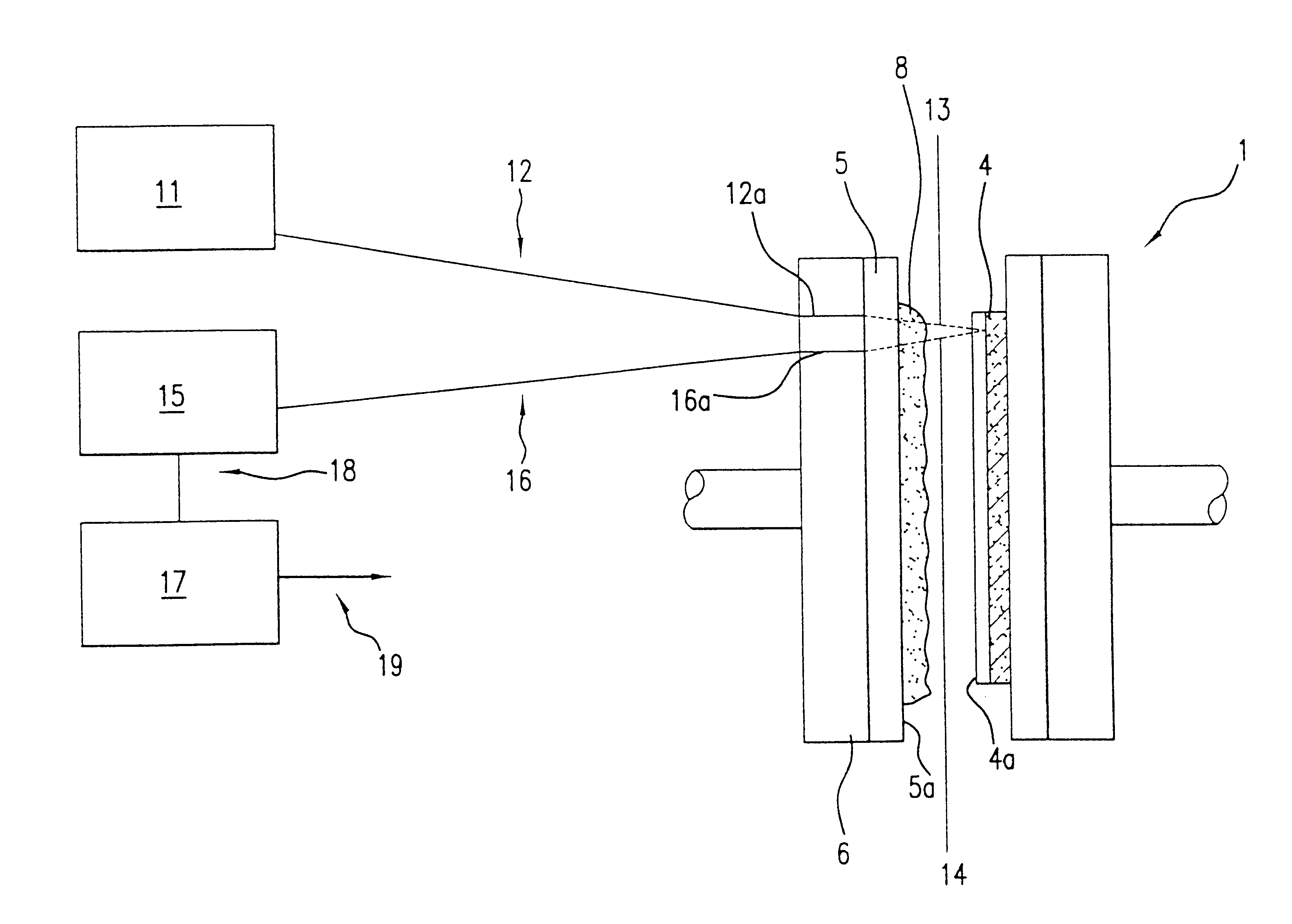
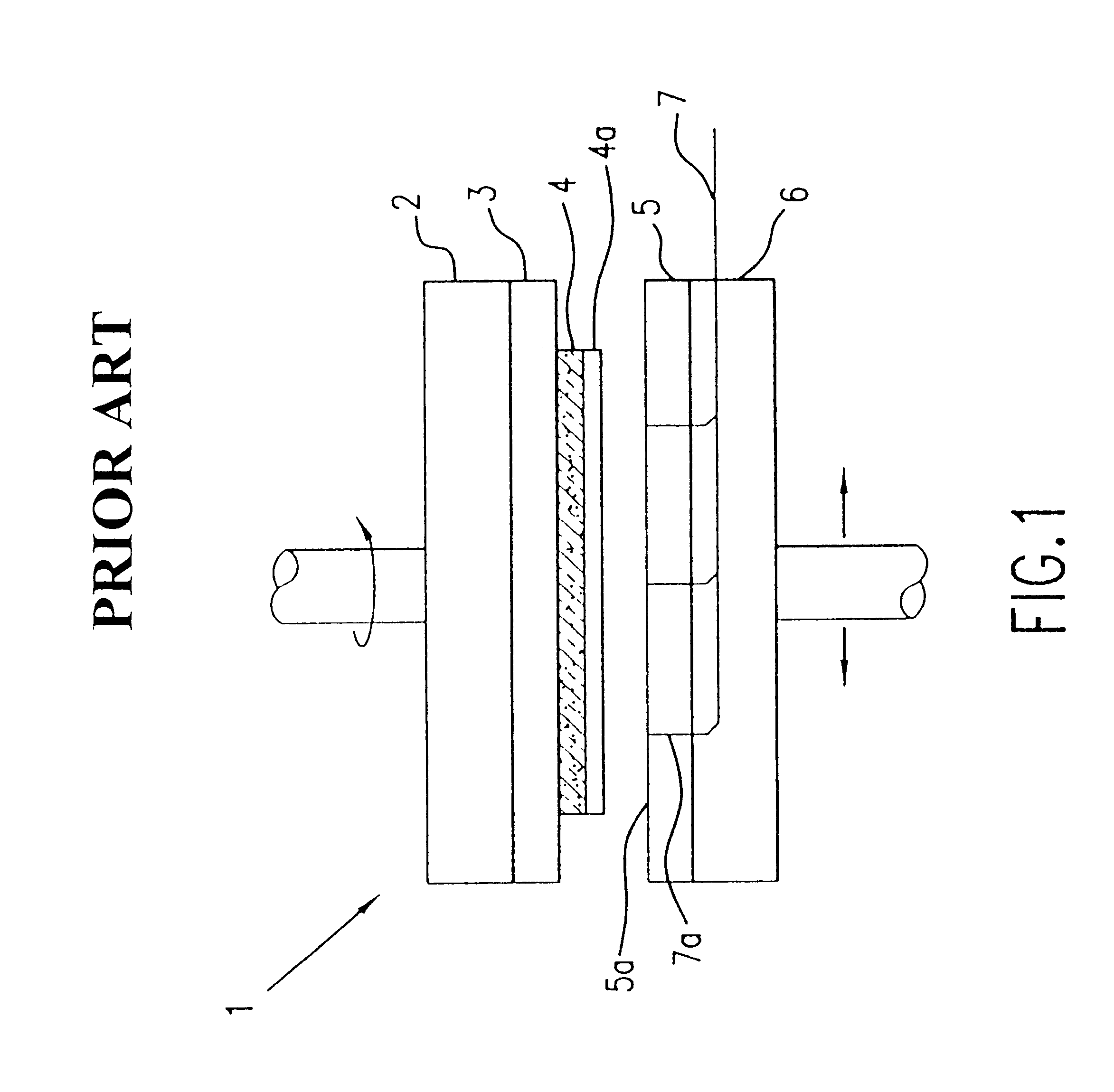
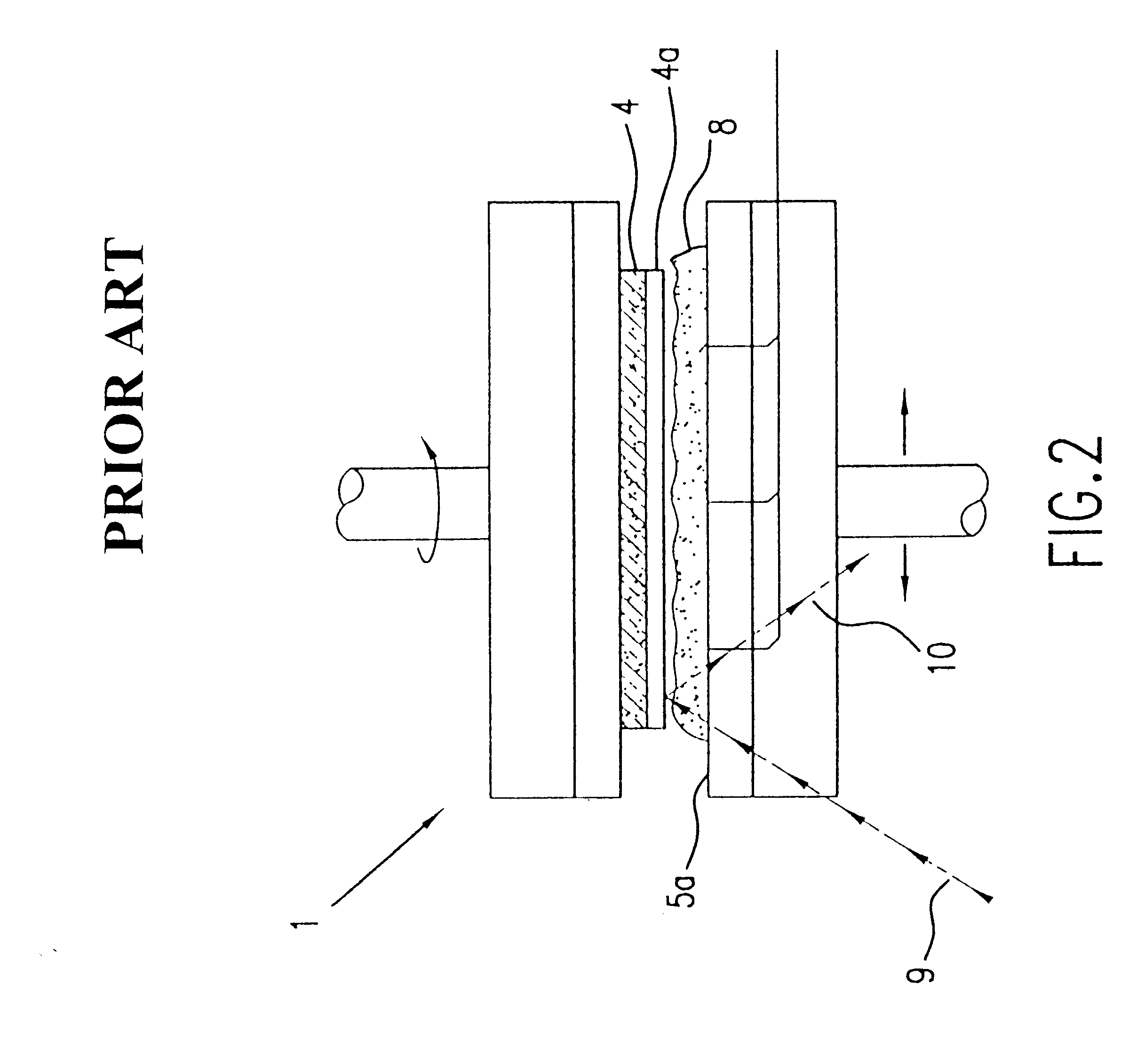
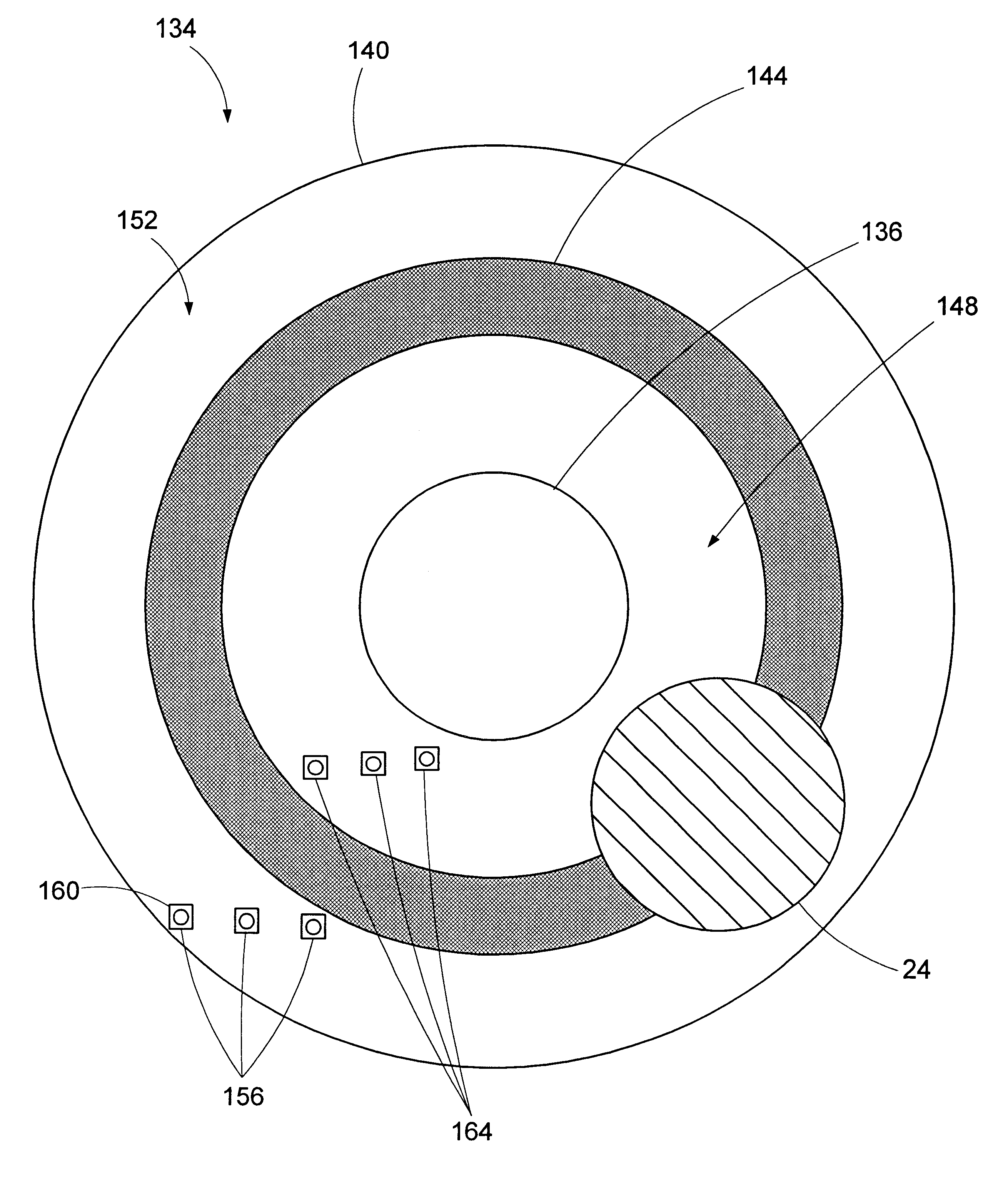
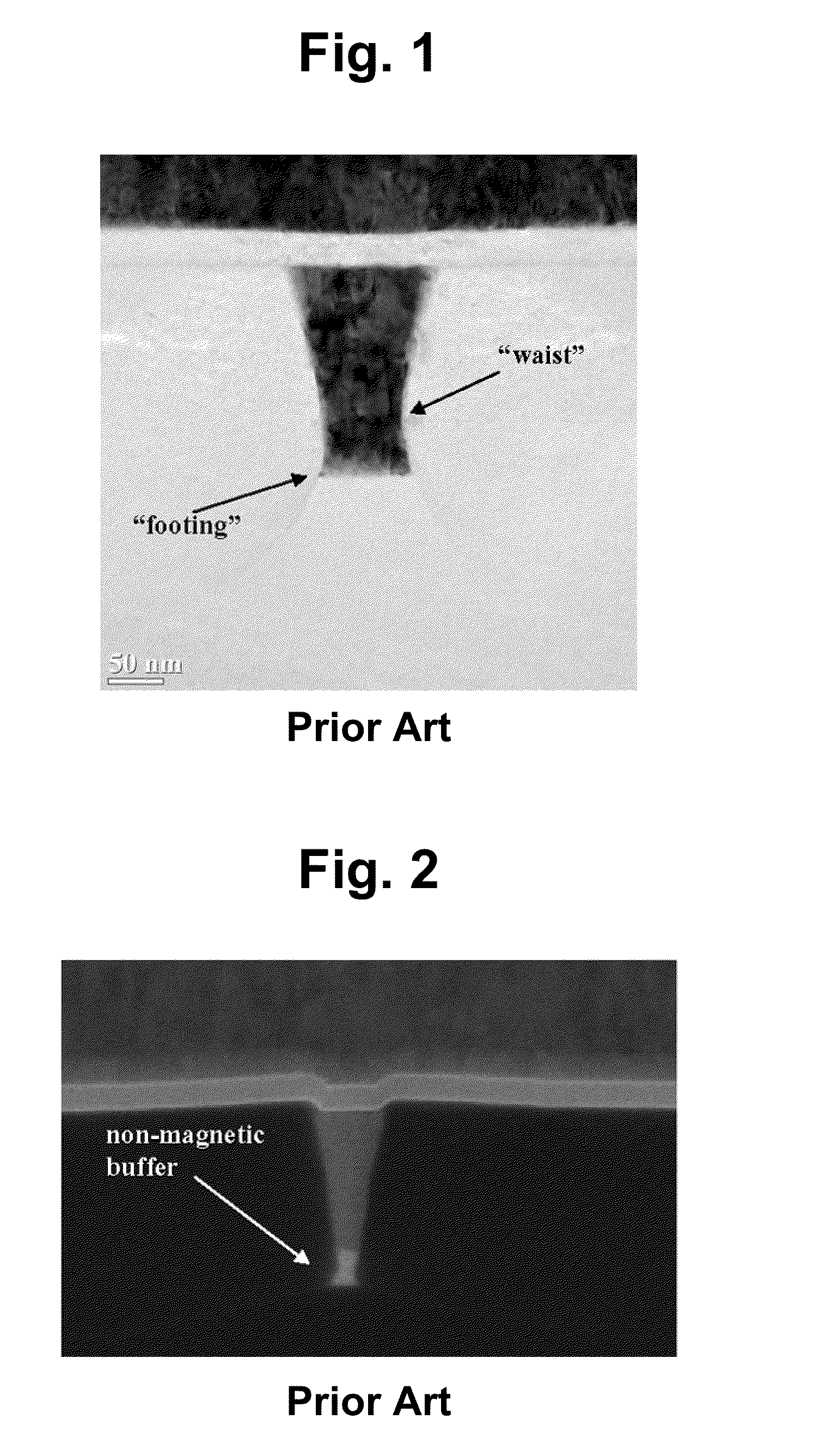
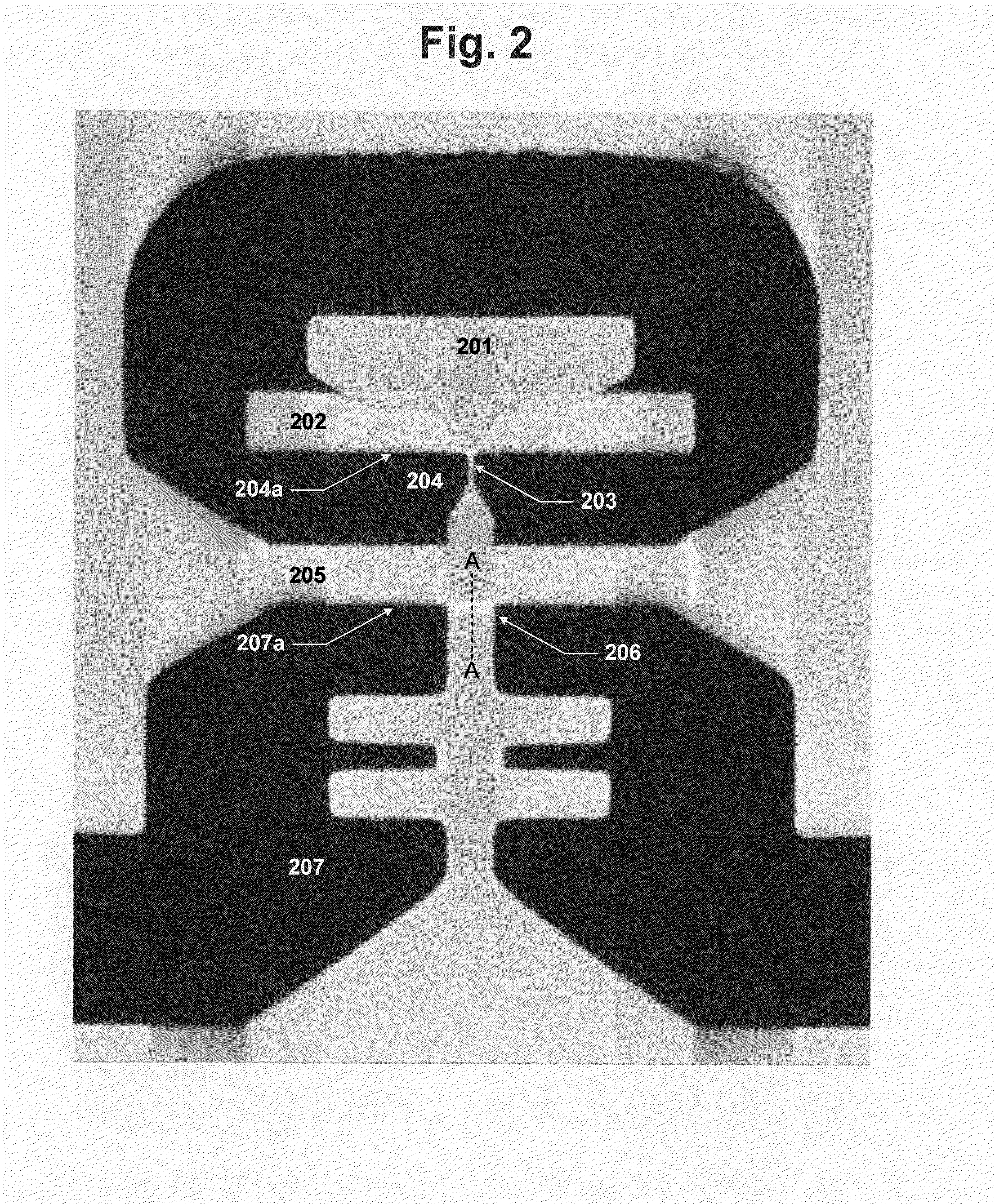Patents
Literature
11093results about "Grinding feed control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
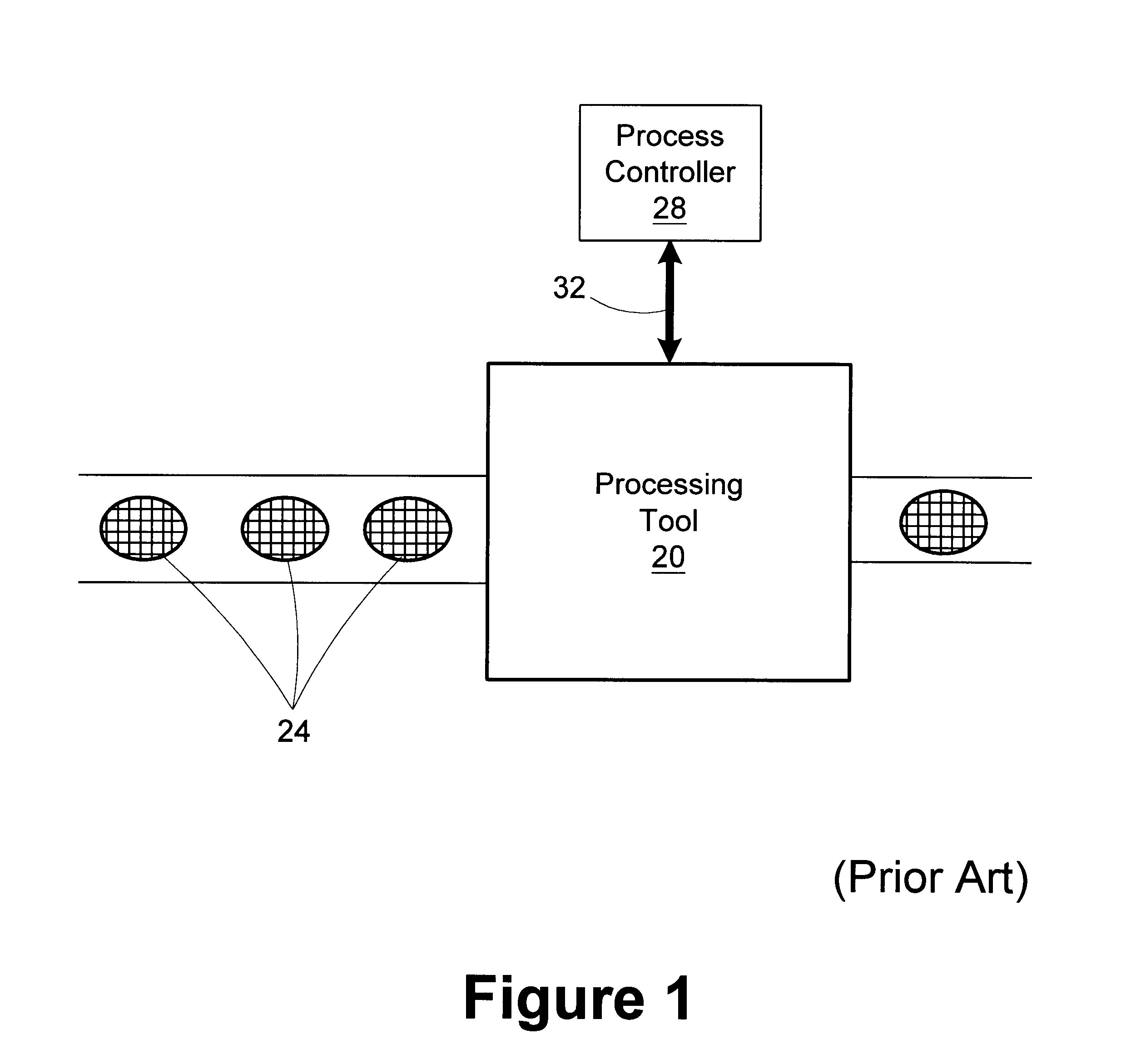
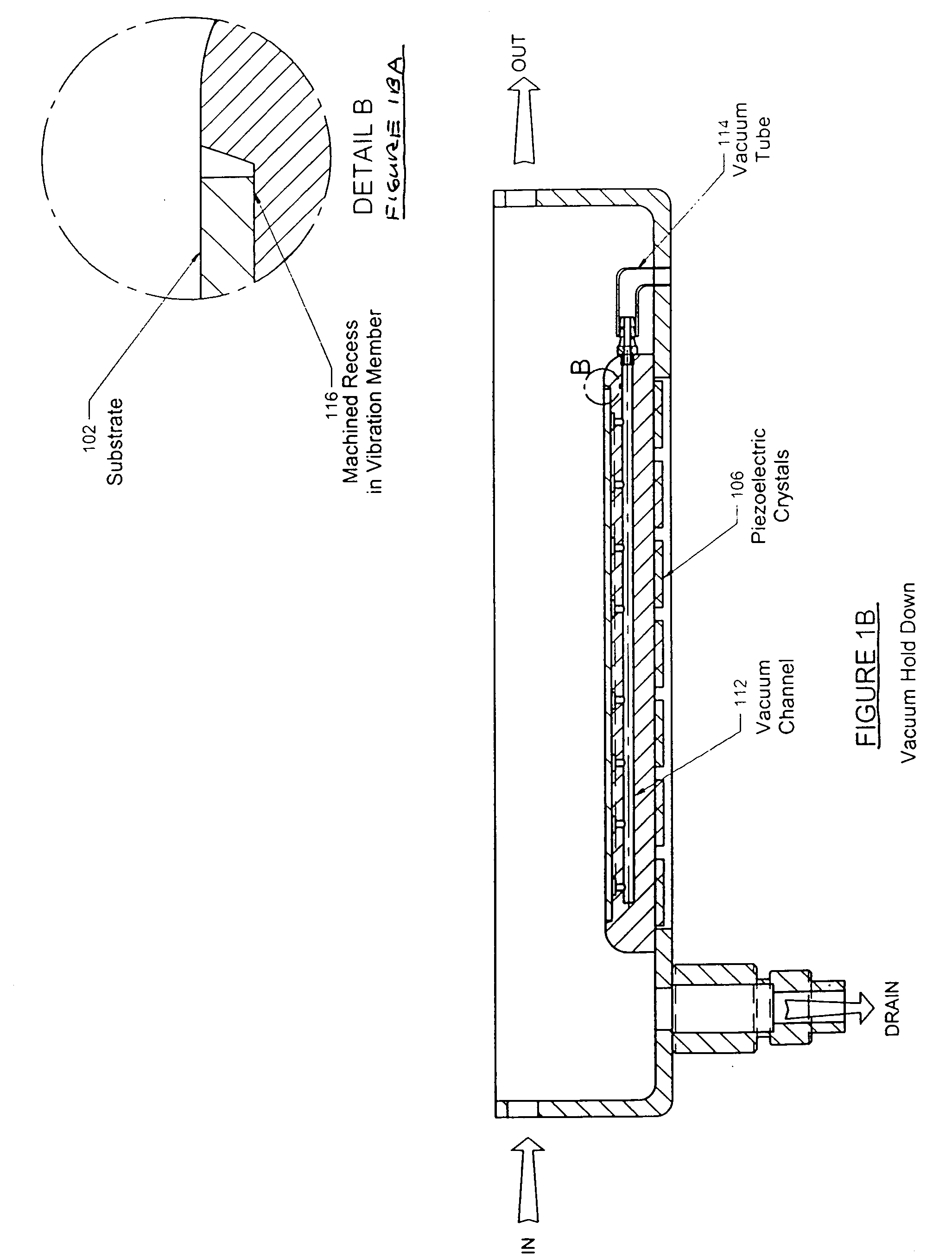
Controlled electro-pneumatic power tools and interactive consumable
Owner:FORGUES SYLVAIN +1
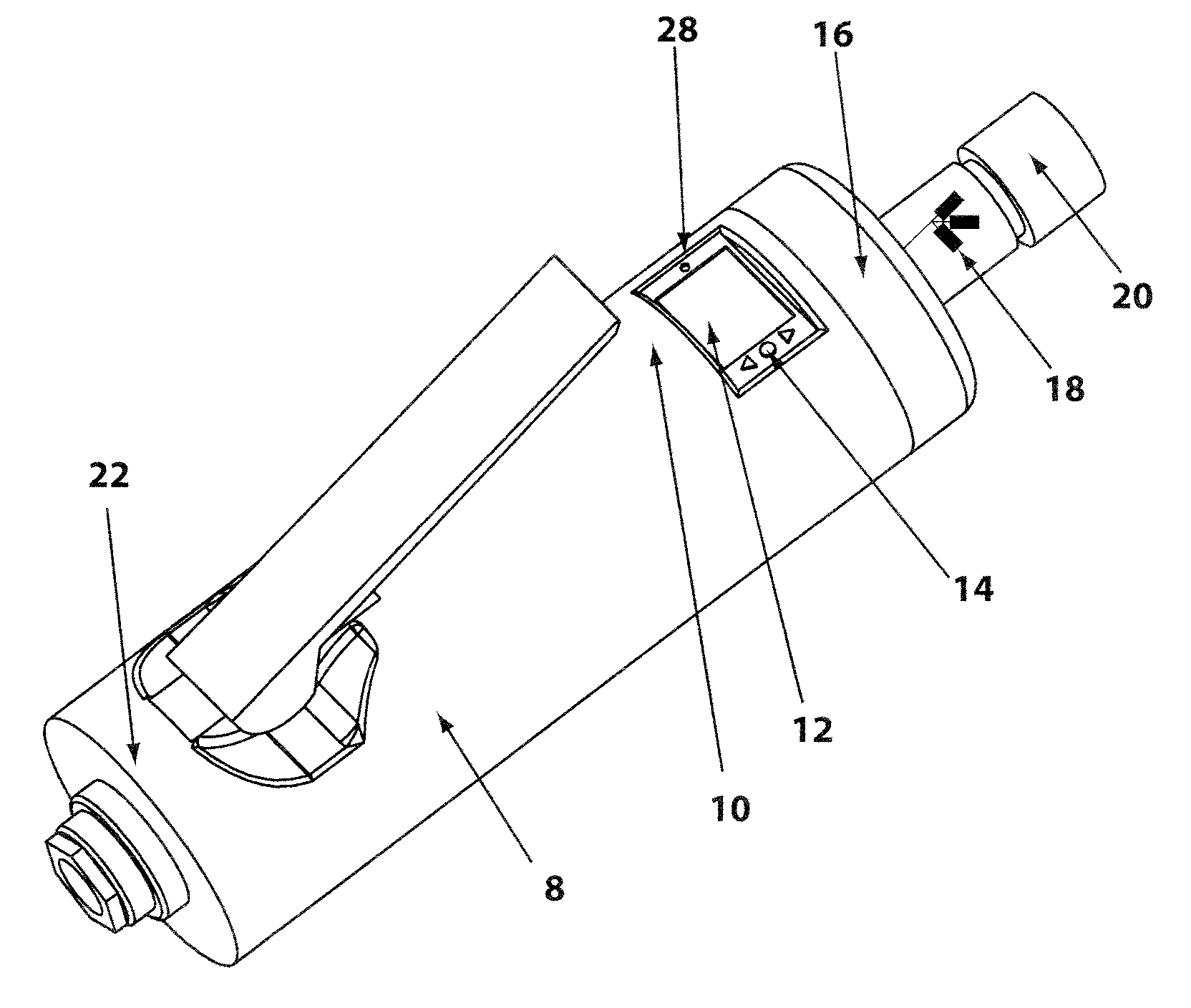
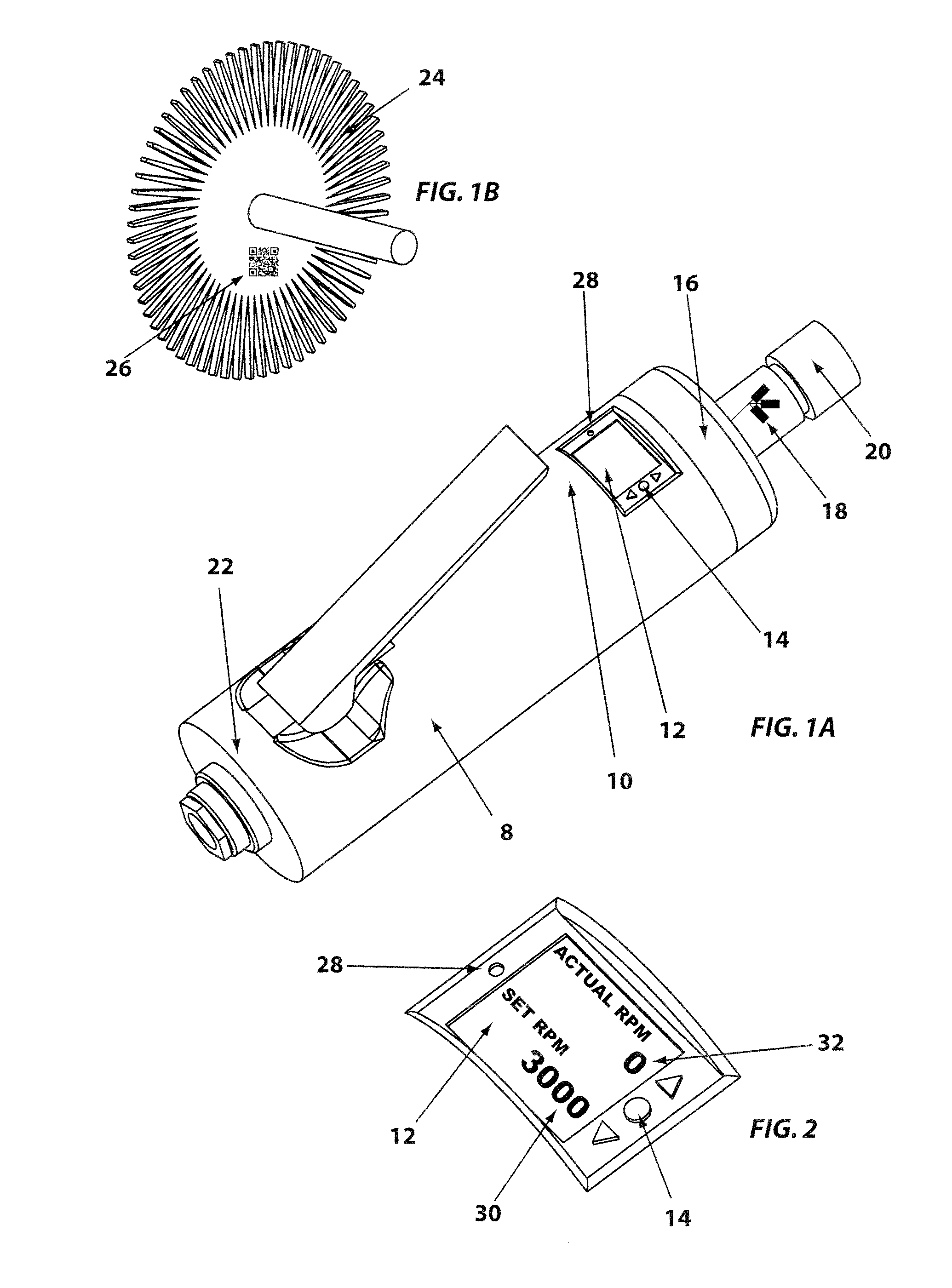
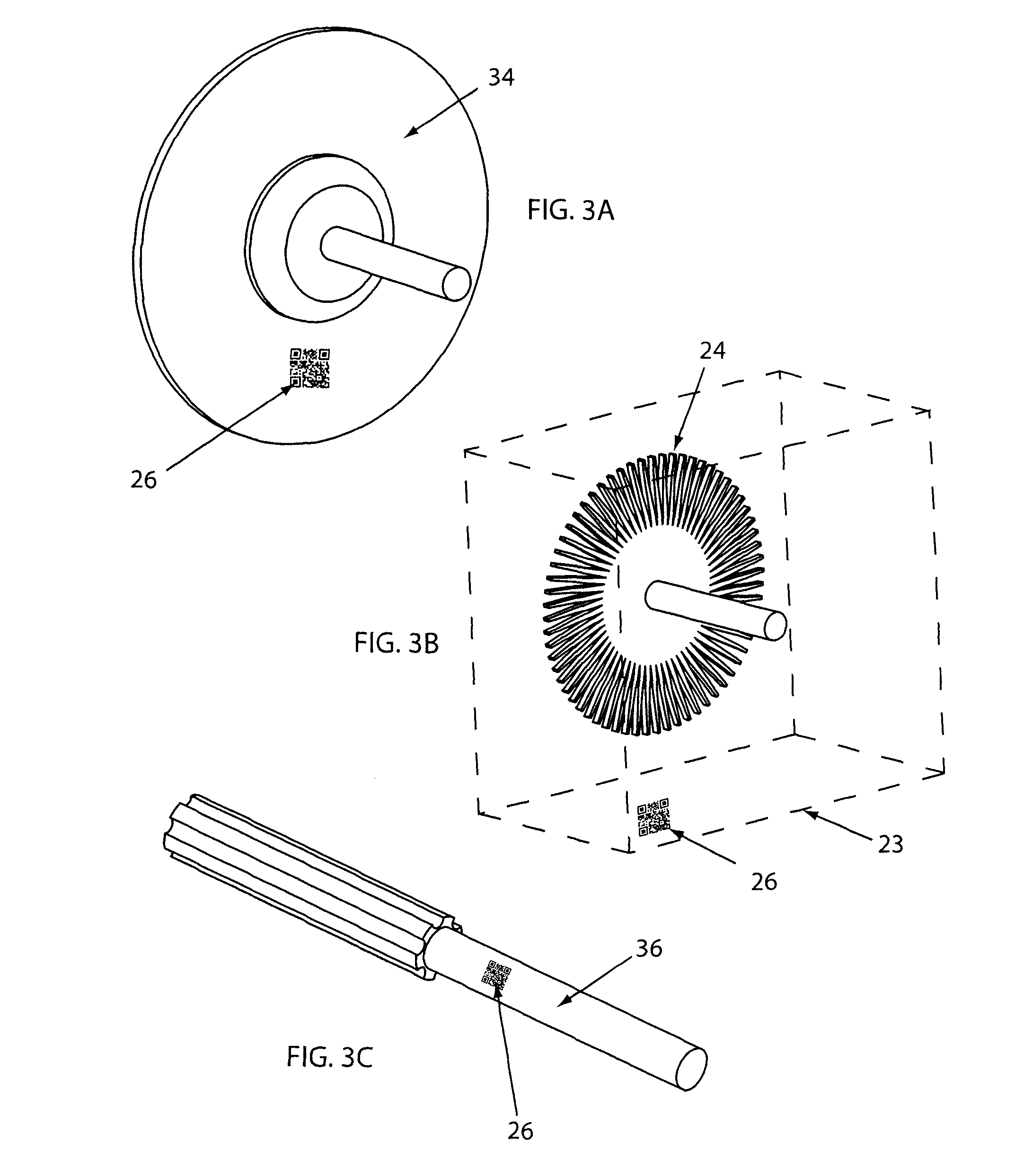
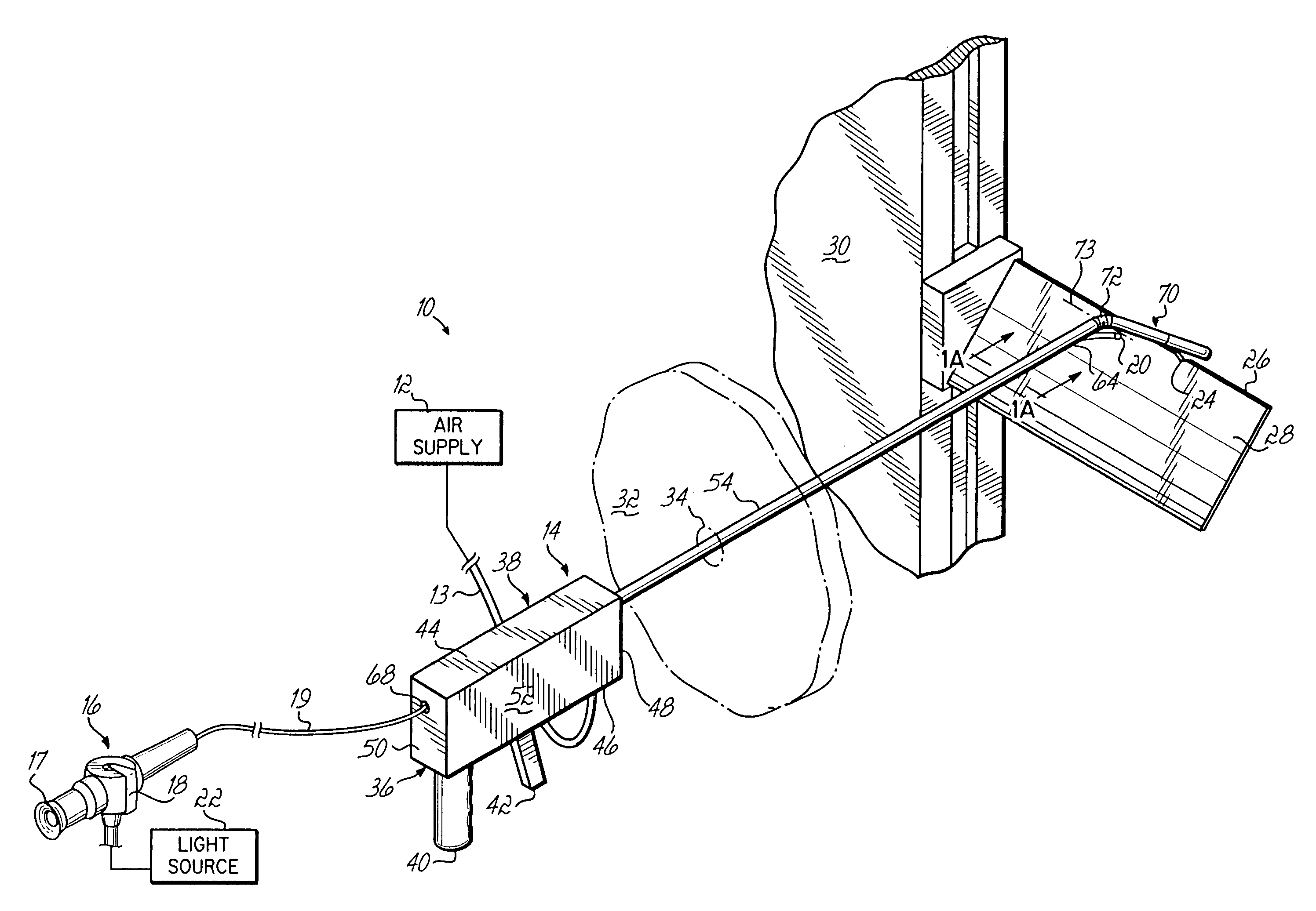
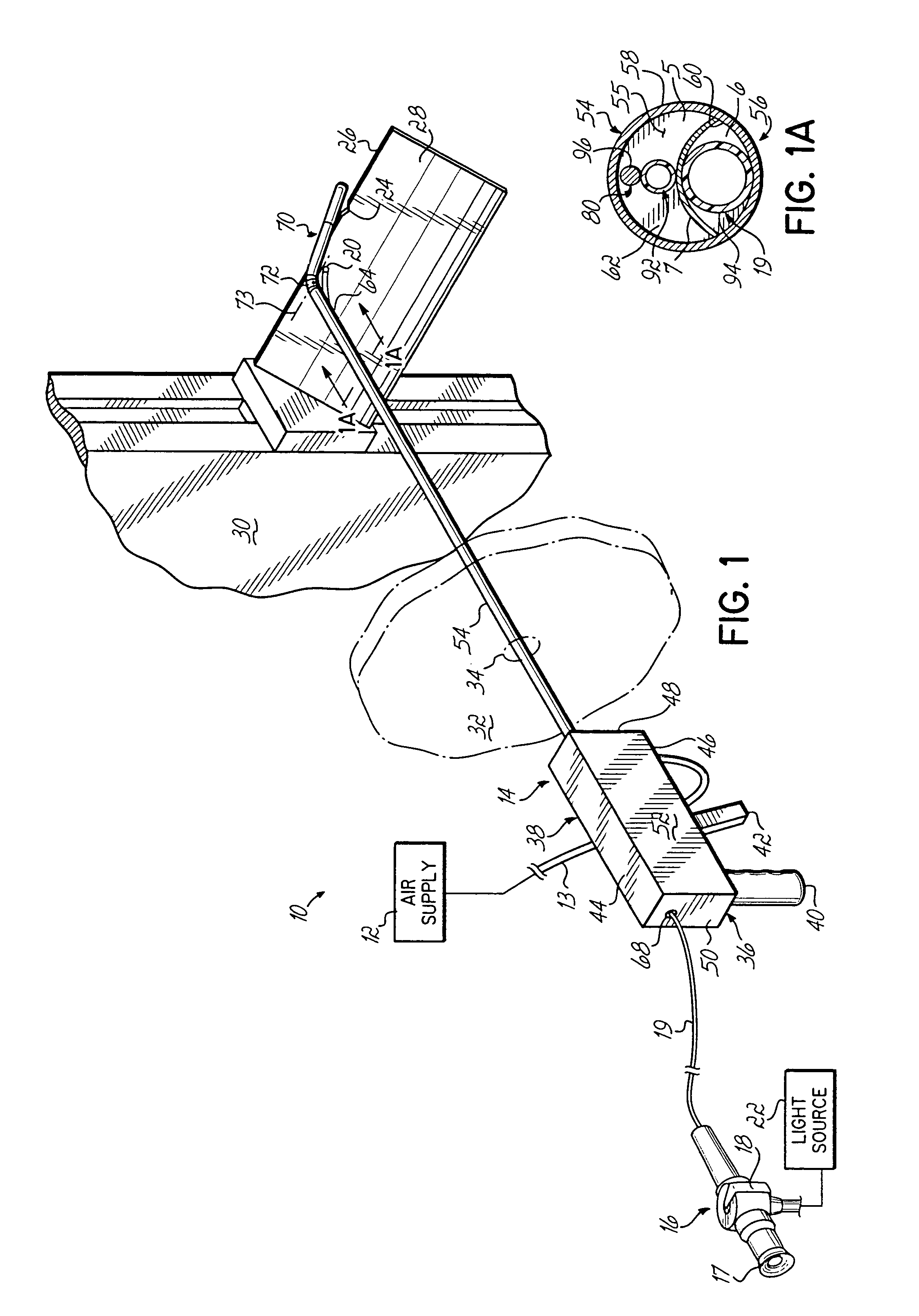
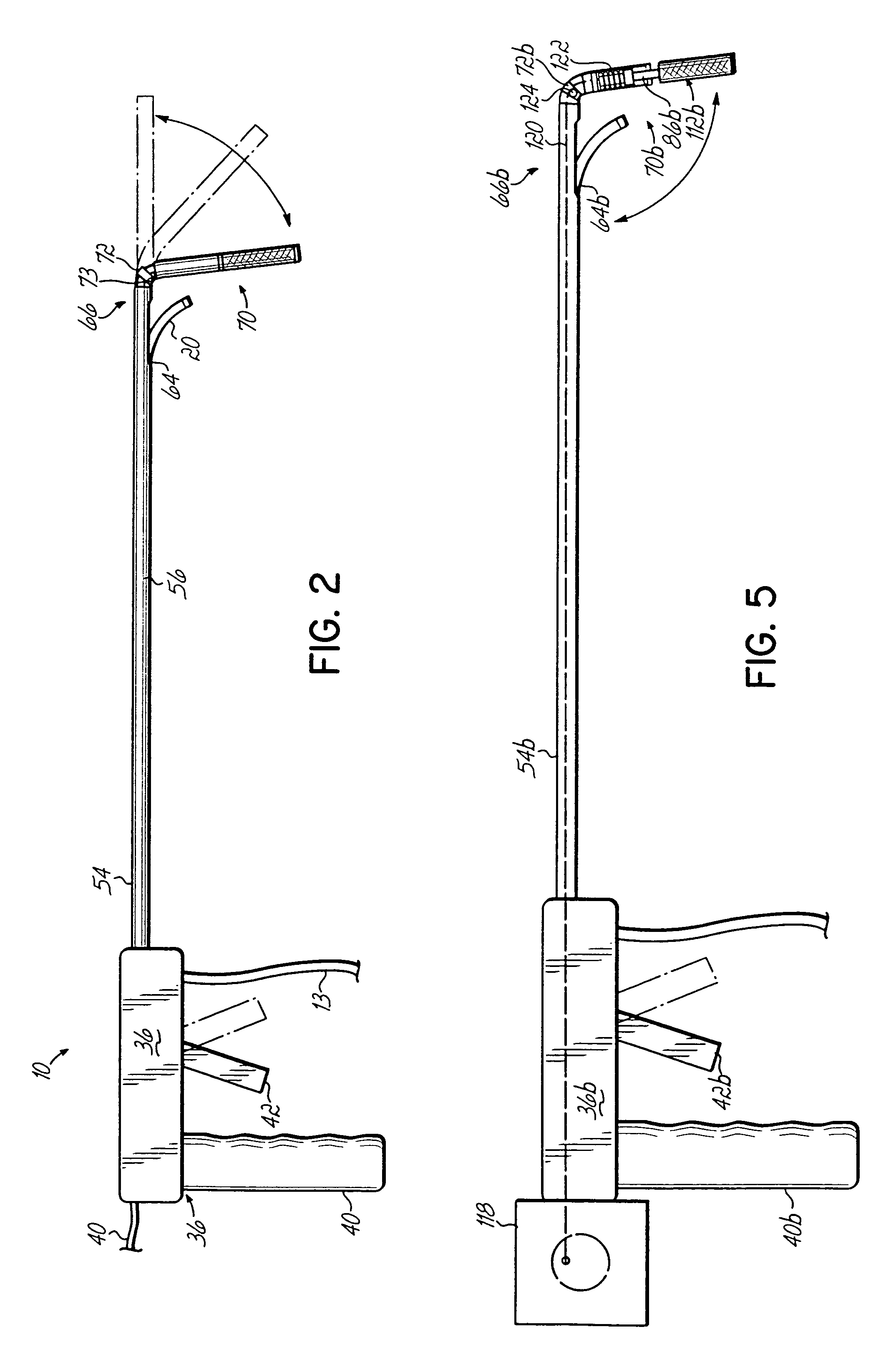
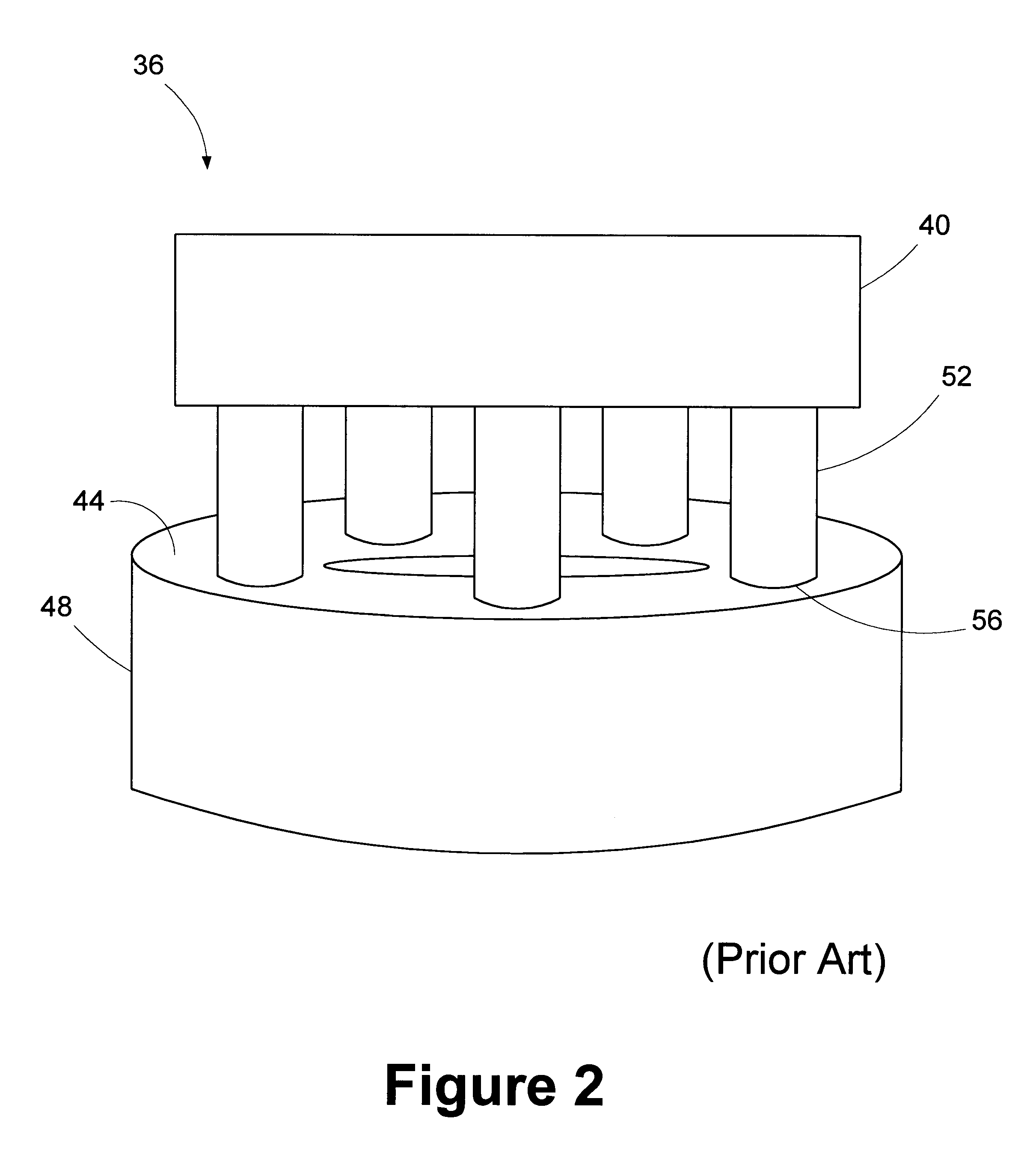
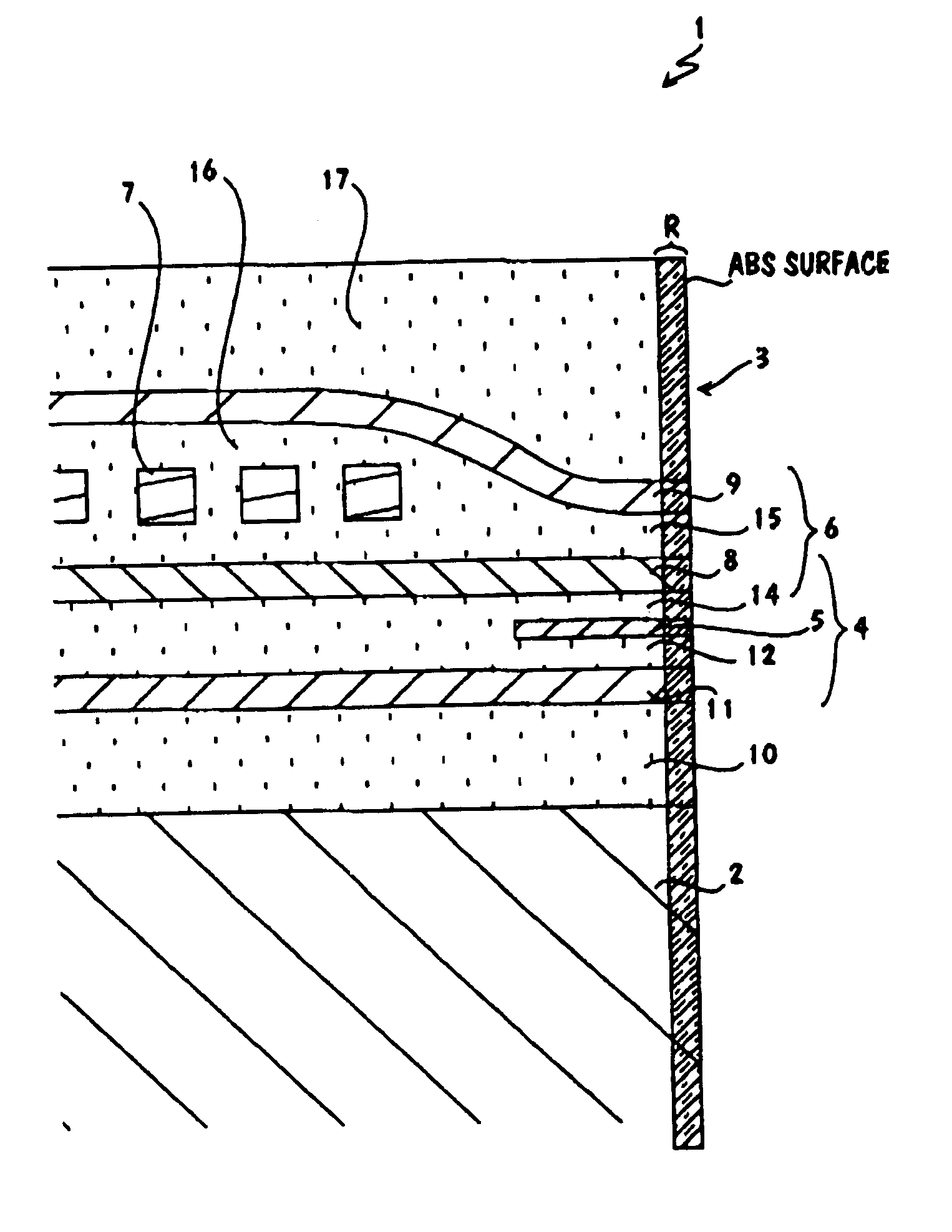
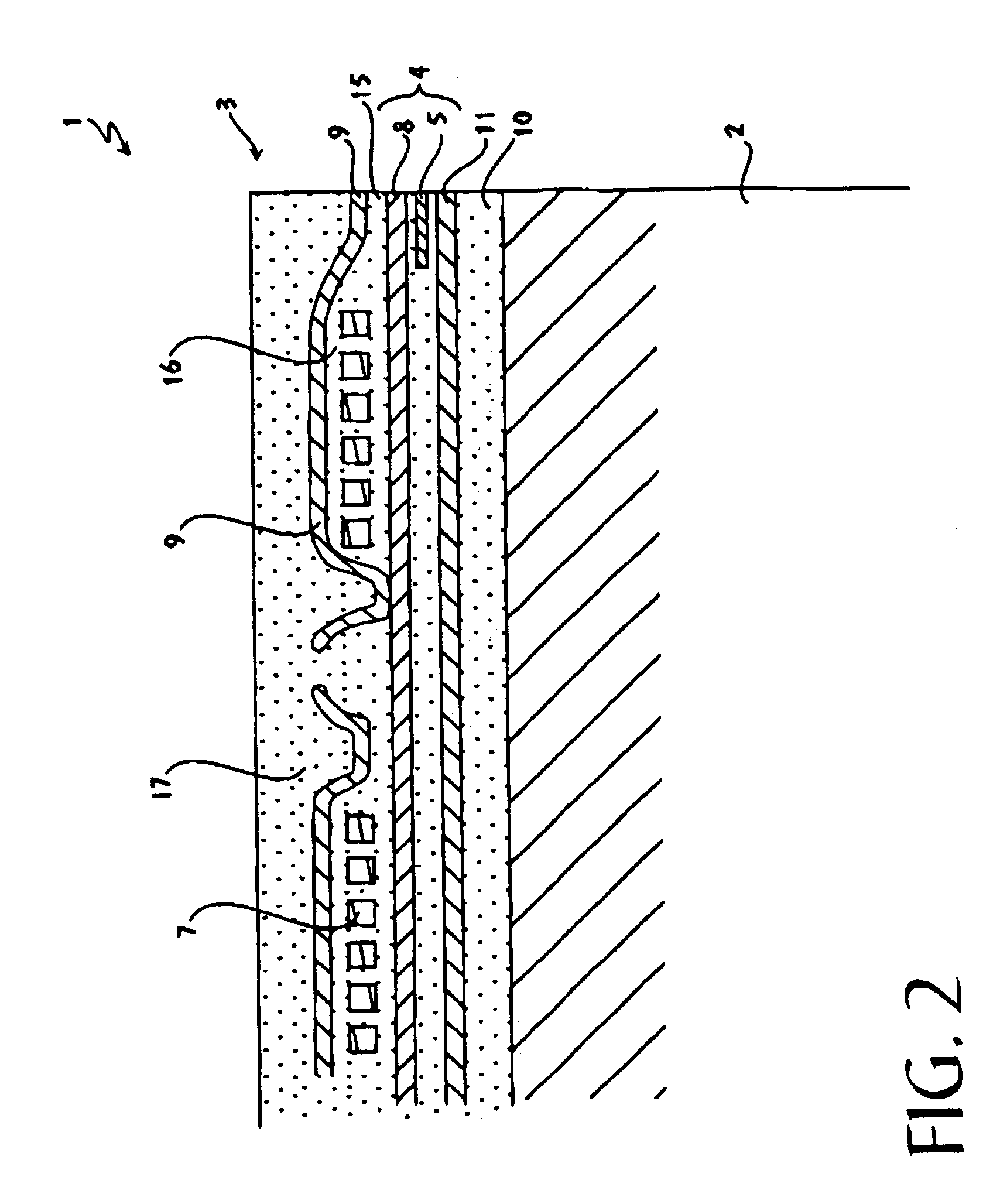
Grinding apparatus for blending defects on turbine blades and associated method of use
InactiveUS6899593B1Revolution surface grinding machinesBlade accessoriesReciprocating motionTurbine blade
A grinding apparatus for use with an endoscope for viewing and blending defects on a turbine engine blade is provided. In one preferred embodiment air pulses from an air supply cause a grinding head on the end of a grinding tool to reciprocate at a predetermined speed. The position of the grinding head is fixed via the operator via a trigger on the grinding tool which articulates an outer portion of a support tube of the grinding tool. In another preferred embodiment, fluid is used to reciprocate the grinding head.
Owner:MOELLER DIETER +2
Wafer carrier checker and method of using same
ActiveUS20060252351A1Grinding drivesBelt grinding machinesSemiconductorElectrical and Electronics engineering
A tool and method for assessing whether a disk carrier, and especially a carrier for holding semiconductor disks, is properly dimensioned. The tool has a body that includes a socket in which a portion of the disk carrier will seat fully if the disk carrier is properly dimensioned. Alignment structures may be provided in the socket to align with features of the carrier to assist in determining whether the disk carrier is properly dimensioned. The socket may include two spaced apart cavities that correspond with end portions of walls of the disk carrier.
