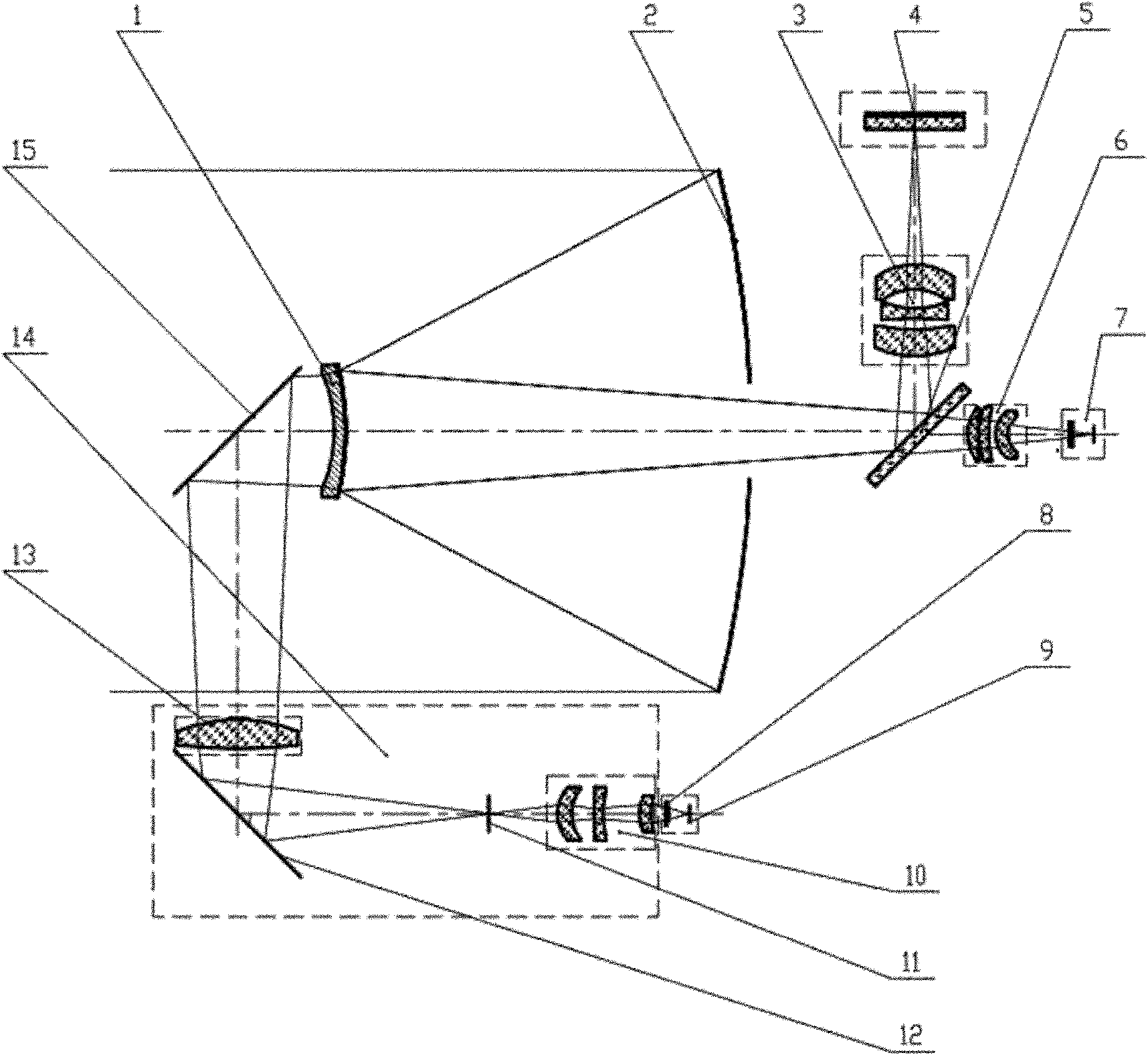
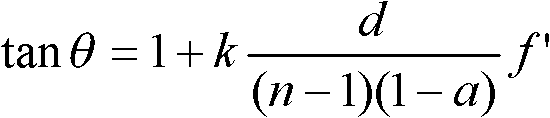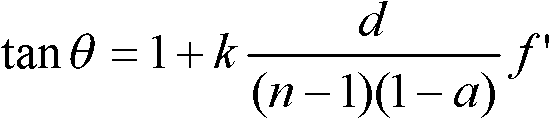Patents
Literature
930 results about "Secondary mirror" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
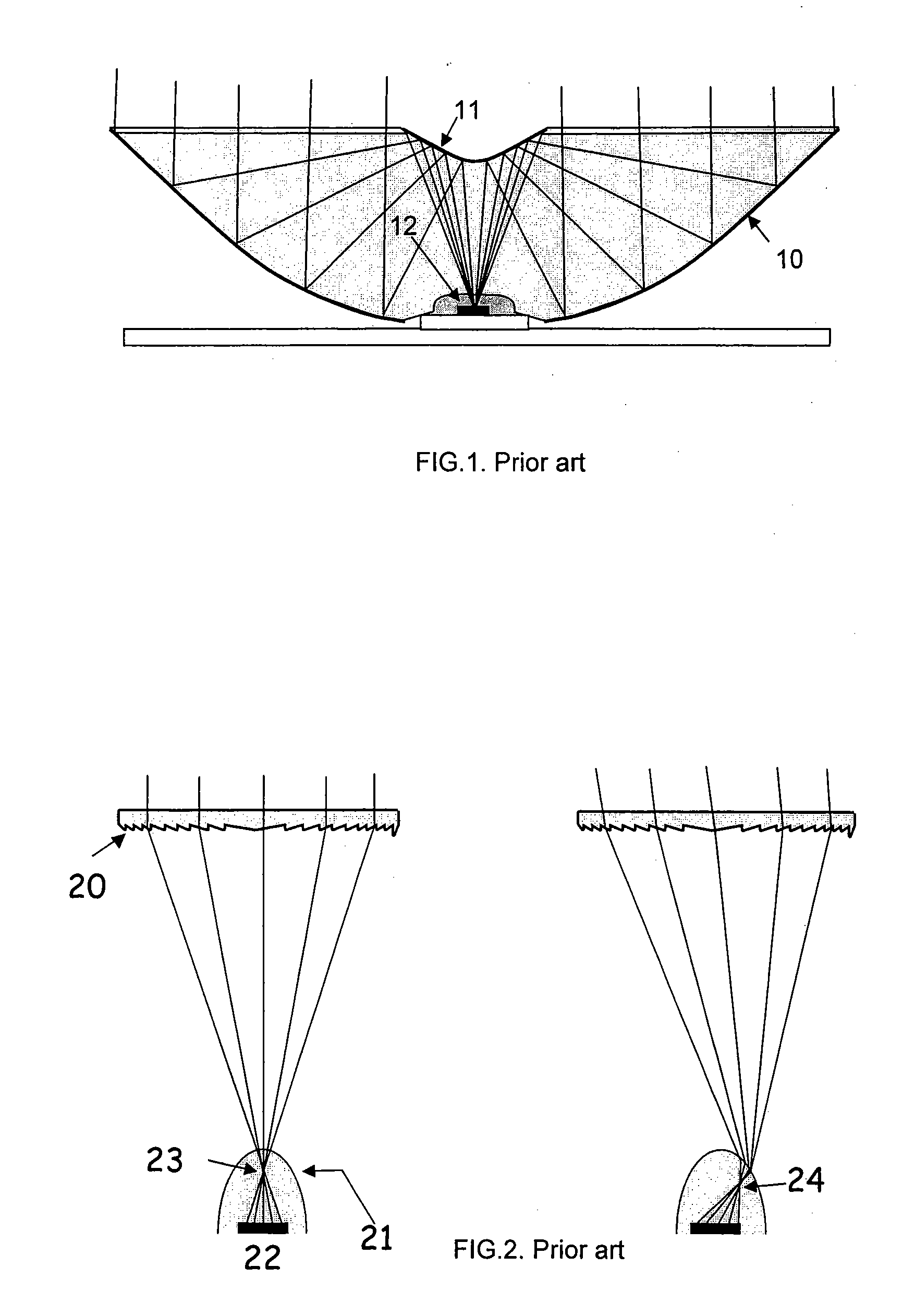
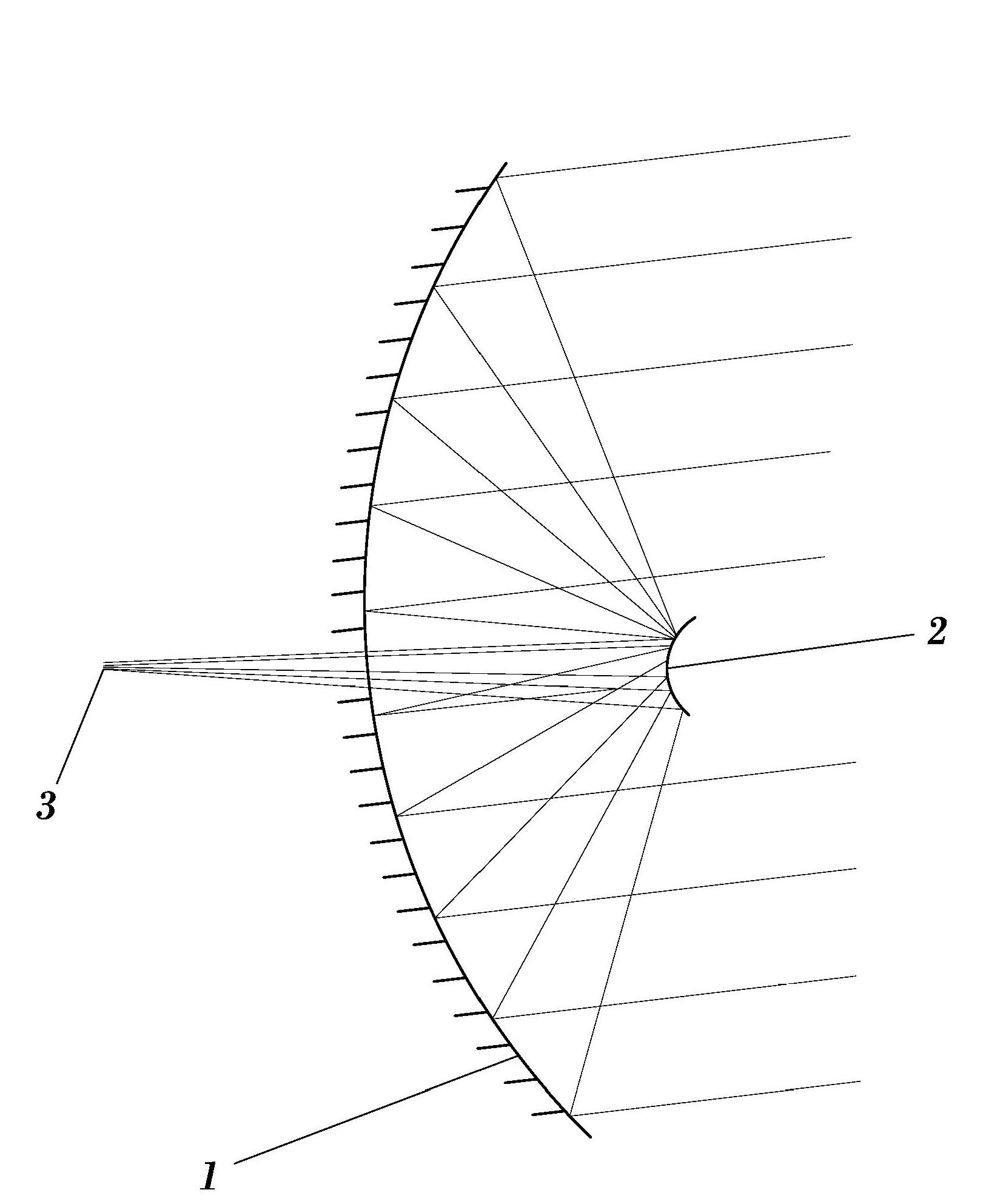
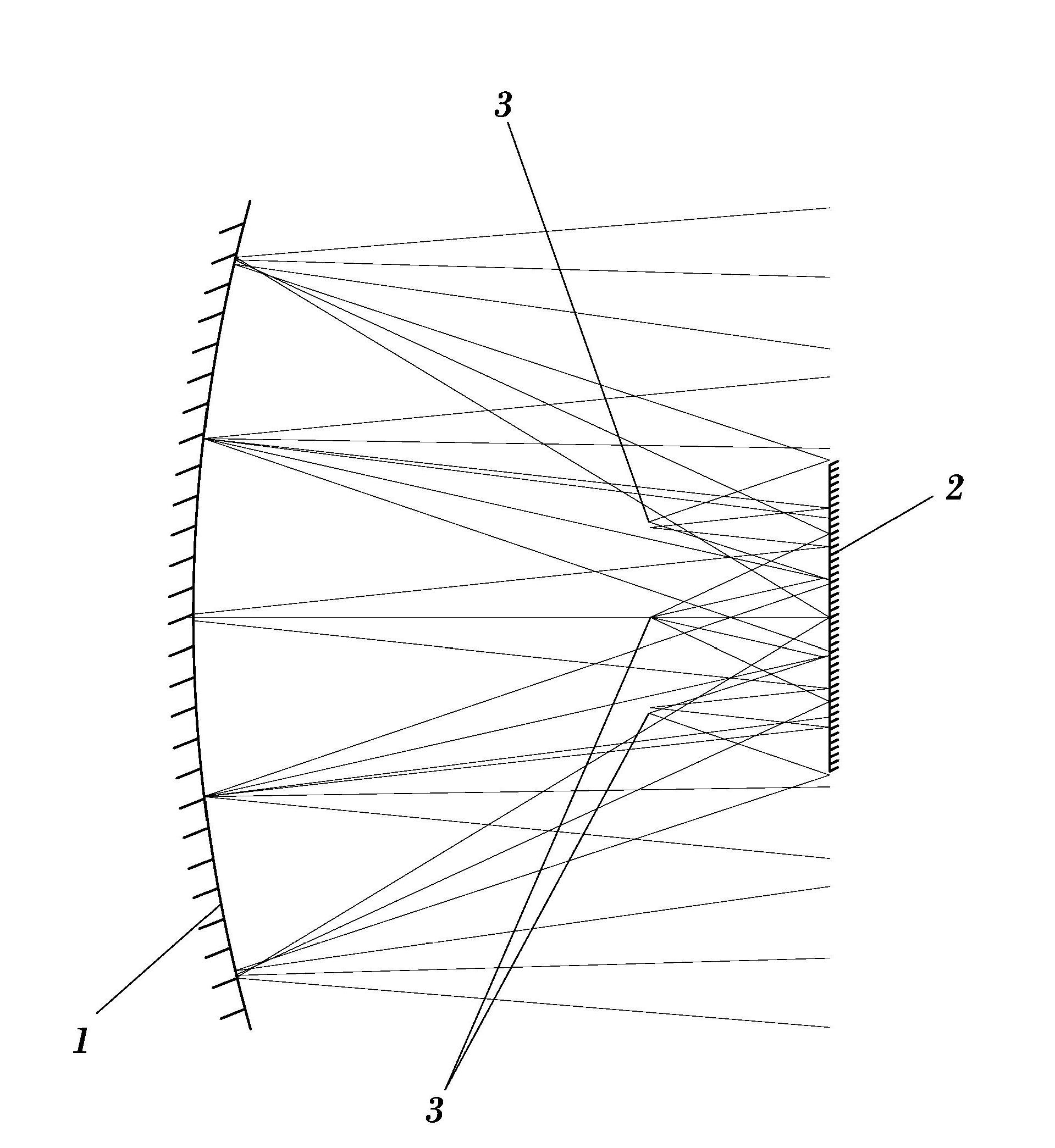
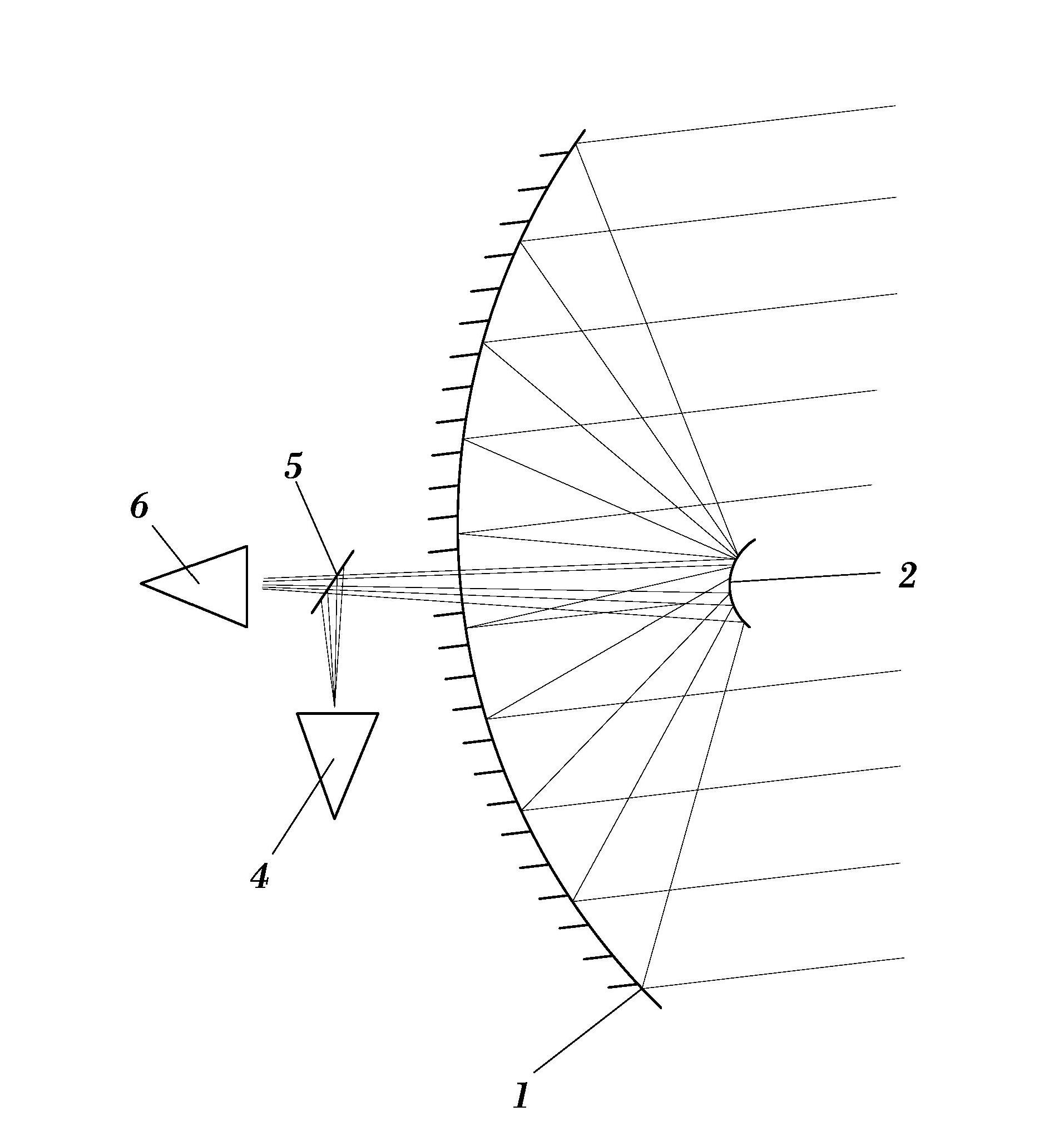
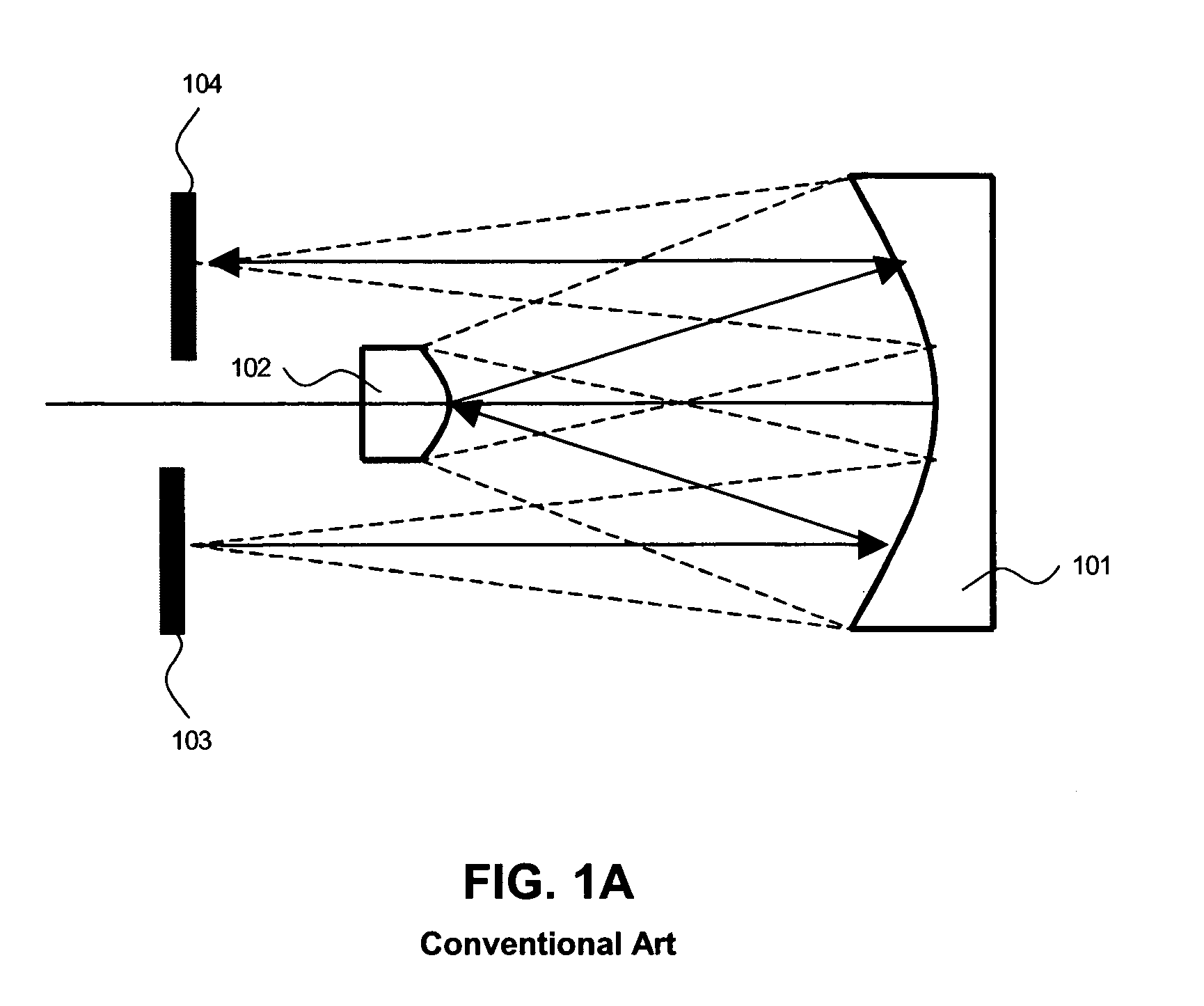
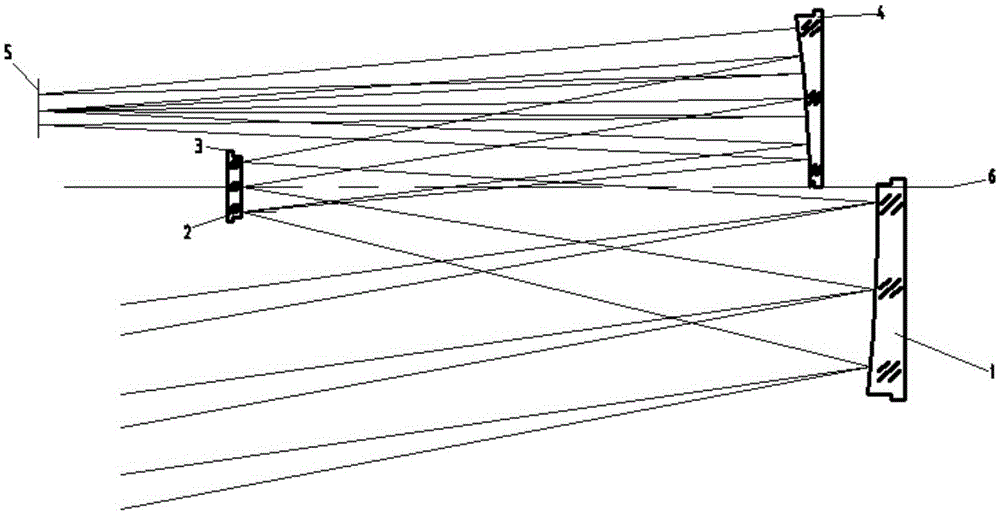
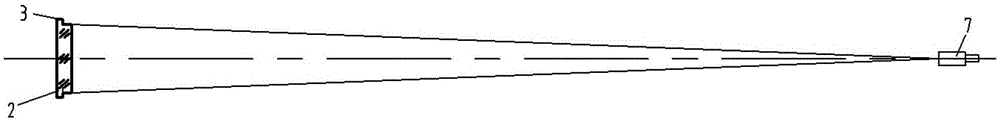
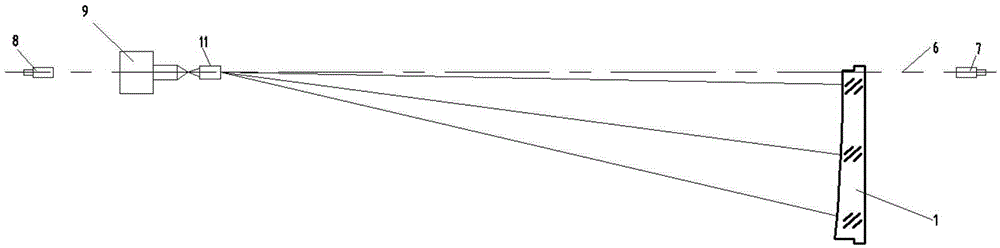
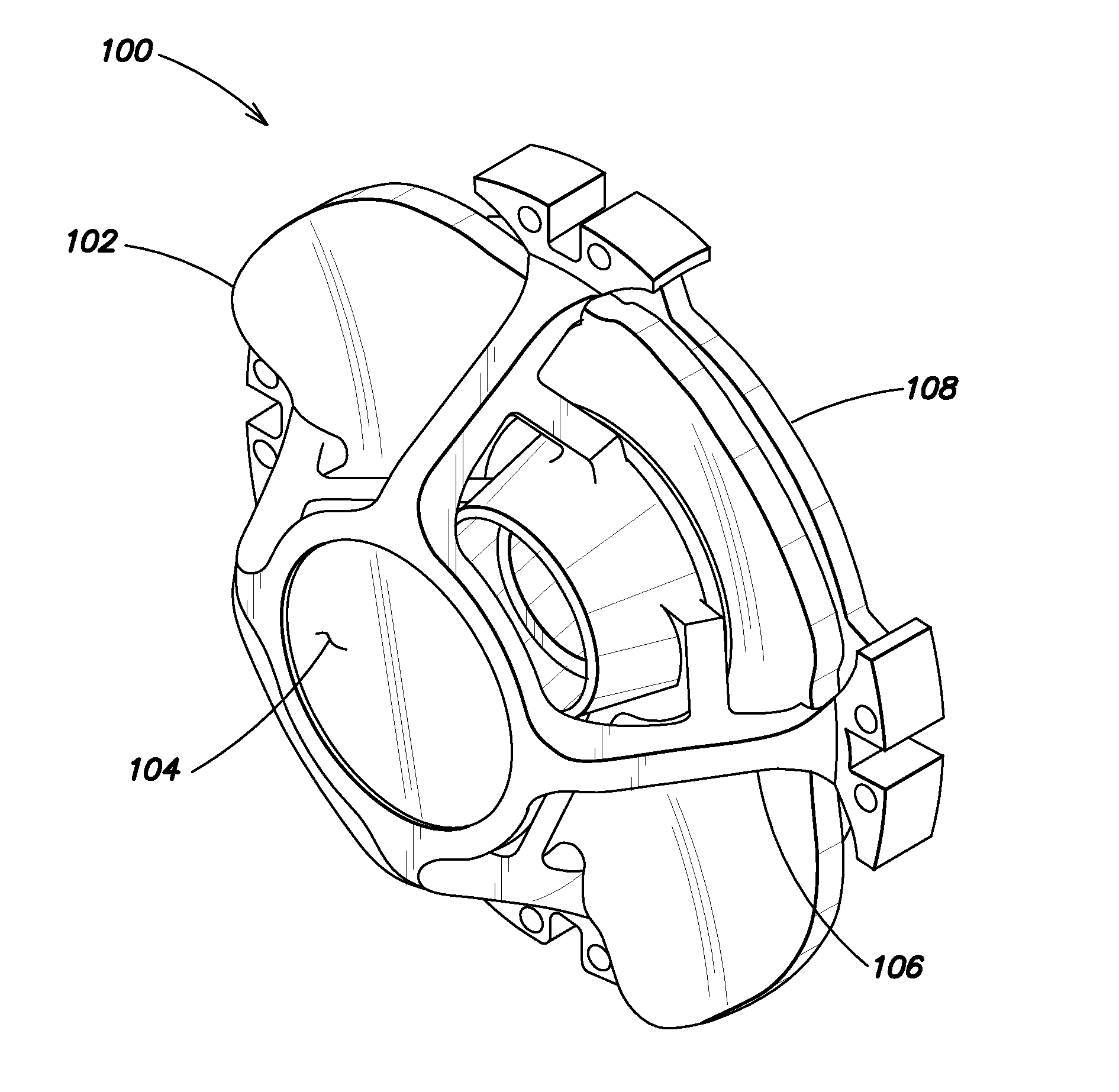
A secondary mirror (or secondary) is the second deflecting or focusing mirror element in a reflecting telescope. Light gathered by the primary mirror is directed towards a focal point typically past the location of the secondary. Secondary mirrors in the form of an optically flat diagonal mirror are used to re-direct the light path in designs such as Newtonian reflectors. They are also used to re-direct and extend the light path and modify the final image in designs such as Cassegrain reflectors.
