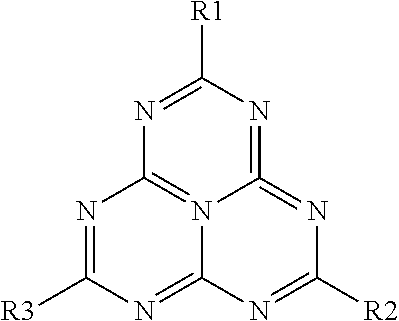
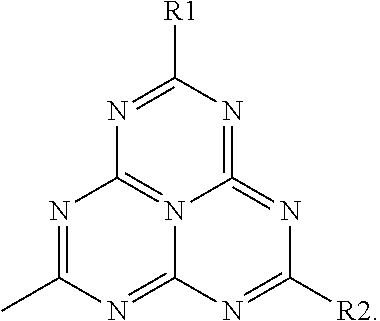
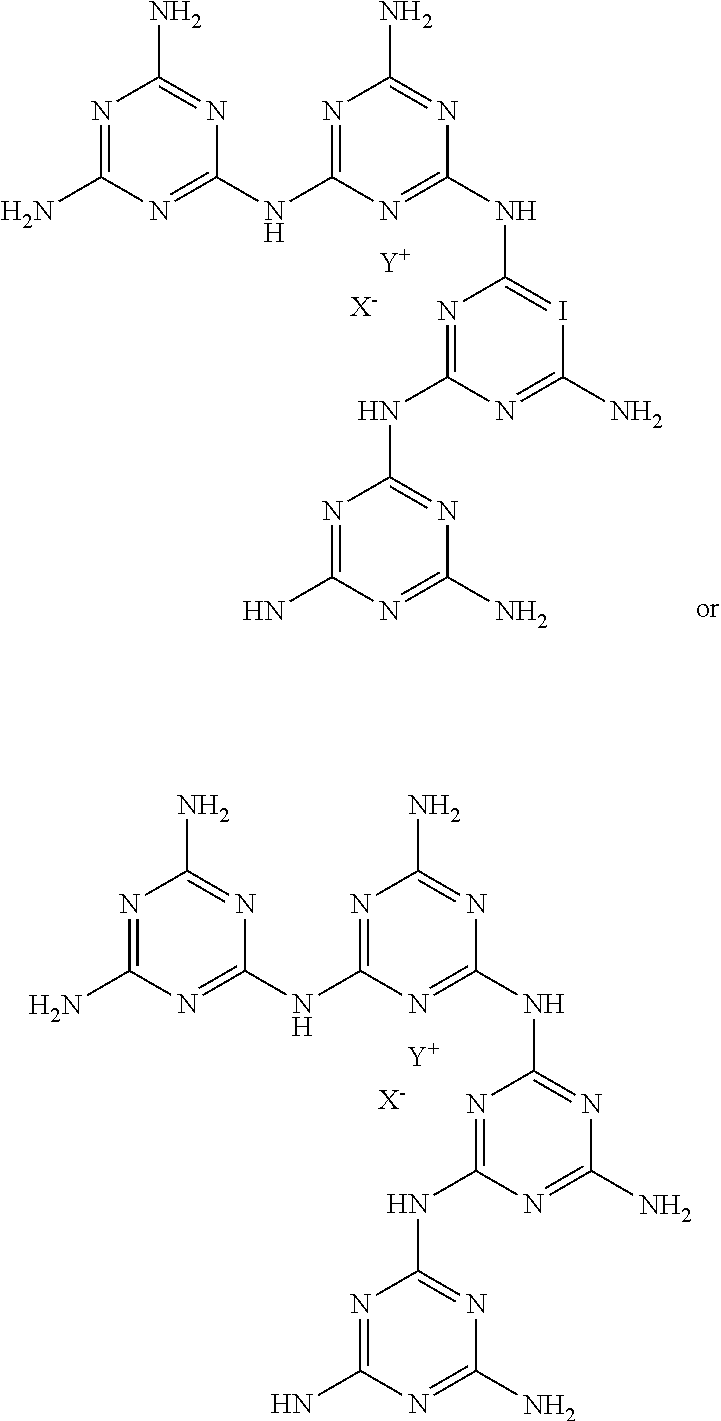
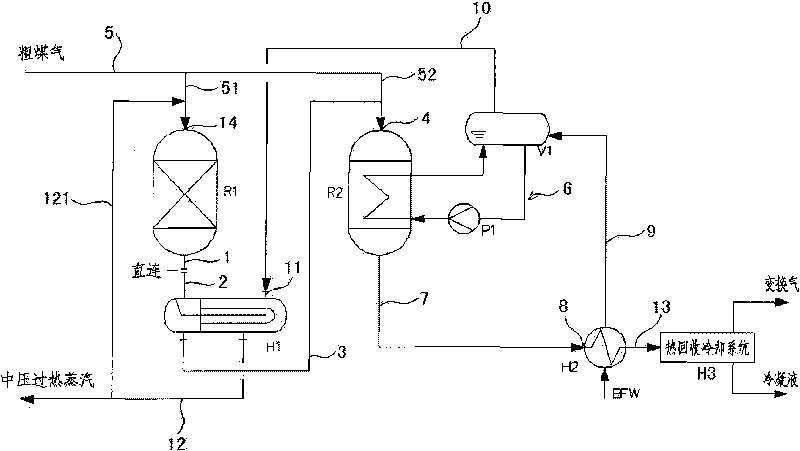
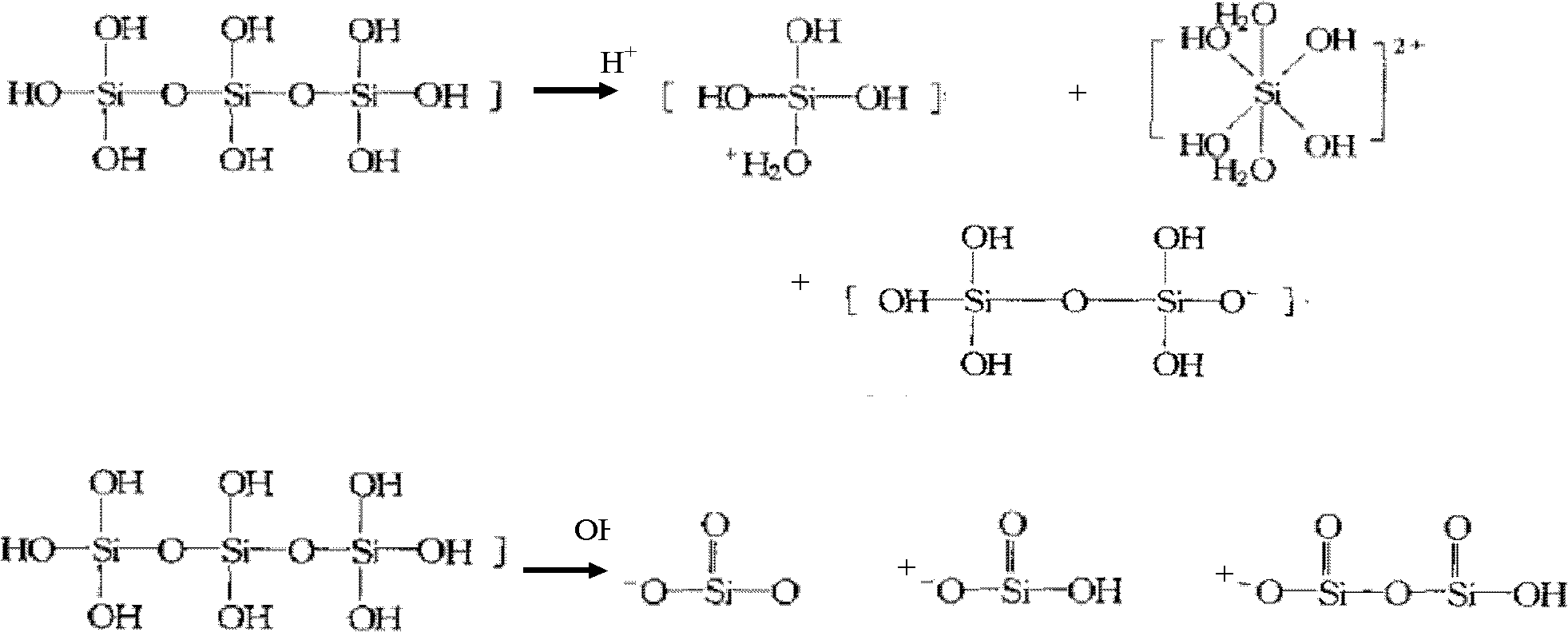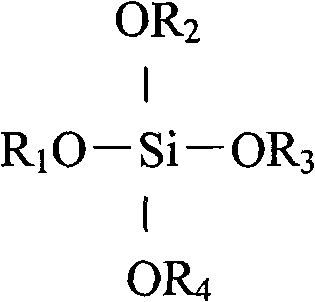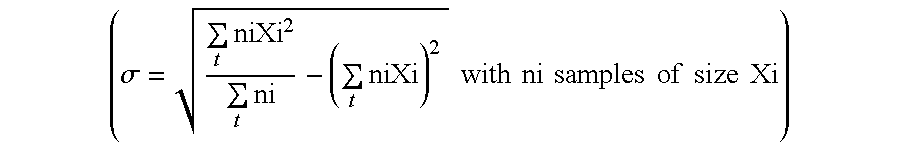Patents
Literature
1605 results about "Conversion reaction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for preparing salvianolic acid A by catalytically converting salvianolic acid B
InactiveCN102212004AShorten the timeHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationSalvianolic acid KSalvianolic acid B
The invention discloses a method for preparing salvianolic acid A by catalytically converting salvianolic acid B. The method is characterized in that the converted raw material is a salvia miltiorrhiza aqueous extract (salvianolic acid B=>50%) primarily purified through combined chromatography; the concentration of the raw material salvianolic acid B is 0.5-2%; urea is taken as the catalyst; the mole ratio of urea to the salvianolic acid B is 0.3-0.7; the conversion reaction temperature is 100-125 DEG C; and the reaction time is 3-6 hours. The method has the following beneficial effects: urea is taken as the catalyst, thus greatly shortening the time for which the salvianolic acid B is in easily destroyed state and remarkably increasing the yield of the salvianolic acid A; the primarily purified salvia miltiorrhiza extract is taken as the converted raw material, thus not only removing the metal ions which are not beneficial to conversion but also removing most colloid-like impurities and frontal impurities which are not beneficial to following separation of the salvianolic acid; and the directional conversion rate of the salvianolic acid B to the salvianolic acid A prepared by the method is not less than 10% and even reaches 60%.
