Patents
Literature
573 results about "Core temperature" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
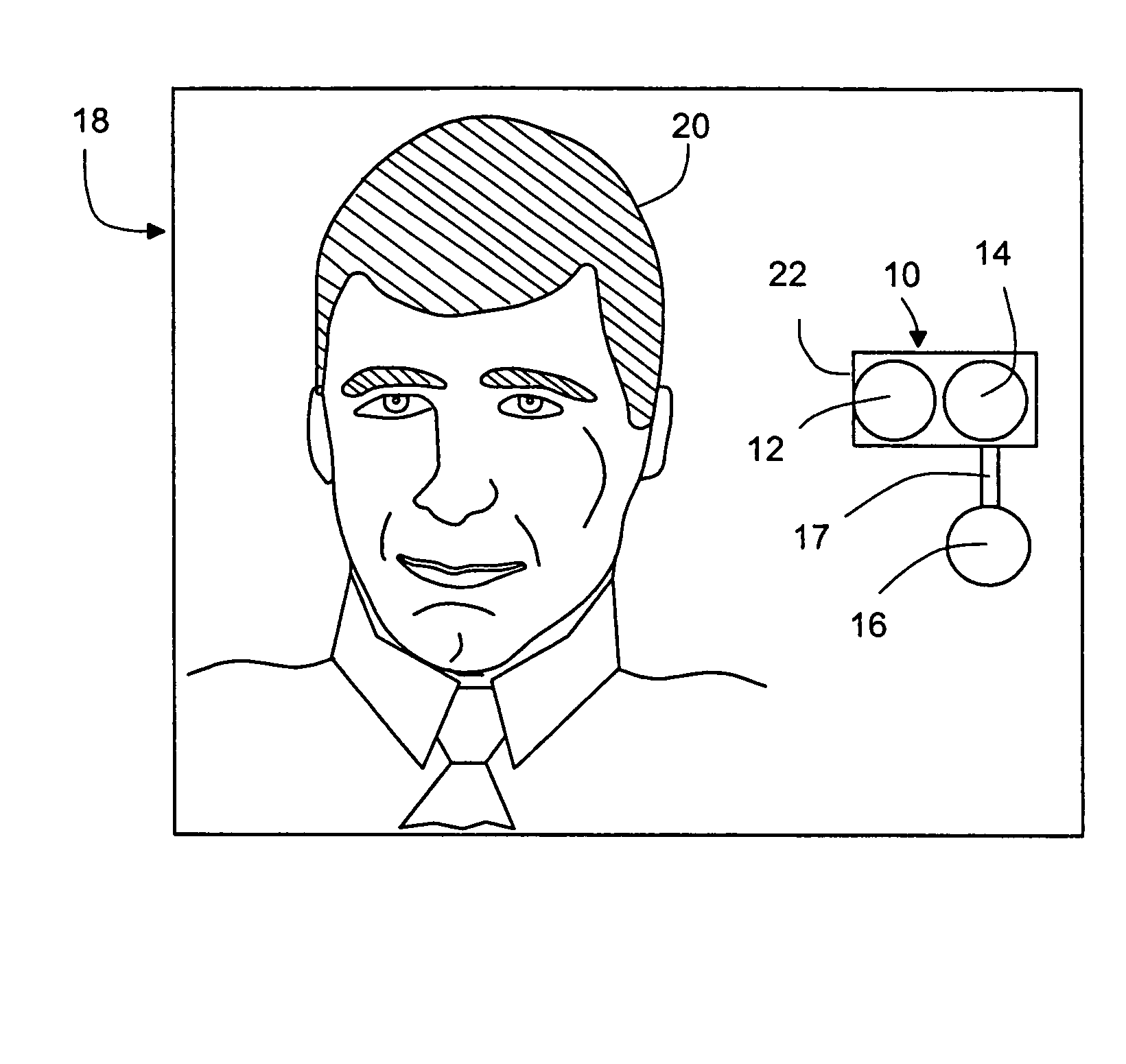
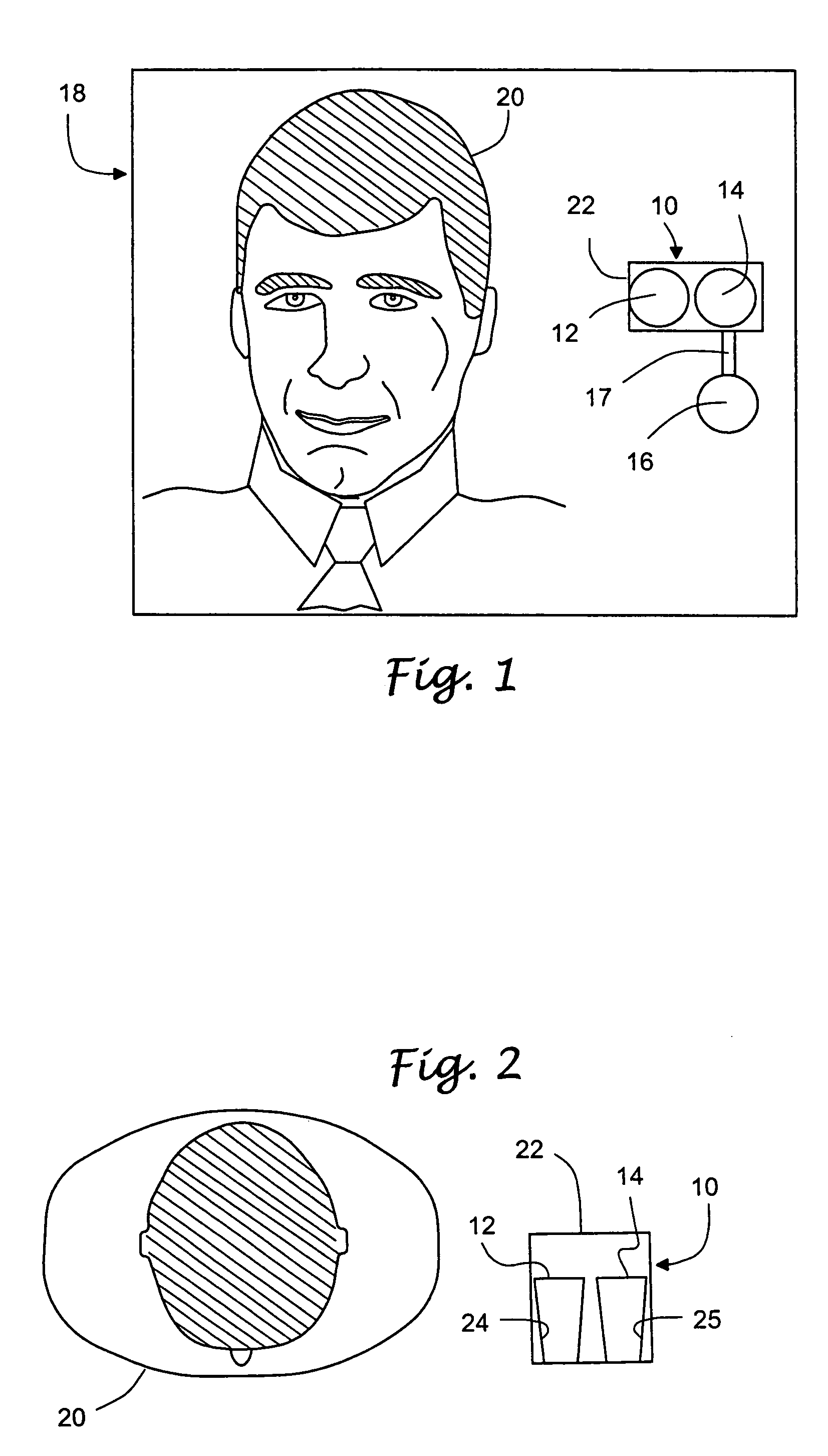
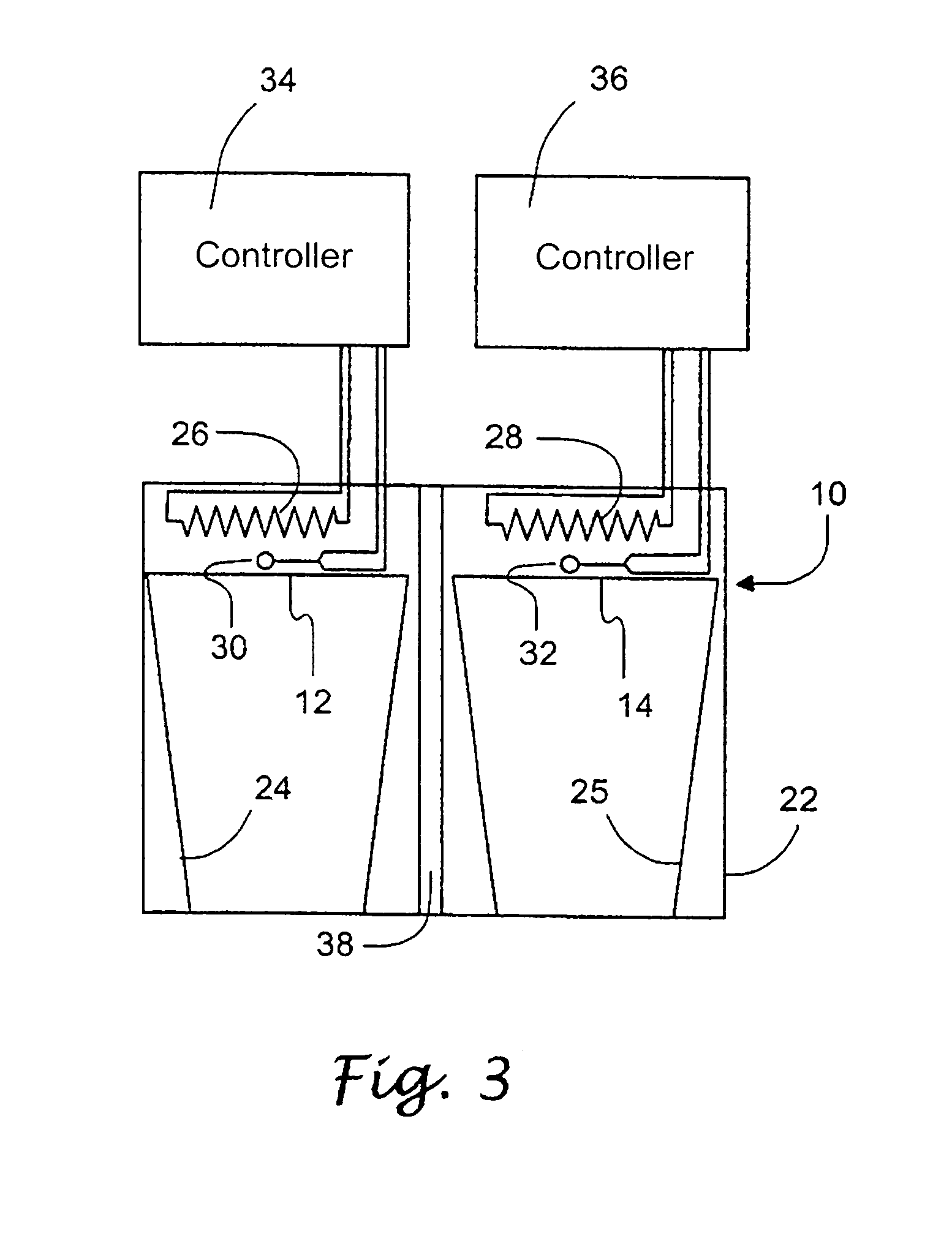
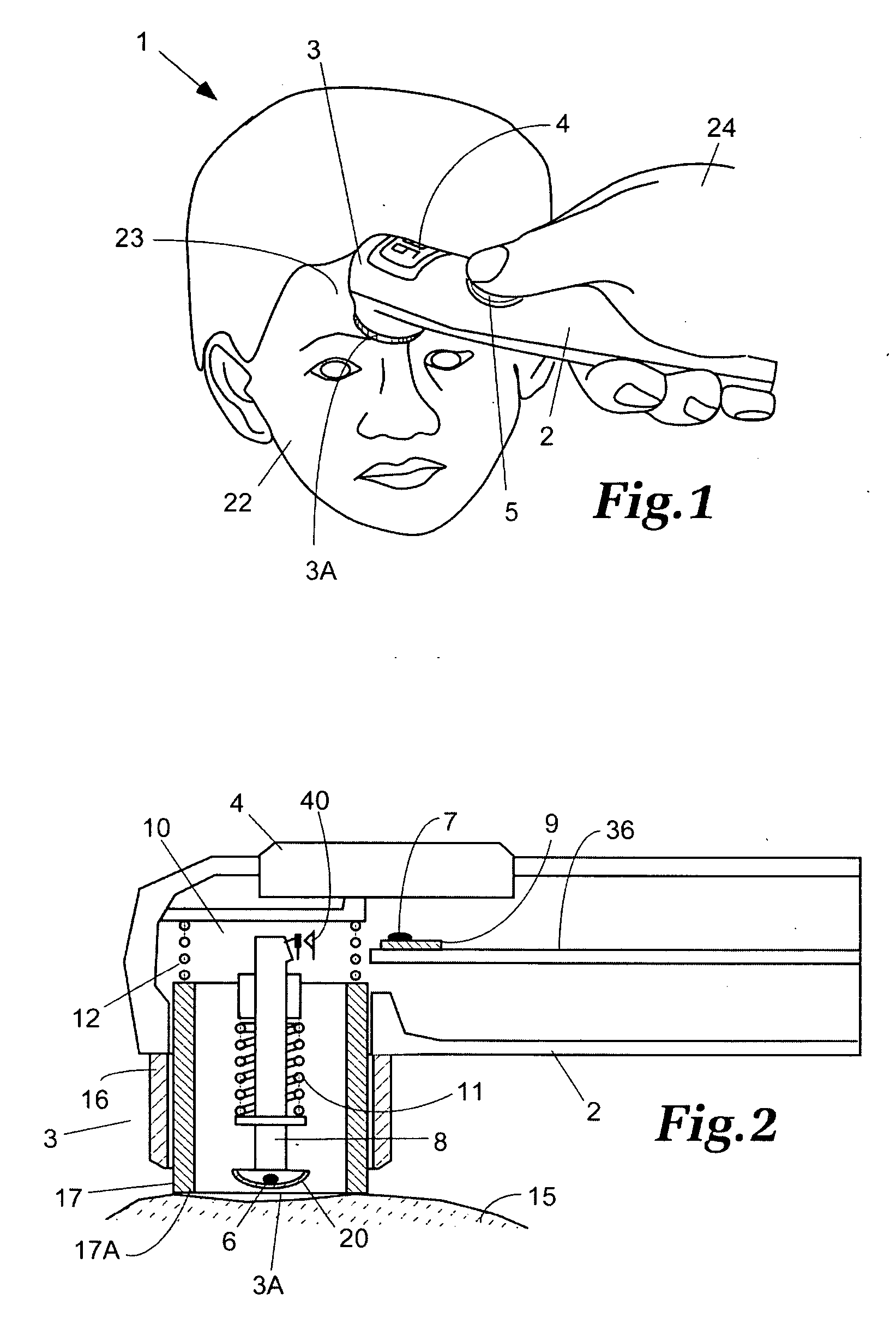
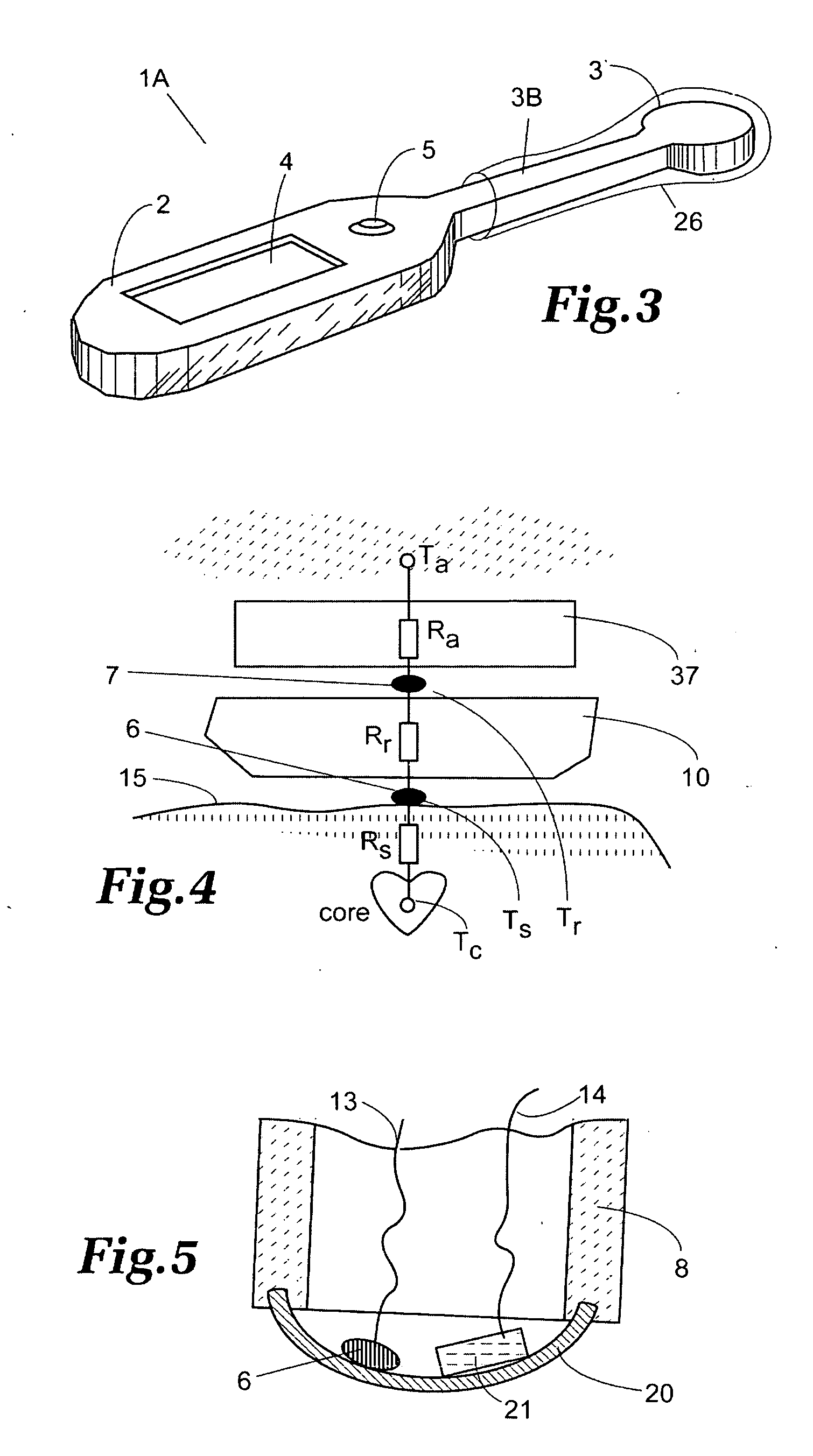
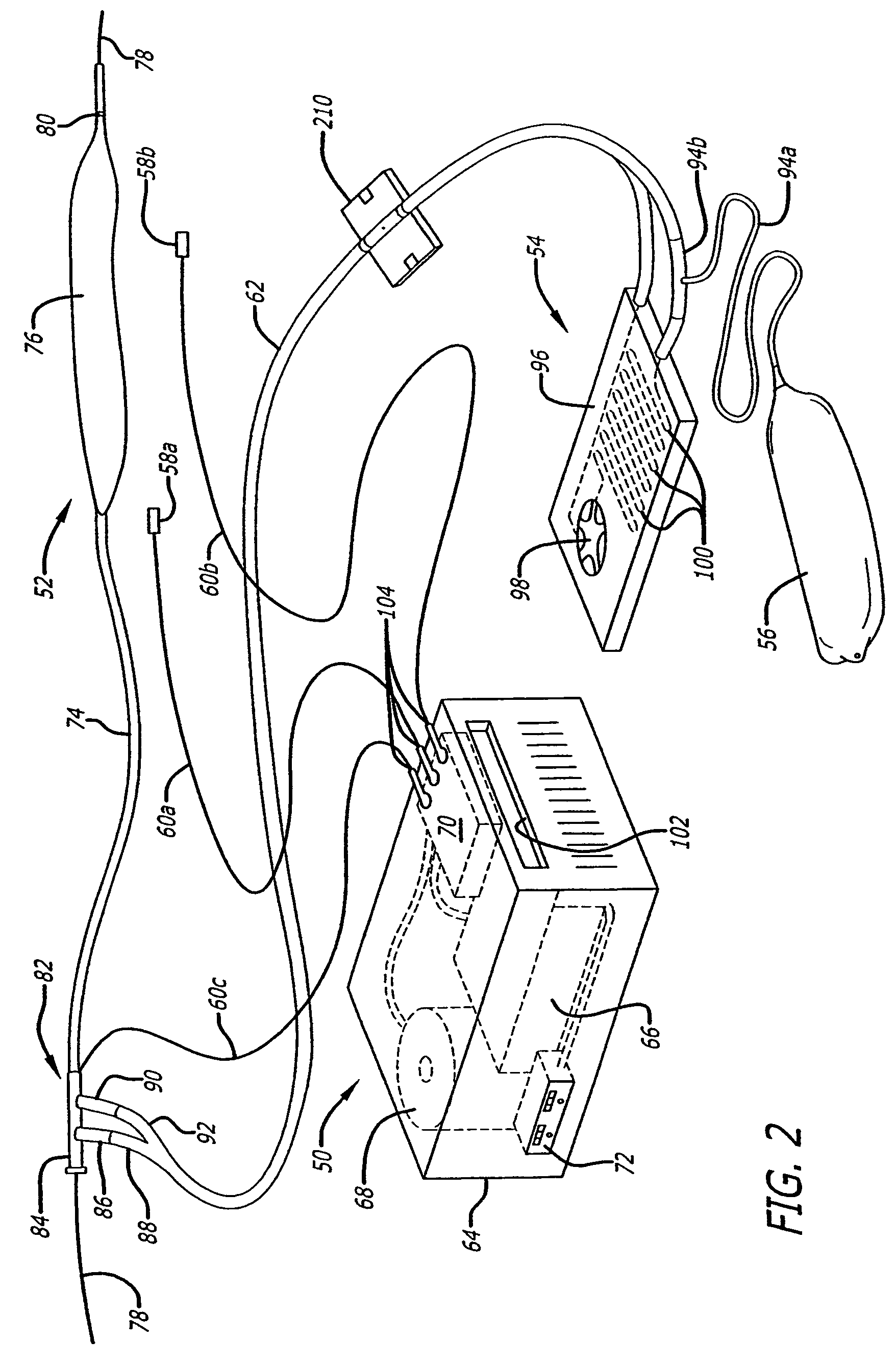
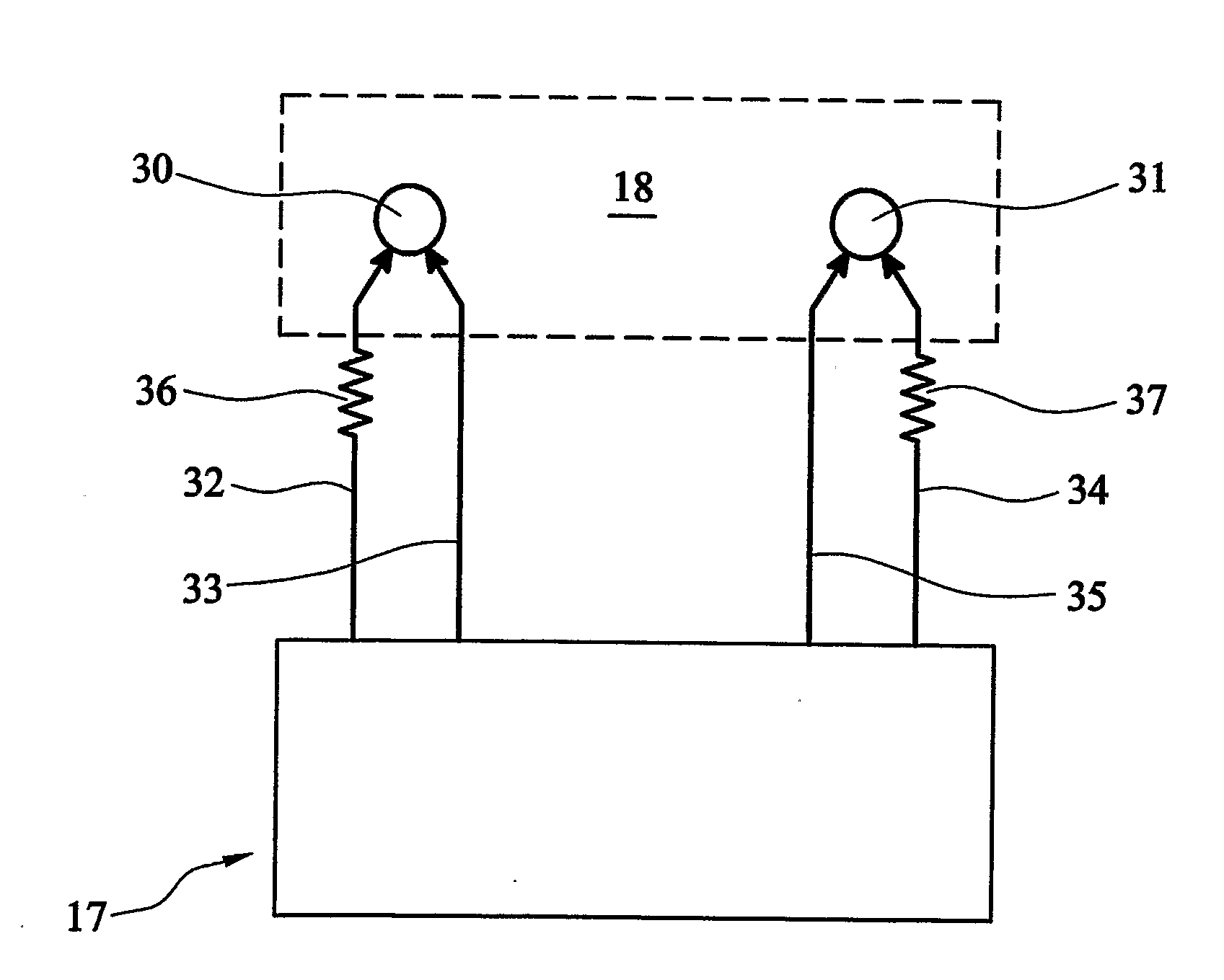
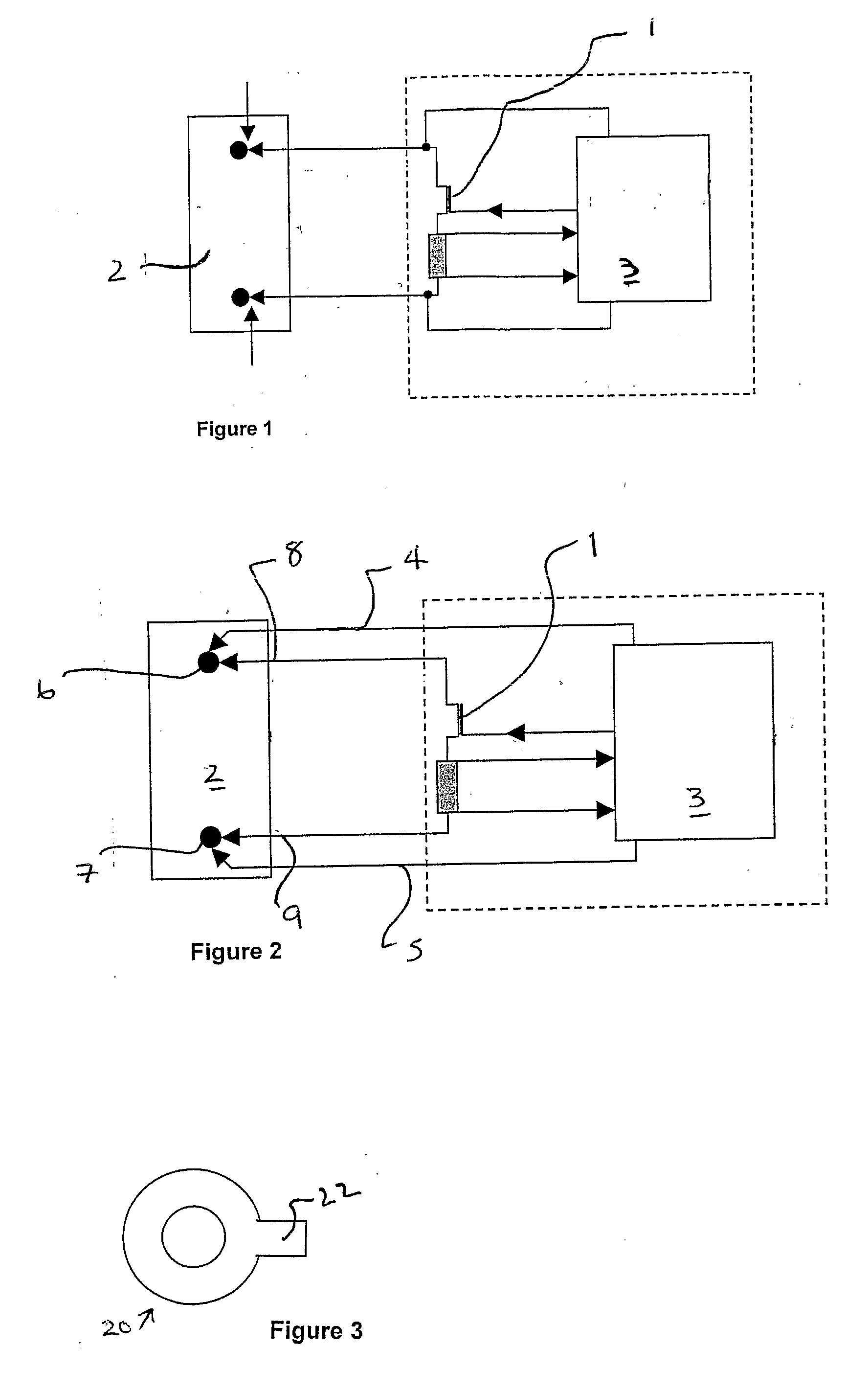
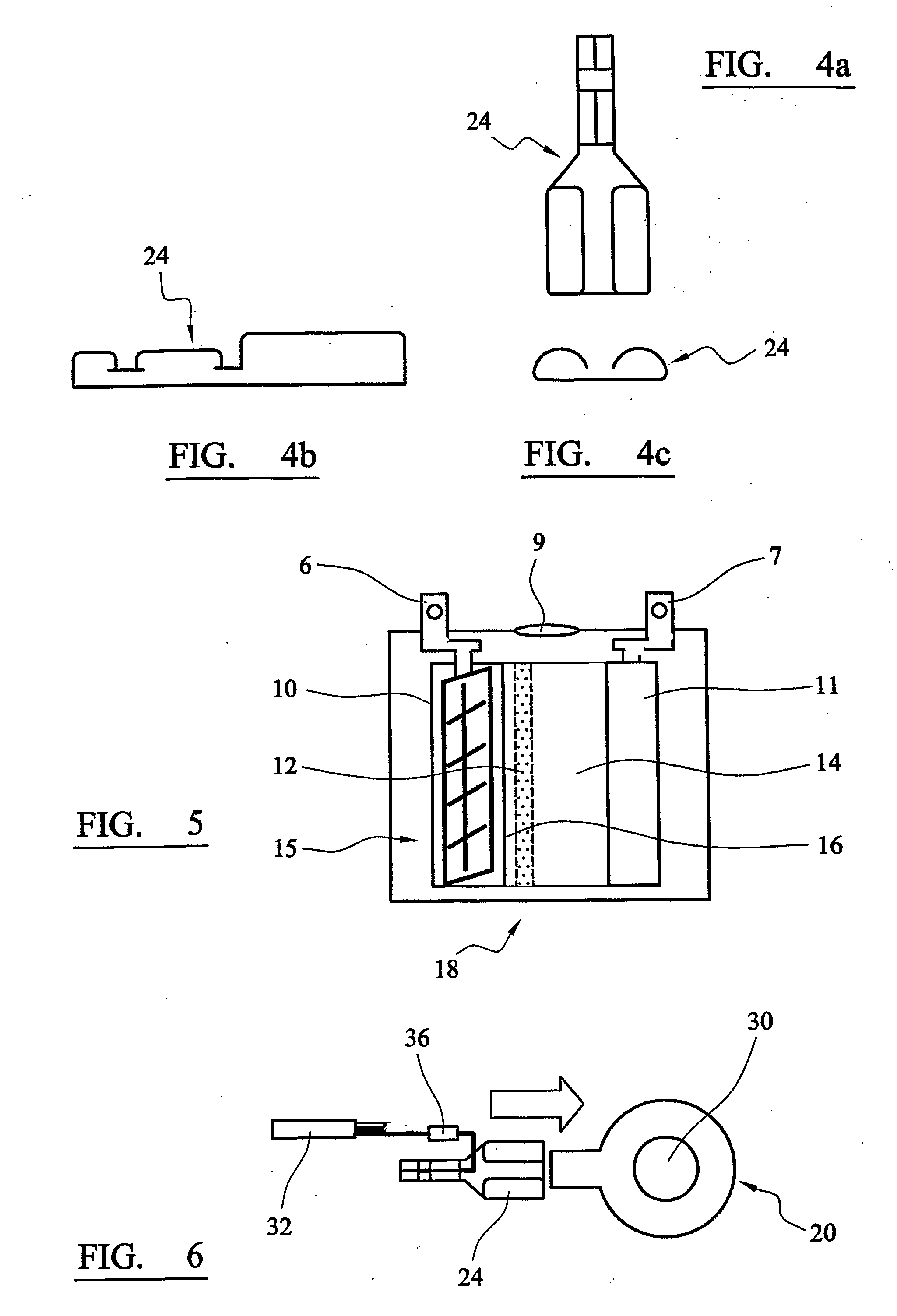
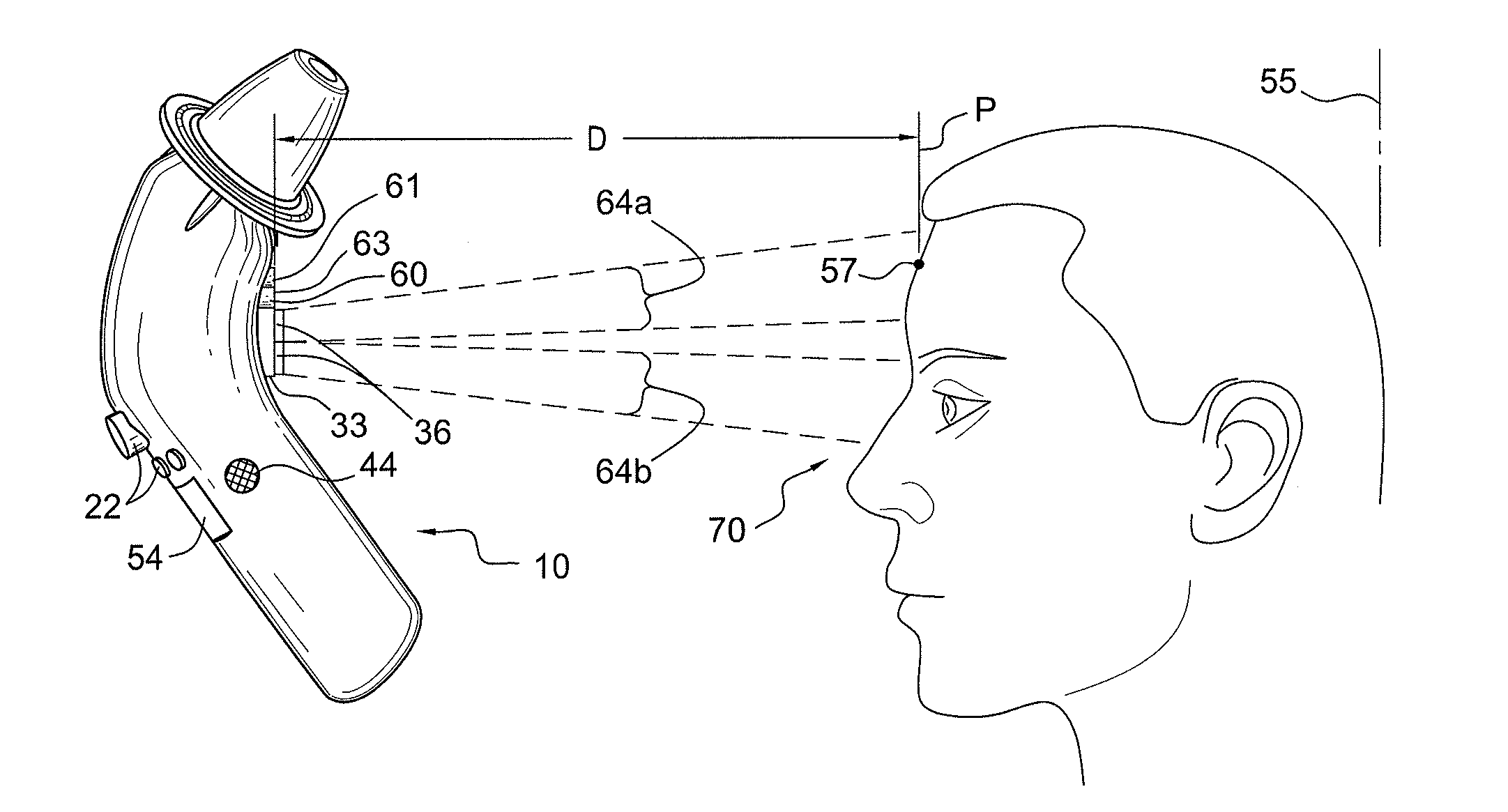
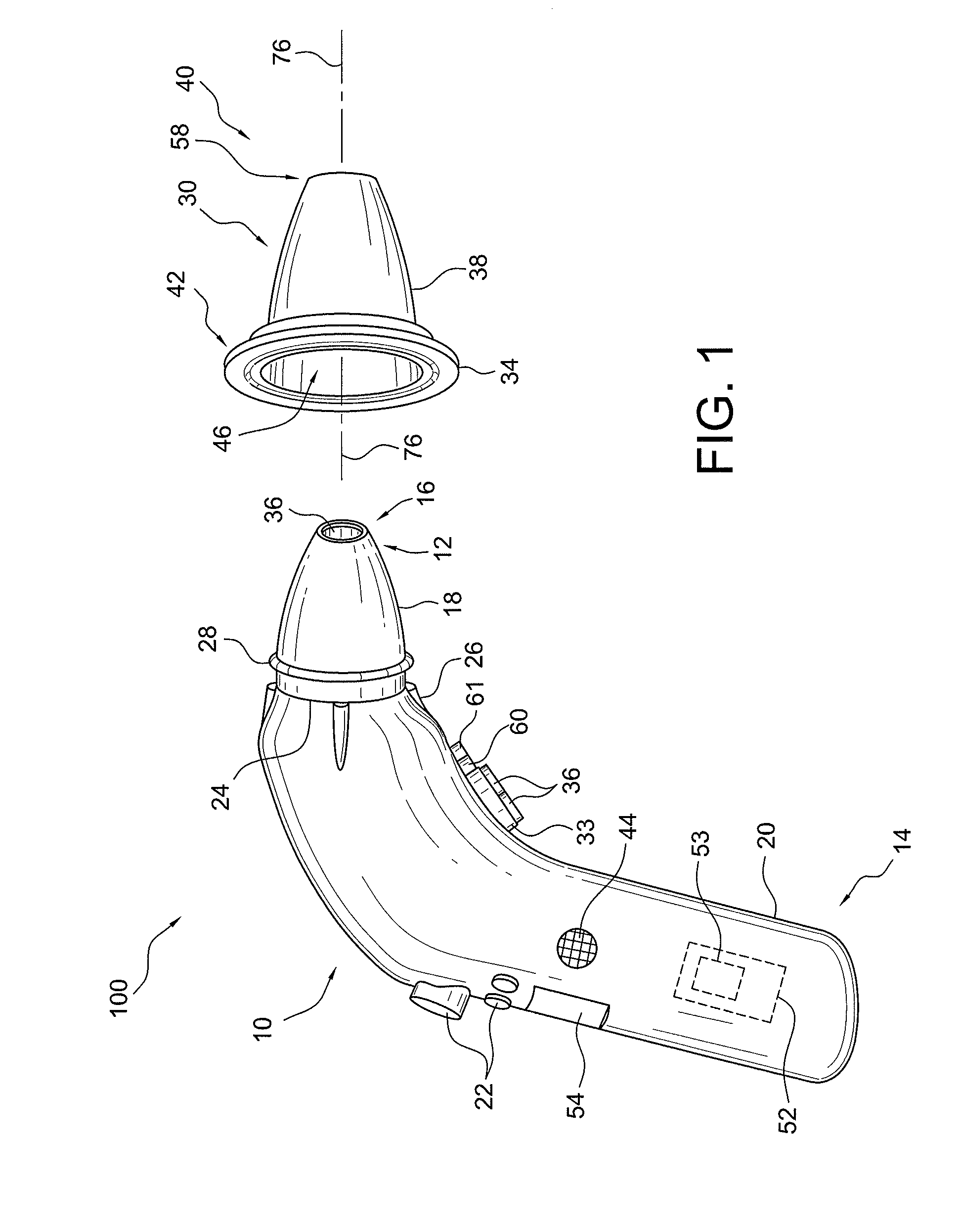
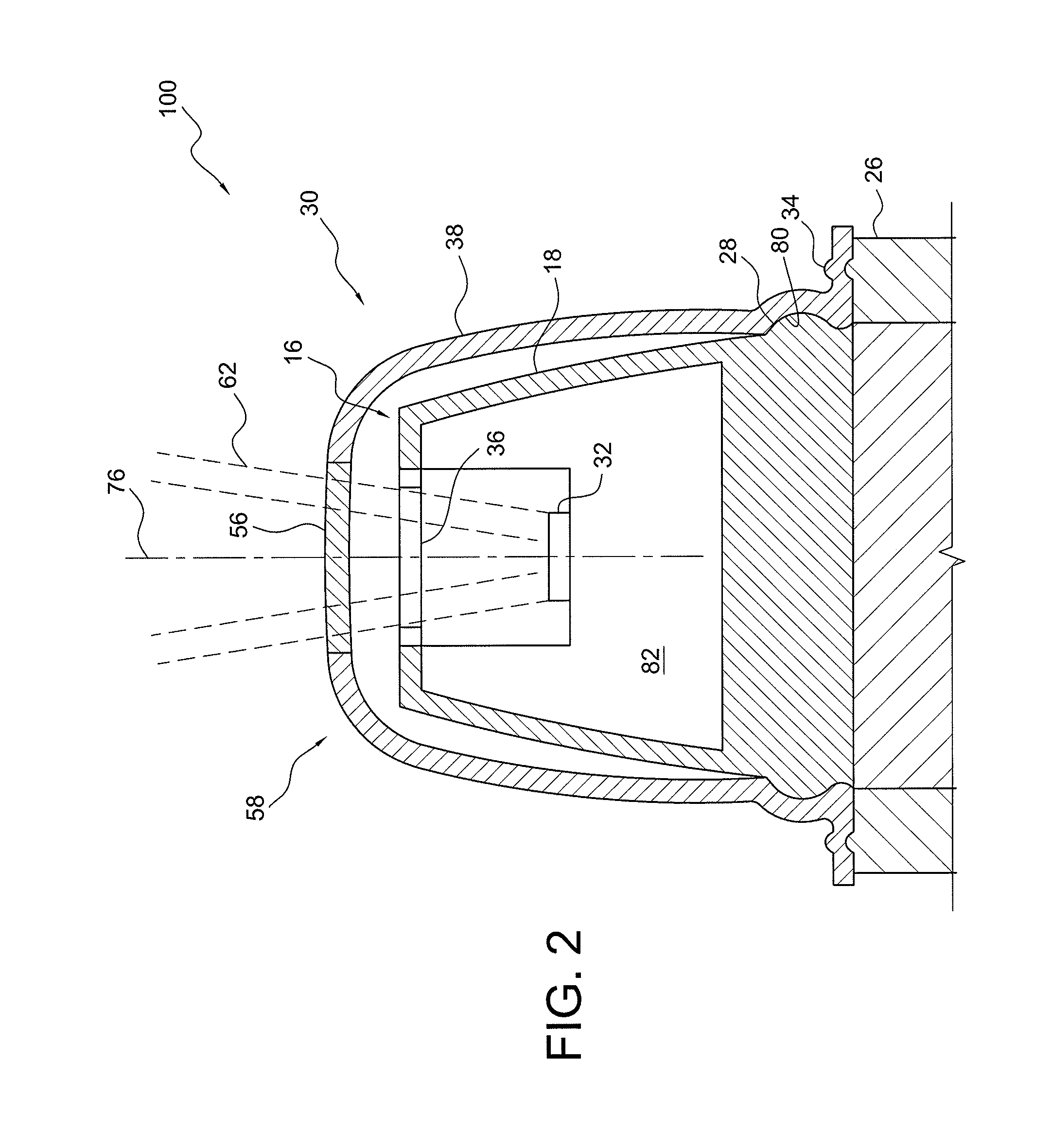
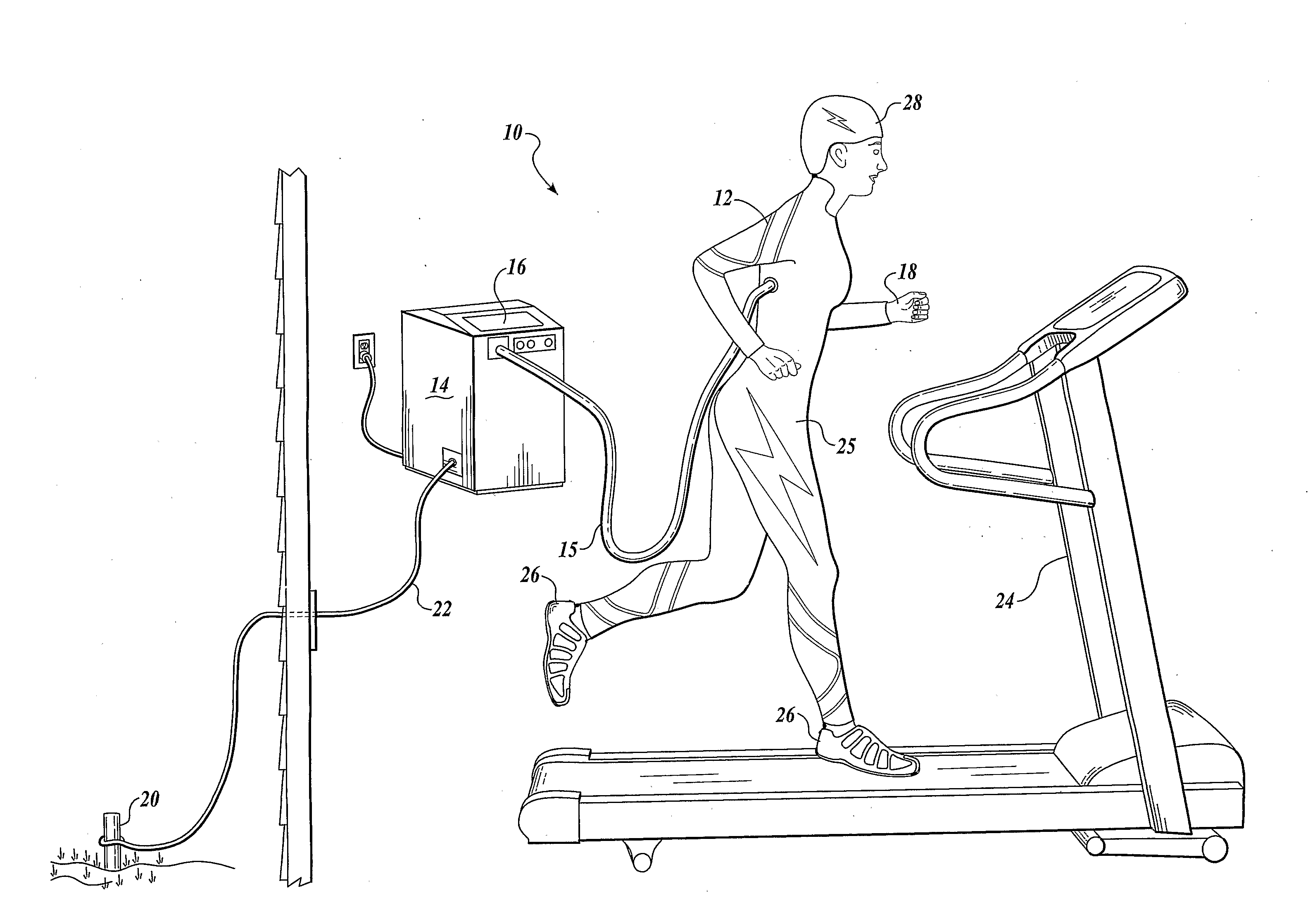
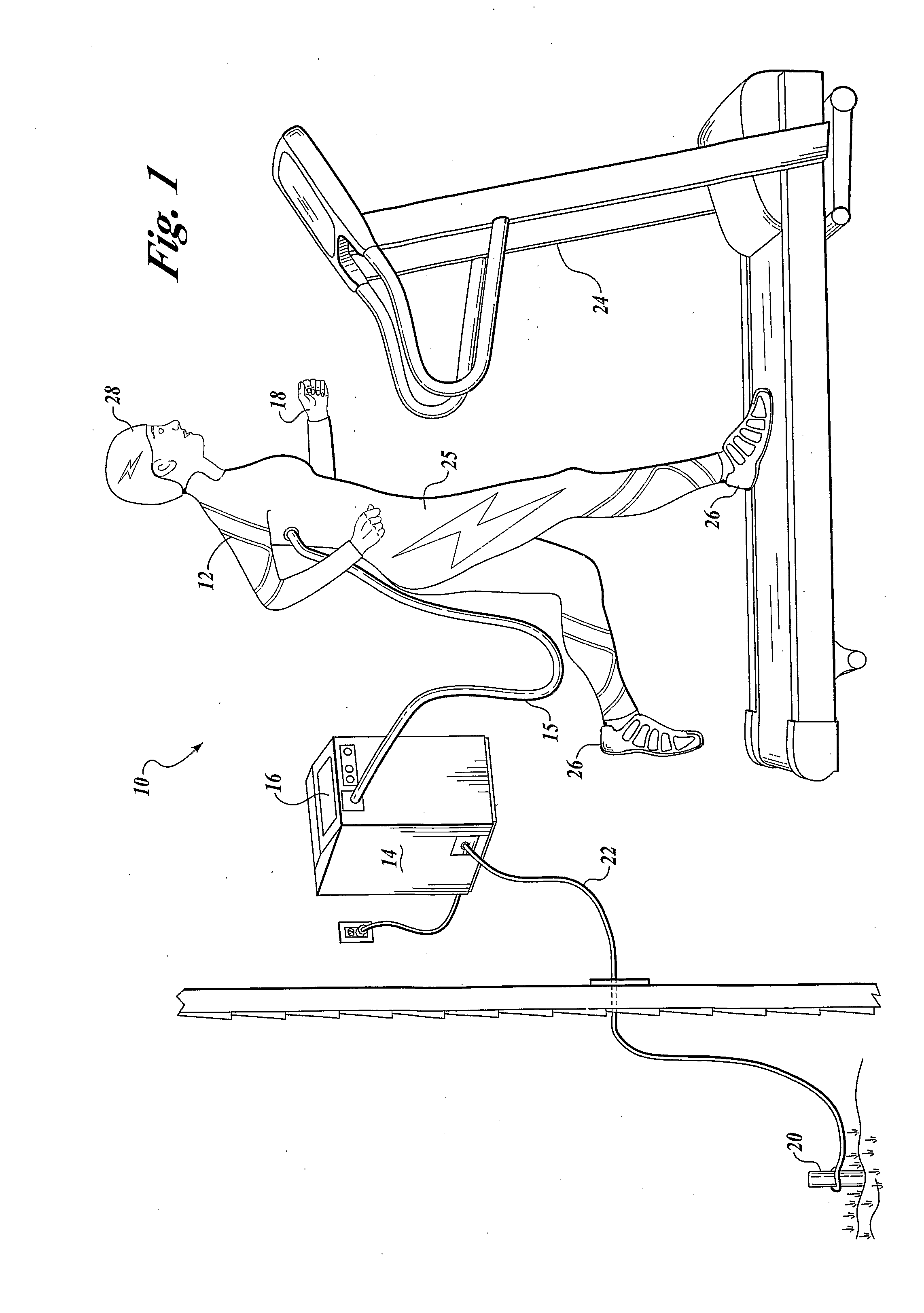
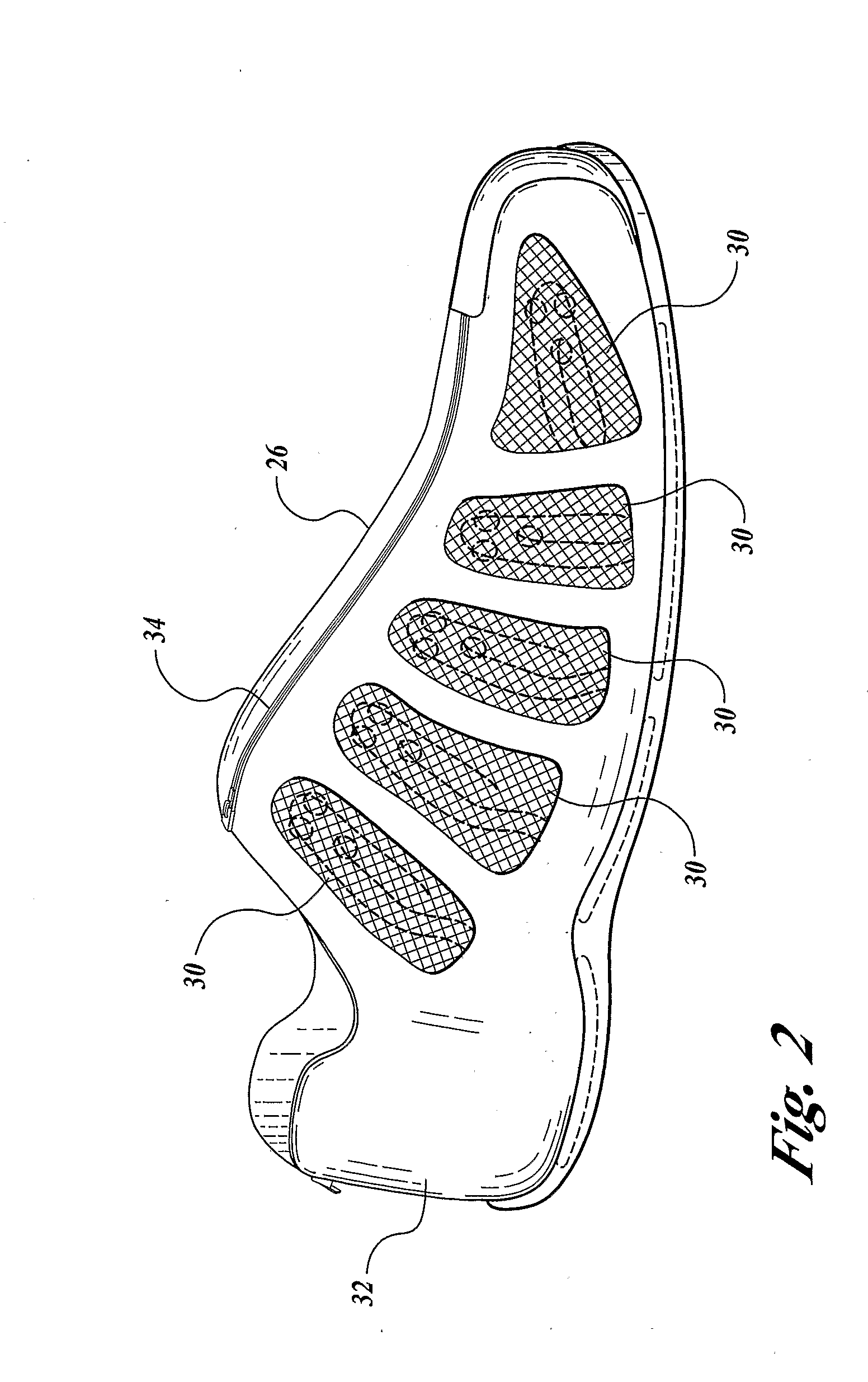
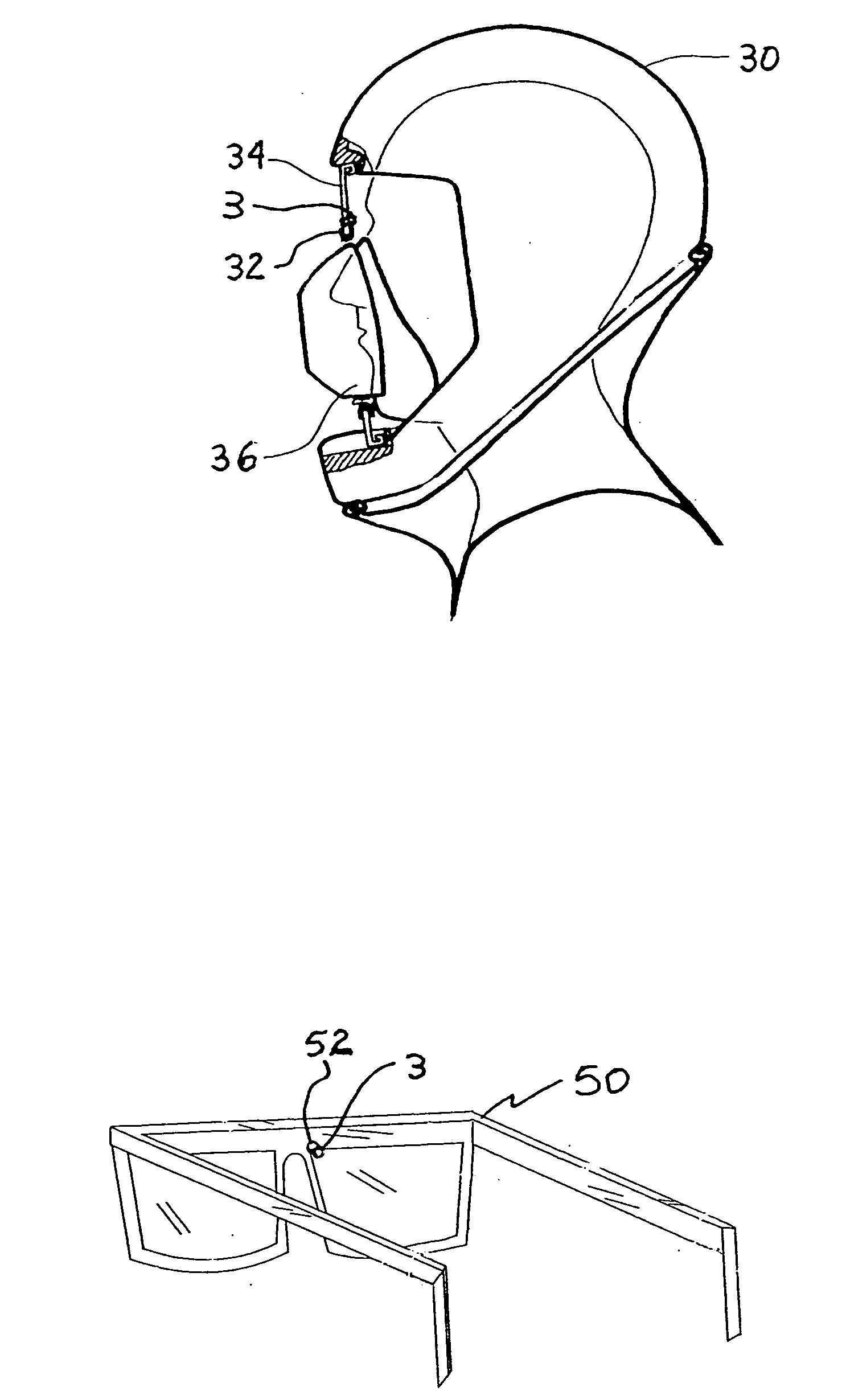
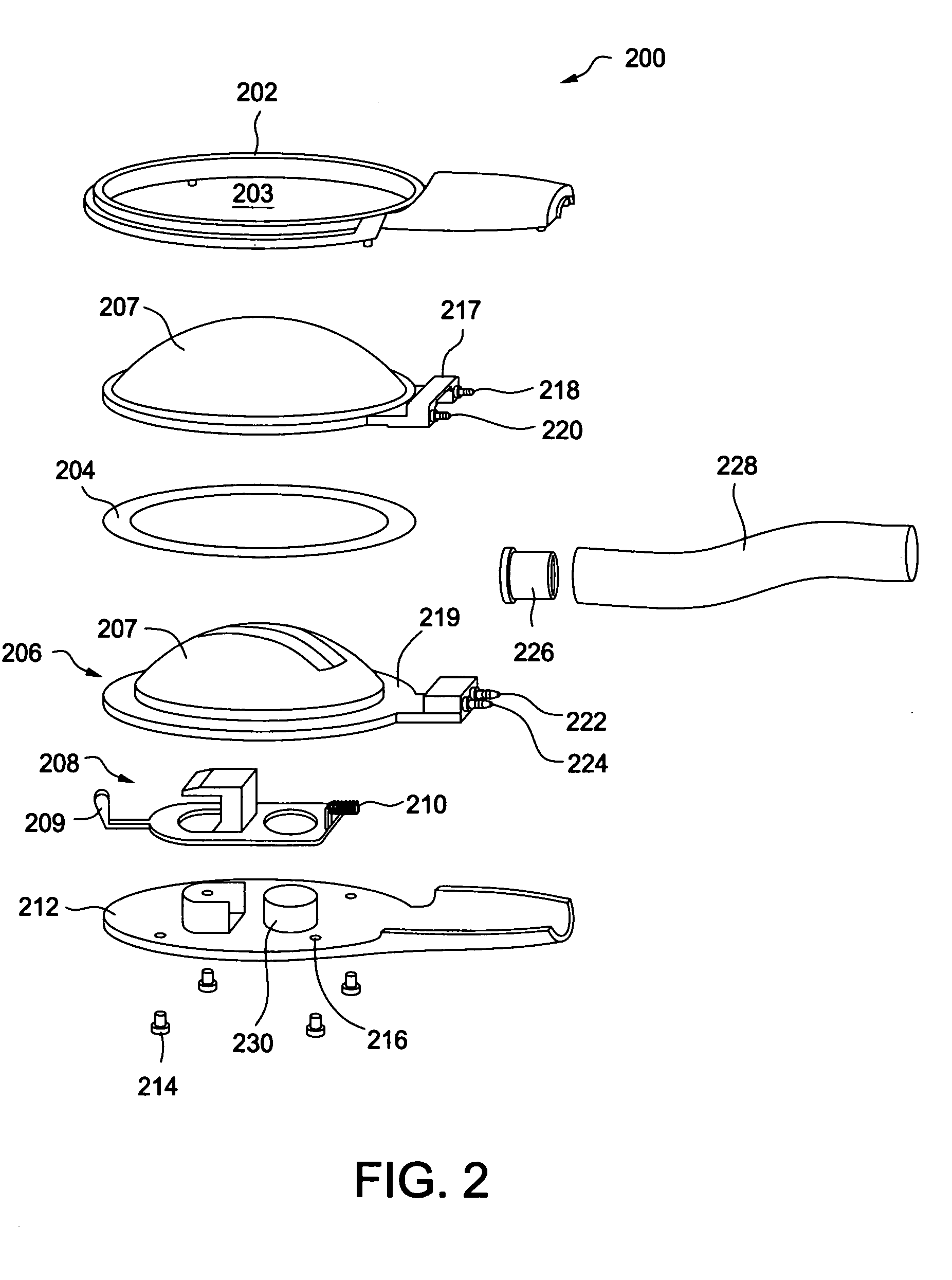
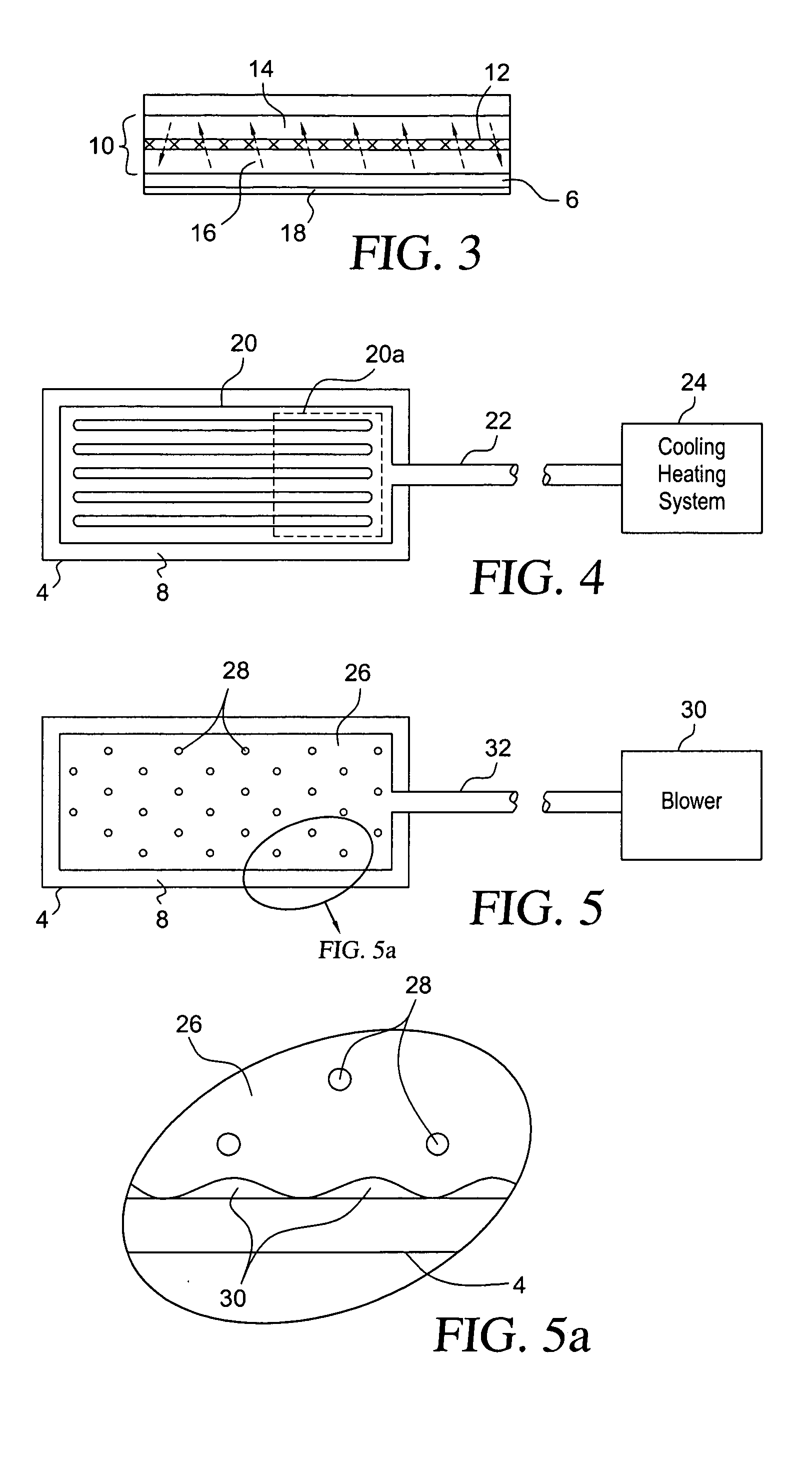
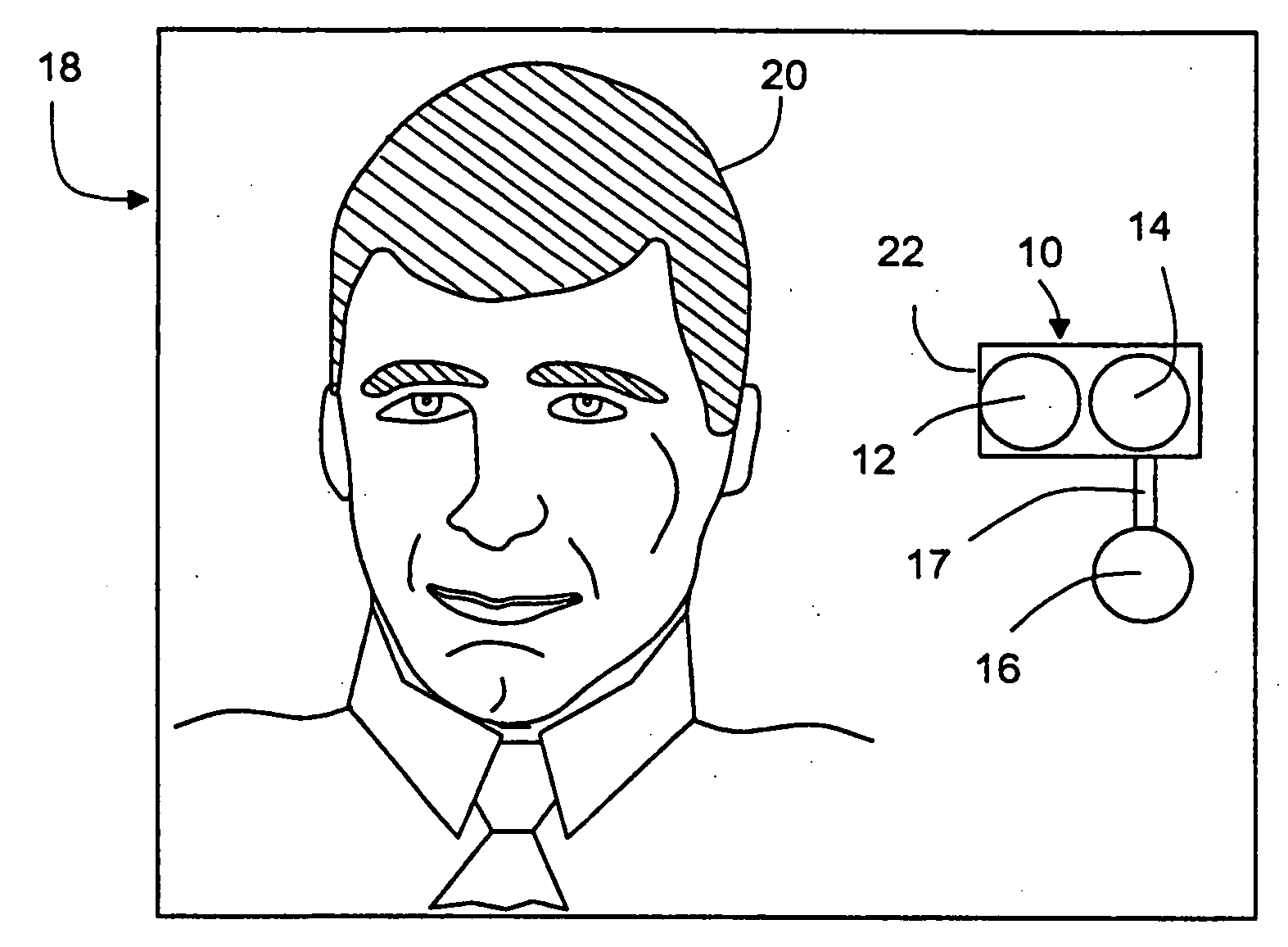
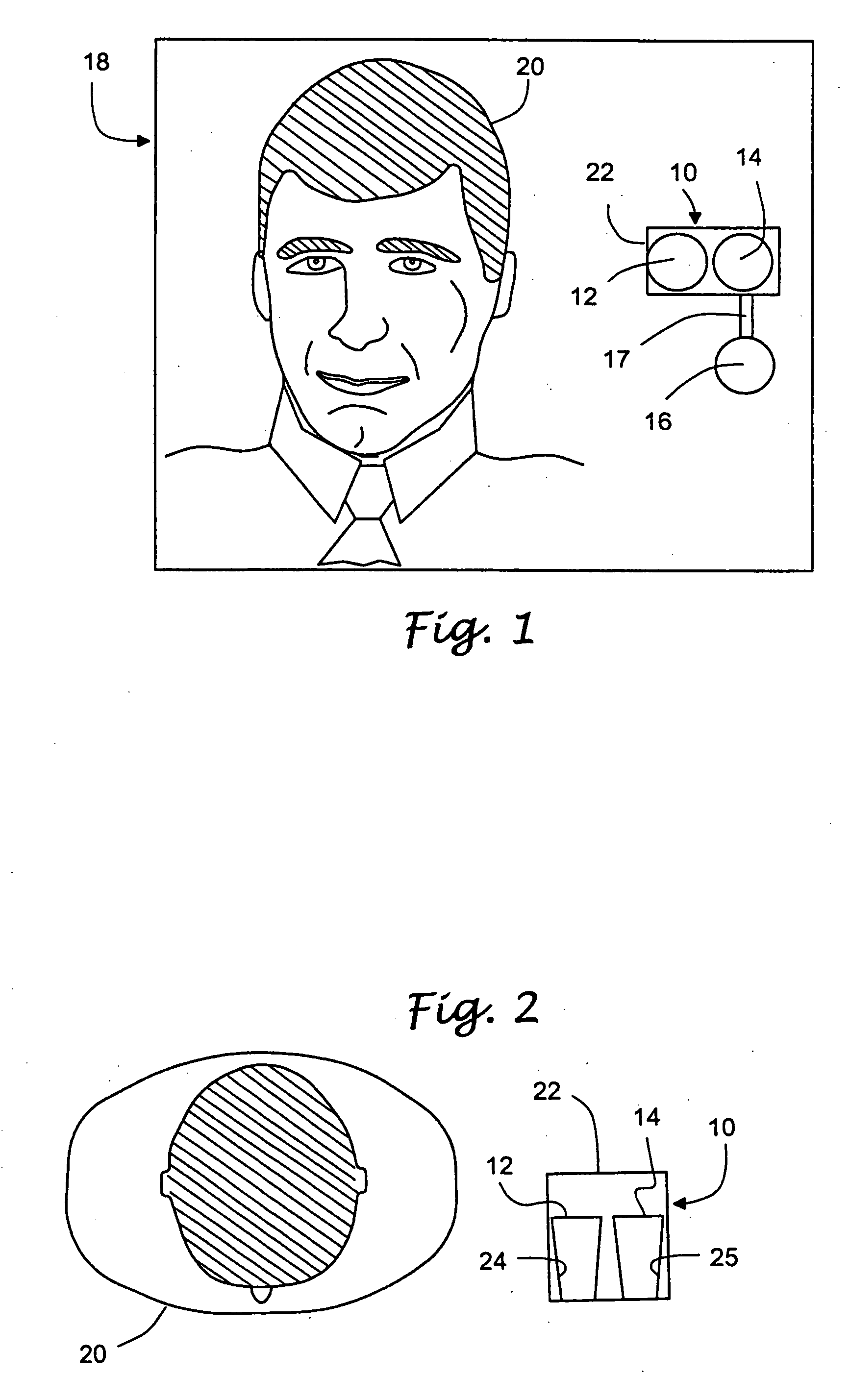
Vital signs probe
InactiveUS20050209516A1Improve performanceAccurate calculationEvaluation of blood vesselsSensorsPulse oximetryCore temperature
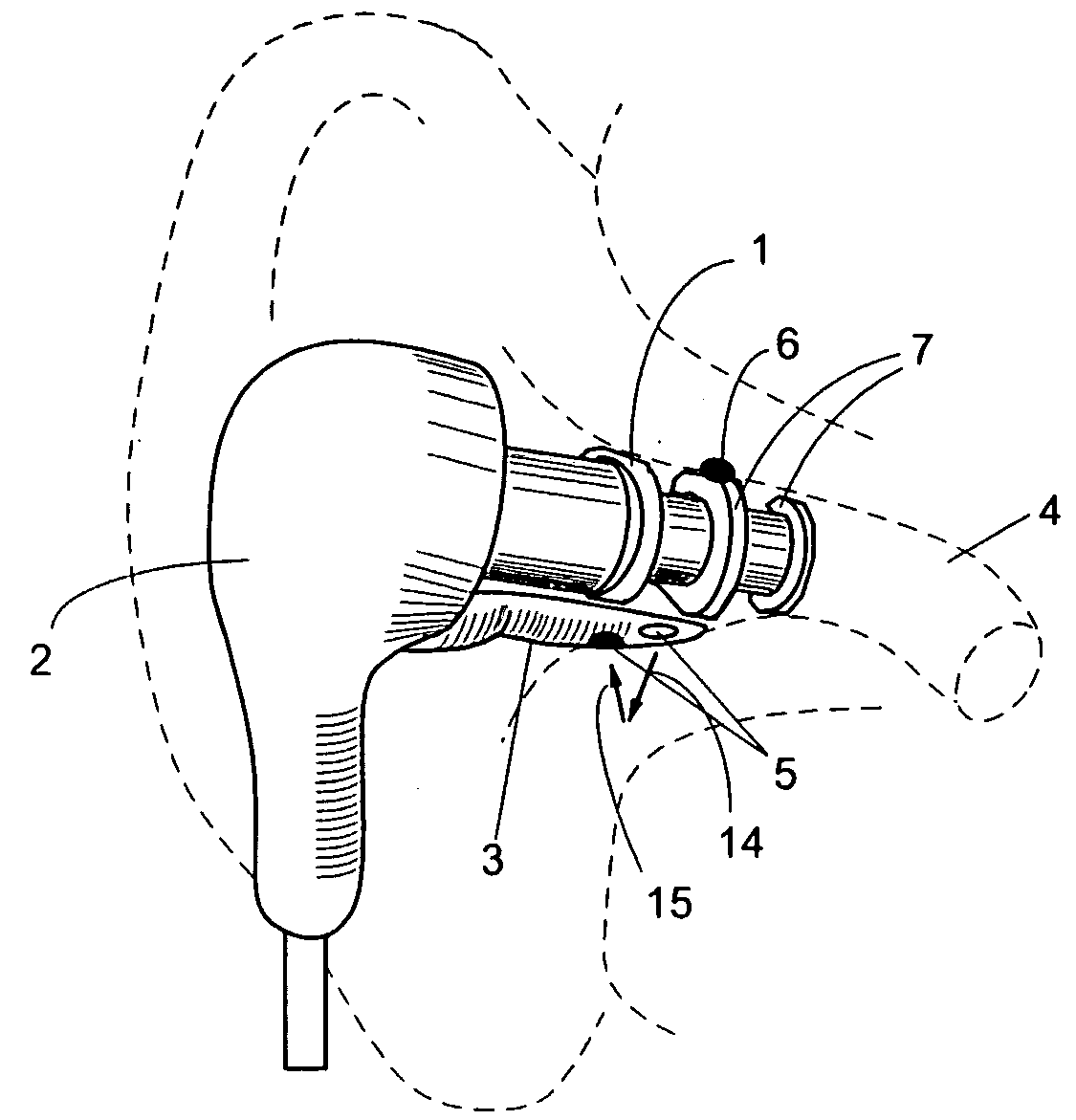
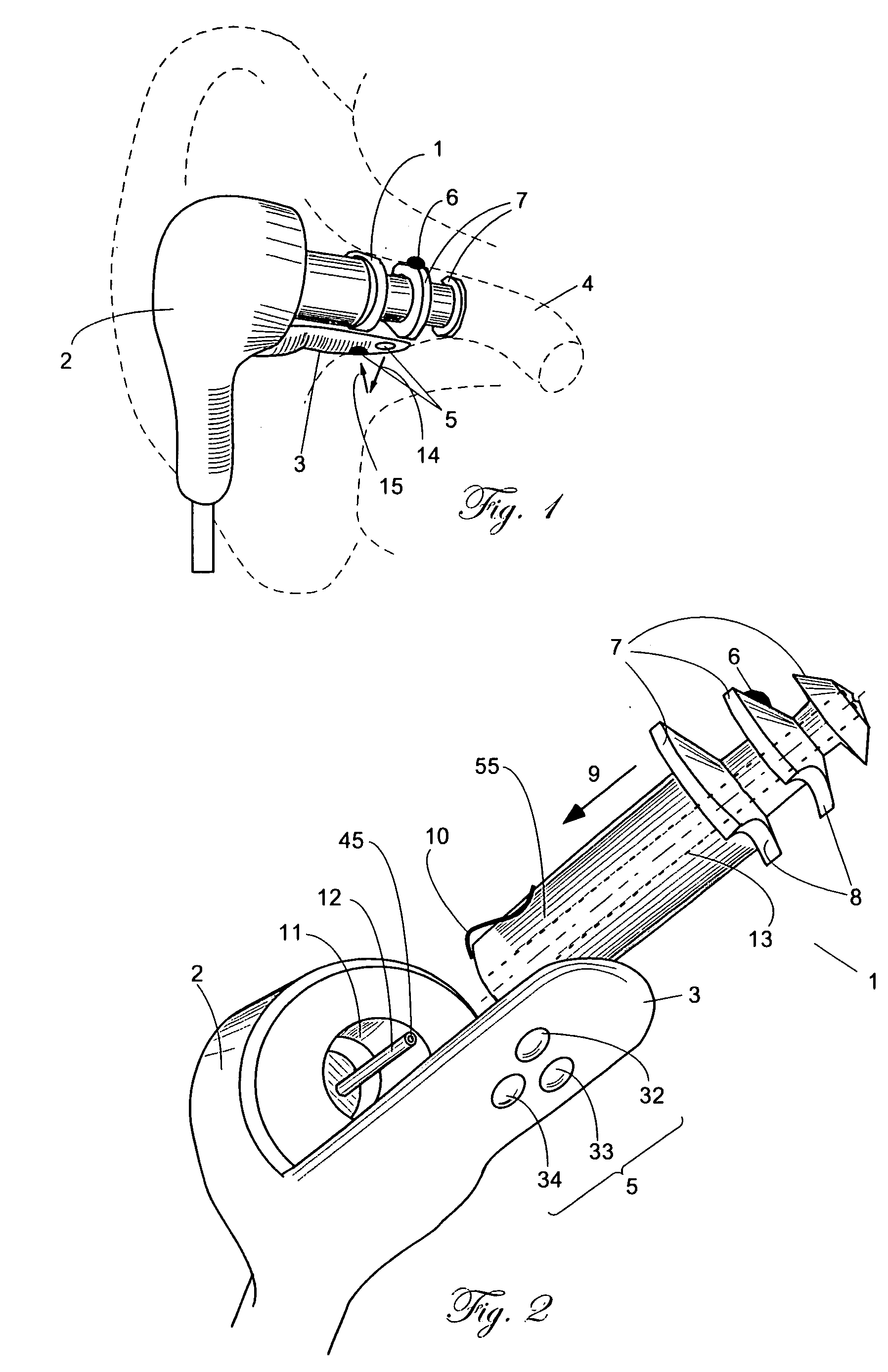
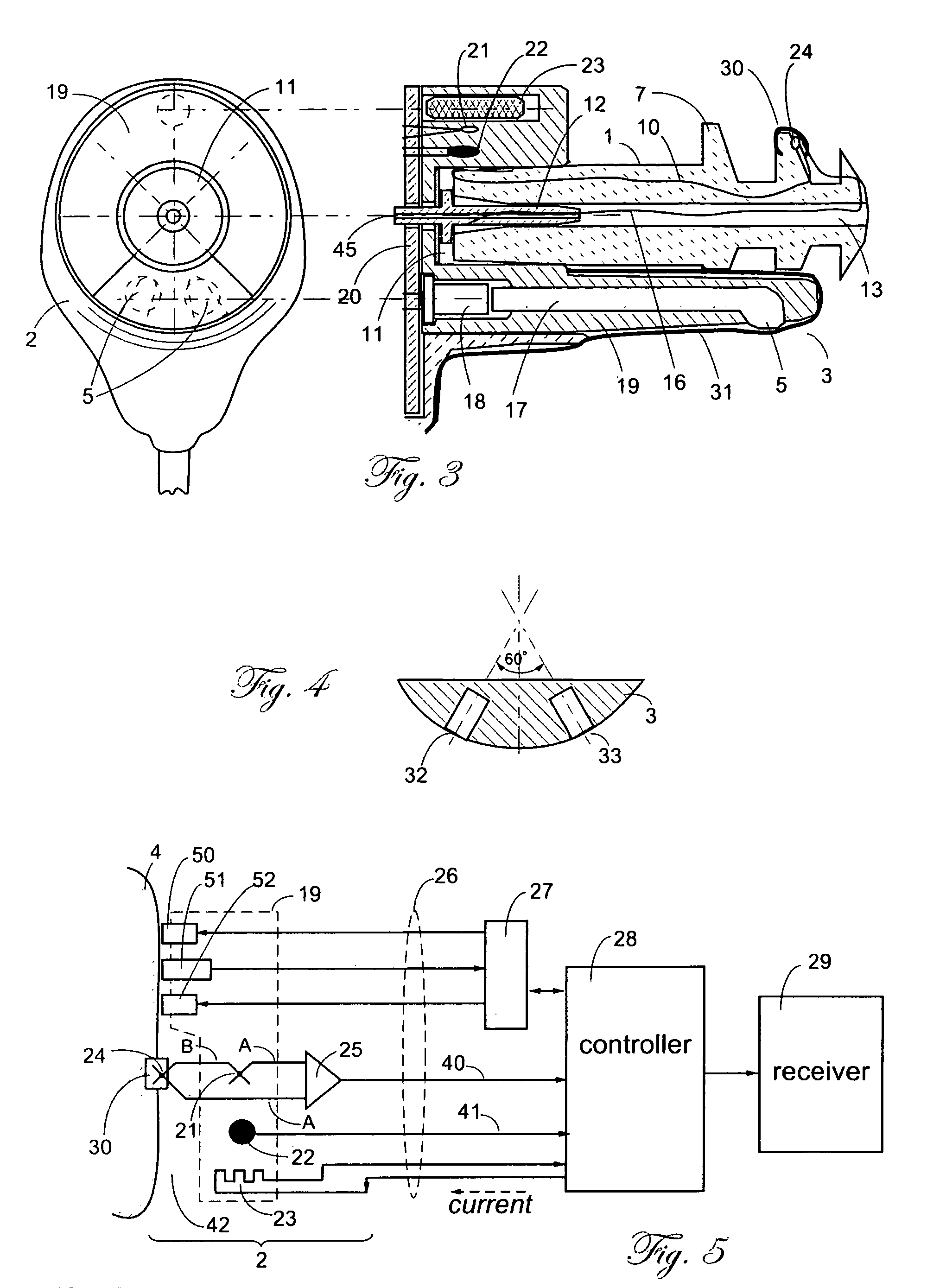
