Patents
Literature
1706results about "Flexible-parts wheels" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Controlled electro-pneumatic power tools and interactive consumable
Owner:FORGUES SYLVAIN +1
Methods for using polishing pads
Polymer-based pads useful for polishing objects, particularly integrated circuits, having interconnected porosity which is uniform in all directions, and where the solid portion of said pad consists of a uniform continuously interconnected polymer material of greater than 50% of the gross volume of the article, are produced directly to final shape and dimension by pressure sintering powder compacts of thermoplastic polymer at a temperature above the glass transition temperature but not exceeding the melting point of the polymer and at a pressure in excess of 100 psi in a mold having the desired final pad dimensions. In a preferred version, a mixture of two polymer powders is used, where one polymer has a lower melting point than the other. When pressure sintered at a temperature not to exceed the melting point of the lower melting powder, the increased stiffness afforded by incorporation of the higher melting polymer component gives improved mechanical strength to the sintered product. Conditions for producing the pads of this invention are such that the polymer powder particles from which the pads are produced essentially retain their original shape and are point bonded to form the pad.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CMP HLDG INC
Molded polishing pad having integral window
A polishing pad is formed as a one-piece article having a region which is transparent and an adjacent region which is opaque. The article is formed by solidifying a flowable polymeric material which at least initially has a uniform composition. The flowable polymeric material is processed during a molding operation to provide the transparent region and the adjacent opaque region. Types of polymeric material suitable for making the polishing pad include a single thermoplastic material, a blend of thermoplastic materials, and a reactive thermosetting polymer.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CMP HLDG INC
Polishing pads and methods relating thereto
InactiveUS6022268AEnhanced interactionLess-proneRevolution surface grinding machinesOther chemical processesEngineeringTopography
This invention describes improved polishing pads useful in the manufacture of semiconductor devices or the like. The pads of the present invention have an advantageous hydrophilic polishing material and have an innovative surface topography and texture which generally improves predictability and polishing performance.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CMP HLDG INC
