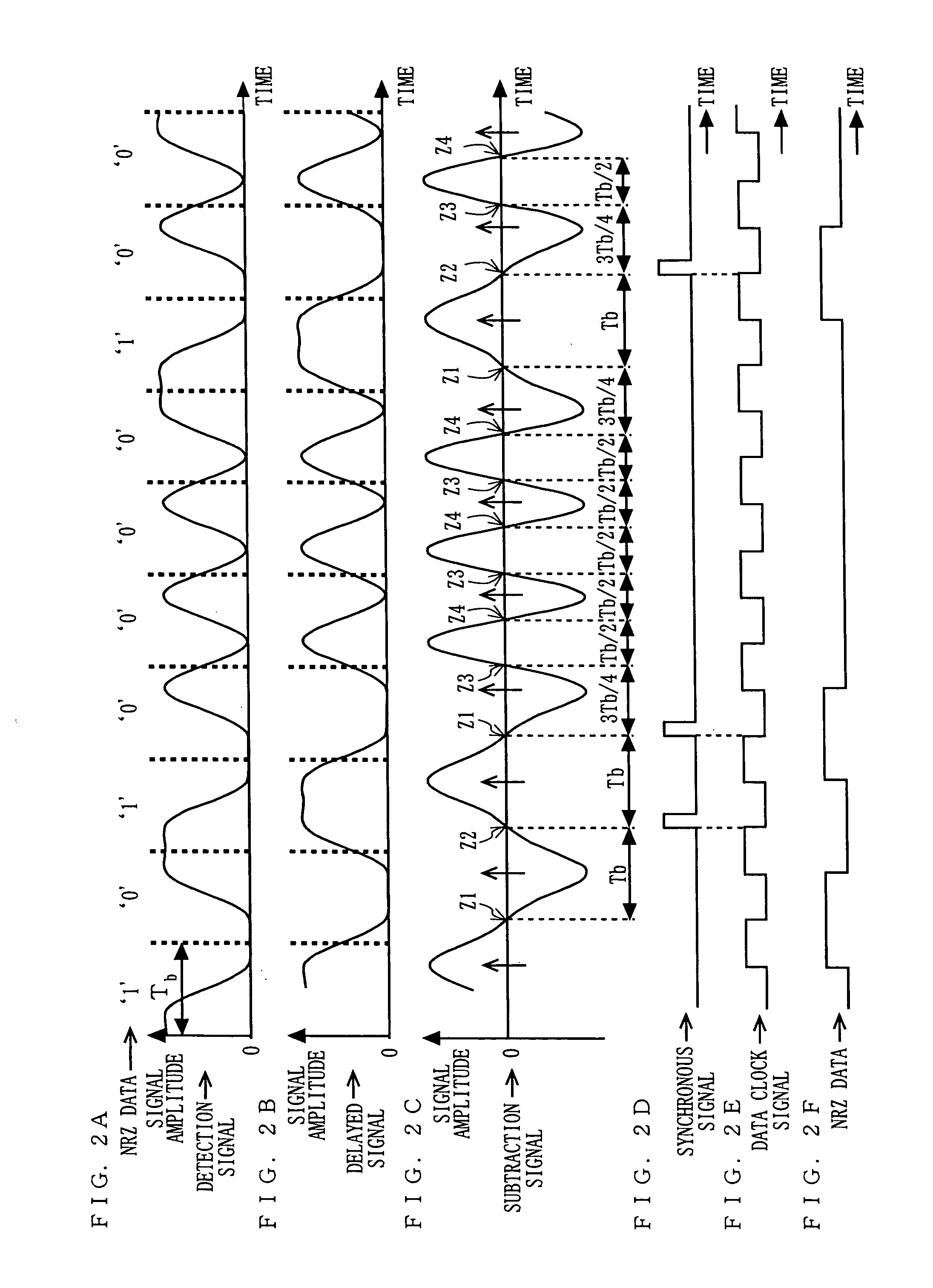
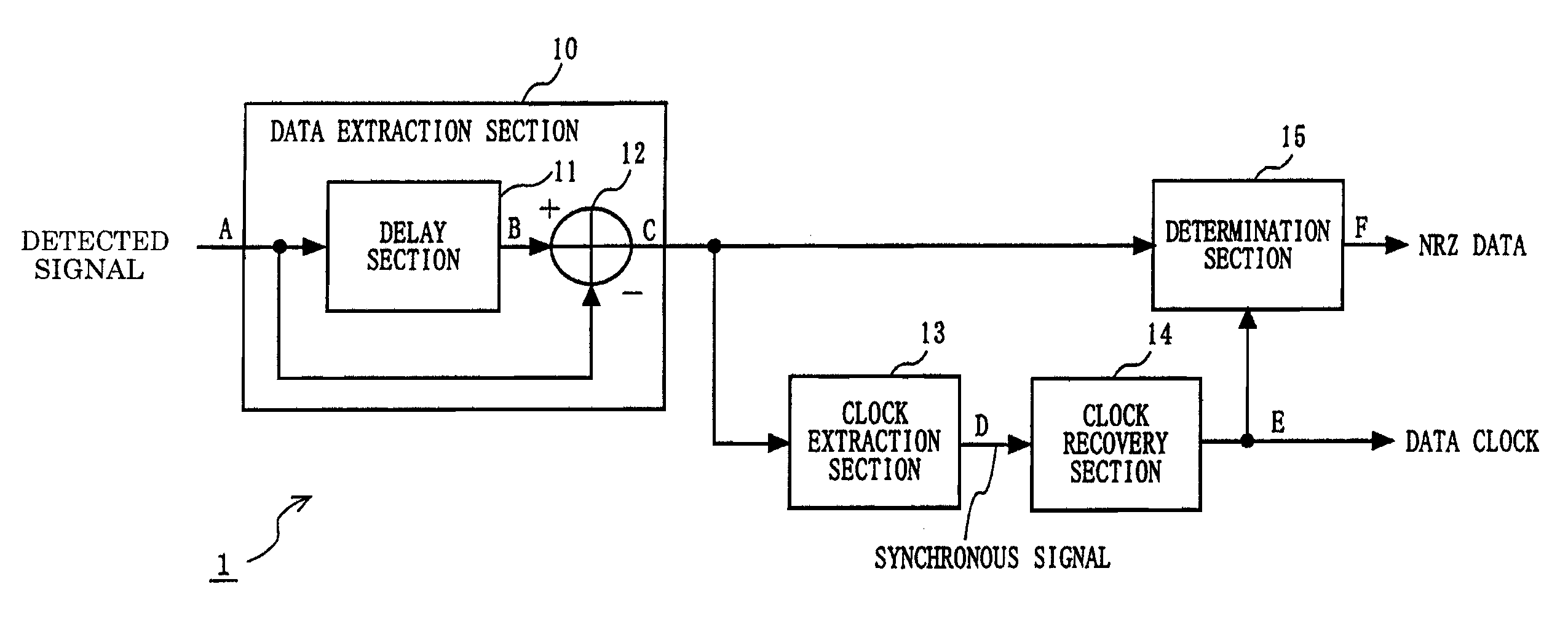
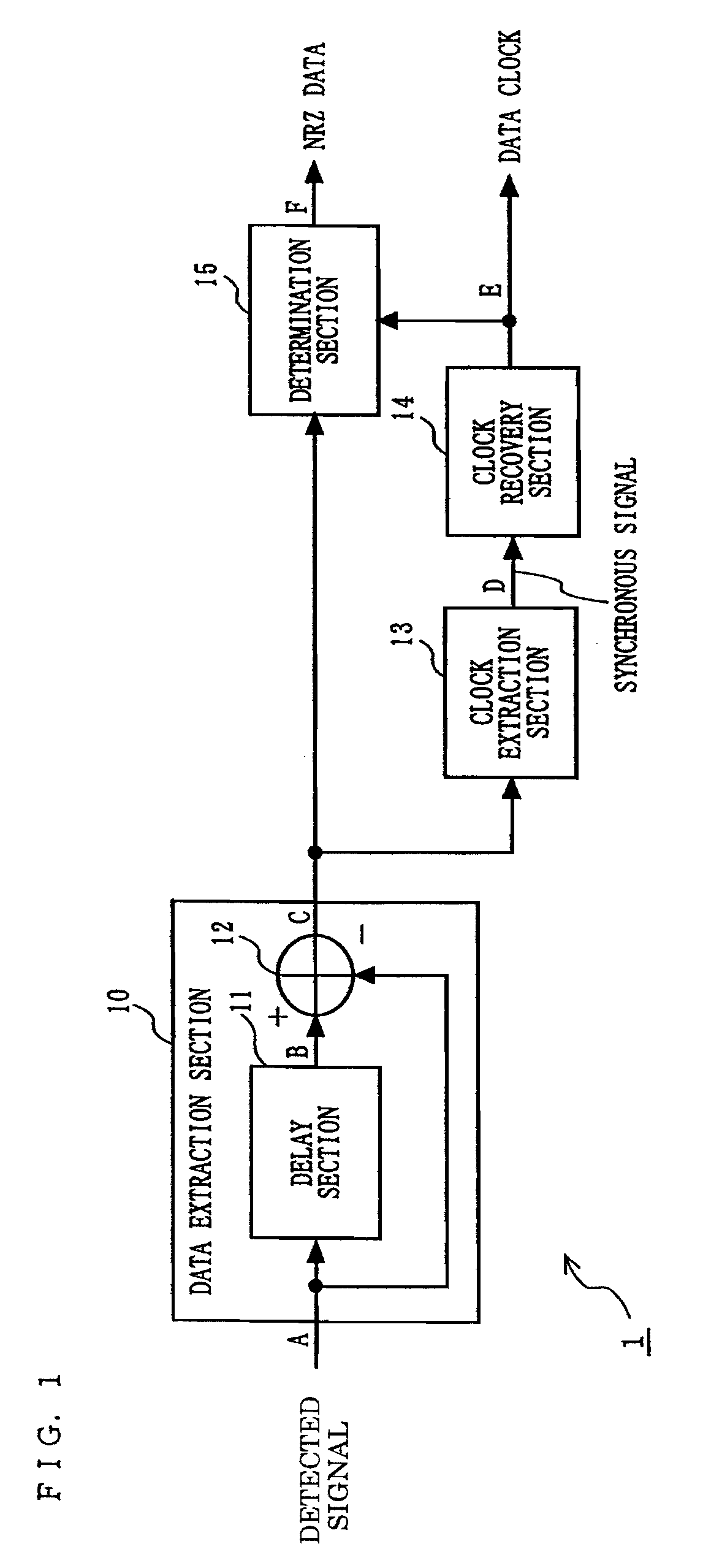
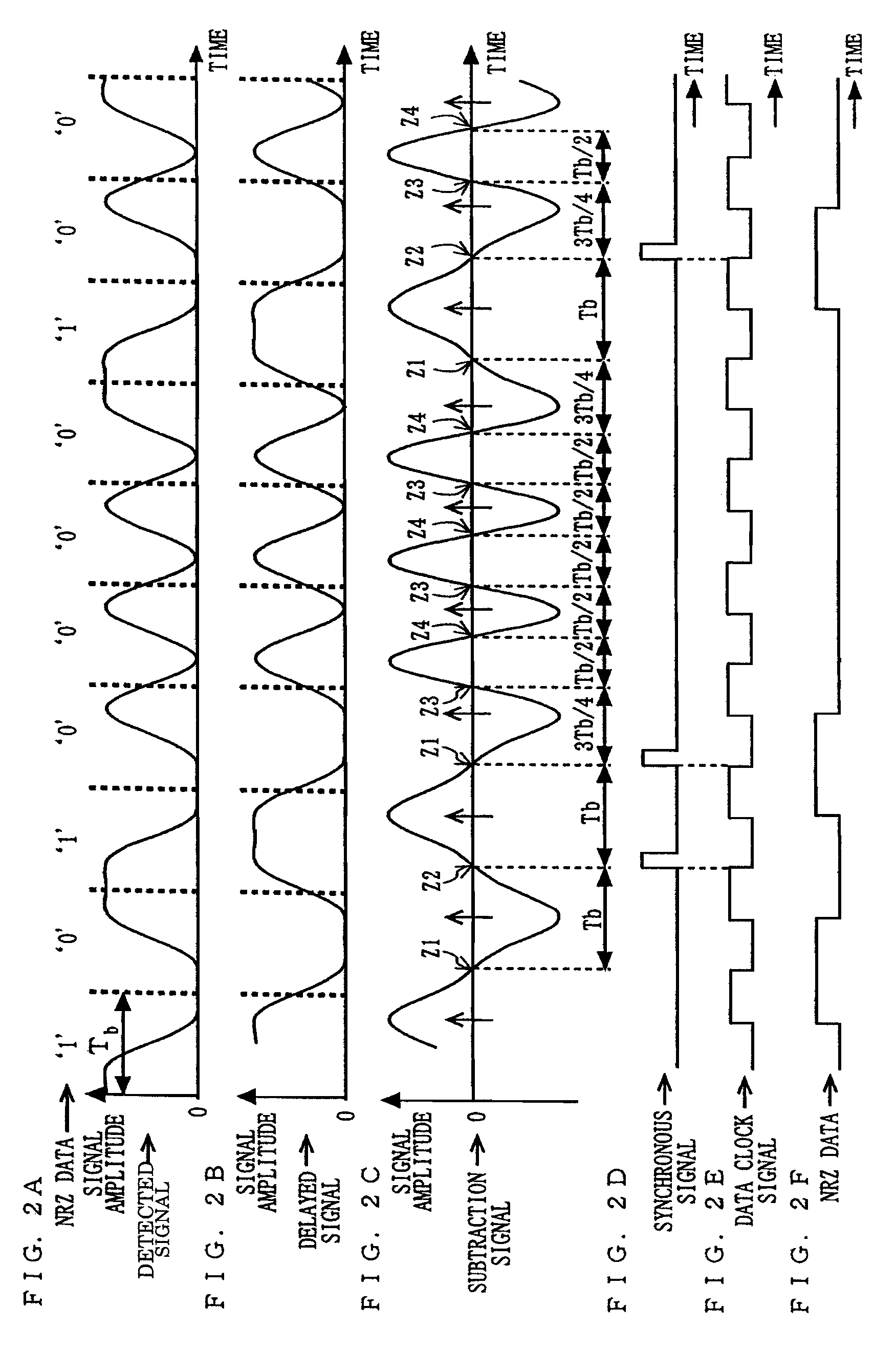
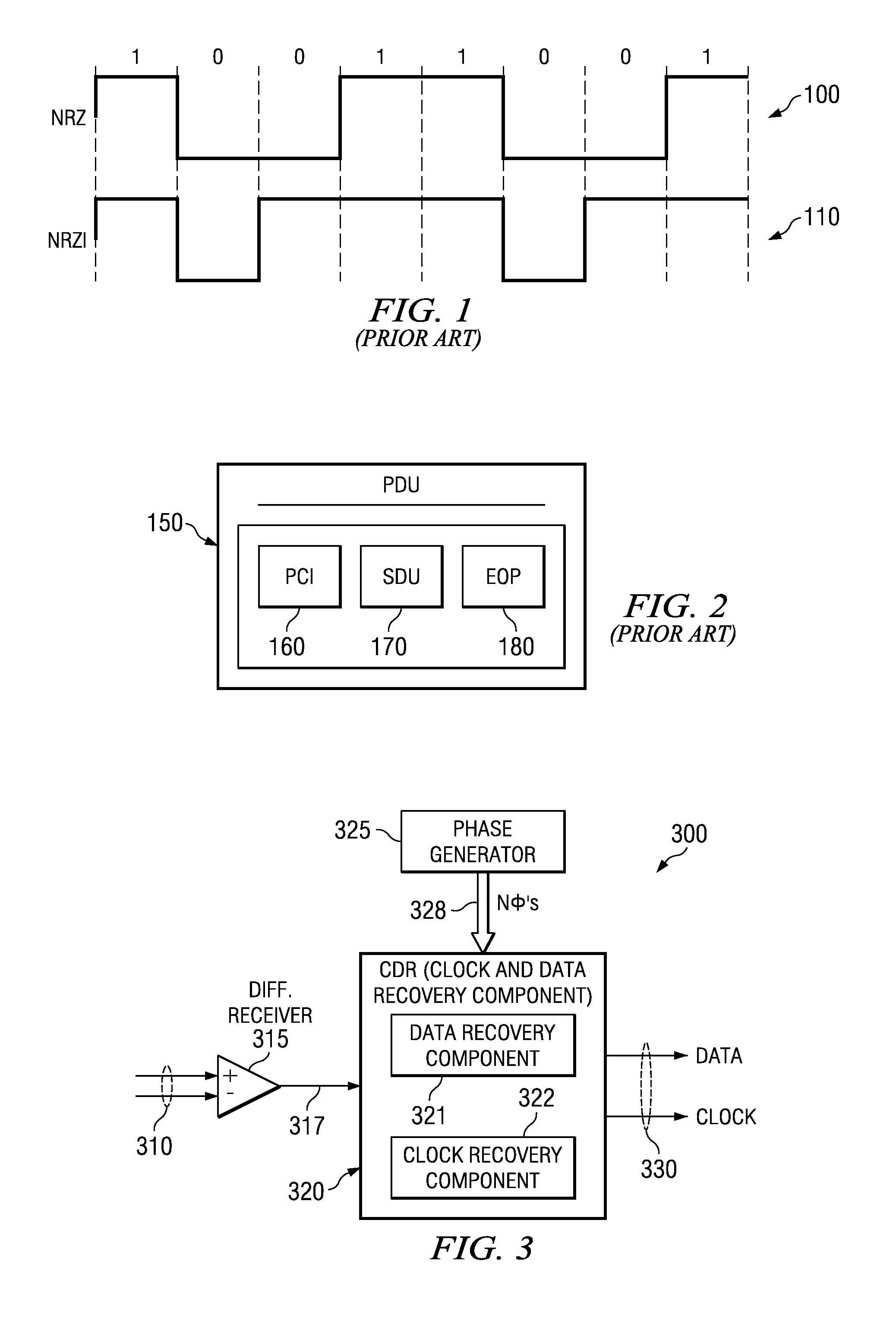
A delay section delays a detected signal by less than one bit time in NRZ data. A subtraction section performs subtraction between a delayed signal and the detected signal, and outputs a resultant signal. A clock extraction section extracts, from crossing points of a subtracted signal, crossing points whose time interval is more than or equal to Tb-α and less than or equal to Tb+β (0<α≦Tb / 8, 0<β≦Tb: Tb is one bit time in the NRZ data), and outputs a synchronous signal synchronized with the extracted crossing point. A clock recovery section synchronizes a clock signal