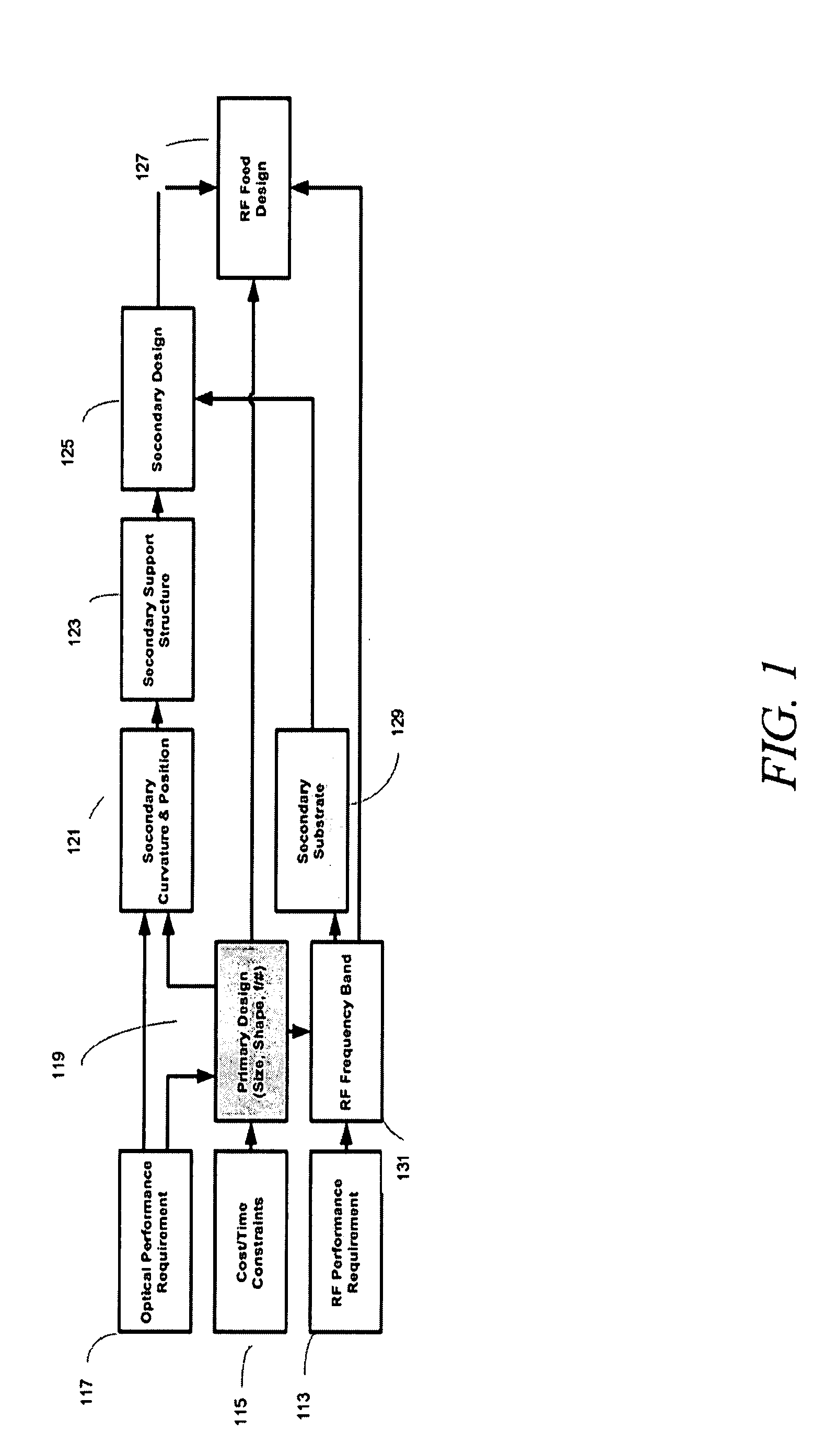
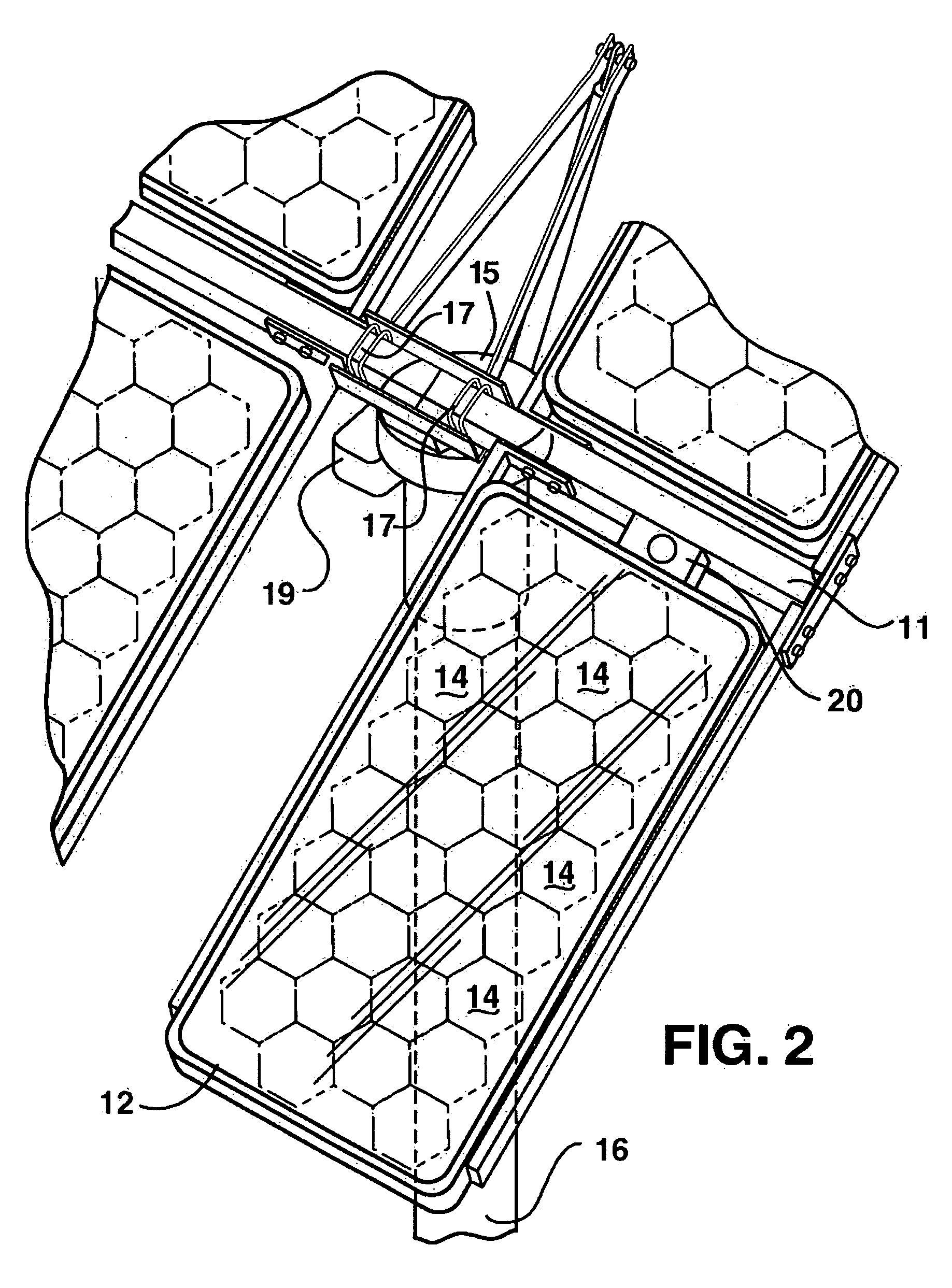
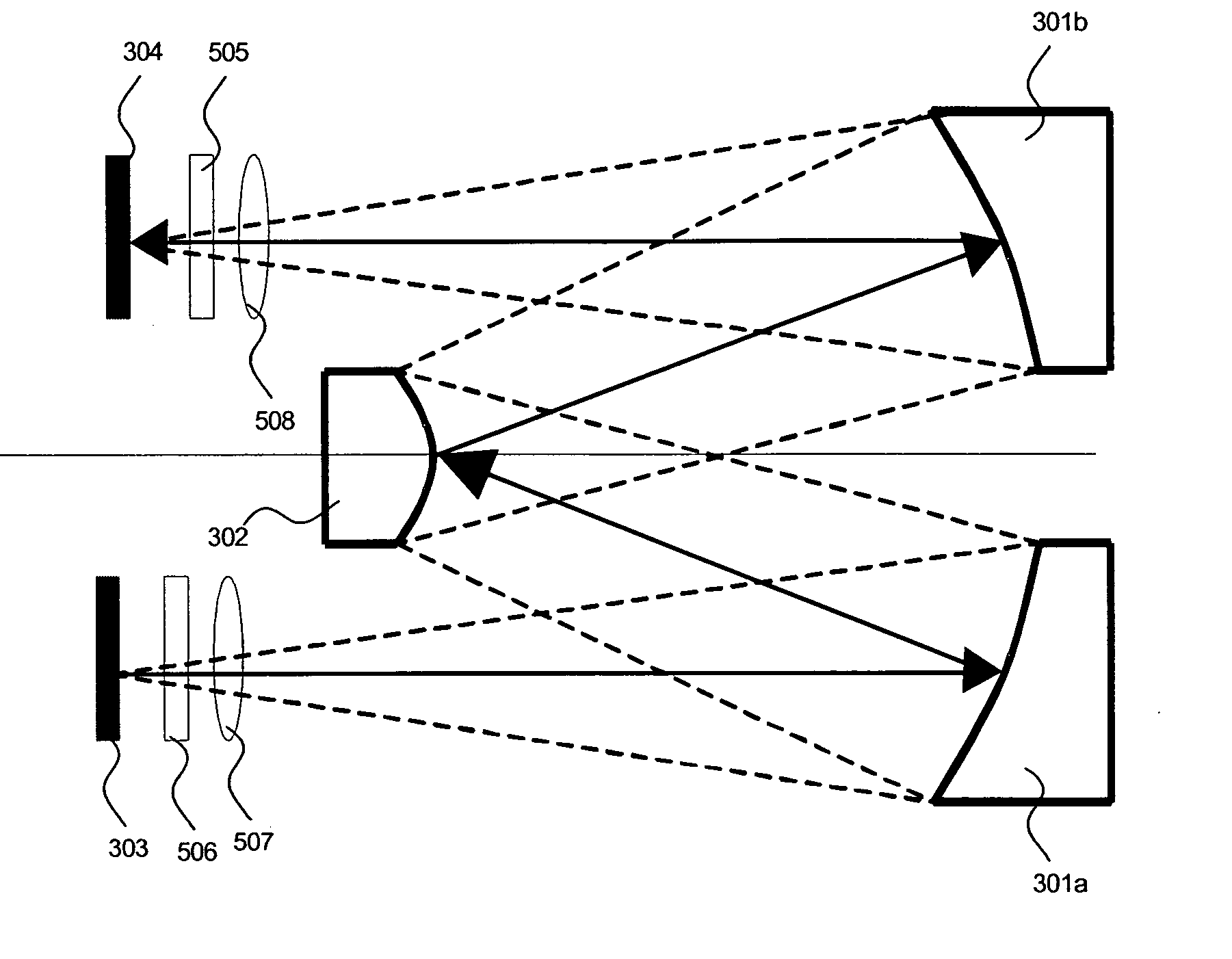
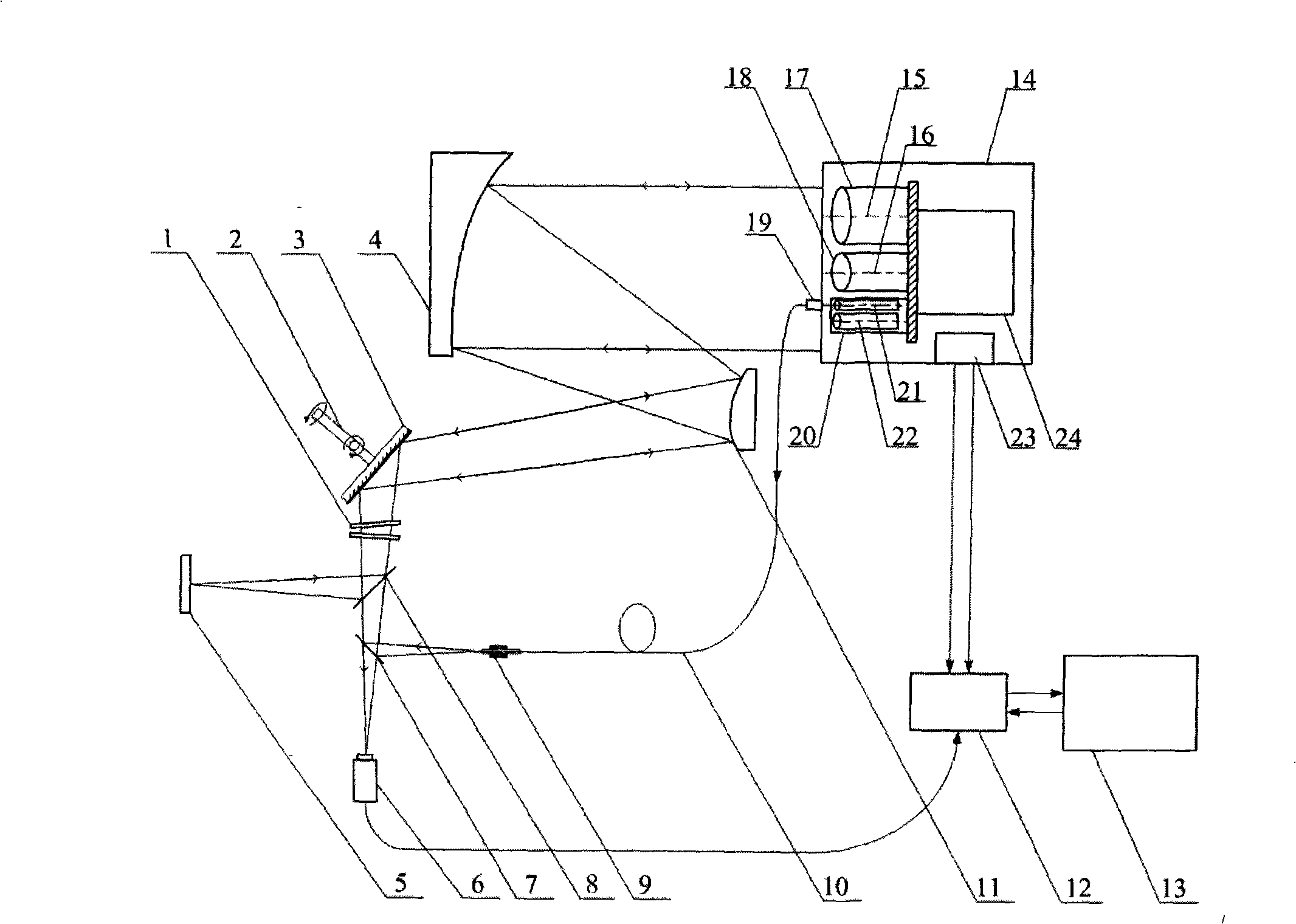
Dual band radio frequency (RF) and optical communications antenna and terminal design methodology and implementation
ActiveUS8094081B1High bandwidthMinimized massAntenna arraysSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna designTransceiver
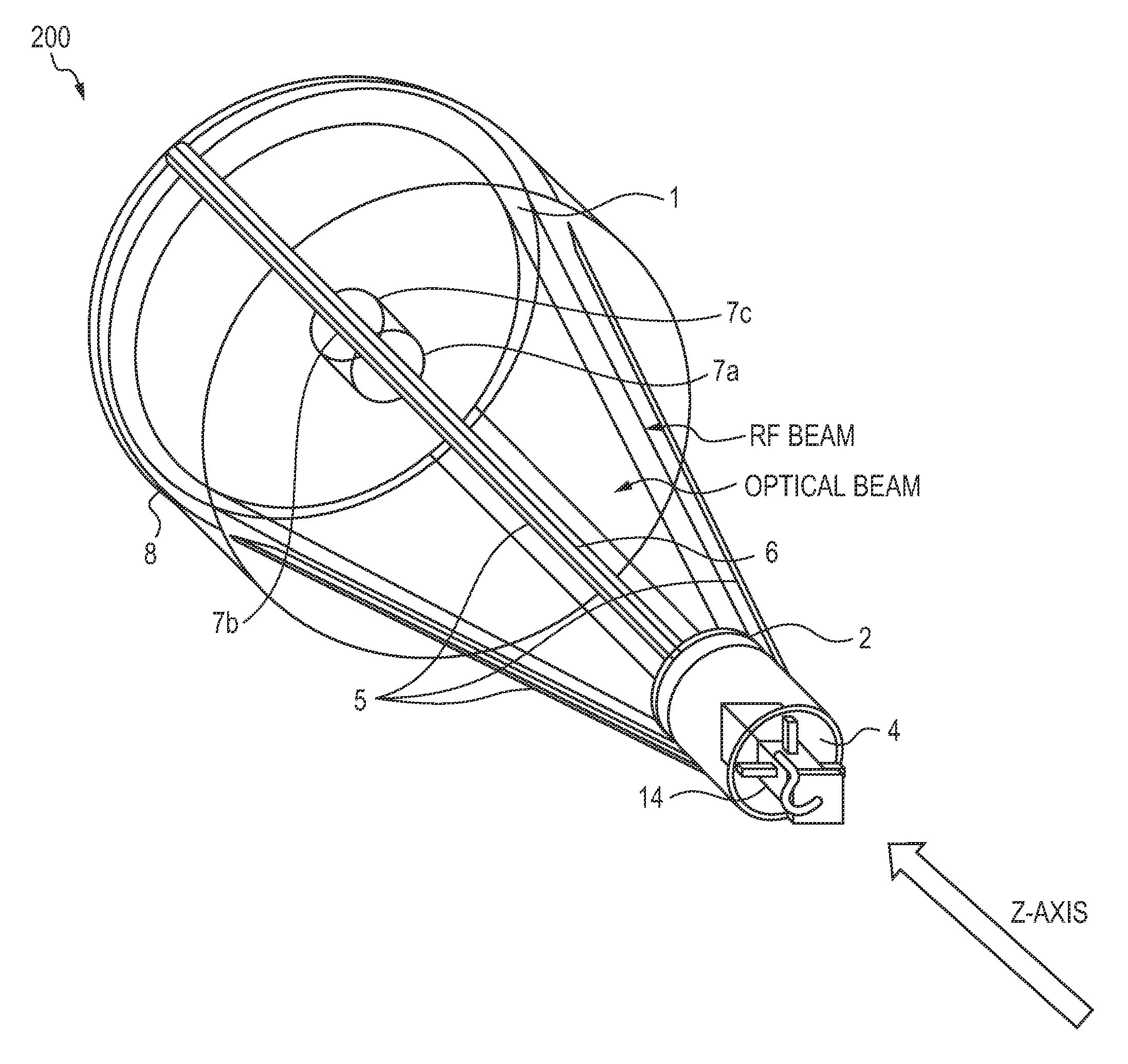
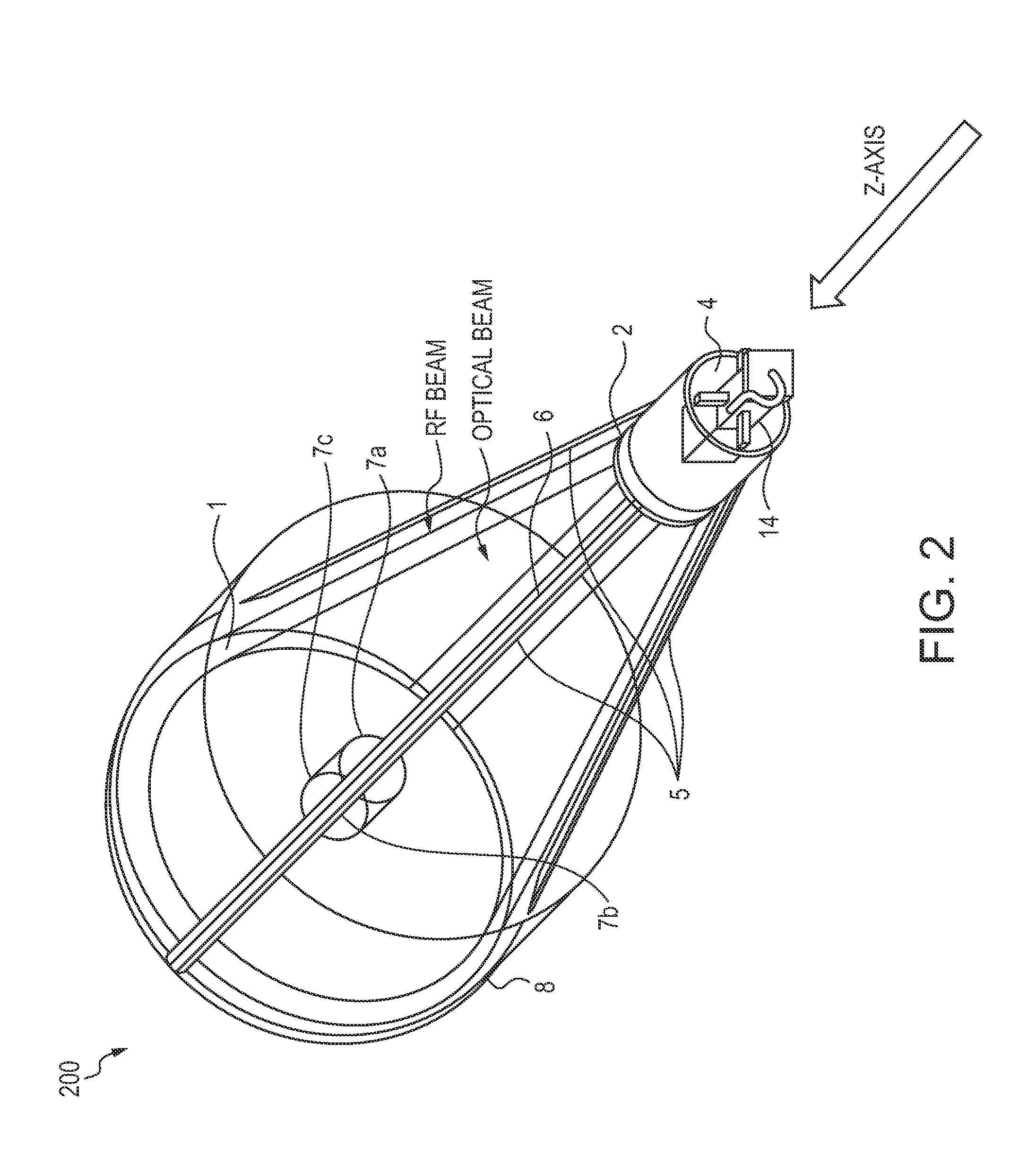
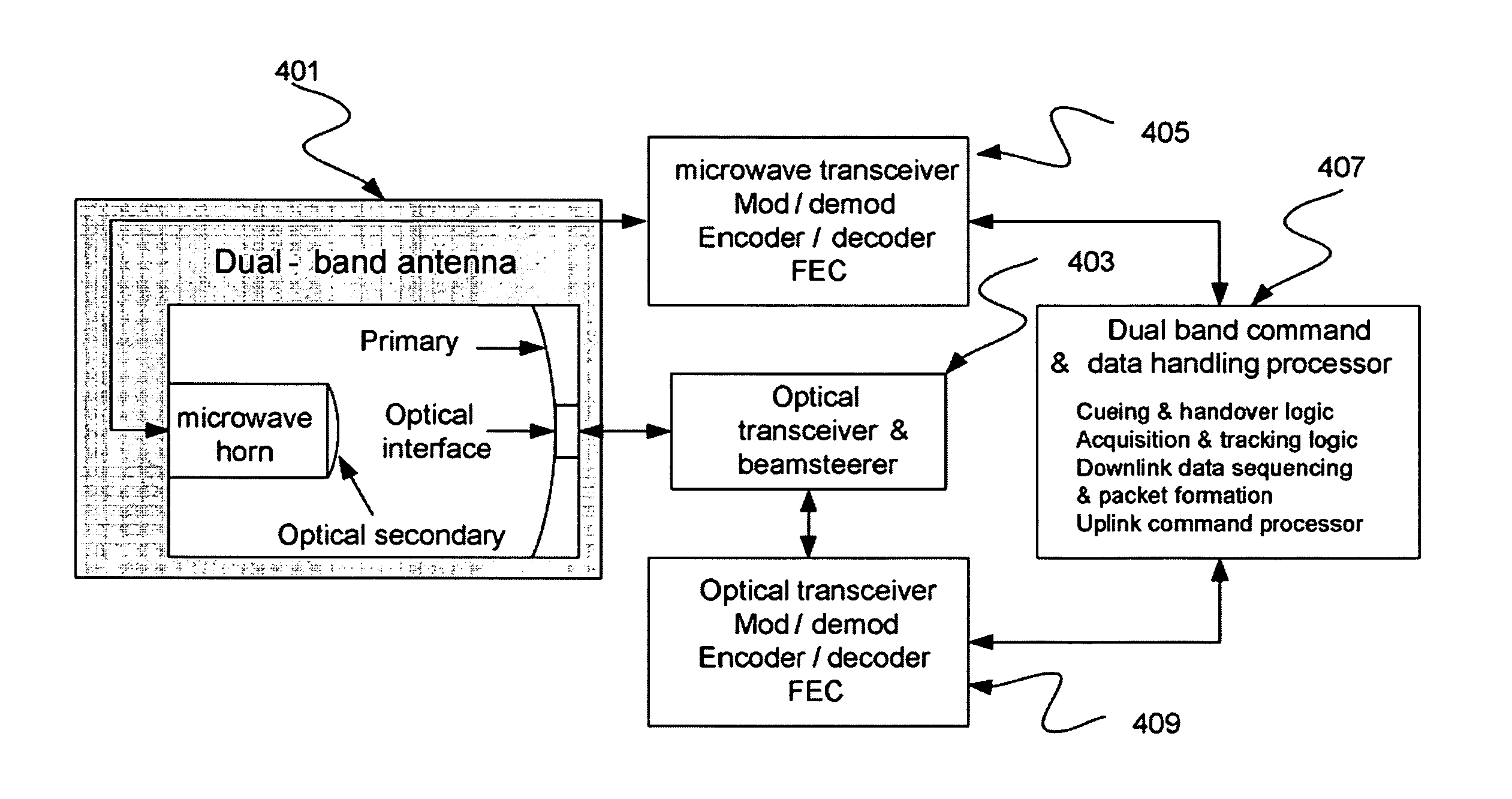
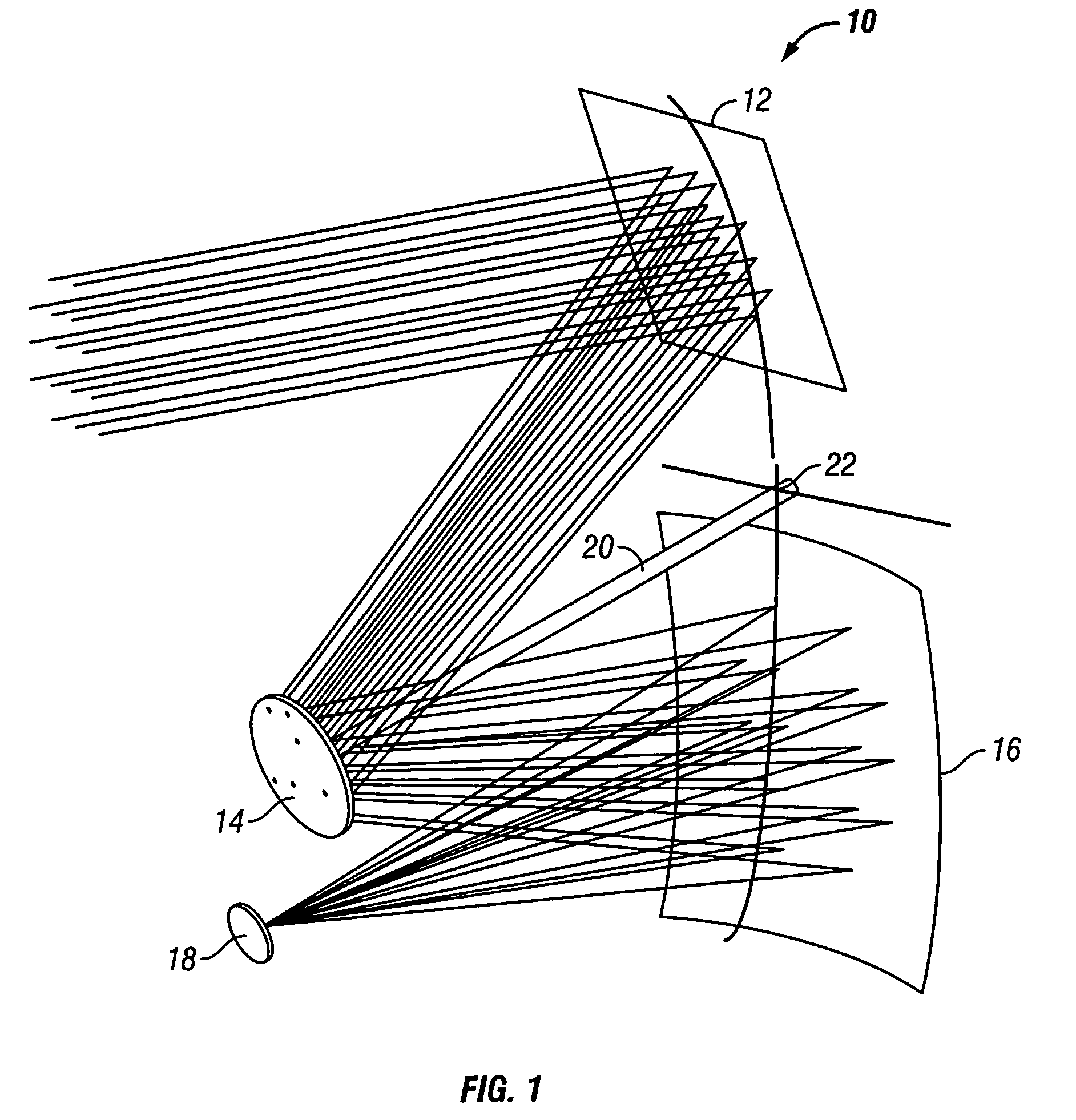
A dual-band antenna is provided that combines two normally disparate communications modes into a single compact aperture minimizing overall mass and volume, while maintaining high performance efficiency and reciprocity of each individual mode. The antenna is compatible with both optical (near-IR / visible) and RF (microwave / millimeter-wave) transceiver subsystems for high bandwidth communications, applicable primarily to long- to extremely long-range (space-to-ground) link distances. The optical link provides high bandwidth while the RF provides a lower data-rate weather backup, accommodation for traditional navigation techniques, and assistance in cueing the extremely tight optical beam by matching the RF beamwidth to an optical fine-steering mechanism field-of-regard. The configuration is built around a near-diffraction-limited high performance primary mirror shared by both a direct-fed RF antenna design and a Cassegrain optical telescope. Material properties are exploited to combine the optical secondary mirror with the RF feed structure, providing a collimated optical beam interface at the antenna vertex.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
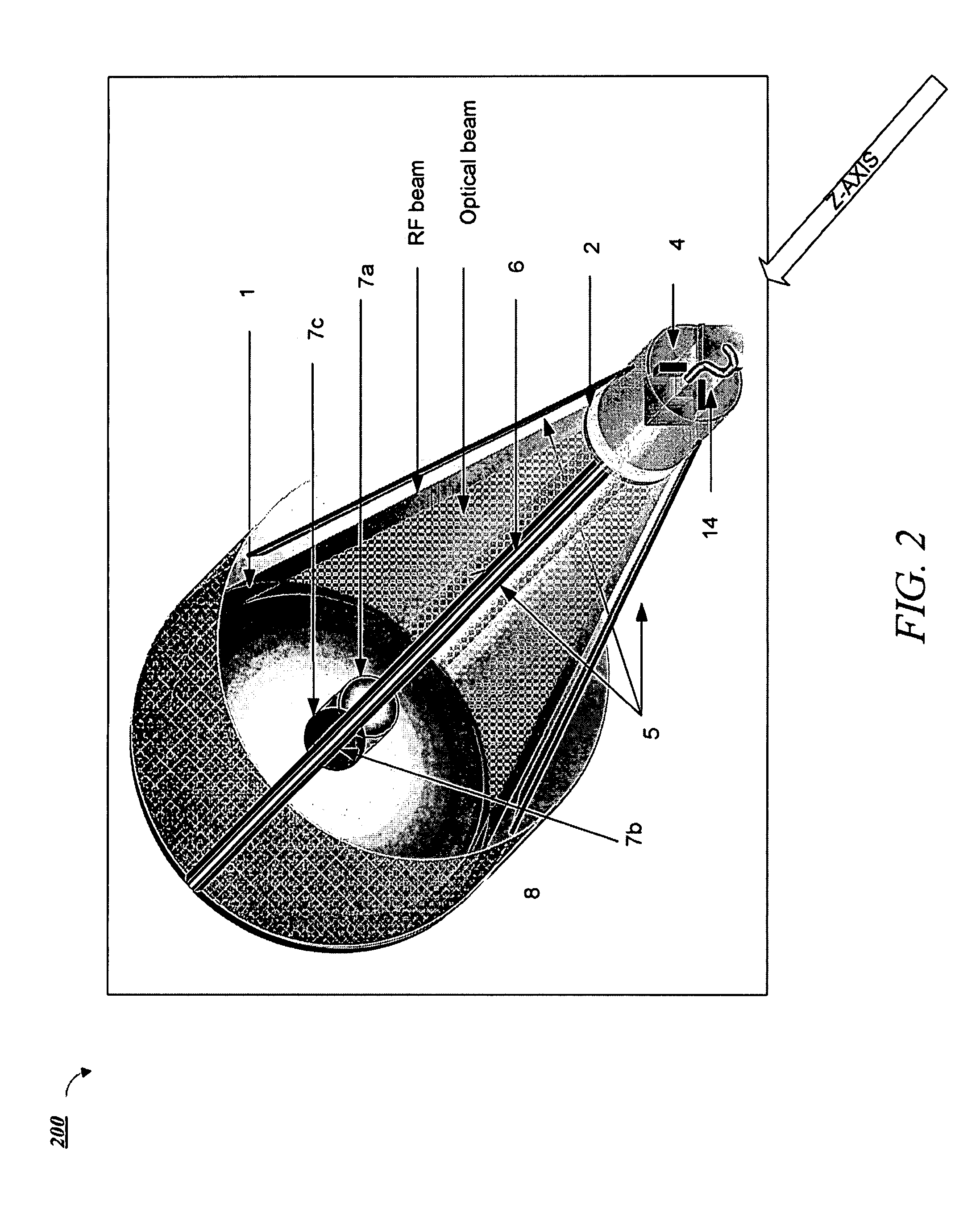
Dual band radio frequency (RF) & optical communications antenna and terminal design methodology and implementation
ActiveUS20120002973A1Increase system capacityLink robustnessWaveguide hornsAntenna arraysAntenna designTransceiver
A dual-band antenna is provided that combines two normally disparate communications modes into a single compact aperture minimizing overall mass and volume, while maintaining high performance efficiency and reciprocity of each individual mode. The antenna is compatible with both optical (near-IR / visible) and RF (microwave / millimeter-wave) transceiver subsystems for high bandwidth communications, applicable primarily to long- to extremely long-range (space-to-ground) link distances. The optical link provides high bandwidth while the RF provides a lower data-rate weather backup, accommodation for traditional navigation techniques, and assistance in cueing the extremely tight optical beam by matching the RF beamwidth to an optical fine-steering mechanism field-of-regard. The configuration is built around a near-diffraction-limited high performance primary mirror shared by both a direct-fed RF antenna design and a Cassegrain optical telescope. Material properties are exploited to combine the optical secondary mirror with the RF feed structure, providing a collimated optical beam interface at the antenna vertex.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
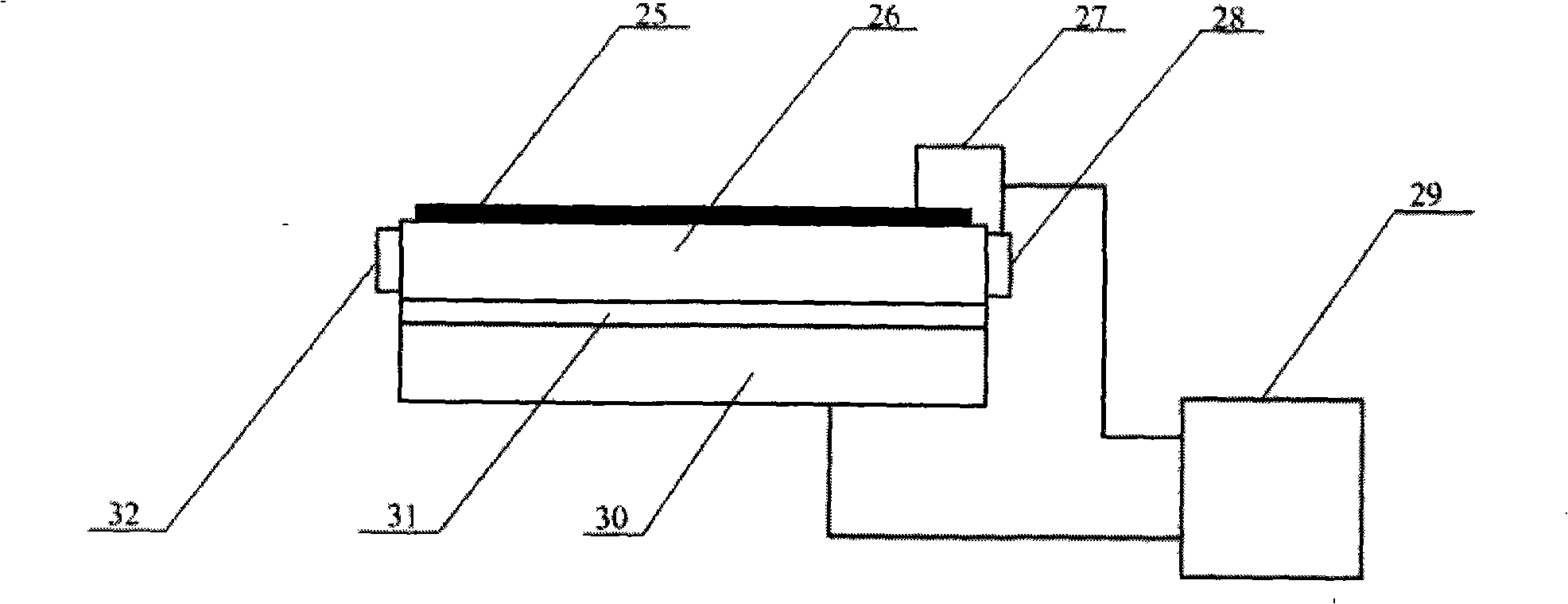
Concentrator solar photovoltaic array with compact tailored imaging power units
InactiveUS20060266408A1Low costEasy to assembleSolar heating energyMirrorsMechanical componentsEngineering
