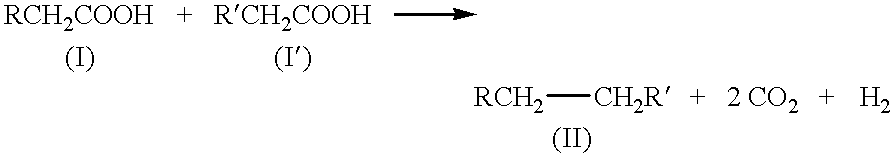
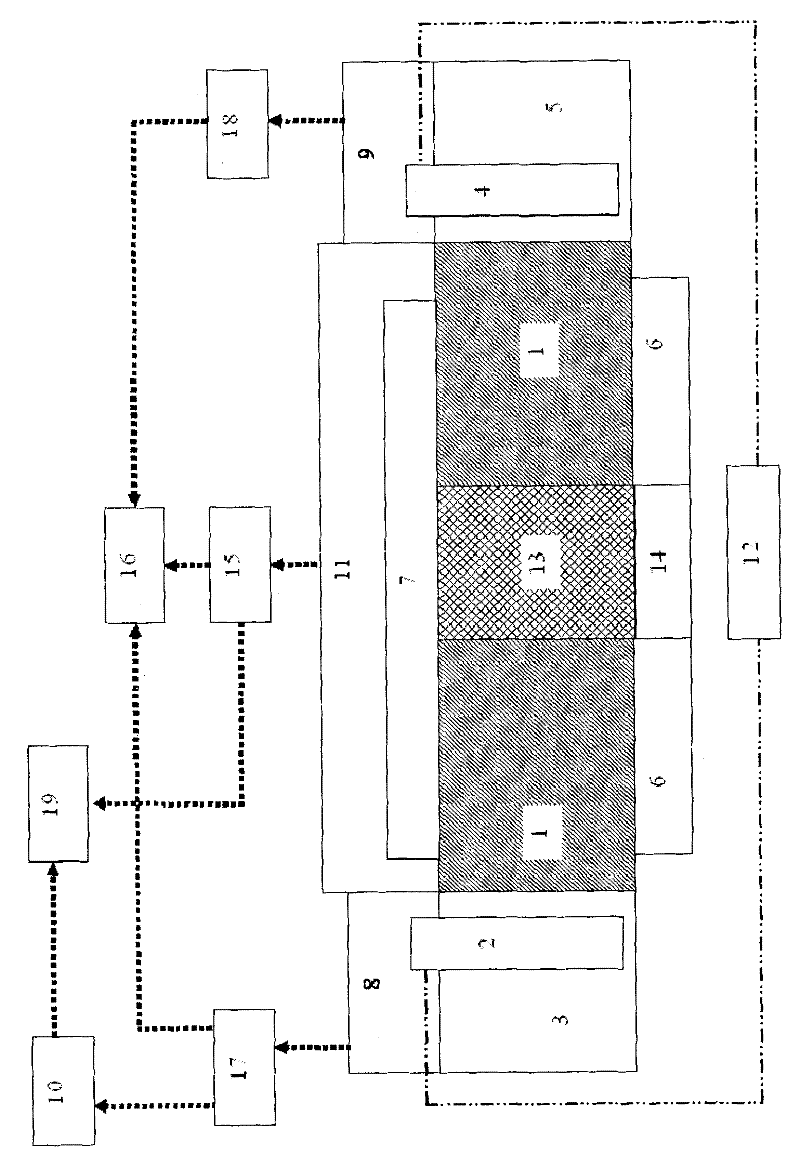
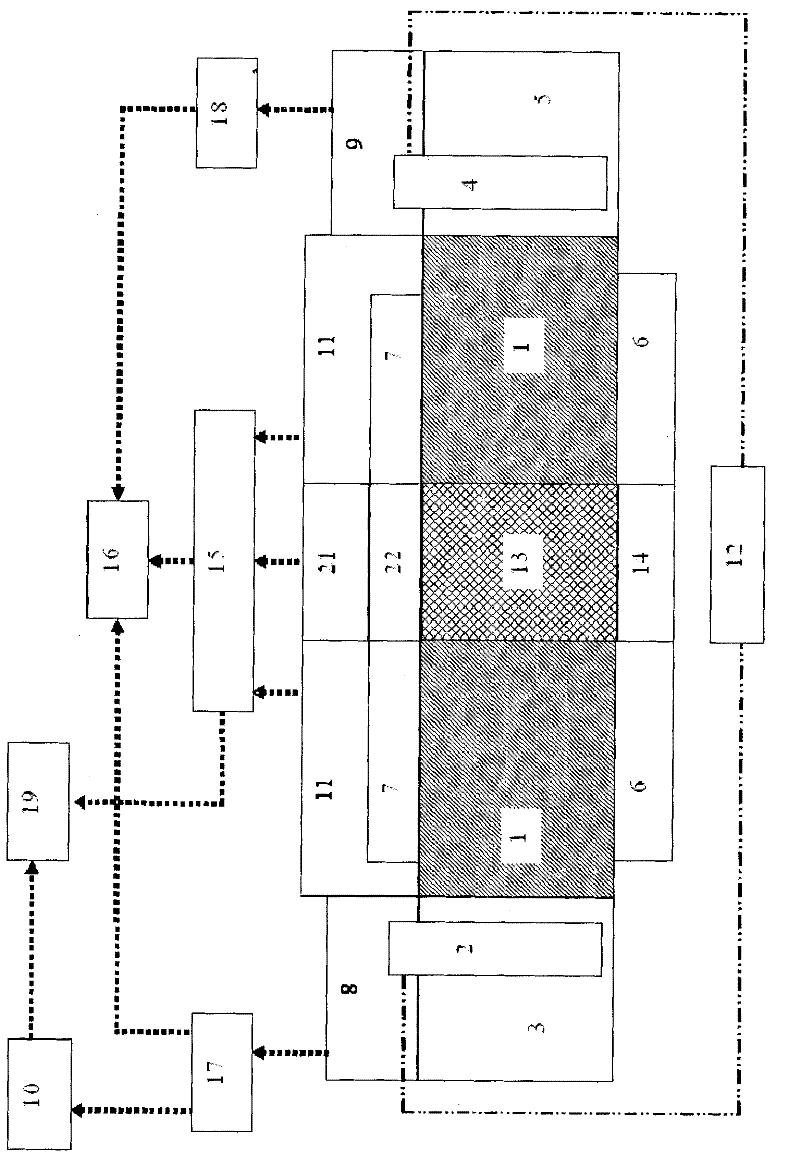
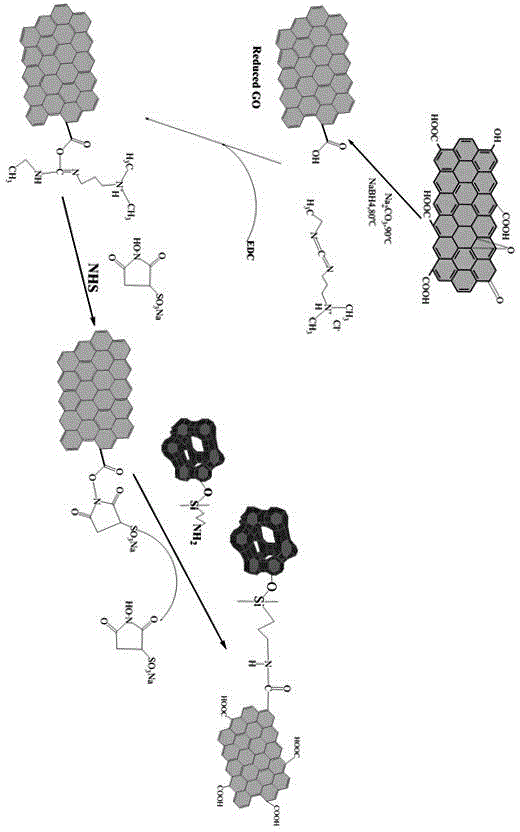
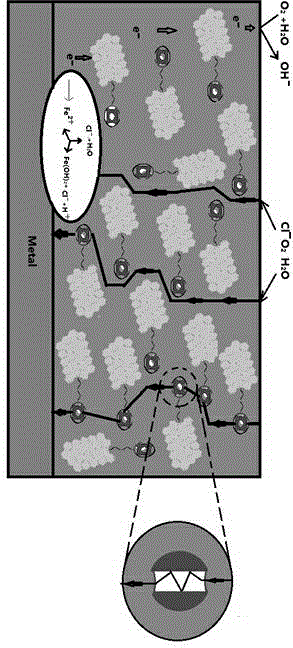
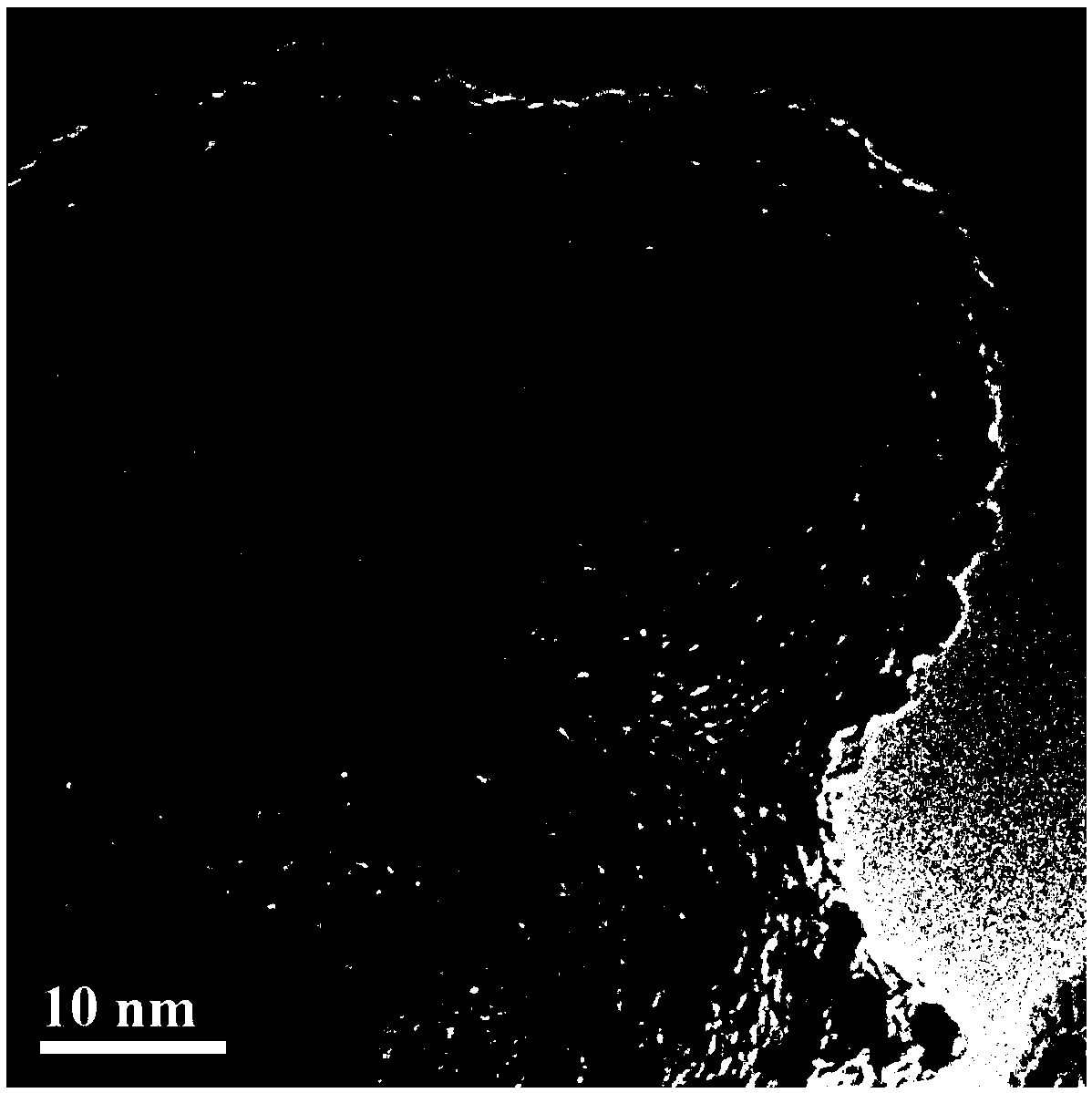
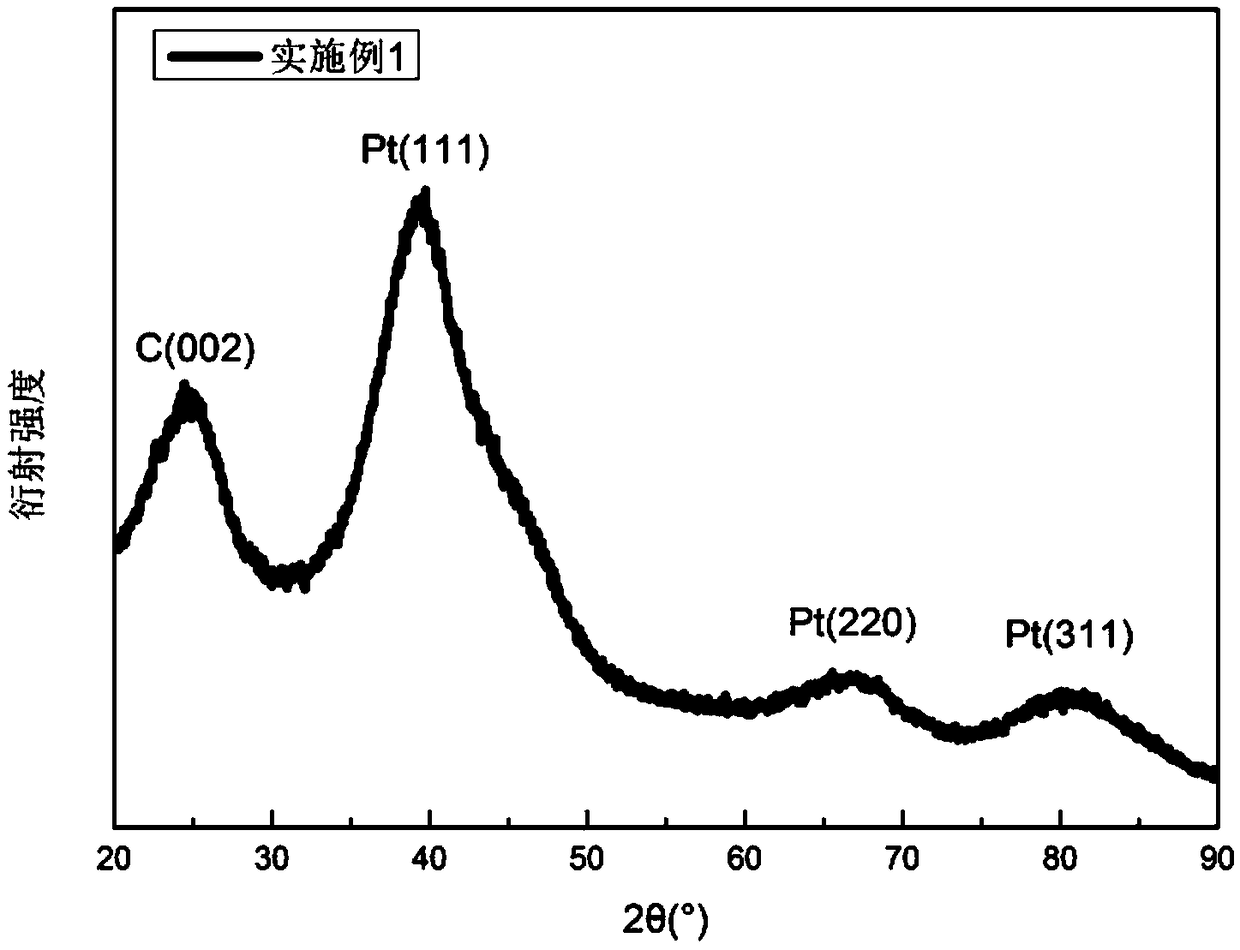
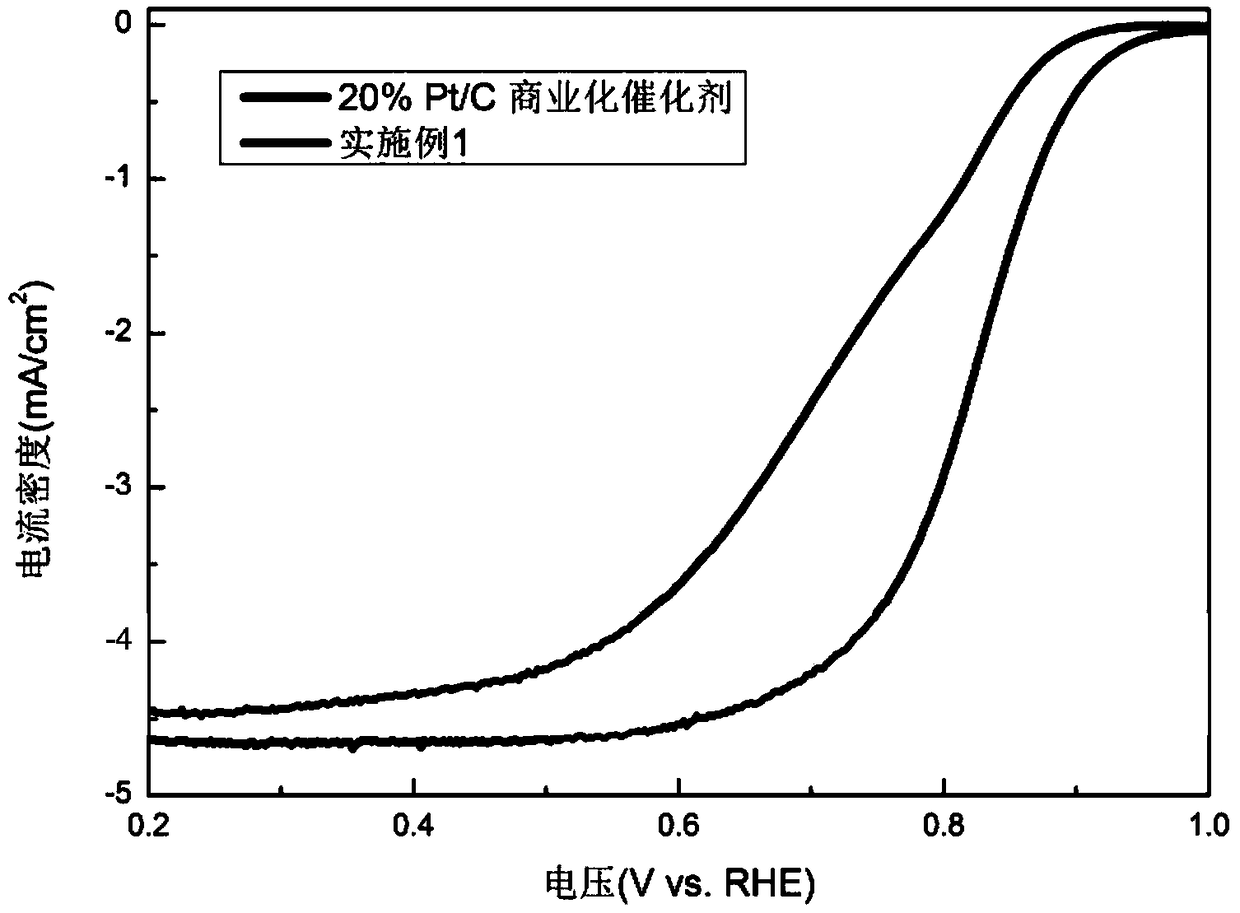
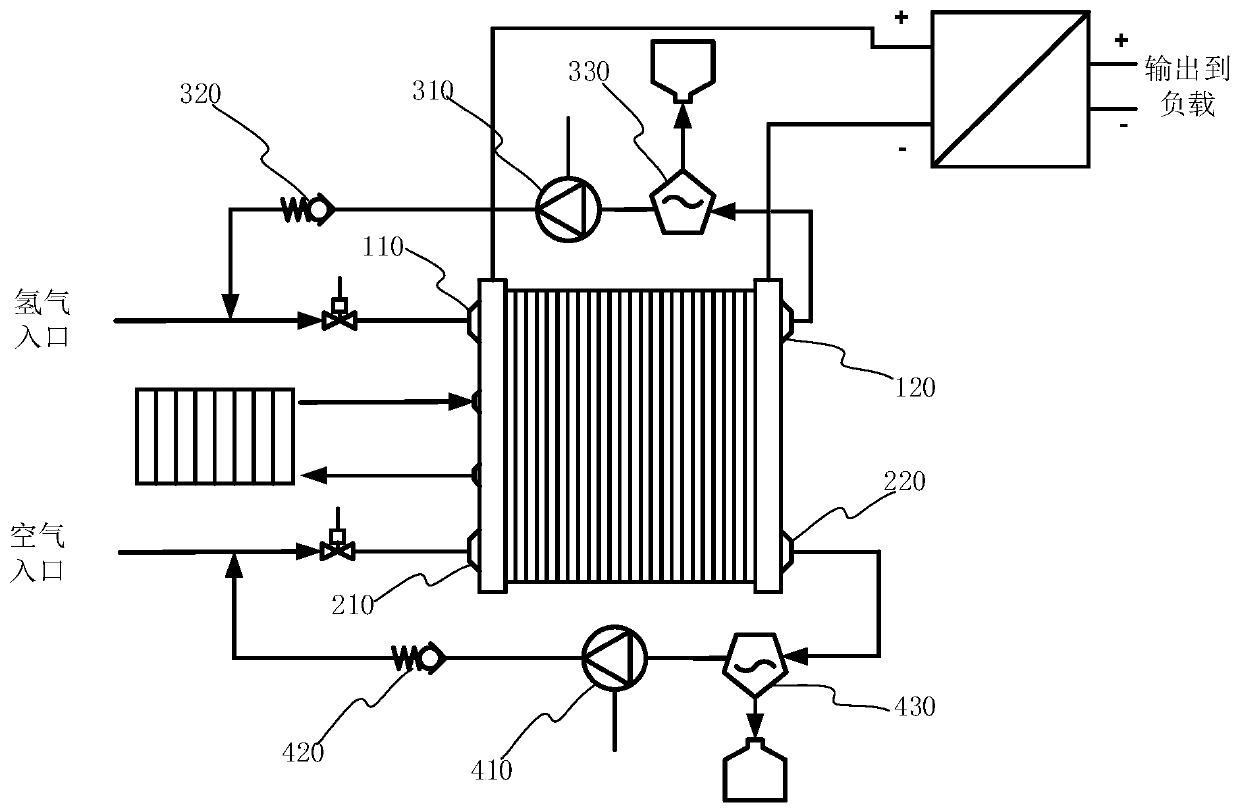
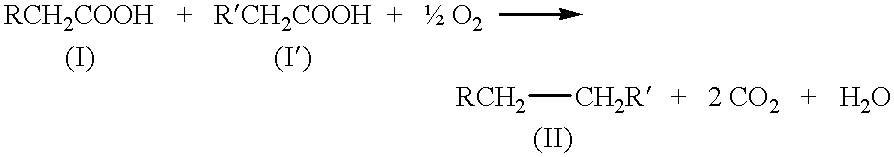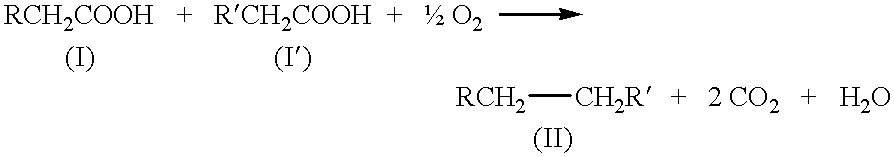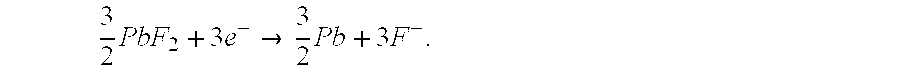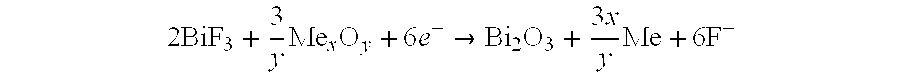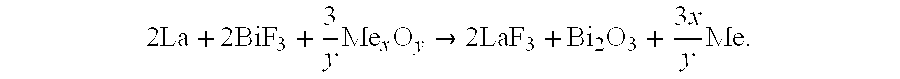Patents
Literature
256 results about "Cathode reaction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cathode is where reduction (gain of electron) occurs. Answer: Therefore, anode reaction is where oxidation occurred, cathode reaction is where reduction happened.
Device for the determination of glycated hemoglobin
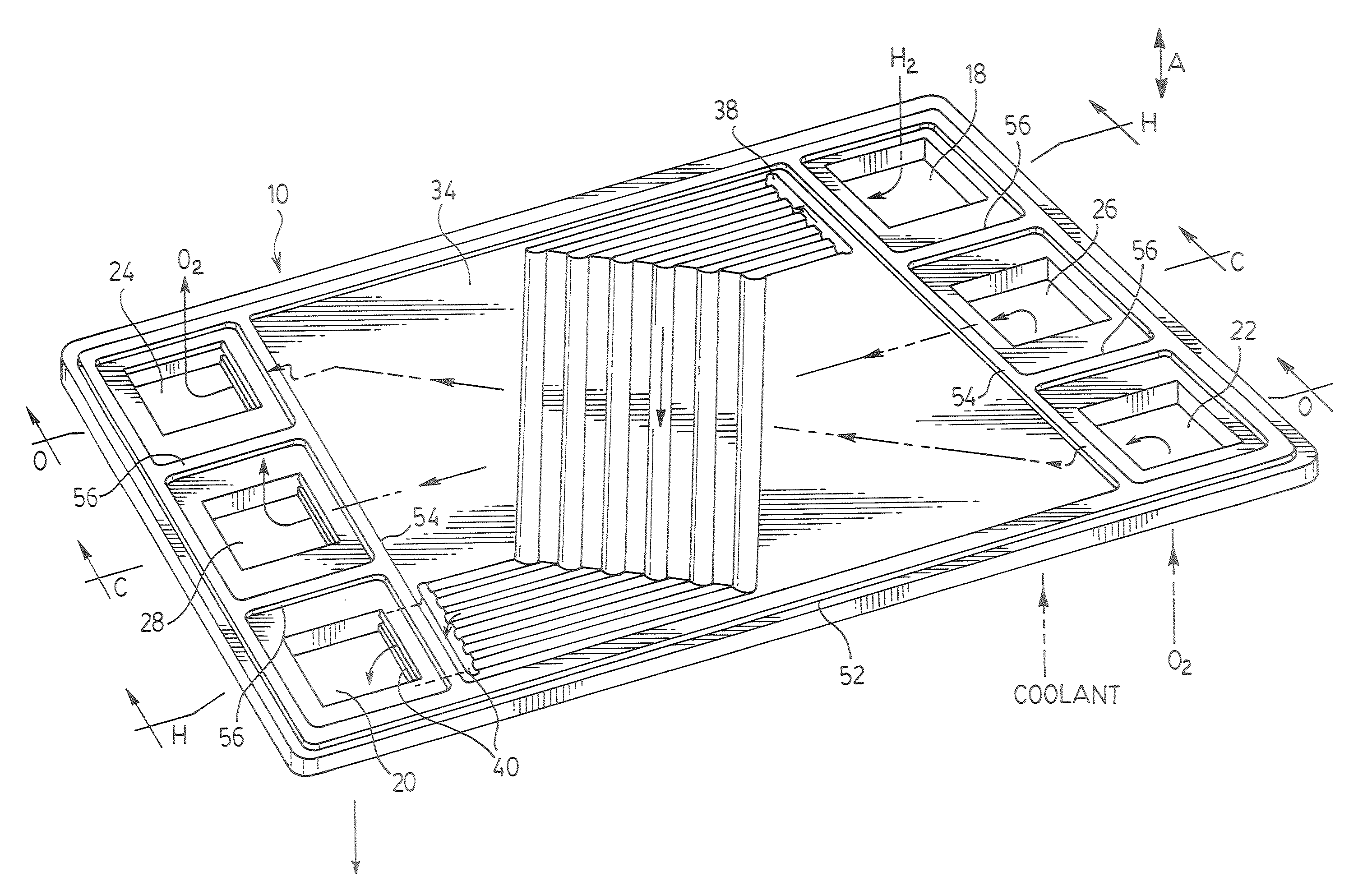
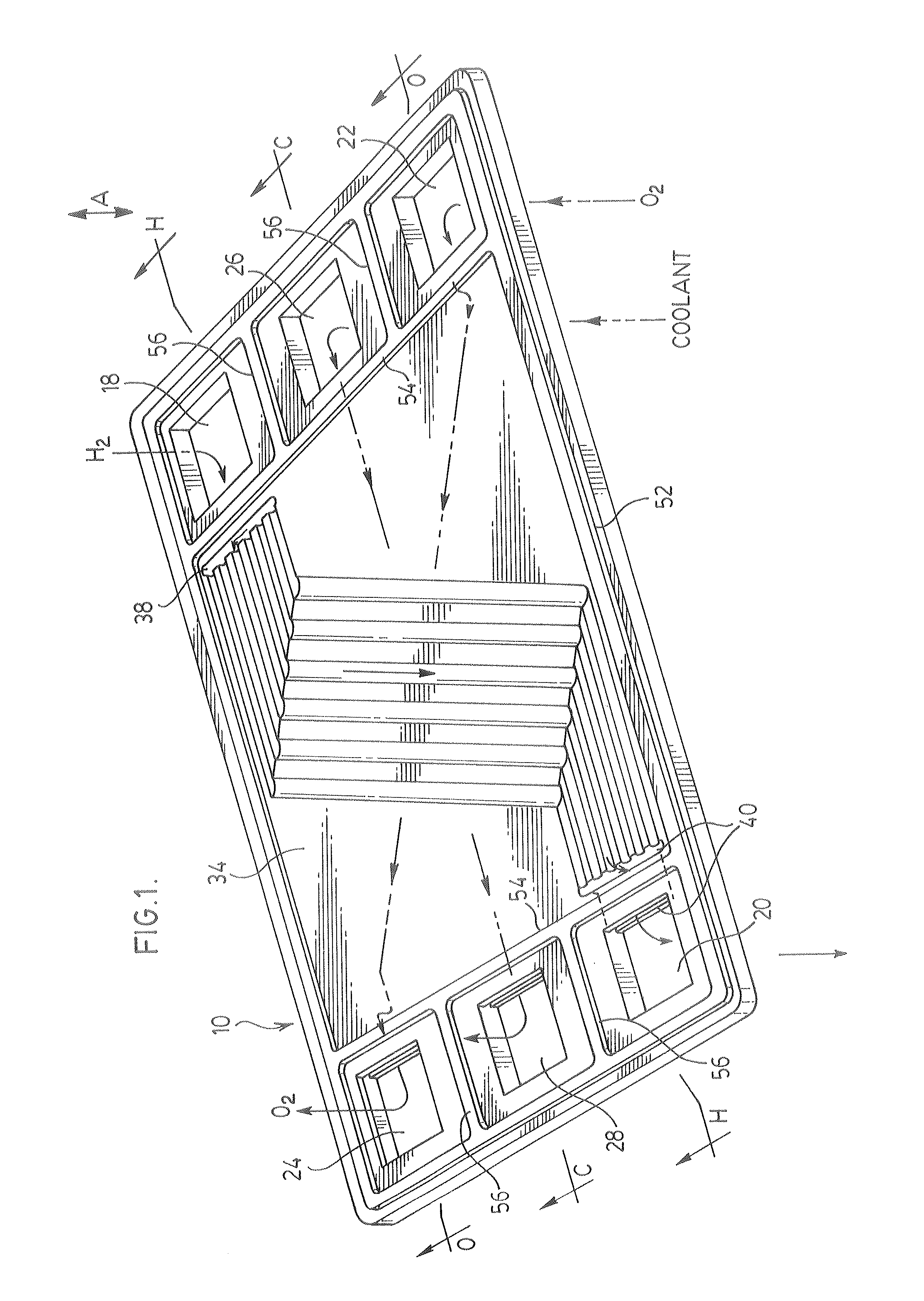
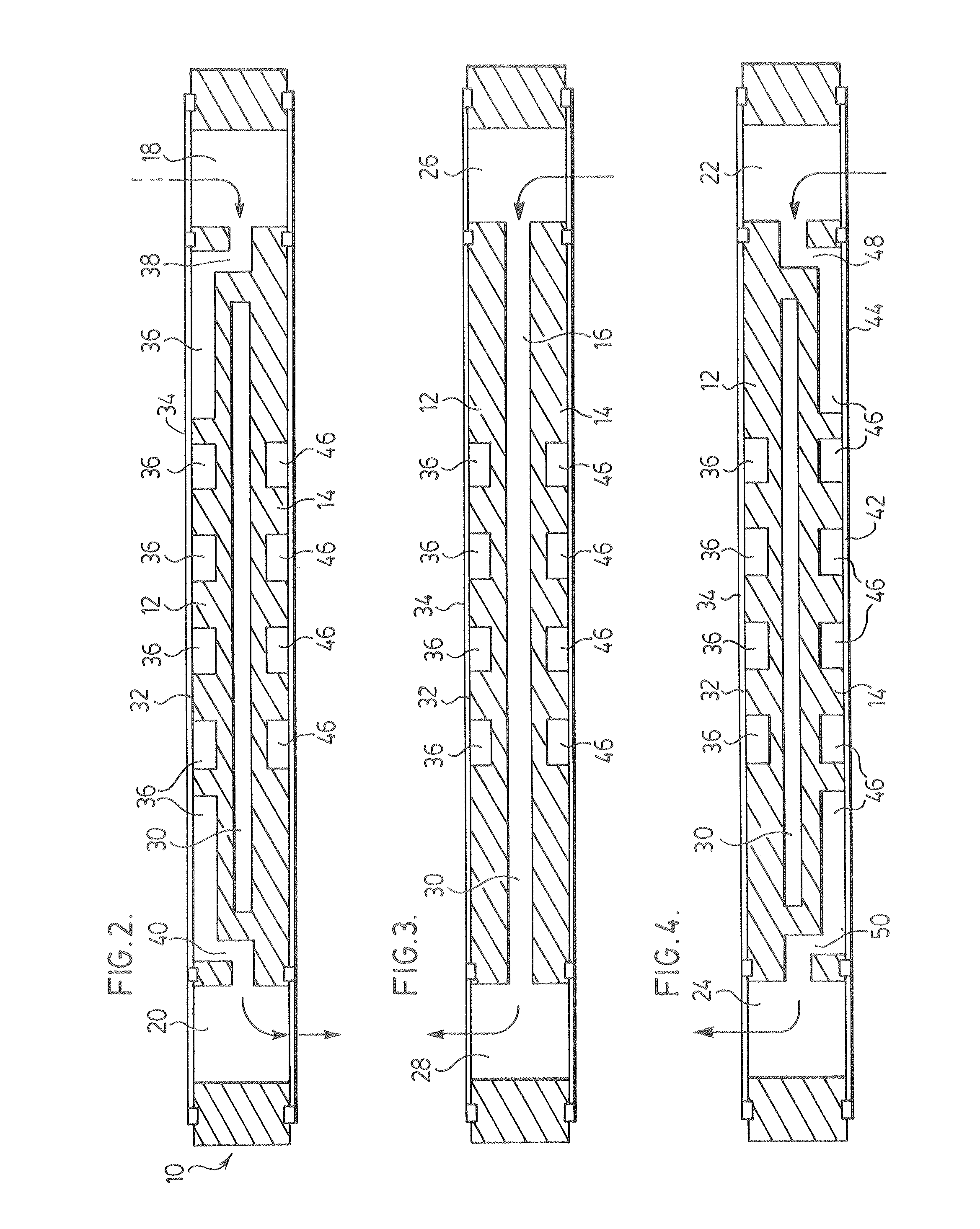
InactiveUS20060205029A1Retain and improve accuracySpeed the ultimate determinationMicrobiological testing/measurementVolume/mass flow measurementTotal hemoglobinCathode reaction
A method of determining the percentage of glycated hemoglobin in a blood sample is disclosed wherein at least one of the assay steps is performed electrochemically. The method includes determining the total amount of hemoglobin in a sample by electrochemically measuring, in an oxygen electroreduction reaction at a cathode, the amount of oxygen in the sample. Because the amount of oxygen dissolved in the sample is known, the total hemoglobin is determined by subtracting the amount of free oxygen from the total oxygen measured, recognizing the fast equilibrium Hb+O2⇄HbO2. This can be followed by determining the amount of glycated hemoglobin in the sample. The cathode reaction is accomplished by contacting the sample with an enzyme, the enzyme being a copper-containing enzyme having four copper ions per active unit. The family of these enzymes includes, for example, laccases and bilirubin oxidases. A device associated with such a process or method is also provided.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Kolbe electrolysis in a polymer electrolyte membrane reactor
InactiveUS6238543B1Electrolysis componentsElectrolytic organic coupling reactionsPlatinumPolymer electrolytes
Disclosed is a process, for the electrolytic coupling of carboxylic acids, carried out in a polymer electrolyte membrane reactor. The reactor design (1) discloses the use of gaseous or neat liquid reactants without the use of organic cosolvents, (2) prevents the loss of platinum, and (3) permits the use of oxygen reduction to water as the cathode reaction.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO +1
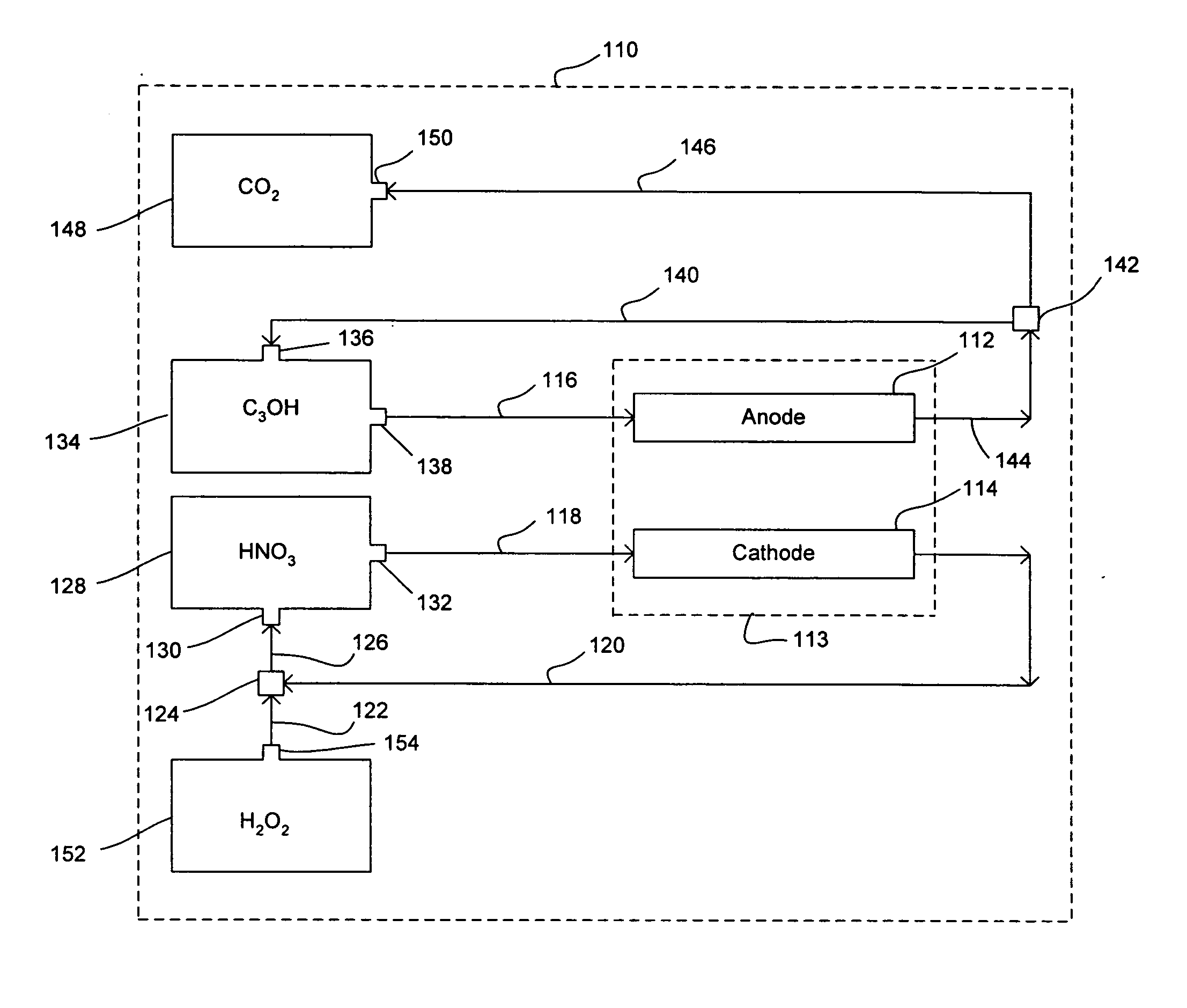
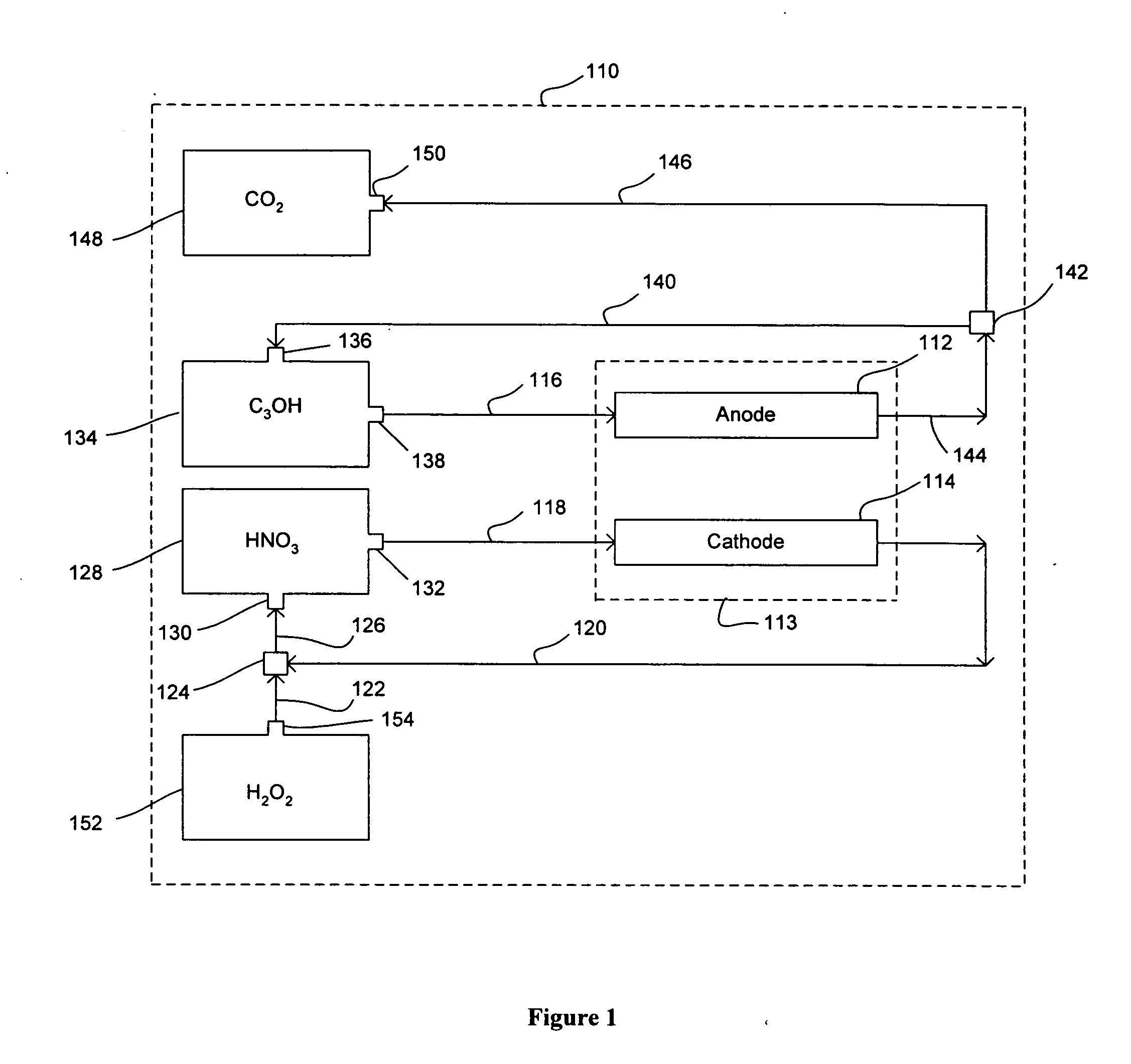
Nitric acid regeneration fuel cell systems
ActiveUS20050084738A1Fuel cell heat exchangeWater management in fuel cellsFuel cellsCathode reaction
The present invention disclosed herein is directed to nitric acid regeneration fuel cell systems that comprise: an anode; a cathode confronting and spaced apart from the anode; an anolyte flowstream configured to flowingly contact the anode, wherein the anolyte flowstream includes a fuel, preferably methanol, for reacting at the anode; a catholyte flowstream configured to flowingly contact the cathode, wherein the catholyte flowstream includes nitric acid for reacting at the cathode to thereby yield cathode reaction products that include nitric oxide and water in a catholyte effluent flowstream; and a hydrogen peroxide flowstream configured to contact and react hydrogen peroxide with the nitric oxide of the catholyte effluent flowstream at a hydrogen peroxide oxidation zone to thereby yield a regenerated nitric acid flowstream. The regenerated nitric acid flowstream is preferably reused in the catholyte flowstream.
Owner:EPD INVESTMENT CO
Solid-state secondary power supply
InactiveUS7722993B2Improve securityAvoid destructionSolid electrolytesElectrode manufacturing processesElectrical conductorDecomposition
