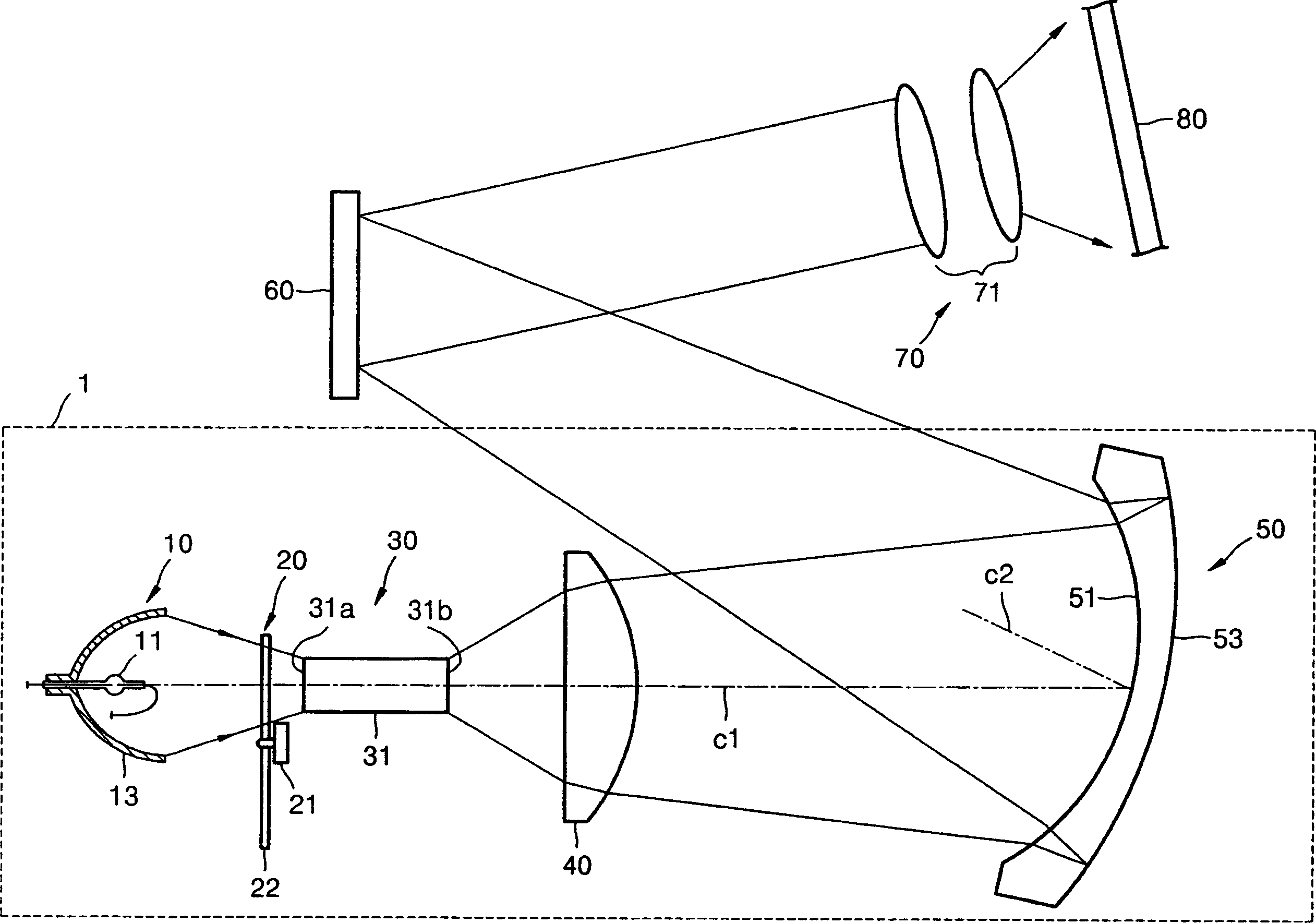
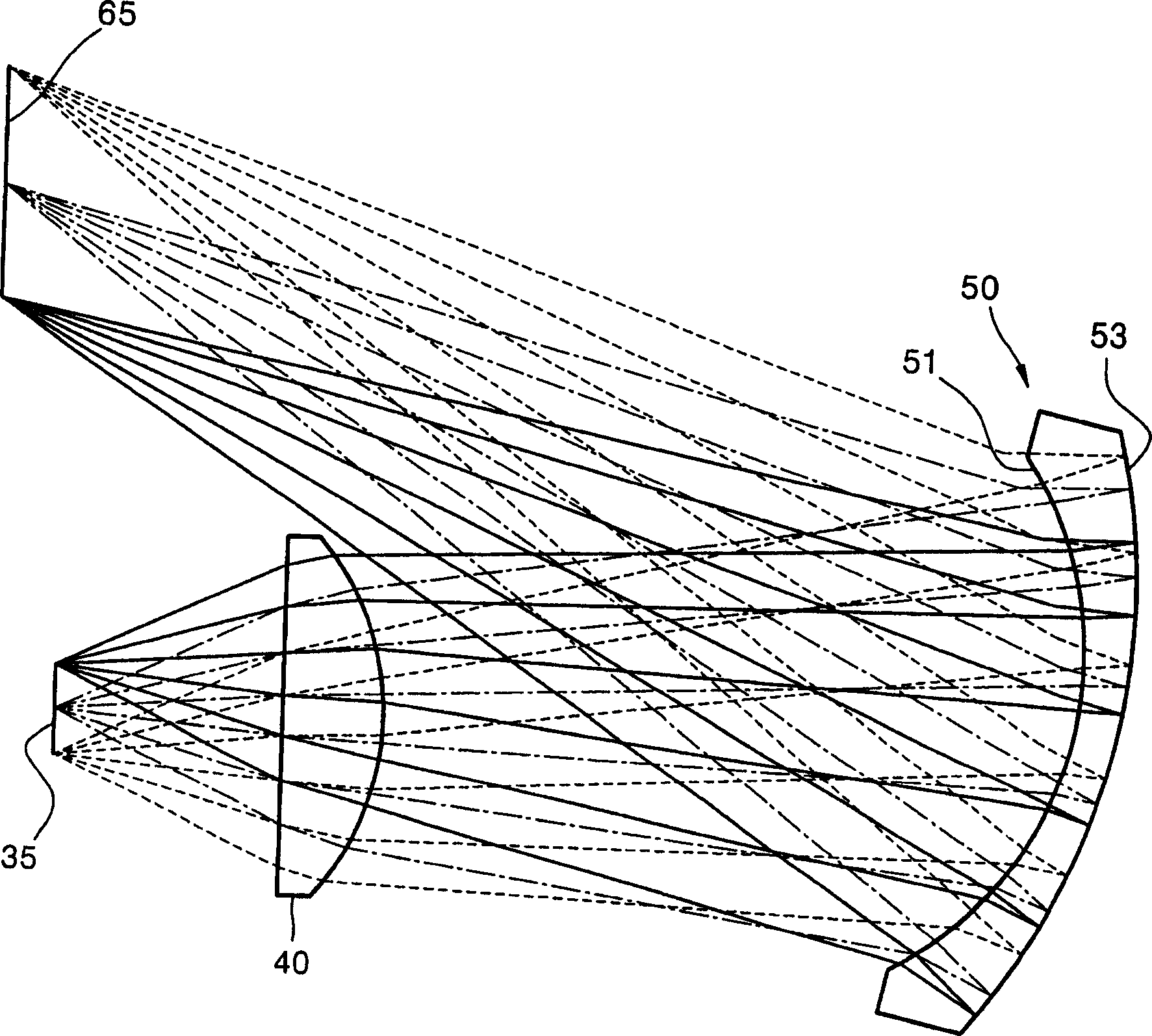
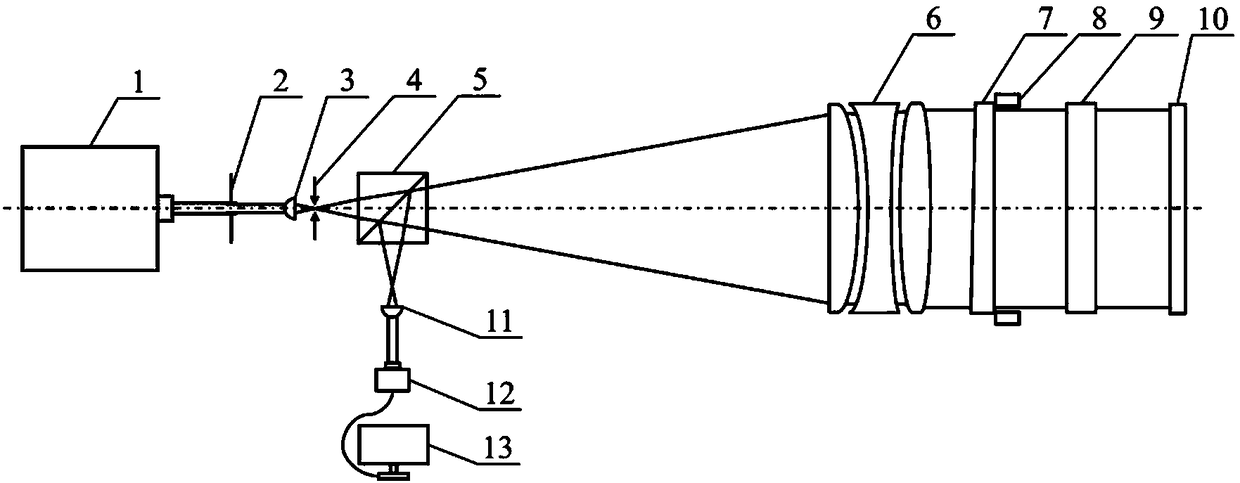
Patents
Literature
41 results about "Mangin mirror" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
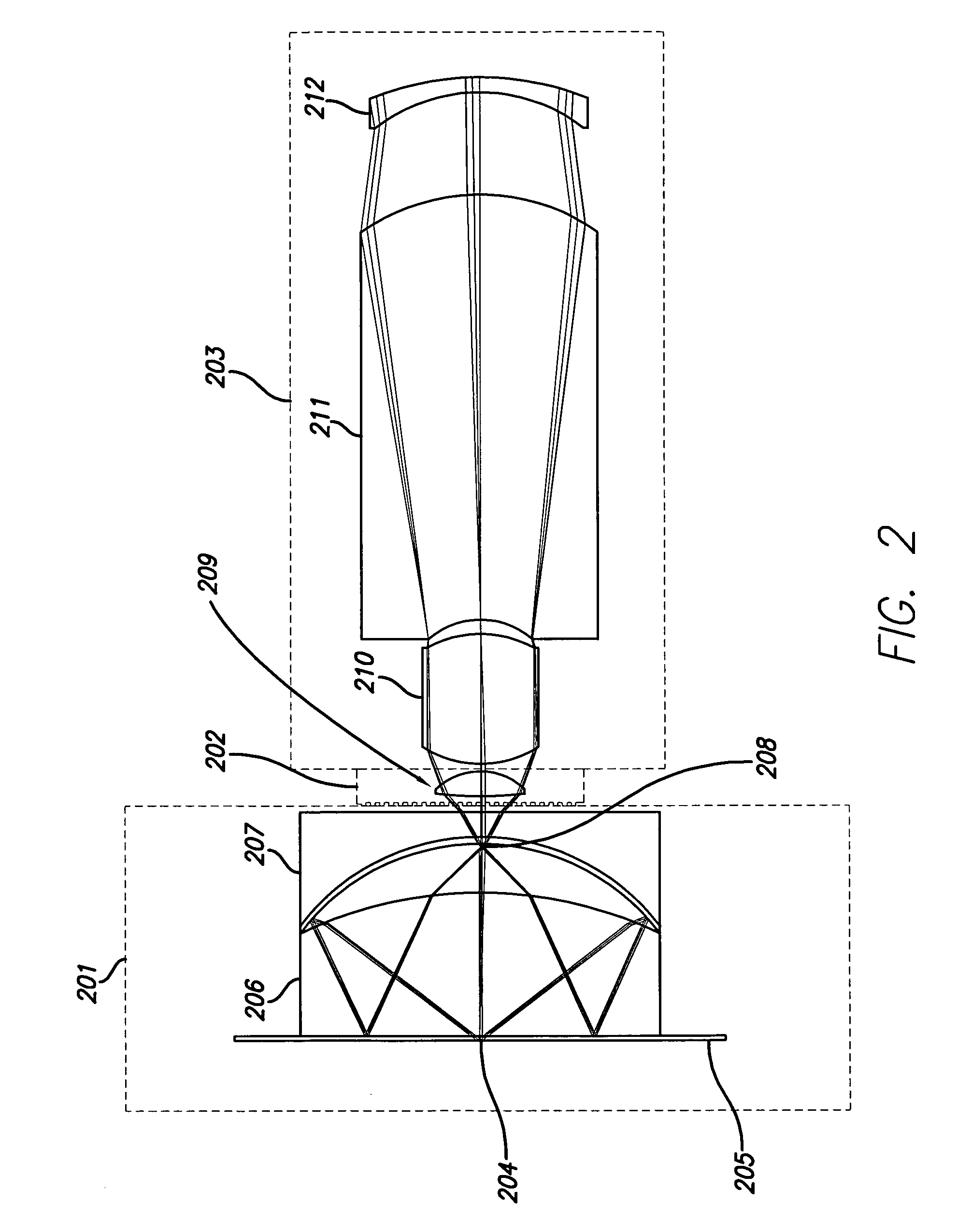
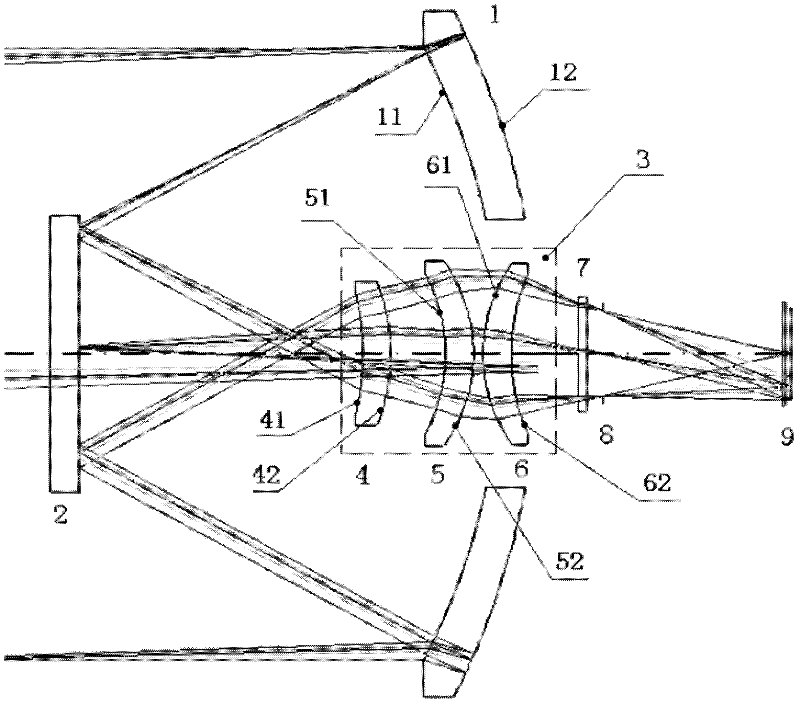
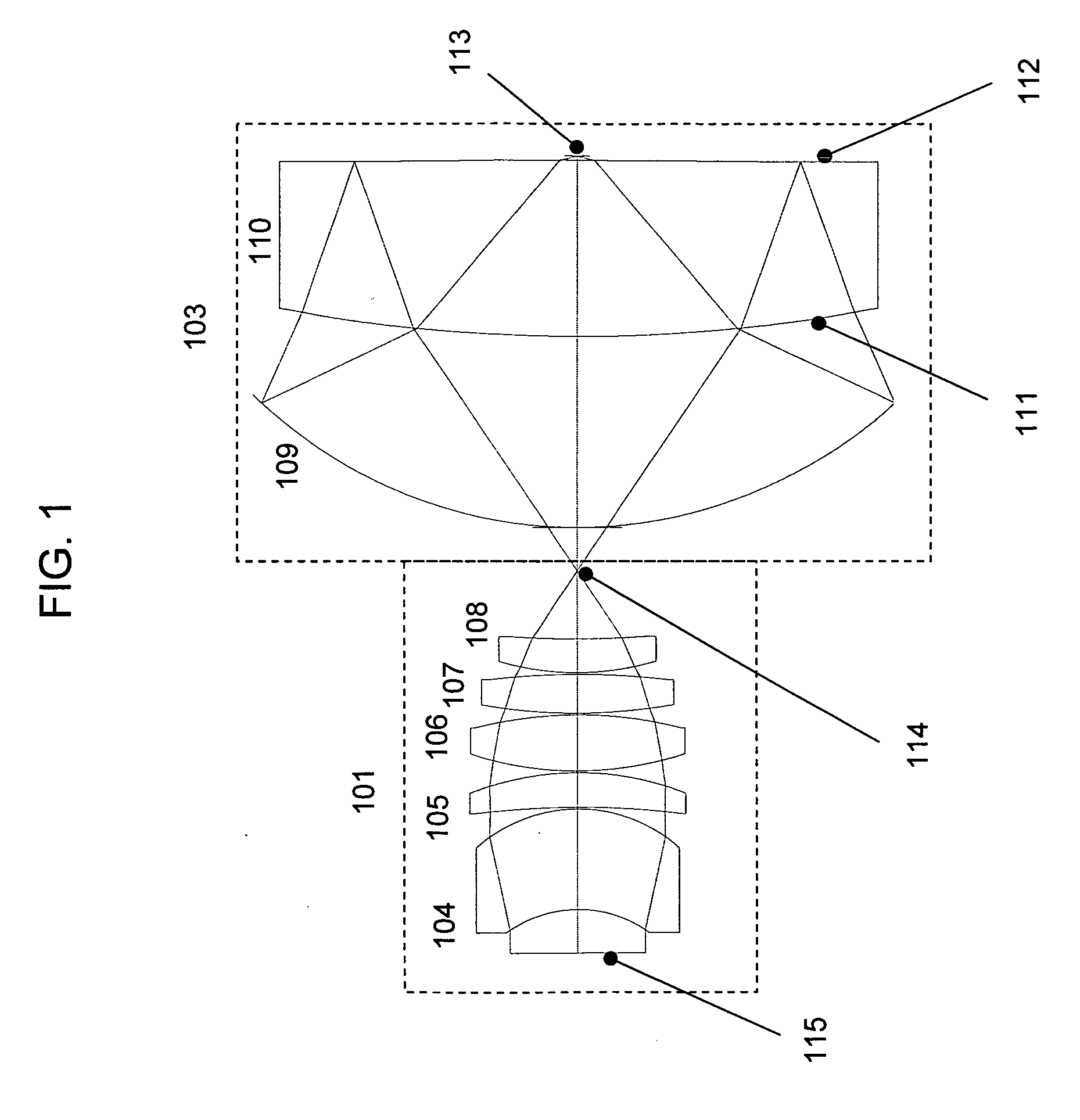
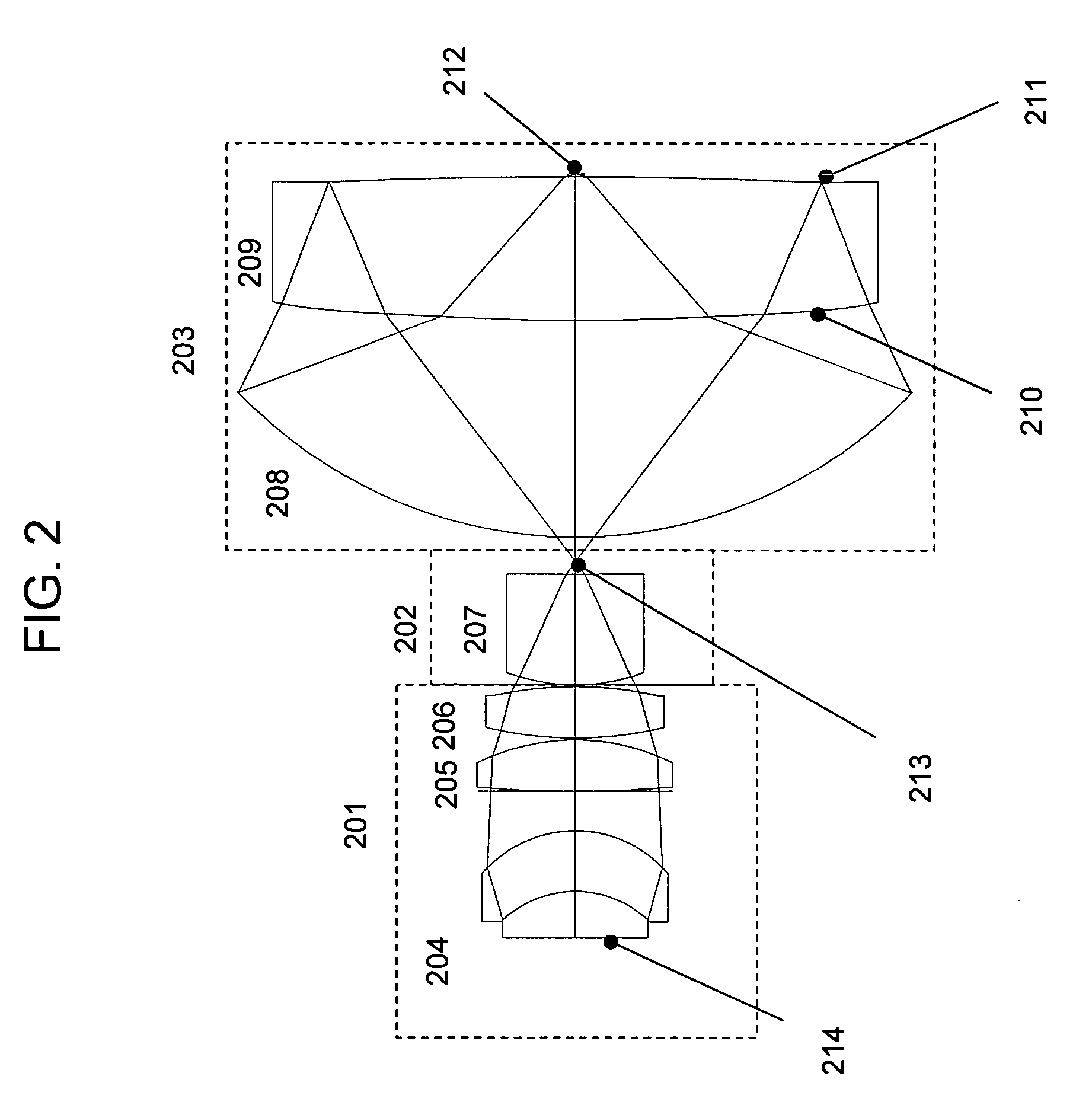
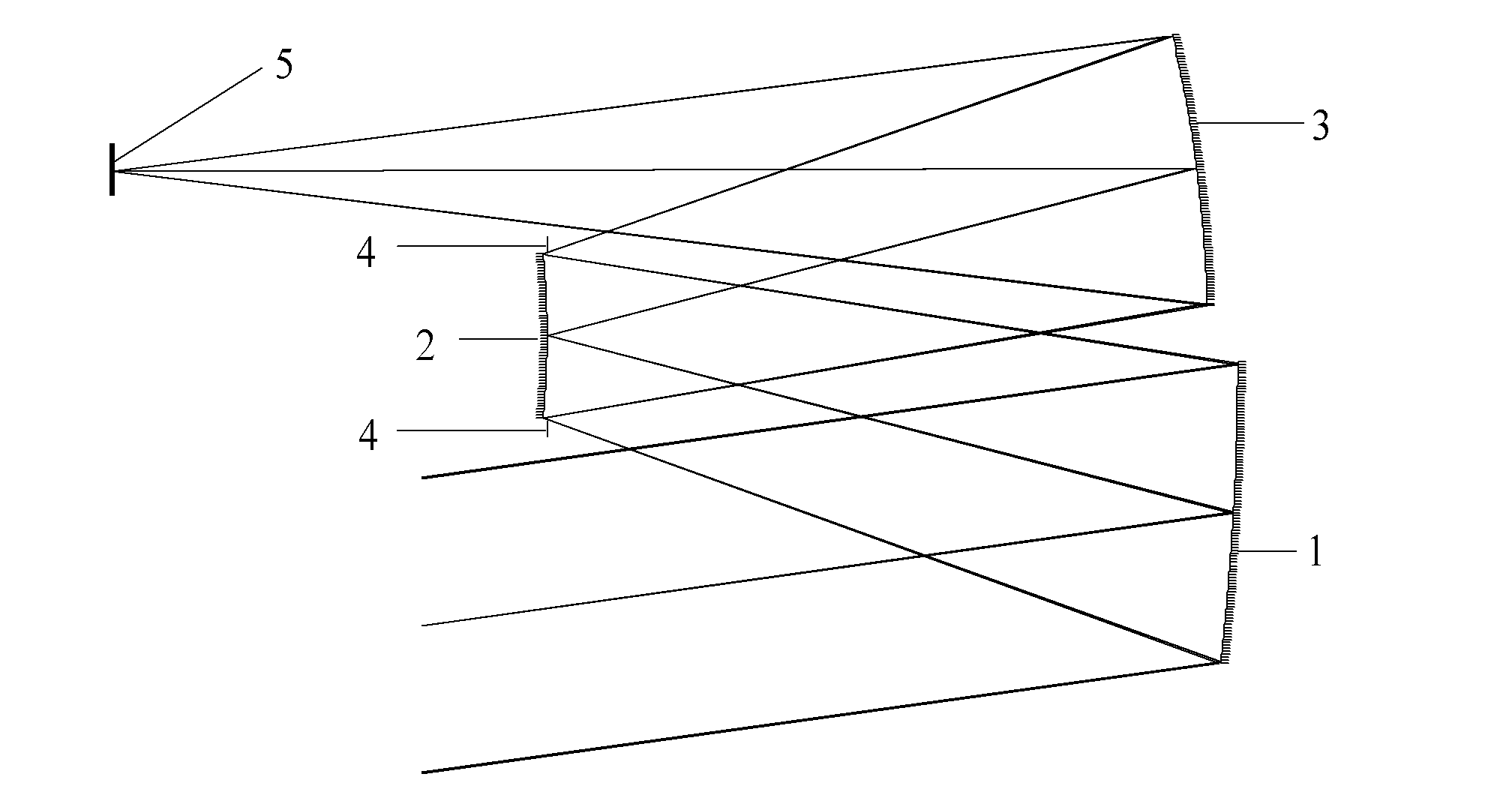
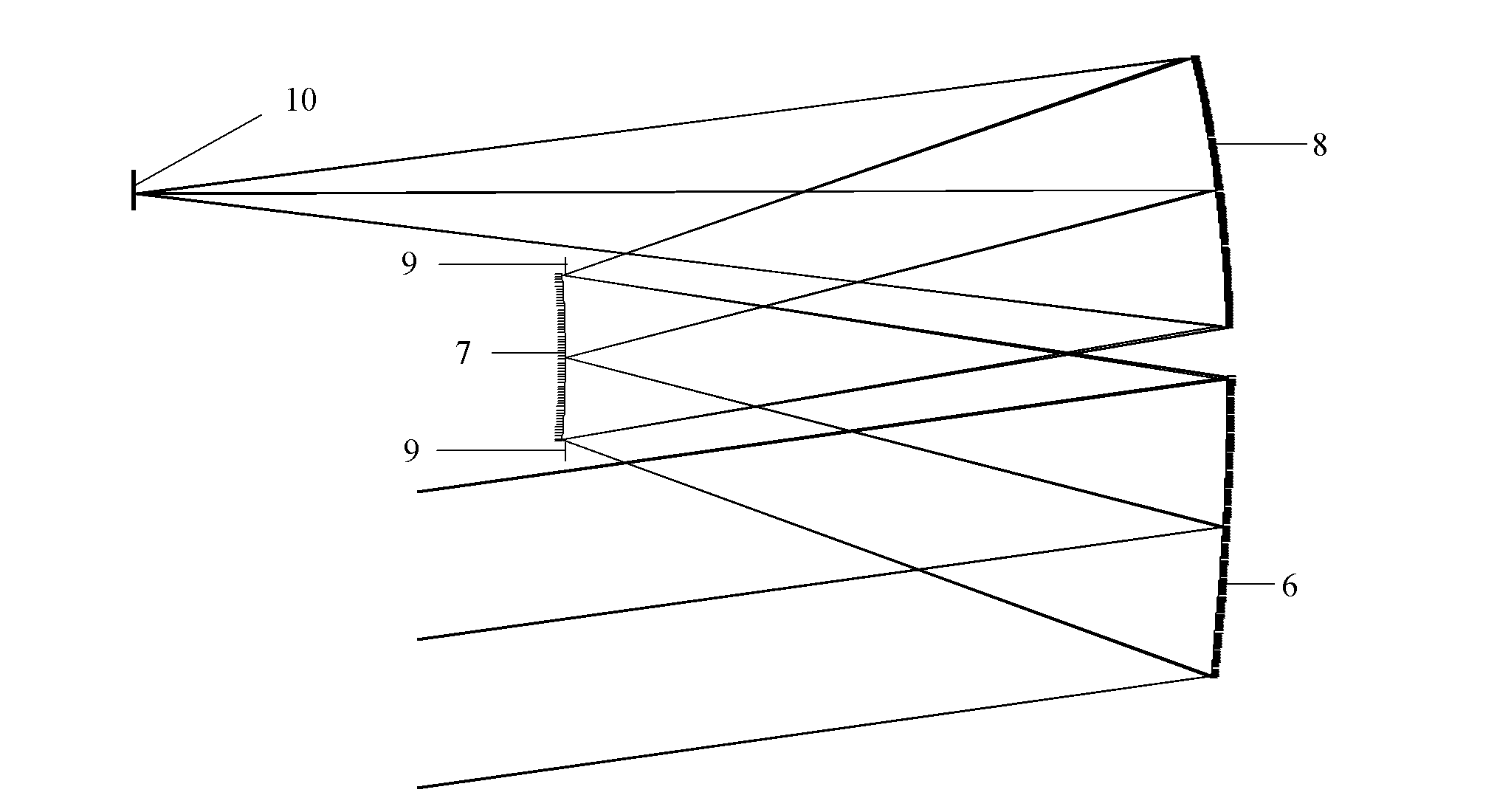
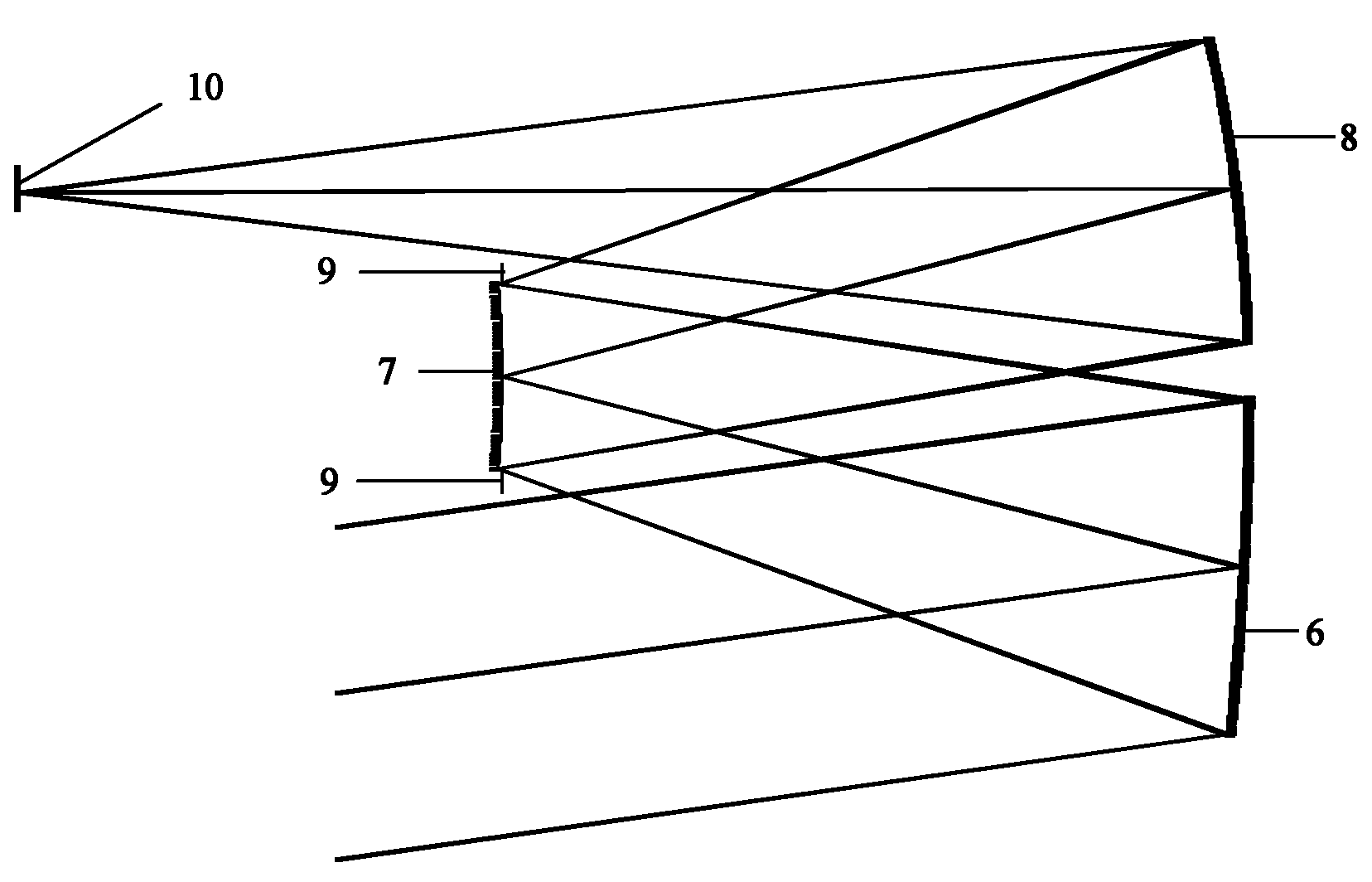
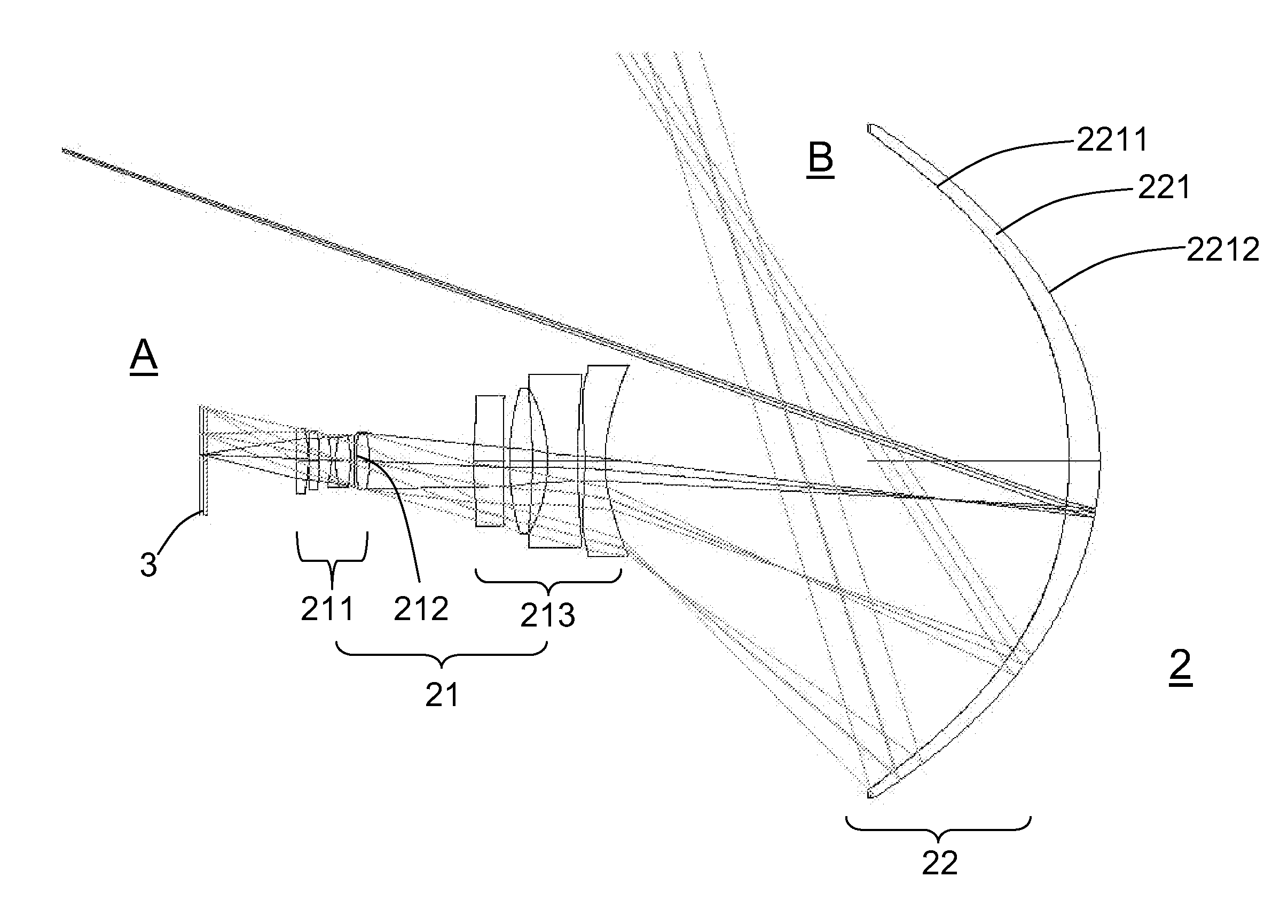
In optics, a Mangin mirror is a negative meniscus lens with the reflective surface on the rear side of the glass forming a curved mirror that reflects light without spherical aberration. This reflector was invented in 1876 by a French officer Alphonse Mangin as an improved catadioptric reflector for search lights and is also used in other optical devices.
