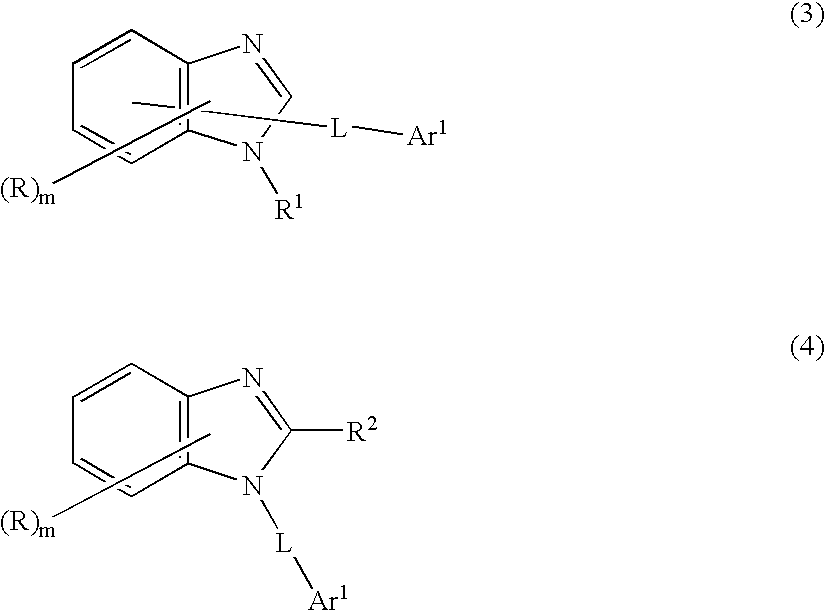
Patents
Literature
10517 results about "Aromatic hydrocarbon" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An aromatic hydrocarbon or arene (or sometimes aryl hydrocarbon) is a hydrocarbon with sigma bonds and delocalized pi electrons between carbon atoms forming a circle. In contrast, aliphatic hydrocarbons lack this delocalization. The term "aromatic" was assigned before the physical mechanism determining aromaticity was discovered; the term was coined as such simply because many of the compounds have a sweet or pleasant odour. The configuration of six carbon atoms in aromatic compounds is known as a benzene ring, after the simplest possible such hydrocarbon, benzene. Aromatic hydrocarbons can be monocyclic (MAH) or polycyclic (PAH).
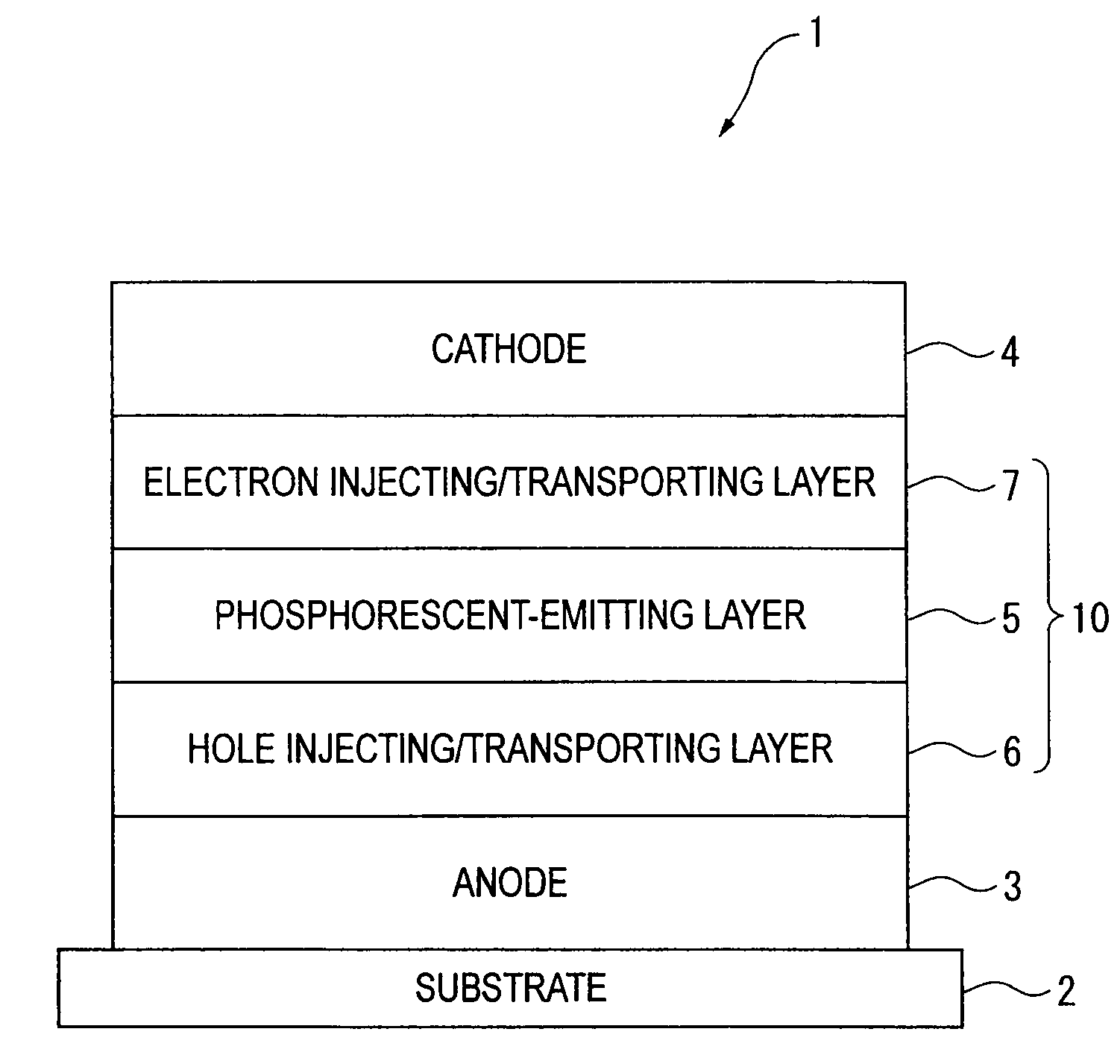
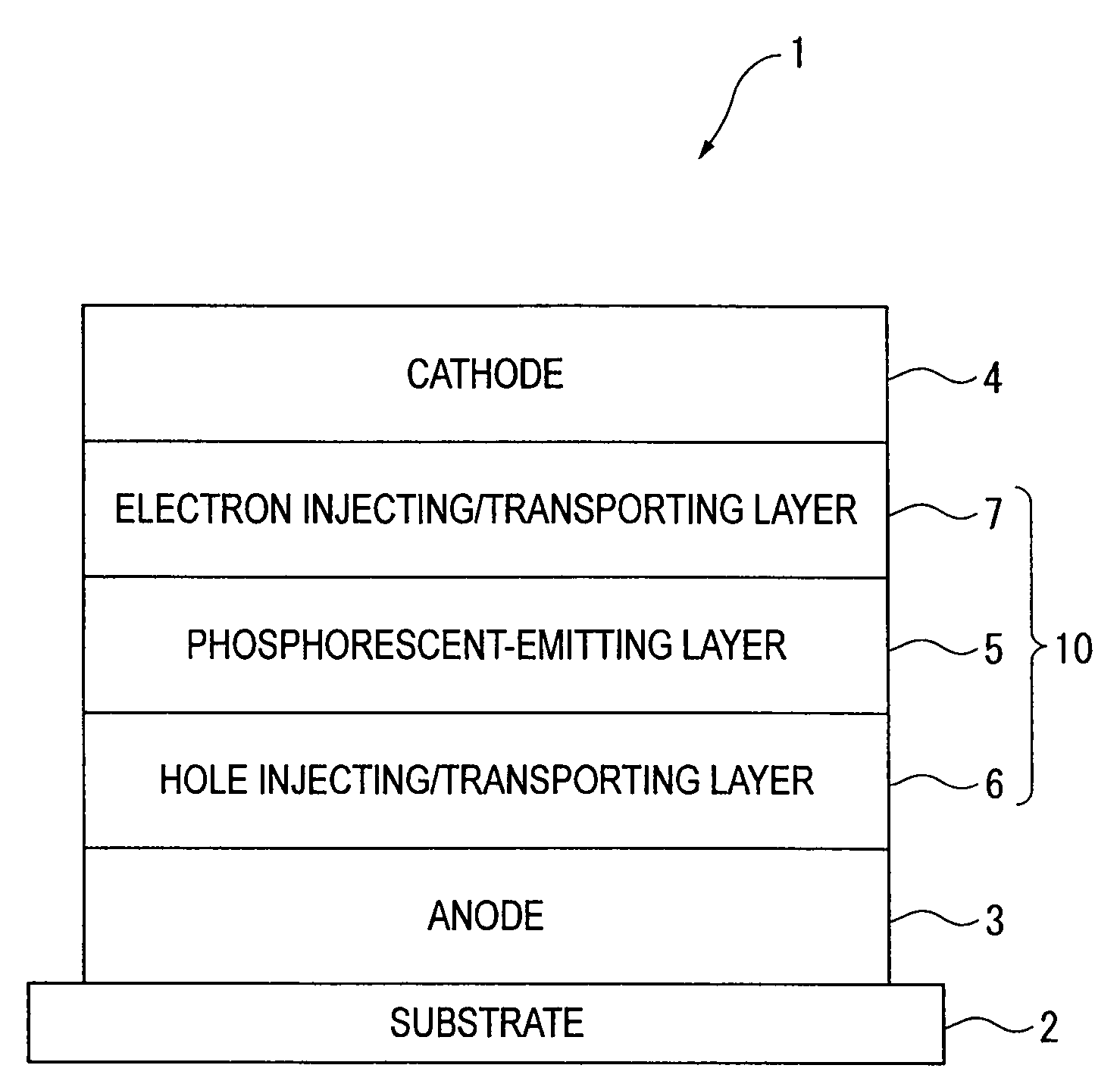
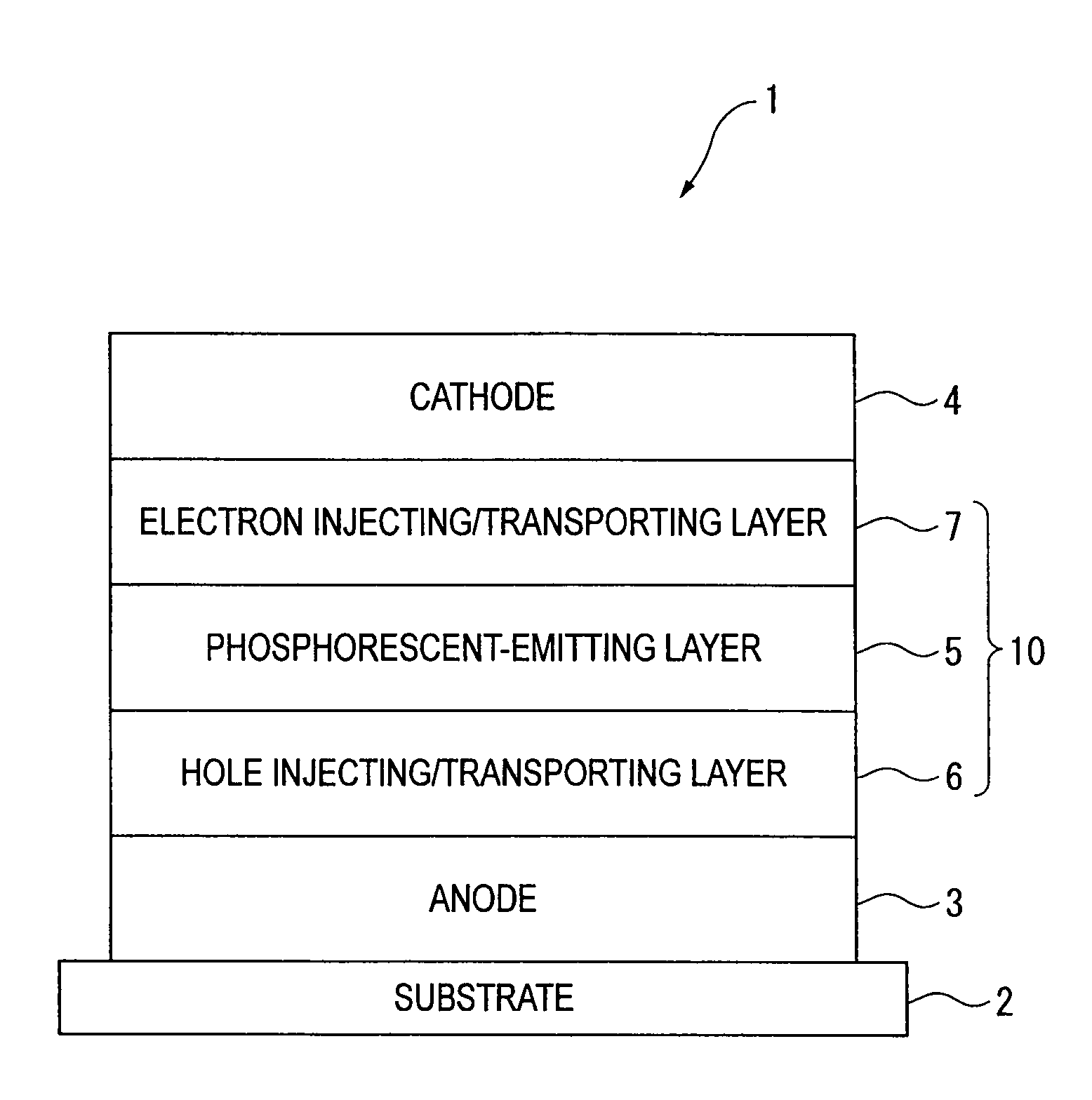
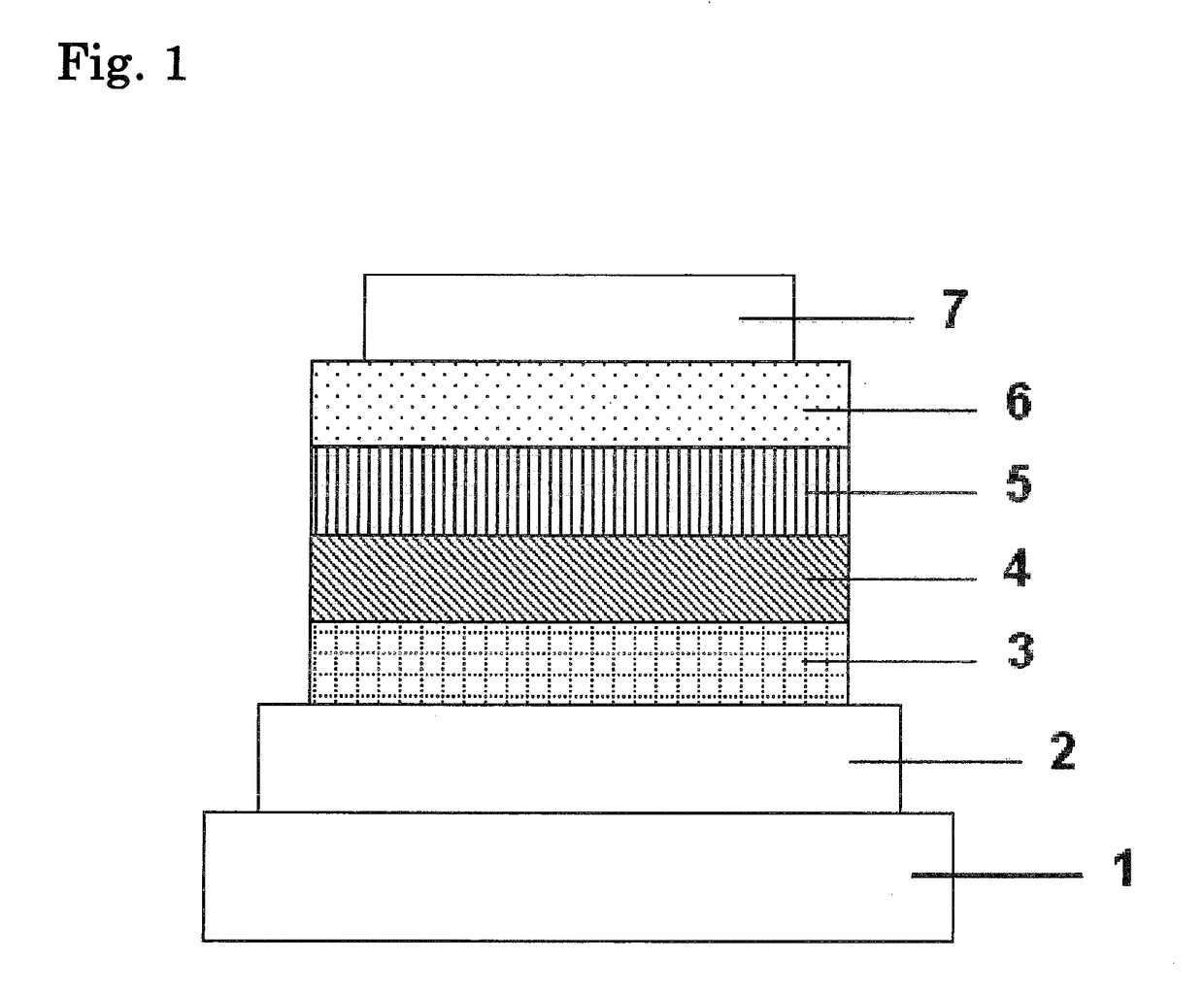
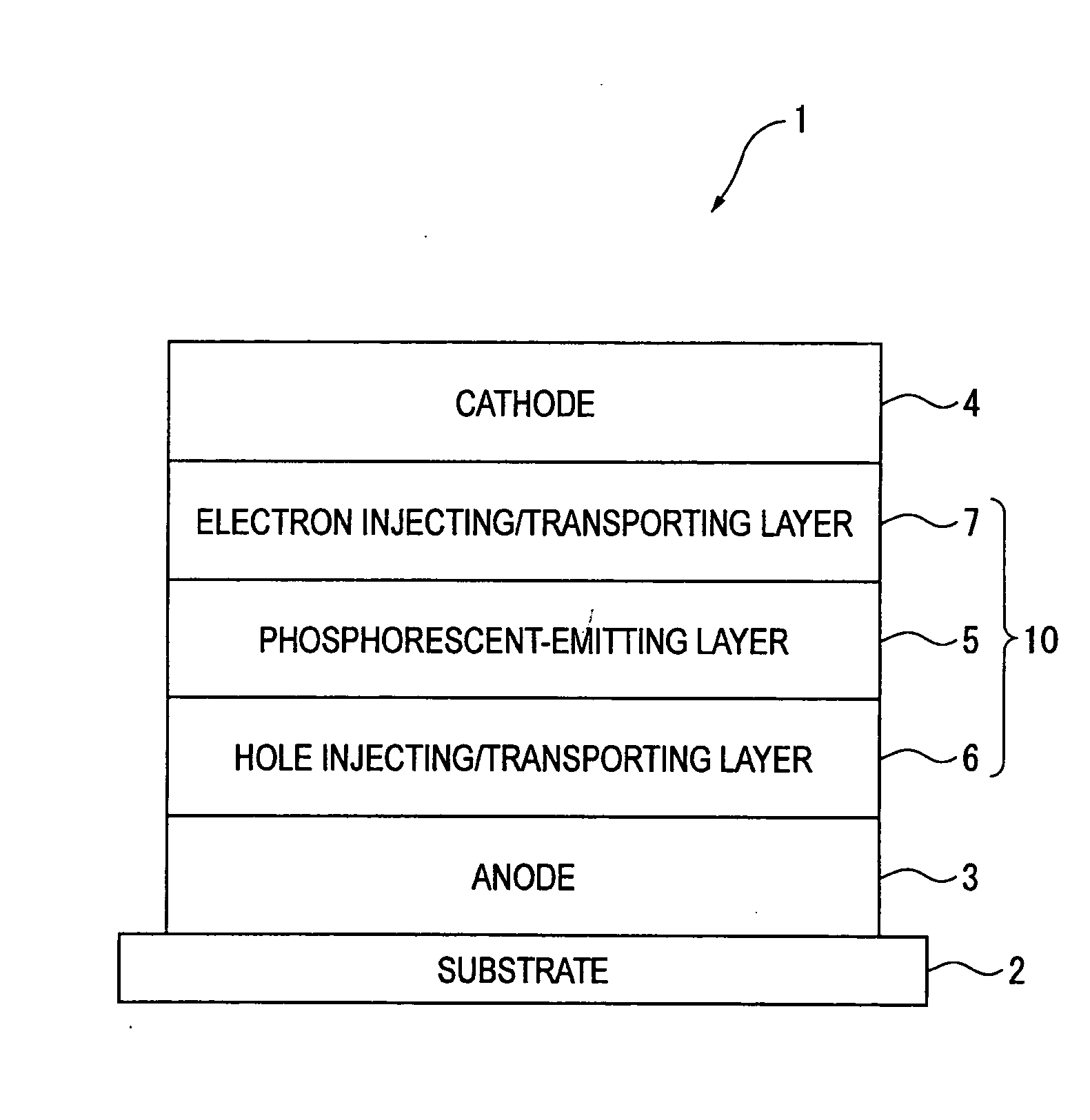
Organic electroluminescence device and material for organic electroluminescence device
ActiveUS20090009065A1Improve efficiencyLong lastingSilicon organic compoundsDischarge tube luminescnet screensOrganic filmBenzo(c)phenanthrene
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
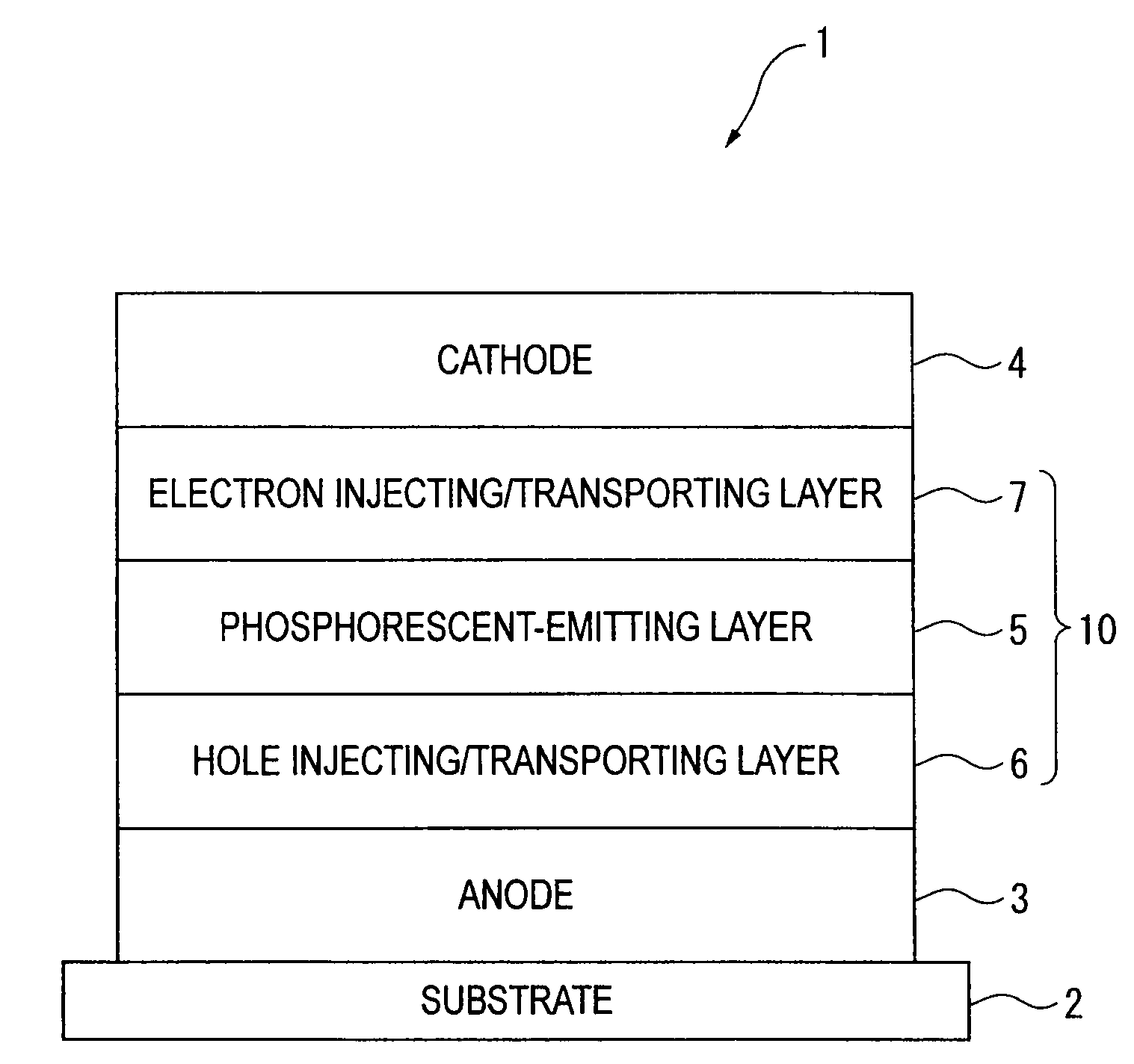
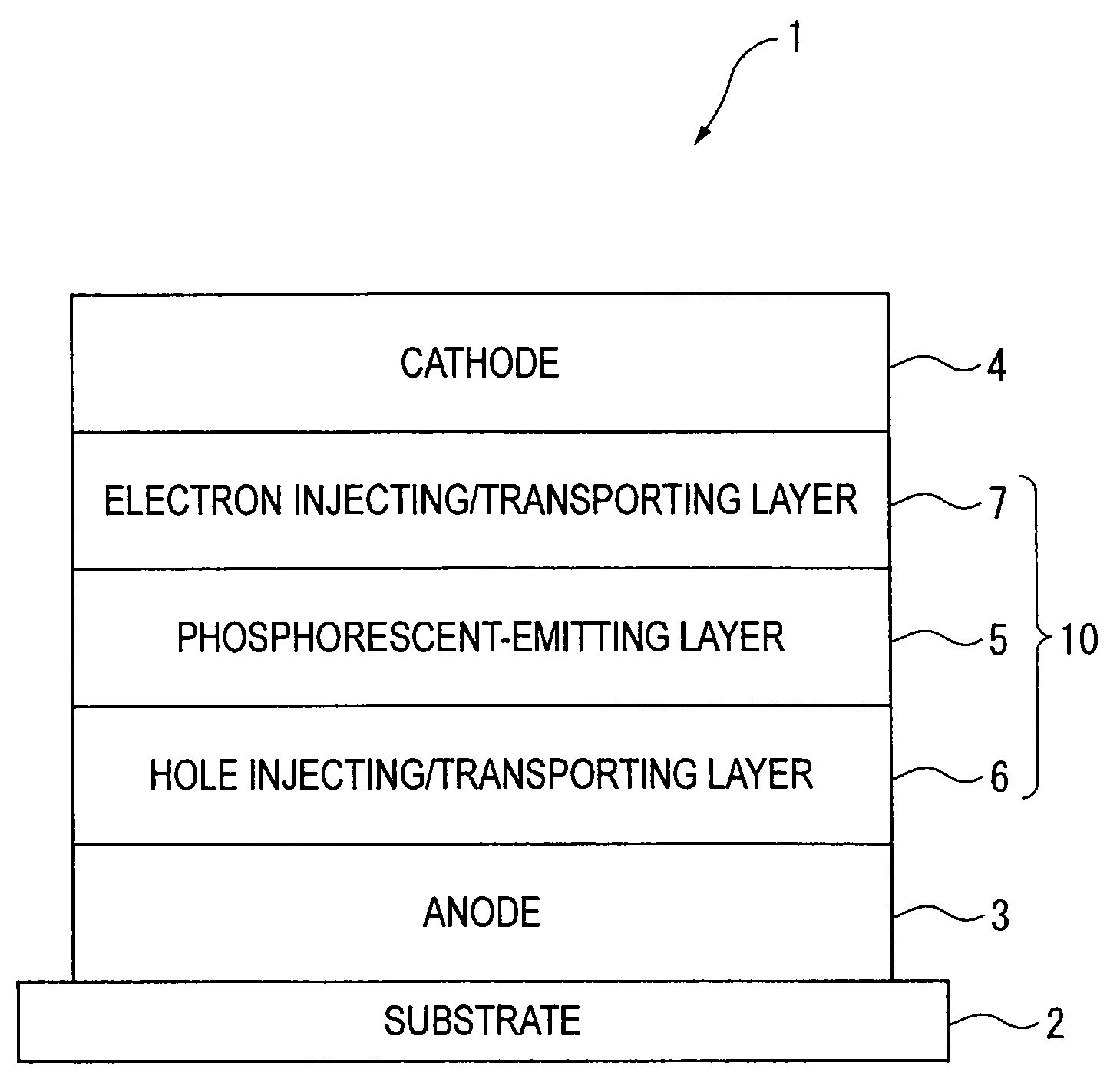
Organic electroluminescence device and material for organic electroluminescence device
InactiveUS20090045731A1Improve efficiencyLong life-timeDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesOrganic filmFluoranthene
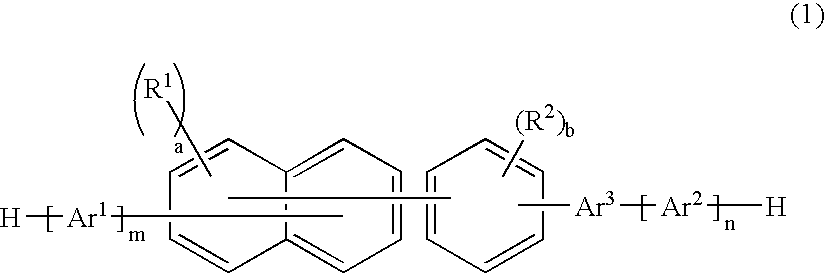
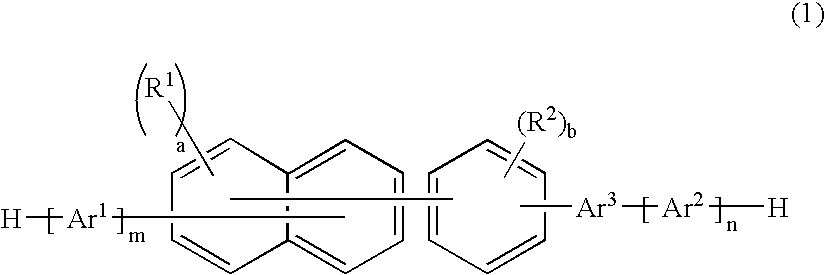
An organic electroluminescence device includes: a cathode; an anode; and a single-layered or multilayered organic thin-film layer provided between the cathode and the anode. The organic thin-film layer includes at least one emitting layer. The at least one emitting layer contains at least one phosphorescent material and a host material represented by the following formula (1).In the formula, Ar1, Ar2, Ar3, B1, B2, B3 and B4 each represent a substituted or unsubstituted benzene ring or a substituted or unsubstituted condensed aromatic hydrocarbon ring selected from a naphthalene ring, a chrysene ring, a fluoranthene ring, a phenanthrene ring, a benzophenanthrene ring, a dibenzophenanthrene ring, a triphenylene ring, a benzo[a]triphenylene ring, a benzochrysene ring, a benzo[b]fluoranthene ring and a picene ring. p is 0 or 1.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