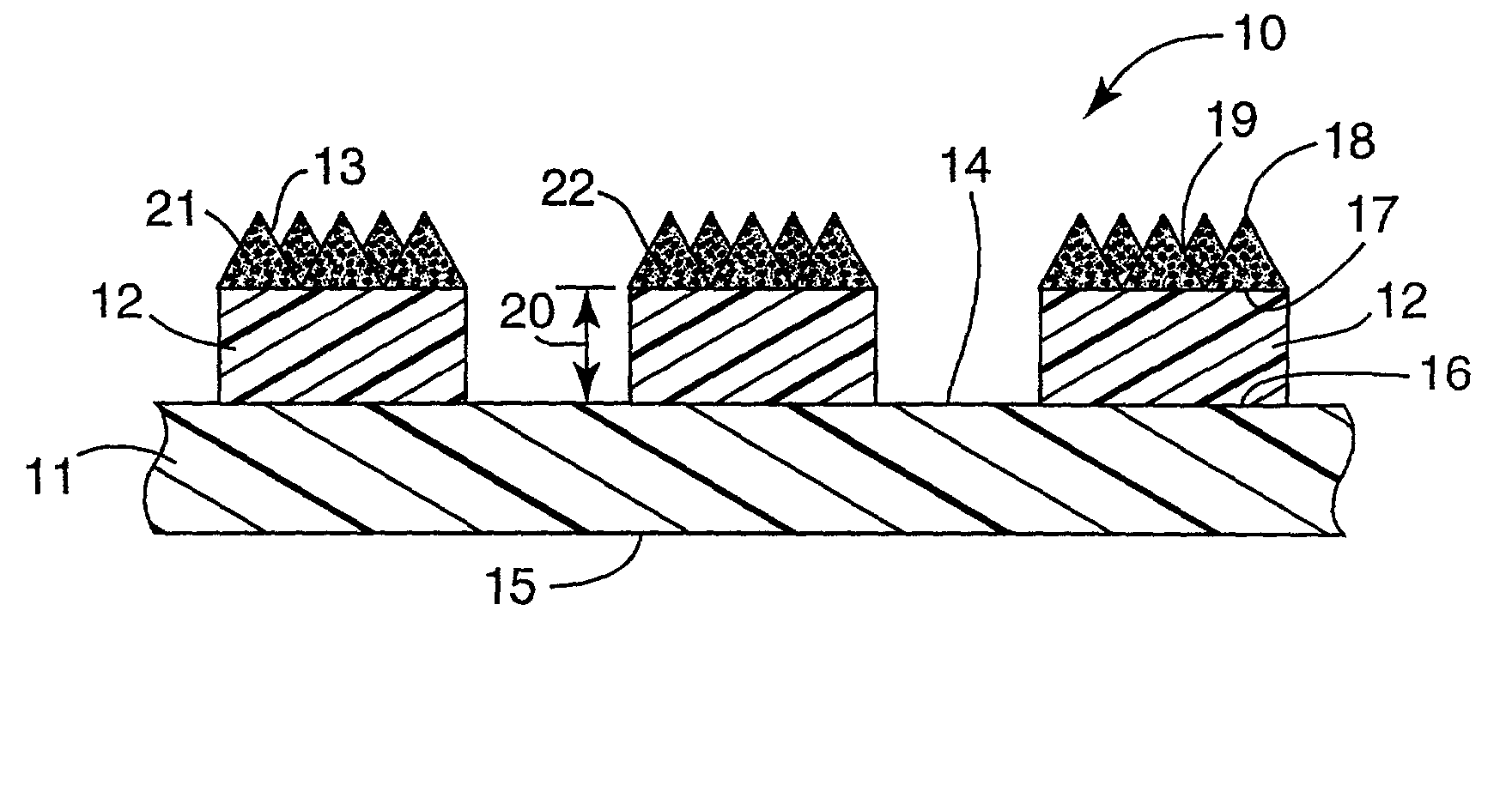
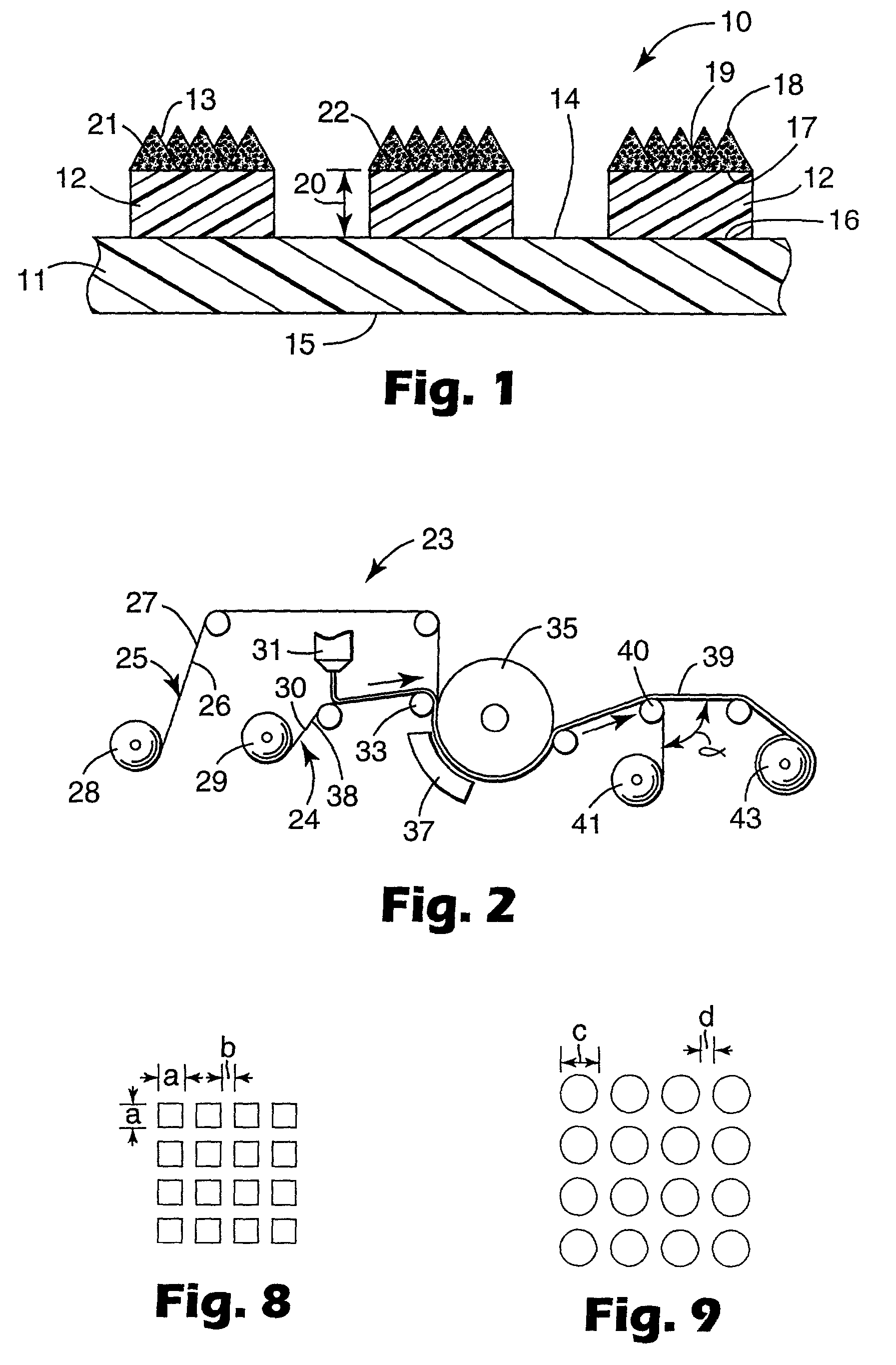
Flexible abrasive product and method of making and using the same
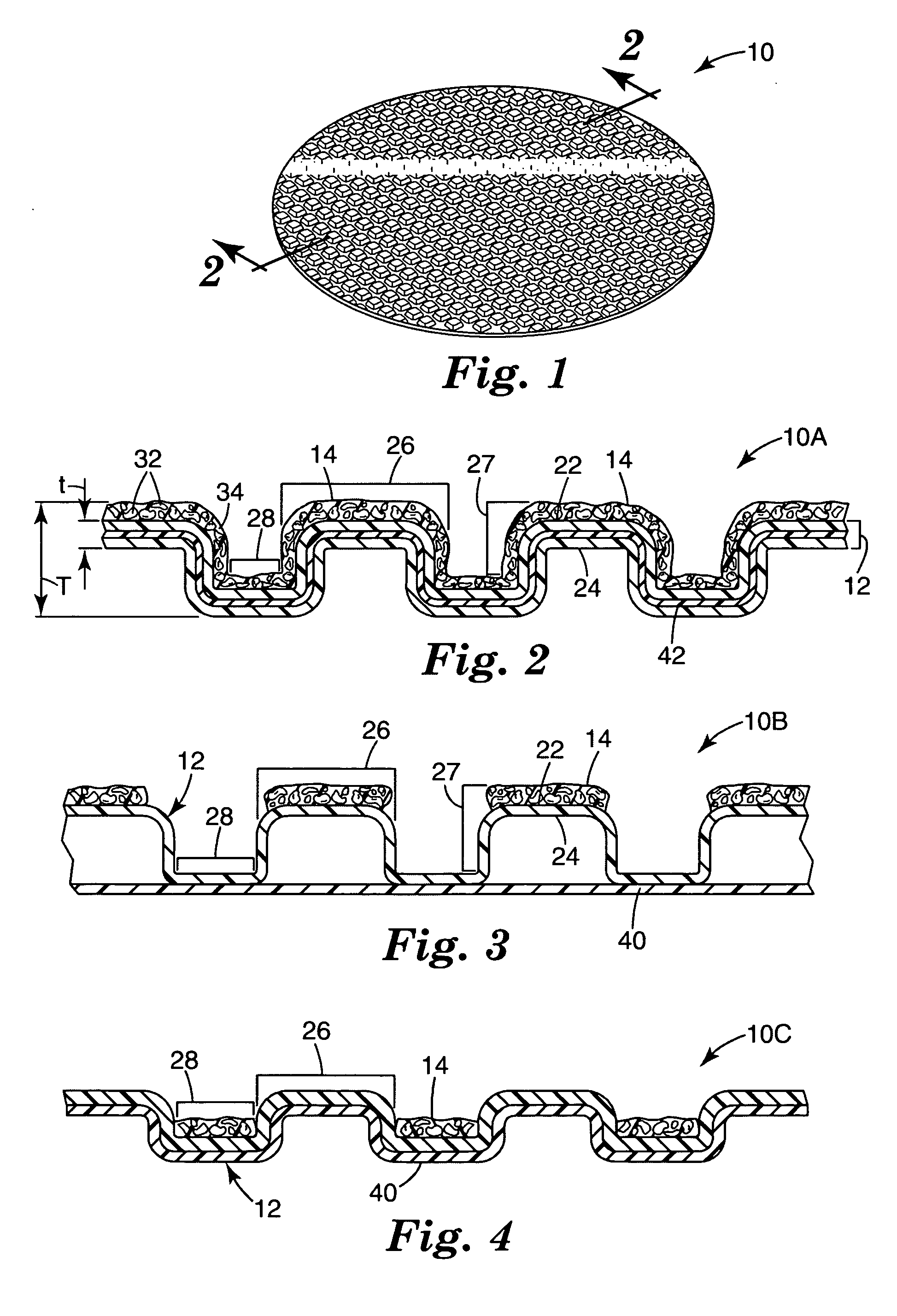
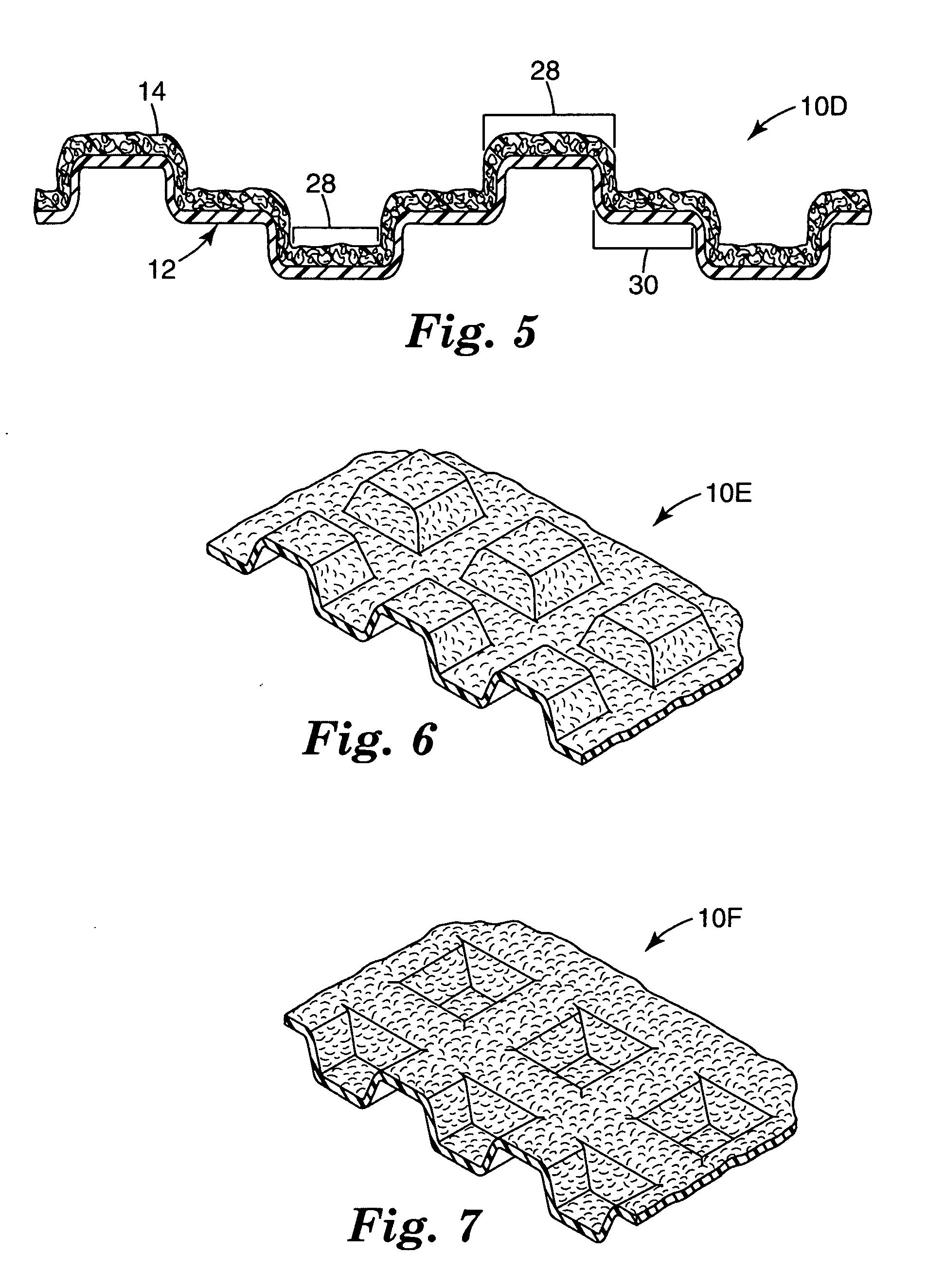
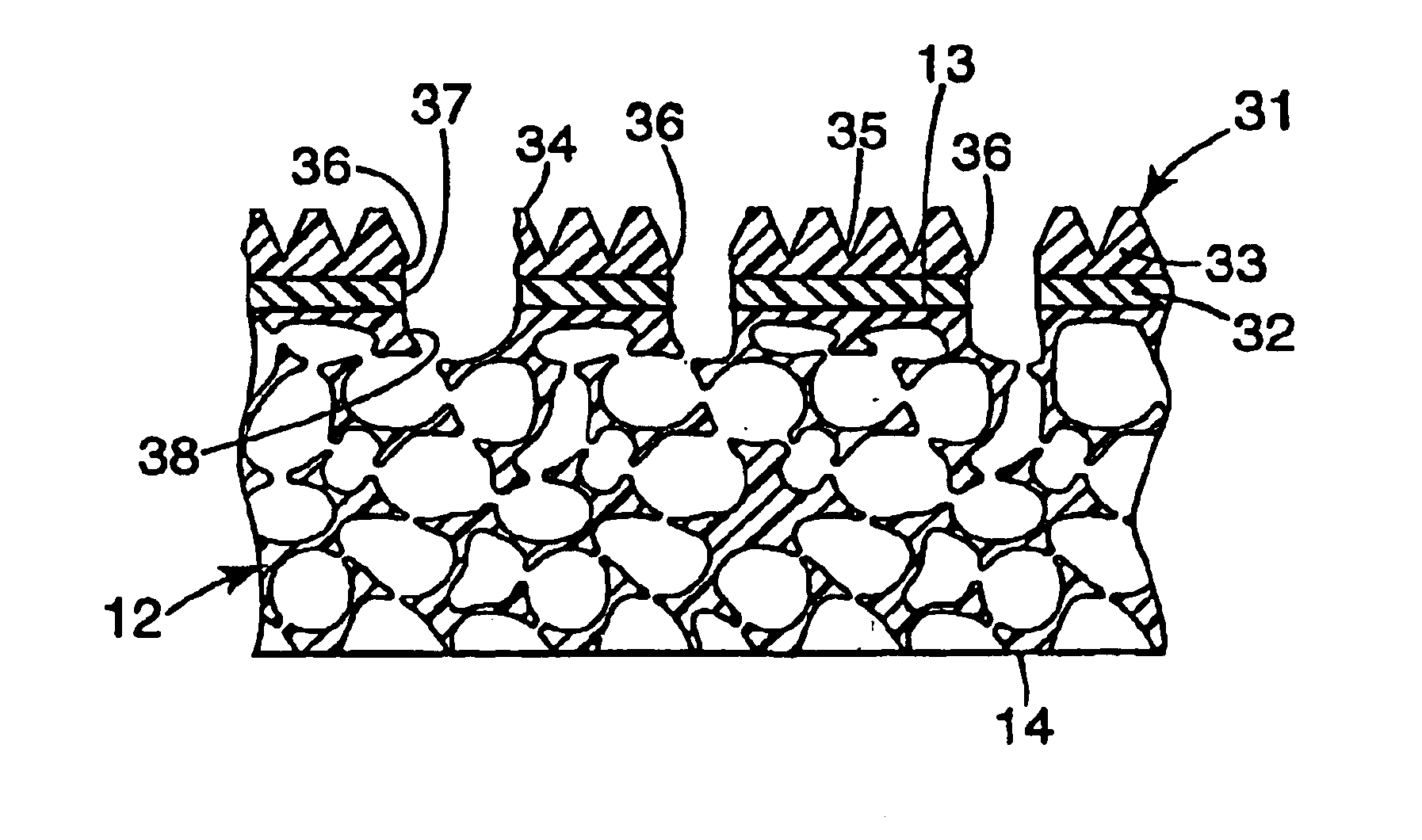
InactiveUS20050020190A1Provide dimensional stabilityFlexible-parts wheelsPlane surface grinding machinesOpen cellCoating
The present invention provides a flexible abrasive product comprised of an open cell foam backing, a foraminous barrier coating and a shaped foraminous abrasive coating. The flexible abrasive article of the invention is made by applying a curable barrier coating over an open cell foam backing, curing the curable barrier coating to provide a foraminous barrier coating having openings therethrough corresponding to openings in the open cell foam, applying a coating composition comprising a curable binder and abrasive particles over the foraminous barrier coating, imparting a textured surface to the coating composition with a production tool which has a textured surface which is the inverse of the textured surface of the abrasive coating and to which production tool textured surface any coating composition coated over an opening of the first major surface may adhere, at least partially curing the binder, and separating the production tool from the textured surface to provide the shaped foraminous abrasive coating.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Polishing pads for chemical mechanical planarization
An improved pad and process for polishing metal damascene structures on a semiconductor wafer. The process includes the steps of pressing the wafer against the surface of a polymer sheet in combination with an aqueous-based liquid that optionally contains sub-micron particles and providing a means for relative motion of wafer and polishing pad under pressure so that the moving pressurized contact results in planar removal of the surface of said wafer, wherein the polishing pad has a low elastic recovery when said load is removed, so that the mechanical response of the sheet is largely anelastic. The improved pad is characterized by a high energy dissipation coupled with a high pad stiffness. The pad exhibits a stable morphology that can be reproduced easily and consistently. The pad surface resists glazing, thereby requiring less frequent and less aggressive conditioning. The benefits of such a polishing pad are low dishing of metal features, low oxide erosion, reduced pad conditioning, longer pad life, high metal removal rates, good planarization, and lower defectivity (scratches and Light Point Defects).
