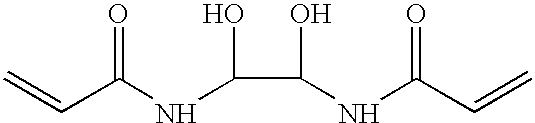
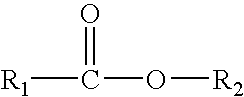
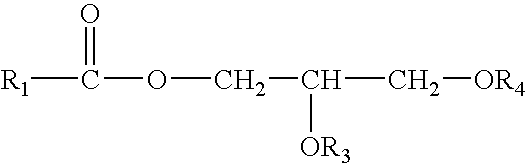
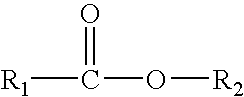
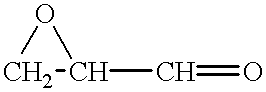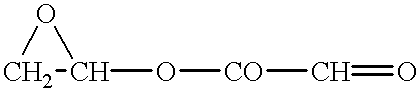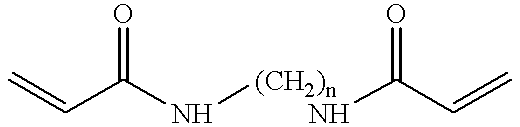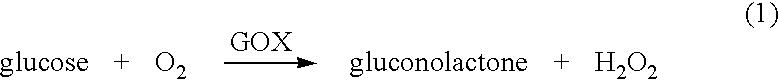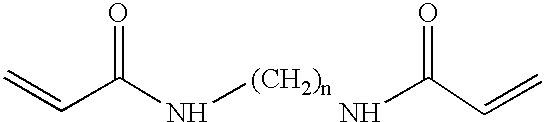Patents
Literature
29752 results about "Hydrogen peroxide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula H₂O₂. In its pure form, it is a very pale blue, clear liquid, slightly more viscous than water. Hydrogen peroxide is the simplest peroxide (a compound with an oxygen–oxygen single bond). It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic. Concentrated hydrogen peroxide, or "high-test peroxide", is a reactive oxygen species and has been used as a propellant in rocketry. Its chemistry is dominated by the nature of its unstable peroxide bond.
Process for producing oxime
InactiveUS7161036B2Speed up the conversion processHigh selectivityOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsKetoneAmmonia
A process for producing an oxime is provided, wherein the process comprises the step of reacting a ketone, hydrogen peroxide and ammonia in the presence of a crystalline titanosilicate having MWW structure under the condition that the ammonia concentration in the liquid portion of the reaction mixture is about 1% by weight or more. By the process, an ammoximation reaction of the ketone can be carried out with a high conversion of the ketone and a high selectivity to the oxime corresponding to the ketone, thereby producing the oxime with a high yield.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
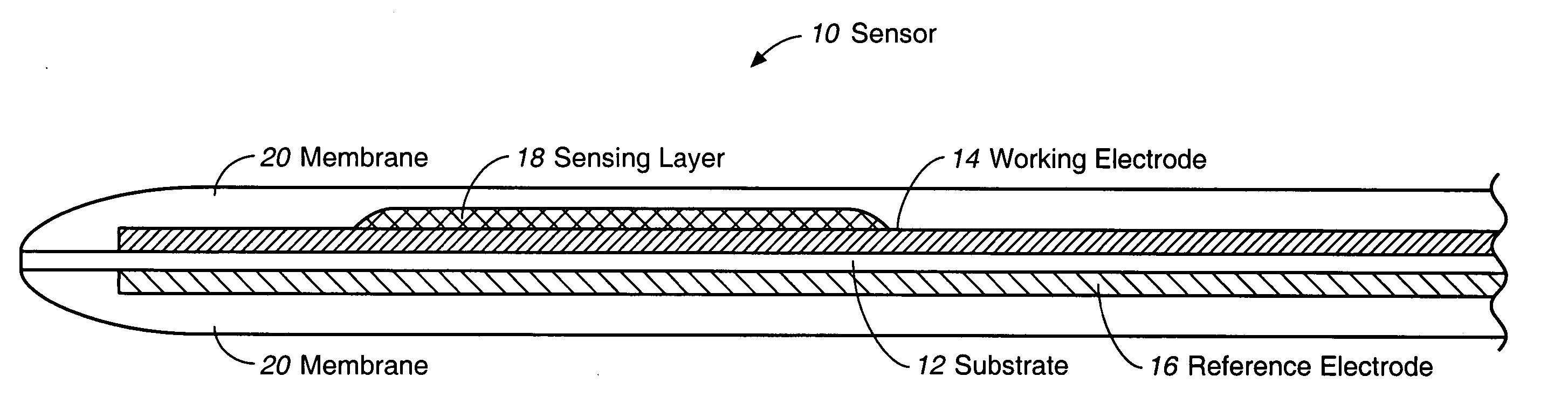
Membrane suitable for use in an analyte sensor, analyte sensor, and associated method
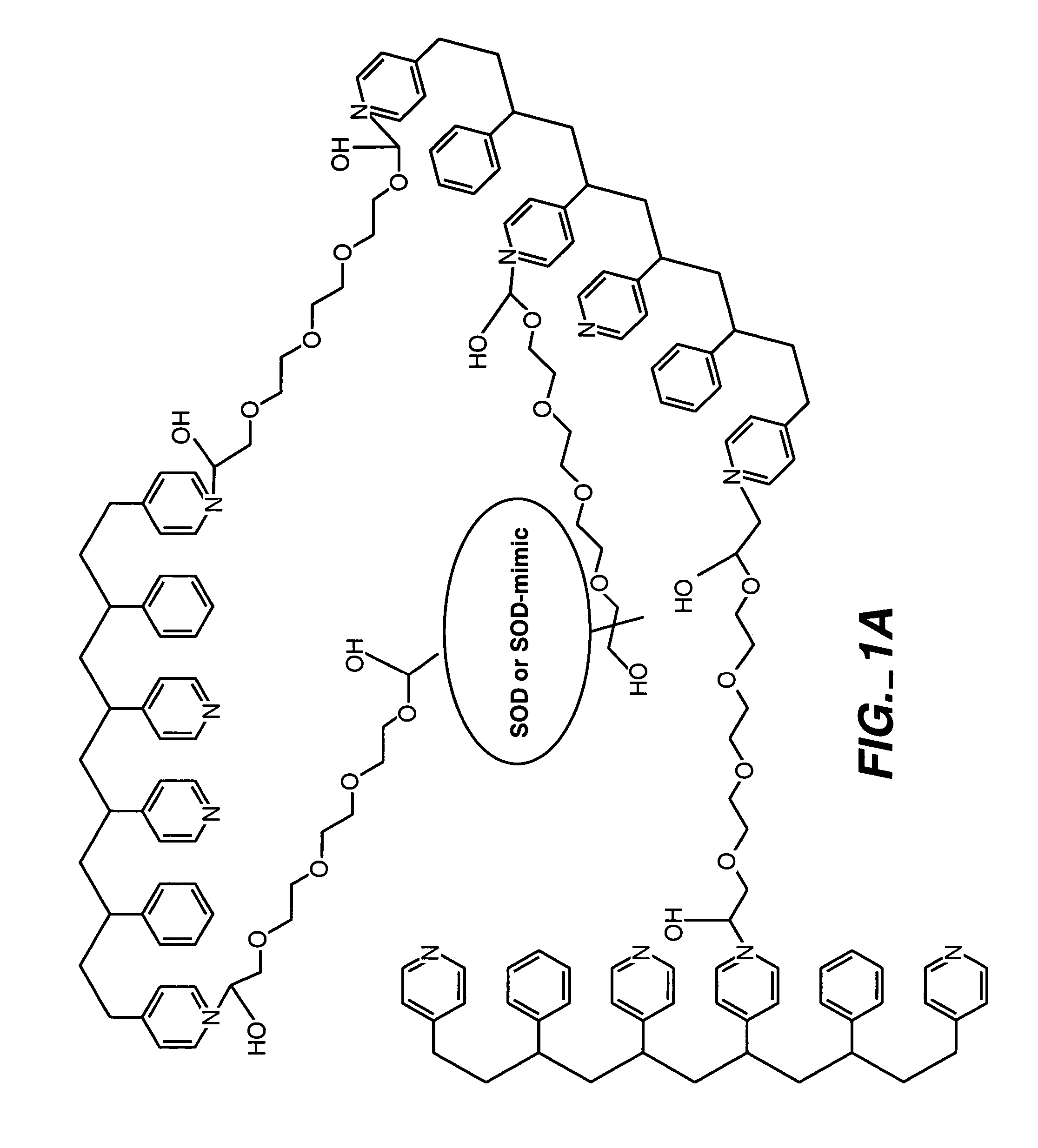
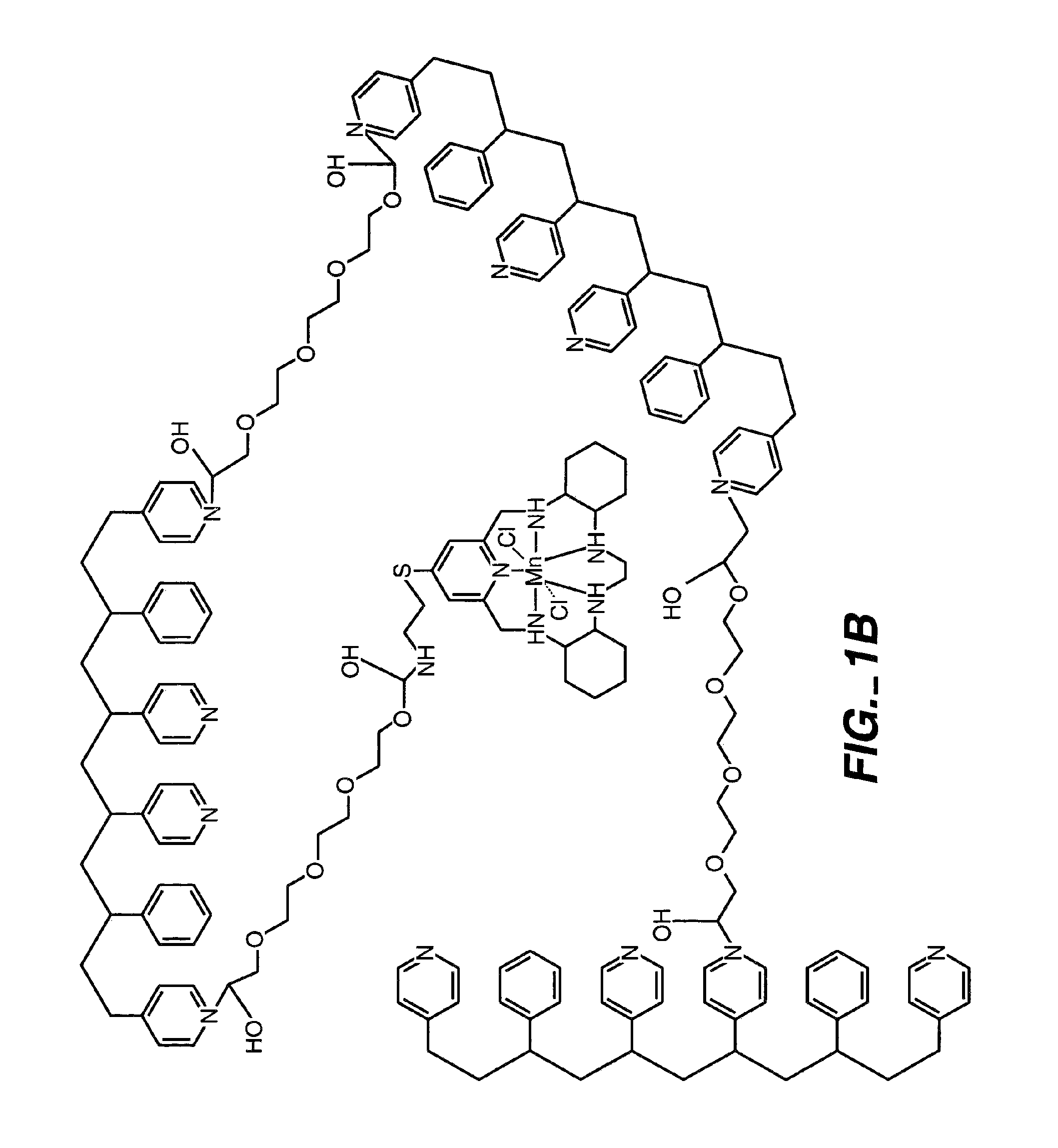
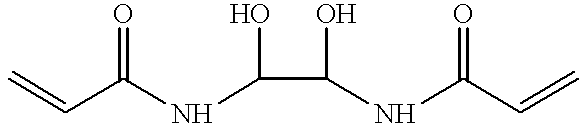
ActiveUS20050173245A1Facilitate linear responsivenessEasy CalibrationImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMetaboliteSuperoxide
A multifunctional membrane is provided. The multifunctional membrane is suitable for use in an analyte sensor. In a particular application, the multifunctional membrane may be used in connection with an amperometric biosensor, such as a transcutaneous amperometric biosensor. Some functions of the membrane are associated with properties of membrane itself, which is comprised of crosslinked polymers containing heterocyclic nitrogen groups. For example, the membrane, by virtue of its polymeric composition, may regulate the flux of an analyte to a sensor. Such regulation generally improves the kinetic performance of the sensor over a broad range of analyte concentration. Other functions of the membrane are associated with functional components, such as a superoxide-dismutating / catalase catalyst, either in the form of an enzyme or an enzyme mimic, that can be bound to the scaffold provided by the membrane. The effect of any such enzyme or enzyme mimic is to lower the concentration of a metabolite, such as superoxide and / or hydrogen peroxide, in the immediate vicinity of the sensing layer of the biosensor. Lowering the concentrations of such metabolites, which are generally deleterious to the function of the sensor, generally protects or enhances biosensor integrity and performance. The membrane is thus an important tool for use in connection with analyte sensors, amperometric sensors, biosensors, and particularly, transcutaneous biosensors. A membrane-covered sensor and a method for making same are also provided.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
CVD nanoporous silica low dielectric constant films
InactiveUS6171945B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSilicon oxideGradual increase
A method and apparatus for depositing nano-porous low dielectric constant films by reaction of a silicon hydride containing compound or mixture optionally having thermally labile organic groups with a peroxide compound on the surface of a substrate. The deposited silicon oxide based film is annealed to form dispersed microscopic voids that remain in a nano-porous silicon oxide based film having a foam structure. The nano-porous silicon oxide based films are useful for filling gaps between metal lines with or without liner or cap layers. The nano-porous silicon oxide based films may also be used as an intermetal dielectric layer for fabricating dual damascene structures. Preferred nano-porous silicon oxide based films are produced by reaction of 1,3,5-trisilanacyclohexane, bis(formyloxysilano)methane, or bis(glyoxylylsilano)methane and hydrogen peroxide followed by a cure / anneal that includes a gradual increase in temperature.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
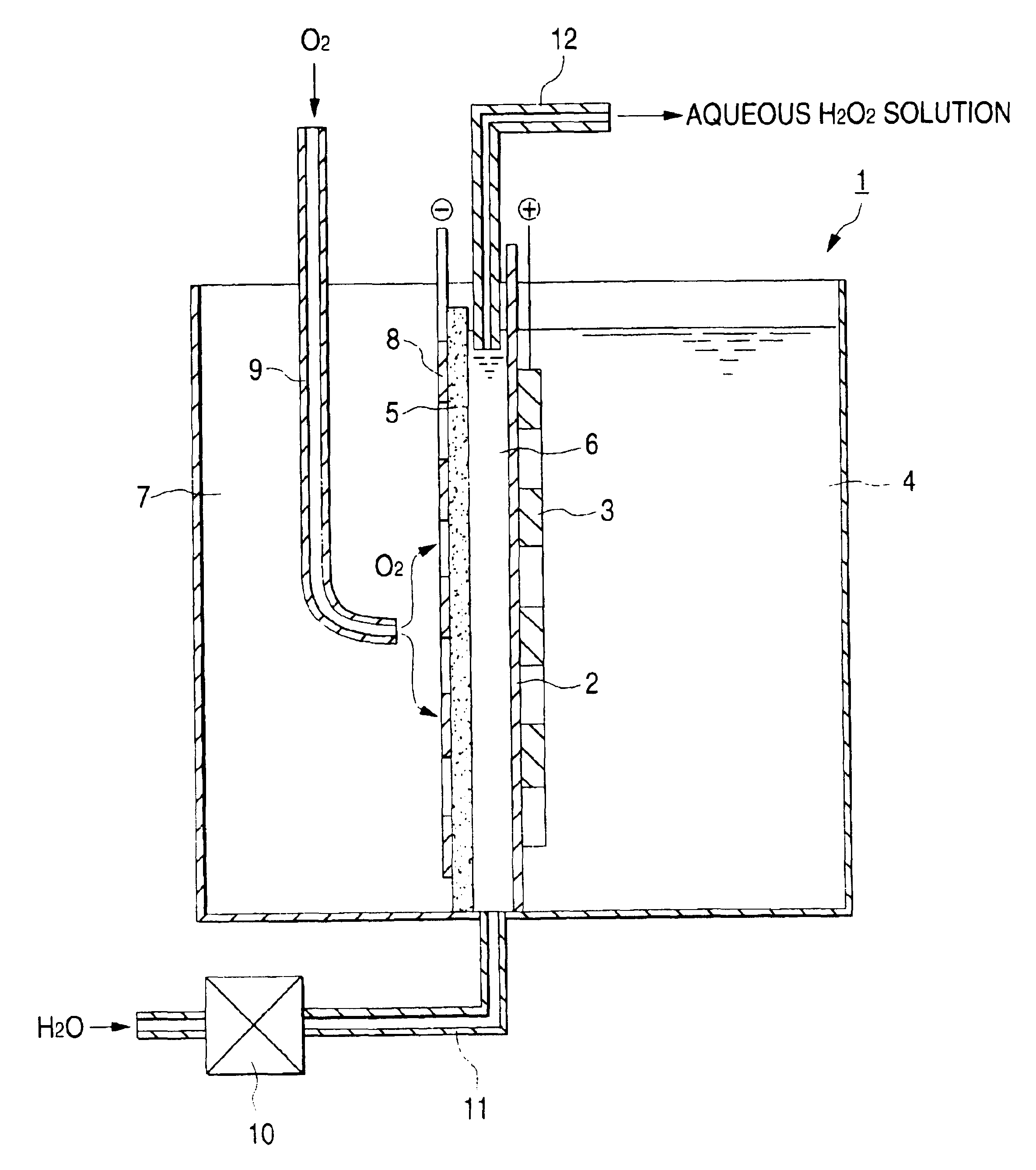
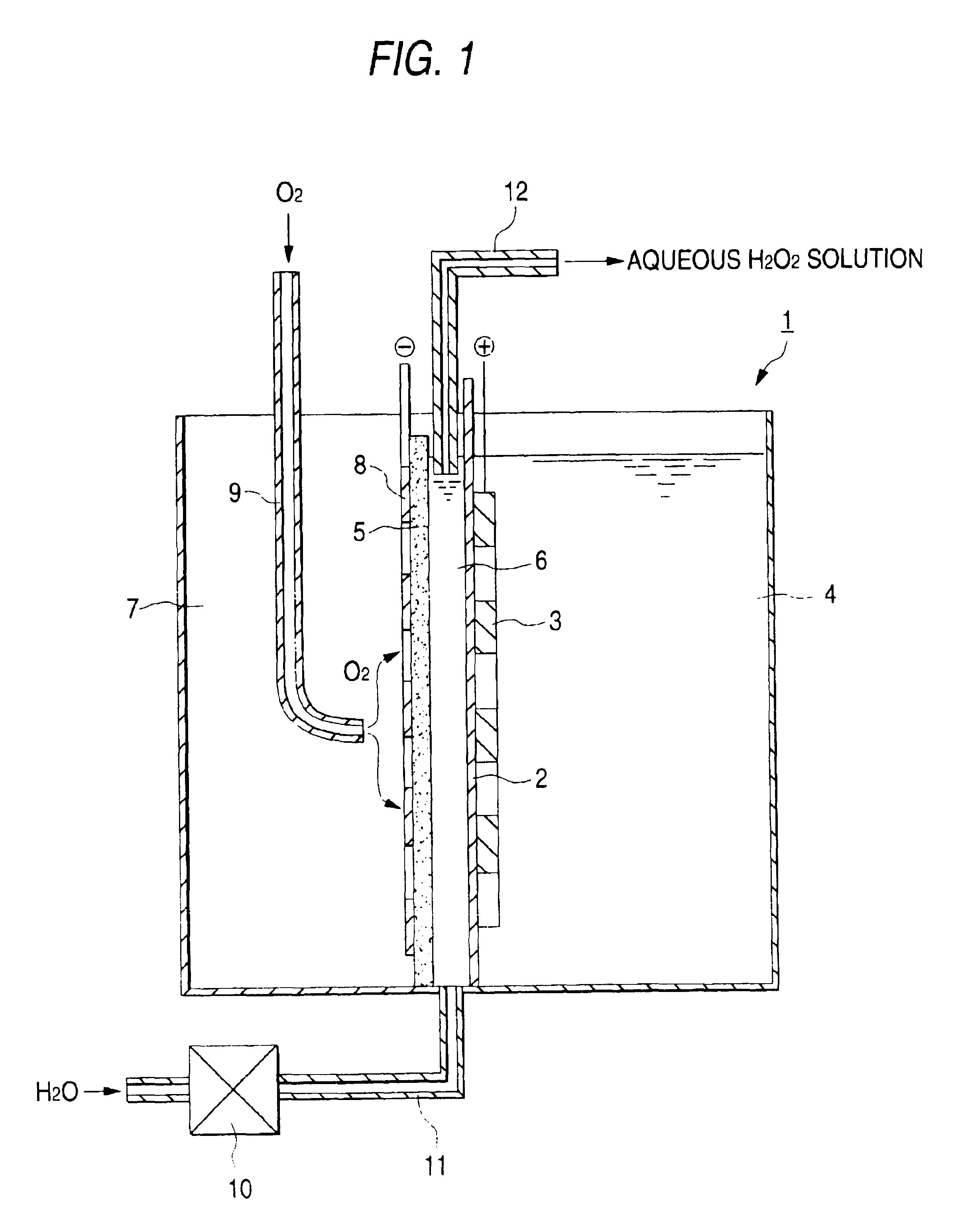
Electrolytic cell for hydrogen peroxide production and process for producing hydrogen peroxide
InactiveUS6767447B2CellsPeroxides/peroxyhydrates/peroxyacids/superoxides/ozonidesSodium sulfateNuclear chemistry
An electrolytic cell and method of electrolysis for producing hydrogen peroxide at a moderate current density while preventing metal deposition on the cathode surface. A feed water from which multivalent metal ions have been removed and in which a salt of a univalent metal, e.g., sodium sulfate, has been dissolved in a given concentration is prepared with an apparatus for removing multivalent metal ions and dissolving a salt in low concentration. The feed water is supplied to an electrolytic cell. Even when electrolysis is continued, almost no deposition of a hydroxide or carbonate occurs on the cathode because multivalent metal ions are not present in the electrolytic solution. Due to the dissolved salt, a sufficient current density is secured to prevent an excessive load from being imposed on the electrodes, etc. Thus, stable production of hydrogen peroxide is possible over a long period of time.
