Patents
Literature
10724 results about "Optical communication" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Optical communication, also known as optical telecommunication, is communication at a distance using light to carry information. It can be performed visually or by using electronic devices. The earliest basic forms of optical communication date back several millennia, while the earliest electrical device created to do so was the photophone, invented in 1880.
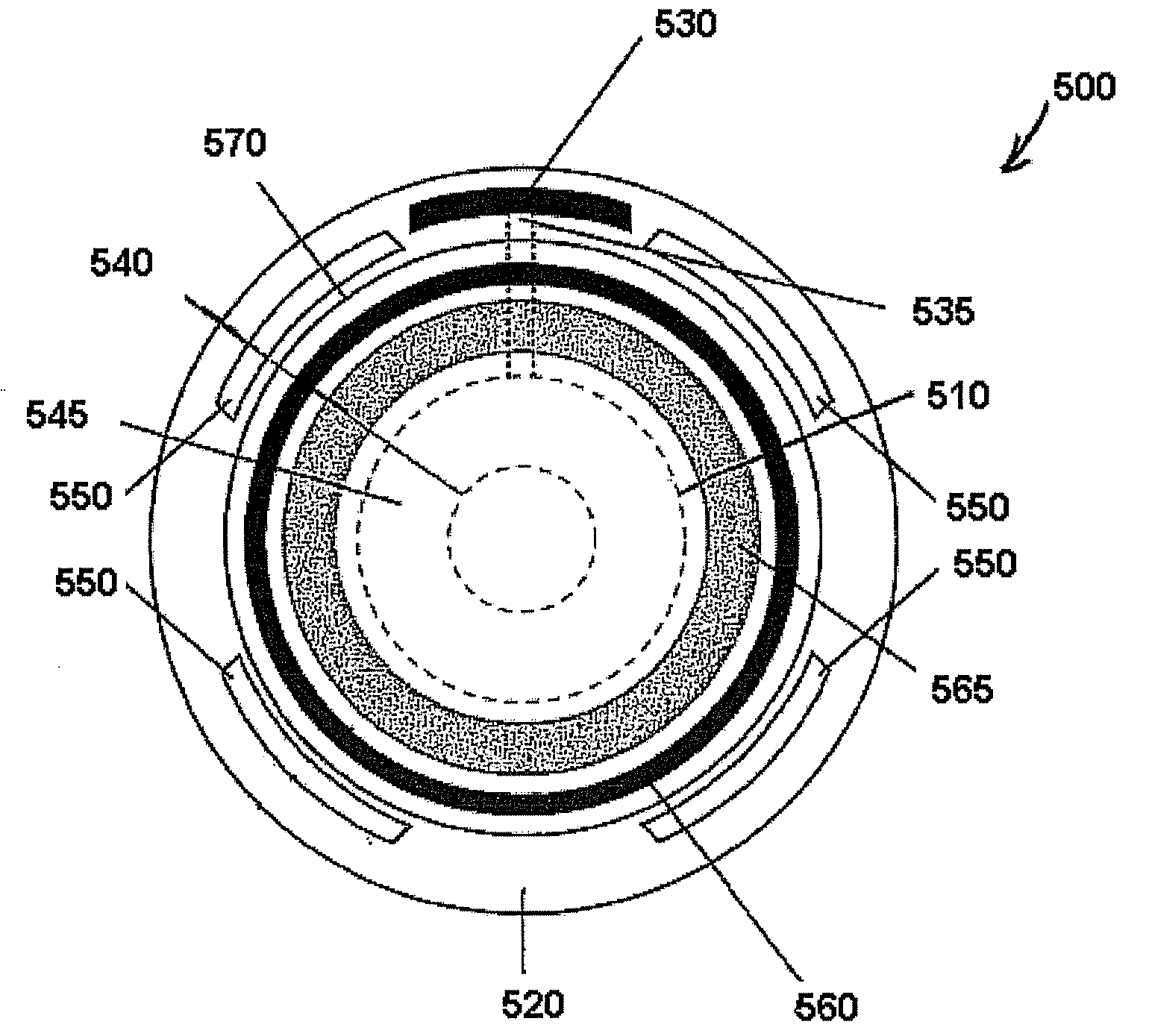
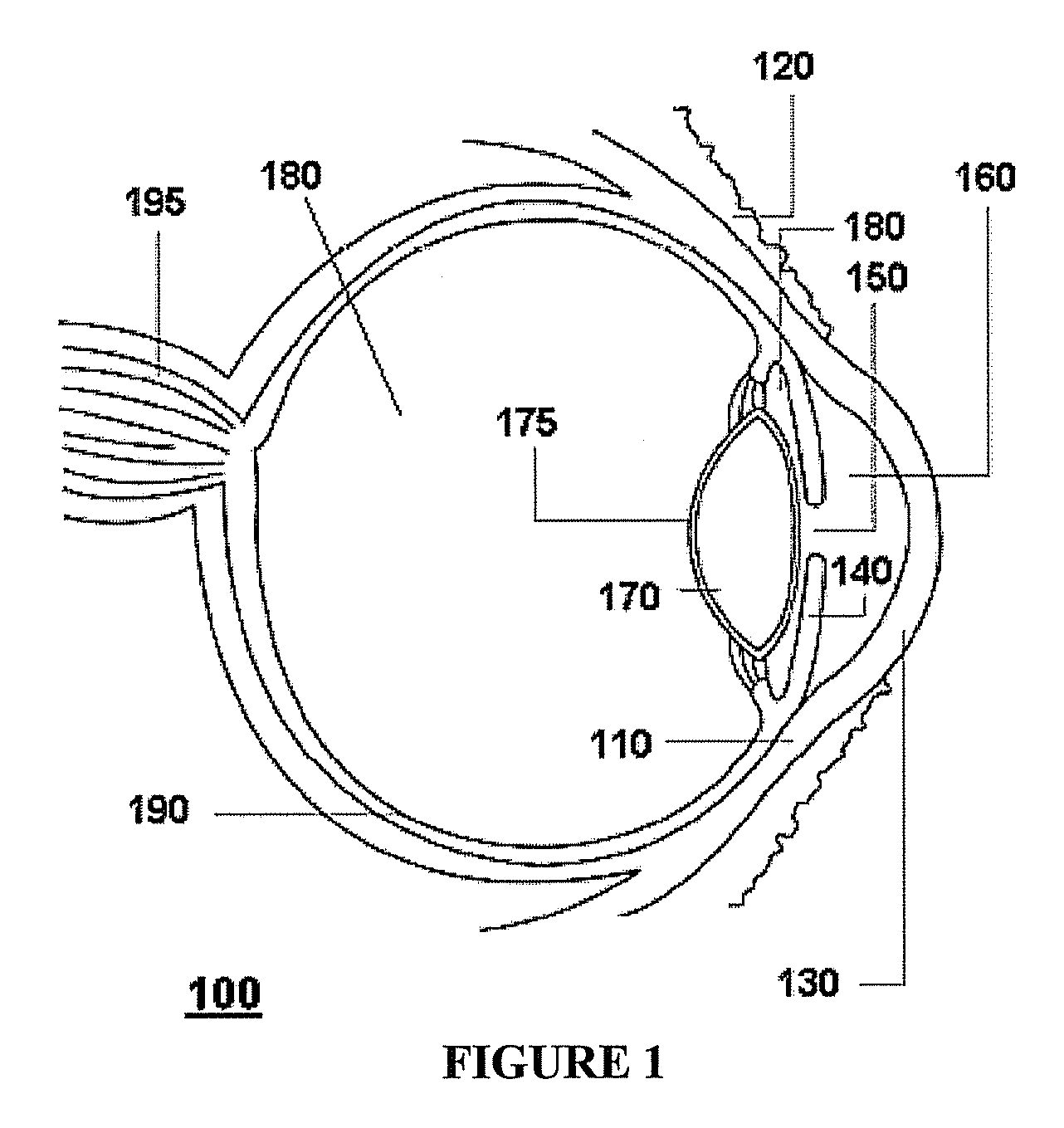
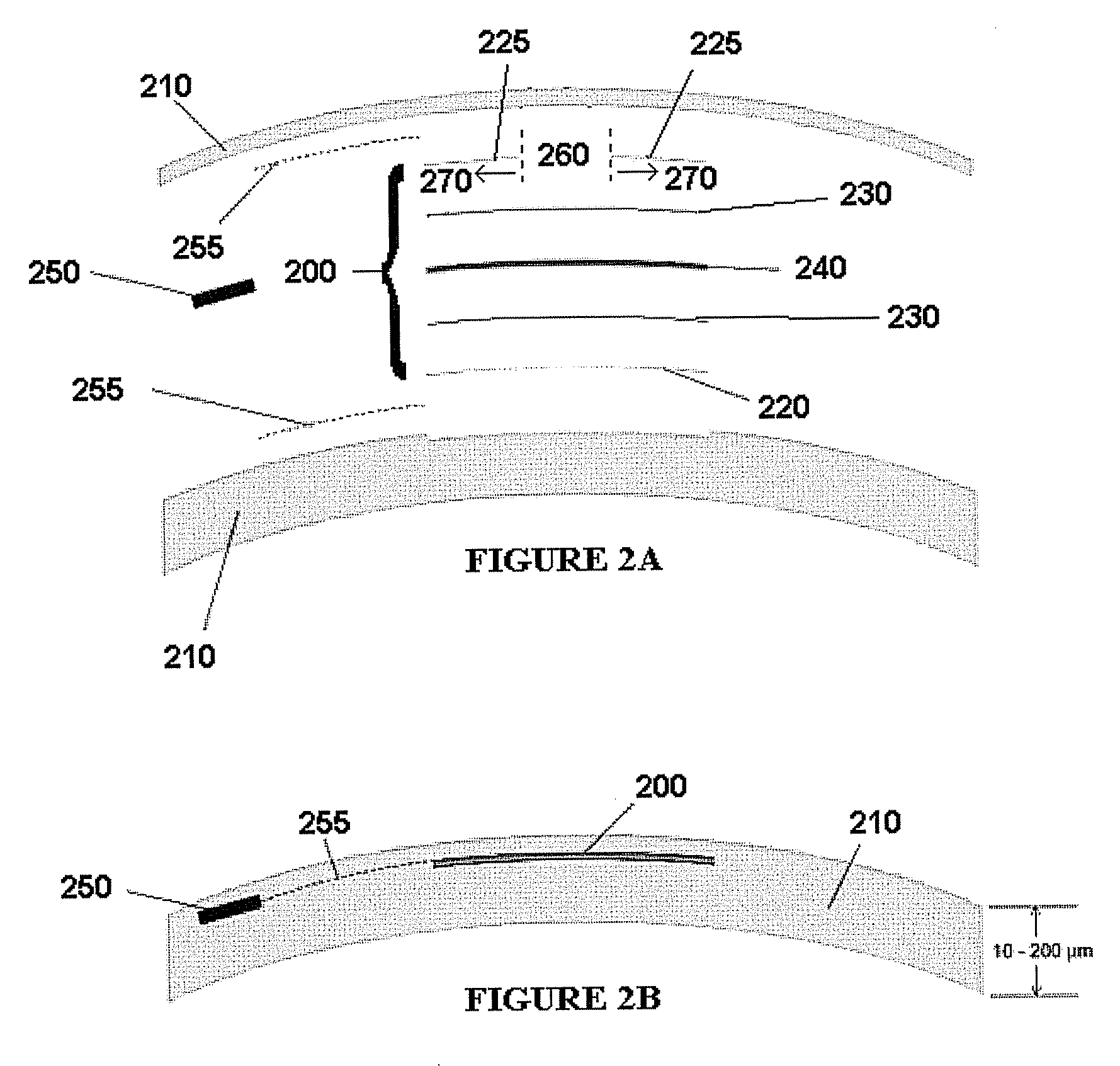
Ophthalmic dynamic aperture
ActiveUS20090033863A1Increase heightAdd depthSpectales/gogglesIntraocular lensCorneal inlayDynamic aperture
Embodiments of the present invention relate to an electro-active element having a dynamic aperture. The electro-active element provides increased depth of field and may be used in a non-focusing ophthalmic device that that is spaced apart from but in optical communication with an intraocular lens, a corneal inlay, a corneal onlay, a contact lens, or a spectacle lens that provide an optical power. The electro-active element provides increased depth of field and may also be used in a focusing or non-focusing device such as an intraocular optic, an intraocular lens, a corneal inlay, a corneal onlay, or a contact lens which may or may not have an optical power. By changing the diameter of dynamic aperture either increased depth of field or increased light reaching the retina may be achieved.
Owner:E VISION LLC +1
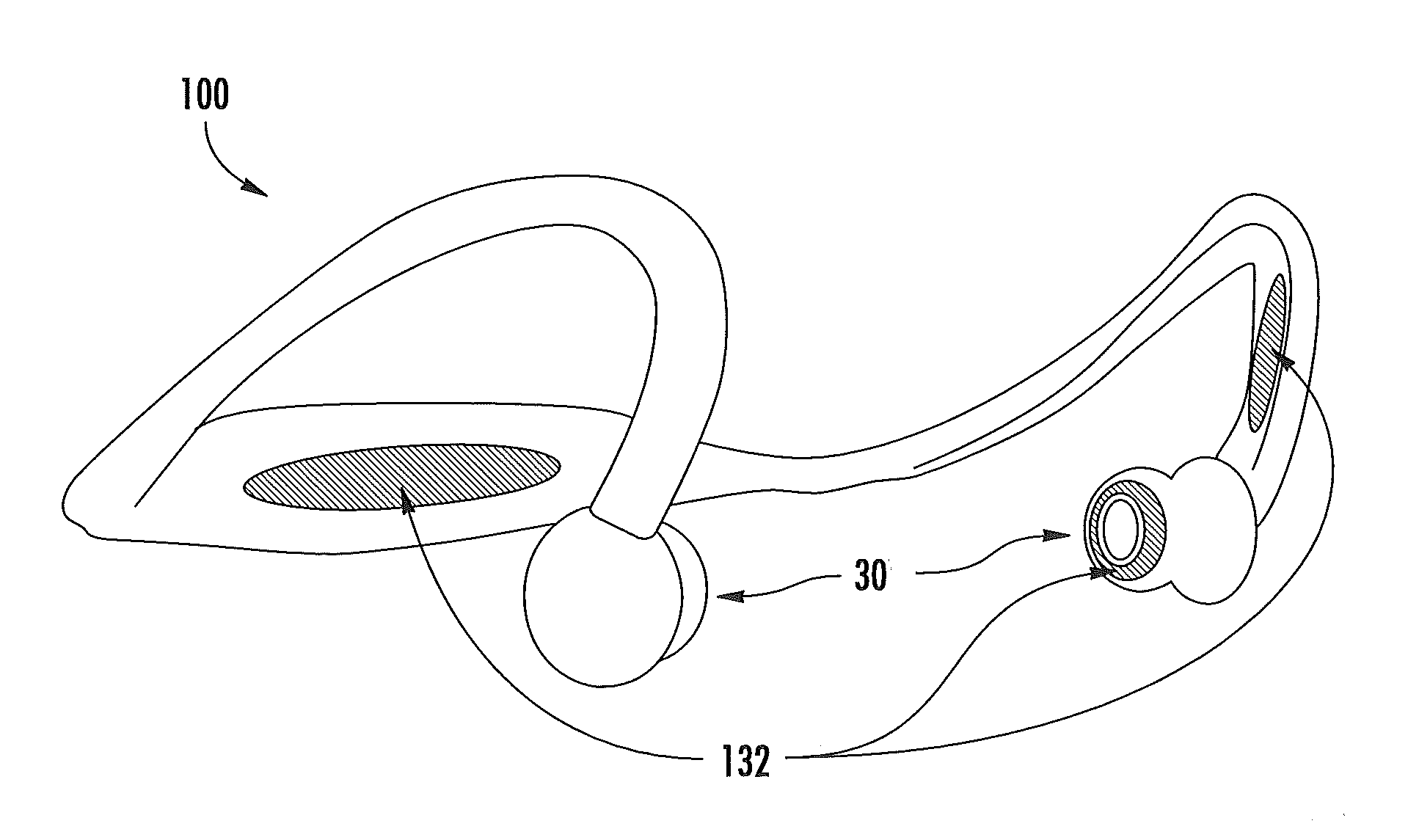
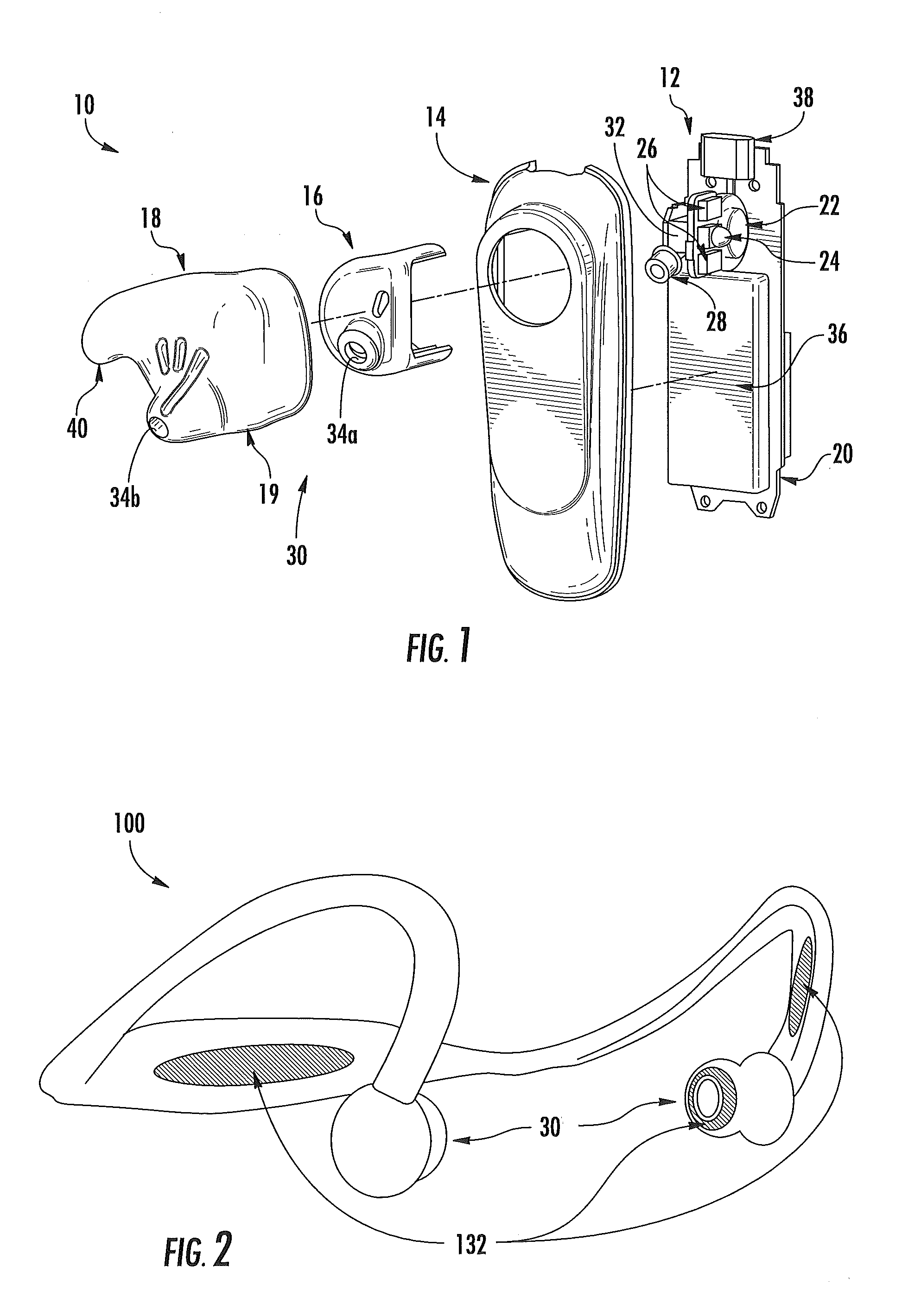
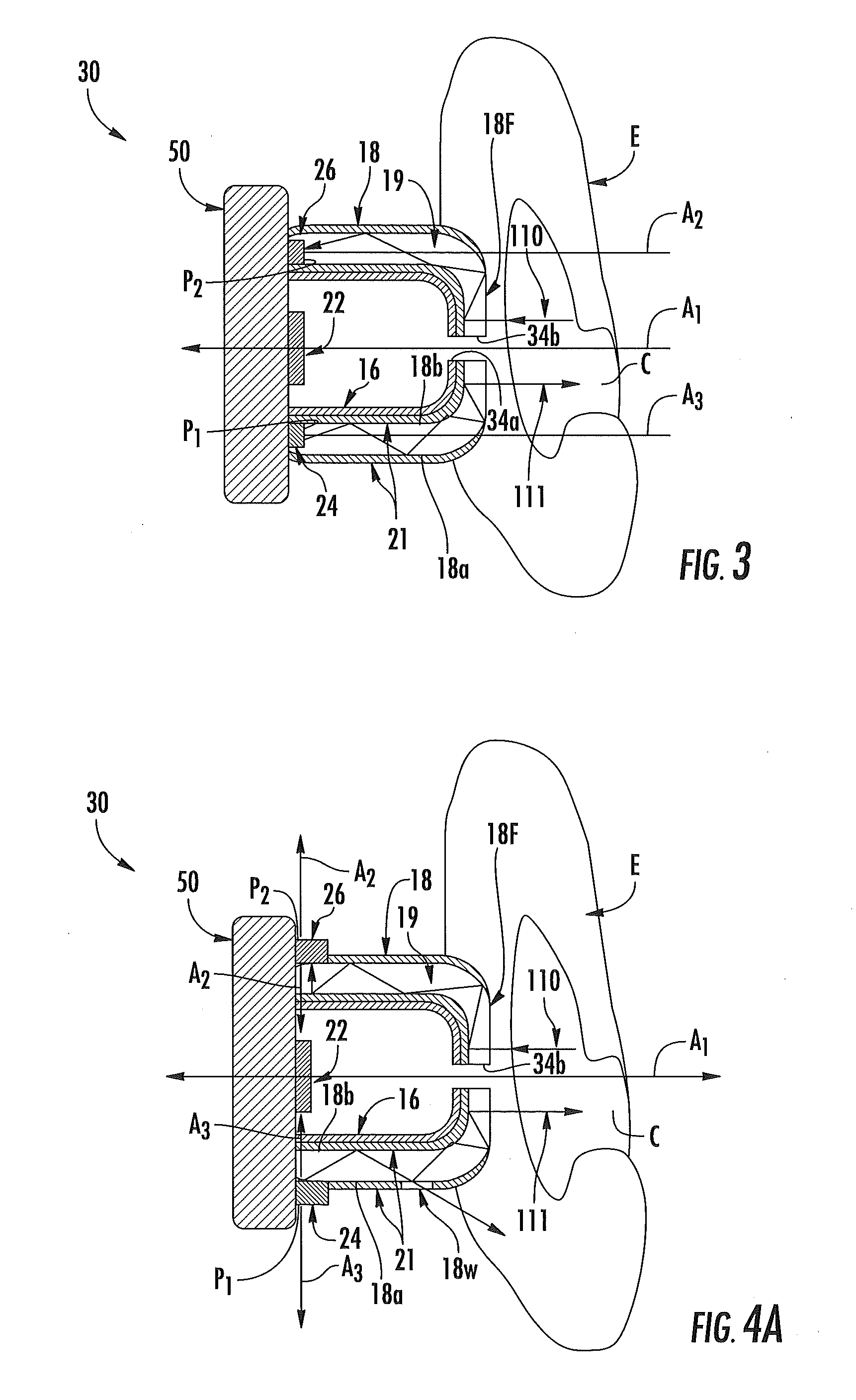
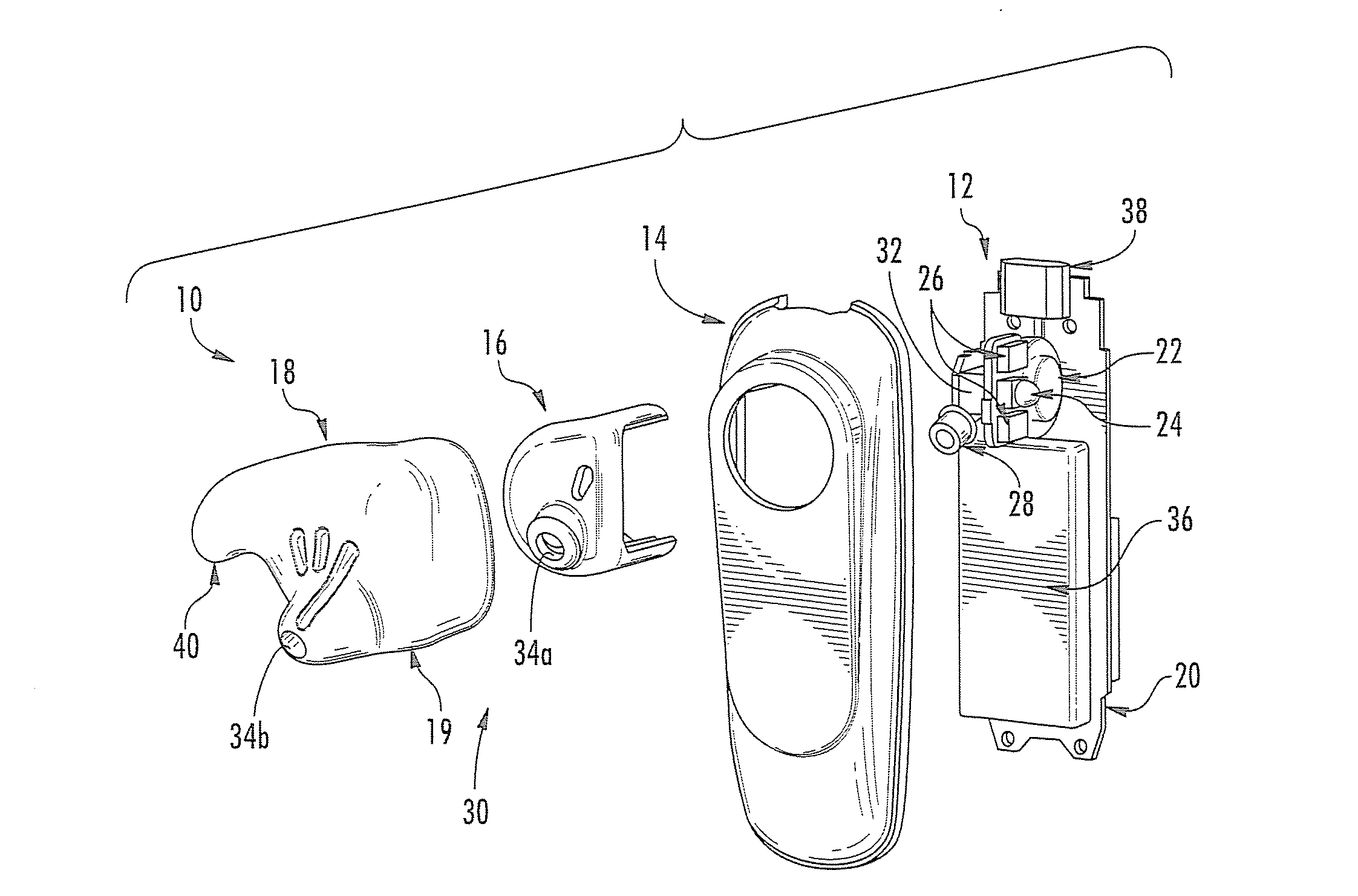
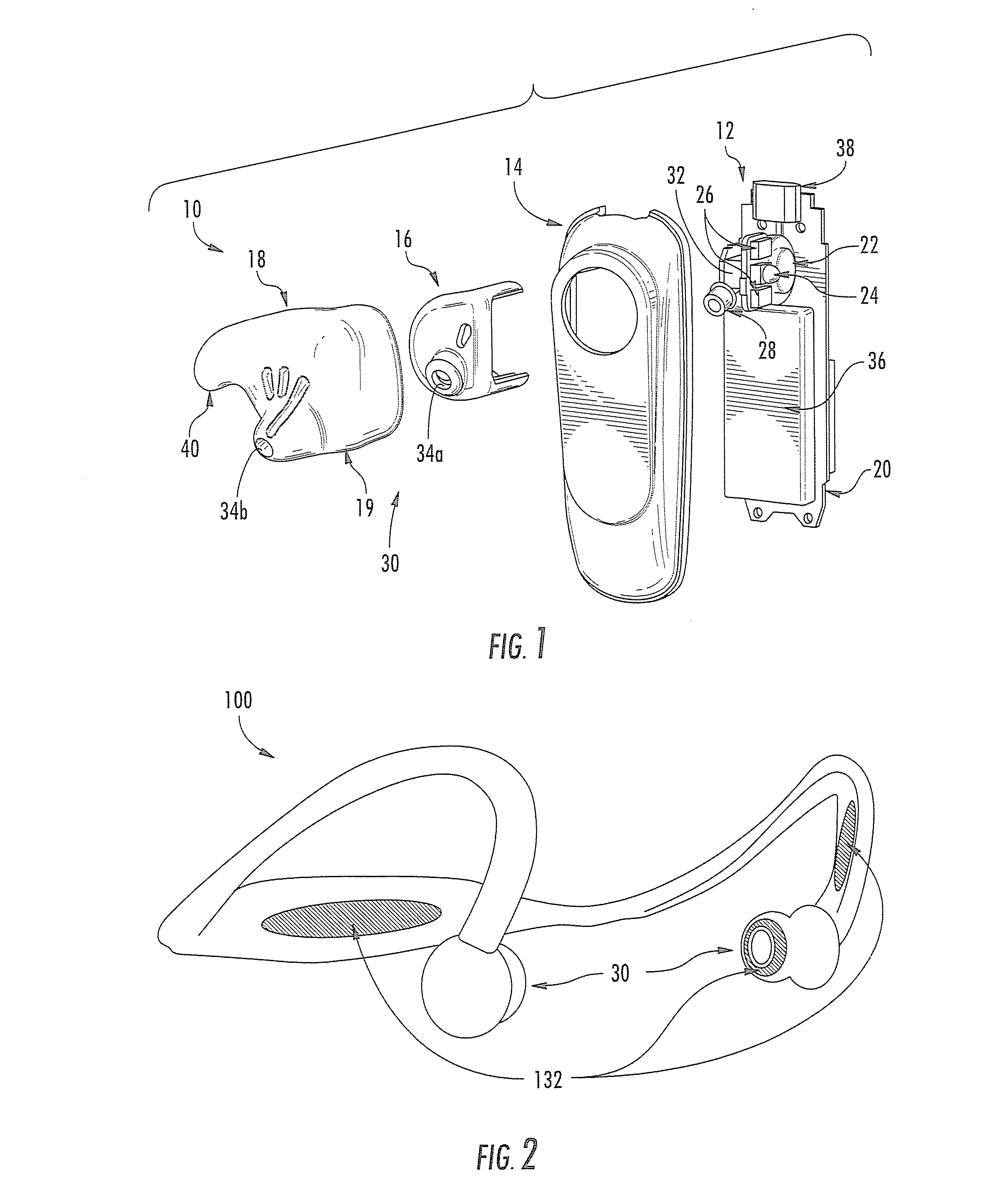
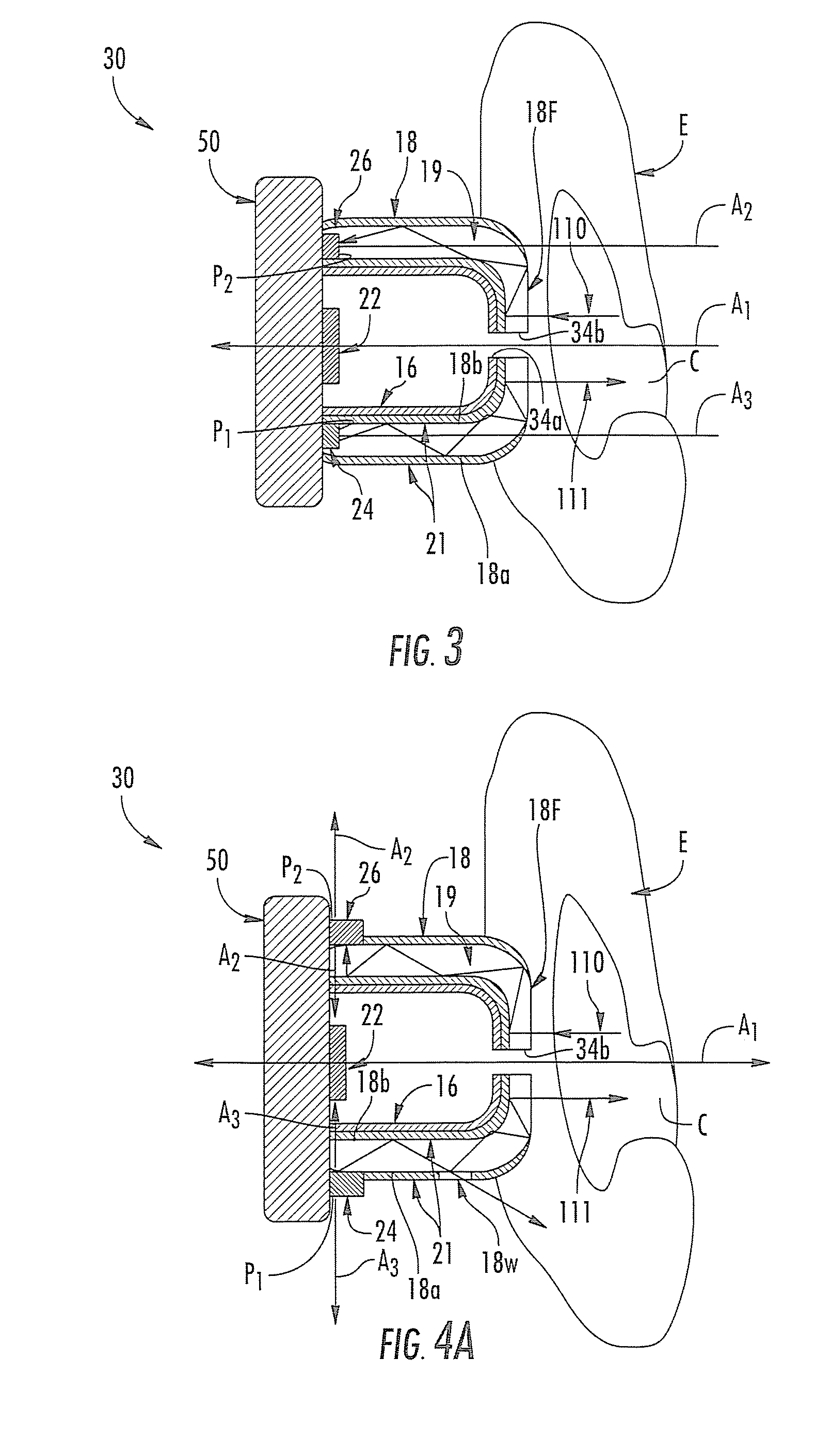
Light-guiding devices and monitoring devices incorporating same
A monitoring device configured to be attached to the ear of a person includes a base, an earbud housing extending outwardly from the base that is configured to be positioned within an ear of a subject, and a cover surrounding the earbud housing. The base includes a speaker, an optical emitter, and an optical detector. The cover includes light transmissive material that is in optical communication with the optical emitter and the optical detector and serves as a light guide to deliver light from the optical emitter into the ear canal of the subject wearing the device at one or more predetermined locations and to collect light external to the earbud housing and deliver the collected light to the optical detector.