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CMP HLDG INC
Polishing pad with high optical transmission window
ActiveUS6984163B2Spread the wordPolishing machinesRevolution surface grinding machinesEngineeringIsocyanate
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CMP HLDG INC
Controlled electro-pneumatic power tools and interactive consumable
ActiveUS20120007748A1Electric signal transmission systemsTelemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsMicrocontrollerElectrical battery
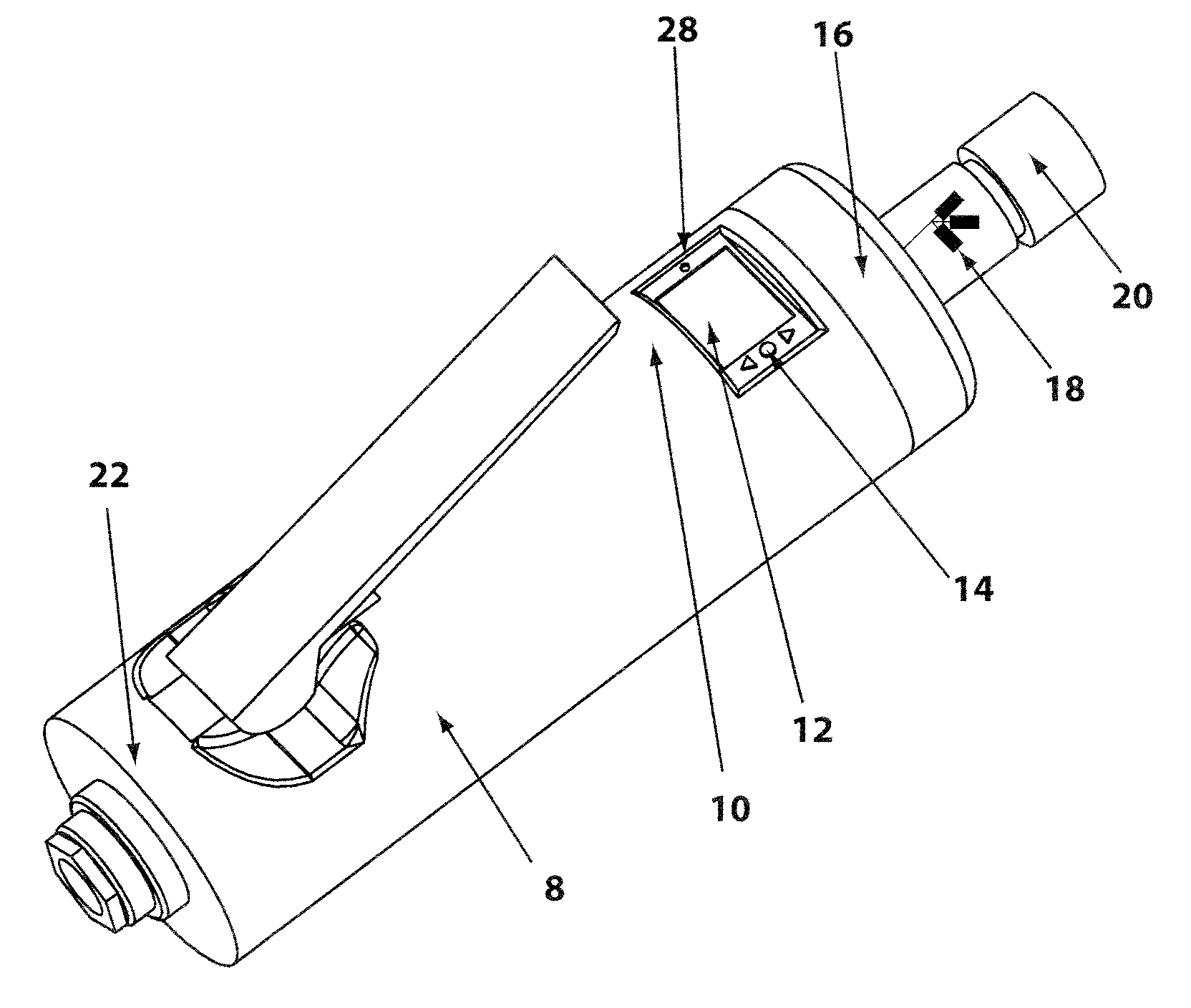
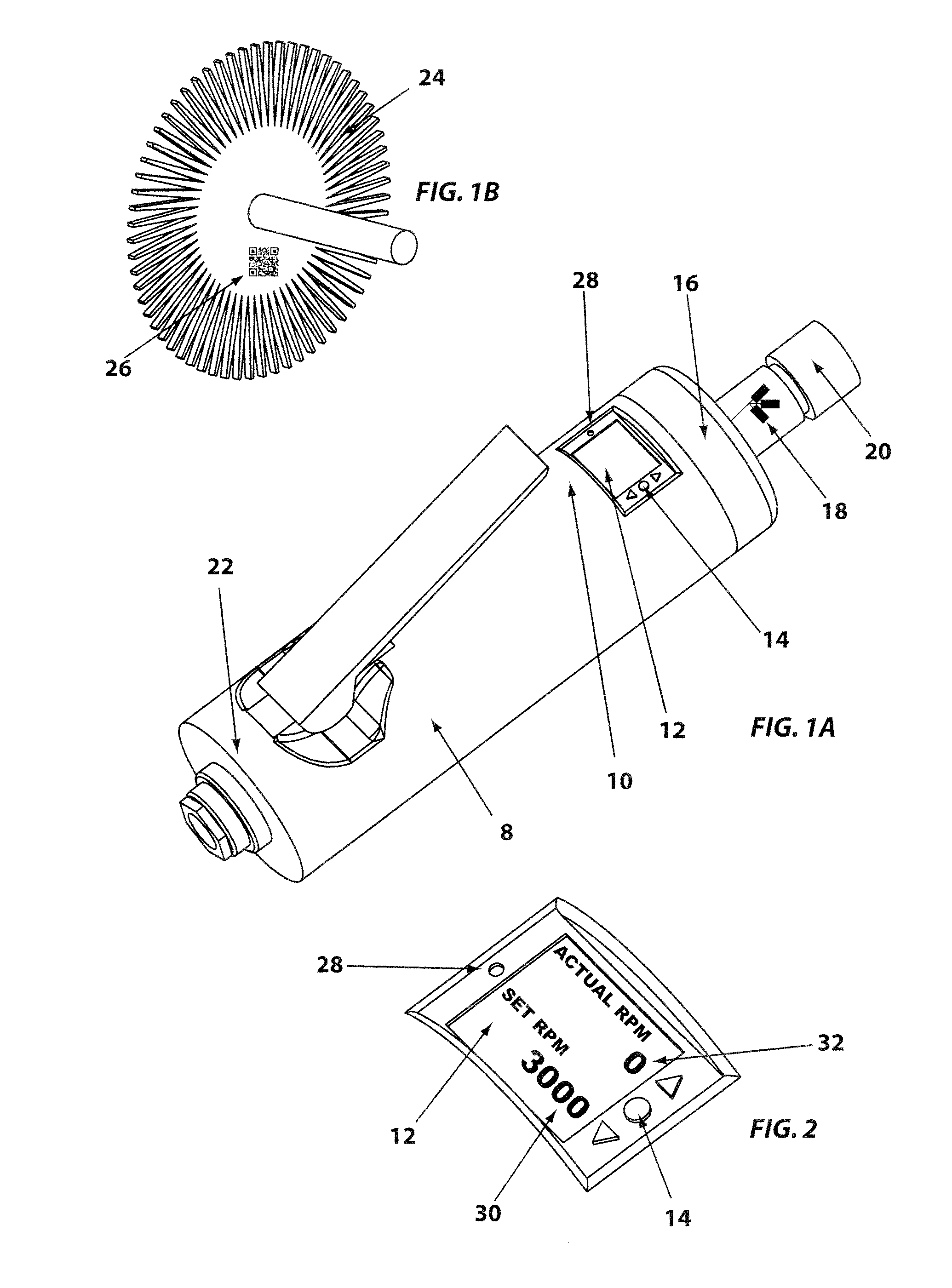
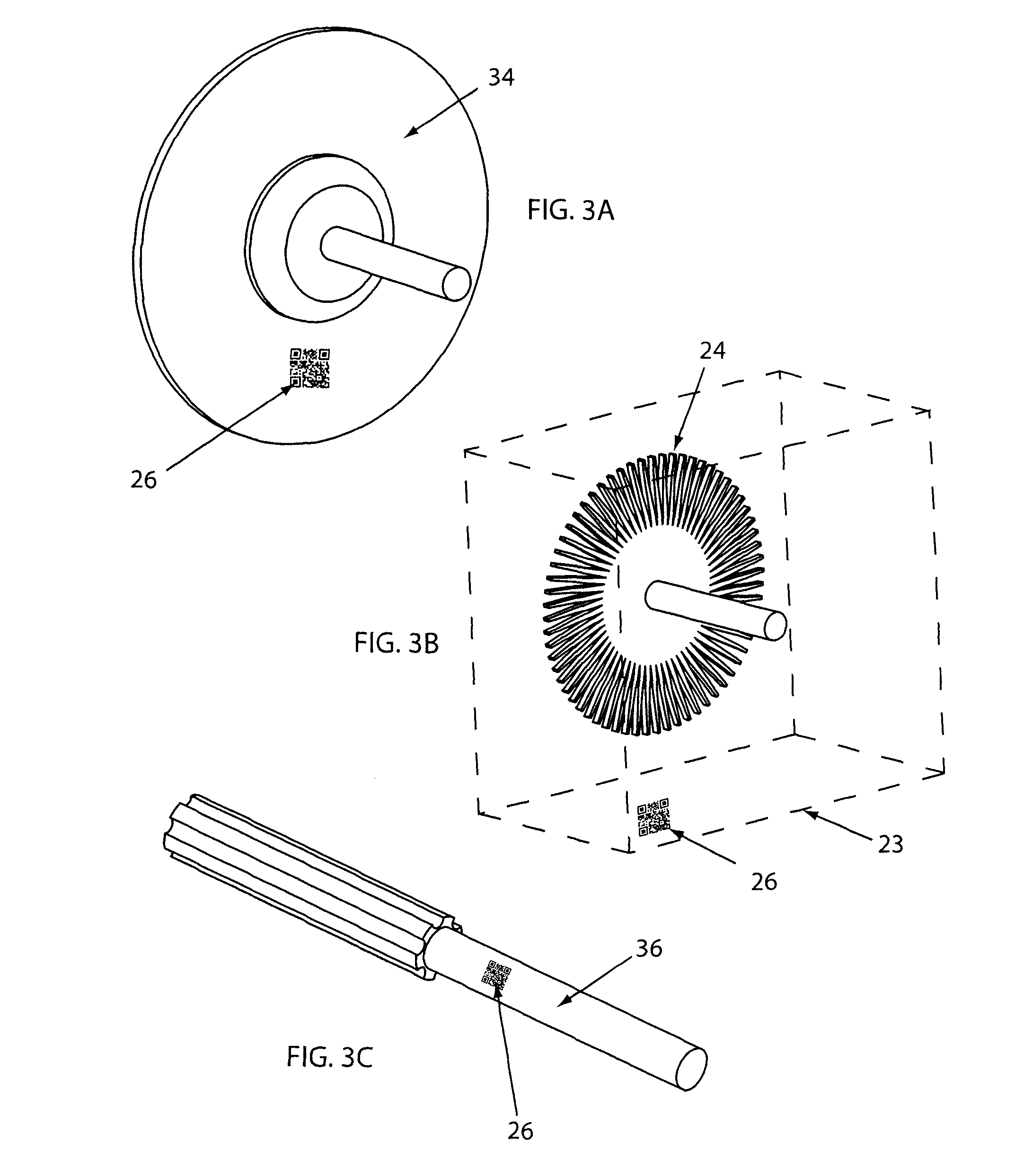
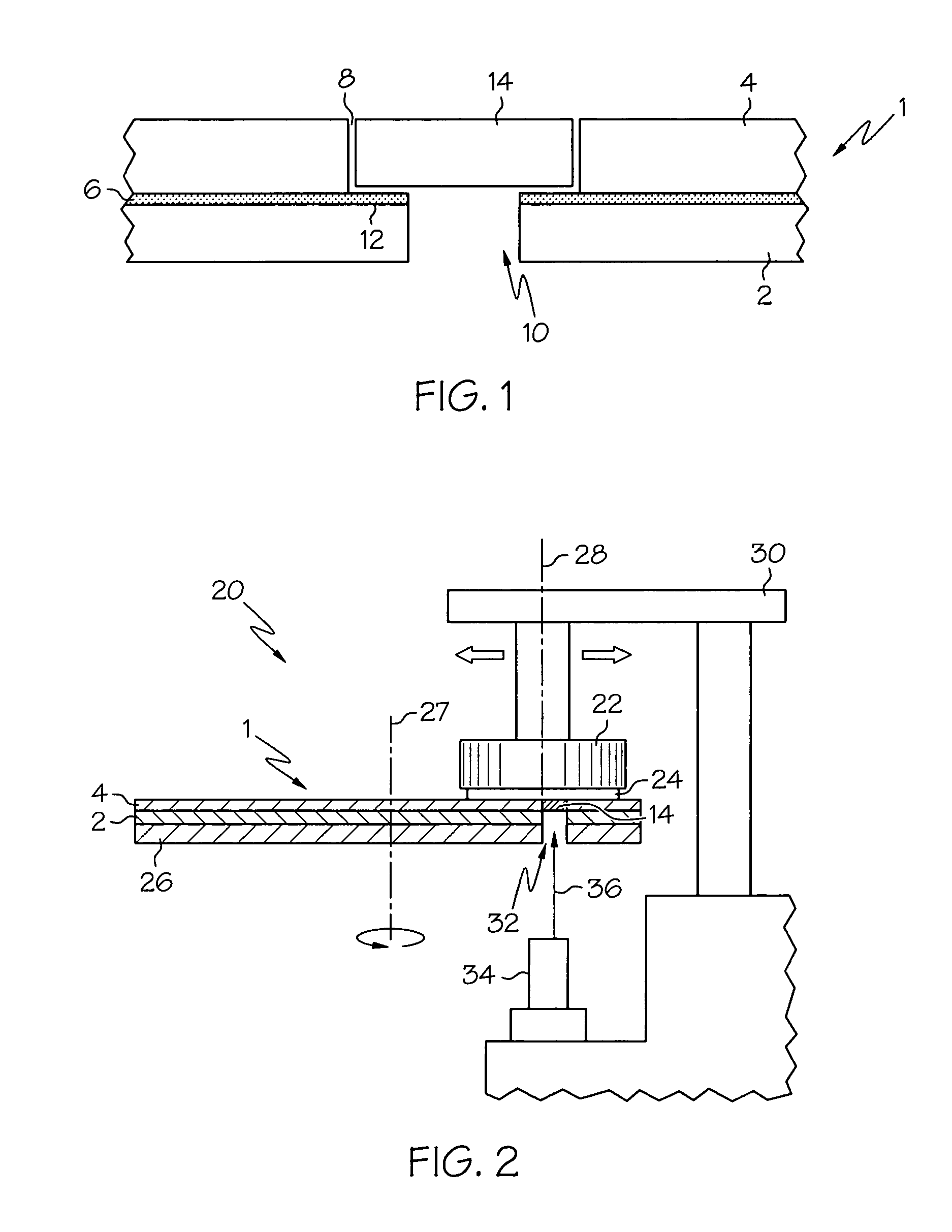
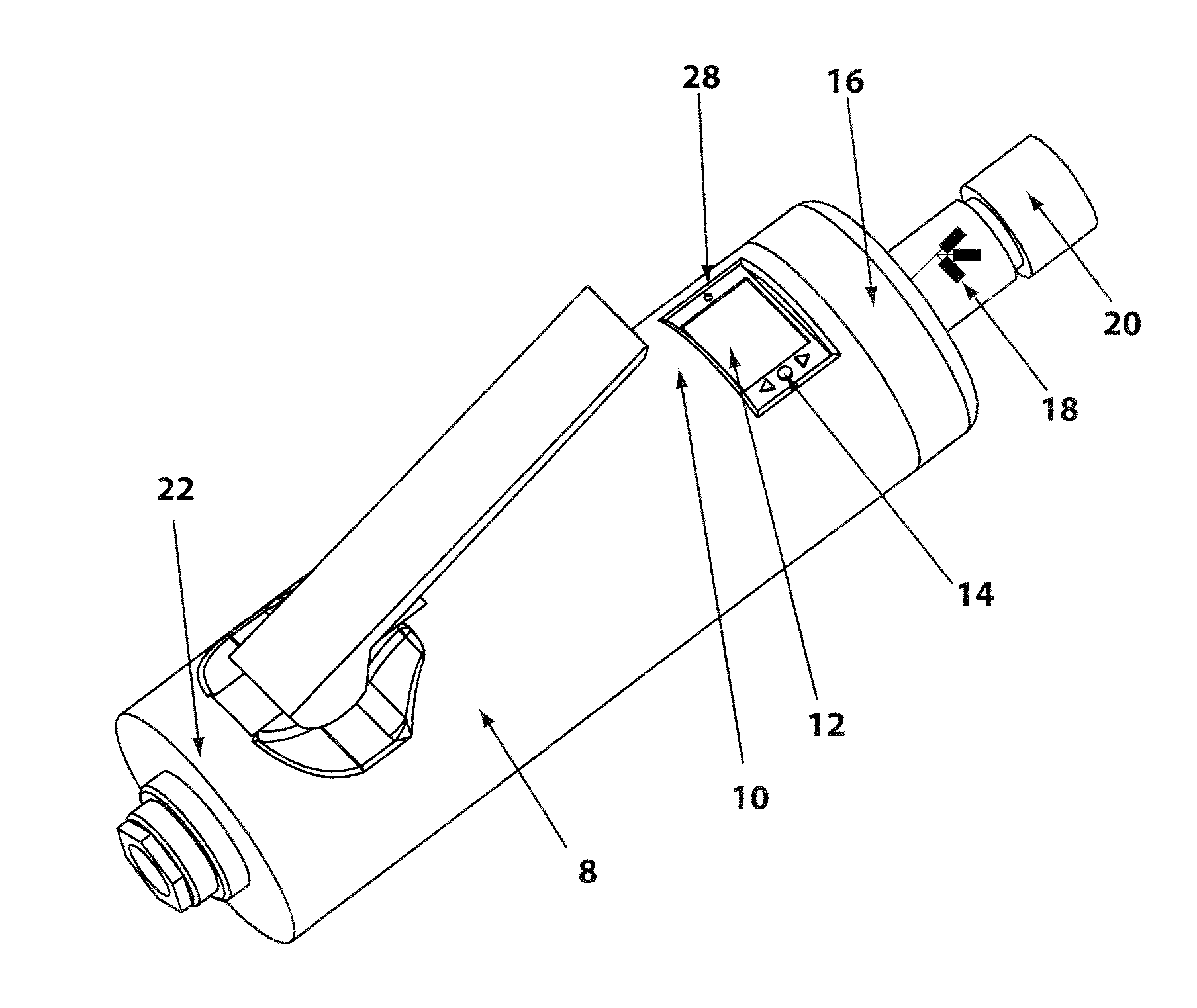
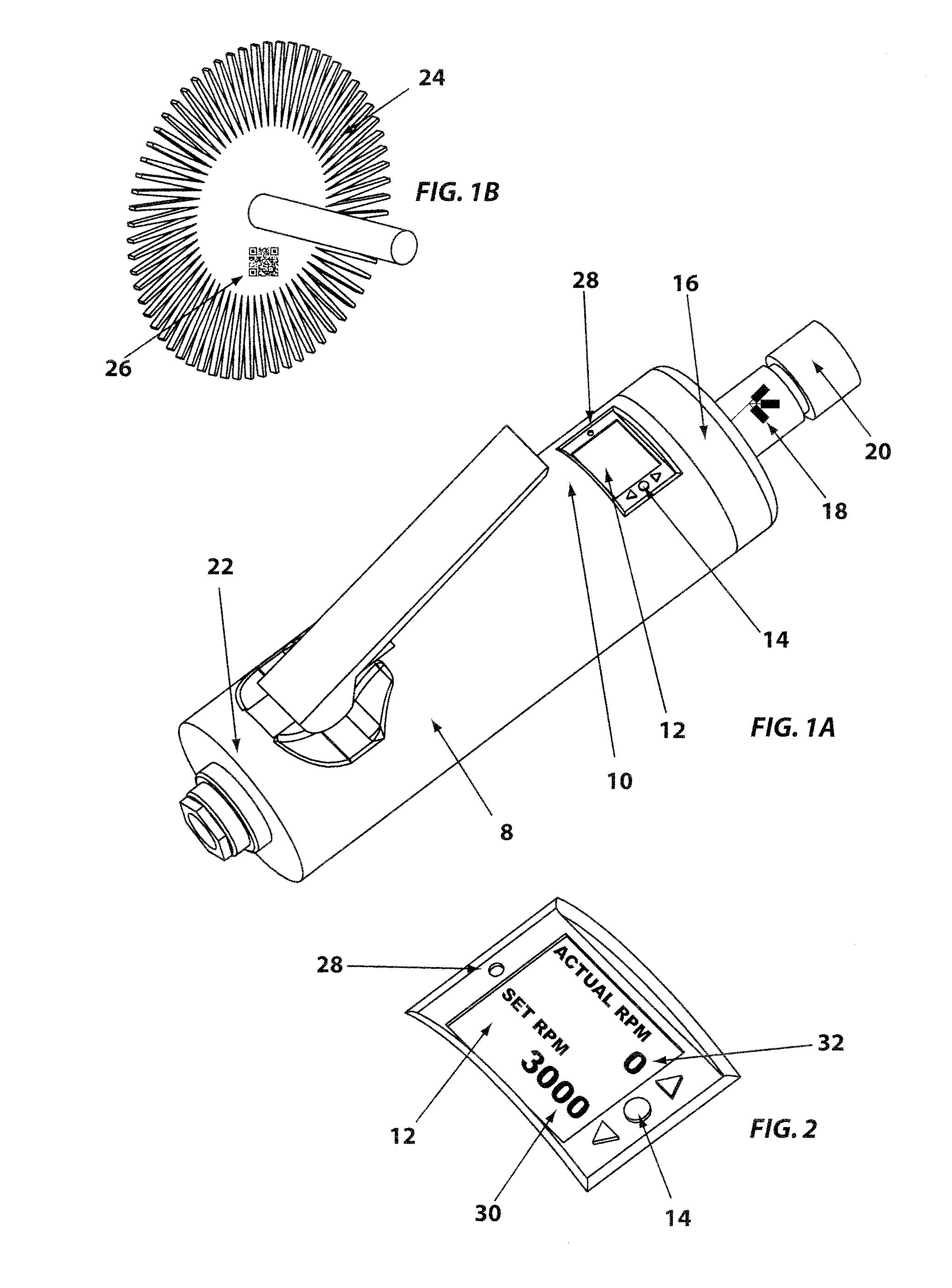
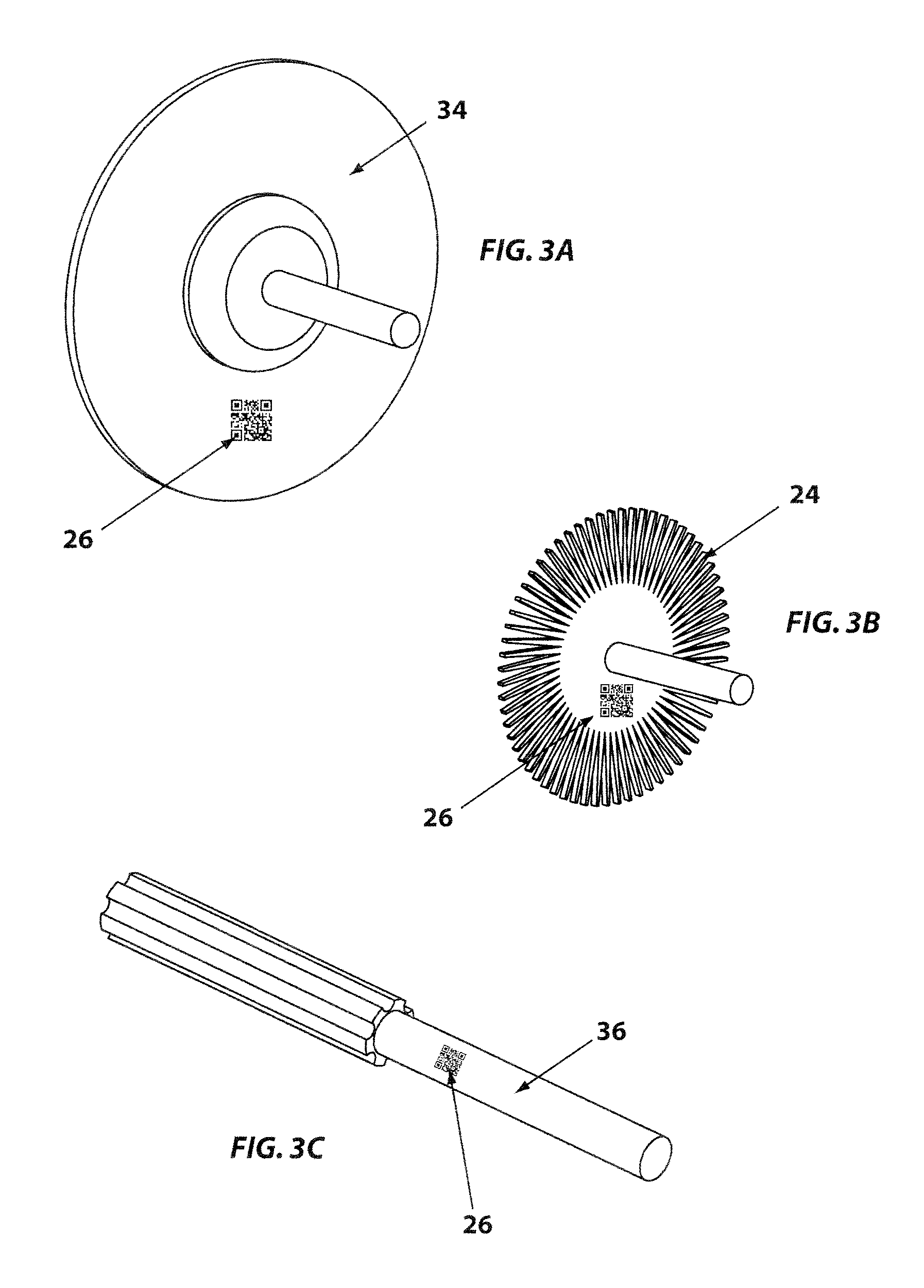
A controlled electro-pneumatic power tool includes an electro-mechanical adjustable valve, a pneumatic motor and a rotational speed sensor connected to a microcontroller for the selection, monitoring and adjustement of the rotational speed in real time. The electro-pneumatic power tool may include input buttons, data ports to save data and a communication port to read / write data from an interactive consumable. The electo-pneumatic power tool may also include a battery and a generator as well as a variable speed transmission with flexible shaft and lightweight handpiece. Using the communication port, important data for the consumable, such as optimum rotation speed, optimum applied pressure and average usage time, can be transmitted to the controlled electro-pneumatic power tool. The controlled electro-pneumatic power tool can read and utilise the transmitted data to select, adjust and maintain the optimum process parameters for the consumable without any input from the operator person. Furthermore, the communicated data can be used to warn the operator person that the tool used is inadequate for the selected consumable, to caution the operator person if he is using the consumable inadequately and to advise him when the consumable should be replaced for safe operation. This will increase the safety of the operator person, improve the quality of the work performed with pneumatic power tools and limit potential damages to the parts being treated.
