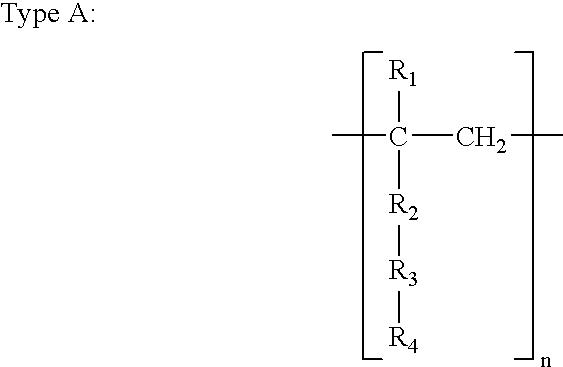
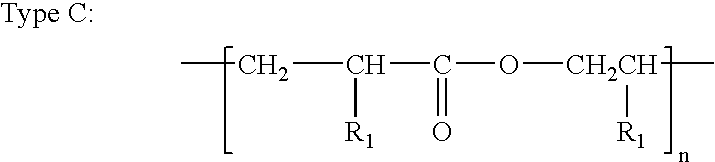
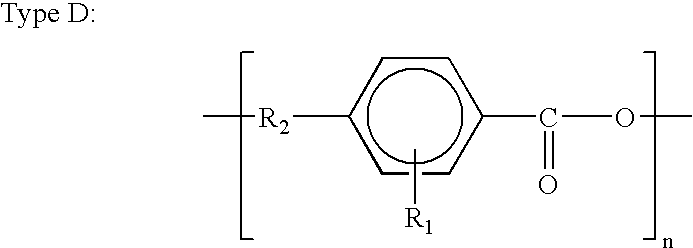
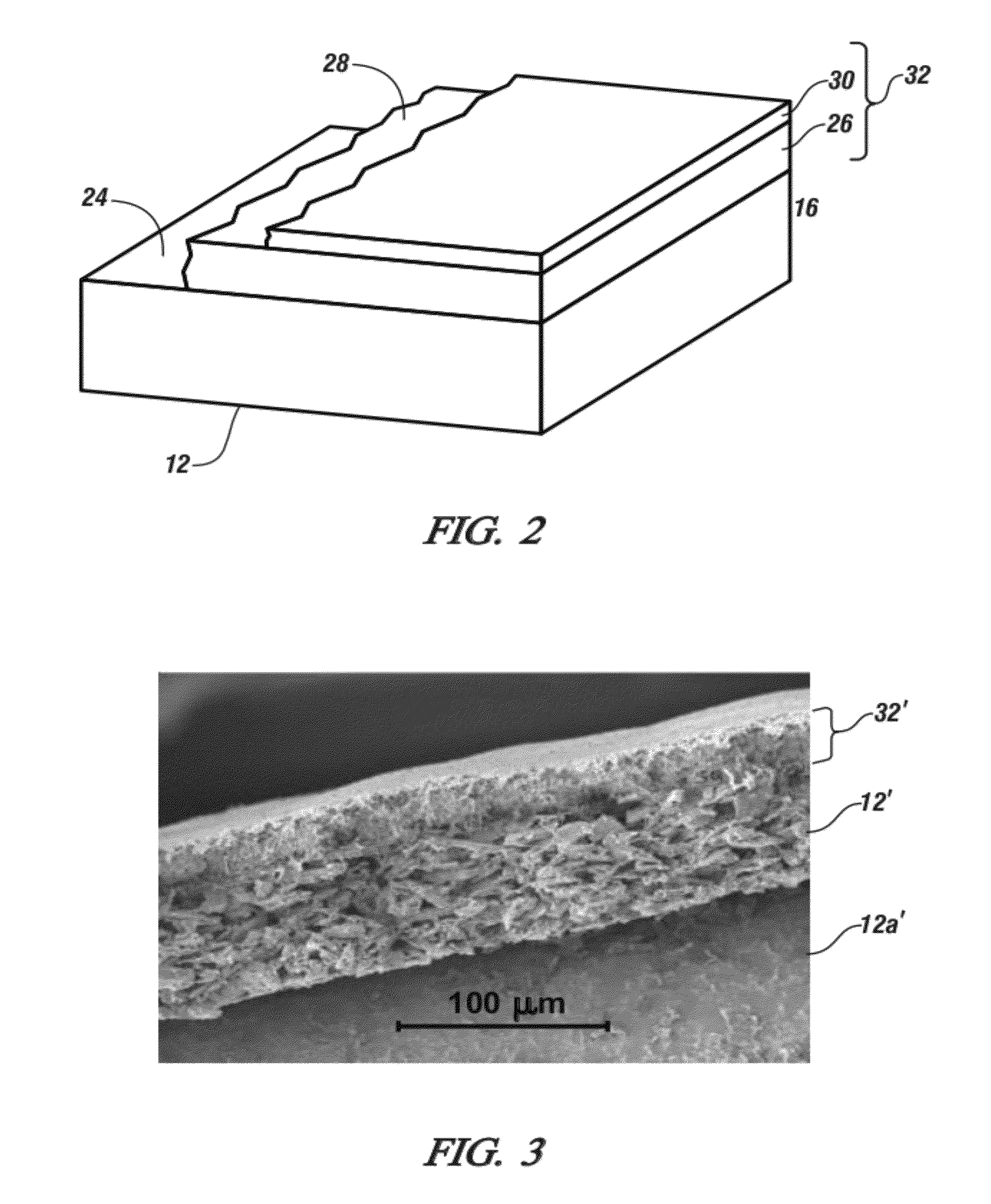
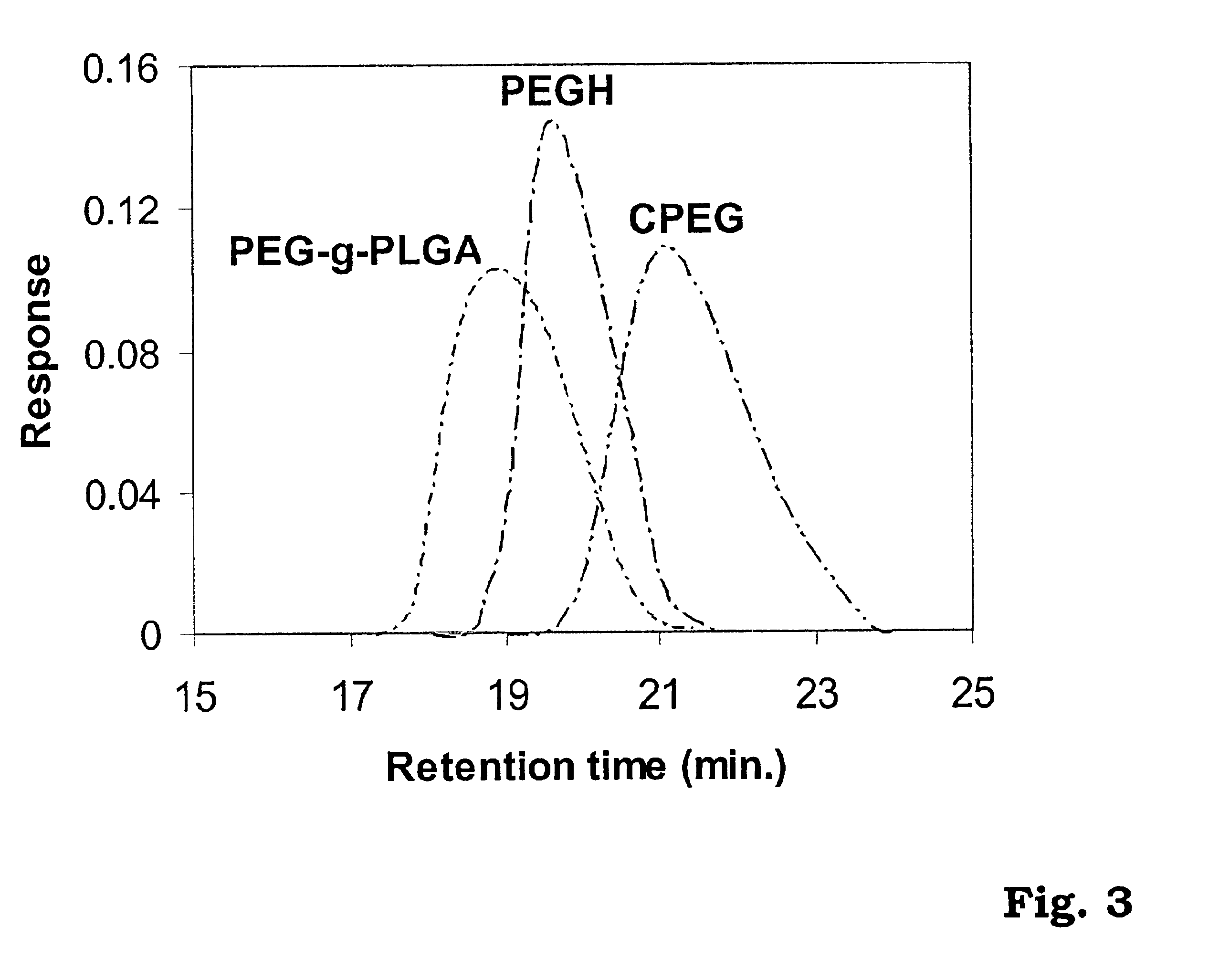
Patents
Literature
5025 results about "Polymer solution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Polymer solutions are solutions containing dissolved polymers. These may be liquid solutions (e.g. in aqueous solution), or solid solutions (e.g. a substance which has been plasticized). The introduction into the polymer of small amounts of a solvent (plasticizer) reduces the temperature of glass transition, the yield temperature, and the viscosity of a melt. An understanding of the thermodynamics of a polymer solution is critical to prediction of its behavior in manufacturing processes — for example, its shrinkage or expansion in injection molding processes, or whether pigments and solvents will mix evenly with a polymer in the manufacture of paints and coatings.
Polymer solution for nanoimprint lithography to reduce imprint temperature and pressure
InactiveUS20040110856A1Reduce pressureReduce the temperatureNanostructure manufactureDecorative surface effectsCross-linkVitrification
A method of forming features on substrates by imprinting is provided. The method comprises: (a) forming a polymer solution comprising at least one polymer dissolved in at least one polymerizable monomer; and (b) depositing the polymer solution on a substrate to form a liquid film thereon; and then either: (c) curing the liquid film by causing the monomer(s) to polymerize and optionally cross-linking the polymer(s) to thereby form a polymer film, the polymer film having a glass transition temperature (Tg); and imprinting the polymer film with a mold having a desired pattern to form a corresponding negative pattern in the polymer film, or (d) imprinting the liquid film with the mold and curing it to form the polymer film. The temperature of imprinting is as little as 10° C. above the Tg, or even less if the film is in the liquid state. The pressure of the imprinting can be within the range of 100 to 500 psi.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Microparticle coated medical device
A drug-loaded microparticle is applied to a medical device for subsequent application to biological tissues. A method of formulating a drug-loaded microparticle and applying it to the surface of a medical device, such as a stent, is disclosed. The drug-loaded microparticle is formulated by combining a drug with various chemical solutions. Specified sizes of the microparticles and amounts of drug(s) contained within the microparticles may be varied by altering the proportions of the chemicals / solutions. In addition to various drugs, therapeutic substances and radioactive isotopes may also be loaded into the microparticles. The drug-loaded microparticle are suspended in a polymer solution forming a polymer matrix. The polymer matrix may be applied to the entire surface or only selected portions of the medical device via dipping, spraying or combinations thereof.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Compositions and methods for mucosal delivery
Mucosal surface-coat-forming film dosage units containing a water-soluble hydrocolloid, an effective dose of an active agent and a mucosal adhesion enhancer; wherein the active agent is encapsulated within a polymer which is chemically or physically distinct from the hydocolloid; wherein the mucosal adhesion enhancer is a starch graft copolymer; wherein the film exhibits a dry tack value of less than 3.5 g, a wet tack of greater than 35 g, a gelation temperature that is greater than 70° C. for a 2% polymer solution, a dry film thickness of less than 20 mil, a water content of 0.5 to 10%, a tensile strength greater than 1500 psi, a modulus in the range of 35,000 to 300,000 psi, a % elongation of less than 20%, a tear probagation resistance of 0.001 to 1 N, and a dissolution time in the range of 1 to 600 seconds upon application to an oral mucosal surface.