Owner:VALENCELL INC
Light-Guiding Devices and Monitoring Devices Incorporating Same
ActiveUS20100217102A1Easy alignmentPhysical therapies and activitiesTransducer detailsLight guideEngineering
A monitoring device configured to be attached to the ear of a person includes a base, an earbud housing extending outwardly from the base that is configured to be positioned within an ear of a subject, and a cover surrounding the earbud housing. The base includes a speaker, an optical emitter, and an optical detector. The cover includes light transmissive material that is in optical communication with the optical emitter and the optical detector and serves as a light guide to deliver light from the optical emitter into the ear canal of the subject wearing the device at one or more predetermined locations and to collect light external to the earbud housing and deliver the collected light to the optical detector.
Owner:VALENCELL INC
Leadless Implantable Intravascular Electrophysiologic Device for Neurologic/Cardiovascular Sensing and Stimulation
ActiveUS20080119911A1Enhances specificity/integrityRestricted blood flowHeart defibrillatorsInternal electrodesOptical communicationRadio frequency
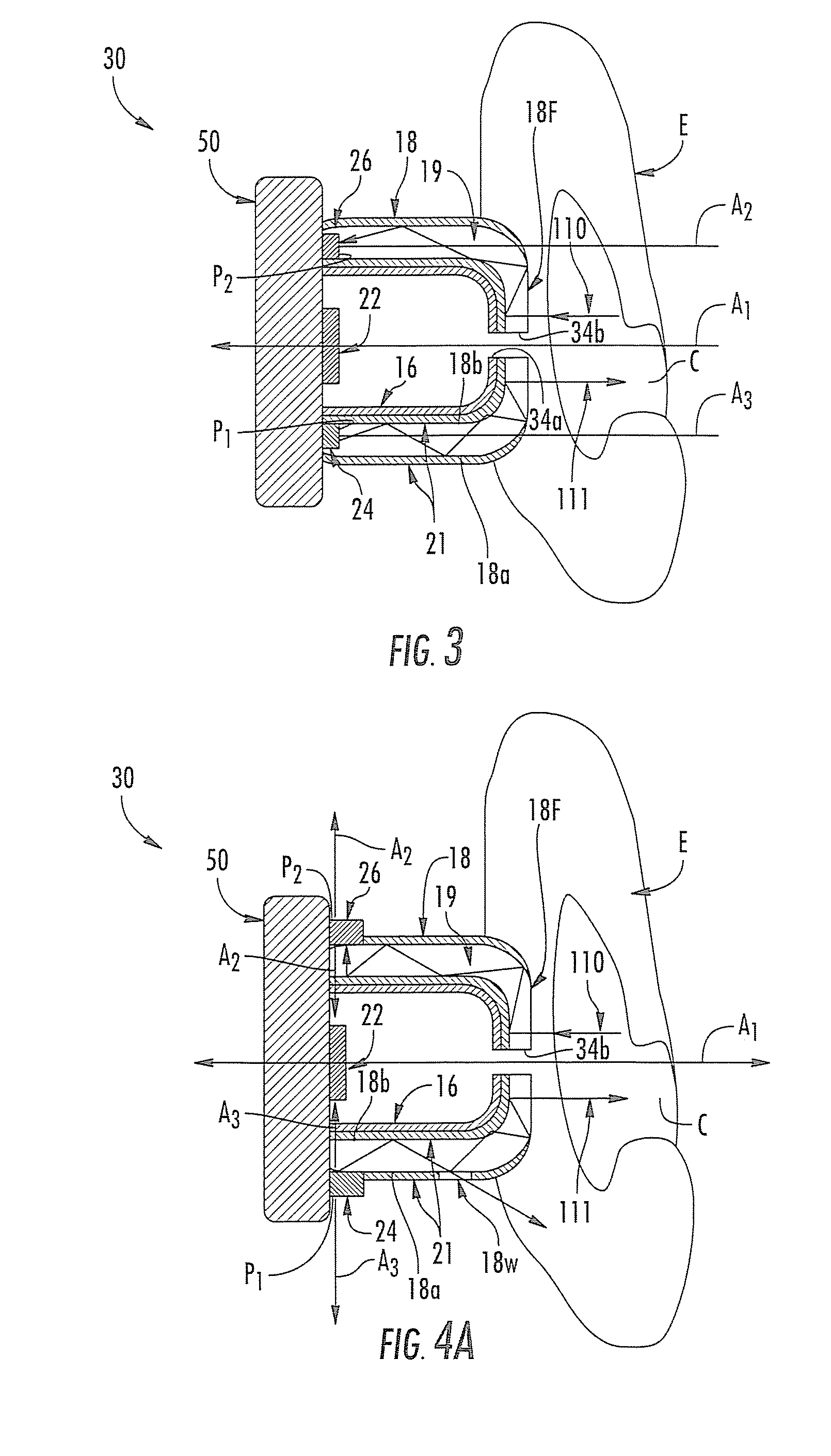
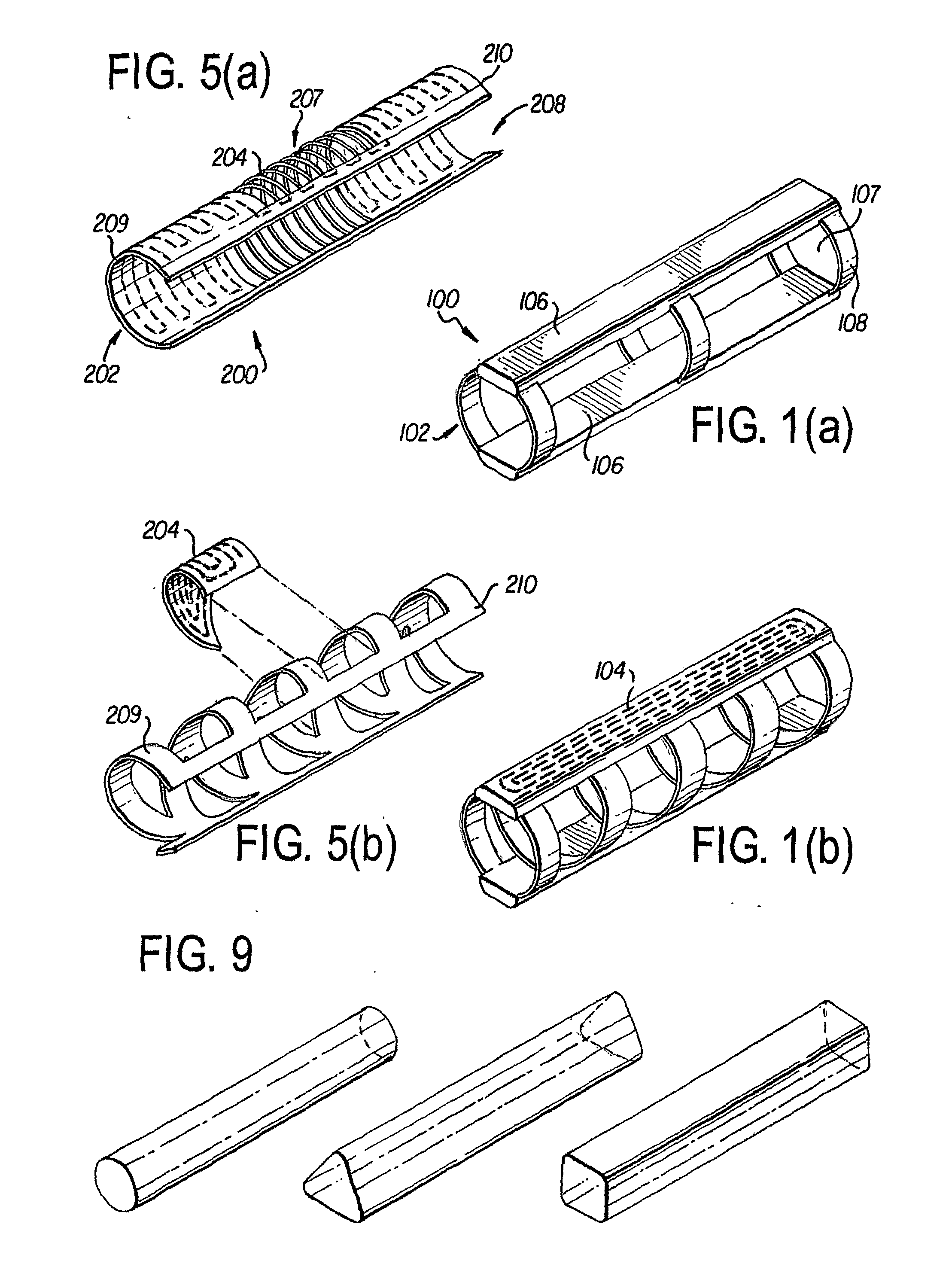
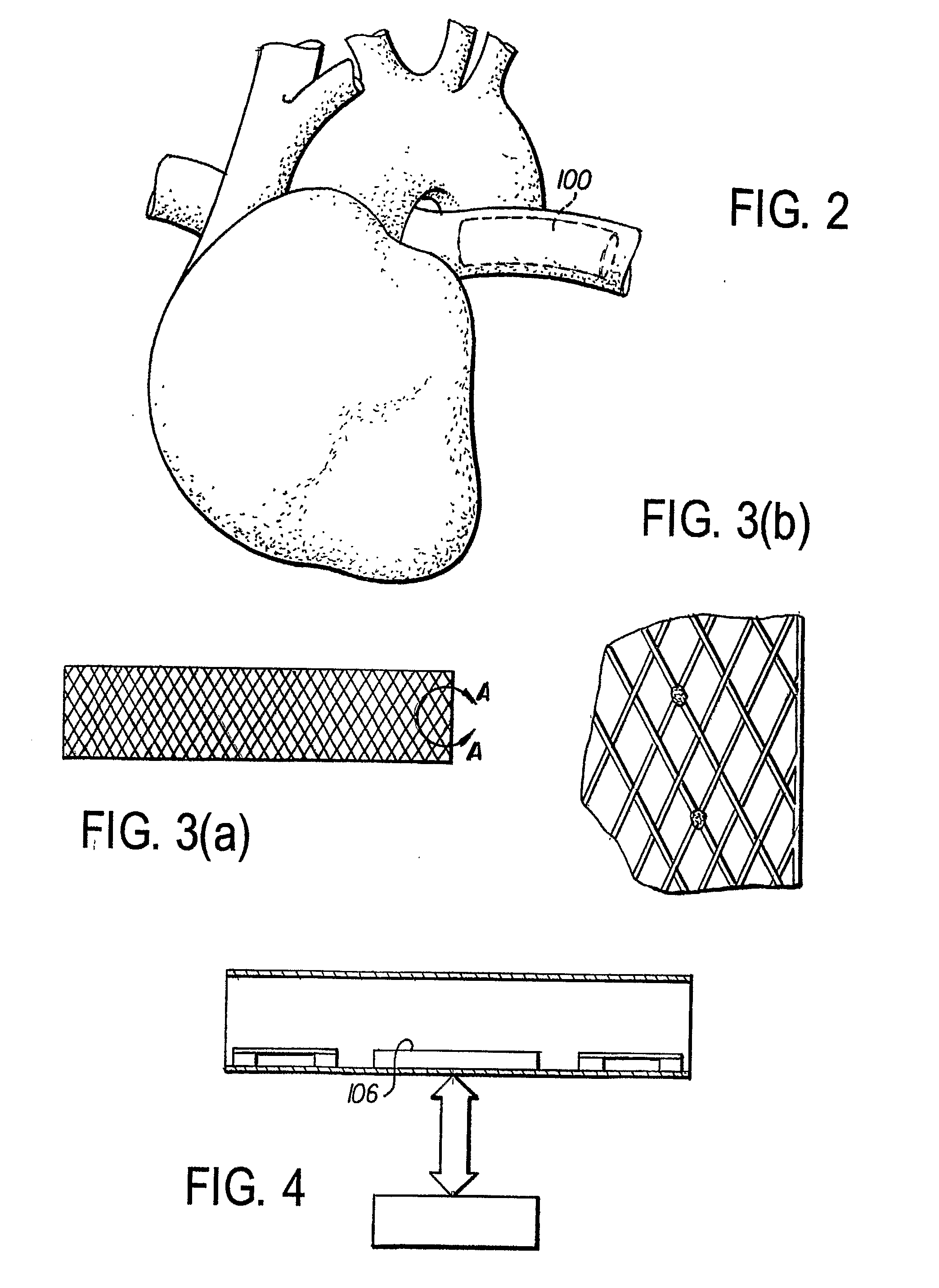
A leadless intravascular sensor (100, 200) uses the body tissue as a communication medium. The implantable intravascular device has a tubular stent-like structure (102) for intravascular fixation with embedded microcircuits to allow bipolar and unipolar sensing of cardiac and neurologic electrical activity, sensing of other physiologic signals, local electrical stimulation (cardiac pacing and defibrillation; neurologic stimulation and seizure therapy) as well as the ability to communicate with other implanted and non implanted devices via radio frequency and / or optical communication and / or analog signal communication using the body tissue as the conducting medium. The device can also be used in the extravascular or perivascular space. In this form, it has an open / flexible ring that can be adjusted, or self-adjusts to provide no pressure or required contact around the vessel or target region.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
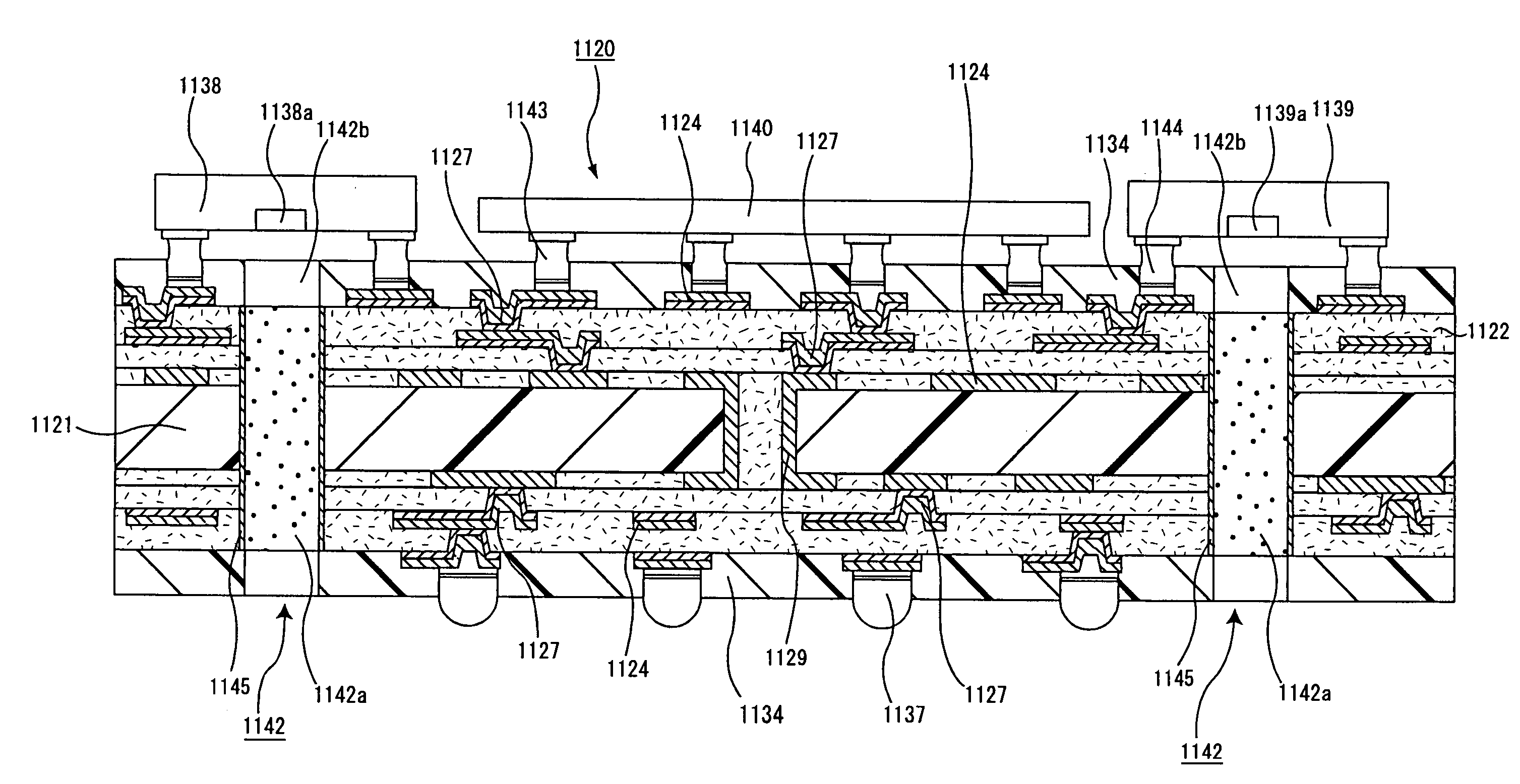
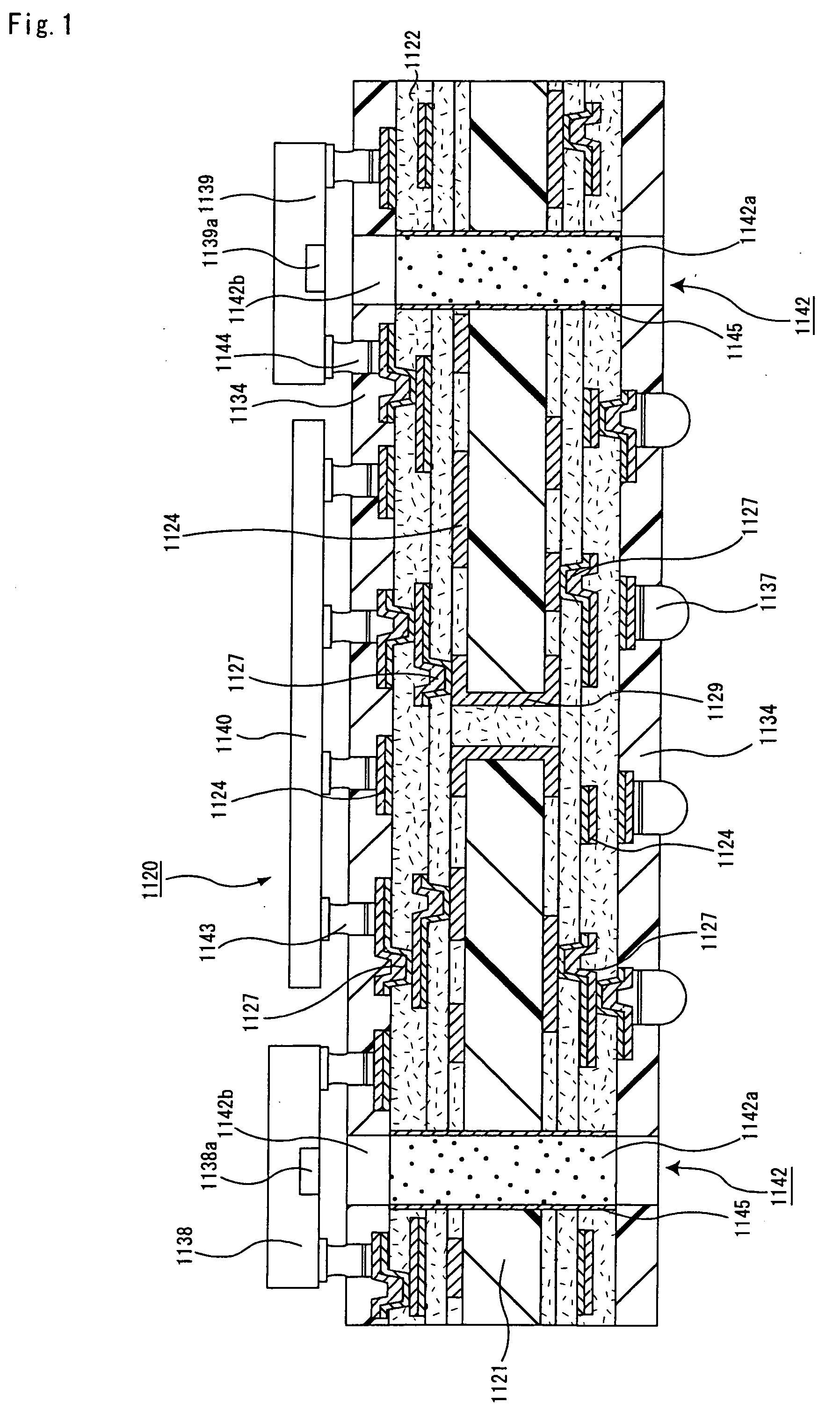
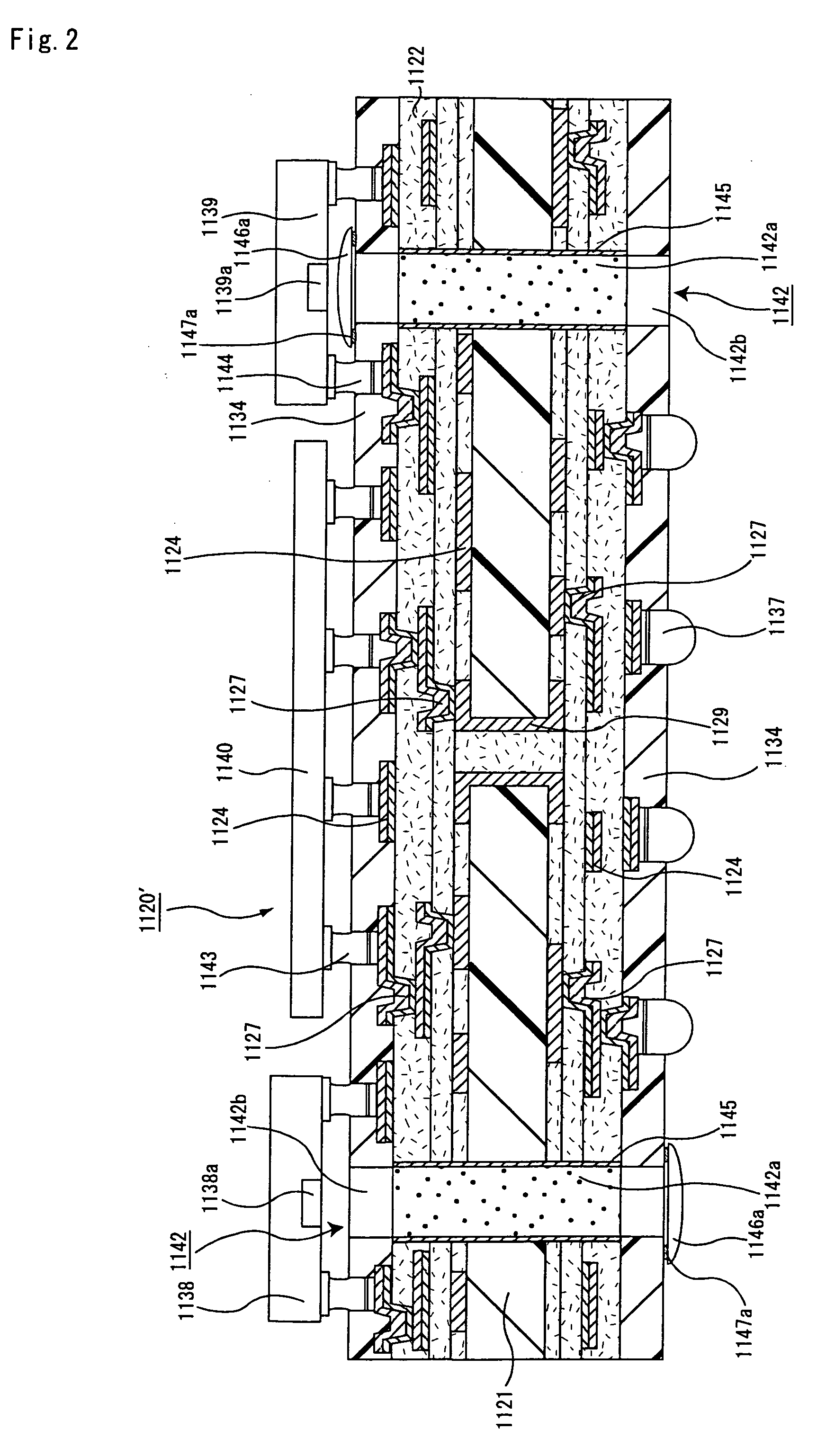
Ic chip mounting substrate, ic chip mounting substrate manufacturing method, optical communication device, and optical communication device manufacturing method
InactiveUS20060012967A1Improve connection reliabilitySmall sizeCircuit optical detailsSolid-state devicesResistElectrical conductor
An object of the present invention is to provide a substrate for mounting an IC chip which is a component for optical communication having an IC chip and an optical component integrally provided thereon, which can ensure a short distance between the IC chip and the optical component, which is excellent in electric signal transmission reliability and which can transmit optical signal through an optical path for transmitting optical signal. The substrate for mounting an IC chip of the present invention is a substrate for mounting an IC chip comprising: a substrate and, as serially built up on both faces thereof, a conductor circuit and an interlaminar insulating layer in an alternate fashion and in repetition; a solder resist layer formed as an outermost layer; and an optical element mounted thereto, wherein an optical path for transmitting optical signal, which penetrates the substrate for mounting an IC chip, is disposed.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
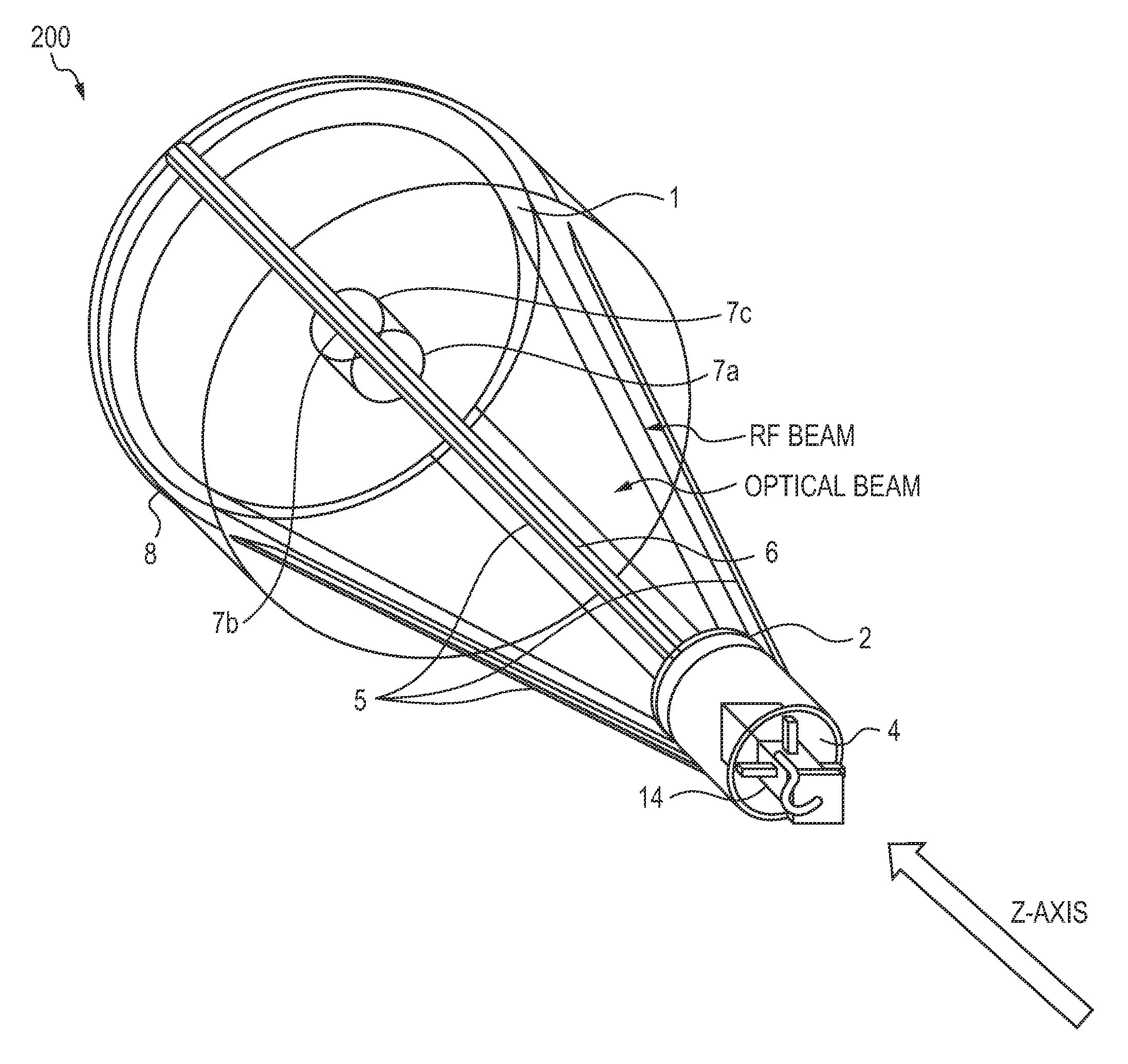
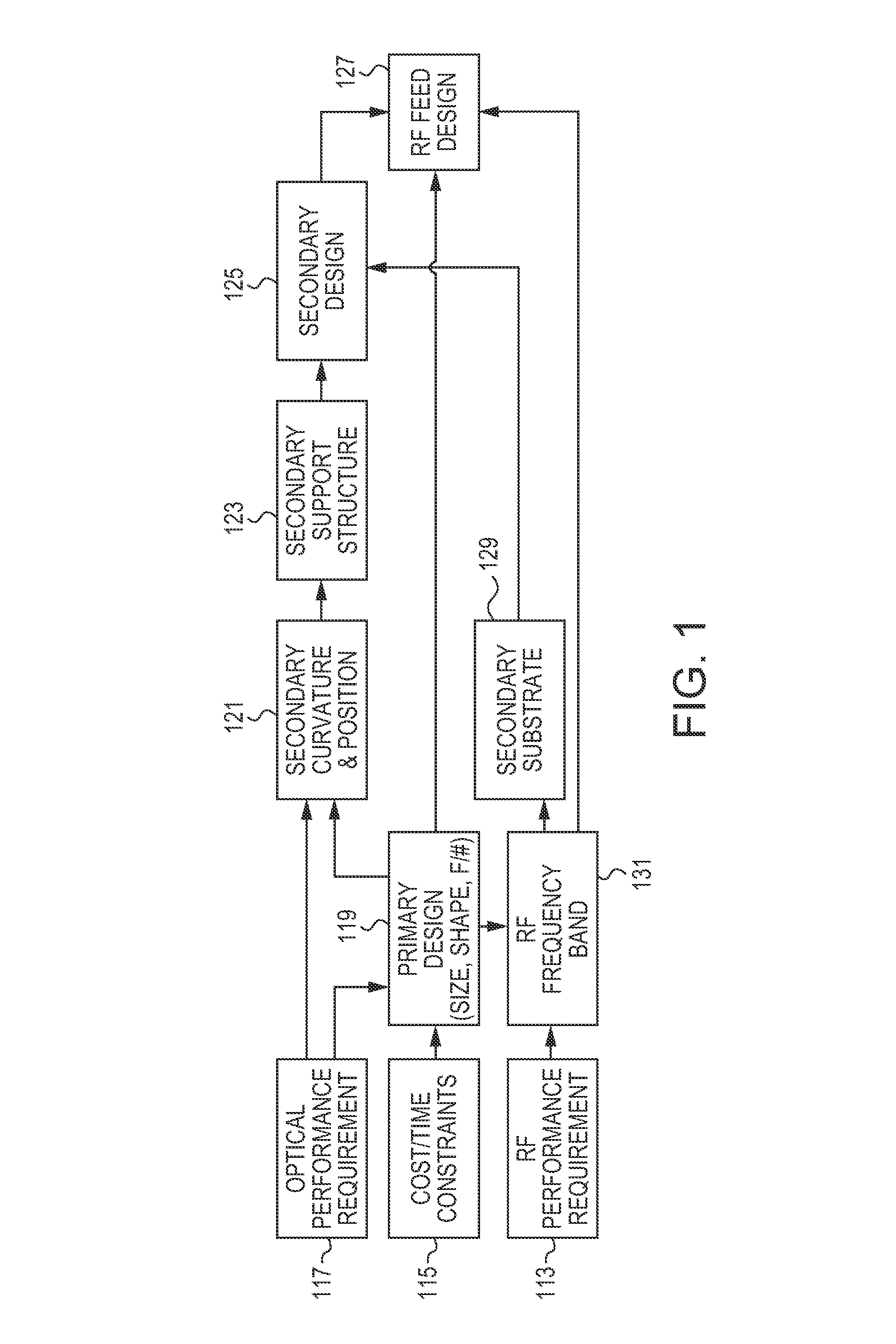
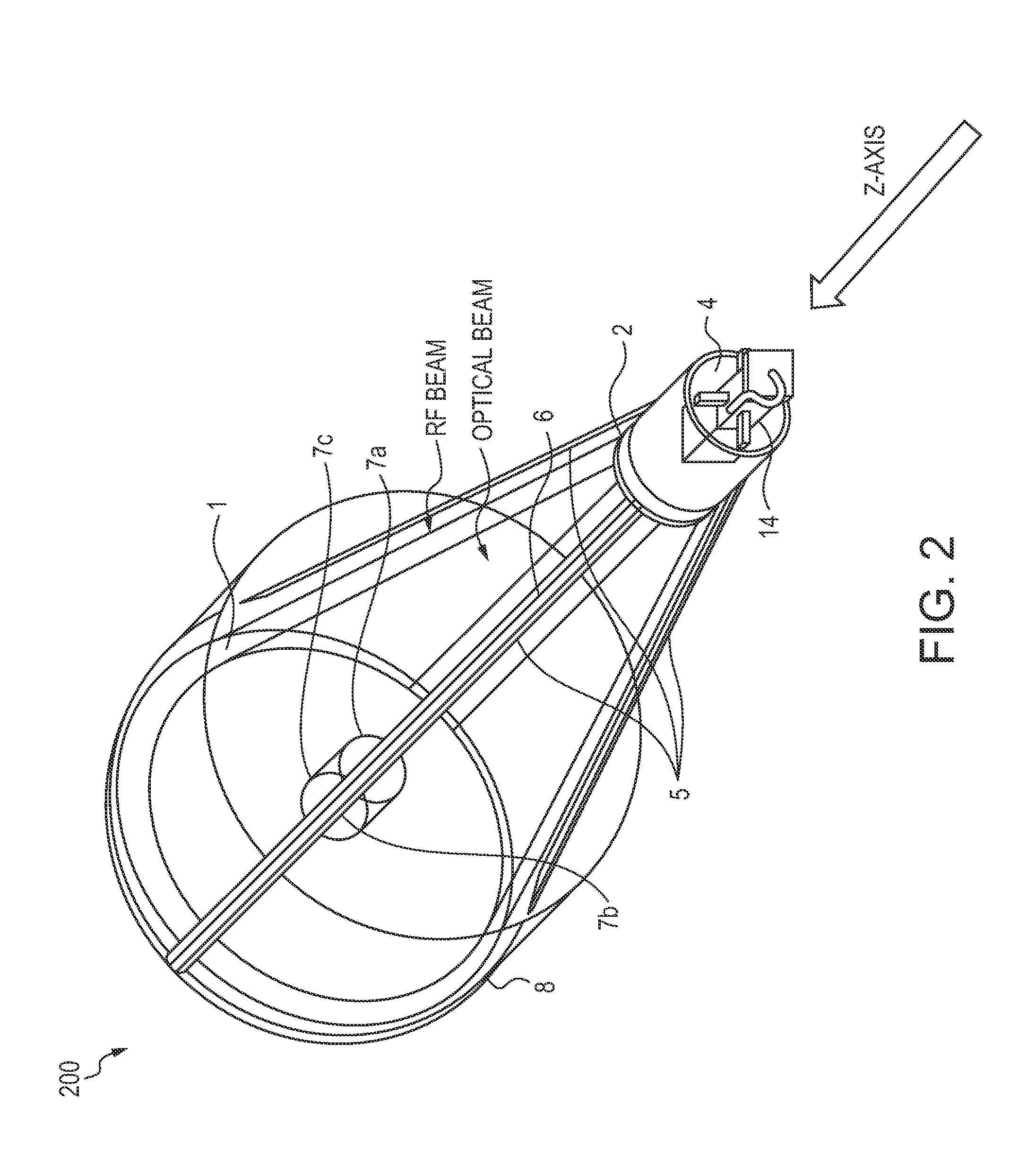
Dual band radio frequency (RF) and optical communications antenna and terminal design methodology and implementation