Owner:SUZHOU LEINA PHARMA RES DEV +1
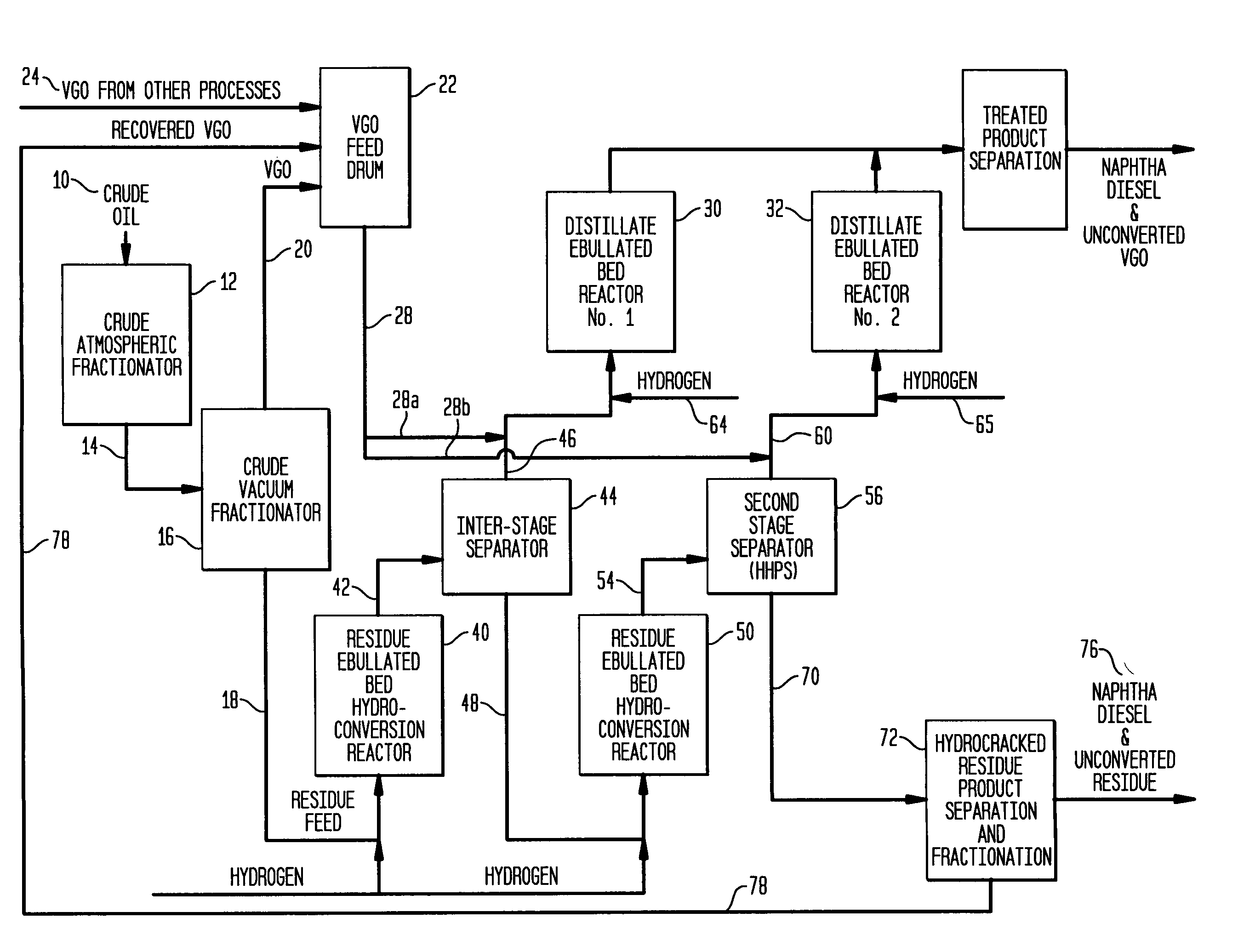
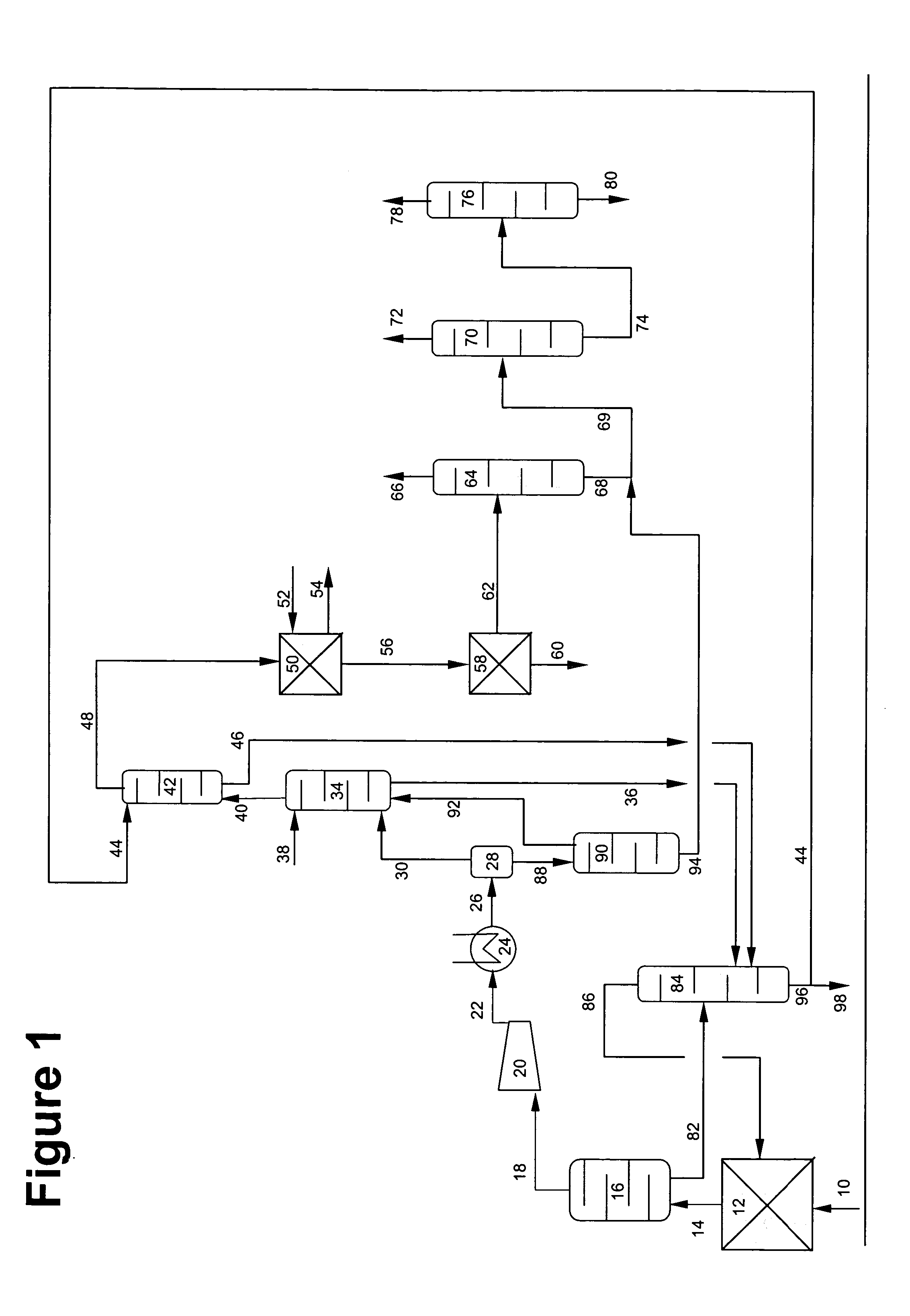
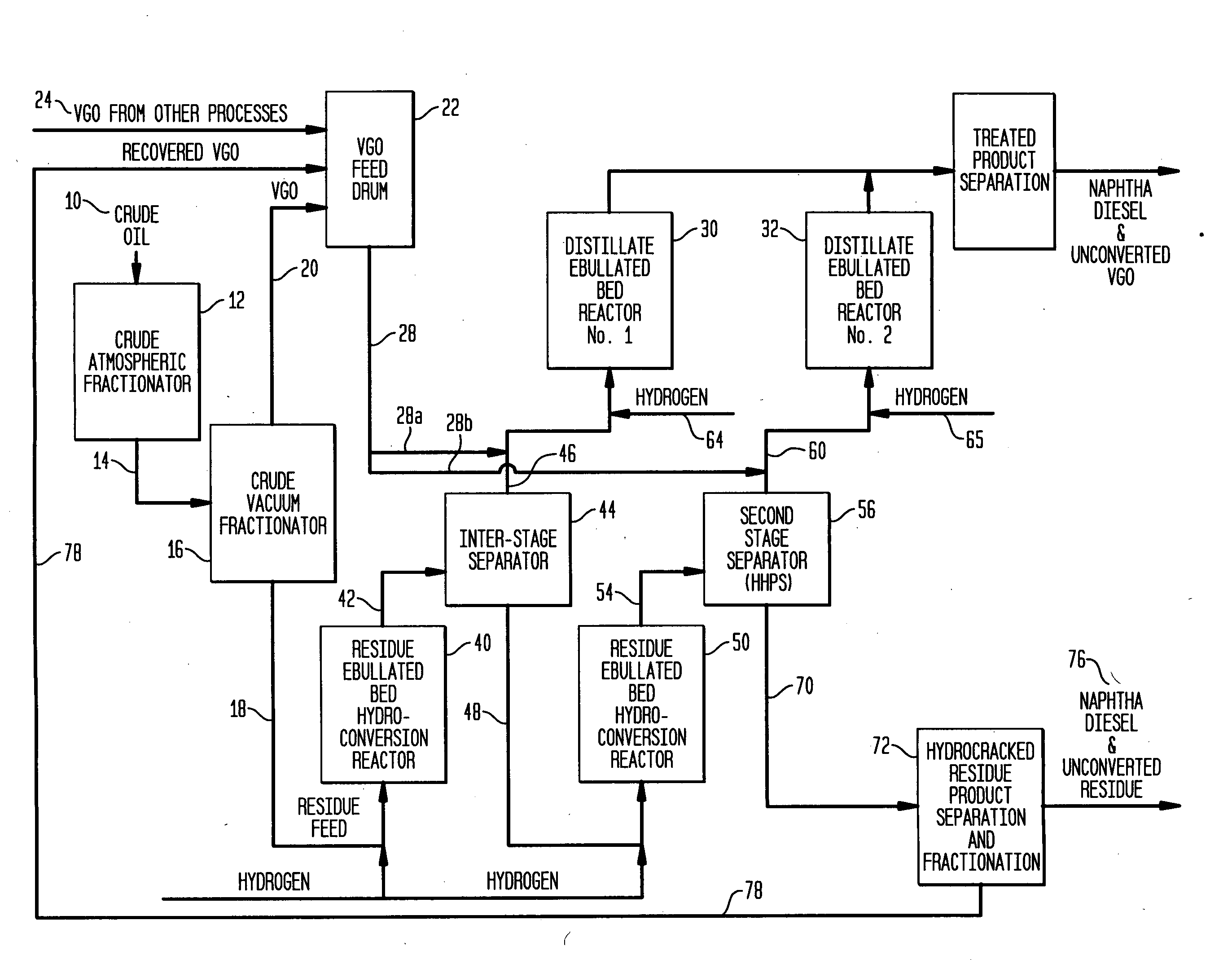
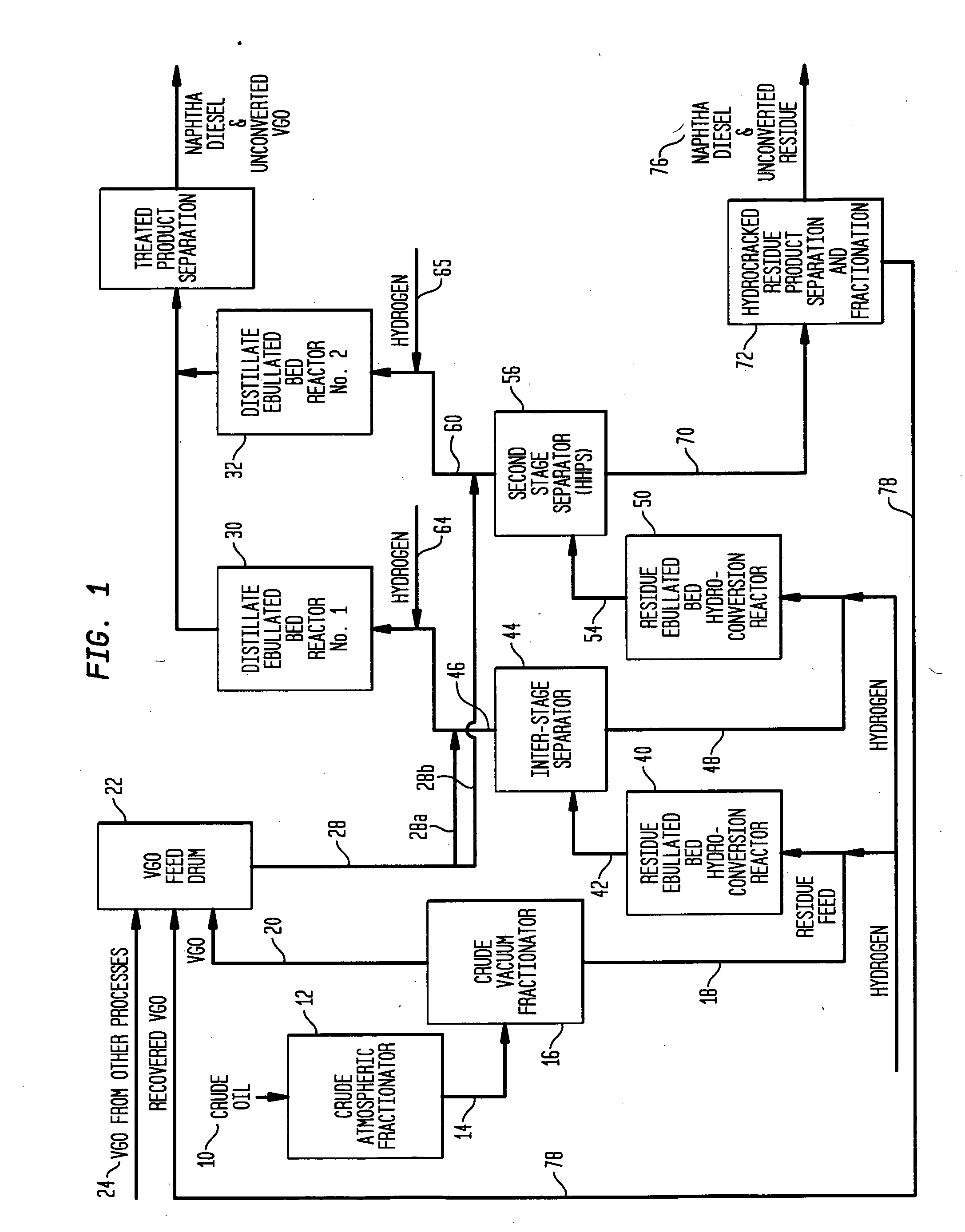
Process for multistage residue hydroconversion integrated with straight-run and conversion gasoils hydroconversion steps
InactiveUS7938952B2Improve throughputMitigate issueTreatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyMolecular sieve catalystsVapor liquidLiquid product
This invention relates to a novel integrated hydroconversion process for converting heavy atmospheric or vacuum residue feeds and also converting and reducing impurities in the vacuum gas oil liquid product. This is accomplished by utilizing two residue hydroconversion reaction stages, two vapor-liquid separators, and at least two additional distillate ebullated-bed hydrocracking / hydrotreating reaction stages to provide a high conversion rate of the residue feedstocks.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Method for screening stereoselective alpha-hydroxy acid dehydrogenase
InactiveCN102660631AOvercoming time-consuming and laboriousOvercoming demandsMicrobiological testing/measurementWater bathsAlpha hydroxy acid
The invention provides a method for screening stereoselective alpha-hydroxy acid dehydrogenase, comprising the following steps: (1) dissolving a sample to be detected containing alpha-hydroxy acid dehydrogenase in a buffer with pH of 6-9, adding an alpha-hydroxy acid chiral monomer as a substrate, and carrying out conversion reaction in water-bath at 20-50 DEG C; and (2) after the conversion reaction, adding the conversion solution in an FeCl3 developer solution to conduct color development reaction for 5-30 min, when the color development reaction finishes, judging the result according to the color appeared in the reaction solution. The method has no need to carry out derivatization on the substrate which is intend to screen, can rapidly identify the dehydrogenase activity and optical selectivity of the selected microbe by using simple colourimetry, has the advantages of simple screening flow, fast speed, low request for devices, strong versatility and the like, and offers great conveniences to the obtainment of optically pure products by using racemic mandelic acid and related derivatives as substrates to carry out resolution through biological enzymatic method.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Tin in an active support matrix
An anode material made from nanoparticles, said anode material including a homogeneous mixture of lithium-alloying nanoparticles with active support matrix nanoparticles, is provided. The active support matrix nanoparticle is a compound that participates in the conversion reaction of the lithium battery. The compound is preferably a transition metal compound, with said compound including a nitride, carbide, oxide or combination thereof.An electrode manufactured from the anode material preferably has a porosity of between 5 and 80% and more preferably has a porosity between 10 and 50%. The anode material nanoparticles preferably have a mean linear dimension of between 2 and 500 nanometers, and more preferably have a mean linear dimension of between 2 and 50 nanometers.
