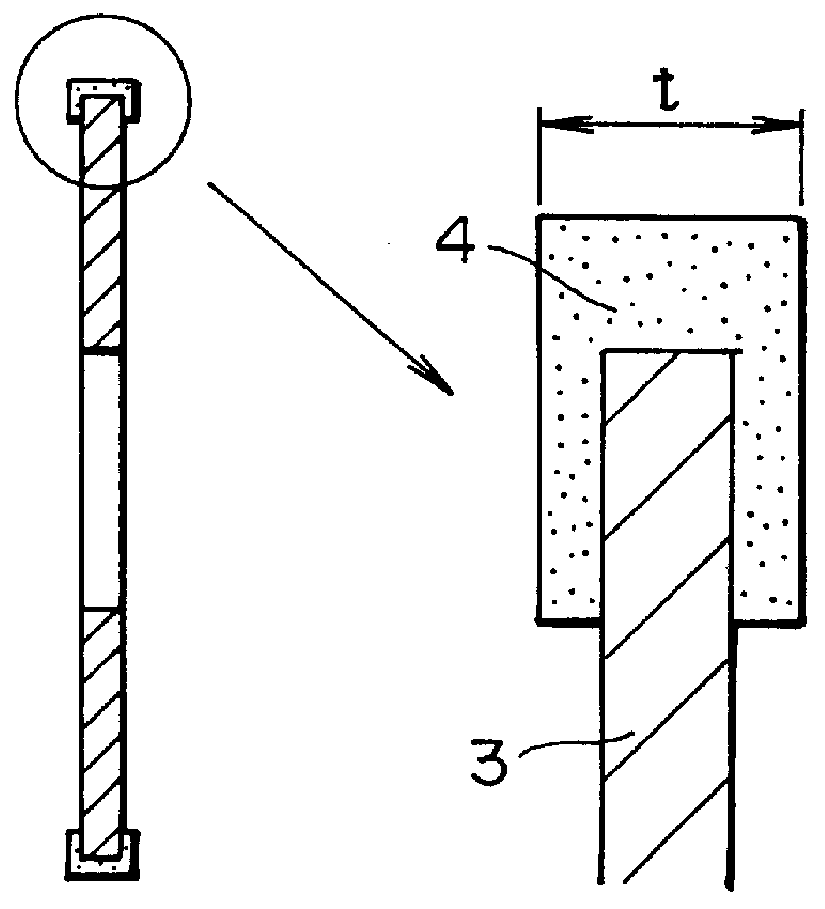
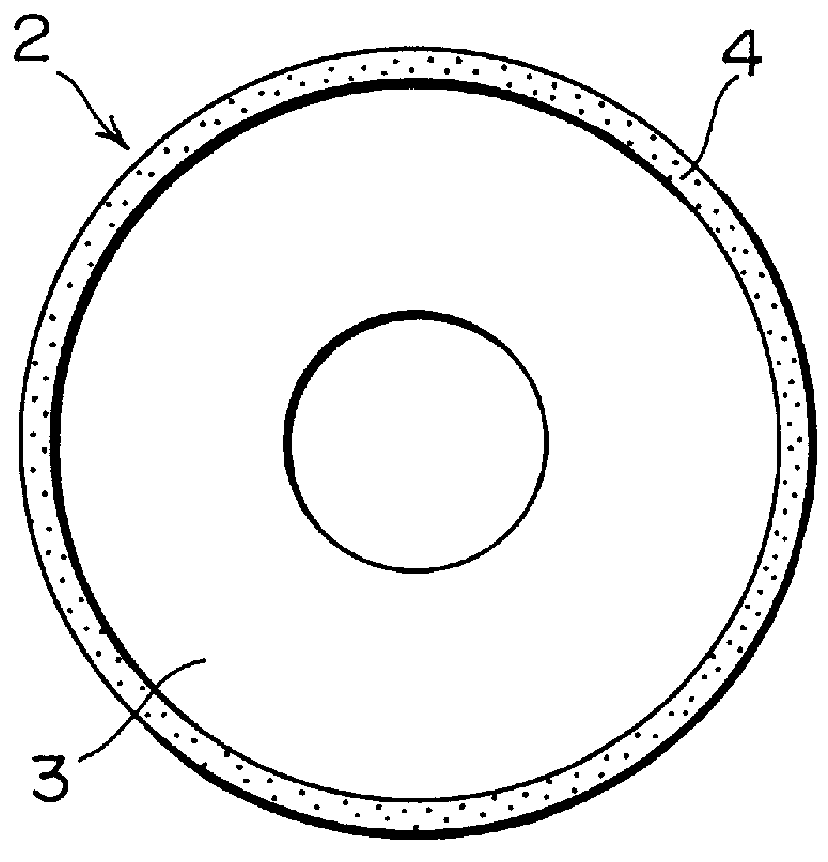
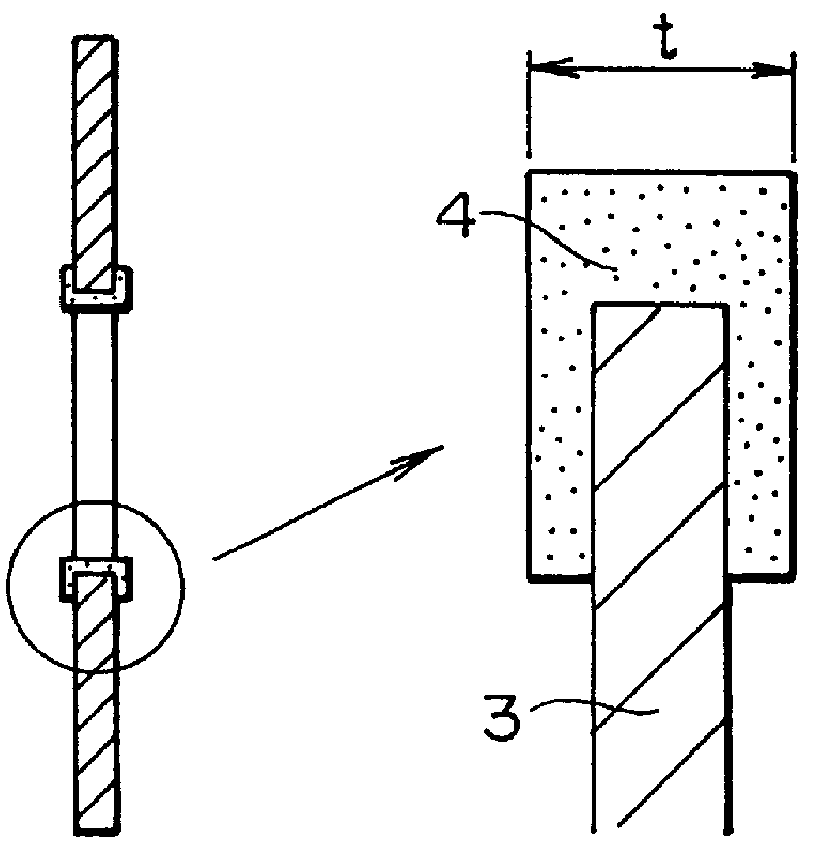
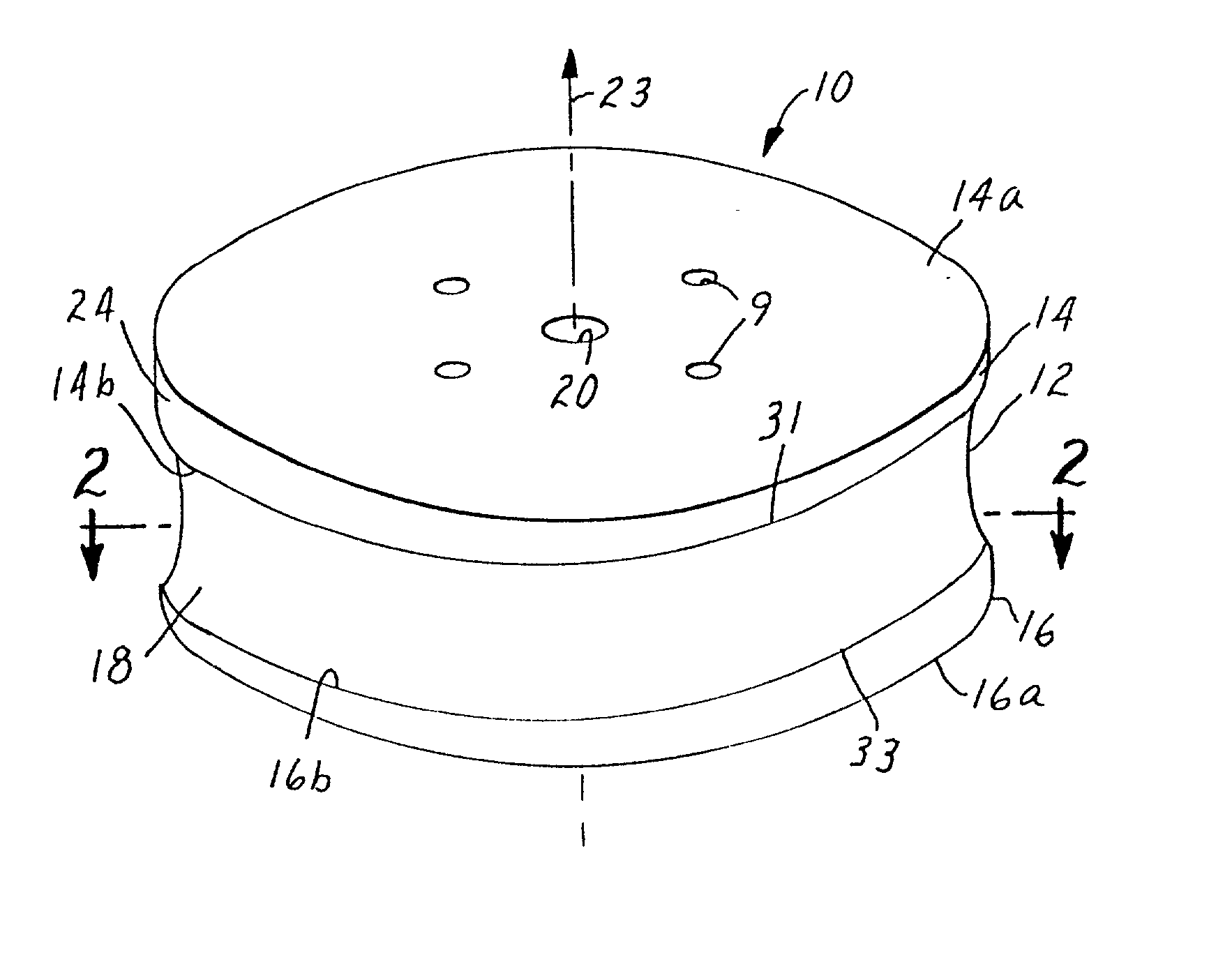
Patents
Literature
2899results about "Bonded abrasive wheels" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
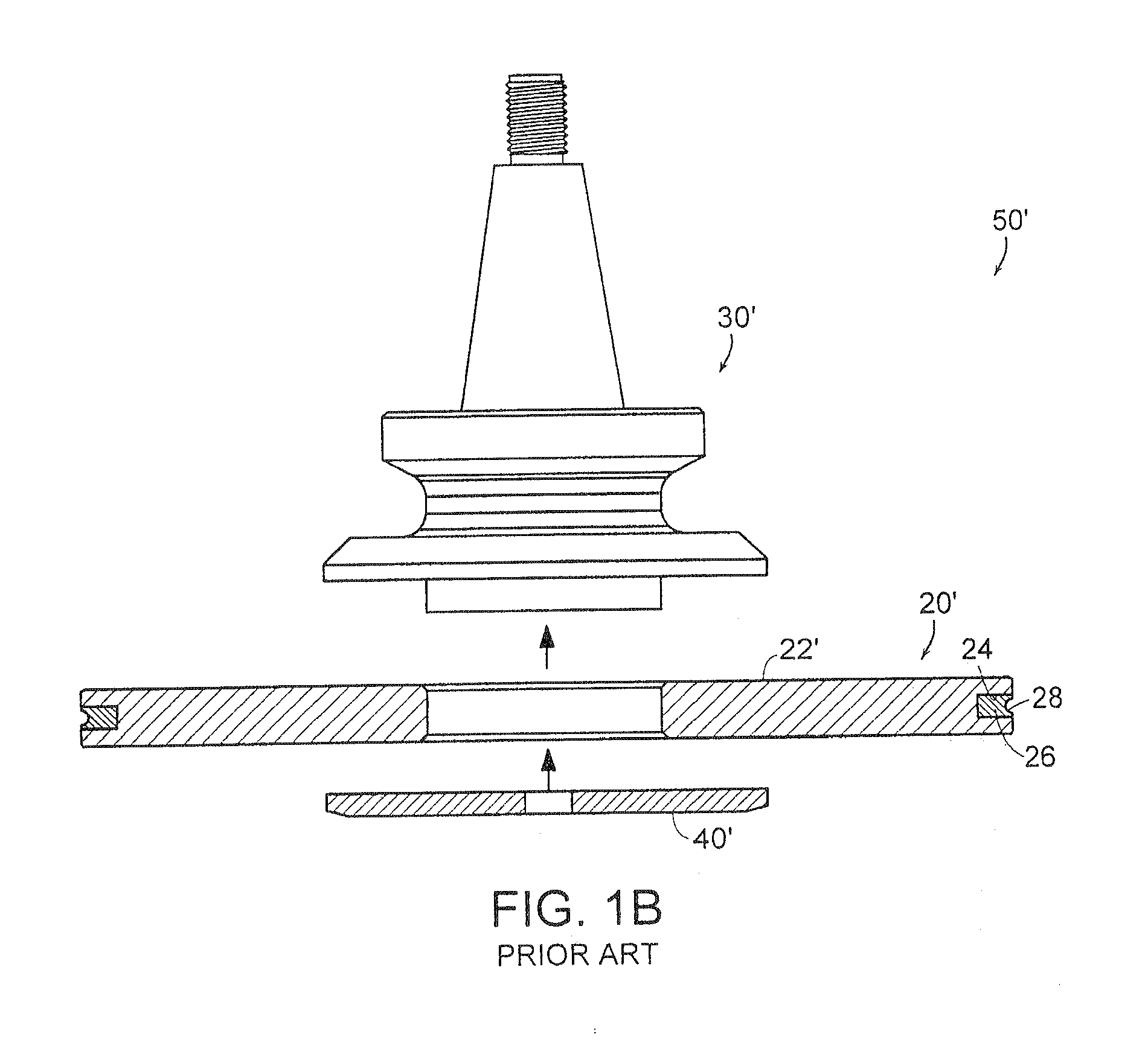
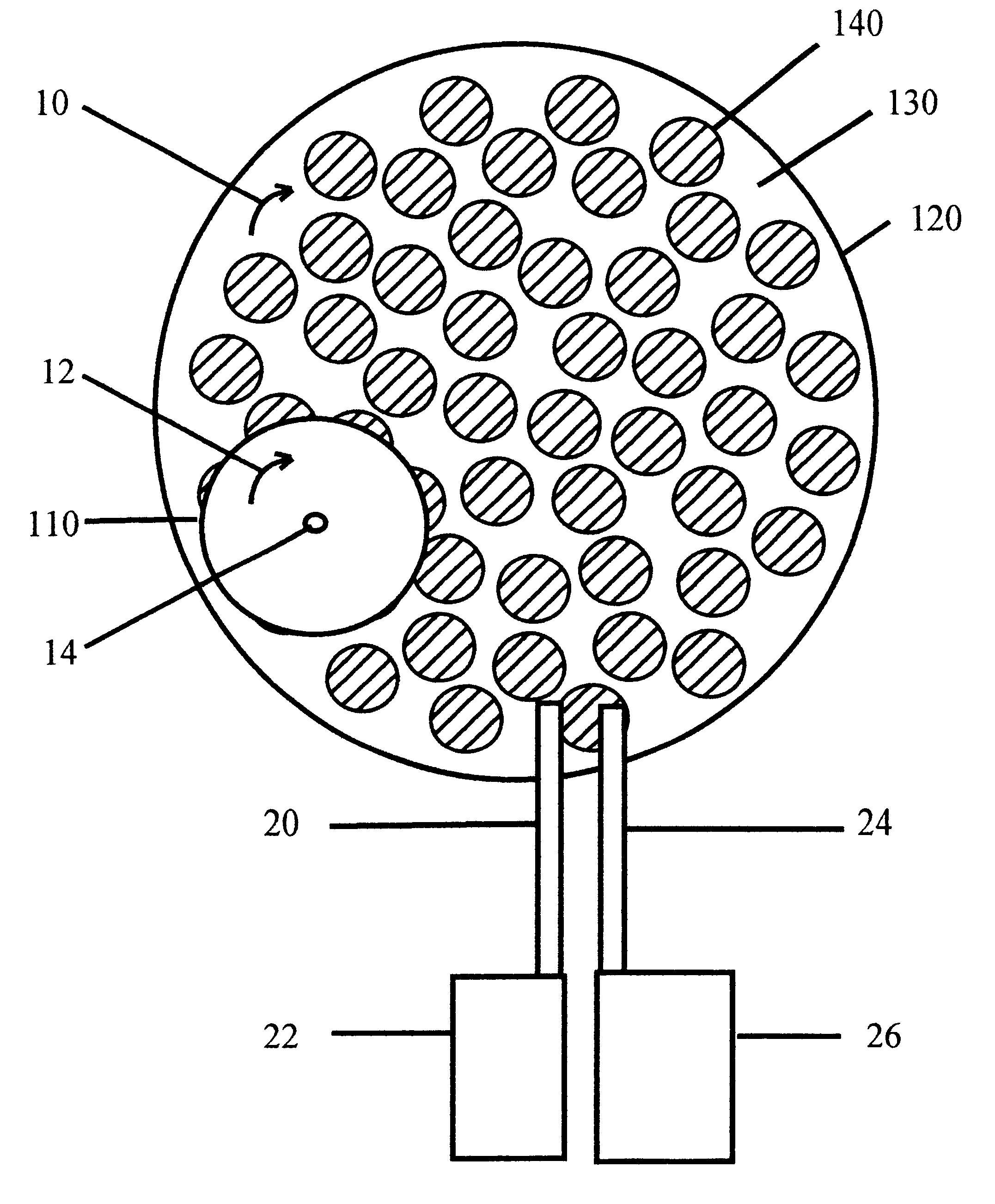
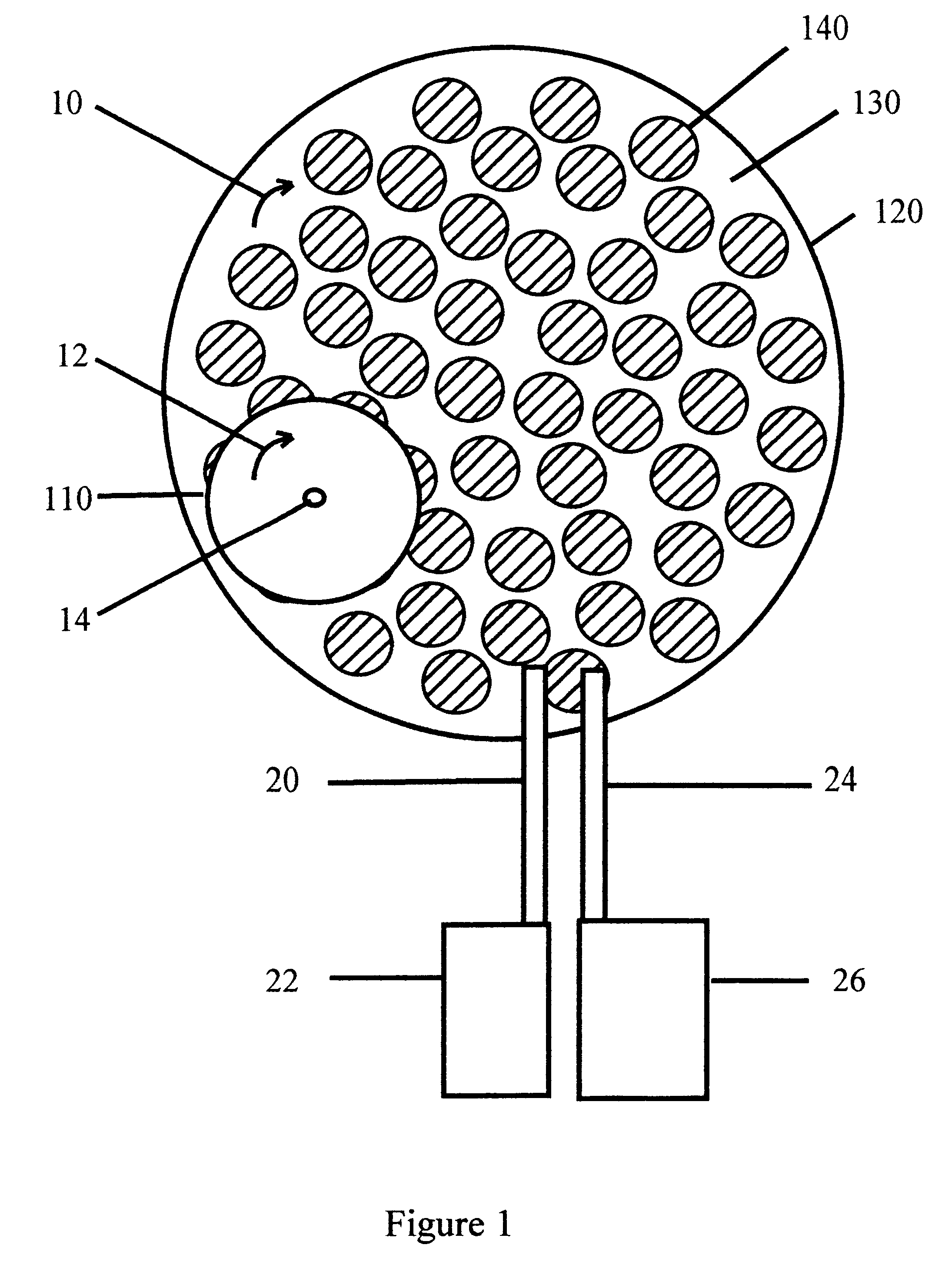
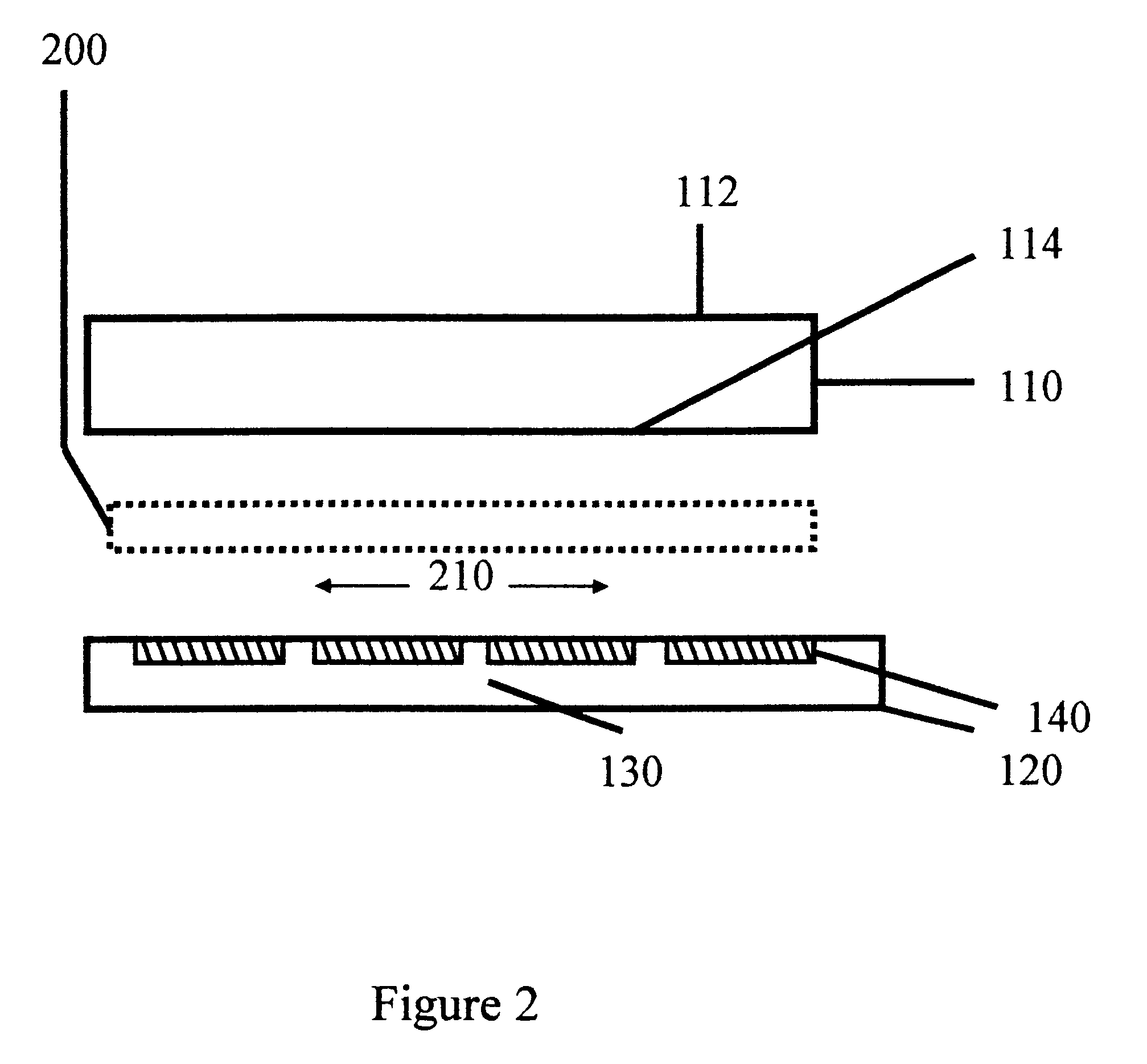
Controlled electro-pneumatic power tools and interactive consumable
Owner:FORGUES SYLVAIN +1
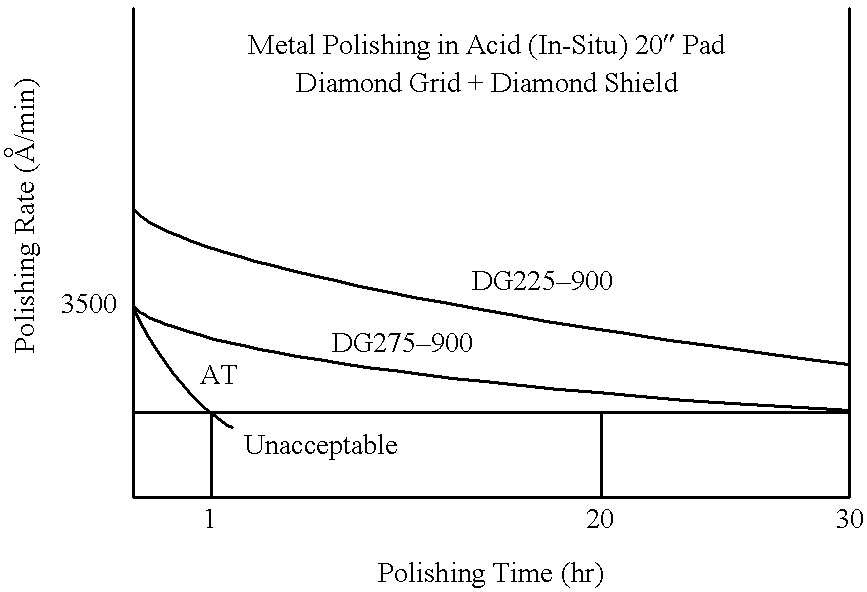
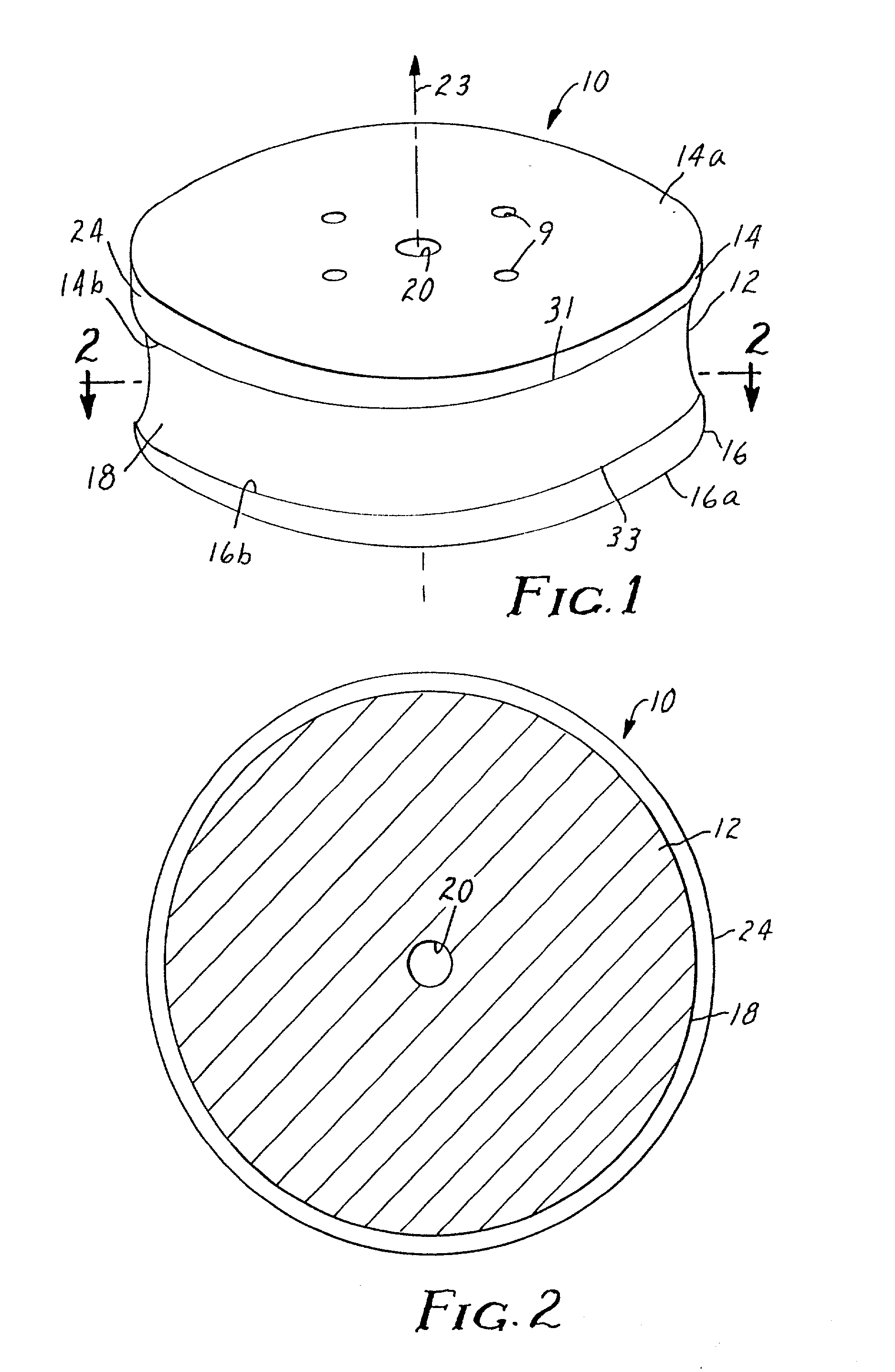
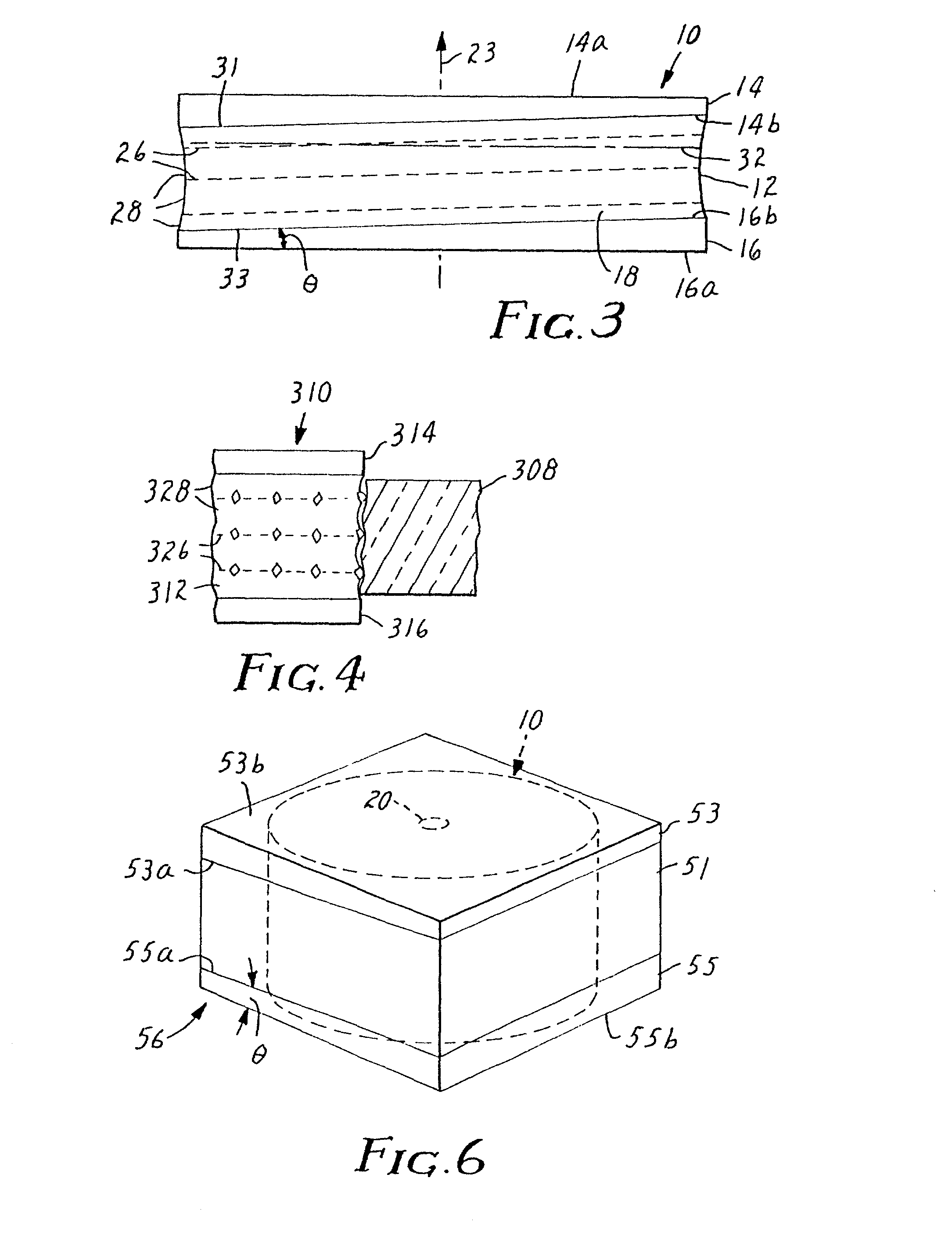
Diamond grid CMP pad dresser
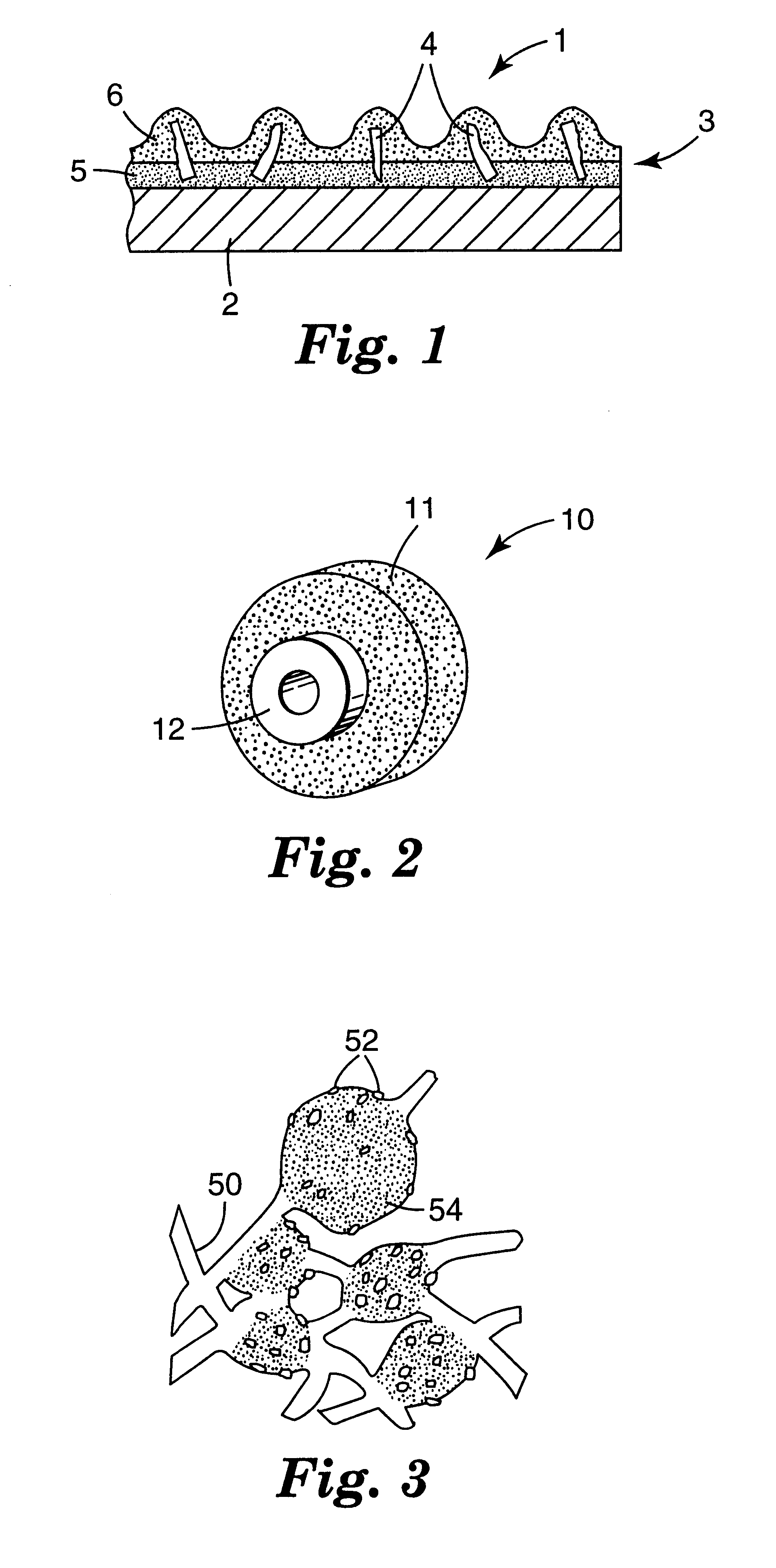
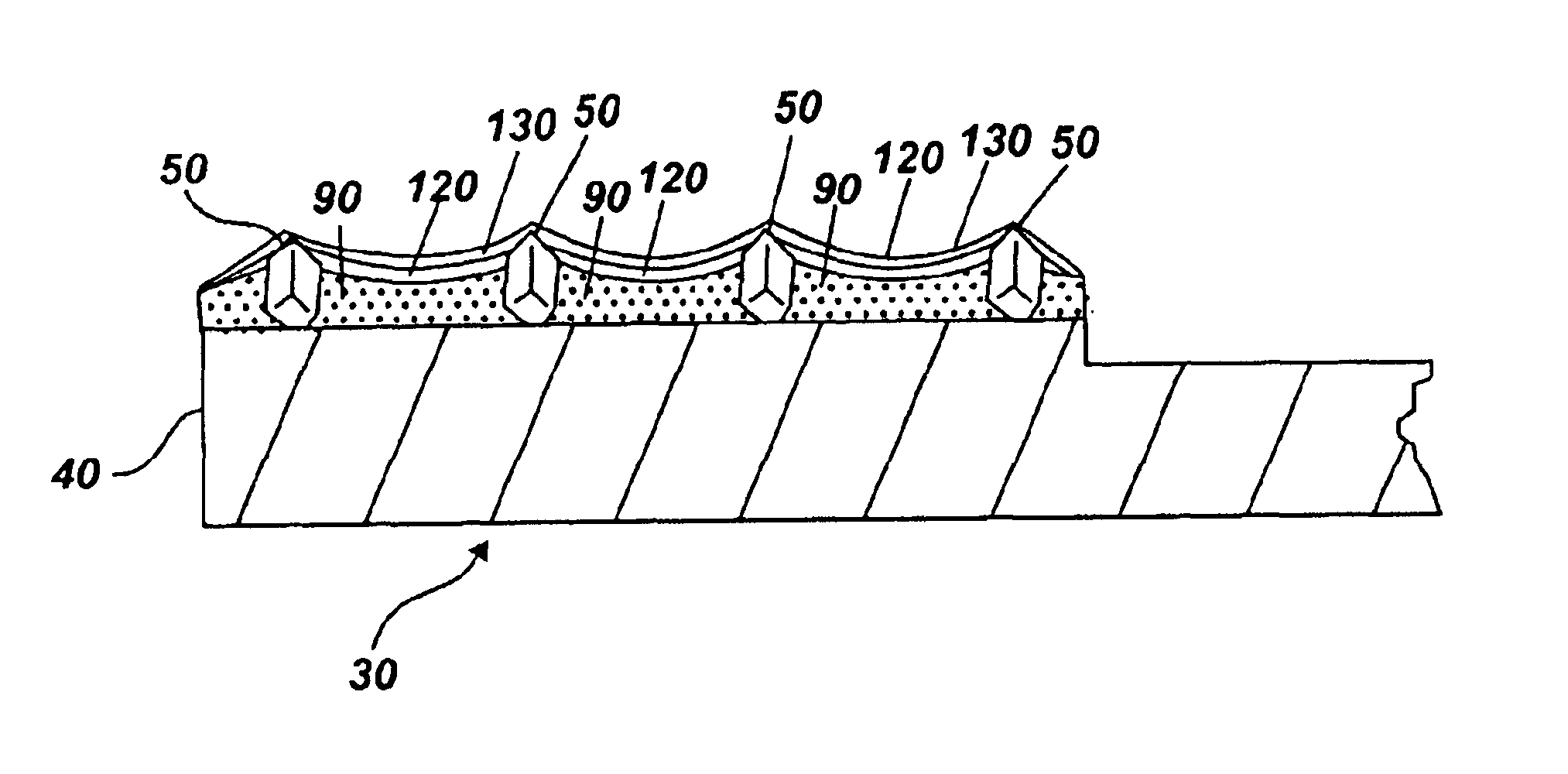
InactiveUS6368198B1Improve polishing efficiencyExtended service lifePolishing machinesRevolution surface grinding machinesSuperhard materialDiamond-like carbon
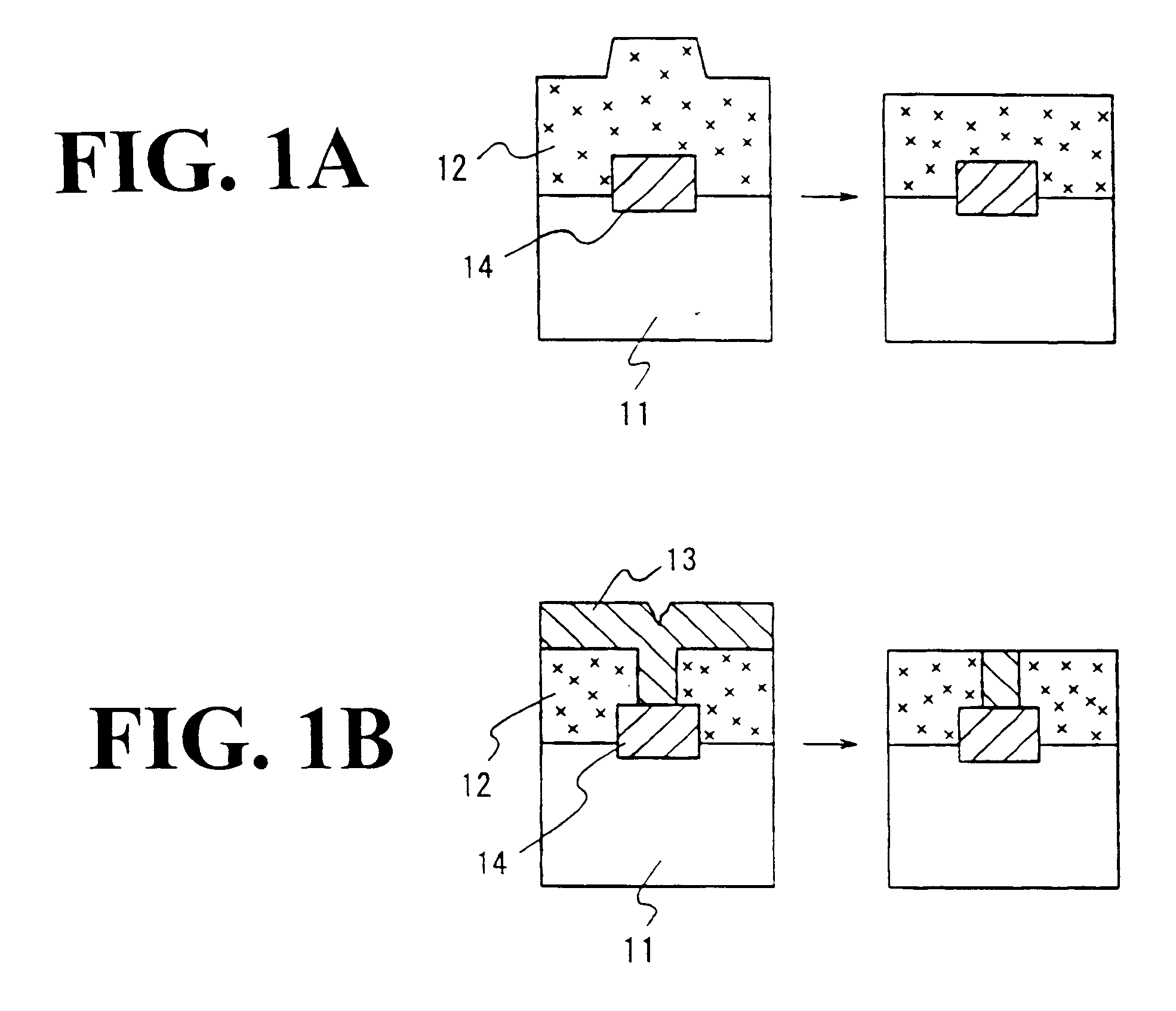
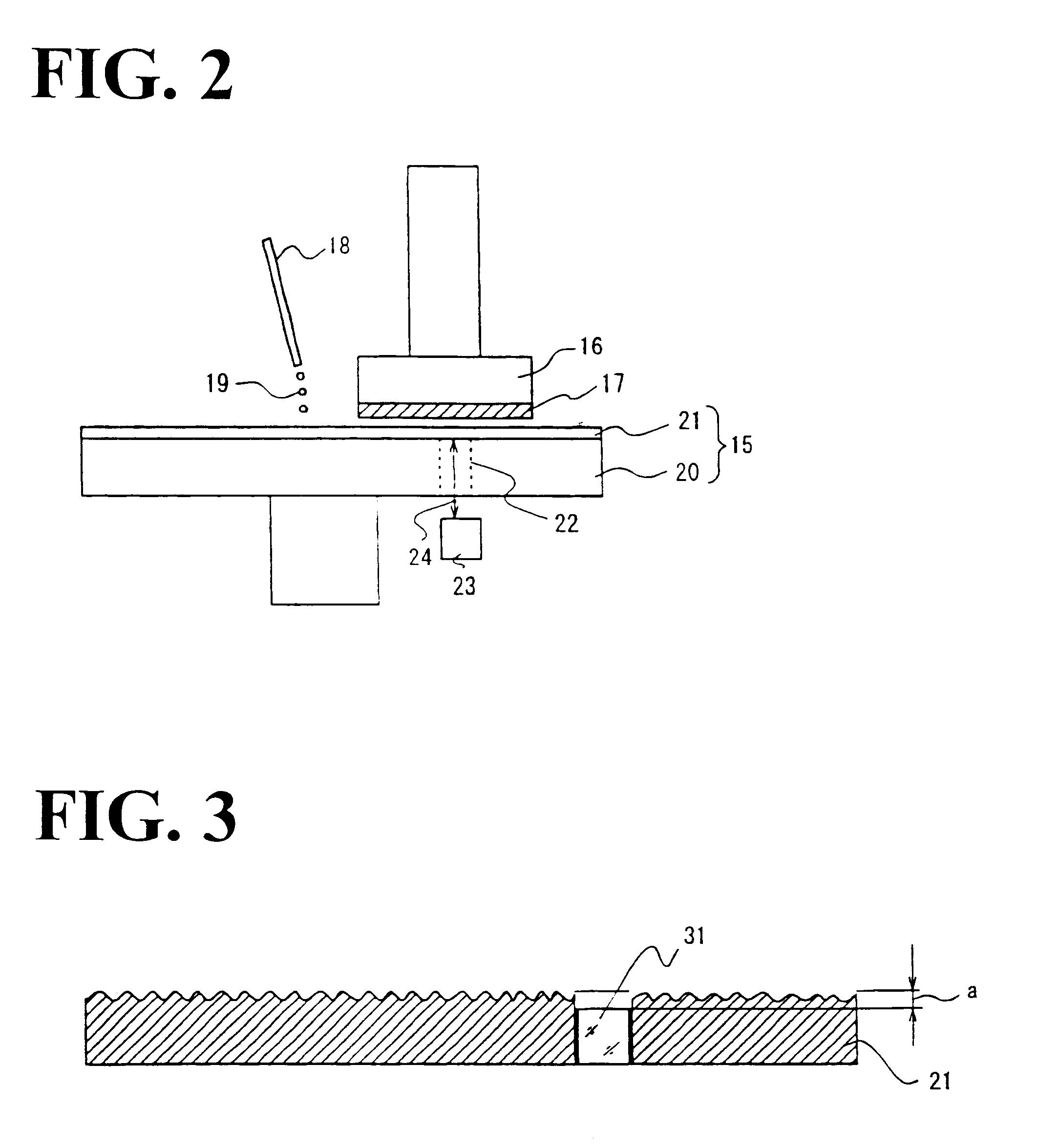
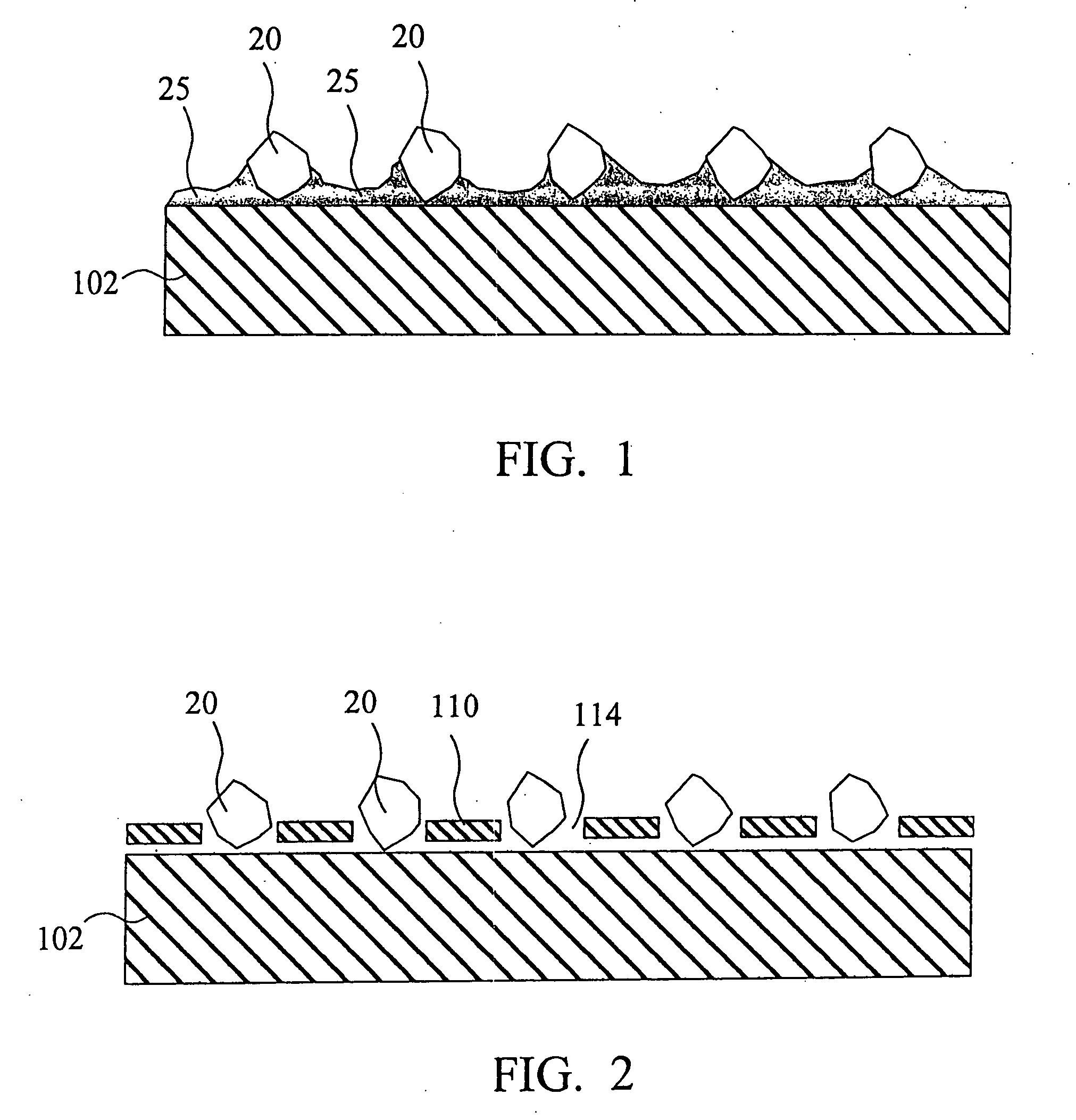
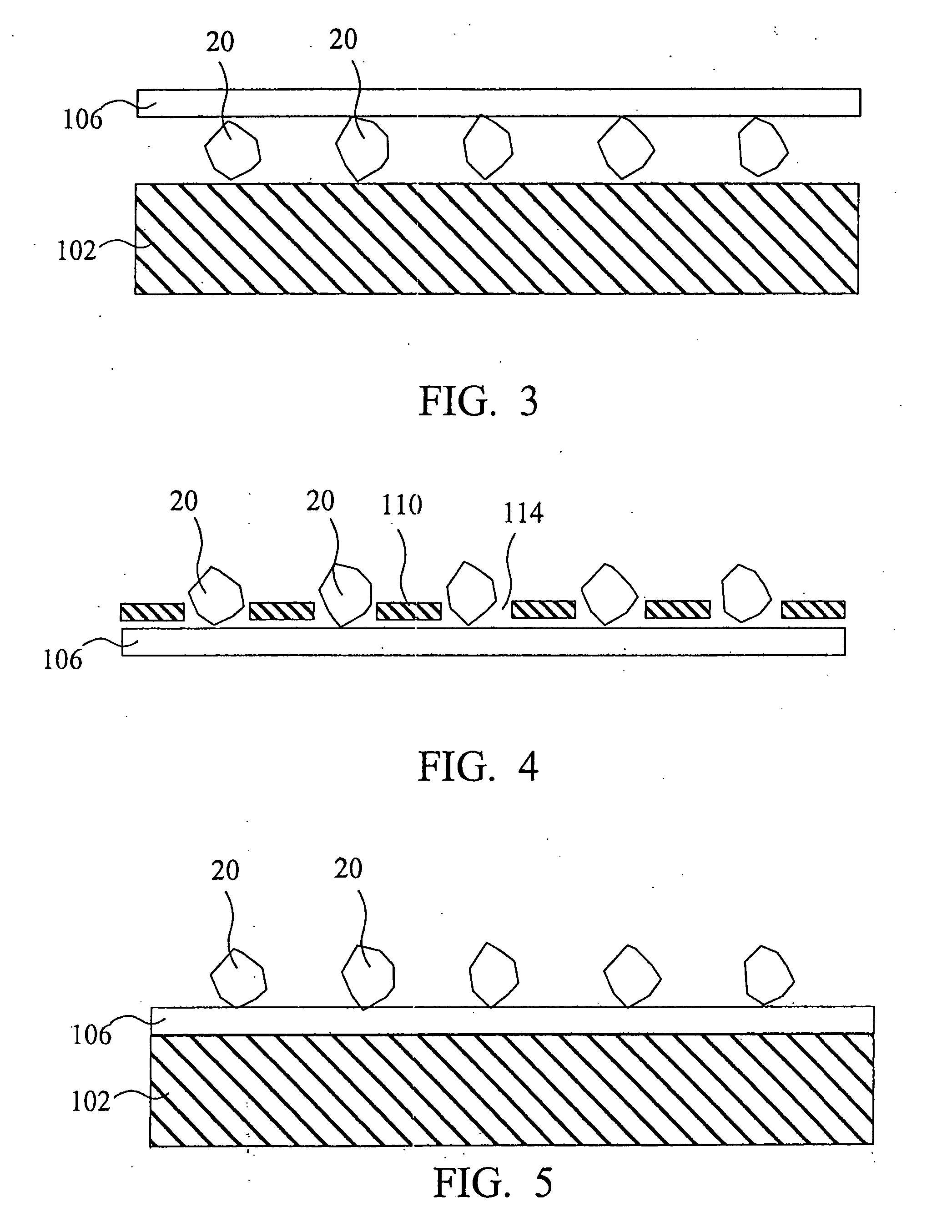
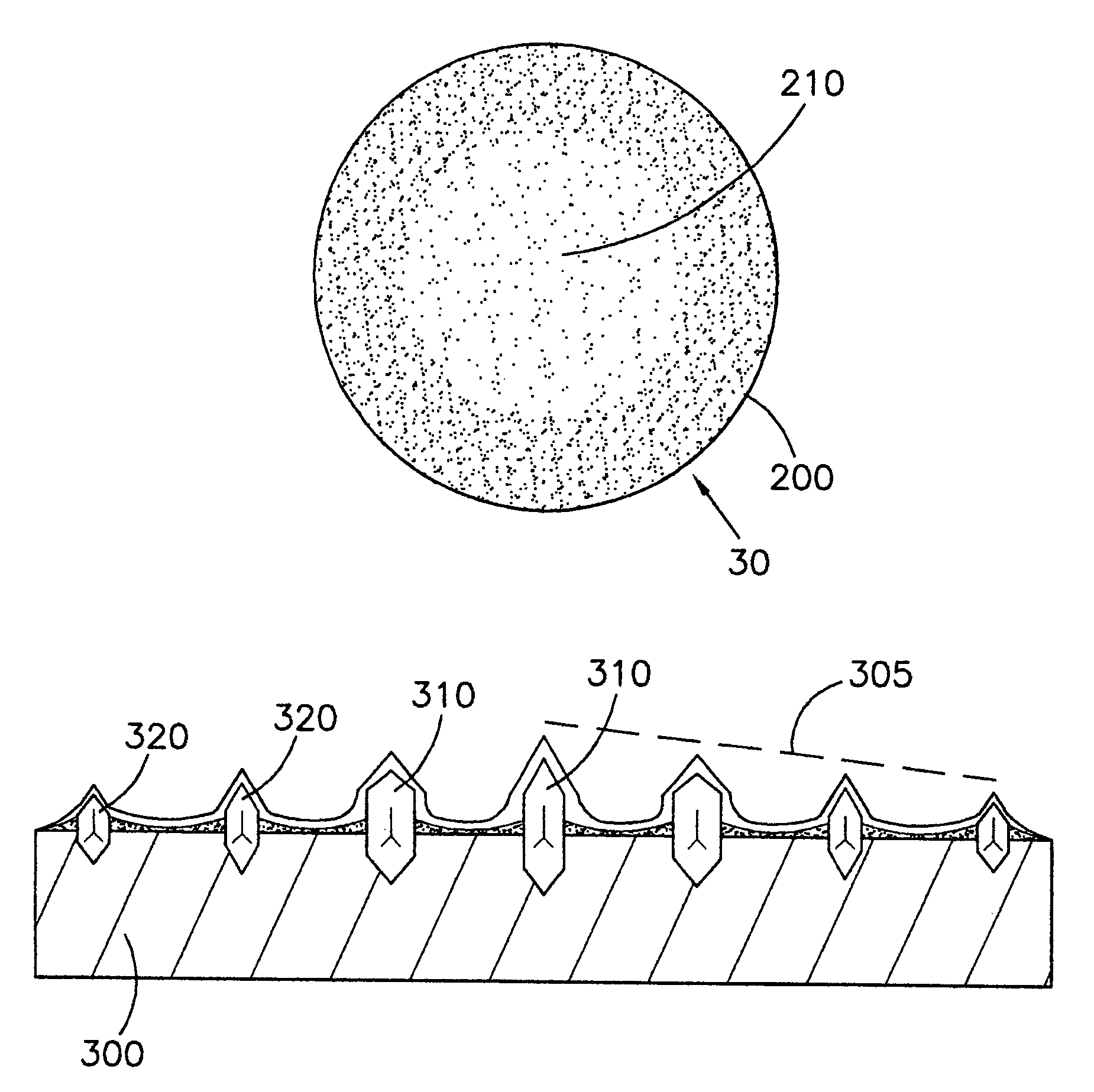
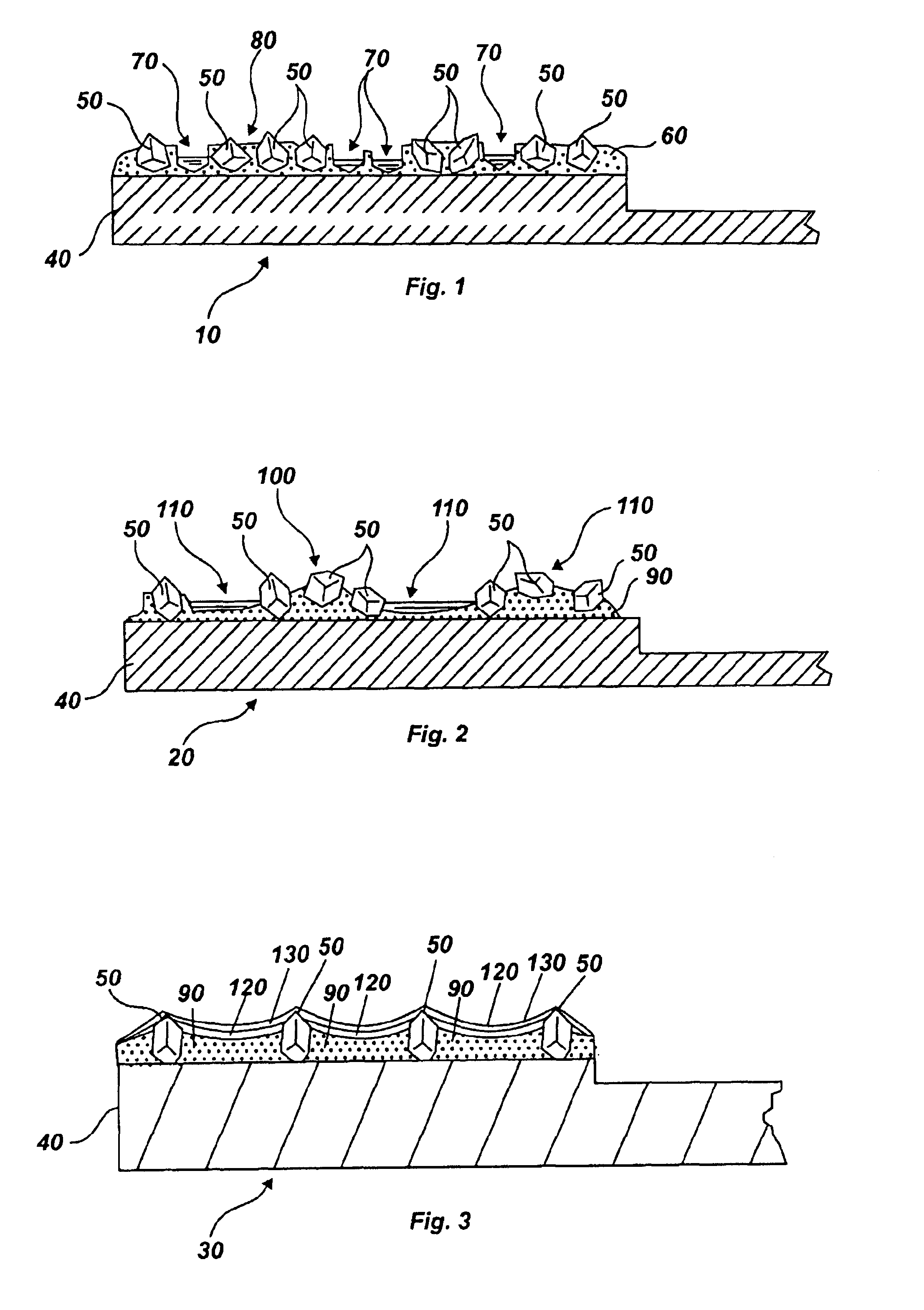
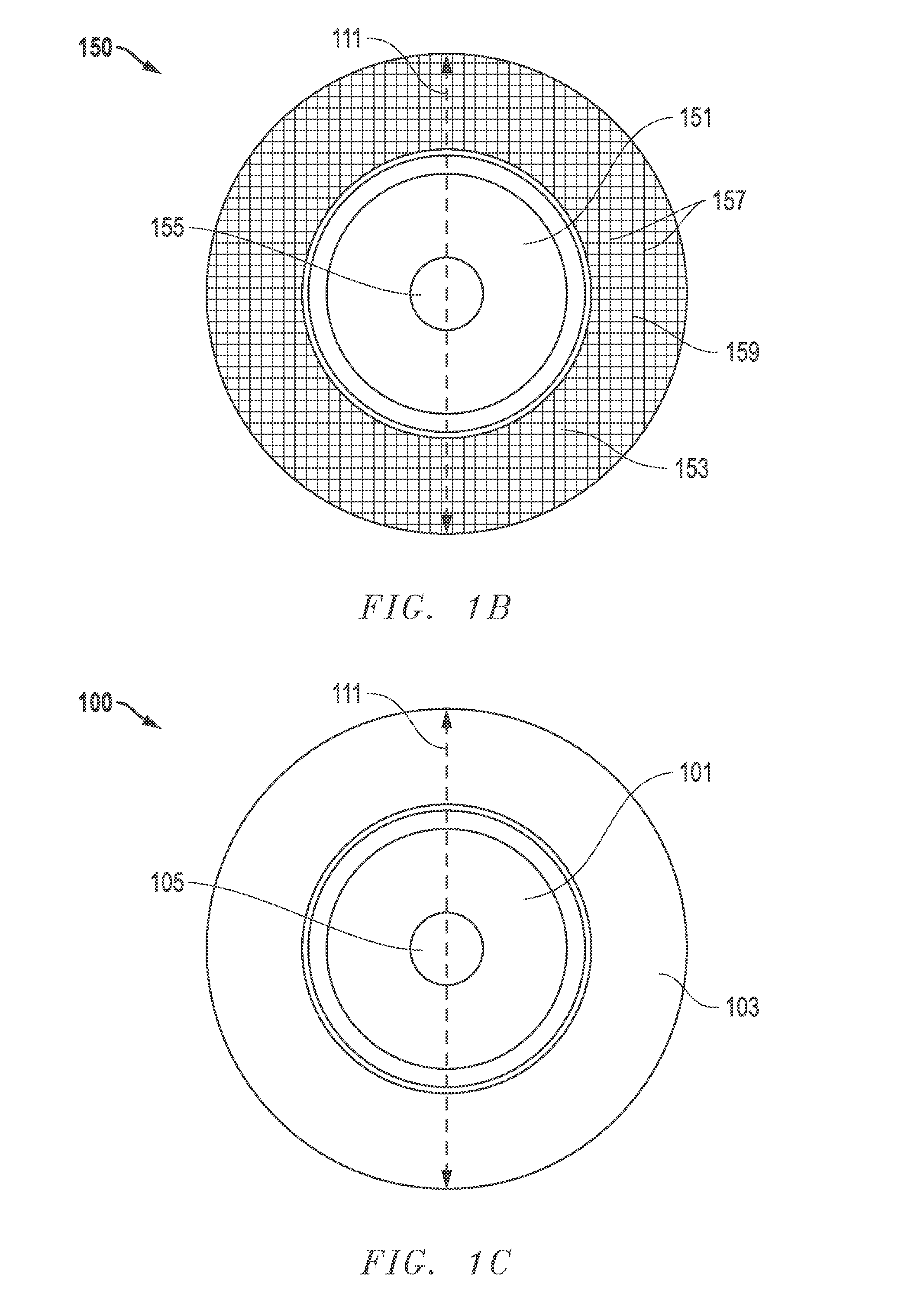
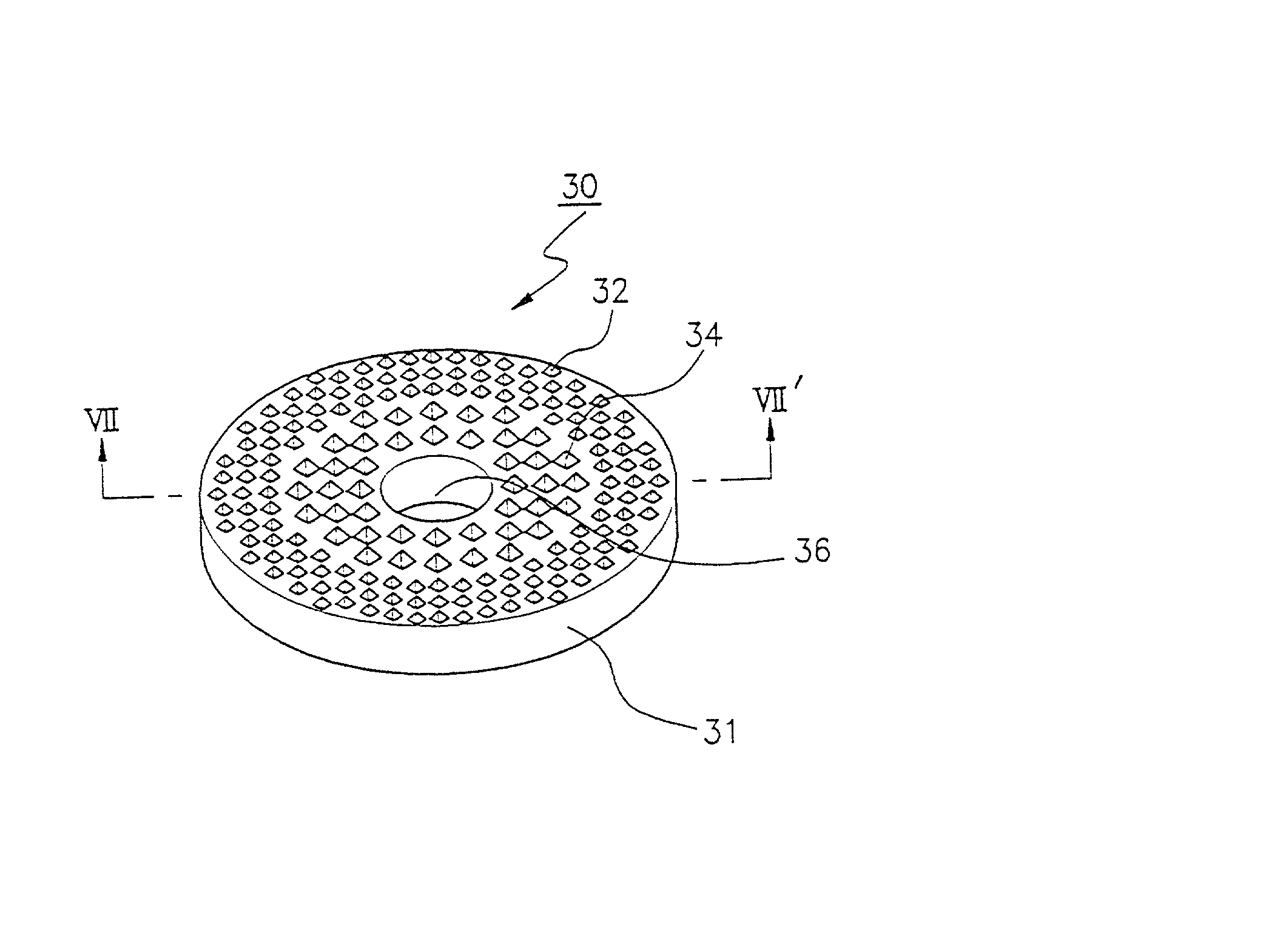
The present invention discloses a CMP pad dresser which has a plurality of uniformly spaced abrasive particles protruding therefrom. The abrasive particles are super hard materials, and are typically diamond, polycrystalline diamond (PCD), cubic boron nitride (cBN), or polycrystalline cubic boron nitride(PcBN). The abrasive particles are brazed to a substrate which may be then coated with an additional anti-corrosive layer. The anti-corrosive layer is