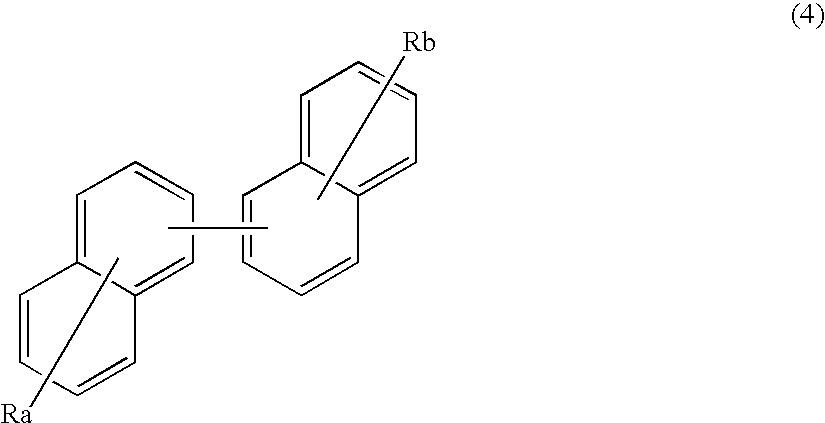
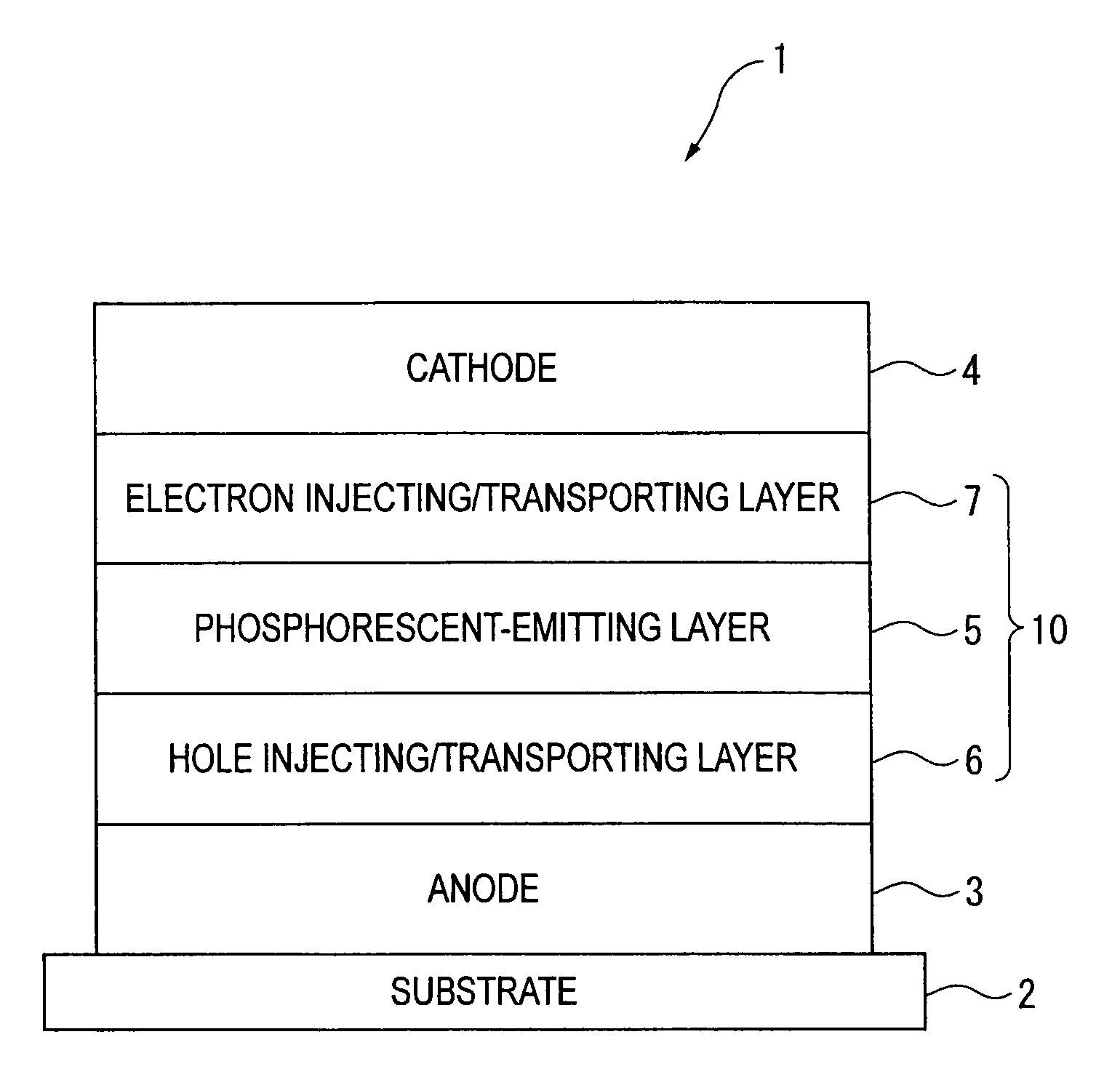
Organic electroluminescence device and material for organic electroluminescence device
ActiveUS20090045730A1Improve efficiencyLong life-timeOrganic chemistryDischarge tube luminescnet screensOrganic filmBenzo(c)phenanthrene
An organic electroluminescence device includes: a cathode; an anode; and a single-layered or multilayered organic thin-film layer provided between the cathode and the anode. The organic thin-film layer includes at least one emitting layer. The at least one emitting layer contains at least one phosphorescent material and a host material represented by the following formula (1).Ra-Ar1-Rb (1)In the formula, Ar1, Ra and Rb each represent a substituted or unsubstituted benzene ring or a condensed aromatic hydrocarbon ring selected from a substituted or unsubstituted naphthalene ring, a substituted or unsubstituted chrysene ring, a substituted or unsubstituted fluoranthene ring, a substituted or unsubstituted phenanthrene ring, a substituted or unsubstituted benzophenanthrene ring, a substituted or unsubstituted dibenzophenanthrene ring, a substituted or unsubstituted triphenylene ring, a substituted or unsubstituted benzo[a]triphenylene ring, a substituted or unsubstituted benzochrysene ring, a substituted or unsubstituted benzo[b]fluoranthene ring and a substituted or unsubstituted picene ring. Substituents for Ra and Rb are not aryl groups.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
Materials for use in electrophoretic displays
The image stability of electrophoretic media, comprising a plurality of particles disposed in a fluid and capable of moving through the fluid upon application of an electric field to the medium, can be improved by including in the fluid either a polystyrene or an aggregating diblock copolymer which forms micelle-like structures in the fluid, the diblock copolymer having a first block soluble in the fluid and a second block not swellable by the fluid. In variable transmission electrophoretic media, haze can be reduced by using as the fluid a mixture of a partially hydrogenated aromatic hydrocarbon and a terpene.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Precursor source mixtures