ActiveUS8094081B1High bandwidthMinimized massAntenna arraysSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna designTransceiver
A dual-band antenna is provided that combines two normally disparate communications modes into a single compact aperture minimizing overall mass and volume, while maintaining high performance efficiency and reciprocity of each individual mode. The antenna is compatible with both optical (near-IR / visible) and RF (microwave / millimeter-wave) transceiver subsystems for high bandwidth communications, applicable primarily to long- to extremely long-range (space-to-ground) link distances. The optical link provides high bandwidth while the RF provides a lower data-rate weather backup, accommodation for traditional navigation techniques, and assistance in cueing the extremely tight optical beam by matching the RF beamwidth to an optical fine-steering mechanism field-of-regard. The configuration is built around a near-diffraction-limited high performance primary mirror shared by both a direct-fed RF antenna design and a Cassegrain optical telescope. Material properties are exploited to combine the optical secondary mirror with the RF feed structure, providing a collimated optical beam interface at the antenna vertex.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
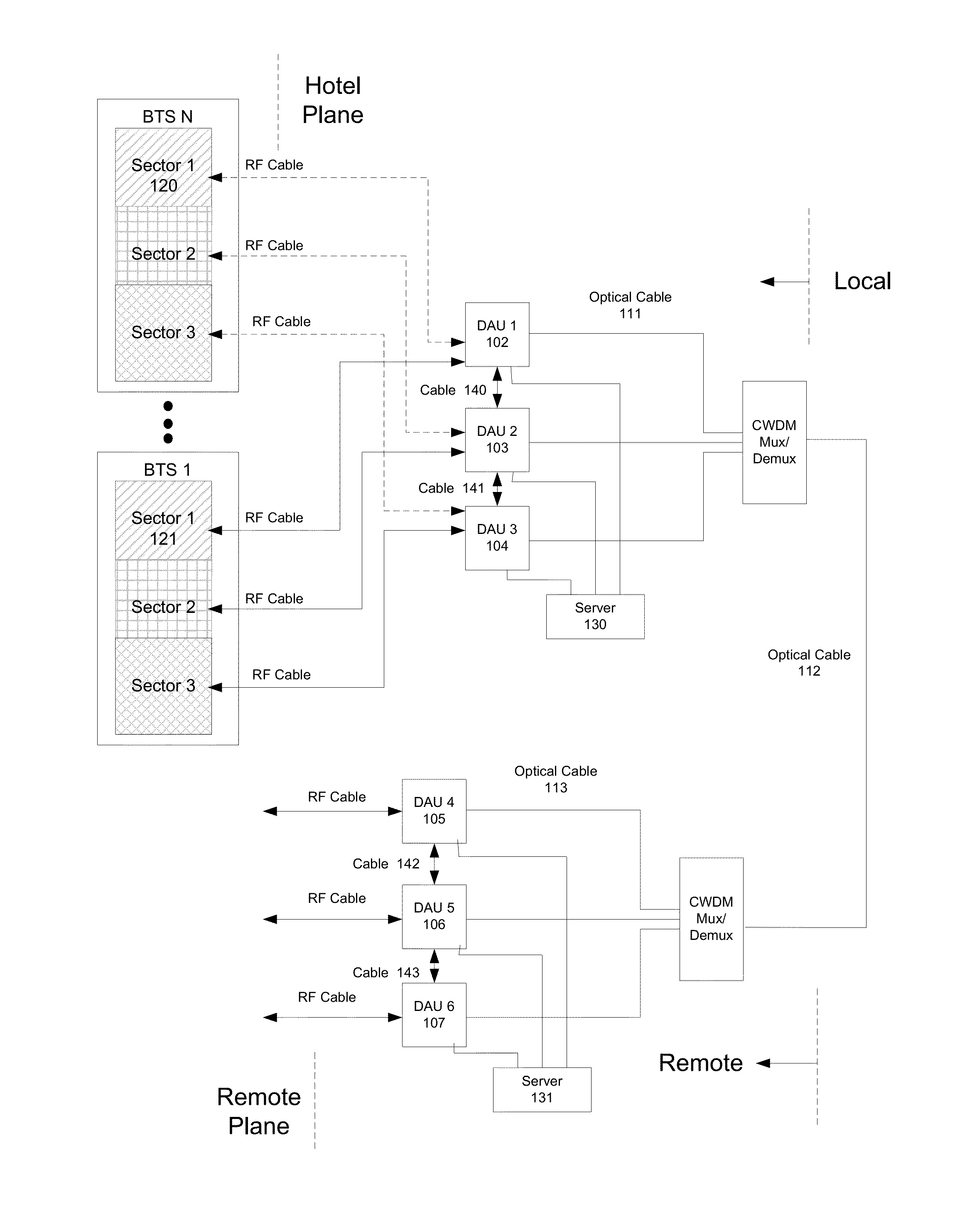
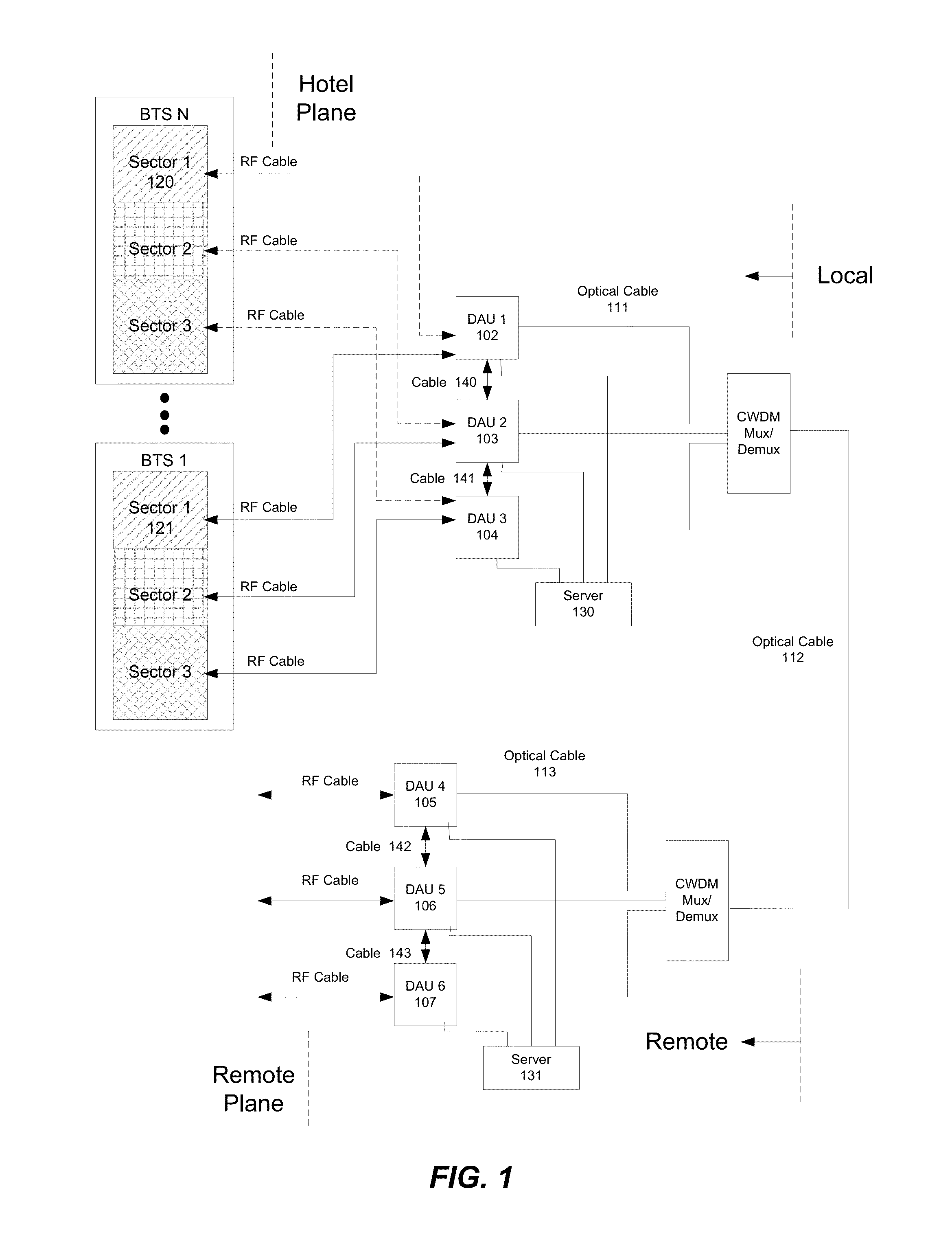
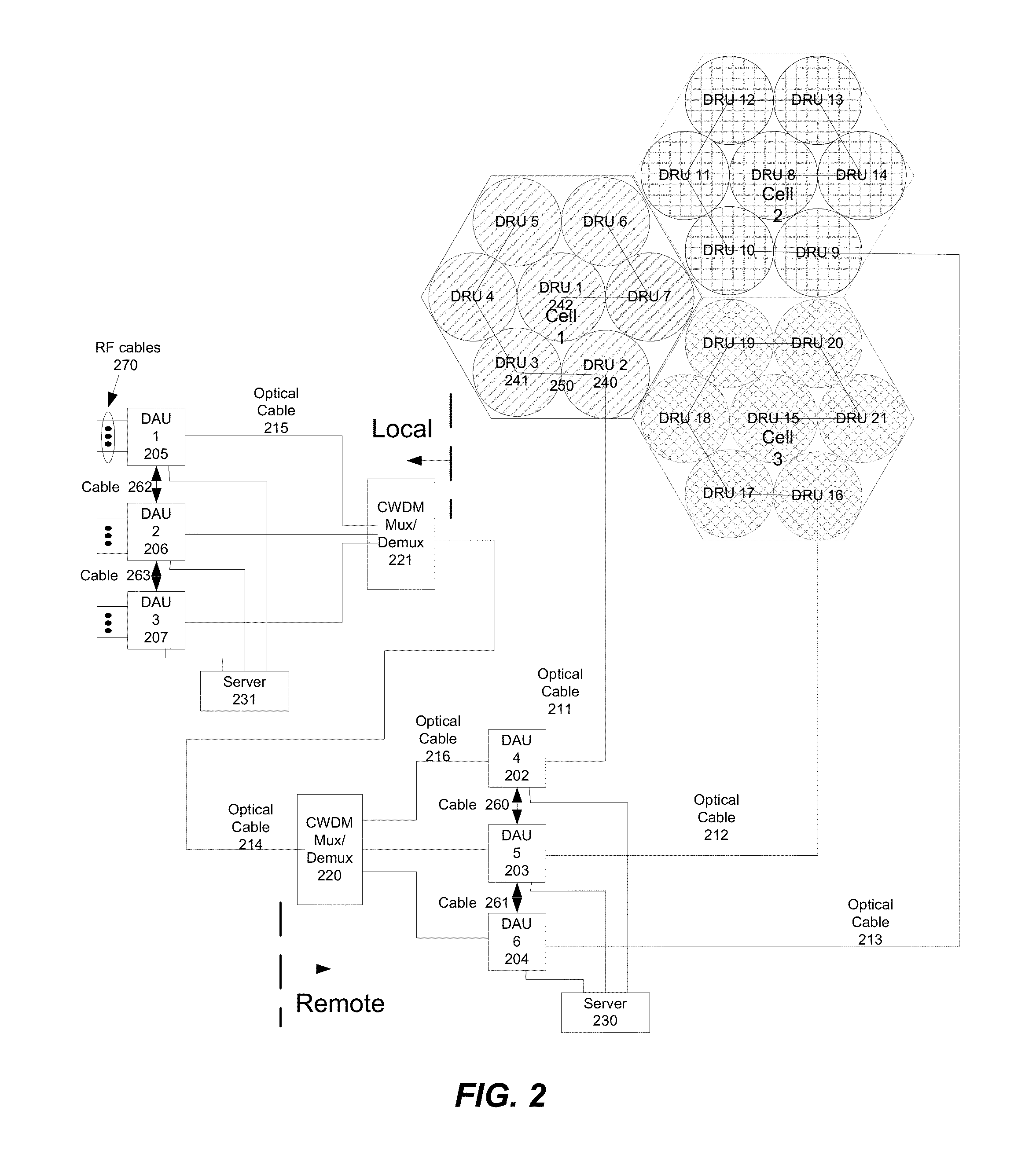
Hybrid data transport for a virtualized distributed antenna system
ActiveUS20140072299A1Electromagnetic network arrangementsOptical multiplexVirtualizationDistributed antenna system
A system for data transport in a Distributed Antenna System (DAS) includes a plurality of remote Digital Access Units (DAUs) located at a Remote location. The plurality of remote DAUs are coupled to each other and operable to transport digital signals between the plurality of remote DAUs. The system also includes a plurality of central hubs. Each of the plurality of central hubs is in communication with one of the remote DAUs using an electrical communications path. The system further includes a plurality of transmit / receive cells. Each of the plurality of transmit / receive cells includes a plurality of remote hubs. Each of the remote hubs in one of the plurality of transmit / receive cells is in communication with one of the plurality of central hubs using an optical communications path.
Owner:DALI WIRELESS
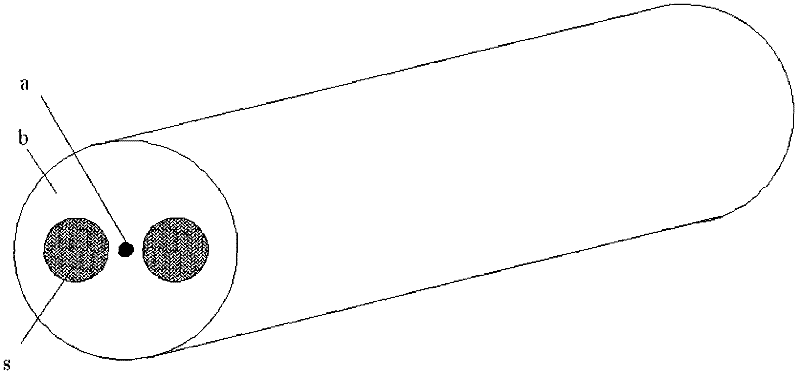
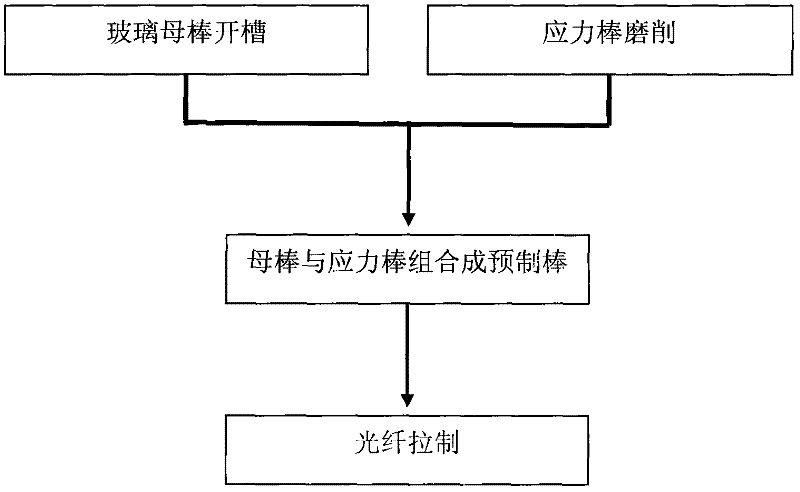
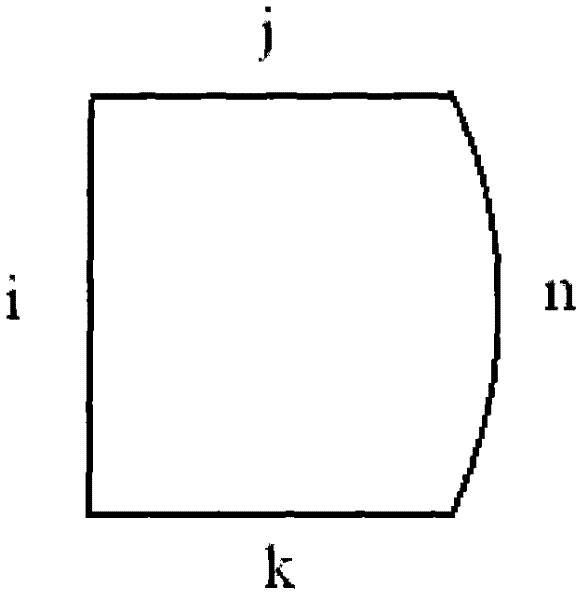
Manufacture method for polarization maintaining fiber and polarization maintaining fiber
InactiveCN102351415AImprove the finishImprove processing efficiencyGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with polarisationSurface finishPolarization-maintaining optical fiber
The invention provides a manufacture method for polarization maintaining fiber and a polarization maintaining fiber, and relates to optical waveguide fibers in the field of fiber-optical communication and fiber optical sensors. The method comprises the following steps that: (1) two oppositely arranged open slots with a same shape are inwardly provided at a side surface of a glass mother rod, stress rods are machined to obtain a shape matching the open slots, and the centers of the cross sections of the two open slots and the center of circle in the cross section of the glass mother rod are in a same line; (2) the stress rods are respectively inserted into each open slot on the glass mother rod, and the assembled glass mother rod and stress rods are put in a cannula to form a preformed rod of the polarization maintaining fiber; (3) the preformed rod of the polarization maintaining fiber is drew to form the polarization maintaining fiber. According to the invention, the glass mother rod is provided with the open slots, and the stress rods are embedded in the open slots, thereby obtaining high process repeatability; inner surfaces of the open slots have high fineness, and the open slots have good symmetry, thereby improving processing efficiency; therefore, the optical performance and reliability of the polarization maintaining fiber are substantially improved.