usually a diamond or diamond-like carbon which is coated over the surface of the disk to prevent erosion of the brazing alloy by the chemical slurry used in conjunction with the CMP pad. This immunity to chemical attack allows the CMP pad dresser to dress the pad while it is polishing a workpiece. In addition to even spacing on the substrate, the abrasive particles extend for a uniform distance away from the substrate, allowing for even grooming or dressing of a CMP pad both in vertical and horizontal directions. A method of producing such a CMP pad dresser is also disclosed.
Owner:KINIK
Molded polishing pad having integral window
A polishing pad is formed as a one-piece article having a region which is transparent and an adjacent region which is opaque. The article is formed by solidifying a flowable polymeric material which at least initially has a uniform composition. The flowable polymeric material is processed during a molding operation to provide the transparent region and the adjacent opaque region. Types of polymeric material suitable for making the polishing pad include a single thermoplastic material, a blend of thermoplastic materials, and a reactive thermosetting polymer.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CMP HLDG INC
Abrasive cutter containing diamond particles and a method for producing the cutter
InactiveUS6238280B1Eliminate disadvantagesAvoid attenuationRevolution surface grinding machinesBonded abrasive wheelsMetal coatingDiamond crystal
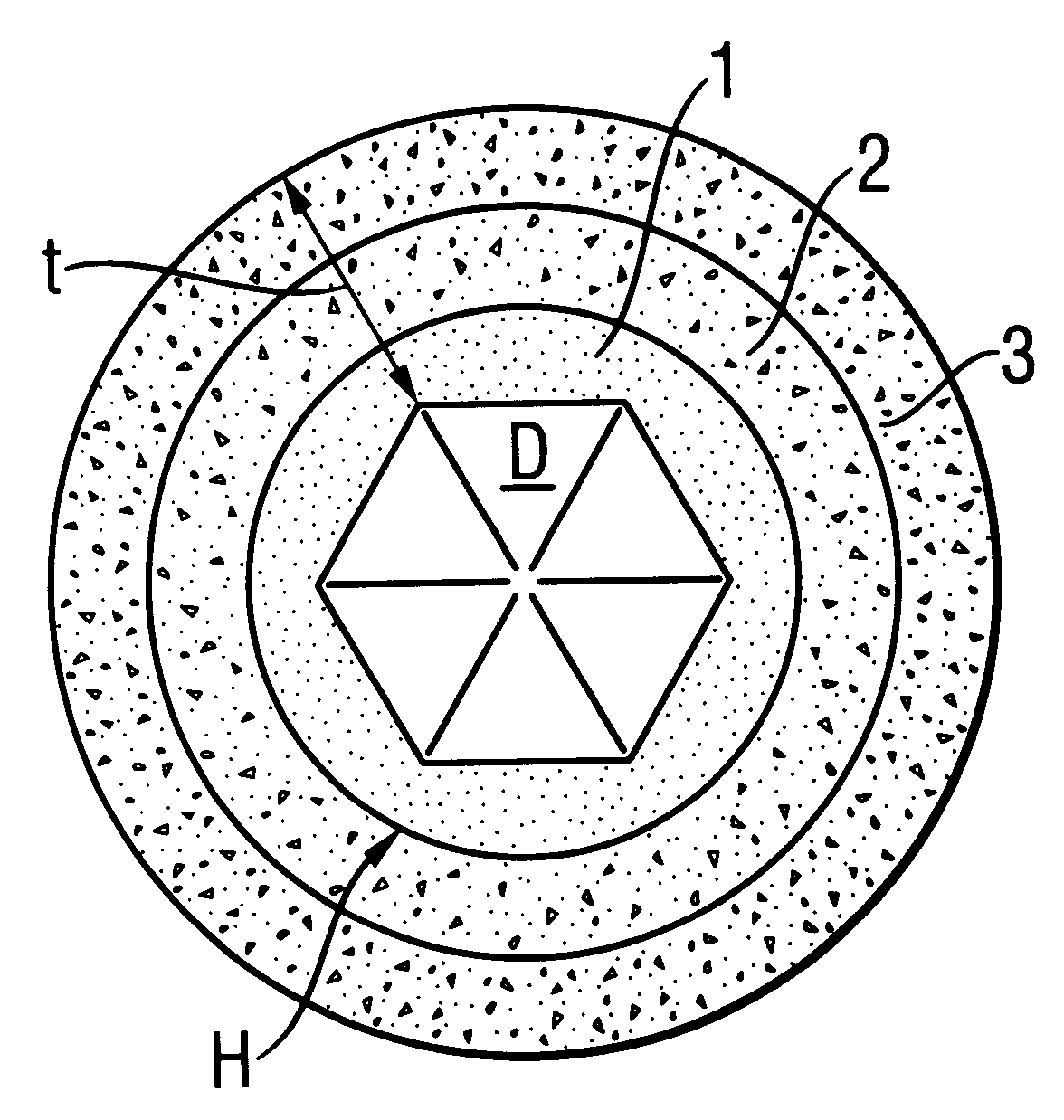
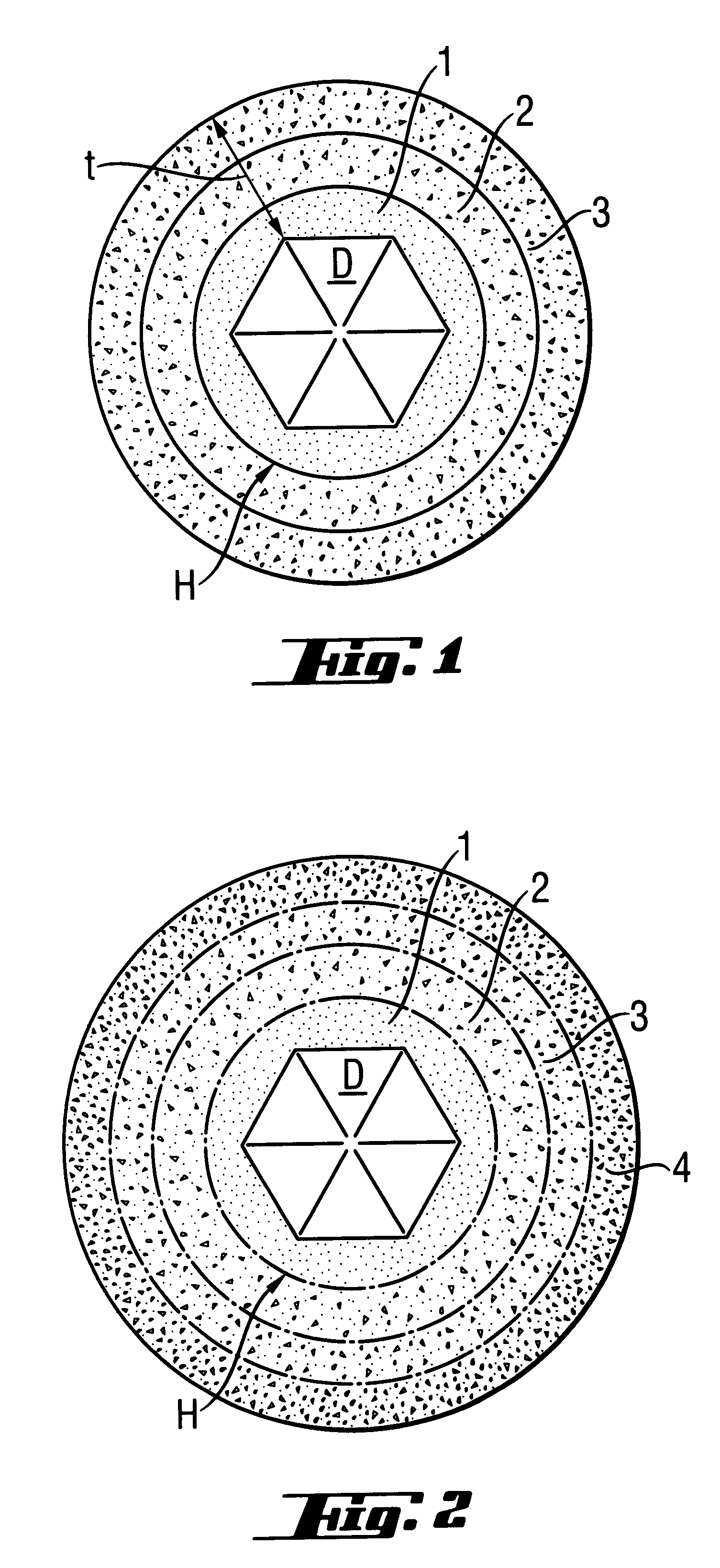
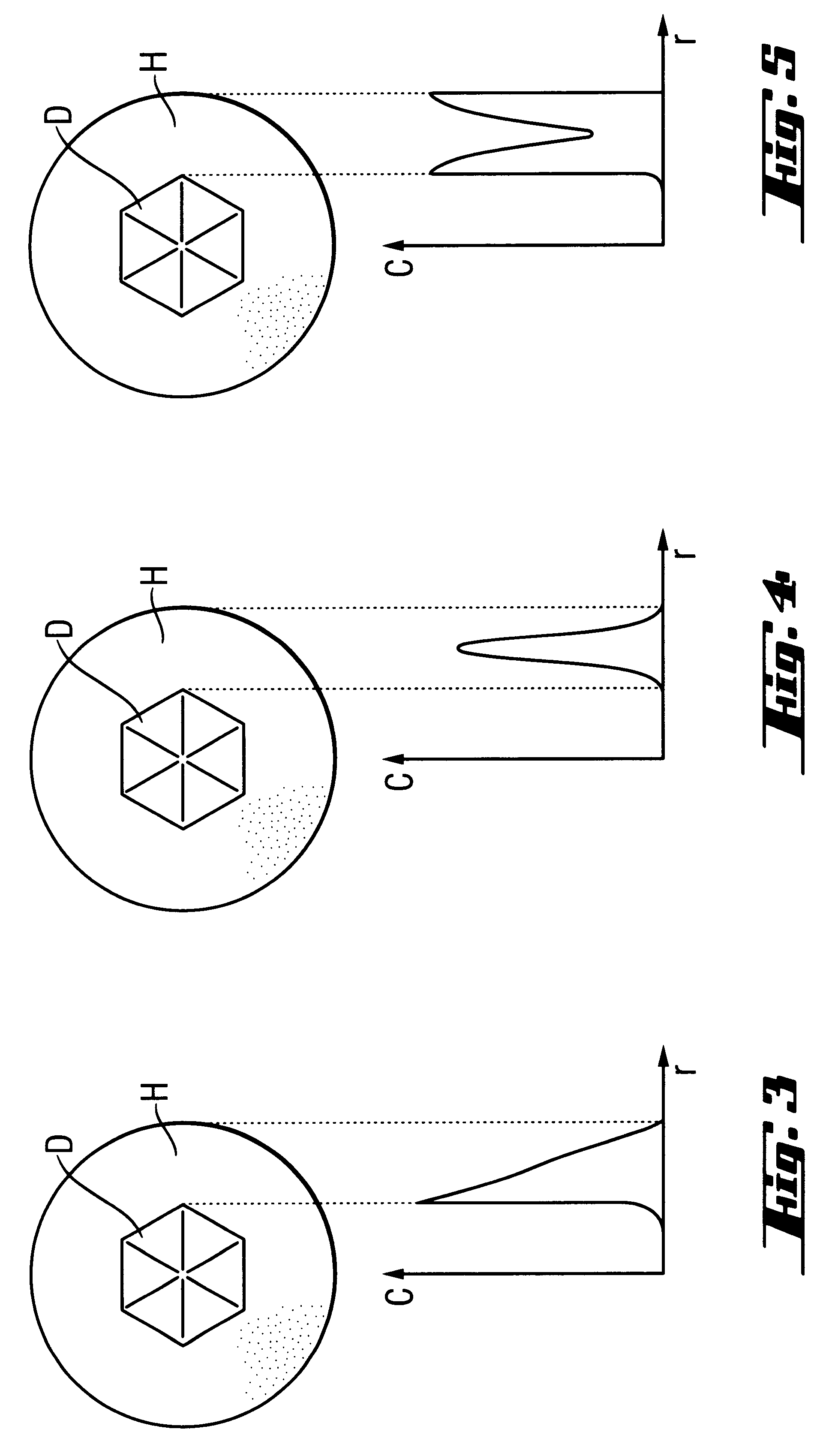
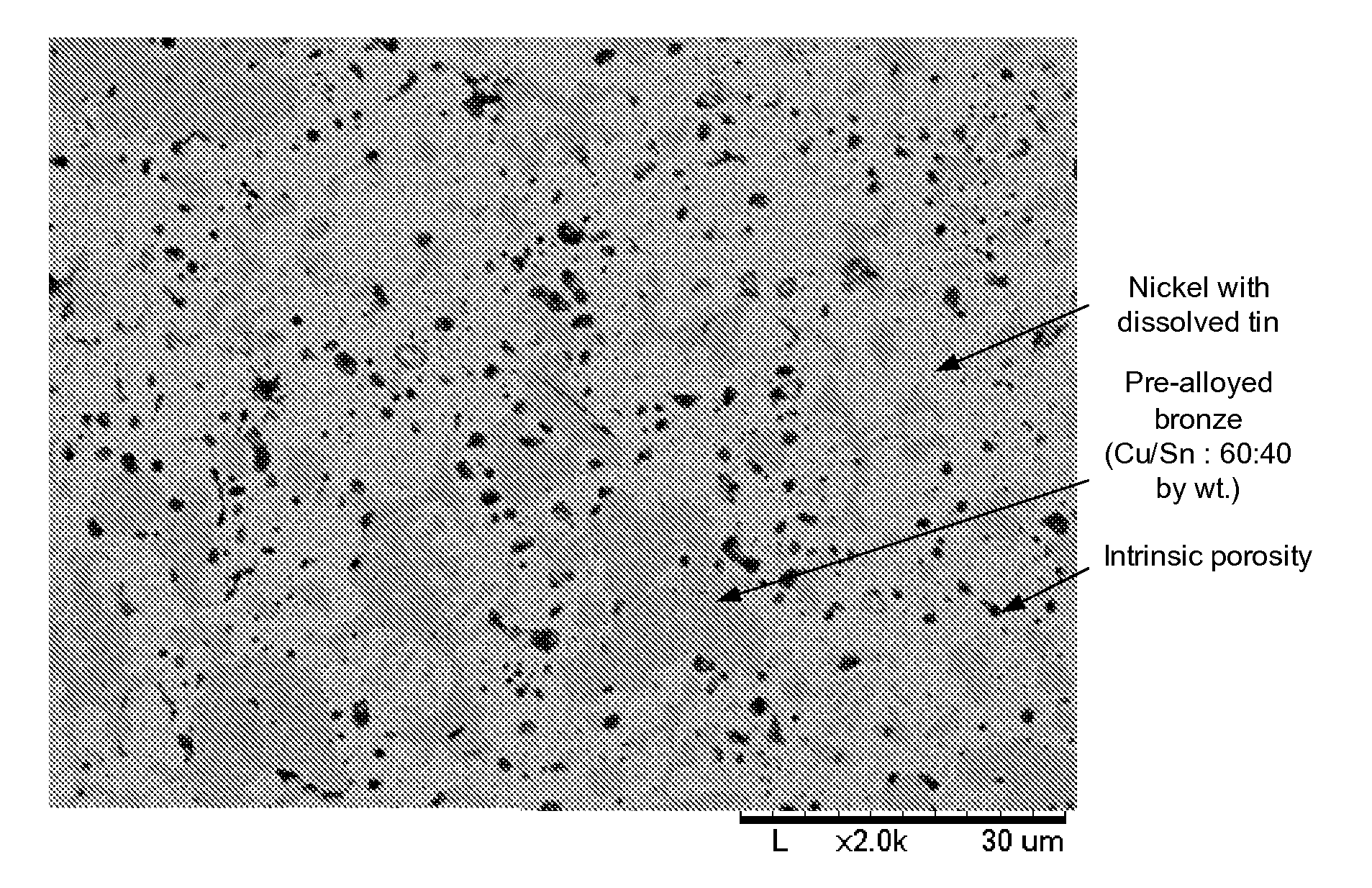
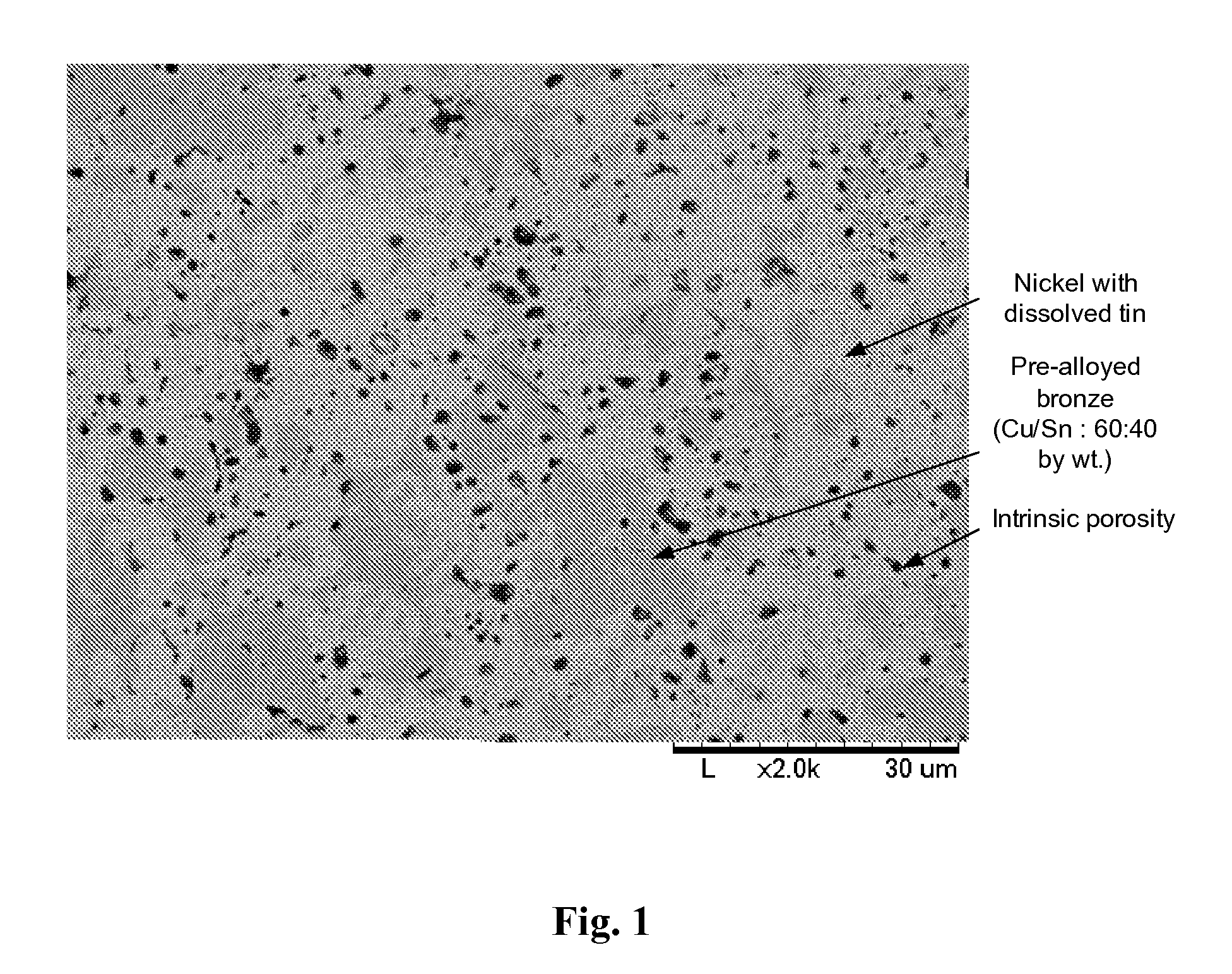