A precursor source mixture useful for CVD or ALD of a film comprising: at least one precursor composed of an element selected from the group consisting of Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Fr, Be, Mg, Ti, Zr, Hf, Sc, Y, La, V, Nb, Ta, Cr, Mo, W, Mn, Re, Fe, Ru, Os, Co, Rh, Ir, Ni, Pd, Pt, Cu, Ag, Au, Zn, Cd, Hg, B, Al, Ga, In, Tl, Si, Ge, Sn, Pb, As, P, Sb and Bi, to which is bound at least one ligand selected from the group consisting of hydride, alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkenyl, aryl, alkyne, carbonyl, amido, imido, hydrazido, phosphido, nitrosyl, nitryl, nitrate, nitrile, halide, azide, alkoxy, siloxy, silyl, and halogenated, sulfonated or silyated derivatives thereof, which is dissolved, emulsified or suspended in an inert liquid selected from the group consisting of aliphatic hydrocarbons, aromatic hydrocarbons, alcohols, ethers, aldehydes, ketones, acids, phenols, esters, amines, alkylnitrile, halogenated hydrocarbons, silyated hydrocarbons, thioethers, amines, cyanates, isocyanates, thiocyanates, silicone oils, nitroalkyl, alkylnitrate, and mixtures thereof. The precursor source mixture may be a solution, emulsion or suspension and may consist of a mixture of solid, liquid and gas phases which are distributed throughout the mixture.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Hydroalkylation of aromatic hydrocarbons
InactiveUS6037513AHigh activityHigh selectivityMolecular sieve catalystsOrganic compound preparationBenzeneX-ray
There is described a process and a catalyst for the hydroalkylation of an aromatic hydrocarbon, particularly benzene, wherein the catalyst comprises a first metal having hydrogenation activity and a crystalline inorganic oxide material having a X-ray diffraction pattern including the following d-spacing maxima 12.4+ / -0.25, 6.9+ / -0.15, 3.57+ / -0.07 and 3.42+ / -0.07.
Owner:MOBIL OIL CORP
Organic electroluminescent device
InactiveUS20070104977A1Improve efficiencyHigh color purityDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsDopantAryl
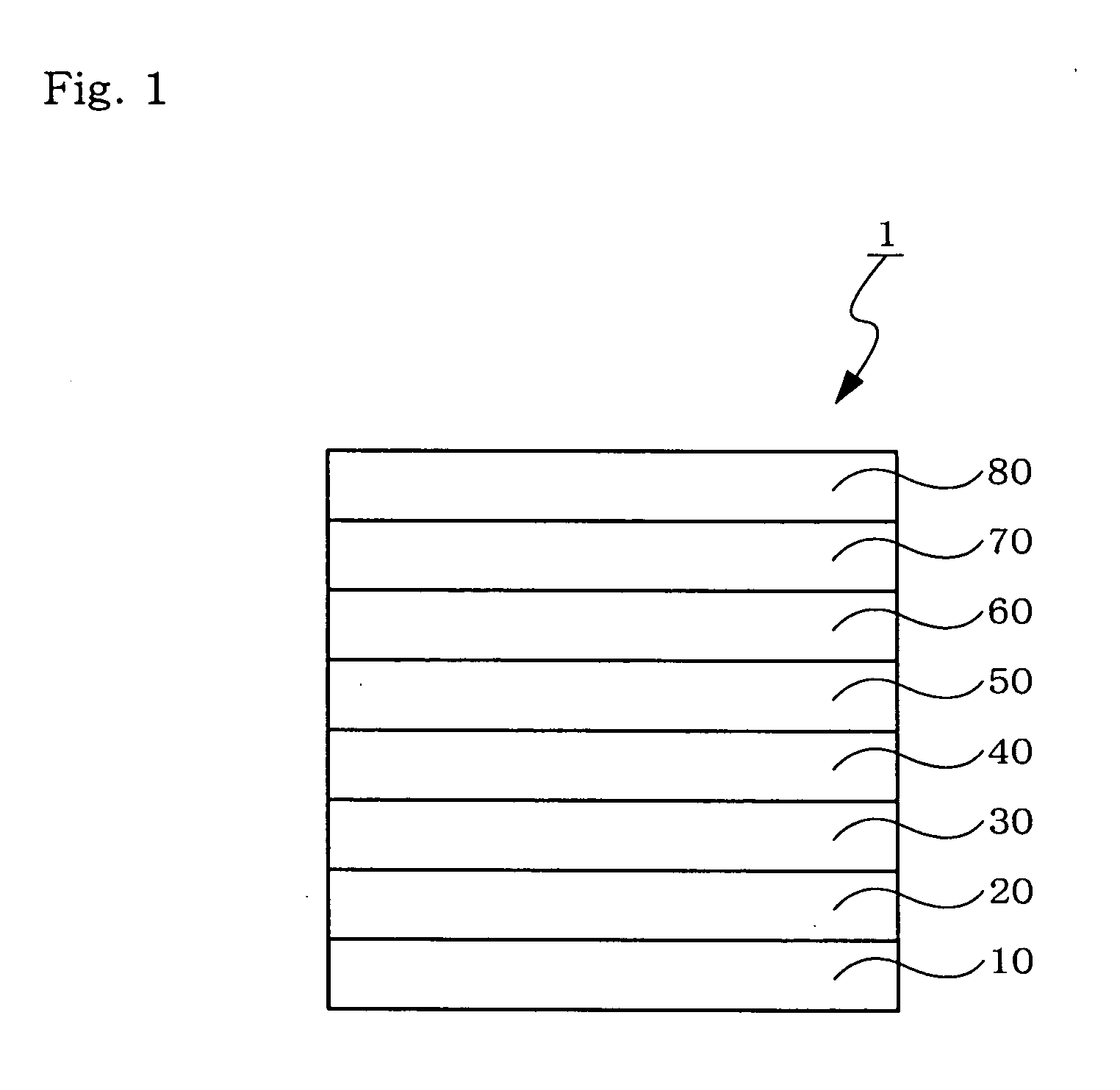
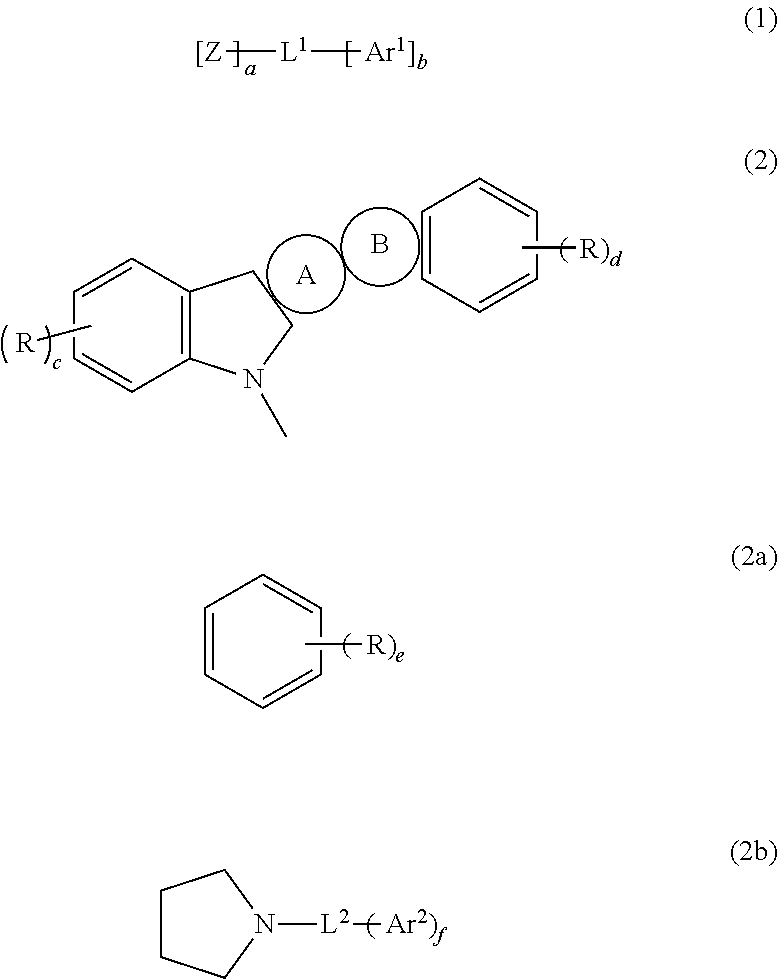
An organic electroluminescent device 1 comprising, an emitting layer (50) and an electron-transporting layer (60) between a cathode (80) and an anode (20), the electron-transporting layer (60) comprising a compound represented by formula (1), the emitting layer (50) comprising a host material which is a compound with an energy gap of 2.8 eV or less represented by formula (2) and a dopant which is an indenoperylene derivative, A-B (1) wherein A is an aromatic hydrocarbon group with three or more carbocycles and B is a substituted or unsubstituted heterocyclic group, X—(Y)n (2) wherein X is a condensed aromatic ring group with three or more carbocycles, Y is a group selected from substituted or unsubstituted aryl, substituted or unsubstituted diarylamino, substituted or unsubstituted arylalkyl and substituted or unsubstituted alkyl groups, and n is an integer of 1 to 6, provided that Ys may be the same or different when n is 2 or more.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
