Patents
Literature
173 results about "Severe acute respiratory syndrome" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A respiratory disease caused by corona virus infection.
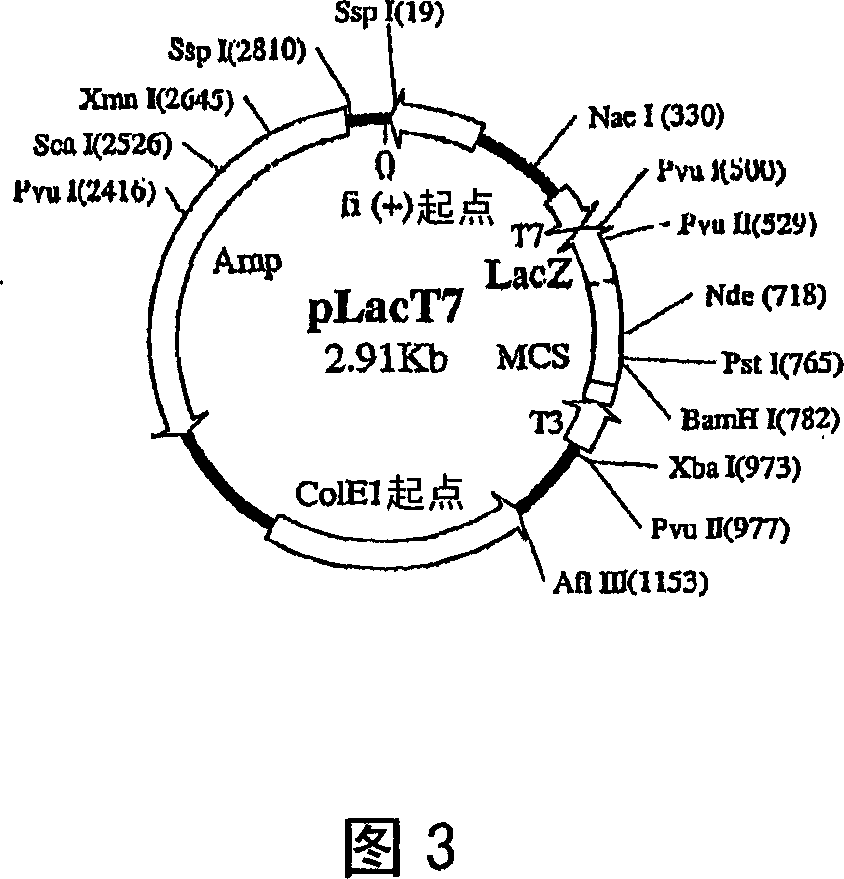
Compositions and methods for the treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)
The present invention provides design and synthesis of oligomeric compounds and compositions that can be administered to reduce the activity of SARS virus in vivo or in vitro, to prevent or treat SARS virus-associated disease, to detect AARS virus, and to diagnose SARS virus-associated diseases.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
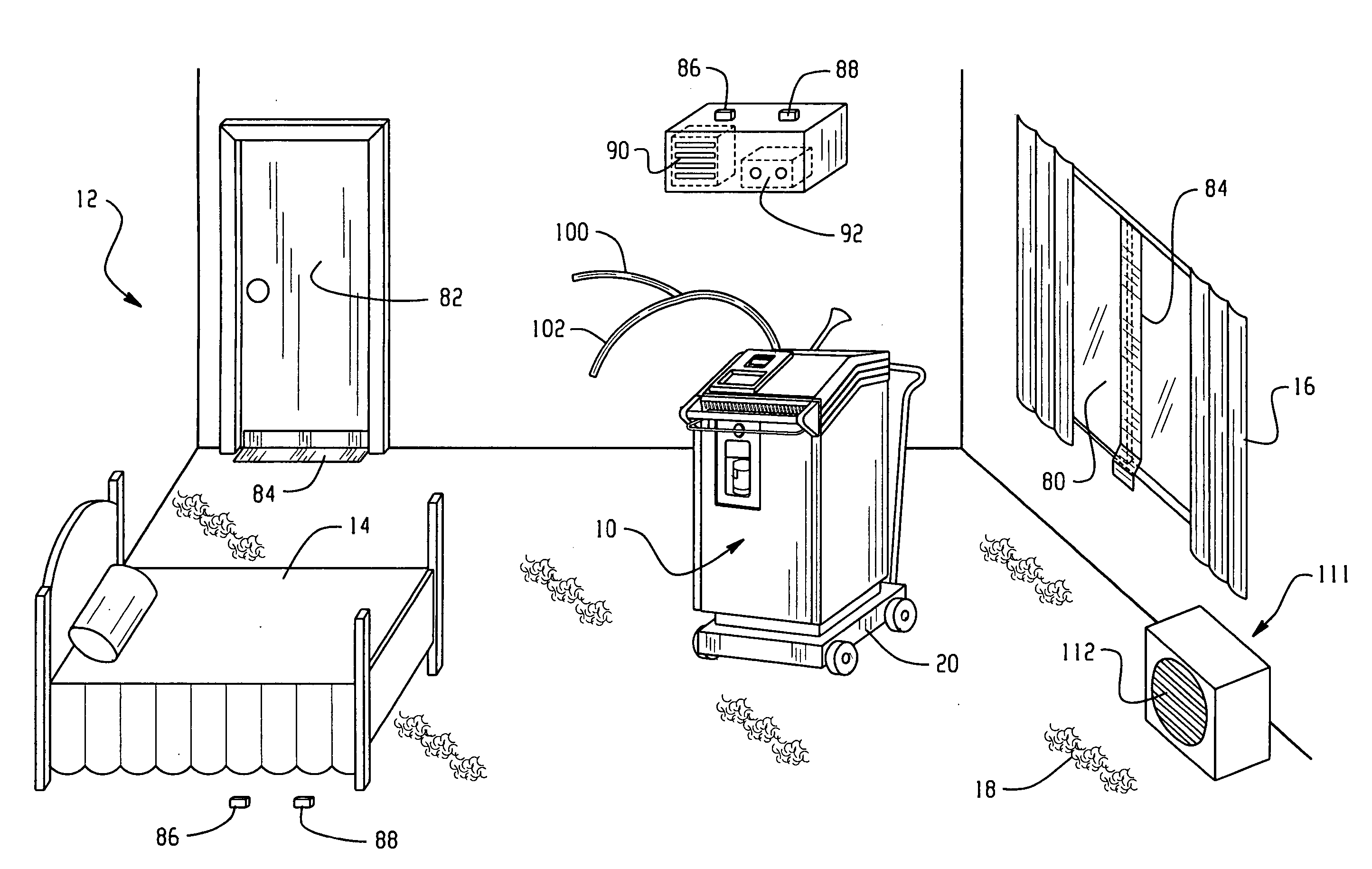
Room decontamination with hydrogen peroxide vapor
ActiveUS20060008379A1Reduce or even removeMinimize residual amountGaseous substancesDeodrantsHotel roomVapor generator
A system for microbially and / or chemically decontaminating a room such as a hotel room includes a vapor generator which supplies a decontaminant vapor, such as hydrogen peroxide vapor to the room. The room is then aerated to a level at which it is safe for normal occupants to enter. By using a two step aeration, with a second step at lower humidity than the first, the concentration of residual hydrogen peroxide is reduced rapidly to safe levels of 1 ppm or less, typically about 0.5 ppm, in under four hours. The room is rendered substantially free of contaminants, such as those responsible for Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS), Norwalk virus, and unpleasant odors.
Owner:STERIS CORP
Methods and apparatus for a remote, noninvasive technique to detect core body temperature in a subject via thermal imaging
ActiveUS7340293B2Accurate of core body temperatureConvenience and securitySensing radiation from moving bodiesDiagnostic recording/measuringDiseaseEngineering
An approach to noninvasively, remotely and accurately detect core body temperature in a warm-blooded subject, human or animal, via thermal imaging. Preferred features such as the use of in-frame temperature references, specific anatomical target regions and a physiological heat transfer model help the present invention to overcome pitfalls inherent with existing thermal imaging techniques applied to physiological screening applications. This invention provides the ability to noninvasively, remotely and rapidly screen for diseases or conditions that are characterized by changes in core body temperature. One human application of this invention is the remote screening for severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), since fever is a common, early symptom. Other diseases and conditions that affect the core body temperature of humans or animals may also be noninvasively and remotely detected with this invention.
Owner:CARDIOWAVE
Compositions and methods for the treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)
The present invention provides design and synthesis of oligomeric compounds and compositions that can be administered to reduce the activity of SARS virus in vivo or in vitro, to prevent or treat SARS virus-associated disease, to detect AARS virus, and to diagnose SARS virus-associated diseases.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
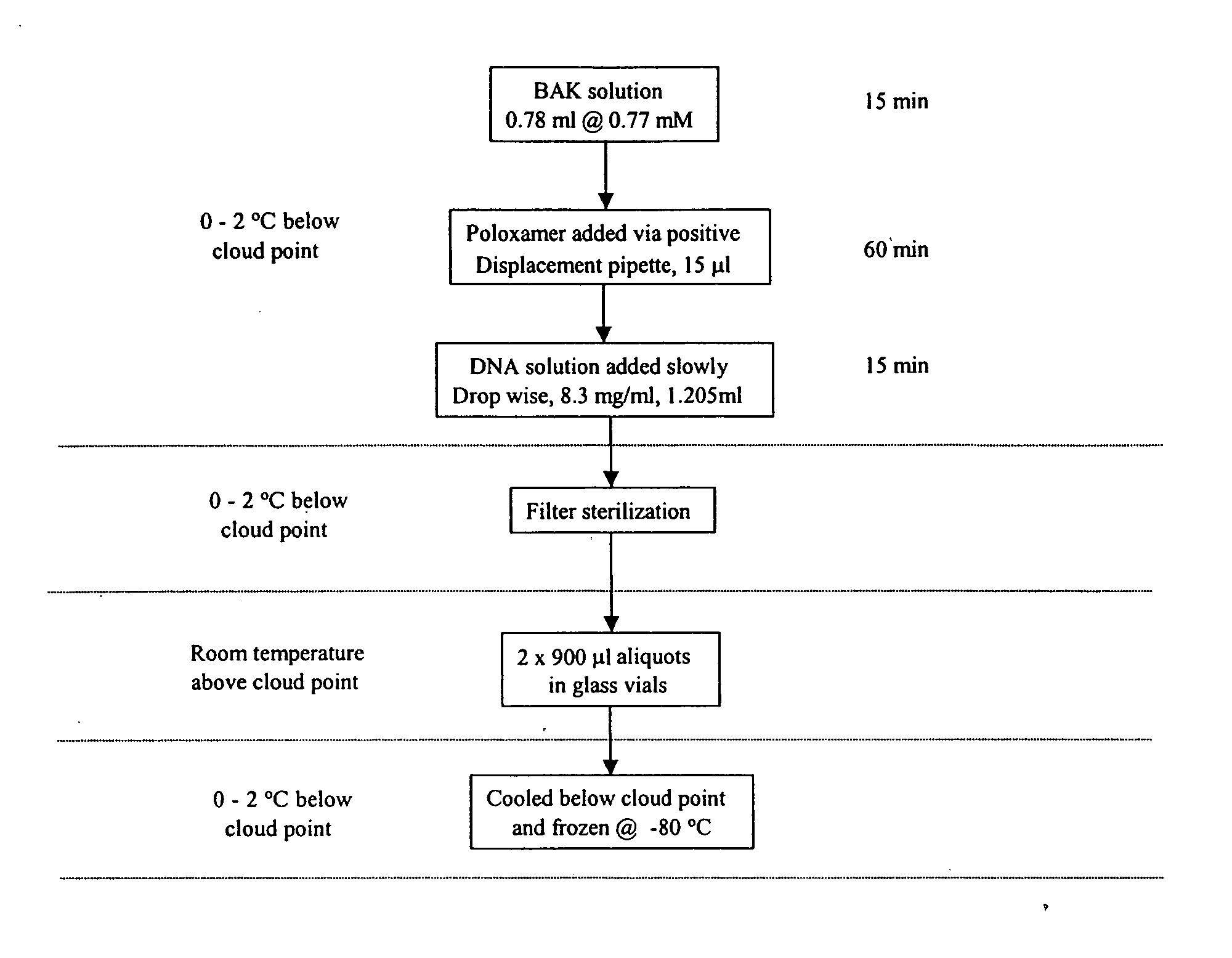
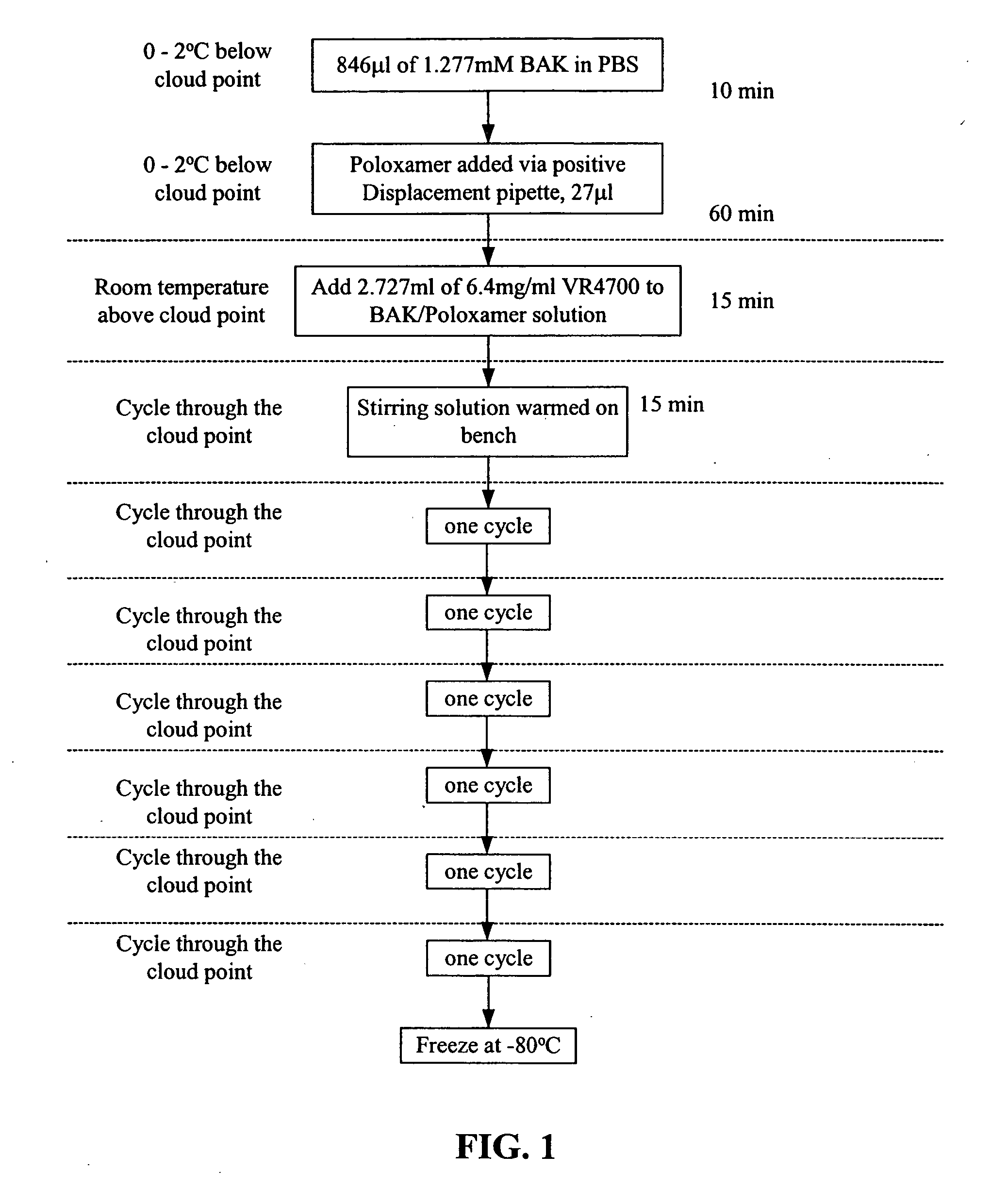
Severe acute respiratory syndrome DNA vaccine compositions and methods of use
The present invention is directed to raising a detectable immune response in a vertebrate by administering in vivo, into a tissue of the vertebrate, at least one polynucleotide comprising one or more regions of nucleic acid encoding a SARS-CoV protein or a fragment, a variant, or a derivative thereof. The present invention is further directed to raising a detectable immune response in a vertebrate by administering, in vivo, into a tissue of the vertebrate, at least one SARS-CoV protein or a fragment, a variant, or derivative thereof. The SARS-CoV protein can be, for example, in purified form. The polynucleotide is incorporated into the cells of the vertebrate in vivo, and an immunologically effective amount of an immunogenic epitope of a SARS-CoV polypeptide, fragment, variant, or derivative thereof is produced in vivo. The SARS-CoV protein is also administered in an immunologically effective amount.
