Patents
Literature
166results about How to "Keep the flow" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
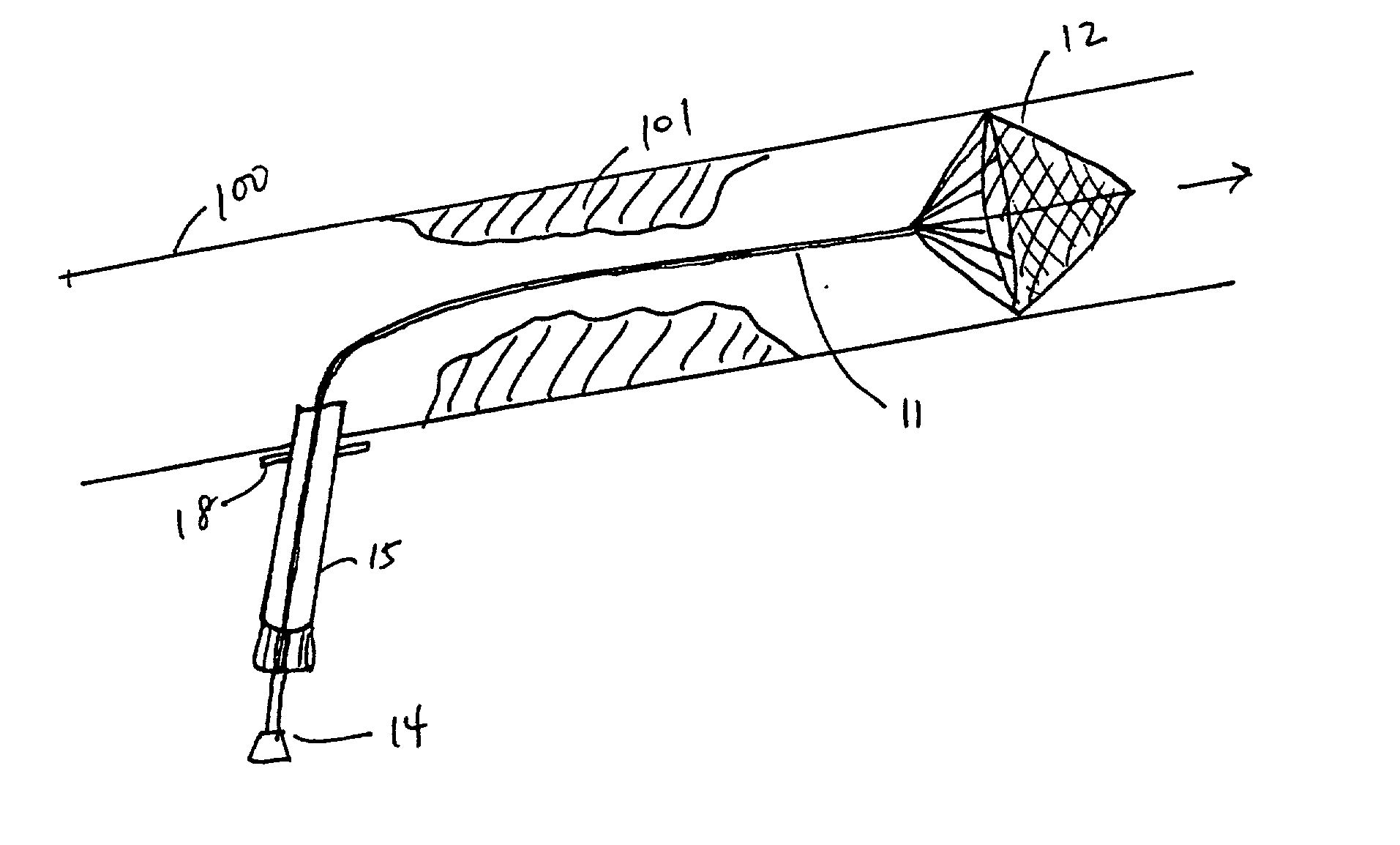
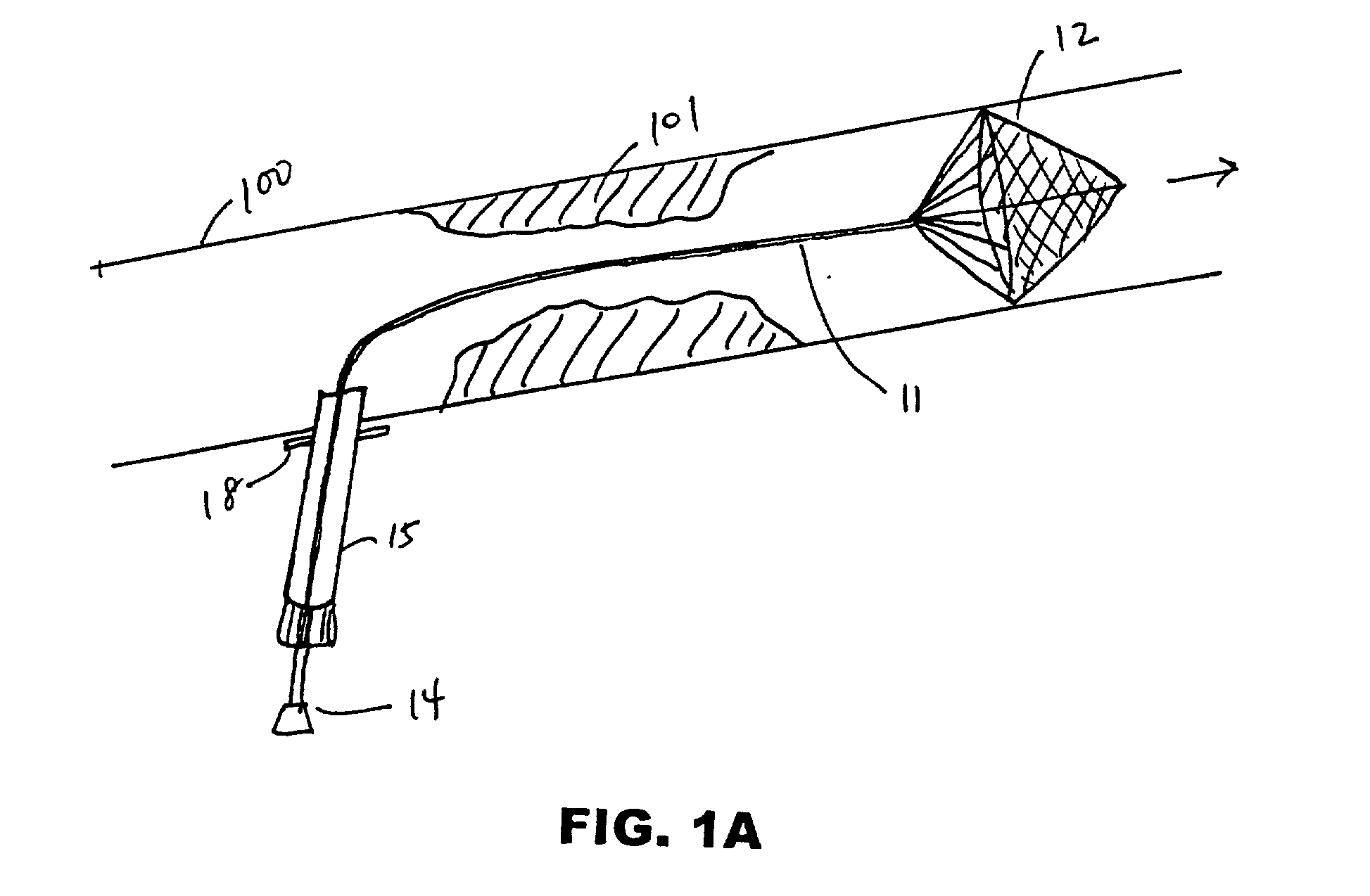
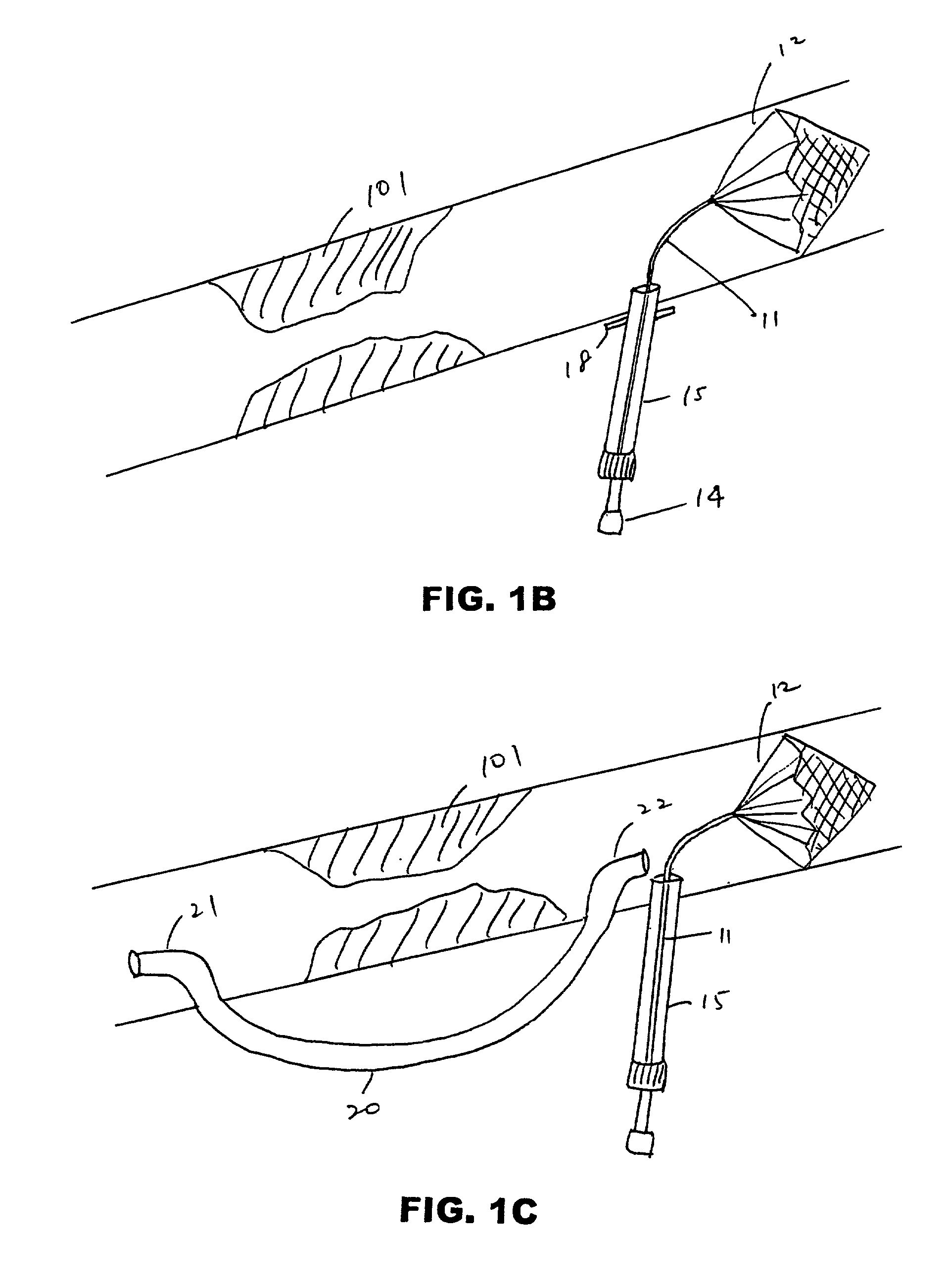
Cerebral protection during carotid endarterectomy and methods of use
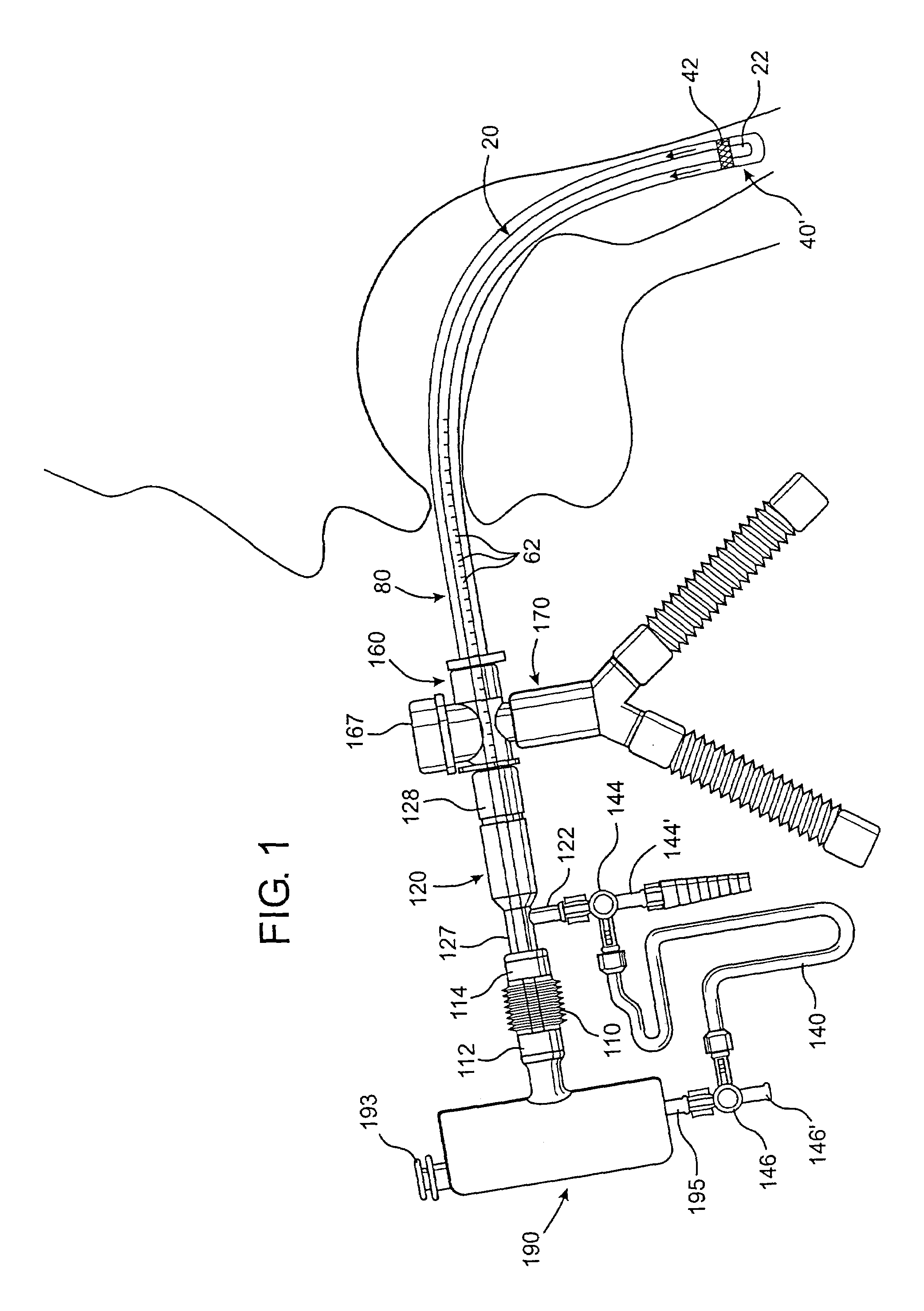
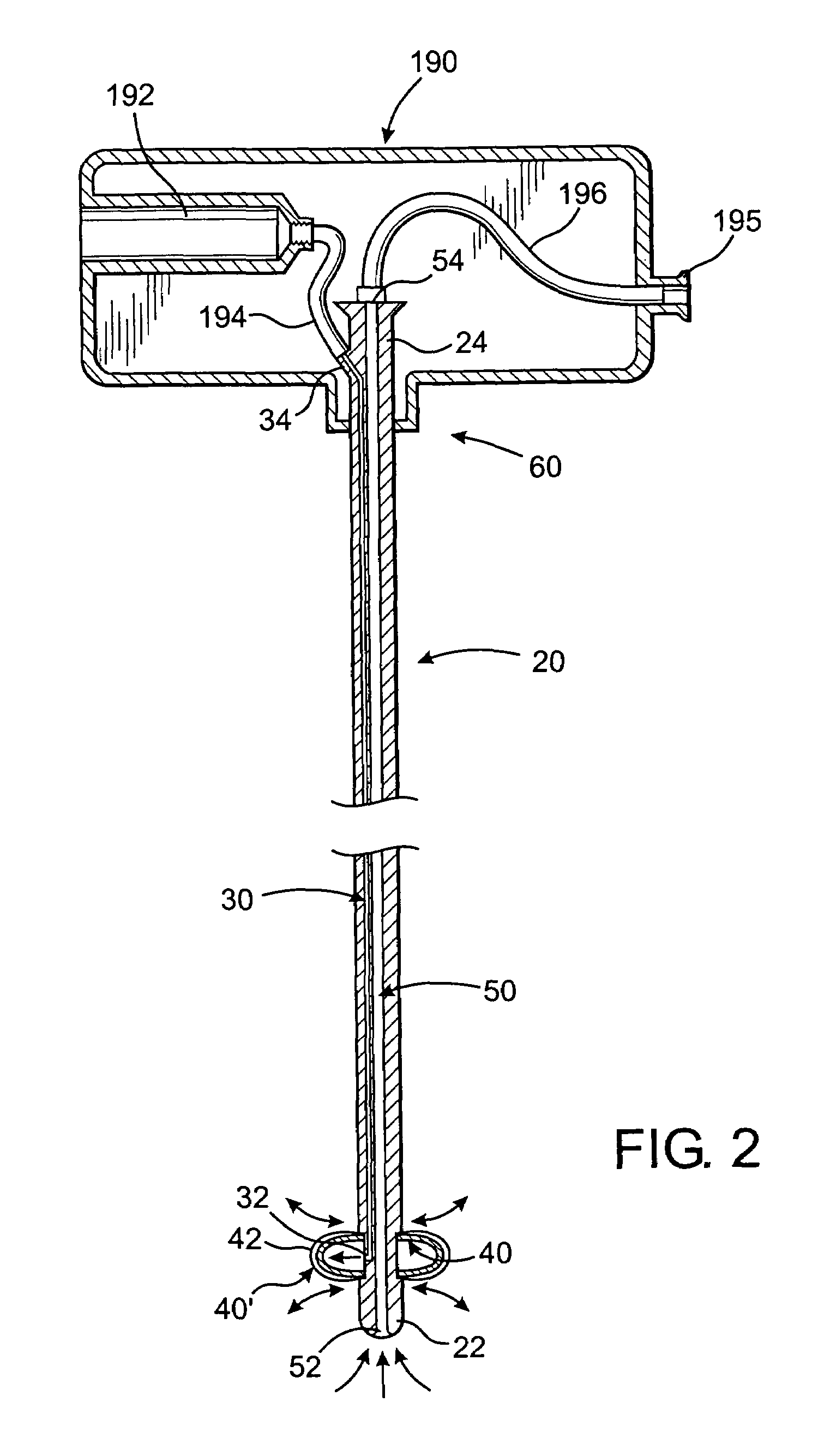
A shunt and method of use for maintaining distal blood flow during an arteriotomy procedure is disclosed. The shunt includes first and second tubular members having proximal ports, distal ports, and lumens therebetween. The distal port of the second tubular member is adapted for releasable attachment to the proximal port of the first tubular member. A second lumen merges and communicates at its distal end with the lumen of the first tubular member and includes a hemostatic valve attached to its proximal end. In using the apparatus for performing open endarterectomy, a filter device is inserted into the vessel and deployed downstream the region of interest in the internal carotid artery. The distal end of the shunt is advanced over the filter device and secured onto the artery. The proximal end of the shunt is inserted upstream the region of interest, typically in the common carotid artery.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
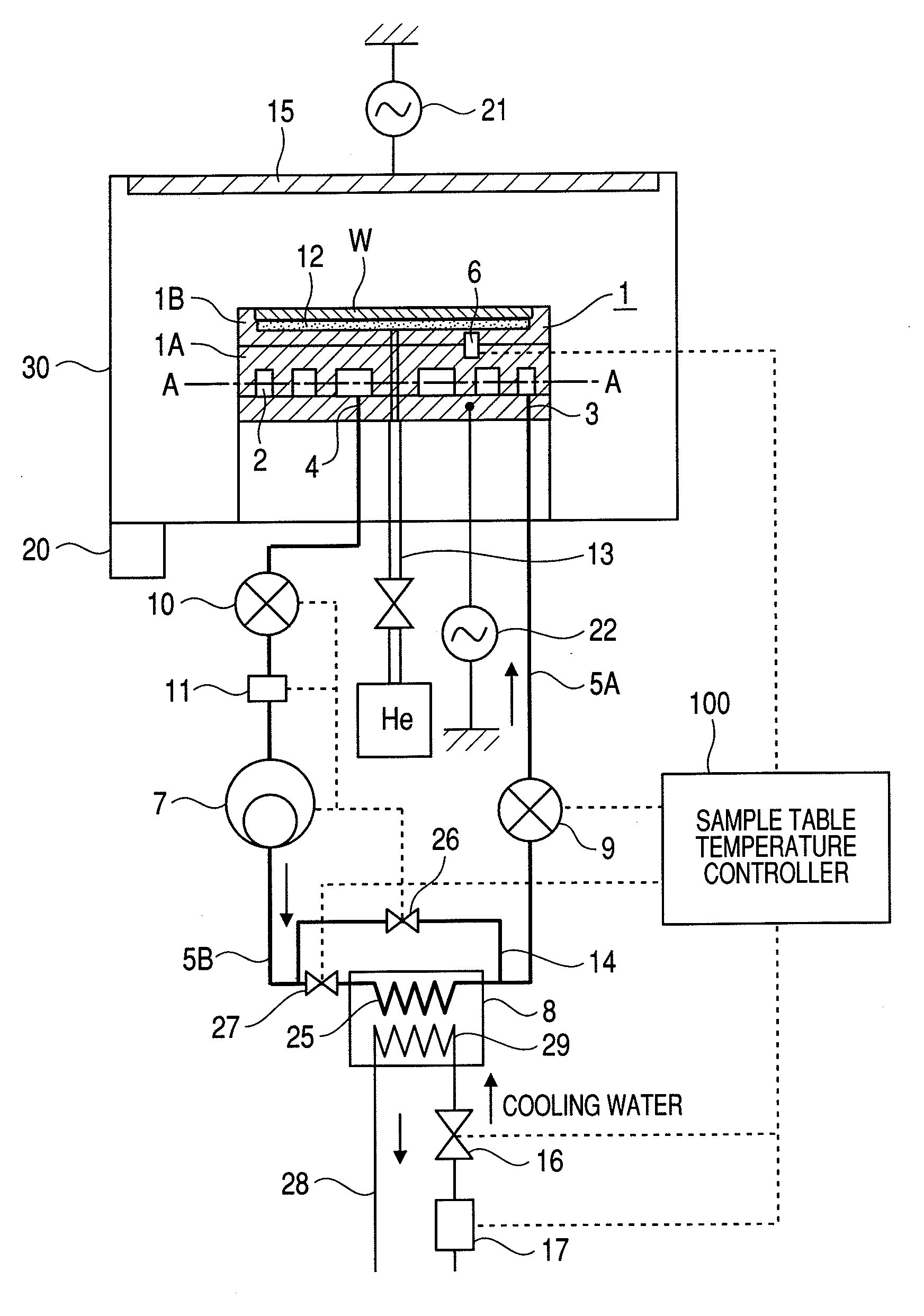
Plasma processing apparatus
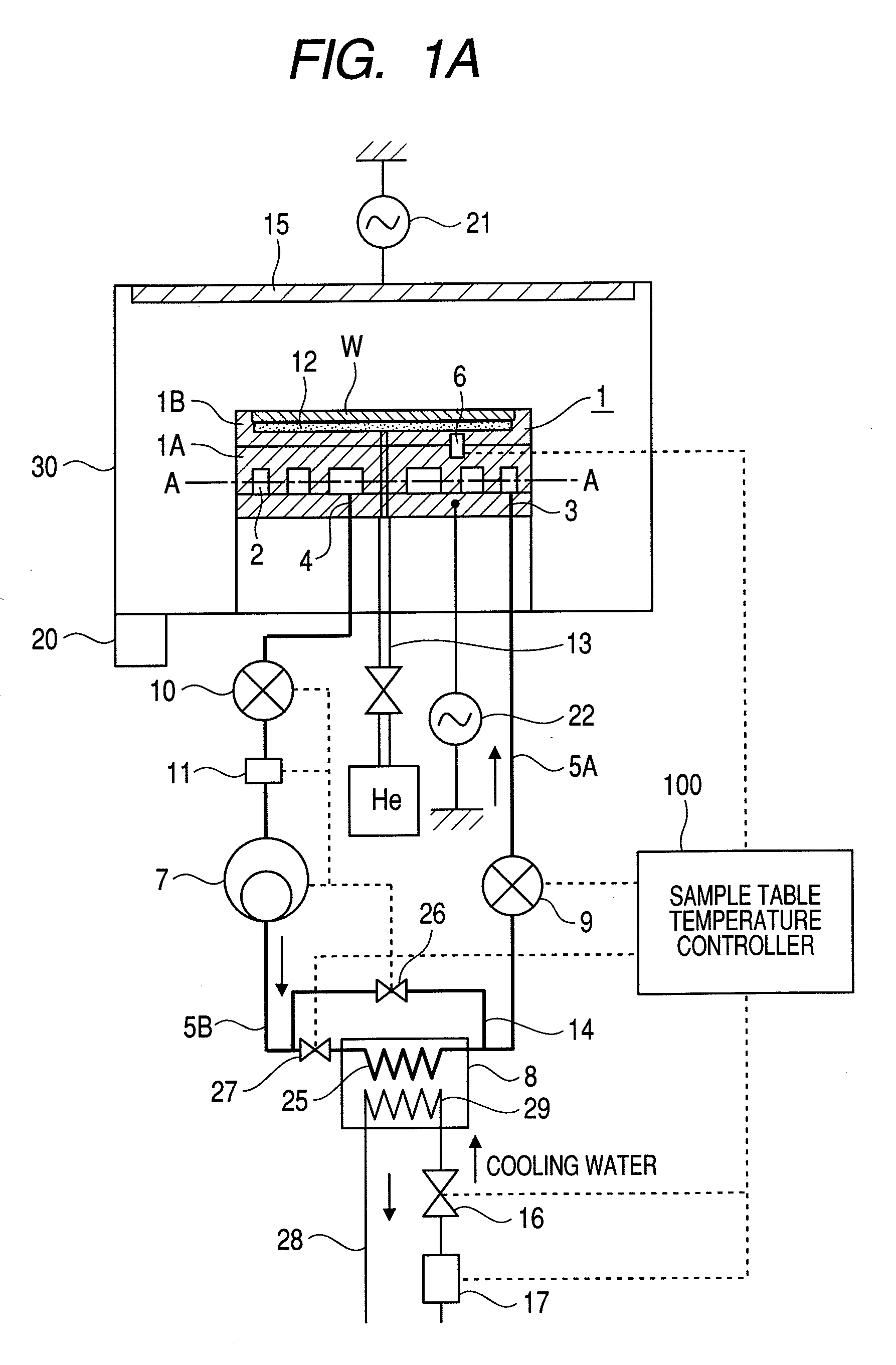
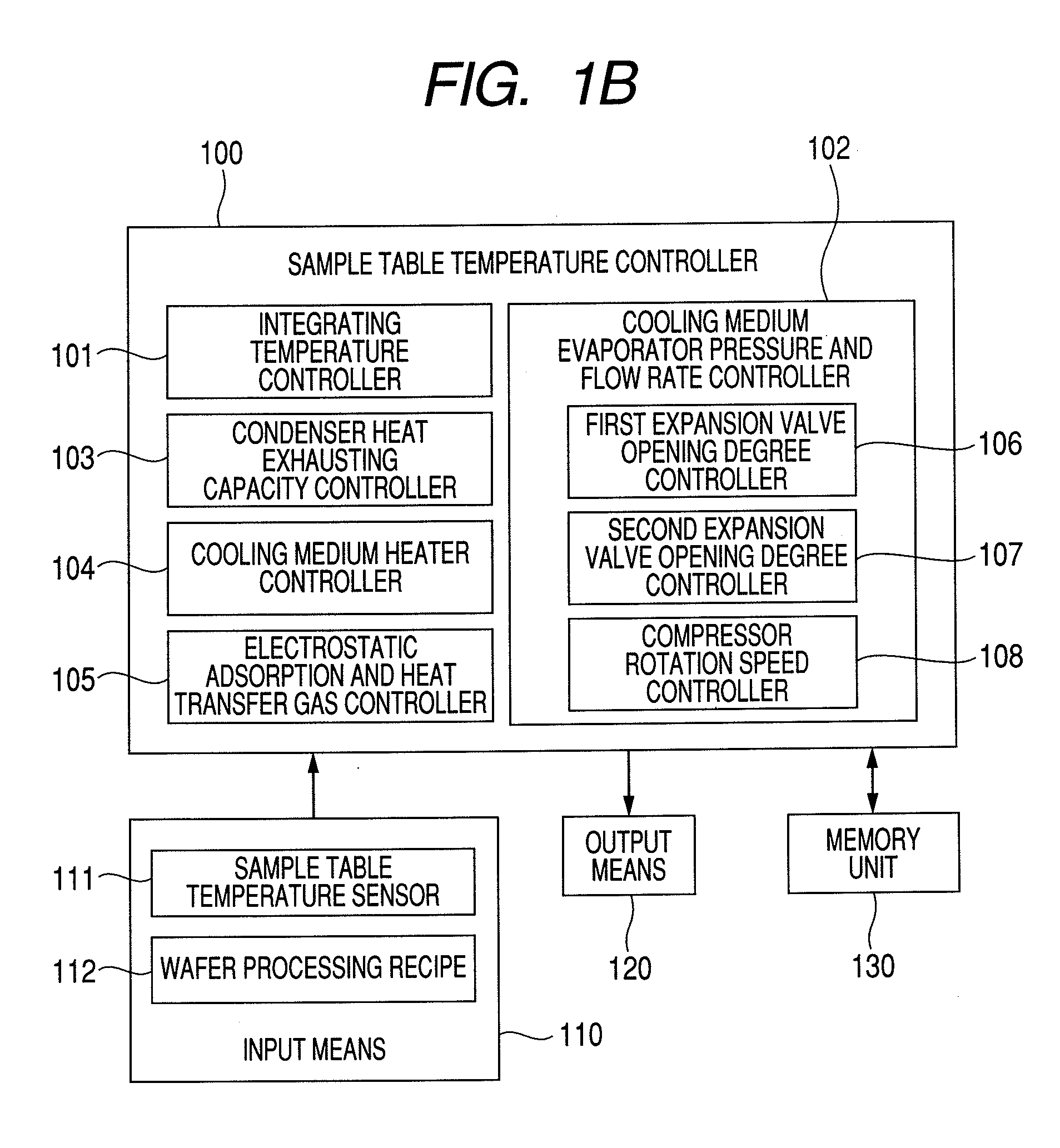
InactiveUS20100126666A1Uniform processingUnified controlElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIn planeEngineering
In a plasma processing apparatus; a refrigerant flow passage being formed in the sample table and constituting an evaporator of a cooling cycle and the in-plane temperature of the sample to be processed is controlled uniformly by controlling the enthalpy of the refrigerant supplied to the refrigerant flow passage and thereby keeping the flow mode in the refrigerant flow passage, namely in the sample table, in the state of a gas-liquid two-phase. If by any chance dry out of the refrigerant occurs in the refrigerant flow passage because the heat input of plasma increases with time or by another reason, it is possible to increase speed of a compressor and inhibit the dry out from occurring in the refrigerant flow passage. Further, if the refrigerant supplied to the refrigerant flow passage is liquefied, it is kept in the gas-liquid two-phase state.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
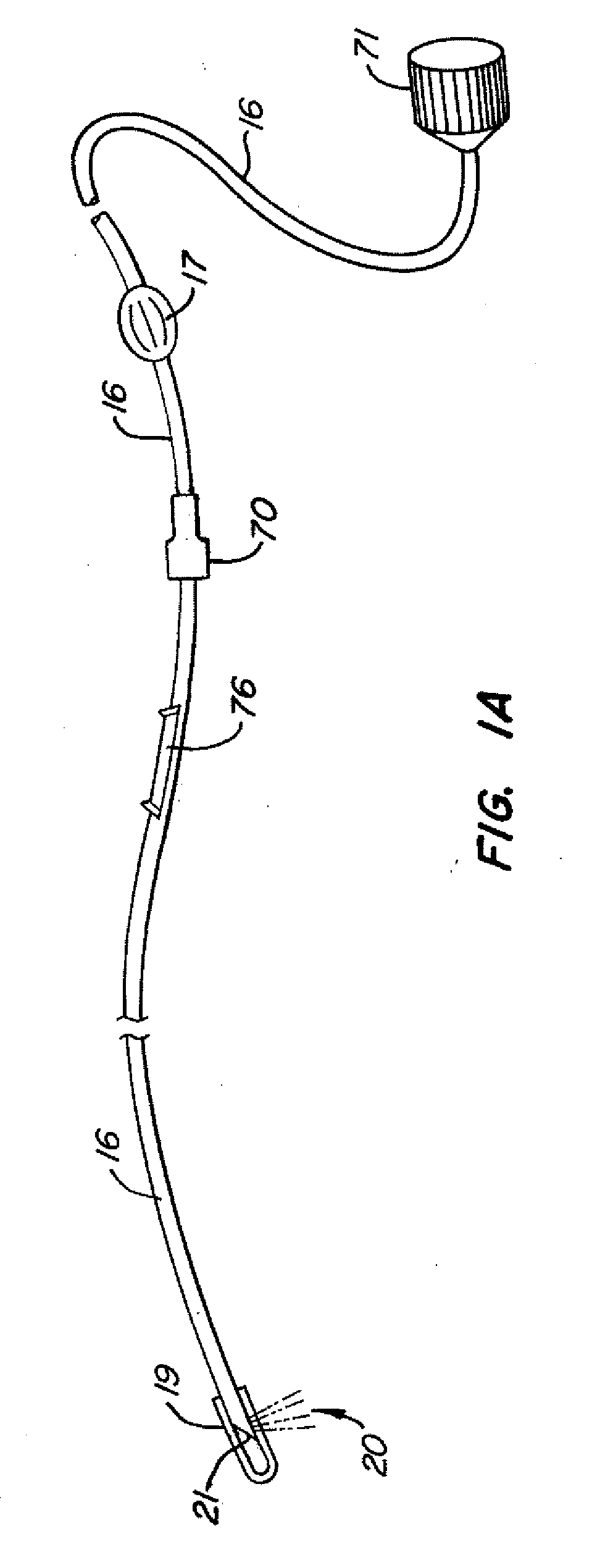
Subcutaneous port catheter system and associated method
A subcutaneous port catheter system includes a reservoir defining a chamber therein. The catheter system also includes a guide catheter attached to the reservoir. The guide catheter has a guide lumen and a distal guide orifice. The catheter system further includes an inner catheter attached to the reservoir. The inner catheter is positioned within the guide lumen and extends through the distal guide orifice. A method of advancing fluid into a blood vessel of a body of a patient is also disclosed.
