Patents
Literature
140 results about "Egress router" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
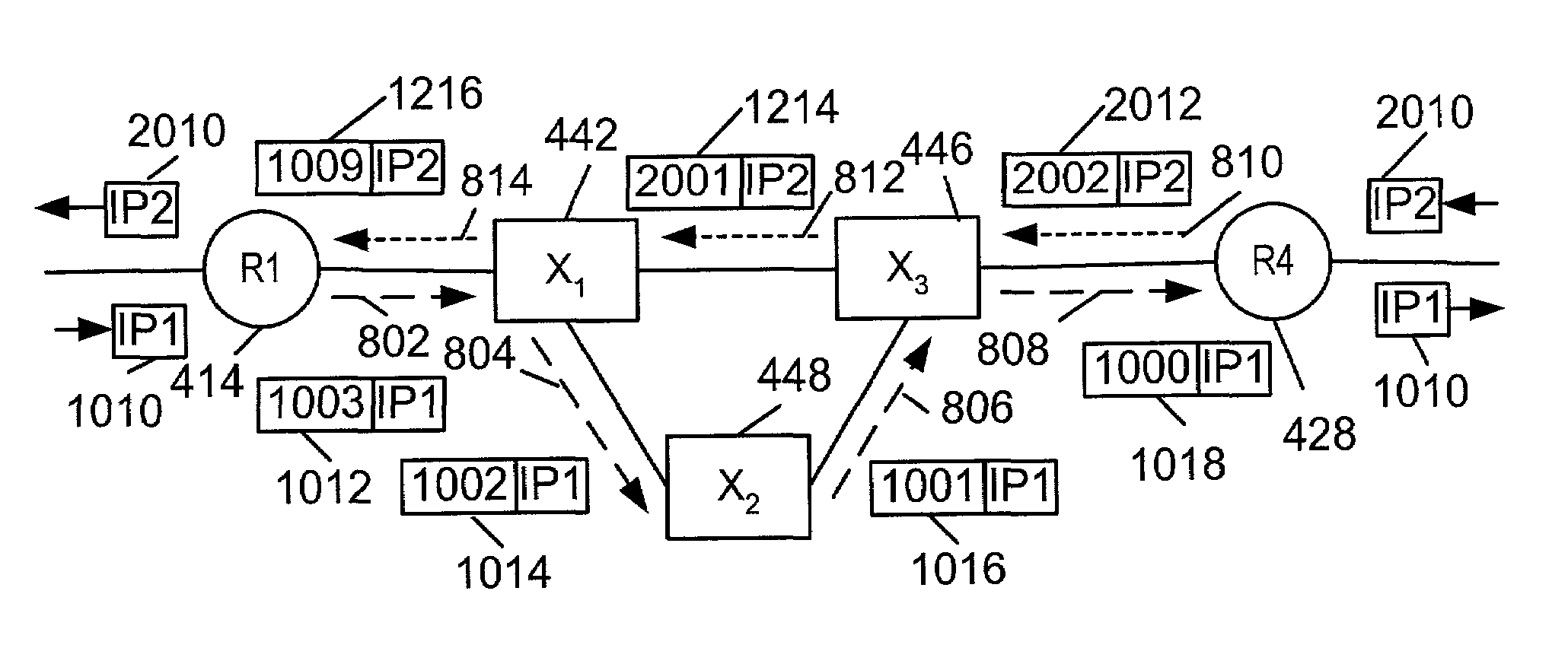
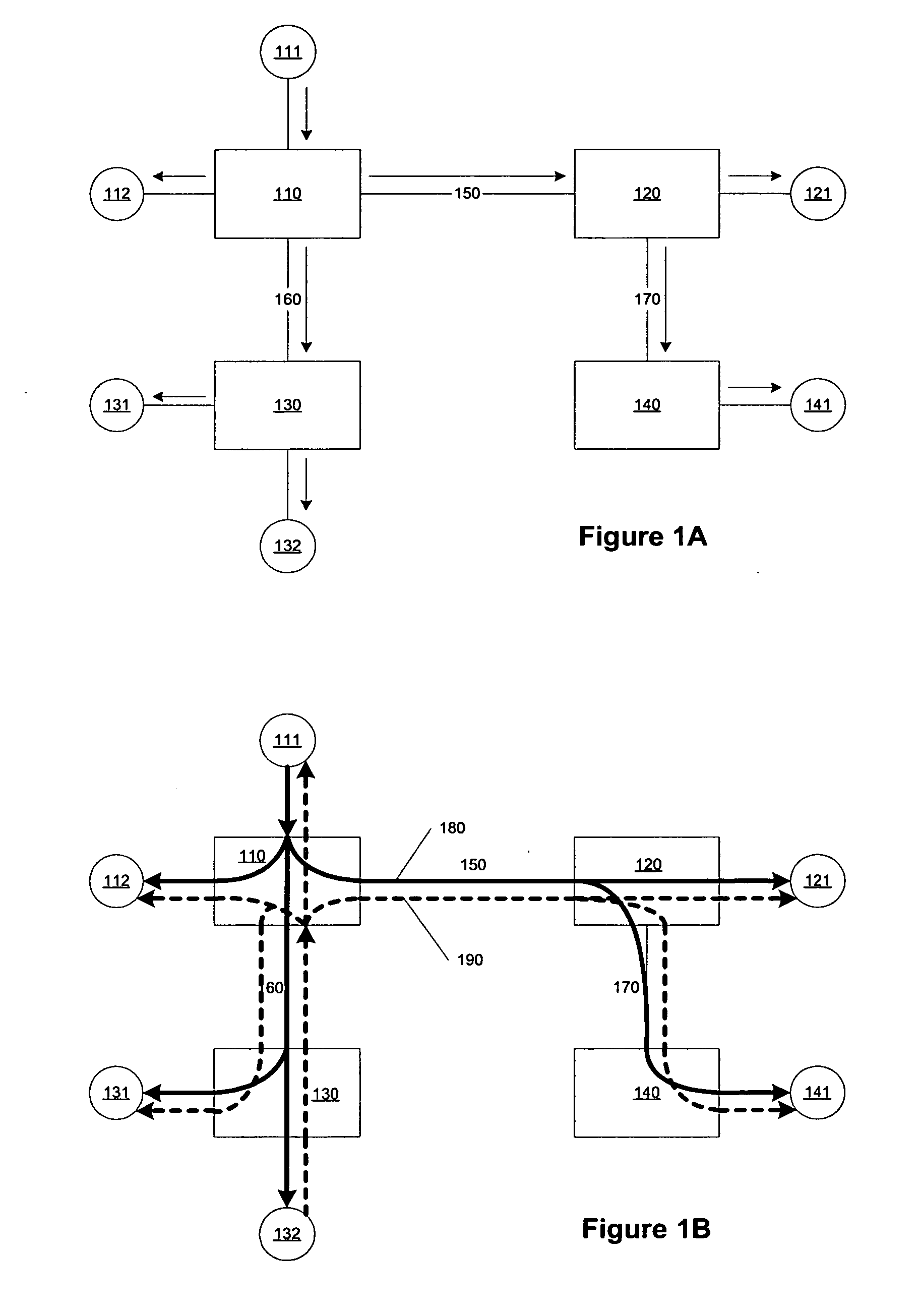
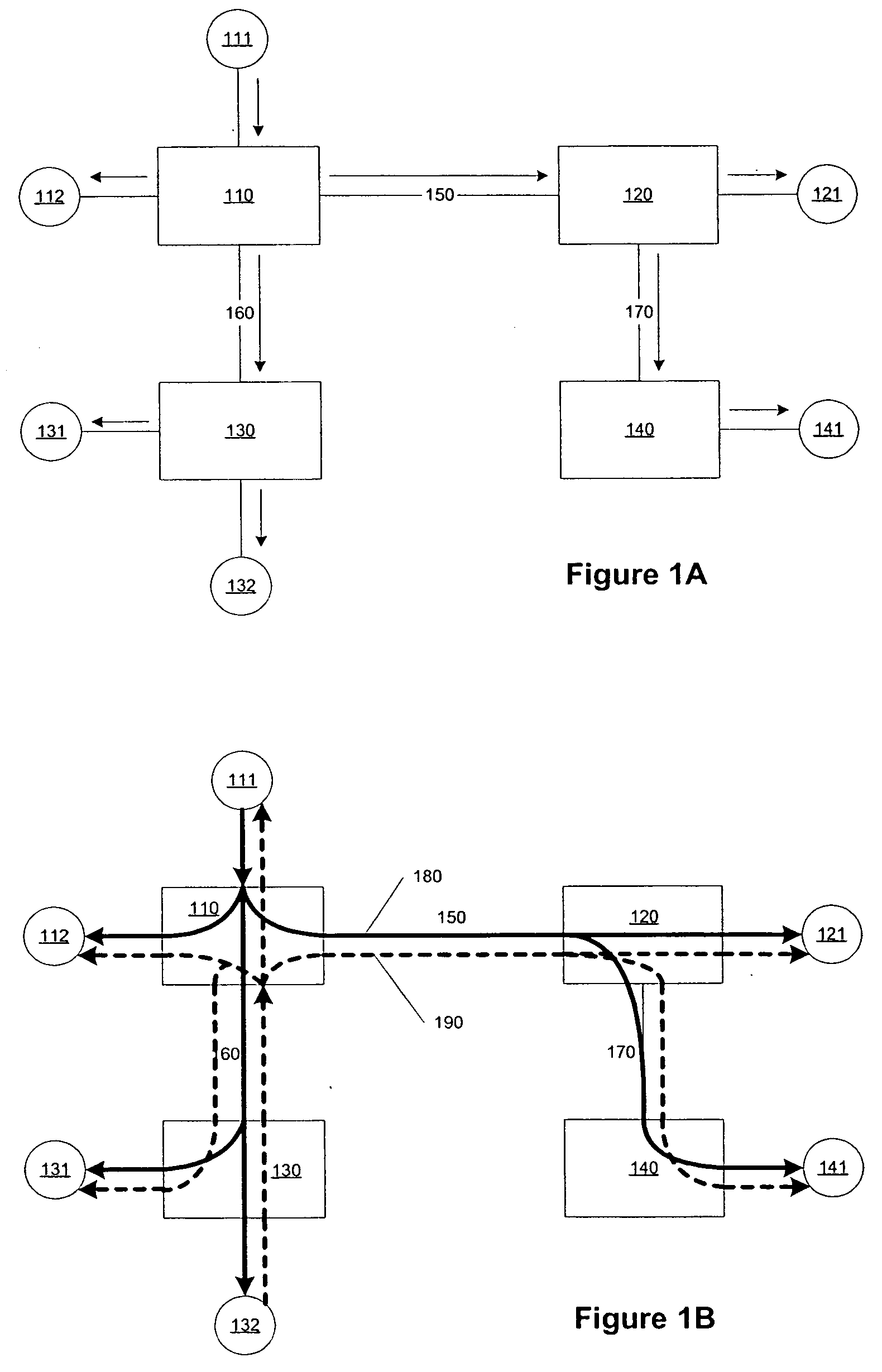
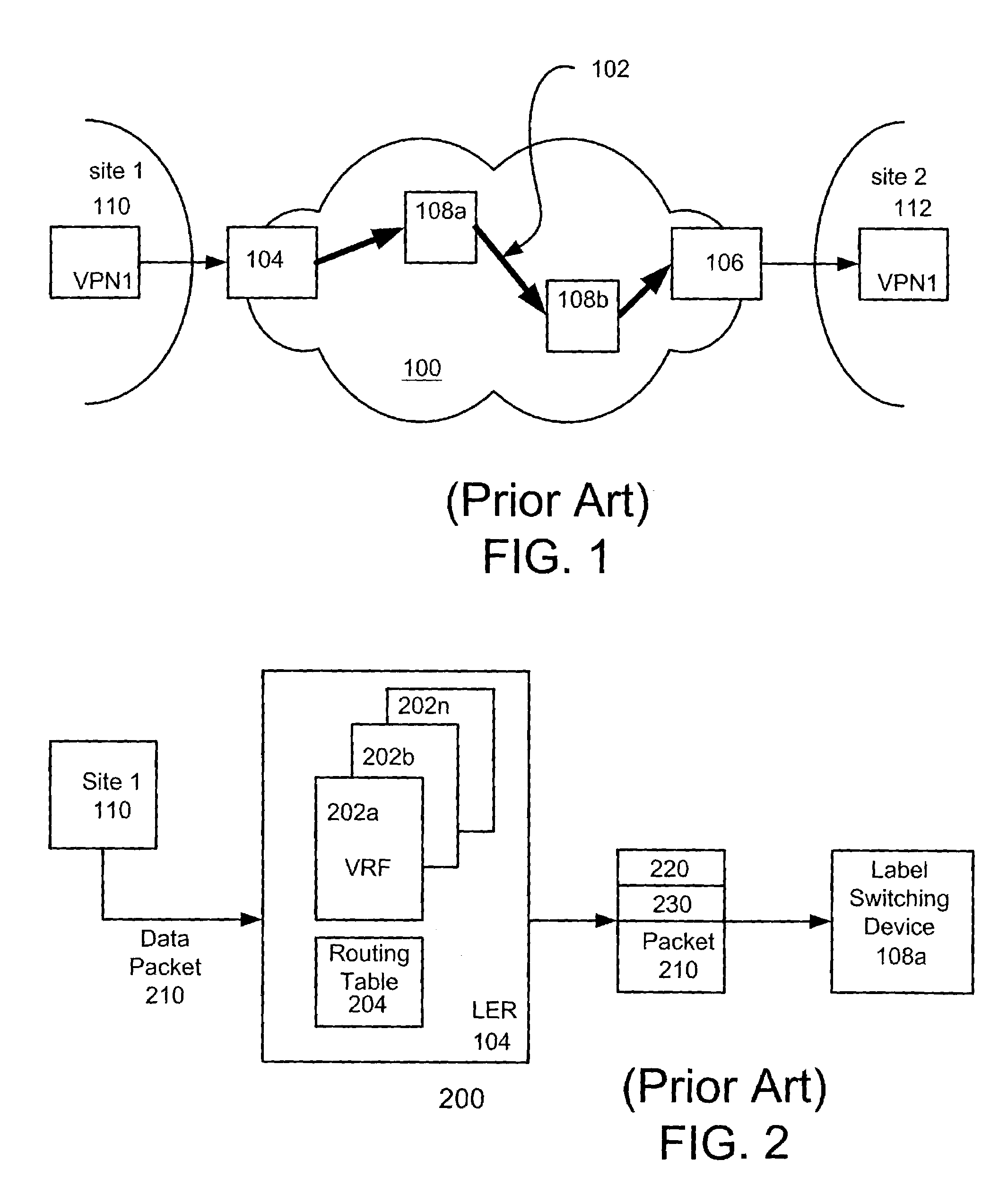
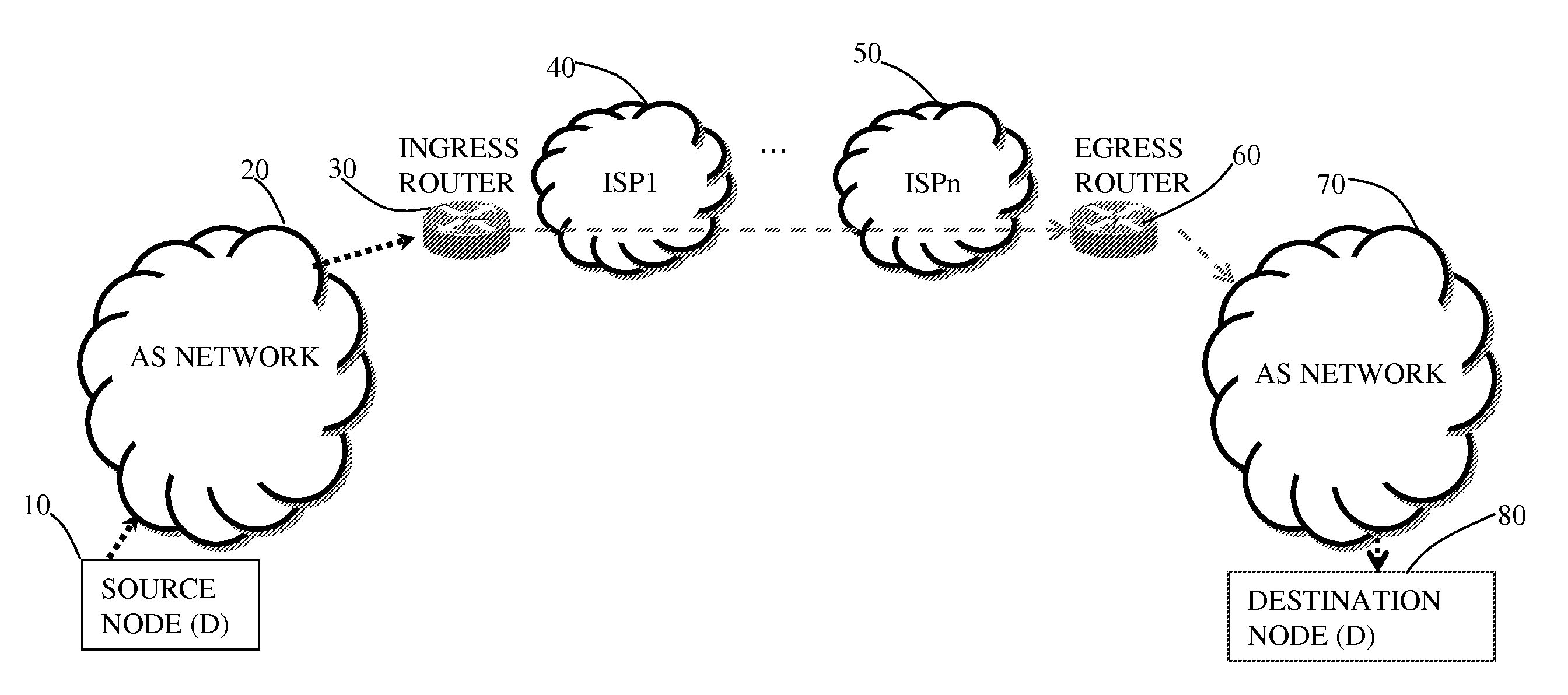
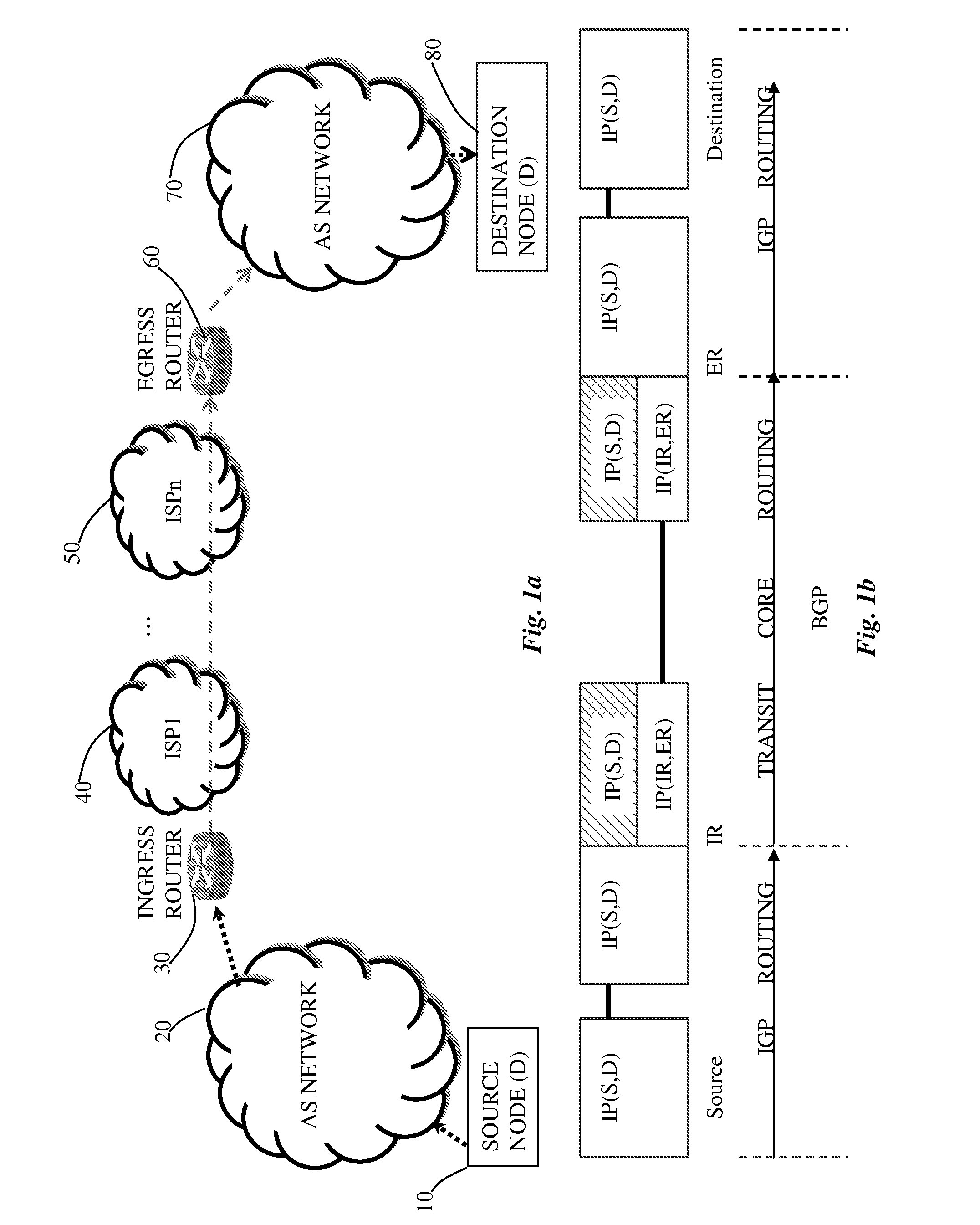
An egress router is a Label Switch Router that is an end point (drain) for a given Label Switched Path (LSP). An egress router may be an ingress router or an intermediate router for any other LSP(s). Hence the role of egress and ingress routers is LSP specific. Usually, the MPLS label is attached with an IP packet at the ingress router and removed at the egress router, whereas label swapping is performed on the intermediate routers.