Owner:VICAL INC
Infectious disease epidemic situation predicative analysis method based on nonlinear and coefficient variation predictive model
InactiveCN101794342ASpecial data processing applicationsSusceptible populationSevere acute respiratory syndrome
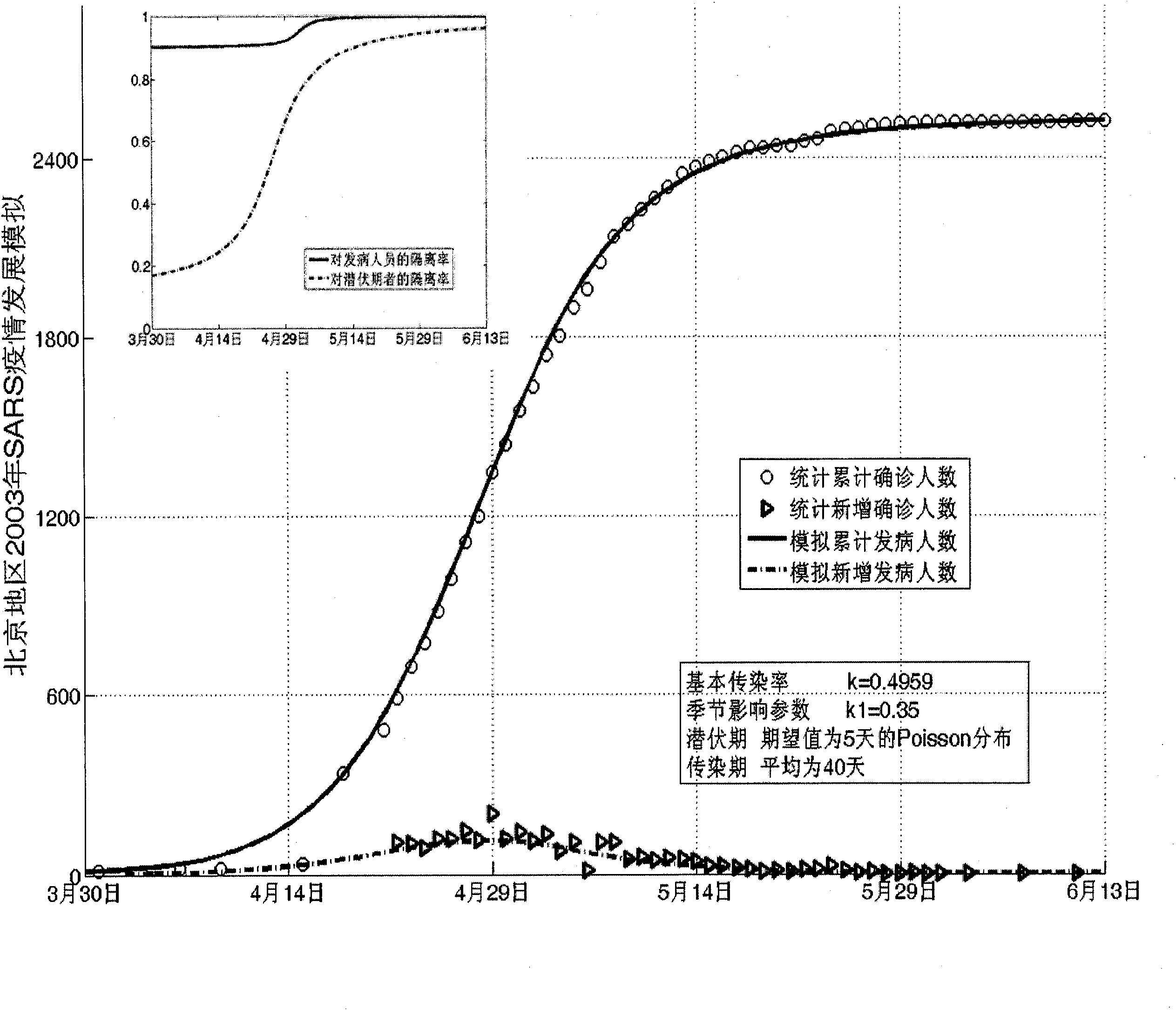
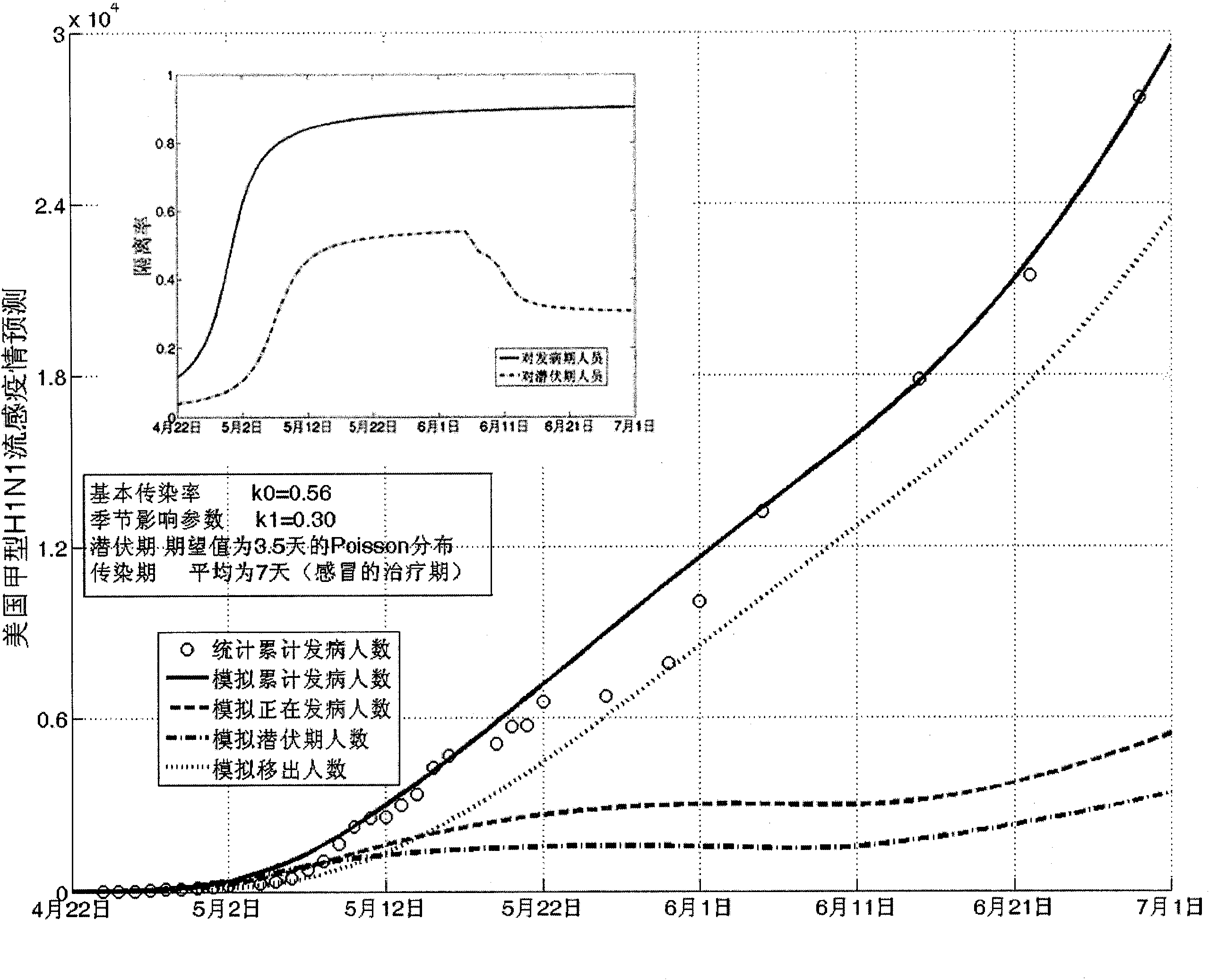
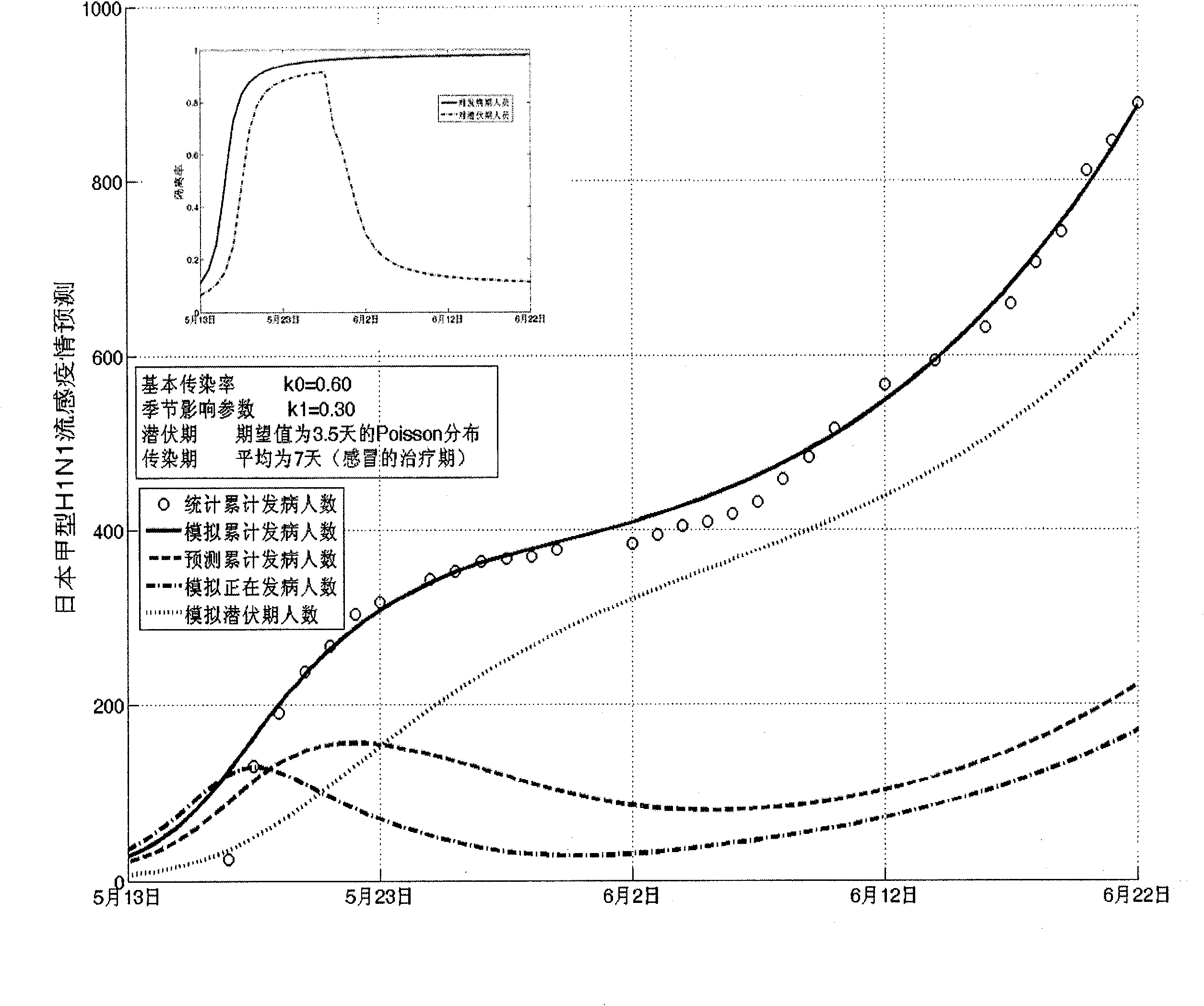
The invention establishes a nonlinear and coefficient variation infectious disease predictive model aiming at epidemic diseases with viruses which have infectivity at a latent period and a period of onset, provides an epidemic situation control function directly related to the model, simulating and predicting effects of different control measures and different control degrees on the basis of prediction in consideration of the control measures, considers the epidemic situation control as a continuous change process, integrally simulating and predicting development and control of the epidemic situation and provides crucial quantitative information for decision-making departments to optimally decide and control the epidemic situation with the smallest cost. By adopting the invention, a relative error for simulating SARS (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndromes) in Beijing areas in 2003 is 0.98% and predictive results for influenza A virus subtype H1N1 in US and Japan are well matched with the actual epidemic situation development, a quantified control factor for preventing the influenza A virus subtype H1N1 at an initial development stage and controlling the spread of the epidemic situation is obtained and epidemic situation development conditions of different control intensities and different susceptible people are predicted.