Electron transporting compounds and organic electroluminescent devices using the same
InactiveUS20140284580A1Prolonged lifetime stabilityLow working voltageSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectronic transmissionPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
Disclosed is a novel compound of Formula 1 and an organic electroluminescent device using the same. In Formula 1, X and Y independently represents a hydrogen, an aromatic or a hetero aromatic hydrocarbon having C5 to C10 carbons; X and Y may be the same or different; Ar1 to Ar2 each represent a hydrogen, an unsubstituted or substituted aromatic hydrocarbon having C4 to C12 carbons, or an unsubstituted or substituted condensed polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon having C4 to C12 carbons; Ar1 to Ar2 can form a fused aromatic ring system with the adjacent aromatic hydrocarbons. The compound of Formula 1 is present in the electron injection or a transport material, or an exciton blocking layer in the organic light emitting device, and thereby improving the device stability, lowering the operational voltage.
Owner:E RAY OPTOELECTRONICS TECH
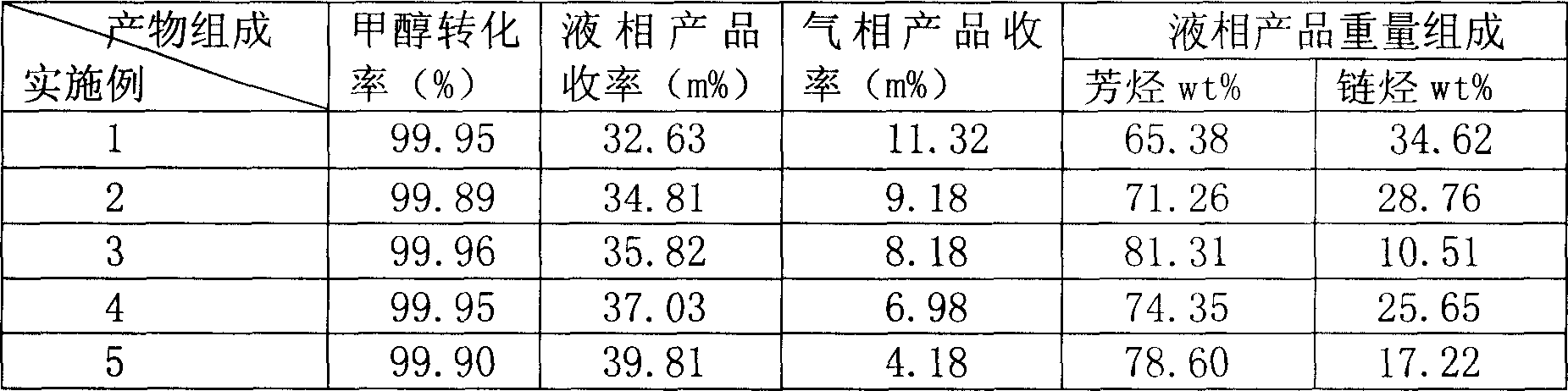
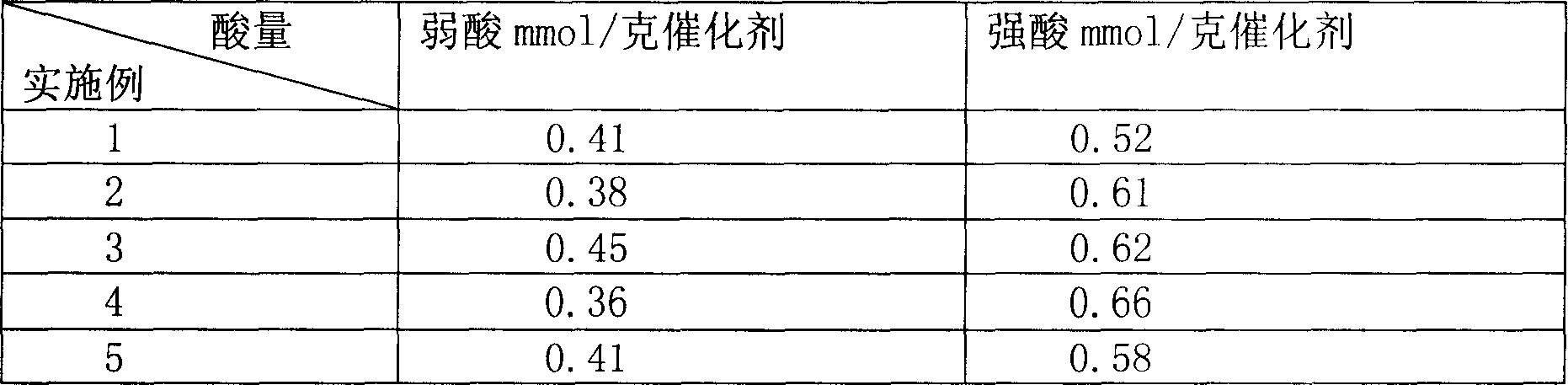
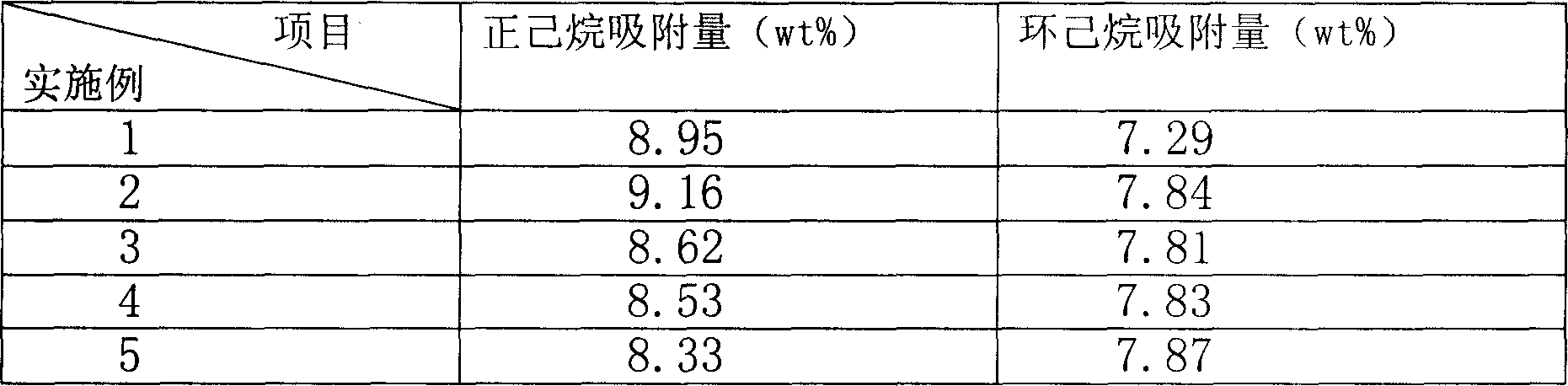
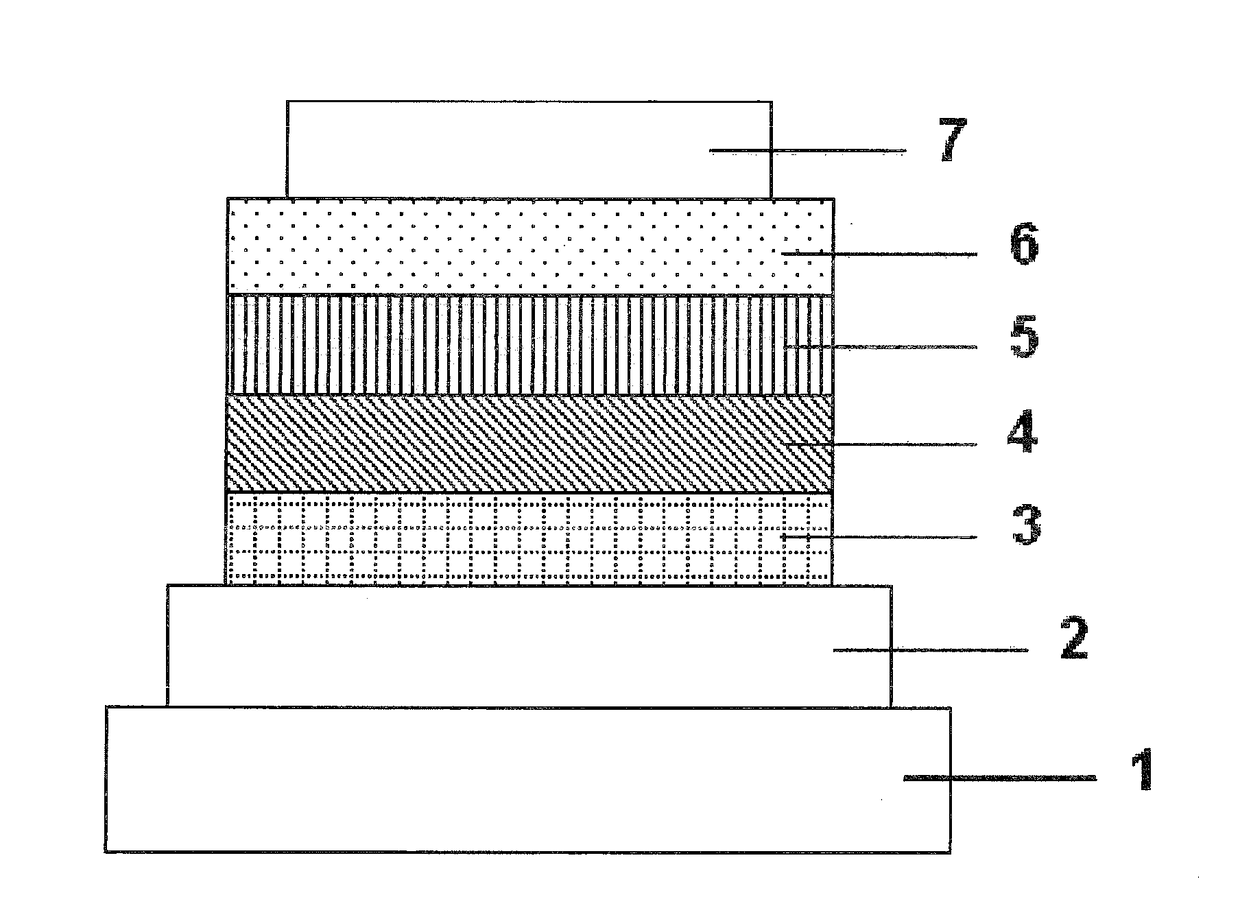
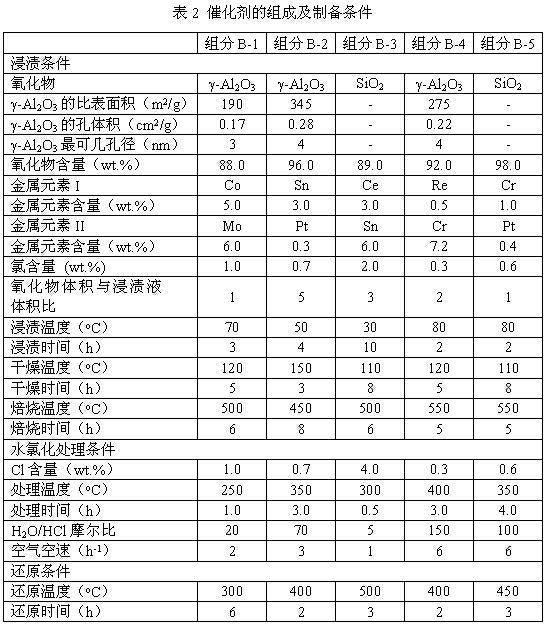
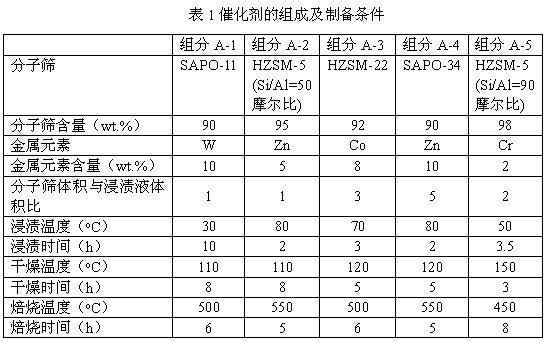
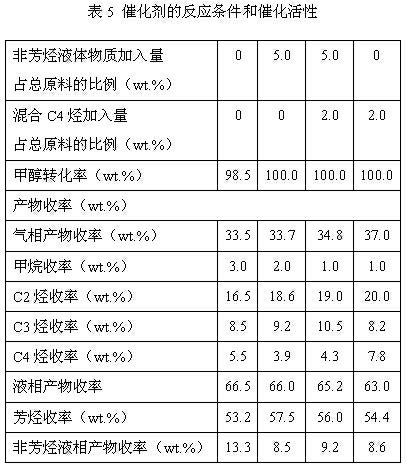
Process of methanol conversion for preparing arene and catalyst and catalyst preparation method
InactiveCN1880288AHigh selectivityHigh flexibility in process operationMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbonsGas phaseAromatic hydrocarbon
This invention relates to a process for transforming methanol to aromatic hydrocarbons, comprising: use methanol as raw material, with modified ZSM-5 molecular sieve as catalyst, under conditions of operation pressure 0.1-5.0Mpa, operation temperature 300-460Deg C, raw material liquid air speed 0.1-6.0h-1, transformed to products with aromatic hydrocarbons as main components; separate the gas-phase products lower carbon hydrocarbons from the liquid-phase C5+ hydrocarbons by cooling separation; the liquid-phase C5+ hydrocarbons then can be separated to be aromatic hydrocarbons and non-aromatic hydrocarbons by extracting separation. This invention is characterized of high total selectivity of aromatic hydrocarbons and flexible process operation.
