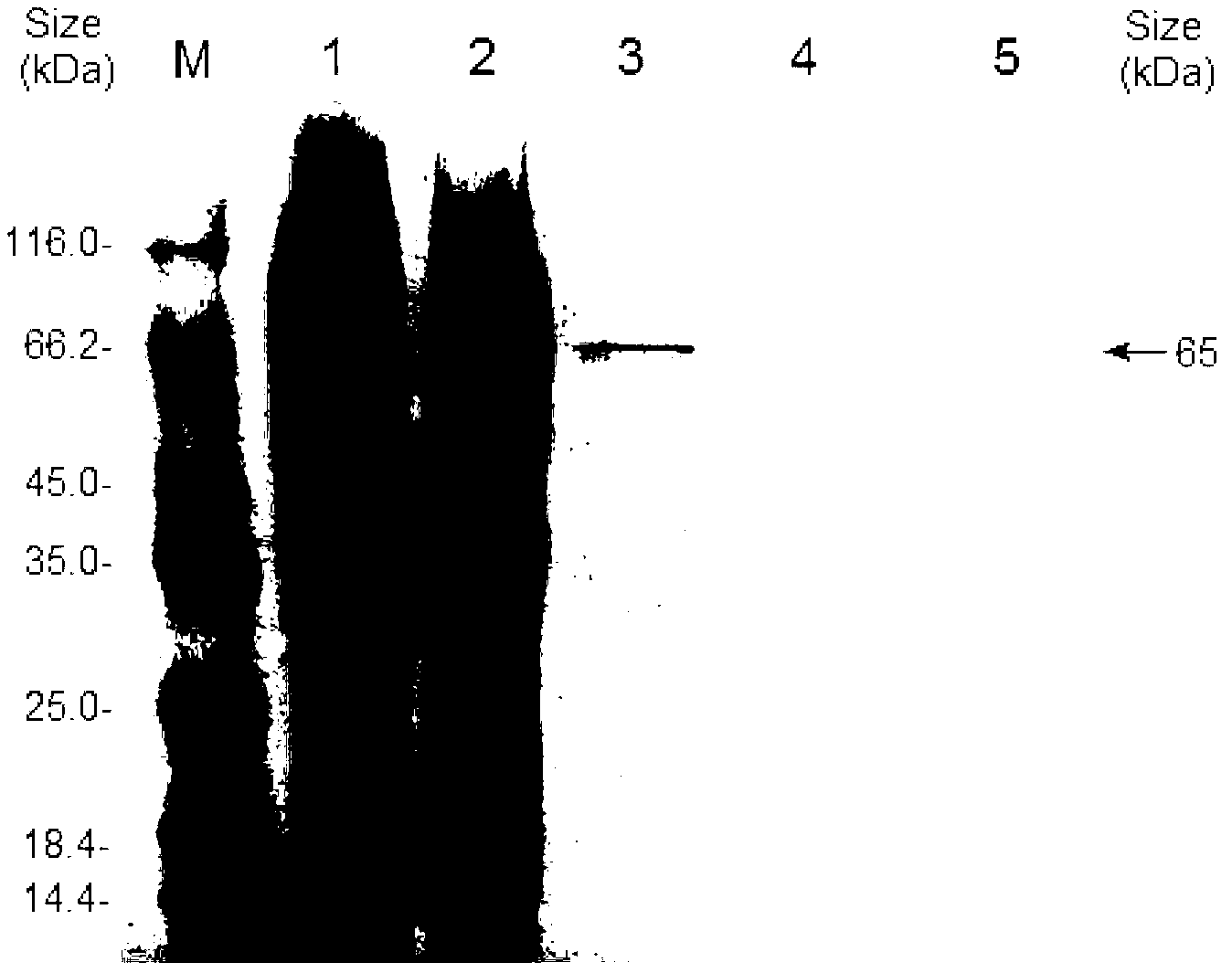Patents
Literature
1193 results about "Laccase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Laccases (EC 1.10.3.2) are copper-containing oxidase enzymes found in many plants, fungi, and microorganisms. Laccases act on phenols and similar substrates, performing one-electron oxidations, leading to crosslinking. For example, laccases play a role in the formation of lignin by promoting the oxidative coupling of monolignols, a family of naturally occurring phenols. Other laccases, such as those produced by the fungus Pleurotus ostreatus, play a role in the degradation of lignin, and can therefore be classed as lignin-modifying enzymes. Laccases catalyze ring cleavage of aromatic compounds.
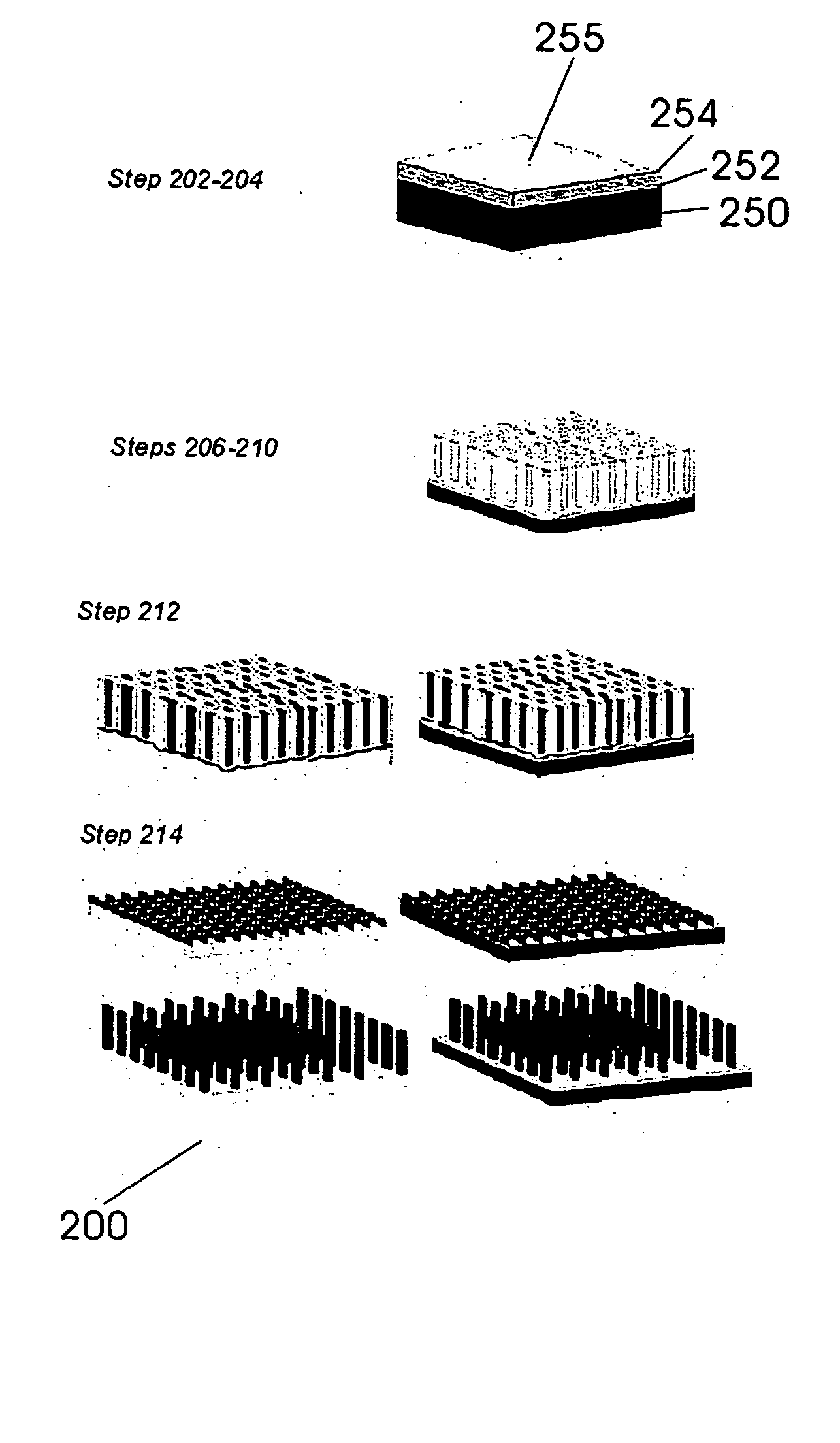
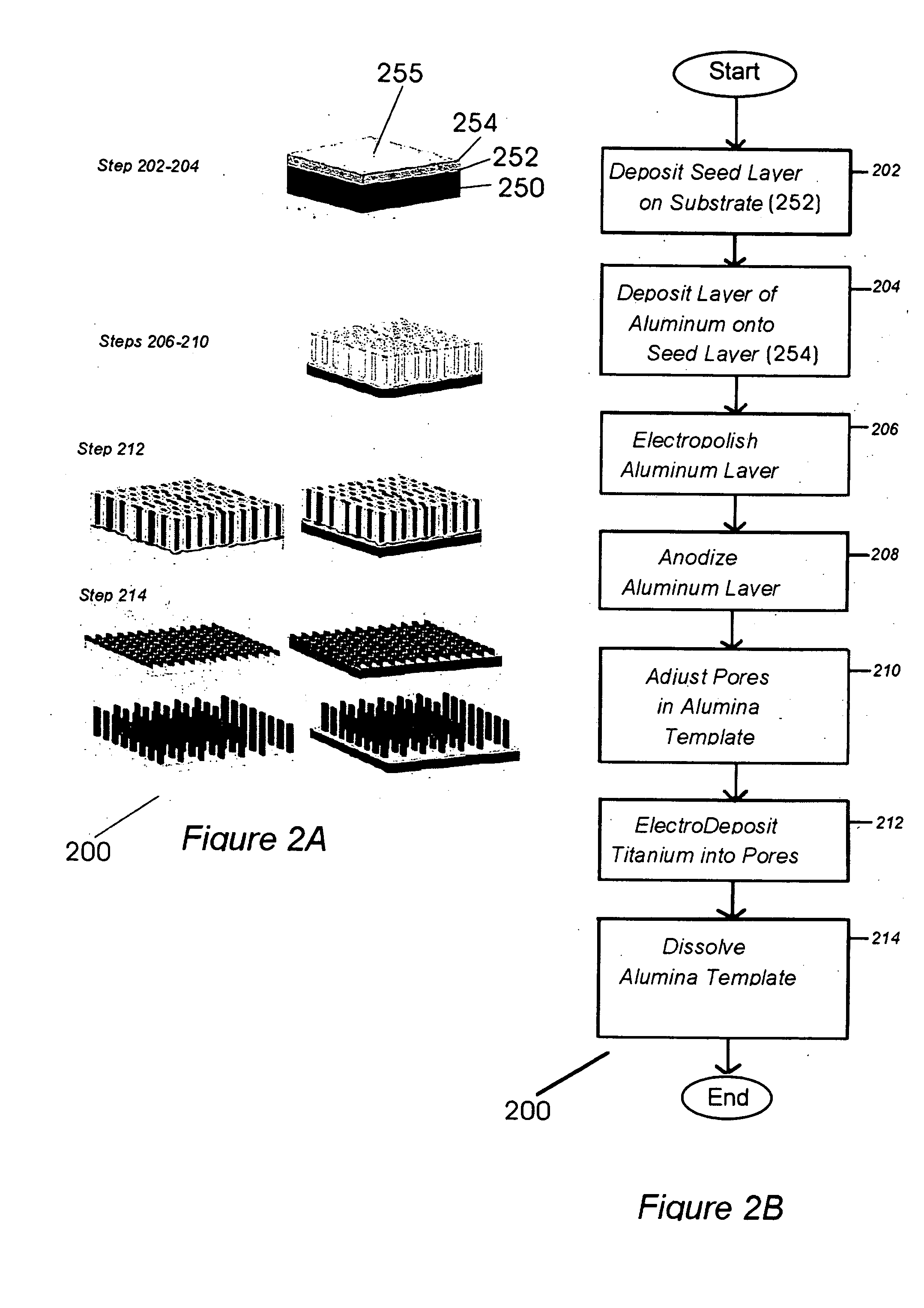
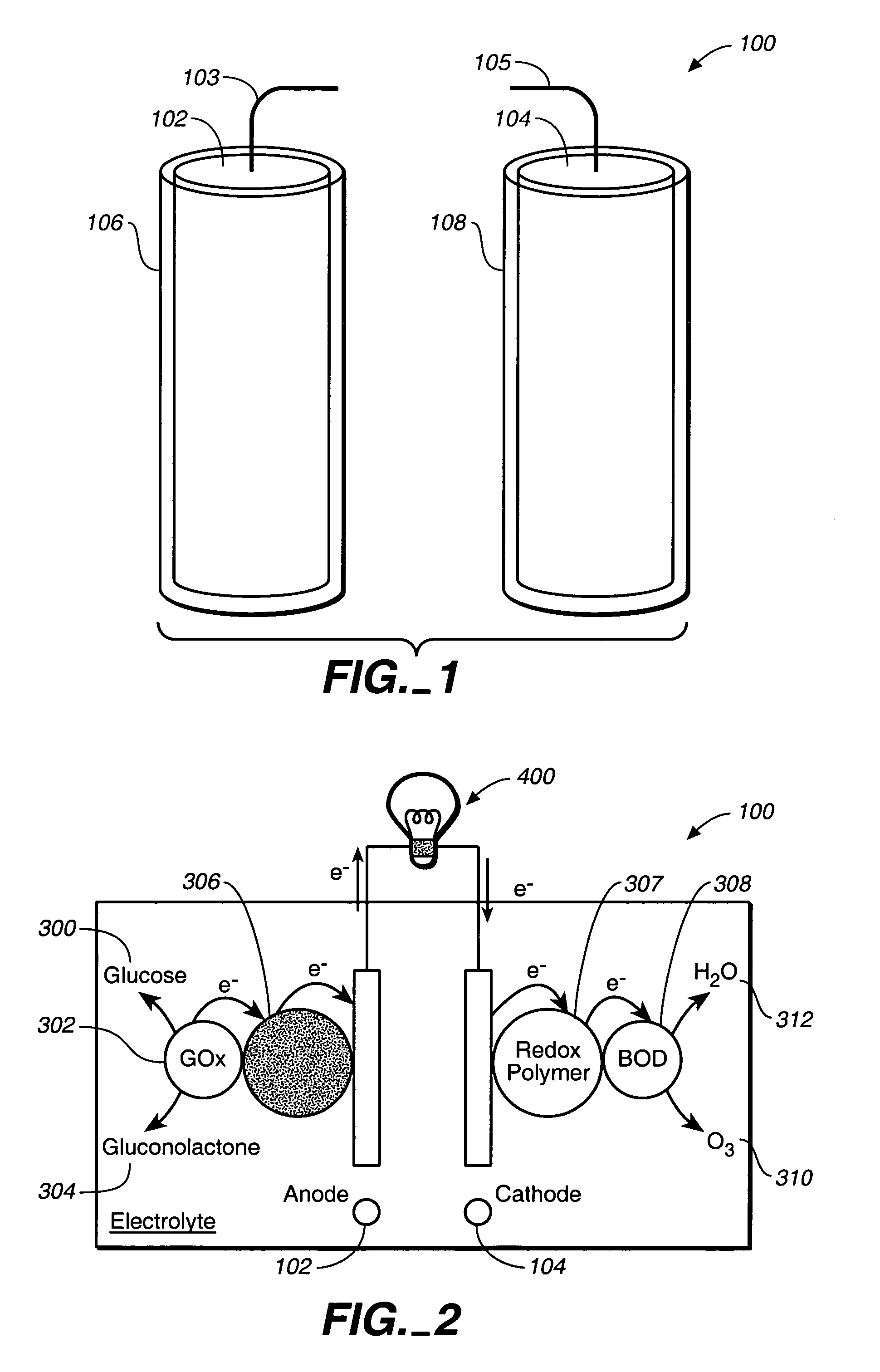
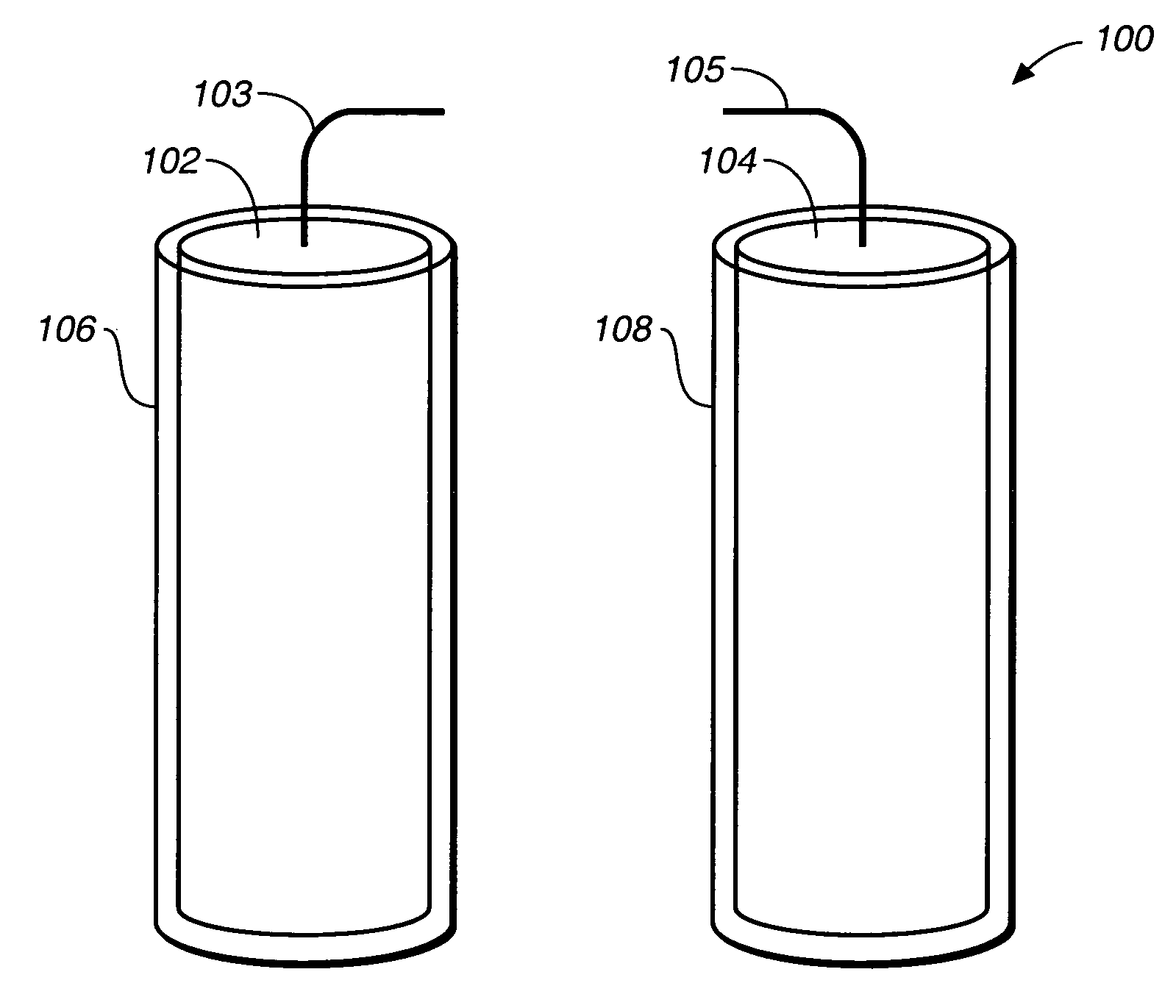
Implantable biofuel cell system based on nanostructures
InactiveUS20050118494A1Increase powerImprove power densityMaterial nanotechnologyFuel cell auxillariesCarbon nanotubeMolecular level
A bio-implantable electrochemical cell system for active implantable medical devices. In one embodiment, the fuel cell includes an electrode structure consisting of immobilized anode and cathode enzymes deposited on nanostructured high-surface-area metal nanowires or carbon nanotube electrodes. The anode enzyme comprises immobilized glucose oxidase and the cathode enzyme comprises immobilized laccase. Glucose is oxidized at the surface of the anode and oxygen is reduced at the surface of the cathode. The coupled glucose oxidation-oxygen reduction reactions provide a self-generating current source. In another embodiment, the nanowires or carbon nanotubes, along with the adjacent surface anode and cathode electrodes, are coated with immobilized glucose oxidase and immobilized laccase containing biocolloidal substrates, respectively. This results in the precise construction of an enzyme architecture with control at the molecular level, while increasing the reactive surface area and corresponding output power by at least two orders of magnitude.
Owner:NANOSOLUTIONS
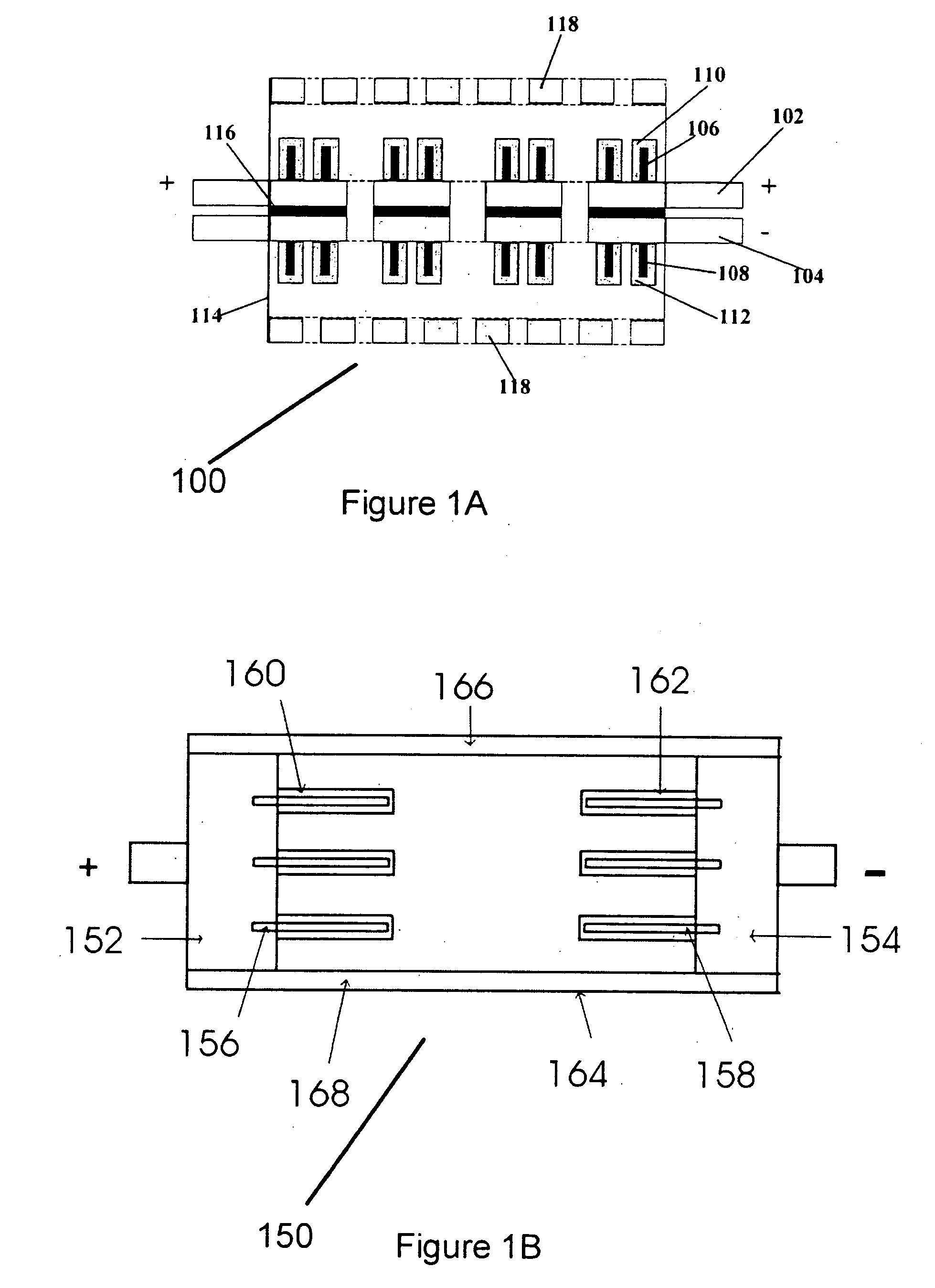
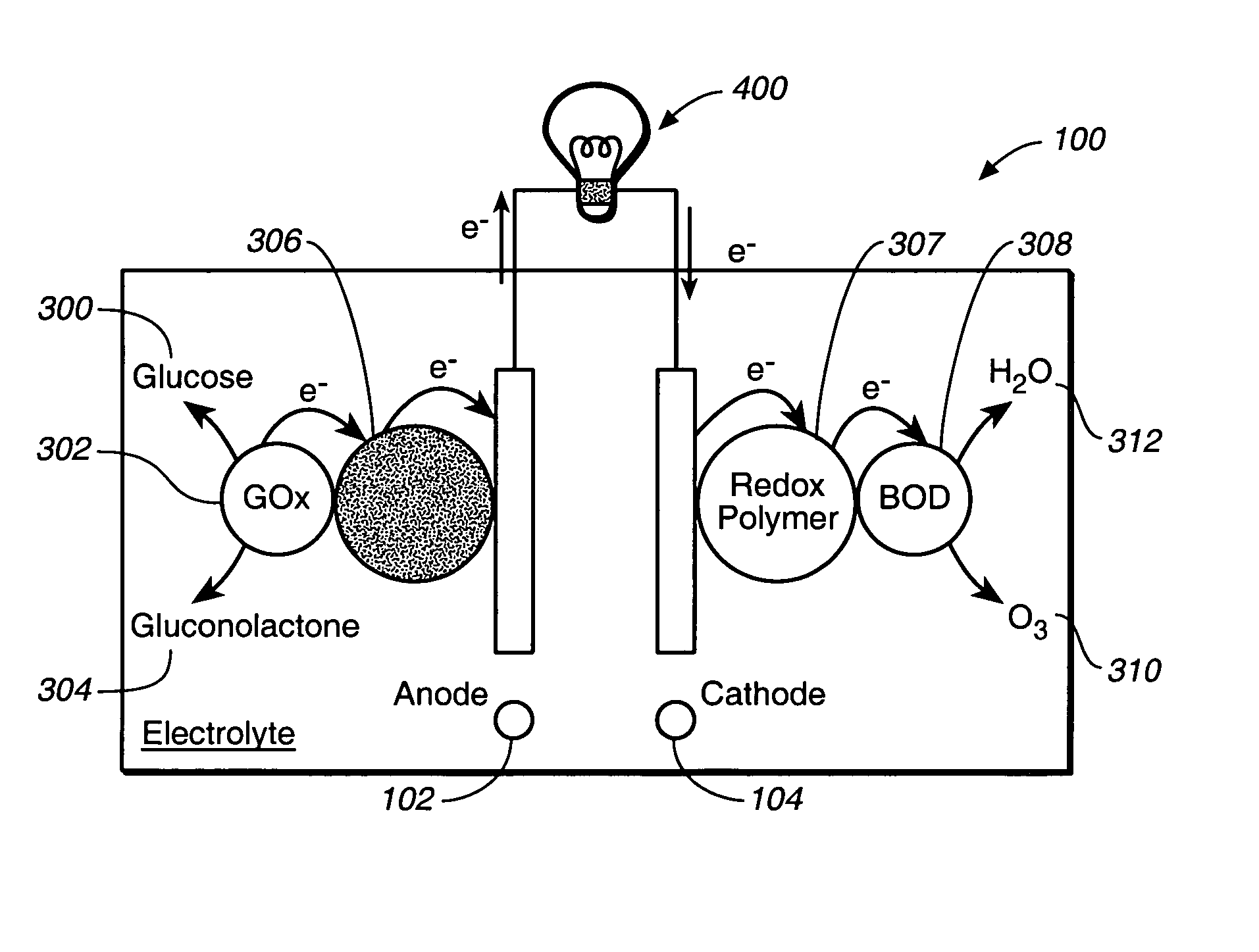
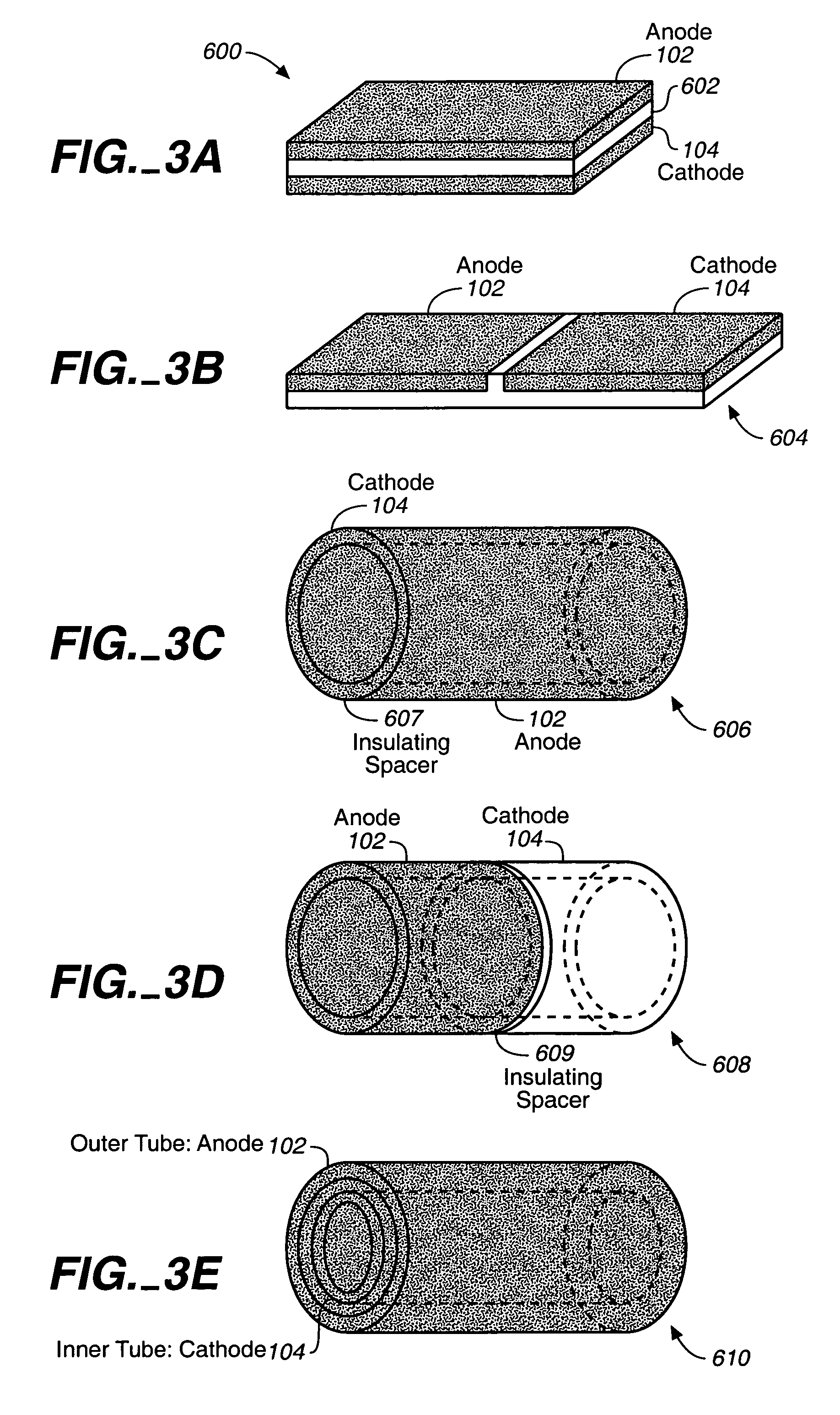
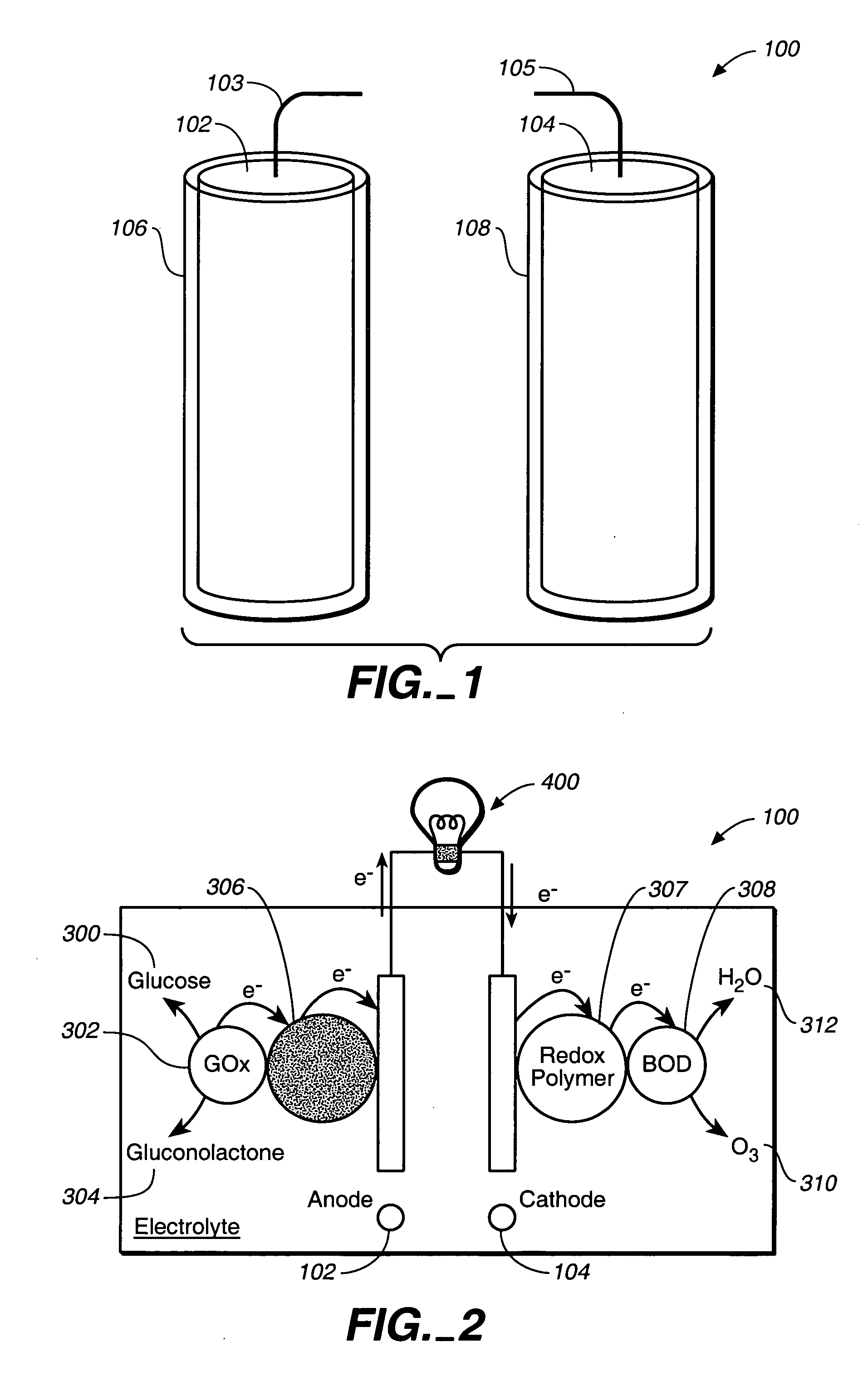
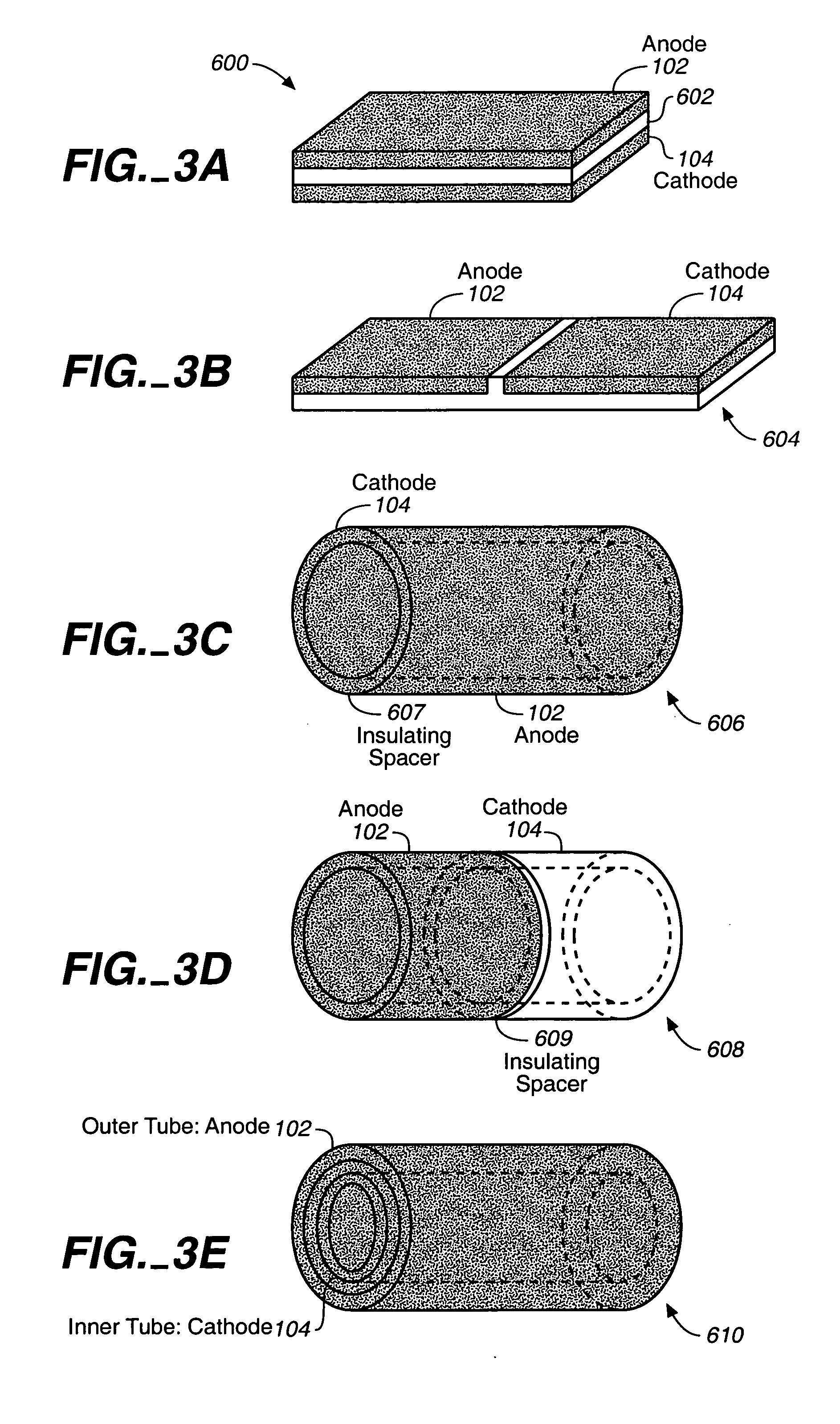
Miniature biological fuel cell that is operational under physiological conditions, and associated devices and methods
InactiveUS7368190B2Reduce physical sizeReduced dimensionMicrobiological testing/measurementVolume/mass flow measurementOperabilityRedox polymers