Owner:中国人民解放军防化指挥工程学院
SARS-CoV-2 (severe acute respiratory syndrome-corona virus disease-2) inhibitor and application thereof
InactiveCN111333722AHigh affinityRealize standardized productionBiological material analysisImmunoglobulins against virusesPhage antibodiesAntibody fragments
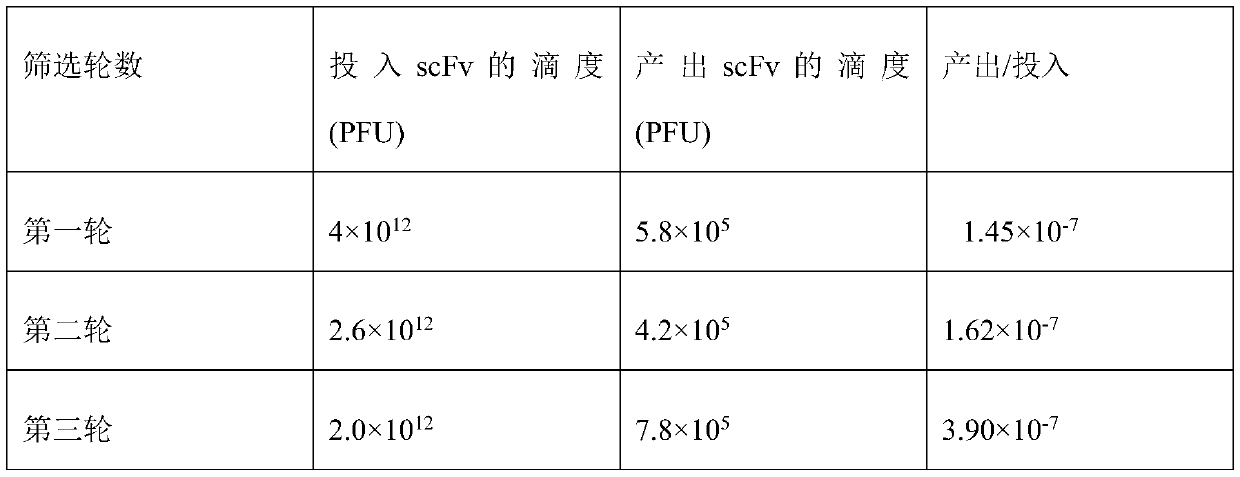
The invention relates to an SARS-CoV-2 (severe acute respiratory syndrome-corona virus disease-2) inhibitor and application thereof and in particularly relates to a neutralizing antibody for SARS-CoV-2 and application of the neutralizing antibody. According to the antibody, a phage display technology is adopted to construct a high-capacity human immunity phage antibody library, and an SARS-CoV-2 protein is adopted a target, human antibody single-chain antibody fragments are screened, and an antibody with a good neutralizing function on SARS-CoV-2 viruses is obtained. The antibody provided by the invention can be used for treating diseases caused by infection of novel corona viruses, and has significant clinical application value.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCIAL CENT FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION PUBLIC HEALTH RES INST OF JIANGSU PROVINCE
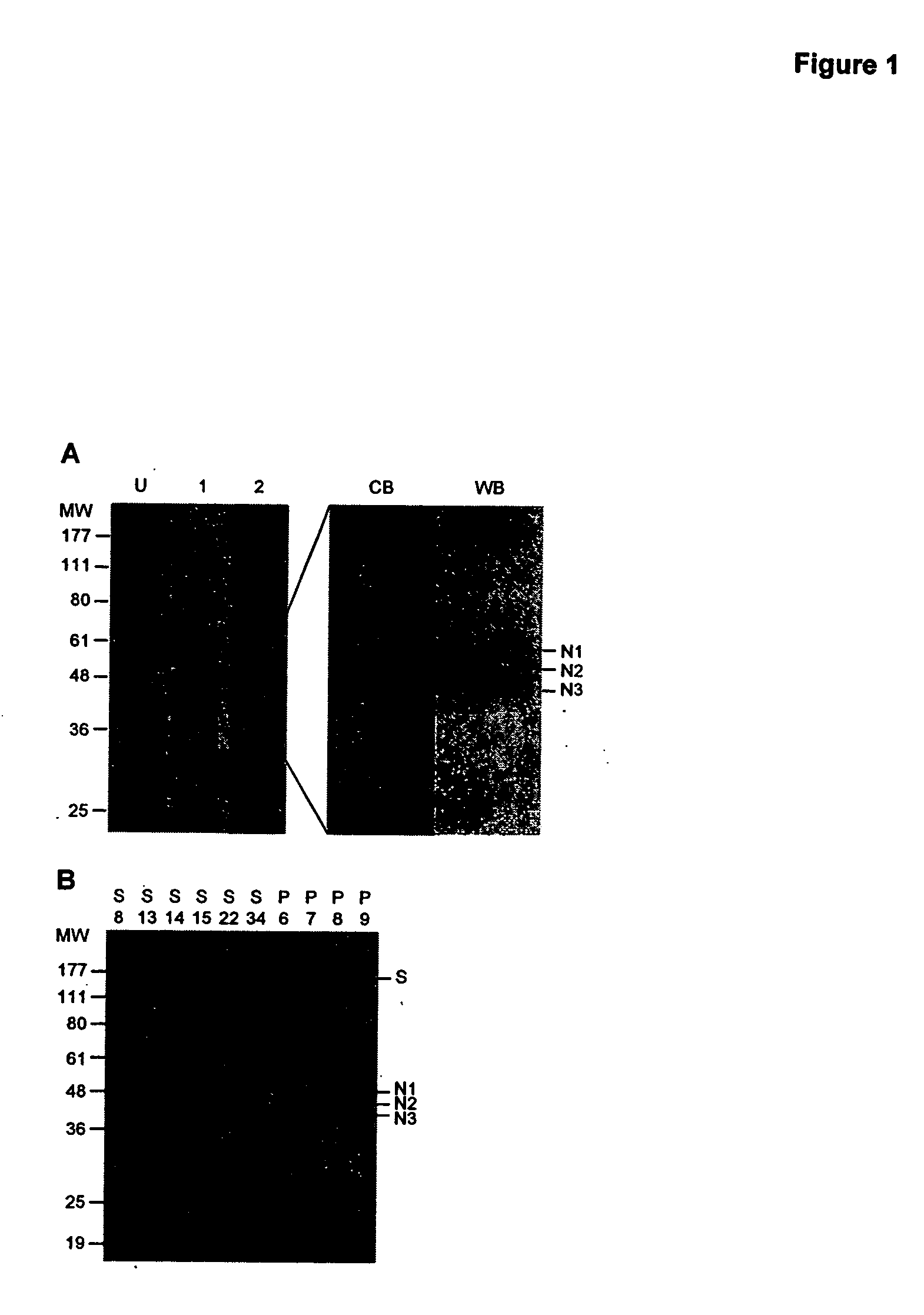
High-throughput diagnostic assay for the human virus causing severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)
InactiveUS20050181357A1Rapid and reliable diagnostic assayHigh detection sensitivitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDiagnostic testPresent method
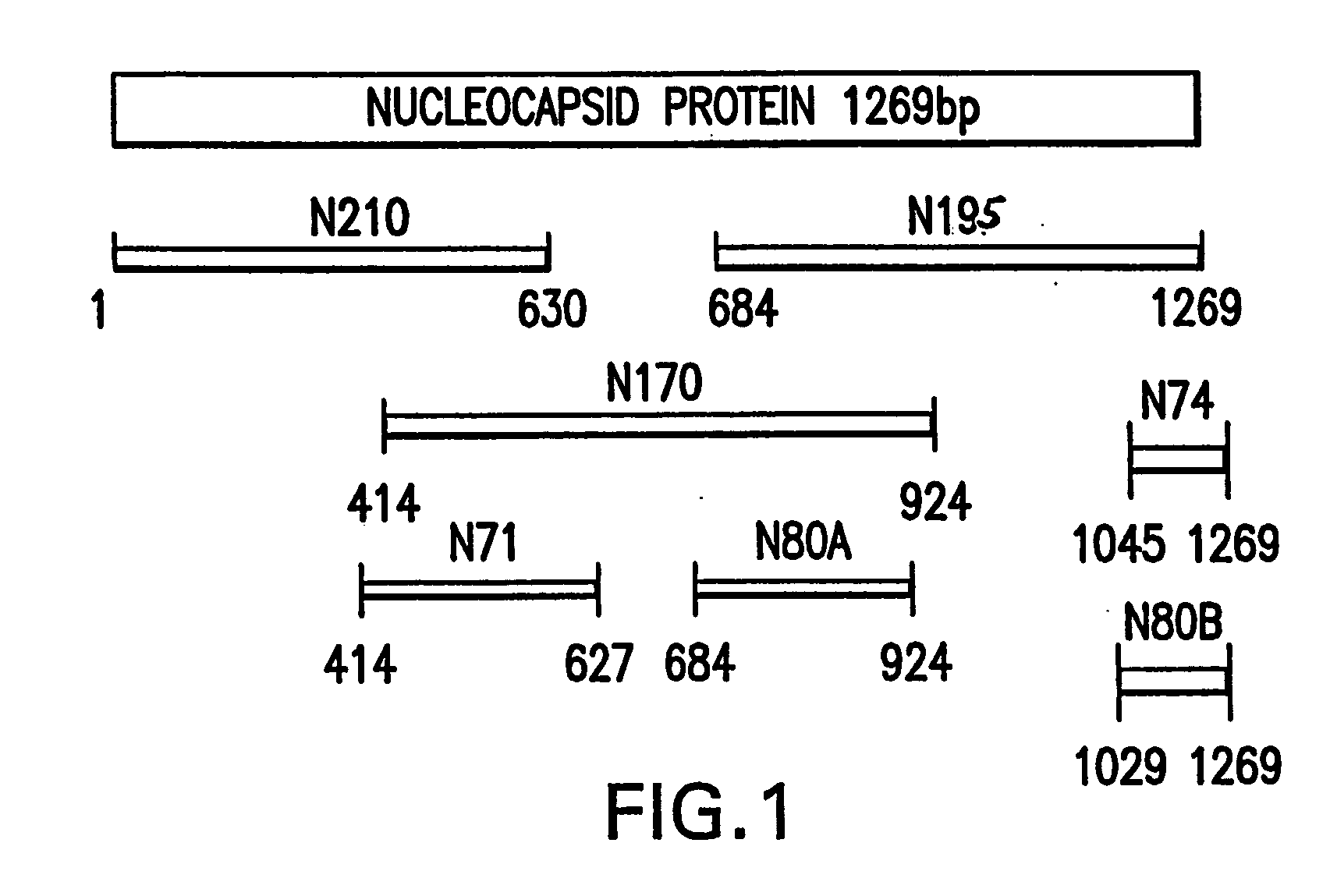
The present invention relates to a high-throughput diagnostic assay for the virus causing Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) in humans (“hSARS virus”). In particular, the invention relates to a high-throughput reverse transcription-PCR diagnostic test for SARS associated coronavirus (SARS-CoV). The present assay is a rapid, reliable assay which can be used for diagnosis and monitoring the spread of SARS and is based on the nucleotide sequences of the N (nucleocapsid)-gene of the hSARS virus. The present method eliminates false negative results and provides increased sensitivity for the assay. The invention also discloses the S (spike)-gene of the hSARS virus. The invention further relates to the deduced amino acid sequences of the N-gene and S-gene products of the hSARS virus and to the use of the N-gene and S-gene products in diagnostic methods. The invention further encompasses diagnostic assays and kits comprising antibodies generated against the N-gene or S-gene product.
