Coating composition of nano cellulose, its uses and a method for its manufacture
一种纳米纤维素、组合物的技术,应用在水性涂料组合物领域
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1a
[0082] Example 1a. Preparation of Microfibrillated Cellulose (Nanocellulose)
[0083] The cellulose selected for the production of microfibrillated cellulose was obtained from Bleached long-fiber kraft kraft pulp (Kraft pulp) (fully bleached kraft pulp mainly based on spruce that is completely chlorine-free). Kraft pulp was mechanically treated in a Claflin cone homogenizer using a specific energy consumption of 2000 kWh / ton combined with homogenization. Homogenization was done using a high pressure homogenizer (model 12.56VH, APV, Rannie LAB) at a consistency of 0.5 to 1% with 5 passes and a pressure of 1000 bar [8].
Embodiment 1b
[0084] Example 1b. Preparation of Microfibrillated Cellulose (Nanocellulose)
[0085] The cellulose selected for the production of microfibrillated cellulose was obtained from Bleached long-fiber kraft kraft pulp (fully bleached kraft pulp mainly based on spruce that is completely chlorine-free). Kraft pulp was mechanically treated in a Claflin cone homogenizer using a specific energy consumption of 2000 kWh / ton combined with homogenization. Homogenization was done using a high pressure homogenizer (model 12.56VH, APV, Rannie LAB) at a consistency of 0.5 to 1% with 5 passes and a pressure of 1000 bar [8].