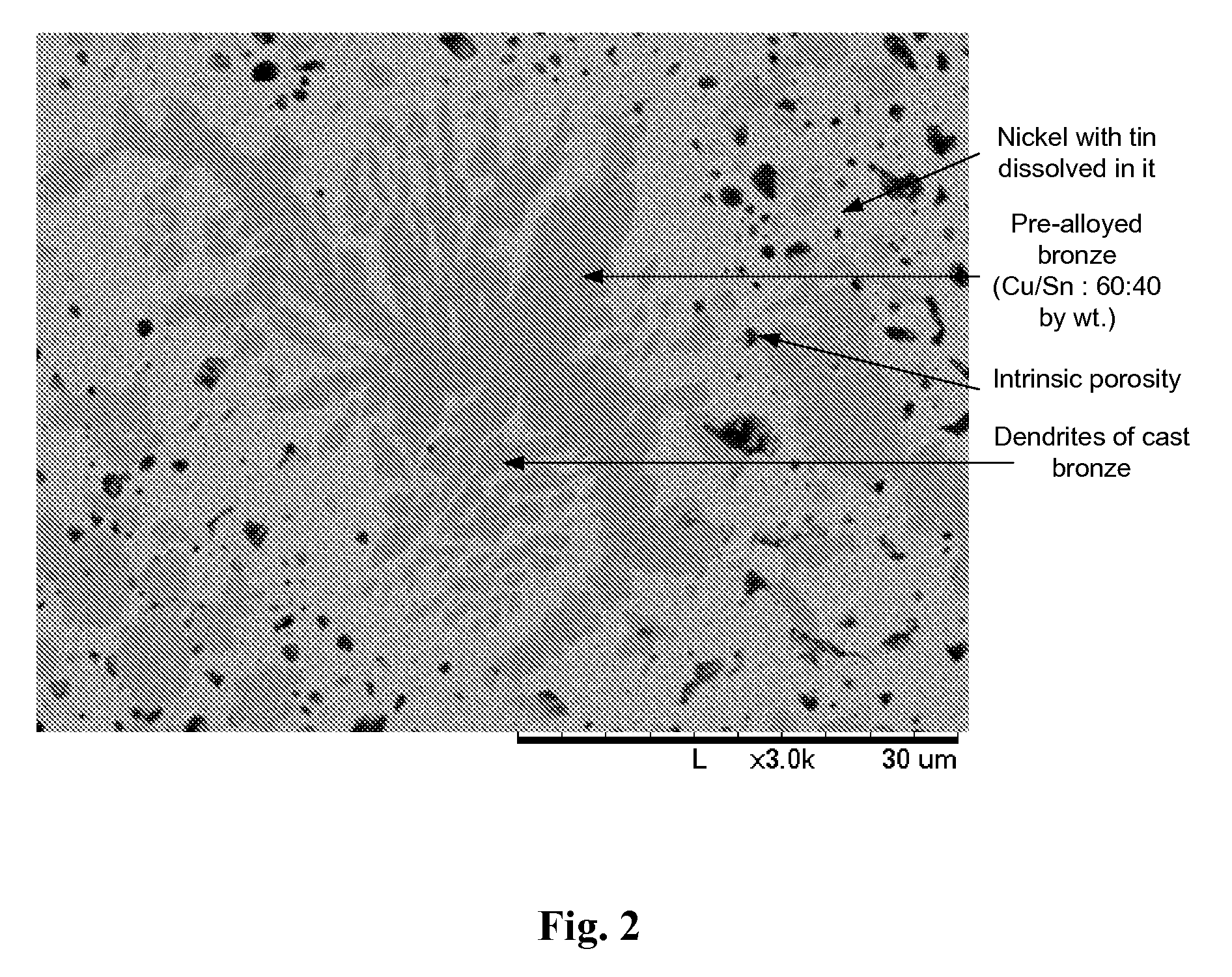
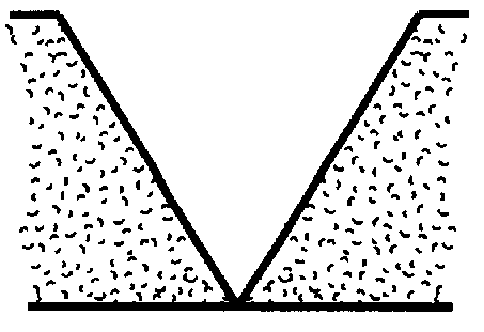
An abrasive cutter formed of at least one diamond particle, preferably at least one mono-diamond crystal and metallic binder material distinguished by the fact that the diamond particle (D) has a size of about 50 mum to about 500 mum and each diamond particle (D) is enclosed by a coating (H) produced in a fluidized bed with the coating having a wall thickness of about 10 mum to about 200 mum. The volume of the coating (H) constitutes at least 30% of the volume of the diamond particles (D) in the fully consolidated state following individual sintering of the coated diamond particles (D, H). The abrasive cutters can be applied directly onto an abrasive tool. Further they can be processed to form composite cutters or cutting segments. In the method of forming the abrasive cutter, the diamond particle (D) is brought into a fluidized bed reactor and enclosed in a metallic coating (H). Coated diamond particle (D, H) can be processed into larger cutters or segments in each case individually sintered and fixed directly on an abrasive tool.
Owner:HILTI AG
Fused Al2O3-MgO-rare earth oxide eutectic abrasive particles, abrasive articles, and methods of making and using the same
InactiveUS20010027623A1Improve grinding performanceLower performance requirementsPigmenting treatmentMangesium aluminatesRare earthAbrasive
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Brazed diamond tools and methods for making the same
Owner:SUNG CHIEN MIN
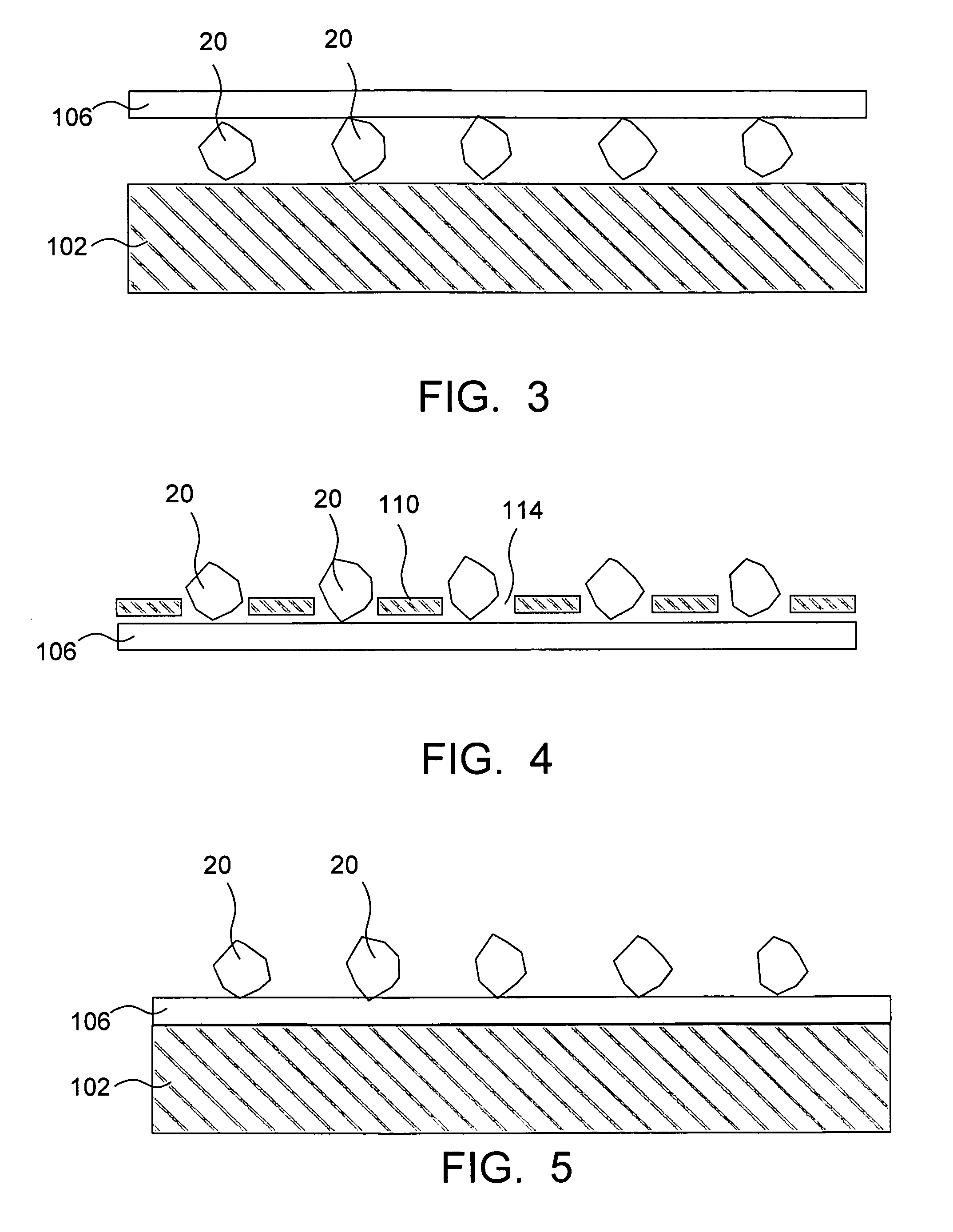
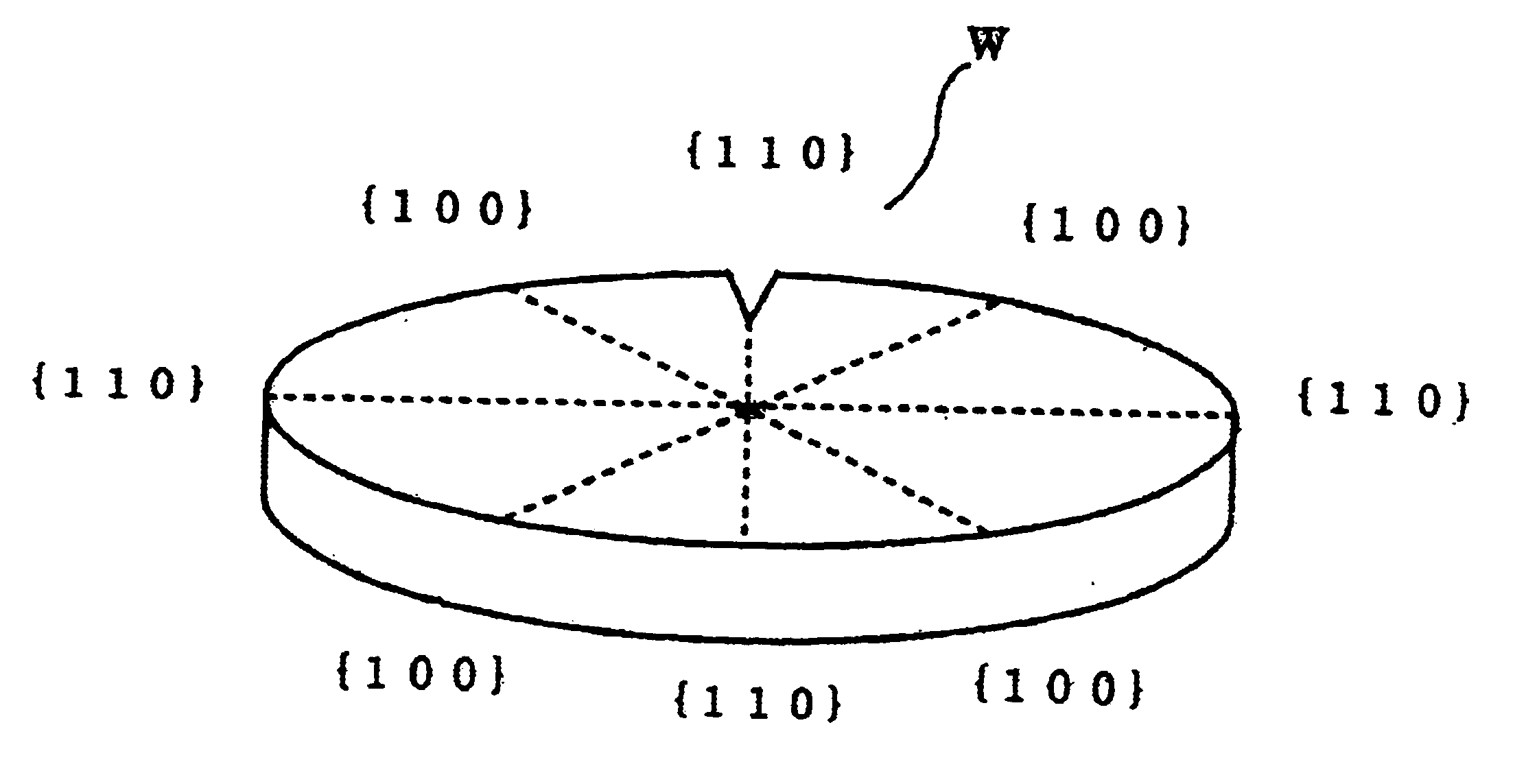
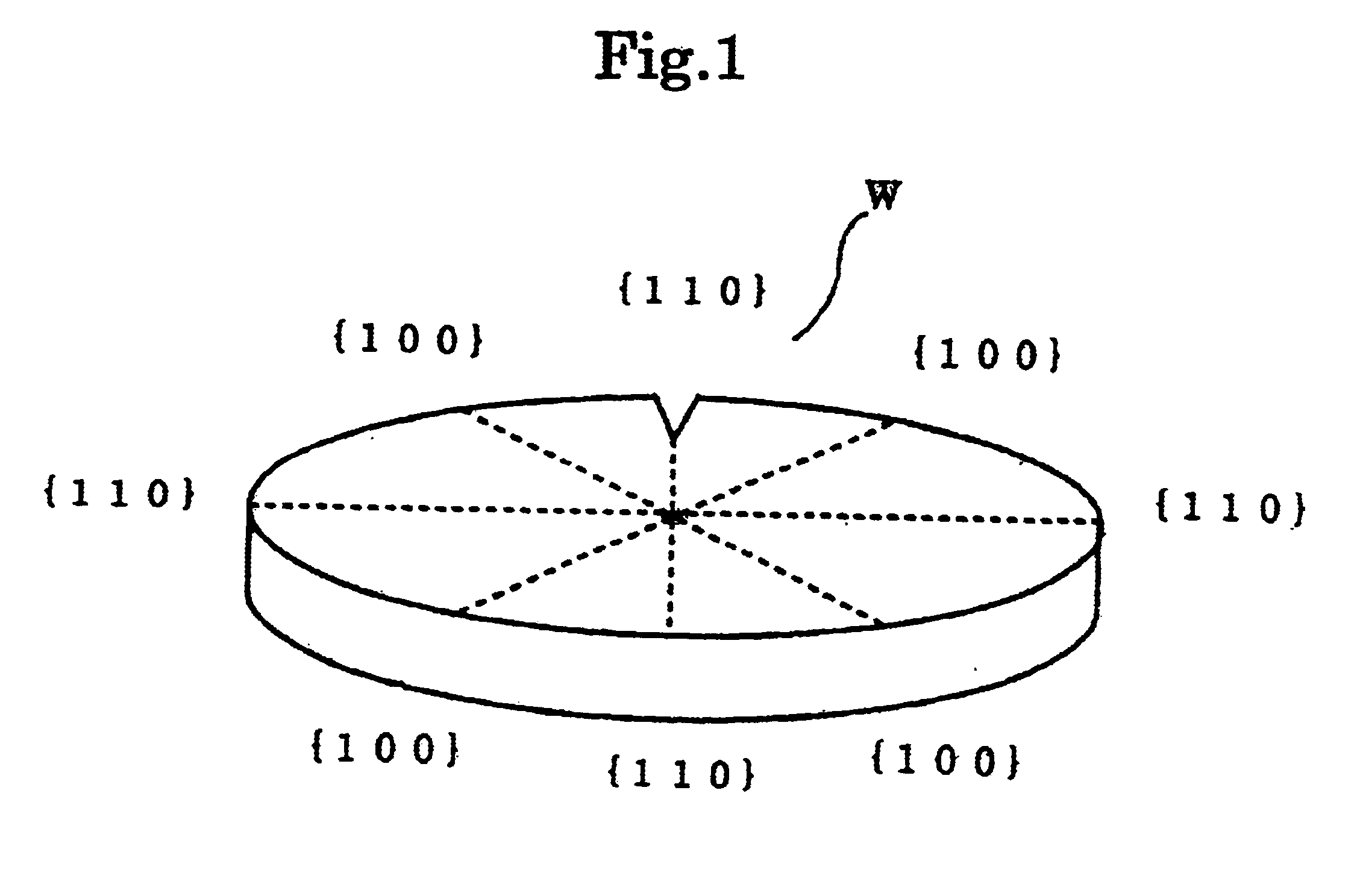
Method for apparatus for polishing outer peripheral chamfered part of wafer