A combination of a patient core temperature sensor and the dual-wavelength optical sensors in an ear probe or a body surface probe improves performance and allows for accurate computation of various vital signs from the photo-plethysmographic signal, such as arterial blood oxygenation (pulse oximetry), blood pressure, and others. A core body temperature is measured by two sensors, where the first contact sensor positioned on a resilient ear plug and the second sensor is on the external portion of the probe. The ear plug changes it's geometry after being inserted into an ear canal and compress both the first temperature sensor and the optical assembly against ear canal walls. The second temperature sensor provides a reference signal to a heater that is warmed up close to the body core temperature. The heater is connected to a common heat equalizer for the temperature sensor and the pulse oximeter. Temperature of the heat equalizer enhances the tissue perfusion to improve the optical sensors response. A pilot light is conducted to the ear canal via a contact illuminator, while a light transparent ear plug conducts the reflected lights back to the light detector.
Owner:FRADEN JACOB
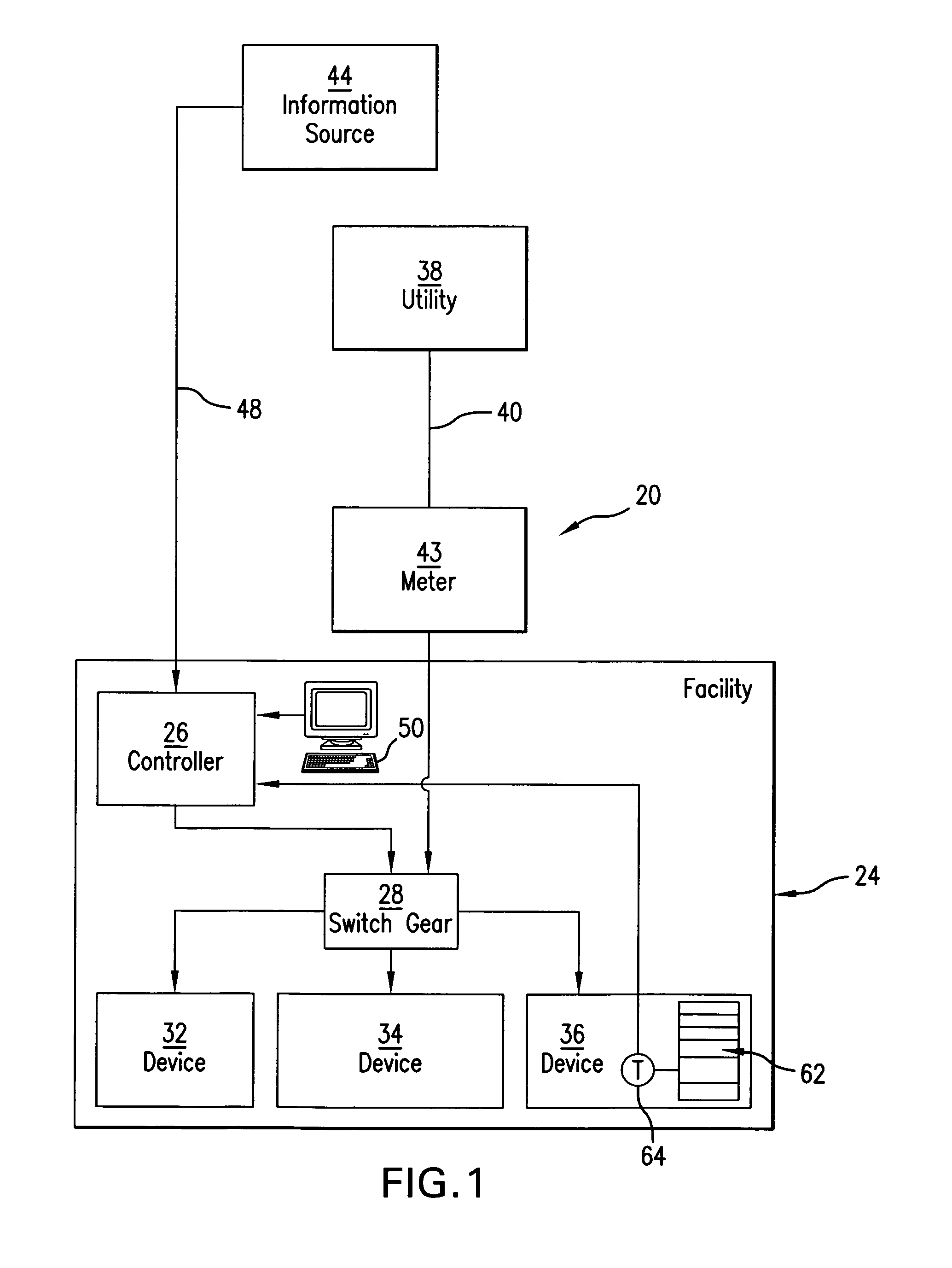
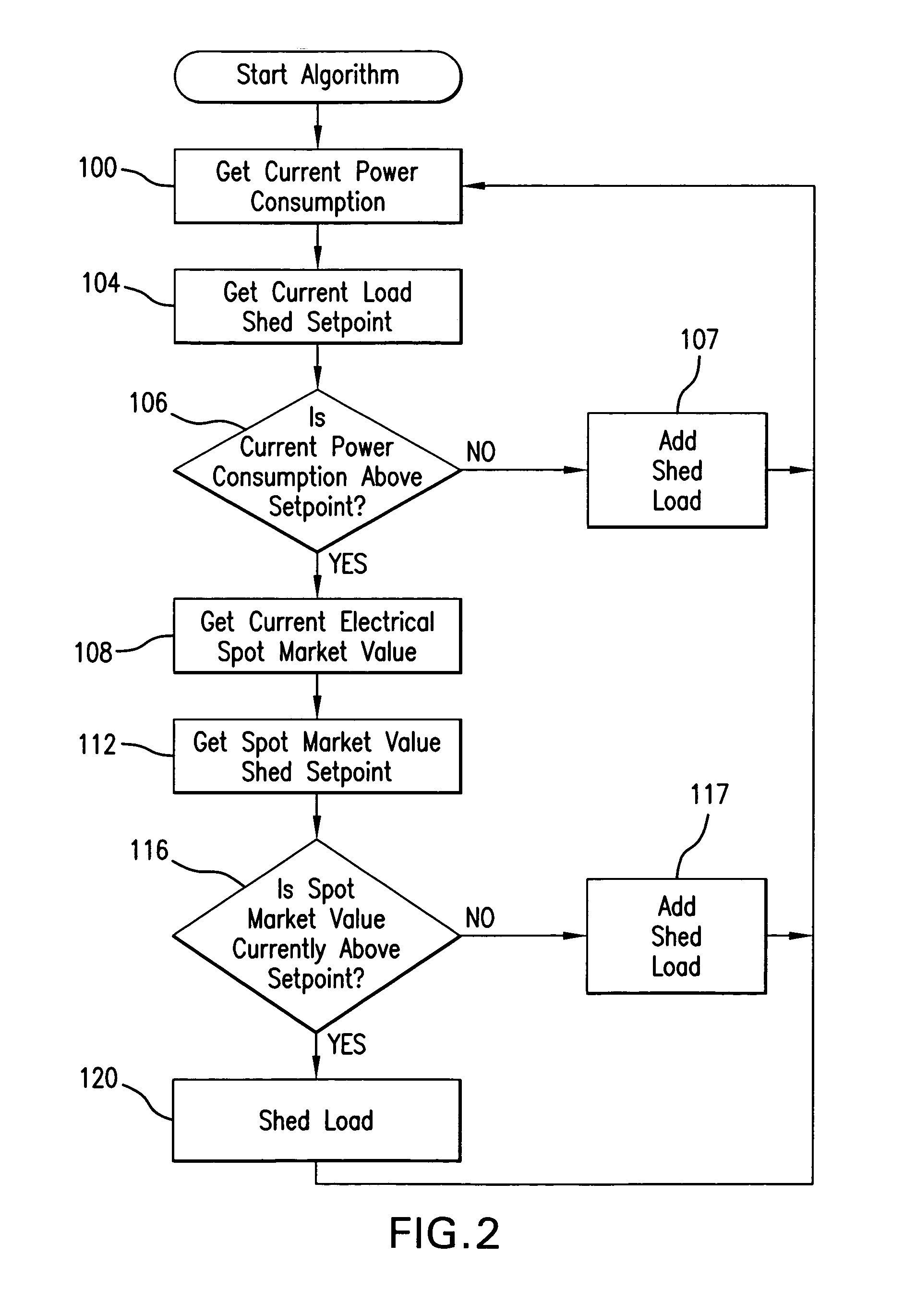
Method and apparatus for controlling power consumption
InactiveUS7062361B1Aggressive in load shedding strategyContinuous monitoringMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlLoad SheddingElectricity
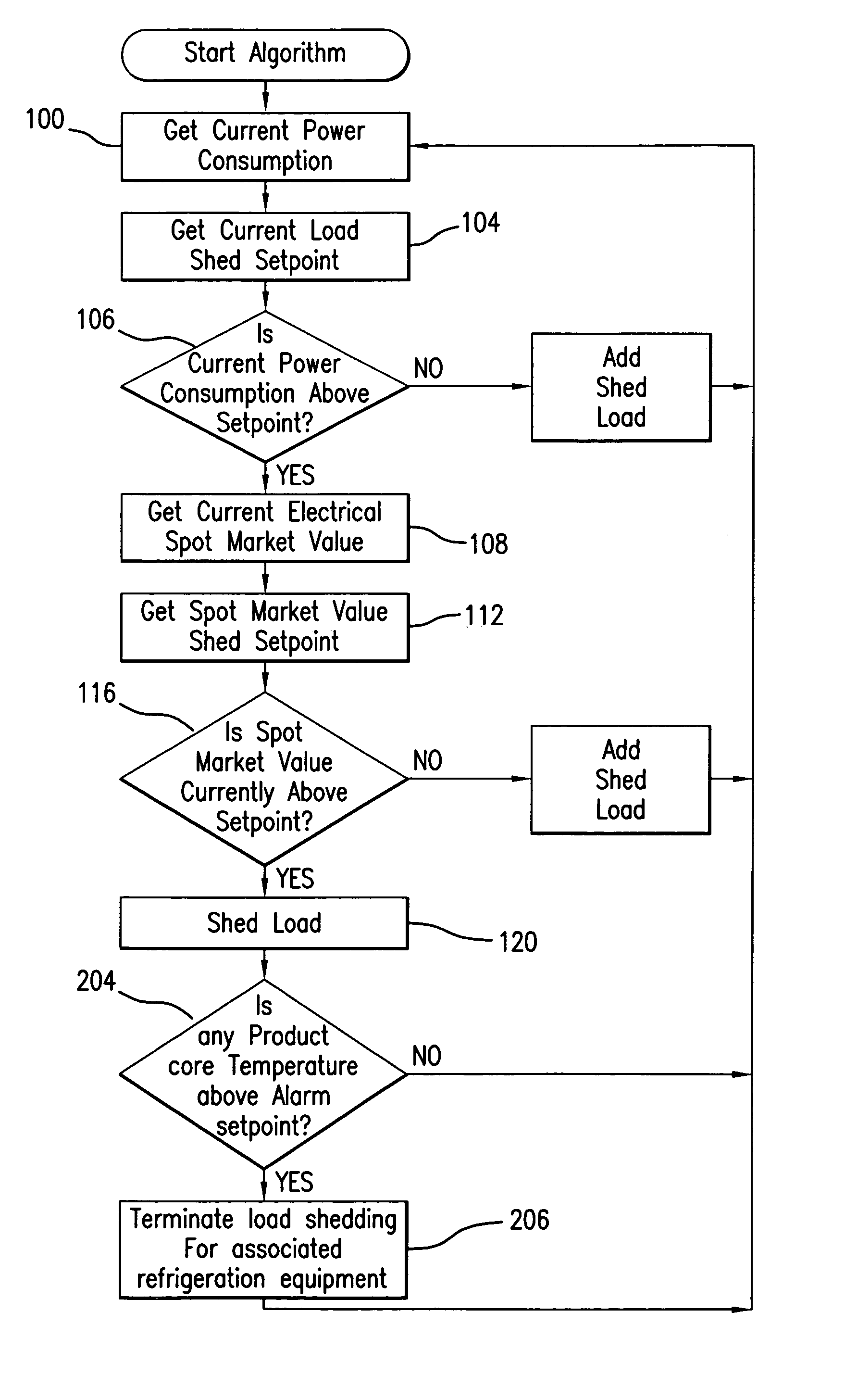
A method and apparatus for controlling power consumption of a facility, building or simply a collection of one or more devices, by load shedding when power consumption is above, or is predicted to be above, a preselected setpoint, but only if electrical power on the spot market cannot be purchased at or below a preselected price. The apparatus and method of the invention optimizes power usage by taking advantage of the buying of electricity as a commodity on the spot market. As a further aspect of the invention, in the situation of a supermarket for example, which refrigerates food products, artificial product core temperature sensors or direct insertion product sensors can be used to continuously monitor the refrigerated temperature of perishable products. A controller would constantly monitor these temperatures to allow a precise load shedding routine to be implemented.