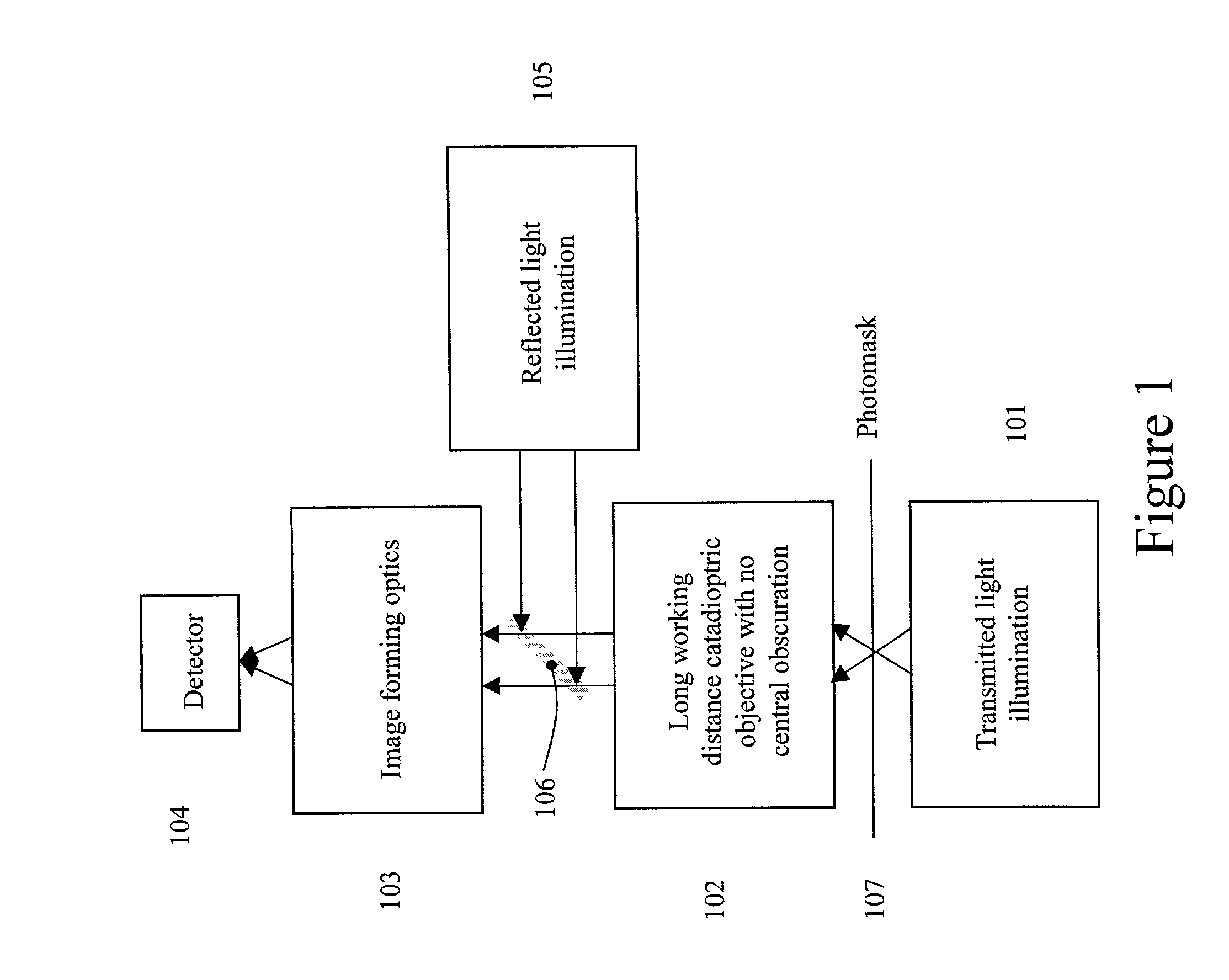
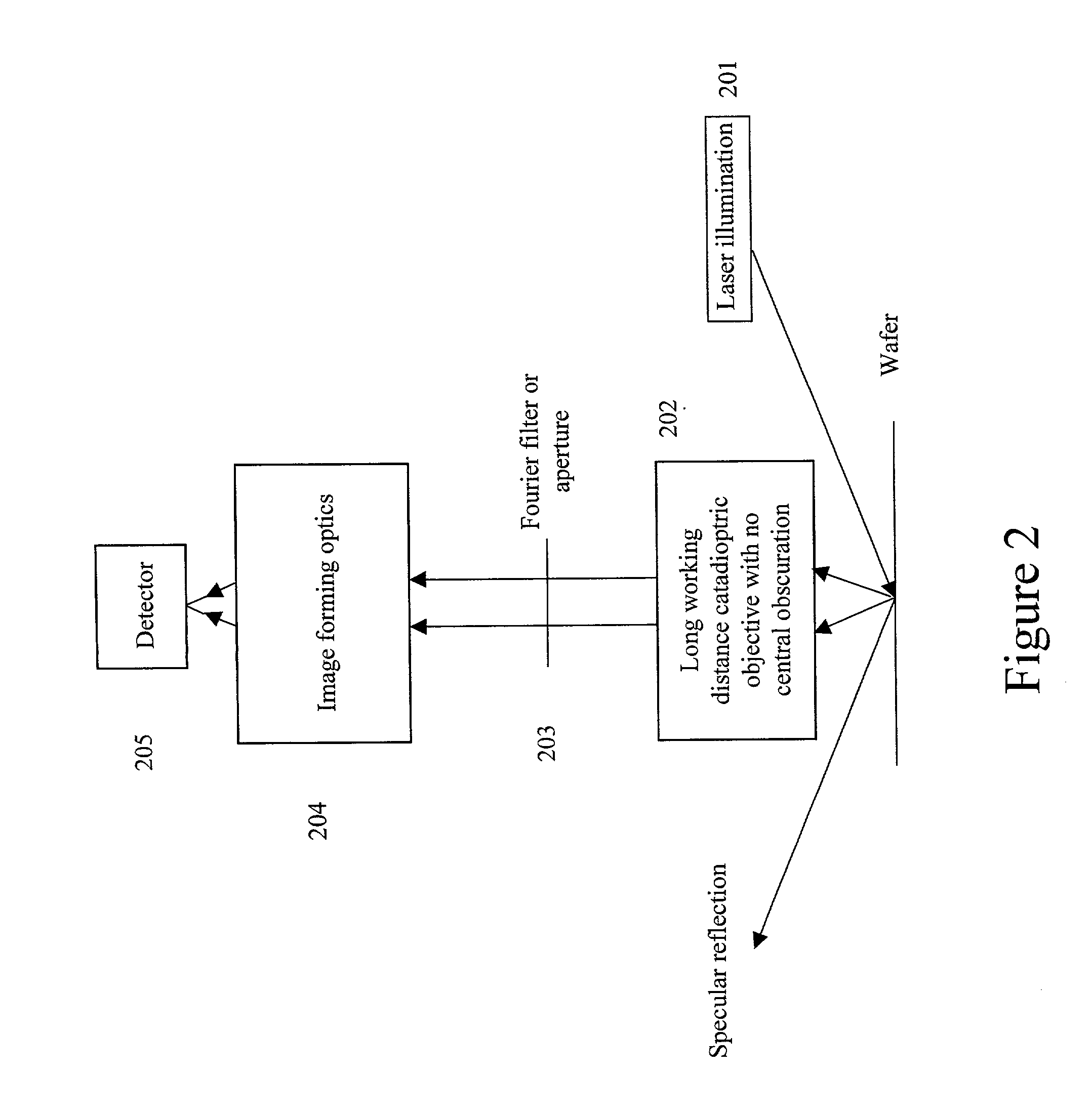
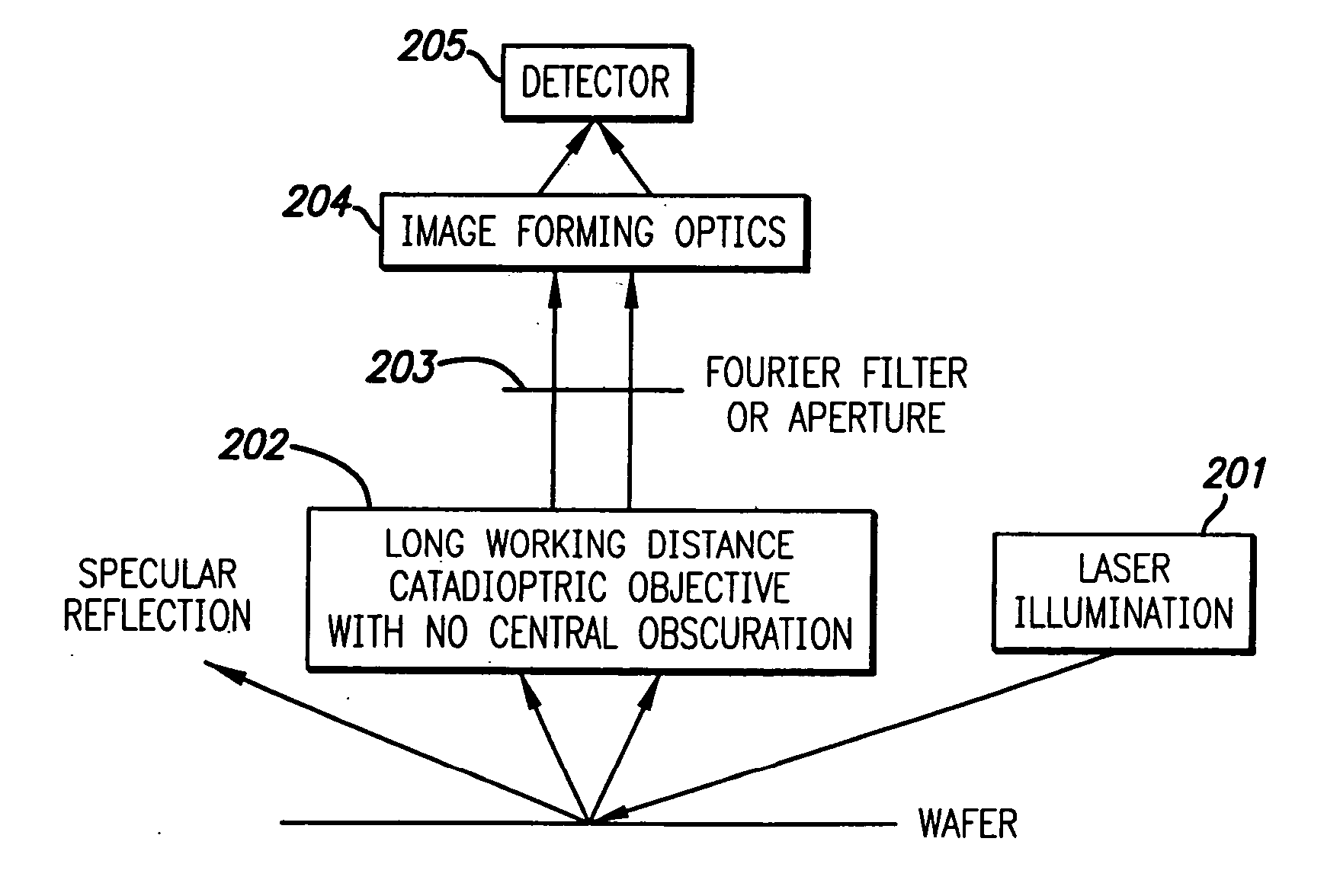
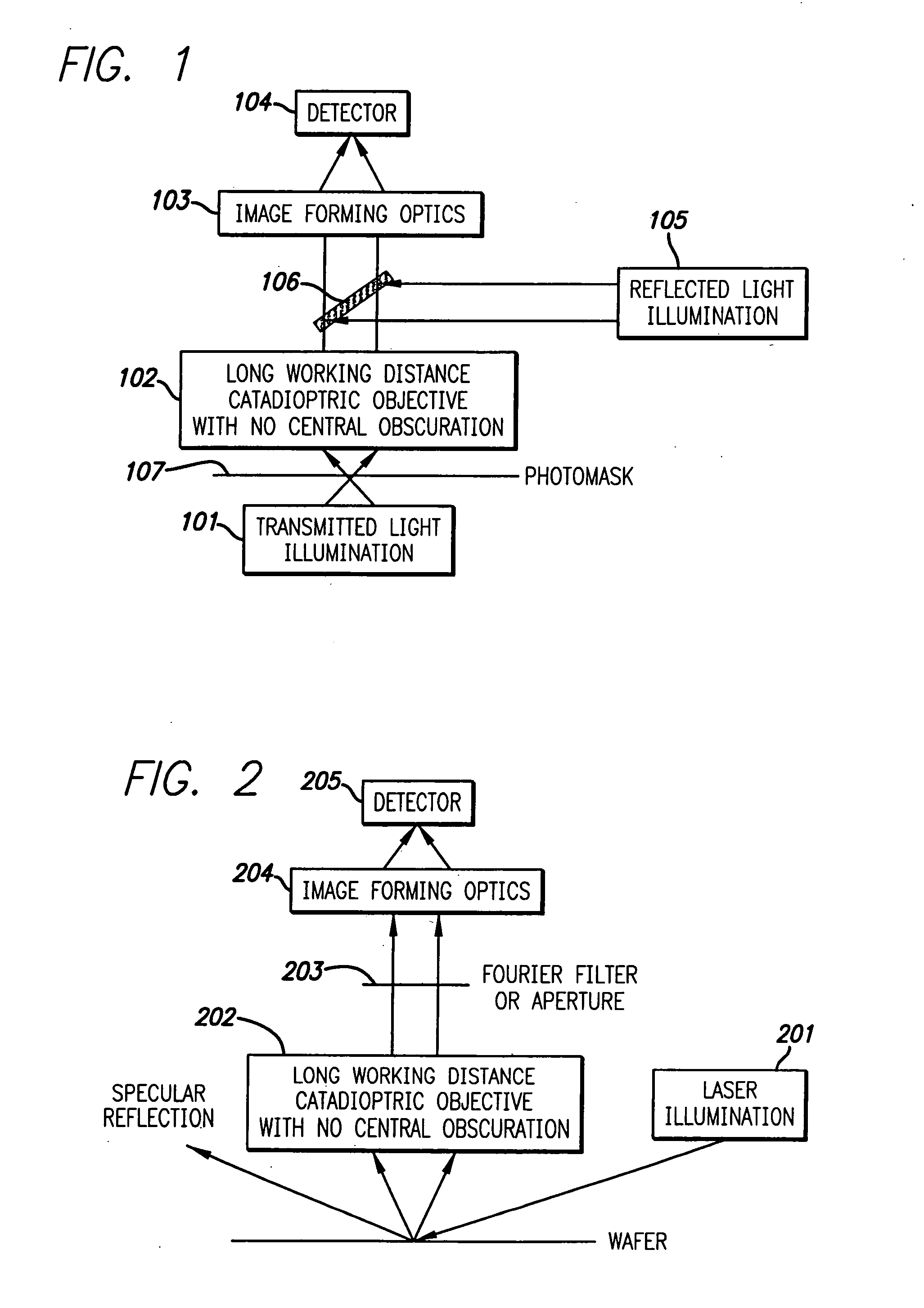
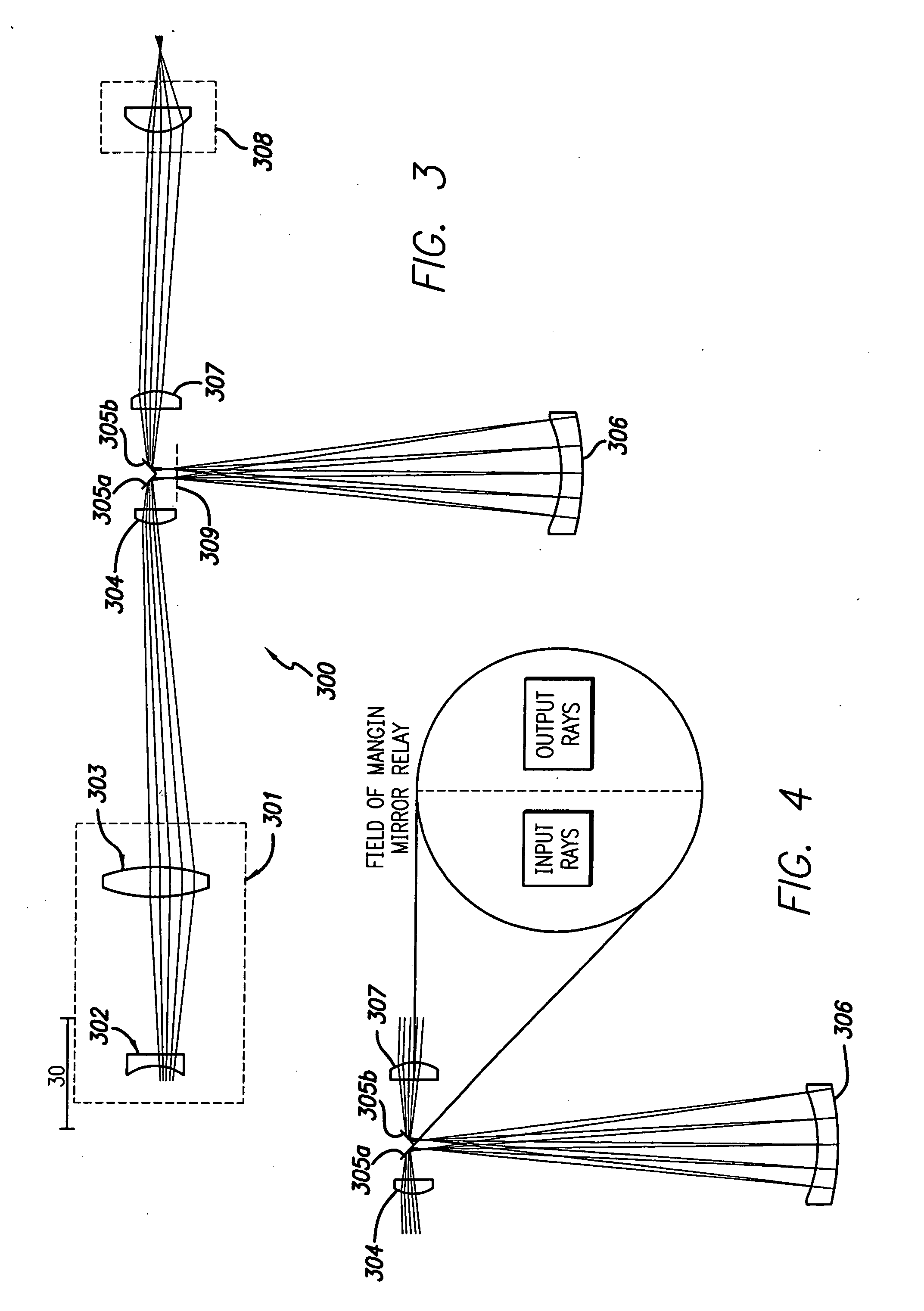
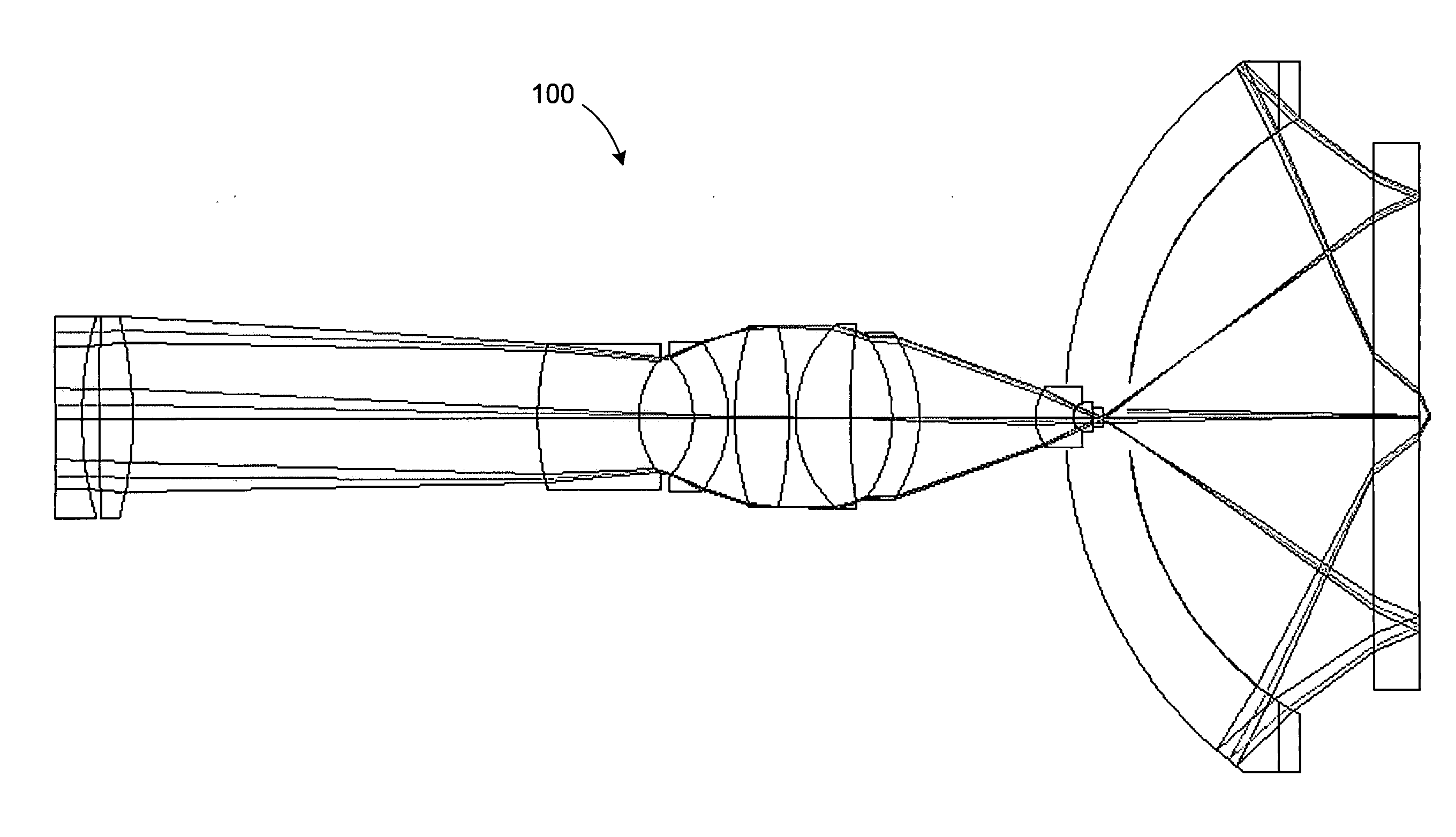
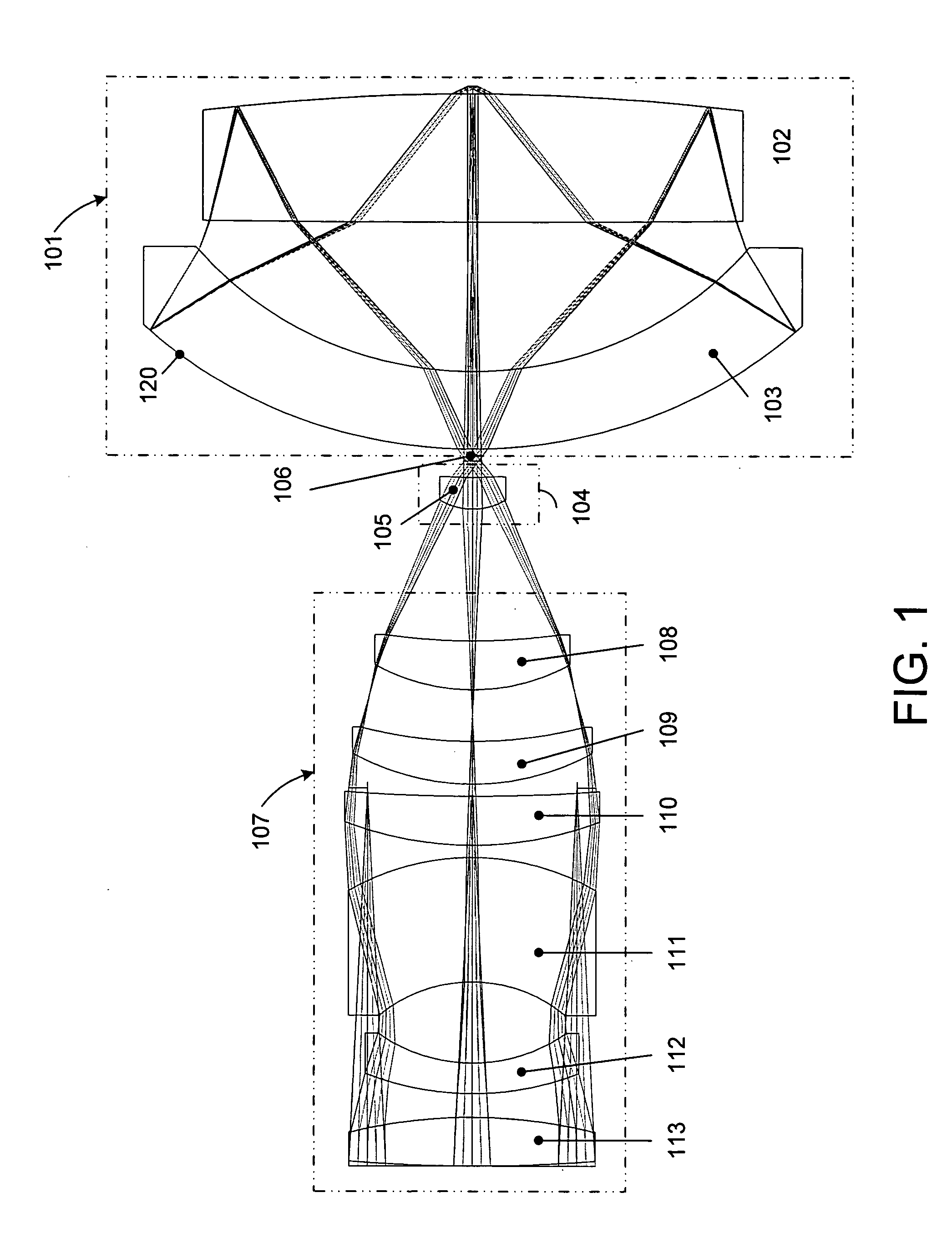
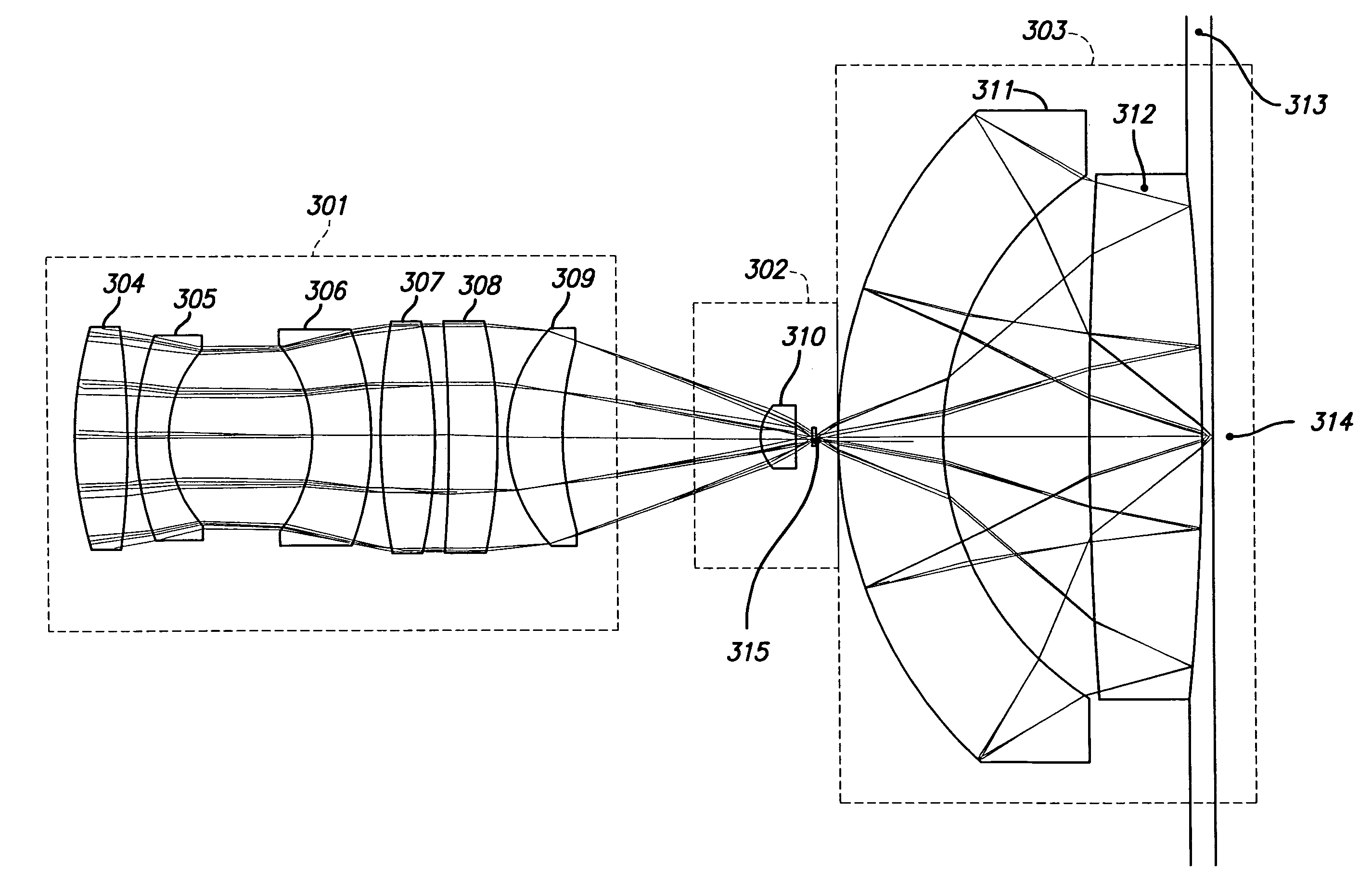
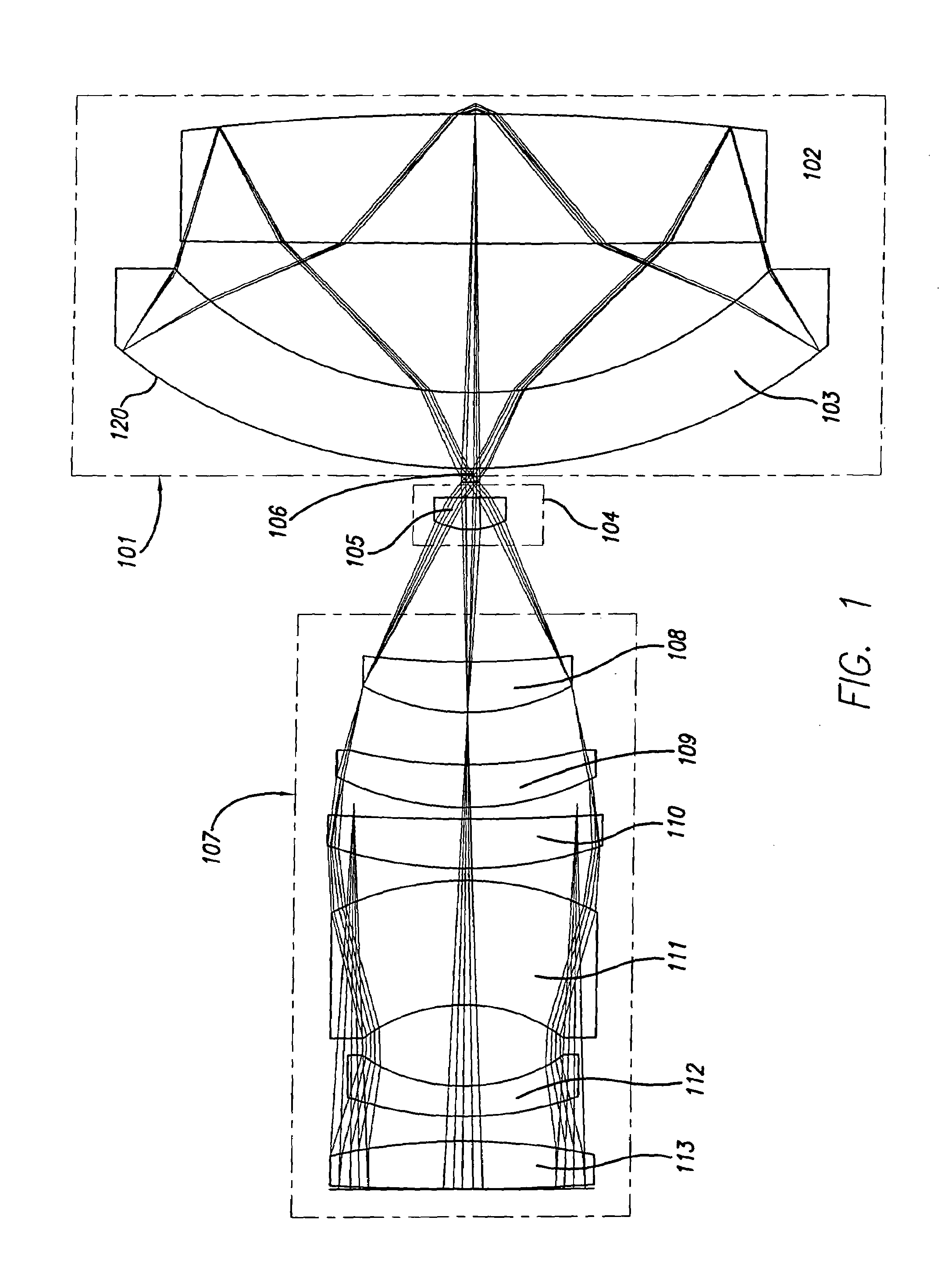
Broad band deep ultraviolet/vacuum ultraviolet catadioptric imaging system
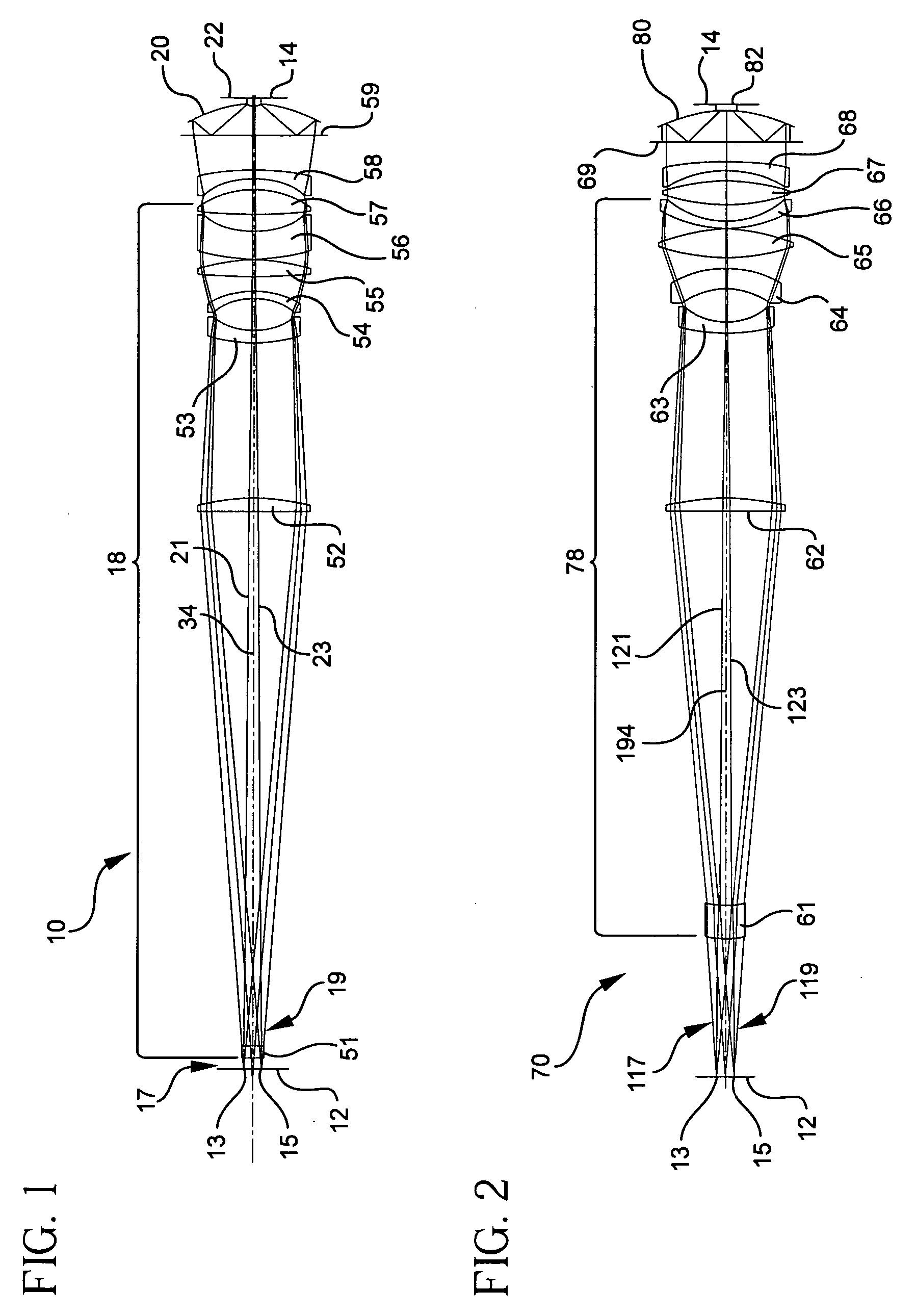
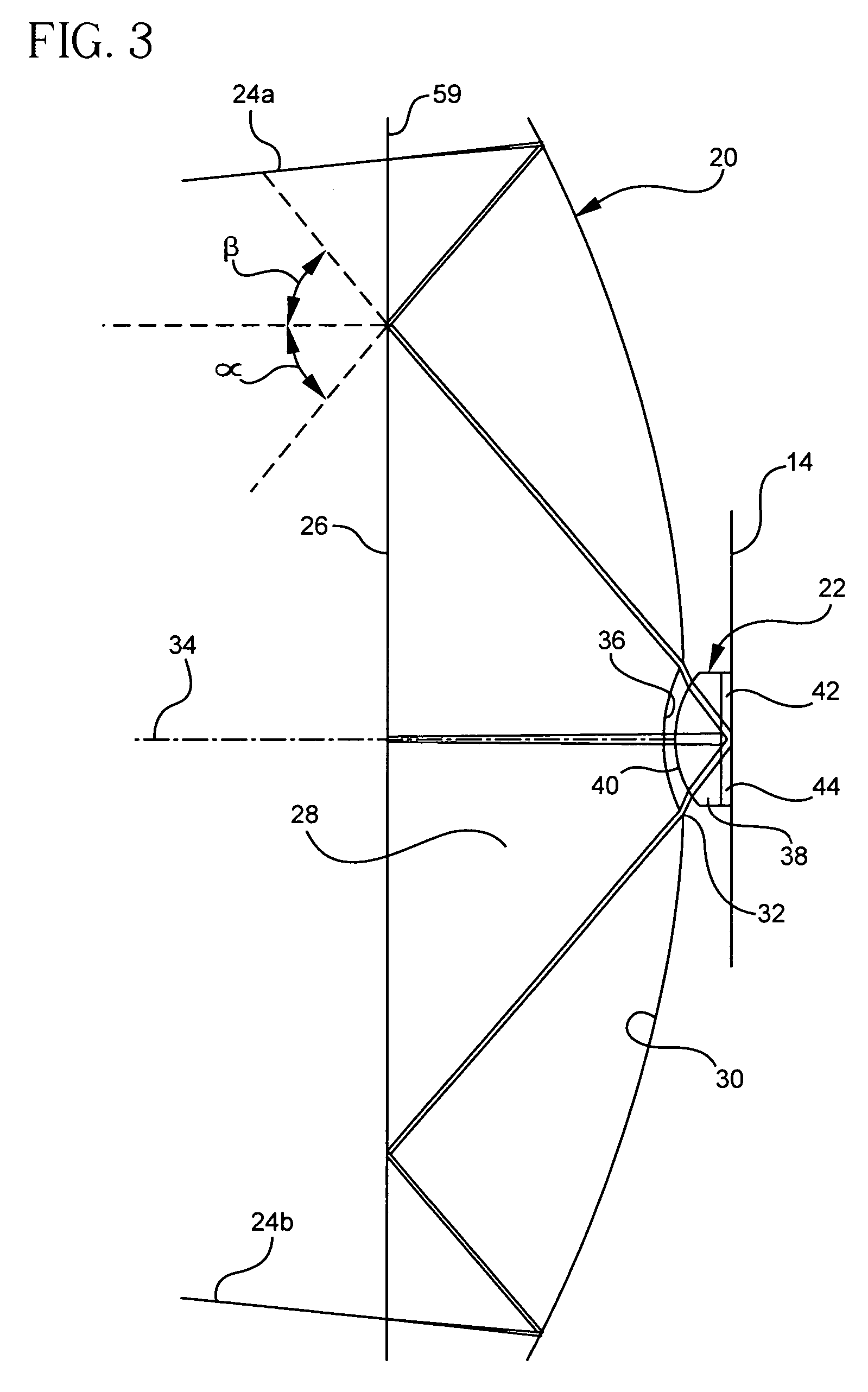
InactiveUS20010040722A1Increase spectral bandwidthRelaxed manufacturing toleranceMirrorsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementMangin mirrorUltraviolet
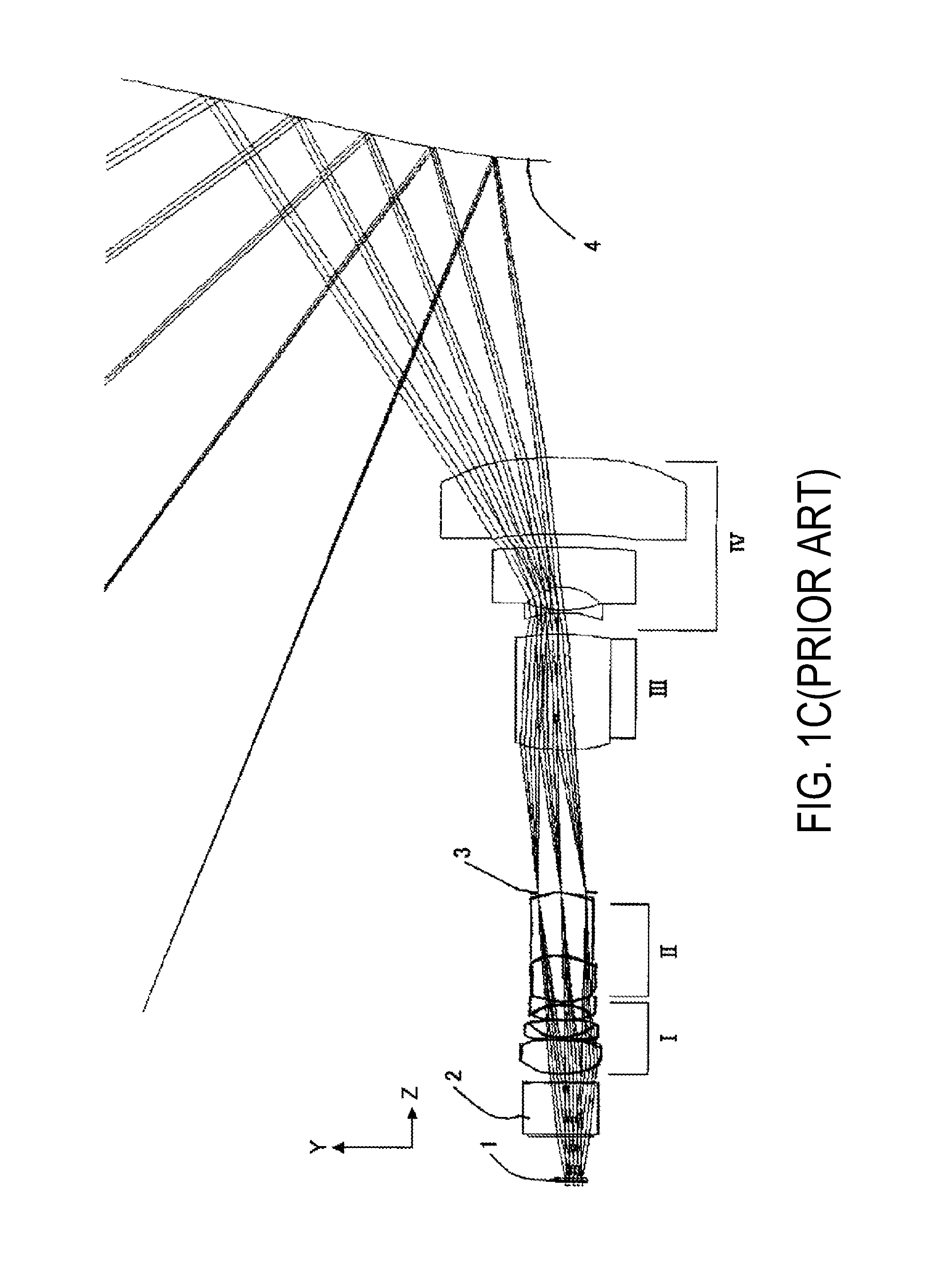
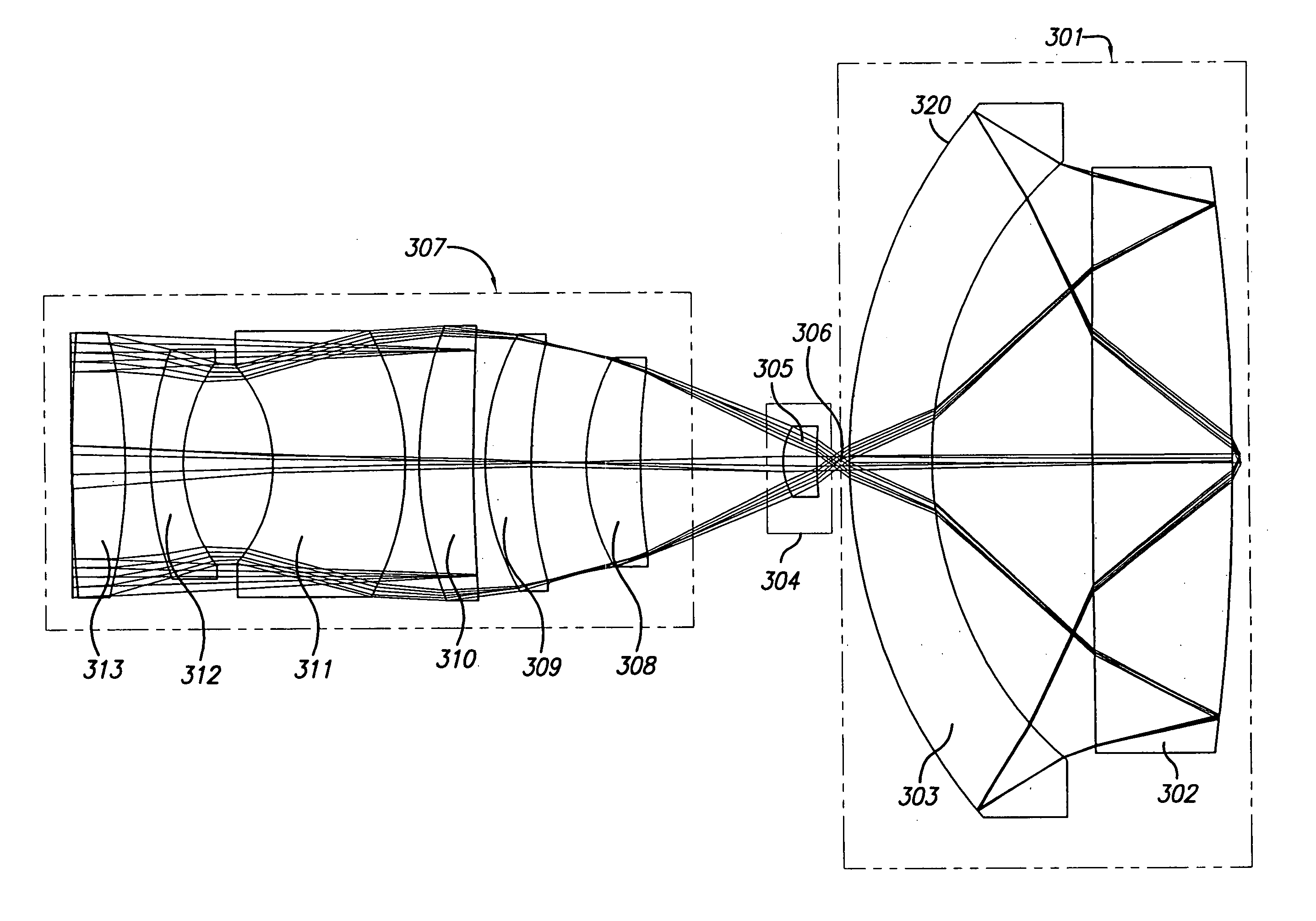
A design for inspecting specimens, such as photomasks, for unwanted particles and features such as pattern defects is provided. The system provides no central obscuration, an external pupil for aperturing and Fourier filtering, and relatively relaxed manufacturing tolerances, and is suited for both broad-band bright-field and laser dark field imaging and inspection at wavelengths below 365 nm. In many instances, the lenses used may be fashioned or fabricated using a single material. Multiple embodiments of the objective lensing arrangement are disclosed, all including at least one small fold mirror and a Mangin mirror. The system is