Owner:RUIGUANG TELECOMM TECH CO LTD
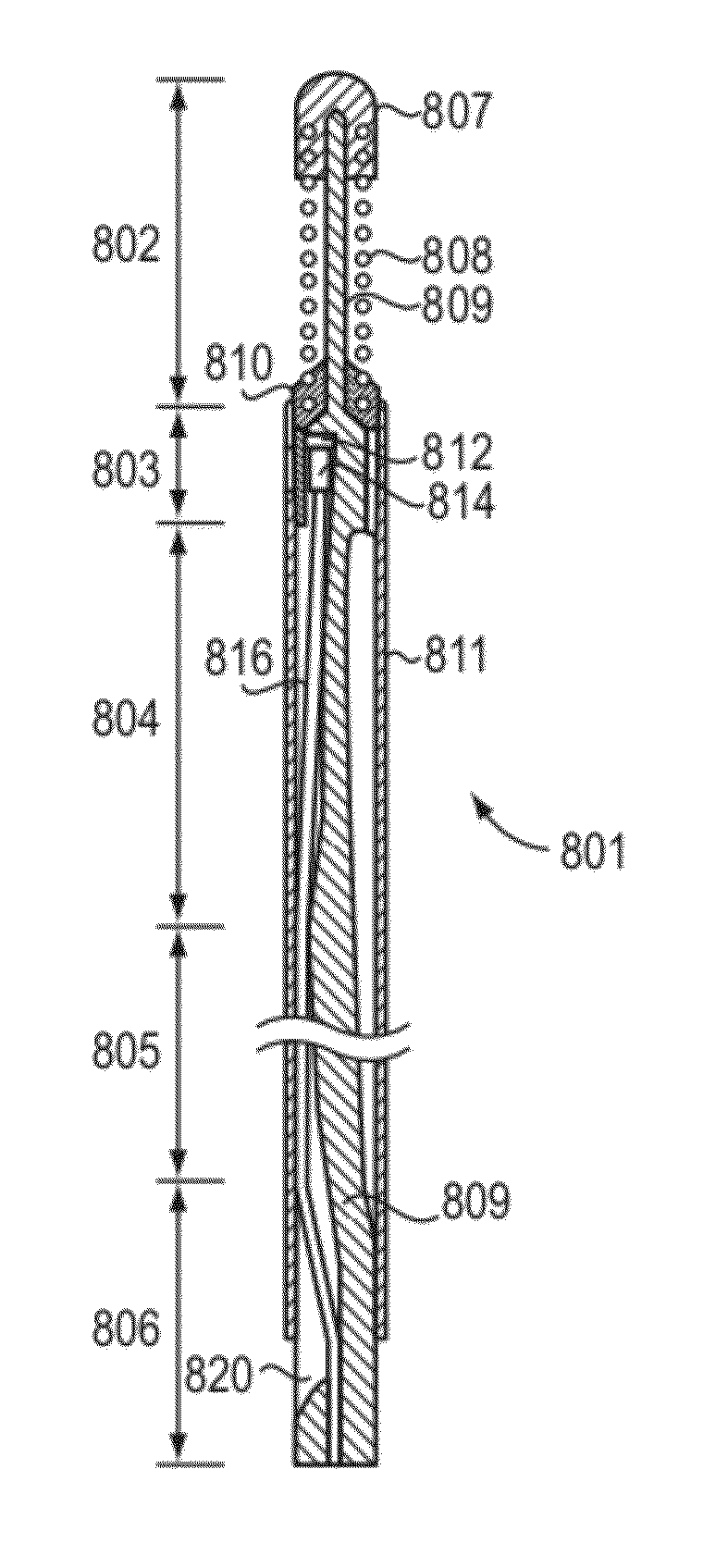
Imaging catheter with integrated reference reflector
In part, the invention relates to a lens assembly. The lens assembly includes a micro-lens; a beam director in optical communication with the micro-lens; and a substantially transparent film. The substantially transparent film is capable of bi-directionally transmitting light, and generating a controlled amount of backscatter. In addition, the film surrounds a portion of the beam director.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
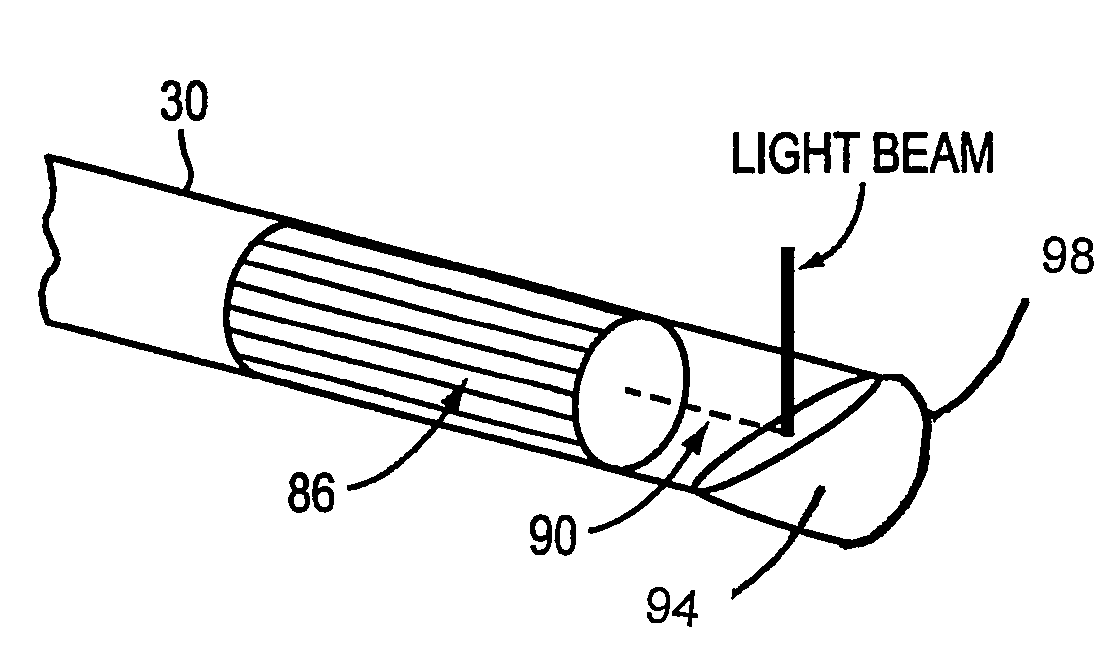
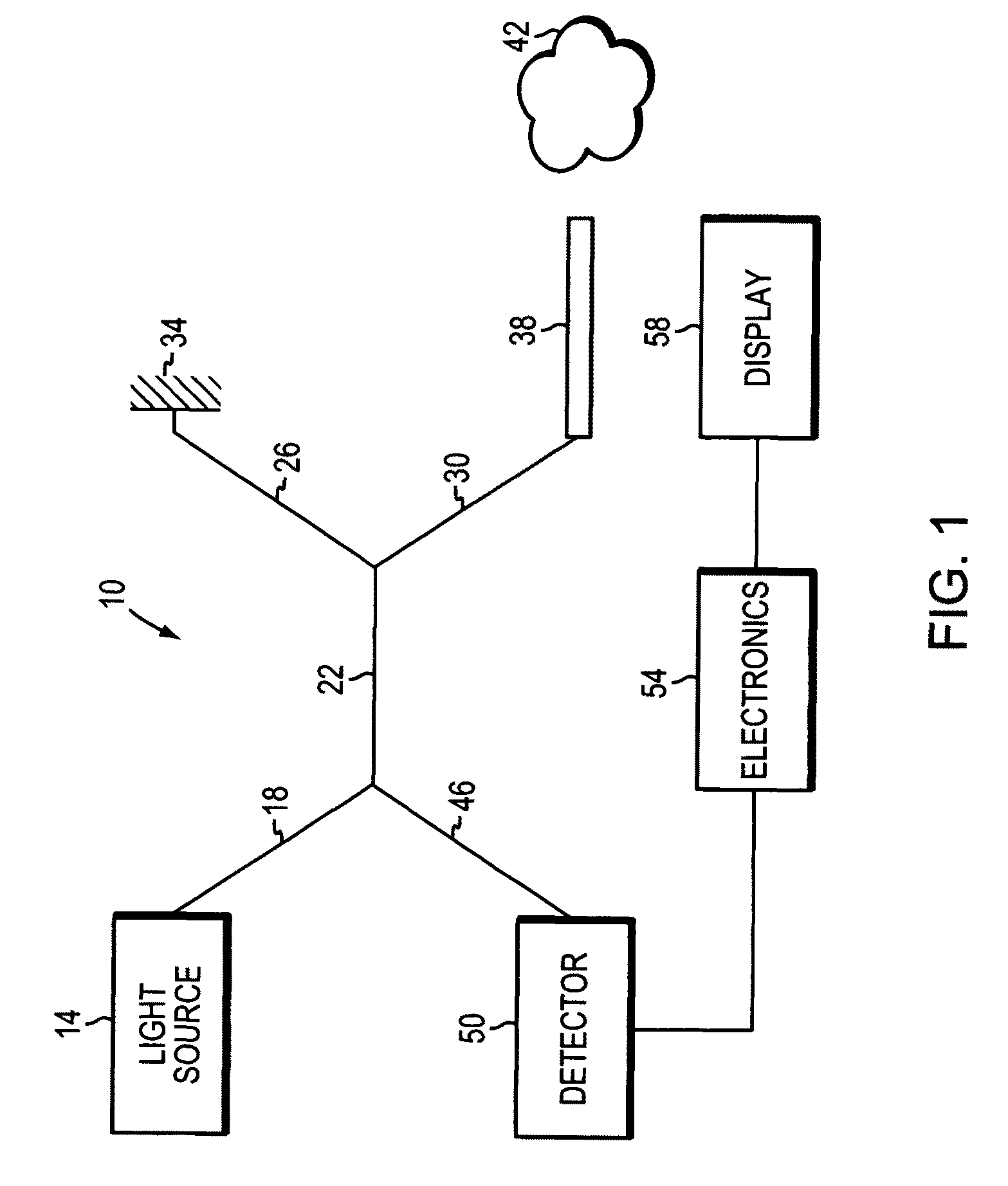
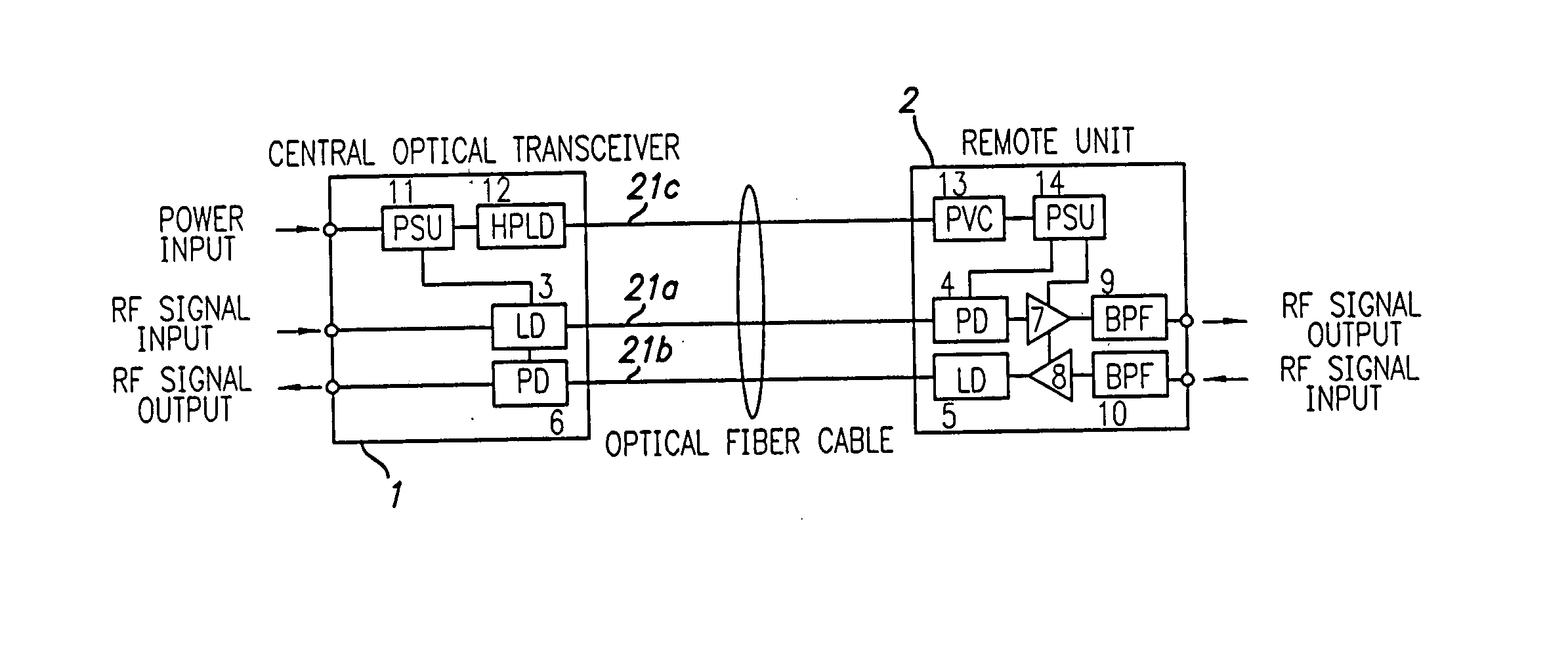
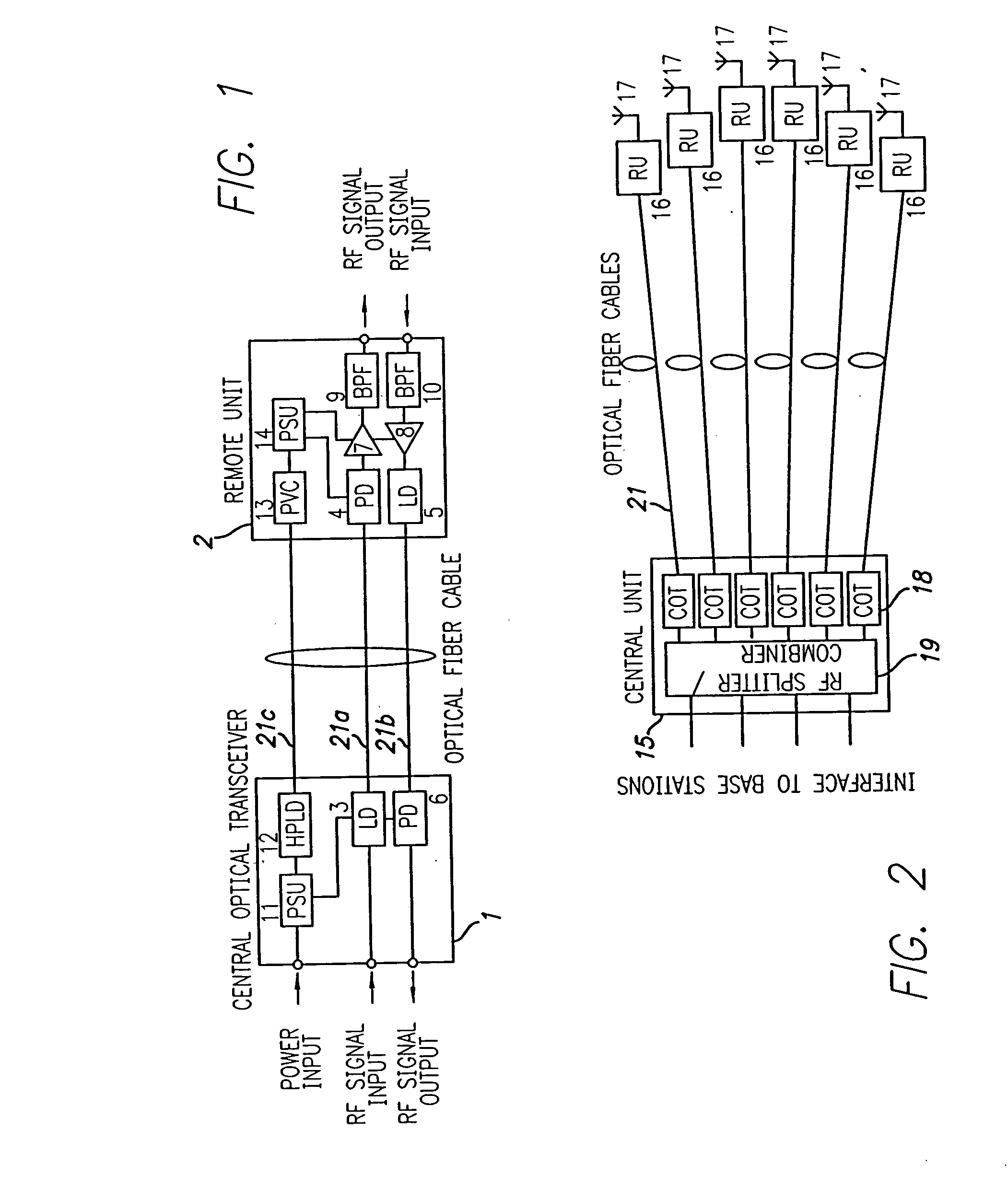
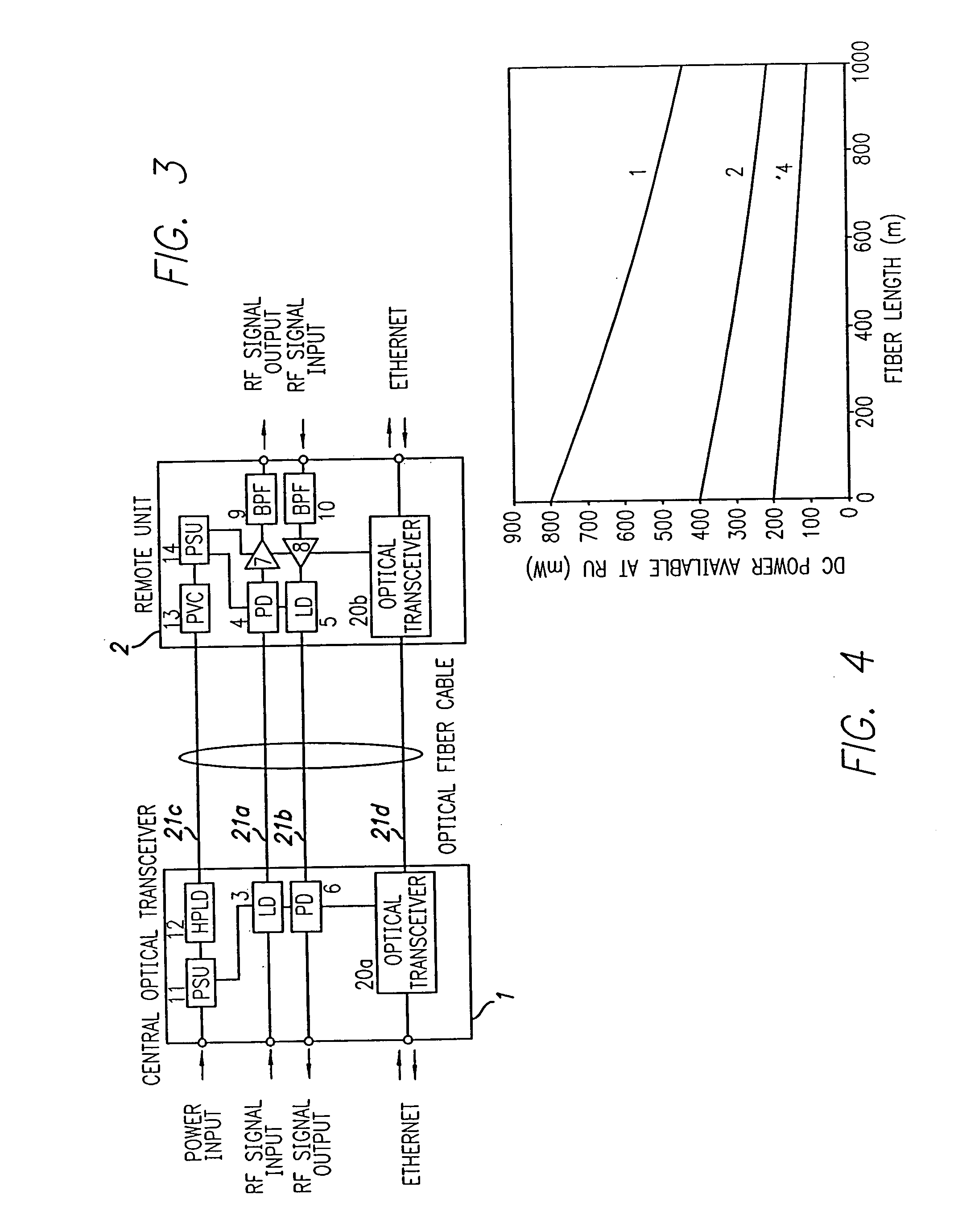
Optical fiber communications method and system without a remote electrical power supply
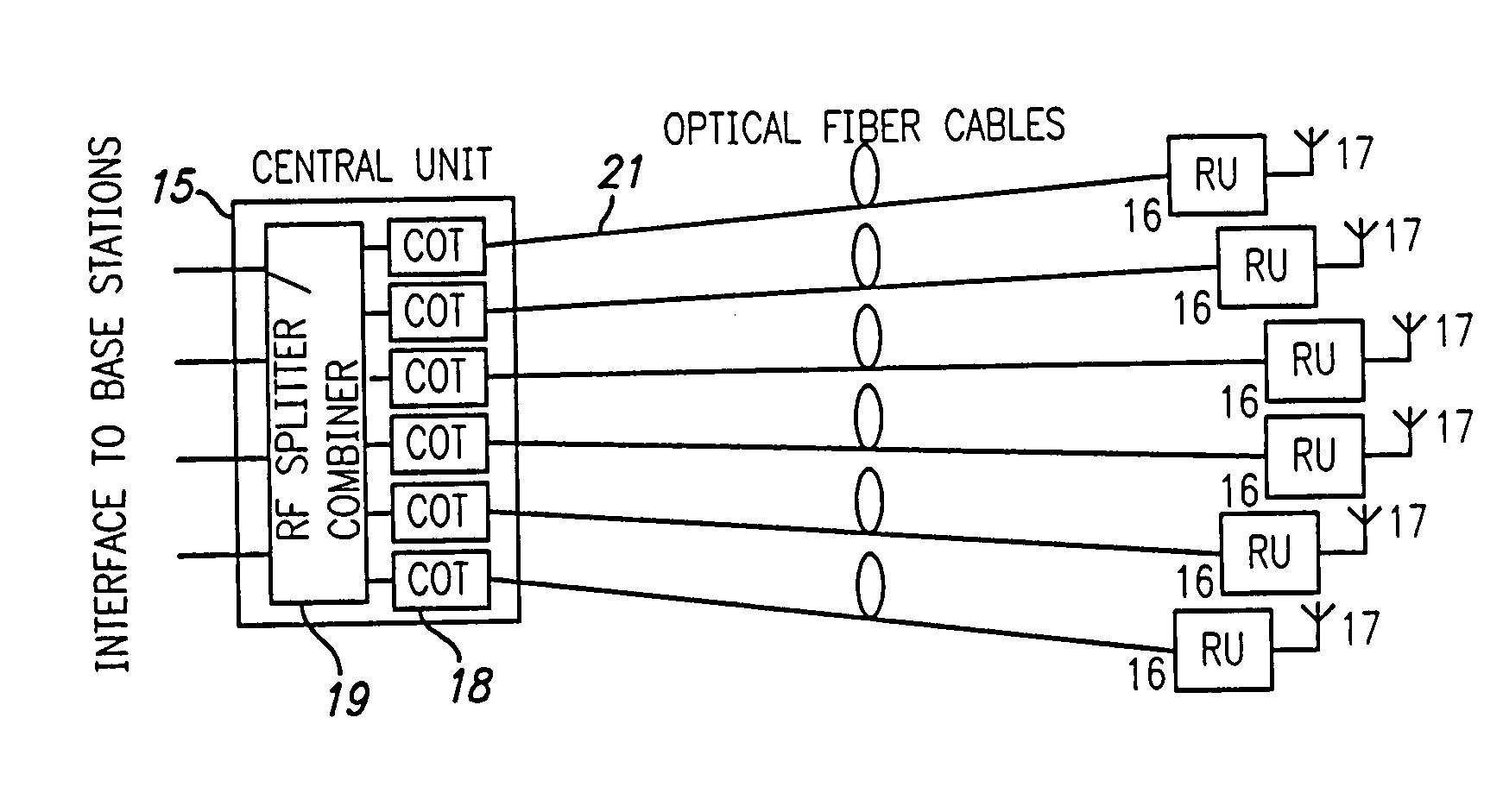
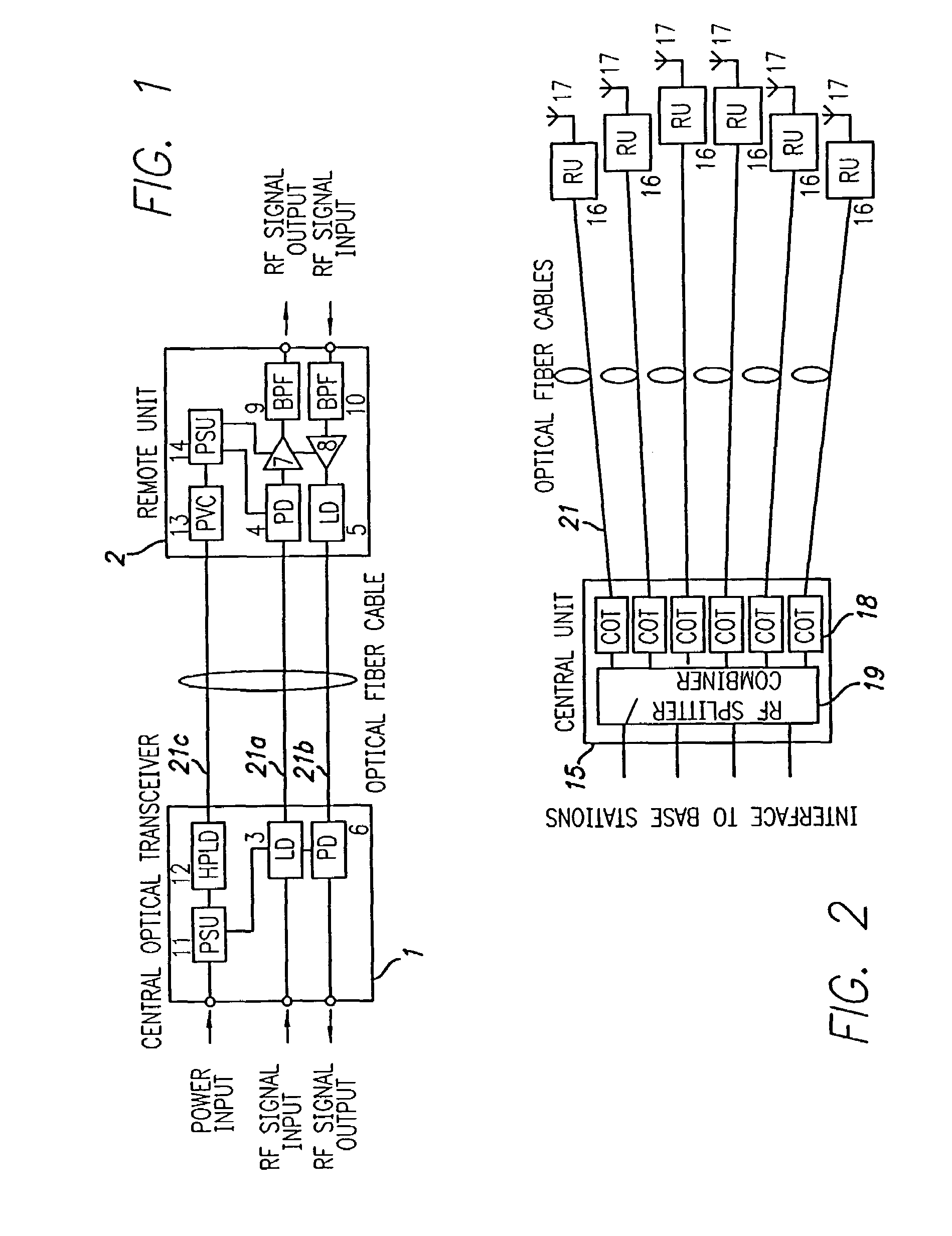
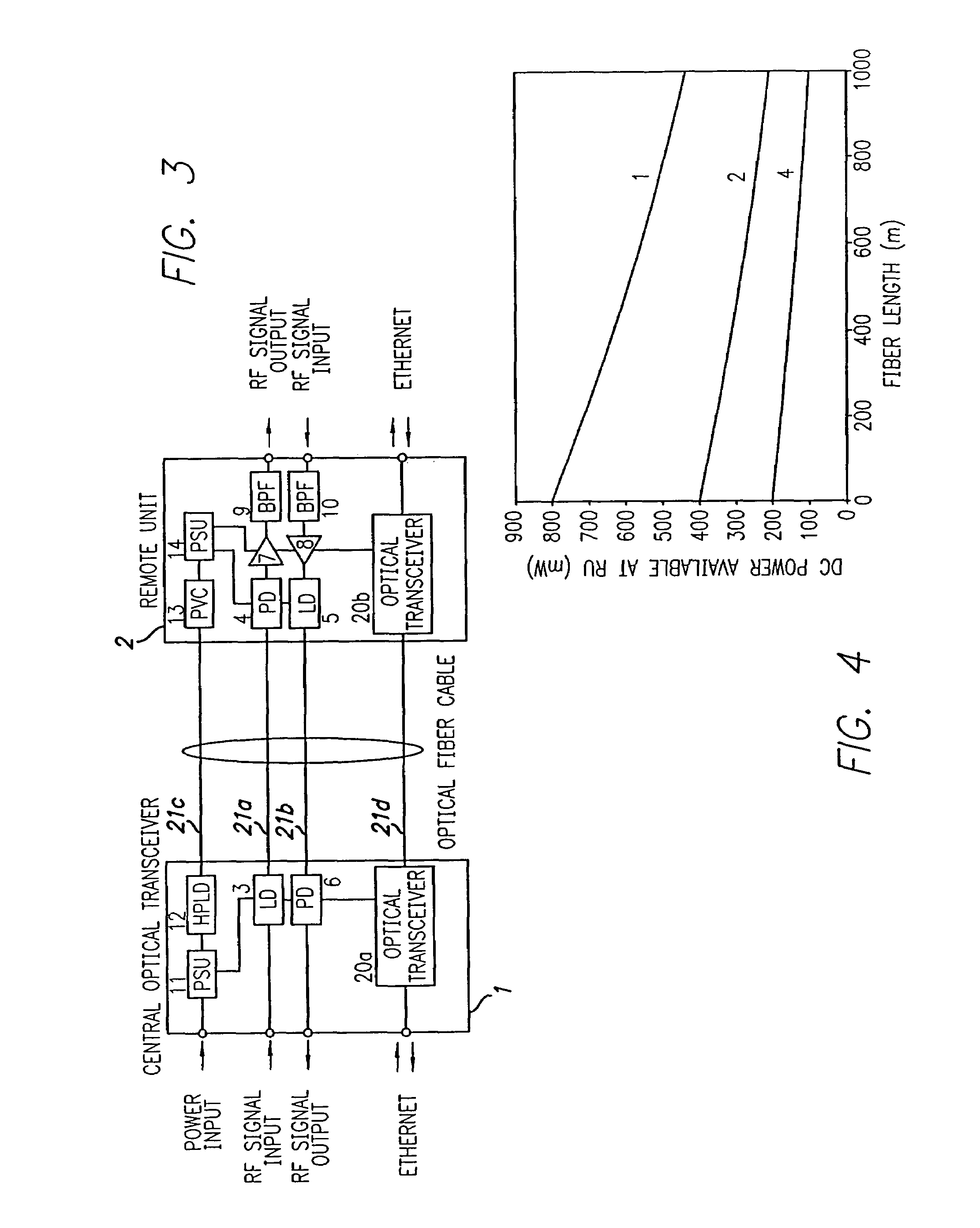
ActiveUS20050226625A1Reduce power consumptionReduced Power RequirementsElectromagnetic transmissionWireless communicationElectrical conductorOptical communication
The present invention allows remote antenna units for radio frequency signal transmission and receipt to operate without the requirement for remote electrical power supplies or for connecting cables that incorporate electrical conductors. According to an aspect of the present invention, an optical communications system employing radio frequency signals comprises a central unit; at least one remote unit having at least one optoelectronic transducer for converting optical data signals to radio frequency signals and converting radio signals to optical signals and at least one antenna to receive and send radio frequency signals; at least one optical fiber data link between the central unit and the remote unit for transmitting optical data signals therebetween; and at least one optical fiber power link between the central unit and the remote unit for providing electrical power at the remote unit.
Owner:NEXTG NETWORKS INC
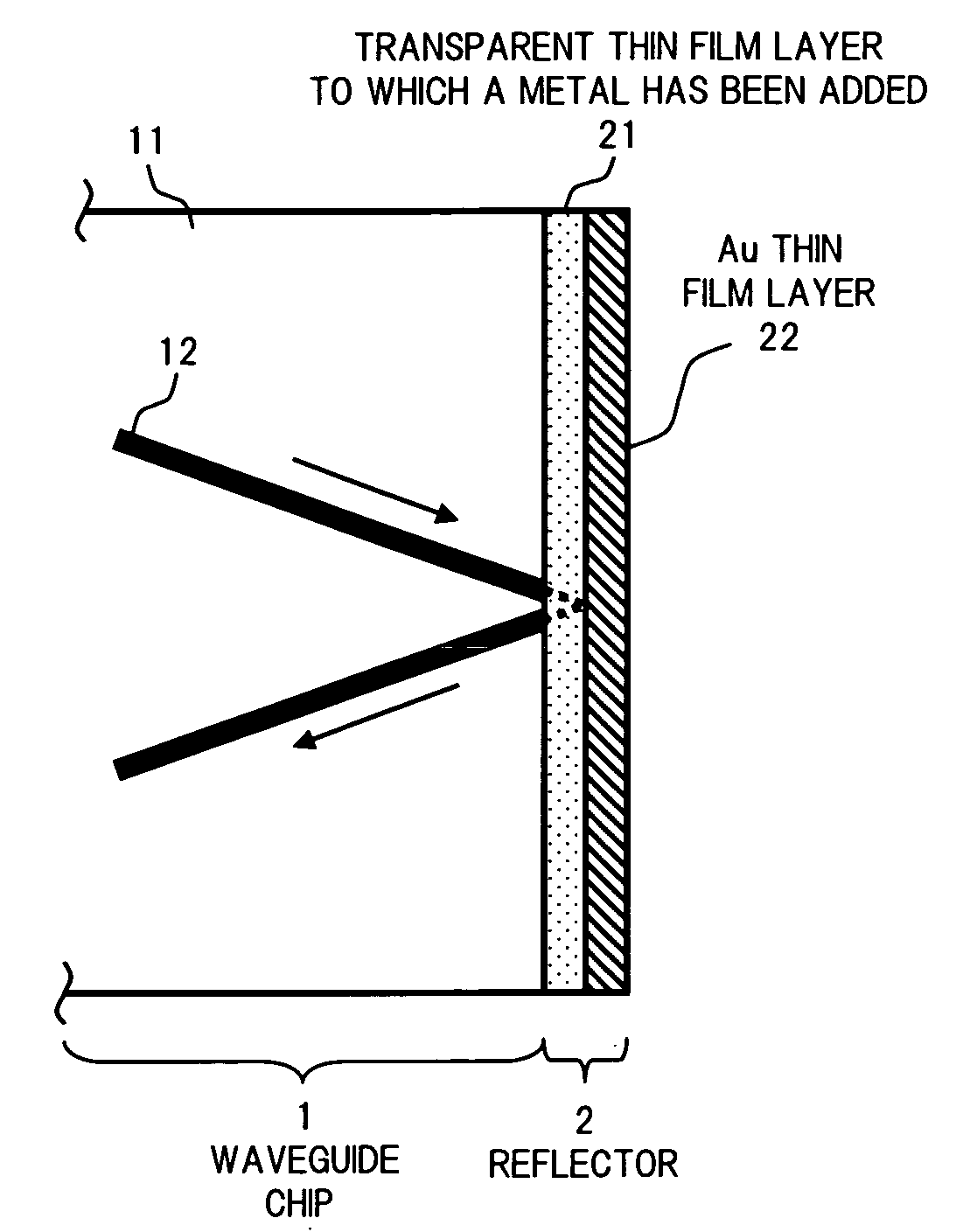
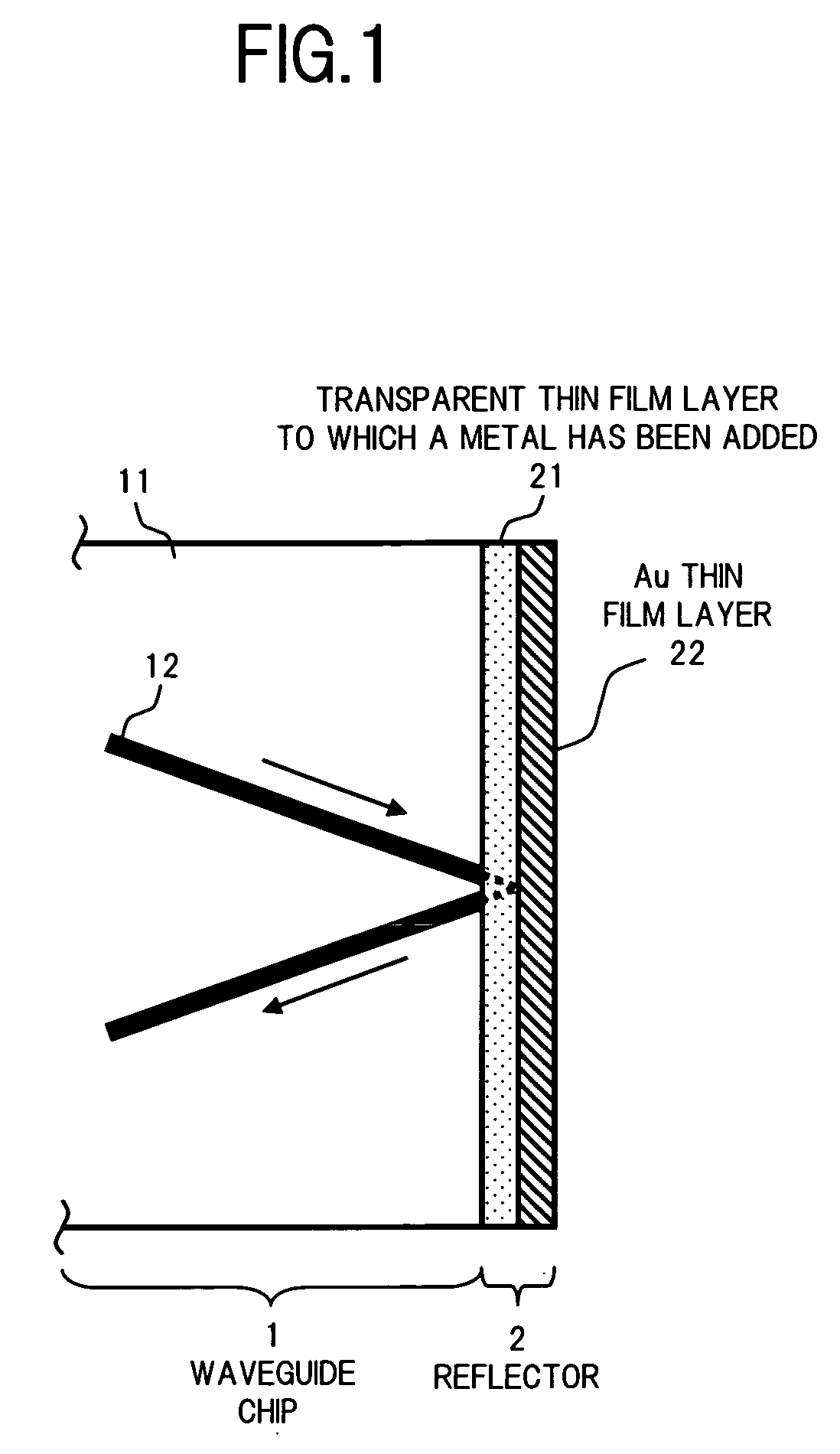
Optical communication device provided with a reflector and method for forming a reflector in an optical communication device
InactiveUS20070070490A1Small lossHigh bonding strengthMirrorsCoupling light guidesCompound (substance)Optical communication
An optical communication device of the invention includes a reflector for reflecting the light that has reached one end surface of a waveguide chip to turn the optical path of the light. The reflector includes a transparent thin film layer formed on one end surface of the waveguide chip by using a material to which a metal that forms an intermetallic compound or the like with Au is added to a substance that is transparent to the light that propagates through the waveguide, as well as an Au thin film layer formed on the front surface of the transparent thin film layer. This allows formation of a reflector having an Au thin film layer as a reflecting surface in an optical medium with high adhesion strength. Thus, an optical communication device can be provided having a high reliability with little loss.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Transverse-mode multiplexing for optical communication systems
ActiveUS20100329671A1Reverses effectOptical mode multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesMultiplexingCommunications system