Owner:TOYOTA MOTOR CO LTD +1
Pnictide containing catalysts for electrochemical conversion reactions and methods of use
ActiveUS20160233487A1Increase electrode kineticsReducing electrode charge transfer resistanceFinal product manufacturePositive electrodesLithium–sulfur batteryLithium sulfur
This patent application describes graphitic carbon nitride materials that are useful in electrochemical cells such as Lithium-Sulfur batteries. Also disclosed are lithium-sulfur batteries designed to incorporate these materials and methods of manufacturing the same. Batteries that include this material exhibit increased electrode kinetics of the lithium-sulfur electrochemical couple, phenomena that improve the specific capacity, usable lifetime and other desirable characteristics of these batteries.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
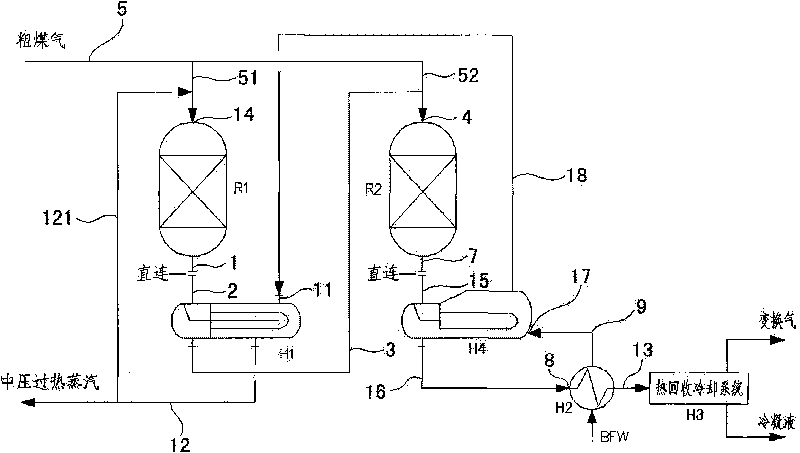
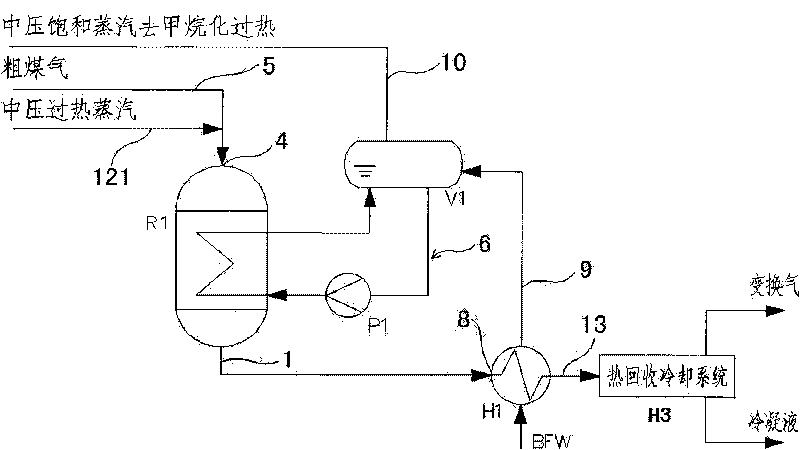
Shunting-type isothermal sulfur-tolerant conversion process and equipment thereof
ActiveCN101704513ASatisfy conversion rate requirementsMeet the requirements of adiabatic conversion control temperature riseHydrogenChemical industryShunt typesSulfur
The invention discloses a shunting-type isothermal sulfur-tolerant conversion process. The process comprises the following steps: shunting raw coal gas from exterior into at least two parts; leading overheat stream in the first part of the raw coal gas to increase the temperature to 200-300 DEG C; and then entering a first-stage conversion reaction step to carry out a conversion reaction and generate first conversion gas; and conveying the other part of the raw coal gas to next-stage conversion reaction step to carry out a conversion reaction. The catalyst bed of a shift converter has the advantages of stable temperature, simple control, convenient operation and low output CO content. The invention has the advantages of short conversion flows, few equipment, reduced resistance, great byproduct stream amount, high overheat temperature, stream pressure and heat recovery rate, and the like, thereby achieving the aims of reducing conversion stages, equipment number and resistance fall, decreasing investment, having great byproduct stream amount and high overheat temperature, stream pressure and heat recovery rate, reducing conversion stream consumption and outward wastewater discharge, protecting the environment and easily maximizing the device equipment. The invention also discloses shunting-type isothermal sulfur-tolerant conversion equipment used by the process.
Owner:SHANGHAI INT ENG CONSULTING
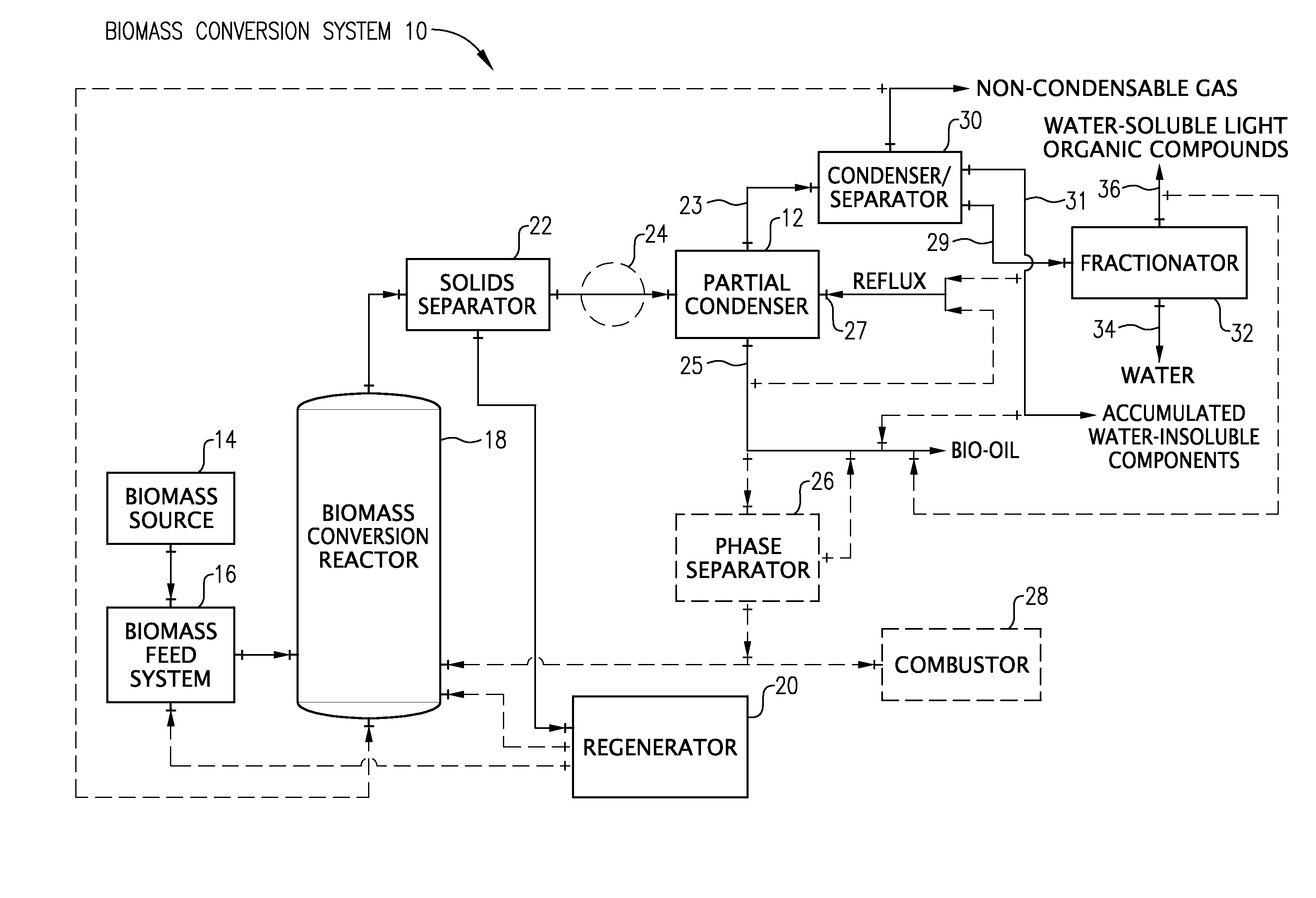
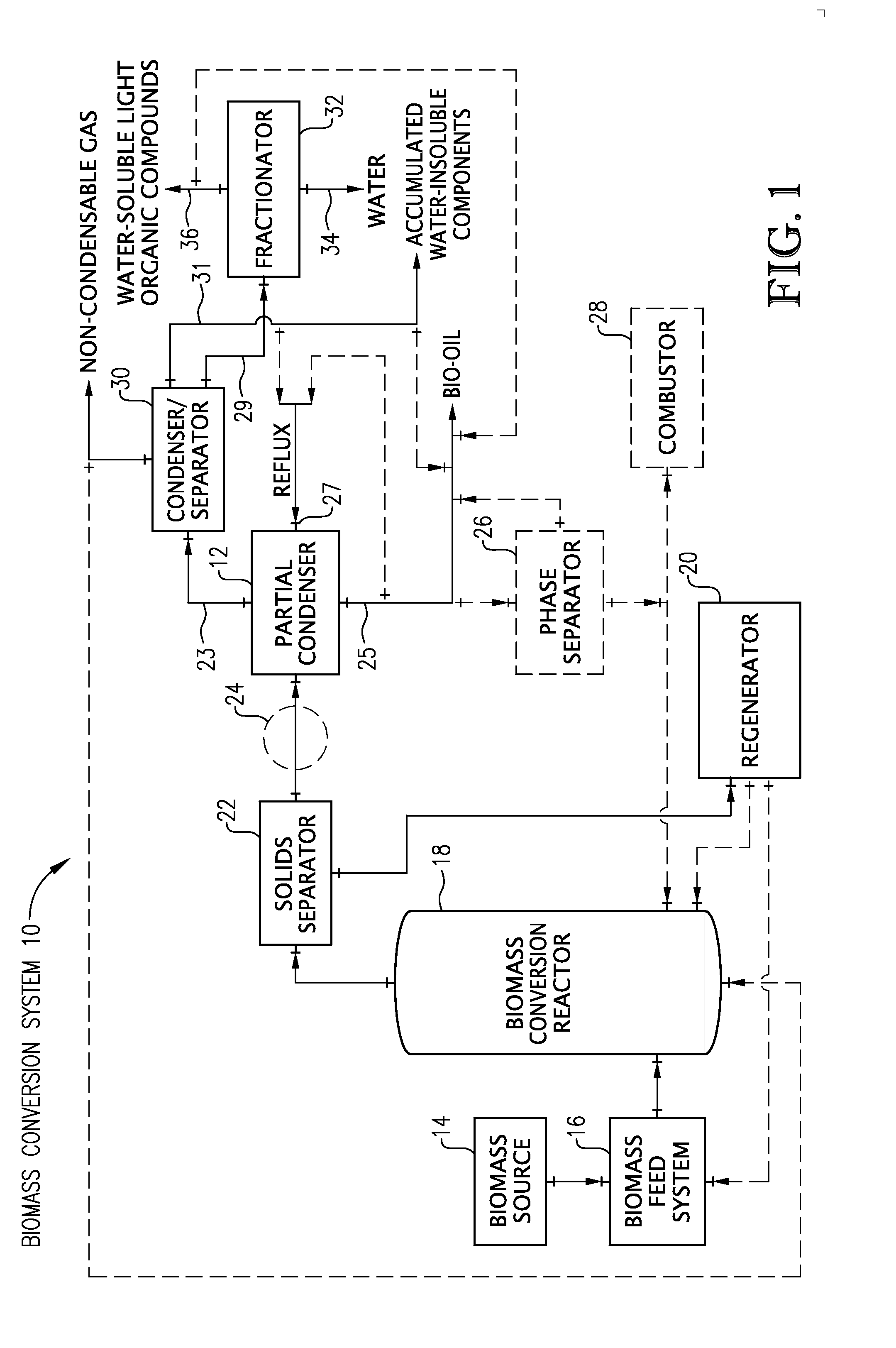
Removal of water from bio-oil
A process and system for separating water from bio-oil by using a partial condenser. The process comprises partially condensing vapor conversion products from a biomass conversion reaction to produce a water-rich overhead stream and a water-depleted stream comprising condensed bio-oil. The partial condenser removes a substantial portion of the water from the bio-oil, while providing an effective and flexible process for producing bio-oil.
Owner:MARD INC
High rate reactor system
PendingUS20140109465A1Increase valueImprove propertiesThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingAlkaneHigh rate
A process and system for upgrading an organic feedstock including providing an organic feedstock and water mixture, feeding the mixture into a high-rate, hydrothermal reactor, wherein the mixture is rapidly heated, subjected to heat, pressure, and turbulent flow, maintaining the heat and pressure of the mixture for a residence time of less than three minutes to cause the organic components of the mixture to undergo conversion reactions resulting in increased yields of distillate fuels, higher-quality kerosene and diesel fuels, and the formation of high octane naphtha compounds. Hydrocarbon products are cooled at a rate sufficient to inhibit additional reaction and recover of process heat, and depressurizing the hydrocarbon products, and separating the hydrocarbon products for further processing. The process and system can include devices to convert olefinic hydrocarbons into paraffinic hydrocarbons and convert olefinic byproduct gas to additional high-octane naphtha and / or heavier hydrocarbons by one of hydrogenation, alkylation, or oligomerization.