Owner:MAGINOT CATHETER TECH
Implant device for trans myocardial revascularization
InactiveUS6258119B1Direct accessPrevent implant detachmentStentsEar treatmentCardiac muscleAngiogenesis growth factor
A myocardial implant for insertion into a heart wall for trans myocardial revascularization (TMR) of the heart wall. The TMR implant provides for means to promote the formation of new blood vessels (angiogenesis), and has a flexible, elongated body that contains a cavity and openings through the flexible, elongated body from the cavity. The TMR implant includes a coaxial anchoring element integrally formed at one end for securing the TMR implant in the heart wall.
Owner:MYOCARDIAL STENTS
Enhanced cross stream mechanical thrombectomy catheter with backloading manifold
InactiveUS20060129091A1High trafficEnhanced cross stream mechanical thrombectomyMulti-lumen catheterMedical devicesSuction forceJet flow
An enhanced cross stream mechanical thrombectomy catheter with backloading manifold having a distal end with outflow and inflow orifices at one side for producing concentrated cross stream jet flow for selective and concentrated thrombus ablation during thrombectomy procedures. The invention provides for suitable distancing of high powered ablation or suction forces from the near walls of the vasculature. Cross stream flow emanating from the one side of the distal end of the catheter resultantly urges the distal end of the catheter and thus the opposing non-orificed side of the distal end of the catheter toward and against the vascular wall to inhibit contact of the inflow orifice with the vascular wall. Features of the invention include a geometrically configured insert to facilitate the backloading or exchange of guidewires.
Owner:MEDRAD INC.
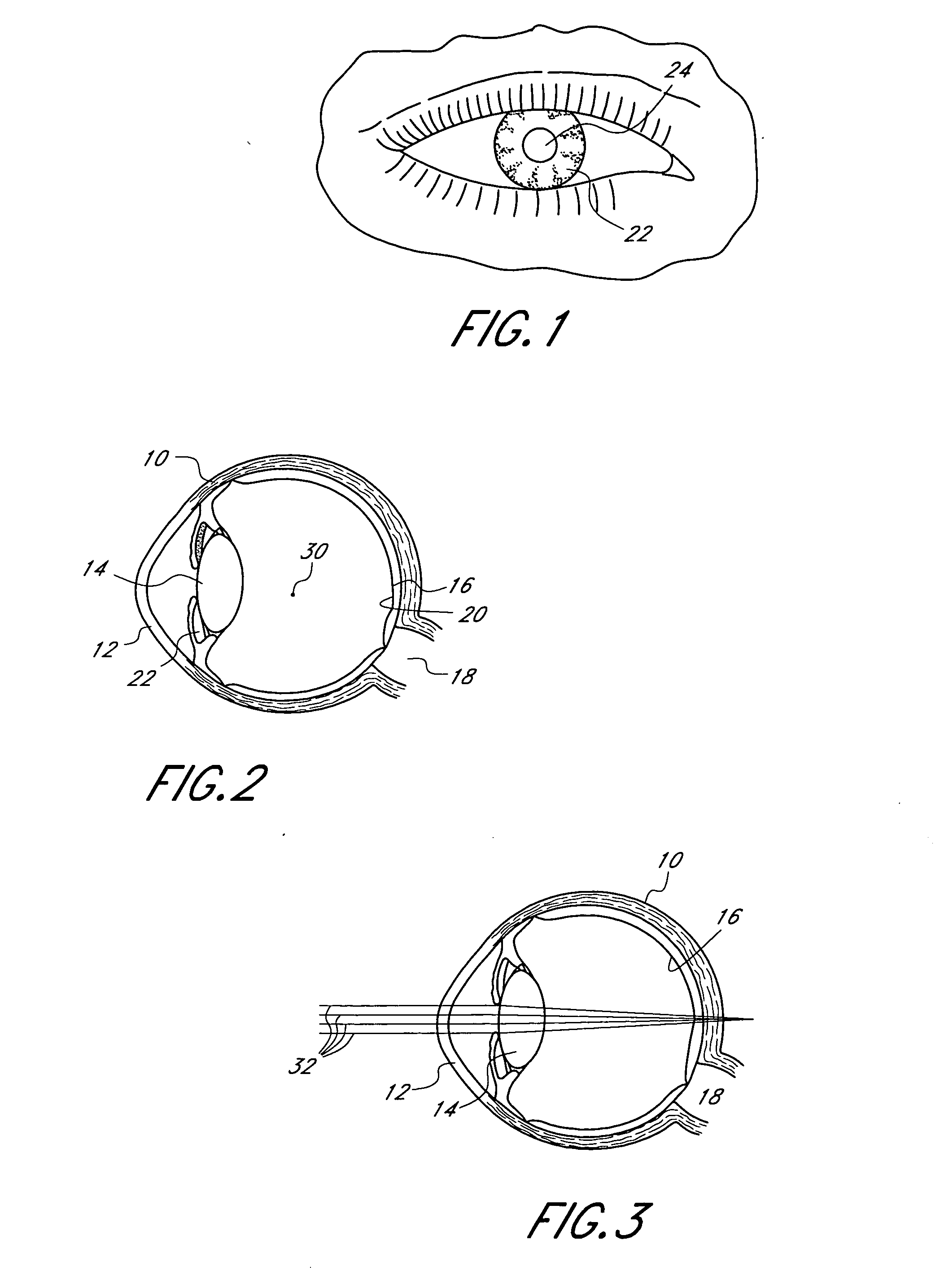
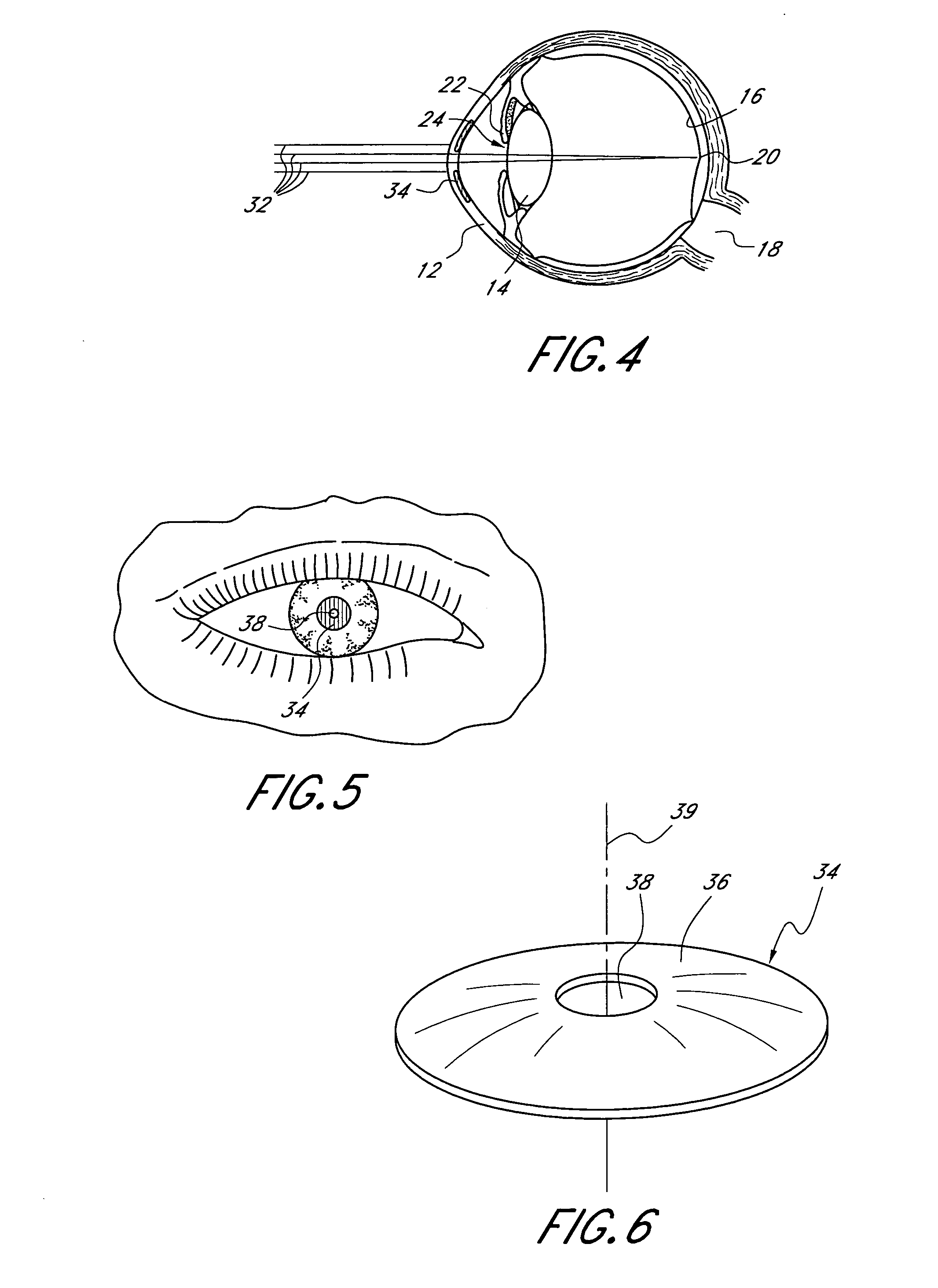
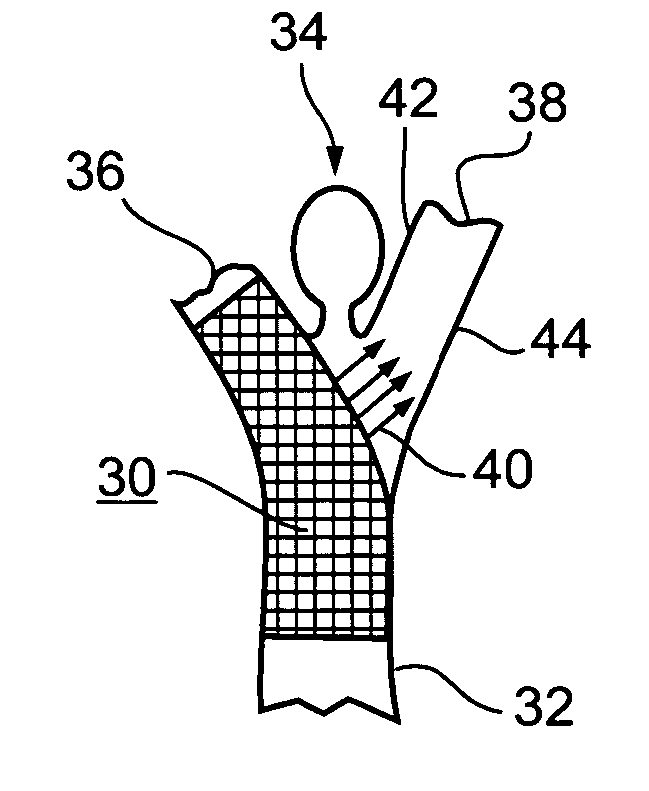
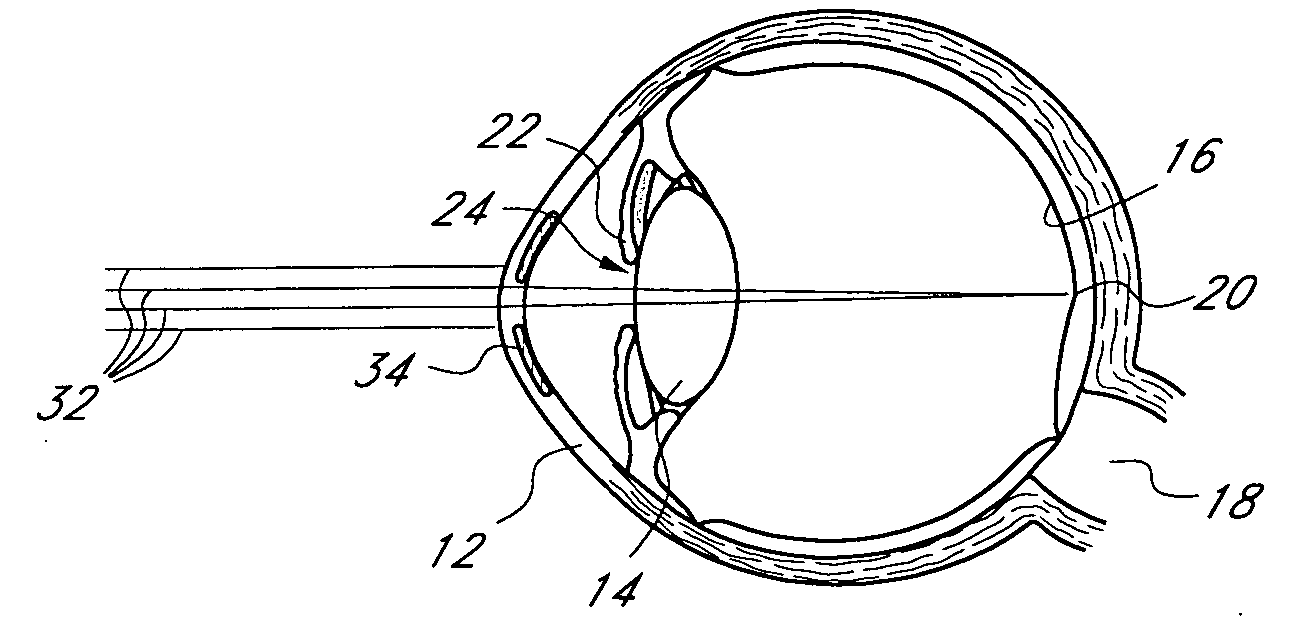
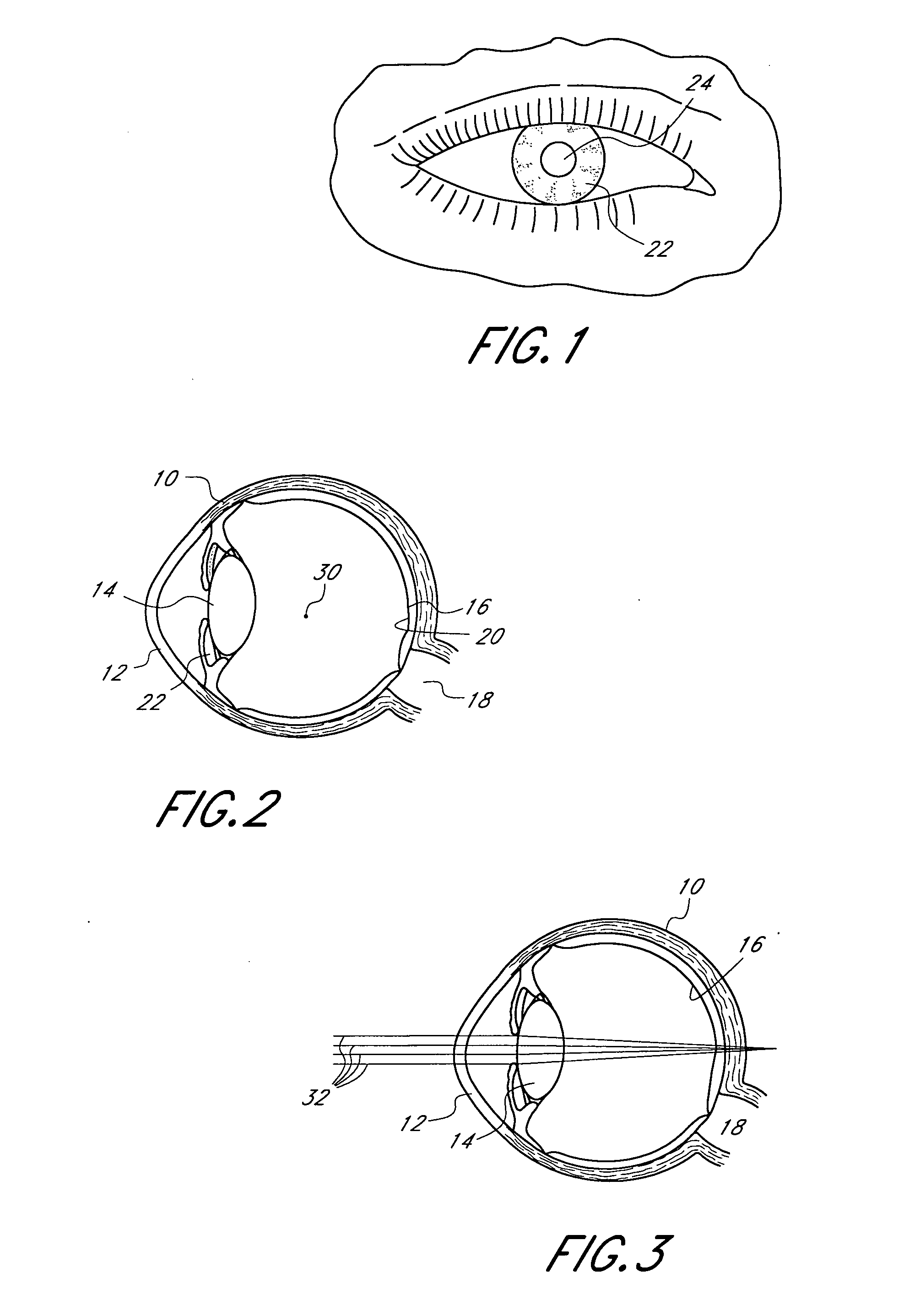
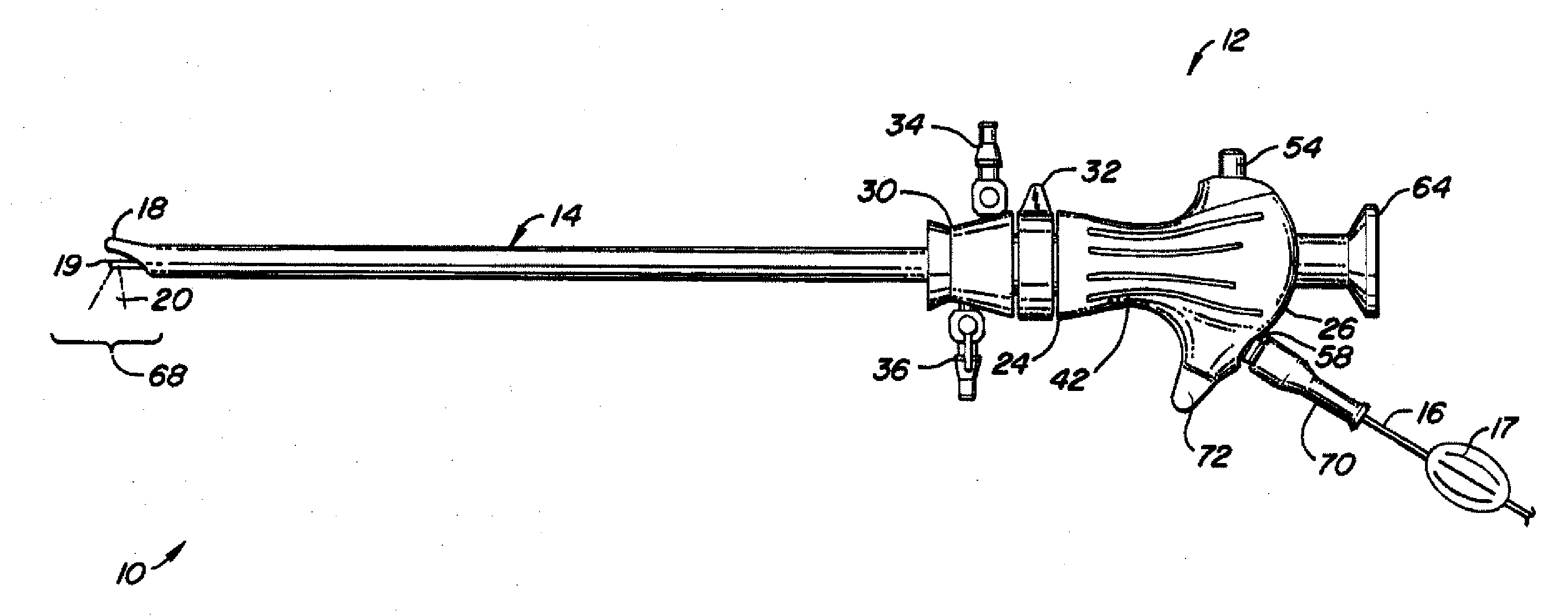
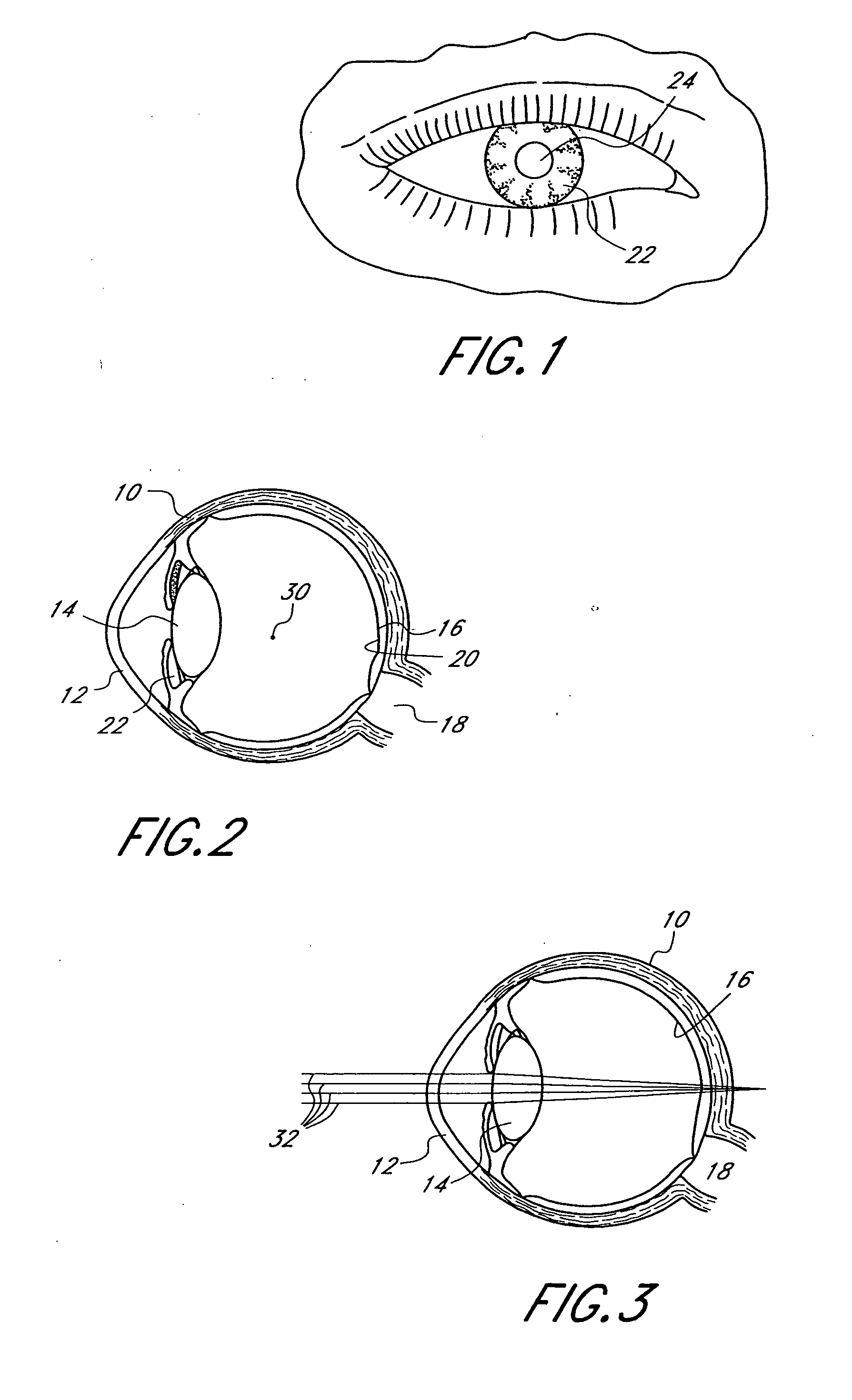
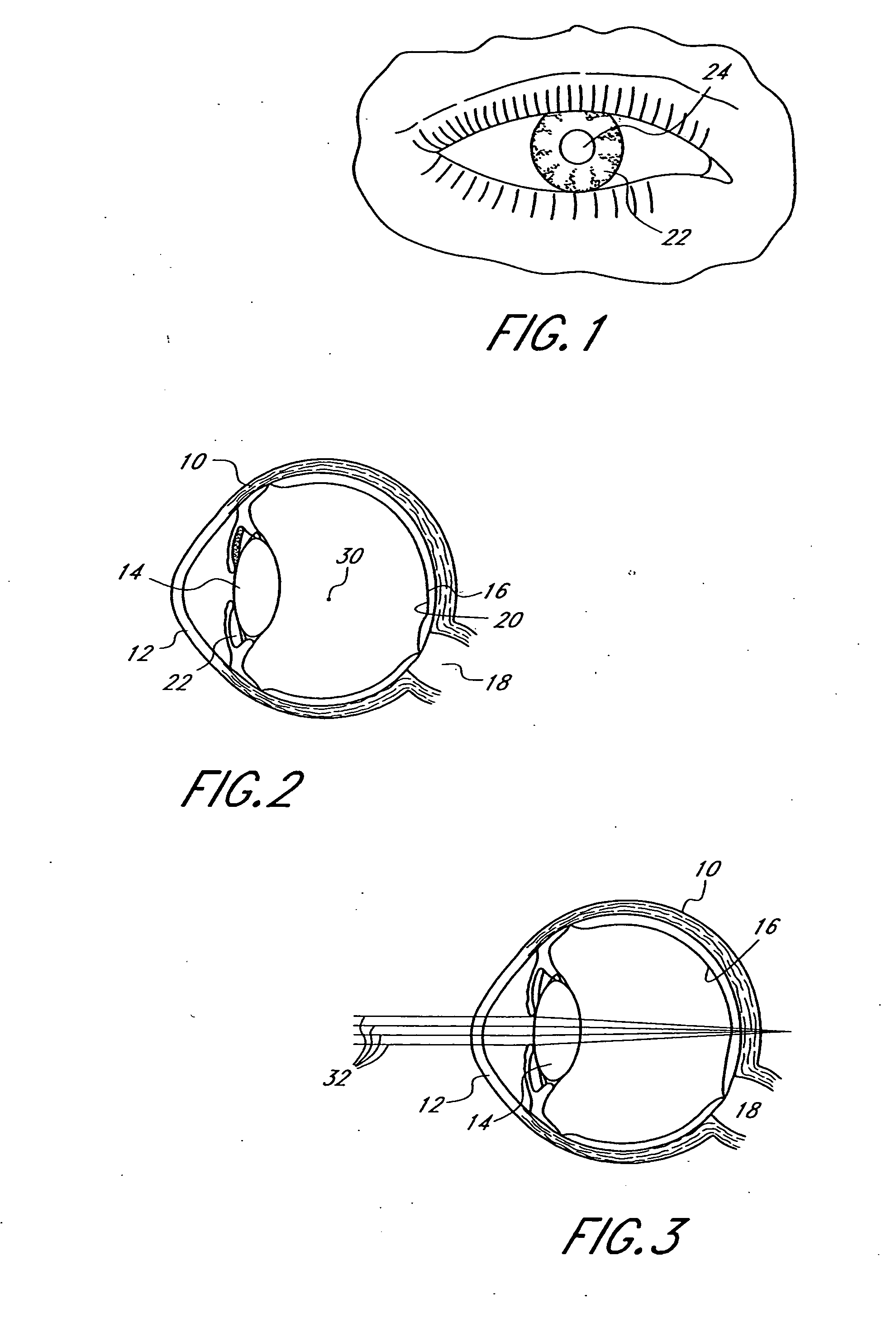
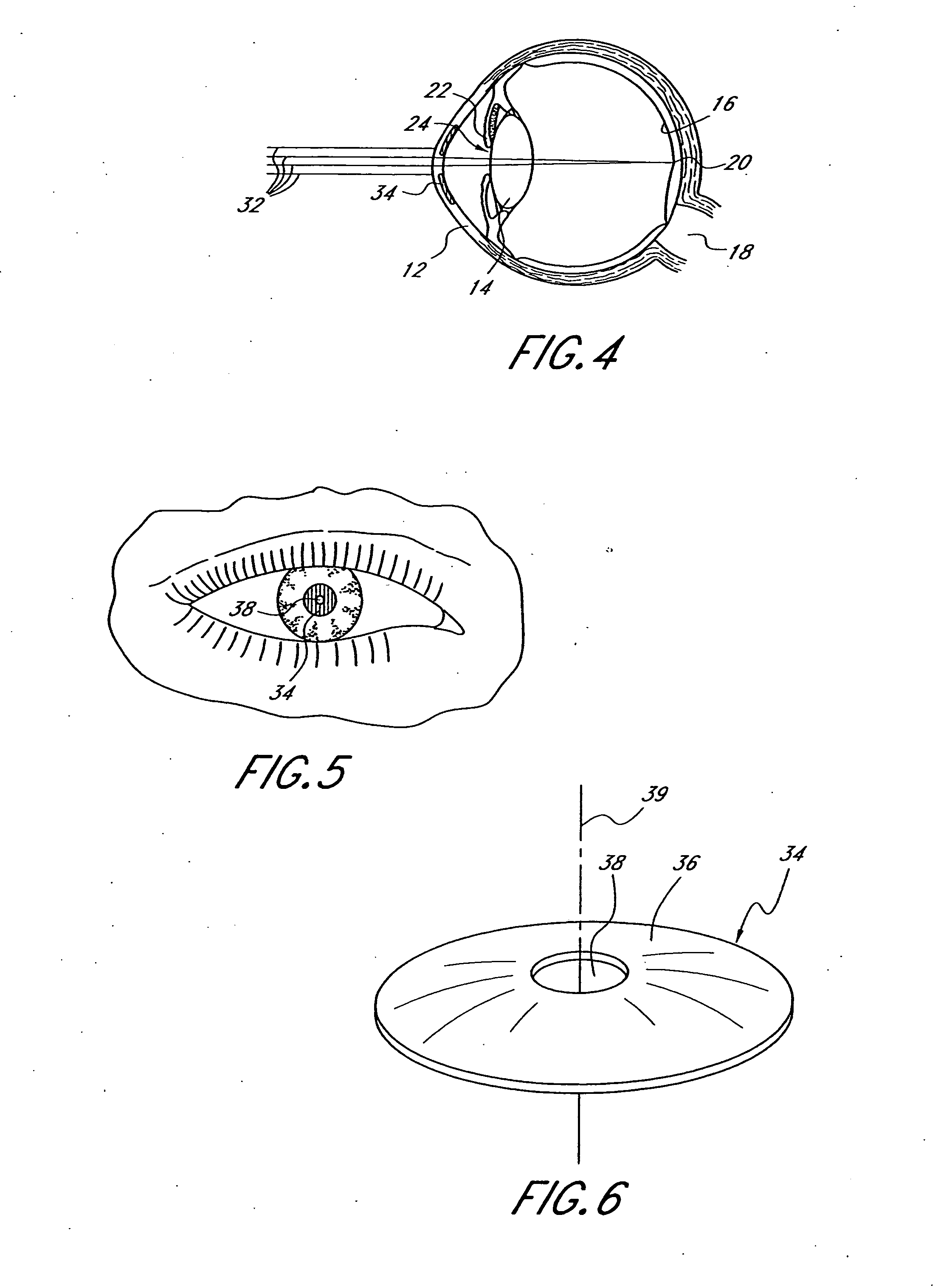
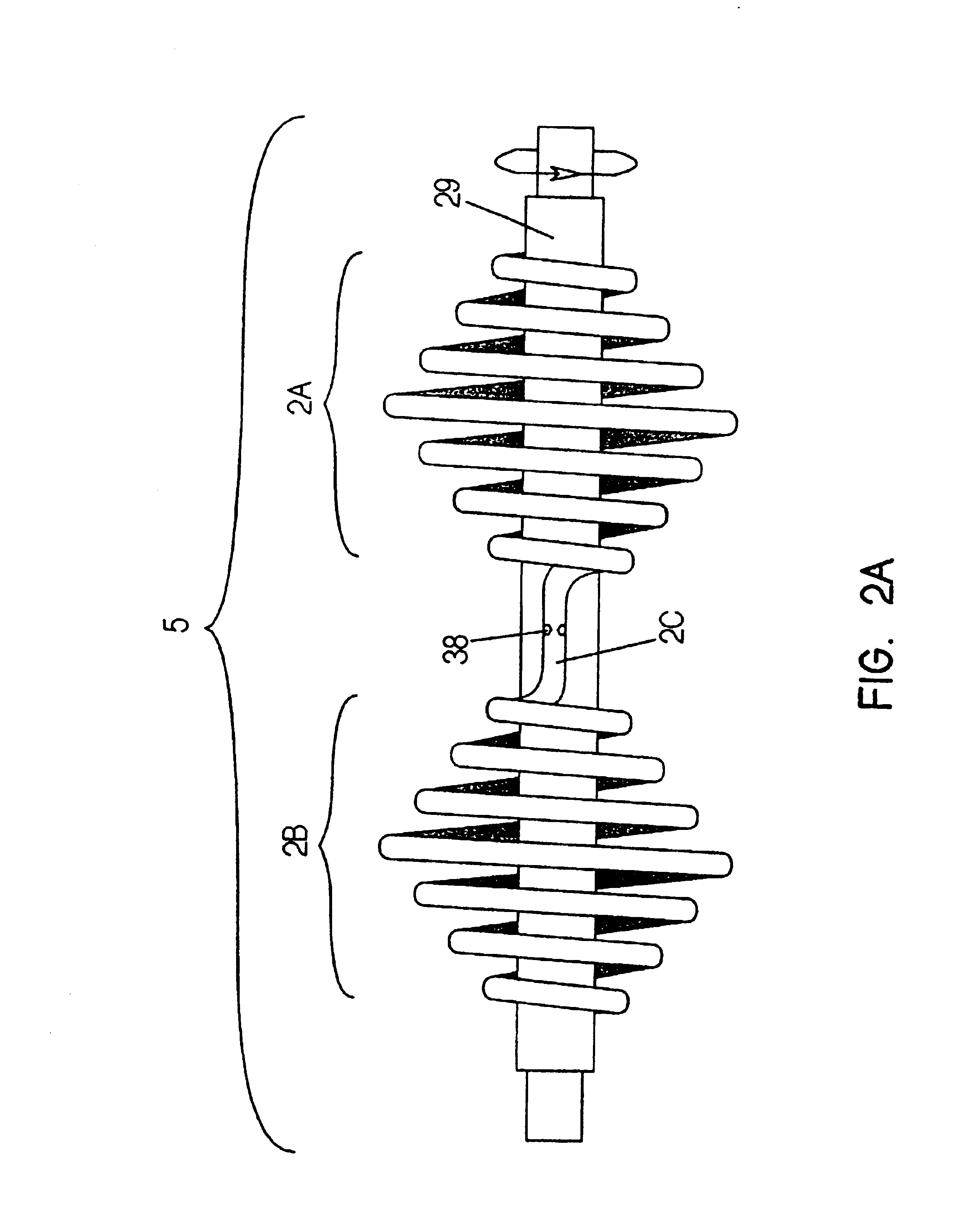
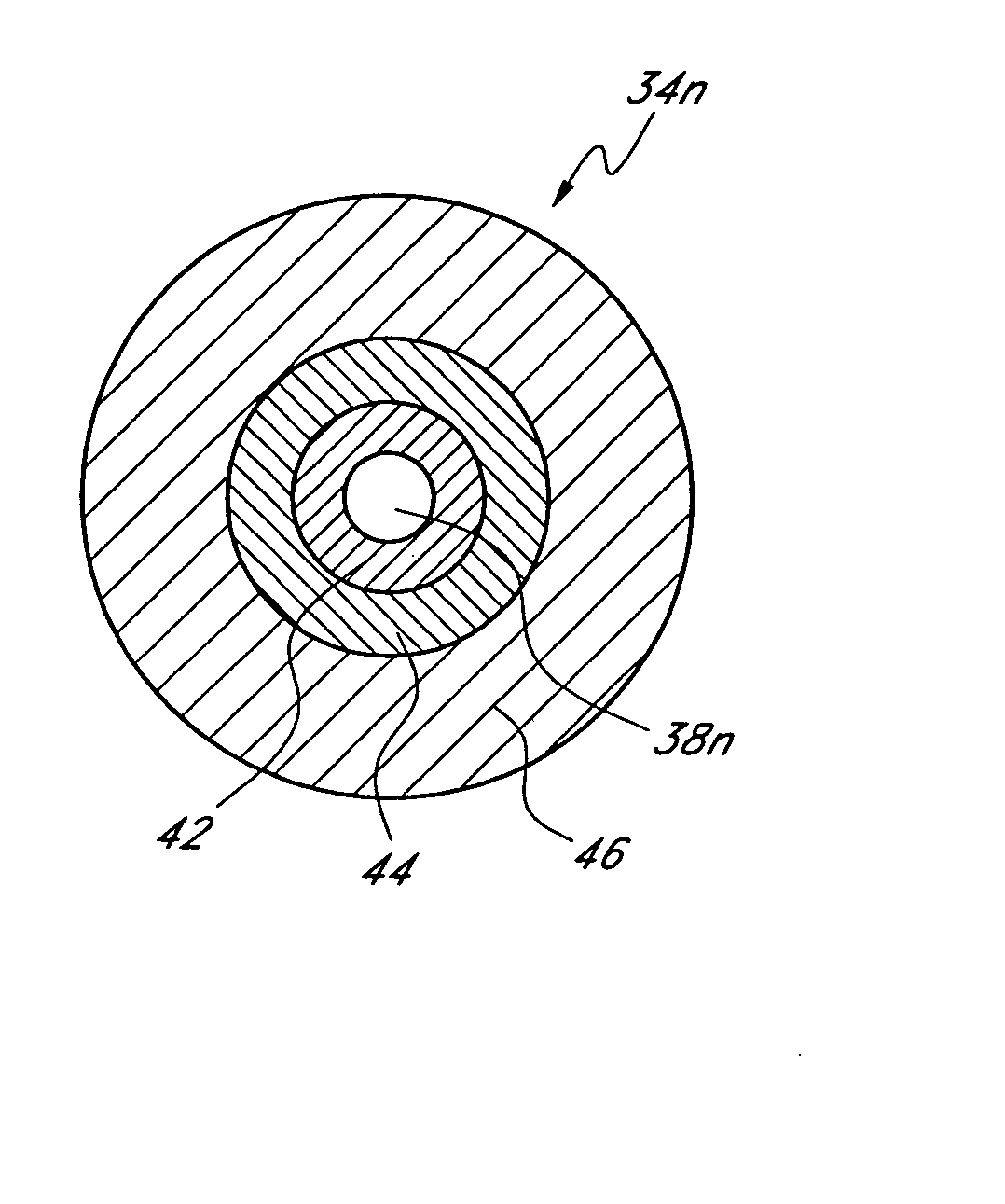
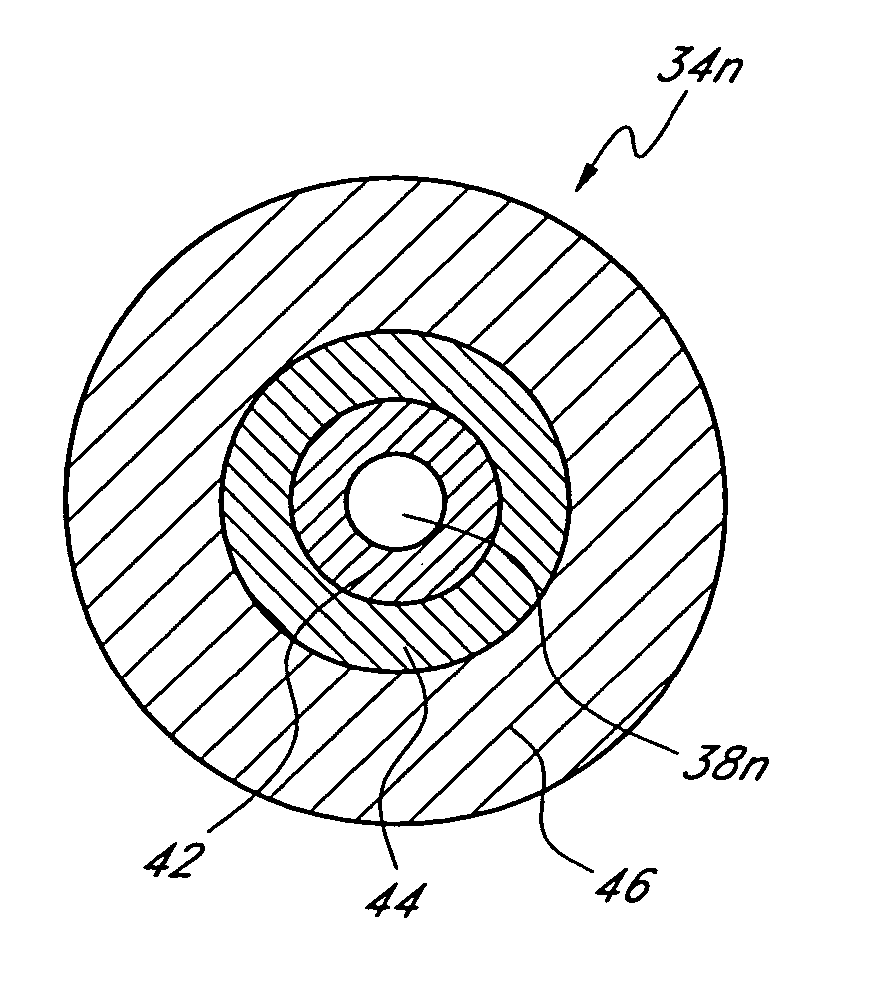
Mask configured to maintain nutrient transport without producing visible diffraction patterns
InactiveUS20050033420A1Increase depth of focusEliminate visible diffraction patternSpectales/gogglesSenses disorderAnterior surfaceCorneal layer
A mask configured to be implanted in a cornea of a patient to increase the depth of focus of the patient includes an anterior surface, a posterior surface, and a plurality of holes. The anterior surface is configured to reside adjacent a first corneal layer. The posterior surface is configured to reside adjacent a second corneal layer. The plurality of holes extends at least partially between the anterior surface and the posterior surface. The holes of the plurality of holes are configured to substantially eliminate visible diffraction patterns.