Owner:THALLIUM HLDG CO LLC
Sustained-release microcapsule of amorphous water-soluble pharmaceutical active agent
InactiveUS6117455AHigh entrapment of a water-soluble drugSmall initial releaseNanotechGogglesEmulsionOrganic solvent
A sustained-release microcapsule contains an amorphous water-soluble pharmaceutical agent having a particle size of from 1 nm-10 mu m and a polymer. The microcapsule is produced by dispersing, in an aqueous phase, a dispersion of from 0.001-90% (w / w) of an amorphous water-soluble pharmaceutical agent in a solution of a polymer having a wt. avg. molecular weight of 2,000-800,000 in an organic solvent to prepare an s / o / w emulsion and subjecting the emulsion to in-water drying.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Antimicrobial compositions containing colloids of oligodynamic metals
InactiveUS7179849B2Reduced settlingReduce agglomerationOrganic active ingredientsPretreated surfacesSolubilityCatheter
Owner:CR BARD INC
Multifunctional and biologically active matrices from multicomponent polymeric solutions
The present invention relates to a biologically active functionalized electrospun matrix to permit immobilization and long-term delivery of biologically active agents. In particular the invention relates to a functionalized polymer matrix comprising a matrix polymer, a compatibilizing polymer and a biomolecule or other small functioning molecule. In certain aspects the electrospun polymer fibers comprise at least one biologically active molecule functionalized with low molecular weight heparin. Examples of active molecules that may be used with the multicomponent polymer of the invention include, for example, a drug, a biopolymer, for example a growth factor, a protein, a peptide, a nucleotide, a polysaccharide, a biological macromolecule or the like. The invention is further directed to the formation of functionalized crosslinked matrices, such as hydrogels, that include at least one functionalized compatibilizing polymer capable of assembly.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE
Systems for applying cross-linked mechanical barriers
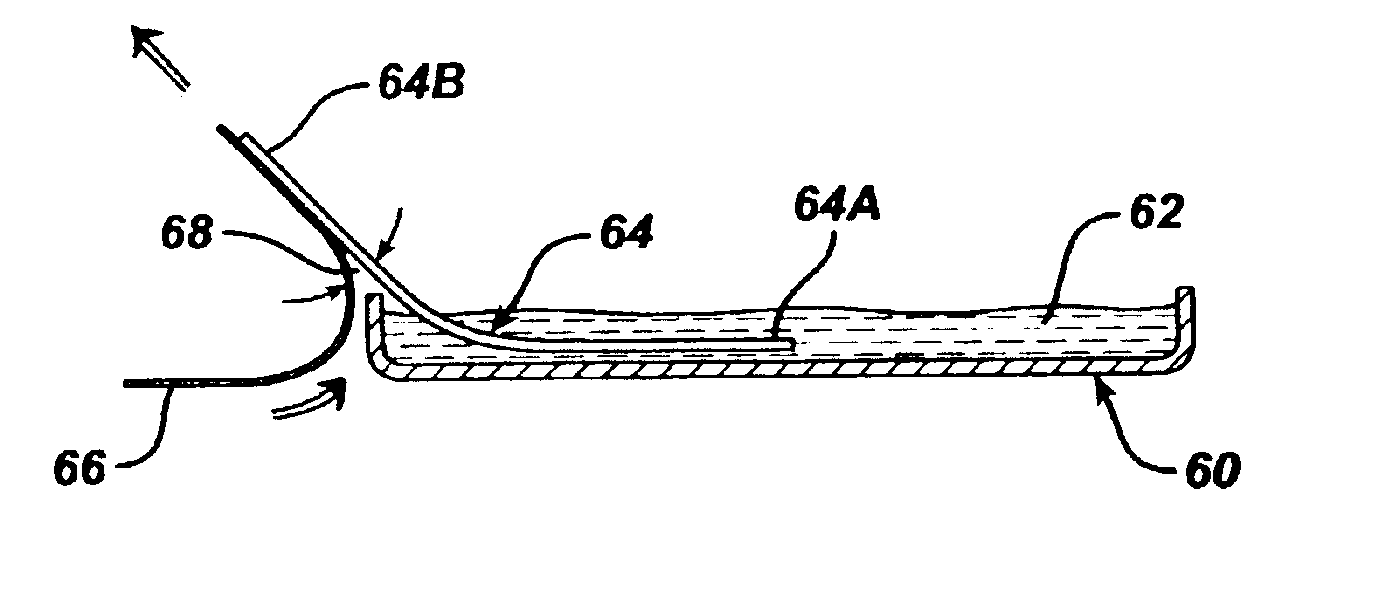
A delivery device applies a biocompatible and biodegradable barrier material to a tissue region, e.g., to seal a vascular puncture site. The material comprises two liquid components, which are pre-packaged in individual dispensers. Upon mixing, the liquid components cross-link to create a barrier matrix. A holder attaches to the delivery device. The holder mutually supports the first and second dispensers while the protein solution and polymer solution are conveyed from the dispensers into a fluid delivery channel. The protein and polymer solutions mix as a result of flow through the channel.