Owner:APPLIED RES ASSOCS INC
Process for producing olefins
A process is described for producing an olefins stream from a first vapor effluent stream from an oxygenate to olefin conversion reaction, said first vapor effluent stream comprising C2 and C3 olefins, C4 hydrocarbons, and C2 to C6 carbonyl compounds. In the process, the temperature and pressure of the first vapor effluent stream are adjusted to produce a second vapor effluent stream having a pressure ranging from about 100 psig to about 350 psig (790 to 2514 kPa) and a temperature ranging from about 70° F. to about 120° F. (21 to 49° C.), said second vapor effluent stream containing about 50 wt. % or more C4 hydrocarbons based upon the total weight of C4 hydrocarbons in the first vapor effluent stream. The second vapor effluent stream is then washed with a liquid alcohol-containing stream to produce a third vapor effluent stream, whereafter the third vapor effluent stream is washed with liquid water to provide a fourth vapor effluent stream comprising the C2 and C3 olefins and about 1.0 wt. % or less C2 to C6 carbonyl compounds.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
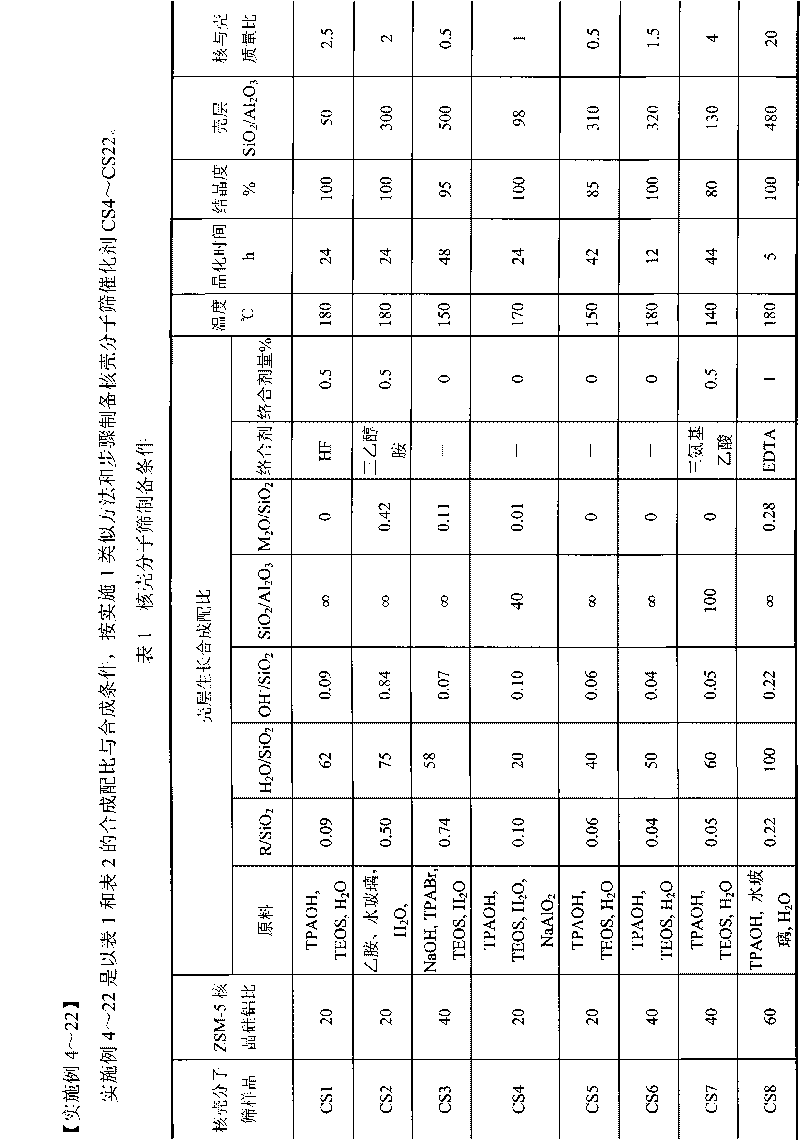
Synthetic method of ZSM-5 zeolites
ActiveCN102502696AReduce the degree of polymerizationHigh activityPentasil aluminosilicate zeolitePetrochemicalCrystallinity
The invention belongs to the synthesis field of aluminosilicate ZMS (Zeolite Molecular Sieve), and relates to a synthetic method of ZSM-5 zeolite molecular sieves. ZSM-5 zeolites are high-silicon micro-porous zeolites with unique three-dimensional ten-membered ring crossing aperture passages, the diameters of the aperture passages are close to the sizes of benzene rings, and the ZSM-5 zeolites can be widely applied to petroleum refining, petrochemical industry and fine chemicals synthesis. Particularly, nano-sized ZSM-5 zeolites achieve larger external surface area and higher intracrystalline diffusion rate, and have higher activity and selectivity as well as strong coking deactivation-resisting capability in hydrocarbons catalysis conversion reactions. The synthetic method regulates the polymerization degrees of silicon sources and aluminum sources respectively by adding acid and alkali so as to obtain highly reactive reactants, and can rapidly achieve nucleus formation in large quantities in a system so as to obtain nano-sized zeolites. The synthetic method is not limited by the types of the silicon sources and the aluminum sources, has strong applicability to raw materials, changes the activity of the raw materials through simple regulation, and can rapidly synthesize products of the nano-sized ZSM-5 zeolites with well crystallinity under the dosage conditions of no template and low-cost templates.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
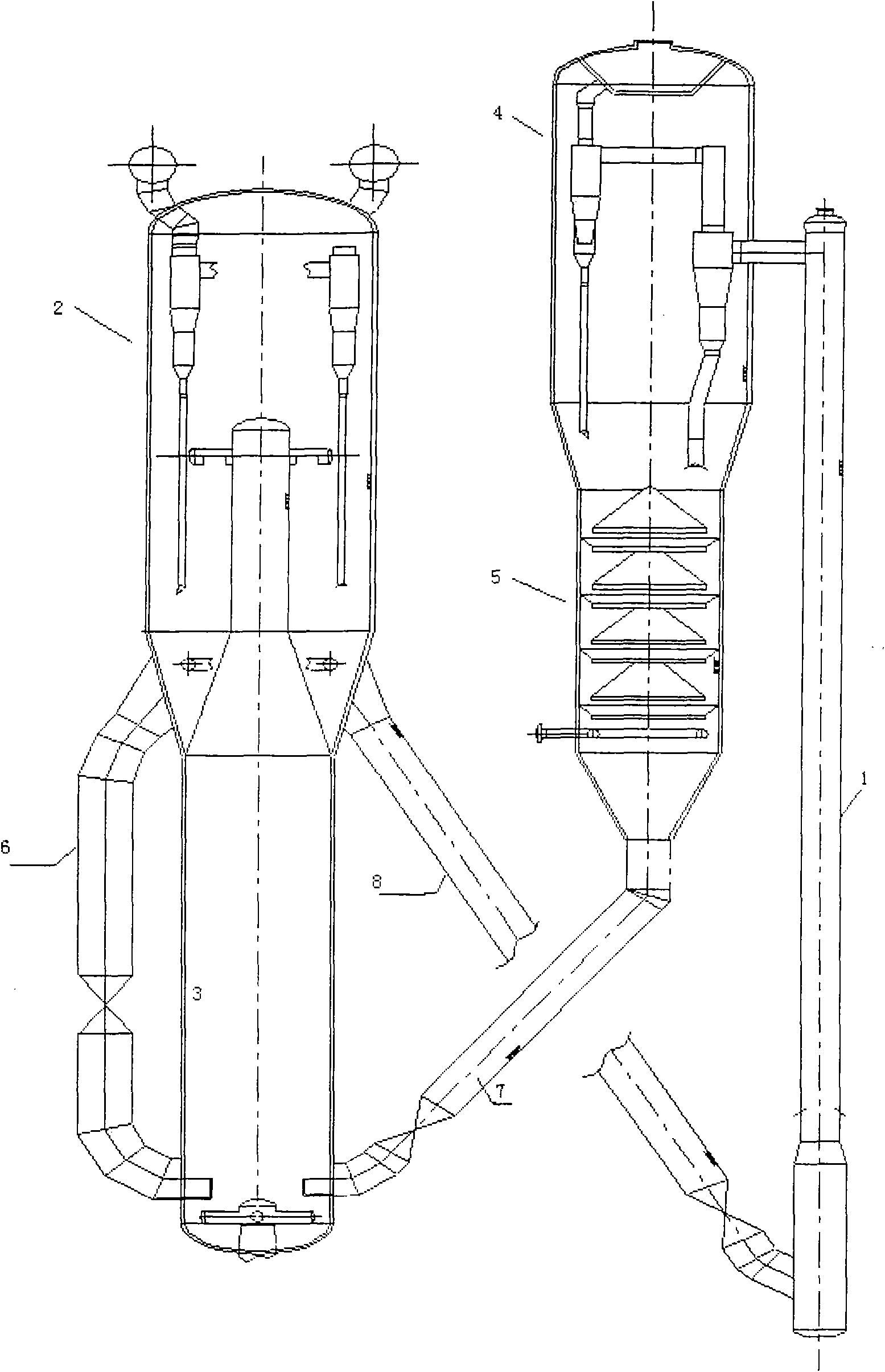
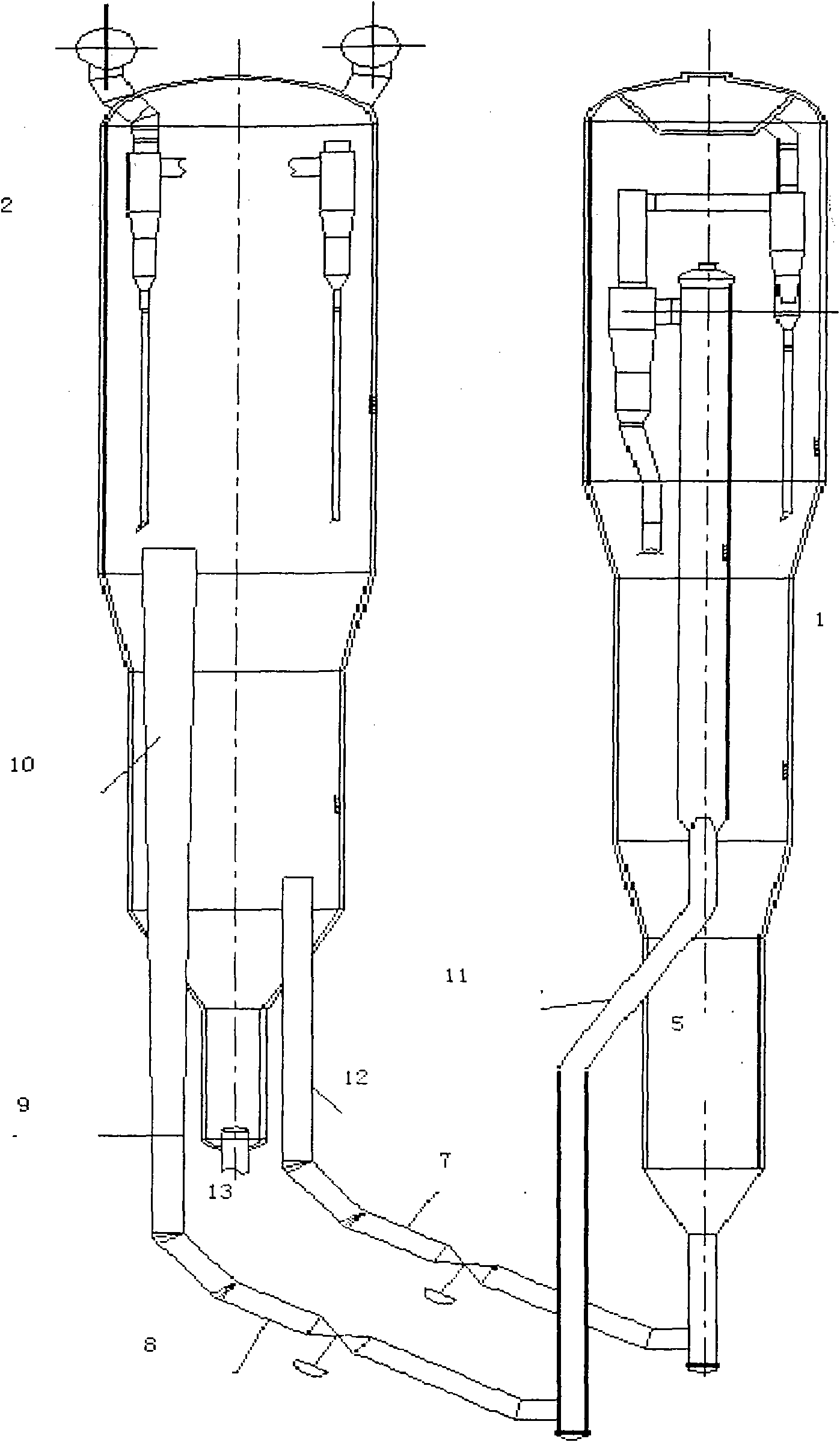
Technology device and method for preparing propylene by dehydrogenating propane or propane-enriched low carbon hydrocarbon
ActiveCN102040445AReduce energy consumptionLow unit priceHydrogen separationDistillation purification/separationGas phaseAlkali metal oxide
The invention provides a technology device and method for preparing propylene by dehydrogenating propane or propane-enriching low carbon hydrocarbon. The device comprises a reacting / regenerating part and a product fractionating part. A reacting / regenerating system is divided into a parallel type arrangement scheme and a coaxial type arrangement scheme by a fluidized bed reacting / regenerating technology, wherein a raising pipe of the parallel type reacting / regenerating system is an internal or external raising pipe, and a raising pipe of the coaxial type reacting / regenerating system is an external raising pipe. The method comprises the steps: leading raw materials and reaction products to enter into a raising pipe reactor after heat exchange; performing a dehydrogenating conversion reaction under the conditions that the reaction temperature is 500-700 DEG C, the pressure is 0.1-0.4MPa, and the ratio of a microspherical catalyst to oil is 5-60, wherein the microspherical catalyst consists of chromium, rare earth oxides, alkali metal oxides and a gamma-Al2O3 carrier, preferably, the temperature is 550-670 DEG C, the pressure is 0.1-0.15MPa, and the ratio of the microspherical catalyst to oil is 6-14; leading the reaction products and the raw materials to enter into a gas-oil separator to separate a gas phase, a liquid phase from a water phase after heat exchange and cooling; leading the separated gas to enter into a gas compressor to be compressed and be transported to an absorbing / stabilizing part; pumping the liquid to an absorbing tower; transporting the liquefied gas from a return tank at the top of a stabilizing tower to a propylene / propane separating tower by a charging pump of a propylene tower; discharging the fine propylene separated from the top of the tower out of the device as a product; discharging the separated byproduct hydrogen out of the device; and returning products at bottom of the tower to the reacting / regenerating part to be recycled.