Owner:RTP CONTROLS
Packer sealing element with shape memory material
A packer or bridge plug uses a sealing element made from a shape memory polymer (SMP). The packer element receives heat or other stimulus to soften the SMP while the element is compressed and retained. While so retained, the heat or other stimulus is removed to allow the SMP to get stiff so that it effectively seals a surrounding tubular. High expansion rates are possible as the softness of the material under thermal input allows it to be reshaped to the surrounding tubular or to the surrounding open hole from a smaller size during run in and to effectively retain a sealed configuration after getting stiff on reduction in its core temperature while longitudinally compressed. The SMP or equivalent material whose modulus is changeable can be covered on the outside, the inside or both with an elastic material that protects the SMP and enhances the seal in the wellbore and against the mandrel.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
System and method for determining and controlling core body temperature
Systems and methods for accurate temperature modification of a patient, or selected regions thereof, including inducing hypothermia. The temperature modification is accomplished using an in-dwelling heat exchange catheter within which a fluid heat exchange medium circulates. A heat exchange cassette attached to the circulatory flow lines of the catheter, the heat exchange cassette being sized to engage a cavity within a control unit. A temperature measurement scheme for obtaining body core temperature is provided, including methods of obtaining and analyzing temperature data to provide feedback to the control unit for use in controlling the heating and cooling of the heat exchange medium so as to heat or cool a patient to a desired target temperature.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Methods and apparatus for a remote, noninvasive technique to detect core body temperature in a subject via thermal imaging
ActiveUS7340293B2Accurate of core body temperatureConvenience and securitySensing radiation from moving bodiesDiagnostic recording/measuringDiseaseEngineering
An approach to noninvasively, remotely and accurately detect core body temperature in a warm-blooded subject, human or animal, via thermal imaging. Preferred features such as the use of in-frame temperature references, specific anatomical target regions and a physiological heat transfer model help the present invention to overcome pitfalls inherent with existing thermal imaging techniques applied to physiological screening applications. This invention provides the ability to noninvasively, remotely and rapidly screen for diseases or conditions that are characterized by changes in core body temperature. One human application of this invention is the remote screening for severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), since fever is a common, early symptom. Other diseases and conditions that affect the core body temperature of humans or animals may also be noninvasively and remotely detected with this invention.
Owner:CARDIOWAVE
Medical thermometer for determining body core temperature
InactiveUS20070055171A1Thermometer detailsThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsMedical thermometerContact type
A temperature sensing device including at least a first contact type temperature sensing element determines body core temperature of a warm blooded animal or human based on an estimated skin temperature of the patient which is computed based on temperature measurements obtained by the first sensing element.
Owner:HELEN OF TROY LIMITED
System and method for determining and controlling core body temperature
Systems and methods for accurate temperature modification of a patient, or selected regions thereof, including inducing hypothermia. The temperature modification is accomplished using an in-dwelling heat exchange catheter within which a fluid heat exchange medium circulates. A heat exchange cassette attached to the circulatory flow lines of the catheter, the heat exchange cassette being sized to engage a cavity within a control unit. A temperature measurement scheme for obtaining body core temperature is provided, including methods of obtaining and analyzing temperature data to provide feedback to the control unit for use in controlling the heating and cooling of the heat exchange medium so as to heat or cool a patient to a desired target temperature.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
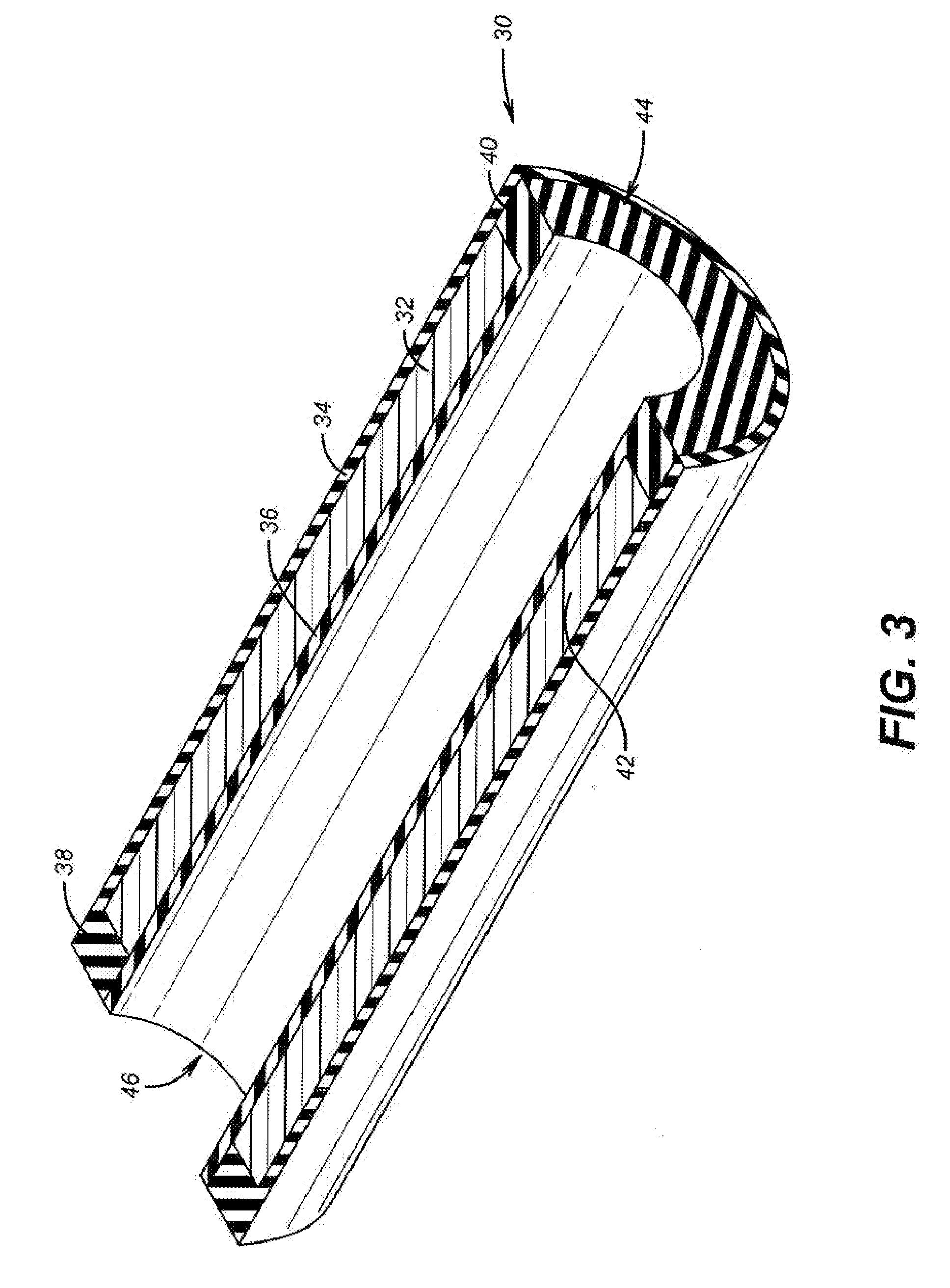
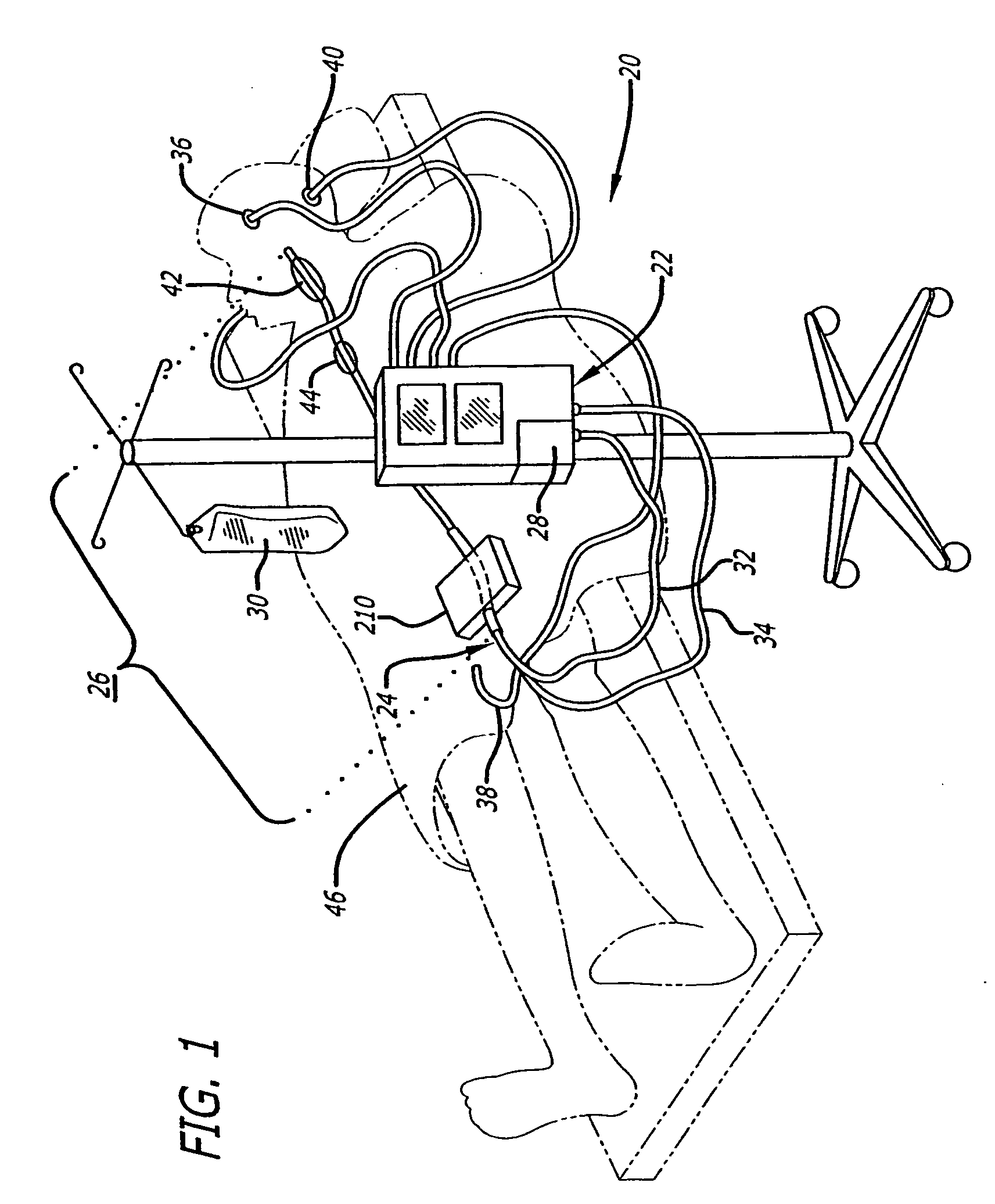
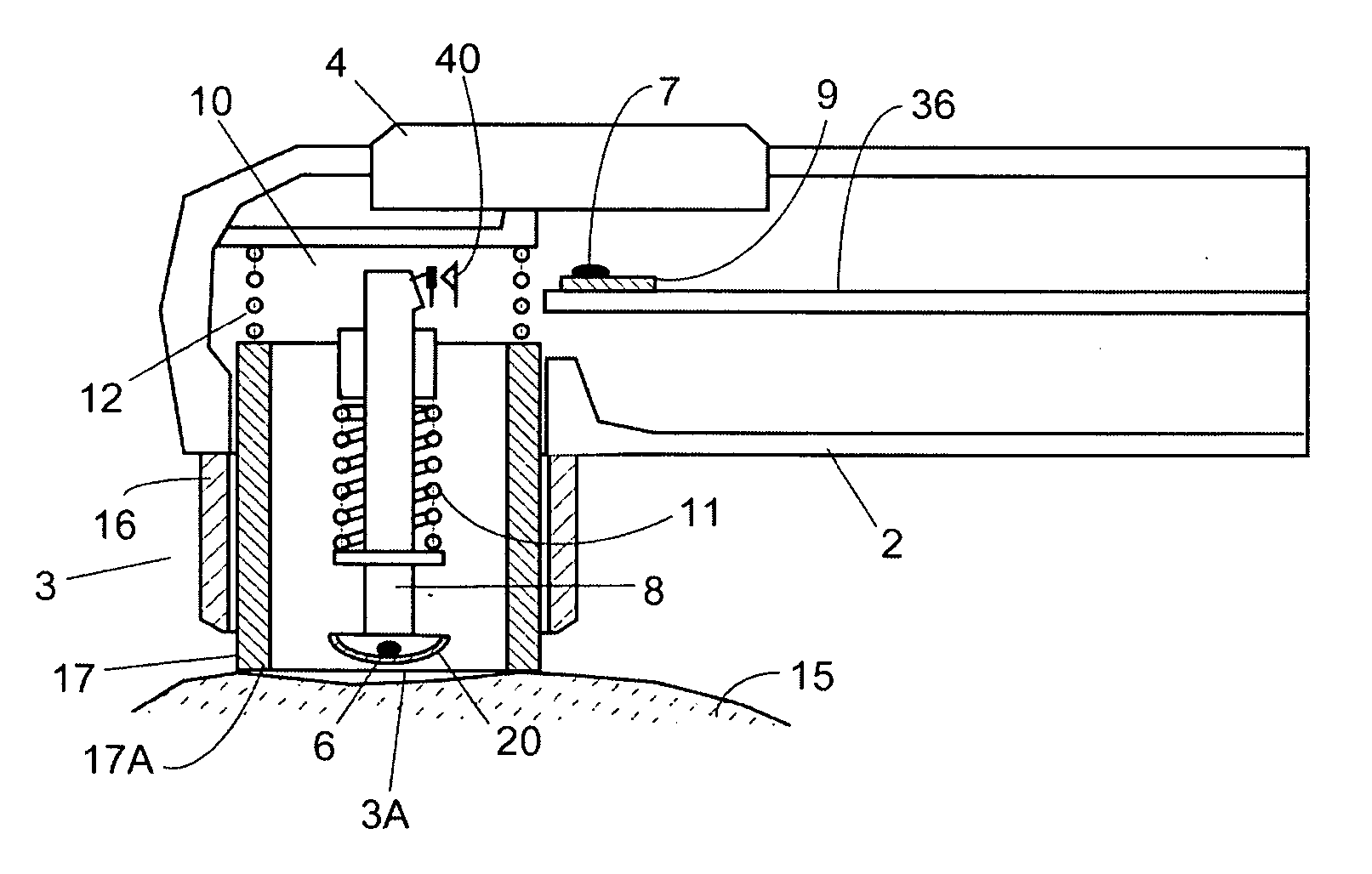
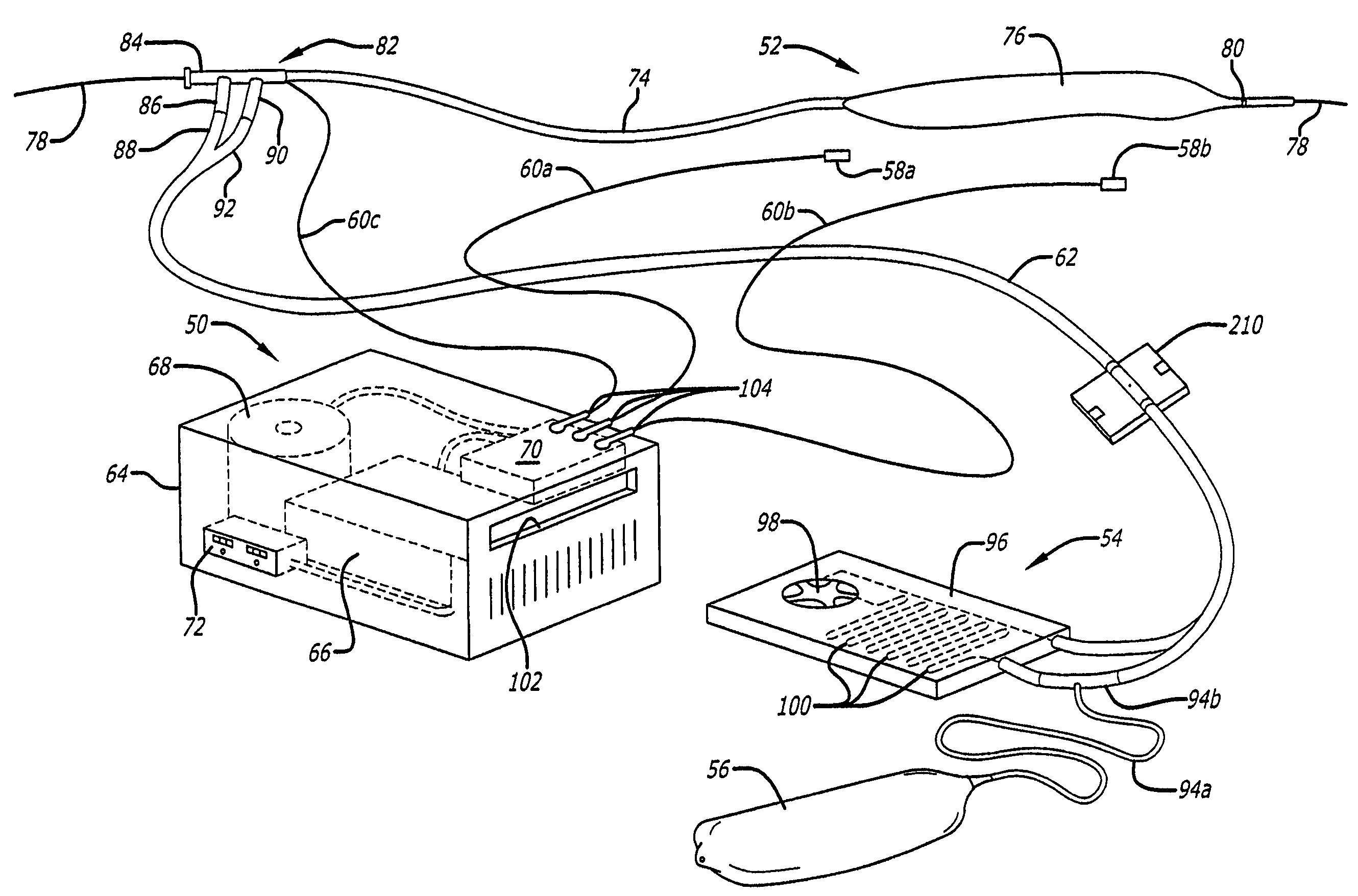
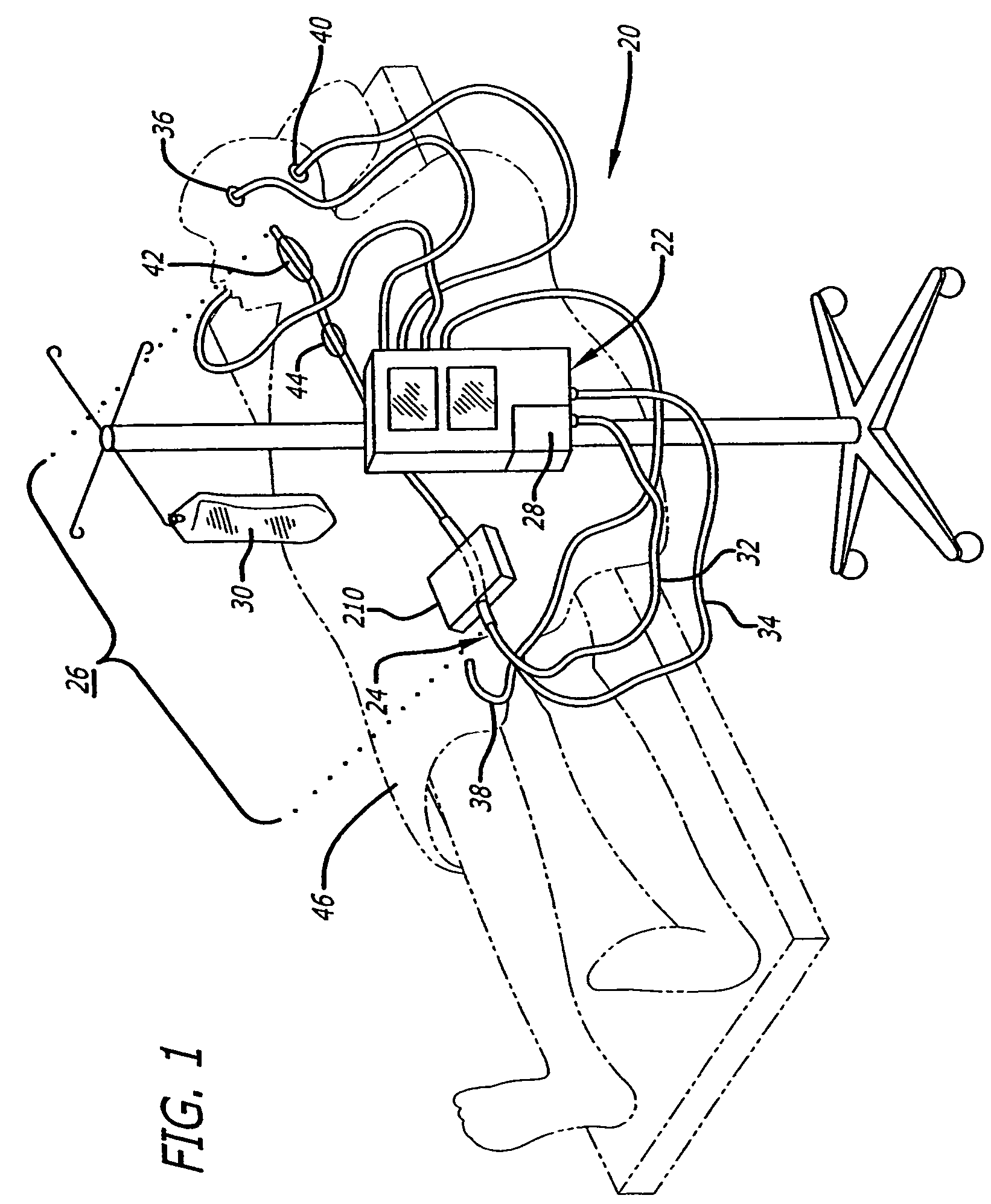
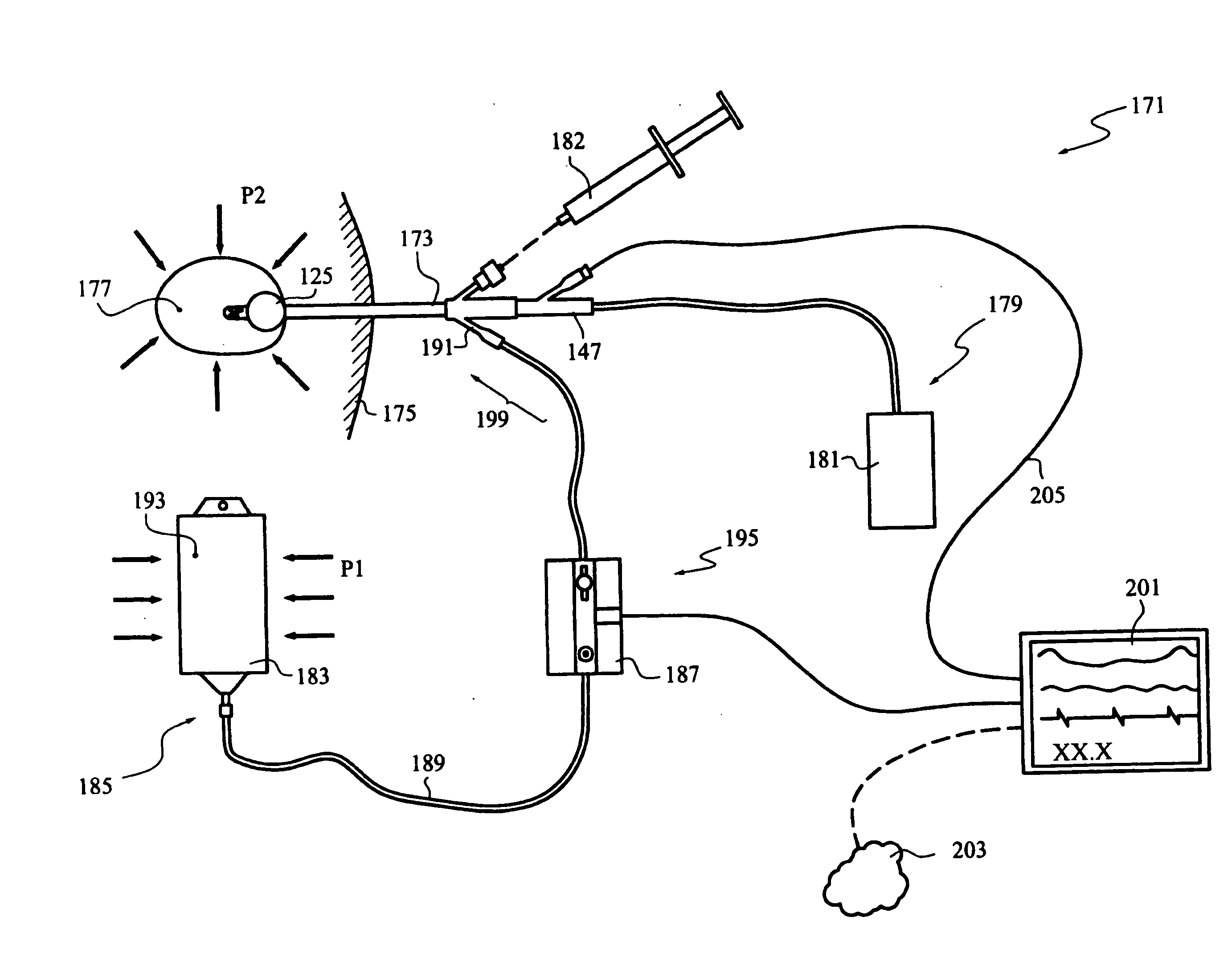
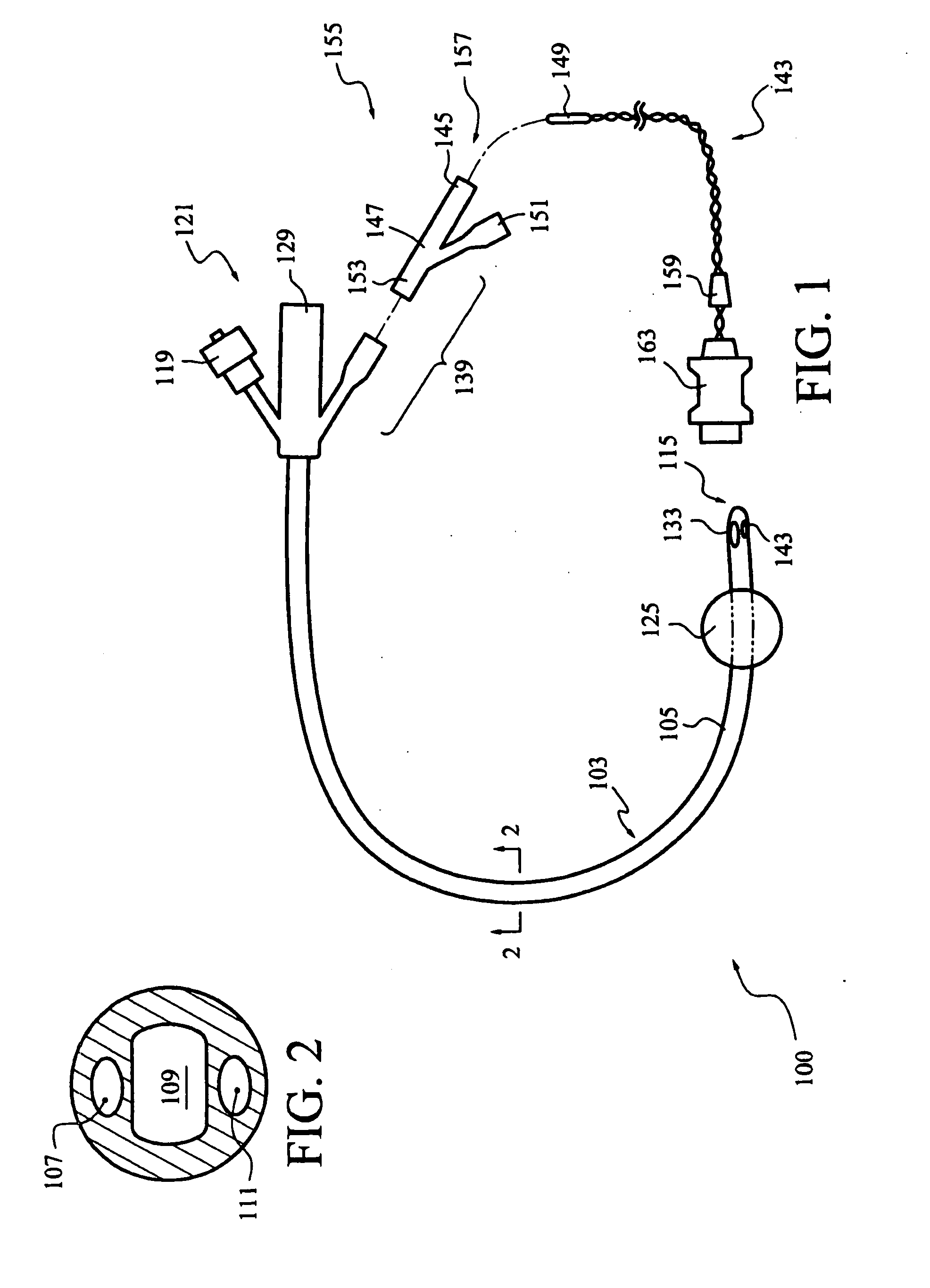
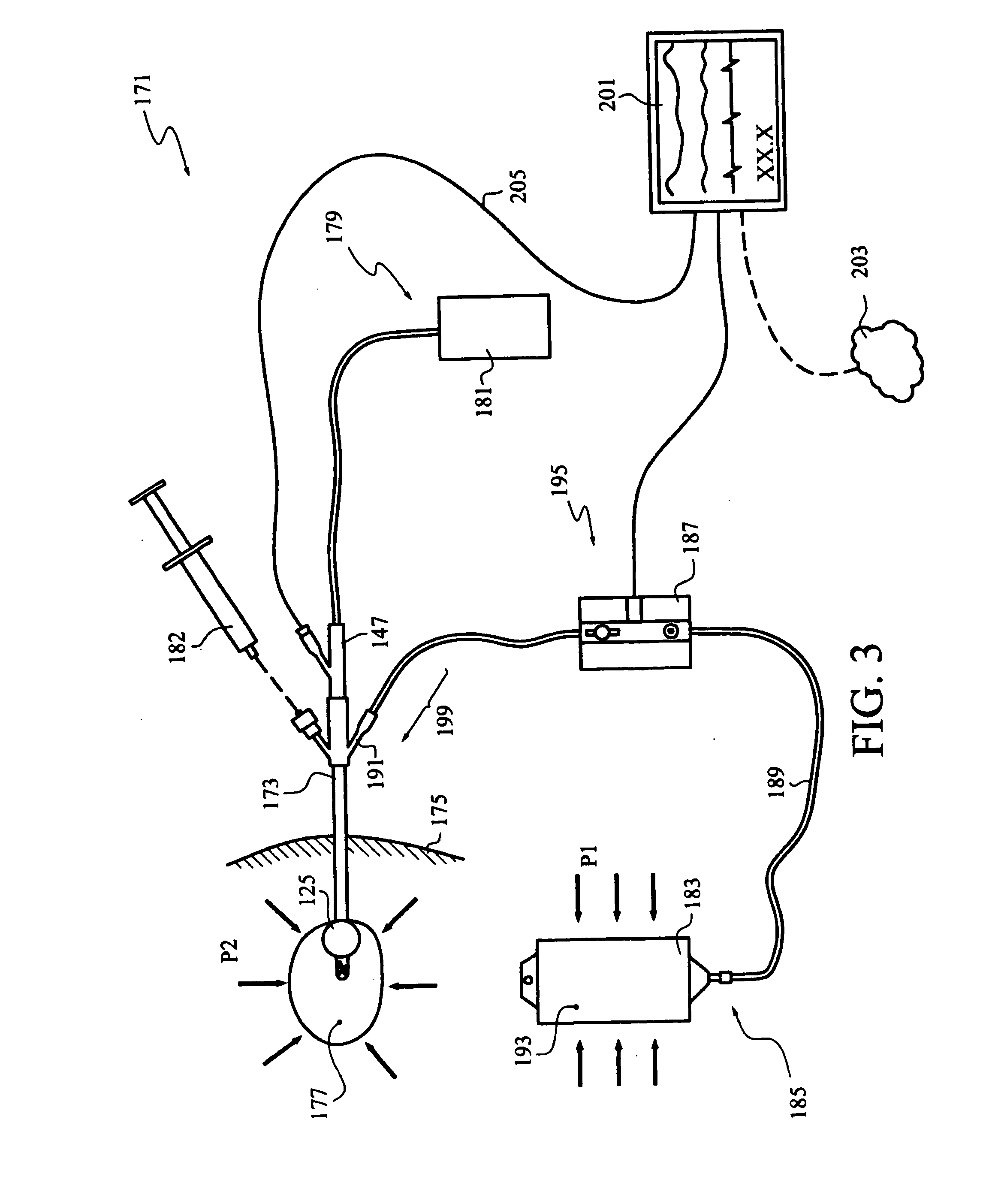
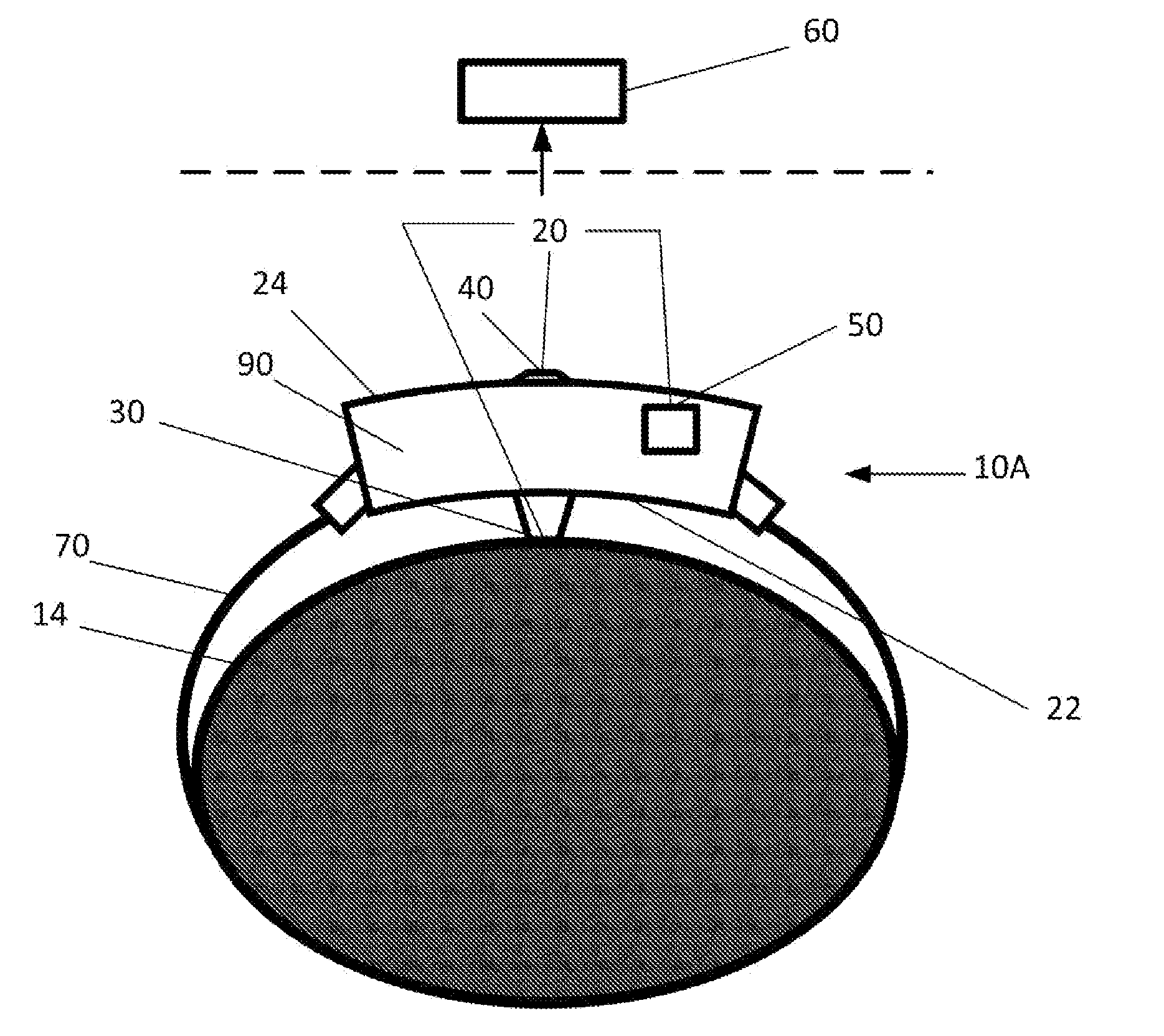
Continuous Intra-Abdominal Pressure Monitoring Urinary Catheter With Optional Core Temperature Sensor
A device structured to generate an input signal to a monitor (201) to visually indicate a value for one or more physiological state variables measured by one or more transducers (203) associated with a medical patient. Preferred embodiments include a pressure transducer (195) placed in fluid communication with the patient's bladder (177) effective to infer intra-abdominal pressure P2. Embodiments may also include a temperature transducer (143) configured to measure the temperature of fluid in / near the bladder (177) to infer core body temperature. Certain embodiments of the invention may include a second pressure transducer (235) configured to measure arterial blood pressure. In the latter case, signals received from the two pressure transducers (177, 235) may be manipulated to produce a third signal corresponding to abdominal perfusion pressure, which can then be indicated on a numeric display device (233).