Owner:NEOMEND INC
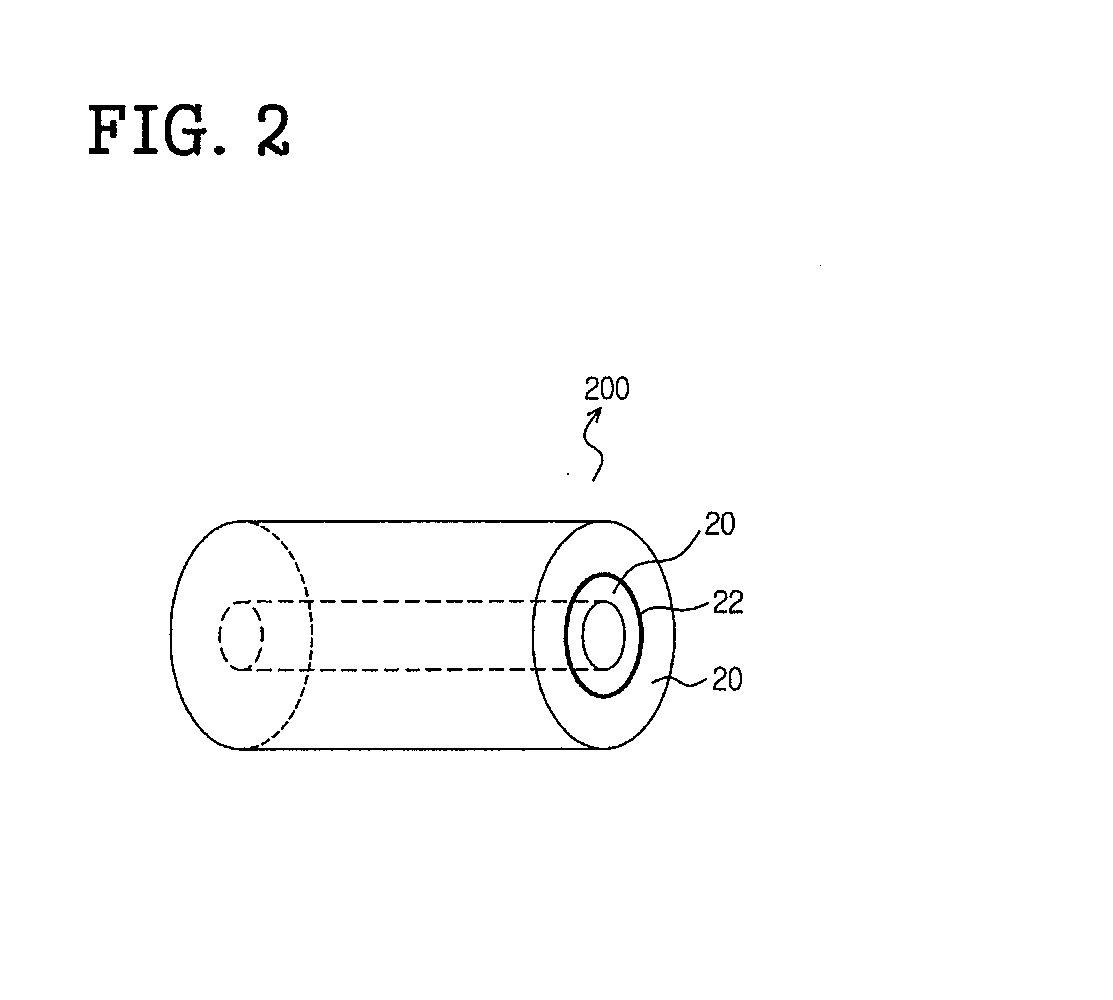
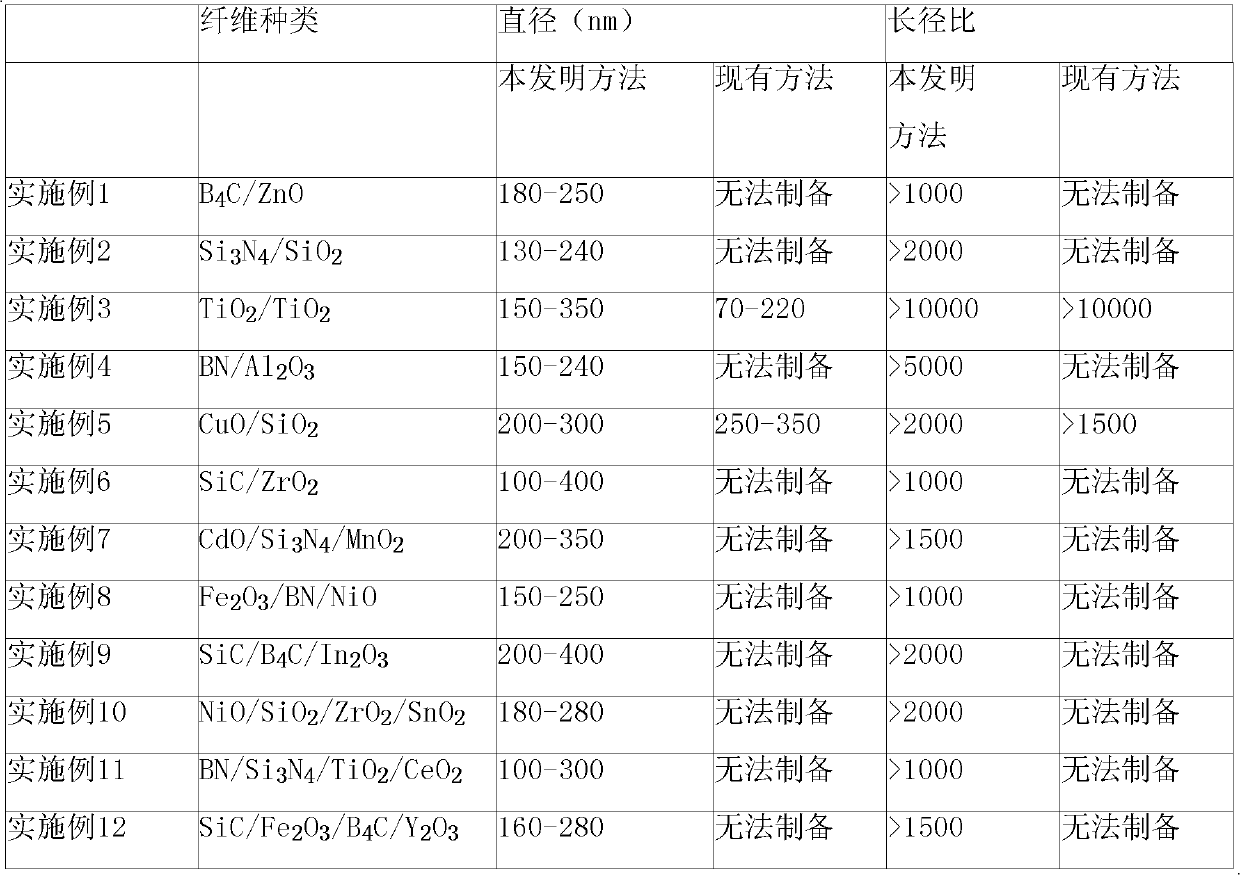
Functional polymer nano composite material and preparation method and uses thereof
ActiveCN101161705AEvenly dispersedStable structureBiocideOther chemical processesEcological environmentPolymer solution
The present invention relates to a polymer nano-composite of the functional inorganic nano-particle with intermingle prepared by electrospinning method, and the use of the composite. The precursory sol of the functional inorganic nano-particle is prepared by the sol-gel method, and is mixed with the polymer solution to form spinning fluid, adding precursor of dopant if necessary, and then the mixed spinning fluid is sprayed on to the electric collecting board with the action of the electric field force by electrospinning method to obtain functional polymer nano-composite with intermingle. The equipment of the invention is simple, the operation is easy, the components, structure and characteristics of the composite is easy to control, the structure is stable, the inorganic nano-particle is dispersed uniformly. According to the difference of the functionality of the inorganic nano-particles, the composite can be used in conducting material, antistatic material, magnetic material, electrochromic material, photocatalysis and ecology environment material, antibiosis material and biomaterial.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
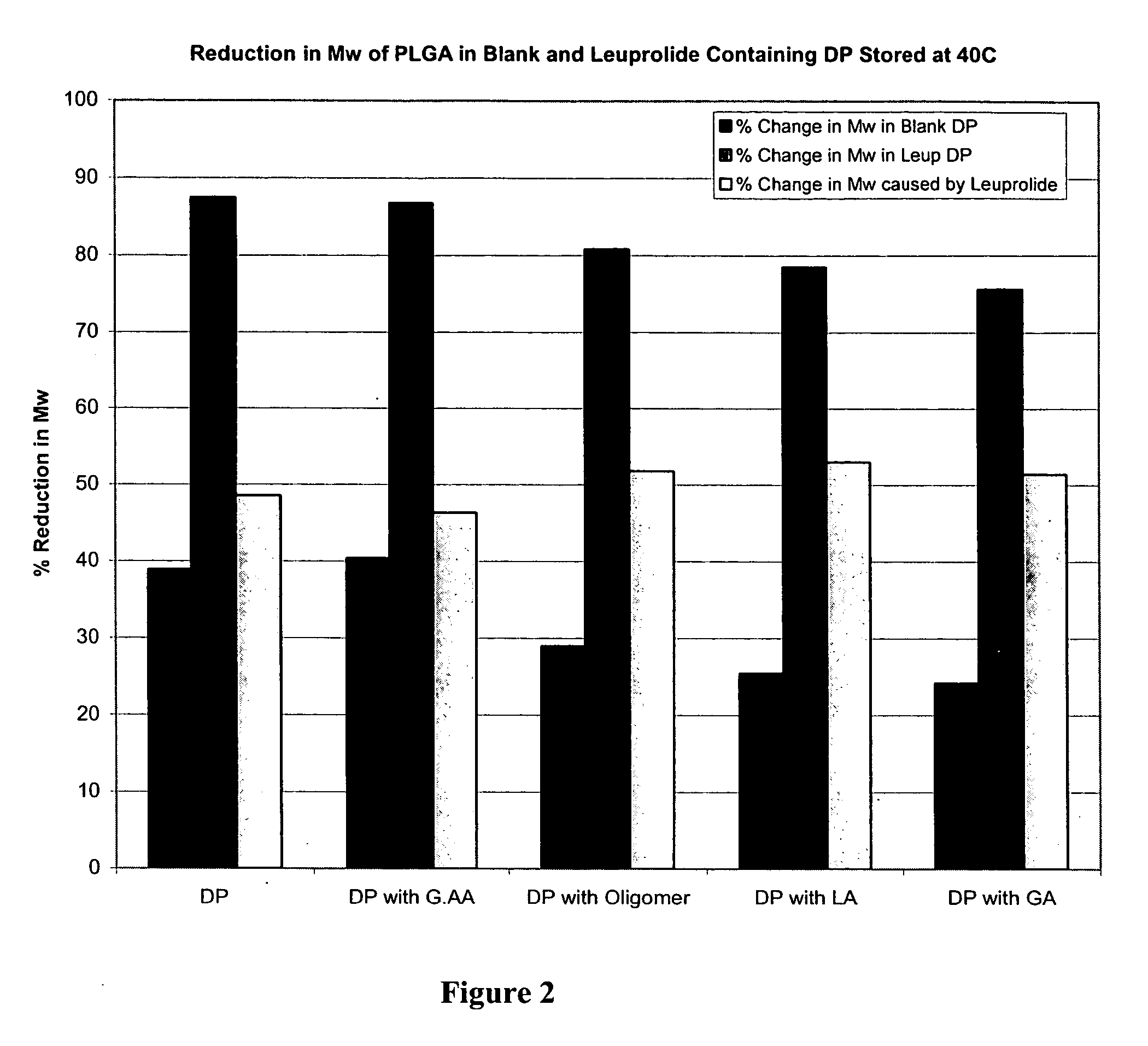
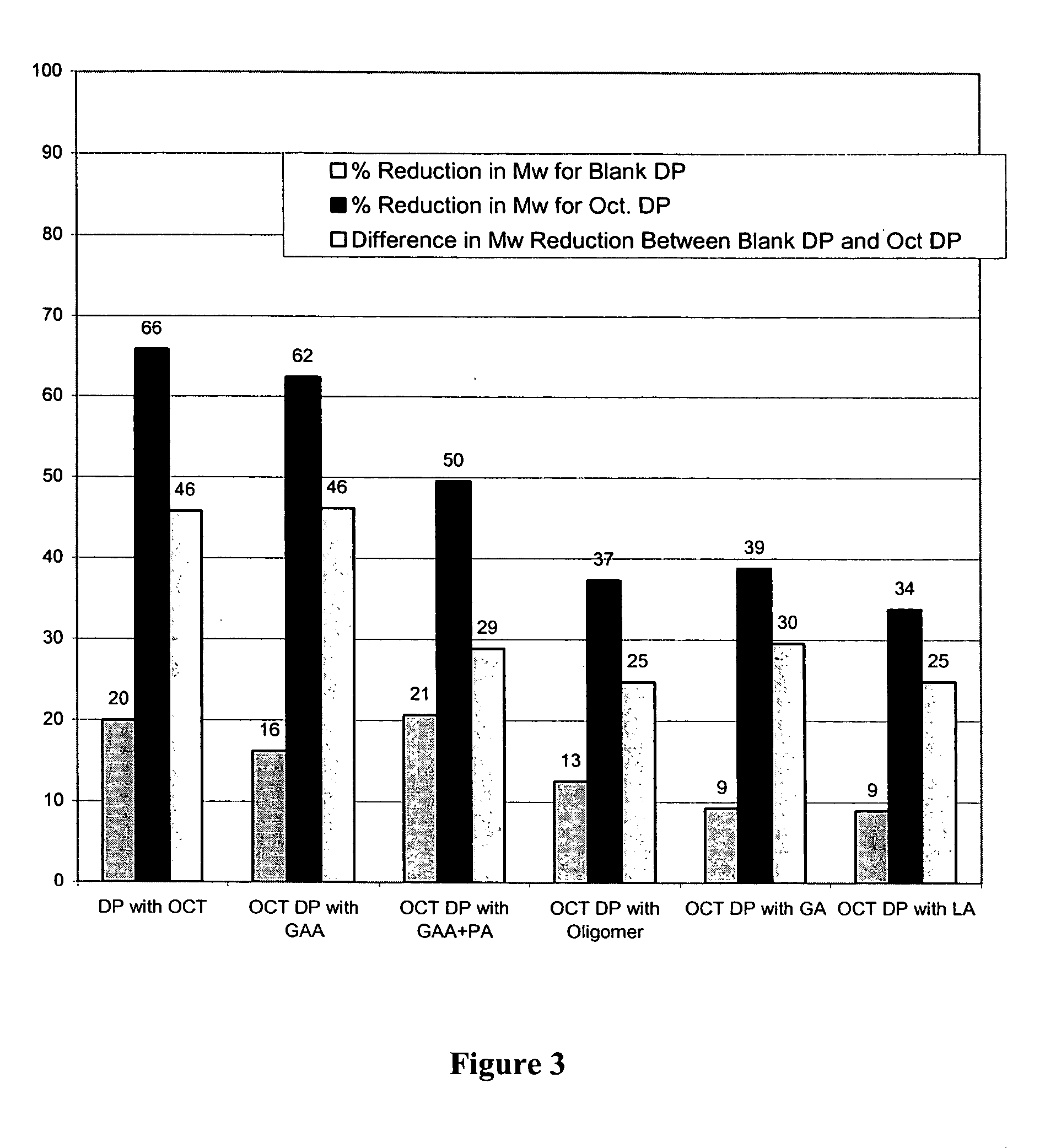
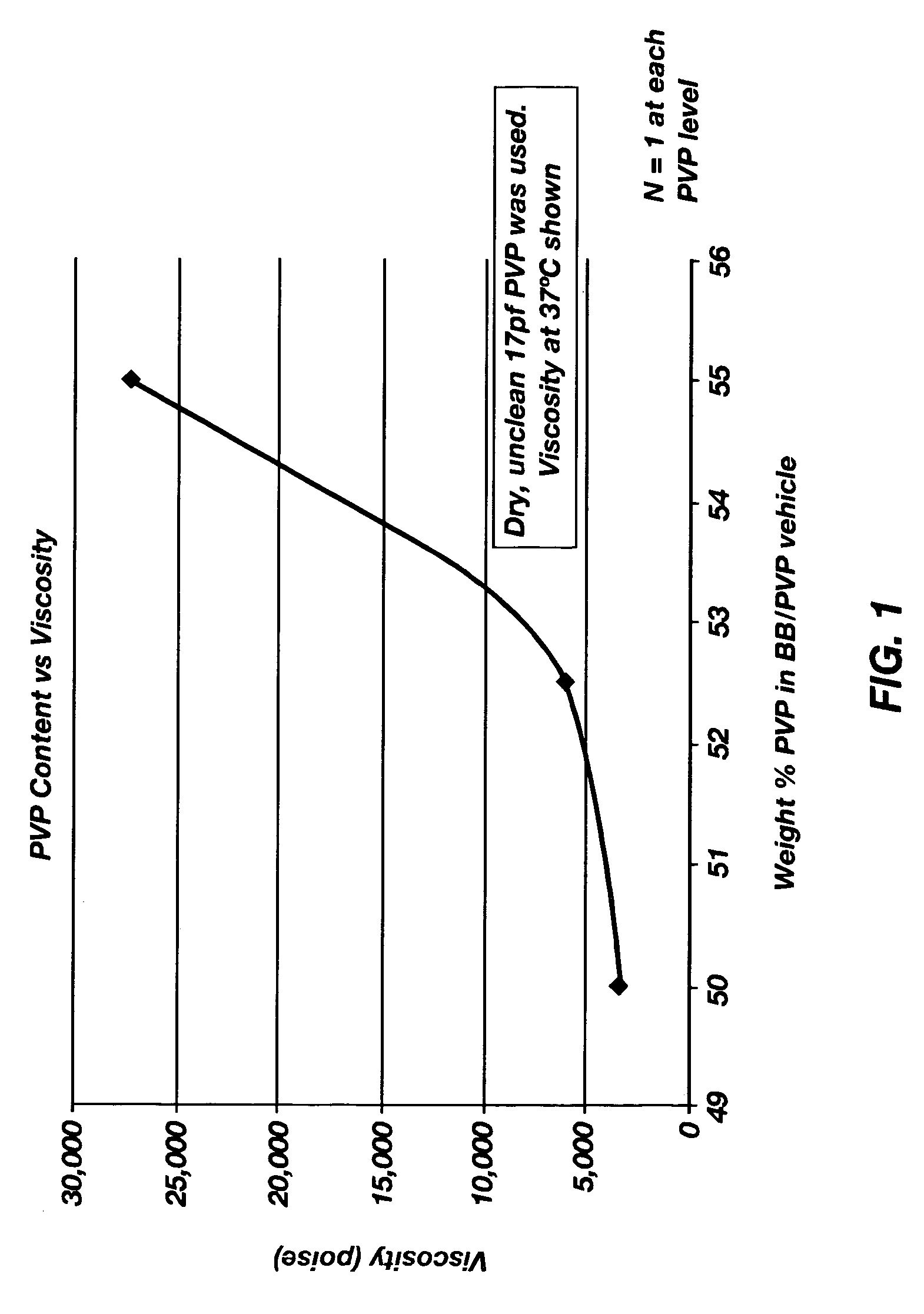
Prevention of molecular weight reduction of the polymer, impurity formation and gelling in polymer compositions
ActiveUS20050042294A1Reduce and eliminate molecular weight reductionReduce molecular weightPowder deliveryBiocideSolubilityActive agent
Polymer and drug containing compositions and method of preparing such compositions are disclosed. The dispersed phase formulation has a polymer, a pharmaceutically or biologically active agent and a small fraction of low pKa acid additive. Stable, filter sterilizable, non-gelling solutions containing GnRH analogues at least at levels typically used in sustained release formulations and a method of increasing solubility of a high level of a GnRH analogue or a freeze-dried antgonist of GnRH in a polymer containing solution are also disclosed. The amount of the acid additive in the polymer solution is such that it is sufficient to increase the solubility of the high level of the GnRH analogue in the polymer solution without affecting the release characteristics of the microspheres prepared therefrom.