Methods and apparatus for implementing bi-directional signal interfaces using label switch paths
InactiveUS7061921B1Special service provision for substationData switching by path configurationCommunications systemEgress router
Methods and apparatus for implementing bi-directional logical signal interfaces (LSIs) in communications systems which use uni-directional label switched paths (LSPs), e.g., MPLS networks, are described. To implement an LSI, two uni-directional LSPs between the same end points, e.g., routers, and extending in opposite directions, are associated together. The association of LSPs may be done by setting LSI configuration information in the routers at both ends of an LSI. Each router at the end of an LSI serves as an egress router for one of the LSPs associated with the LSI and an ingress router for the other LSP associated with the LSI. To enable an egress router to determine which, if any, LSI a packet or message corresponds to, a real as opposed to a null label is used when sending packets over an LSI LSP to an LSI LSP egress router.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
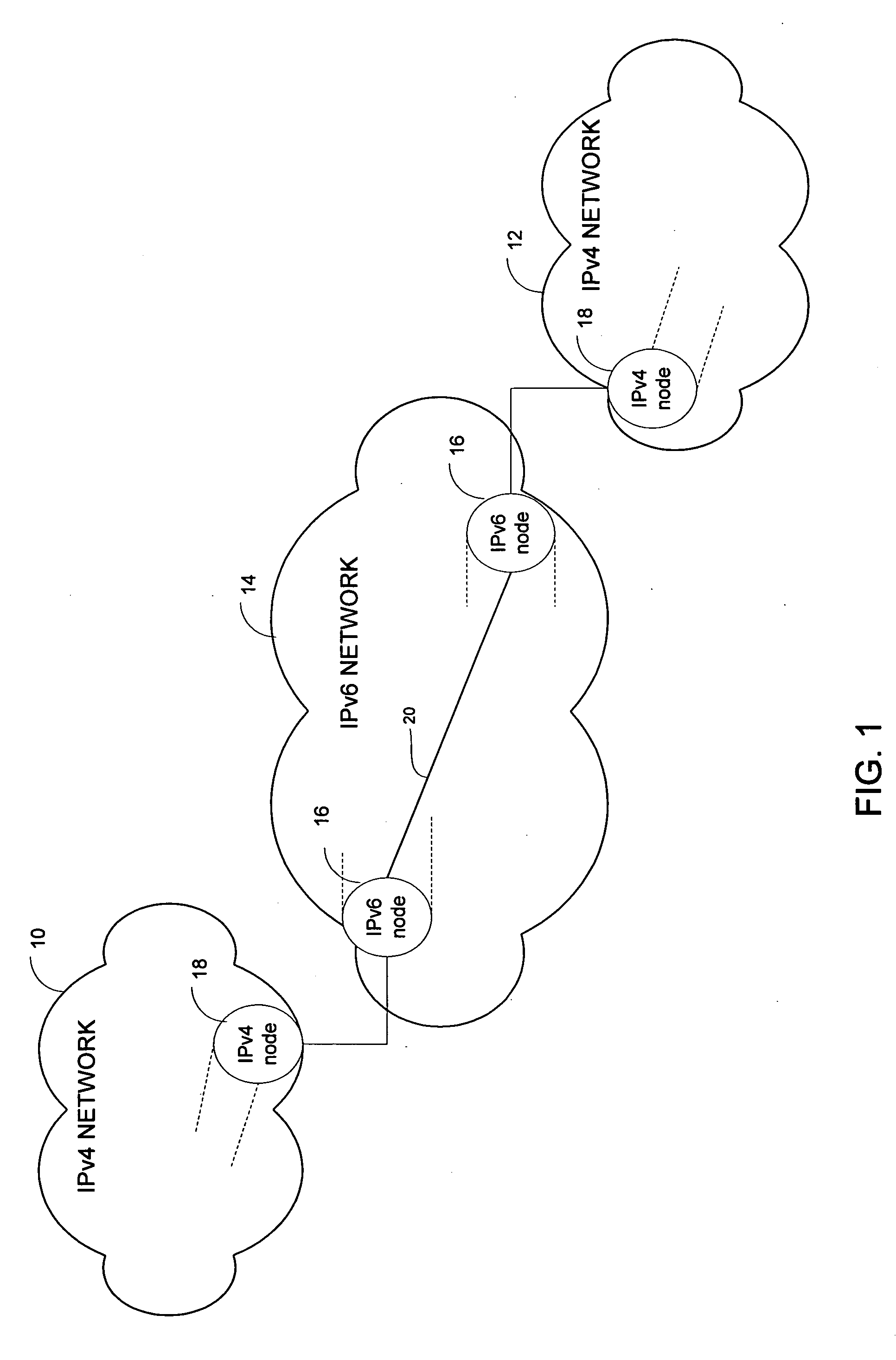
Method and system for automatically interconnecting IPv4 networks across an IPv6 network
InactiveUS20060209885A1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationIPv6 packetEgress router
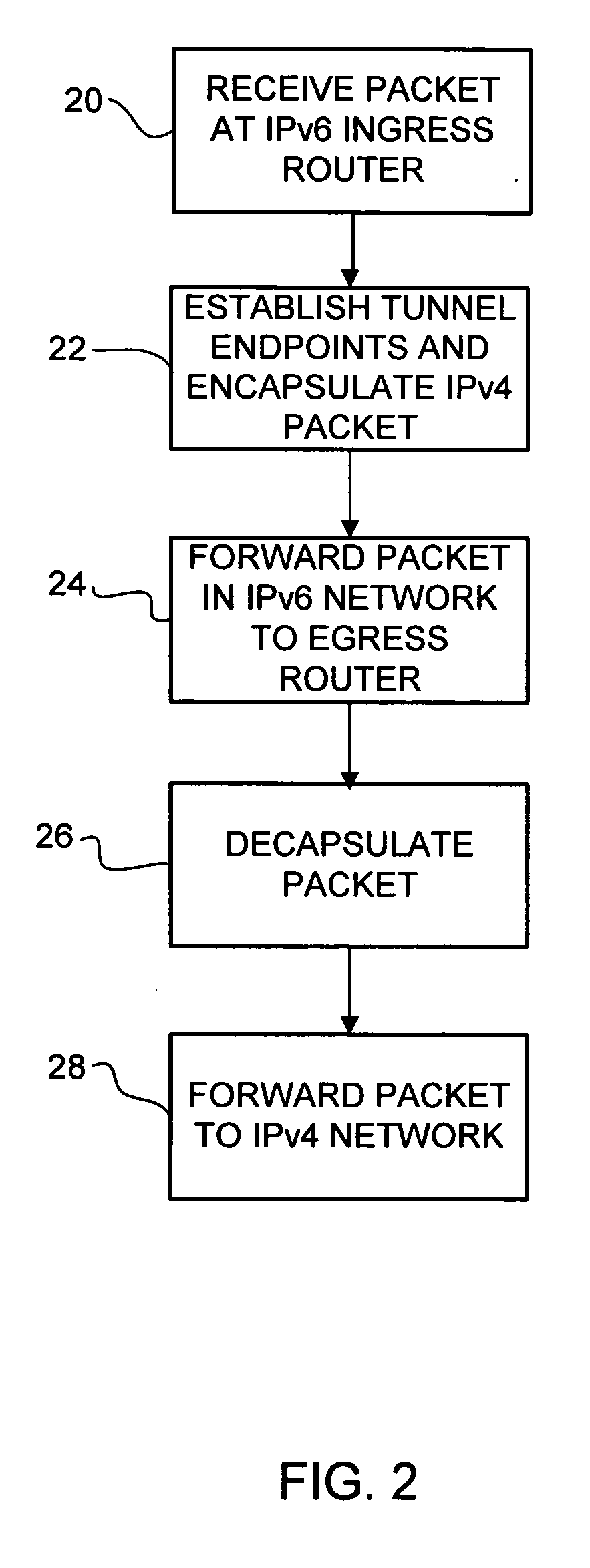
A method and system for automatically interconnecting IPv4 networks across an IPv6 network are disclosed. The method includes receiving an IPv4 packet at an ingress router in the IPv6 network and finding the longest match IPv4 routing entry for IPv4 addresses in the received packet to identify an egress router in the IPv6 network. The IPv4 packet is encapsulated to create an IPv6 packet, wherein destination and source addresses of the encapsulated packet identify a subnet router anycast corresponding to the ingress router and the egress router in the IPv6 network. The encapsulated packet is forwarded to the egress router.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Content based data packet routing using labels
InactiveUS20060165053A1Fast and efficientImprove performanceData switching by path configurationRouting tableEgress router
Disclosed is a content based router, system and method of operation. Upon receipt of a data packet at in ingress router, the ingress router matches the content of the data packet against stored user subscriptions. In one embodiment, the content is described using XML data and the user subscriptions are defined by XML queries. The router assigns a routing label to the data packet based on the matching, and transmits the data packet to a second network router. Intermediate routers along the packets path then use the assigned label in combination with stored routing tables in order to determine next hop routing. Upon receipt at an egress router, the content of the message is matched against user subscriptions for those users serviced by the egress router, and the egress router provides the data packet to those end users whose subscriptions match the content. The assigned routing labels may define routing paths or routing trees.
Owner:NEC CORP +1
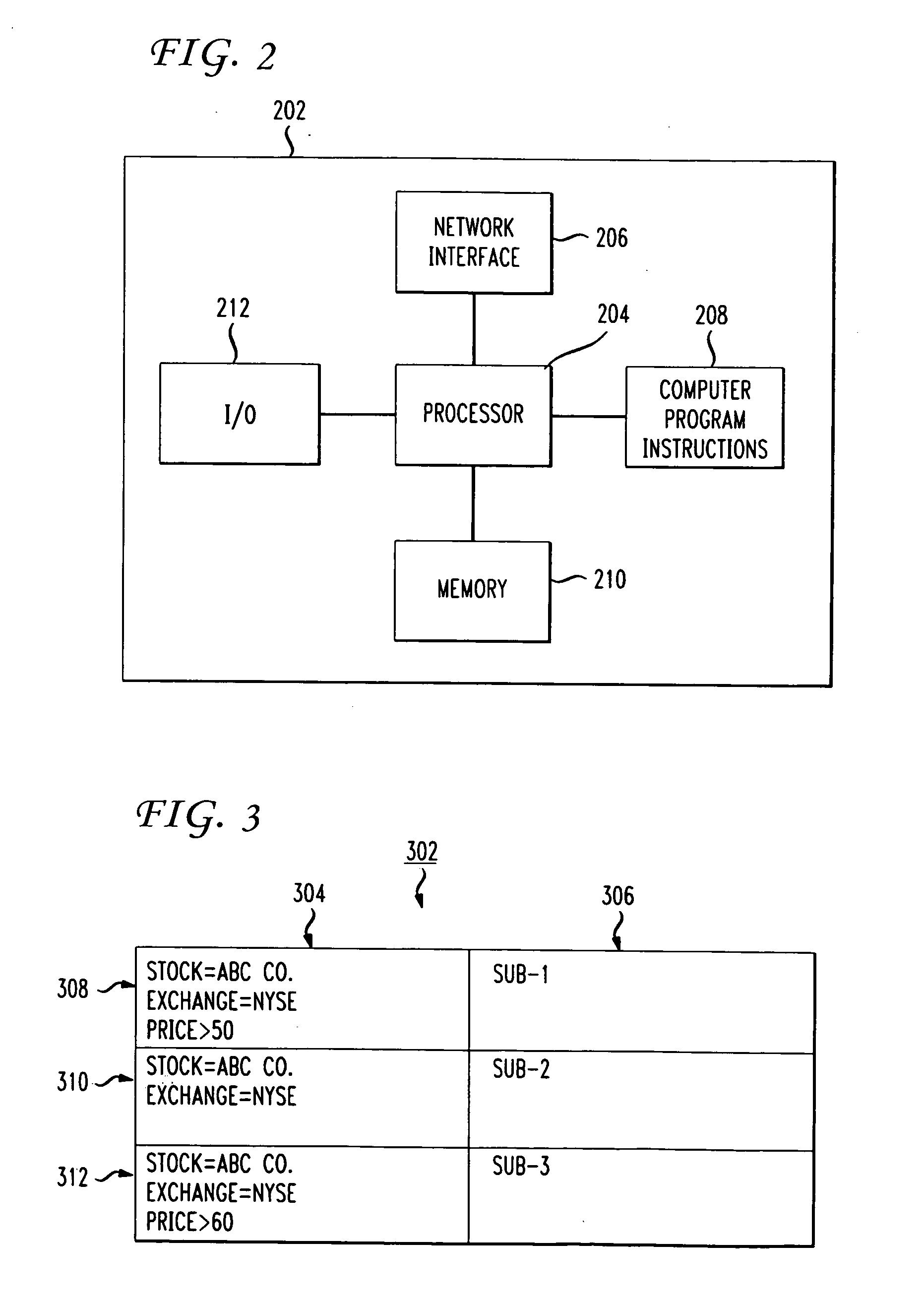
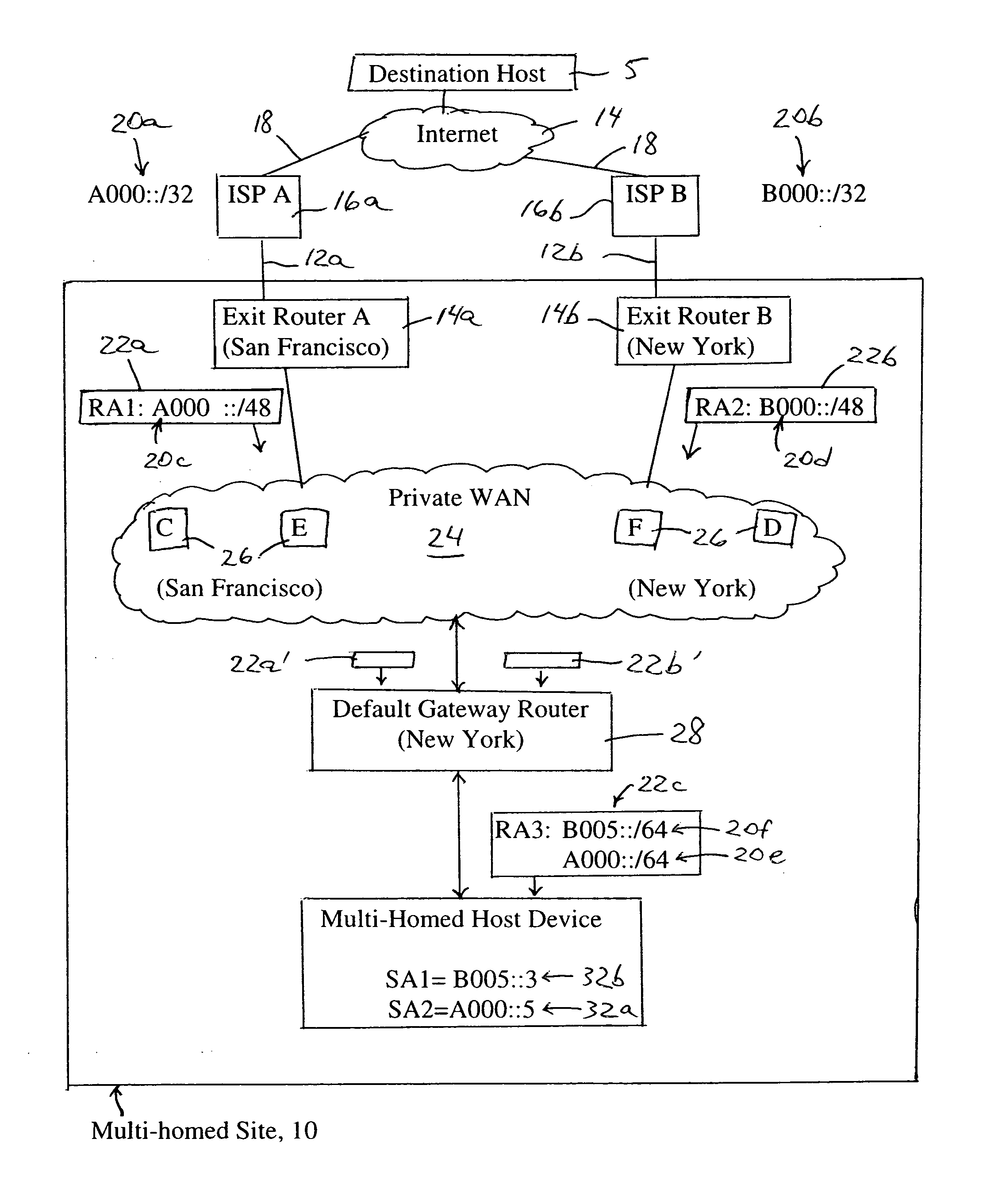
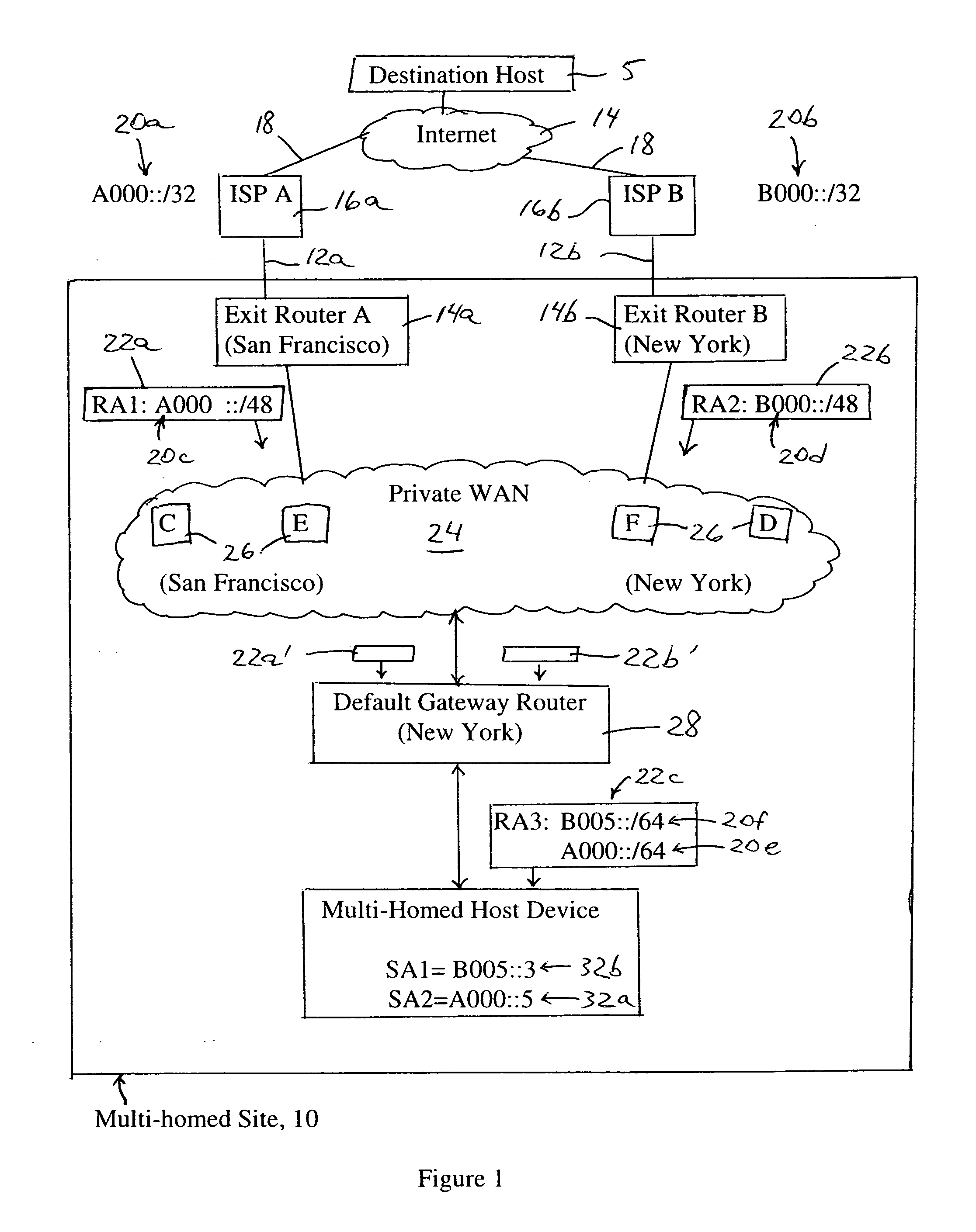
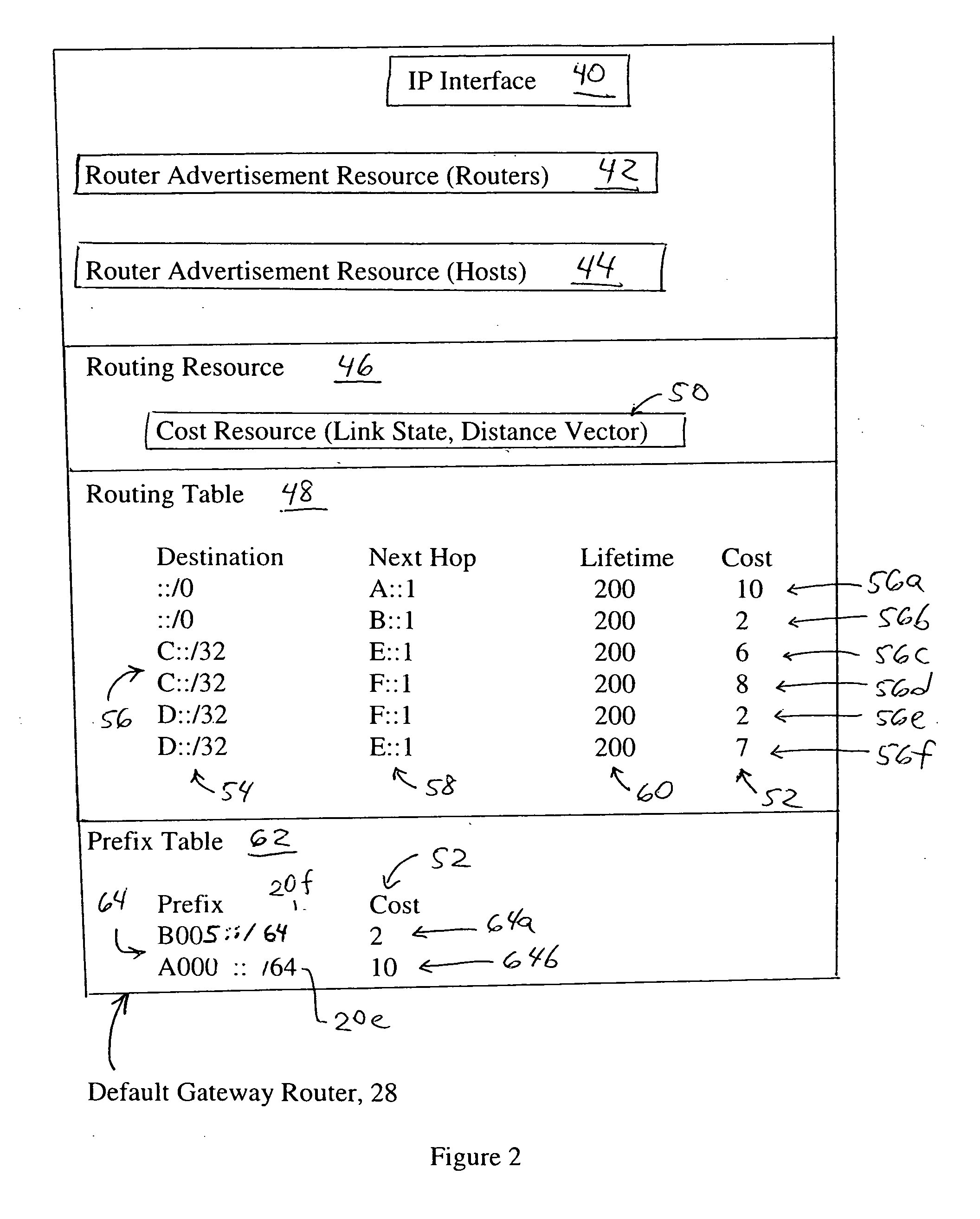
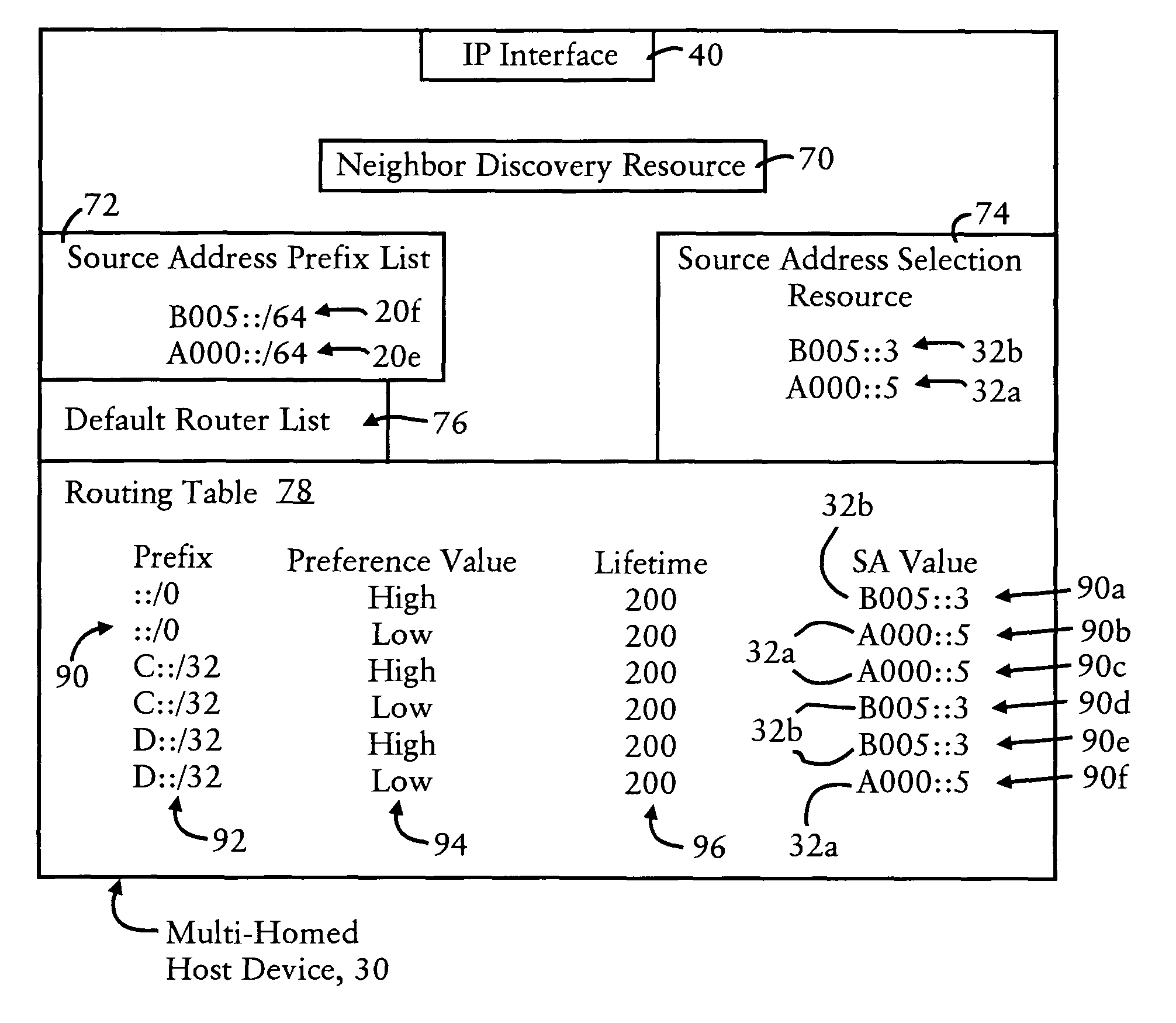
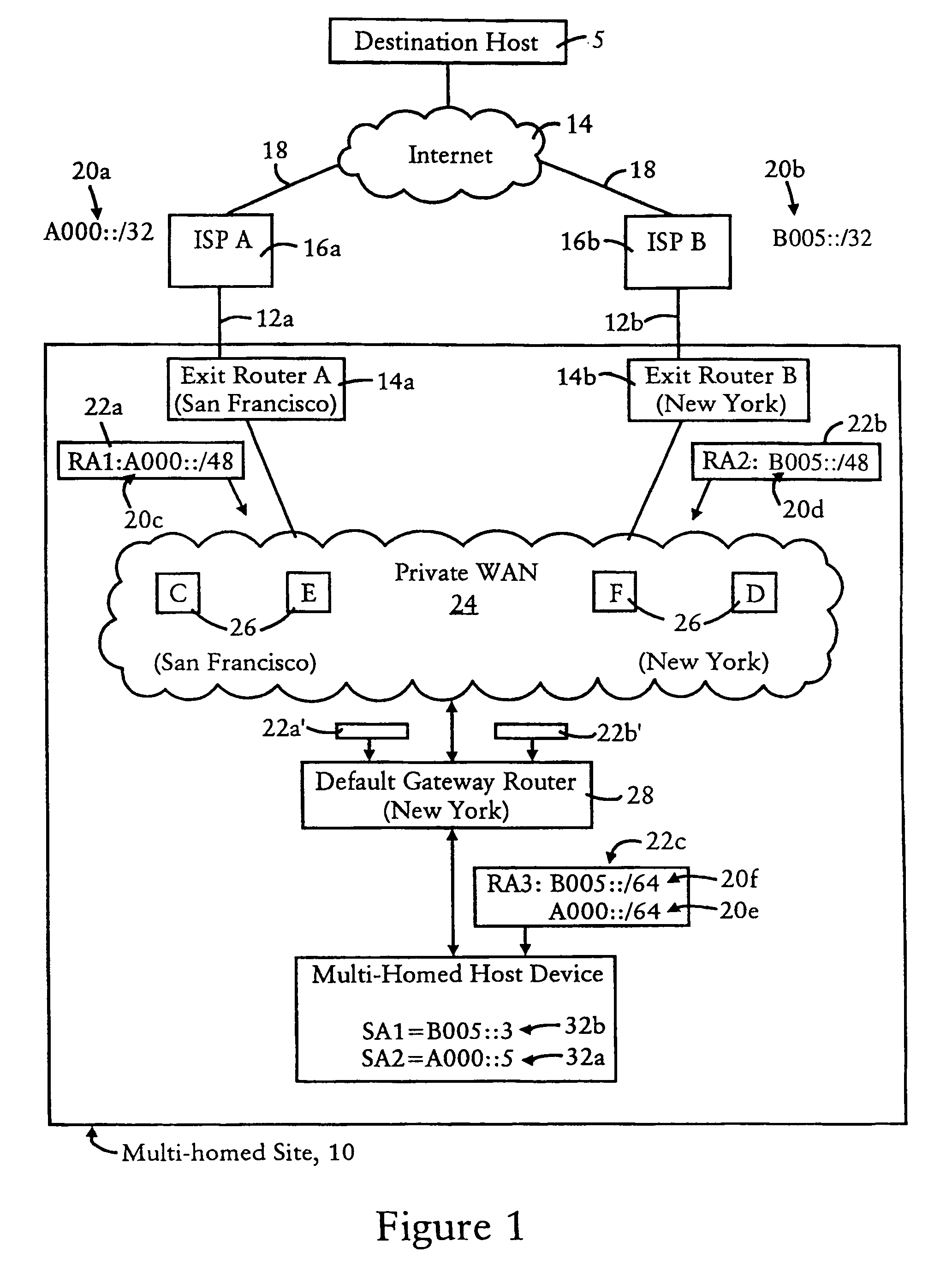
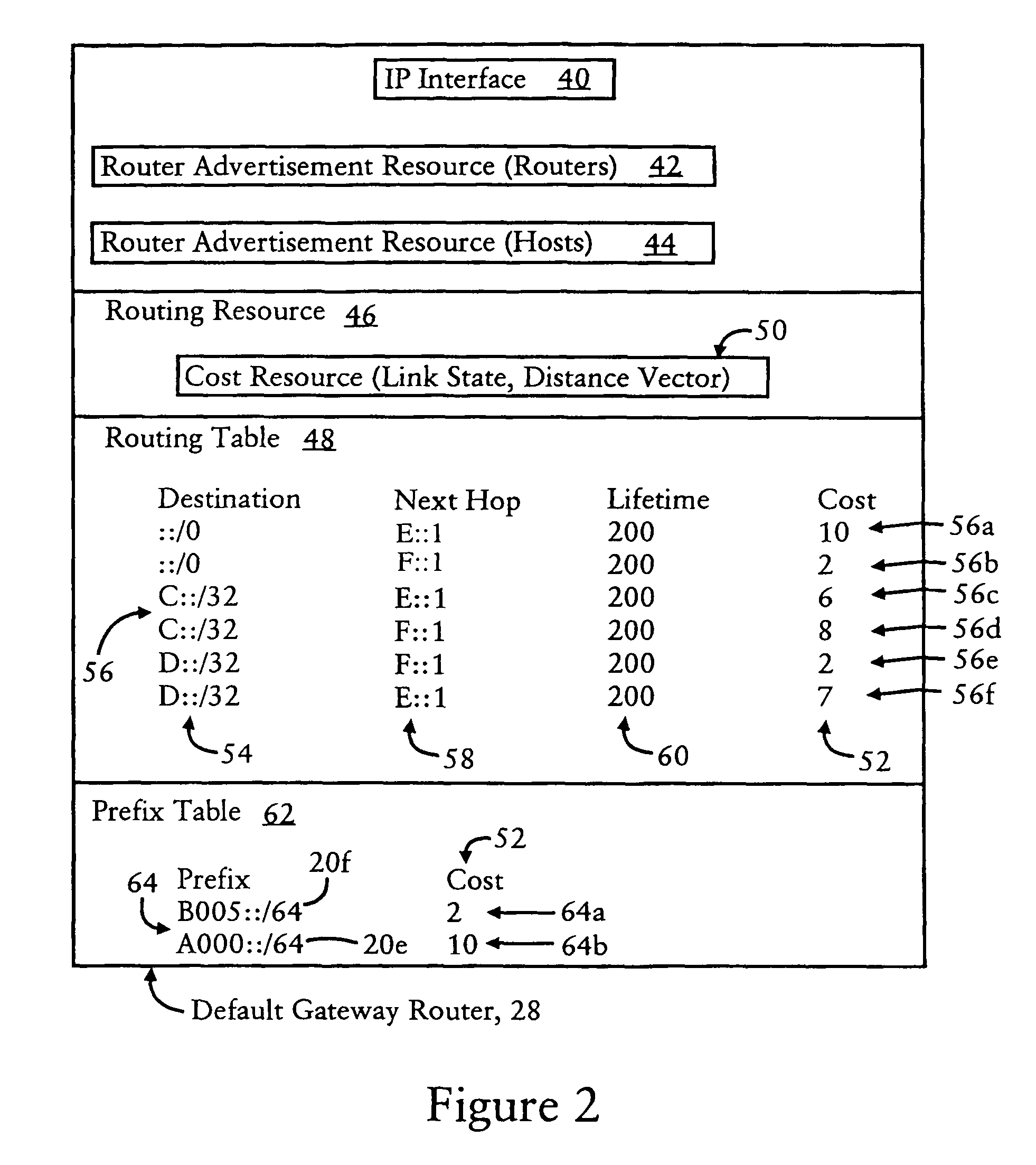
