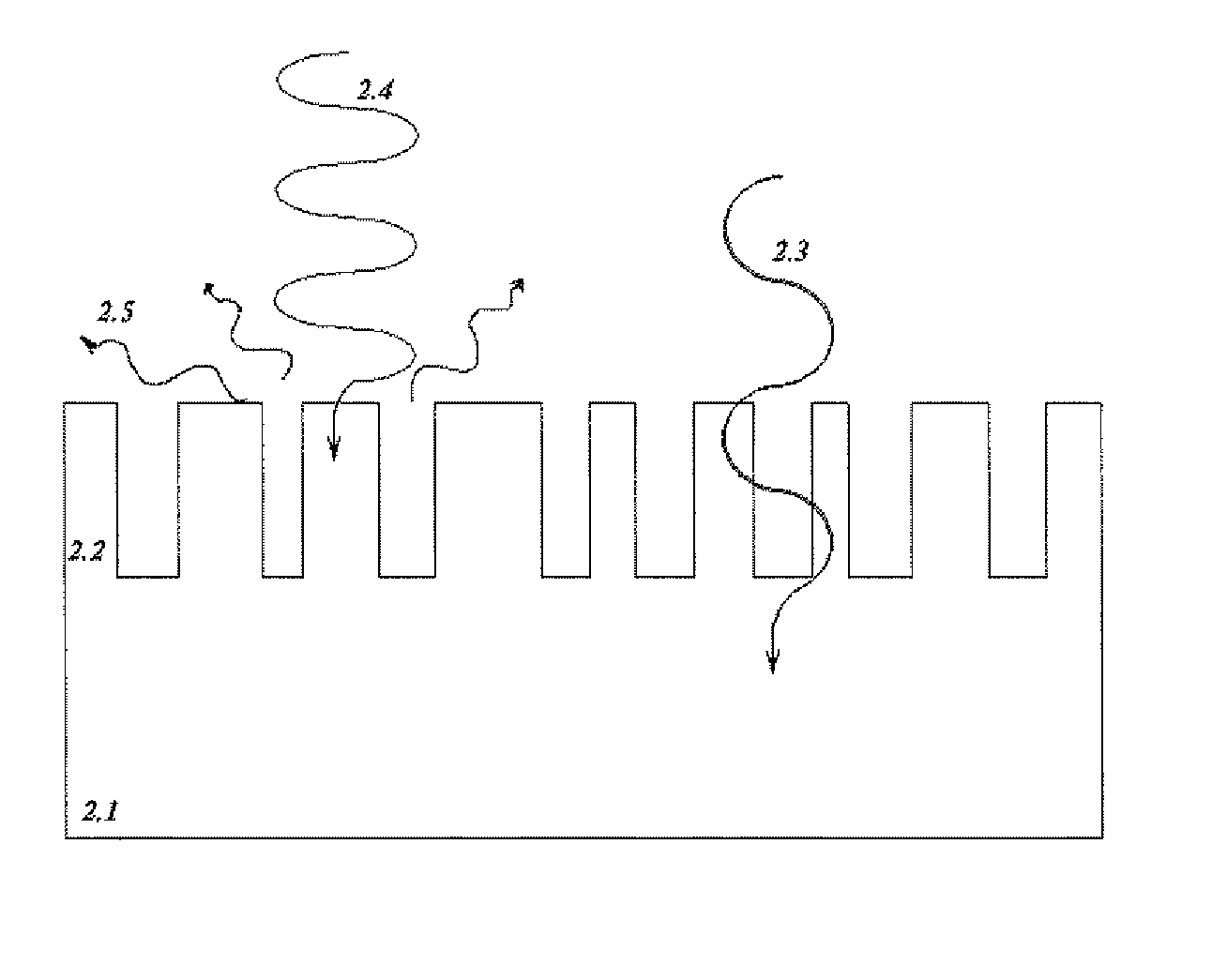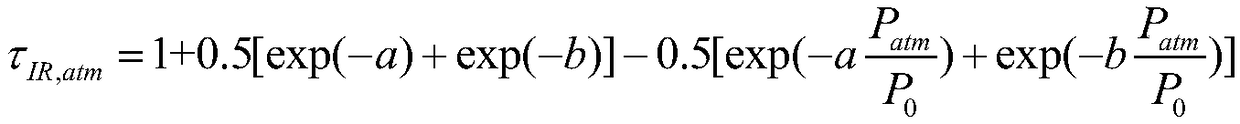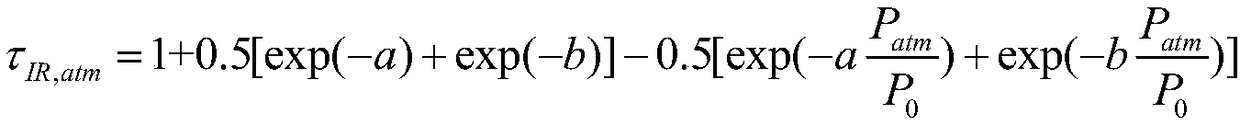Patents
Literature
109 results about "Long wave radiation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The atmosphere is most transparent in the wavelength range from 8 to 12μm and from 17 to 18μm (the so-called atmospheric windows). The long-wave radiation spectrum of clouds (water drops) is close to the spectrum of water vapor but is more intense. Dense clouds are virtually opaque to long-wave radiation.
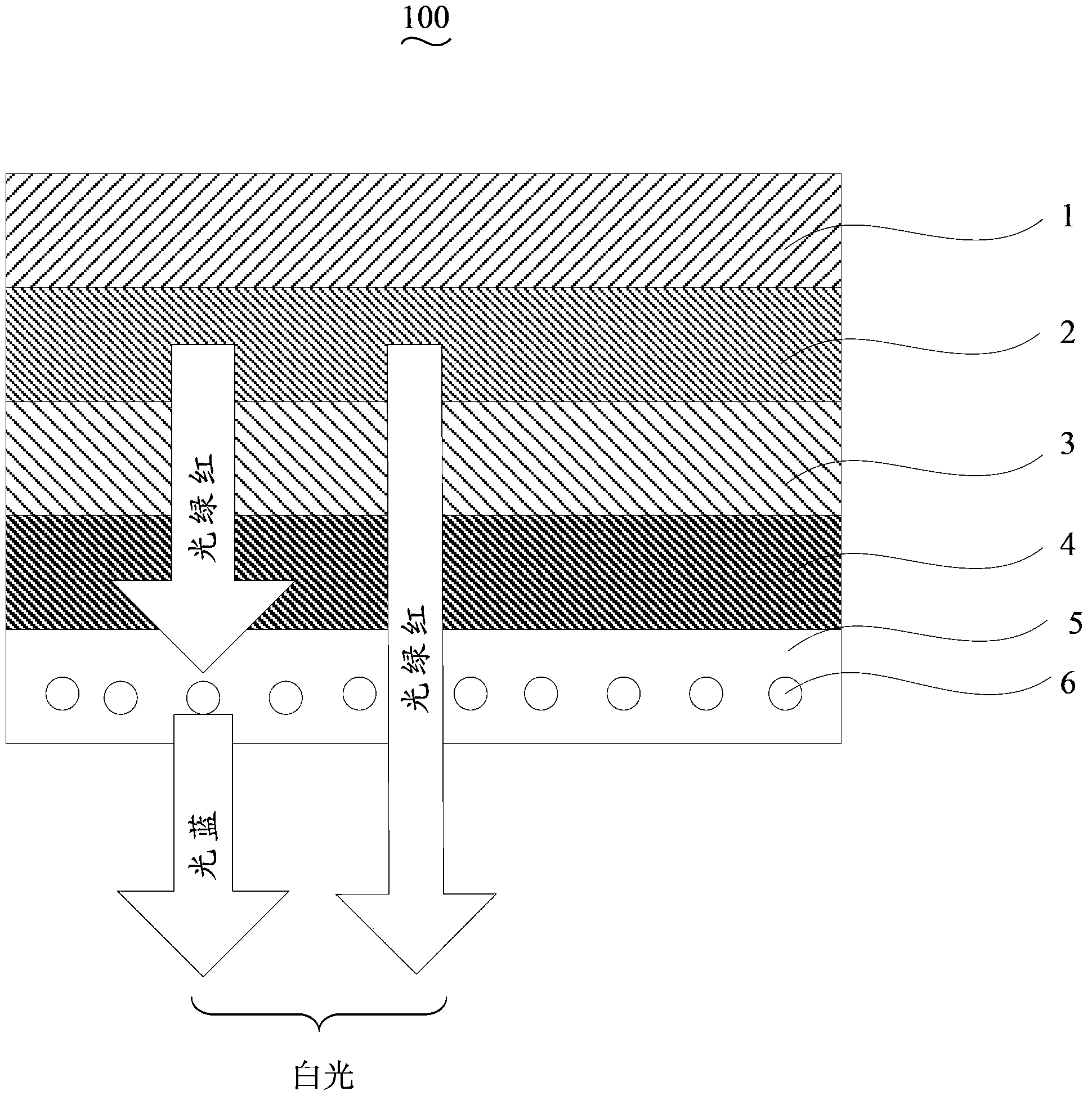
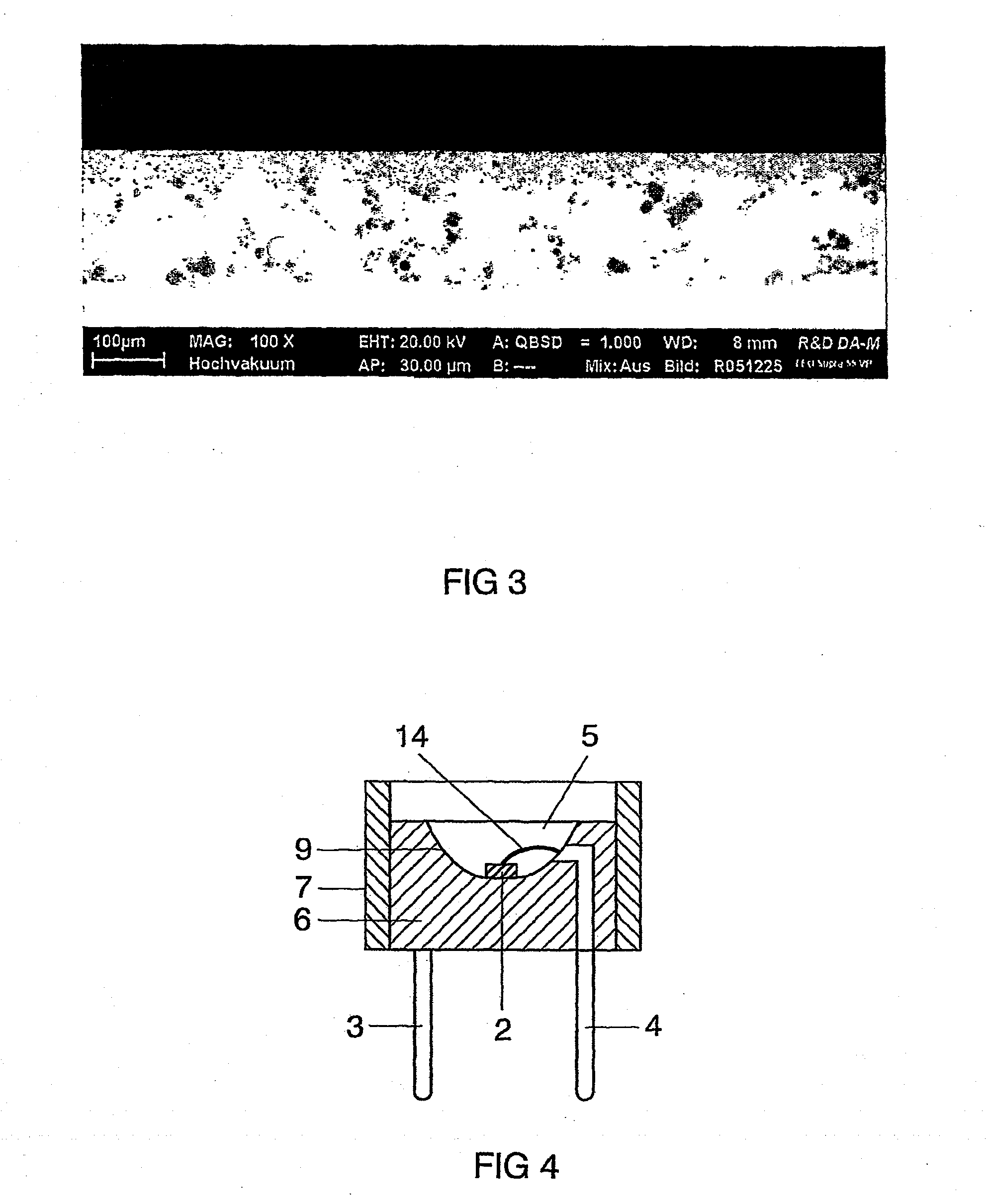
Luminescence conversion led
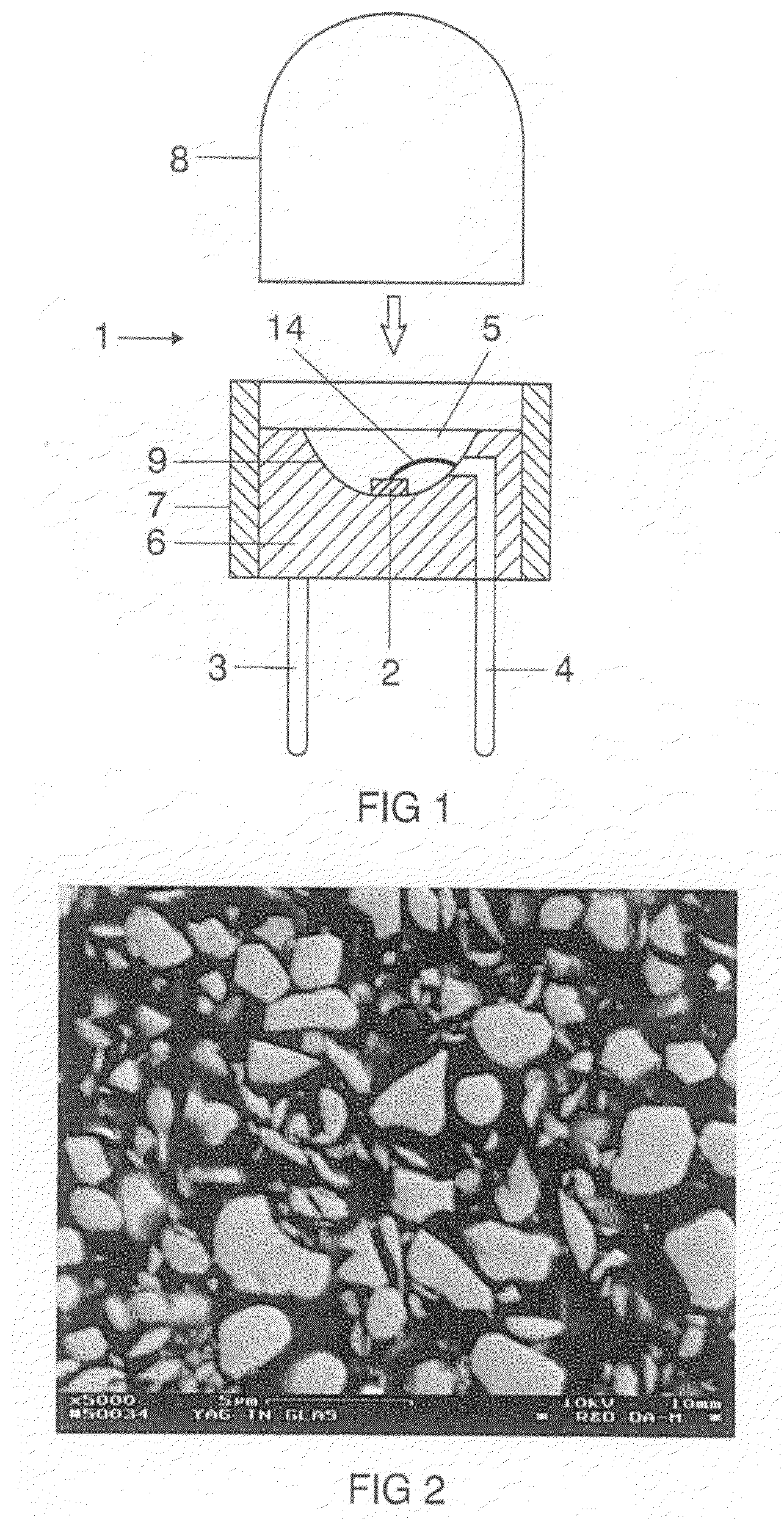
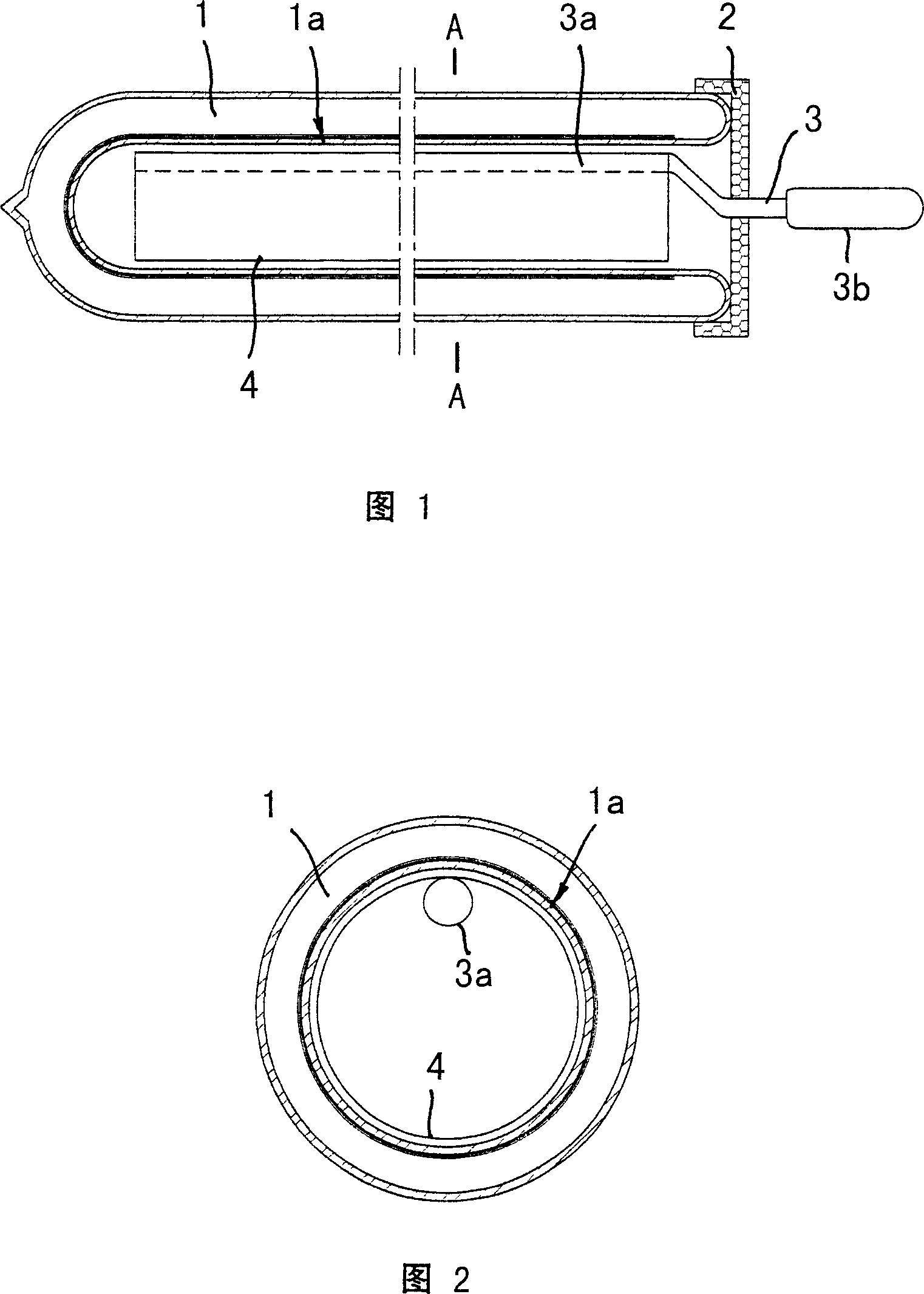
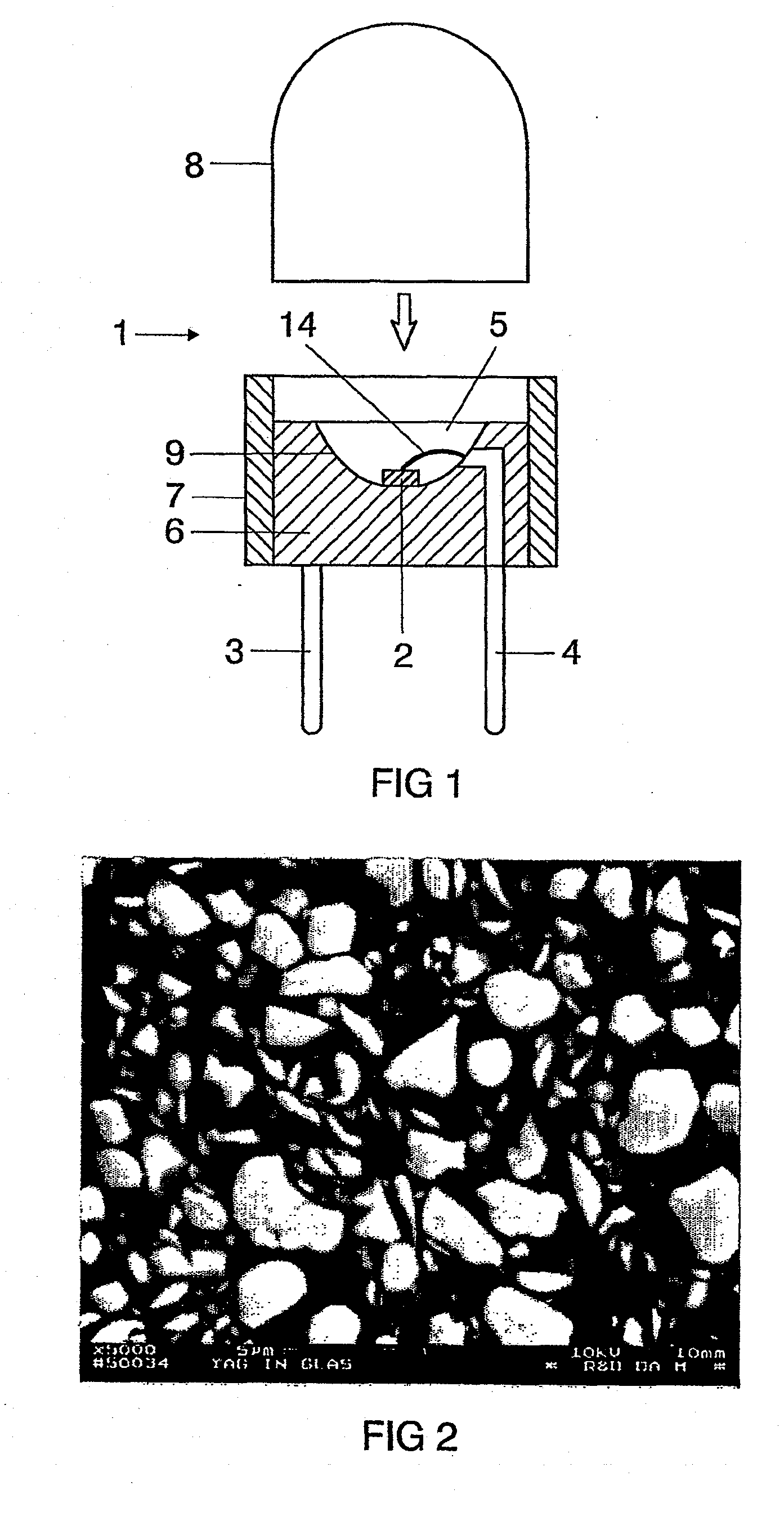
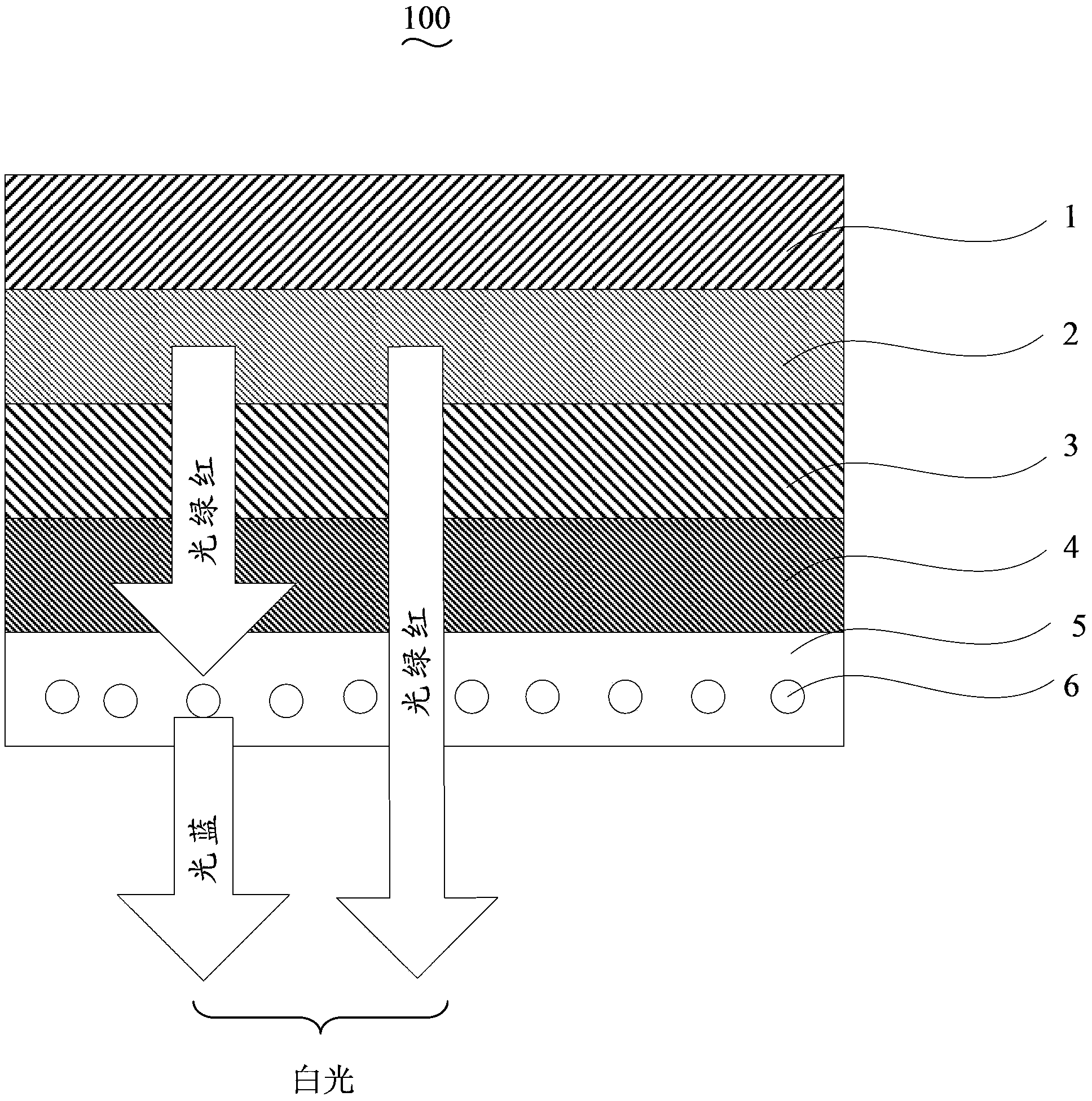