[0086] Nanocellulose concentrates (1% to 4%) are obtained by centrifugation or evaporation from 0.5% to 1.0% aqueous dispersions of nanocellulose produced by the homogenization process. Centrifugation was performed in a Heraeus 400R (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) at 2500 rpm and 22°C during 60 minutes. This treatment is repeated until the desired con...
Embodiment 2
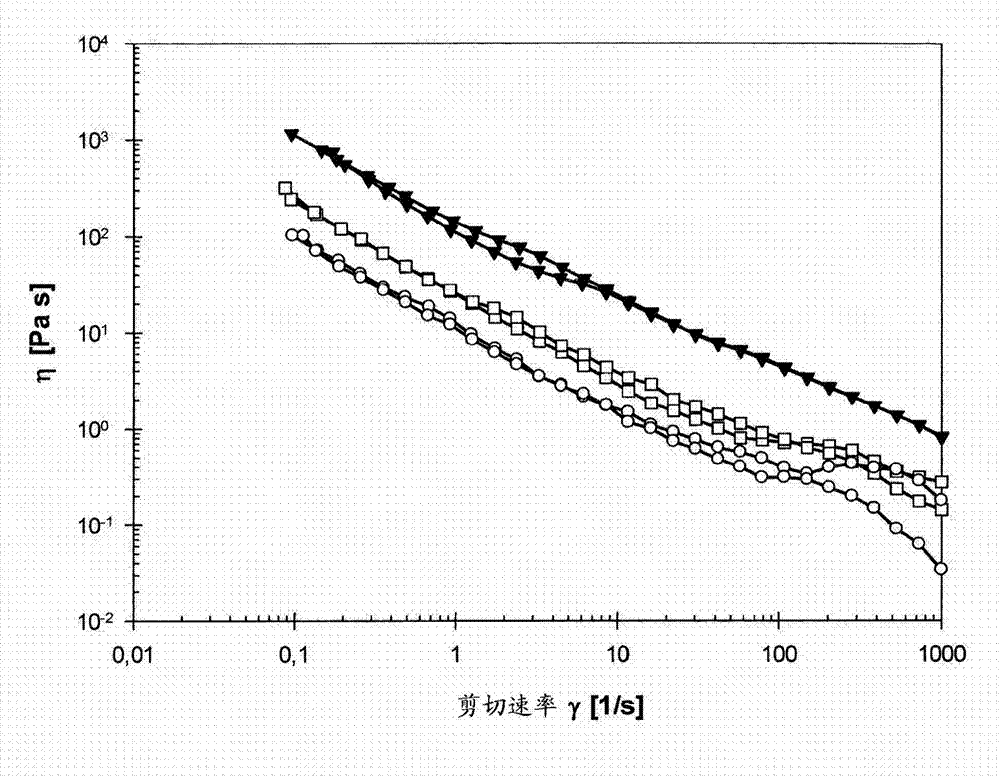
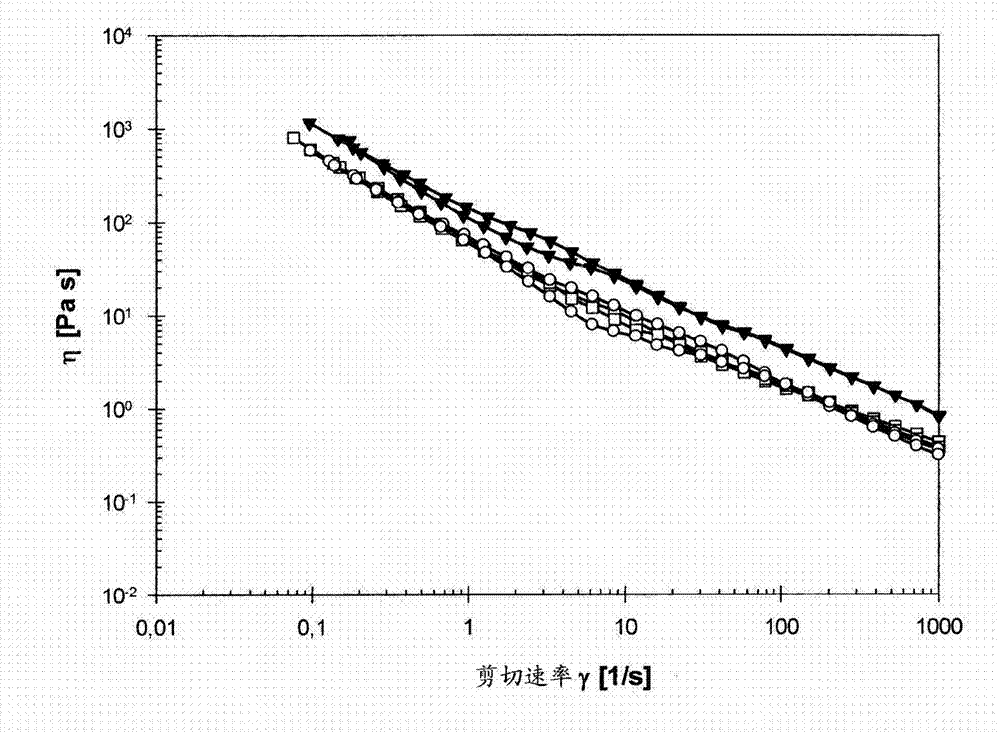
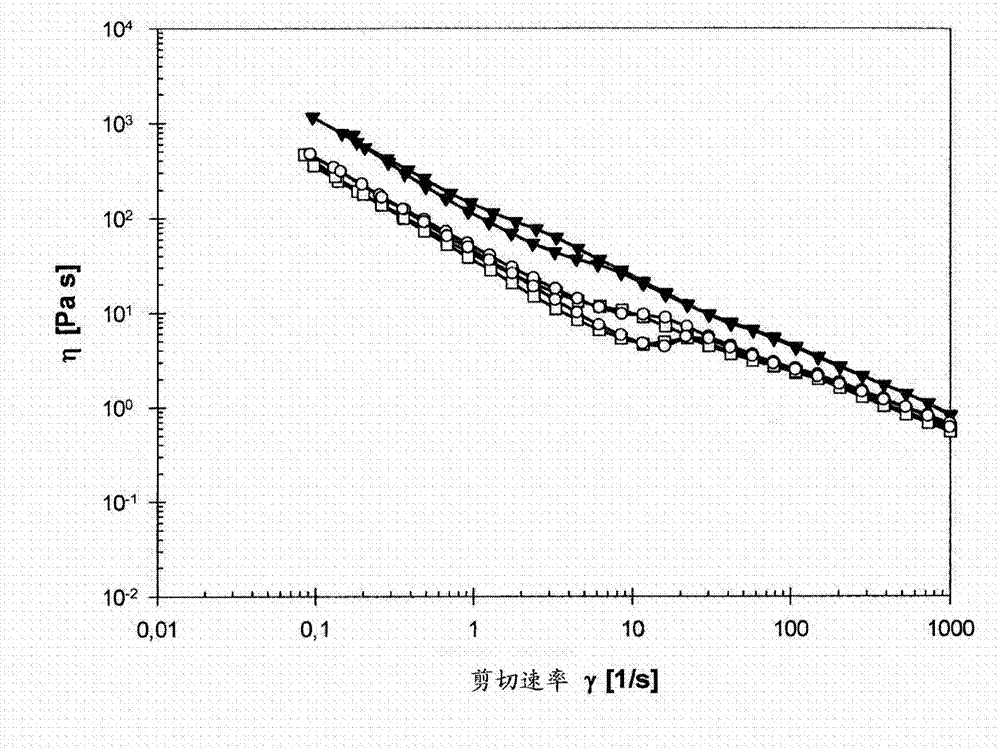
[0087] Example 2. Preparation and testing of compositions according to the invention
[0088] Table 1: Surfactants selected for testing
[0089]
[0090] According to principles known to those skilled in the art, cationic surfactants according to Table 2 were added to 1% to 4% of the aqueous dispersion of nanocellulose (Example 1b). The composition was stirred for 10 minutes after adding the surfactant and the pH of the composition was adjusted to neutral pH (pH 6 to 7) by adding HCl and / or NaOH. The compositions were evaporated to different dry matter contents (2.24% to 5.55%) in an oven at 75°C. A summary about sample preparation and its rheological testing is shown in Table 2.
[0091] Table 2: Summary table of tests performed on different solutions
[0092]
[0093] Rheological measurement
[0094] The low-shear and oscillatory rheological properties of the nanocellulose dispersions were measured on a Physica MCR 301 (Anton Paar GmbH, Graz, Austria) rotationa...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| base weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| coating mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com