with the phase of the synchronous signal, and outputs a data clock signal. A determination section determines the polarity of the subtracted signal outputted from the subtraction section in accordance with the data clock signal, and outputs the determination result as NRZ data.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
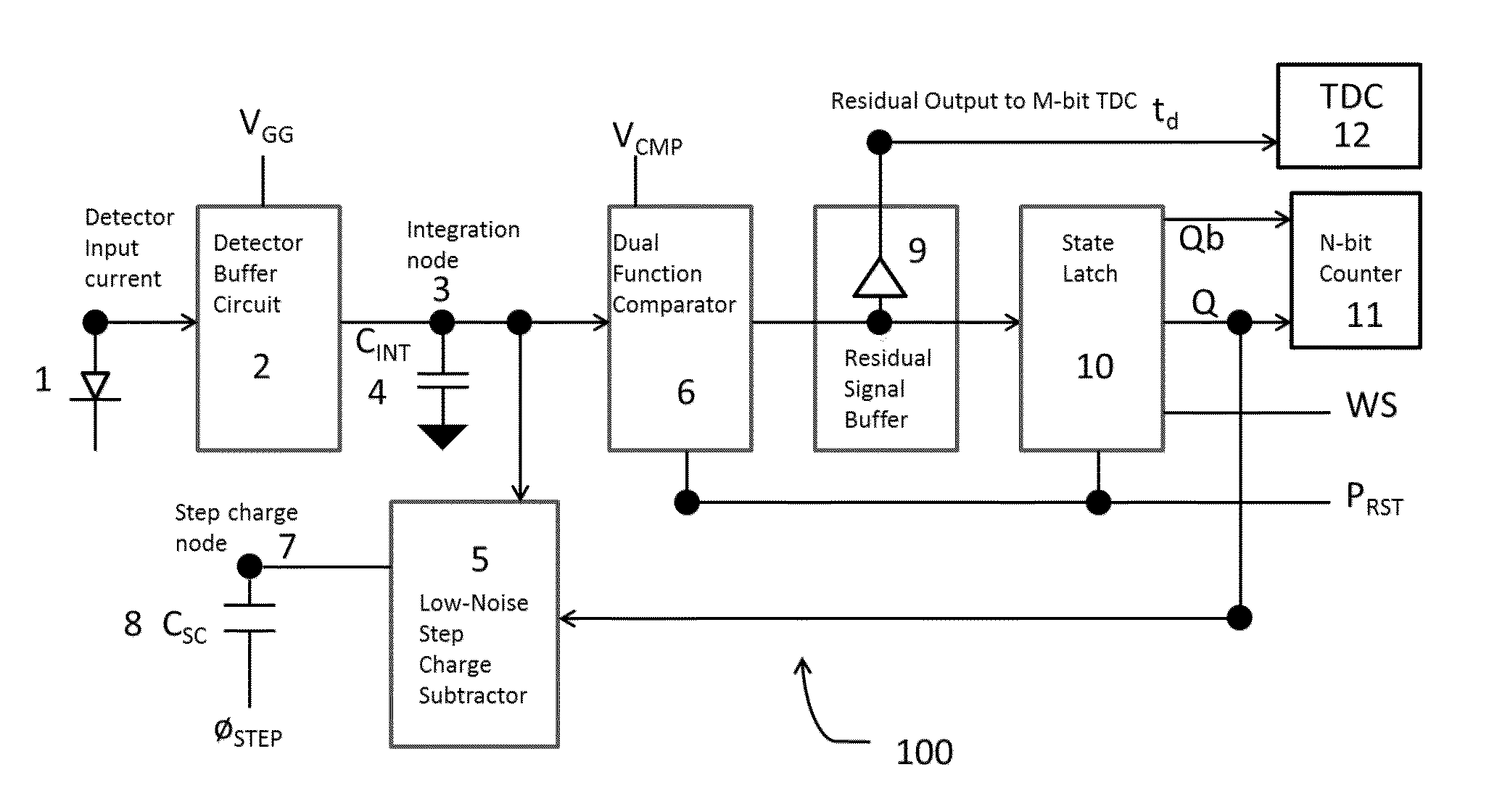
Low power ADC for high dynamic range integrating pixel arrays
ActiveUS9197233B2Low costTelevision system detailsColor television detailsAnalog signal processingDual function
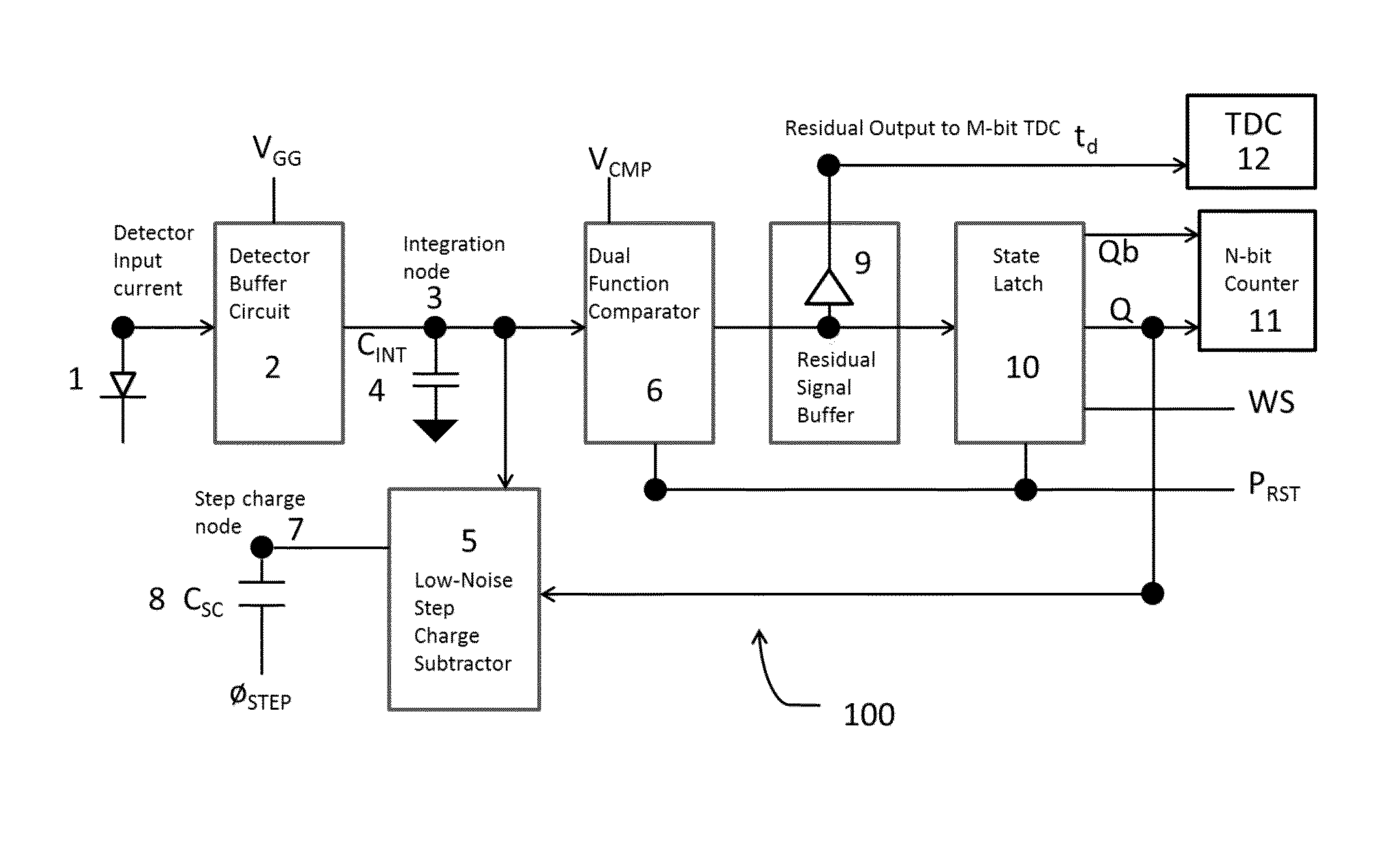
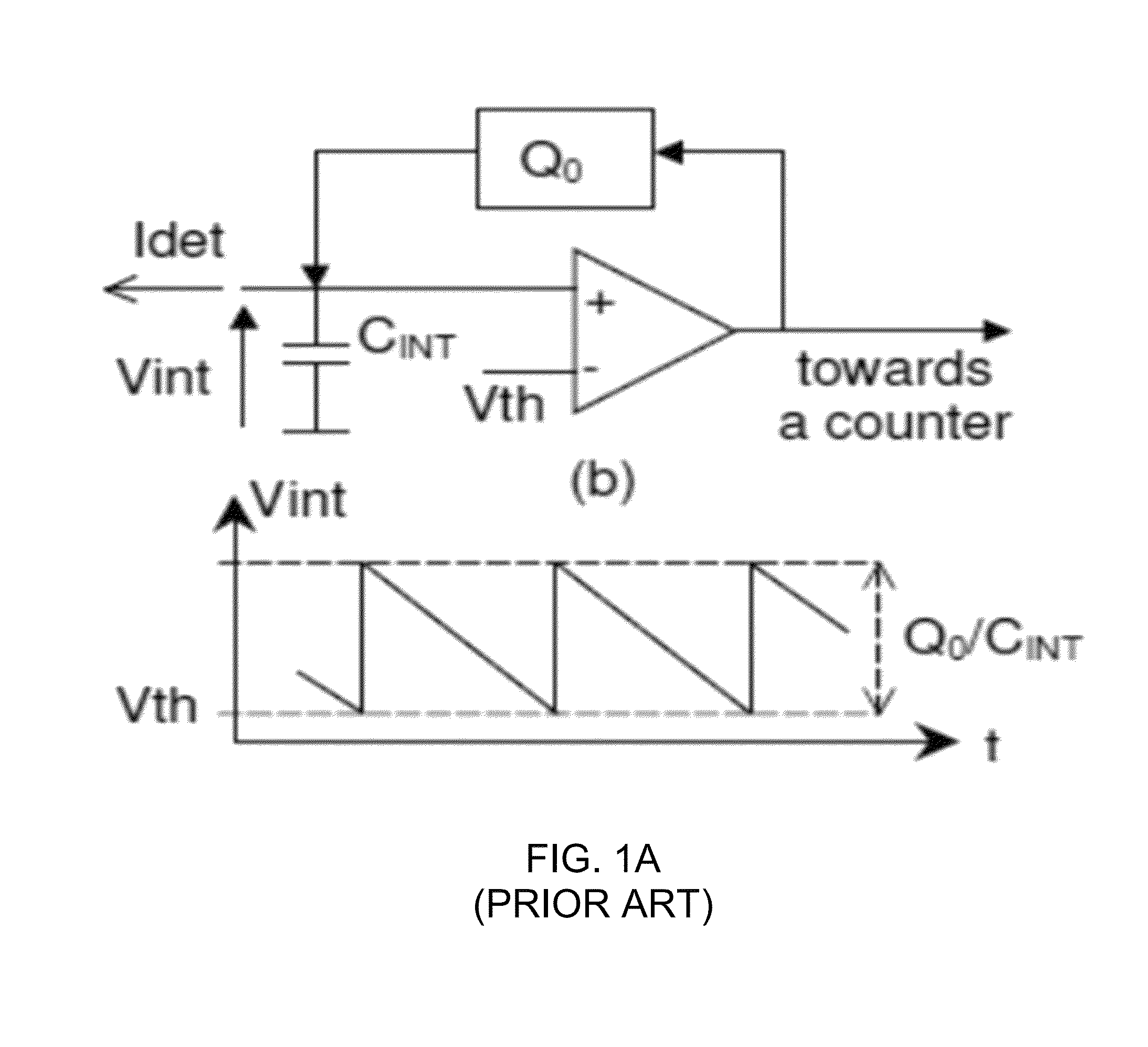
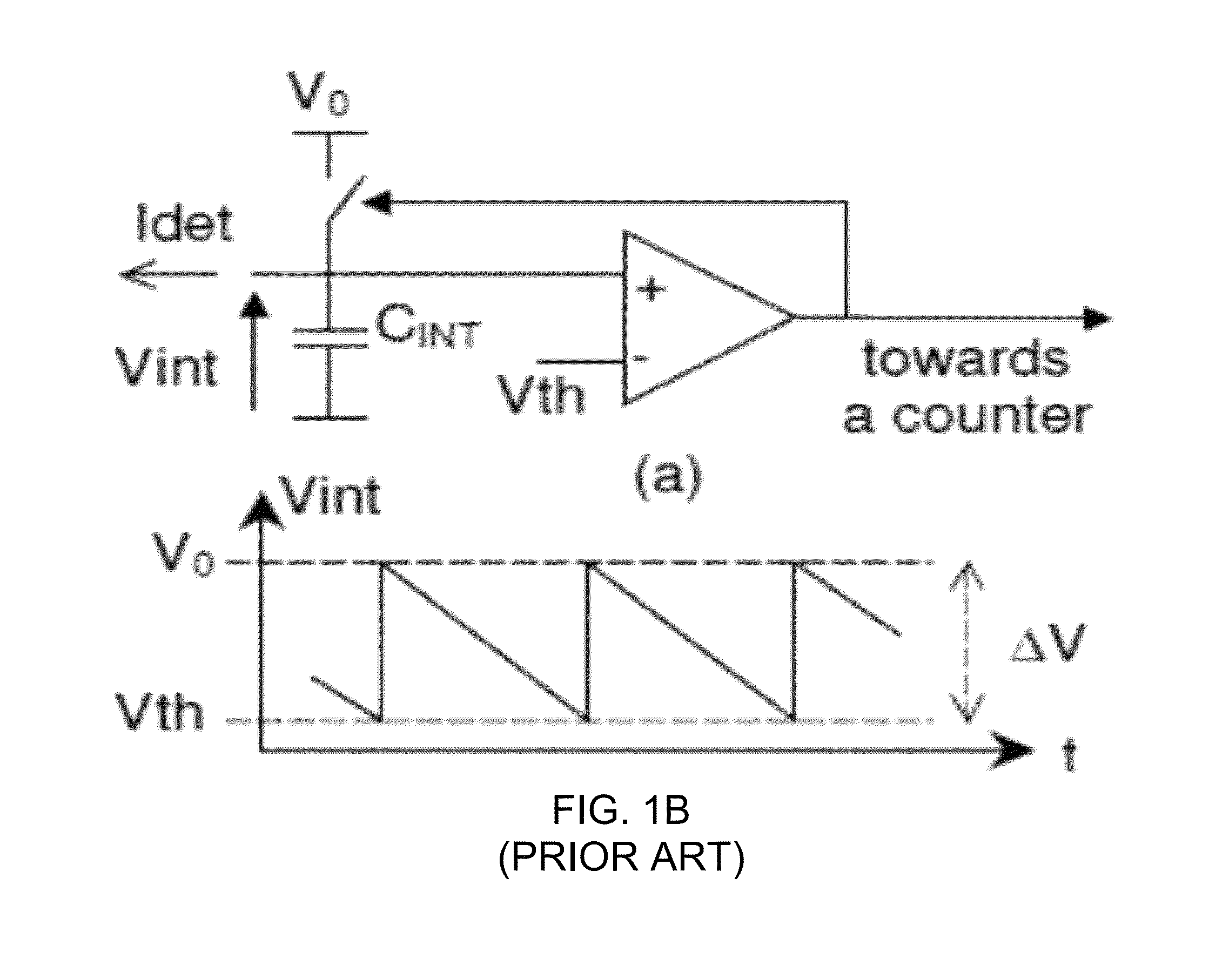
In one or more embodiments, an apparatus and method for processing an analog signal into a digital signal includes an input current buffer circuit, a signal charge integration node, a dual function comparator, a step charge subtractor, a state latch, a coarse N-bit counter, an optional residue signal buffer and a residue signal M-bit time-to-digital (TDC) converter. The circuitry is free running, meaning that it is never reset. Instead, what is tracked for each frame is how much additional charge has been accumulated since the end of the previous integration period. Between each frame, the state of the counter and the amount of charge residing in the integration node are recorded. This information from the beginning and end of a given frame is differenced and to this is added the amount of charge indicated by the number of times the counter overflowed during the integration period.