InactiveUS20090206352A1Improve conversion efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingVitreous BodiesElectrical connection
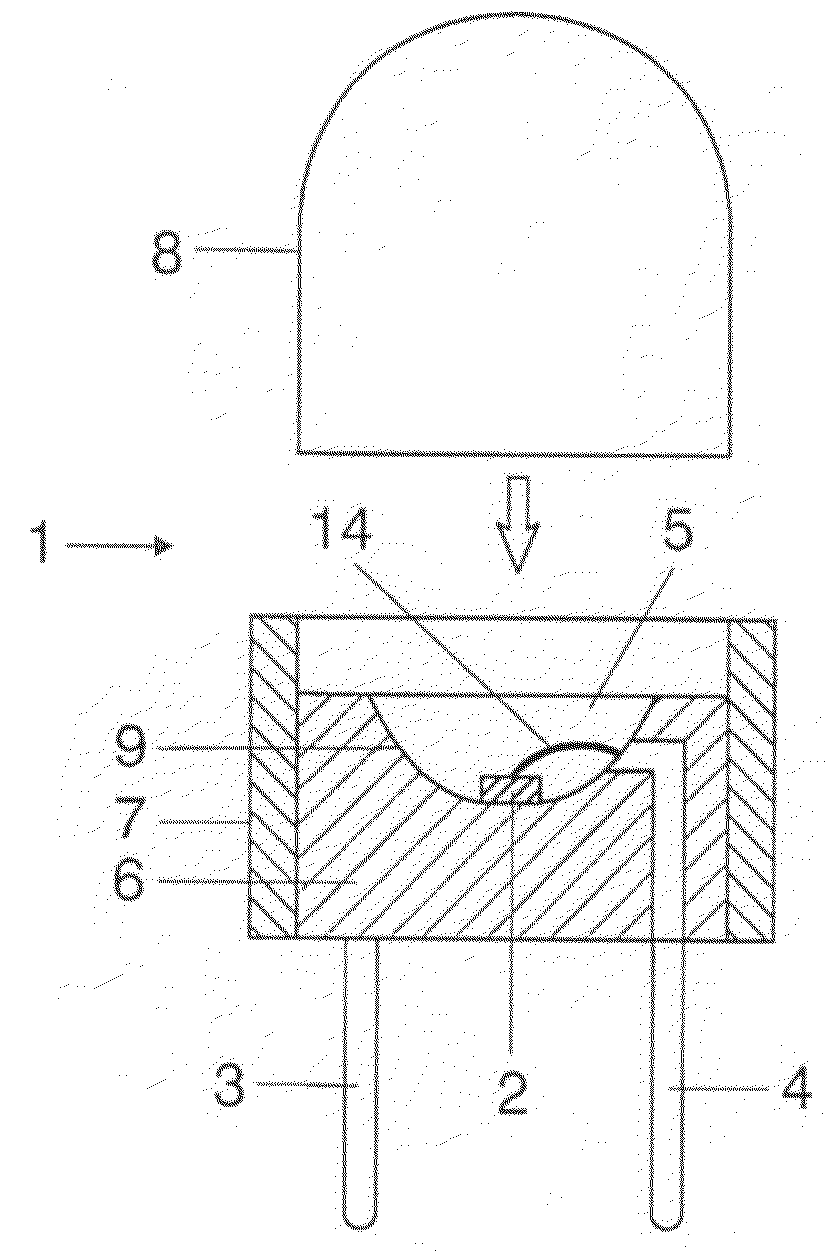
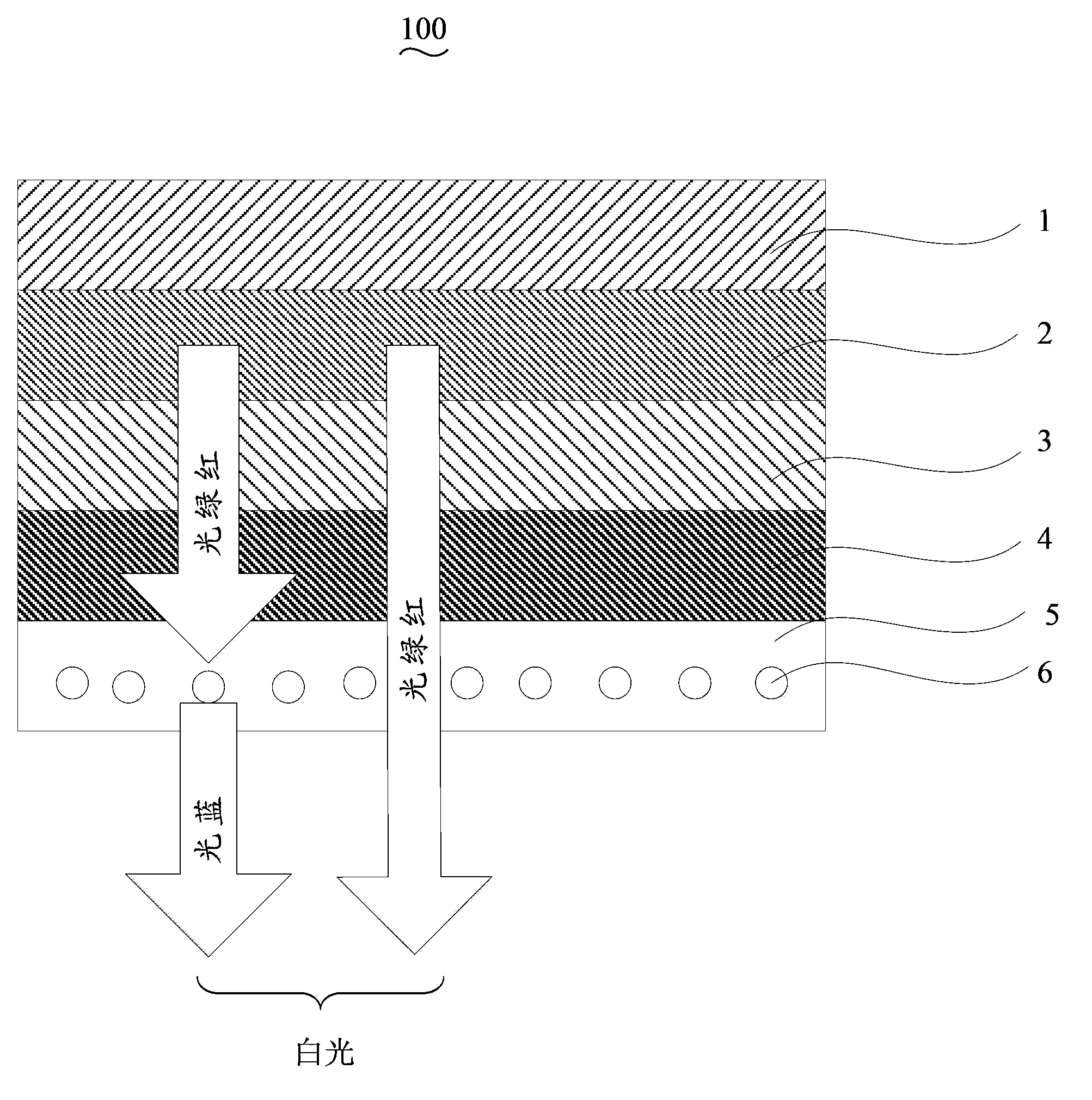
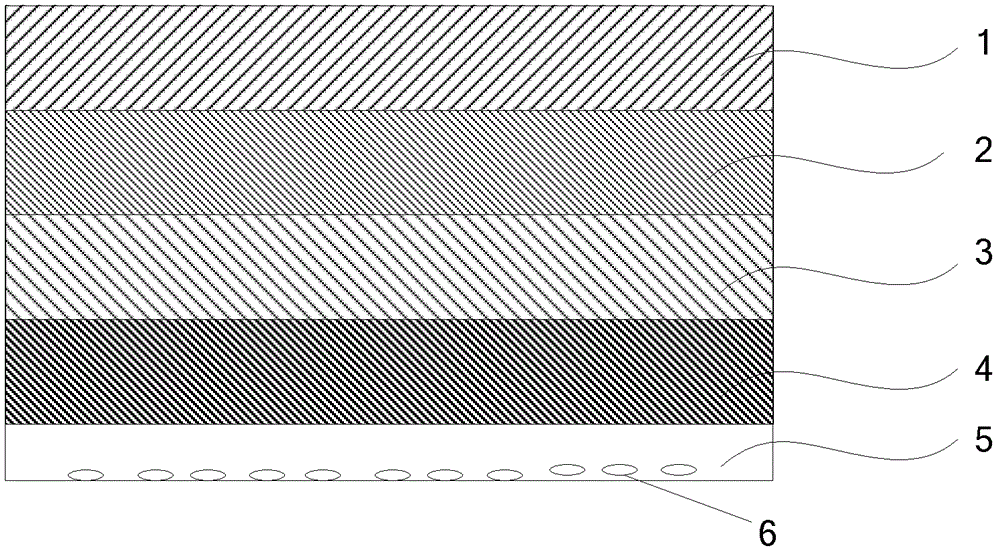
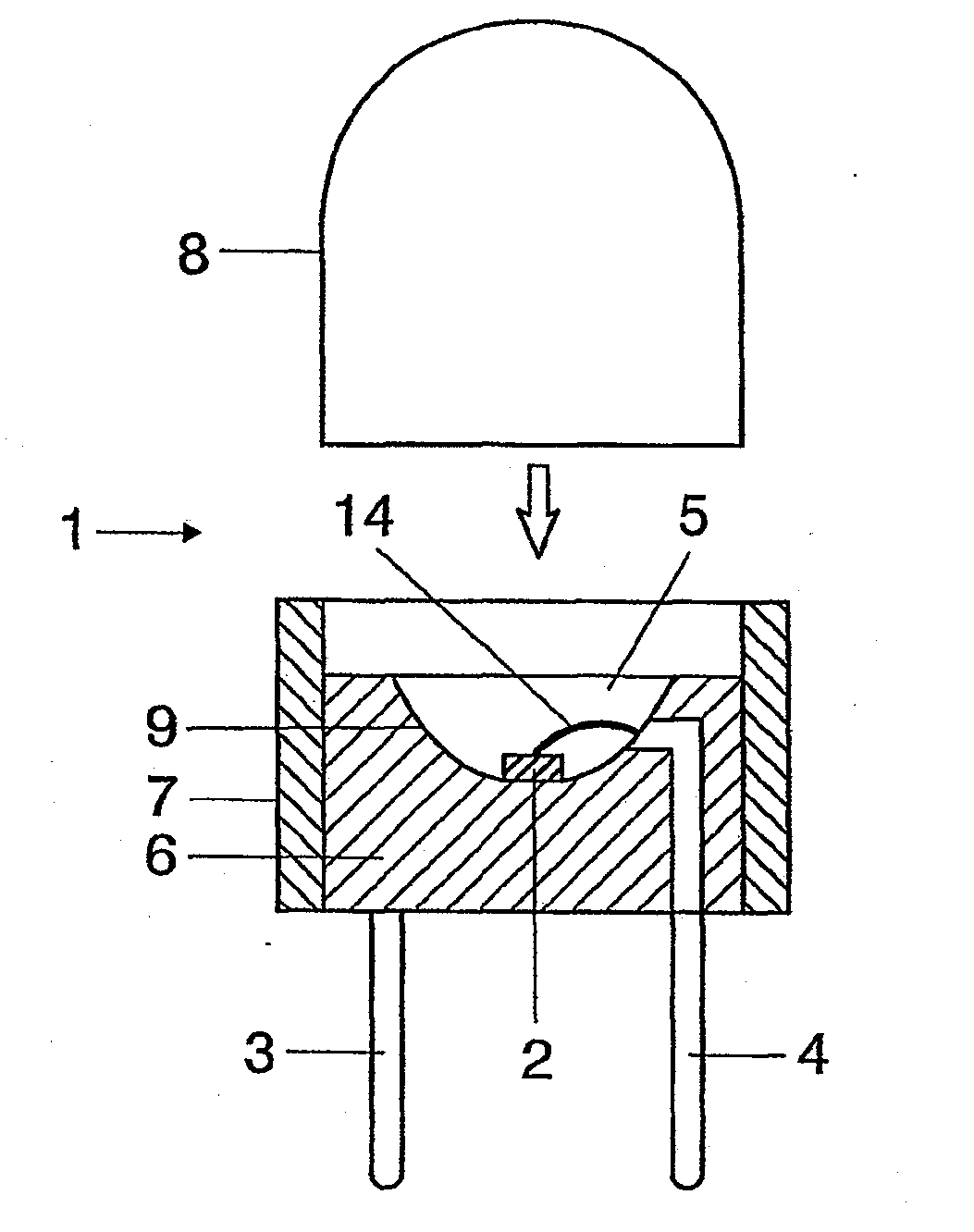
A luminescence conversion LED having a radiation emitting chip that is connected to electrical connections and is surrounded by a housing that comprises at least a basic body and a cap, the chip being seated on the basic body, in particular in a cutout of the basic body, and the primary radiation of the chip being converted at least partially into longer wave radiation by a conversion element, wherein the cap is formed by a vitreous body, the conversion means being contained in the vitreous body, the refractive index of the vitreous body being higher than 1.6, preferably at least n=1.7.