Application: in electric equipment as a secondary current source (storage battery). Nature of the invention: Solid-state secondary current source, consisting from an anode (An0), in a form of a metal or an alloy of metals, whose fluorination leads to generation of fluoride or fluorides with high isobar generation potential, an electrolyte in a form of solid-state fluorine-ionic conductor with high ionic conductivity and low electronic conductivity and a cathode (KtF0) in a form of fluoride or solid solution of fluorides with low isobar generation potential, with cathodic reaction during discharge KtF0+e−→F−+Kt′ and anodic during discharge An0+F−→An′F+e−, in which anode and cathode are reversible with respect to fluorine-ions with cathode reaction during charge-discharge: KtFx0+Xe−XF−+Kt′ and anodic during charge-discharge An0+XF−An′Fx+Xe− at voltages that are below voltages of solid electrolyte decomposition, and anode, electrolyte and cathode contain in their composition at least one component that prevents destruction of solid-state battery during charge-discharge cycles. Technical result: the composition of secondary solid-state current source allows achieving high specific energy characteristics of secondary batteries with high number of charge / discharge cycles, ensuring safety of their utilization and lengthy retention of electric energy.
Owner:AWESOM ENERGY BV
Electrochemical composite decomposition manufacturing method and device of laser light tube electrode
ActiveCN103572341ADoes not affect transmissionEfficient compositeCellsOptical elementsSolid lightDecomposition
The invention relates to an electrochemical composite decomposition manufacturing method and an electrochemical composite decomposition manufacturing device of a laser light tube electrode. Solid pulse laser is changed into an annular hollow laser beam with central light strength as zero by a light beam modulating system; compression shock is generated for electrochemical deposition in a non-solid light tube electrode by utilizing annular laser to irradiate expansion of plasma; decomposition stress is removed, a cathode reaction gas is exhausted, and material density is improved; moreover, the deposition reaction is only generated on the light beam with central laser energy as zero, so that the electrochemical composite deposition processing, repairing and surface performance strengthening which are high in quality and good in locality are realized. The electrochemical composite decomposition manufacturing method and the electrochemical composite decomposition manufacturing device disclosed by the invention are suitable for processing, repairing and surface performance strengthening of micro high-performance metal components, and belong to the field of micro quick forming and processing.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Fuel cell using biofilms as catalyst for the cathode reaction an/or the anode reaction
InactiveUS20060234110A1Promote catalysisContinuously replenishedFuel cell auxillariesActive material electrodesFuel cellsBiofilm growth
The present invention relates to a process for the treatment of at least one of the electrodes (cathode and / or anode) of a fuel cell, before the said cell is operated, and before or after the said electrode is placed in the said cell, comprising the step consisting in forming a biofilm on at least part of the surface of the said electrode, by immersing the said electrode in a medium capable of causing the growth of biofilms, the said biofilm being intended to catalyse the reaction at the electrode, and the step consisting simultaneously in subjecting the said electrode to a polarization potential. The invention also relates to a fuel cell comprising at least one electrode covered with a biofilm, obtained before the said electrode is placed in the cell, and to the electrode.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +1
Cathode material used for lithium-sulfur secondary battery
InactiveCN105932242AEasy accessEasy to manufactureCell electrodesLi-accumulatorsLithium sulfurIntermediate product