Owner:BFE ACQUISITION SUB II LLC D B A BLACK FOREST ENG
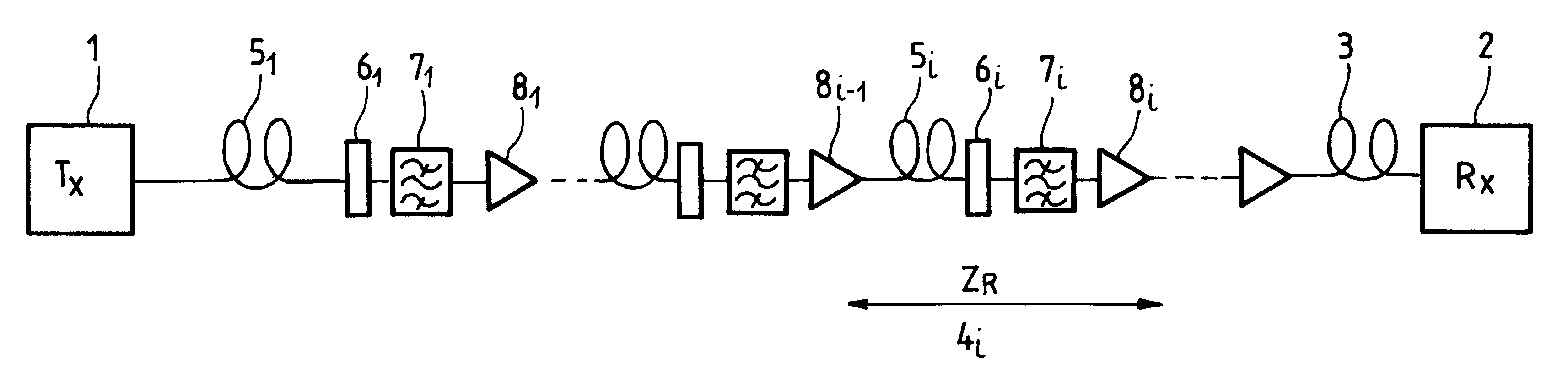
Optical fiber transmission system for soliton signals with wavelength multiplexing and saturable absorbers
InactiveUS6327061B1Avoid disadvantagesWavelength-division multiplex systemsTransmission monitoringMultiplexingActive component
An optical fiber transmission system for soliton signals with wavelength multiplexing in which the bit times of the various channels lambd1 to lambdn of the multiplex are substantially synchronous, at least at one point. At least one saturable absorber is located at this point. The channels can be made synchronous by an appropriate selection of wavelengths, or by using optical delay lines, or the like. The saturable absorber then modulates the intensity of the soliton signals in the various channels of the multiplex. It is possible to use a clock for remotely driving the saturable absorber. The invention also relates to a corresponding transmission method. The invention makes it possible to transmit over long distances without using active components.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
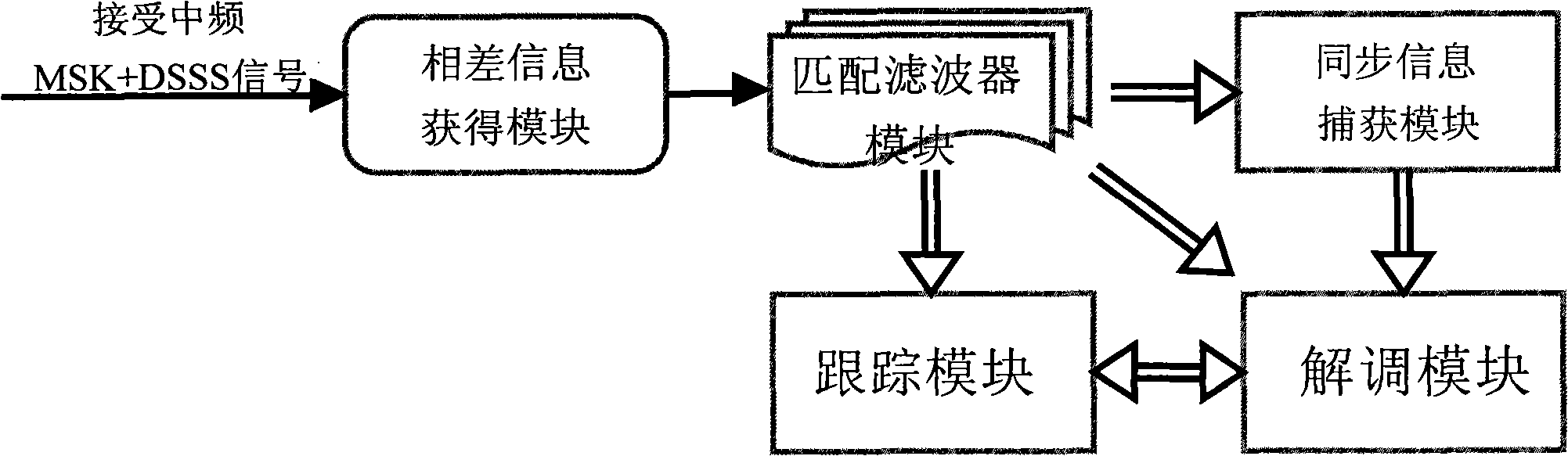
Method for jointly demodulating MSK and DSSS and demodulator thereof
InactiveCN101515915AReduce consumptionReduce power consumptionMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksCommunications systemFrequency compensation
The invention belongs to the technology filed of wireless communication, relating to a method for jointly demodulating MSK (minimum shift keying) and DSSS (direct sequence spread spectrum) and a demodulator thereof. The demodulator comprises an error information obtaining module, a match filter module, a synchronous information trapping module, a demodulating module and a tracking module; and the method for jointly demodulating MSK and DSSS comprises the following steps of: (1) obtaining error information, (2) matching and filtering the error information, (3) trapping synchronous information, (4) demodulating, (5) tracking, or the like, and sending demodulation results to parent process so as to complete communication process. The invention has the advantage of better frequency compensation ability, thereby, solving the problems that a method for dispreading and demodulating direct sequence spread spectrum signals needs to be frequency offset estimated, complex extraction of PN code synchronization and bit synchronization, etc. Compared with the existing dispreading and demodulating method, the invention is simple as needing no carrier recovery module nor bit timing module, and is applicable to the wireless communication system.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Ask demodulation device and wireless device using the same
ActiveUS7450666B2Amplitude demodulation by homodyne/synchrodyne circuitsIndividual digits conversionClock recoveryEngineering