Owner:OSRAM GMBH +1
Heat supply load forecasting method based on a comprehensive temperature
ActiveCN106096781ASolve wasteForecastingRenewable energy source integrationLoad forecastingBuilding energy
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH +1
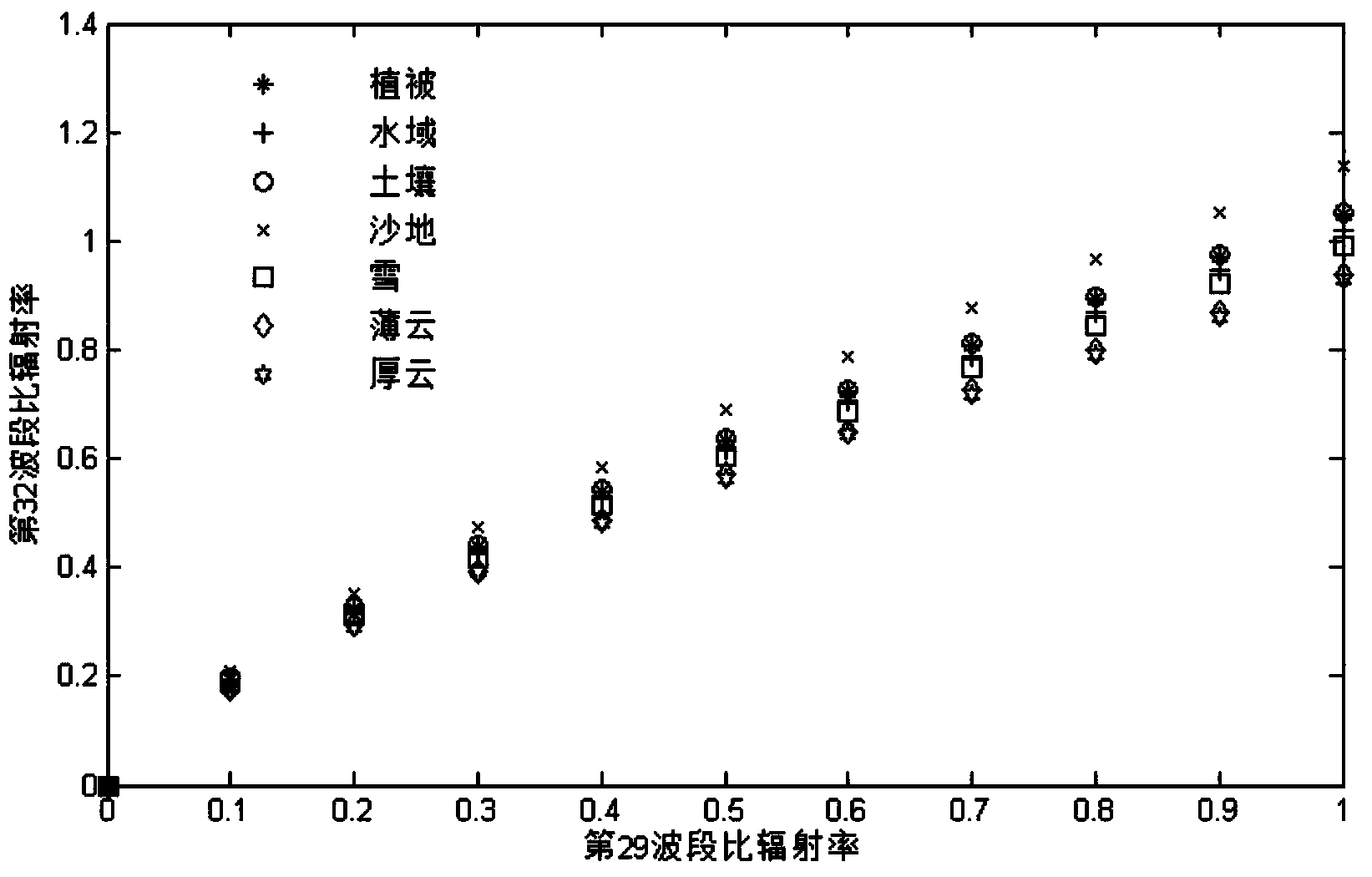
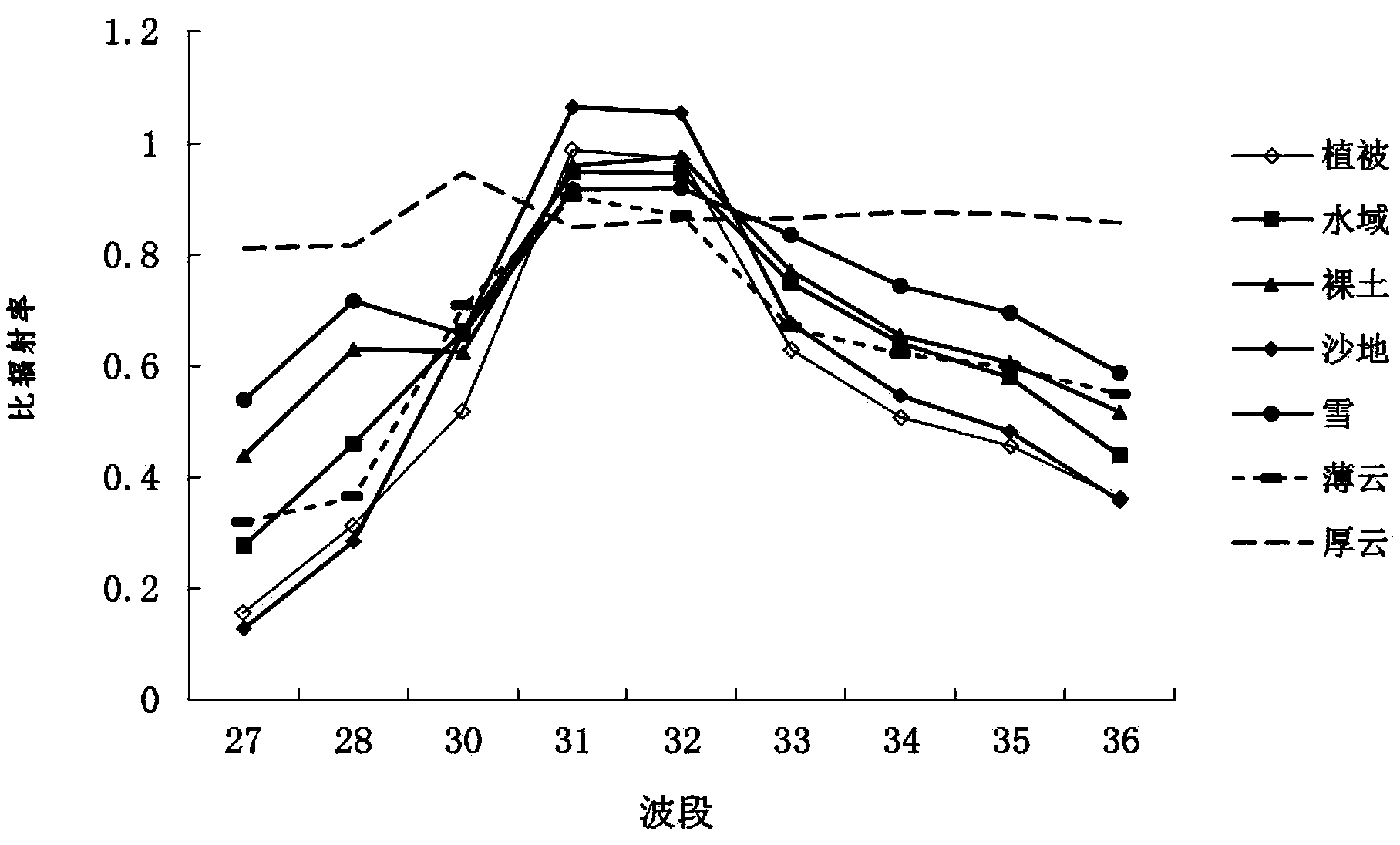
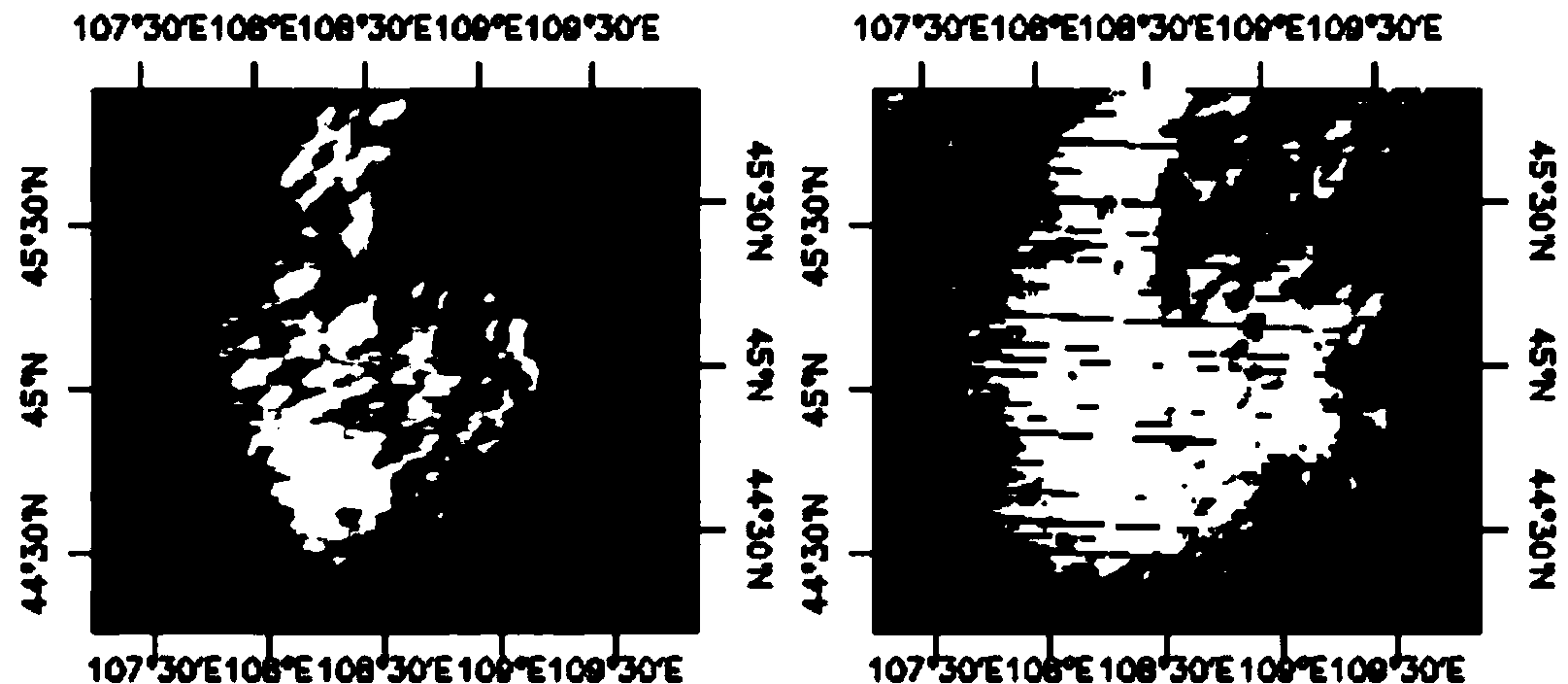
Cloud detection method by using MODIS remote sensing thermal infrared data
The invention discloses a cloud detection method by using MODIS remote sensing thermal infrared data, which involves mainly utilizing the emissivity difference between a cloud and an underlay object in a MODIS data long wave radiated wave band for cloud detection. Since the cloud is different from such underlay objects as vegetation, exposed soil, snow, sand, water area and the like in terms of substance properties and surface conditions, their emissivity in a long wave band are different. The invention further provides a cloud index (TCDI) method which involves cloud detection by using the emissivity difference between the cloud and other underlay objects, is free from the influence of sunlight, and is capable of the cloud detection in both the day time and at night.
Owner:海全胜
Town thermal island characteristic prediction technique and system based on digital image analysis
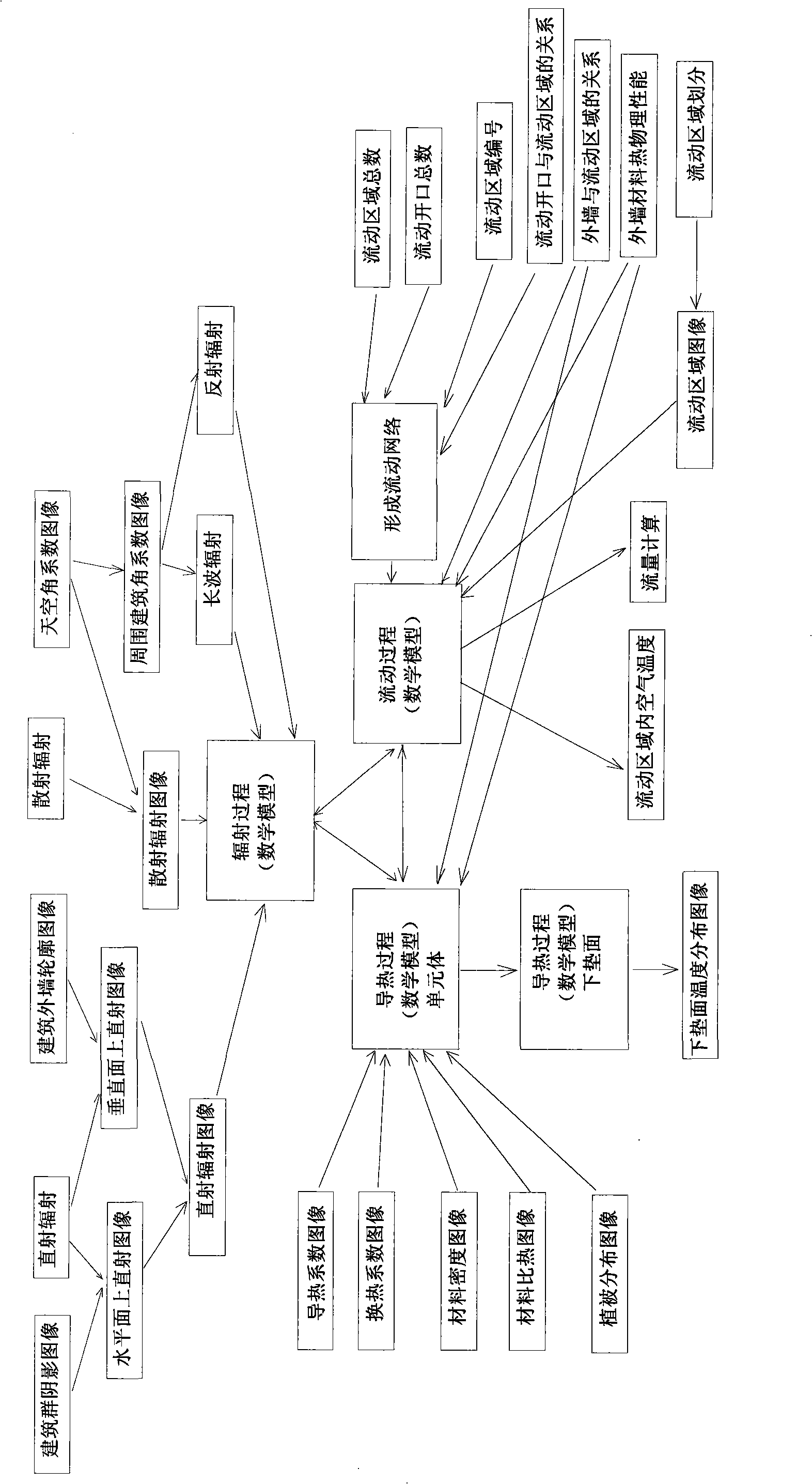
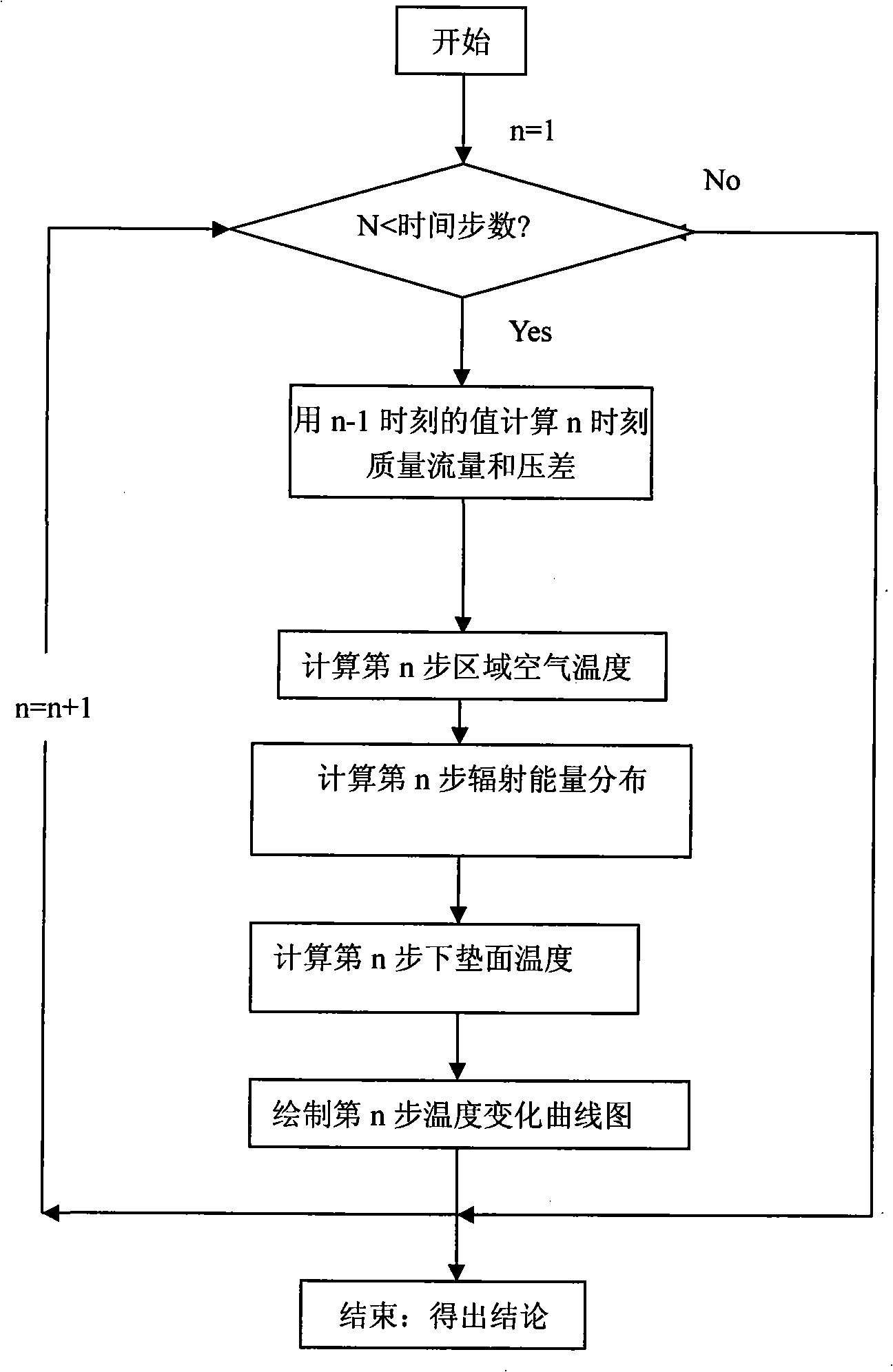
The invention provides a prediction method and a system for protecting a town heat island characteristics which are based on the digital image analysis, and relates to the field of environmental engineering. A town digital elevation model DEM is established according to a town planning map; a flow region network model is established by taking the flow region of buildings as a 'node' and taking the flow opening as a 'branch'; the mass conservation equation, the loop pressure equation, the flow relation equation and the heat balance equation are established according to the flow region network model; the air mass flux, the pressure difference and the air temperature between the town buildings are calculated, and the flow region in which each pixel is positioned is identified; the direct solar radiation, the diffuse solar radiation, the long-wave radiation and the reflected radiation energy distribution of an analysis surface are calculated; the specific heat, the density and the thermal coefficient of each pixel in an underlying surface image are obtained; therefore the temperatures of the underlying surface and each wall surface are calculated, and the town heat island characteristics are predicted. The invention uses the digital image processing technology, and thus the problem of dynamic boundary in a town outdoor heat environment is successfully solved; the purpose of optimizing the town heat environment is realized.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Photocatalyst material for absorbing full sunlight spectrum and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107185565AIncrease profitRealize full spectrum utilizationPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationMicro nanoHigh energy
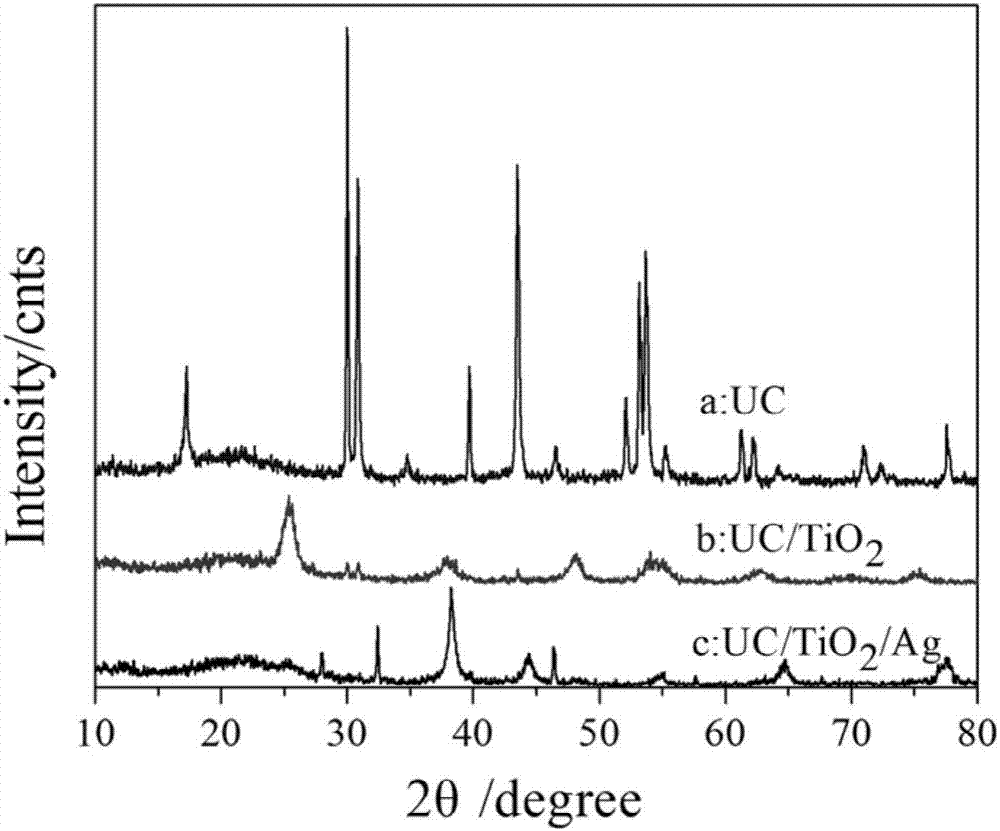
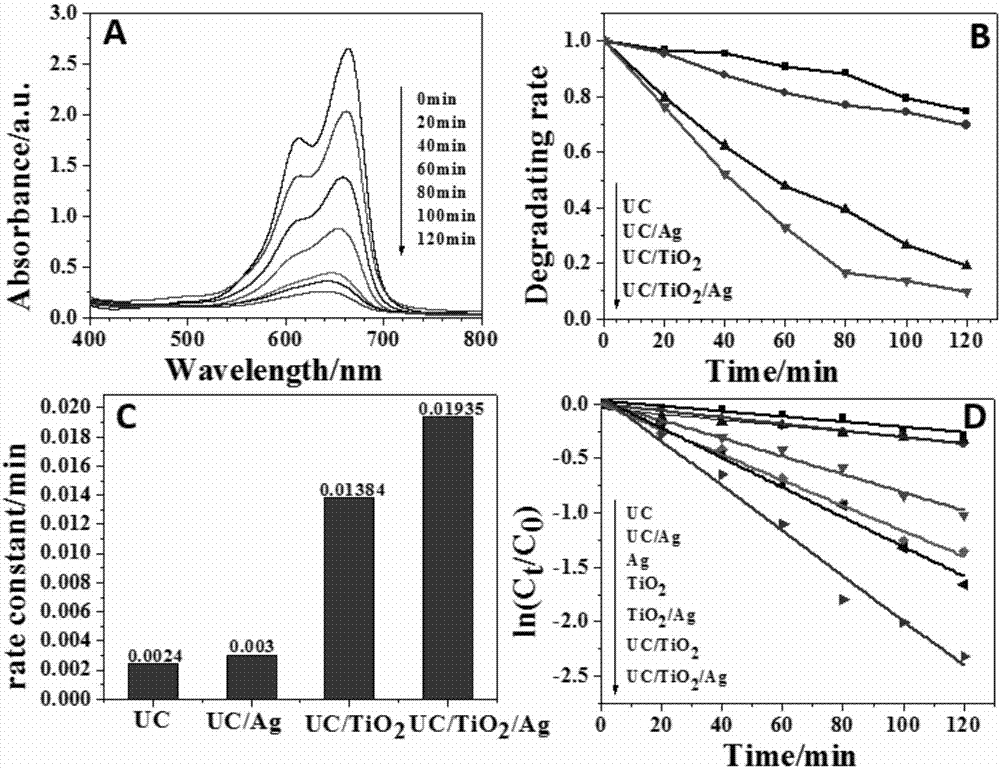
The invention provides a photocatalyst material for absorbing a full sunlight spectrum and a preparation method thereof and relates to the technical field of composite micro-nano materials. The material uses an upconversion material NaYF4: Yb,Er as a template, and the surface of the template is sequentially modified with TiO2 and Ag nanoparticles. Firstly, the upconversion material is obtained through hydro-thermal synthesis reaction, then is used as the template and is successively modified with the TiO2 and Ag nanoparticles through reduction reaction, and the UC / TiO2 / Ag composite micro-nano photocatalyst material is obtained. The photocatalyst material retains the advantage of efficiently absorbing ultraviolet and visible wavebands of high-energy excitation of a traditional photocatalyst material, meanwhile can also convert long-wave radiation of an infrared waveband in sunlight into visible waveband shortwave radiation which can be directly absorbed by the material, the sunlight utilization rate is further improved, full spectrum utilization of sunlight is achieved, and the photocatalyst material is hopeful to serve as a photocatalyst for sunlight-based efficient catalytic degradation of organic pollutants.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV
Heat preservation type sunshade and energy-saving device
ActiveCN102650189ARaise the room temperatureImprove insulation effectClimate change adaptationLight protection screensEmissivityHigh absorption
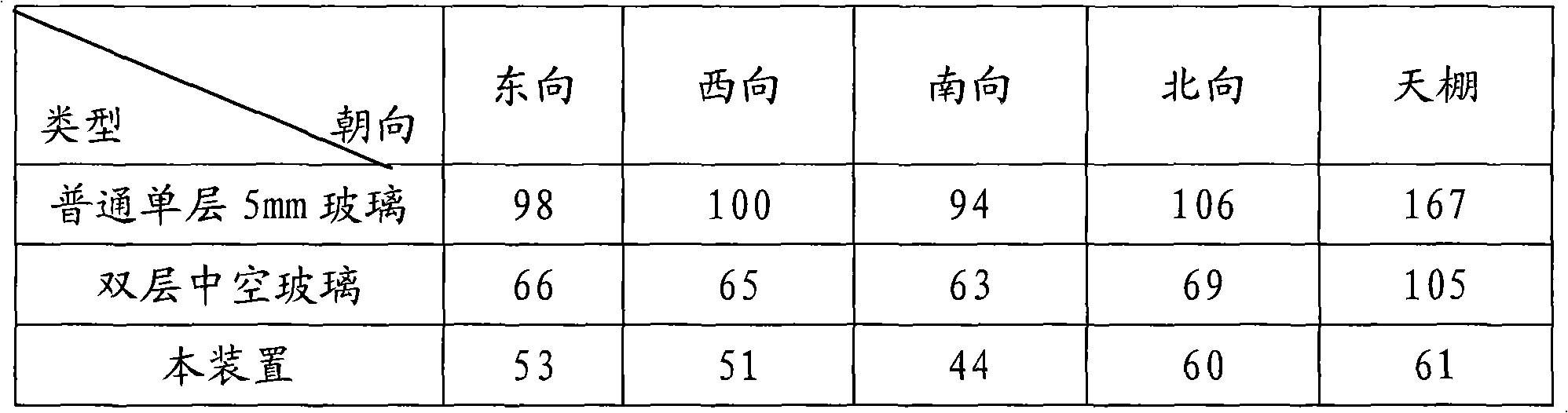
The invention relates to a glass window sunshade device, and particularly discloses a heat preservation type sunshade and energy-saving device. The device comprises a hollow glass body, multiple louvers which are arranged in parallel, and a drive device for driving the louvers to rotate; the internal part of the hollow glass body is formed into a closed cavity; the louvers are installed in the closed cavity; a high absorption rate coating and a high reflectance coating are respectively arranged at the front surface and the back surface of each louver; and a low reflectance plating film is arranged on the cavity wall at one side of the closed cavity facing to outside. According to the device provided by the invention, the high absorption rate coating is combined with the low reflectance plating film, the long wave radiation produced by the louvers and the indoor long wave radiation are reflected to indoor through the low reflectance plating film, thus, the louvers and indoor heat are prevented from losing outwards through the long wave radiation, and a better heat preservation effect can be played.
