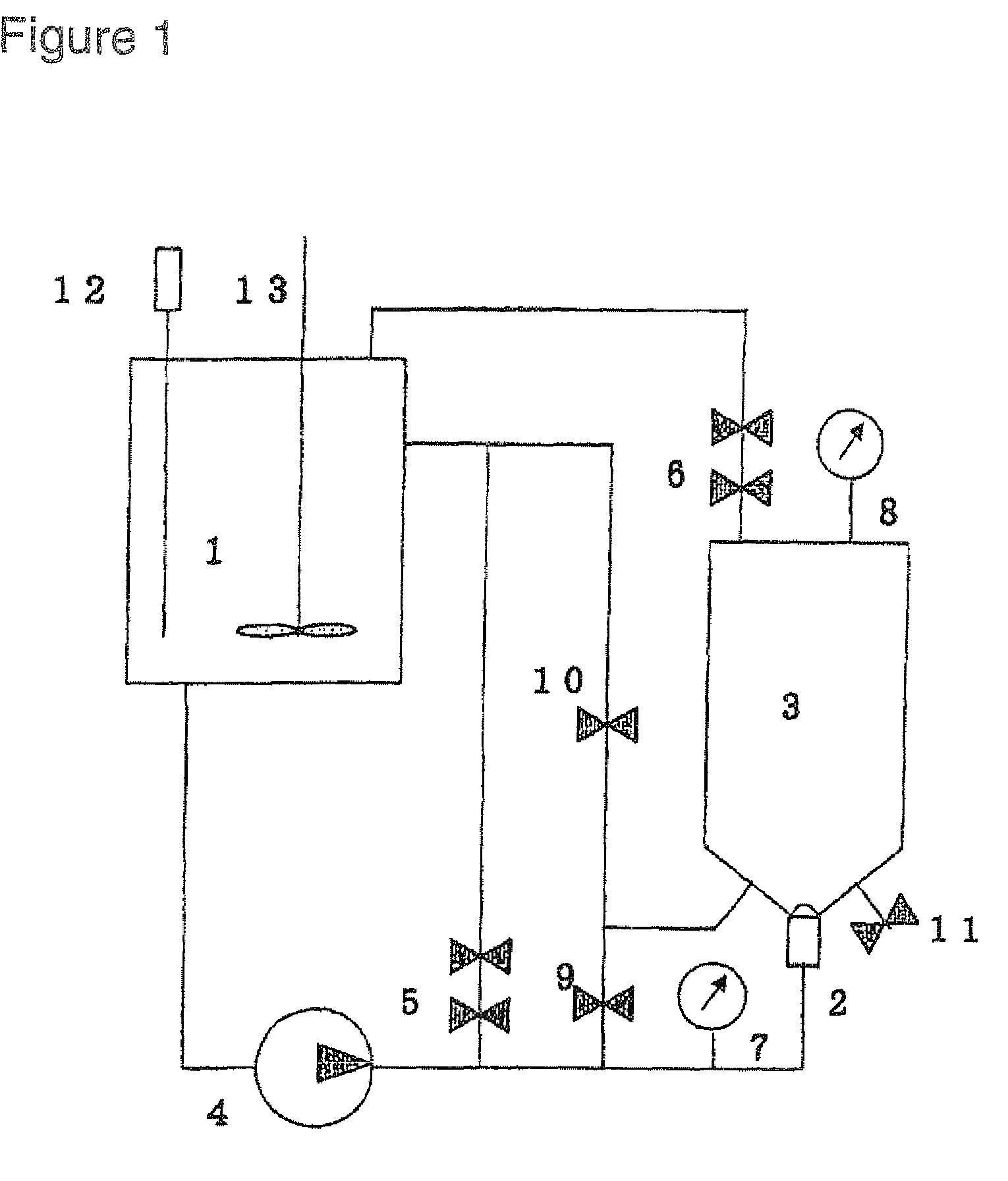
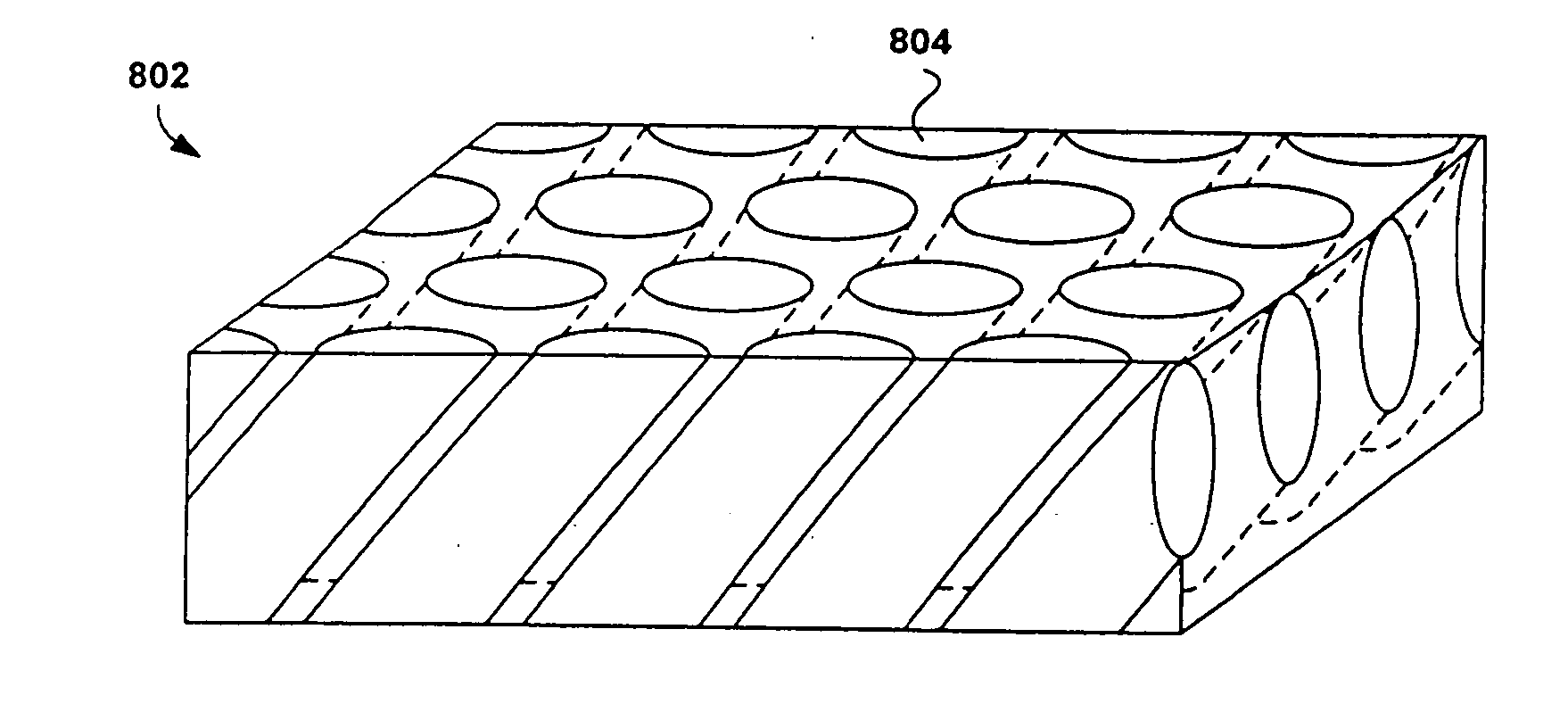
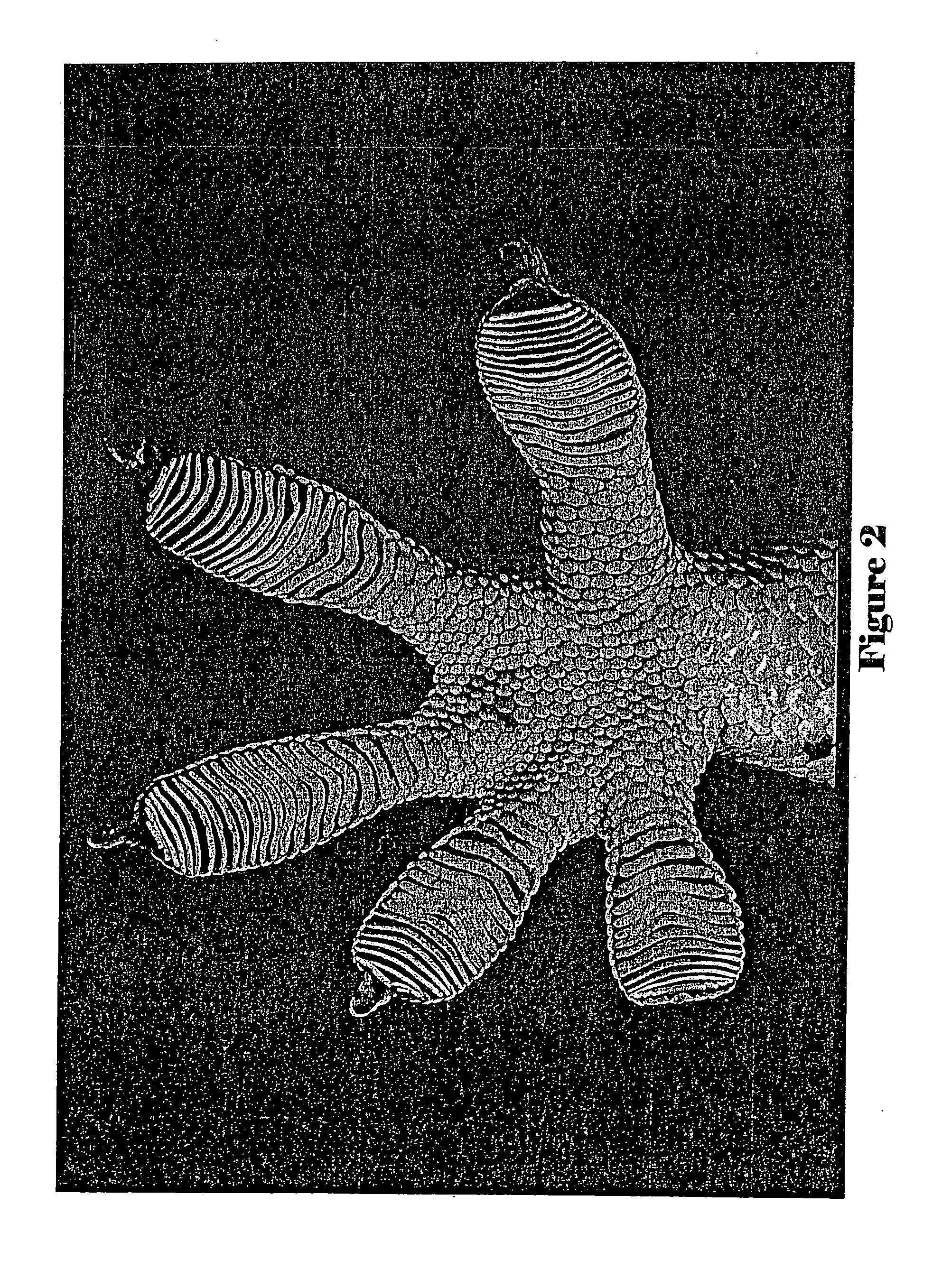
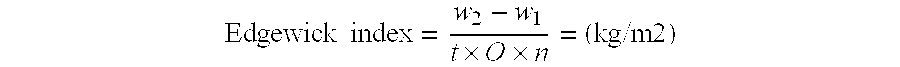Patents
Literature
109 results about "Microfibril" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
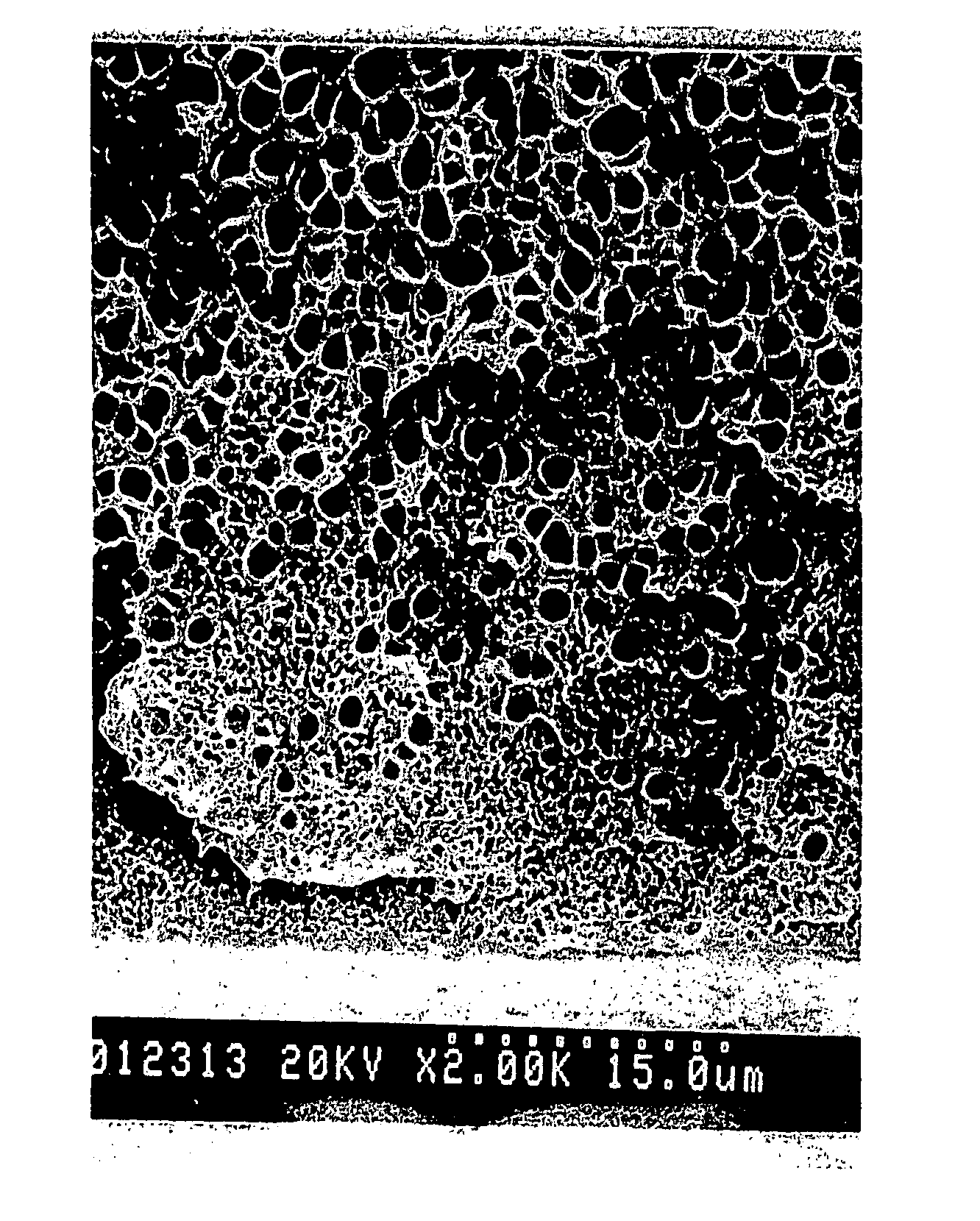
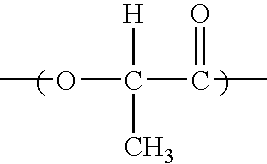
A microfibril is a very fine fibril, or fiber-like strand, consisting of glycoproteins and cellulose. It is usually, but not always, used as a general term in describing the structure of protein fiber, e.g. hair and sperm tail. Its most frequently observed structural pattern is the 9+2 pattern in which two central protofibrils are surrounded by nine other pairs. Cellulose inside plants is one of the examples of non-protein compounds that are using this term with the same purpose. Cellulose microfibrils are laid down in the inner surface of the primary cell wall. As the cell absorbs water, its volume increases and the existing microfibrils separate and new ones are formed to help increase cell strength.