An optical communication system having an optical transmitter and an optical receiver optically coupled via a multi-path fiber. The optical transmitter launches, into the multi-path fiber, an optical transverse-mode-multiplexed (TMM) signal having a plurality of independently modulated components by coupling each independently modulated component into a respective transverse mode of the multi-path fiber. The TMM signal undergoes inter-mode mixing in the multi-path fiber before being received by the optical receiver. The optical receiver processes the received TMM signal to reverse the effects of inter-mode mixing and recover the data carried by each of the independently modulated components.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Methods and systems for simultaneous real-time monitoring of optical signals from multiple sources
ActiveUS20070188750A1Increase speedLower levelRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationDetector arrayOptical communication
Methods and systems for real-time monitoring of optical signals from arrays of signal sources, and particularly optical signal sources that have spectrally different signal components. Systems include signal source arrays in optical communication with optical trains that direct excitation radiation to and emitted signals from such arrays and image the signals onto detector arrays, from which such signals may be subjected to additional processing.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Optical coherence tomography apparatus and methods
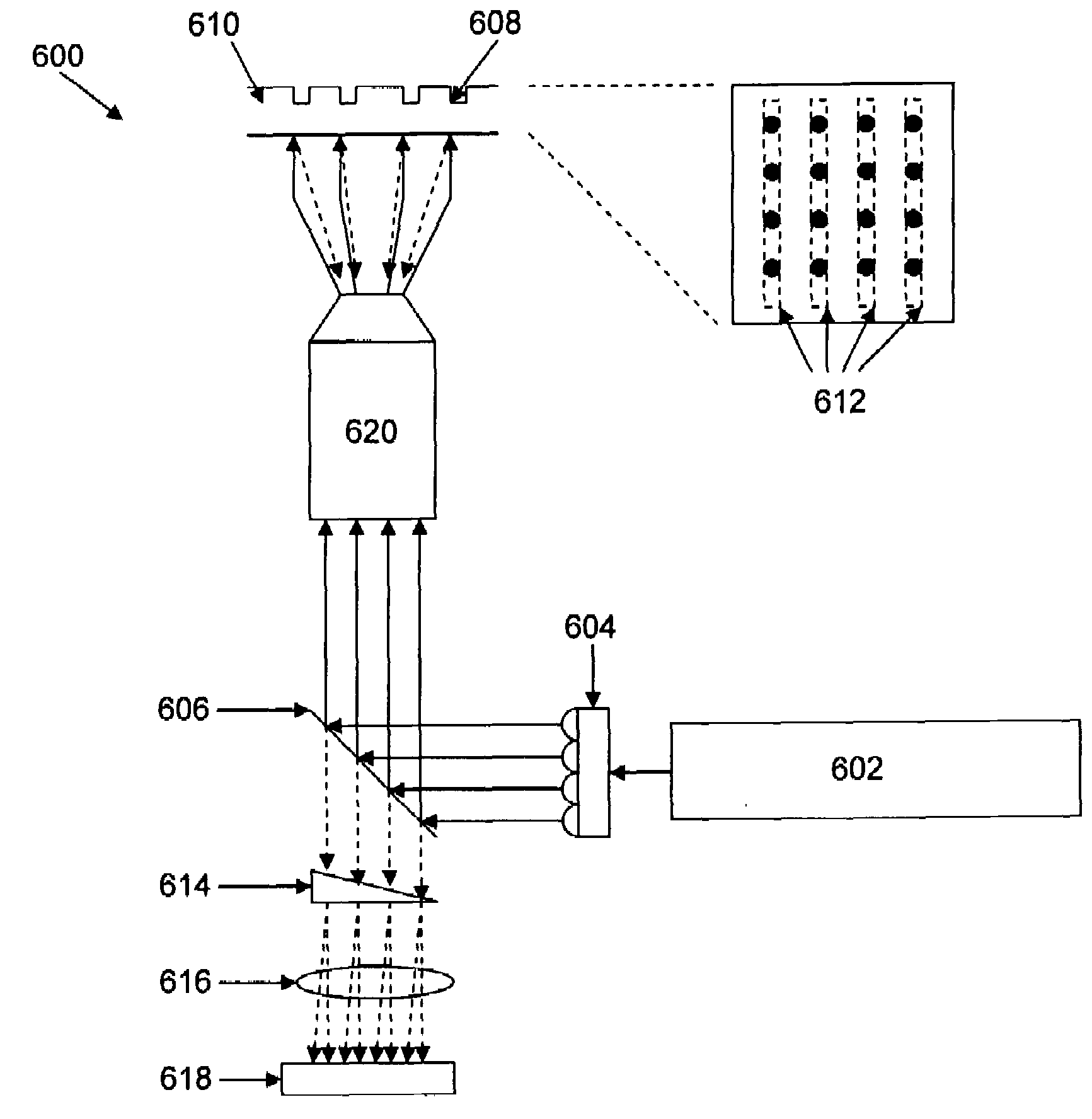
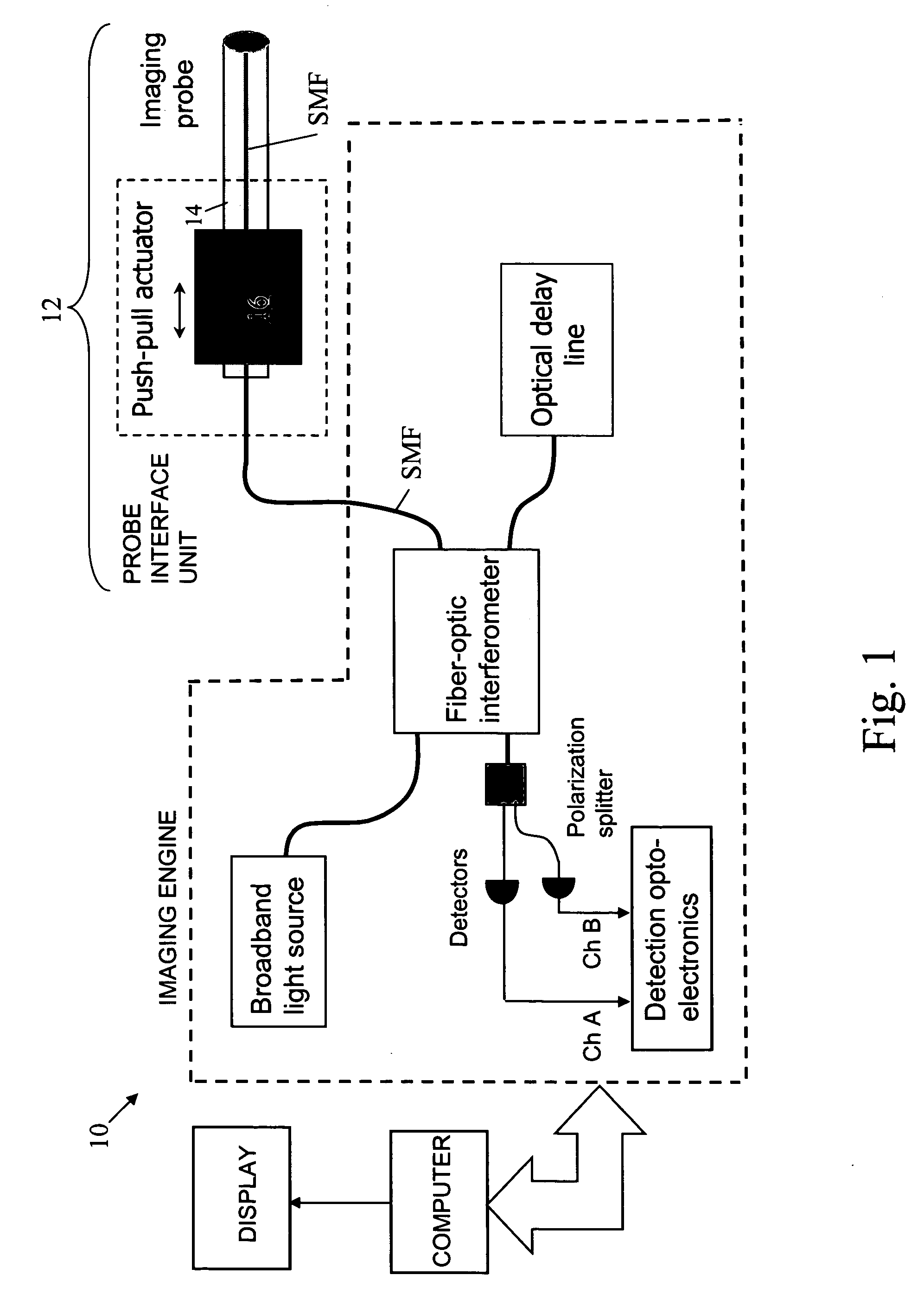
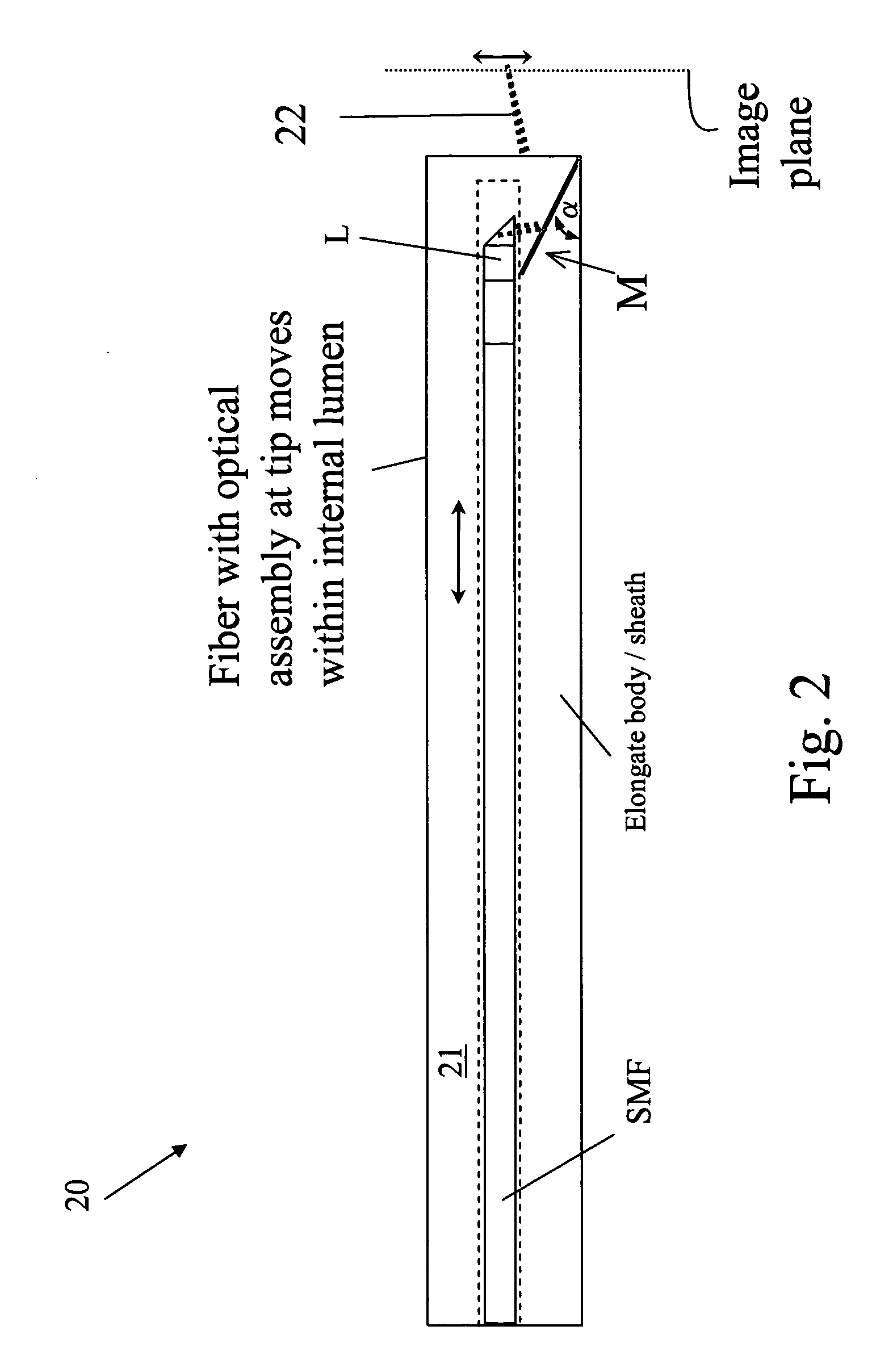
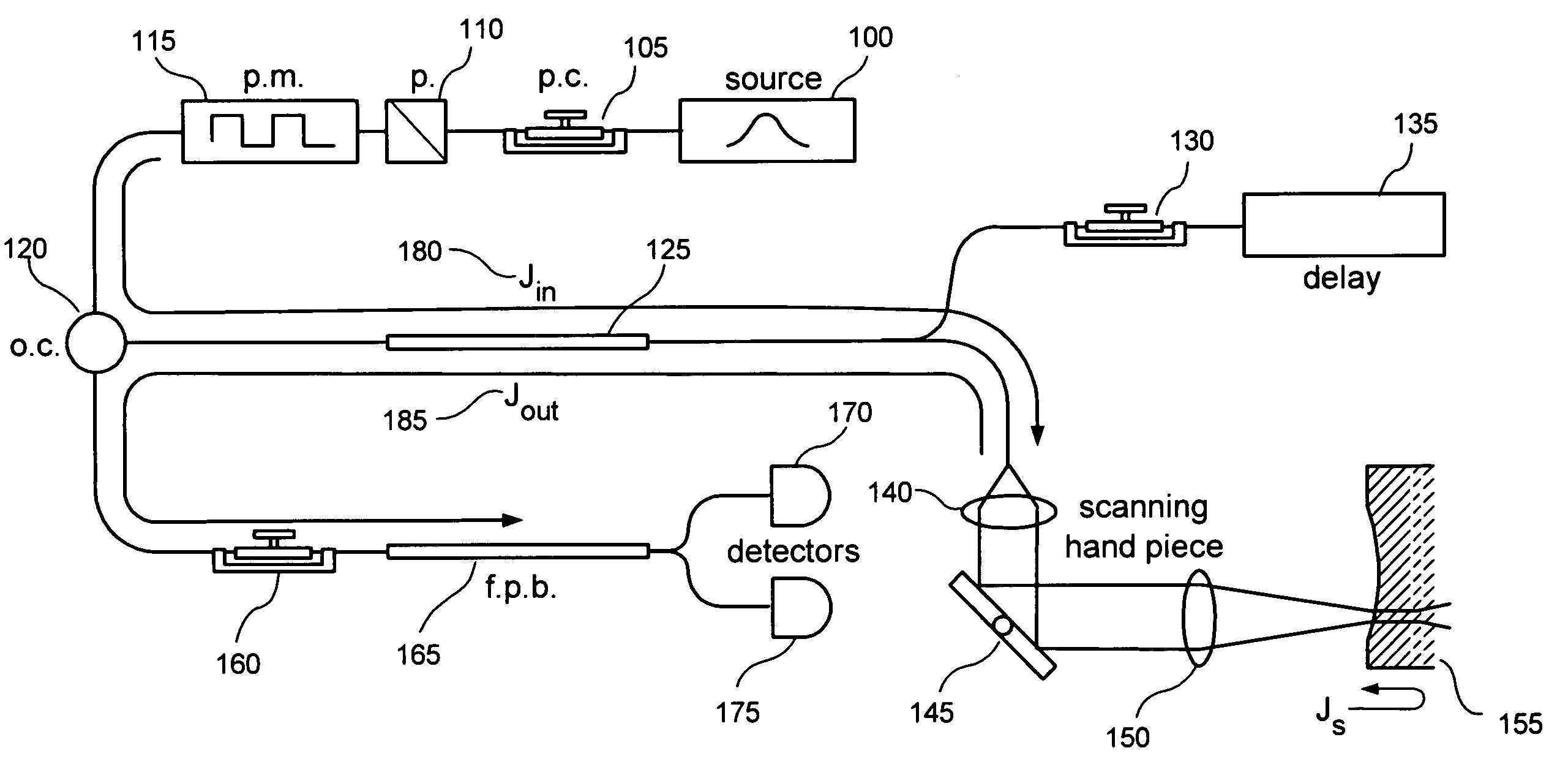
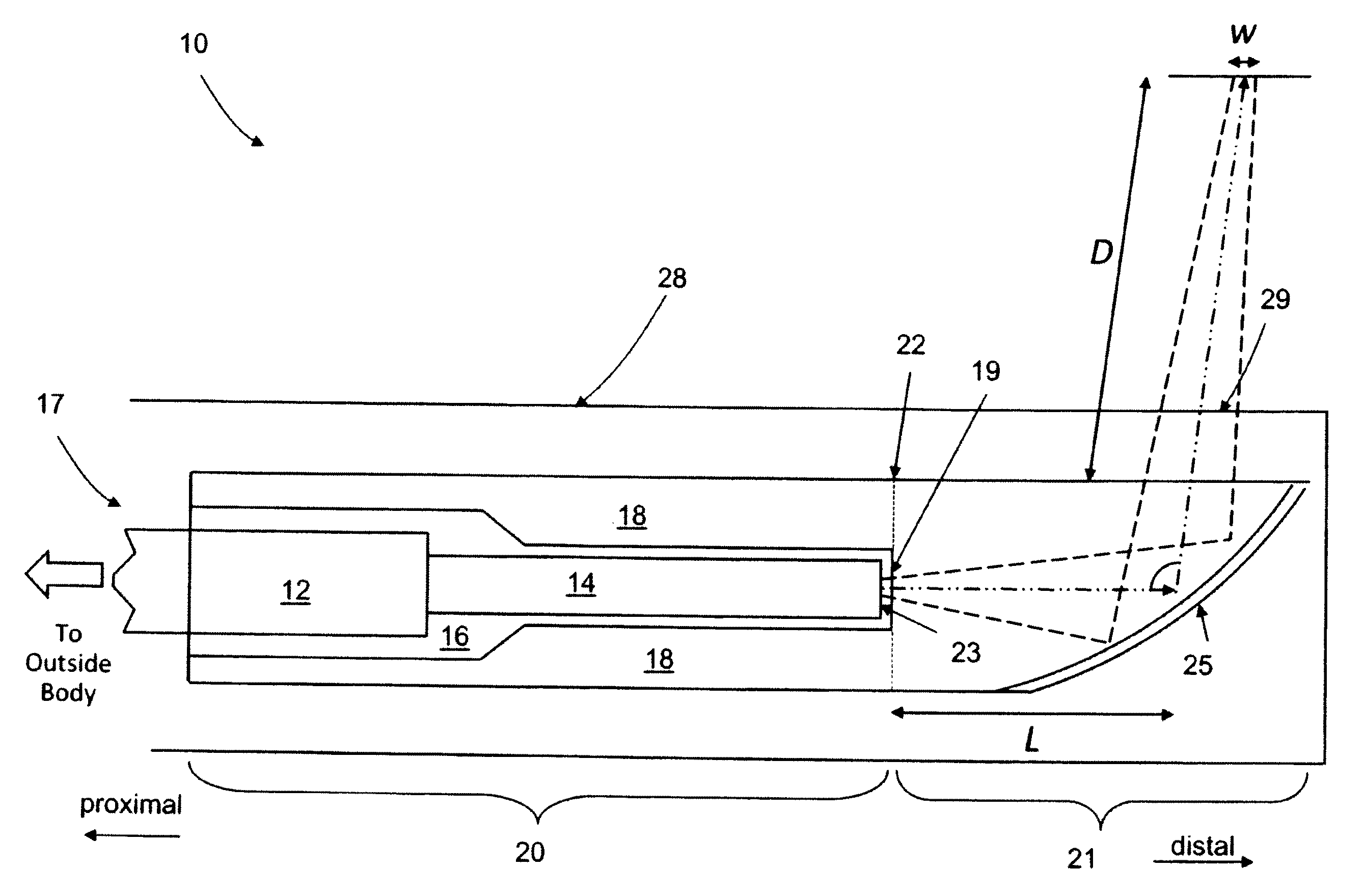
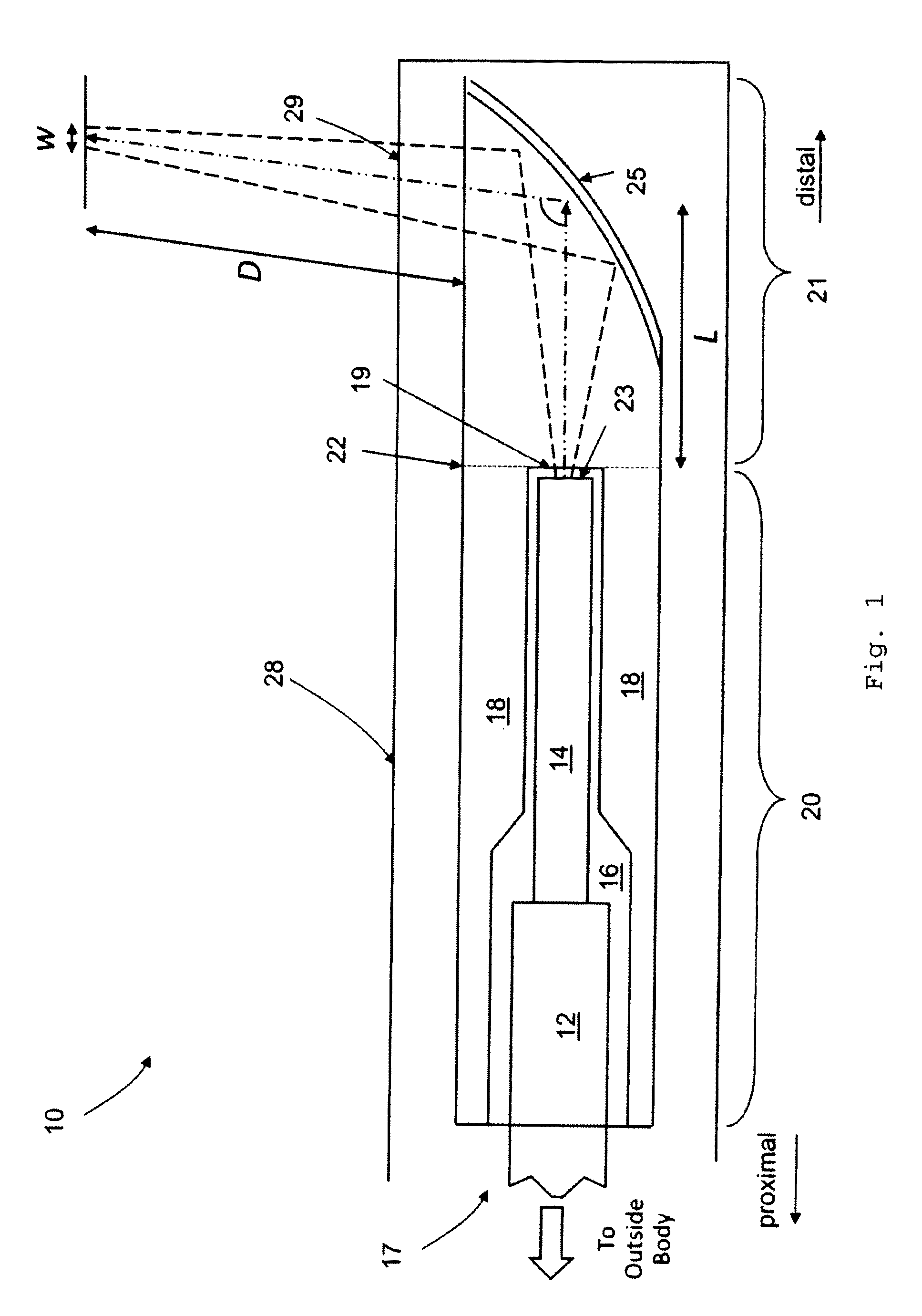
In one aspect, the invention relates to an imaging probe. The imaging probe includes an elongate body having a proximal end and distal end, the elongate body adapted to enclose a portion of a slidable optical fiber, the optical fiber having a longitudinal axis; and a first optical assembly attached to a distal end of the fiber. The first optical assembly includes a beam director adapted to direct light emitted from the fiber to a plane at a predetermined angle to the longitudinal axis, a linear actuator disposed at the proximal portion of the elongated body, the actuator adapted to affect relative linear motion between the elongate body and the optical fiber; and a second optical assembly located at the distal portion of the elongate body and attached thereto, the second optical assembly comprising a reflector in optical communication with the first optical assembly, the reflector adapted to direct the light to a position distal to the elongate body.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
Reactor and method of processing a semiconductor substrate
InactiveUSRE37546E1Accurately determineEliminate needThermometer detailsRadiation pyrometryGas syringeEngineering
Owner:KOKUSAI SEMICON EQUIP CORP
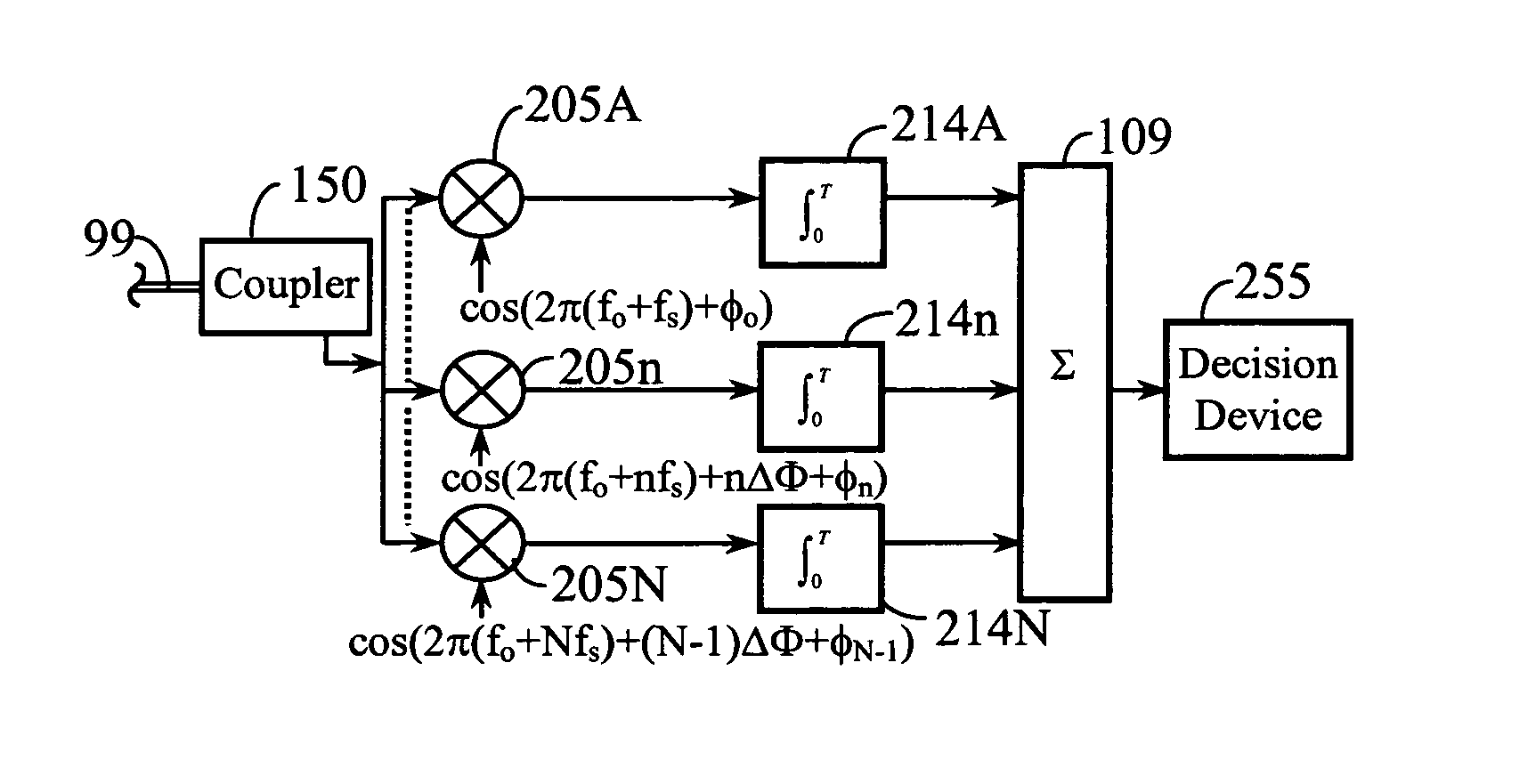
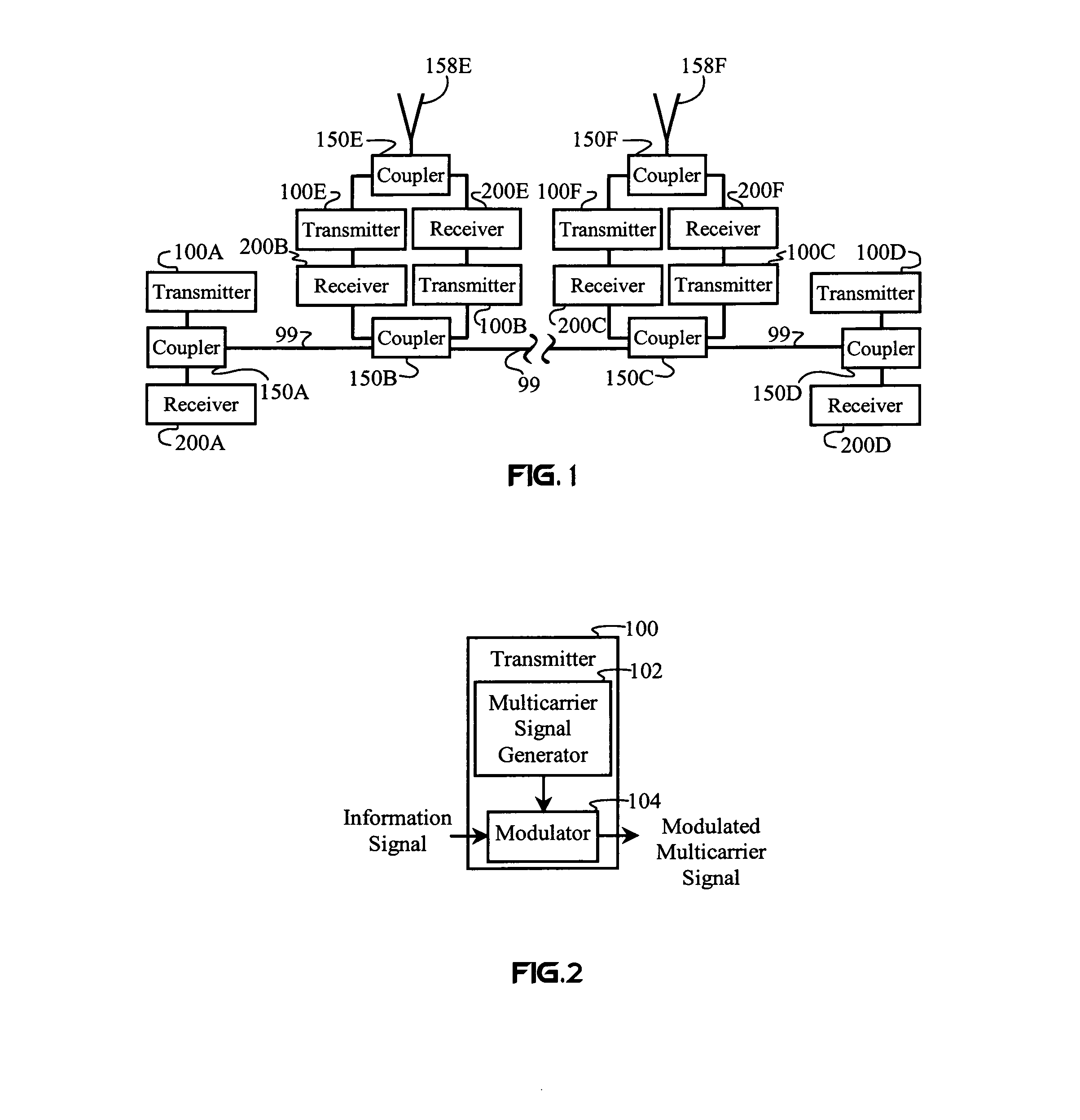
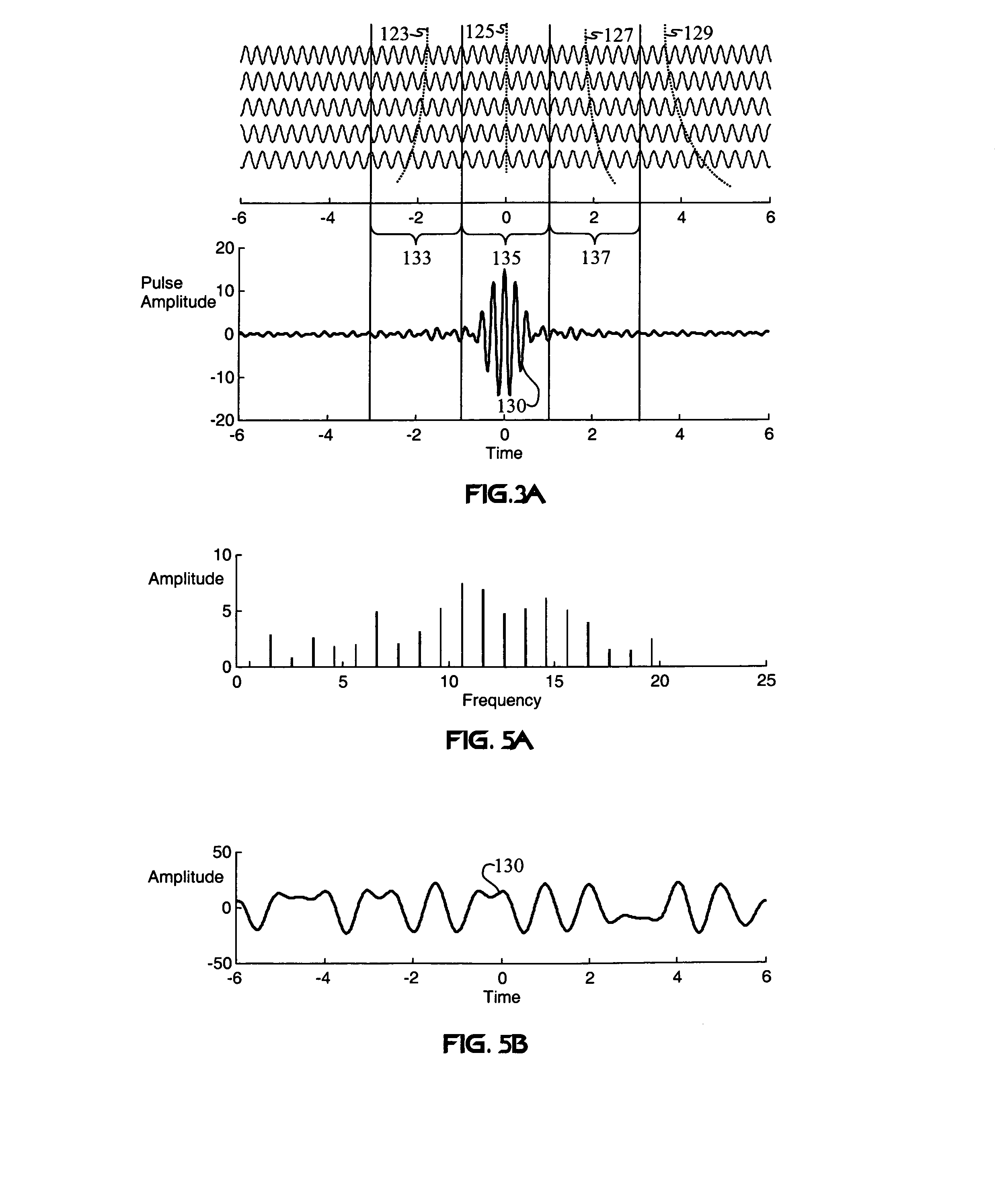
Method and apparatus for using multicarrier interferometry to enhance optical fiber communications
InactiveUS7076168B1Increase diversityImprove efficiencyEnergy efficient ICTModulated-carrier systemsSignal qualityFrequency reuse
A redundently modulated multicarrier protocol known as Carrier Interference Multiple Access (CIMA) is used in an optical-fiber network having wireless links at network nodes. CIMA is a protocol that can be used to create wireless protocols (such as TDMA and CDMA) having enhanced capacity and reduced system complexity. A CIMA optical-fiber network uses dispersion to enhance signal quality and facilitate switching. CIMA achieves both diversity benefits and capacity enhancements by providing redundancy in at least one diversity parameter while providing orthogonality in another diversity parameter. This basic operating principle of CIMA may be combined with multi-user detection to achieve frequency reuse and improved power efficiency. In the wireless link, diversity may be used to reduce the effects of small-scale fading on interferometry multiplexing.