Solar panels and assembled arrays thereof include a collection of relatively compact, high-capacity power units. Optical components of each power unit include a front window or surface glazing, a primary mirror, secondary mirror and receiver assembly. Primary and secondary mirrors are defined by respective perimeters, at least a portion of which may be substantially coplanar and in contact with the front window. Some primary mirrors are configured with a perimeter of alternating full and truncated sections, and are curved to a base portion forming a pilot hole therein. Receiver assembly mechanical components include an alignment tube for mating with the primary mirror's pilot hole and for housing a photovoltaic solar cell. A base plate provided adjacent to the alignment tube serves to radiate heat emitted by the solar cell, and in some embodiments an additional heat sink provides further passive cooling. A tapered optical rod also provided within the receiver assembly directs received sunlight to the solar cell where electrical current is generated.
Owner:H2GO
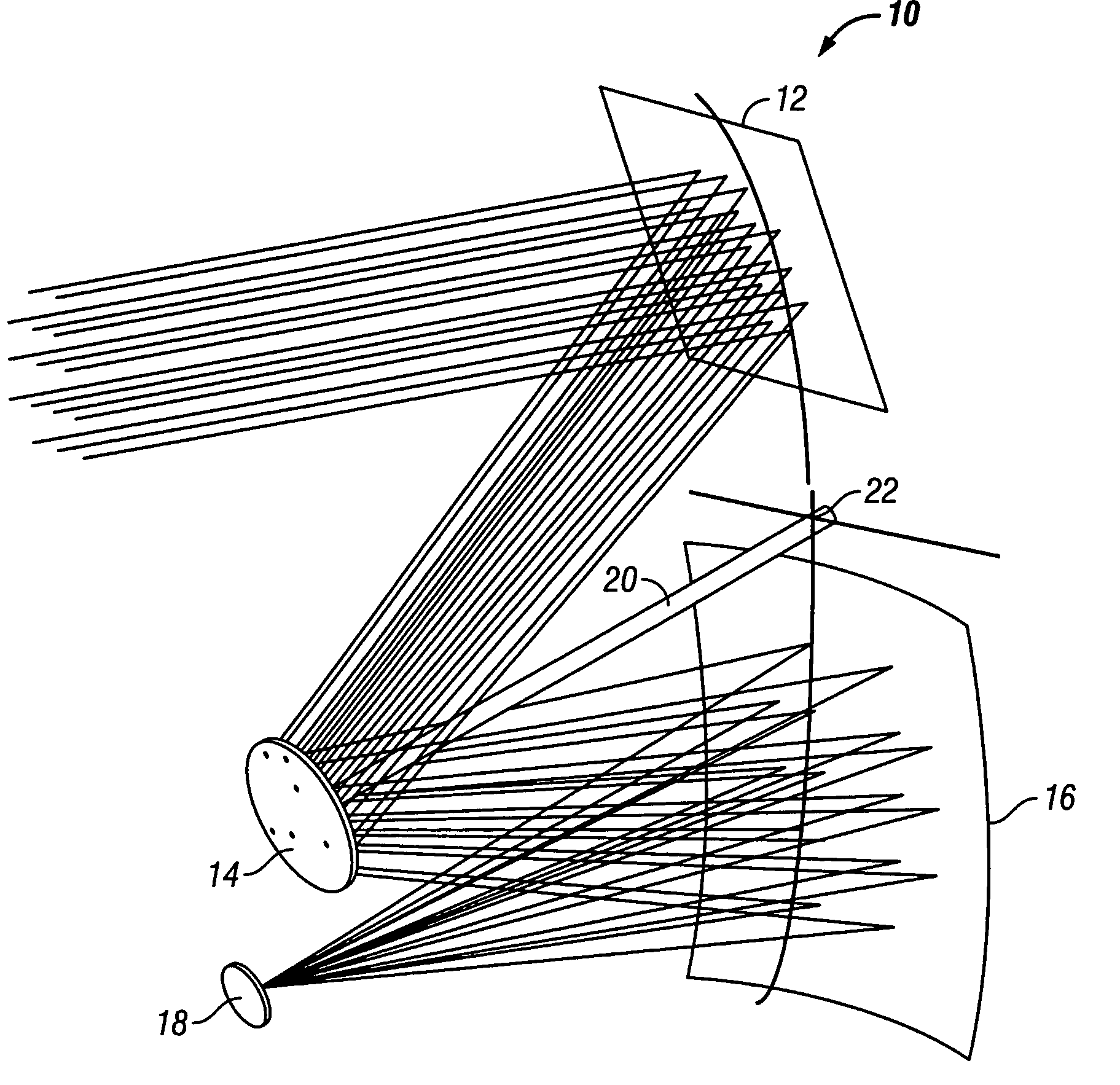
Multi-junction solar cells with a homogenizer system and coupled non-imaging light concentrator
InactiveUS20080047605A1High solar fluxEfficient electrical outputSolar heating energyMirrorsOptic systemMultijunction photovoltaic cell
Optical systems and methods that concentrate light from a distant source, such as the sun, onto a target device, such as a solar cell. Light impinging from the distant source, is focused or imaged by a plurality of primary reflective segments of a primary mirror element onto a plurality of corresponding secondary reflective segments. The secondary mirror segments image the corresponding primary segments onto an exit aperture such that the exit aperture is uniformly illuminated. A target cell may be located proximal to the exit aperture, or an entry aperture of a non-imaging concentrator may be positioned proximal the exit aperture, wherein the concentrator concentrates the reflected light onto the target cell.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Concentrator solar photovol taic array with compact tailored imaging power units
InactiveUS20070089778A1Low costReduced dimensionSolar heating energySolar heat devicesMechanical componentsEngineering
Solar panels and assembled arrays thereof include a collection of relatively compact, high-capacity power units. Optical components of each power unit include a front window or surface glazing, a primary mirror, secondary mirror and receiver assembly. Primary and secondary mirrors are defined by respective perimeters, at least a portion of which may be substantially coplanar and in contact with the front window. Some primary mirrors are configured with a perimeter of alternating full and truncated sections, and are curved to a base portion forming a pilot hole therein. Receiver assembly mechanical components include an alignment tube for mating with the primary mirror's pilot hole and for housing a photovoltaic solar cell. A base plate provided adjacent to the alignment tube serves to radiate heat emitted by the solar cell, and in some embodiments an additional heat sink provides further passive cooling. A tapered optical rod also provided within the receiver assembly directs received sunlight to the solar cell where electrical current is generated.
