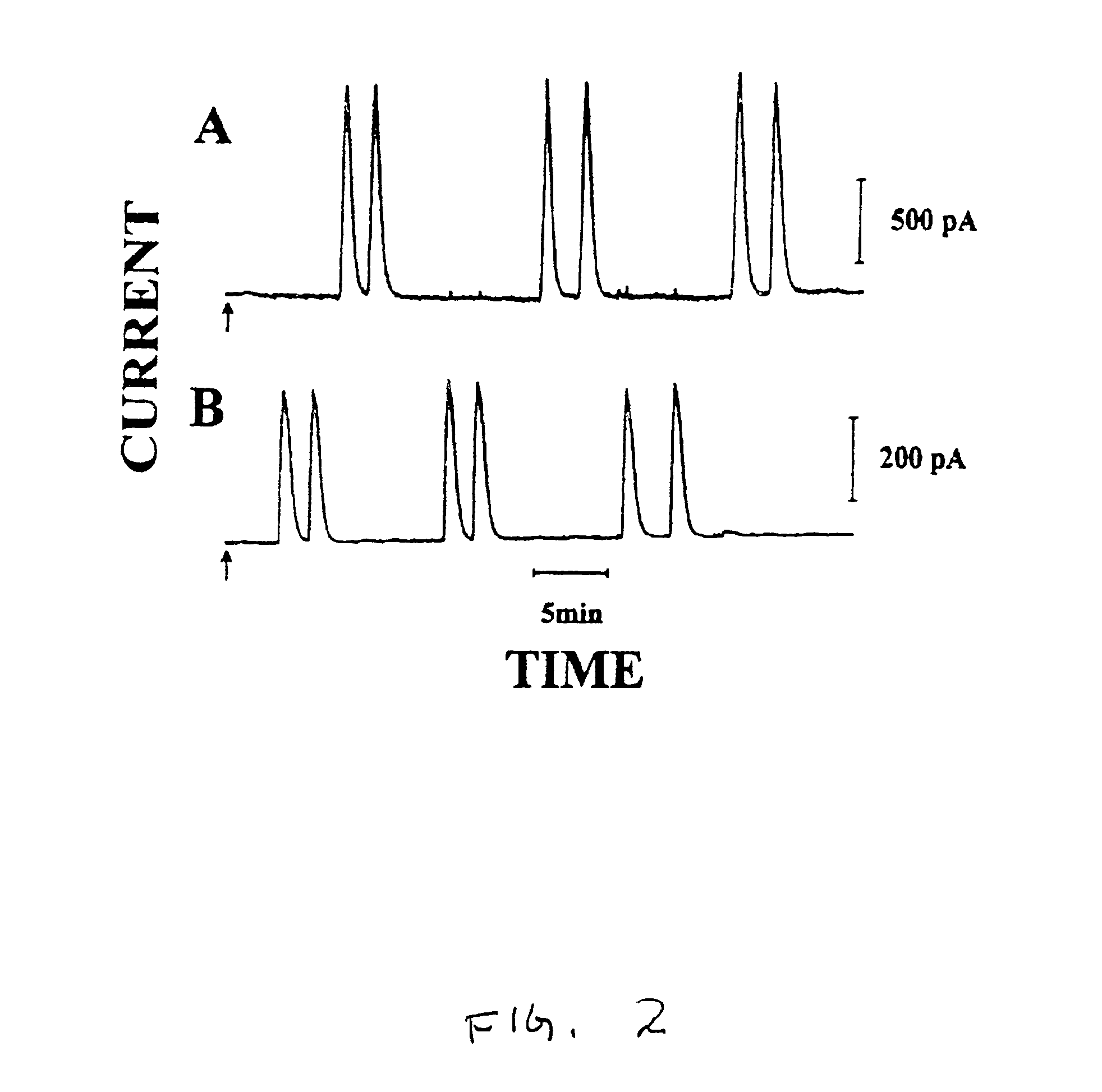
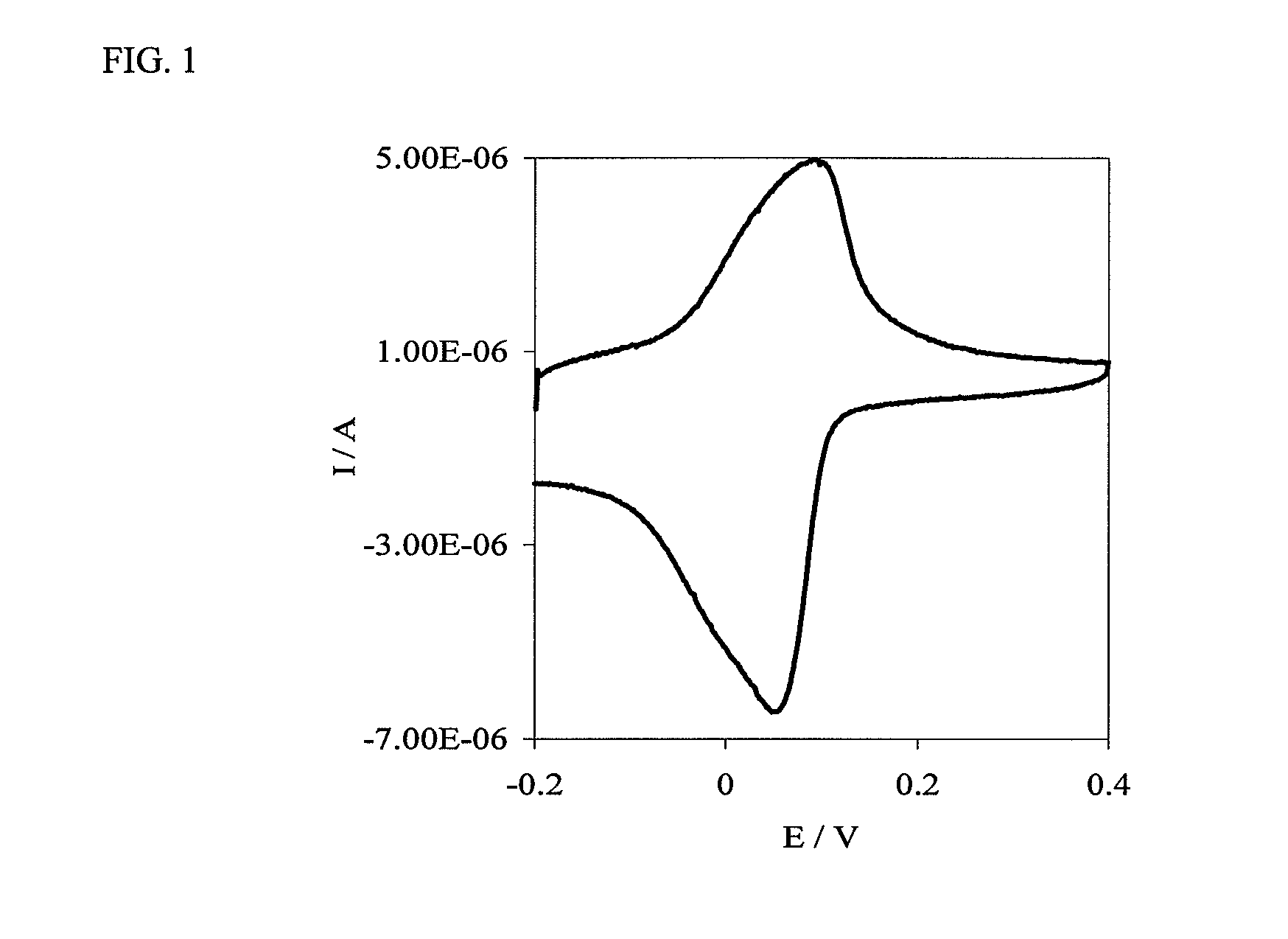
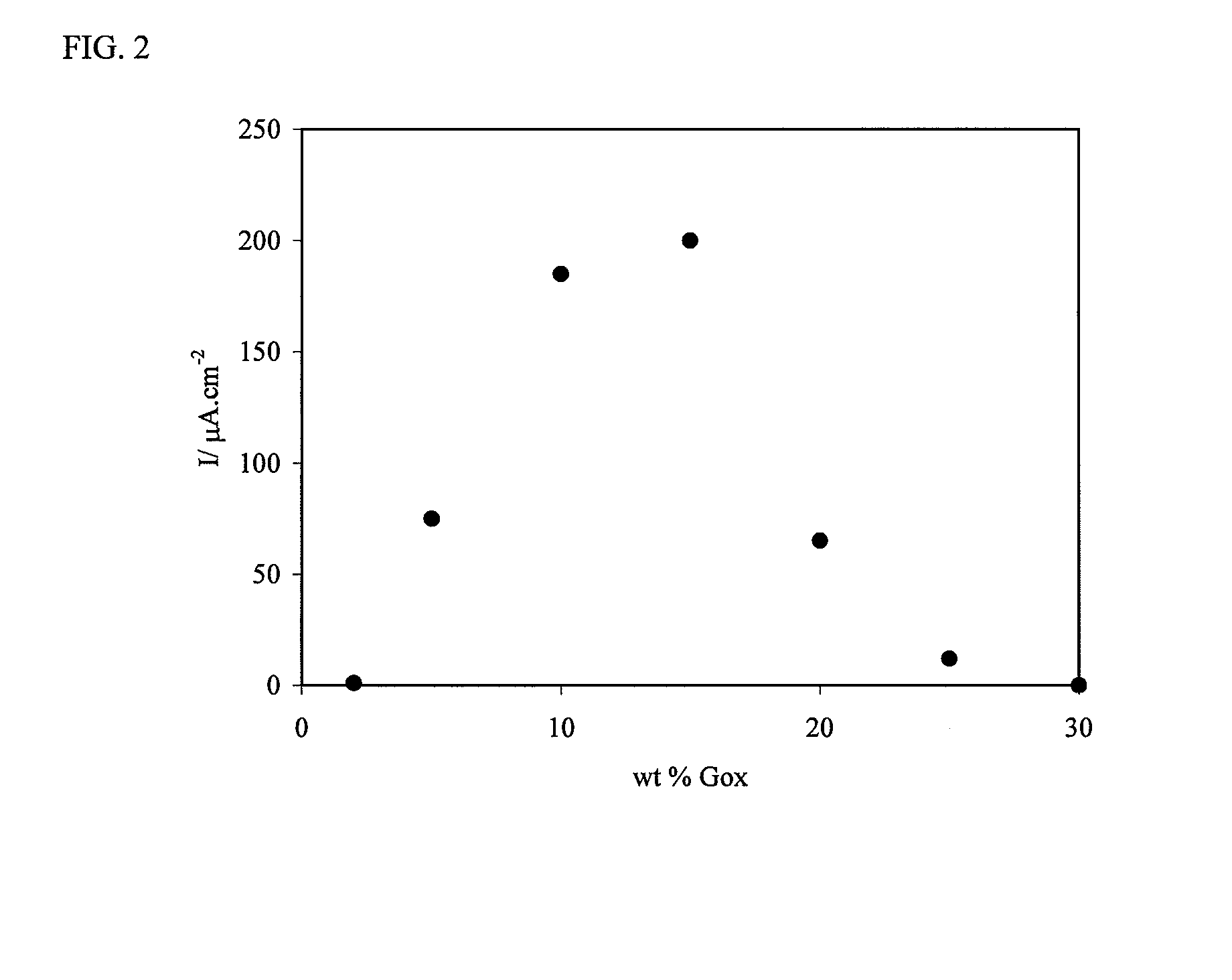
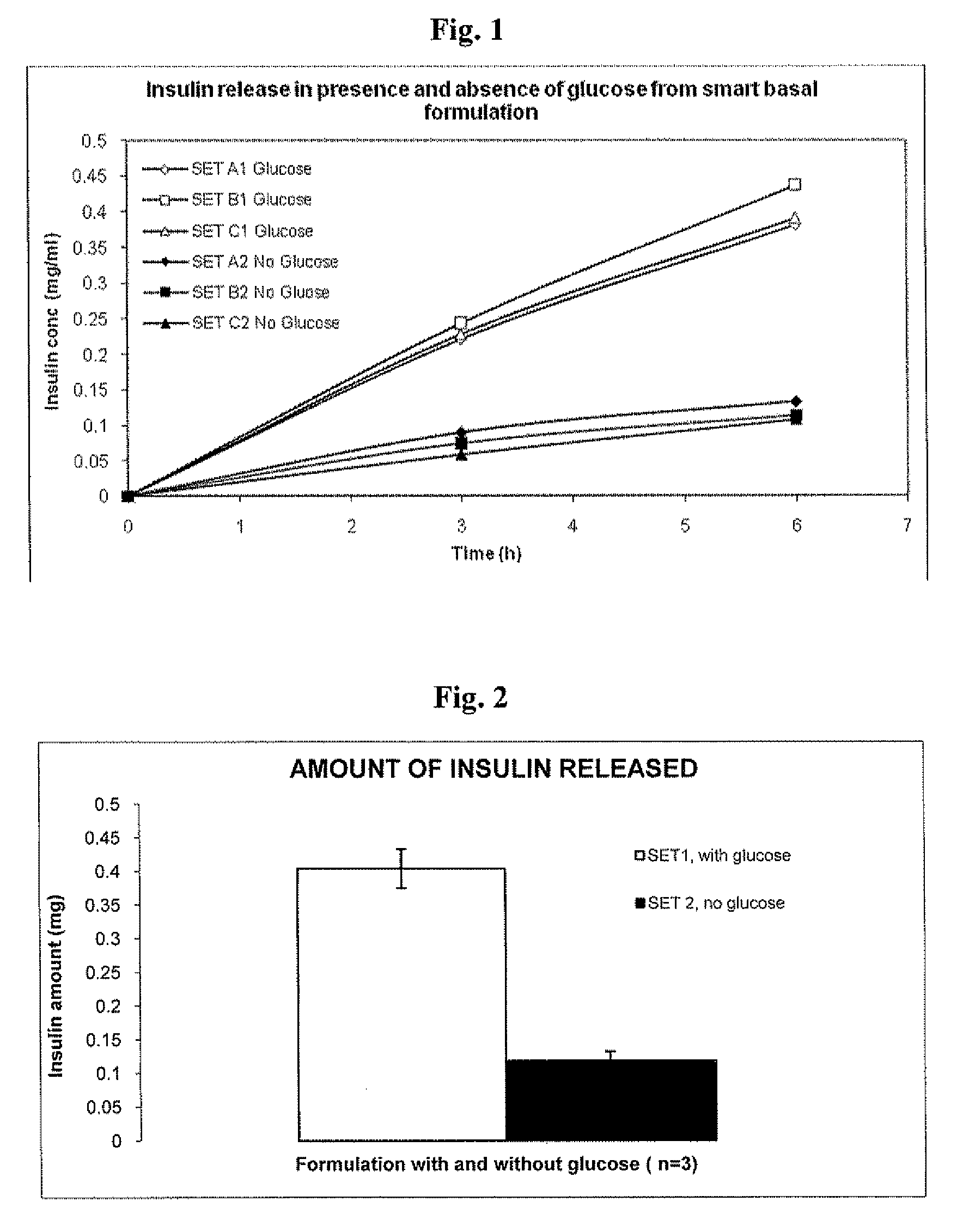
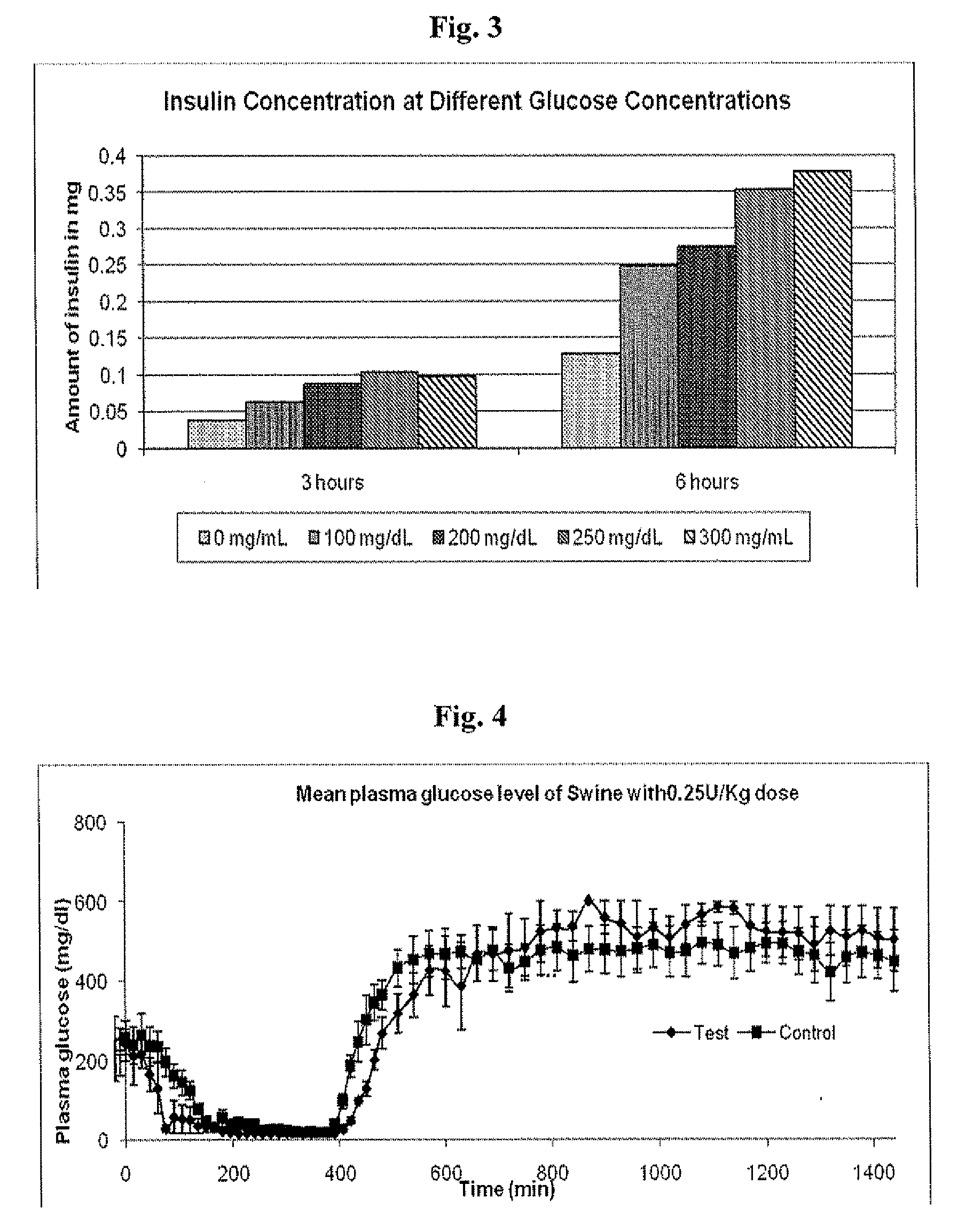
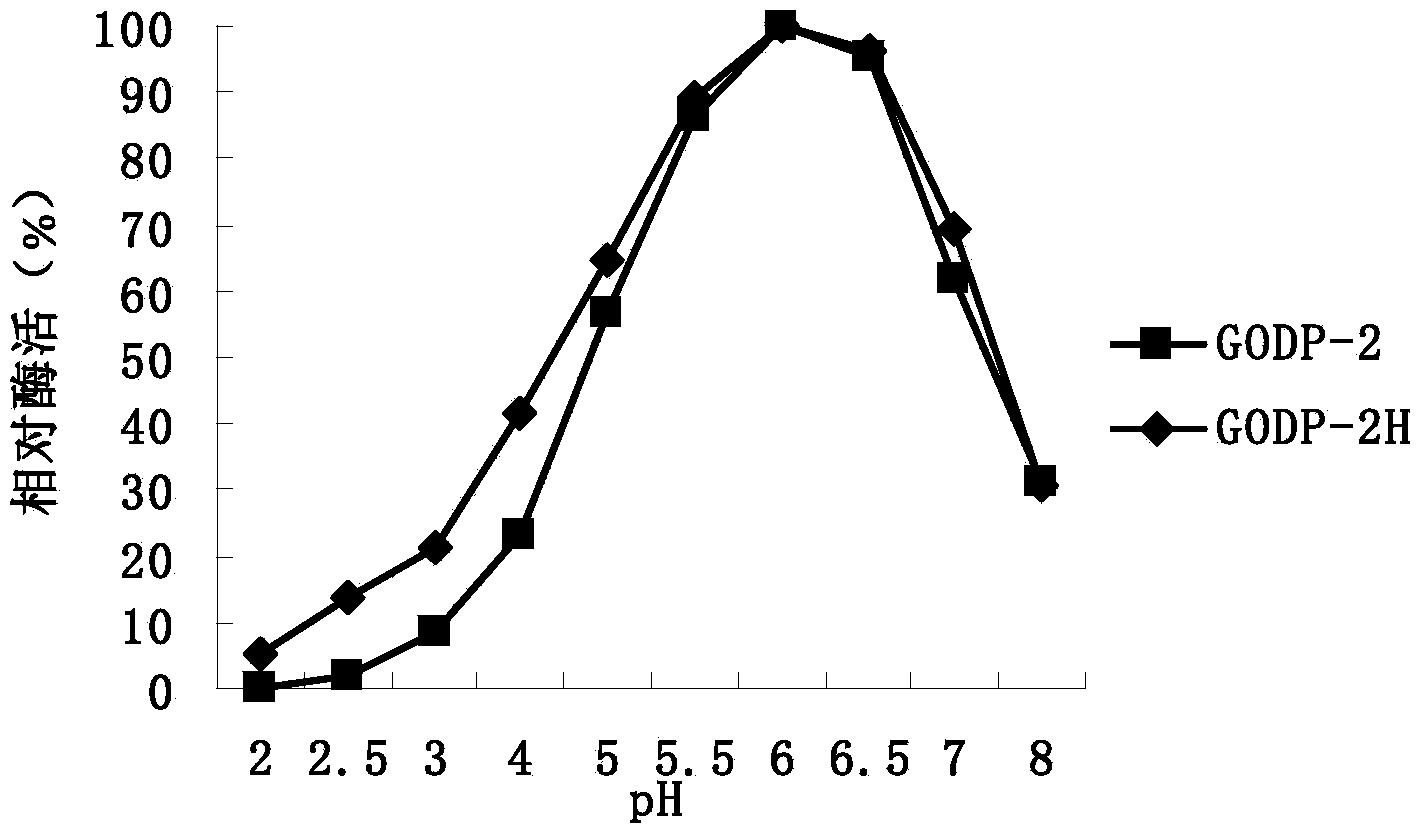Patents
Literature
1742 results about "Glucose oxidase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
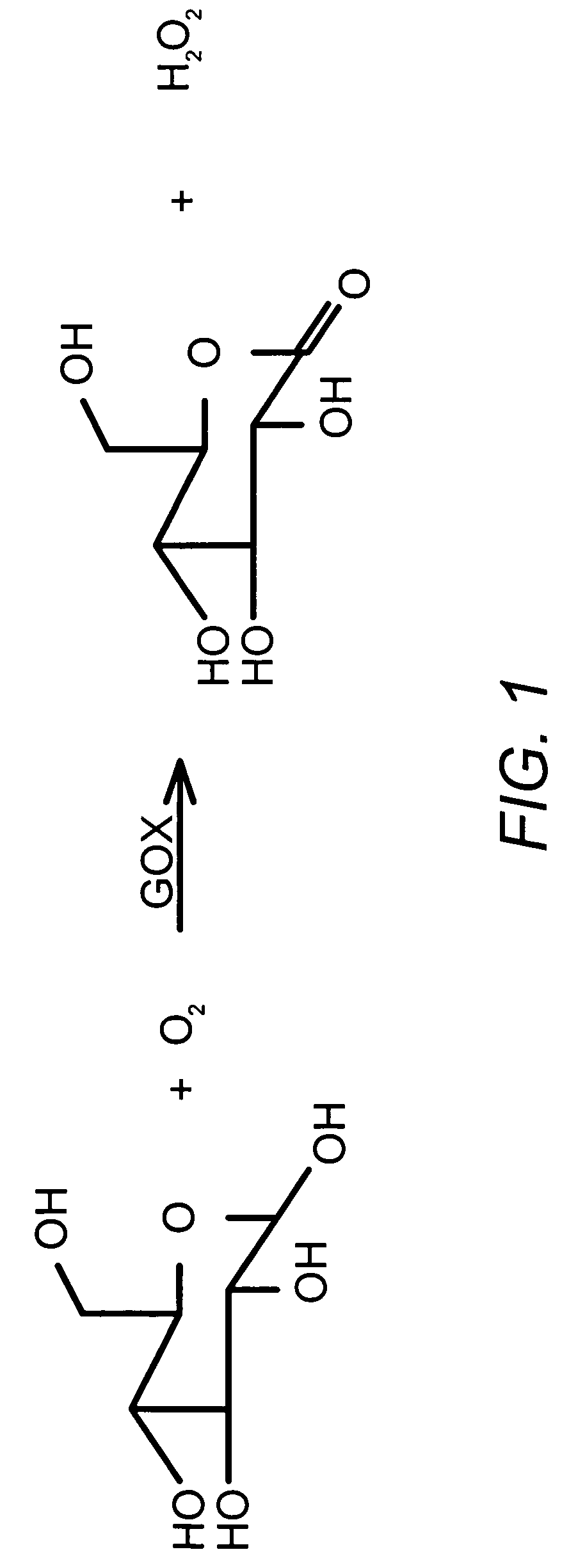
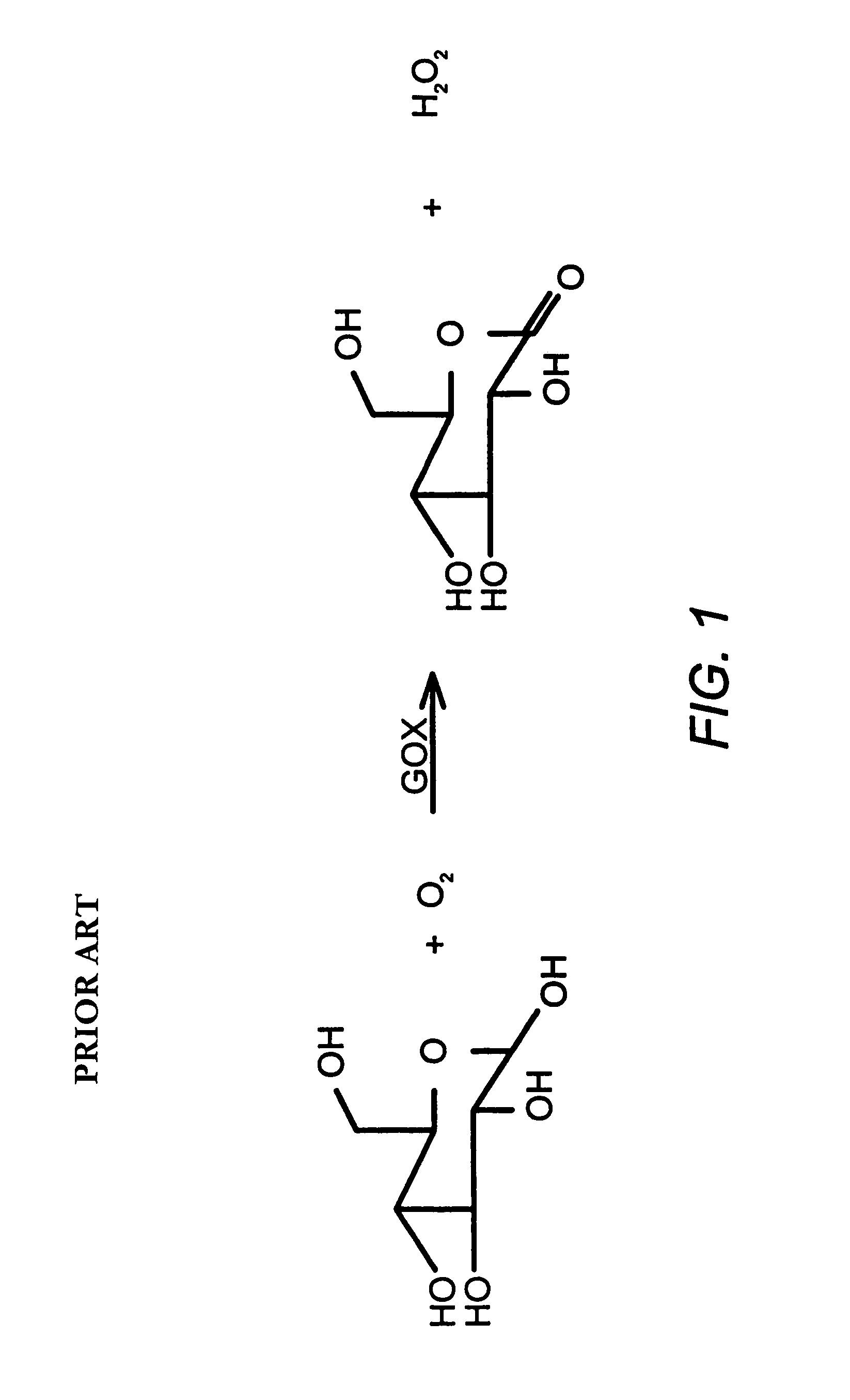
The glucose oxidase enzyme (GOx or GOD) also known as notatin (EC number 1.1.3.4) is an oxido-reductase that catalyses the oxidation of glucose to hydrogen peroxide and D-glucono-δ-lactone. This enzyme is produced by certain species of fungi and insects and displays antibacterial activity when oxygen and glucose are present.