implemented off axis such that the returning second image is displaced laterally from the first image so that the lateral separation permits optical receipt and manipulation of each image separately. The objective designs presented have the optical axis of the Mangin mirror image relay at ninety degrees to the optical axis defined by the focusing lenses, or an in-line or straight objective having one ninety degree bend of light rays.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
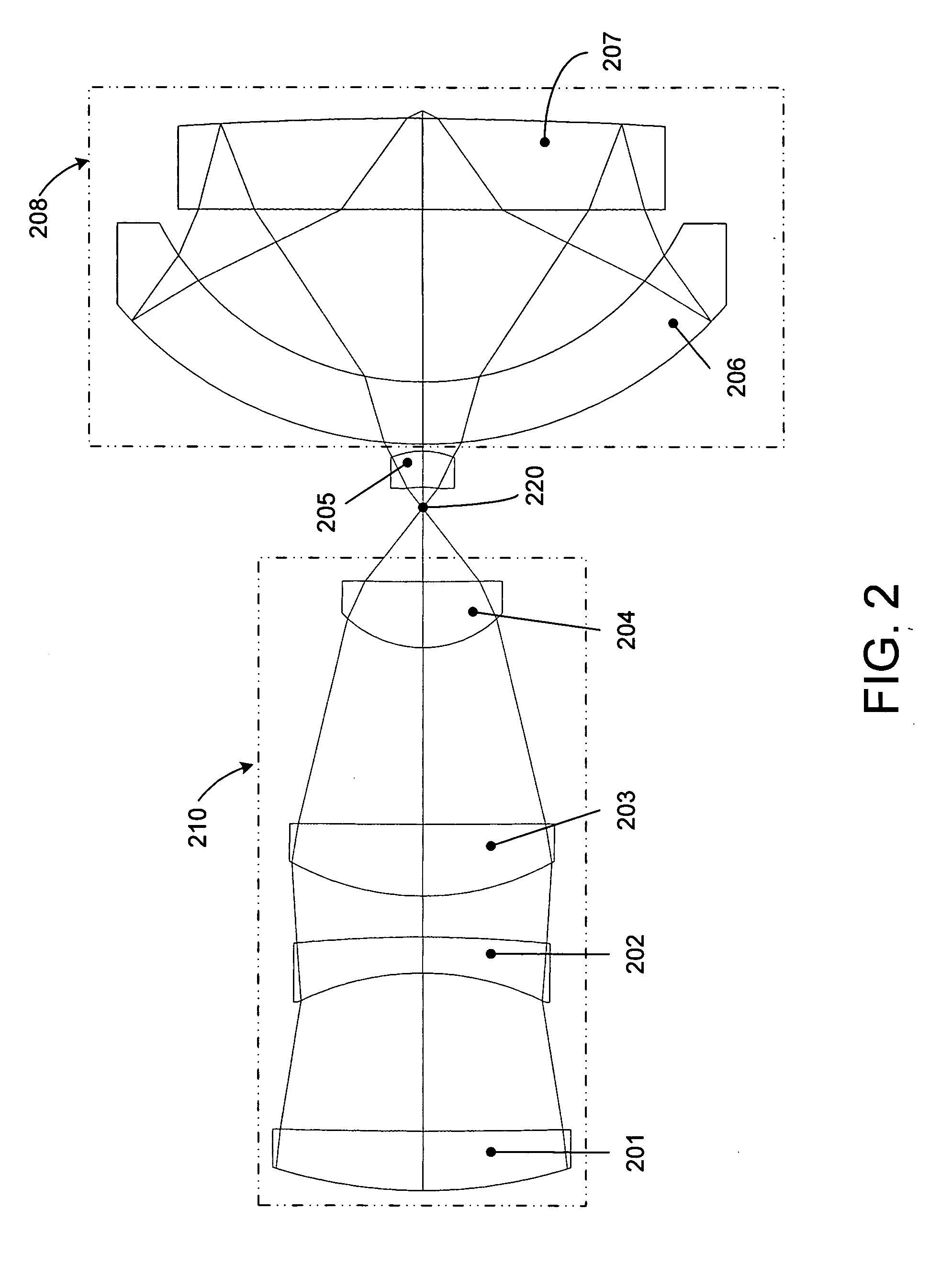
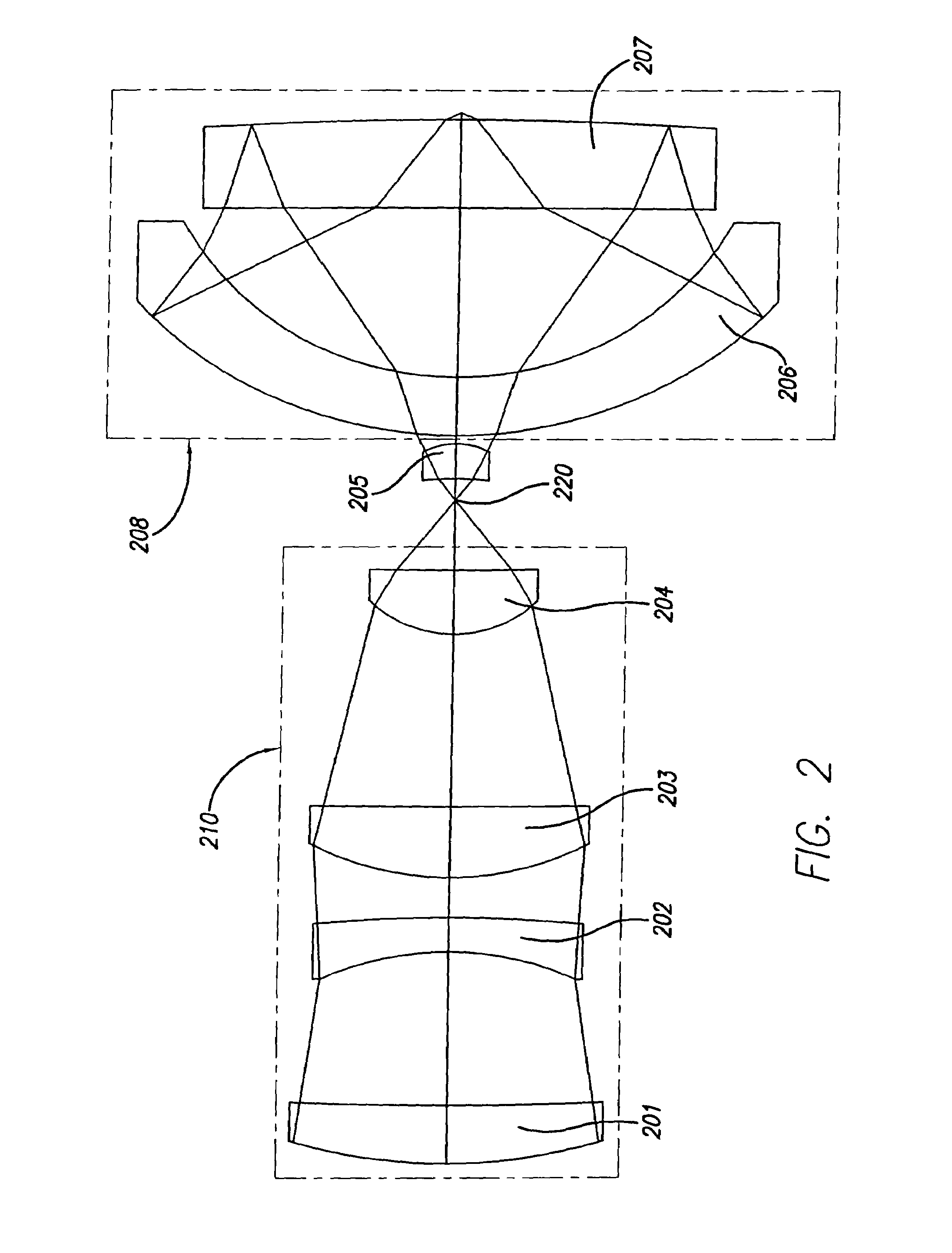
Catadioptric imaging system for high numerical aperture imaging with deep ultraviolet light
InactiveUS20050179994A1Reduces TM polarization componentReduce componentsPolarising elementsMicroscopesAngle of incidenceMangin mirror
A catadioptric imaging system for micro-lithographic projection features a high numerical aperture objective where most of the focusing power is produced by reflection and refraction angles are limited to avoid additional aberration. A field correcting optic is appended to a Mangin mirror in an immersive configuration for raising the numerical aperture. The optical connection between the Mangin mirror and the field correcting optic is arranged to control refraction angles by limiting angles of incidence or refractive index differences. A radially symmetric polarizing effect is achieved in a pupil to improve image contrast.