Owner:FORGUES SYLVAIN +1
Abrasive product and method of making and using the same
InactiveUS20030022604A1Long useful lifeIncrease ratingsFlexible-parts wheelsCoatingCeramic materials
The present invention relates to an abrasive article having a shaped abrasive coating on a shaped backing and to a method of making and using the flexible abrasive article. The flexible abrasive article includes a backing bearing separated, shaped non-abrasive structures having a distal end spaced from the backing which are coated with a shaped abrasive coating. The method comprises providing the backing, applying to one surface of the backing a plurality of separated, shaped non-abrasive structures with distal ends, coating the distal ends with a curable composition containing abrasive particles, imparting a shaped configuration to the uncured coating and curing the coating.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Nonwoven abrasive articles and methods
ActiveUS20050223649A1Improve cutting performancePigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesMaterials scienceCoating
Nonwoven abrasive articles, particularly lofty nonwoven abrasive articles, with a textured, non-planar surface and an abrasive coating thereon. The coating may cover the entire surface or only portions of the surface. The textured surface, composed of peaks or high regions and valleys or recessed regions, provides improved cut performance over nonwoven abrasive articles having a generally planar abrading surface.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Flexible abrasive product and method of making and using the same
InactiveUS6929539B2Provide dimensional stabilityFlexible-parts wheelsGrinding/polishing apparatusOpen cellCoating
The present invention provides a flexible abrasive product comprised of an open cell foam backing, a foraminous barrier coating and a shaped foraminous abrasive coating. The flexible abrasive article of the invention is made by applying a curable barrier coating over an open cell foam backing, curing the curable barrier coating to provide a foraminous barrier coating having openings therethrough corresponding to openings in the open cell foam, applying a coating composition comprising a curable binder and abrasive particles over the foraminous barrier coating, imparting a textured surface to the coating composition with a production tool which has a textured surface which is the inverse of the textured surface of the abrasive coating and to which production tool textured surface any coating composition coated over an opening of the first major surface may adhere, at least partially curing the binder, and separating the production tool from the textured surface to provide the shaped foraminous abrasive coating.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Disposable scrubbing product
InactiveUS20050129897A1Resists effect of waterMaintain stiffnessStampsWrappersEngineeringFibrous layer
The present invention discloses a disposable scrubbing product for use in household cleaning or personal care applications. The scrubbing product of the invention is a multi-layer laminate product and generally includes at least two distinct layers, an abrasive layer and an absorbent fibrous layer such as a layer tissue made from papermaking fibers, a layer of coform, an airlaid web, or combinations thereof. The abrasive layer is formed primarily of polymeric fibers in a disordered or random distribution as is typical of fibers deposited in meltblown or spunbond processes so as to form an open, porous structure. In one embodiment, multiple layers of an abrasive structure are releasably attached together. In this manner, the top or outermost layer may be removed after being used in order to expose an unused abrasive structure located below the discarded layer.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Air duct seal for HVAC case
An HVAC duct sealing system has an air duct wall, a sealing surface, such as an HVAC case, against which the air duct wall is biased, and a seal member interposed between the duct wall and the sealing surface. The seal member is interposed between the air duct wall and the sealing surface and is molded directly onto the air duct wall using a two-shot or double shot method of forming. The seal can be rubber or any flexible, pliable material capable of creating a seal with a surface. The seal has a seal base that is attached to and surrounds an end part and two sides of the air duct wall. The seal has a flexible tip portion extending from the seal base that is biased against and bends against the sealing surface in accordance with an amount of pressing force to create a seal. The flexible tip bends between 0 and 100 degrees from its pre-installation position.
Owner:DENSO INTERNATIONAL AMERICA
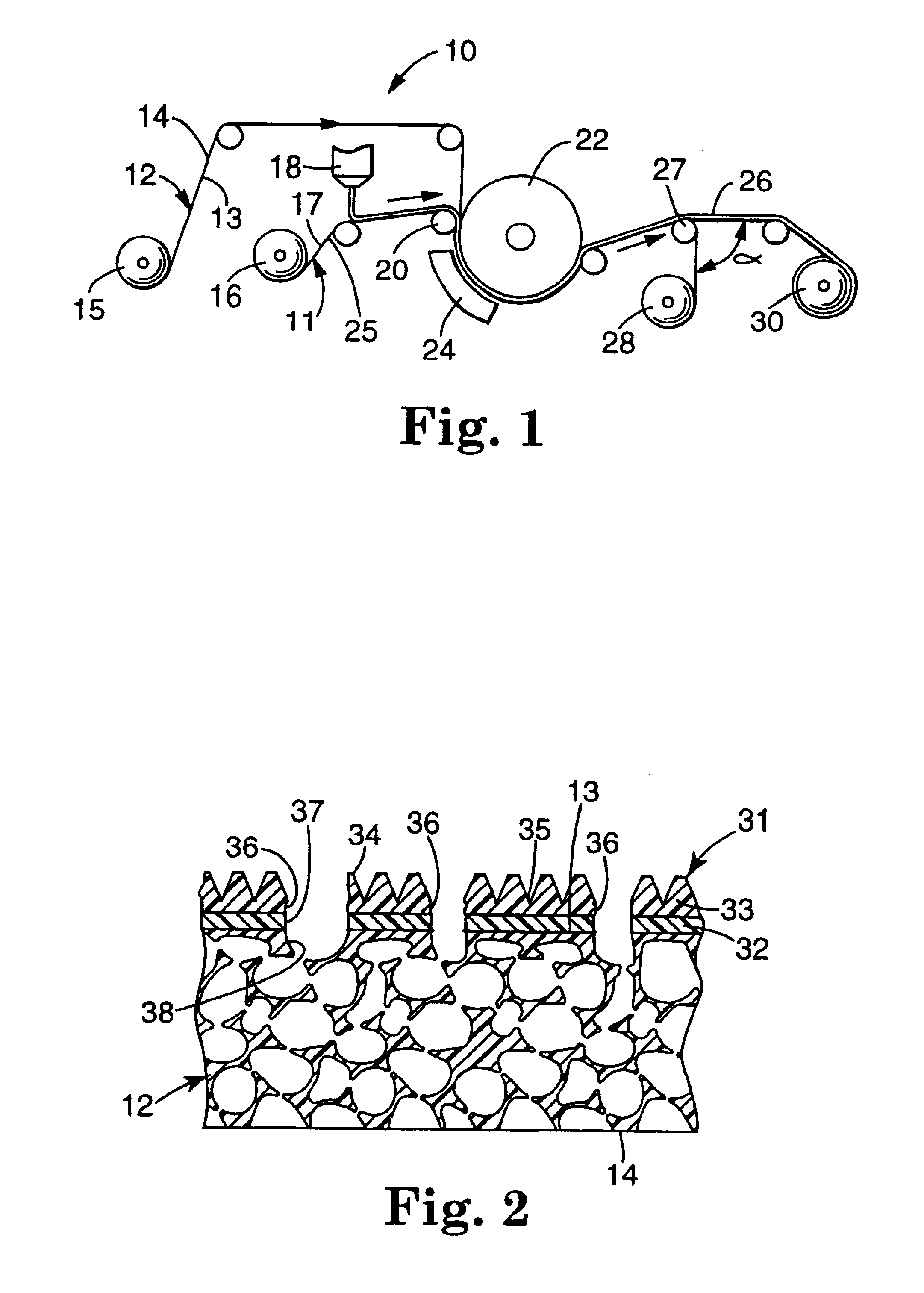
Sanding disks
InactiveUS6312325B1Risk minimizationProtect from harmRevolution surface grinding machinesSupport wheelsAngle grinderEngineering
Accessories for an angle grinder include a disposable rotary sanding disk having quite large shaped ventilating / viewing apertures, for use with a resilient backing plate also having shaped ventilating apertures. The apertures of one or both parts are shaped so that snagging of the apertures on projections from the work surface is minimized and to facilitate air flow across the work surface during use. This air flow helps in cooling the work and ejecting detritus, so minimising clogging effects. The ventilating apertures also facilitate viewing the work to be sanded through the spinning disk during the abrasion process, so that operator feedback is immediate. The holes also give the sanding disk more resilience so that a greater area comes in contact with the work and the disk wears more evenly over its abrasive surface.
Owner:MORTON CO
Polishing pad with microporous regions
The invention provides a polishing pad for chemical-mechanical polishing comprising a polymeric material comprising two or more adjacent regions, wherein the regions have the same polymer formulation and the transition between the regions does not include a structurally distinct boundary. In a first embodiment, a first region and a second adjacent region have a first and second non-zero void volume, respectively, wherein the first void volume is less than the second void volume. In a second embodiment, a first non-porous region is adjacent to a second adjacent porous region, wherein the second region has an average pore size of about 50 μm or less. In a third embodiment, at least two of an optically transmissive region, a first porous region, and an optional second porous region, are adjacent. The invention further provides methods of polishing a substrate comprising the use of the polishing pads and a method of producing the polishing pads.
Owner:CMC MATERIALS INC
Multi-layer polishing pad material for CMP
InactiveUS6884156B2Polishing machinesRevolution surface grinding machinesAdhesiveBiomedical engineering
The invention is directed to a multi-layer polishing pad for chemical-mechanical polishing comprising a polishing layer and a bottom layer, wherein the polishing layer and bottom layer are joined together without the use of an adhesive. The invention is also directed to a polishing pad comprising an optically transmissive multi-layer polishing pad material, wherein the layers of the polishing pad material are joined together without the use of an adhesive.
Owner:CMC MATERIALS INC
Polishing pads for chemical mechanical planarization
InactiveUS6860802B1Revolution surface grinding machinesFlexible-parts wheelsHigh energyRelative motion
An improved pad and process for polishing metal damascene structures on a semiconductor wafer. The process includes the steps of pressing the wafer against the surface of a polymer sheet in combination with an aqueous-based liquid that optionally contains sub-micron particles and providing a means for relative motion of wafer and polishing pad under pressure so that the moving pressurized contact results in planar removal of the surface of said wafer, wherein the polishing pad has a low elastic recovery when said load is removed, so that the mechanical response of the sheet is largely anelastic. The improved pad is characterized by a high energy dissipation coupled with a high pad stiffness. The pad exhibits a stable morphology that can be reproduced easily and consistently. The pad surface resists glazing, thereby requiring less frequent and less aggressive conditioning. The benefits of such a polishing pad are low dishing of metal features, low oxide erosion, reduced pad conditioning, longer pad life, high metal removal rates, good planarization, and lower defectivity (scratches and Light Point Defects).