Owner:WOLFE TORY MEDICAL
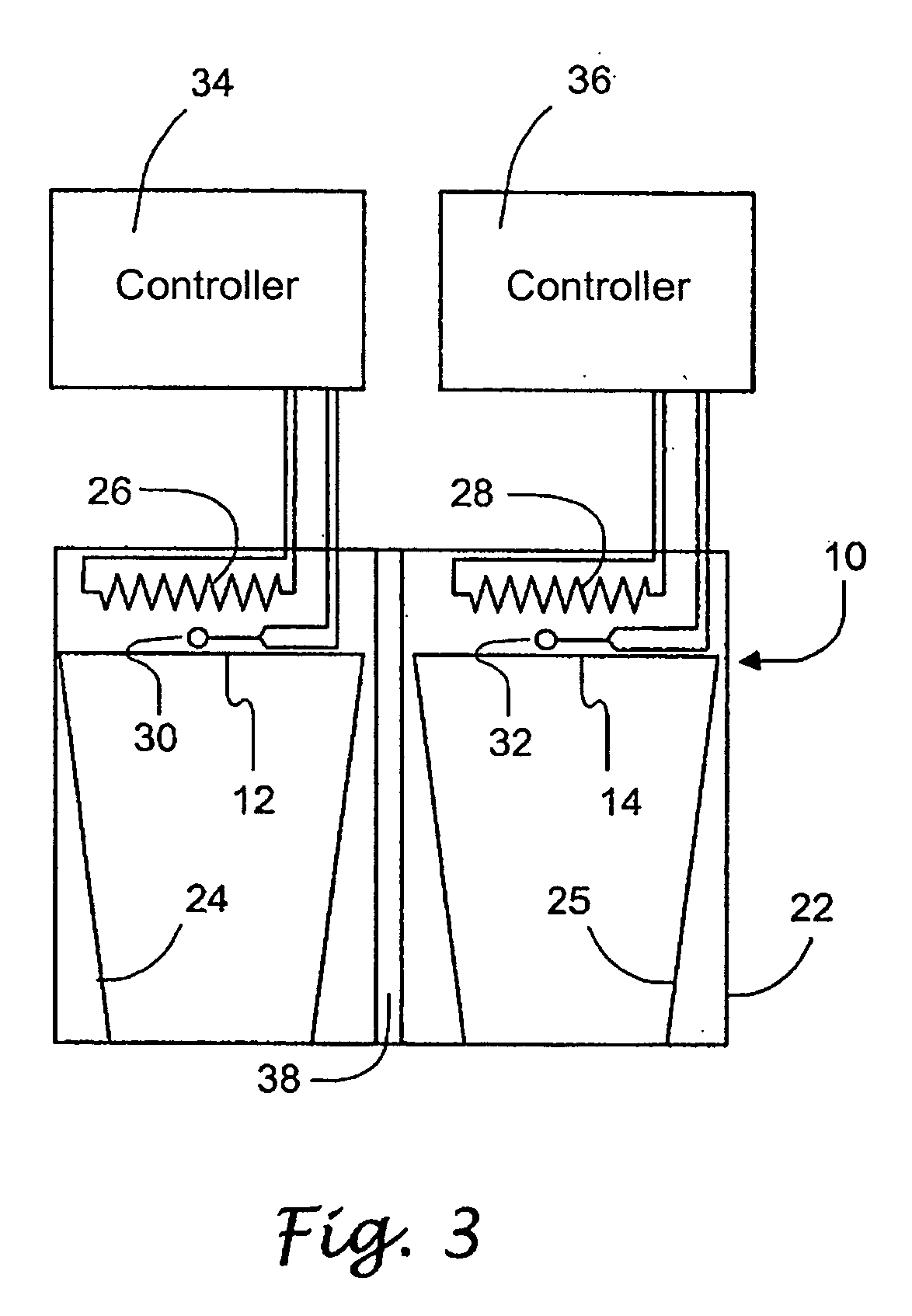
Kelvin Connector Including Temperature Sensor
The electrical measuring apparatus (17) and temperature sensing apparatus minimises the number of connections required for each contact (30, 31) of a battery (18). The present invention measures the core temperature of the battery (18) which is useful in monitoring the health of the battery (18). The apparatus comprises first connection means to connect to the first contact (30) of the battery (18) and second connection means to connect to the second contact (31) of the battery (18). The apparatus includes a thermistor (36) which connects in series with one lead (32) of the connecting means. Accordingly, the apparatus does not require the temperature sensor (36) to be independently connected to the battery (18).
Owner:LIAISONS ELECTRONIQUES MECANIQUES LEM
Temperature measurement system
ActiveUS20140046192A1Body temperature measurementSensing radiation from moving bodiesCore temperatureNuclear medicine
A method of determining a temperature of a patient includes measuring a first temperature of the patient with a temperature device without contacting the patient with the device, and measuring a second temperature of the patient by contacting a measurement site of the patient with the device. The method also includes determining a temperature value indicative of a core temperature of the patient based on the first and second temperatures.
Owner:WELCH ALLYN INC
Passive Microwave Assessment of Human Body Core to Surface Temperature Gradients and Basal Metabolic Rate
InactiveUS20120029369A1Enhances ability to quantifyEnhances to mapThermometers using value differencesBody temperature measurementDiseaseHuman body
A passive microwave thermography apparatus uses passive microwave antennas designed for operation, for example, at WARC protected frequencies of 1.400 to 1.427 GHz and 2.690 to 2.70 GHz (for core body gradient temperature measurement) and 10.68 to 10.700 GHz or higher microwave frequency (for surface body gradient temperature measurement) and a related directional antenna or antenna array to measure microwave radiation emanating from an animal, especially, a human body. The antennae may be radially directed toward a point within or on the surface of a human body for comparison with known temperature distribution data for that point and a given ambient temperature. Each frequency band may provide a plurality of adjacent noise measuring channels for measuring microwave noise naturally emitted by the human body. The apparatus measures short-term changes in, for example, core and body surface temperatures to establish a basal metabolic rate. Changes in core body temperature may be stimulated by the administration of food or certain organic and drug-related substances or stress to induce a change in basal metabolic rate over time. These changes correlate directly with a human subject's metabolism rate at rest and under certain dietary constraints and can be used to determine courses of treatment for obesity, metabolic disease, and other disorders. The apparatus can also be used to remotely monitor patients and subjects without physical contact.
Owner:ICOVE DAVID +3
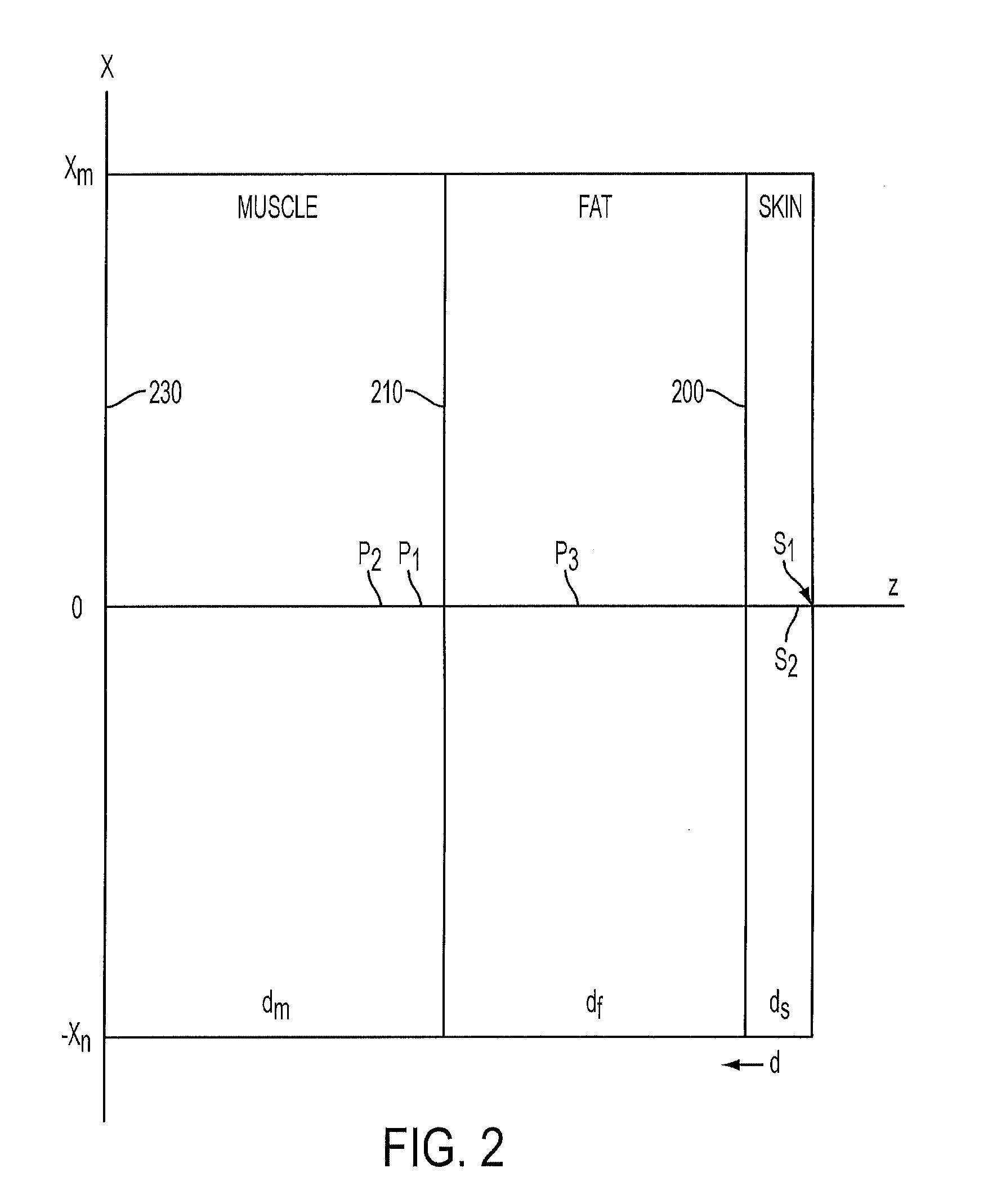
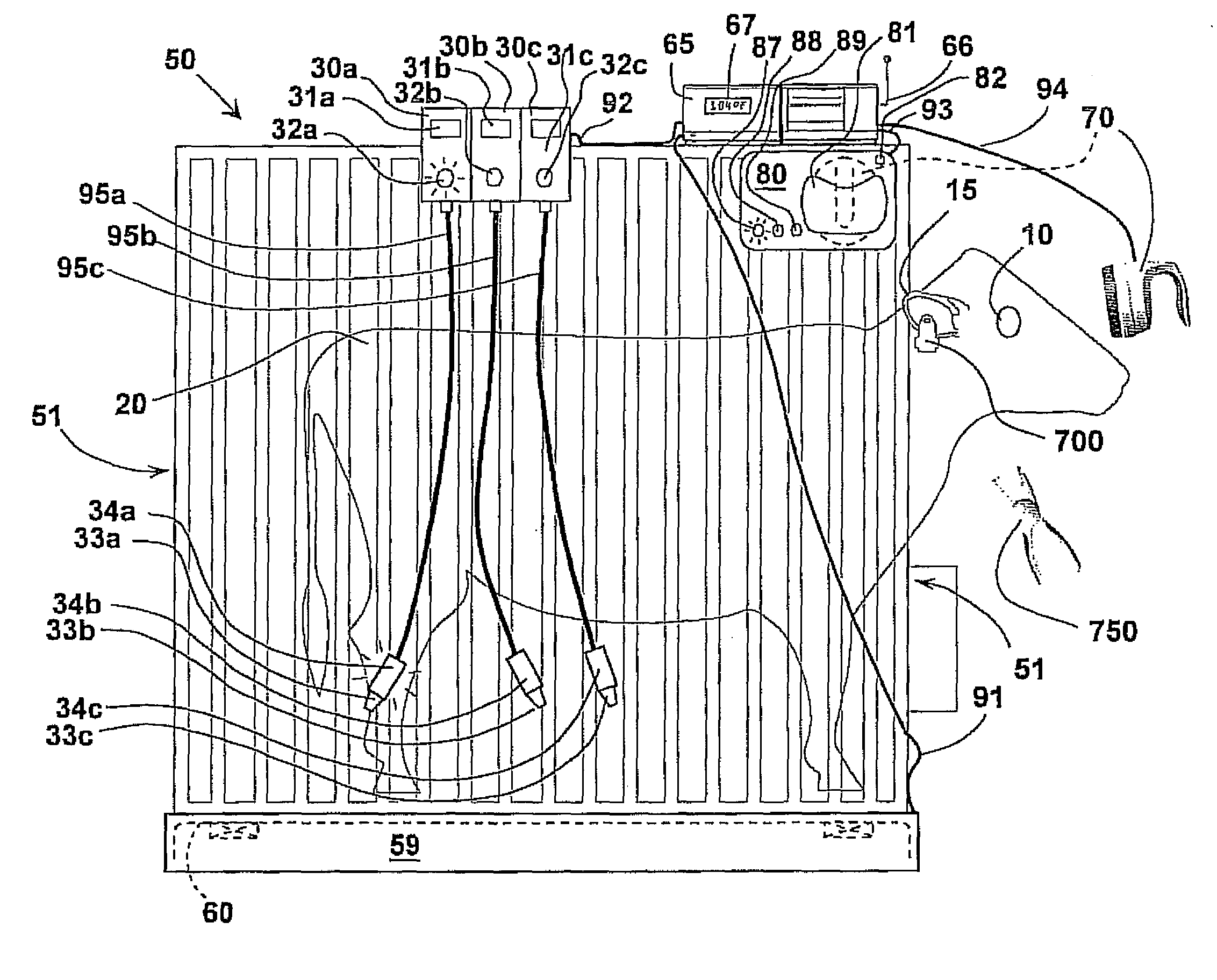
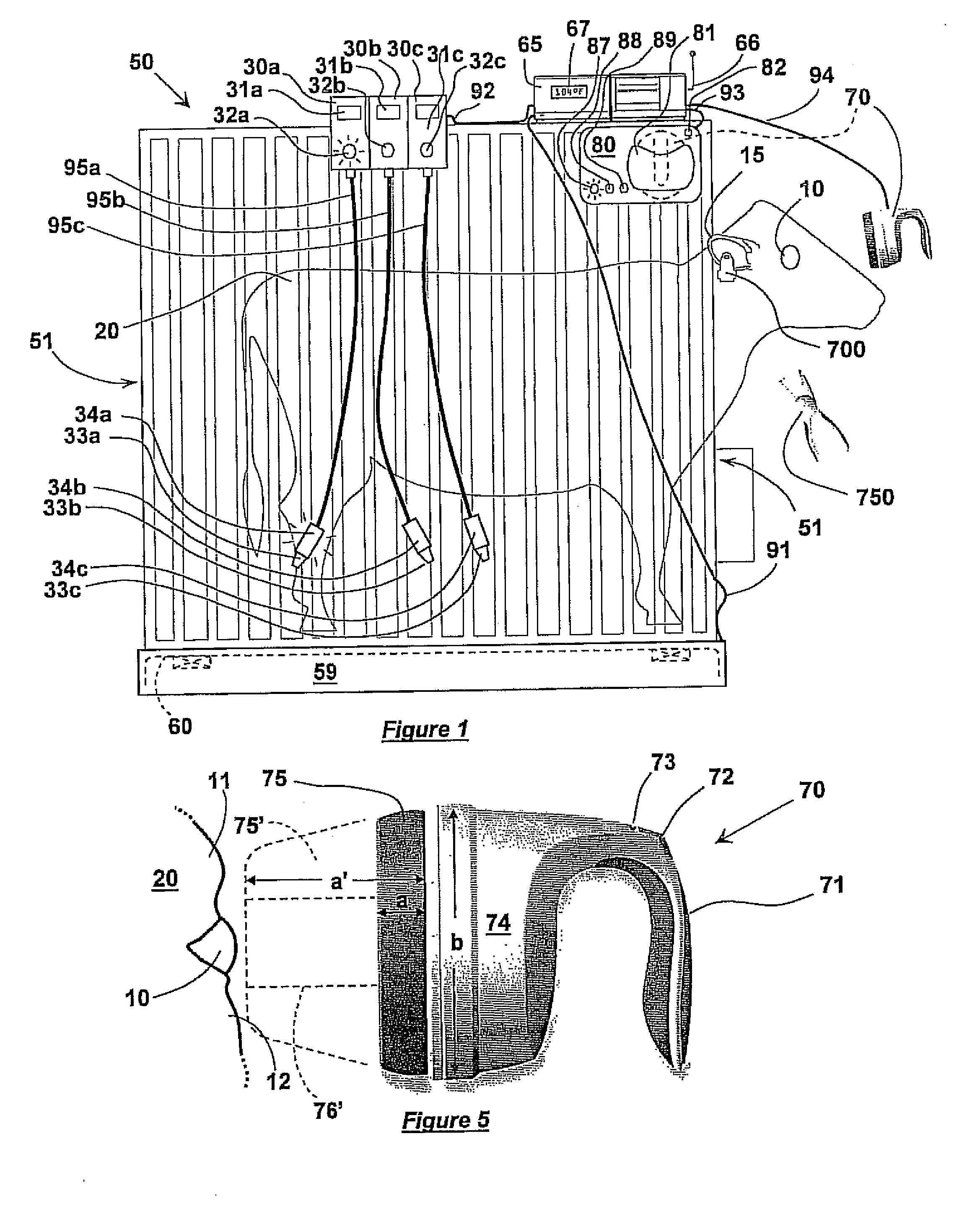
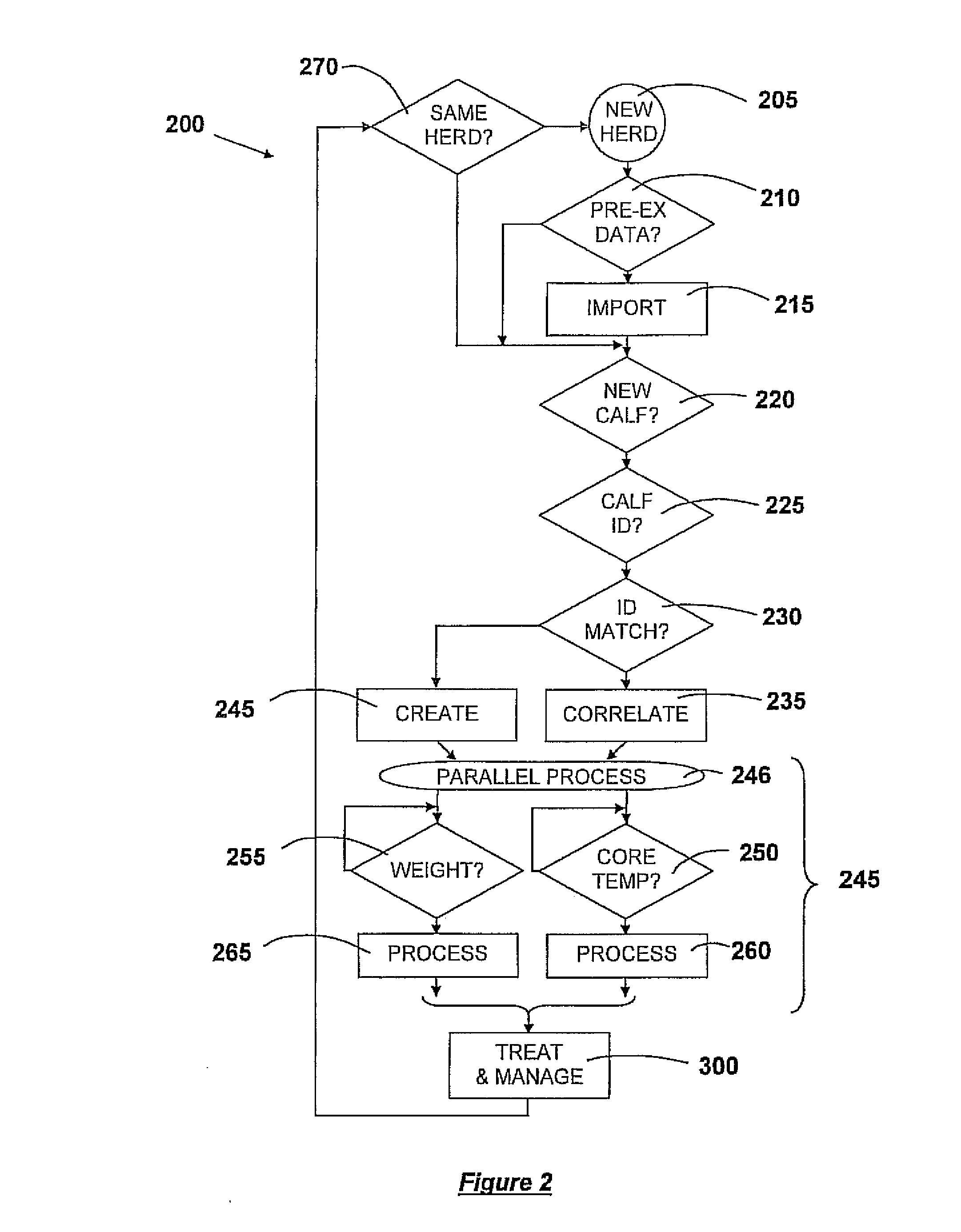
Core-Temperature Based Herd Management System and Method
InactiveUS20100160809A1Increase profitabilityLow costMedical devicesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCore temperatureHerd management
A system and method for managing a herd of animals possibly requiring medical treatment, such as cows in a feedlot. The animals are herded individually into a chute, where identification data is collected from a tag, and core temperature data is collected using a special non-contacting core temperature sensor. The animal is tagged with a color coded tag representing a range of temperatures into which that animal's temperature falls. The animal is then delivered to a pen corresponding to that range of temperatures, where appropriate medicinal treatment is automatically dosed and applied to the animal.
Owner:HERDX
Grounded Pressure Cooling
ActiveUS20080234788A1Prevent perspirationRelieve stressSurgical instruments for heatingFootwearCore temperatureBlood vessel
Owner:VASPER SYST
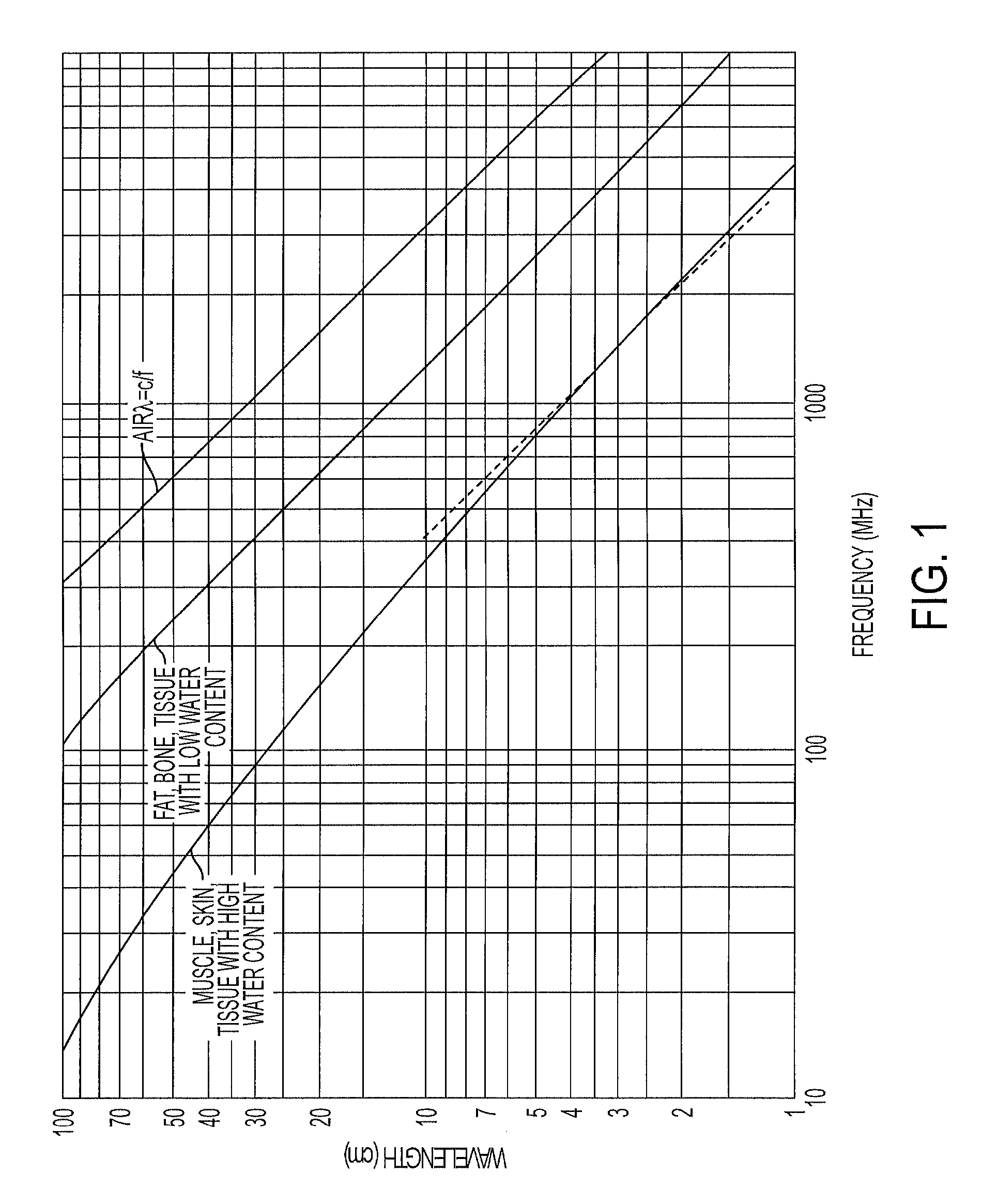
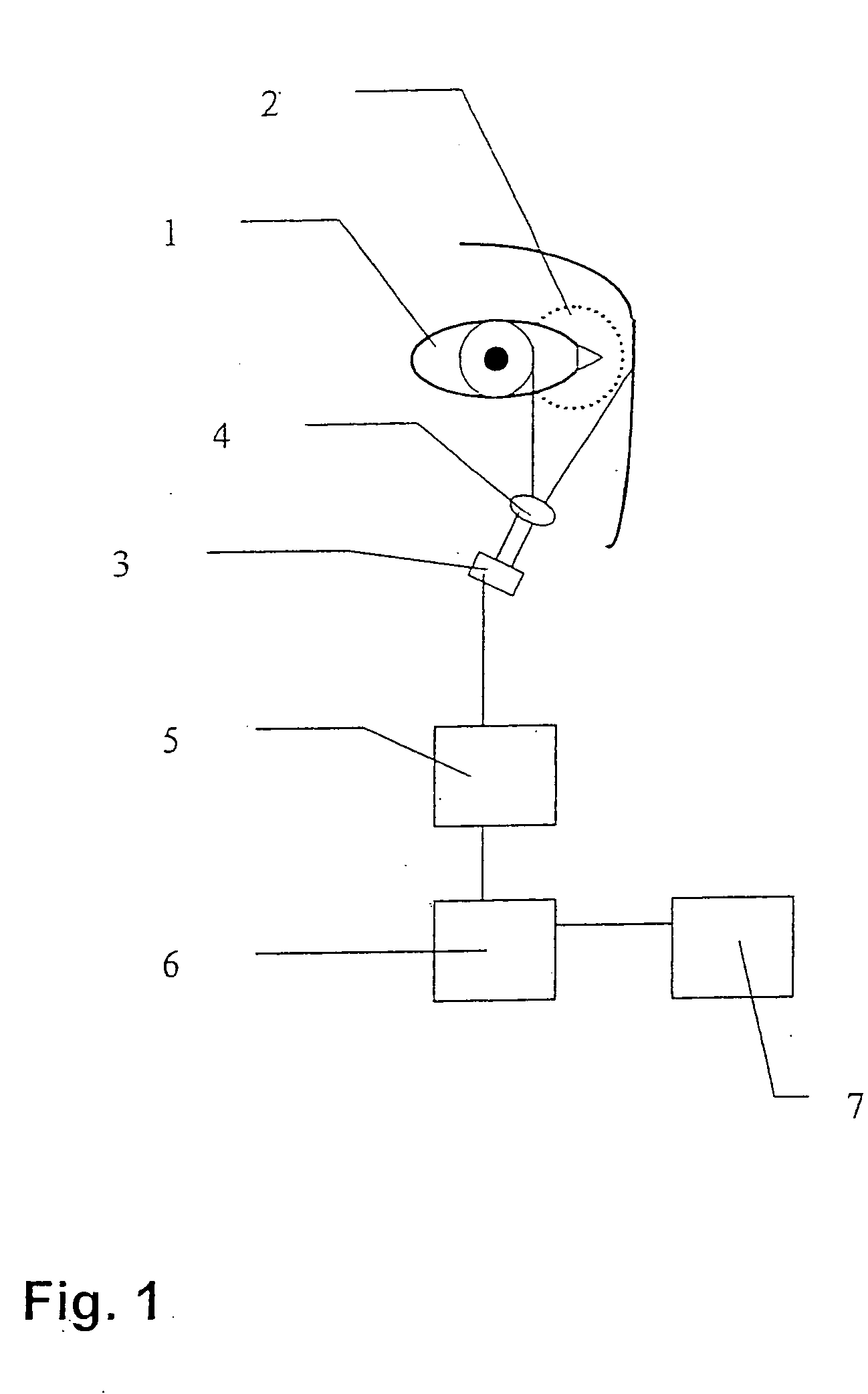
Measuring system and method for the contactless determination of the body core temperature
InactiveUS20050271117A1Reliable correlationThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsBody temperature measurementDisplay deviceEngineering
A measuring system and method for the contactless and continuous determination of the body core temperature of a person / subject preferably includes a matrix-like infrared sensor (3) that is directed toward the nose-side area of the canthus. The infrared sensor (3) is connected with an evaluating unit (5) for the evaluation of the infrared signals and the selection of the maximum in the matrix. The evaluating unit (5) is connected with a computing unit (6) for the calculation of the body core temperature from the maximum determined and for displaying via a display (7) and / or transmission of the measured signals and / or the calculated value for the body core temperature.