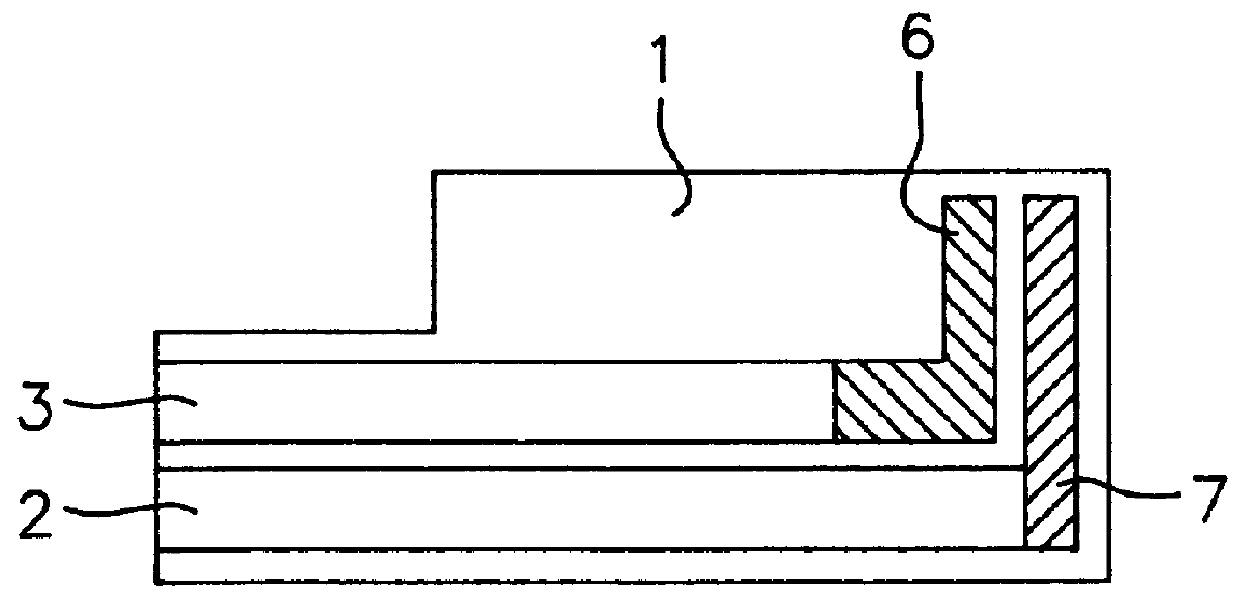
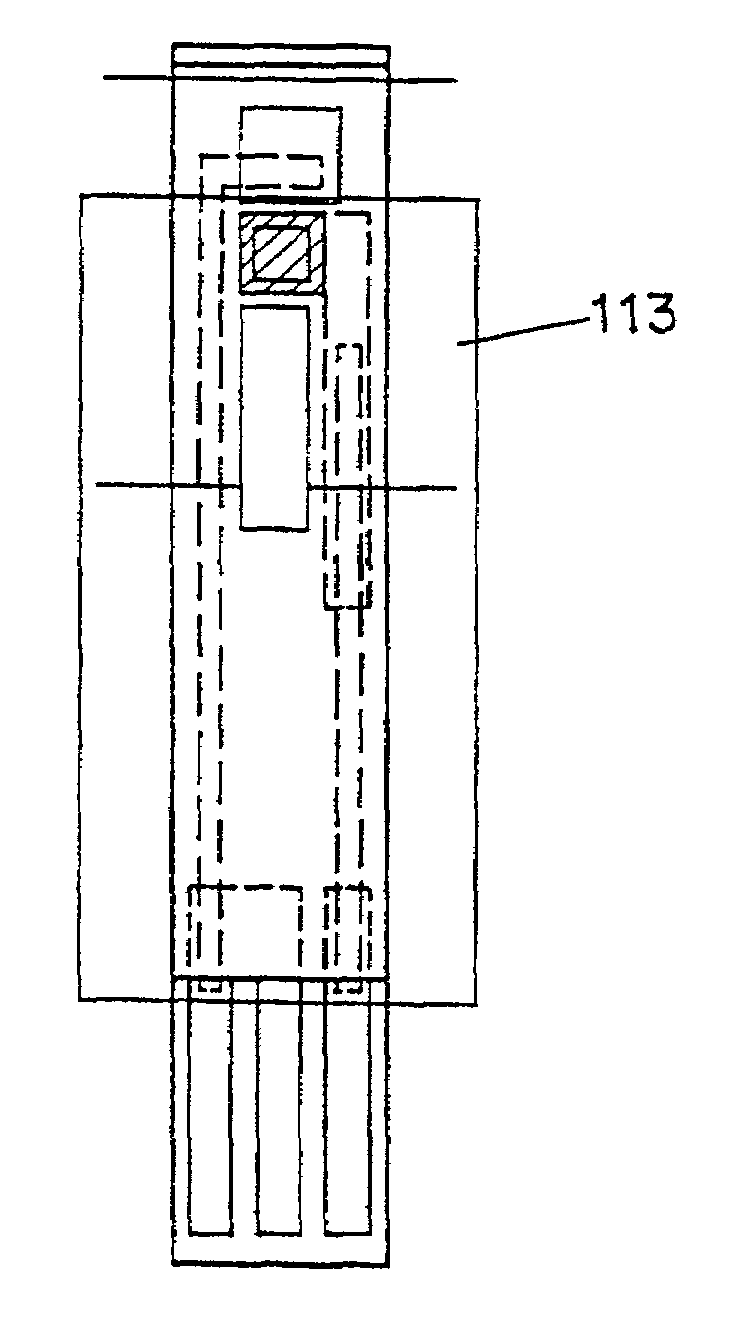
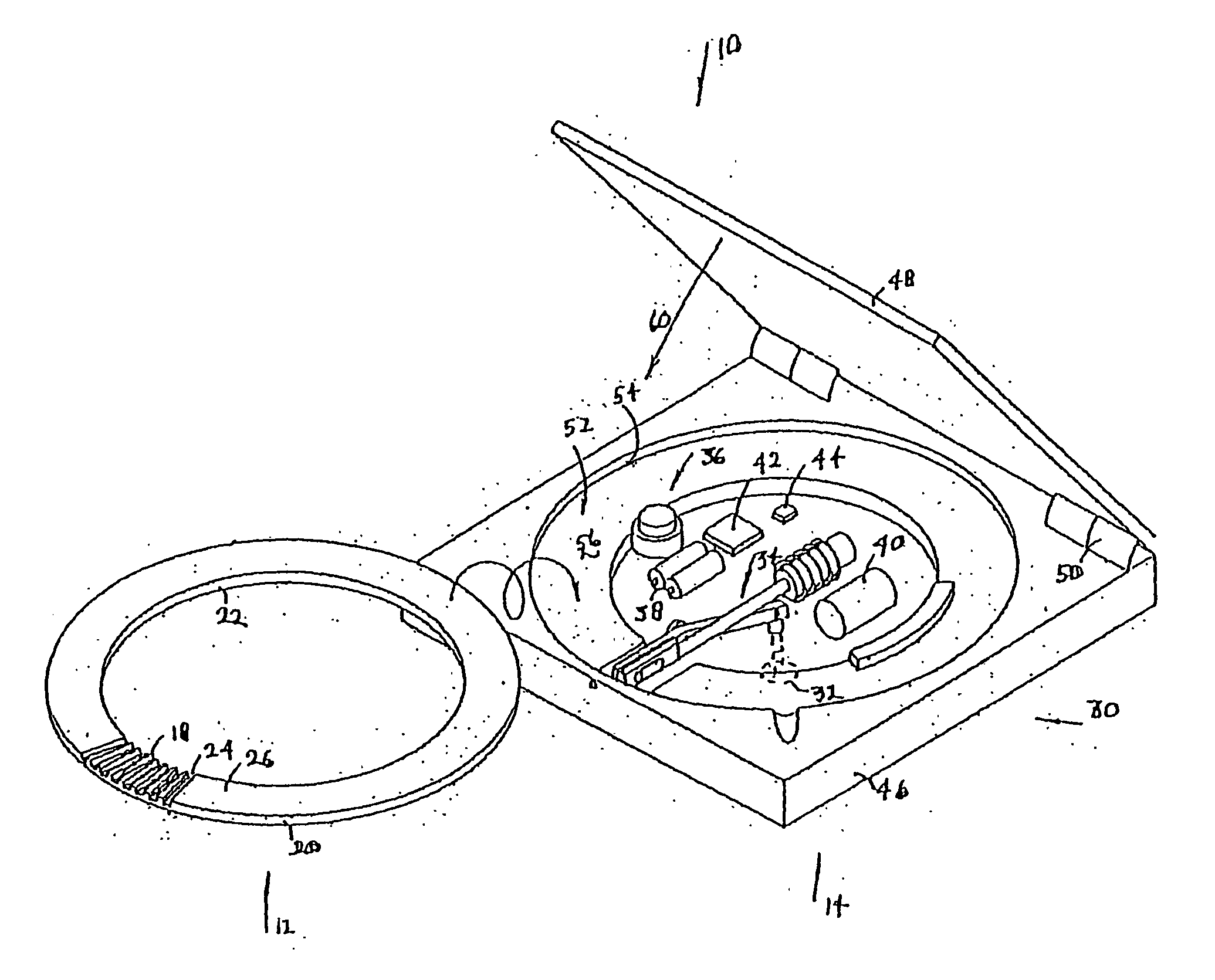
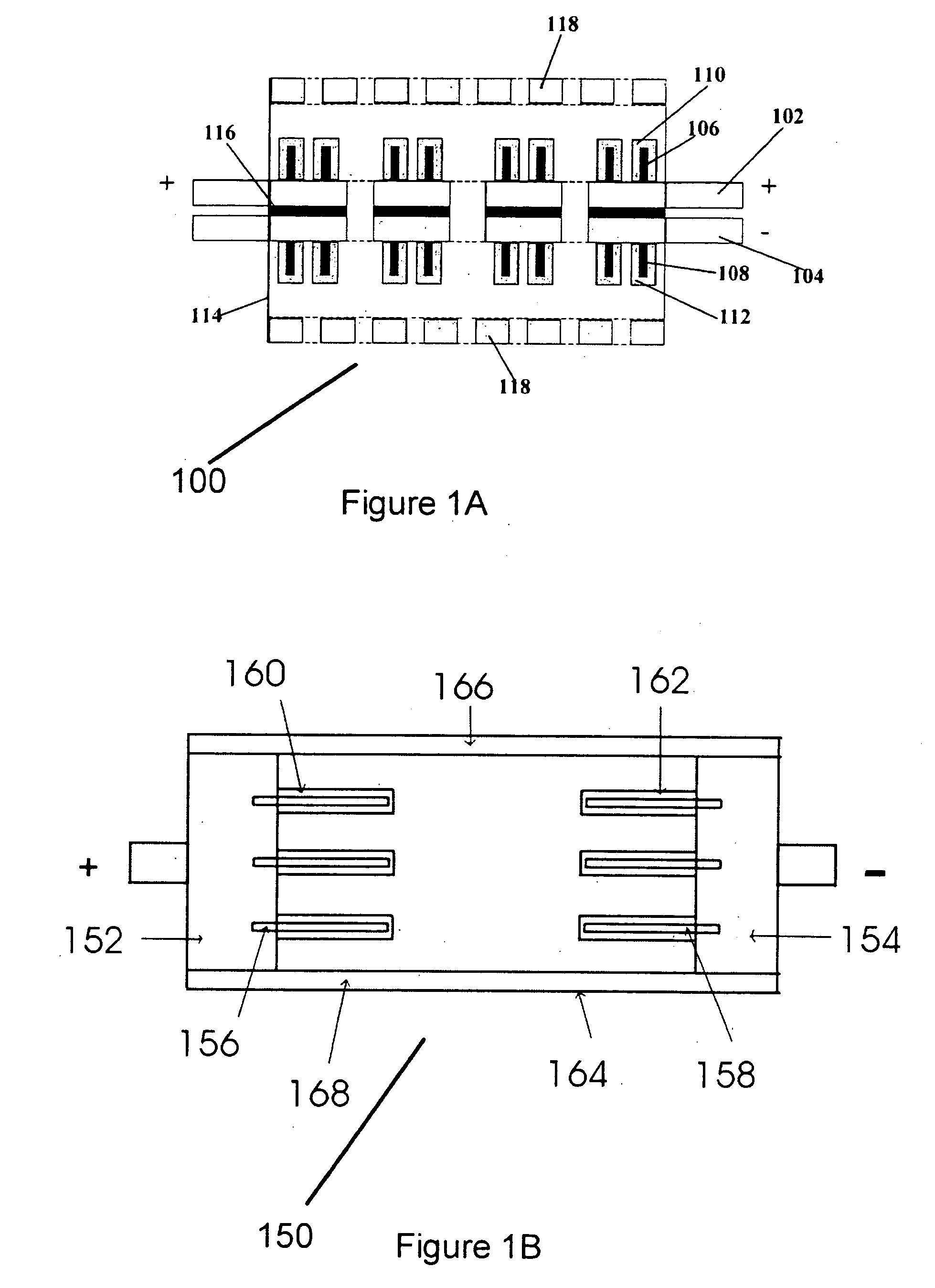
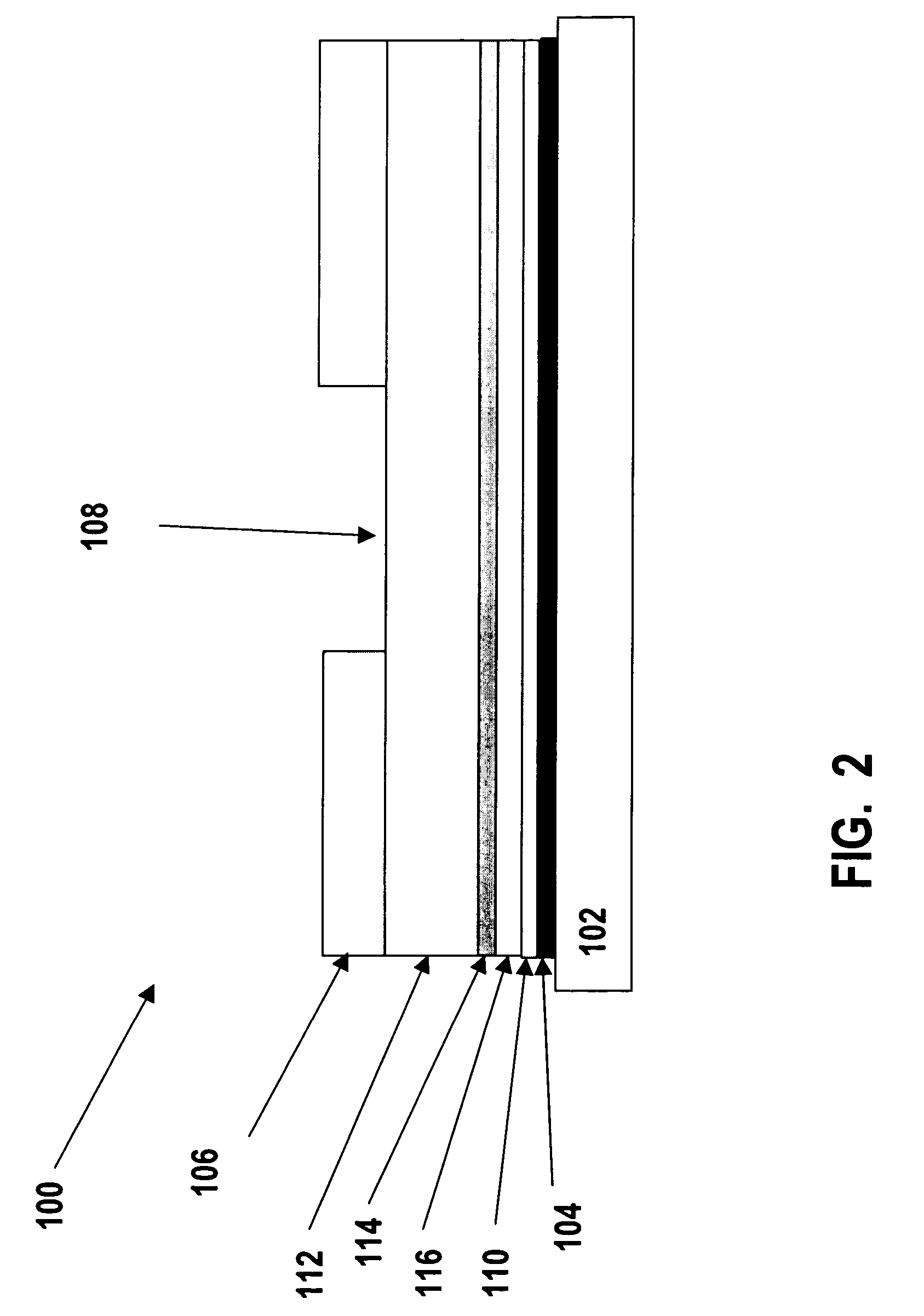
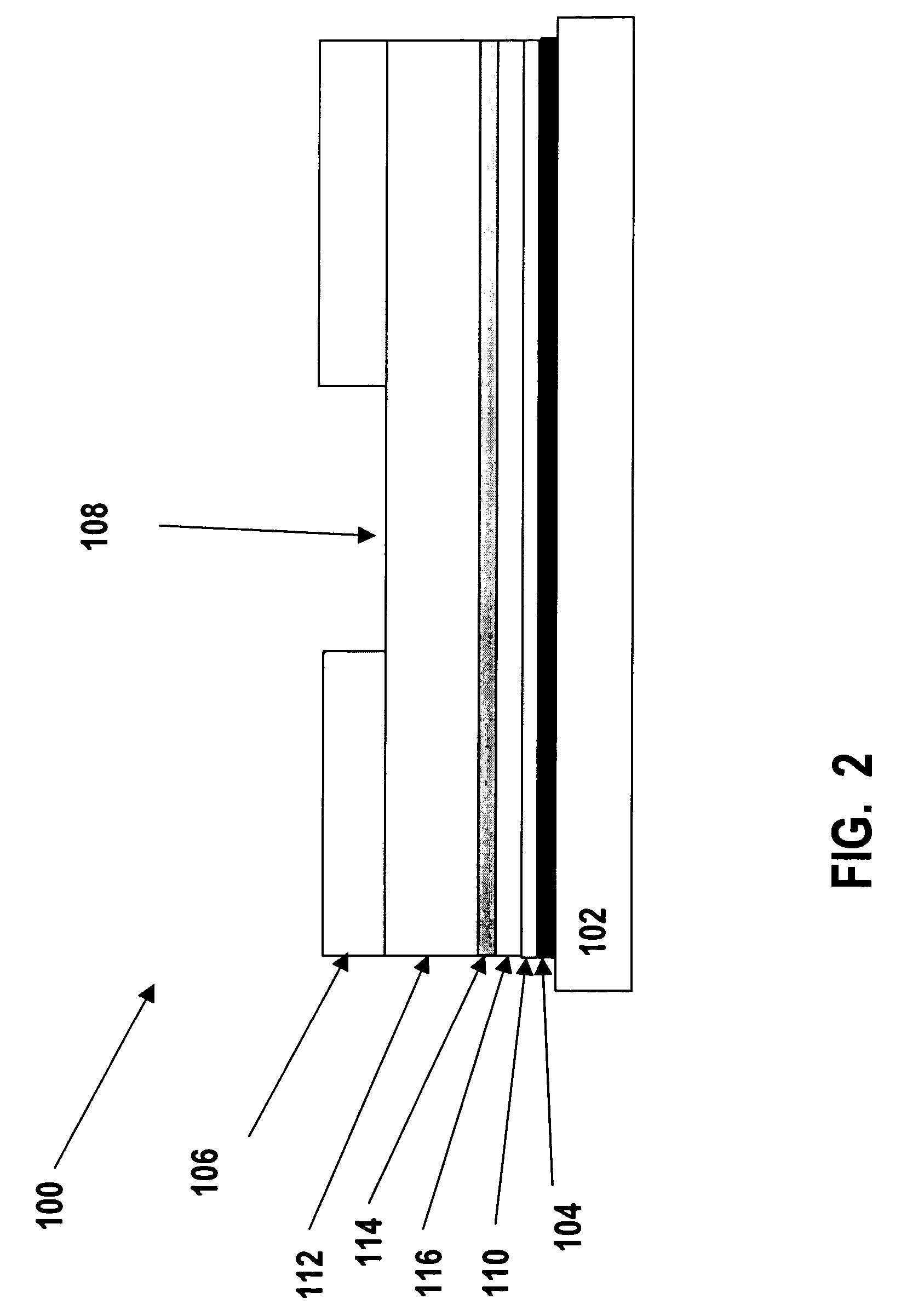
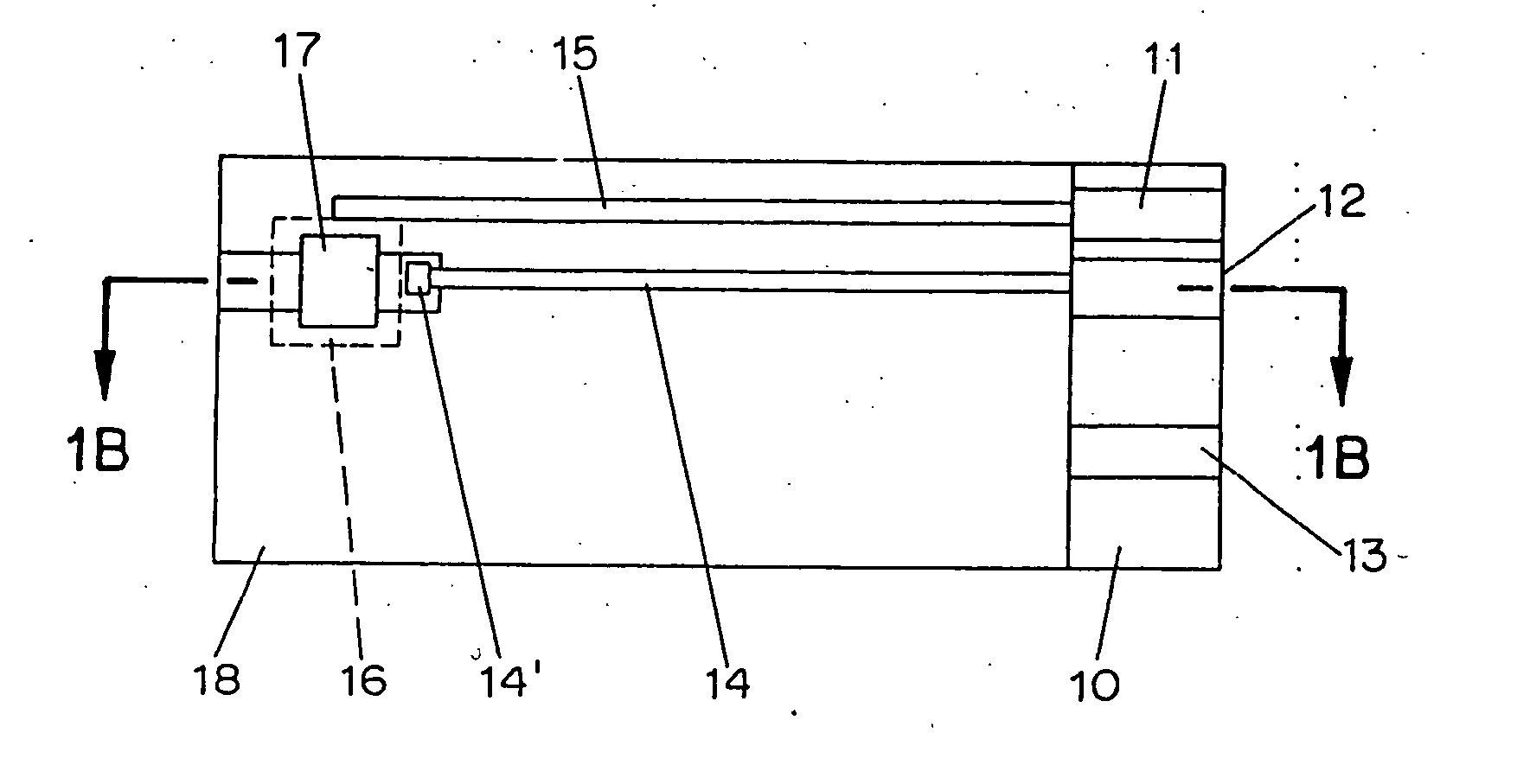
Enzyme electrode structure
InactiveUS6071391AEasy to manufactureEasy to measureImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsEnzyme electrodeWorking electrode
A biosensor comprises a space part for sucking and housing a sample formed of two upper and lower plates, the two plates being stuck together by an adhesive layer, the space part for sucking and housing the sample being constituted so as to be partially opened in the peripheral part and partially closed by the adhesive layer, and has a working electrode having at least glucose oxidase immobilized thereon and a counter electrode on the same plane of the plate.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Microsensors for glucose and insulin monitoring
InactiveUS6893552B1Simultaneous measurementLacking and neededImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsOxidative enzymeD-Glucose
A dual sensor for the simultaneous amperometric monitoring of glucose and insulin, wherein the glucose probe is based on the biocatalytic action of glucose oxidase, and the insulin probe is based on the electrocatalytic activity of metal oxide. Further provided is an oxidase enzyme composite electrode with an internal oxygen-rich binder. The present invention also optionally includes metallizing components within the carbon paste to eliminate signals from interfering compounds. The present invention includes embodiments for both in vitro and in vivo uses.
Owner:ARROWHEAD CENT
Nano-chem-FET based biosensors
ActiveUS7303875B1Facilitate membrane potential studiesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNanowireGlucose polymers