InactiveUS6884154B2Improve productivityShorten polishing timeEdge grinding machinesPolishing machinesProduction rateHardness
In a process for polishing the chamfered peripheral part of a wafer using a polishing cloth while supplying a polishing slurry in order to improve productivity of the process by reducing a polishing time, at least two steps of polishing processes are performed in sequence. The process comprises a first polishing process to polish a particular part, e.g. the part corresponding to the {110} plane of a peripheral part of the wafer and a second polishing process in which the whole part of a peripheral part of the wafer is polished for finishing by means of varying a hardness of the polishing clothes and / or a particle size of abrasives in the slurry such as the hardness of the polishing cloth in the second polishing process being softer than that of in the first polishing process and a particle size of abrasives in the slurry in the second polishing process being finer than that of in the first polishing process.
Owner:SHIN-ETSU HANDOTAI CO LTD
Abrasive Slicing Tool for Electronics Industry
InactiveUS20100000159A1Superior wheel stiffnessProlong lifePigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesPorosityElectronic industry
A bond matrix for metal bonded abrasive tools includes a metal bond system, porosity and an optional filler. Tools according to embodiments of the invention exhibit long tool life, produce an acceptable quality of cut and can have self-dressing properties. The bond matrix can be used, for example, in abrasives tools configured for the electronics industry, such as 1A8 wheels for slicing ball grid arrays (BGAs) and other such slicing operations.