Owner:DE NORA PERMELEC LTD
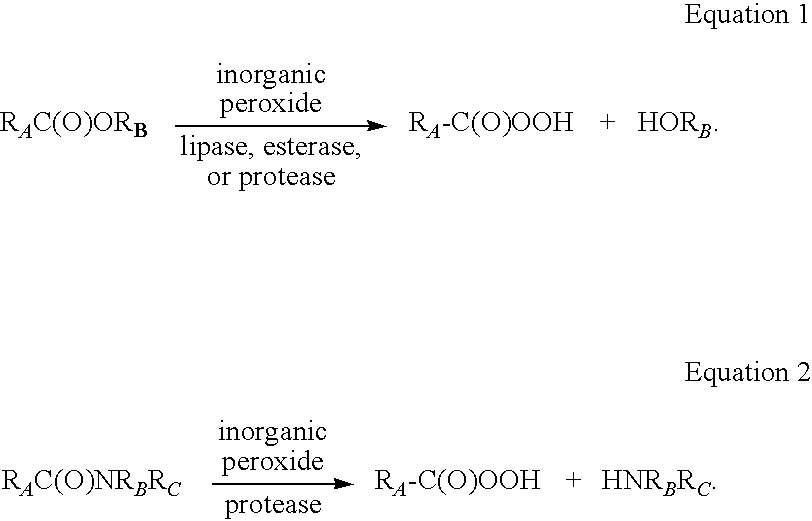
Production of peracids using an enzyme having perhydrolysis activity
A process is provided for producing peroxycarboxylic acids from carboxylic acid esters. More specifically, carboxylic acid esters are reacted with an inorganic peroxide, such as hydrogen peroxide, in the presence of an enzyme catalyst having perhydrolysis activity. The present perhydrolase catalysts are classified as members of the carbohydrate esterase family 7 (CE-7) based on the conserved structural features. Further, disinfectant formulations comprising the peracids produced by the processes described herein are provided.
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
Slurry compositions for chemical mechanical polishing of copper and barrier films
InactiveUS20050090104A1High selectivityShorten the counting processSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPolishing compositions with abrasivesSlurryPolymer
Owner:INNOVATIUM TECH
Membrane suitable for use in an analyte sensor, analyte sensor, and associated method
ActiveUS7699964B2Facilitate linear responsiveness and calibration and stabilityPreserve and improve performance of sensorImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMetaboliteAmperometric biosensor
A multifunctional membrane is provided. The multifunctional membrane is suitable for use in an analyte sensor. In a particular application, the multifunctional membrane may be used in connection with an amperometric biosensor, such as a transcutaneous amperometric biosensor. Some functions of the membrane are associated with properties of membrane itself, which is comprised of crosslinked polymers containing heterocyclic nitrogen groups. For example, the membrane, by virtue of its polymeric composition, may regulate the flux of an analyte to a sensor. Such regulation generally improves the kinetic performance of the sensor over a broad range of analyte concentration. Other functions of the membrane are associated with functional components, such as a superoxide-dismutating / catalase catalyst, either in the form of an enzyme or an enzyme mimic, that can be bound to the scaffold provided by the membrane. The effect of any such enzyme or enzyme mimic is to lower the concentration of a metabolite, such as superoxide and / or hydrogen peroxide, in the immediate vicinity of the sensing layer of the biosensor. Lowering the concentrations of such metabolites, which are generally deleterious to the function of the sensor, generally protects or enhances biosensor integrity and performance. The membrane is thus an important tool for use in connection with analyte sensors, amperometric sensors, biosensors, and particularly, transcutaneous biosensors. A membrane-covered sensor and a method for making same are also provided.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Methods for microdispensing patterened layers
InactiveUS6306594B1Efficient couplingShort response timeMicrobiological testing/measurementBurettes/pipettesAnalyteClinical settings
An efficient method for the microfabrication of electronic devices which have been adapted for the analyses of biologically significant analyte species is described. The techniques of the present invention allow for close control over the dimensional features of the various components and layers established on a suitable substrate. Such control extends to those parts of the devices which incorporate the biological components which enable these devices to function as biological sensors. The materials and methods disclosed herein thus provide an effective means for the mass production of uniform wholly microfabricated biosensors. Various embodiments of the devices themselves are described herein which are especially suited for real time analyses of biological samples in a clinical setting. In particular, the present invention describes assays which can be performed using certain ligand / ligand receptor-based biosensor embodiments. The present invention also discloses a novel method for the electrochemical detection of particular analyte species of biological and physiological significance using an substrate / label signal generating pair which produces a change in the concentration of electroactive species selected from the group consisting of dioxygen and hydrogen peroxide.
Owner:I STAT CORP
Multiple fluid closed system dispensing device
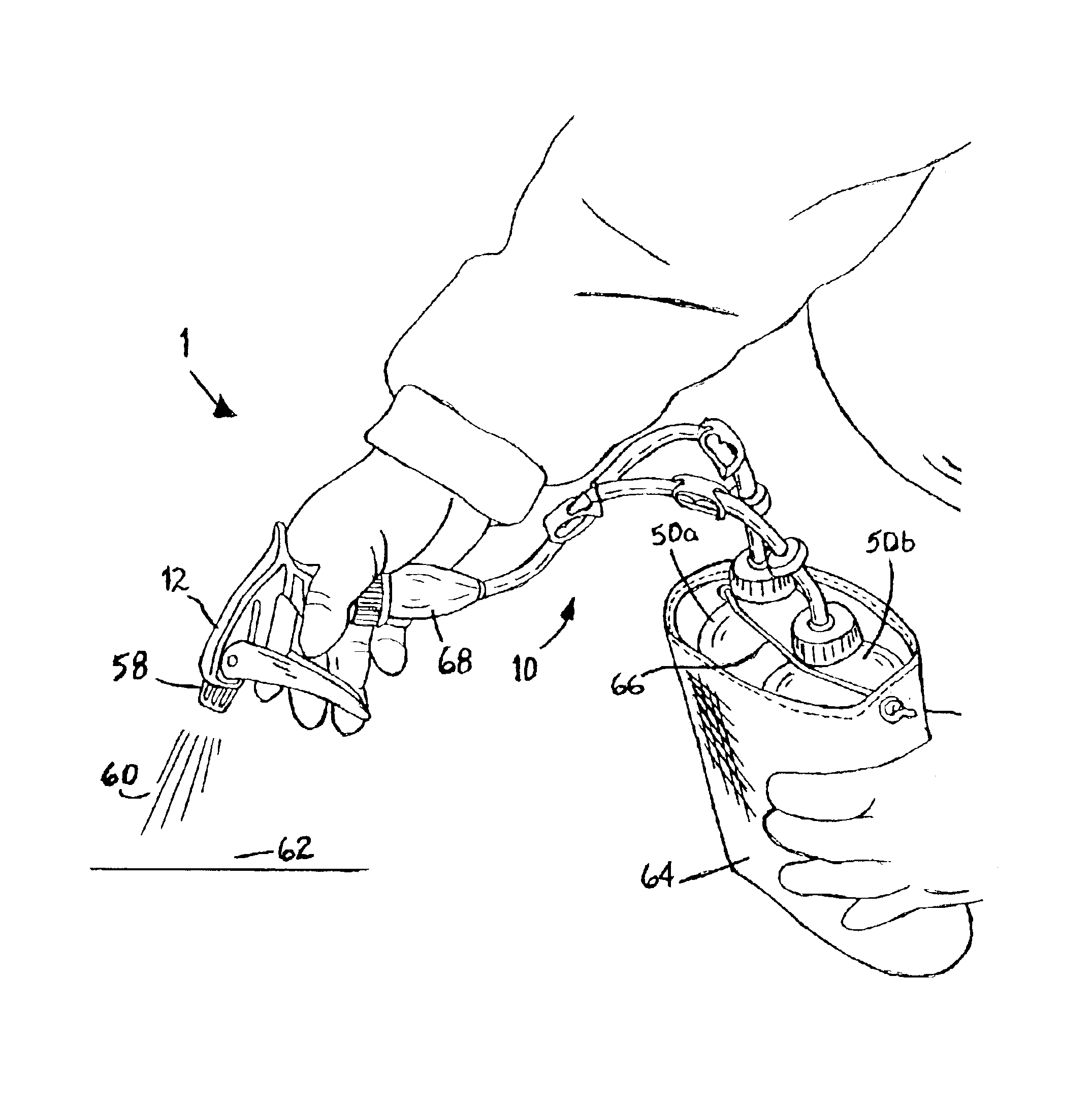
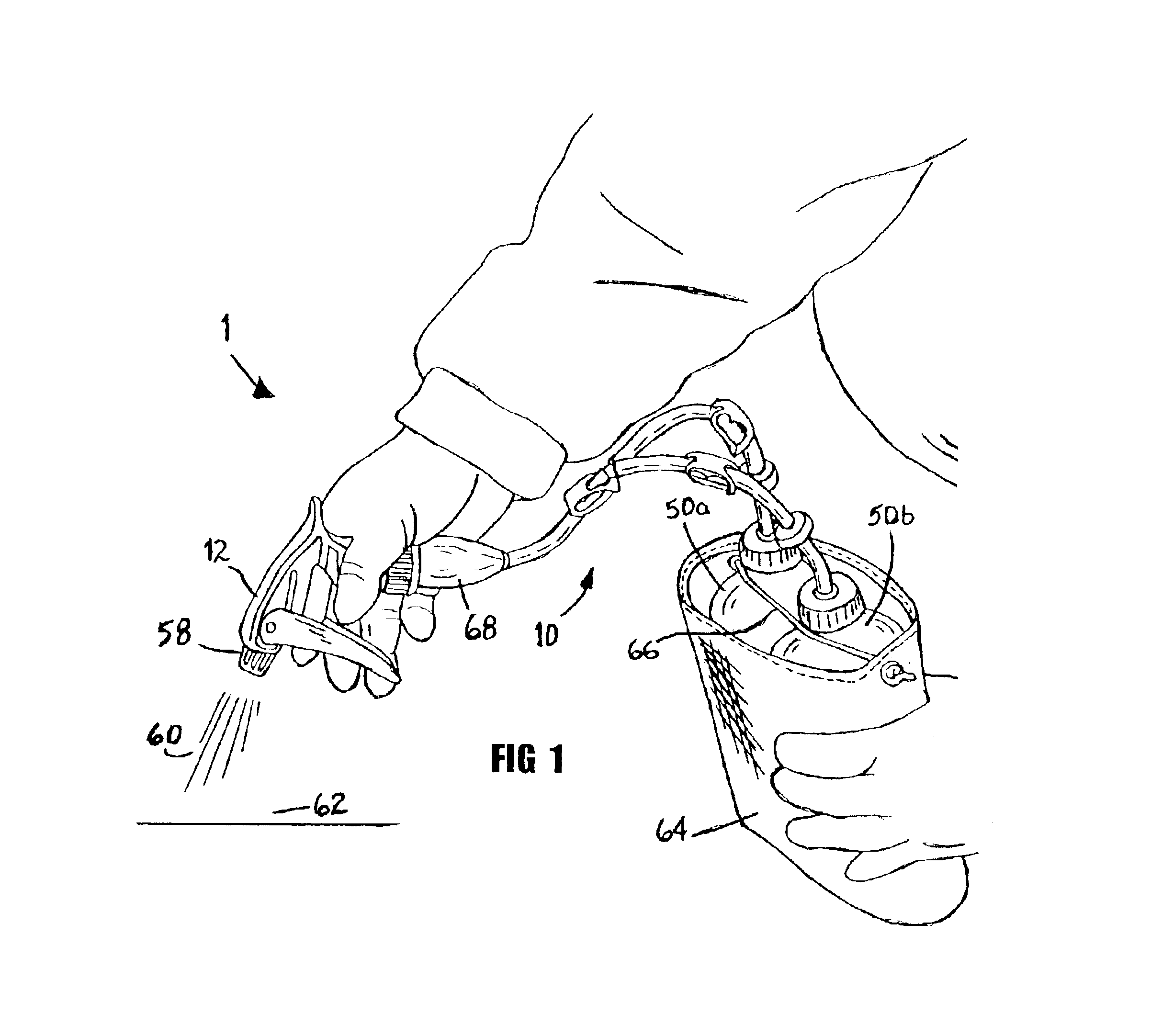
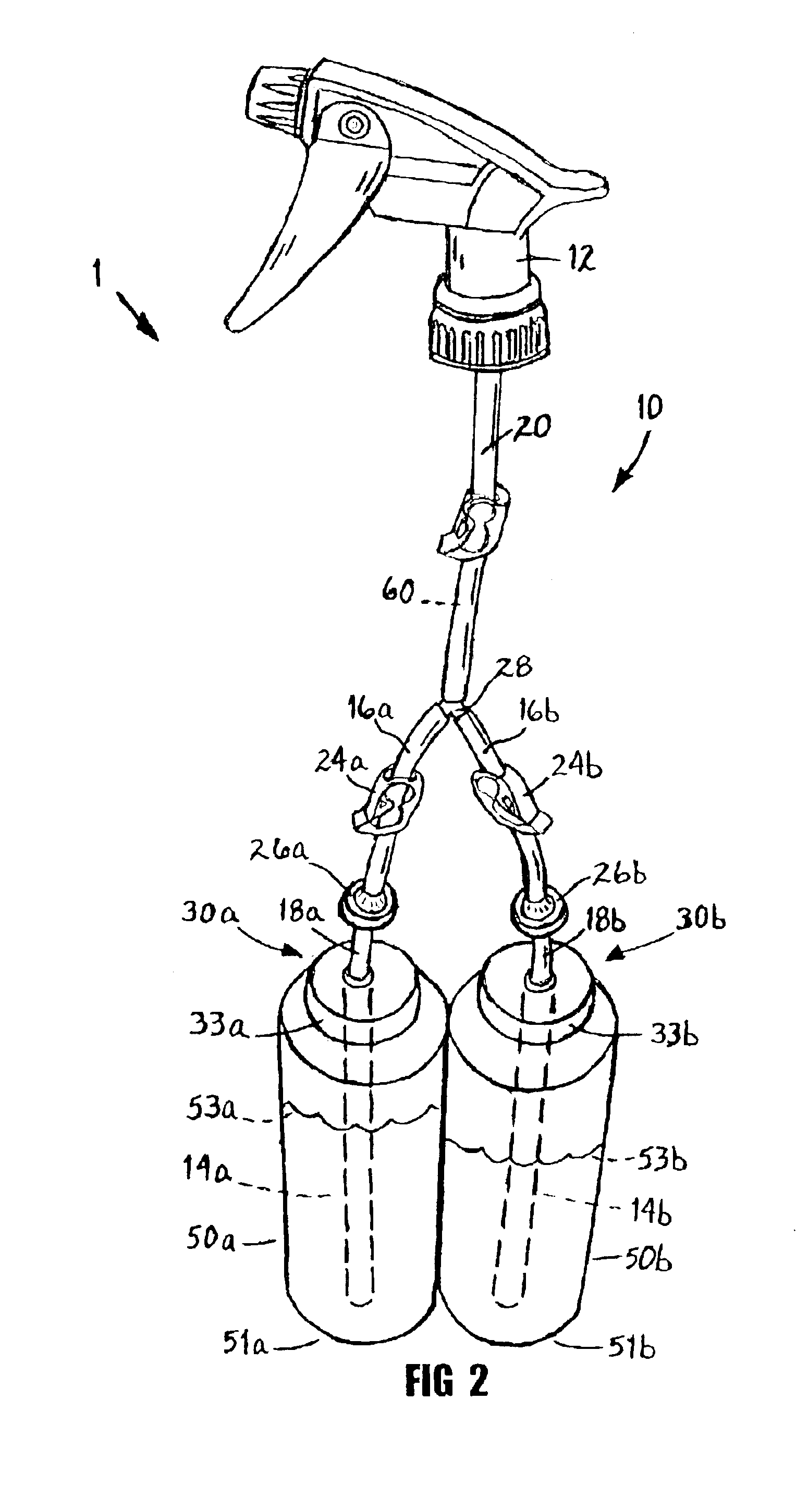
InactiveUS6843390B1Improve efficiencyEffective alternativeLiquid transferring devicesSolid materialTarget surfaceEngineering
A dispensing device (1) with multi-arm tubing assembly (10) connected to a single source pumping means (12) draws and mixes multiple fluids from plurality of flexible walled sealed supply containers (50a,b) then expels the mixture (60) through nozzle (58) to a target surface (62). Dispensing device (1) provides a closed system whereby no venting occurs, rather supply containers (50a,b) contract in size equal to the volume of fluid expelled. Unstable fluids thus remain protected from exposure to outside air. Additionally, a new use of a repressurization device is disclosed for maintaining the potency of unstable fluids like hydrogen peroxide and a kit is provided which allows user to choose from various components and accessories as needed to suit their multi-chemical dispensing needs.