Owner:VERSITECH LTD
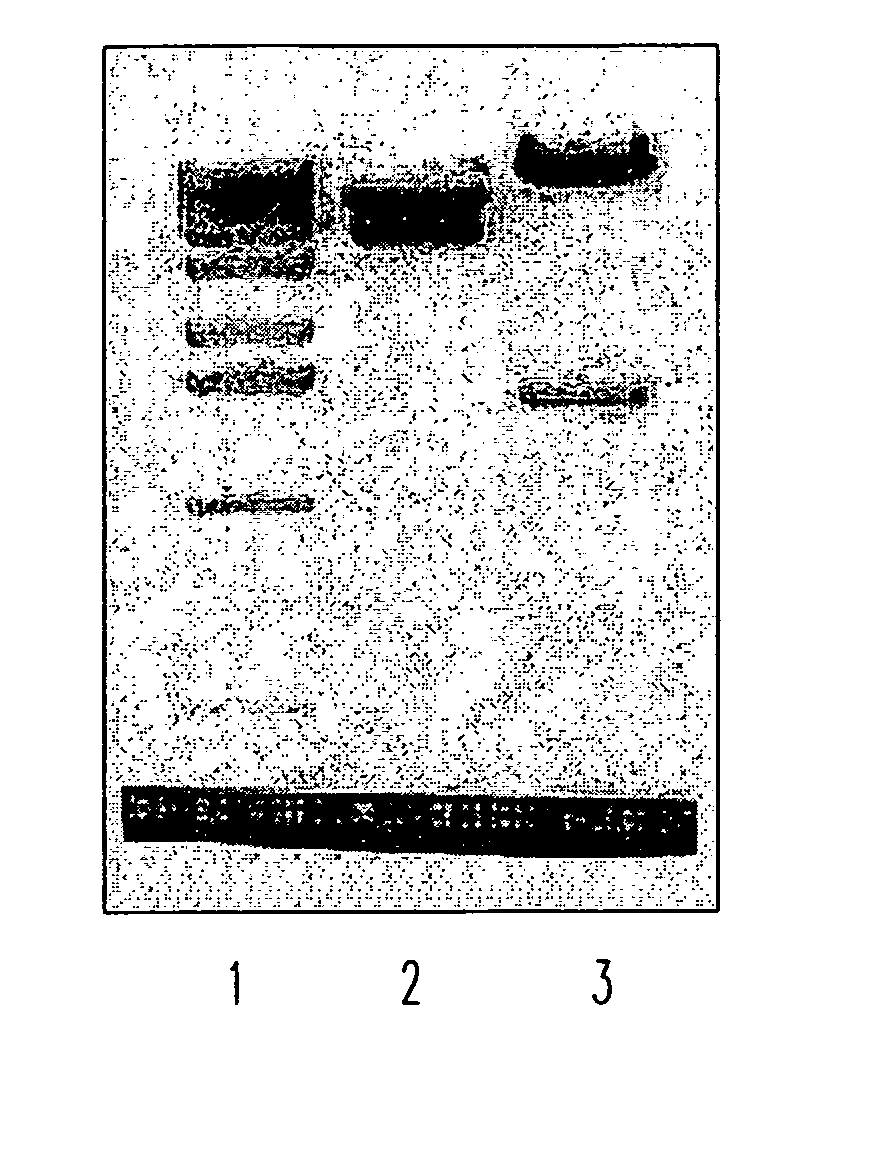
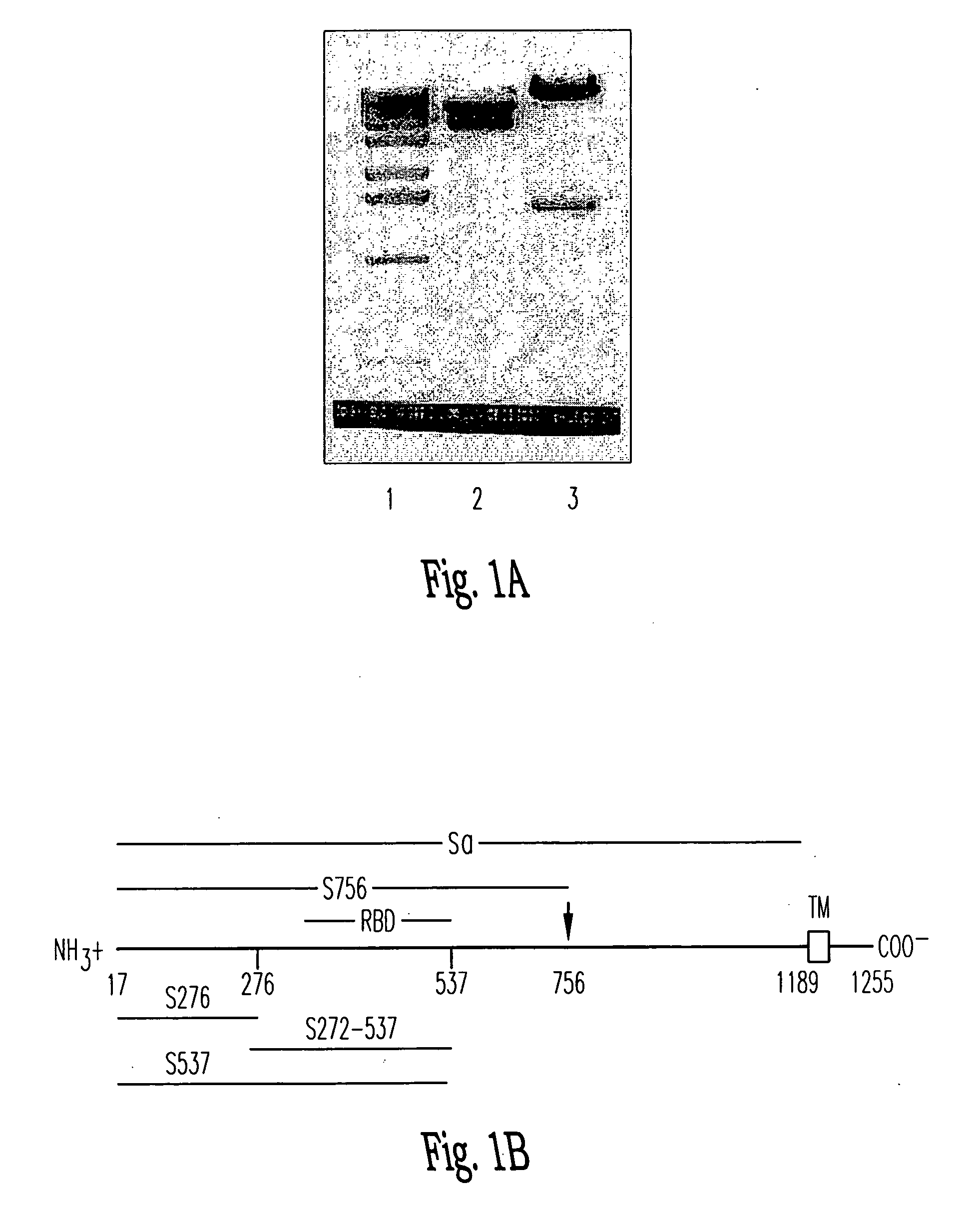
Soluble fragments of the SARS-CoV spike glycoprotein
InactiveUS20060240515A1Easy to produceImprove resistance to degradationSsRNA viruses positive-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAptamerVaccination
The invention relates to the spike protein from the virus (SARS-CoV) that is etiologically linked to severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS); polypeptides and peptide fragments of the spike protein; nucleic acid segments and constructs that encode the spike protein, polypeptides and peptide fragments of the spike protein, and coupled proteins that include the spike protein or a portion thereof; peptidomimetics; vaccines; methods for vaccination and treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome; antibodies; aptamers; and kits containing immunological compositions, or antibodies (or aptamers) that bind to the spike protein.
Owner:HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES GOVERNMENT OF US SEC THE DEPT OF
Diagnostic assay for the human virus causing severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)
ActiveUS7267942B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPcr assaySevere acute respiratory syndrome
The present invention relates to a diagnostic assay for the virus causing Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) in humans (“hSARS virus”). In particular, the invention relates to a real-time quantitative PCR assay for the detection of hSARS virus using reverse transcription and polymerase chain reaction. Specifically, the quantitative assay is a TaqMan® assay using the primers and probes constructed based on the genome of the hSARS virus. The invention further relates to a diagnostic kit that comprises nucleic acid molecules for the detection of the hSARS virus.
Owner:HONG KONG THE UNIV OF +1
Methods and apparatus for a remote, noninvasive technique to detect core body temperature in a subject via thermal imaging
InactiveUS20080154138A1Convenience and securityGuarantee economic securitySensing radiation from moving bodiesDiagnostic recording/measuringDiseaseEngineering
Owner:MCQUILKIN GARY L
Compositions and methods for diagnosing and preventing severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)
InactiveUS20050112559A1Reduce usageSuitable for detectionSsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsBiologic DMARDImmunologic function