Owner:CORNING INC
Compact catadioptric long-wave infrared athermal imaging optical system
InactiveCN102520506AAchieve long focal length imagingCompact structureOptical elementsMangin mirrorLight beam
The invention relates to a compact catadioptric long-wave infrared athermal imaging optical system, which comprises a secondary lens, a primary reflective lens and a relay lens. The secondary lens is a catadioptric optical component with negative focal power and comprises an annular light transmission part and a central Mangin mirror; a light beam from an object is transmitted into the primary reflective lens through the annular light transmission part of the secondary lens and is then transmitted into the Mangin mirror of the secondary lens after reflection by the primary reflective lens, and catadioptric focusing is carried out by the Mangin mirror so that the target is imaged on a first image plane; the target on the first image plane is then transferred by the relay lens and focuses again on a second image plane; and the second image plane is overlapped with the focal plane of an image receiver. Image of long focal length can be realized, and the system has a compact structure and a large view field and can be applied in the optical imaging field of aviation and aerospace.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Broad band deep ultraviolet/vacuum ultraviolet catadioptric imaging system
InactiveUS20050111081A1High degreeImprove performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMangin mirrorUltraviolet
A design for inspecting specimens, such as photomasks, for unwanted particles and features such as pattern defects is provided. The system provides no central obscuration, an external pupil for aperturing and Fourier filtering, and relatively relaxed manufacturing tolerances, and is suited for both broad-band bright-field and laser dark field imaging and inspection at wavelengths below 365 nm. In many instances, the lenses used may be fashioned or fabricated using a single material. Multiple embodiments of the objective lensing arrangement are disclosed, all including at least one small fold mirror and a Mangin mirror. The system is implemented off axis such that the returning second image is displaced laterally from the first image so that the lateral separation permits optical receipt and manipulation of each image separately. The objective designs presented have the optical axis of the Mangin mirror image relay at ninety degrees to the optical axis defined by the focusing lenses, or an in-line or straight objective having one ninety degree bend of light rays.
Owner:KLA CORP
Catadioptric imaging system employing immersion liquid for use in broad band microscopy
InactiveUS20050152027A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationMicroscopesMangin mirrorLight energy
A reduced size catadioptric inspection system employing a catadioptric objective and immersion substance is disclosed. The objective may be employed with light energy having a wavelength in the range of approximately 190 nanometers through the infrared light range, and can provide numerical apertures in excess of 0.9. Elements are less than 100 millimeters in diameter and may fit within a standard microscope. The objective comprises a focusing lens group, a field lens, a Mangin mirror arrangement, and an immersion substance or liquid between the Mangin mirror arrangement and the specimen. A variable focal length optical system for use with the objective in the catadioptric inspection system is also disclosed.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
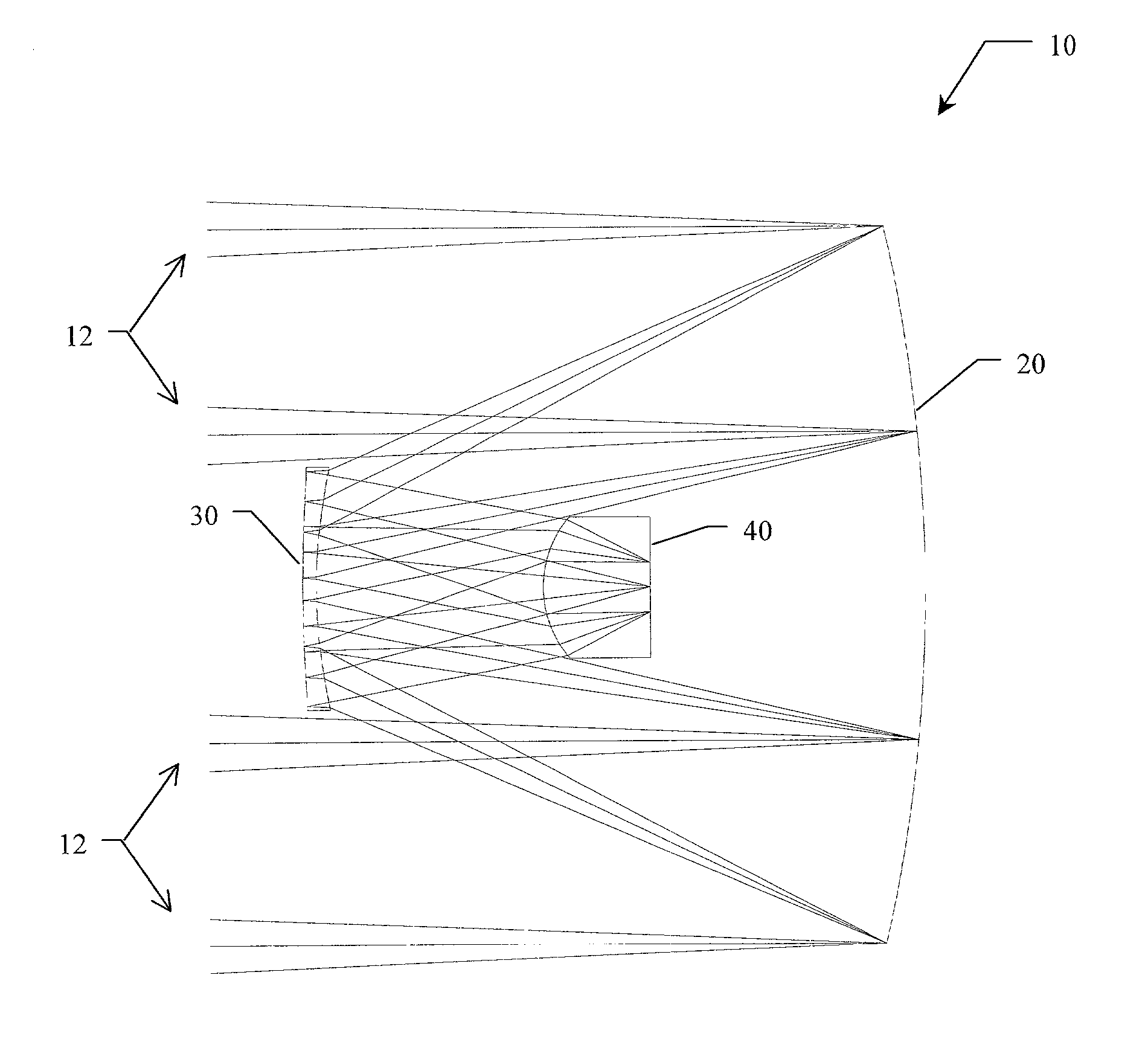
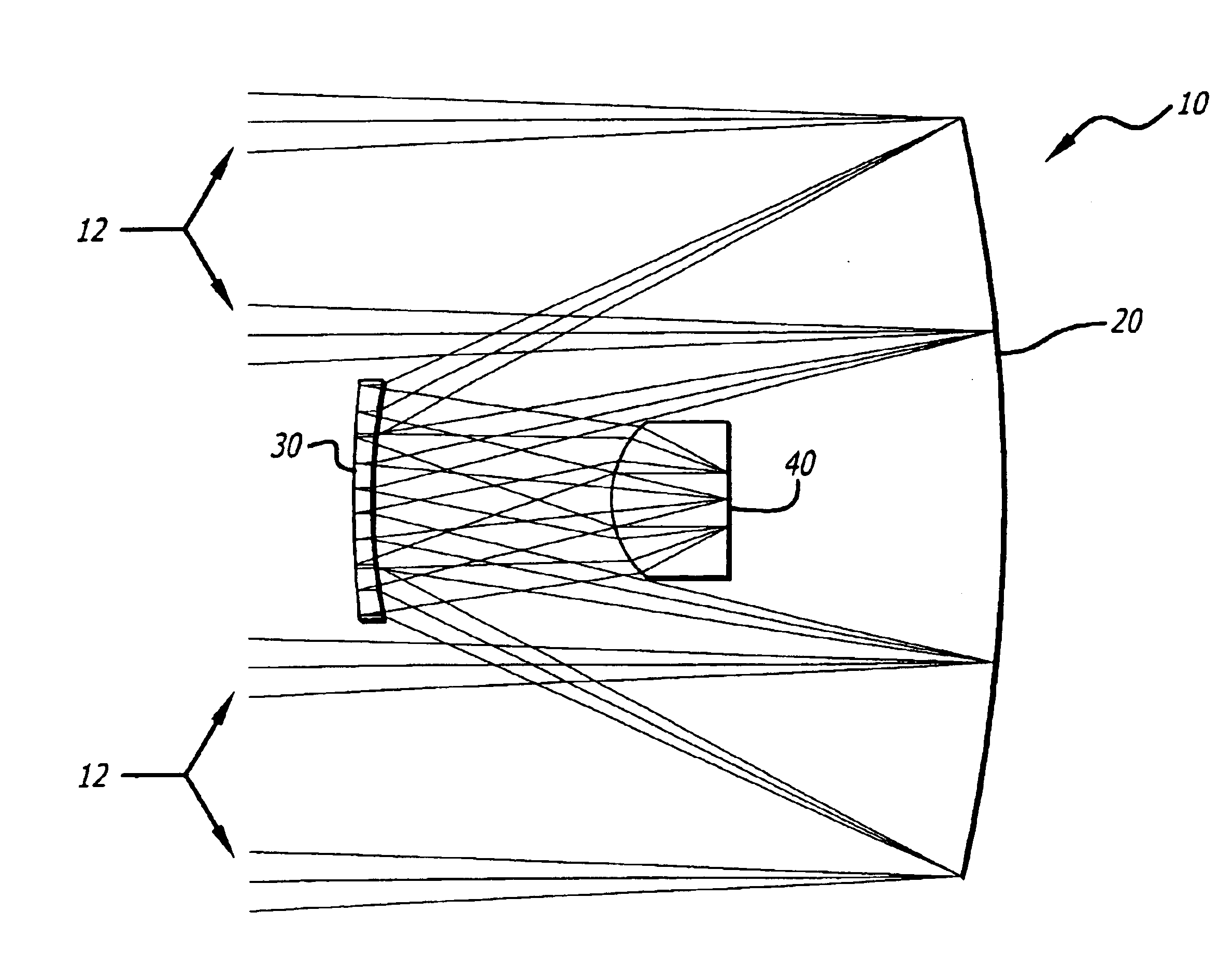
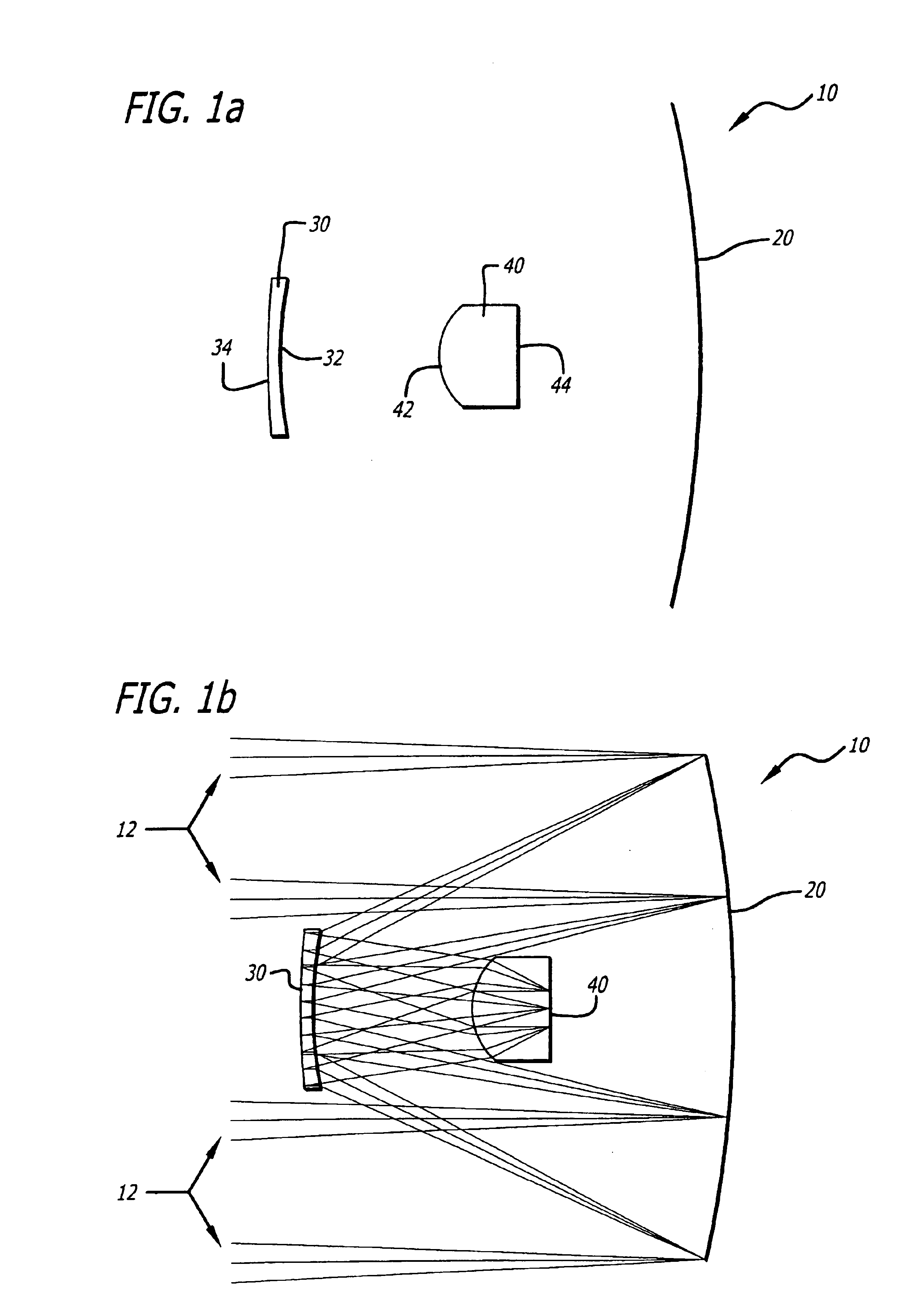
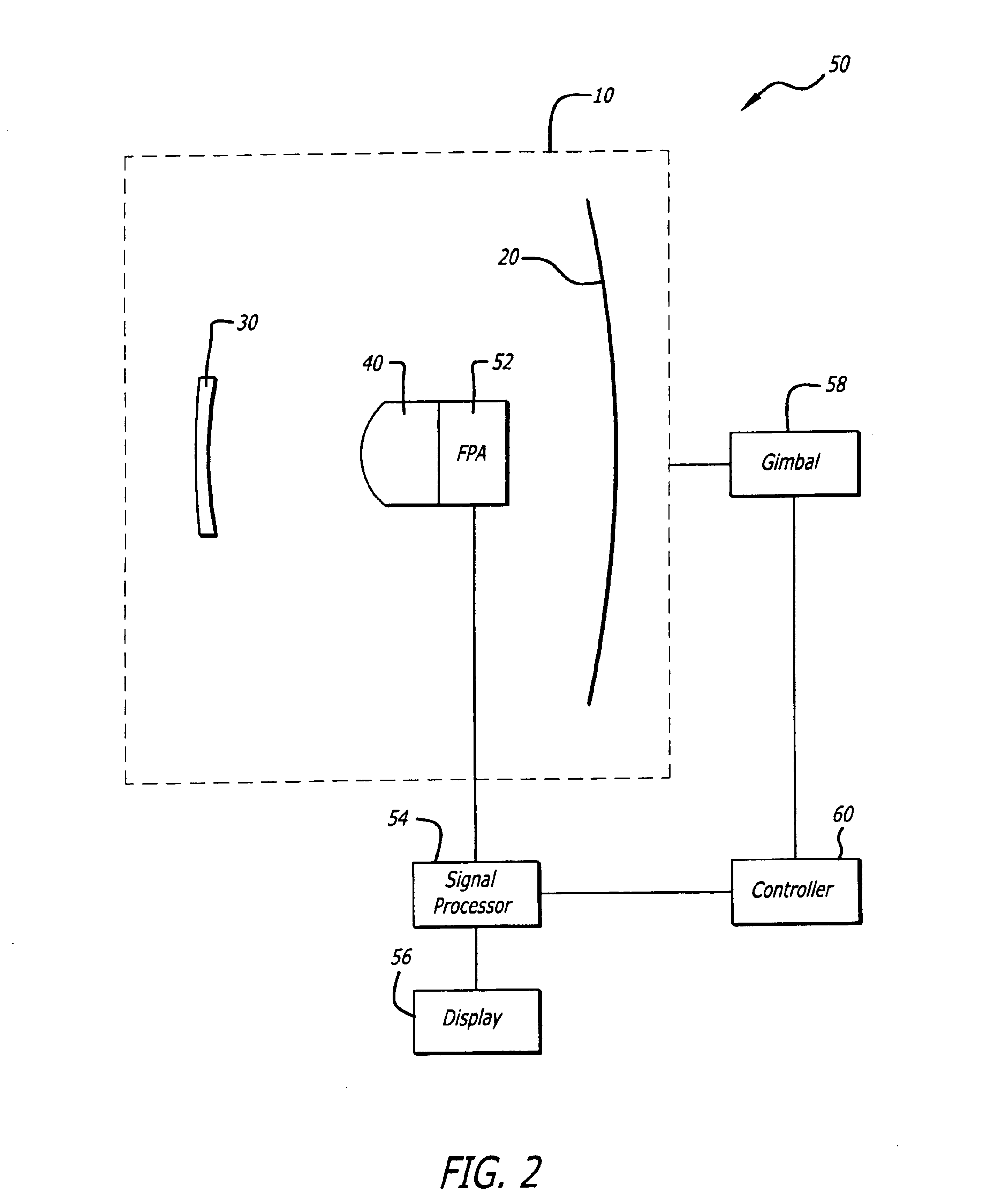
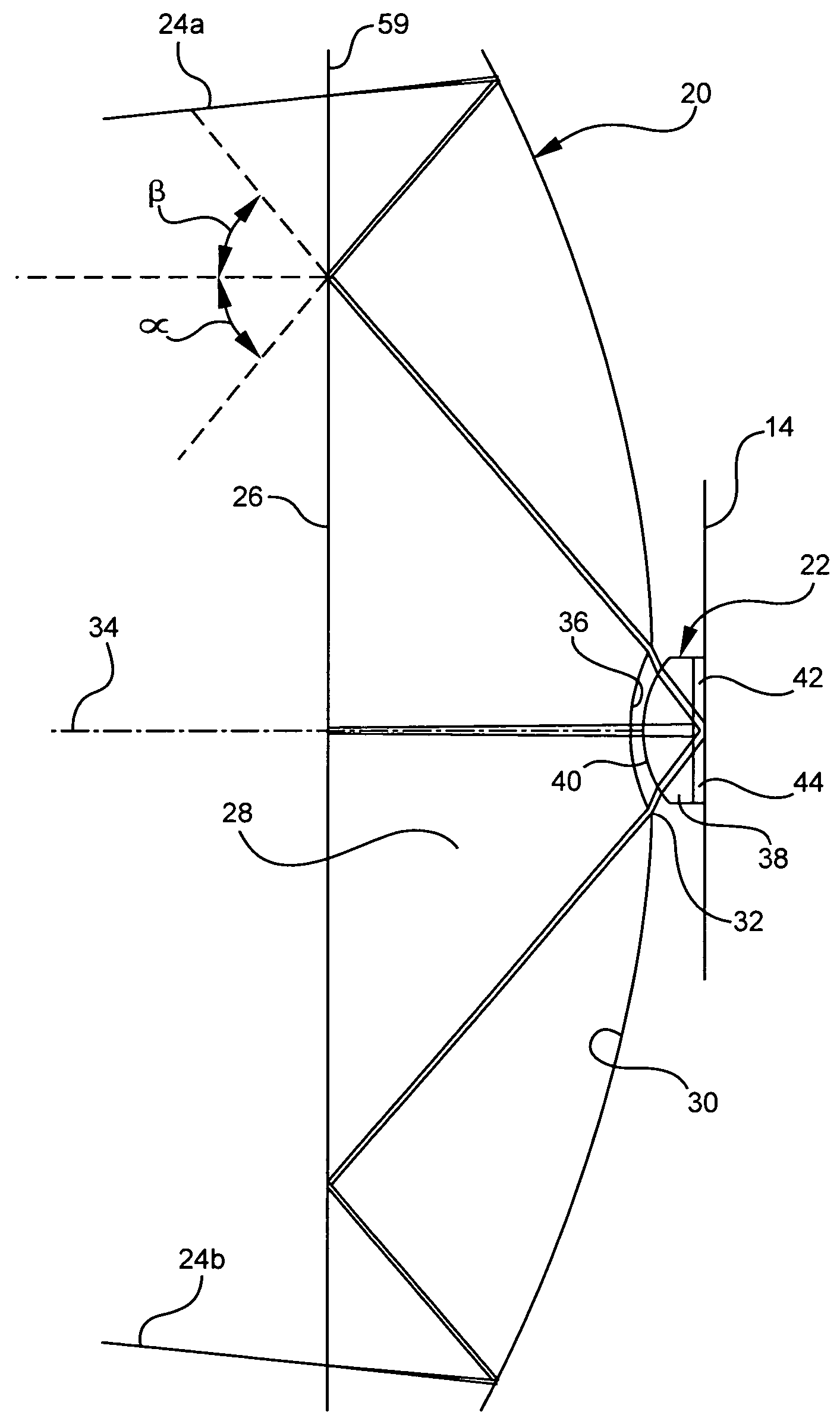
Optical system for simultaneous imaging of LWIR and millimeter wave radiation
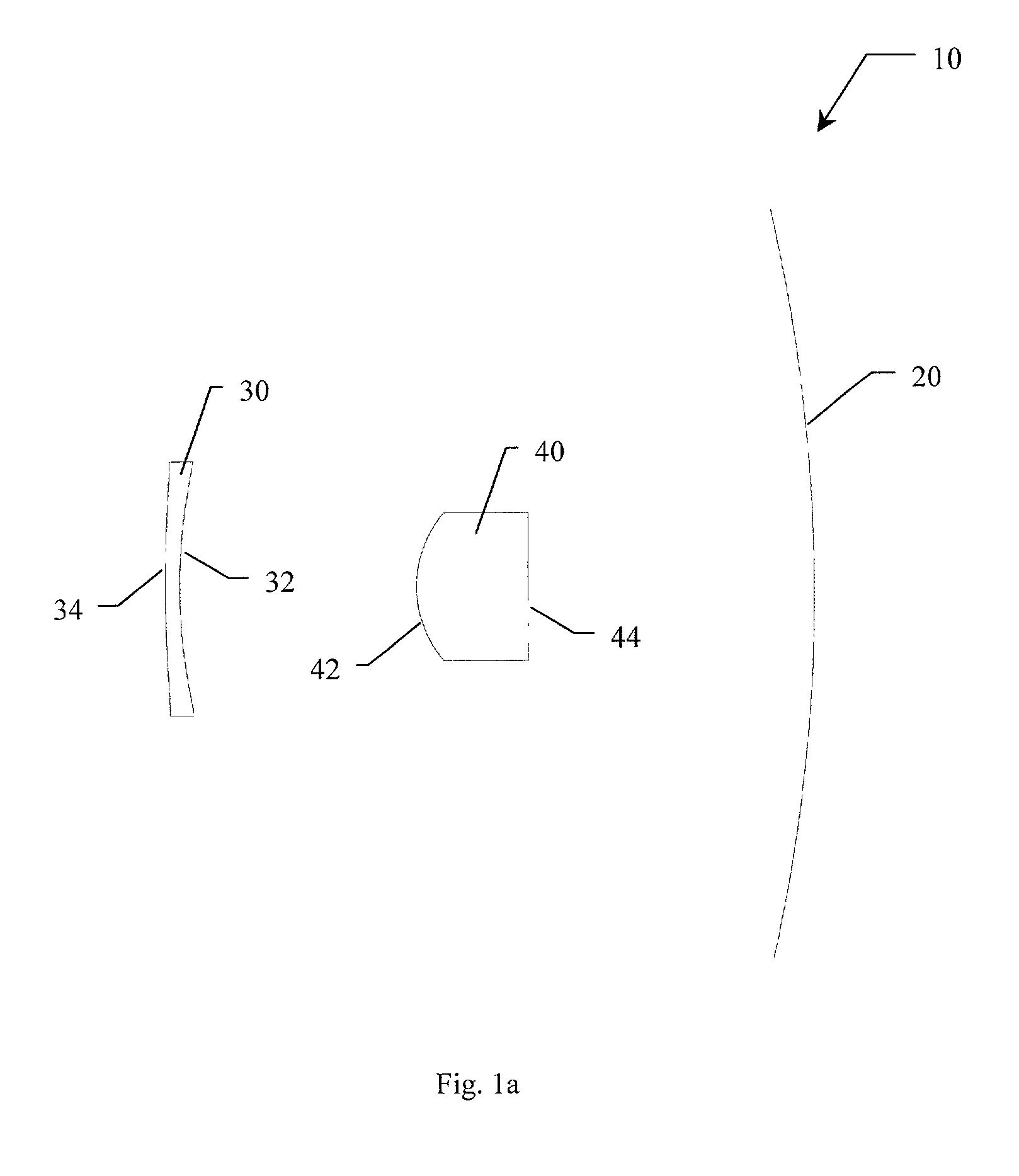
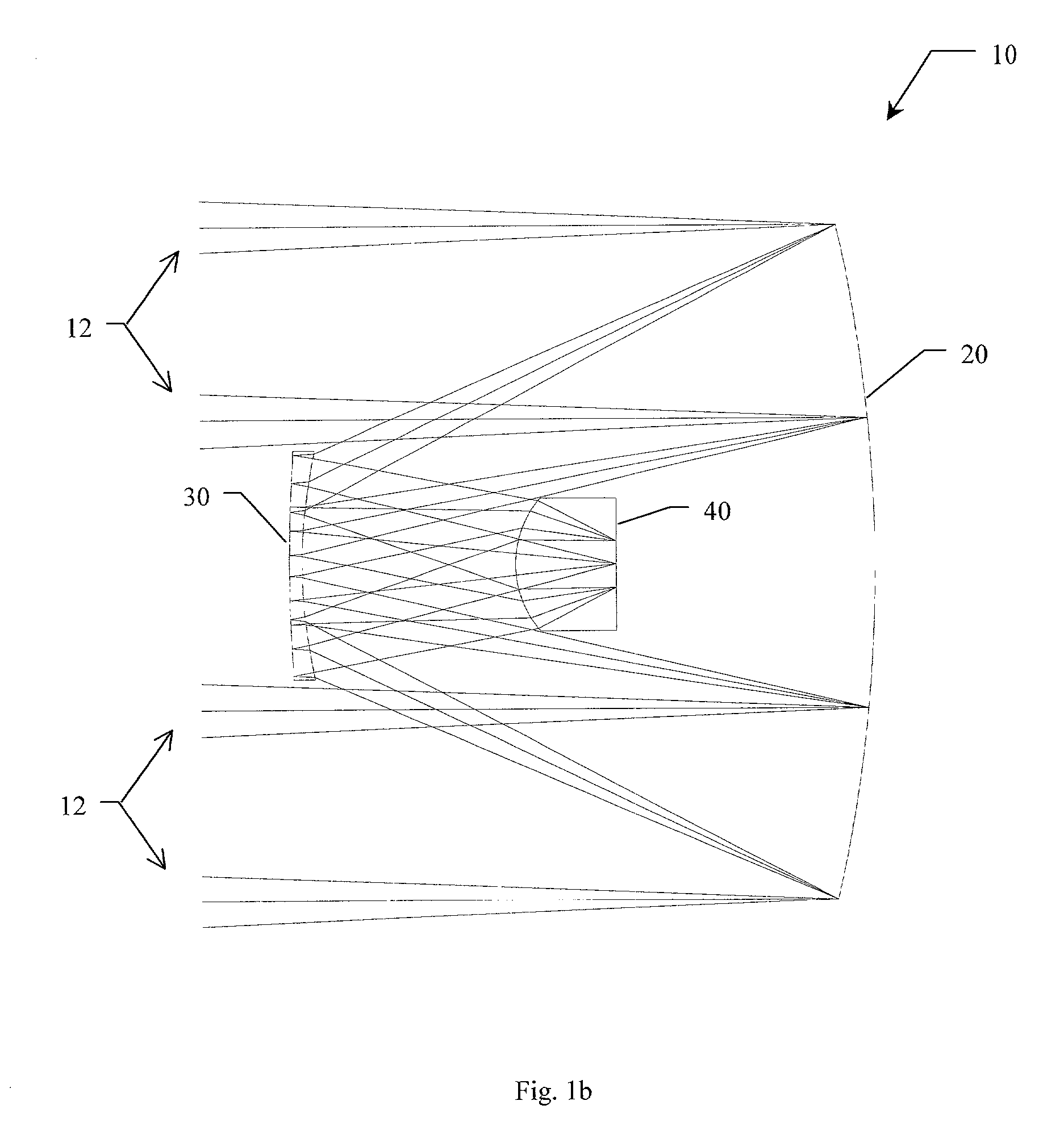
A system and method for simultaneous imaging of both infrared and millimeter wave radiation. The novel optical system (10) includes a primary mirror (20), a Mangin secondary mirror (30) positioned to receive energy reflected from the primary mirror (20), and an immersion lens (40) for focusing energy received from the Mangin mirror (30). In the illustrative embodiment, the primary mirror (20) and Mangin mirror (30) are arranged in a Cassegrain configuration. Central to this invention is the use of a negative power refractive Mangin mirror (30) as the Cassegrain secondary mirror, so that the field curvature of the secondary mirror (30) and immersion lens (40) can be made to cancel. The immersion lens (40) effectively decreases the wavelength of the millimeter wave radiation, allowing a smaller detector to collect the same amount of radiation as would a larger detector in air. In the illustrative embodiment, the system (10) further includes a detector array (52) placed in intimate contact with the immersion lens (40).