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CMP HLDG INC
Polishing pad and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS20060037699A1Detection accuracy meetsHigh measurement accuracySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLapping machinesWaferingDevice material
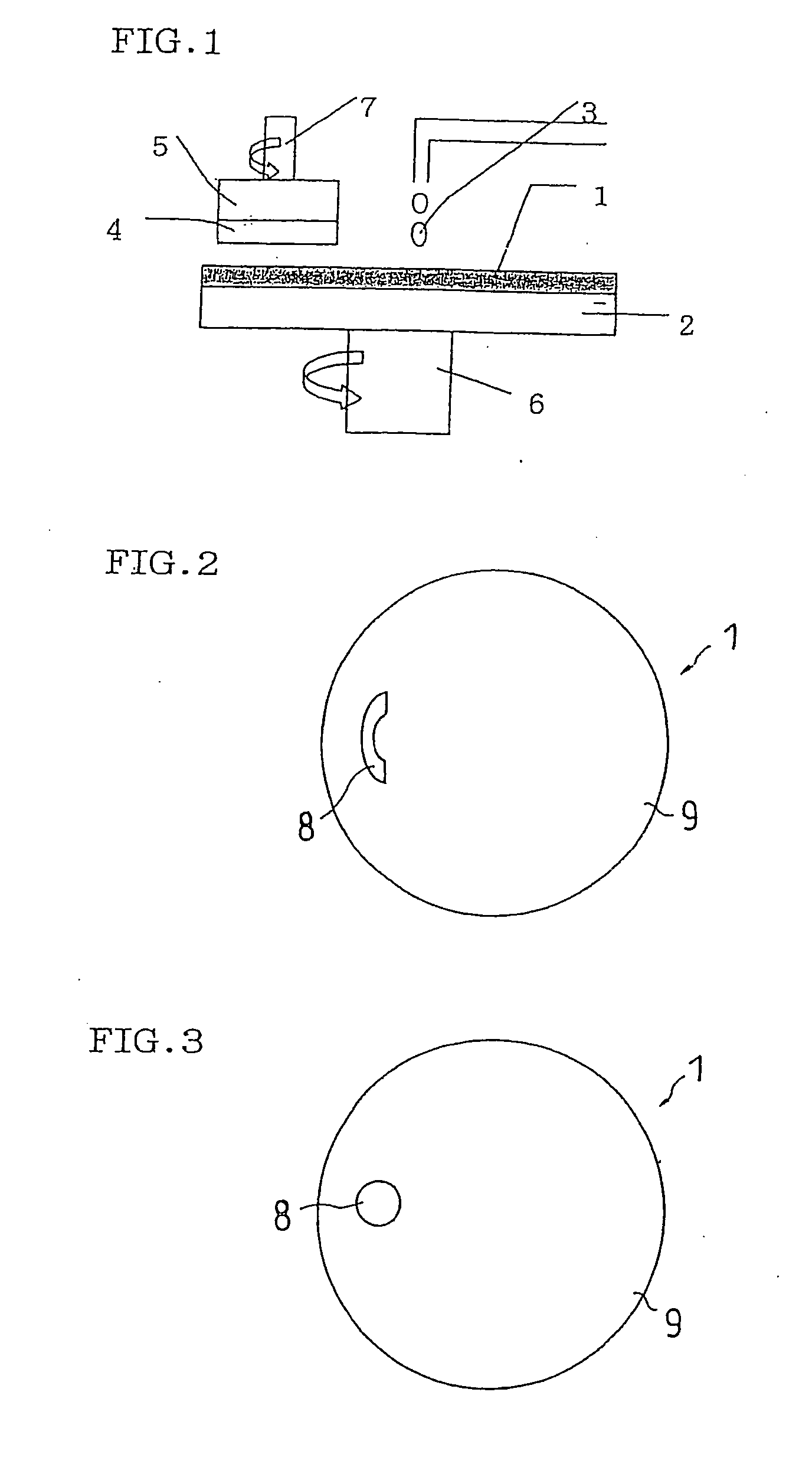
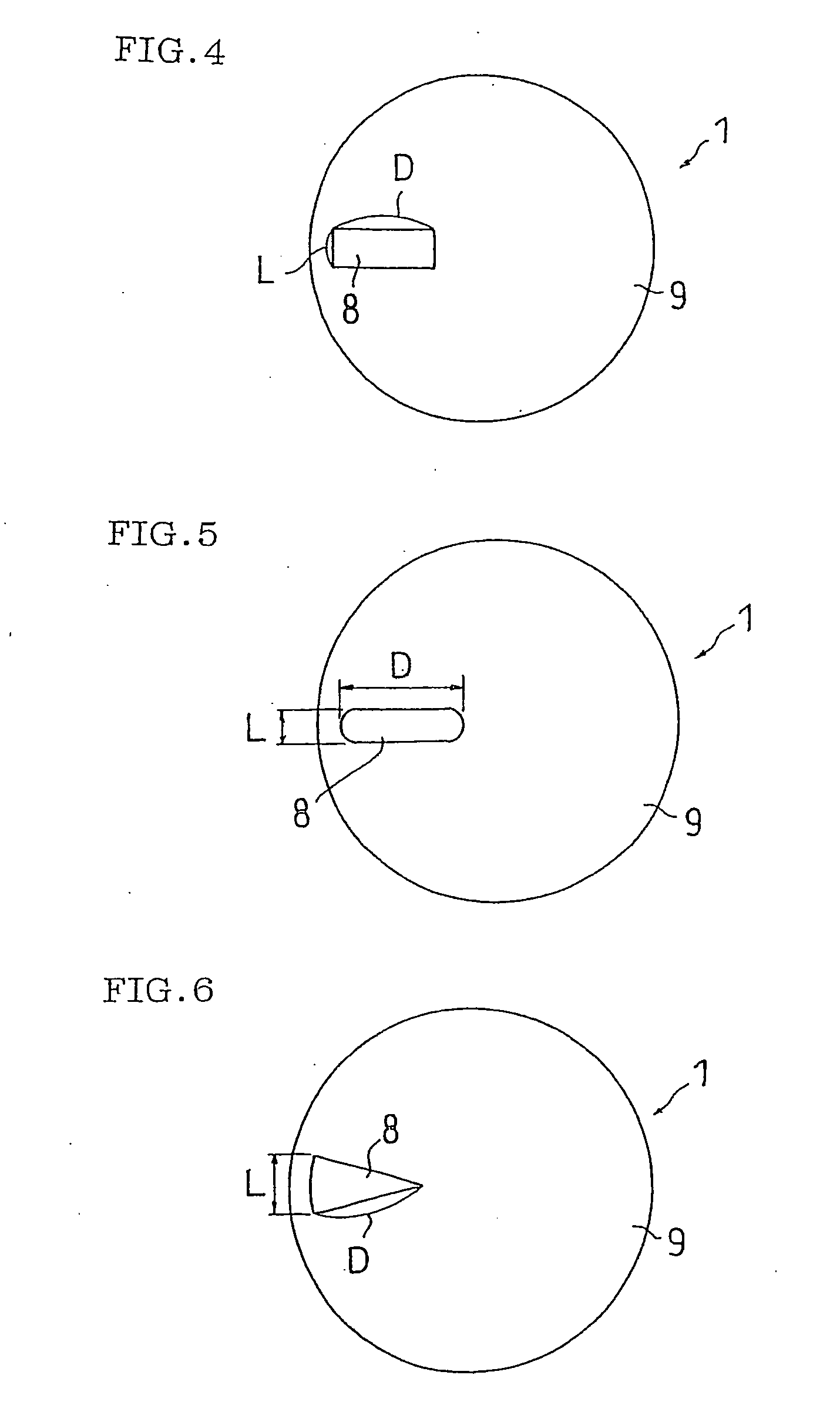
A polishing pad enabling a highly precise optical endpoint sensing during the polishing process and thus having excellent polishing characteristics (such as surface uniformity and in-plane uniformity) is disclosed. A polishing pad enabling to obtain the polishing profile of a large area of a wafer is also disclosed. A polishing pad of a first invention comprises a light-transmitting region having a transmittance of not less than 50% over the wavelength range of 400 to 700 nm. A polishing pad of a second invention comprises a light-transmitting region having a thickness of 0.5 to 4 mm and a transmittance of not less than 80% over the wavelength range of 600 to 700 nm. A polishing pad of a third invention comprises a light-transmitting region arranged between the central portion and the peripheral portion of the polishing pad and having a length (D) in the diametrical direction which is three times or more longer than the length (L) in the circumferential direction.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CMP HLDG INC
Conductive polishing article for electrochemical mechanical polishing
InactiveUS6962524B2Easy to moveSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFlexible-parts wheelsEngineeringContact element
Embodiments of a ball assembly are provided. In one embodiment, a ball assembly includes a housing, a ball, a conductive adapter and a contact element. The housing has an annular seat extending into a first end of an interior passage. The conductive adapter is coupled to a second end of the housing. The contact element electrically couples the adapter and the ball with is retained in the housing between seat and the adapter.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
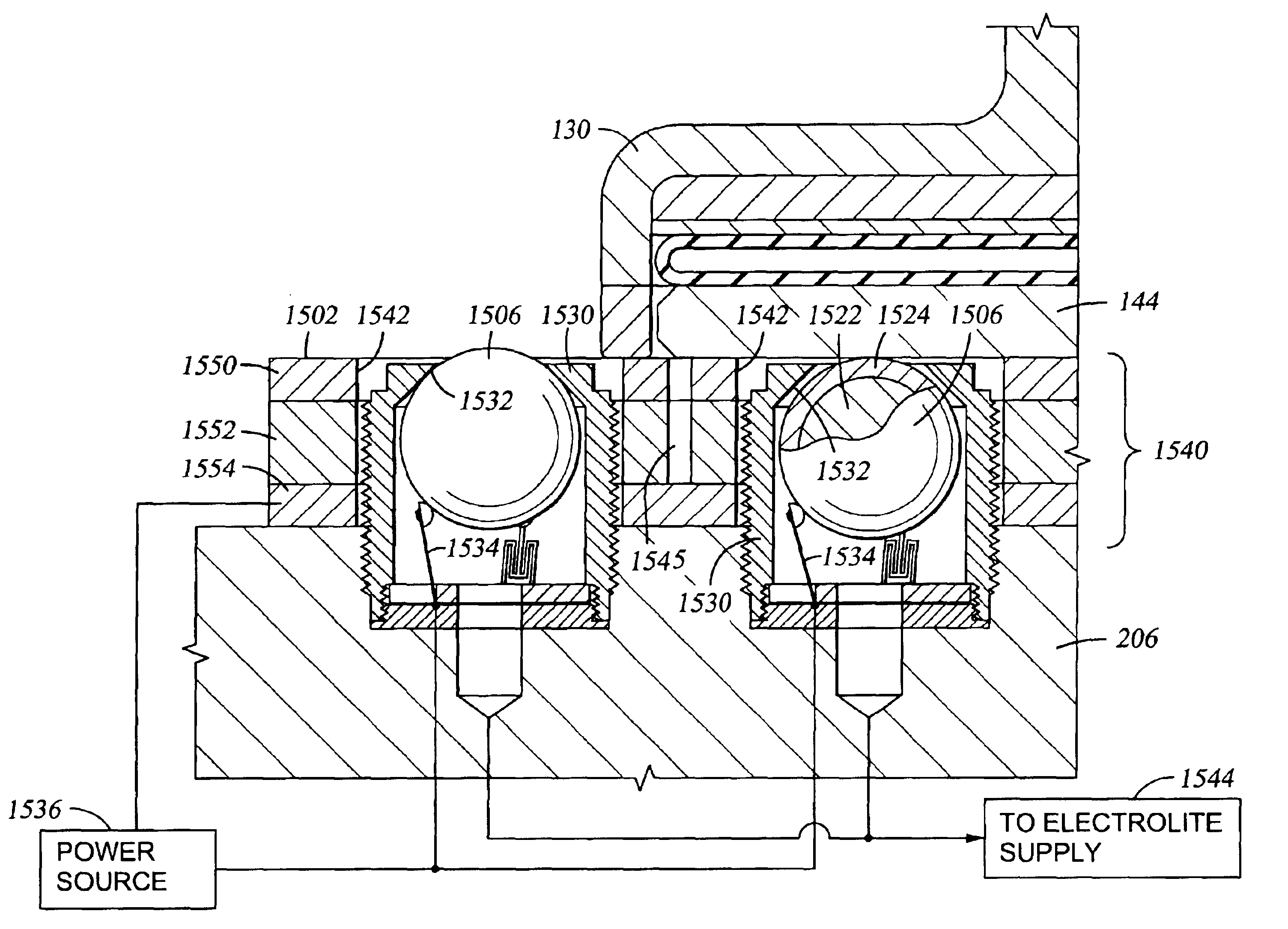
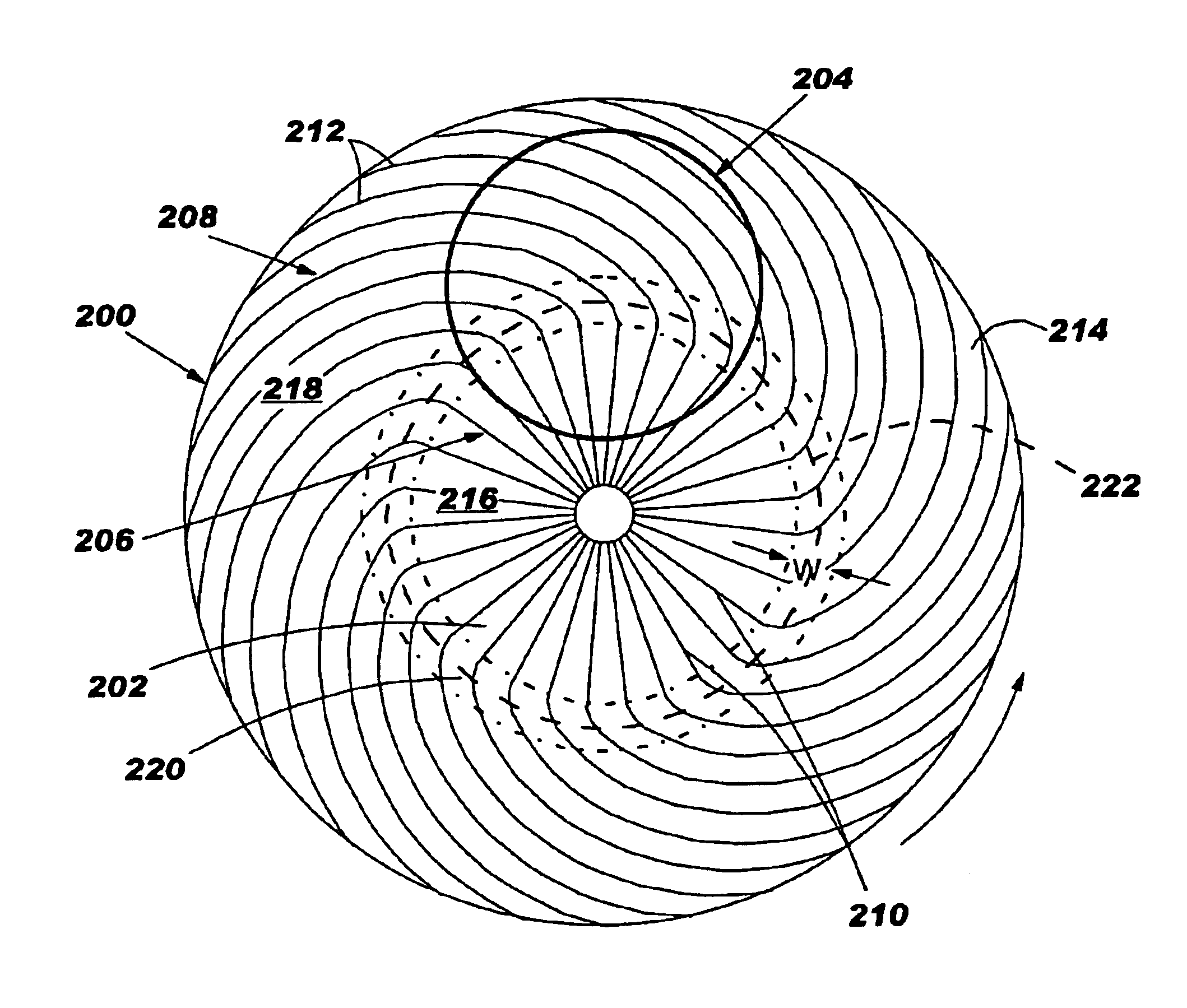
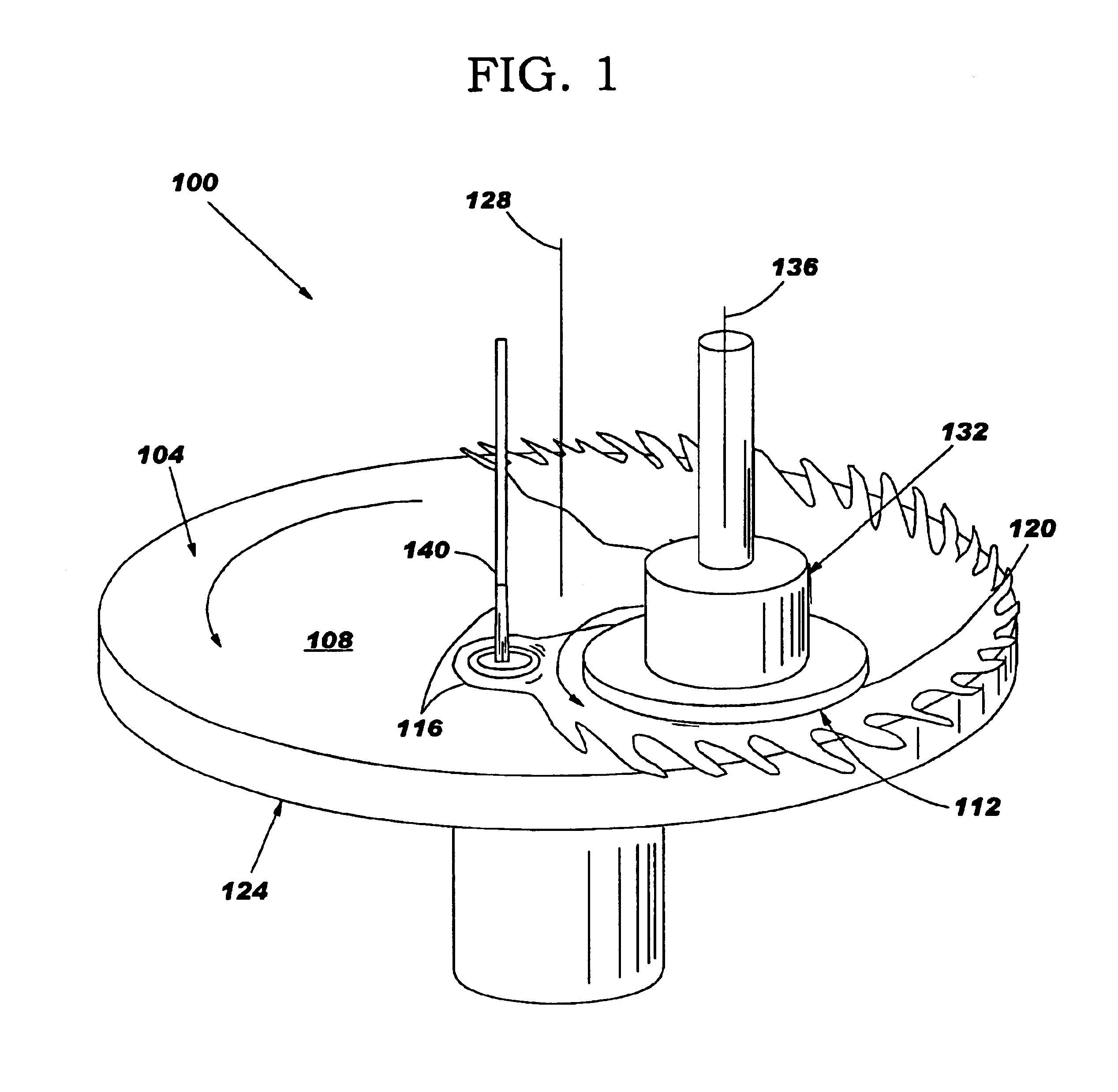
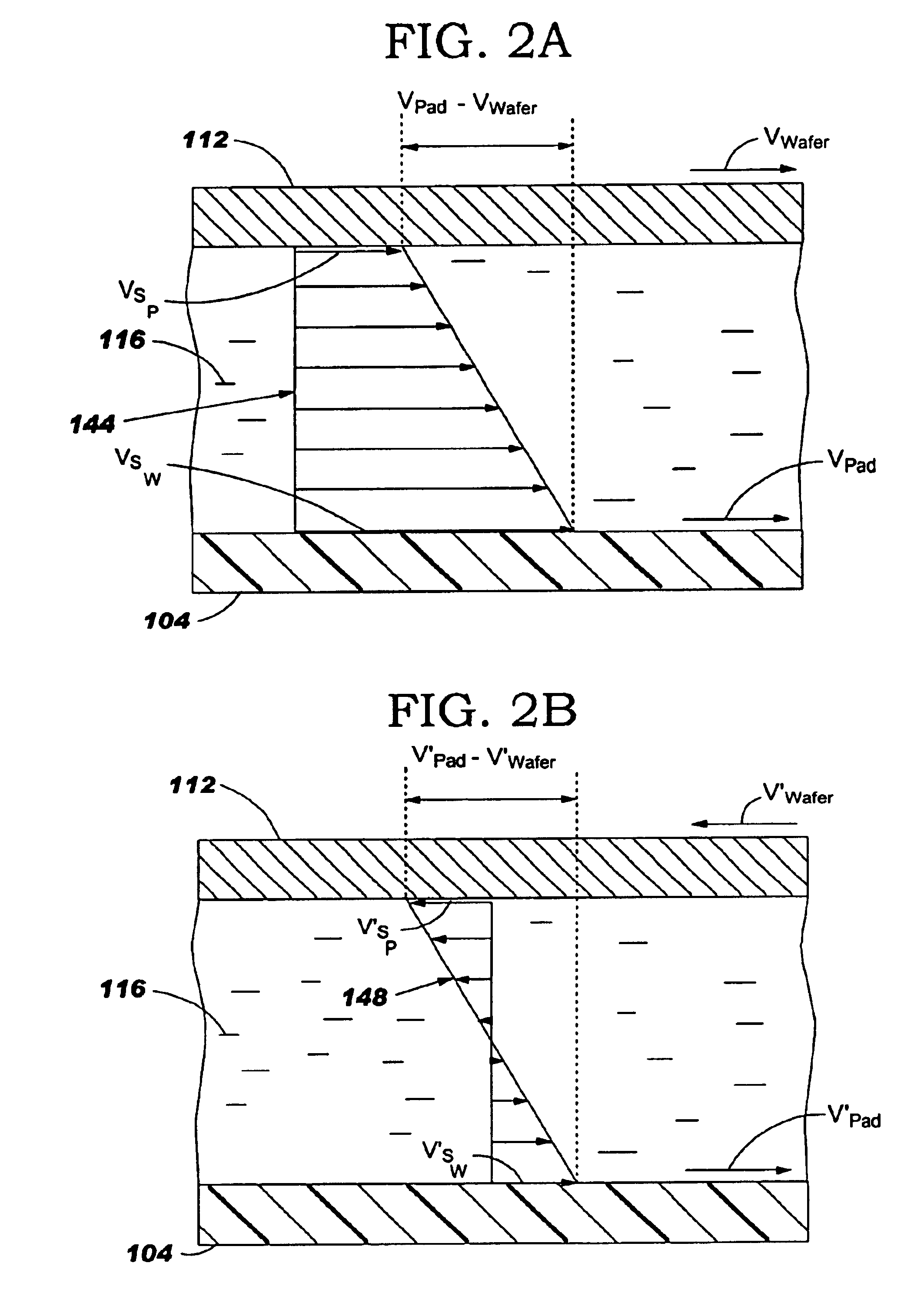
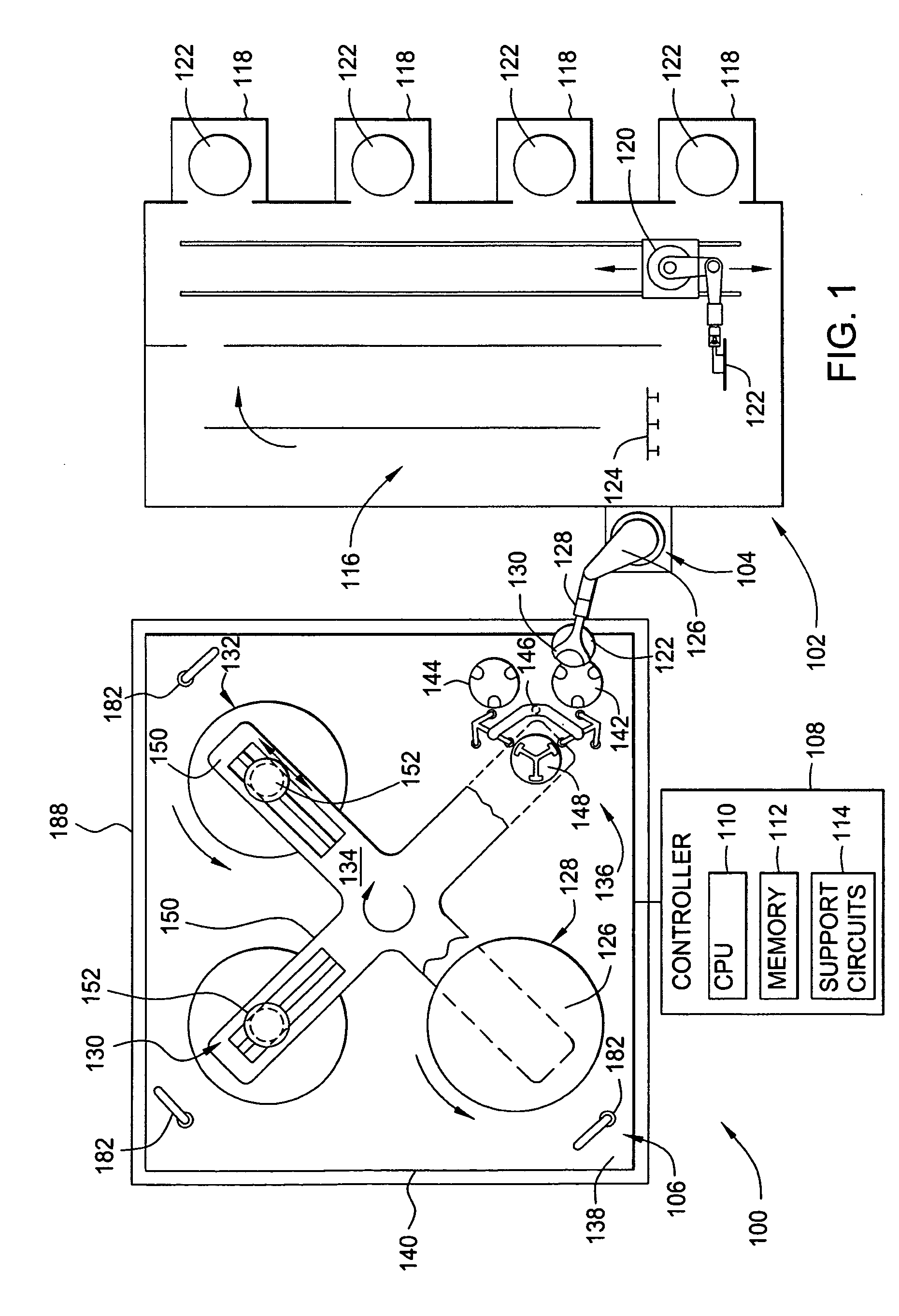
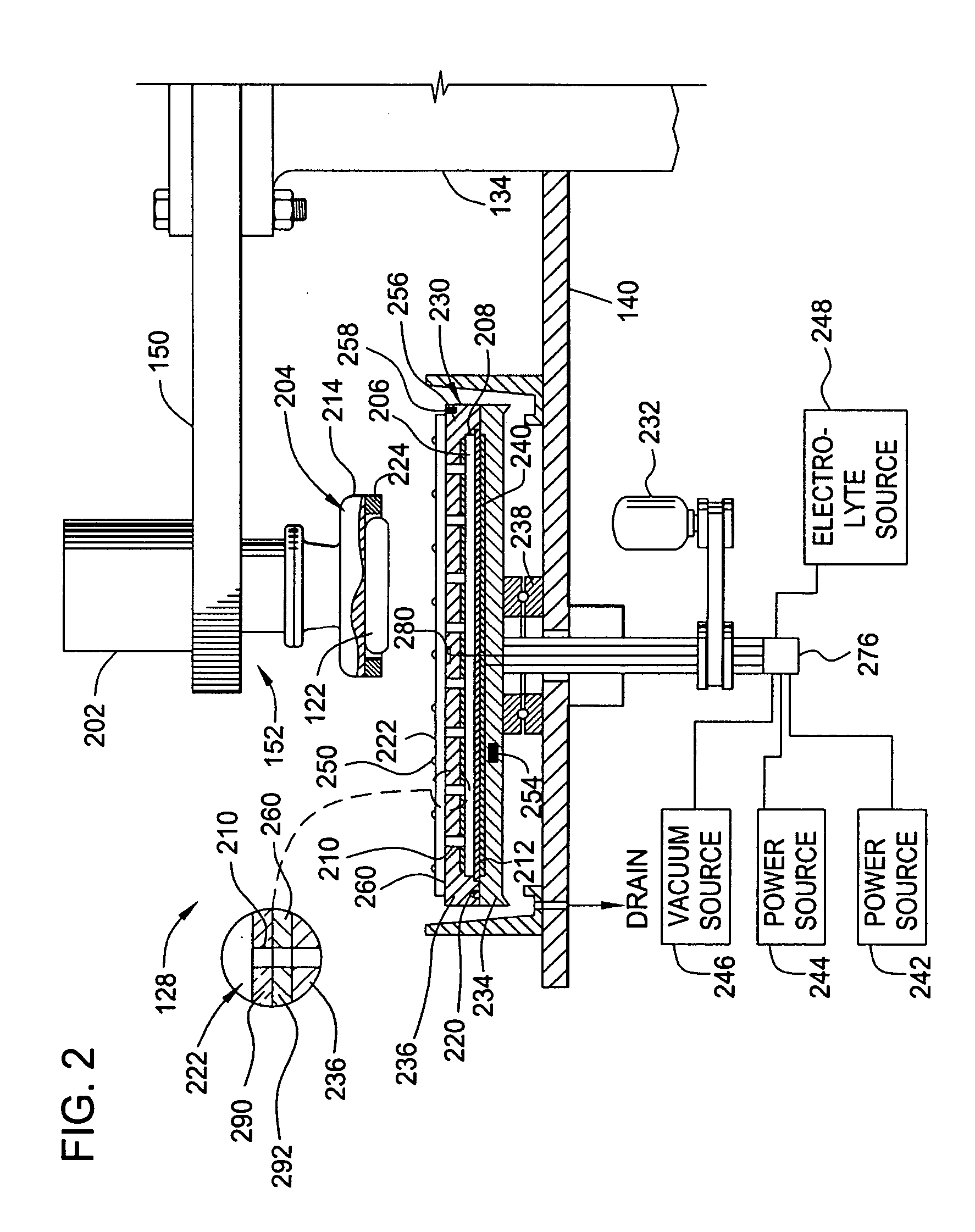
Chemical mechanical polishing pad having a process-dependent groove configuration