Owner:DEPARTMENT 13 INC
OCT using spectrally resolved bandwidth
The present invention is related to a system for optical coherence tomographic imaging of turbid (i.e., scattering) materials utilizing multiple channels of information. The multiple channels of information may be comprised and encompass spatial, angle, spectral and polarization domains. More specifically, the present invention is related to methods and apparatus for utilizing optical sources, systems or receivers capable of providing (source), processing (system) or recording (receiver) a multiplicity of channels of spectral information for optical coherence tomographic imaging of turbid materials. In these methods and apparatus the multiplicity of channels of spectral information that can be provided by the source, processed by the system, or recorded by the receiver are used to convey simultaneously spatial, spectral or polarimetric information relating to the turbid material being imaged tomographically. The multichannel optical coherence tomographic methods can be incorporated into an endoscopic probe for imaging a patient. The endoscope comprises an optical fiber array and can comprise a plurality of optical fibers adapted to be disposed in the patient. The optical fiber array transmits the light from the light source into the patient, and transmits the light reflected by the patient out of the patient. The plurality of optical fibers in the array are in optical communication with the light source. The multichannel optical coherence tomography system comprises a detector for receiving the light from the array and analyzing the light. The methods and apparatus may be applied for imaging a vessel, biliary, GU and / or GI tract of a patient.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
System and method for providing Jones matrix-based analysis to determine non-depolarizing polarization parameters using polarization-sensitive optical coherence tomography
InactiveUS20080007734A1Reduced polarization effectsEasy to detectMaterial analysis by optical meansDiagnostics using tomographyPolarization sensitiveOptical communication
Arrangement, system and method for a polarization effect for a interferometric signal received from sample in an optical coherence tomography (“OCT”) system are provided. In particular, an interferometric information associated with the sample and a reference can be received. The interferometric information is then processed thereby reducing a polarization effect created by a detection section of the OCT system on the interferometric signal. Then, an amount of a diattenuation of the sample is determined. The interferometric information can be provided at least partially along at least one optical fiber which is provided in optical communication with and upstream from a polarization separating arrangement. In another exemplary embodiment of the present invention, apparatus and method are provided for transmitting electromagnetic radiation to the sample. For example, at least one first arrangement can be provided which is configured to provide at least one first electromagnetic radiation. A frequency of radiation provided by the first arrangement can vary over time. At least one polarization modulating second arrangement can be provided which is configured to control a polarization state of at least one first electromagnetic radiation so as to produce at least one second electromagnetic radiation. Further, at least one third arrangement can be provided which is configured to receive the second electro-magnetic radiation, and provide at least one third electromagnetic radiation to the sample and at least one fourth electromagnetic radiation to a reference. The third and fourth electromagnetic radiations may be associated with the second electromagnetic radiation.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Zoomable spot module
A lamp (10, 30, 80) includes an LED module (16, 36, 86) having at least one LED (12, 32, 82) arranged on a substrate (14, 34, 84). An optical system includes at least one lens (18, 38, 88) in optical communication with the LED module (16, 36, 86). A zoom apparatus (20, 40, 90) selectively adjusts the relative axial separation of the optical system and the LED module (16, 36, 86). In one embodiment (30), the zoom apparatus (40) is slidably adjustable. In a another embodiment (80), the zoom apparatus (90) is rotatably adjustable.
Owner:GELCORE LLC (US)
Miniature Optical Elements for Fiber-Optic Beam Shaping
ActiveUS20100253949A1Avoid disruptionAvoid damageMirrorsEndoscopesFiberDiagnostic Radiology Modality
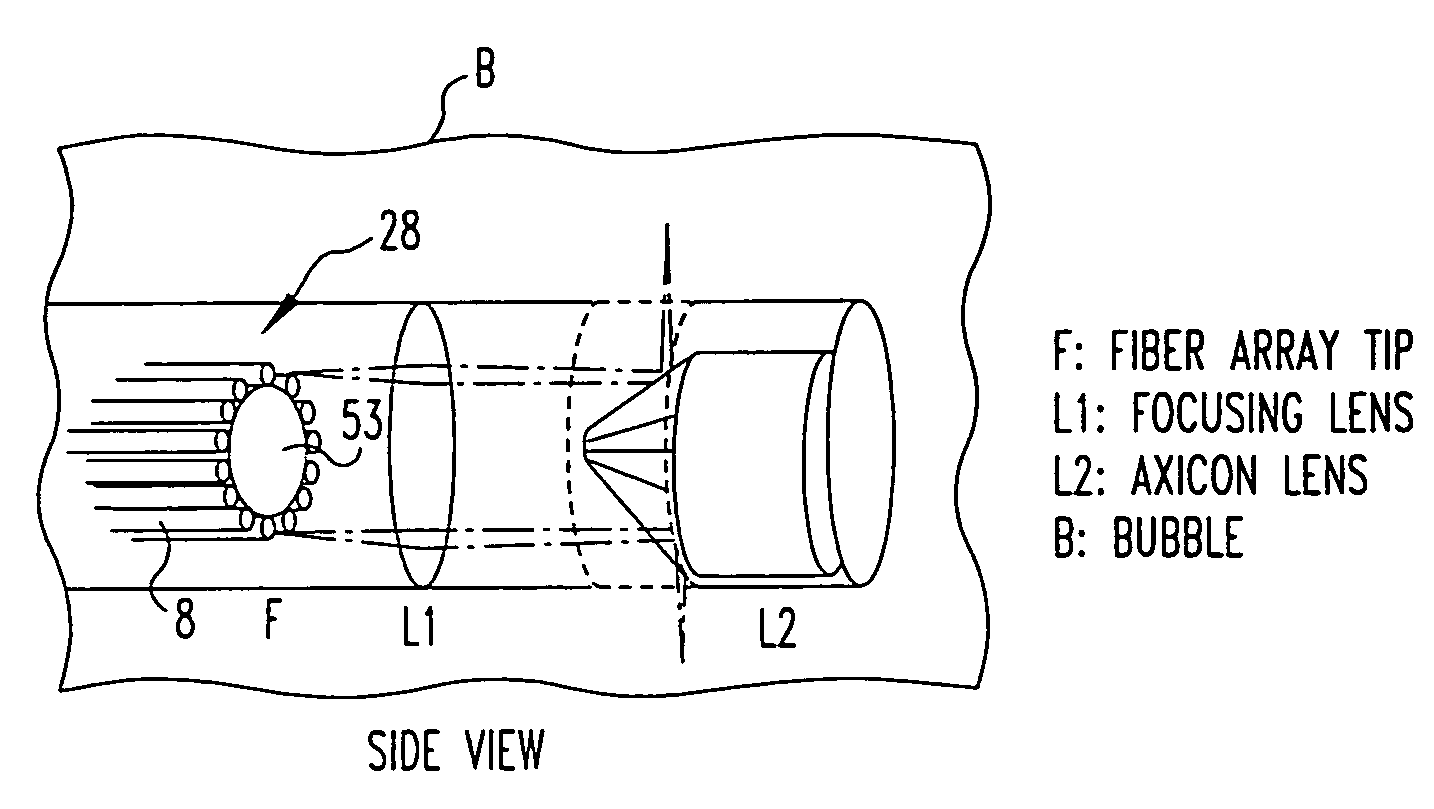
In part, the invention relates to optical caps having at least one lensed surface configured to redirect and focus light outside of the cap. The cap is placed over an optical fiber. Optical radiation travels through the fiber and interacts with the optical surface or optical surfaces of the cap, resulting in a beam that is either focused at a distance outside of the cap or substantially collimated. The optical elements such as the elongate caps described herein can be used with various data collection modalities such optical coherence tomography. In part, the invention relates to a lens assembly that includes a micro-lens; a beam director in optical communication with the micro-lens; and a substantially transparent film or cover. The substantially transparent film is capable of bi-directionally transmitting light, and generating a controlled amount of backscatter. The film can surround a portion of the beam director.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
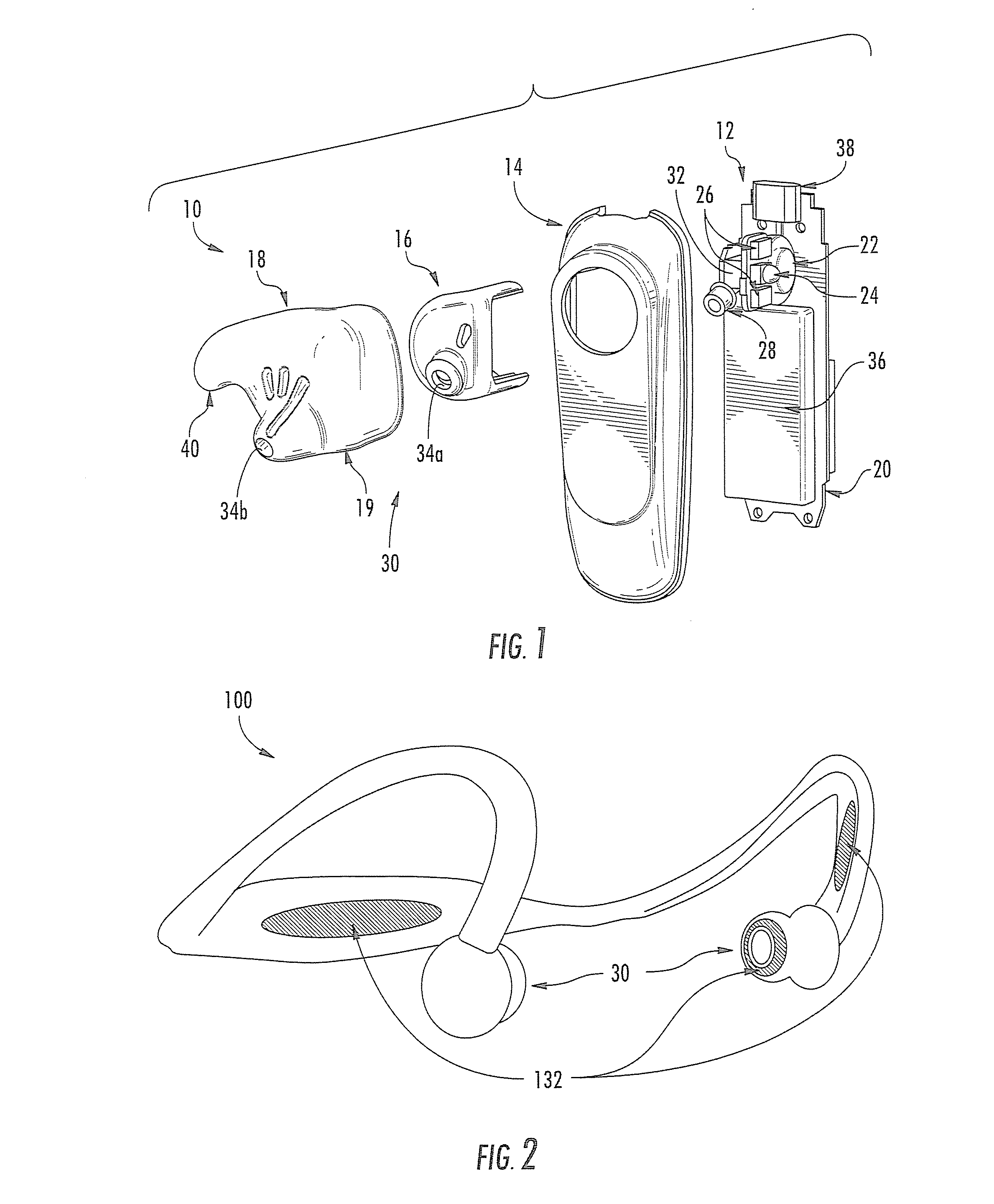
Light-guiding devices and monitoring devices incorporating same
ActiveUS8700111B2Easy alignmentPhysical therapies and activitiesTransducer detailsLight guideEngineering
A monitoring device configured to be attached to the ear of a person includes a base, an earbud housing extending outwardly from the base that is configured to be positioned within an ear of a subject, and a cover surrounding the earbud housing. The base includes a speaker, an optical emitter, and an optical detector. The cover includes light transmissive material that is in optical communication with the optical emitter and the optical detector and serves as a light guide to deliver light from the optical emitter into the ear canal of the subject wearing the device at one or more predetermined locations and to collect light external to the earbud housing and deliver the collected light to the optical detector.
Owner:VALENCELL INC
Multimodal Imaging System, Apparatus, and Methods
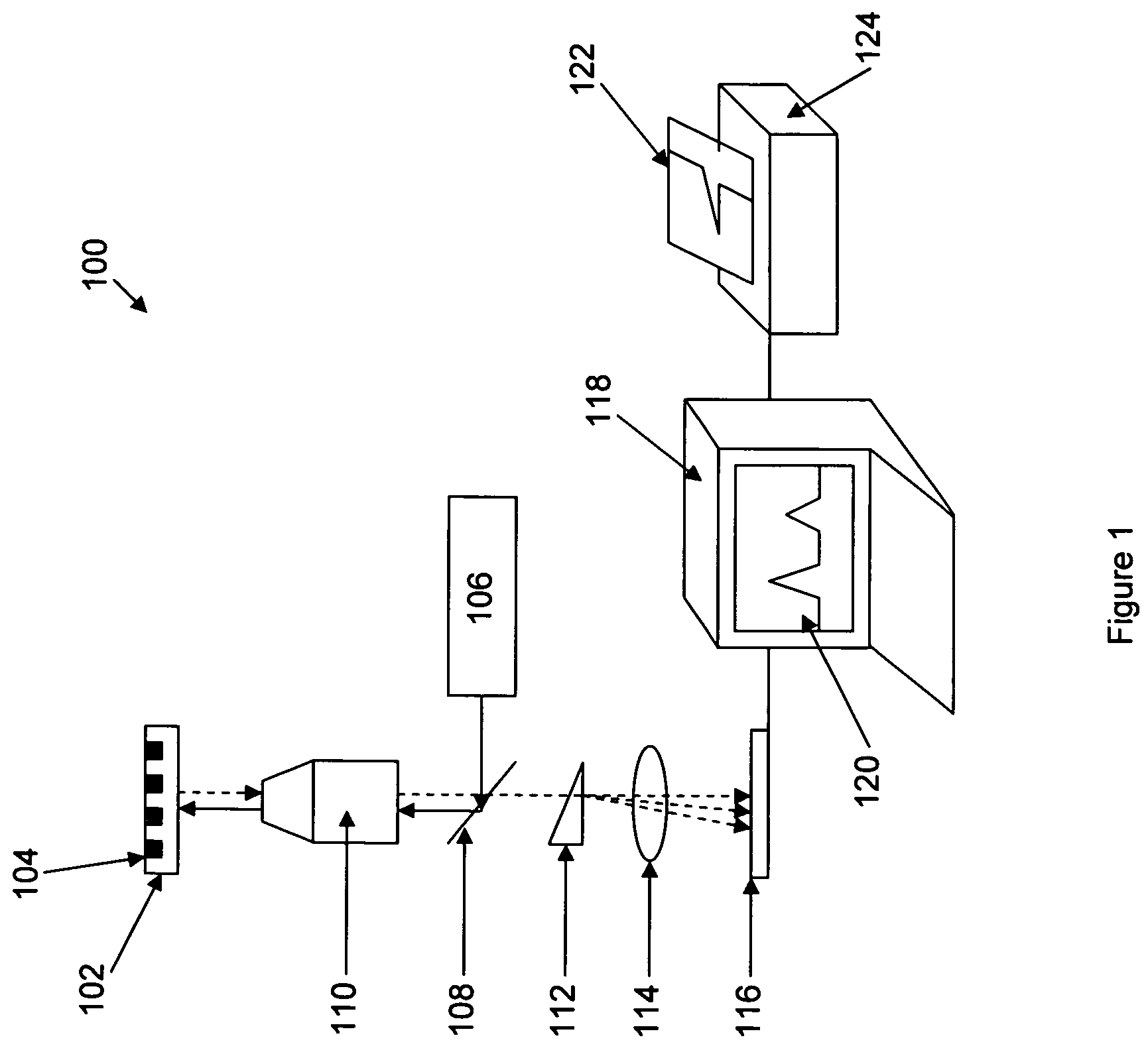
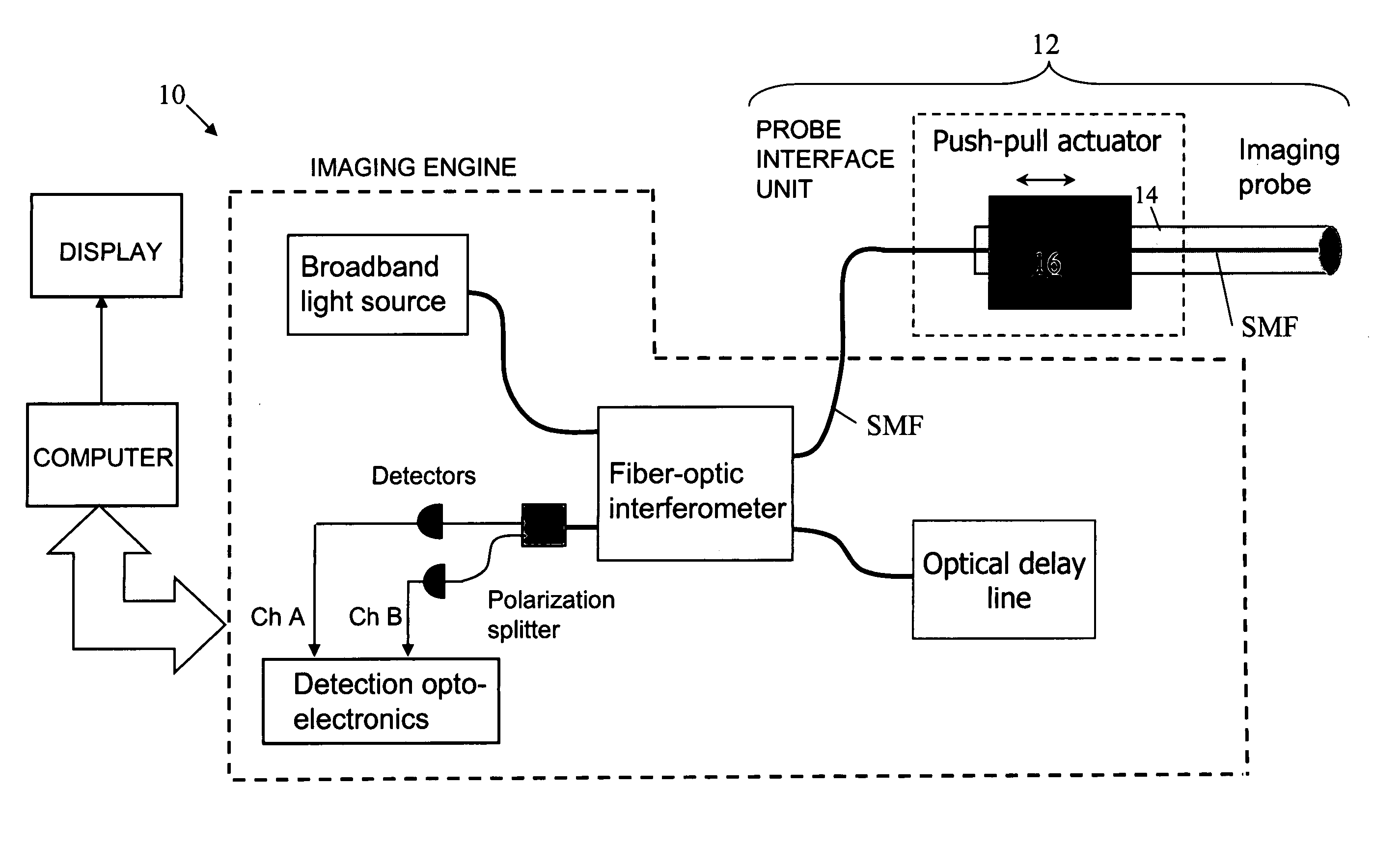
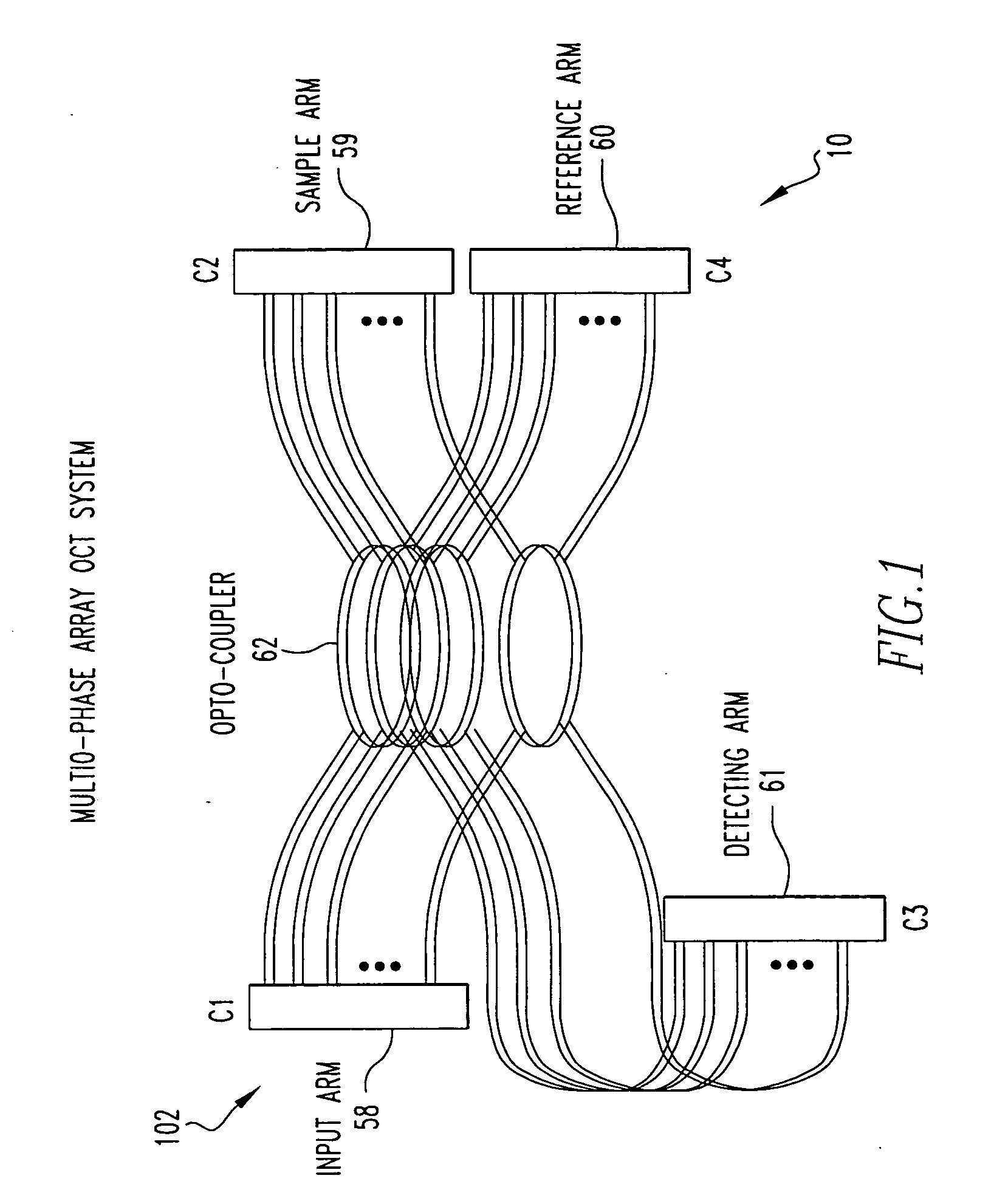
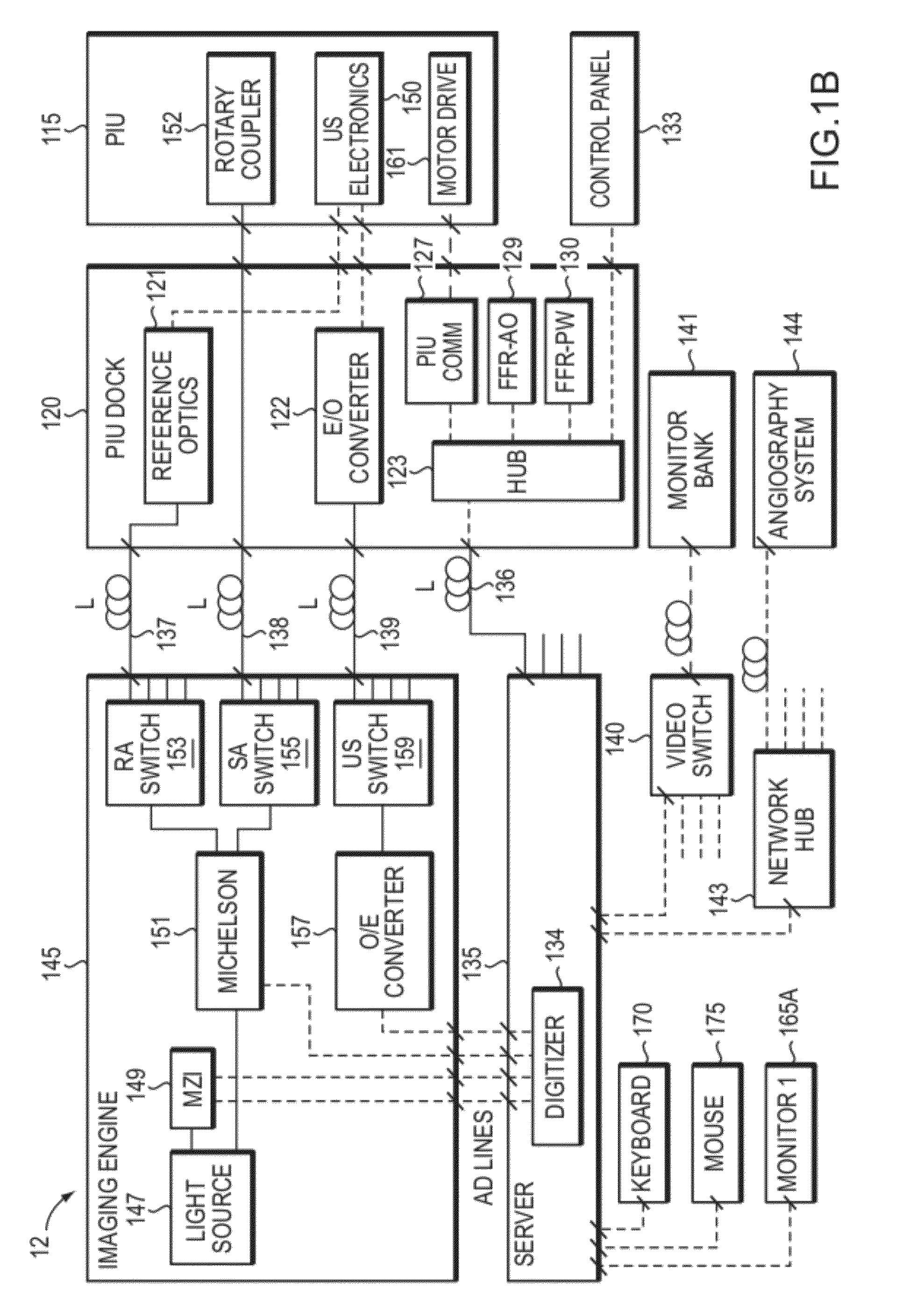
In part, the invention relates to an image data collection system. The system can include an interferometer having a reference arm that includes a first optical fiber of length of L1 and a sample arm that includes a second optical fiber of length of L2 and a first rotary coupler configured to interface with an optical tomography imaging probe, wherein the rotary coupler is in optical communication with the sample arm. In one embodiment, L2 is greater than about 5 meters. The first optical fiber and the second optical fiber can both be disposed in a common protective sheath. In one embodiment, the system further includes an optical element configured to adjust the optical path length of the reference arm, wherein the optical element is in optical communication with the reference arm and wherein the optical element is transmissive or reflective.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
Method and apparatus for correcting faults in a passive optical network
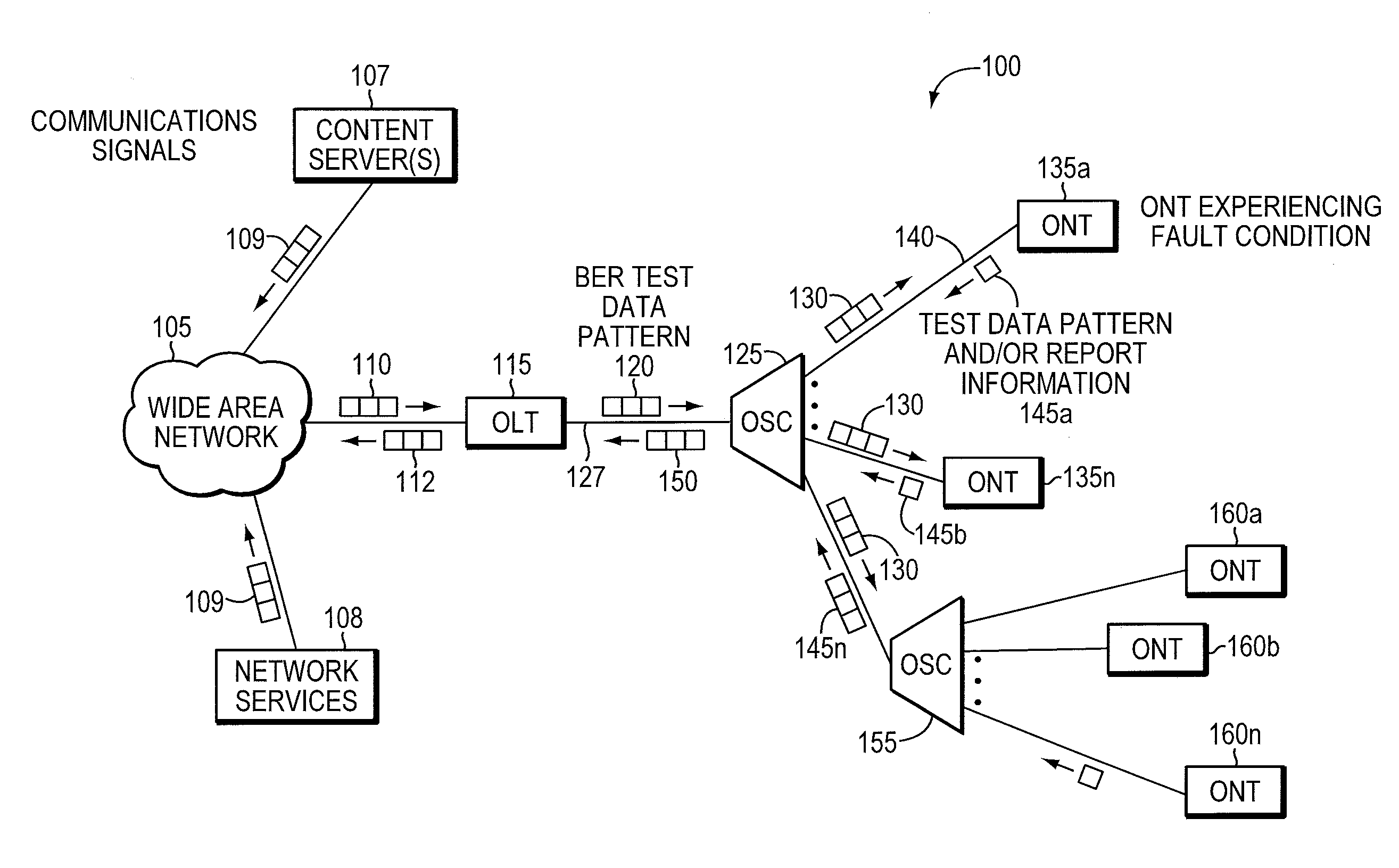
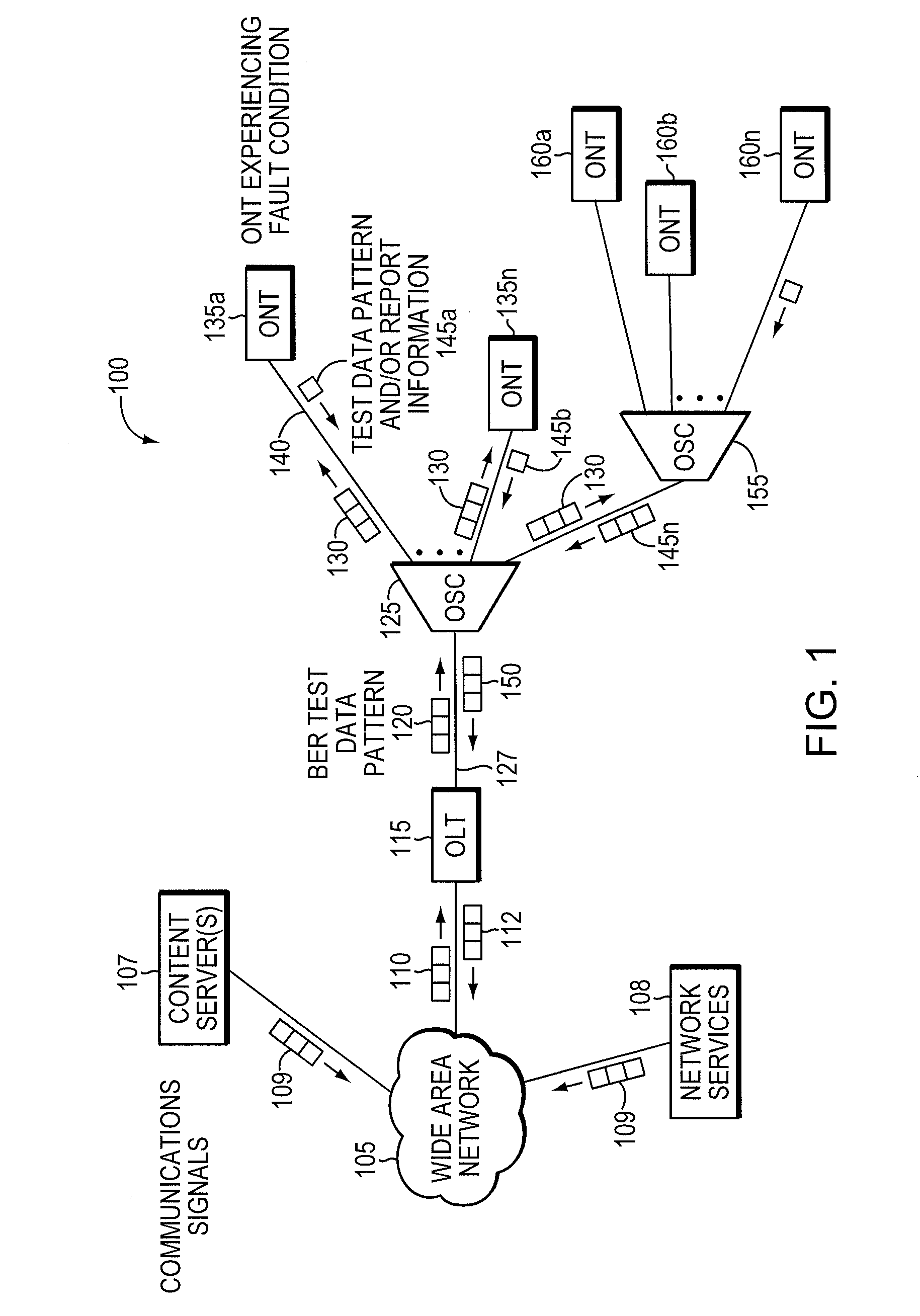
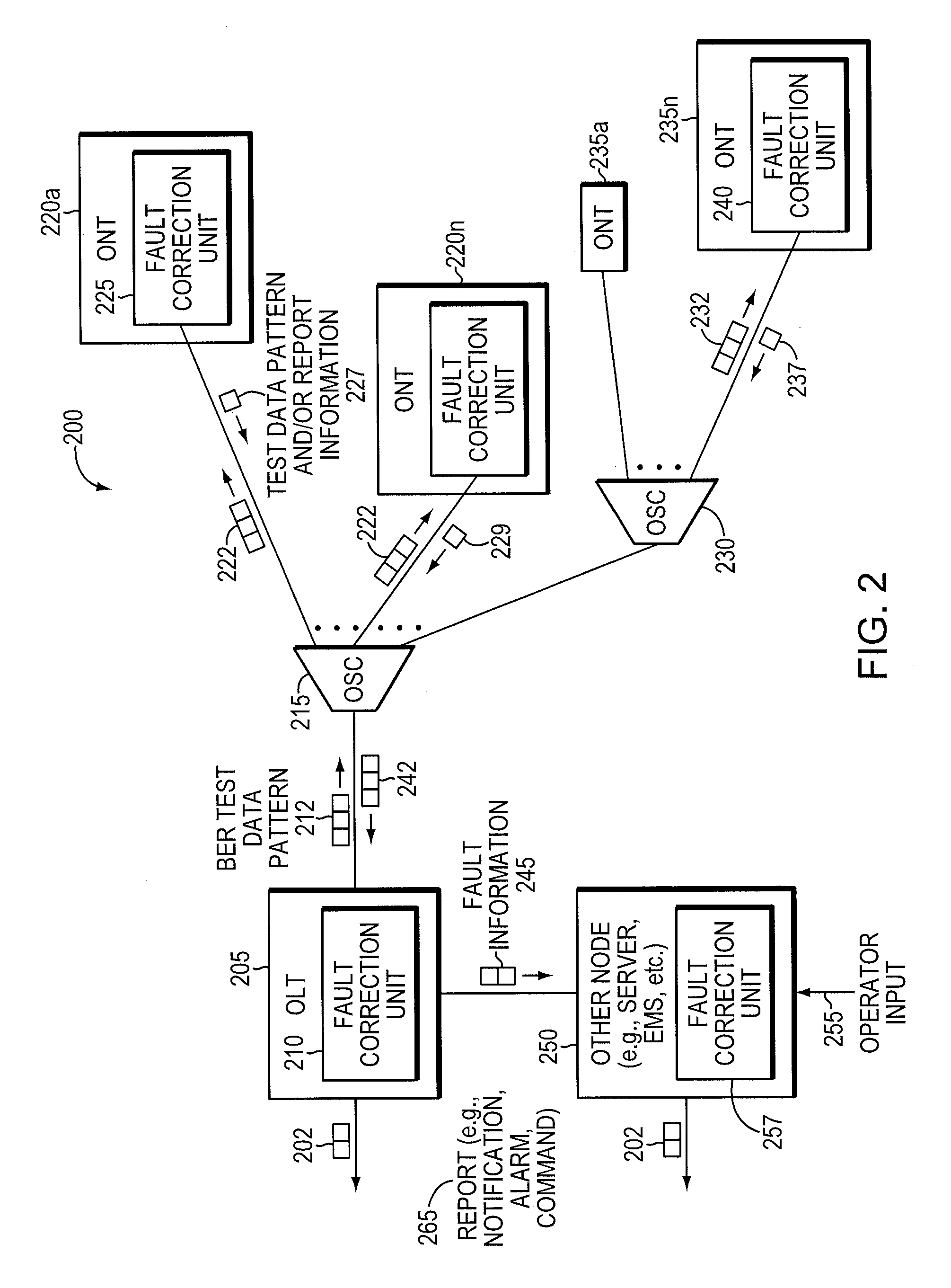
ActiveUS8090258B2Transmission monitoringTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Engineering
Component malfunctions in passive optical networks (PON) can increase bit error rates and decrease signal-to-noise ratio of communications signals. These faults may cause the receivers of the signals, either the optical line terminal (OLT) or optical network terminals (ONTs), to experience intermittent faults and / or may result in misinterpreted commands that disrupt other ONT's communication, resulting in a rogue ONT condition. Existing PON protocol detection methods may not detect these types of malfunctions. An embodiment of the present invention identifies faults in a PON by transmitting a test series of data patterns via an optical communications path from a first optical network node to a second optical network node. The test series is compared to an expected series of data patterns. An error rate may be calculated as a function of the differences between the test series and expected series. The error rate may be reported to identify faults in the PON. Through use of the embodiment, network faults can be identified and optionally automatically corrected, saving a network service provider from expending technician time and maintaining an operating state of the network.