Owner:HORNE STEPHEN JOHN +1
System and method for nanostructure apodization mask for transmitter signal suppression in a duplex telescope
Disclosed herein is a system for an apodization mask composed of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) for absorbing unwanted stray light. An apodization mask is a precise pattern or shape that is mathematically derived using light scattering measurement techniques to achieve optimal light absorption.Also disclosed herein is an apparatus for a duplex telescope with stray light suppressing capabilities comprising: a primary mirror for transmitting and receiving light; a secondary mirror for defocusing transmitted light onto the primary mirror and for focusing received light; a photodetector which receives light; a laser transmitter which transmits light; and an apodization mask for absorbing stray transmitted light.
Owner:NASA
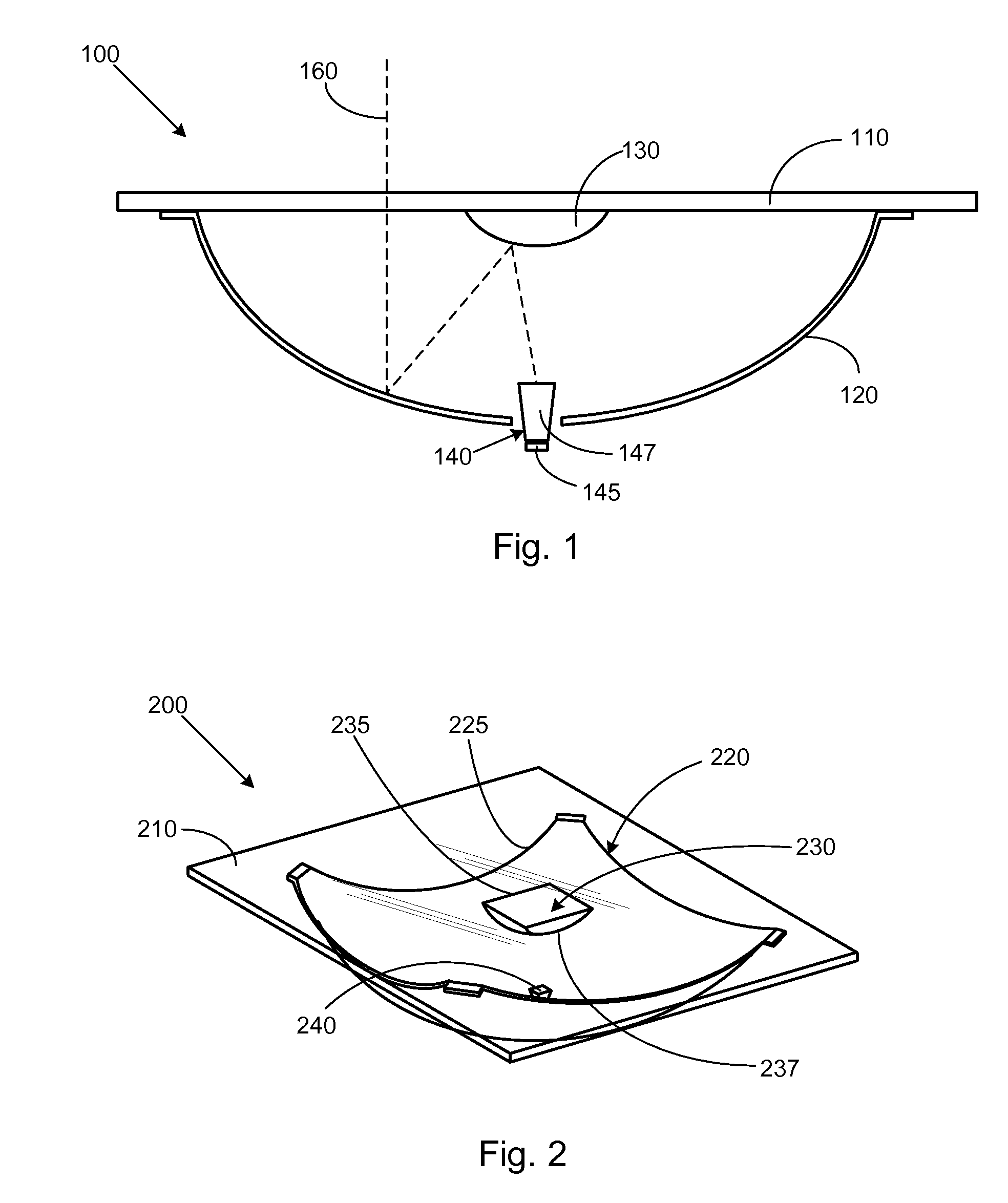
Dual magnification folding travel mirror with annular illuminator
ActiveUS7090378B1Light weightSufficiently smallLighting elementsShaving accessoriesMagnifying glassEngineering
A portable travel mirror device includes a base, a handle pivotably mounted to the base, and a dual mirror assembly mounted to the handle which is pivotable and telescopically extendable between compact transport and upright use configurations, and includes a circular primary mirror frame holding a magnifying mirror encircled by a ring-shaped lamp energized by a power source within the base, and overlain by a diffuser ring. A secondary mirror pivotably and swivelably attached to the primary mirror frame has a different magnification factor, e.g., 1×, and is pivotable upwards from a travel position overlying and protecting the primary mirror to an upright use position, and is also swivelable into contact with the primary mirror frame, whereby light from the lamp is transmitted through the diffuser ring and a transparent secondary mirror bezel to illuminate objects in front of the primary or secondary mirror.
Owner:ZADRO INC
Conversion of solar energy to electrical and/or heat energy
InactiveUS20080163922A1Improve efficiencyIncrease light intensitySolar heating energyMirrorsEngineeringSpecular surface
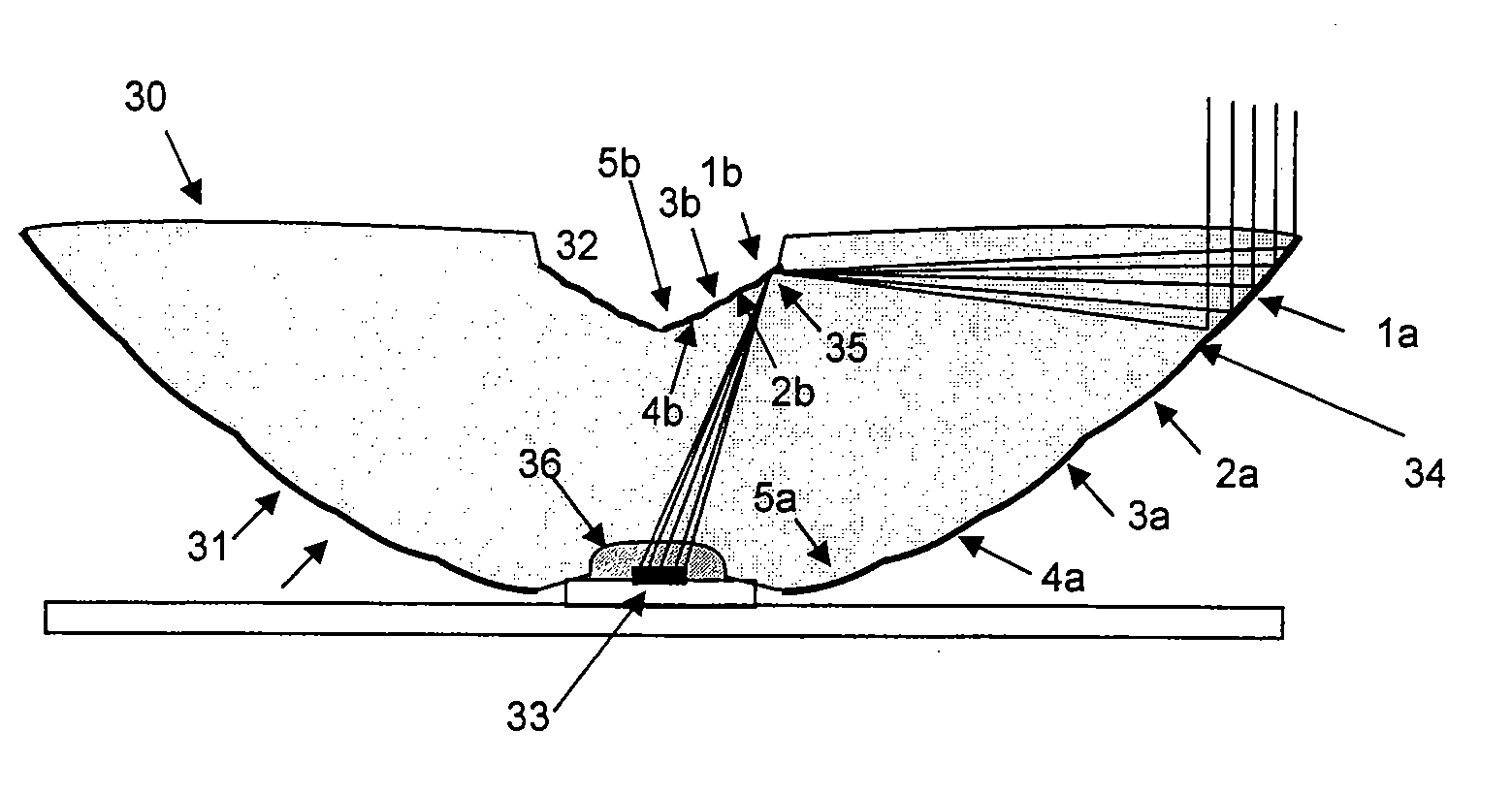
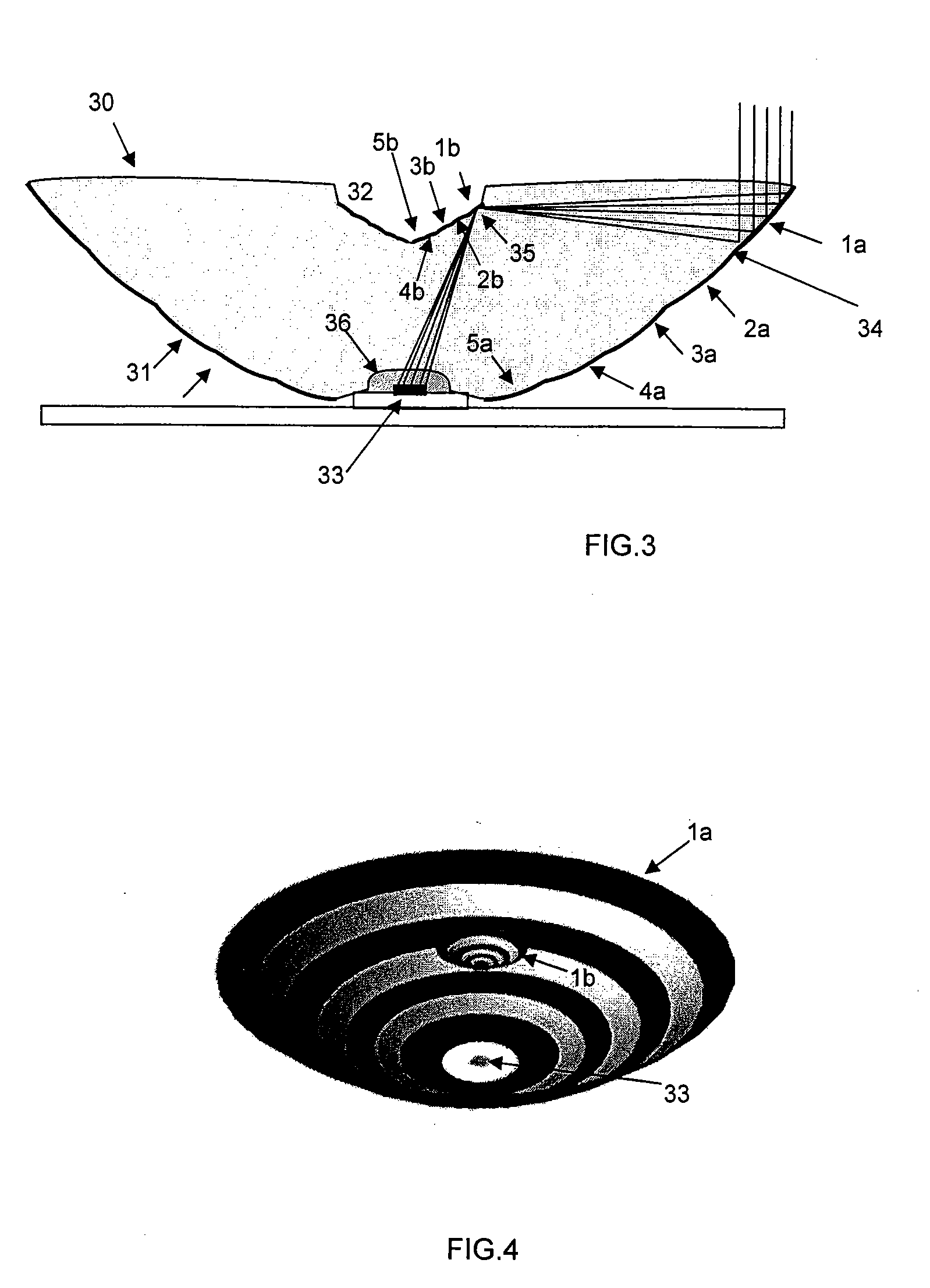
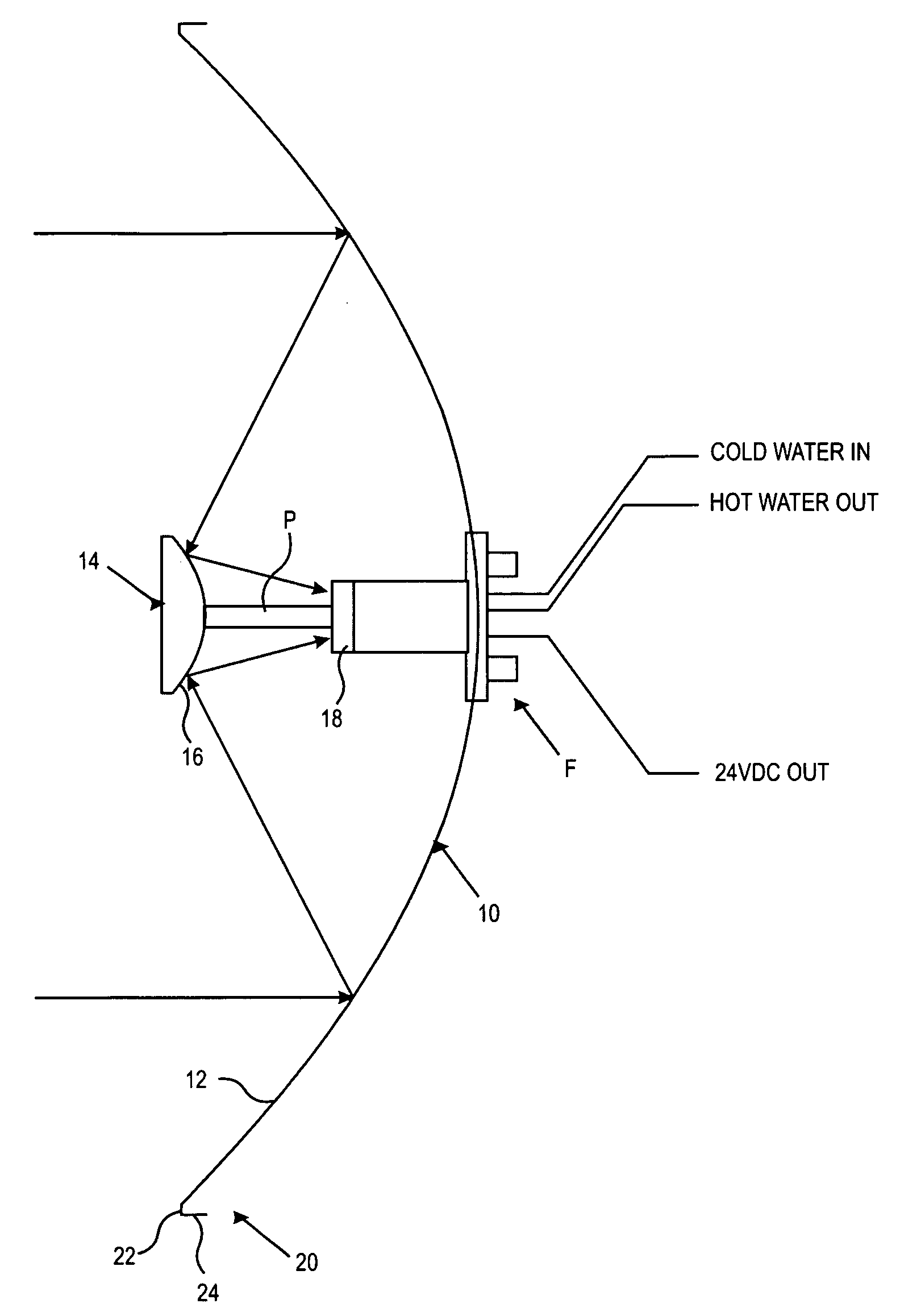
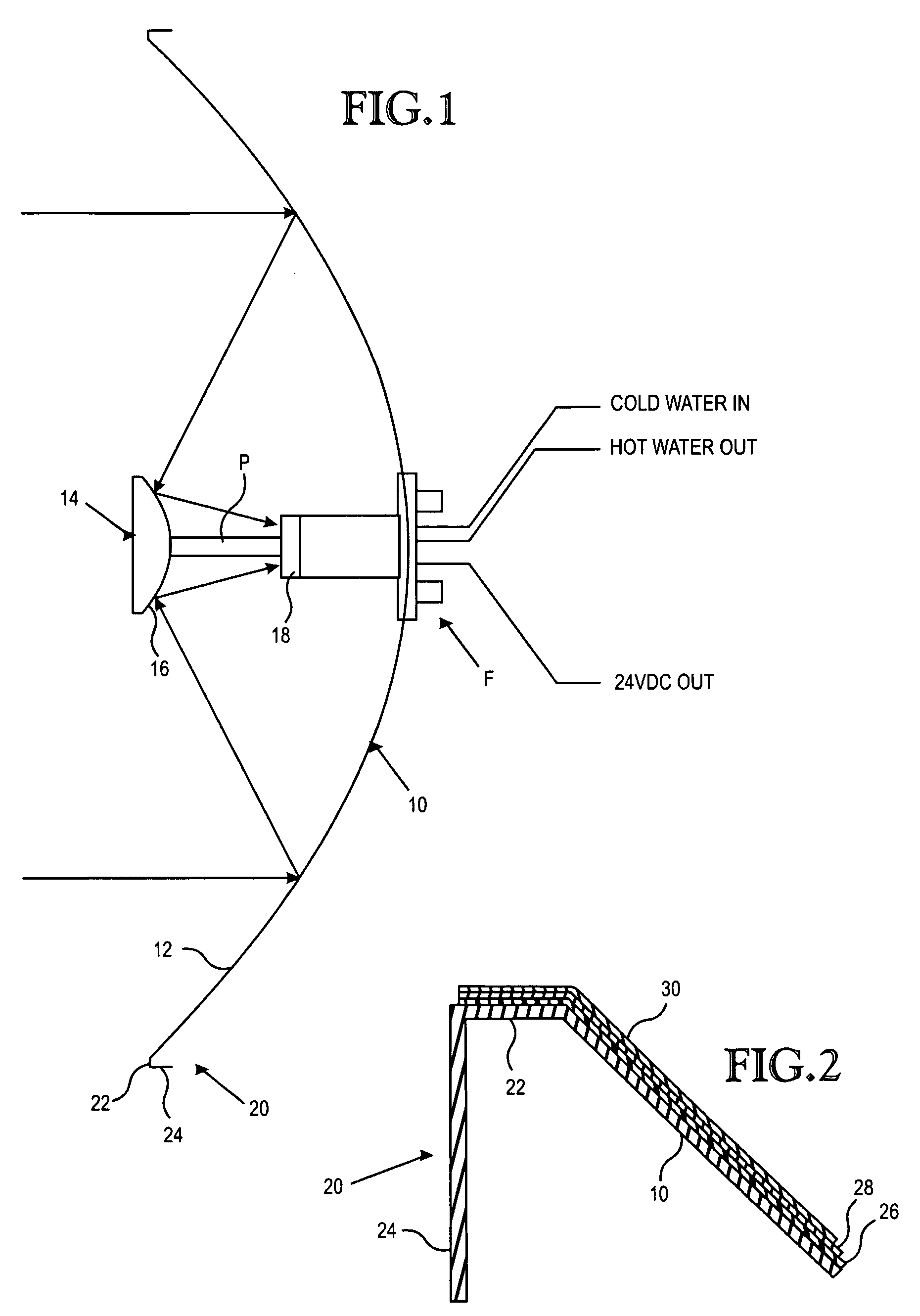
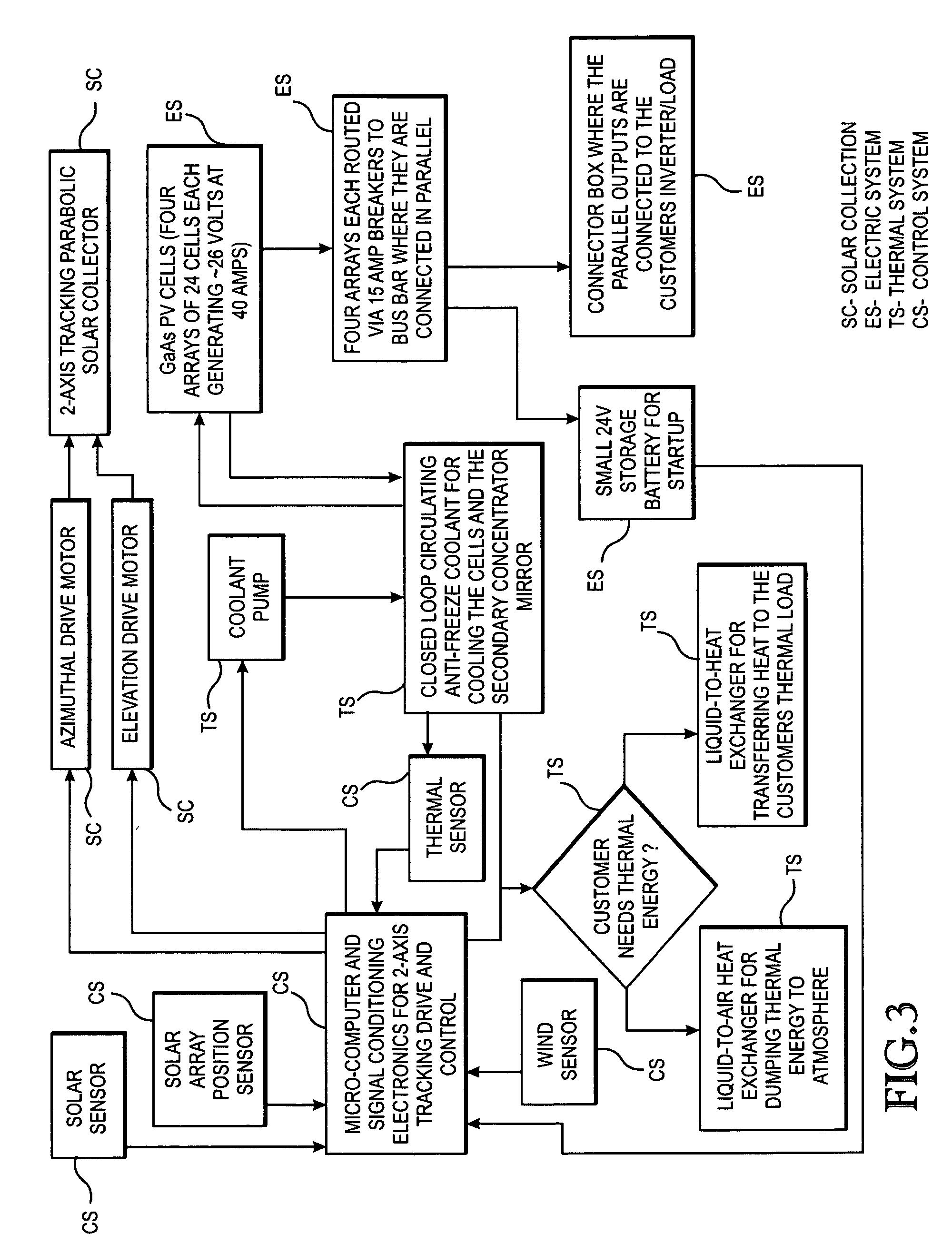
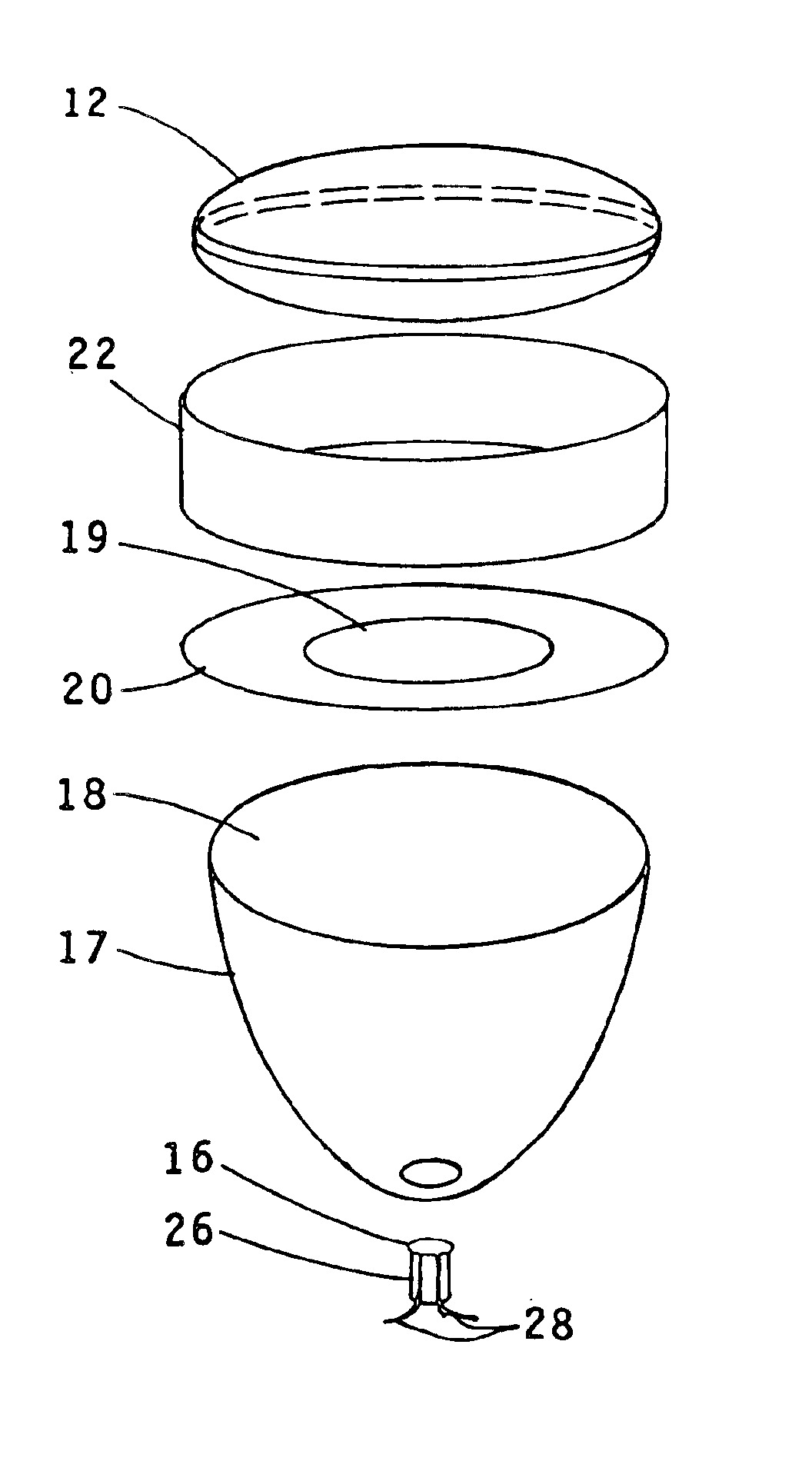
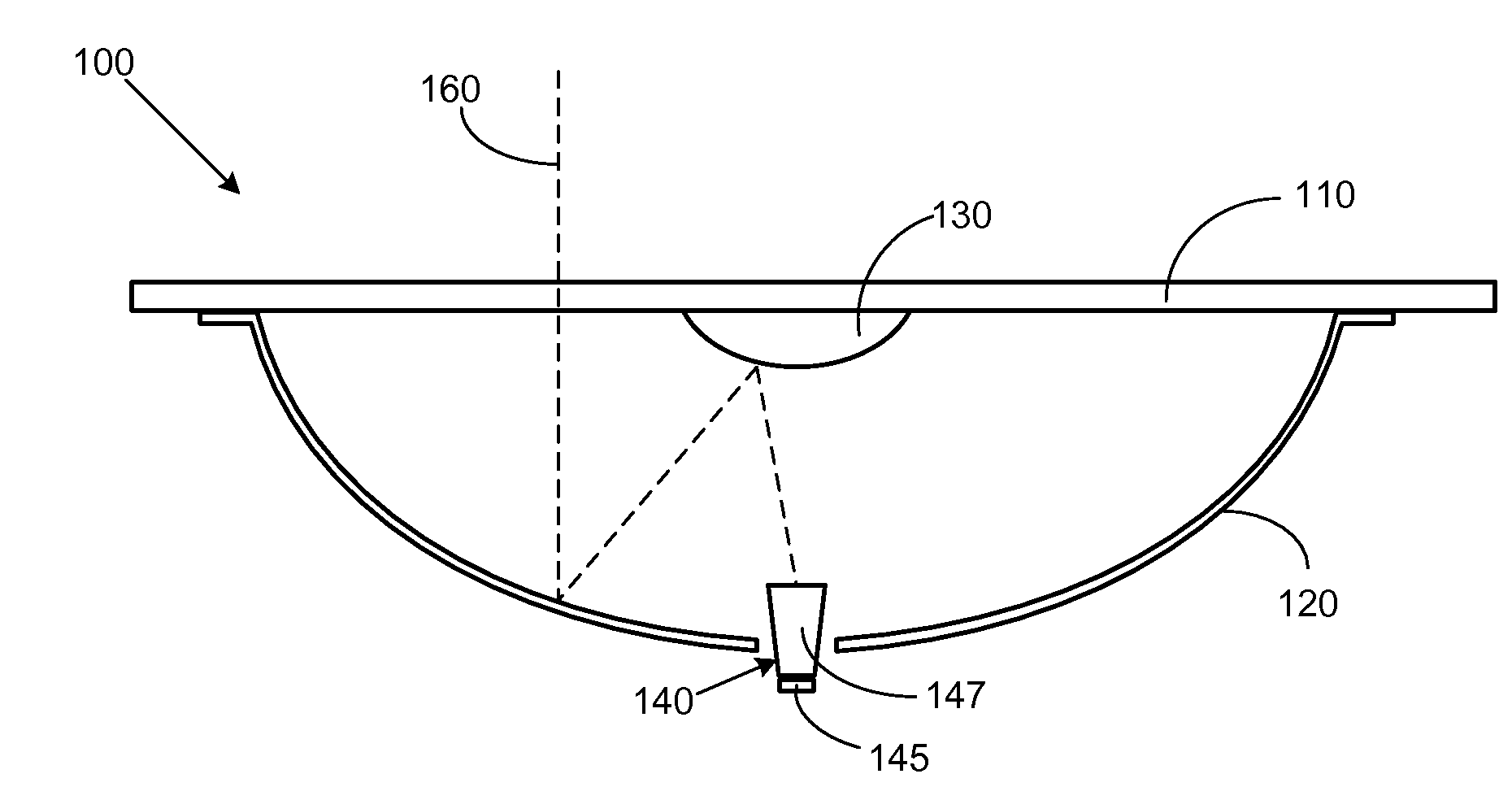
A parabolic primary mirror (10) has a concave specular surface (12) that is constructed and positioned to receive solar energy and focus it towards a focal point. A secondary mirror (14) having a convex specular surface (16) is constructed and positioned to receive focused solar energy from the primary mirror and focus it onto an annular receiver (18). The annular receiver (18) may include an annular array of optical elements (100) constructed to receive solar energy from the secondary specular surface (14) and focus it onto a ring of discreet areas. A ring of solar-to-electrical conversion units are positioned on the ring of discreet areas. A sun sensor that allows accurate solar tracking to keep mirror system aligned with the sun.
Owner:EDTEK INC
Solar energy collection system
InactiveUS6881893B1Simpler less complexLess expensiveSolar heat devicesPV power plantsCollection systemMagnifying glass
Sunlight is localized at a solar cell by means of a lens in conjunction with a solar energy trap with very low losses. The lens is a standard magnifying lens which concentrates the sunlight to a spot which is a small percentage of the total area of the lens. The lens is fixed at a tilt angle which is in accordance with the latitude of the site of the solar collection. The daily arc of the sun across the face of the lens produces a smooth arc path of the spot in three dimensional spaces. At or near the smooth arc in space, a guide which may be a secondary mirror surface or an opening guides the light into a solar trap. The solar trap is a fully mirrored enclosed space which permits light to enter but not leave the trap. The light in the trap is guided to a solar cell within the trap with reflected and scattered light being absorbed by the solar cell.
Owner:COBERT DAVID M
Catadioptric imaging system and a projection exposure apparatus provided with said imaging system
InactiveUS6639734B2Avoiding deterioration of image forming performanceInhibit deteriorationPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusOptic systemRadiation
The object of the present invention is to provide a catadioptric imaging system, or the like, which is capable of obtaining a desired image-side NA and an image circle without increasing the size of a reflecting mirror with a smaller number of lenses. This catadioptric imaging system comprises a first imaging optical system and a second imaging optical system, wherein the first imaging optical system is provided with a positive first lens group, an aperture stop, and a positive second lens group in the order from the object side, and the second imaging optical system is provided with a primary mirror comprising a concave first reflecting surface having a first radiation transmitting portion at the center thereof, and a secondary mirror comprising a second reflecting surface having a second radiation transmitting portion at the center thereof. In this case, all of the refracting members for constituting the optical system is formed of the same optical material, or at least one of the refracting surfaces and the reflecting surfaces is formed to be aspherical, or a refracting member is disposed to be separated from the first reflecting surface or the second reflecting surface.