Methods of detecting components of interest, e.g., nucleic acids and sugars, are provided. The methods comprise contacting one or more nanowires comprising a functional group with a sample containing the component or components of interest. In one embodiment, the functional group comprises a hairpin oligonucleotide, e.g., a hairpin that changes conformation upon binding the component of interest, e.g., a nucleic acid. The change in conformation produces a change in charge that is detected. In another embodiment, the functional group comprises an enzyme, e.g., glucose oxidase, which produces a change in pH when glucose is present in a sample.
Owner:SHOEI CHEM IND CO LTD
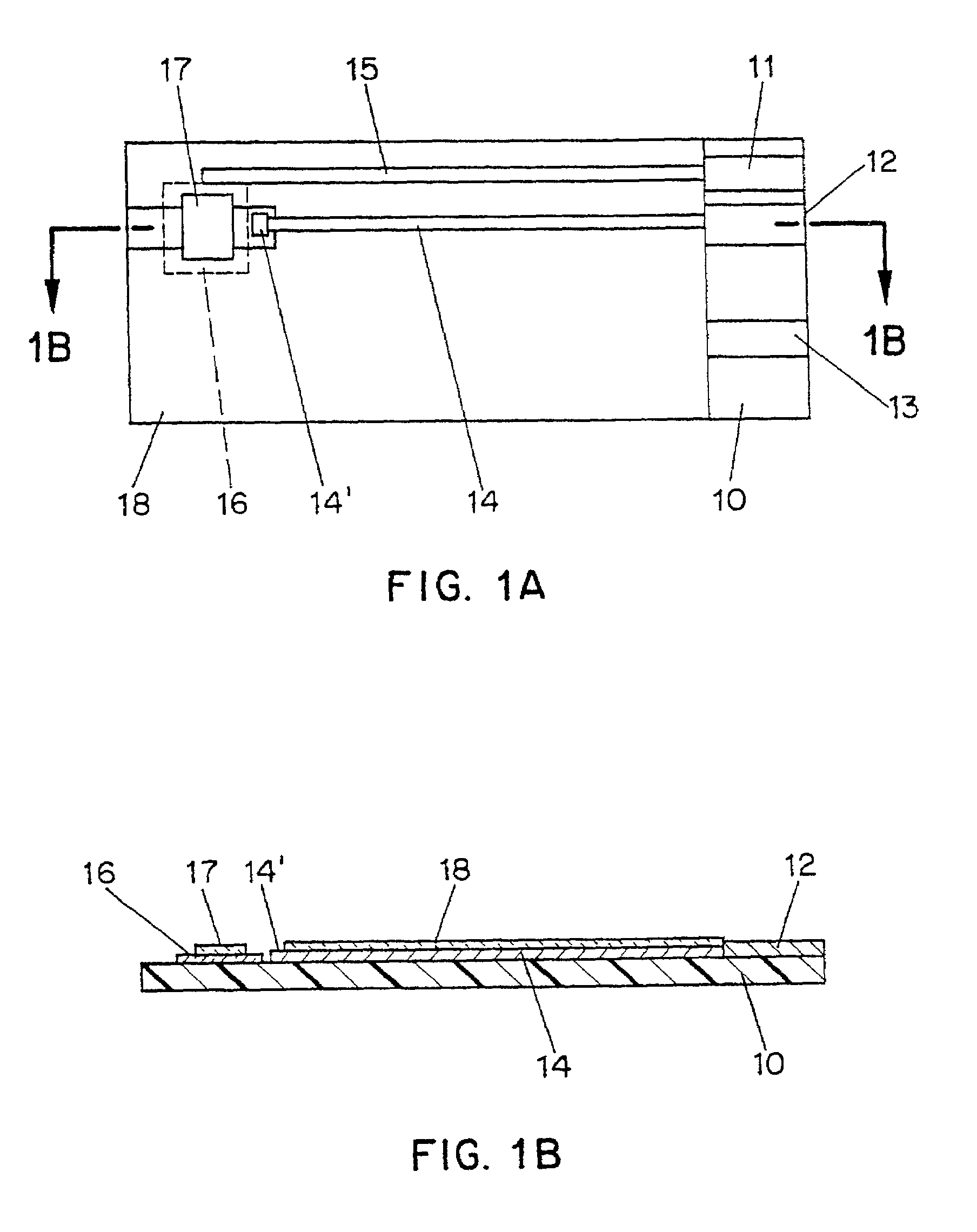
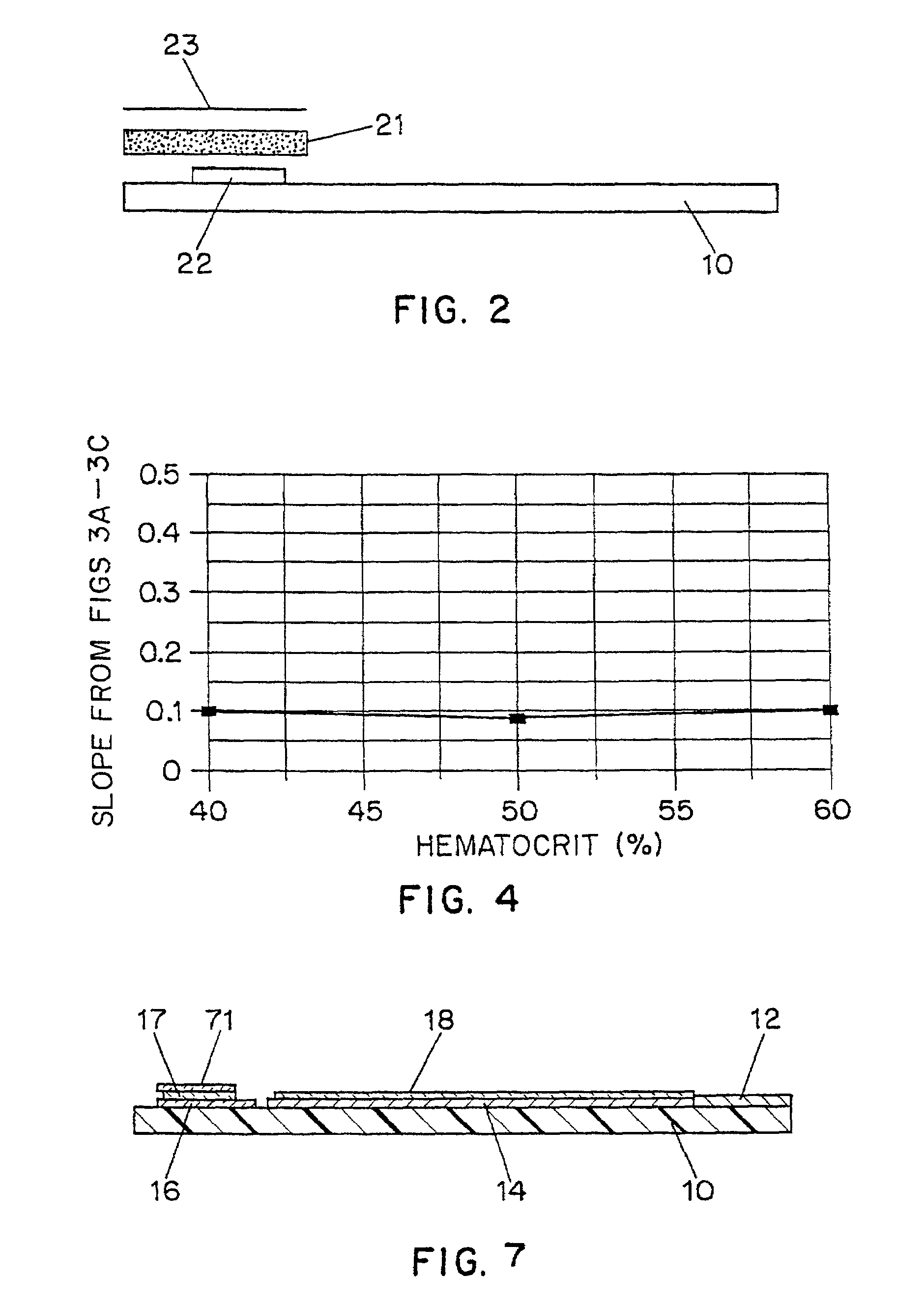
Disposable test strips with integrated reagent/blood separation layer
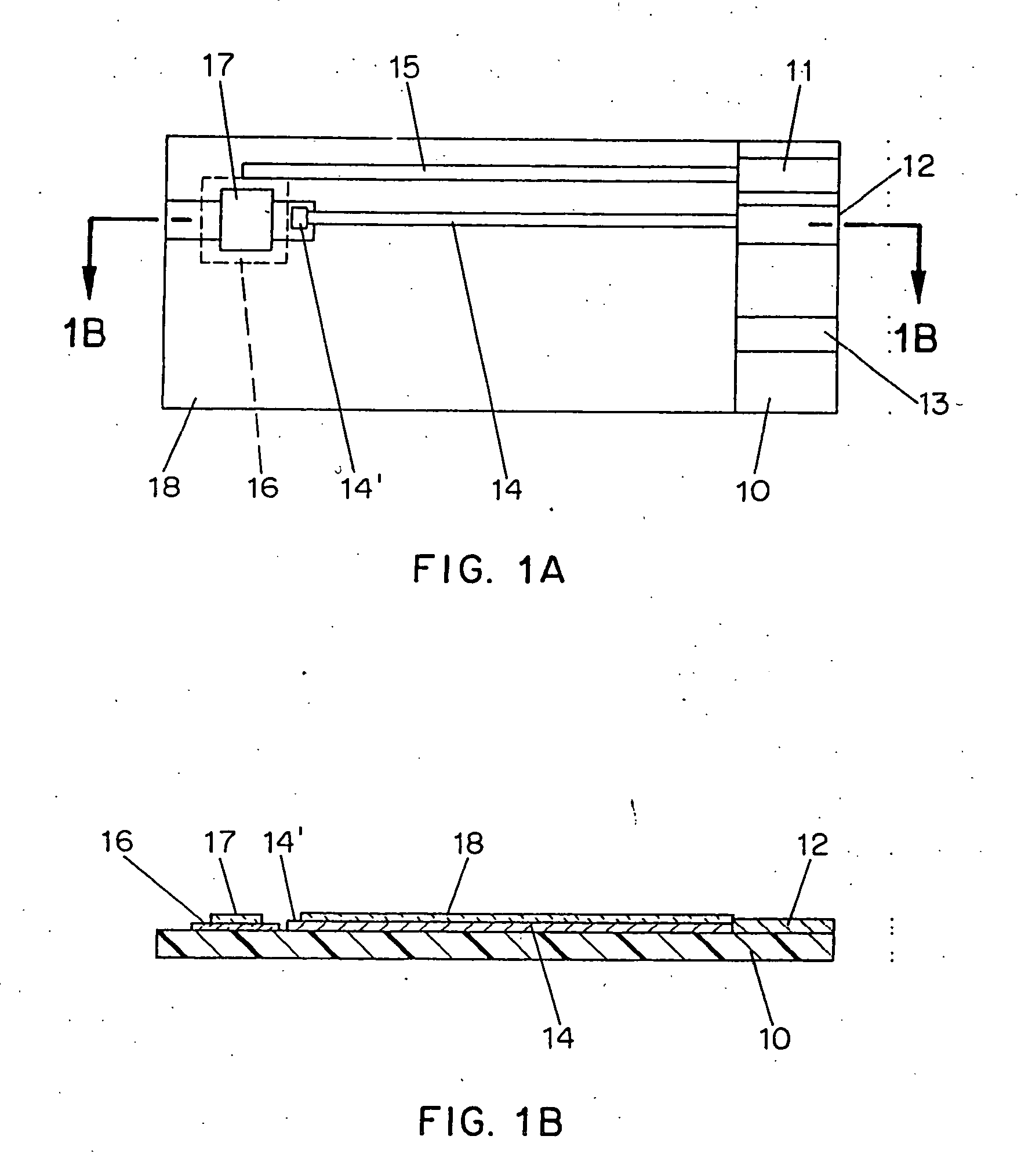
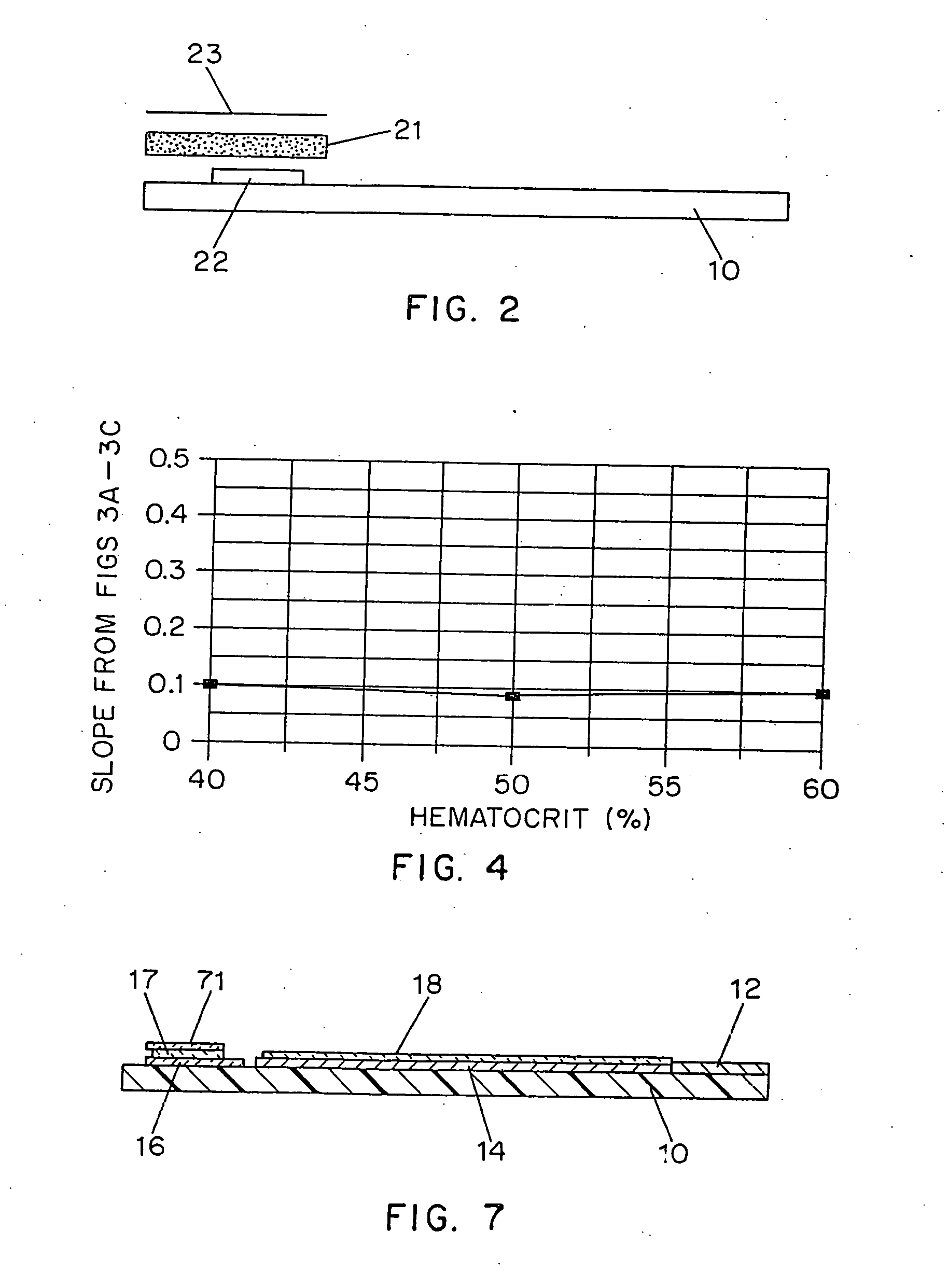
An improved disposable glucose test strip for use in a test meter of the type which receives a disposable test strip and a sample of blood from a patient and performs an electrochemical analysis using a non-conductive integrated reagent / blood separation layer (17) containing a filler, an enzyme effective to oxidize glucose, e.g., glucose oxidase, and a mediator effective to transfer electrons from the enzyme. The integrated layer formulation is printed over a conductive carbon element (16) to form a working electrode. The filler, for example a silica filler, is selected to have a balance of hydrophobicity such that on drying it forms a two-dimensional network on the surface of the conductive element. The response of this test strip is essentially temperature independent over relevant temperature ranges and is substantially insensitive to the hematocrit of the patient.
