Heat supply load forecasting method based on a comprehensive temperature
A load and heat supply technology, applied in forecasting, renewable energy integration, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of not considering outdoor wind speed, solar radiation, indoor heat gain and heat supply, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0050] Specific implementation mode one: the heating load forecasting method based on comprehensive temperature comprises the following steps:
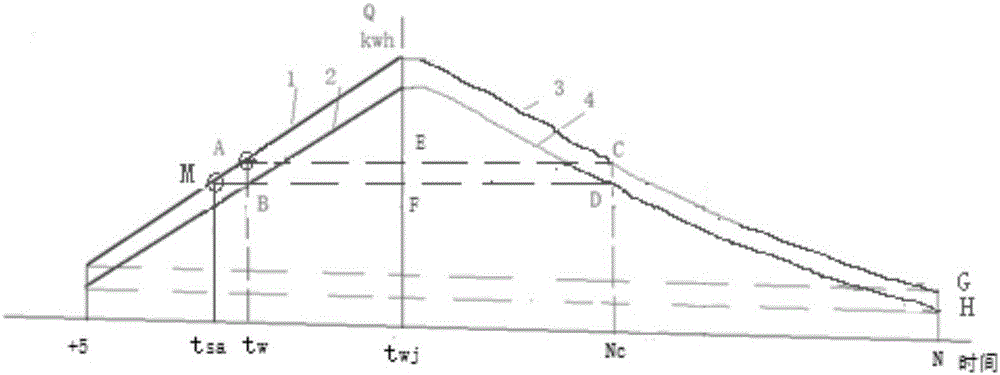
[0051]Firstly, a building with multiple surfaces, each with different thermal properties, is simplified to an equivalent building with the same surface properties. Then convert all the buildings and all pipe networks within the range supplied by the heat source into a comprehensive equivalent building to obtain the equivalent thermal characteristic coefficient of the building. The heating load forecast is carried out on the basis of replacing the dry bulb temperature with the comprehensive temperature and considering the indoor heat gain, taking into account the solar radiation capacity absorbed by the outer surface of the wall, the long-wave radiation exchange between the building and the external environment, and the indoor heat gain. In order to solve the problem of traditional heating load prediction using dry bulb temperature, th...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0109] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: Δt in the step four y By the formula (4) get:
[0110] Δt y = ρI y α e - - - ( 4 )
[0111] Wherein said ρ is solar radiation absorption coefficient, is checked by relevant manual; I y It is the predicted value of solar irradiance on the horizontal or vertical plane, which is obtained by statistical method according to the test data, and the unit is W / m 2 ; e is the heat transfer coefficient of the outer surface, according to the outdoor wind speed, it can be obtained from the relevant manual, and the unit is W / (m 2 ·°C).
specific Embodiment approach 3
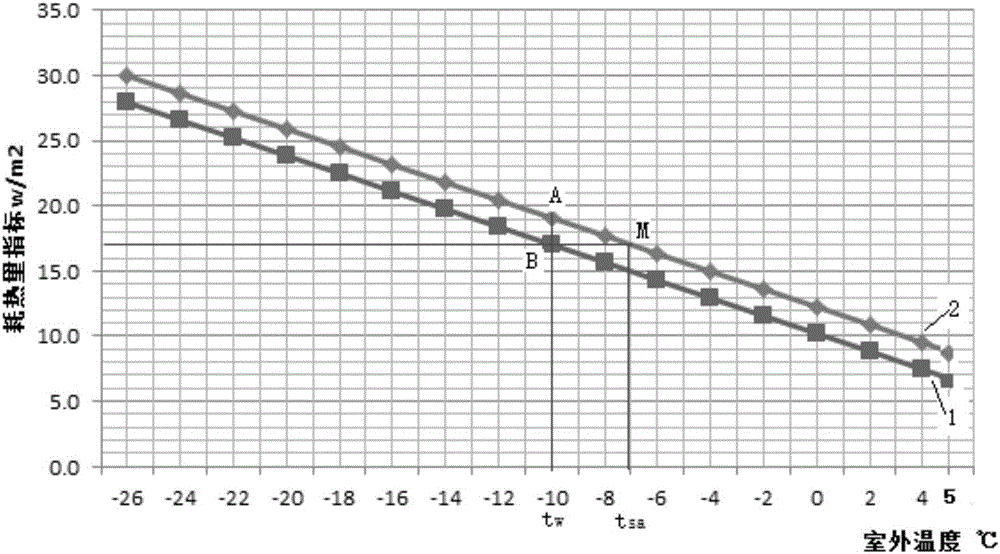
[0112] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is that: in the step five, the predicted value of the comprehensive equivalent building heat consumption index is calculated according to formula (5), and can also be calculated according to t say check figure 1 Sure( figure 1 t in say The intersection point M with curve 2 is the predicted value):
[0113] q H y 1 = ( t n - t s a y ) 1000 × A 0 × γ - q I H - ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com