Owner:NIKON CORP
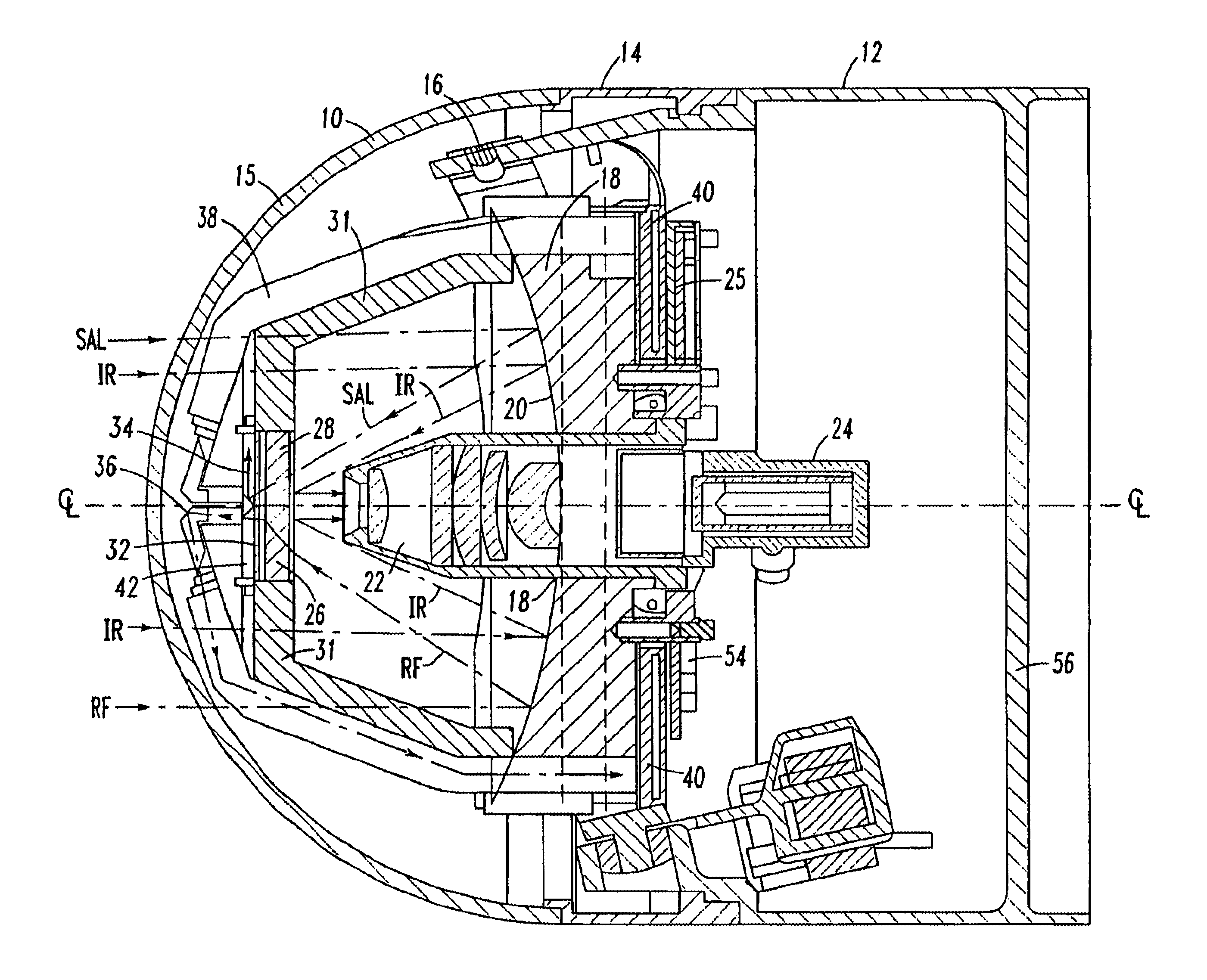
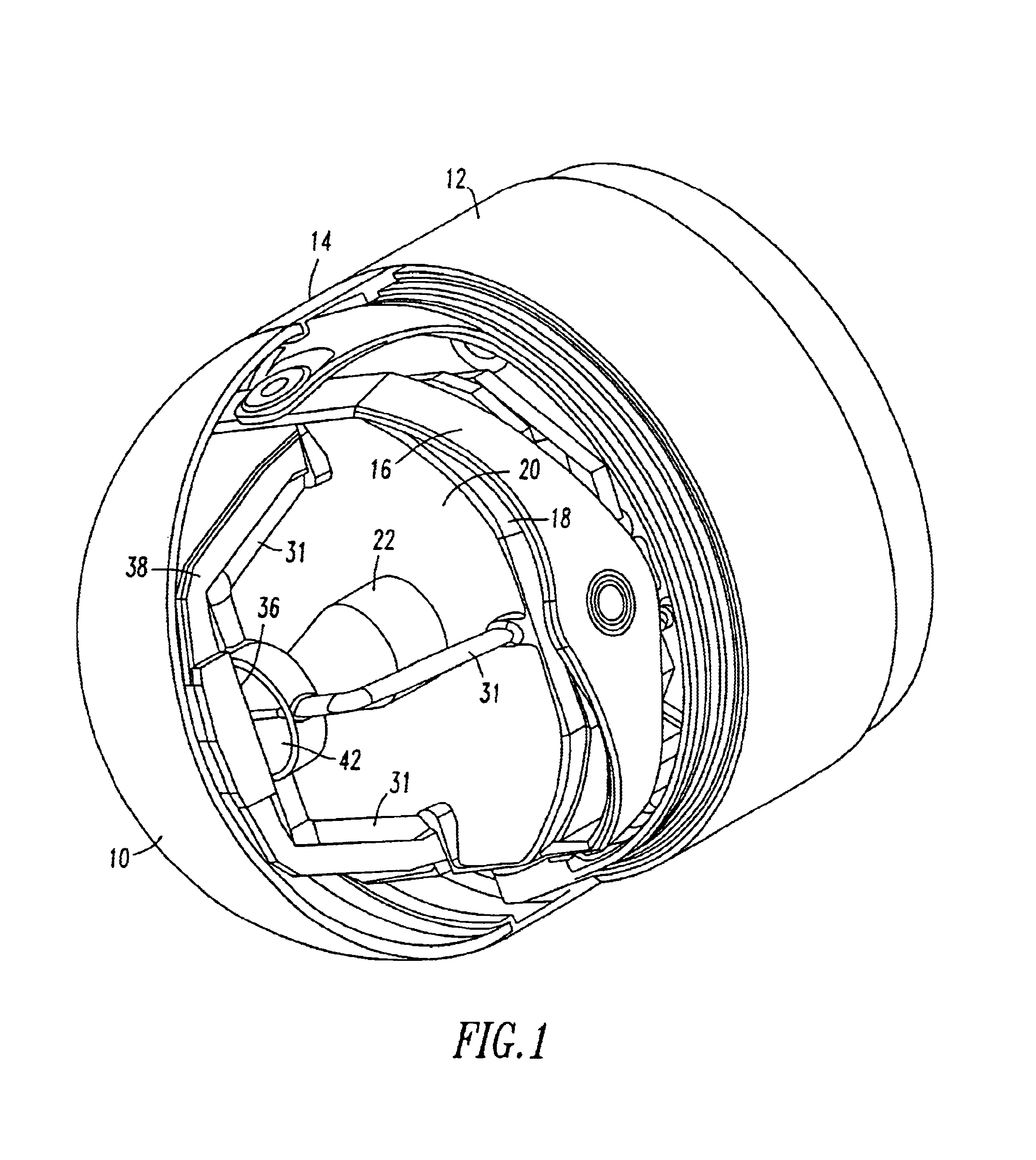
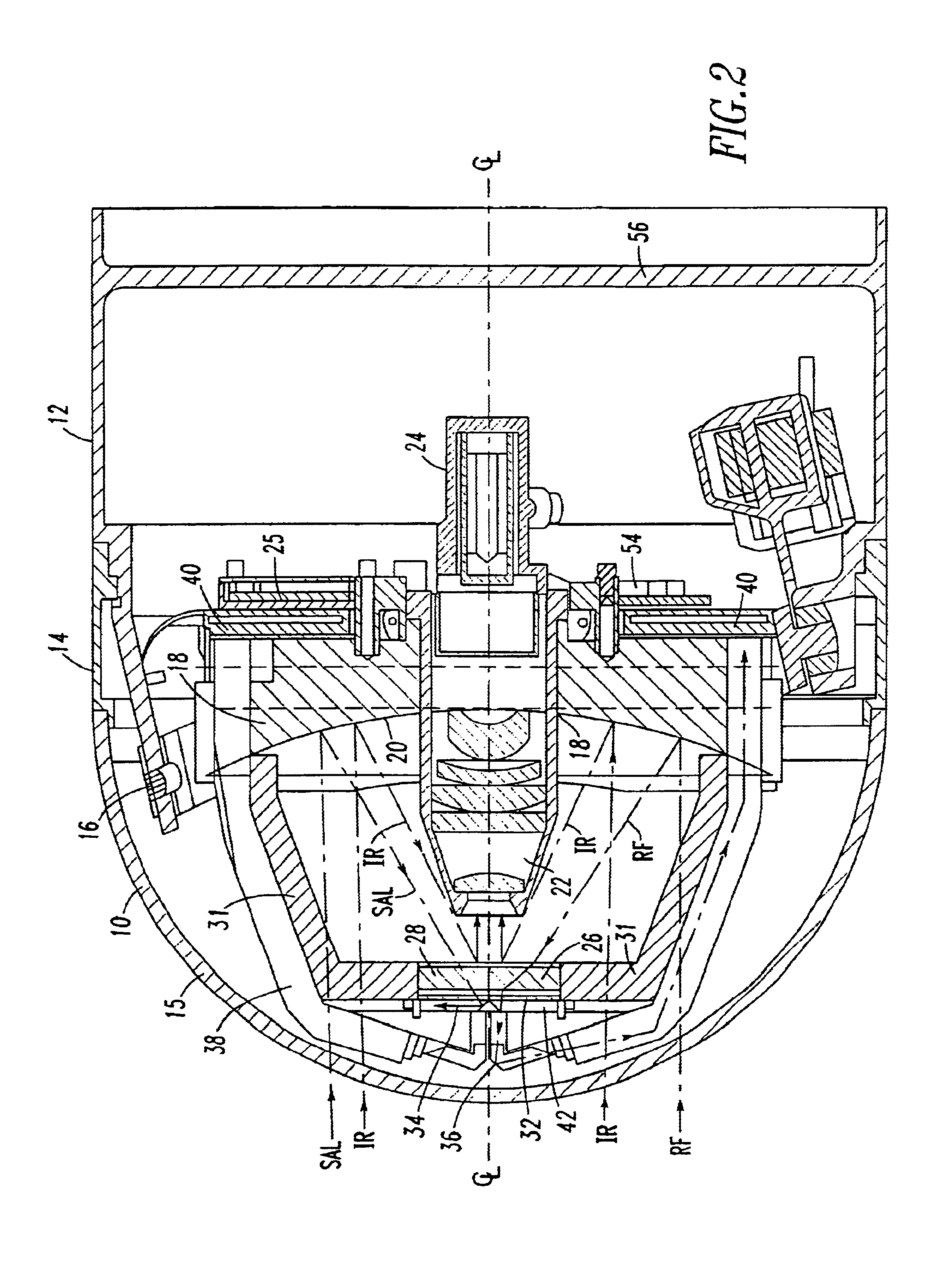
Tri-mode co-boresighted seeker
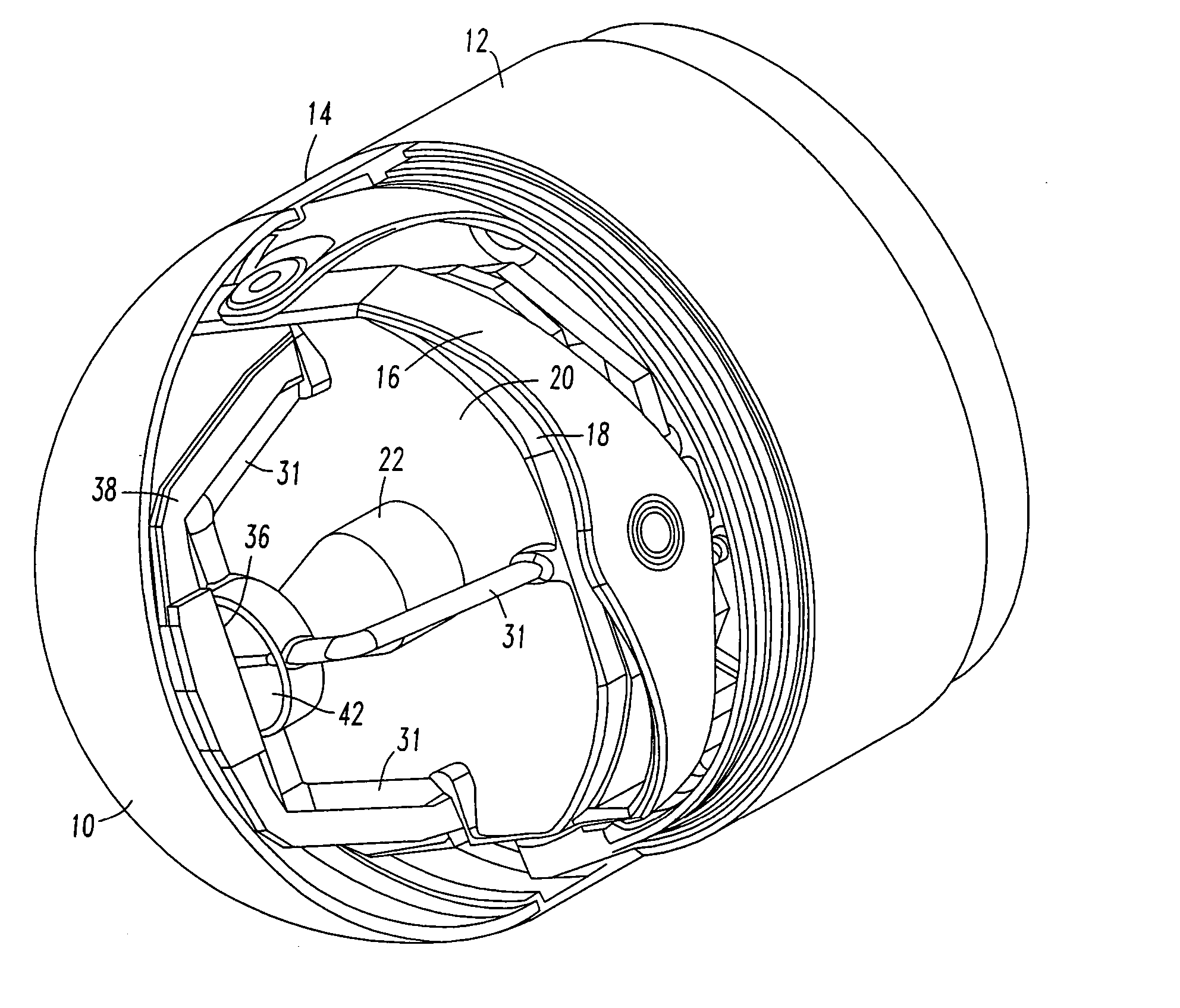
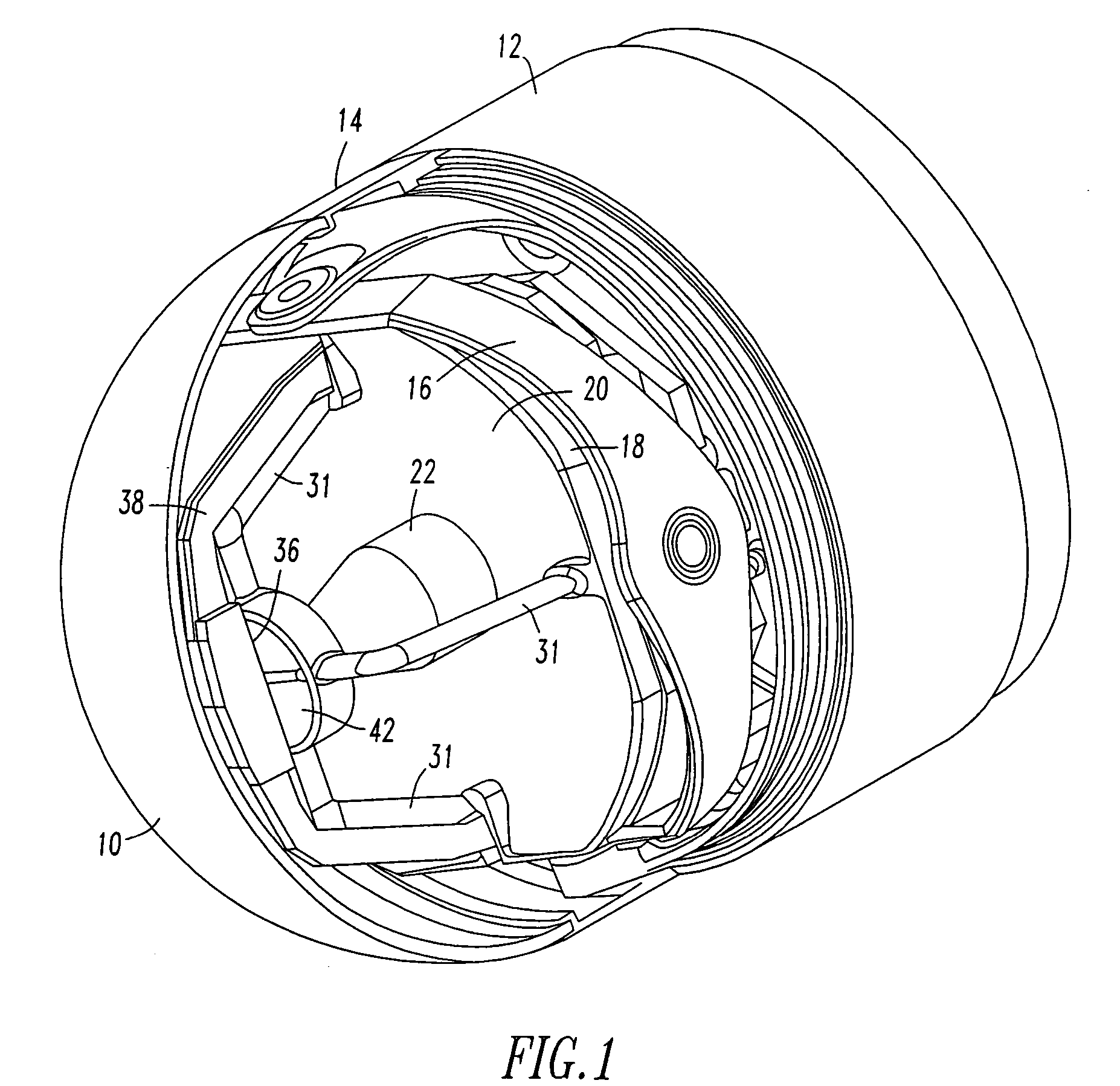
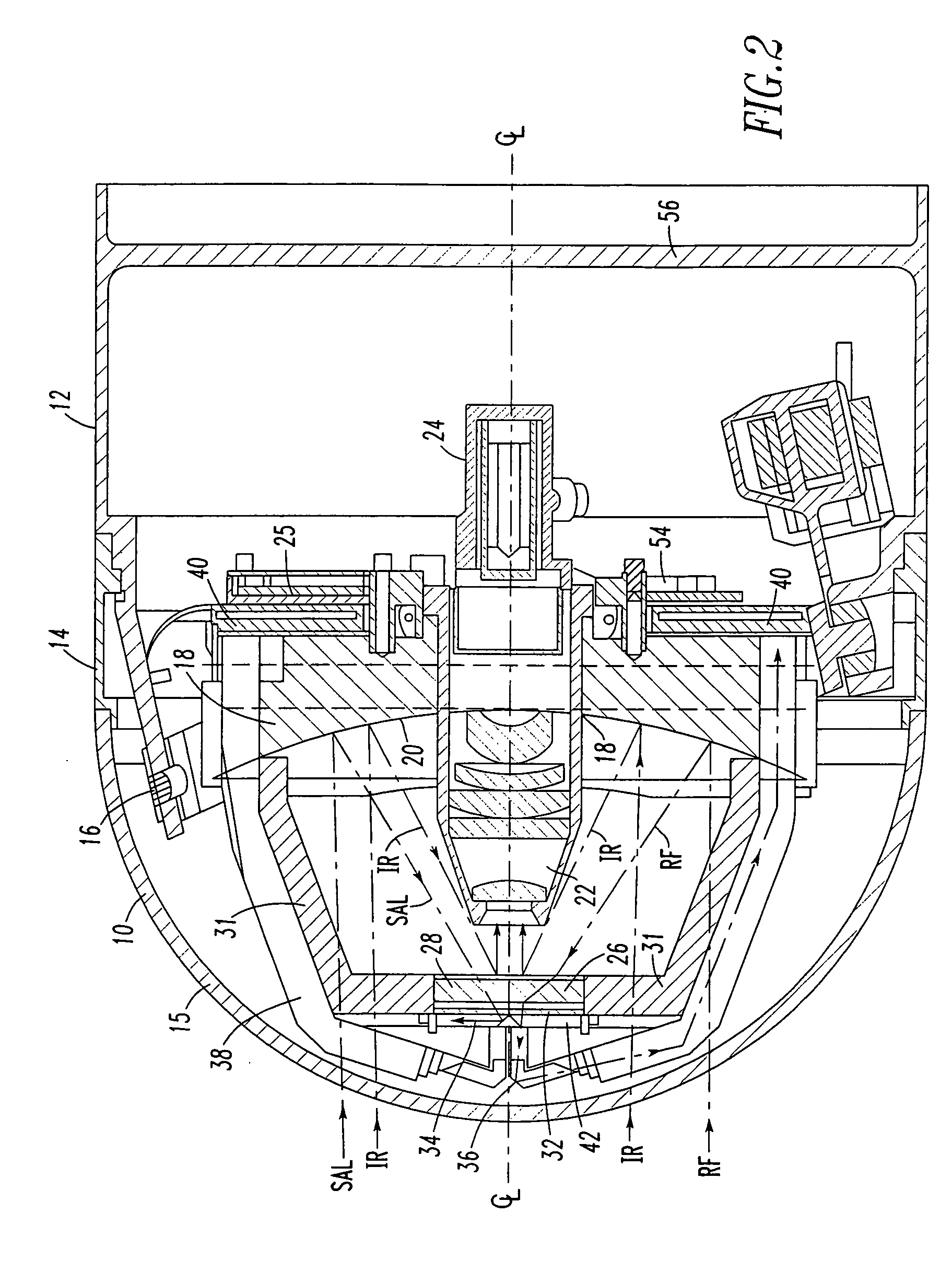
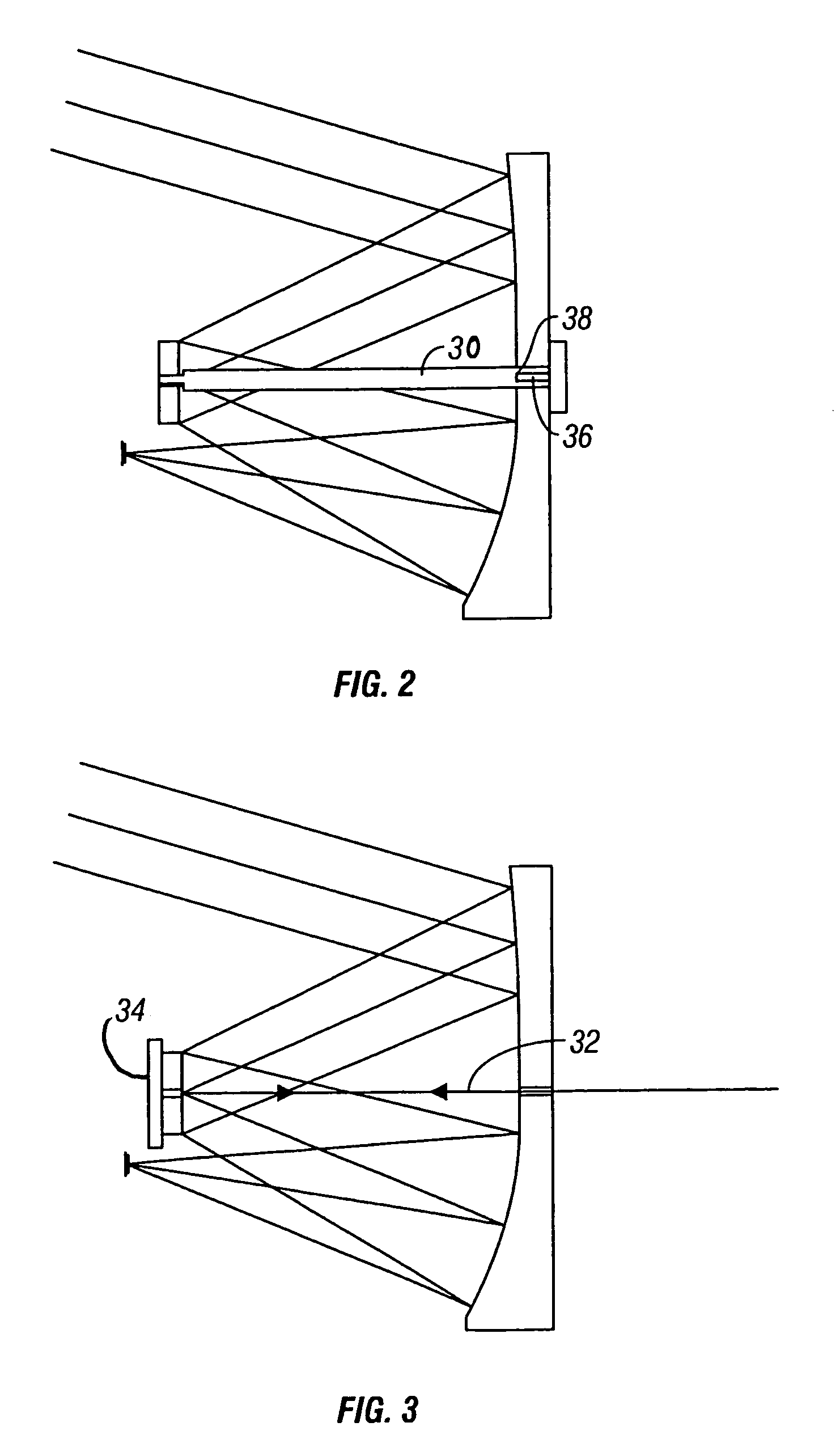
A tri-mode co-boresighted seeker including a primary collecting mirror assembly having a parabolic surface and a forwardly located dielectric secondary mirror assembly including a dielectric mirror coating which reflects infrared (IR) energy to an IR detector assembly located on a central longitudinal axis on one side of the secondary mirror while providing substantially unobstructed propagation of millimeter wave RF energy and laser energy in a joint or common signal path therethrough to means located on the other side of the secondary mirror for extracting and diverting laser energy away from the common RF-optical signal path to a laser sensor assembly while causing little or no disturbance to the RF signal as it propagates to a co-located bifurcated waveguide assembly which couples the RF energy to an RF sensor means located behind the primary mirror.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Compact multispectral scanning system
Owner:ALFA IMAGING
Solar concentrator with square mirrors
InactiveUS20090114213A1Efficient throughput of lightMinimal shadingSolar heating energySolar heat devicesEngineeringSolar concentrator
The present invention is a solar concentrator system incorporating a square primary mirror, a square secondary mirror, and an optical receiver. The square secondary mirror provides highly efficient throughput of light in combination with the square primary mirror, with minimal shading. Manufacturing features may be incorporated into the square secondary mirror to assist in simplifying fabrication issues and assembly steps related to its non-circular shape. An optional heat shield around the optical receiver may be included, further enhancing performance of the solar concentrator system.
Owner:SOLFOCUS
Large field of view protection optical system with aberration correctability for flat panel displays
InactiveUS7158215B2Improve performanceReadingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCatoptricsDisplay device
An exposure system for manufacturing flat panel displays (FPDs) includes a reticle stage adapted to support a reticle. A substrate stage is adapted to support a substrate. A reflective optical system is adapted adapted to image the reticle onto the substrate. The reflective optical system includes a primary mirror including a first mirror and a second mirror, and a secondary mirror. The reflective optical system has sufficient degrees of freedom for both alignment and correction of third order aberrations when projecting an image of the reticle onto the substrate by reflections off the first mirror, the secondary mirror, and the second mirror.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
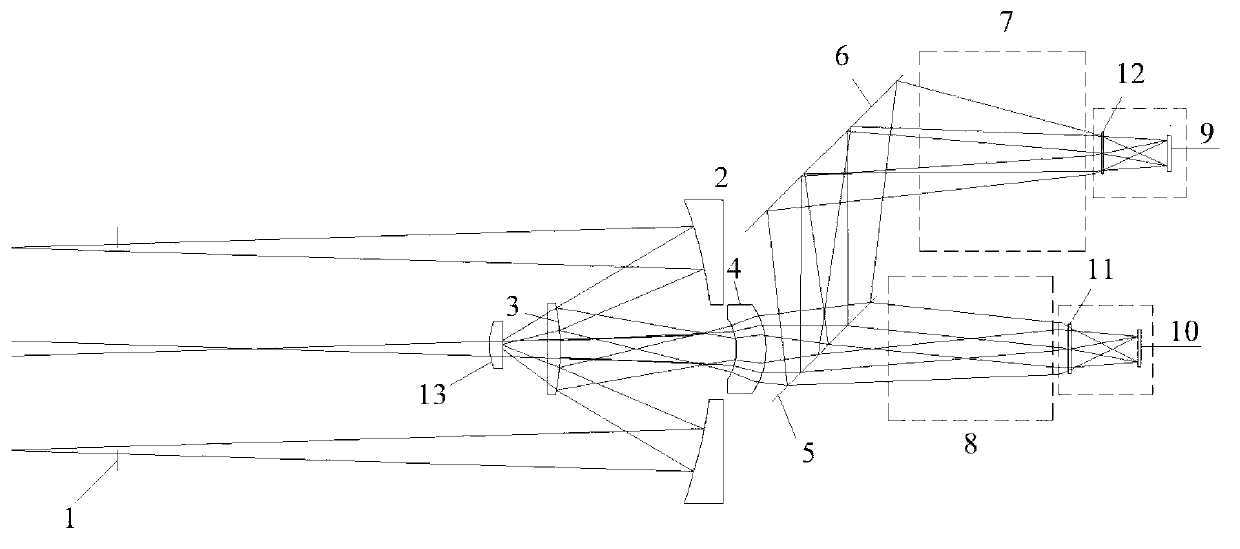
Laser and middle- and long-wavelength infrared common-aperture three-band imaging system
ActiveCN103278916AReduce volumeExcellent aberration correctionOptical elementsBeam splitterImaging quality
The invention relates to a laser and middle- and long-wavelength infrared common-aperture three-band imaging system, which comprises an entrance pupil shared by each band, a primary mirror, a secondary convex mirror, a middle / long-wavelength infrared optical path imaging lens group, a laser converging light spot receiving unit, a middle- and long-wavelength infrared band beam splitter, a middle- and long-wavelength infrared dual-band imaging lens group and a detection image surface, wherein the reflection surface of the primary mirror is a concave surface, and a hole is formed in the center of the primary mirror. The system can be used for realizing the common-aperture collection of scene infrared radiation energy of the same object and laser echo energy reflected by the object; and the entrance pupil is positioned in front of the primary mirror, the secondary mirror is used for the beam splitting of laser and middle- and long-wavelength infrared bands, and a dichroic mirror is inclined to split middle-wavelength infrared light and long-wavelength infrared light, so that the system is compact in structure, the utilization rates of optical energy and space of the system are increased, the aberration correction and beam focusing of middle- and long-wavelength infrared bands are facilitated respectively, and the imaging quality is remarkably improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
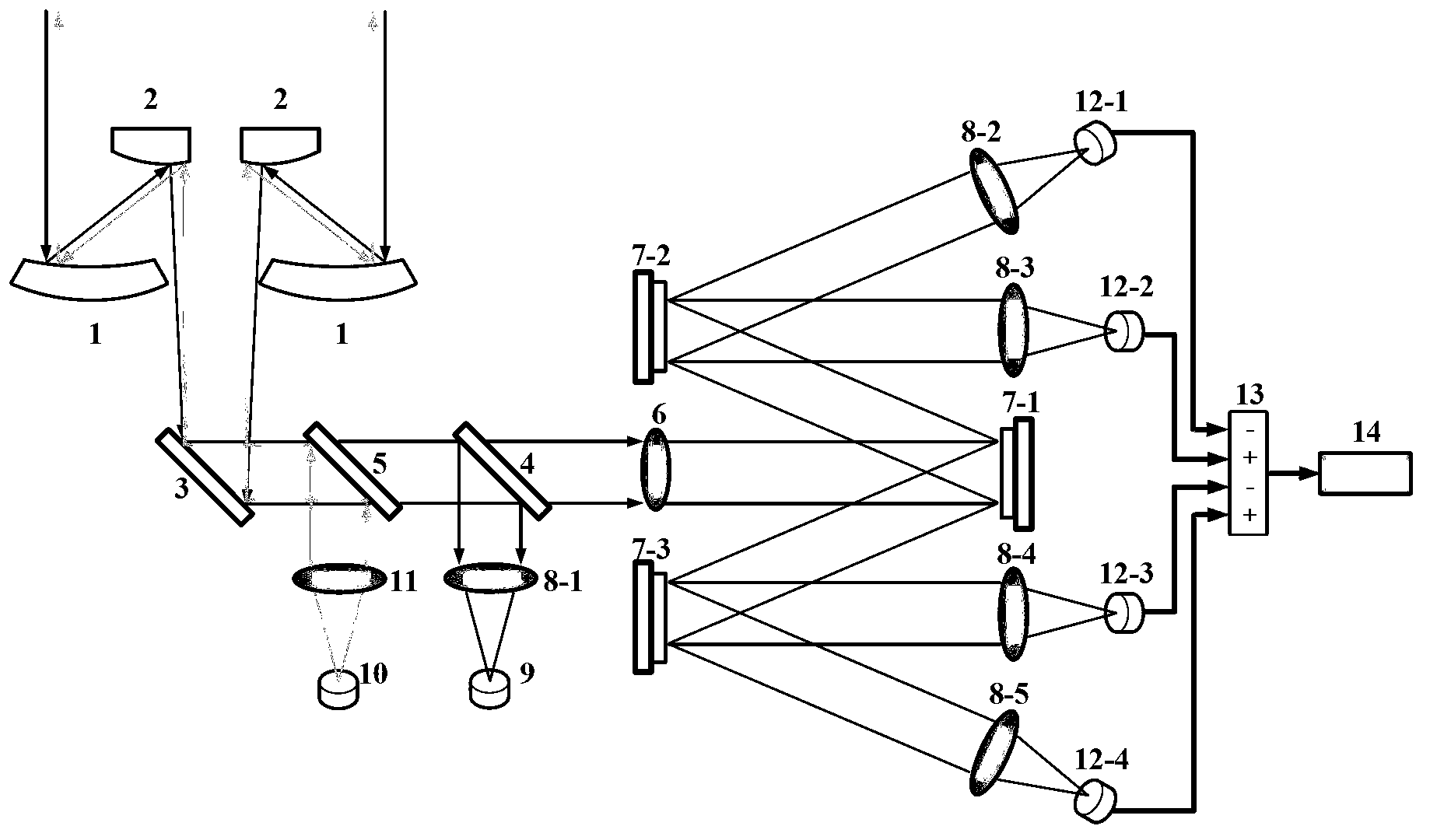
Free space optical-communication APT system and method based on compressive sensing receiver
ActiveCN103326780AGuaranteed stabilityImplementing a Coarse Tracking LoopFree-space transmissionBeam splitterSpatial light modulator
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
Tri-mode co-boresighted seeker
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
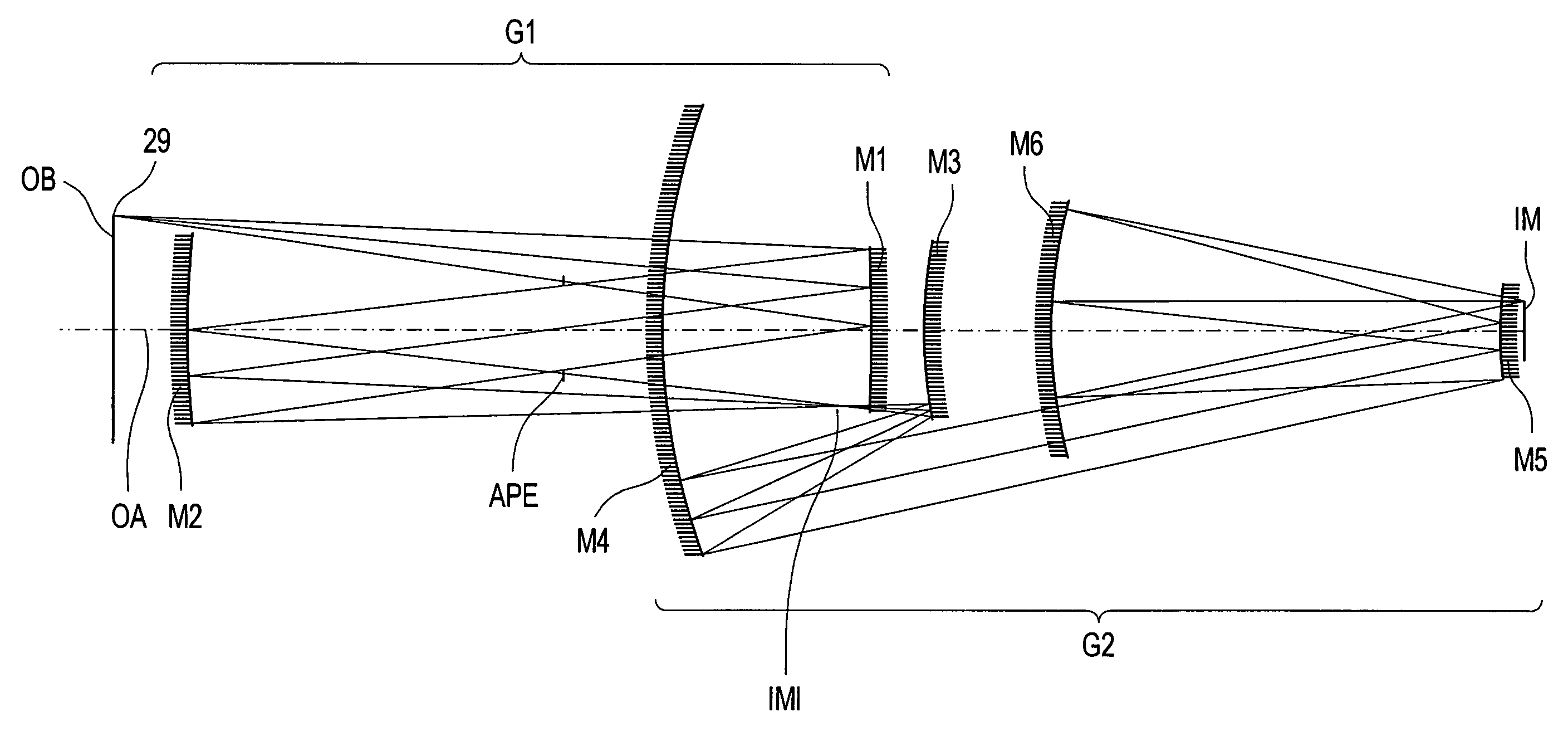