Owner:许鹏
Long wave pass infrared filter based on porous semiconductor material and the method of manufacturing the same
Scattering-type long wave pass filters for the infrared region of the spectrum offer high levels of suppression of the unwanted short-wave radiation, good levels of transmission of the desired long wave radiation combined with good control of the rejection edge position and shape and good mechanical stability of the filter layer. Such filters are well suited for the wide range of applications and can be used in various environments including cryogenic temperatures. Several methods of fabrication of such filters based on electrochemical etching of semiconductor materials in order to form porous layer are provided.
Owner:LAKE SHORE CRYOTRONICS INC
Dysprosium and ytterbium co-doped alkali yttrium fluoride glass up-conversion luminescent material, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104342153ASolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRubidiumPotassium
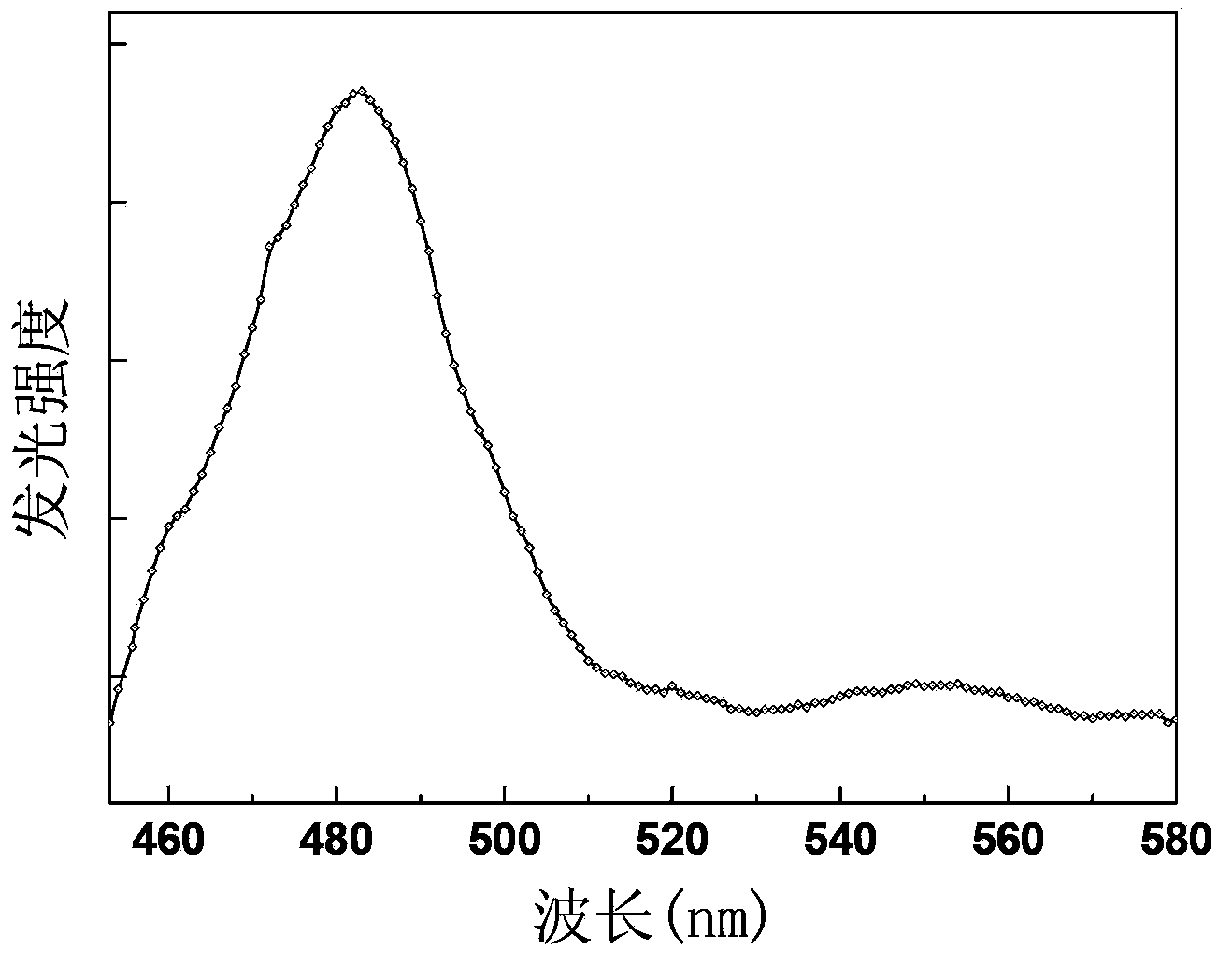
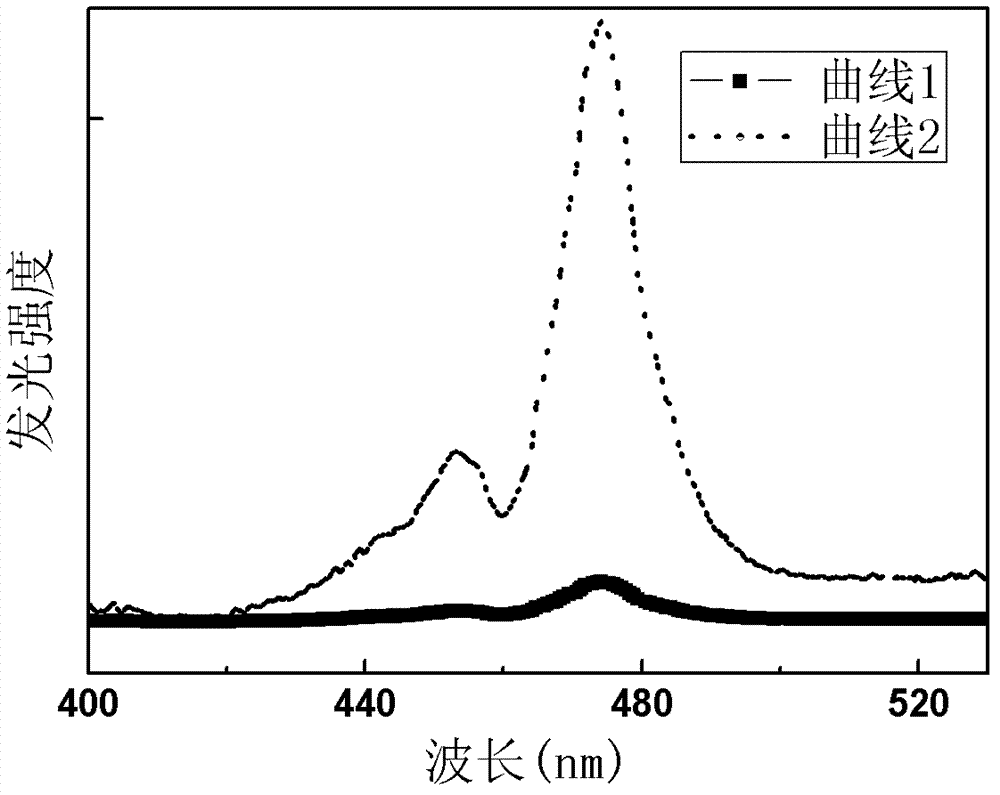
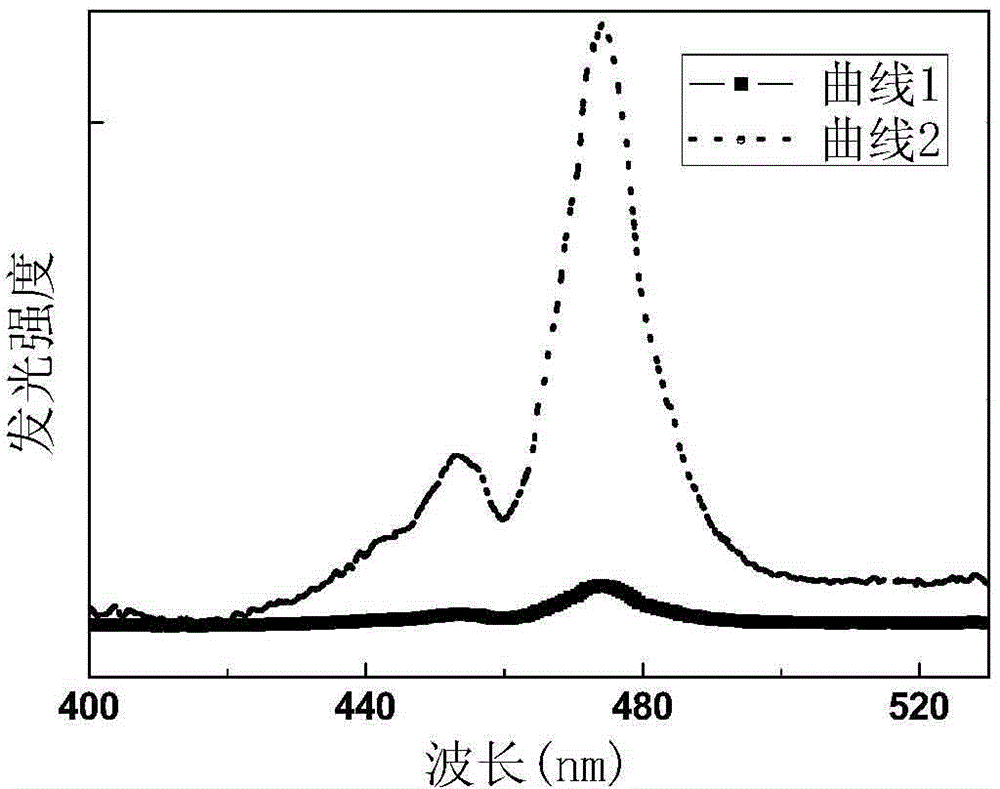
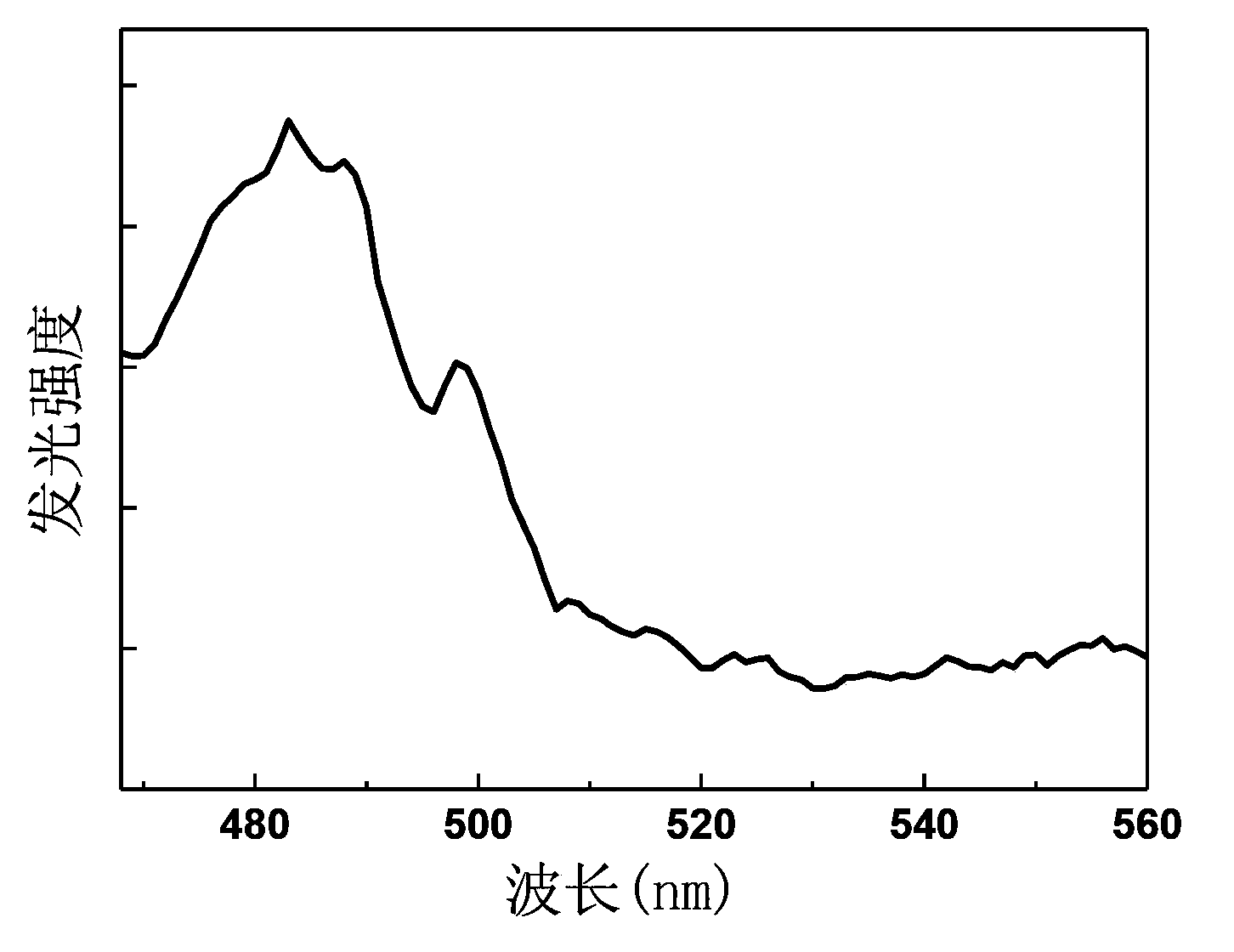
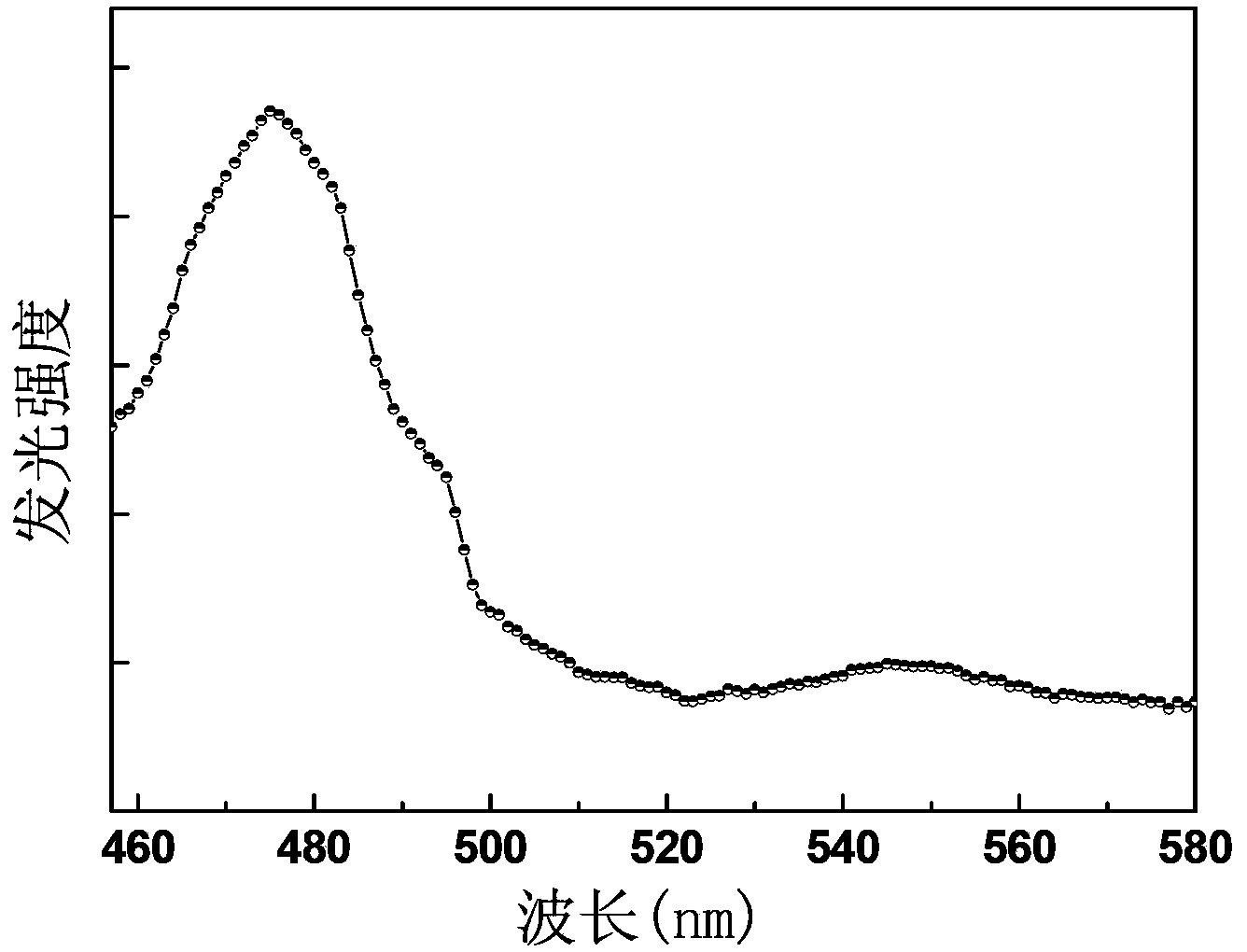
The invention relates to a dysprosium and ytterbium co-doped alkali yttrium fluoride glass up-conversion luminescent material with a chemical formula of RYF4:xDy<3+>,yYb<3+>, wherein x is 0.01-0.06, y is 0.01-0.04, and R is at least one selected from lithium element, sodium elemental, potassium element, rubidium element and caesium element. The dysprosium and ytterbium co-doped alkali yttrium fluoride glass up-conversion luminescent material excitation wavelength is 796nm; and a 482nm light emission peak is corresponding to light emission peak formed by Dy<3+> ion <4>F9 / 2 to <6>F15 / 2 transition radiation, such that blue-light short-wave luminescence excited by long-wave radiation of infrared to green light is realized. The invention also provides a preparation method and an application of the dysprosium and ytterbium co-doped alkali yttrium fluoride glass up-conversion luminescent material.