Owner:SELFCARE +1
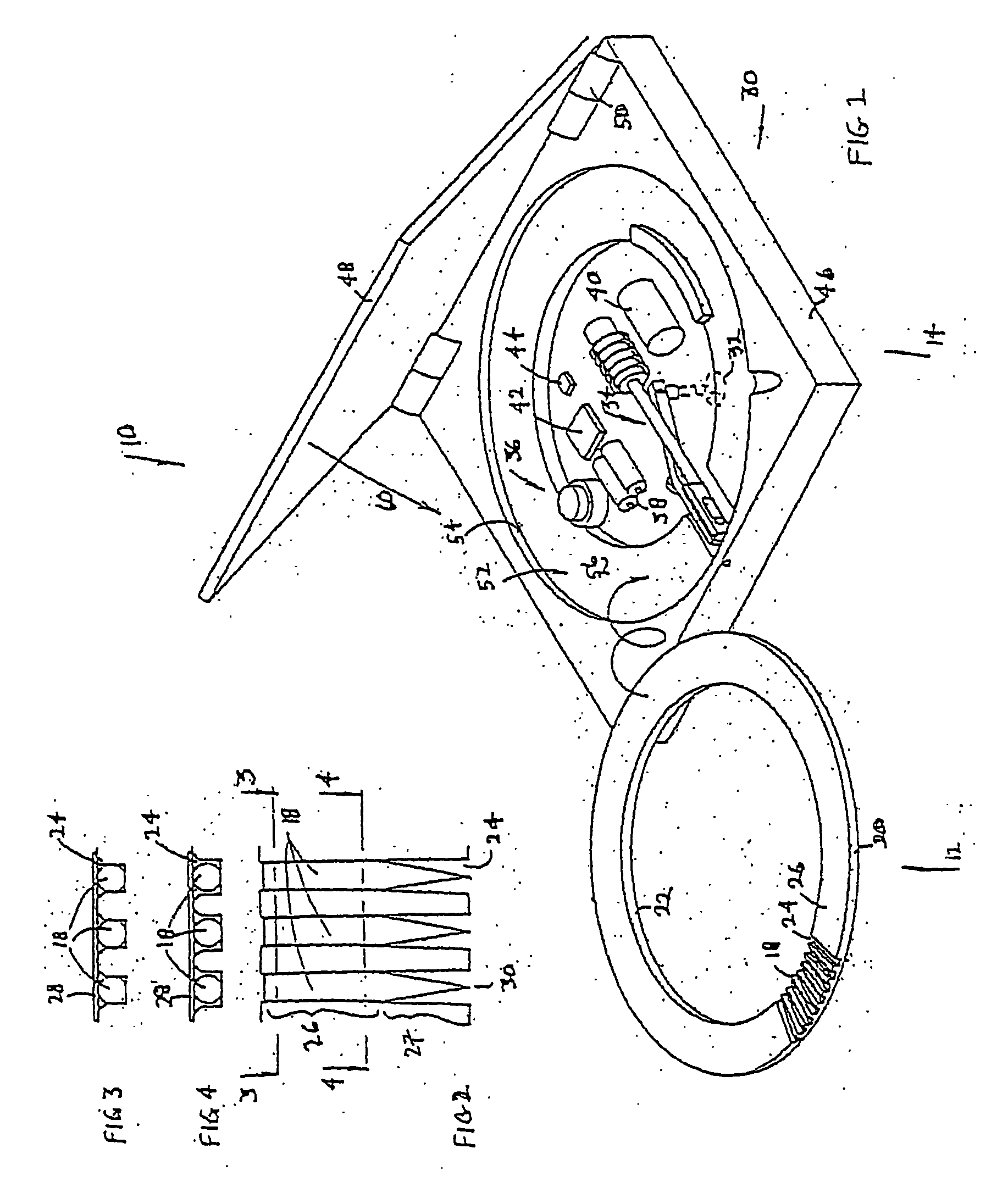
Enzyme electrode structure
InactiveUS6156173AEasy to manufactureEasy to measureImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsEnzyme electrodeWorking electrode
A biosensor comprises a space part for sucking and housing a sample formed of two upper and lower plates, the two plates being stuck together by an adhesive layer, the space part for sucking and housing the sample being constituted so as to be partially opened in the peripheral part and partially closed by the adhesive layer, and has a working electrode having at least glucose oxidase immobilized thereon and a counter electrode on the same plane of the plate.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Polymer matrix containing catalase co-immobilized with analytic enzyme that generates hydrogen peroxide
InactiveUS6858403B2Enhancing swelling kineticsLong useful lifePowder deliveryBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteHydrogen peroxide degradation
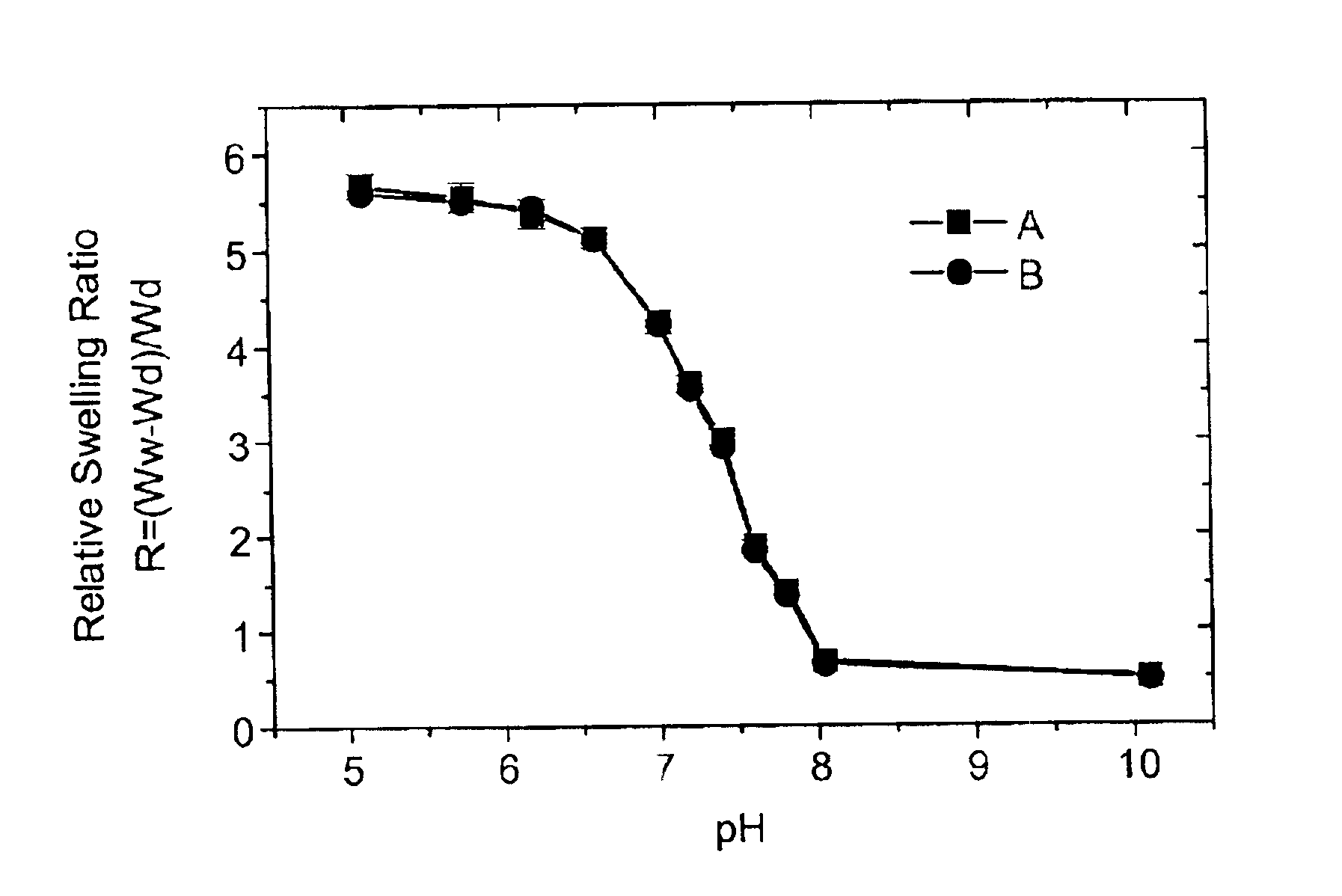
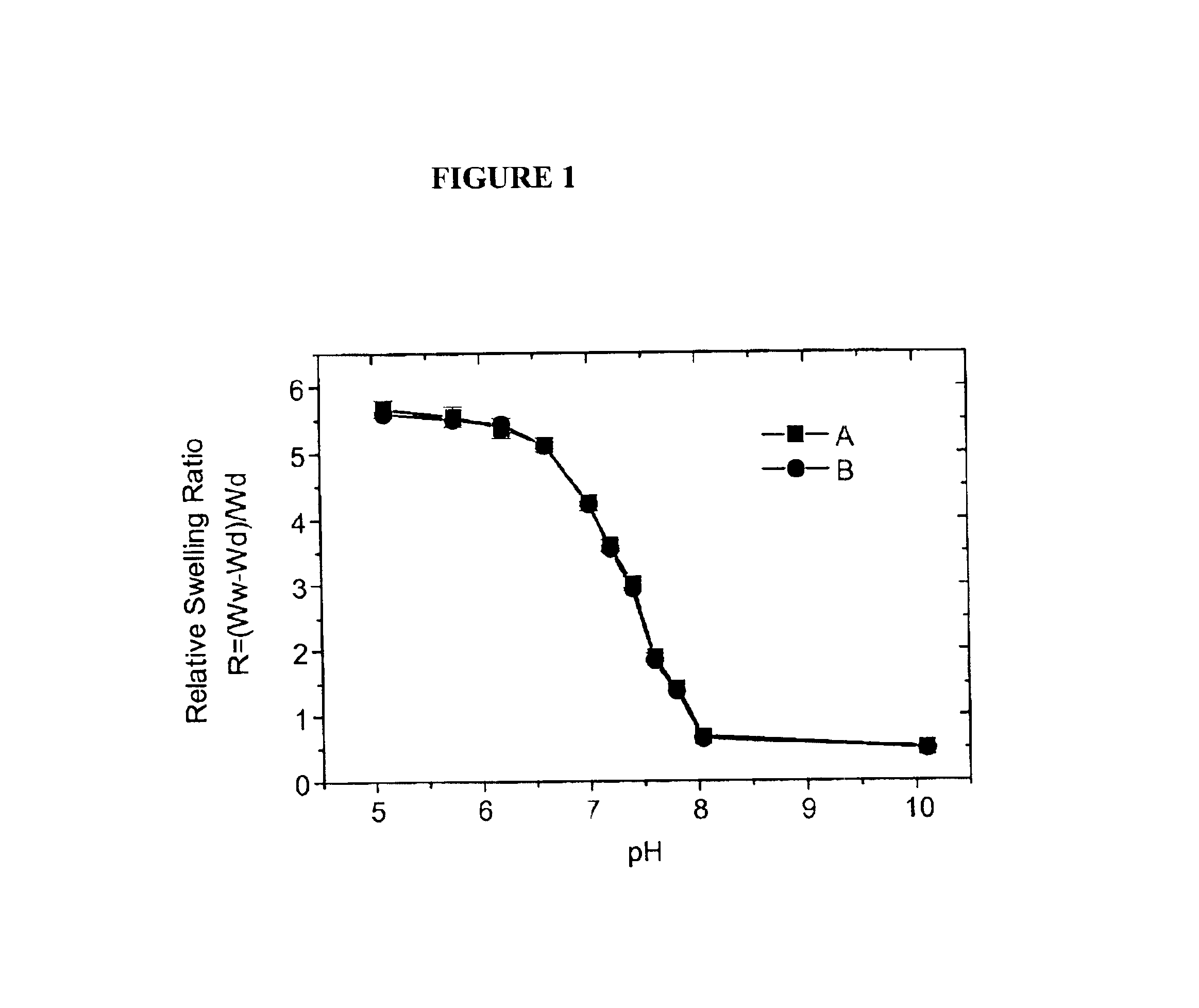
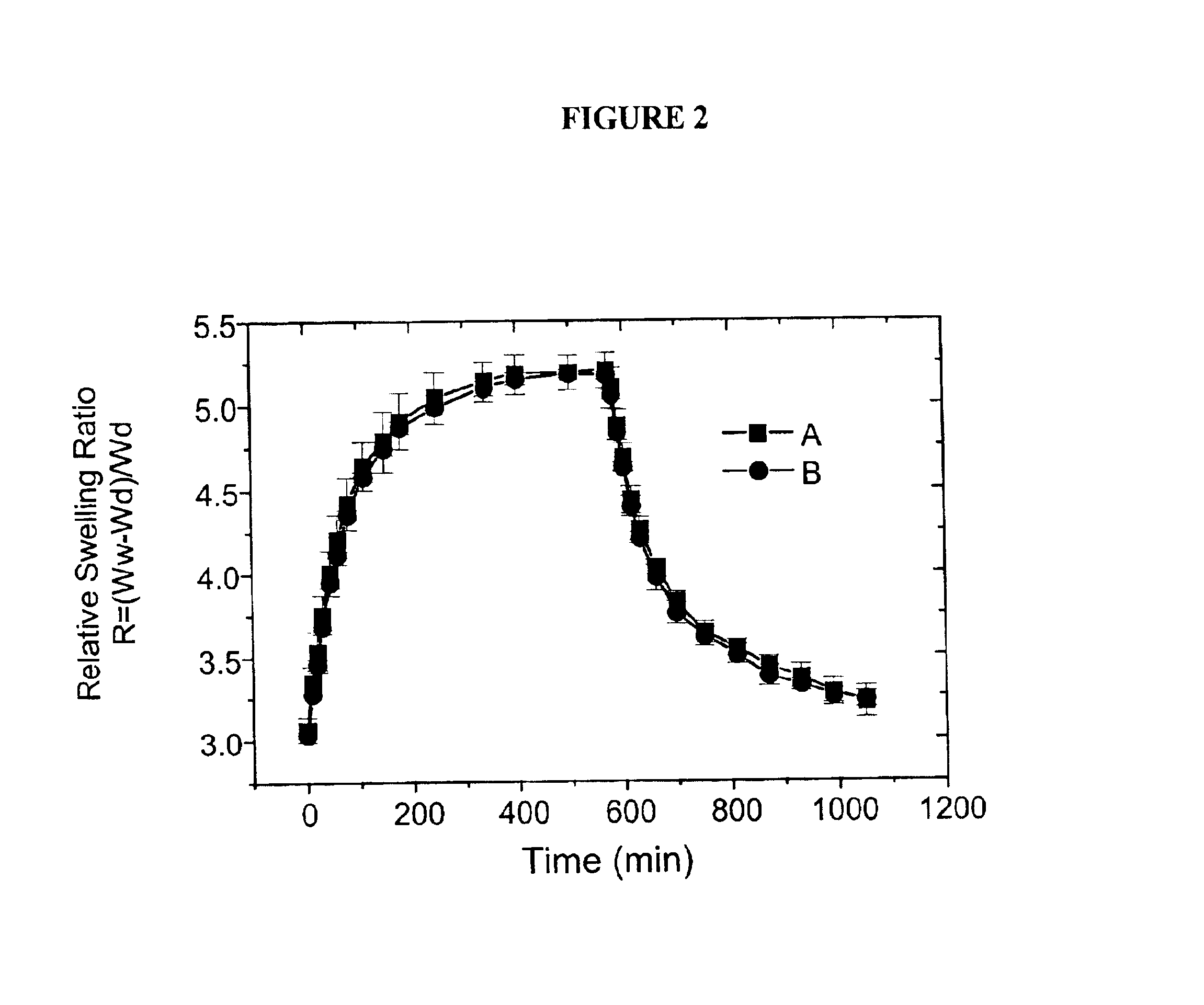
Hydrogels containing catalase co-immobilized with an analyte-sensitive enzyme such as glucose oxidase are disclosed. The hydrogels may be pH-sensitive, and preferably are thin and lightly crosslinked. The catalase is present in concentrations ranging generally from 100 units / ml to about 1000 units / ml. These hydrogels have much faster swelling response times as compared to hydrogels without catalase, and are useful in biosensors and analyte-responsive drug delivery devices. The hydrogels also have an increased useful life, due to protection of the immobilize analyte-sensitive enzyme from degradation by hydrogen peroxide.
Owner:M BIOTECH
Method and apparatus for measuring analytes
InactiveUS20060200044A1Cancel noiseImprove accuracyMaterial nanotechnologyNanoinformaticsAnalyteReady to use
A device comprises a cartridge (12) and a plurality of analyte detecting members (18) mounted on said cartridge. The cartridge may have a radial disc shape. The analyte detecting members may be a three-electrode system wherein only a working electrode is covered with a glucose oxidase. In one embodiment, the device may also include a fluid spreader (28) positioned over at least a portion of said analyte detecting member to urge fluid toward one of the detecting members. A plurality of analyte detecting members may be used. Each analyte detecting member may be a low volume device.
Owner:PELIKAN TECH INC
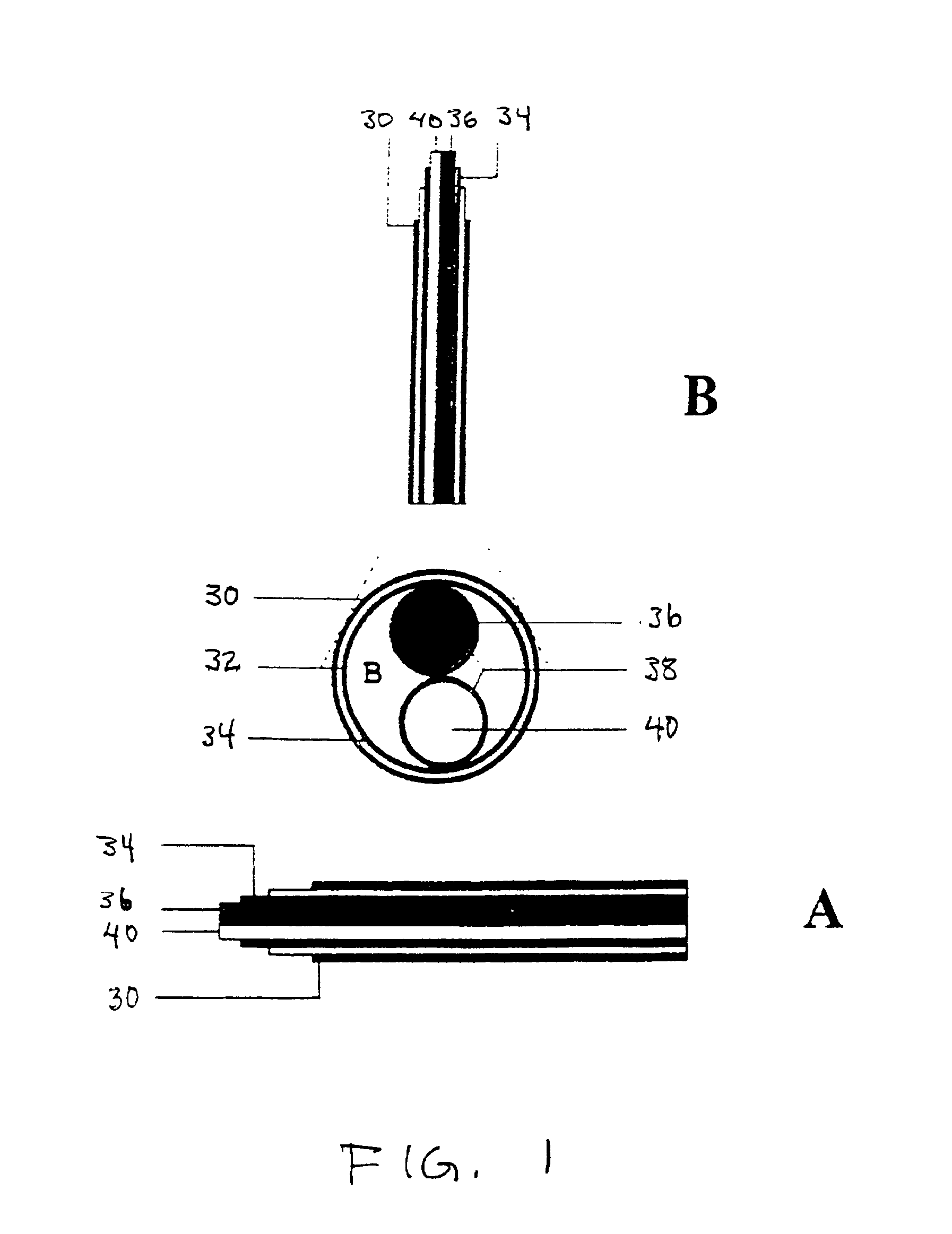
Implantable biofuel cell system based on nanostructures
InactiveUS20050118494A1Increase powerImprove power densityMaterial nanotechnologyFuel cell auxillariesCarbon nanotubeMolecular level
A bio-implantable electrochemical cell system for active implantable medical devices. In one embodiment, the fuel cell includes an electrode structure consisting of immobilized anode and cathode enzymes deposited on nanostructured high-surface-area metal nanowires or carbon nanotube electrodes. The anode enzyme comprises immobilized glucose oxidase and the cathode enzyme comprises immobilized laccase. Glucose is oxidized at the surface of the anode and oxygen is reduced at the surface of the cathode. The coupled glucose oxidation-oxygen reduction reactions provide a self-generating current source. In another embodiment, the nanowires or carbon nanotubes, along with the adjacent surface anode and cathode electrodes, are coated with immobilized glucose oxidase and immobilized laccase containing biocolloidal substrates, respectively. This results in the precise construction of an enzyme architecture with control at the molecular level, while increasing the reactive surface area and corresponding output power by at least two orders of magnitude.