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Catadioptric microscope objective employing immersion liquid for use in broad band microscopy
An objective for imaging specimens is disclosed. The objective receives light energy from a light energy source configured to provide light energy in a wavelength range of approximately 480 to 660 nanometers, employs a Mangin mirror arrangement in conjunction with an immersion liquid to provide a numerical aperture in excess of 1.0 and a field size in excess of 0.05 millimeters, where every element in the objective has a diameter of less than approximately 40 millimeters.
Owner:KLA CORP
Optical-compensation athermalizing long-wave infrared optical system
InactiveCN102540436AQuality improvementRealize thermal difference eliminationOptical elementsMangin mirrorPlane mirror
The invention relates to an optical-compensation athermalizing long-wave infrared optical system which comprises a primary mirror, a secondary mirror and a relay mirror; wherein the primary mirror is a Mangin mirror, the refracting surface of the Mangin mirror has a negative focal power, and the reflecting surface of the Mangin mirror is a concave surface, and the secondary mirror is a planar mirror; and an object target is refracted from the refracting surface of the primary mirror to the reflecting surface of the primary mirror, refracted by the refracting surface of the primary mirror for the second time and turned and reflected by the secondary mirror to irradiate on an image surface of a refrigeration type infrared detector sequentially through the relay mirror and a detector window.According to the optical-compensation athermalizing long-wave infrared optical system, as the Mangin mirror is adopted by the primary mirror, the optical system has a wide viewing field and compact structure.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optical system for simultaneous imaging of LWIR and millimeter wave radiation
A system and method for simultaneous imaging of both infrared and millimeter wave radiation. The novel optical system (10) includes a primary mirror (20), a Mangin secondary mirror (30) positioned to receive energy reflected from the primary mirror (20), and an immersion lens (40) for focusing energy received from the Mangin mirror (30). In the illustrative embodiment, the primary mirror (20) and Mangin mirror (30) are arranged in a Cassegrain configuration. Central to this invention is the use of a negative power refractive Mangin mirror (30) as the Cassegrain secondary mirror, so that the field curvature of the secondary mirror (30) and immersion lens (40) can be made to cancel. The immersion lens (40) effectively decreases the wavelength of the millimeter wave radiation, allowing a smaller detector to collect the same amount of radiation as would a larger detector in air. In the illustrative embodiment, the system (10) further includes a detector array (52) placed in intimate contact with the immersion lens (40).
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
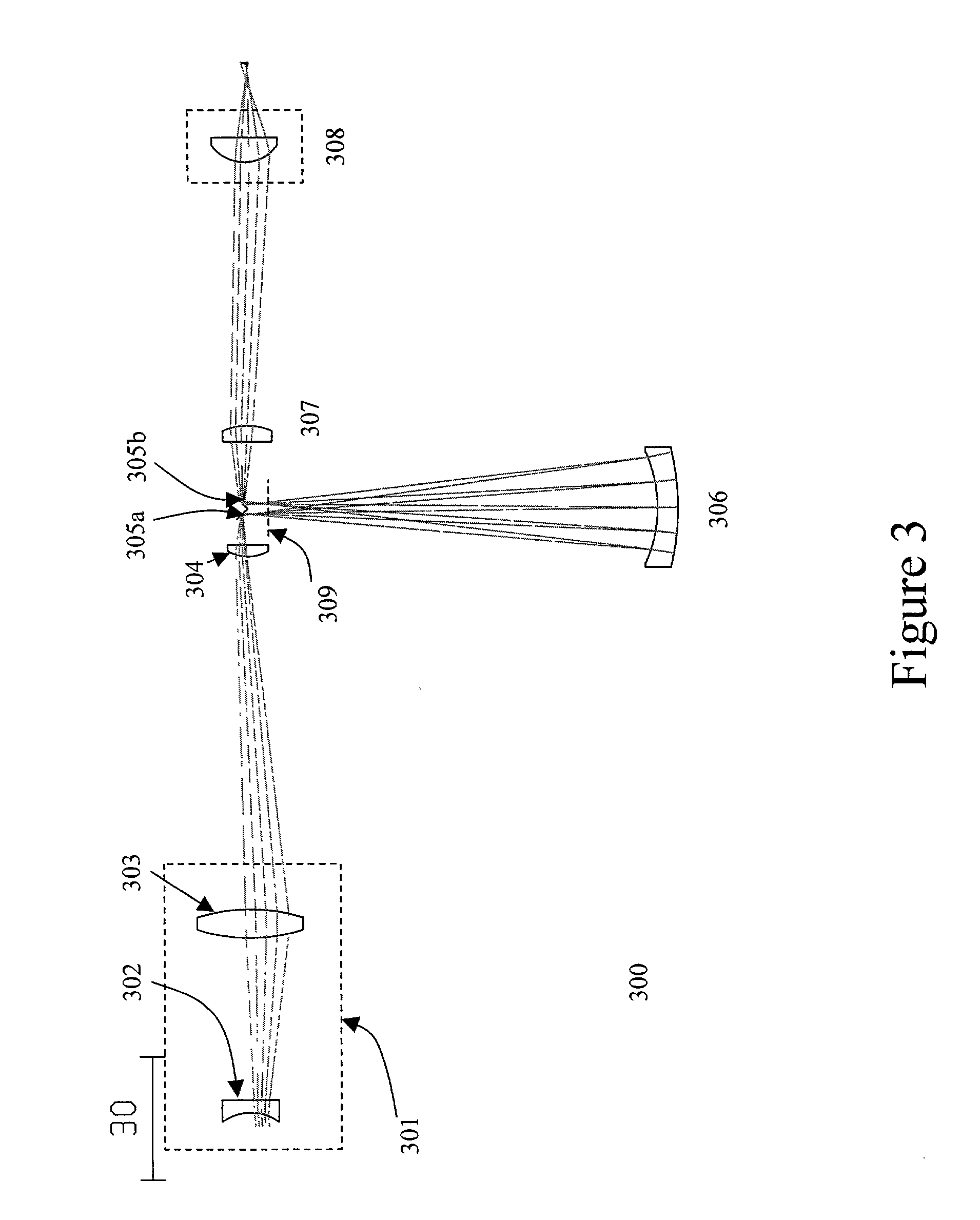
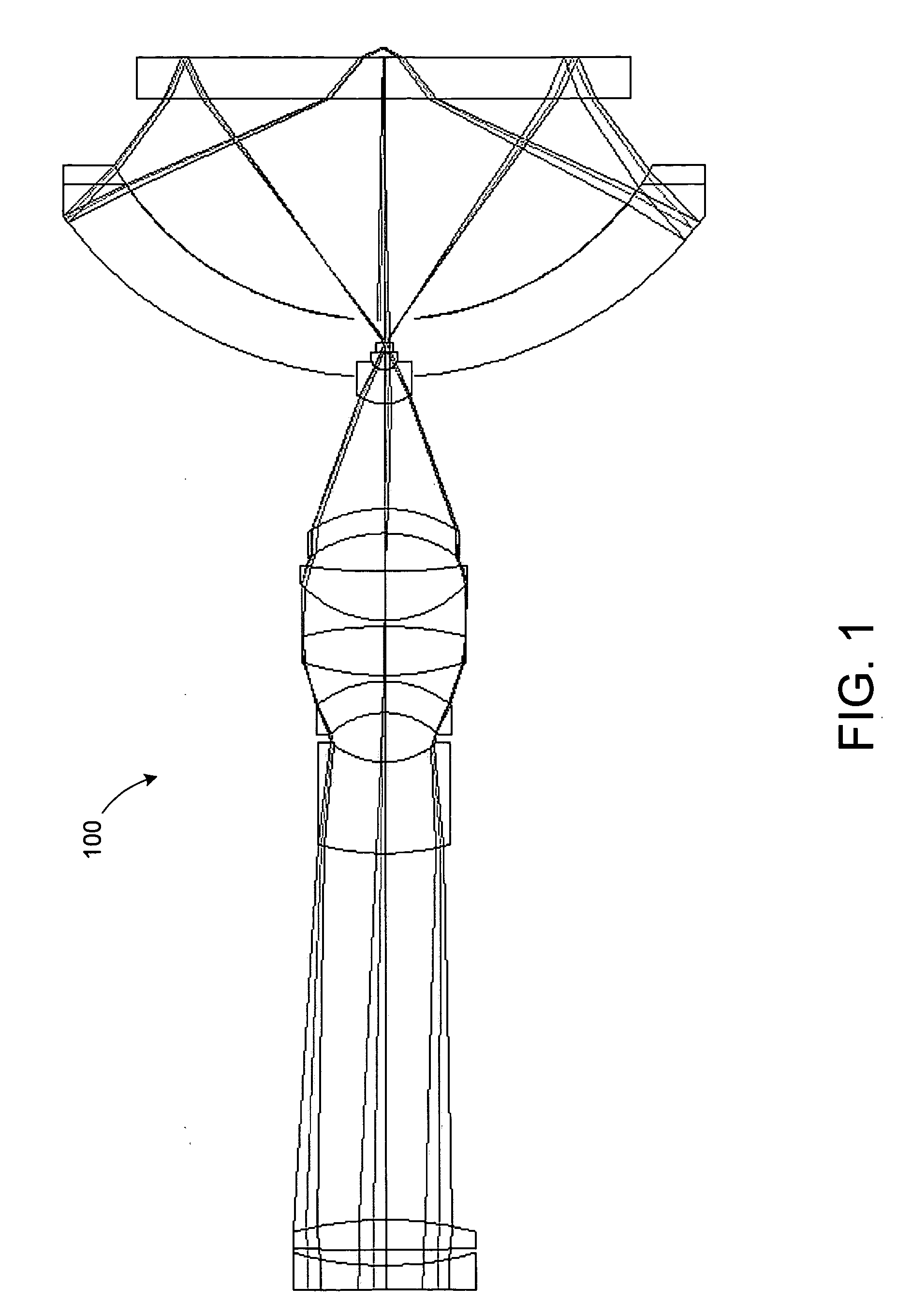
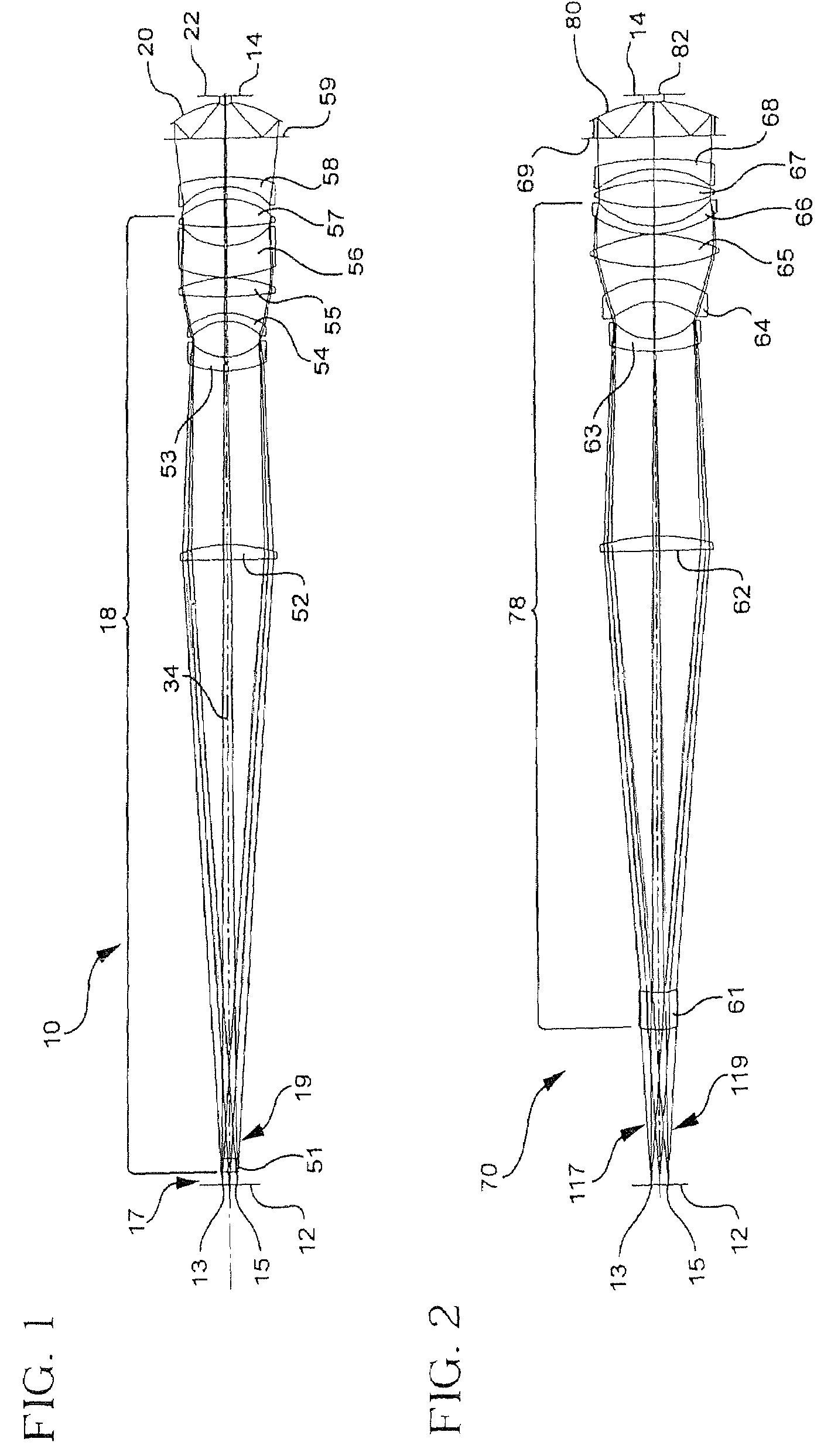
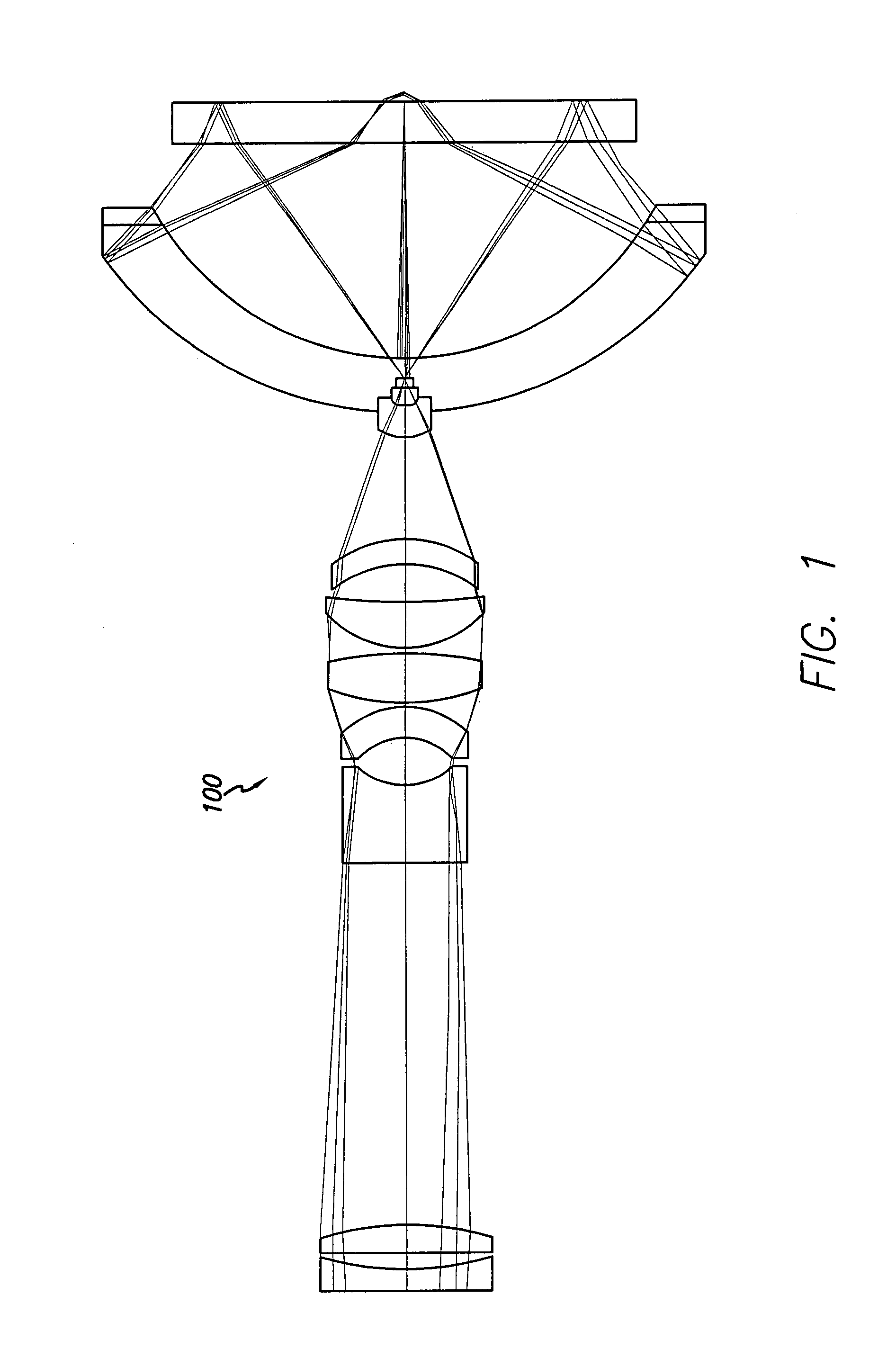
Small ultra-high NA catadioptric objective using aspheric surfaces
A relatively high NA objective employed for use in imaging a specimen and method for imaging a specimen is provided. The objective comprises a lens group having at least one focusing lens configured to receive light energy and form an intermediate image, at least one field lens oriented to receive the intermediate image and provide intermediate light energy, and a Mangin mirror arrangement positioned to receive the intermediate light energy and apply light energy to the specimen. One or more elements may employ an aspheric surface. The objective may provide, in certain instances, an uncorrected spectral bandwidth up to approximately 193 to 266 nanometers and can provide numerical apertures in excess of 0.9. Elements are less than 100 millimeters in diameter and may fit within a standard microscope. The field lens may comprise more than one lens and may be formed of a material different from at least one other lens in the objective.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
An imaging system with 15° field of view telecentric three mirrors coaxial
InactiveCN102279047AIncreased frame widthImprove Earth Observation CapabilitiesRadiation pyrometryMirrorsMangin mirrorMirror plane
The invention provides a telecentric imaging system with field of view of 15 degrees and three coaxial reflectors, belongs to the space optics technical field, and relates to a telecentric off-axis three-reflector imaging system. A technical problem to be solved is providing a telecentric imaging system with field of view of 15 degrees and three coaxial reflectors. A technical scheme is as follows: the imaging system comprises a main mirror, a second mirror, a third mirror, an aperture diaphragm and an imaging surface, the main mirror, the second mirror, the third mirror and the aperture diaphragm are coaxial, and the main mirror and the third mirror are coplanar; the second mirror is placed on a reflected light path of the main mirror, the third mirror is placed on a reflected light pathof the second mirror, and the aperture diaphragm is placed on a mirror plane edge of the second mirror; in order to realize telecentric image space, a distance from the aperture diaphragm to the third mirror is half of a summit radius of curvature length of the third mirror; in order to realize wide field of view of 15 degrees, the second mirror is a convex spherical mirror, and the main mirror and the third mirror are concave quarticsurface mirrors; a distance from the second mirror to the third mirror is larger than half of a system image space focal length. According to the system, abundant ground resource information is obtained, and the system has low processing and adjusting difficulty.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Wide-angle projection optical system
ActiveCN104698574AAddress security risksLarge field cornerOptical elementsOptical propertyMangin mirror
The invention relates to a wide-angle projection optical system between an object side and an image side. The wide-angle projection optical system comprises a first optical system and a second optical system. The first optical system comprises a first lens unit and a second lens unit. The second optical system comprises a Mangin mirror. The first lens unit with positive effective optical power comprises an aperture diaphragm, provides the optical feature matching projection light rays of the object side and collects the light rays onto the aperture diaphragm. The second lens unit behind the first lens unit has the positive effective optical power. Relative to the first lens unit, the aperture diaphragm and the second lens unit, the Mangin mirror is closer to the image side. The first lens unit and the second lens unit form distortion real images at the front of the Mangin mirror which is provided with a penetration face and a reflection face, in this way, the light rays are subjected to the secondary refraction and the primary reflection, so that an image distortionless after zooming is generated on a screen and thinned, with aberration thereof reduced.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