Owner:卓润生 +1
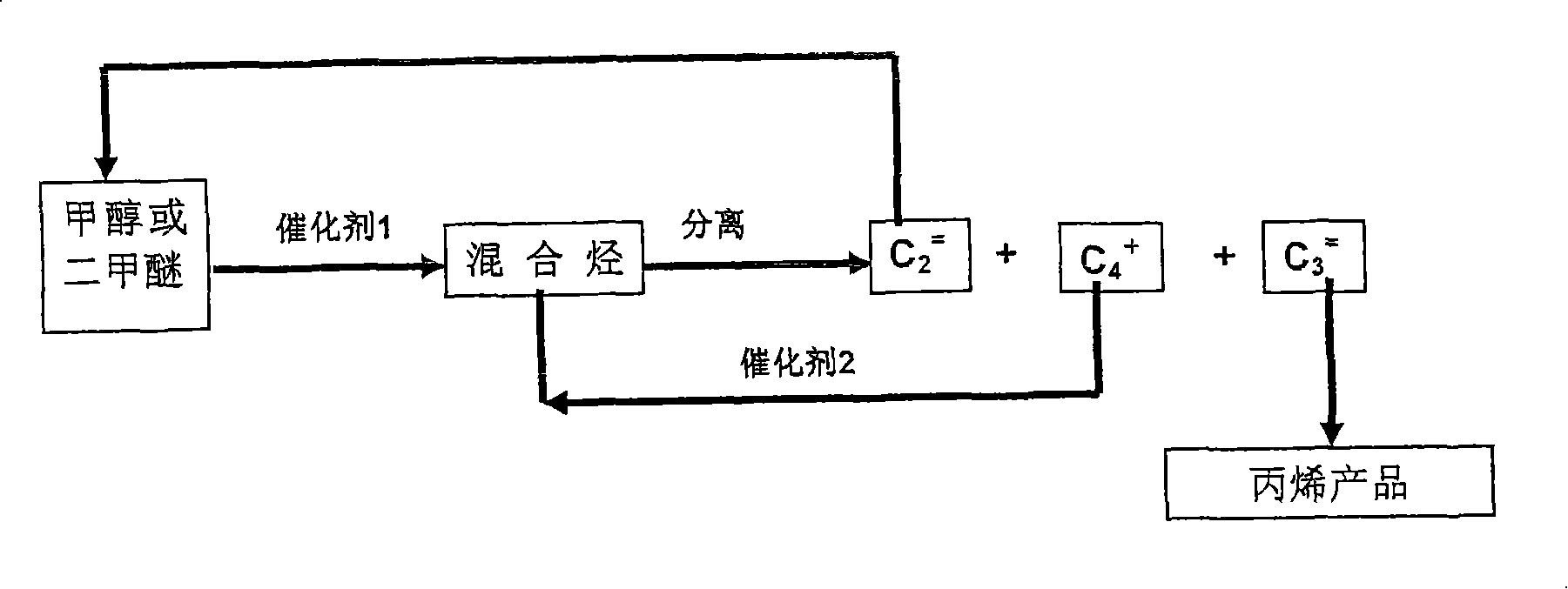
Method for producing propylene by carbinol or dimethyl ether
ActiveCN101177374AHighly selective preparationHydrocarbon from oxygen organic compoundsEthylene productionHydrocarbon mixturesMoving bed
The invention relates to a method for preparing olefin by methanol or dimethyl ether, in particular to a high selectivity preparation method of propylene, which comprises a conversion reaction of methanol or dimethyl ether, alkylation of methanol and ethylene and a catalytic cracking reaction of a plurality of heavy components above C4. A hydrocarbon mixture rich in propylene is generated by preheated material contacting with a first catalyst in a circulating fluidized bed or a moving bed reactor. After the propylene is separated from the hydrocarbon mixture, a plurality of light components of the hydrocarbon mixture comprising hydrogen and methane return to a methanol conversion reactor, the propylene is generated by the alkylation of methanol and ethylene in the light components. The invention is characterized in that the C4 and the heavy components above C4 separated from separation system are contacted with cracking catalyst in the circulating fluidized bed, generating hydrocarbonmixture contained ethylene, propylene and other light components by the catalytic cracking reaction, then the hydrocarbon mixture returns to the separation system for obtaining propylene.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
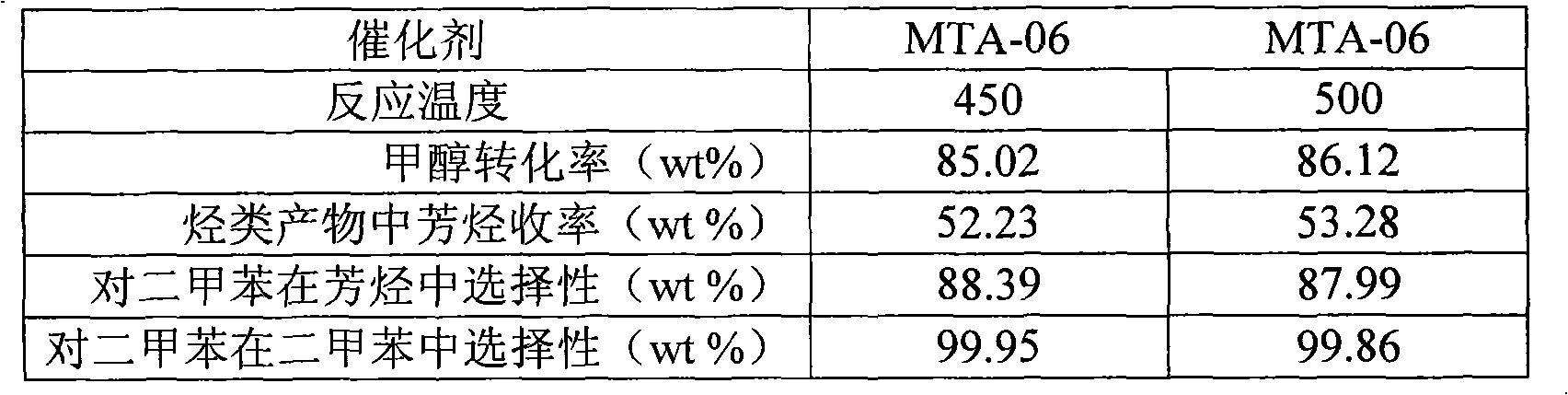
High yield preparation method of paraxylene by methanol/dimethyl ether conversion
InactiveCN101607864AMolecular sieve catalystsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsMolecular sieveAromatic hydrocarbon
The invention relates to a high yield preparation method of paraxylene by methanol / dimethyl ether conversion and the method can increase the yield of paraxylene in the converted products of methanol / dimethyl ether by adopting molecular sieve based catalyst which is modified with metals or through silylanization and adding aromatic hydrocarbons in the raw materials. The aromatic hydrocarbons is the separated benzene and / or toluene which is generated through the methanol / dimethyl ether conversion reaction and part or whole of aromatic hydrocarbons is recycled in the reaction system; otherwise, additional benzene and / or toluene is added in the raw materials. By adopting the method, the content of aromatic hydrocarbons in the products of the methanol / dimethyl ether conversion reaction can be more than 50wt%; wherein, the content of paraxylene in aromatic hydrocarbons is more than 80wt% and the selectivity of paraxylene in xylene isomers is more than 99wt%.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +2
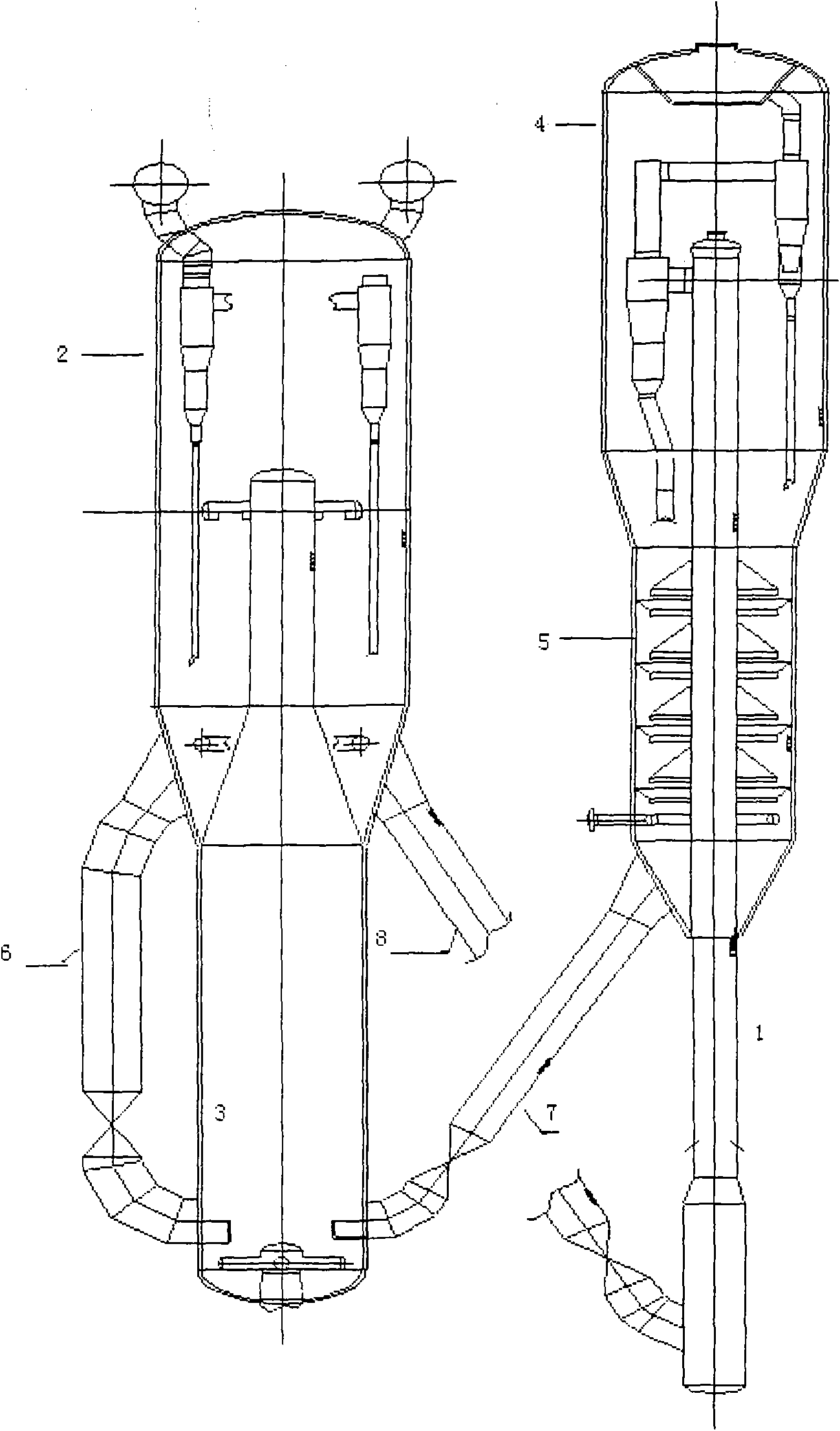
Residue conditioning system
The present invention provides a system for converting the residue of a carbonaceous feedstock gasification or incineration process into an inert slag and a gas having a heating value. The residue is converted by plasma heating in a refractory-lined residue conditioning chamber. The gas produced is optionally passed through a gas conditioning system for cooling and cleaning to provide a product gas that is suitable for use in downstream applications. The system also comprises a control subsystem for optimizing the conversion reaction
Owner:PLASCO ENERGY GROUP INC
Catalyst for heavy oil fixed bed hydrogenating treatment and its preparation process
The invention relates to a heavy oil fixed-bed hydrotreating catalyst and a preparation method thereof. The catalyst has a large pore size and high activity, is suitable for conversion reactions of macromolecular components such as asphaltene and heavy colloids, and is hydrogenated with conventional heavy and residual oils. The treatment catalyst is used together to obtain a higher rate of impurity removal, especially the rate of carbon residue removal and heavy metal removal is greatly improved. When the catalyst of the present invention is combined with the existing catalyst, it should be installed after the desulfurization catalyst and before the denitrogenation catalyst. It has an ideal treatment effect on various heavy and residual oil raw materials, and is especially suitable for residual oil raw materials with high residual carbon value. Hydrotreating process.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Conversion reactions for organic compounds
InactiveUS6482997B2High activityReduce interactionOrganic reductionHydrocarbon by hydrogenationOrganic compoundAverage size