Owner:ACUFOCUS
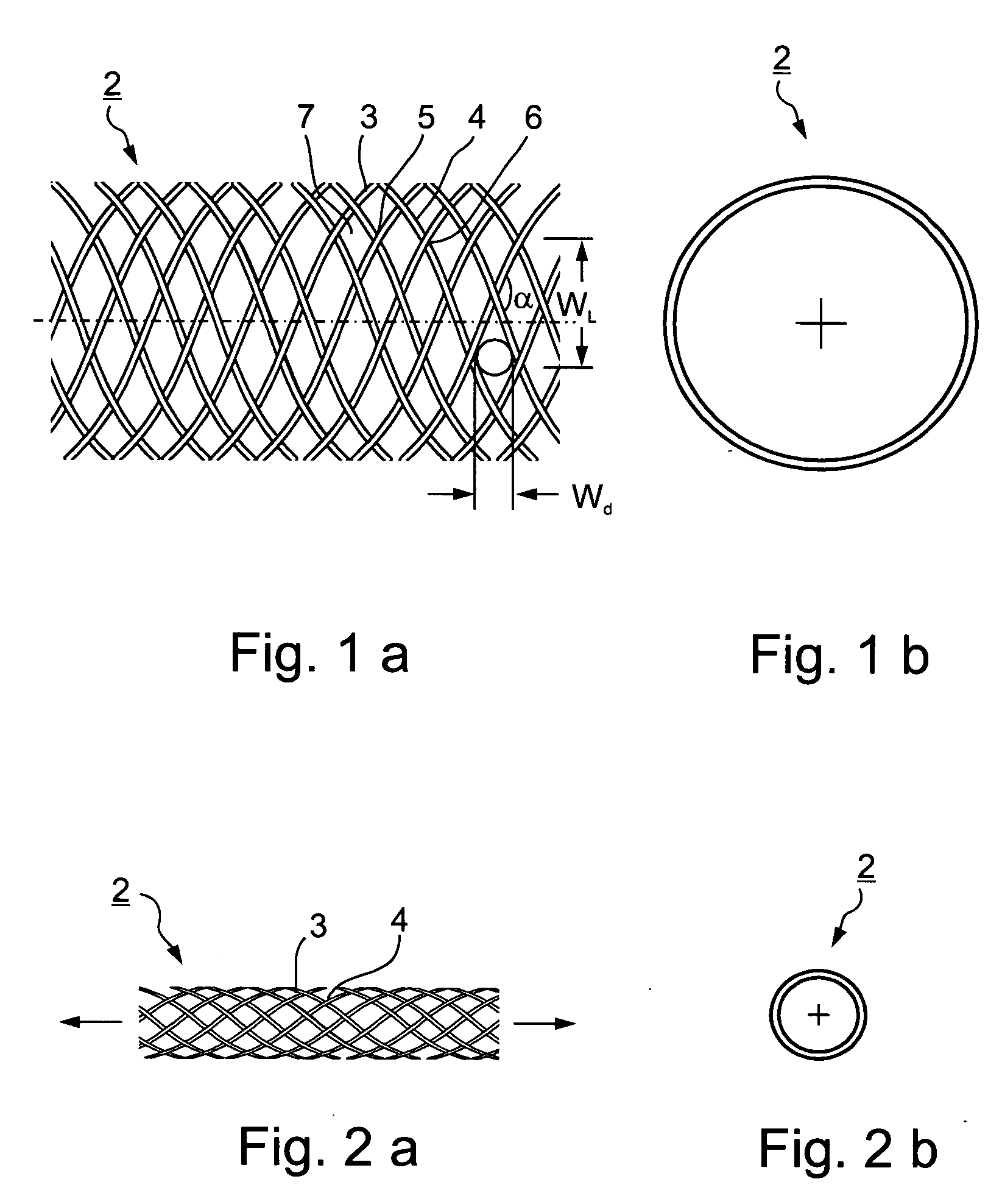
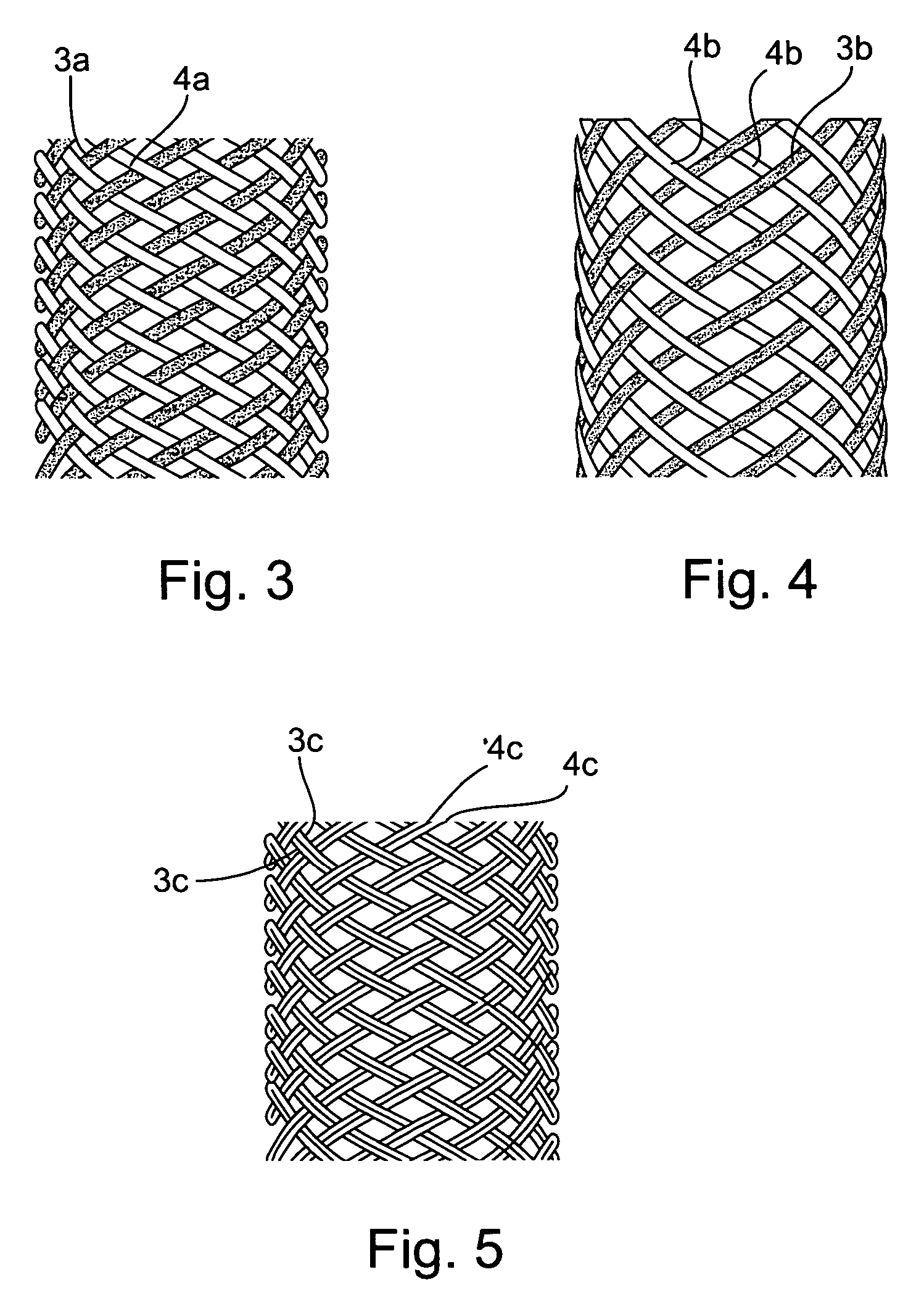
Implantable intraluminal device and method of using same in treating aneurysms
InactiveUS20050010281A1Sufficiently flexibleSufficiently pliableStentsBlood vesselsPorosityProximate
Owner:STRYKER CORP +1
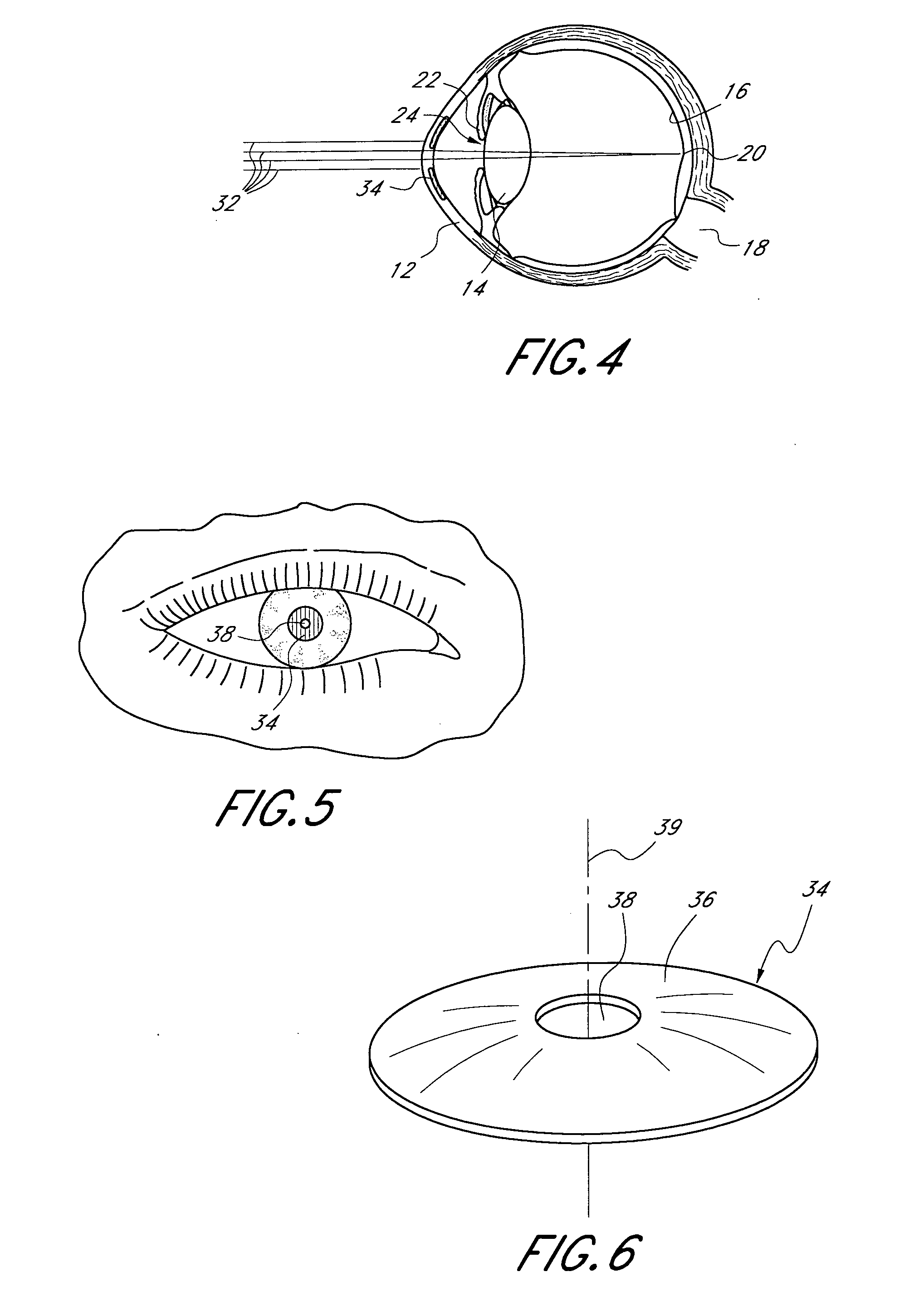
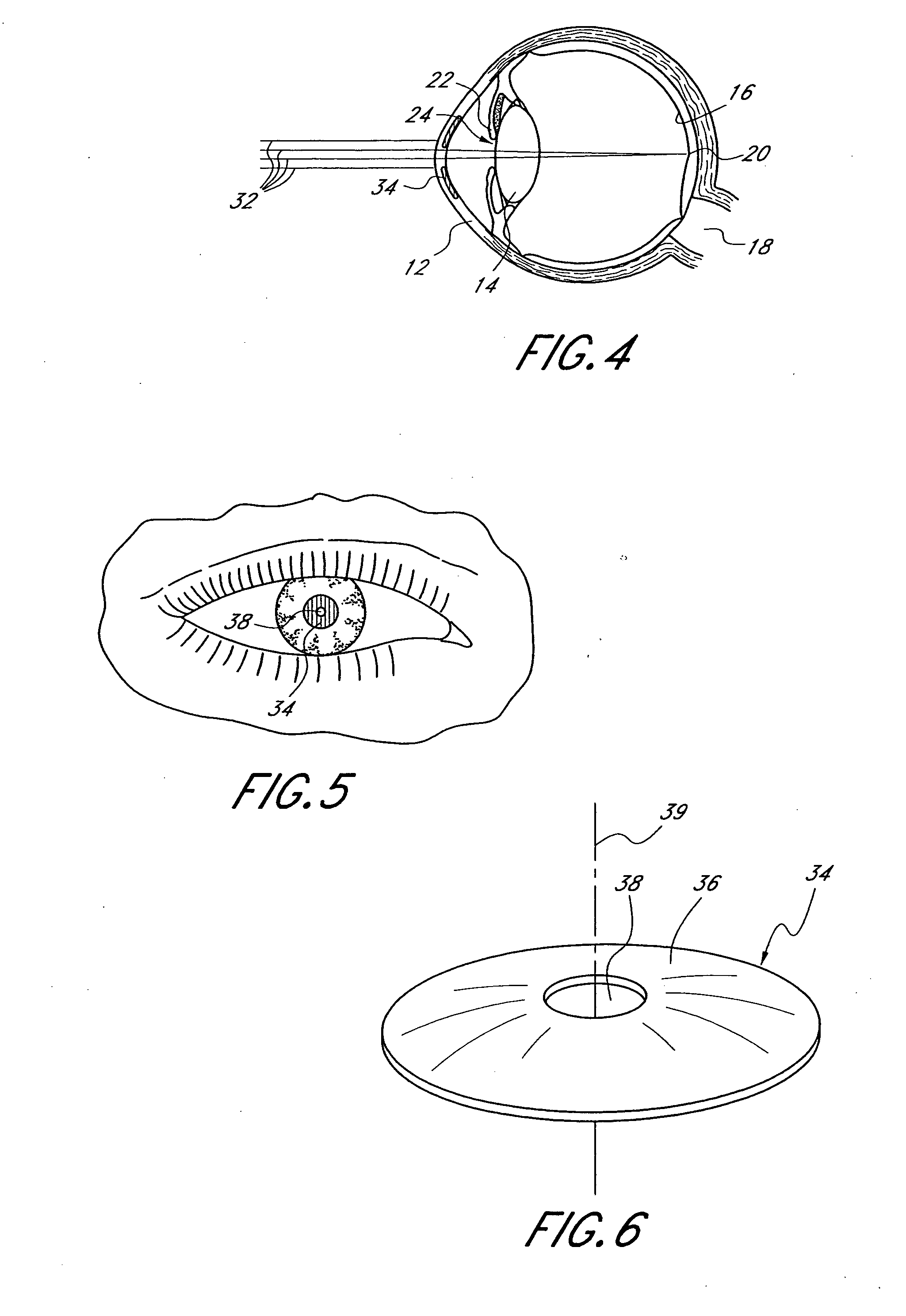
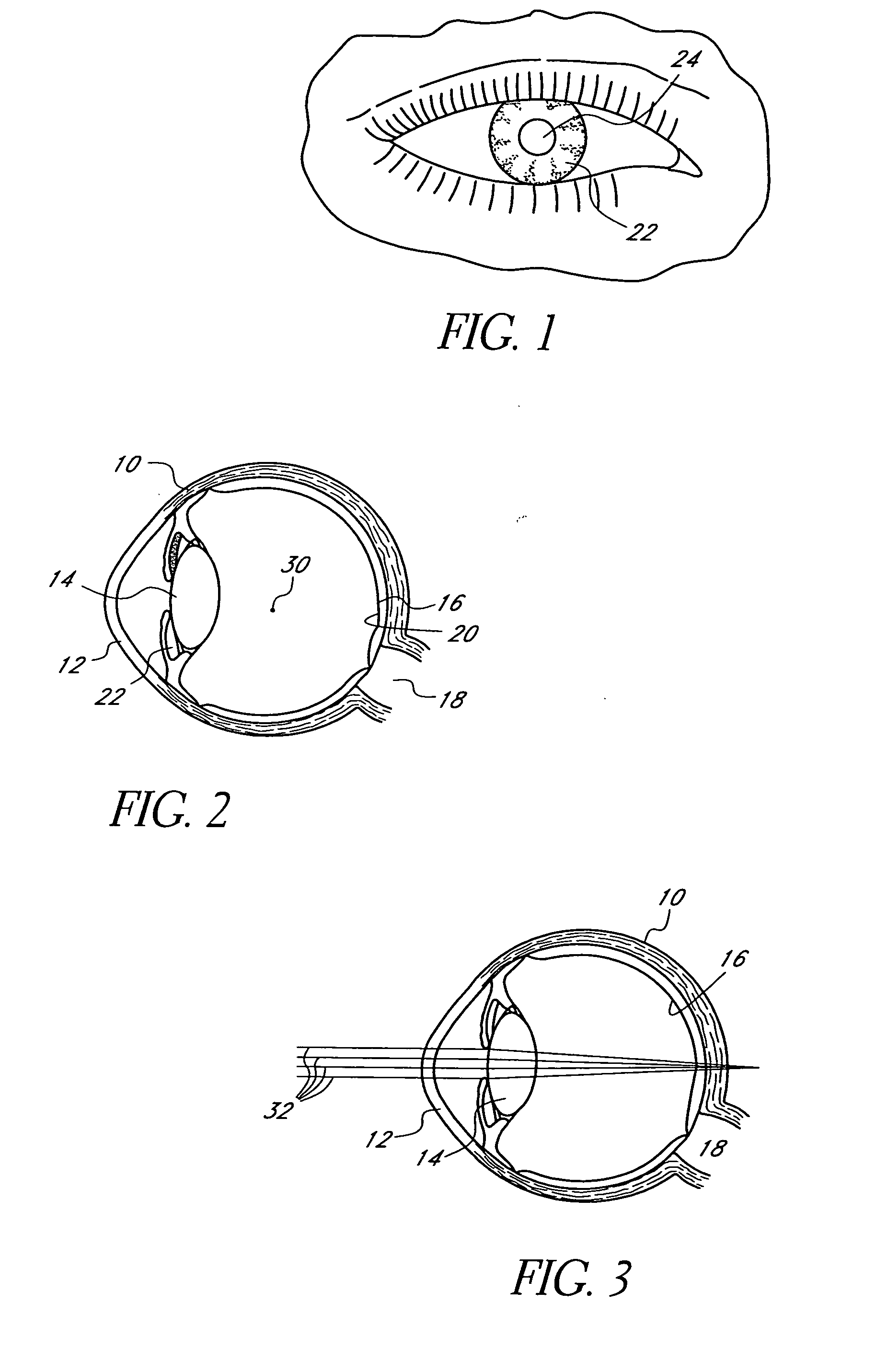
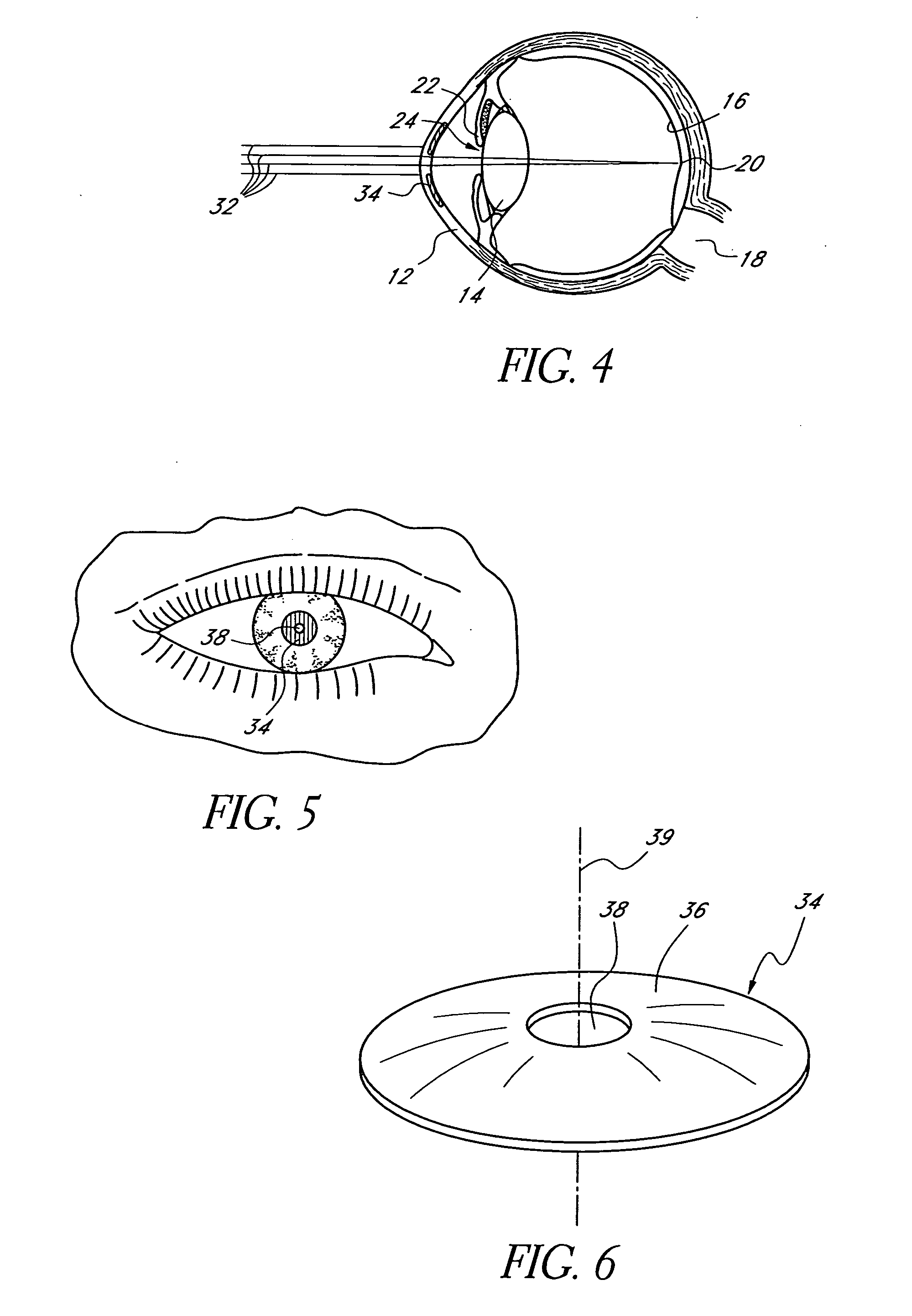
Method and apparatus for aligning a mask with the visual axis of an eye
InactiveUS20050046794A1Increase depth of focusMaintain alignmentEye diagnosticsOptometryDepth of focus
A method is provided for increasing the depth of focus of an eye of a patient. A visual axis of the eye is aligned with an instrument axis of an ophthalmic instrument. The ophthalmic instrument has an aperture through which the patient may look along the instrument axis. A first reference target is imaged on the instrument axis at a first distance with respect to the eye. A second reference target is imaged on the instrument axis with the ophthalmic instrument at a second distance with respect to the eye. The second distance is greater than the first distance. Movement is provided such that the patient's eye is in a position where the images of the first and second reference targets appear to the patient's eye to be aligned. A mask comprising a pin-hole aperture having a mask axis is aligned with the instrument axis such that the mask axis and the instrument axis are substantially collinear. The mask is applied to the eye of the patient while the alignment of the mask axis and the instrument axis is maintained. Maintaining alignment of the mask axis and the instrument axis may be facilitated by capturing an image of the eye.