The invention relates to a cathode material used for a lithium-sulfur secondary battery. The cathode material is characterized in that transition metal nitrides are contained in the cathode material. The transition metal nitrides are anchored on the surface of a carbon substrate well to form a conductive network together by using higher conductivity of the transition metal nitrides and affinity with the carbon substrate; moreover, the redox liquid phase conversion reaction speed of a polysulfide intermediate product is strengthened in the cathode reaction process of the lithium-sulfur battery by using the polarity characteristics of the metal nitrides, the utilization rate of the sulfur active material in the lithium-sulfur battery is improved, and the cathode material is beneficial for promoting the practicability of sulfur in the lithium-sulfur secondary battery.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method and device for remediating polluted soil and treating solid waste by using electric energy
InactiveCN102284474AImprove temperature distribution uniformityImprove solubilitySolid waste disposalContaminated soil reclamationSolubilityOxygen
The invention relates to a method and device for restoring polluted soil and treating solid wastes. A cathode reaction tank and an anode reaction tank are respectively arranged at the two ends of soil / solid wastes, a water supply layer is arranged at the bottom of the soil / solid wastes and contains a chemical agent which can improve the solubility of organic pollutants and heavy metals in water, and a replaceable pollutant collecting layer covers the top of the soil / solid wastes which are internally provided with a replaceable artificial focal zone. The temperature value of the soil / solid wastes is increased to dozens of degrees even hundreds of degrees by applying a high voltage and large current; volatile organic pollutants volatile from the soil / solid wastes due to a high temperature, and nonvolatile organic pollutants and the heavy metals rise to the collecting layer along with water and are left in the collecting layer after the water is evaporated; and partial heavy metal ions are transferred to the electrode tank and the artificial focal zone along the electric field direction. Hydrogen and oxygen generated at a cathode and an anode are respectively collected for burning the volatile pollutants in the collecting layer and the focal zone; and the oxygen also can be made into ozone for oxygenizing pollutants in the soil / solid wastes or be cleared out.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Preparation method of waterborne epoxy composite anticorrosive coating
InactiveCN104877517APrevent restackingAvoid gatheringAnti-corrosive paintsEpoxy resin coatingsEpoxyElectrochemical corrosion
The invention provides a preparation method of a waterborne epoxy composite anticorrosive coating and relates to a preparation method of a composite coating material. The waterborne epoxy composite anticorrosive coating provided by the invention is prepared by adopting carbodiimide (EDC) mediated condensation reaction to integrate zeolite and graphene, and then filling the integrated zeolite and graphene into waterborne epoxy resin. By adopting the method, the characteristics of more pore passages and large specific surface area of zeolite are combined with high strength and electron mobility of graphene; corrosive particles can be blocked from passing through a coating layer to reach a metal matrix and the time for the corrosive particles to pass through the coating layer to reach the metal matrix can be prolonged in the process of anticorrosive application of the coating; and the cathode reaction during corrosion can be transferred to an interface between the coating layer and air by virtue of the electrical conductivity of graphene, thereby slowing down the happening of electrochemical corrosion reaction. By adopting the method, the defects that the current waterborne anticorrosive coating layer is generally poor in barrier property and short in anticorrosion cycle are overcome, and the anticorrosion performance of the waterborne coating layer is greatly improved.