Owner:NANOSOLUTIONS
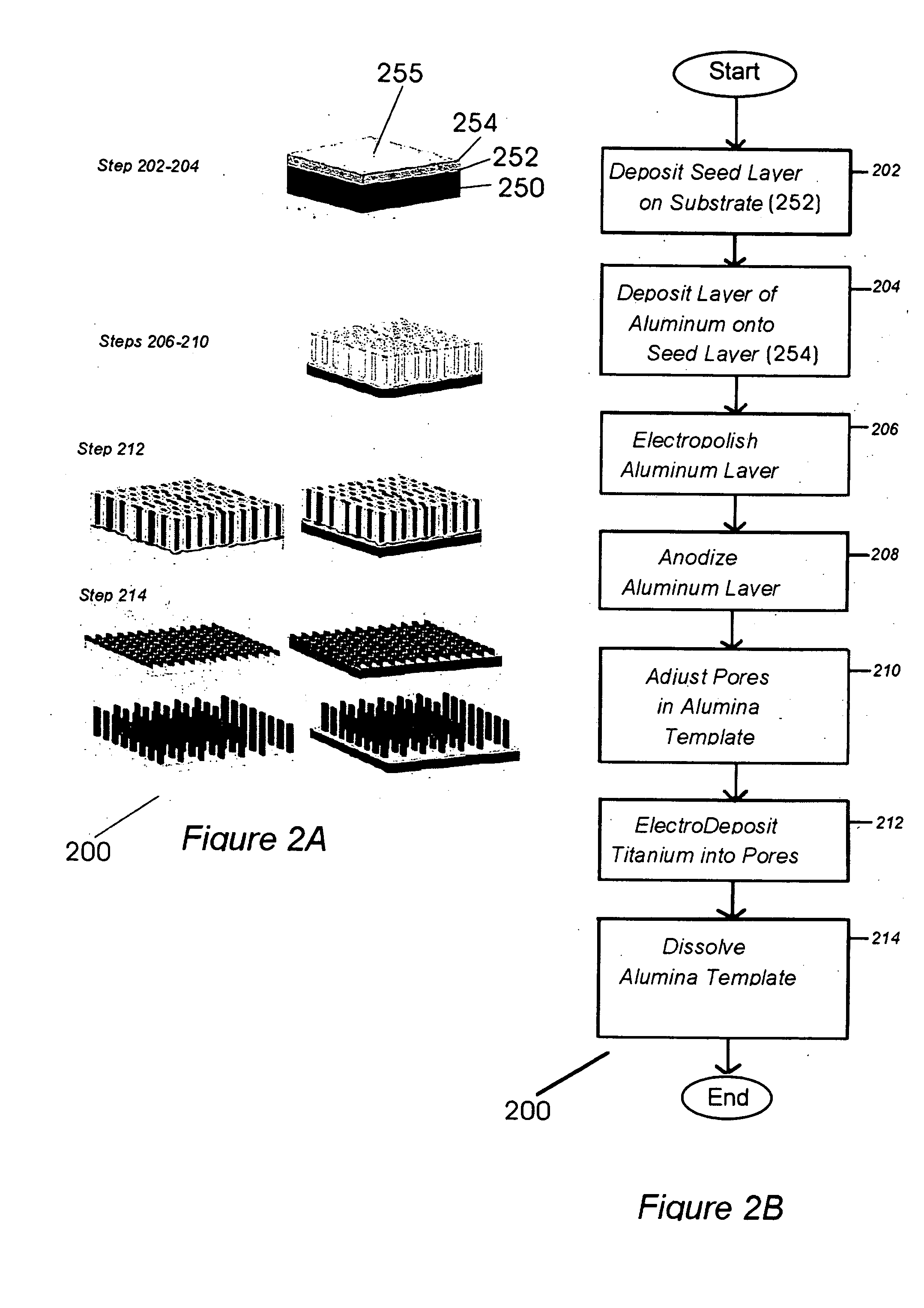
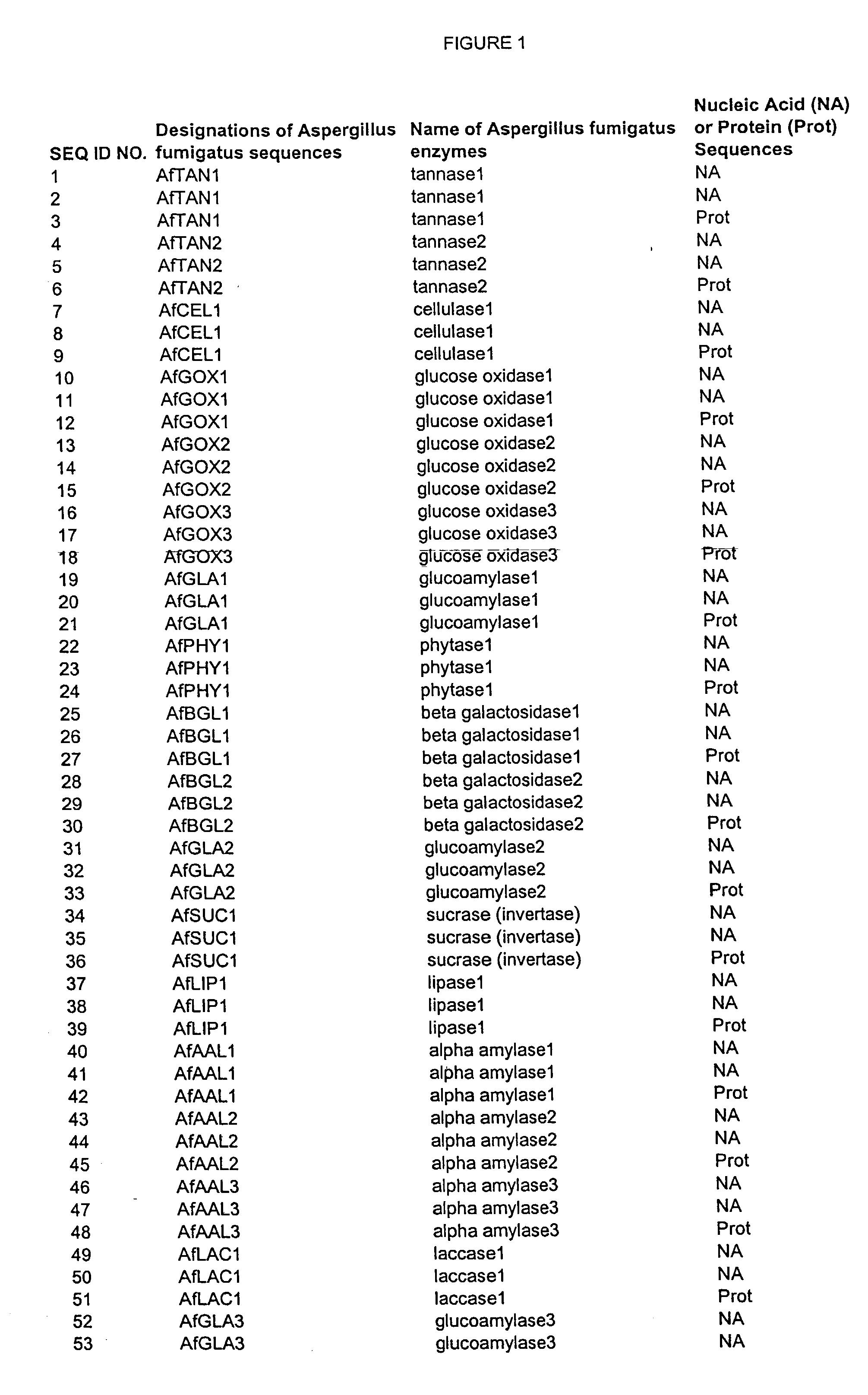
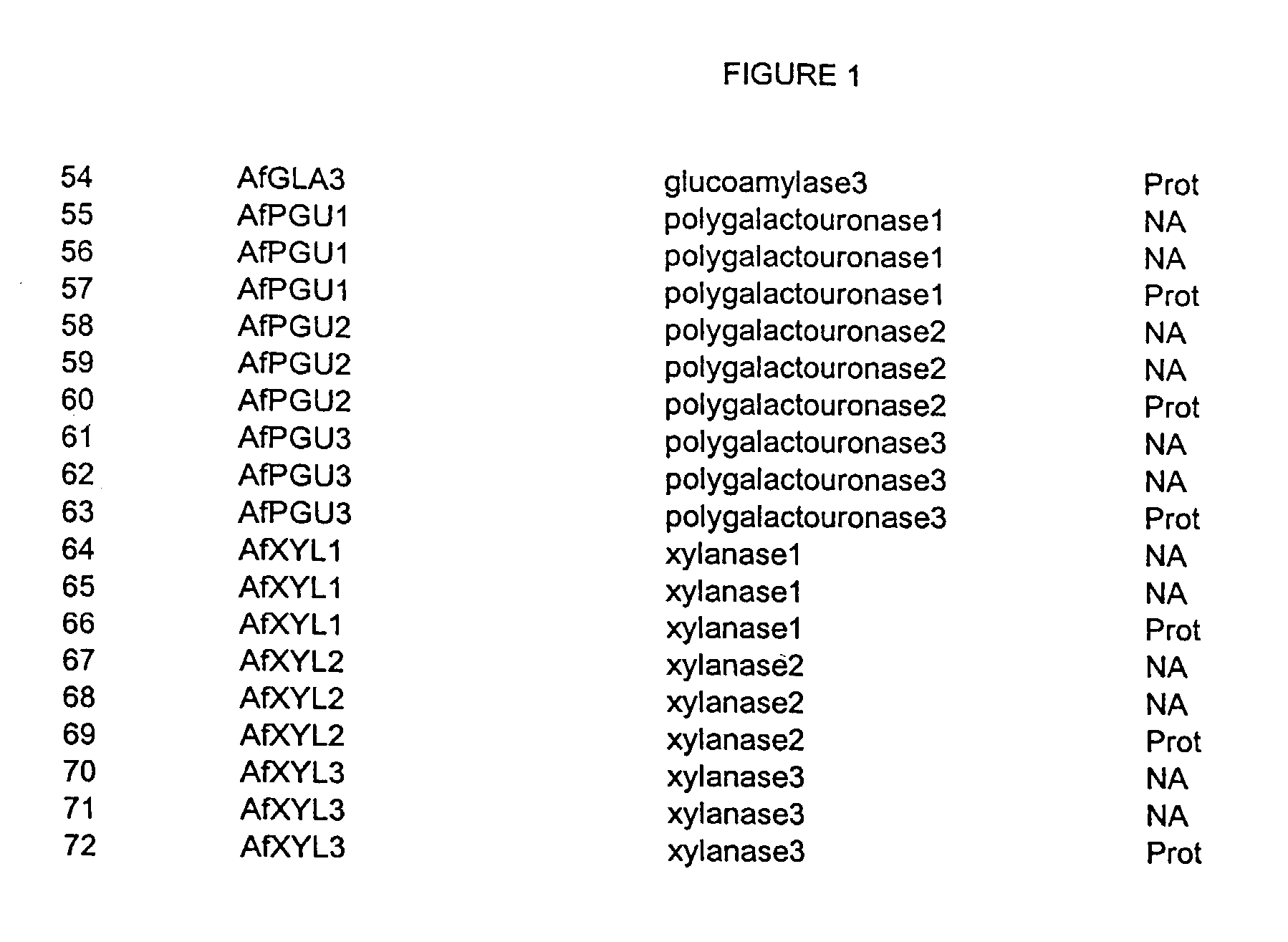
Nucleic acids of aspergillus fumigatus encoding industrial enzymes and methods of use
The present invention provides nucleotide sequences of Aspegillus fumigatus that encode proteins which exhibit enzyme activities. Vectors, expression constructs, and host cells comprising the nucleotide sequences of the enzyme genes are also provided. The invention further provides methods for producing the enzymes, and methods for modifying the enzymes in order to improve their desirable characteristics. The activities displayed by the enzymes of the invention include those of a tannase, cellulase, glucose oxidase, glucoamylase, phytase, beta-galactosidases, invertase, lipase, alpha-amylase, laccase, polygalacturonase or xylanase. The enzymes of the invention can be used in a variety of industrial processes. Enzymatically active compositions in various forms as well as antibodies to the enzymes and fragments thereof, are also provided.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC
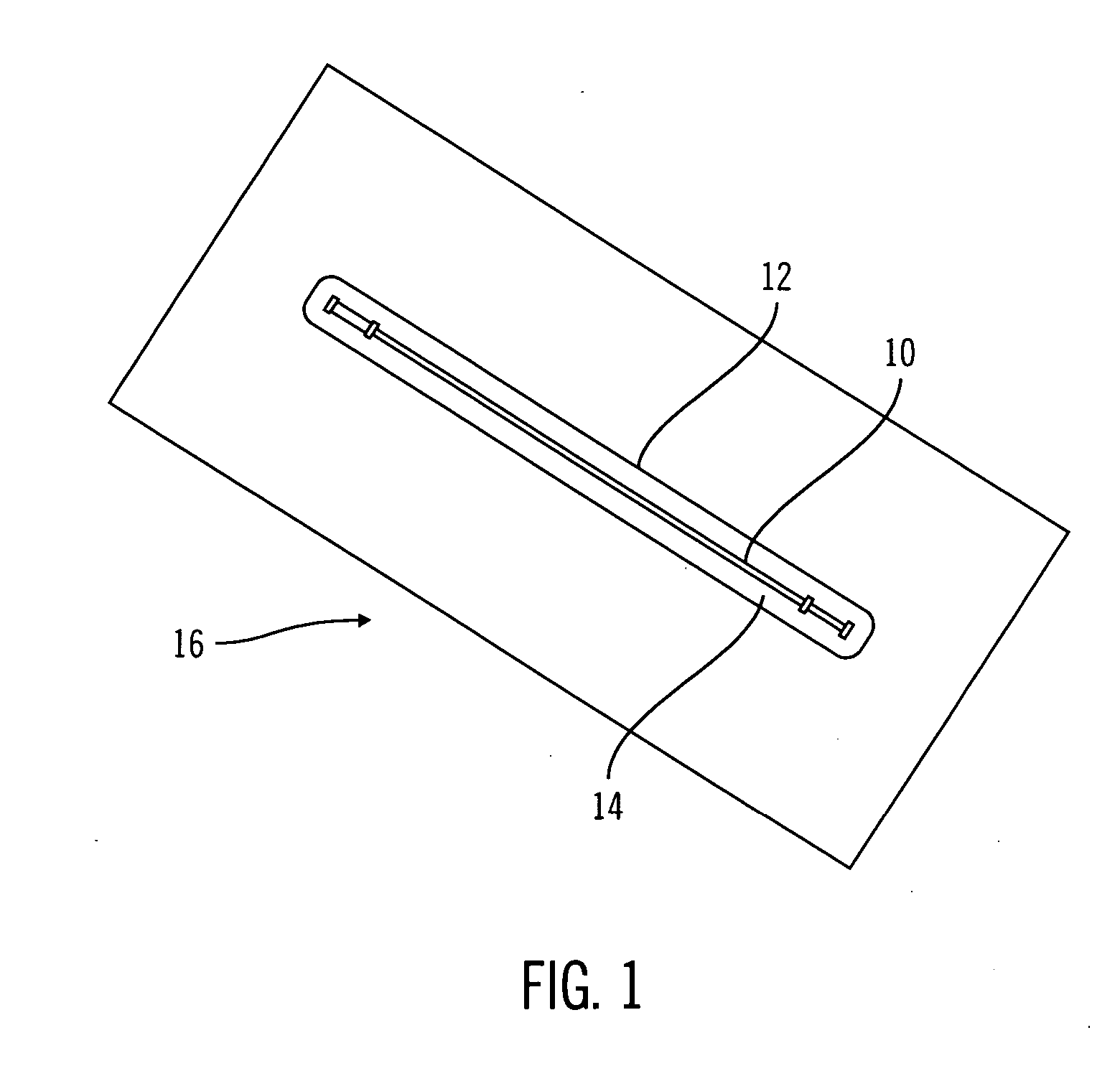
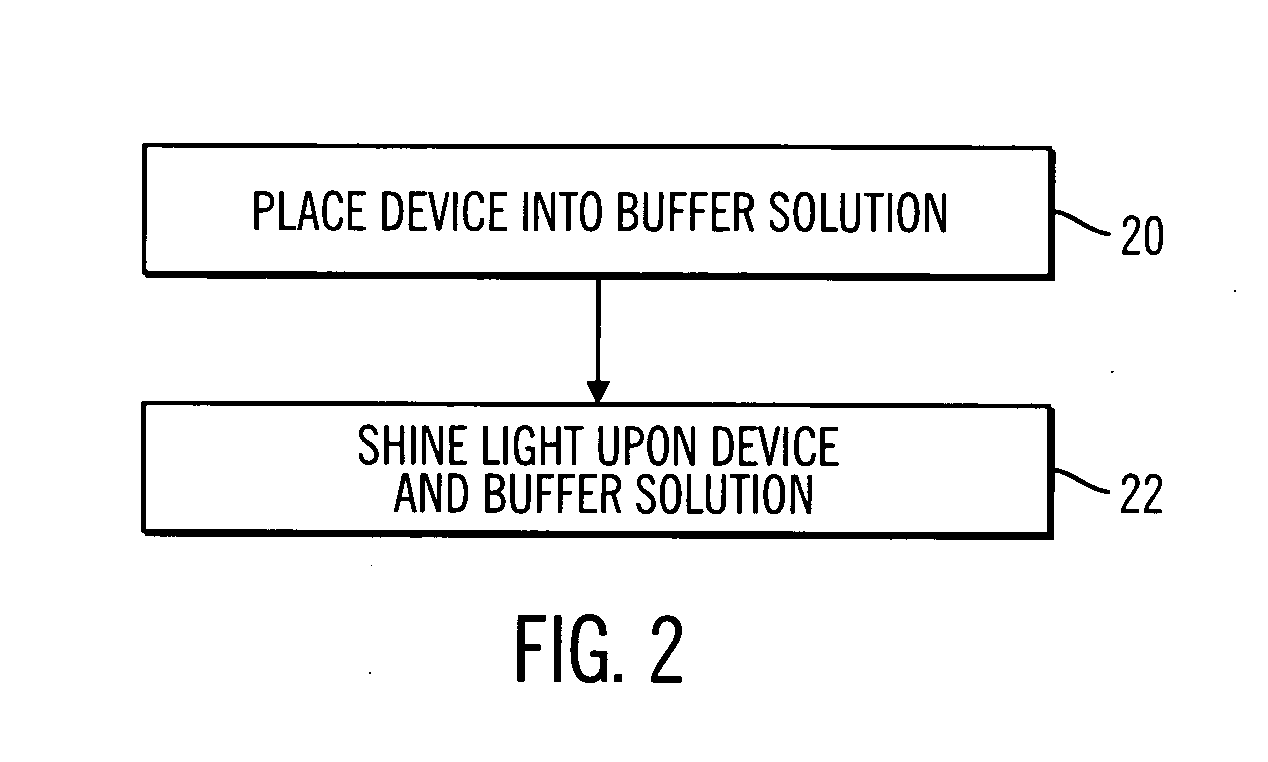
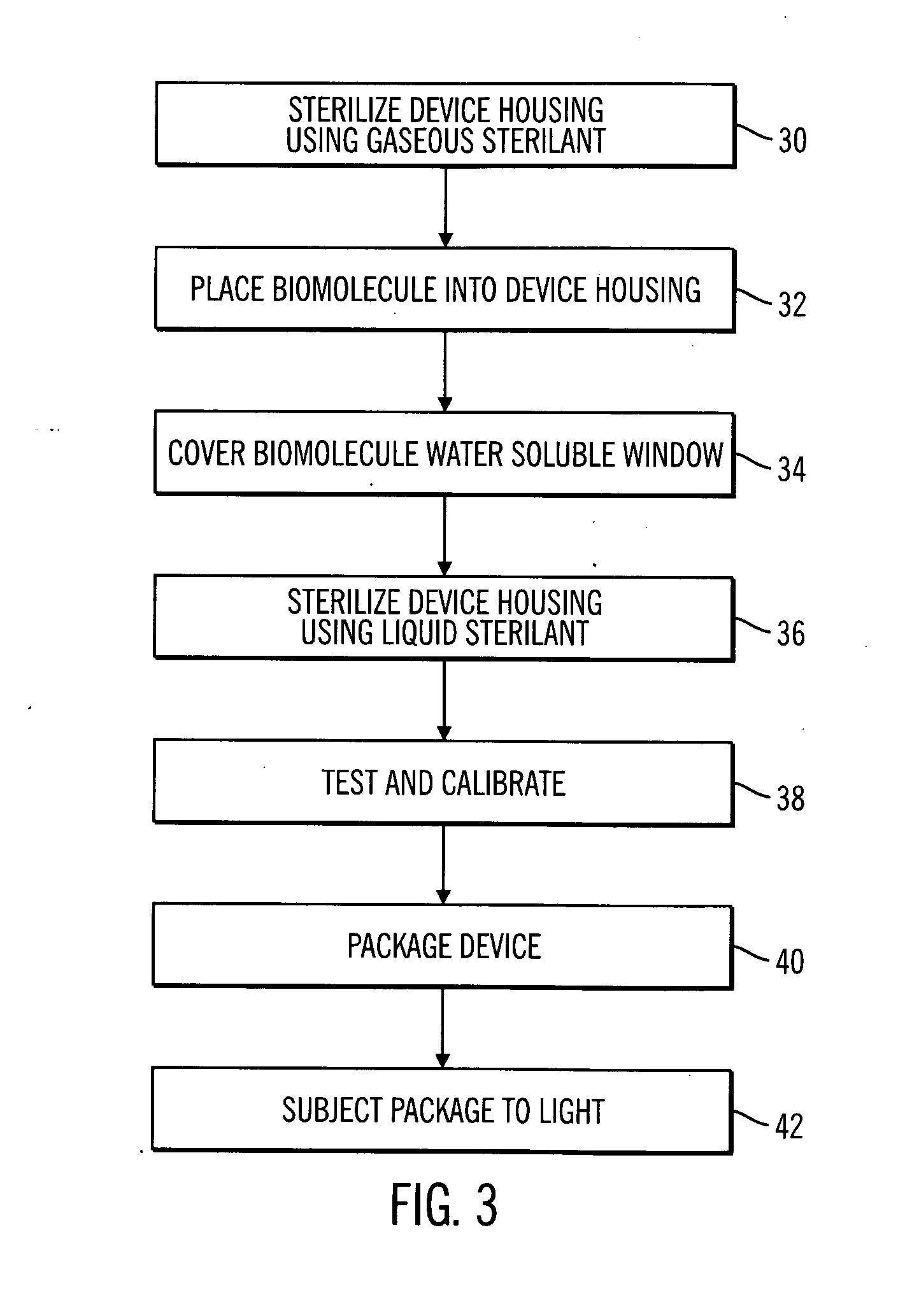
Sterile device and method for producing same
A sterile device immersed in a sterile buffer and a method for providing same. The sterile device may be a medical device such as a biosensor having a biomolecule as a sensing element such as, for example, a glucose oxidase enzyme. The buffer may be a bicarbonate solution. Both the device and the buffer may be packaged and stored over long term while maintaining sterilization. The sterilization method may comprise a combination of gaseous, liquid and light sterilization.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Polypeptide formulations and methods for making, using and characterizing them
ActiveUS20060183178A1Improve performancePeptide/protein ingredientsComponent separationGlucose sensorsDiabetes management
Embodiments of the invention include polypeptide formulations and methods for making, using and characterizing them. Embodiment of the invention include stabilized polypeptide formulations, for example stable glucose oxidase formulations that can be used with glucose sensors used in the management of diabetes. Another embodiment of the invention includes methods to characterize the concentration of nonionic surfactants in stabilized polypeptide formulation for example stable insulin formulations that can be used in the treatment of diabetes.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Polypeptide formulations and methods for making, using and characterizing them
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Wound dressings comprising hydrated hydrogels and enzymes
InactiveUS20060034816A1Prevents undesired migrationAvoid injuryPeptide/protein ingredientsPlastersWound dressingPeroxidase
A skin dressing, particularly a wound dressing, comprises oxidoreductase enzyme and, optionally, peroxidase enzyme, wherein the enzyme(s) are present in hydrated condition, e.g. being present in one or more hydrated hydrogels. The dressing is used by being located on the skin of a human or animal e.g. over a wound. The oxidoreductase enzyme catalyses a reaction that produces hydrogen peroxide from an appropriate substrate, the substrate either being naturally present in body fluids and / or being supplied separately and / or being incorporated into the dressing. The currently preferred oxidoreductase enzyme is glucose oxidase. The catalyses reaction of β-D-glucose substrate to give hydrogen peroxide and gluconic acid. A mixture of oxidoreductase enzyme can undergo reaction (optionally catalysed by the peroxidase enzyme) to produce a variety of species including reactive oxygen intermediates that have antimicrobial properties and that can therefore assist in promoting wound healing.