Owner:MICREL
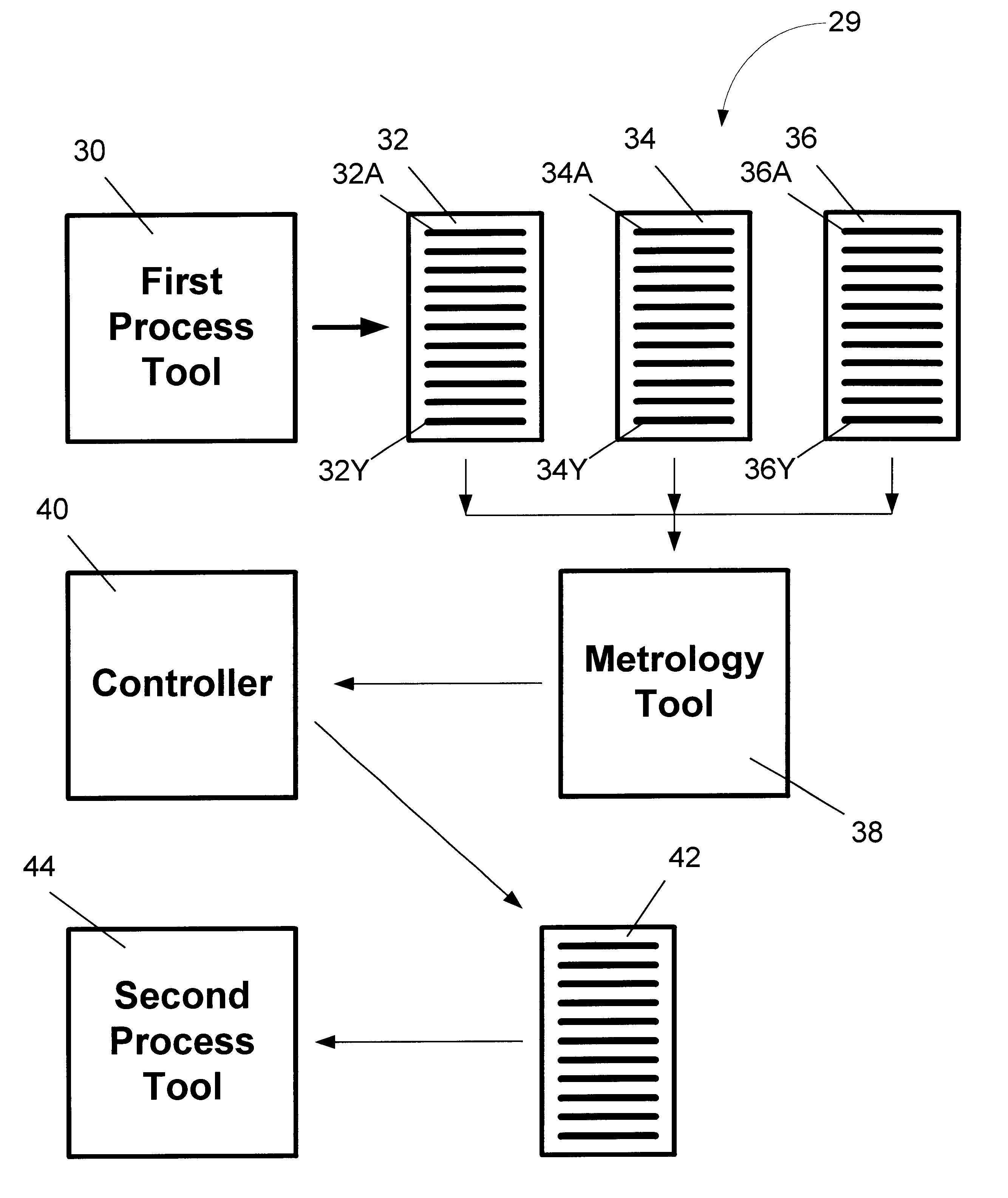
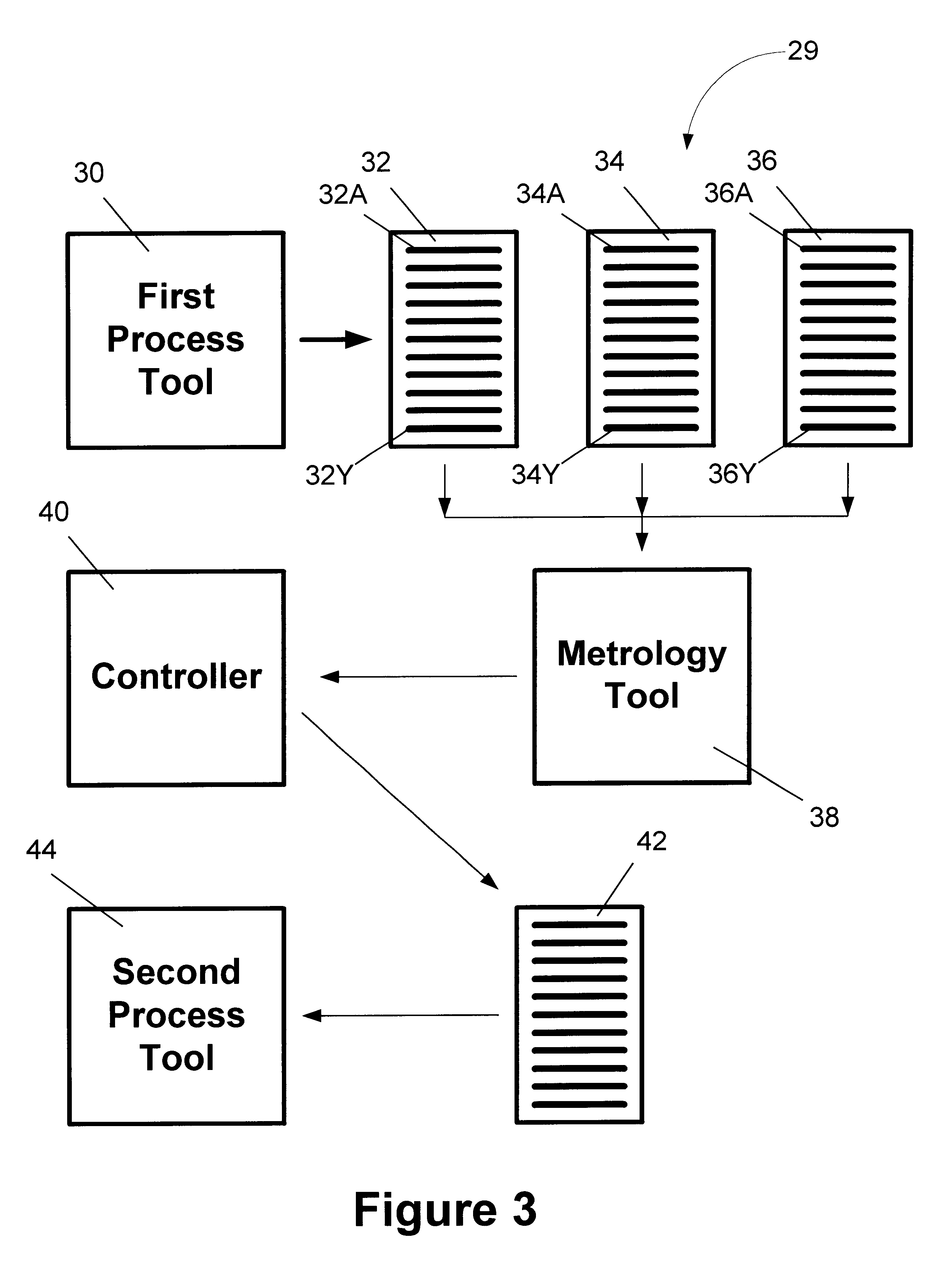
Dynamic lot allocation based upon wafer state characteristics, and system for accomplishing same
InactiveUS6746308B1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementGrinding feed controlEngineeringProcess operation
In one illustrative embodiment, the method comprises providing a plurality of wafer lots, each of the lots comprising a plurality of wafers, performing at least one process operation on at least some of the wafers in each of the plurality of lots, identifying processed wafers having similar characteristics, re-allocating the wafers to lots based upon the identified characteristics, and performing additional processing operations on the identified wafers having similar characteristics in the re-allocated lots. In one illustrative embodiment, the system comprises a first processing tool for performing processing operations on each of a plurality of wafers in each of a plurality of wafer lots, a controller for identifying processed wafers having similar characteristics and re-allocating the wafers to lots based upon the identified characteristics, and a second processing tool adapted to perform additional processing operations on the identified wafers having similar characteristics in the re-allocated lot.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
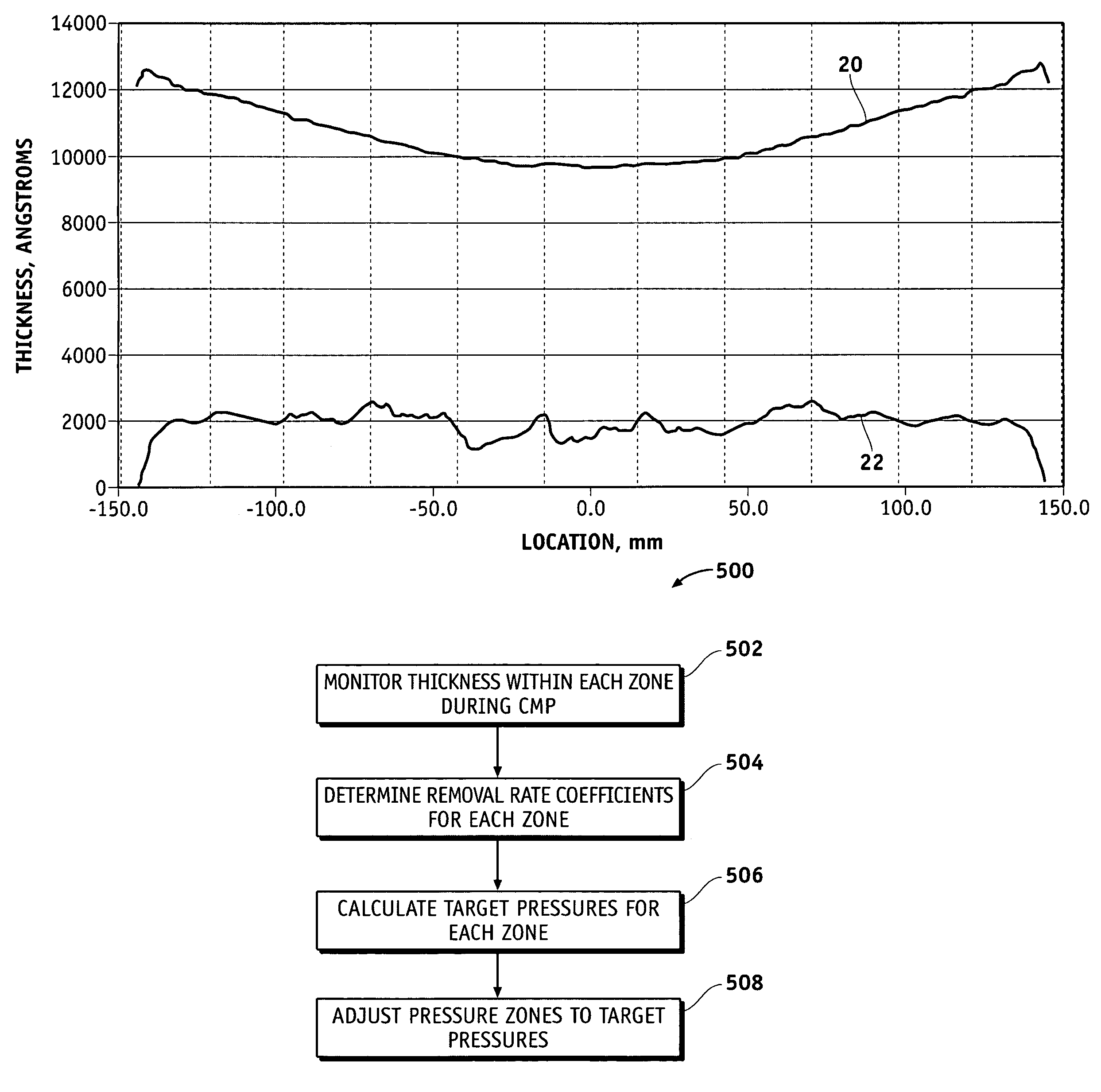
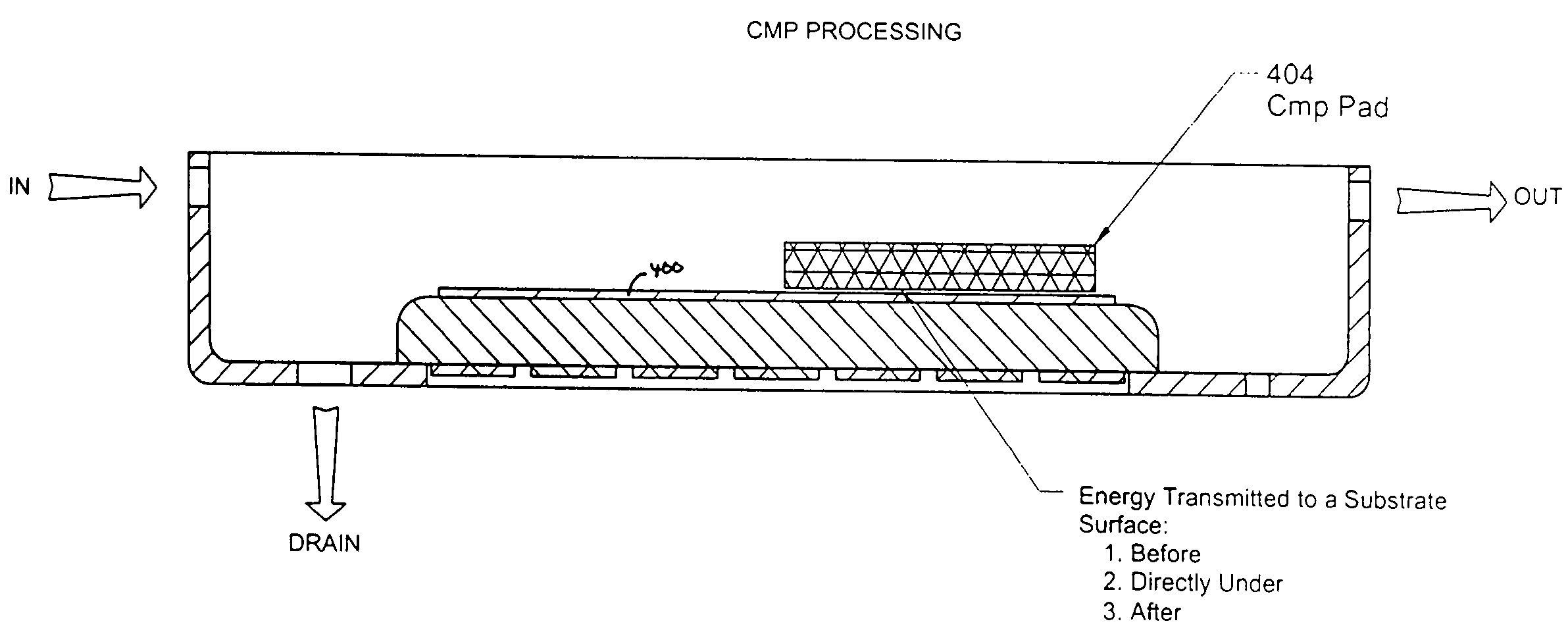
Methods for controlling the pressures of adjustable pressure zones of a work piece carrier during chemical mechanical planarization
ActiveUS7115017B1Polishing machinesRevolution surface grinding machinesEngineeringChemical-mechanical planarization
Methods are provided for controlling adjustable pressure zones of a CMP carrier. A method comprises determining a first thickness of a layer on a wafer underlying a first zone of the carrier. A first portion of the layer underlying the first zone is removed. The first zone is configured to exert a first pressure against the second surface of the wafer. A second thickness of the layer underlying the first zone is determined and a target thickness corresponding to a predetermined thickness profile is selected. A second pressure for the first zone is calculated using the first thickness, the second thickness, the first pressure, and the target thickness. The pressure exerted by the first zone against the second surface of the wafer is adjusted to the second pressure and the steps are repeated for a second zone.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
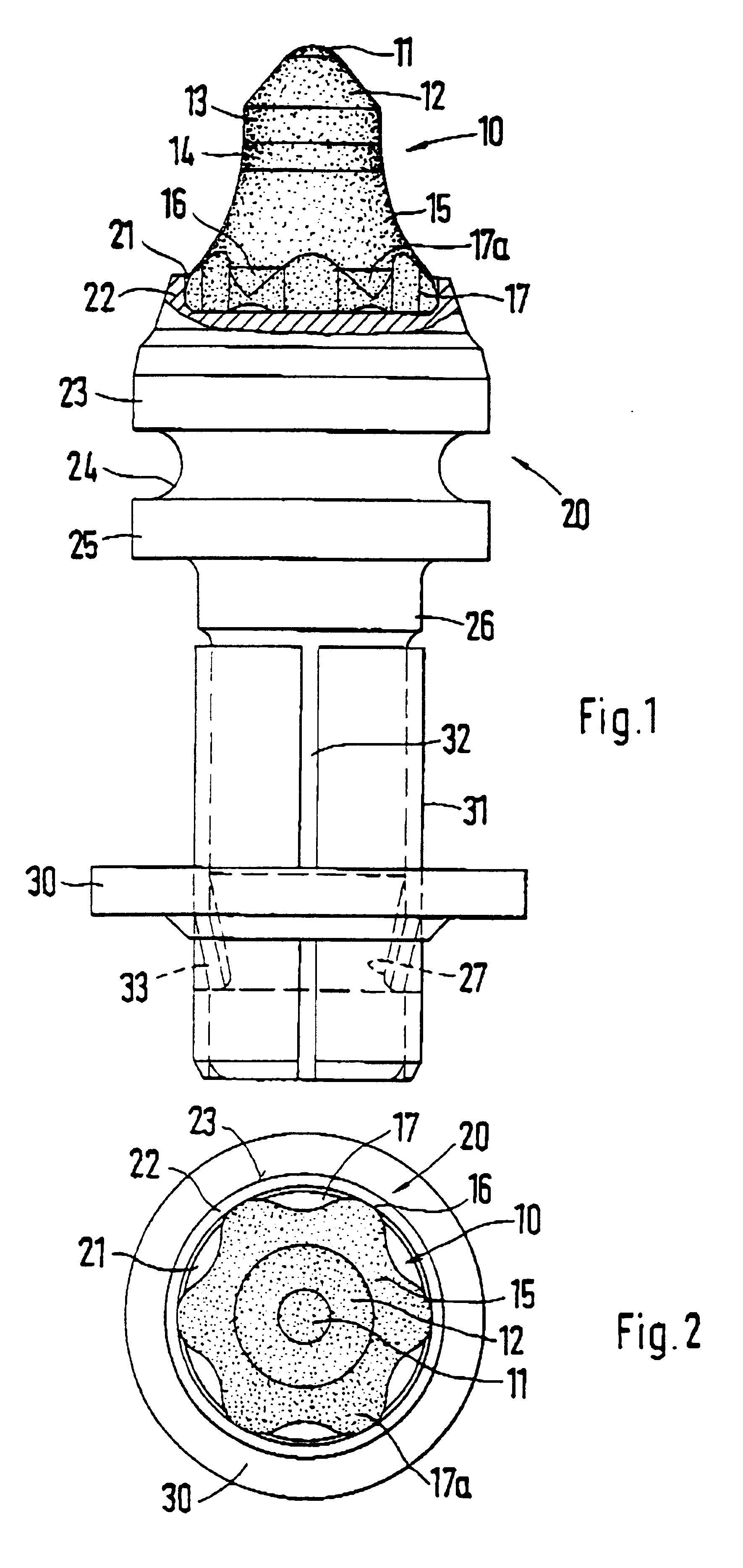
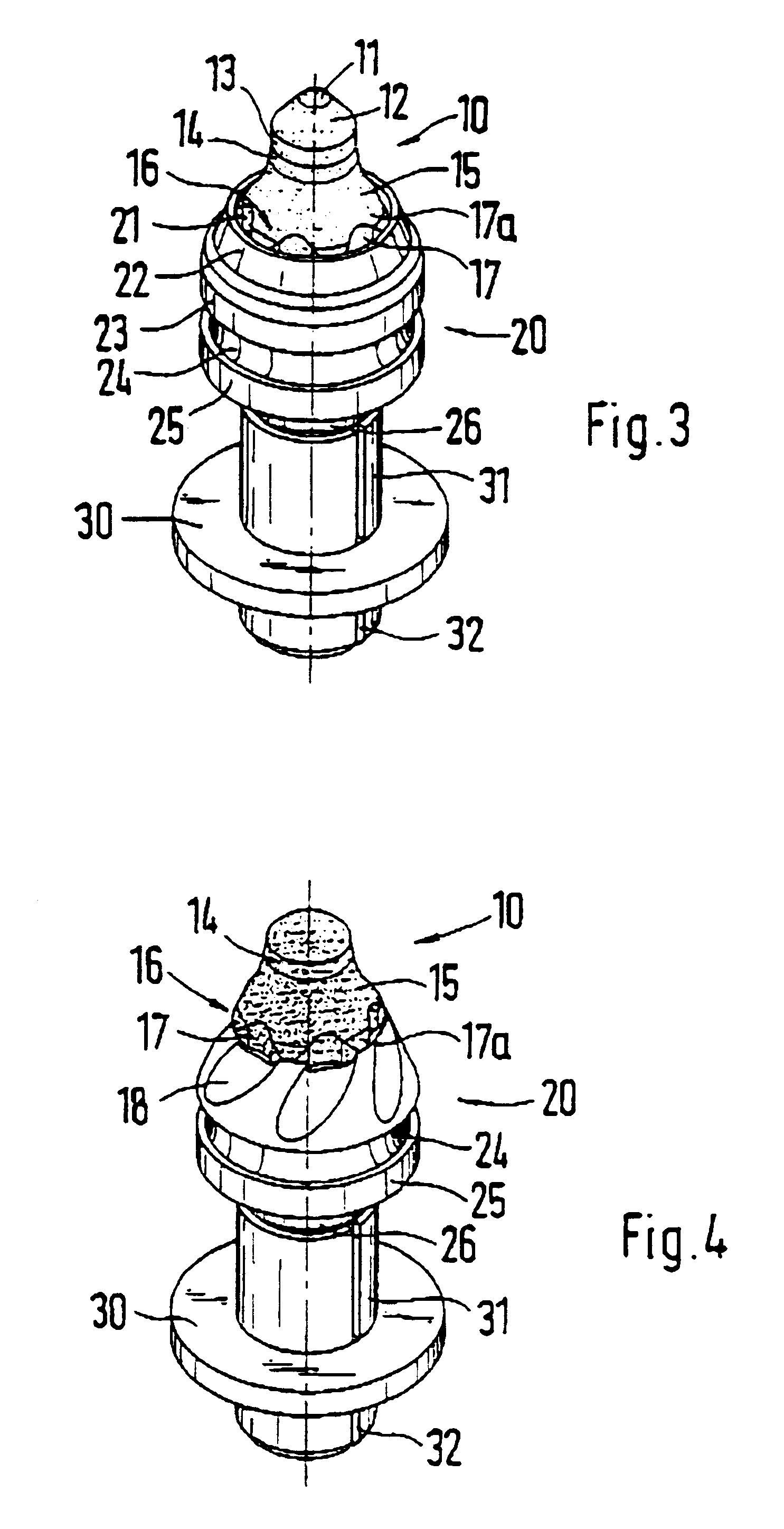
Round-shank bit for a coal cutting machine
InactiveUS6199956B1Sufficient supportLess stressPolishing machinesRevolution surface grinding machinesMaximum diameterEngineering
A round-shank bit for a coal cutting machine or the like, having a bit head and a bit shank, wherein the bit head has a bit tip, maintained by a base element in a receptacle of the bit head. Starting at the base element, the bit tip tapers in a direction toward the free end of the bit tip, wherein the base element forms a maximum diameter of the bit tip, and wherein the bit tip has recesses on its outer contour. In order to assure good rotational behavior over the entire length of the operating time, the base element has the recesses on an outer circumference forming the maximum diameter.
Owner:BETEK BERGBAU UND HARTMETALLTECHN KARL HEINZ SIMON
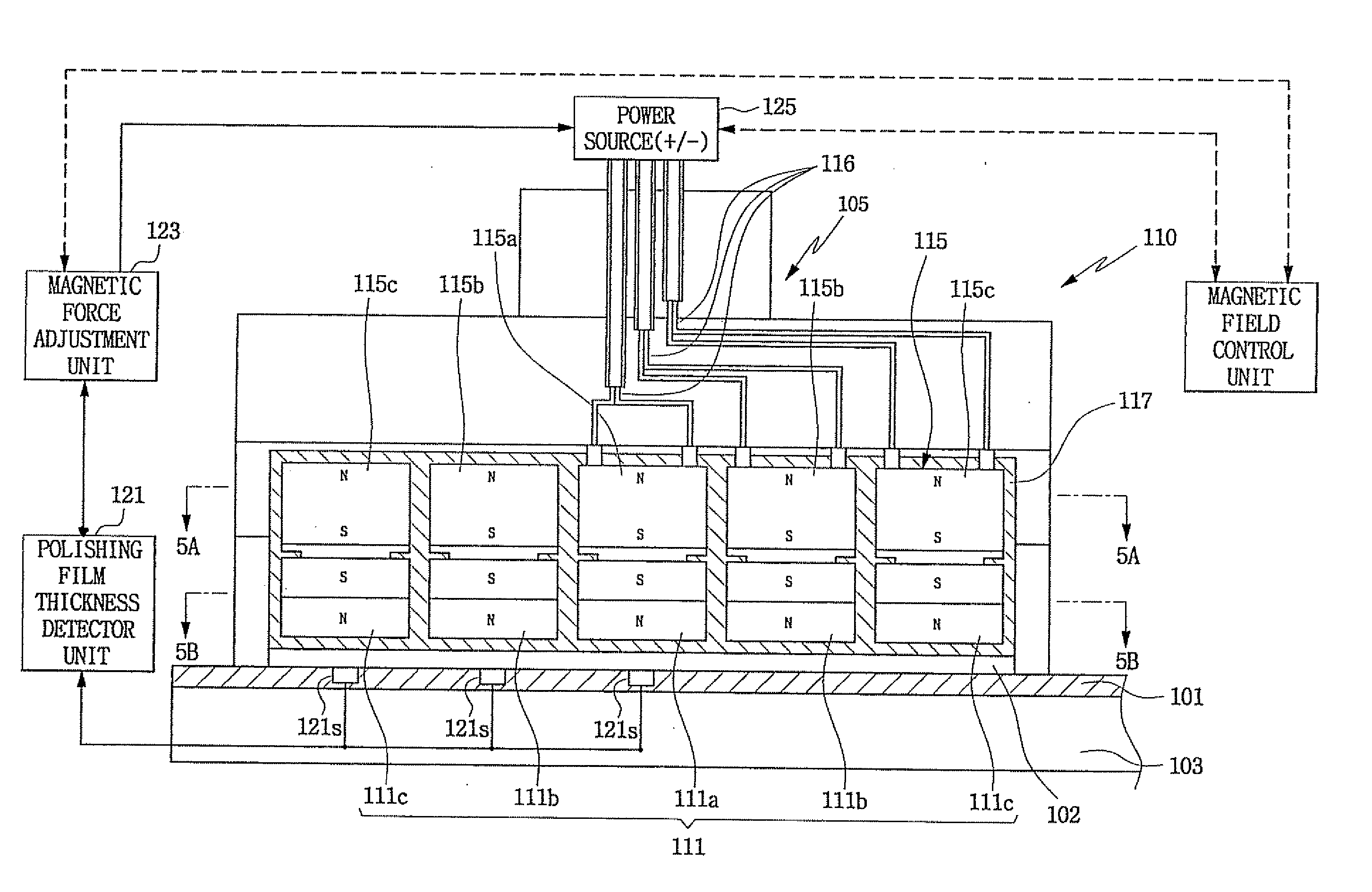
Polishing apparatus and related polishing methods
InactiveUS20060189259A1Uniform thicknessPolishing machinesRevolution surface grinding machinesEngineeringMagnetic field
Polishing apparatus and related methods employ aligned first and second magnetic field sources to adjust the compressive force and / or pressure applied by a carrier head against a target workpiece (such as a wafer) by selectively and controllably generating a repellant or attractive force between the two magnetic field sources.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
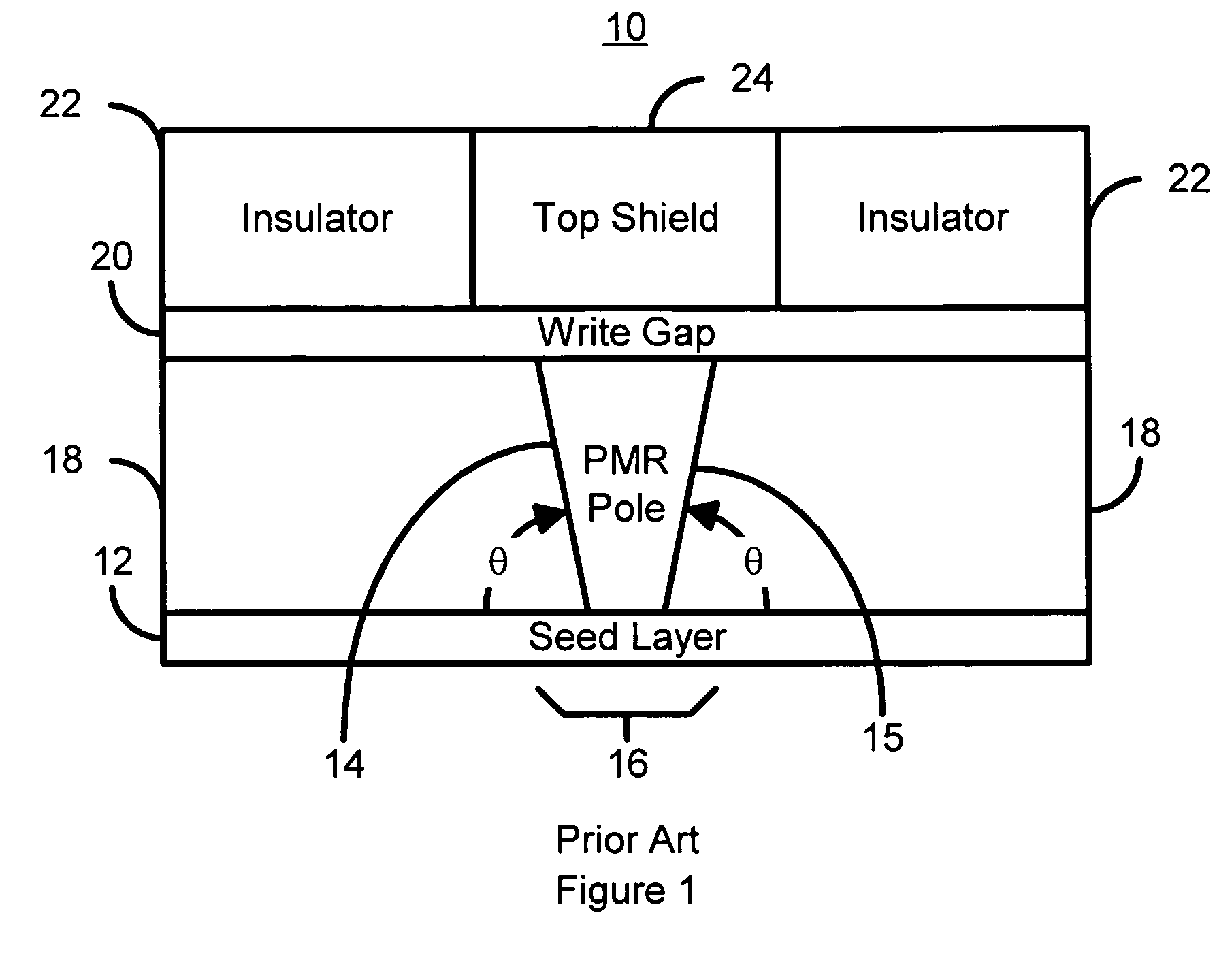
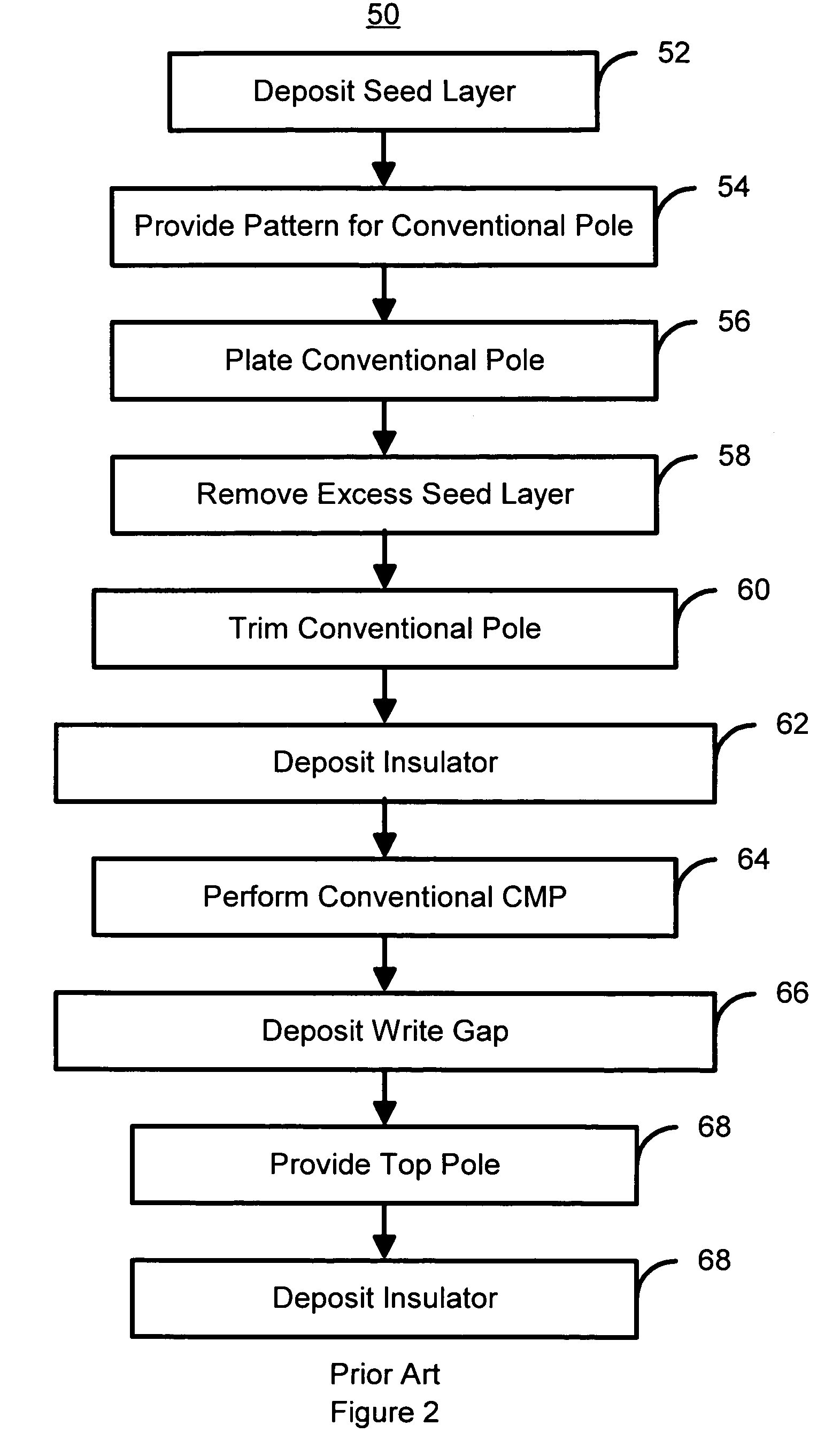
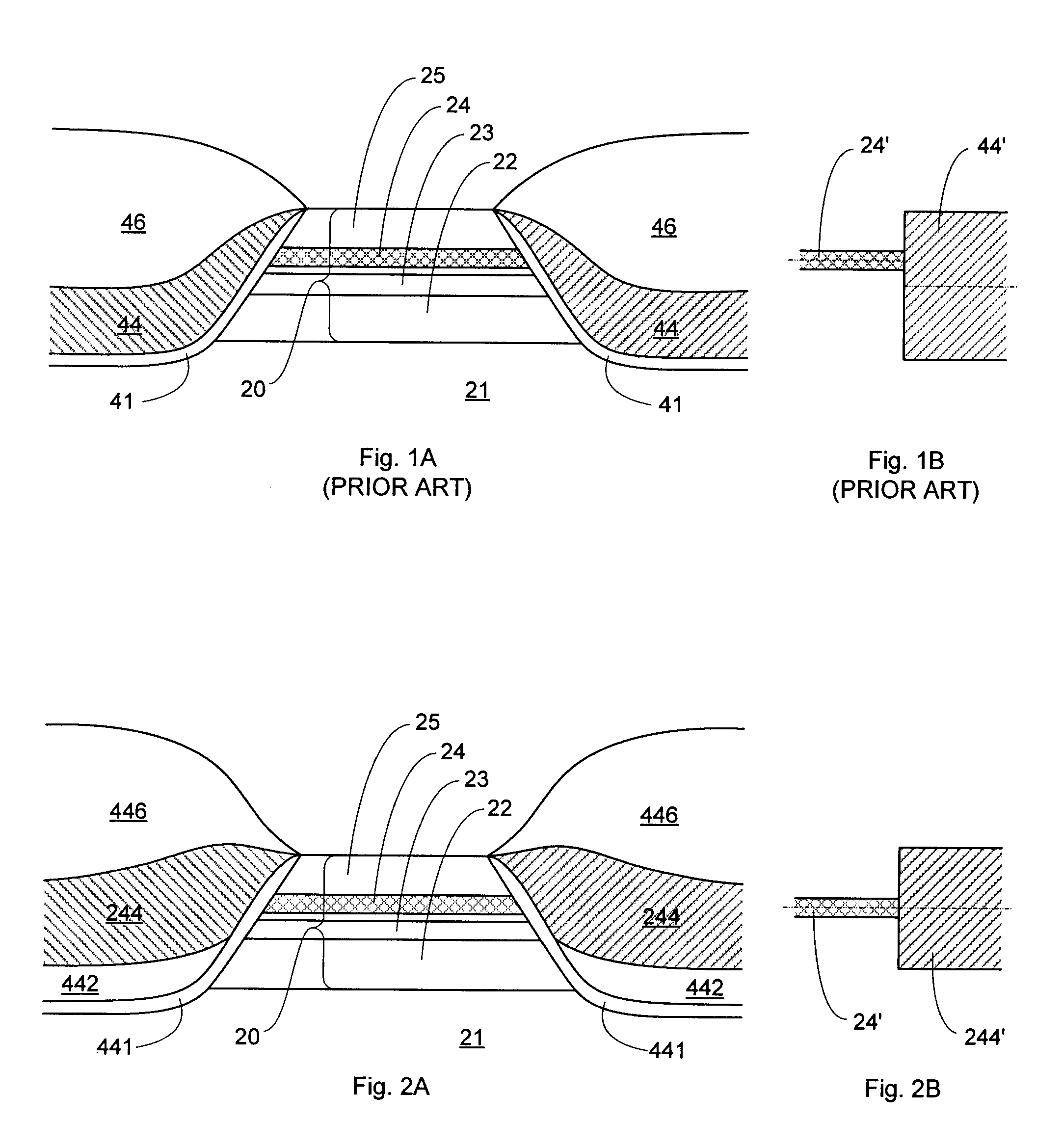
Damascene process for fabricating poles in recording heads
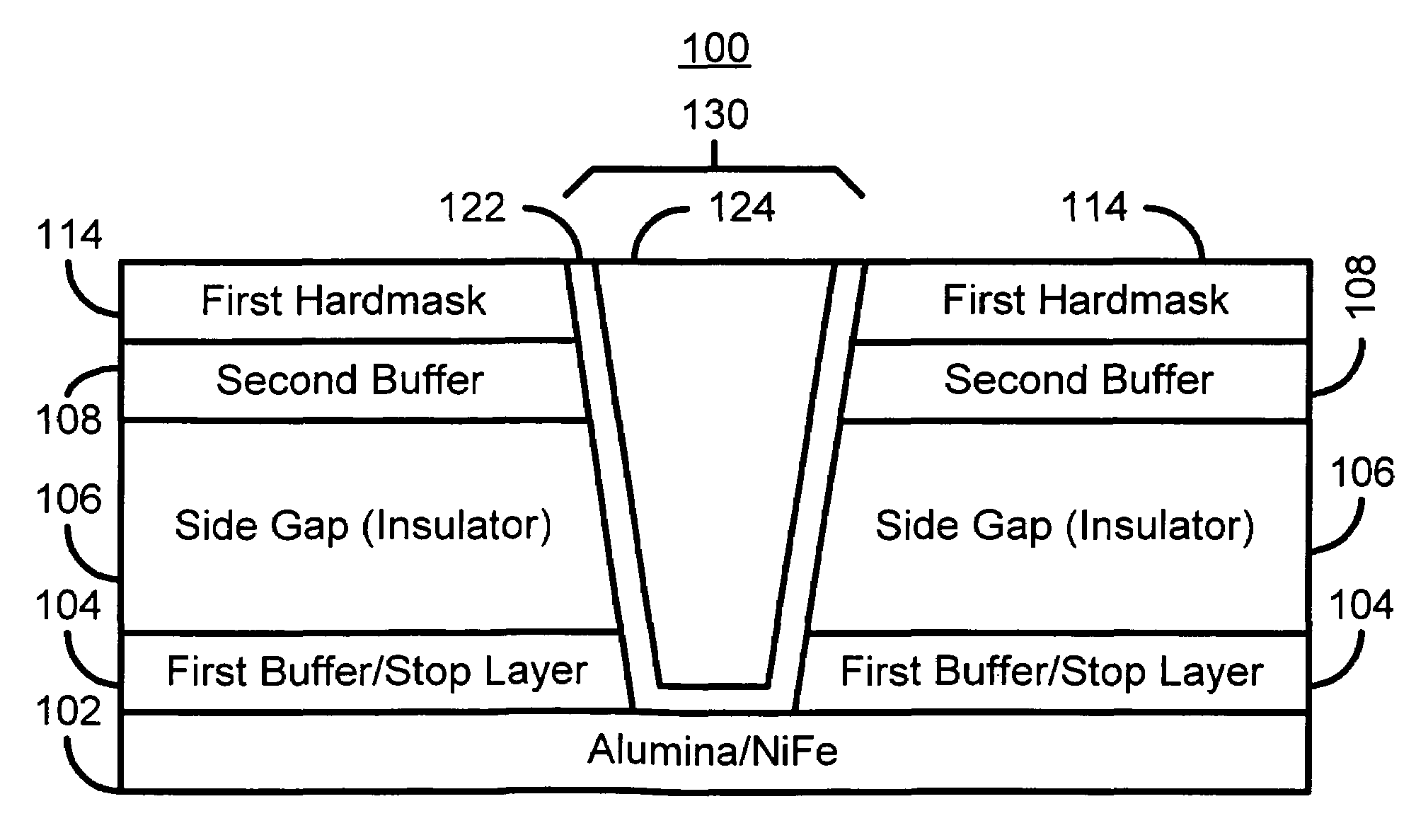
A method and system for manufacturing a pole for a magnetic recording head. The method and system include providing an insulator and fabricating at least one hard mask on the insulator. The at least one hard mask has an aperture therein. The method and system also include removing a portion of the insulator to form a trench within the insulator. The trench is formed under the aperture. The method and system further include depositing at least one ferromagnetic material. The pole includes a portion of the ferromagnetic material within the trench.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Rapid and accurate end point detection in a noisy environment
Methods and apparatus for film measurement and endpoint detection in a noisy environment, such as CMP processing of semiconductor wafers, are disclosed, characterized by the use of spectral analysis of intensity data derived from light reflected off the sample to estimate film thickness or detect an endpoint condition.