Owner:WANDERS INC
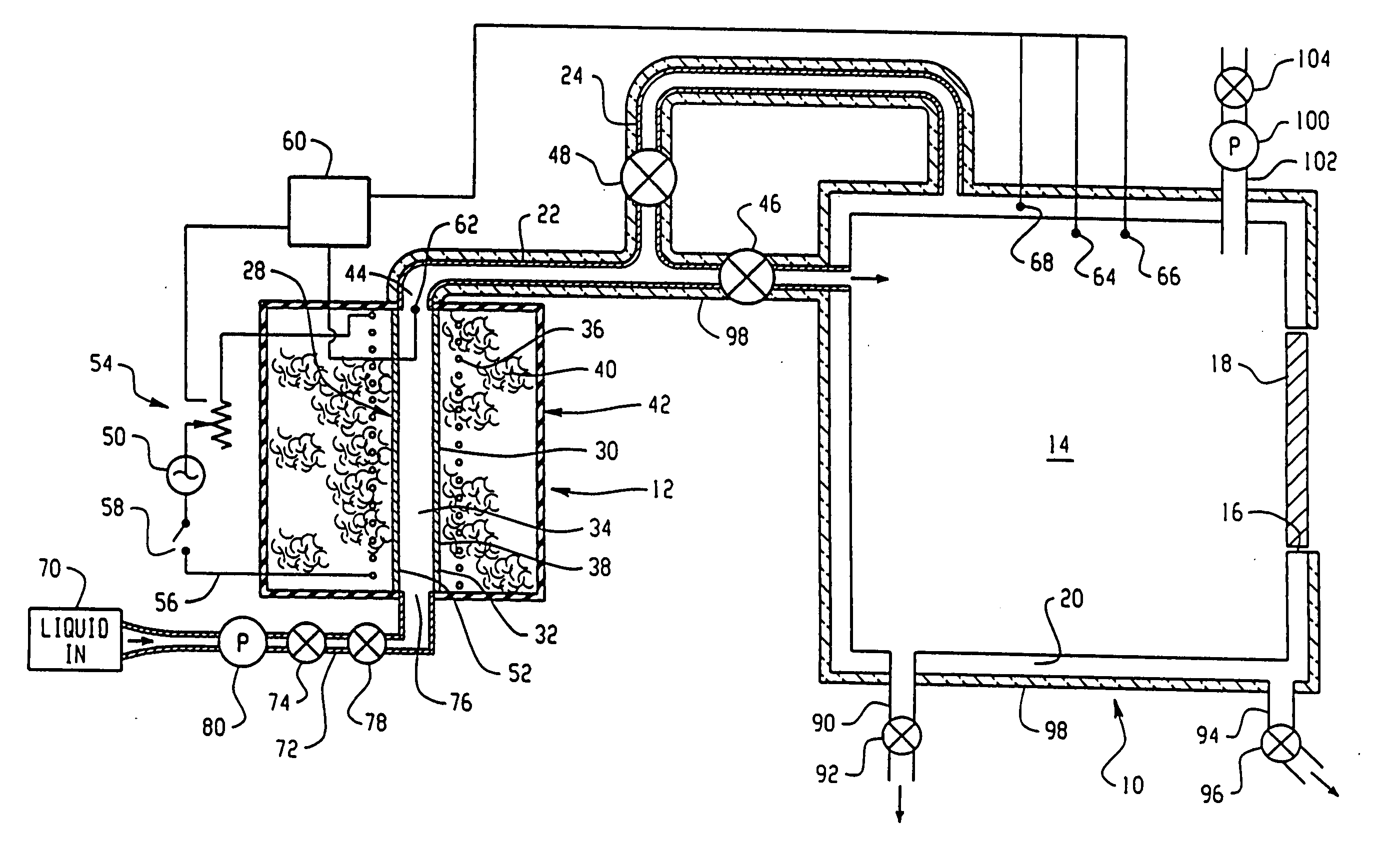
Catalyst and process for direct catalytic production of hydrogen peroxide, (H2O2)
InactiveUS6168775B1High catalytic activityHigh activityHydrogen peroxideCatalyst activation/preparationParticulatesHydrogen
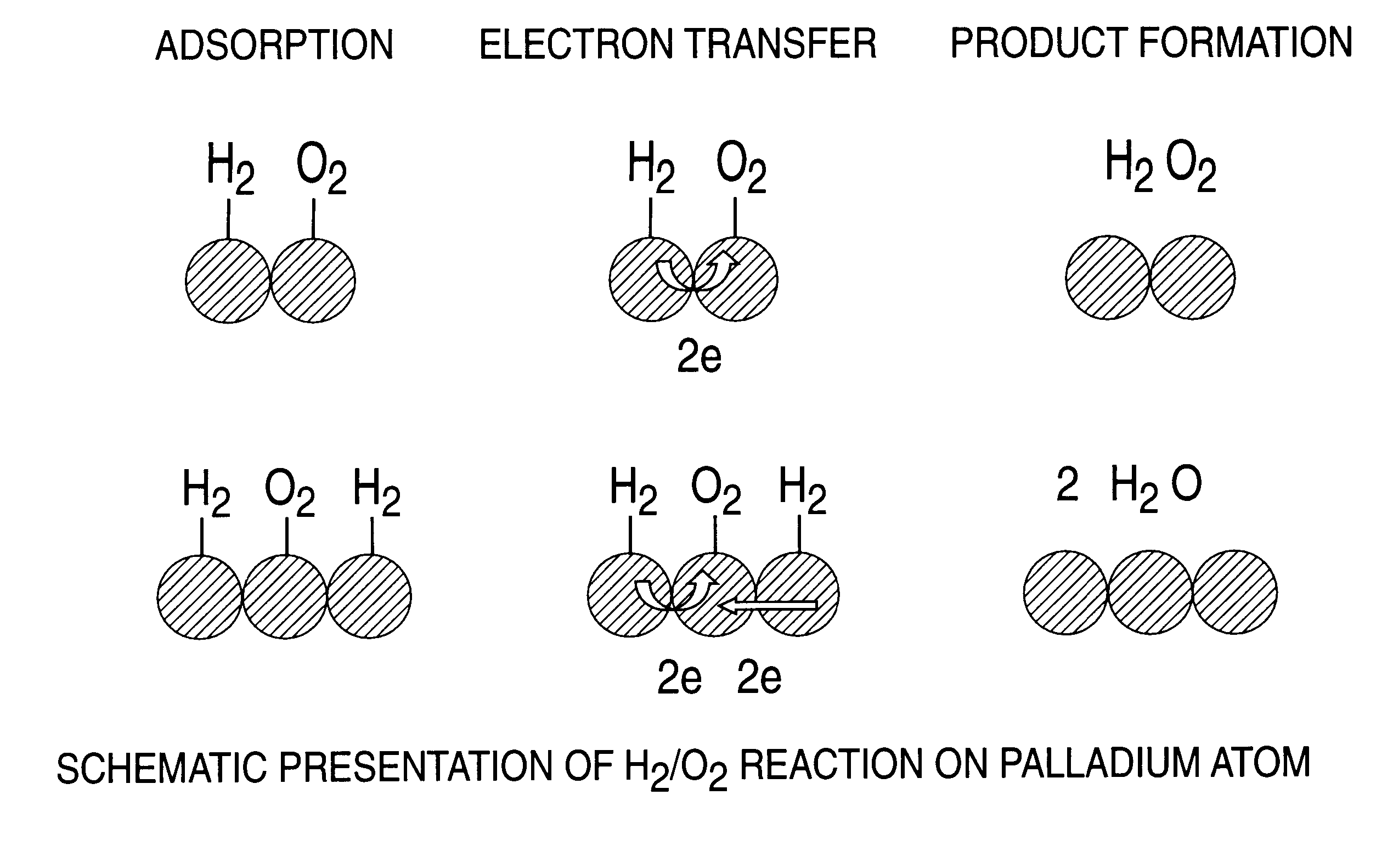
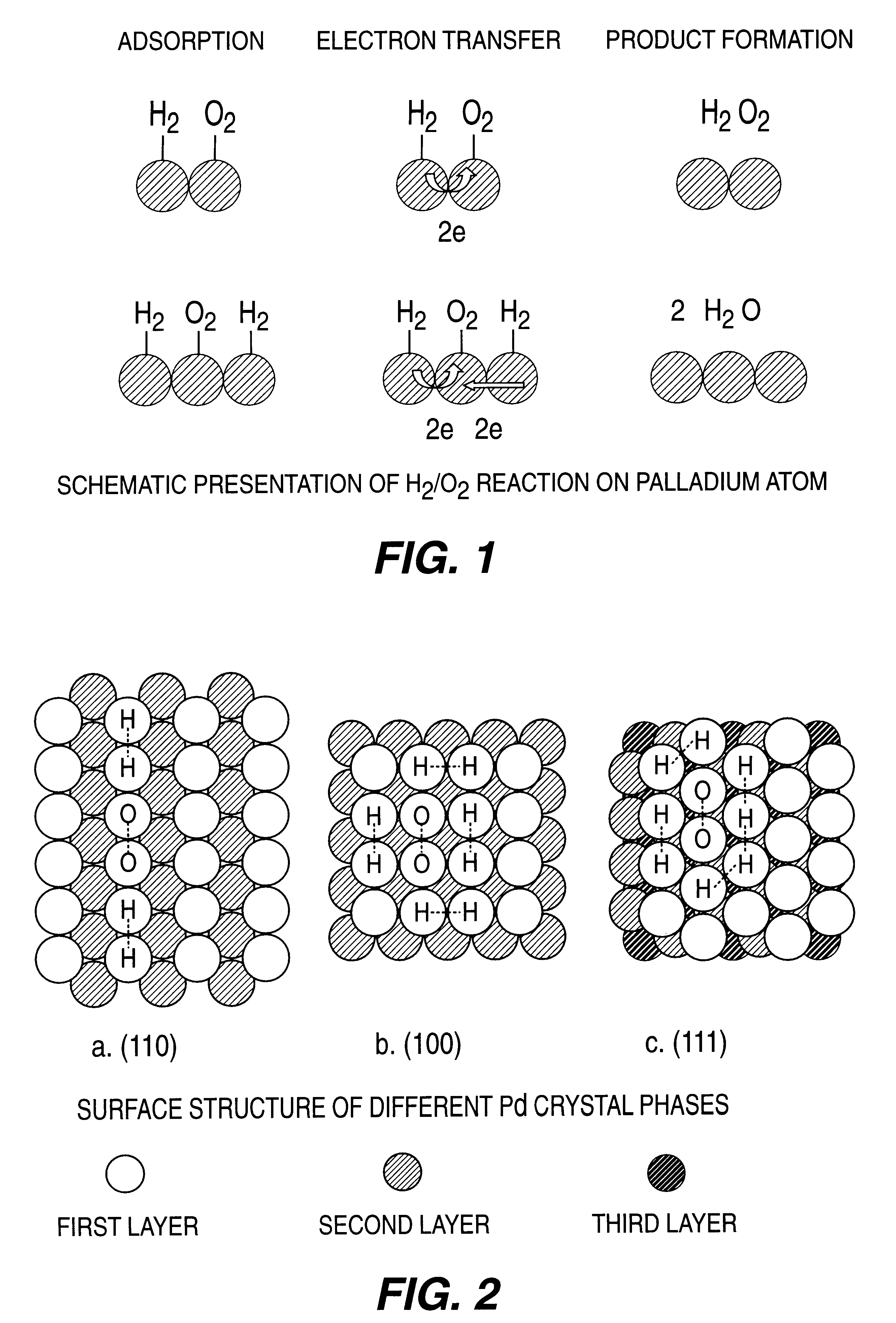
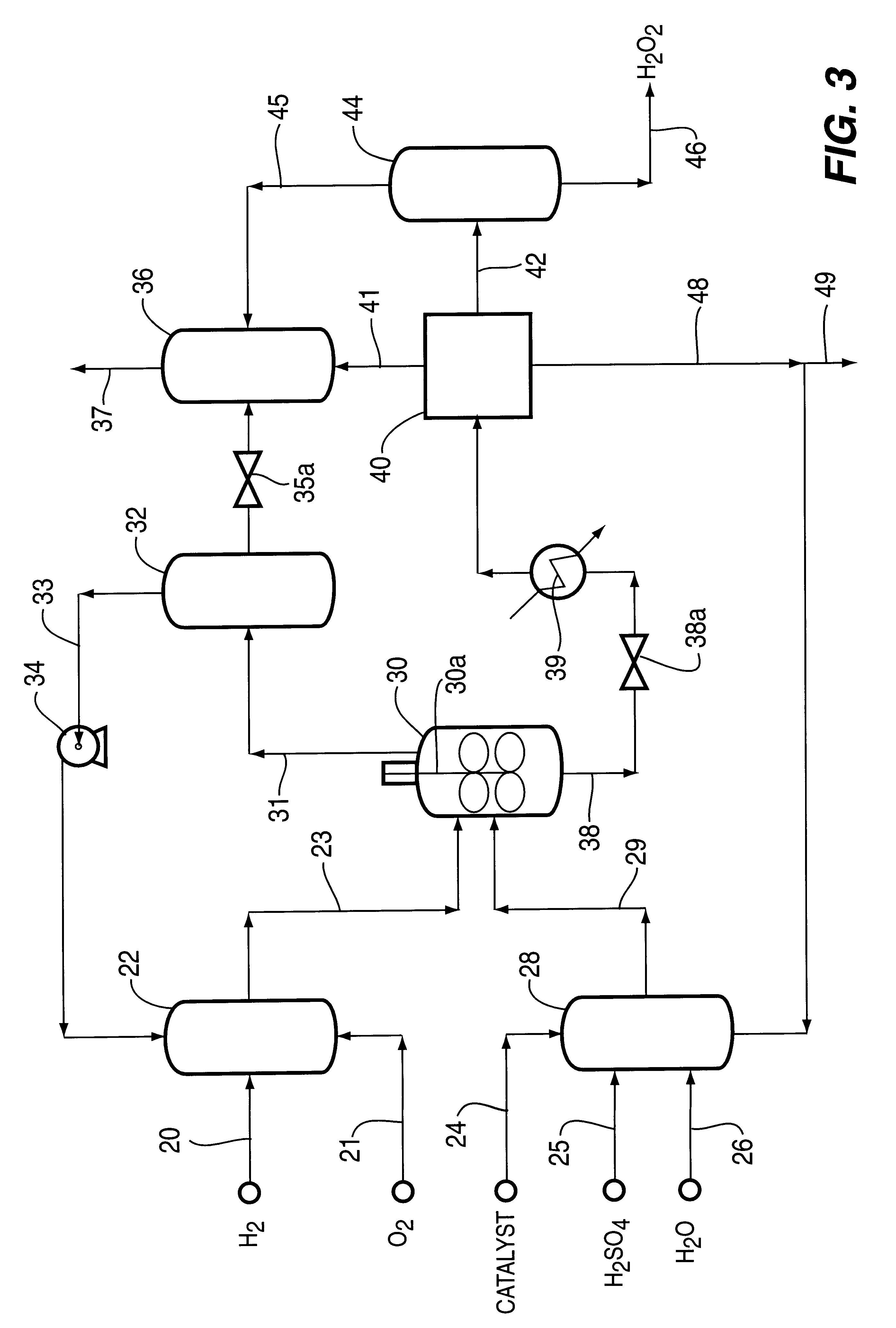
A particulate supported noble metal phase-controlled catalyst material having 5-1000 mum surface area of 50-500 m2 / gm is provided for use in direct catalytic production of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) product from hydrogen and oxygen-containing feedstreams. The catalyst is made by depositing phase controlled crystals of a noble metal such as palladium on a suitable particulate support material such as carbon black, by utilizing a precursor solution of the metal and a suitable control ionic polymer having molecular weight of 300-8000 such as sodium polyacrylate in a selected metal to polymer molar ratio of 1:0.1 to 1:10, which procedure provides desired phase control of the noble metal atoms to form widely dispersed minute noble metal crystals on the support material. The invention includes methods for making the catalyst, and also a process for utilizing the catalyst to directly produce high yields of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) product from hydrogen and oxygen-containing gaseous feedstreams.