Owner:蓬莱禄源漆业有限公司
Polymer supershort fiber reinforced fuel cell proton exchange membrane and its preparing method
InactiveCN101071873AReduce penetrationImprove performanceCell electrodesCell component detailsPolymer scienceFiltration
The invention provides a polymer ultra short fiber enhancement fuel cell proton exchange membrane and its preparation method. In this proton exchange membrane the polymer ultra short fiber mass percent is 0.01%-5%,others are proton exchange resin mass percent, the polymer ultra short fiber diameter is 0.01-1 micro meter, the length usually is 0.01-500 microns. The preparation craft is: 1) add the polymer ultra short fiber dispersion liquid in solvent, add dispersing agent to prepare dispersion liquid 2) add the polymer ultra short fiber dispersion fluid to the proton exchange resin solution for dispersing to obtain blend liquid of polymer ultra short fiber and proton exchange resin 3) pour cast the blend liquid into the Teflon casting membrane horizontally placed, dry and strip the membrane, boil in the H2SO4 solution, wash by deionized water to obtain the polymer ultra-short fiber reinforced proton exchange membrane. Advantes: good mechanicl strength and size stability, reduced filtration of cathode reaction gases and raised performance and durability of fuel cell.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
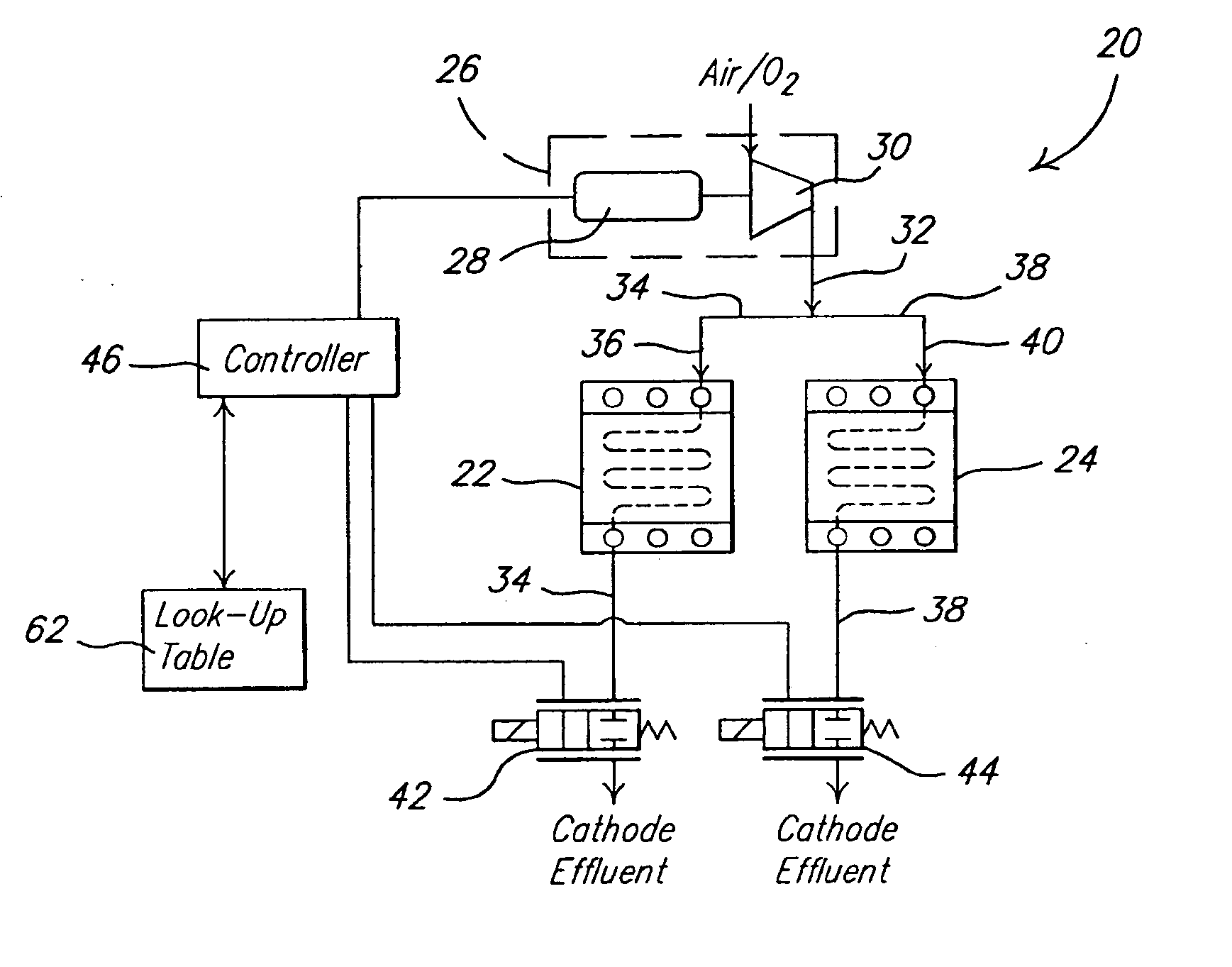
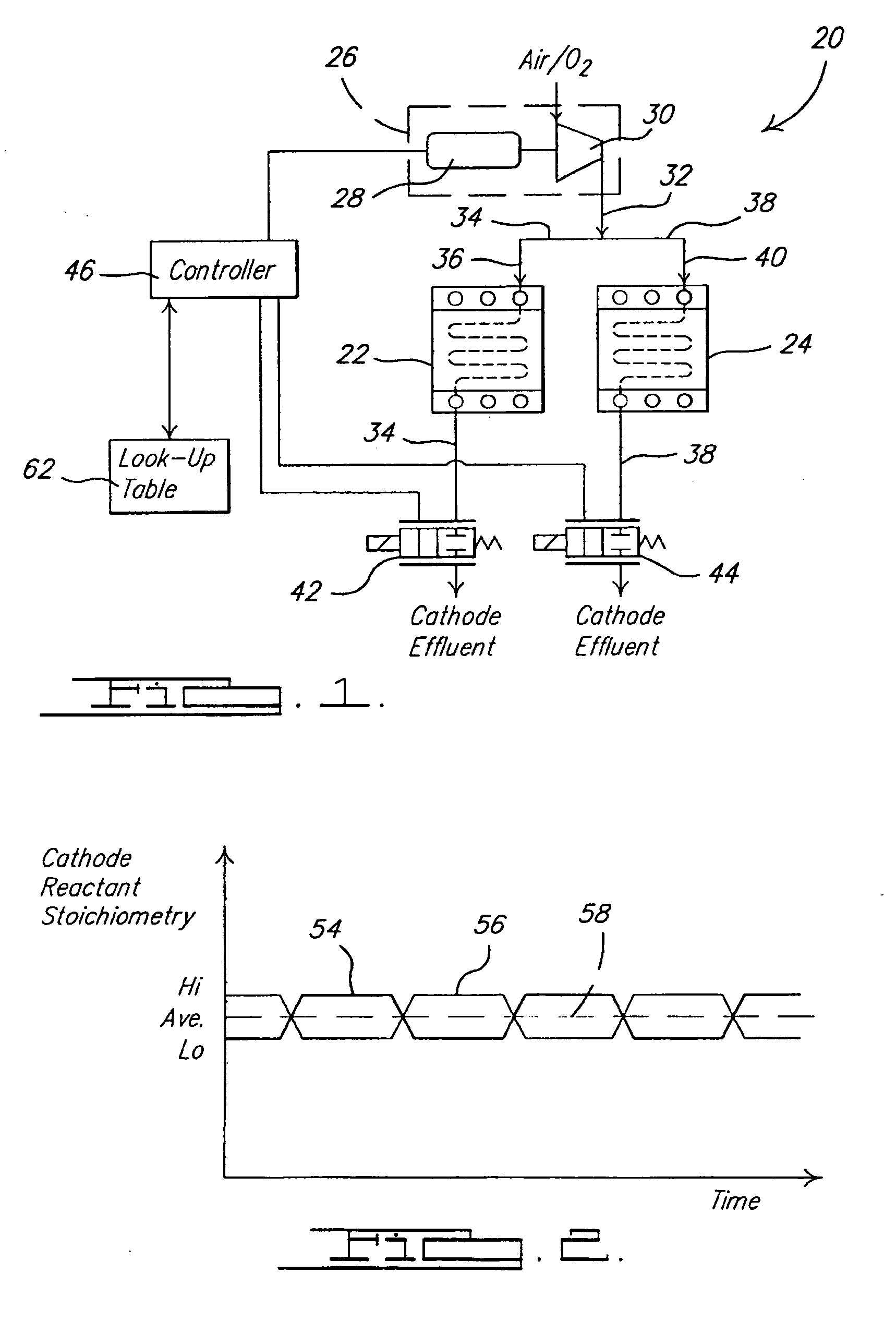
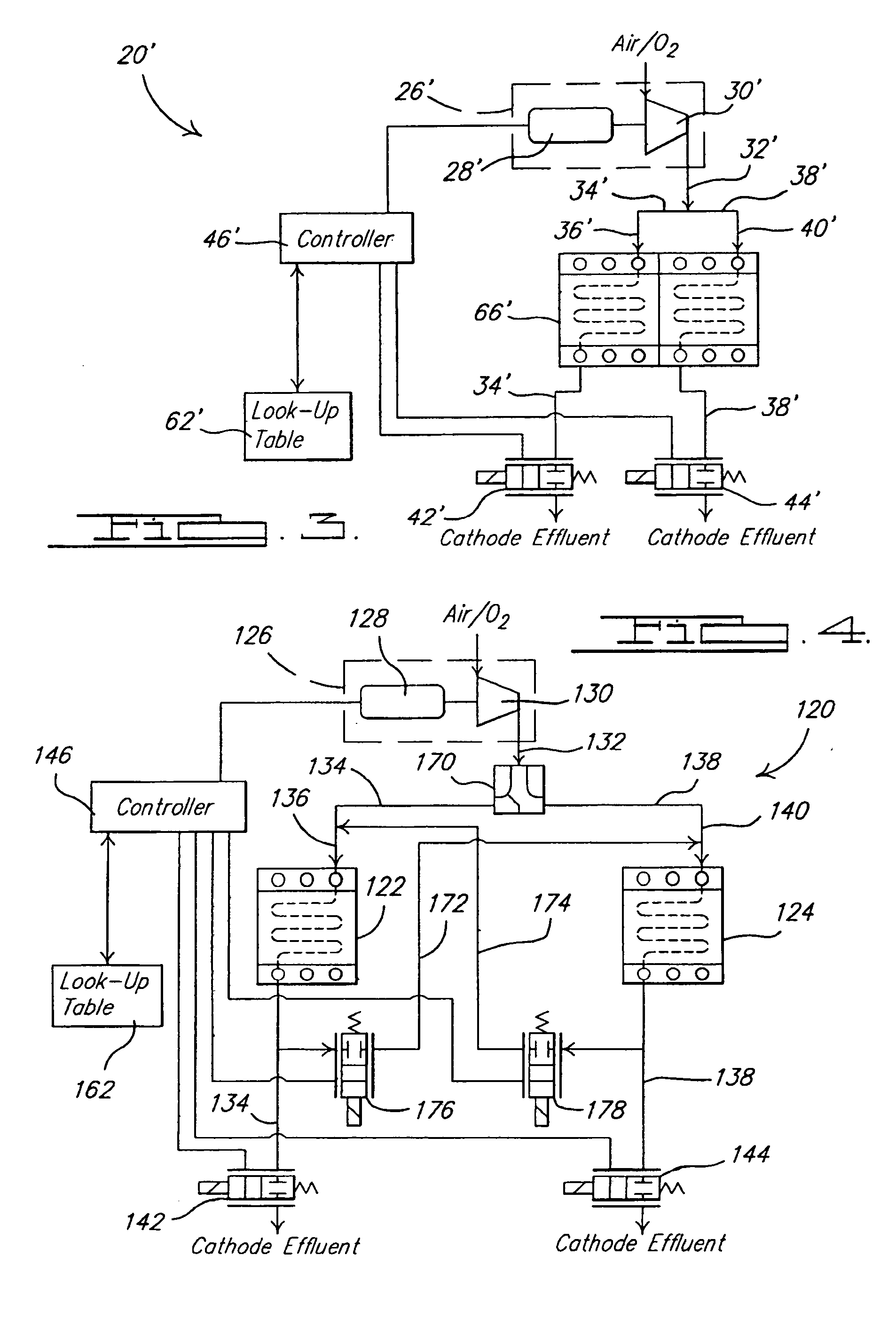
Dynamic cathode gas control for a fuel cell system
InactiveUS20060234093A1Reduced Power RequirementsSatisfies needReactant parameters controlFuel cells groupingChemical measurementFuel cells
A fuel cell system utilizes at least one flow restricting device to vary the stoichiometric quantity of cathode reactant flowing to two discrete cathode sides of the fuel cell system. The varying of the stoichiometric quantity of cathode reactant can be between two predetermined values. The varying of the stoichiometric quantity can be during a steady state power demand placed on the system and / or during transients in a power demand placed on the system. The airmover that supplies the cathode reactant stream can be operated in a substantially continuous manner during a continuous power demand placed on the fuel cell system.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method for biological treatment of sulfate wastewater employing synchronous electric catalysis of anode and cathode
ActiveCN103319002AImprove the reduction of SO
<sub>4</sub>
<sup>2-</sup>
rateReduce consumptionTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesSulfate-reducing bacteriaSulfur
The invention provides a method for biological treatment of sulfate wastewater employing synchronous electric catalysis of an anode and a cathode. The method comprises the following concrete steps of: (1) building an electric catalytic bioreactor, which includes a cathode reaction zone, a buffer zone and an anode reaction zone; (2) inoculating mixed bacteria of sulfate reducing bacteria inside the cathode reaction zone, leading to a culture medium, electrifying and acclimatizing, and cultivating for 3-5 days at 28-34 DEG C, so as to achieve cathode hanging membrane of the sulfate reducing bacteria; (3) inoculating sulfur-oxidizing bacteria inside the anode reaction zone, leading to the culture medium to cultivate for 5-7 days at 25-30 DEG C; and (4) starting a reactor, leading the sulfate wastewater to the cathode reaction zone of the reactor, and enabling the sulfate wastewater to flow out of the reactor after flowing inside the anode reaction zone through the buffer zone. By adopting the method, control of an S<2->oxidization process is achieved when the reduction speed of the sulfate reducing bacteria for reducing SO4<-2> is improved. Thus, the yield of S produced by biological metabolism of the wastewater is improved.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A solvothermal reduction carbon-supported platinum-based catalyst for fuel cell and a preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN108963282AGuaranteed stabilityEnsure consistencyMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesPtru catalystAlcohol fuel
The invention discloses a method for preparing a carbon-supported platinum-based catalyst of a fuel cell by a solvothermal method, which is applied to a proton exchange membrane fuel cell and comprises the steps of: In the cathode reaction of oxygen fuel cell and direct alcohol fuel cell, it belongs to the electrochemical catalytic reaction field. A solvothermal reduction process is used, A support carbon material is sufficiently dispersed in a solvent, A metal precursor solution is added with stirring, that mass percentage of the active ingredient reaches 20 to 60 wt% in the prepared catalyst, the pH value of the solution is adjusted to above 9 by an alkaline solution, and the mixture is react in a high-temperature and high-pressure sealed reaction vessel. After the reaction, the pH valuewas adjusted to less than 5 by acidic solution, and the reaction solution was filtered, washed, dried and ground to obtain carbon-supported platinum-based electrocatalyst. The catalyst active ingredient prepared by the invention has small particle diameter and is uniformly dispersed on a carbon carrier, and has high activity. The preparation process of the invention is simple in operation, rapidin reaction, low in energy consumption, low in cost, and easy to realize mass industrial production.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