Owner:FILMETRICS
Apparatus for determining metal CMP endpoint using integrated polishing pad electrodes
A polishing system includes a polishing tool having a platen, a polishing pad, and a controller. The platen is adapted to have the polishing pad attached thereto. The polishing pad includes a polishing surface and a back surface that is opposite the polishing surface. At least one sender electrode and at least one response electrode is disposed in the polishing pad. The controller is coupled to the polishing tool. A method includes polishing a conductive process layer of a wafer using a polishing pad of a polishing tool having at least one sender electrode and at least one response electrode disposed therein. A signal is provided to the at least one sender electrode. The signal provided to the at least one sender electrode is monitored with at least one of a group of the at least one response electrode, the at least one response electrode communicating with the at least one sender electrode through the conductive process layer of the wafer. Endpoint of the polishing process is determined based on the signal received by the at least one response electrode.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
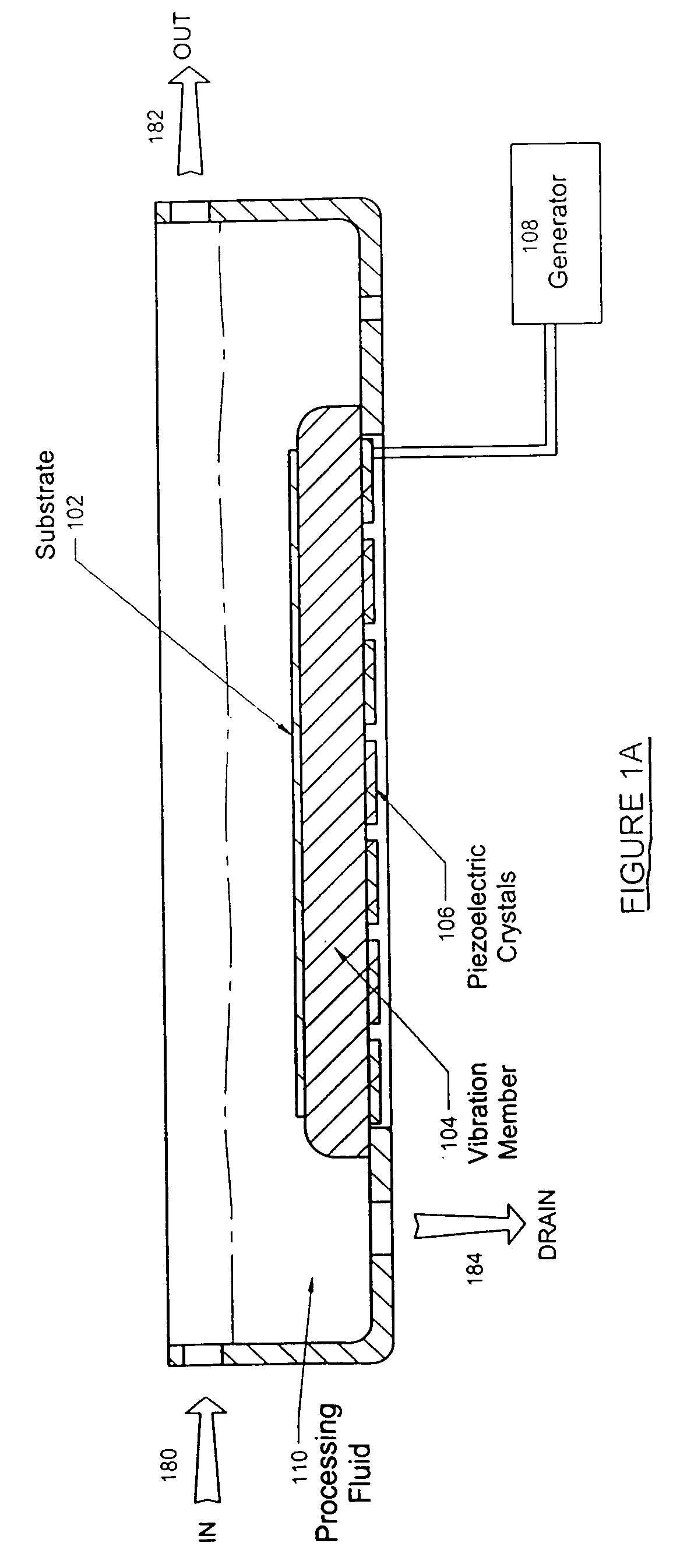
Method and apparatus to process substrates with megasonic energy
ActiveUS20050003737A1Uniform energyImprove uniformityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsLiquid surface applicatorsEngineeringSubstrate surface
A variety of techniques may be employed, alone or in combination, to enhance contact between a processed substrate and applied megasonic energy. In accordance with one embodiment of the new invention, the vibration plate is brought into intimate contact with one surface of the substrate, while cleaning or processing fluid contacts the other. In accordance with an alternative embodiment of the present invention, a reflecting surface may be provided to cause emanated energy to be reflected back into the near field and make it more uniform. In accordance with another alternative embodiment of the present invention, energy may be transferred across a substrate bounded on both sides by liquid with incidence of megasonic energy that is either normal to the substrate surface or within a critical range of incident angles. In yet another embodiment, generated dilatational waves may be converted to surface waves prior to contacting the substrate.
Owner:P C T SYST
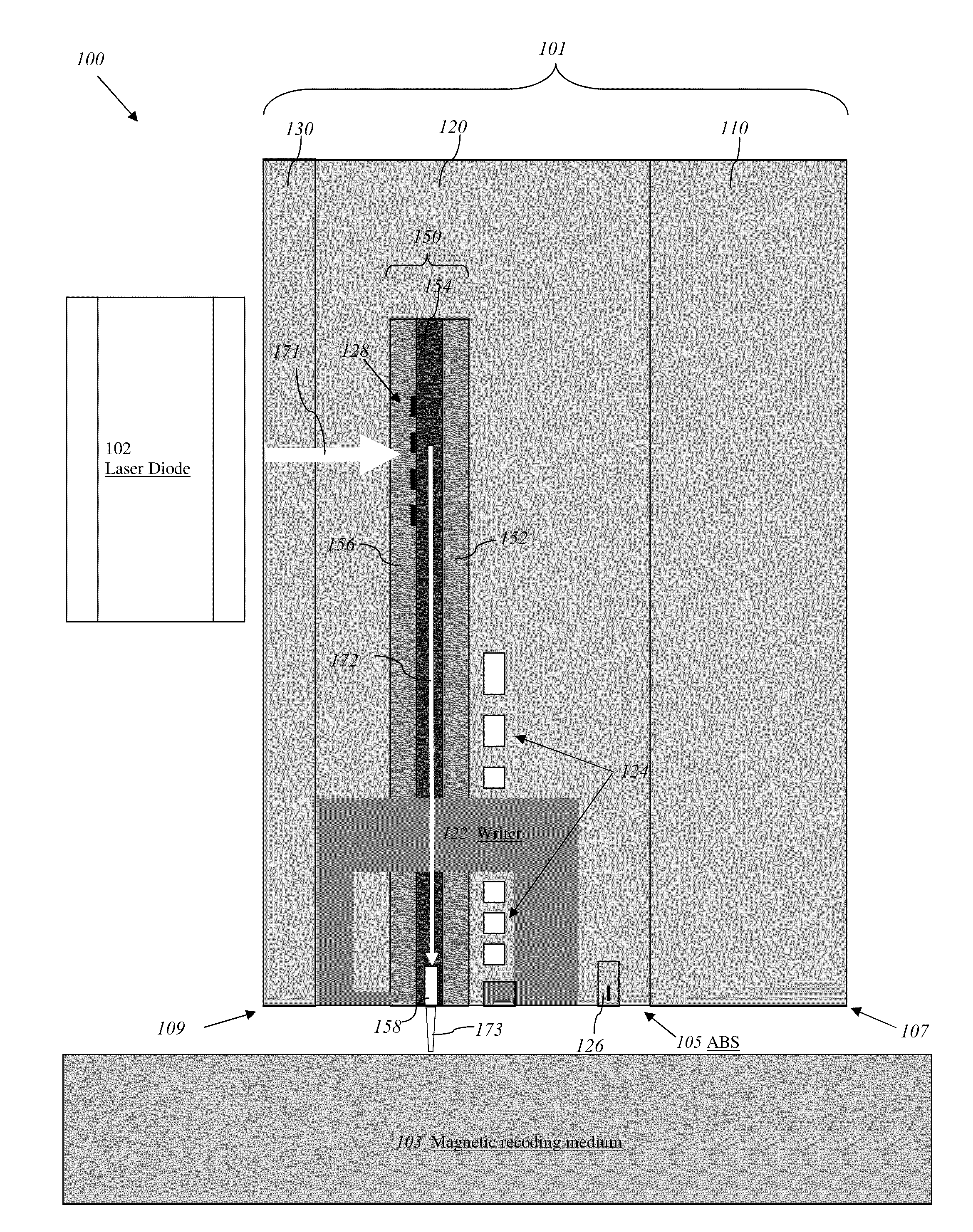
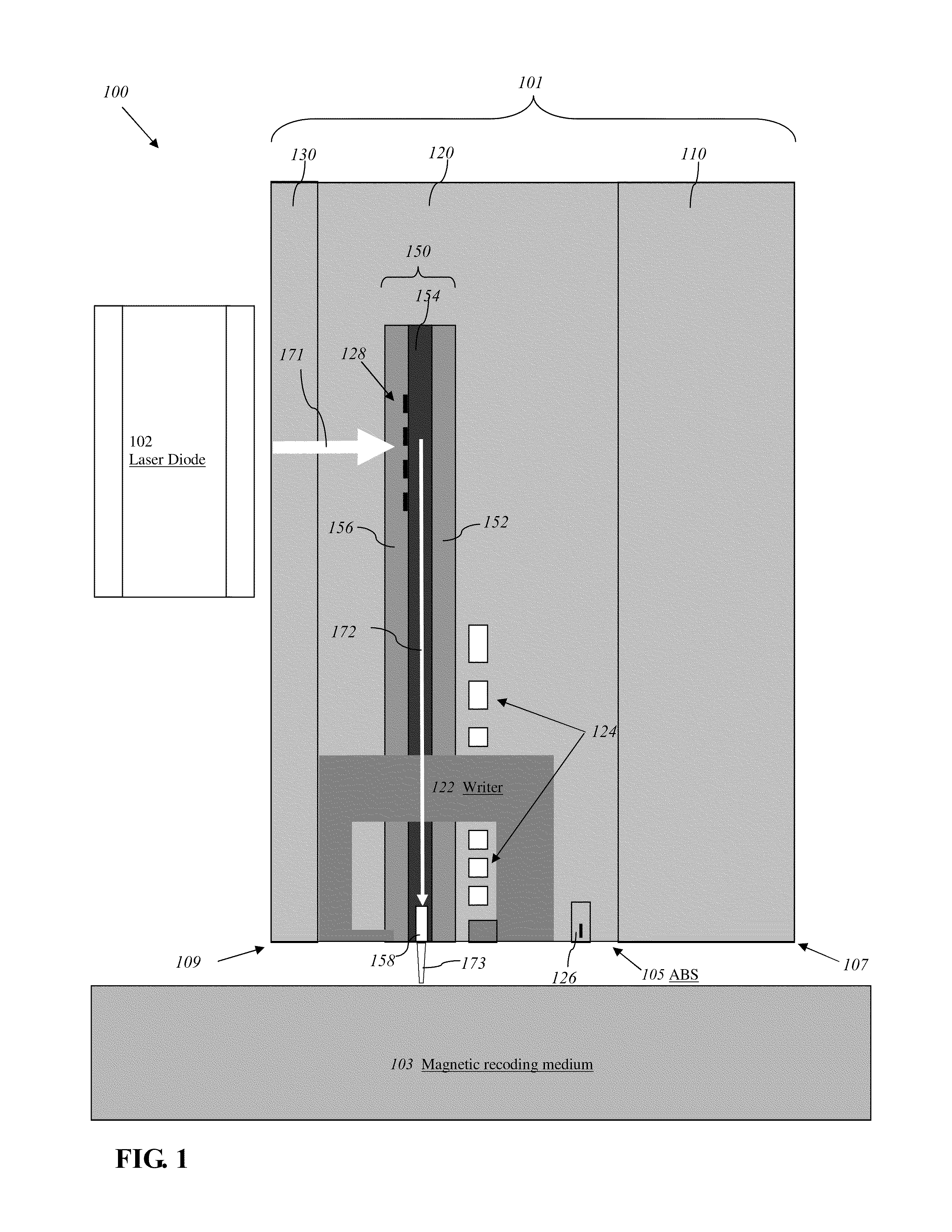
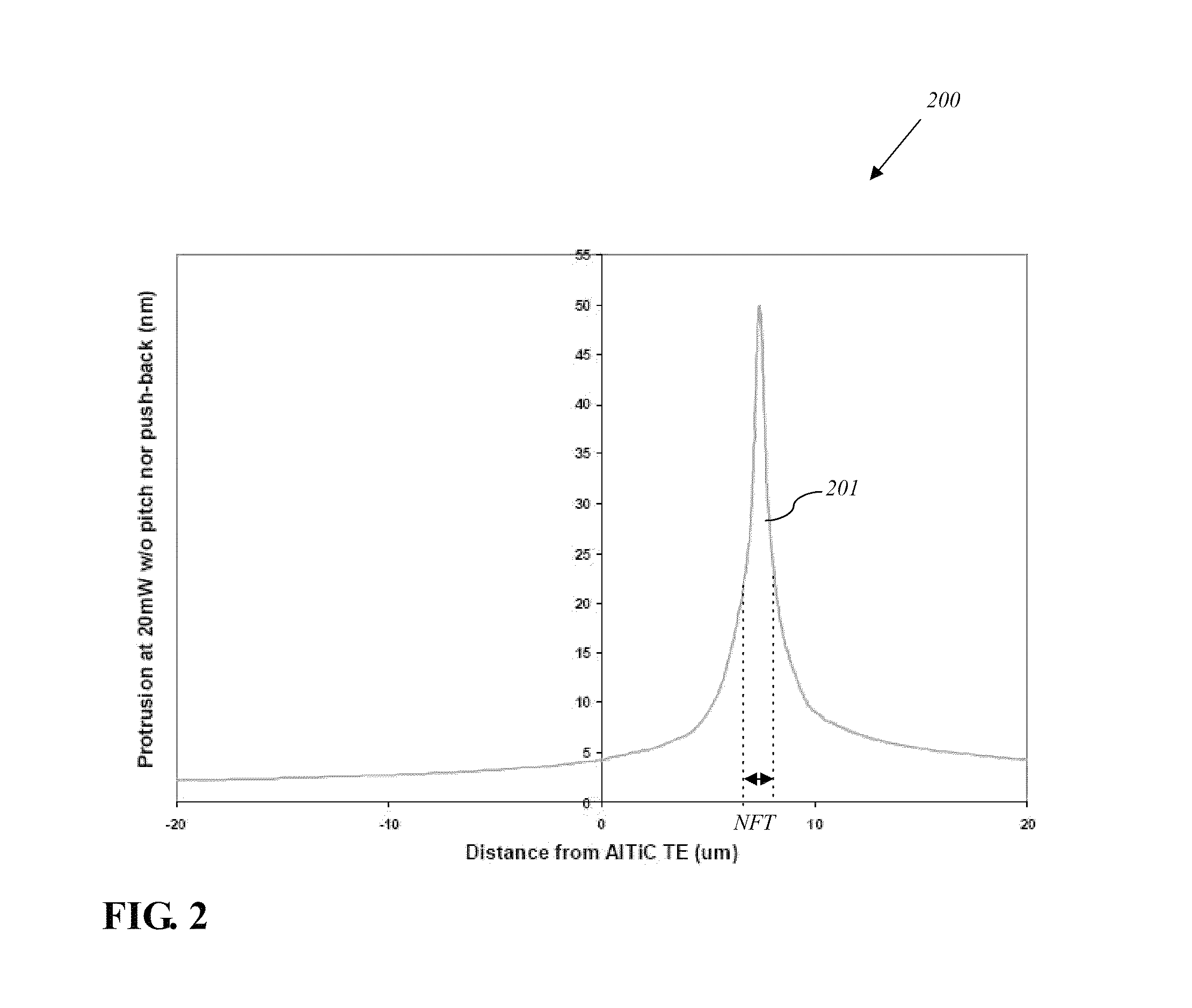
Reducing thermal protrusion of a near field transducer in an energy assisted magnetic recording head
ActiveUS8077418B1Preventing protrusion-related damageImprove reliabilityCombination recordingElectrical transducersTransducerOptical power
Methods of fabricating an energy-assisted magnetic recording (EAMR) head to compensate for a heat-induced protrusion of a near field transducer formed therein are disclosed. The methods can include applying optical power to the near field transducer to generate heat therein. The near field transducer protrudes beyond an air bearing surface of the EAMR head by the generated heat. The methods can further include removing a protruded portion of the near field transducer.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
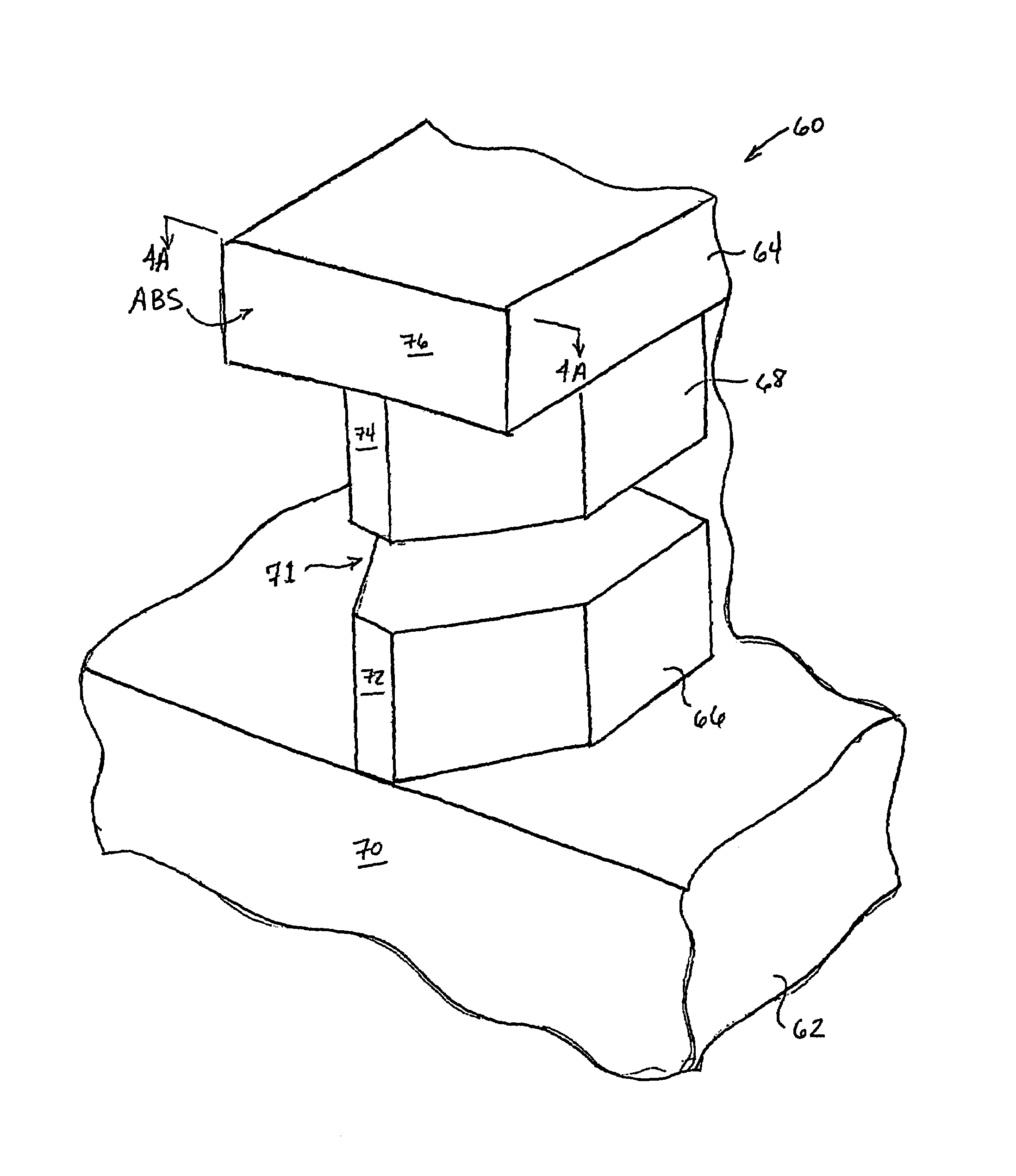
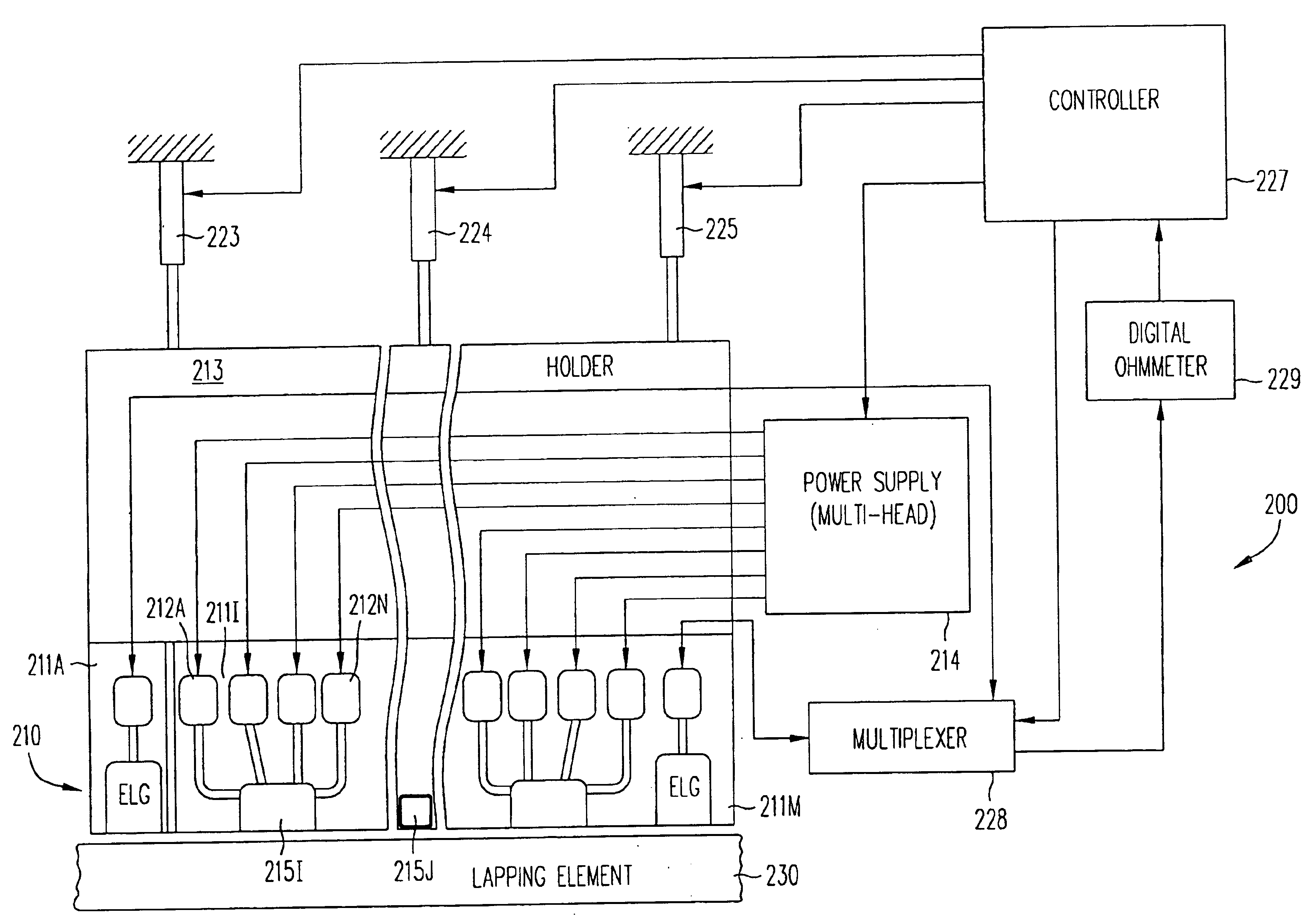
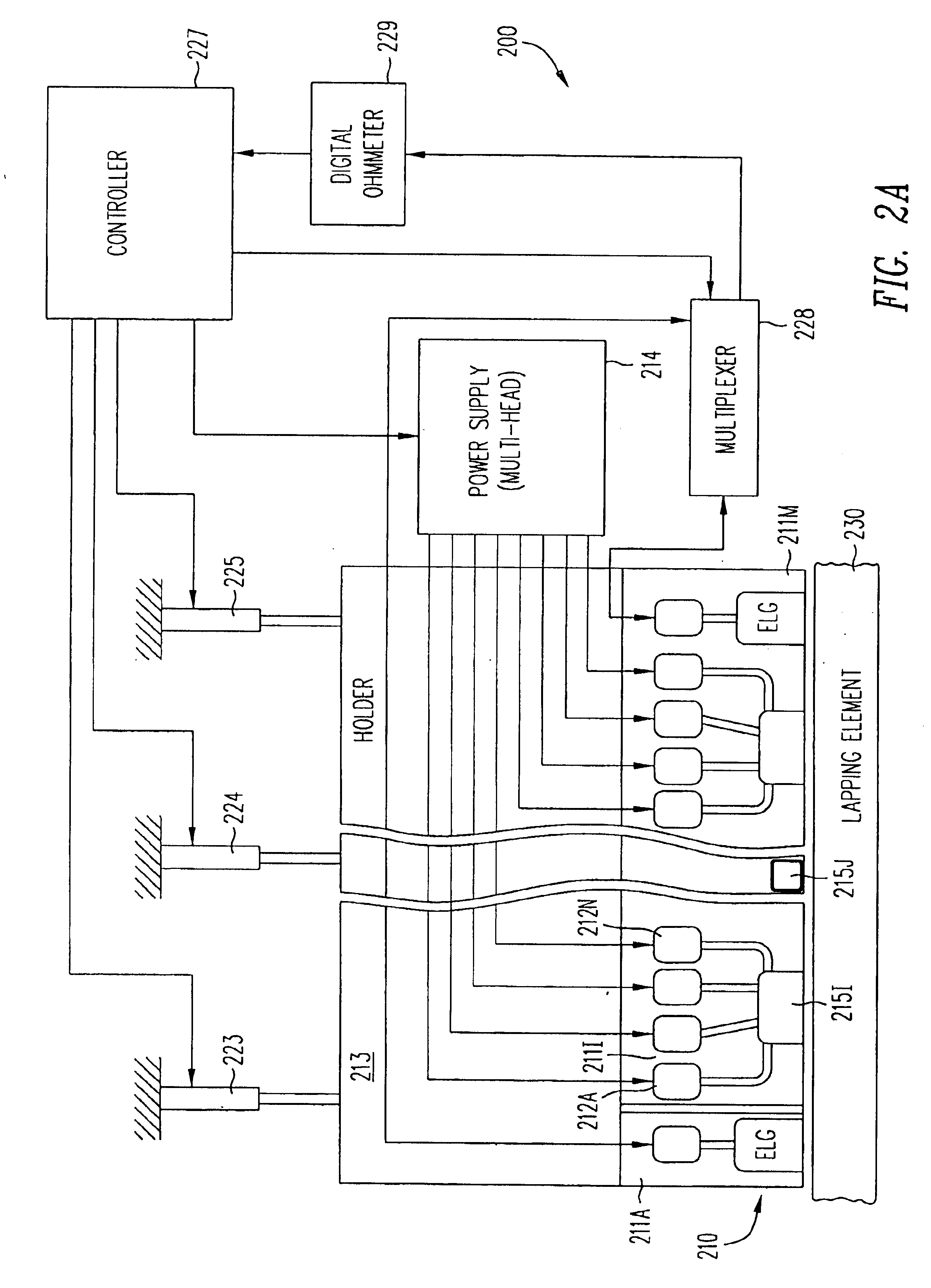
Method for providing an electronic lapping guide corresponding to a near-field transducer of an energy assisted magnetic recording transducer
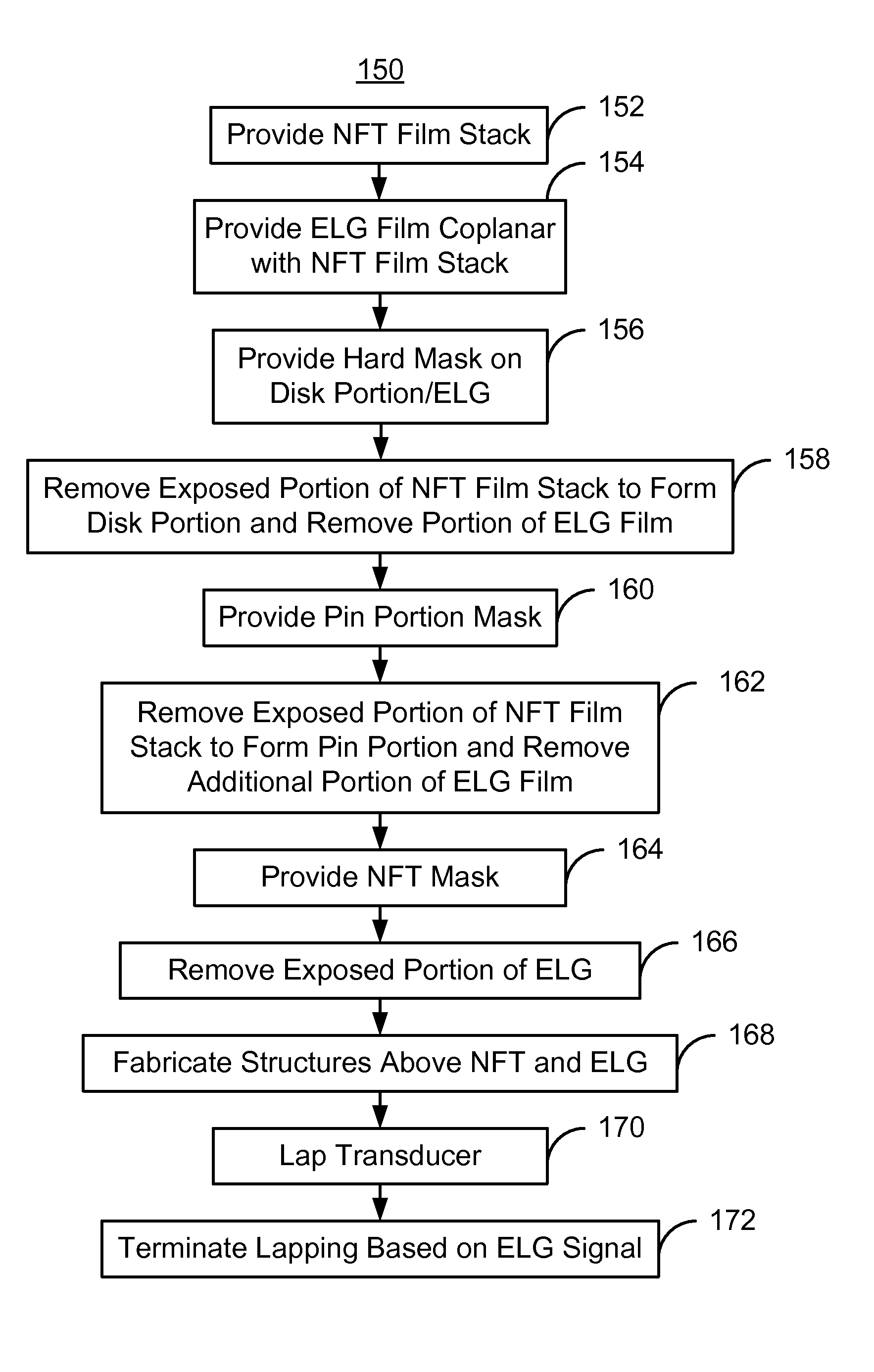
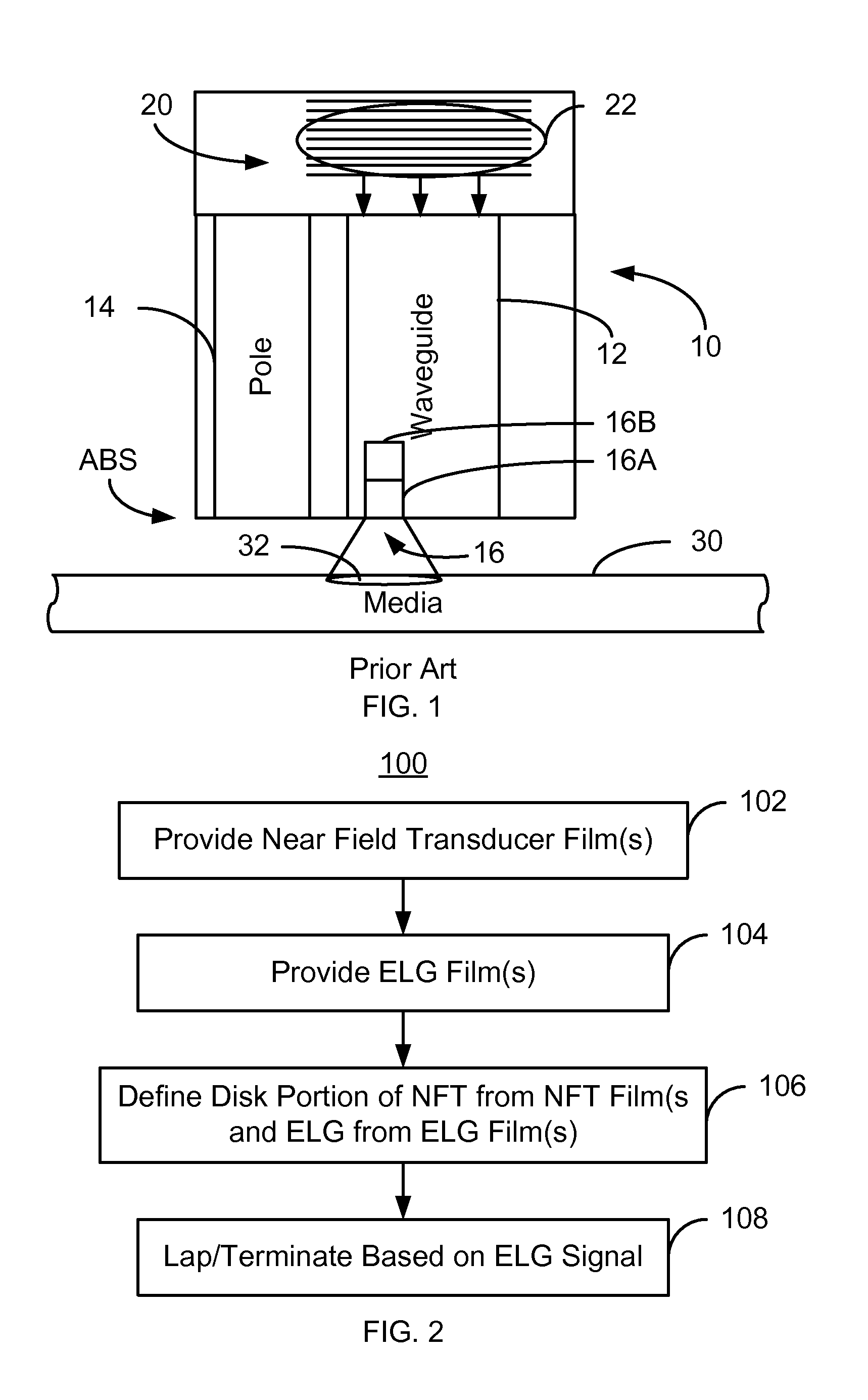
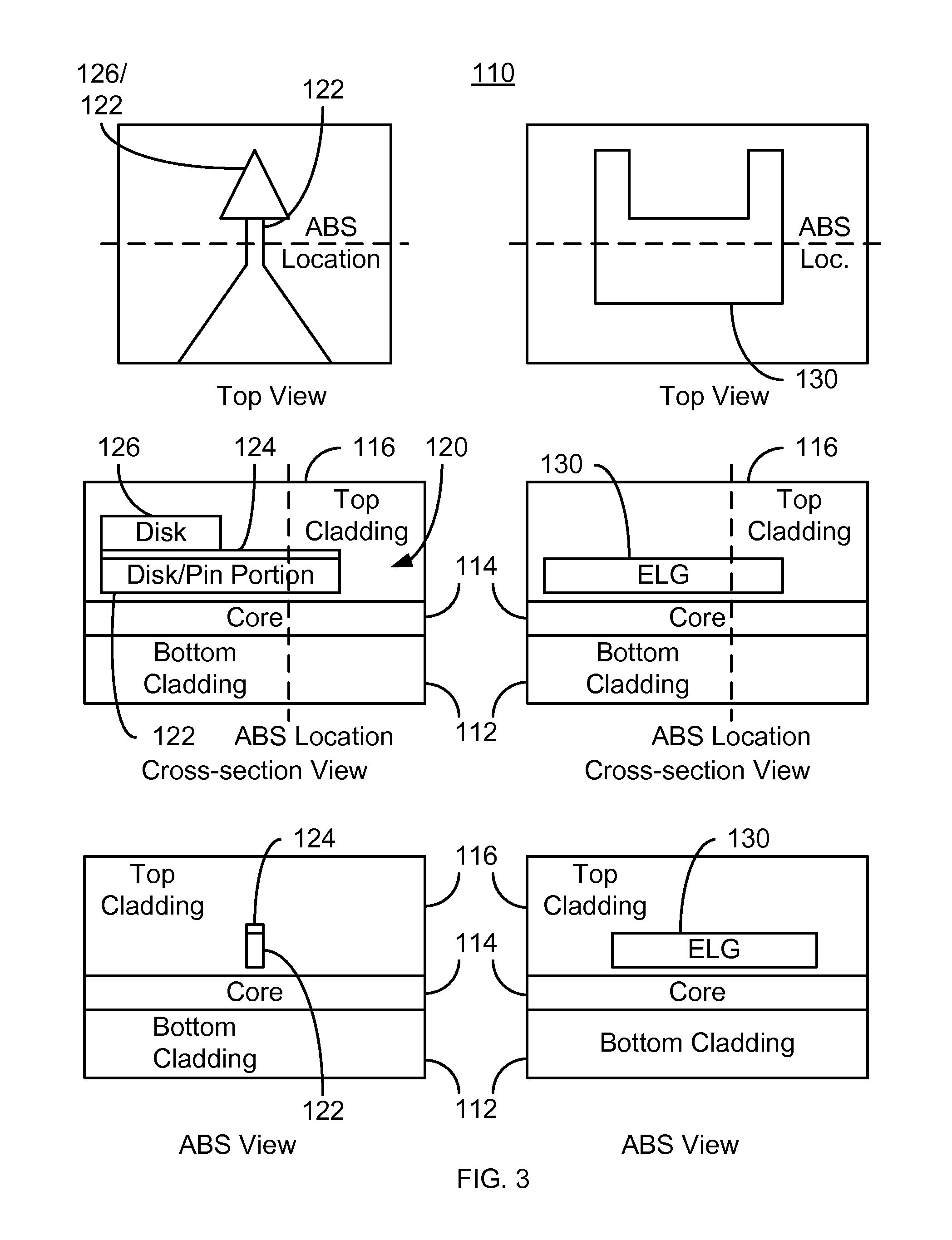
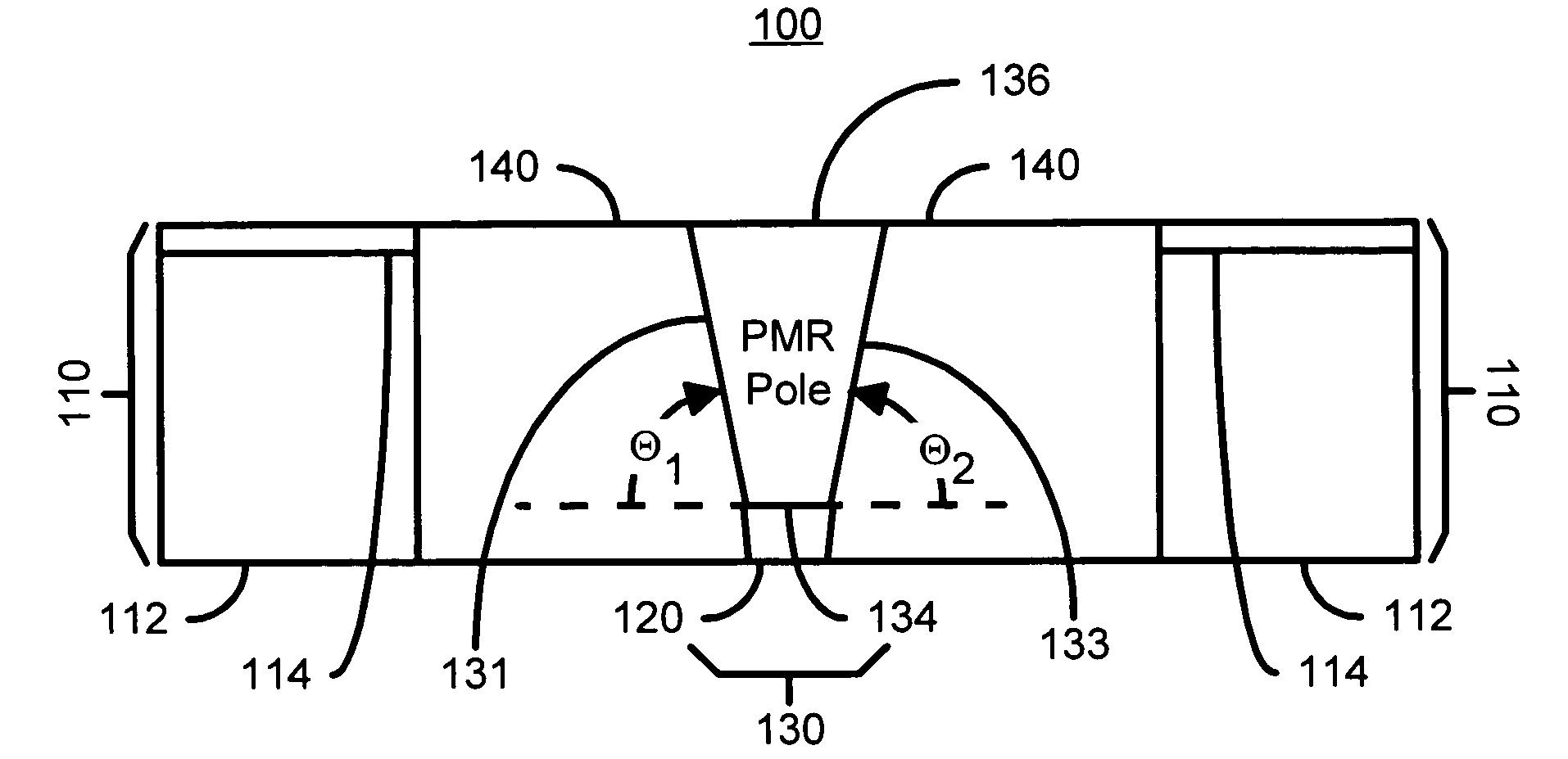
A method fabricates a transducer having an air-bearing surface (ABS). The method includes providing at least one near-field transducer (NFT) film and providing an electronic lapping guide (ELG) film substantially coplanar with a portion of the at least one NFT film. The method also includes defining a disk portion of an NFT from the portion of the at least one NFT film and at least one ELG from the ELG film. The disk portion corresponds to a critical dimension of the NFT from an ABS location. The method also includes lapping the at least one transducer. The lapping is terminated based on a signal from the ELG.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