A fuel cell is provided with an anode and a cathode. The anode is in electrical communication with an anode enzyme and the cathode is in electrical communication with a cathode enzyme. The anode enzyme is preferably an oxidase or a dehydrogenase. The cathode enzyme is a copper-containing enzyme, such as a laccase, an ascorbate oxidase, a ceruloplasmine, or a bilirubin oxidase. Preferably, the cathode enzyme is operable under physiological conditions. Redox polymers serve to wire the anode enzyme to the anode and the cathode enzyme to the cathode. The fuel cell can be very small in size because it does not require a membrane, seal, or case. The fuel cell can be used in connection with a biological system, such as a human, as it may operate at physiological conditions. By virtue of its size and operability at physiological conditions, the fuel cell is of particular interest for applications calling for a power source implanted in a human body, such as a variety of medical applications.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
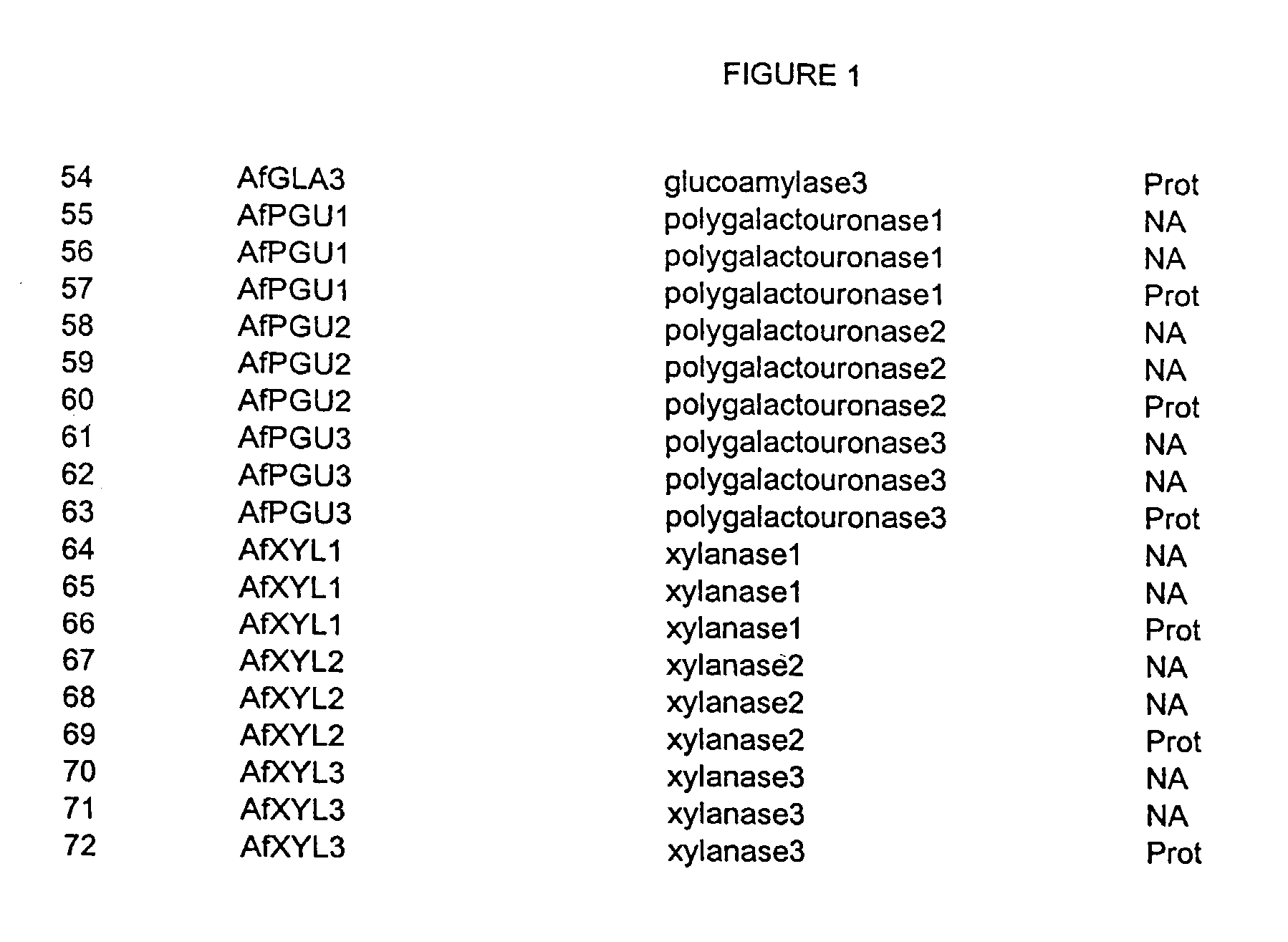
Nucleic acids of aspergillus fumigatus encoding industrial enzymes and methods of use
The present invention provides nucleotide sequences of Aspegillus fumigatus that encode proteins which exhibit enzyme activities. Vectors, expression constructs, and host cells comprising the nucleotide sequences of the enzyme genes are also provided. The invention further provides methods for producing the enzymes, and methods for modifying the enzymes in order to improve their desirable characteristics. The activities displayed by the enzymes of the invention include those of a tannase, cellulase, glucose oxidase, glucoamylase, phytase, beta-galactosidases, invertase, lipase, alpha-amylase, laccase, polygalacturonase or xylanase. The enzymes of the invention can be used in a variety of industrial processes. Enzymatically active compositions in various forms as well as antibodies to the enzymes and fragments thereof, are also provided.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC
Miniature biological fuel cell that is operational under physiological conditions, and associated devices and methods
InactiveUS20080044721A1Reduce physical sizeReduced dimensionMicrobiological testing/measurementVolume/mass flow measurementOperabilityRedox polymers