Fibers comprising starch and biodegradable polymers
Owner:PROCTER & GAMBLE CO
Highly absorbent composite and method of making the same
InactiveUS20100063470A1Promote resultsIncrease stickinessNon-fibrous pulp additionLayered productsFiberMaterials science
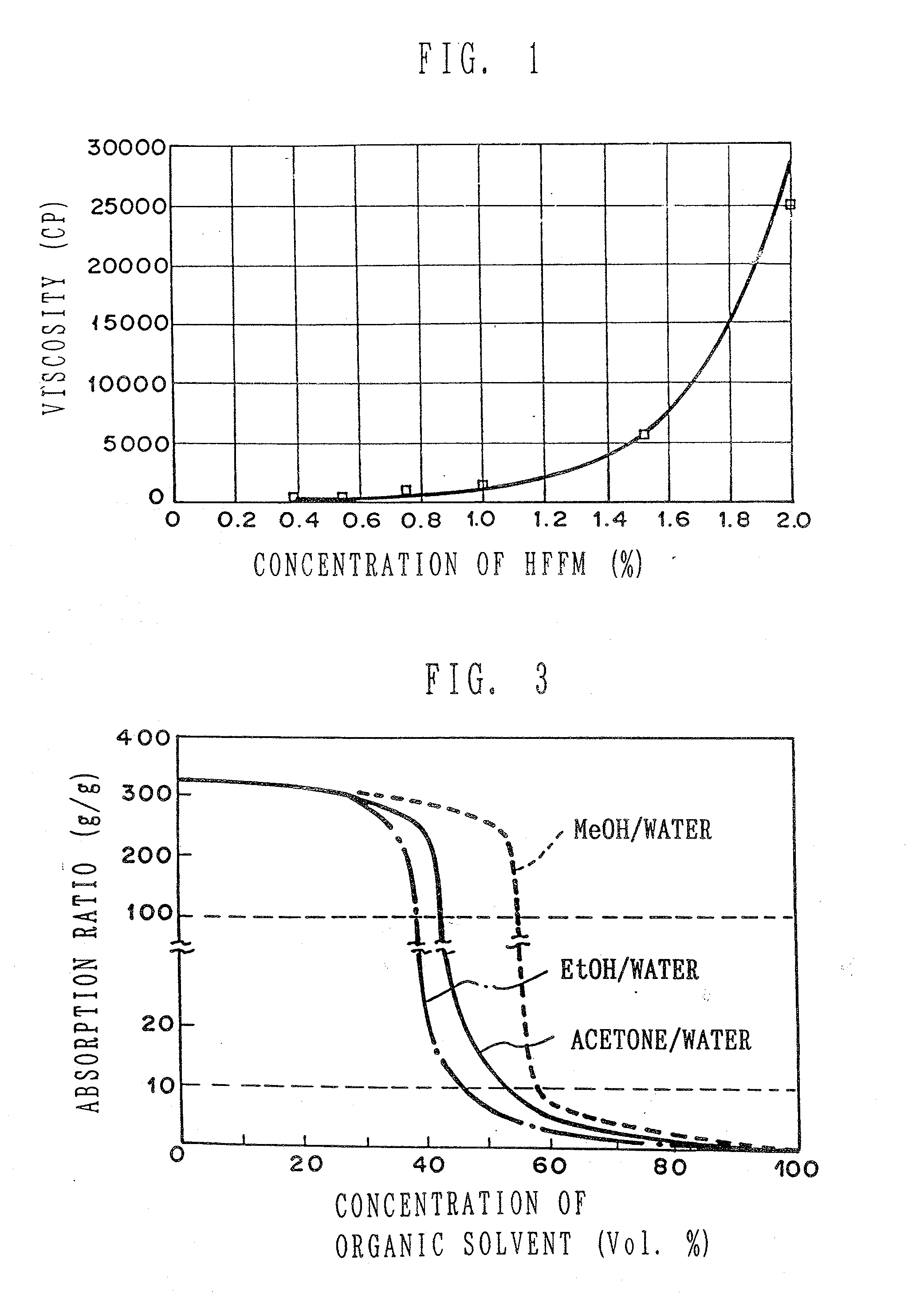
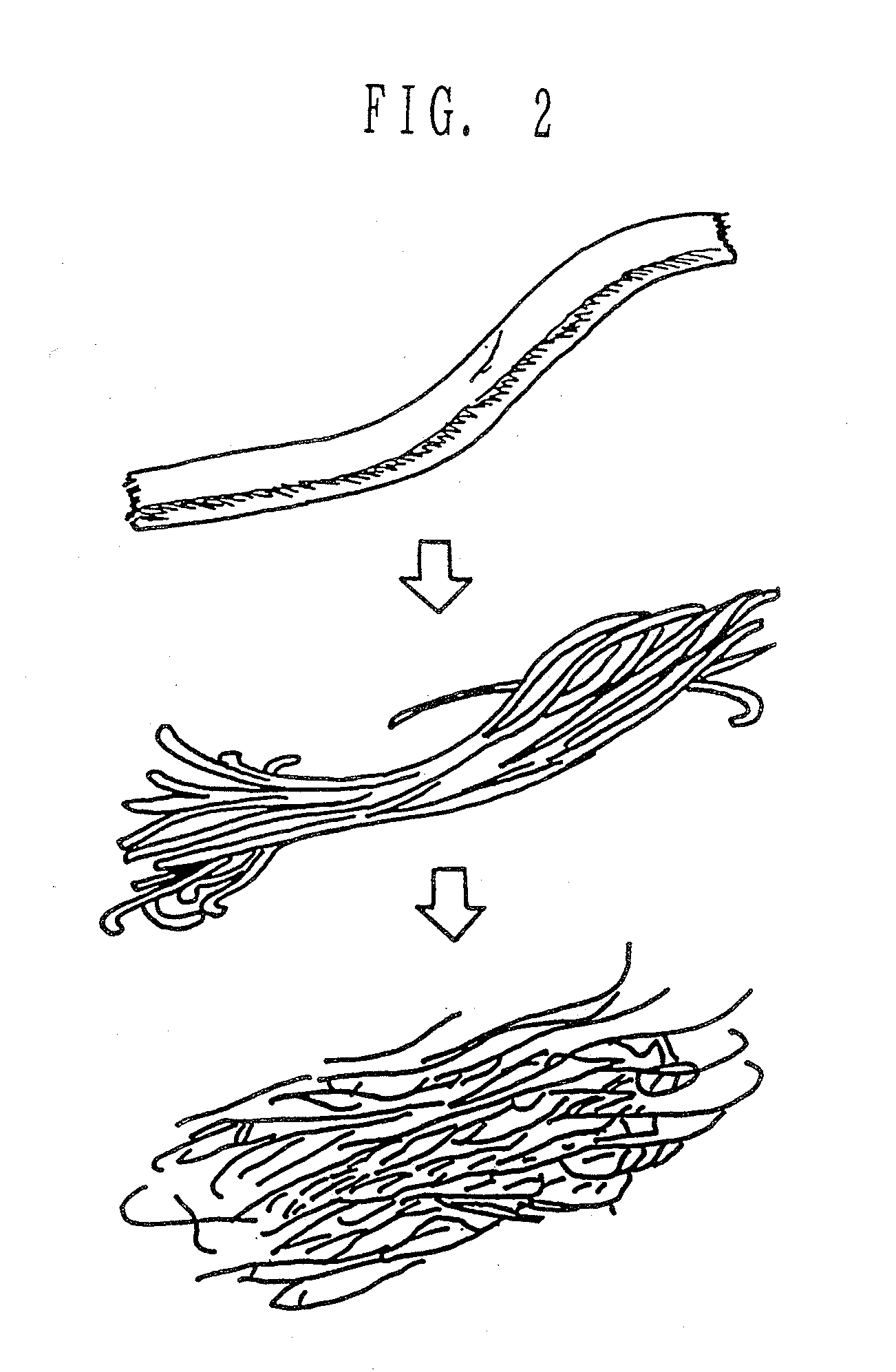
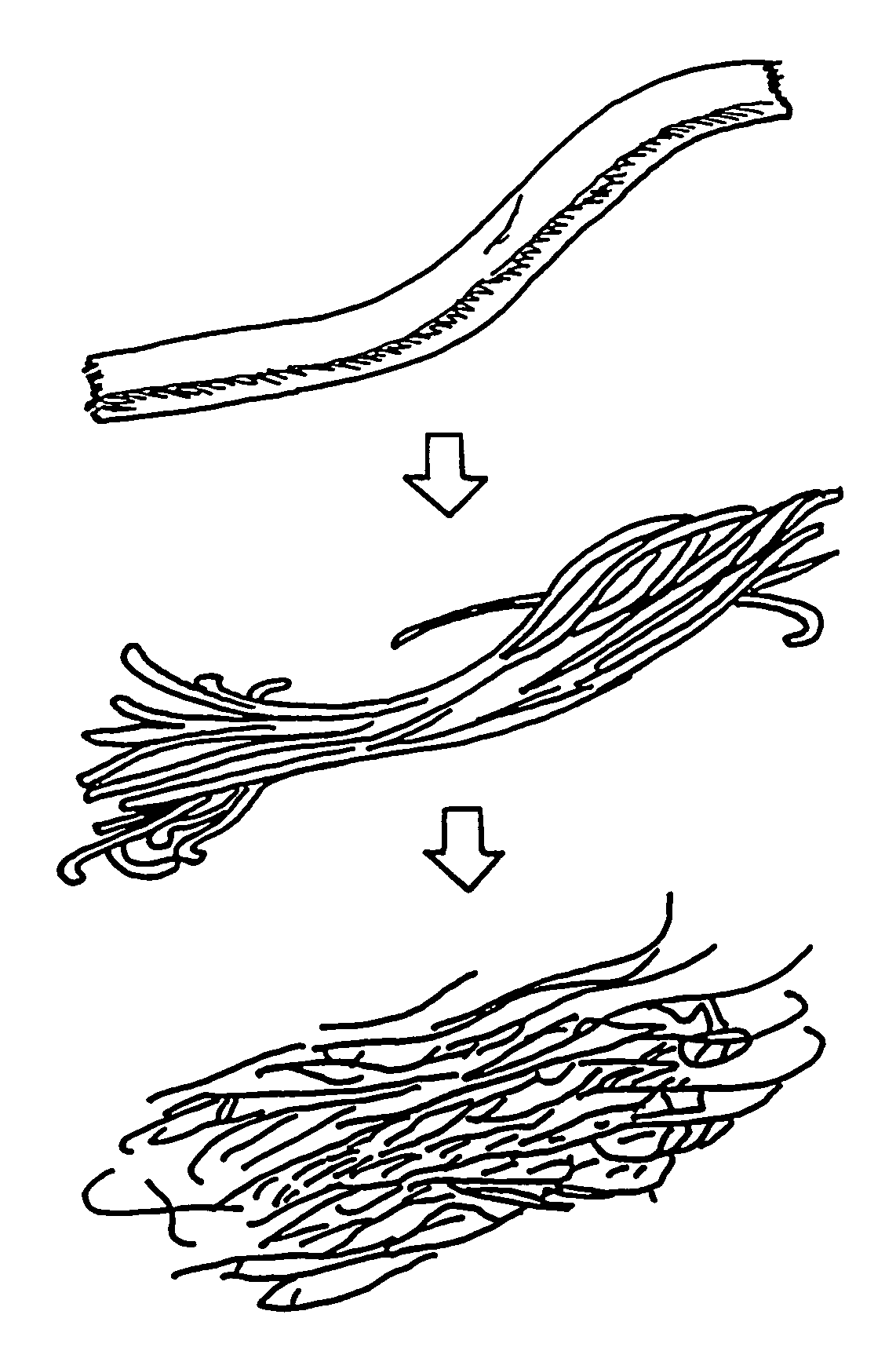
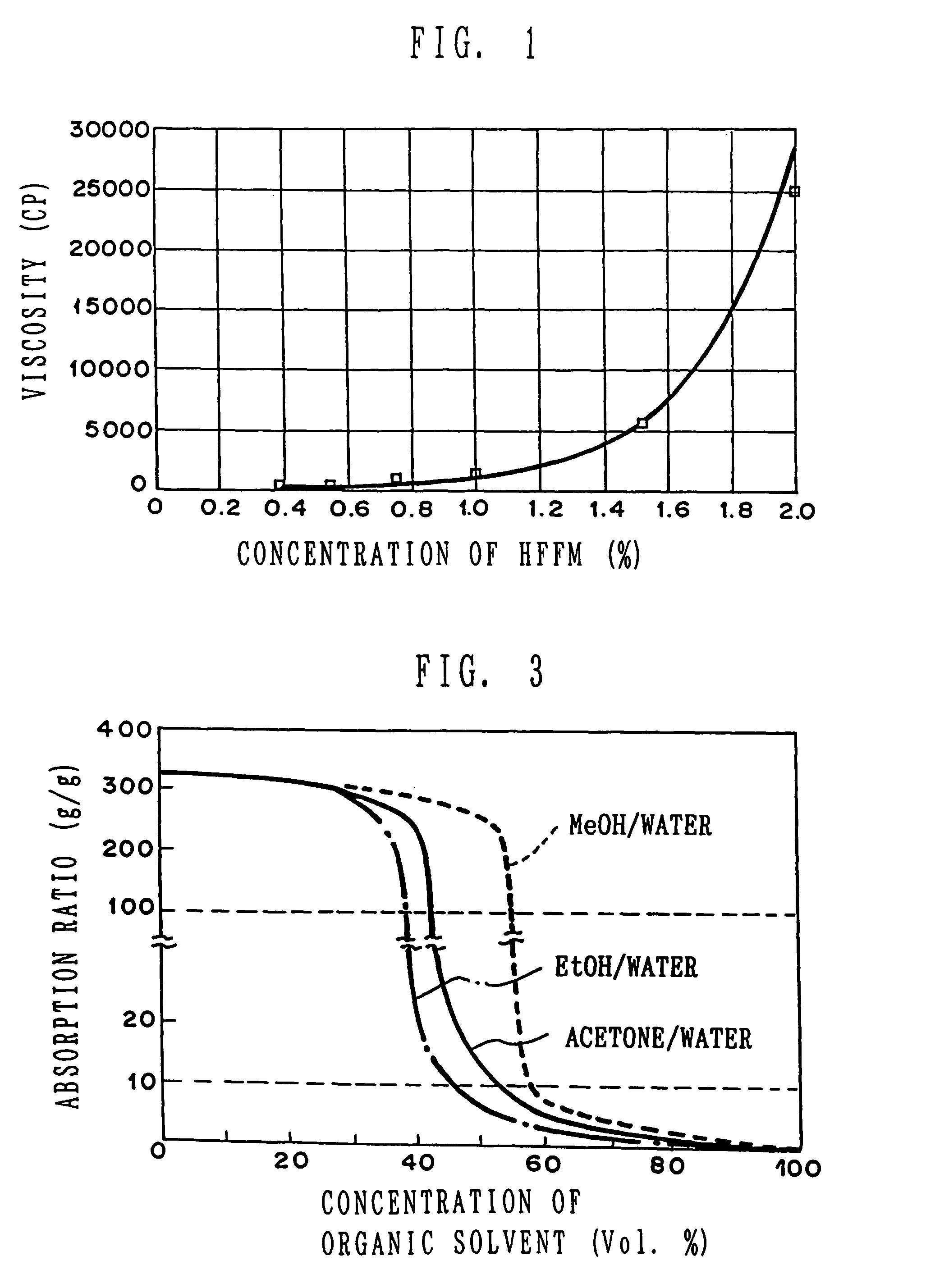
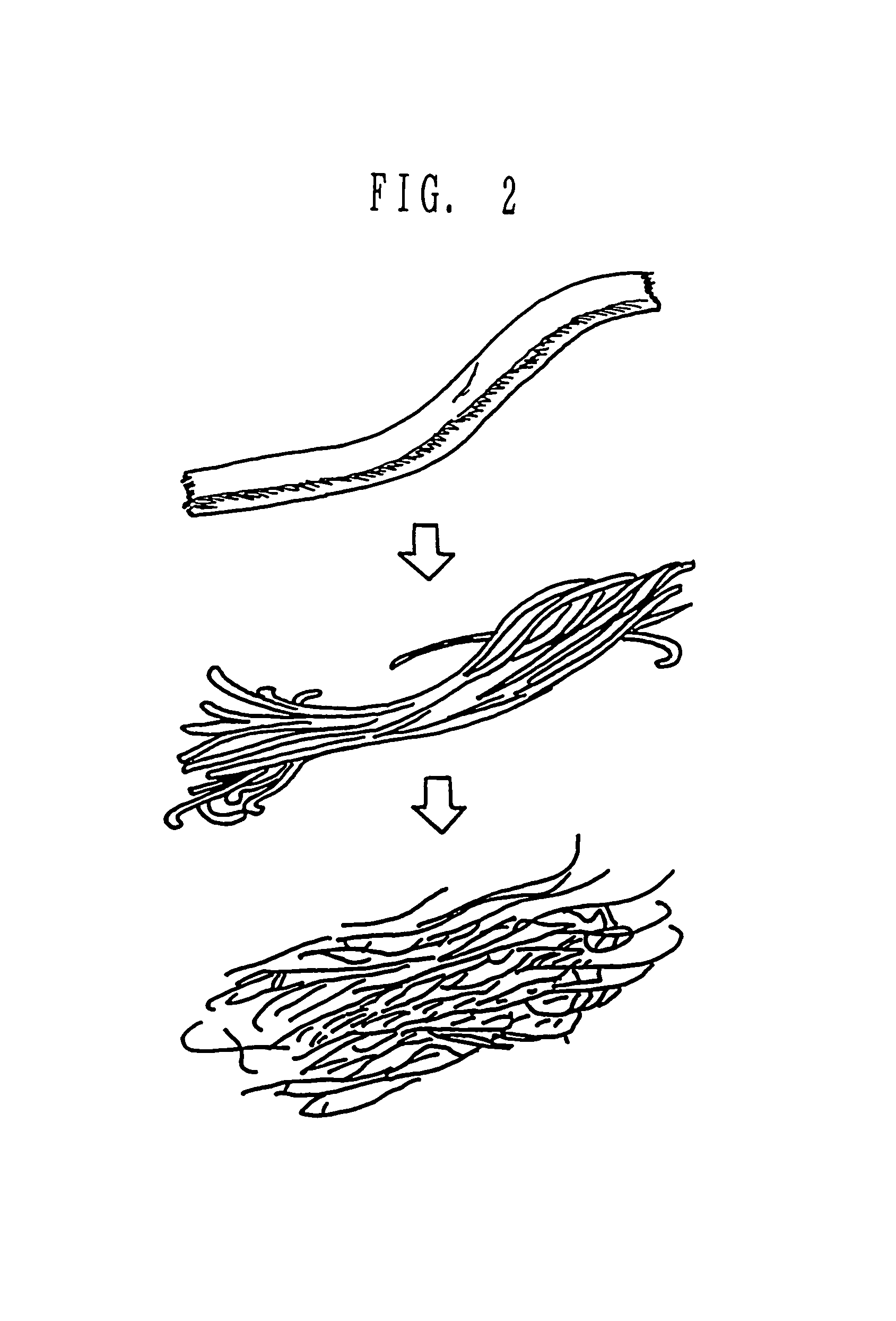
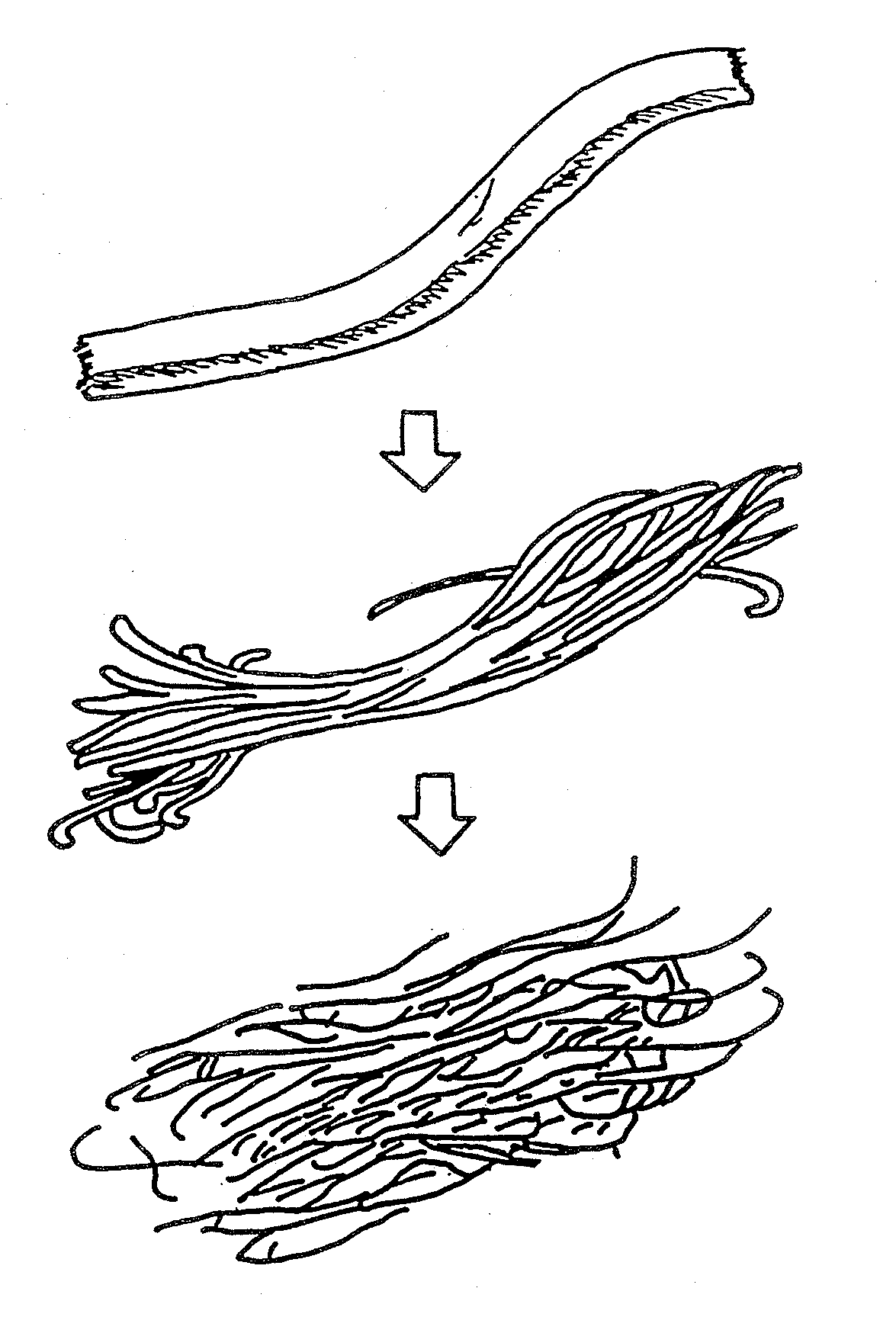
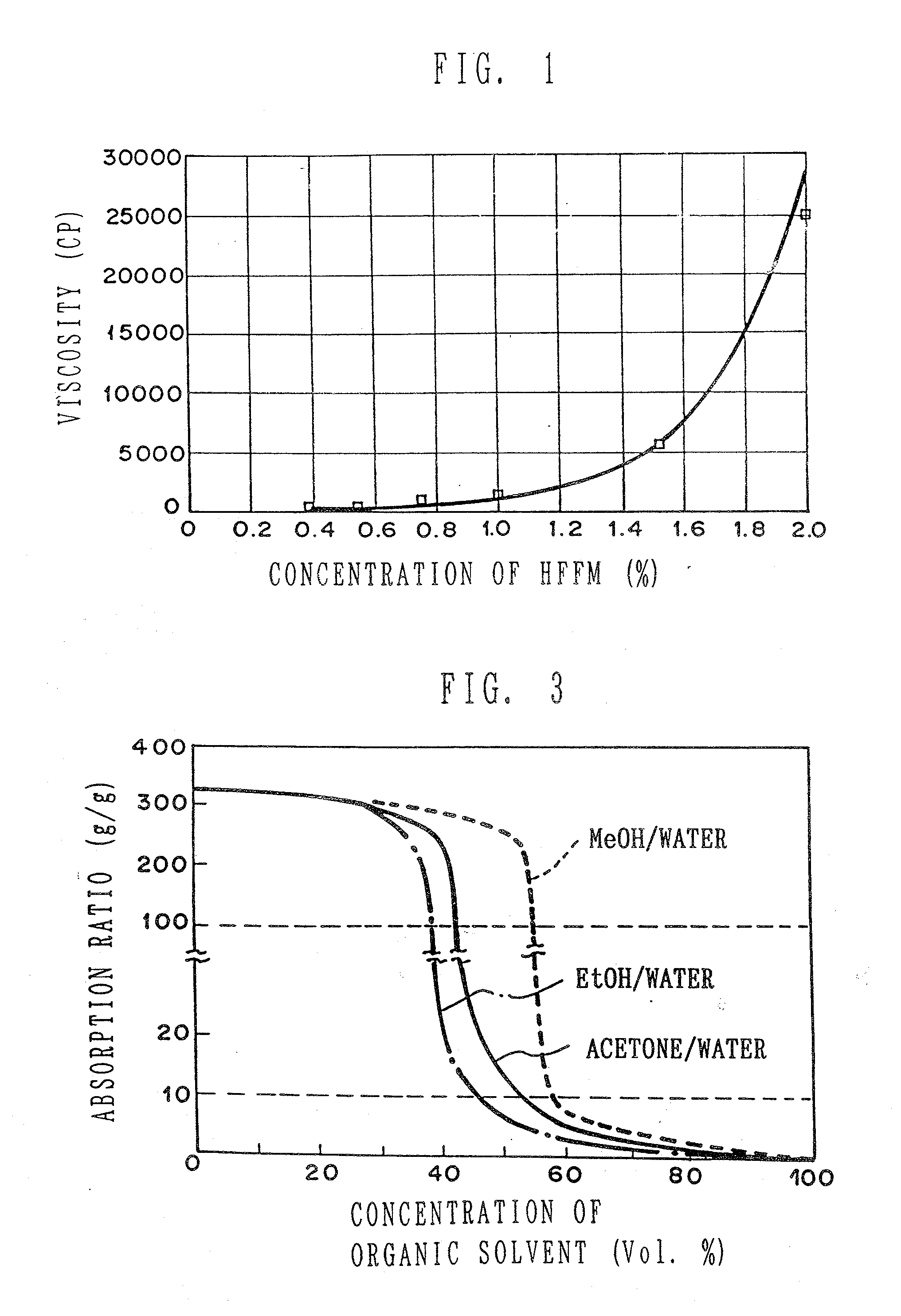
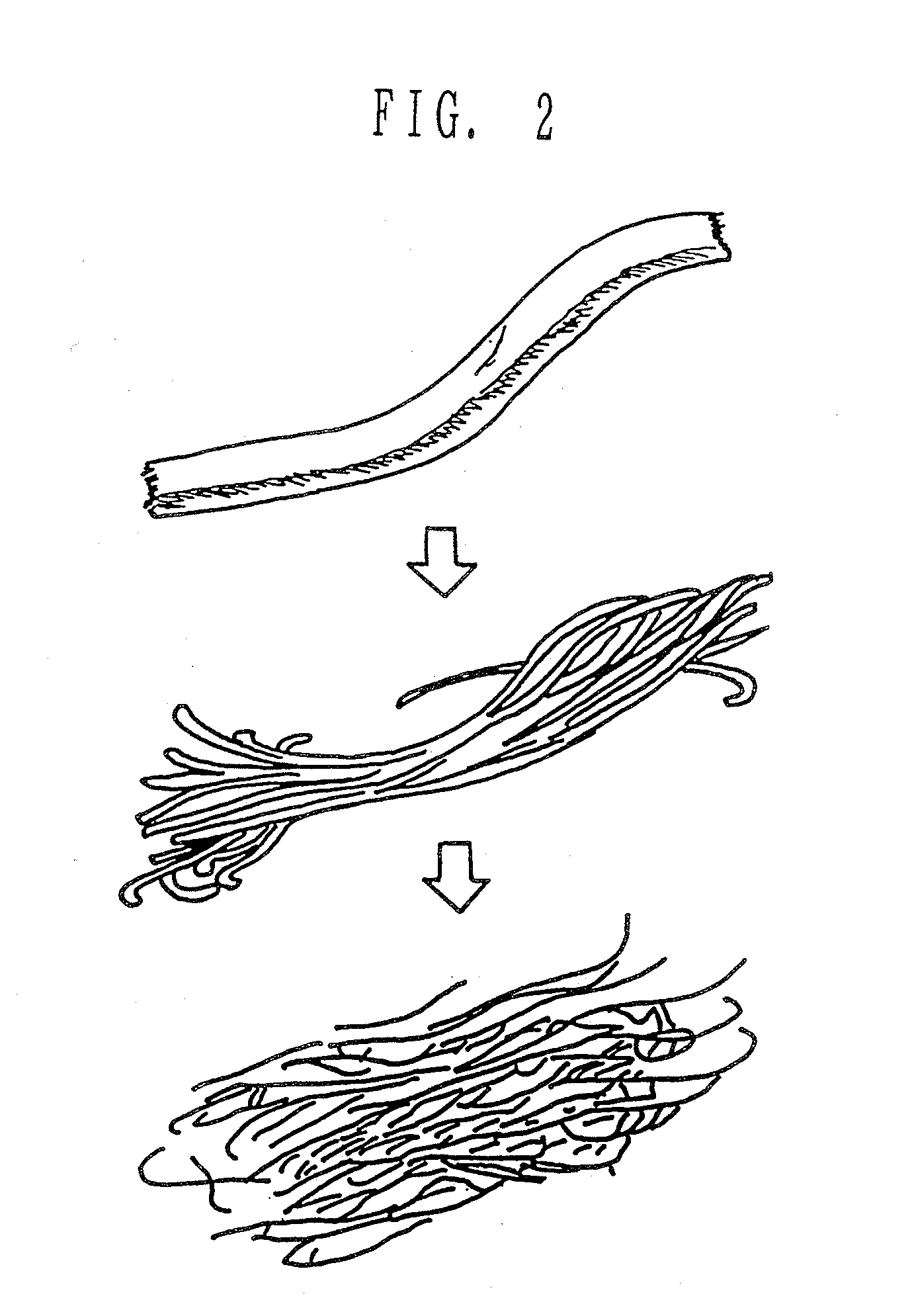
A composite structure mainly composed of hydratable fine fibers in the form of microfibril and a water swellable solid body, the fibers being obtained from cellulose or derivatives thereof, and at least part of the surface of the solid body is covered with the fine fibers. The absorbent composite can be formed in various form of, for example, particle, pellet, sheet and the like, especially of a sheet type with a supporting sheet of a non-woven fabric. The present invention further provides a method of making the composite structure.
Owner:SUZUKI MIGAKU +2
Highly absorbent composite compositions, absorbent sheets provided with the compositions, and process for producing the same
InactiveUS8268424B1Good dimensional stabilityEfficient designNon-fibrous pulp additionPreformed elementsFiberPolymer chemistry
A composite structure mainly composed of hydratable fine fibers in the form of microfibril and a water swellable solid body, the fine fibers being obtained from cellulose or a derivative thereof, and at least part of the surface of the solid body is covered with the fine fibers. The absorbent composite can be formed in various form of, for example, particle, pellet, sheet and the like, especially of a sheet type with a supporting sheet of a non-woven fabric. The present invention further provides a method of making the composite structure.
Owner:DSG INT LTD
Highly absorbent composite and method of making the same
InactiveUS20100062934A1Promote resultsIncrease stickinessNon-fibrous pulp additionOther chemical processesFiberSolid body
A composite structure mainly composed of hydratable fine fibers in the form of microfibril and a water swellable solid body, the fibers being obtained from cellulose or derivatives thereof, and at least part of the surface of the solid body is covered with the fine fibers. The absorbent composite can be formed in various form of, for example, particle, pellet, sheet and the like, especially of a sheet type with a supporting sheet of a non-woven fabric. The present invention further provides a method of making the composite structure.
Owner:SUZUKI MIGAKU +2
Cellulose-based fibrous materials
InactiveUS8012312B2Low densityImprove surface qualityCellulosic pulp after-treatmentCalendersFiberPolymer science
The present invention aims to provide cellulose-based fibrous materials for obtaining papers and sheets having low density, high surface quality, good size stability despite of high strength, and high opacity. Cellulose-based fibrous materials having external fibrils consisting of an assembly of scale-like microfibrils exhibit a higher fiber stiffness, a lower water retention value and a higher specific surface area as compared with fibrous materials having filamentous external fibrils at the same freeness. Papers and sheets having low density, high surface quality, good size stability and high opacity can be obtained by using such fibrous materials.
Owner:NIPPON PAPER IND CO LTD
Method for preparing nano cellulose microfibril reinforced polymer composite material
ActiveCN102344685AUniform structureTransparent structureConjugated cellulose/protein artificial filamentsConjugated synthetic polymer artificial filamentsSolubilityFiber