Owner:SHANXI INST OF COAL CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Organic electroluminescent element
InactiveUS20170263869A1Reduce the driving voltageSolve low luminous efficiencyOrganic chemistryElectroluminescent light sourcesDopantHost material
Provided is a homogeneous organic EL device having a low driving voltage, high luminous efficiency, and a long lifetime. The device is an organic electroluminescent device including a light-emitting layer between an anode and a cathode opposite to each other, in which: the light-emitting layer contains a host material and a light-emitting dopant material; the host material is a material obtained by preliminarily mixing two or more kinds of compounds selected from compounds each having a structure in which two nitrogen atoms of an indolocarbazole ring are each substituted with an aromatic hydrocarbon group or an aromatic heterocyclic group; and the light-emitting layer is formed by co-depositing the preliminarily mixed host material and the light-emitting dopant material in a vacuum.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CHEMICAL CO LTD
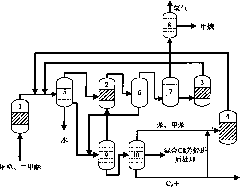
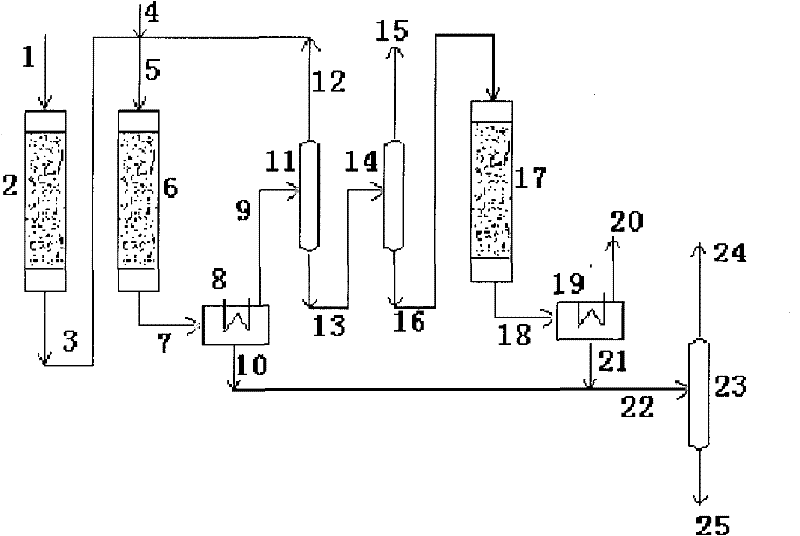
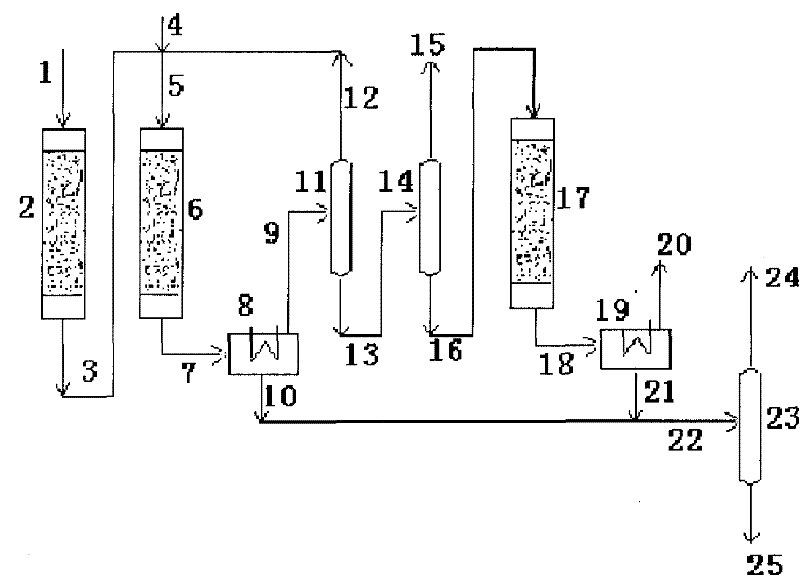
System and process for preparing aromatic hydrocarbon by converting methanol or dimethyl ether
ActiveCN101823929AHigh yieldHigh selectivityHydrogen separation using liquid contactHydrocarbon from oxygen organic compoundsAromatizationAromatic hydrocarbon
The invention relates to a system and a process for preparing aromatic hydrocarbon by converting methanol or dimethyl ether and belongs to the technical field of aromatic hydrocarbon production. The methanol or the dimethyl ether serving as a raw material firstly reacts in an aromatization reactor; a reaction product is separated; H2, methane, mixed C8 aromatic hydrocarbon and partial C9s + hydrocarbons serving as products are output from the system; and C2+ non-aromatic hydrocarbon and aromatic hydrocarbons except the mixed C8 aromatic hydrocarbon and the partial C9s + hydrocarbons are take as a circular material flow and return to corresponding reactors for further aromatization reaction. By separating and recycling the product obtained in the process of aromizing the methanol or the dimethyl ether, the system and the process improve the yield and selectivity of the aromatic hydrocarbon; and moreover, the process is flexible, and target products can be changed according to market demands.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Fluorinated surfactants for use in making a fluoropolymer