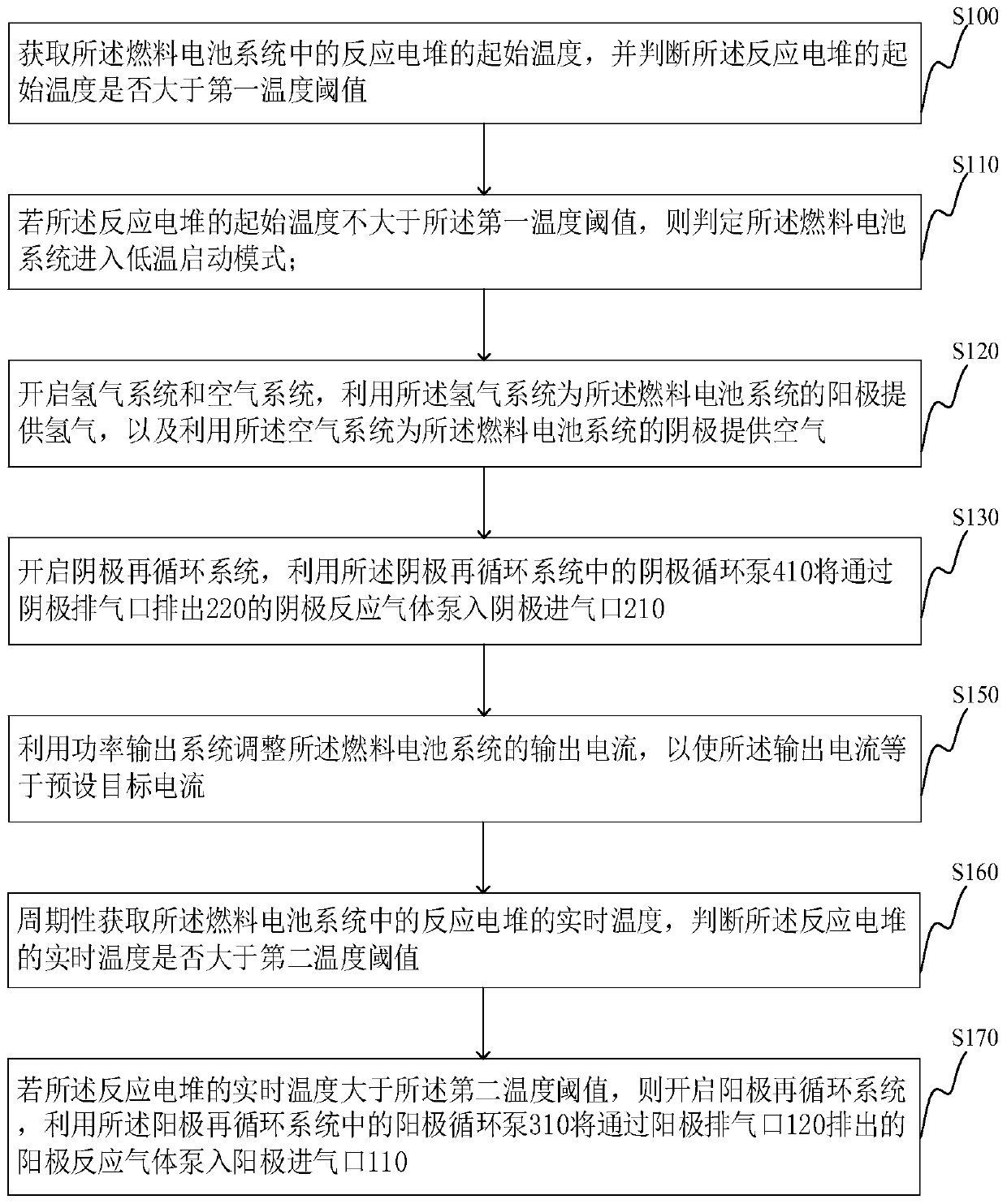
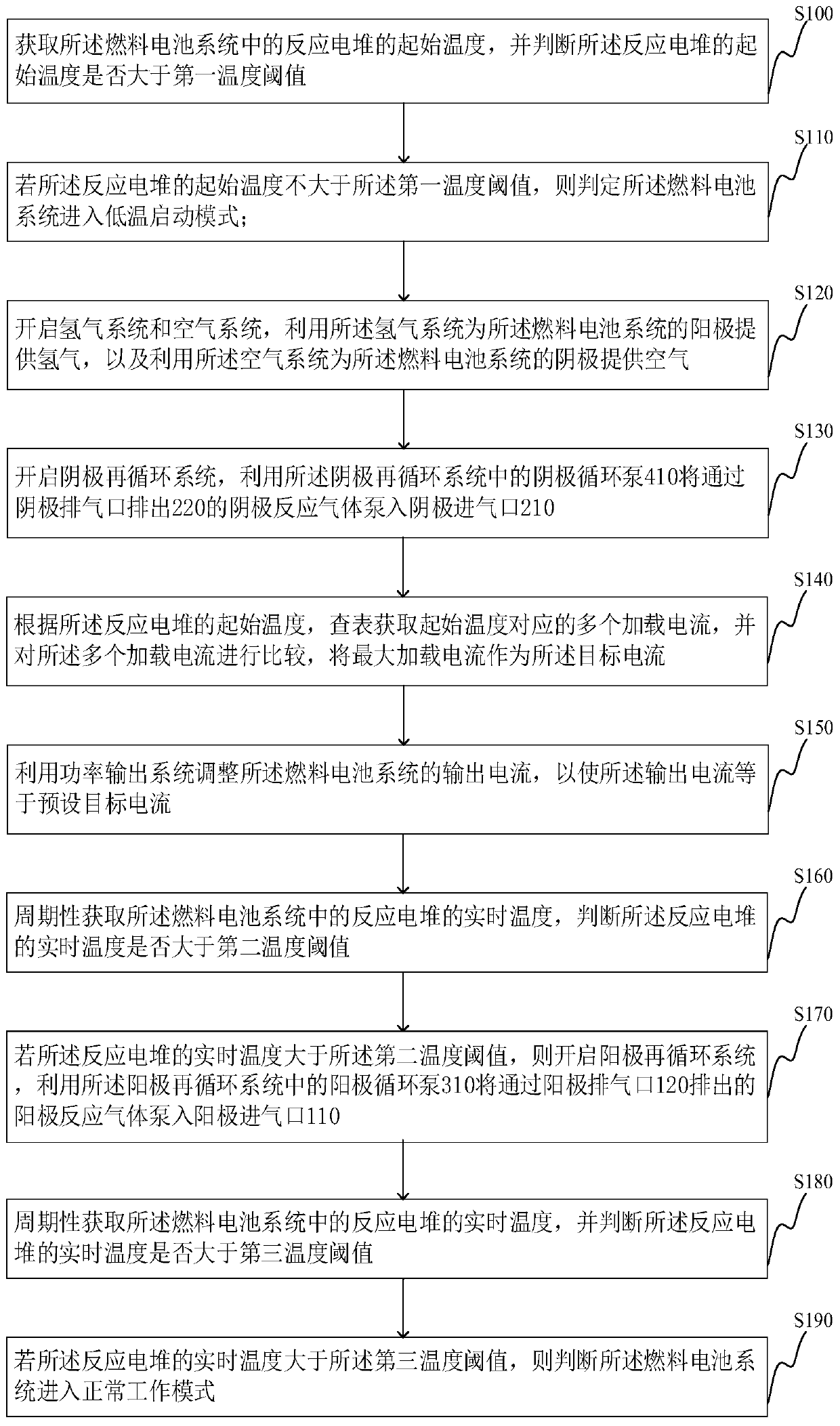
Low temperature starting methods for fuel cell system, computer equipment and memory medium
ActiveCN109904494AReduce power generation efficiencyFast heat productionFuel cell controlPower flowFuel cells
The invention provides low temperature starting methods for a fuel cell system, computer equipment and a memory medium. A low temperature starting method comprises the steps of obtaining and judging whether an initial temperature of a reaction stack in the fuel cell system is greater than a first temperature threshold or not; judging whether the fuel cell system enters a low temperature starting mode or not if the initial temperature is not greater than the first temperature threshold; providing hydrogen for an anode the fuel cell system through utilization of a hydrogen system, and providingair for a cathode of the fuel cell system through utilization of an air system; pumping cathode reaction gas exhausted from a cathode exhaust port into a cathode air inlet through utilization of a cathode circulation pump in a cathode recirculation system; adjusting an output current of the fuel cell system through utilization of a power output system, thereby enabling the output current to be equal to a preset target current; periodically obtaining and judging whether a real-time temperature of the reaction stack is greater than a second temperature threshold or not; and starting an anode recirculation system if the real-time temperature is greater than the second temperature threshold.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Separated area current detecting system for proton exchange film fuel cell
InactiveCN1945887AAchieving tightnessAchieve insulationElectrical testingSolid electrolyte fuel cellsReaction fieldProton
This invention relates to a regional current test system for proton exchange membrane fuel batteries including an anode collecting board, a membrane electrode and a cathode collecting board, in which, an anode gas flow field is processed on the anode collecting board to provide a flow channel for the anode gas, collect current generated by the membrane electrode and bring out the current, besides, the membrane electrode provides reaction field for anode and cathode reaction gas, and the proton exchange membrane conducts proton and water to finish the reaction, cathode and anode provide reaction field for various gas and convey current to the collecting board. A reaction gas flow field is processed on the cathode collecting board to provide a flow channel for the cathode gas and collect current generated by the membrane electrode to carry it to outside current.
Owner:北京飞驰绿能电源技术有限责任公司
Device and method for treating organic wastewater with TiO2 photocatalysis rotary disc fuel cell
InactiveCN102398955APrevent invalid compoundingReduce compound lossWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment by electrochemical methodsFuel cellsPhotocathode
The invention provides a device and a method for treating organic wastewater with a TiO2 photocatalysis rotary disc fuel cell. TiO2 photocatalyst is loaded on a photo-anode rotary disc substrate to serve as a photoanode rotary disc, and a photocathode rotary disc and the photoanode rotary disc are respectively placed in a photocathode reaction tank and a photoanode reaction tank, which are partitioned from each other by an ion exchange membrane in between. A motor is started, a speed controller is utilized to control the rotation speed of the rotary discs, and thereby a layer of liquid film is formed on the surface of each rotary disc. An excitation light source is used for irradiating the photoanode rotary disc, and while the light absorbed by the organic wastewater is greatly reduced, the utilization rate of the excitation light and the efficiency of photocatalytic degradation are increased as well. The double reaction tanks can effectively prevent the ineffective compounding of oxidation product and reduction product in solution, moreover, different types of organic wastewaters with different concentrations can be degraded in the two reaction tanks, meanwhile, the combination loss of photoinduced electrons and holes on the TiO2 surface can be reduced, consequently, the utilization rate of the excitation light and the efficiency of pollutant degradation are increased, and high efficiency and low consumption are achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
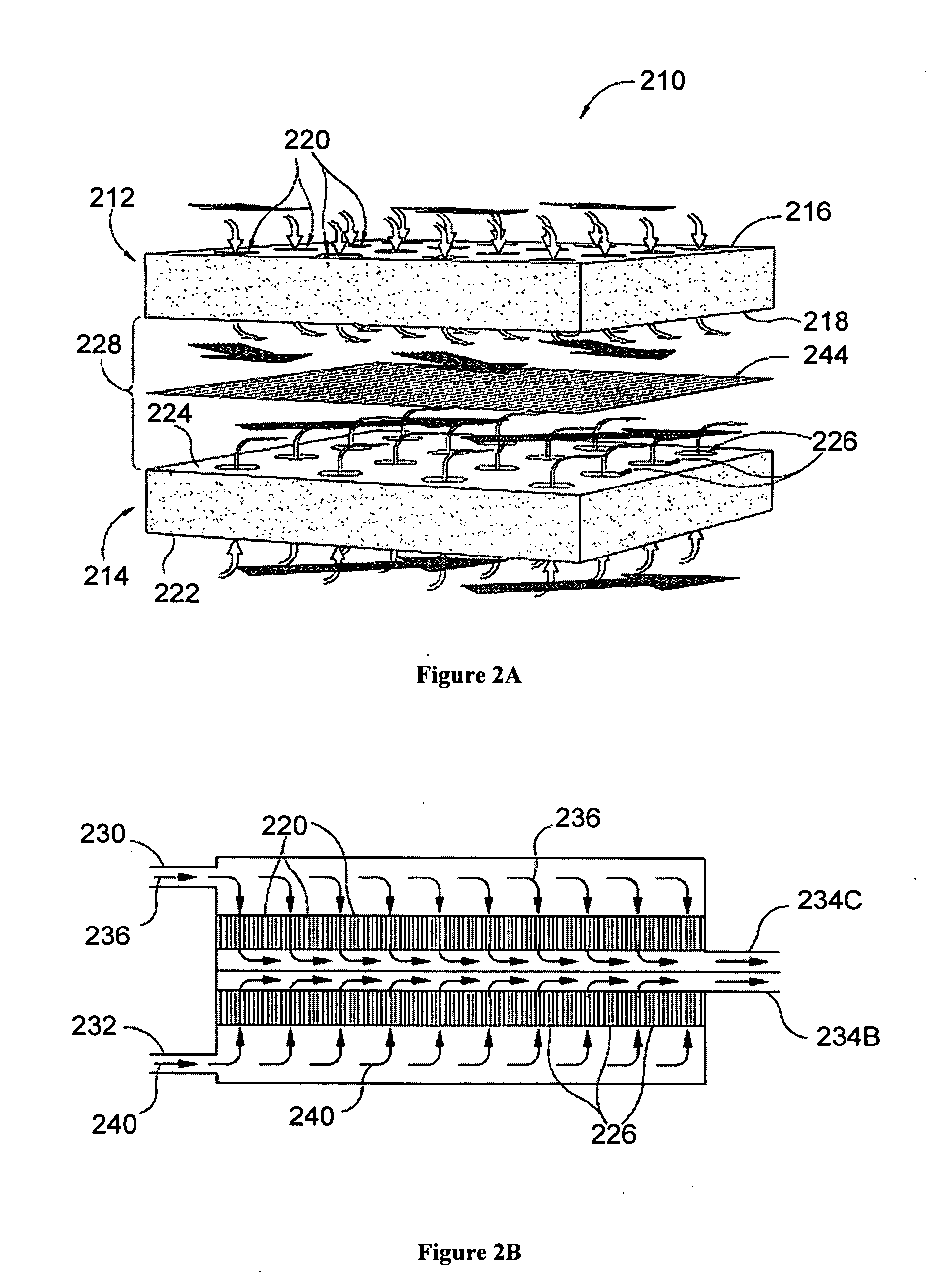
Fuel cell assemblies with integrated reactant-conditioning heat exchangers
A fuel cell assembly in which at least one heat exchanger for conditioning either the anode or cathode reactant gas is integrated with the fuel cell stack and located at the end of the fuel cell stack, to isolate the fuel cell stack from contact with the end plates of the stack. The heat exchanger may preferably be comprised of a stack of plates which may preferably be the same as the plates as the fuel cell stack, with outer and inner end plates to direct the flow of reactant gases, waste gases and coolant to and from the fuel cell stack. The assembly is preferably configured to include reactant conditioning heat exchangers at both ends of the fuel cell stack.