Owner:SYSTAGENIX WOUND MANAGEMENT (US) INC
Freezing flour-dough improver and uses thereof
ActiveCN101411344AOvercome stabilityOvercome volumeDough treatmentPre-baking dough treatmentYeastVitamin C
The invention discloses a frozen dough modifying agent, which is prepared by evenly mixing an enzyme preparation (including one or a plurality of alpha-amylase, cellulose, hemicellulase, pentosanase, lipase, glucose oxidase, glutamine transaminage and so on), vitamin C, an emulsifying agent, a thickening agent, wheat gluten powder, lecithin and stuffing according to certain proportion. The frozen dough modifying agent has the advantages that the frozen dough modifying agent can effectively improve the stability of dough during fermentation and roasting processes, improve the freezing resistance property of yeasts, increase the volume of finished products, improve the tissue of the finished products, reduce the loss of the vitality of the yeasts during the freezing process, and effectively delay the aging of the finished products.
Owner:ANGELYEAST CO LTD
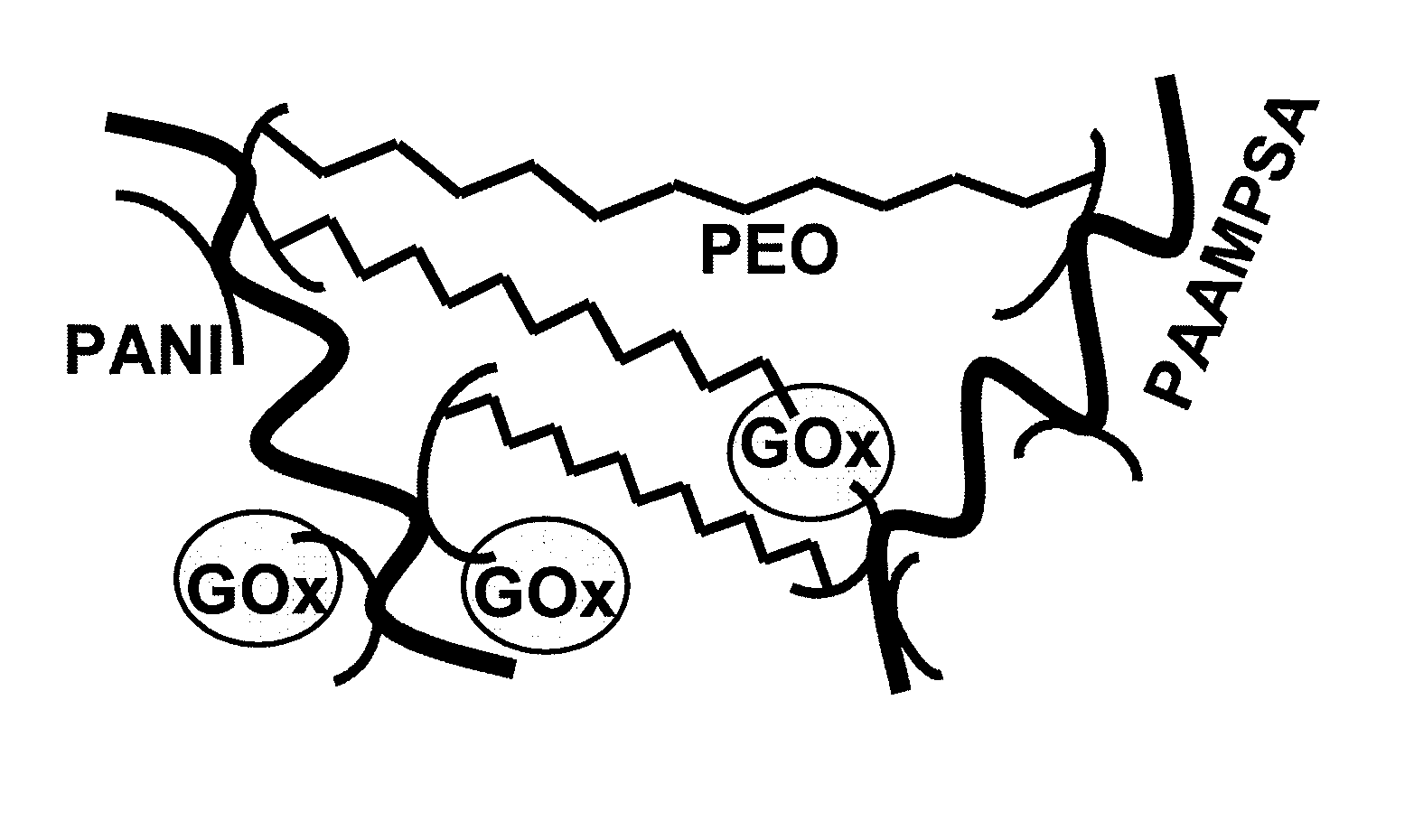
Electron-conducting crosslinked polyaniline-based redox hydrogel, and method of making
ActiveUS20090321277A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRedox enzymesPolymer science
A polymer matrix that may coated on an electrode is created by co-crosslinking (1) an adduct of a polyaniline formed by templated oxidative polymerization on a polymer acid; (2) a water-soluble crosslinker; and (3) a redox enzyme. The polymer matrix may be hydrated, and the absorbed water may make it permeable to, for example, glucose. The polyaniline may be polyaniline itself or a substituted polyaniline; the water-soluble crosslinker may be poly(ethylene glycol) diglycidyl ether, and the redox enzyme may be glucose oxidase. The polymer matrix may be produced by co-crosslinking (1) an adduct of an electrically conductive polymer and a polymer acid; (2) a water-soluble crosslinker; and (3) a redox enzyme in a single step at an about neutral pH, curing by drying. After hydration, the crosslinked polymer matrix may form a 3-dimensional glucose-permeable bioelectrocatalyst, catalyzing the electrooxidation of glucose.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Insulin formulations for insulin release as a function of tissue glucose levels
InactiveUS20090175840A1Reduce productionRaise the pHPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderInjections insulinReducing agent
Injectable insulin formulations that are capable of modifying the amount of insulin released based on the patient's tissue glucose levels, methods for making and using these formulations are described herein. The formulation may be administered via subcutaneous, intradermal or intramuscular administration. In one preferred embodiment, the formulations are administered via subcutaneous injection. The formulations contain insulin, an oxidizing agent or enzyme and a reducing agent or enzyme, a diluent and optionally one or more thickening agents. If a thickening agent is present in the formulation, the thickening agent increases the viscosity of the formulation following administration. Preferably the formulation contains an insulin, a diluent, glucose oxidase and peroxidase. Following administration to a patient, the insulin is released from the formulations as a function of the patient's tissue glucose level, which in turn maintains the patient's blood glucose level within an optimum range. The formulation is often referred to as a “smart” formulation since it modifies its release rate of insulin according to the patient's needs at a particular time. In a preferred embodiment, the formulation is designed to release insulin into the systemic circulation over time with a basal release profile following injection in a patient. In another embodiment, the formulation is designed to release insulin into the systemic circulation over time with a non-basal release profile following injection in a patient, such as a regular human insulin release profile or a prandial release profile.
Owner:BIODEL
Methods for producing potato products
The present invention relates to methods for producing consumable products from potatoes, comprising: (a) treating a potato substance with an effective amount of one or more exogenous enzymes selected from the group consisting of an amyloglucosidase, glucose oxidase, laccase, lipase, maltogenic amylase, pectinase, pentosanase, protease, and transglutaminase, and (b) processing the enzyme-treated potato substance to produce a potato product. The invention also relates to consumable products obtained from potatoes by the methods of the present invention.
Owner:NOVO NORDISKBIOTECH INC
Compound enzyme preparation for fermentation of pu'er tea and application
InactiveCN102492665APromote decompositionImprove the unique quality of connotationHydrolasesPre-extraction tea treatmentBiotechnologyPhytase
The invention relates to a compound enzyme preparation for fermentation of pu'er tea, which is formed by compounding 10% to 20% of cellulase, 10% to 20% of pectinase, 5% to 15% of polyphenol oxidase, 5% to 10% of glucose oxidase, 5% to 10% glucoamylase, 5% to 10% xylanase, 5% to 10% of beta-glucanase, 5% to 10% of beta-mannase, 5% to 10% of tannase, 5% to 10% of acidic protease, 5% to 10% of lipase, 1% to 5% of alpha-amylase and 1% to 5% of phytase. By the aid of coordination of the enzyme system, polysaccharide and other substances in tea including cellulose and hemicellulose can be effectively decomposed, so that various physiochemical substances in cells can be dissolved. Meanwhile, oxidation and condensation of tea polyphenol, decomposition of protein, amino acid and carbonhydrate, a series of reactions of various products including polymerization and condensation and the like are accelerated and promoted.
Owner:YUNNAN NORMAL UNIV
Electrochemical biosensor
ActiveUS20100285514A1Promote resultsImprove electrochemical performanceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectrochemical biosensorFluorescence
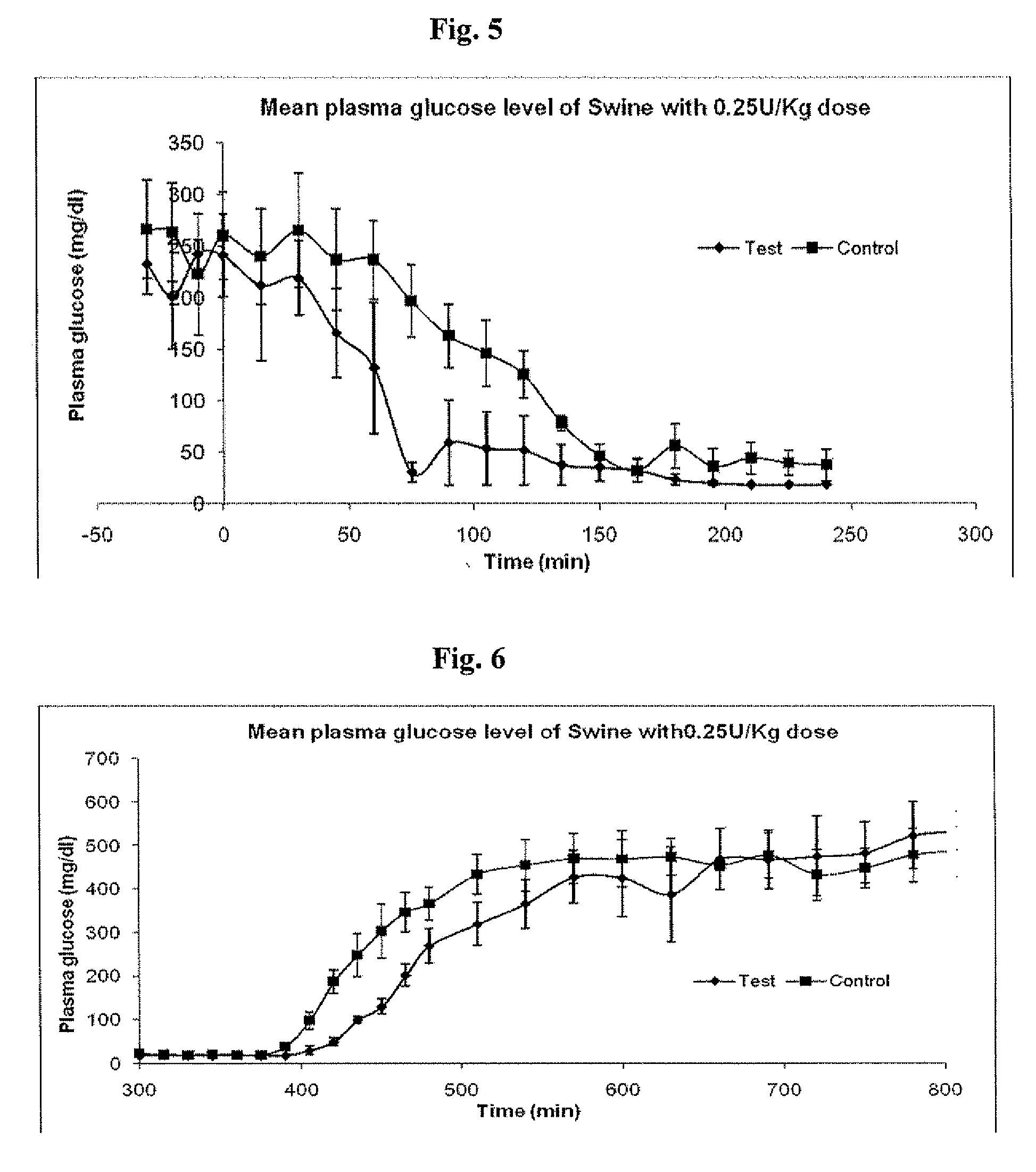
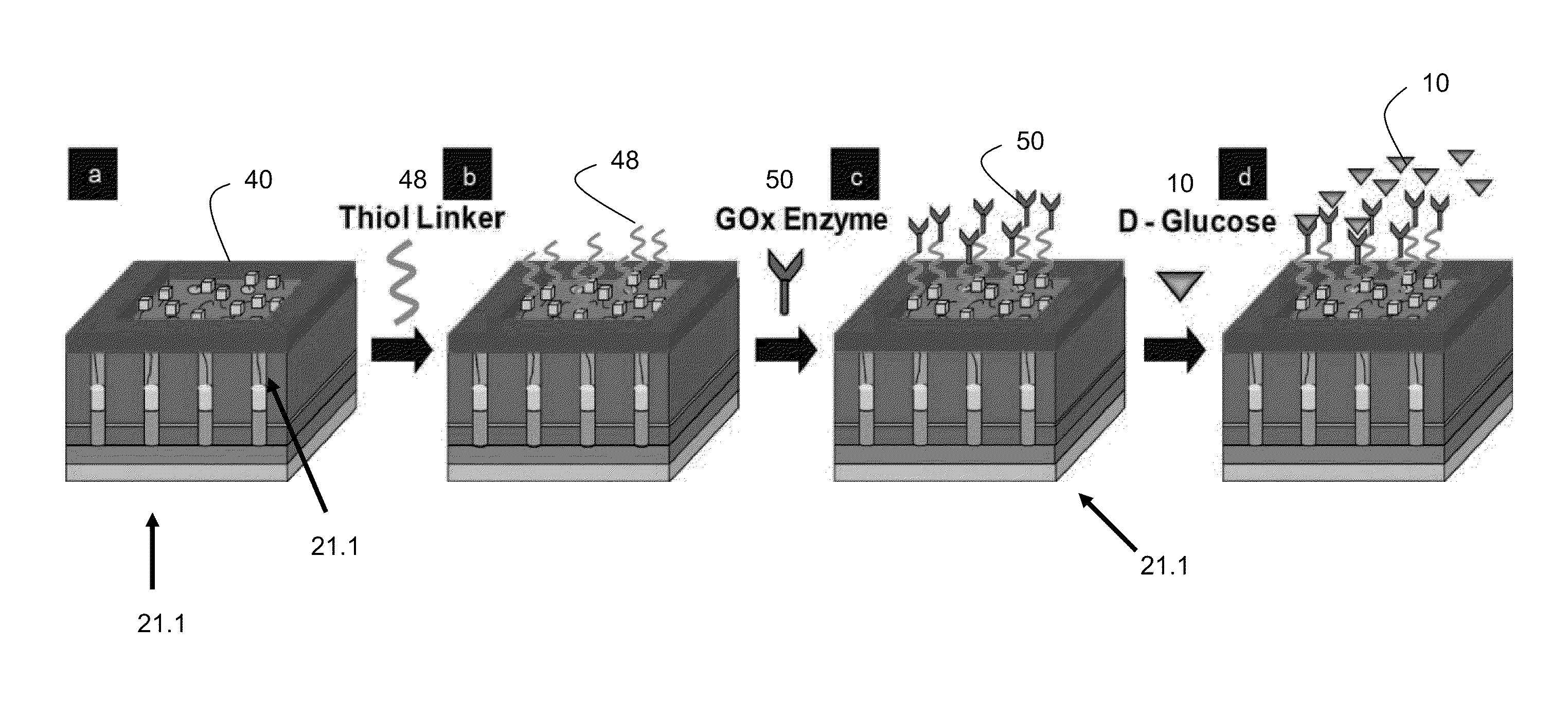
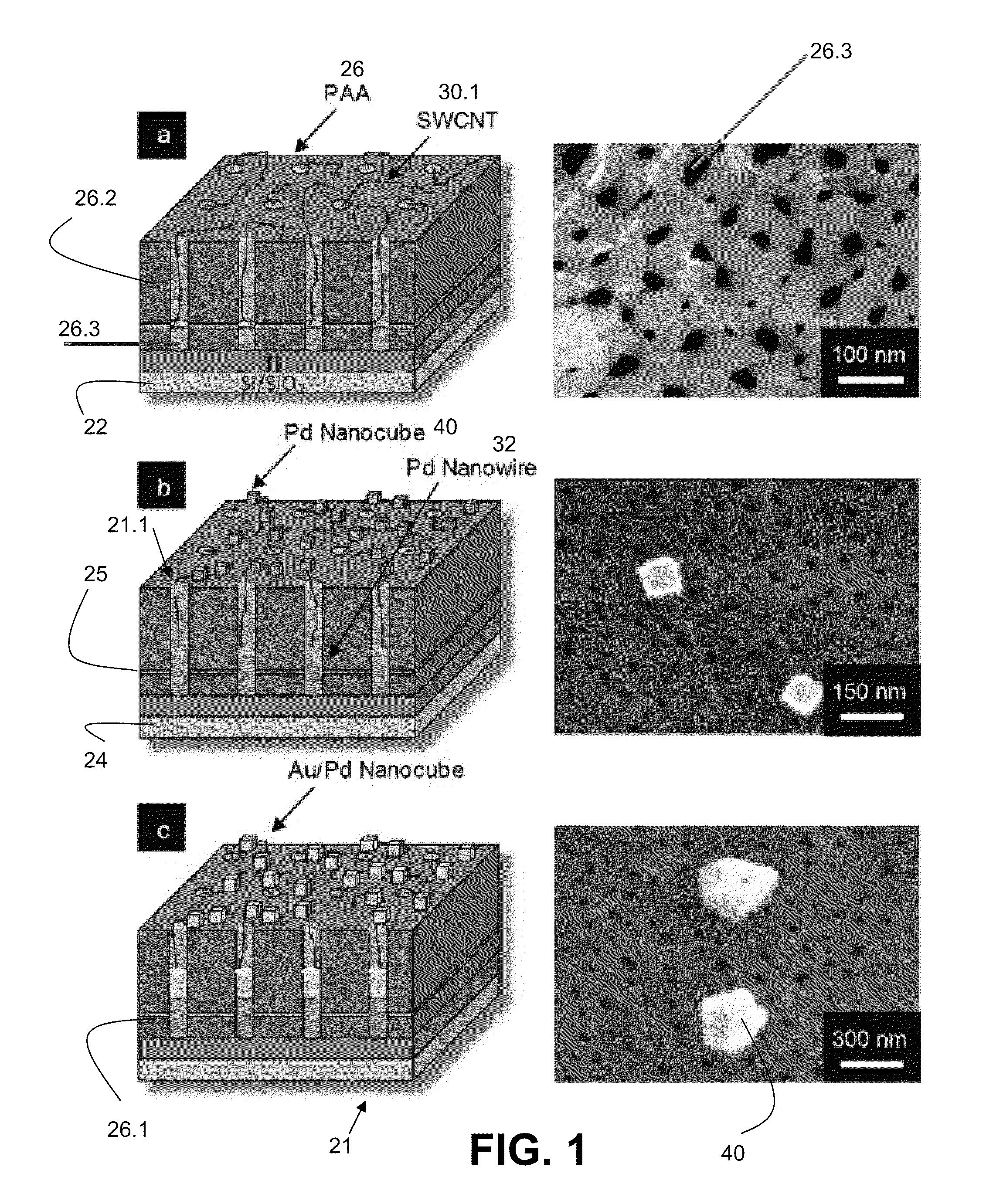
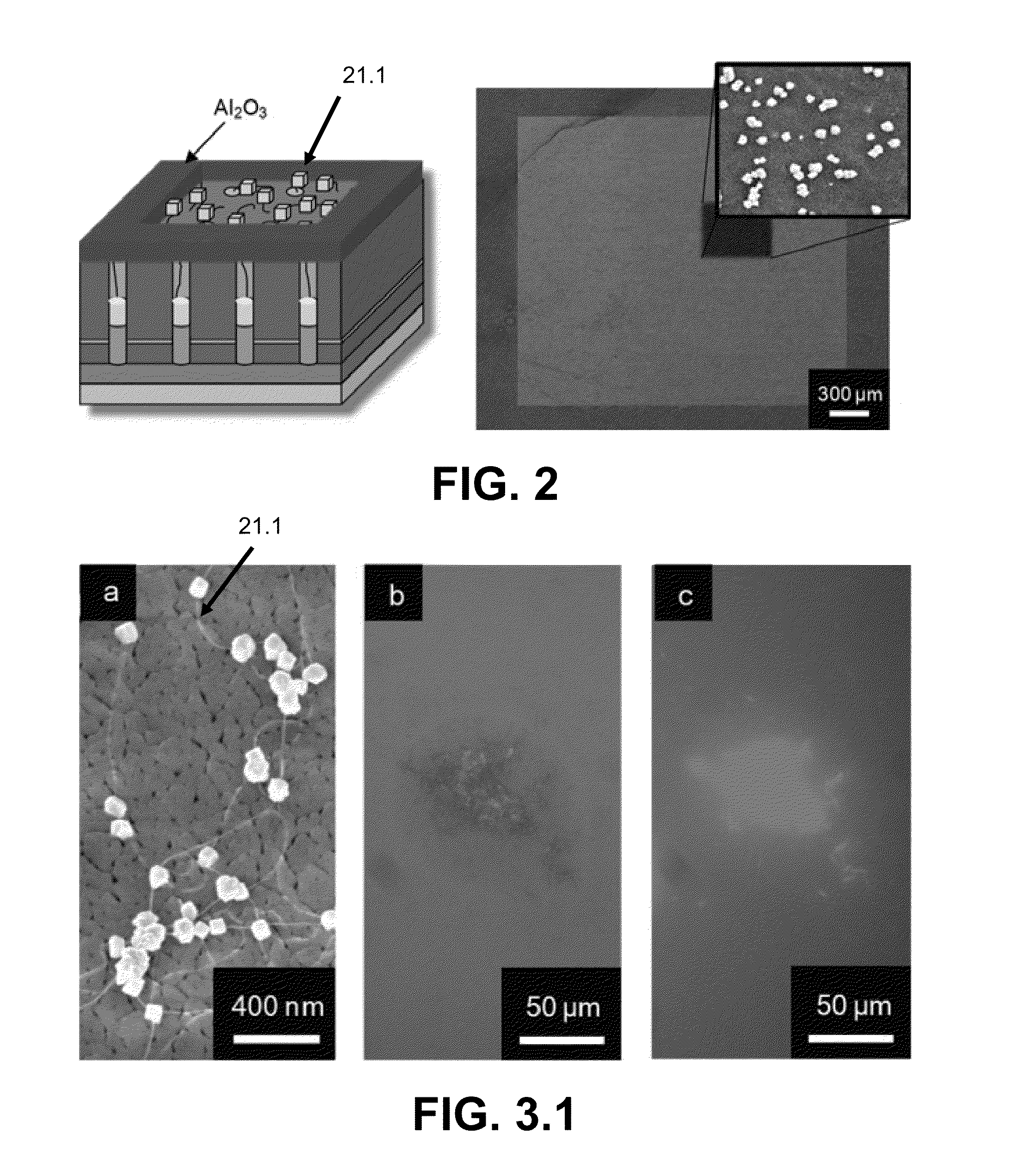