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN ABRASIVES INC +1
Polishing body, polishing apparatus, polishing apparatus adjustment method, polished film thickness or polishing endpoint measurement method, and semiconductor device manufacturing method
After a hole is formed in a polishing pad, a transparent window plate is inserted into the hole. Here, a gap is left between the upper surface of the transparent window plate and the outermost surface constituting the working surface of the polishing pad. During polishing, the polishing head holding the wafer applies a load to the polishing pad by means of a load-applying mechanism, so that the polishing pad and transparent window plate are compressed. In this case, the system is arranged so that the gap remains constant, and so that a dimension equal to or greater than a standard value is maintained. Since the upper surface of the transparent window plate is recessed from the upper surface of the polishing pad, there is no scratching of the surface of the transparent window plate during dressing. Accordingly, the polishing pad has a long useful life.
Owner:NIKON CORP
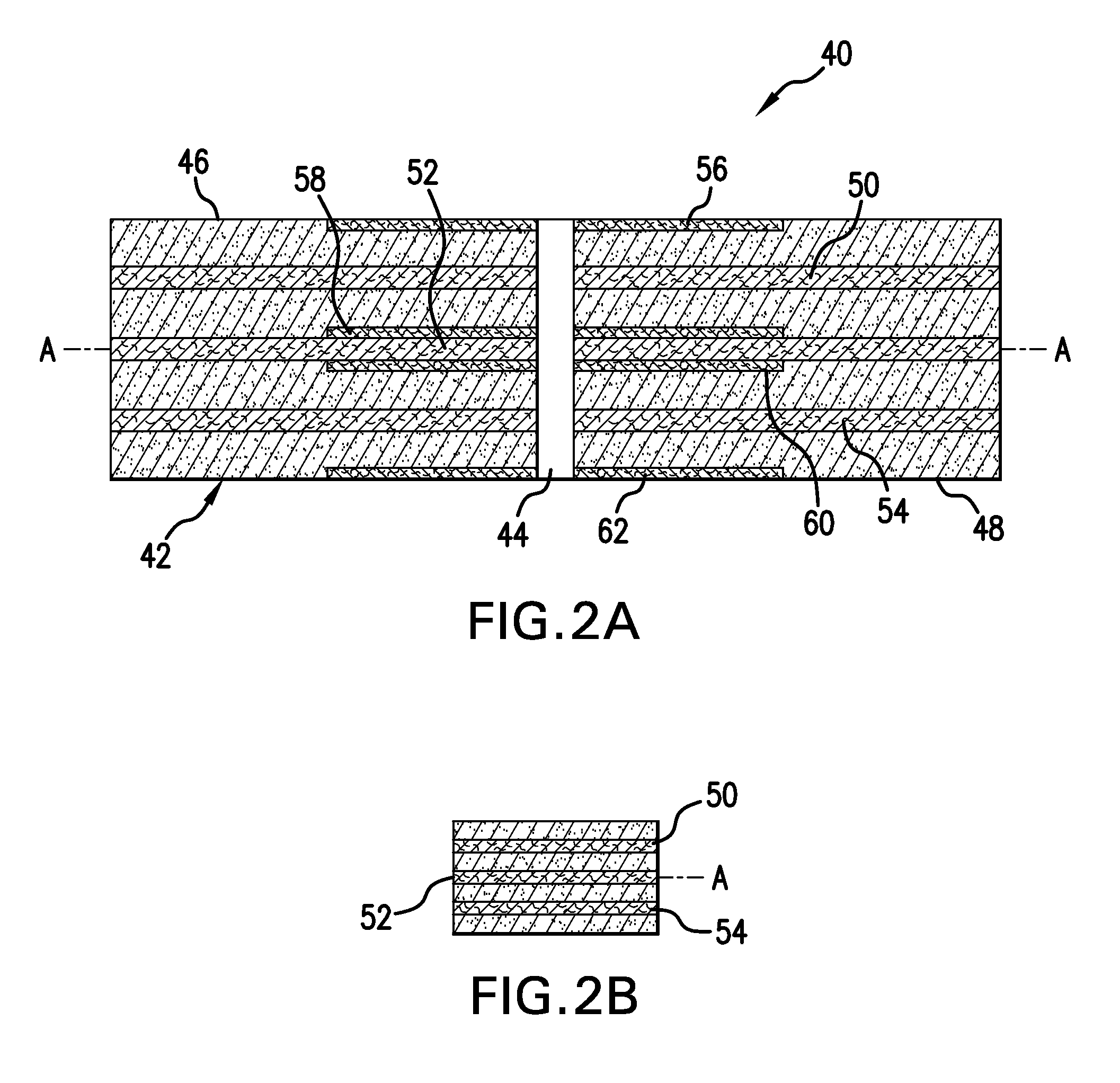
Reinforced Bonded Abrasive Tools
InactiveUS20100190424A1Improve performanceReduce the amount requiredPigmenting treatmentRevolution surface grinding machinesFiberFiberglass mesh
Bonded abrasive tools, e.g., grinding wheels, can be reinforced using, for instance, one or more fibreglass web(s) having a surface of glass per unit of at least 0.2. Alternatively or in addition, the fibreglass web has a thickness of 2 mm or less. The web can be designed to provide improved adhesion between the fibreglass reinforcement and the mixture employed to form the bonded abrasive tool. In some examples, the middle reinforcement at the neutral zone of the wheel can be eliminated or minimized.
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN ABRASIVES INC +1
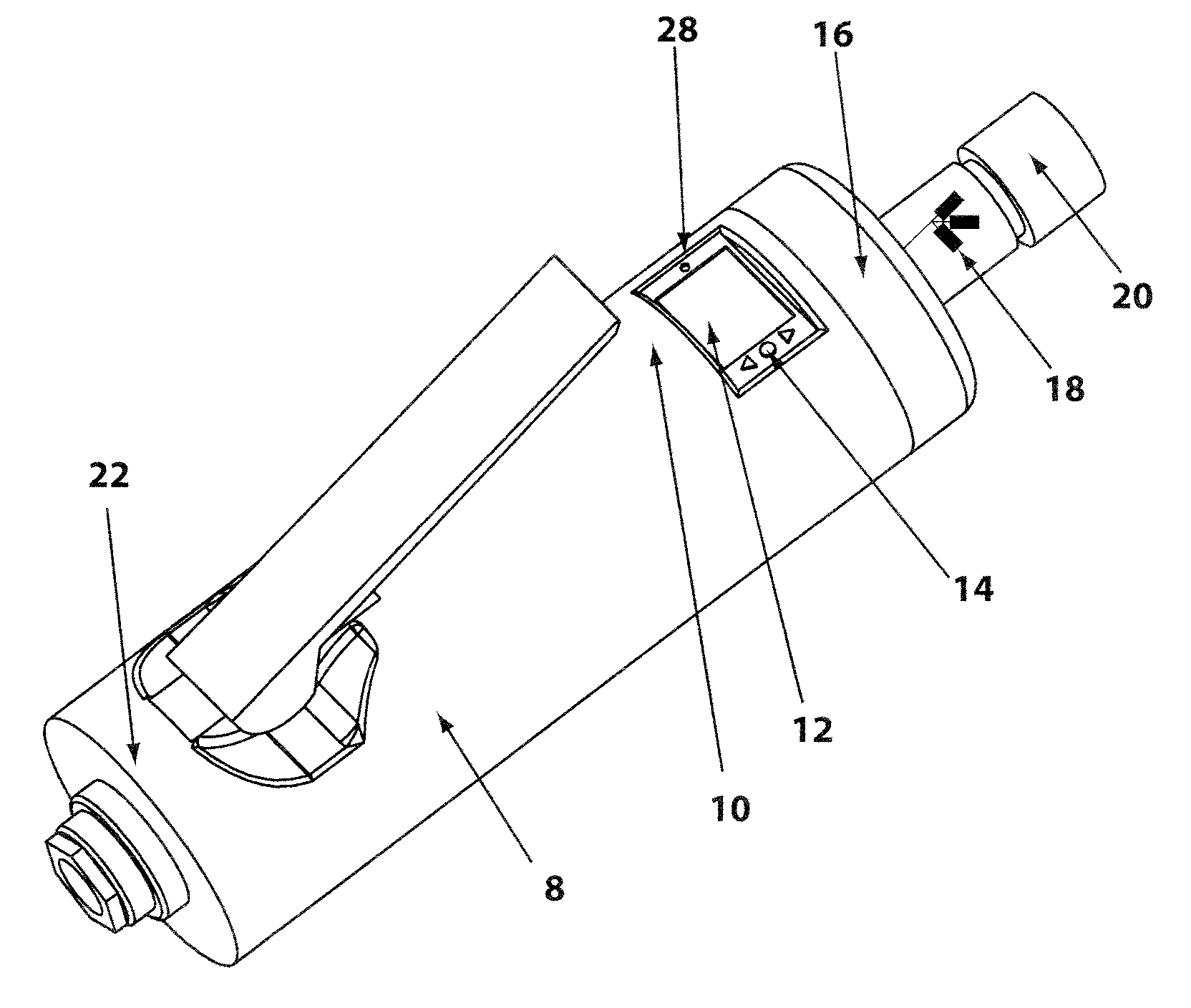
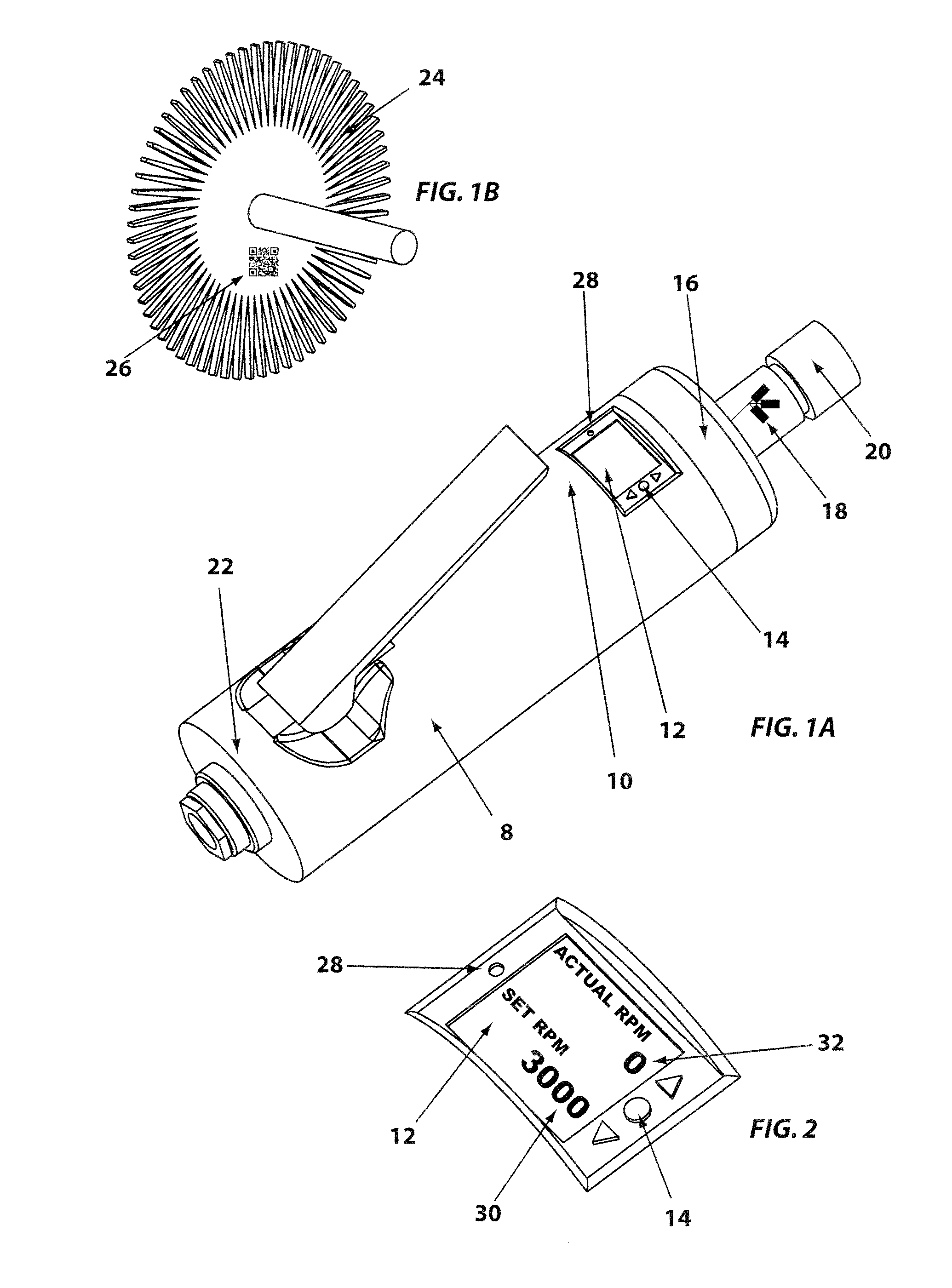
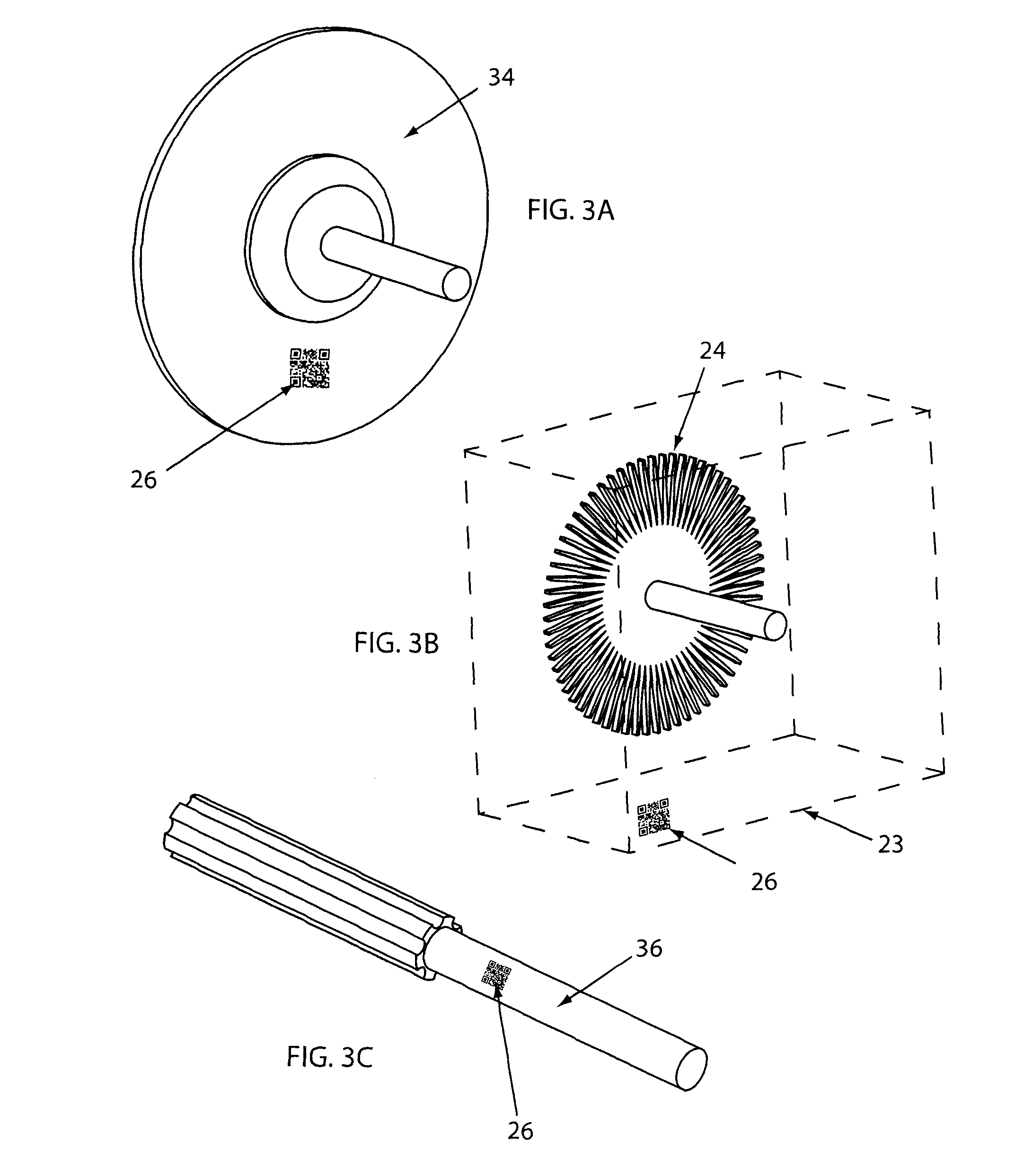
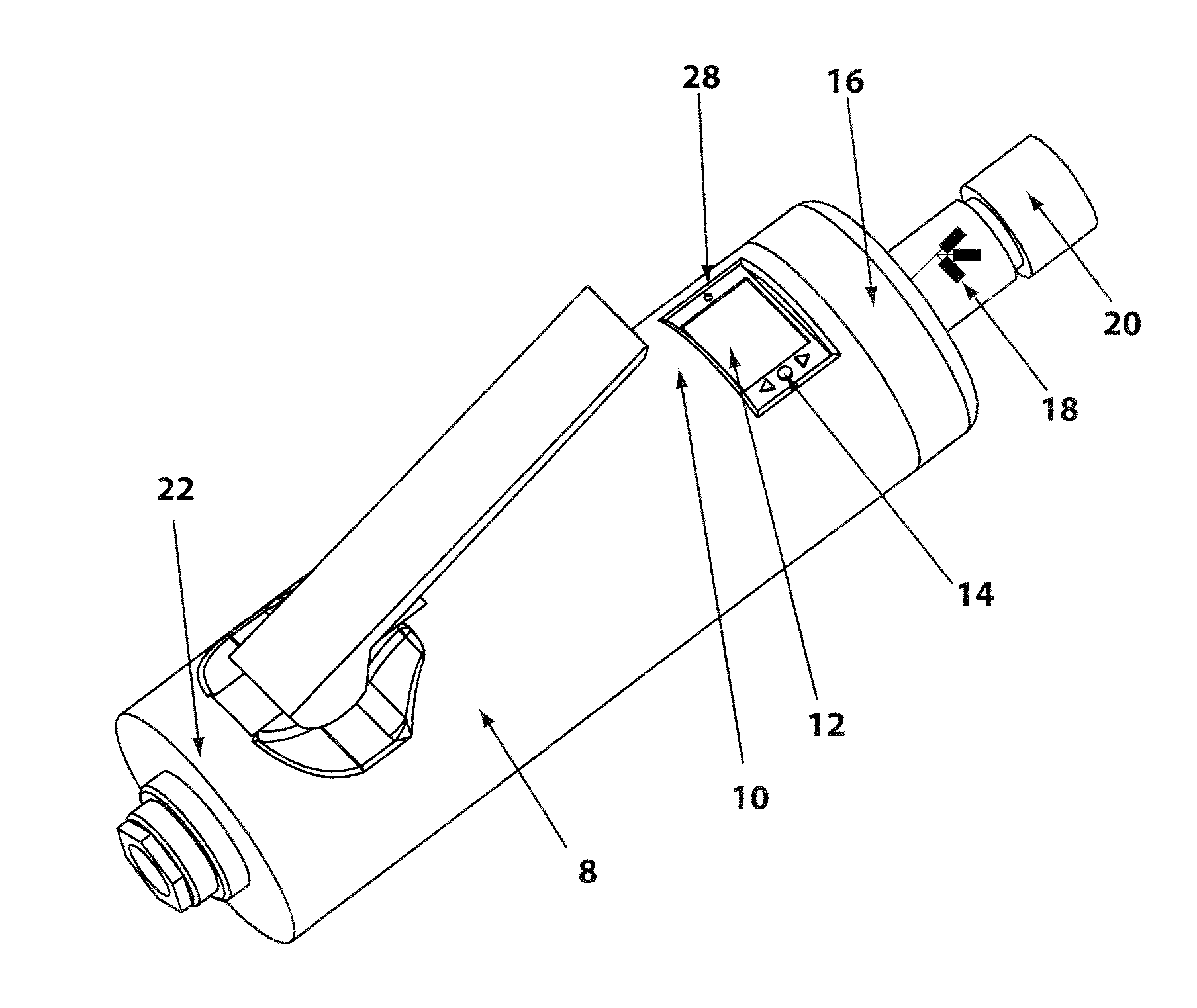
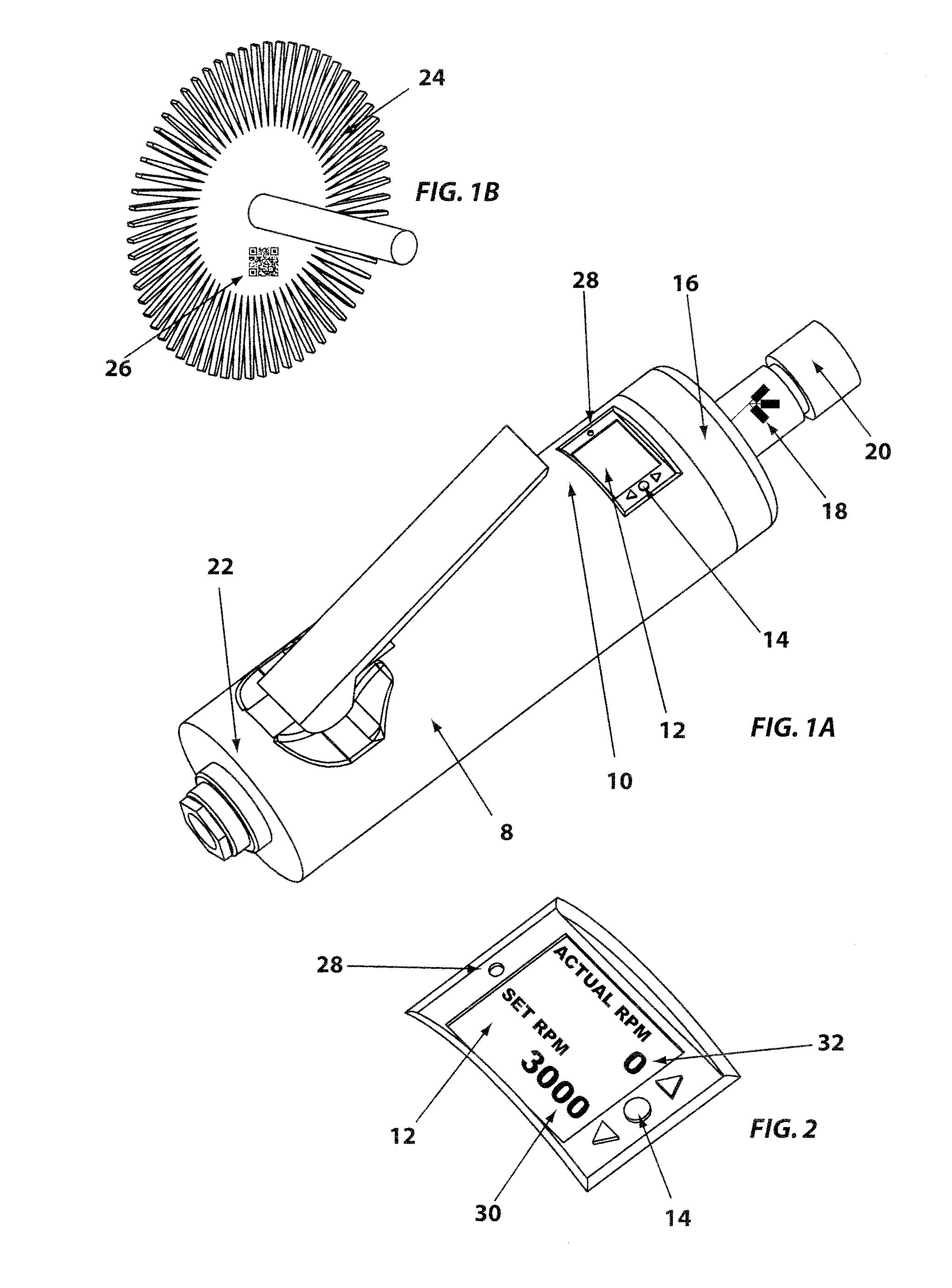
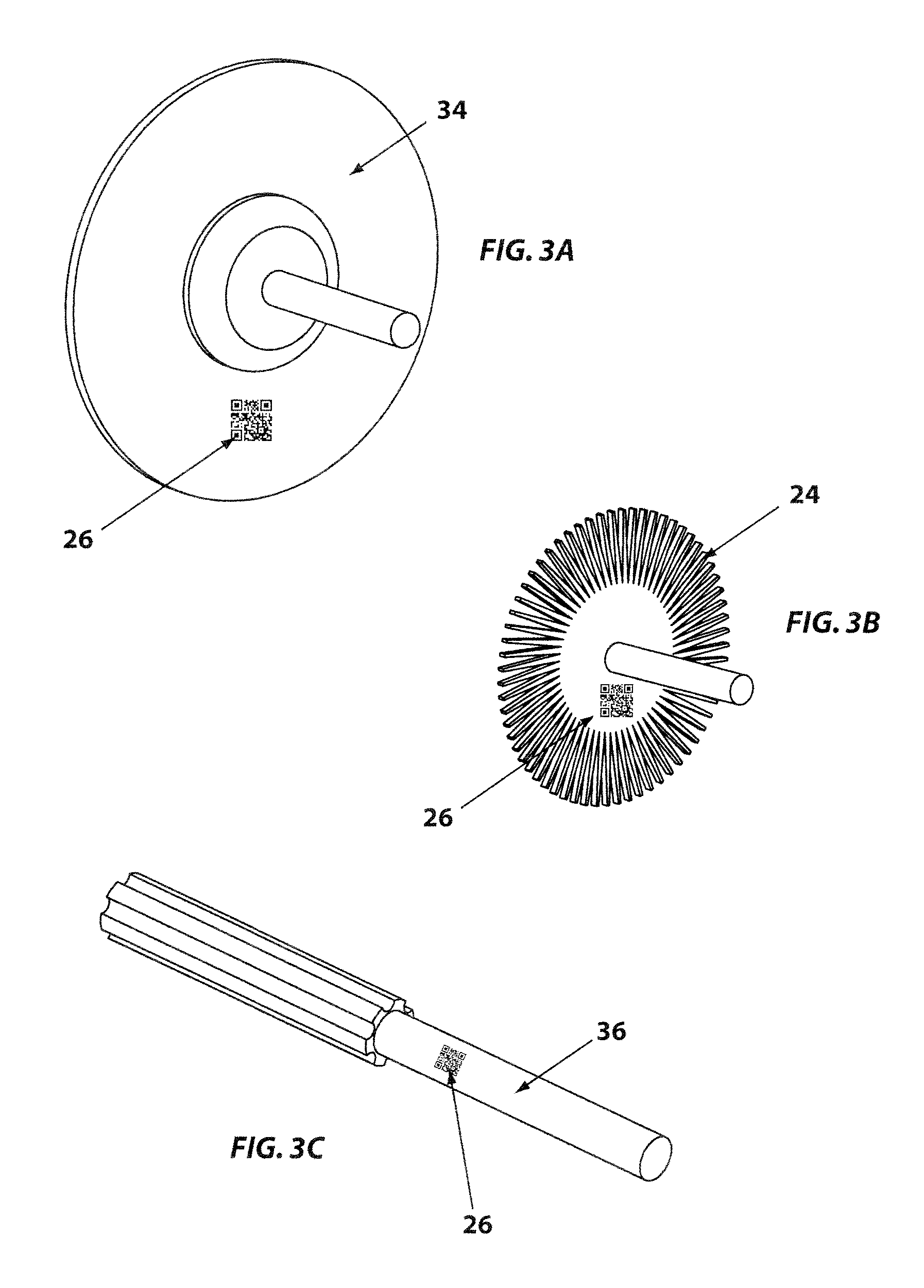
Controlled electro-pneumatic power tools and interactive consumable
ActiveUS20120007748A1Electric signal transmission systemsTelemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsMicrocontrollerElectrical battery
A controlled electro-pneumatic power tool includes an electro-mechanical adjustable valve, a pneumatic motor and a rotational speed sensor connected to a microcontroller for the selection, monitoring and adjustement of the rotational speed in real time. The electro-pneumatic power tool may include input buttons, data ports to save data and a communication port to read / write data from an interactive consumable. The electo-pneumatic power tool may also include a battery and a generator as well as a variable speed transmission with flexible shaft and lightweight handpiece. Using the communication port, important data for the consumable, such as optimum rotation speed, optimum applied pressure and average usage time, can be transmitted to the controlled electro-pneumatic power tool. The controlled electro-pneumatic power tool can read and utilise the transmitted data to select, adjust and maintain the optimum process parameters for the consumable without any input from the operator person. Furthermore, the communicated data can be used to warn the operator person that the tool used is inadequate for the selected consumable, to caution the operator person if he is using the consumable inadequately and to advise him when the consumable should be replaced for safe operation. This will increase the safety of the operator person, improve the quality of the work performed with pneumatic power tools and limit potential damages to the parts being treated.