Owner:DRAGER SAFETY
Methods and apparatus for adjusting body core temperature
Owner:AVACORE TECH
Hydration Monitor
ActiveUS20080234600A1Performance maximizationPrevent dehydrationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMedicineCore temperature
Owner:INOVA DESIGN SOLUTIONS
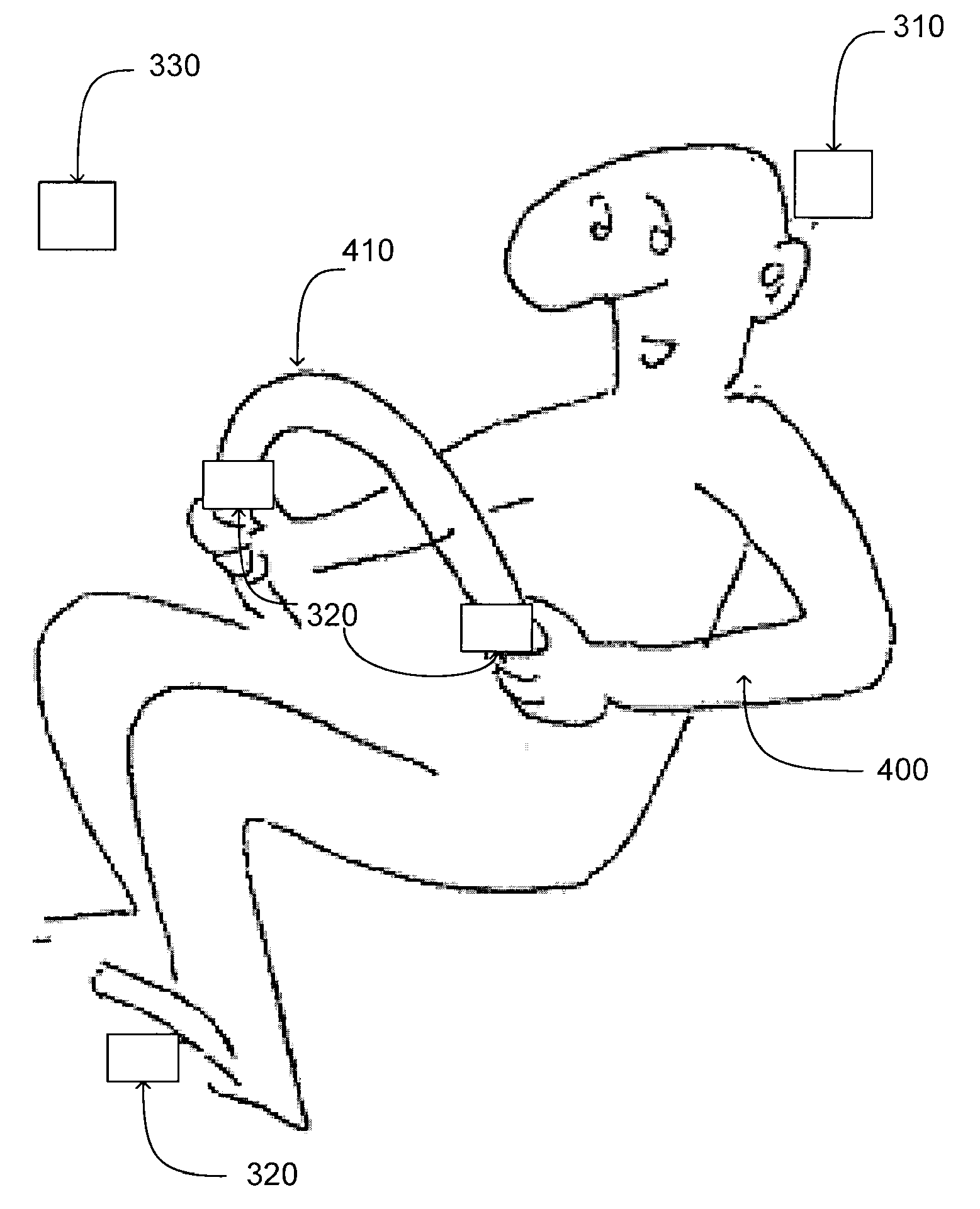
Method and apparatus for manipulating driver core temperature to enhance driver alertness
ActiveUS20080180235A1Shorten the timeLower core temperatureDiagnostic recording/measuringOptical signallingDriver/operatorCore temperature
The present invention provides a system, method and apparatus for reducing a vehicle driver's core temperature to offset drowsiness. In one embodiment, a temperature sensor records data describing a vehicle driver core temperature and communicates the data describing the vehicle driver core temperature to a temperature regulator. The temperature regulator determines whether the vehicle driver core temperature is similar to one or more circadian temperatures associated with wakefulness. If the vehicle driver core temperature is similar to a circadian temperature associated with sleep, the temperature regulator reduces the vehicle driver core temperature. In an embodiment the temperature regulator cools a material physically contacting the venous plexuses or arteriovenous anastomoses to cool the portions of the vehicle driver's anatomy which most efficiently cool the vehicle driver.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Temperature probe for an oven, oven and method for operating an oven
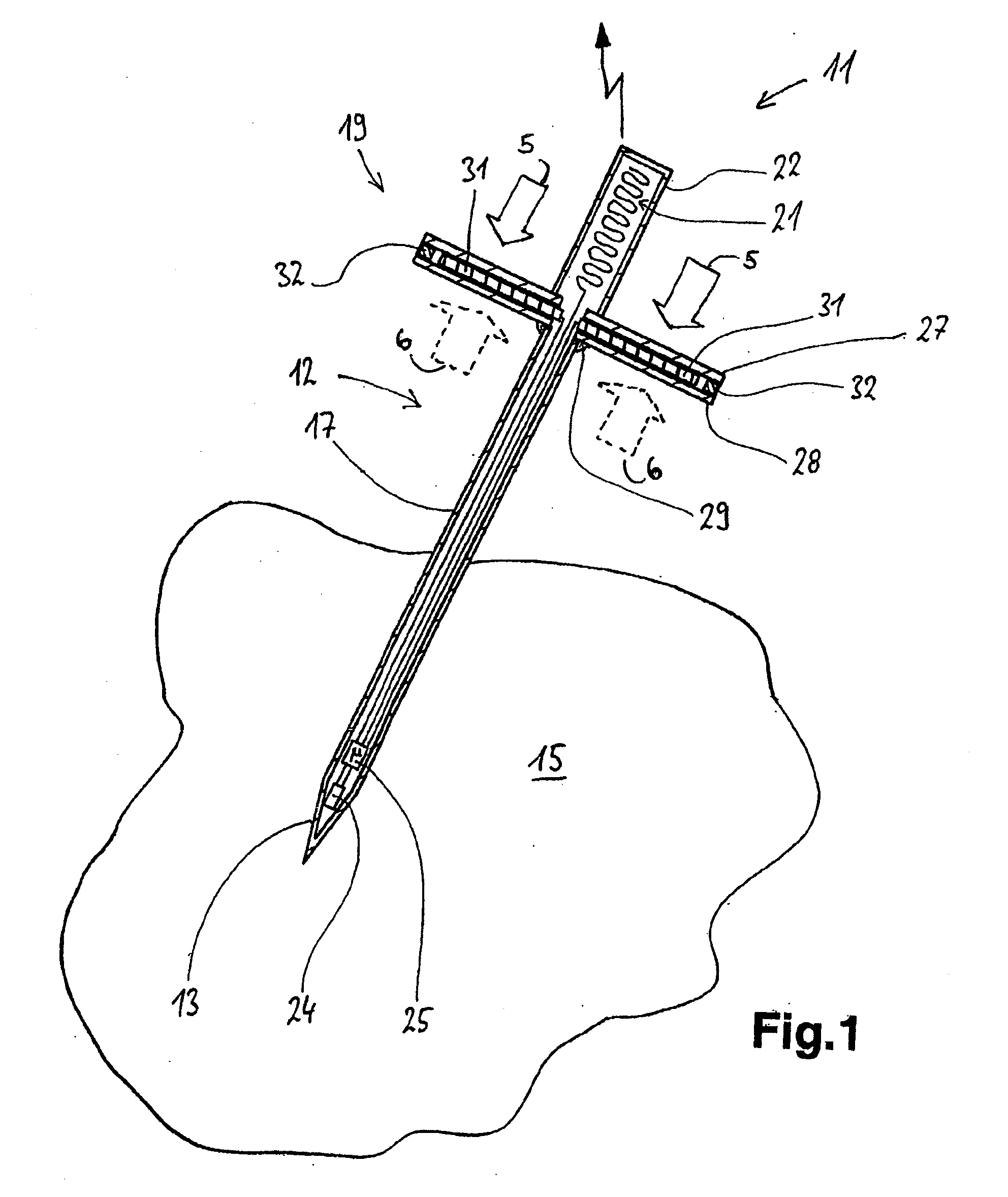
InactiveUS20100012645A1Easy and handlingRequired emitting powerThermometer detailsTemperature measurement in household appliancesTemperature differenceCore temperature
The invention relates to a temperature probe for an oven, comprising in one embodiment a longitudinal housing in the form of a spit. A temperature sensor and an electronic unit are arranged in a tip and are connected at the other end to emitting means. The temperature probe comprises a thermogenerator for producing energy. The thermogenerator uses a temperature difference between a higher temperature inside the oven and a lower core temperature in a food product, such as roast, in which the temperature probe is inserted, for producing energy for operating the emitting means.
Owner:E G O ELEKTRO GERAETEBAU GMBH
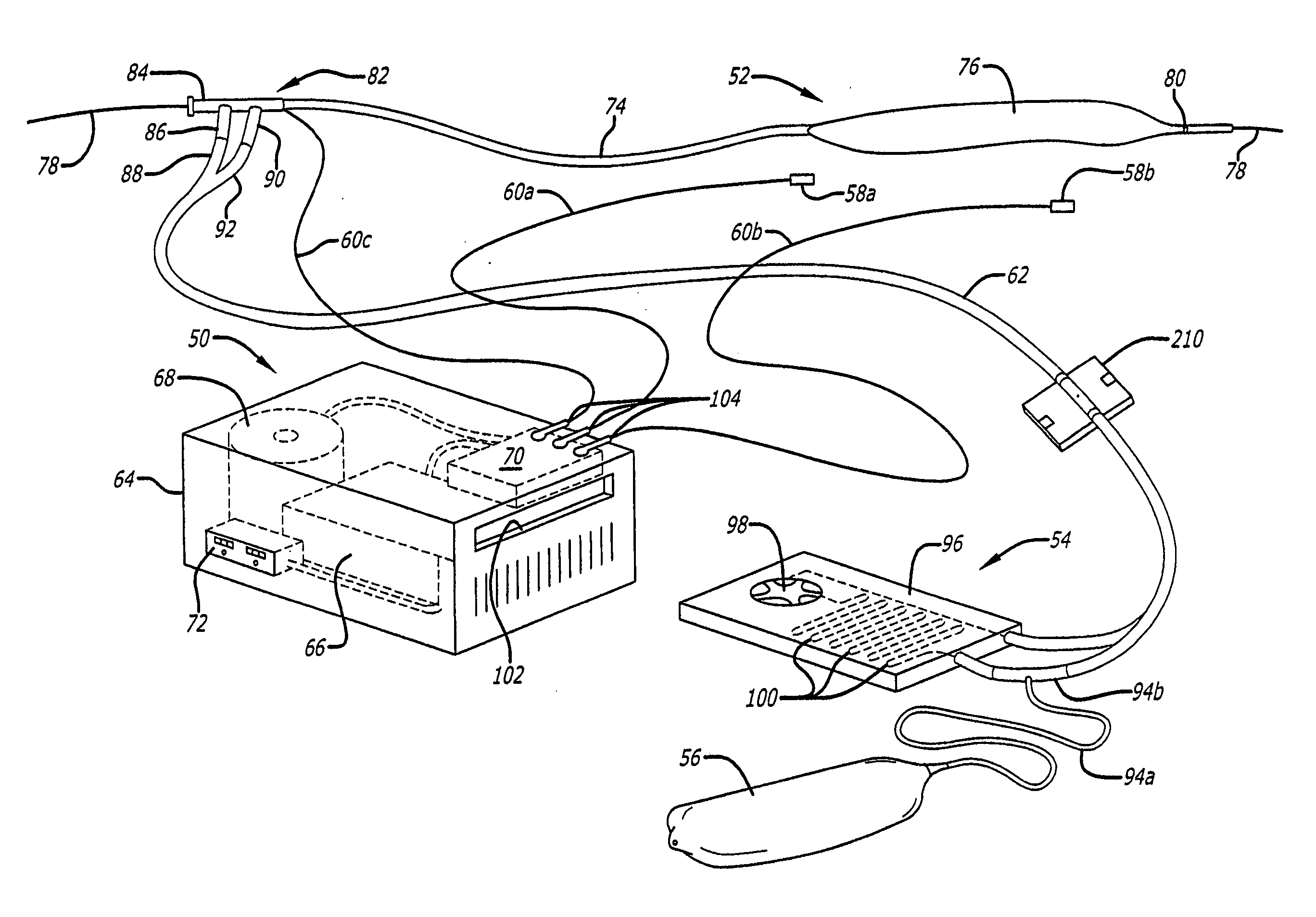
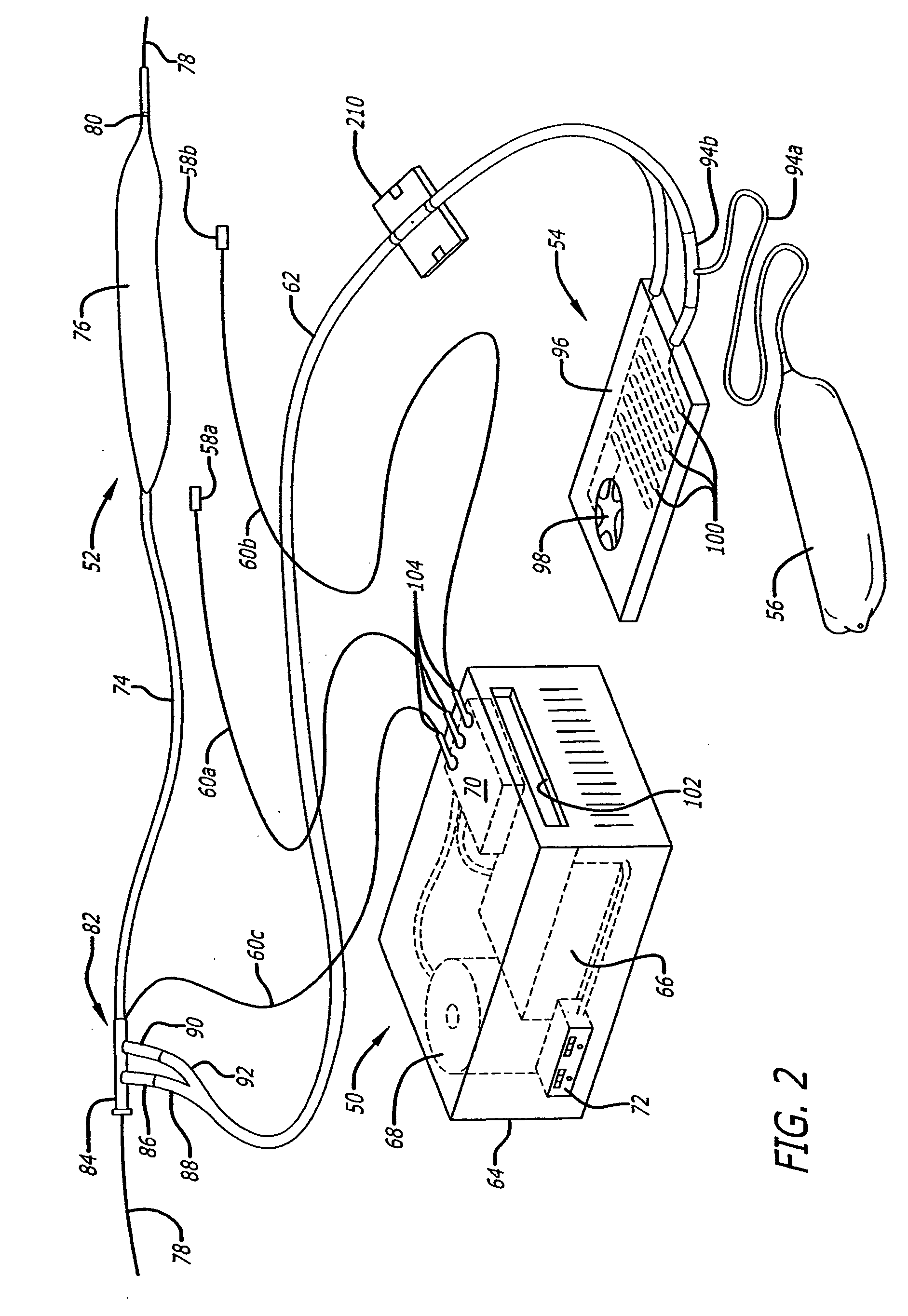
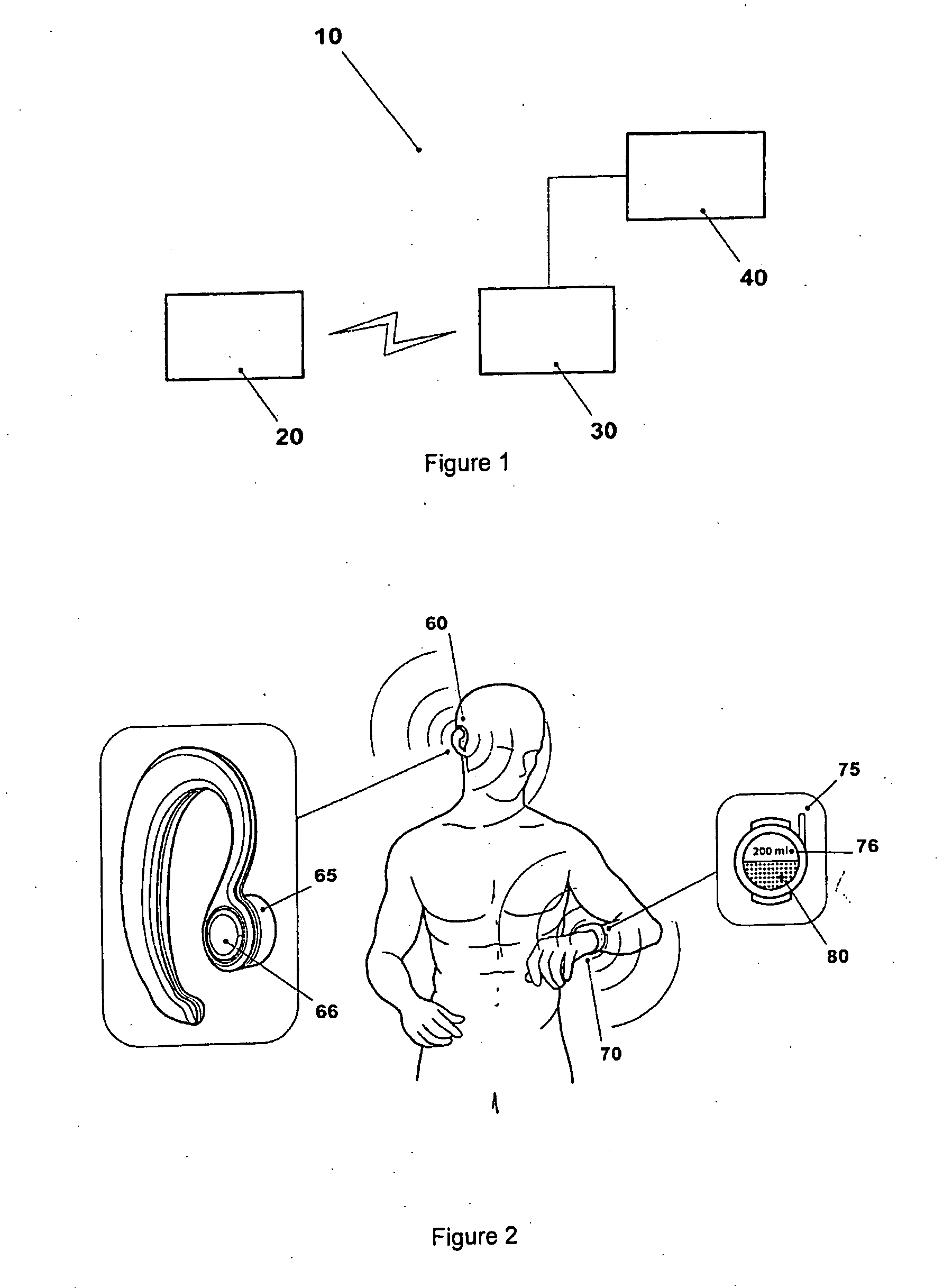
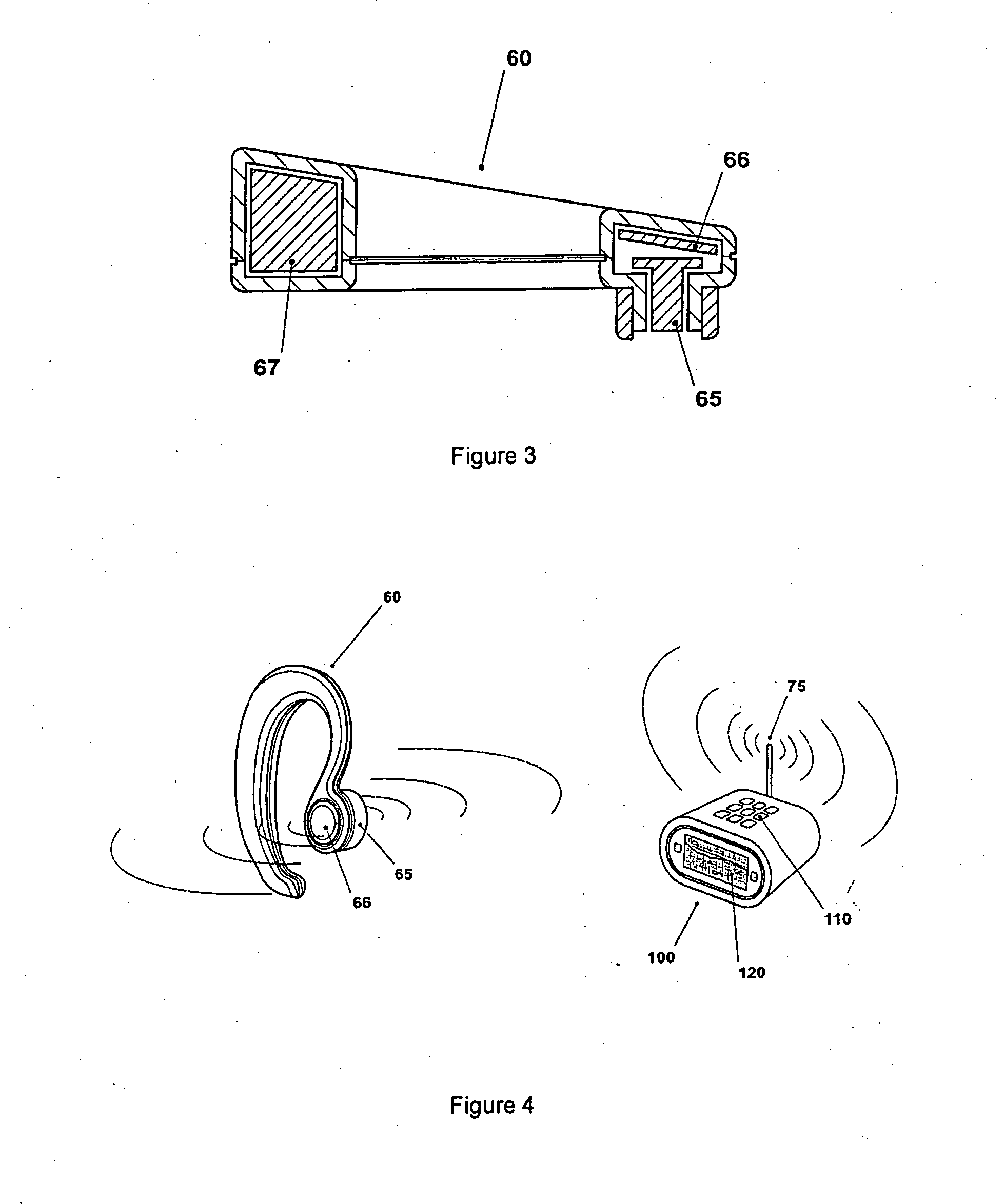
Wireless medical probe
InactiveUS20060047214A1Thermometers using electric/magnetic elementsBody temperature measurementTransducerBlood pressure
A wireless medical transducer that is attached to a patient's body contains one or more sensing assemblies for continuous, wireless and non-invasive monitoring of vital signs. These include EKG, core temperature, arterial blood pressure, arterial blood oxygenation, and others. A transducer may be configured either as a two-unit device where the units are connected by a short cable or a single unit. Sharing various components allows different vitals signs to be monitored with greater efficiency. Multiple radio transmitters may operate in the same environment without interfering with each other.