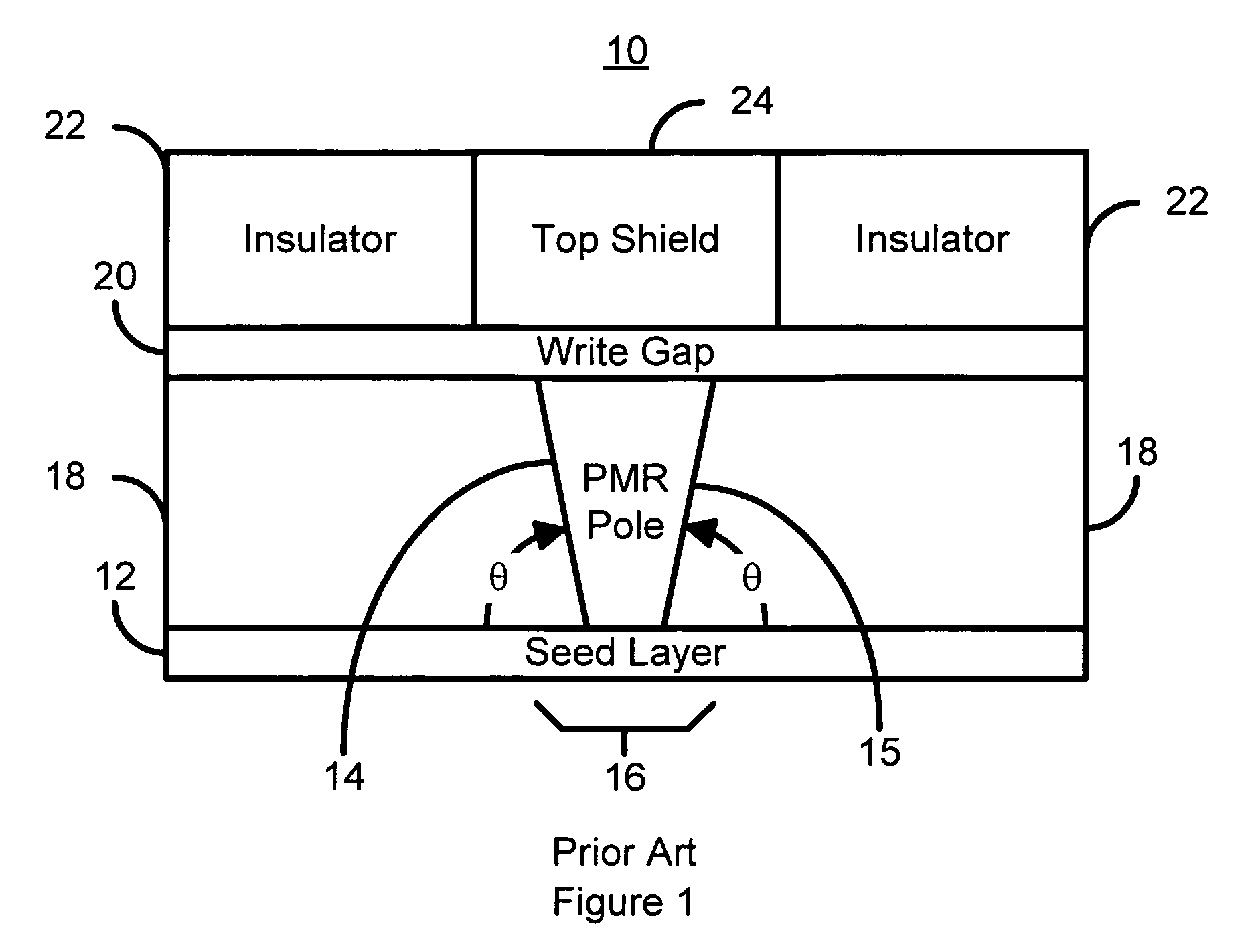
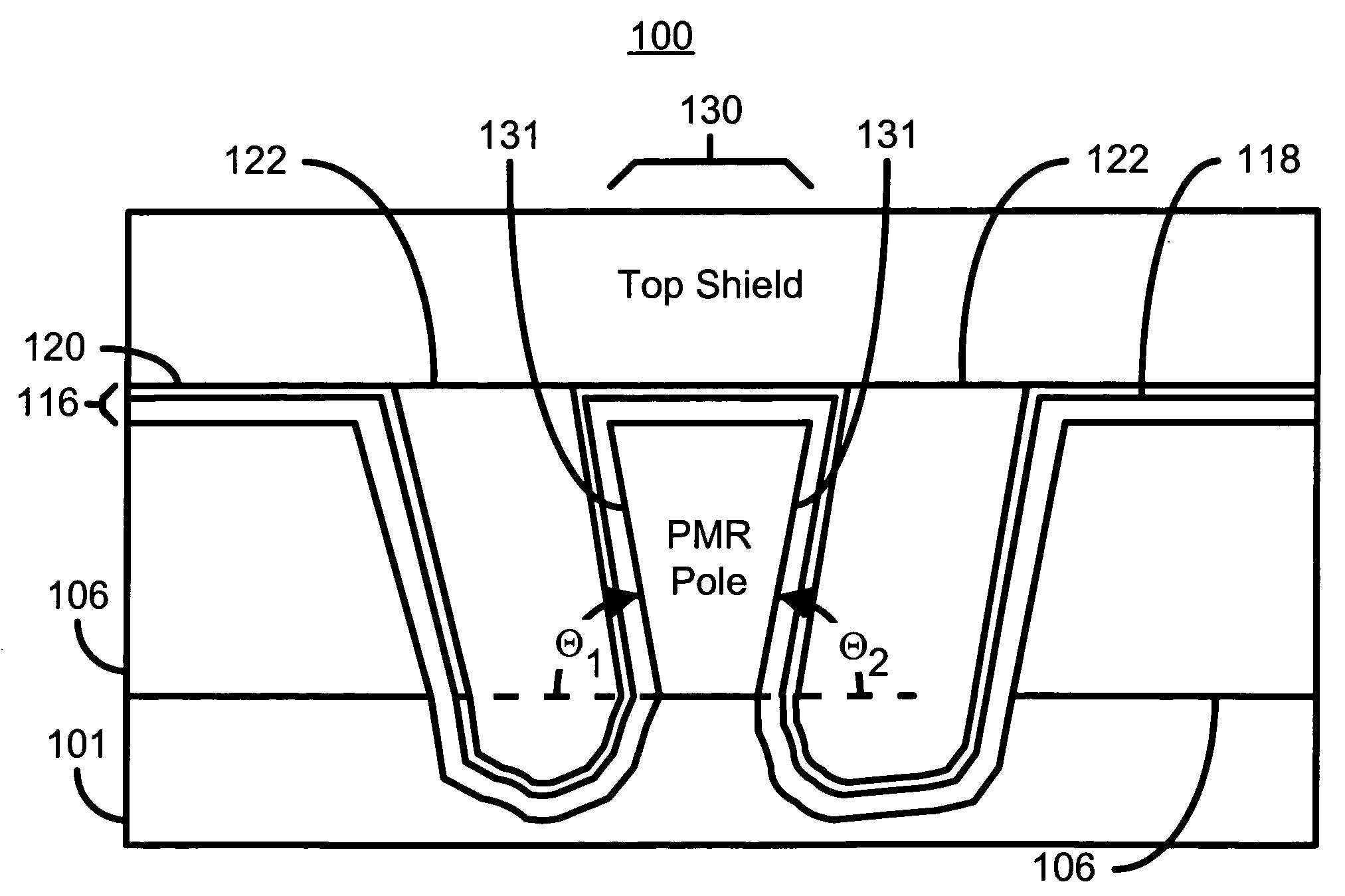
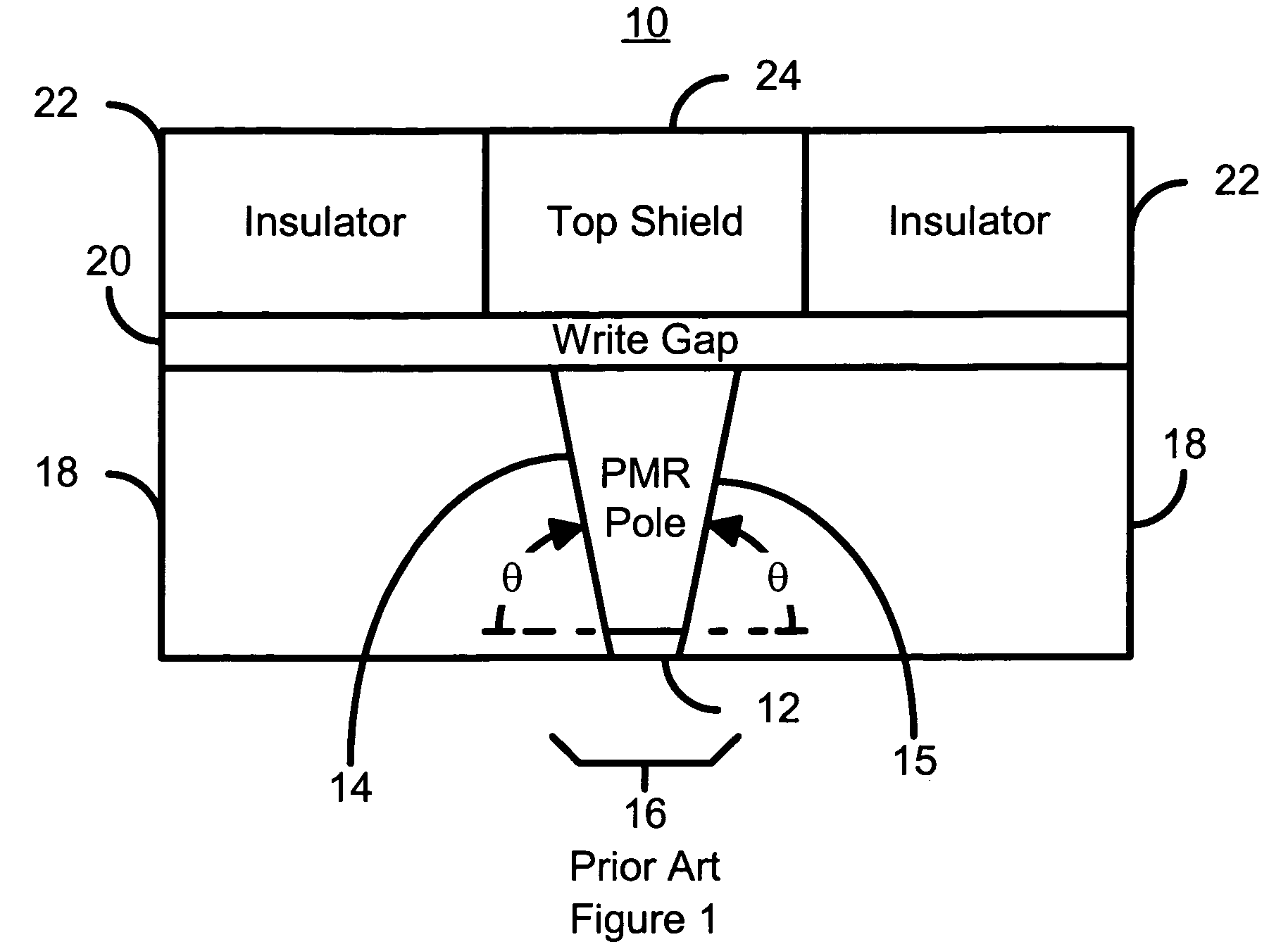
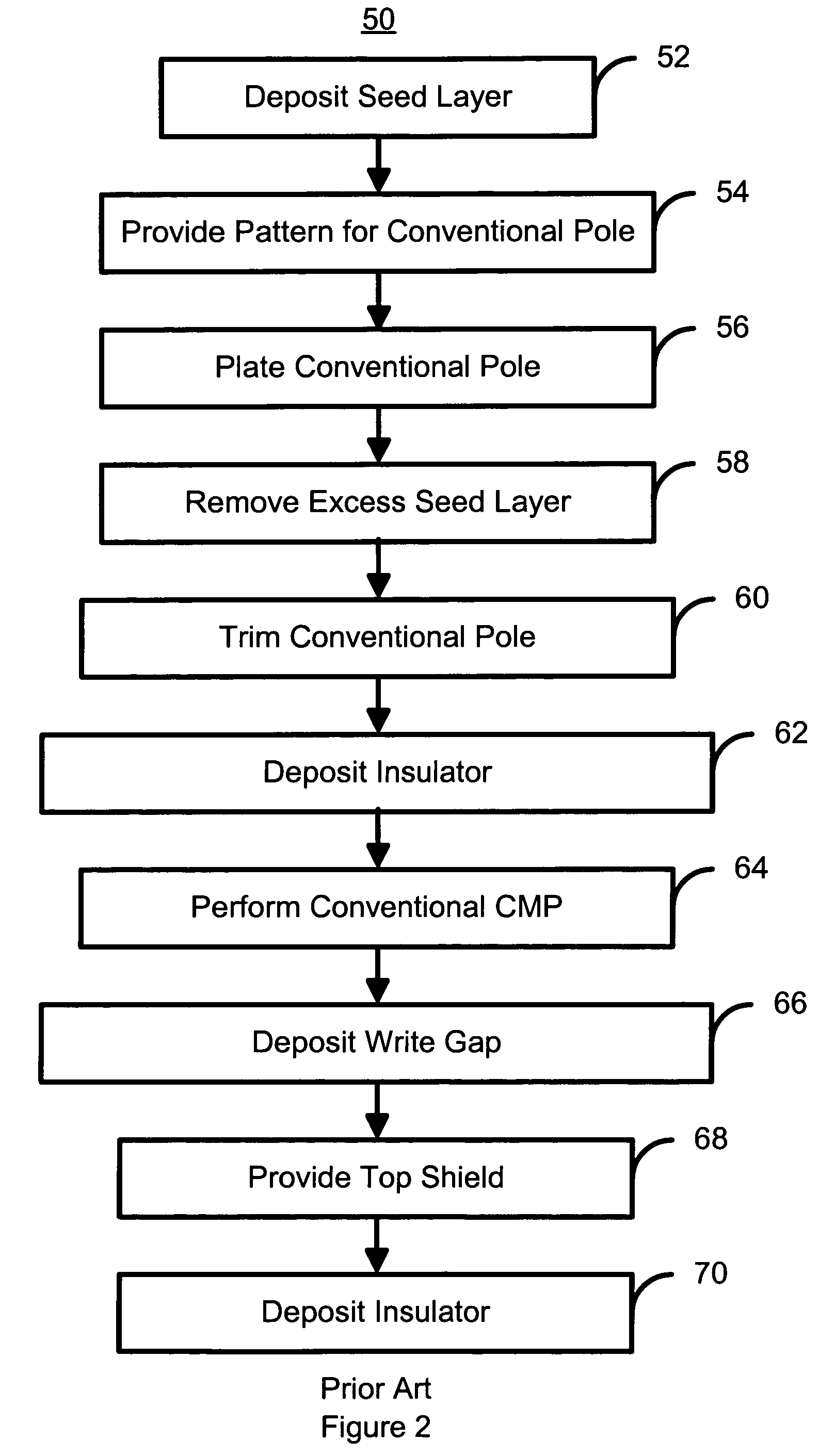
Method for manufacturing a perpendicular magnetic recording head
InactiveUS7296339B1Construction of head windingsElectrical transducersEngineeringChemical-mechanical planarization
A method and system for manufacturing a perpendicular magnetic recording head is disclosed. The method and system include providing a chemical mechanical planarization (CMP) uniformity structure having an aperture therein and forming a perpendicular magnetic recording pole within the aperture. The CMP uniformity structure may include a CMP barrier layer. The method and system further include fabricating an insulator after formation of the perpendicular magnetic recording pole and performing a CMP to remove a portion of the insulator, expose a portion of the perpendicular magnetic recording pole and planarize an exposed surface of the perpendicular magnetic recording head.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Method of forming a fully wrapped-around shielded PMR writer pole
InactiveUS8533937B1Reduce and eliminate shadowing effectGood deposition coverageElectrical transducersManufacture head surfaceEngineeringNon magnetic
A method or forming a wrapped-around shielded perpendicular magnetic recording writer pole is disclosed. A structure comprising a leading shield layer and an intermediate layer disposed over the leading shield layer is provided, the intermediate layer comprising a pole material and a dielectric material. A trench is formed in the dielectric material. A non-magnetic layer in the trench is removed via an ion beam etching process. A seed layer is deposited in the trench and over the pole material. A magnetic material comprising a side shield layer is deposited on at least a portion of the seed layer.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
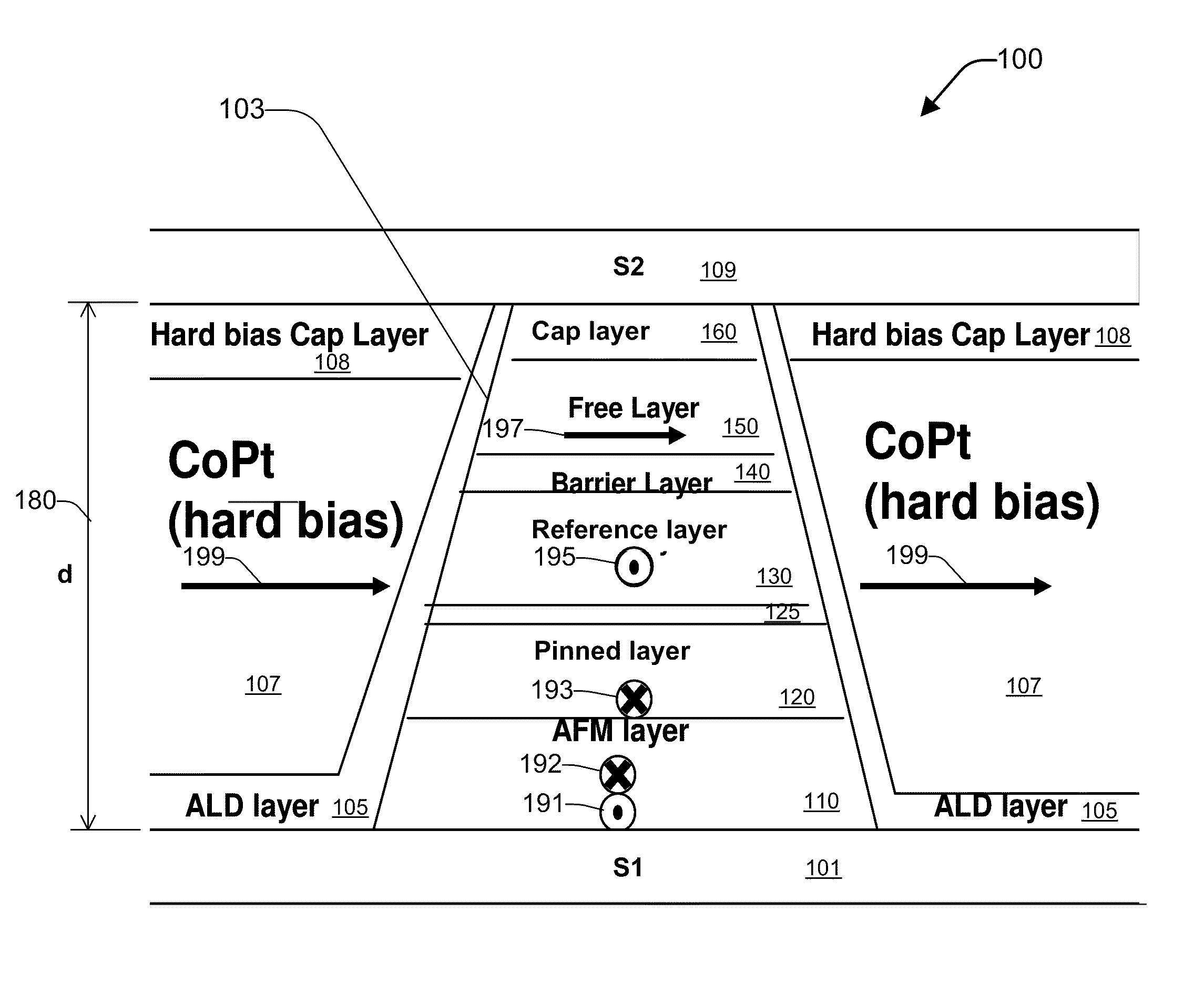
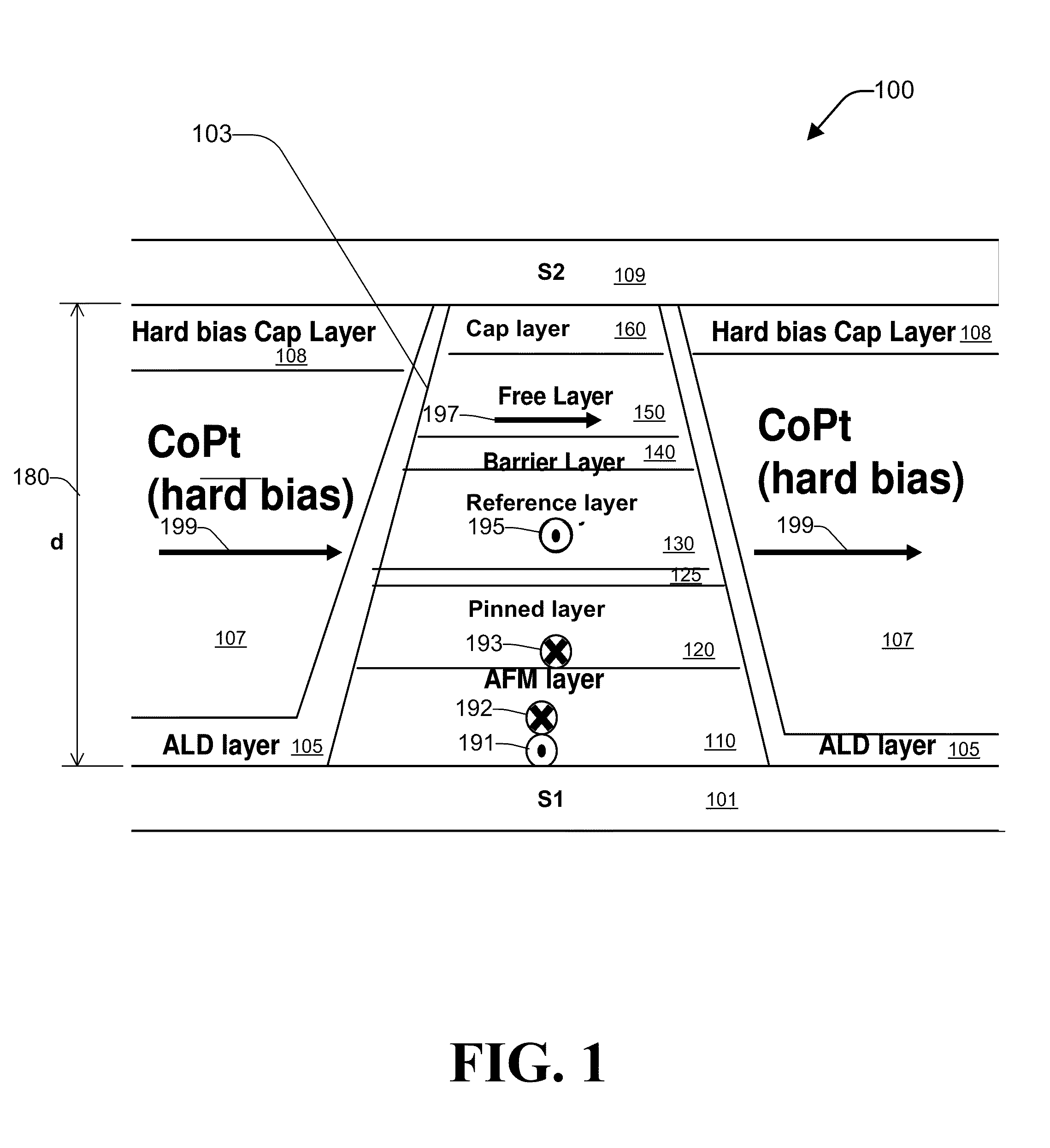
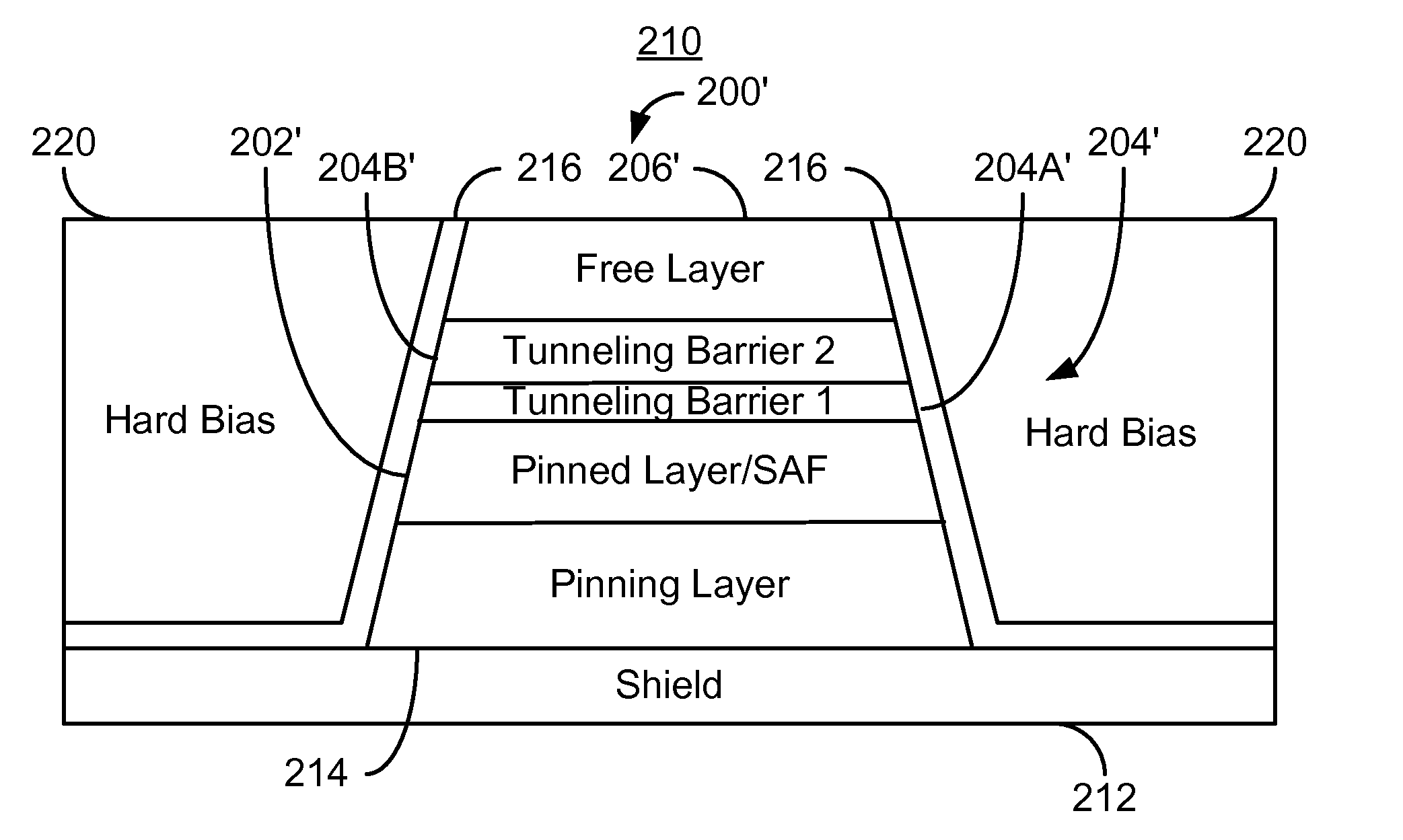
Method for forming a hard bias structure in a magnetoresistive sensor
A method for forming a hard bias structure in a magnetoresistive sensor is disclosed. A magnetoresistive sensor having a soft magnetic bias layer, spacer layer, and a magnetoresistive layer, is formed over a substrate having a gap layer. A mask is formed over a portion of the magnetoresistive sensor structure to define a central region. The masked structure is ion milled to remove portions not shielded by the mask, to form the central region with sloped sides, and to expose a region of the gap layer laterally adjacent the sloped sides. A first underlayer is deposited onto at least the sloped sides at a high deposition angle. A second underlayer is deposited to at least partially overlap the first underlayer, and at a first lower deposition angle. A hard bias layer is deposited over at least a portion of the second underlayer, and at a second lower deposition angle.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Method of forming a magnetoresistive device
A method of forming a head comprises forming a write transducer on a wafer, cutting the wafer to produce a slider bar with a cut surface, and planarizing the cut surface of the slider bar. Forming the write transducer can include forming a first pole layer and forming a first pole pedestal layer over the first pole layer, where the first pole pedestal layer includes a tapered portion defined by a first end having a nose width less than a desired final nose width, and a second end having a zero throat width greater than the desired final nose width. Planarizing the cut surface of the slider bar exposes the first pole pedestal layer until a width thereof approximately equals the desired final nose width.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Self-aligned method for fabricating a high density GMR read element
