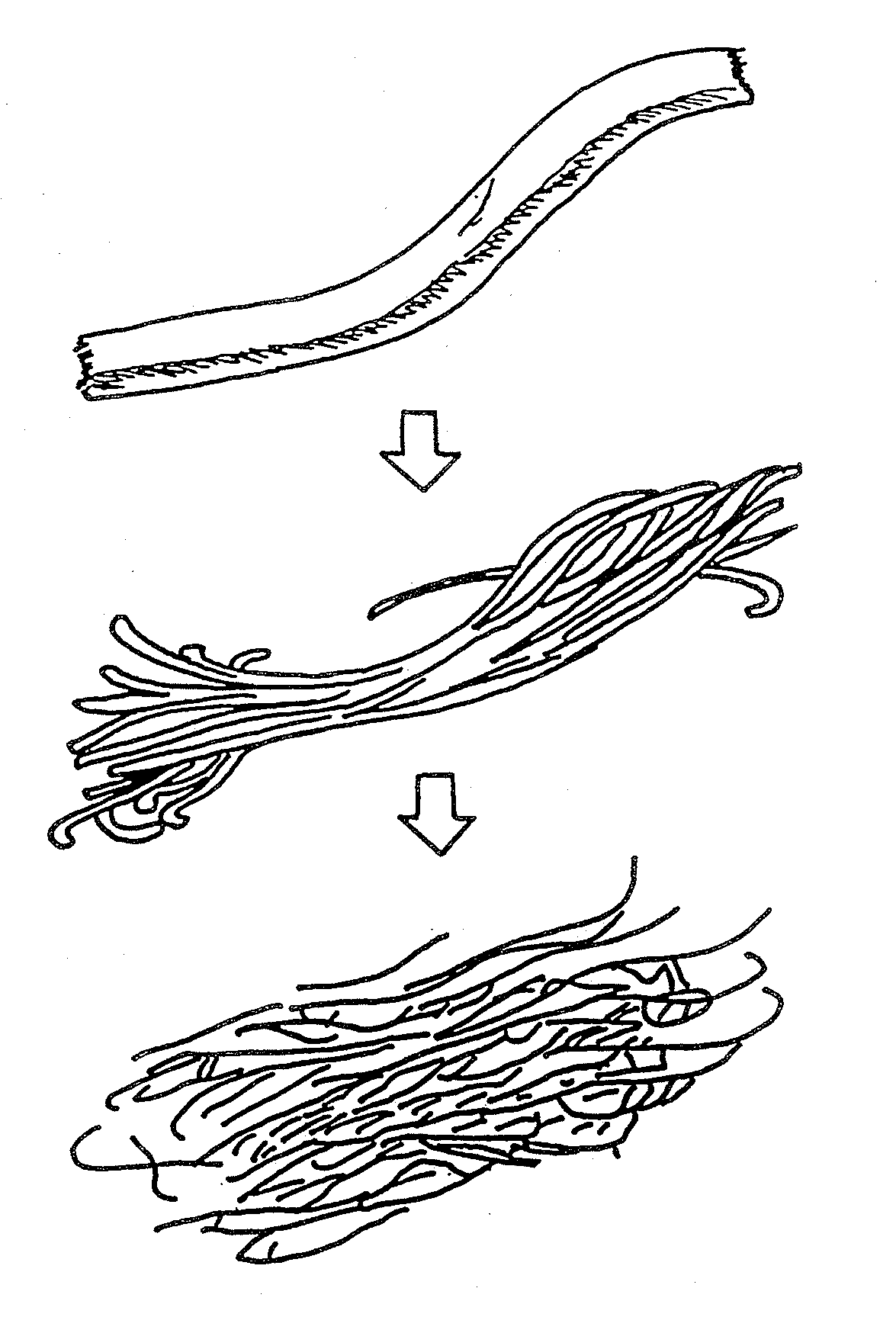
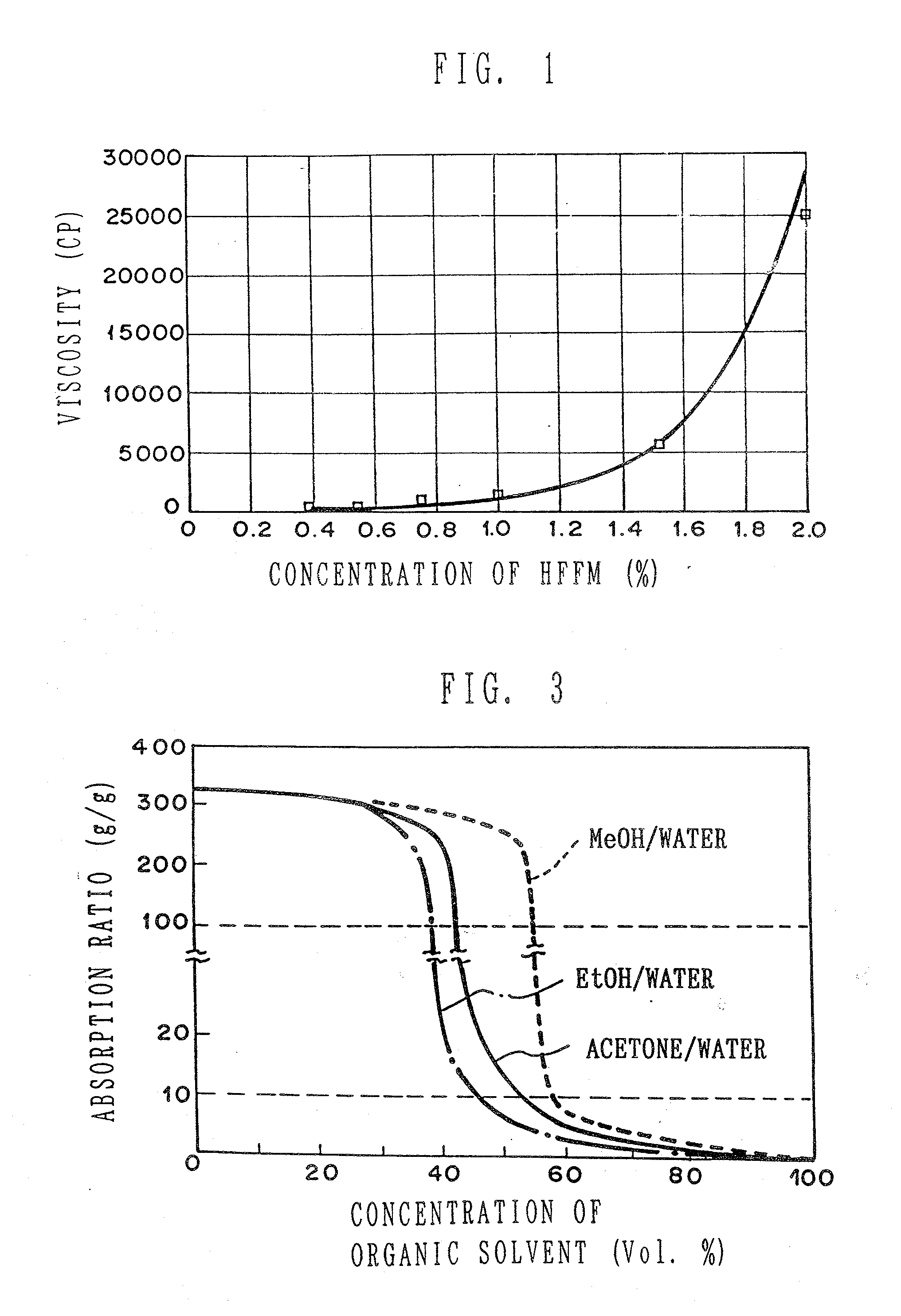
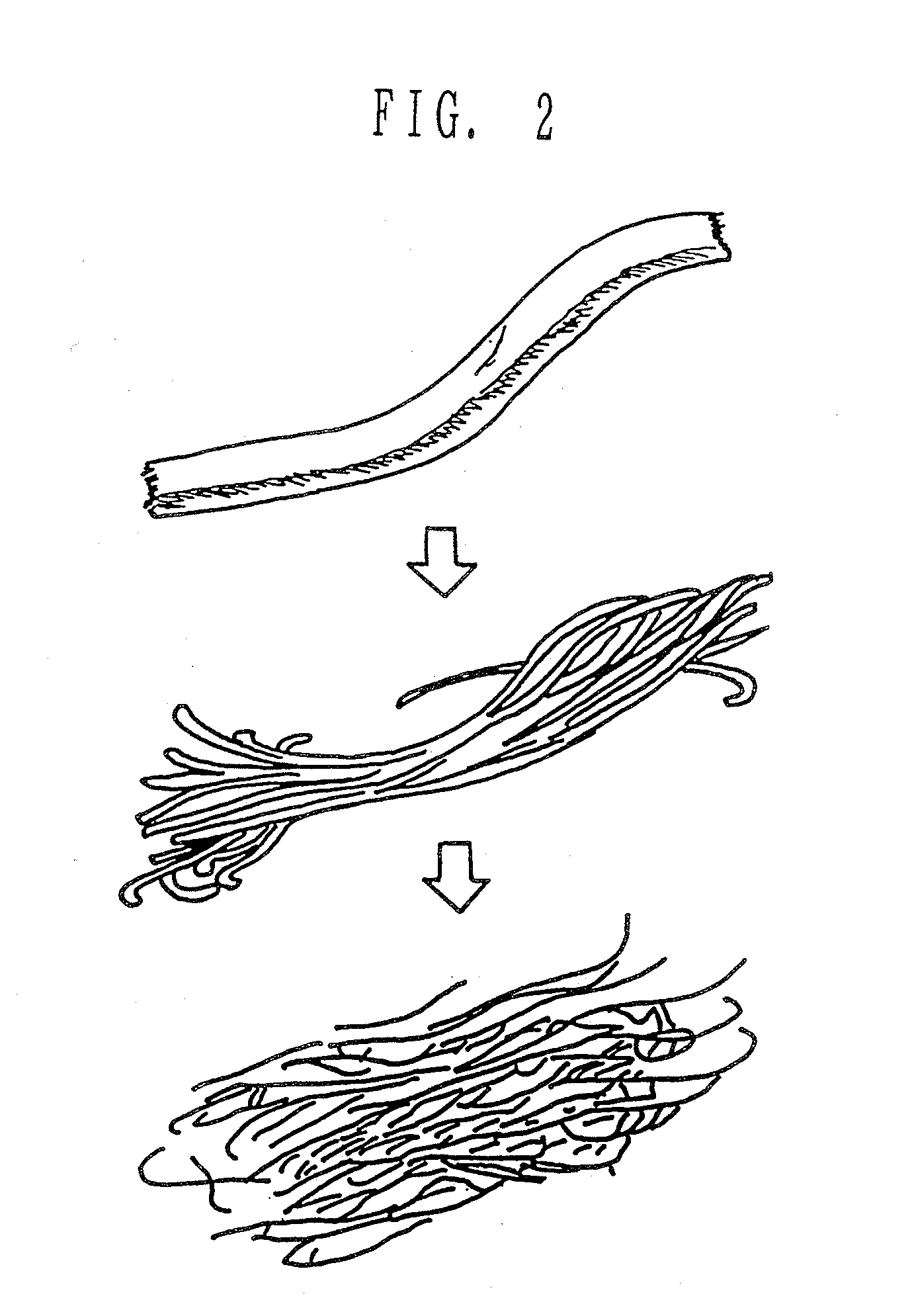
Highly absorbent composite and method of making the same
a composite and high-absorption technology, applied in the field of new-type absorbent composites, can solve the problems of no successful commercialization examples reported, no effective absorbent products have been developed, and initial absorbing is very fast, so as to achieve high viscosity, improve the effect, and hold stably in a small spa
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparing the HFFM Dispersion Liquids
[0310]Ethyl alcohol and ion-exchanged water were added to a dispersion liquid of the S-MFC (made by Tokushu Paper Mfg. Co., Ltd.) in gel state of 3.0% water dispersion as a stock liquid, to make three kinds of microfibril dispersion liquid where the ratio of ethyl alcohol / water was 70 / 30 and the concentrations of the S-MFC were 0.25%, 0.5% and 1%, respectively.
Preparing the HFFM / SAP Coexistent Dispersion Liquids
[0311]10 grams of the SAP (made by Sanyo Chemical Industries, Ltd. under the trademark “IM-6700”) passed by 60 to 100 mesh was added to 50 cc of each of the above-mentioned three kinds of the HFFM dispersion liquid to prepare the HFFM / SAP dispersion slurry.