A polishing body, e.g., pad (200, 230, 260, 300) or belt (400, 500) having a polishing layer (214, 404) that includes a backmixing region (202, 232, 262, 308, 416, 508) wherein backmixing can occur within a slurry (116) between a wafer (204, 234, 264, 304, 408), or other article, and the polishing layer under certain conditions. The polishing layer includes a first groove configuration (206, 236, 266, 312, 428, 504) within the backmixing region and a second grove configuration (208, 238, 268, 320, 432, 520) outside of the backmixing region that is different from the first groove configuration. The first groove configuration is designed based upon whether or not the presence of spent slurry within the backmixing region is detrimental or beneficial to polishing the wafer.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CMP HLDG INC
Molding a polishing pad having integral window
A polishing pad is formed by solidifying a flowable polymeric material at different rates of cooling to provide a polishing pad with a transparent region and an adjacent opaque region. Types of polymeric material suitable for making the polishing pad include a single thermoplastic material, a blend of thermoplastic materials, and a reactive thermosetting polymer.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CMP HLDG INC
Installation for heating and/or ventilating the passenger compartment of a vehicle employing selective extraction of air
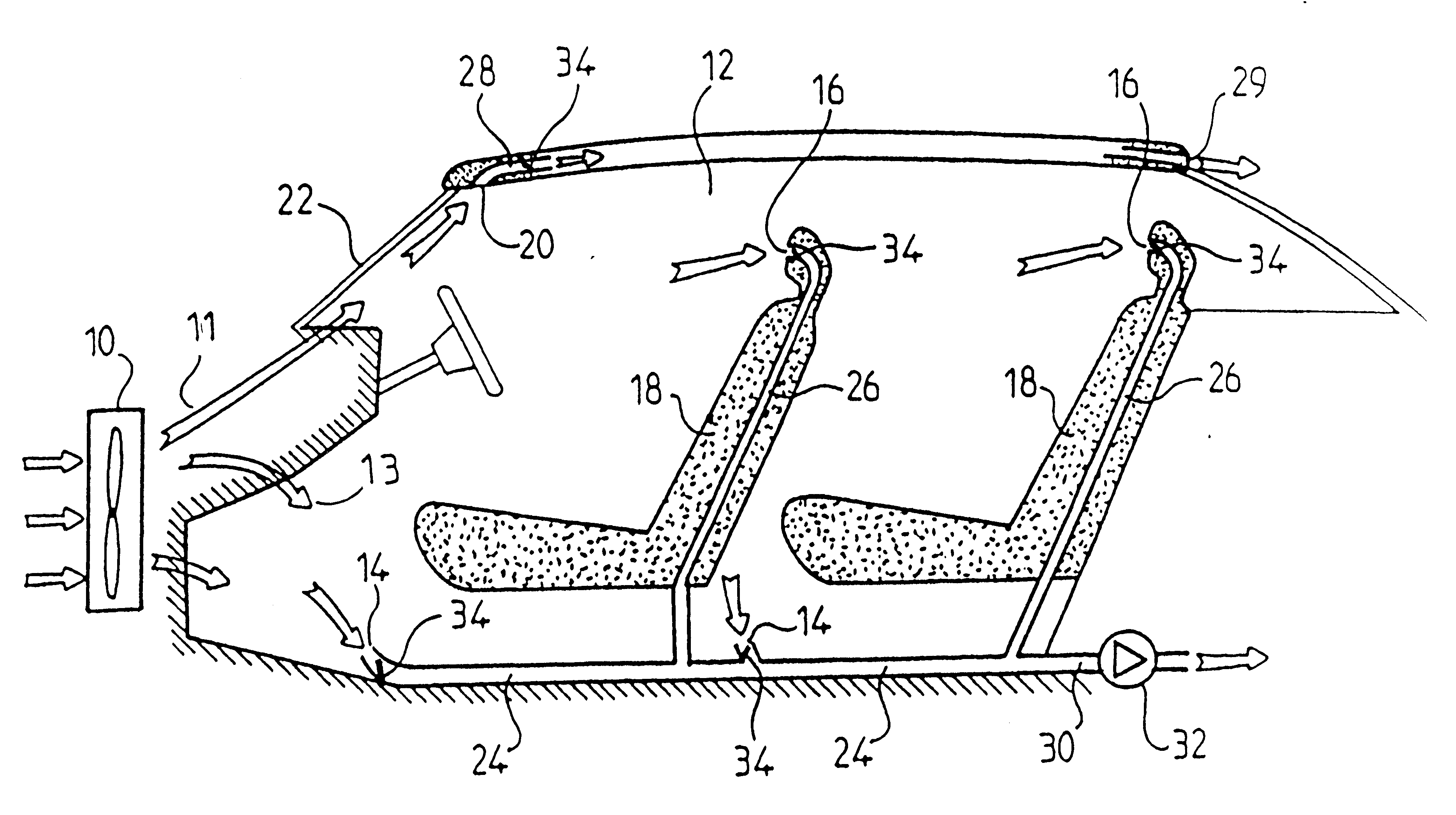
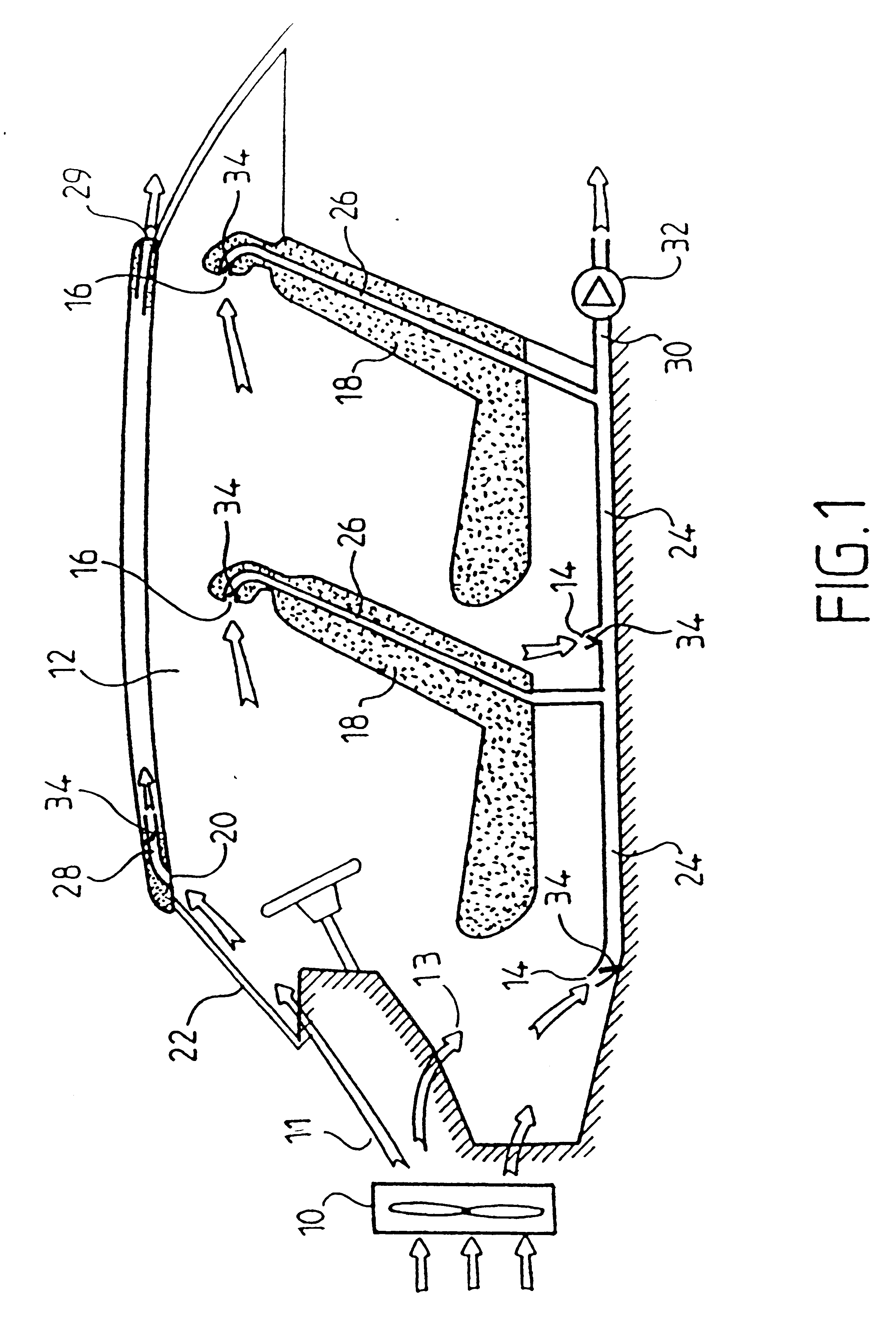
InactiveUS6497275B1Increase in exchangeImprove ventilationVehicle seatsAir-treating devicesCold airAirflow
A fan causes a flow of cold air and warm air into the internal space of the passenger compartment of a vehicle. Air extraction channels connected to corresponding extraction vents are distributed at different locations in the passenger compartment. Controllable flaps selectively apportion and control the distribution of the extracted airflow between the different extraction channels.
Owner:VALEO SYST THERMIQUES
Method and apparatus for electrochemical mechanical processing
InactiveUS20050000801A1CellsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProcess chemistryEngineering
Embodiments of the invention generally provide a method and apparatus for processing a substrate in an electrochemical mechanical planarizing system. In one embodiment, a cell for polishing a substrate includes a processing pad disposed on a top surface of a platen assembly. A plurality of conductive elements are arranged in a spaced-apart relation across the upper planarizing surface and adapted to bias the substrate relative to an electrode disposed between the pad and the platen assembly. A plurality of passages are formed through the platen assembly between the top surface and a plenum defined within the platen assembly. In another embodiment, a system is provided having a bulk processing cell and a residual processing cell. The residual processing cell includes a biased conductive planarizing surface. In further embodiments, the conductive element is protected from attack by process chemistries.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Flexible abrasive product and method of making and using the same