Owner:FRADEN JACOB
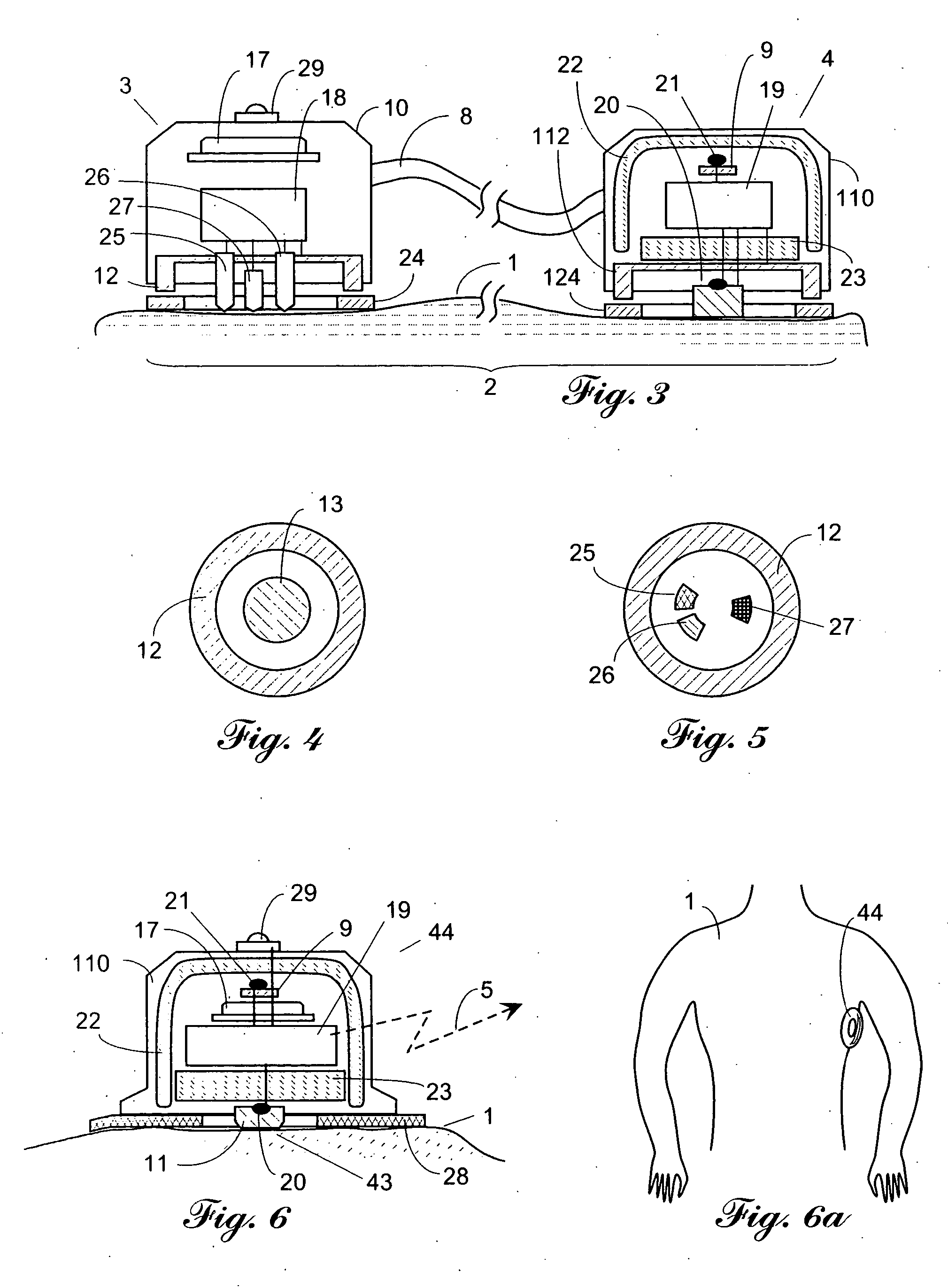
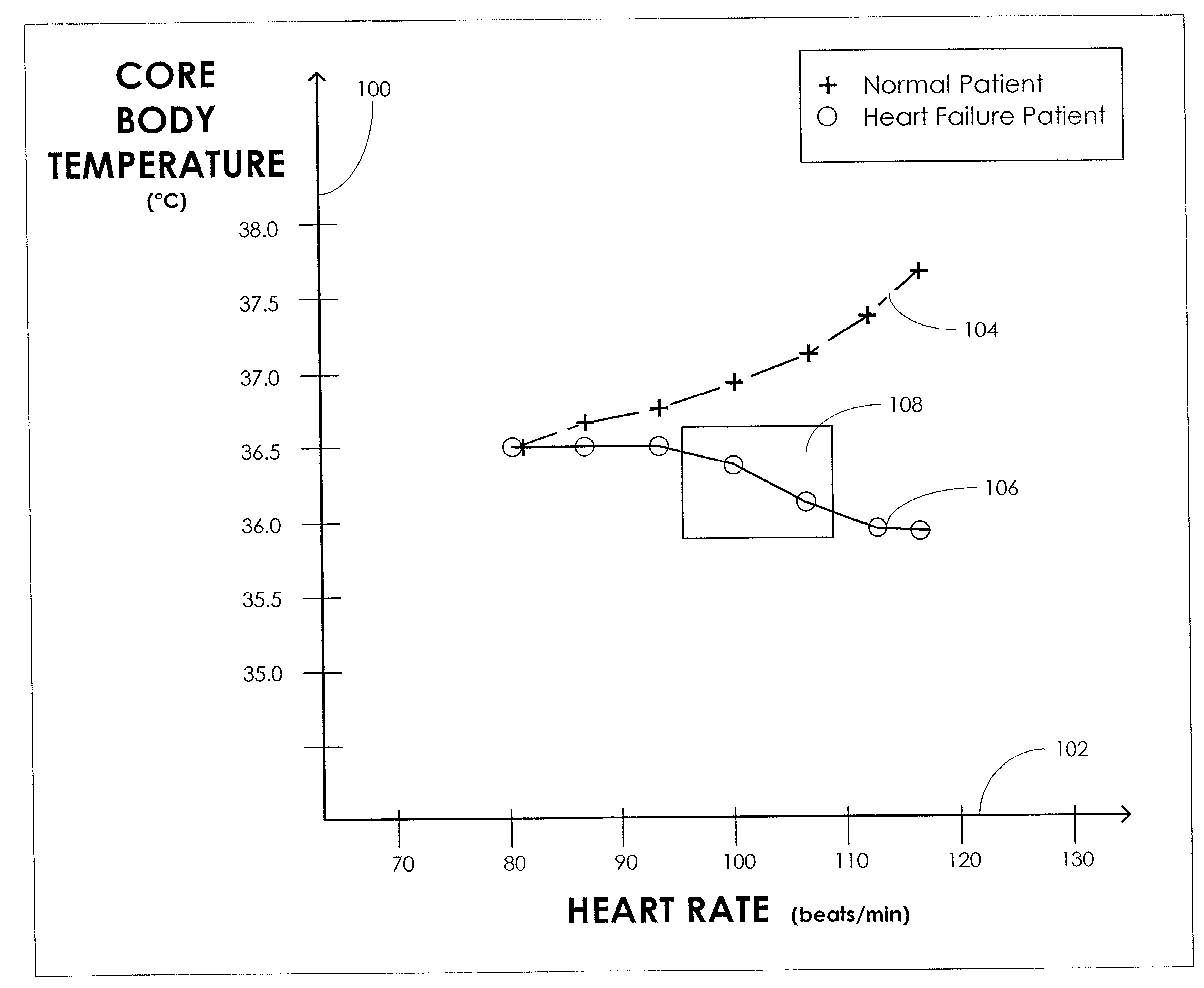
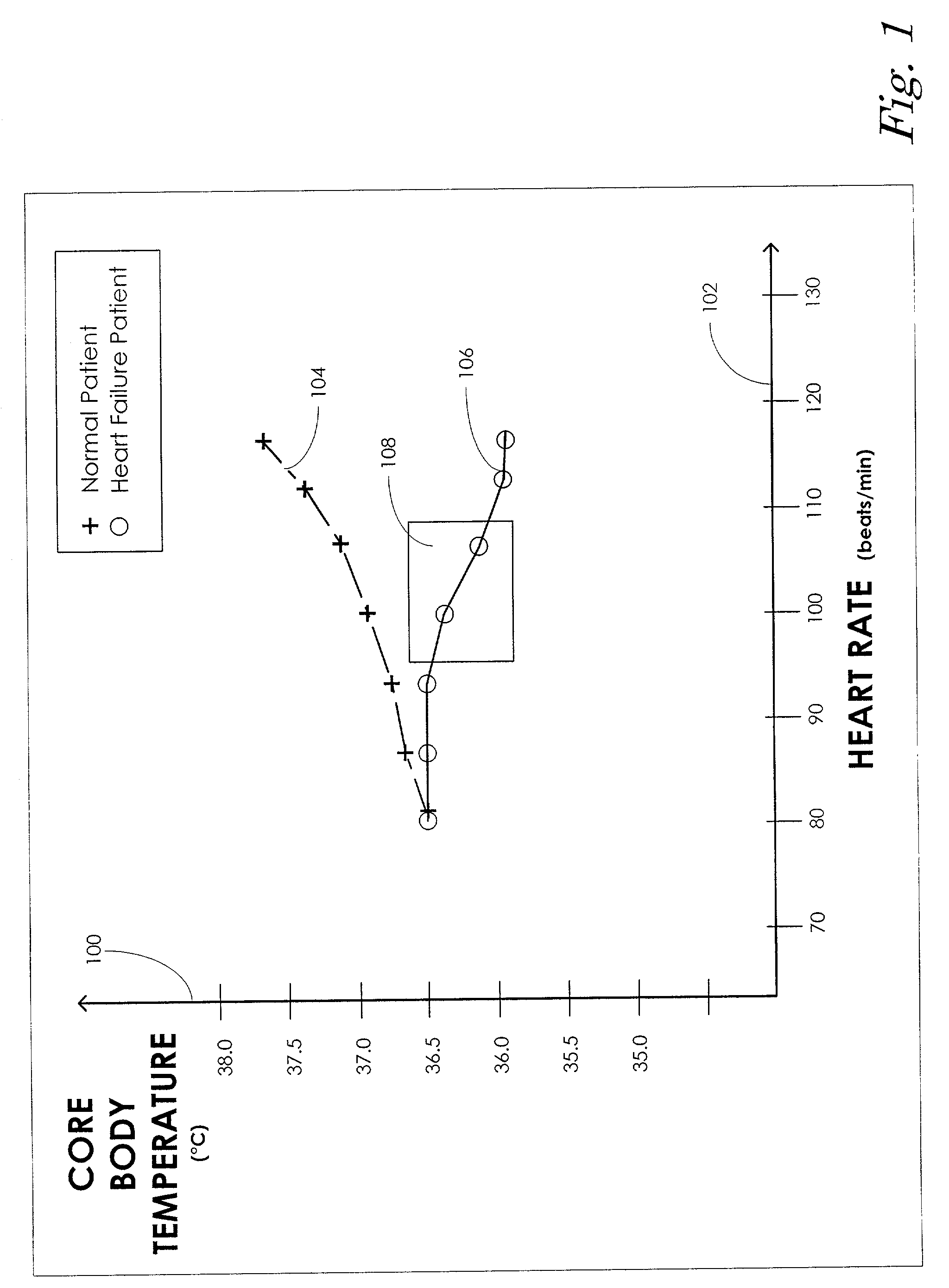
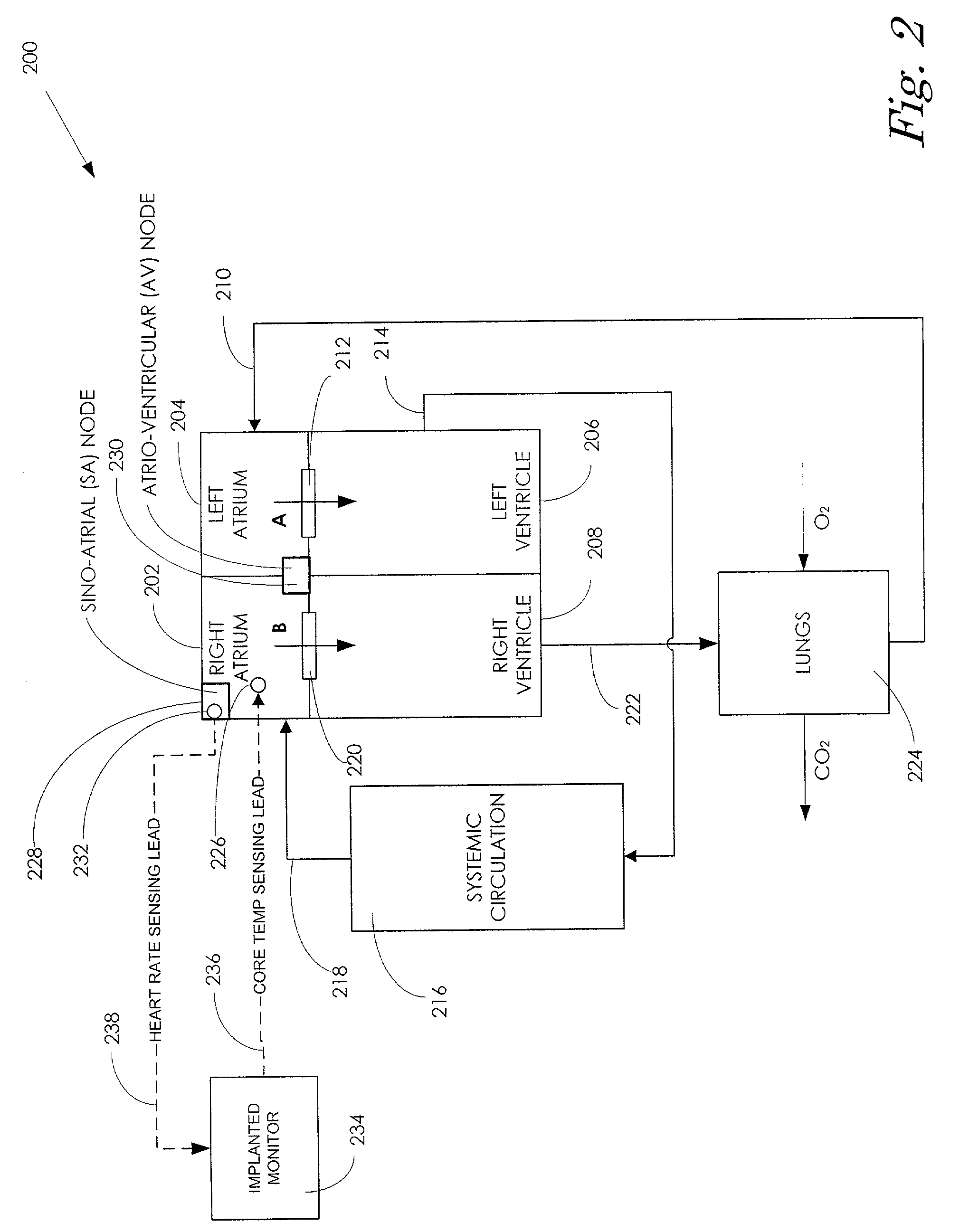
Core body temperature monitoring in heart failure patients
An implanted heart monitor includes sensors that measure various aspects of the heart failure patient's heart. A remote heart monitoring system connects the implanted heart monitor to a care provider, such as a physician. The data provided by the implanted heart monitor permits the care provider to obtain valuable data on the heart in order to make health care decisions affecting the heart failure patient's treatment. In many cases, the measurement of core body temperature and other patient data will enable the care provider to alter the patient's treatment to address the patient's condition. The implanted heart monitor can communicate over a wireless communication link with an external monitor. The implanted heart monitor may be implemented as part of a pacing device (i.e., pace maker) or may be a separate unit devoted to monitoring functions. The external monitor communicates with a monitoring station over a communication link. The monitoring station can operate as a centralized data collection unit, collecting data from multiple external monitors and multiple implanted heart monitors. Various other aspects of a heart failure patient's heart and / or body can be monitored, such as heart rate, blood pH levels, blood CO2 levels, and any other indications of the heart failure patient's activity. Various predetermined thresholds may be set to trigger alarms and / or data reports.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Temperature compensation circuit used for avalanche photodiode
InactiveCN101593786AImproved Gain Control AccuracyElectric variable regulationSemiconductor devicesWorking temperatureComputer module
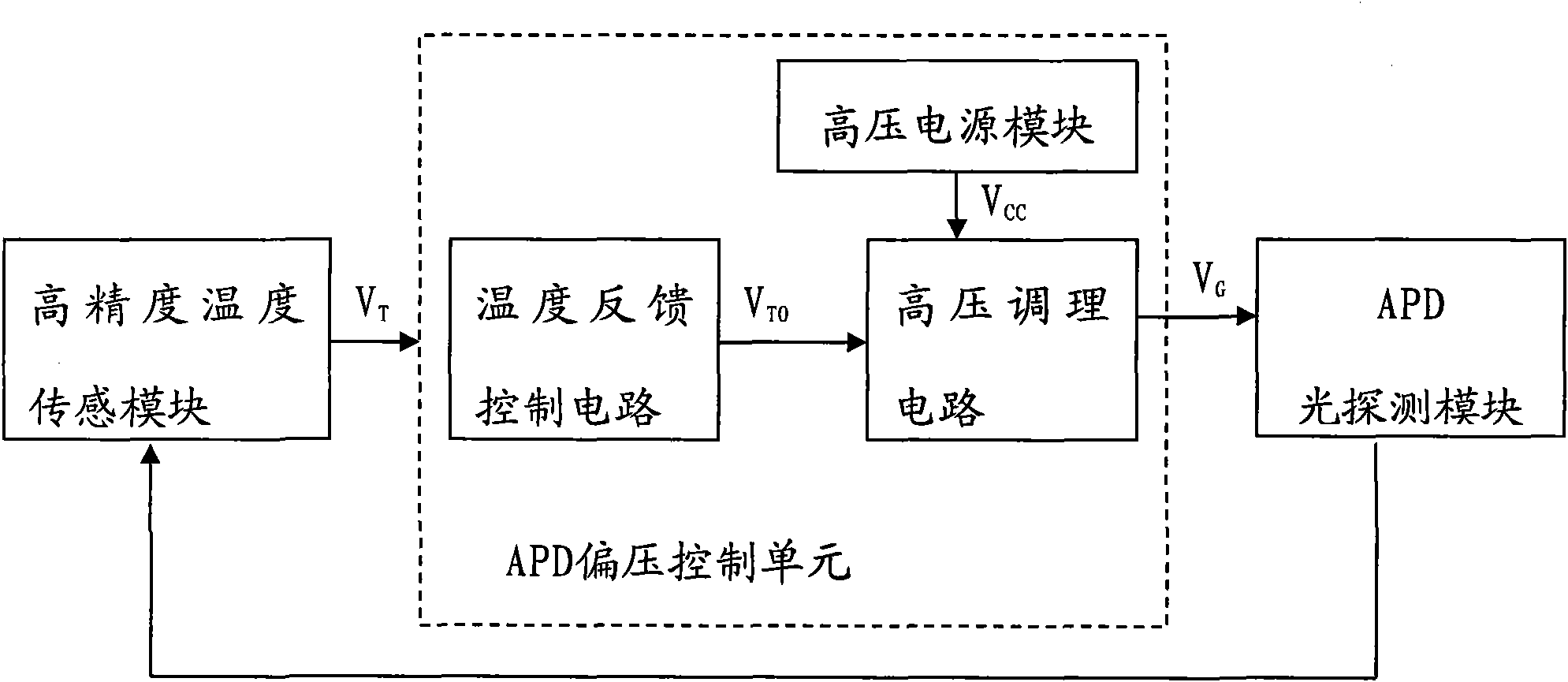
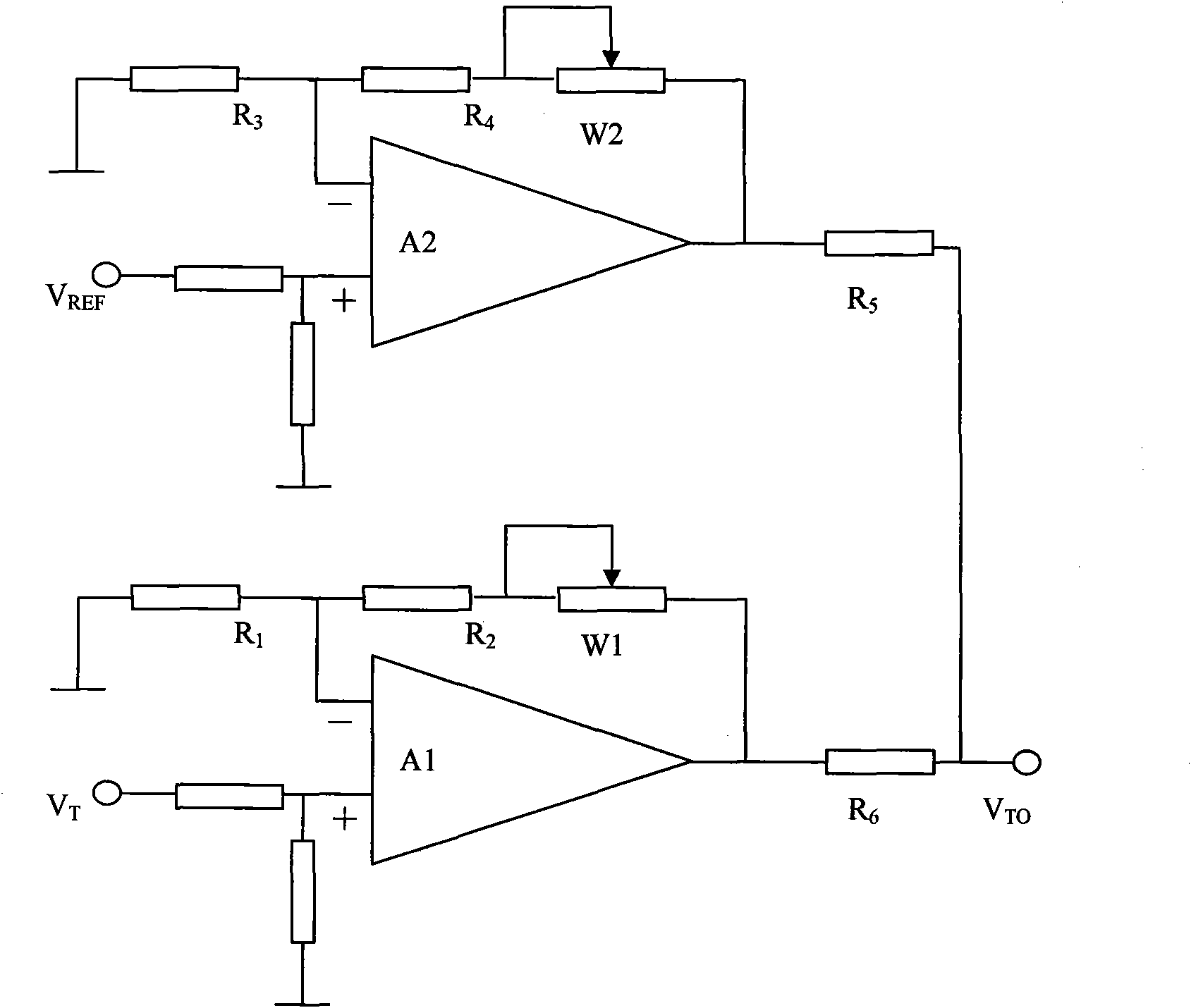
The invention discloses a temperature compensation circuit used for an avalanche photodiode (APD), which comprises a high-precision temperature sensing module, an APD bias control unit and an APD optical detection module, wherein the high-precision temperature sensing module is used for converting a tube core temperature of the APD into an analog voltage signal, an input end of the high-precisiontemperature sensing module is connected with the APD optical detection module, and an output end of the high-precision temperature sensing module is connected with the APD bias control unit; the APD bias control unit is used for converting the voltage signal output by the high-precision temperature sensing module into a bias signal for controlling the APD; and the APD optical detection module is used for feeding back the tube core temperature and making the gain of the APD constant under the control of the bias signal, an input end of the APD optical detection module is connected with the APDbias control unit, and an output end of the APD optical detection module is connected with the high-precision temperature sensing module. The practical high-precision APD bias controlled temperature compensation circuit is designed by using the APD bias control unit consisting of high-voltage controllers and related auxiliary circuit modules, the constant gain working temperature range of the APDis between zero and 50 DEG C, and the gain control precision is higher than 0.5 percent.
Owner:SHANGHAI BOOM FIBER SENSING TECH +1
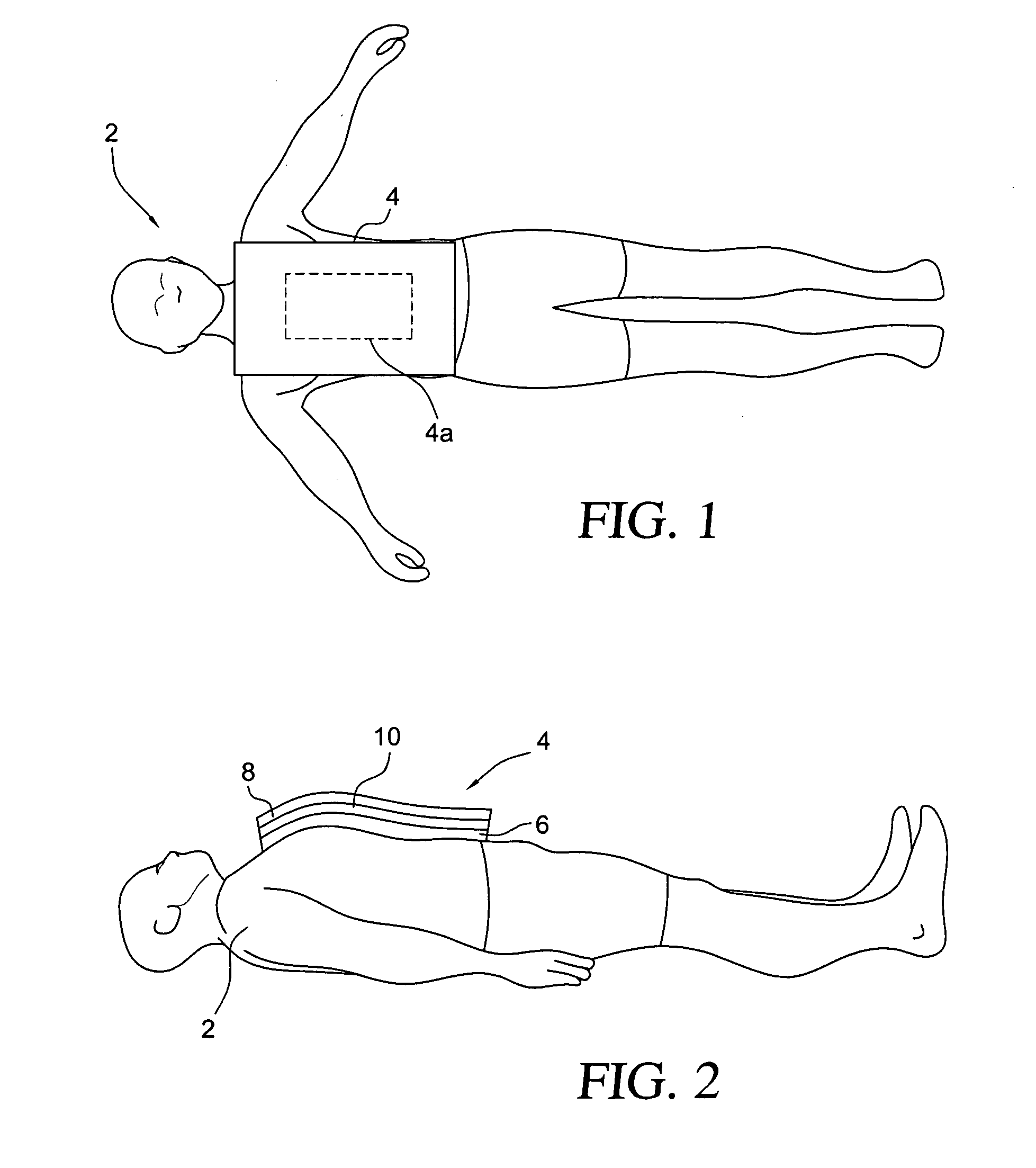
Heating system to alleviate hypothermia
ActiveUS20070049997A1Aggressive treatmentFacilitates patient insertionTherapeutic coolingTherapeutic heatingCold exposureBody area
A medical, electrically powered thermal cover for fitting predominantly the trunk and head of a person experiencing or potentially experiencing traumatic or cold-exposure hypothermia. The thermal cover encases all of the torso and neck, and portions of other body areas. Heating may be distinctly non-uniform, being applied to the body surface only in special regions where the body's capacity for heat uptake may be relatively high. In sum, the system may monitor deep body core temperature, direct heat to the body core where it may be most needed, and controls therapy over time to restore normothermia.
Owner:GRI ALLESET INC
Transpirationcooled wind driven generator stator
ActiveCN1960126AReduce lossNo maintenanceMagnetic circuit stationary partsWind drivenCore temperature
The tightly closed space of the stator consists of the stator chassis, the non-magnetic stainless steel isolated sleeve, the tightly closed end cap and the pressuring ring. The cooling loop consists of the liquid-lead groove between the stator core sections, the stator winding / stator end winding, the stator vaporizing space and the air condenser (AC). Via the gas entering tube and the liquid returning tube, AC connects to the stator chassis to form a main cooling circle loop. The heat produced due to the consumption of the stator components transfers to the vaporization cooling media (VCM) to raise its temperature. When the temperature reaches the saturation value based on inner pressure, VCM in the capacitor vaporize and occur phase-changing decalescence, then cool down by AC and finally liquidize. The invention causes stator core temperature distributing evenly. Features are: safe and reliable, simple structure, small volume, and large power density.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
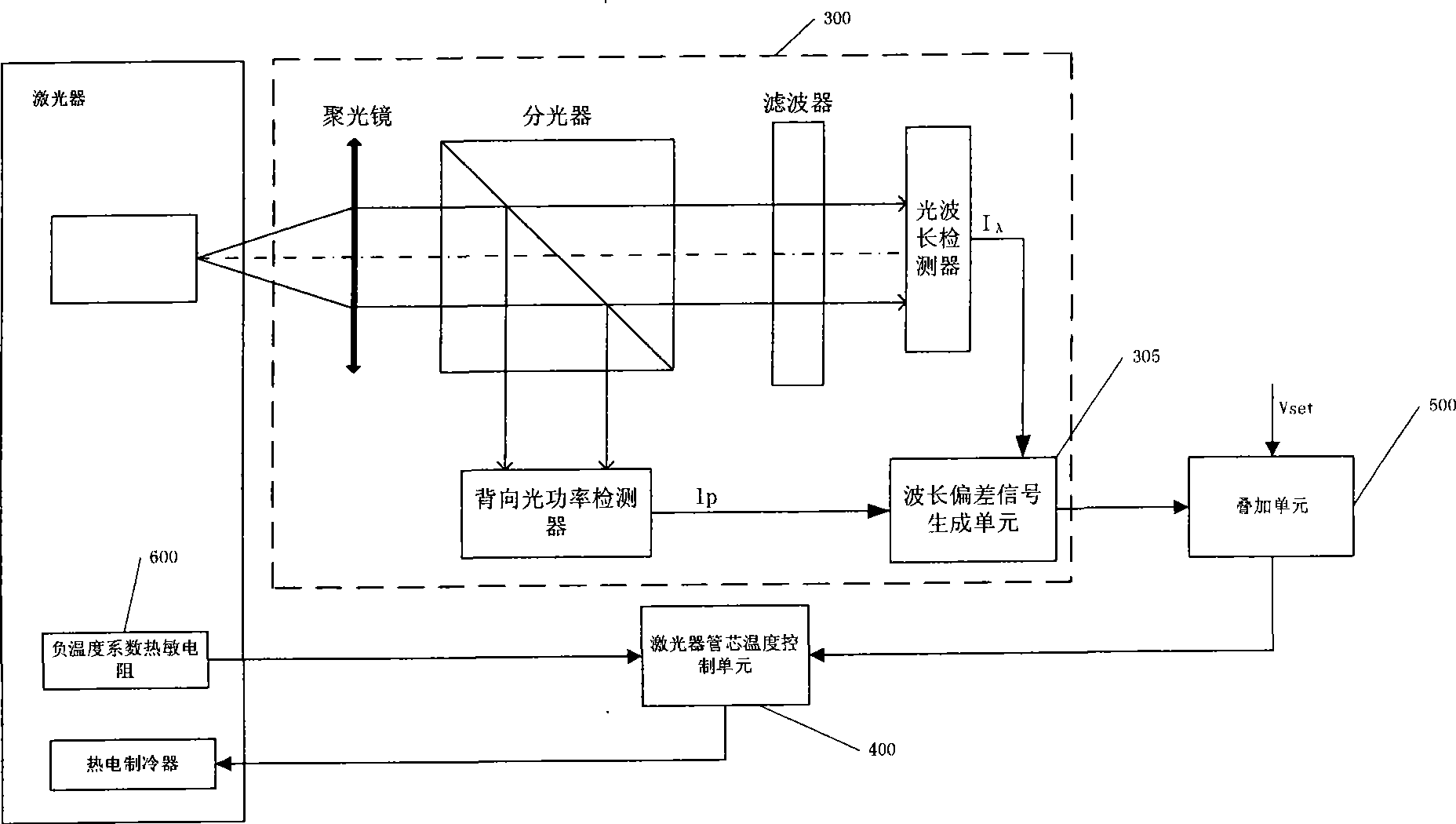
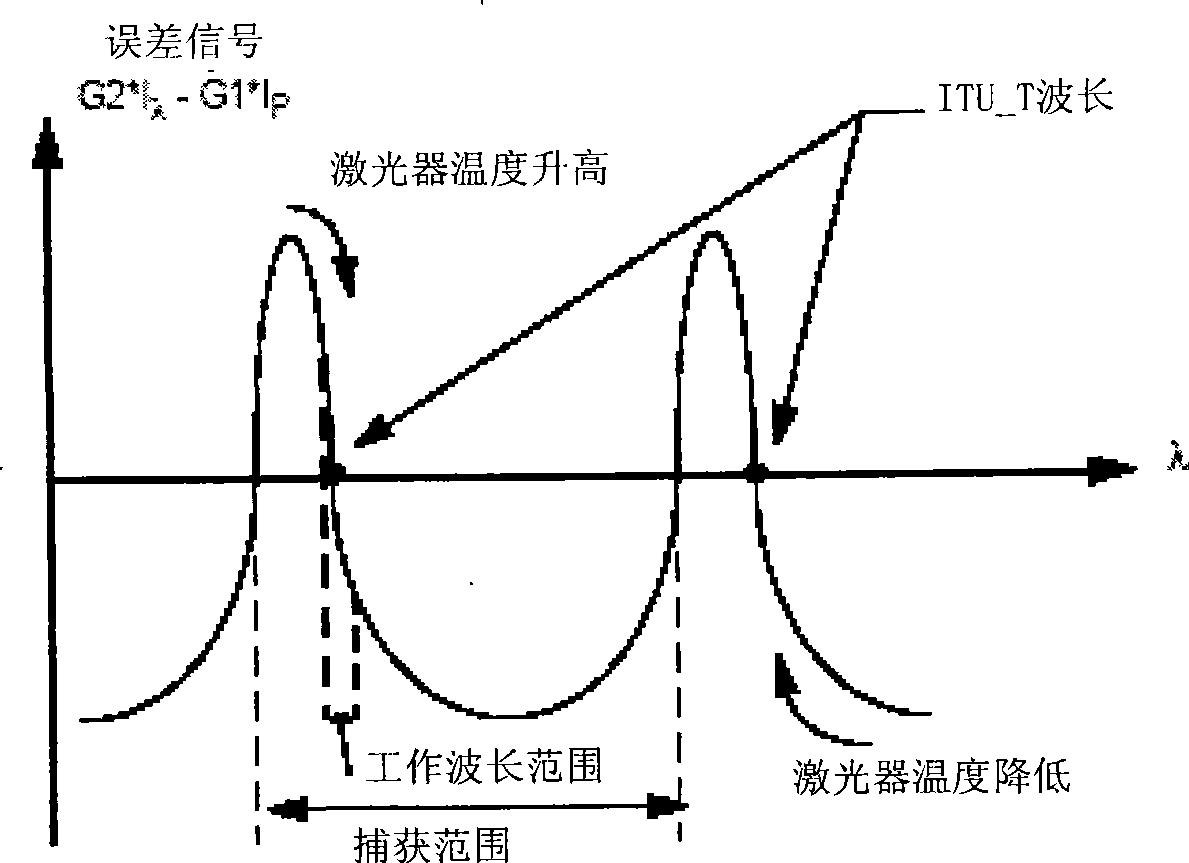
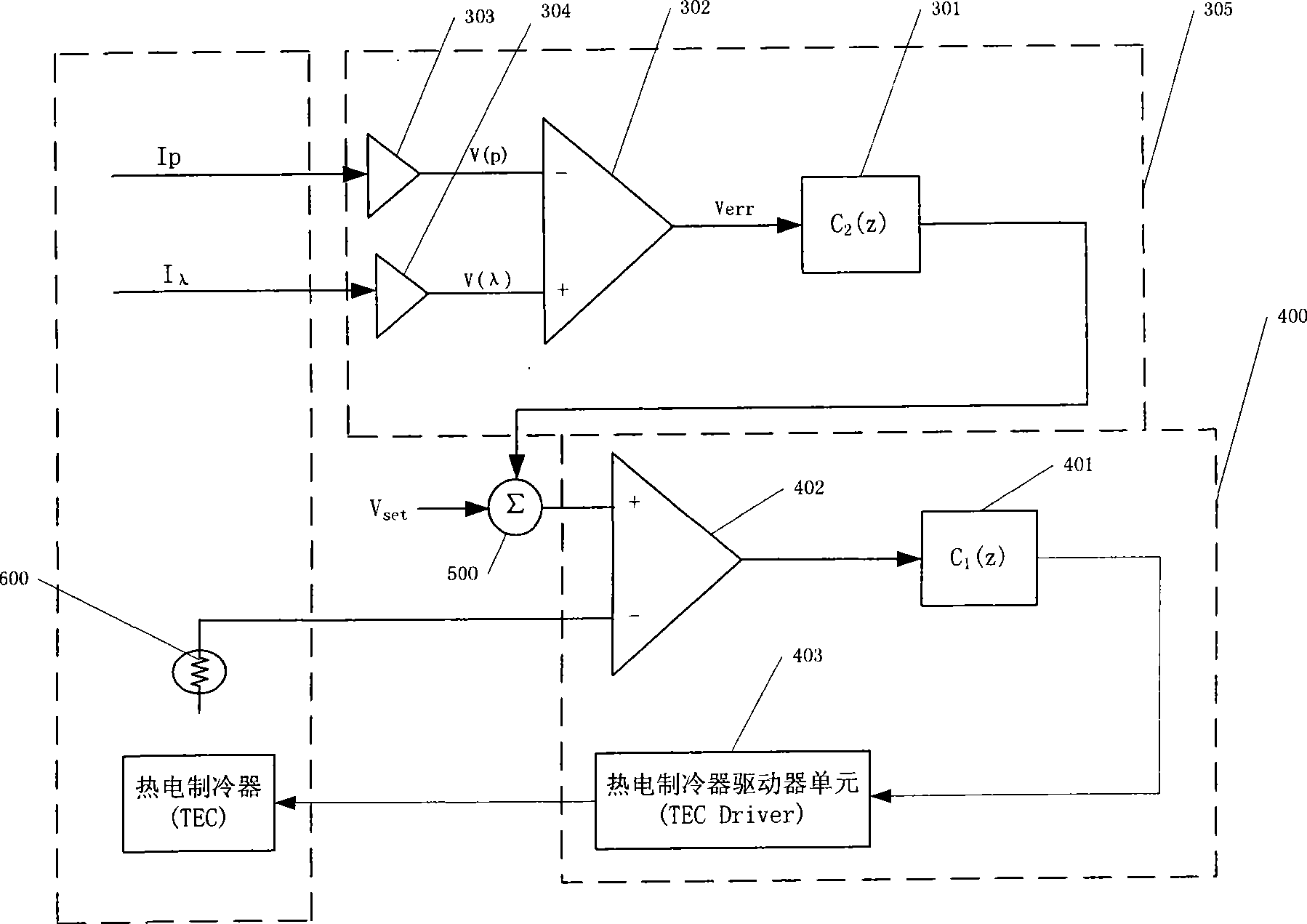
Control device for implementing optical module wavelength locking and method thereof
ActiveCN101369713AImprove stabilityHigh precisionLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersControl signalHeat sensitive
The invention discloses a control device and method for implementing optical module wavelength lock, wherein the apparatus includes: a laser tube core temperature control unit, for obtaining a feedback signal of laser build-in negative temperature coefficient thermistor, and comparing the feedback signal with a presetting signal to generate a control signal inputted to a laser build-in thermoelectric cooler; a wavelength autocontrol unit, for detecting laser output optical signal, and obtaining a wavelength deviation signal for implementing wavelength lock; a superpose unit, for superposing the wavelength deviation signal onto the presetting signal and sending to the laser tube core temperature control unit. The invention overcomes the defect of large offset of optical module output wavelength, and resolves the problem of neighboring channel signal crosstalk of the DWDM system.