Default gateway router supplying IP address prefixes ordered for source address selection by host device
A default gateway router of a multi-homed site is configured for supplying, to a host device, a plurality of address prefixes having been advertised by respective exit routers providing respective connecting links for the multi-homed site to a wide area network. The default gateway router sends the address prefixes to the host device in a determined order based on a determined preference in the default gateway router for reaching the respective exit routers. The host device is configured for selecting a source address according to the determined order supplied by the default gateway router. The address also prefixes may be grouped according to identified destination prefixes, enabling the host device to select, for a given identified destination prefix, the source address according to the ordering of address prefixes within the corresponding group.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Port-to-port, non-blocking, scalable optical router architecture and method for routing optical traffic
InactiveUS20090074414A1Maximize throughputMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsCross connectionStructure of Management Information
Owner:MIND FUSION LLC
Dynamic multipoint tree rearrangement
A mechanism to dynamically map a multicast session to a transport tree to reduce flooding of egress routers on the transport tree is provided. A mechanism to reduce the length of time in which transient flooding can occur while the transport tree is being chosen or configured is also provided. The disclosed dynamic mapping mechanisms avoid interruption of an established multicast session. One mechanism disclosed provides for remapping of a multicast session by cloning an original transport tree with which the multicast session is associated, associating the multicast session with the cloned transport tree, and then reconfiguring the cloned transport tree in accord with edge egress routers that have subscribers to that multicast session.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
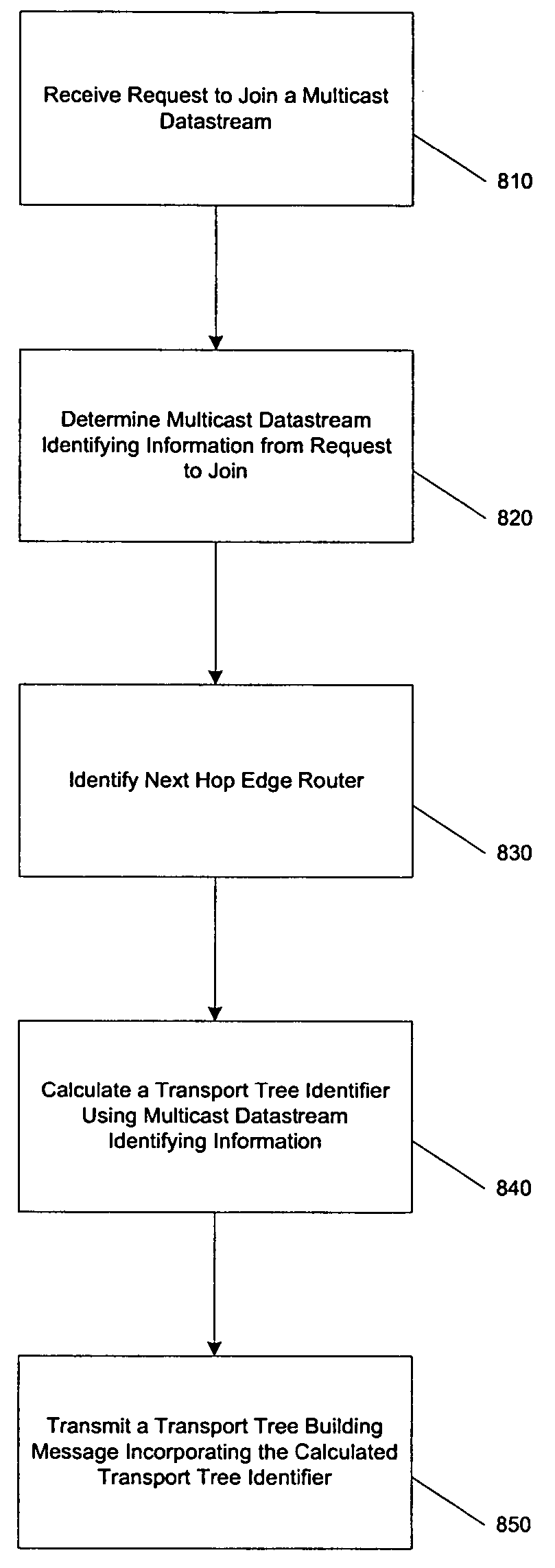
In-band multicast signaling using LDP
A mechanism is provided by which a transport tree identifier can be generated using one or more identifiers for a multicast datastream. The transport tree identifier can then be used in the process of building a transport tree across a transport network. A transport network egress router can receive a request to join a multicast datastream from a downstream node outside of the transport network. The information contained in the join message that identifies the desired multicast datastream can be encoded in the transport tree identifier. The transport tree identifier can be related to one or more of a multicast group destination address, a multicast datastream source address, and a broadcast domain identifier.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
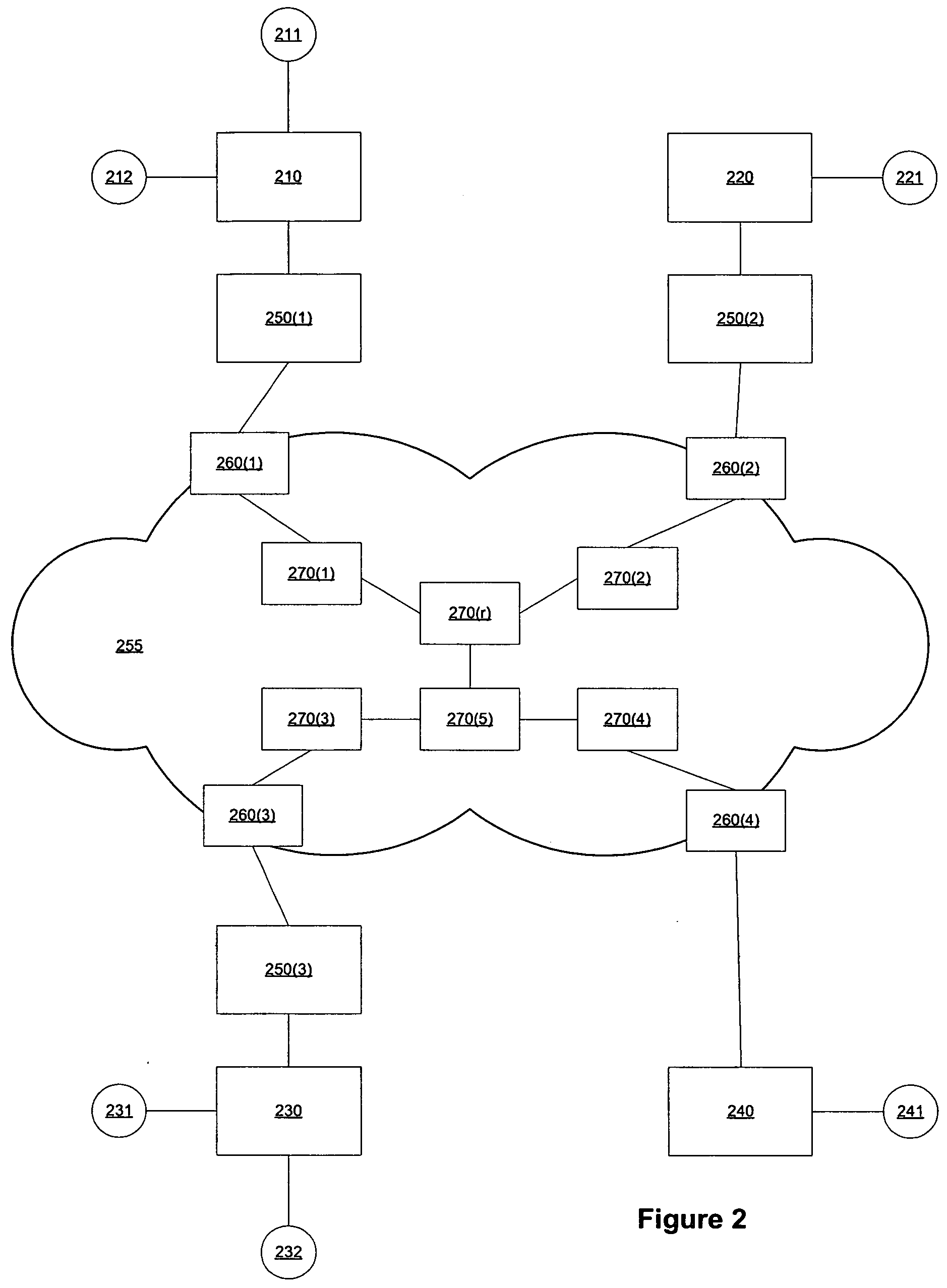
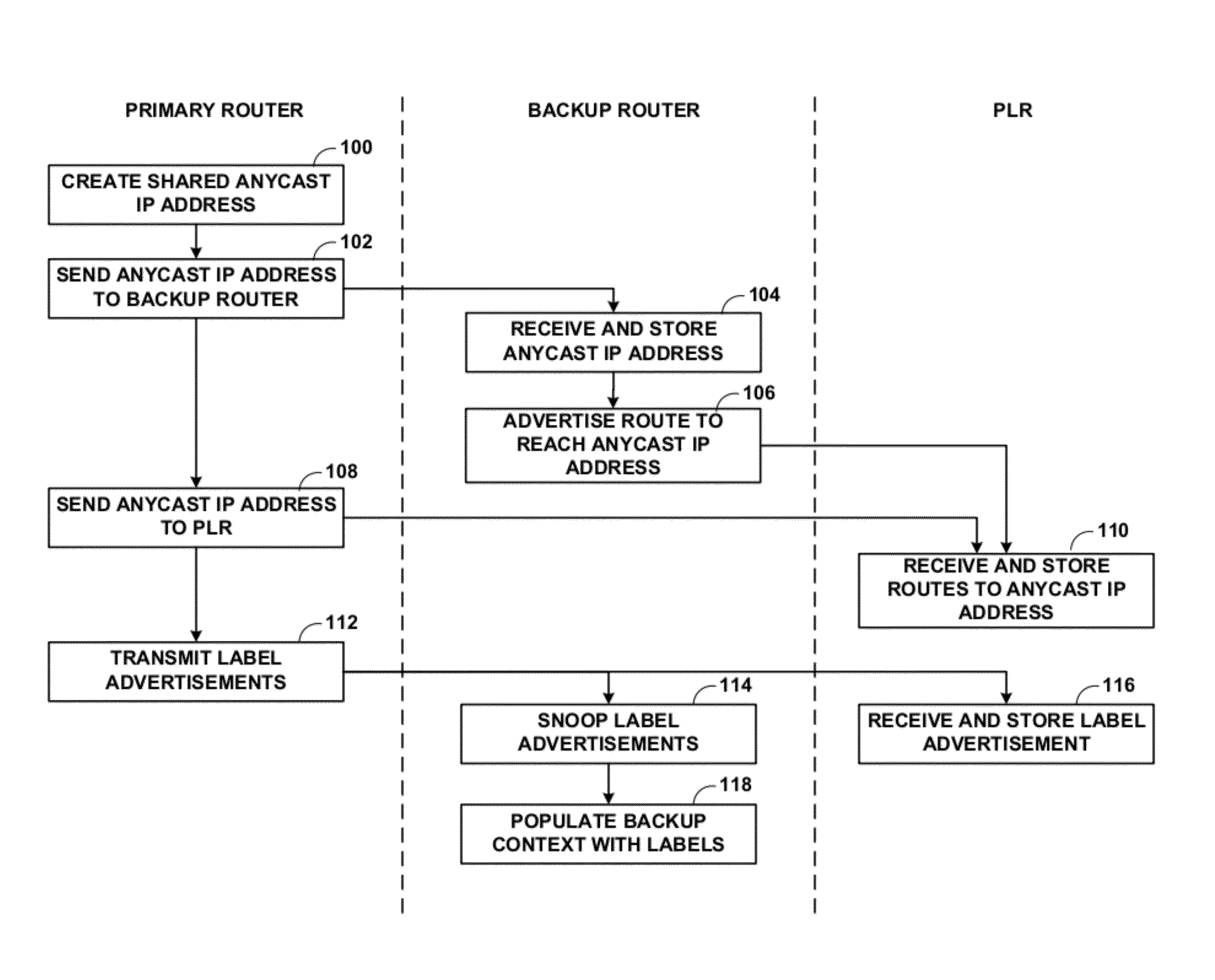
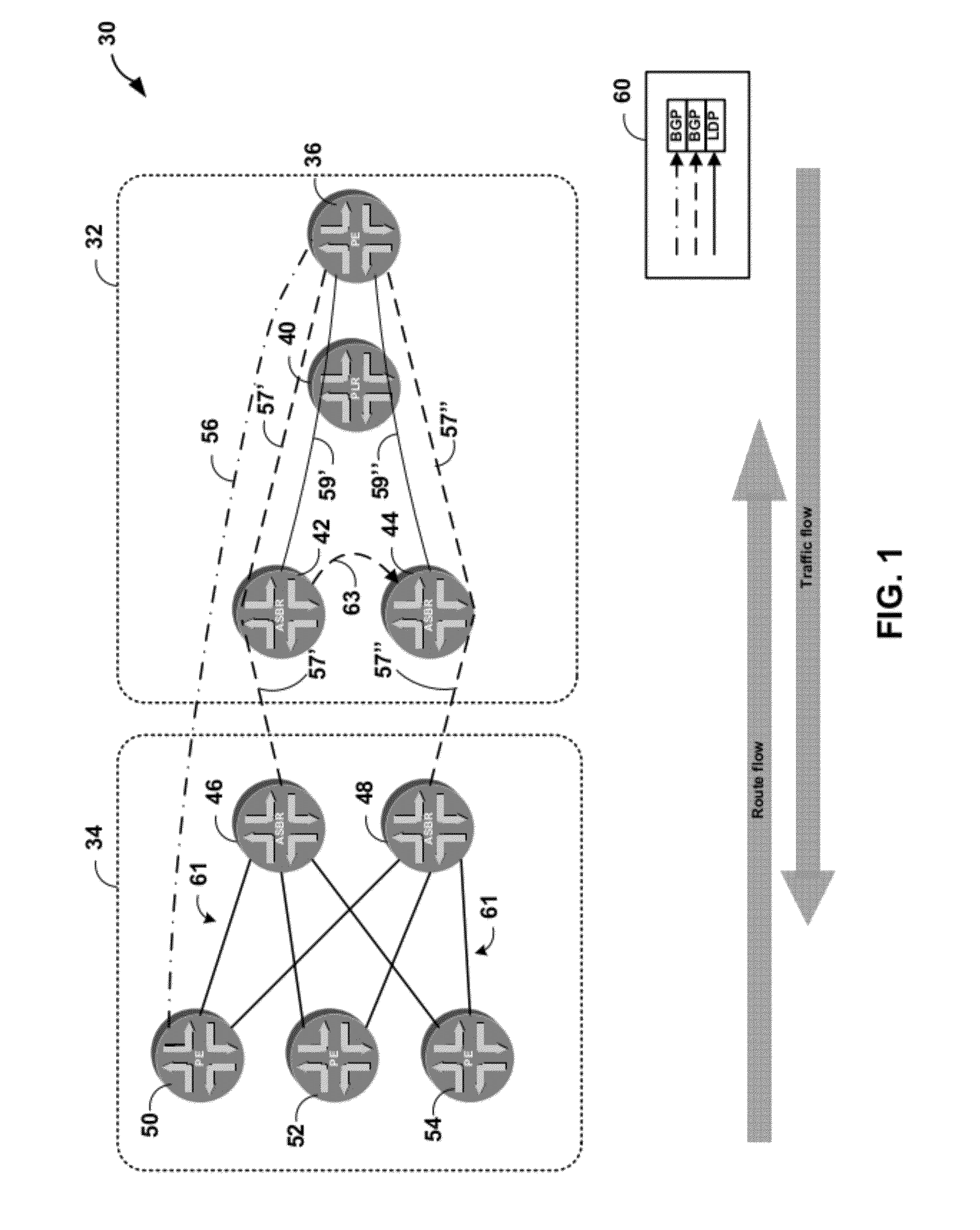
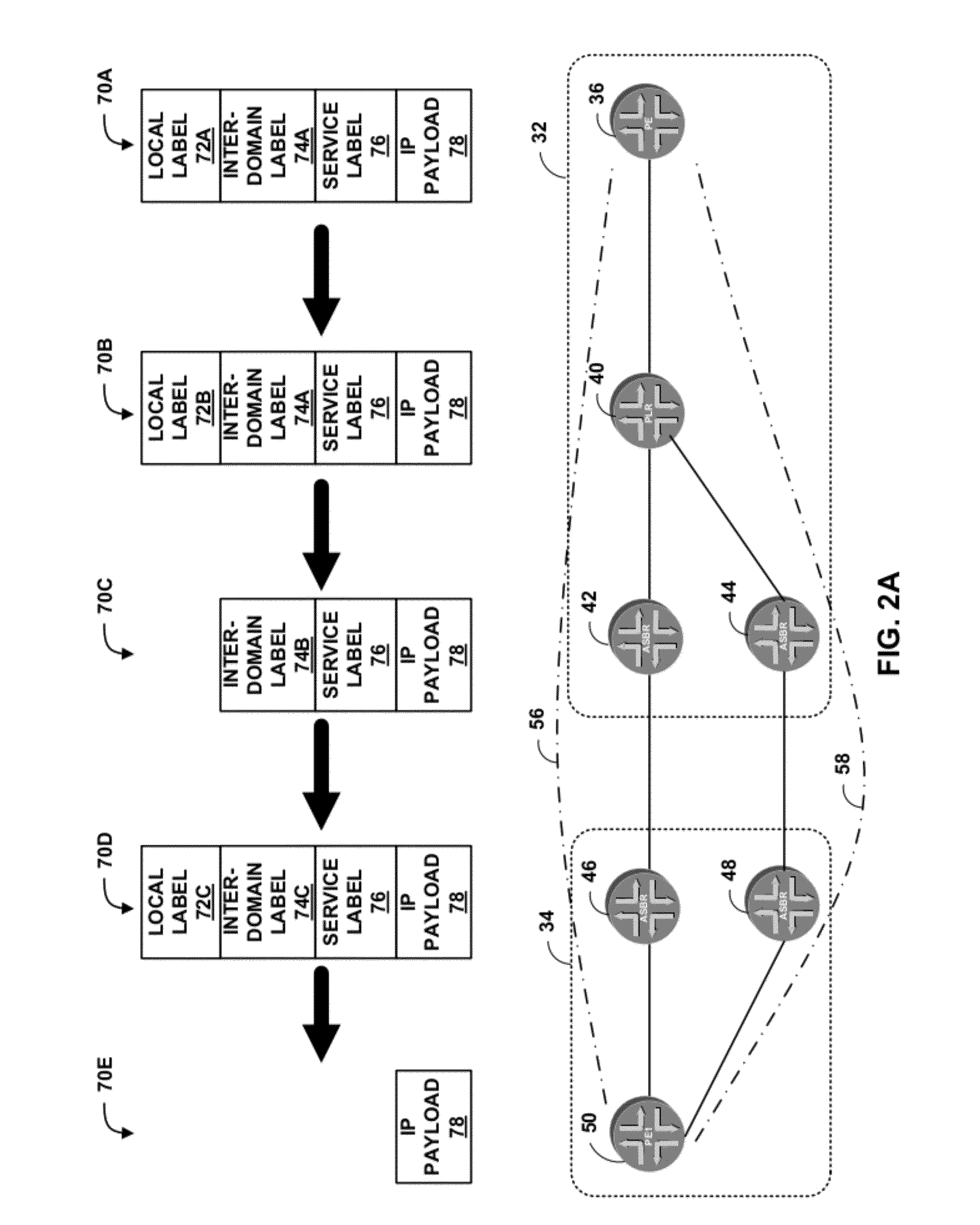
Egress protection for label switched paths
ActiveUS8259564B1Protection to failError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsIp addressEgress router