The invention discloses a method for in situ generating a nano cellulose microfibril reinforced polymer composite material, comprising the following steps: using ionic liquid as a primary solvent, dissolving cellulose, or mixing cellulose with other polymers via solution mixing, and controlling the solubility of the cellulosic material in the solvent to maintain naturally occurring nano cellulose microfibril in the cellulosic material, so as to in situ obtain the nano cellulose microfibril reinforced polymer composite material. The nano microfibril can be observed under a transmission microscope obviously, which is different from the completely dissolved cellulose solution. In the preparing process, the dissolving temperature is controlled within 30-150 DEG C, and stirring and vacuum deaeration are used as auxiliary. By controlling the dissolving time, solution concentration and ratio of mixing, a polymer solution containing cellulose microfibril with dimension of 5-300 nanometers can be obtained. The polymer solution can be used for preparing composite material fiber, hollow fibrous membrane, diaphragm, film, gel, porous material and other known applications of enhanced material.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Hierarchically-dimensioned-microfiber-based dry adhesive materials
InactiveUS20050271870A1Film/foil adhesivesDecorative surface effectsHigh dimensionalAdhesive materials
Embodiments of the present invention include hierarchically-dimensioned, microfiber-based dry adhesive materials featuring dense arrays of microfibers with free tips terminating in numerous microfibrils. In certain embodiments, more than two levels of microfiber-dimension hierarchy may be employed, each dimension involving smaller microfibrils emanating from the tips of the microfibers or microfibrils of the next highest dimensional level. Various additional embodiments of the present invention are directed to methods for preparing hierarchically-dimensioned, microfiber-based dry adhesive materials. These methods include single-pass or multi-pass imprint-lithography, pattern masking and etching, and imprinting fiber-embedded substrates followed by etching.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Cellulose-based fibrous materials
ActiveUS20090065164A1Low densityImprove surface qualityCellulosic pulp after-treatmentReinforcing agents additionFiberPolymer science
The present invention aims to provide cellulose-based fibrous materials for obtaining papers and sheets having low density, high surface quality, good size stability despite of high strength, and high opacity. Cellulose-based fibrous materials having external fibrils consisting of an assembly of scale-like microfibrils exhibit a higher fiber stiffness, a lower water retention value and a higher specific surface area as compared with fibrous materials having filamentous external fibrils at the same freeness. Papers and sheets having low density, high surface quality, good size stability and high opacity can be obtained by using such fibrous materials.
Owner:NIPPON PAPER IND CO LTD
Vulcanized rubber composition, pneumatic tire and the process of producing the same
InactiveUS8022136B2Improve featuresReduce energy lossSpecial tyresPneumatic tyre reinforcementsPolymer scienceRolling resistance
By using a vulcanized rubber composition containing a rubber component composed of at least any one of a natural rubber, a modified natural rubber and a synthetic rubber, and chemically modified microfibril cellulose, it is possible to provide a vulcanized rubber composition that is environmentally conscious and that exhibits excellent rupture characteristics and a low energy loss, and a pneumatic tire that is excellent in rolling resistance property, steering stability and durability.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD +1
Polyolefin microporous membrane
InactiveUS20060103055A1Highly uniform surface porous structureImprove permeabilityMembranesSemi-permeable membranesFiberPolyolefin
The present invention provides a polyolefin microporous membrane having a surface structure comprising fine spaces formed by partitioning micro-fibrils and a network formed by uniform dispersion of said micro-fibrils, wherein the average diameter of the micro-fibrils is 20 to 100 nm and the average distance between the micro-fibrils is 40 to 400 nm; and a process for producing said poly-olefin microporous membrane.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI CHEM CORP
Fibers comprising starch and biodegradable polymers
InactiveUS20050026529A1Speed up the descentWoven fabricsNon-woven fabricsPlasticizerPolymer chemistry