A fuel cell is provided with an anode and a cathode. The anode is in electrical communication with an anode enzyme and the cathode is in electrical communication with a cathode enzyme. The anode enzyme is preferably an oxidase or a dehydrogenase. The cathode enzyme is a copper-containing enzyme, such as a laccase, an ascorbate oxidase, a ceruloplasmine, or a bilirubin oxidase. Preferably, the cathode enzyme is operable under physiological conditions. Redox polymers serve to wire the anode enzyme to the anode and the cathode enzyme to the cathode. The fuel cell can be very small in size because it does not require a membrane, seal, or case. The fuel cell can be used in connection with a biological system, such as a human, as it may operate at physiological conditions. By virtue of its size and operability at physiological conditions, the fuel cell is of particular interest for applications calling for a power source implanted in a human body, such as a variety of medical applications.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Device for the determination of glycated hemoglobin
InactiveUS20060205029A1Retain and improve accuracySpeed the ultimate determinationMicrobiological testing/measurementVolume/mass flow measurementTotal hemoglobinCathode reaction
A method of determining the percentage of glycated hemoglobin in a blood sample is disclosed wherein at least one of the assay steps is performed electrochemically. The method includes determining the total amount of hemoglobin in a sample by electrochemically measuring, in an oxygen electroreduction reaction at a cathode, the amount of oxygen in the sample. Because the amount of oxygen dissolved in the sample is known, the total hemoglobin is determined by subtracting the amount of free oxygen from the total oxygen measured, recognizing the fast equilibrium Hb+O2⇄HbO2. This can be followed by determining the amount of glycated hemoglobin in the sample. The cathode reaction is accomplished by contacting the sample with an enzyme, the enzyme being a copper-containing enzyme having four copper ions per active unit. The family of these enzymes includes, for example, laccases and bilirubin oxidases. A device associated with such a process or method is also provided.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Methods for producing potato products
The present invention relates to methods for producing consumable products from potatoes, comprising: (a) treating a potato substance with an effective amount of one or more exogenous enzymes selected from the group consisting of an amyloglucosidase, glucose oxidase, laccase, lipase, maltogenic amylase, pectinase, pentosanase, protease, and transglutaminase, and (b) processing the enzyme-treated potato substance to produce a potato product. The invention also relates to consumable products obtained from potatoes by the methods of the present invention.