InactiveUS20070117914A1Convenient and easy preparationPrepared cost-effectivelyOrganic active ingredientsOrganic compound preparationEmulsion polymerizationCarboxylic acid
The present invention provides a fluorinated surfactant having the general formula:[Rf—(O)t—CQH—CF2—O]n—R-G (I)wherein Rf represents a partially or fully fluorinated aliphatic group optionally interrupted with one or more oxygen atoms, Q is CF3 or F, R is an aliphatic or aromatic hydrocarbon group, G represents a carboxylic or sulphonic acid or salt thereof, t is 0 or 1 and n is 1, 2 or 3. The surfactant is particularly useful in polymerizing fluorinated monomers in an aqueous emulsion polymerization.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Hydroalkylation of aromatic hydrocarbons
InactiveUS6730625B1High activityHigh selectivityMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieve catalystBenzeneX-ray
There is described a process and a catalyst for the hydroalkylation of an aromatic hydrocarbon, particularly benzene, wherein the catalyst comprises a first metal having hydrogenation activity and a crystalline inorganic oxide material having a X-ray diffraction pattern including the following d-spacing maxima 12.4±0.25, 6.9±0.15, 3.57±0.07 and 3.42±0.07.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CORP (US)
Organometallic complex and light emitting element, light emitting device, and electronic device using the organometallic complex
InactiveUS20070244320A1High light emitting efficiencyReduce power consumptionGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsSolid-state devicesArylHydrogen
An organometallic complex having a structure represented by the following general formula (G1) is provided. (In the formula, A represents an aromatic hydrocarbon group having 6 to 25 carbon atoms. Further, Z represents any one of hydrogen, an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, an alkoxy group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, or an aryl group having 6 to 25 carbon atoms. In addition, Ar1 represents an aryl group having 6 to 25 carbon atoms. R1 represents any one of hydrogen, an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, or an alkoxy group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms. Further, M is a central metal and represents an element belonging to Group 9 or Group 10.)