A method is provided for fabricating a read element with leads that overlay a top surface of a sensor of the read element. The method includes forming a mask over a sensor layer, then using the mask to define the sensor from the sensor layer. The mask is then narrowed and a lead layer is formed that overlays both ends of the top surface of the sensor without covering a center portion of the top surface.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Method for making high speed, high areal density inductive write structure
InactiveUS7007372B1Excellent magnetic propertiesIncrease coverageDecorative surface effectsVacuum evaporation coatingMagnetic mediaMagnetic poles
An inductive write element is disclosed for use in a magnetic data recording system. The write element provides increased data rate and data density capabilities through improved magnetic flux flow through the element. The write element includes a magnetic yoke constructed of first and second magnetic poles. The first pole includes a pedestal constructed of a high magnetic moment (high Bsat) material, which is preferably FeRhN nanocrystalline films with lamination layers of CoZrCr. The second pole includes a thin inner layer of high Bsat material (also preferably FeRhN nanocrystalline films with lamination layers of CoZrCr), the remainder being constructed of a magnetic material capable of being electroplated, such as a Ni—Fe alloy. An electrically conductive coil passes through the yoke between the first and second poles to induce a magnetic flux in the yoke when an electrical current is caused to flow through the coil. Magnetic flux in the yoke produces a fringing field at a write gap whereby a signal can be imparted onto a magnetic medium passing thereby.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
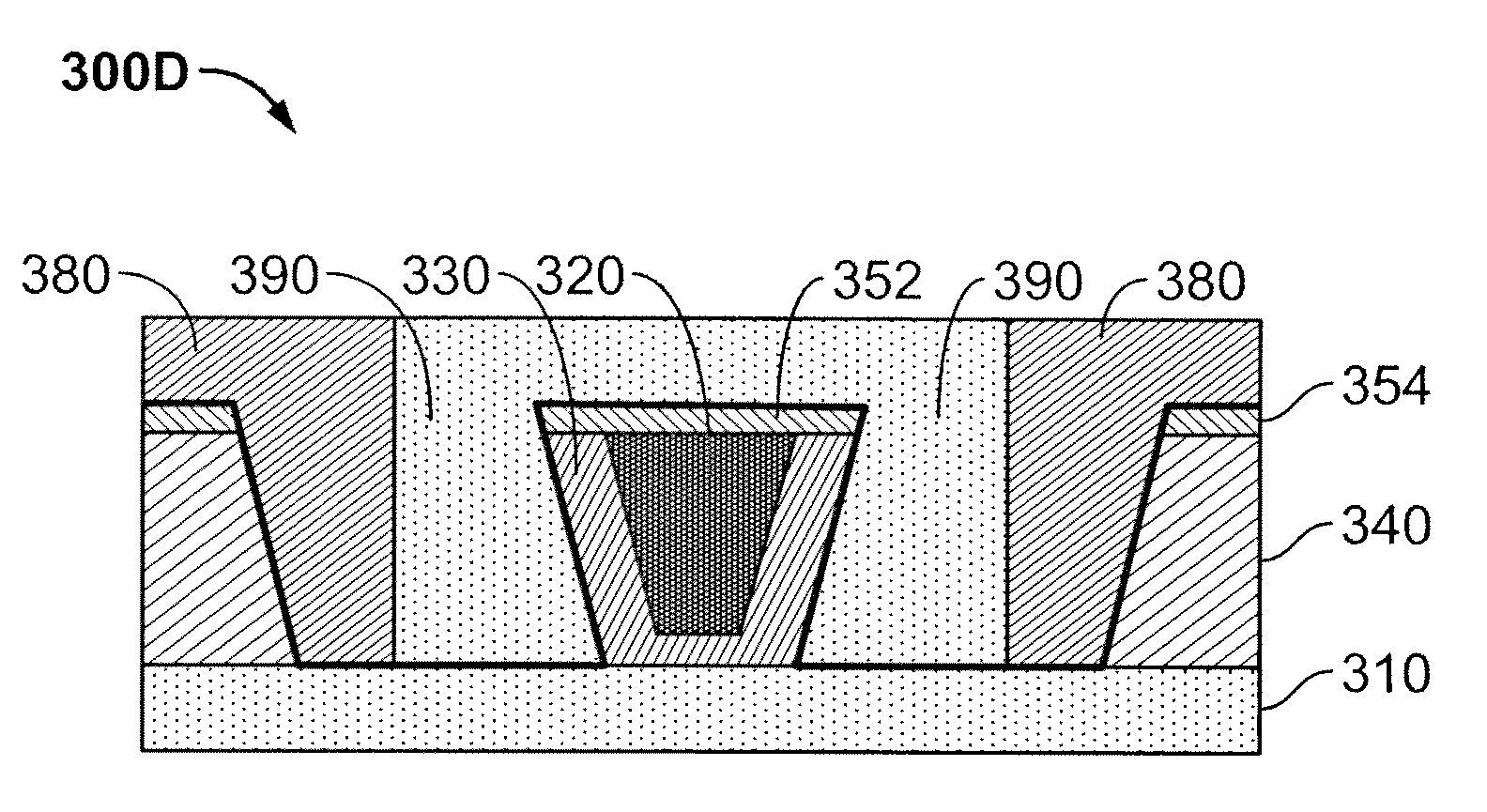
Method for providing a wrap-around shield for a magnetic recording transducer
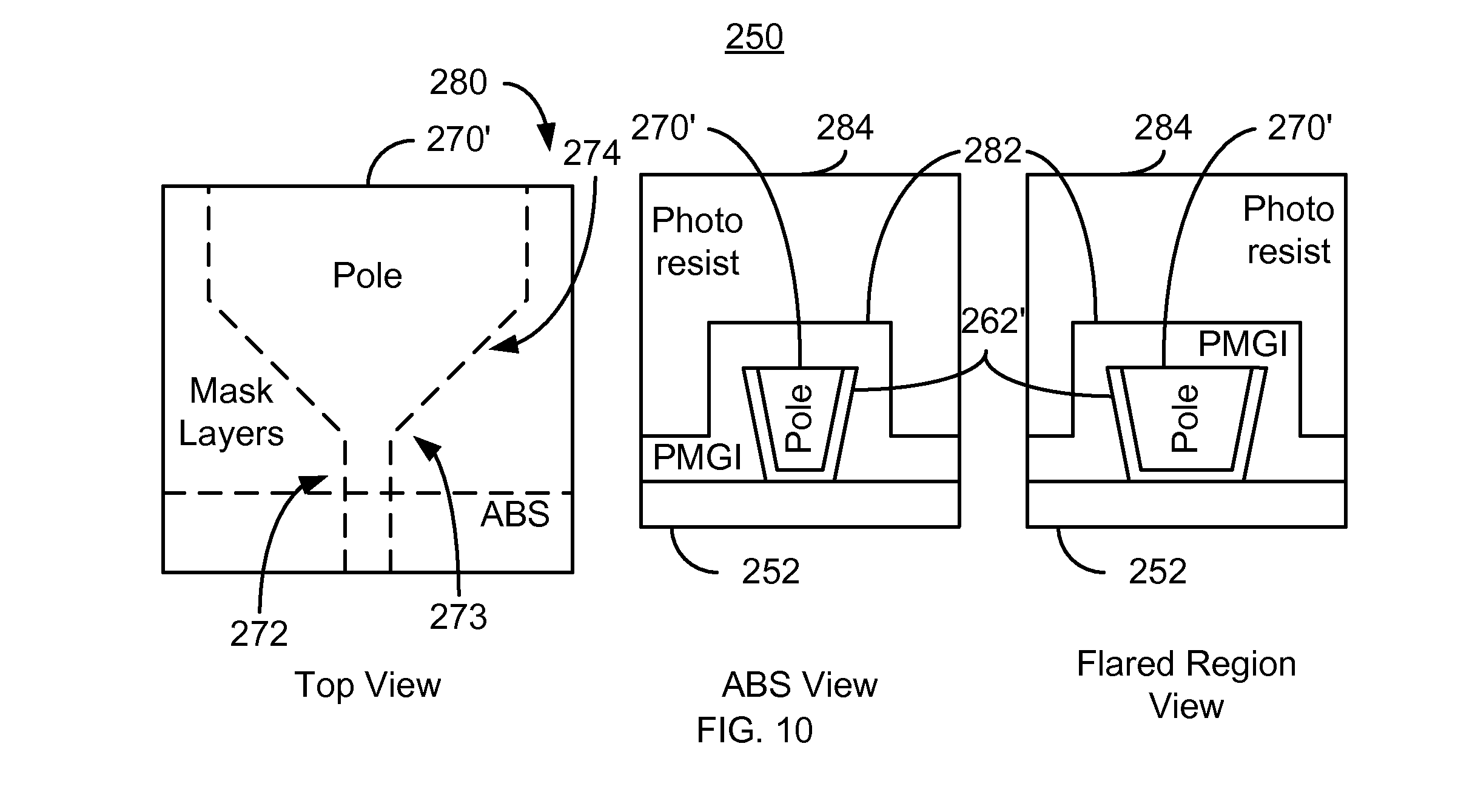
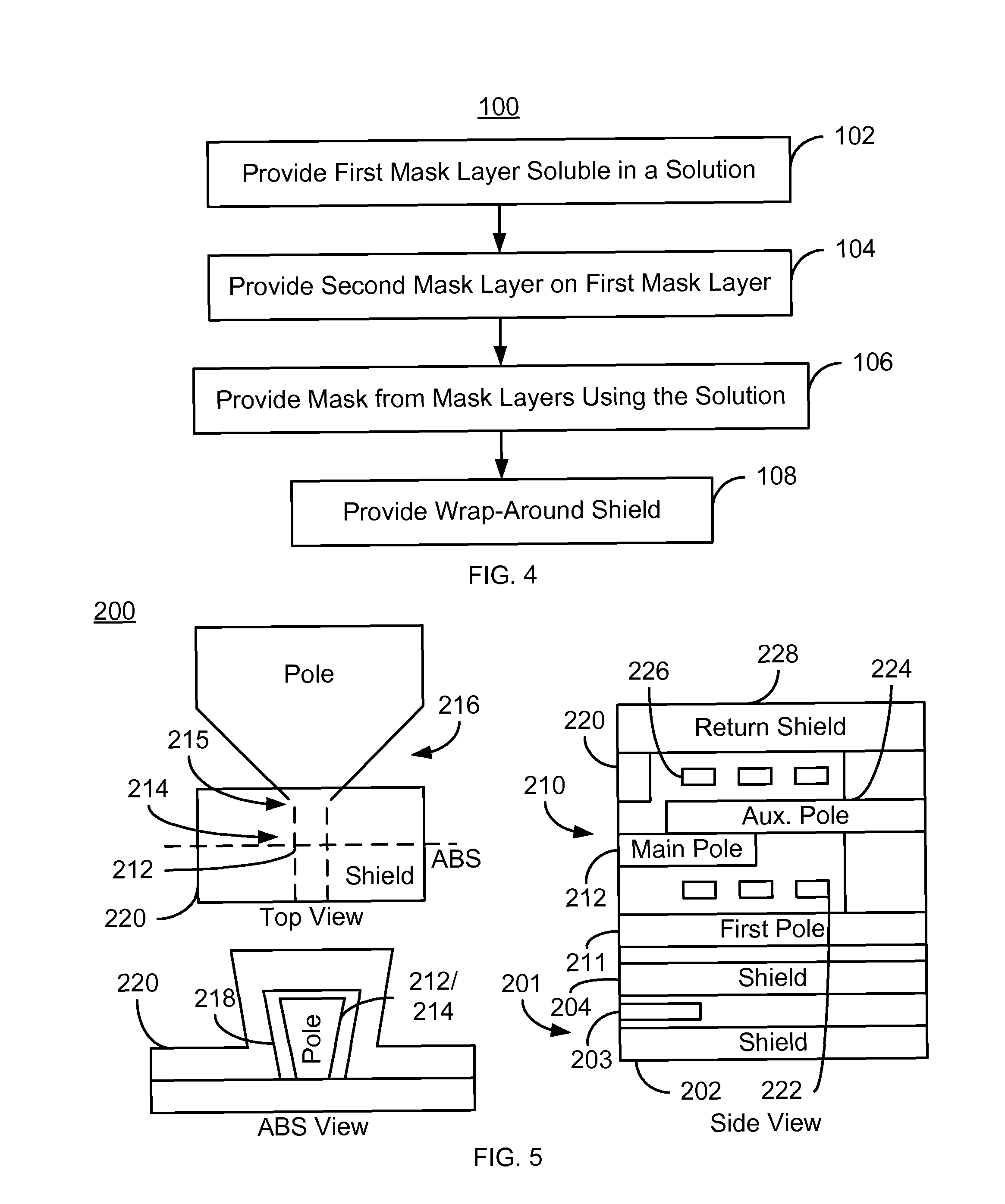
A method for fabricating a magnetic transducer is described. The magnetic transducer includes a pole having a pole tip and a flared region. The method Includes providing a first mask layer on the pole and providing a second mask layer on the first mask layer. The first mask layer is soluble in a predetermined solution and has a first thickness. The second mask layer has a second thickness greater than the first thickness. The method also includes forming a mask from the first mask layer and the second mask layer. The step of forming the mask layer includes using the predetermined solution. The mask has a pattern that exposes a portion of the pole tip and covers a portion of the flared region. The method also includes providing a wrap-around shield on at least the pole tip.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Method for fabricating a magnetic recording transducer
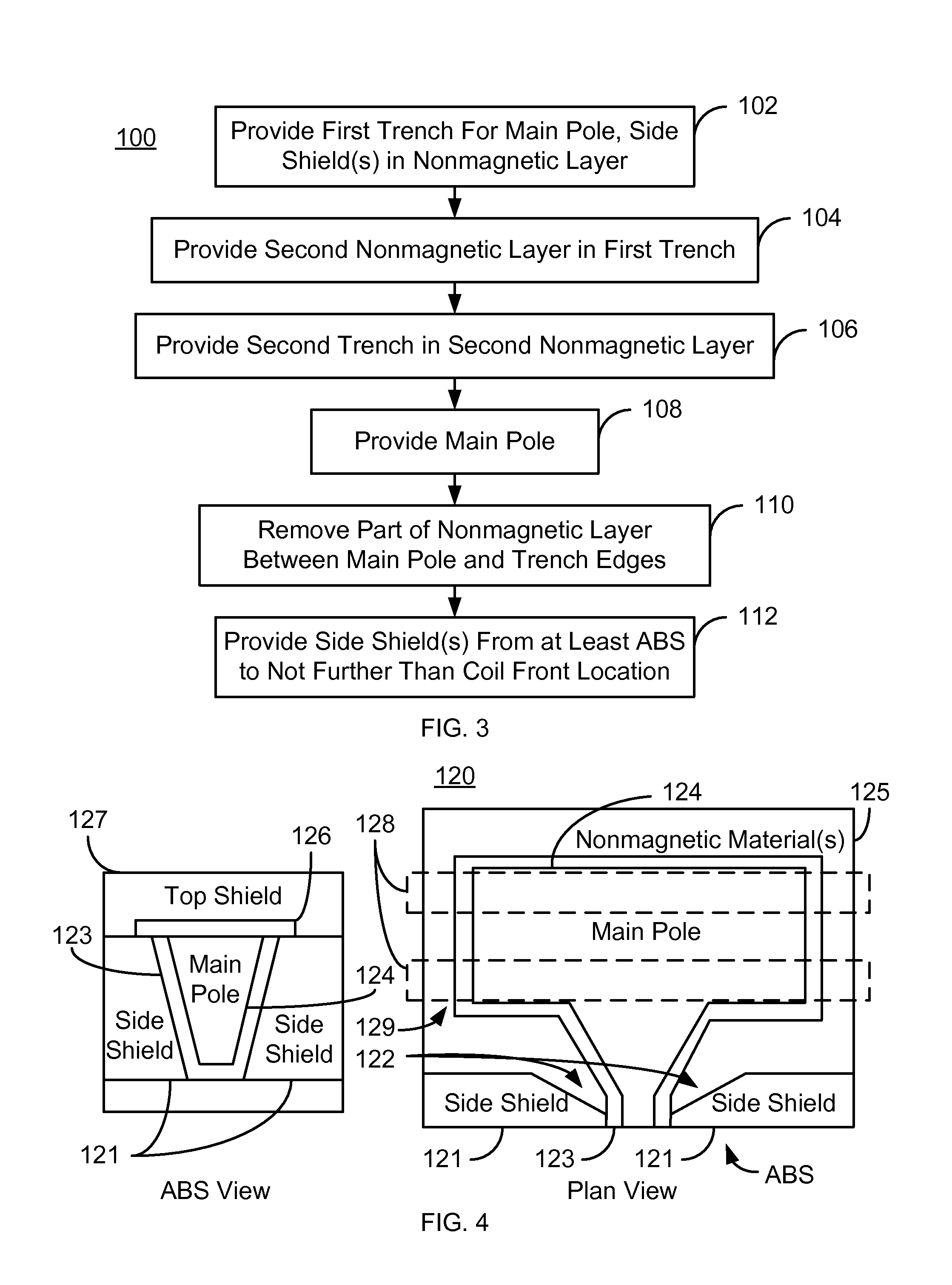
ActiveUS8276258B1Manufacture head surfaceElectrical transducersMagnetic transducersAir bearing surface
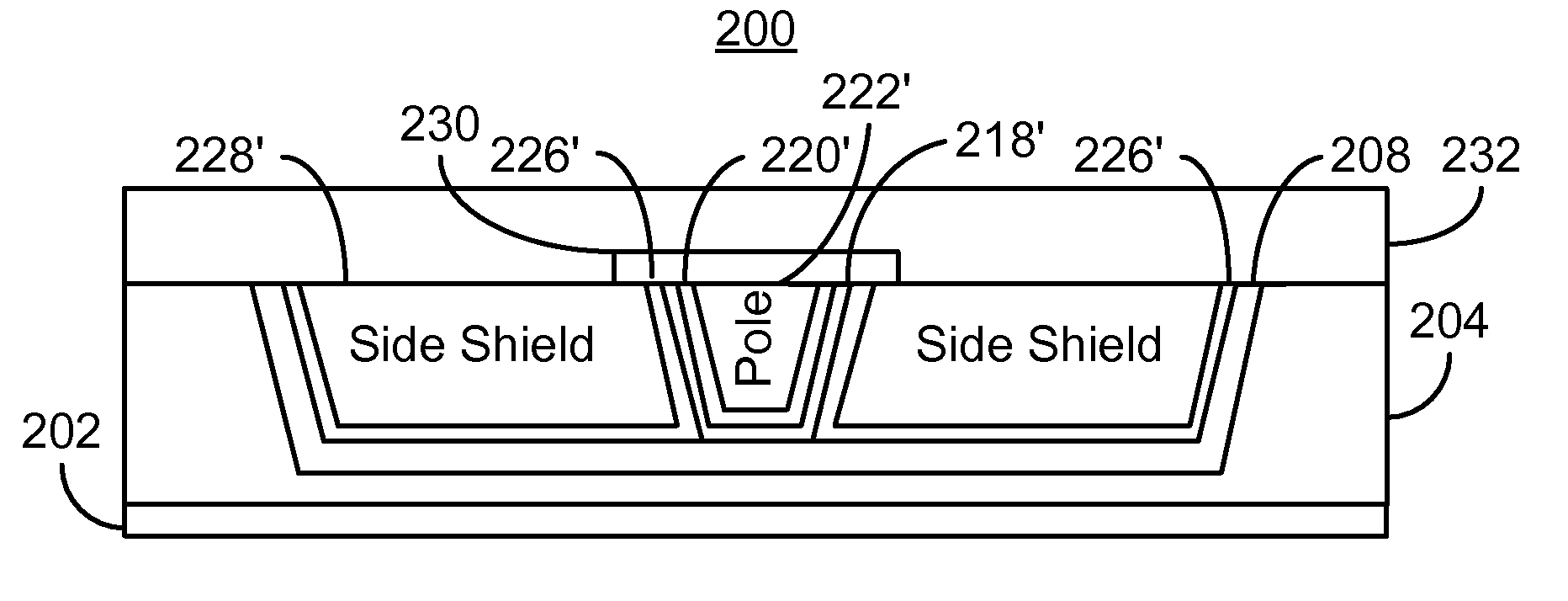
A method and system provide a magnetic transducer that includes an underlayer and a first nonmagnetic layer on the underlayer. The method and system include providing a first trench in the first nonmagnetic layer. The first trench has at least one edge corresponding to at least one side shield. The method and system also include providing a second nonmagnetic layer in the first trench and providing a second trench in the second nonmagnetic layer. The method and system include providing the main pole. At least part of the main pole resides in the second trench. The method and system further include removing at least a portion of the second nonmagnetic layer between the edge(s) and the main pole. The method and system also provide the side shield(s) in the first trench. The side shield(s) extend from at least an air-bearing surface location to not further than a coil front location.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
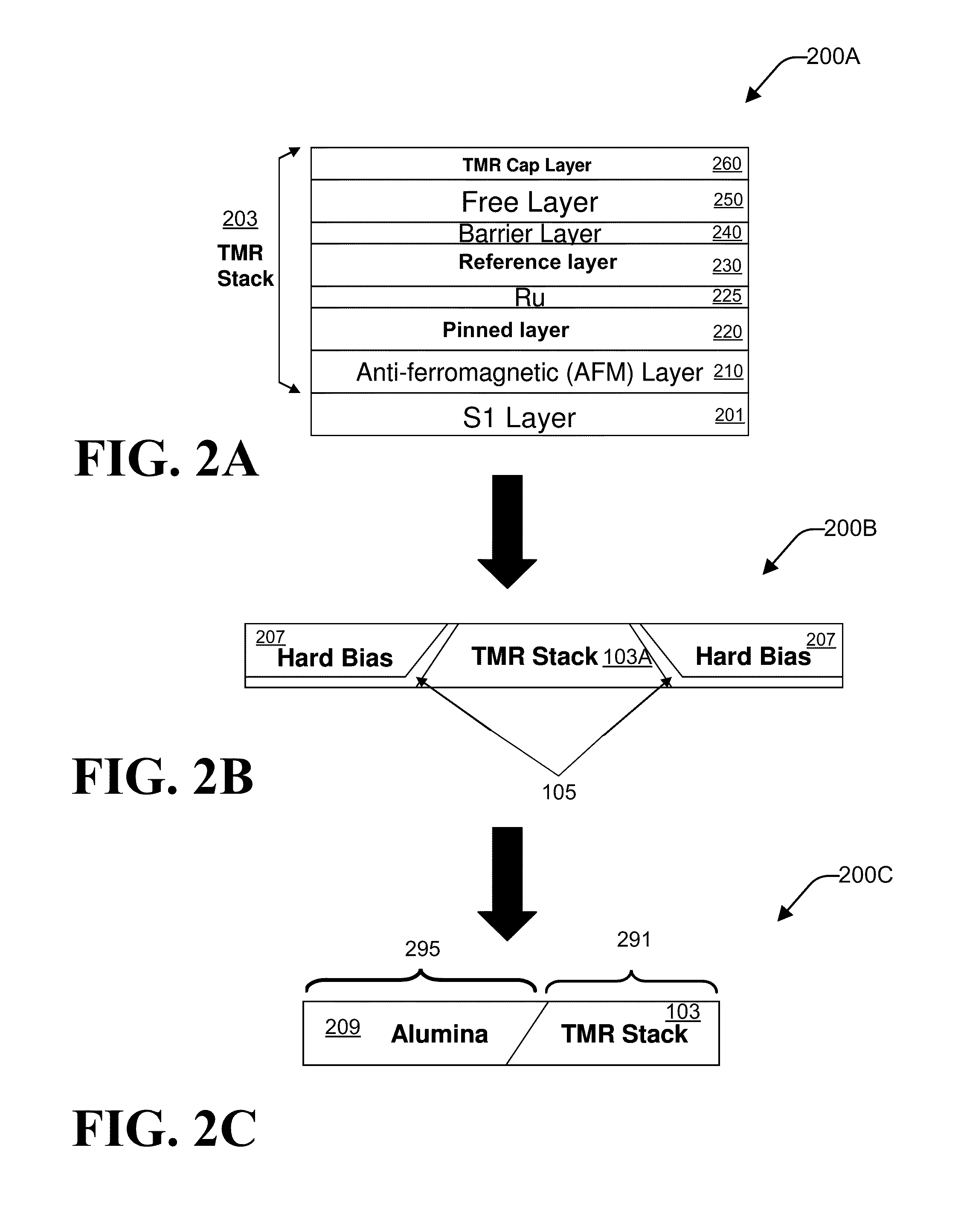
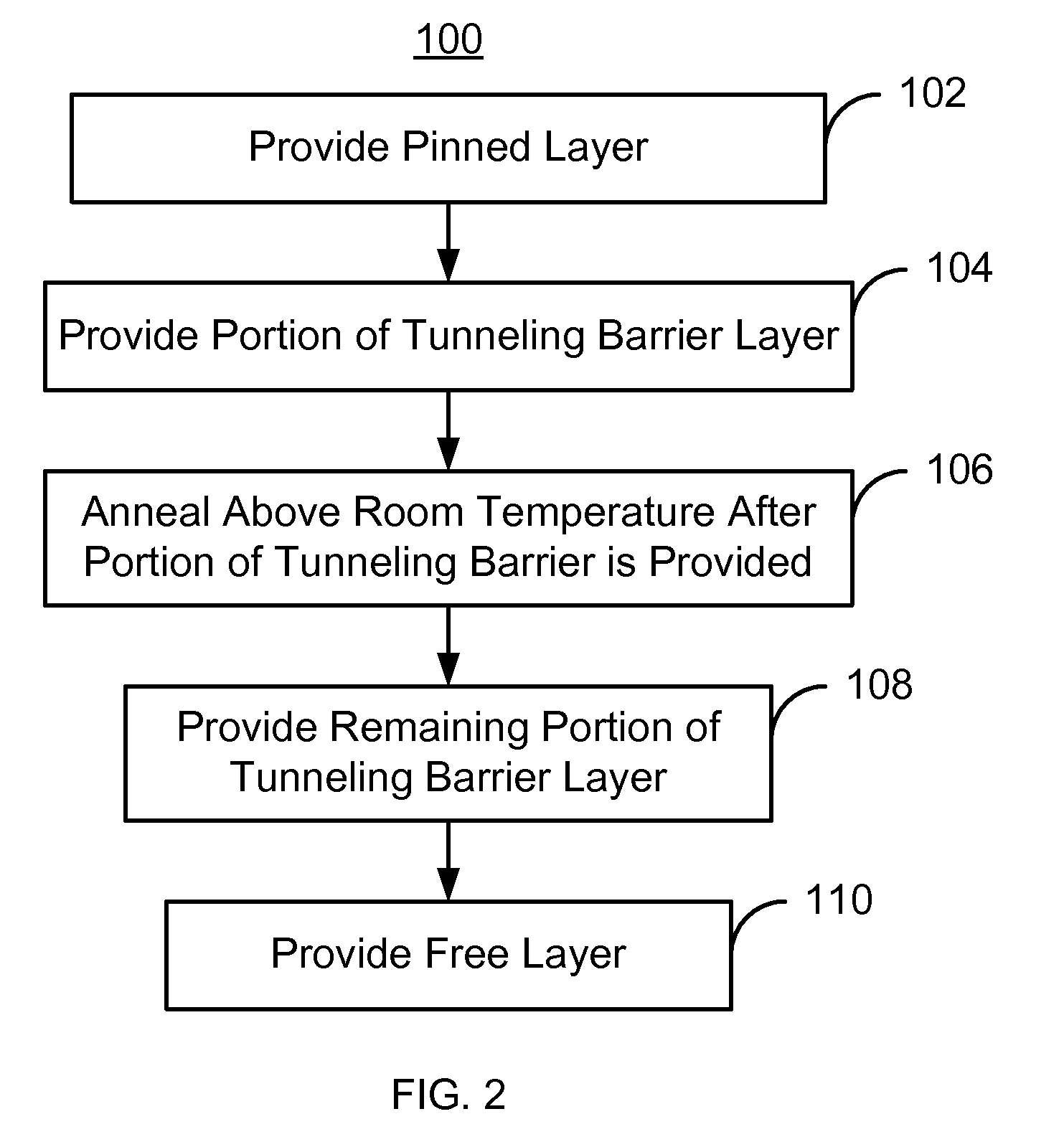
Method of fabricating a tunneling magnetoresistive (TMR) reader