Owner:NOVO NORDISKBIOTECH INC
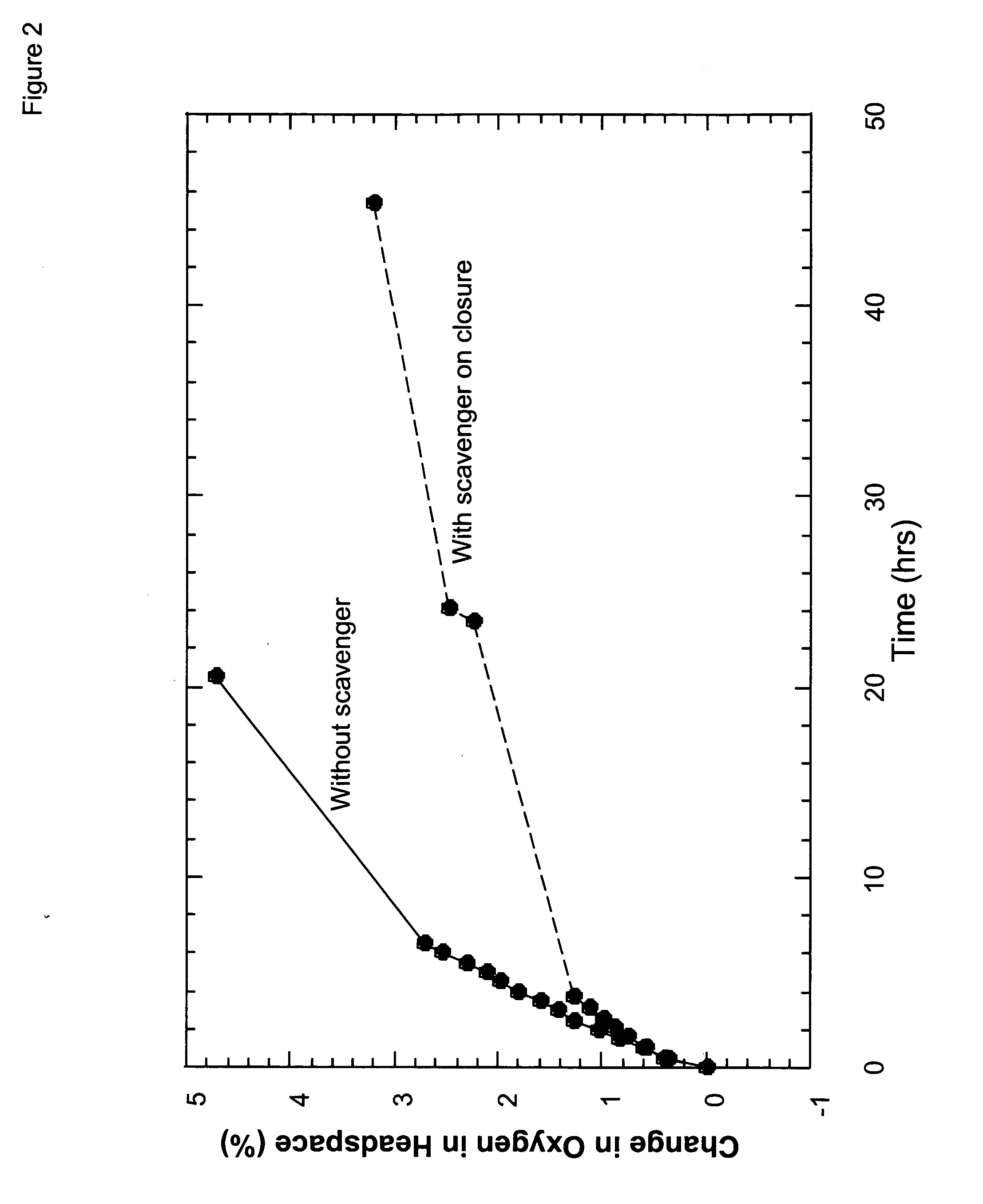
Oxygen scavenging compositions and methods of use
InactiveUS20050205840A1Efficient use ofHydrogenOther chemical processesWater useBiological activation
Oxygen is removed or maintained in a sealed container by electrochemically reducing the oxygen to water using an enzymatic O2 scavenging system based on a laccase enzyme. Activation of the O2 scavenging system typically occurs by water (liquid or vapor) adsorption; in preferred embodiments, ascorbate and isoascorbate (and their corresponding acids) are especially advantageous for their dual role as reductant and hygroscopic agent. The capacity of the O2 scavenging system can be manipulated by altering the concentration of reductant that is included in the O2 scavenging composition. The O2 scavenging system can be prepared in a variety of formats (e.g., inks, labels, packets, liners, patches, caps, within the packaging material itself) and is readily produced by apparatuses conventionally used in the industry on a high speed continuous basis.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
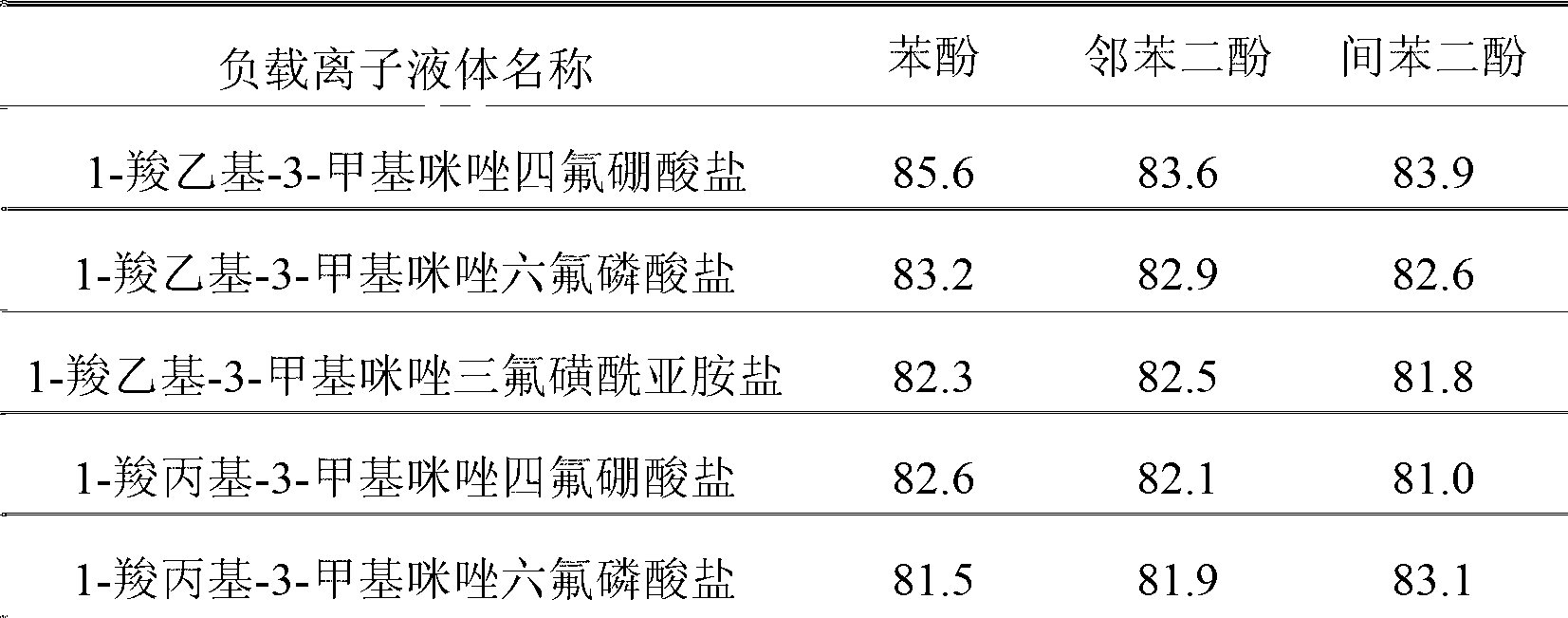
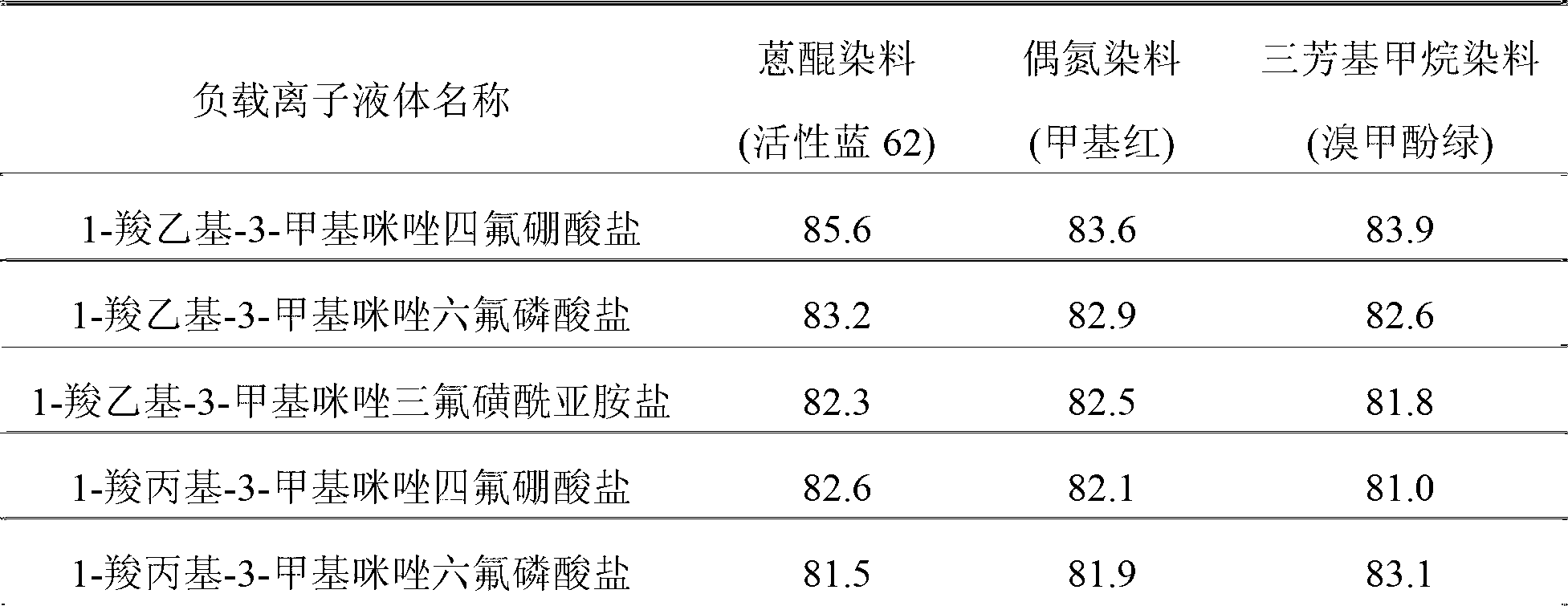
Magnetic nanoparticle-based immobilized laccase and ionic liquid composite particle and application thereof
InactiveCN103007847AImprove stabilityHigh reuse rateOn/in inorganic carrierMicroballoon preparationSilicic acidSilanes
The invention discloses a magnetic nanoparticle-based immobilized laccase and an ionic liquid composite particle, a preparation method thereof and application in removal of contaminants in water. The preparation method comprises the steps that carbonyl iron is taken as an iron source and is synthesized to be gamma-Fe2O3 nano-particles through a chemical precipitation method; the magnetic nanoparticles are taken as cores, tetraethoxysilane and a silane coupling agent are taken as a silicon source, and by means of a sol-gel method, surface amino-functionalized nano core-shell type magnetic silicon dioxide is prepared; 1-ethyl-(3-dimethyllaminopropyl) carbodiie hydrochlide is taken as a coupling agent, and laccase is bonded on the surface of the nano core-shell type magnetic silicon dioxide in a covalent bond manner to obtain the immobilized laccase of the magnetic nanoparticle silicon dioxide particles; and then the immobilized laccase is reacted with a functionalized ionic liquid which is synthesized by reacting N,N-carbonyldiimidazole and an ionic carboxy contained liquid to prepare the magnetic nanoparticle immobilized laccase and ionic liquid composite particle, and the composite particle is applied to the removal of the contaminants in water.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Multienzyme organic fertilizer
InactiveCN102432400AImprove internal environmentIncrease productionFertilising methodsFertilizer mixturesPectinaseCellulose
The invention discloses a multienzyme organic fertilizer, wherein the fertilizer can increase soil organic matter contents and varieties of bioactivators, and improve physical, chemical and biological characteristics for soil, and improve soil fertility, and alleviate soil hardened state, and reduce pesticide residue in the soil; on the other hand, the fertilizer can provide progressive, continuous and complete nutrients for plant growth, and improve inner environment of crops at the same time such that the crops have abilities of full digestion and nutrient absorption. The invention can not only improve the yields of the crops, but also can improve qualities of agricultural products, and enhance healthcare functions for agricultural products. The fertilizer is suitable to be used by field crops and greenhouse vegetables, land vegetables, fruits, flowers, commercial crops and so on. The multienzyme organic fertilizer is composed of the following raw materials in percentages by weight: 10-15% of laccase, 5-10% of neutral protease, 10-15% of phytase, 5-10% of cellulose, 1-5% of xylanase, 1-5% of pectinase, 1-5% of amylase and 55-60% of organic fertilizer powder.