This disclosure describes techniques for protecting an endpoint of a label switched path. In one embodiment, a system includes an ingress router, a primary egress router, backup router, and a point of local repair (PLR) router. The ingress router, the PLR router, and the first egress router form a first label switched path. The backup router provides protection for the primary egress router such that the backup router provides routing services for the first egress router when the first egress router is not available. The primary egress router and the backup router share an anycast IP address. The backup router advertises a route to reach the primary egress router, but upon receiving a packet intended for the primary egress router, the backup router identifies the destination of the packet and forwards the packet to the destination instead of the primary egress router along a different route.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
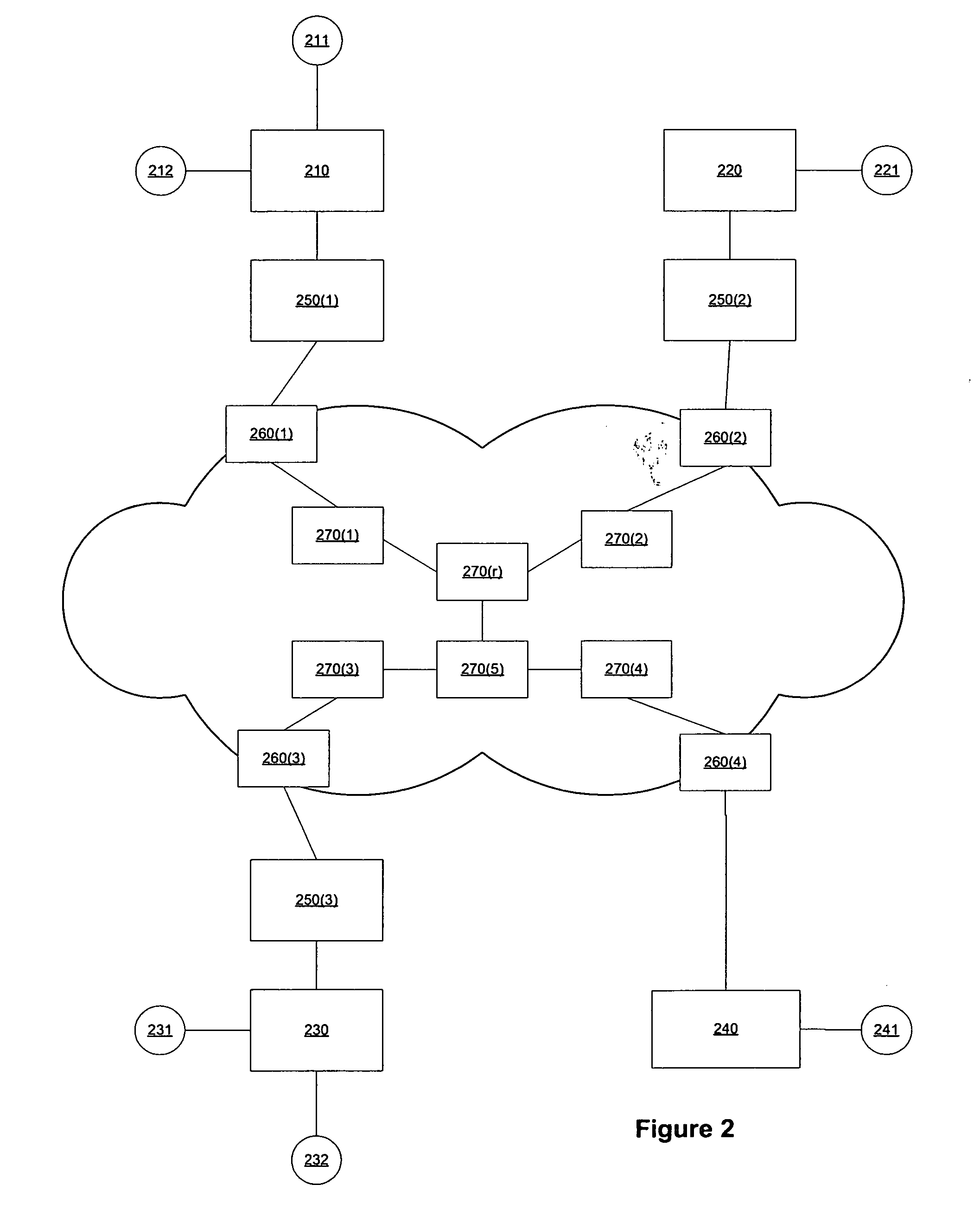
Method and system for forwarding data units
InactiveUS20050068933A1SaveSave bandwidthTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationCommunications systemForwarding equivalence class
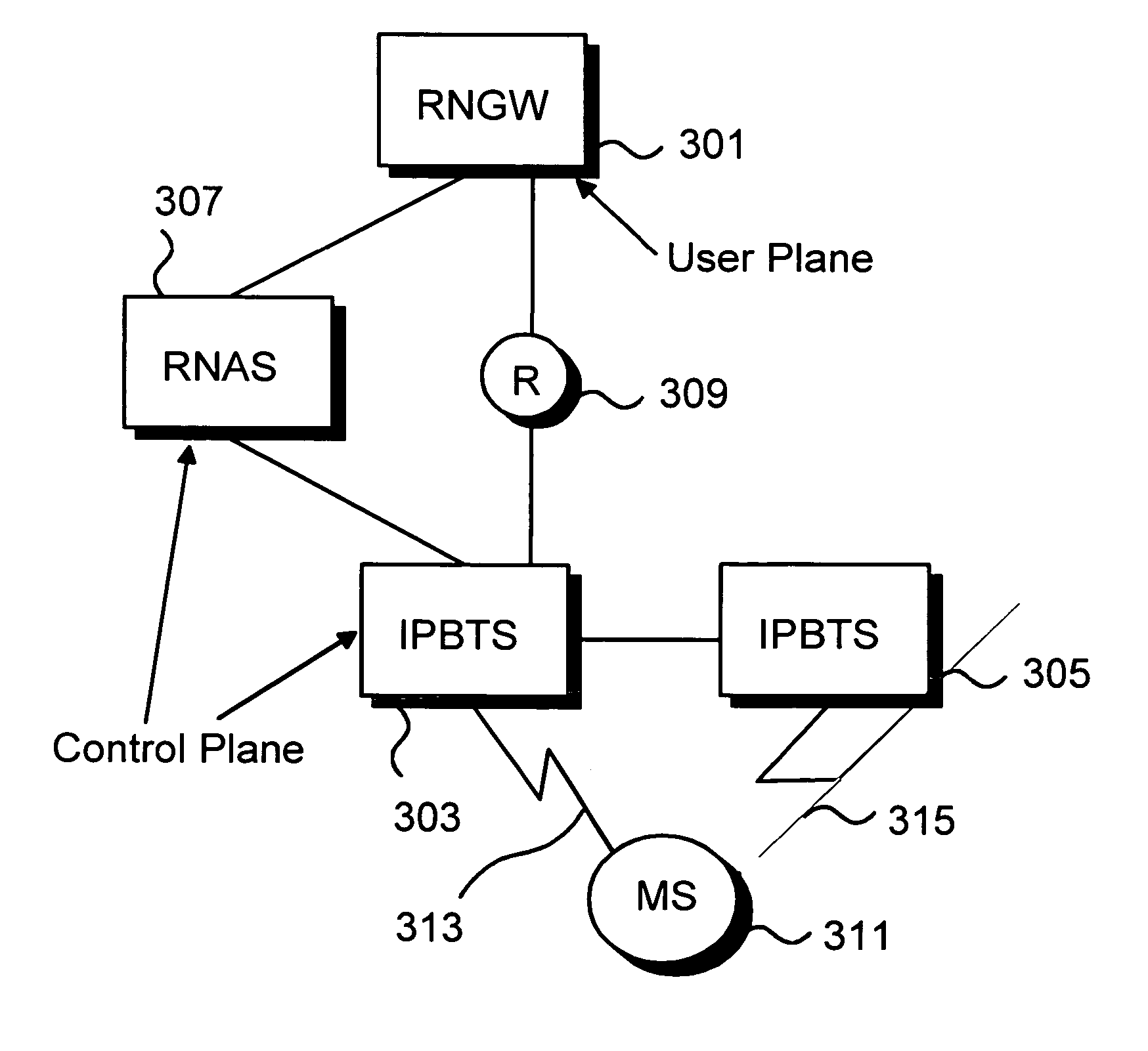
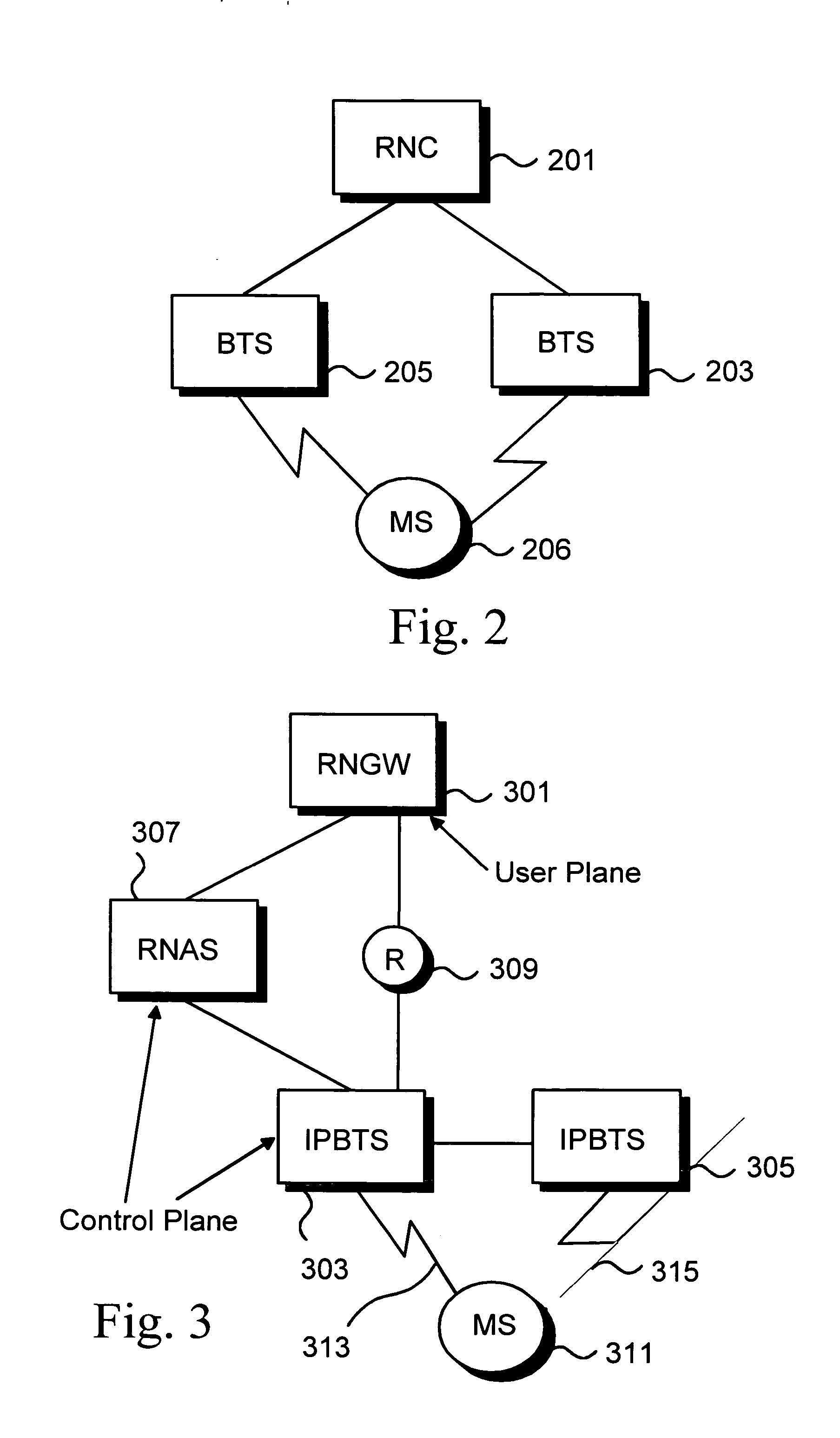
A method and system for forwarding data units in a communications system, that comprises: ingress routers (901) capable of forwarding data units and containing a Forwarding Equivalence Class table (911) that contains mapping information, intermediate routers (905, 907, 909) capable of forwarding data units, egress routers (903) capable of forwarding data and containing a Forwarding Equivalence Class table (919) that contains mapping information. The method comprising the steps of: assigning a first label on data unit and a second label on data unit based on mapping information, sending data unit in to egress router via one or more intermediate router (905, 907, 909), receiving (903) data unit, identifying data unit based on mapping information on Forwarding Equivalence Class table (919) and based on second label. The method further comprises the steps of: creating a Forwarding Equivalence Class for radio access network specific data units; and storing information about Forwarding Equivalence Class in Forwarding Equivalence class table (FEC).
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
Method for optimizing the use of network resources for the transmission of data signals, such as voice, over an IP-packet supporting network
ActiveUS7486661B2Efficient use of bandwidthHigh resource reservationNetwork traffic/resource managementSpeech analysisMultiplexingComputer network
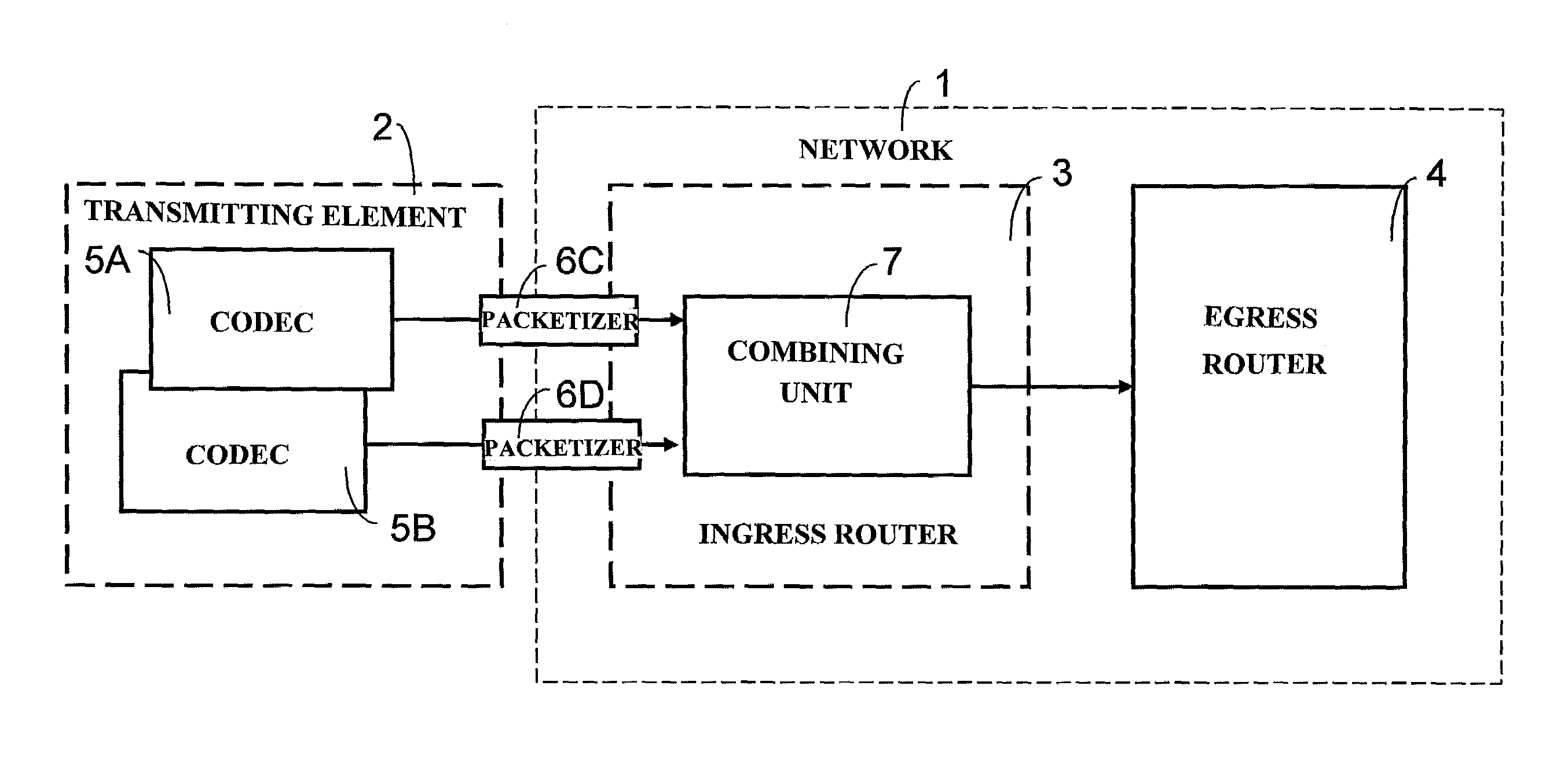
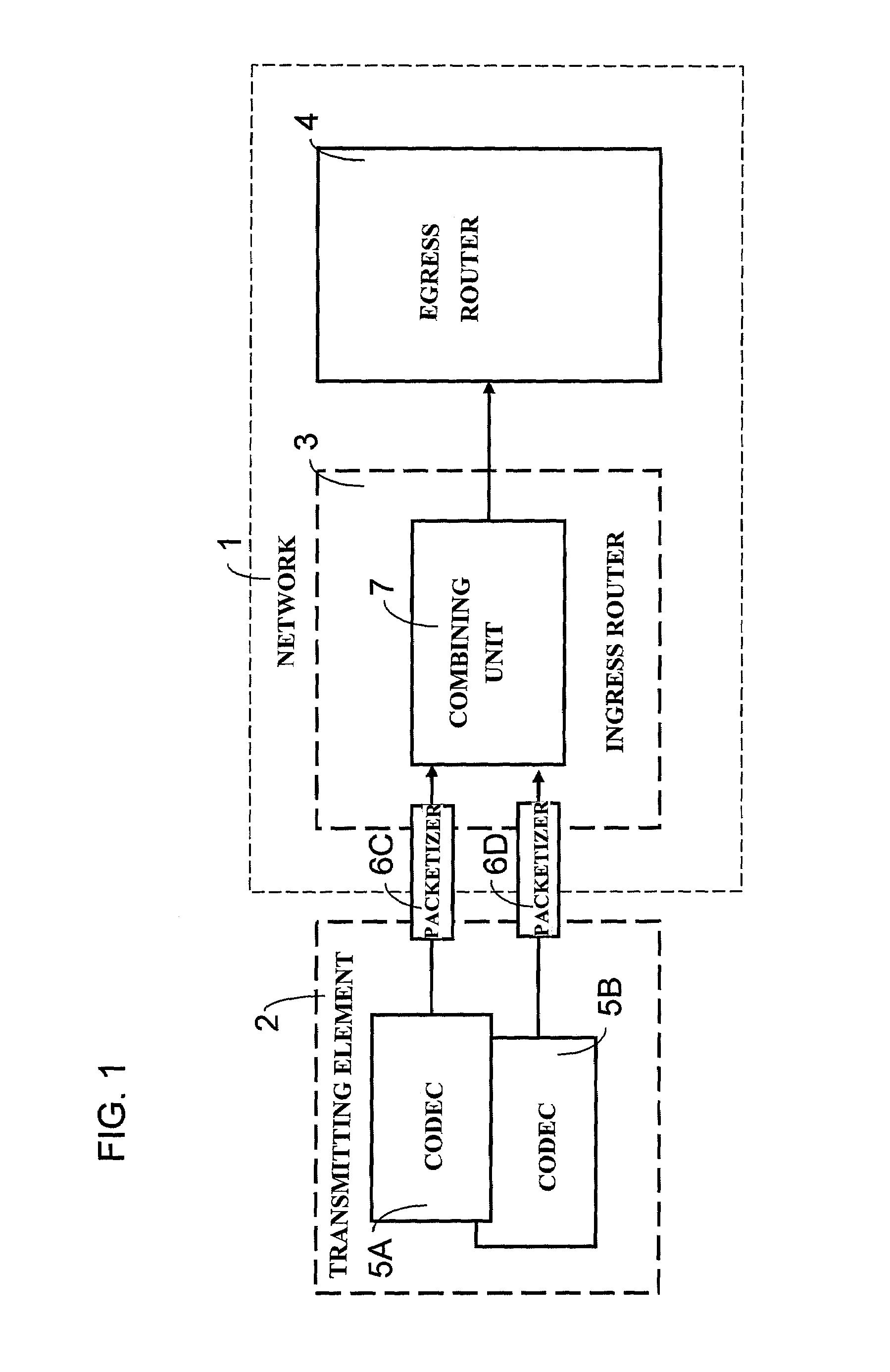
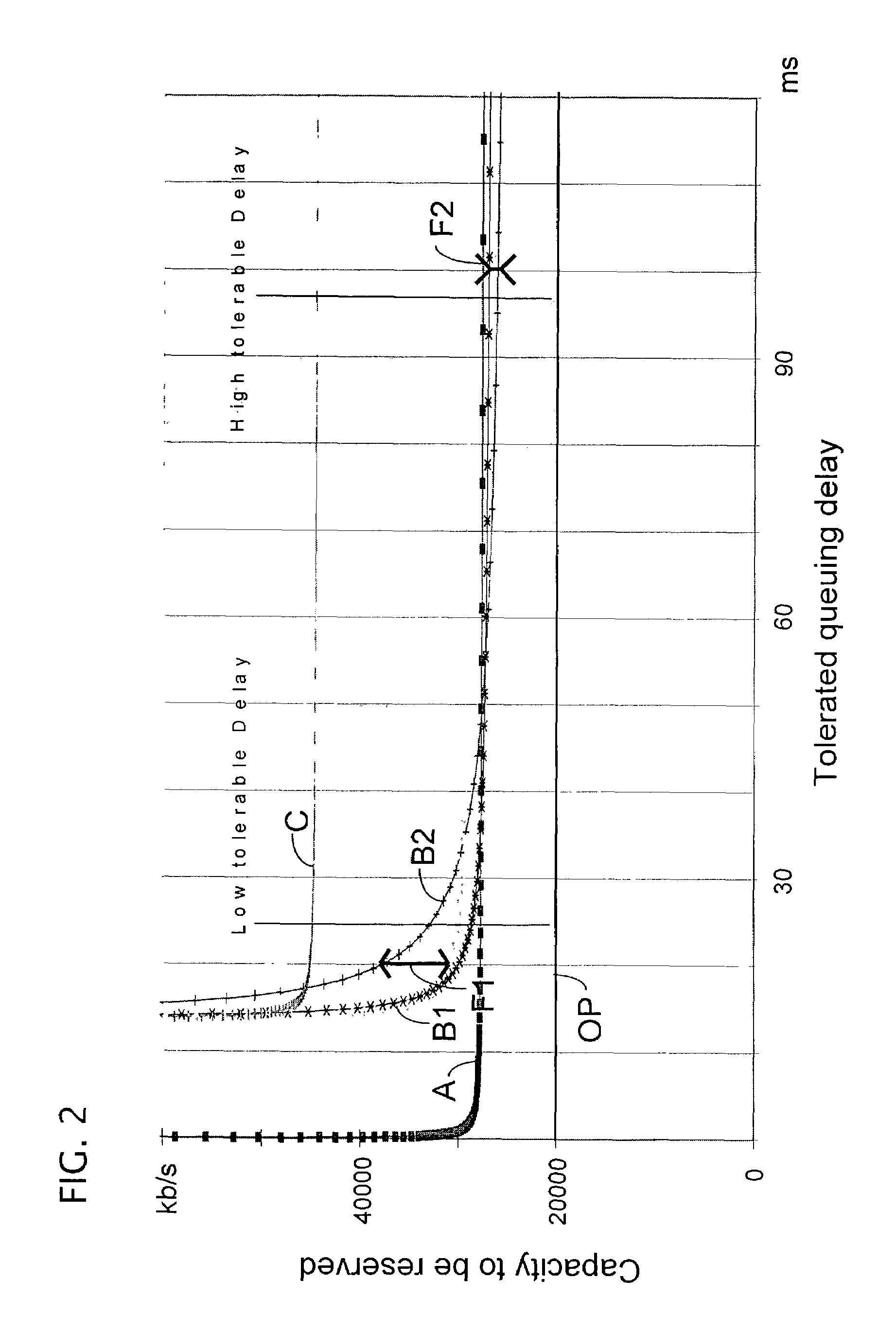
A method for optimizing the use of network resources for the transmission of data signals, such as voice frames, between network units over an IP-packet supporting network. The data frames are obtained using codecs, which may have a different mouth-to-ear transmission delay, from data samples, e.g. voice samples, that are formatted and to which a data frame header is added. The method includes attributing codec categories to each of the data or voice frames according to the codecs by means of which the data samples are generated, each codec category corresponding to a different mouth-to-ear delay budget range for the data frames; sorting the data frames according to their codec categories; generating multiplexed cells from data frames of a same codec category, each multiplexed cell being obtained by multiplex aggregation of a predetermined number of voice samples; and transporting the multiplexed cells from an ingress router to an egress router in the IP-network.