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Luminescent element material and luminescent element comprising the same
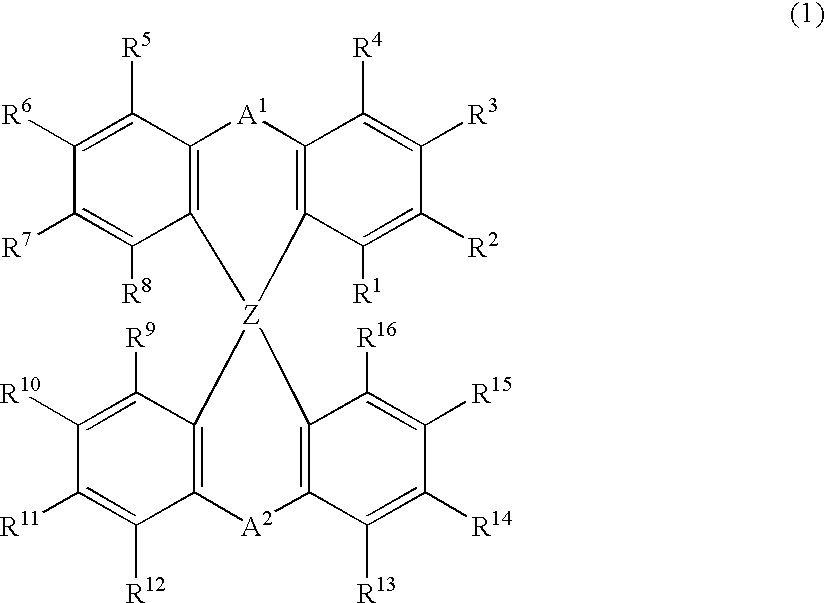
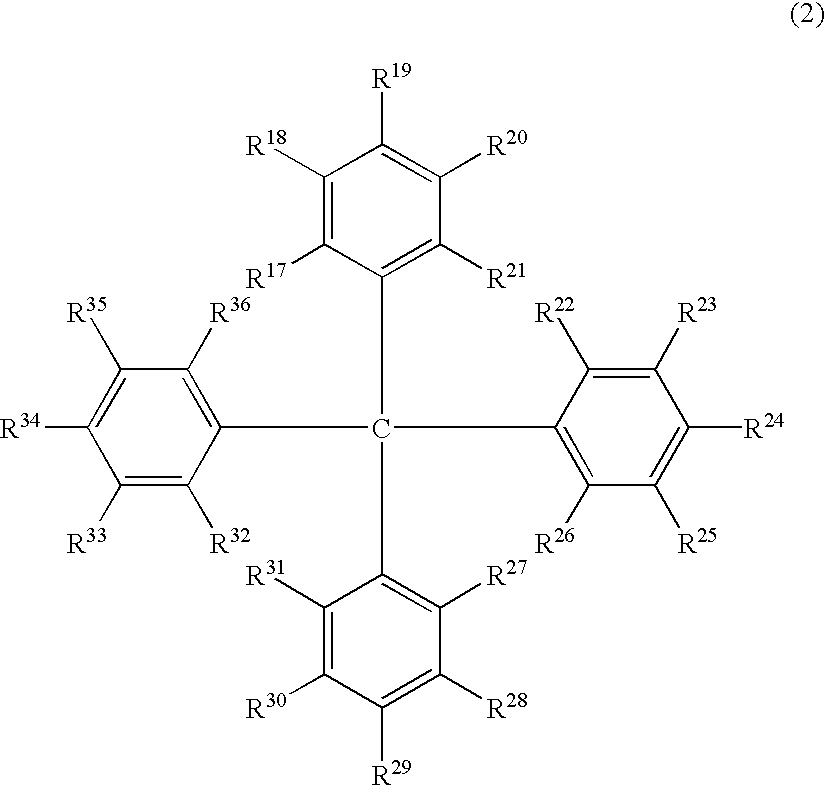
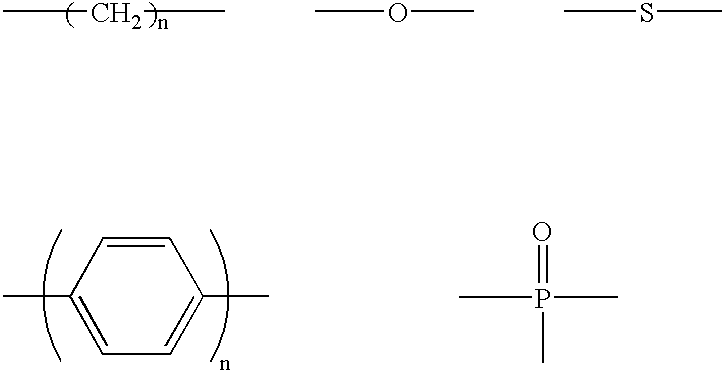
The light emitting device of the present invention relates to a light emitting device which is characterized in that it is a device with an emissive substance present between an anode and cathode, and which emits light by means of electrical energy, and said device has a least one type of compound denoted by (a) to (d) below. (a) A compound having a plurality of 1,7-phenanthroline skeletal structures (b) A benzoquinoline derivative (c) A spiro compound represented by general formula (1) A1 and A2 are each selected from single bonds, substituted or unsubstituted alkyl chains, ether chains, thioether chains, ketone chains and substituted or unsubstituted amino chains. However, A1<> A2. Z represents carbon or silicon. R1 to R16 are each selected from hydrogen, alkyl group, cycloalkyl group, aralkyl group, alkenyl group, cycloalkenyl group, alkynyl group, hydroxyl group, mercapto group, alkoxy group, alkylthio group, aryl ether group, aryl thioether group, aryl group, heterocyclic group, halogen, haloalkane, haloalkene, haloalkyne, cyano group, aldehyde group, carbonyl group, carboxyl group, ester group, carbamoyl group, amino group, nitro group, silyl group, siloxanyl group and a cyclic structure formed with an adjacent substituent. (d) A tetraphenylmethane derivative represented by general formula (2) R17 to R36 are each selected from hydrogen, alkyl group, cycloalkyl group, aralkyl group, alkenyl group, cycloalkenyl group, alkynyl group, hydroxyl group, mercapto group, alkoxy group, alkylthio group, aryl ether group, aryl thioether group, aryl group, heterocyclic group, halogen, haloalkane, haloalkene, haloalkyne, cyano group, aldehyde group, carbonyl group, carboxyl group, ester group, carbamoyl group, amino group, nitro group, silyl group, siloxanyl group and a cyclic structure formed with an adjacent substituent. However, at least one of R17 to R36 is selected from substituents represented by general formula (3). -X-Ar (3) X is a single bond or is selected from the following, and Ar denotes a condensed aromatic ring or heteroaromatic ring. In the case where X is phosphorus oxide, then Ar represents an aromatic hydrocarbon or heteroaromatic ring. n is an natural number.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Method for preparing aromatic hydrocarbons and propylene simultaneously employing methanol/dimethyl ether
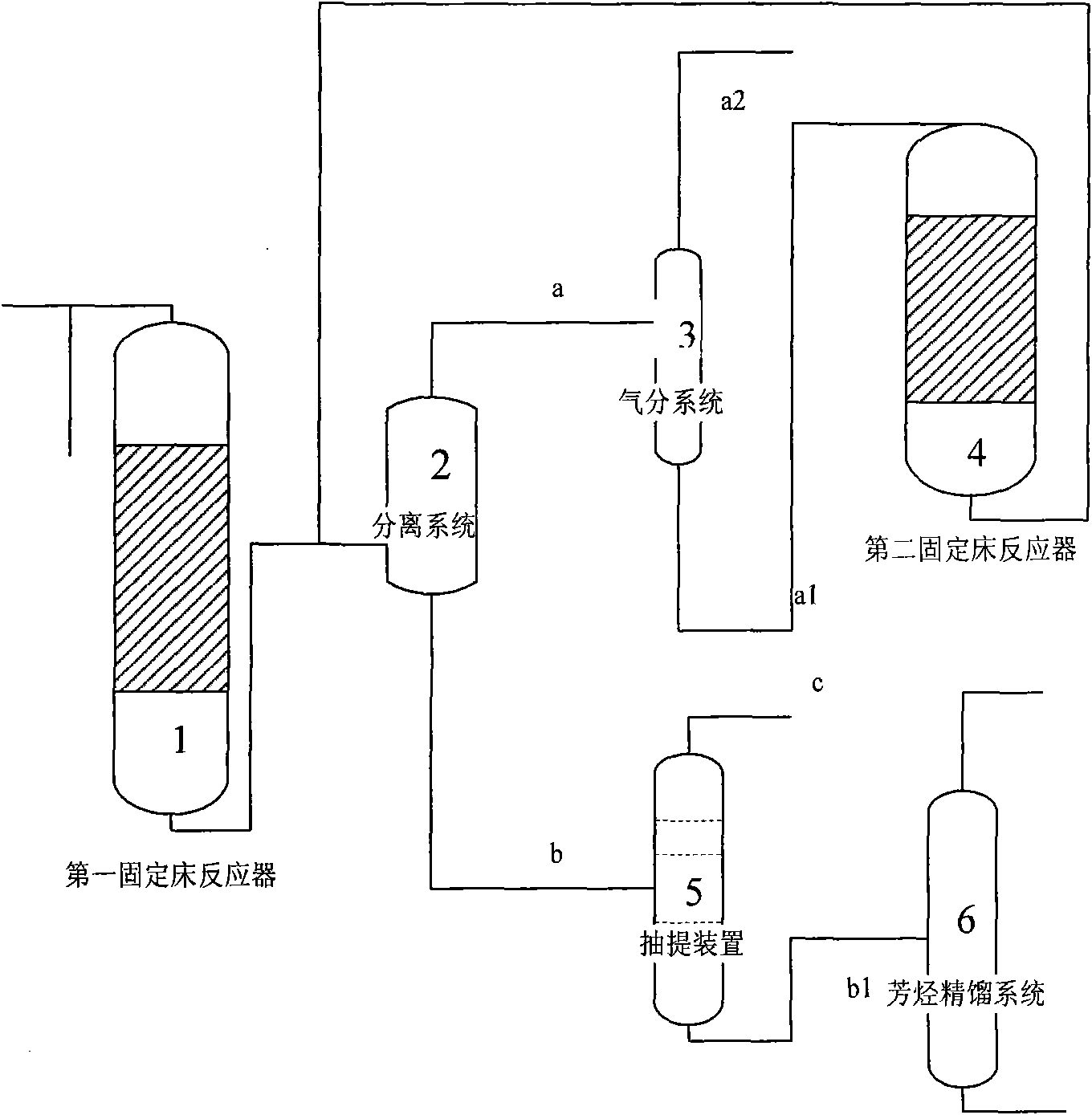
InactiveCN101607858AHigh selectivityIncrease added valueMolecular sieve catalystsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsMolecular sieveFixed bed
The invention discloses a method for preparing aromatic hydrocarbons and propylene simultaneously employing methanol / dimethyl ether, comprising the following steps: 1) placing raw materials containing methanol or / and dimethyl ether, metals and molecular sieve based catalyst which is modified through silanizing in a first fixed bed reactor to perform catalytic reaction; 2) separating the products obtained in step 1) to obtain propylene, then placing propylene in a second fixed bed reactor with molecular sieve based catalyst which is modified by using metals to react, then performing aromatization on the obtained product in step 1) and obtaining aromatic hydrocarbons; then separating to obtain toluene and sending toluene back to the outlet of the first fixed bed reactor as a raw material. In the method, methanol is converted and prepared to aromatic hydrocarbons while propylene is produced at the same time and the content of paraxylene in aromatic hydrocarbons is high. In the products prepared by the method, the content of propylene can reach above 20%, the content of aromatic hydrocarbons can reach above 58wt% and the content of paraxylene in aromatic hydrocarbons is more than 35wt%.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +2
Light emitting device and electronic appliance using the same
InactiveUS20060292394A1Easy to changeDistanceDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesVanadium oxideOrganic compound
A light emitting device comprises a pair of electrodes and a mixed layer provided between the pair of electrodes. The mixed layer contains an organic compound which contains no nitrogen atoms, i.e., an organic compound which dose not have an arylamine skeleton, and a metal oxide. As the organic compound, an aromatic hydrocarbon having an anthracene skeleton is preferably used. As such an aromatic hydrocarbon, t-BuDNA, DPAnth, DPPA, DNA, DMNA, t-BuDBA, and the like are listed. As the metal oxide, molybdenum oxide, vanadium oxide, ruthenium oxide, rhenium oxide, and the like are preferably used. Further, the mixed layer preferably shows absorbance per 1 μm of 1 or less or does not show a distinct absorption peak in a spectrum of 450 to 650 nm when an absorption spectrum is measured.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