Owner:郝伟星
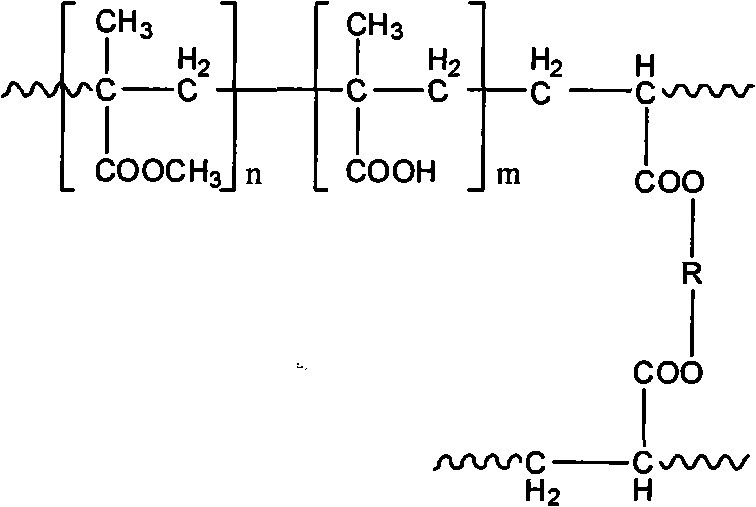
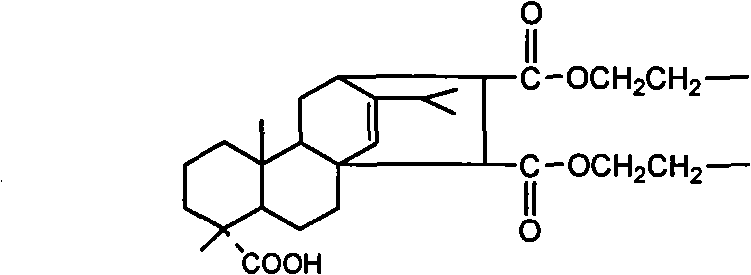
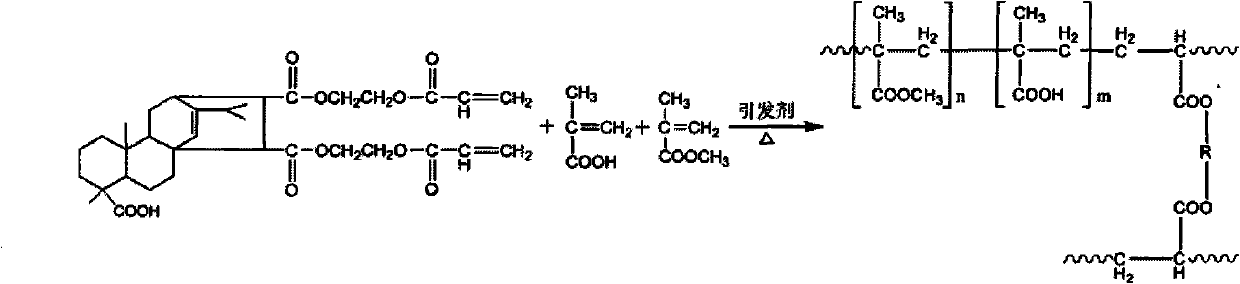
Abietyl-containing terpolymer and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an abietyl-containing terpolymer and a preparation method thereof, the chemical name of the abietyl-containing terpolymer is maleic rosin ethylene glycol acrylate-(methyl) acrylic acid-methyl methacrylate polymer. The preparation method is as follows: taking maleic rosin ethylene glycol acrylate, (methyl) acrylic acid and methyl methacrylate polymer as raw materials, and ethyl acetate as solvent, preparing the maleic rosin ethylene glycol acrylate-(methyl) acrylic acid-methyl methacrylate polymer by using a suspension polymerization method under the action of an initiator. The polymer has -COOH radicals, can be used for natural product separation such as separating berberine hydrochloride, ligustrazine hydrochloride and the like and used as the carrier of immobilized enzymes such as immobilized amylase, lipase and laccase.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV FOR NATITIES +1
Lignocellulose degrading bacteria and application thereof
InactiveCN101974436AReduce biotransformation timeImprove qualityBio-organic fraction processingFungiFungicidePenicillium bilaiae
The invention discloses lignocellulose degrading bacteria and application thereof. The lignocellulose degrading bacteria is expanded penicillium W4 with the preservation number of CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection) No.4077. The stain can generate cellulose and laccase and degrade straw lignocellulose, can be used as a main effective component of microbial fungicides of a mushroom culture medium and has the effects of shortening the biological transformation time of the mushroom culture medium and improving the quality of the mushroom culture medium. Particularly for the biological transformation of a small quantity of packed mushroom culture media of a family workshop, the lignocellulose degrading bacteria has obvious advantage in environment with lower temperature.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Method for preparing xylooligosaccharide, lignin and microcrystalline cellulose by completely utilizing straws
The invention discloses a method for preparing xylooligosaccharide, lignin and microcrystalline cellulose by completely utilizing straws, belonging to the technical fields of food and chemical engineering. The method comprises the following steps: by using straws of wheat, rice, corn and other agricultural crops as raw materials, pulverizing, soaking in water, carrying out certain-intensity steam explosion depolymerization treatment, adding xylanase for enzymolysis, filtering, and carrying out membrane separation on the filtrate to obtain the xylooligosaccharide; carrying out certain-intensity steam explosion treatment on the filtration residue, adding cellulase and laccase for enzymolysis, filtering, carrying out high-pressure value equalizing on the filtrate, decolorizing, concentrating and drying to obtain the microcrystalline cellulose; and immersing the filtration residue in a solution with a certain pH value, reacting at specific temperature, carrying out vacuum filtration under reduced pressure, carrying out solid-liquid separation, and drying to obtain the refined lignin. By adopting the steam explosion and composite enzymolysis, the method has the advantage of mild conditions, avoids using toxic reagents, and implements complete utilization of the hemicellulose, cellulose and lignin components in the straws.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Deinking Technique for news bogus paper through enzyme
InactiveCN1563567AImprove bleachabilityPaper recyclingChemical paints/ink removersDeinkingPulp and paper industry
A waste new print zyme deinking technology includes crushing the pulp, deinking, suspension selection, washing, bleaching among which, deinking agent, laccase, amboceptor are added into the pulped with waste newsprints and waster to be inlet with oxygen and the pulp concentration is controlled at 3%-18%, temperature 20-70deg.C pulping, keeping warmth.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
Novel Laccases, Compositions And Methods of Use
Novel laccases, nucleic acid sequences encoding such laccases, and vectors and host cells for expressing the laccases are described. The novel laccase enzymes may be employed in conjunction with mediators to provide an improved method for bleaching denim fabrics.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Novel laccase enzyme and use thereof
ActiveUS20060063246A1Reduce the amount requiredReduce usageCosmetic preparationsBacteriaNucleic acid sequencingGenus
The present invention relates to a novel laccase enzyme obtainable from the strains of genus Thielavia. The invention relates also to the nucleic acid sequence encoding the enzyme, a recombinant host into which the nucleic acid sequence has been introduced and a method for the production of the enzyme in a recombinant host. The enzyme of the invention is suitable for several applications, in particular for increasing the lightness of denim.
Owner:AB ENZYMES OY
Ultrasonic synthesis method and application of different single-metal and double-metal two-dimensional MOFs nano-enzymes
InactiveCN111330643AUnique ultra-thin two-dimensional sheet structureSonosynthesis is simpleOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationPeroxidaseActive agent
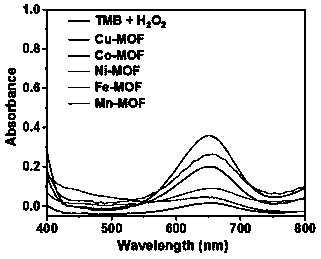
The invention discloses an ultrasonic synthesis method of different single-metal and double-metal two-dimensional MOFs nano-enzymes and application of the nano-enzymes. The invention relates to the technical field of nanometer materials, catalysis and analytical chemistry. The ultrasonic synthesis method is simple, low in cost and mild in condition, the synthesized different single-metal and double-metal two-dimensional MOFs nano-enzyme materials are high in yield, uniform in morphology, good in performance and free of surfactants, and the defects that a traditional hydrothermal method is complex in process, large in energy consumption, difficult in MOFs volume and morphology control and the like are overcome. The different single-metal and double-metal two-dimensional MOFs nano-enzymes synthesized by the method disclosed by the invention have various biomimetic catalysis characteristics, such as peroxidase-like activity, chloroperoxidase-like activity, glucose oxidase-like activity, laccase-like activity and NADH enzyme-like activity, show unique oxidative activity of peroxidase and chloroperoxidase in an organic solvent, and can be used for indole oxidation.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
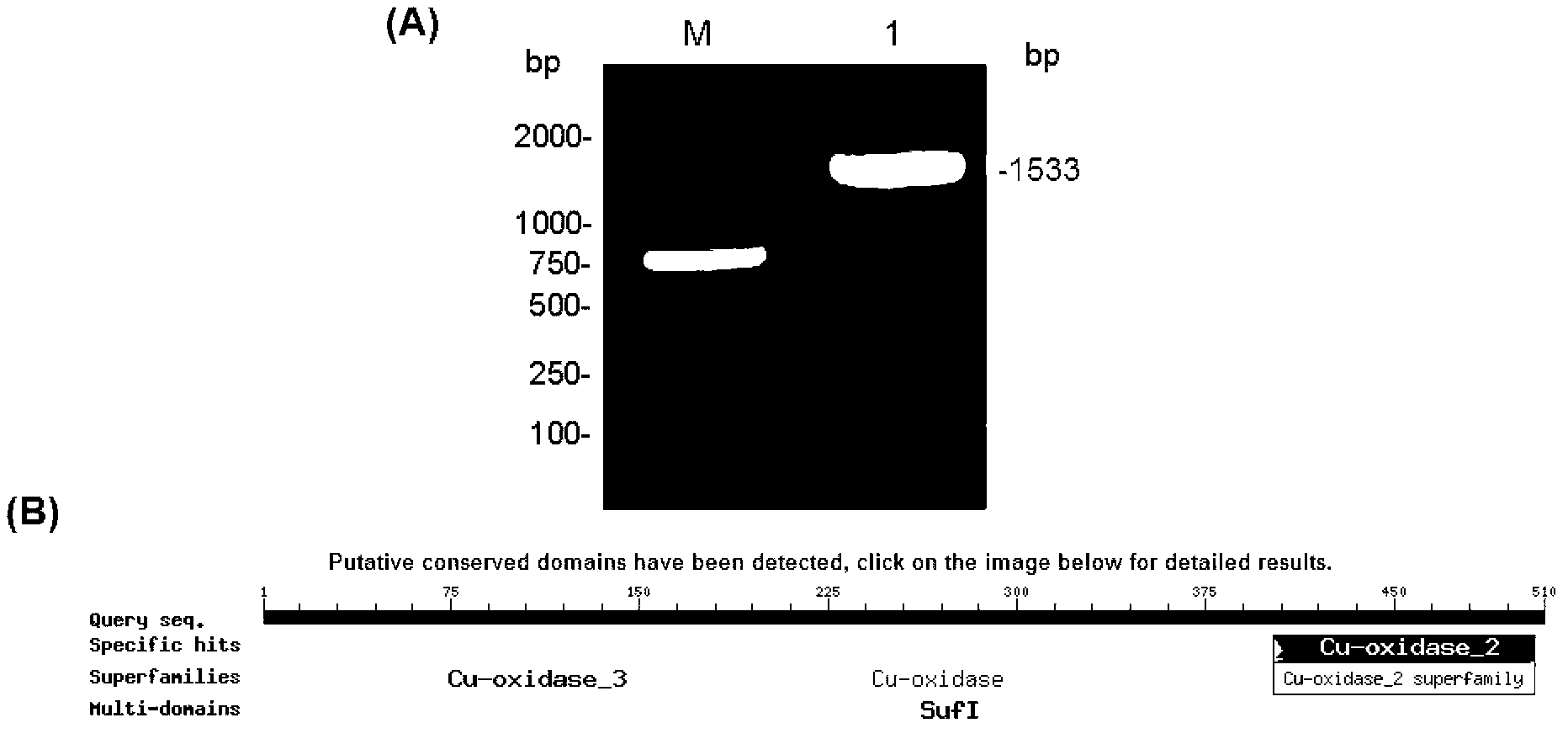
Bacterial laccase mutant protein, recombinant expression plasmid, transformed engineered strain and fermentation preparation method thereof
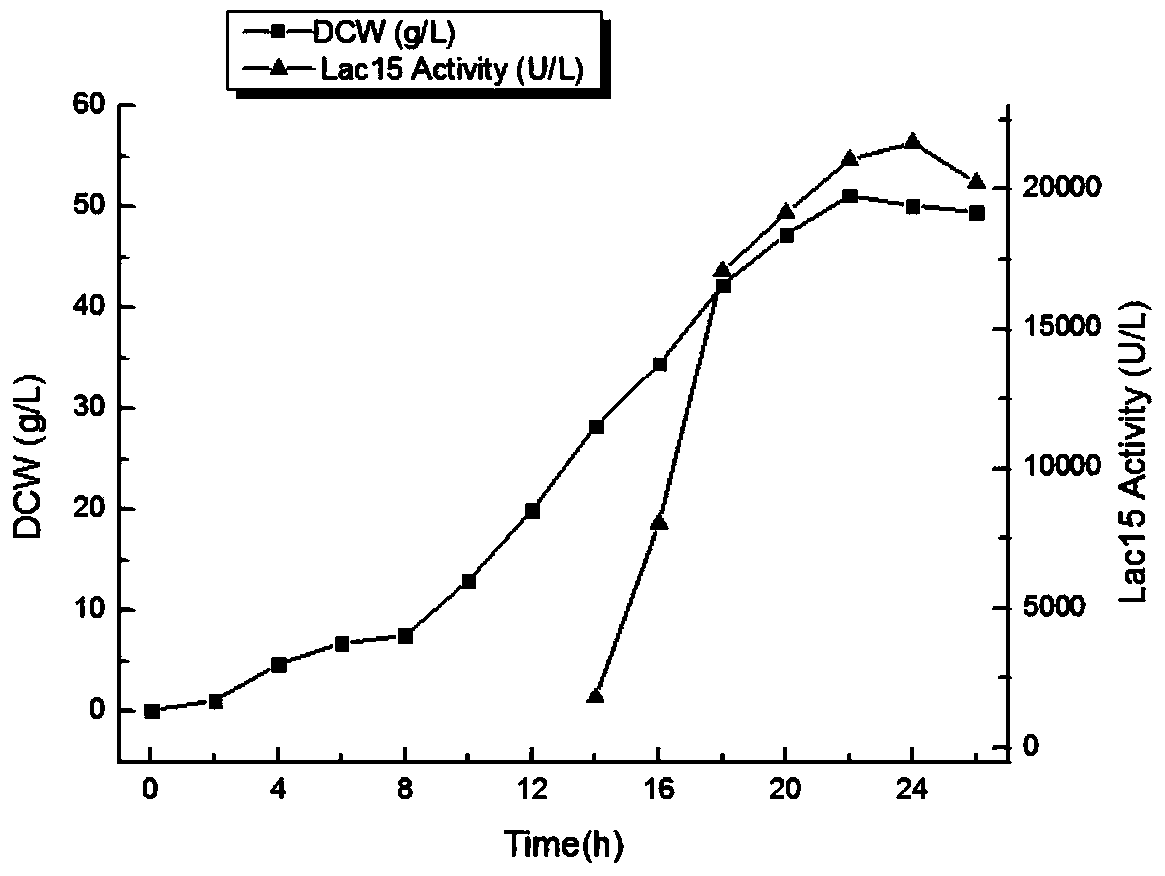
ActiveCN104087560AImprove stabilityIncrease temperatureBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMutated proteinGenetic engineering
The invention discloses a bacterial laccase mutant protein, which is characterized in that the mutant protein amino acid sequence is obtained by deletion mutation of the 323rd glycine residue to the 332rd glycine residue in the bacterial laccase amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID No.1. Through a genetic engineering reconstruction method, a stability improved bacterial laccase protein coding gene, its expression plasmid and engineered bacteria can be obtained, and after large-scale fermentation and induced expression of the engineered bacteria, the stability improved bacterial laccase protein can be obtained. According to the invention, the marine uncultured microorganism source bacterial laccase Lac15 is taken as the foundation, and by means of genetic engineering reconstruction, mutant gene can be obtained. At the same time, a recombinant escherichia coli is employed to conduct high-density culture for high-efficiency expression of the bacterial laccase mutant protein. According to the invention, the stability and yield of the bacterial laccase are greatly improved.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Traditional Chinese medicine multi-enzyme bacterium straw composite feed for livestock and poultry
InactiveCN102894215AIncrease profitImprove meat qualityAnimal feeding stuffPhytaseMonopotassium phosphate
The invention provides a traditional Chinese medicine multi-enzyme bacterium straw composite feed for livestock and poultry. The feed is mainly prepared from saccharomyces cerevisiae, protease, phytase, cellulose, xylanase, glucanase, laccase, pectase, amylase, Aspergillus niger, traditional Chinese medicinal preparations consisting of Radix Astragali, jerusalem artichoke, Poria cocos, purslane, dandelion and the like, straw, corn flour, potassium dihydrogen phosphate and magnesium sulfate magnesium sulfate. According to the invention, a complex enzyme system and microbes exert action on the straw, and synergism between traditional Chinese medicines and potassium dihydrogen phosphate and magnesium sulfate is used at the same time; so output of bifidobacteria in the livestock and poultry is increased, disease-resistant immunity of the livestock and poultry is improved, and bifidobacteria exerts effects on assisting digestion and decomposing plant barriers in coarse cereals so as to realize easy absorption of the coarse cereals by intestines and stomachs and assist the livestock and poultry in rapid digestion and absorption of foods. Thus, the livestock and poultry like flocks and herds are allowed to have healthy and strong bodies, an enhanced digestive function and an improved farrowing rate, fattening and marketing time is shortened, and breeding cost is reduced.