Owner:FORGUES SYLVAIN +1
Customized polishing pads for CMP and methods of fabrication and use thereof
ActiveUS20060276109A1Easy to controlImpact on polishing propertyAdditive manufacturing apparatusLapping machinesPorositySurface engineering
The present application relates to polishing pads for chemical mechanical planarization (CMP) of substrates, and methods of fabrication and use thereof. The pads described in this invention are customized to polishing specifications where specifications include (but not limited to) to the material being polished, chip design and architecture, chip density and pattern density, equipment platform and type of slurry used. These pads can be designed with a specialized polymeric nano-structure with a long or short range order which allows for molecular level tuning achieving superior themo-mechanical characteristics. More particularly, the pads can be designed and fabricated so that there is both uniform and nonuniform spatial distribution of chemical and physical properties within the pads. In addition, these pads can be designed to tune the coefficient of friction by surface engineering, through the addition of solid lubricants, and creating low shear integral pads having multiple layers of polymeric material which form an interface parallel to the polishing surface. The pads can also have controlled porosity, embedded abrasive, novel grooves on the polishing surface, for slurry transport, which are produced in situ, and a transparent region for endpoint detection.
Owner:CMC MATERIALS INC
Reinforced abrasive wheels
InactiveUS6942561B2Minimize empty spaceSaving in layer materialGrinding machine componentsRevolution surface grinding machinesGlass fiberEngineering
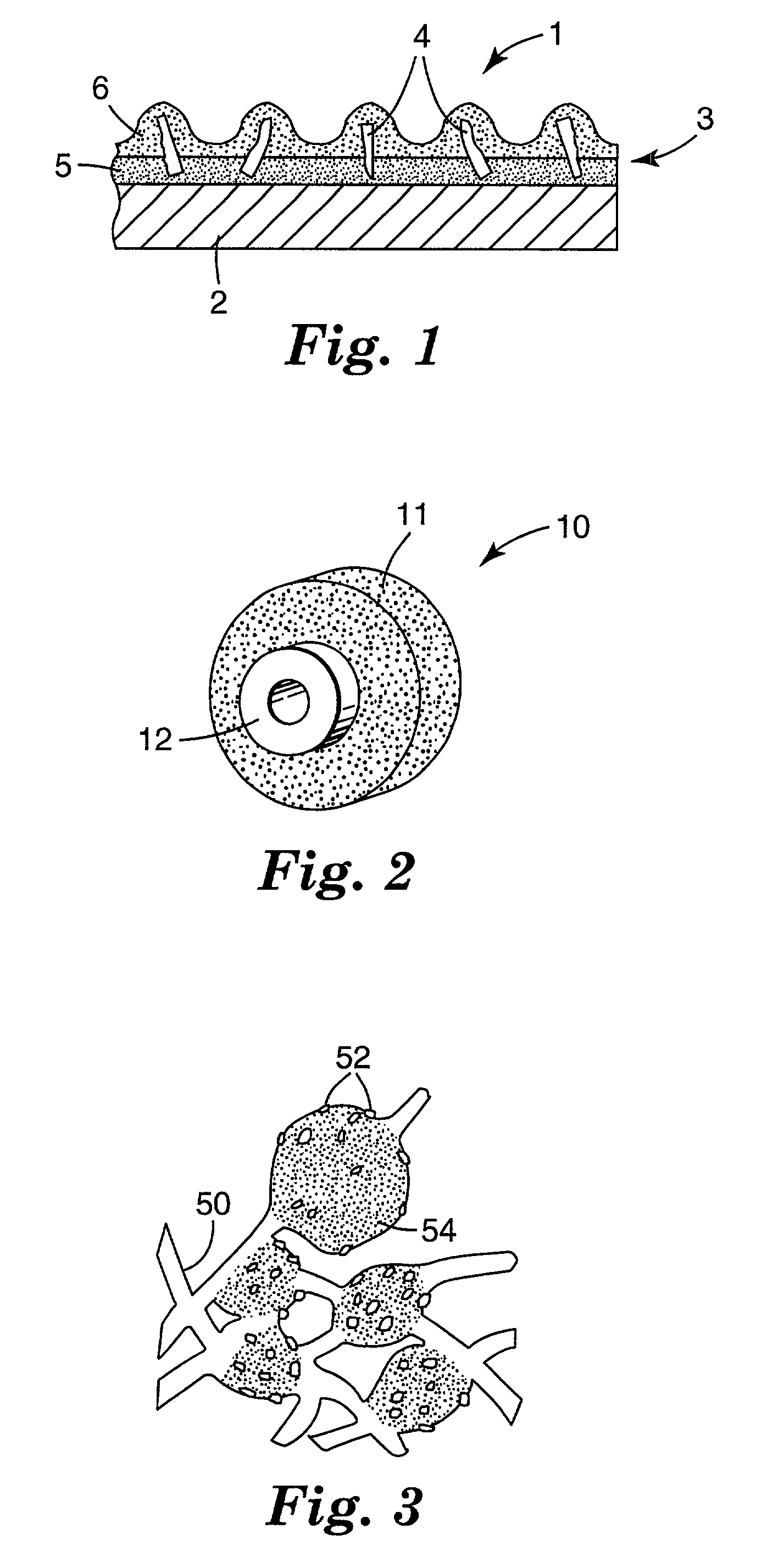
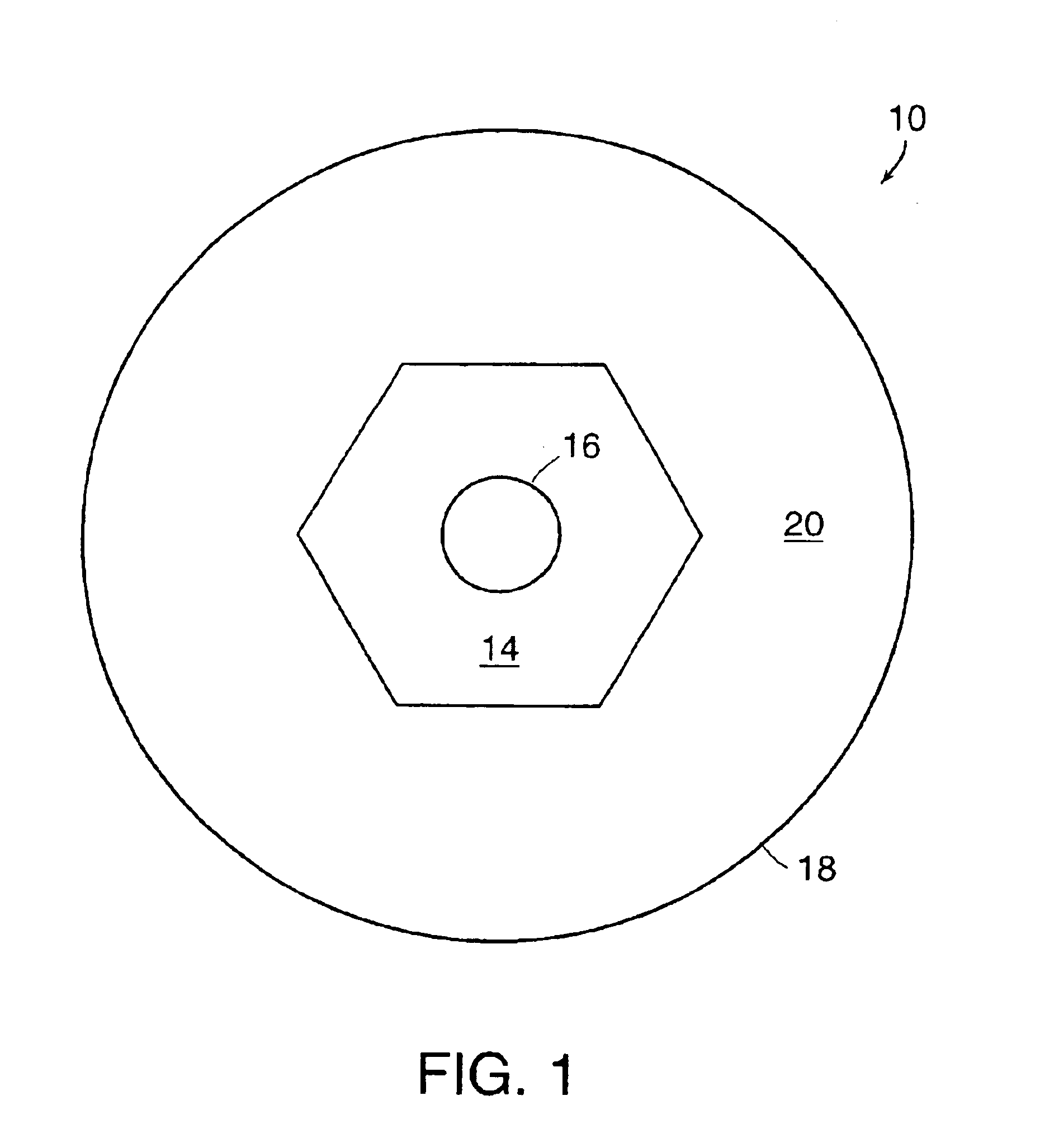
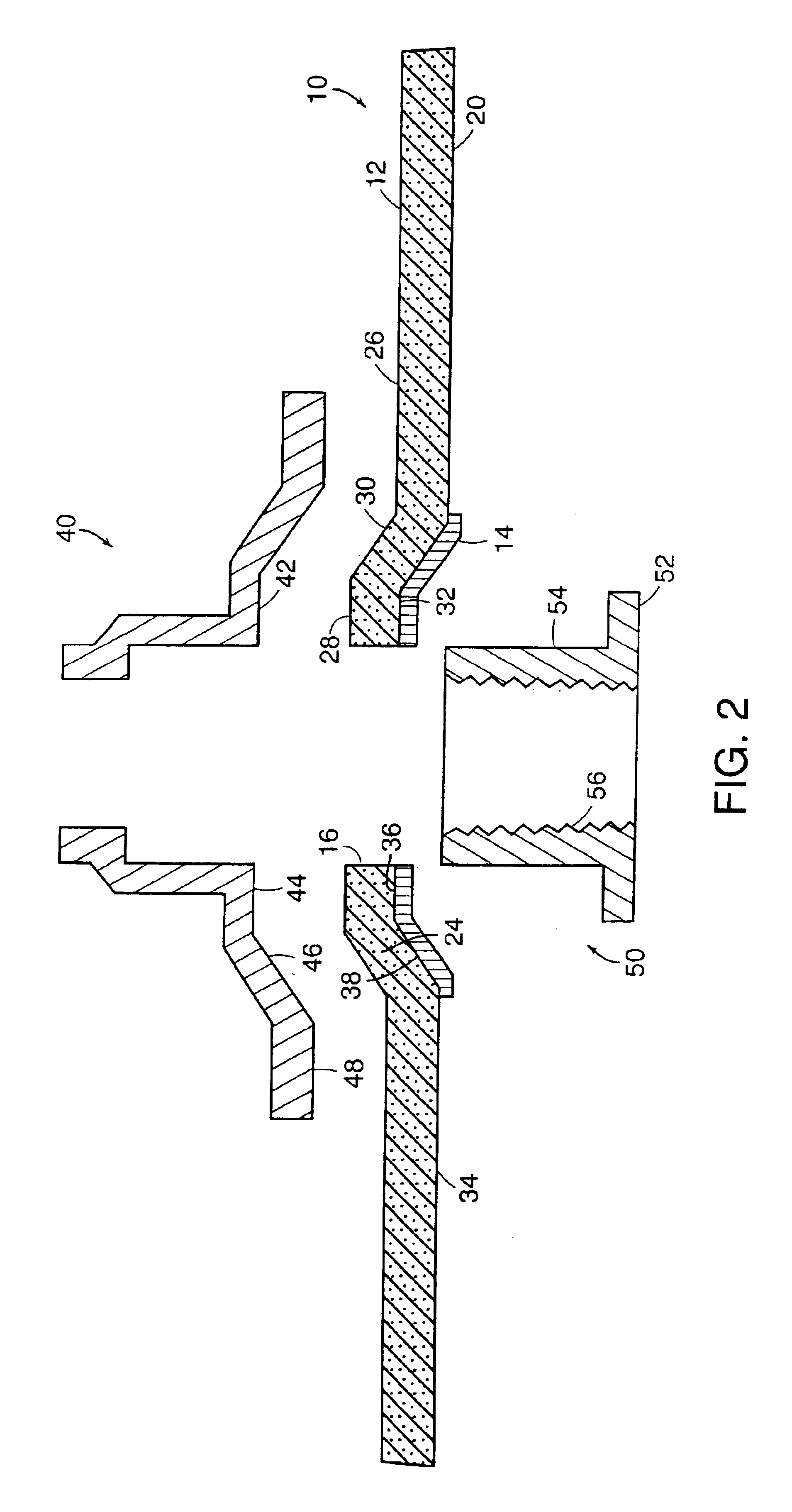
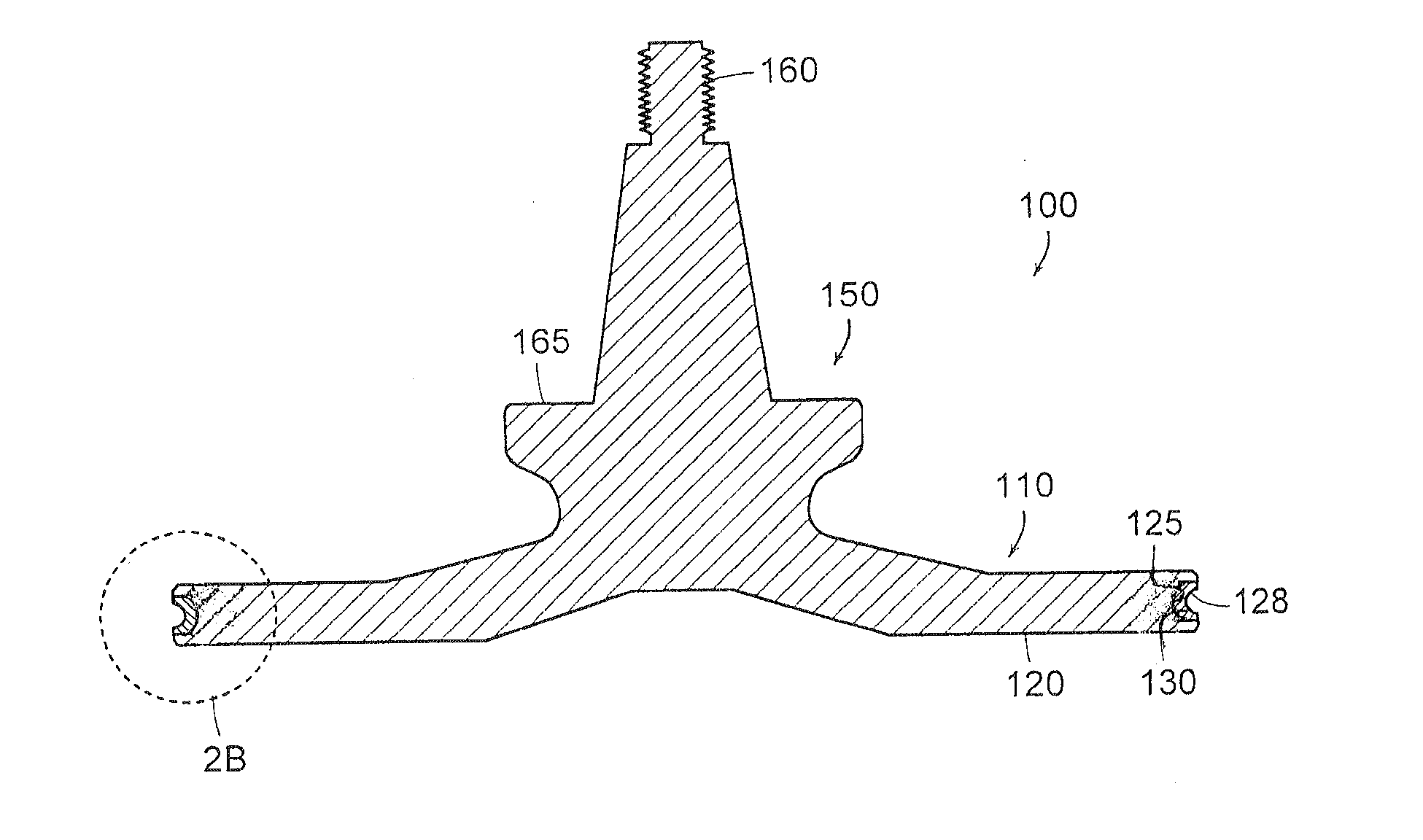
In a depressed-center abrasive wheel assembly a reinforcement layer of polygonal shape is located between a front face of the abrasive wheel and a front flange. The reinforcement layer is dimensioned to entirely cover the depressed center portion of the wheel. An example of polygonal reinforcement layer has a hexagonal shape and is made of fiberglass cloth. A polygonal shape reinforcement layer can also be employed between the front flange and the front face in an abrasive flat wheel assembly that employs a wheel without internal reinforcement.
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN ABRASIVES INC
Single-use edging wheel for finishing glass
InactiveUS20090017736A1Uniform thicknessEdge grinding machinesPigmenting treatmentFlat glassMaterials science
A single-use grinding tool includes a wheel portion having a profiled recess (e.g., such as a U, V, or bowl shape) extending circumferentially along the wheel portion's periphery. A multi-layered bonded abrasive (e.g., 3-dimensional matrix of abrasive grains and bond material, or multiple layers of abrasive tape) is conformably coated or otherwise applied in a uniform thickness along the profiled recess. The bonded abrasive in one particular case includes a metal bond with diamonds. However, organic, resinous, vitrified, and hybrid bonds, as well as other abrasive grit types, can be used. The wheel portion is supported by an arbor portion which may be removably coupled to the wheel portion, or formed integrally with the wheel portion. The tool is useful, for example, in edge grinding a workpiece, such as sheet glass. Methods of tool use and tool manufacture are disclosed as well.
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN ABRASIFS INC +1
Finishing element including discrete finishing members
Unitary finishing elements having discrete finishing members fixedly attached to unitary resilient body are disclosed for finishing semiconductor wafers. The discrete finishing members can be comprised of a multiphase polymeric composition. The new unitary finishing elements have lower cost to manufacture and high precision. The unitary finishing elements can reduce unwanted surface defect creation on the semiconductor wafers during finishing.
Owner:SEMCON TECH +1
Sanding disks
InactiveUS6312325B1Risk minimizationProtect from harmRevolution surface grinding machinesSupport wheelsAngle grinderEngineering
Accessories for an angle grinder include a disposable rotary sanding disk having quite large shaped ventilating / viewing apertures, for use with a resilient backing plate also having shaped ventilating apertures. The apertures of one or both parts are shaped so that snagging of the apertures on projections from the work surface is minimized and to facilitate air flow across the work surface during use. This air flow helps in cooling the work and ejecting detritus, so minimising clogging effects. The ventilating apertures also facilitate viewing the work to be sanded through the spinning disk during the abrasion process, so that operator feedback is immediate. The holes also give the sanding disk more resilience so that a greater area comes in contact with the work and the disk wears more evenly over its abrasive surface.
Owner:MORTON CO
Brazed diamond tools and methods for making the same
InactiveUS20040112359A1Avoid large movementsImprove cutting efficiencyDrill bitsConstructionsChemical LinkageBraze alloy
Superabrasive tools and methods for the making thereof are disclosed and described. In one aspect, superabrasive particles are chemically bonded to a matrix support material according to a predetermined pattern by a braze alloy. The brazing alloy may be provided as a powder, thin sheet, or sheet of amorphous alloy. A template having a plurality of apertures arranged in a predetermined pattern may be used to place the superabrasive particles on a given substrate or matrix support material.
Owner:SUNG CHIEN MIN
Contoured CMP pad dresser and associated methods
InactiveUS7201645B2Increase loadImprove permeabilityPolishing machinesRevolution surface grinding machinesEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:KINIK
Detection system for chemical-mechanical planarization tool
InactiveUS20050026542A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementLapping machinesReflectance spectroscopySemiconductor
Methods and apparatus are provided for endpoint detection in a chemical mechanical planarization (CMP) process. Reflectance spectra data is taken periodically in different areas of a surface of a semiconductor wafer during a chemical mechanical planarization process. Three different reflectance spectra are identified to determine a status of the CMP process. A first reflectance spectra data corresponds to light reflected predominately from a layer of material on the surface of the semiconductor wafer. A second reflectance spectra corresponds to the layer of material being thinned such that the second reflectance spectra is modified by an underlying layer of material. A third reflectance spectra corresponds to light reflected predominately from the underlying layer of material.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Abrasive-bladed cutting wheel
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Grinding wheel
InactiveUS20020068518A1Removal from surfaceReduce grooveRevolution surface grinding machinesBonded abrasive wheelsGrinding wheelAbrasive
A cylindrical, abrasive grinding wheel having a cylindrical abrasive region with an abrasive surface at an outer circular band thereof. The abrasive region includes layers of abrasive particles. The layers of abrasive particles can be tilted with respect to an axis of rotation of the grinding wheel or they can such that grooving in the grinding wheel and a workpiece ground by the grinding wheel can be reduced. Alternatively, the abrasive region can be formed from a plurality of abrasive segments each having layers of abrasive particles. The layers of abrasive particles can be staggered in the direction of the axis of rotation from one segment to another. This can also reduce grooving in the grinding wheel and workpieces.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Molding a polishing pad having integral window
A polishing pad is formed by solidifying a flowable polymeric material at different rates of cooling to provide a polishing pad with a transparent region and an adjacent opaque region. Types of polymeric material suitable for making the polishing pad include a single thermoplastic material, a blend of thermoplastic materials, and a reactive thermosetting polymer.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CMP HLDG INC
Fused Al2O3-Y2O3 eutectic abrasive particles, abrasive articles, and methods of making and using the same
InactiveUS6592640B1Improve grinding performanceLower performance requirementsPigmenting treatmentMangesium aluminatesMaterials scienceAbrasive
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Diamond grid CMP pad dresser
InactiveUS6884155B2Easy to monitorUniform sizePolishing machinesRevolution surface grinding machinesSuperhard materialDiamond-like carbon
The present invention discloses a CMP pad dresser which has a plurality of uniformly spaced abrasive particles protruding therefrom. The abrasive particles are super hard materials, and are typically diamond, polycrystalline diamond (PCD), cubic boron nitride (cBN), or polycrystalline cubic boron nitride(PcBN). The abrasive particles are brazed to a substrate which may be then coated with an additional anti-corrosive layer. The anti-corrosive layer is usually a diamond or diamond-like carbon which is coated over the surface of the disk to prevent erosion of the brazing alloy by the chemical slurry used in conjunction with the CMP pad. This immunity to chemical attack allows the CMP pad dresser to dress the pad while it is polishing a workpiece. In addition to even spacing on the substrate, the abrasive particles extend for a uniform distance away from the substrate, allowing for even grooming or dressing of a CMP pad both in vertical and horizontal directions. A method of producing such a CMP pad dresser is also disclosed.