Owner:ACUFOCUS
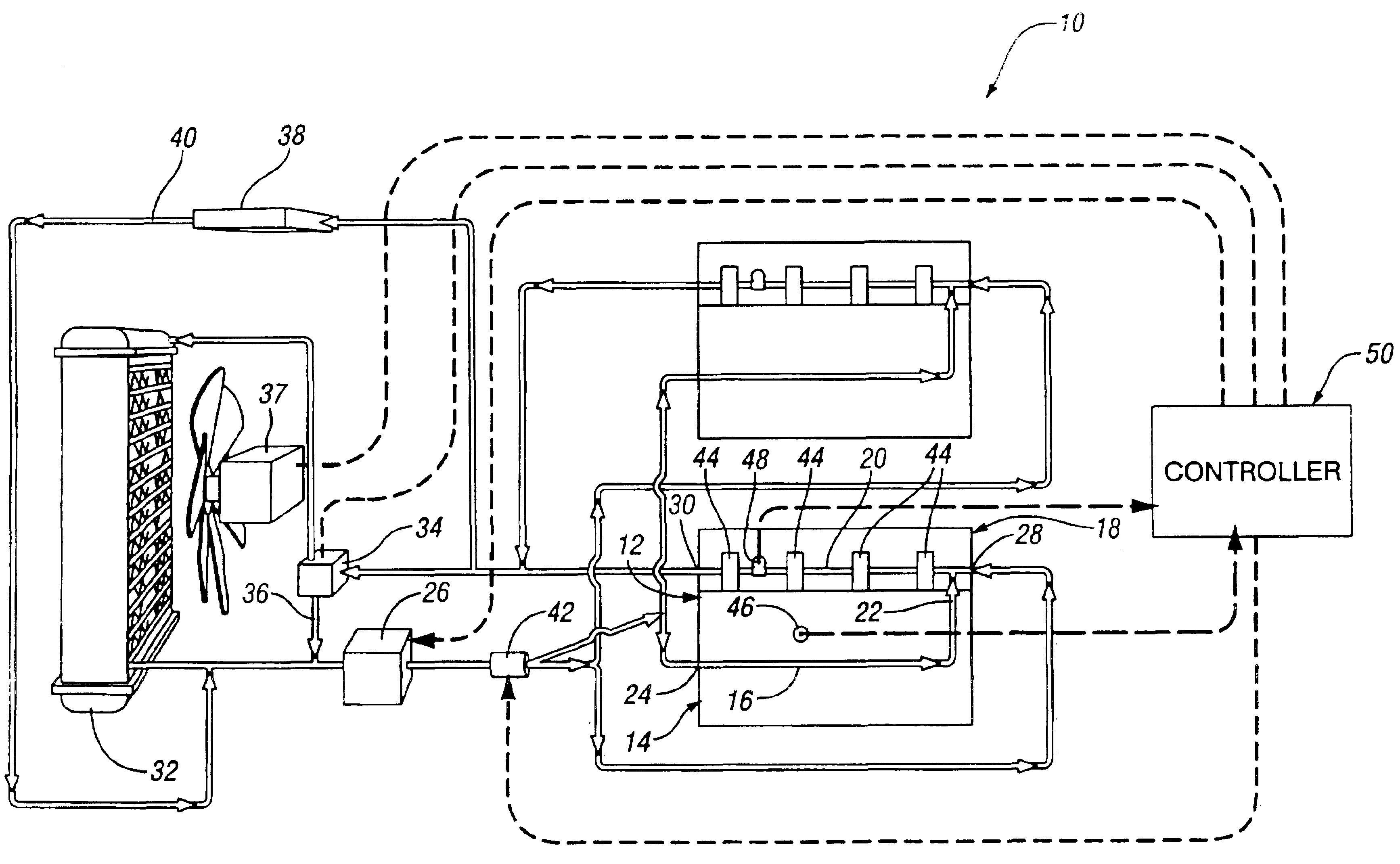
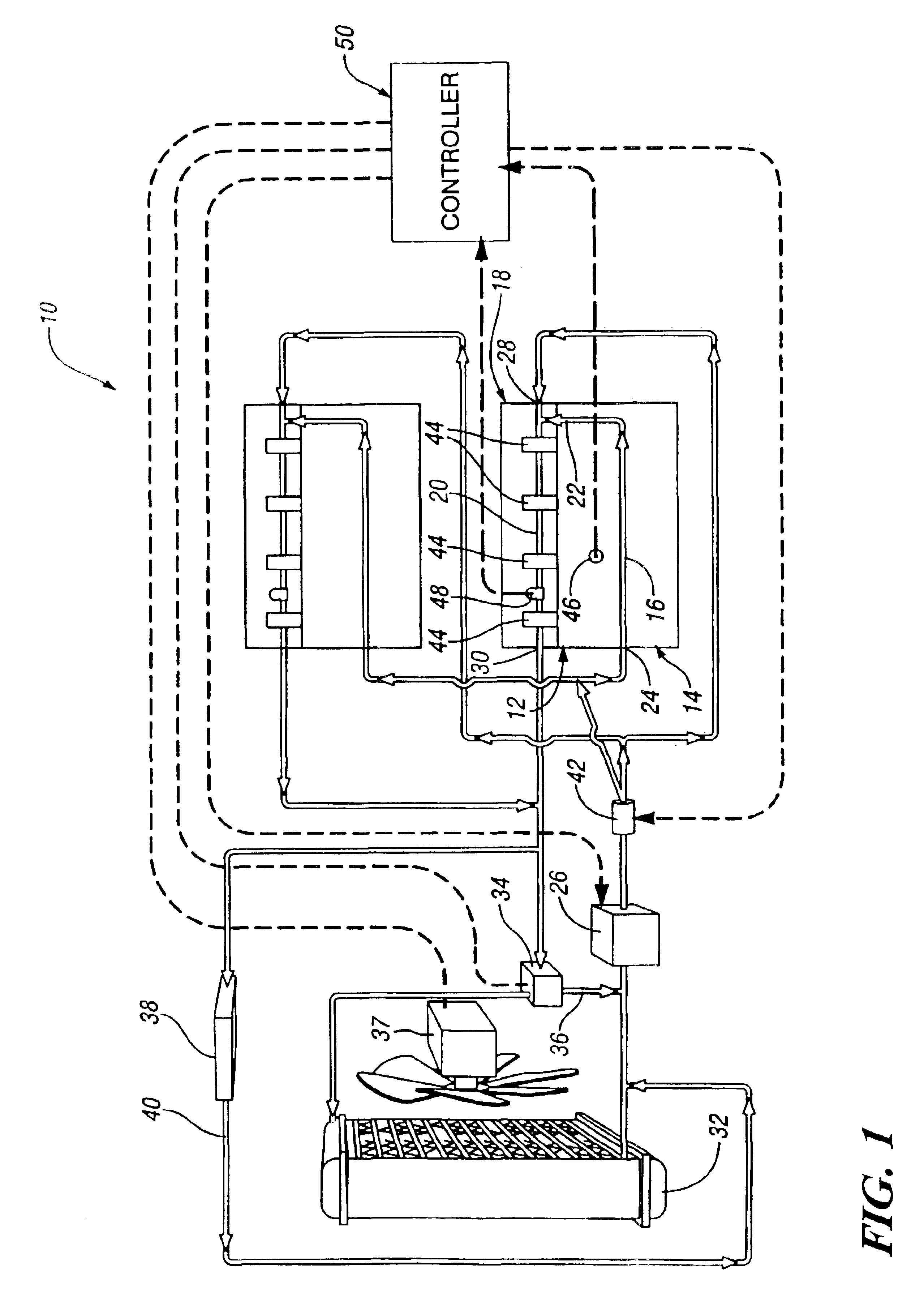
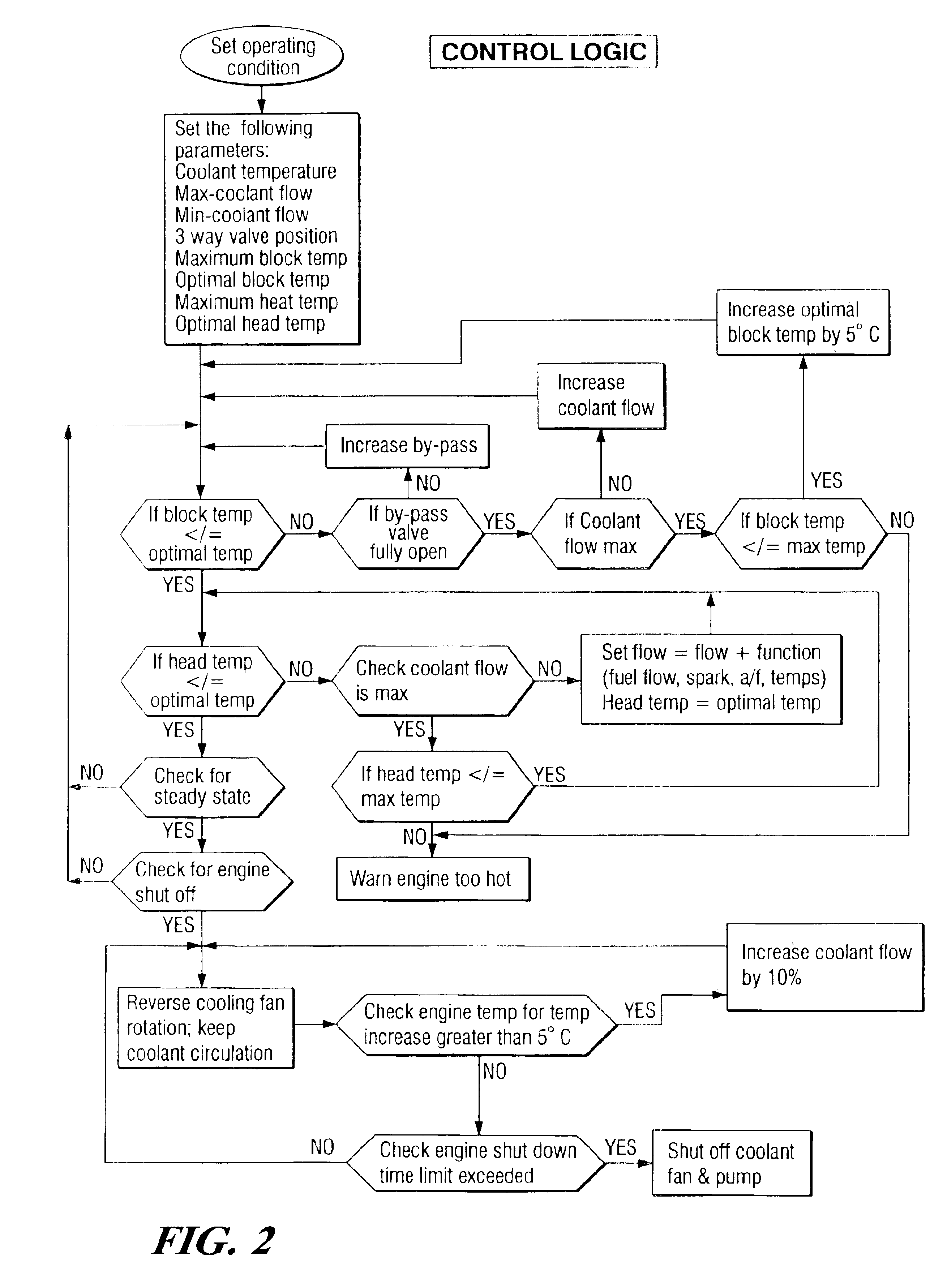
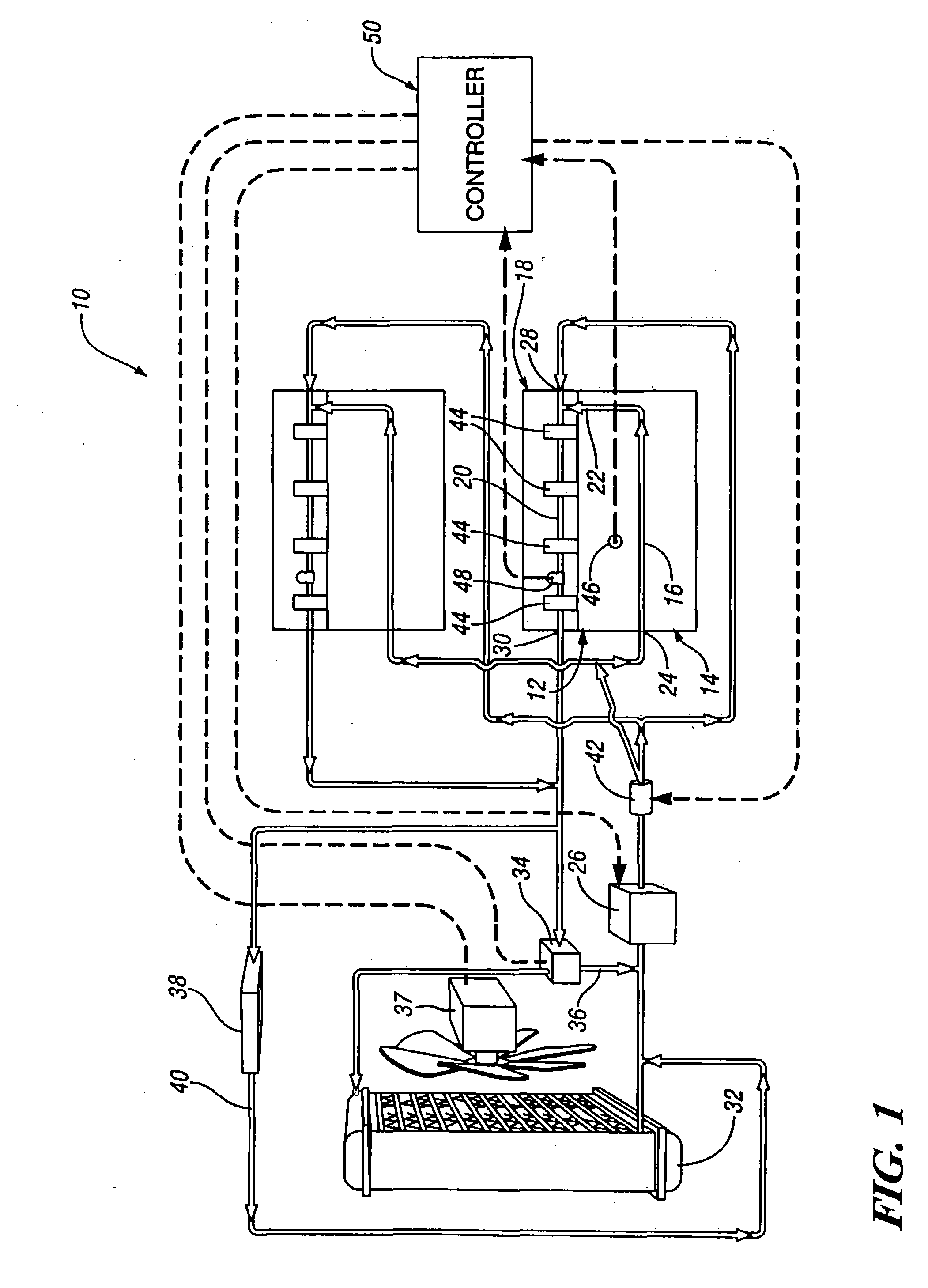
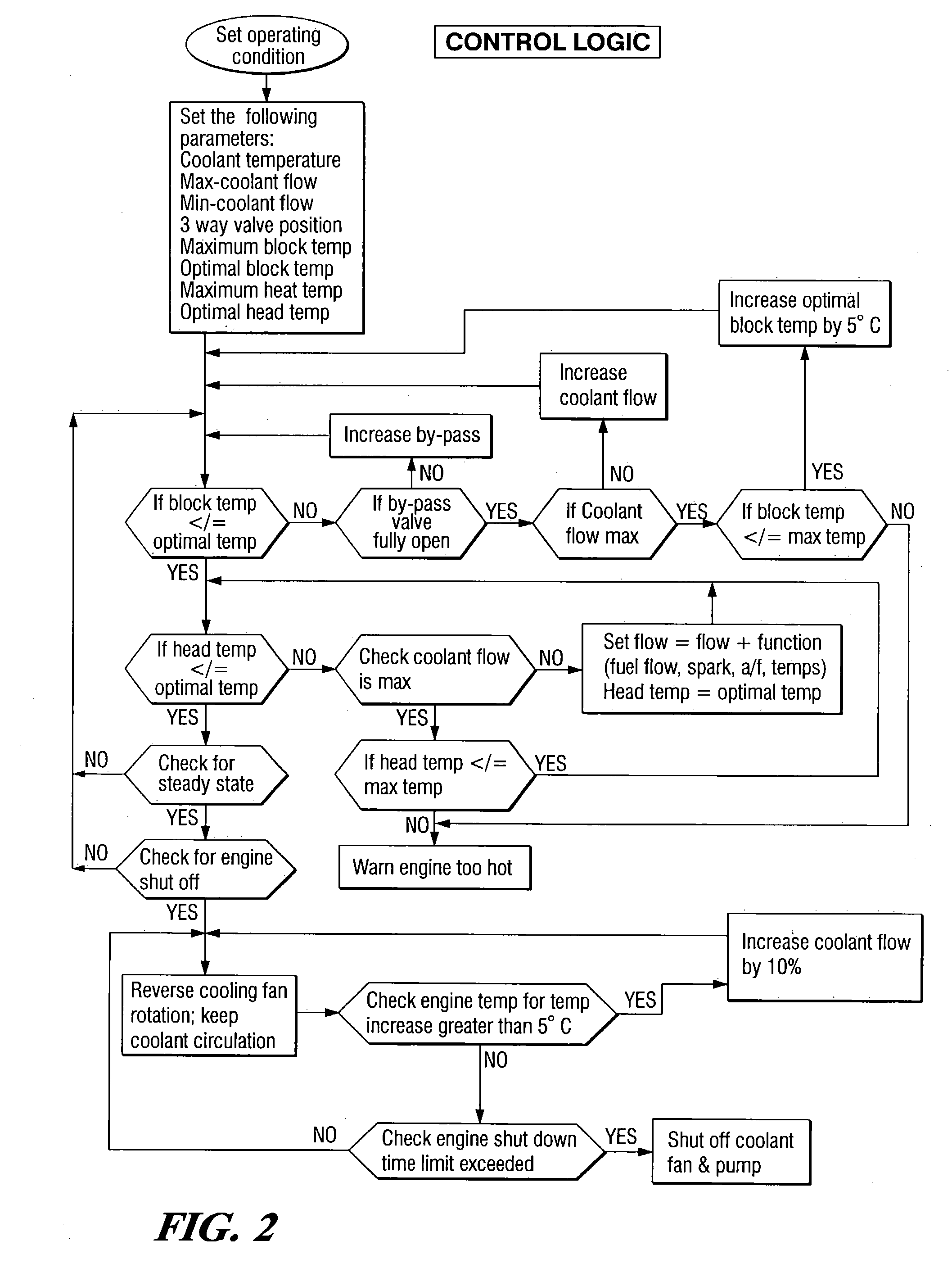
Engine cooling system
InactiveUS6955141B2Minimizes parasitic lossIncrease and decrease flow of coolantLiquid coolingCoolant flow controlCoolant flowCylinder head
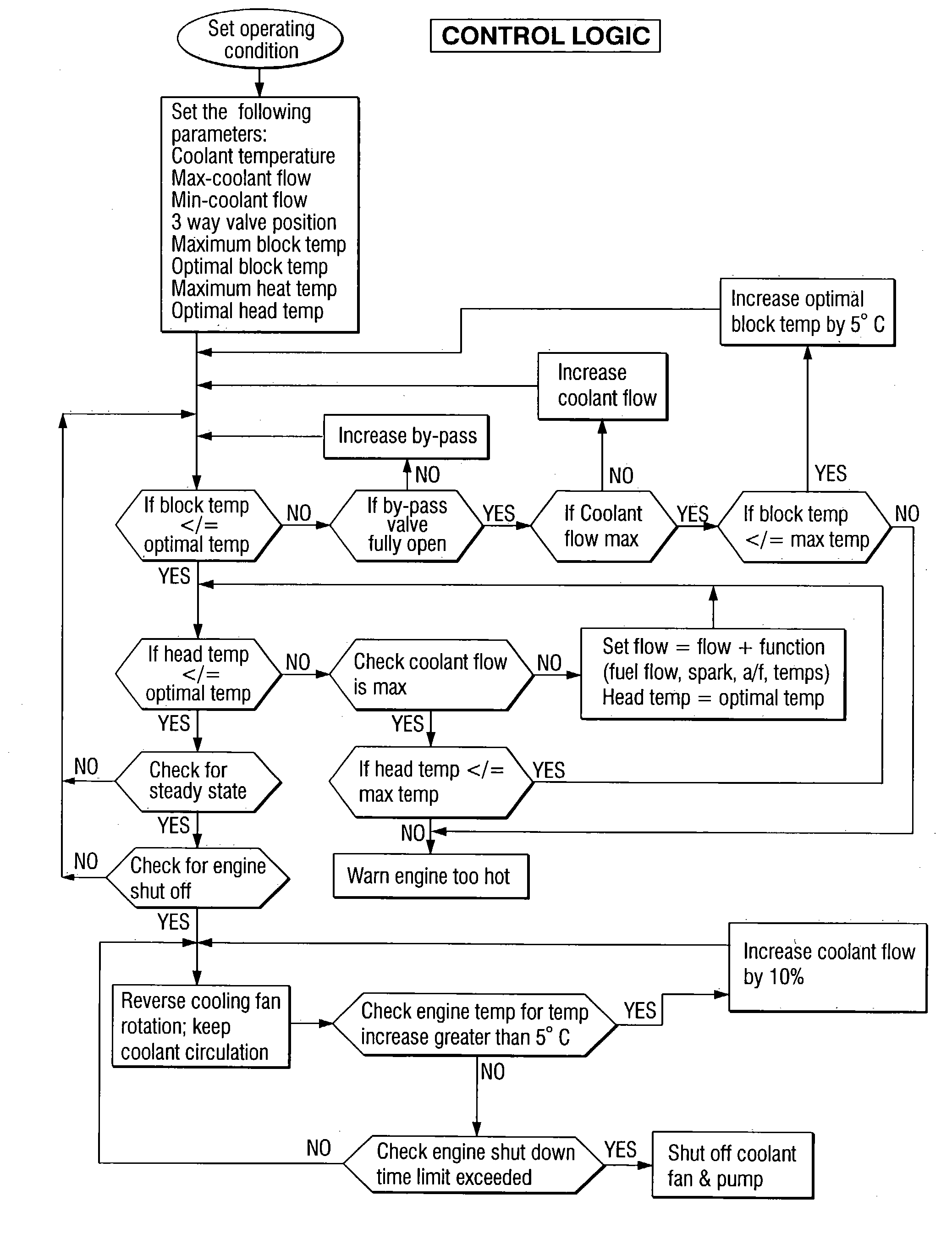
A cooling system has a diverter valve to selectively control the flow of coolant through an internal combustion engine having a cylinder block with a cooling jacket and a cylinder head mounted on the block with a cooling jacket. A controller, responsive to the temperature of the block and the head, controls the diverter valve and a water pump to provide adequate coolant flow through the head and the block as needed to maintain optimal operating temperatures. After the engine is shut off, the controller continues to operate the water pump and a cooling fan to continue to cool the engine for a period of time.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
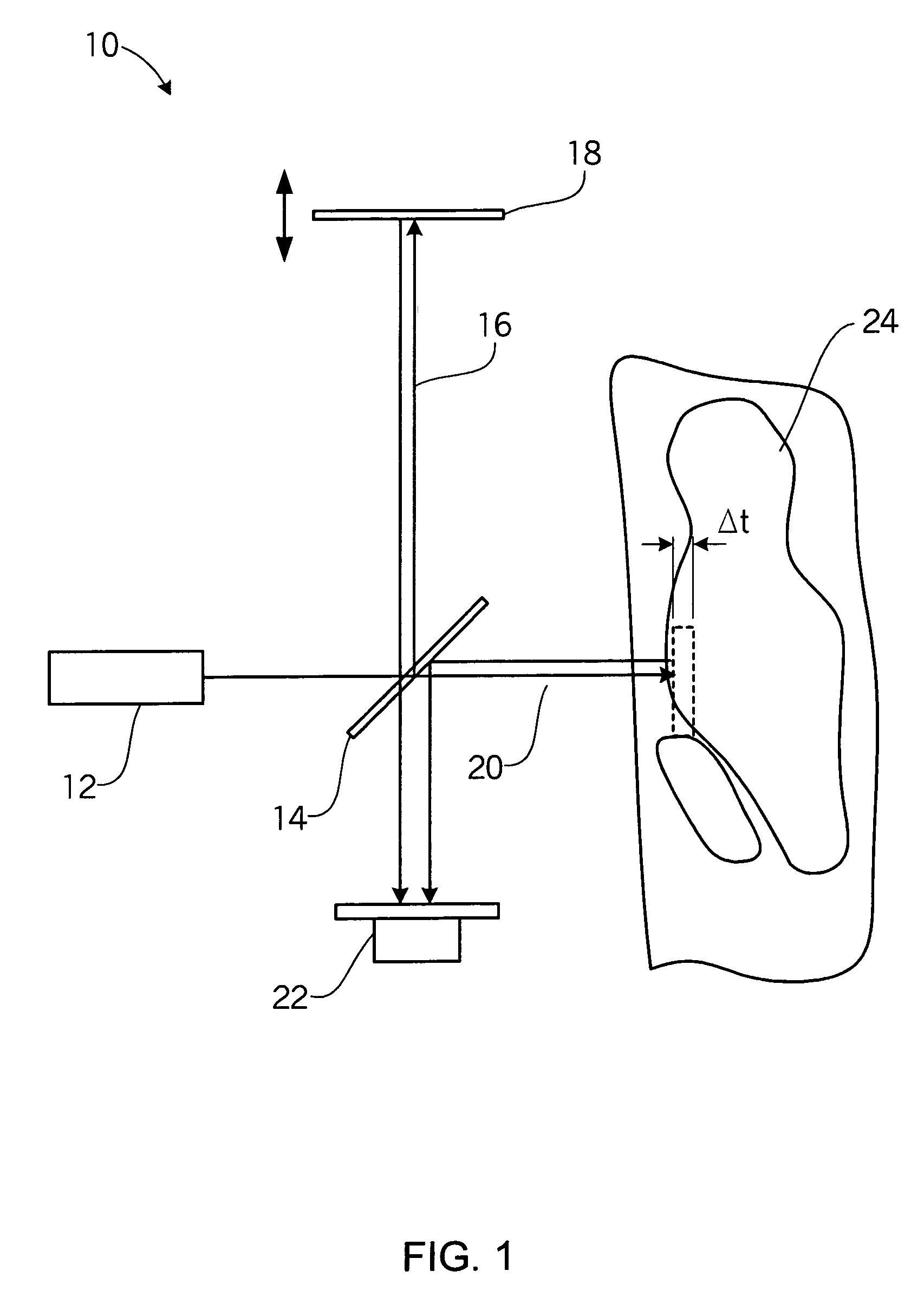
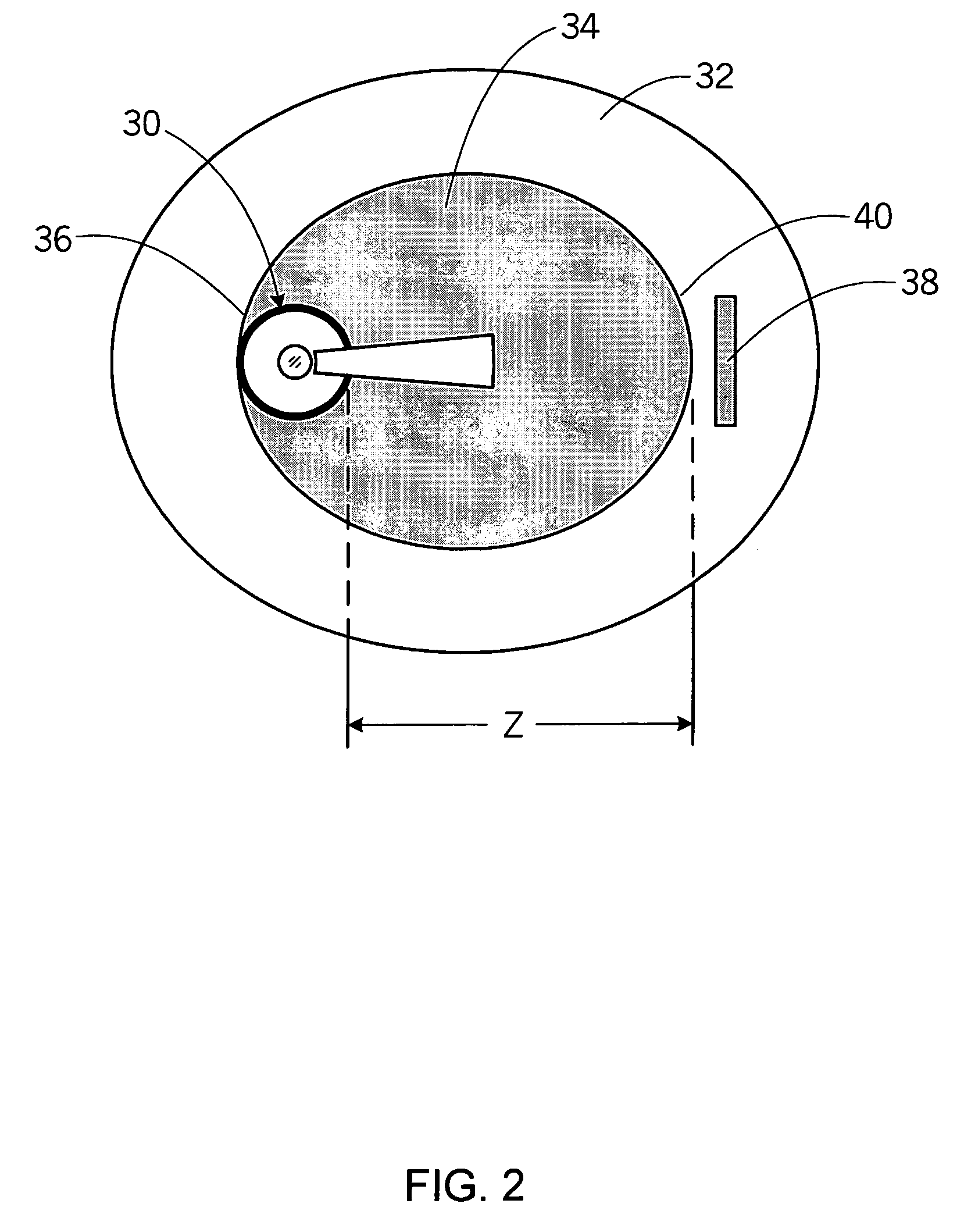
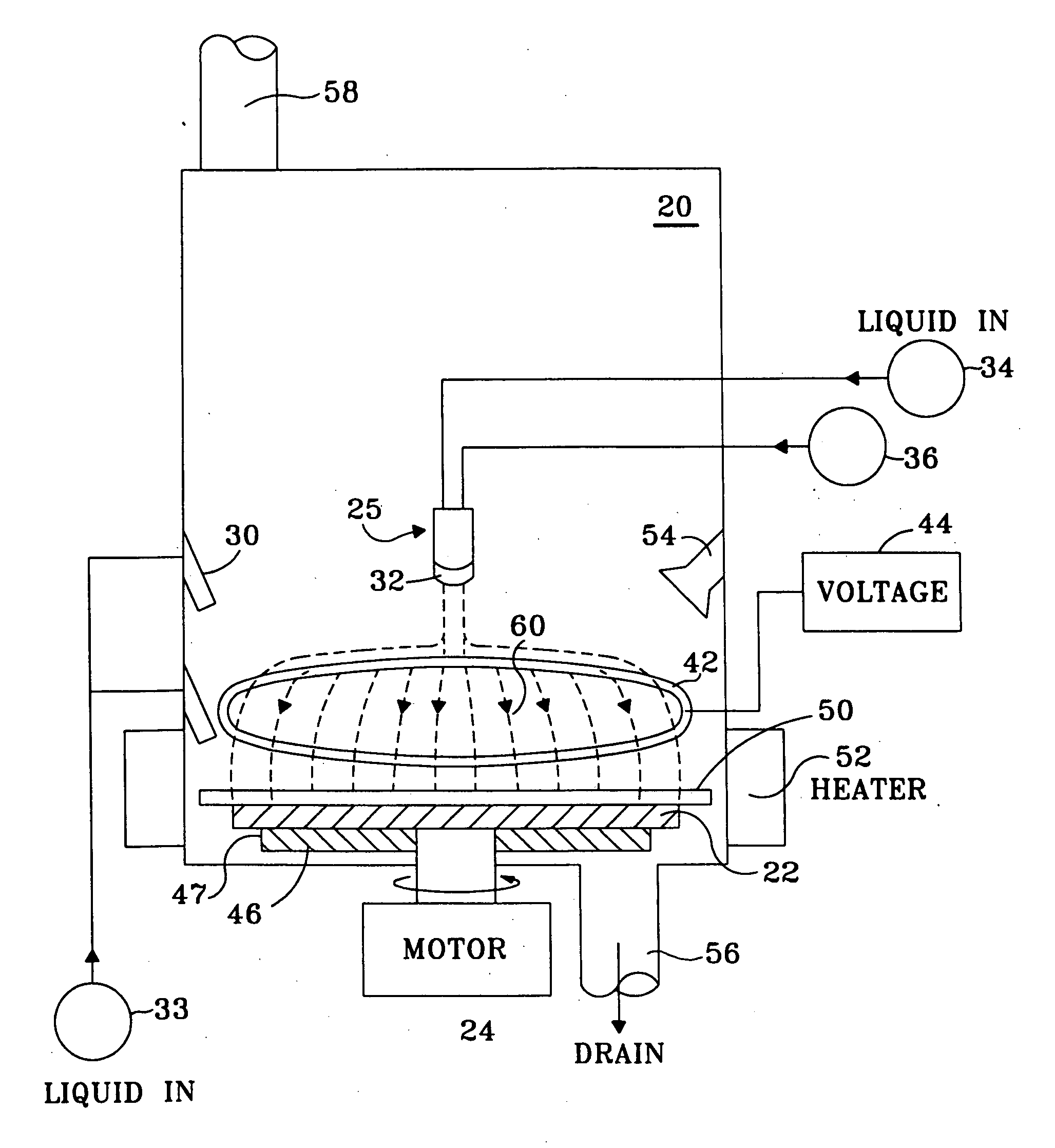
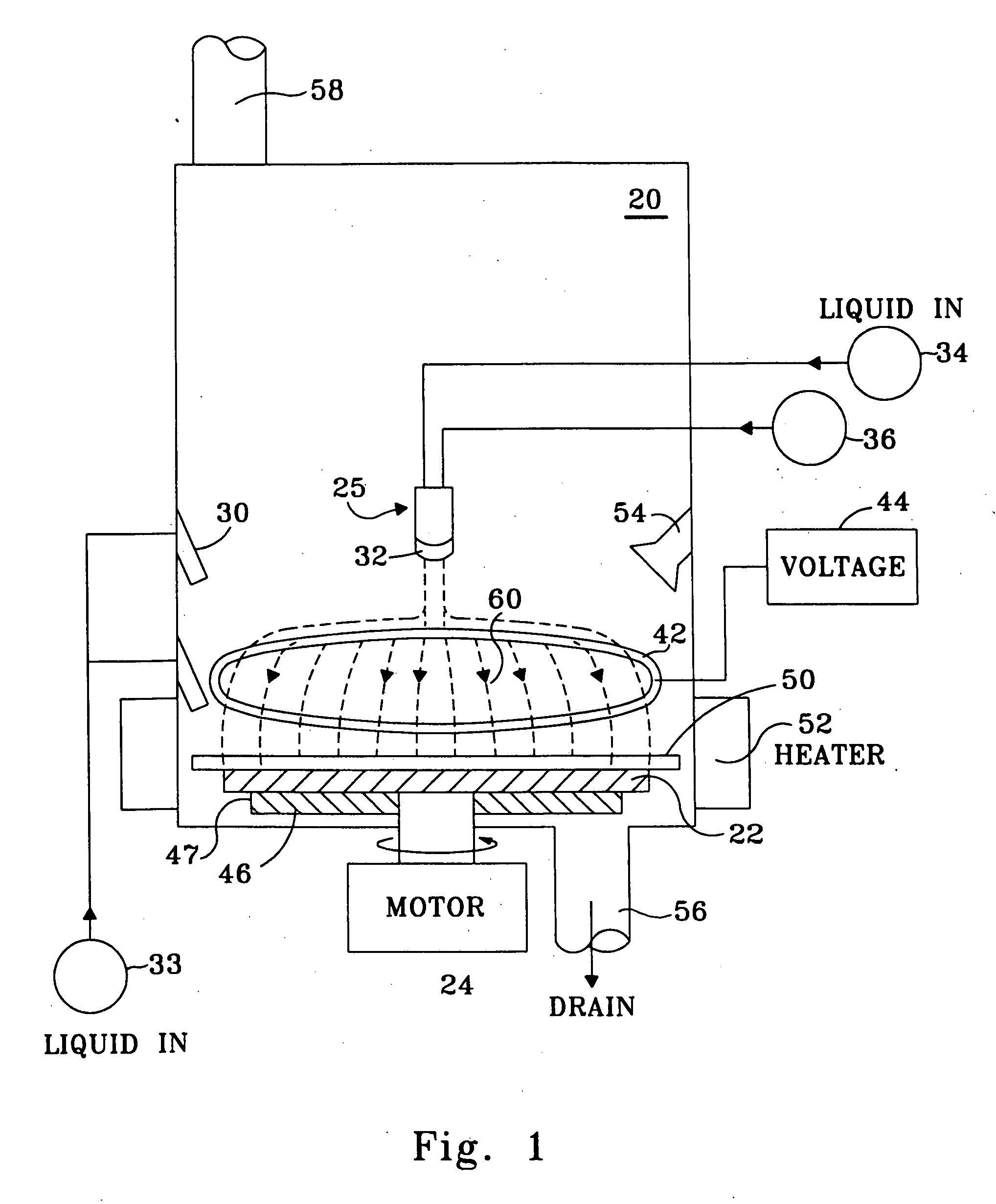
Device for tissue characterization
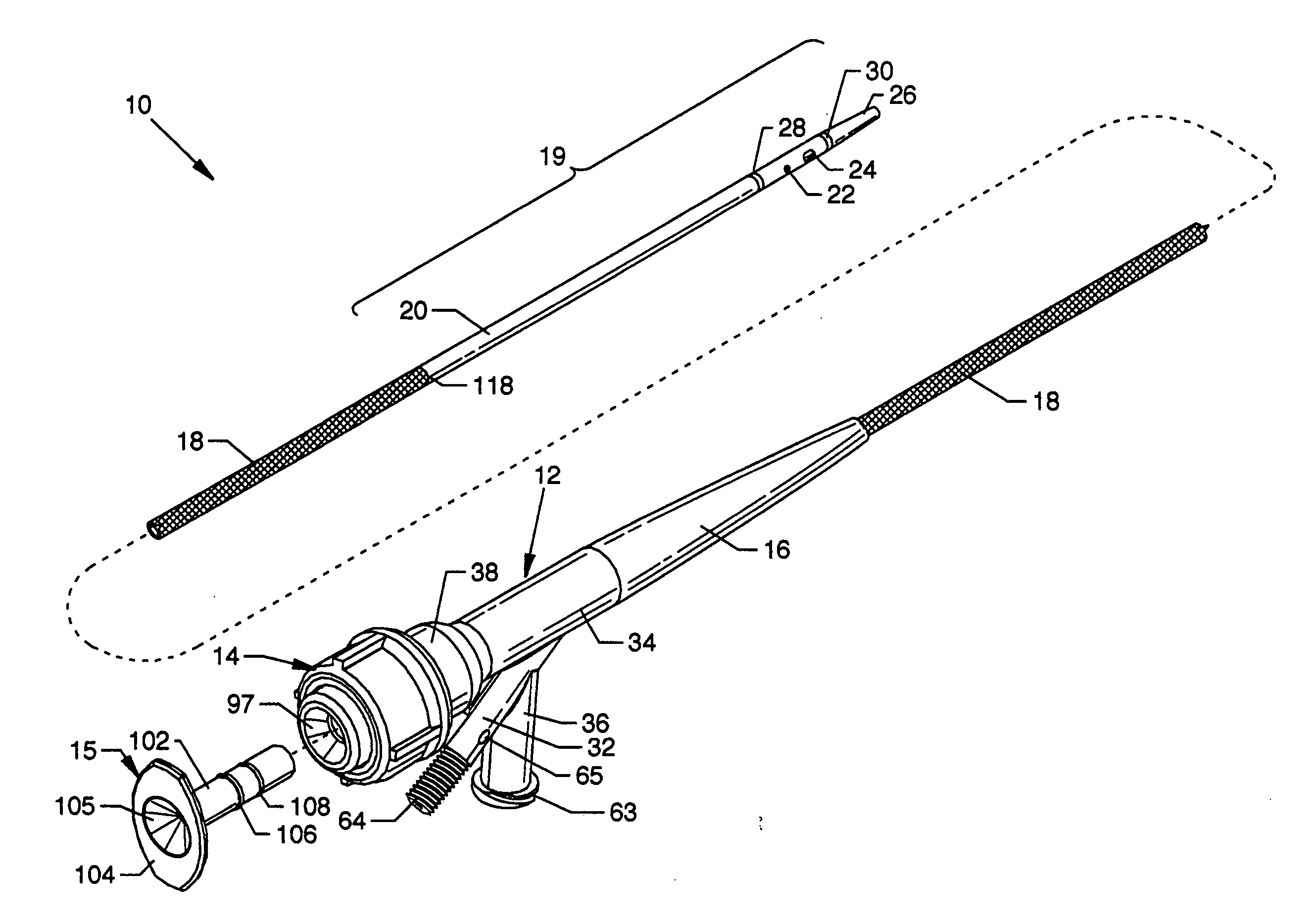
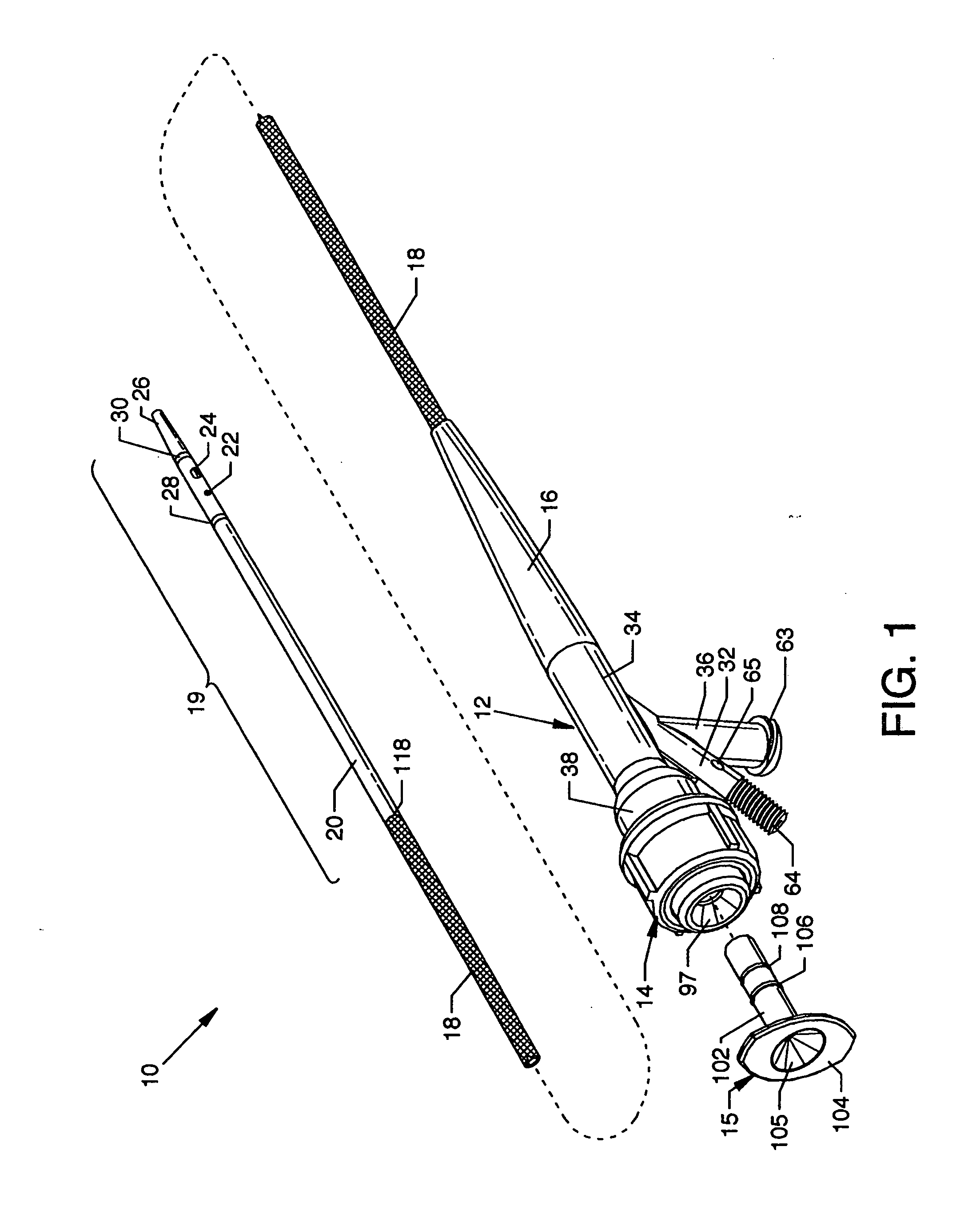
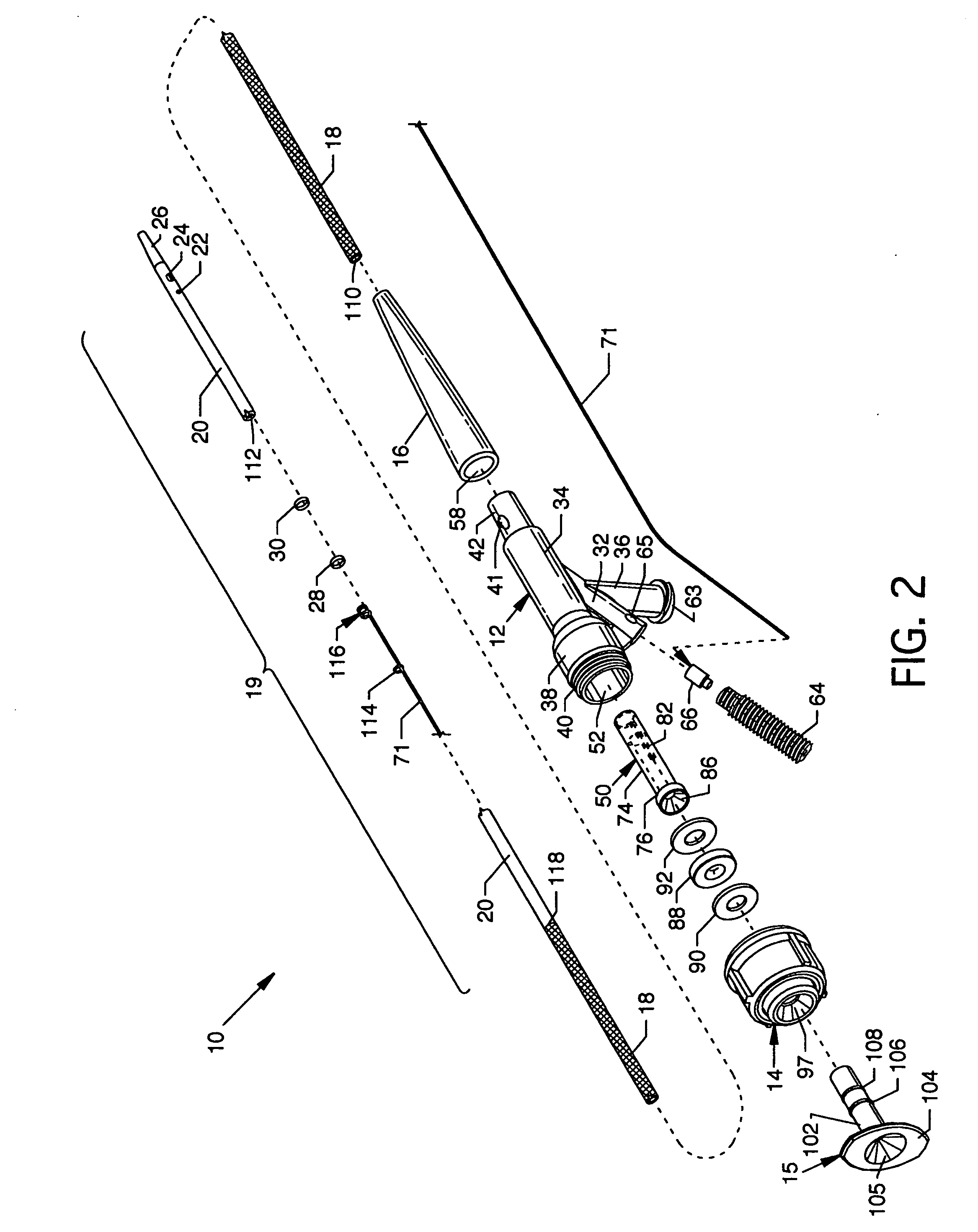
InactiveUS7242832B2Keep the flowMaintain normal flowPhase-affecting property measurementsSurgeryDistal portionTissue characterization
Owner:MEDEIKON
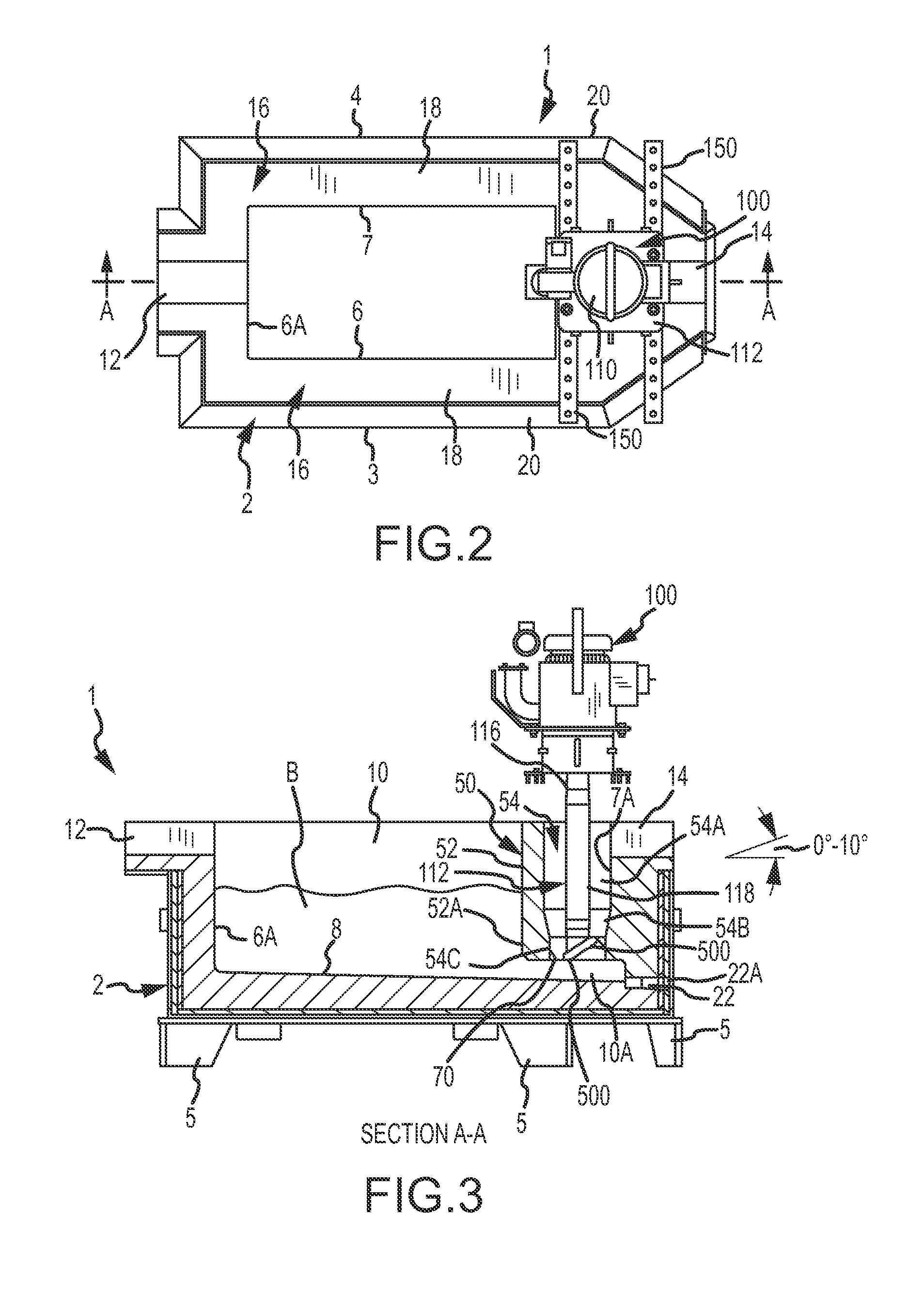
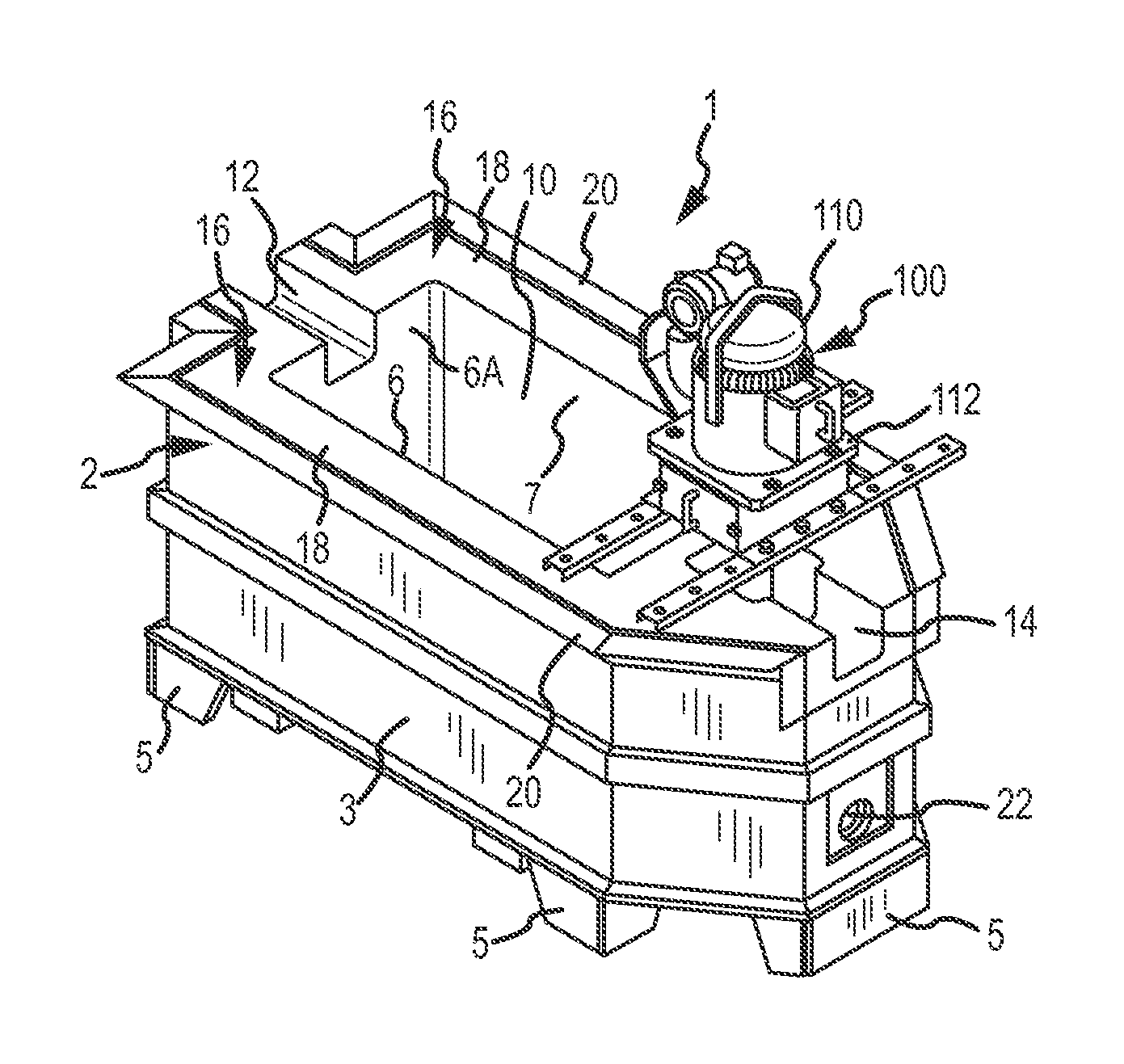
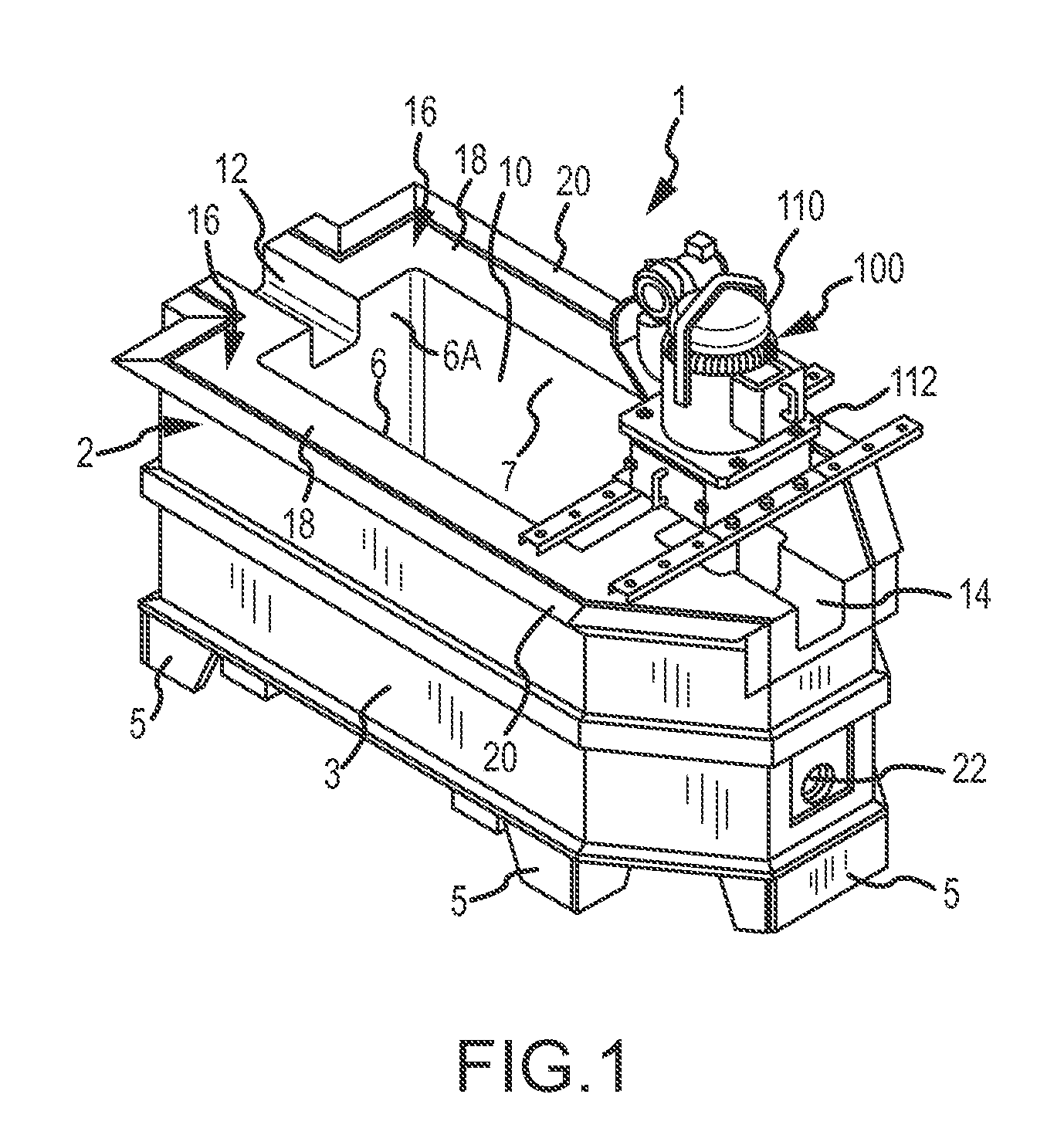
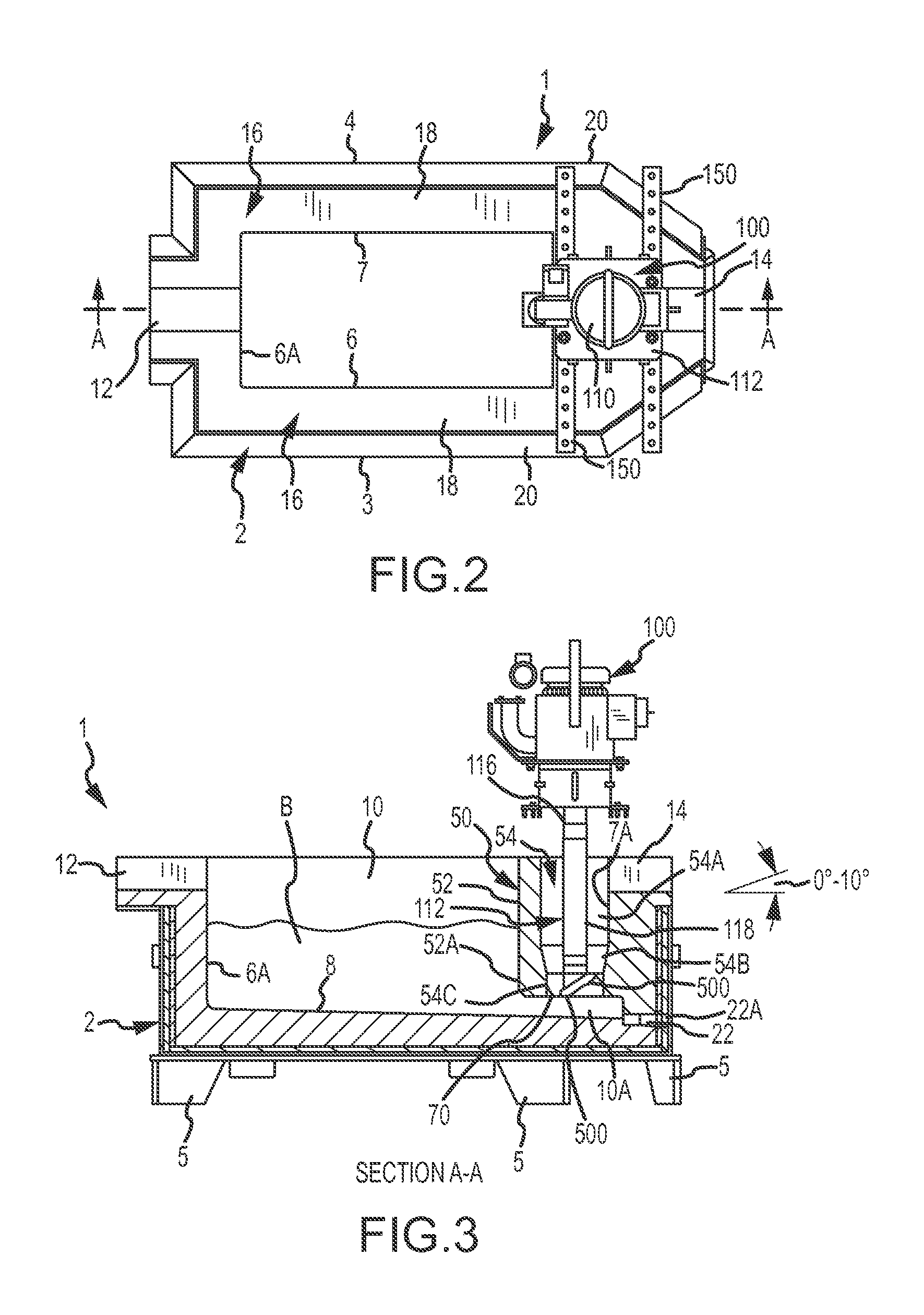
Molten metal transfer and degassing system
ActiveUS20130306687A1Keep the flowReduce the possibilityMelt-holding vesselsMolten metal pouring equipmentsEngineeringMolten metal