Owner:JILIN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for producing fiberboards by lignocelluloses as raw materials
InactiveCN102650108AEnvironmentally friendlyFunctionalWood working apparatusDomestic articlesCelluloseAdhesive
The invention provides a method for producing fiberboards by lignocelluloses as raw materials. The method comprises the steps as follows: degrading and transforming the lignocelluloses through the biological modification effect of special basidiomycetes; enabling the modified lignocelluloses to have a physical structure with stronger adhesion effect, and chemical properties; and carrying out compression of various density fiberboards on the modified lignocelluloses through a hot press process so as to prepare the density fiberboards free of chemical adhesives. An effective solution is provided for new material preparation, environmental protection and low-carbon economy. According to the method, the chemical adhesives are not added, the fiberboards do not need to be produced by the biological modification-thermocompression bonding process for the basidiomycetes of the added expensive laccases, and the problems of environmental pollution due to formaldehyde released by the chemical adhesives used in the conventional fiberboards, high cost due to treatment of the directly added laccases on the lignocelluloses, or the like is effectively solved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
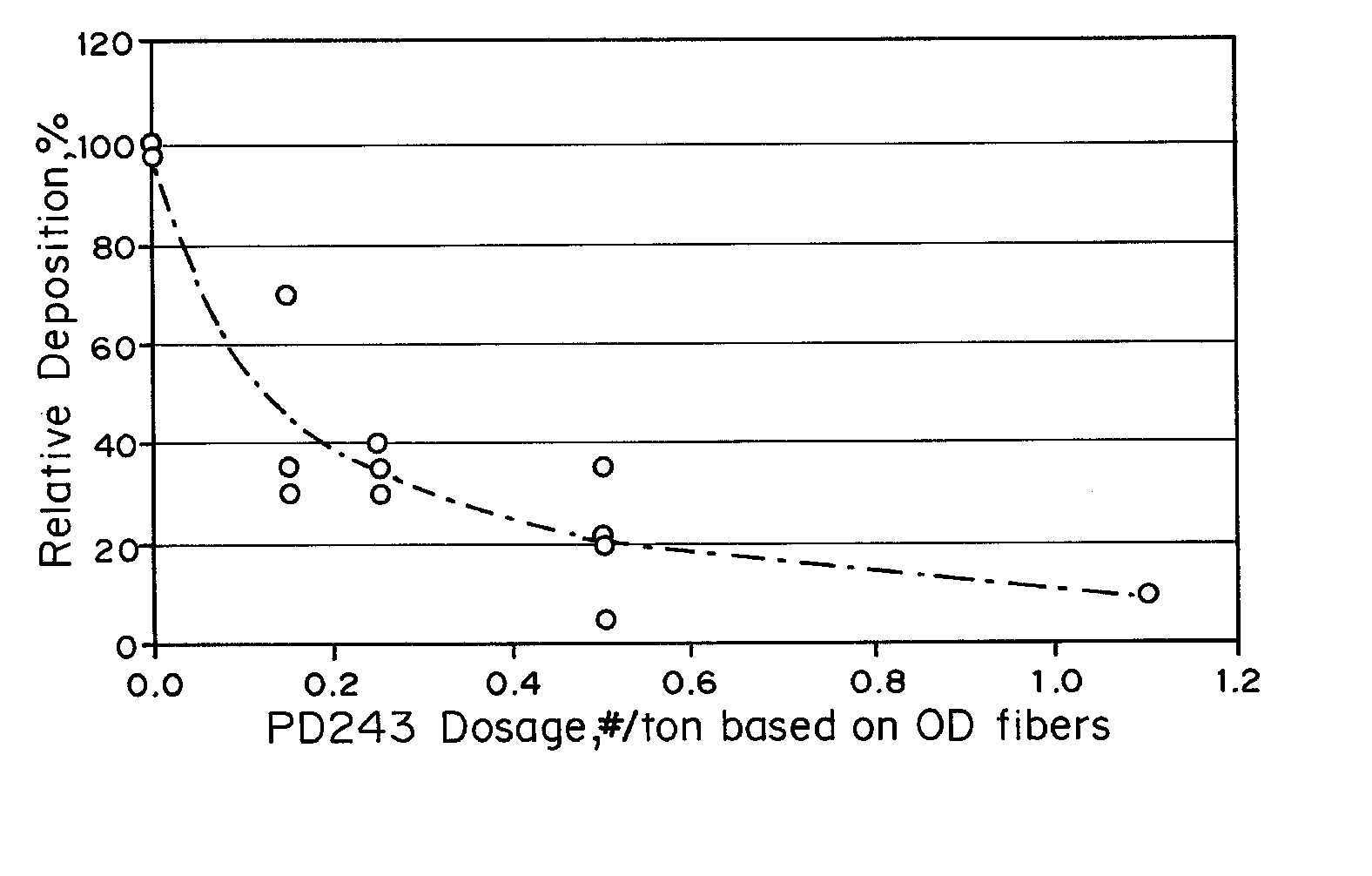
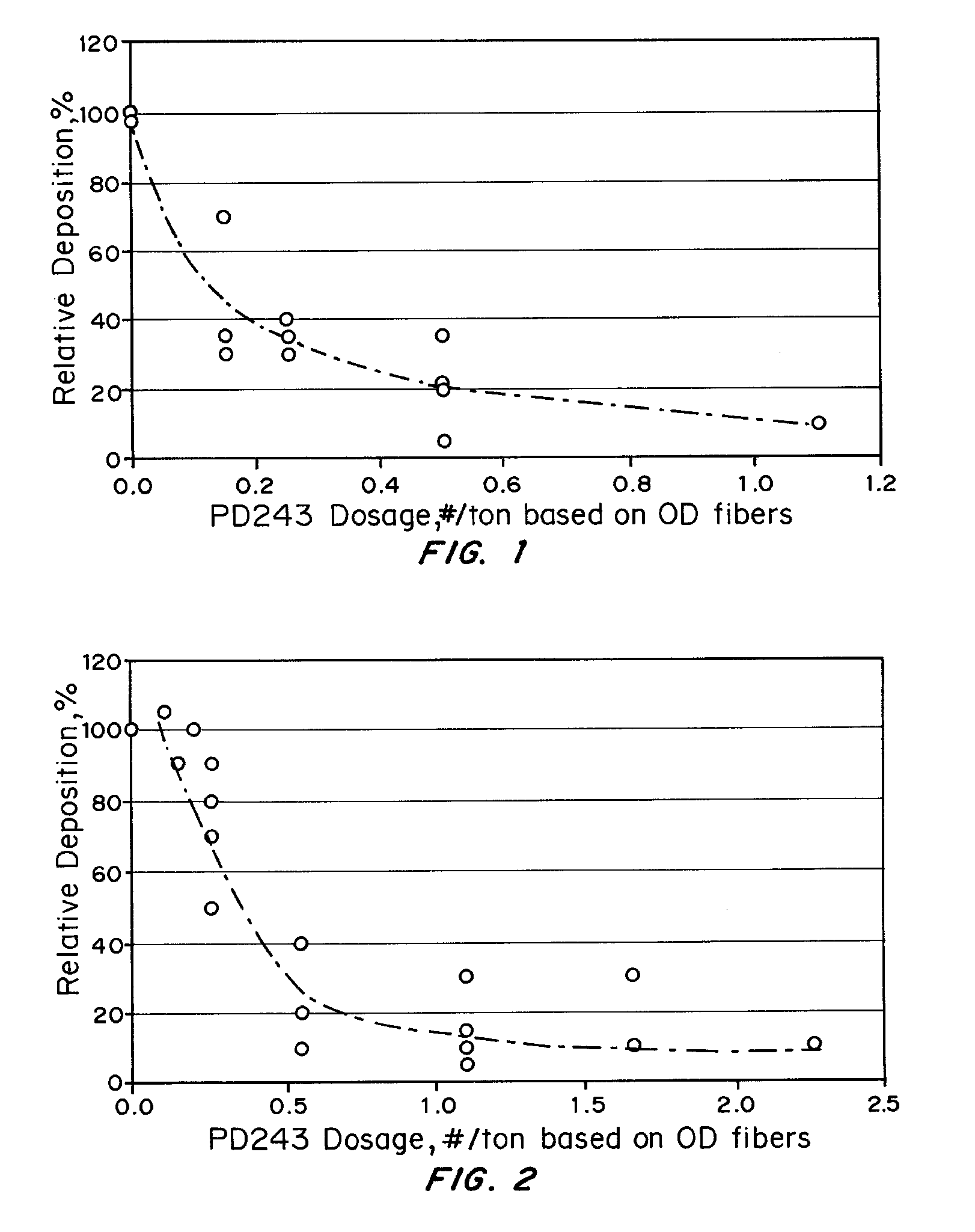
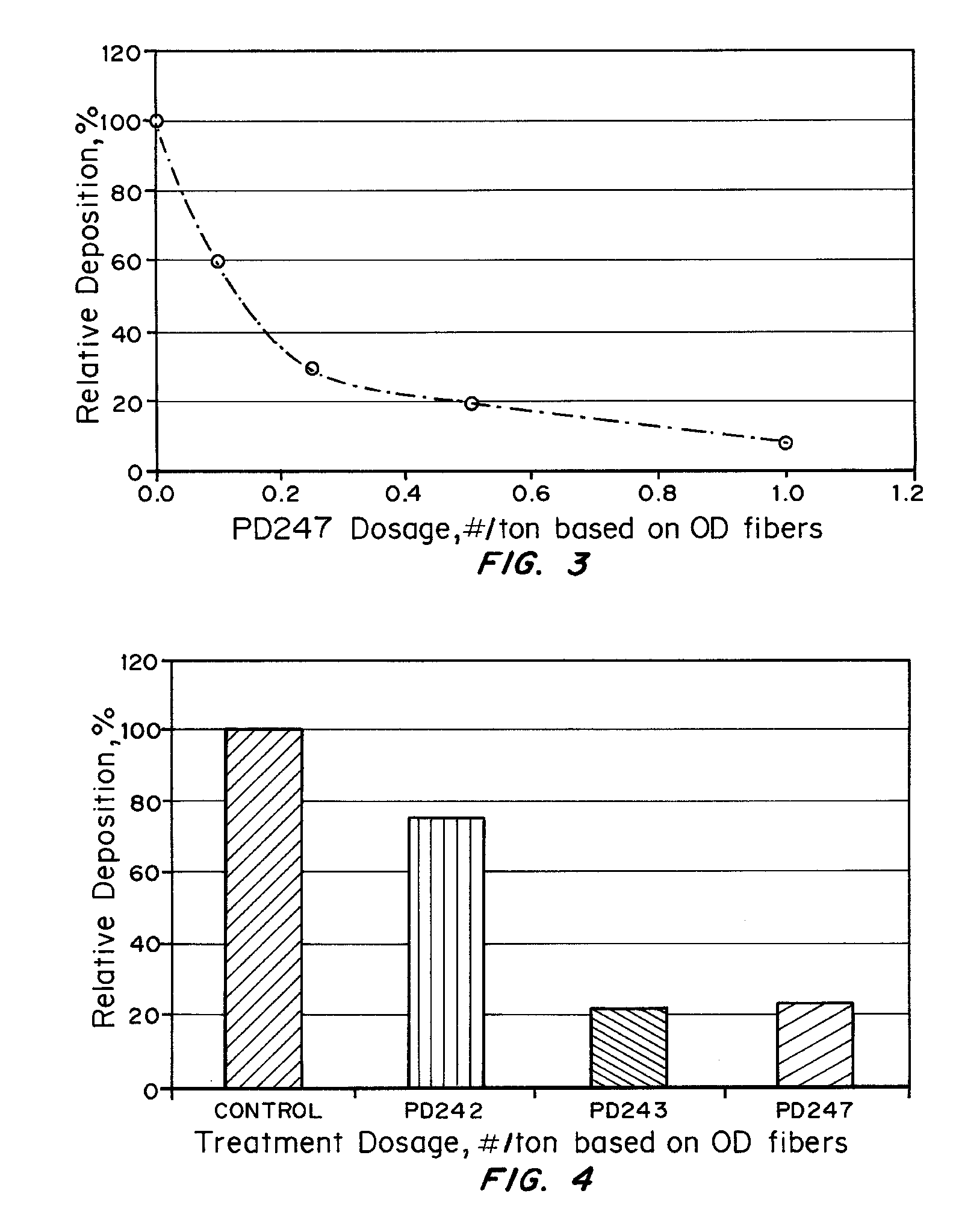
Treatment of Pulp Stocks Using Oxidative Enzymes to Reduce Pitch Deposition
InactiveUS20070261806A1Lower energy requirementsImprove paper strengthPulp liquors combustionFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpTime rangeResin acid
Methods of treating pulp stocks with an enzyme formulation containing one or more oxidative enzymes, to reduce pitch deposition, control pitch related problems, modify the physical and / or chemical properties of tri, di-, and mono-glycerides, fatty acids, resin acids, esters of fatty acids and resin acids, and metal soaps of fatty acids and resin acids, or change the concentration of triglycerides, fatty acids, resin acids, and esters of fatty acids and resin acids, have been developed. The pulp stock is treated with an enzyme formulation containing laccases, peroxidases, esterases, and / or combinations thereof. The enzyme formulations may also contain a laccase mediator and / or a dispersant. The enzyme formulation can be applied at any of several locations during the pulping and / or papermaking process. The enzyme formulation is typically applied as a solution to the pulp stock. The enzyme treatment is effective at a temperature of between about 30° C. to about 95° C., more preferably from about 50° C. to about 80° C. The pH of the pulp stock is from about 4.0 to about 7.0, more preferably from about 4.5 to 5.5. The stock can be treated for a period of time ranging from about 5 minutes to about 10 hours.