The present invention relates to the fields of immunology and molecular biology and describes compositions and methods for using proteins, peptides and nucleic acids related to the SARS CoV nucleocapsid protein and the spike glycoprotein. In particular, the present invention provides immunostimulatory preparations, prophylactic pharmaceutical preparations, diagnostic assays and kits for identifying and preventing SARS infections.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
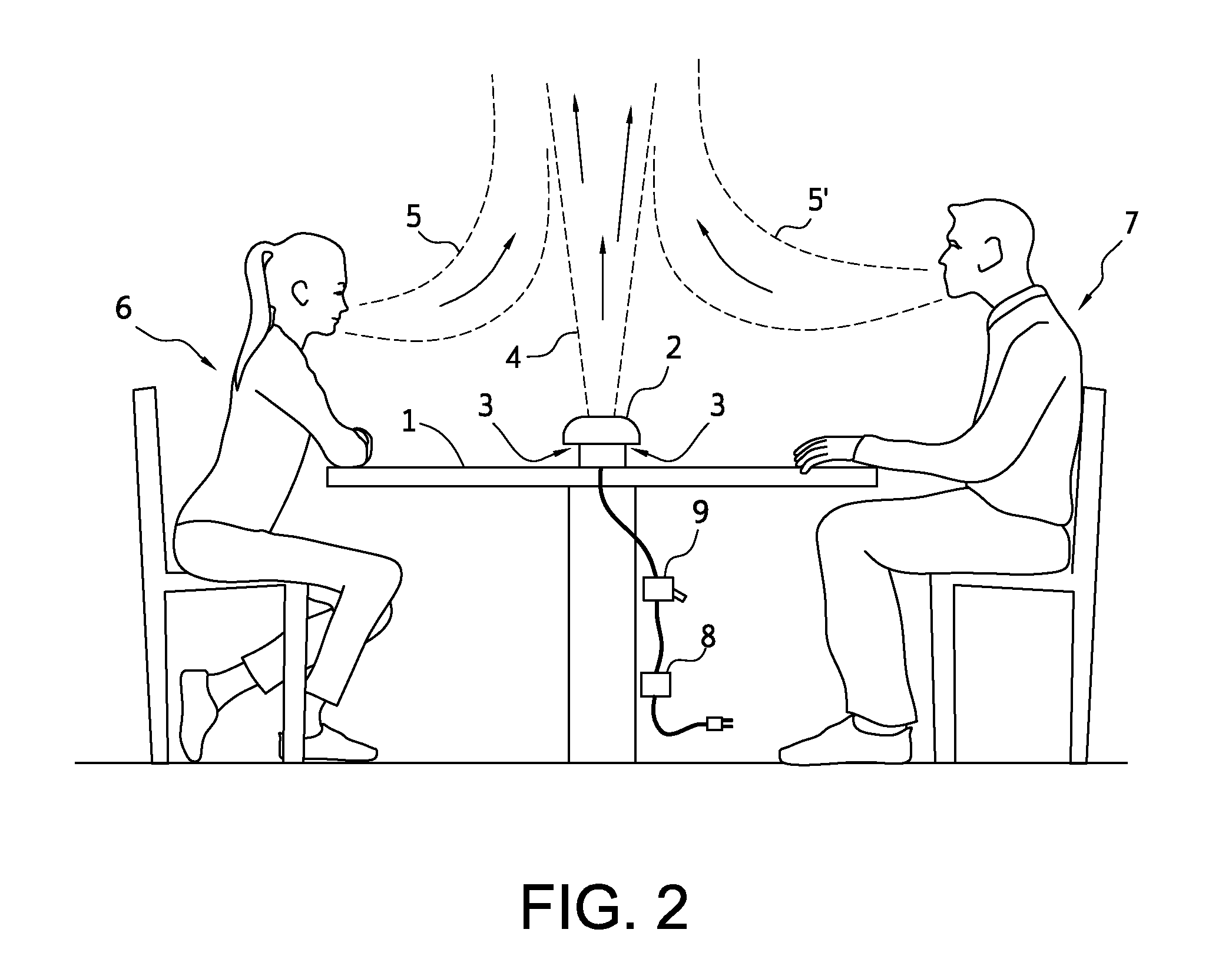
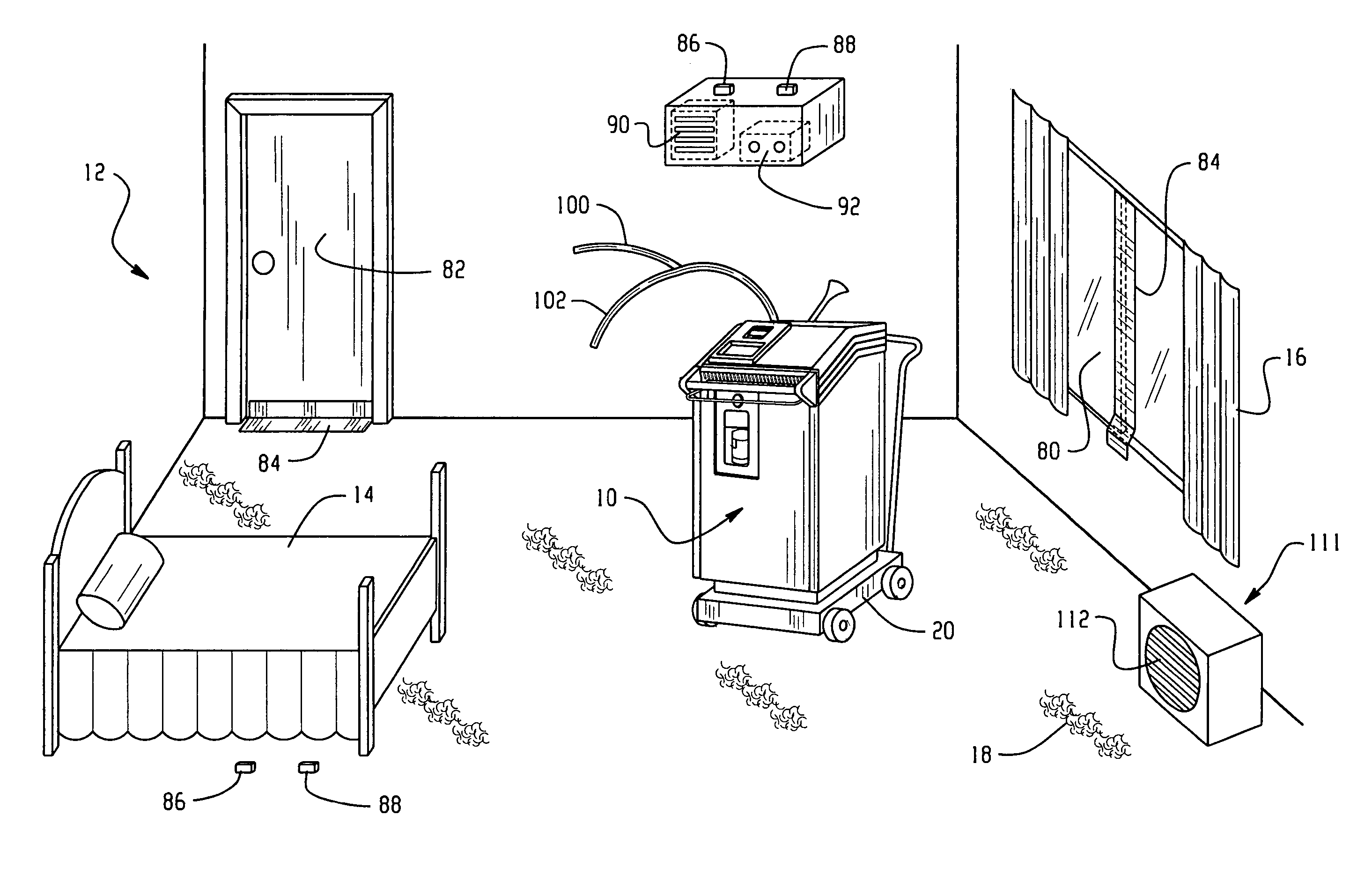
Close proximity airborne influenza/pathogen mitigator
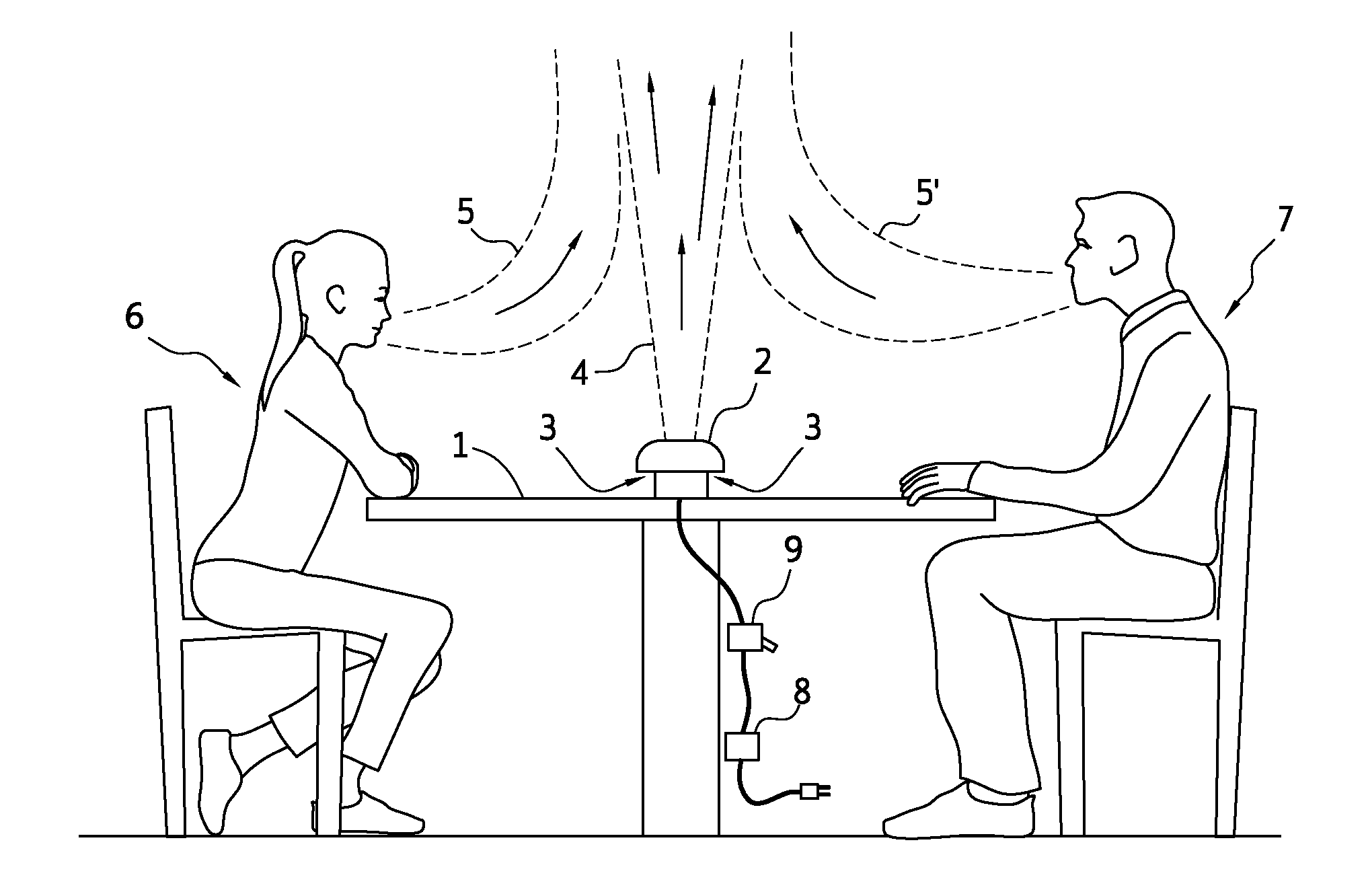
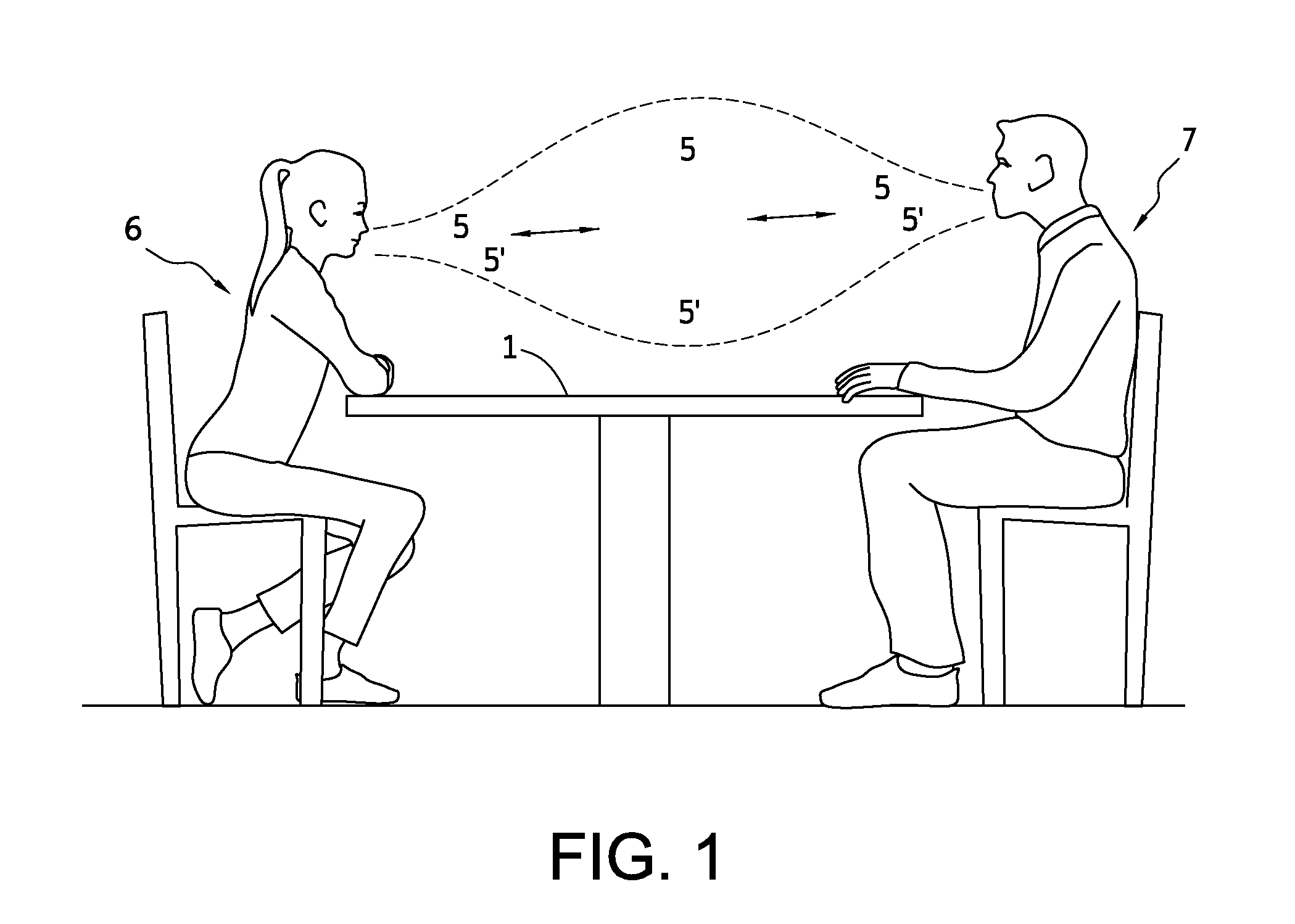
Close proximity, including conversations at closer than three (3) feet apart, facilitates disease transfer via airborne pathogens. This transfer can be mitigated by the present invention, which is directed towards methods, systems and apparatuses to produce a predictably shaped and minimally intrusive air barrier that may comprise an airborne disinfectant, to divert and or render harmless and to divert and negate close proximity airborne pathogens, such as influenza and severe acute respiratory syndrome, etc., and other airborne particulates transferred from an infected person towards the face of an unfortunate recipient at normal conversational distances apart from each other, and / or to divert and render harmless such airborne particulates.
Owner:CARR PETER
High-throughput diagnostic assay for the human virus causing severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)
InactiveUS7547512B2Rapid and reliable diagnostic assayHigh detection sensitivitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPresent methodSevere acute respiratory syndrome
The present invention relates to a high-throughput diagnostic assay for the virus causing Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) in humans (“hSARS virus”). In particular, the invention relates to a high-throughput reverse transcription-PCR diagnostic test for SARS associated coronavirus (SARS-CoV). The present assay is a rapid, reliable assay which can be used for diagnosis and monitoring the spread of SARS and is based on the nucleotide sequences of the N (nucleocapsid)-gene of the hSARS virus. The present method eliminates false negative results and provides increased sensitivity for the assay. The invention also discloses the S (spike)-gene of the hSARS virus. The invention further relates to the deduced amino acid sequences of the N-gene and S-gene products of the hSARS virus and to the use of the N-gene and S-gene products in diagnostic methods. The invention further encompasses diagnostic assays and kits comprising antibodies generated against the N-gene or S-gene product.