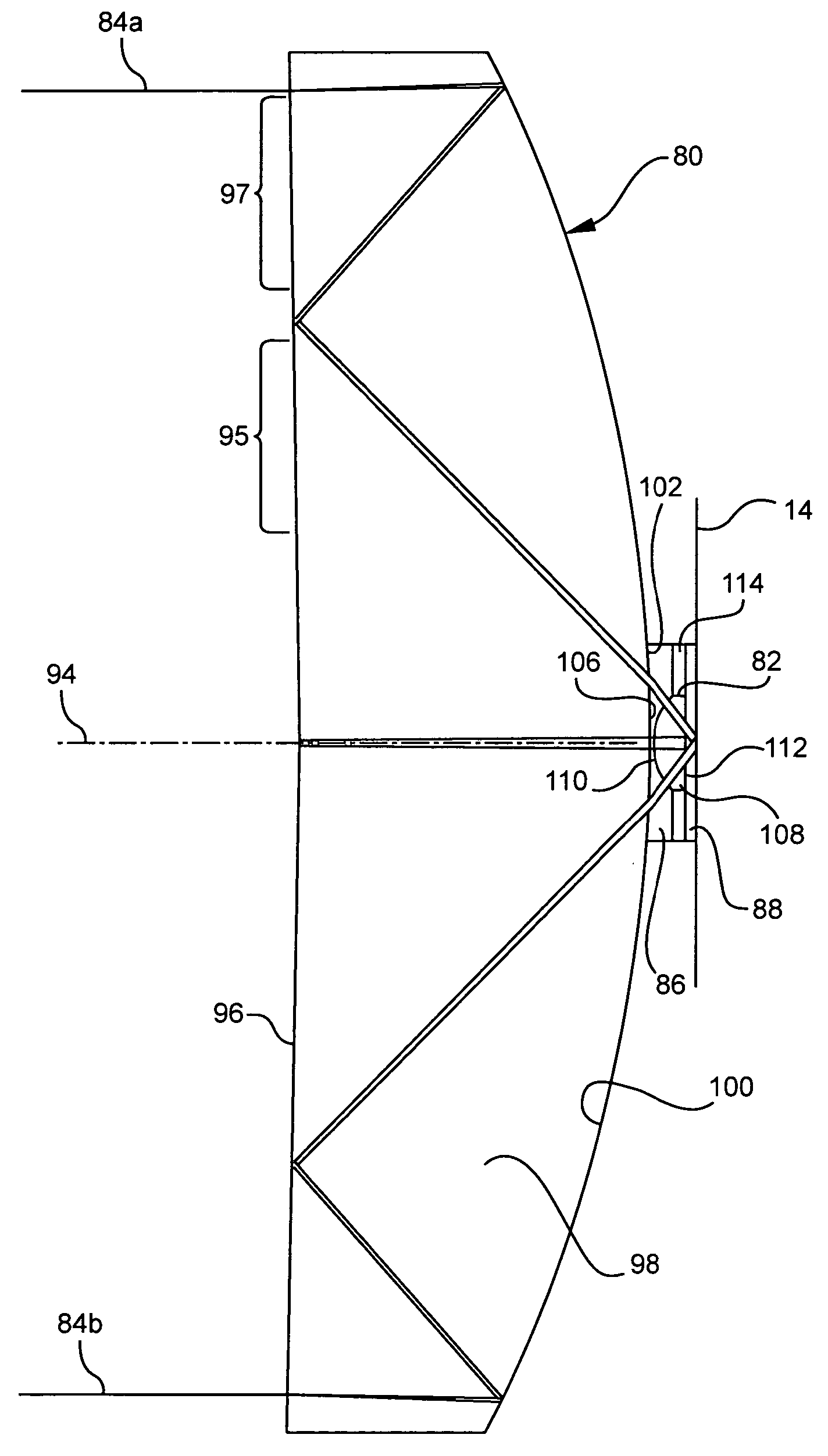
IR microscope with image field curvature compensation, in particular with additional illumination optimization
ActiveUS20130188034A1Easy to useAvoid chromatic aberrationRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansMangin mirrorFlat detector
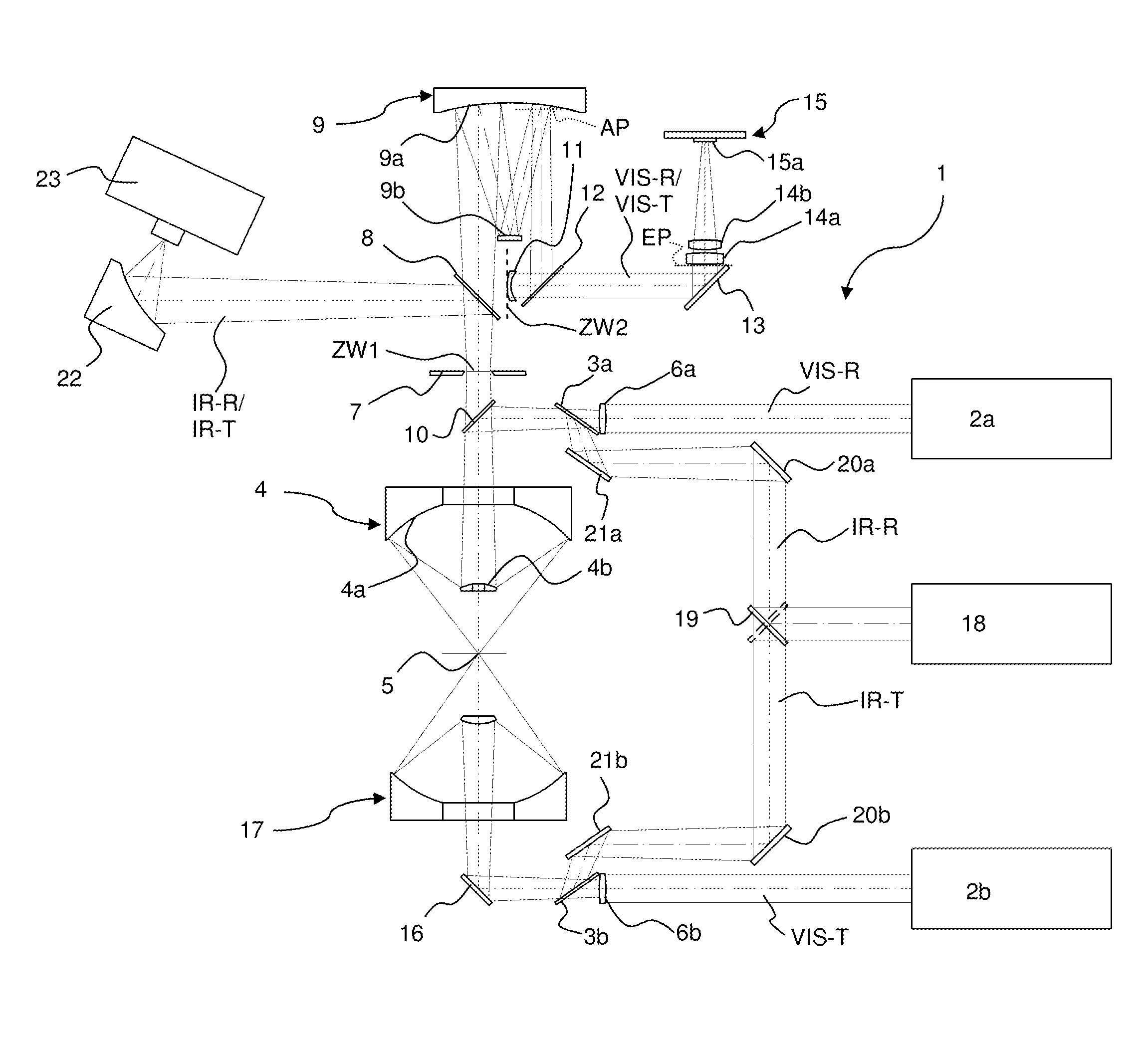
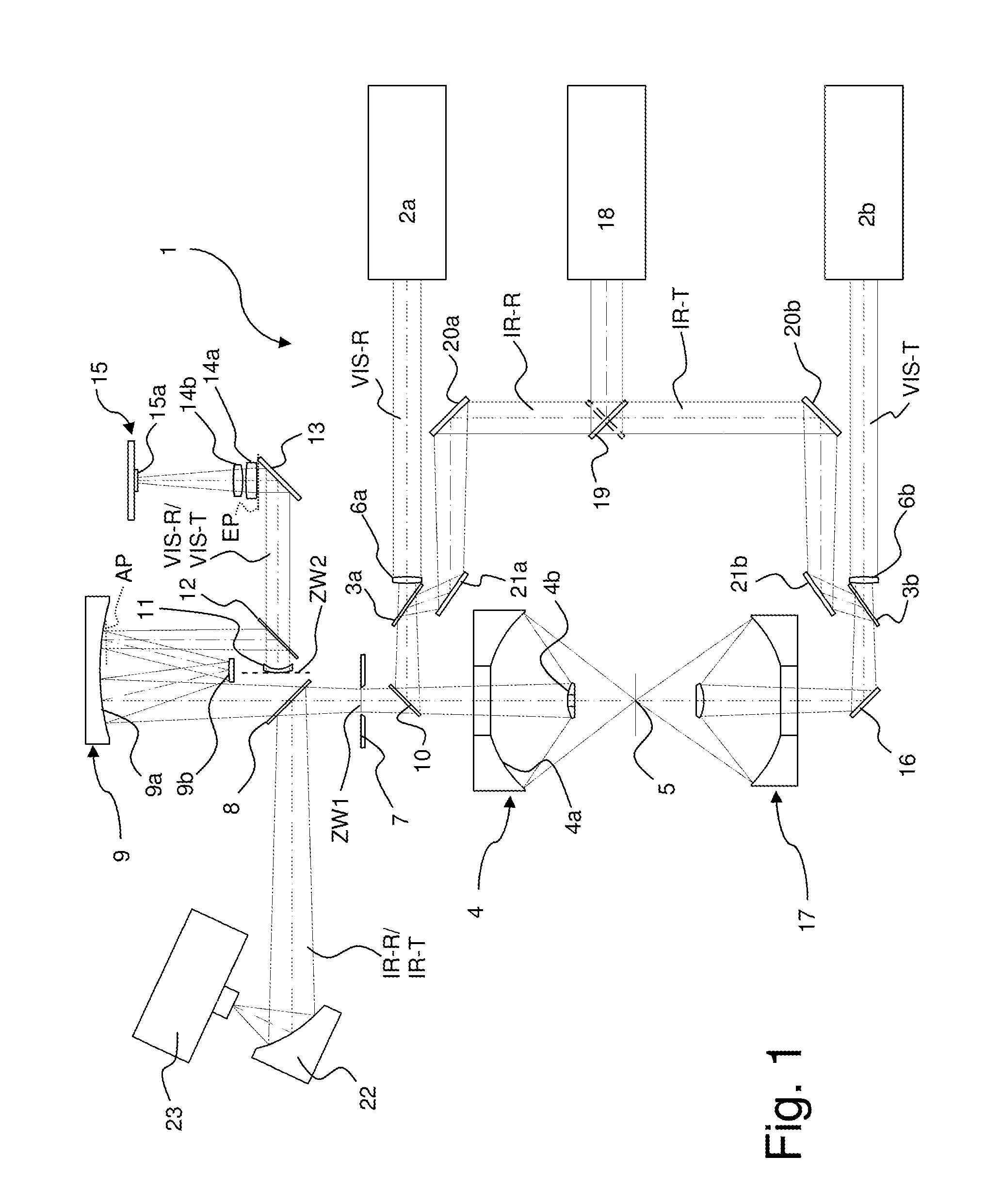
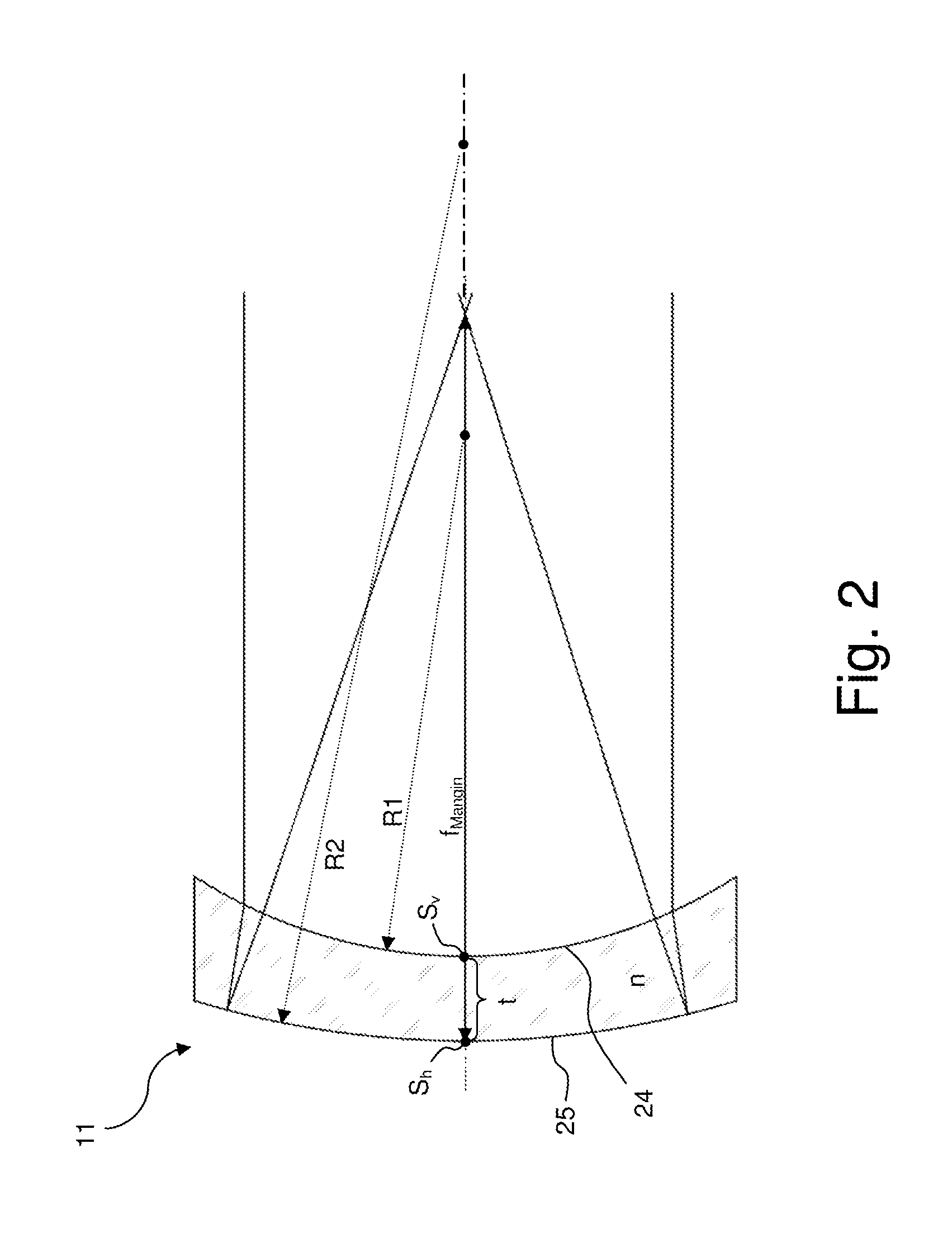
An IR microscope (1) is constituted such that, in an optical viewing mode in a beam path of visible light (VIS-R, VIS-T), a first intermediate focus (ZW1) is imaged onto a flat detector surface (15a) of a camera. The IR microscope (1) is constituted such that, in the beam path of the visible light (VIS-R, VIS-T), the first intermediate focus (ZW1) is imaged onto a second intermediate focus (ZW2), and, in the second intermediate focus (ZW2), a Mangin mirror (11) is disposed that corrects a field curvature of the Cassegrain objective (4). The invention provides an IR microscope in which the field curvature generated by the Cassegrain objective is corrected in a simple manner in the optical viewing mode when detection is performed using a flat detector and without restricting the spectral range of the IR microscope.
Owner:BRUKER OPTICS GMBH & CO KG
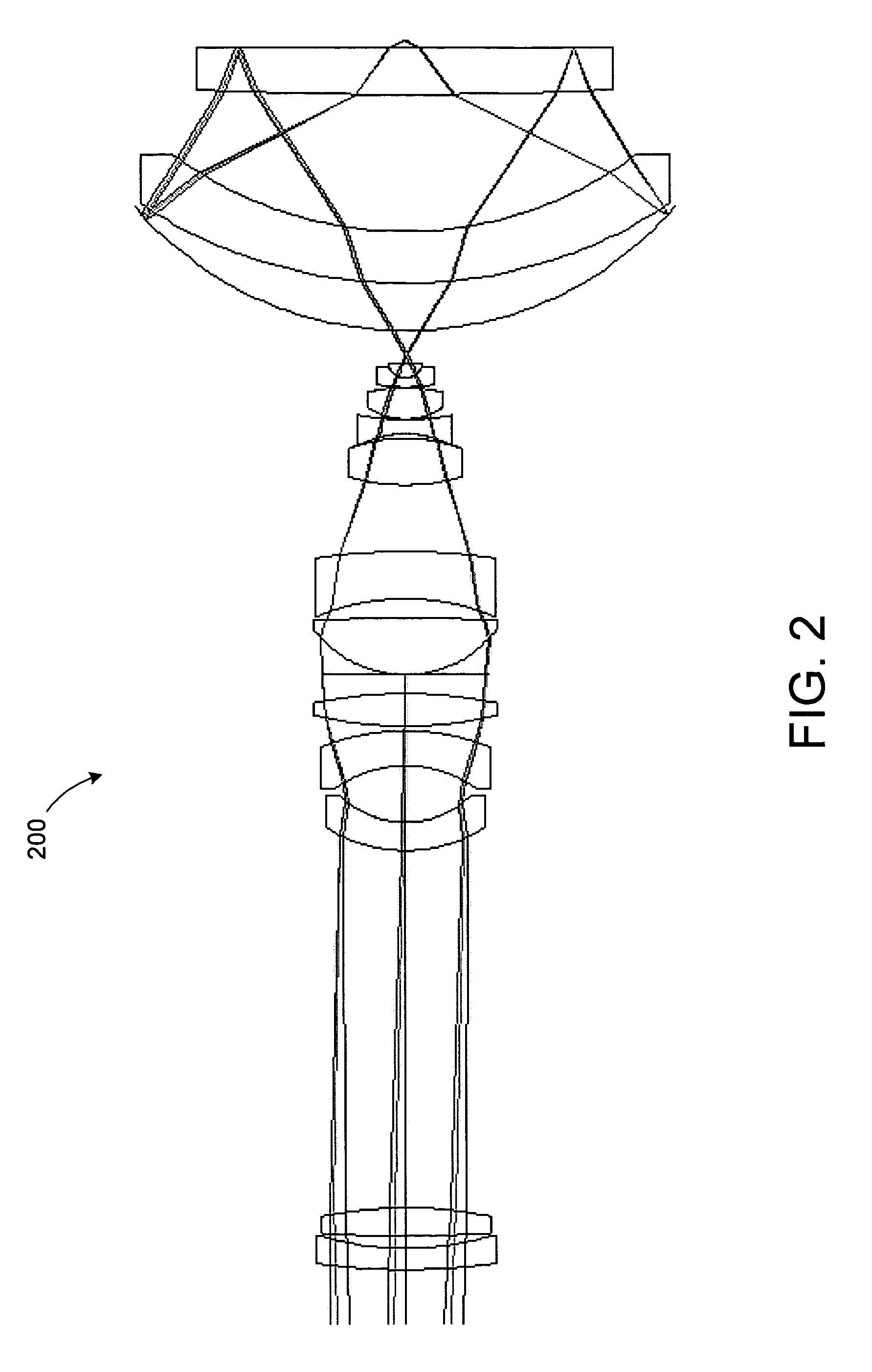
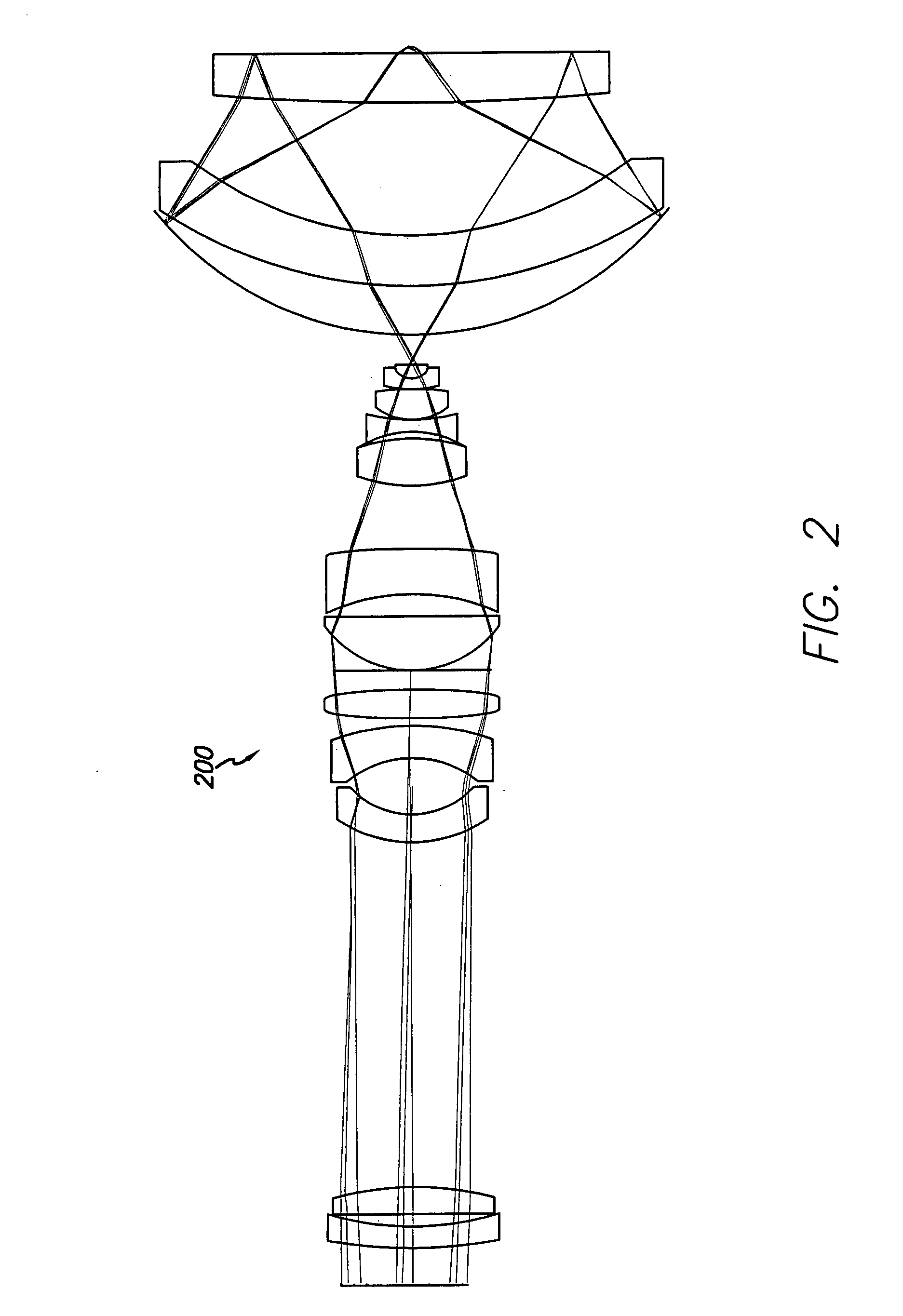
Catadioptric imaging system exhibiting enhanced deep ultraviolet spectral bandwidth
InactiveUS20050259318A1Increase spectral bandwidthMirrorsOptical filtersIntermediate imageMangin mirror
A relatively high spectral bandwidth objective employed for use in imaging a specimen and method for imaging a specimen is provided. The objective comprises a lens group having at least one focusing lens configured to receive light energy and form an intermediate image, at least one field lens oriented to receive the intermediate image and provide intermediate light energy, and a Mangin mirror arrangement positioned to receive the intermediate light energy and apply light energy to the specimen. The objective may provide, in certain instances, a spectral bandwidth up to approximately 193 to 266 nanometers and can provide numerical apertures in excess of 0.9. Elements are less than 100 millimeters in diameter and may fit within a standard microscope. The field lens may comprise more than one lens and may be formed of a material different from at least one other lens in the objective.
Owner:KLA TENCOR CORP
Catadioptric imaging system for high numerical aperture imaging with deep ultraviolet light
InactiveUS7564633B2Reduce refractionReduces TM polarization componentPolarising elementsMicroscopesAngle of incidenceMangin mirror
A catadioptric imaging system for micro-lithographic projection features a high numerical aperture objective where most of the focusing power is produced by reflection and refraction angles are limited to avoid additional aberration. A field correcting optic is appended to a Mangin mirror in an immersive configuration for raising the numerical aperture. The optical connection between the Mangin mirror and the field correcting optic is arranged to control refraction angles by limiting angles of incidence or refractive index differences. A radially symmetric polarizing effect is achieved in a pupil to improve image contrast.
Owner:CORNING INC
Optical illumination system and image projection system including the same
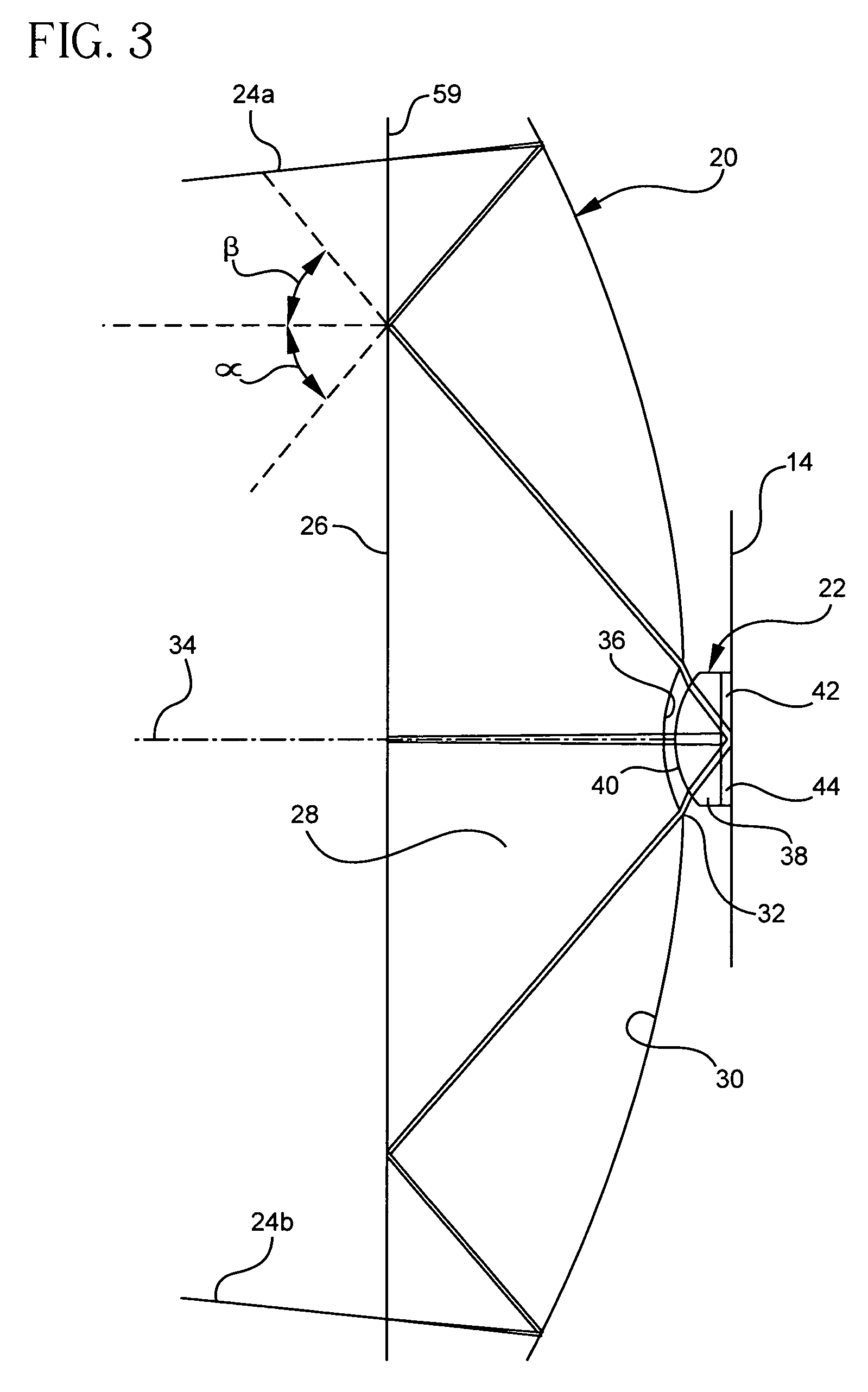
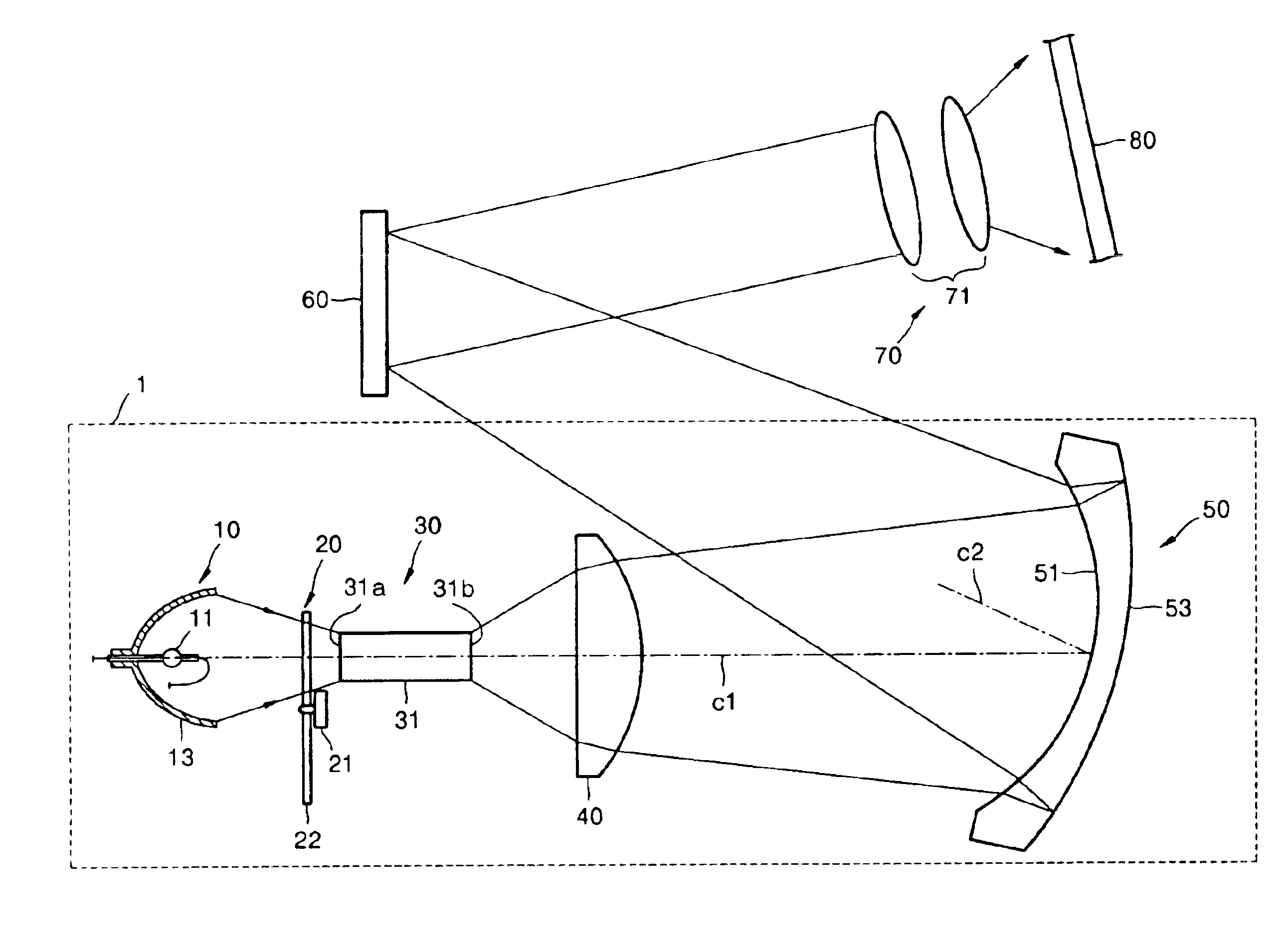
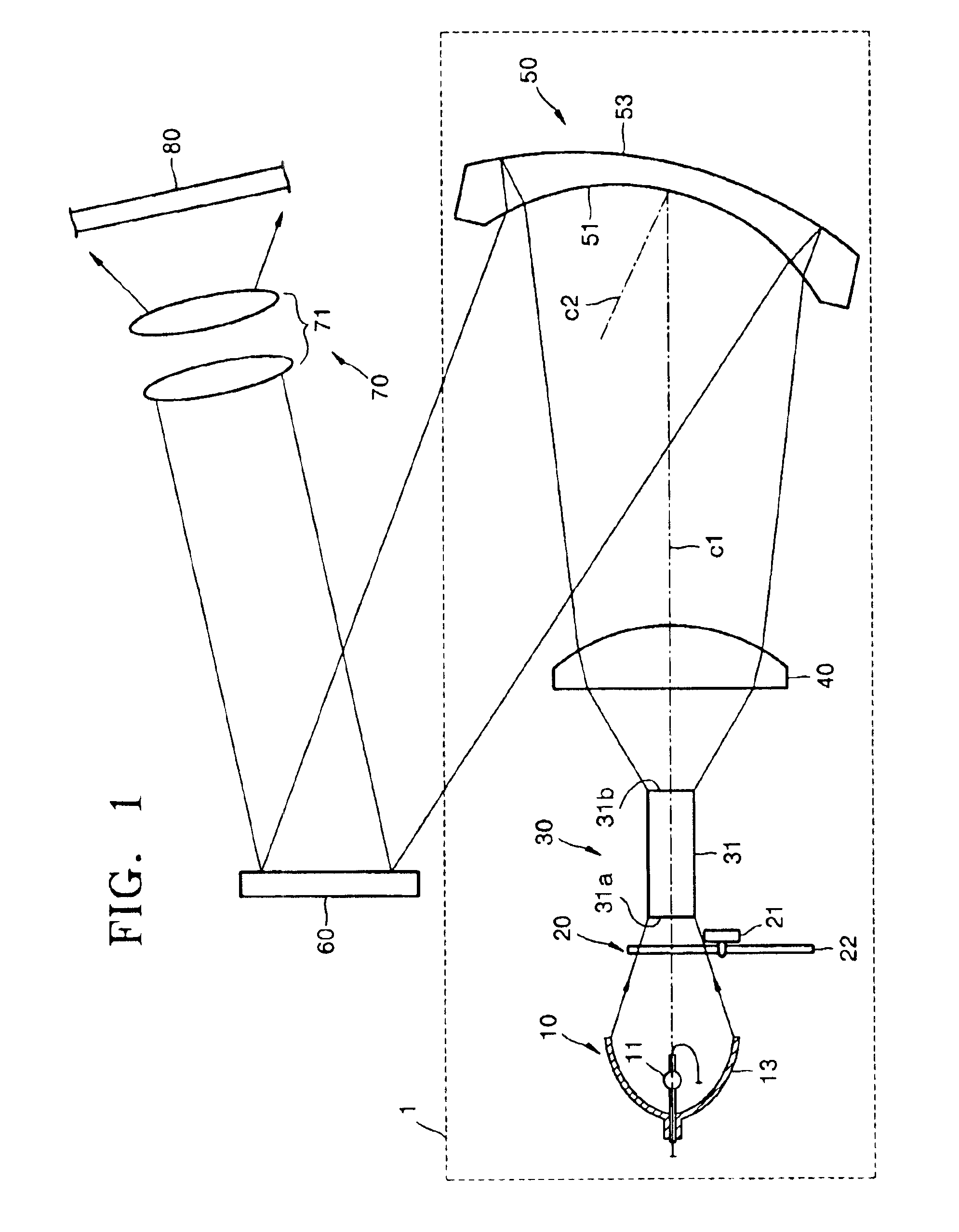
InactiveUS6908199B2Reduce manufacturing costEliminate degradationProjectorsElectric lightingMangin mirrorProjection system
An optical illumination system and an image projection system including the same include a light source, at least one illuminating lens and a Mangin mirror that illuminate light emitted from the light source on a predetermined reflective device, the Mangin mirror including a concave refracting surface that refracts and transmits light incident from the illuminating lens, and a convex reflecting surface disposed behind the concave refracting surface to internally reflect the light refracted by the concave refracting surface back toward the concave refracting surface and tilted with respect to the illuminating lenses. The light reflected from the convex reflecting surface and then refracted through the concave refracting surface propagates along a path that is different from a path of the light emitted from the illuminating lens.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Wide-angle projection optical system
InactiveUS20150160441A1Eliminate dangerShort effective focal lengthProjectorsLensOptical propertyMangin mirror
A wide-angle projection optical system includes, between an object side and an image side, a first optical system including a first lens group having an aperture stop and a second lens group disposed behind the aperture stop, and a second optical system including a Mangin mirror. The first and second lens groups have positive power. The first lens group provides optical characteristics to match with a light coming from the object side and converges the light toward the aperture stop. The first and second lens groups are configured to form an aberrated real image. The Mangin mirror is disposed closer to the image side than others. The Mangin mirror includes a refracting surface and a reflecting surface for refracting the light two times and reflecting the light one time, thereby producing an enlarged real image on a screen. Therefore, the image distortion is reduced, and the image quality is enhanced.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
High performance catadioptric imaging system
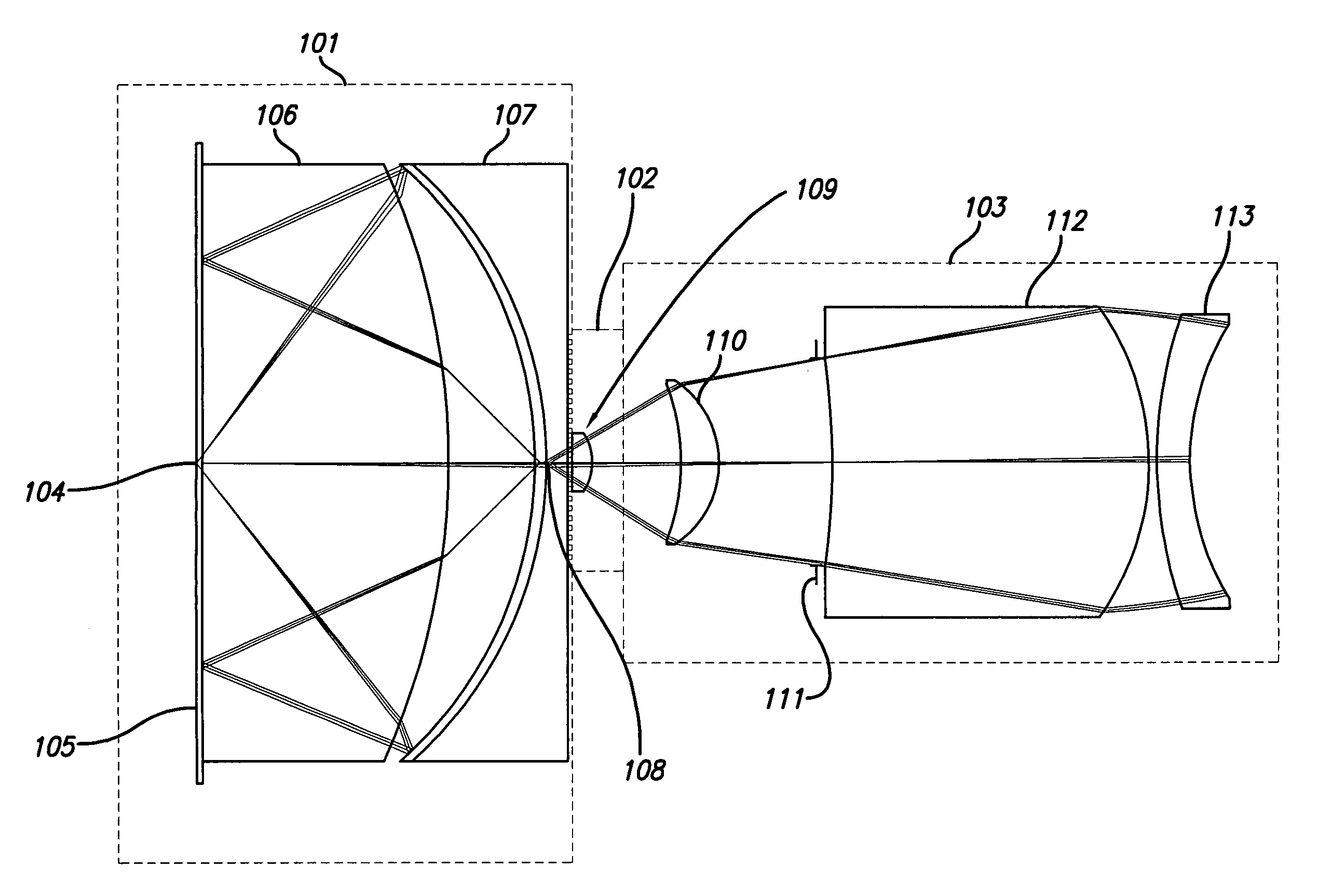
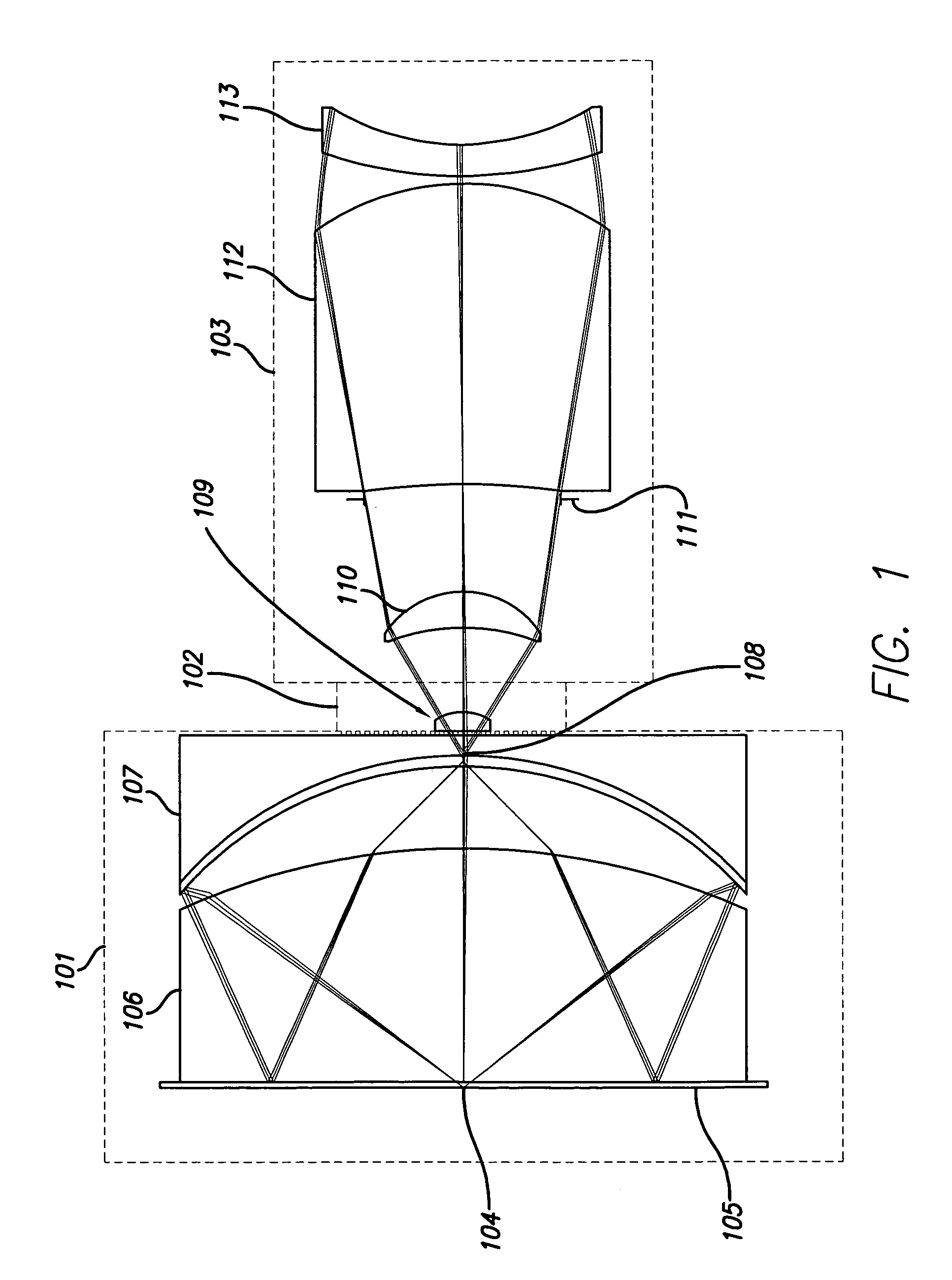