Owner:RPX CORP
System, device and method for limiting tunnel traffic in an information communication network
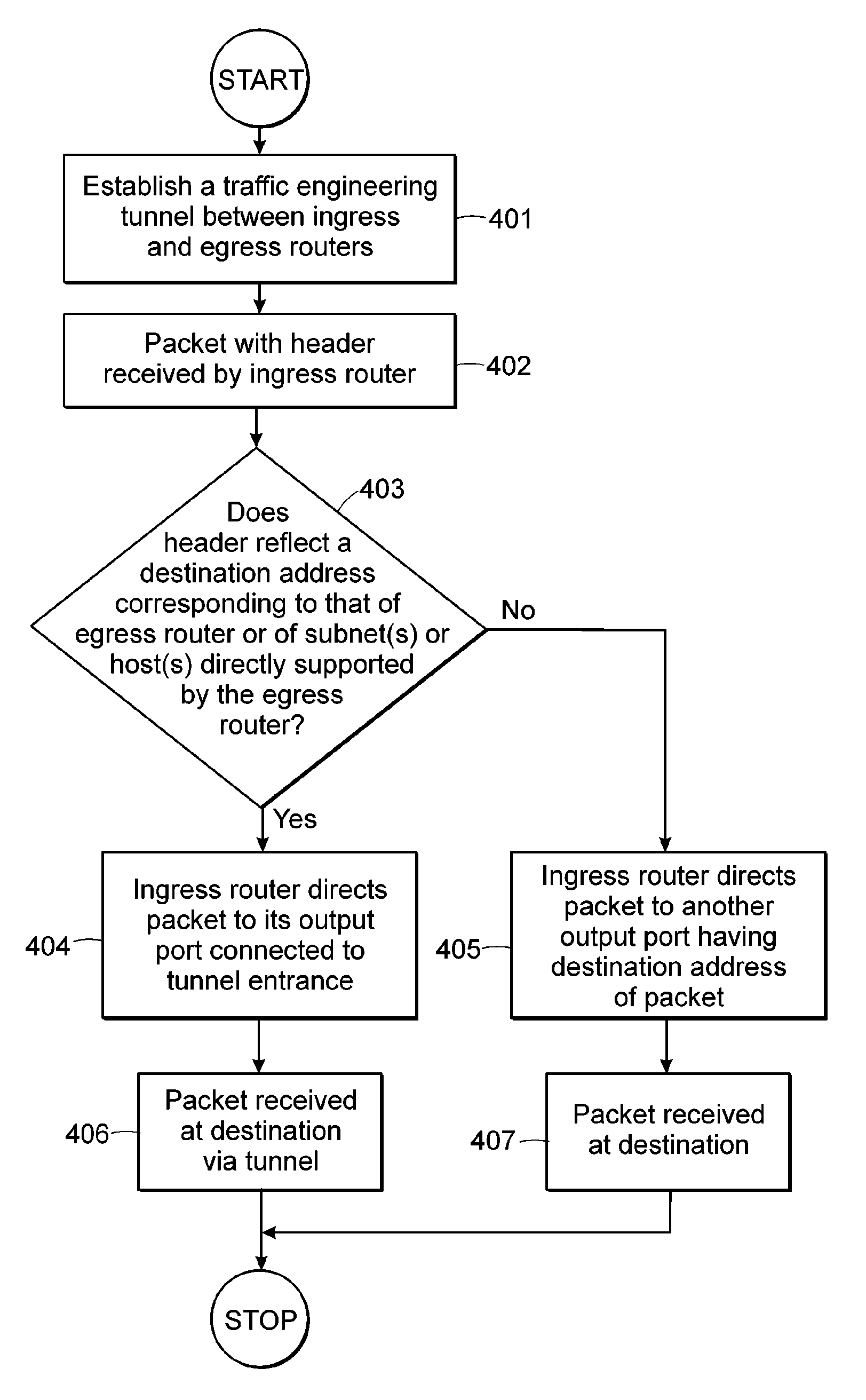
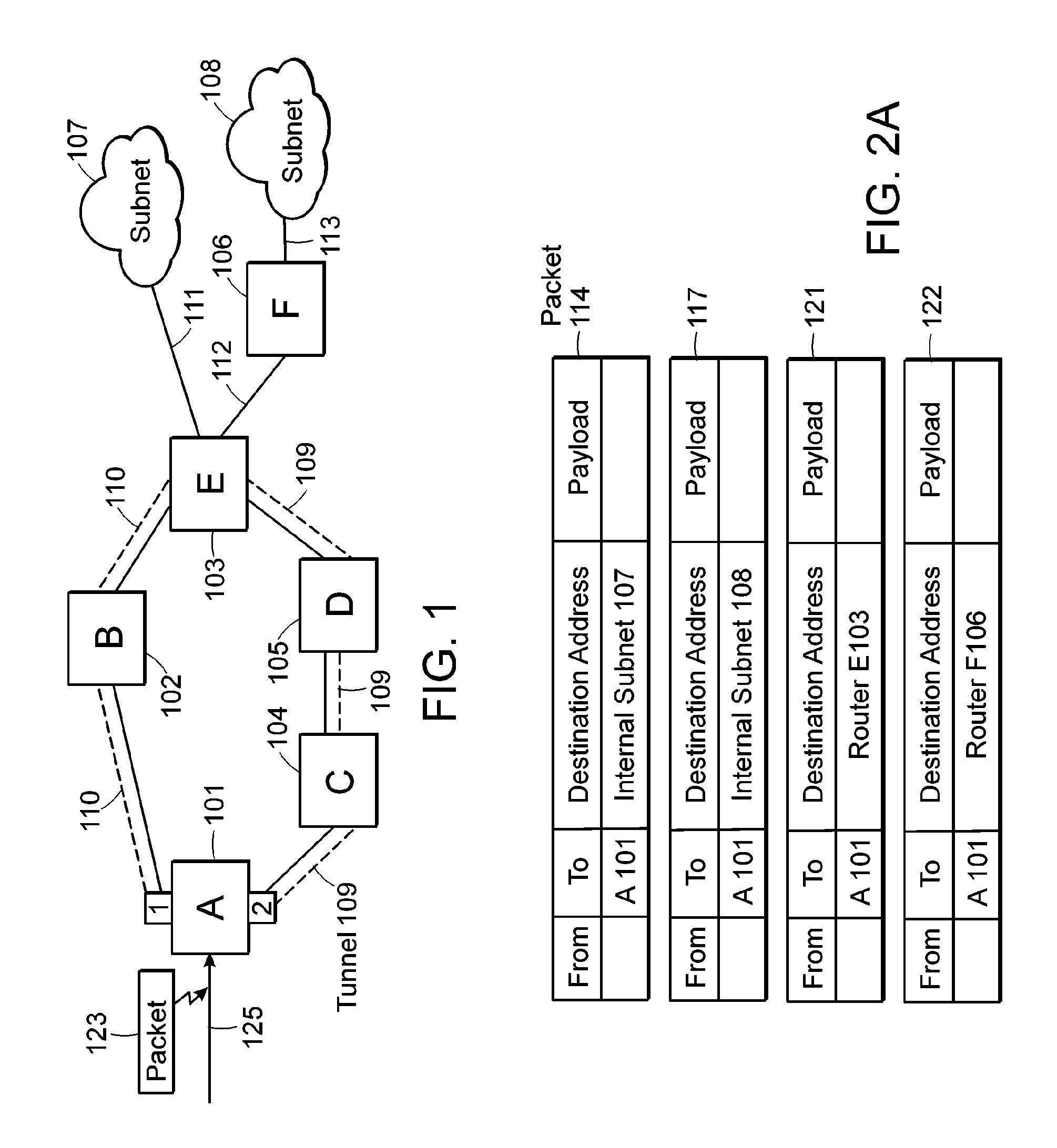
ActiveUS7123587B1Avoid destabilizationAvoid congestion problemsError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityForwarding equivalence class
There is disclosed an apparatus and method for limiting tunnel traffic in a network. Traffic engineering tunnels are used to direct traffic along a predefined path, which may differ from the path that internet protocol (IP) routing would determine. Interior gateway protocol (IGP) cut through will allow the forwarding of all destinations downstream of a tunnel through the tunnel, without the operator needing to specify a forwarding equivalence class (FEC). But congestion in the tunnel and network instability may result from this approach. A solution to these problems is disclosed which limits the traffic in the tunnel to only that with destination addresses of the tunnel's egress router or nodes directly supported thereby. Other solutions are disclosed which allow tunnel traffic to nodes having destination addresses other than those being directly supported by the tunnel's egress router. All of these solutions are achieved in both pre-determined forwarding entry and dynamic packet-by packet embodiments.
Owner:AVAYA INC
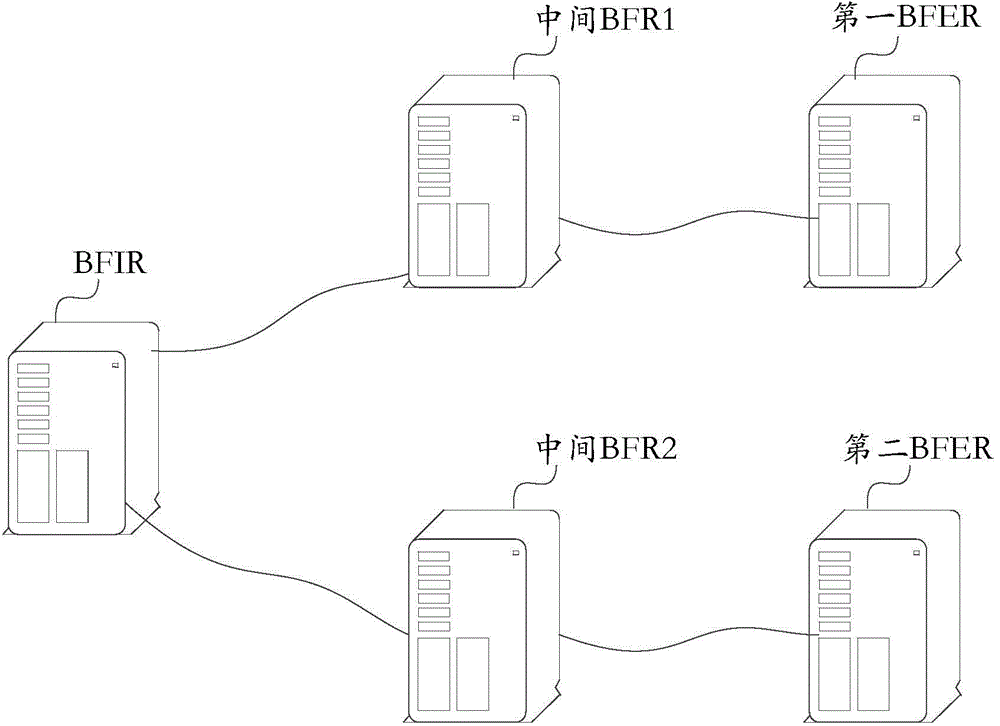
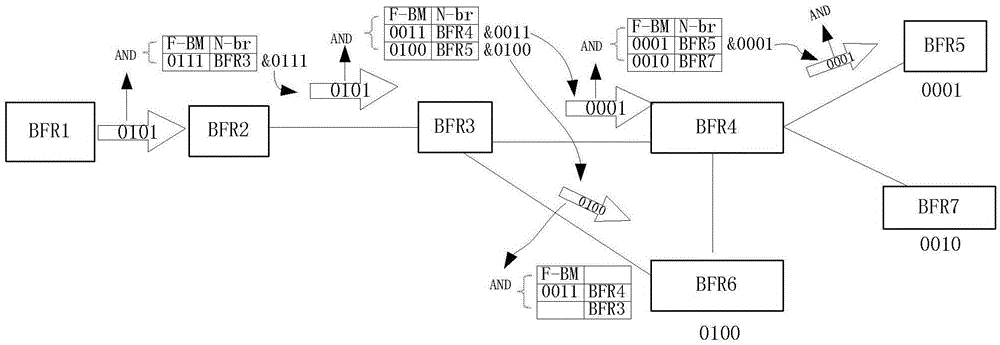
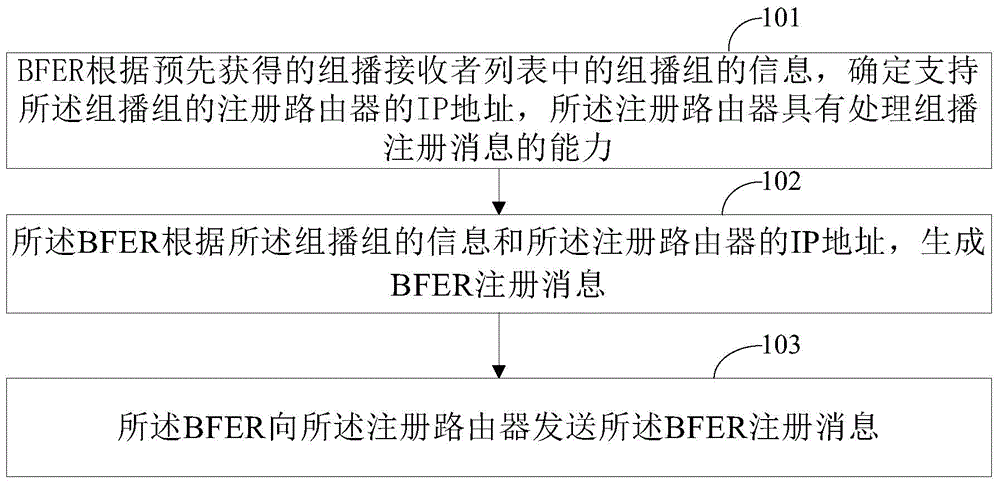
Bit-forwarding ingress router, bit-forwarding router and operation administration maintenance detection method
ActiveCN105812197ASave resourcesImprove detection efficiencySpecial service provision for substationMulticast networkEgress router
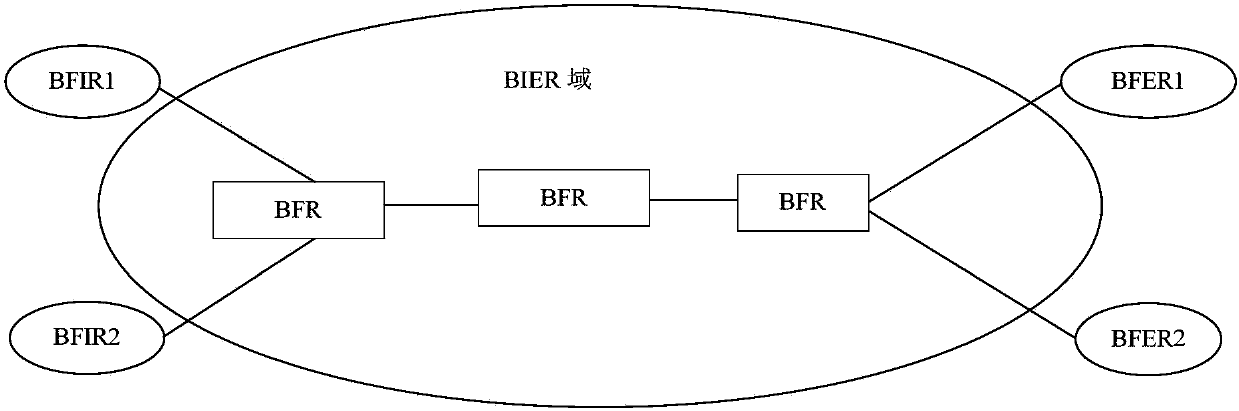
The invention provides a bit-forwarding ingress router (BFIR), a bit-forwarding router (BFR) and an operation administration maintenance (OAM) detection method and belongs to the multicast network field. An OAM request message from the BFIR is received through a first BFR; a target BFR corresponding to the OAM request message is determined by the first BFR to be the first BFR according to the OAM request message; a first OAM response message is acquired by the first BFR according to the ID of the BFIR, and the first OAM response message is sent to the BFIR. Through the method and the device, a problem that a transmission fault generated in a transmission process of a multicast message can not be diagnosed or processed by the BFIR can be solved, connectivity detection can be facilitated through the OAM message, and detection on multiple bit-forwarding egress routers (BFER) can be realized.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Switching system
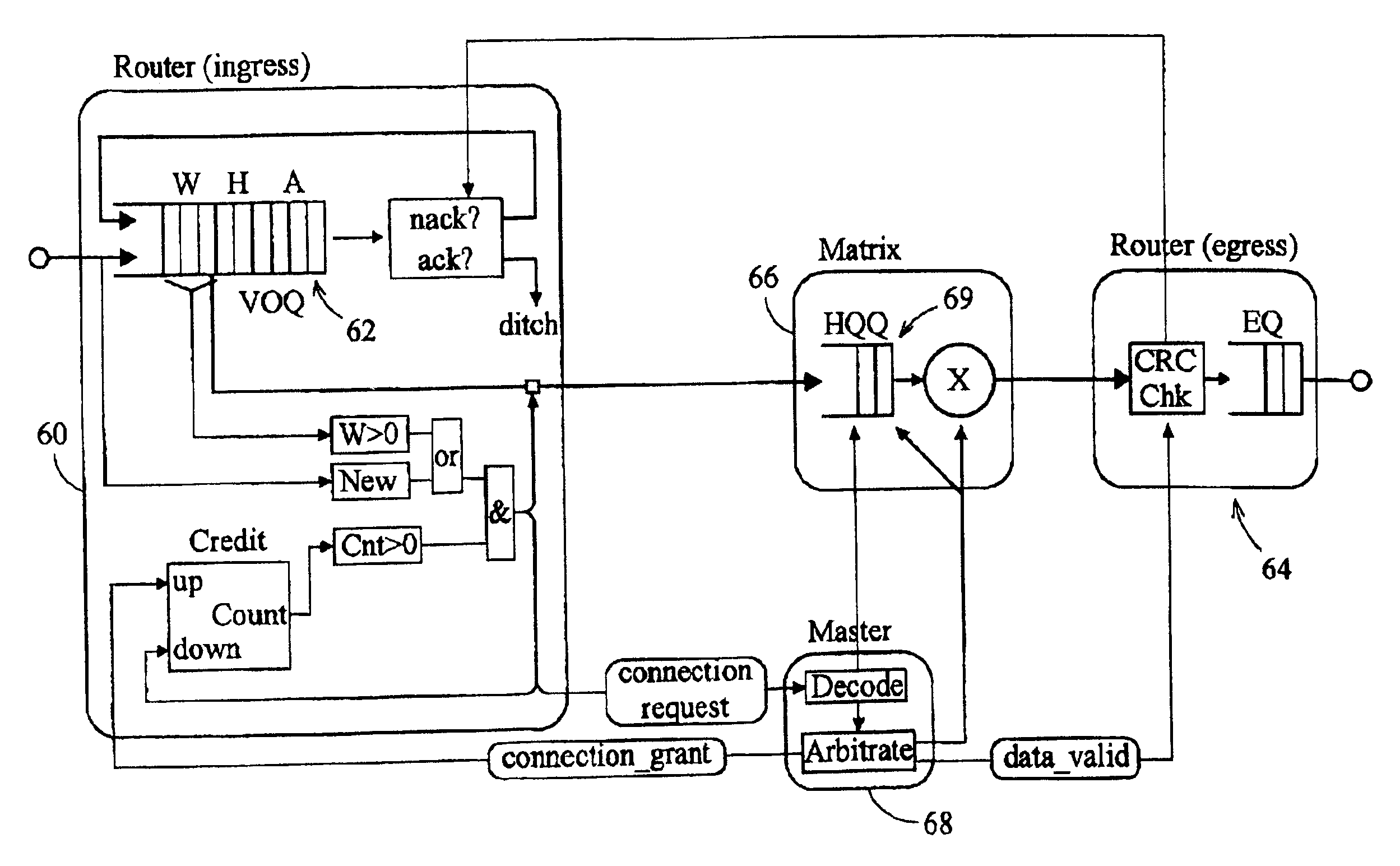
InactiveUS6876663B2Data switching by path configurationTime-division multiplexing selectionEgress routerData interchange
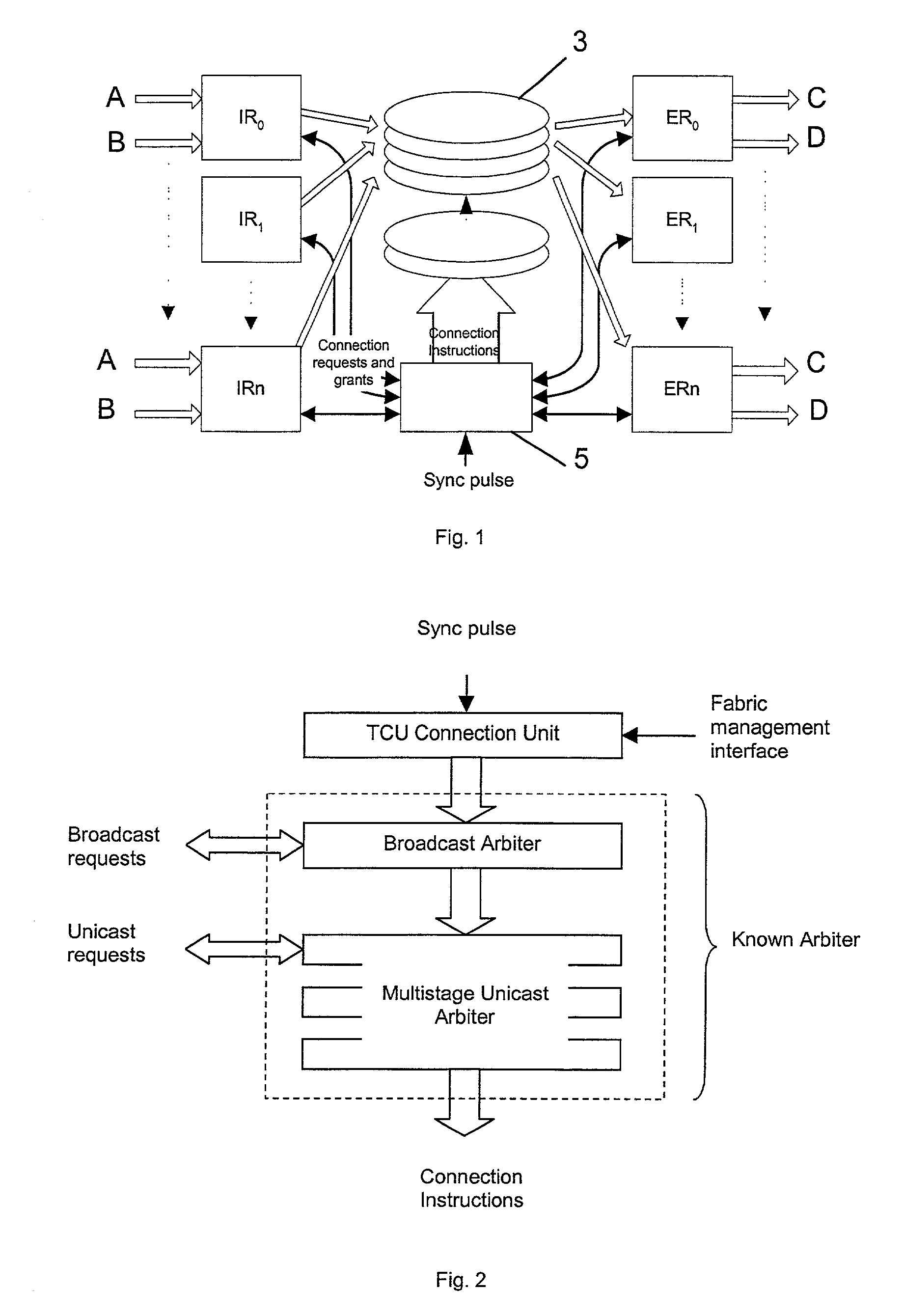
A data switching device has ingress routers and egress routers interconnected by a switching matrix controlled by a controller. Each ingress router maintains one or more virtual output queues for each egress router. The switching matrix itself maintains a head-of queue buffer of cells which are to be transmitted. Each of these queues corresponds to one of the virtual output queues, and the cells stored in the switching matrix are replicated from the cells queuing in the respective virtual output queues. Thus, when it is determined that a connection is to be made between a given input and output of the switching matrix, a cell suitable for transmission along that connection is already available to the switching matrix. Upon receipt of a new cell by one of the ingress routers, the cell is stored in one of the virtual output queues of the ingress router corresponding to the egress router for the cell, and also written the corresponding head of queue buffer, if that buffer has space. If not, the cell is stored, and written to the head of queue buffer when that buffer has space for it.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Data switch and a method for controlling the data switch
ActiveUS20020141397A1Reduce, or even eliminate, variation in the latency of the throughputMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexControl dataEgress router
A data switch is proposed of the type having virtual queue ingress routers interconnected with egress routers by way of a memoryless switching matrix controlled by a control unit which performs an arbitration process to schedule connections across the switch. This scheduling is performed to ensure that data cells which arrive at the ingress routers at unpredictable times are transmitted to the correct egress routers. Each ingress router further includes a queue for time division multiplex traffic, and at times when such traffic exists, the control unit overrides the arbitration process to allow the time division multiplex traffic to be transmitted through the switch.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Message forwarding method and device
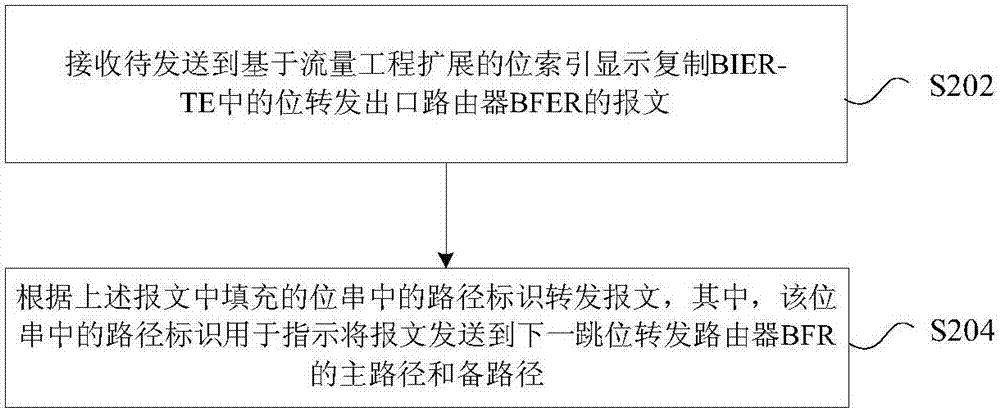
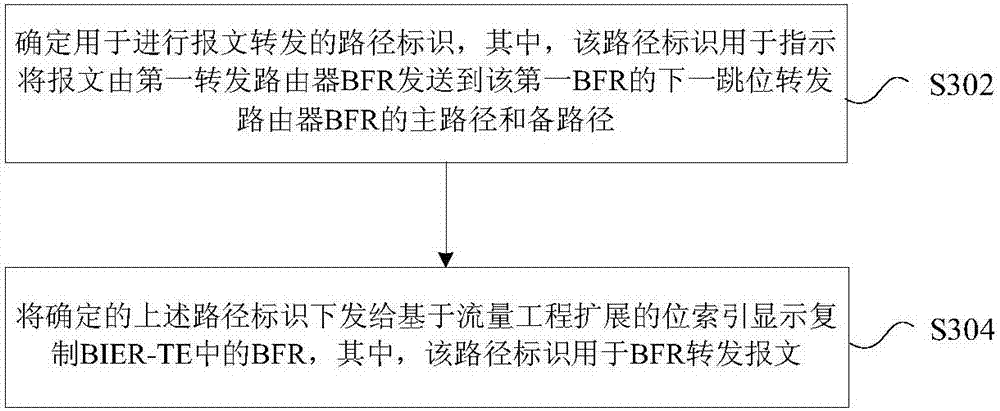
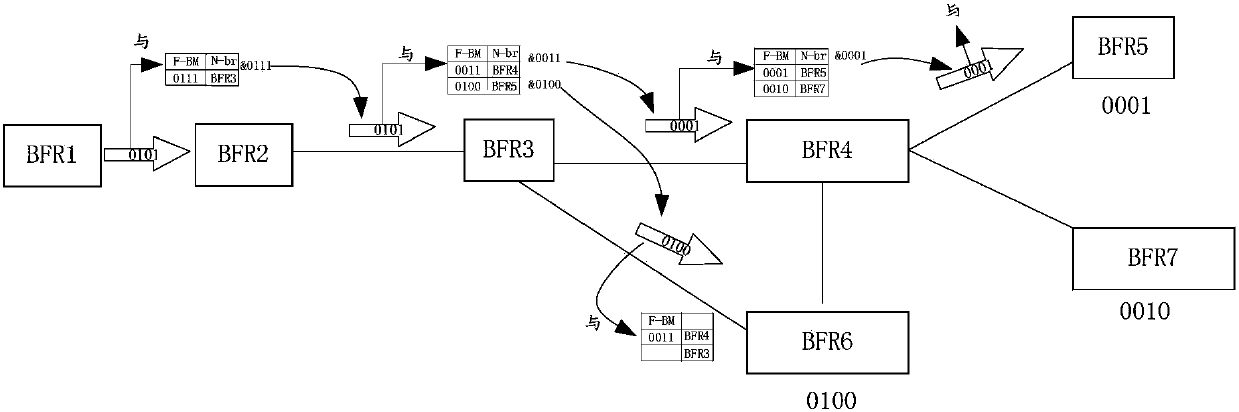
The invention provides a message forwarding method and device. The method comprises the steps of: receiving a message to be sent to BFER (Bit-Forwarding Egress Routers) in BIER-TE (Bit Index Explicit Replication-Traffic Engineering), and a route identifier, wherein the route identifier is used for indicating a primary route and a standby route for sending the message to a next hop bit of BFR(Bit Forwarding Router) of a first BFR from the first BFR; according to the router identifier, determining a bitstring for forwarding the message to the BFER; and filling the bitstring into the message, and according to the bitstring, forwarding the message. By the message forwarding method and device provided by the invention, the problem of resource waste in the related art, which is caused by a case that route protection cannot be correctly and reasonably configured, is solved, thereby achieving effects of reasonably and effectively configuring route protection and avoiding resource waste.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Secure hidden route in a data network
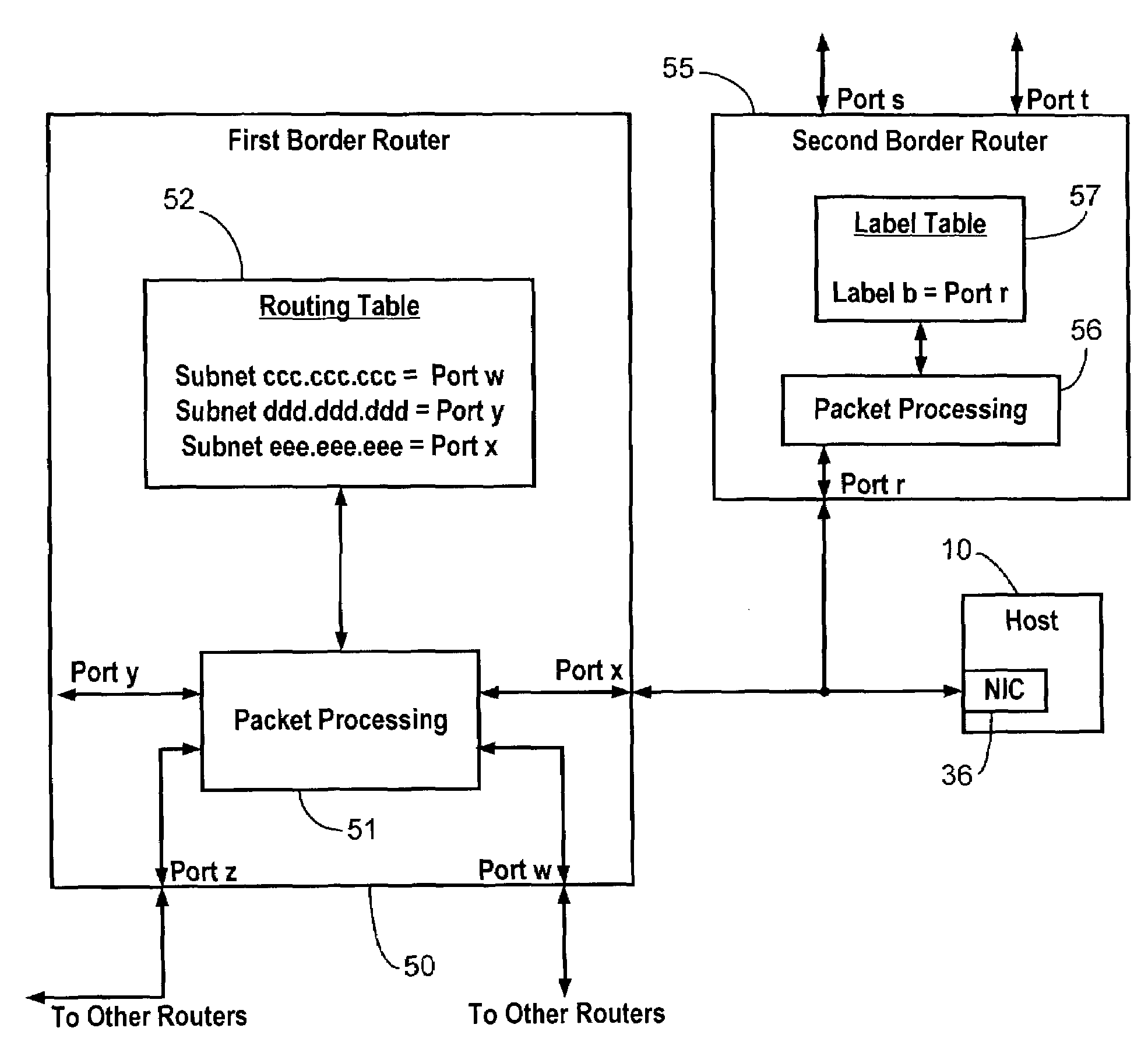
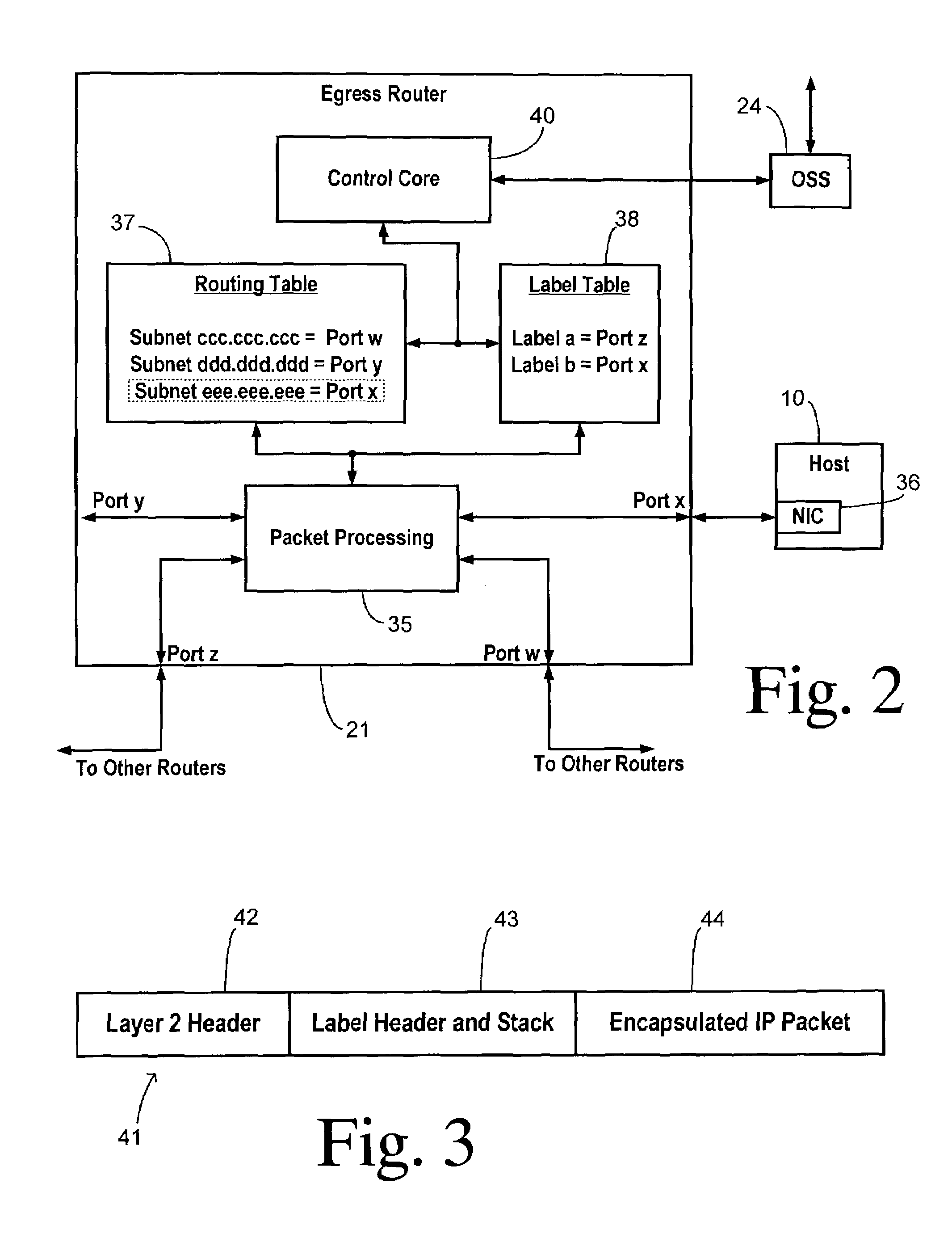
A hidden pathway to a host is provided in an internetwork having an egress router coupled to the host. A selected port of the egress router is connected to the host as a hidden access port. A label table in the egress router is configured to associate the selected port with a predetermined label. Distribution of the predetermined label is restricted to one or more controlled access points so that access to the hidden pathway is restricted to the controlled access points. The controlled access points may reside at the users themselves, but are preferably contained within proxy devices coupled to the internetwork using secure connections.