[0312]The prepared dispersion slurry is described as follows:
TABLE 2ExperimentEthylConcentrationS-MFC / SAP ×No.alcohol / waterof S-MFC (%)100 (%)No. 170 / 300.20.1No. 270 / 300.52.5No. 370 / 301.05.0
Forming the HFFM / SAP Composite Sheet Material
[0313]Each of the dispersion liquids while stirred wa...
example 2
Concentration of the HFFM and the Properties of a Composite Sheet Material
[0318]Preparing the HFFM Dispersion Liquid
[0319]Preparing a Bacteria Cellulose (BC) Stock Solution
[0320]BC (made by B.P.R.) where the concentration of solids was 30% was stirred and dissolved in ion-exchanged water by a mixer for approximately 2 hours to prepare a stock solution where the concentration of solids was 1.2%.
Preparing Ethyl Alcohol / Water Dispersion Liquids of BC
[0321]Ethyl alcohol and water were added to a prescribed amount of the stock solution to prepare BC dispersion liquids of 0.02% to 0.80% BC.
Preparing the HFFM / SAP Coexistent Dispersion Liquid
[0322]5 grams of the SAP (made by Sanyo Chemical Industries, Ltd.) was added to 50 cc of each of the dispersion liquids of 0.02% to 0.8% BC to prepare BC / SAP dispersion liquids. In case the concentration of the BC was lower in the dispersion liquid, the SAP settled, but as the concentration of the BC became higher, it became stabilized. By stirring with...
example 3
Continuous Coating Experiments
[0328]A highly absorbent composite was made by using an apparatus as shown in FIG. 61 provided with a coating unit as shown in FIG. 63, using the following materials:
(1) Microfibril: S-MFC (made by Tokushu Paper Mfg. Co., Ltd.)
(2) SAP: 1M-4000 (made by Hoechst-Celanese Co.)
(3) Suspension medium: Acetone / water system
(4) Coating composition:
Component% by weightS-MFC0.4SAP30.0Acetone48.8Water20.8
(5) Supporting sheet: A two-layered through-air thermal bond web non-woven fabric (40 g / cm2, apparent specific density of 0.06) having the following composition was used:
[0329]Upper layer: Mixed web of rayon (4 denier×45 mm length (70%)) and PE / PET (2 denier×45 mm length (30%)), approximately 25 g / cm2
[0330]Lower layer: Single web of PE / PET bicomponent fiber (2 denier×45 mm length), approximately 15 g / cm2.
[0331]A mixture dispersion liquid of the composition in (4) above was continuously applied in approximately 10 mm width at an interval of 5 mm width onto the surf...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com