A method of fabricating a tunneling magnetoresistance (TMR) reader is disclosed. A TMR structure comprising at least one ferromagnetic layer and at least one nonmagnetic insulating layer is provided. A first thermal annealing process on the TMR structure is performed. A reader pattern definition process performed on the TMR structure to obtain a patterned TMR reader. A second thermal annealing process is performed on the patterned TMR reader.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
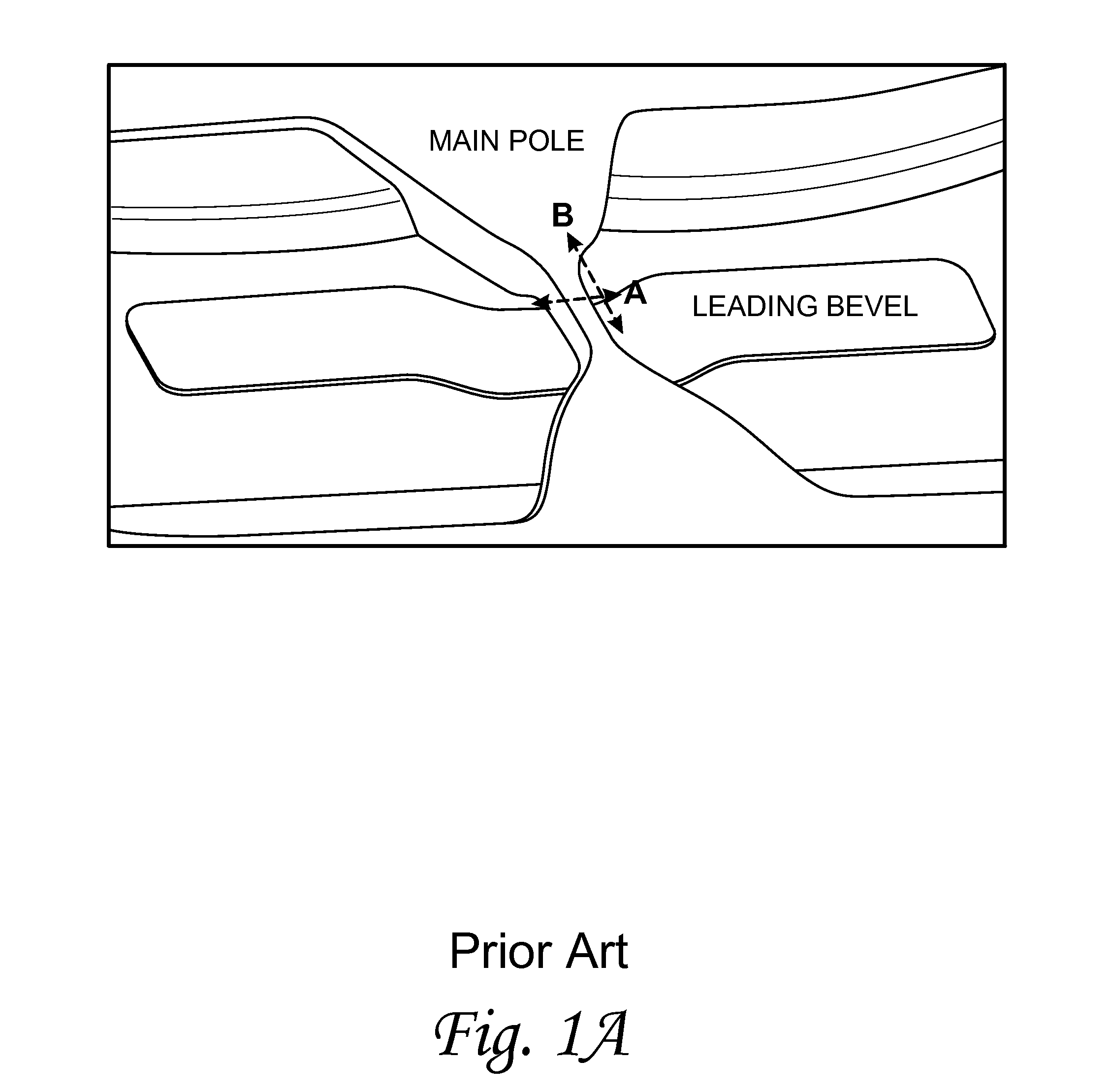
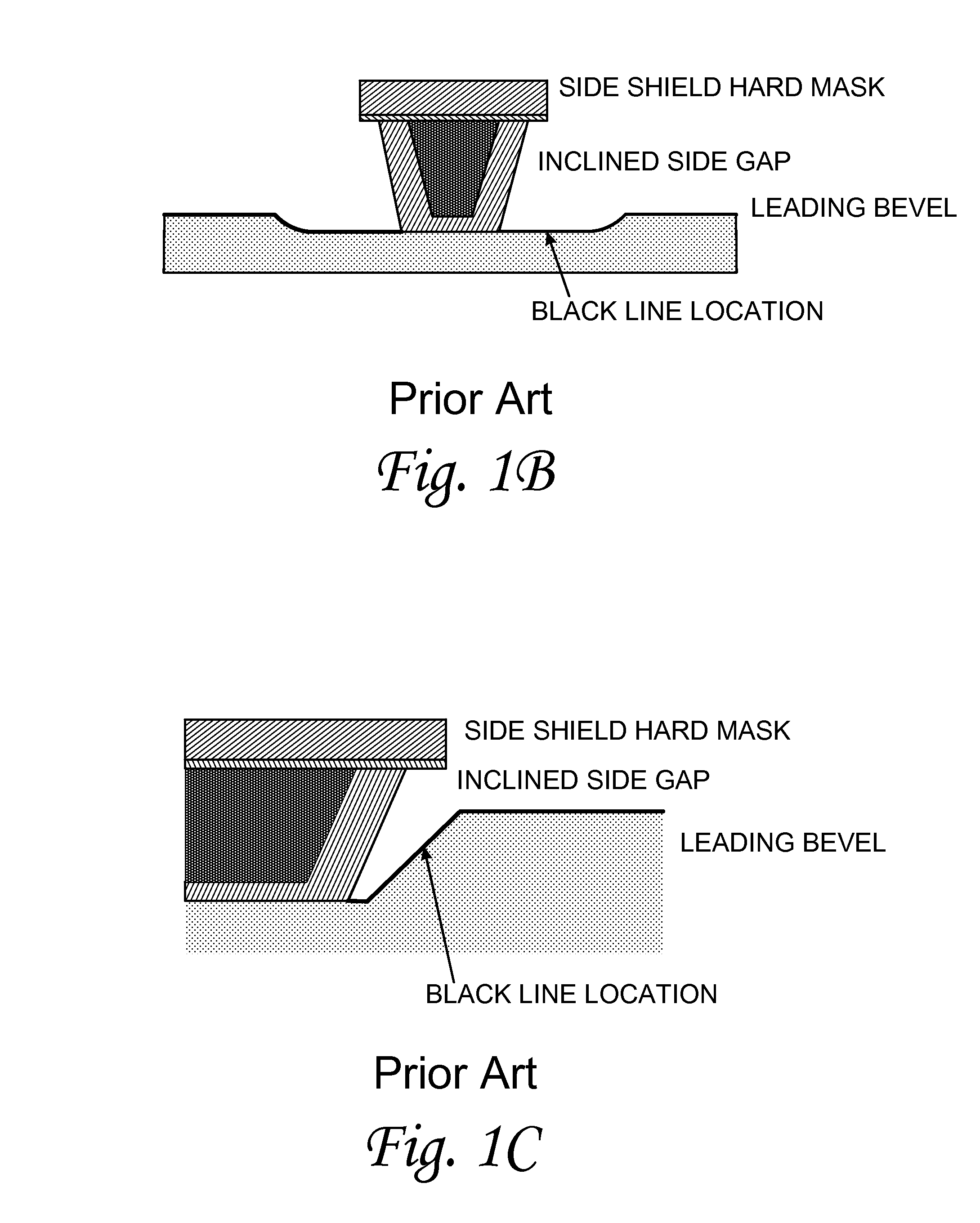
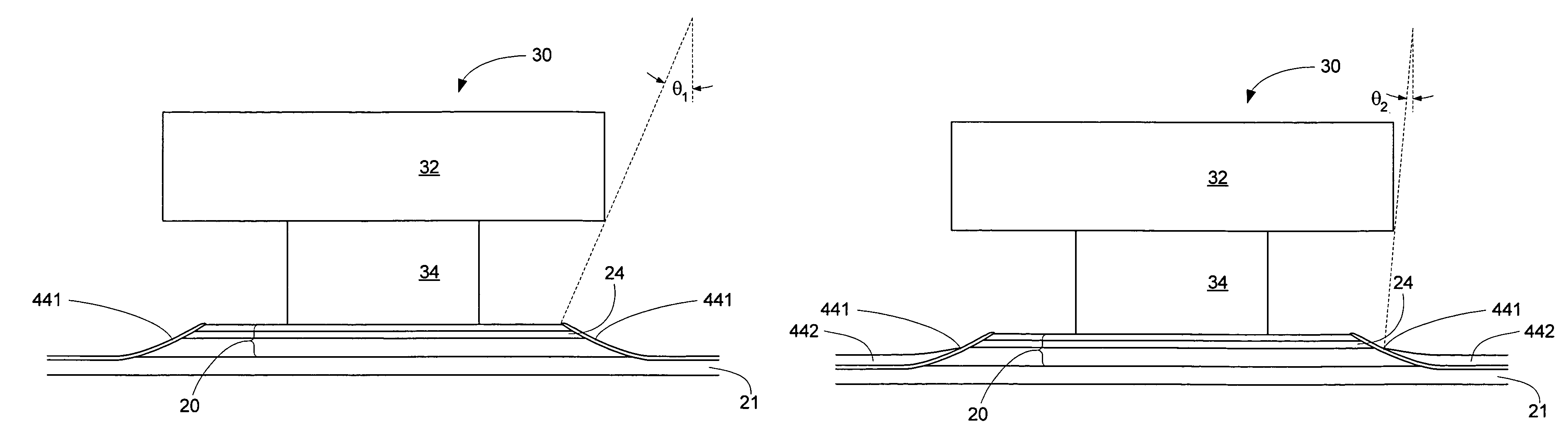
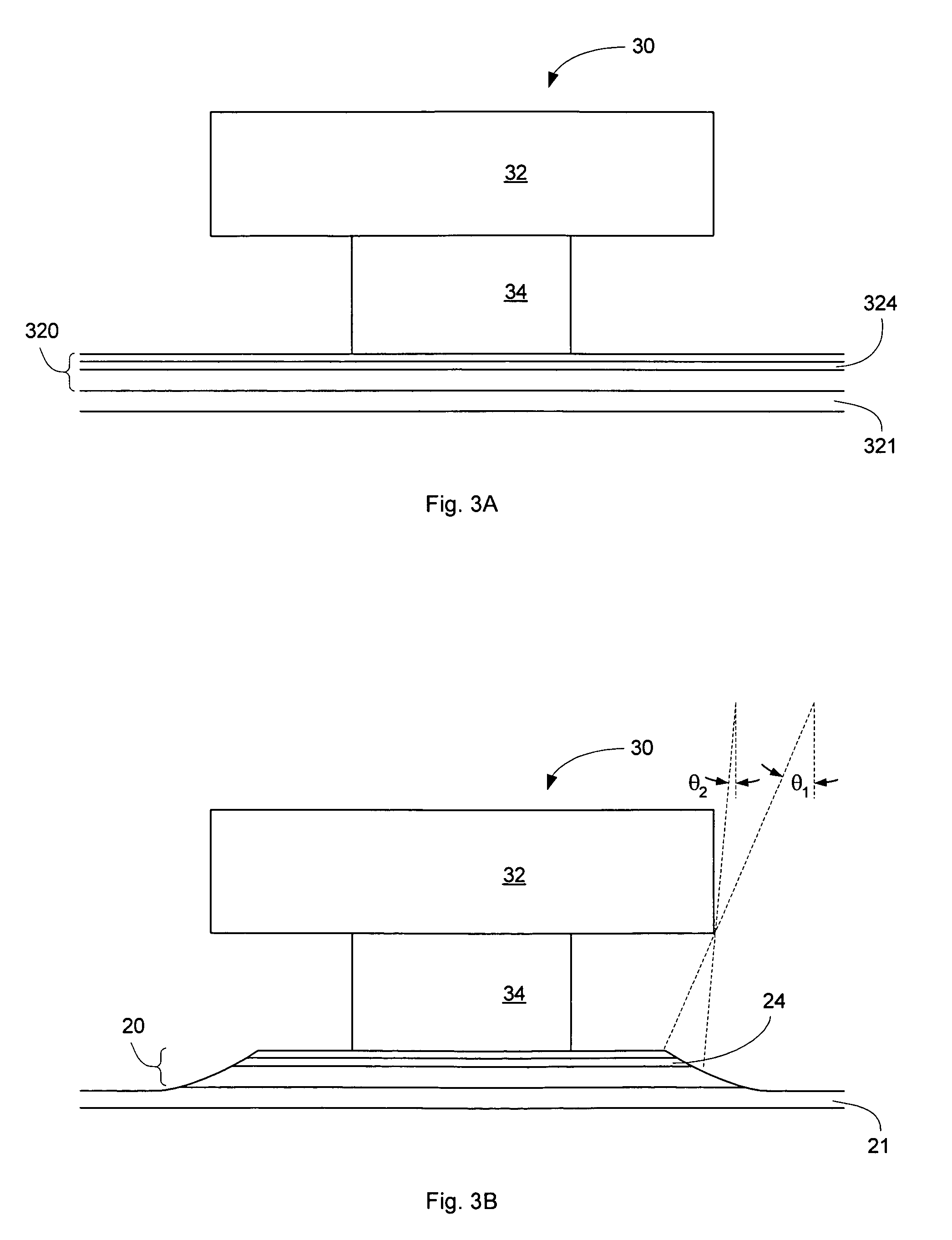
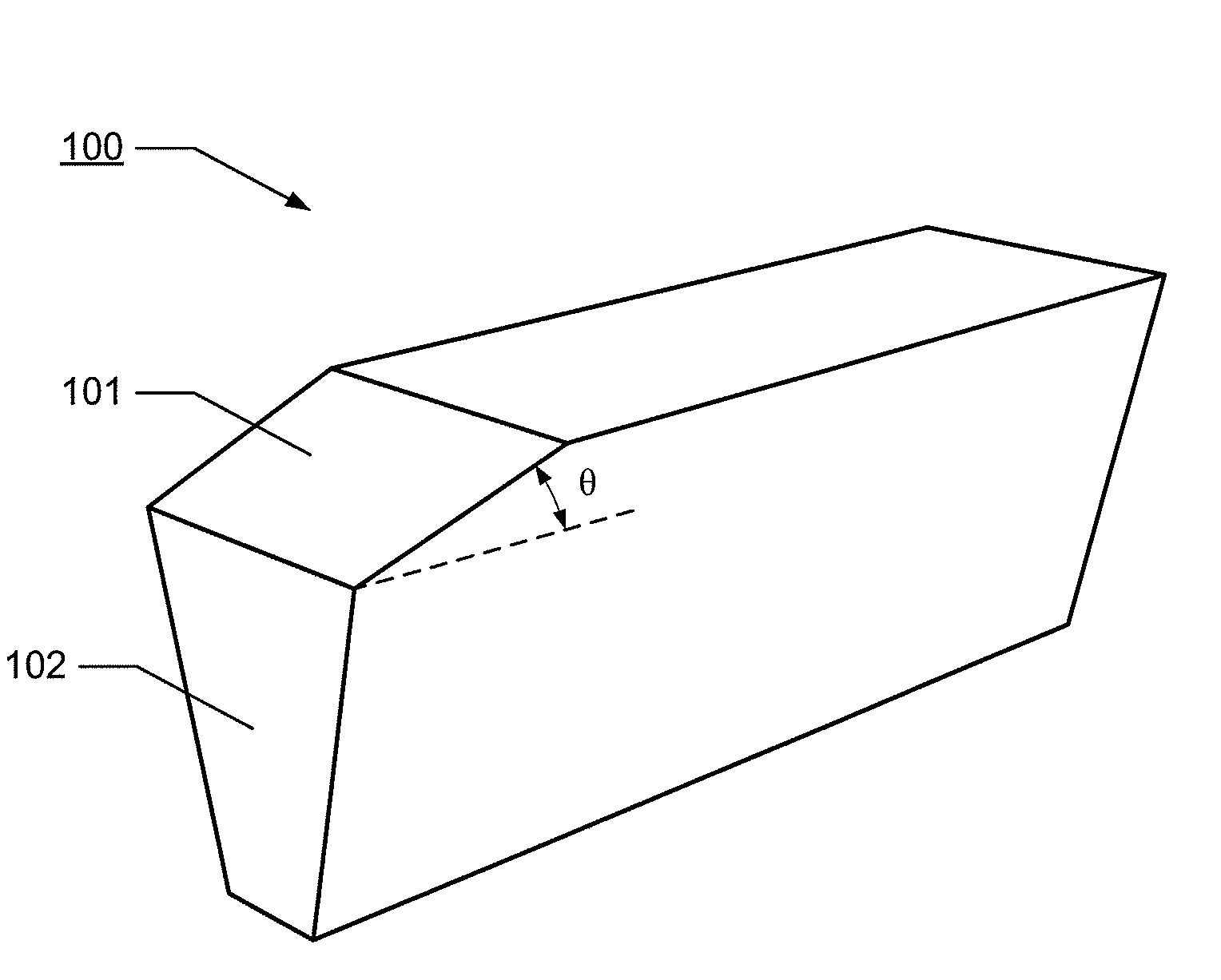
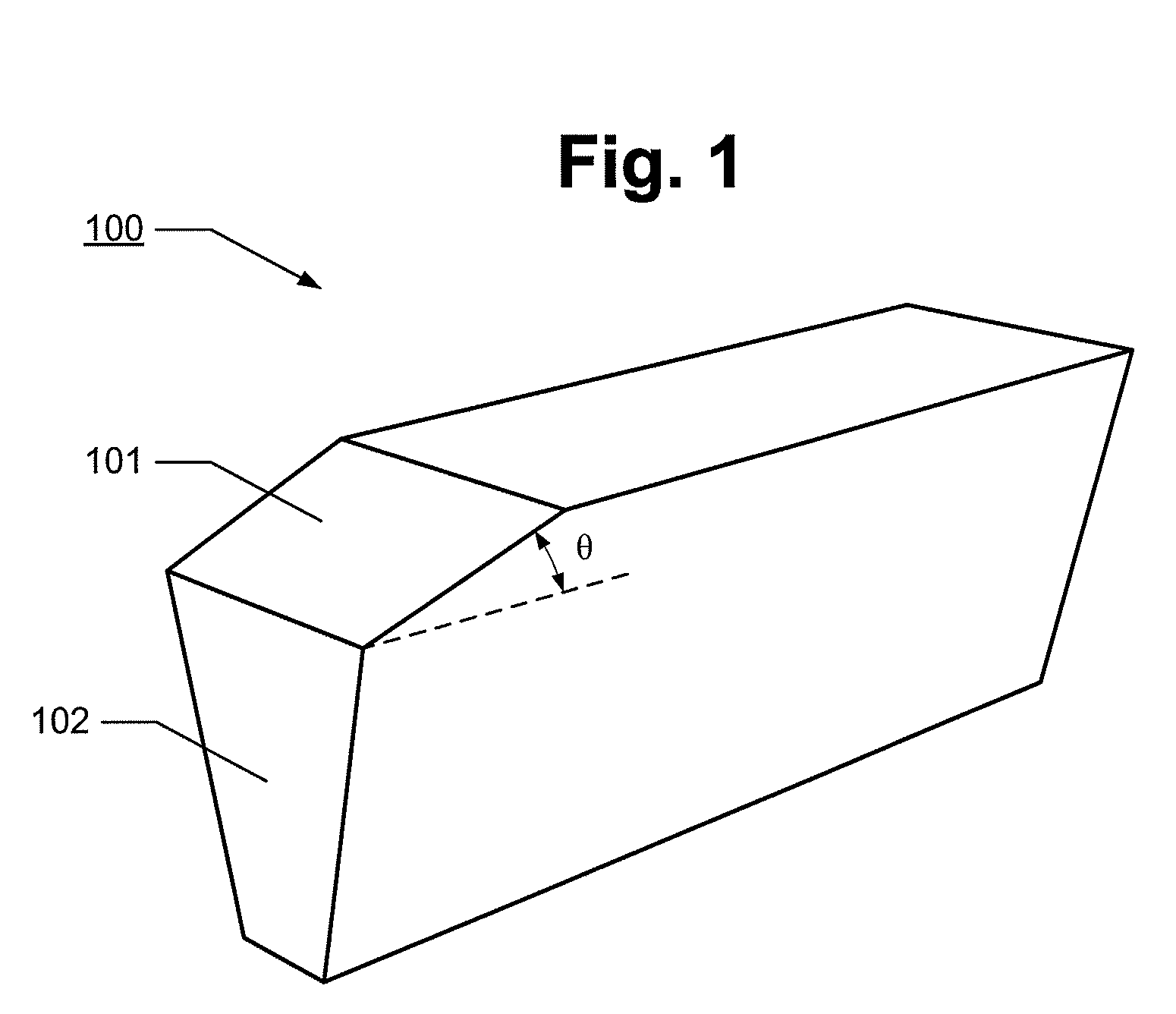
Method of measuring a bevel angle in a write head
A method of measuring a bevel angle in a write pole comprises the step of providing a mask over a wafer containing the write pole. The mask has a first opening over the write pole and a second opening over a sacrificial region of the wafer. The sacrificial region comprises a same material as the write pole. The method further comprises the steps of performing a beveling operation on the write pole and the sacrificial region to form a first bevel in the write pole and a second bevel in the sacrificial region, and measuring an angle of the second bevel in the sacrificial region to determine the bevel angle of the write pole.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Method for providing a magnetic recording transducer
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
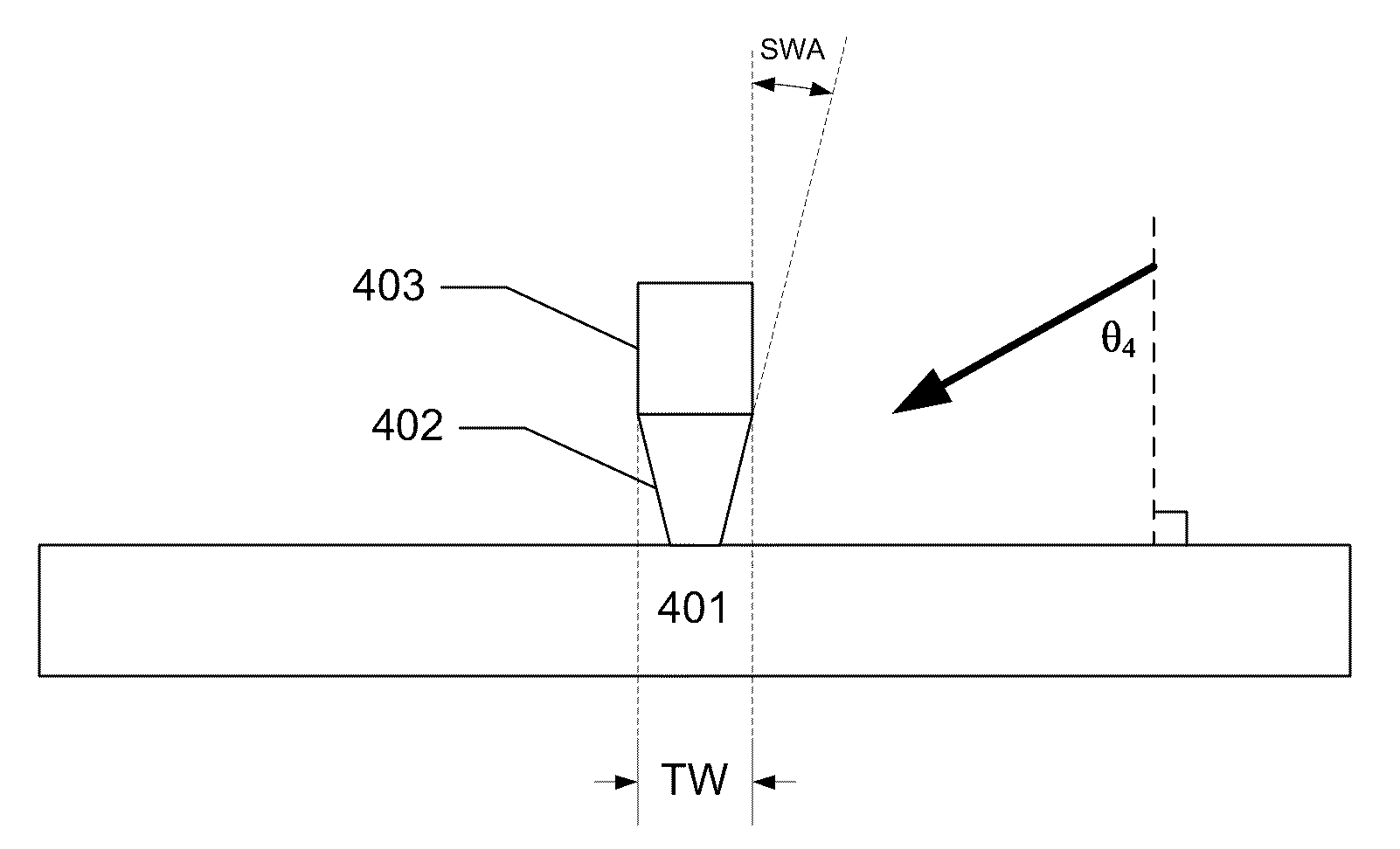
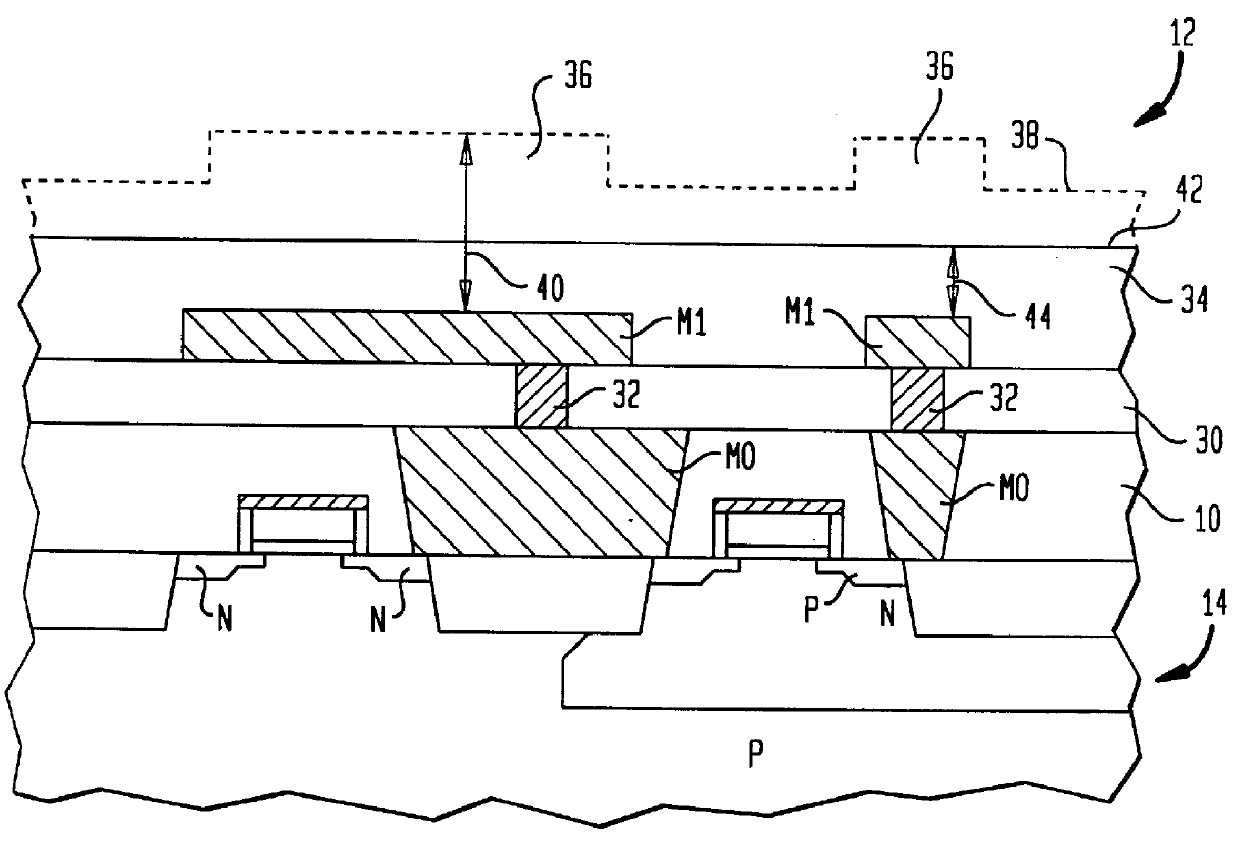
Tunable pole trim processes for fabricating trapezoidal perpendicular magnetic recording (PMR) write poles
A method of forming a write pole for a magnetic recording device is provided. The method comprises providing a layer of magnetic material covered with a secondary hard mask layer and a patterned primary hard mask, milling at a first milling angle to transfer a pattern from the patterned primary hard mask to the secondary hard mask, and milling at a second milling angle to transfer the pattern from the secondary hard mask to the layer of magnetic material to form the write pole. The second milling angle is greater than the first milling angle. The method further comprises milling at a third milling angle to adjust a side wall angle of the write pole to about a desired side wall angle, and milling at a fourth milling angle to reduce a track width of the write pole to a desired track width.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Method and apparatus for in-line oxide thickness determination in chemical-mechanical polishing
InactiveUS6020264ASemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementResistance/reactance/impedenceElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
In-line thickness measurement of a dielectric film layer on a surface of a workpiece subsequent to a polishing on a chemical-mechanical polishing machine in a polishing slurry is disclosed. The workpiece includes a given level of back-end-of-line (BEOL) structure including junctions. The measurement apparatus includes a platen and an electrode embedded within the platen. A positioning mechanism positions the workpiece above the electrode with the dielectric layer facing in a direction of the electrode. A slurry dam is used for maintaining a prescribed level of a conductive polishing slurry above the electrode, the prescribed level to ensure a desired slurry coverage of the workpiece. A capacitance sensor senses a system capacitance C in accordance with an RC equivalent circuit model, wherein the RC equivalent circuit includes a resistance R representative of the slurry and workpiece resistances and the system capacitance C representative of the dielectric material and junction capacitances. Lastly, a capacitance-to-thickness converter converts the sensed capacitance to a dielectric thickness in accordance with a prescribed system capacitance / optical thickness calibration, wherein the prescribed calibration corresponds to the given level of BEOL structure of the workpiece.