Networks of single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) decorated with Au-coated Pd (Au / Pd) nanocubes are employed as electrochemical biosensors that exhibit excellent sensitivity (2.6 mA mM−1 cm−2) and a low estimated detection limit (2.3 nM) at a signal-to-noise ratio of 3 (S / N=3) in the amperometric sensing of hydrogen peroxide. Biofunctionalization of the Au / Pd nanocube-SWCNT biosensor is demonstrated with the selective immobilization of fluorescently labeled streptavidin on the nanocube surfaces via thiol linking. Similarly, glucose oxidase (GOx) is linked to the surface of the nanocubes for amperometric glucose sensing. The exhibited glucose detection limit of 1.3_M (S / N=3) and linear range spanning from 10 μM to 50 mM substantially surpass other CNT-based biosensors. These results, combined with the structure's compatibility with a wide range of biofunctionalization procedures, would make the nanocube-SWCNT biosensor exceptionally useful for glucose detection in diabetic patients and well suited for a wide range of amperometric detection schemes for biomarkers.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
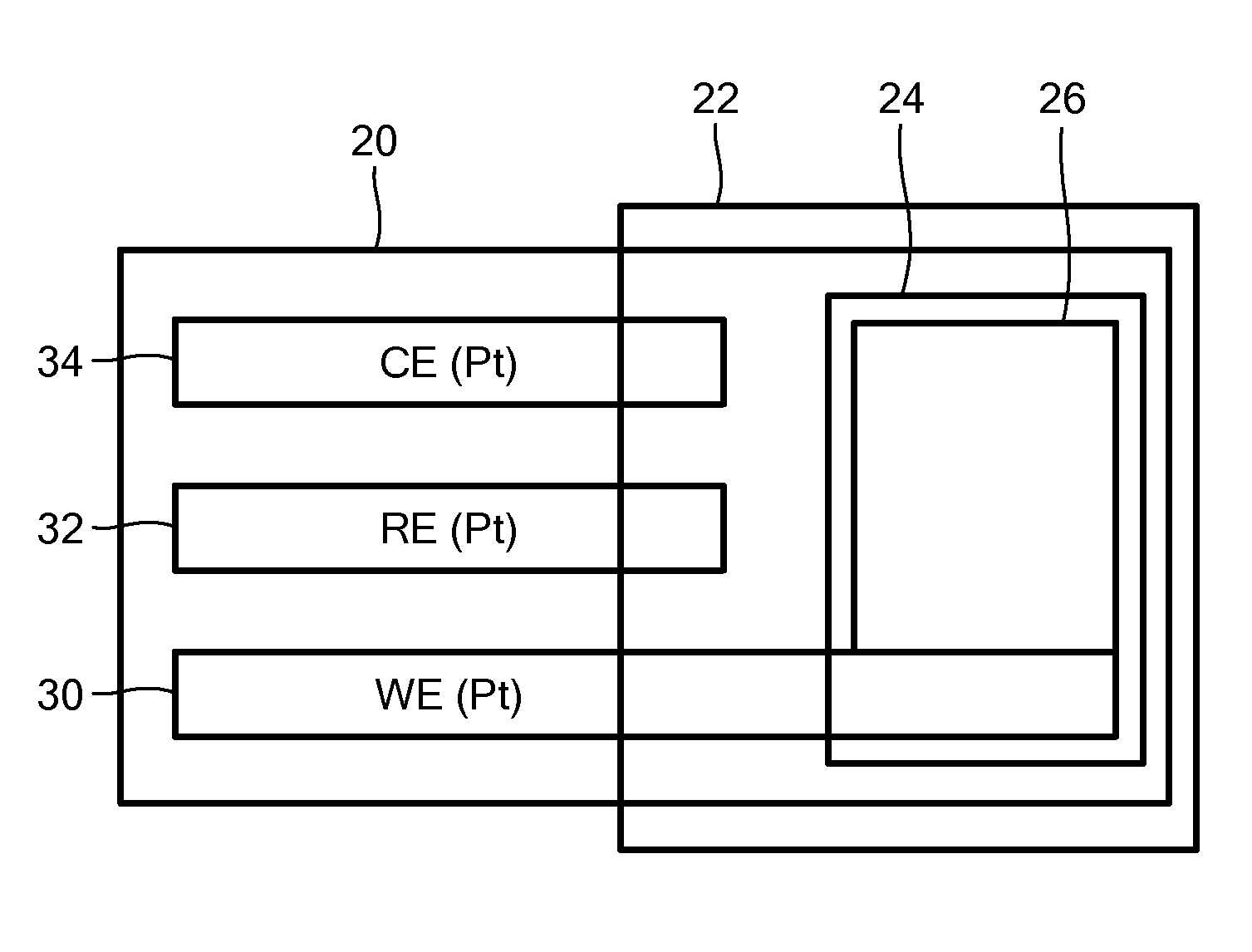
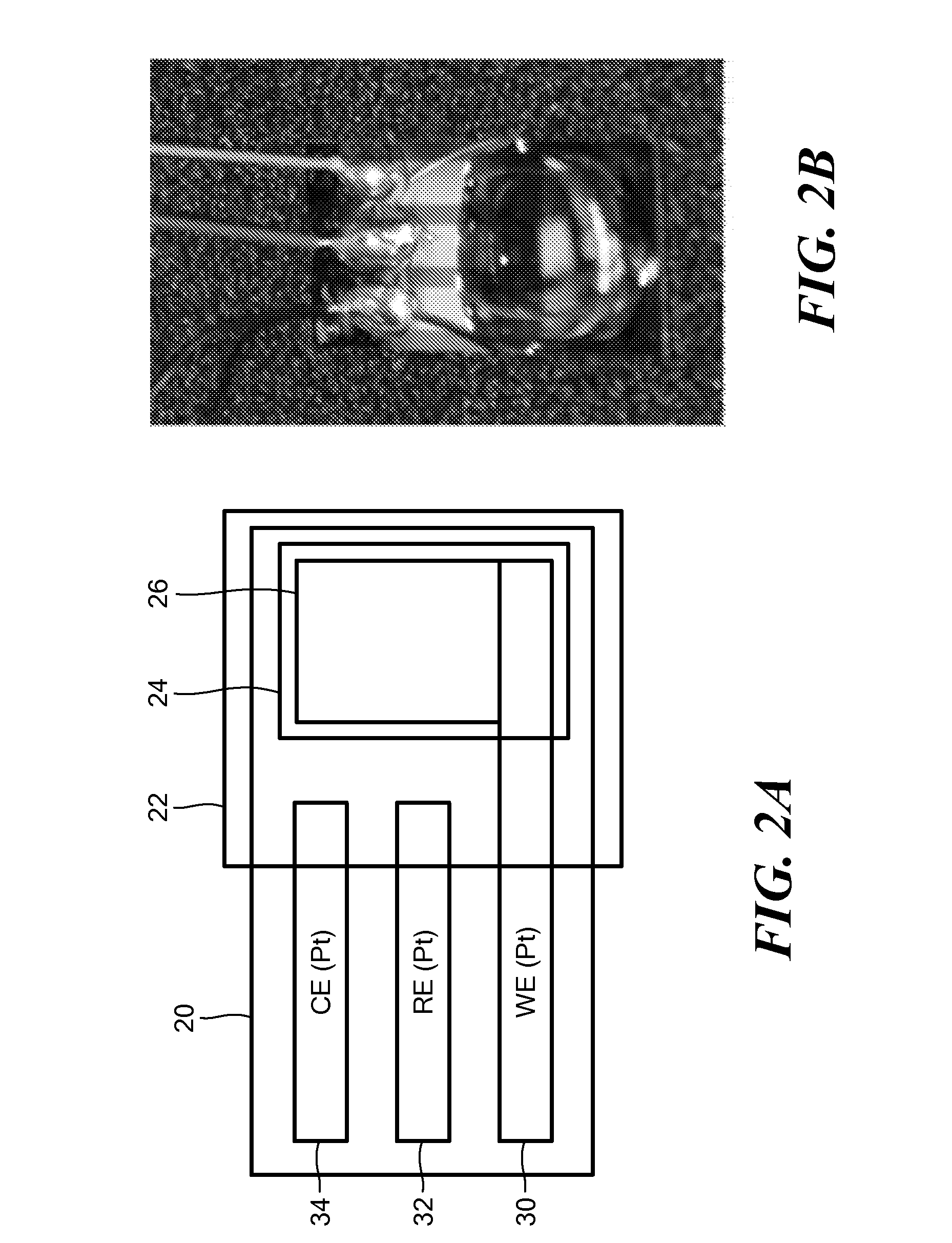
Saliva Glucose Monitoring System
ActiveUS20140197042A1Exposure was also limitedProtective coatingImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrochemical detectorClinical settings
A glucose sensor suitable for measuring glucose levels in human saliva is provided. Systems containing the glucose sensor and methods for making and using the sensor are also provided. The glucose sensor is highly sensitive and can detect glucose levels at least down to 5 ppm. Fabrication of the sensor involves depositing single-walled carbon nanotubes onto the surface of a working electrode in a 3 electrode electrochemical detector and functionalizing the nanotubes by depositing layers of polymers, metallic nanoparticles, and glucose oxidase enzyme onto the nanotubes. The sensor can be used as a disposable, single-use device or as part of an analytical system, such as a microfluidics system, for the analysis of multiple analytes. The sensor enables the diagnosis and monitoring of diabetes to be performed without pain or the need for finger pricks in a home or clinical setting.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Intelligent polymerized crystalline colloidal array carbohydrate sensors
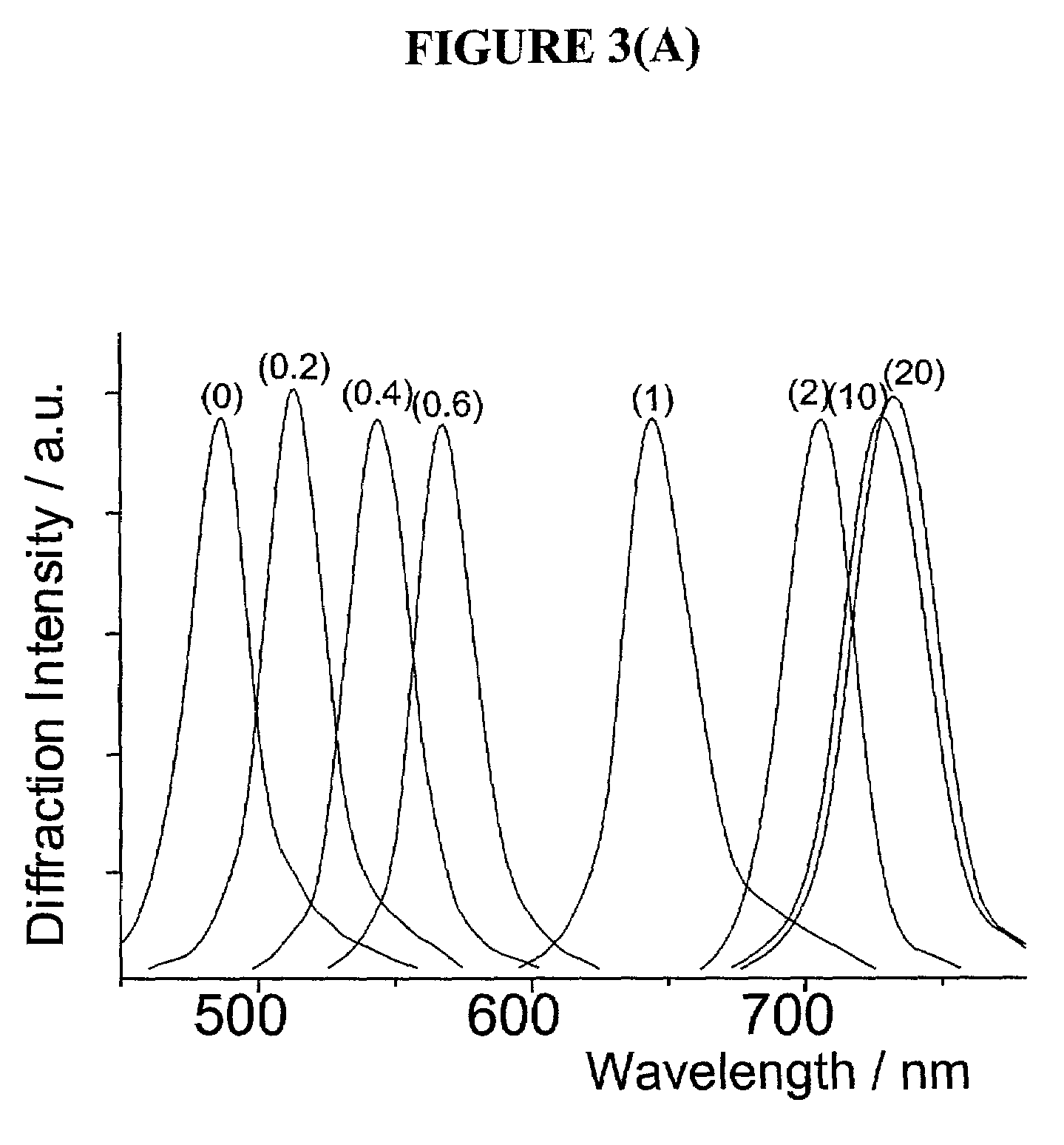
InactiveUS7105352B2Material analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorSpectrum generation using diffraction elementsGlucose sensorsConcentrations glucose
The present invention is related to glucose sensors that are capable of detecting the concentration or level of glucose in a solution or fluid having either low or high ionic strength. The glucose sensors of the present invention comprise a polymerized crystalline colloidal array (PCCA) and a molecular recognition component capable of responding to glucose. The molecular recognition component may be a boronic acid, such as a phenylboronic acid, glucose oxidase, a combination of phenylboronic acid and poly(ethylene)glycol or crown ether, or another component capable of detecting glucose in various fluids and solutions. The glucose sensors of the present invention may be useful in the development of noninvasive or minimally invasive in vivo glucose sensors for patients having diabetes mellitus.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Glucose detection sensor, and preparation and application methods thereof
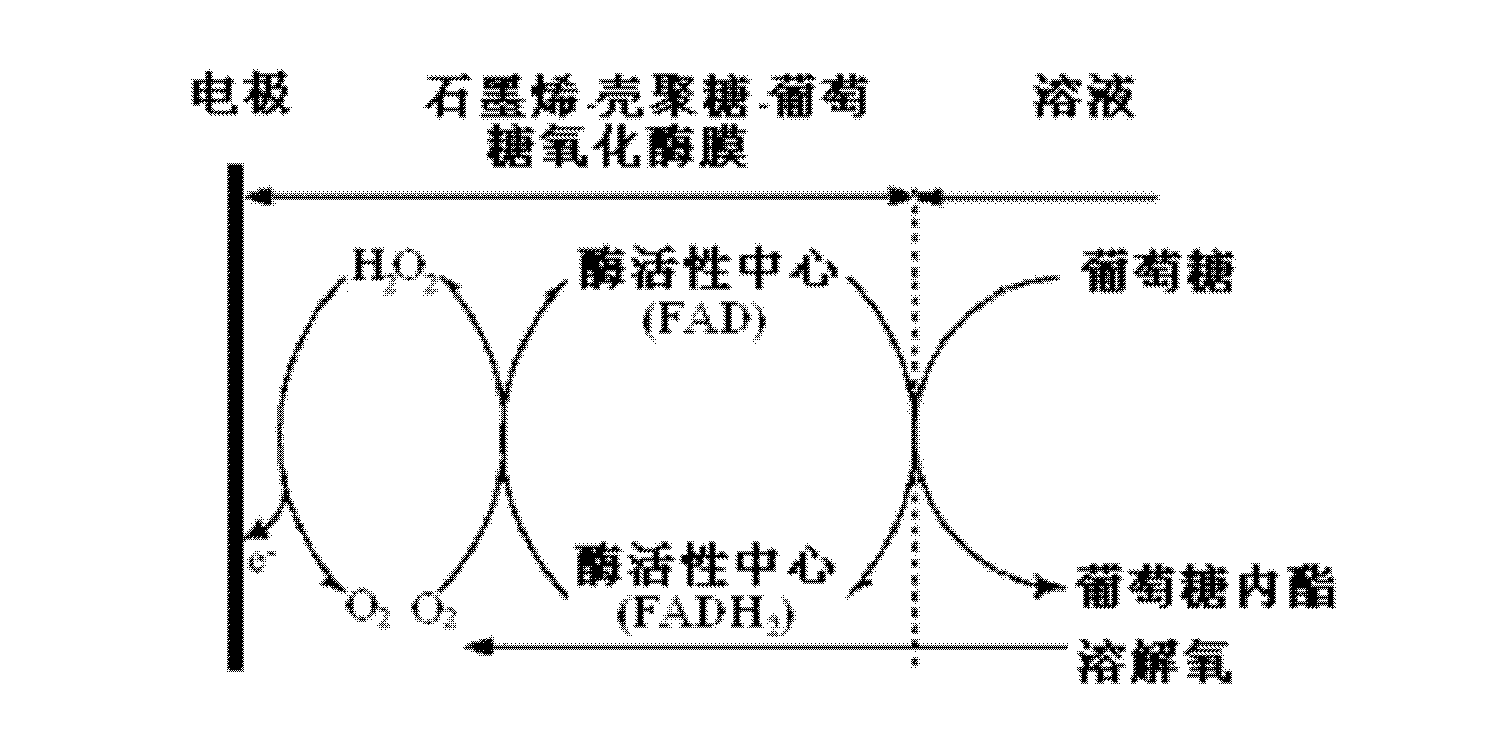
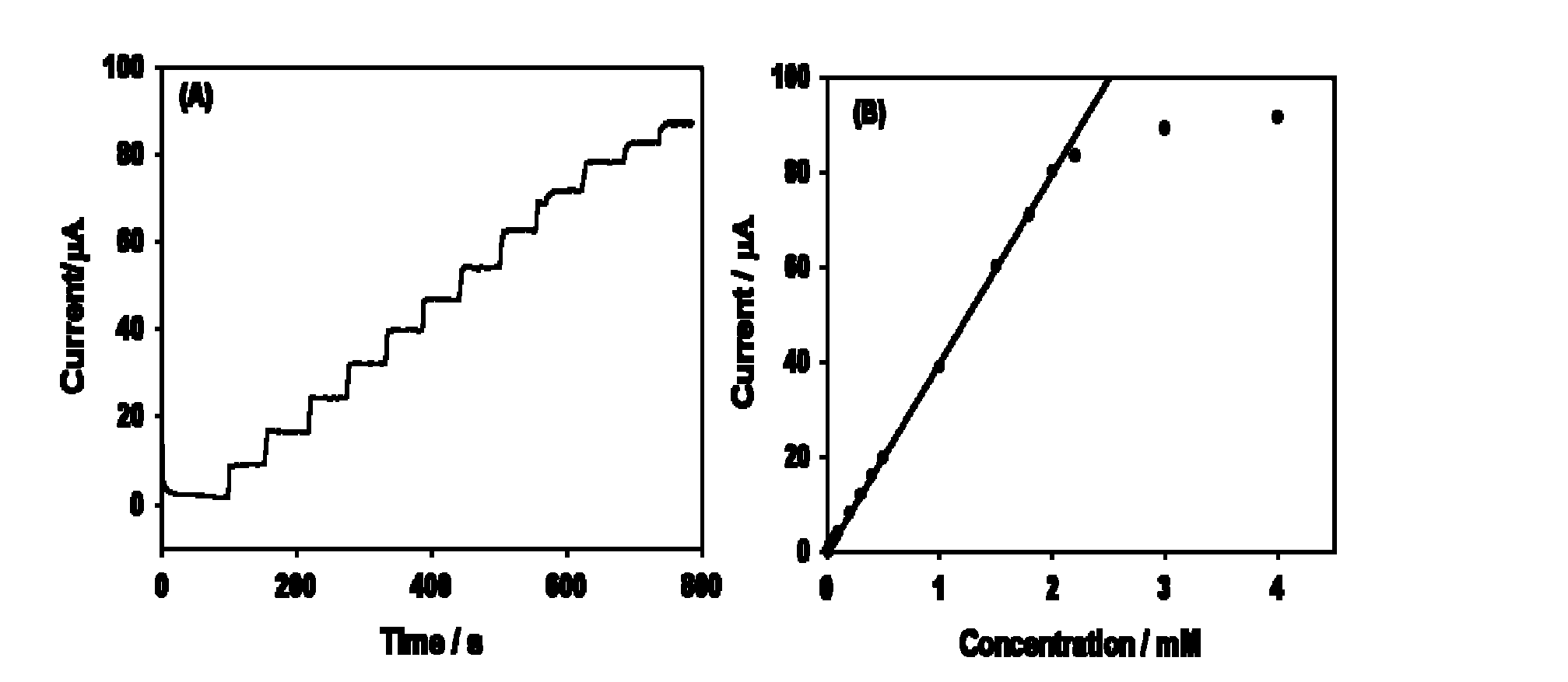
InactiveCN102636540ASpecific fastStrong specificityMaterial electrochemical variablesGlucose sensorsChemistry
The invention discloses a glucose detection sensor, and preparation and application methods thereof. The sensor comprises a three-electrode system, wherein a graphene / chitosan / glucose oxidase deposition modified glassy carbon electrode is used as a working electrode, a platinum sheet is used as a counter electrode, and a calomel electrode is used as a reference electrode. In the detection process, by using the graphene / chitosan / glucose oxidase deposition modified glassy carbon electrode as the working electrode, the platinum sheet as the counter electrode and the calomel electrode as the reference electrode, an electrochemical work station is utilized to determine the glucose content. Compared with the traditional method, the invention has the advantages of higher sensitivity and higher specificity, and the low detection limit is 4.0*10<-7> mol / L; and meanwhile, the glucose sensor has the advantages of simple preparation process, stable performance and short sample detection time, can be recycled, and is convenient to operate.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Method for detecting hydrogen peroxide or glucose based on enzyme simulation by ferroferric oxide magnetic nanometer particle
InactiveCN101387606AGood choiceHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorColor/spectral properties measurementsPeroxidaseD-Glucose
The invention relates to a method for detecting hydrogen peroxide or glucose, based on ferroferric oxide nanometer particle mimetic enzyme, wherein the ferroferric oxide nanometer particle mimetic enzyme is obtained by co-precipitation method, the ferroferric oxide nanometer particle mimetic enzyme has the catalysis property similar to peroxidase, and the ferroferric oxide nanometer particle mimetic enzyme can be used to detect hydrogen peroxide for real-time presenting the colorimetric detection of hydrogen peroxide. The detected limit of hydrogen peroxide is 3x10<-6>mol / L, the linear range is 5x10<-6> to 1x10<-4>mol / L. The ferroferric oxide nanometer particle mimetic enzyme can be combined with glucose oxidase to realize the colorimetric detection of glucose. The detection limit of glucose is 3x10<-5>mol / L and the linear range is 5x10<-5> to 1x10<-3>mol / L. The colorimetric detection of glucose has high selectivity and sensitivity, without complex instruments.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Fresh shrimp freezing and antistaling agent as well as fresh shrimp freezing and antistaling method
InactiveCN105341137AGreat tasteReduce lossesMeat/fish preservation by freezing/coolingMeat/fish preservation using chemicalsAquatic productZoology
The invention discloses a fresh shrimp freezing and antistaling agent as well as a fresh shrimp freezing and antistaling method. The antistaling agent is a mixture containing tea polyphenol, chitosan, antibacterial peptide, nisin, glucose oxidase, sodium chloride, lactic acid and trehalose. The antistaling agent is used for freezing and fresh-keeping of fresh shrimps; the fresh shrimp freezing and antistaling agent has natural components, and can be used for better protecting freshness of aquatic products, maintaining original appearance and state, reducing loss of proteins and other nutrients, inhibiting generation of bacteria, and substantially prolonging shelf-life and storage life.