Owner:DANA CANADA CORP
Rotary proton exchange film fuel battery
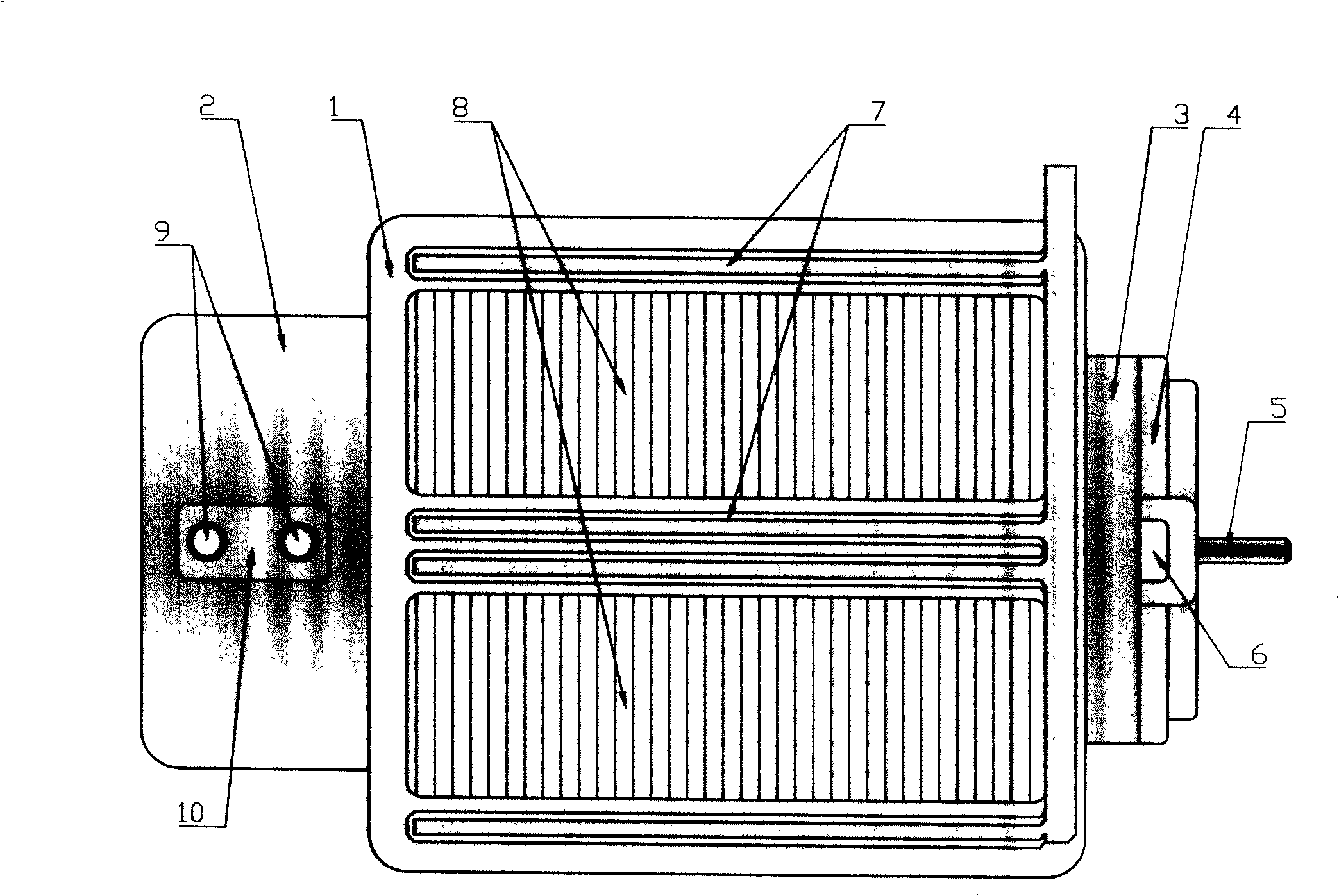
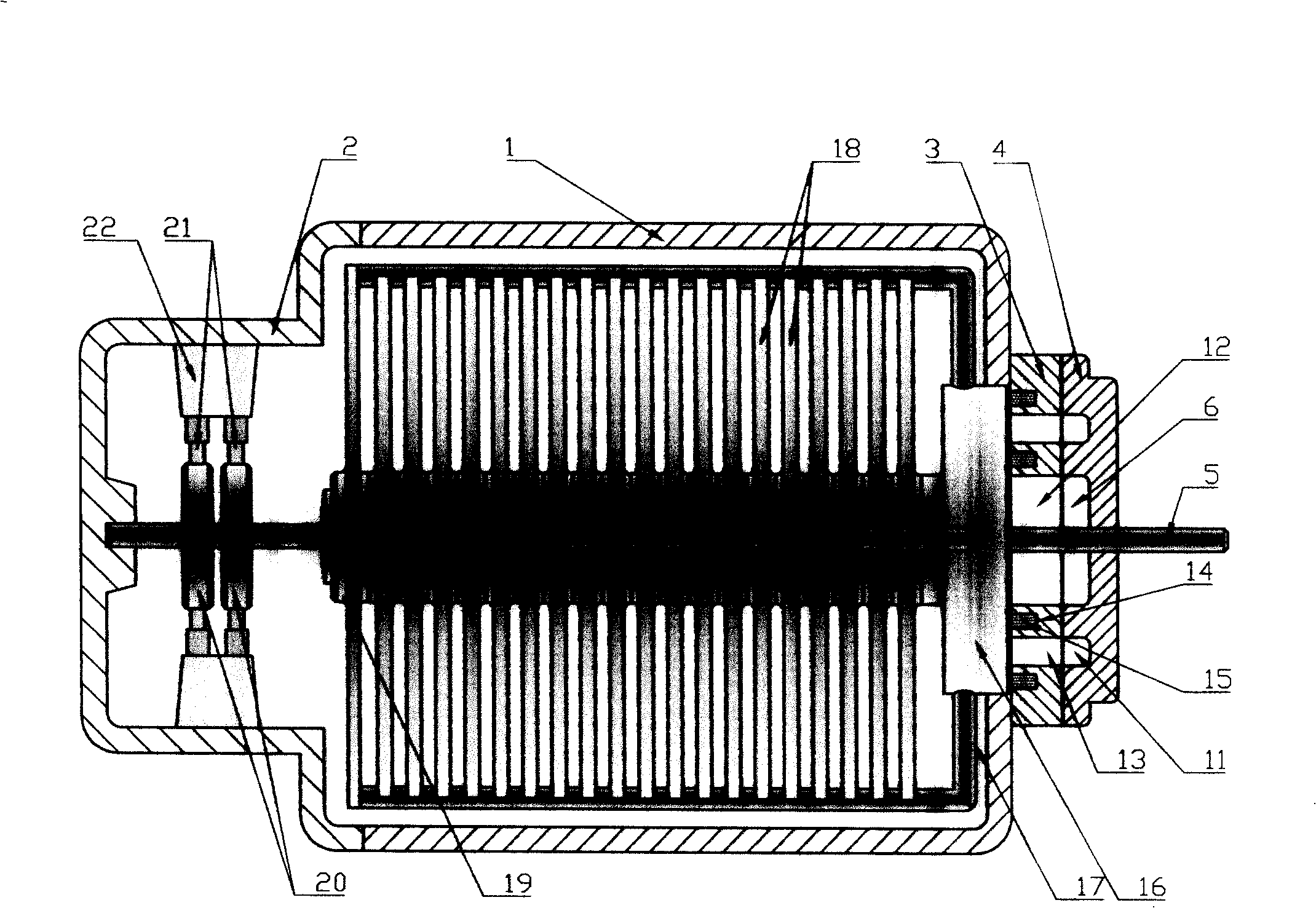
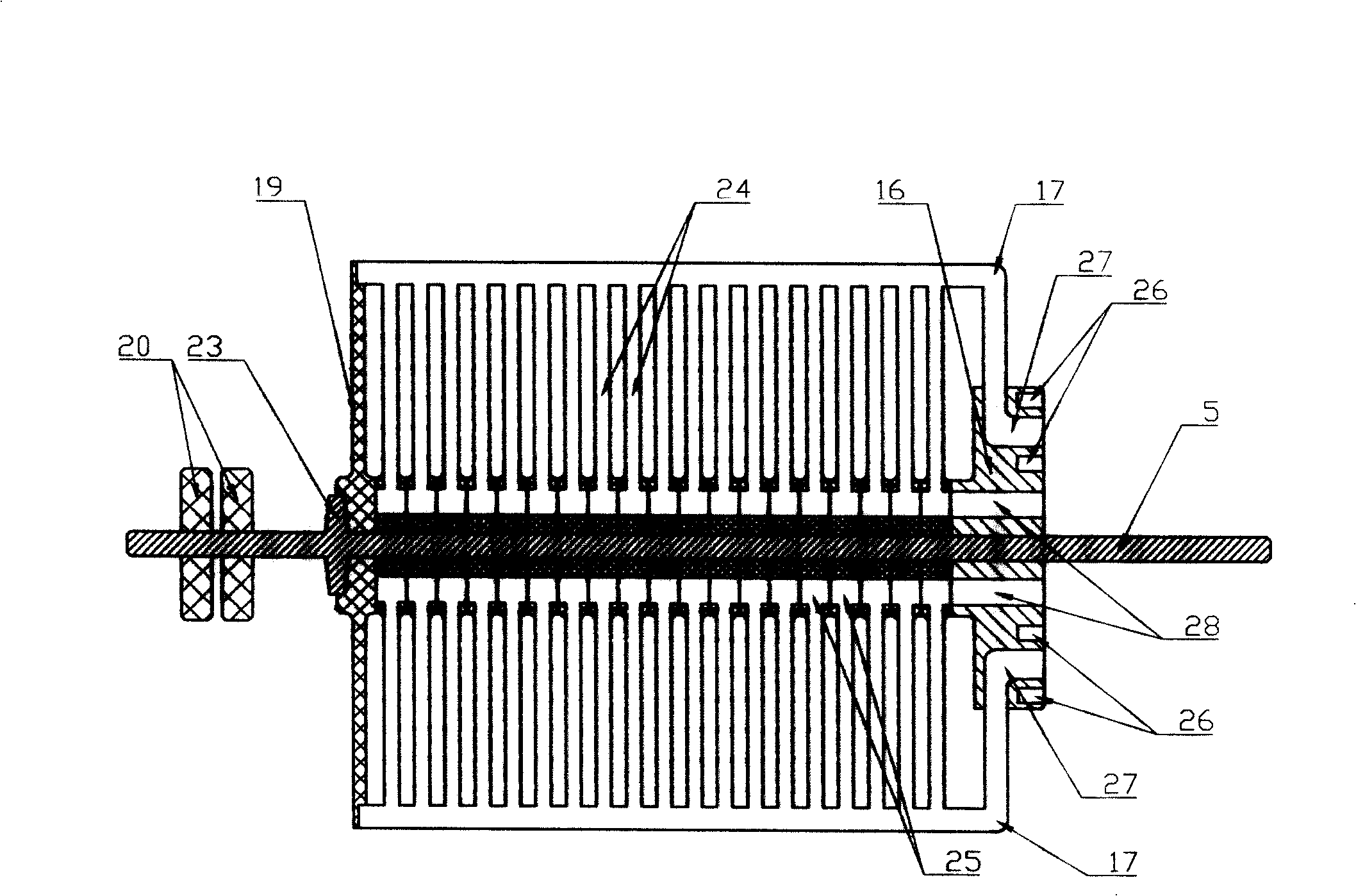
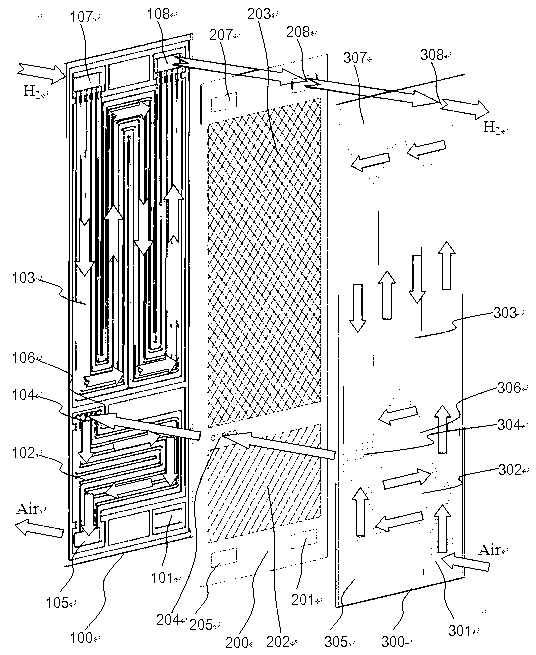
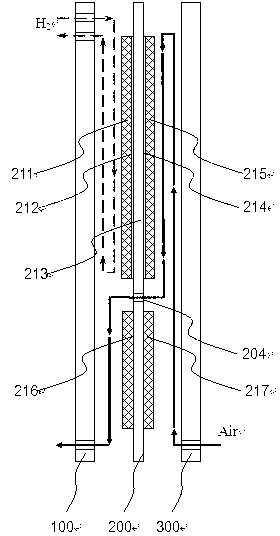
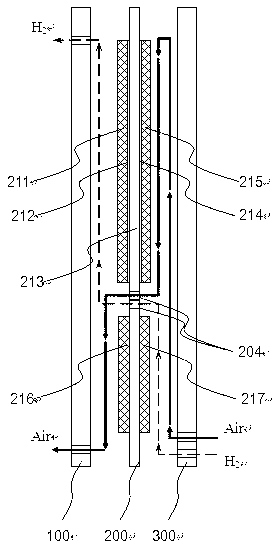
InactiveCN101262071AIncrease profitHigh or low utilizationSolid electrolyte fuel cellsFuel cell detailsProtonCathode reaction
The invention discloses a proton exchange membrane flue cell of rotating disk type, which comprises a rotating disk that can rotate around a centre axle vertical to the surface of the disk; the rotating disk comprises a disk rack 4 with certain thickness and a fixing device 5 arranged on the disk rack used for fixing a proton exchange membrane 2 that is clamped and overlapped by anode parts 3 and cathode parts 1, and the surface of the external wall of the rotating disk is formed by the cathode parts, and the surface of side wall of the internal chamber of the rotating disk is formed by the anode parts. The chamber and the outer side of the rotating disk in cathode reaction atmosphere are sealed and separated; the chamber of the disk is connected with a path of anode reaction gas through an air inlet 6, an air-inlet duct 8 and an air-outlet duct 7 which are arranged in the disk rack and an air outlet 9. The proton exchange membrane flue cell of rotating disk type of the invention can evenly spread reaction gas on the surface of the cathode and anode in operation through self rotating of the rotating disk, actively and evenly discharge excess water, conveniently adjust humidity and temperature of the membrane and electrode and has comparatively high membrane utilization rate and low overall cost.
Owner:田浩
Magnesium water battery
The invention relates to a magnesium water battery which comprises a magnesium or magnesium alloy anode, a diaphragm, a hydrogen-evolution-catalyst-carried cathode and a cathode reactant water, wherein the anode and cathode are arranged in opposite; the diaphragm is arranged between the anode and cathode; and the anode, cathode and diaphragm are arranged in water. Compared with the prior art, the magnesium water battery is simple in structure and convenient to use, and is not restricted by the dissolved oxygen concentration in seawater when being used in seawater. The underwater magnesium water battery solves the problem of dependence of the traditional magnesium dissolved oxygen seawater battery on the oxygen concentration in seawater, and can operate normally even in an oxygen-free environment as long as the anode and cathode of the battery are isolated by the diaphragm and a hydrogen evacuation channel is left. Compared with the traditional magnesium dissolved oxygen seawater battery which needs a larger open space to ensure the continuous renewal of fresh seawater, the magnesium water battery has the advantages of compact structure, small size and obviously higher volumetric specific energy. The battery can operate normally as long as seawater enters.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
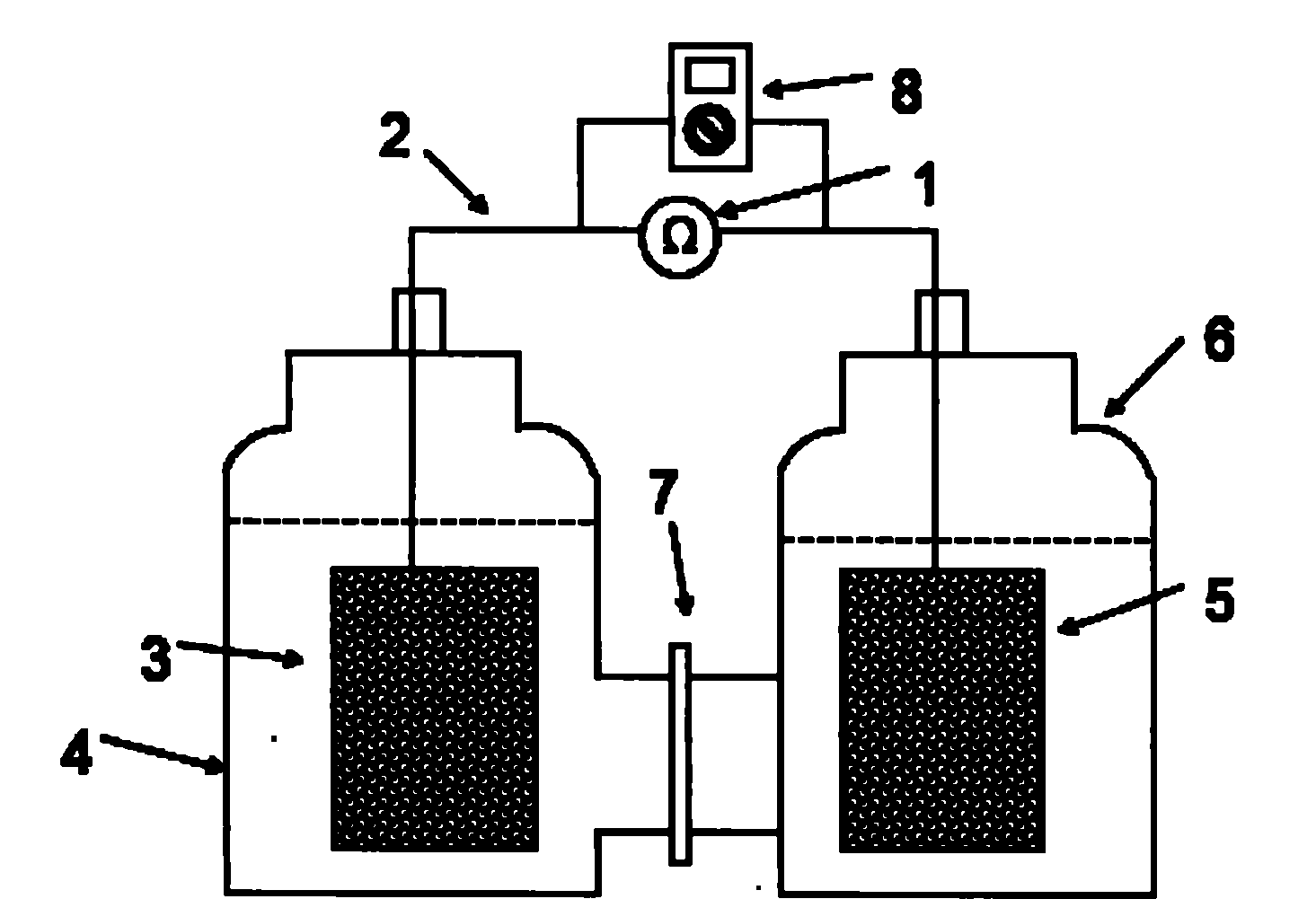
Shewanella-decolorationis-based microbial fuel cell and using method thereof
InactiveCN102315471ASimplify how to runImprove environmental adaptabilityFinal product manufactureBiochemical fuel cellsElectron donorOxygen
The invention discloses a Shewanella-decolorationis-based microbial fuel cell and a using method thereof. The microbial fuel cell comprises an anode chamber, a cathode chamber, an anode electrode, a cathode electrode, a proton permeation film and an external circuit, wherein a microorganism is inoculated in the anode chamber; the anode chamber is also filled with a culture solution and electron donors of the microorganism; the cathode chamber is filled with cathode reaction liquid; and the microorganism is Shewanella decolorationis. The microbial fuel cell takes the Shewanella decolorationis as an anode microorganism; and the Shewanella decolorationis has extremely high environmental suitability and a variety of breathing mechanisms. In the nutrient-rich anode culture solution, the Shewanella decolorationis can metabolize and reproduce quickly, and consume dissolved oxygen to maintain an anaerobic environment around the anode electrode in an extremely short time; therefore, the step of blowing nitrogen to manufacture the anaerobic environment and keep an anaerobic reaction condition of a common microbial fuel cell before starting or in operation can be eliminated; an operation operating method is simplified; and the Shewanella-decolorationis-based microbial fuel cell has a good application prospect in the treatment and the recycling of environmental pollutants.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROORGANISM
Underground water nitrate removal method and denitrification reactor
ActiveCN106986440AReduce interactionAdjustable pHTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesWater contaminantsGroundwater nitrateElectrolysis
The invention discloses an underground water nitrate removal method and a denitrification reactor; electrochemistry, heterotrophic aerobic denitrification and anaerobic autotrophic denitrification are combined to construct an autotrophic-heterotrophic synergic denitrification apparatus capable of providing hydrogen and oxygen. The denitrification reactor comprises an anode reaction area and a cathode reaction area which are used for carrying out heterotrophic aerobic denitrification and anaerobic hydrogenotrophic denitrification independently; denitrifying bacteria are fixed to filler by means of film colonization; since an anode and a cathode are in contact with the filler and anode and cathode plates penetrate the filler layer, gases produced may be distributed evenly in the whole reaction area during electrolytic production of hydrogen and oxygen, and denitrification efficiency is improved. A nitrate sensor is arranged in an inflow water tank to monitor the quality of inflow water in real time, an electrolytic power supply can be controlled through feedback adjustment, the magnitude of electrolytic current is adjusted, and oxygen supply and hydrogen supply are changed accordingly. The apparatus is simple in overall structure, controllable in gas supply and convenient to operate.