Owner:IBM CORP
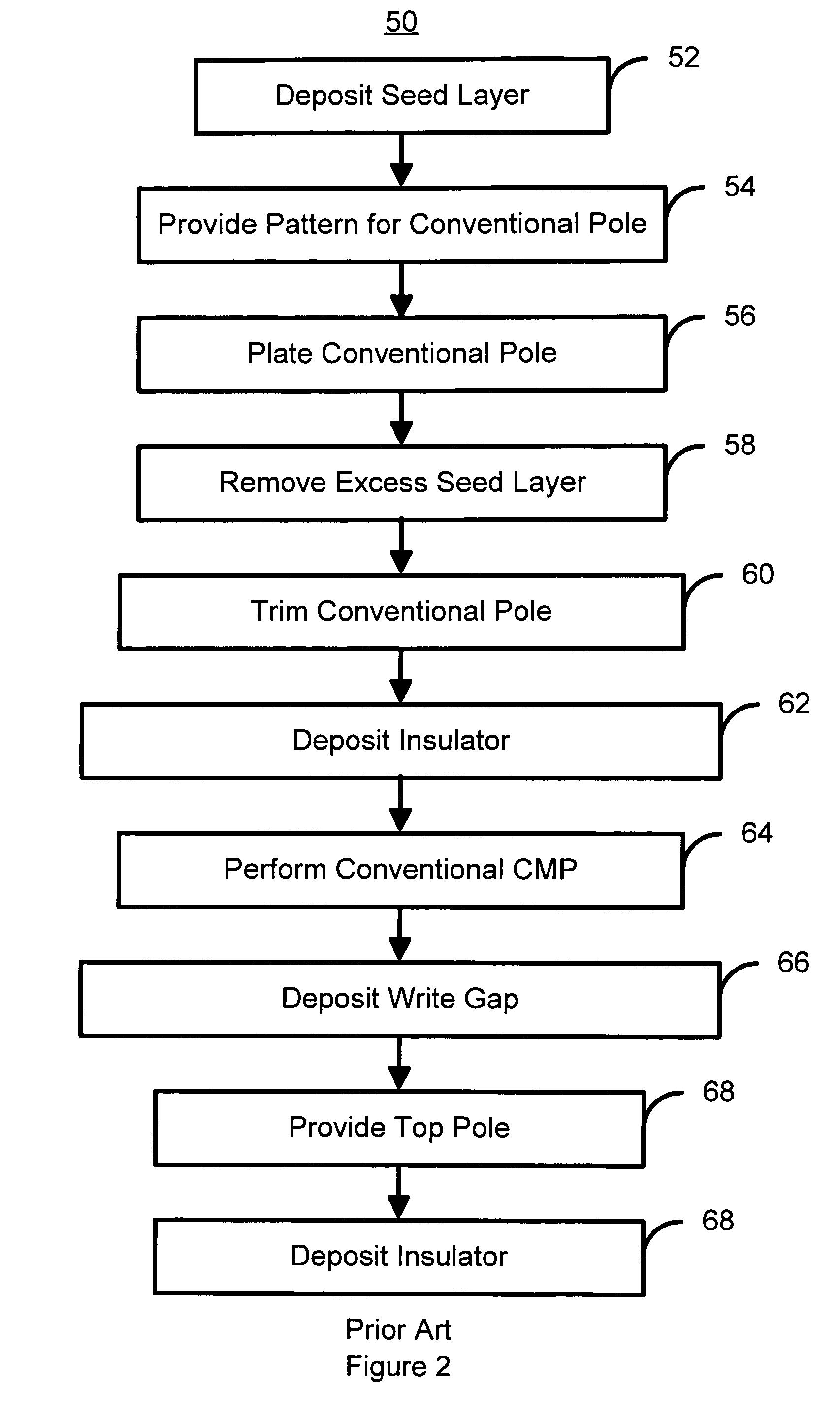
Method for manufacturing a pole for a magnetic recording head
A method and system for manufacturing a pole on a recording head is disclosed. The method and system include sputtering at least one ferromagnetic layer and fabricating a hard mask on the ferromagnetic layer. The method and system also include defining the pole and depositing a write gap on the pole. A portion of the pole is encapsulated in an insulator.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Method of manufacturing a magnetic head device
InactiveUS7114241B2Electrical transducersManufacture head surfaceSubject matterElectrical and Electronics engineering
A method of manufacturing a magnetic head device includes forming a thin film magnetic head element over a substrate, the thin film magnetic head element including a magnetoresistance (MR) element. The substrate is cut such that the MR element is exposed on a side surface of the substrate. The side surface is then polished. Afterward, a magnetically degenerated layer is removed from the thin film magnetic head element along the side surface. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract that will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
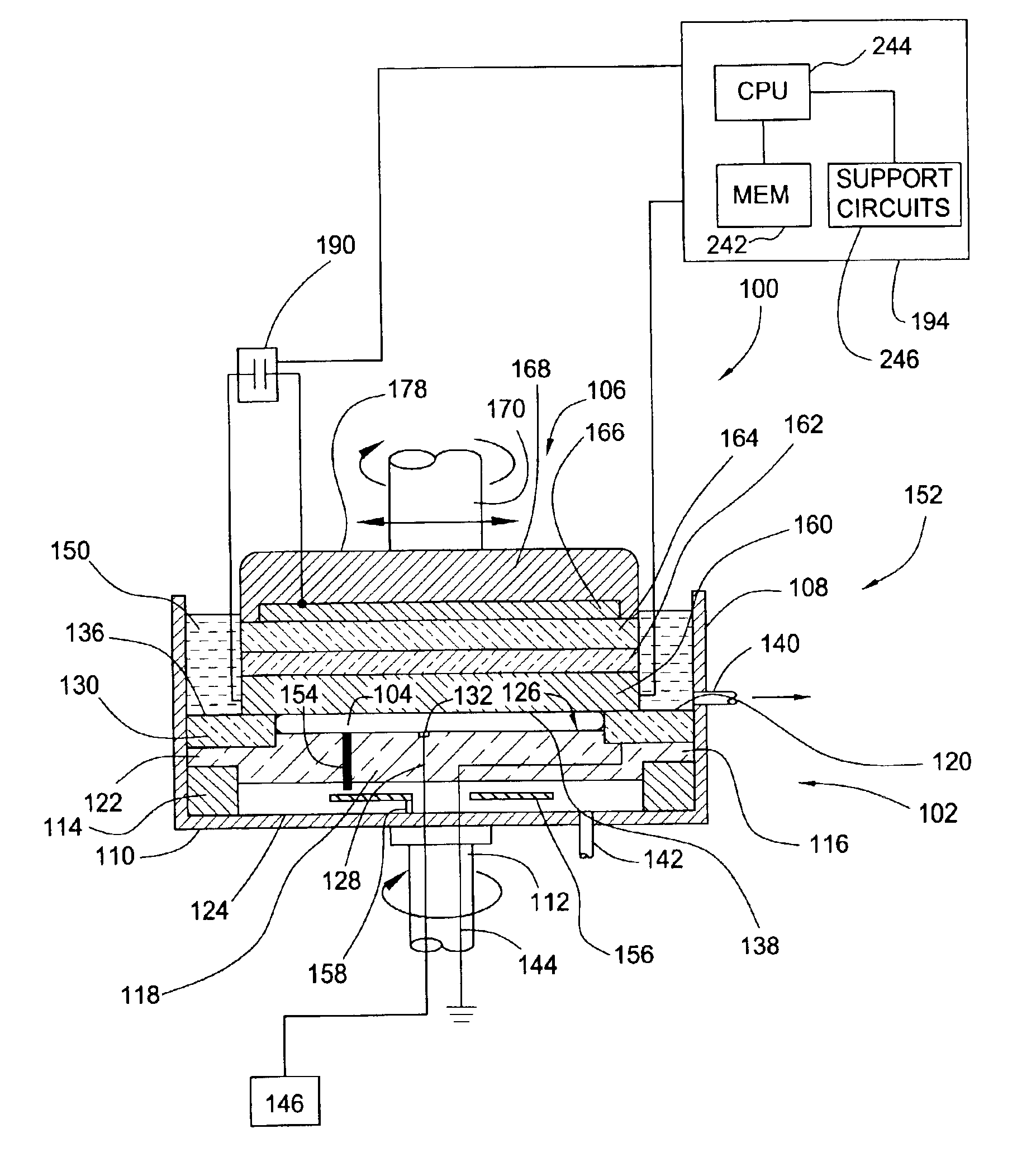
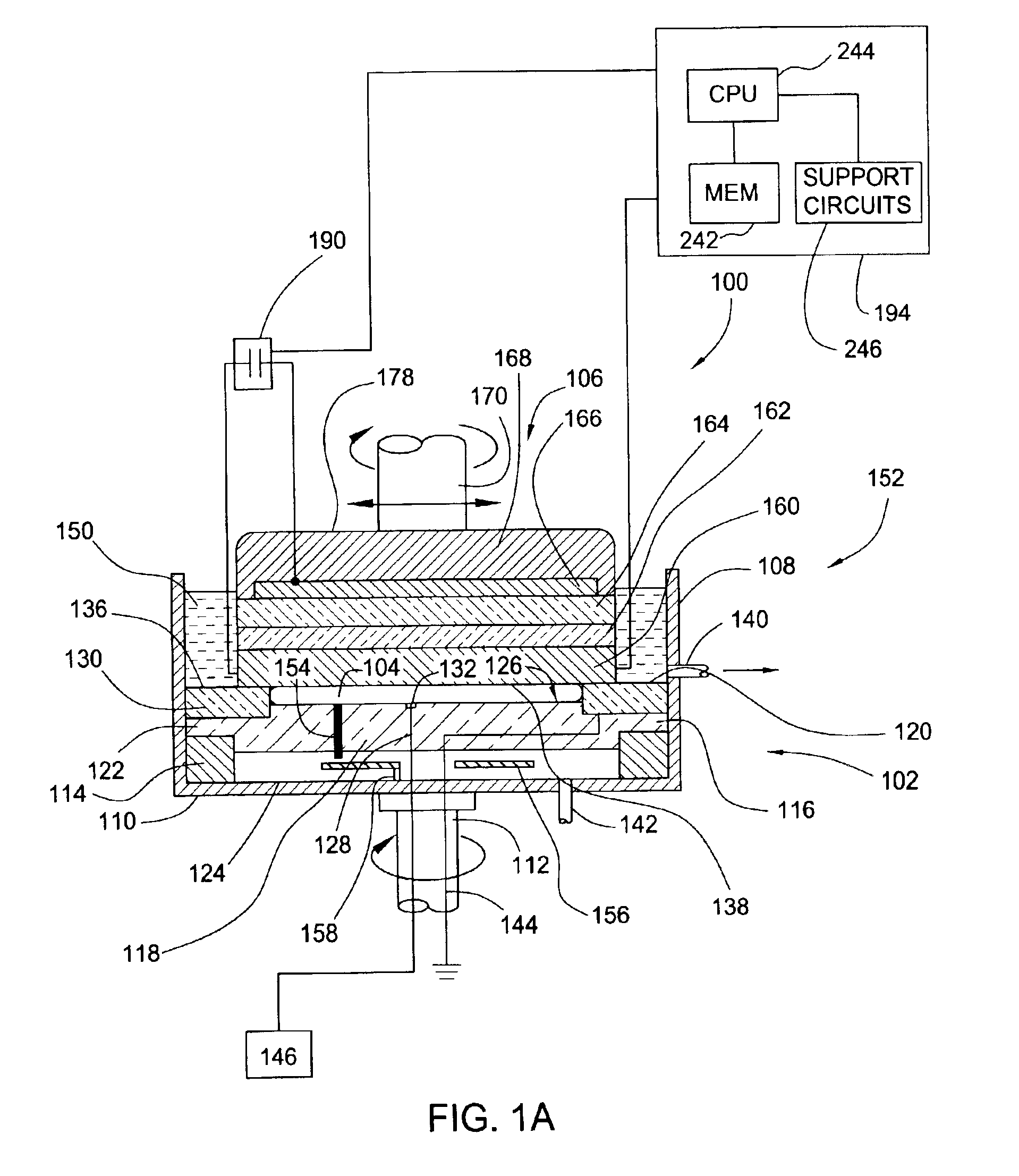
Process control in electrochemically assisted planarization
InactiveUS6848970B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLapping machinesEngineeringElectrochemical dissolution
Aspects of the invention generally provide a method for polishing a material layer using electrochemical deposition techniques, electrochemical dissolution techniques, polishing techniques, and / or combinations thereof. In one aspect of the invention, the polishing method comprises applying a separate electrical bias, such as a voltage, to each of a plurality of zones of an electrode. Determining the separate biases comprises determining a time that at least one portion of the material layer is associated with each of the zones of the counter-electrode.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
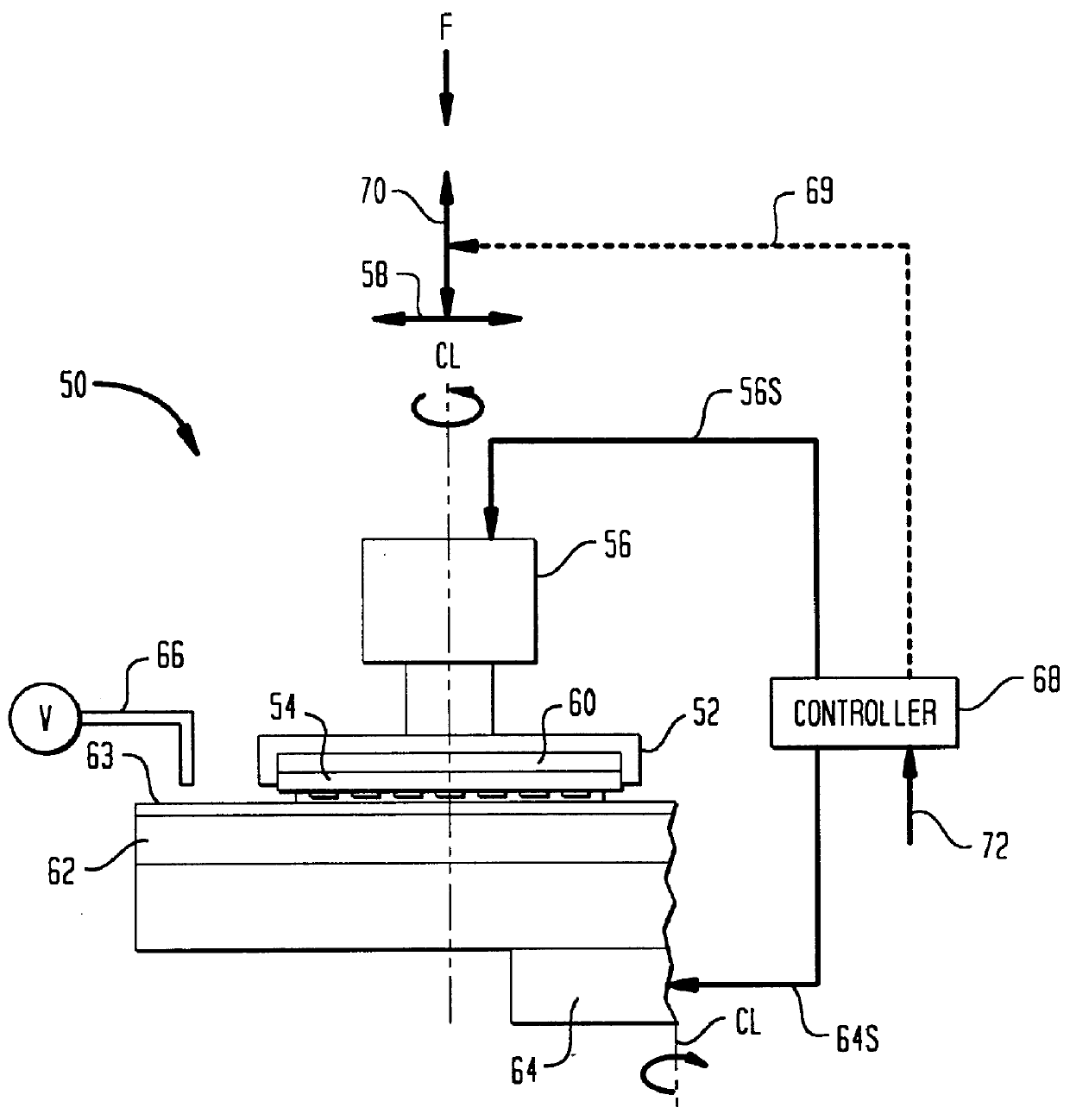
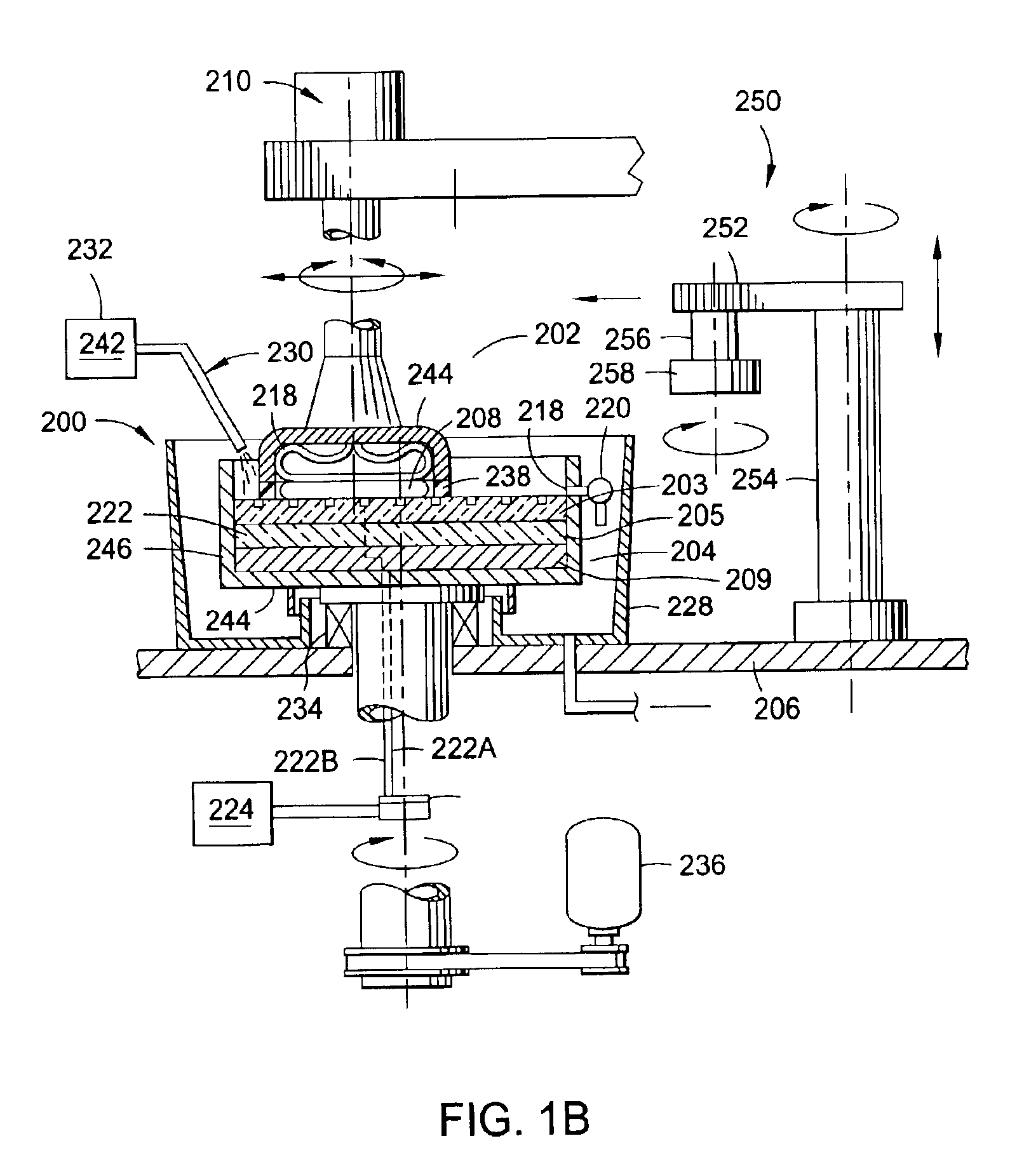
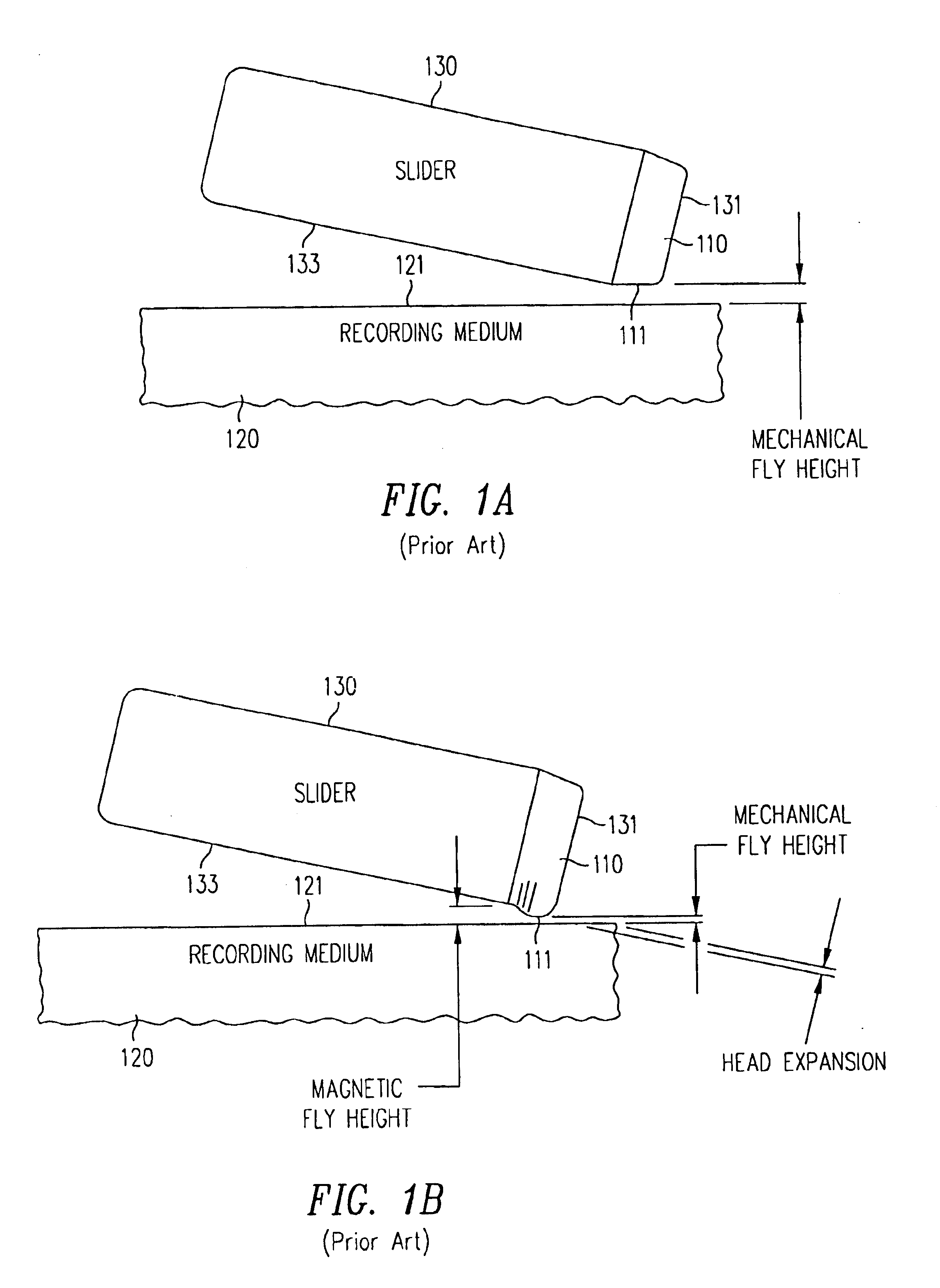
Lapping a head while powered up to eliminate expansion of the head due to heating
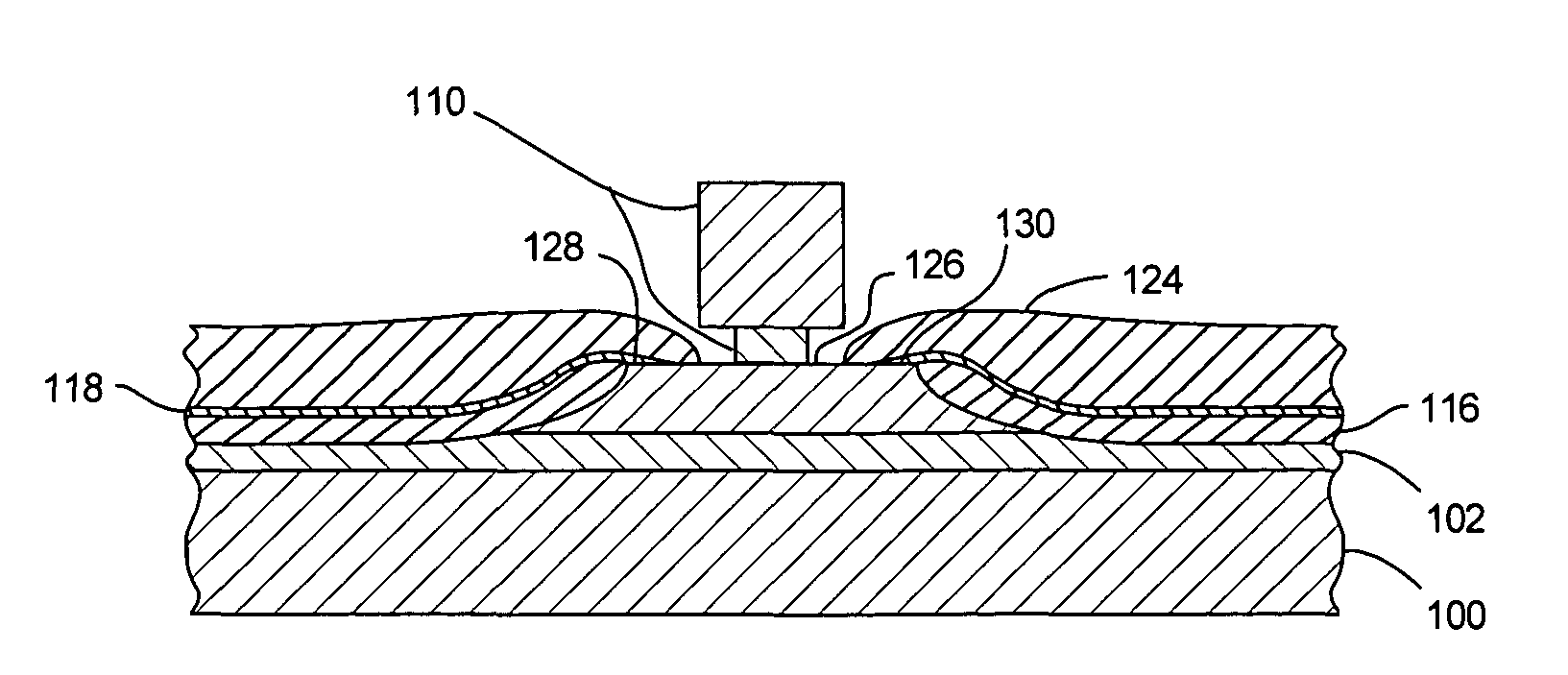
A head is fabricated using photolithography, and the head is purposely powered up during a material removal process, such as lapping, so that the head's expansion (that would be formed on being powered up during normal usage in a drive) is planarized. Specifically, the head is energized in a manner identical (or similar) to energization of circuitry in the head during normal operation in a drive, even though fabrication of the head has not yet been completed. When energized, a shape that the head would have during normal operation is replicated (or approximated). Therefore, the head's shape includes a expansion of the pole tip region, although the head is only partially fabricated. Thereafter, a portion of the head in the expansion is partially or completely removed, by lapping while energized. The depth of material removal from the head is monitored e.g. by a controller sensitive to a change in electrical characteristic of a device (such as a resistor) that is normally fabricated during photolithography of the head.
Owner:WD MEDIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com