InactiveUS6923840B2Provide dimensional stabilityPigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesOpen cellCoating
The present invention provides a flexible abrasive product comprised of an open cell foam backing, a foraminous barrier coating and a shaped foraminous abrasive coating. The flexible abrasive article of the invention is made by applying a curable barrier coating over an open cell foam backing, curing the curable barrier coating to provide a foraminous barrier coating having openings therethrough corresponding to openings in the open cell foam, applying a coating composition comprising a curable binder and abrasive particles over the foraminous barrier coating, imparting a textured surface to the coating composition with a production tool which has a textured surface which is the inverse of the textured surface of the abrasive coating and to which production tool textured surface any coating composition coated over an opening of the first major surface may adhere, at least partially curing the binder, and separating the production tool from the textured surface to provide the shaped foraminous abrasive coating.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
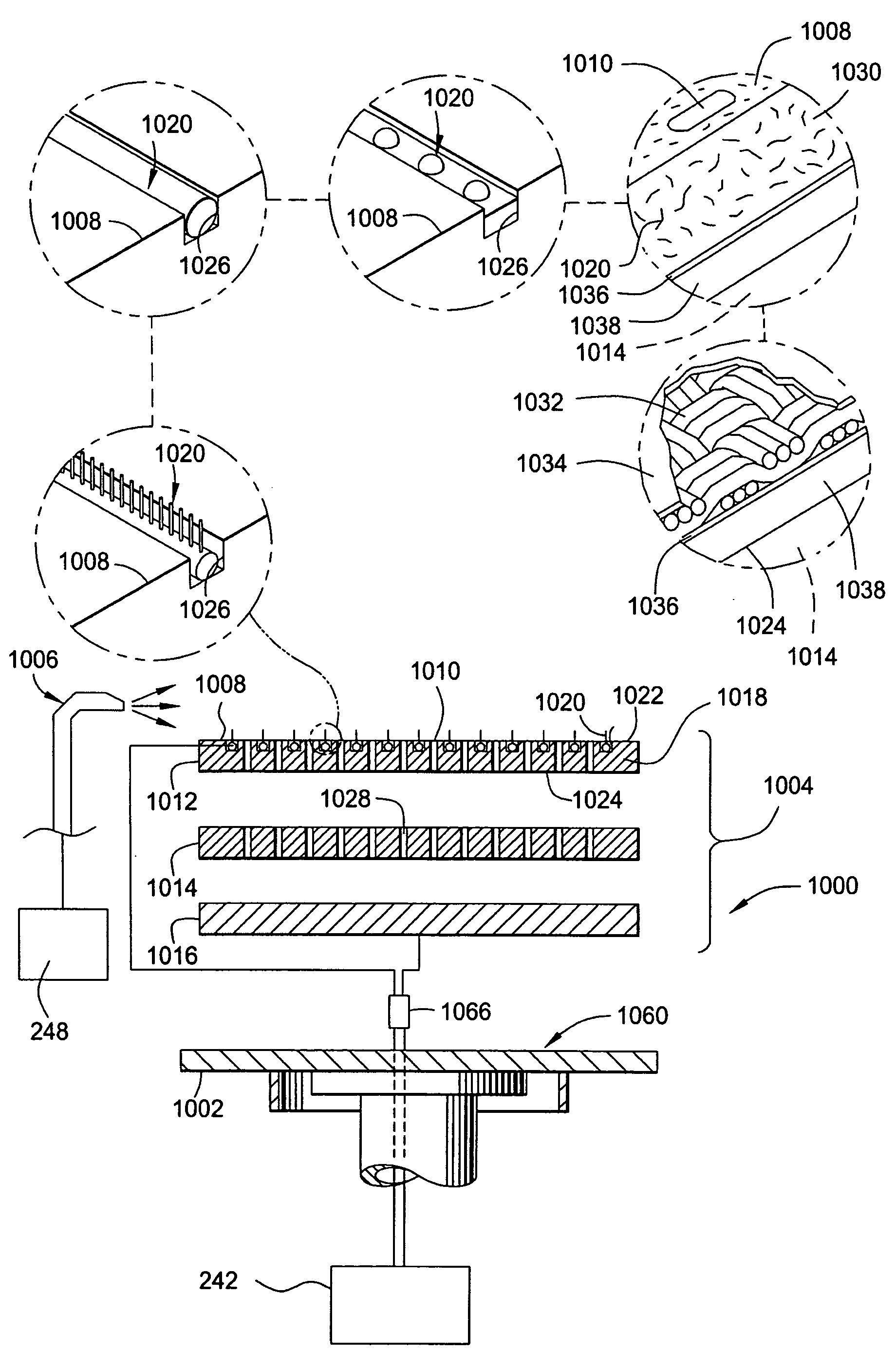
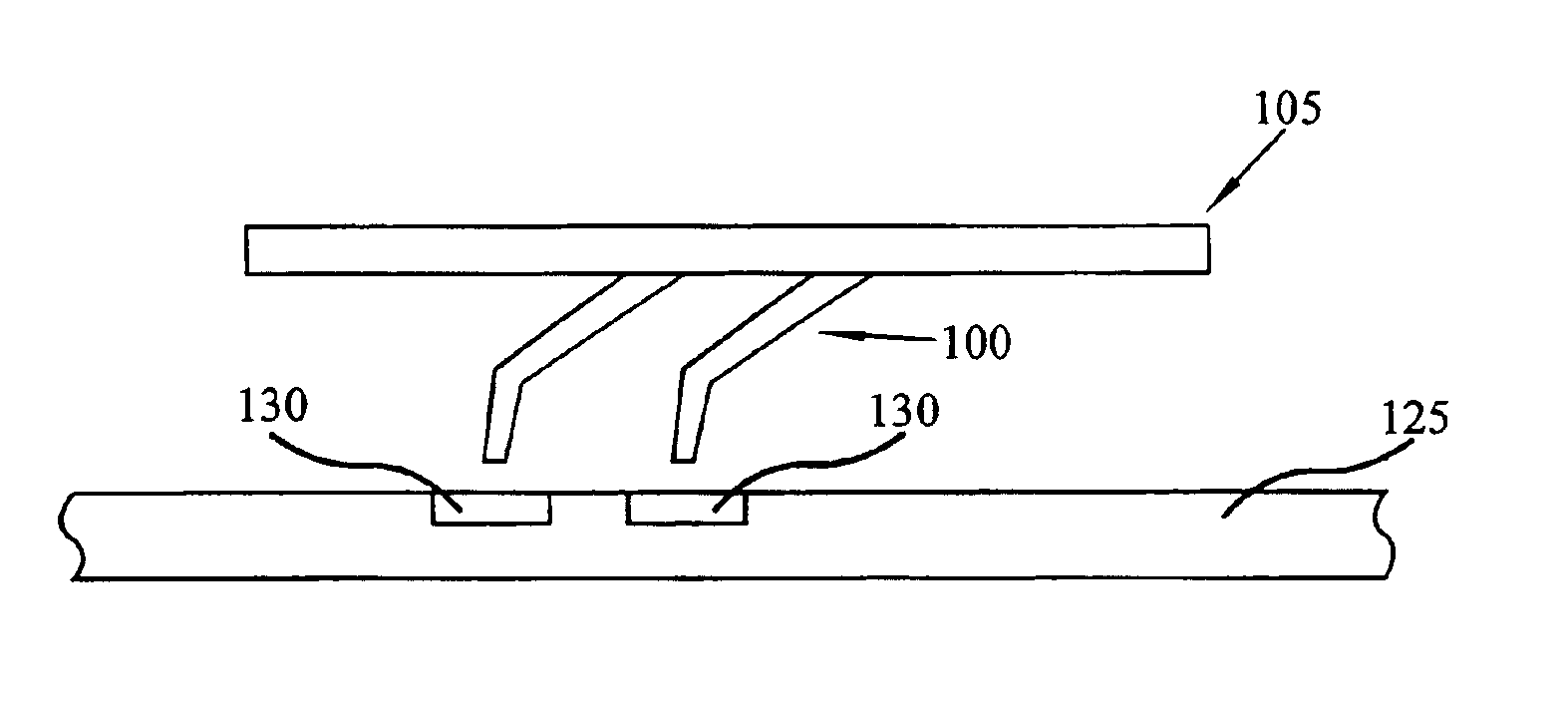
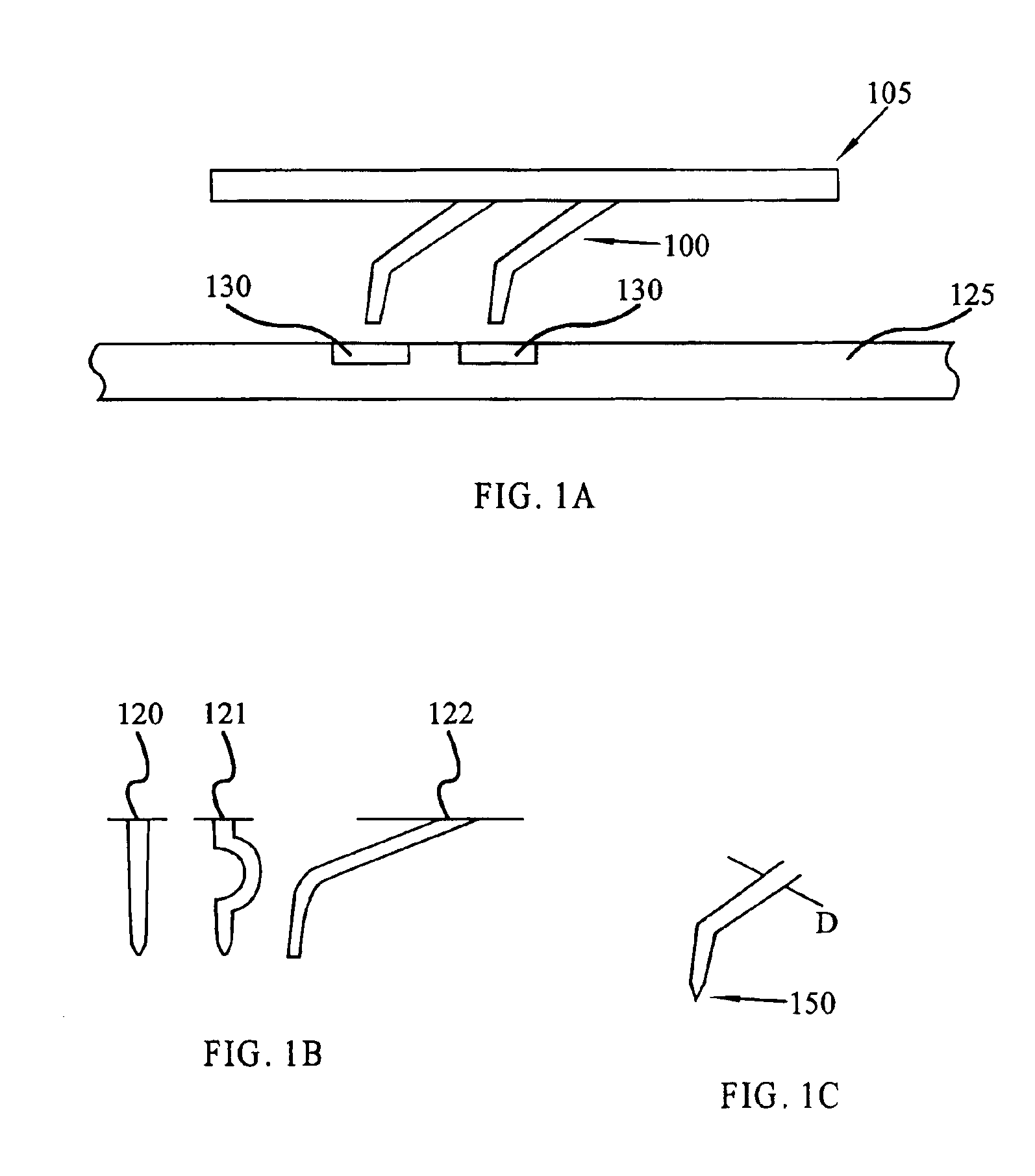
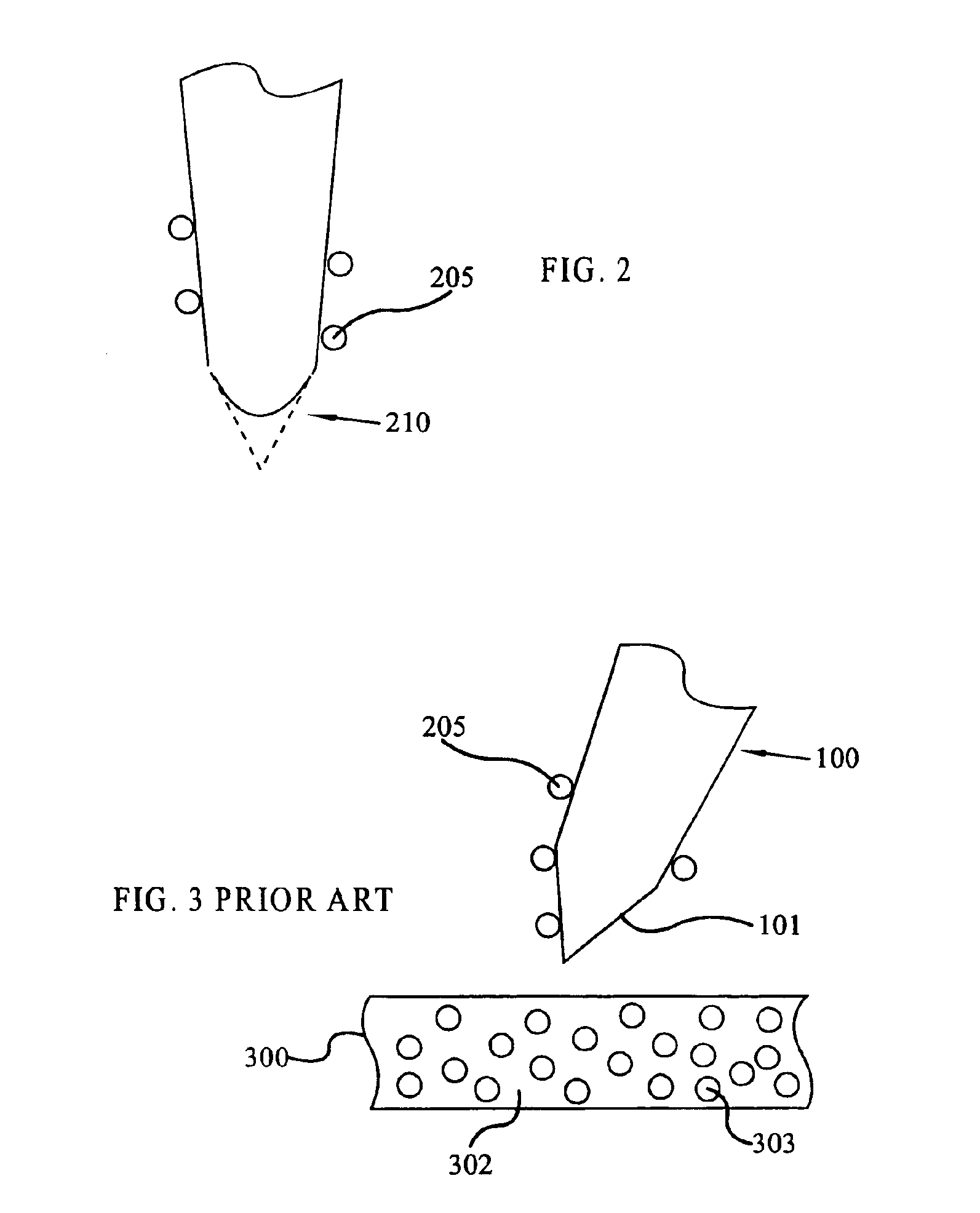
Method and apparatus for probe tip cleaning and shaping pad
A method and apparatus is provided for cleaning and shaping a probe tip using a multi-layer adhesive and abrasive pad. The multi-layer adhesive and abrasive pad is constructed on the surface of a support structure, such as a silicon wafer, and is made of an adhesive in contact with abrasive particles. Adhesive is applied in layers with abrasive particles in-between each layer of adhesive. Abrasive particles may vary in size and material from layer to layer to achieve cleaning, shaping and polishing objectives.
Owner:SV PROBE PTE LTD
Surface textured microporous polishing pads
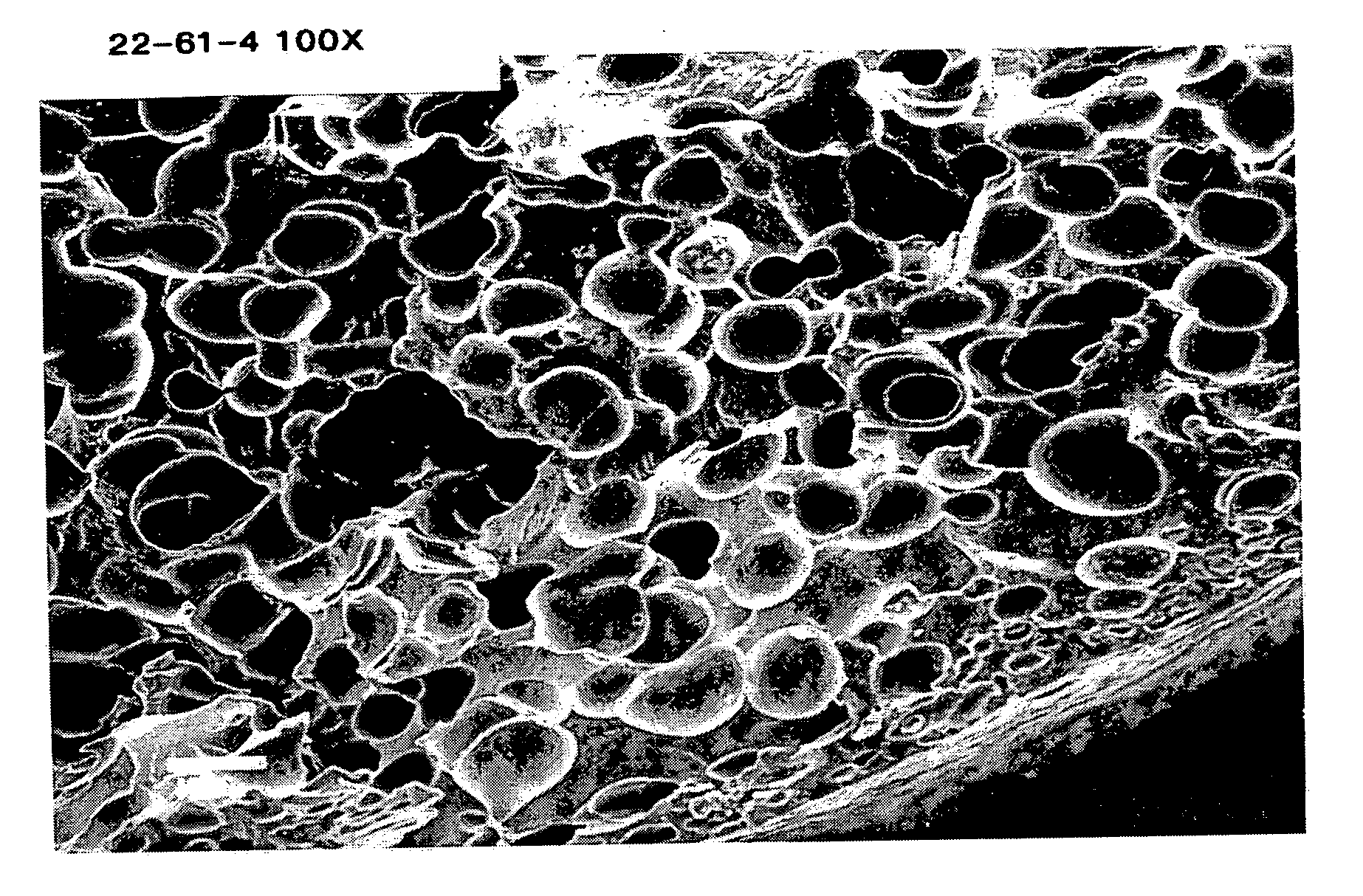
InactiveUS20050276967A1Reduce unevennessHigh removal rateLayered productsFlexible-parts wheelsCompound (substance)Surface roughness