Owner:ZTE CORP
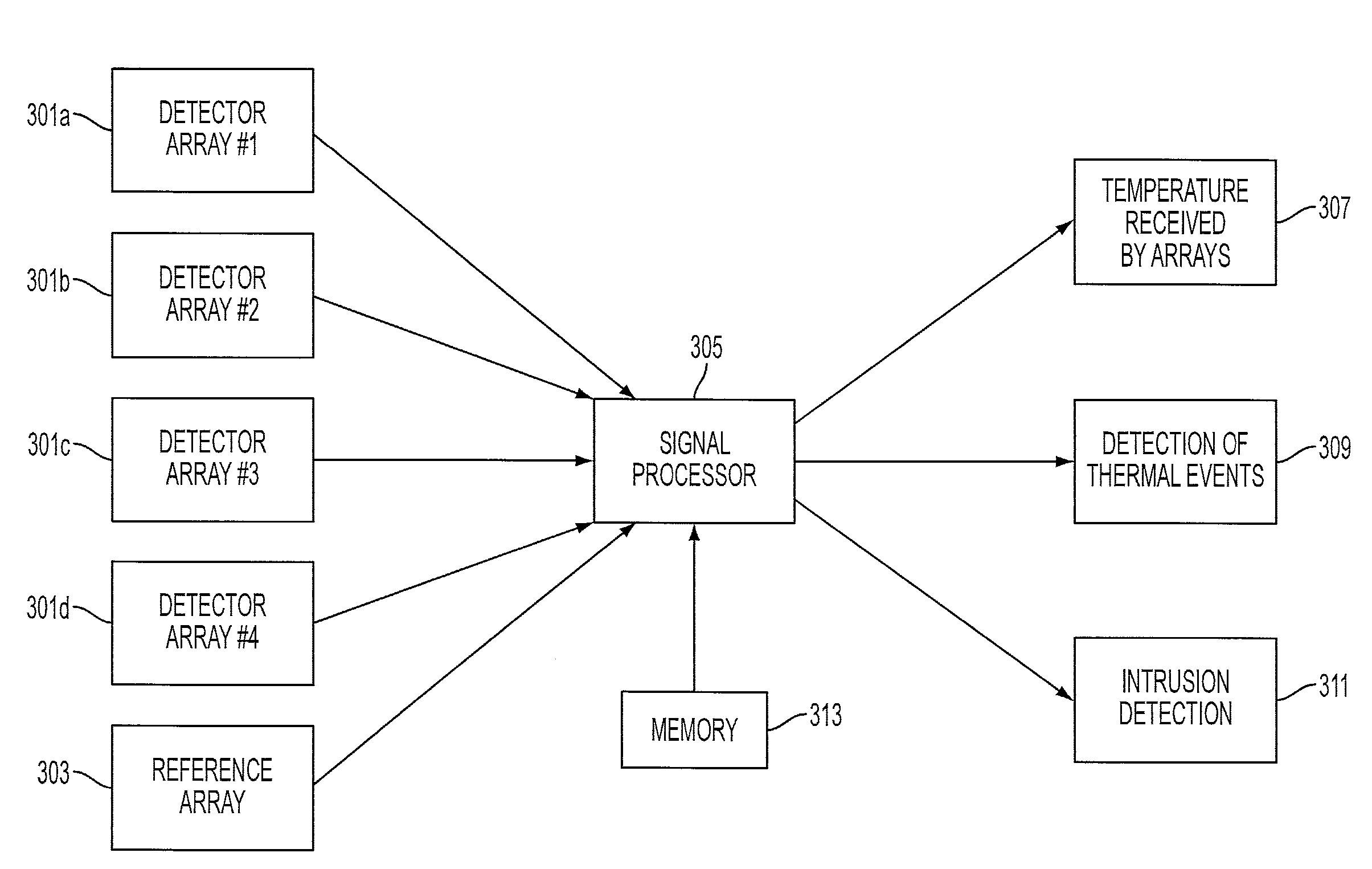
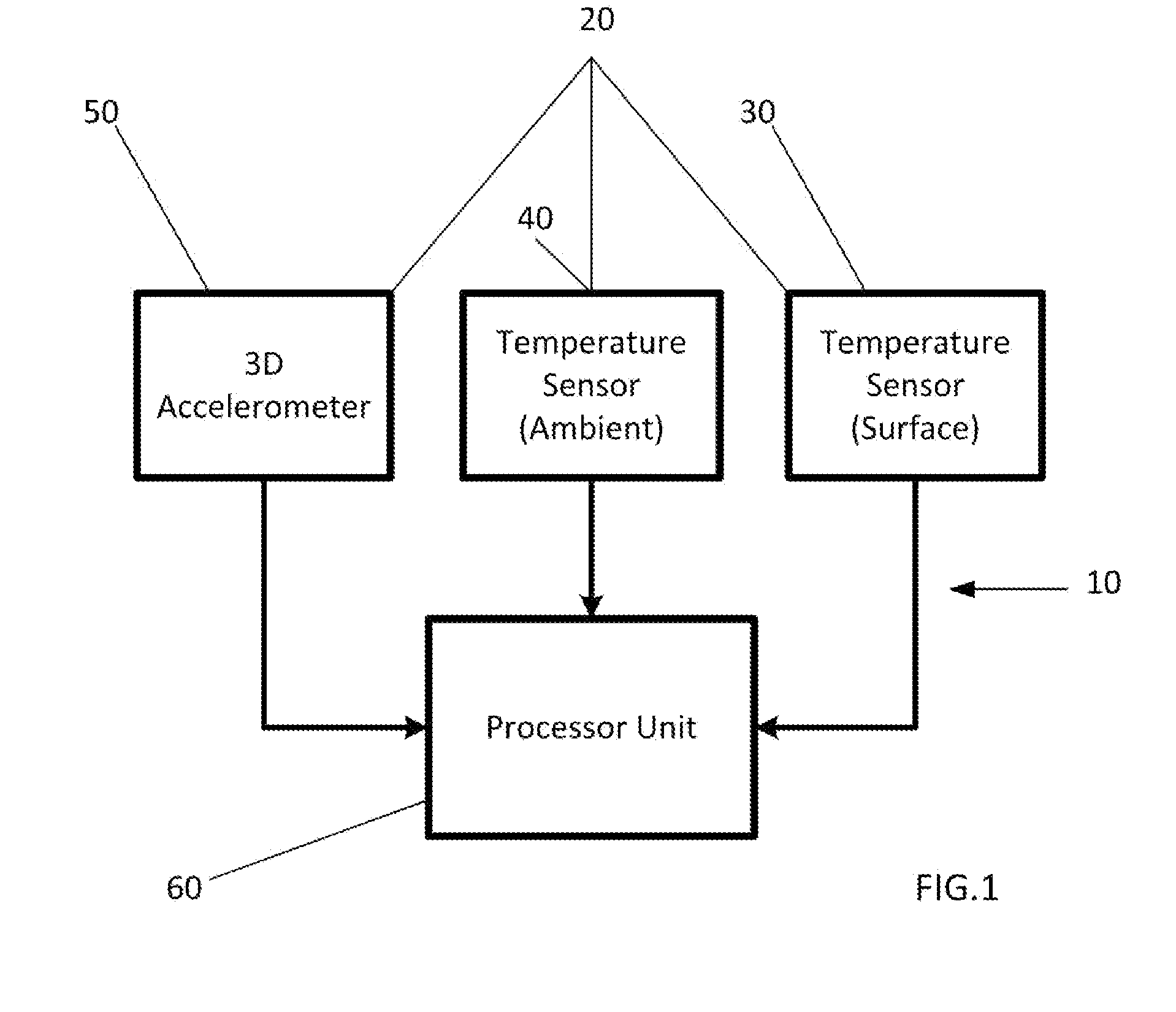
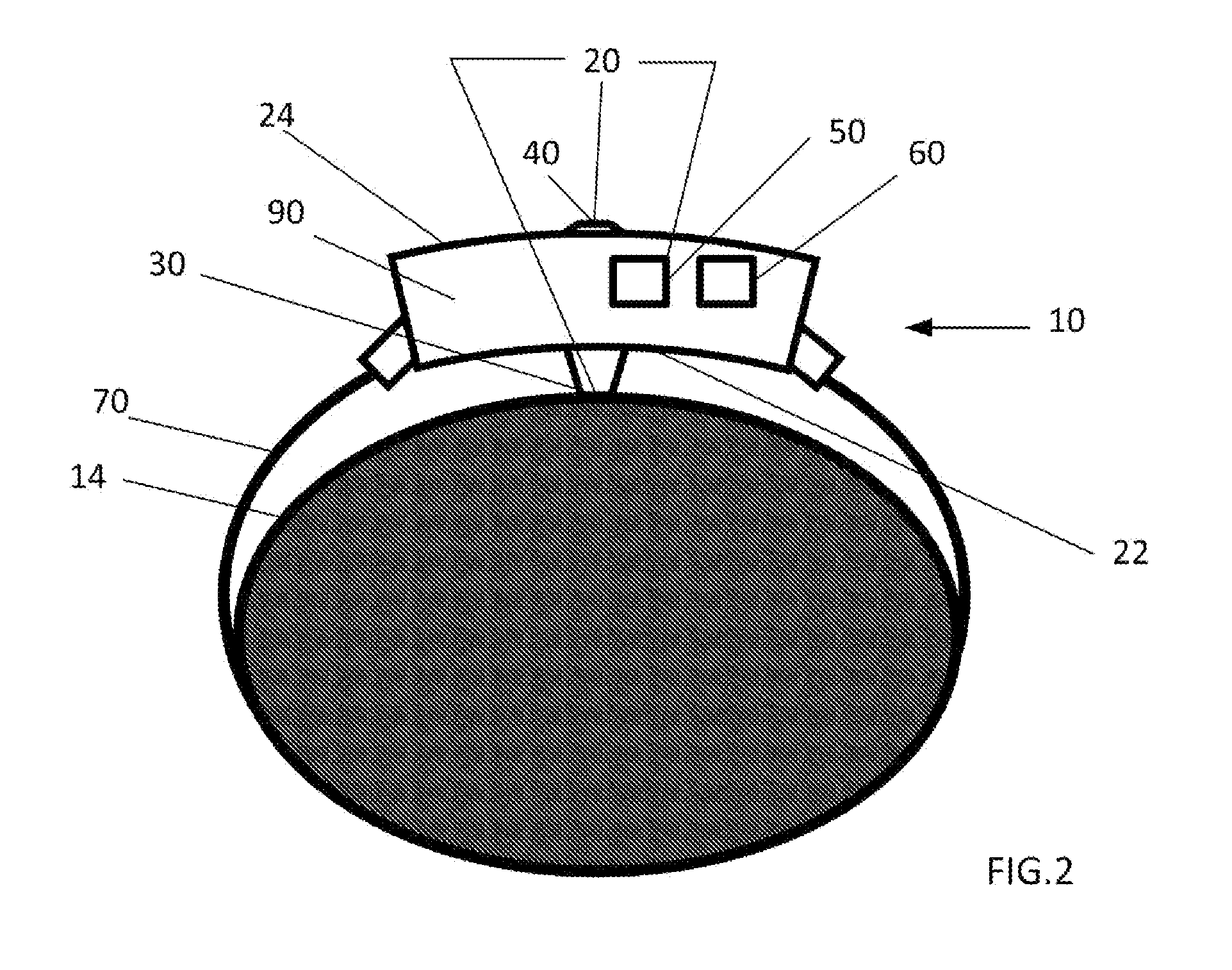
Non-invasive automatic monitoring of pet animal's core temperature
ActiveUS20150057963A1Thermometers using electric/magnetic elementsDigital computer detailsAccelerometerCore temperature
A system, device and method monitoring whether a core temperature of a warm-blooded pet animal is within a normal range for the pet animal comprises a sensing assembly including (i) a skin temperature sensor positioned such that a sensing surface of the skin temperature sensor faces the animal, the skin temperature sensor configured to produce a skin temperature output, (ii) an ambient temperature sensor spaced away from the animal and configured to produce an ambient temperature output, and (iii) an accelerometer for sensing an acceleration of the pet animal and producing an acceleration output; and a processor for receiving the outputs, calculating an activity level from the acceleration data and determining whether the core temperature of the pet animal is within the normal range based on a pre-defined function relating the skin temperature TS, the ambient temperature TA, and the activity level of the pet animal.
Owner:PETPACE
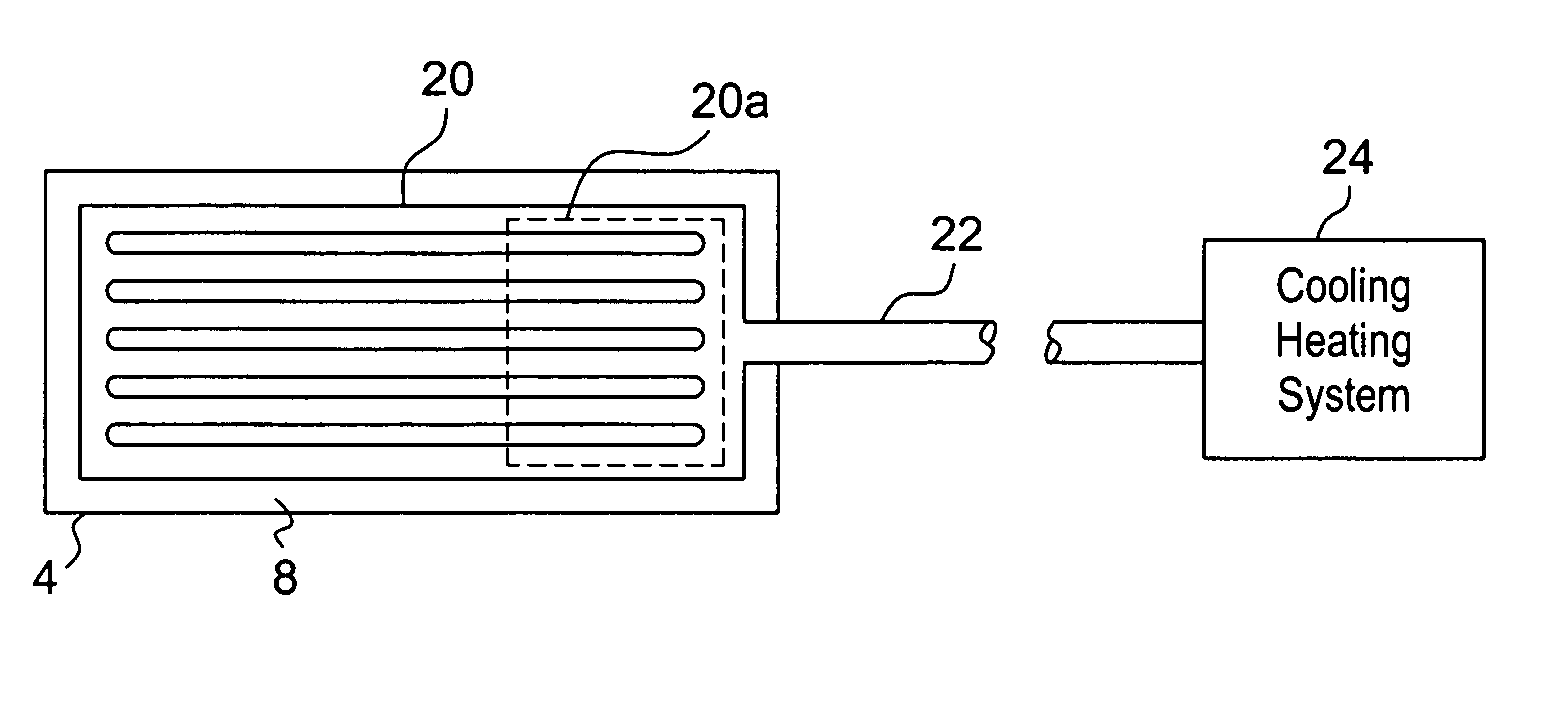
Patient heat transfer device
InactiveUS20090228082A1Controlled and rapid induced hypothermiaQuick controlIndirect heat exchangersTherapeutic coolingLiquid stateMedicine
To rapidly induce hypothermia to a patient, in the event the patient has a stroke, hyperthermia or some other temperature related heath problems which requires prompt action to regulate the temperature of the patient, a flat flexible structure conformable to the body of the patient is placed into contact with the patient. The structure has at least two heat transfer portions. One of heat transfer portions is positioned in contact with the body of the patient. The structure is hermetically sealed and a fluidized medium responsive to temperature change is provided in the structure between the heat transfer portions. The fluid is changeable between a liquid state and a gaseous state, when it is exposed to heat and cold. The heat absorbed by the heat transfer portion in contact with the patient is carried by the fluidized medium, as latent heat in the gas that results when the liquid is vaporized to its gaseous state, to the heat transfer portion layer not in contact with the patient, so that the latent heat in the gaseous vapor is dissipated. Upon dissipation, the gaseous vapor is condensed and the fluidized medium returns to its liquid state. The structure may be formed from a flat flexible heat pipe and may also be configured as a rib cage shaped jacket to embrace the torso of the patient. A cooling circuit or mechanism may be added to the structure to facilitate the removal of heat therefrom. The structure may also be used to raise the core temperature of a patient.
Owner:SMITHS MEDICAL ASD INC
Bituminous products, the mixture thereof with aggregates and the use thereof
ActiveUS20090088499A1Bituminous mix production temperatureMaintain managementIn situ pavingsTransportation and packagingRoad surfaceCore temperature
The invention relates to anhydrous bituminous products containing one or several specific additives which make it possible to substantially reduce a temperature for producing aggregate and bituminous product mixtures in such a way that it ranges from 20 to 40° C., wherein the temperature of the aggregate and the bituminous product mixture during spreading ranges from 10 to 40° C. and the temperature in the core of the aggregate and bituminous product mixtures during compacting can be raised to 50° C. without degrading the standardized properties of the bituminous product and the bituminous product and aggregate mixture and ensuring the process continuity from transport to compacting according to the state of the art. The inventive aggregate and bituminous product mixtures are particularly suitable for tightening, building and servicing road surfaces, pavements and airfield runways.
Owner:ARKEMA FRANCE SA
Methods and apparatus for a remote, noninvasive technique to detect core body temperature in a subject via thermal imaging
InactiveUS20080154138A1Convenience and securityGuarantee economic securitySensing radiation from moving bodiesDiagnostic recording/measuringDiseaseEngineering
Owner:MCQUILKIN GARY L
Automatic temperature control apparatus of pump laser for ASE broadband light source
ActiveCN101404376ACompact designImprove reliabilityTemperatue controlLaser cooling arrangementsAutomatic controlControl signal
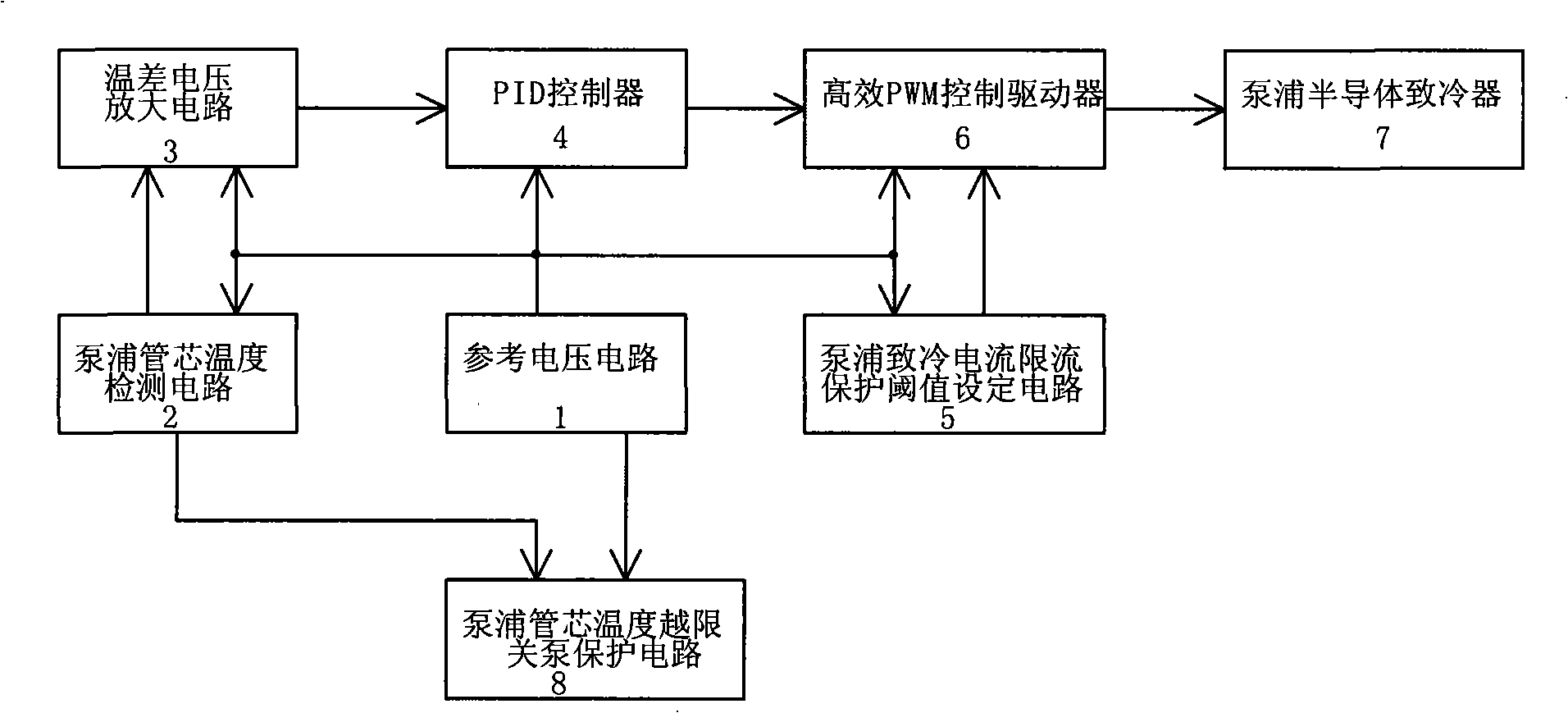
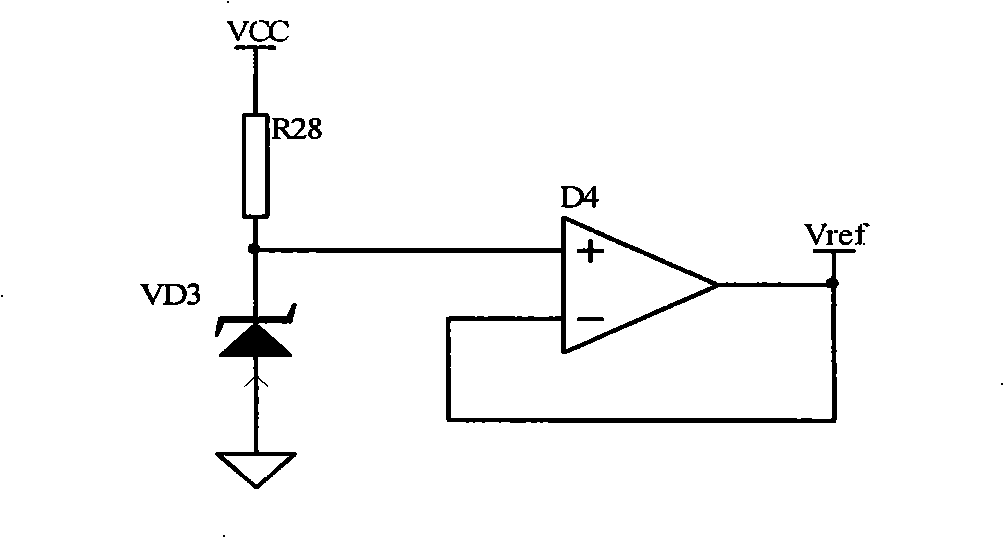
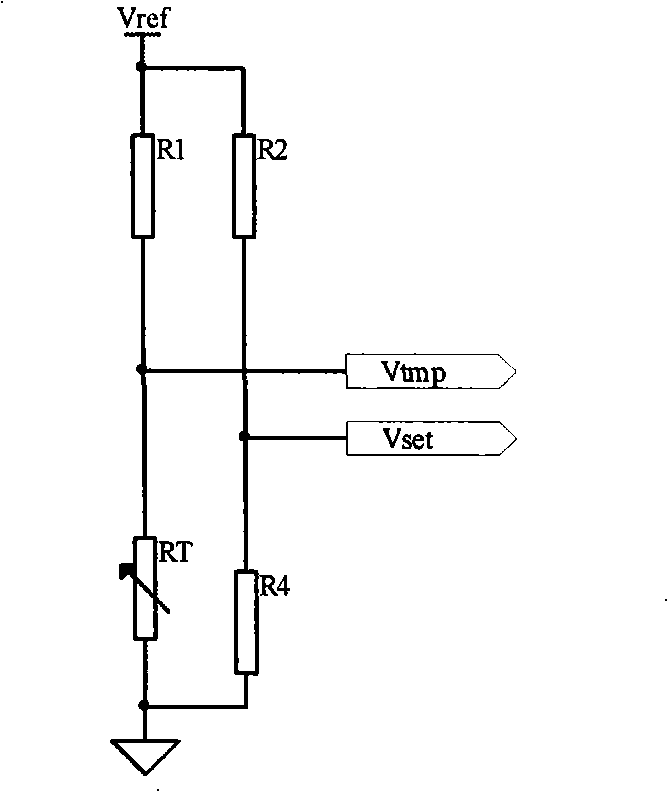
The invention designs an automatic temperature control circuit which has exact control, reliable and stable performance and complete protective measures, and is used for executing effective real time control on the temperature of a tube core of a pump laser in ASE broadband light source. The control device adopts the design proposal of a temperature control system based on Proportion Integration Differentiation (PID) control and pulse-width modulation (PWM) braking mechanism and realizes the designs by adopting a pure hardware circuit; the control device comprises a reference voltage circuit, a pumping tube core temperature testing circuit, a thermoelectric voltage amplifier circuit, a PID controller, a pumping refrigeration current limiting protective threshold set circuit, an efficient PWM control driver, a pumping semiconductor refrigerator and a pumping tube core temperature out-of-limit close protective circuit. The whole circuit has simple and compact design, high reliability as well as heating and refrigerating efficiency, and little self heating, thereby greatly reducing the power consumption and volume of a pumping temperature controller; as the control device has the complete protective function, when the temperature of the pumping tube core exceeds the set range of operating temperature, the circuit sends out the gang control signal to automatically close a drive circuit of the pumping. The pumping refrigeration current limiting protective circuit limits the refrigeration current within the range of the preset maximum refrigeration current range to prevent the pumping from being damaged.
Owner:WUXI TACLINK OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
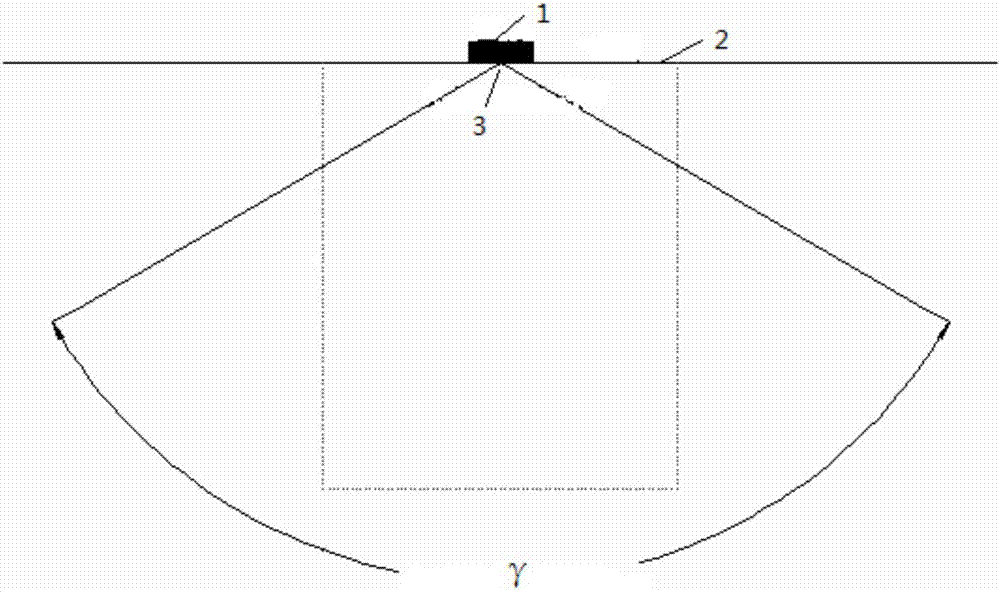
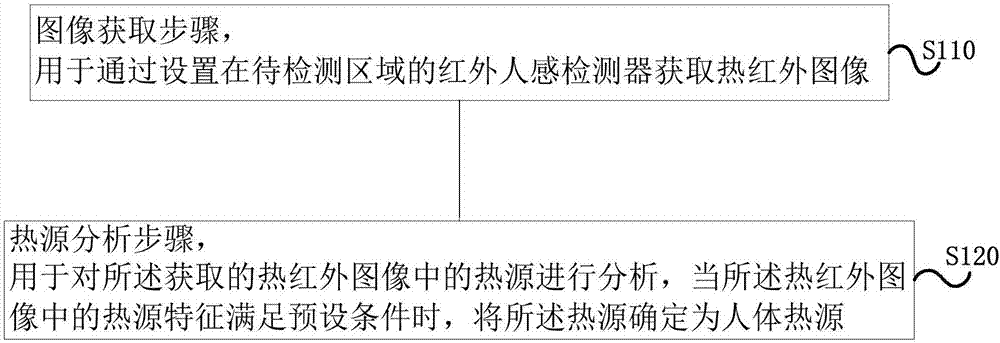
Human body heat source recognition method and device and equipment having device
ActiveCN107084795AAccurate identificationAccurate feedbackMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsLower limitHuman body
The invention provides a human body heat source recognition method and device and equipment having the device. The human body heat source recognition method comprises an image acquisition step which is used for acquiring a thermal infrared image through an infrared human sensing detector arranged in an area to be detected; and a heat source analysis step which is used for analyzing the heat source in the acquired thermal infrared image and determining the heat source as a human body heat source when the heat source characteristics in the thermal infrared image meet the preset conditions, wherein the preset conditions include that the temperature of the heat source is greater than or equal to the lower limit value of normal human body temperature and less than or equal to the upper limit value of the normal human body temperature, and the difference value of the heat source core temperature and the background temperature is greater than or equal to a preset temperature difference threshold. According to the technical scheme, the human body heat source can be accurately recognized, the human body position is monitored in real time and the recognition accuracy is high so that the position information of the human body heat source can be accurately fed back and the human body heat source area is constantly maintained to have great comfort level experience effect.
Owner:GREE ELECTRIC APPLIANCES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com