Aspects of the invention include a transfer chamber constructed inside of or next to a vessel used to retain and degas molten metal. The transfer chamber is in fluid communication with the vessel so molten metal from the vessel is pulled through the vessel by the pump as it is degassed. This helps maintain a generally constant flow of molten metal through the degassing vessel. Other aspects relate to a system and method for efficiently performing maintenance on components positioned in a vessel.
Owner:MOLTEN METAL EQUIP INNOVIATIONS LLC
System and method for component maintenance
InactiveUS20140265068A1Keep the flowReduce the possibilityCharge manipulationManufacturing convertersMarine engineeringMolten metal
Aspects of the invention include a transfer chamber constructed inside of or next to a vessel used to retain and degas molten metal. The transfer chamber is in fluid communication with the vessel so molten metal from the vessel is pulled through the vessel by the pump as it is degassed. This helps maintain a generally constant flow of molten metal through the degassing vessel. Other aspects relate to a system and method for efficiently performing maintenance on components positioned in a vessel.
Owner:MOLTEN METAL EQUIP INNOVIATIONS LLC
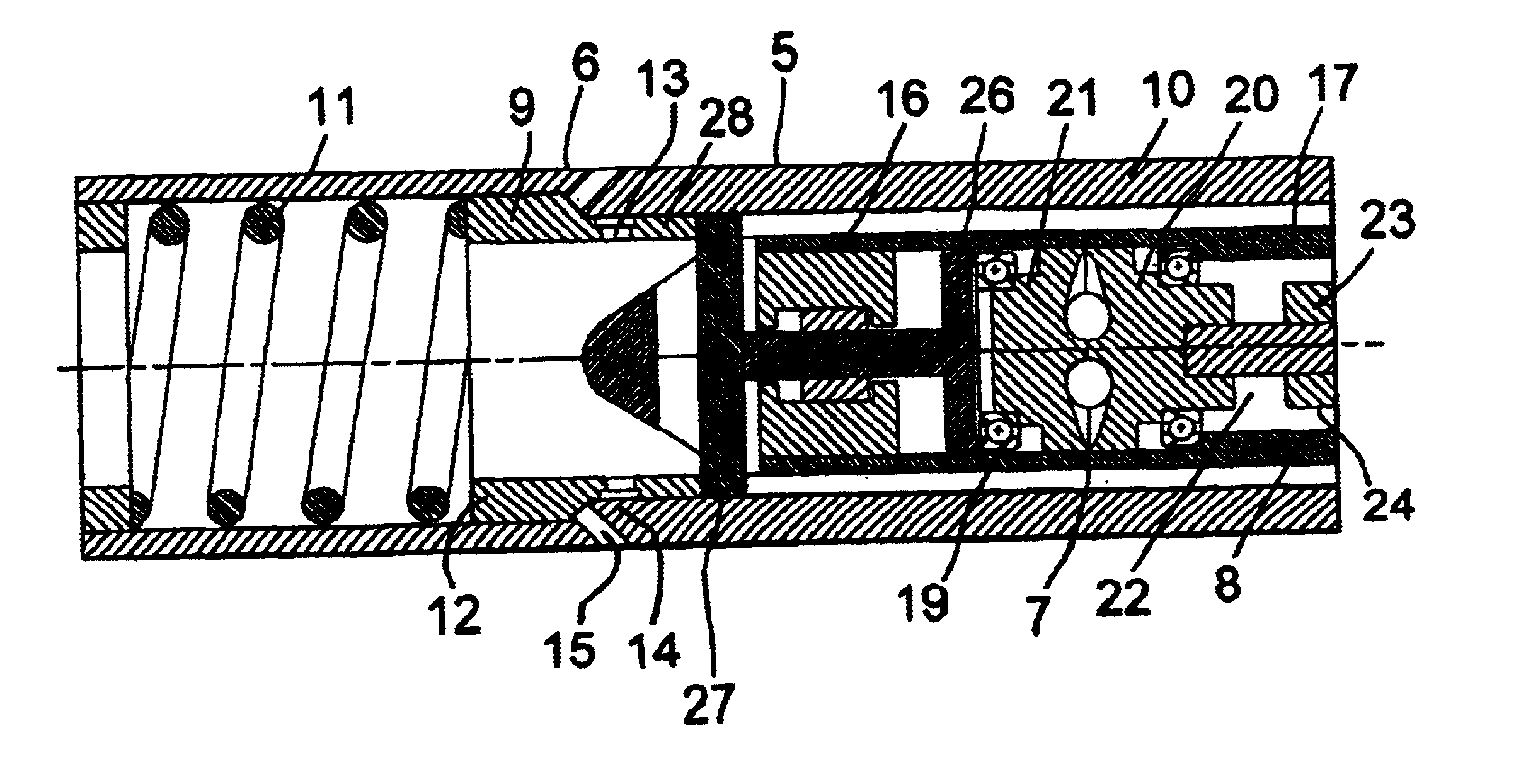
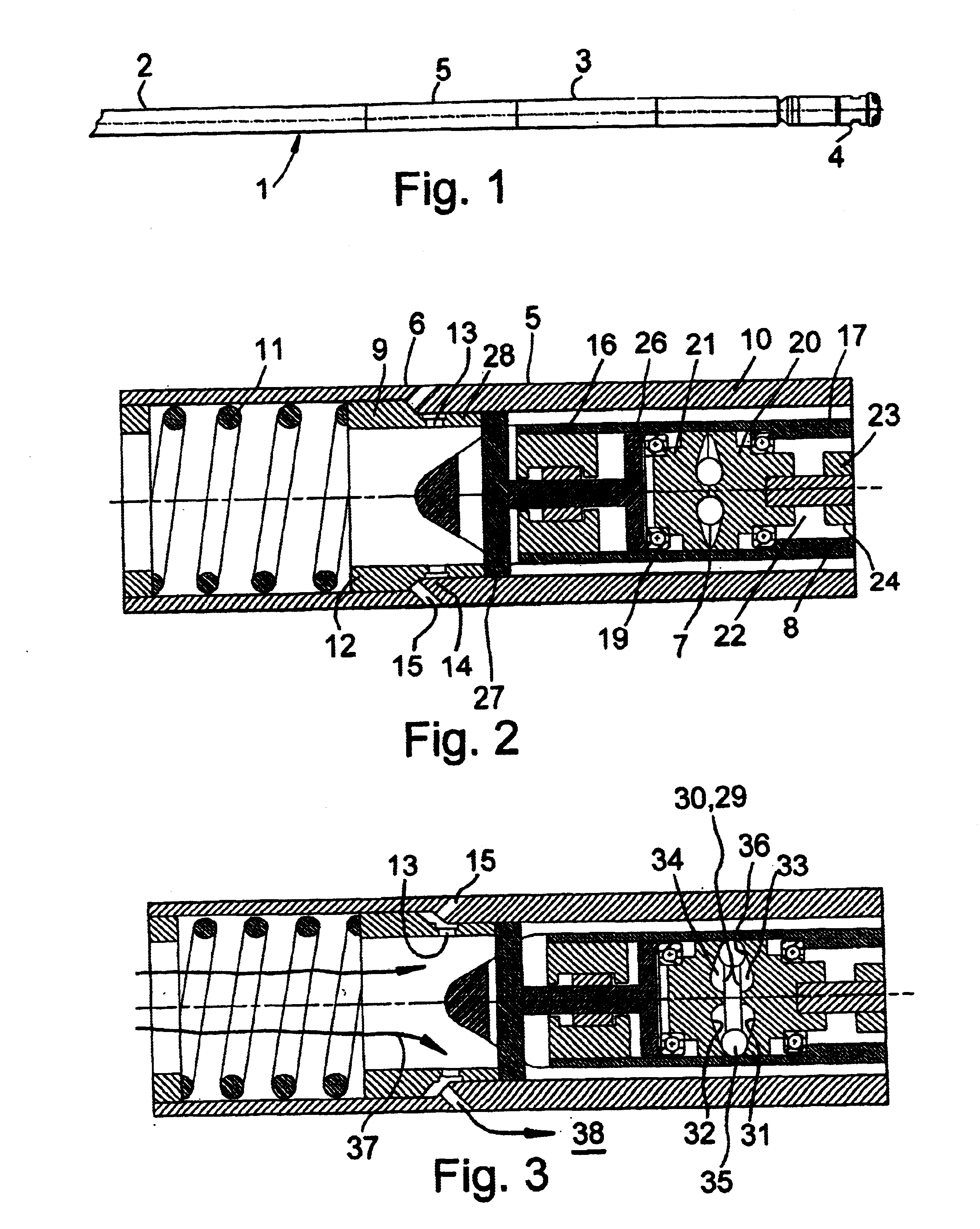
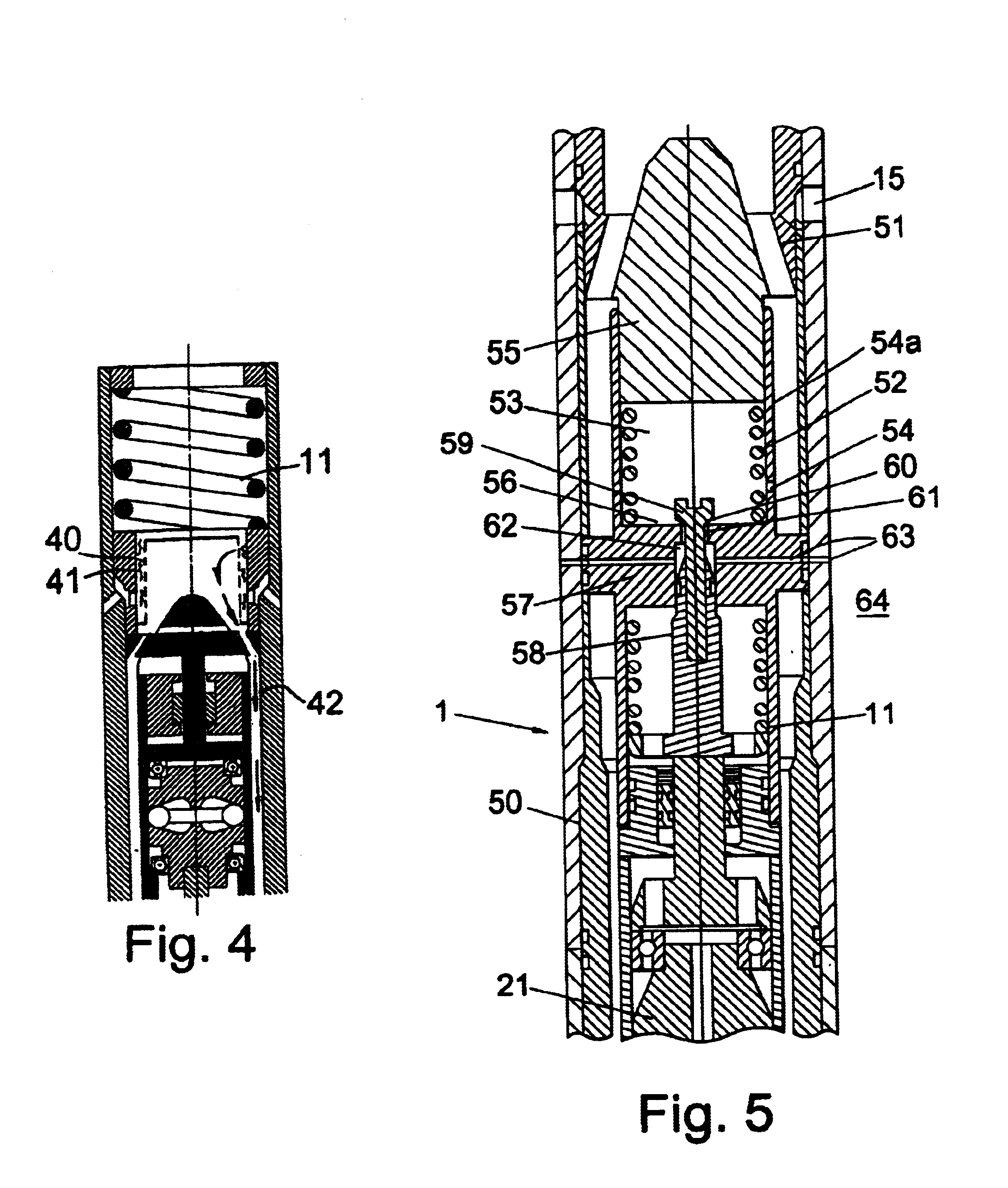
Speed governor
InactiveUS6854953B2Convenient and efficient mannerPrevent speedingWind motor controlServomotorsActuatorControl valves
The present invention provides a speed governor (5) suitable for use in a fluid driven down-hole tool (3). The speed governor comprises an actuator (7) operatively coupled to a motive fluid flow control valve (6). The actuator is and arranged so as to be activatable, directly or indirectly, in response to the running speed of the tool (3), for opening of the control valve (6) with increasing rotational speed of the motor (3) above a predetermined speed limit thereby to limit the rotational speed of the downhole tool (3).