Owner:OAKWOOD LAB LLC
Electrospinning of fine hollow fibers
A method for electrospinning nanofibers having a core-sheath, tubular, or composite structure is disclosed. The process uses a spinneret having first and second capillaries that channel first and second fluids in the spinneret, the second capillary surrounding the first. A high voltage is applied between the spinneret and a spaced conductive collector. In one embodiment, the first fluid is a mineral oil and the second fluid is a polymeric solution that may include a polymer, a catalyst, a solvent, and a sol-gel precursor. The as-spun nanofiber includes an oil core and a composite sheath. The oil may be removed to produce a composite tubular fiber or the polymer and oil may be removed by calcination to produce a ceramic tubular fiber. In other embodiments, miscible fluids are used to produce porous nanofibers, selected additives functionalize the surfaces of the nanofibers and / or conjugated polymers are used.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
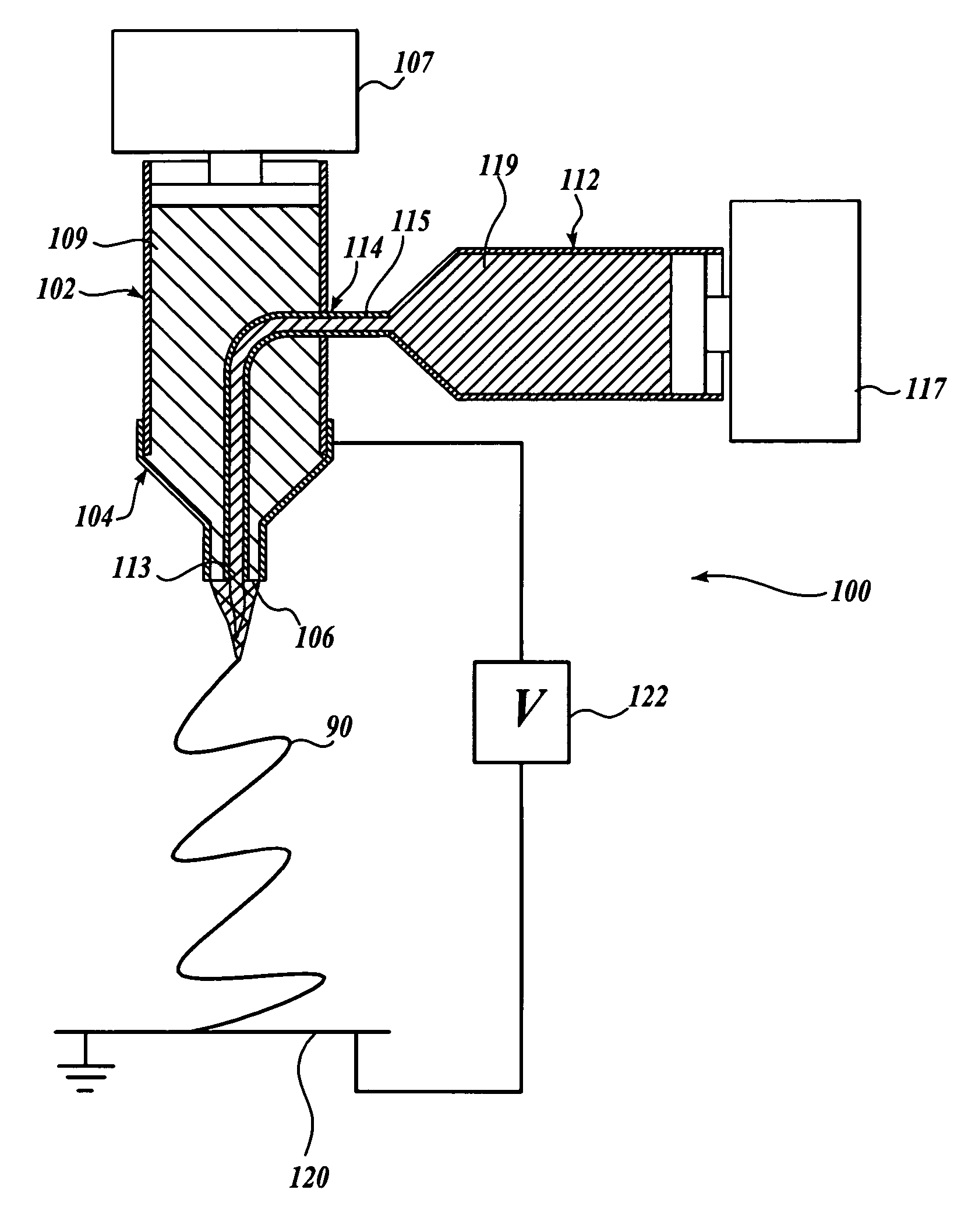
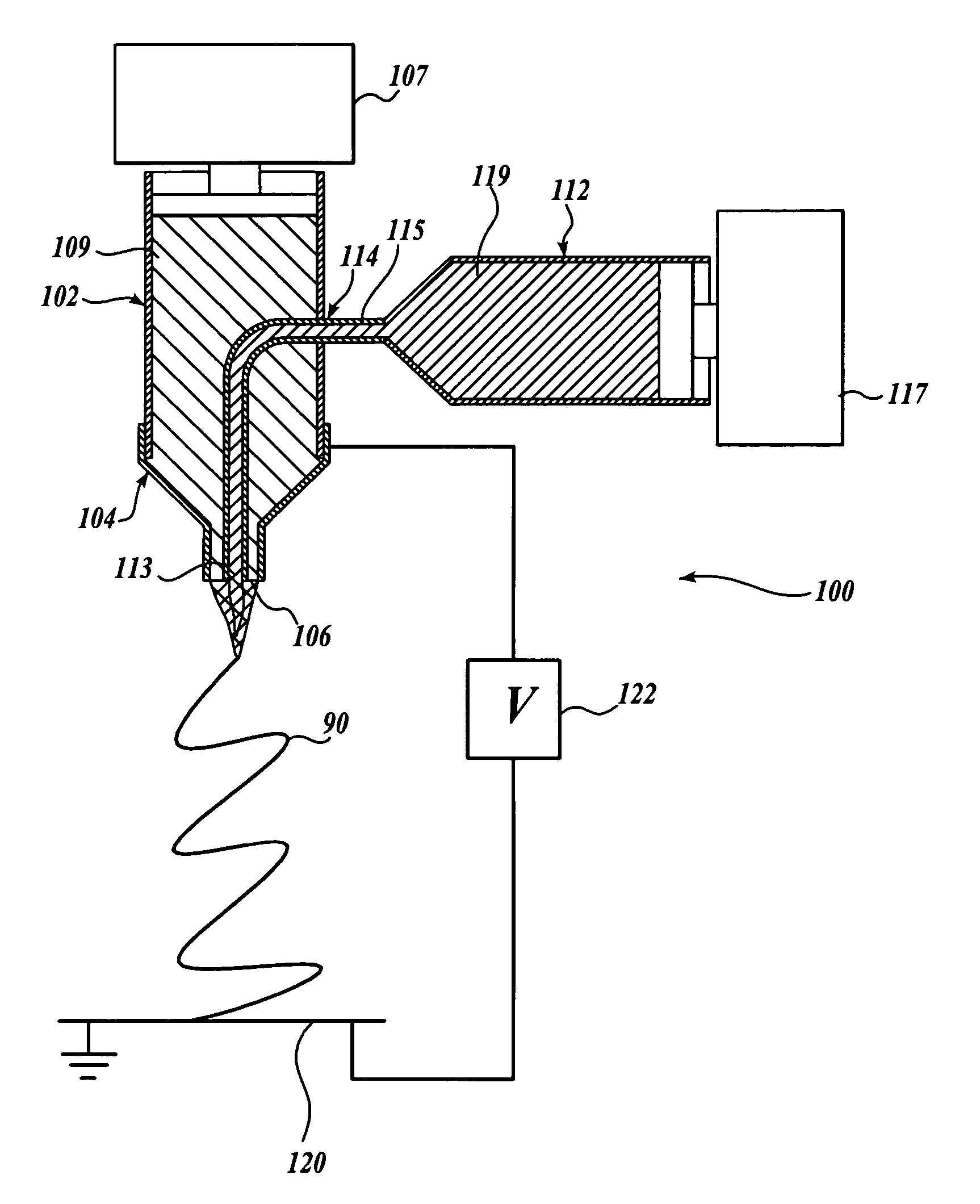
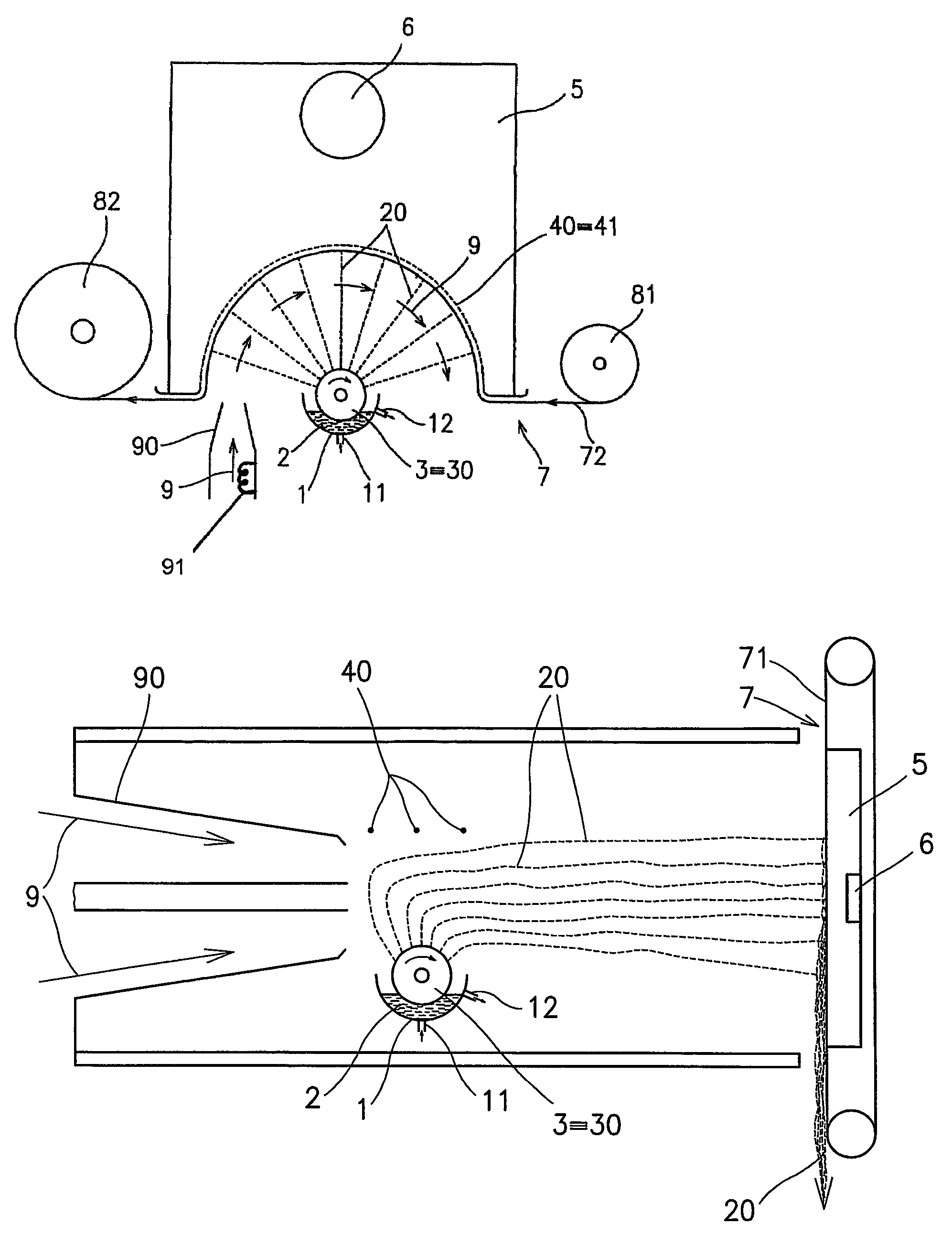
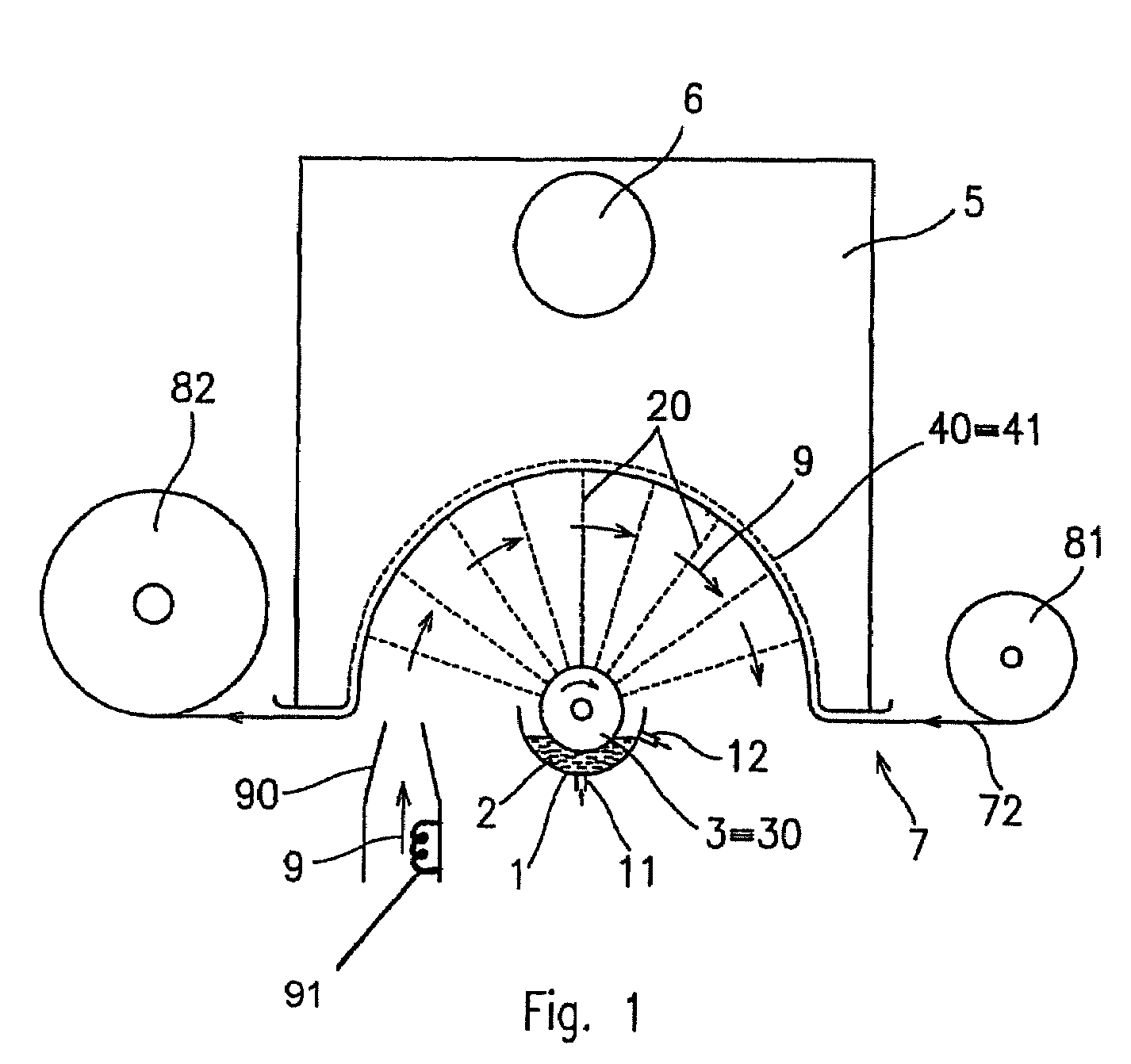
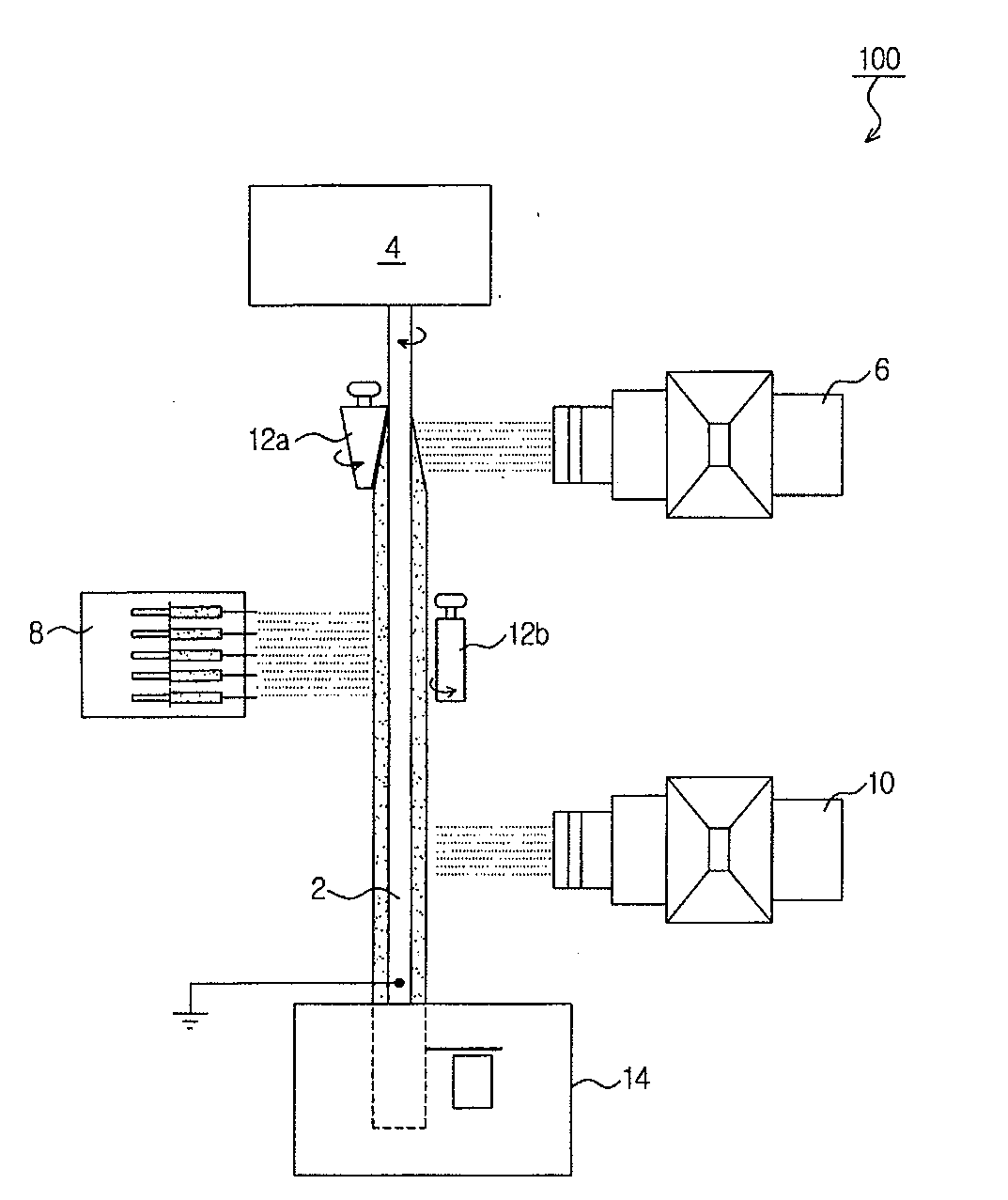
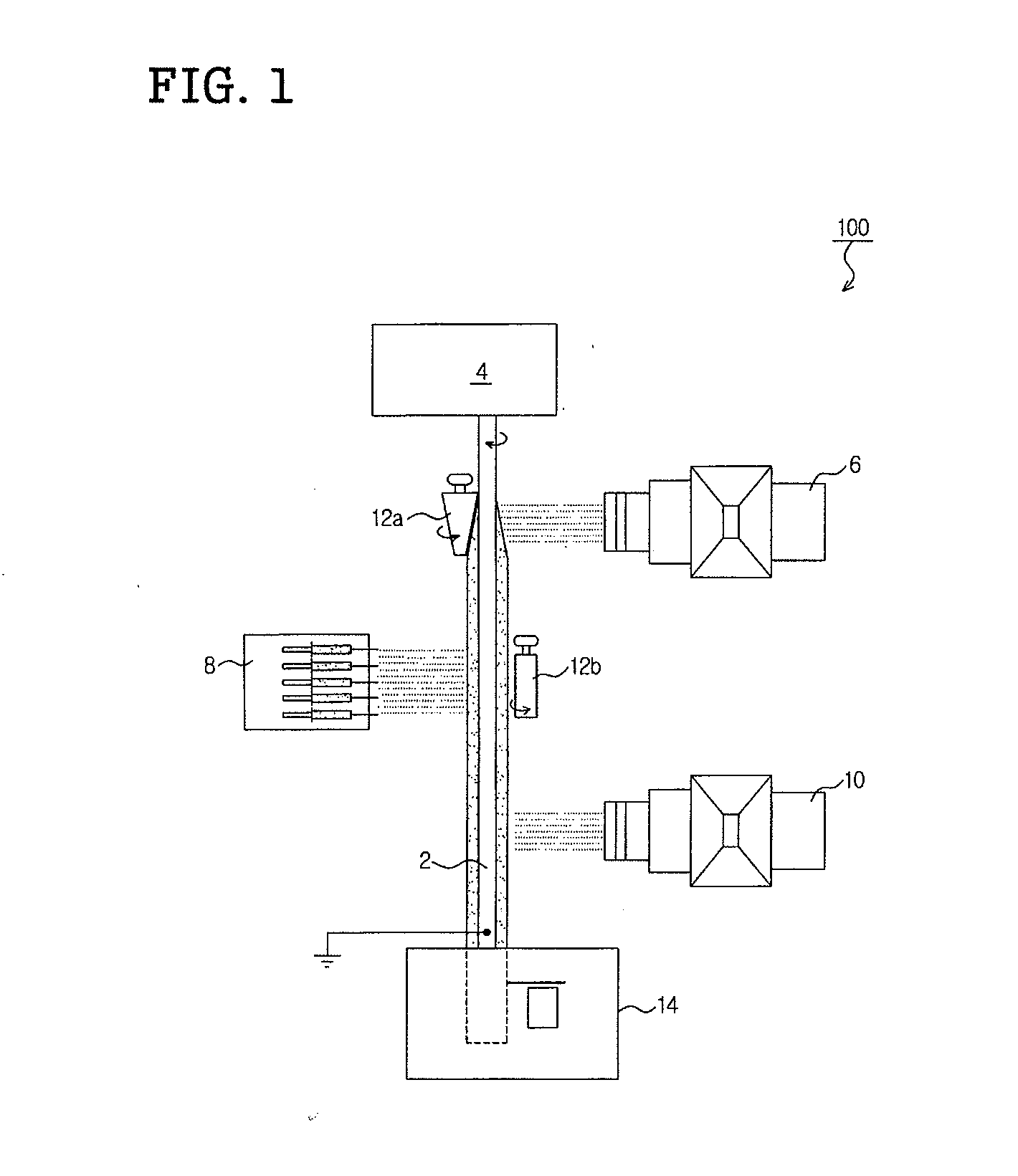
Method of nanofibres production from a polymer solution using electrostatic spinning and a device for carrying out the method
ActiveUS7585437B2High quality and uniformity of layerSpinnerette packsNanotechnologyPotential differenceElectrospinning
A method of nanofibers production from a polymer solution uses electrostatic spinning in an electric field created by a potential difference between a charged electrode and a counter electrode. The polymer solution for spinning is supplied into the electric field using the surface of a rotating charged electrode. On a part of the circumference of the charged electrode near to the counter electrode, a spinning surface is created for attaining a high spinning capacity. In a device for carrying out the method, the charged electrode is pivoted and part of its circumference is immersed in the polymer solution. The free part of the circumference of the charged electrode is positioned opposite the counter electrode.
Owner:TECHNICKA UNIVEZITA V LIBERCI
Polymer compositions containing colloids of silver salts