Owner:KINIK
Side-emitting LED package having scattering area and backlight apparatus incorporating the LED lens
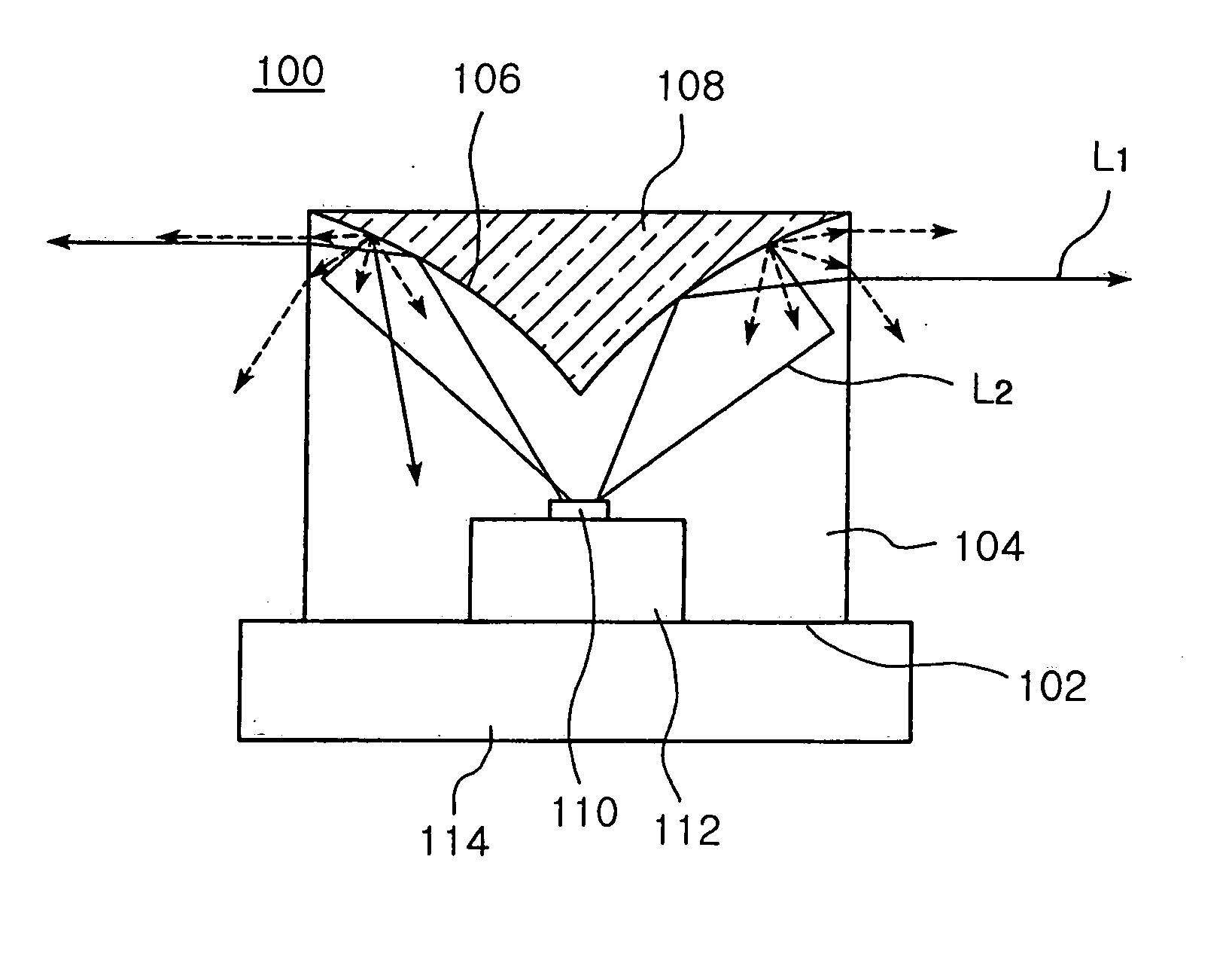
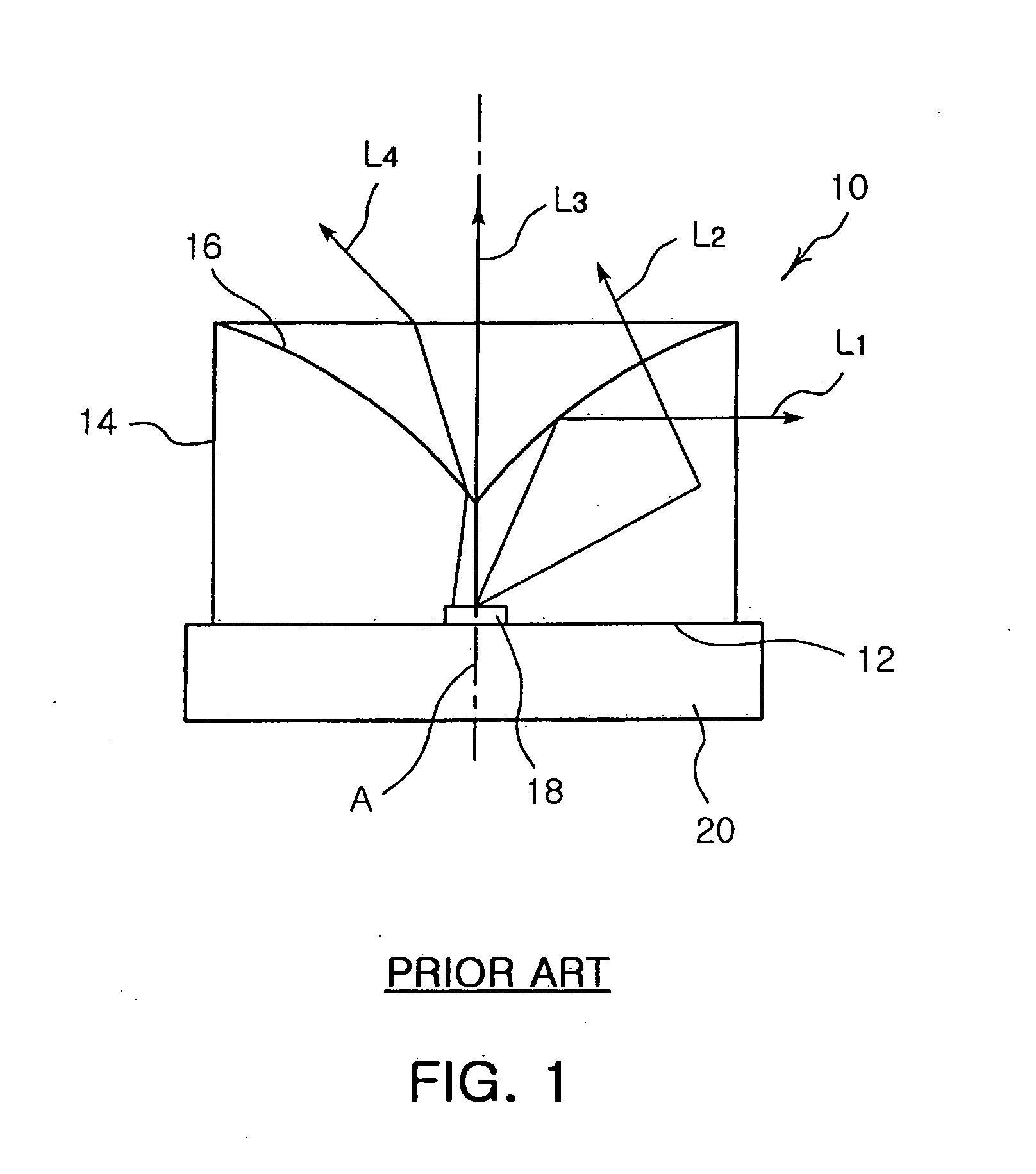
ActiveUS20060208269A1Avoid light lossPoint-like light sourceSolid-state devicesOptoelectronicsExit surface
The invention provides an LED package and a backlight device incorporating the LED lens. The LED package has a bottom surface and a light exiting surface cylindrically extended around a central axis of the package from the bottom surface. Also, a reflecting surface is positioned on an opposite side of the bottom surface and symmetrical around the central axis such that light incident from the bottom surface is reflected toward the light exiting surface. Further, a scattering area is formed on the reflecting surface. According to the invention, by applying scattering materials on the reflecting surface of the LED package, a reflecting paper does not need to be attached, thereby simplifying a process and reducing the manufacture time and cost.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for manufacturing microporous CMP materials having controlled pore size
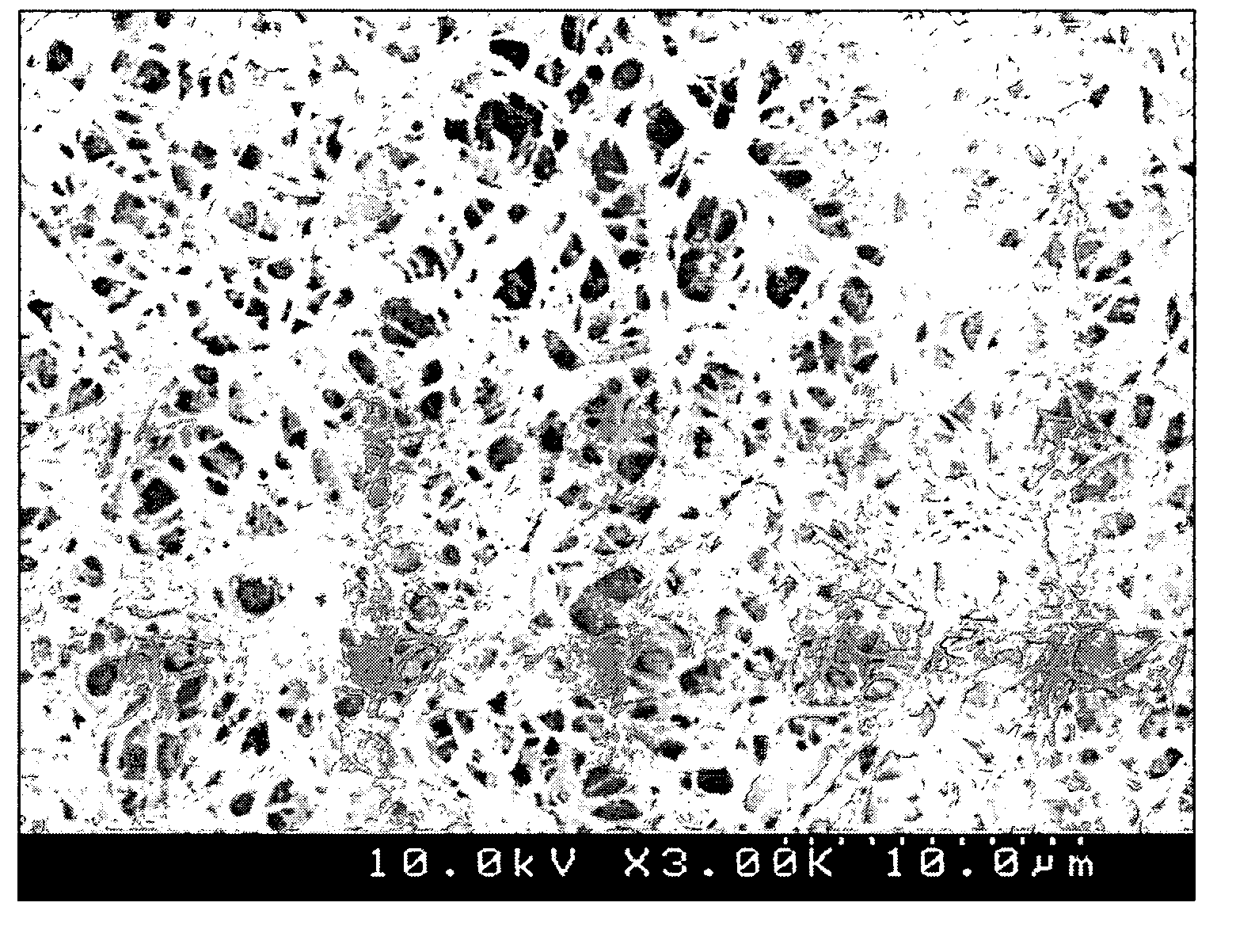
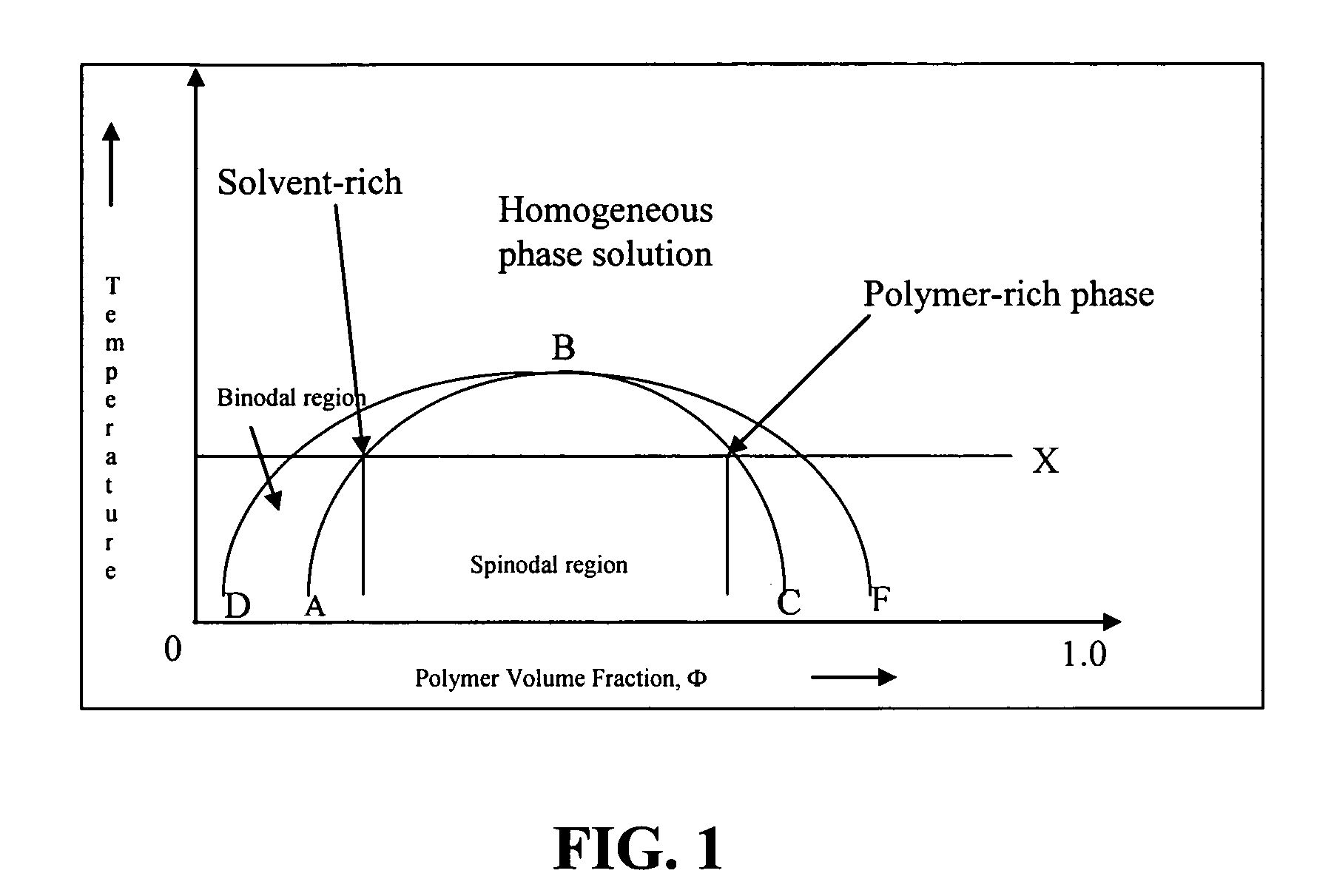
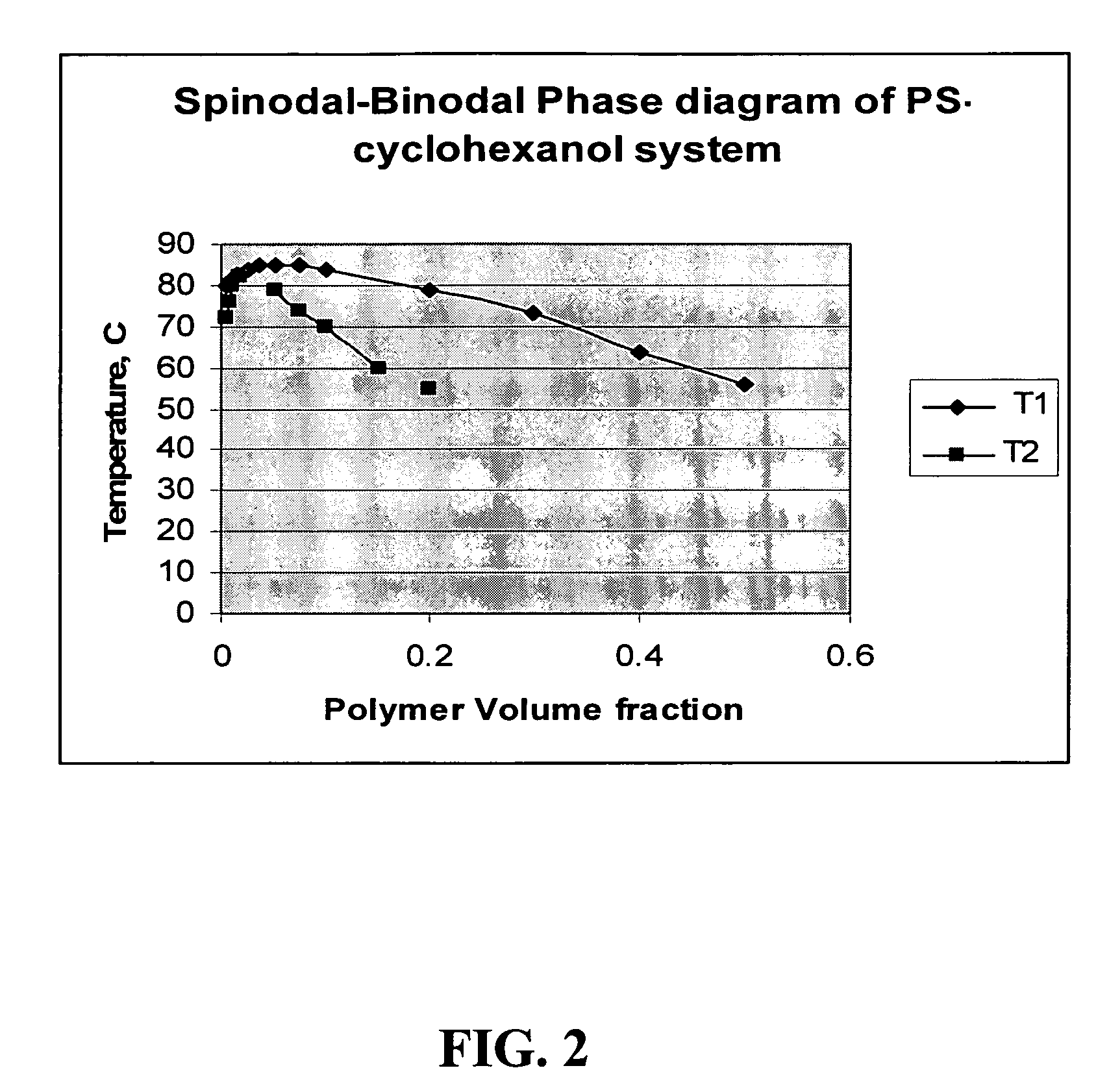
A method of manufacturing a chemical-mechanical polishing (CMP) pad comprises the steps of (a) forming a layer of a polymer resin liquid solution (i.e., a polymer resin dissolved in a solvent); (b) inducing a phase separation in the layer of polymer solution to produce an interpenetrating polymeric network comprising a continuous polymer-rich phase interspersed with a continuous polymer-depleted phase in which the polymer-depleted phase constitutes about 20 to about 90 percent of the combined volume of the phases; (c) solidifying the continuous polymer-rich phase to form a porous polymer sheet; (d) removing at least a portion of the polymer-depleted phase from the porous polymer sheet; and (e) forming a CMP pad therefrom. The method provides for microporous CMP pads having a porosity and pore size that can be readily controlled by selecting the concentration polymer resin in the polymer solution, selecting the solvent based on the solubility parameters of the polymer in the solvent polarity of solvent, selecting the conditions for phase separation, and the like.
Owner:CMC MATERIALS INC
Abrasive tool with metal binder phase
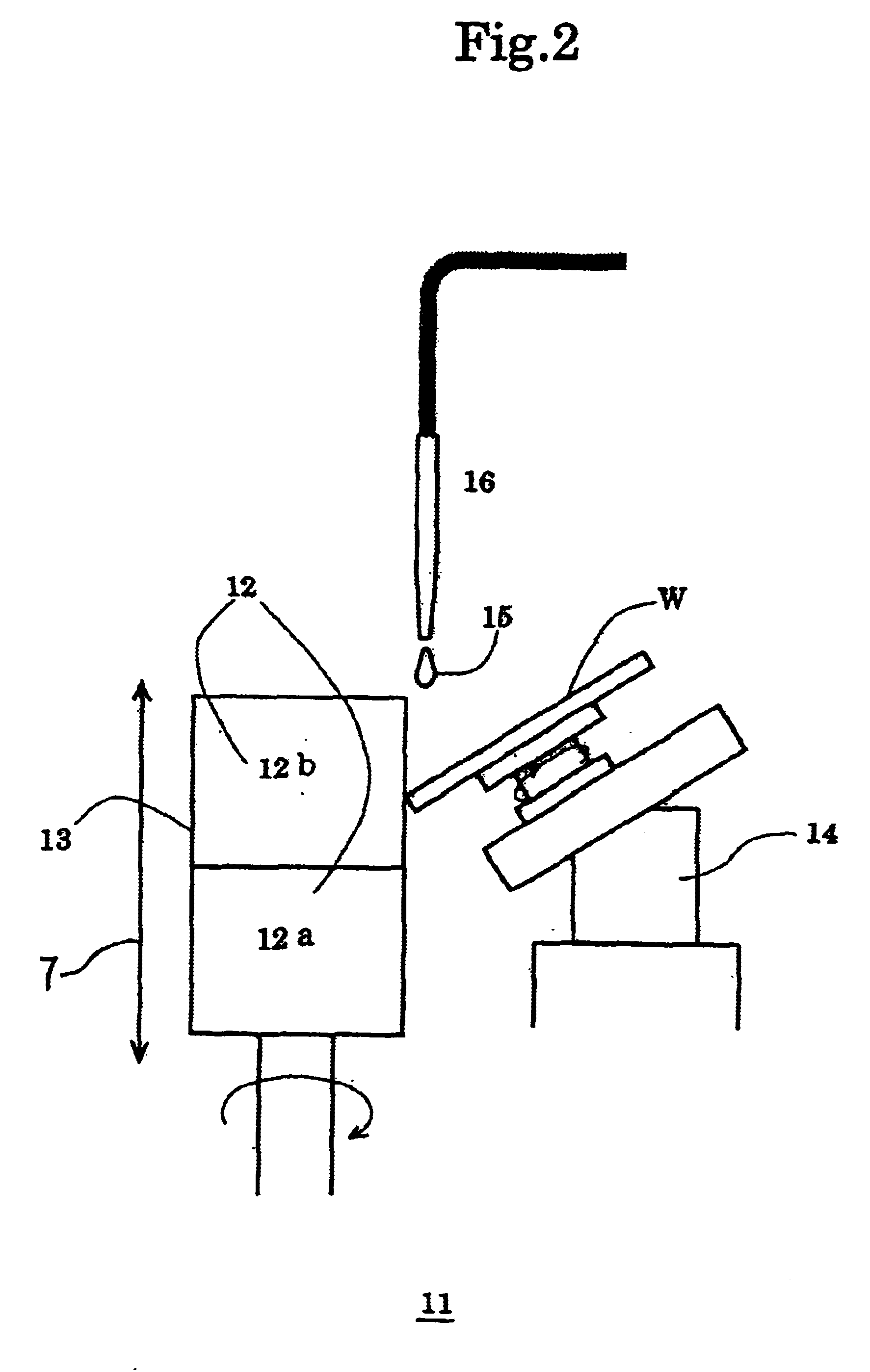
InactiveUS6419574B1Sufficient sharpnessImprove discharge performanceRevolution surface grinding machinesGrinding drivesWear particleMetal
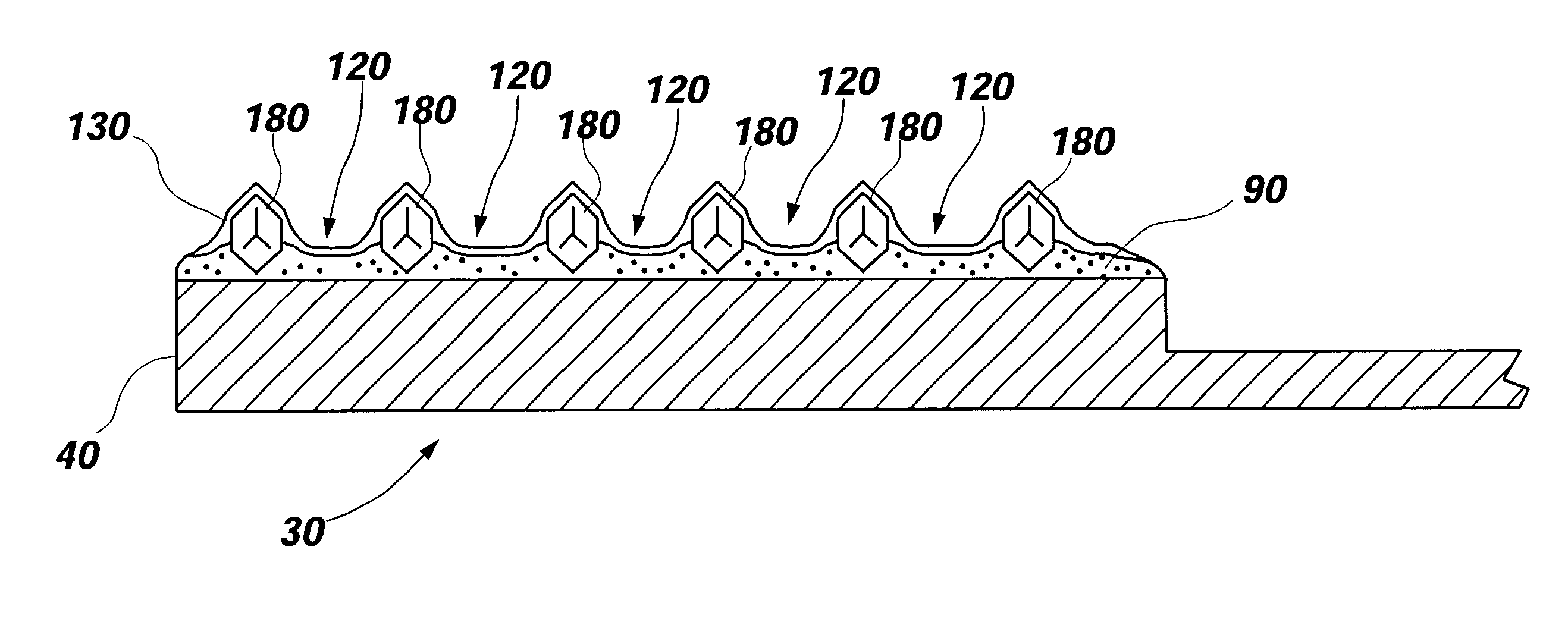
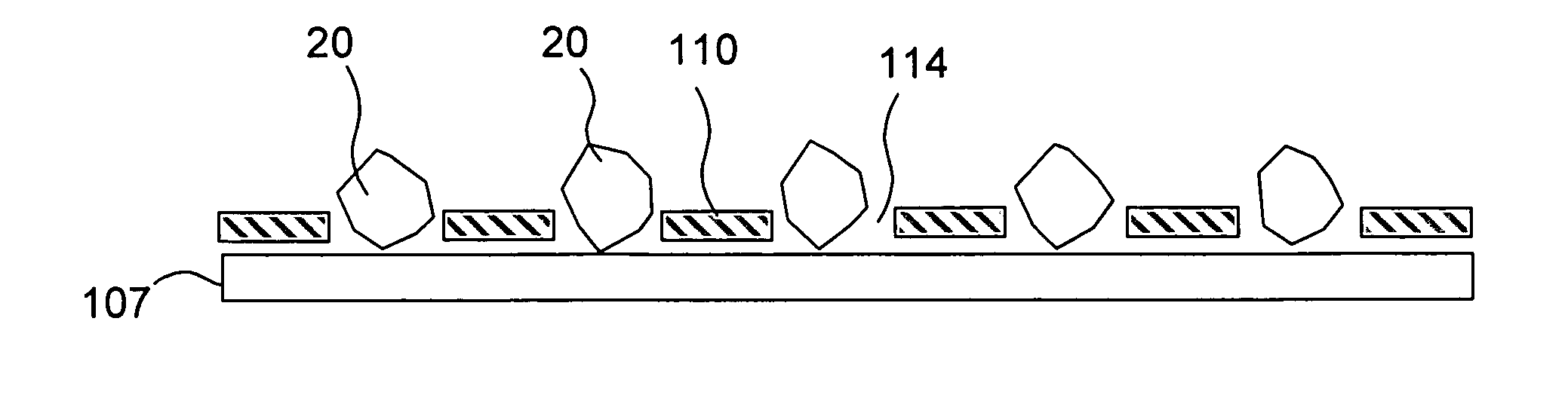
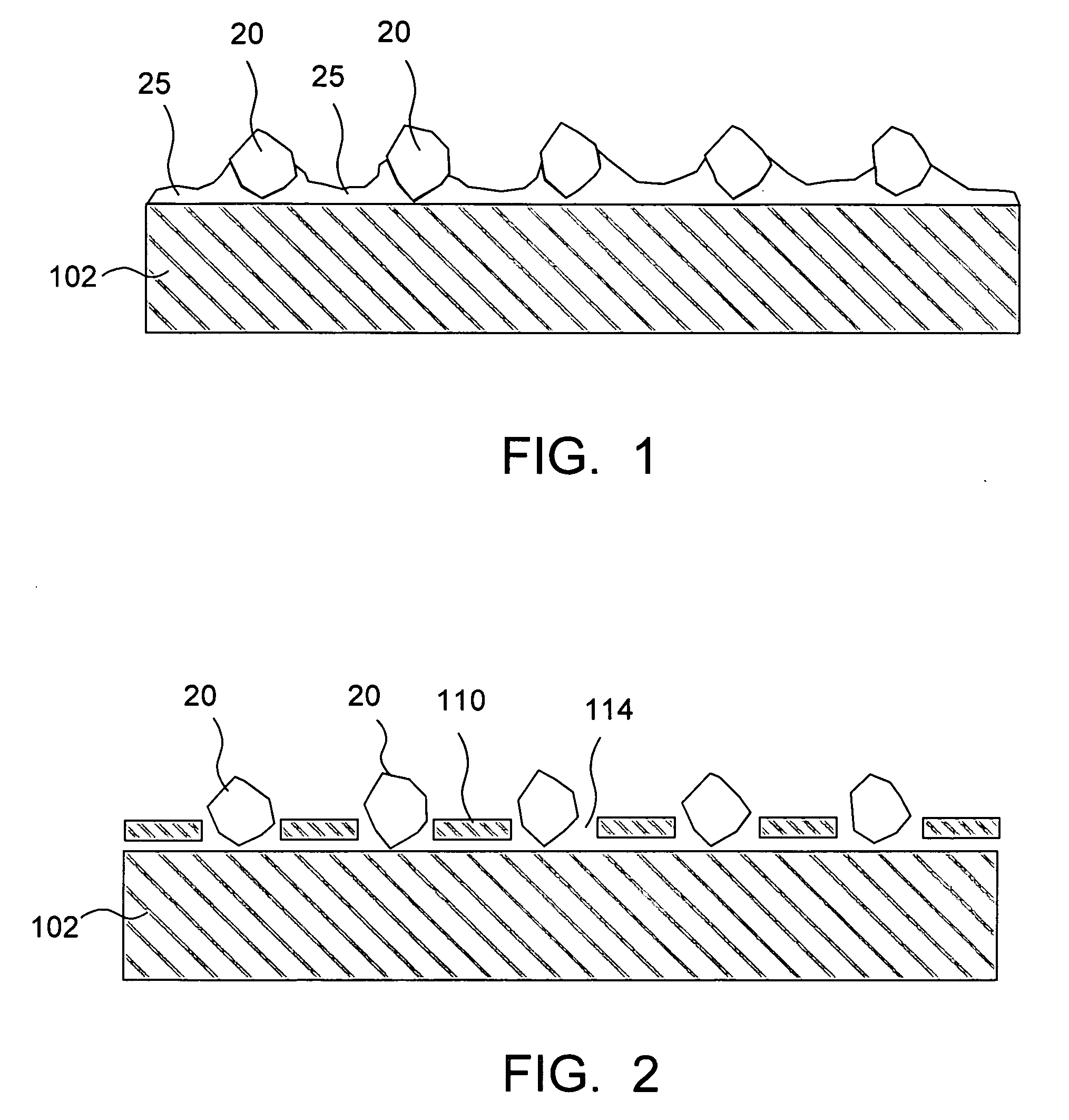
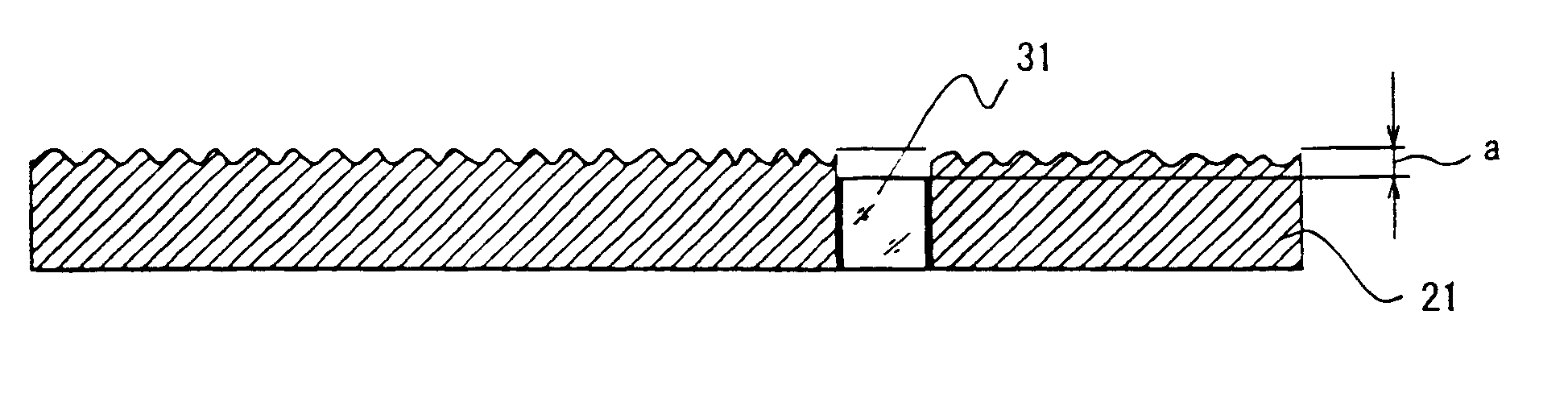
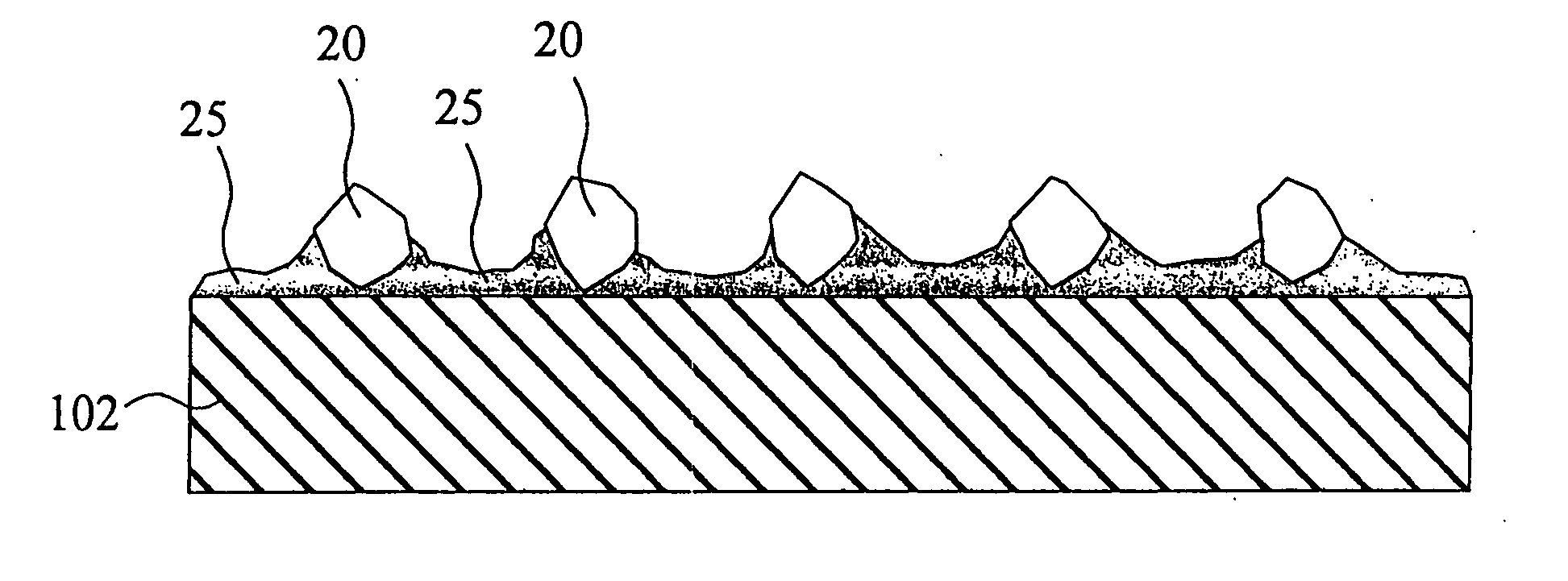
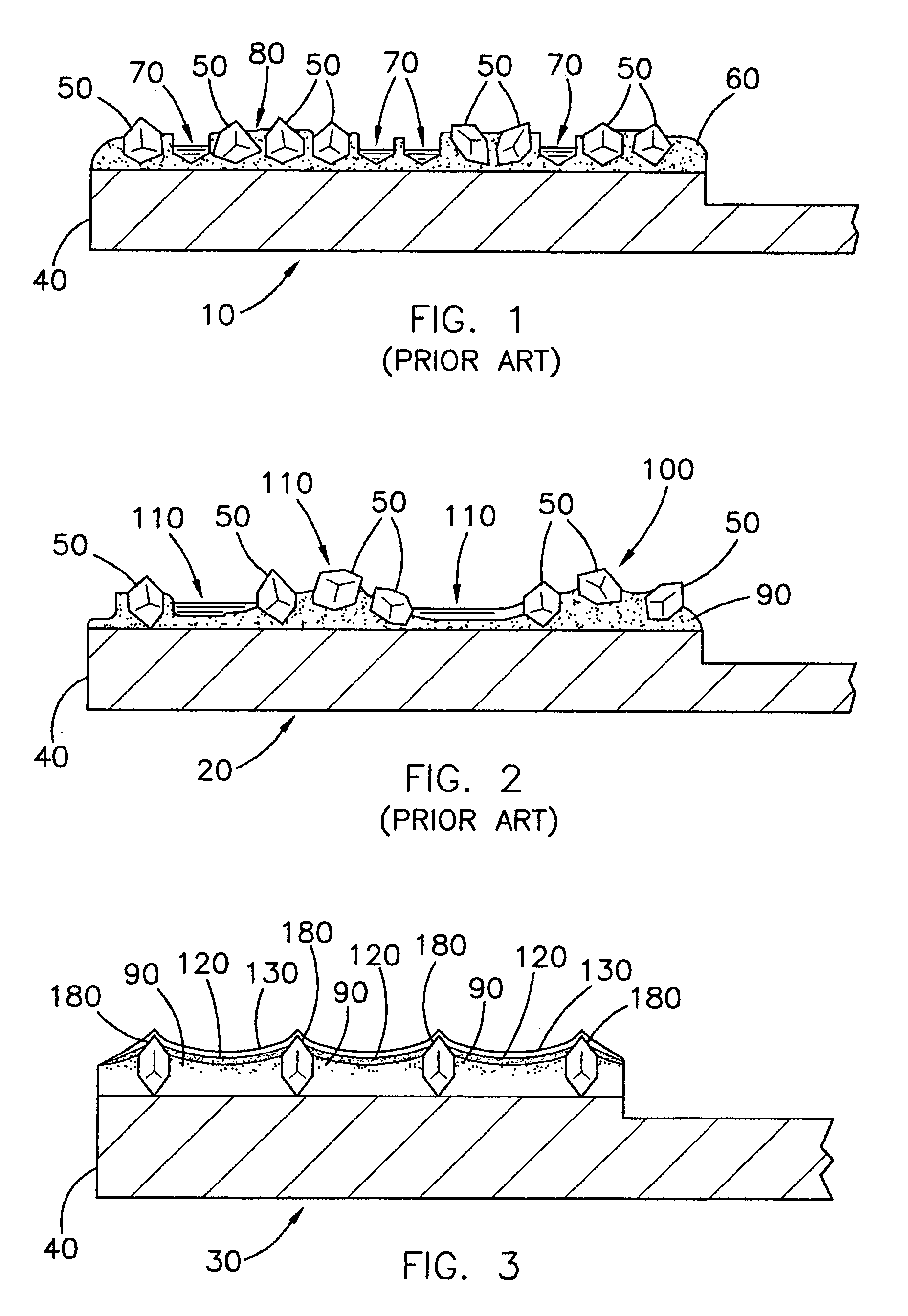
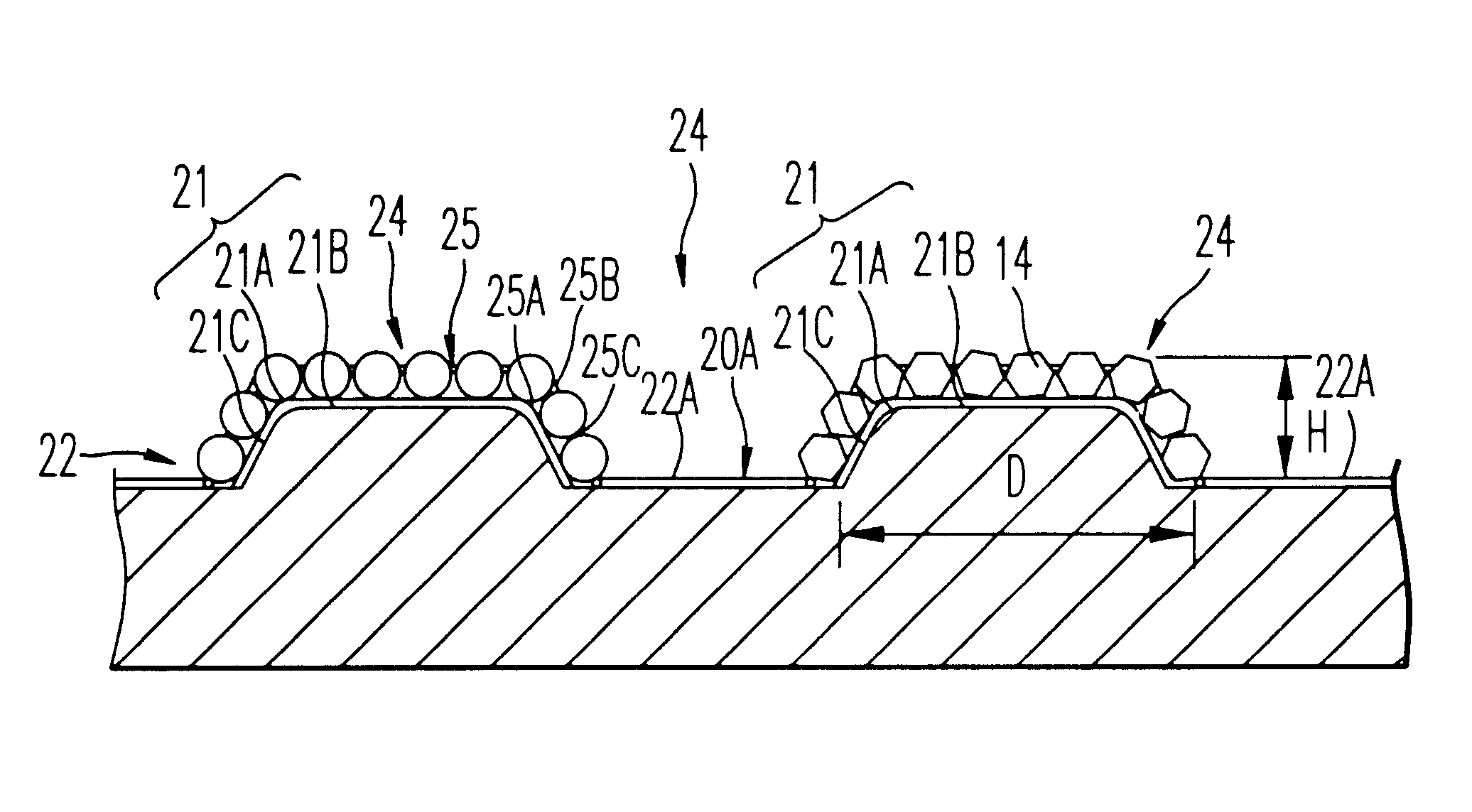
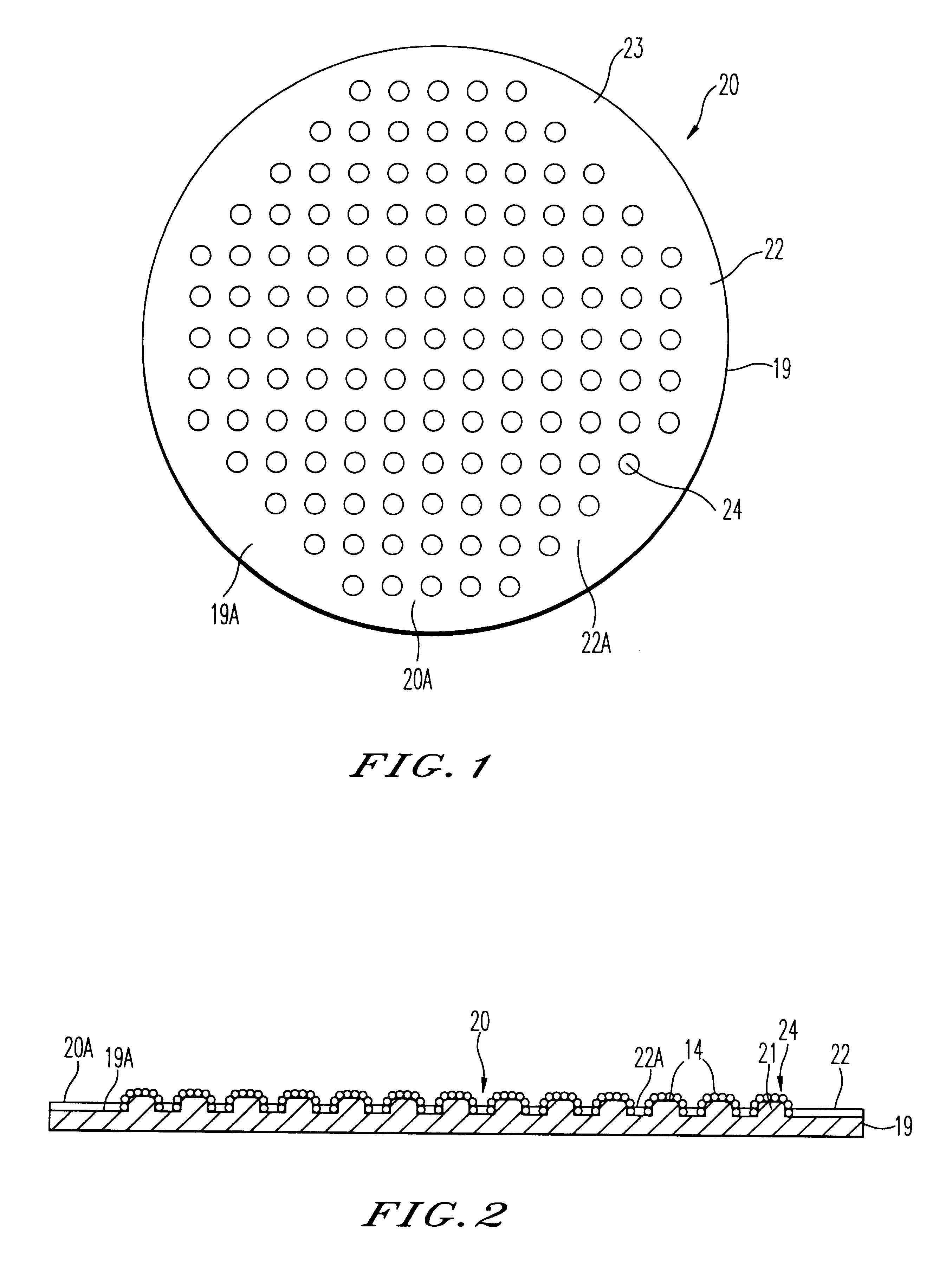
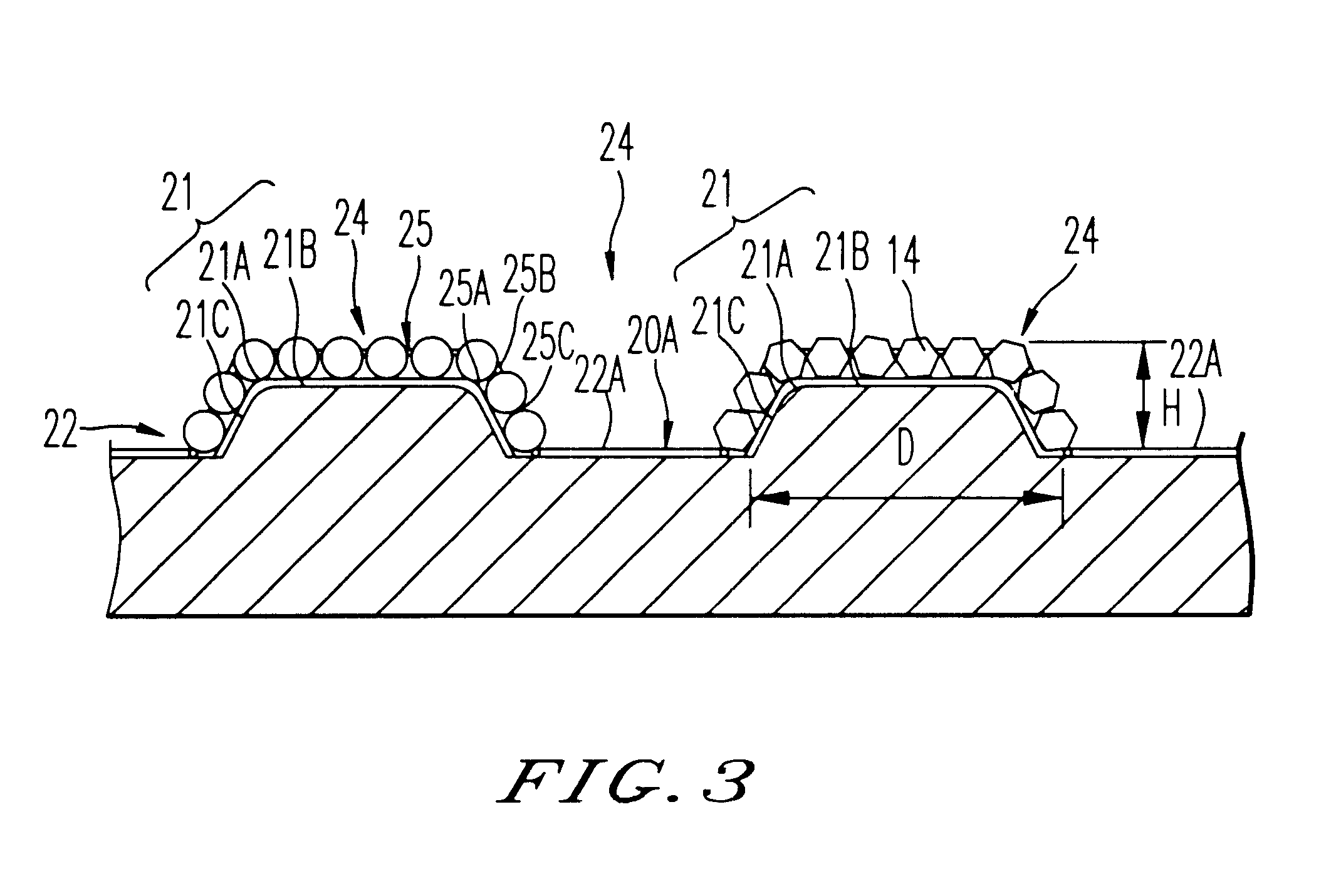