Owner:ROTECH GROUP
Mask configured to maintain nutrient transport without producing visible diffraction patterns
InactiveUS20060079959A1Increase depth of focusEliminate DiffractionSpectales/gogglesSenses disorderAnterior surfaceCorneal layer
A mask configured to be implanted in a cornea of a patient to increase the depth of focus of the patient includes an anterior surface, a posterior surface, and a plurality of holes. The anterior surface is configured to reside adjacent a first corneal layer. The posterior surface is configured to reside adjacent a second corneal layer. The plurality of holes extends at least partially between the anterior surface and the posterior surface. The holes of the plurality of holes are configured to substantially eliminate visible diffraction patterns.
Owner:CHRISTIE BRUCE A +2
Endoscope and optical fiber assembly
ActiveUS20070270788A1Restricts lateral movementKeep the flowEndoscopesSurgical instrument detailsFiberFiber coupler
An endoscope for an optical fiber provides for inflow and outflow of irrigant. A telescope is included having a field of view directed into a working region. The endoscope defines a “hooded region” with an extended, blunt tip. The optical fiber fits within the endoscope has a side or end firing tip with an emission surface. A guide element is adapted to movably support the optical fiber in a position spaced away from the working region, and limit lateral movement of the tip without preventing longitudinal and rotational movement. An irrigant flow arrangement operates to direct inflowing irrigant over the emission surface of the tip. The fiber is assembled with a fiber coupler, a handle, a fiber port cap, and a travel limiter fixed to the fiber at a predetermined distance from the tip. The travel limiter cooperates with the endoscope and the fiber port cap to limit longitudinal and rotational movement of the fiber.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Method and apparatus for aligning a mask with the visual axis of an eye
InactiveUS20060271026A1Increase depth of focusMaintain alignmentSurgical instrument detailsEye diagnosticsOptometryDepth of focus
A method is provided for increasing the depth of focus of an eye of a patient. A visual axis of the eye is aligned with an instrument axis of an ophthalmic instrument. The ophthalmic instrument has an aperture through which the patient may look along the instrument axis. A first reference target is imaged on the instrument axis at a first distance with respect to the eye. A second reference target is imaged on the instrument axis with the ophthalmic instrument at a second distance with respect to the eye. The second distance is greater than the first distance. Movement is provided such that the patient's eye is in a position where the images of the first and second reference targets appear to the patient's eye to be aligned. A mask comprising a pin-hole aperture having a mask axis is aligned with the instrument axis such that the mask axis and the instrument axis are substantially collinear. The mask is applied to the eye of the patient while the alignment of the mask axis and the instrument axis is maintained. Maintaining alignment of the mask axis and the instrument axis may be facilitated by capturing an image of the eye.
Owner:SILVESTRINI THOMAS A +3
Soft breastshield
Owner:MEDELA HLDG AG
Engine cooling system
ActiveUS20050028756A1Minimizes parasitic lossIncrease and decrease flow of coolantLiquid coolingCoolant flow controlTemperature controlCylinder head
A cooling system has a diverter valve to selectively control the flow of coolant through an internal combustion engine having a cylinder block with a cooling jacket and a cylinder head mounted on the block with a cooling jacket. A controller, responsive to the temperature of the block and the head, controls the diverter valve and a water pump to provide adequate coolant flow through the head and the block as needed to maintain optimal operating temperatures. After the engine is shut off, the controller continues to operate the water pump and a cooling fan to continue to cool the engine for a period of time.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Grounded Pressure Cooling
ActiveUS20080234788A1Prevent perspirationRelieve stressSurgical instruments for heatingFootwearCore temperatureBlood vessel
Owner:VASPER SYST
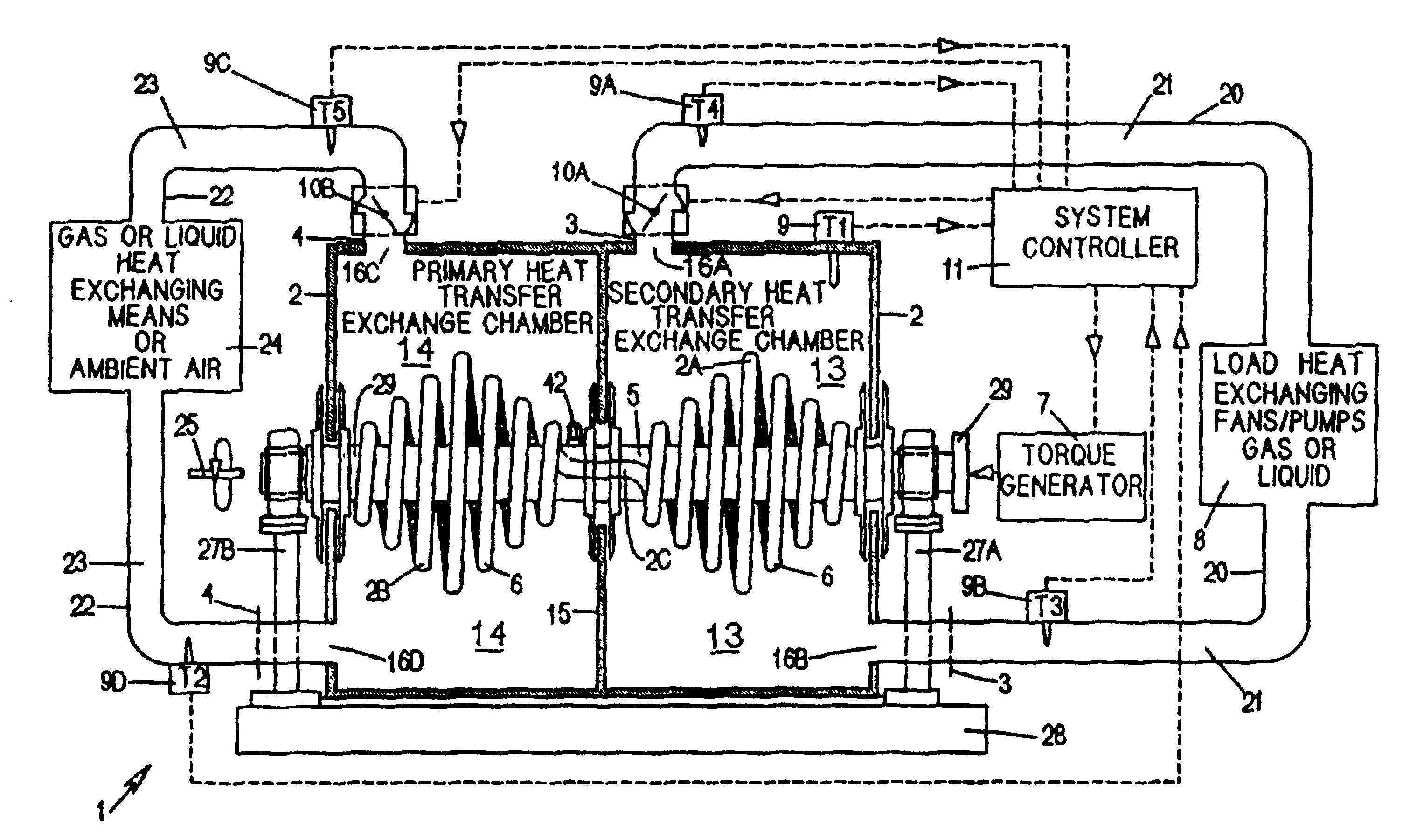
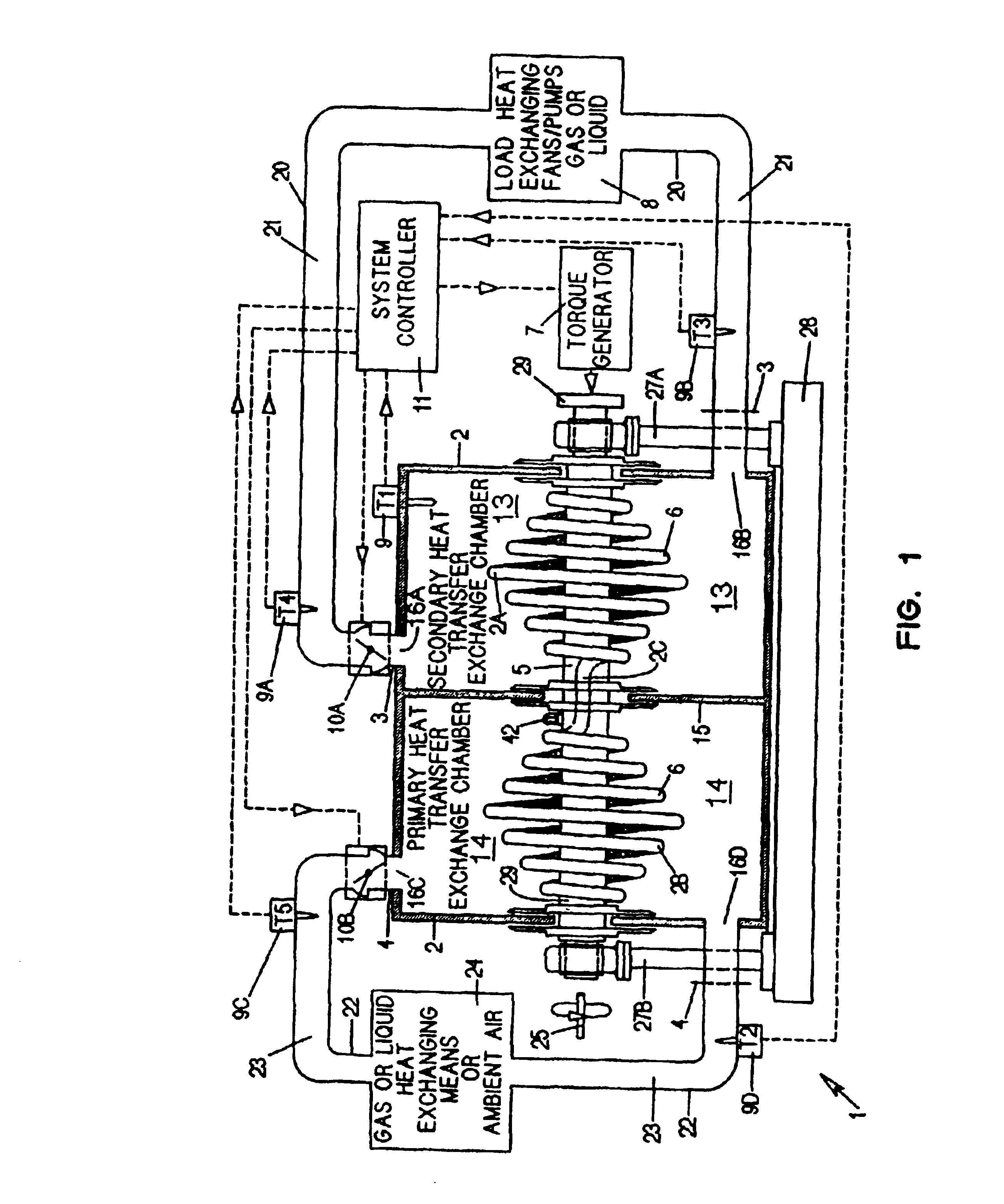
Centrifugal heat transfer engine and heat transfer systems embodying the same
InactiveUS20030145621A1Simple methodReduce the introductionSelf-contained rotary compression machinesCompression machines with non-reversible cycleRotational axisThermal isolation
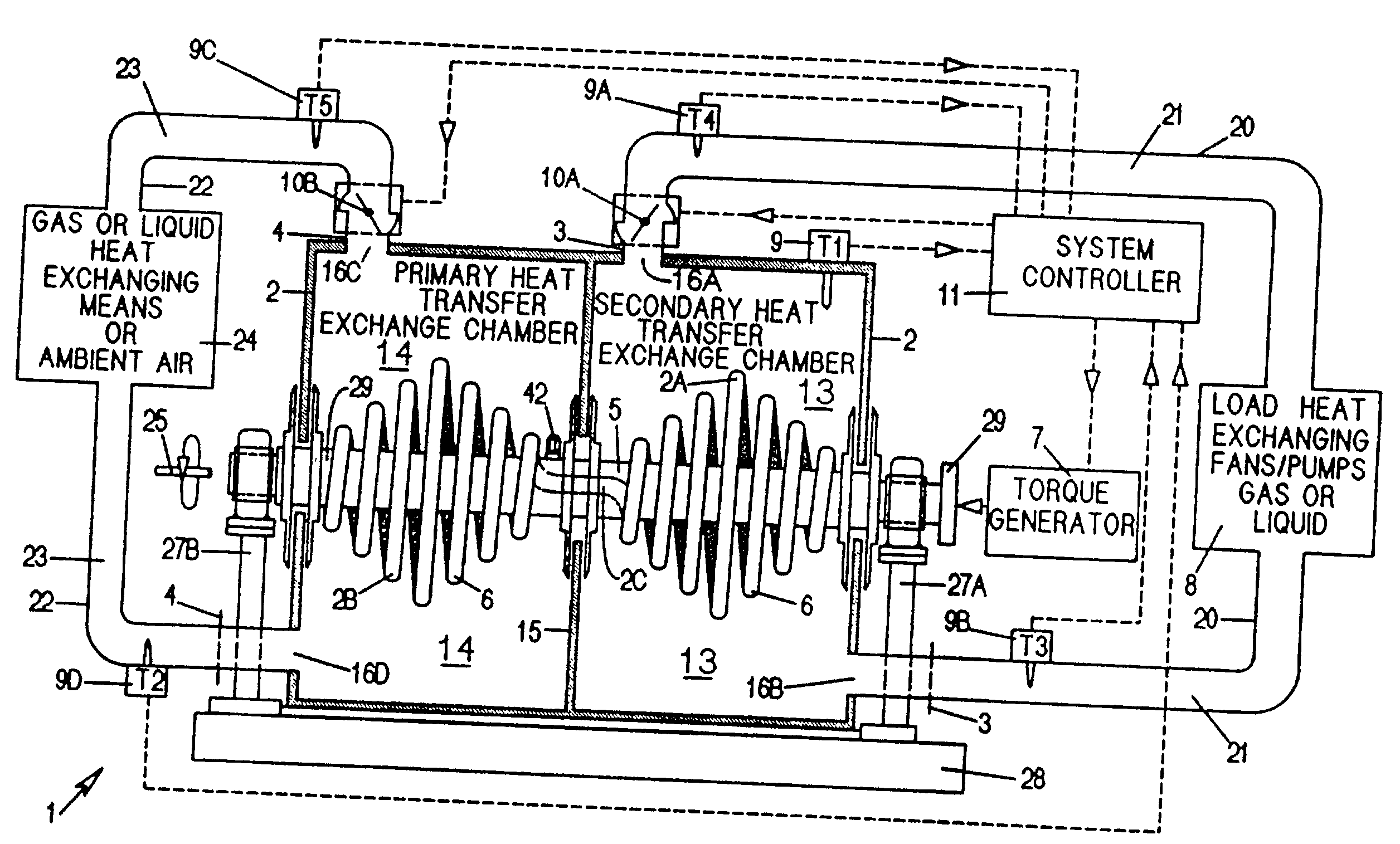
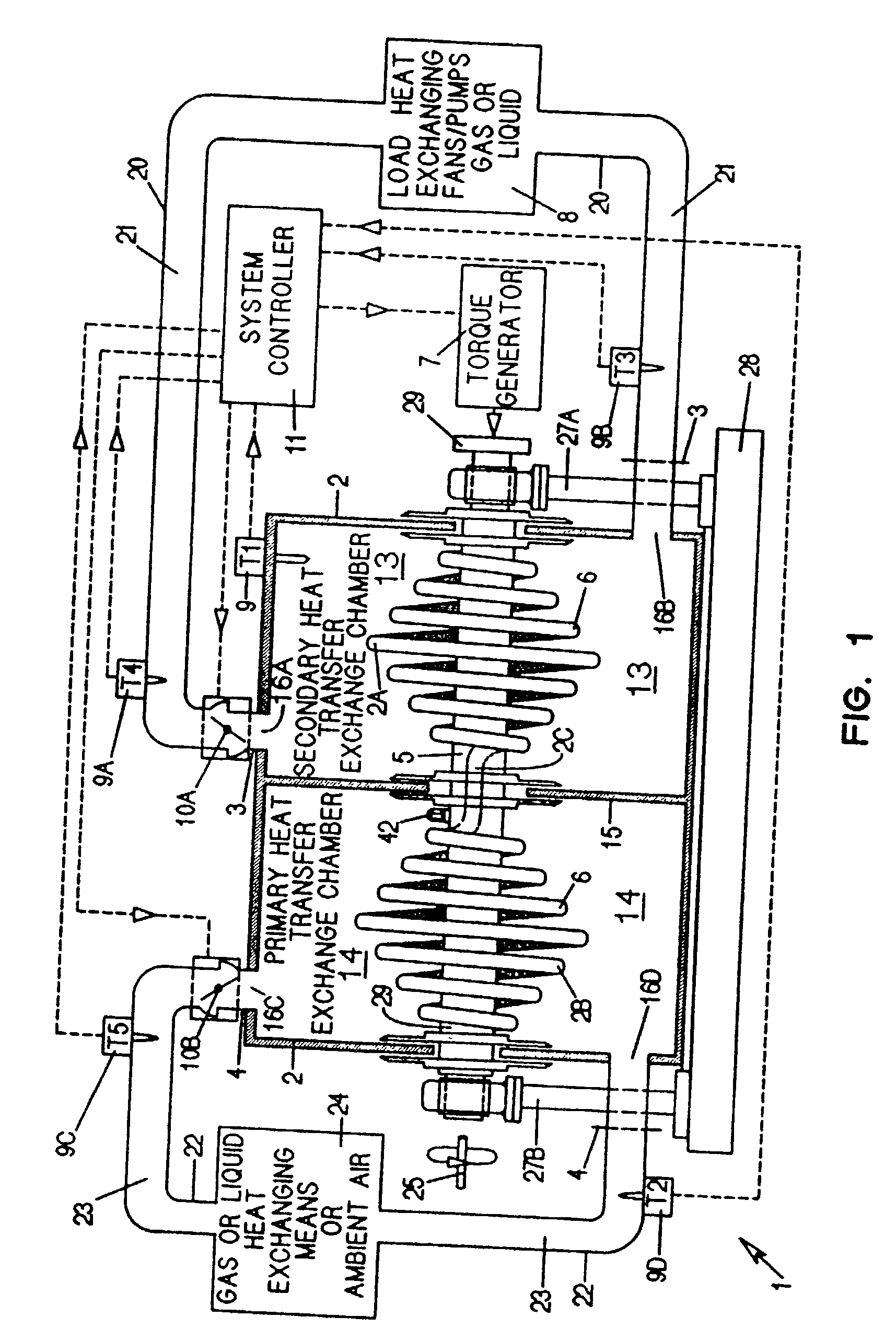
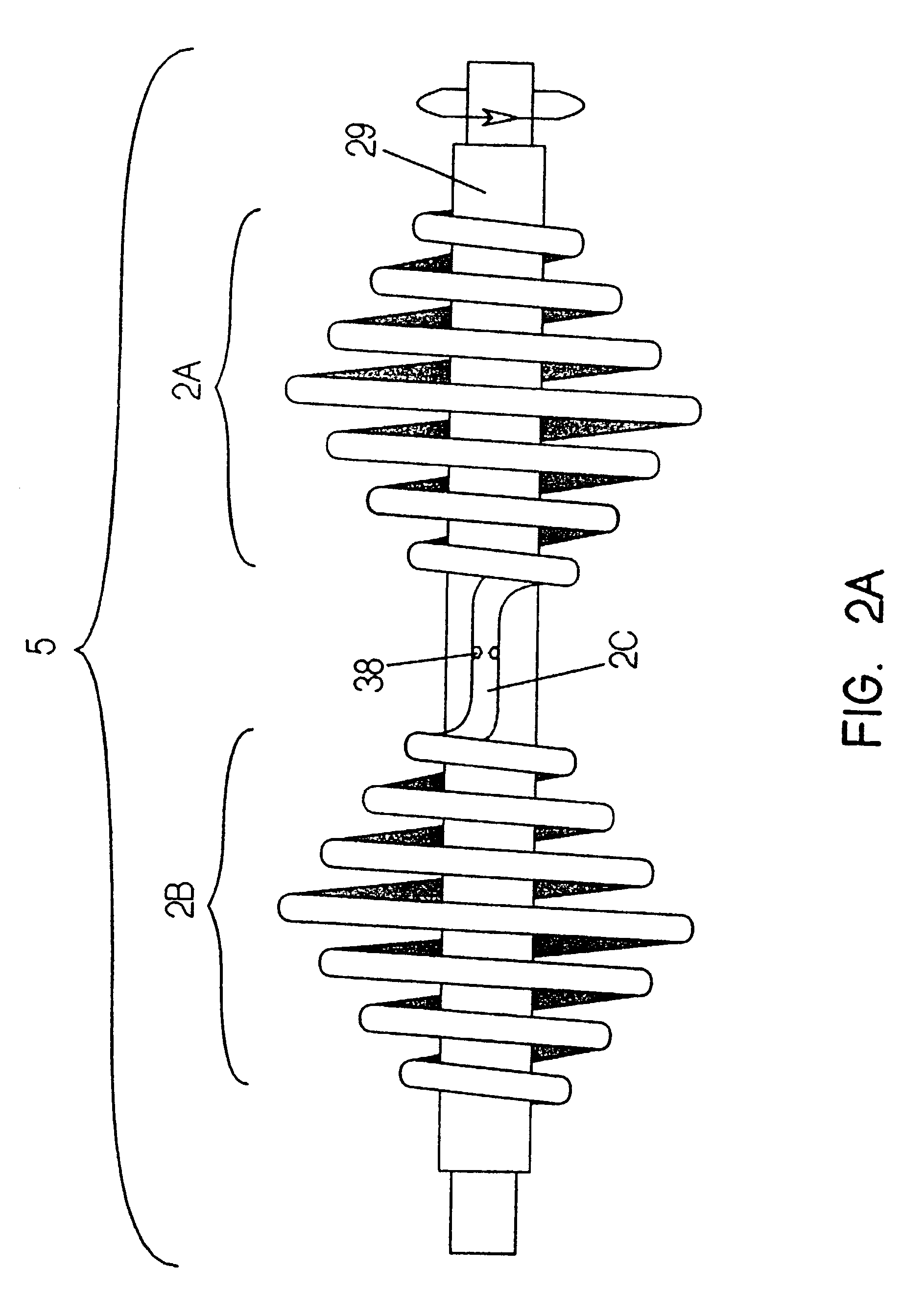
A heat transfer engine having cooling and heating modes of reversible operation, in which heat can be effectively transferred within diverse user environments for cooling, heating and dehumidification applications. The heat transfer engine of the present invention includes a rotor structure which is rotatably supported within a stator structure. The stator has primary and secondary heat exchanging chambers in thermal isolation from each other. The rotor has primary and secondary heat transferring portions within which a closed fluid flow circuit is embodied. The closed fluid flow circuit within the rotor has a spiraled fluid-return passageway extending along its rotary shaft, and is charged with a refrigerant which is automatically circulated between the primary and secondary heat transferring portions of the rotor when the rotor is rotated within an optimized angular velocity range under the control of a temperature-responsive system controller. During the cooling mode of operation, the primary heat transfer portion of the rotor carries out an evaporation function within the primary heat exchanging chamber of the stator structure, while the secondary heat transfer portion of the rotor carries out a condenser function within the secondary heat exchanging chamber of the stator. During the cooling mode of operation, a vapor-compression refrigeration process is realized by the primary heat transfer portion of the rotor performing an evaporation function within the primary heat exchanging chamber of the stator structure, while the secondary heat transfer portion of the rotor performs a condenser function within the secondary heat exchanging chamber of the stator. During the heating mode of operation, a vapor-compression refrigeration process is realized by the primary heat transfer portion of the rotor performing a condenser function within the primary heat exchanging chamber of the stator structure, while the secondary heat transfer portion of the rotor performs an evaporation function within the secondary heat exchanging chamber of the stator. By virtue of the present invention, a technically feasible heat transfer engine is provided which avoids the need for conventional external compressors, while allowing the use of environmentally safe refrigerants. Various embodiments of the heat transfer engine are disclosed, in addition to methods of manufacture and fields and applications of use.