The present invention relates to antimicrobial compositions, methods for the production of these compositions, and use of these compositions with medical devices, such as catheters, and implants. The compositions of the present invention advantageously provide varying release kinetics for the active ions in the compositions due to the different water solubilities of the ions, allowing antimicrobial release profiles to be tailored for a given application and providing for sustained antimicrobial activity over time. More particularly, the invention relates to polymer compositions containing colloids comprised of salts of one or more oligodynamic metal, such as silver. The process of the invention includes mixing a solution of one or more oligodynamic metal salts with a polymer solution or dispersion and precipitating a colloid of the salts by addition of other salts to the solution which react with some or all of the first metal salts. The compositions can be incorporated into articles or can be employed as a coating on articles such as medical devices.
Owner:CR BARD INC
Static spinning device and its industrial use
InactiveCN1715463AHigh speedImprove mechanical propertiesFilament/thread formingElectrospinningMagnification
The present invention provides electrostatic spinning apparatus and its industrial application. The apparatus includes polymer solution conveying machine, spinning nozzle device connected to the outlet of the polymer solution conveying machine, spinning bath below the spinning nozzle device, fiber turning guide roller set inside the spinning bath and electrodes set on the spinning nozzle device and the spinning bath. The apparatus of the present invention is used in spinning polymer, and has greatly raised wet spinning speed, great fiber drafting magnification, well oriented fiber molecule chain, compact fiber structure, greatly raised mechanical performance of fiber, wide solvent selecting range, simplified electrostatic spinning equipment, raised solvent recovering rate and less environmental pollution caused by the solvent.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Hemostatic wound dressings and methods of making same
The present invention is directed to methods of making wound dressings that include the steps of contacting a fabric substrate having properties effective for use as a hemostat and containing fibers prepared from a biocompatible polymer, with a solution of a water-soluble or water-swellable biocompatible polymer under conditions effective to distribute the polymer solution substantially homogenously on and through the fabric substrate, transferring the fabric substrate to a lyophilization unit under conditions effective to maintain the homogeneous distribution on and throughout the substrate, and lyophilizing the fabric having the polymer solution distributed on and there through.