In the electrodeposited abrasive wheel 20 of the abrasive tool according to the present invention, plural mound parts 21, which are upheaved at the central domain of base metal 19 in almost columnar shape, are arranged mostly in the shape of lattice. An abrasive grain layer 22 is formed on a base metal 19, and plural ultra abrasive grains 14 are adhered only to each mound parts 21 by electrodeposited metal phase 25, and referred as the small abrasive-grain-layer parts 24, respectively. Ultra abrasive grains are laid out at corner R part 21a and top 21b of the mound parts 21 at the small abrasive-grain-layer parts 24. Ultra abrasive grains at each small abrasive-grain-layer parts are set as 11-500 pieces, and the rate which ultra abrasive grains occupy to the whole area of abrasive grain layer accounted by plane projection is set as 20%-80% of the range. At the time of grinding, only ultra abrasive grains contact to grinding work piece, then high abutment pressure is maintained, and sharpness and the discharge performance of ground wastes are good.
Owner:MITSUBISHI MATERIALS CORP
Mosaic polishing pads and methods relating thereto
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CMP HLDG INC
Abrasive article and method of making same
An abrasive article may include an abrasive body having a grinding layer, where the grinding layer may include a bond and abrasive particles contained within the bond. The abrasive body also may include a volumetric ratio GLVb / GLVap of at least about 0.4, where GLVb is a volume percent of bond for a total volume of the grinding layer and GLVap is a volume percent of abrasive particles for a total volume of the grinding layer. The abrasive particles may include seeded sol-gel ceramic and may have an average particle size of at least about 600 microns. In addition, the abrasive particles may include a coupling agent that may include an organic material with a silane functional group. Prior to formation of the abrasive article, the abrasive particles may be coated by the coupling agent at a ratio ACOA / AAB of at least about 0.1, where CCOA is the amount of coupling agent in grams in a pre-formation mixture and AAB is the amount of abrasive particles in pounds (lbs) in the pre-formation mixture.
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN ABRASIVES INC +1
Conditioner and conditioning disk for a CMP pad, and method of fabricating, reworking, and cleaning conditioning disk
InactiveUS20020127962A1Effective conditioningProlong lifeGrinding drivesBelt grinding machinesSize differenceCleaning methods
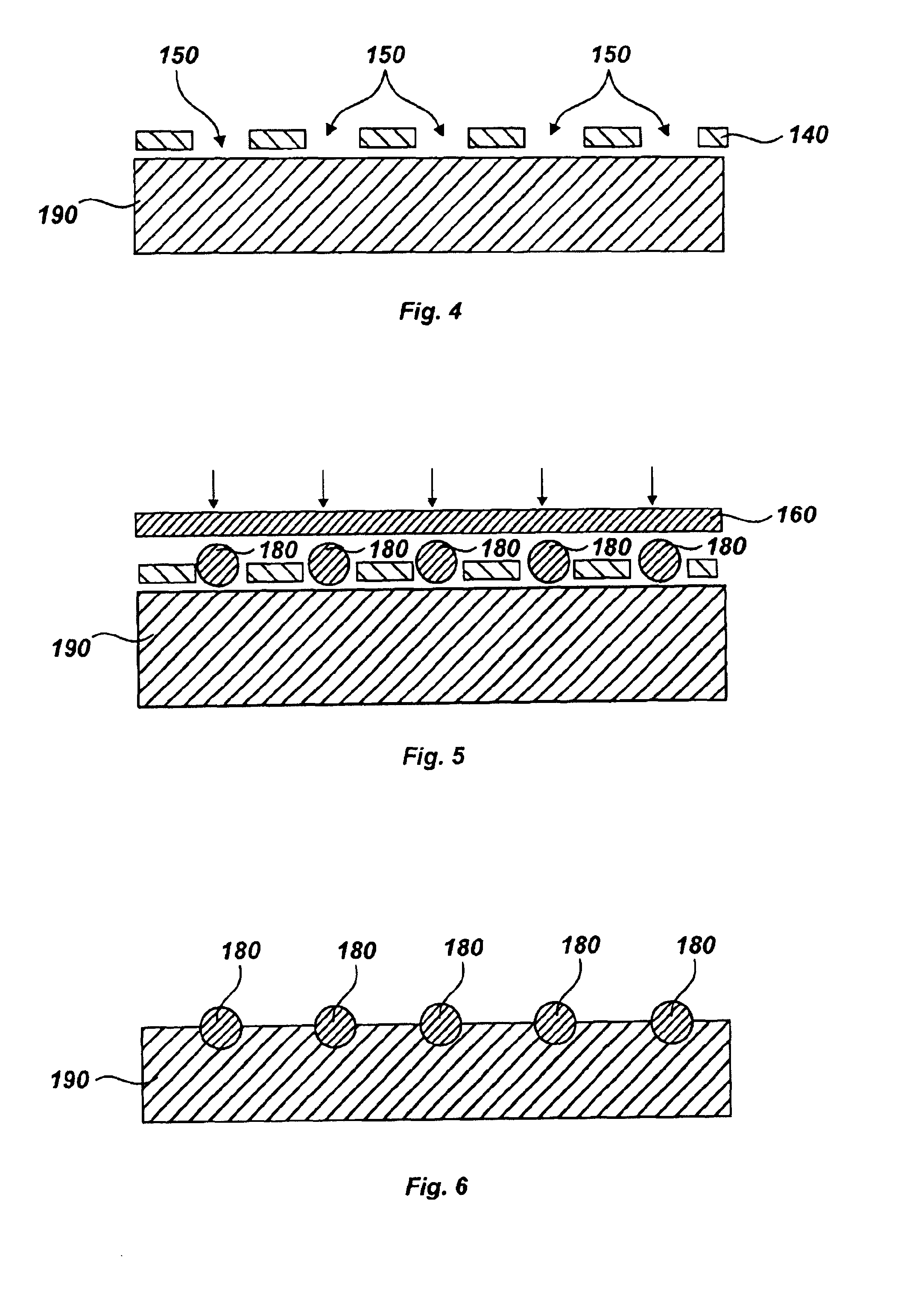
A conditioning disk and a conditioner for a chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) pad, and a method of fabricating, reworking, and cleaning the conditioning disk, are utilized to improve conditioning efficiency, and to reduce production expenses. The conditioning disk for a CMP pad is divided into regions defined by a size difference of abrasive grains formed on the body surface in each region of the conditioning disk. The method of fabricating the conditioning disk is performed by forming adhesive films for attaching the abrasive grains onto the body surface multiple times. In addition, a used conditioning disk may be reworked by detaching the abrasive grains from the body, and attaching new abrasive grains. A used conditioning disk can also be cleaned of by-products of the conditioning process by a cleaning method using a HF solution or BOE (buffered oxide etch) solution.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com