Owner:BORAL IP HLDG
Polymer matrix containing catalase co-immobilized with analytic enzyme that generates hydrogen peroxide
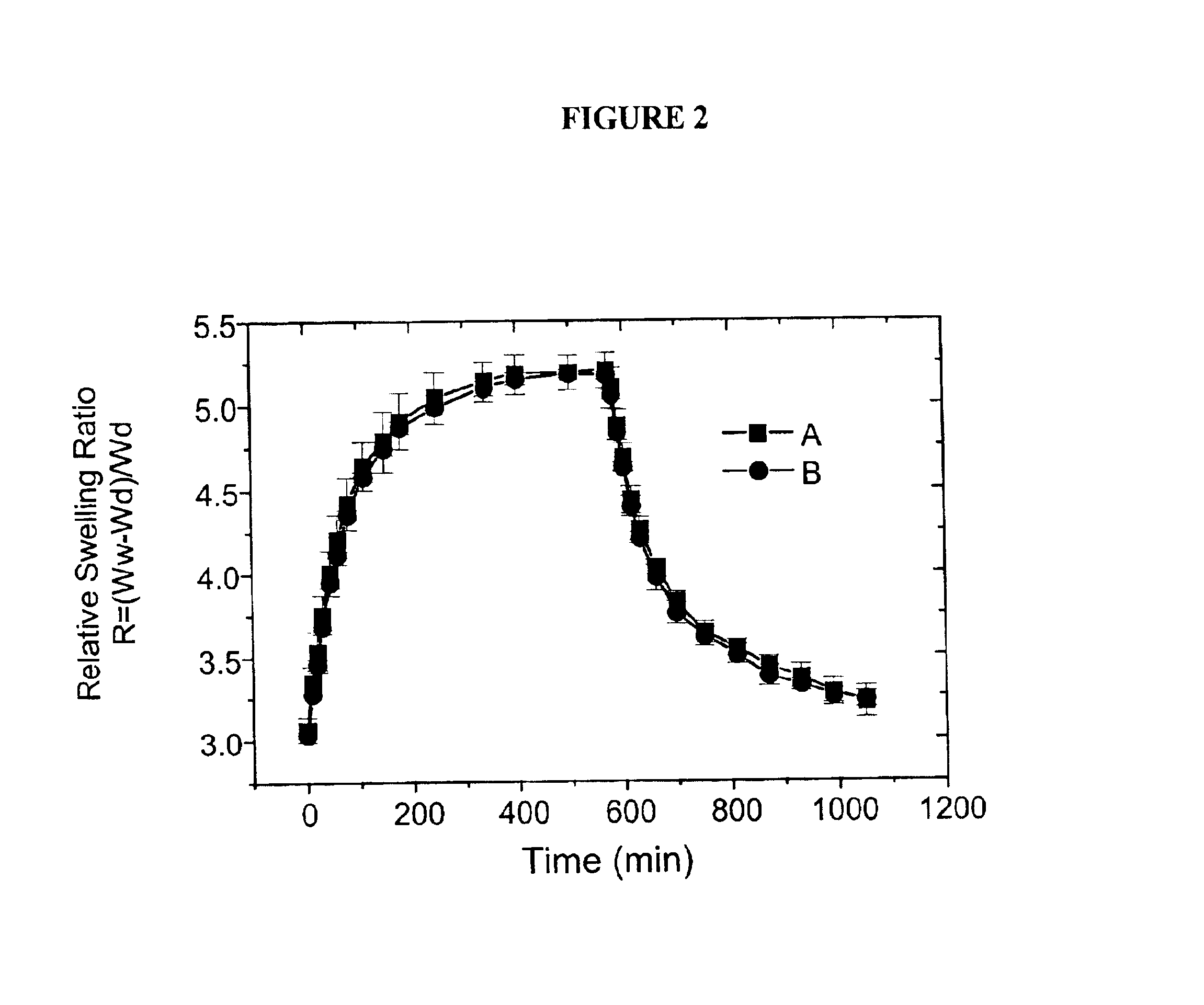
InactiveUS6858403B2Enhancing swelling kineticsLong useful lifePowder deliveryBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteHydrogen peroxide degradation
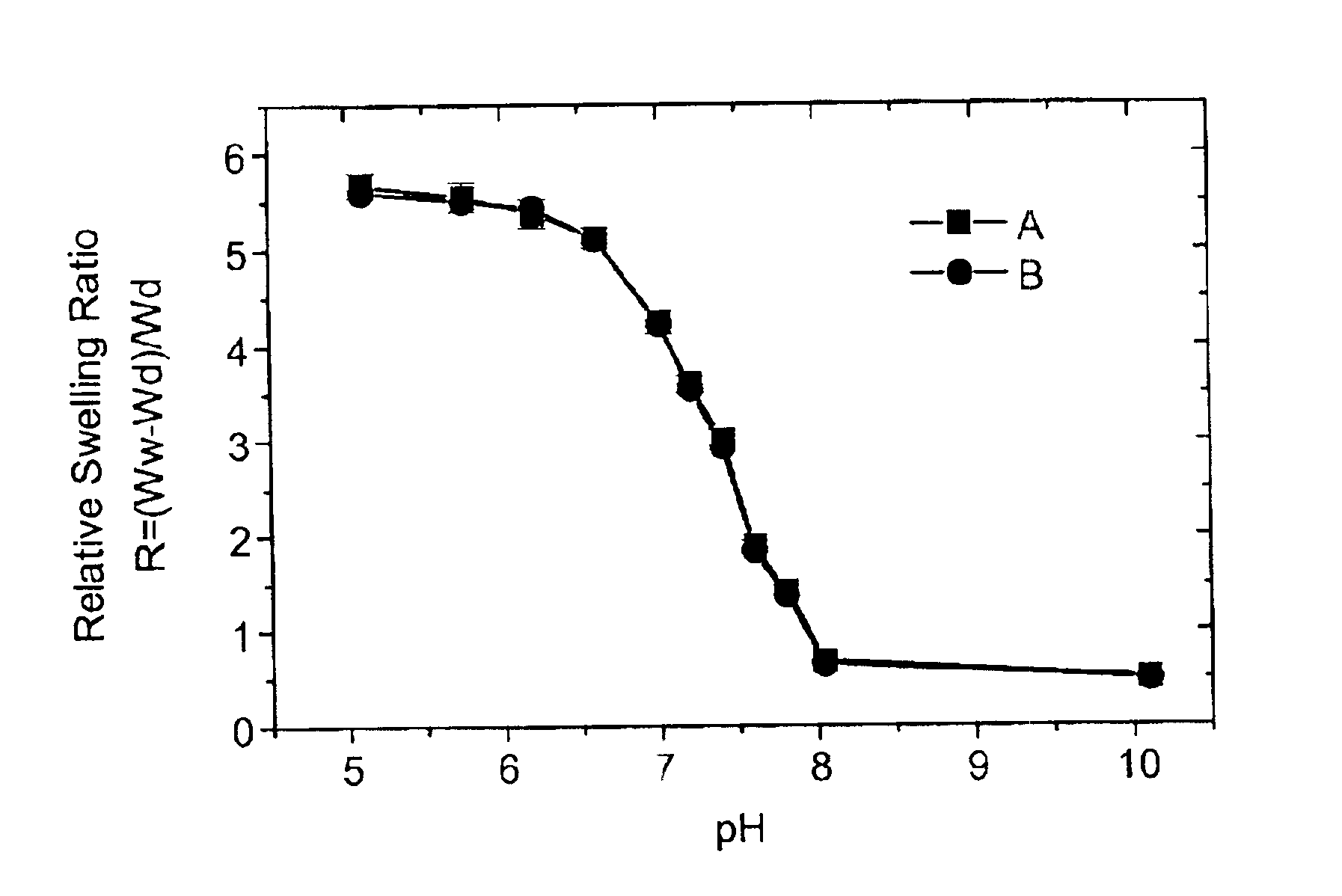
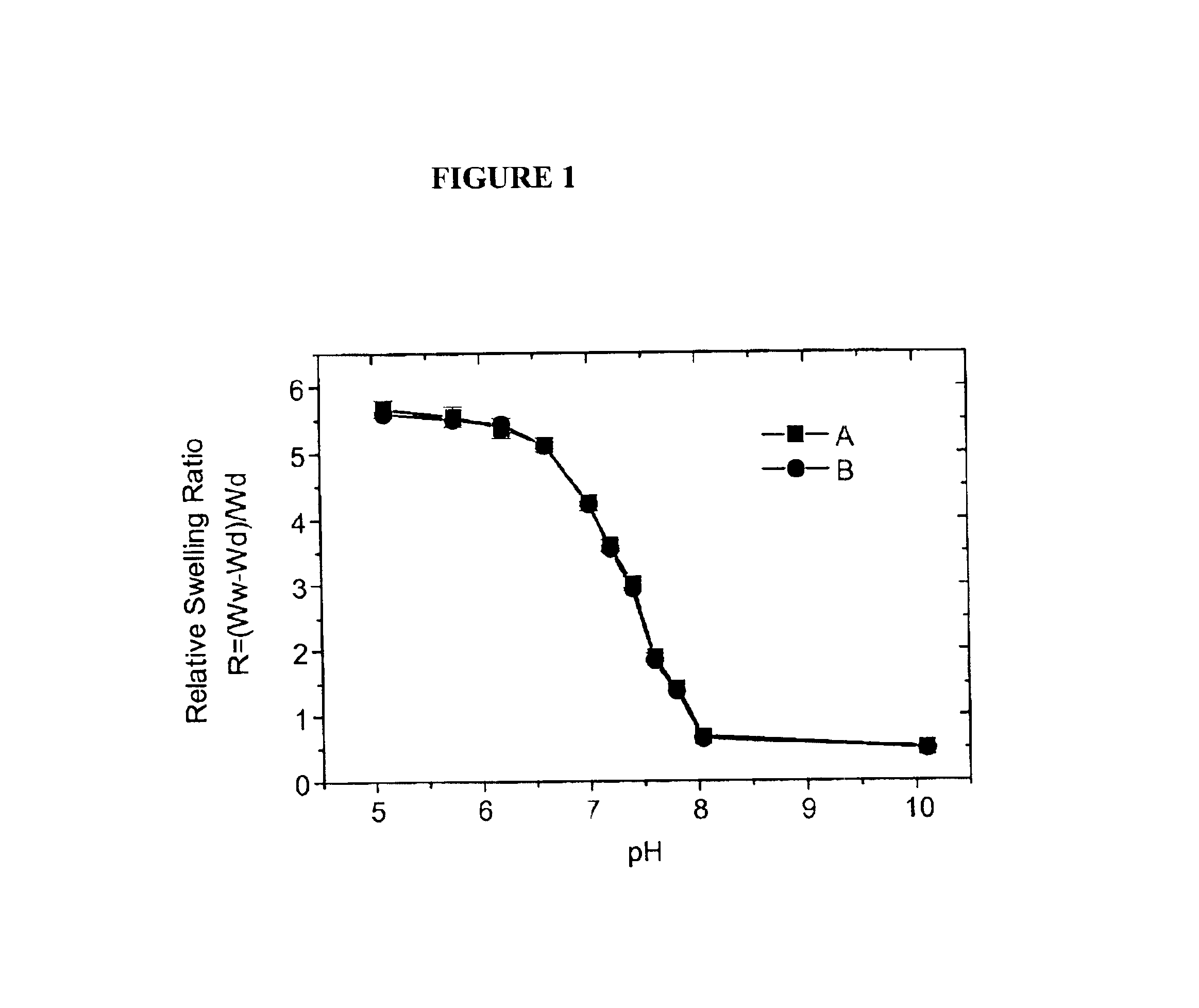
Hydrogels containing catalase co-immobilized with an analyte-sensitive enzyme such as glucose oxidase are disclosed. The hydrogels may be pH-sensitive, and preferably are thin and lightly crosslinked. The catalase is present in concentrations ranging generally from 100 units / ml to about 1000 units / ml. These hydrogels have much faster swelling response times as compared to hydrogels without catalase, and are useful in biosensors and analyte-responsive drug delivery devices. The hydrogels also have an increased useful life, due to protection of the immobilize analyte-sensitive enzyme from degradation by hydrogen peroxide.
Owner:M BIOTECH
Production of Peracids Using An Enzyme Having Perhydrolysis Activity
ActiveUS20080176783A1Efficient implementationReduce concentrationBiocideHydrolasesMedicinal chemistryPeroxide
A process is provided for producing peroxycarboxylic acids from carboxylic acid esters. More specifically, carboxylic acid esters are reacted with an inorganic peroxide, such as hydrogen peroxide, in the presence of an enzyme catalyst having perhydrolysis activity. The present perhydrolase catalysts are classified as members of the carbohydrate esterase family 7 (CE-7) based on the conserved structural features. Further, disinfectant formulations comprising the peracids produced by the processes described herein are provided.
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
Integrate chemical processes for industrial utilization of seed oils
ActiveUS20050154221A1Easy to operateHigh olefin conversionFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteOxygen-containing compound preparationPolyesterAmino esters
Integrated processes of preparing industrial chemicals starting from seed oil feedstock compositions containing one or more unsaturated fatty acids or unsaturated fatty acid esters, which are essentially free of metathesis catalyst poisons, particularly hydroperoxides; metathesis of the feedstock composition with a lower olefin, such as ethylene, to form a reduced chain olefin, preferably, a reduced chain α-olefin, and a reduced chain unsaturated acid or ester, preferably, a reduced chain α,Ω-unsaturated acid or ester. The reduced chain unsaturated acid or ester may be (trans)esterified to form a polyester polyolefin, which may be epoxidized to form a polyester polyepoxide. The reduced chain unsaturated acid or ester may be hydroformylated with reduction to produce an α,Ω-hydroxy acid or α,Ω-hydroxy ester, which may be (trans)esterified with a polyol to form an α,Ωpolyester polyol. Alternatively, the reduced chain unsaturated acid or ester may be hydroformylated with reductive amination to produce an α,Ω-amino acid or α,Ω-amino ester, which may be (trans)esterified to form an α,Ωpolyester polyamine.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
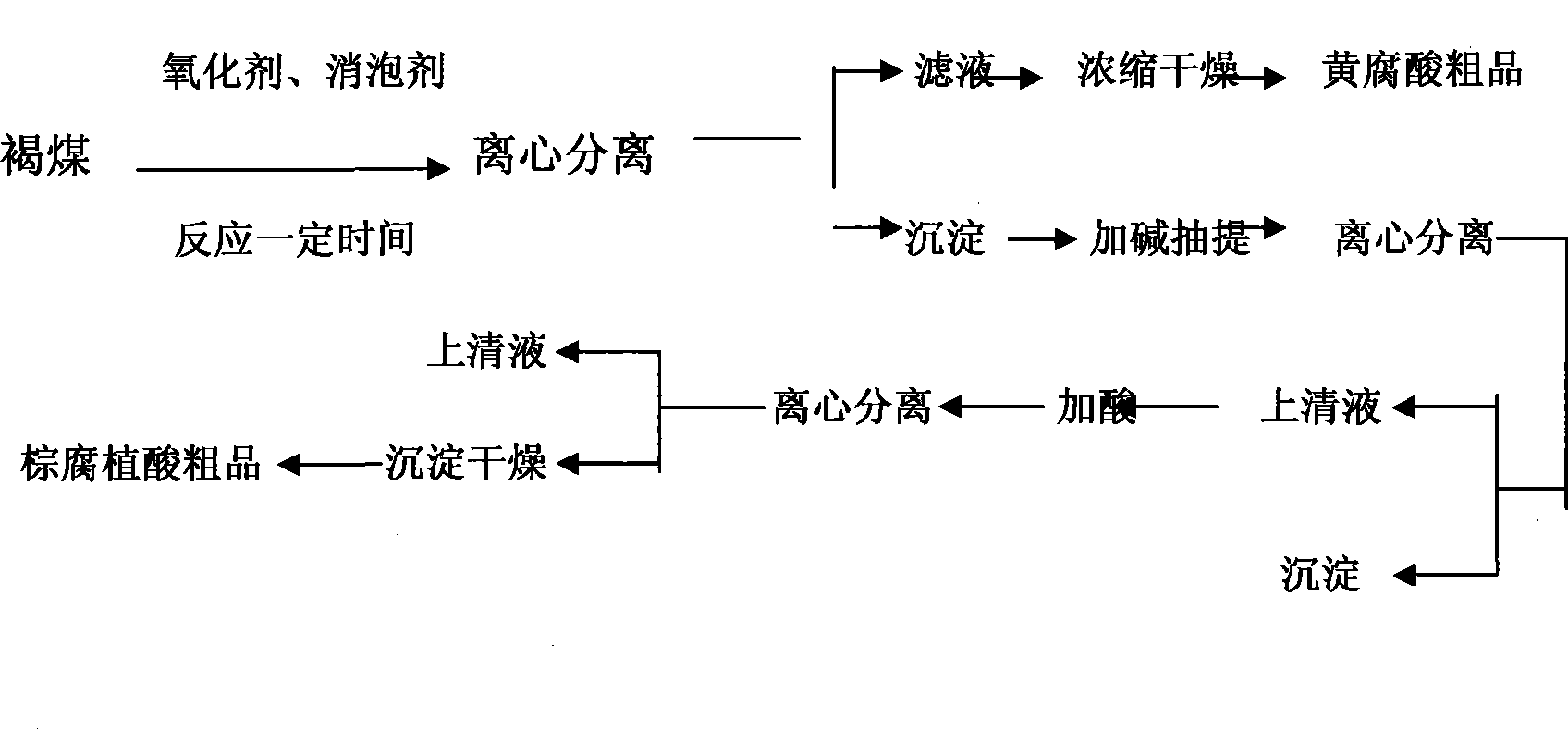
Method for preparing humic acid and salt thereof by oxidation and degradation of brown coal
The invention discloses a method for producing humic acid and salt thereof through the oxidative degradation of young lignite. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out the oxidation reaction of the lignite containing the humic acid and aqueous hydrogen peroxide solution; after the reaction, obtaining water soluble fulvic acid through centrifugal separation, supernatant filtration, concentration and drying; adding alkali into the fulvic acid to prepare a fulvic acid salt product; carrying out the alkaline extraction and centrifugal separation of the residue deposit of the production of the fulvic acid, adding acid into the supernatant till the pH value is 1 to 2, carrying out a reaction at an increased temperature or room temperature, carrying out centrifugal separation after the reaction is finished, and obtaining purified ulmic acid after precipitation and drying; and directly concentrating and drying the supernatant in the previous step to obtain the humate. The method can improve the yield of the fulvic acid and total humic acid in the young lignite, and simultaneously increase the active group in the humic acid. The method can be used for producing fulvic acid, fulvic acid salt, ulmic acid and ulmic acid salt products. In particular, the method puts an end to the environmental pollution caused by the nitric acid which is taken as an oxidation degradation agent. In addition, the method has a short technological line, low cost, simple requirements on equipment, and moderate conditions. The method which can be applied to the industrialized production has good application prospect.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +4