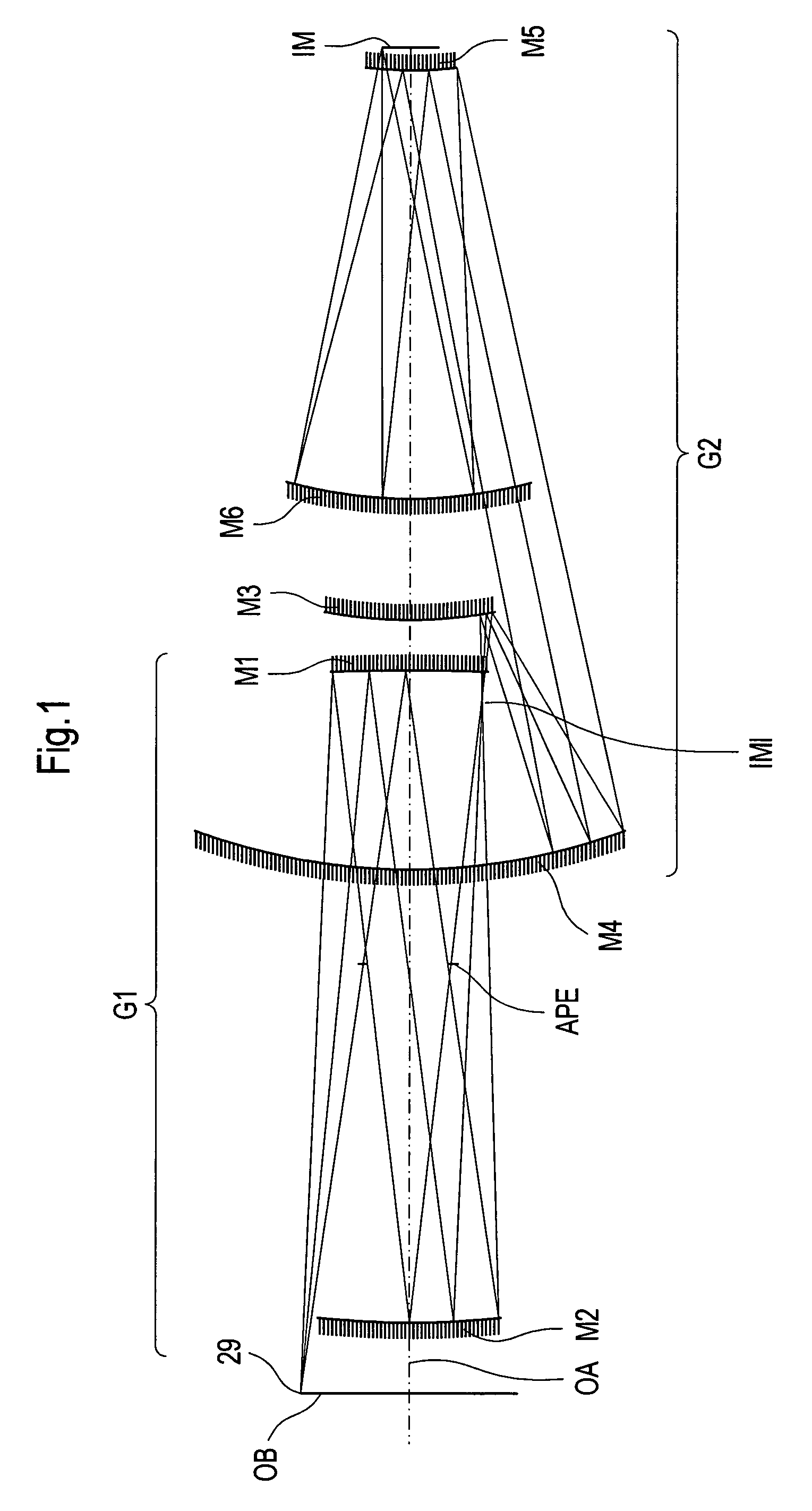
Projection system for EUV lithography
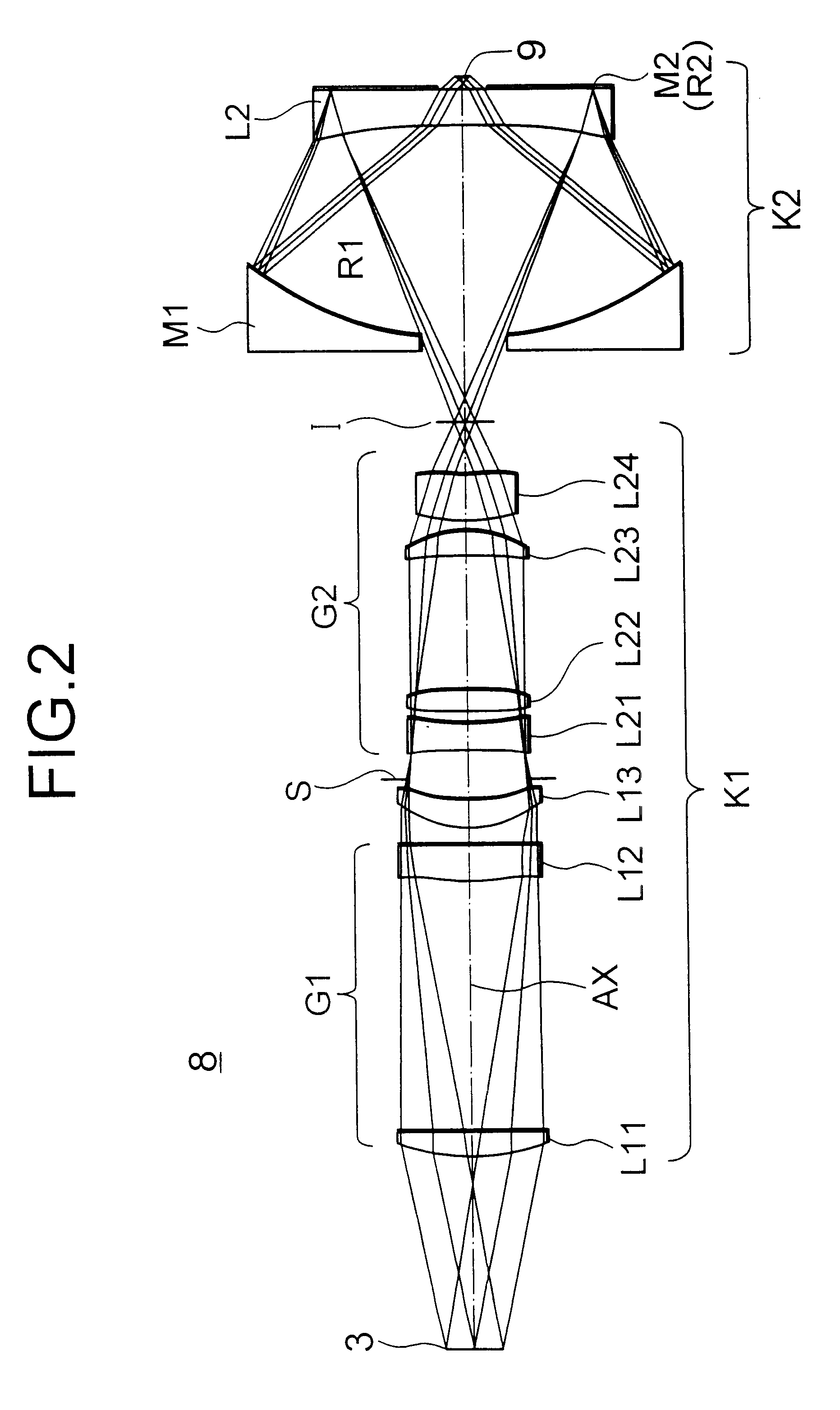
InactiveUS6985210B2Preventing Image Quality DeteriorationEasy mounting and adjustingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusIntermediate imageOptical axis
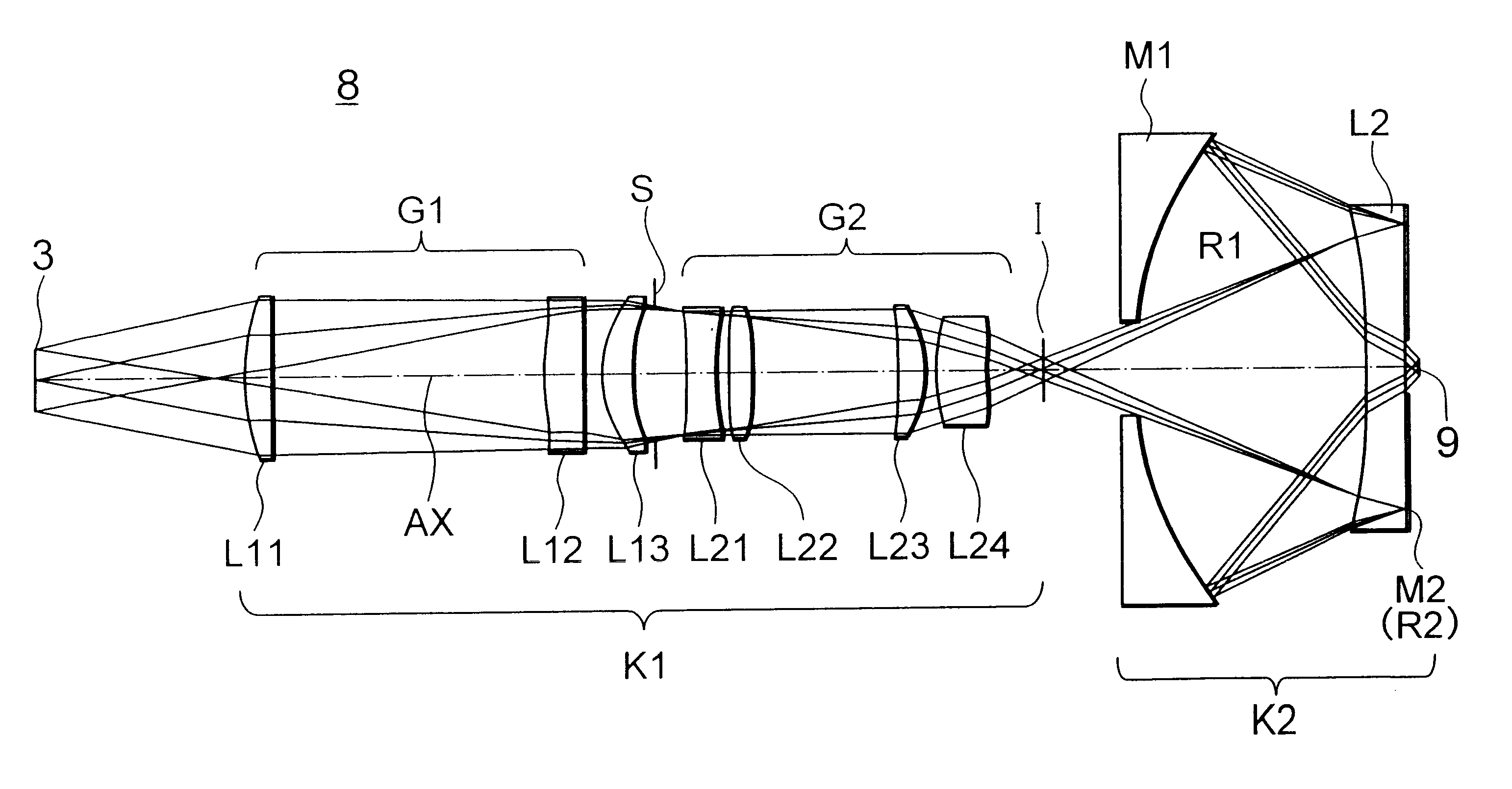
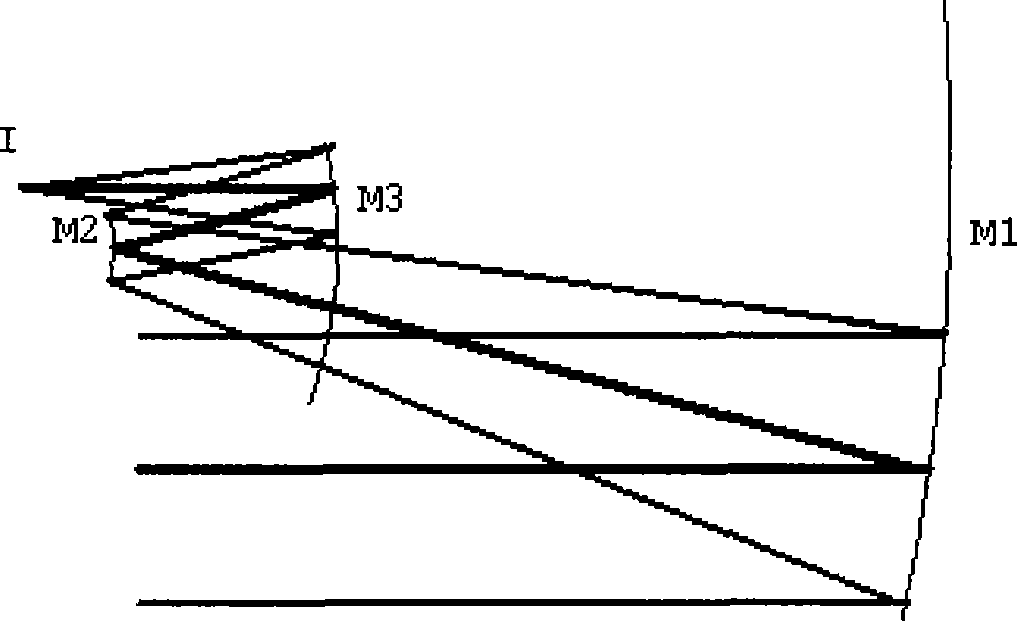
An EUV optical projection system includes at least six reflecting surfaces for imaging an object (OB) on an image (IM). The system is preferably configured to form an intermediate image (IMI) along an optical path from the object (OB) to the image (IM) between a secondary mirror (M2) and a tertiary mirror (M3), such that a primary mirror (M1) and the secondary mirror (M2) form a first optical group (G1) and the tertiary mirror (M3), a fourth mirror (M4), a fifth mirror (M5) and a sixth mirror (M6) form a second optical group (G2). The system also preferably includes an aperture stop (APE) located along the optical path from the object (OB) to the image (IM) between the primary mirror (M1) and the secondary mirror (M2). The secondary mirror (M2) is preferably concave, and the tertiary mirror (M3) is preferably convex. Each of the six reflecting surfaces preferably receives a chief ray (CR) from a central field point at an incidence angle of less than substantially 15°. The system preferably has a numerical aperture greater than 0.18 at the image (IM). The system is preferably configured such that a chief ray (CR) converges toward the optical axis (OA) while propagating between the secondary mirror (M2) and the tertiary mirror (M3).
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Solar Concentrator
InactiveUS20090114265A1Improve manufacturabilityHeat dissipationLine/current collector detailsPV power plantsSolar cellSolar concentrator
The present invention is an improved solar concentrator array utilizing a monolithic array of primary mirrors with a metal layer deposited on its backside for electrical purposes and for dissipating heat. The array of primary mirrors may be formed by glass slumping. The size of the primary mirrors is chosen to accommodate design aspects related to performance, manufacturing processes, cost, and thermal management. An electrical package, which in one embodiment is a molded leadframe, provides the electrical circuitry between a solar cell and the metal layer. The electrical package may be configured with features such as an aperture or side edges to enhance manufacturability of the solar concentrator array. An array of secondary mirrors may be integrally formed with a front panel of the solar concentrator.
Owner:SOLFOCUS
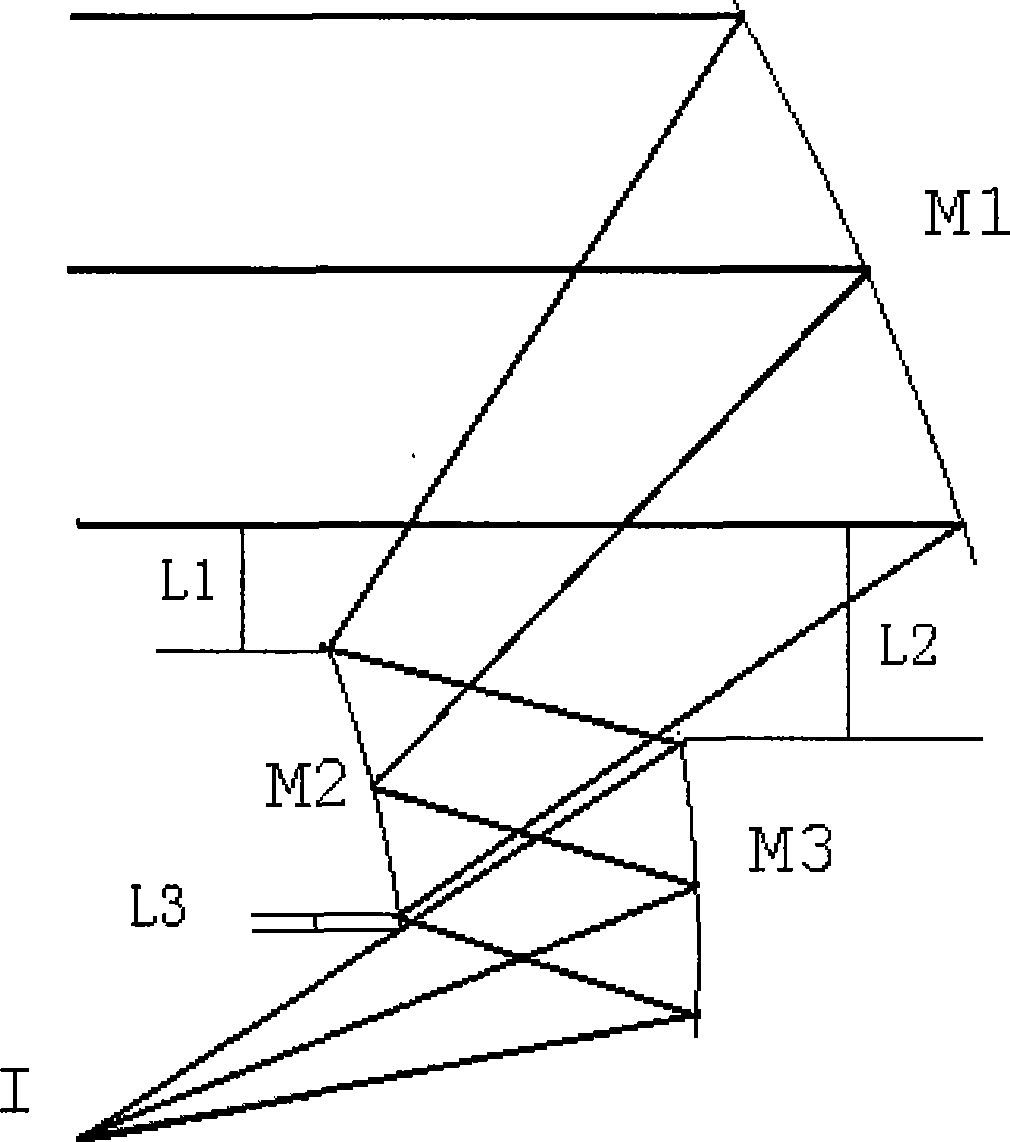
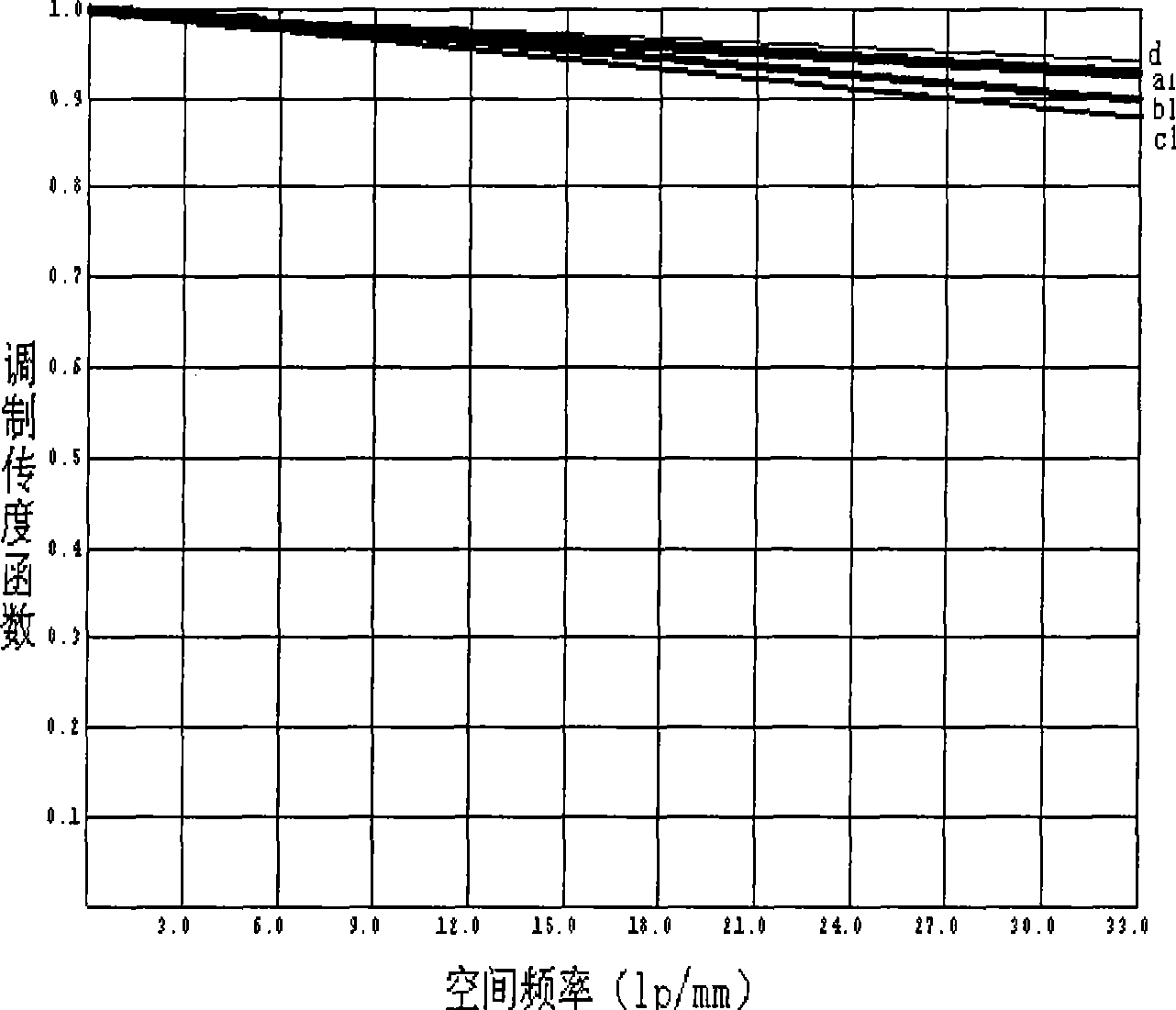
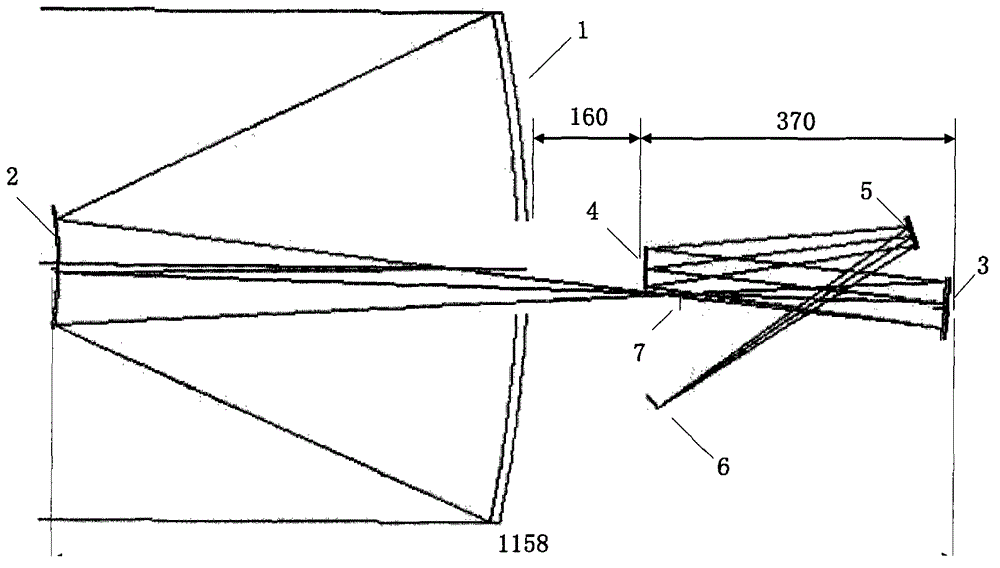
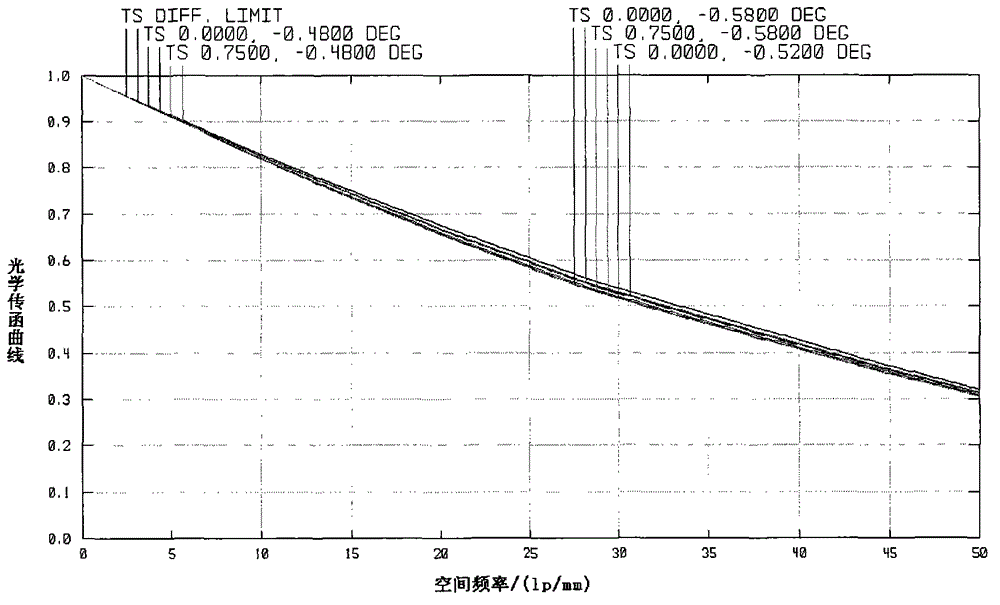
Large view field off-axis three-reflector system and adjusting method
ActiveCN105242387ASimple structureReduce the difficulty of assembly and adjustmentOptical elementsHyperboloidSystems design
The invention relates to a large view field off-axis three-reflector system and an adjusting method. The large view field off-axis three-reflector system comprises a main mirror, a secondary mirror, an aperture diaphragm, a third mirror and a focal plane. The main mirror is an off-axis hyperboloid reflector; the secondary mirror is a protruding spherical surface reflection mirror; the third mirror is an off-axis secondary recessed flat spherical mirror; the master axes of the master mirror and the third mirror are superposed as a reference axis; the aperture diaphragm is successively arranged on the secondary mirror; the optical axis of the secondary mirror is superposed with the master axis of the third mirror; a target light ray from infinity enters the secondary mirror after reflection of the main mirror and enters the third mirror through the reflection of the secondary mirror; and then the light ray is imaged on the focal surface. The invention solves the contradiction between the large view field off-axis three-reflector system, the processing and adjusting. The large view field off-axis three-reflector system adopts a simple structure and can realize the wide width imaging, wherein the effective view field reaches 12 degree*3.5 degree.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Bi-polymer infrared optics for high-g applications
ActiveUS20130208367A1Low costSacrificing optical qualityMirrorsDirection controllersCamera lensHigh acceleration
Optical systems configured to withstand operation in high acceleration and varying temperature environments, and methods of assembling the same. In one example, an imaging optical apparatus includes a primary minor made of an unreinforced polymer, a secondary mirror made of the unreinforced polymer and optically coupled to the primary minor, a field lens optically coupled to the secondary minor, and a strut having a plurality of cross-struts and mounting features configured to mount the primary minor, the secondary mirror and the field lens. In some examples, the imaging optical apparatus further includes an outer retainer disposed behind the primary minor and coupled to the strut, and an inner retainer disposed behind the field lens and coupled to the strut, the outer and inner retainers configured to structurally support the primary minor and the field lens and to accommodate deflections of the primary minor.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Compact catadioptric long-wave infrared athermal imaging optical system