Owner:T MOBILE INNOVATIONS LLC
Inter-area exit route dynamic selection method and system
InactiveCN102780605AReduce management and maintenance costsShort response timeData switching networksQuality of serviceRouting table
The invention provides an inter-area exit route dynamic selection method and system. The method comprises the following steps that each area exit router collects self information regularly; the transmission performance evaluated value of each area exit router is calculated; an inter-area router acquires the transmission performance evaluated value; priority levels are generated; the inter-area router carries out priority level sequencing on the area exit routers according to the transmission performance evaluated values; and the inter-area router selects the router with the maximal transmission performance evaluated value as the next-hop address of the exit router, wherein the area exit routers refer to routers which are used for connecting an inter-area network and an extra-area network and have direct communication capability, and the inter-area router refers to a router which is directly connected with the exit routers but does not have capability of directly communicating with the extra-area network. According to the method and the system which are provided by the invention, an existing route protocol is not required to be changed, the allocation of a static route table is automatically completed by the system, and the defect that the QoS (Quality of Service) is not considered in a traditional method is effectively overcome.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Wireless Mesh network self-adapting routing method based on throughput performance
ActiveCN101296180AImpact of reduced throughputNetwork connectionsWireless communicationWireless mesh networkPacket loss
The invention discloses a wireless Mesh network self-adapting routing method based on throughput performance. Each node maintains a link quality database according to the packet loss ratio of probe packets by broadcasting the probe packets outwards and receiving the probe packets sent by neighbor nodes; a hidden node is introduced to the occupied weight and calculation of throughput; a database records the link quality information between the node and the neighbor nodes thereof and a metric value is used for expression; the metric value is used for calculating the quality of each specific route. A route request is flooded into the whole network as required, and a router having an optimal metric value is taken as an optimal router to be recorded by each node. By broadcasting gateway information, a gateway node maintains the knowability and accessibility in the whole wireless Mesh network, namely, the active trace of an egress router by all nodes. The method solves the problem of performance degradation caused by the insufficient consideration about the hidden node.
Owner:SHANGHAI MAXTROPY DATA TECH
Message sending method and apparatus and message cross-domain forwarding network architecture
InactiveCN107592262ASolve technical problems that occupy more network resourcesSave network resourcesData switching networksNetwork architectureEgress router
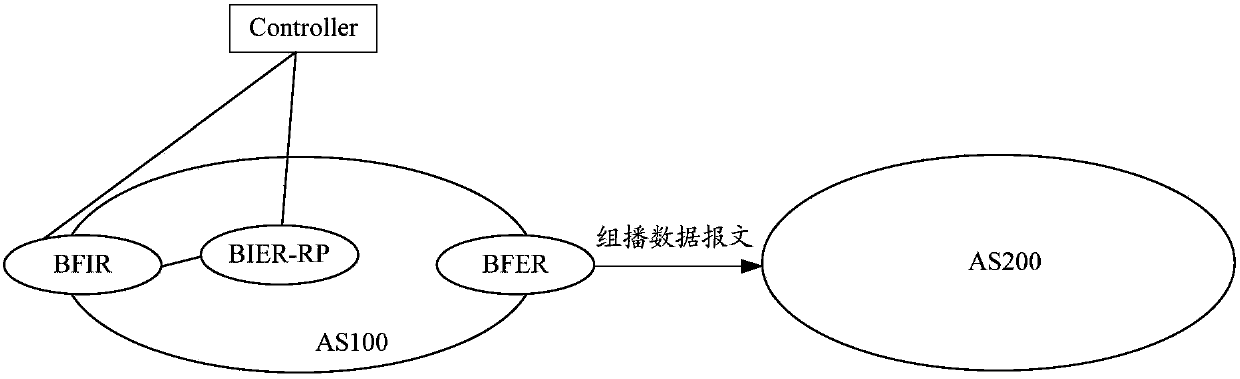
The invention provides a message sending method and apparatus and a message cross-domain forwarding network architecture. The message sending method comprises steps: a bit indexed explicit replication-rendezvous point (BIER-RP) device of a first domain announces an address of a cross-domain multicast group to a controller; and after a bit-index forwarding ingress router (BFIR) of the first domainreceives a multicast data message requesting to be transmitted across a domain to a second domain, the BFIR transmits the multicast data message to a bit-index forwarding egress router (BFER) of the first domain, and the BFER forwards the multicast data message to the second domain. The technical problem that many network resources need to be occupied when the multicast data message is transmittedin a related technology can be solved.
Owner:ZTE CORP
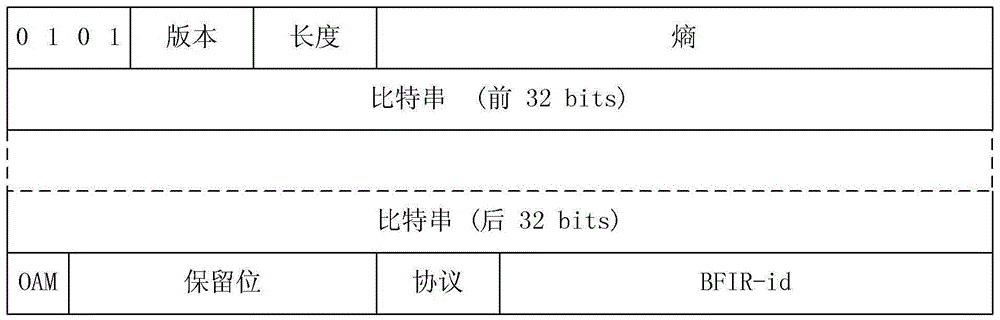
Transmission method, apparatus and system of BIER control information
InactiveCN106656524APrevent leakageShorten the timeSpecial service provision for substationMemory footprintEgress router
The invention discloses a transmission method, apparatus and system of BIER (Bit Indexed Explicit Replication) control information, which can transmit control information in an easy and highly efficient manner and prevent control information overload. The method includes the following steps: a bit forwarding ingress router (BFIR) constructs a BIER datagram, a datagram header carries indication information used for indicating that the BIER datagram carries control information, and a datagram body carries the control information. A system comprises a bit forwarding ingress router (BFIR) and a bit forwarding egress router (BFER). The BFIR comprises a first construction module and a second construction module. The BFER comprises a receiving module and a de-packaging module. Through the scheme of the embodiment of the invention, access information related to mlticasting is only sensed at boundary nodes, the memory occupaion processing time and mechanism of intermediate forwarding nodes is saved, and information leakage at unrelated nodes is prevented.
Owner:ZTE CORP
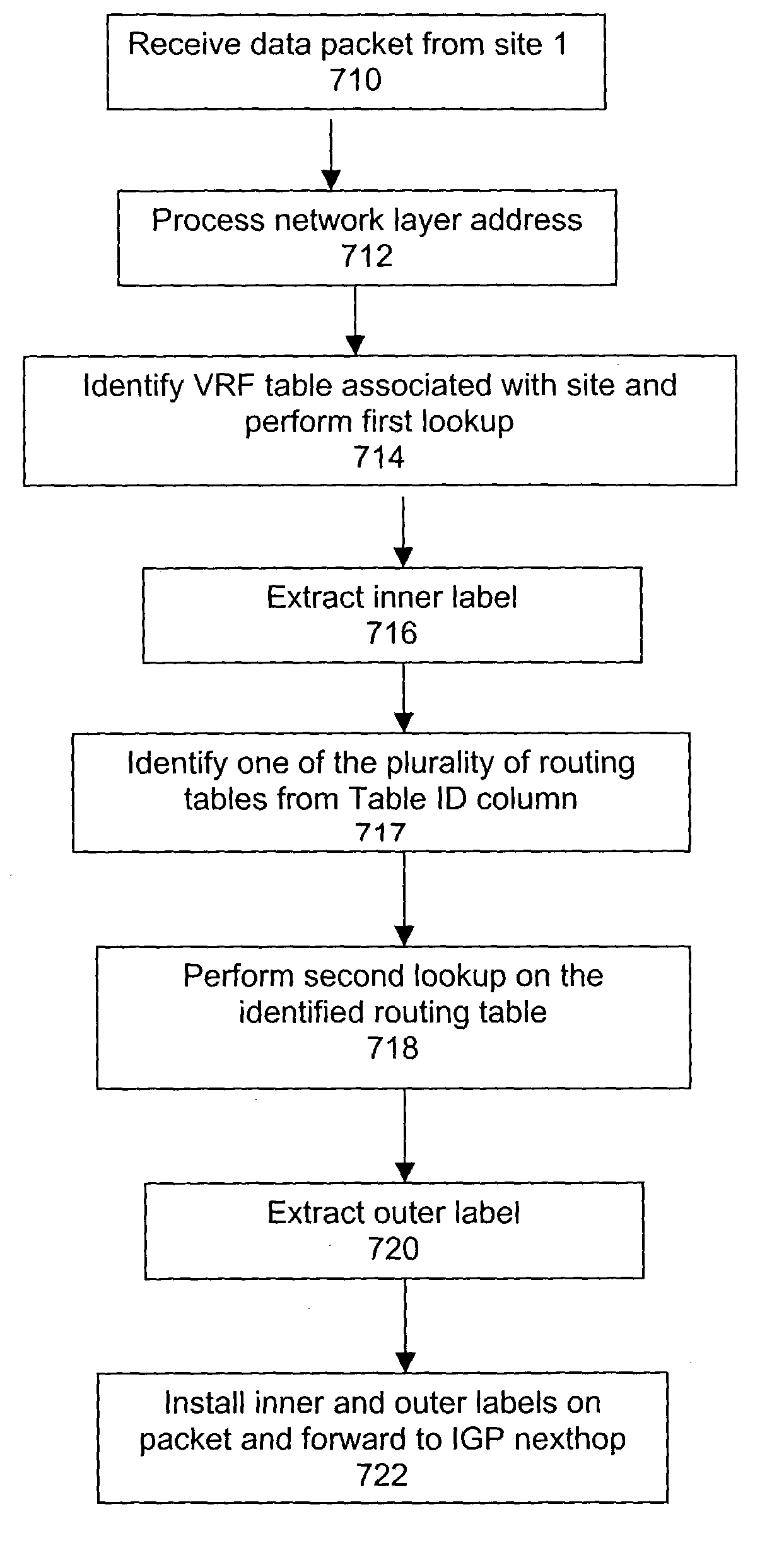
Method and system for supporting a dedicated label switched path for a virtual private network over a label switched communication network
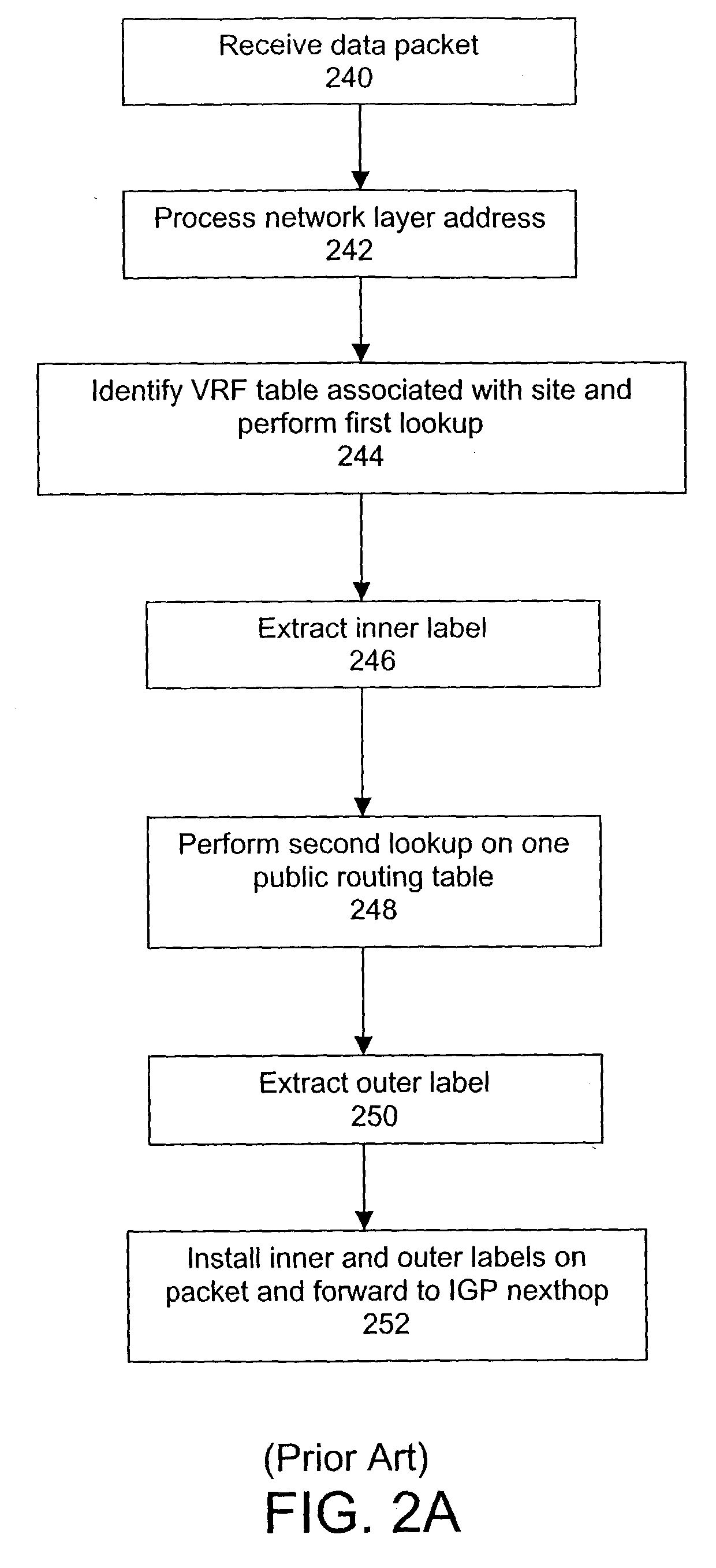
A system and method for transmitting data from a first site to a second site over a shared Multi-Protocol Label Switched (MPLS) network comprising a plurality of routers, including an ingress router in communication with the first site and an egress router in communication with the second site, includes configuring a plurality of label switching paths between the ingress router and the egress router over a plurality of label switching devices. The method further includes performing a first lookup on one of at least one virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) table stored in the ingress router, whereby the first lookup identifies one routing table from a plurality of routing tables stored in the ingress router, each routing table being associated with one of the plurality of label switched paths, and performing a second lookup on the one routing table, wherein the routing table defines the associated label switched path between the ingress router and the egress router for a virtual private network (VPN) between the first site and the second site.