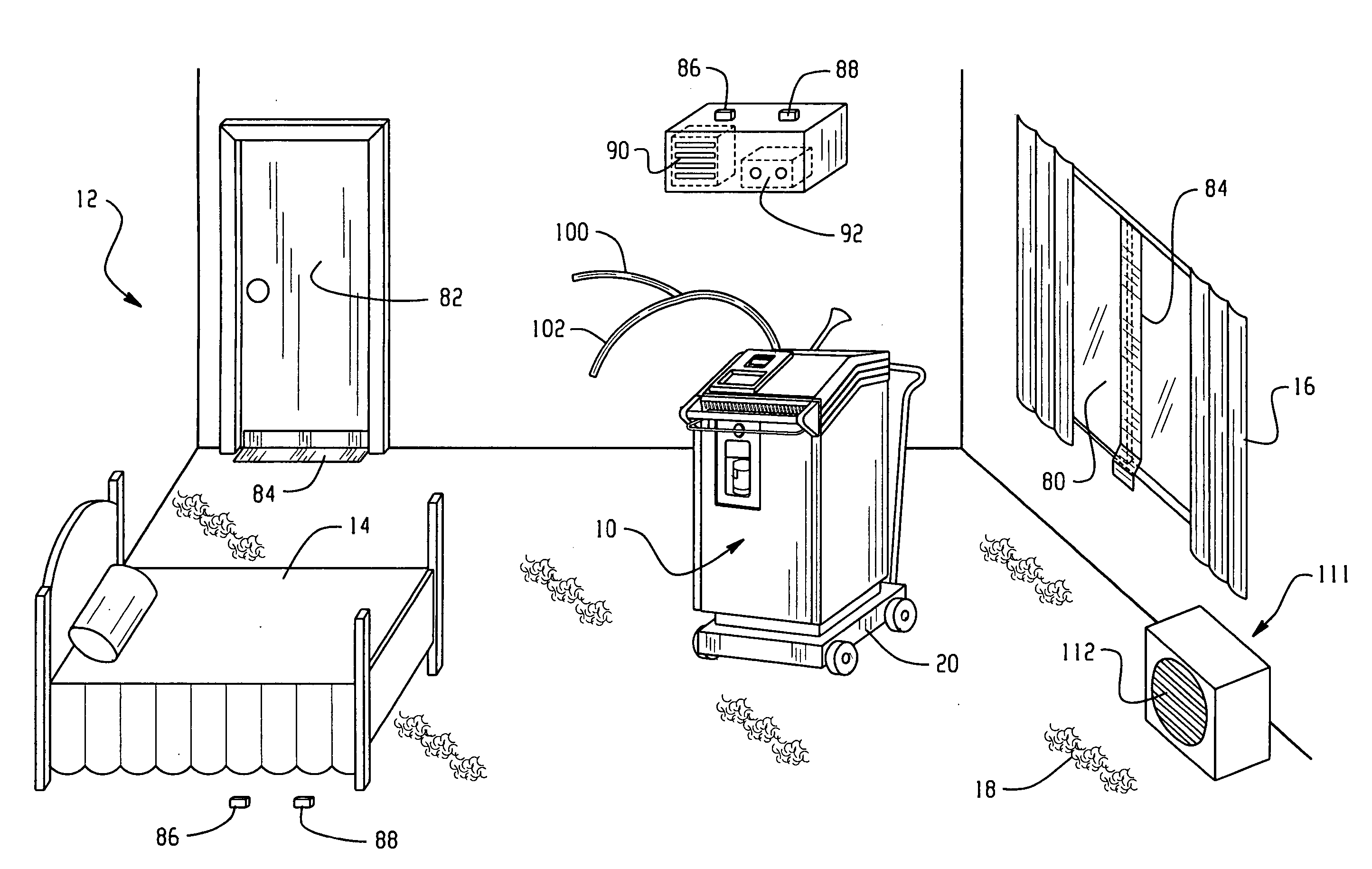
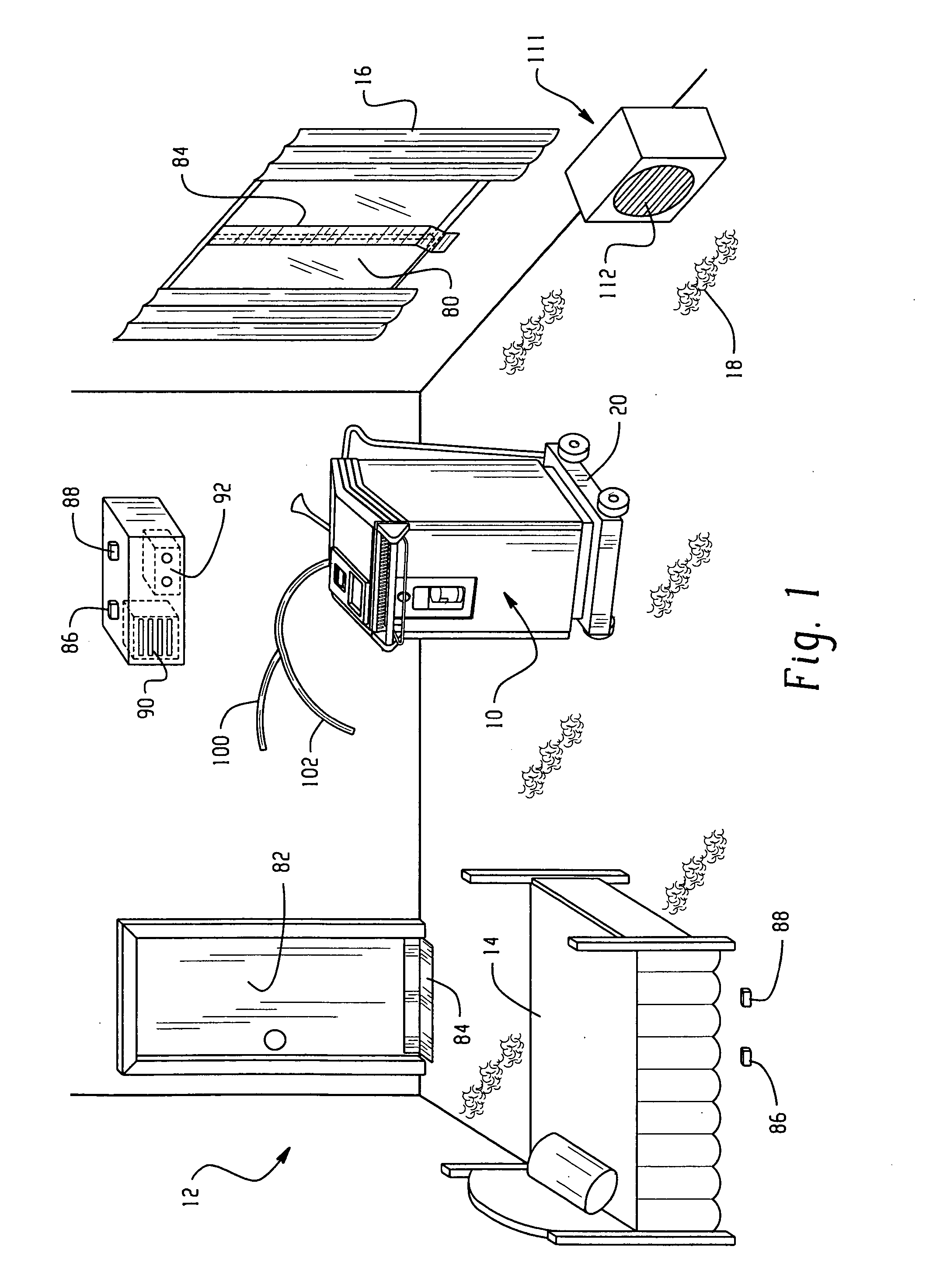
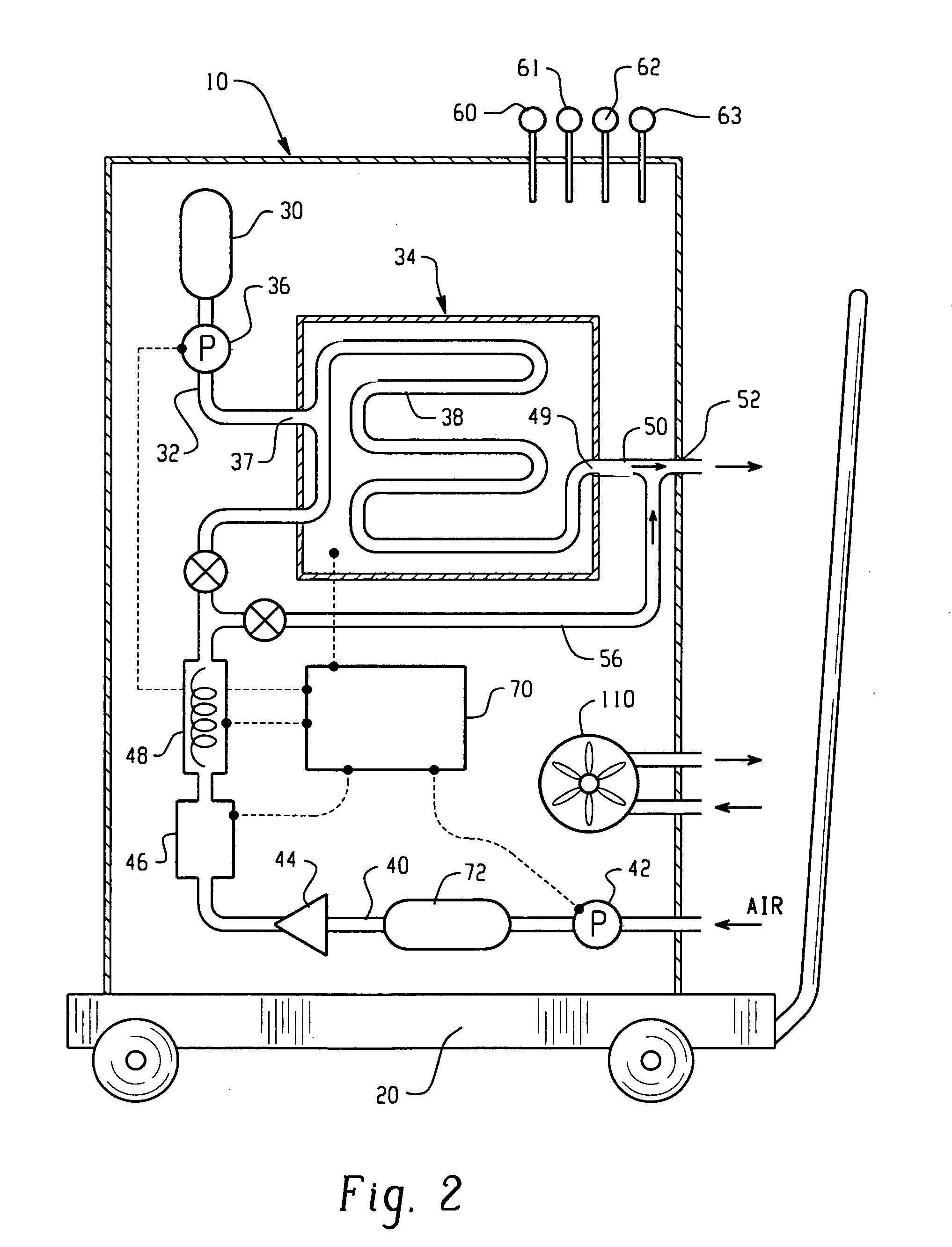
Room decontamination with hydrogen peroxide vapor
ActiveUS20060008379A1Reduce or even removeMinimize residual amountGaseous substancesDeodrantsHotel roomVapor generator
A system for microbially and / or chemically decontaminating a room such as a hotel room includes a vapor generator which supplies a decontaminant vapor, such as hydrogen peroxide vapor to the room. The room is then aerated to a level at which it is safe for normal occupants to enter. By using a two step aeration, with a second step at lower humidity than the first, the concentration of residual hydrogen peroxide is reduced rapidly to safe levels of 1 ppm or less, typically about 0.5 ppm, in under four hours. The room is rendered substantially free of contaminants, such as those responsible for Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS), Norwalk virus, and unpleasant odors.
Owner:STERIS CORP
System and method of microdispensing and arrays of biolayers provided by same
InactiveUS20020090738A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsReal time analysisClinical settings
Owner:ABBOTT POINT CARE
Heat and hydrogen peroxide gas sterilization of container
The present invention discloses a method and apparatus for sterilizing containers with gas-phase hydrogen peroxide and heat on a linear form, fill and seal packaging machine. A partially formed container is subjected to multiple applications of gaseous hydrogen peroxide and hot air within a sterilization tunnel. The sterilization tunnel is maintained at a temperature greater than the condensation temperature of hydrogen peroxide. The present invention sterilizes the container allowing for filling of the container with a high acid product such as orange juice for ambient distribution. The container may be any number of possibilities such as TETRA REX TM gable top cartons, plastic bottles, and the like. The invention allows for the efficacious use of hydrogen peroxide gas having a concentration of up to 53%.
Owner:TETRA LAVAL HLDG & FINANCE SA
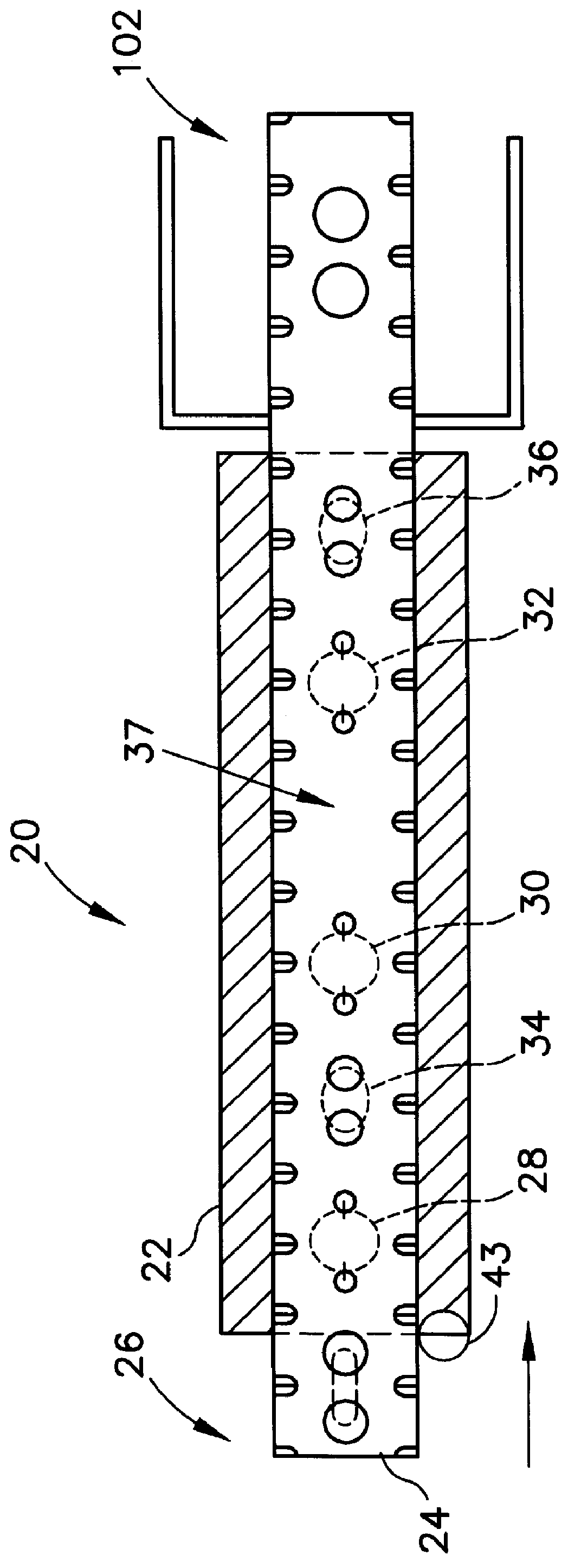
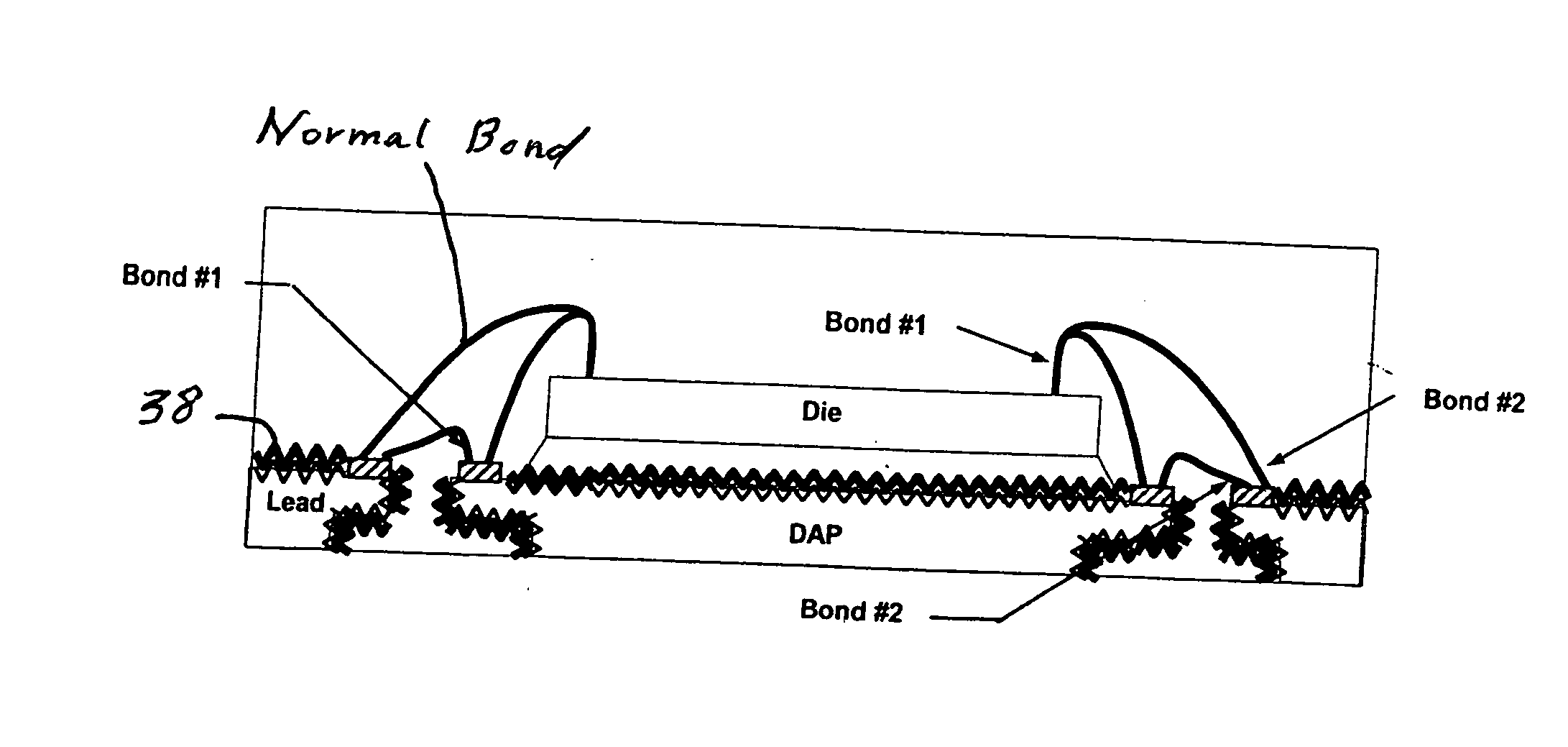
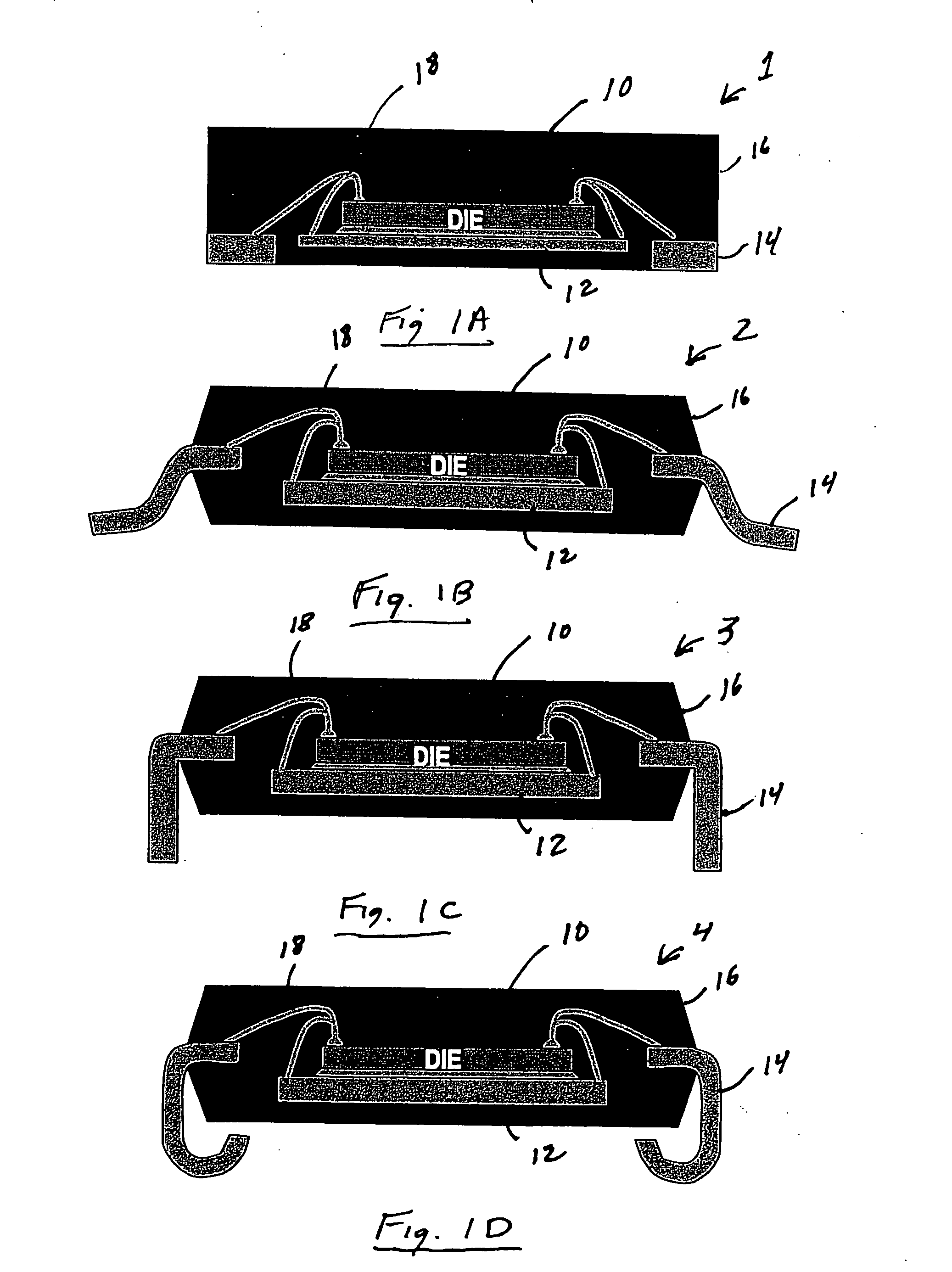
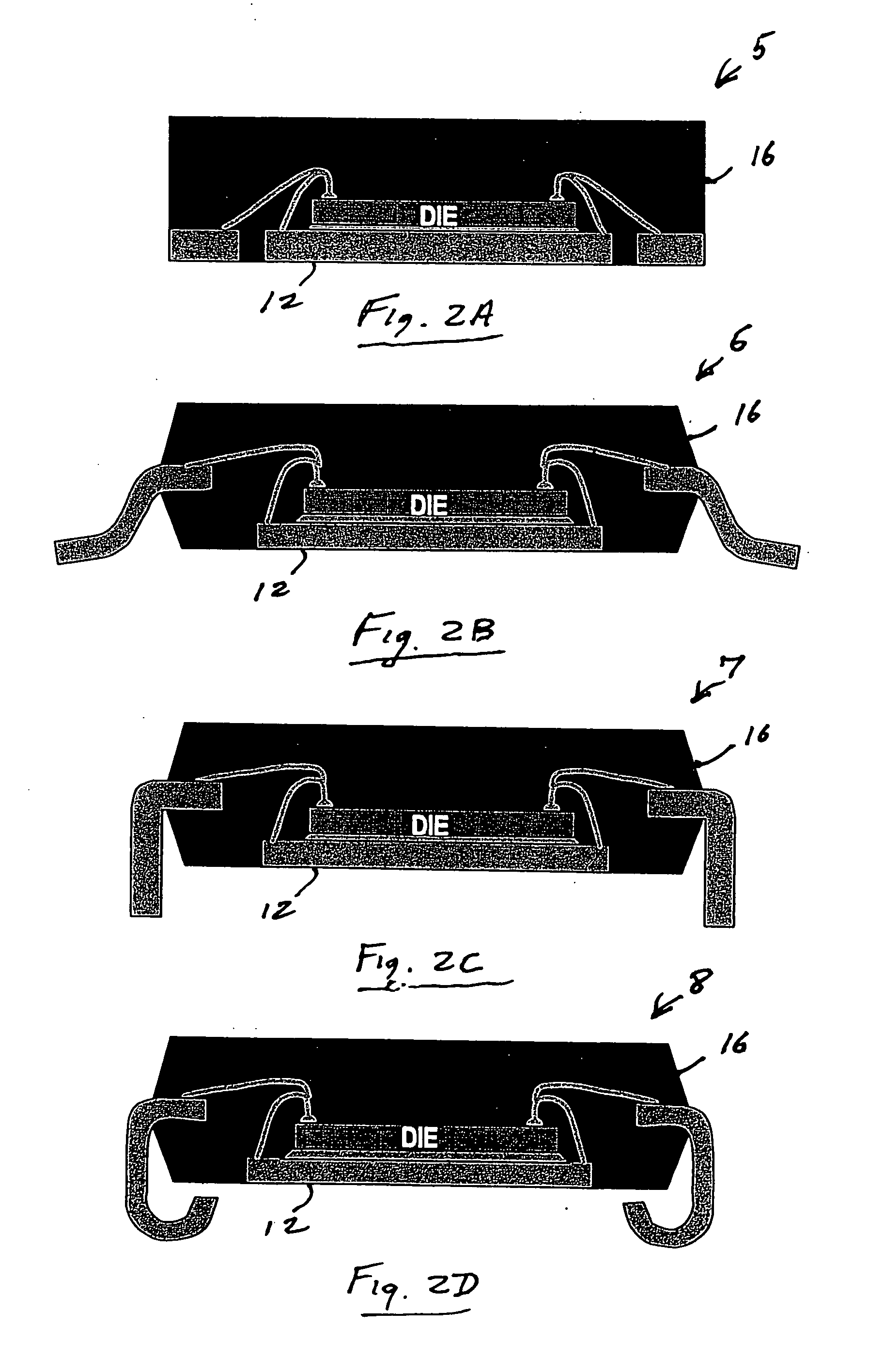
Semiconductor package including leadframe roughened with chemical etchant to prevent separation between leadframe and molding compound
InactiveUS20060097366A1Improve adhesionTrend downSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCompound aSemiconductor package
A semiconductor package contains a metal leadframe that has been specially treated by roughening it with a chemical etchant. The roughening process enhances the adhesion between the leadframe and the molten plastic during the encapsulation of the leadframe and thereby reduces the tendency of the package to separate when exposed to moisture and numerous temperature cycles. In one embodiment, the leadframe made of copper is roughened with a chemical etchant that contains sulfuric acid and hydrogen peroxide.
Owner:UTAC HEADQUARTERS PTE LTD
Filter cake degradation compositions and methods of use in subterranean operations
InactiveUS7195068B2Cleaning apparatusLiquid/gas jet drillingAcid derivativeHydrogen peroxide degradation
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for degrading filter cakes in subterranean formations, and more specifically, to improved methods and compositions for degrading filter cakes that comprise acid-soluble portions and polymeric portions. In one embodiment, the present invention provides a method of degrading a filter cake comprising an acid-soluble portion and a polymeric portion in a subterranean formation comprising the steps of: introducing a filter cake degradation composition comprising a delayed-release acid component and a delayed-release oxidizer component to a well bore penetrating the subterranean formation; allowing the delayed-release acid component to release an acid derivative and the delayed-release oxidizer component to release an acid-consuming component; allowing the acid-consuming component to interact with the acid derivative to delay a reaction between at least a portion of the acid derivative and at least a portion of the acid-soluble portion of the filter cake and to produce hydrogen peroxide; allowing the acid derivative to degrade at least a portion of the acid-soluble portion of the filter cake after a delay period; and allowing the hydrogen peroxide to degrade at least a portion of the polymeric portion of the filter cake.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Production of peracids using an enzyme having perhydrolysis activity