Owner:XI'AN UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND TECHNOLOGY
Novel sufficient metal air battery oxygen electrode and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102509806AReduced risk of cloggingGood diffusion distanceCell electrodesCollectors/separatorsChemical physicsElectrical battery
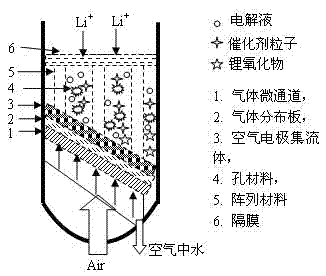
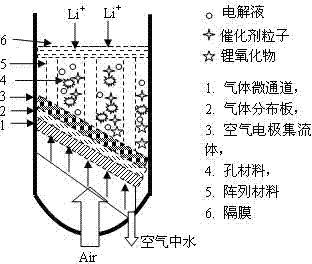
The invention relates to a novel sufficient metal air battery oxygen electrode and a preparation method thereof, belongs to a high performance chemical electric power source and the relative field. The oxygen electrode and the preparation method can be used for solving technical problems of eliminating the phenomenon that a reaction is stopped caused by an oxidative product deposits on a gas path when metal is discharged, the reaction efficiency and loop stability of the oxygen electrode of a chargeable metal air battery are effectively improved, a three-phase reaction interface is reduced, and poison of moisture in the air to an electrode reaction and corrosion to an electrode are reduced. In the technical scheme provided by the invention, a gas micro channel is adopted to reduce moisture in the air, a gas distribution plate is used for improving airflow direction and a gas distribution state, a hole carbon material and an array materials combine to form a high efficiency three dimensional electrode, and a cathode reaction chamber is separated from a metal anode through a diaphragm. The oxygen electrode provided by the invention has the advantages of high catalytic reaction efficiency, good loop stability, short diffusion distance of gas and metallic ions, full air liquid solid three-phase contact; and unblocked gas path, reasonable gas distribution, strong metal oxide deposition resistance, good mass transferring and diffusion process effect, strong operability, and is suitable for a high energy density power supply occasions in a long term repeatedly.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Microbial fuel cell and application thereof to degradation of azo dye pollutant
ActiveCN102315469AOvercome energy consumption,Overcome the disadvantages caused by practical difficultiesCell electrodesTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesCulture fluidElectron donor
The invention discloses a microbial fuel cell and application thereof to degradation of azo dye pollutants. The microbial fuel cell comprises an anode chamber, a cathode chamber, an anode electrode, a cathode electrode, a proton permeable membrane and an external circuit. Electrochemical active microbes are inoculated in the anode chamber. Culture solution for the microbes, a carbon source and electron donors are also contained in the anode chamber. Cathode reaction liquid is contained in the cathode chamber and consists of Shewanella decolorationis and culture solution thereof. Electron acceptors of the Shewanella decolorationis are also contained in the cathode chamber. The microbial fuel cell oxidizes an organic substrate in the solution through the microbes in the anode chamber, generated electrons are transferred to the anode electrode and the electrons on the anode electrode are transferred to the cathode electrode through the external circuit. In the cathode chamber, the Shewanella decolorationis accepts the electrons on the cathode electrode, grows and metabolizes. The electrons are transferred to end electron acceptors such as the azo dye pollutants through a respiratory chain to reduce and degrade the azo dye pollutants. Therefore, the microbial fuel cell can be used for the treatment of the pollutants.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
Materials for cathode in solid oxide fuel cells
InactiveUS20050201919A1Promote absorptionReduce overpotentialActive material electrodesSolid electrolyte fuel cellsAlkaline earth metalOxygen vacancy
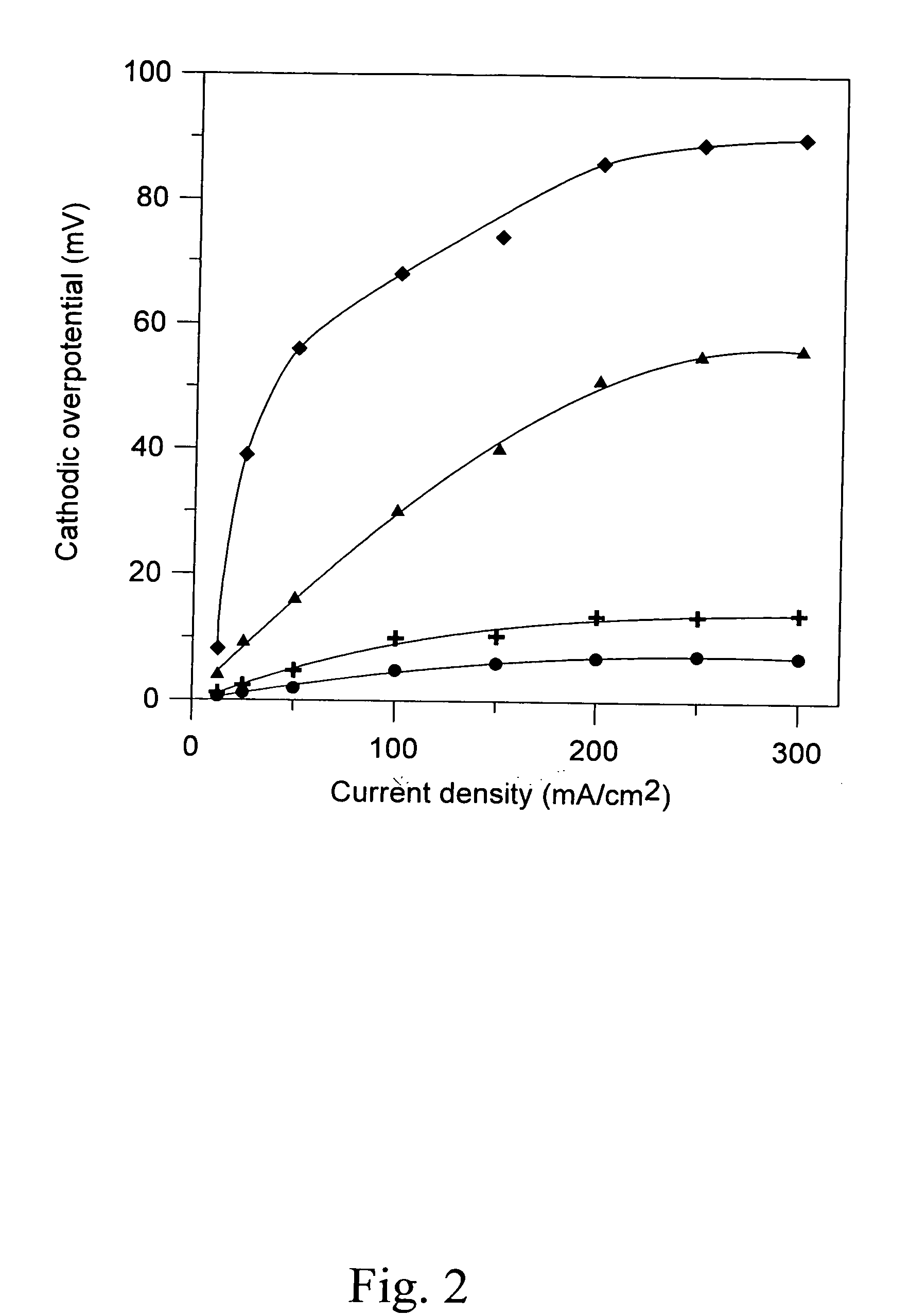
The present invention relates to materials for cathode in solid oxide fuel cells, more particularly, an oxide having high oxygen vacancies and high conductivity as cathode, which is able to accelerate absorption of oxygen molecule and diffusion of oxygen ion for reducing internal resistance of cells, in other words, reducing overpotential of cathode, and improvement of electric generation efficiency of fuel cells. General form of the cathode materials is Ln1-xAxCu1-yByO2.5±δ, wherein Ln is lanthanide ion, A is alkaline-earth metal, B is metal. Cathode dope different alkaline-earth metal on A side to converse partly copper (Cu) to trivalence copper ion for forming perovskite having oxygen vacancies with regularity sequence, by utilizing catalytic of cathode electrode accelerating cathode reaction and compound electron being conducted though external circuit with conversing oxygen to form oxygen ion for obtaining anode and hydrogen reaction by diffusing oxygen ion to electrolyte.
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
Self-humidifying fuel cell
InactiveCN102800876AImprove stabilityImprove power densityFuel cell auxillariesElectrochemical responseUninterruptible power supply
The invention discloses a self-humidifying fuel cell. The fuel cell is formed by superposing a plurality of monomers, wherein each monomer comprises a cathode flow field plate, an anode flow field plate, a sealing piece and a film electrode; the film electrode consists of a reaction area and a humidifying area; corresponding reaction areas and humidifying areas are contained in the anode flow field plate and the cathode flow field plate; the cathode reaction air enters the fuel cell monomers, passes through the humidifying area of the cathode flow field plate and enters the reaction area to participate an electrochemical reaction; the completely reacted air enters the humidifying area on the anode flow field plate through a gas channel formed on the film electrode; and the air passing through the reaction area has high humidity, and the water can humidify the inlet cathode reaction air through the proton exchange film of the humidifying area on the film electrode. The inlet air is humidified by directly utilizing the air exhaust, the humidifying area and the reaction area are positioned on the same film electrode, the fuel cell is simple in structure, the fuel cell stack integration is not influenced, the water management problem of the fuel cell can be greatly solved, and the power density of a fuel cell system is improved. The fuel cell can be applied to various fields of various electronic equipment power supplies, the uninterrupted power system, the electric automobile engine system and the like.
Owner:JIANGSU ICE CITY INSULATION MATERIALS STOCK
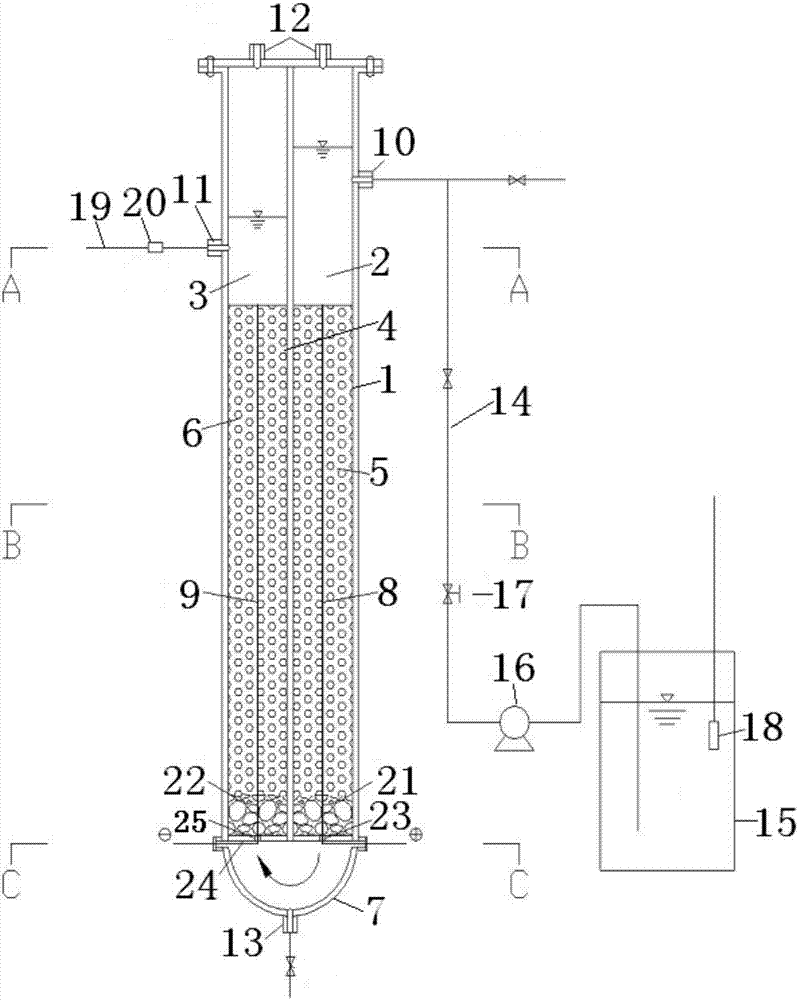
Integrated electrochemical treatment device for deep treatment and deep treatment method
InactiveCN105585082AExtend the reaction pathSync removalWater treatment parameter controlWater treatment compoundsPeristaltic pumpSludge
The invention provides an integrated electrochemical treatment device for deep treatment and a deep treatment method, relates to an electrochemical treatment device and a method for performing deep treatment through the device and aim to solve the problem that only a single pollutant is treated in the existing electrochemical treatment process. The device comprises a cylinder, a water inlet, a water outlet, a cathode, an anode, an iron net, a peristaltic pump, a direct-current stabilized power supply, an air blower, a first baffle, a second baffle, a third baffle, a fourth baffle, a fifth baffle, a sixth baffle, a microporous aeration pipe, an annular partition board, an outer cylinder sludge discharge port, an inner cylinder sludge discharge port and a water tank. The method comprises steps as follows: 1, the peristaltic pump is started, wastewater in the water tank enters a cathode reaction region from the water inlet through the peristaltic pump, and the air blower is started; 2, the air blower is shut off, the stabilized power supply is started, then water flows out naturally from the water outlet, after the reaction ends, a valve at the sludge discharge port is opened, and precipitated sludge is discharged out from the sludge discharge port. The integrated electrochemical treatment device for deep treatment and the deep treatment method are used for the field of sewage treatment.