Owner:TELLABS PETALUMA
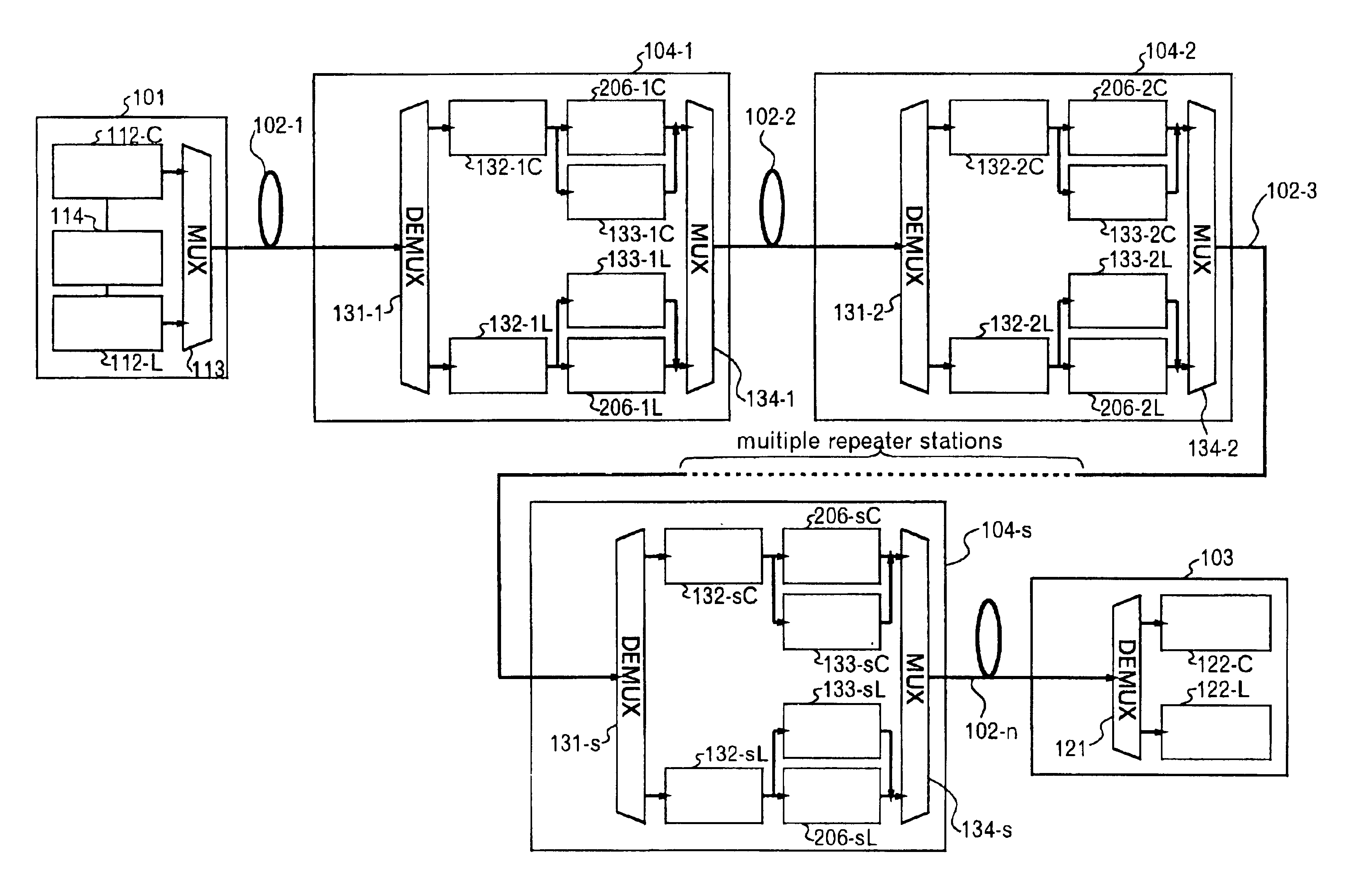
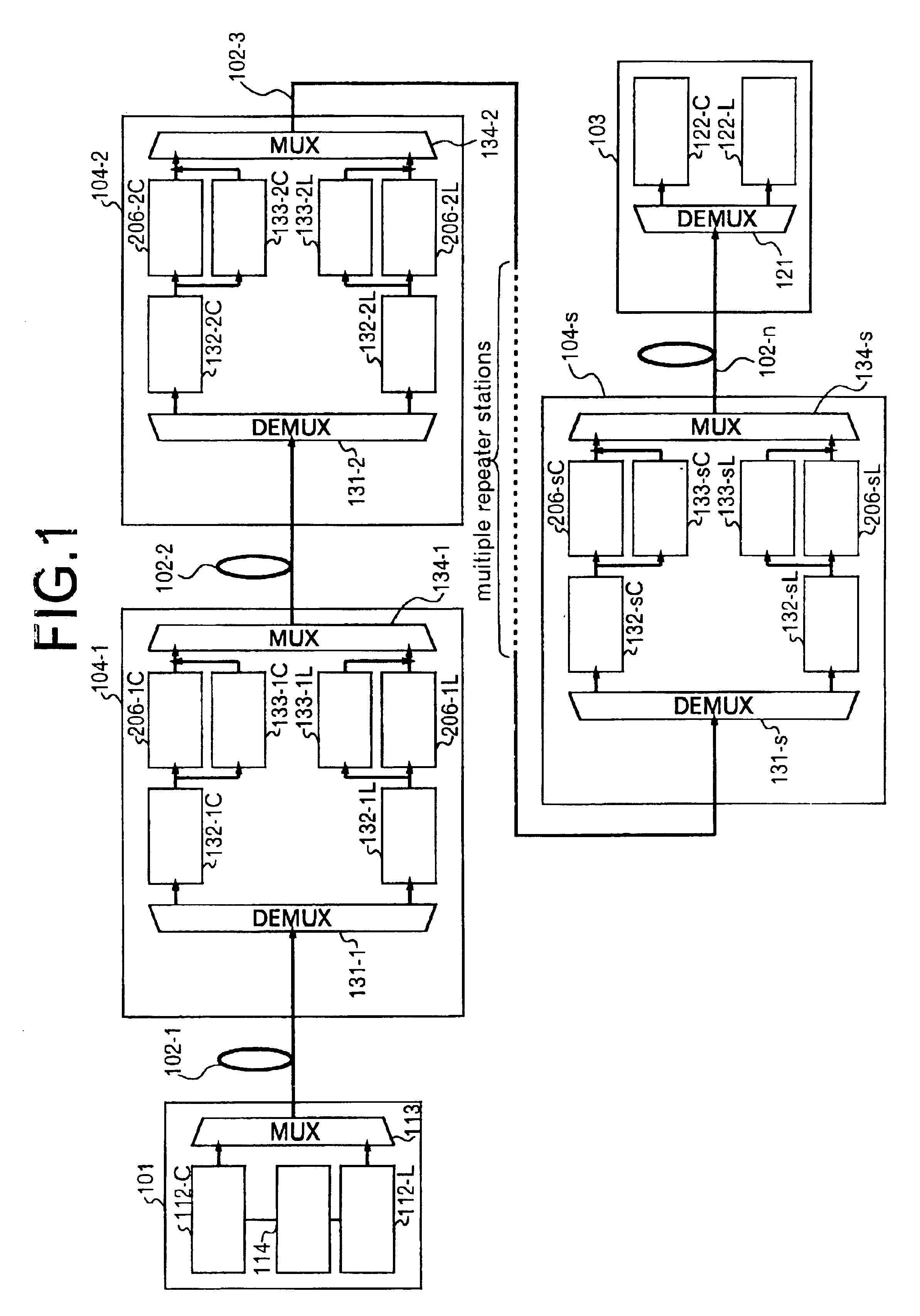
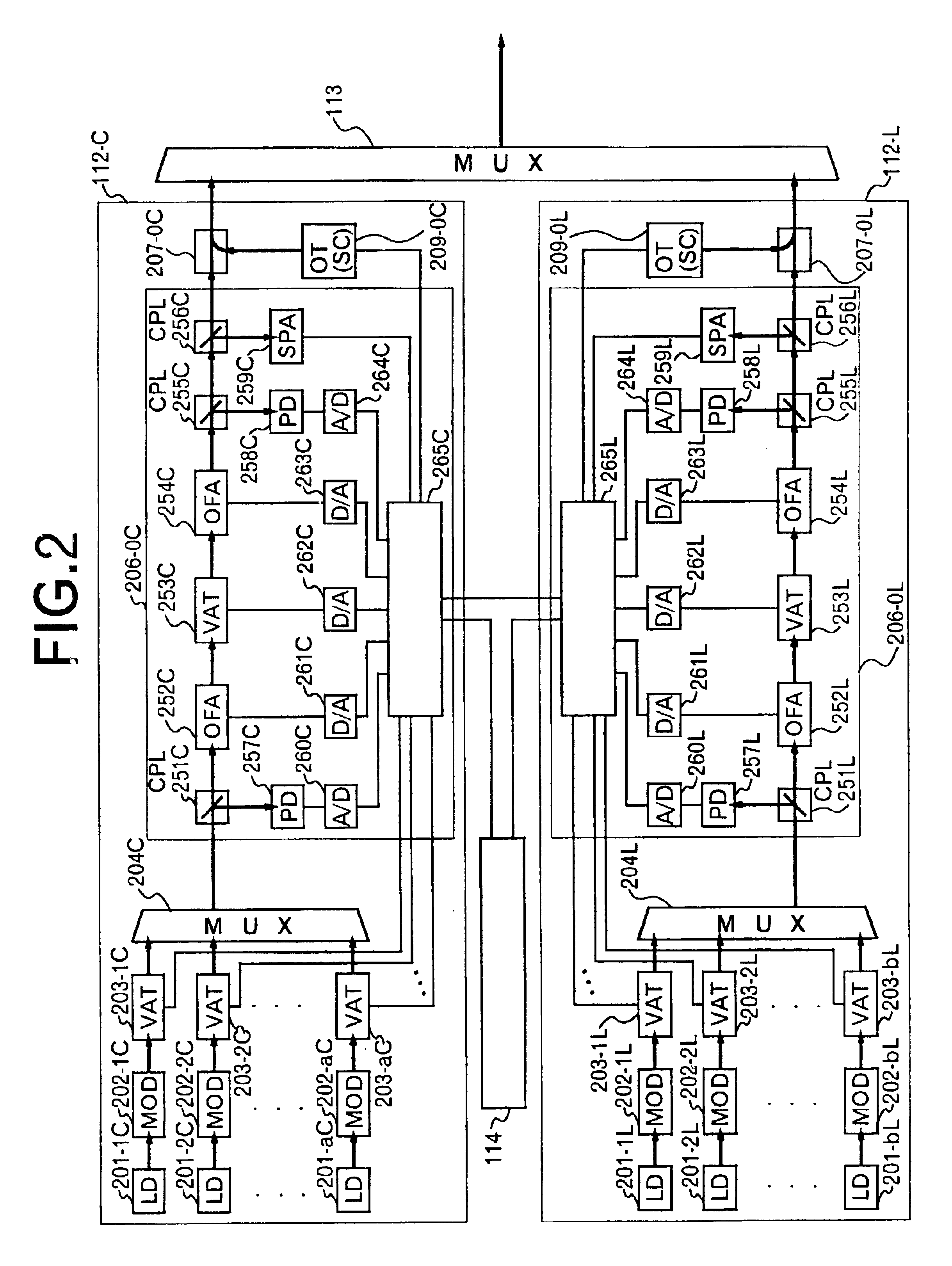
Method of activating optical communication system, channel increasing/decreasing method, and computer-readable recording medium
InactiveUS6839160B2Improve reliabilityLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsAudio power amplifierCommunications system
The invention relates to a method of activating an optical communication system comprising a plurality of optical amplifiers having an optical amplifier, between optical transmission lines in which wavelength-division multiplex optical signals are transmitted. The method comprises steps of: generating a desired slope in a desired wavelength range of a gain wavelength curve of the optical amplifier; adjusting an output of the optical amplifier to a desired output level; performing the above two steps in a plurality of optical repeater stations, the steps being carried out in sequence from the first to the last optical repeater stations; and adjusting a level in each optical signal in the wavelength-division multiplex optical signal so as to have substantially constant optical signal-to-noise ratios in the optical signals to be received. Activating the optical communication system according to this procedure allows proper execution of gain slope compensation, output control, and pre-emphasis control.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
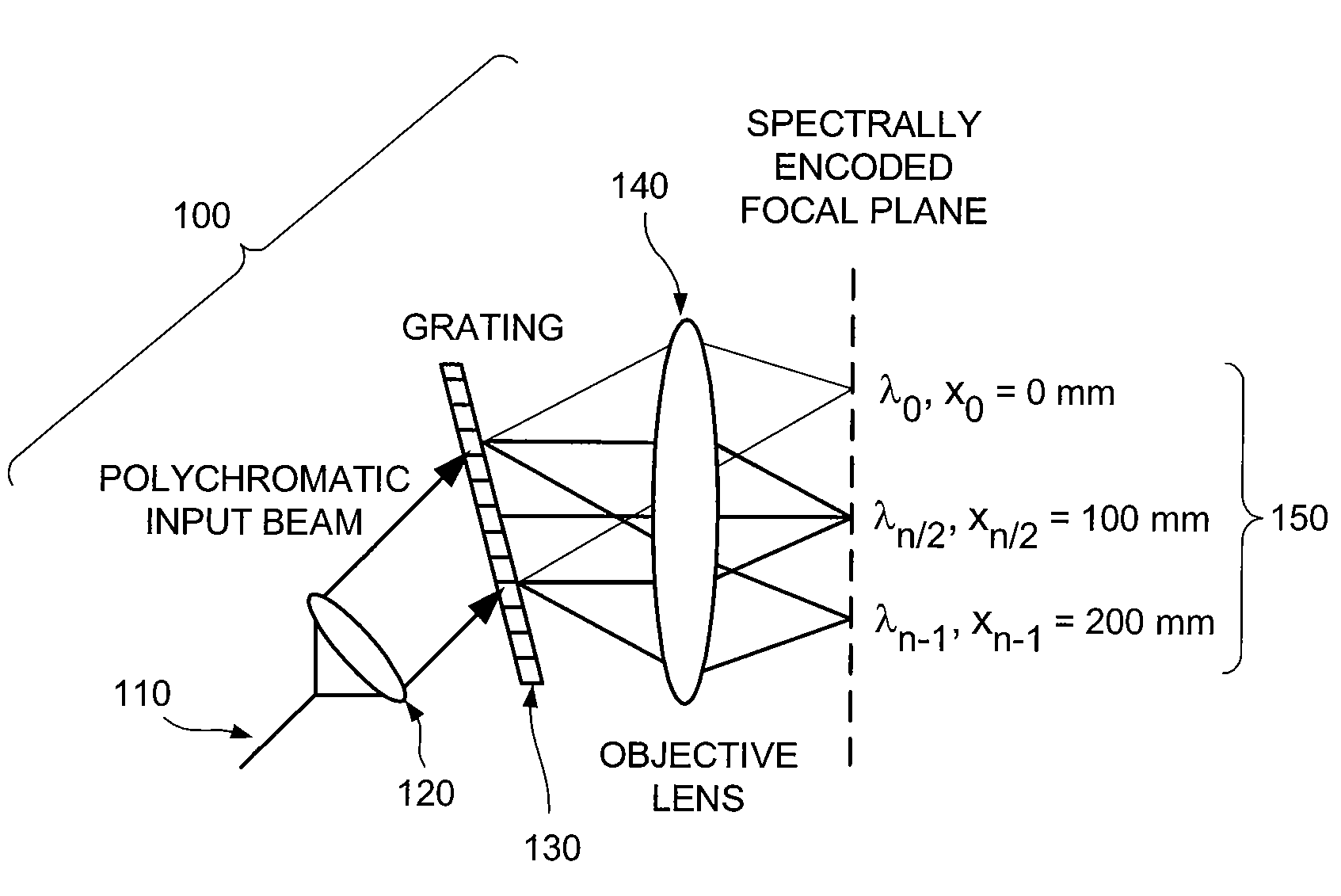
Apparatus for obtaining information for a structure using spectrally-encoded endoscopy teachniques and methods for producing one or more optical arrangements
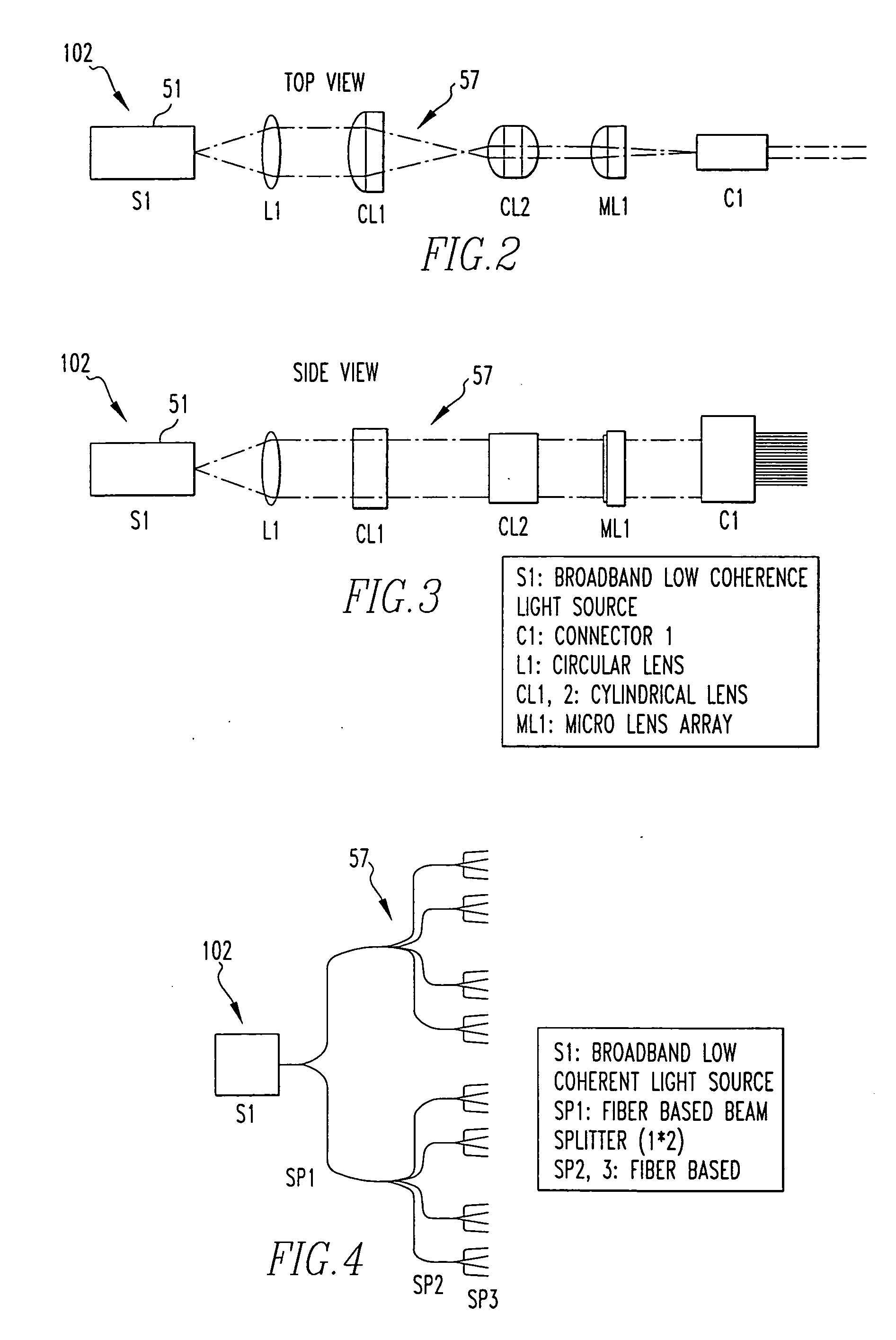
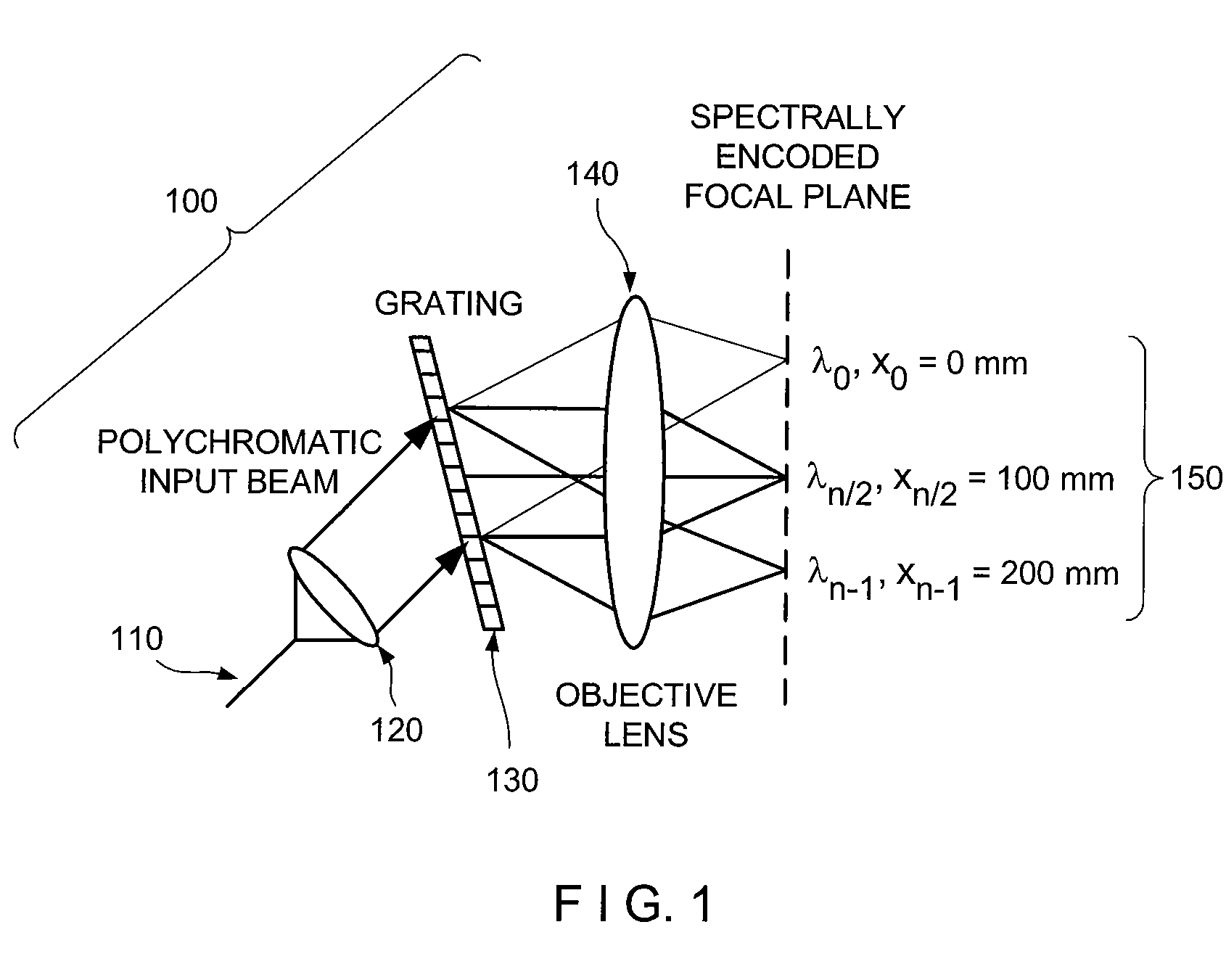
ActiveUS20070188855A1Improve collection efficiencyMinimizing speckleEdge grinding machinesSpectrum generation using diffraction elementsFiberEngineering
Exemplary apparatus for obtaining information for a structure can be provided. For example, the exemplary apparatus can include at least one first optical fiber arrangement which is configured to transceive at least one first electromagnetic radiation, and can include at least one fiber. The exemplary apparatus can also include at least one second focusing arrangement in optical communication with the optical fiber arrangement. The second arrangement can be configured to focus and provide there through the first electromagnetic radiation. Further, the exemplary apparatus can include at least one third dispersive arrangement which is configured to receive a particular radiation which is the first electromagnetic radiation and / or the focused electromagnetic radiation, and forward a dispersed radiation thereof to at least one section of the structure. At least one end of the fiber can be directly connected to the second focusing arrangement and / or the third dispersive arrangement. In addition, an exemplary embodiment of a method for producing an optical arrangement can be provided. For example, a first set of optical elements having a first size in a first configuration and a second set of optical elements in cooperation with the second set and having a second size in a second configuration can be provided. The first and second sets can be clamped into a third set of optical elements. The third set can be polished, and a further set of optical elements may be deposited on the polished set.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
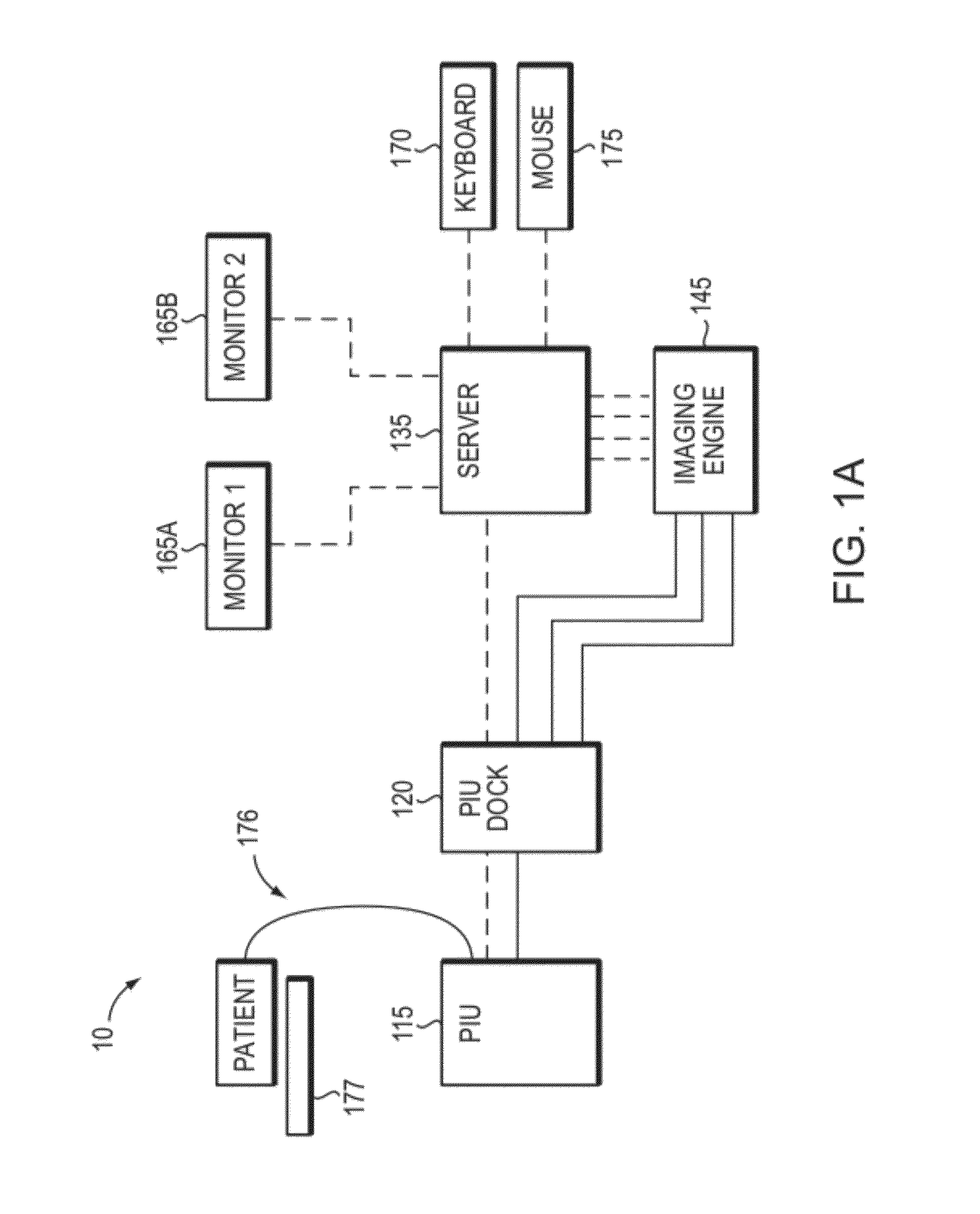
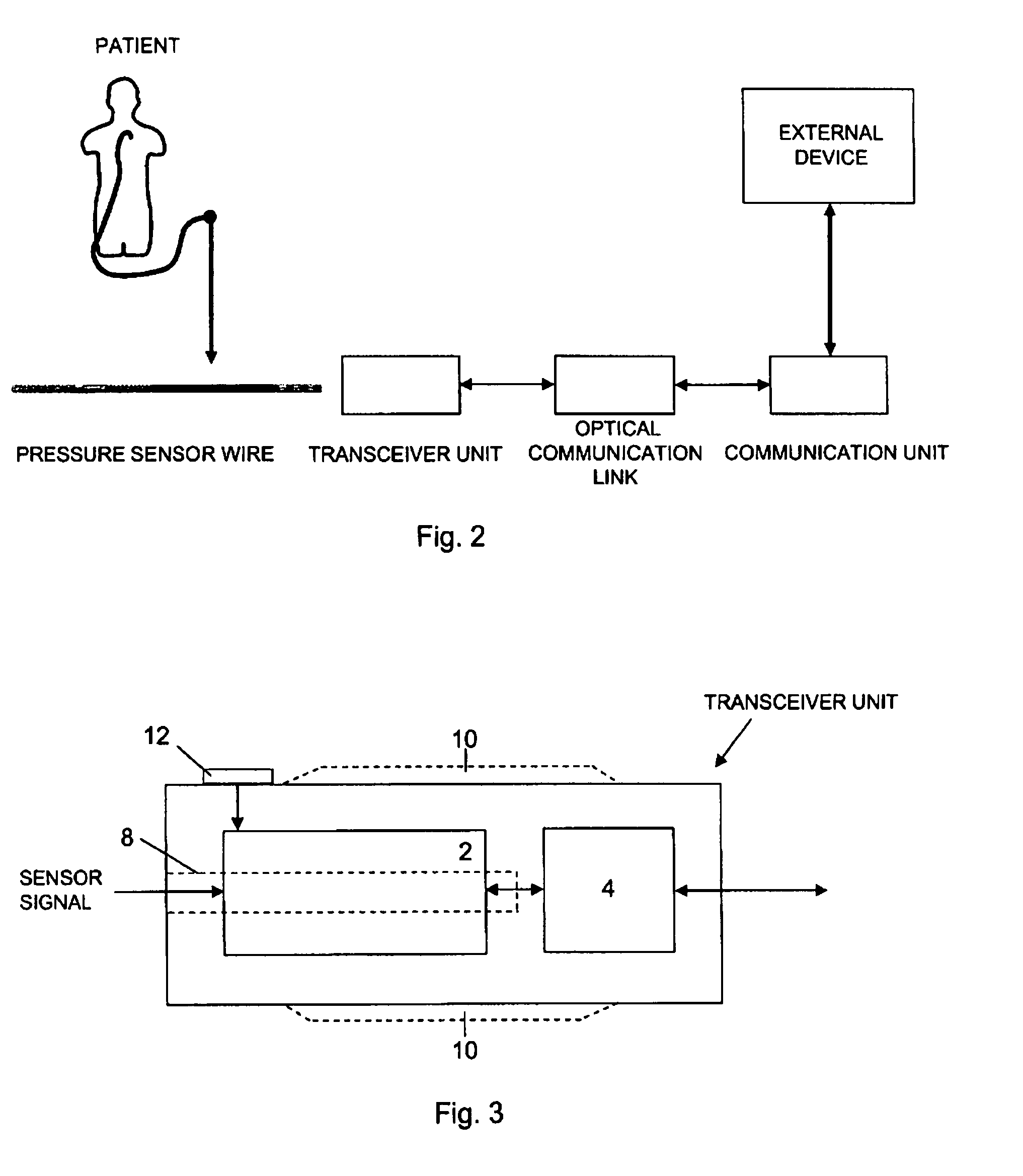
Measurement system to measure a physiological condition in a body
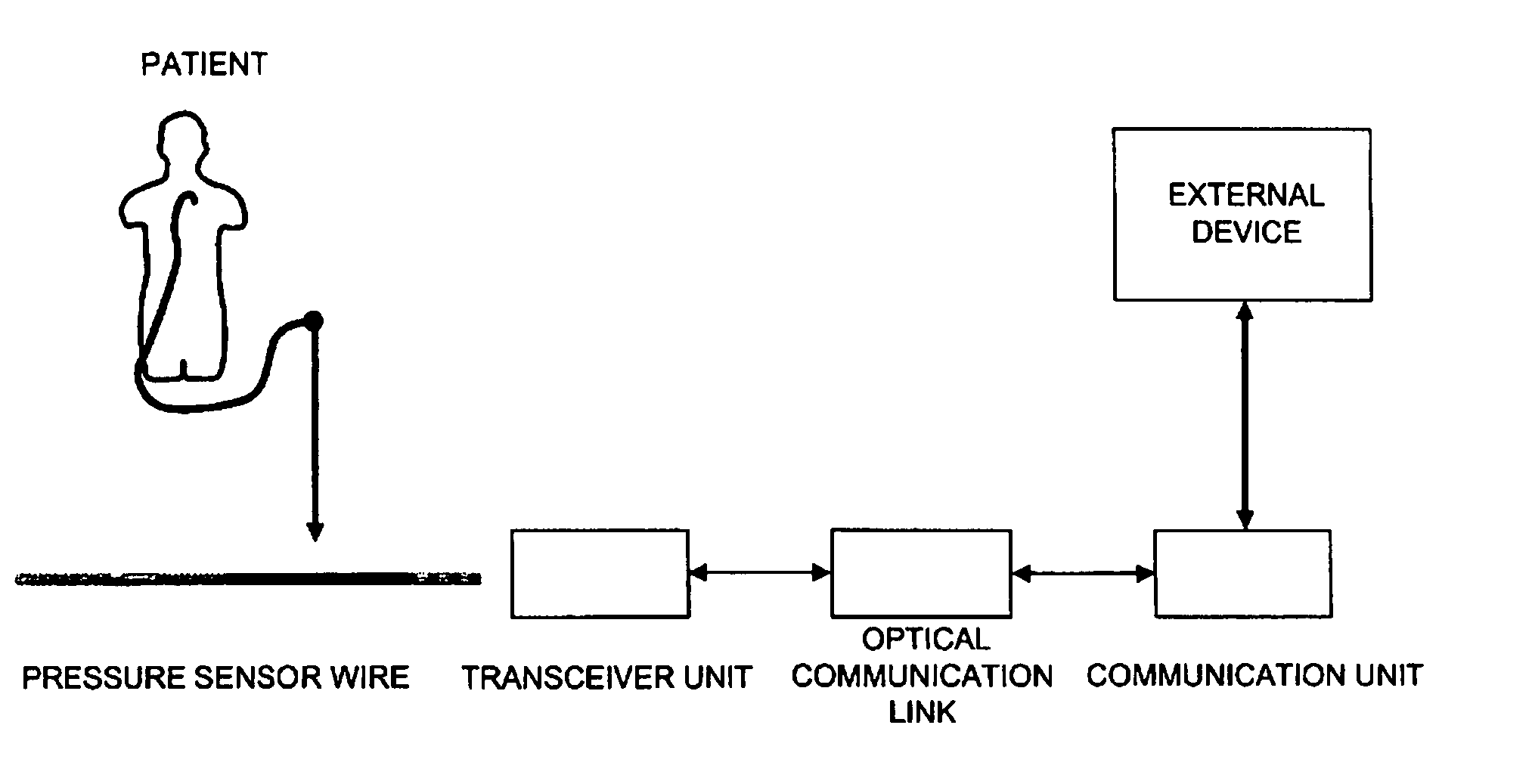
InactiveUS7946997B2Eliminate needEasy to useGuide wiresDiagnostic recording/measuringCommunication unitTransceiver
Measurement system comprising a sensor wire provided, at its distal end, with a physiological condition sensor to measure a physiological condition inside a patient, and to provide measured data to an external device, the measurement system comprises a transceiver unit adapted to be connected to the proximal end of the sensor wire, and a communication unit arranged in connection with the external device. The transceiver unit is adapted to communicate, by a communication signal, with the communication unit, in order to transfer measured data to the external device. The communication signal, including the measured data, is generated by the transceiver unit and transferred as an output signal and the communication unit is arranged to be connected to a standard input / output connector of the external device and to communicate with the external device in accordance with an established standard, or in accordance with relevant parts of an established standard, e.g. BP22 or USB. The measurement system further comprises a physical optical communication link arranged between the transceiver unit and the communication unit, wherein the communication signal is an optical signal transferred by the optical communication link. The transceiver unit also comprises an energy means adapted to energize the sensor, the transceiver unit and also the optical communication link.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL COORDINATION CENT