Owner:ENZYMATIC DEINKING TECH LLC
Bacillus pumilus laccase gene as well as expression and application thereof
InactiveCN103320453AIncrease productionEasy to meet industrial application requirementsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliBacillus pumilus
The invention relates to a bacillus pumilus (Bacillus pumilus) L-9 laccase gene cotA as well as recombinant expression and application thereof, belonging to the field of bioengineering. The cotA is separated from the bacillus pumilus (Bacillus pumilus) L-9, an expression vector pColdII-cotA is constructed, and an escherichia coli expression strain BL21(DE3) is transformed to realize high-efficiency expression. The obtained recombinase laccase has the advantages of high alkaline environment resistance and high high-temperature resistance, has a good effect of discoloring azo dyes and anthraquinone dyes and has high application potential.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Processing method of waste water containing heavy metal and dye
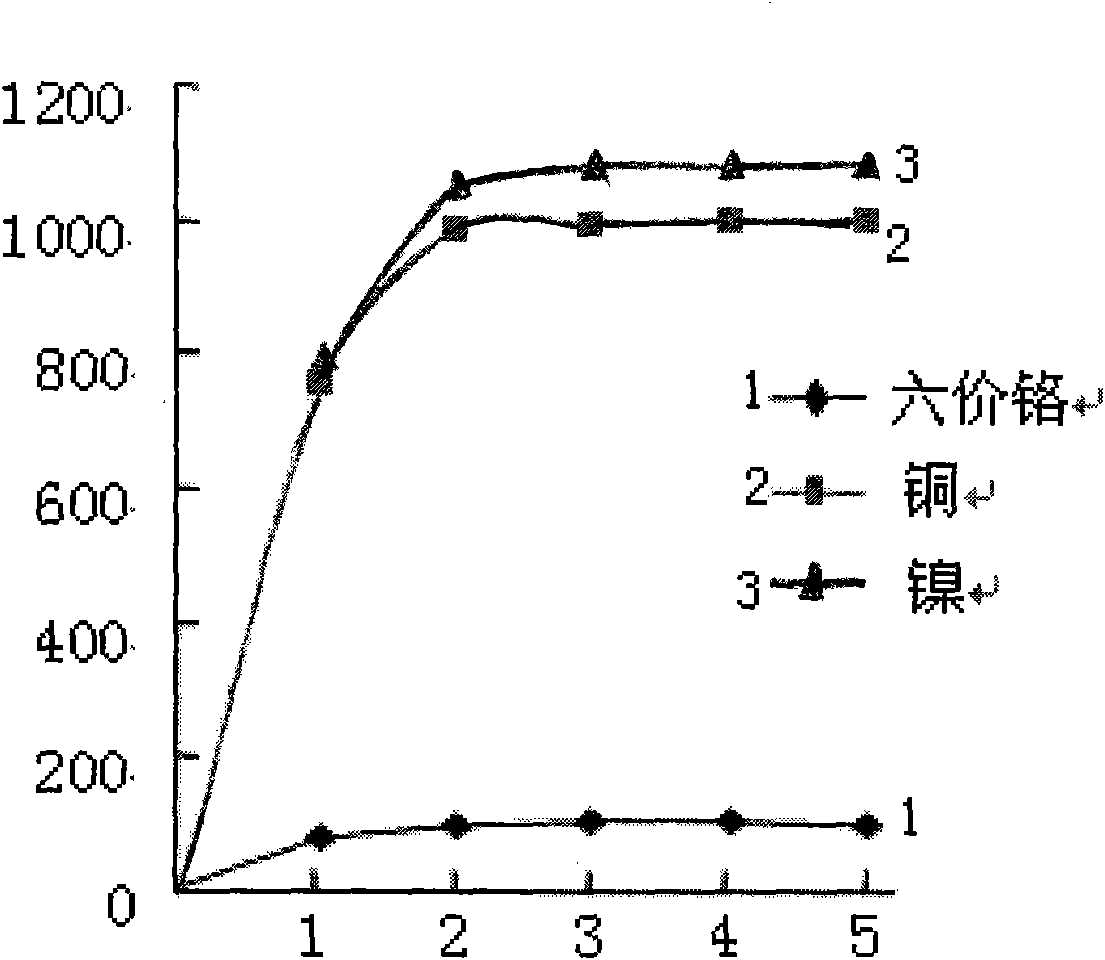
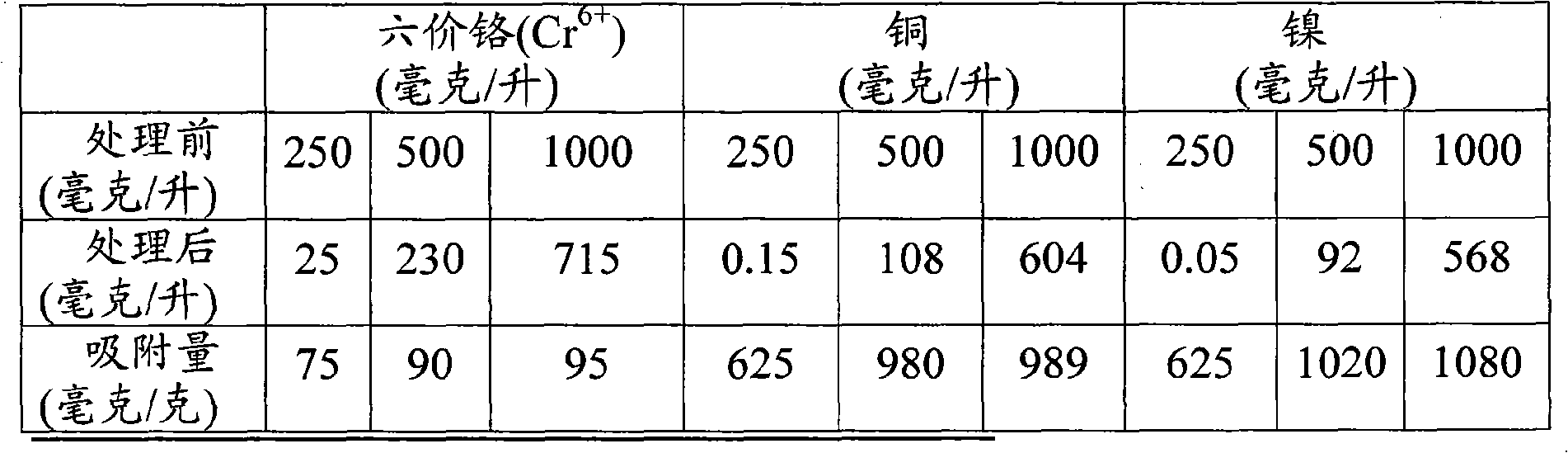
InactiveCN101570377AImprove adsorption capacityEasy to handleMultistage water/sewage treatmentWaste water treatment from plant processingSorbentHydroquinone Compound
The invention discloses a processing method of waste water containing heavy metal and dye. In the method, a sorbent is utilized to process the waste water containing heavy metal and dye, and the sorbent contains ferroferric oxide micro-magnetic particles and laccase. The laccase is hydroquinone dioxygen oxidoreductase containing copper, and the class number is EC 1.10.3.2. The ferroferric oxide micro-magnetic particles and the lasscase are in cross-linkage combination through assistance of a cross linkage agent. Heavy metal and dye in the waste water can be fast adsorbed and recovered with high efficiency by the ferroferric oxide micro-magnetic particles and the laccase, thereby the waste water containing heavy metal and dye is effectively processed, and the environment is protected.
Owner:GUANGZHOU LANTAO WATER TREATMENT CO LTD
Elastic polyester-cotton fabric dyeing and finishing pretreatment method
InactiveCN103821006AReduce energy consumptionLow processingBiochemical fibre treatmentBleaching apparatusPolyesterTextile printer
The invention relates to an elastic polyester-cotton fabric dyeing and finishing pretreatment method and belongs to the field of a textile printing and dyeing technology. The invention aims to raise whiteness and water absorbability of a product and minimize reduction of mechanical properties of fabric. Firstly, hot-water preshrinking and pre-setting treatment are carried out on fabric so as to raise external dimension stability of the elastic fabric; then, dyeing and finishing pretreatment is carried out with amylase, pectase and the like so as to remove most non-fibrous symbiont; and finally, hydrogen peroxide bleaching and deoxygenation treatment are combined to remove a few pigment and impurities in the elastic fabric so as to finish dyeing and finishing pretreatment of the fabric. The method comprises the following technological steps: preshrinking and pre-setting; bio-enzyme (amylase, pectase, laccase and cellulose) treatment; hydrogen peroxide bleaching; and catalase deoxygenation. In comparison with a traditional alkali pretreatment process, the method provided by the invention has advantages as follows: production energy consumption is reduced, and quality of the elastic polyester-cotton fabric is raised.