Owner:ETHICON INC
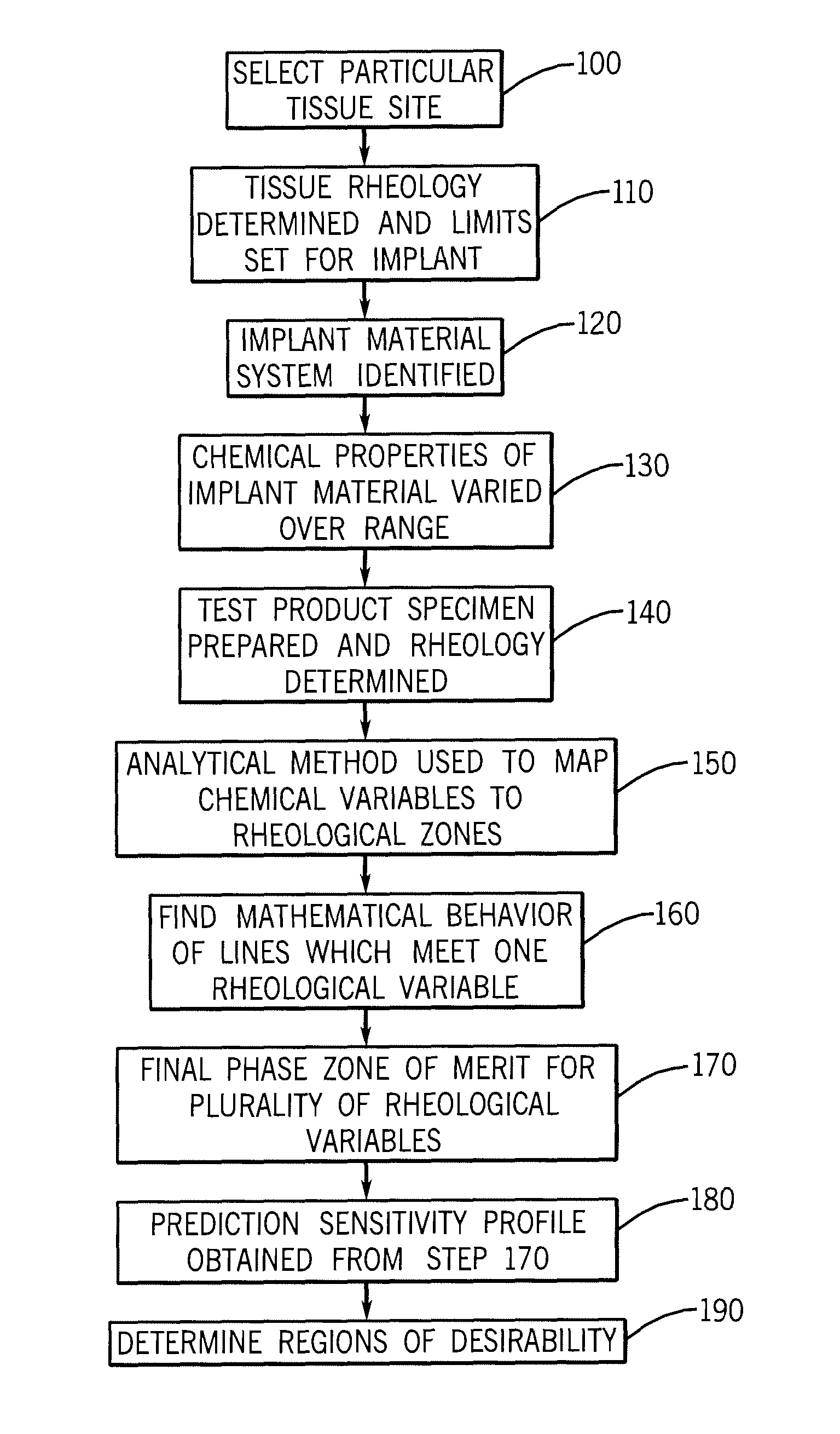
Implantation Compositions for Use in Tissue Augmentation
InactiveUS20100041788A1Good compatibilityMinimized immuno-histo tissue responseOrganic active ingredientsSurgical adhesivesPolymer solutionPolysaccharide
A composition of matter and method for preparation of a tissue augmentation material. A polysaccharide gel composition is prepared with rheological properties selected for a particular selected application. The method includes preparing a polymeric polysaccharide in a buffer to create a polymer solution or gel suspending properties in the gel and selecting a rheology profile for the desired tissue region.
Owner:MERZ AESTHETICS
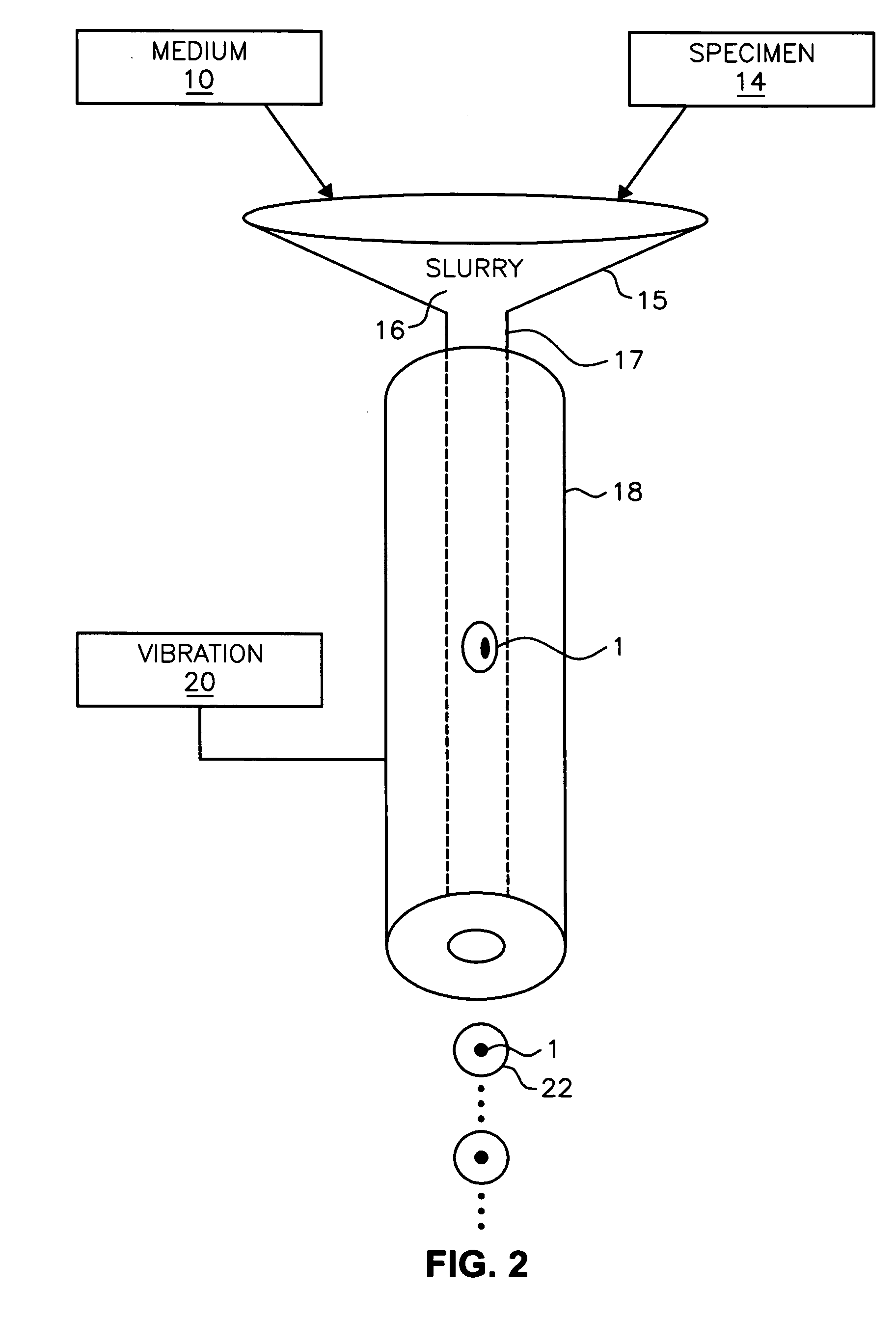
System and method for preparation of cells for 3D image acquisition
InactiveUS20050085708A1Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPolymer science3d image
The present invention provides a method for embedding particles in a solid structure including the steps of extruding a slurry of particles and a polymeric solution into a linear polymer medium having particles embedded into a polymer portion; and curing the polymer portion of the linear polymer medium.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON +1
Solvent/polymer solutions as suspension vehicles
A nonaqueous, single-phase vehicle that is capable of suspending an active agent. The nonaqueous, single-phase vehicle includes at least one solvent and at least one polymer and is formulated to exhibit phase separation upon contact with an aqueous environment. The at least one solvent may be selected from the group consisting of benzyl benzoate, decanol, ethyl hexyl lactate, and mixtures thereof and the at least one polymer may be selected from the group consisting of a polyester, pyrrolidone, ester of an unsaturated alcohol, ether of an unsaturated alcohol, polyoxyethylenepolyoxypropylene block copolymer, and mixtures thereof. In one embodiment, the at least one solvent is benzyl benzoate and the at least one polymer is polyvinylpyrrolidone. A stable, nonaqueous suspension formulation that includes the nonaqueous, single-phase vehicle and an active agent, and a method of forming the same, are also disclosed.
