Nondestructive detection method of mechanical properties of standing timbers
A technology of non-destructive testing and standing trees, which is applied in the direction of wood testing, material inspection products, etc., and can solve problems such as narrow applicability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
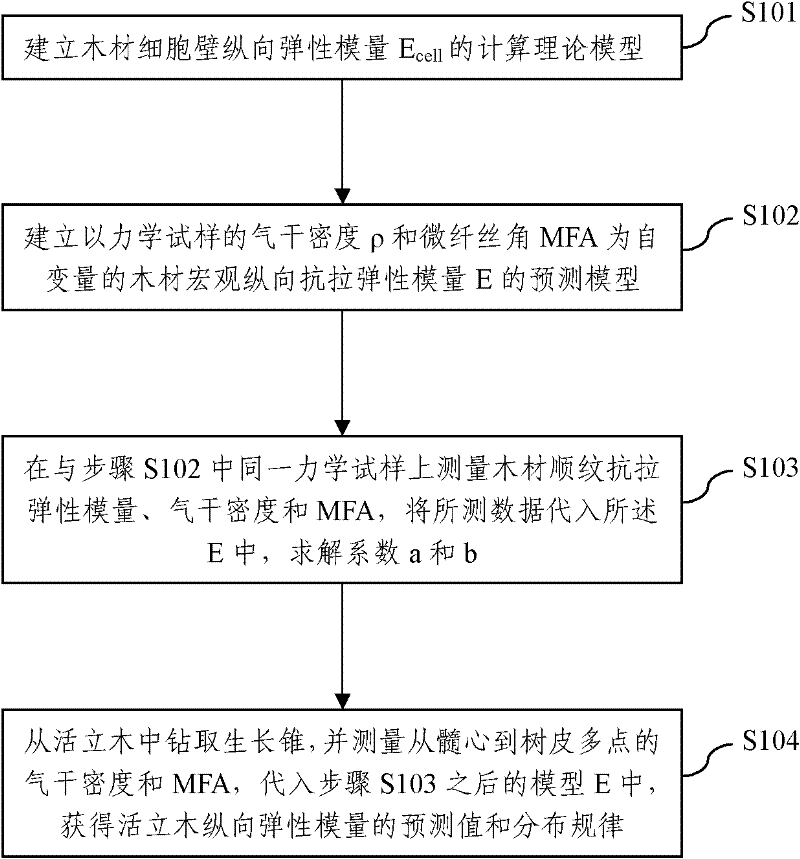
[0030] The present invention is based on the multi-wall layer structure of wood cell wall, applies the stiffness prediction theory and classical laminate theory in the mesomechanics of composite materials, and combines the mechanical properties of the main components of the cell wall and the main characteristics of the wall layer structure to establish the longitudinal elastic modulus of the wood cell wall. Quantitative prediction model to measure the mechanical properties of standing trees, the specific process is as follows figure 1 shown, including:
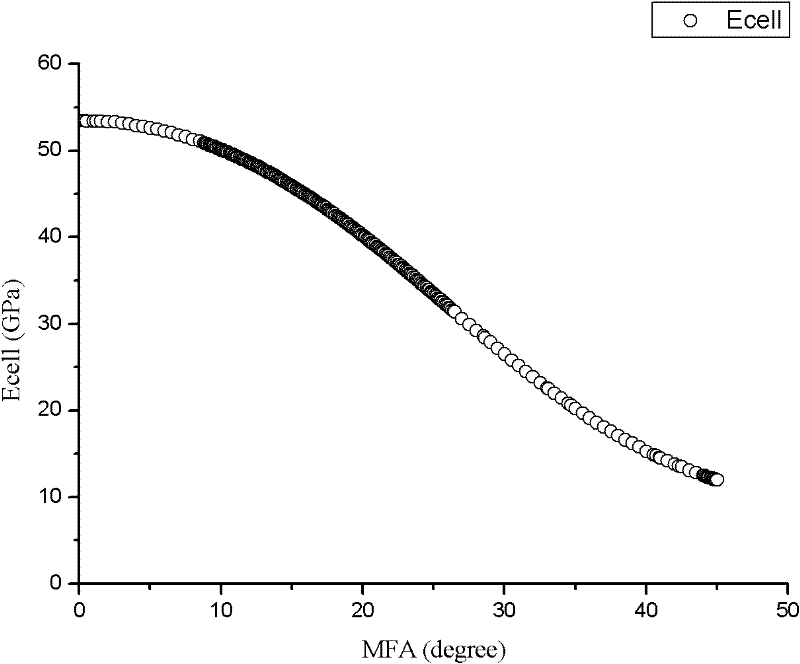
[0031] Step S101, establishing the longitudinal elastic modulus E of the wood cell wall cell Theoretical model of computation:
[0032] E. cell =f(MFA);
[0033] (Refer to the specific content of the model: YU Yan, JIANG Ze-hui, TIAN Gen-lin. Size effect on longitudinal MOE of microtomed wood sections and relevanttheoretical explanation. Forestry Study in China, 2009, 11(4): 243-248)
[0034] When establishing the model, i...
Embodiment 2
[0068] Taking fir wood as the processing object, the processing is carried out according to the following steps:
[0069] Step 1, referring to Step 1 to Step 3 in Example 1 to establish a prediction model for the longitudinal modulus of elasticity of the cell wall of coniferous wood;
[0070] Step 2. After measuring the elastic modulus of the Chinese fir wood tensile national standard sample along the grain, intercept the effective part in the middle of the sample, select a long thin sheet non-standard sample with a thickness between 1mm and 3mm, and use X-ray Diffractometer to measure density and microfibril angle;
[0071] Step 3. Use 2 / 3 of the data set measured in step 2 for modeling, and directly substitute into the prediction model of the macroscopic longitudinal tensile elastic modulus E of wood:
[0072] E=a×(ρ / ρ cell )E cell +b
[0073] Obtain the coefficients a and b, and establish a prediction model for the longitudinal elastic modulus of Chinese fir based on na...
Embodiment 3
[0077] Take poplar tomentosa as the processing object, and proceed as follows:
[0078] Step 1, step 1 to step 3 in the reference embodiment 2 set up the predictive model of Populus tomentosa longitudinal modulus of elasticity;
[0079] Step 2, after measuring the modulus of elasticity of the poplar wood along the grain of the tensile national standard sample, the effective part in the middle of the sample is intercepted, and the X-ray diffractometer is used to measure the density and the microfibril angle;
[0080] Step 3. Use 2 / 3 of the data set measured in step 2 for modeling, and directly substitute into the prediction model of the macroscopic longitudinal tensile elastic modulus E of wood:
[0081] E=a×(ρ / ρ cell )E cell +b
[0082] The coefficients a and b are obtained, and the prediction model of the longitudinal elastic modulus of Populus tomentosa is established:
[0083] E = 1.2293 × ρ 1.5 ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Elastic modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com