Owner:OCEANS KING LIGHTING SCI&TECH CO LTD +2
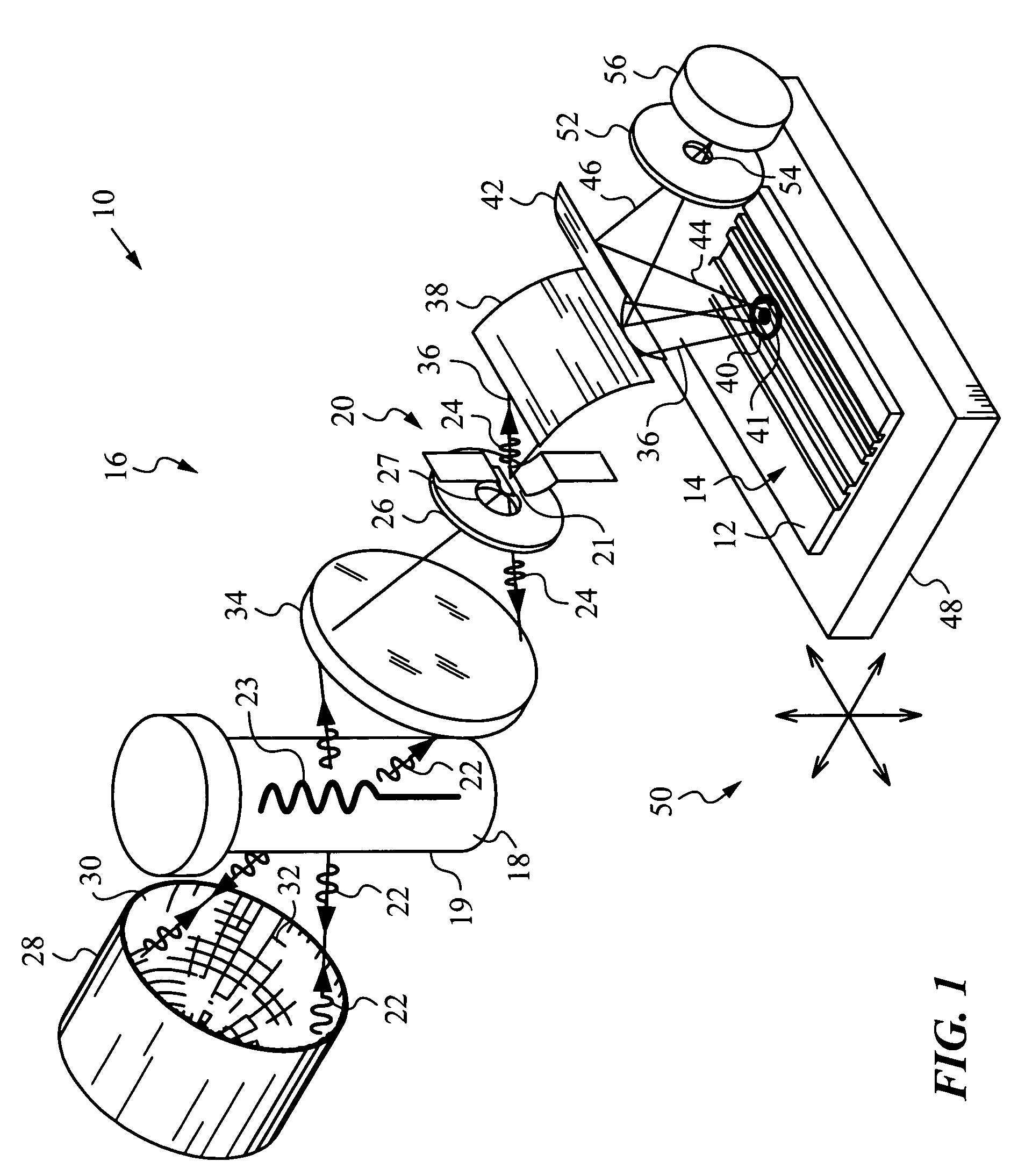
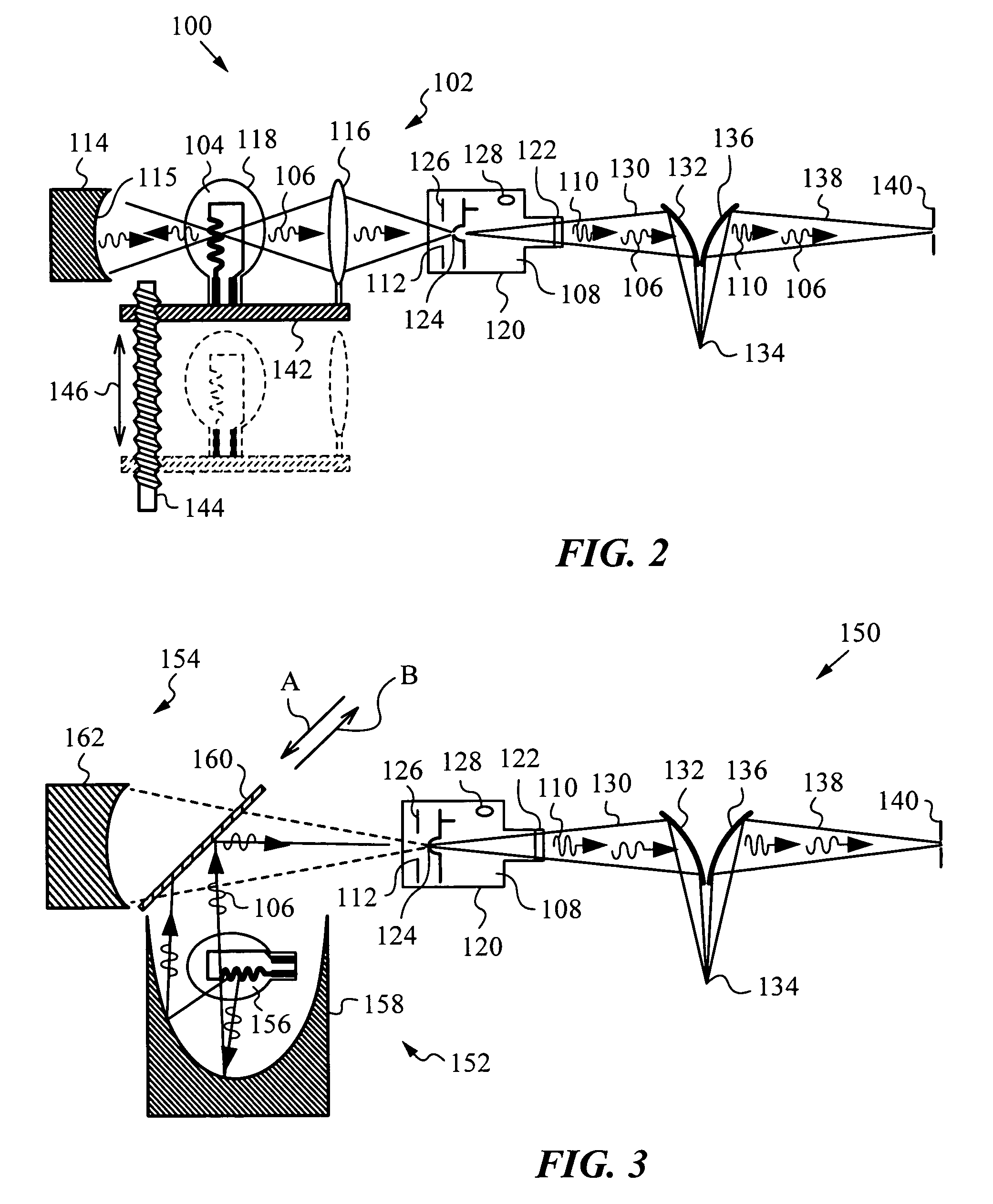
System and method for high intensity small spot optical metrology
ActiveUS7349103B1High strengthEasy to operateMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansBeam steeringOptical metrology
An apparatus and method for examining features of a sample with a broadband beam of light obtained from a long-wavelength source that may include two distinct emitters that emit a long-wavelength radiation and a short-wavelength source that emits a short-wavelength radiation. A passage is positioned between the sources and a reflective beam combining optics is provided for shaping the long-wavelength radiation to enter the short-wavelength source via the passage and also for shaping the short-wavelength radiation that exits through the passage and propagates toward the long-wavelength source. The reflective beam combining optics shape the short-wavelength radiation such that it re-enters the short-wavelength source via the passage and is combined with the long-wavelength radiation into the broadband beam that exits the short-wavelength source. A beam steering optics projects the broadband beam to a spot on the sample, and a scattered broadband radiation from the spot is intercepted and shaped to a broadband signal beam, which is passed through a sampling pinhole that passes a test portion of it on to a detector for optical examination; the test portion that is passed can correspond to a center portion of the spot.
Owner:N & K TECH
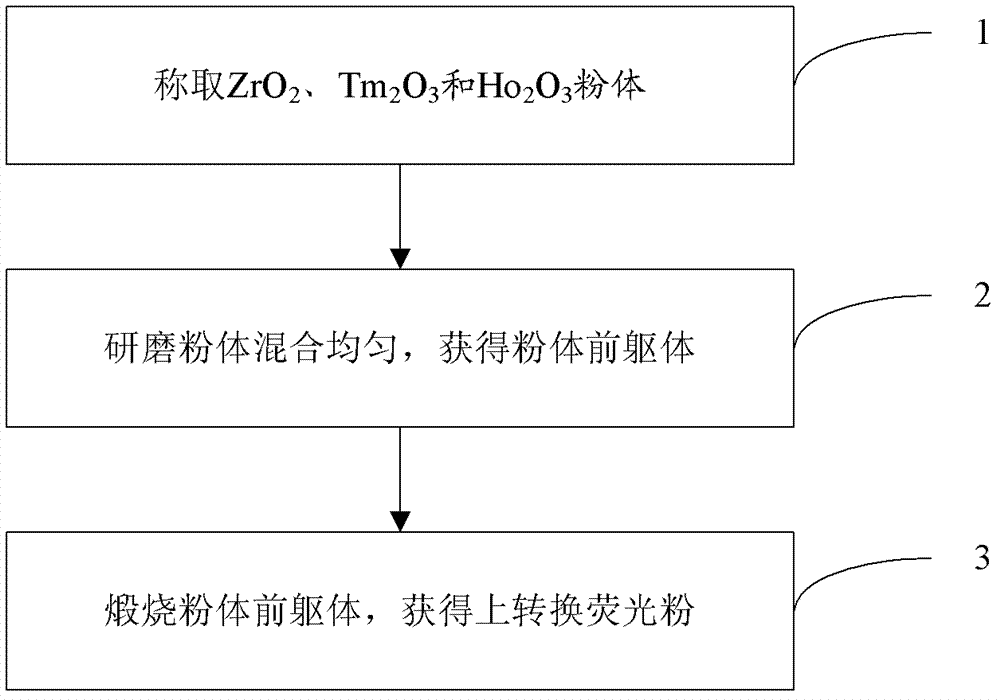
Thulium-holmium co-doped zirconia upconversion phosphor and preparation method thereof
The invention belongs to the field of phosphor, and discloses thulium-holmium co-doped zirconia upconversion phosphor and a preparation method thereof. The general chemical formula of the upconversion phosphor is Zr1-y-xO2:xTm3+, yHo3+, wherein Zr1-y-xO2 is a matrix, Tm and Ho are doping elements, the value range of x is 0.01-0.06, and the value range of y is 0.01-0.1. According to the invention, the thulium-holmium co-doped zirconia upconversion phosphor is prepared by magnetron sputtering equipment, and can realize blue-light short-wave luminescence excited by long-wave radiation from infrared to green light; therefore, the phosphor can make up deficiencies of blue-light materials in current display and luminescent materials.
Owner:OCEANS KING LIGHTING SCI&TECH CO LTD +1
Estimation methods of optical remote sensing image land surface temperature under cloud and emission long wave radiation
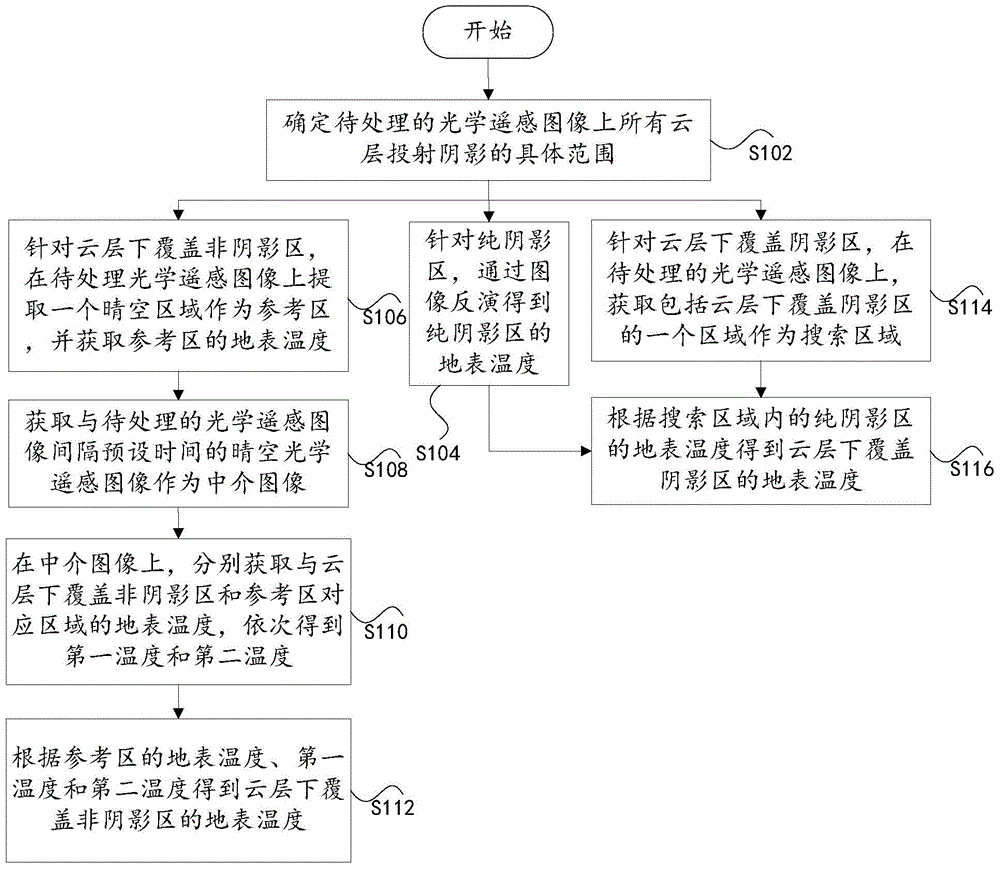
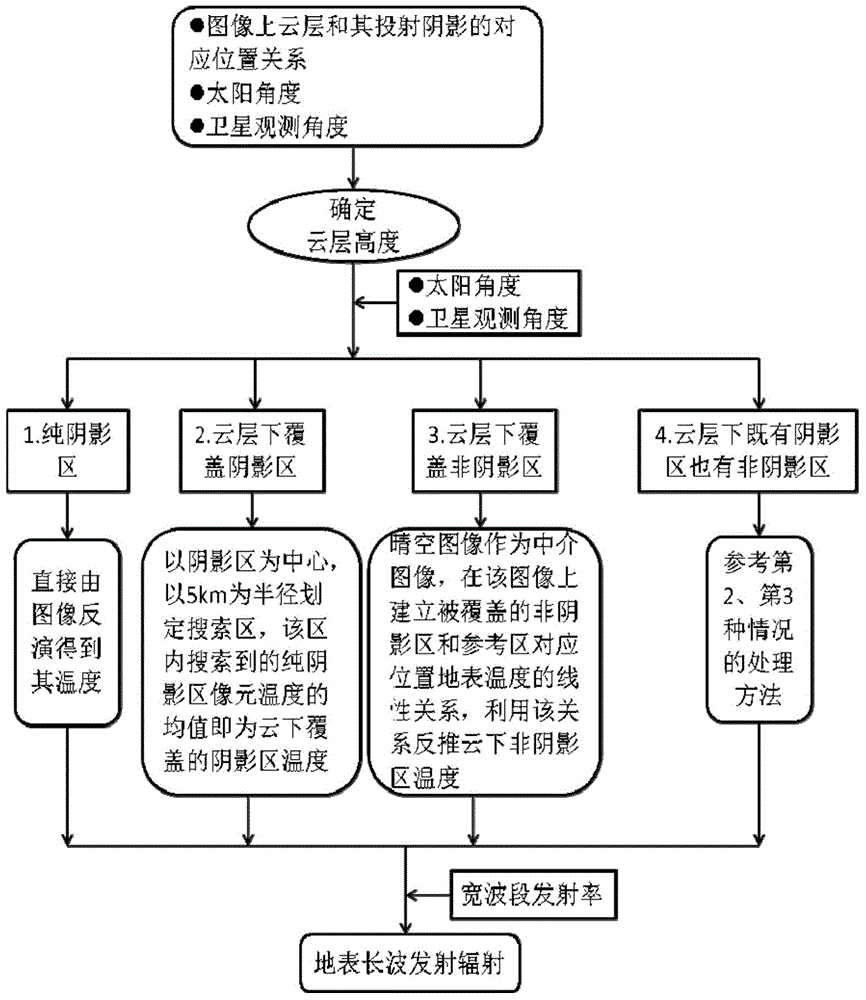
The present invention discloses estimation methods of optical remote sensing image land surface temperature under cloud and emission long wave radiation. The estimation methods of optical remote sensing image land surface temperature under cloud comprises a step of determining the specific scope of all cloud layer cast shadows on an optical remote sensing image to be processed and obtaining the land surface temperature of a pure shadow area through image retrieval, a step of selecting a clear sky image with the interval of a preset time with the image to be processed as an intermediary image for a cloud layer coverage non-shadow area, determining one reference area on the optical remote sensing image to be processed, and obtaining the land surface temperature of the cloud layer coverage non-shadow area according to the temperature of the reference area, a step of determining a search area in the optical remote sensing image to be processed for the cloud layer coverage non-shadow area, and a step of obtaining the land surface temperature of a cloud layer coverage shadow area according to the land surface of the pure shadow area in the search area so as to realize the estimation of the land surface temperature in the condition of a cloud layer. Through the estimation methods, the estimation of the land surface temperature in the condition of the cloud layer can be realized.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Heat pipe solar water heater with convergent-divergent nozzle
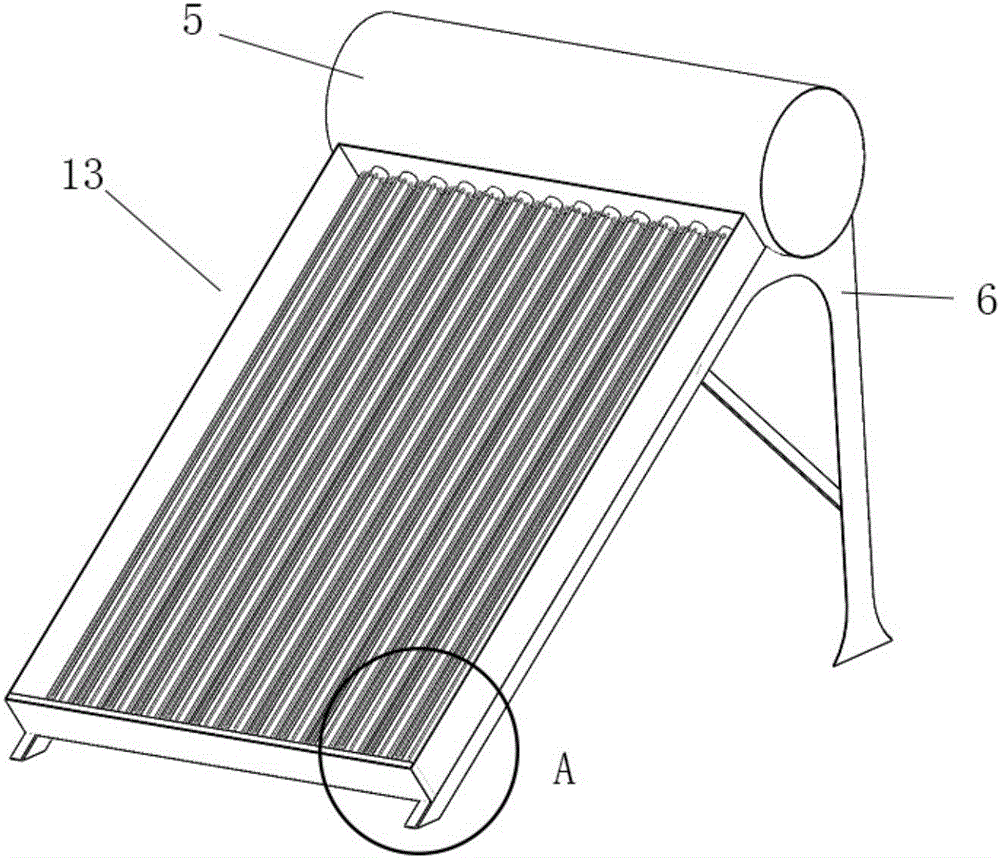
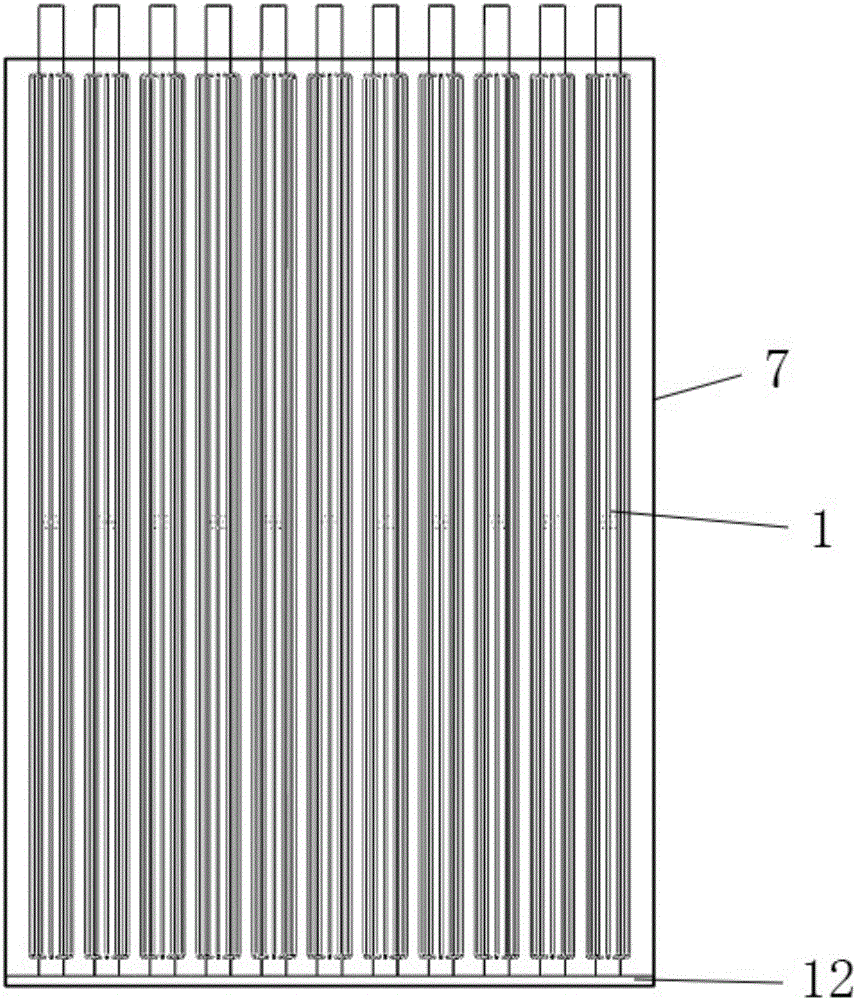
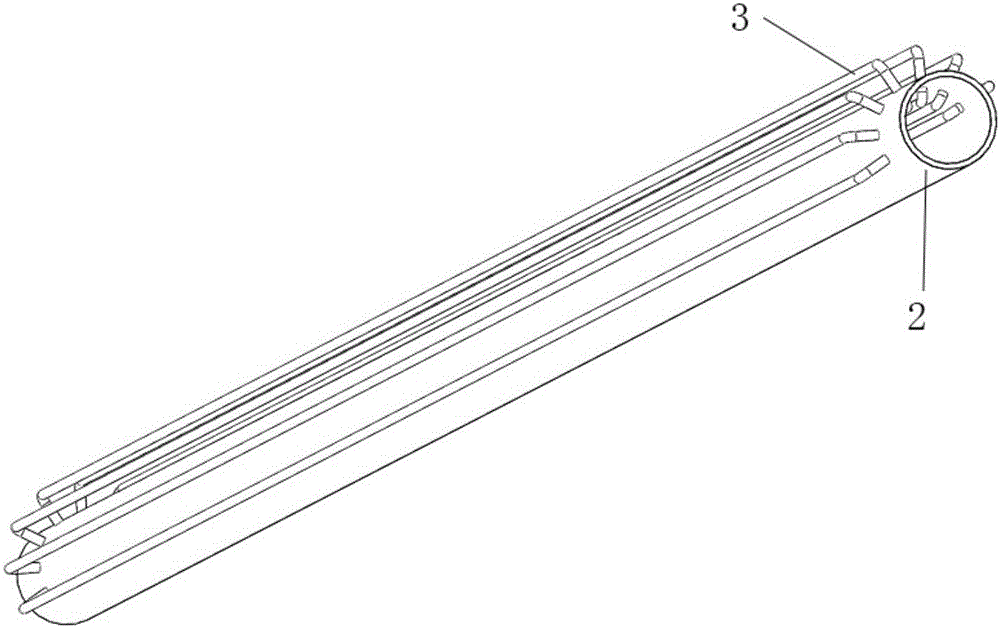
ActiveCN106288452AReduce thermal resistanceThermal resistance is obviousSolar heating energySolar heat devicesGlass coverSolar water
The invention discloses a heat pipe solar water heater with a convergent-divergent nozzle. The heat pipe solar water heater comprises a solar water tank (5), a support (6) and a heat collector (13). The lower portion of the solar water tank (5) is connected with the heat collector (13), the heat collector (13) comprises heat-collecting tubes (1), an open warm-keeping box (7), a glass cover plate (8), heat-absorbing plates (9), a phase change heat storage layer (10) and a warm-keeping layer (11), and the multiple heat-collecting tubes (1) are transversely arranged inside the open warm-keeping box (7). The adopted hollow glass cover plate has the advantages of preventing heat conduction, convection heat exchange and long-wave radiation; the heat tubes have the characteristic of one-way heat transfer, so that heat will not be transferred in the opposite direction of gravity, and the heat loss of the solar water heater is greatly restrained on cloudy or rainy days.