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Device for the recovery and diffluence of sulfur dioxide and the system and method thereof
ActiveCN100475313CReduce dosageReduce volumeDispersed particle separationSulfur preparation/purificationRecovery methodSulfur
Owner:XIAN ZHONGYU SOFTWARE TECH
Comminution and densification of biomass particles
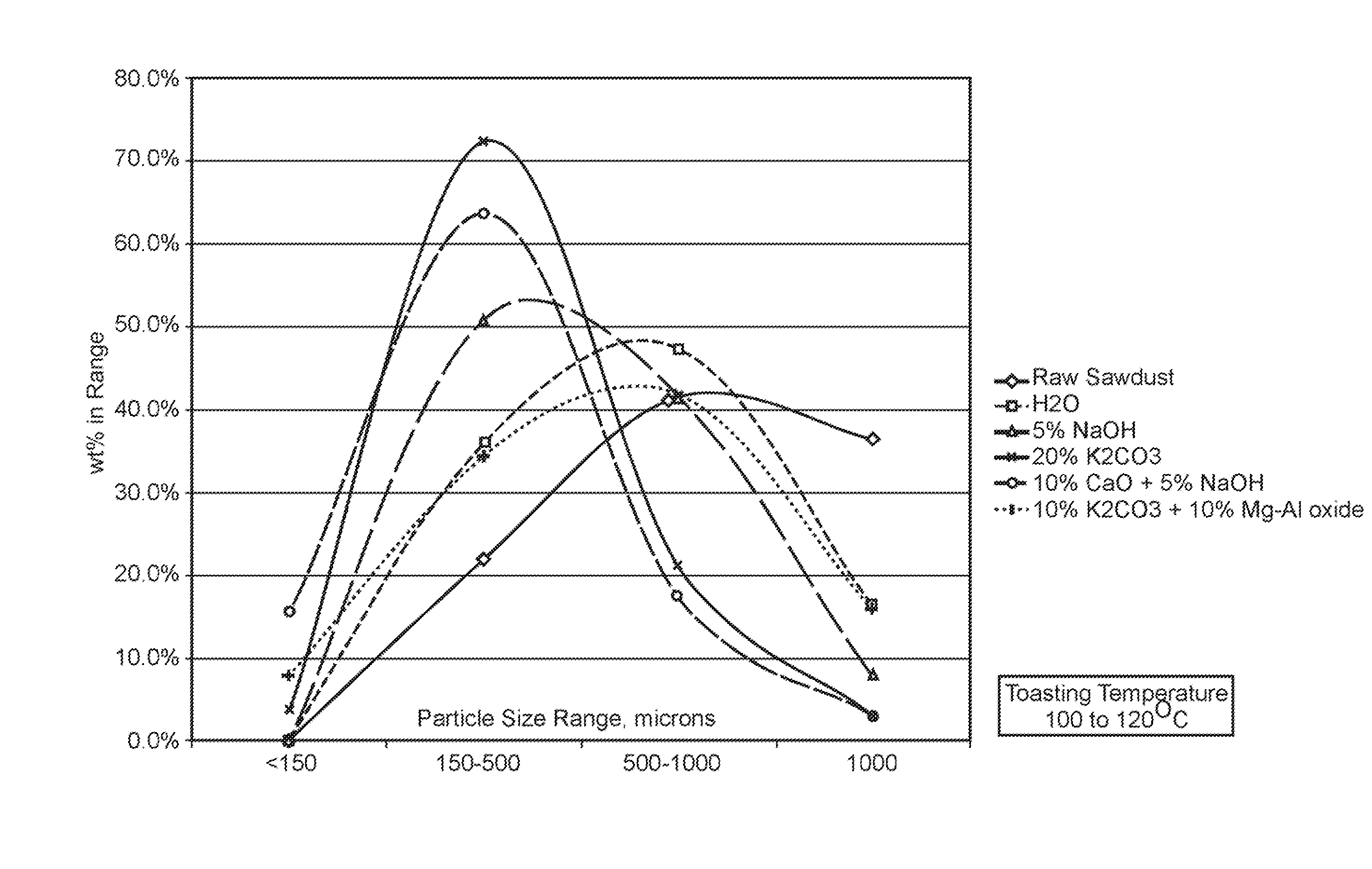
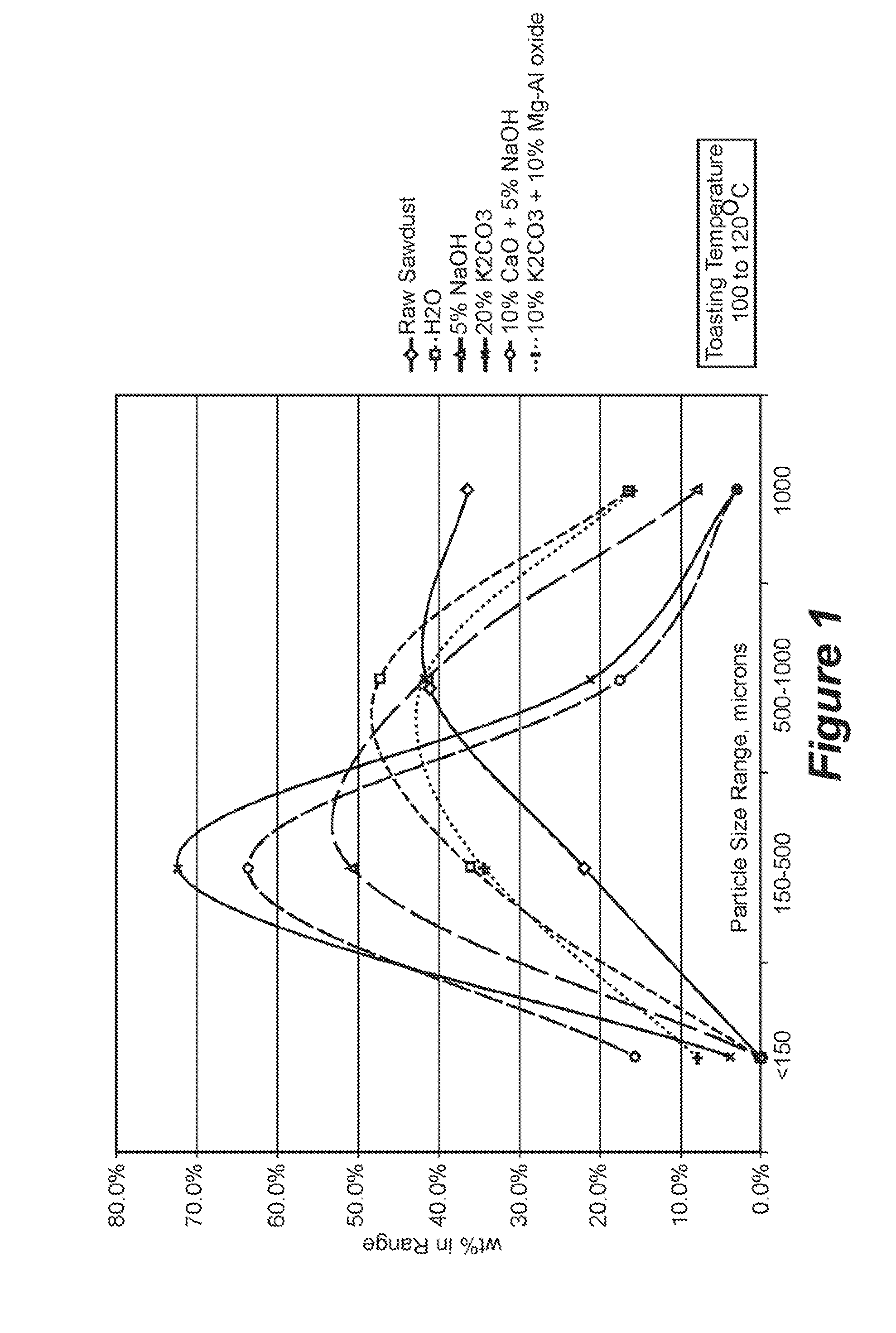
A method is disclosed for reducing the mechanical strength of solid biomass material, in particular ligno-cellulosic biomass. The method comprises heating the solid biomass material to a temperature in the range of 105° C. to 200° C. The heat treatment, which is referred to as “toasting”, significantly reduces the mechanical energy required for reducing the particle size of the solid biomass material.The method is particularly suitable as a pretreatment step to a conversion reaction of the solid biomass material.
Owner:MARD INC
Residue Conditioning System
The present invention provides a system for converting the residue of a carbonaceous feedstock gasification or incineration process into an inert slag and a gas having a heating value. The residue is converted by plasma heating in a refractory-lined residue conditioning chamber. The gas produced is optionally passed through a gas conditioning system for cooling and cleaning to provide a product gas that is suitable for use in downstream applications. The system also comprises a control subsystem for optimizing the conversion reaction
Owner:PLASCO ENERGY GROUP INC
Hydrogen-making method by utilizing catalytic cracked regenerated flue gas
InactiveCN1400159AIncrease contentSolve the pollution of the environmentHydrogenChemical recyclingHydrogenFlue gas
The method for making hydrogen by utilizing catalytic cracking regenerated flue gas includes the following steps: (1). contacting hydrocarbon oil raw material with catalytic cracking catalyst and making them produce reaction; (2). separating reaction oil vapour and catalyst of carbon deposit, feeding oil vapour into subsequent separation system, and stripping the catalyst of carbon deposit and feeding it into first regenerator; (3). in first regenerator contacting the catalyst of carbon deposit with oxygen-containing gas for 2-2.5 sec. at 500-660 deg.C and empty bed gas speed of 0.2-0.8 m / s, feeding regenerated flue gas into subsquent hydrogen-making process; (4). separating CO from regenerated flue gas, making CO and water vapour produce conversion reaction and separating hydrogen from the obtained gas product.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Chitosan modified alginate hydrogel three-dimensional porous bracket and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101773683ARich sourcesControllable physical and chemical propertiesProsthesisPhosphateFreeze-drying
The invention relates to a chitosan modified alginate hydrogel three-dimensional porous bracket with specific in-vitro degradability and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving sodium alga acid serving as a raw material in phosphate buffer solution; performing amidation reaction of a carboxyl group in the sodium alga acid and an amino group in a cross-linking agent cystamine or dimethyl cystinate under the activation of water-soluble carbodiimide to form a chemically crosslinked hydrogel; performing freeze drying on the hydrogel to obtain a porous bracket material of the hydrogel; and performing surface modification on the porous bracket by using chitosan. In solution of a reducing agent such as cysteine with an appropriate concentration, a disulfide bond in a hydrogel cross-bridge is degraded through a disulfide bond-sulfydryl conversion reaction, so the porous bracket is decomposed and dissolved and disappears. Therefore, the porous bracket can be used as an in-vitro cell culture template material. The hydrogel porous bracket researched by the invention has the characteristics of simple preparation, rich raw material source, low cost and availability. Various physiochemical performances, mechanical strength, degradation rate and surface properties of the bracket material are controllable within a large range.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
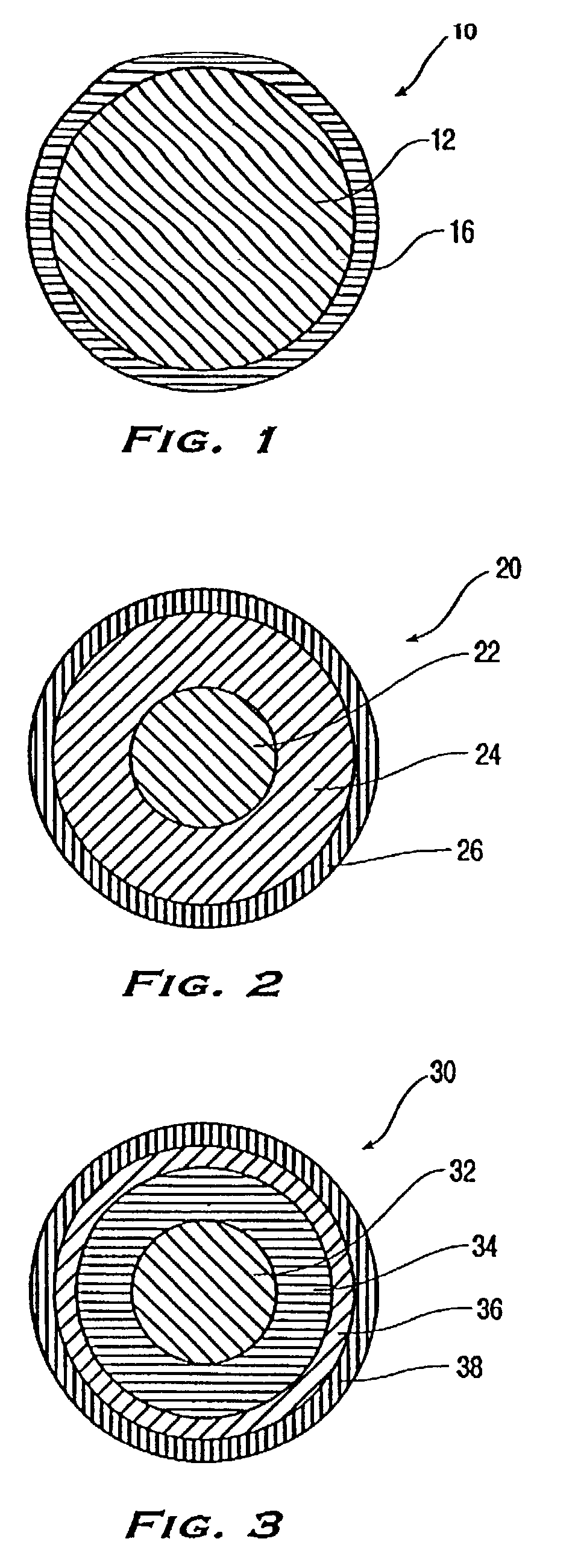
Core-shell type aromatic conversion catalyst, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101722033AGuaranteed to be completely wrappedDecrease the external area char rateMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon by metathesis reactionAlcoholCore shell