A delay section delays a detected signal by less than one bit time in the NRZ data. A subtraction section performs subtraction between a delayed signal and the detected signal, and outputs a resultant signal. A clock extraction section extracts, from crossing points of a subtracted signal, crossing points whose time interval is more than or equal to (Tb-alpha) and less than or equal to (Tb+beta) (wherein 0<alpha<=Tb / 8, 0<beta<=Tb: Tb is one bit time in the NRZ data), and outputs a synchronous signal synchronized with the extracted crossing point. A clock recovery section synchronizes a clock signal with the phase of the synchronous signal, and outputs a data clock signal. A determination section determines the polarity of the subtracted signal outputted from the subtraction section in accordance with the data clock signal, and outputs the determination result as the NRZ data.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Transition-time control in a high-speed data transmitter
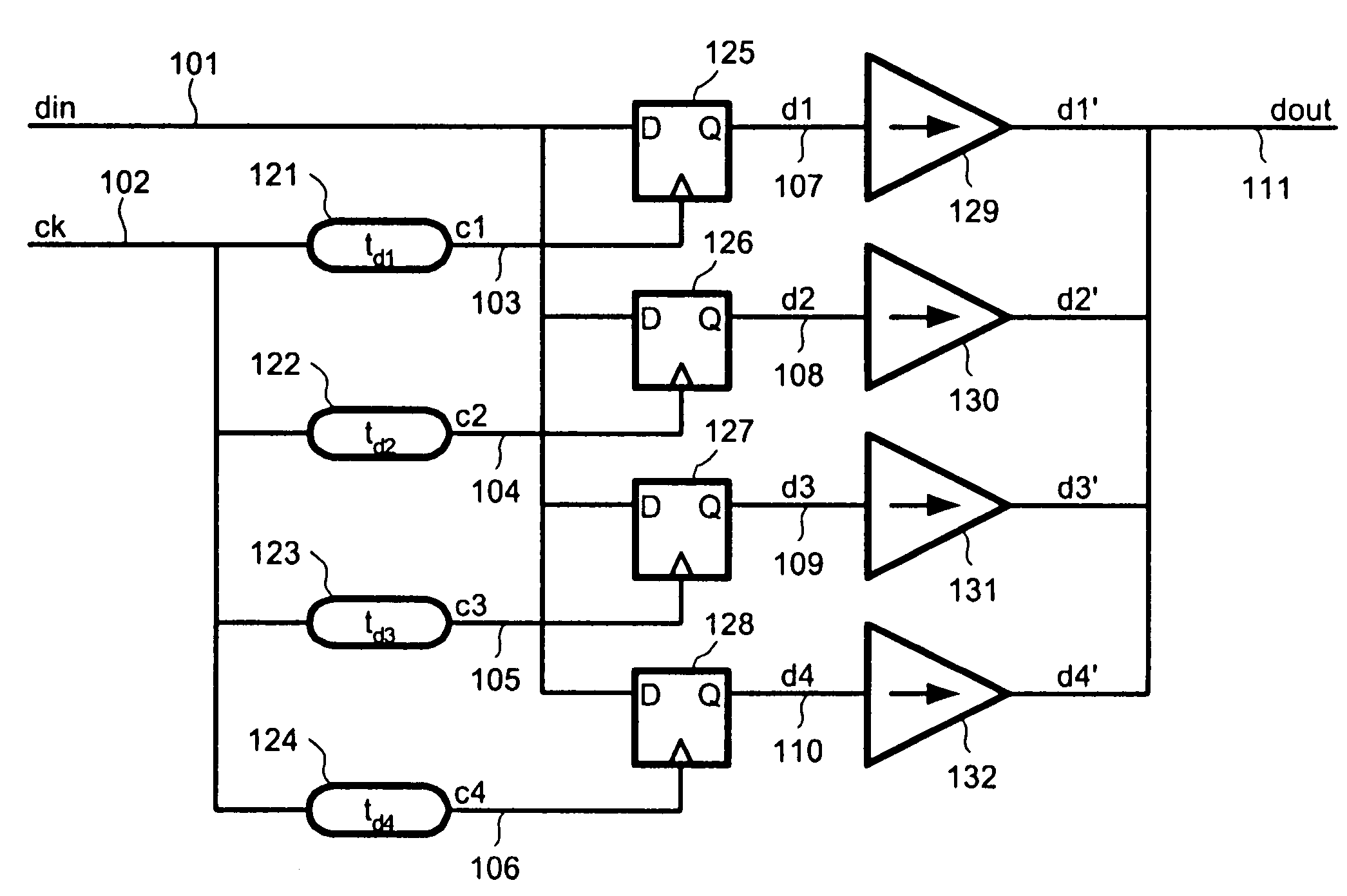
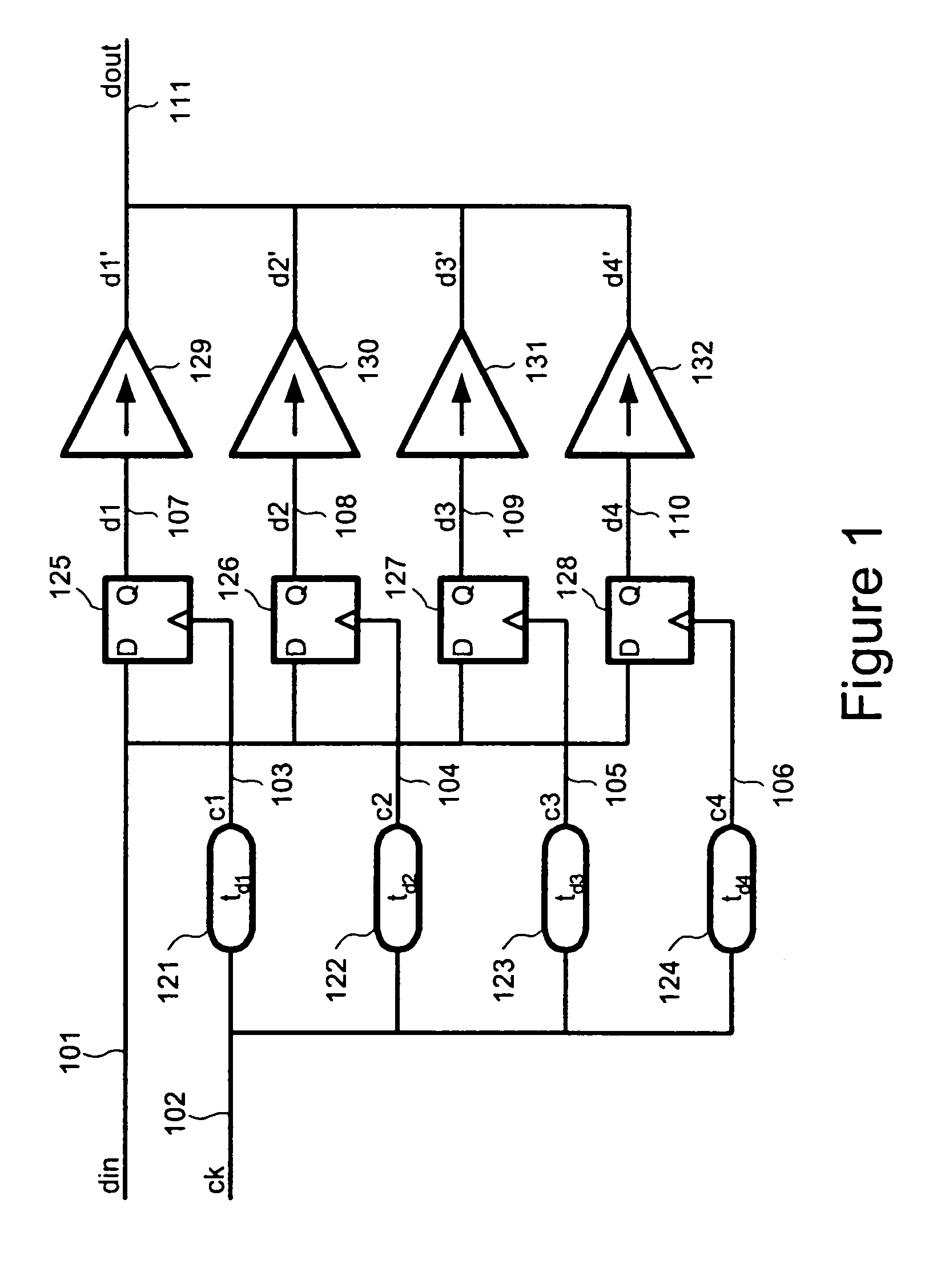
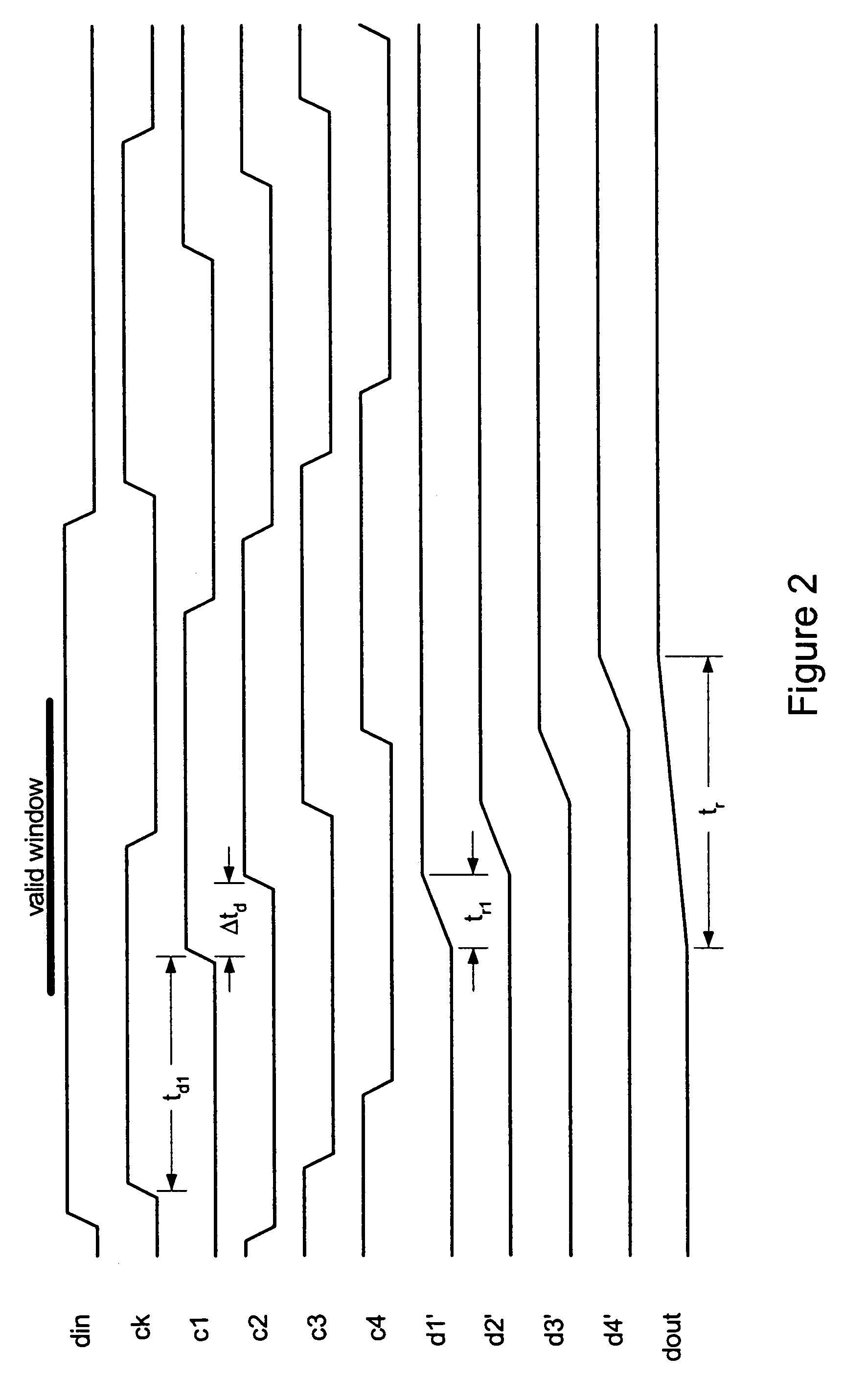
InactiveUS7187721B1Increase computing speedAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsTransmission line coupling arrangementsControl delayTransition time
Transition time of a data signal is controlled by applying different delays to the data signal and combining the delayed data signals. The transition time of the data output is determined by difference in delays applied to the data input and may be proportional to bit time of the bit clock. The data input may be applied directly to the delay elements or may be clocked by clock signals delayed by the delay elements. The delayed data is applied to parallel driver circuits. Supply voltage to the delay elements can be controlled to compensate for production and environmental variations. The supply voltage controller includes parallel delay elements of different delays and a phase comparator, the output of which controls the supply voltage applied to the delay elements.
Owner:FINISAR +1
Multiple bit rate optical communication method, optical network unit and optical line terminal
InactiveUS7653312B2Reduce upgrade costsLow costTime-division optical multiplex systemsTime-division multiplexOptical communicationOptical network unit
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
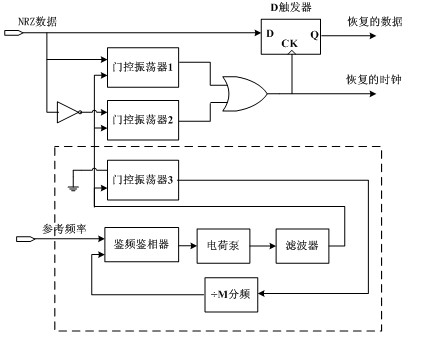
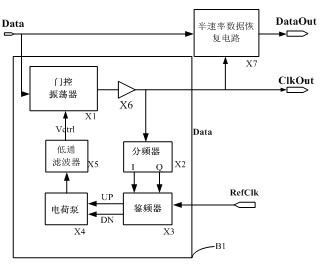
Ultrahigh-speed burst mode clock restoring circuit based on gate-control oscillator
InactiveCN102611440AAchieve monolithic integrationLow costPulse automatic controlLow-pass filterControl signal
The invention provides an ultrahigh-speed burst mode clock restoring circuit based on a gate-control oscillator, comprising the gate-control oscillator, four frequency dividers, a frequency-discrimination device, a charge pump, a low-pass filter, an interior clock buffer and a semi-velocity data restoring circuit. The ultrahigh-speed burst mode clock restoring circuit is characterized in that an output clock of the gate-control oscillator can restore a clock signal from input data of any phases within a plurality of bit times when data turn over under traction