Owner:TIANJIN CHENGJIAN UNIV
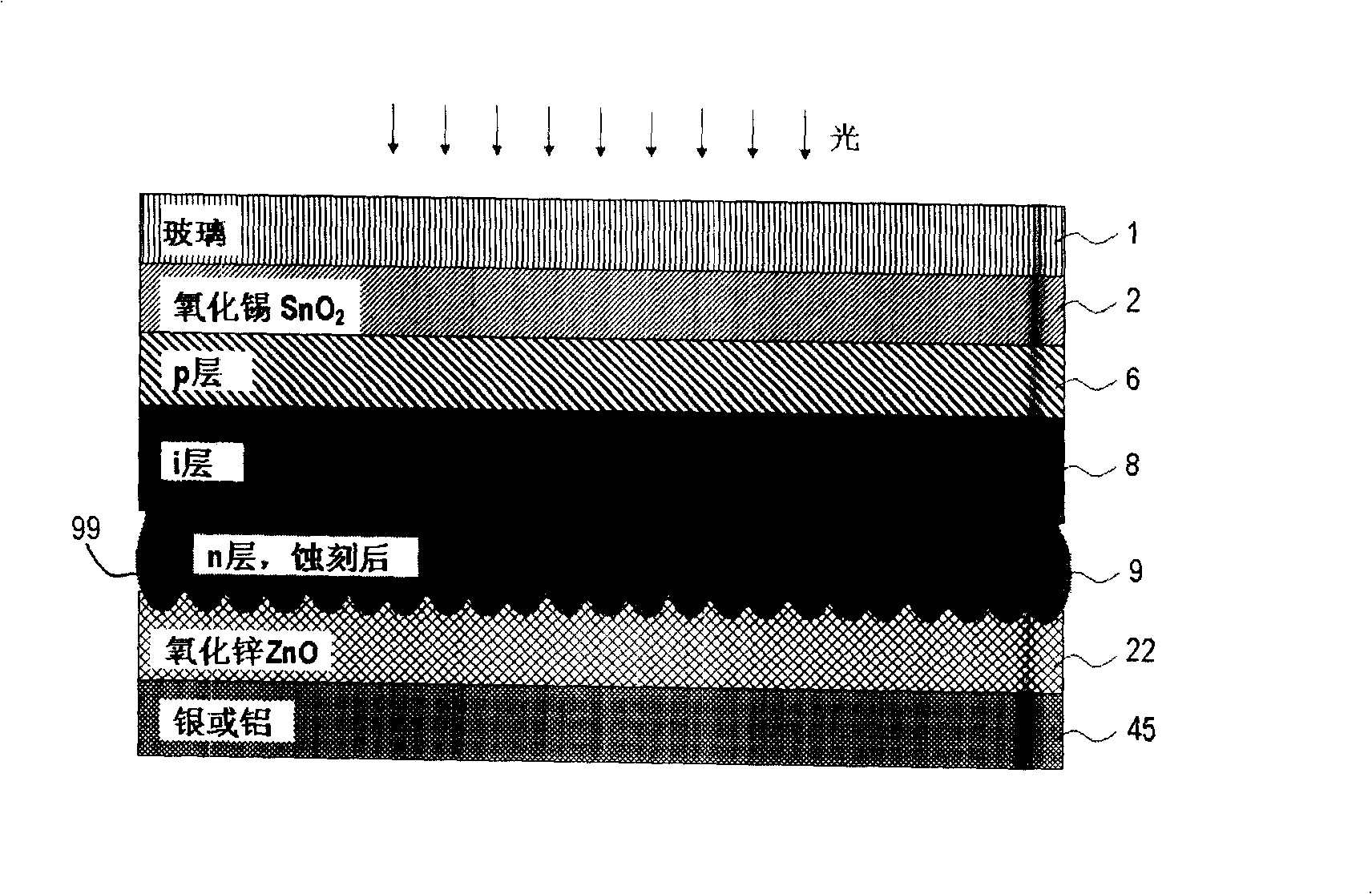
Method for reinforcing optical capturing effect of thin film photovoltaic device
InactiveCN101246922APhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesLong wave radiationSolar cell
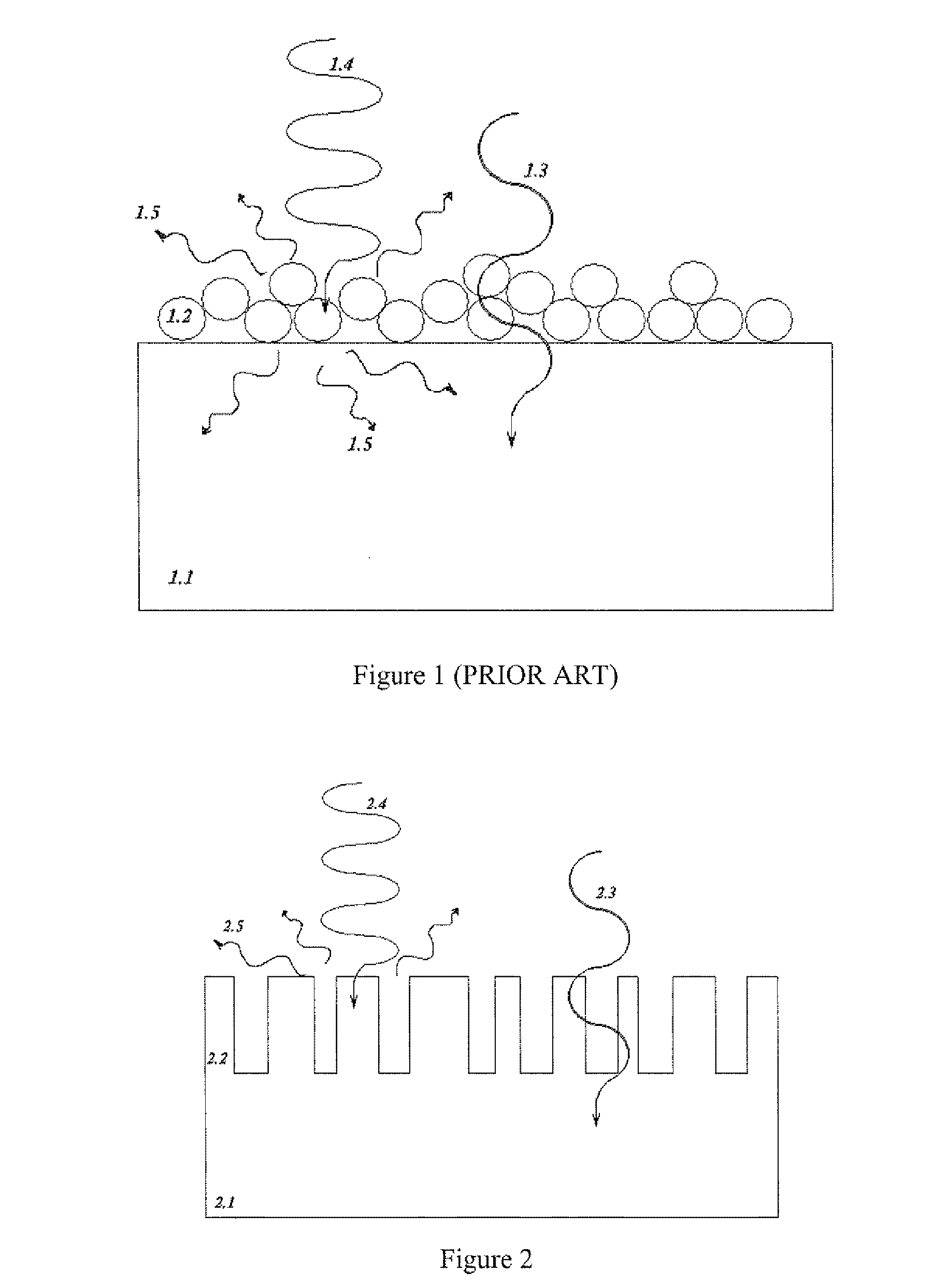
The present invention discloses a method for inducing long wave radiation of improved film silicon p-i-n type solar cell which is characterized of etching process a thicker n layer to make it has a non-flat structure with micron dimension, and the high reflection back electrode on the back makes the long wave light not be absorbed entering photovoltaic conversion layer again with bigger angle. So the whole inner reflection effect is gained, and the capture of weak absorption light is improved, and the conversion efficiency of silicon film solar photovoltaic device is improved.
Owner:BEIJING XINGZHE MULTIMEDIA TECH
Simulated telemetry system and method for infrared extinction and particle size of bio-aerosol
InactiveCN102507401ASimple structureEasy to operateParticle size analysisParticle suspension analysisParticulatesBlack-body radiation
The invention discloses a simulated telemetry system and a simulated telemetry method for infrared extinction and particle size of bio-aerosol. According to the system, an aerosol generator fills sample powder in a sample cell, the sample powder is fully dispersed by a fan to form a bio-aerosol cloud, the size distribution of particles is measured by a spectrometer, black body radiation generated by a large surface source black body radiation source positioned at a light inlet of the sample cell is used for simulating ground feature long wave radiation, and the light is attenuated by the sample cell, and is received by a medium field receiving telescope and a Fourier conversion infrared spectrometer which are positioned at the light outlet of the sample cell, so that the bio-aerosol cloud is subjected to infrared extinction measurement and telemetry simulation under typical ground feature backgrounds. The simulated telemetry system has a simple structure, is used for telemetry simulation of the spectrum extinction and size distribution of the aerosol under the laboratory conditions, and verifies a bio-aerosol infrared telemetry technology; and the invention is easy to operate, reliable and stable, and can simultaneously measure multiple components and multiple optical parameters.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Visible light super-transmissible coating material for Low-E glass and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104448963AAchieve diversificationHigh visible light transmittanceAlkali metal silicate coatingsArchitectural glassMass ratio
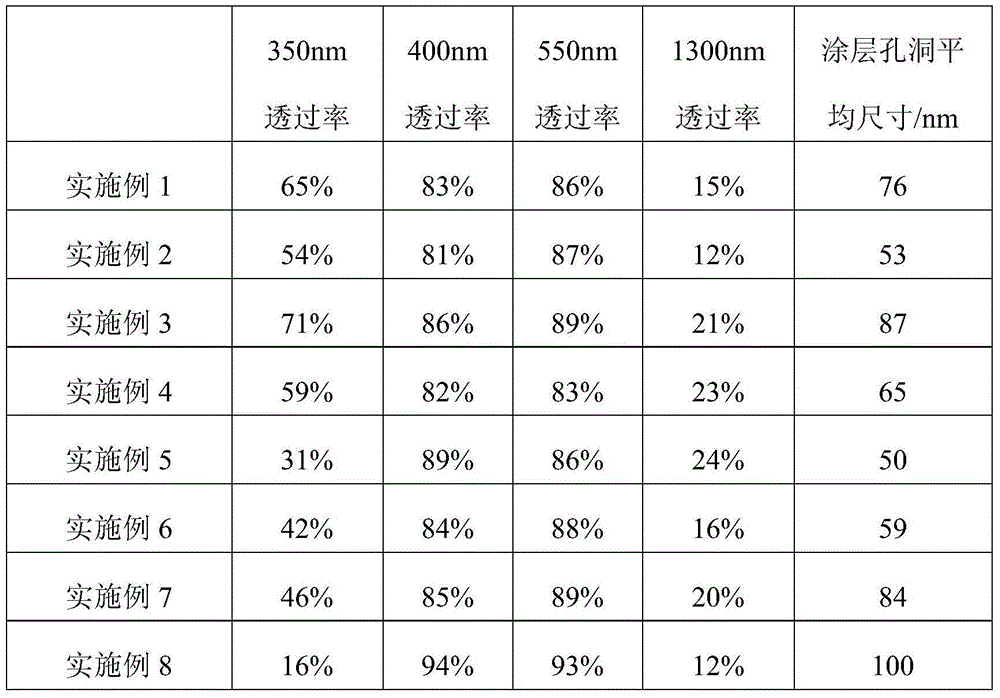
The invention discloses a visible light super-transmissible coating material for Low-E (low-emission) glass and a preparation method thereof. The coating material is mainly composed of a solution system formed by an acrylic organic polymer and a silicon dioxide inorganic precursor. The solution system has a solid content of 1.5-3.5wt.%, wherein the acrylic organic polymer and the silicon dioxide inorganic precursor are in a mass ratio of 0.5-1.5:1. The coating material has a porous structure of 50-100nm pores, and refractive index of the coating material reaches 1 / 2th power of the product of the air refractive index and the glass refractive index, the diffraction reflectivity of medium-long wavelength infrared radiation reaches 76%-88%, and also visible light transmittance is increased and heat loss caused by long-wave radiation is inhibited. Also, the coating material is formed mainly by coating, film forming and inorganic curing of the film, high temperature and high vacuum coating conditions are unnecessary, the processing equipment and operation are simple, and diversification of architectural glass functions can be realized.