Owner:TREND MICRO INC
Dynamic multipoint tree rearrangement
InactiveUS7808930B2Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationEgress routerTree rearrangement
A mechanism to dynamically map a multicast session to a transport tree to reduce flooding of egress routers on the transport tree is provided. A mechanism to reduce the length of time in which transient flooding can occur while the transport tree is being chosen or configured is also provided. The disclosed dynamic mapping mechanisms avoid interruption of an established multicast session. One mechanism disclosed provides for remapping of a multicast session by cloning an original transport tree with which the multicast session is associated, associating the multicast session with the cloned transport tree, and then reconfiguring the cloned transport tree in accord with edge egress routers that have subscribers to that multicast session.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Source address selection scheme suitable for multi-home environment
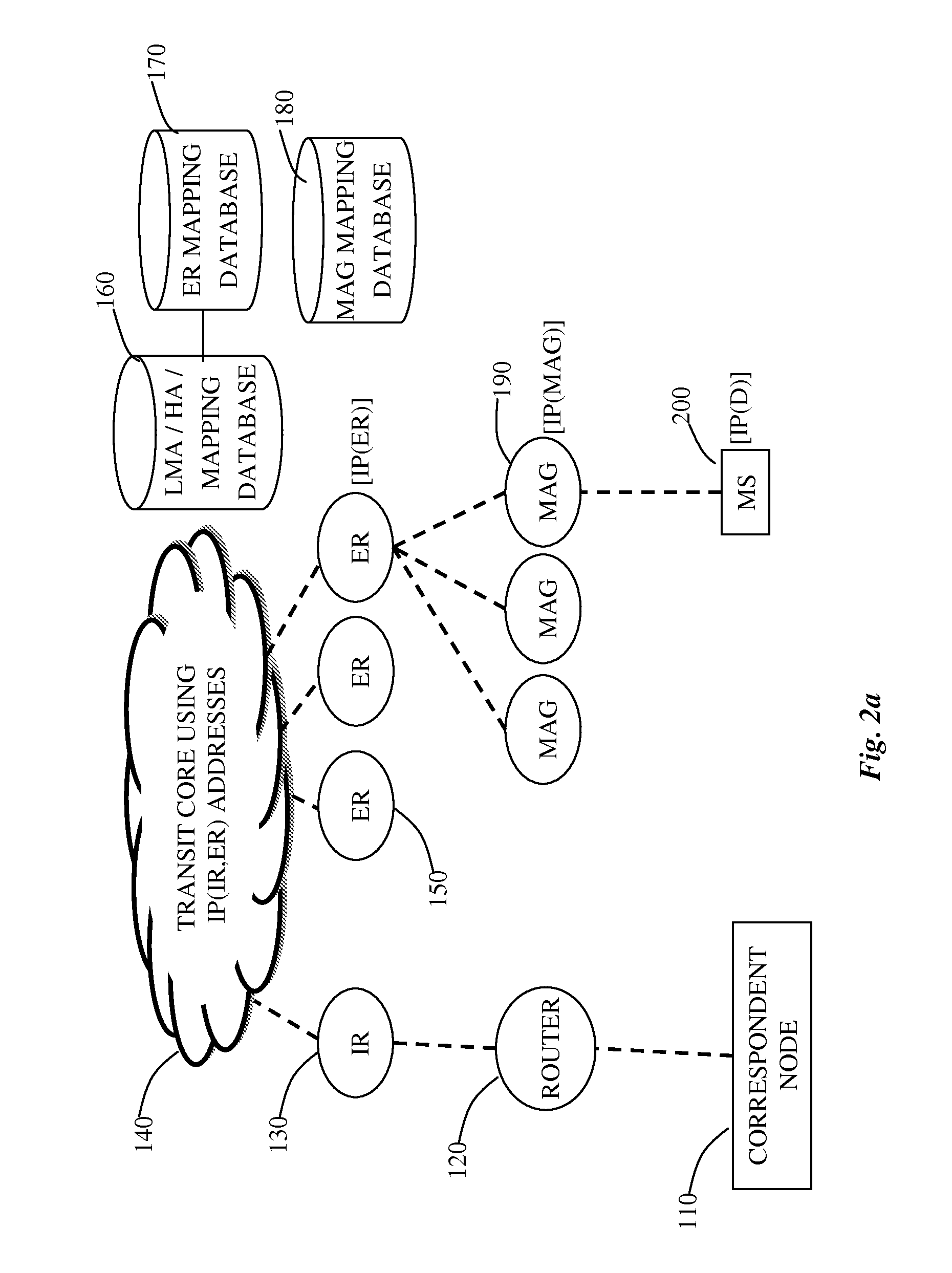
InactiveUS20050102415A1Environmental efficiencyEfficient use ofData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsComputer networkService provision
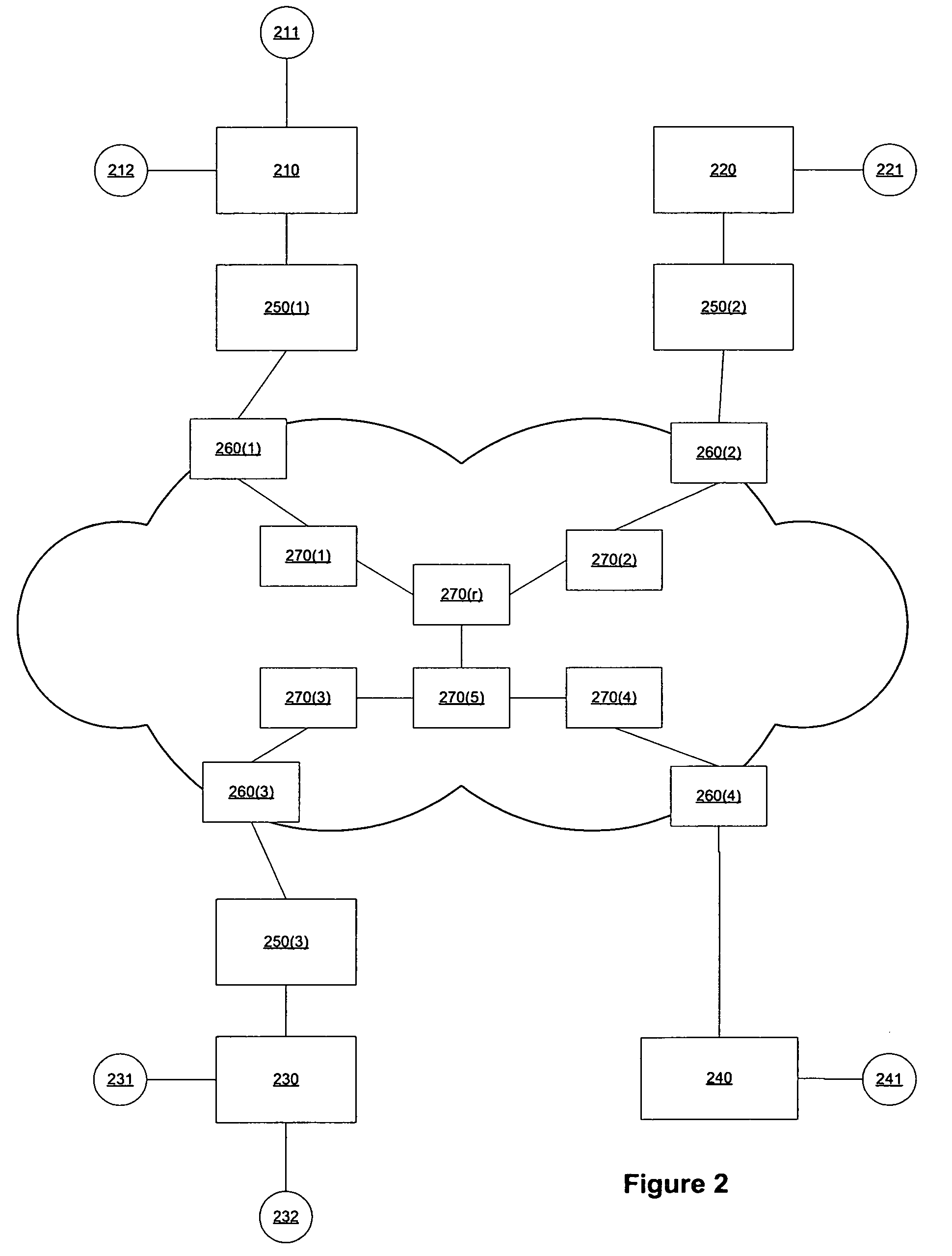
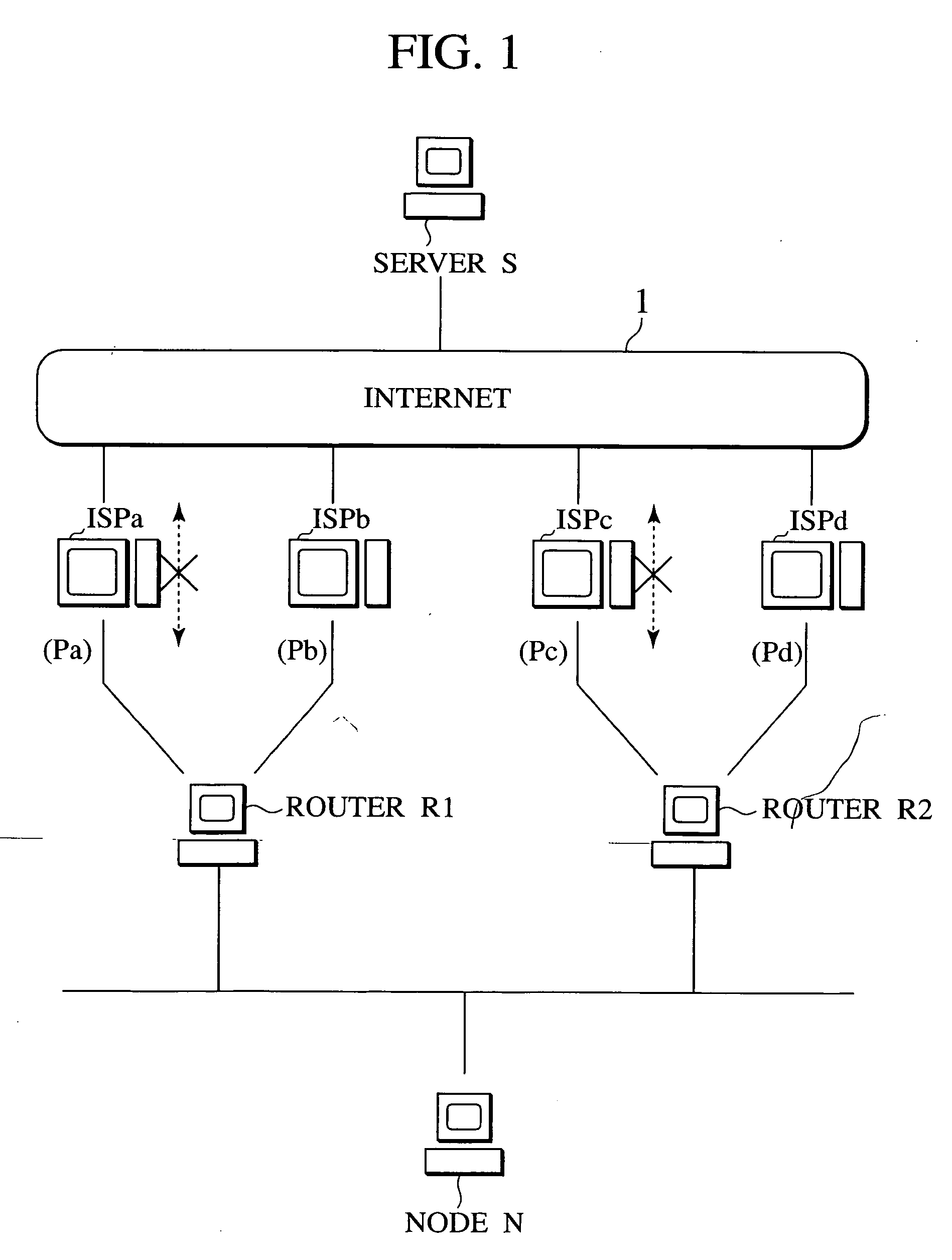
In a source address selection system containing a router device connected to a plurality of Internet service providers, and a communication node connected to the router device, it becomes possible to utilize the multi-home environment effectively, by enabling the selection of the source address according to the egress router with respect to the Internet, by accounting for the state of connection with the Internet service provider.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
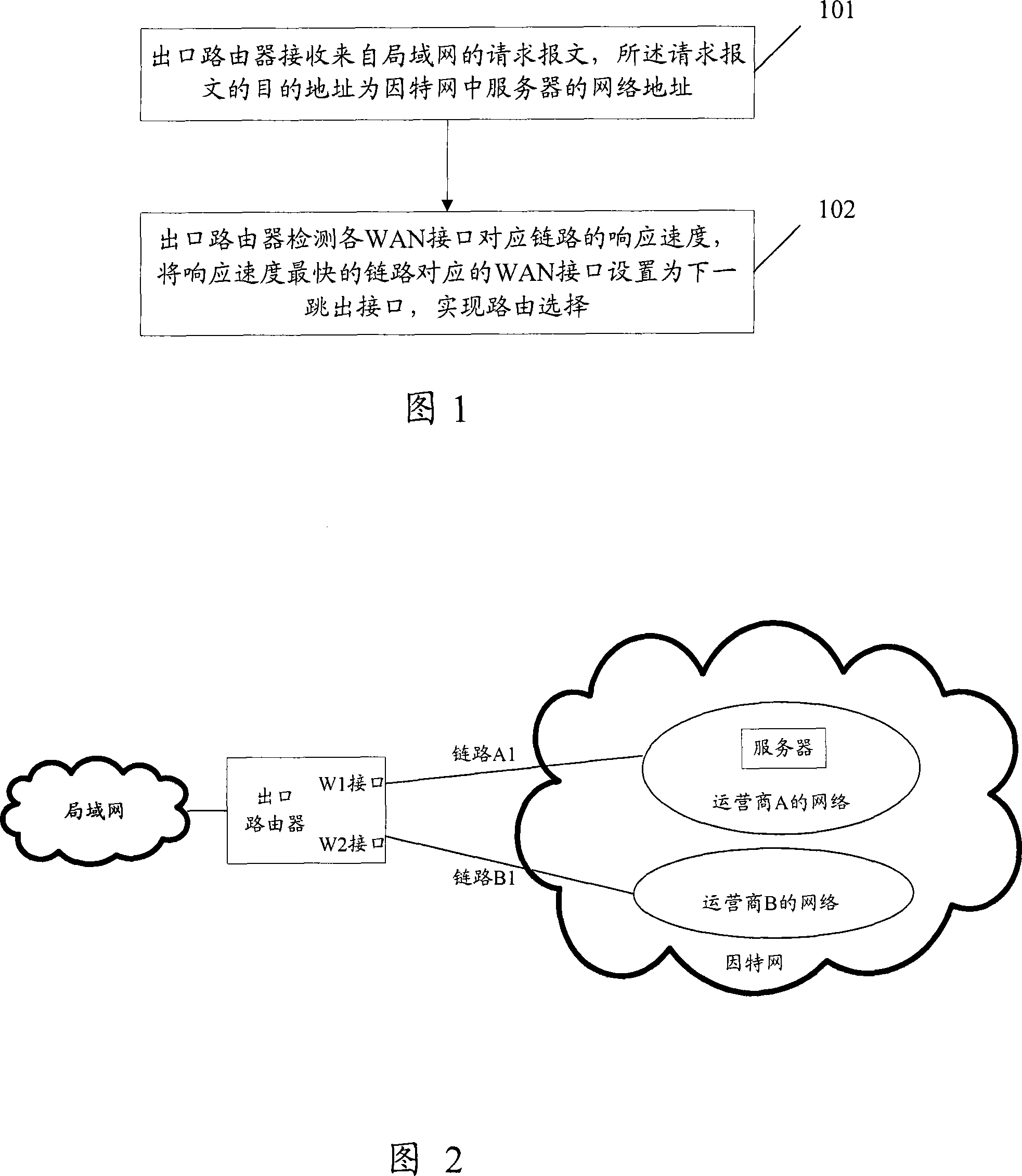
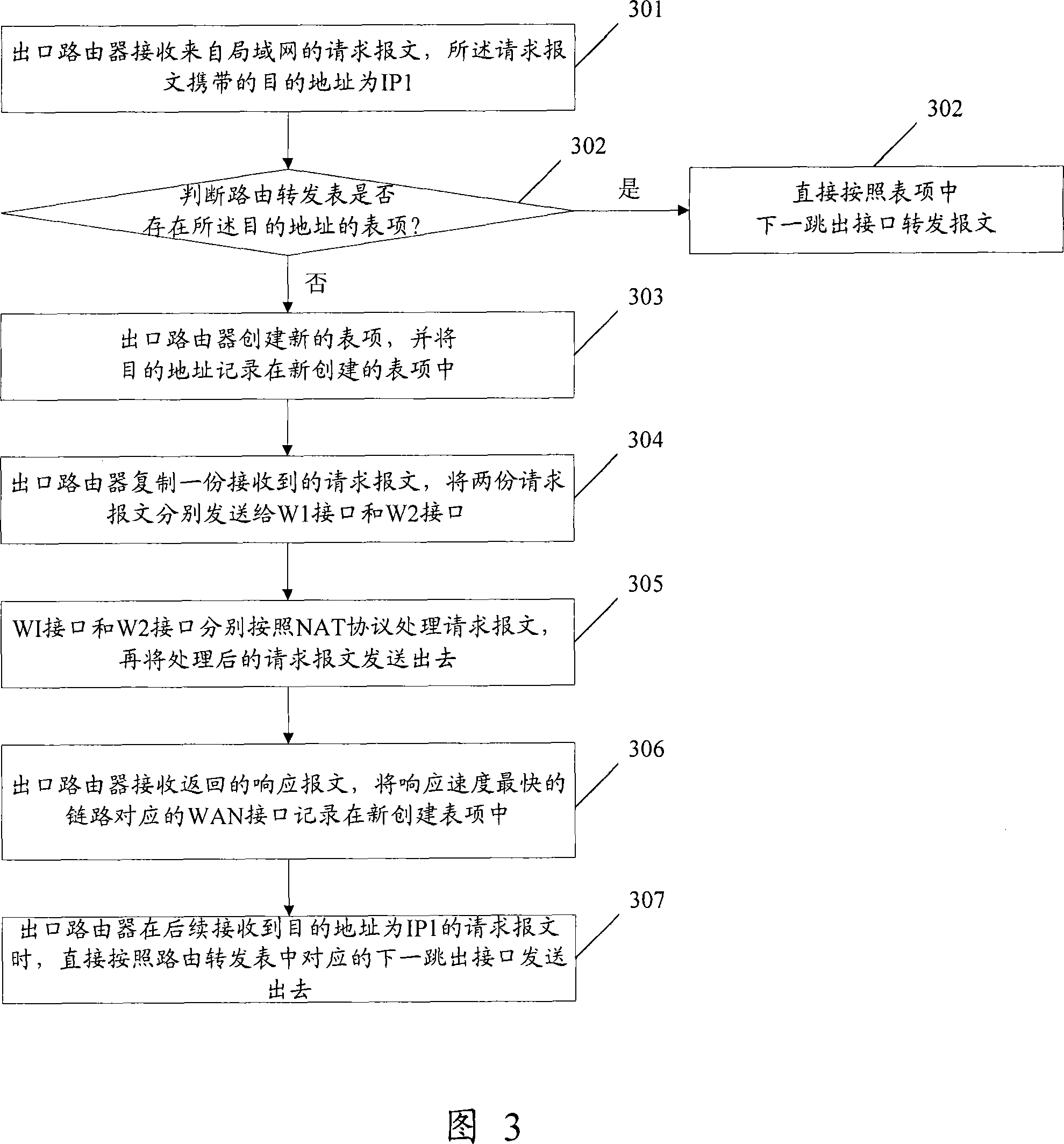
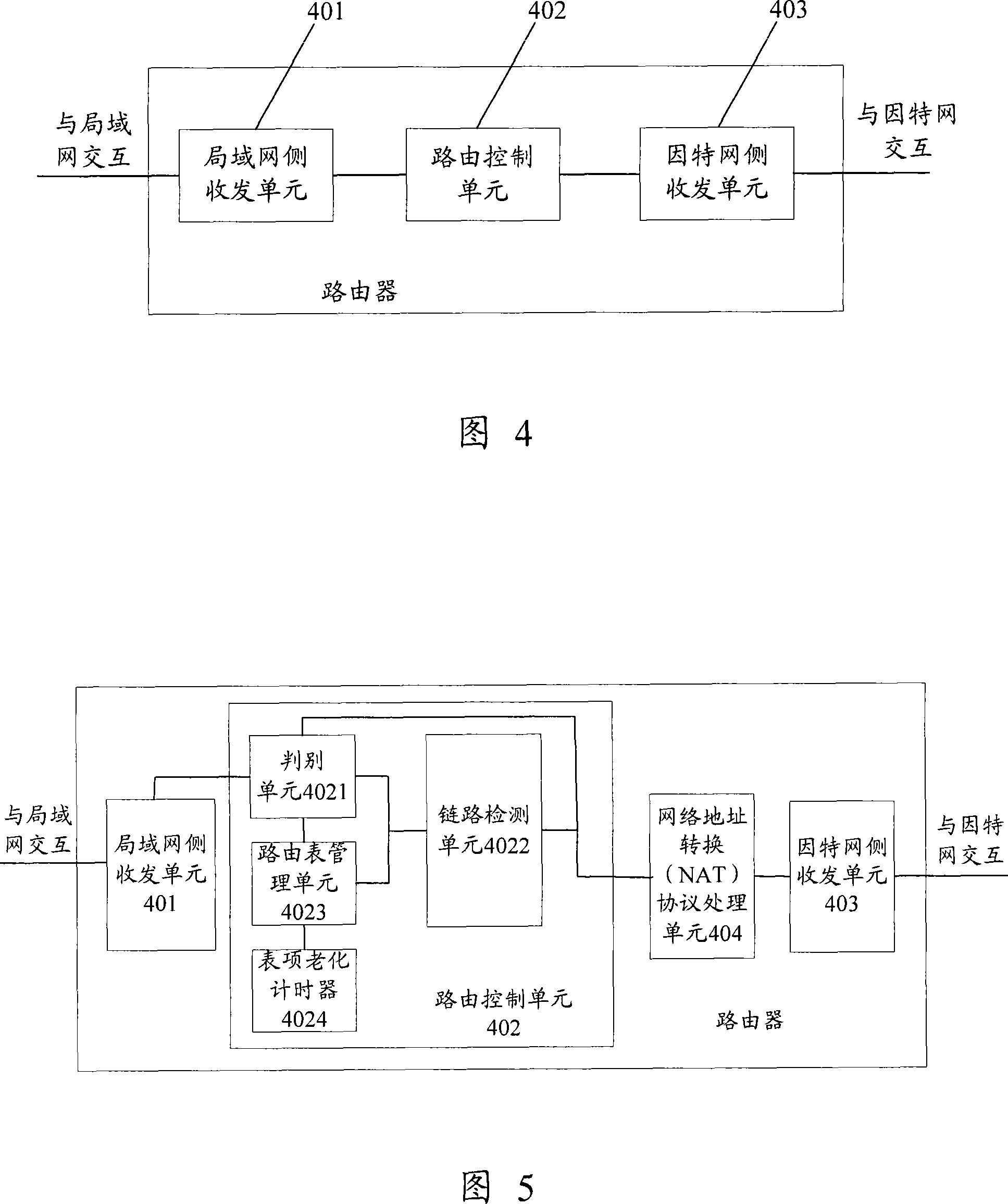
Route selecting method and router
InactiveCN101026589AReduce workloadEasy accessData switching by path configurationNetwork addressingThe Internet
The method includes steps: exit router receives request message from LAN, and the target address of the request message is network address of server in Internet; using the request message, the exit router detects response speed of link corresponding to each WAN interface; setting up WAN interface corresponding the link with fastest response speed as exit interface of next hop corresponding to target address so as to realize route selection. The invention does not need to collocate exit router by handwork, instead uses request message to determine route directly. The invention guarantees that LAN accesses server in Internet according to optimal route.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
Handover in Core-Edge Separation Technology in Wireless Communications
ActiveUS20110002301A1Easy to useWireless commuication servicesData switching networksSeparation technologyNetwork packet
In one embodiment of the invention, a method for wireless communication includes receiving a packet destined to a destination node at a first egress router. The destination node is supported by a second egress router. A destination address of the packet is the first egress router. The received packet is redirected to the second egress router.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
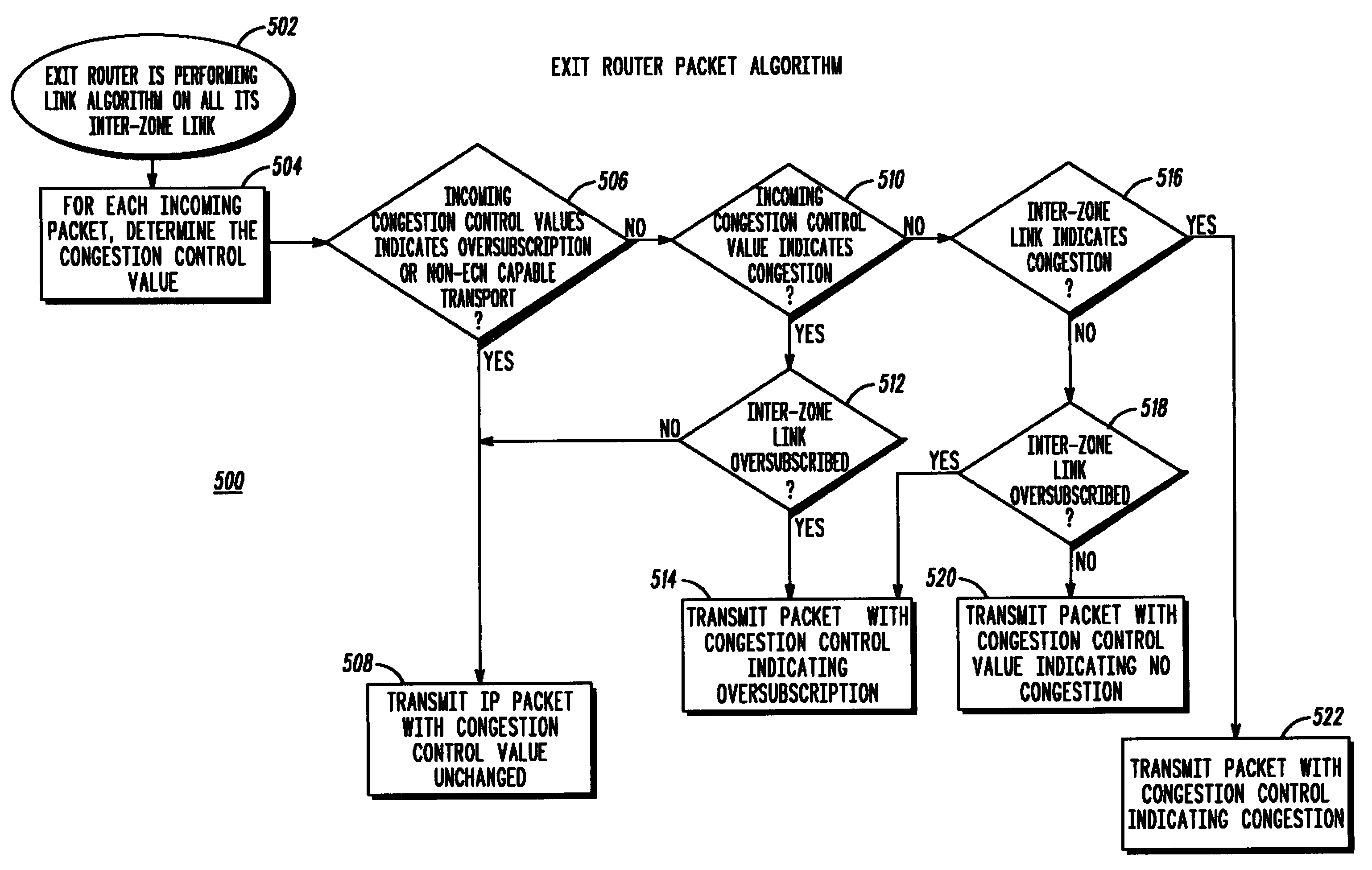
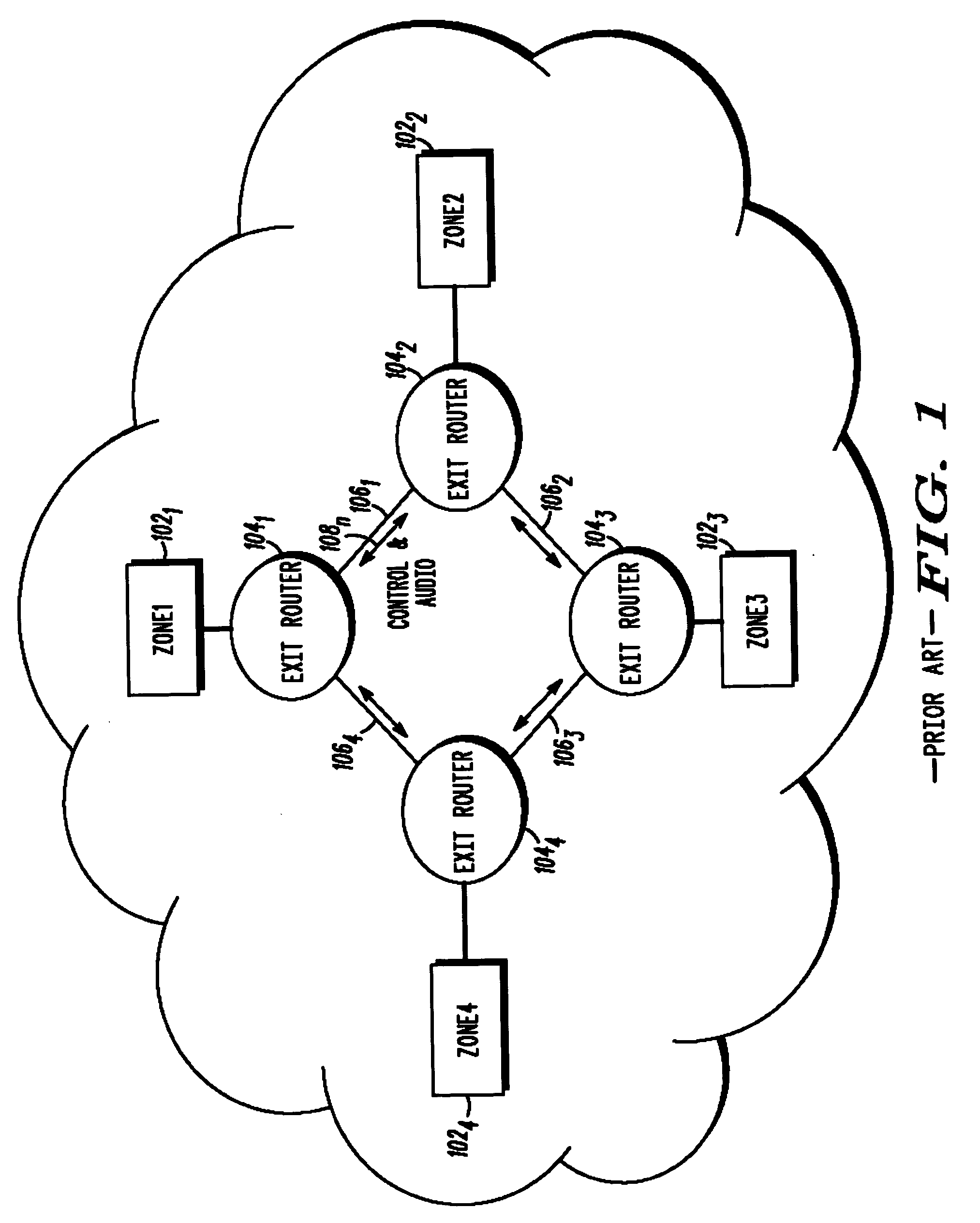
Method for managing inter-zone bandwidth in a two-way messaging network
InactiveUS20060015639A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionTraffic capacityEgress router
A congestion control level method for a messaging system having a plurality of exit routers (104) coupled to a plurality of zone controllers (102) which includes determining a congestion control value based on the traffic type, and notifying the plurality of zone controllers over the control plane of the congestion control level on the audio plane based on the congestion control value. The traffic type can be audio, voice and / or data as described herein.
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
Packet transmission method based on network dual exit and exit router
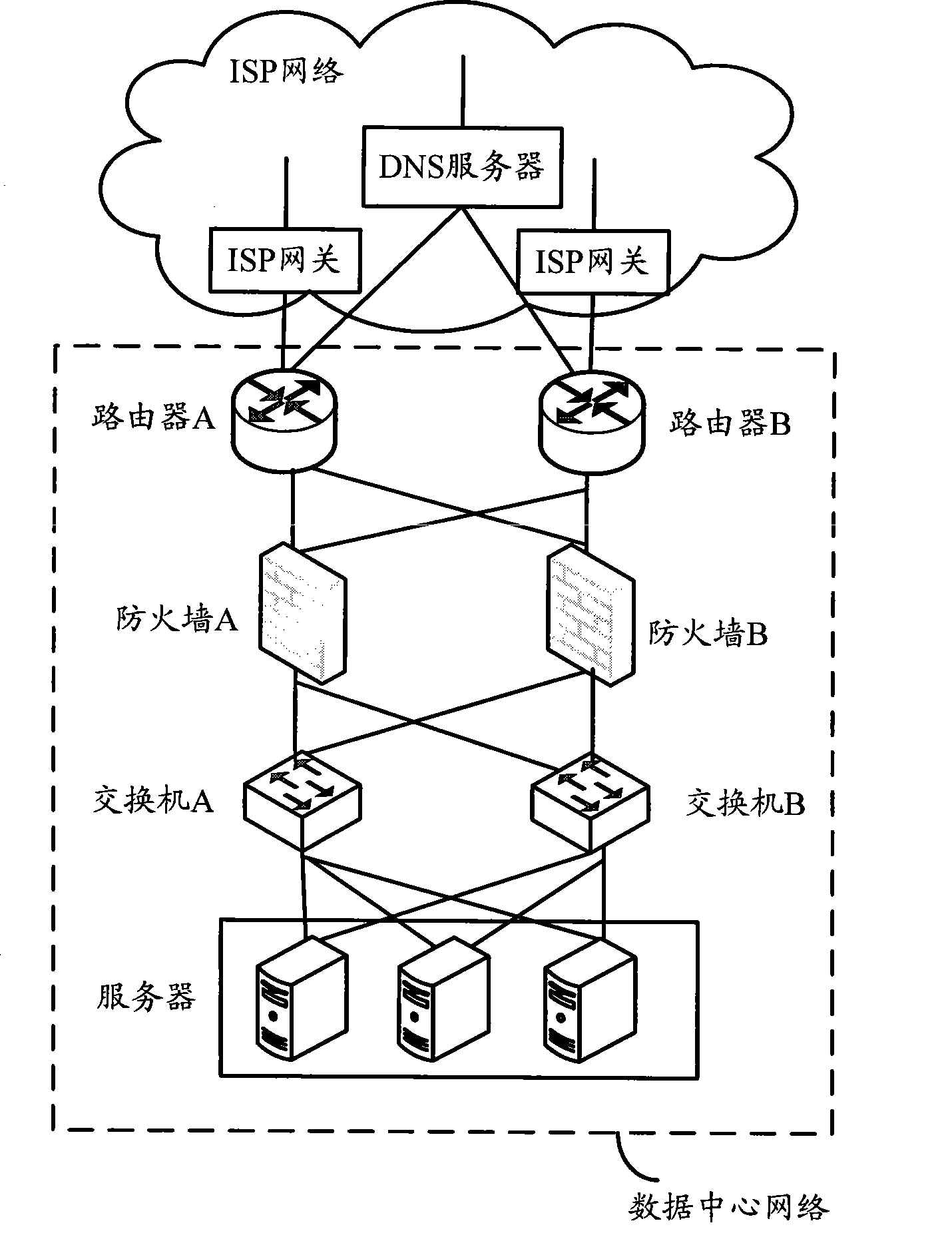
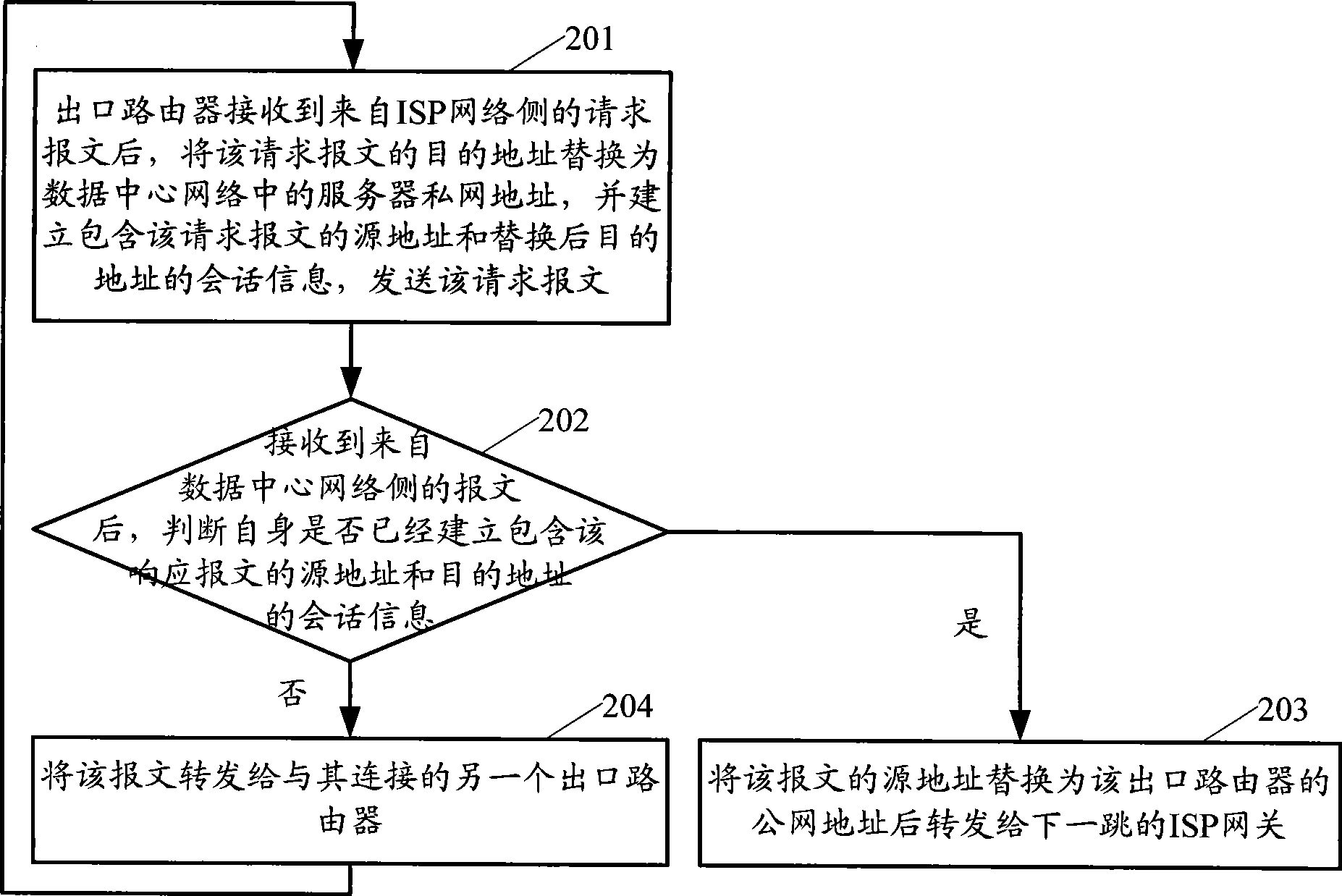