A method is provided for producing peroxycarboxylic acids from carboxylic acid esters. More specifically, carboxylic acid esters are reacted with an inorganic peroxide, such as hydrogen peroxide, in the presence of an enzyme catalyst having perhydrolysis activity derived from Bacillus sp. to produce peroxycarboxylic acids.
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
Oral care composition with cross-linked polymer peroxide
InactiveUS20060045854A1Low costImprove convenienceCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsCross-linkWhitening Agents
Oral care compositions comprising: (a) a peroxide complex comprising a peroxide component and an N-vinyl heterocyclic polymer (e.g., poly-N-vinyl polylactam, or poly-N-vinyl-polyimide); (b) a whitening agent (e.g., hydrogen peroxide); and (c) an orally acceptable carrier. In one embodiment, the carrier comprises a film forming material. Methods are also provided for making an oral care composition comprising: (a) mixing a whitening agent, silicone adhesive and carrier fluid to form a homogenous mixture; (b) adding a peroxide complex to said homogenous mixture, wherein said complex comprises hydrogen peroxide and an N-vinyl heterocyclic polymer; and (c) mixing under vacuum.
Owner:COLGATE PALMOLIVE CO
Enzymatic production of peracids using perhydrolytic enzymes
A process is provided to produce a concentrated aqueous peracid solution in situ using at least one enzyme having perhydrolase activity in the presence of hydrogen peroxide (at a concentration of at least 500 mM) under neutral to acidic reaction conditions from suitable carboxylic acid esters (including glycerides) and / or amides substrates. The concentrated peracid solution produced is sufficient for use in a variety of disinfection and / or bleaching applications.
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
Hydrogen peroxide disinfectant with increased activity
InactiveUS6346279B1High activityReduced activityBiocideInorganic phosphorous active ingredientsDisinfectantPhosphoric acid
An acidic aqueous hydrogen peroxid solution is provided, with improved disinfectant activity. Concentrated solutions preferably contain up to about 8% and as-used concentrations contain about 0.5% peroxide. The solution also contains from 0.1 to 5.0% of at least one acid compound, e.g. phosphoric and / or a phosphonate with from 1 to 5 phosphonic acid groups, and from 0.02 to 5% of at least one anionic surfactant. The surfactant is selected from C8 to C16-alkyl aryl sulphonic acids, sulphonated C12 to C22 carboxylic acids, C8 to C22-alkyl diphenyl oxide sulphonic acids, naphthalene sulphonic acids, C8 to C22 alkyl sulphonic acids, and alkali metal and ammonium salts thereof, and alkali metal C8 to C18 alkyl sulphates, and mixtures thereof. Most preferably the solution has an emulsifier, e.g. a salt of an alkylated diphenyl oxide. The solution may also contain corrosion inhibitors and / or lower alcohols.
Owner:VIROX TECH
Integrated oxygen generation and carbon dioxide absorption method apparatus and systems
InactiveUS20050031522A1Improvement in mission durationLower acquisition costsFuel cell auxillariesMachines/enginesChemical speciesCo2 absorption
A method for producing oxygen and absorbing carbon dioxide in a single operation using a solution that contains an oxygen source and a redox partner that can react to form oxygen and a chemical species that can form an insoluble carbonate to precipitate and chemically store carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide is introduced into the solution and the carbonate precipitates as the oxygen is generated. In particular, the invention uses an aqueous solution of permanganate and hydrogen peroxide that react in the presence of a catalyst to produce oxygen and manganese (II) ions. Carbon dioxide gas introduced into the solution reacts with the manganese (II) ions to precipitate manganese carbonate. Other cations capable of reacting with carbon dioxide to form an insoluble carbonate, for example calcium, barium and magnesium, may also be added to the solution to precipitate carbonate salts. Calcium permanganate may used as a source of both calcium and permanganate.