Owner:KUNSHAN CHUNYANG DOOR & WINDOW DECORATION ENG
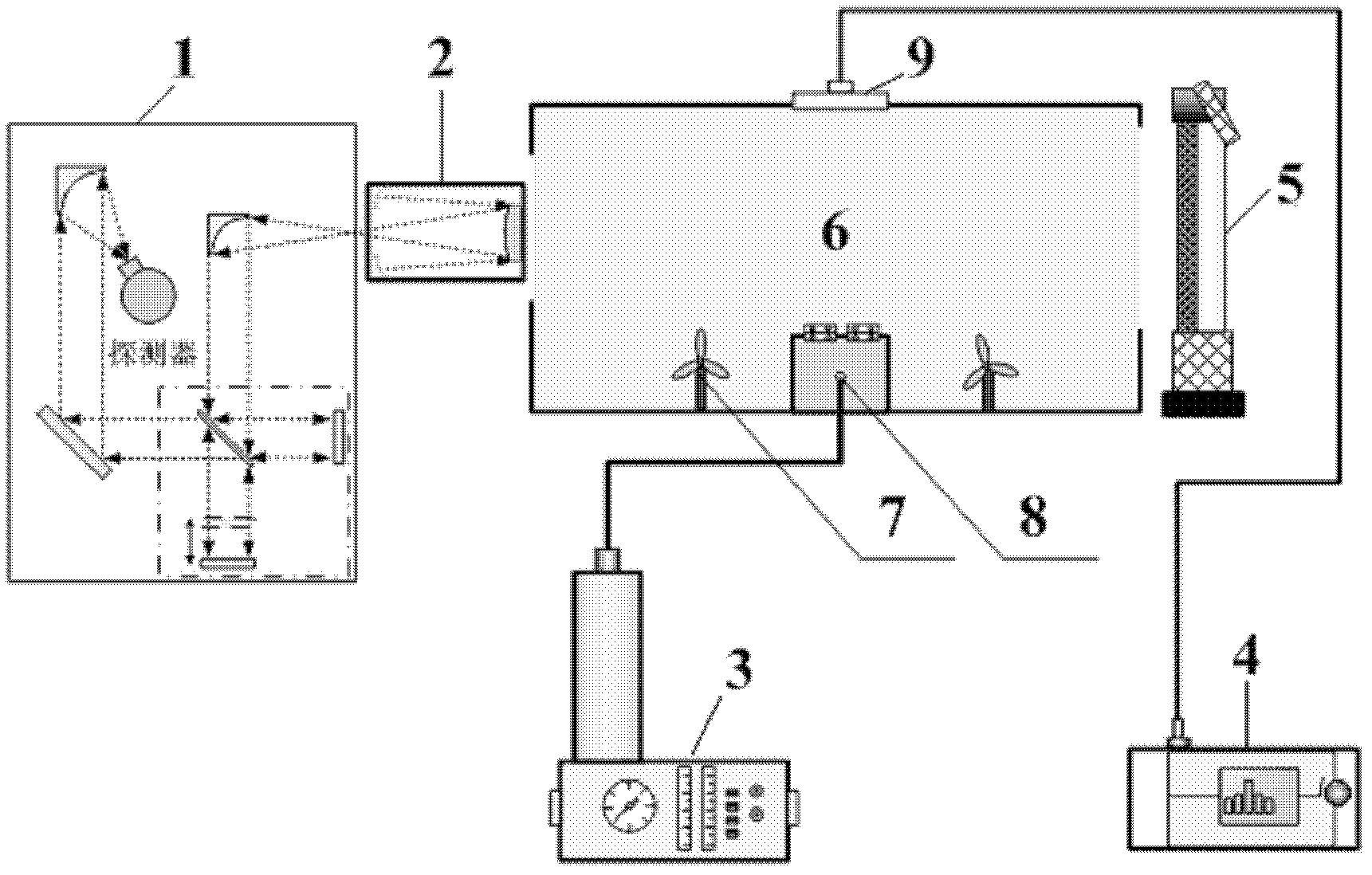
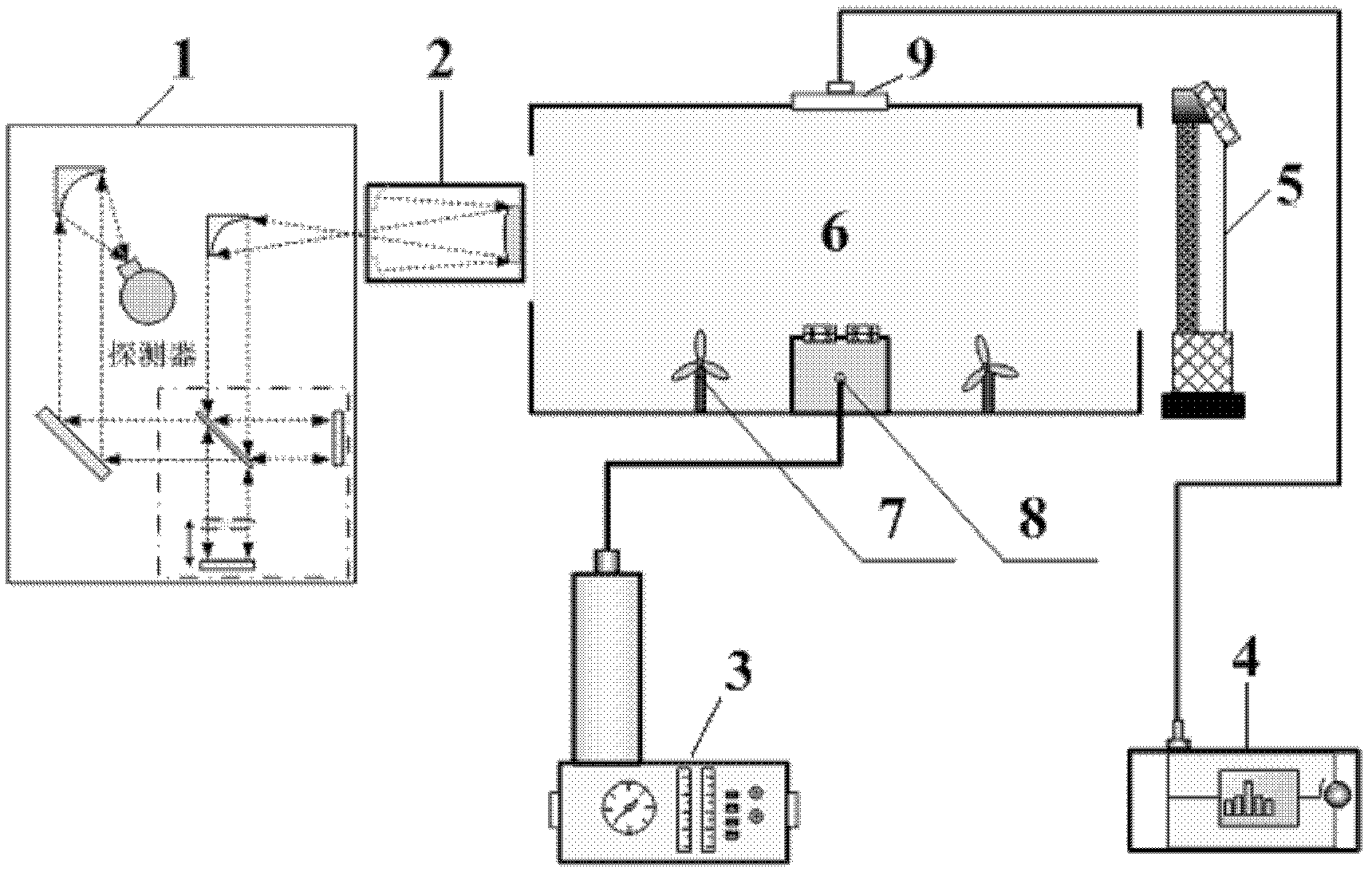
Manual target for measuring downward atmospheric long-wave radiation and method for producing same
InactiveCN105509896AEasy to transportAvoid inconvenient transportationRadiation pyrometryObservational errorTarget array
The invention provides a manual target for measuring downward atmospheric long-wave radiation and a method for producing the same. The manual target comprises a target body, a temperature-measuring system, and a master control system. The temperature-measuring system is connected with the target body and measures the temperature of the target body. The master control system is connected with the temperature-measuring system and displays and stores measured temperature data. The target body is N-row M-column target array formed by seamlessly splicing N*M child targets. The manual target is convenient to transport. Inconvenience of transporting the manual targets at a large scale is avoided. The manual target increases the measurement precision of downward atmospheric long-wave radiation values, decreases measurement errors, is greatly reduced in cost, satisfies ground close-quarter measurement, and is suitable for infrared load calibration on aerial work platforms, airborne platforms, and balloon platforms.
Owner:ACAD OF OPTO ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
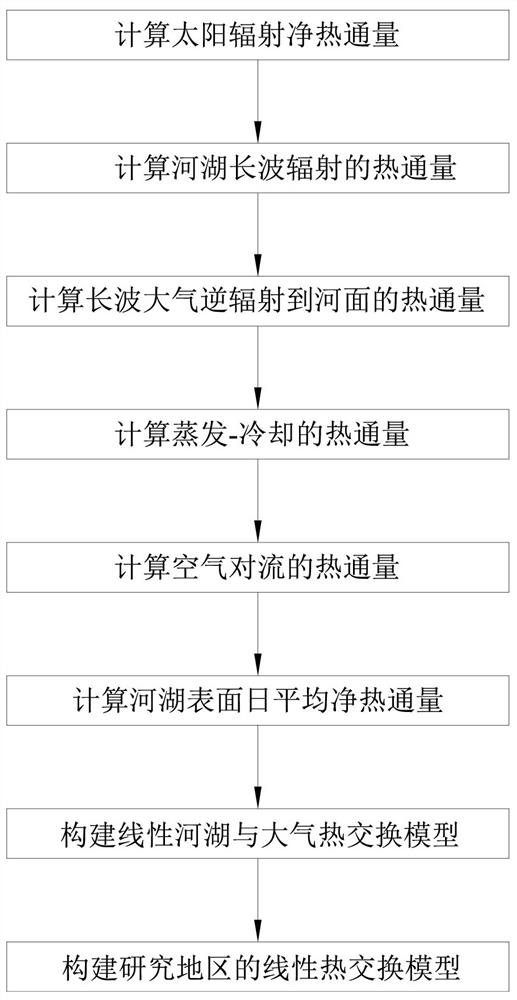
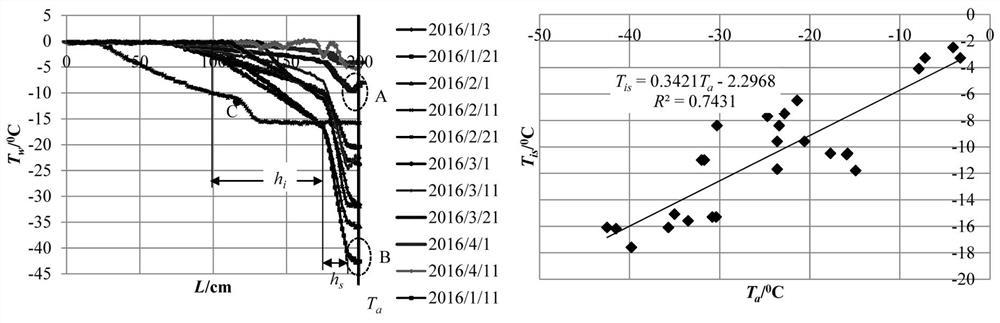
Method for constructing linear model for heat exchange between rivers, lakes and atmosphere in ice period
ActiveCN112541275ASolve the problem of large difference in valuesDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsHeat fluxLong wave radiation
The invention relates to a method for constructing a linear model for heat exchange between rivers, lakes and atmosphere in an ice period. The method comprises the following steps: calculating solar radiation net heat flux; calculating the heat flux of long-wave radiation of rivers and lakes; calculating the heat flux of long-wave atmospheric reverse radiation to the river surface; calculating theheat flux of evaporative-cooling; calculating the heat flux of air convection; calculating the daily average net heat flux of the river and lake surfaces; constructing a linear river and lake and atmosphere heat exchange model; and constructing a linear heat exchange model of the research area. A nonlinear heat exchange model suitable for the iced rivers and lakes and the atmosphere is established and comprises solar radiation, long-wave radiation, evaporative cooling and convection, it is found that the surface temperature of the iced rivers and lakes is close to the measured air temperature1.5 m above the river surface and comprises snow covers and exposed ice cover surfaces, and the nonlinear heat exchange model of the rivers and lakes and the atmosphere is linearized, a linear regression method is adopted based on historical daily average weather data of a meteorological station, and the problem that the values of heat exchange coefficients are greatly different is solved.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES
Dysprosium-holmium-codoped titanium dioxide up-conversion luminescence material, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103571471ASolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLong wave radiationTitanium dioxide
The invention provides a dysprosium-holmium-codoped titanium dioxide up-conversion luminescence material. The chemical formula of the dysprosium-holmium-codoped titanium dioxide up-conversion luminescence material is TiO2:xDy<3+>,yHo<3+>, wherein x is 0.002-0.06, and y is 0.002-0.04. The dysprosium-holmium-codoped titanium dioxide up-conversion luminescence material can be excited through long wave radiation to emit blue light. The invention also provides a preparation method of the dysprosium-holmium-codoped titanium dioxide up-conversion luminescence material, and an application of the dysprosium-holmium-codoped titanium dioxide up-conversion luminescence material.
Owner:OCEANS KING LIGHTING SCI&TECH CO LTD +1
Thulium-holmium co-doped chlorosilicate upconversion light-emitting fluorescent powder as well as preparation method thereof and organic light-emitting diode
InactiveCN104673284AAchieve preparationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRubidiumPotassium
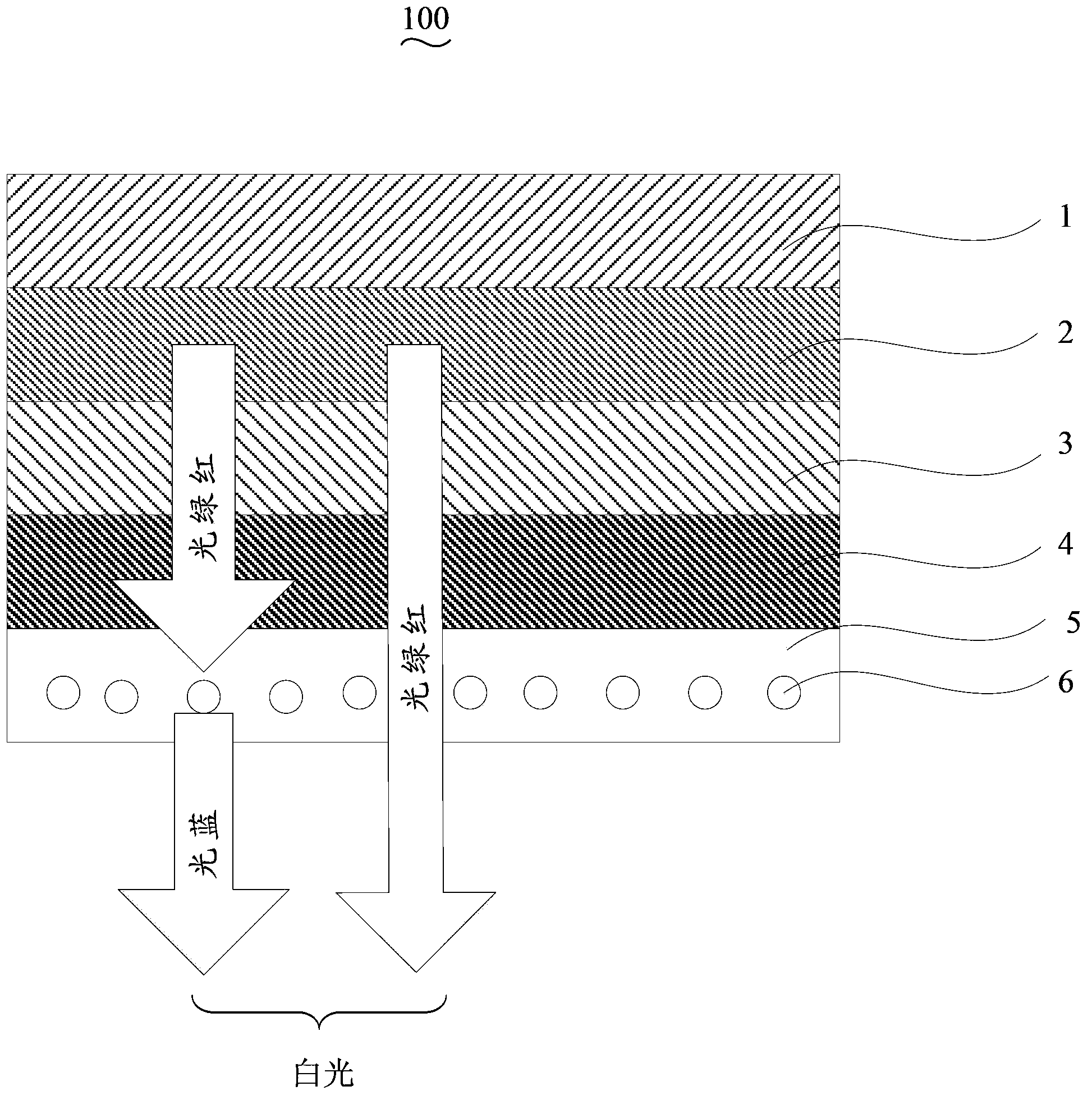
The invention relates to thulium-holmium co-doped chlorosilicate upconversion light-emitting fluorescent powder as well as a preparation method thereof and an organic light-emitting diode. A chemical formula of the fluorescent powder is R2SiCl6:xTm<3+>, yHo<3+>, wherein R2SiCl6 is a doped matrix, Tm and Ho are doped elements, x ranges from 0.002 to 0.06, y ranges from 0.002 to 0.04; and R is lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium or cesium. The thulium-holmium co-doped chlorosilicate upconversion light-emitting fluorescent powder disclosed by the invention can realize excite blue-light shot-wave light due to infrared-green long-wave radiation, so that part of red green light in the organic light-emitting diode is converted into blue light, and the rest of the red green light is synthesized into white light, and thus, preparation of a white-light lighting product is realized.
Owner:OCEANS KING LIGHTING SCI&TECH CO LTD +2
Praseodymium-holmium-codoped lanthanum fluoride up-conversion luminescence material, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103571491ASolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHolmiumLanthanum fluoride
The invention provides a praseodymium-holmium-codoped lanthanum fluoride up-conversion luminescence material. The chemical formula of the praseodymium-holmium-codoped lanthanum fluoride up-conversion luminescence material is LaF3:xPr3+,yHo<3+>, wherein x is 0.002-0.06, and y is 0.002-0.04. The praseodymium-holmium-codoped lanthanum fluoride up-conversion luminescence material can be excited through long wave radiation to emit blue light. The invention also provides a preparation method of the praseodymium-holmium-codoped lanthanum fluoride up-conversion luminescence material, and an application of the praseodymium-holmium-codoped lanthanum fluoride up-conversion luminescence material.
Owner:OCEANS KING LIGHTING SCI&TECH CO LTD +1
A method for estimating radiant thermal environment characteristics of a floating device
PendingCN109446559AReduce mistakesDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsRadiant heatAtmospherics
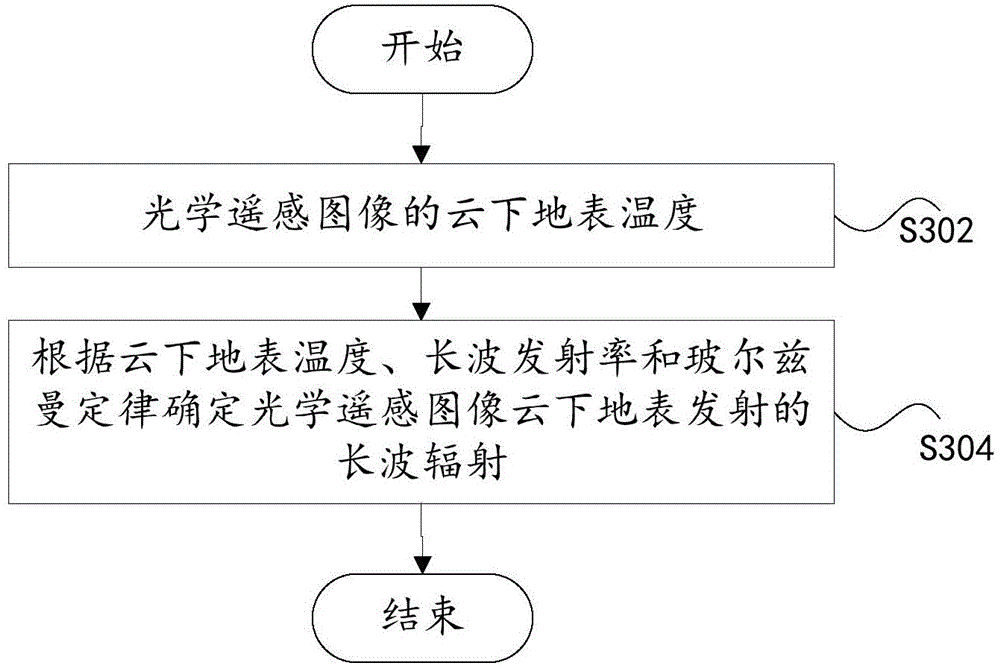
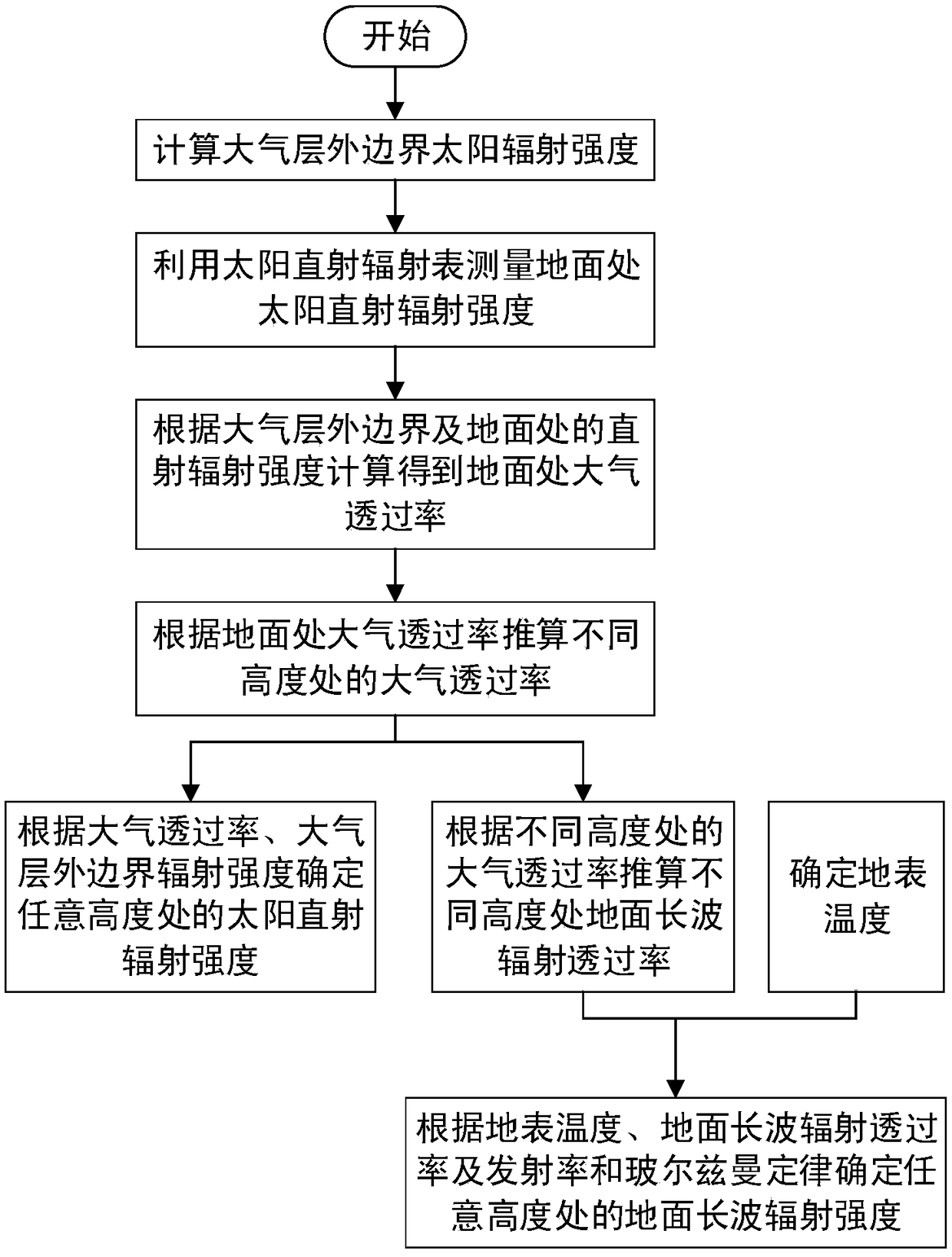
The invention belongs to the field of thermal environment analysis of a floating device, in particular to a method for estimating radiant thermal environment characteristics of the floating device. The method comprises the steps of calculating an outer atmospheric boundary radiation intensity Isun; calculating the intensity of direct solar radiation Id, 0; calculating the atmospheric transmittancetau atm, 0, tau atm, 0=Id, 0 / Isun; calculating the atmospheric transmittance tau atm at the height H according to the atmospheric transmittance tau atm at the surface, 0; according to the atmospherictransmittance tau atm at H and the outer boundary radiation intensity Isun, determining the direct solar radiation intensity Id at H, Id=Isun*tau atm; calculating the atmospheric transmittance tau IR, atm of surface long wave radiation at altitude H; determining the surface temperature Tground, and determining the surface long-wave radiation intensity according to the surface long-wave radiationtransmittance and emissivity and Boltzmann law. The invention estimates the radiant heat environment characteristic parameters at different altitudes H of the floating device released from the targetsite according to the less measured data, reduces the error of the calculation of the thermal characteristics of the floating device caused by the altitude and the geographical environment, and has guiding significance in the aspects of the thermal design of the floating device, skin material selection, flight test safety and the like.