action of the input data, wherein the phase of the clock signal is aligned with the phase of the input data; the four frequency dividers, the frequency-discrimination device, the charge pump, the low-pass filter and the interior clock buffer are used for analyzing relation of output lock signal frequency and reference frequency and providing a control signal for the gate-control oscillator, and the semi-velocity data restoring circuit resets the data according to the restored clock signal to generate a restored data signal. The ultrahigh-speed burst mode clock restoring circuit disclosed by the invention is suitable for an optical fiber communication system, and in particular relates to a burst mode optical communication system taking a ten-gigabit Ethernet passive optical network technology as representation.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
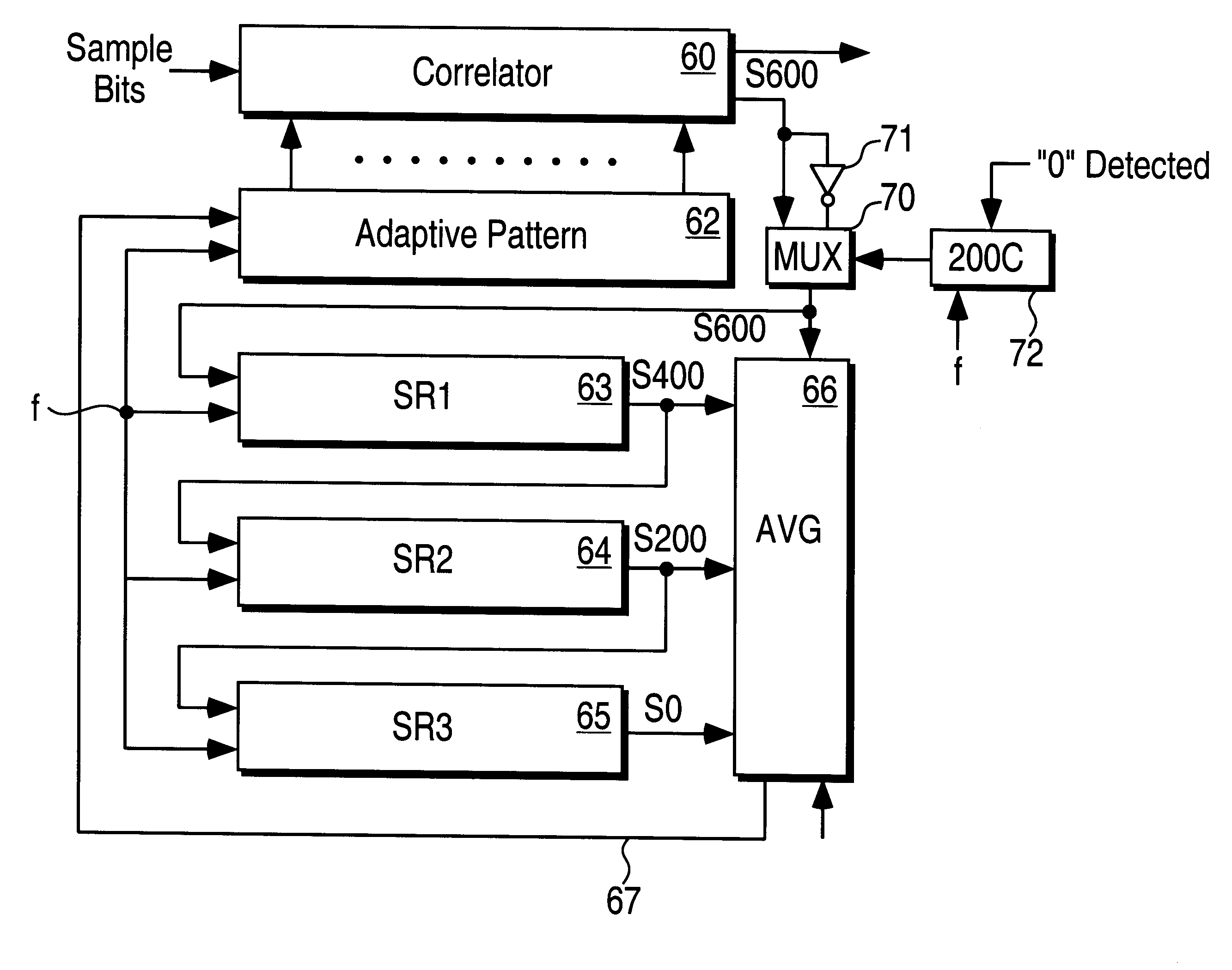
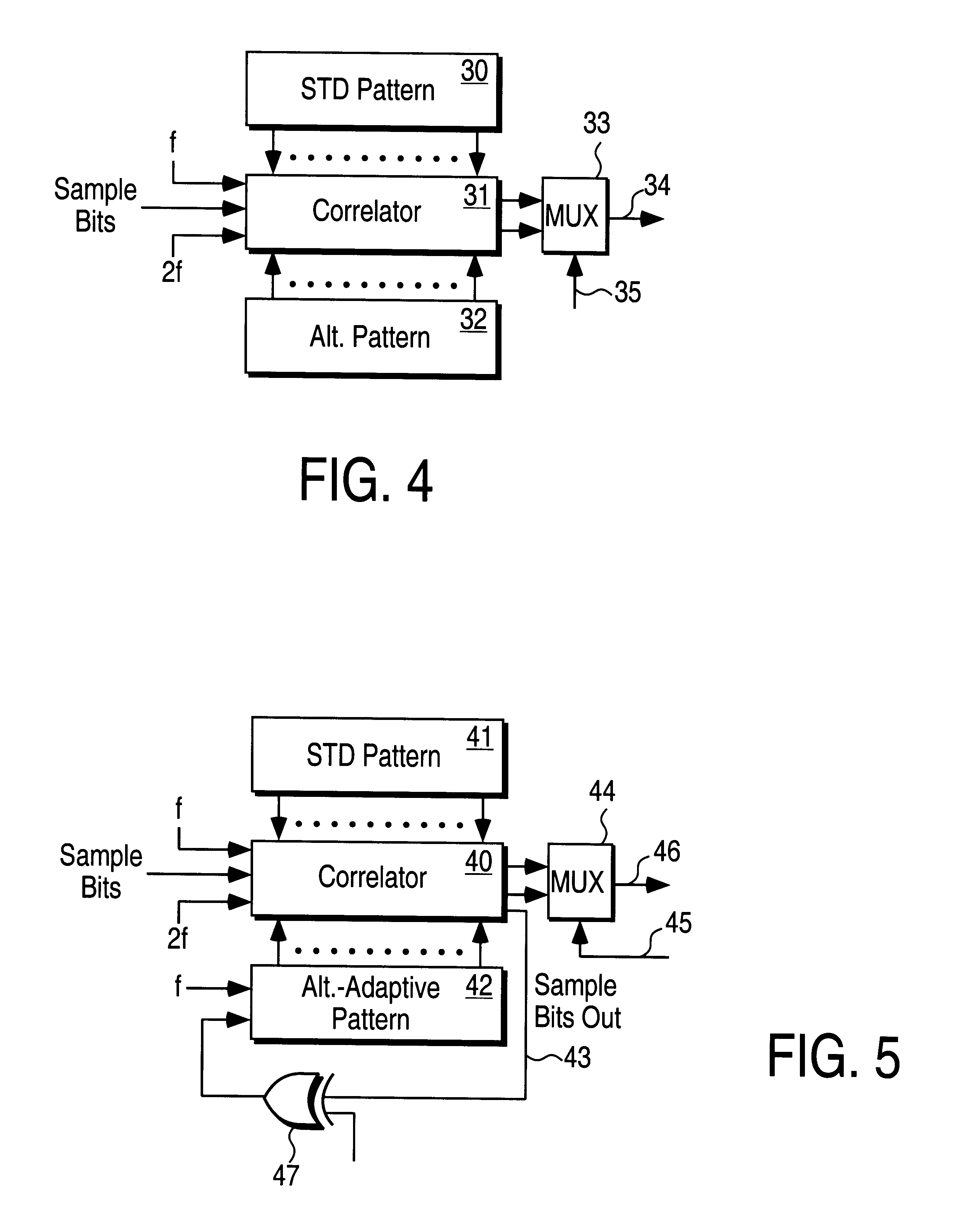
Adaptive reference pattern for spread spectrum detection
InactiveUS6473450B1Electric signal transmission systemsTransmission/receiving by adding signal to waveCarrier signalSignal correlation
Owner:ECHELON CORP
Low power ADC for high dynamic range integrating pixel arrays
ActiveUS20150288376A1Reduction in CLow costTelevision system detailsElectric signal transmission systemsAnalog signal processingDual function
In one or more embodiments, an apparatus and method for processing an analog signal into a digital signal includes an input current buffer circuit, a signal charge integration node, a dual function comparator, a step charge subtractor, a state latch, a coarse N-bit counter, an optional residue signal buffer and a residue signal M-bit time-to-digital (TDC) converter. The circuitry is free running, meaning that it is never reset. Instead, what is tracked for each frame is how much additional charge has been accumulated since the end of the previous integration period. Between each frame, the state of the counter and the amount of charge residing in the integration node are recorded. This information from the beginning and end of a given frame is differenced and to this is added the amount of charge indicated by the number of times the counter overflowed during the integration period.
Owner:BFE ACQUISITION SUB II LLC D B A BLACK FOREST ENG
Clock recovery system for encoded serial data with simplified logic and jitter tolerance
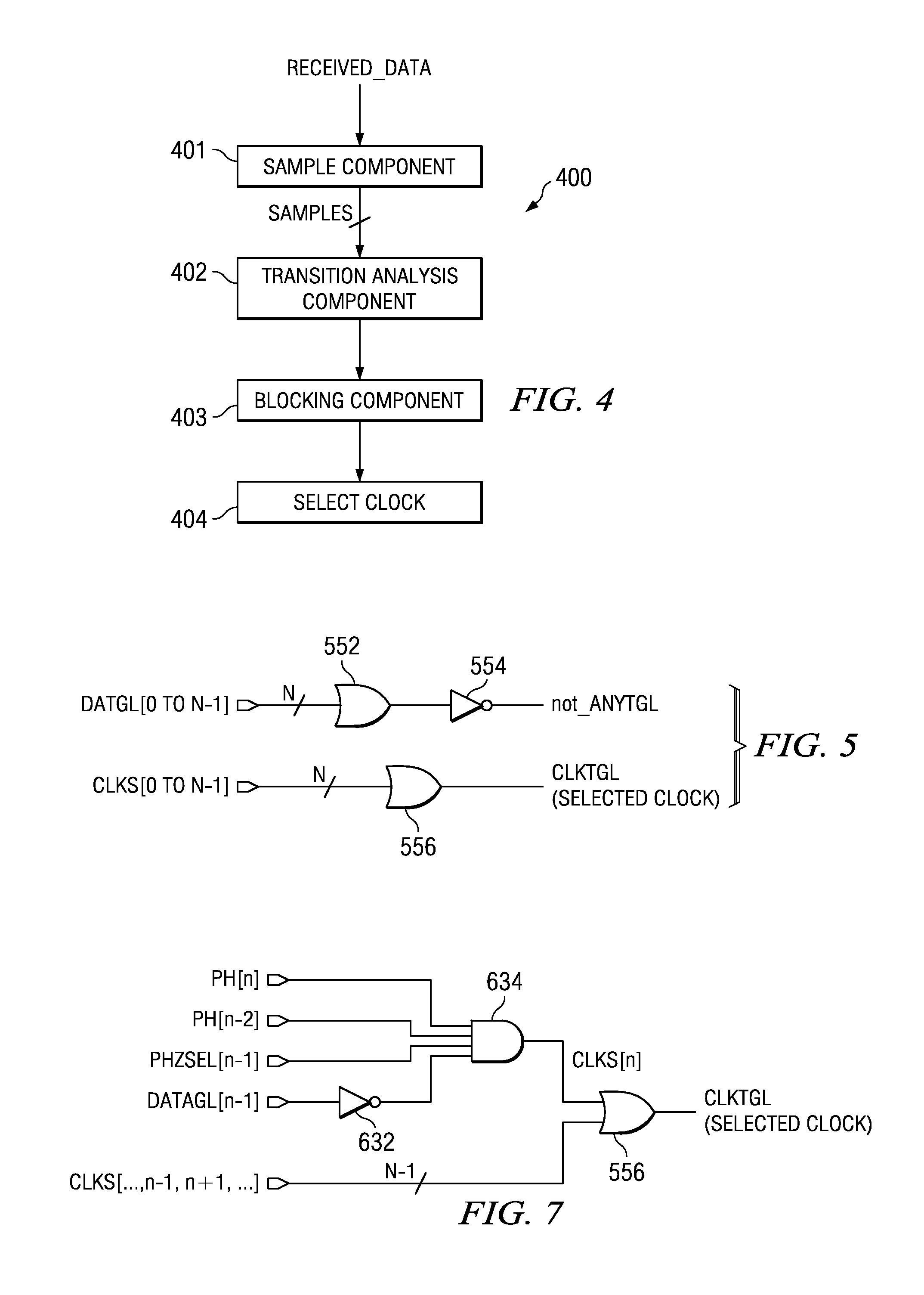
ActiveUS20050091559A1Facilitate data communicationImprove toleranceElectronic circuit testingError detection/correctionData streamClock recovery
The present invention facilitates clock and data recovery for serial data streams by selecting a clock phase for each input data transition and generating a recovered clock. In order to identify data transitions, the received serial data stream is sampled N times per ideal bit time, where the minimum value for N must be greater than 2 / (1−(2*jitter_ratio)) and jitter_ratio is the fractional representation of the portion of the ideal bit time during which transitions can be expected or estimated to occur. On identifying a transition, a toggle phase is set. In order to avoid stale clock phase selection resulting from jitter and the like, one phase after the toggle phase is blocked or prevented from being selected for the clock. Finally, a clock phase is selected N / 2 phases from the toggle phase and a recovered clock is generated by combining the individually selected clock phases.