The invention relates to a core-shell type aromatic conversion catalyst, a preparation method and application thereof, mainly solving the problems of strong acidity of an outside surface, rapid inactivation speed and low selectivity of aromatic shape selective catalysis in previous molecular sieve based catalysts. The invention adopts the following technical scheme: the preparation method that ZSM-5 crystal grain is taken as a core and a high silicon MF1 molecular sieve shell layer is formed on the outside surface of the core crystal by secondary growth is used for synthesizing the core-shell type zeolite molecular sieve with tightly-bonded core and shell and communicated pore canals, then the catalyst is prepared by shaping and baking 10-100% of core-shell type zeolite molecular sieves and the balance binder in terms of weight percent to better solve the above problems. The invention can be used in industrial production of aromatic conversion reactions of toluene disproportionation, toluene methylation, xylene isomerisation, trimethylbenzene cracking, cumin cracking and styralyl alcohol alkylating.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
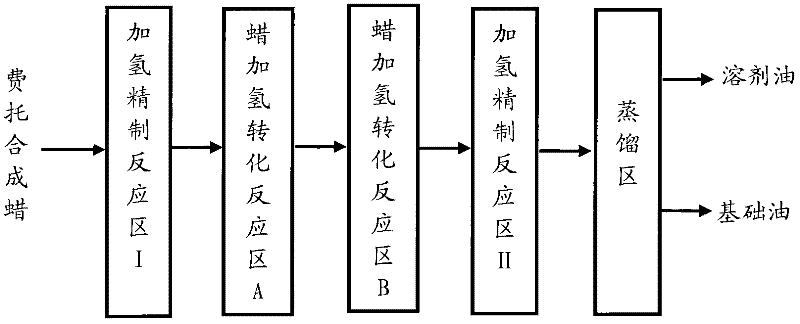
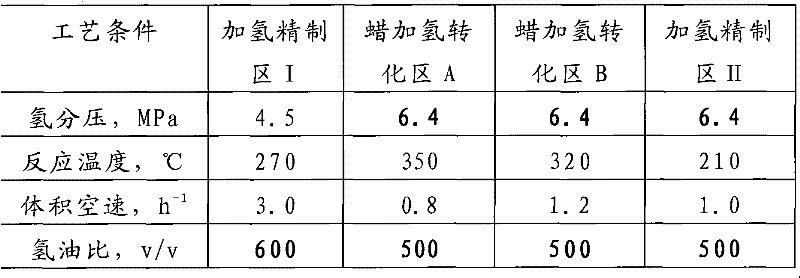
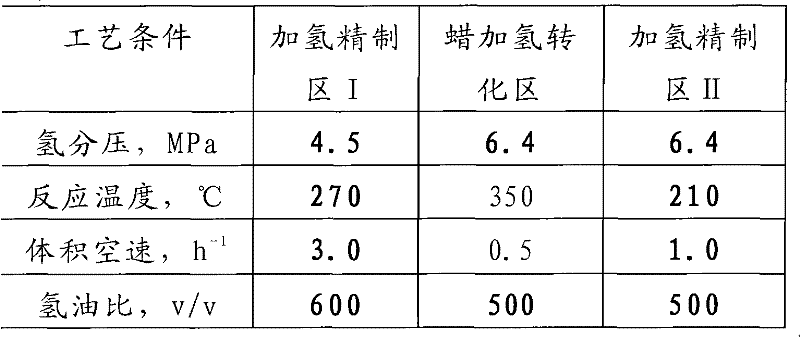
Method for producing base oil of lubricating oil by using Fischer-Tropsch synthesis wax
ActiveCN102533329AHigh yieldTreatment with hydrotreatment processesLubricant compositionWaxIsomerization
The invention relates to a method for producing base oil of lubricating oil by using Fischer-Tropsch synthesis wax. The method comprises the following steps of: (a) enabling the Fischer-Tropsch synthesis wax to be in contact with a hydrofining catalyst in a hydrofining reaction region I to obtain the Fischer-Tropsch synthesis wax subjected to hydrogenating alkene saturation and deoxidization; (b) enabling the Fischer-Tropsch synthesis wax obtained in the step (a) to be in contact with a hydrogenating isomerization catalyst in a wax hydrogenating conversion reaction region A to obtain wax converting generation oil with depression of pour point; (c) enabling the wax converting generation oil obtained in the step (b) to be in contact with the hydrogenating isomerization catalyst in a wax hydrogenating conversion reaction region B to obtain a wax converting generation oil with further depression of pour point; (d) enabling the wax converting generation oil with further depression of pour point, obtained in the step (c), to be in contact with the hydrofining catalyst in a hydrofining reaction region II to obtain wax converting generation oil subjected to hydrofining; and (e) separating the generation oil obtained in the step (d) in a distillation region to obtain the base oil of the lubricating oil.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
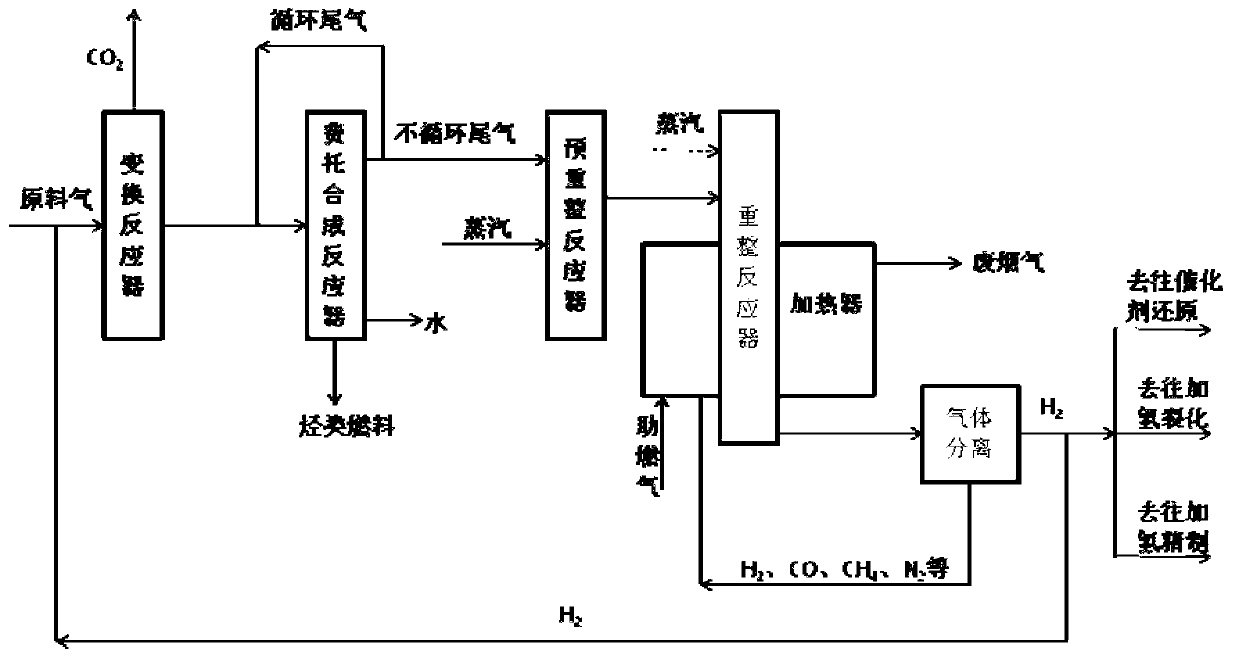
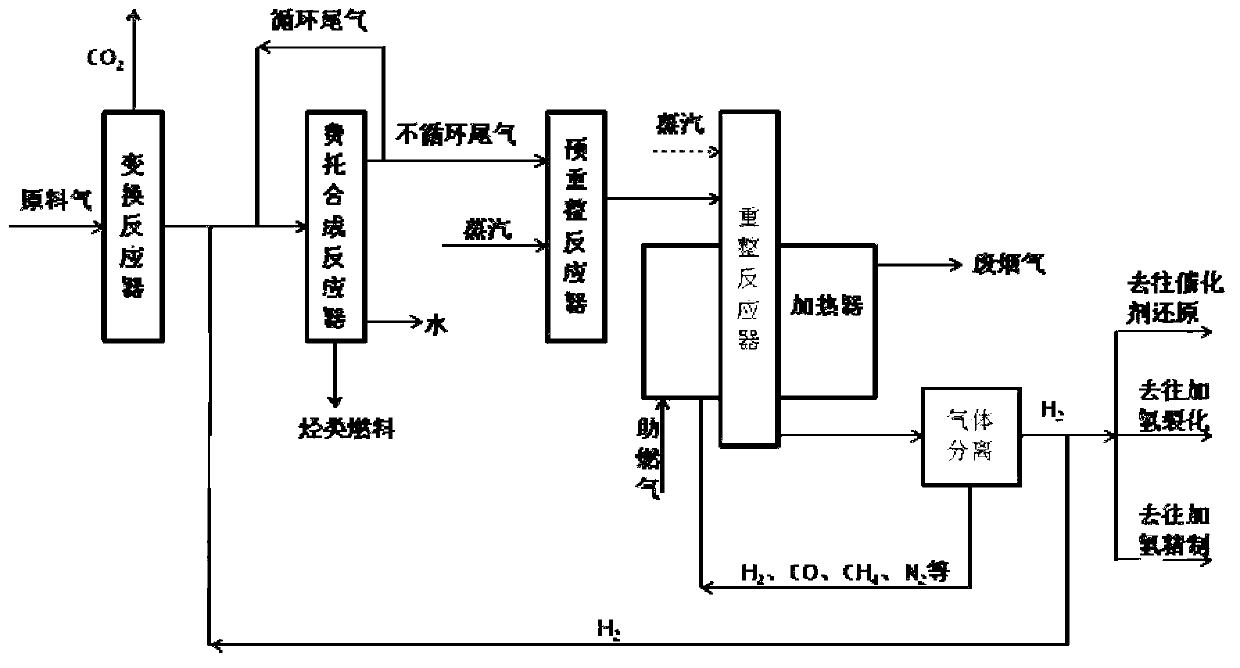
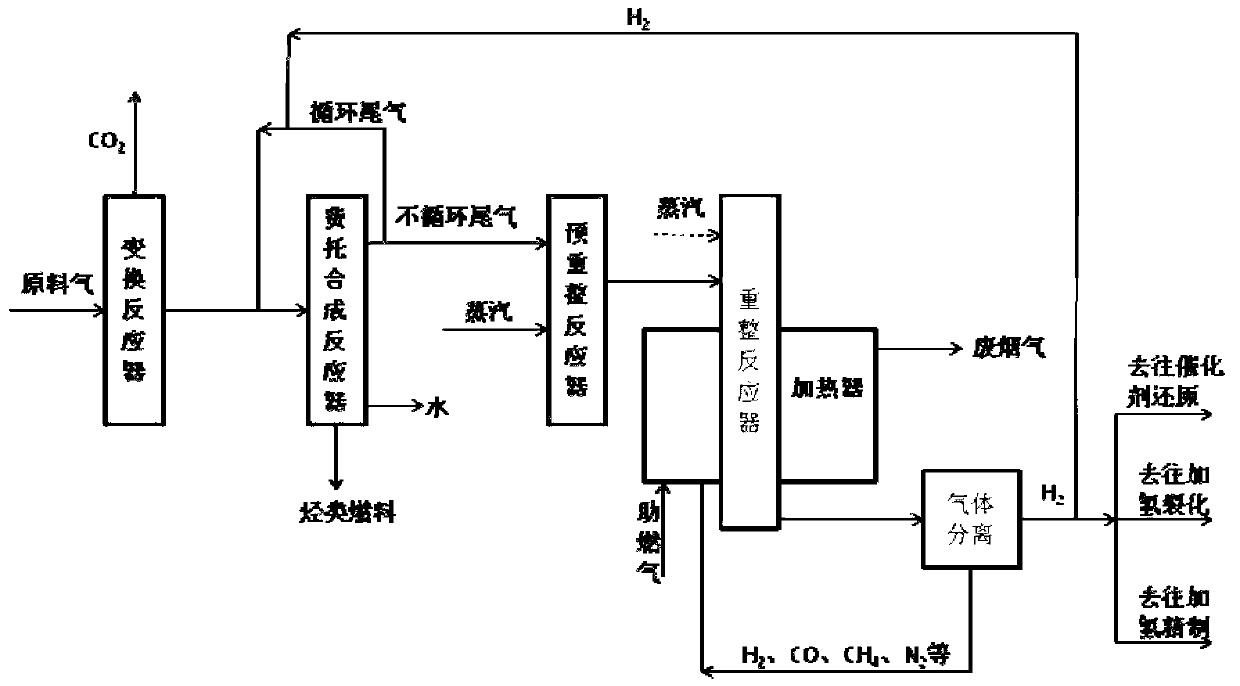
Comprehensive utilization process for low-carbon-emission Fischer-Tropsch synthesis tail gas
ActiveCN102730637AEfficient use ofImprove utilization efficiencyHydrogenChemical industryHydrogenWater vapor
The invention discloses a comprehensive utilization process for a low-carbon-emission Fischer-Tropsch synthesis tail gas. The process is used for converting the non-circular tail gas generated after the Fischer-Tropsch synthesis reaction into synthesis gas containing hydrogen through water vapor reforming, and then separating and extracting high-purity hydrogen from the synthesis gas containing hydrogen for use. The comprehensive utilization process comprises the following steps: 1) obtaining converted gas through a water vapor conversion reaction, 2) obtaining a hydrocarbon fuel through a Fischer-Tropsch synthesis reaction, 3) converting a hydrocarbon compound containing two or more than two carbon atoms into methane after a pre-reforming reaction, 4), converting methane and water vapor into hydrogen and carbon monoxide through a reforming reaction, 5) separating gases respectively containing hydrogen and carbon monoxide, 6) and providing heat for a reforming reactor. The process disclosed by the invention can be used for effectively utilizing the Fischer-Tropsch synthesis tail gas, especially the tail gas containing a large amount of inert components, and converting the tail gas into the hydrogen for use. Meanwhile, the comprehensive utilization process disclosed by the invention can be used for effectively utilizing residual combustible components after the hydrogen in the reforming gas is separated, thereby enhancing the utilization efficiency of the energy.