InactiveCN102520506AAchieve long focal length imagingCompact structureOptical elementsMangin mirrorLight beam
The invention relates to a compact catadioptric long-wave infrared athermal imaging optical system, which comprises a secondary lens, a primary reflective lens and a relay lens. The secondary lens is a catadioptric optical component with negative focal power and comprises an annular light transmission part and a central Mangin mirror; a light beam from an object is transmitted into the primary reflective lens through the annular light transmission part of the secondary lens and is then transmitted into the Mangin mirror of the secondary lens after reflection by the primary reflective lens, and catadioptric focusing is carried out by the Mangin mirror so that the target is imaged on a first image plane; the target on the first image plane is then transferred by the relay lens and focuses again on a second image plane; and the second image plane is overlapped with the focal plane of an image receiver. Image of long focal length can be realized, and the system has a compact structure and a large view field and can be applied in the optical imaging field of aviation and aerospace.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multi-light axis consistency test device based on multiband target plate and rotating reflection mirror
InactiveCN101319884ARealize dynamic testingImprove test accuracyUsing optical meansTesting optical propertiesPlane mirrorOptical fiber coupler
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Common axis three mirror anastigmatic optic
A three mirror anastigmatic optic (and corresponding method of making) comprising a primary mirror, a secondary mirror, a tertiary mirror, and a vertex common to the primary and tertiary mirrors.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Laser radar emission and receiving light path parallel regulating system and method
InactiveCN101216558AAvoid damageGuaranteed parallelWave based measurement systemsRadar systemsOptical axis
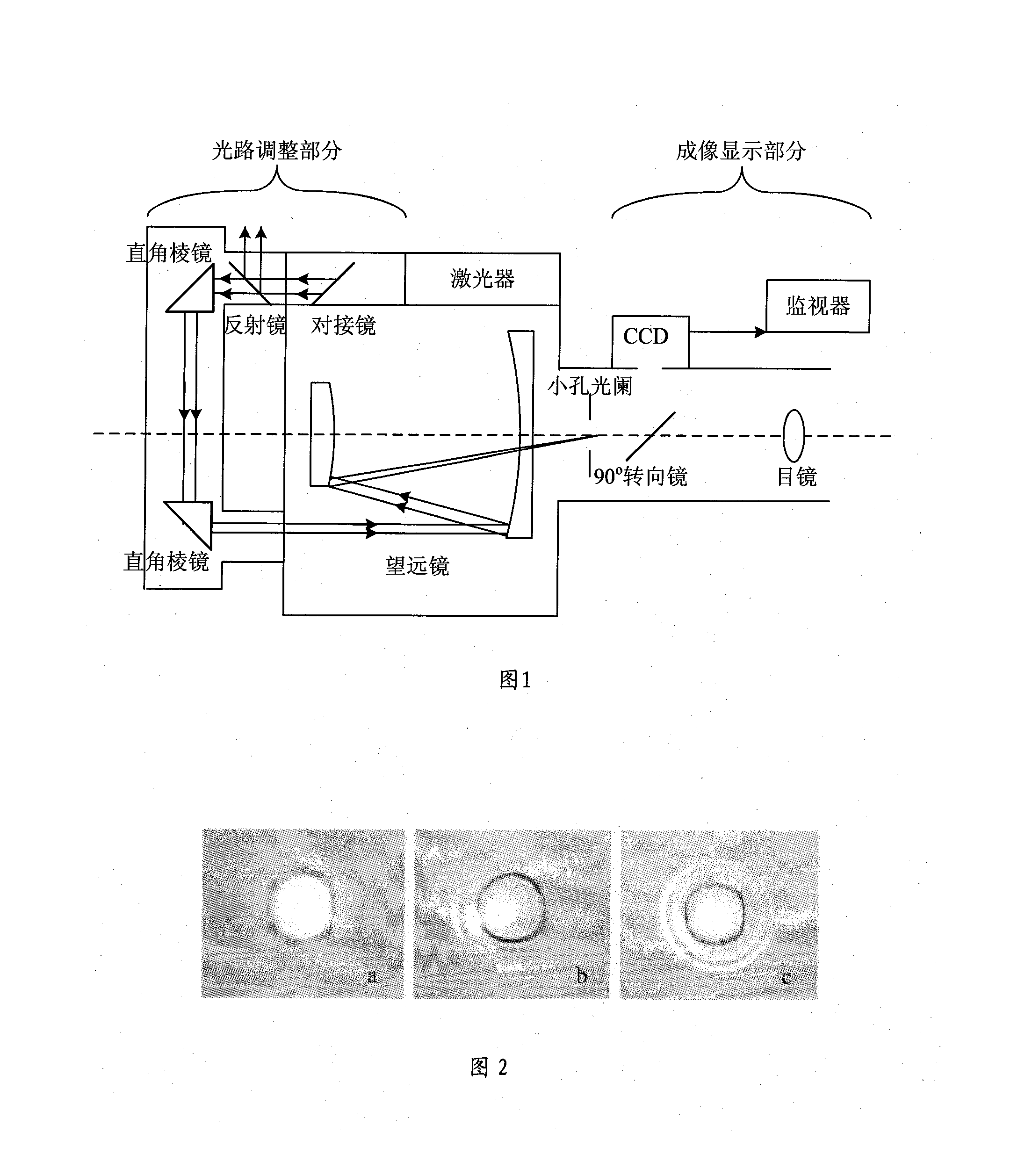
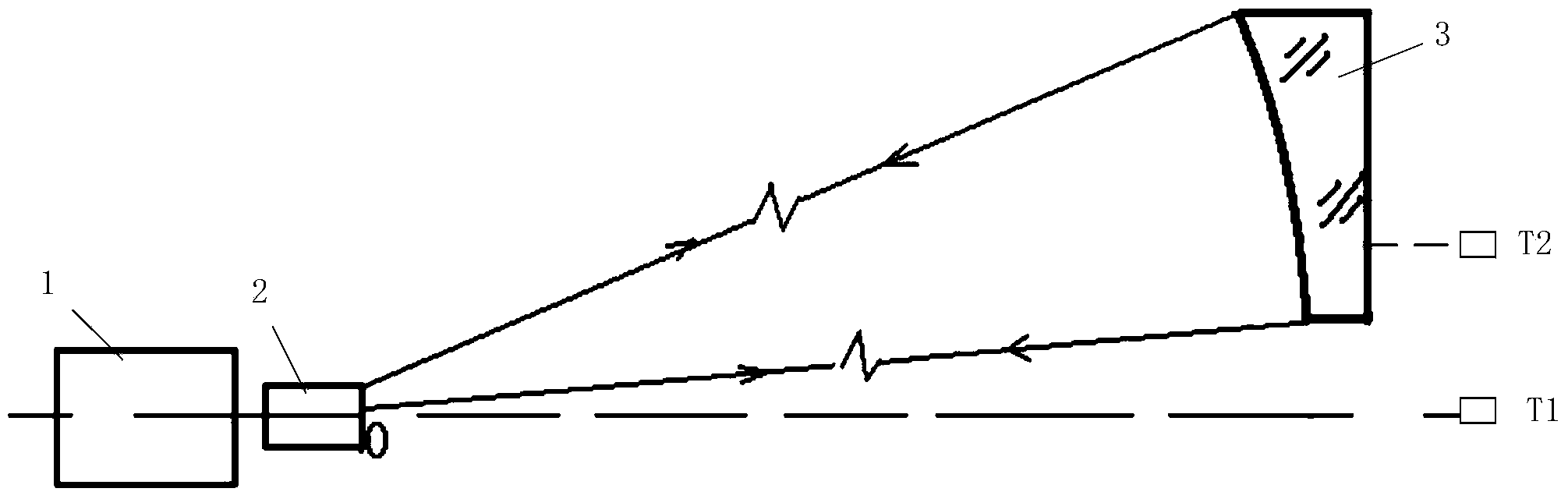
The invention discloses a parallel adjustment system of emission and receiving light paths of laser radar and a method. The system comprises a laser fixedly arranged on the tube of a receiving telescope and having the direction of the emission light parallel to the optical axis direction of the telescope, and a connection mirror, a total reflection mirror and an angle reflector consisting of a pair of right-angle prisms arranged in front of the tube of the receiving telescope, which are arranged in the optical path in front of the laser. The laser beam emitted from the angle reflector enters the tube of the receiving telescope and focuses on a combined focal plane of the primary mirror and the secondary mirror of receiving telescope. The focusi laser spot forms an image on a CCD after turning the direction through a 90-DEG turning mirror, and the clear laser spot image can be viewed on a monitor. The parallelism of the optical paths can be determined and adjusted according to the shape of the laser spot. The invention has the advantages of simple structure and higher accuracy, and has been successfully applied in developed laser radar system.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Initial assembly positioning method for four off-axis lenses
Disclosed is an initial assembly positioning method for four off-axis lenses. The four off-axis lenses include the main mirror, the secondary mirror, the third mirror and the plane mirror, wherein the main mirror and the third mirror are off-axis aspheric mirrors. A zero compensator is utilized for calibrating the direction of the optical axes of the off-axis mirrors. The reference is provided for adjusting the space positions of the mirrors through four-rod positioning. Initial assembly positioning of the mirror assembly is achieved through multi-theodolite networking. According to the initial assembly positioning method for the four off-axis lenses, by the combination of the optical axis introduction and four-rod positioning technology, the certain precision of the initial assembly of the four off-axis lenses is achieved, and a reasonable initial point is built for optical system computer-assisted adjustment.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF SPATIAL MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH
Variable range millimeter wave method and system
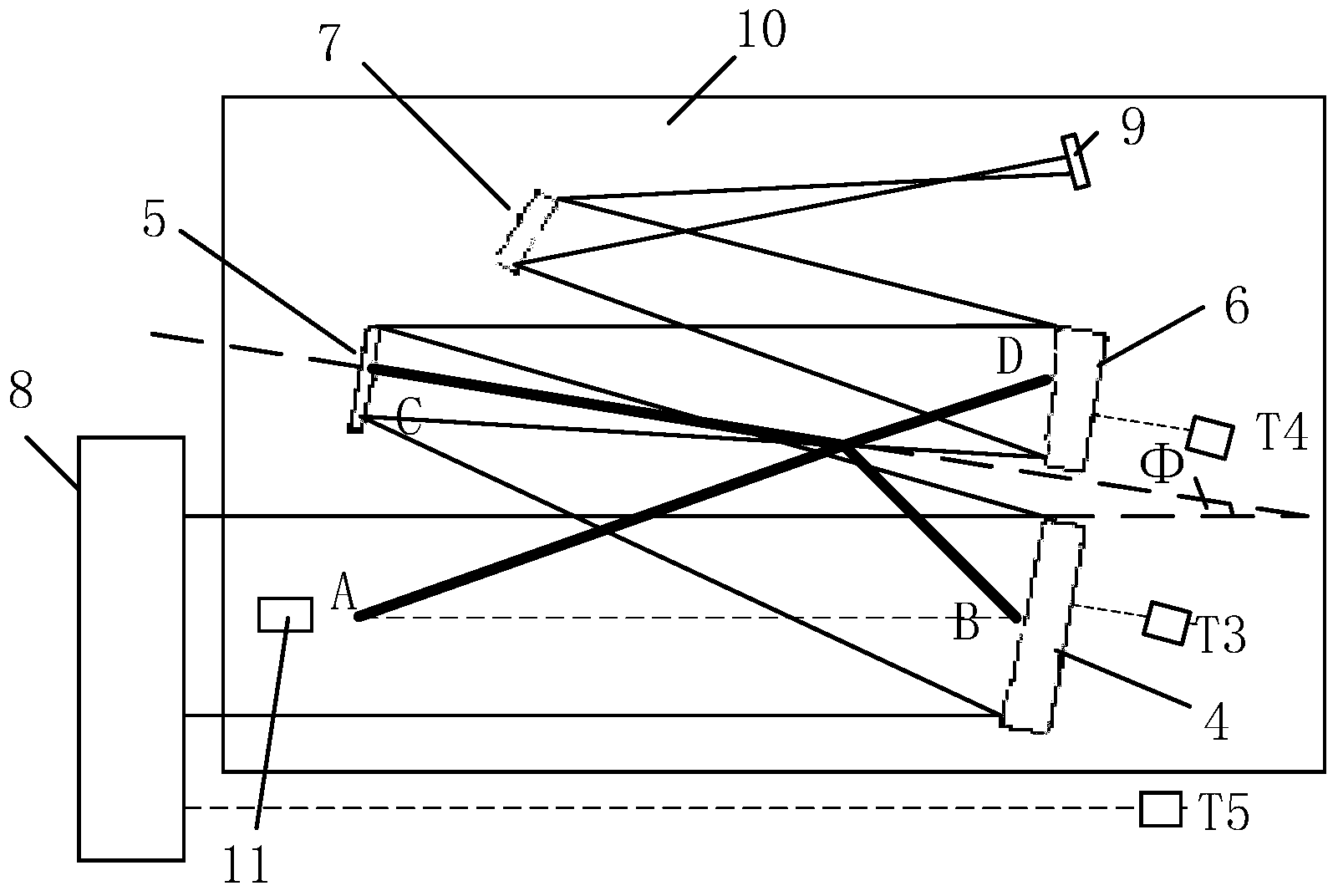
InactiveUS20110084868A1Eliminate legal concernImage processing can be alteredRadio wave reradiation/reflectionMillimetre waveVideo image
A variable range millimeter wave method and system is disclosed. In a particular embodiment, the system includes a primary mirror having an aperture to reflect millimeter wave energy to a secondary mirror, where the secondary mirror is disposed in front of the primary mirror and adapted to redirect the millimeter wave energy to a millimeter wave sensor / detector of a millimeter wave camera. The millimeter wave camera is configured to process the millimeter wave energy to visually detect concealed objects hidden on a target and an operating frequency of the millimeter wave camera is between 225 GHz and 275 GHz. In addition, the system includes a laser rangefinder, GPS and altimeter to determine a location of the target and to optimize a focus of the millimeter wave camera. A video monitor displays millimeter wave imagery and video images spatially and temporally relative to the millimeter wave imagery to aid targeting.