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Clock recovery system for encoded serial data with simplified logic and jitter tolerance
ActiveUS7200782B2Facilitate data communicationImprove toleranceElectronic circuit testingError detection/correctionData streamClock recovery
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Clock-signal adjusting method and device
ActiveUS7760840B2Pulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionClock rateWave shape
A clock-signal adjusting method and device is used for adjusting a frequency of a clock signal according to a frequency of an input data. The input data is sampled with a sampling frequency m times of the clock frequency to obtain a data transition waveform indicating data transition timing distribution. A unitary bit time of the input data is divided into m zones. A frequency relationship between the clock signal and the input data is determined according to a shift of the data transition waveform relative to the zones. The frequency of the clock signal is adjusted according to the frequency relationship.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
Data recovery using data eye tracking
Owner:SUPER INTERCONNECT TECH
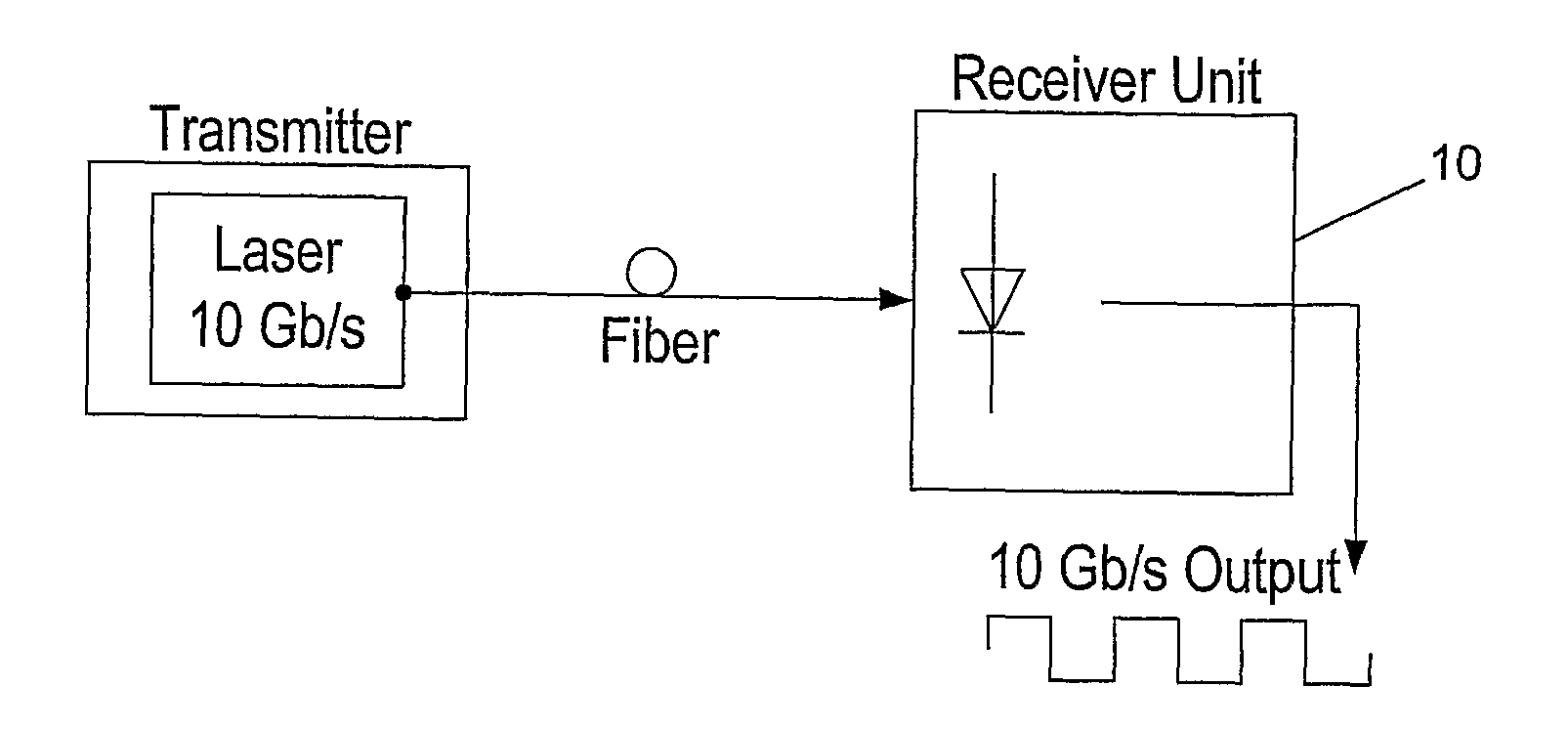
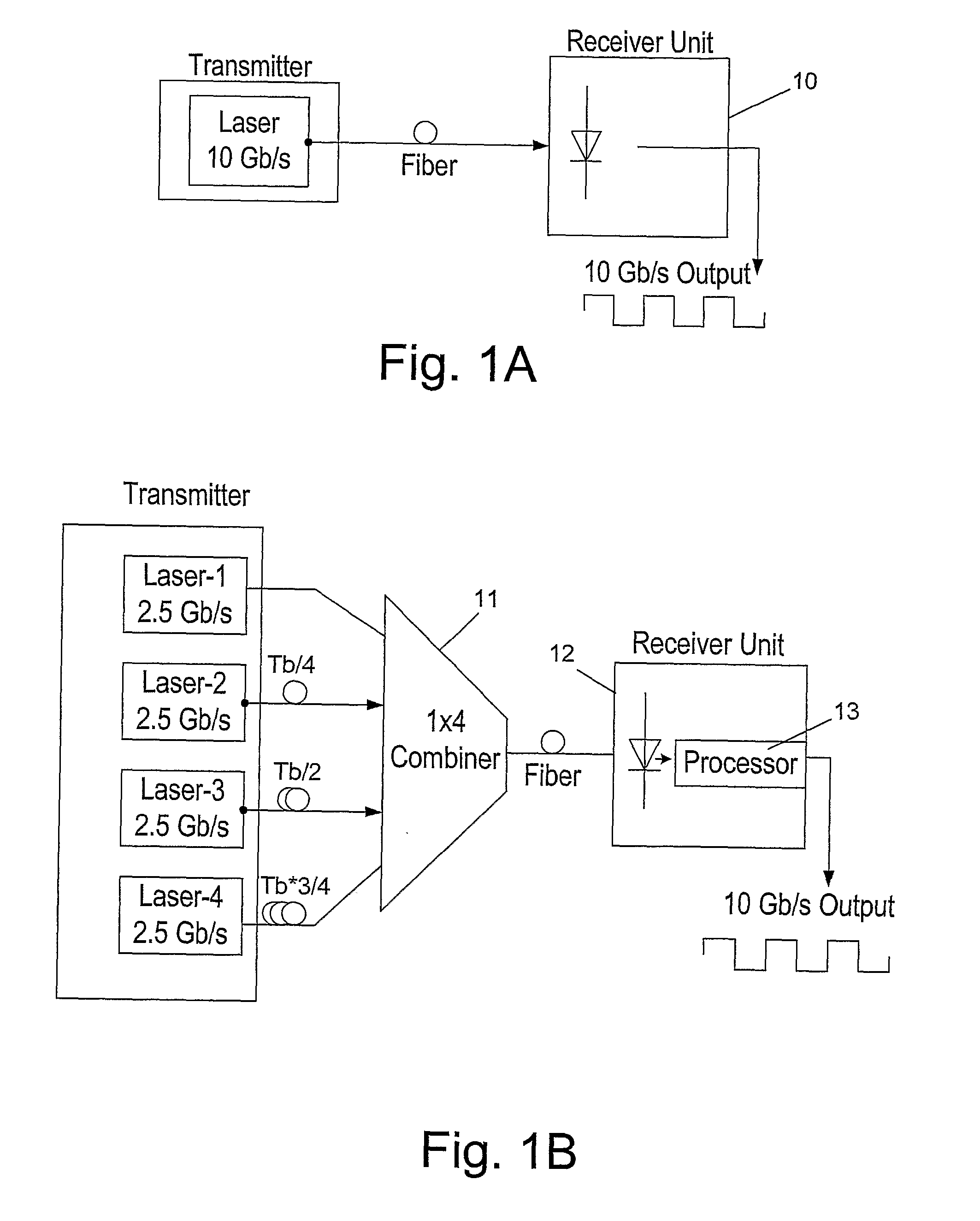
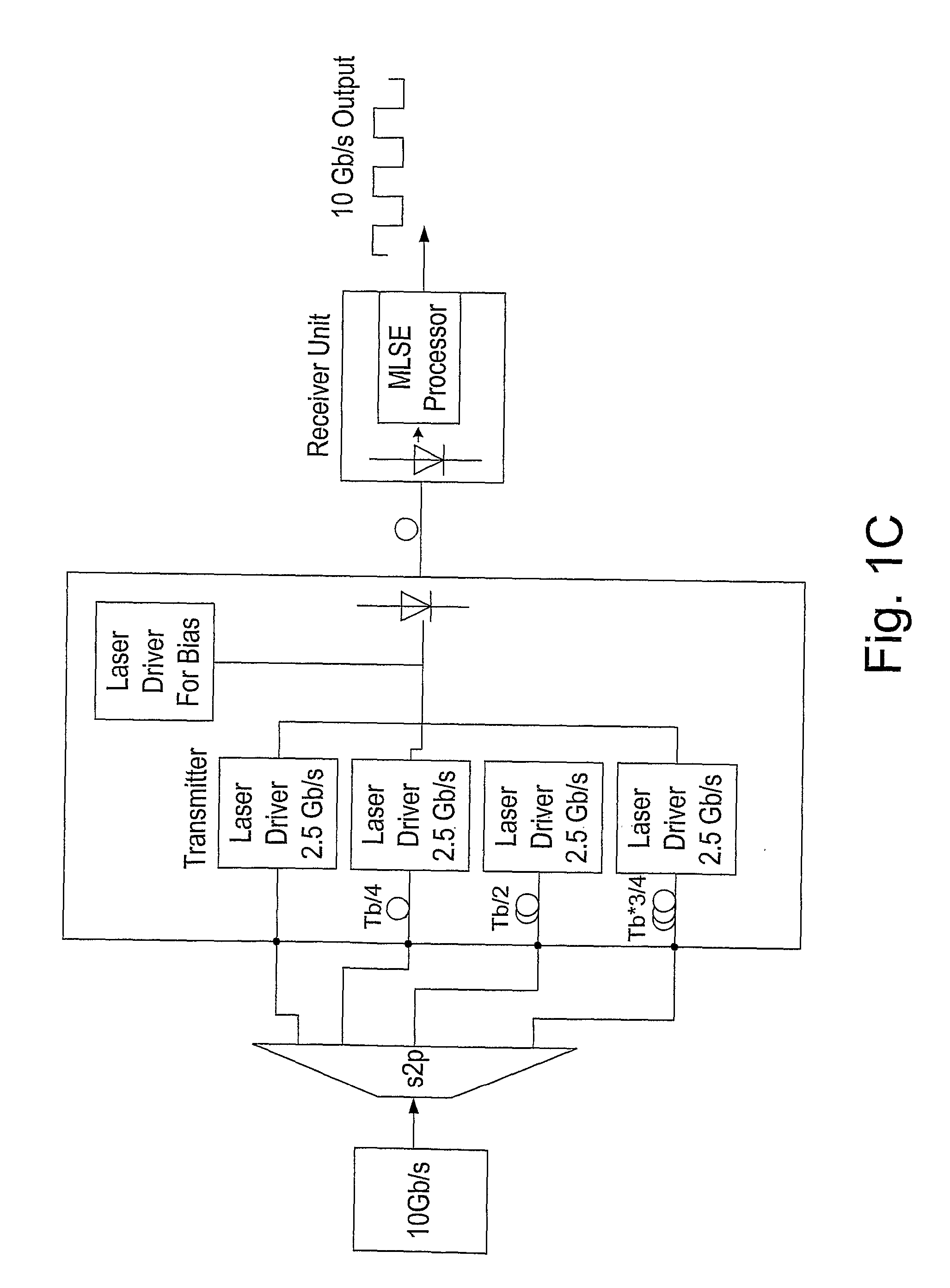
Method and Apparatus for Increasing the Capacity of A Data Communication Channel
ActiveUS20100247107A1Increase data capacityLow costTime-division multiplexElectromagnetic receiversData streamTime delays
Method for efficiently increasing the capacity of an optical channel which can operate in a given data rate B, by generating N modulated data streams with a bit rate of B / N and a bit-time of N / B at the transmission end, to be simultaneously transmitted from a transmission end to a receiving end of the channel. A shift of 1 / B*N between the first modulated data stream and each of its N−1 subsequent modulated data streams is generated using time delay or phase shifting and then the first modulated data stream and its shifted subsequent modulated data streams are combined into a composite multilevel signal with up to N levels and the composite multilevel signal is transmitted to a receiving end of the channel. At the receiving end, the composite multilevel signal is sampled N times during each bit-time, in order to obtain a vector with N elements at each time, such that each element has N+1 possible values and corresponds to the order of a sample. Each of the N modulated data streams are reconstructed by vectorial MLSE, preformed for each element by calculating the joint conditional PDF.