Environmentally degradable finely attenuated fibers produced by melt spinning a composition comprising destructurized starch, a biodegradable thermoplastic polymer, and a plasticizer are disclosed. The present invention is also directed to highly attenuated fibers containing thermoplastic polymer microfibrils which are formed within the starch matrix of the finely attenuated fiber. Nonwoven webs and disposable articles comprising the highly attenuated fibers are also disclosed.
Owner:BOND ERIC BRYAN +4
Hierarchically-dimensioned-microfiber-based dry adhesive materials
InactiveUS20050271869A1Film/foil adhesivesSynthetic resin layered productsHigh dimensionalAdhesive materials
Embodiments of the present invention include hierarchically-dimensioned, microfiber-based dry adhesive materials featuring dense arrays of microfibers with free tips terminating in numerous microfibrils. In certain embodiments, more than two levels of microfiber-dimension hierarchy may be employed, each dimension involving smaller microfibrils emanating from the tips of the microfibers or microfibrils of the next highest dimensional level. Various additional embodiments of the present invention are directed to methods for preparing hierarchically-dimensioned, microfiber-based dry adhesive materials. These methods include single-pass or multi-pass imprint-lithography, pattern masking and etching, and imprinting fiber-embedded substrates followed by etching.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Vulcanized rubber composition, pneumatic tire and the process of producing the same
ActiveUS20100076118A1Improve featuresReduce energy lossSpecial tyresTyre tread bands/patternsPolymer scienceRolling resistance
By using a vulcanized rubber composition containing a rubber component composed of at least any one of a natural rubber, a modified natural rubber and a synthetic rubber, and chemically modified microfibril cellulose, it is possible to provide a vulcanized rubber composition that is environmentally conscious and that exhibits excellent rupture characteristics and a low energy loss, and a pneumatic tire that is excellent in rolling resistance property, steering stability and durability.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD +1
Fibers comprising starch and polymers
The present invention is directed to highly attenuated fibers produced by melt spinning a composition comprising destructurized starch, a thermoplastic polymer, and a plasticizer. The present invention is also directed to highly attenuated fibers containing microfibrils which are formed within the starch matrix. Nonwoven webs and disposable articles comprising the highly attenuated fibers are also disclosed.
Owner:BOND ERIC BRYAN +5
Liquid detergent composition with abrasive particles
InactiveUS20120071383A1Non-surface-active detergent compositionsDetergent compounding agentsWaxCellulose
The present invention relates to a dishwashing composition comprising abrasive particles and a suspending aid selected from the group consisting of crystalline wax structurants, micro-fibril-cellulose, amido-gellants, di-benzylidene polyol acetal derivatives, and mixtures thereof, and the process and use thereof.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Surface sizing solution, and surface sizing solution used sized paper
The invention provides a surface sizing solution used in the papermaking field. The surface sizing solution contains a product and water, the product is obtained after a cross-linking reaction of nano fibrillated cellulose, starch and a cross-linking agent, the nano fibrillated cellulose is single microfibrils of cellulose having a length of 100-2000nm and a diameter of 3-200nm obtained through defibrating cellulose raw materials, wherein bone dry mass parts of the nano fibrillated cellulose, the starch and the cross-linking agent are 0.1-10, 85-99.75 and 0.15-5 respectively. The invention also provides a sized paper made by using the surface sizing solution. The surface sizing surface containing the nano fibrillated cellulose is coated on the surface of paper to realize enforcing and toughening effects in order to effectively improve the flexibility resistance of the sized paper.