Optical fiber communications method and system without a remote electrical power supply
ActiveUS7469105B2Reduce power consumptionReduced Power RequirementsElectromagnetic transmissionWireless communicationElectrical conductorEngineering
The present invention allows remote antenna units for radio frequency signal transmission and receipt to operate without the requirement for remote electrical power supplies or for connecting cables that incorporate electrical conductors. According to an aspect of the present invention, an optical communications system employing radio frequency signals comprises a central unit; at least one remote unit having at least one optoelectronic transducer for converting optical data signals to radio frequency signals and converting radio signals to optical signals and at least one antenna to receive and send radio frequency signals; at least one optical fiber data link between the central unit and the remote unit for transmitting optical data signals therebetween; and at least one optical fiber power link between the central unit and the remote unit for providing electrical power at the remote unit.
Owner:NEXTG NETWORKS INC
High resolution proton beam monitor
InactiveUS20070181815A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingLight beamProton
A method and apparatus for monitoring a scanning beam of penetrating radiation, such as a scanning proton beam used to irradiate tissue. The position of the beam is tracked in real time by interposing a scintillator film between a source and an object of irradiation. An imaging detector, in optical communication with the scintillator, provides an output that is indicative of the position of the radiation and its variation with time. The accumulated dose over a scan may also be monitored.
Owner:LEXITEK
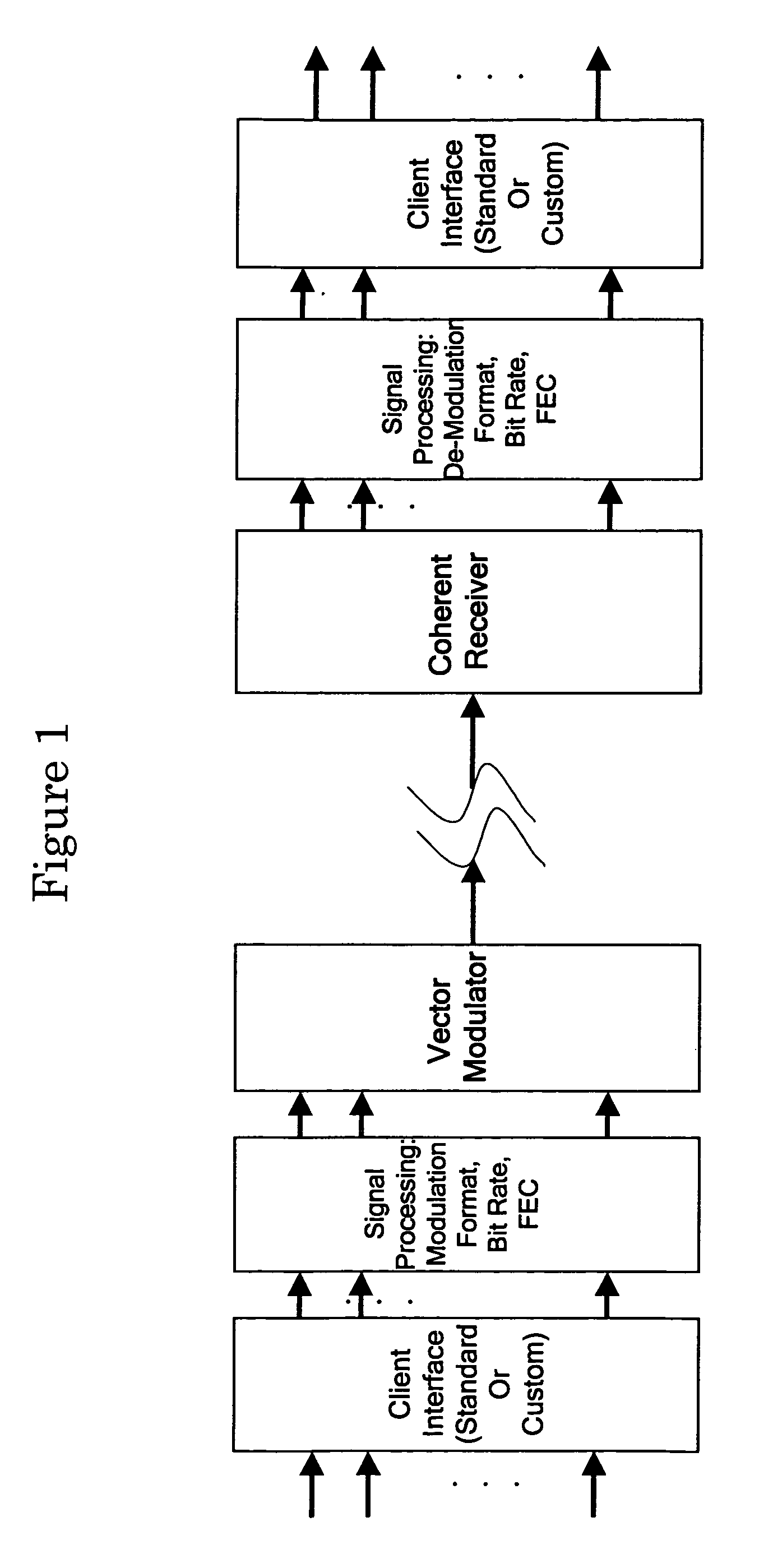
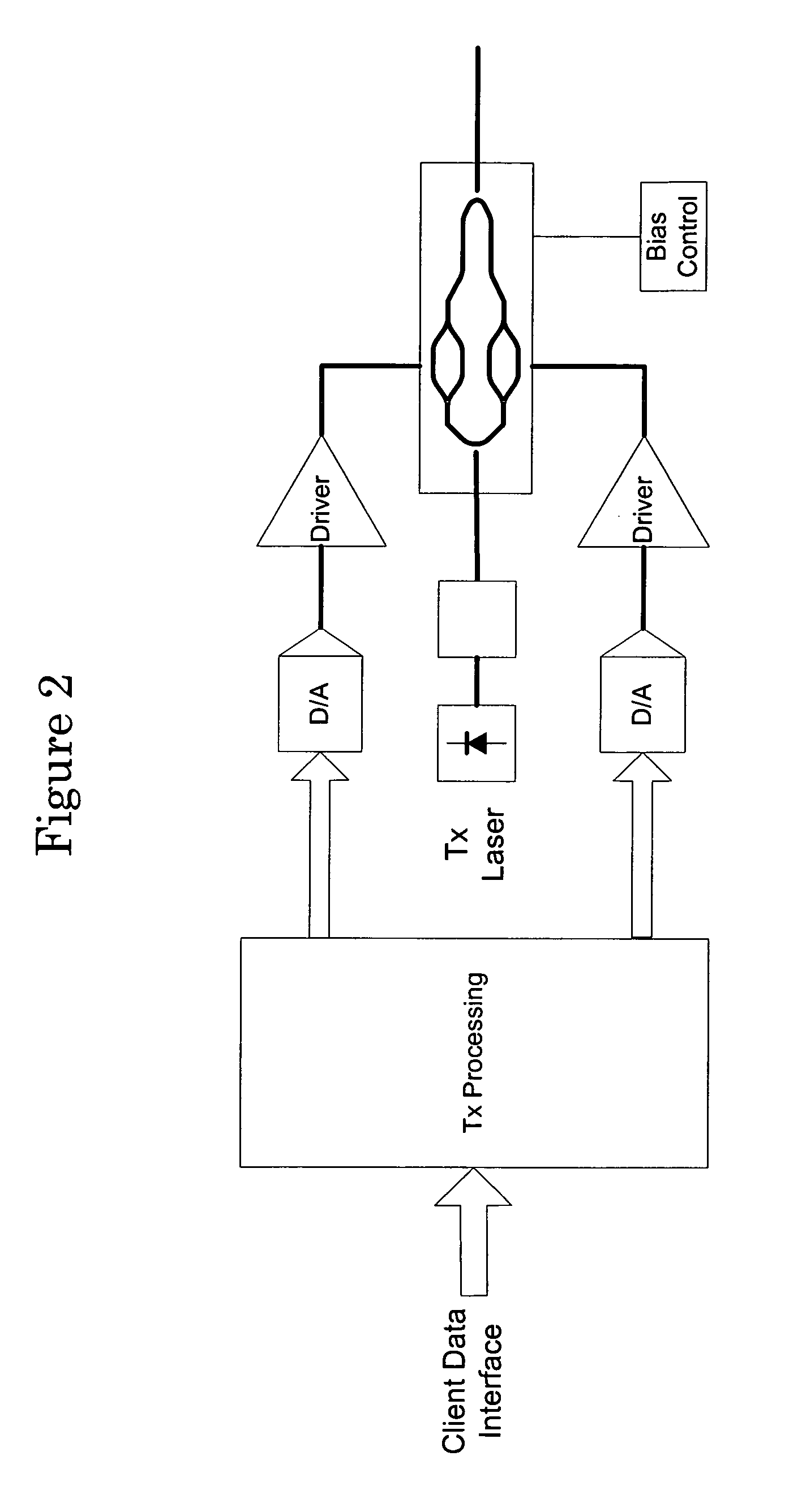
Optical transmission apparatuses, methods, and systems
InactiveUS7826752B1Robust optical communicationFree-space transmissionElectromagnetic transmittersTransport systemModem device
Apparatuses, systems, and methods are disclosed that provide for an agile coherent optical modem that can generate agile RF waveforms and data rates on a generic opto-electronic hardware platform. An “agile coherent optical modem” [ACOM] approach to optical communications by employing a software configurable and adaptive technologies to the transport system. The ACOM generate agile RF waveforms and data rates on a generic opto-electronic hardware platform. By employing advanced communication techniques to the optical domain such as wavelength agility, waveform agility, and symbol rate agility, it is possible to enable robust optical communications. The ACOM allows for the transport capacity of a communications link to be varied, thereby accommodating variations in transport conditions, range, opacity, etc.
Owner:OPTIC153 LLC
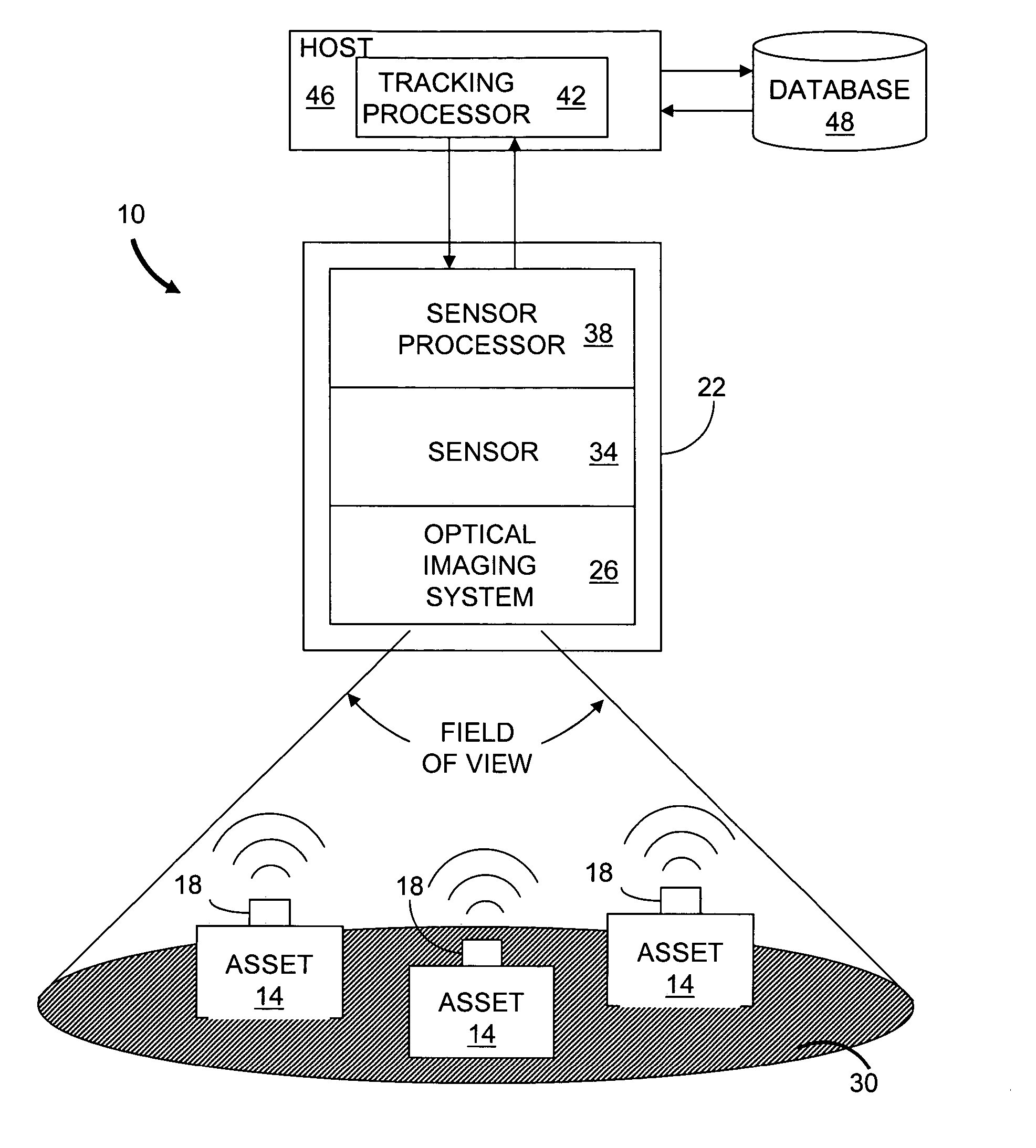
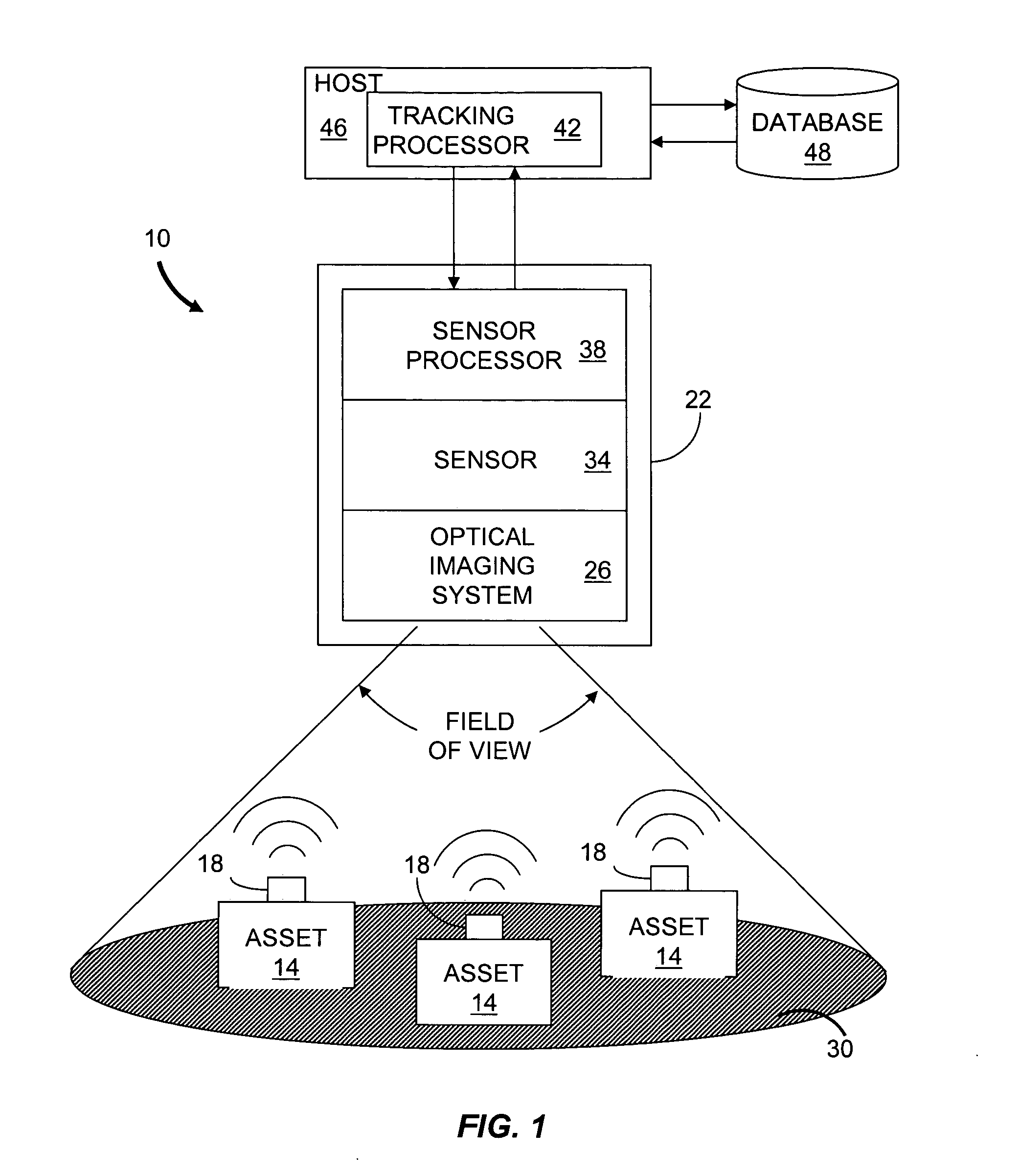
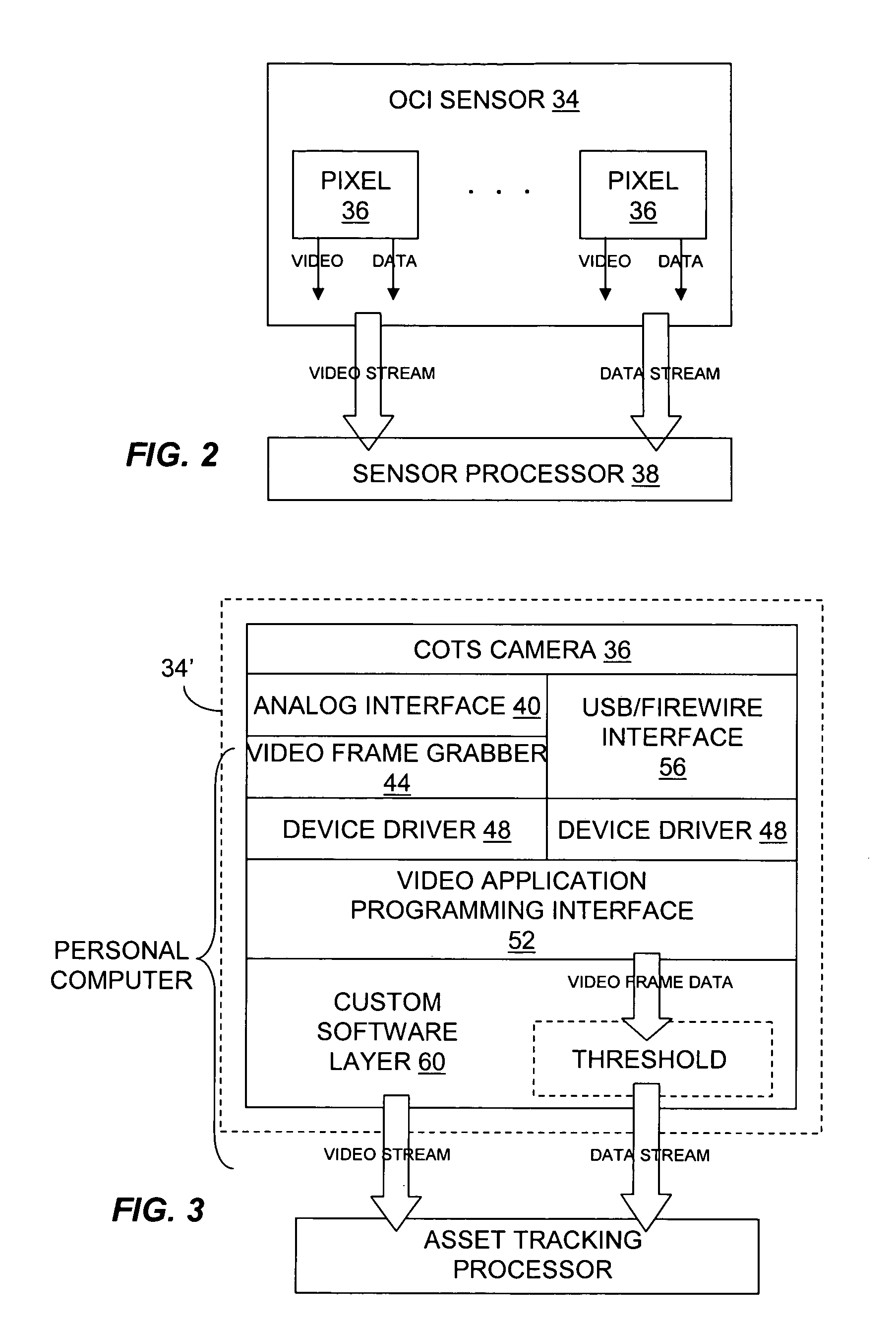
Optical asset tracking system
InactiveUS20050116821A1Electric signal transmission systemsDigital data processing detailsDigital videoElectricity
Described are a system and a method for optical tracking of assets. The system includes a sensor having a plurality of pixels. Each pixel is adapted to produce an electrical signal responsive to an incident optical data signal emitted by an optical tag attached to an asset. The system also includes a sensor processor in communication with the sensor and configured to generate an electrical data signal based on optical data signals incident on the pixels. The sensor processor also generates asset data in response to the electrical data signals from the pixels. The sensor and sensor processor can be implemented as an optical communications imager in which each pixel generates a communication data signal based on incident light. Alternatively, the sensor can include a digital video camera or an analog video camera for lower bandwidth communications.
Owner:CELEVATORON LABS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com