A reduced size catadioptric objective and system is disclosed. The objective may be employed with light energy having a wavelength in the range of approximately 190 nanometers through the infrared light range. Elements are less than 100 mm in diameter. The objective comprises a focusing lens group configured to receive the light energy and comprising at least one focusing lens. The objective further comprises at least one field lens oriented to receive focused light energy from the focusing lens group and provide intermediate light energy. The objective also includes a Mangin mirror arrangement positioned to receive the intermediate light energy from the field lens and form controlled light energy for transmission to a specimen. The Mangin mirror arrangement imparts controlled light energy with a numerical aperture in excess of 0.65 and up to approximately 0.90, and the design may be employed in various environments.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Long-wave infrared optical system for observing devices using the principle of the Cassegrain telescope
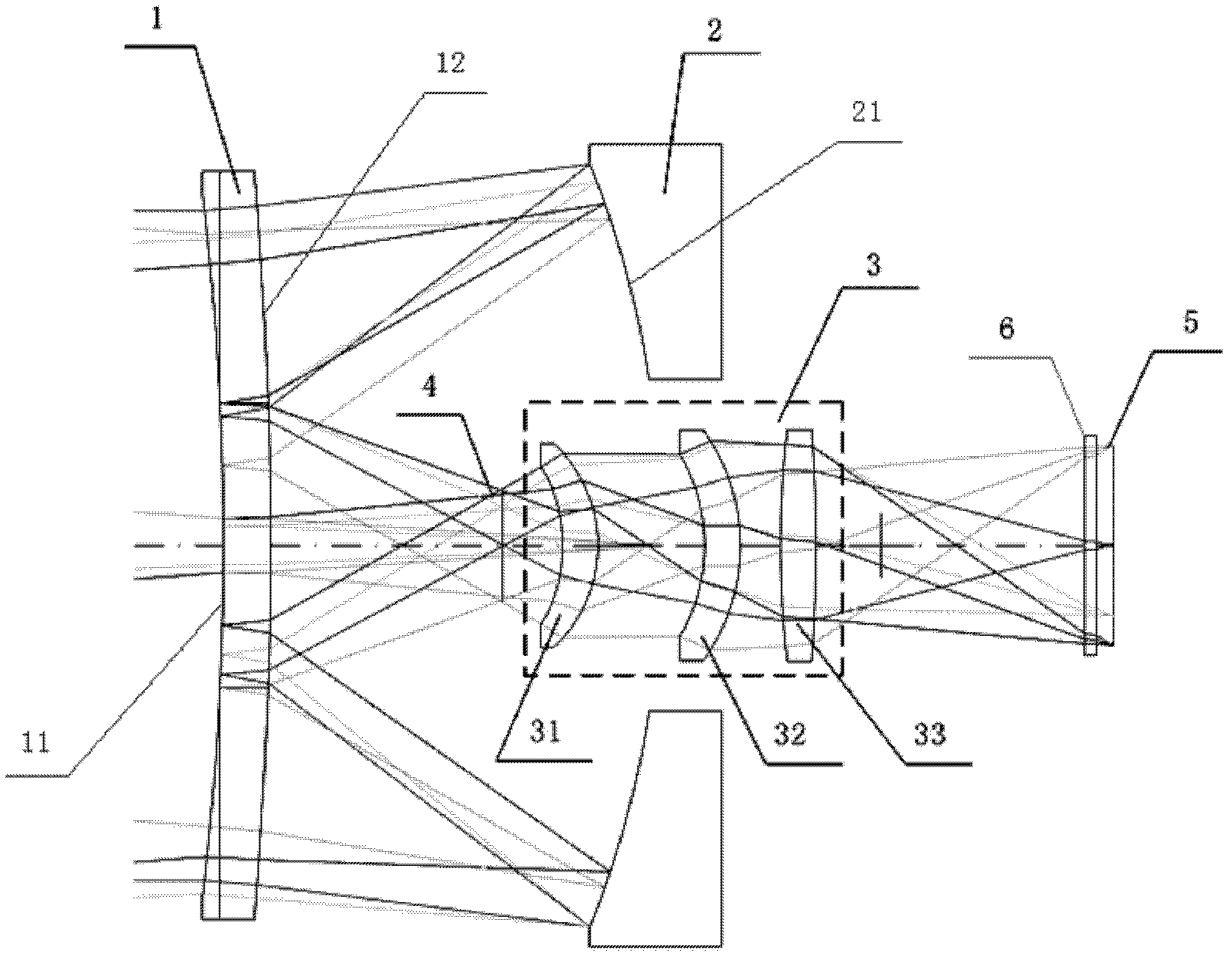
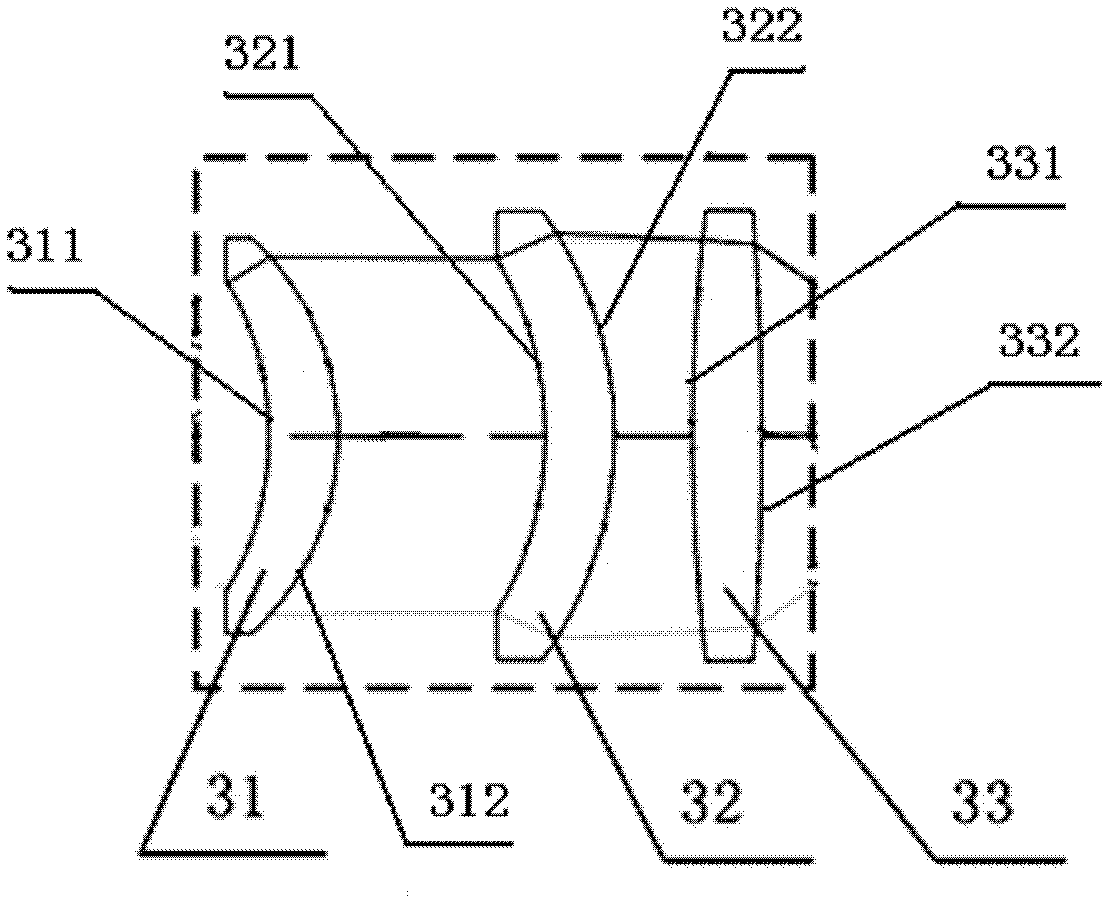
The invention proposed the design of an optical system using the principle of Cassegrain telescopes for a long wave radiation range, which consists of two main components: the first component comprising the two reflective mirrors, in which surface distortion of mirror 1 is parabolic, surface distortion of mangin mirror 2 is aspheric; the second component is a relay consisting of three lenses: lens 1, lens 2, and lens 3 arranged after the medial image plane correspondingly; it plays an important role in fixing the pupil's position to match the position of the cold shield of the sensor and eliminating absolutely the aberration to ensure receiving good quality image at the sensor plane.
Owner:VIETTEL GRP
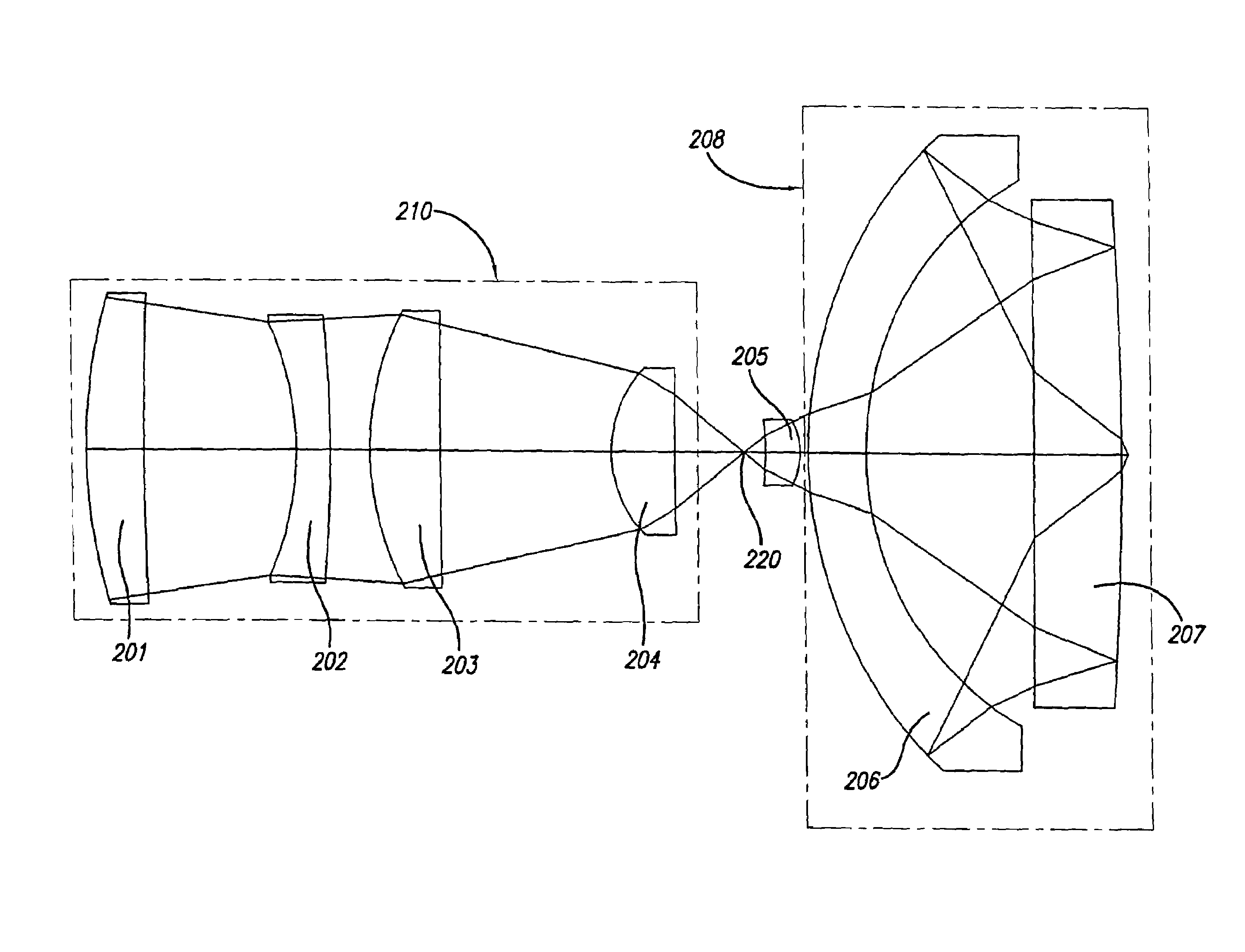
Catadioptric imaging system for broad band microscopy
A system and method for inspection is disclosed. The design includes an objective employed for use with light energy having a wavelength in various ranges, including approximately 266 to 1000 nm, 157 nm through infrared, and other ranges. The objective includes a focusing lens group having at least one focusing lens configured to receive light, a field lens oriented to receive focused light energy from said focusing lens group and provide intermediate light energy, and a Mangin mirror arrangement positioned to receive the intermediate light energy from the field lens and form controlled light energy. Each focusing lens has a reduced diameter, such as a diameter of less than approximately 100 mm, and a maximum corrected field size of approximately 0.15 mm. An immersion substance, such as oil, water, or silicone gel, may be employed prior to passing controlled light energy to the specimen inspected.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
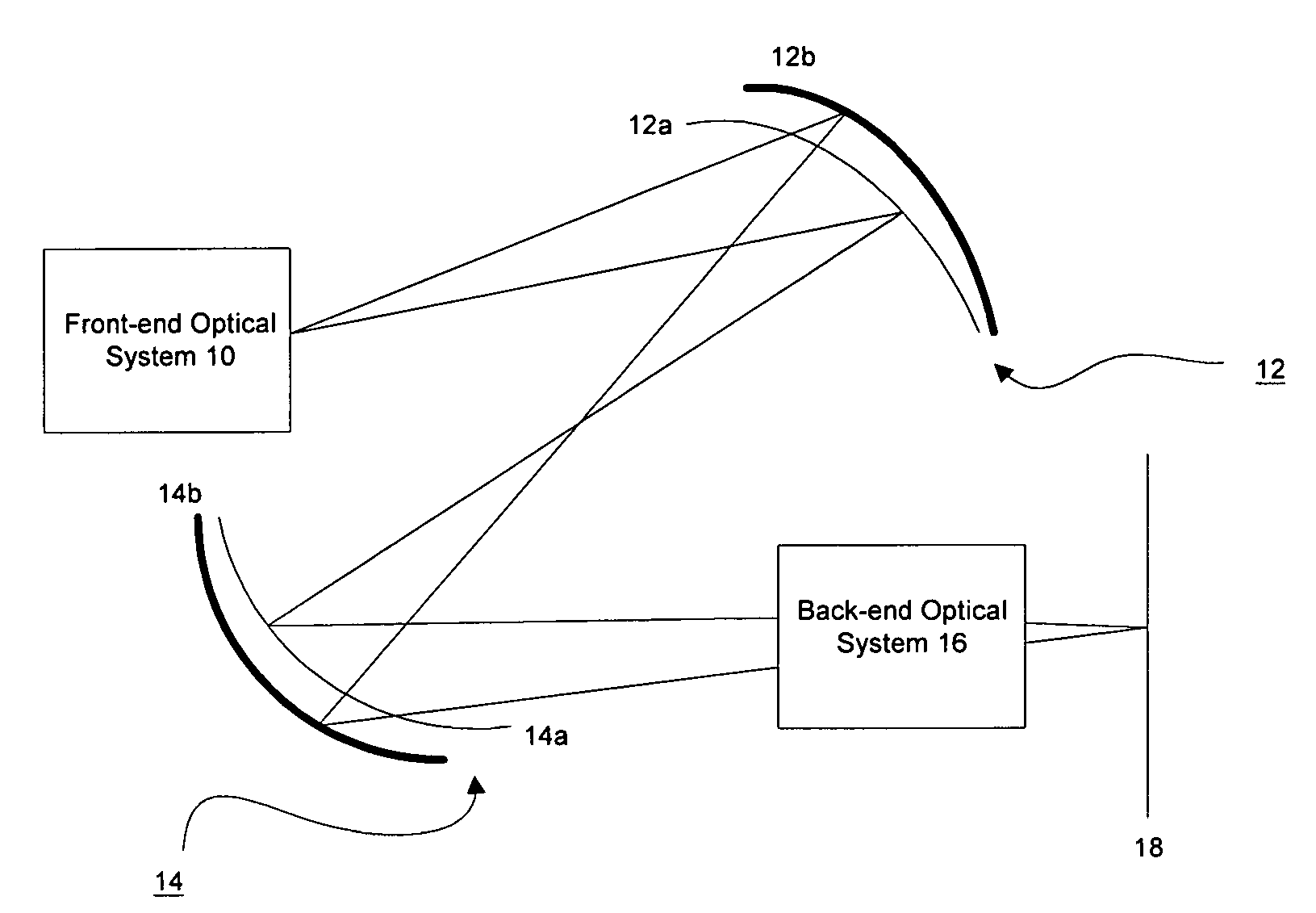
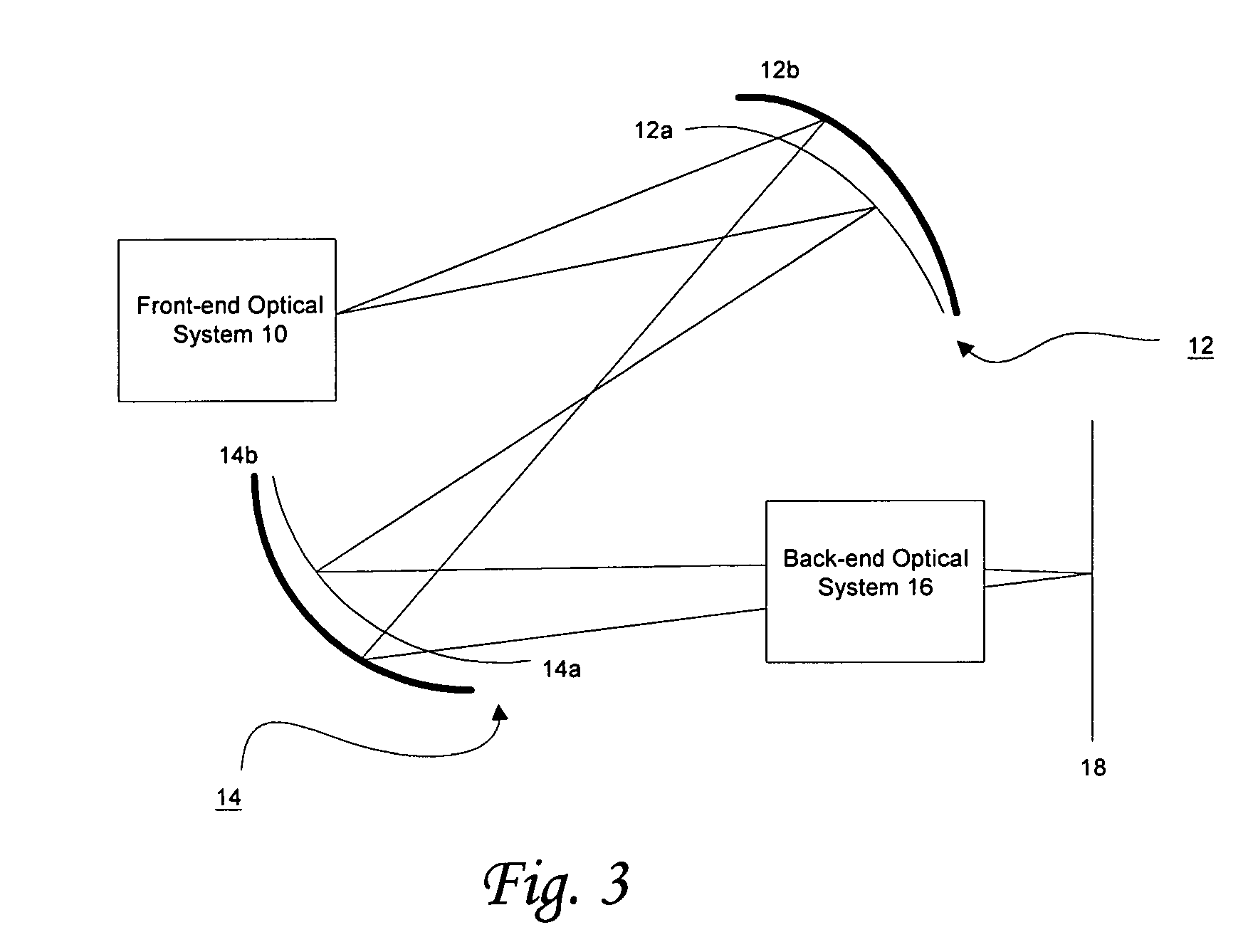
Dichroic mangin mirror
InactiveUS7333271B2Certain degreeEliminate dispersionRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansMangin mirrorLight beam
An optical system having at least one dichroic Mangin mirror. The optical system has a front-end optical sub-system or a light source operative to emit an optical beam. The optical beam is dispersed into at least a first color beam and a second color beam and has certain degree of monochromatic aberration. The dichroic Mangin mirror is disposed along the optical paths of both the first and second color beams. The dichroic Mangin mirror includes a first surface operative to transmit the first color beam only, but reflects the second color beam. Therefore, upon incident on the dichroic Mangin mirror, the second color beam is reflected, while the first color beam transmits through the first surface and is then reflected off from the second surface. Thereby, the first and second color beams can be focused at the same position, which is referred as an achromatic system focus. Thereby, the chromatic aberration caused by the dispersion can be eliminated.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Wide-angle projection optical system
ActiveUS20160274344A1Eliminate dangerShort effective focal lengthProjectorsOptical elementsImaging qualityMangin mirror
A wide-angle projection optical system includes, between an object side and an image side, a first optical system including a first lens group having an aperture stop and a second lens group disposed behind the aperture stop, and a second optical system including a Mangin mirror and a glass plate disposed between the second lens group and the Mangin mirror. The first and second lens groups have positive power. The first lens group provides optical characteristics to match with a light coming from the object side. The first and second lens groups are configured to form an aberrated real image. The Mangin mirror is disposed closer to the image side than others. The Mangin mirror includes a refracting surface and a reflecting surface for refracting the light two times and reflecting the light one time, thereby producing an enlarged real image on a screen. Therefore, the image quality is enhanced.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Optical path of multispectral polarization scanning radiometer based on reflecting telescope system
ActiveCN104634742AReduced Variation Factors in Polarization Measurement AccuracySmall residual polarizationMaterial analysis by optical meansLight polarisation measurementReflecting telescopeMangin mirror
The invention discloses an optical path of a multispectral polarization scanning radiometer based on a reflecting telescope system. The optical path comprises a pre-posed scanning mirror set, a telescope system and a main measuring optical path, wherein the pre-posed scanning mirror set is composed of a first planar mirror and a second planar mirror both which are orthogonal and installed on a remote sensing platform; the film layers of the first and second planar mirrors are silver reflection films respectively; the telescope system comprises a main mirror, a secondary mirror and a field diaphragm; the main mirror and the second mirror are concave parabolic mirrors and each plated with the a silver reflection film; the main measuring optical path comprises a polarizing component, multiple color separation filters, multiple reflector plates, multiple focusing lenses, multiple narrow band filters and multiple detectors. Because the reflecting telescope system is applied, the difference factors affecting the polarization measurement precision are reduced; the system is low in residual system polarization, wide in spectral range, flexible in amounts and positions of spectrums, high in transmittance, low in processing and installing precision and system cost.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optical lighting system and image projection system containing it
InactiveCN1536391AReduce manufacturing costEliminate deteriorationTelevision system detailsProjectorsMangin mirrorLight beam
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
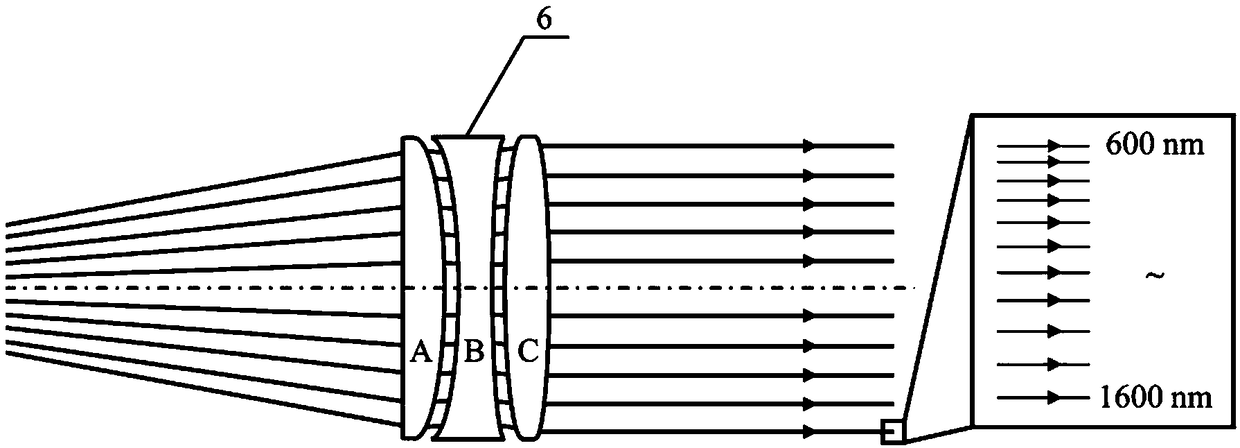
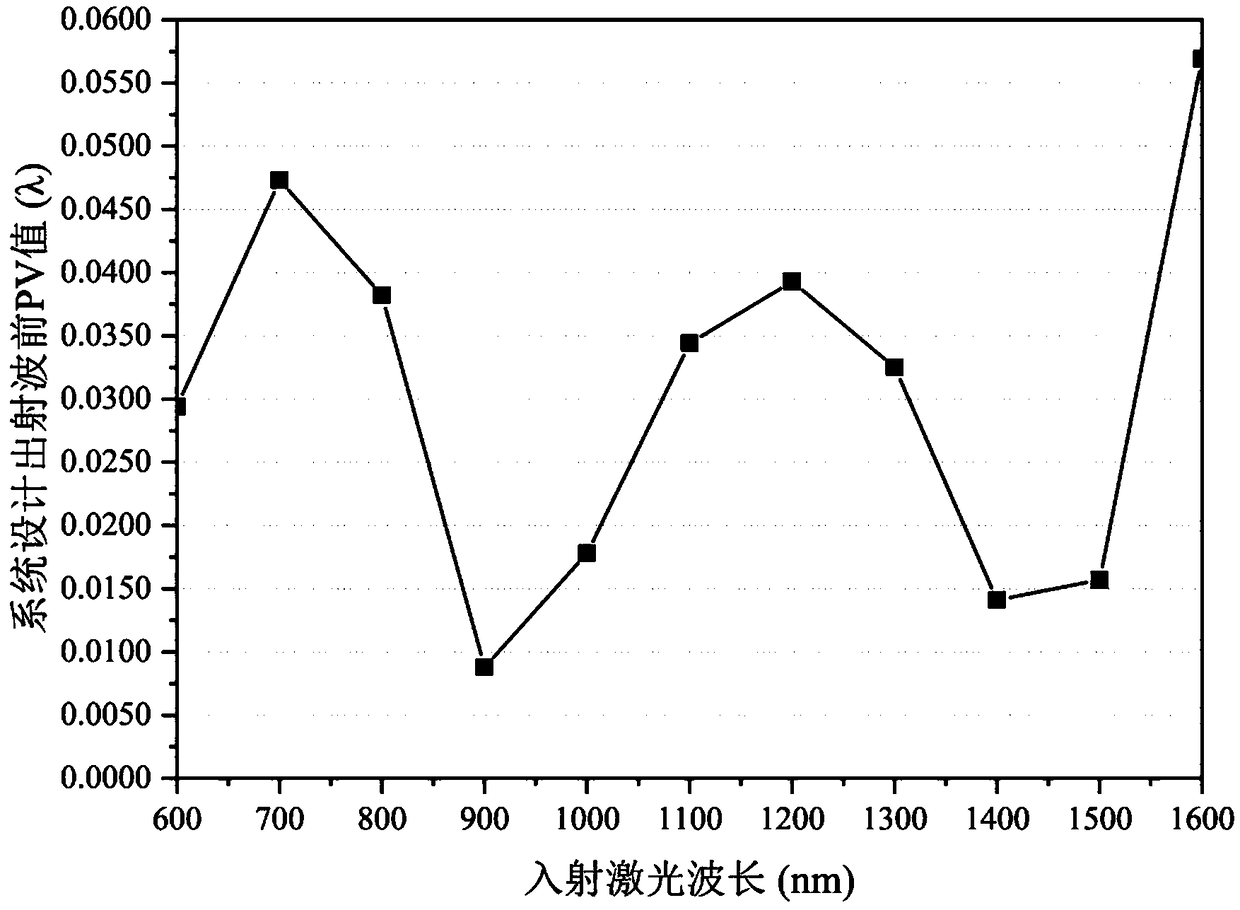
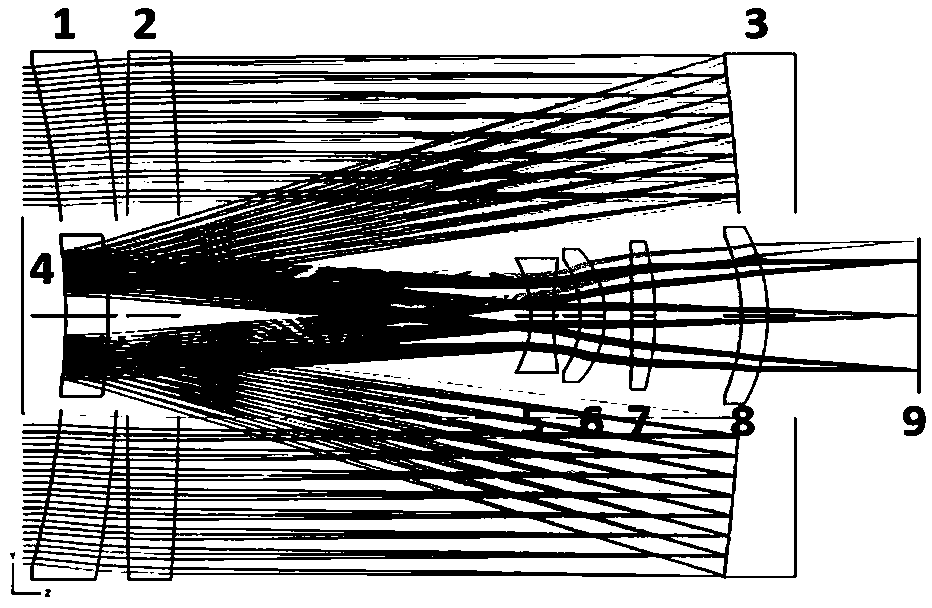