Owner:WUHAN KAIDI ENG TECH RES INST CO LTD
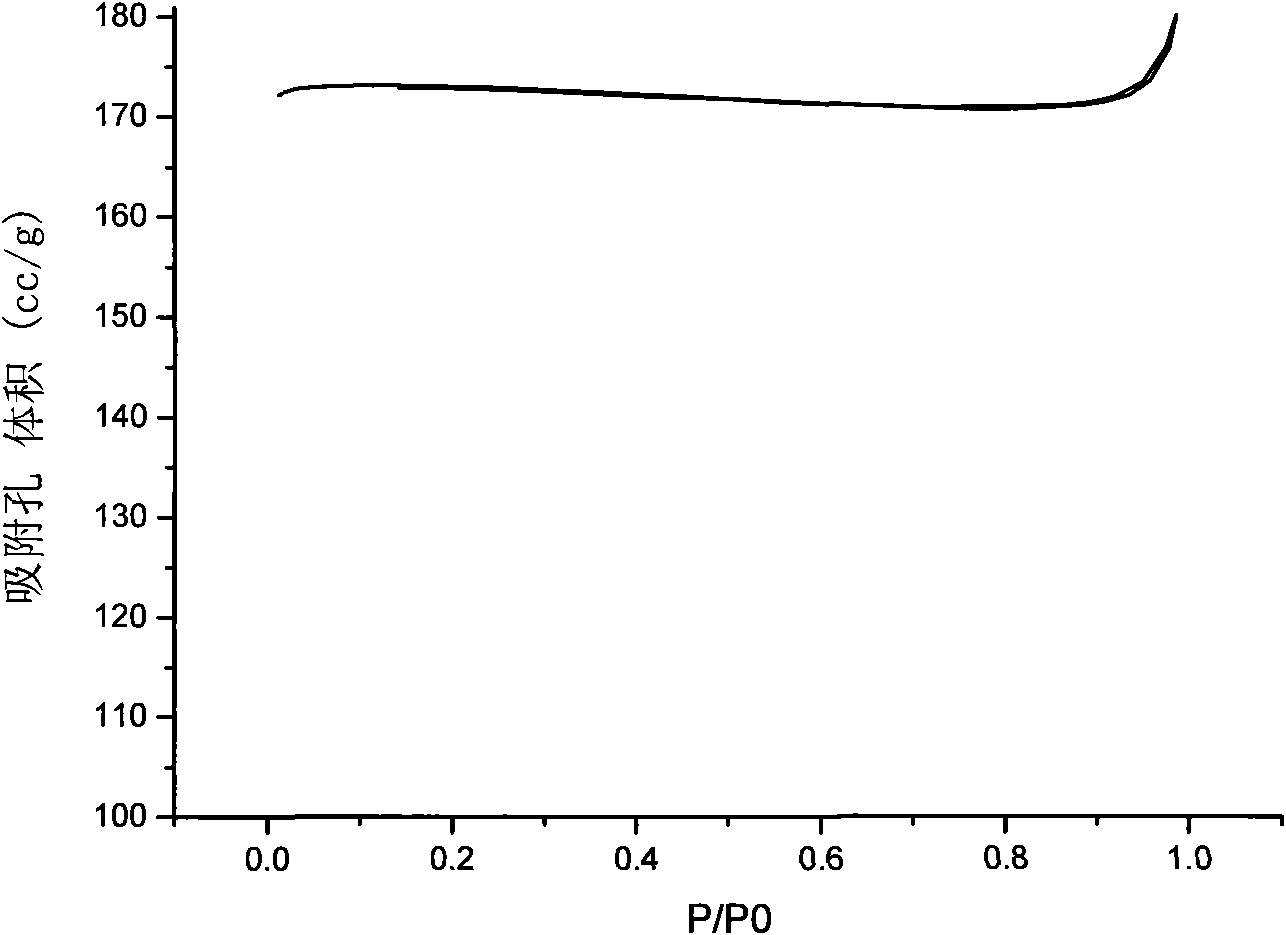
SAPO-34 molecular sieve and synthesis method thereof
ActiveCN101633508AMolecular-sieve and base-exchange phosphatesMolecular-sieve silicoaluminophosphatesHysteresisSynthesis methods
The invention provides an SAPO-34 molecular sieve and a synthesis method thereof. A hysteresis loop is arranged between nitrogen adsorption isotherm and desorption isotherm of the molecular sieve; and a molecular sieve crystal comprises topographies such as hollow shells, holes, concave-convex, cracks, nuclear shells and the like. The molecular sieve is obtained by mixing an aluminum source, a phosphorous source, a silicon source and an organic template agent to form gel and hydrothermally crystallizing the gel for 4 to 500 hours at the temperature of between 100 and 250 DEG C, wherein the organic template agent is added in two steps, one part is added during forming the gel, and the rest is added during hydrothermal crystallization. The molecular sieve is a catalyst of active components, can be used for conversion reaction of oxygenated organic compounds, and also can be used for conversion reaction of hydrocarbons, or used as a hydrogen conversion catalyst of hydrocarbons after supporting metals.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
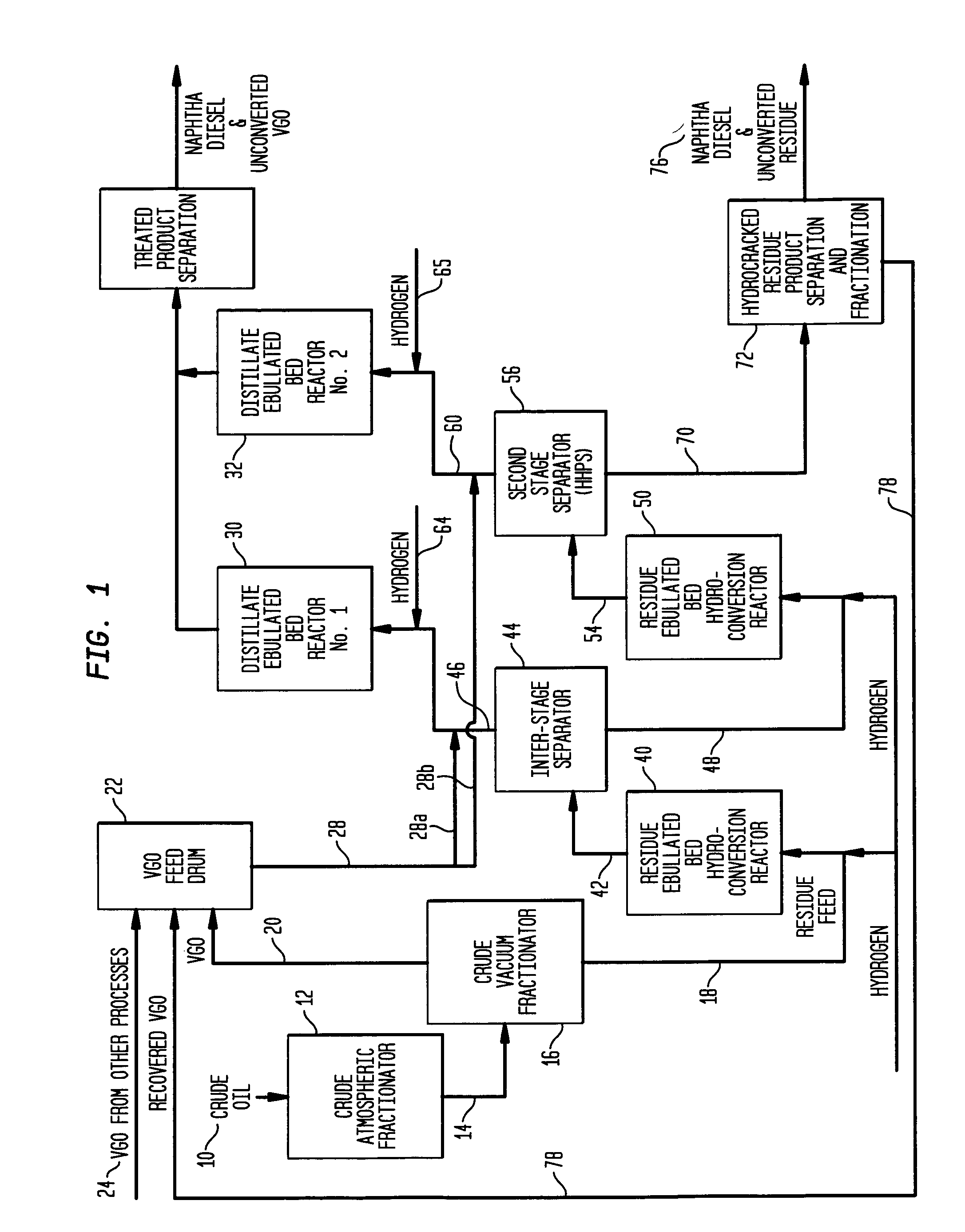
Process for multistage residue hydroconversion integrated with staight-run and conversion gasoils hydroconversion steps
ActiveUS20090288986A1High throughput rateImprove throughputTreatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyMolecular sieve catalystsVapor–liquid separatorGasoline
This invention relates to a novel integrated hydroconversion process for converting heavy atmospheric or vacuum residue feeds and also converting and reducing impurities in the vacuum gas oil liquid product. This is accomplished by utilizing two residue hydroconversion reaction stages, two vapor-liquid separators, and at least two additional distillate ebullated-bed hydrocracking / hydrotreating reaction stages to provide a high conversion rate of the residue feedstocks.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Solids Circulation System and Method for Capture and Conversion of Reactive Solids
ActiveUS20120111109A1Specific gravity by measuring pressure differencesGasifier mechanical detailsCycloneFluid transport
A solids circulation system receives a gas stream containing char or other reacting solids from a first reactor. The solids circulation system includes a cyclone configured to receive the gas stream from the first reactor, a dipleg from the cyclone to a second reactor, and a riser from the second reactor which merges with the gas stream received by the cyclone. The second reactor has a dense fluid bed and converts the received materials to gaseous products. A conveying fluid transports a portion of the bed media from the second reactor through the riser to mix with the gas stream prior to cyclone entry. The bed media helps manipulate the solids that is received by the cyclone to facilitate flow of solids down the dipleg into the second reactor. The second reactor provides additional residence time, mixing and gas-solid contact for efficient conversion of char or reacting solids.
Owner:THERMOCHEM RECOVERY INT
Process to control conversion of C4+ and heavier stream to lighter products in oxygenate conversion reactions
InactiveUS6844476B2Convenient lightingProduction is limitedMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieve catalystReaction zoneChemistry
A method for converting heavy olefins present in a product stream exiting a first reaction zone into light olefins and carbonaceous deposits on a catalyst without separation of the heavy olefins from the product stream exiting the first reaction zone. The method comprises creating the product stream exiting the first reaction zone, the product stream exiting the first reaction zone comprising the heavy olefins, moving the product stream exiting the first reaction zone to a second reaction zone without separation of the heavy olefins from the product stream exiting the first reaction zone, and contacting the product stream exiting the first reaction zone with the catalyst under conditions effective to form the light olefins, the contacting causing the carbonaceous deposits to form on at least a portion of the catalyst.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Process for the preparation of multimetallic catalysts that can be used in reactions for transformation of hydrocarbons
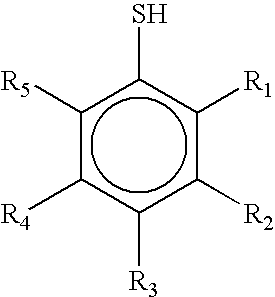
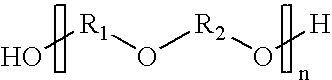
InactiveUS20070191651A1Loss of selectivityAvoid problemsOxygen-containing compound preparationOther chemical processesDissolutionColloid
The invention relates to a process for the preparation of a catalyst comprising:a) The preparation of a colloidal oxide suspension of a first metal M1 that consists in the neutralization of a basic solution by an acidic mineral solution that contains the precursor of the metal M1,b) Bringing into contact the precursor of the promoter M2, either directly in its crystallized form or after dissolution in aqueous phase, with the colloidal suspension that is obtained in stage a),c) Bringing into contact the colloidal suspension that is obtained in stage b) with the substrate,d) Drying at a temperature of between 30° C. and 200° C., under a flow of air.The invention also relates to a process for the treatment of an olefinic fraction that uses the catalyst prepared [by] said preparation process.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Low compression, resilient golf balls with rubber core
A low compression, resilient golf ball having a center including a material formed from the conversion reaction of sufficient amounts of polybutadiene, a free radical source, and a cis-to-trans catalyst to convert a portion of cis-isomer to trans-isomer in the polybutadiene, wherein said material has an amount of trans-isomer greater than the amount of trans-isomer present before the conversion reaction, and wherein the reaction product is susbstantially free of antioxidant.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com