Owner:CAPITAL MANAGEMENT +1
Membrane and electrode structure for implantable sensor
ActiveUS7336984B2Limited accessDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEnvironmental designExcess oxygen
The invention is the design of a biological measuring device for the determination of the concentration of biomolecules (e.g. glucose) in an environment which is designed for implantation into an individual or for use in the context of an external apparatus. The device contains a composite membrane that is essentially entirely permeable to oxygen and permeable to larger biomolecules only in discrete hydrophilic regions. The membrane diffusionally limits the access of biomolecules to an enzyme, present in the hydrophilic region that catalyzes the oxidation of the biomolecule to produce hydrogen peroxide. A sensor in communication with the hydrophilic region is used to determine the amount of product produced or the amount of excess oxygen present allowing for the concentration of the biomolecule to be determined.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Functional coatings and designs for medical implants
InactiveUS20050159805A1Function increaseFunctionality can be affectedStentsSurgeryHydrogen peroxide breakdownHydrogen
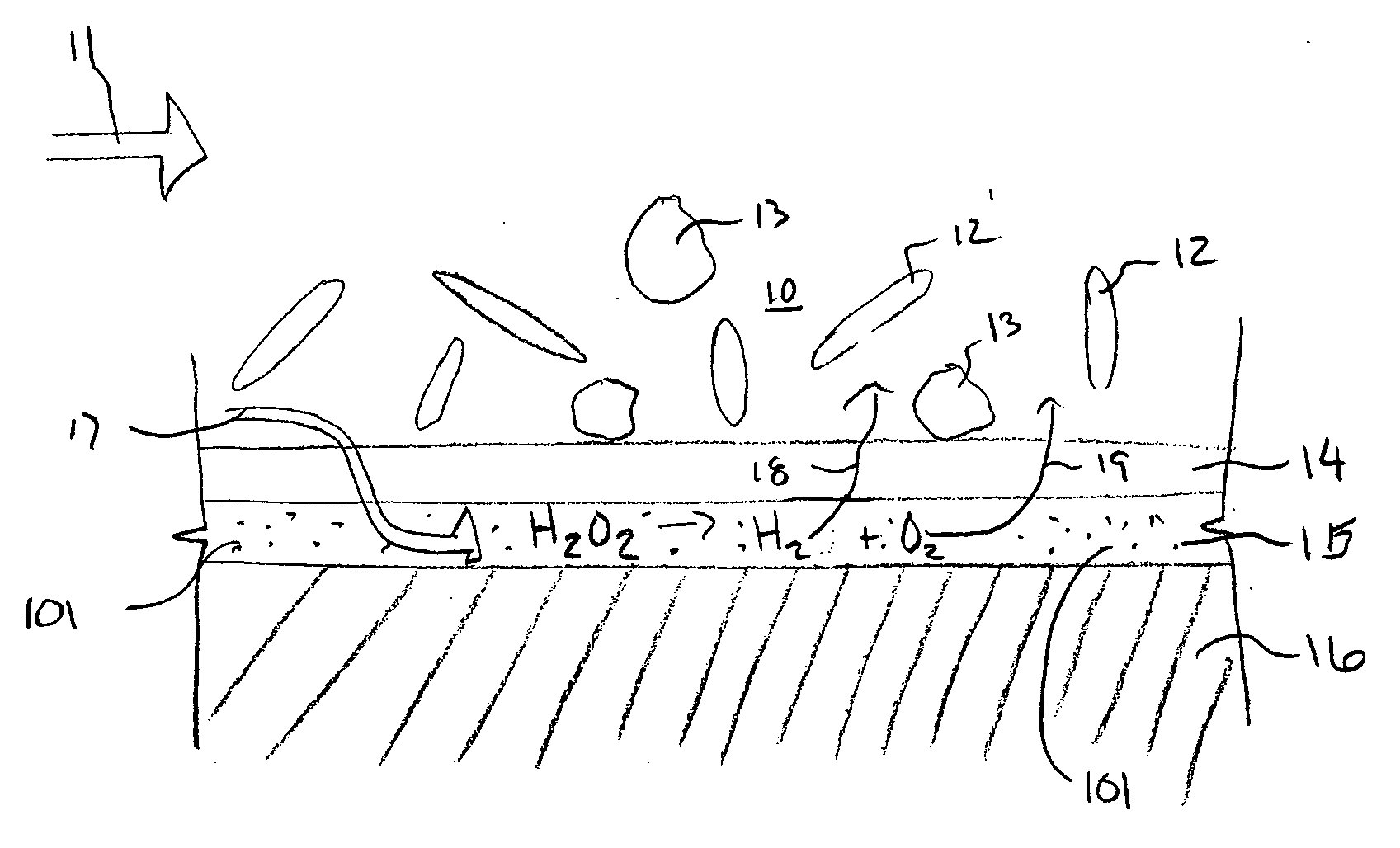
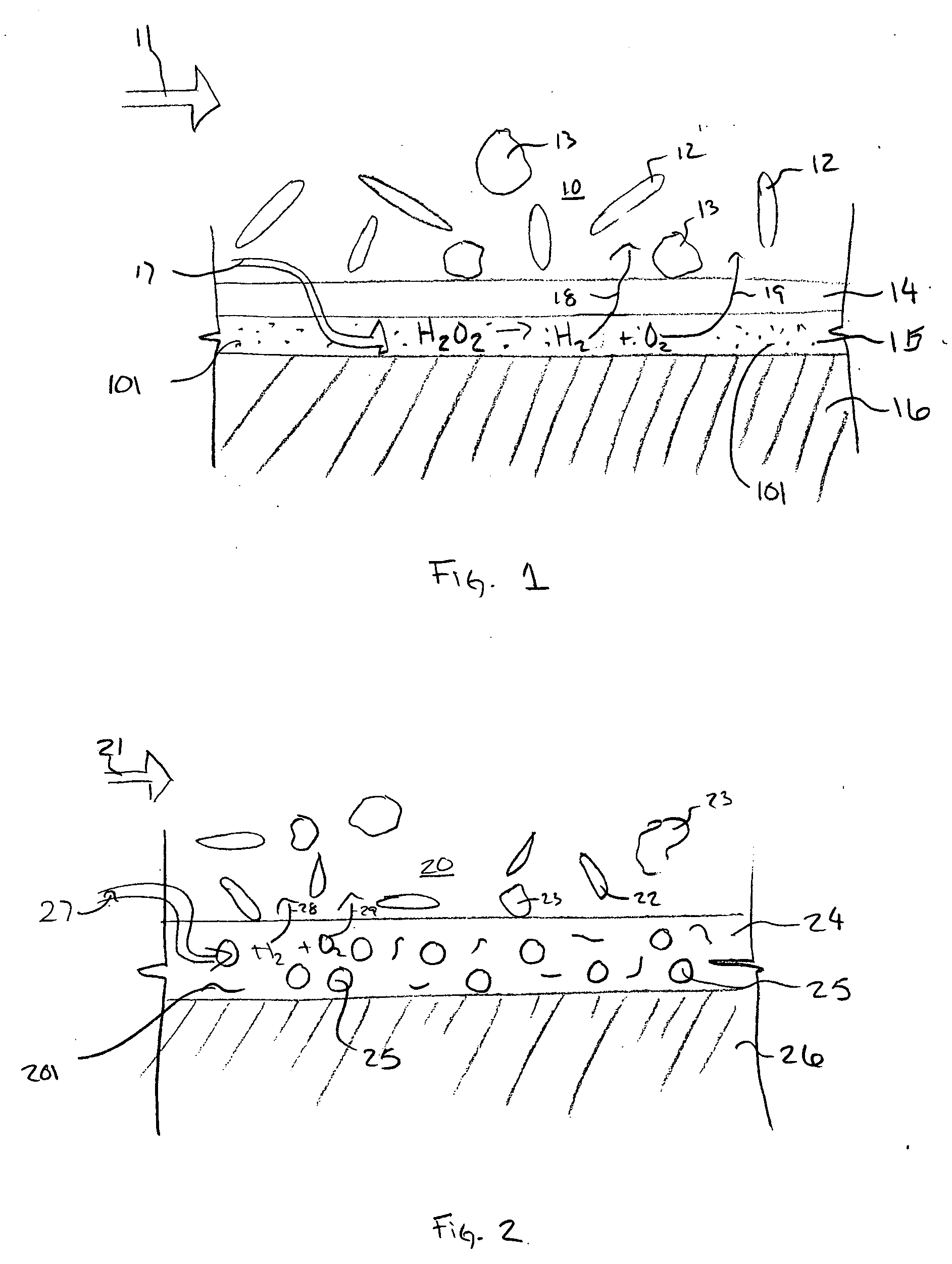
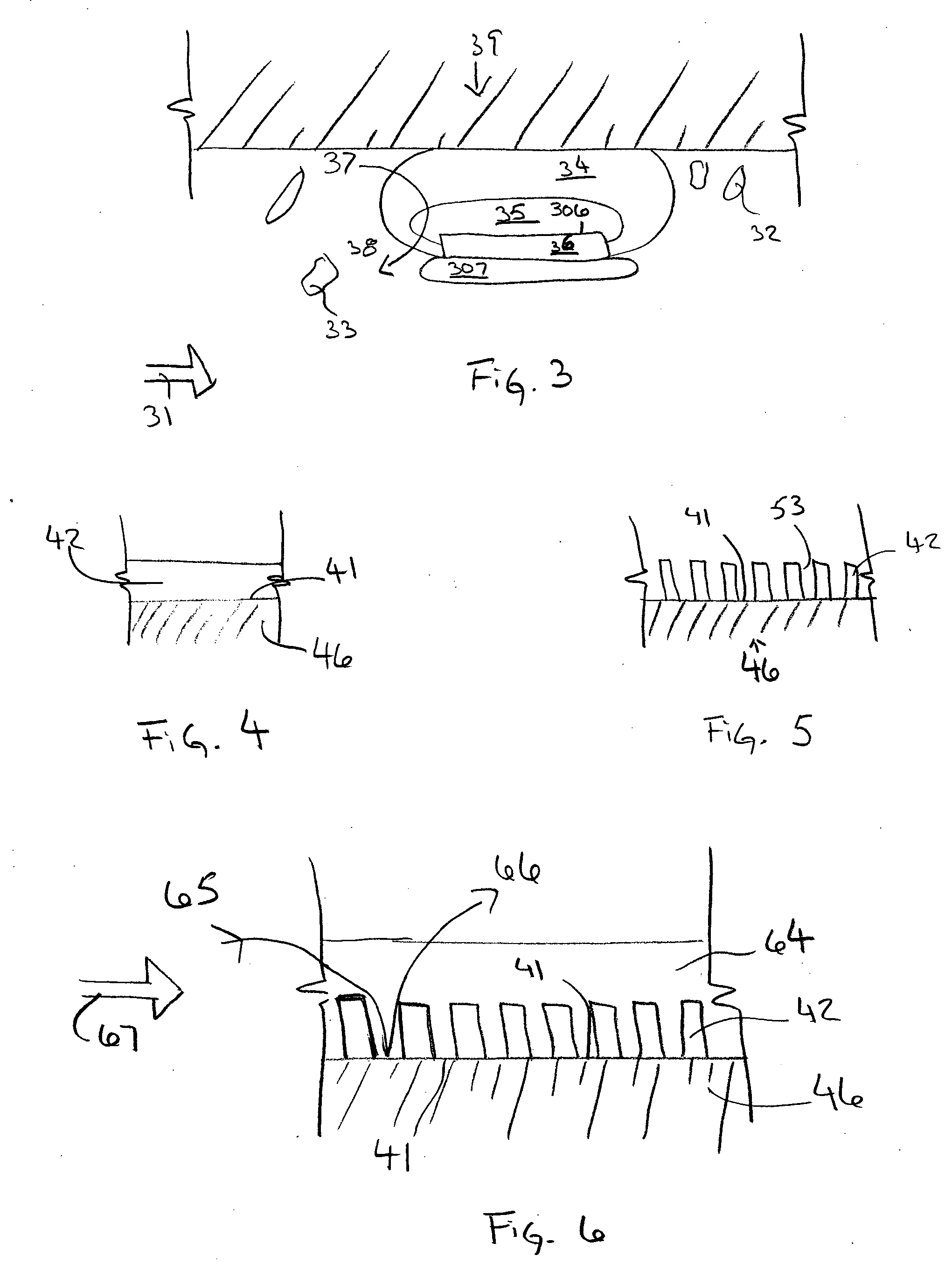
The present invention regards an implant that may be uniquely shaped to enhance its functionality and that may also be coated with a coating system that affects its functionality. In one embodiment the implant may have a first surface that is covered with a filter material, the filter material being in contact with a catalyst that promotes the decomposition of Hydrogen Peroxide into Hydrogen and Oxygen. In this and other embodiments, this filter material may be made from ceramic materials and may be meso-porous. In another embodiment, the implant may or may not be coated with this system and may have at least one strut with a tapered cross-section, the cross-section becoming smaller in area when moving from a reference point on the inside of the implant to the outside of the implant.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Method for vaporizing a fluid using an electromagnetically responsive heating apparatus
InactiveUS20050095168A1Increase productionReduced resistive electrical power loadSteam generation heating methodsGrinding feed controlElectromagnetic responseEngineering
A vaporizer heating apparatus is comprised of electromagnetically responsive material and electrically non-conductive material. A antimicrobial fluid to be vaporized, such as water or hydrogen peroxide solution, is supplied to the heating apparatus where it is converted to a vapor. In one embodiment of the present invention, electromagnetically responsive material particulate is embedded into the electrically non-conductive material. In another embodiment of the present invention, a microwave generator is used to produce heat.
Owner:AMERICAN STERILIZER CO
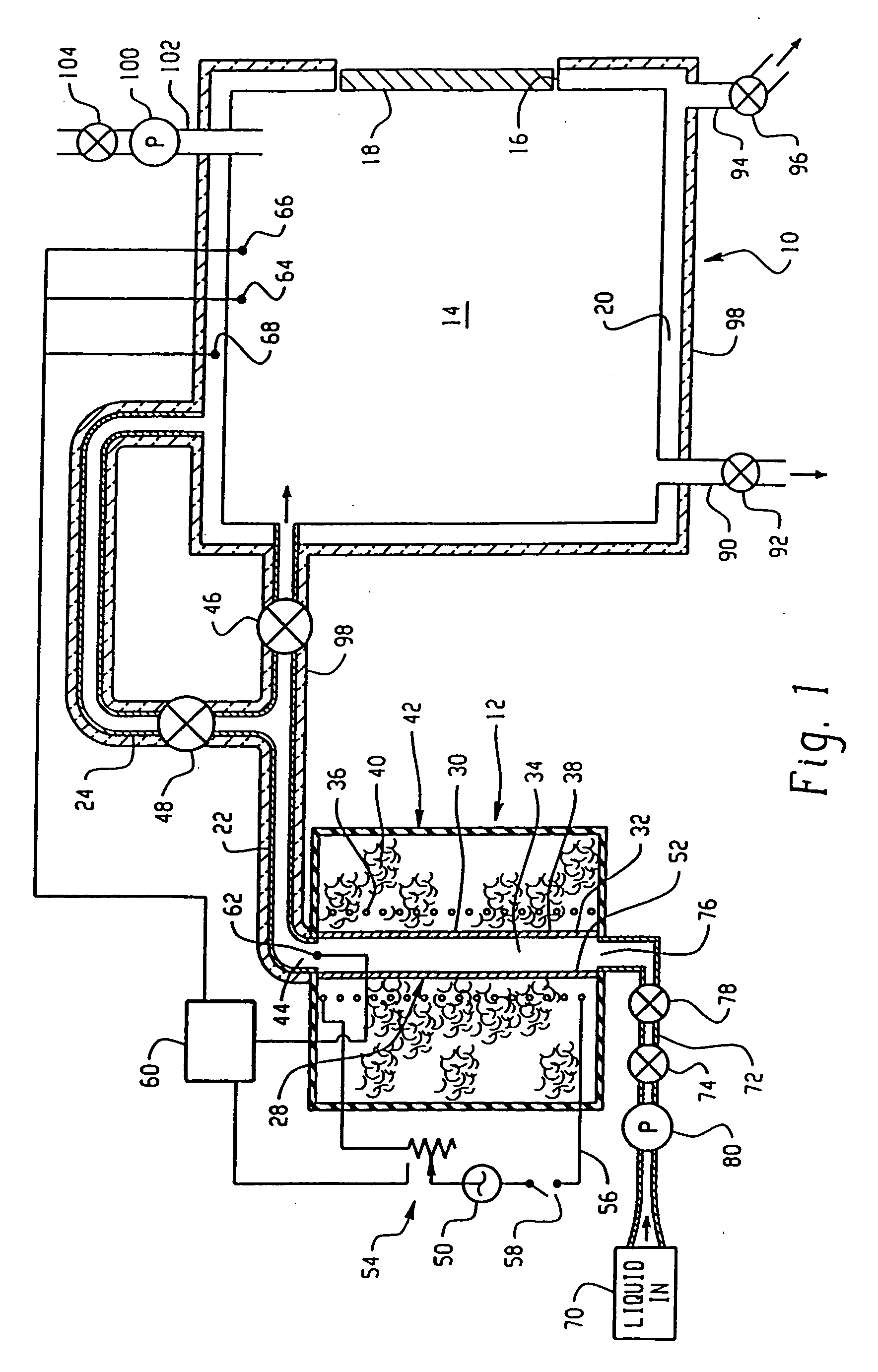
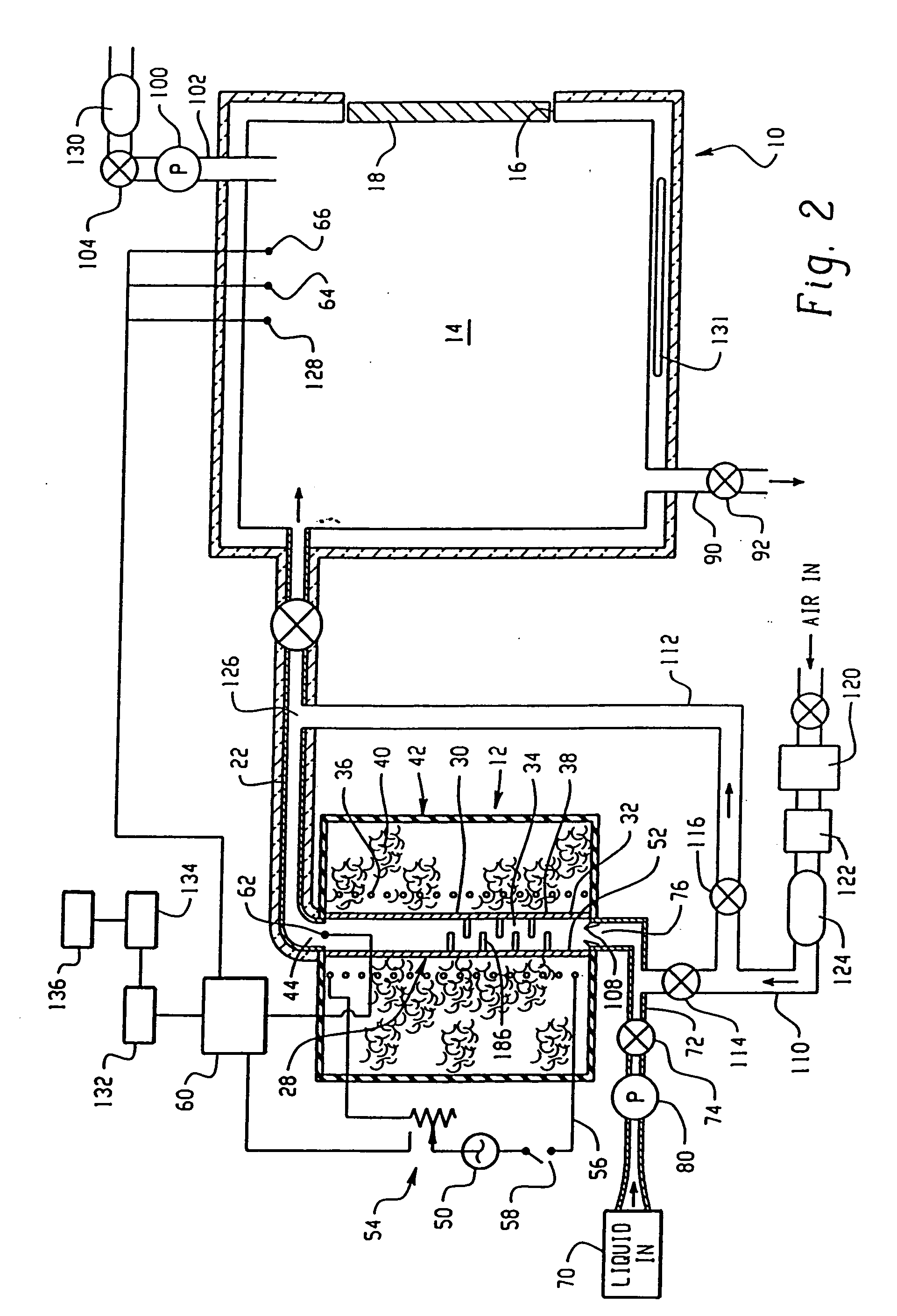
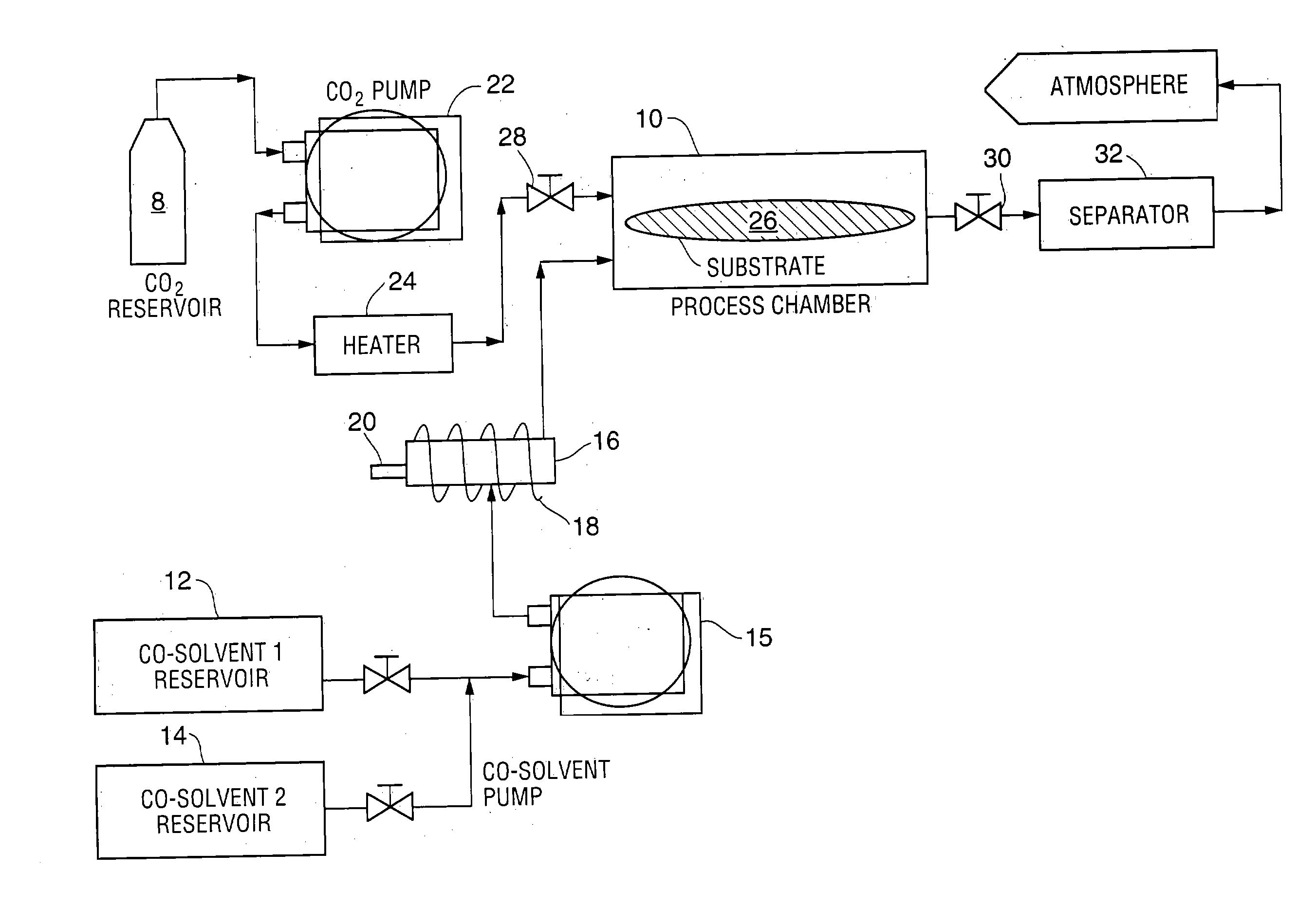
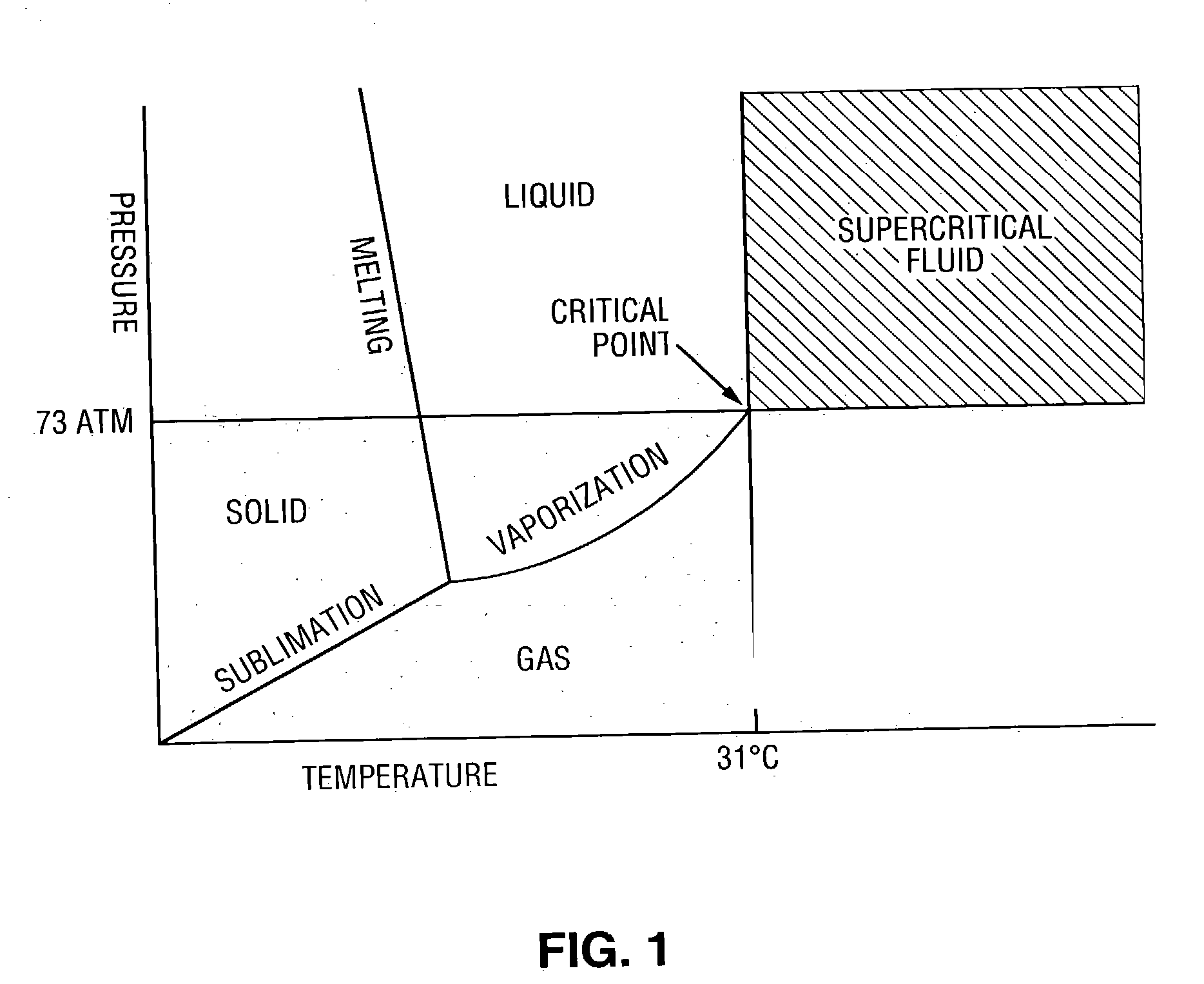
Compositions and method for removing photoresist and/or resist residue at pressures ranging from ambient to supercritical