Owner:GOLD EAST PAPER JIANGSU
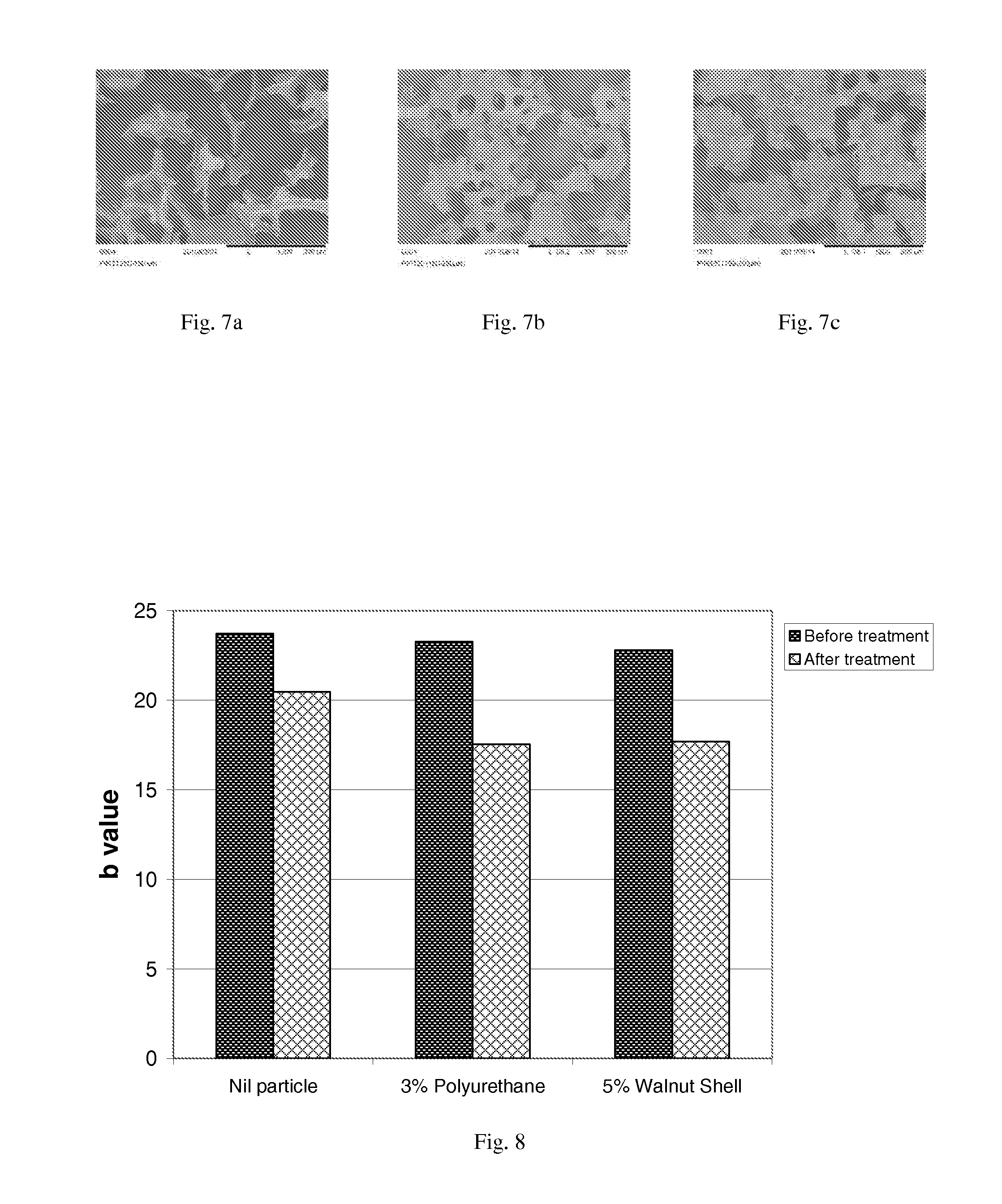
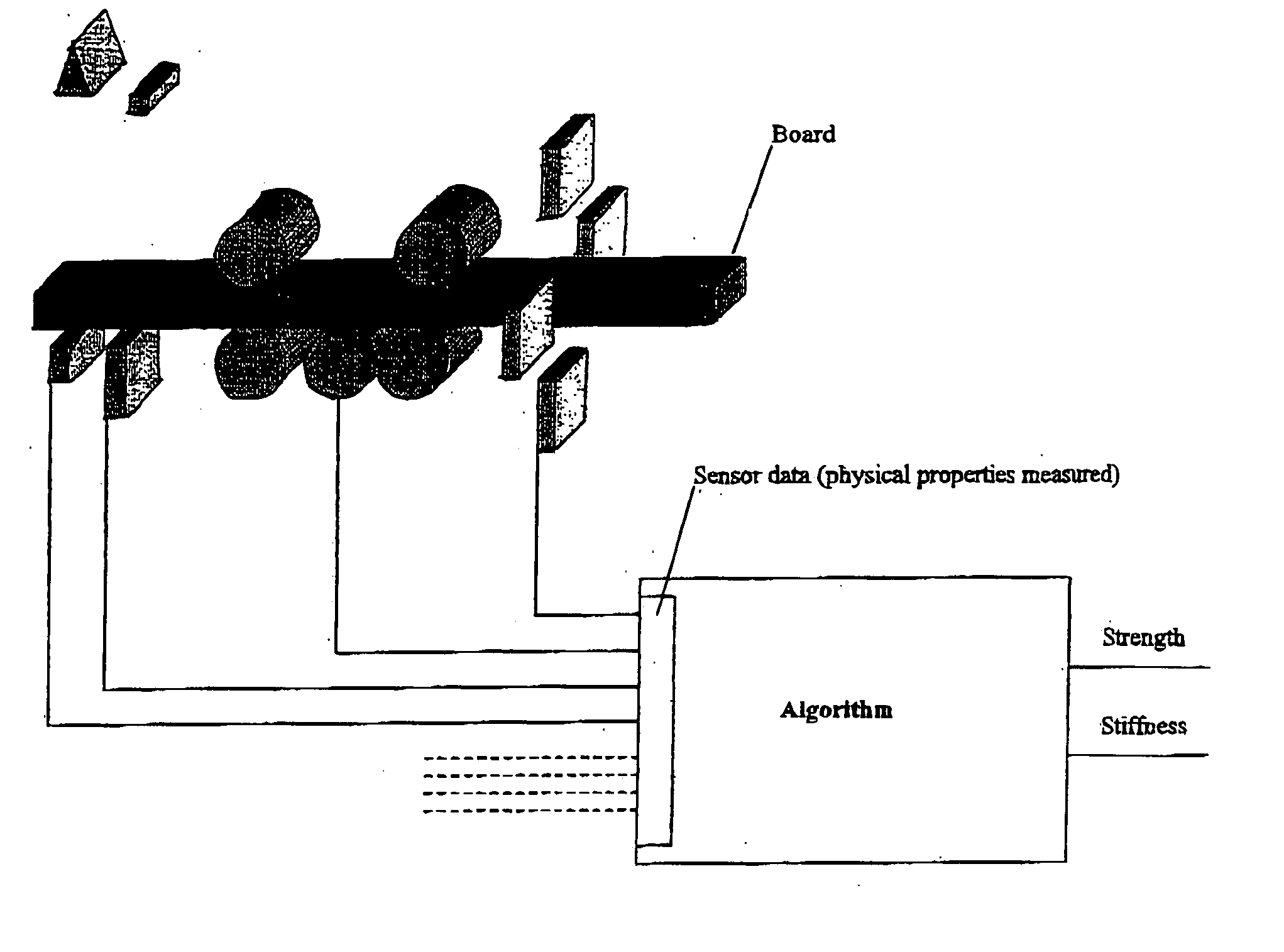
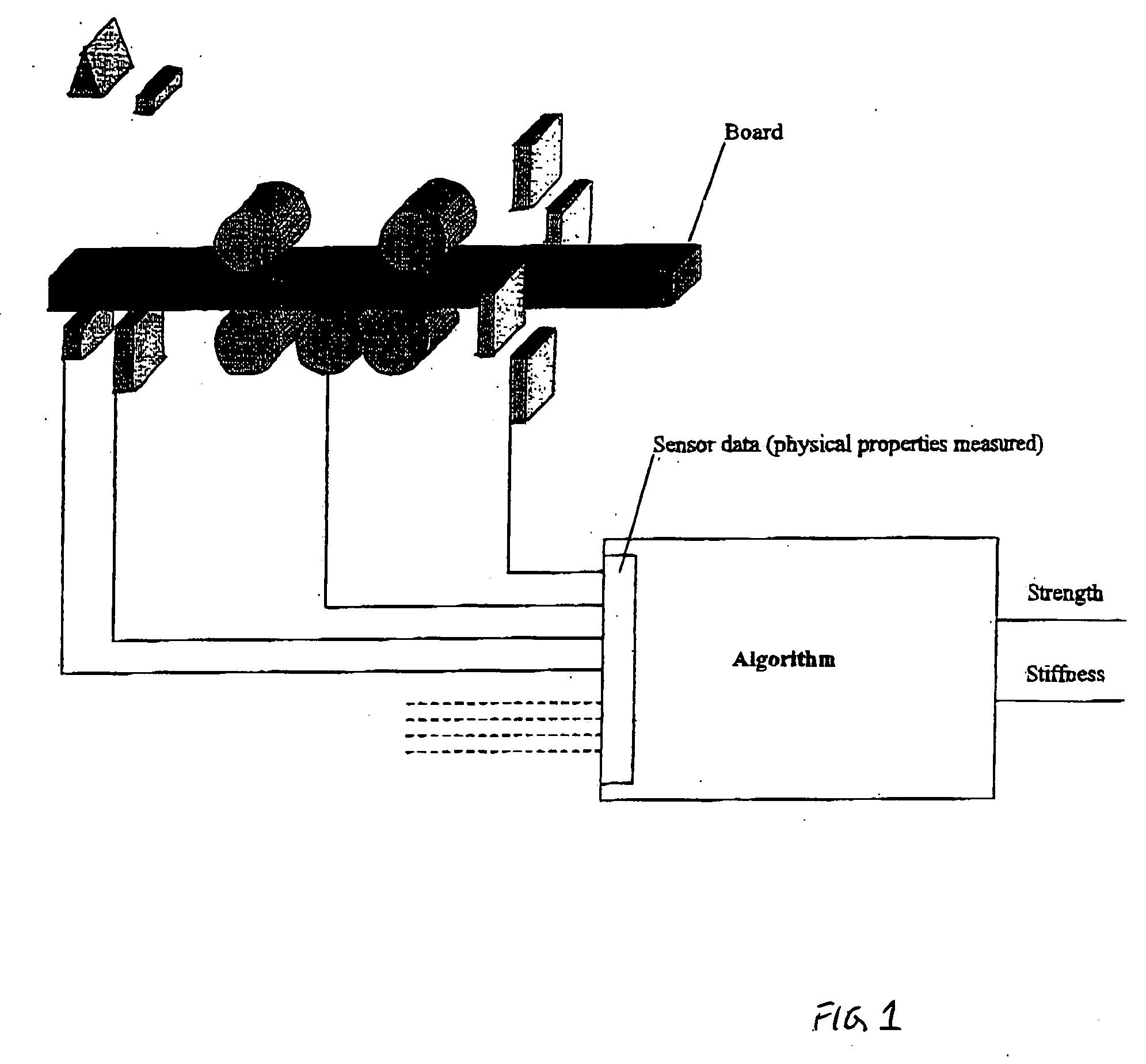
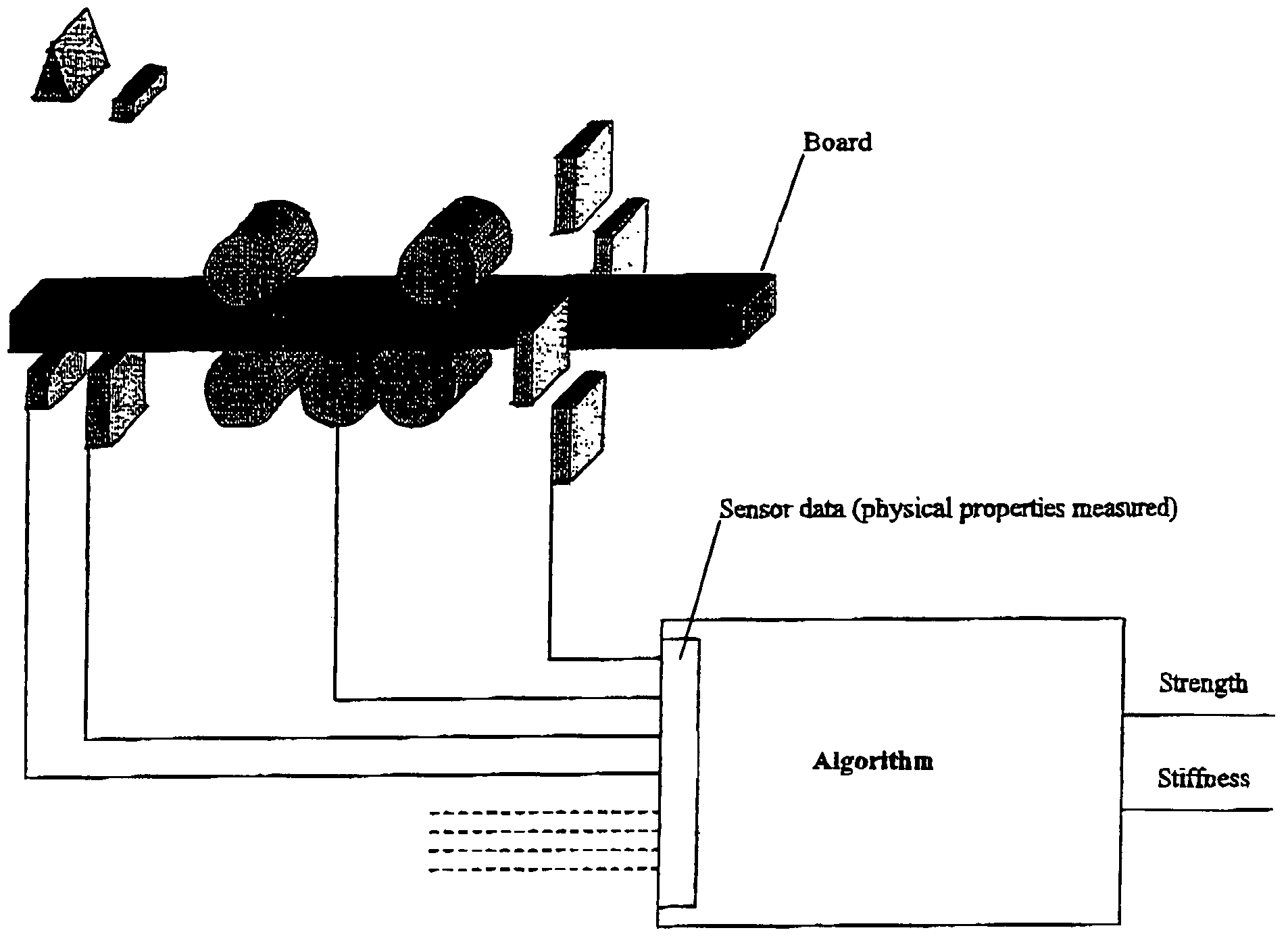
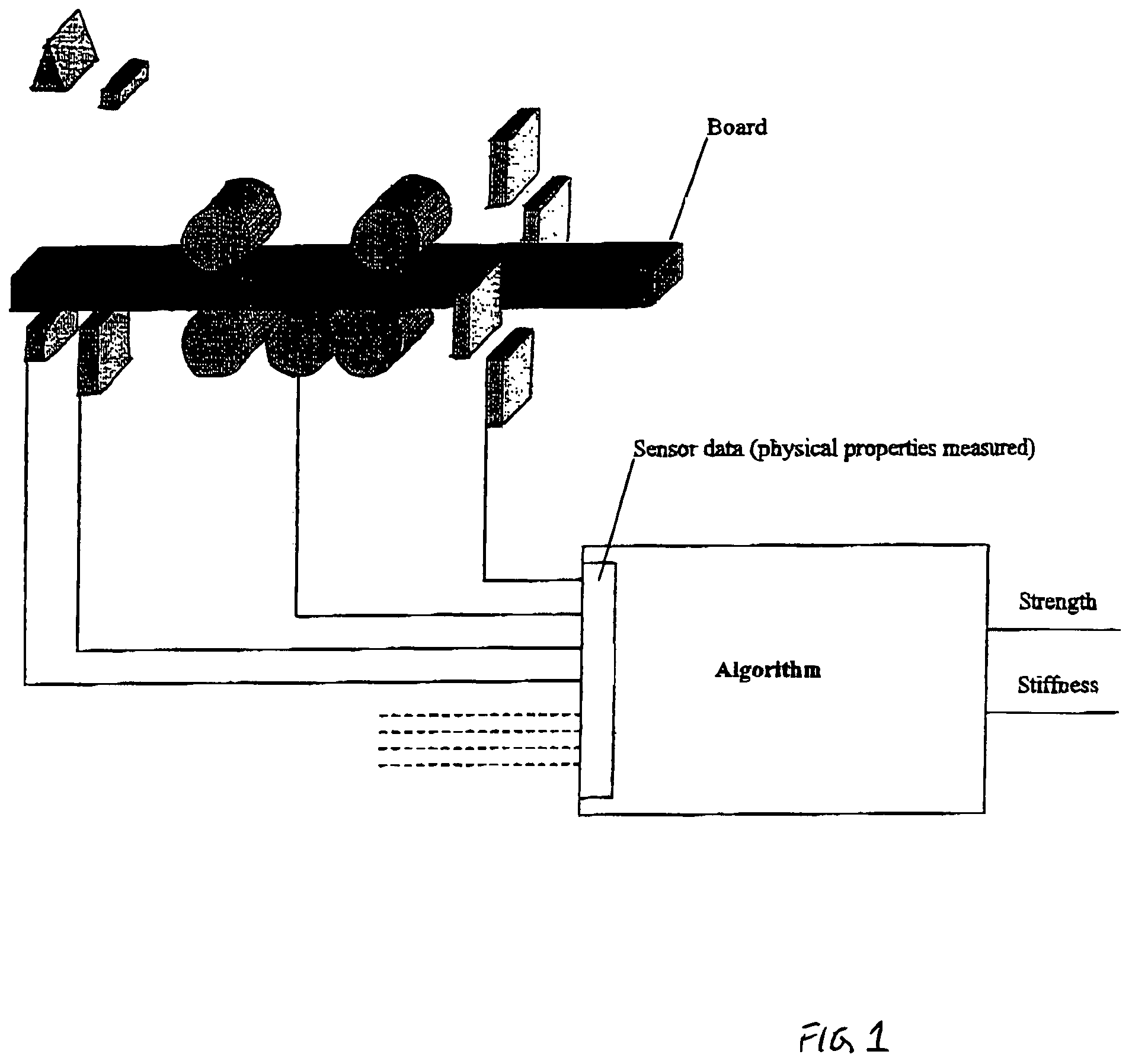
Method of wood strength and stiffness prediction
ActiveUS20050031158A1Improve forecast accuracyDiffering accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisNon destructiveFiber
A method of non-destructive testing of a wood piece using a multiplicity of sensors. The method may include the steps of sensing the wood piece; collecting information from the sensors; and integrating the information into a physical model providing for strength and stiffness prediction. The collected information relate to material characteristics of the wood piece and to fiber quality characteristics of the wood piece. The material characteristics may include one or more of the following material characteristics of the wood piece: growth ring thickness; grain angle deviation; clear wood density; knot location; knot density; knot type; knot size; location in the tree from which the wood piece was cut. The fiber quality characteristics may include one or more of the following fiber quality characteristics: microfibril angle, juvenile wood, biodeterioration; reaction wood species; and manufacturing or drying defects including one or more of the following defects: sawcuts, checks, shake; size of actual cross-section, and species.
Owner:WEYERHAEUSER NR CO
Preparation method of nano-cellulose aerogel
The invention discloses a preparation method of nano-cellulose aerogel and relates to the preparation method of the nano-cellulose aerogel. The preparation method aims at solving the problem of poor dispersion of the existing cellulose aerogel in an organic solvent. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1) dissolving absorbent cotton in a sulfuric acid solution for acidolysis, centrifugalizing, and then washing a white sol precipitate with deionized water to be neutral; 2) adding the nano-cellulose sol precipitate into the organic solvent, uniformly stirring, and then placing into an ultrasonic cleaning instrument for ultrasonic dispersion; and 3) placing a nano-cellulose suspension at the temperature of minus 18-minus 25 DEG C for freezing, and then further placing into a freeze-drying machine for freeze-drying. The nano-cellulose aerogel prepared by the invention has obvious nano-microfibril and nano-porous structure and can be rapidly dispersed in the organic solvent, such as dimethylformamide, dimethylacetamide and the like, the particle size of dispersed cellulose is nano-scale, and the good dispersion is shown. The preparation method disclosed by the invention can be applied to catalyst carriers, adsorbents and other fields.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY +1
Method and equipment for measurement of intact pulp fibers
InactiveUS20100020168A1Real-time measurementAvoid dataRadiation pyrometryImage analysisNon destructiveMicrophotograph
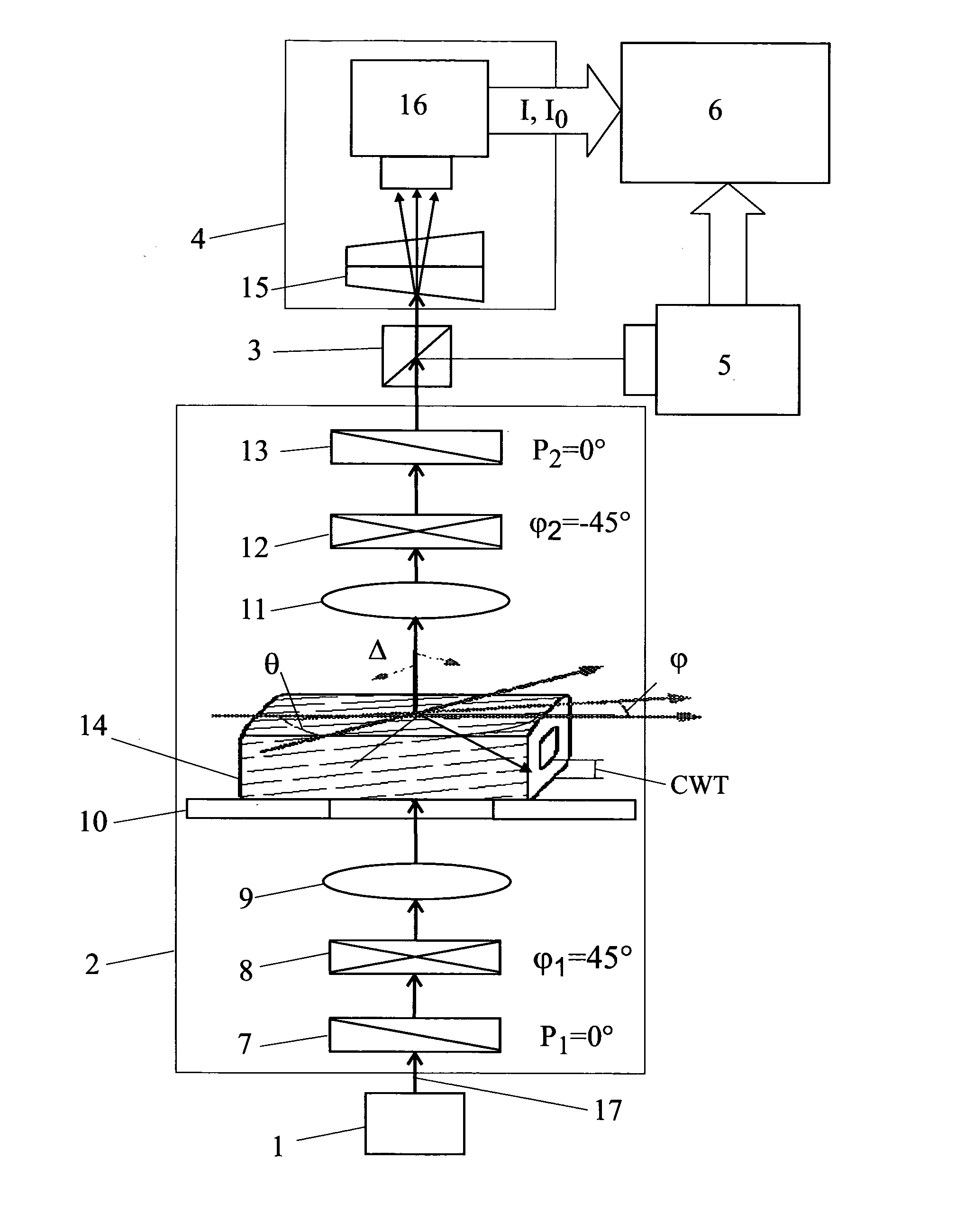
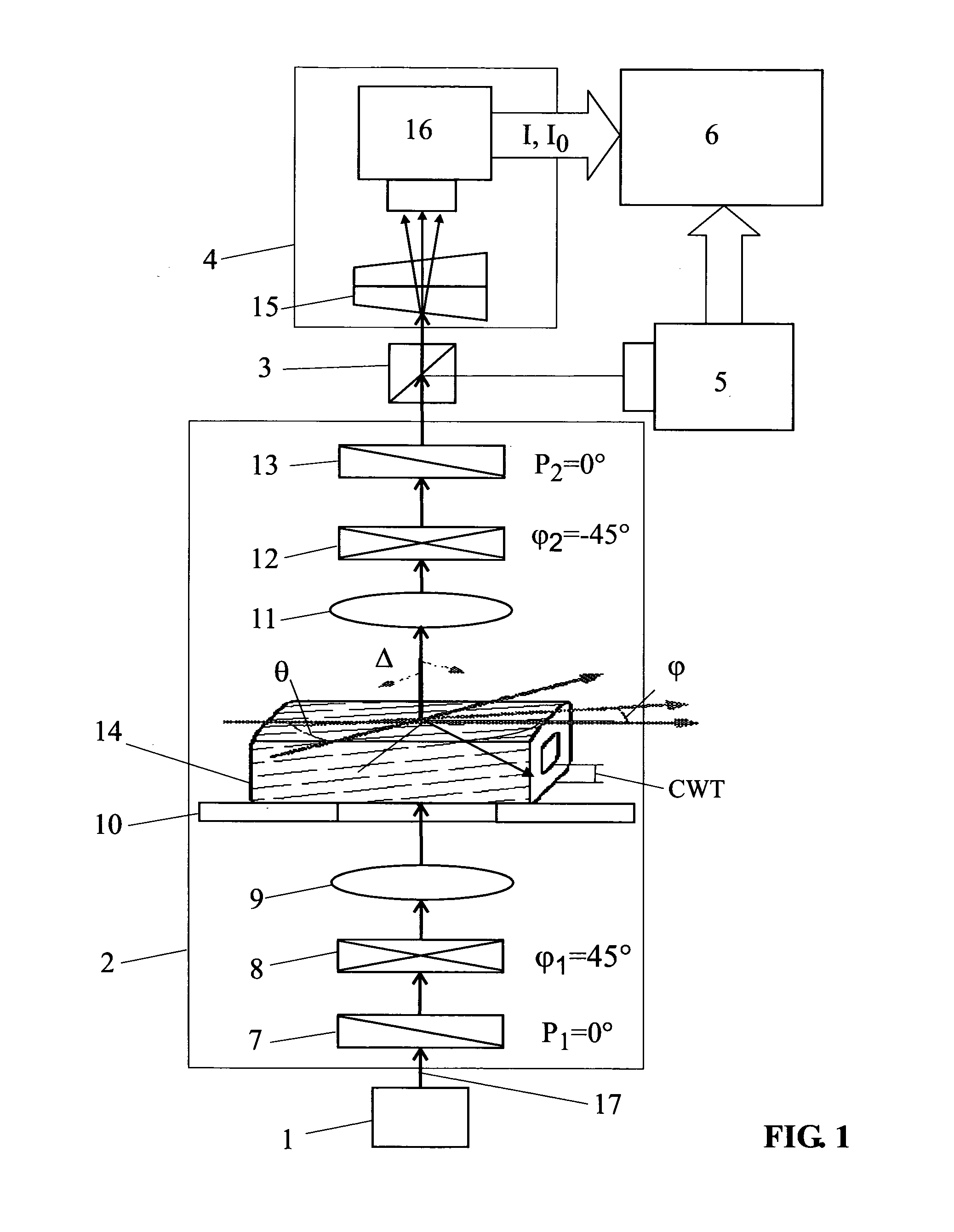
A non-destructive method capable of real-time or on-line measurement of a wood or pulp fiber without sample pretreatment for the microfibril angle and the path difference. A circular polariscope in combination with a line spectral camera generating a micrograph insensitive to the orientation of a fiber and determined only by the fiber's properties related to polarized light. A line image across the fiber is captured and dispersed it into a spectral image to perform a real-time spectral analysis of the fiber's image.