Owner:VERSITECH LTD
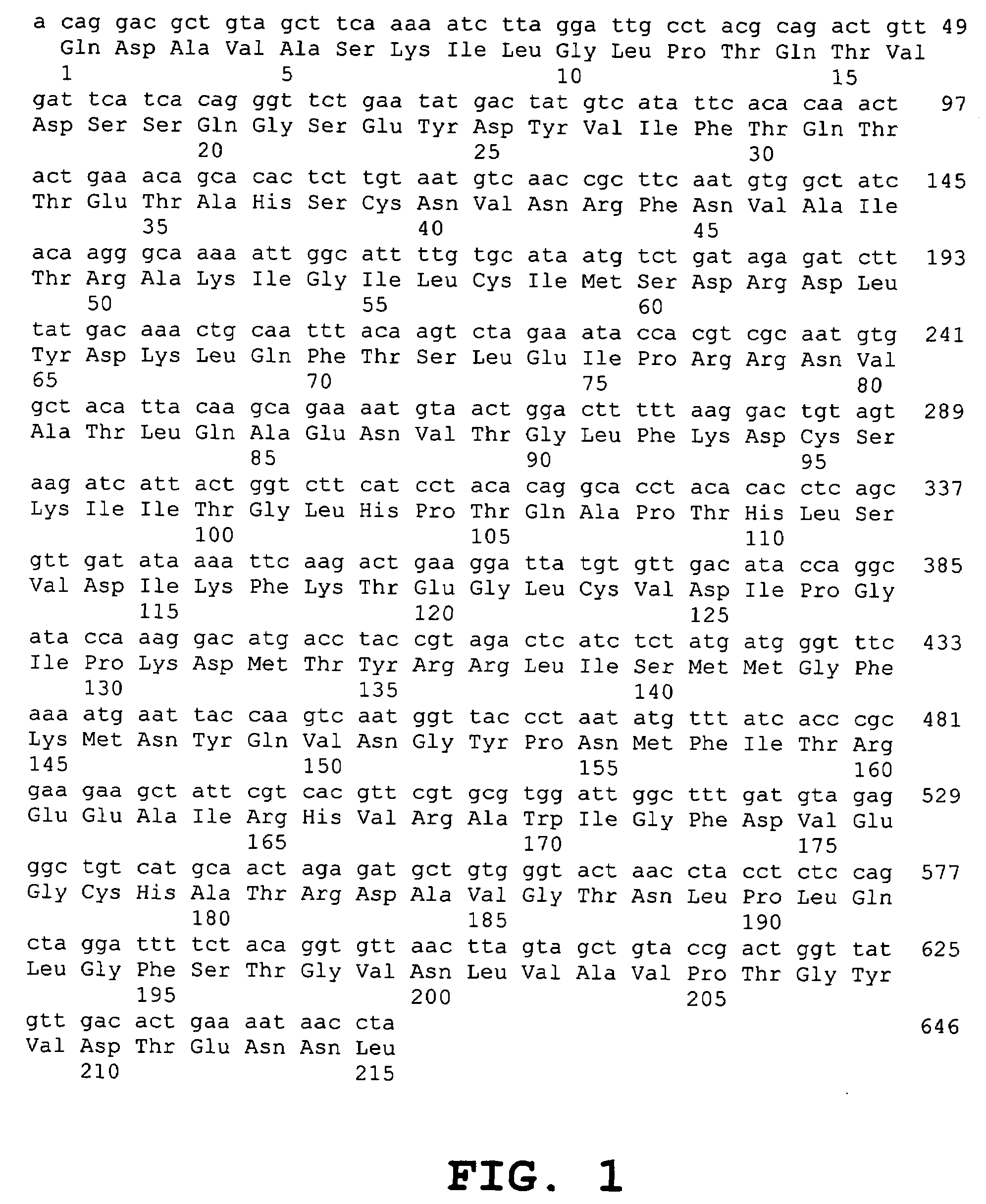
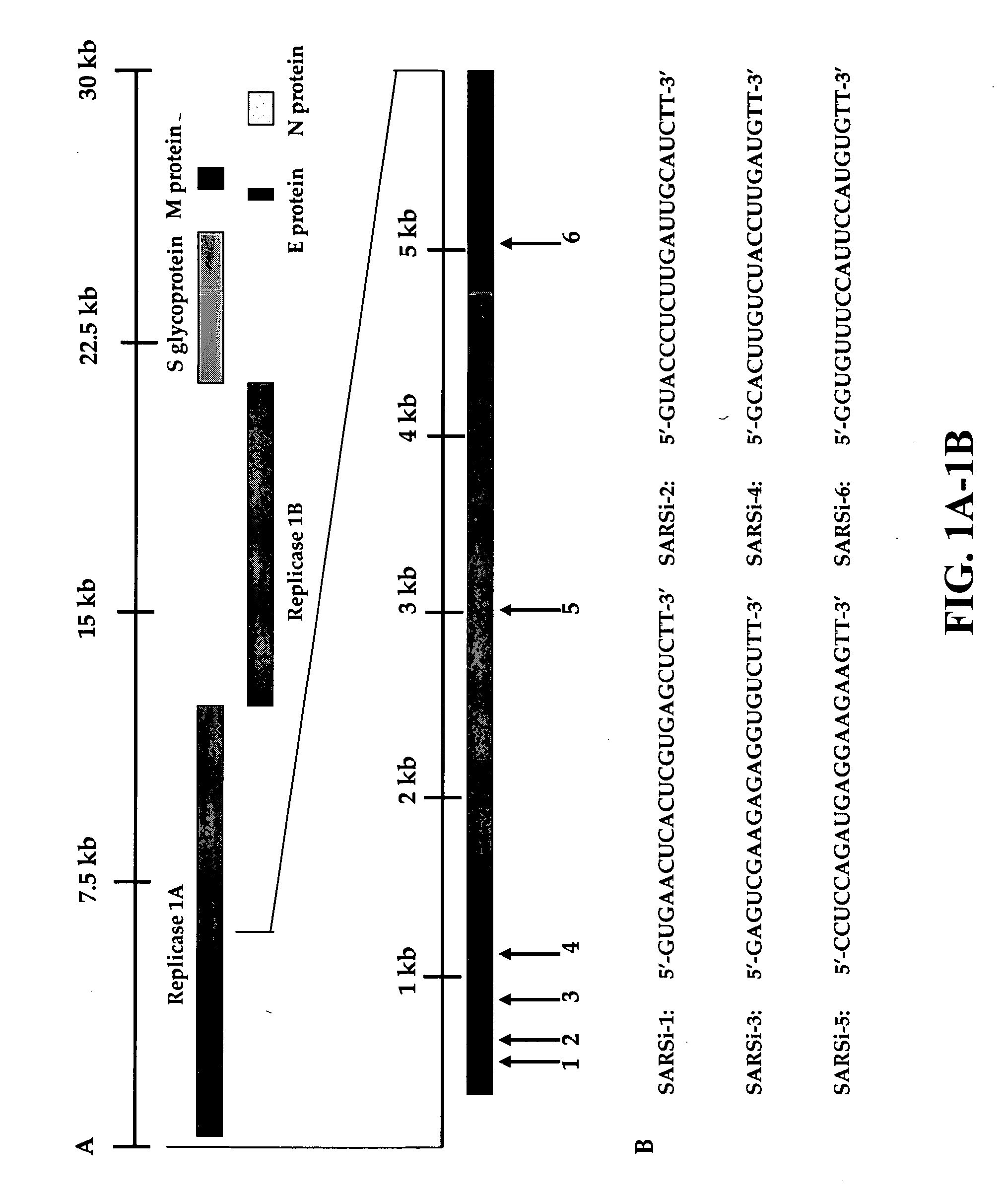
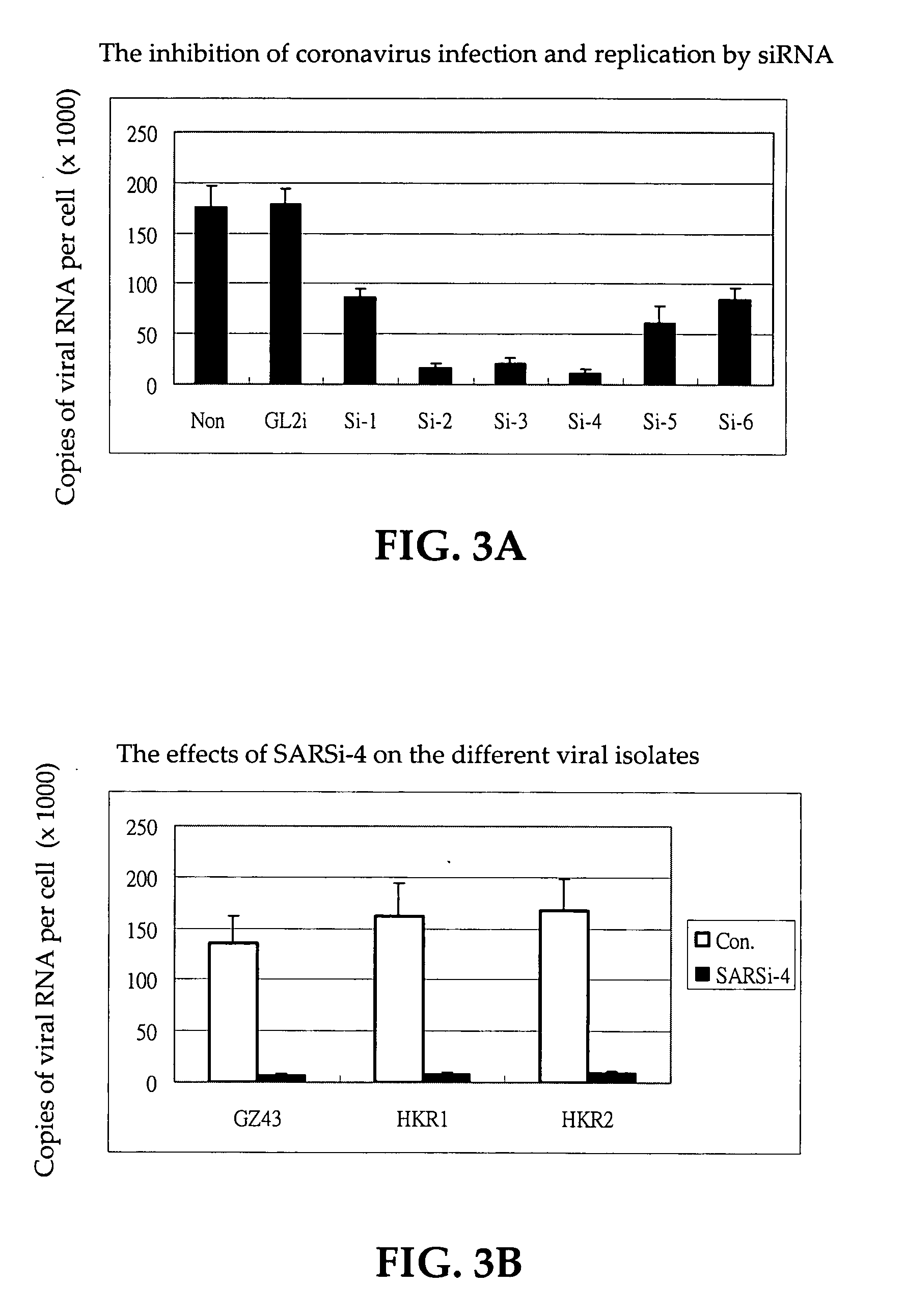
Inhibition of SARS-associated coronavirus (SCoV) infection and replication by RNA interference
The present invention relates to therapeutic agents useful for the treatment of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) in humans. In particular, the present invention relates to RNA interference (RNAi) molecules useful for inhibiting the infection and replication of hSARS virus. Preferably, the RNAi molecules target the replicase region of the hSARS virus, or combinations of different sites of hSARS virus genes. The present invention further encompasses methods of using the RNAi molecules for preventing and / or treating SARS. Vaccines and kits comprising therapeutically effective amounts of the RNAi molecules are also encompassed.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Sars vaccines and methods to produce highly potent antibodies
InactiveCN101098710APeptide preparation methodsAntibody medical ingredientsAntigenSARS-associated coronavirus
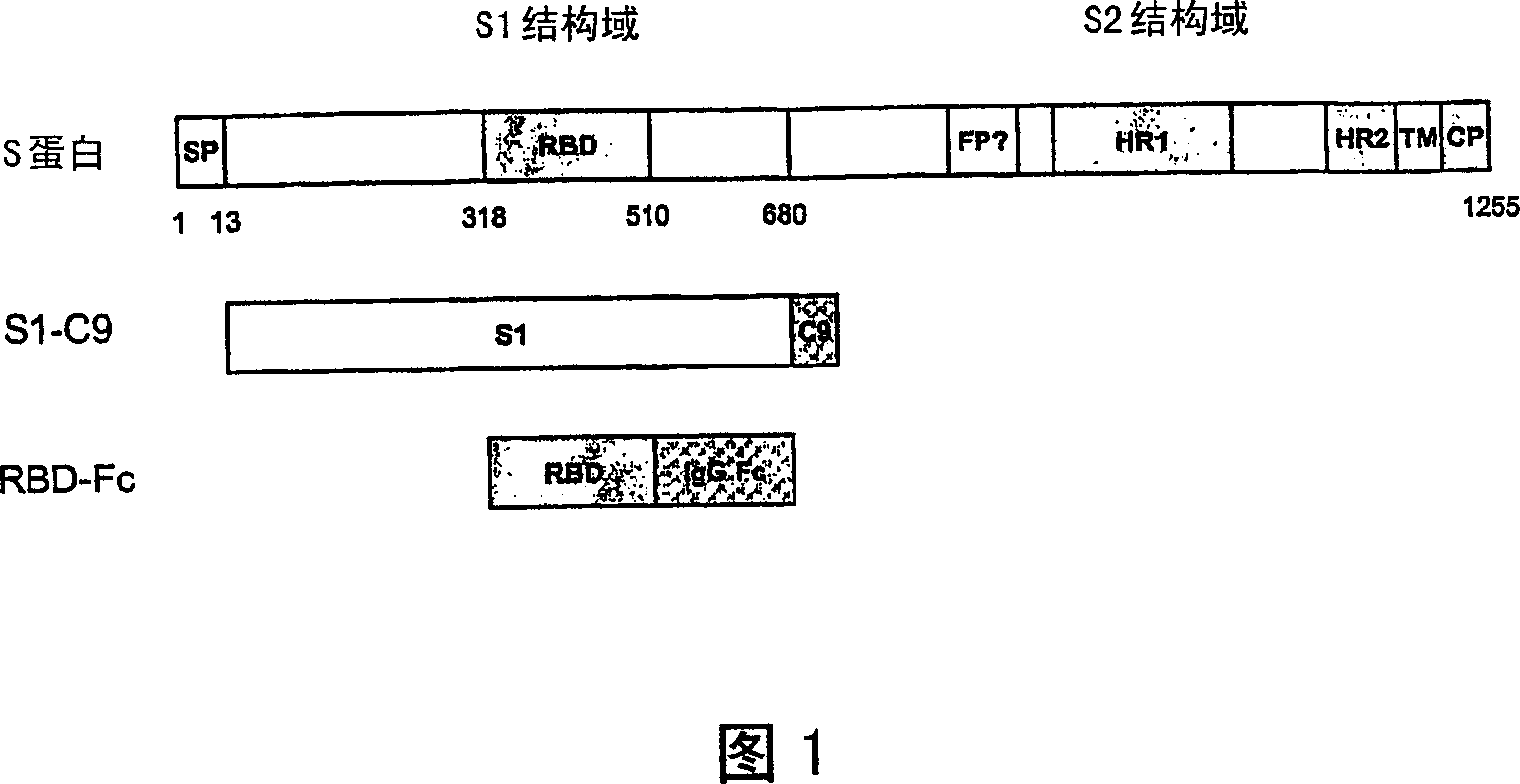
This invention provides a vaccine comprising an effective amount of an isolated polypeptide or recombinant protein containing the sequence of the receptor-binding domain in the SARS associated coronavirus spike protein or a functional fragment thereof, or a nucleic acid molecule comprising the sequence of a fragment which encodes the sequence of the receptor-binding domain in the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome associated coronavirus spike protein or a functional fragment thereof. This invention provides a composition for increasing the immunogenicity of an antigen comprising an effective amount of an antigen and an IgG Fc domain, its functional fragment, or a substance containing an IgG Fc domain or its functional fragment. The antigen and the IgG Fc may be linked or unlinked. Finally, this invention also provides method for using any of the above compositions for immunization.
Owner:NEW YORK BLOOD CENT
Uses of interferons with altered spatial structure
InactiveUS20090220456A1Preventing and treating Severe AcutePeptide/protein ingredientsMicroorganismsSpatial structureInterferon alpha
This invention provides a method for preventing or treating Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome in a subject comprising administering to the subject an effective amount of recombinant super-compound interferon or a functional equivalent thereof. This invention provides a method for inhibiting the causative agent of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome comprising contacting the agent with an effective amount of super-compound interferon or its equivalent.