Owner:NAT ENG RES CENT OF URBAN WATER RESOURCE
Microbial fuel cell and application thereof in degradation of polybrominated diphenyl ethers
ActiveCN102315472AEasy to handleResource optimizationTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesBiochemical fuel cellsElectron donorFire retardant
The invention discloses a microbial fuel cell and application thereof in degradation of polybrominated diphenyl ethers. The microbial fuel cell comprises an anode chamber, a cathode chamber, an anode electrode, a cathode electrode, a proton permeation film and an external circuit, wherein an electrochemical active microorganism is in the anode chamber; the anode chamber is also filled with a culture solution, a carbon source and electron donors of the microorganism; cathode reaction liquid is filled in the cathode chamber; bromide flame retardant polluted water body sediment is inoculated in the anode chamber to serve as the electrochemical active microorganism; and polybrominated diphenyl ethers or polybrominated-diphenyl-ethers-containing pollutants are also in the anode chamber. In themicrobial fuel cell, under the action of the microorganism in the bromide flame retardant polluted water body sediment, the polybrominated diphenyl ethers in the cathode solution are degraded into low bromination biphenyl ethers even bromine-free diphenyl ethers, and simultaneously electrical energy is output, so that good effects of environmental pollution treatment and recycling are achieved. The microbial fuel cell can operate steadily in a long time, and has a very good application prospect in the degradation of polybrominated diphenyl ether materials in various types of waste water and polluted water bodies.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
Apparatus for preparing sterilizing water and process for sterilizing water
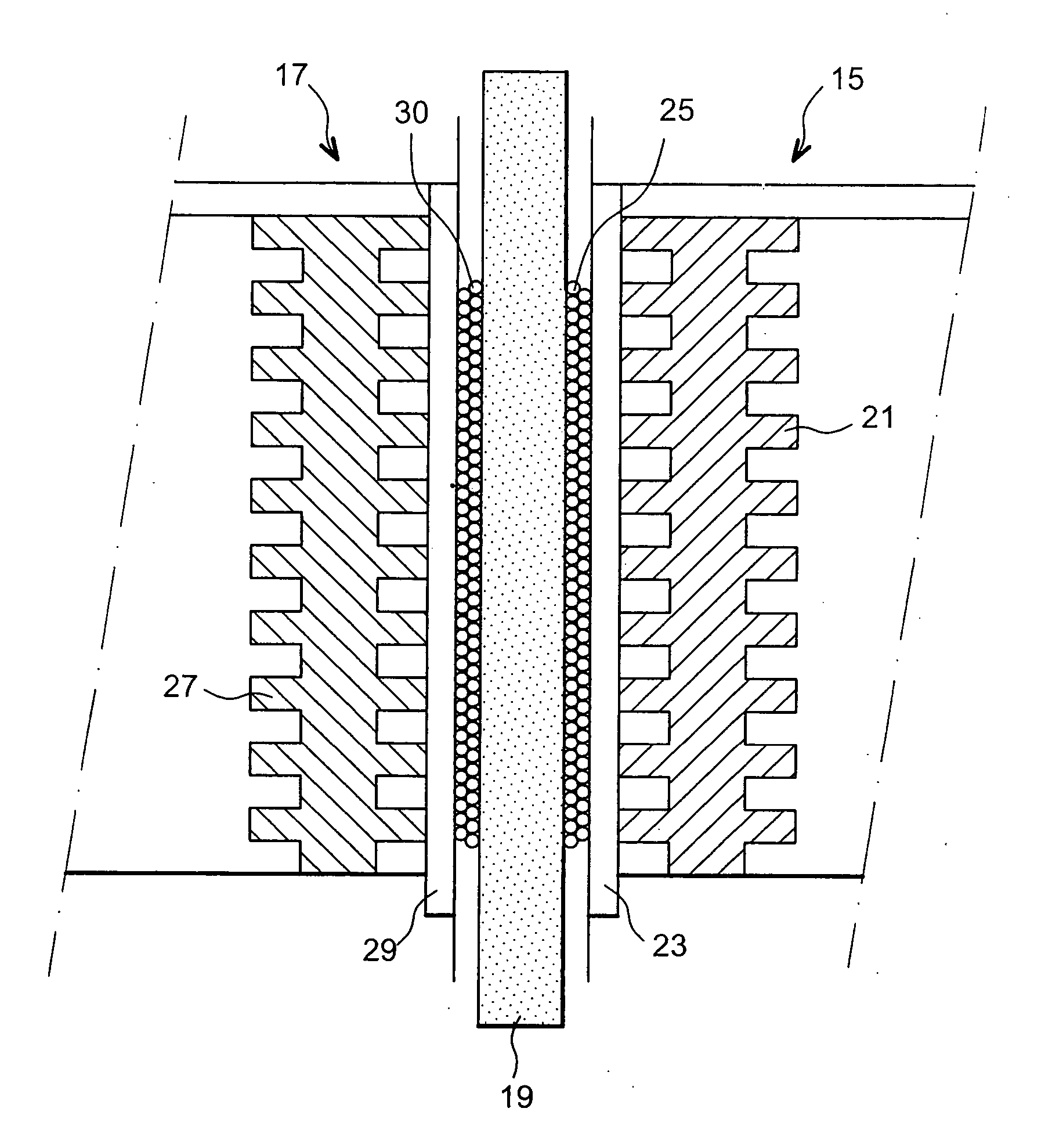
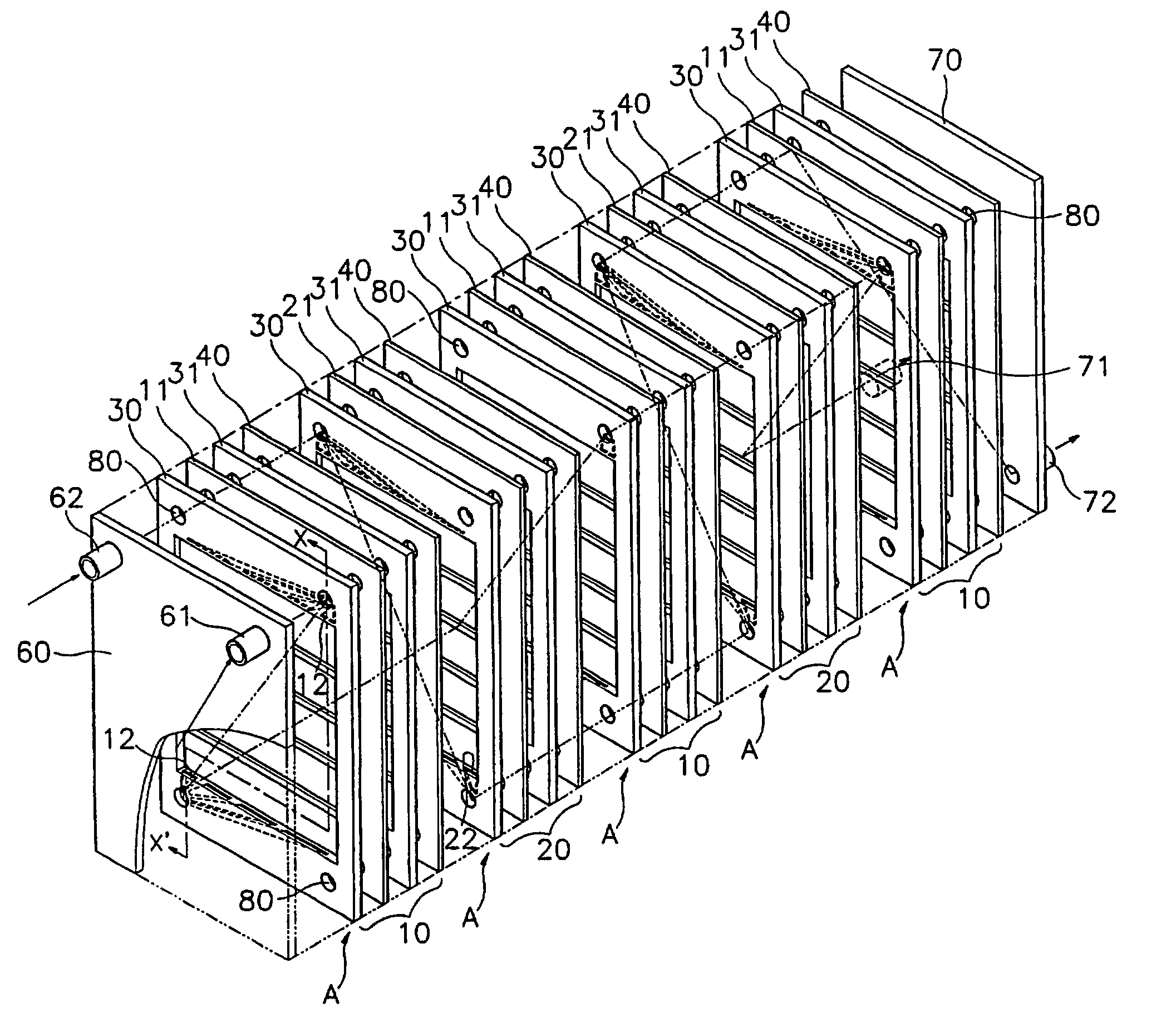
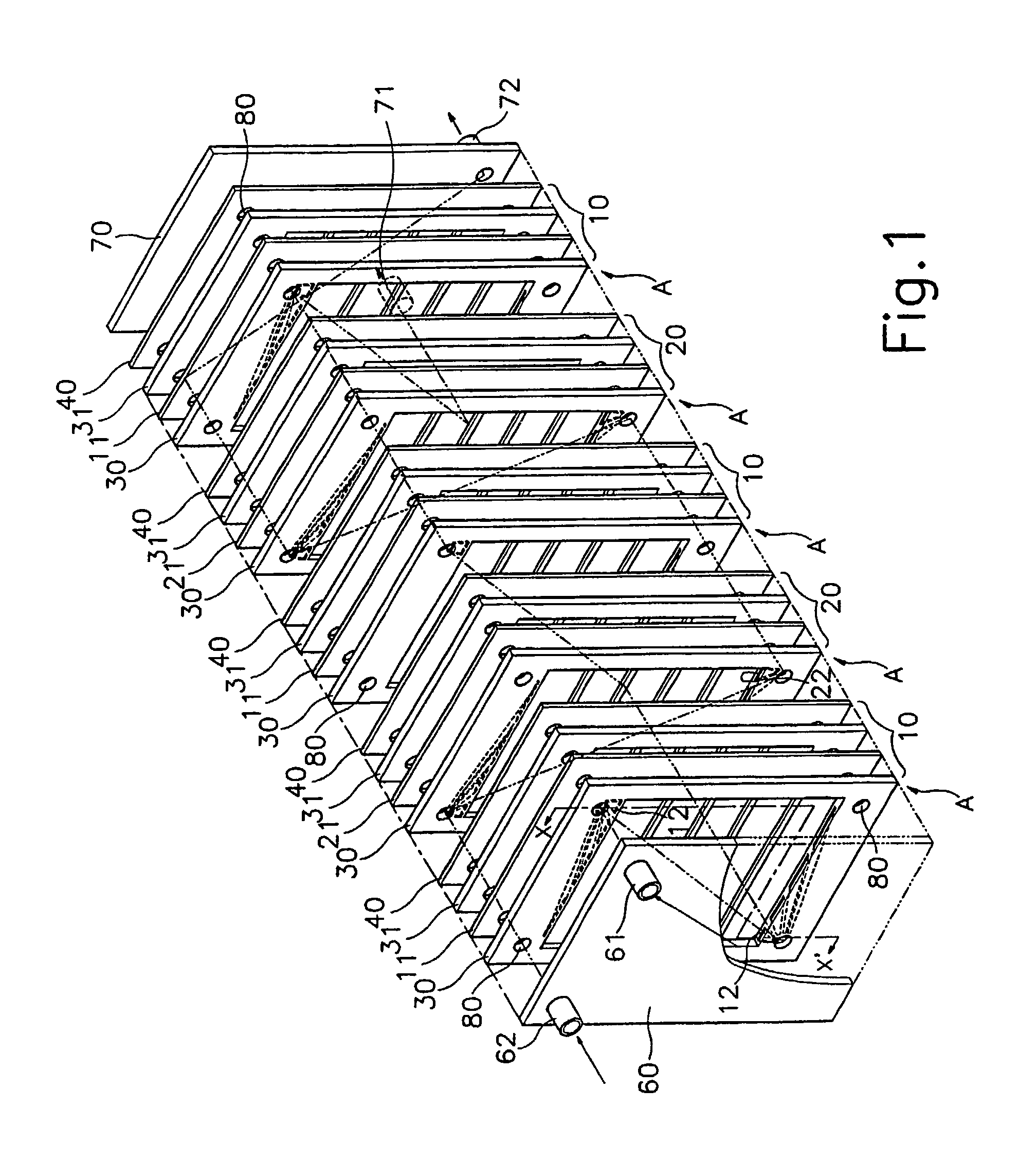
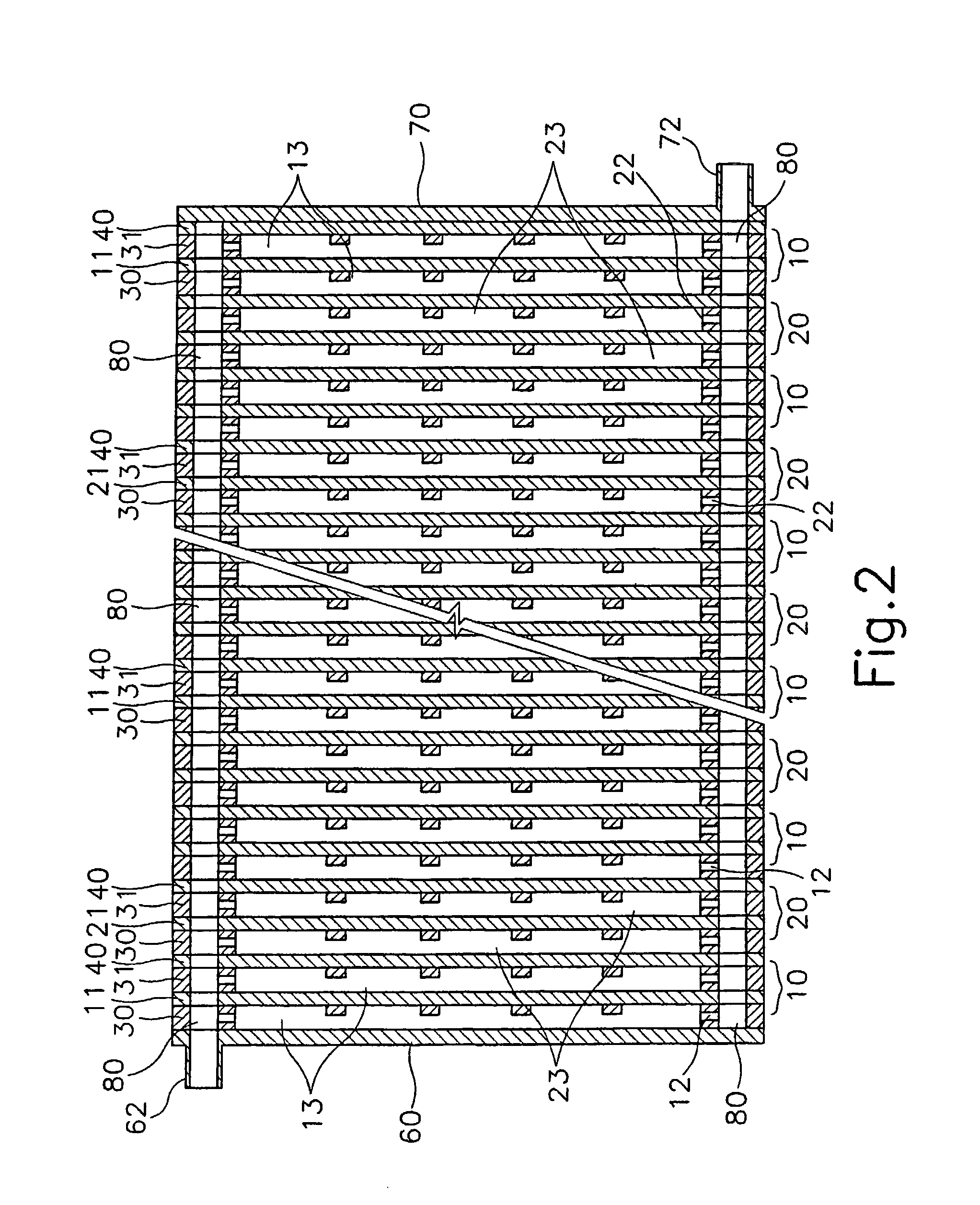
InactiveUS7001493B1Weather/light/corrosion resistanceVolume/mass flow measurementDiagonalCathode reaction
The present invention provides an apparatus for preparing sterilizing water, which comprises an electrolyzer wherein an anode chamber (10) and a cathode chamber (20) partitioned by an ion exchange membrane (40) form a unit cell (A), being alternately arranged and successively equipped with close relation; water inlets (61, 62) and water outlets (71, 72) are provided on the end plate (60, 70) at both ends of the electrolyzer; said anode chamber (10) and cathode chamber (20) having circulative openings at the vicinity of each edge at both sides centered from anode plate (11) and cathode plate (21), of which two circulative openings of diagonal direction among them have plural passages of fan-shape, in order for water introduced through the openings to pass through the passages to rapidly go through each electrode; and a gap-control gasket (30) and a gasket for preventing leakage of electrolyte (31) having plural horizontal members are provided at the center to form an anode reaction chamber (13) and a cathode reaction chamber (23).
Owner:KIM HEE JUNG
Non-diaphragm electrochemical waste water treatment device
InactiveCN101671066AGuaranteed uptimeLow investment costWater/sewage treatmentWastewaterCathode reaction
The invention relates to a non-diaphragm electrochemical waste water treatment device which comprises an electrode reactor, wherein a waste water guide pipe, an anode, a feed cathode and a large metalparticle collecting device are arranged in the electrode reactor; a waste water inlet is arranged at the bottom of the electrode reactor, the upper side of the waste water inlet is longitudinally provided with the waste water guide pipe, and a space is reserved between the lower end of the waste water guide pipe and the waste water inlet; in addition, the upper end of the waste water guide pipe is provided with an anode protective baffle; the anode is arranged on the outer wall of the waste water guide pipe, and the feed cathode is arranged at the bottom of the electrode reactor; moreover, afeeding device is arranged on the electrode reactor; and the large metal particle collecting device is arranged below the anode protective baffle. Therefore, the non-diaphragm electrochemical waste water treatment device can effectively maintain particles in the electrode reactor to be fluidized and also prevent the metal particles from entering an anode reaction area. Under the condition of no need of a diaphragm, a cathode reaction area and an anode reaction rear are separated, thereby thoroughly solving various problems brought by using the diaphragm.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Couple corrosion sensor
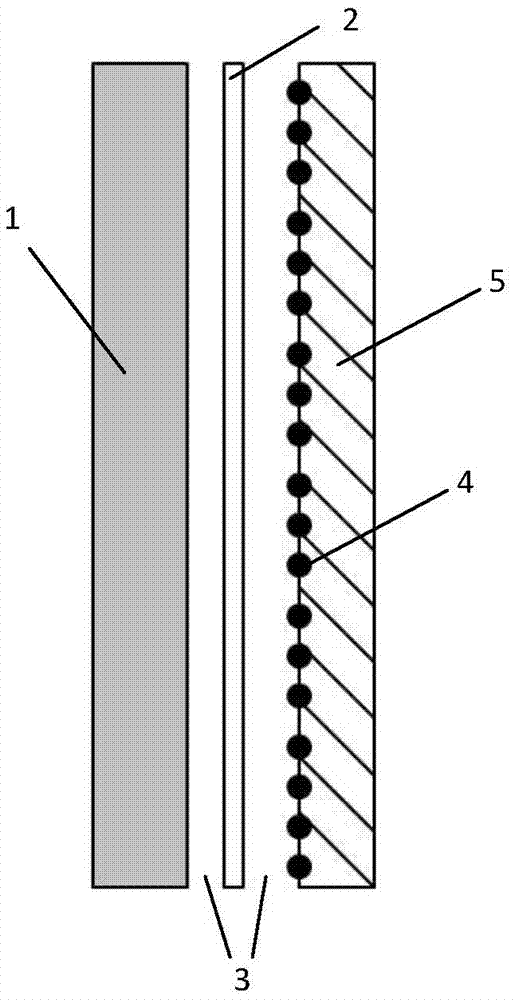
ActiveCN103018299AImprove effectivenessAccurate monitoringMaterial electrochemical variablesElectricityCarbon film
The invention provides a couple corrosion sensor which comprises a body. The body is composed of a metal electrode, an insulating sheet and a carbon film electrode successively superposed from top to bottom, wherein the metal electrode and the carbon film electrode are both in electric connection with an electrode outlet wire, and the body is provided with a plurality of through holes penetrating the metal electrode, the insulating sheet and the carbon film electrode. The invention has the following beneficial effects: when the carbon film electrode made of graphite is used as a cathode and exposed in an environment, corrosion does not occur, so cathode reaction conditions do not change, and no influence is exerted on weak corrosion current. A coating material and technology used for preparation of the surface of the metal electrode are identical to those of a metal to be monitored, so validity of monitoring is enhanced. Arrangement of the plurality of through holes amplifies the weak corrosion current, so monitoring is more accurate.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com