Owner:YE CHUN
Production of aromatic copolymide fiber dissolving pulp
InactiveCN1456719AAchieve reuseNo protection issuesArtificial filament recoveryPlastic recyclingDissolving pulpAramid
Owner:上海依极科技有限公司
Micropatterned structures for forming a seal with the face skin and other surfaces and method of make
ActiveUS20150329743A1Good contact/sealIncrease frictionFilm/foil adhesivesSynthetic resin layered productsFiberAdhesive
The present invention is directed towards an article suitable for attachment to facial skin or other surfaces, which comprises microfibrils and continuous microribbons. The article provides good sealing when used on a regular skin, and on a challenge skin surface with facial hair, sweat and acnes. The article also provides good adhesion and sealing on any other rough surfaces, and can be used repeatedly against different surfaces. These dry adhesives can be used for improving sealing of mask respirators, swimming goggles, or for other applications such as medical bandage, working gloves, and protective clothing seal.
Owner:METNA
Method of producing a paper product
The invention relates to a method of producing a laminate paper product comprising at least two layers, said method comprising (i) providing an aqueous suspension comprising cellulosic fibers (ii) adding to the suspension microfibrillar polysaccharide in an amount to yield from about 0.05 to about 50 wt % based on the weight of the cellulosic fibers (iii) dewatering the obtained suspension and forming a first layer having a density from about 150 to about 500 kg / m3 of said laminate paper product. The invention also relates to a method comprising (i) providing an aqueous suspension comprising cellulosic fibers (ii) adding to the suspension microfibrillar polysaccharide in an amount to yield from about 0.05 to about 50 wt % based on the weight of the cellulosic fibers (iii) dewatering the obtained suspension and forming at least a first and a second layer of said laminate whereby at least one of said at least first and second layer is formed from an aqueous suspension obtained in step (ii) containing microfibrillar polysaccharide; and joining said layers in such way that the laminate product obtains a density from about 150 to about 800 kg / m3. The invention also relates to a laminate paper product which can be obtained by the method and the use thereof.
Owner:KEMIRA OY
Sintered microfibrillar structure micrometer size granule porous composite material and production method
InactiveCN1762909AContinuously adjustable network orificePorosity can be continuously adjustedCeramicwareAdhesiveSorbent
The sintered composite material contains microfibril oxide and micron level grains of catalyst, adsorbent, magnetic material, etc. and its oxide microfibrils have sintered combining points to form 3D netted structure to bind up the micron level grains. The preparation process of the sintered composite material includes: mixing microfibril, micron level grains, adhesive and water in certain proportion to form slurry; filtering in forming mold to form the precursor; drying the precursor and sintering at certain temperature and atmosphere to form the composite material. The composite material has the advantages of excellent anticorrosive performance, excellent antioxidant performance, controllable netted structure, high micron level grain supporting amount, easy production and low cost.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Coating composition of nano cellulose, its uses and a method for its manufacture
InactiveCN104781081ADuplicating/marking methodsCellulose coatingsActive agentOctadecyltrimethylammonium bromide
The invention relates to an aqueous coating composition of nano cellulose (e.g. microfibrillated cellulose), characterized in that has a dry matter concentration of 2%-12% of nano celluloseand comprises at least one cationic surfactant, which may be chosen among Hexadecyltrimethyl-ammonium bromide,Octadecyltrimethyl- ammonium bromide,Hexadecylpyridinium chloride andTetradecyltrimethyl- ammonium bromide, Dodecylpyridinium chloride. The invention also pertains to use of the composition as a coating layer and as an oxygen barrier layer. Further it relates to substrates, e.g. board, cardboard or paper coated with the composition. Moreover, the invention pertains to a process for preparing the coating composition.
Owner:PAPER & FIBER RES INST
Modified bacterial cellulose
InactiveUSRE38792E1Young's modulas are improvedIncrease modulusSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationBacteroidesFiber
This invention provides a bacterial cellulose comprising ribbon-shaped microfibrils having a thickness of 10 to 100 nm and a width of 160 to 1000 nm or a bacterial cellulose comprising ribbon-shaped microfibrils having a thickness of 10 to 100 nm and a width of 50 to 70 nm. The former bacterial cellulose can be produced by culturing cellulose-producing bacteria in a culture medium containing a cell division inhibitor, and the latter can be produced by culturing the bacterium in a culture medium containing an organic reducing agent. The bacterial cellulose is modified from conventional bacterial cellulose in the major axis, and is improved in Young's modulus, etc.This invention provides a bacterial cellulose comprising ribbon-shaped microfibrils having a thickness of 1 to 9 nm and a width of 160 to 1000 nm or a bacterial cellulose comprising ribbon-shaped microfibrils having a thickness of 1 to 9 nm and a width of 50 to 70 nm. The former bacterial cellulose can be produced by culturing cellulose-producing bacteria in a culture medium containing a cell division inhibitor, and the latter can be produced by culturing the bacterium in a culture medium containing an organic reducing agent. The bacterial cellulose is modified from conventional bacterial cellulose in the major axis, and is improved in Young's modulus, etc. <?insert-end id="INS-S-00001" ?>
Owner:CP KELCO
Method for regulating mechanical property of polyethylene terephthalate/polyolefin mixture by using magnetic field
InactiveCN101168605AEffectively control mechanical propertiesImprove mechanical propertiesPolymer sciencePolyolefin
The invention discloses a method for adjusting and controlling the mechanical properties of a polyethylene terephthalate (PET) / polyolefin blend material by utilizing the action of a magnetic field. The present invention takes general-purpose polyolefin as continuous phase, as polypropylene, polyethylene and copolymers thereof, polyethylene terephthalate as dispersed phase, prepares polymer blend, as the PET of dispersed phase in shearing, Microfibrils are formed under stretching, which reinforces the blend. A magnetic field is applied during the preparation of the blend, and the magnetic field affects the orientation of the PET molecular chains and the de-orientation of the oriented molecular chains after shearing and stretching, and can adjust the orientation degree of the molecular chains in the PET microfibers and the microfibrils. Mechanical properties, so as to effectively control the mechanical properties of the blend material.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method of wood strength and stiffness prediction
ActiveUS7680304B2Improve forecast accuracyDiffering accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisNon destructiveFiber
A method of non-destructive testing of a wood piece using a multiplicity of sensors. The method may include the steps of sensing the wood piece; collecting information from the sensors; and integrating the information into a physical model providing for strength and stiffness prediction. The collected information relate to material characteristics of the wood piece and to fiber quality characteristics of the wood piece. The material characteristics may include one or more of the following material characteristics of the wood piece: growth ring thickness; grain angle deviation; clear wood density; knot location; knot density; knot type; knot size; location in the tree from which the wood piece was cut. The fiber quality characteristics may include one or more of the following fiber quality characteristics: microfibril angle, juvenile wood, biodeterioration; reaction wood species; and manufacturing or drying defects including one or more of the following defects: sawcuts, checks, shake; size of actual cross-section, and species.
Owner:WEYERHAEUSER NR CO
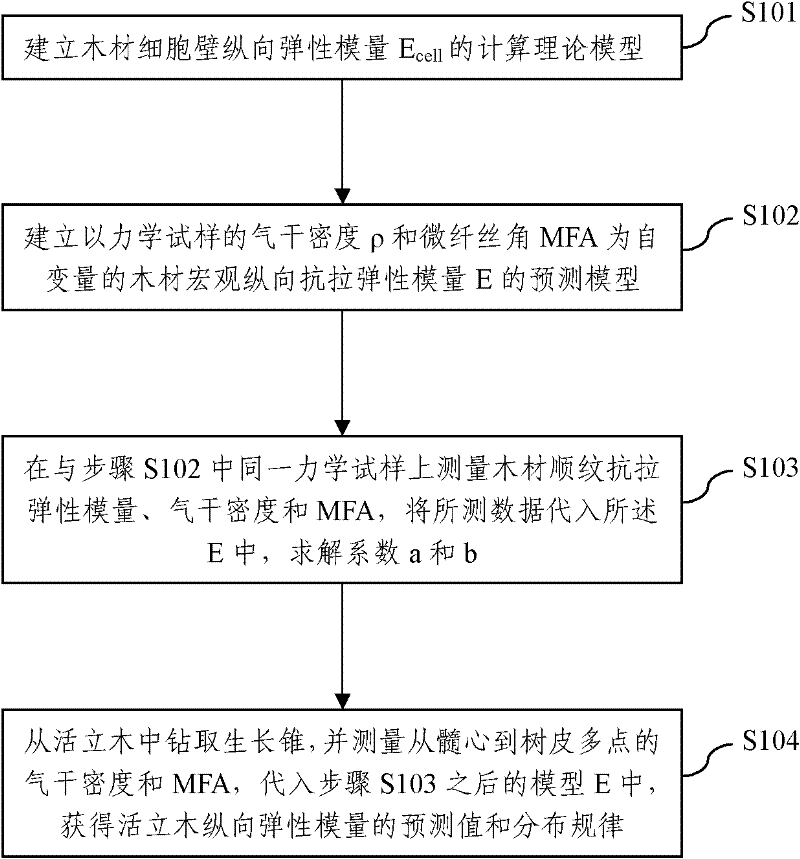
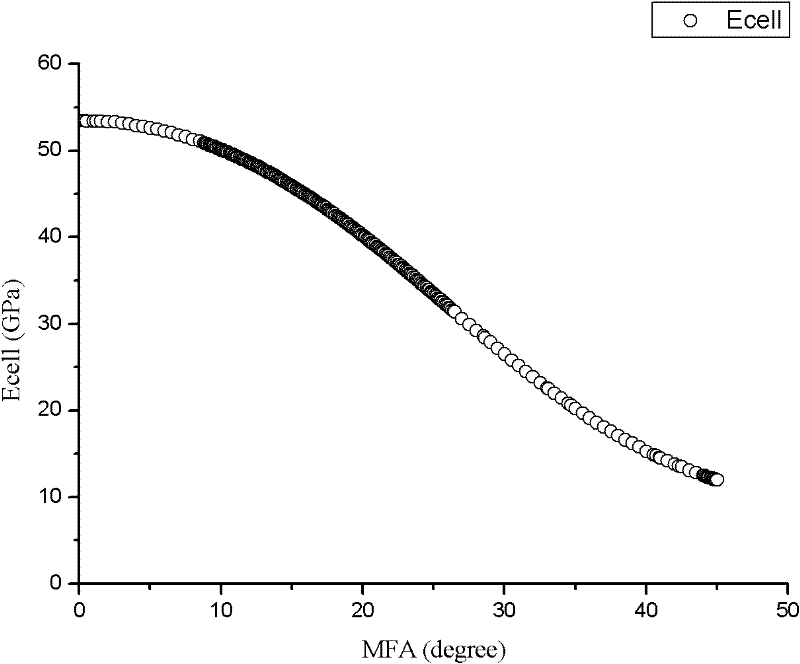
Nondestructive detection method of mechanical properties of standing timbers
The invention discloses a nondestructive detection method of mechanical properties of standing timbers. The method comprises the following steps of: S1, establishing a prediction model Ecell of a longitudinal elastic modulus of a wood cell wall; S2, establishing a prediction model of a wood macroscopic longitudinal elastic tensile modulus E taking the air-dry density rho and a microfibril angle MFA of a mechanical sample as independent variables: E=a*( rho / rhocell) Ecell+b; S3, measuring the elastic tensile modulus of wood rift grains, the air-dry density and the MFA on the same one mechanical sample, putting the measured data into E and carrying out linear regression to obtain coefficients a and b, and completing the establishment of the wood macroscopic longitudinal elastic tensile modulus E; and S4, drilling the standing timbers to take a growth cone, detecting the air-dry density and the MFA of the growth cone from a pith to bark multipoint, and putting into the model E after the step S3 so as to obtain the predicted value and regularities of distribution of the longitudinal elastic modulus of the standing timbers. According to the nondestructive detection method, the nondestructive and accurate measurement to the mechanical properties of the standing timbers is realized.