A surface-textured polishing pad suitable for chemical-mechanical polishing comprises a porous polymeric foam having an average pore cell size in the range of about 60 μm or less. At least about 75% of the pores in the foam have a pore cell size within about 30 μm of the average pore cell size. The pad has at least one textured surface that includes divots having a depth in the range of about 25 μm to about 1150 μm, a width in the range of about 0.25 μm to about 380 μm, and a length-to-width aspect ratio of about 1 to about 1000. In addition, the at least one textured surface of the pad includes at least about 10 divots per square centimeter of surface area, and has an average surface roughness of at least about 5 μm. Preferably, at least one textured surface has at least one pattern of spaced, parallel grooves imprinted thereon.
Owner:CABOT MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Polishing pads and methods relating thereto
InactiveUS6217434B1Improve the level ofLow levelRevolution surface grinding machinesOther chemical processesTopographySemiconductor
This invention describes improved polishing pads useful in the manufacture of semiconductor devices or the like. The pads of the present invention have an advantageous hydrophilic polishing material and have an innovative surface topography and texture which generally improves predictability and polishing performance.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CMP HLDG INC
Mosaic polishing pads and methods relating thereto
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CMP HLDG INC
Polishing pad and multi-layer polishing pad
InactiveUS20040014413A1Improve flatnessEffectively suppressed from occurringSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFlexible-parts wheelsSurface roughnessBiomedical engineering
The present invention intends to provide a polishing pad and a multi-layer polishing pad that can particularly effectively suppress scratch from occurring. The polishing pad of the invention comprises at least one part selected from a groove (a) having at least one kind of shape selected from annular, lattice-like and spiral form on a polishing surface side, a concave portion (b) and a through hole (c). In the above, surface roughness of an inner surface of the part is 20 mum or less and the polishing pad is used for chemical mechanical polishing.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON
Polishing pad
A polishing pad is useful planarizing semiconductor substrates. The polishing pad comprises a polymeric material having a porosity of at least 0.1 volume percent, a KEL energy loss factor at 40° C. and 1 rad / sec of 385 to 750 1 / Pa and a modulus E′ at 40° C. and 1 rad / sec of 100 to 400 MPa.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CMP HLDG INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com