Owner:KELIX HEAT TRANSFER SYST
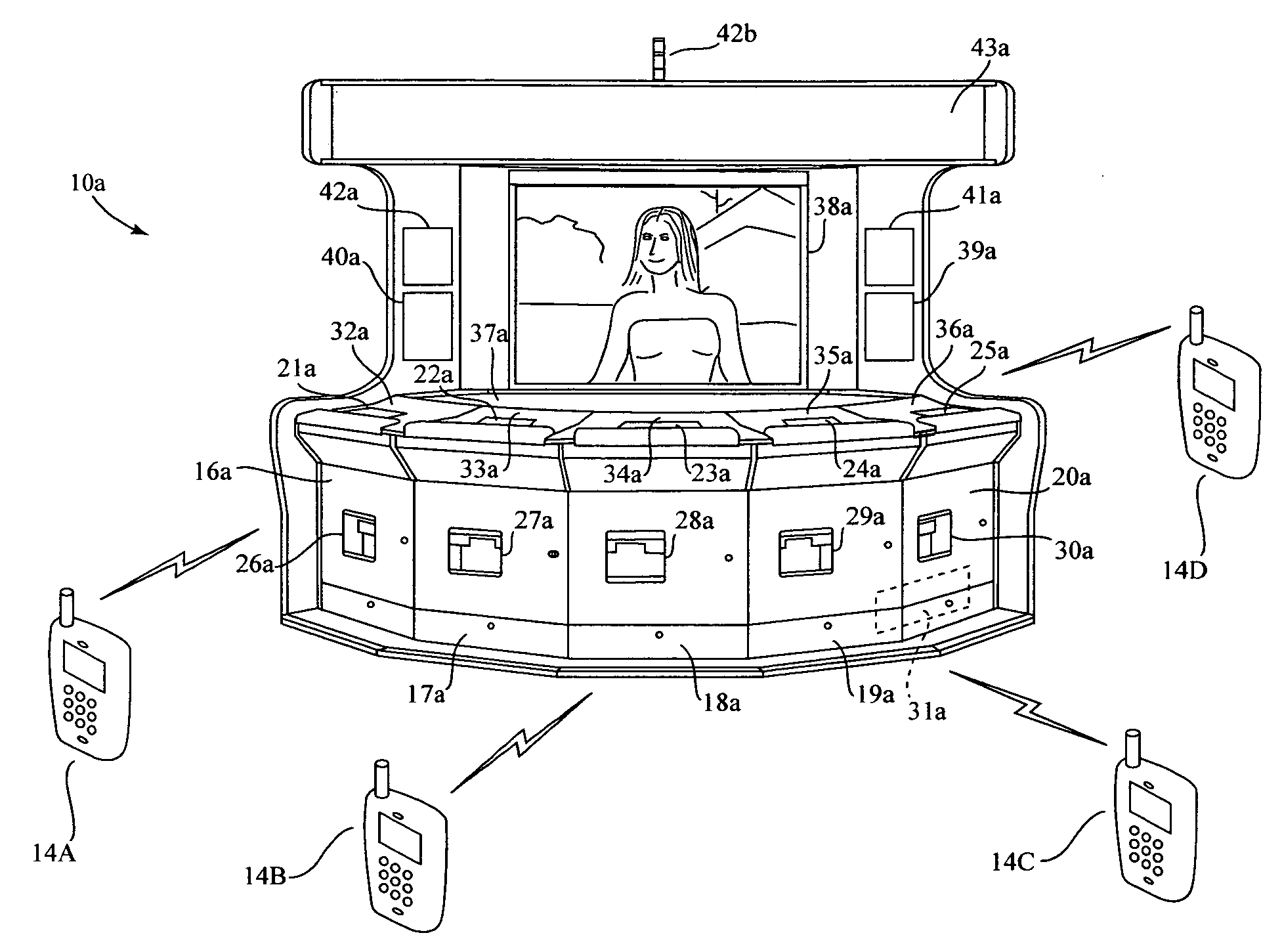
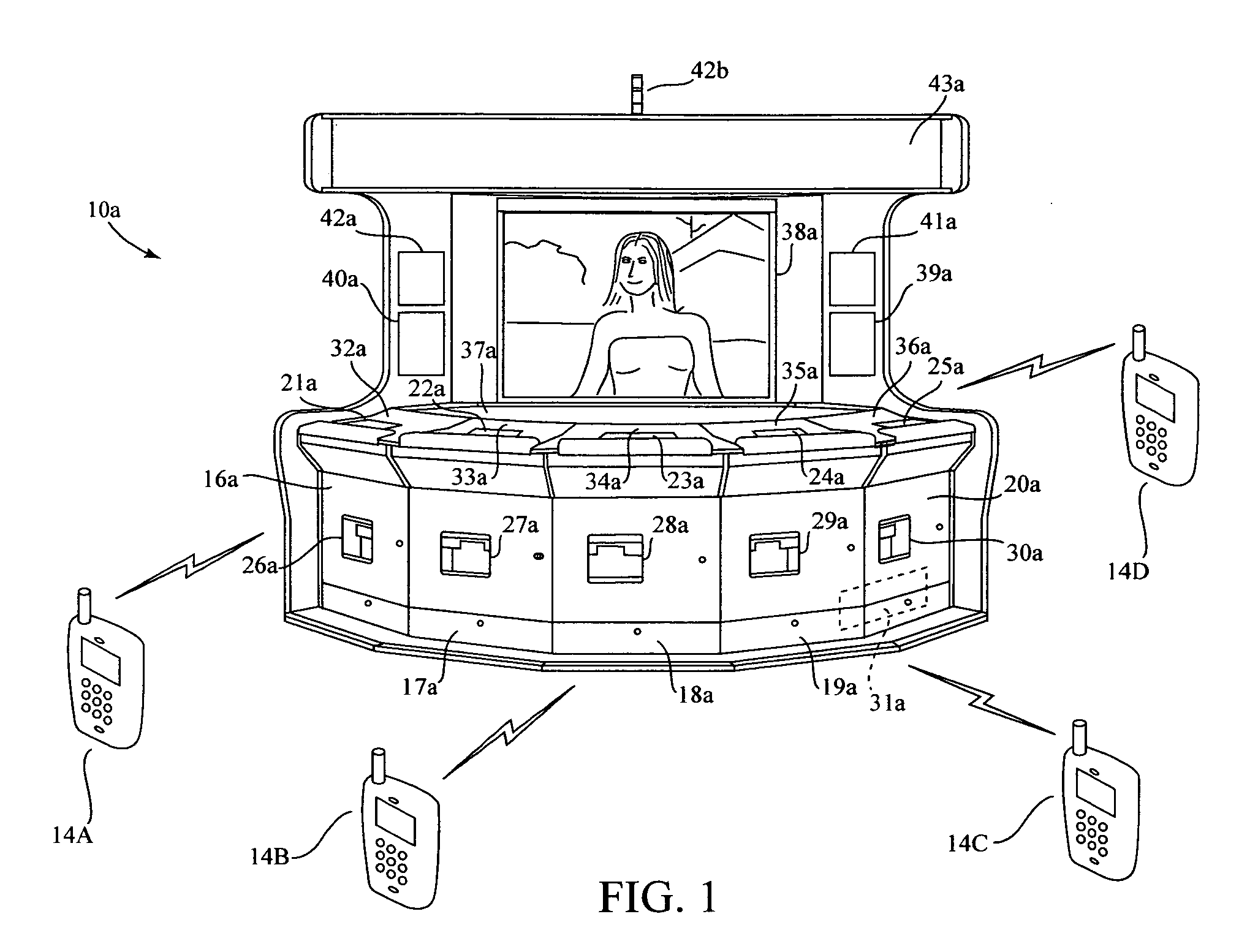
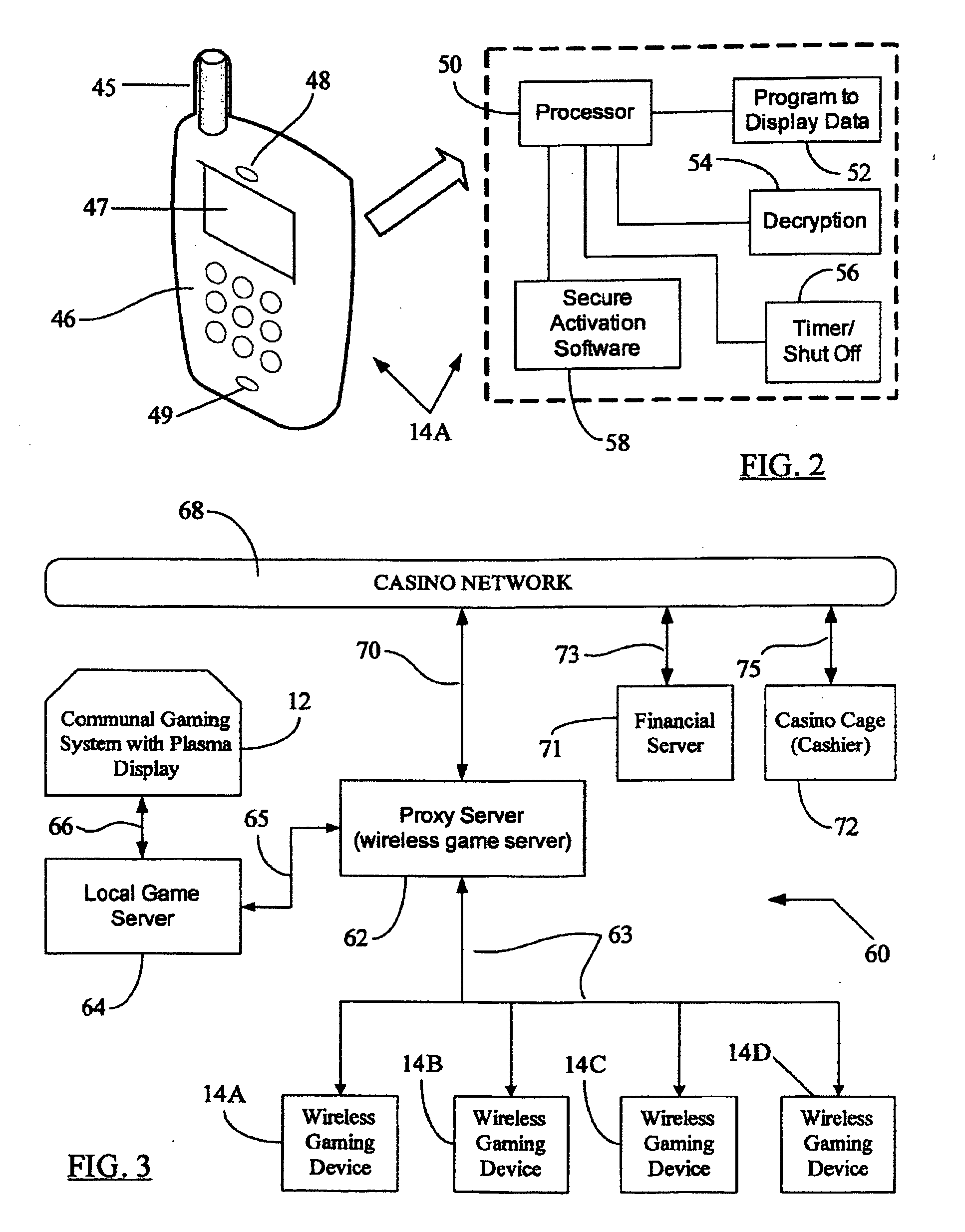
Wireless bet withdrawal gaming system
InactiveUS20090075724A1Improve mobilityWithout reducing speed of playBoard gamesCard gamesWireless transmissionUser input
A system for wireless gaming comprises a central game processor having wireless transmission and reception ability. The game processor has a device server and a local game server. Multiple user input devices having a visual display and wireless transmission and reception ability are provided. The wireless devices are used to play a game in which a player places a multiple part wager comprising at least two distinct wagers to participate in a game. At least a partial hand of cards is provided to each player, and at least one common card is provided. Players are given an opportunity to withdraw a portion of the wager after viewing the player cards. The at least one common card is revealed and play is resolved. All wagers not withdrawn by the player are resolved
Owner:BALLY GAMING INC
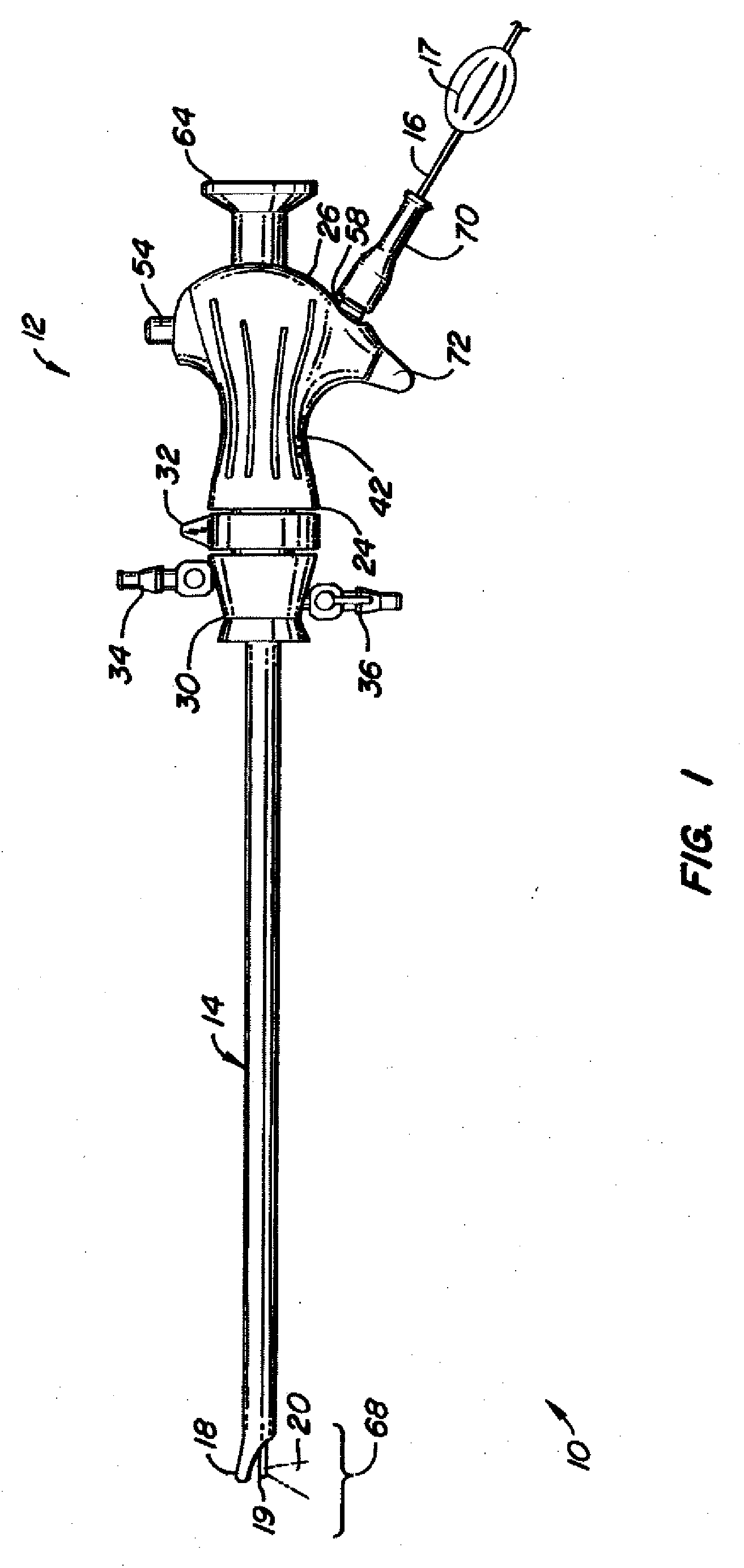
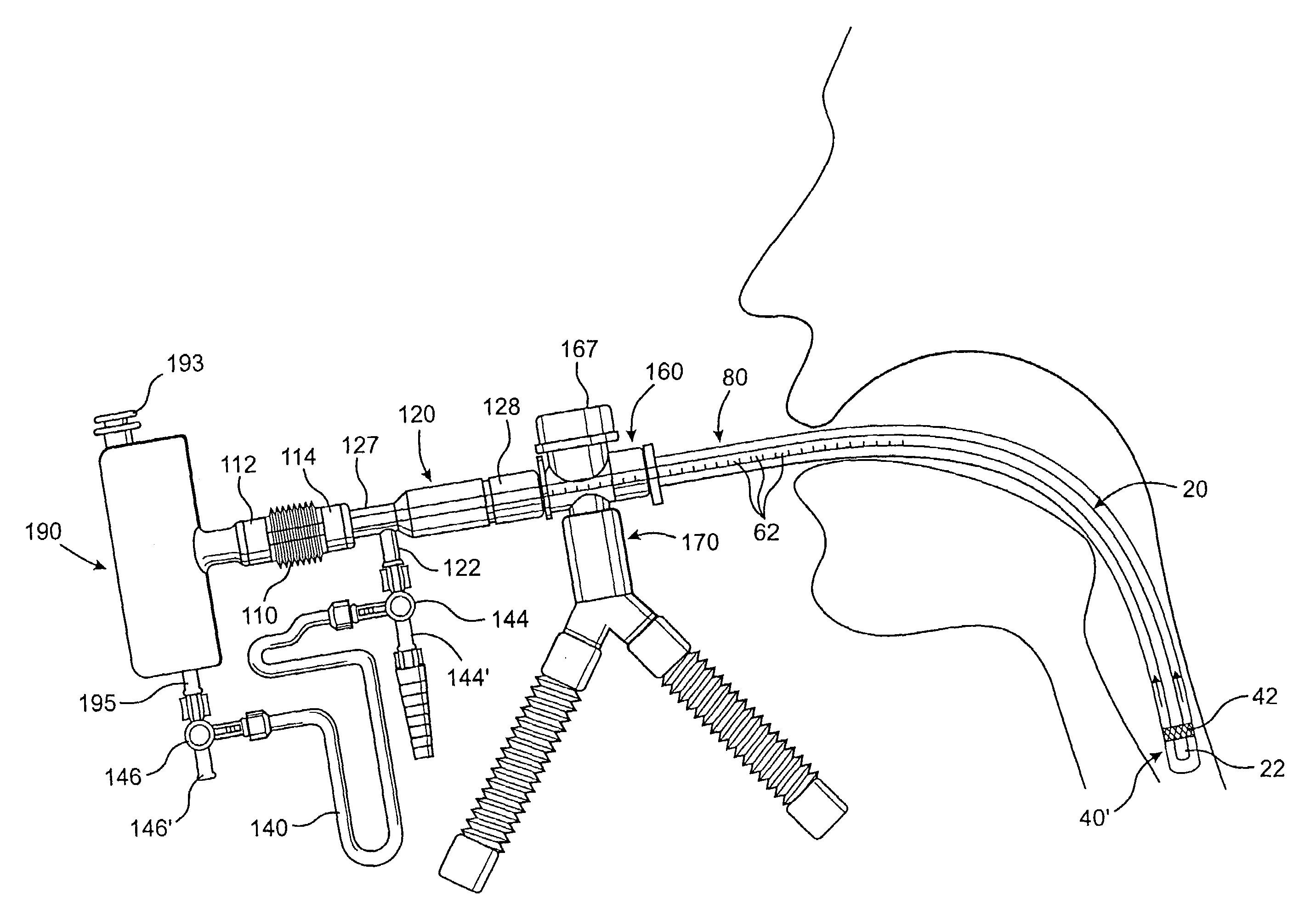
Endotracheal tube cleaning apparatus and method
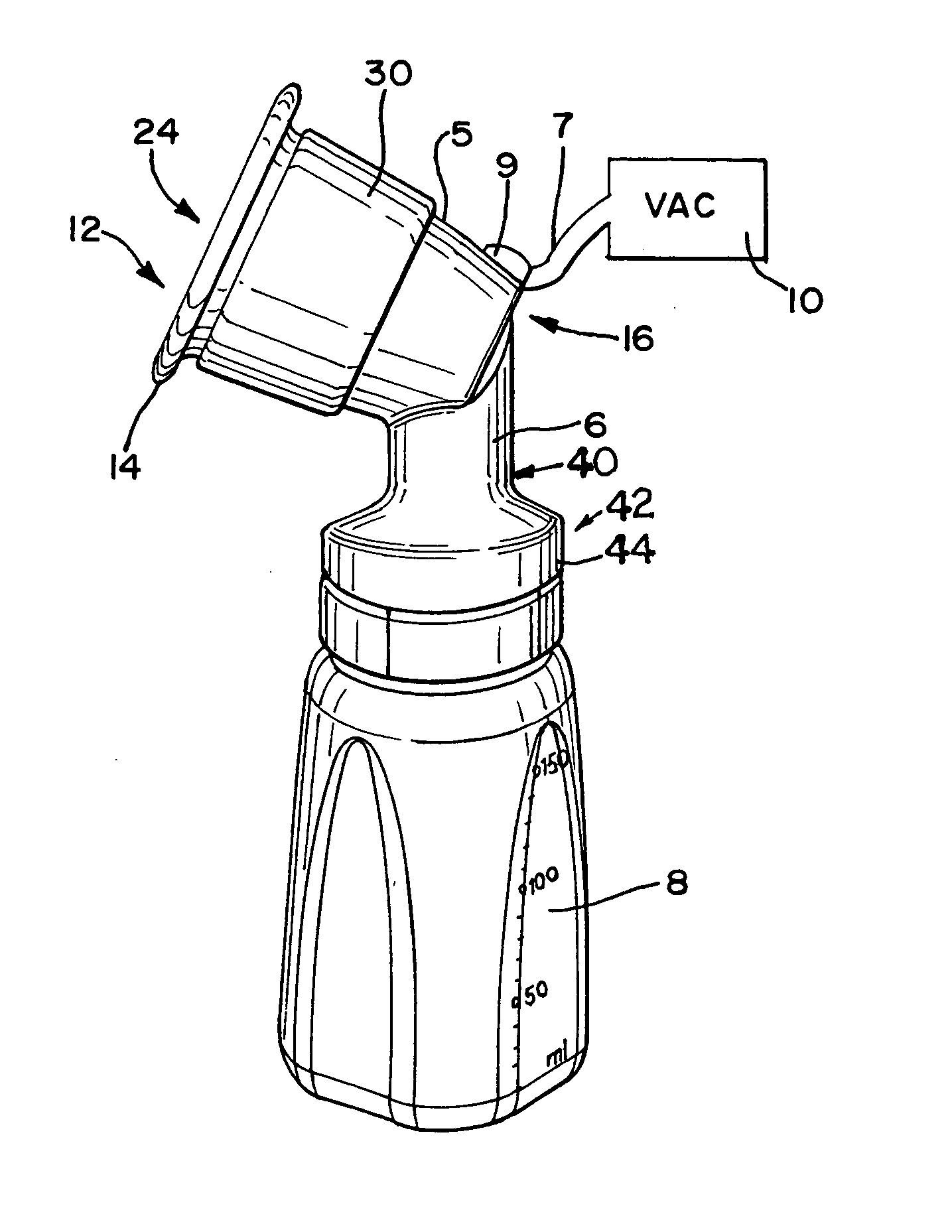
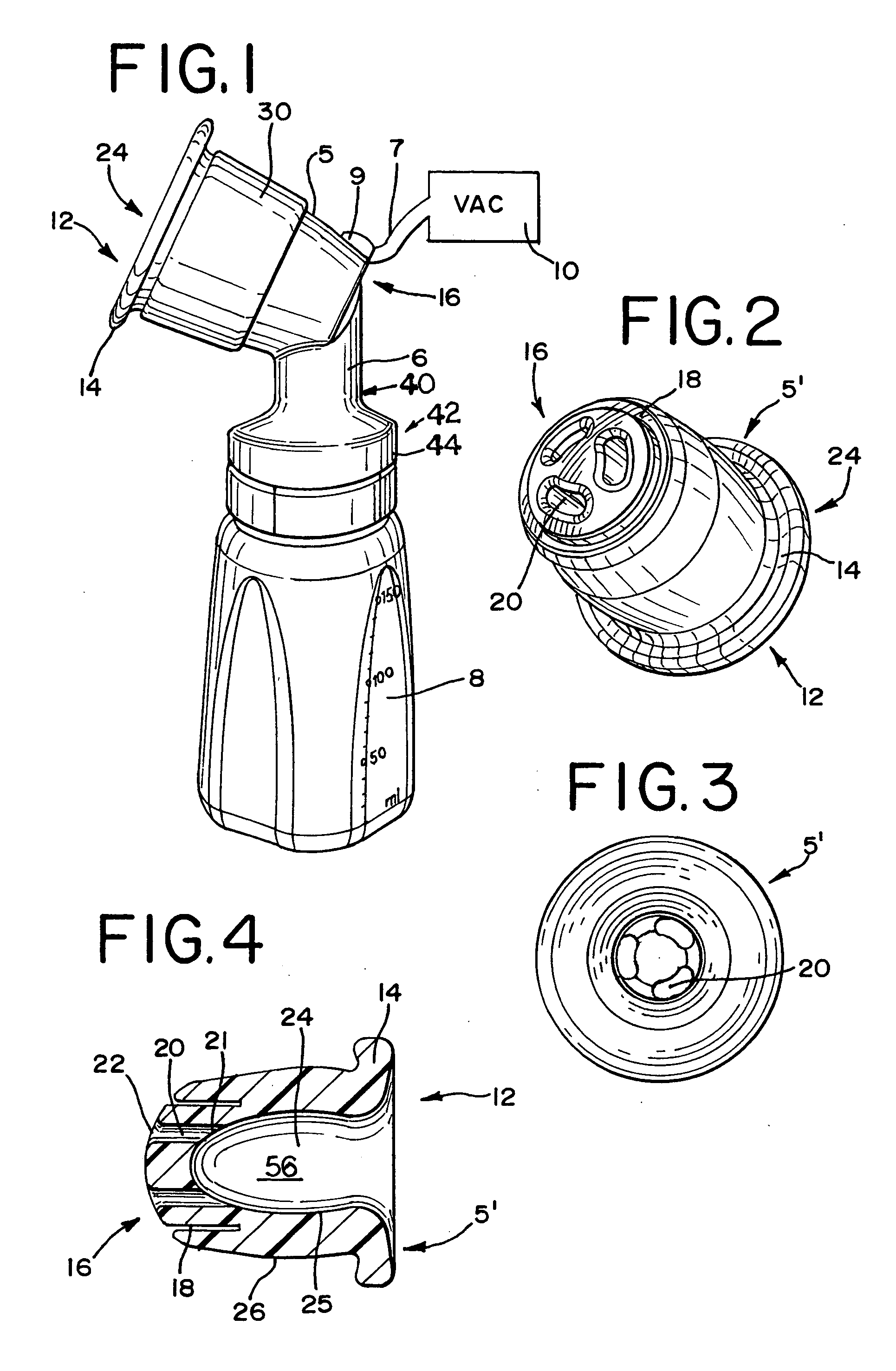
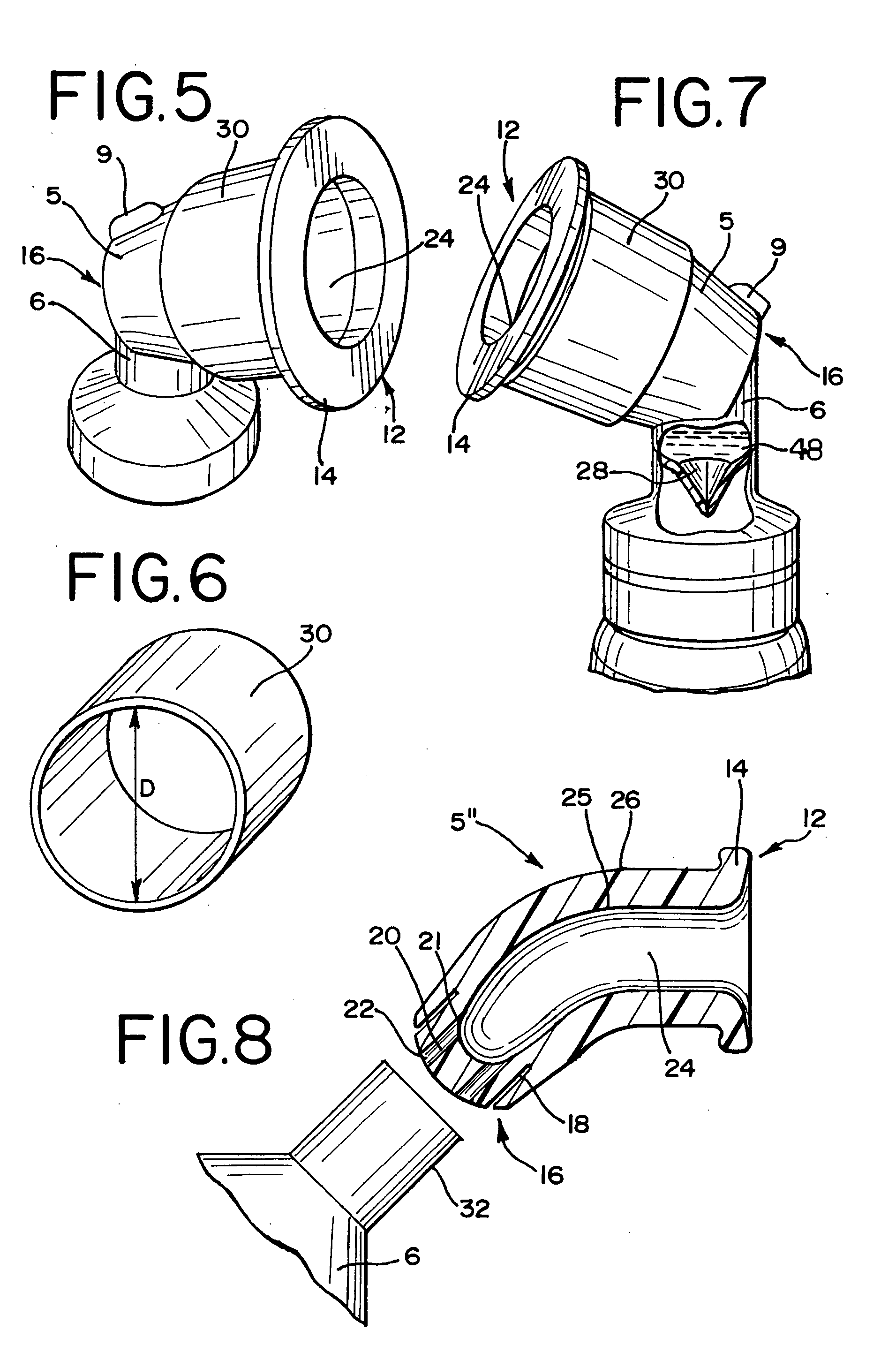
A cleaning apparatus and method to be used with an endotracheal tube and including an elongate tubular member that extends into the endotracheal tube. A cleaning assembly which may include an irregular outer surface is provided at a distal end of the elongate tubular member and is radially expandable to engage the interior wall of the endotracheal tube for cleaning thereof. A ventilator coupling is further provided and is connected to the endotracheal tube, a first inlet port of the ventilator coupling being coupled to a ventilator assembly to supply air to a patient, and a second inlet port of the ventilator coupling being structured to receive the elongate tubular member there through into the endotracheal tube. Also, a bypass coupling assembly is connected between the channel of the elongate tubular member and the ventilator assembly so as to automatically direct air from the ventilator assembly into the channel of the elongate tubular member, and out the distal end of the channel, upon occlusion of a flow of the air through the endotracheal tube at a point of the endotracheal tube upstream of the distal end of the channel.
Owner:MOREJON ORLANDO
Cleaning with electrically charged aerosols
InactiveUS20060118132A1Easy to cleanEasy maintenanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrostatic cleaningLiquid layerAerosol droplet
In a method for cleaning a wafer, the wafer is placed a processing chamber. A layer or film of liquid is provided on the wafer. Electrically charged aerosol droplets of a liquid are formed and directed to the workpiece. The charged aerosol particles accumulate on the workpiece. This creates an electrical charge on the workpiece. Contaminant particles on the workpiece are released and / or repelled by the electrical charge and are carried away in the liquid layer. The liquid layer is optionally continuously replenished with fresh liquid. The liquid layer may be thinned out in a localized aerosol impingement area, via a jet of gas, to allow the electrical charge of the aerosol to better collect on or near the surface of the workpiece.
Owner:SEMITOOL INC
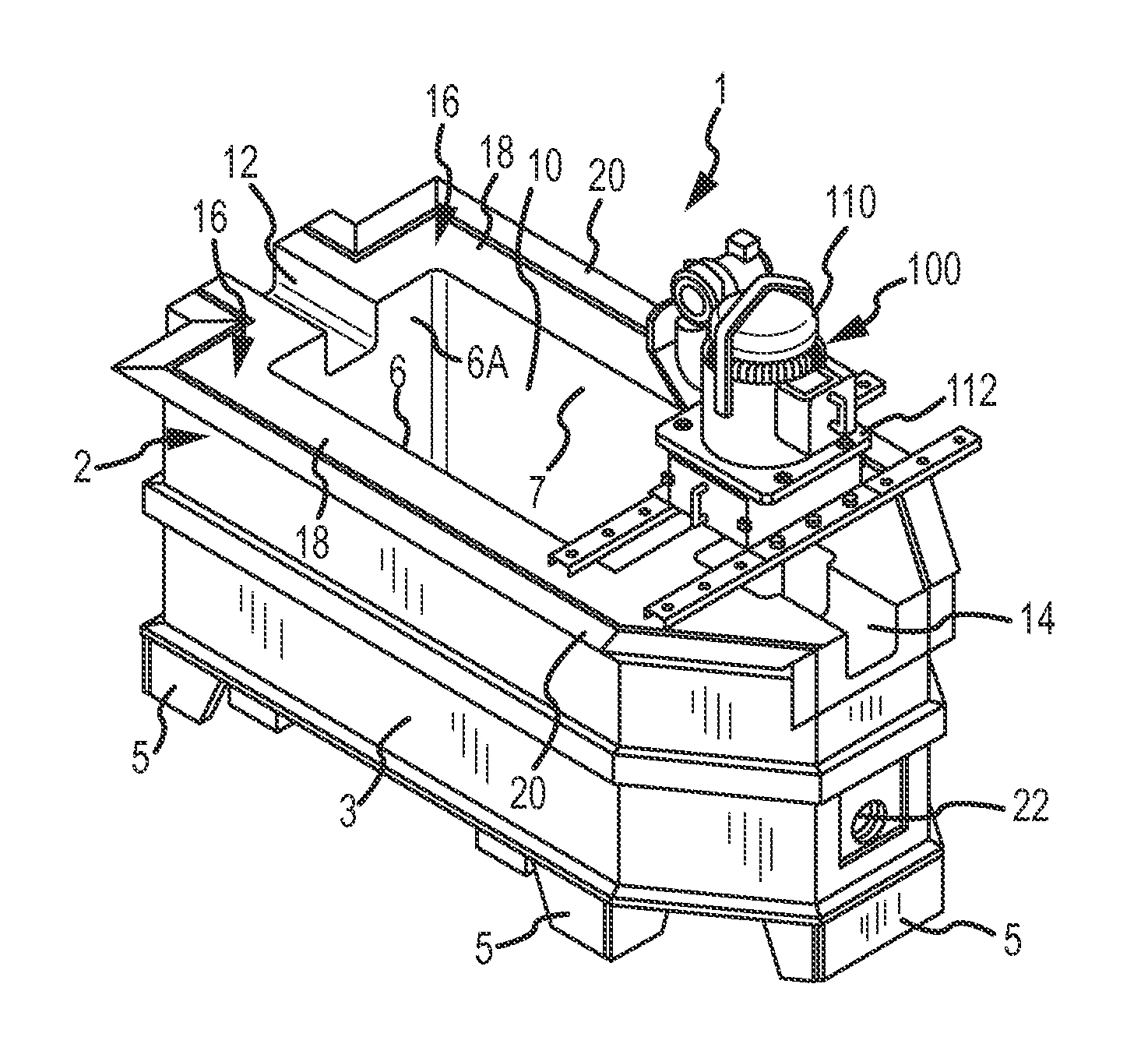
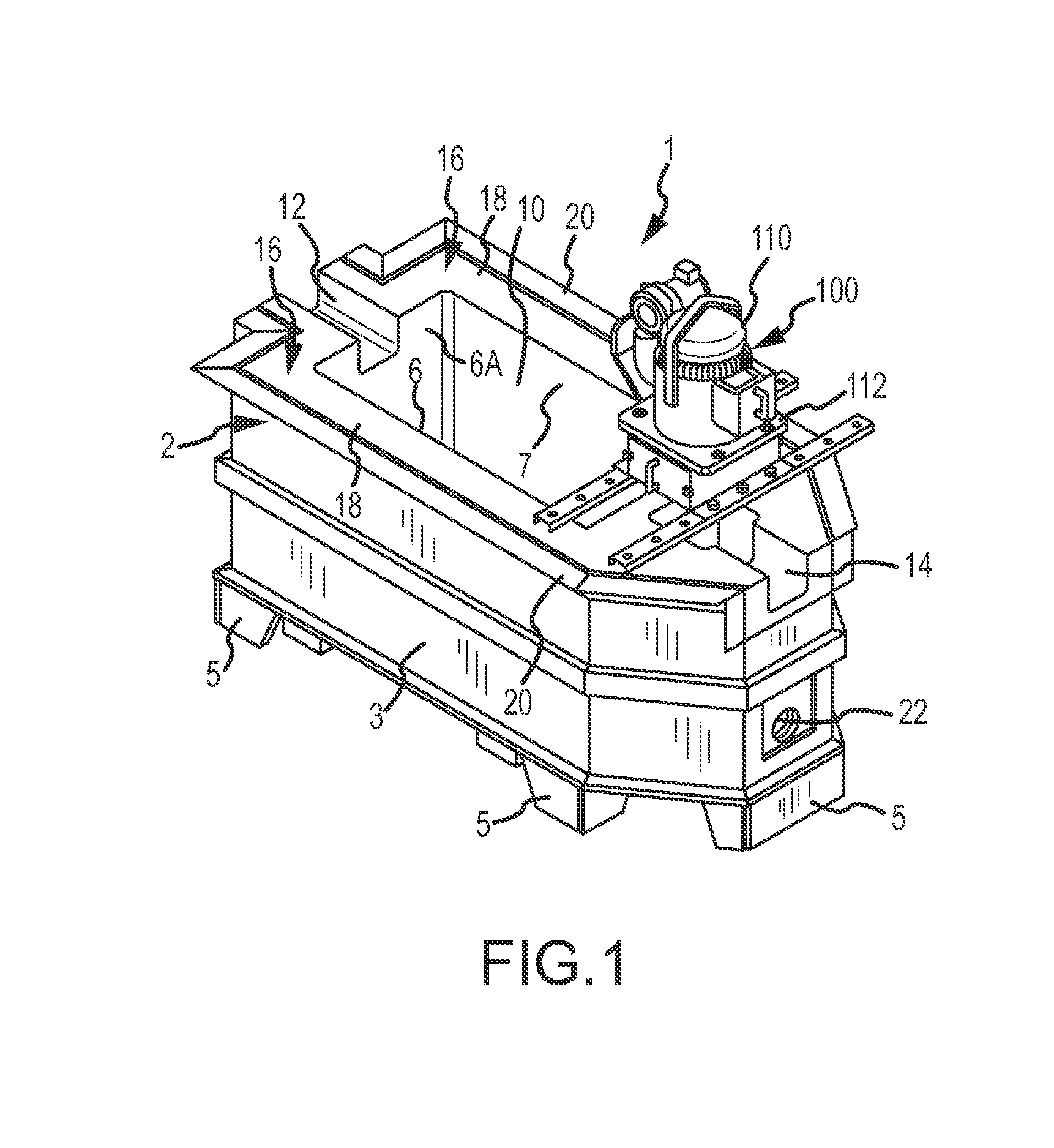
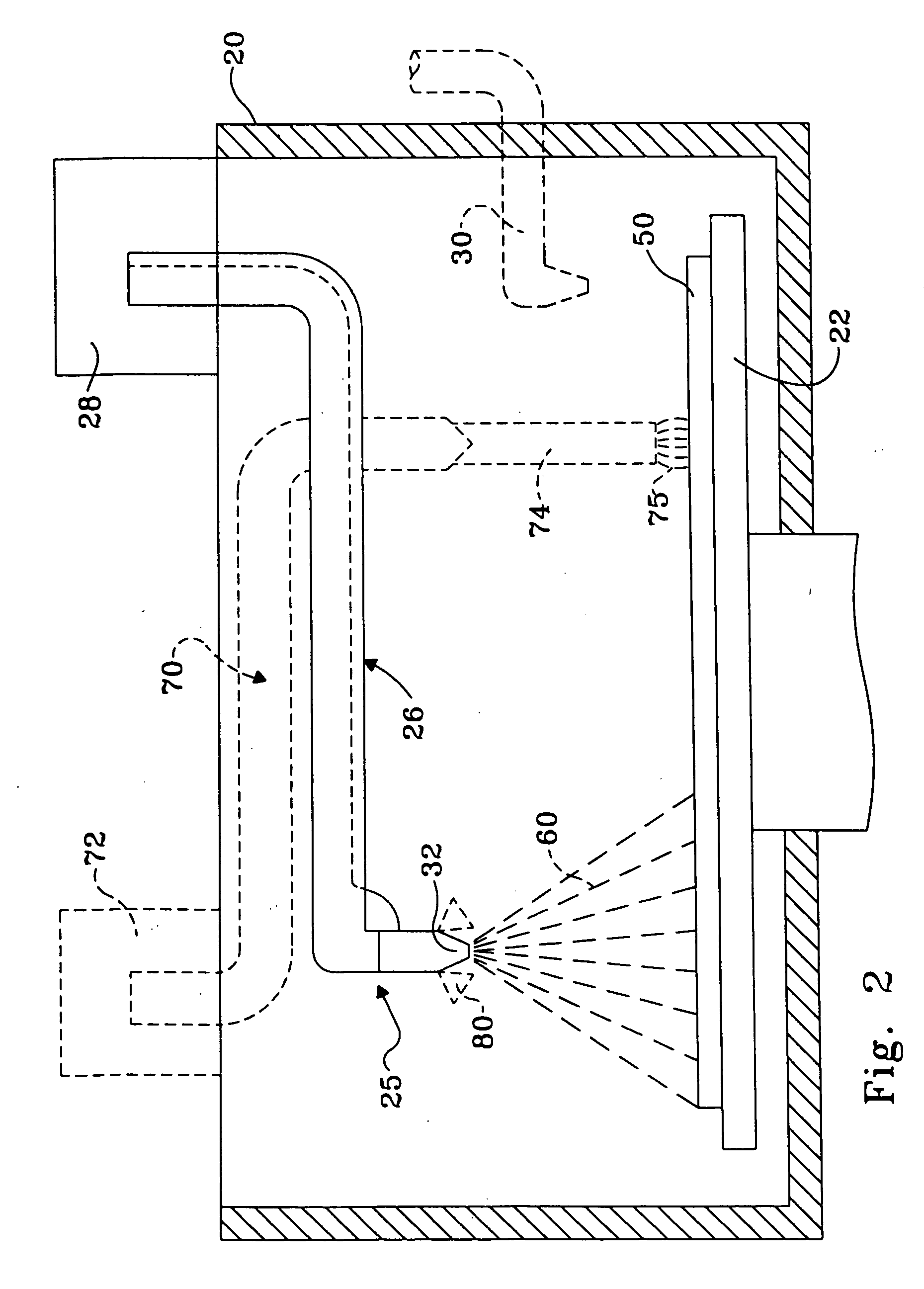
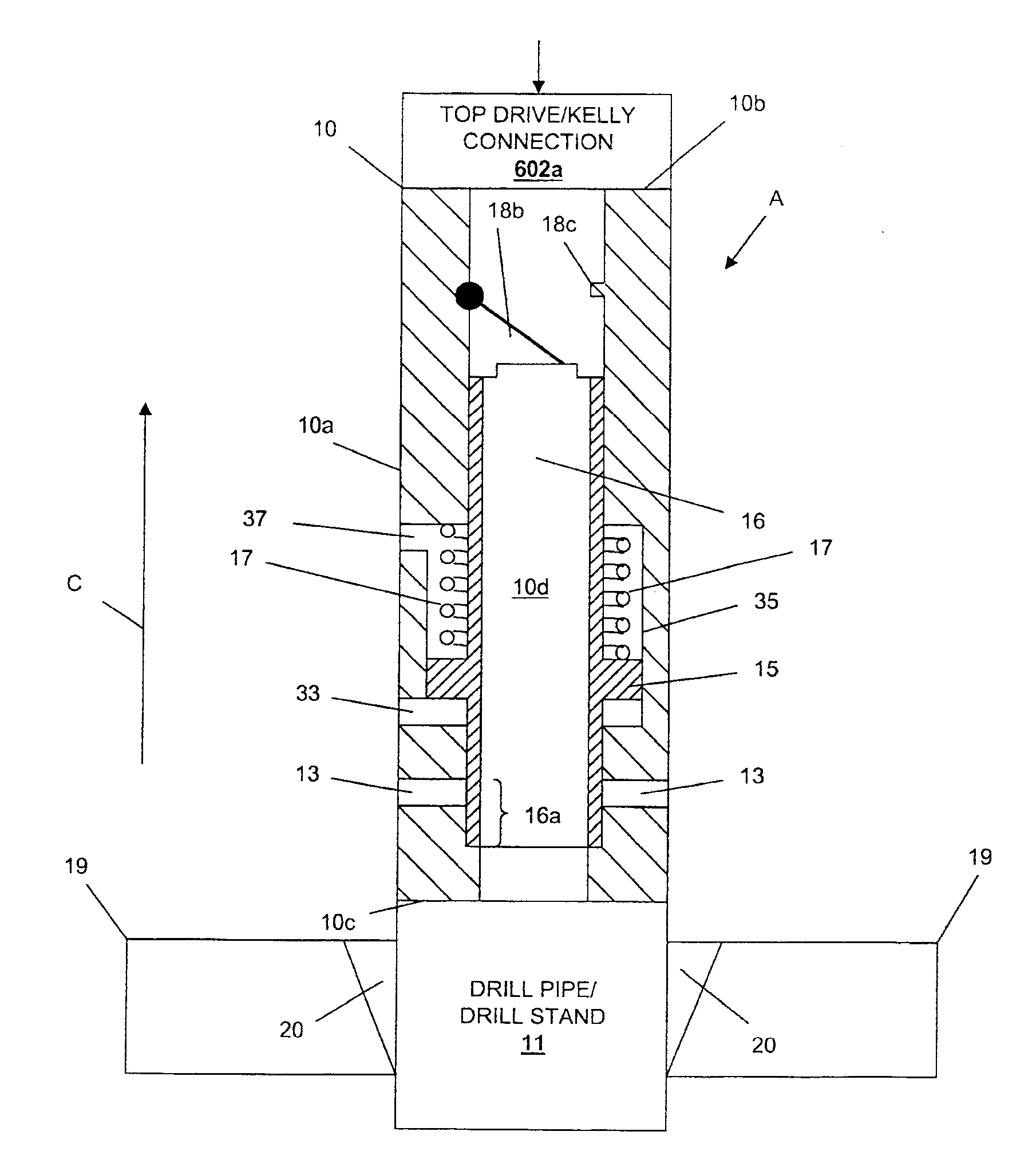
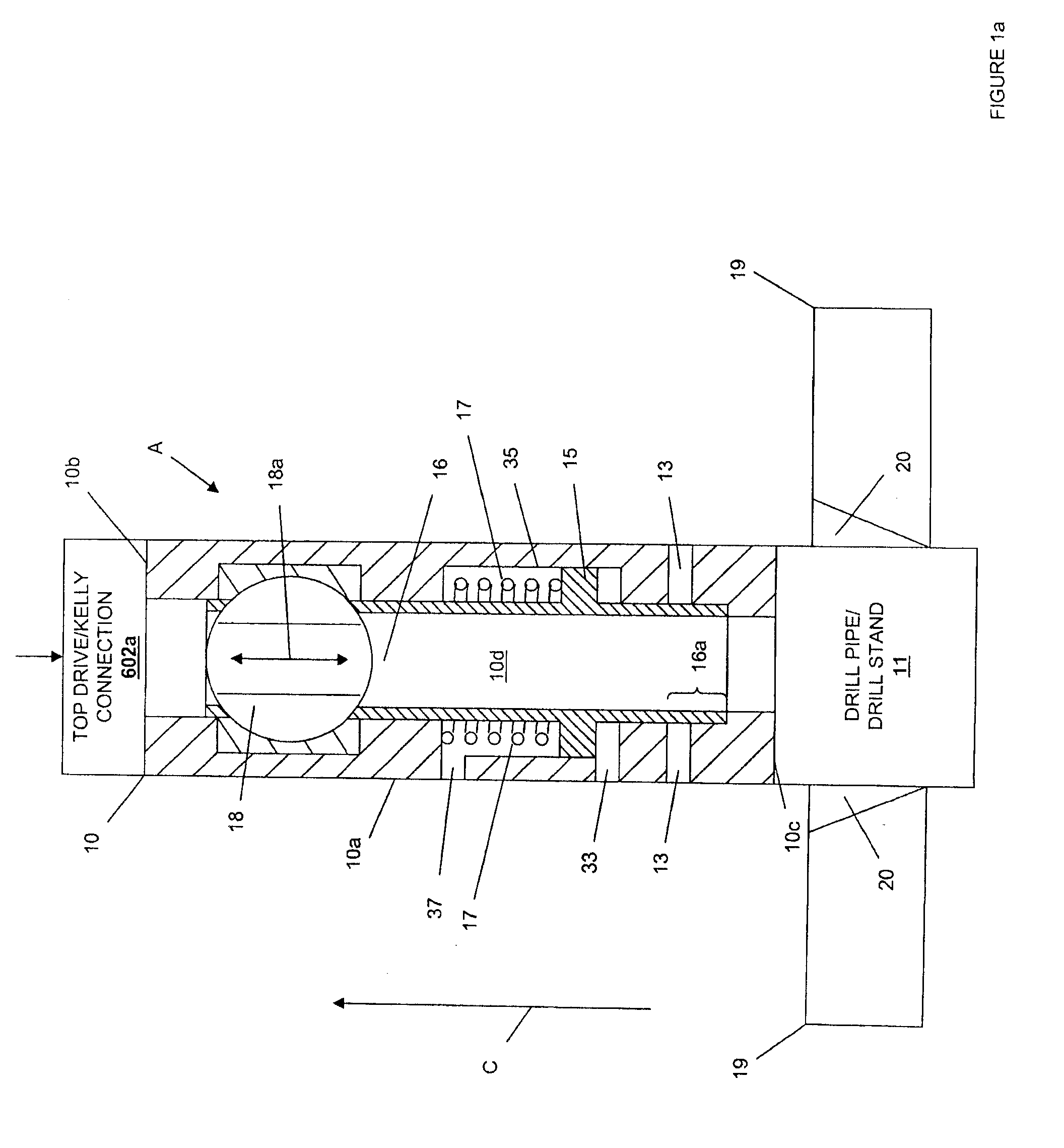
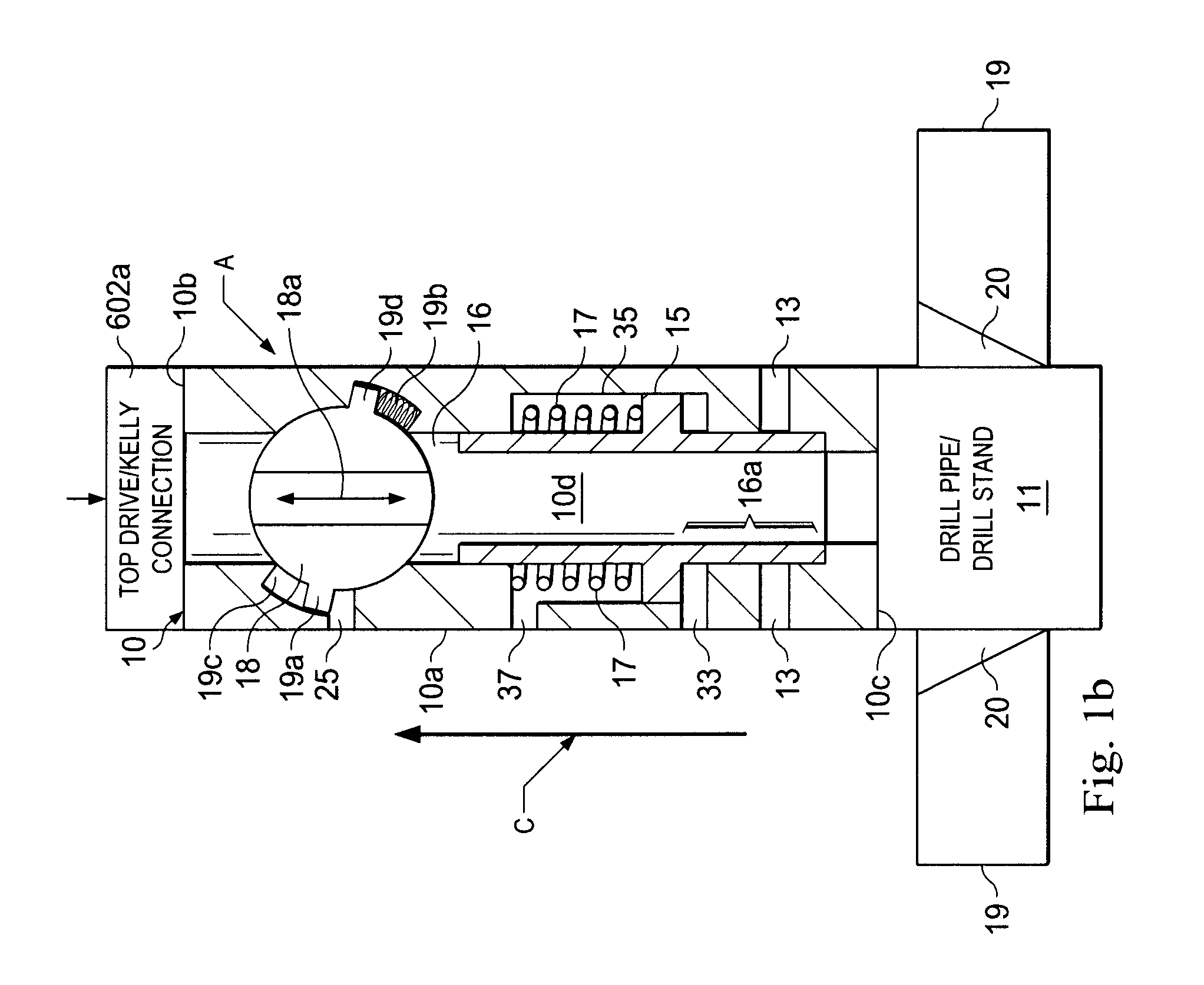
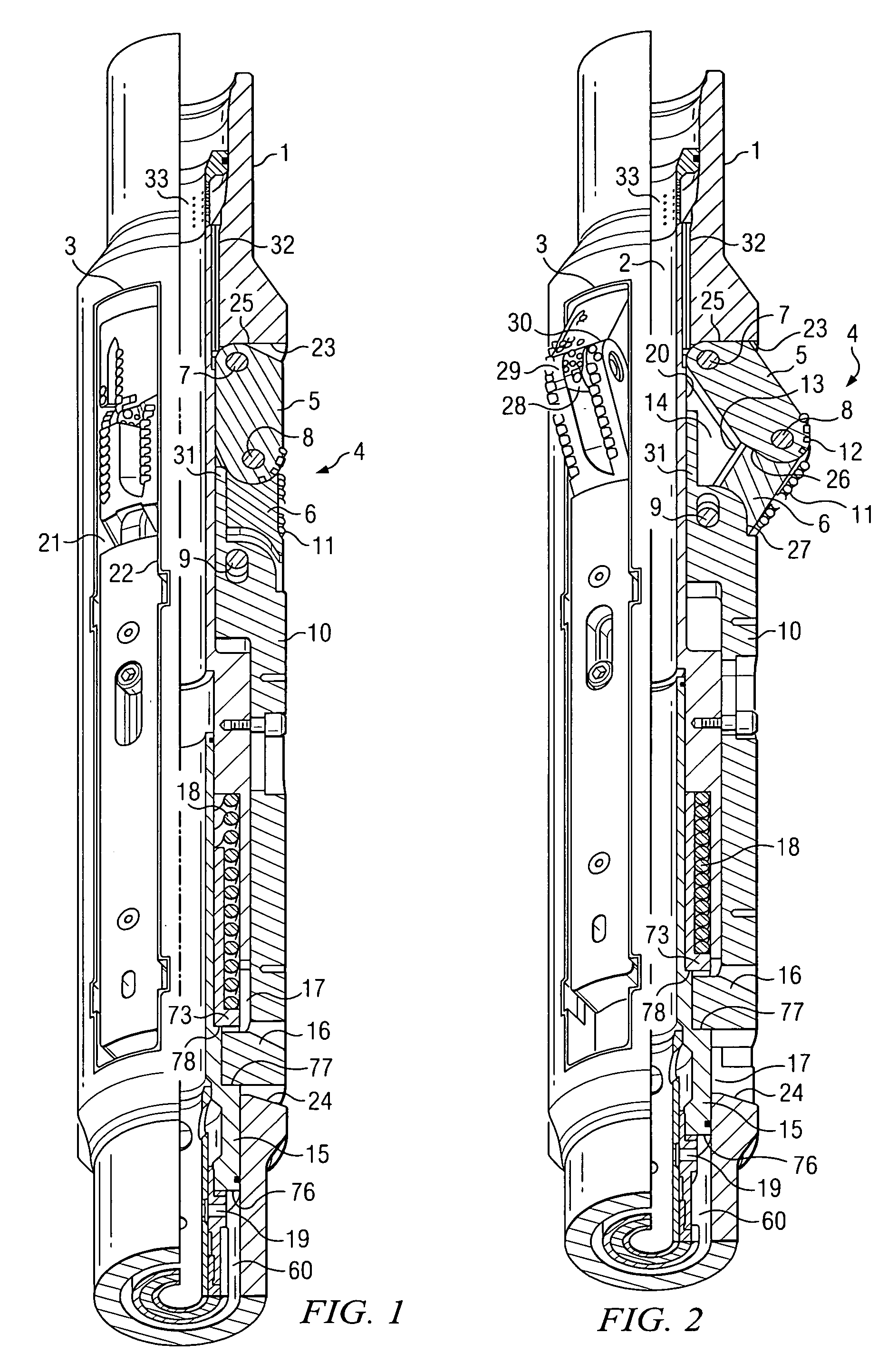
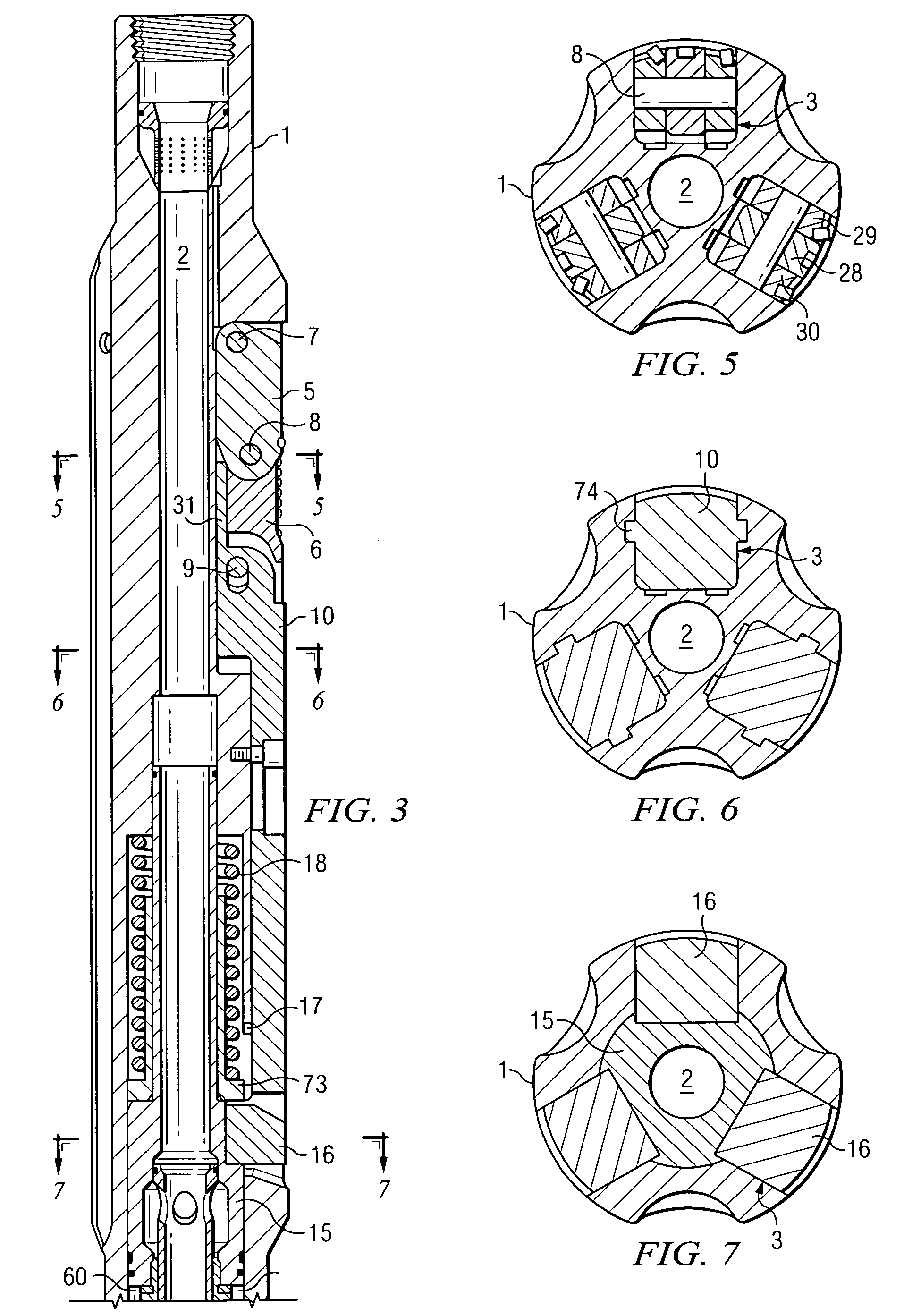
Continuous Circulating Sub for Drill Strings
A system and method for maintaining continuous flow through a drill string during drill pipe connection includes establishing drilling fluid flow axially through the length of a tubular sub attached to the top of a drill string. The sub is then engaged with a collar disposed at least partially around the perimeter of the sub so as to define an exterior flow path along the exterior of the sub. Radial flow is then initiated into the sub through said collar and along said exterior flow path. Axial flow is then terminated through the length of the tubular sub while maintaining radial flow into the sub. A pipe joint is then attached to the top of the tubular sub, axial flow is reestablished through the length of the tubular sub, radial flow is terminated into the sub, and the collar is disengaged from the sub.
Owner:DUAL GRADIENT SYST
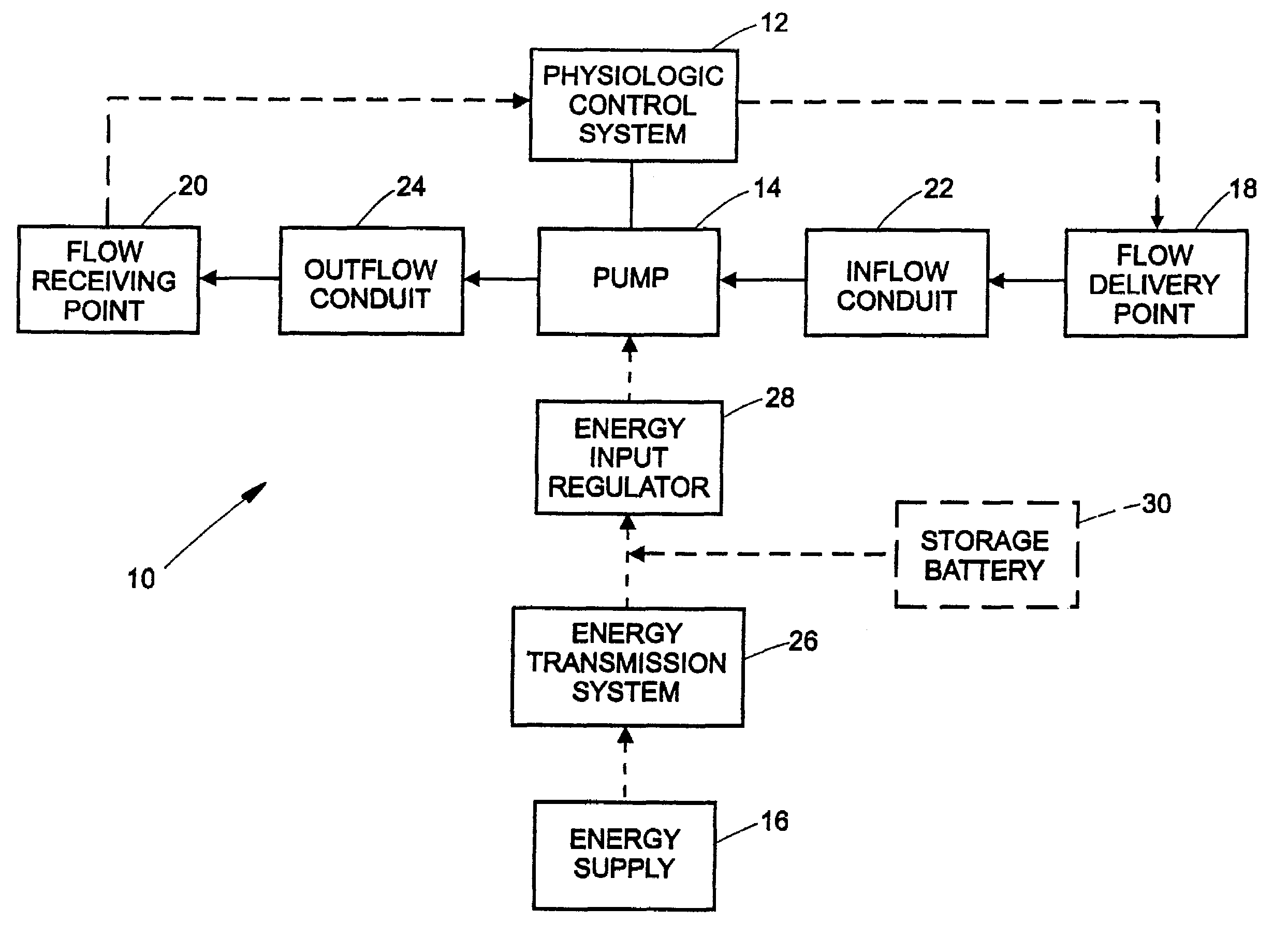
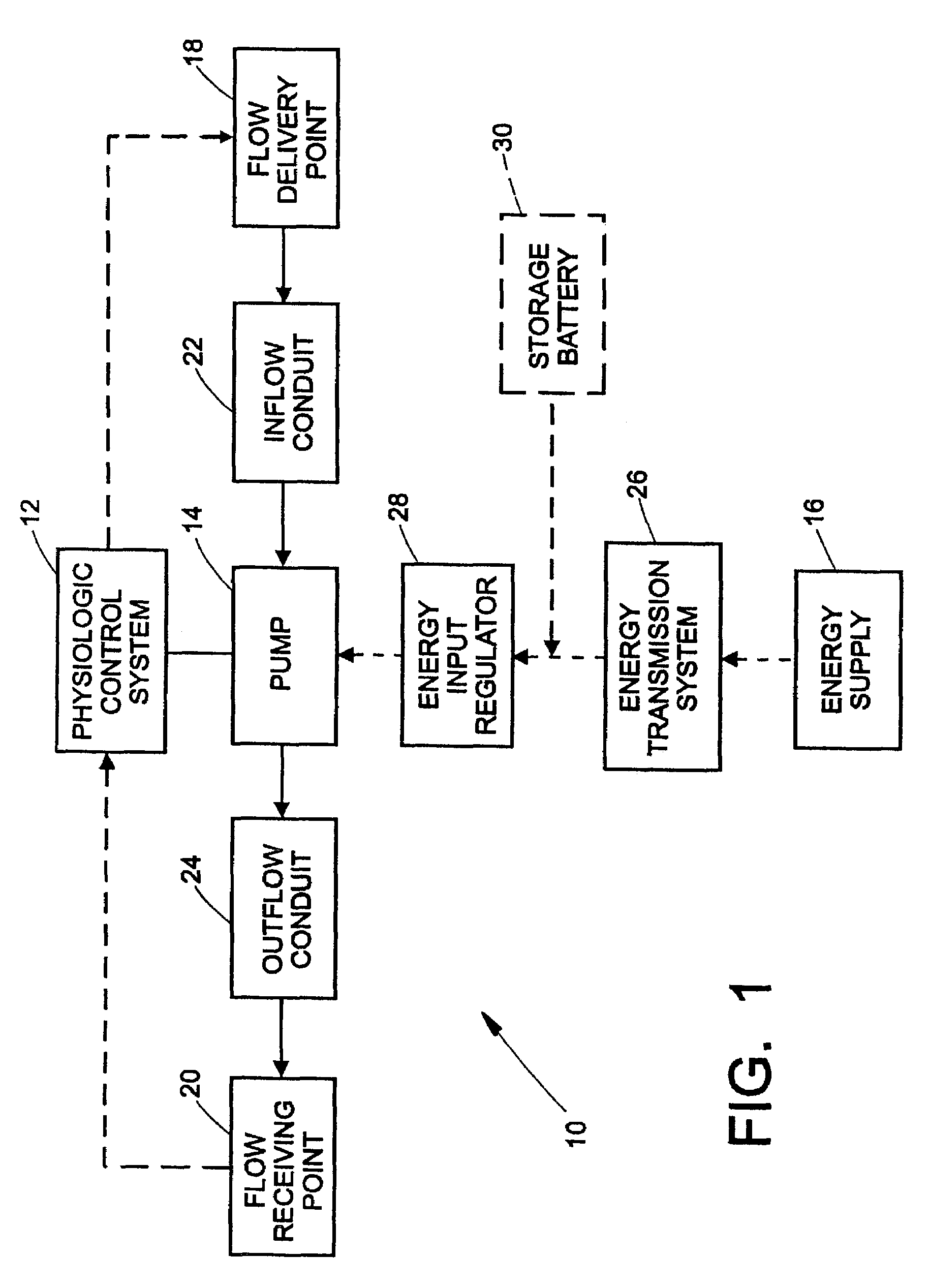
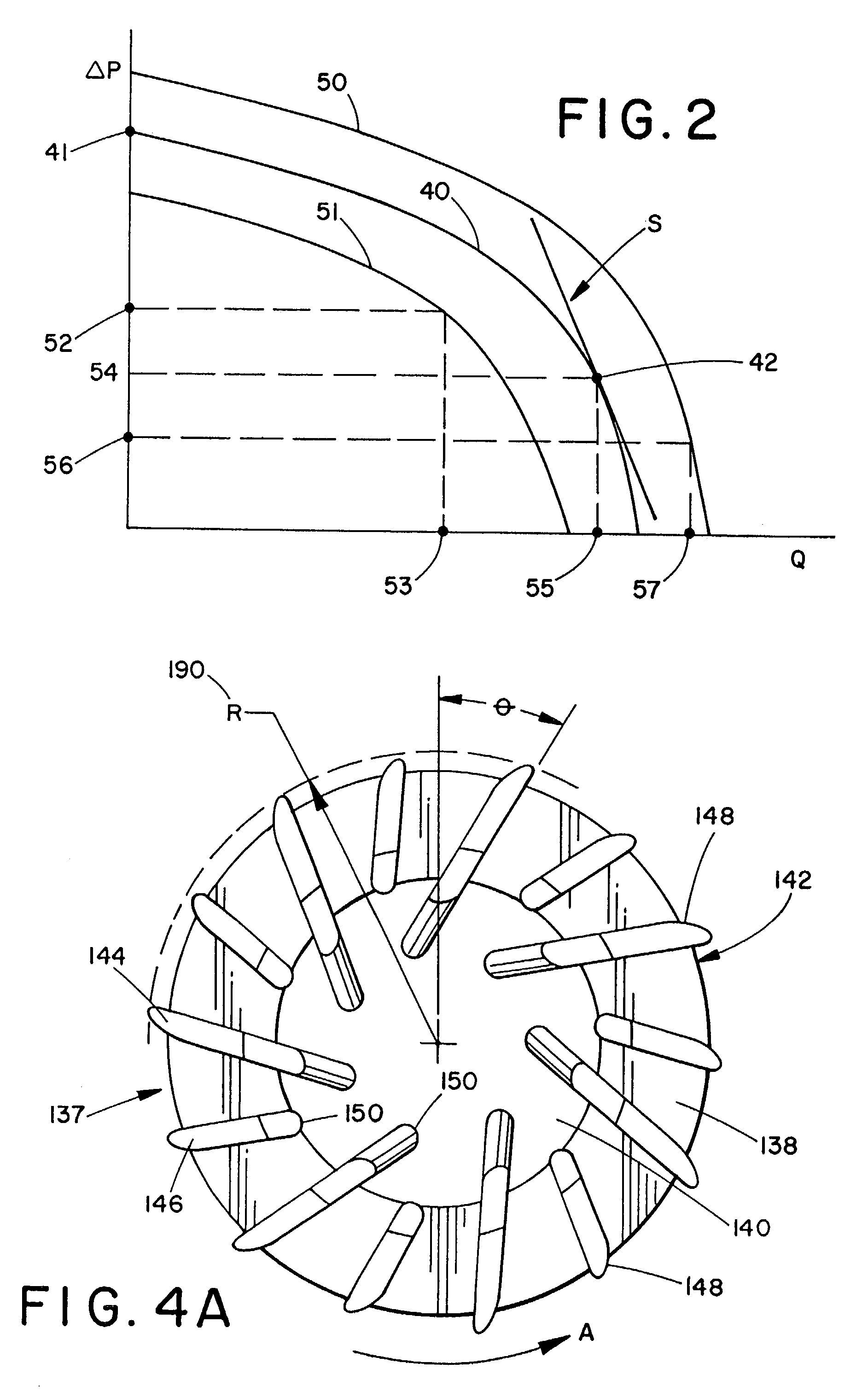
Flow controlled blood pump system
InactiveUS7435059B2Increase rotation speedStrengthen the pressure effectControl devicesBlood pumpsTraffic capacityPower flow
A system for pumping blood to assist or assume the cardiac function of a patient is characterized by a blood pump that exhibits a steep performance curve such that only small changes in pump flow occur for large changes in differential pressure across the pump. The pump therefore exhibits flow-limiting characteristics to protect the physiological system against harmful flow rates or pressures. Pump flow may also be limited by controlling the current provided to a driver from a power supply or by suitable restrictions within or external to the pump housing.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Method and apparatus for aligning a mask with the visual axis of an eye