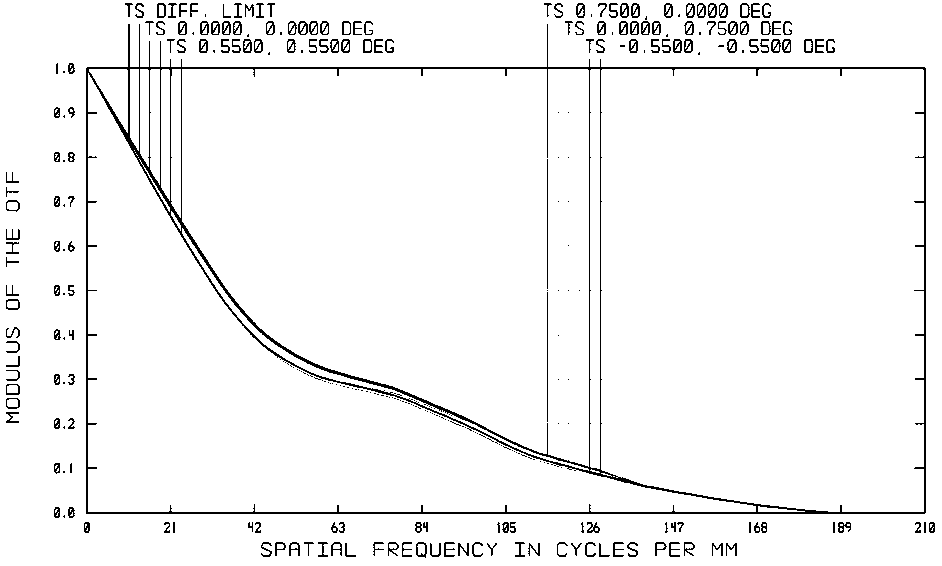
Multi-wavelength laser interferometer
ActiveCN109029244AResolved only at 632.8nmSolving 1053nmUsing optical meansBeam splitterMangin mirror
A multi-wavelength laser interferometer comprises a laser, an aperture diaphragm, a beam expanding secondary mirror, a pinhole diaphragm, a beam splitter prism, a collimating main mirror, a transmission standard mirror, a piezoelectric ceramic transducer, a to-be-measured plane element, a reflection standard mirror, an imaging lens, a hyperspectral camera and a computer. The collimating main mirror in the interferometer is composed of three lenses, and the imaging lens and the beam expanding secondary mirror are identical in parameter and are both single lenses; and in order to reduce the processing difficulty of the lenses in the interferometer and the difficulty of light path adjustment of a whole system, the beam expanding secondary mirror and the collimating main mirror are each provided with one surface which can be a plane. The multi-wavelength laser interferometer can be used for measuring transmission wavefront or reflected wavefront of the to-be-measured plane optical elementin the wavelength range of 600 nm-1600 nm.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
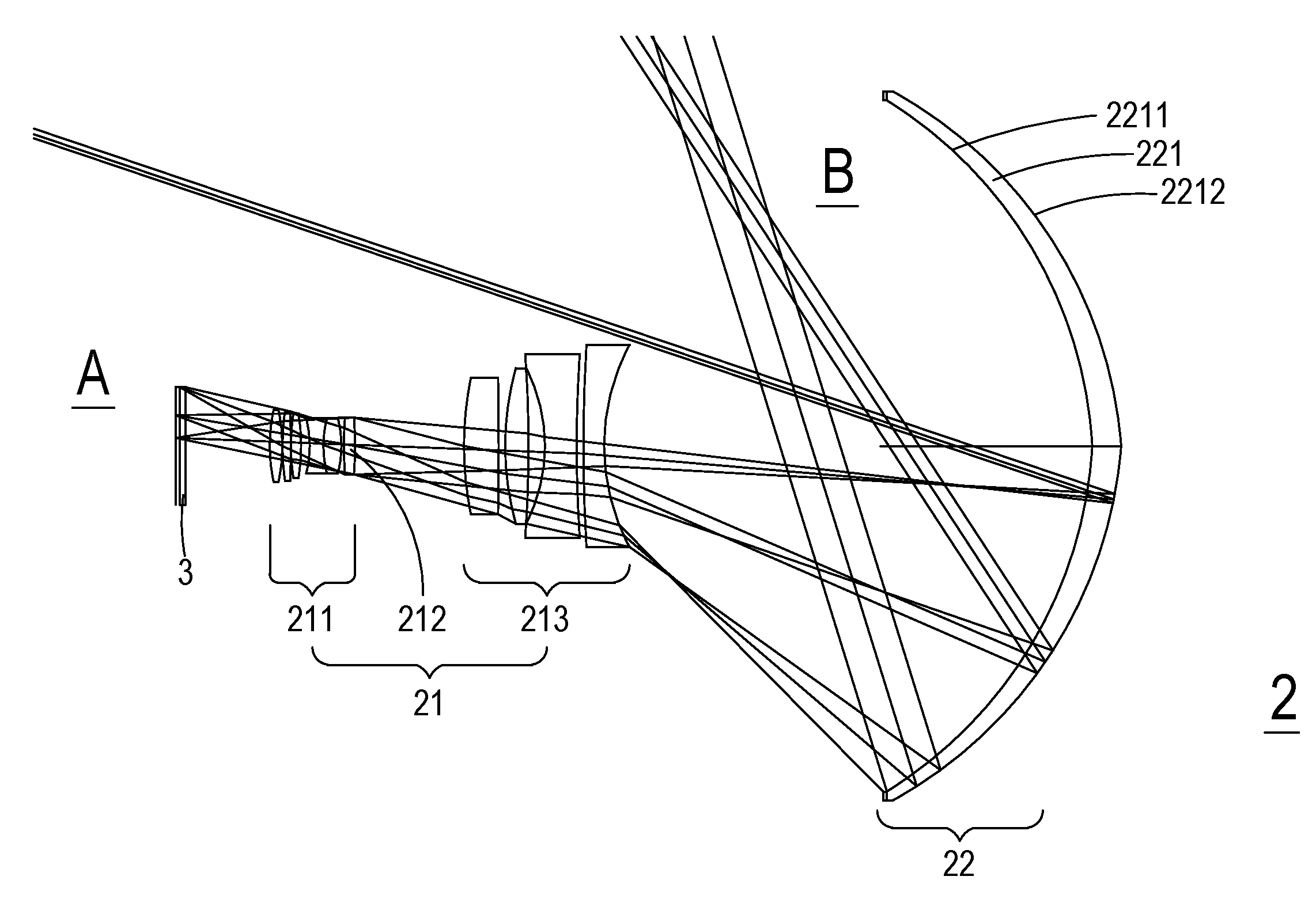
Compact type coaxial refraction and reflection type telescope objective
The invention discloses a compact type coaxial refraction and reflection type telescope objective. The surfaces of all components of the telescope objective are spherical surfaces. The telescope objective comprises a front-group concave lens, a front-group positive lens, a main reflecting mirror, a Mangin mirror, a rear-group concave lens and three rear-group positive lenses, wherein the telescopeobjective is in rotational symmetry relative to a main optical axis, and an aperture diaphragm is positioned on a main reflecting mirror; the middle of the front-group concave lens, the middle of thefront-group positive lens and the middle of the main reflecting mirror are independently provided with a hole; after an incident ray from ground scenery is refracted through the front-group lenses, the incident ray reaches the main reflecting mirror; after the incident ray is focused, the incident ray passes through the front surface, the rear surface and the front surface of the Mangin mirror insequence without hindering in sequence; and after the incident ray is refracted by the rear-group concave lens and three rear-group positive lenses in sequence, the incident ray passes through the center hole of the main reflecting mirror without hindering to finally reach an image surface. The telescope objective has the advantages of long focal length, low cost, small volume, light weight, compact structure, good imaging quality, easiness in processing and adjustment and the like.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Inspection system using small catadioptric objective
A system for use with a reduced size catadioptric objective is disclosed. The system including the reduced size objective includes various subsystems to allow enhanced imaging, the subsystems including illumination, imaging, autofocus, positioning, sensor, data acquisition, and data analysis. The objective may be employed with light energy having a wavelength in the range of approximately 190 nanometers through the infrared light range, and elements of the objective are less than 100 mm in diameter. The objective comprises a focusing lens group and at least one field lens oriented to receive focused light energy from the focusing lens group and provide intermediate light energy. The objective also includes a Mangin mirror arrangement. The design imparts controlled light energy with a numerical aperture in excess of 0.65 and up to approximately 0.90 to a specimen for imaging purposes, and the design may be employed in various environments.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Catadioptric imaging system employing immersion liquid for use in broad band microscopy
A reduced size catadioptric inspection system employing a catadioptric objective and immersion substance is disclosed. The objective may be employed with light energy having a wavelength in the range of approximately 190 nanometers through the infrared light range, and can provide numerical apertures in excess of 0.9. Elements are less than 100 millimeters in diameter and may fit within a standard microscope. The objective comprises a focusing lens group, a field lens, a Mangin mirror arrangement, and an immersion substance or liquid between the Mangin mirror arrangement and the specimen. A variable focal length optical system for use with the objective in the catadioptric inspection system is also disclosed.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Catadioptric imaging system exhibiting enhanced deep ultraviolet spectral bandwidth
A relatively high spectral bandwidth objective employed for use in imaging a specimen and method for imaging a specimen is provided. The objective includes a lens group having at least one focusing lens configured to receive light energy and form an intermediate image, at least one field lens oriented to receive the intermediate image and provide intermediate light energy, and a Mangin mirror arrangement positioned to receive the intermediate light energy and apply light energy to the specimen. The objective may provide, in certain instances, a spectral bandwidth up to approximately 193 to 266 nanometers and can provide numerical apertures in excess of 0.9. Elements are less than 100 millimeters in diameter and may fit within a standard microscope. The field lens may include more than one lens and may be formed of a material different from at least one other lens in the objective.
Owner:KLA CORP
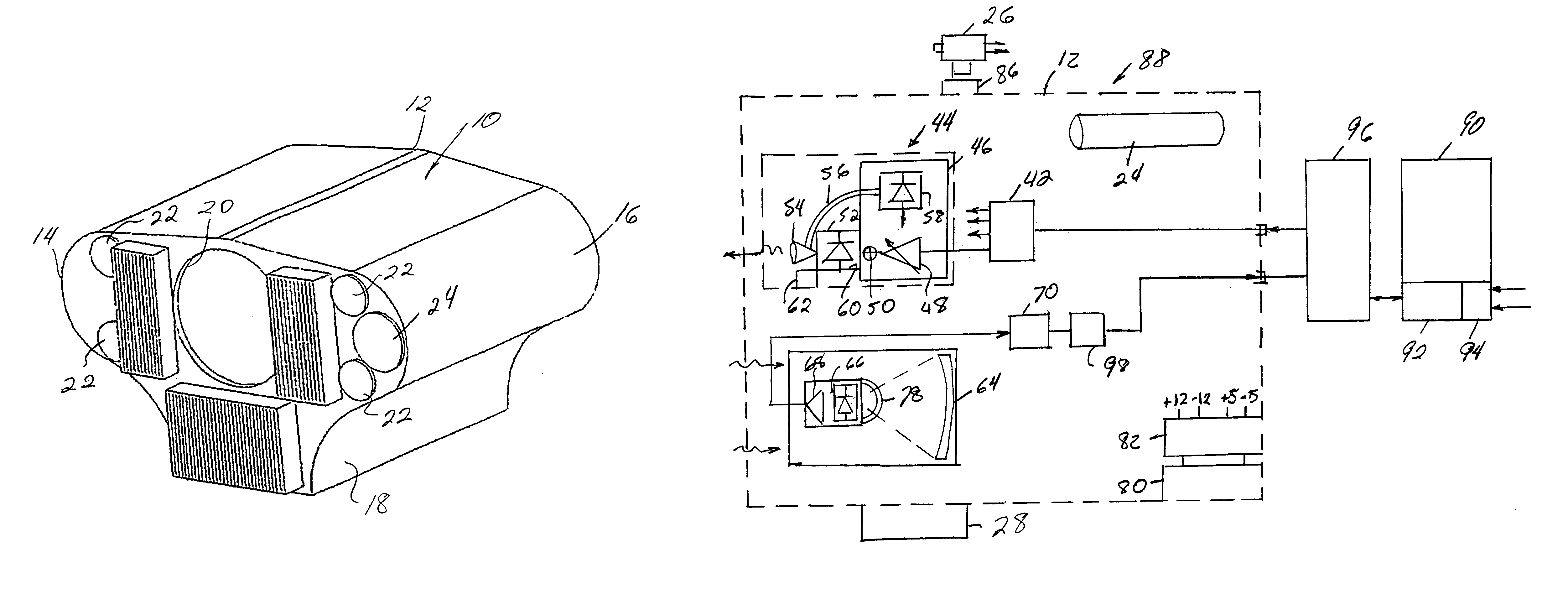
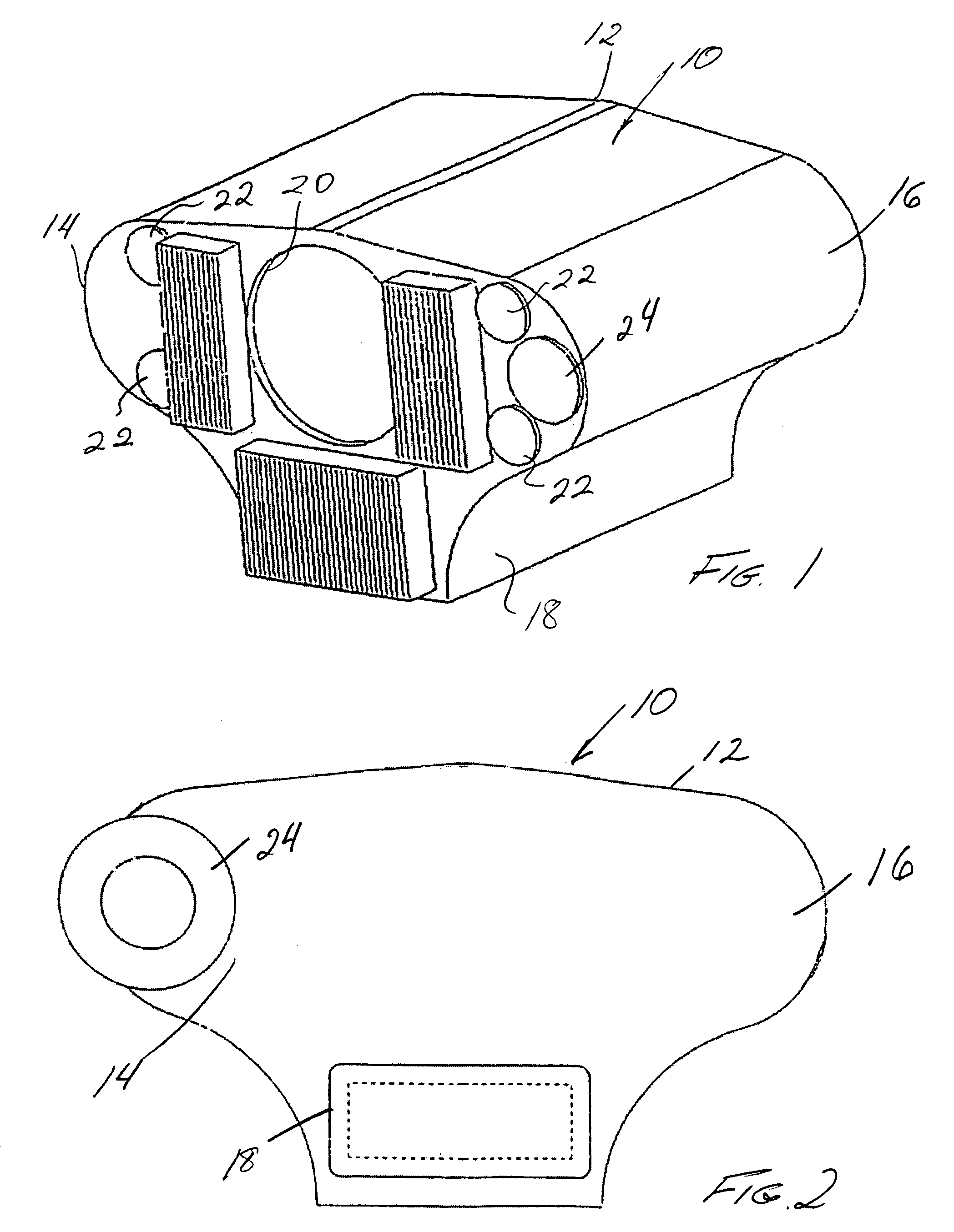
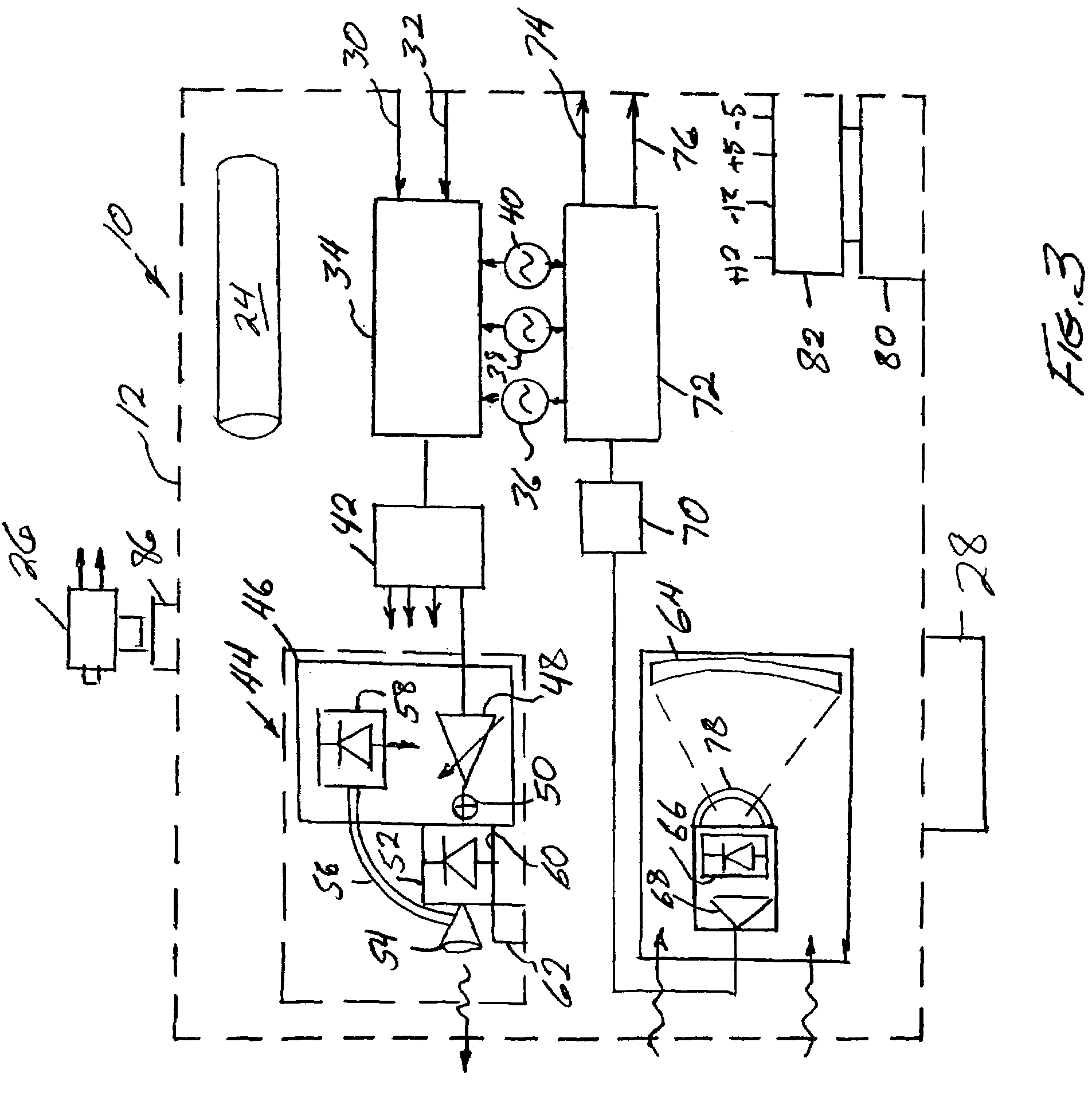
Portable laser transceiver
A portable transceiver of one or more signals includes an input, frequency modulation, a splitter and a plurality of lasers in a transmitter module. A receiver module includes a Mangin mirror aligned with an input aperture. A photodiode receives the signal from the mirror for subsequent demodulation. An interference filter is arranged between the mirror and the photodiode. The filter is hemispherical, having a center of curvature at the focal point of the mirror. The transceiver may include a video camera and gyro-stabilizer accessories. A visual siting scope is aligned with the lasers and the receiver. A separate transceiver for ethernet input signals interfaces with a 10 / 100 ethernet switch and does not employ frequency modulation.
Owner:LASER DIODE SYST
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com