Owner:INTARCIA THERAPEUTICS INC
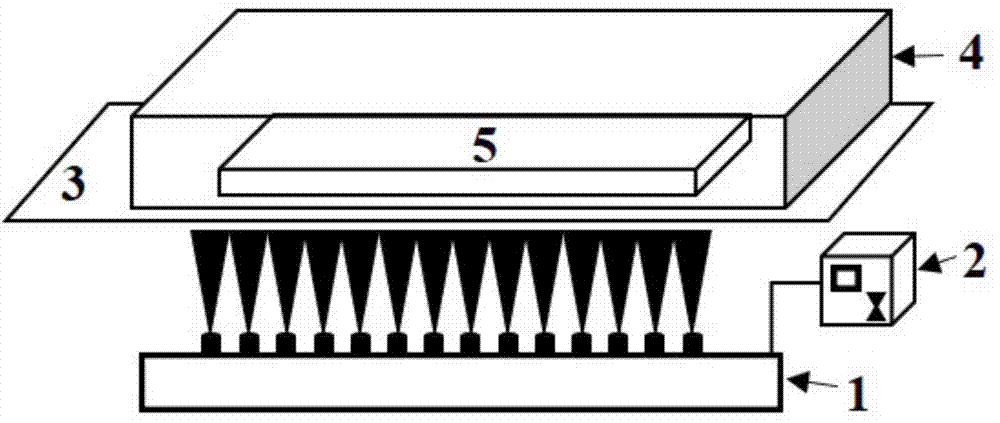
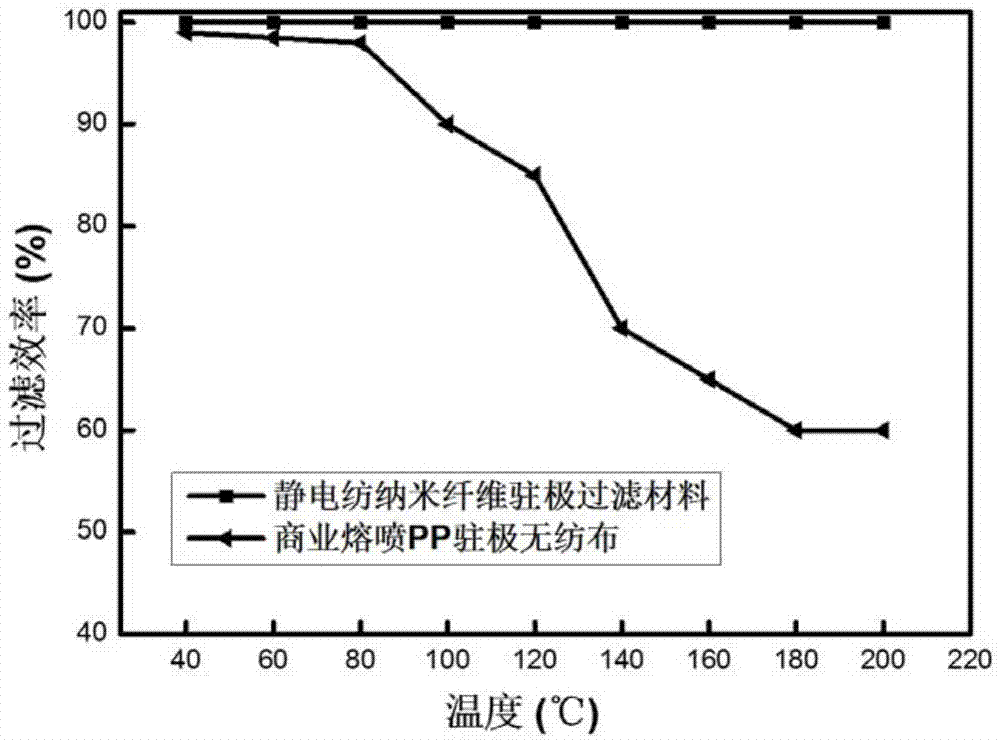
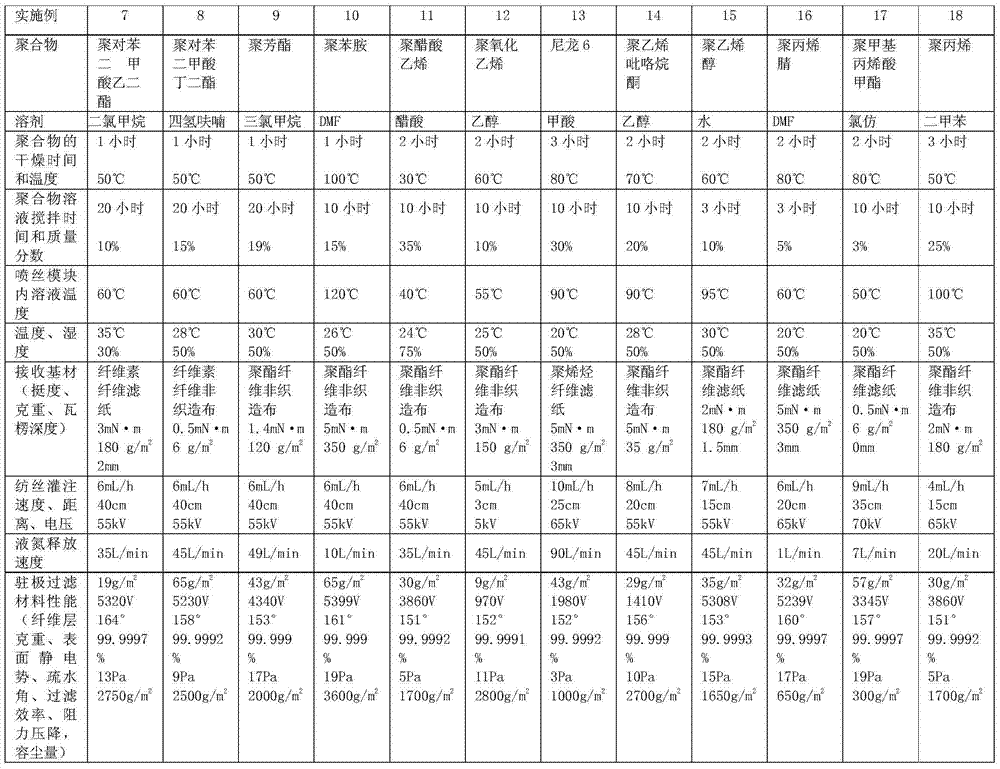
Electrospinning nano-fiber electret filtering material and its preparation method
ActiveCN104289042AHigh surface electrostatic potentialHigh super strong electrostatic adsorption performanceSynthetic resin layered productsFiltration separationPorosityFiber
The invention relates to an electrospinning nano-fiber electret filtering material and its preparation method. The high-efficiency and low-resistsance nano-fiber electret filtering material having no interfibrous adhesion and having a fluffy three-dimensional netted intercommunication structure is prepared through controlling the component and the temperatures of a polymer solution in an electrospinning process and carrying out one-step forming in the nano-fiber forming rapid cooling process, wherein the gram weight of the above nanofiber layer is 0.01-70g / m<2>, and the porosity is not less than 80%. The surface electrostatic potential of the nano-fiber electret filtering material is 800-6000V, and the surface charges have lasting storage stability, the hydrophobic angle is greater than 150DEG, the filtering efficiency of the material to particles of 0.006-1[mu]m can reach above 99.999%, the piezoresistance is less than 20Pa, and the dust containing capacity is 300-3600g / m<2>. The preparation method is simple, and the filtering material has wide application prospects in the fields of individual protection mouth mask filtration, indoor air purification and filtration, and high efficiency / ultrahigh efficiency air filtration.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Implantable drug delivery prosthesis
An apparatus and associated method for delivering a therapeutic substance to a vascular lumen, using an implantable prosthesis, such as a stent, which has grooves or trenches formed thereon. The grooves are formed on specific regions of the stent struts to increase the flexibility of the stent. The grooves also provide a therapeutic material carrying capability for treating intravascular ailments, such as instent restenosis and thrombosis. The therapeutic material loading of the grooves can be accomplished in several ways. For example, a pure therapeutic material or a pre-mixed material with a polymer solution, which enhances the adhesion properties of the material, may be deposited directly in to the grooves using conventional spray or modified dip techniques. In another example, a microextruded monofilament therapeutic material can be wound about the stent, such that the monofilament becomes embedded in the grooves.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Low Viscosity Liquid Polymeric Delivery System
InactiveUS20090181068A1Heavy metal active ingredientsNervous disorderPolymer sciencePolymer solution
Owner:DUNN RES & CONSULTING
Integral bi-layer separator-electrode construction for lithium-ion batteries
InactiveUS20120231321A1Improve temperature resistanceImprove the immunityFinal product manufacturePrimary cellsEvaporationSlurry
A porous bi-layer separator composed of a first layer with a contacting array of non-conducting particles overlaid with a second layer of a microporous polymer layer, may be fabricated on the electrode surface of the anode of a lithium-ion battery to form an integral electrode-separator construction. The bi-layer separator may prevent development of a direct electronic path between the anode and cathode of the battery while accommodating electrolyte solution and enabling passage of lithium ions. Such an integral separator should be mechanically robust and tolerant of elevated temperatures. Exemplary bi-layer separators may be fabricated by sequential deposition of solvent-containing slurries and polymer solutions with subsequent controlled evaporation of solvent. The elevated temperature performance of lithium-ion battery cells incorporating such integral electrode-bi-layer separators was demonstrated to exceed the performance of similar cells using commercial and experimental single layer polymer separators.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method for making a porous Polymeric material
Porous polymers having a plurality of openings or chambers that are highly convoluted, with each chamber being defined by multiple, thin, flat partitions are produced by a new gel enhanced phase separation technique. In a preferred embodiment, a second solvent is added to a polymer solution, the second solvent causing the solution to gel. The gel can then be shaped as needed. Subsequent solvent extraction leaves the porous polymeric body of defined shape. The porous polymers have utility as medical prostheses, the porosity permitting ingrowth of neighboring tissue. The present technique also enhances shape-making capability, for example, of bifurcated vascular grafts, which feature a common entrance region but two or more exit regions.
Owner:KENSEY NASH CORP
Temperature-resistant salt-resistant efficient gel, and preparation and use thereof
InactiveCN101475667AImprove solubilityGood viscosity increasing effectDrilling compositionSulfite saltAging resistance
The invention discloses a temperature resistant salt tolerant high efficiency gel and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method is characterized in that the preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing a comb-shaped associated copolymer PAH containing macromonomers and functional hydrophobic monomers into an aqueous solution having the concentration of 0.1 to 4g / L, the crosslinking agent concentration of 0.01 to 1.0g / L, the surfactant concentration of 0.01 to 8mmol / L and the sodium sulfite thermal stabilizer concentration of 0.005 to 1.0g / L; adding the aqueous solution into a mixing container with a stirring device; stirring the aqueous solution evenly at the room temperature; regulating the pH value of the solution to be equal to between 4 and 11, and obtaining a temperature resistant salt tolerant high efficiency gel polymer solution system used for tertiary oil recovery and scavenge, displacement modification, profile modification or water shutoff. The polymer solution system has micro-crosslinking to form the gel during the flowage inside the oil reservoir. The gel has good elasticity, not easy dehydration, stable gelling performance, and excellent tackification, temperature resistance, salt tolerance, shearing resistance and ageing resistance.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
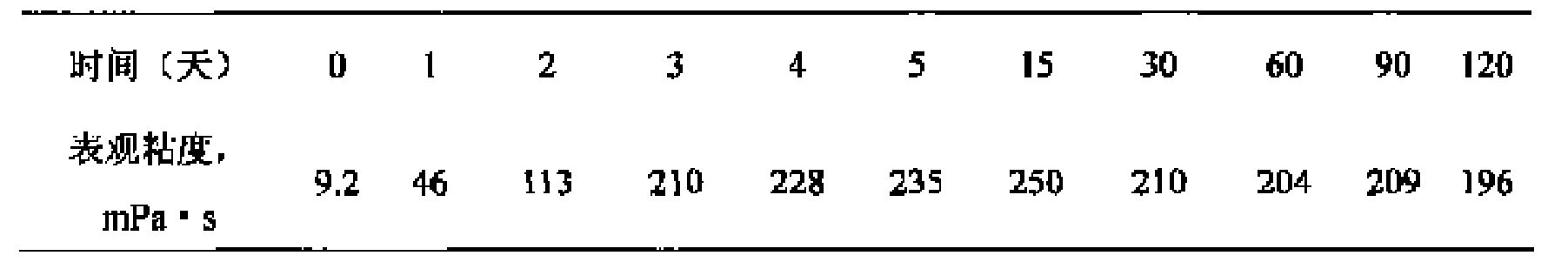
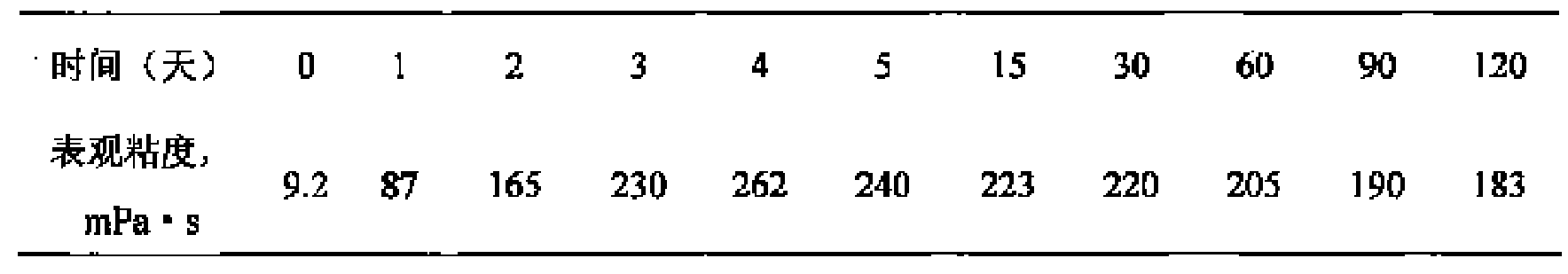
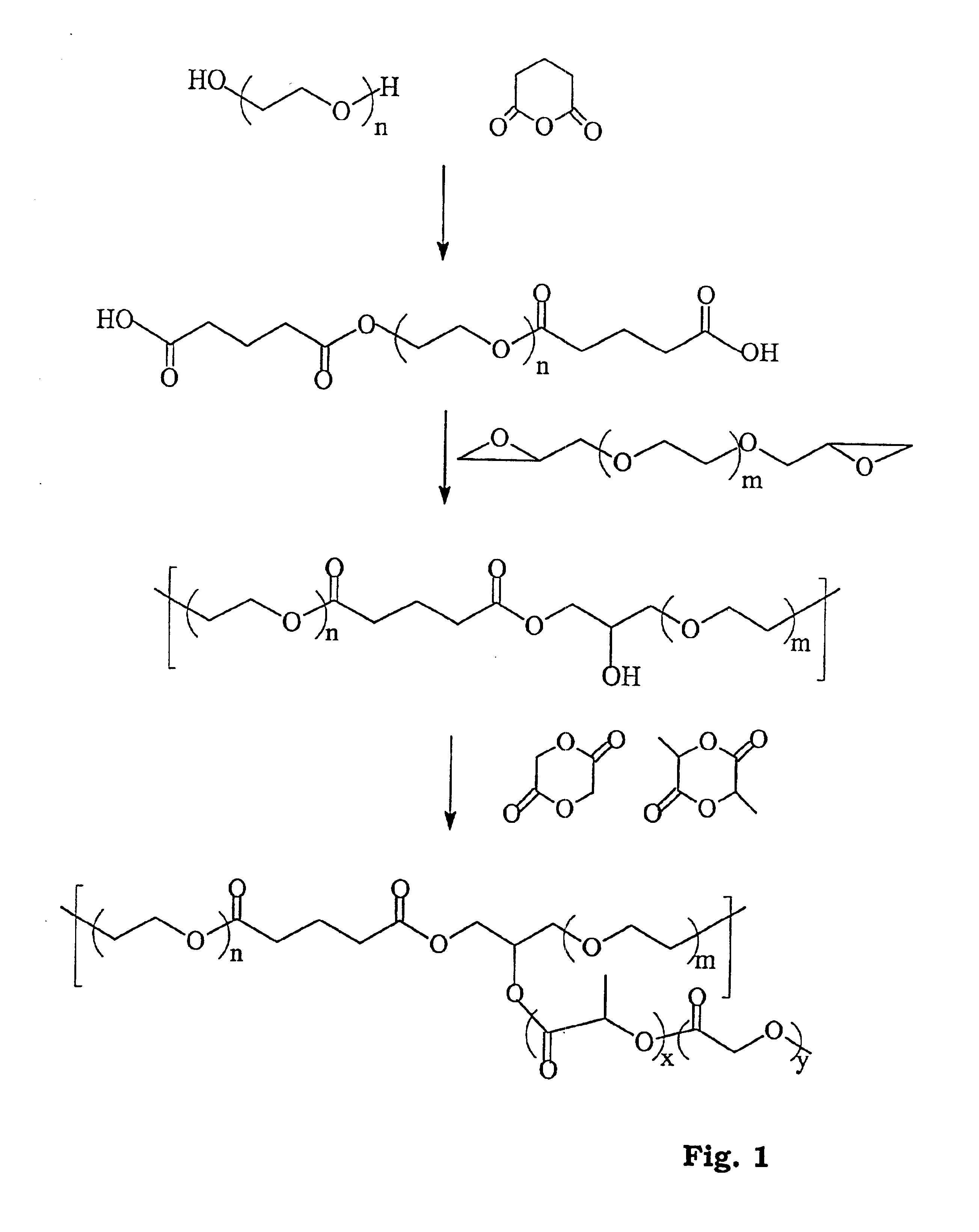
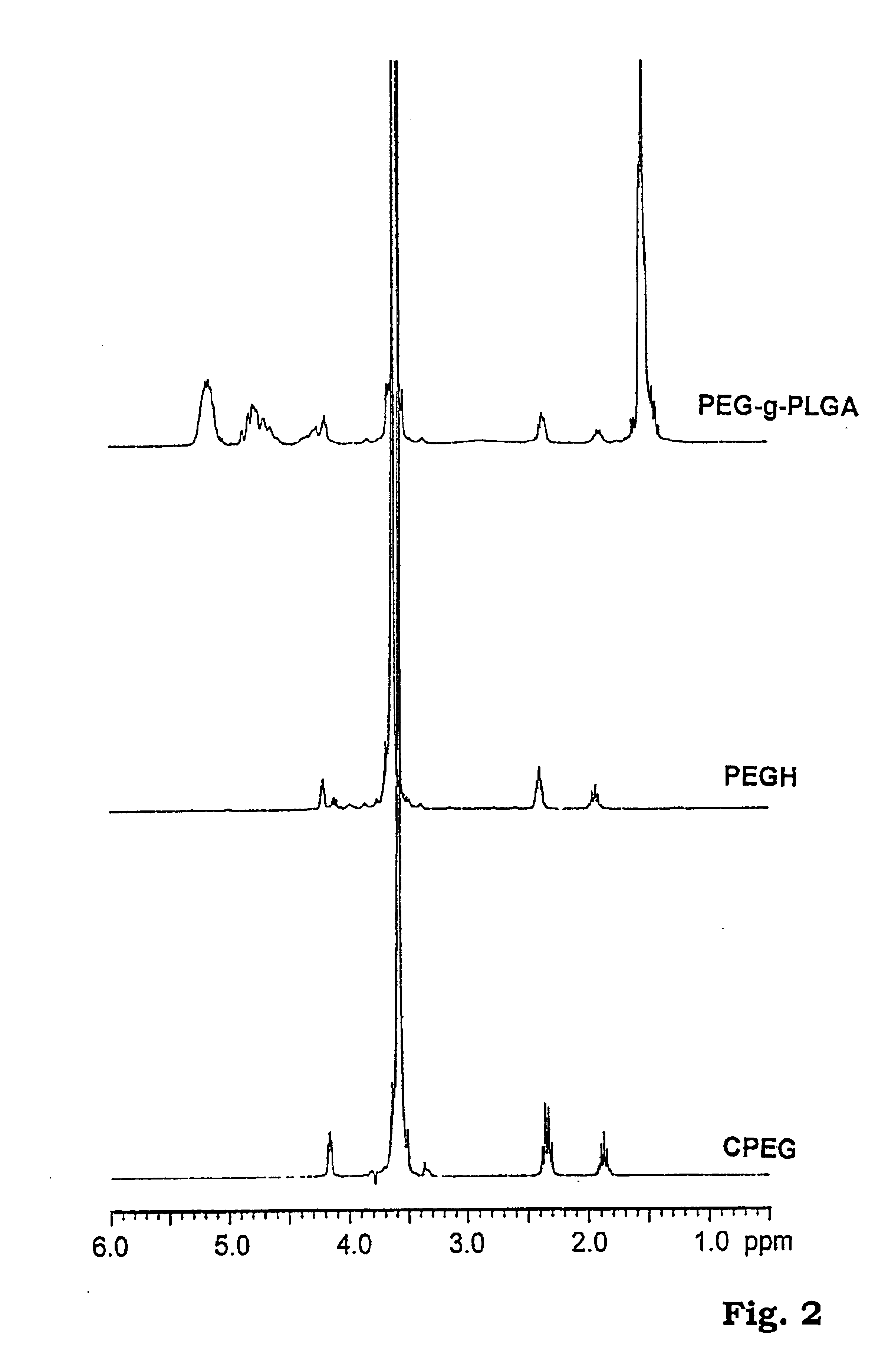
Thermogelling biodegradable aqueous polymer solution
InactiveUS6841617B2Low viscosityEasily manipulatedPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsPolymer sciencePolyethylene glycol
Disclosed is a thermogelling biodegradable aqueous polymer solution useful in providing a bioactive agent delivery system. The present invention provides a thermogelling biodegradable aqueous polymer solution with a polyethylene glycol (PEG) block and a biodegradable polyester block, where the blocks are linked to form a polymer of a general structure comprising the formula of An(B), where n is greater than 2 and A is selected from the group consisting of a polyethylene glycol block and a biodegradable polyester block, B is selected from the group consisting of a polyethylene glycol block and a biodegradable polyester block, and A is different from B.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Umbrella-shaped electrostatic spinning sprayer and electrostatic spinning method