Owner:国际竹藤网络中心
Medical device comprising collagen-vi
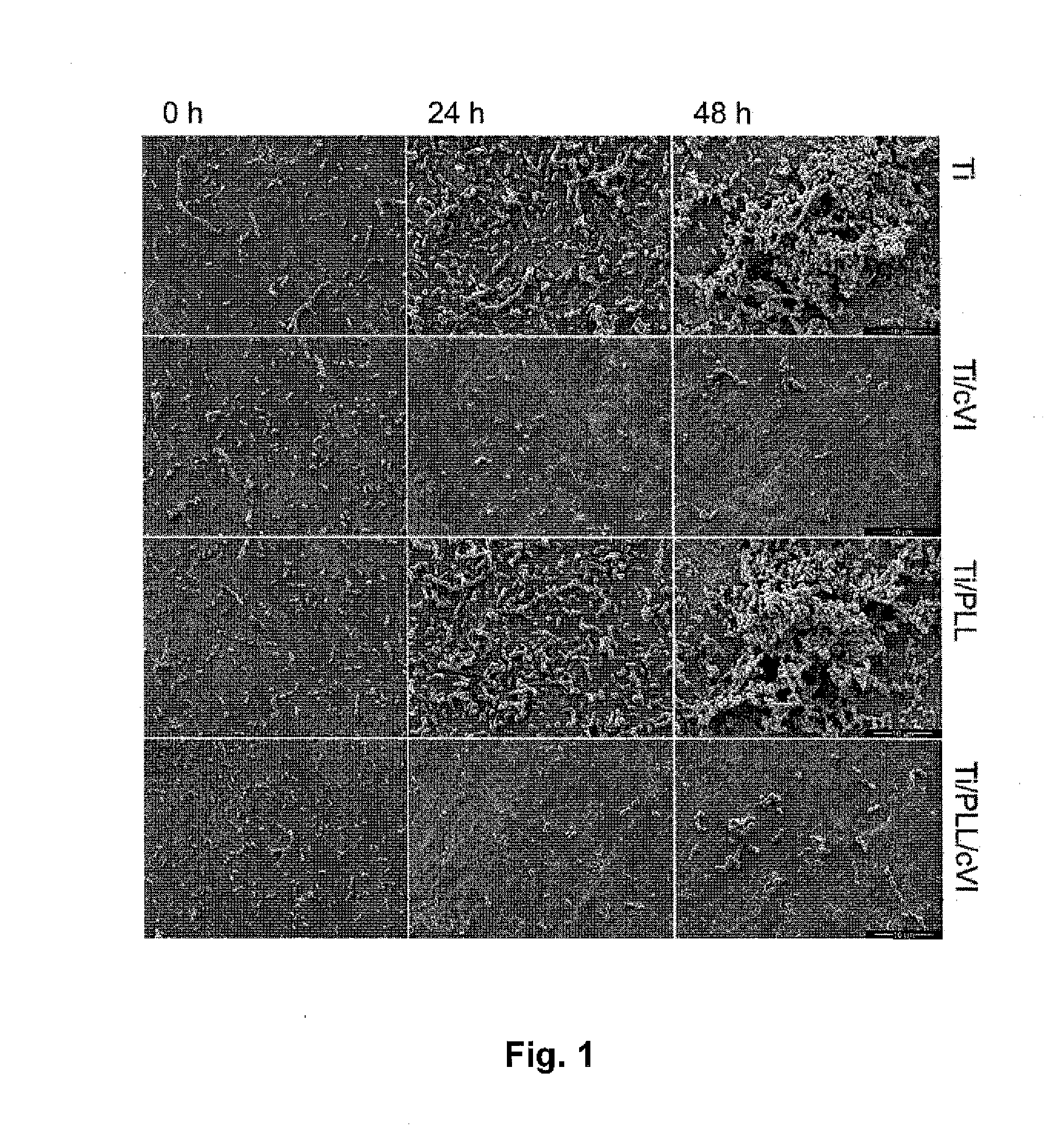
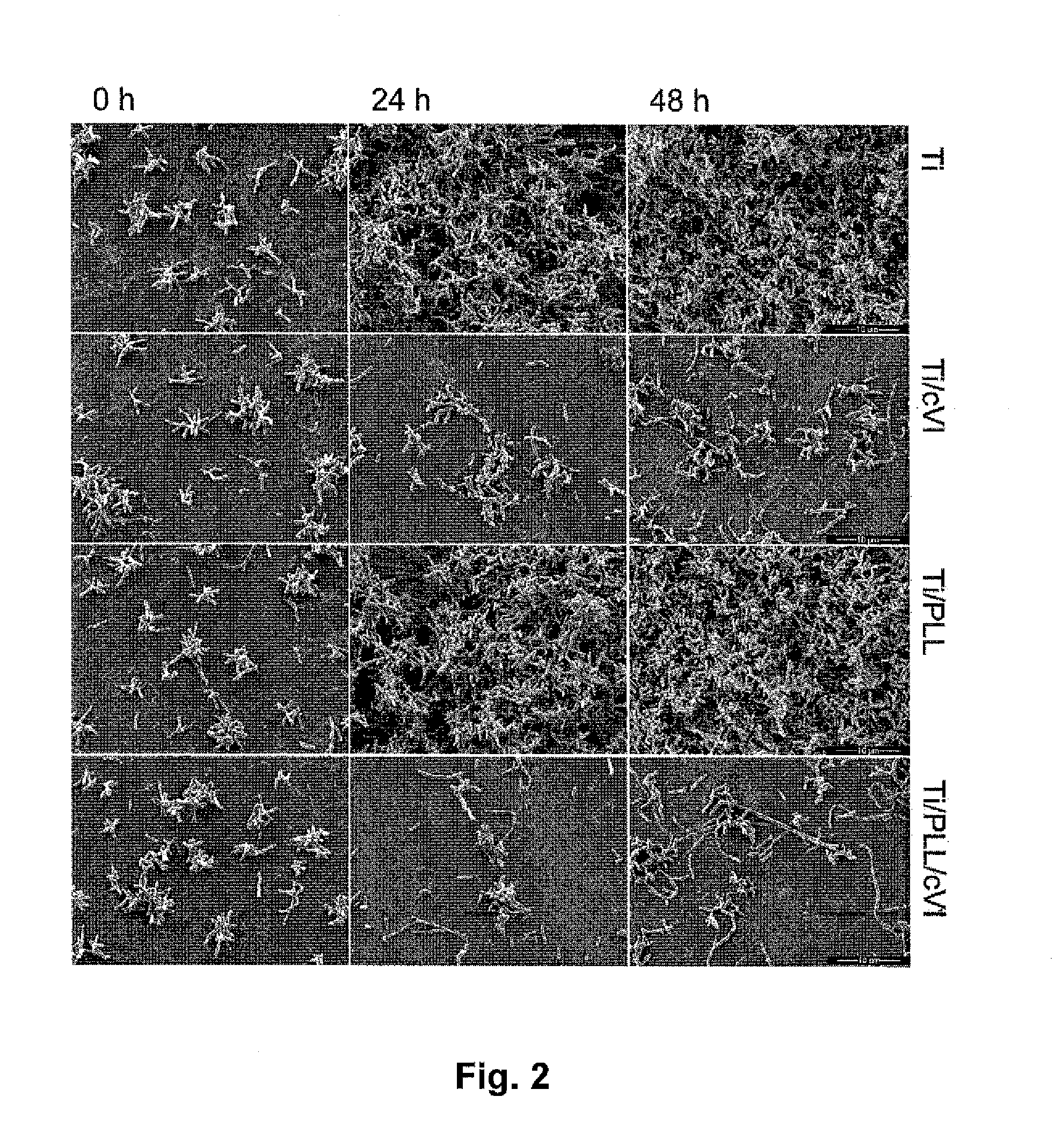
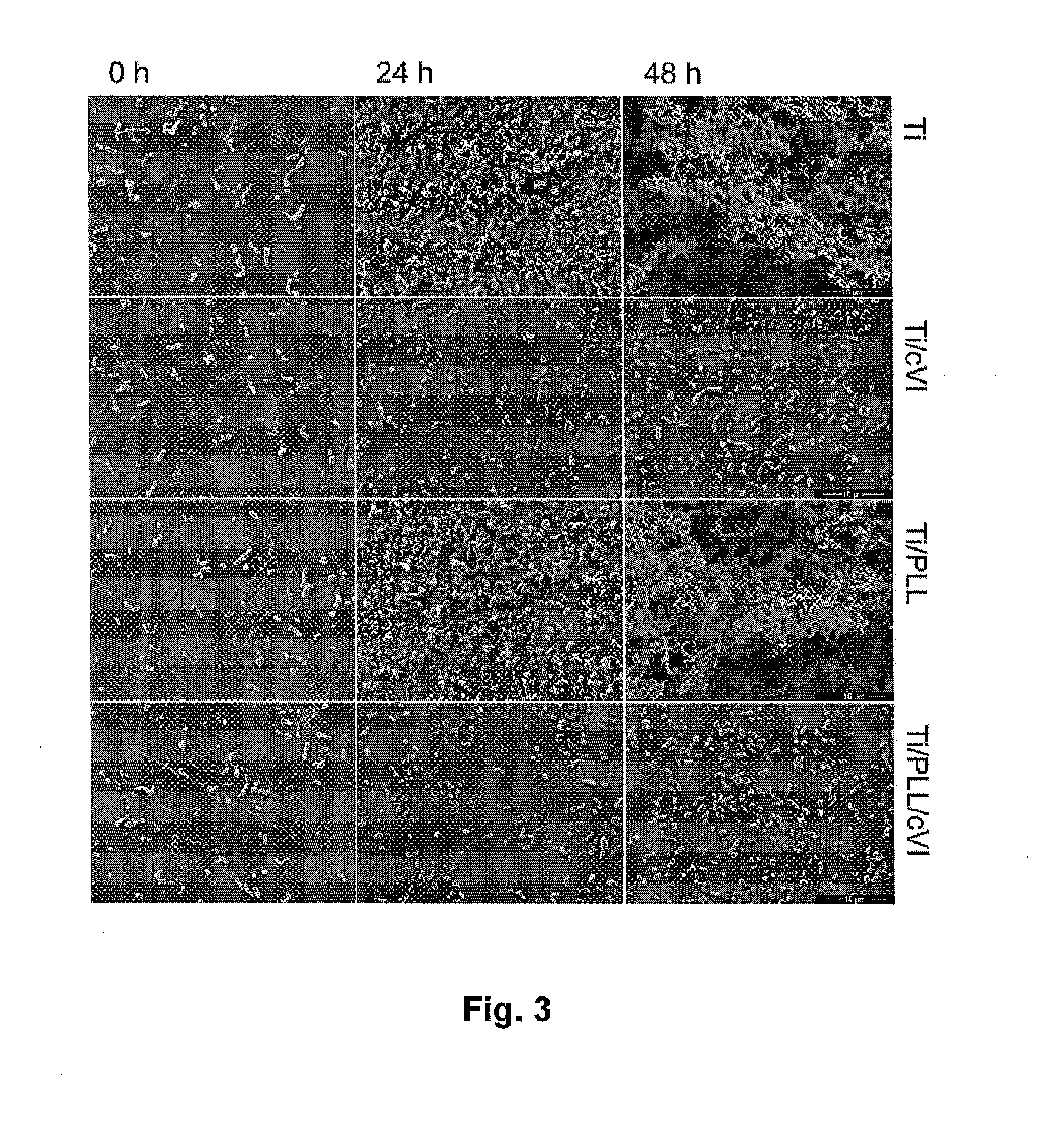
InactiveUS20140377323A1Reduce riskResist attenuationDental implantsPeptide/protein ingredientsMedicineLiving body
A medical device intended for insertion into a living body, which includes a non-biodegradable substrate having a tissue contact surface, wherein said tissue contact surface is at least partially coated with microfibrils of collagen VI.
Owner:DENTSPLY SIRONA INC
A method for the production of a film comprising microfibrillated cellulose, a film and a paper or paperboard product
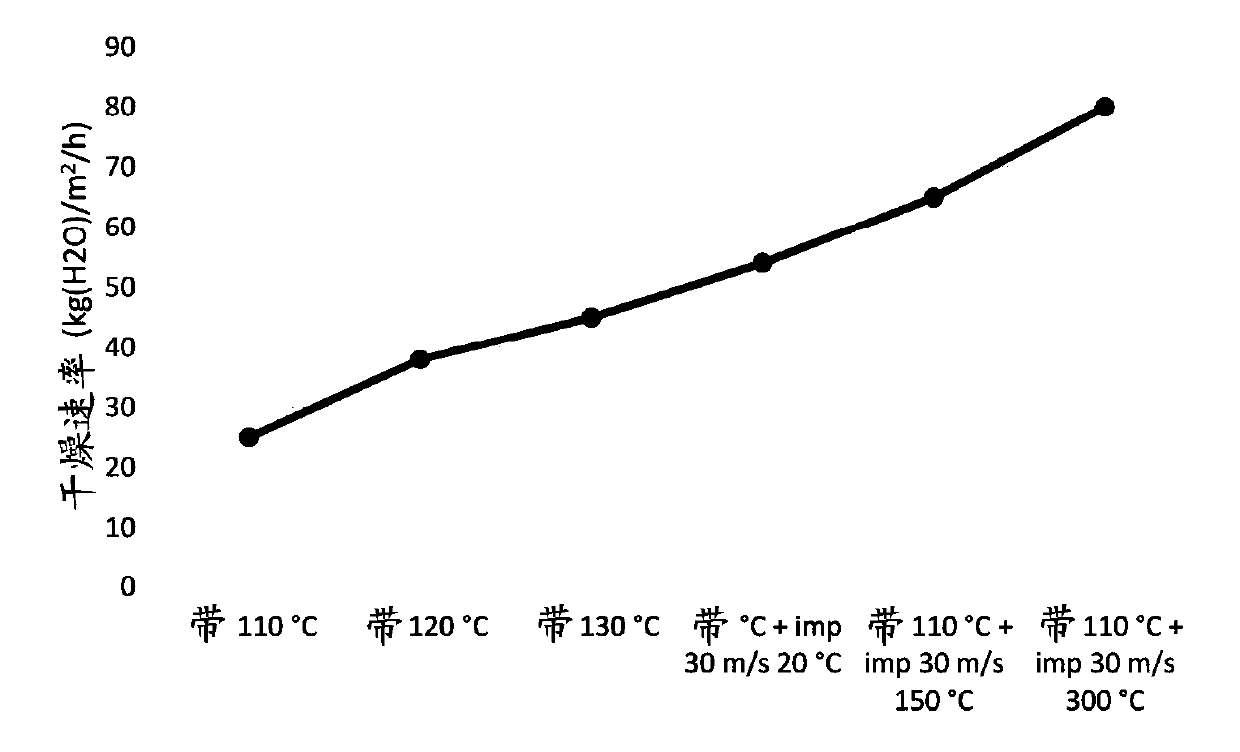
The present invention relates to a method for the production of a film comprising microfibrillated cellulose, wherein the method comprises the steps of; providing a suspension comprising between 70 weight-% to 100 weight-% of microfibrillated cellulose based on total dry weight, forming a fibrous web of said suspension, drying the web in a drying equipment wherein the web is at least partly driedat a drying rate above 75 kg(H2O) / m2 / h by use of hot air whereby a film is formed. The invention also relates to a film produce according to the method and a paper or paperboard substrate comprising said film.
Owner:STORA ENSO OYJ
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com