Owner:MICROSEMI
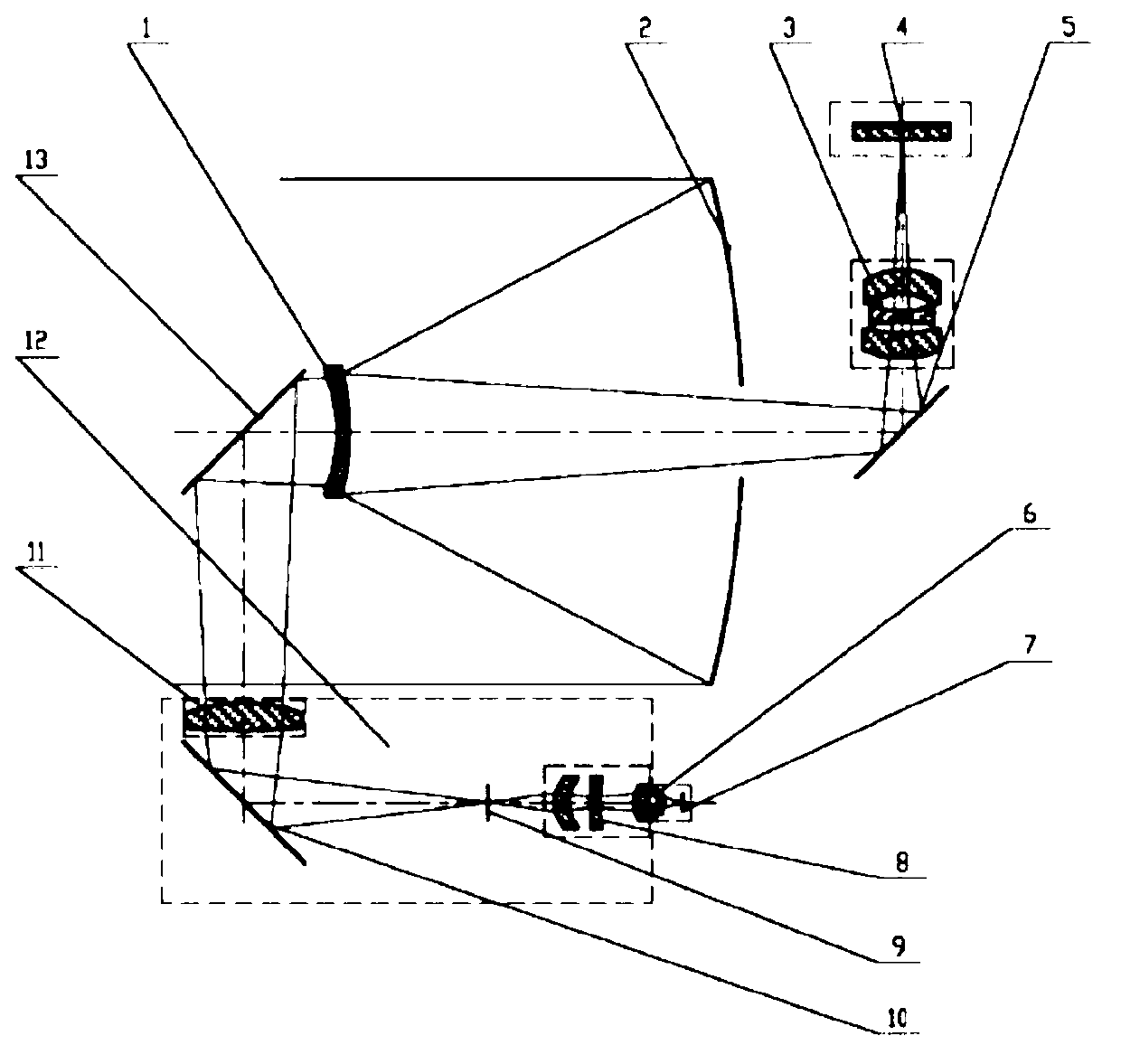
Catadioptric hybrid multispectral imaging system
InactiveCN102116673AImprove transmittanceSave spaceRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationBeam splitterImaging quality
The invention discloses a catadioptric hybrid multispectral imaging system, which comprises a primary mirror, a catadioptric dual-purpose secondary mirror, a wedge-shaped dichroic beam splitter, a medium wave or long wave infrared or medium-long wave infrared dual-waveband imaging mirror assembly, a medium wave or long wave infrared or medium-long wave infrared dichroic detector unit, a visible to near infrared waveband imaging mirror assembly, a visible to near infrared waveband beam splitting device and a detection unit thereof, a short wave infrared waveband imaging mirror assembly, and a short wave infrared waveband beam splitting device and a detection unit thereof, wherein a hole is formed at the center of the primary mirror, and the reflecting surface of the primary mirror is a concave surface; and the incident surface of the catadioptric dual-purpose secondary mirror is a convex surface. The system can realize imaging with common field of view and common aperture of a same object, improve the utilization rate of light energy, save space for the beam splitter and the system, prevent parasitic light from directly leaking into the imaging mirror assembly from the hole formed on the primary mirror, correct asymmetric aberration, be more conductive to realizing large aperture and the larger field of view and significantly improve the imaging quality. The imaging with the same optical axis and the common field of view can enable an image to be easy to register.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF SPATIAL MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH +1
Non-barrier three-reflector optical system
InactiveCN101435913AHas rotational symmetryReduce free variableOptical elementsImaging qualityUltraviolet
The invention discloses an unshielded three-reflector optical system, which can be used in a wide spectral imaging system with wave band from ultraviolet to infrared, and is particularly applicable to a preposed object lens of a spectrum imager. The system consists of a main reflector, a secondary reflector and a third reflector with aperture ratio of 1 / 0.5-1 / 3; the system avoids shielding through inclining elements; a beam path of the system is telecentric beam path in the image side; a principle ray of zero field coverage is spread along links of the vertex of each element; a diaphragm is arranged on the secondary reflector; the secondary reflector is arranged on a focal plane of the third reflector; focal power of the main reflector, the secondary reflector and the third reflector is positive, negative and positive respectively; curvature radiuses of the vertexes of the three reflectors approximately meet the condition of Petzval; and types of the three reflectors are Zernike free surfaces. The system has reasonable residual aberration distribution to greatly improve image quality, and can easily avoid shielding, so that the effective use area of each mirror face is equivalent to an original mirror; and the primary ray of the zero field coverage of the system moves along the links of the vertex of each surface, thereby facilitating the processing, assembly and regulation of the system.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Coaxial four-reflector ultra-low distortion optical system
ActiveCN102866487ACompact structureImprove structural stabilityMirrorsPicture taking arrangementsLow distortionPlane mirror
The invention relates to a coaxial four-reflector ultra-low distortion optical system, which comprises a primary mirror, a secondary mirror, a third mirror, a fourth mirror, a plane mirror and a receiving image plane, wherein optical axes of the primary mirror, the secondary mirror, the third mirror, the fourth mirror and the plane mirror are in a same straight line; the plane mirror is located between the third mirror and the fourth mirror; the primary mirror and the secondary mirror constitute a classical R-C system and form a primary real image, which continues imaging when passing through the third mirror and the fourth mirror and deflects to the receiving image plane through the plane mirror; the primary mirror, the secondary mirror and the third mirror constitute a coaxial TMA system and assume most of focal power; the fourth mirror assumes smaller part of focal power, accounting for 10-20% of the total focal power, in the imaging of the optical system; and an aperture diaphragm of the optical system is located on the primary mirror and the fourth mirror is placed at an exit pupil of the system. The optical system of the invention can be used to realize high image quality, low distortion and high stability and greatly reduce the processing difficulty of a large-aperture primary mirror and is suitable for high-precision satellite-borne stereo mapping cameras.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF SPATIAL MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com