Owner:MULTIPON NETWORKS
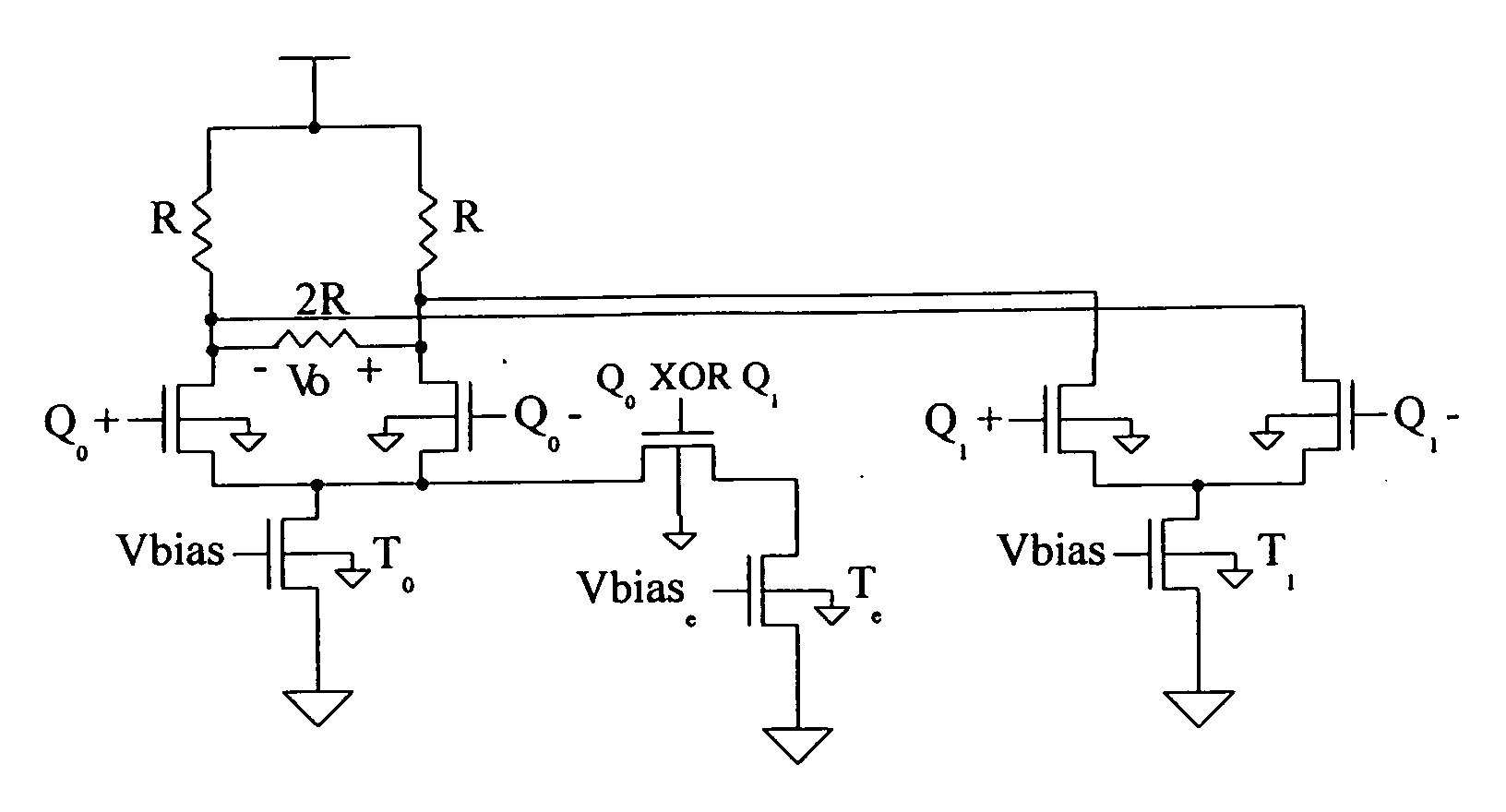
Driver/equalizer with compensation for equalization non-idealities
InactiveUS20060238237A1Reliability increasing modificationsElectronic switchingCommunications systemPower grid
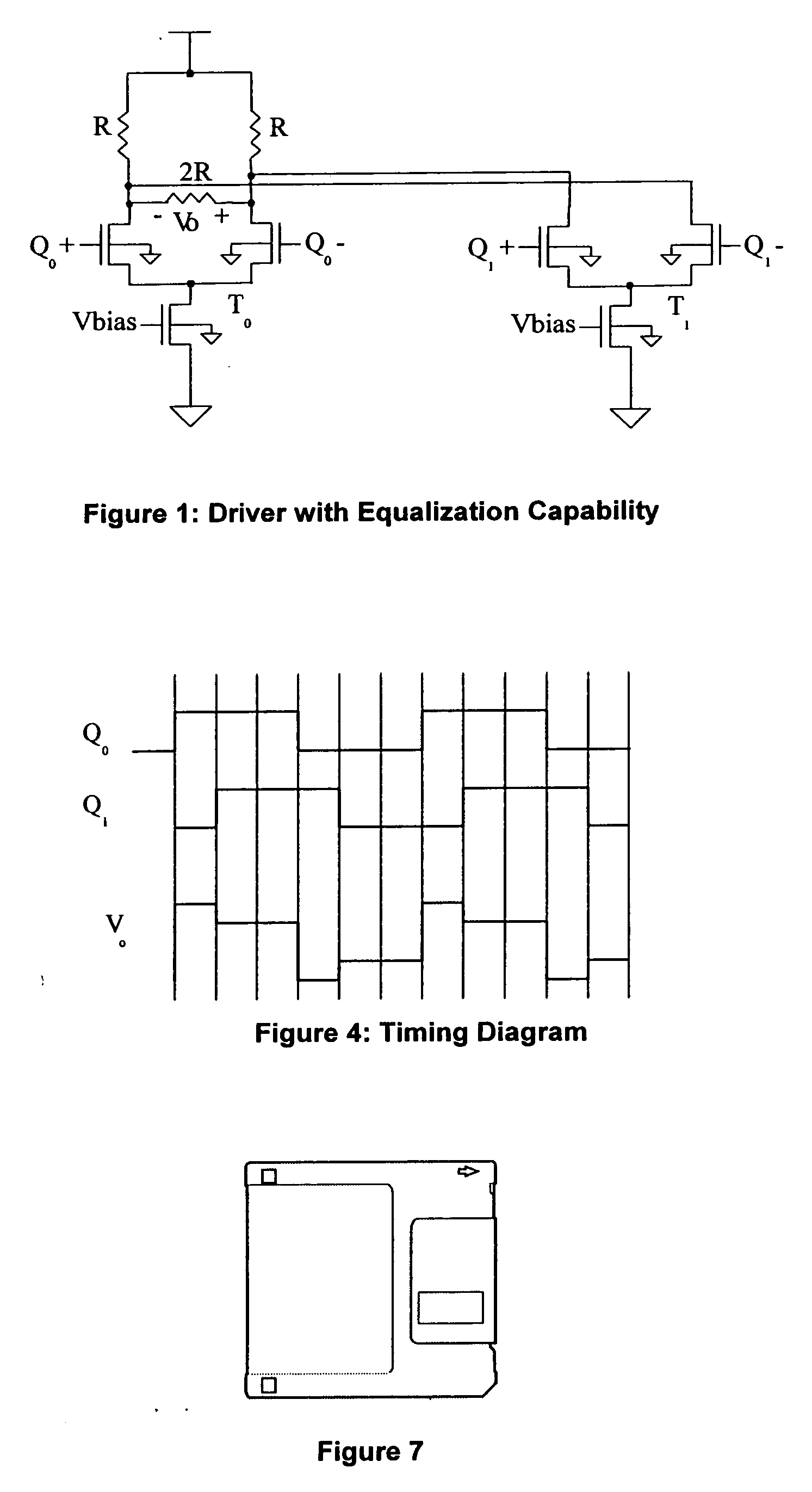
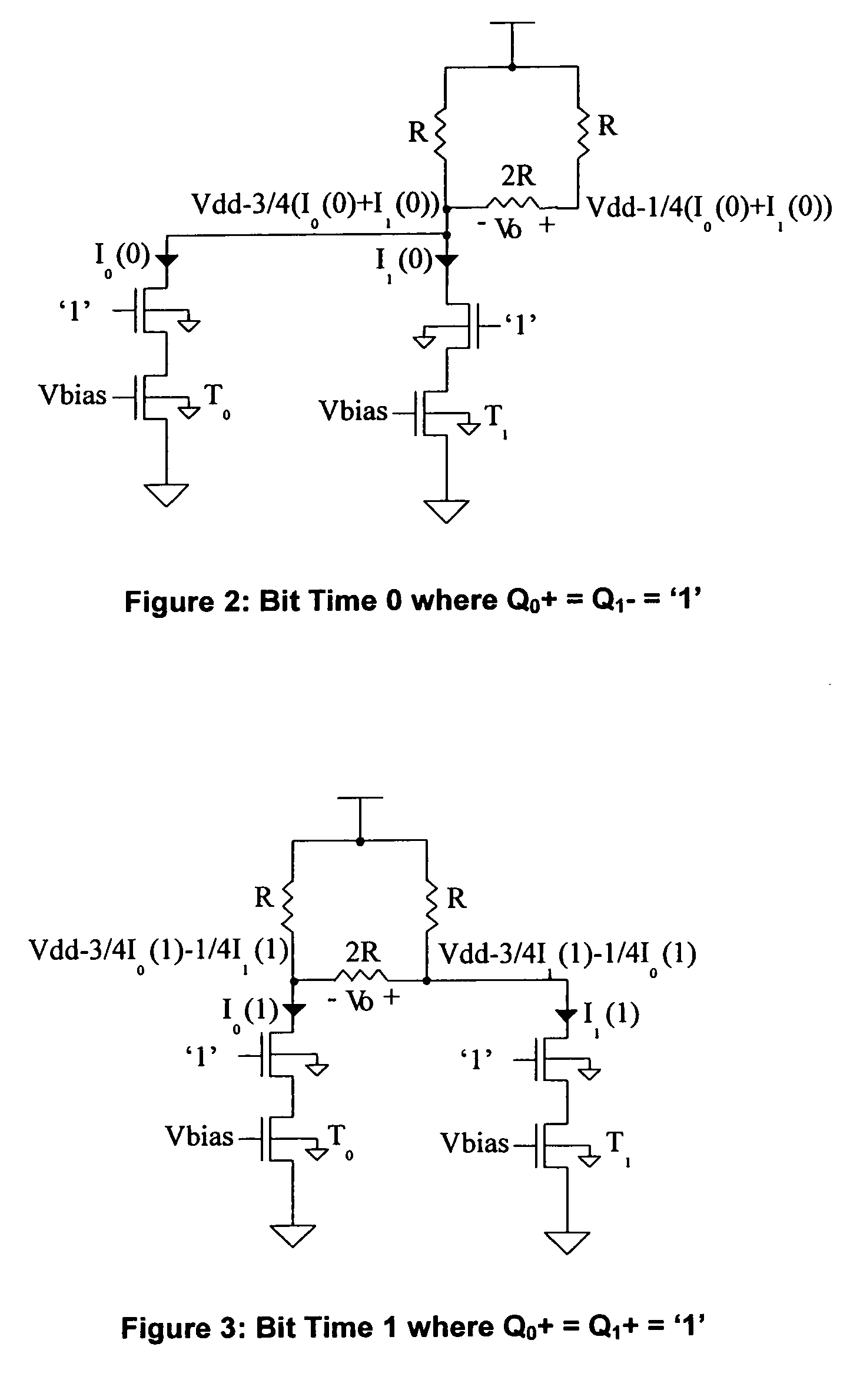
A high speed serial data communication system includes provisions for the correction of equalization errors, particularly those errors introduced by equalizer non-idealities. The equalization is achieved at the data transmitter, and is based on dynamic current subtraction at the output of a differential pair. When bit time>0, the error current is removed or subtracted from the total driver current, thereby maintaining a constant total current from bit time 0 to bit time>0. The same result can also be achieved by subtracting current when bit time>0 using field effect transistors of the opposite gender. The error current can be determined empirically from simulation or through feedback using a replica of the driver. The circuits for achieving equalization error correction and the resulting electrical network analysis are shown and described.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com