InactiveUS20060270946A1Increase depth of focusMaintain alignmentEye diagnosticsOphthalmology departmentOptometry
A method is provided for increasing the depth of focus of an eye of a patient. A visual axis of the eye is aligned with an instrument axis of an ophthalmic instrument. The ophthalmic instrument has an aperture through which the patient may look along the instrument axis. A first reference target is imaged on the instrument axis at a first distance with respect to the eye. A second reference target is imaged on the instrument axis with the ophthalmic instrument at a second distance with respect to the eye. The second distance is greater than the first distance. Movement is provided such that the patient's eye is in a position where the images of the first and second reference targets appear to the patient's eye to be aligned. A mask comprising a pin-hole aperture having a mask axis is aligned with the instrument axis such that the mask axis and the instrument axis are substantially collinear. The mask is applied to the eye of the patient while the alignment of the mask axis and the instrument axis is maintained. Maintaining alignment of the mask axis and the instrument axis may be facilitated by capturing an image of the eye.
Owner:SILVESTRINI THOMAS +3
Centrifugal heat transfer engine and heat transfer systems embodying the same
InactiveUS6964176B2Simple methodReduce the introductionSelf-contained rotary compression machinesCompression machines with non-reversible cycleRotational axisThermal isolation
A heat transfer engine having cooling and heating modes of reversible operation, in which heat can be effectively transferred within diverse user environments for cooling, heating and dehumidification applications. The heat transfer engine of the present invention includes a rotor structure which is rotatably supported within a stator structure. The stator has primary and secondary heat exchanging chambers in thermal isolation from each other. The rotor has primary and secondary heat transferring portions within which a closed fluid flow circuit is embodied. The closed fluid flow circuit within the rotor has a spiraled fluid-return passageway extending along its rotary shaft, and is charged with a refrigerant which is automatically circulated between the primary and secondary heat transferring portions of the rotor when the rotor is rotated within an optimized angular velocity range under the control of a temperature-responsive system controller.
Owner:KELIX HEAT TRANSFER SYST
Mask configured to maintain nutrient transport without producing visible diffraction patterns
InactiveUS20060271182A1Increase depth of focusEliminate DiffractionSpectales/gogglesSenses disorderAnterior surfaceCorneal layer
A mask configured to be implanted in a cornea of a patient to increase the depth of focus of the patient includes an anterior surface, a posterior surface, and a plurality of holes. The anterior surface is configured to reside adjacent a first corneal layer. The posterior surface is configured to reside adjacent a second corneal layer. The plurality of holes extends at least partially between the anterior surface and the posterior surface. The holes of the plurality of holes are configured to substantially eliminate visible diffraction patterns.
Owner:CHRISTIE BRUCE A +2
Mask configured to maintain nutrient transport without producing visible diffraction patterns
InactiveUS20060271180A1Increase depth of focusEliminate DiffractionSpectales/gogglesSenses disorderAnterior surfaceCorneal layer
A mask configured to be implanted in a cornea of a patient to increase the depth of focus of the patient includes an anterior surface, a posterior surface, and a plurality of holes. The anterior surface is configured to reside adjacent a first corneal layer. The posterior surface is configured to reside adjacent a second corneal layer. The plurality of holes extends at least partially between the anterior surface and the posterior surface. The holes of the plurality of holes are configured to substantially eliminate visible diffraction patterns.
Owner:CHRISTIE BRUCE A +2
Reaming and stabilization tool and method for its use in a borehole
ActiveUS20050274546A1Disadvantages and and reduced eliminatedFunctionality reduced eliminatedDrill bitsCutting machinesMechanical engineeringDrill hole
In accordance with an embodiment of the present invention, a drilling tool includes a tubular body defining a longitudinal axial cavity extending therethrough and defining at least one cutter element recess. The drilling tool also includes a cutter element at least partially disposed within the at least one cutter element recess and includes at least first and second cutting arms at least substantially disposed within the cutter element recess in a retracted position. The first and second cutting arms are operable to move from the retracted position to an extended position in which the first and second cutting arms extend at least partially beyond a periphery of the tubular body. The first and second cutting arms and the tubular body enclose a space when the first and second cutting arms are in the extended position.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com