Owner:WEI GUANGWEN
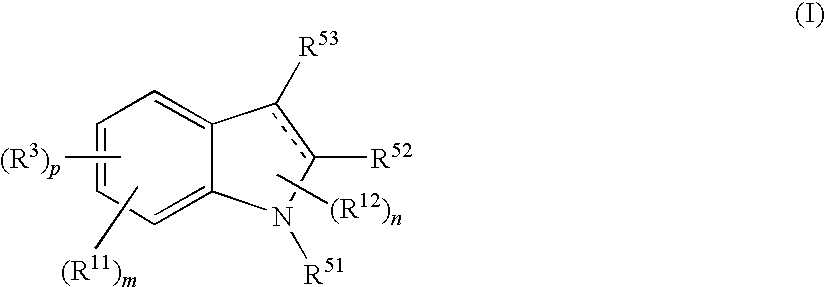
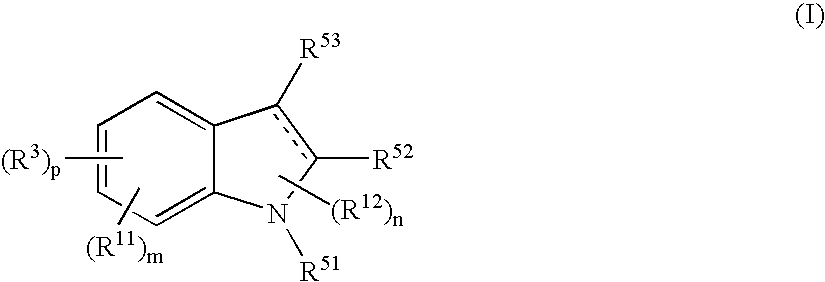
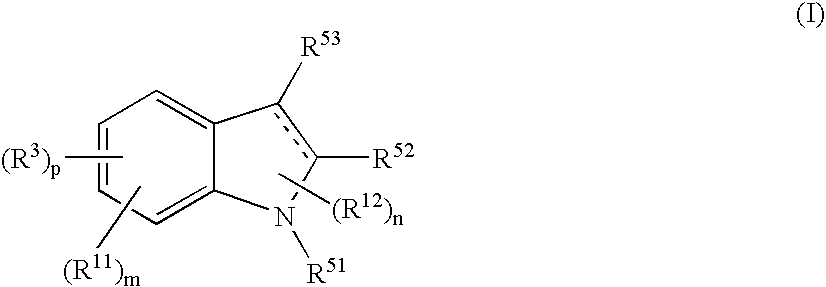
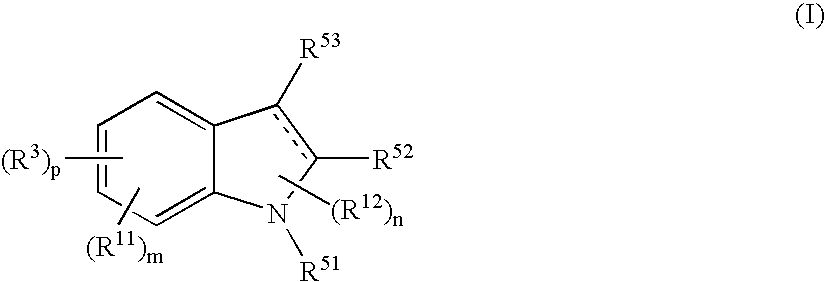
Indole compound and use thereof
InactiveUS7728023B2Increased airway hyperreactivityImprove respiratory functionBiocideSenses disorderClinical trialObstructive Pulmonary Diseases
The present invention relates to a compound represented by the formula (I),wherein all symbols are as defined in the description,a salt thereof, a solvate thereof, or a prodrug thereof, which has a leukotriene receptor antagonistic activity which is expected to be more effective than those of the leukotriene receptor antagonists currently used in clinical trials. Therefore, it is useful as an agent for the prevention and / or treatment of a leukotriene-mediated disease such as a respiratory diseases such as bronchial asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, pulmonary emphysema, chronic bronchitis, pneumonia (e.g. interstitial pneumonia etc.), severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), allergic rhinitis, sinusitis (e.g. acute sinusitis, chronic sinusitis, etc.), or the like, or as an expectorant or an antiitussive.
Owner:ONO PHARMA CO LTD
Coronavirus isolated from humans
Disclosed herein is a newly isolated human coronavirus (SARS-CoV), the causative agent of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS). Also provided are the nucleic acid sequence of the SARS-CoV genome and the amino acid sequences of the SARS-CoV open reading frames, as well as methods of using these molecules to detect a SARS-CoV and detect infections therewith. Immune stimulatory compositions are also provided, along with methods of their use.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Uses of spatial configuration to modulate protein function
ActiveCN101001644APeptide/protein ingredientsMedical atomisersRecombinant Super-compound InterferonInterferon alpha
This invention provides a method for preventing or treating Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome in a subject comprising administering to the subject an effective amount of recombinant super-compound interferon or a functional equivalent thereof. This invention provides a method for inhibiting the causative agent of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome comprising contacting the agent with an effective amount of super-compound interferon or its equivalent.
Owner:SUPERLAB FAR EAST LTD
Room decontamination with hydrogen peroxide vapor
ActiveUS7354551B2Reduce humidityGaseous substancesDeodrantsTwo stepSevere acute respiratory syndrome
A system for microbially and / or chemically decontaminating a room such as a hotel room includes a vapor generator which supplies a decontaminant vapor, such as hydrogen peroxide vapor to the room. The room is then aerated to a level at which it is safe for normal occupants to enter. By using a two step aeration, with a second step at lower humidity than the first, the concentration of residual hydrogen peroxide is reduced rapidly to safe levels of 1 ppm or less, typically about 0.5 ppm, in under four hours. The room is rendered substantially free of contaminants, such as those responsible for Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS), Norwalk virus, and unpleasant odors.
Owner:STERIS CORP
Diagnostics for sars virus
InactiveUS20070092938A1SsRNA viruses positive-senseMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseEpitope
This invention relates to Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome associated coronavirus (SARS virus) isolated and recombinant proteins, in particular the nucleocapsid (N) protein and spike (S) protein, as well as fragments thereof and their use in the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS). The proteins and fragments carry epitopes that are specific for the SARS virus. Thus, detection methods based on these proteins or fragments as well as the monoclonal antibodies against these proteins or fragments are specific for the SARS virus.
Owner:TEMASEK LIFE SCIENCES LABORATORY
Prognostic PCR assay for severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)
InactiveUS20050112558A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPcr assaySARS-CoV infection
Disclosed are nucleic acid primers, probes and standard target sequences that allow for the quantitative assessment of the SARS-CoV viral titer found in a biological specimen from a patient. Quantifying the viral titer in the patient sample allows the practitioner to make a prognostic determination of the severity of the SARS-CoV infection and the necessary treatment regime.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG +1
Novel environmentally-friendly corrosion-resistance peracetic acid disinfectant
The invention relates to a novel environmentally-friendly corrosion-resistance peracetic acid disinfectant, and belongs to the technical field of disinfection product preparation. 100 ml of the novel environmentally-friendly corrosion-resistance peracetic acid disinfectant comprises: 0.1 to 0.5 gram of peracetic acid solution, 0.05 to 0.1 gram of stabilizer sodium ethylenediamine tetracetate, 0.1 to 0.2 gram of surfactant sodium citrate, 0.1 to 0.2 gram of quaternary ammonium salt, 0.005 to 0.02 gram of sodium molybdate, and the balance of water. The disinfectant has broad-spectrum sterilization performance, so that the stability of conventional peracetic acid is obviously improved; additives of the disinfectant obviously inhibit the corrosion of the peracetic acid on metal materials, can be suitable for quick and effective sterilization and disinfection in schools, hospitals, factories, mines and other public places, and also can be used for environment disinfection and sterilization of SARS (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndromes), A(H1N1) and other communicable diseases. The disinfectant has no pollution after use, and is safe and convenient to use.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Novel human virus causing severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and uses thereof
The present invention relates to an isolated novel virus causing Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) in humans (“hSARS virus”). The hSARS virus is identified to be morphologically and phylogenetically similar to known member of Coronaviridae. The present invention provides the complete genomic sequence of the hSARS virus. Furthermore, the invention provides the nucleic acids and peptides encoded by and / or derived from the hSARS virus and their use in diagnostic methods and therapeutic methods, including vaccines. In addition, the invention provides chimeric or recombinant viruses encoded by said nucleotide sequences and antibodies immunospecific to the polypeptides encoded by the nucleotide sequences.
Owner:VERSITECH LTD
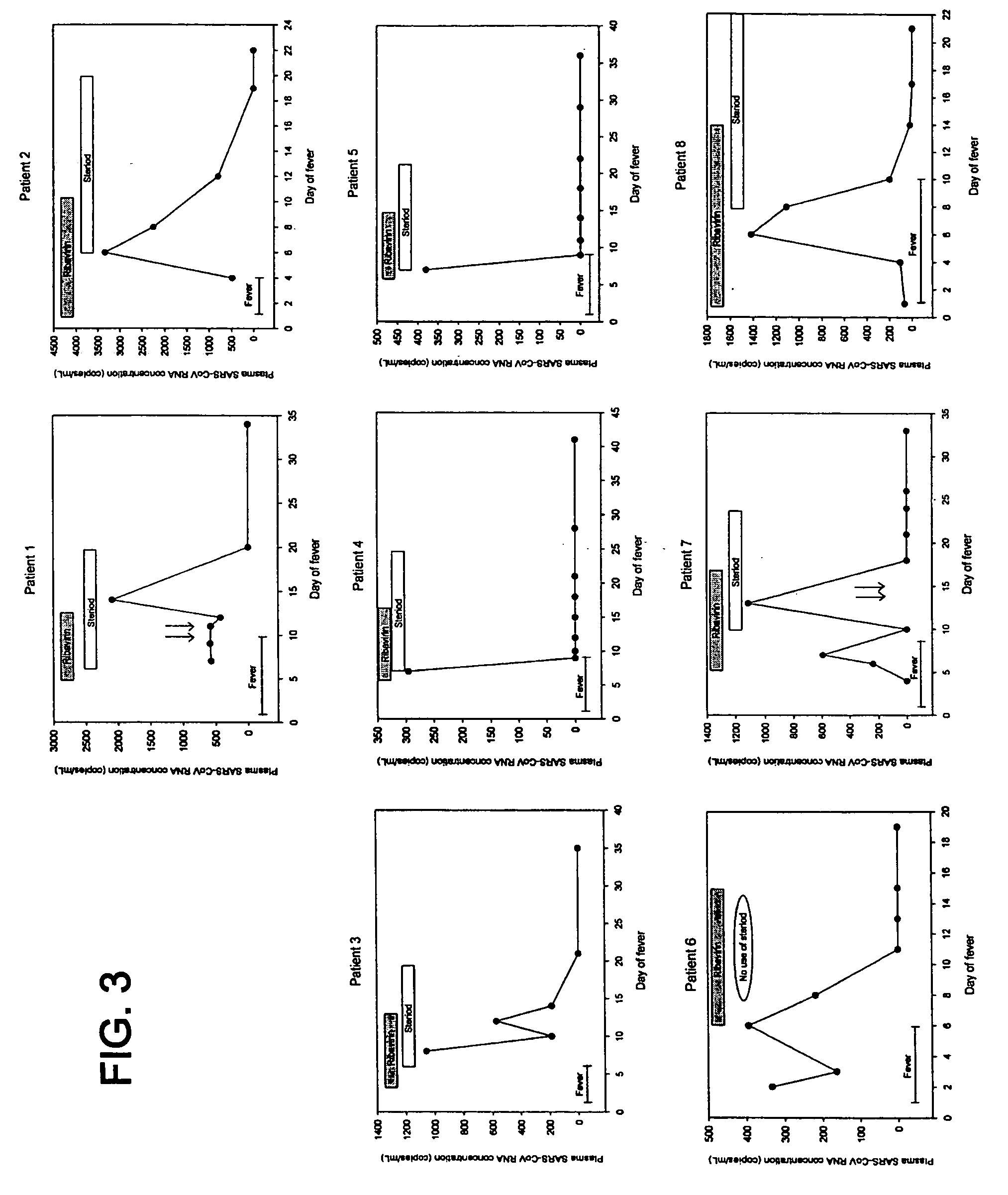
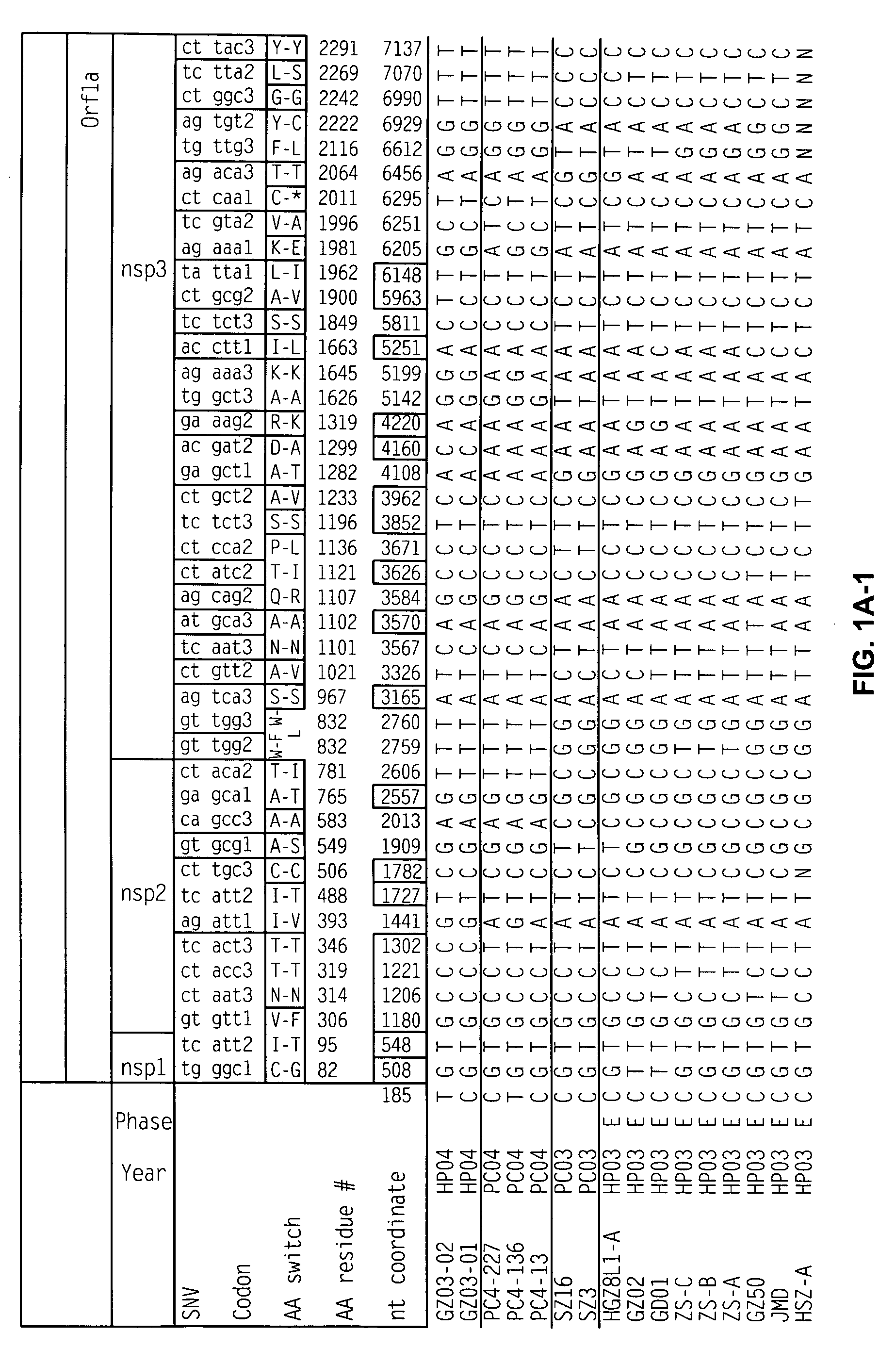
Characterization of the earliest stages of the severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) virus and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050112554A1Insufficient infectivitySsRNA viruses positive-senseSugar derivativesVirulent characteristicsMortality rate
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (“SARS”) is a human respiratory disease of recent origin, widespread infectivity, recurring incidence, and significant mortality. Although there is abundant evidence suggesting that the coronavirus responsible for the disease (“SARS-CoV”) evolves during an outbreak, there is currently little data on the earliest strains of this coronavirus. The present invention is directed to the characterization of the genomic RNA sequences of these earliest SARS coronaviruses, to the identification of nucleotide positions within the SARS-CoV genomic RNA that are characteristic of the different evolutionary stages of the coronavirus, to kits based on these positions for use in diagnosis of the disease in patients, and for the development of vaccines to the disease based on the lowered virulence and contagiousness of these earliest strains of SARS-CoV.