Owner:中国人民解放军63660部队
Thulium-holmium-codoped zirconium dioxide glass up-conversion luminescence material, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103571470ASolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingUpconversion luminescenceHolmium
The invention relates to a thulium-holmium-codoped zirconium dioxide glass up-conversion luminescence material. The chemical formula of the thulium-holmium-codoped zirconium dioxide glass up-conversion luminescence material is ZrO2:xTm<3+>,yHo<3+>, wherein x is 0.002-0.06, and y is 0.002-0.04. The thulium-holmium-codoped zirconium dioxide glass up-conversion luminescence material can be excited through long wave radiation to emit blue light. The invention also provides a preparation method of the thulium-holmium-codoped zirconium dioxide glass up-conversion luminescence material, and an application of the thulium-holmium-codoped zirconium dioxide glass up-conversion luminescence material.
Owner:OCEANS KING LIGHTING SCI&TECH CO LTD +1
Efficient double-glass vacuum heat-pipe solar heat-gathering pipe
InactiveCN1936452AReduced delivery pathwayShorten the pathSolar heating energySolar heat devicesLong wave radiationOptoelectronics
This invention relates to a high efficient double glass vacuum hot tube solar energy heat-collector characterizing that a low radiation membrane of high penetration rate of solar radiation and low rate of long wave radiation is coated on the outside wall of the inner tube of a double glass vacuum tube, so that the sun can irradiate onto the heat tube and its metal heat-collecting rib plates directly via a glass to shorten the path of solar energy in the heat-collecting tube and reduce the long wave radiation in the inner tube of the vacuum tube and heat loss.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Upconversion fluorescent powder on zirconium-gallium sulphide basal body and preparation method of upconversion fluorescent powder
InactiveCN104927852ASimple methodReduce energy consumptionLuminescent compositionsTransition radiationLong wave radiation
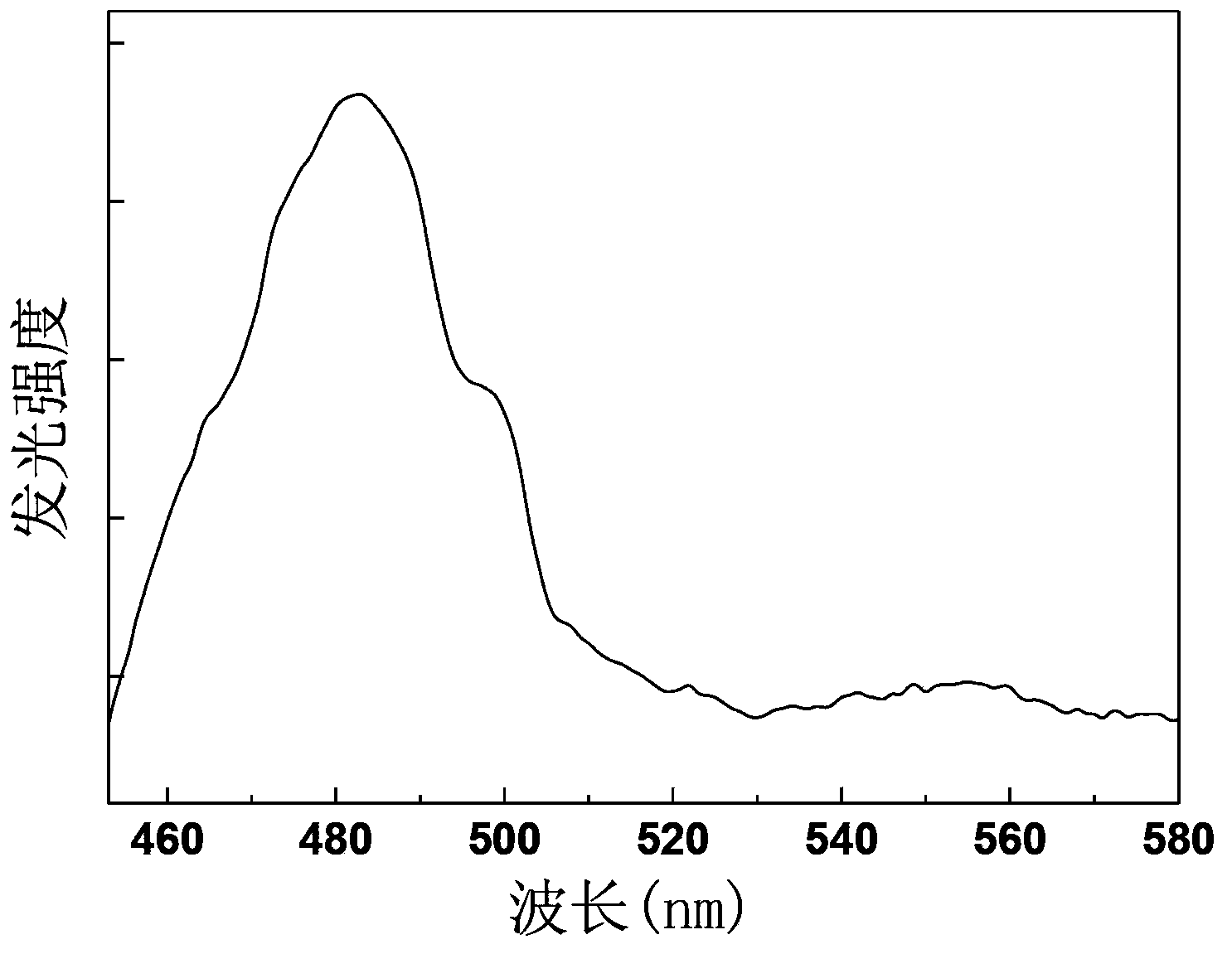
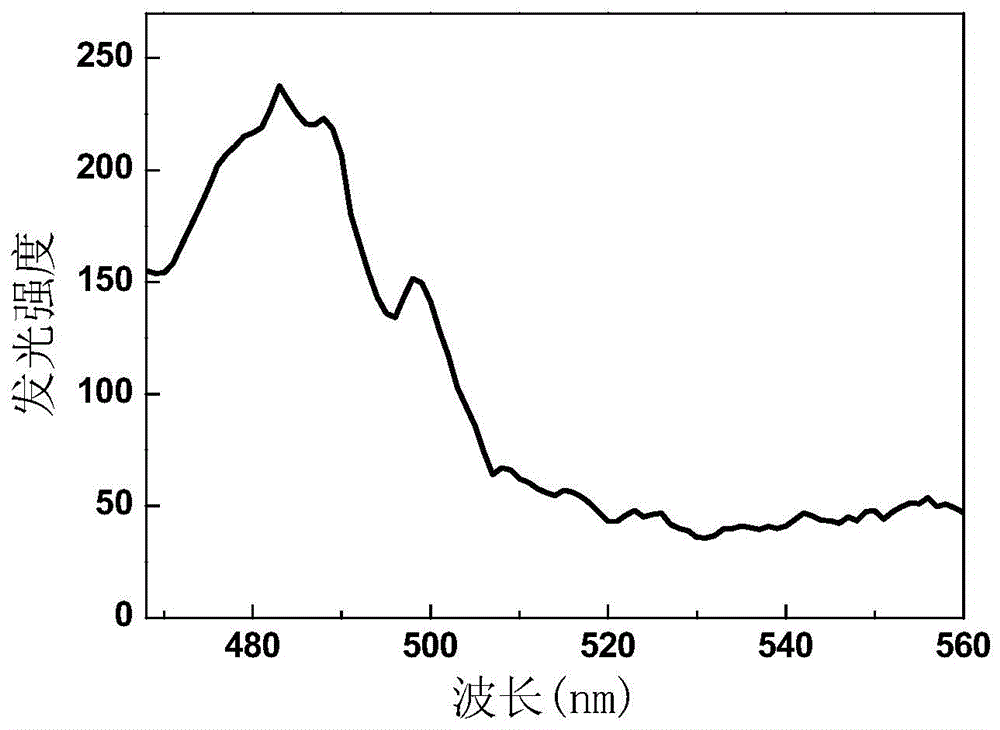
The invention discloses upconversion fluorescent powder of a zirconium-gallium sulphide basal body and a preparation method of the upconversion fluorescent powder. The structural general formula of the fluorescent powder is aZrS-bGa2S3-cR2S: xPr3+ and yYb3+, wherein the aZrS-bGa2S3-cR2S is a substrate, and the Pr3+ and the Yb3+ are doping and activating elements which are used as luminous ion centers in films; the numerical value of a is in 0.57-0.8, the numerical value of b is in 0.12-0.3, the numerical value of c is in 0.03-0.06, the numerical value of x is 0.01-0.06, and the numerical value of y is 0.01-0.04. The upconversion fluorescent powder of the praseodymium-ytterbium co-doping zirconium-gallium sulphide basal body, prepared by the preparation method disclosed by the invention, can realize long-wave radiation excitation from infrared light to green light, and the emission peak of the obtained blue light of which the luminous wavelength is 483nm corresponds to transition radiation emission of Pr3+ ions 3P0 to 3H4.
Owner:OCEANS KING LIGHTING SCI&TECH CO LTD +2
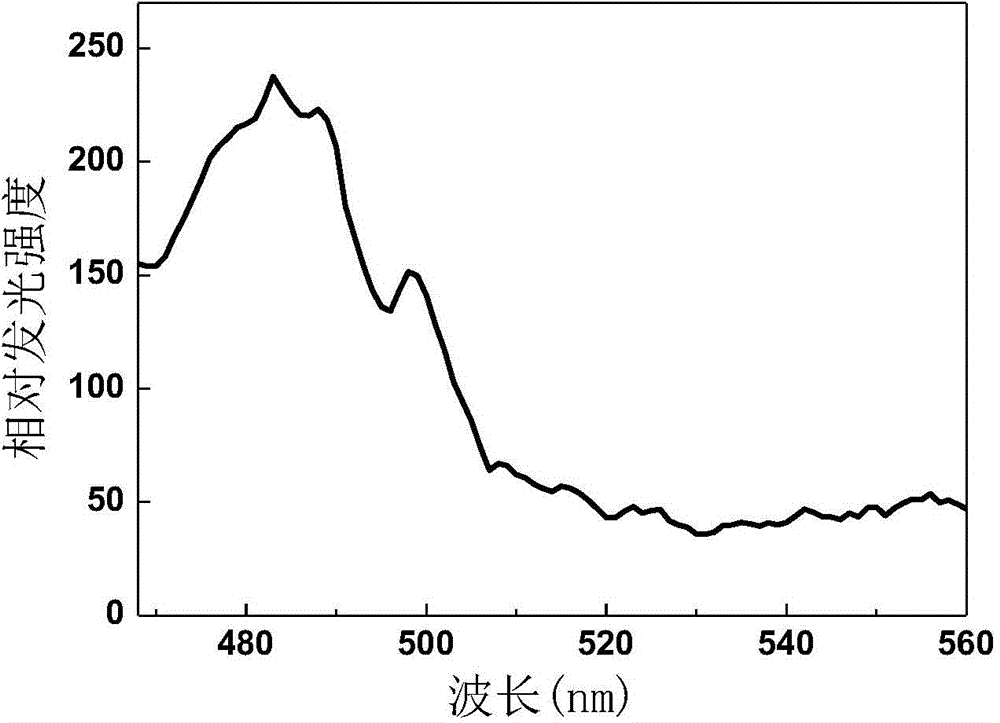
Yttrium silicate upconversion luminous fluorescent powder, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103059858AEasy to prepareLow costSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingUpconversion luminescenceLong wave radiation
The invention belongs to the field of fluorescent powder, and discloses an yttrium silicate upconversion luminous fluorescent powder, and a preparation method and application thereof. The fluorescent powder has a structure of Y2-xSiO5:xHo<3+>; Ho<3+> is a doping ion; and x is in the range from 0.02 to 0.1. The yttrium silicate upconversion luminous fluorescent powder prepared by the invention can realize blue short-wavelength light emitting through excitation by long-wave radiation from infrared to green ray. Therefore, the fluorescent powder can make up for the lack of blue material in current display and luminous material.
Owner:OCEANS KING LIGHTING SCI&TECH CO LTD +1
Simulation experiment method for measuring infrared features of solid target in normal temperature environment
InactiveCN106066340AReduce the difficulty of experimentsReduce experiment costRadiation pyrometryMaterial thermal analysisThermodynamicsRoom temperature
The invention discloses a simulation experiment method for measuring infrared features of a solid target with temperature lower or much higher than ambient temperature in normal temperature environment, and provides the relationship between low temperature long wave radiation and high temperature short wave radiation of solid wall in certain conditions, so that the integral radiation intensity of long wave band of solid wall surface under low temperature and the integral radiation intensity of middle wave band of solid wall surface under high temperature can be calculated mutually. The method can be used for measuring radiation characteristics of high temperature or low temperature solid, and can adjust the temperature of the solid target to slightly higher than the normal temperature on the ground, so as to effectively reduce experiment difficulty, reduce experiment cost, and also improve the measurement accuracy.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
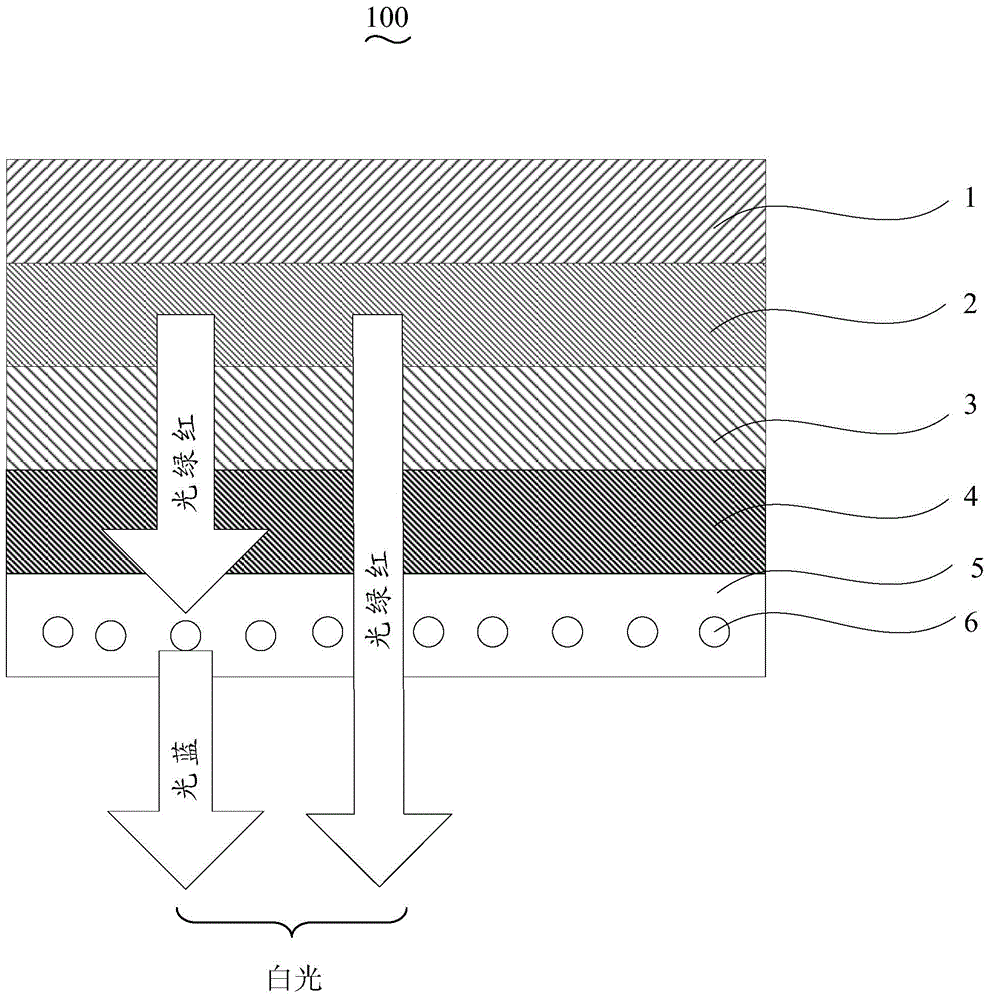
Luminescence Conversion LED
ActiveUS20110143627A1Improve conversion efficiencySolid-state devicesLuminescent coatings applicationRefractive indexVitreous Bodies
A luminescence conversion LED having a radiation emitting chip that is connected to electrical connections and is surrounded by a housing that comprises at least a basic body and a cap, the chip being seated on the basic body, in particular in a cutout of the basic body, and the primary radiation of the chip being converted at least partially into longer wave radiation by a conversion element, wherein the cap is formed by a vitreous body, the conversion means being contained in the vitreous body, the refractive index of the vitreous body being higher than 1.6, preferably at least n=1.7.
Owner:OSRAM OLED
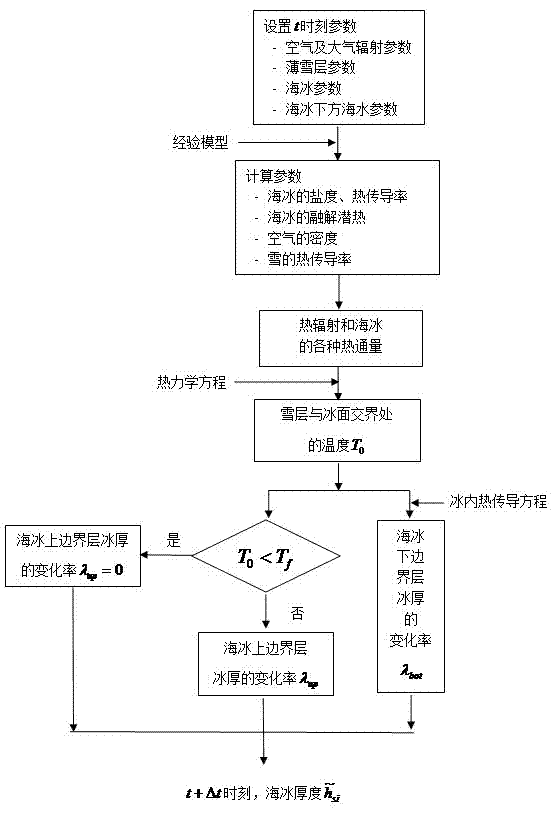
Method for simulating generating and thawing process of sea ice covered by thin snow
InactiveCN102902843AAvoid layered computingImprove computing efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsHeat fluxLong wave radiation
The invention discloses a method for simulating the generating and thawing process of sea ice covered by thin snow. The method comprises the steps of: setting the sea ice covered by the thin snow and environmental parameters of the sea ice; calculating parameters such as salinity, heat conductivity, and melting latent heat of the sea ice; calculating the solar shortwave radiation, the atmosphere long wave radiation and various heat fluxes of the sea ice according to the environmental parameters; calculating the temperature at the boundary of a snow layer and an ice surface according to a thermodynamic equation; and judging whether the upper boundary layer of the sea ice is thawed or not, if so, calculating the change rate of the ice thickness of the upper boundary ice layer; calculating the change rate of the thickness of the lower boundary layer of the sea ice according to an internal heat conduction equation; and finally calculating the thickness of the sea ice according to the change rates of the thicknesses of the upper and lower boundary layers of the sea ice. The method has the characteristic of high calculation efficiency and can be used for the simulation on the generating and thawing process of the sea ice covered by thin snow.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Thulium-doped tellurate glass up-conversion luminescent material, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103421512AEasy to prepareLow costLuminescent compositionsSemiconductor devicesThuliumLong wave radiation
A thulium-doped tellurate glass up-conversion luminescent material has a chemical formula of TeaTibLacOm:dTm<3+>, wherein a is 0.85-0.92, b is 0.02-0.06, c is 0.01-0.08, d is 0.01-0.05, m is 1.935-1.99, and a+b+c+d=1. The thulium-doped tellurate glass up-conversion luminescent material can be excited to emit blue light by long-wave radiation. The invention also provides a preparation method and an application of the thulium-doped tellurate glass up-conversion luminescent material.
Owner:OCEANS KING LIGHTING SCI&TECH CO LTD +1
Praseodymium-holmium-codoped rare earth stannate up-conversion luminescent material and its preparation method and use
InactiveCN104650895ASolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRare earthTransition radiation
The invention discloses a praseodymium-holmium-codoped rare earth stannate up-conversion luminescent material. The praseodymium-holmium-codoped rare earth stannate up-conversion luminescent material has a chemical formula of Me2-x-ySnO5: xPr<3+>, yHo<3+>, wherein x is in a range of 0.002-0.06, y is in a range of 0.002-0.04, and Me represents a lithium element, a lanthanum element, a gadolinium element or a lutecium element. The praseodymium-holmium-codoped rare earth stannate up-conversion luminescent material can be stimulated by long-wave radiation from infrared light to green light, and in a 483nm wavelength zone, Pr<3+> ion 3P0 to 3H4 transition radiation forms a luminescence peak and thus the praseodymium-holmium-codoped rare earth stannate up-conversion luminescent material can be used as a blue-light emission material. The invention also provides a preparation method and use of the praseodymium-holmium-codoped rare earth stannate up-conversion luminescent material.
Owner:OCEANS KING LIGHTING SCI&TECH CO LTD +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com