ActiveCN103088443AOvercoming easy blockageOvercome efficiencySpinnerette packsFilament/thread formingNumerical controlFiber
The invention relates to an umbrella-shaped electrostatic spinning sprayer and an electrostatic spinning method. The sprayer comprises an umbrella-shaped spinning nozzle, a numerical control type infusion device and a solution collecting groove, wherein the numerical control type infusion device mainly comprises a solution propeller and a controller; the middle of the umbrella-shaped spinning nozzle is provided with a cylindrical hollow portion, and an output end of the solution propeller is placed into the cylindrical hollow portion of the umbrella-shaped spinning nozzle; the controller controls flow velocity and flow of spinning solutions; and the solution collecting groove is placed in the bottom of the umbrella-shaped spinning nozzle. The electrostatic spinning method comprises that a binding post on the umbrella-shaped spinning nozzle is connected with a high-voltage positive electrode, conducting polymer solutions are continuously added to the umbrella-shaped spinning nozzle which is horizontally placed through the numerical control type infusion device, electrostatic spinning is started, collection is achieved through a collecting device, and nano-fibers are formed. The sprayer avoids blocking phenomena, and is easy to clean and good in stability; and the electrostatic spinning method improves production efficiency and the yield of electrostatic spinning.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Composite fiber filter comprising nan0-materials, and manufacturing method and apparatus thereof
InactiveUS20080217807A1Improve efficiencyPronounced antibacterial activityLayered productsWood working apparatusYarnElectrospinning
Disclosed herein is a method for manufacturing a composite fiber filter having high efficiency and high functionality, the method comprising: melt-spinning microfiber yarns on a forming rod, which is made of a conductive material, grounded at one end thereof and rotatably driven, using a melt-spinning device, to form on the forming layer a microfiber layer consisting of the microfiber yarns; and electrospinning on the microfiber layer an electrospinnable polymer solution having a given dielectric constant, using an electrospinning device, so as to form on the microfiber layer a nanofiber layers consisting of nanofiber yarns, wherein the microfiber yarns of the microfiber layer and the nanofiber yarns of the nanofiber layer contain silver nanoparticles so as to have an antibacterial function.
Owner:LEE BONG DAE +2
Electrostatic spinning preparation method of ceramic nanometer composite fibers
The invention discloses an electrostatic spinning preparation method of ceramic nanometer composite fibers, comprising the following concrete steps of: firstly, according to volume percentage, weighing 3-10 percent of ceramic nanometer particles with the partilce size of 10-300 nm, 3-20 percent of ceramic precursor, 5-30 percent of spinnable polymer and 40-89 percent of solvent with the total volume of 100 percent; secondly, adding the spinnable polymer into the solvent, heating in water bath and magnetically stirring; thirdly, adding the ceramic precursor into the spinnable polymer solution obtained in the second step, heating in water bath, magnetically stirring and ageing; fourthly, adding the ceramic nanometer particles into the ceramic precursor spinnable solution obtained in the third step, heating at constant temperature in the water bath and forming a spinning solution by carrying out ultrasonic dispersion and constant temperature swelling; fifthly, preparing composite nanometer fibers by the spinning solution according to an electrostatic spinning technology; and sixthly, obtaining the ceramic nanometer composite fibers by sintering the composite nanometer fibers. In the method, raw materials have wide selection conditions and wide optional range.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Electrospun matrices for delivery of hydrophilic and lipophilic compounds
InactiveUS20100166854A1Monocomponent protein artificial filamentElectric discharge heatingFiberCompound a
A method of forming electrospun fiber mats from a plurality of different biodegradable polymeric fibers is provided, in which a plurality of up to six different biodegradable polymer solutions are electrospun together by a method comprising the steps of providing a plurality of up to six different biodegradable polymer solutions each containing at least one biologically or pharmaceutically active material and each in communication with a needle for electrospinning a biodegradable polymer fiber from the solution, and pumping each solution through its respective needle into an electric field under conditions effective to produce uncontrolled charged jet streams of the polymer solutions directed at a grounded rotating mandrel, thereby forming fiber threads of the biologically or pharmaceutically active compounds and polymers in the solutions that are deposited on the mandrel to form an electrospun non-woven fiber mat, wherein the needles are positioned for co-deposition of the fiber threads from the polymer solution streams together on the mandrel to form a fiber mat.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Method for preparing nano cellulose microfibril reinforced polymer composite material
ActiveCN102344685AUniform structureTransparent structureConjugated cellulose/protein artificial filamentsConjugated synthetic polymer artificial filamentsSolubilityFiber
The invention discloses a method for in situ generating a nano cellulose microfibril reinforced polymer composite material, comprising the following steps: using ionic liquid as a primary solvent, dissolving cellulose, or mixing cellulose with other polymers via solution mixing, and controlling the solubility of the cellulosic material in the solvent to maintain naturally occurring nano cellulose microfibril in the cellulosic material, so as to in situ obtain the nano cellulose microfibril reinforced polymer composite material. The nano microfibril can be observed under a transmission microscope obviously, which is different from the completely dissolved cellulose solution. In the preparing process, the dissolving temperature is controlled within 30-150 DEG C, and stirring and vacuum deaeration are used as auxiliary. By controlling the dissolving time, solution concentration and ratio of mixing, a polymer solution containing cellulose microfibril with dimension of 5-300 nanometers can be obtained. The polymer solution can be used for preparing composite material fiber, hollow fibrous membrane, diaphragm, film, gel, porous material and other known applications of enhanced material.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Sustained release and long residing ophthalmic formulation and the process of preparing the same
The present invention relates to sustained release and long residing opthalmic formulation having thermosensitivity, mucoadhesiveness, hydro gel properties and small particle size. The said formulation comprises micelle solution of random block co-polymer having a hydrophobic component and a hydrophillic component of general formula -(X+Y+Z-)m, and at least one hydrophobic drug with the block co-polymer solution. The invention also provides a process of preparing said formulation.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DELHI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com