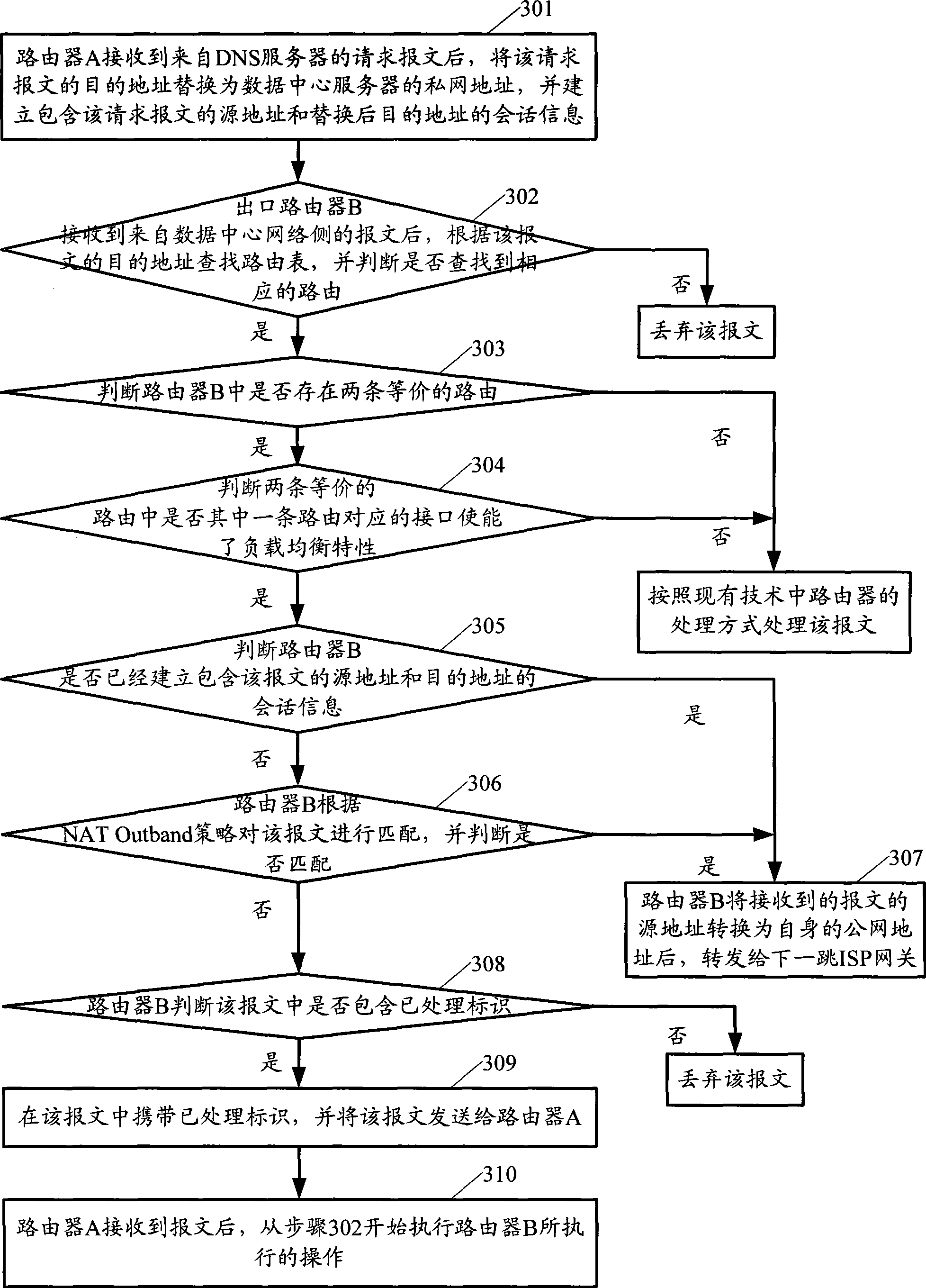
InactiveCN101383778AImprove securityGuaranteed balanceData switching networksData centerEgress router
The invention provides a message transmission method based on double output-ports of the network and output-port routers, which are applied in a data centre network containing two output-port routers, and a connection is established between the two outlet-port routers; after receiving a request message from the (ISP) network side of a service supplier, each output-port router merely conducts the displacement of destination address, and creates a conversation information containing the source address of the request message and the destination address after the displacement, and then sends the request message; after receiving the message from the network side of the data center, by judging whether the self creates the conversation information containing the source address of the message and the destination address, if yes, the output-port router replaces the source address of the message by a public network address of the output-port routers and then transmits the public network address to the ISP gateway of the next hop; otherwise, the output-port router transmits the message to the other output-port router connected with the output-port router. The invention is favorable for realizing safety precautions of the servers in the data center network and improving the security of the data center network.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
Method and device for multicast forwarding
ActiveCN105871565ARealize interconnectionRapid deploymentSpecial service provision for substationIp addressMulticast network
The invention discloses a method and a device for multicast forwarding, which can enable a BFIR (bit-forwarding ingress router) to acquire BFER (bit-forwarding egress router) information included in a multicast group and enable a BIER (bit index explicit replication) multicast network to be quickly deployed. The BFER in the BIER network can determine an IP address of a registered router supporting the multicast group according to information of the multicast group in a pre-acquired multicast receiver list; according to the information of the multicast group and the IP address of the registered router supporting the multicast group, the BFER generates a BFER registration message, wherein the BFER registration message comprises the information of the multicast group, the destination IP address of the BFER registration message is the IP address of the registered router, and the source IP address of the BFER registration message is the IP address of the BFER; the BFER sends the BFER registration message to the registered router; and after the registered router in the BIER network receives the BFER registration message sent by the BFER, a BFER table entry is acquired according to the BFER registration message, wherein the BFER table entry comprises the information of the multicast group and the IP address of the BFER.
Owner:XFUSION DIGITAL TECH CO LTD
Configuring route properties for use in transport tree building
A mechanism is provided by which a transport tree identifier can be generated comprising both an opaque field, containing information that cannot be interpreted by core routers, and a non-opaque field, containing information that can be interpreted by core routers. The transport tree identifier is then used in the process of building a transport tree across a transport network. A transport network egress router can receive a request to join a multicast datastream from a downstream node outside of the transport network. The information contained in the join message that identifies the desired multicast datastream is encoded in the opaque field of the transport tree identifier. Information related to desired route properties is encoded in the non-opaque field, for interpretation by the core routers. The non-opaque field can also include an identifier of a root node core router for the transport tree. Route properties can be provided, for example, by selection and transmission from the customer itself, or route properties can be associated with a particular customer or associated with a port of an egress router coupled to the customer network.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com