Owner:CHINESE HUMAN GENOME CENT AT SHANGHAI
Indole Compound and Use Thereof
InactiveUS20080188532A1Increased airway hyperreactivityImprove respiratory functionBiocideSenses disorderDiseaseBronchial epithelium
The present invention relates to a compound represented by the formula (I),wherein all symbols are as defined in the description,a salt thereof, a solvate thereof, or a prodrug thereof, which has a leukotriene receptor antagonistic activity which is expected to be more effective than those of the leukotriene receptor antagonists currently used in clinical trials. Therefore, it is useful as an agent for the prevention and / or treatment of a leukotriene-mediated disease such as a respiratory diseases such as bronchial asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, pulmonary emphysema, chronic bronchitis, pneumonia (e.g. interstitial pneumonia etc.), severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), allergic rhinitis, sinusitis (e.g. acute sinusitis, chronic sinusitis, etc.), or the like, or as an expectorant or an antiitussive.
Owner:ONO PHARMA CO LTD
Isolation and characterization of the precursor virus of human sars virus: sars-associated corona virus-like virus
ActiveUS20080069839A1SsRNA viruses positive-senseSugar derivativesViunalikevirusSevere acute respiratory syndrome
The present invention relates to isolation and characterization of a class of isolated novel viruses which is the precursor of the virus causing Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) in humans (“hSARS virus”). The precursor virus which is a SARS coronavirus-like virus (“SCoV-like virus”) is identified to be morphologically and phylogenetically similar to hSARS virus. The present invention relates to a nucleotide sequence comprising the genomic sequence of the SCoV-like virus. The invention further relates to nucleotide sequences comprising a portion of the genomic sequence of the SCoV-like virus. The invention also relates to the deduced amino acid sequences of the SCoV-like virus. The invention further relates to the nucleic acids and peptides encoded by and / or derived from these sequences and their use in diagnostic methods and therapeutic methods. The invention further encompasses chimeric or recombinant viruses encoded by said nucleotide sequences and antibodies directed against polypeptides encoded by the nucleotide sequences. Furthermore, the invention relates to vaccine preparations comprising the SCoV-like virus, including recombinant and chimeric forms of said virus.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Diagnostic assay for the human virus causing severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)
ActiveUS20050009009A1Reduce the amount of solutionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPcr assaySevere acute respiratory syndrome
The present invention relates to a diagnostic assay for the virus causing Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) in humans (“hSARS virus”). In particular, the invention relates to a real-time quantitative PCR assay for the detection of hSARS virus using reverse transcription and polymerase chain reaction. Specifically, the quantitative assay is a TaqMan® assay using the primers and probes constructed based on the genome of the hSARS virus. The invention further relates to a diagnostic kit that comprises nucleic acid molecules for the detection of the hSARS virus.
Owner:HONG KONG THE UNIV OF +1
Probes and methods for the simultaneous detection and identification of multiple viruses that cause respiratory infections in humans
InactiveCN101107366AShorten the lengthSynthetic economyMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesEnterovirusSevere acute respiratory syndrome
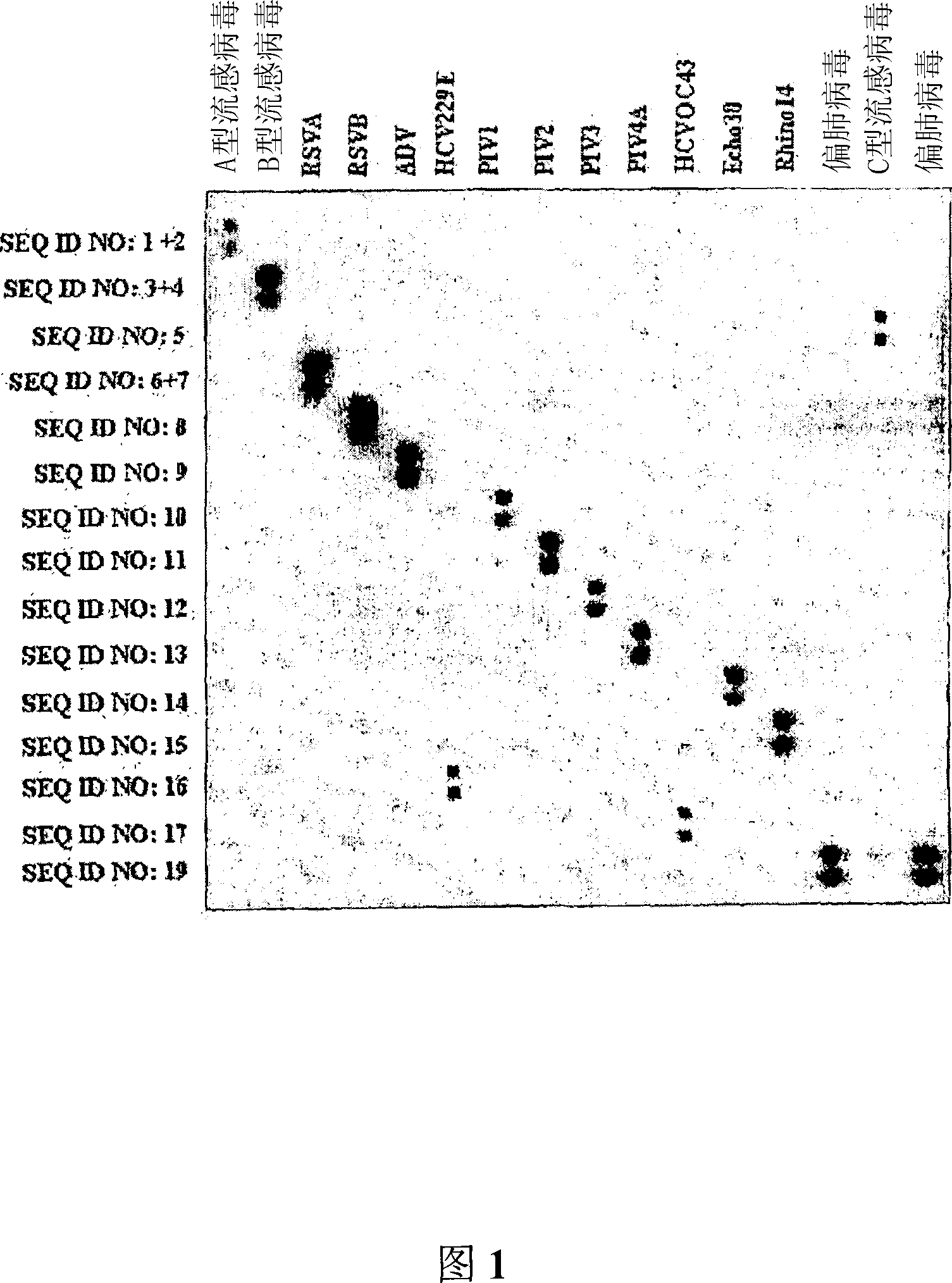
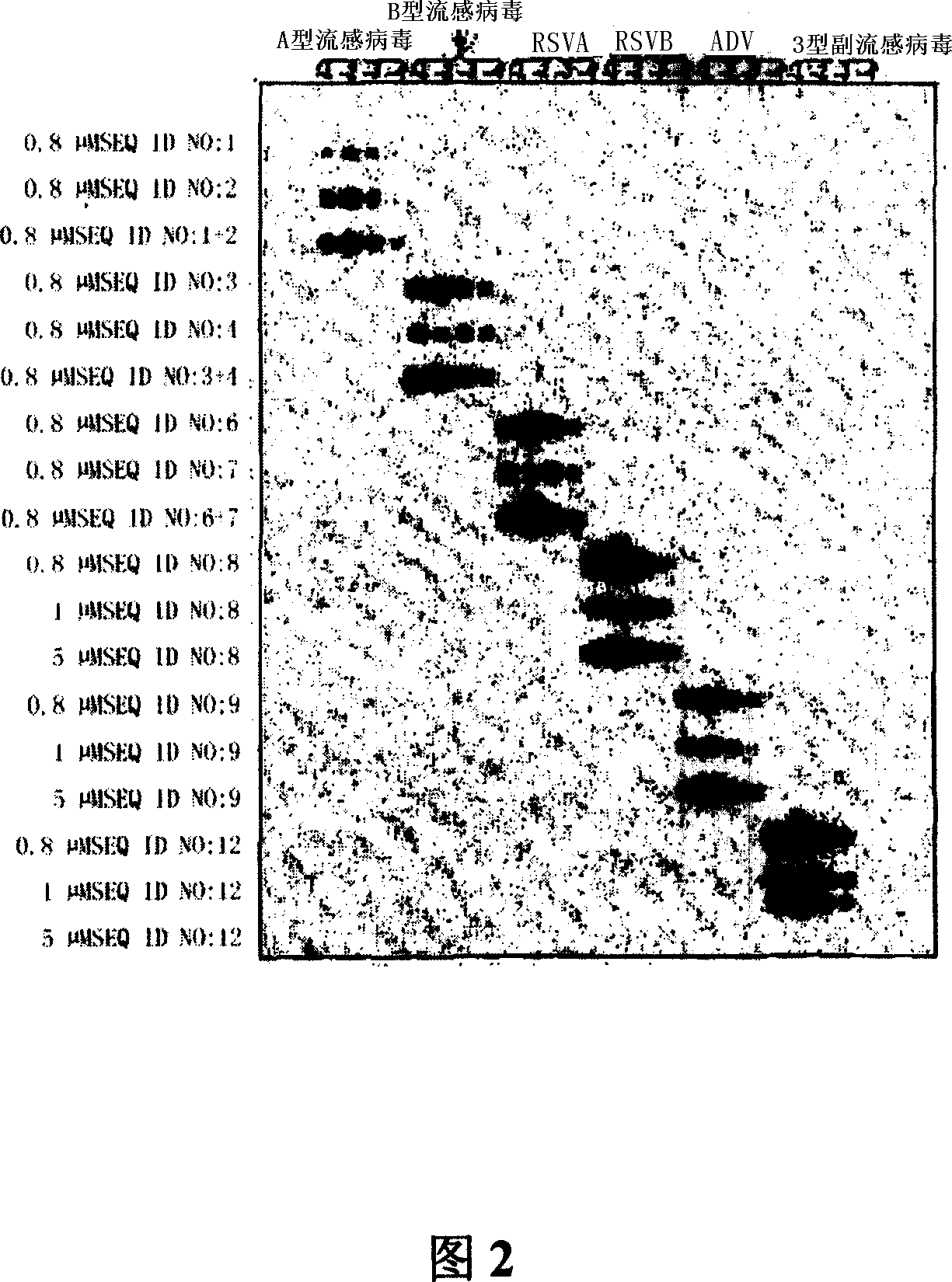
The invention relates to probes and assays which are used for the simultaneous detection, in a single assay sample, of a plurality of nucleic acid sequences of viruses that cause respiratory infections in humans, selected from among influenza virus type A, influenza virus type B, influenza virus type C, human respiratory syncytial virus type A, human respiratory syncytial virus type B, human adenovirus, human parainfluenza virus type 1, human parainfluenza virus type 2, human parainfluenza virus type 3, human parainfluenza virus types 4A and 4B, enterovirus, rhinovirus, human coronavirus type 229E, human coronavirus type OC43, coronavirus that causes severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), human metapneumovirus and combinations thereof.
Owner:INST DE SALUD CARLOS III
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com