InactiveUS20040050406A1Accelerate photoresist strippingImprove reaction kineticsNon-surface-active detergent compositionsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistAlcohol
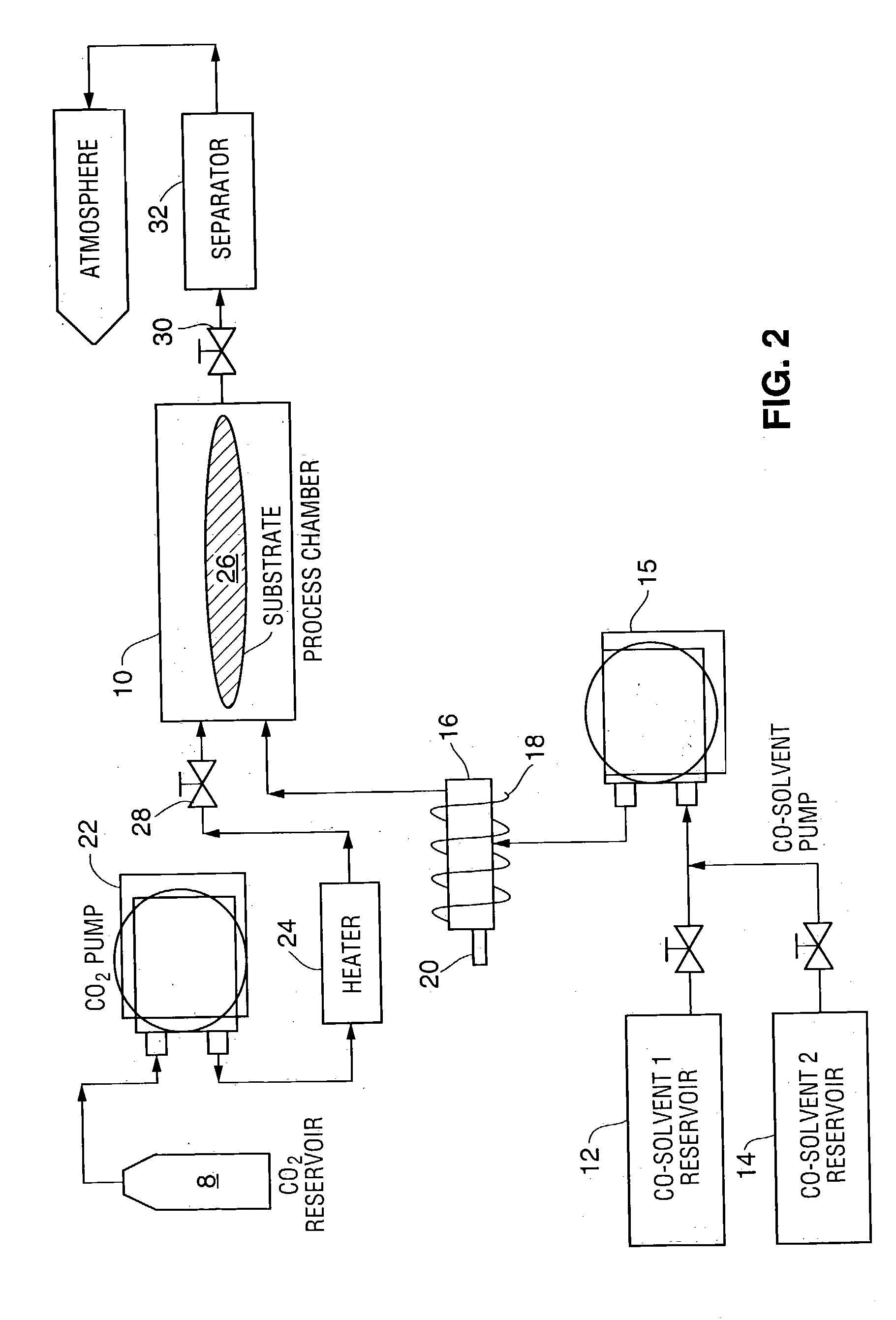
A method of enhancing removal of photoresist and / or resist residue from a substrate includes exposing the substrate to an environmentally friendly, non-hazardous co-solvent mixture comprising a carbonate, an oxidizer and an accelerator. The stripping process may be performed under ambient conditions, or in the presence of a supercritical fluid such as supercritical carbon dioxide with the supercritical cleaning step itself being a desirable "green" process. In one embodiment, the co-solvent mixture includes propylene carbonate, benzyl alcohol, hydrogen peroxide and an accelerator such as formic acid. If desired, supercritical carbon dioxide in combination with a second co-solvent mixture may be subsequently applied to the substrate to rinse and dry the substrate. In one embodiment, the second co-solvent mixture includes a lower alkyl alcohol such as isopropyl alcohol.
Owner:SCP GLOBAL TECH INC
Sterilization method and apparatus
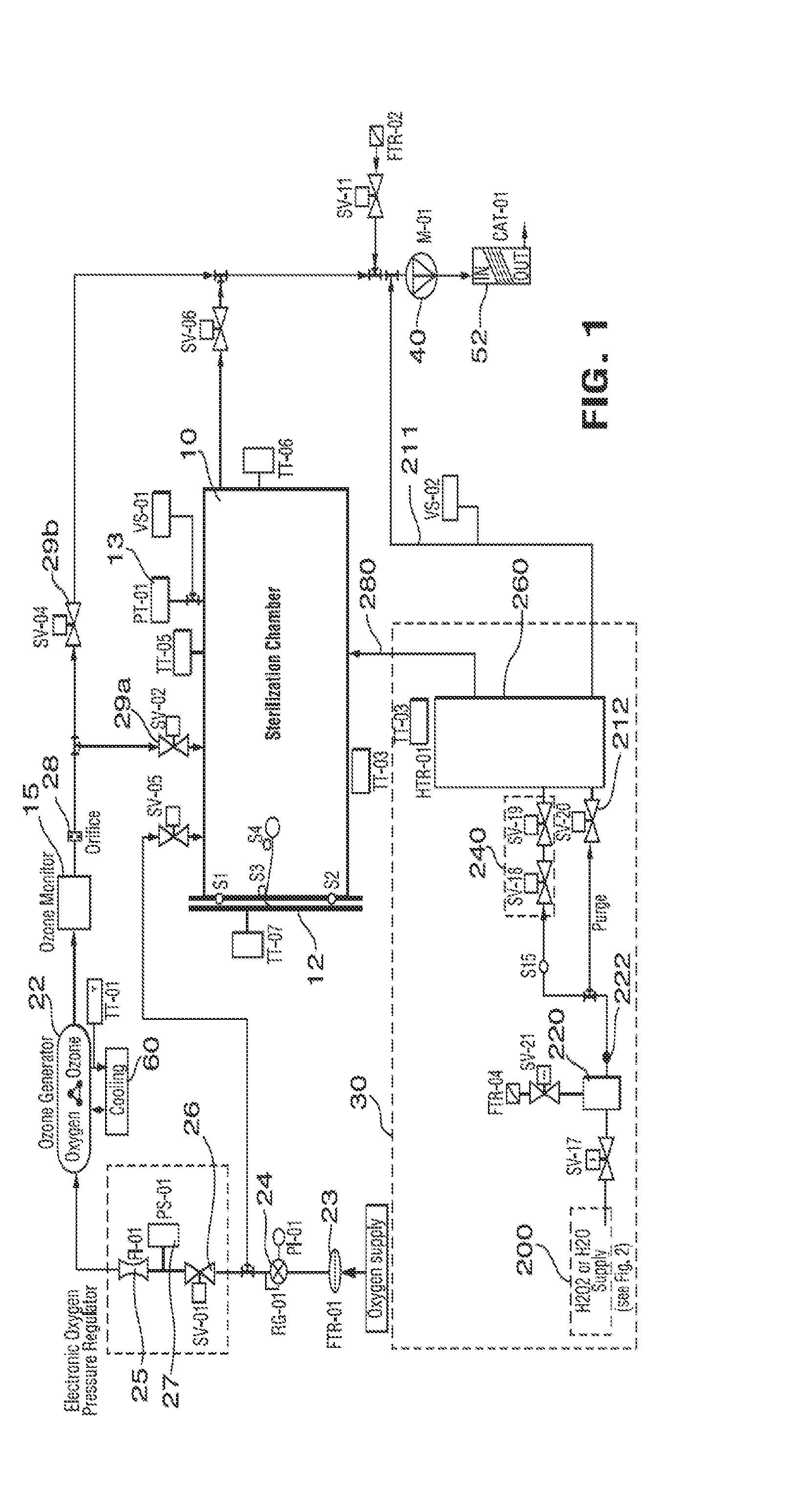
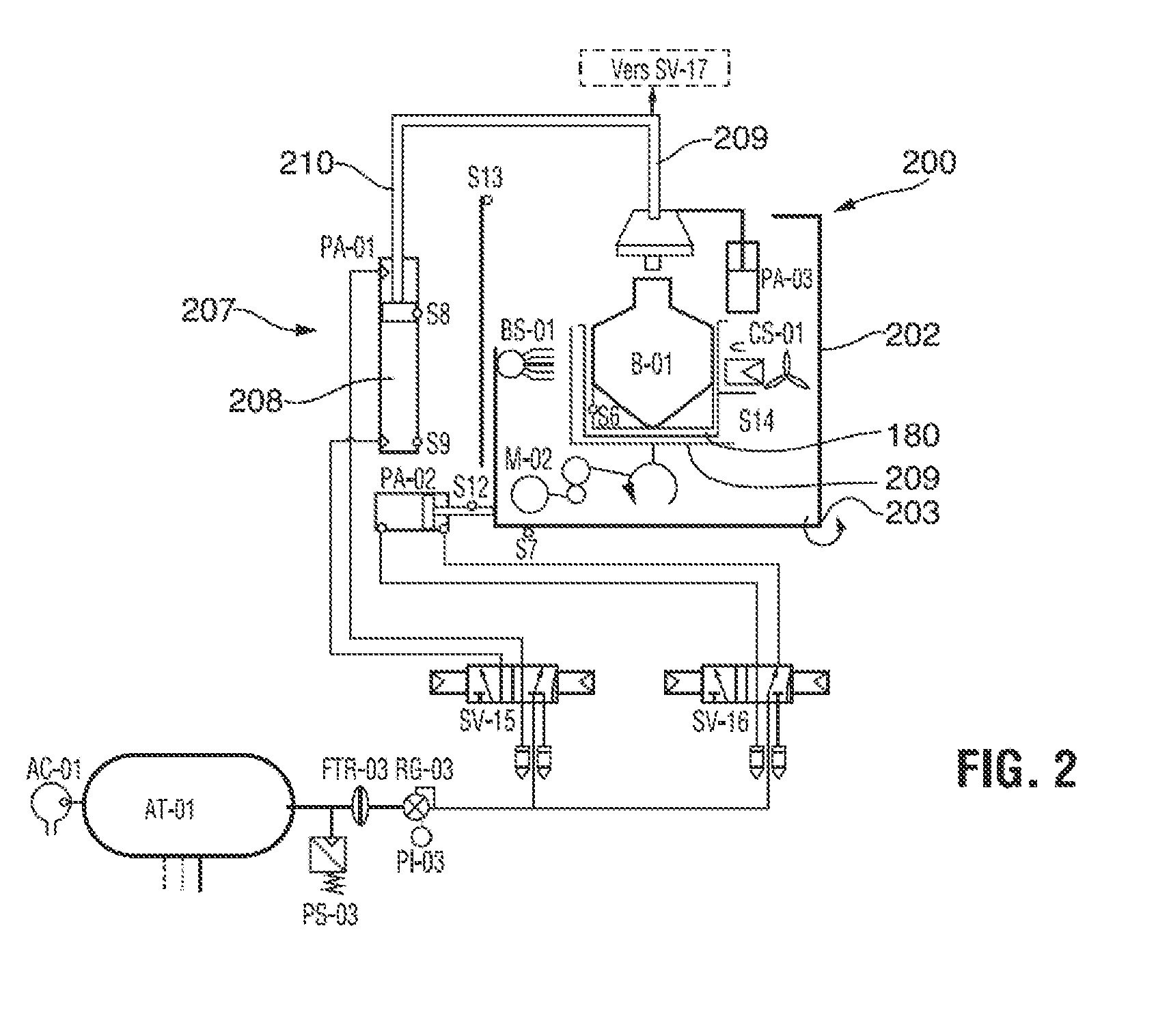
ActiveUS20110076192A1Reduce disadvantagesReduce humiditySamplingSupporting meansDecompositionWater vapor
A method of sterilizing an article by sequentially exposing the article to hydrogen peroxide and ozone is disclosed. The article is exposed under vacuum first to an evaporated aqueous solution of hydrogen peroxide and subsequently to an ozone containing gas. The exposure is carried out without reducing the water vapor content of the sterilization atmosphere, the water vapor content being derived from the aqueous solvent of the hydrogen peroxide solution and from the decomposition of the hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen. The complete sterilization process is carried out while the chamber remains sealed and without removal of any component of the sterilization atmosphere. For this purpose, the chamber is initially evacuated to a first vacuum pressure sufficient to cause evaporation of the aqueous hydrogen peroxide at the temperature of the chamber atmosphere. The chamber is then sealed for the remainder of the sterilization process and during all sterilant injection cycles. Keeping the chamber sealed and maintaining the hydrogen peroxide and its decomposition products in the chamber for the subsequent ozone sterilization step results in a synergistic increase in the sterilization efficiency and allows for the use of much lower sterilant amounts and sterilization cycle times than would be expected from using hydrogen peroxide and ozone in combination.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
Topical formulations and delivery systems
InactiveUS7060253B1Improves effervescenceGood removal effectBiocideAerosol deliveryFoaming agentActive agent
A system for delivering a chemical agent in the form of a spray or foam, which in a preferred embodiment involves the use of an aerosol dispenser to deliver a formulation containing both an anionic surface active agent such as sodium lauryl sulfate as a foaming agent and a chemical agent such as either hydrogen peroxide as a disinfecting chemical agent or natural sea water.
Owner:PHYLOMED CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com