Owner:高邮市应天水产有限公司
Glucose oxidase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN103981159AImprove heat resistanceIncrease specific volumeFungiPre-baking dough treatmentHeat resistanceWild type
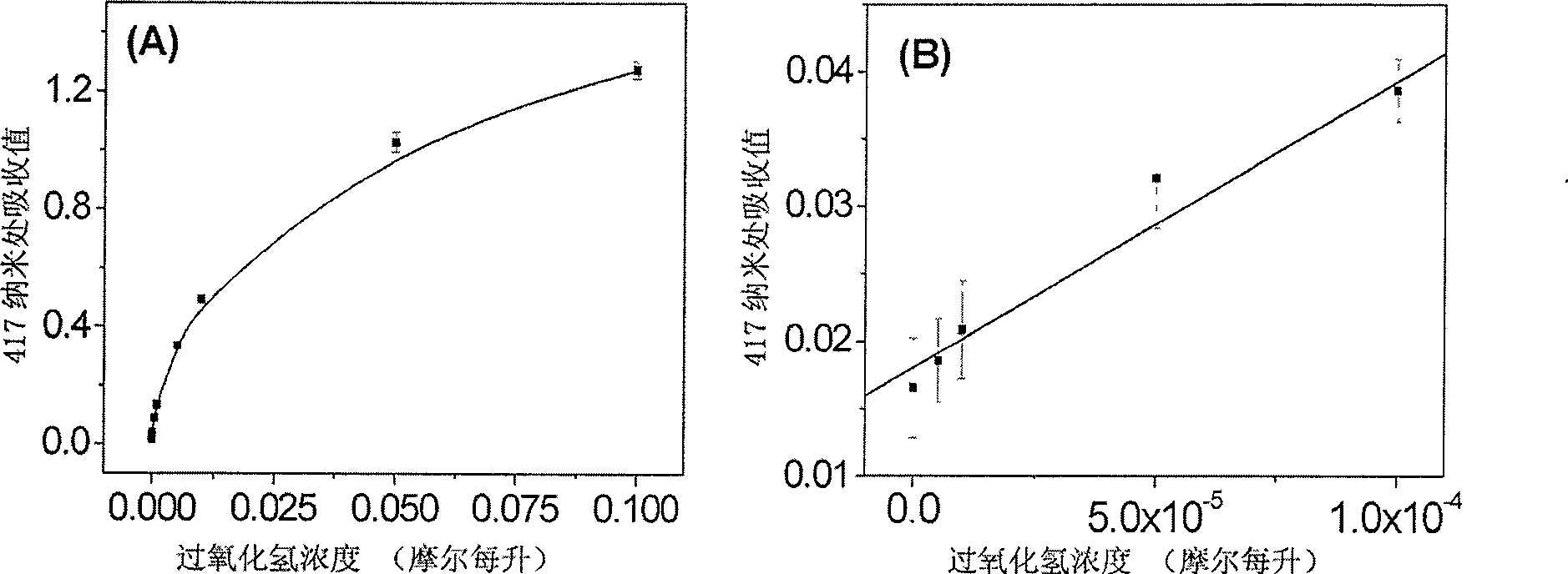
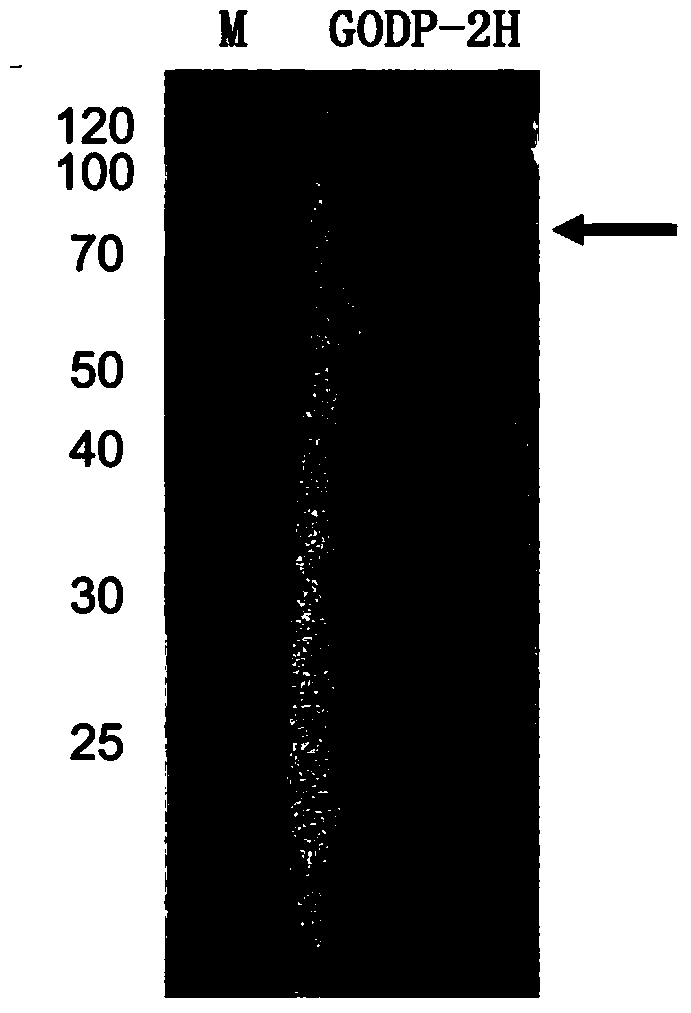
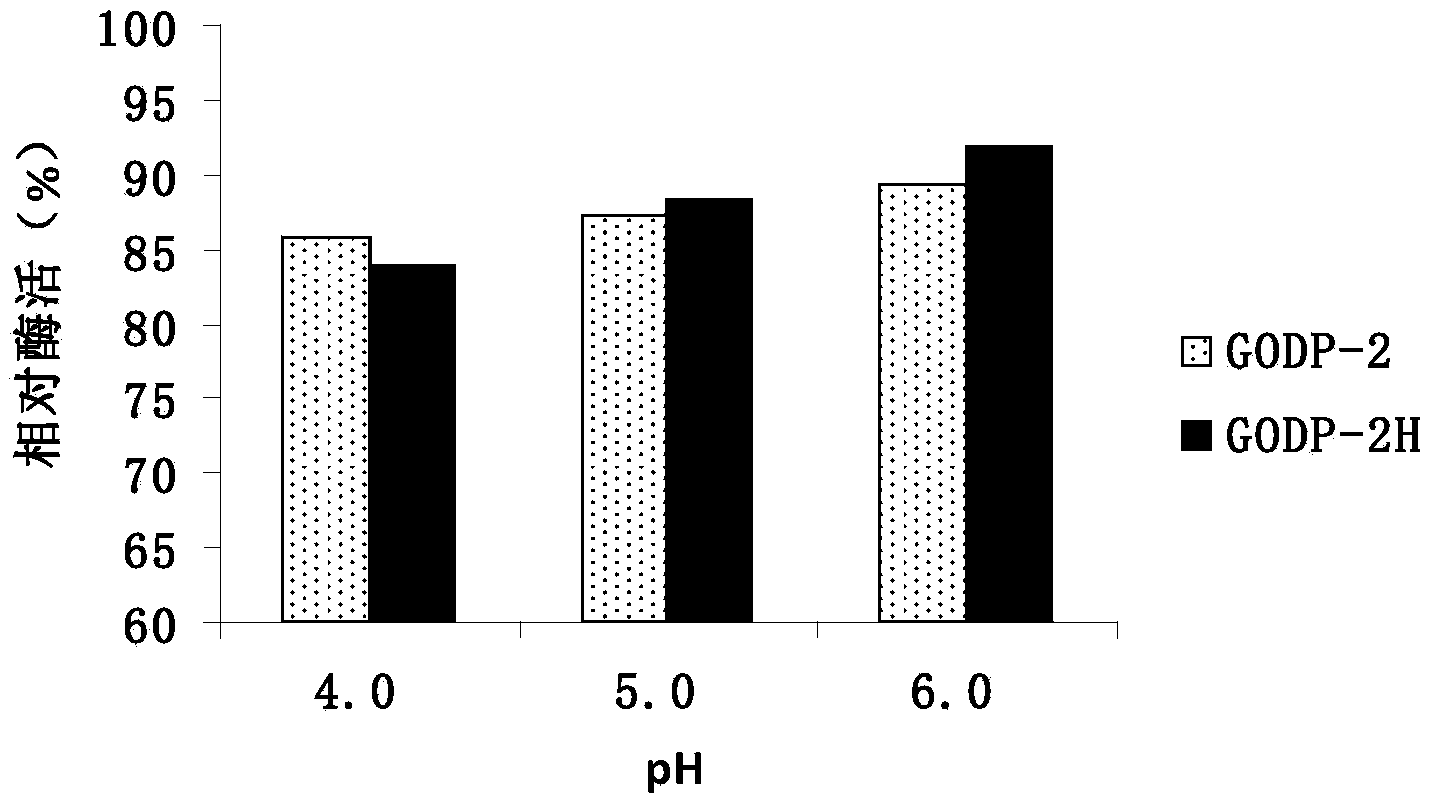
The invention provides a glucose oxidase mutant. According to the glucose oxidase mutant, a 172-nd amino acid of glucose oxidase with an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 is changed to Arg from Asn, and a 525-th amino acid of the glucose oxidase is changed to Asn from Cys. The glucose oxidase mutant has an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 3, and a nucleic acid sequence of a coding gene of the glucose oxidase mutant is shown in SEQ ID NO: 4. The glucose oxidase mutant provided by the invention has the optimal action pH value of 6.0, is very stable in the pH range of 4.0-6.0 and has good pH tolerance which is similar to that of a wild type; the optimal action temperature of the mutant is 40 DEG C; residual enzyme activity still can be maintained at 78.1%, 47.7% and 15.9% after the mutant is respectively treated for 1 hour at the temperature of 60 DEG C, 65 DEG C and 70 DEG C; and the heat resistance is far higher than that of the wild type, which means that the heat resistance of the glucose oxidase is greatly improved due to mutation; therefore, the mutant GODP-2H is more suitable for being applied to industrial production compared with the wild type due to the characteristic.
Owner:QINGDAO VLAND BIOTECH GRP
Immobilized enzyme biological catalyst, preparation method and application
InactiveCN101058824AReduce dosageImprove distributionImmobilised enzymesChemical industryDielectricPotassium
The invention relates to an immobilized enzyme biocatalyst and the manufacturing method and application. The immobilized enzyme biocatalyst regards tubular hollow silica dioxide dielectric hole material as a carrier external surface, inner surface and micropore in the wall of which are fixed biological enzyme molecule. The method includes physical adsorption cast investment or chemical coupling / crosslinking method; the biocatalyst is provided with good enzyme dispersibility and high carrying quantity, high recovery ratio of enzymatic activity, low enzyme flow rate. The invention can fix penicillin acylating enzyme, glucose oxidase, peroxidase, cytase and so on, which also can be used for removing sugar in protein, removing sugar in total egg, removing oxygen in food , microbiological sensing device, antibiosis and disinfection reaction, wherein immobilized penicillin acylating enzyme biocatalyst can be used to hydrolyze penicillin potassium and manufacture 6-APA.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Preparation method for high purity fructo-oligosaccharide
ActiveCN101368195AImprove performanceSuitable for useOn/in organic carrierFermentationSucrosePeroxidase
The invention relates to a preparation method of high purified fructo-oligosaccharide, in particular to a method for preparing the high purified fructo-oligosaccharide by using immobilized enzyme. The preparation method of the invention prepares immobilized fructosyltransferase, immobilized glucose oxidase and immobilized mimic hydrogen peroxidase; then prepared enzymes are used to prepare the high purified fructo-oligosaccharide through an interrupted or continuous production method. In the preparation method, cheap metalporphyrin compounds are used as the mimic hydrogen peroxidase to replace expansive catalase; the fructosyltransferase, the glucose oxidase and the mimic hydrogen peroxidase are all immobilized and all can be recycled and reused; the stability and the operating factor of the enzymes are improved; the production cost for preparing the high purified fructo-oligosaccharide is greatly reduced. The preparation method can use one step method to directly produce the high purified fructo-oligosaccharide from cane sugar.
Owner:量子高科(广东)生物有限公司
Disposable test strips with integrated reagent/blood separation layer
InactiveUS20060260940A1Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsGlucose testSilicon dioxide
An improved disposable glucose test strip for use in a test meter of the type which receives a disposable test strip and a sample of blood from a patient and performs an electrochemical analysis is made using a non-conductive integrated reagent / blood separation layer containing a filler, an enzyme effective to oxidize glucose, e.g., glucose oxidase, and a mediator effective to transfer electrons from the enzyme. The integrated layer formulation is printed over a conductive carbon element to form a working electrode. The filler, for example a silica filler, is selected to have a balance of hydrophobicity and hydrophilicty such that one drying it forms a two-dimensional network on the surface of the conductive element. The response of this test strip is essentially temperature independent over relevant temperature ranges and is substantially insensitive to the hematocrit of the patient.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Expression of the glucose oxidase gene in transgenic organisms
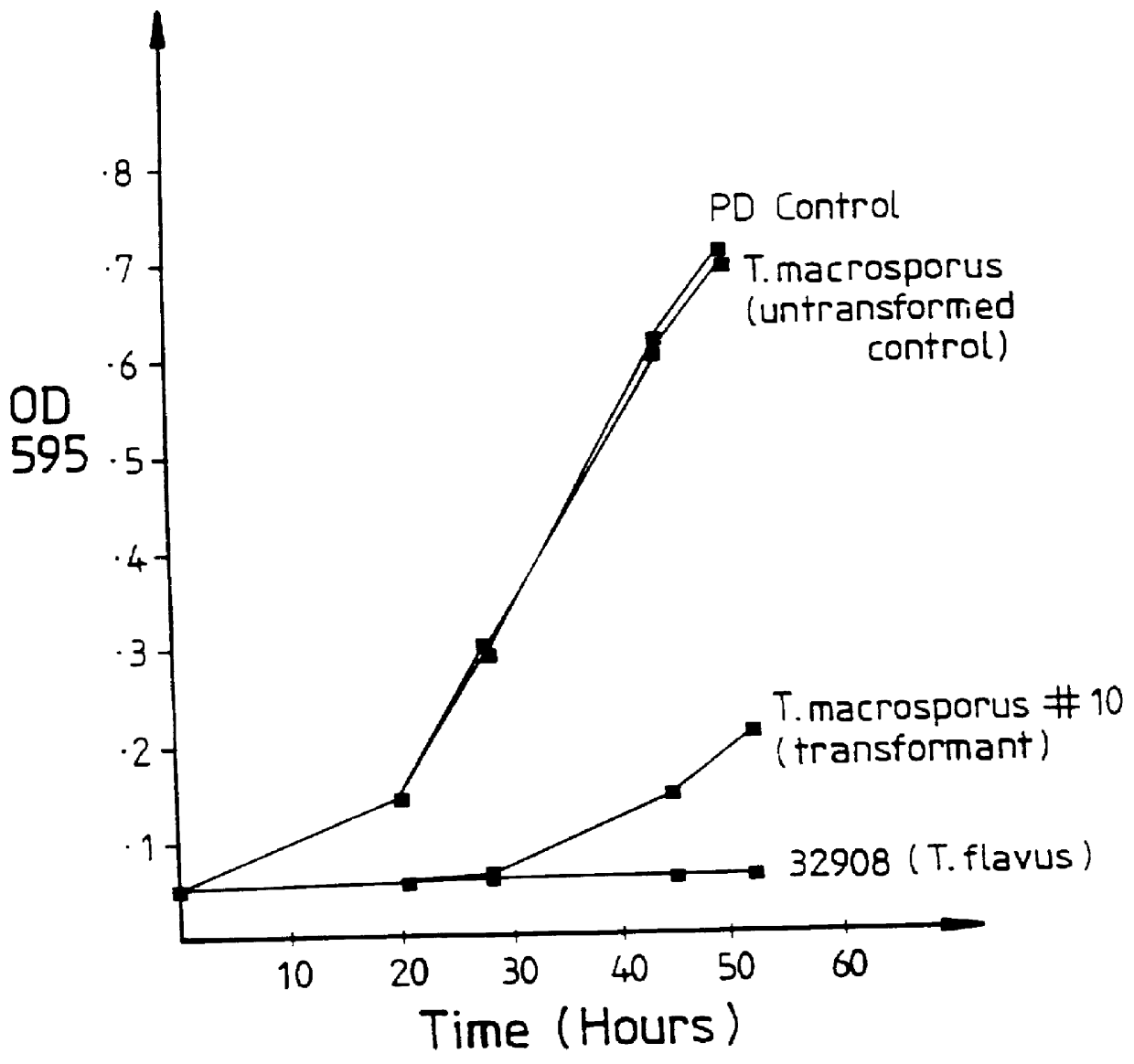
PCT No. PCT / AU95 / 00059 Sec. 371 Date Nov. 11, 1996 Sec. 102(e) Date Nov. 11, 1996 PCT Filed Feb. 10, 1995 PCT Pub. No. WO95 / 21924 PCT Pub. Date Aug. 17, 1995A genetic construct for use in production of transgenic plants with reduced susceptibility or increased resistance to pests or diseases comprises an isolated nucleotide sequence encoding the glucose oxidase enzyme of Talaromyces flavus, the nucleotide sequence being operably linked to a promoter capable of expression in a plant, plant cell or group of plant cells, and further comprises a nucleic acid segment having a nucleotide sequence encoding a signal sequence which directs secretion of the functional glucose oxidase enzyme of T. flavus from plant cells.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
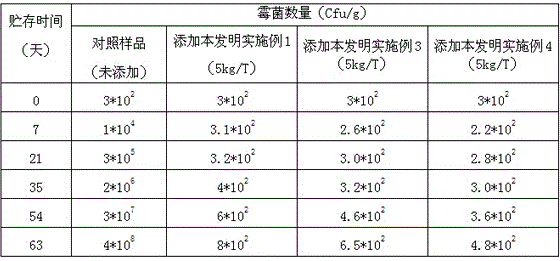
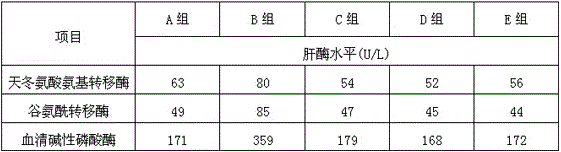
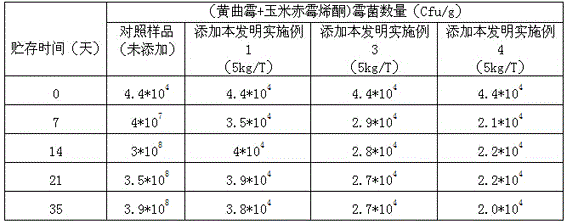
Mildew-proof detoxication and detoxification mixed type feed additive
InactiveCN105594994AGrowth inhibitionEliminate the effects ofAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsDiseaseSnow mold
The invention relates to a mildew-proof detoxication and detoxification mixed type feed additive, and belongs to the technical field of feed additives. The feed additive is prepared from the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 70 to 95 percent of modified montmorillonite, 0.4 to 0.8 percent of bacillus subtilis, 2 to 20 percent of yeast cell wall polysaccharide, 0.6 to 1 percent of glucose oxidase, 0.5 to 4 percent of methionine, 0.5 to 2 percent of alpha-mannatide and 0.5 to 4 percent of VC. The mildew-proof detoxication and detoxification mixed type feed additive has the advantages that the reasonable ingredient preparation is adopted; through reasonable use, mycotoxin can be adsorbed; the mildew growth is inhibited; the influence of mycotoxin on animal physiology is eliminated; the resistivity of animals on diseases is improved; the phenomenon of having loose bowels is reduced; the culture benefits are improved.
Owner:浙江大飞龙动物保健品股份有限公司
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com