Owner:吴江市桃源海润印染有限公司
Method for preparing solid repair agent by using protein peptide and repairing soil by using soil repair agent
ActiveCN102580998AAchieve fixPlant heightContaminated soil reclamationPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonLight pollution
The invention provides a method for preparing a solid repair agent by using protein peptide and repairing soil by using the soil repair agent. The method comprises the steps of: preparing the protein peptide prepared by using a method in the patent ZL200610019063.7 or the protein peptide prepared by using protein-containing waste according to the following formula in site, wherein the formula comprises 1) 5-10 percent of protein peptide, 2-6 percent of molasses and the balance of water; 2) 5-10 percent of protein peptide, 0.5-1.0 percent of laccase crude product, 1-2 percent of laccase strain and the balance of water; and 3), 5-10 percent of protein peptide and the balance of water. The formula 1 is suitable for the soil in which plants are planted and which is seriously polluted by heavy metal ions; the formula 2 is suitable for the soil in which plants are planted and which is seriously polluted by heavy metal ions and is polluted by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon; and the formula 3 is suitable for directly acting on conventional polluted soil with light pollution. The protein peptide soil repair agent can be used as a nutrient in which a microorganism or indigenous microorganism for promoting the enrichment of the plants to the heavy metal ions, so that the polluted soil is repaired. The soil repair agent has low price, high efficiency and good effect.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
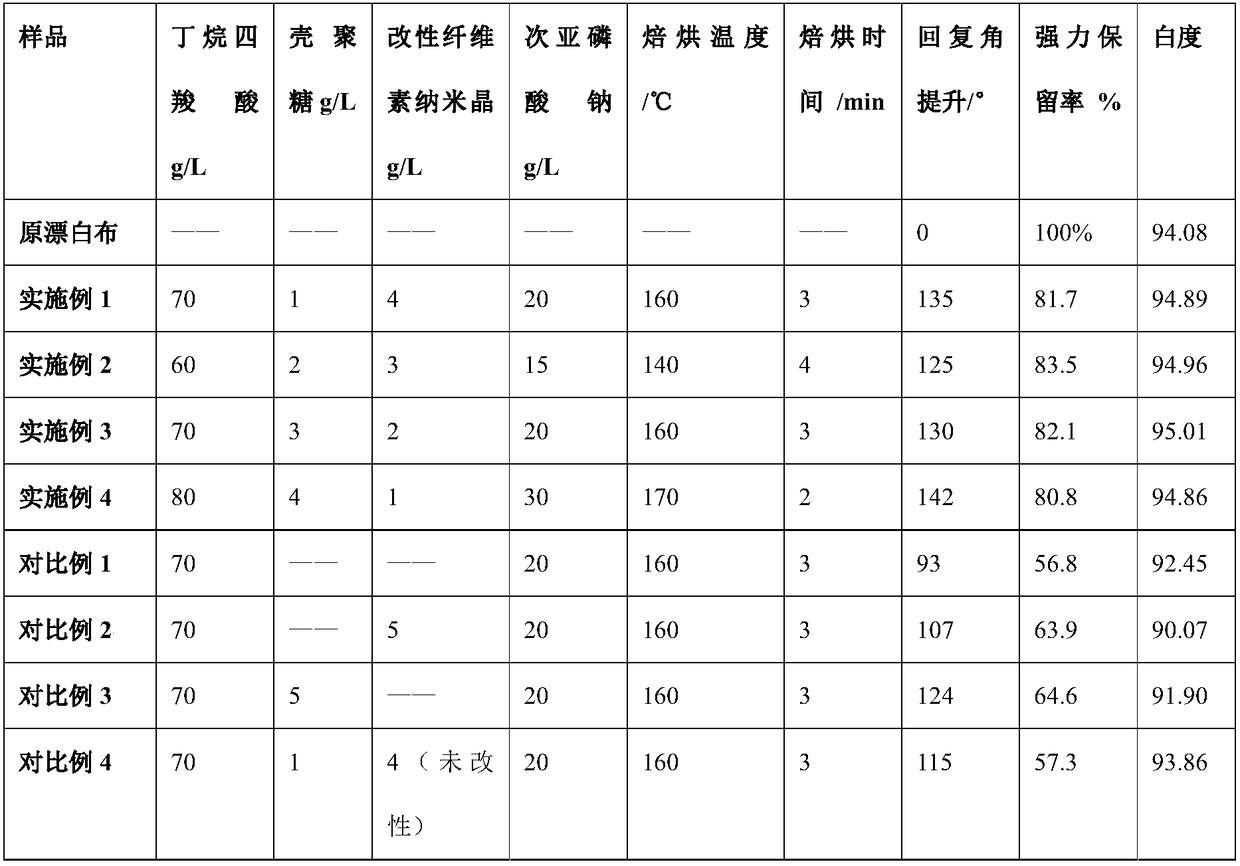
Crease-resistant finishing liquid for cotton fabric and application of crease-resistant finishing liquid
ActiveCN109137499AHigh strengthImprove stabilityWrinkle resistant fibresVegetal fibresFiberCarboxylic acid
The invention discloses crease-resistant finishing liquid for cotton fabric and application of the crease-resistant finishing liquid and belongs to textile finishing. The crease-resistant finishing liquid is characterized in that a laccase / TEMPO system is used to oxidize cellulose nanocrystals into aldehyde groups, the aldehyde groups and Girard's reagent T have Schiff base reaction to prepare positive ion modified cellulose nanocrystals, and the modified cellulose nanocrystals, 1,2,3,4-butanetetracarboxylic acid and chitosan are compounded to apply to the crease-resistant finishing of the cotton fabric. The crease-resistant finishing liquid has the advantages that the chitosan and the cellulose nanocrystals used by the finishing liquid are natural biomass materials and can copolymerize with BTCA on cotton fibers under high temperature to generate a long branched chain structure, and accordingly the cotton fabric after finishing has good crease resistance; in addition, by introducing the cellulose nanocrystals and the chitosan, the break strength retention and dyeing performance of the fabric after the crease-resistant finishing are improved, and the fabric is good in washing resistance stability and meets environment protection standards.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for performing complete cotton knitted fabric dyeing post treatment using immobilization laccase
InactiveCN101302716AIncrease temperatureImprove stabilityBiochemical fibre treatmentOn/in organic carrierEcological environmentPolyethylene glycol
The invention discloses a post processing method for the dyeing of all-cotton knitted fabrics that applies an immobilized laccase, belongs to the technical field of the application of the dyeing and finishing treatment of the knitted fabrics in the printing and dyeing industry, and aims at solving the technical problems that traditional post processing of the knitted fabric dyeing has high soaping temperature, large water consumption and residual washing water with deep chromaticity and achieving the goal for optimizing the post processing effect of the dyeing. The post processing method of the invention adopts calcium alginate and gelatinum as carriers so as to implement the imbedding of the laccase, improves the immobilization efficiency of the laccase in the carriers through glutaraldehyde crosslinking, improves the heat and pH stability of the laccase in the carriers by adding polyethyleneglycol, and realizes the circulation of the immobilized laccase in the post enzyme-washing treatment of the dyeing of the all-cotton knitted fabrics by adding carmowax to improve the thermal stability and the pH stability of the laccase in the carriers. By adopting the post processing method of the invention, the enzyme-washing technique with the immobilized laccase can replace traditional chemical soaping techniques, can not only effectively remove superficial loose color of the dyed all-cotton knitted fabrics and improve the wet processing fastness of the fabrics, but also effectively lower the chromaticity of the post processing residual liquid and release the burden of the sewage treatment of the printing and dyeing, and the post processing method of the invention is favorable for protecting ecological environment.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Biocatalytic clean pulping agent and application process thereof
InactiveCN1844572ANo emissionsNo pollutionPulp liquor regenerationWashing/displacing pulp-treating liquorsForeign matterProcess equipment
The invention relates to a biochemical catalysis cleaning slurry agent and relative application. Said invention is formed by: amylase, laccase, hydroxybenztriazole, calcii chloridum SL-1 slurry braise agent, sodium carbonate, and water. And the application comprises: 1, cutting raw material to be kneaded and dedusted; 2, preparing material with wet method; 3, dipping to remove lignin colloid; 4, extruding slurry to replaced and separated, dipping to filter the left liquid to be recycled; 5, rough milling and combing wire; 6, screening slurry to remove foreign matters; 7, washing slurry; 8, finish milling slurry; 9, poaching slurry; 10, washing poached slurry; 11, stepped treating and recycling used water. The invention is characterized in dipping said raw material in normal temperature and pressure. The left liquid is not discharged, but be recycled. And the pulp is poached pulp. The invention can support industrial production.
Owner:石建凯
Grass fiber bio-separation compound preparation and application method thereof
The invention discloses a grass fiber bio-separation compound preparation and an application method thereof. The grass fiber bio-separation compound preparation comprises bacteria components and enzyme components, wherein the bacteria components comprise white rot fungi and zymogeneous bacteria, and the enzyme components comprise cellulose, xylanase, laccase, protease, thermostable amylase, ligninase and pectinase. According to the grass fiber bio-separation compound preparation, straw serving as the raw material is treated with a biological method, a biological cycle liquid and a waste cooking liquid produced in the treatment process can be recycled without drainage, and lignin can be extracted; and besides, according to the method, straw does not require cutting and dust removal, and the cooking does not require high temperature and high pressure, so that a large quantity of manpower and electric charges is omitted, and the preparation and the method are suitable for a plurality of raw materials such as wheat straw, straw, cotton stalks, reeds and the like, can be used for producing a paddle board, molded pulp, various types packaging paper, office paper and household paper and have the advantages of low cost and environment protection.
Owner:北京秸大环保科技有限公司
Enzyme biological fuel cell and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN102569861AHigh outputLight up successfullyBiochemical fuel cellsInternal resistanceConcentrations glucose
An enzyme biological fuel cell is prepared by the steps of separating a negative pole and a positive pole by phenol proton exchange membrane (DuPontTMPFSA NRE-211), preparing substrate materials of the negative pole and the positive pole to be grapheme-nanu-au composition, respectively loading laccase and glucose oxidase on substrate materials, using the loaded laccase and glucose oxidase to catalyze respectively oxygen and glucose substrate in a cathode chamber and an anode chamber to receive and lose electrons, and forming a loop by the fact that electrons start from the anode, pass through an external circuit and reach the cathode. When glucose concentration of the enzyme biological fuel cell in the anode chamber is 50 mM, open-circuit voltage of the cell is 1.2V, maximum power density of the cell is 1.96+-0.13mW cm-2, and internal resistance of the cell is only 200 omega. Two enzymebiological fuel cells connected in series can light a red or a yellow luminous diode successively. After the enzyme biologica fuel cell is assembled for 70 days, open circuit potential of the cell remains 80% of the best value. The preparing method is also disclosed.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
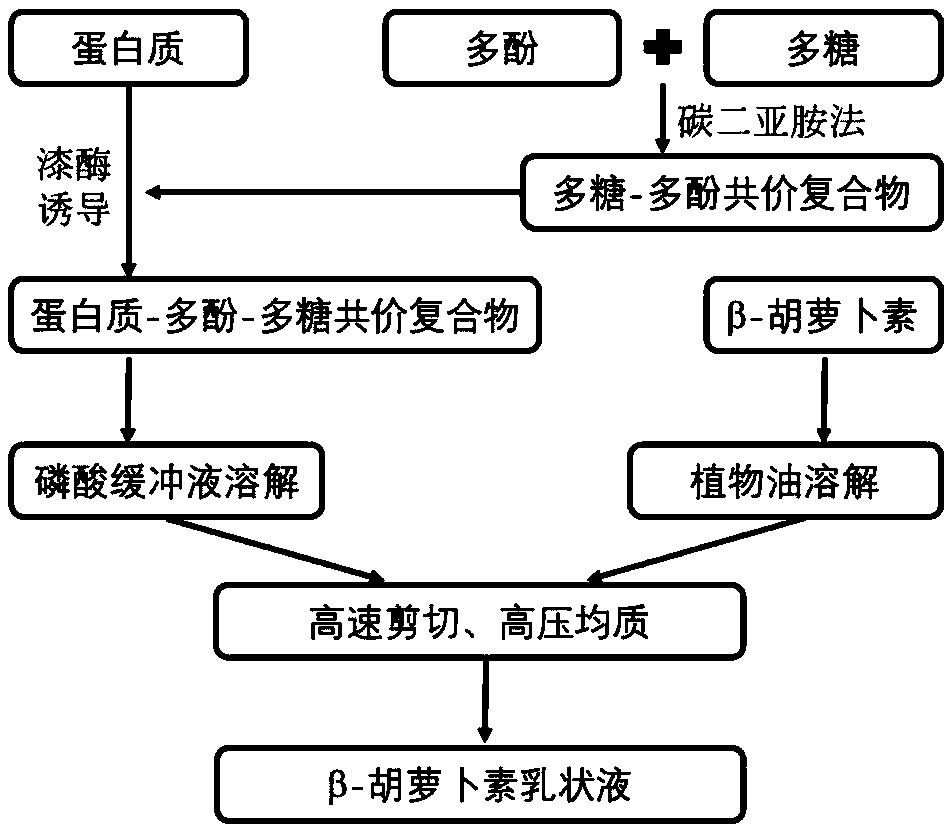
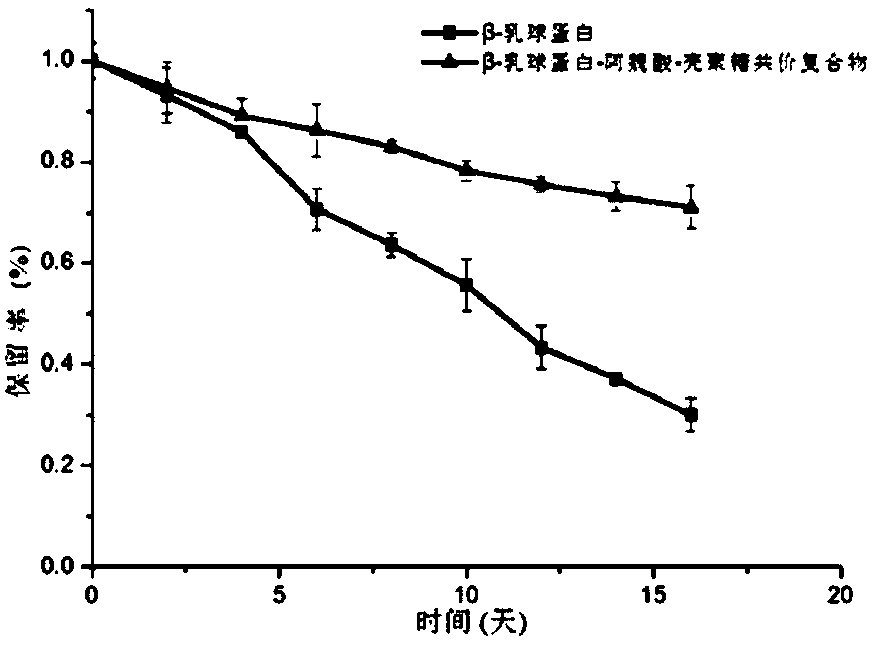
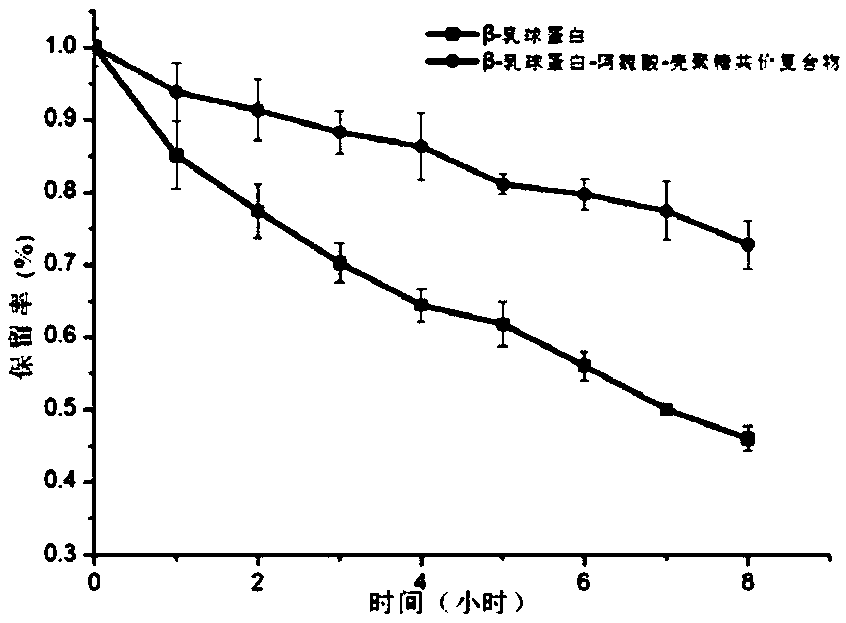
Preparation method of protein-polyphenol-polysaccharide covalent complex and application of protein-polyphenol-polysaccharide covalent complex
ActiveCN108719999AHas antioxidant capacityImprove water holding capacityFood ingredient as emulsifierCross-linkFood additive
The invention discloses a preparation method of a protein-polyphenol-polysaccharide covalent complex which belongs to the technical field of food additives pertaining to food science, and an application of the protein-polyphenol-polysaccharide covalent complex. The preparation method of the protein-polyphenol-polysaccharide covalent complex comprises the following steps of activating carboxyl of polyphenols by using a carbodiimide method, so that the activated carboxyl reacts with polysaccharides so as to produce a polysaccharide-polyphenol covalent complex; and then, inducing covalent cross-linking between proteins and the polysaccharide-polyphenol covalent complex by utilizing laccase so as to obtain the protein-polyphenol-polysaccharide covalent complex. The preparation method of the protein-polyphenol-polysaccharide covalent complex is simple, highly efficient and easy in production process; and the prepared protein-polyphenol-polysaccharide covalent complex has good antioxidant ability and thermal stability. Being used as an emulsifier for preparing a beta-carotene emulsion, the protein-polyphenol-polysaccharide covalent complex is capable of ensuring good physical and chemical stability; and thus, wide application in the fields of food, pharmaceutical and and cosmetic industries is feasible.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com