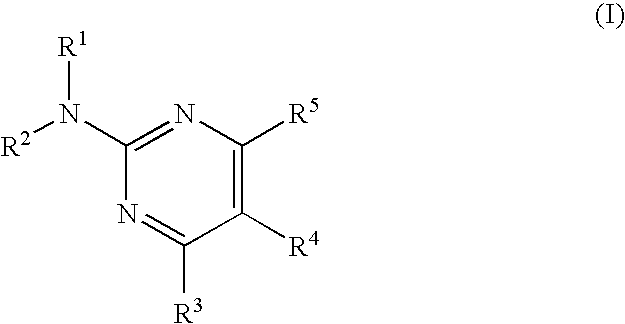
Pyrimidine compound and medicinal composition thereof
The present invention provides a novel pyrimidine compound having an excellent adenosine receptor (A1, A2A, A2B receptor) antagonistic action. More specifically, it provides a compound represented by the following formula, a salt thereof or a solvate of them. In the formula, R1 and R2 are the same as or different from each other and each represents a hydrogen atom, an alkyl group having one to six carbon atoms which may be substituted, an alkenyl group having two to six carbon atoms which may be substituted, an alkynyl group having two to six carbon atoms which may be substituted, a cycloalkyl group having three to eight carbon atoms which may be substituted, a cycloalkenyl group having three to eight carbon atoms which may be substituted, a 5 to 14-membered non-aromatic heterocyclic group which may be substituted, an aromatic hydrocarbon cyclic group having six to fourteen carbon atoms which may be substituted, a 5 to 14-membered aromatic heterocyclic group which may be substituted, an acyl group having one to six carbon atoms which may be substituted or an alkylsulfonyl group having one to six carbon atoms which may be substituted; R3 represents a hydrogen atom, a halogen atom, a cyano group, an alkyl group having one to six carbon atoms which may be substituted, an alkenyl group having two to six carbon atoms which may be substituted, an alkynyl group having two to six carbon atoms which may be substituted, an aromatic hydrocarbon cyclic group having six to fourteen carbon atoms which may be substituted, a 5 to 14-membered aromatic heterocyclic group which may be substituted, a nitrogen atom which may be substituted, an oxygen atom which may be substituted or a sulfur atom which may be substituted; R4 represents an aromatic hydrocarbon cyclic group having six to fourteen carbon atoms which may be substituted, a 5 to 14-membered aromatic heterocyclic group which may be substituted or a 5 to 14-membered non-aromatic heterocyclic group having at least one or more unsaturated bonds which may be substituted; and R5 represents an aromatic hydrocarbon cyclic group having six to fourteen carbon atoms which may be substituted or a 5 to 14-membered aromatic heterocyclic group which may be substituted.
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
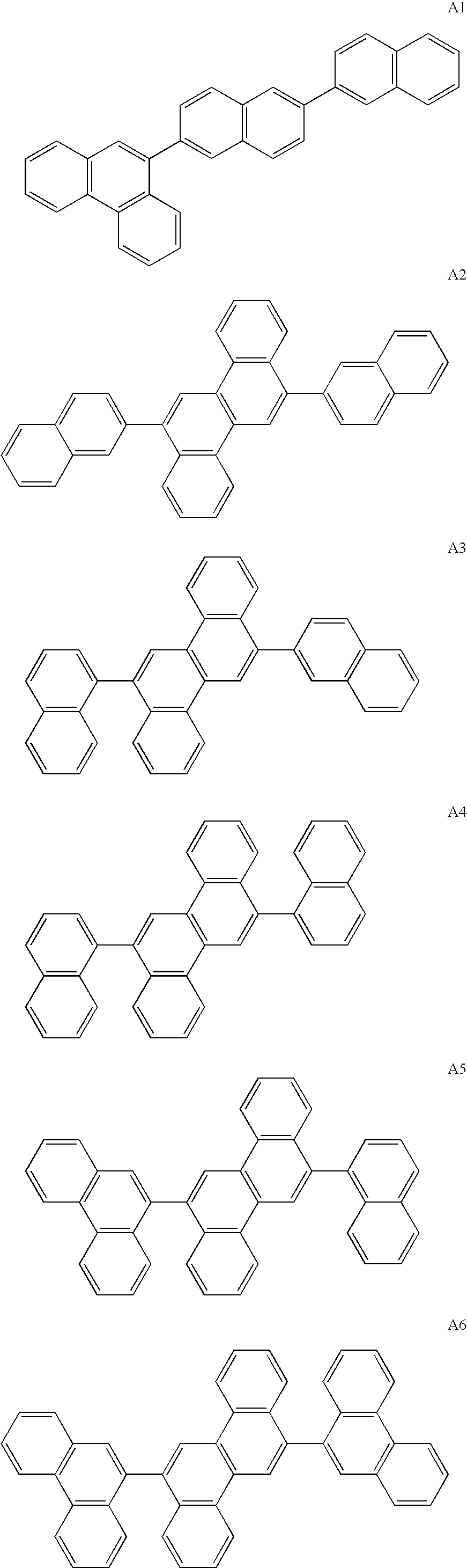
Naphthalene derivative, material for organic electroluminescence device, and organic electroluminescence device using the same
InactiveUS20090008607A1Excellent in luminous efficiency and heat resistance and lifetimeImprove efficiencyOrganic chemistryElectrical apparatusAlkoxy groupOrganic electroluminescence
A naphthalene derivative represented by the following formula (1) is provided. In the formula (1), Ar1 and Ar2 each represent an aromatic hydrocarbon cyclic group having 6 to 18 carbon atoms forming a ring. The aromatic hydrocarbon cyclic group has none of anthracene skeleton, pyrene skeleton, aceanthrylene skeleton and naphthacene skeleton. Ar3 represents a benzene skeleton or a naphthalene skeleton. R1 and R2 each represent an alkyl group, a cycloalkyl group, an alkoxy group, a cyano group, a silyl group or a halogen atom. a and b each represent an integer in a range of 0 to 4. m and n each represent an integer in a range of 1 to 4.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
Organic electroluminescent device
InactiveUS6268071B1Easy to useDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesBenzeneAliphatic hydrocarbon
An organic EL device comprises a substrate, an organic EL structure stacked on the substrate, a sealing plate located on the organic EL structure with a predetermined space therebetween, and a sealing adhesive agent for fixing the sealing plate on the substrate and thereby closing up the organic EL structure. The sealing adhesive agent is a photo-curing type adhesive agent which, upon photo-curing, generates gases under heating conditions of 85° C. and 60 minutes. In these gases, the total amount of a low-molecular straight-chain aliphatic hydrocarbon which may have a substituent, an aromatic hydrocarbon which may have a substituent, an alicyclic hydrocarbon which may have a substituent, and a heterocyclic compound and a siloxane which may have a substituent is 200 mug / g or lower calculated as benzene. The organic EL device of the invention is reduced as much as possible in terms of a deterioration with time, and can maintain its initial performance over a long period of time, so that it can have an ever longer service life.
Owner:FUTABA CORPORATION
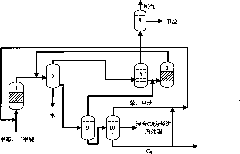
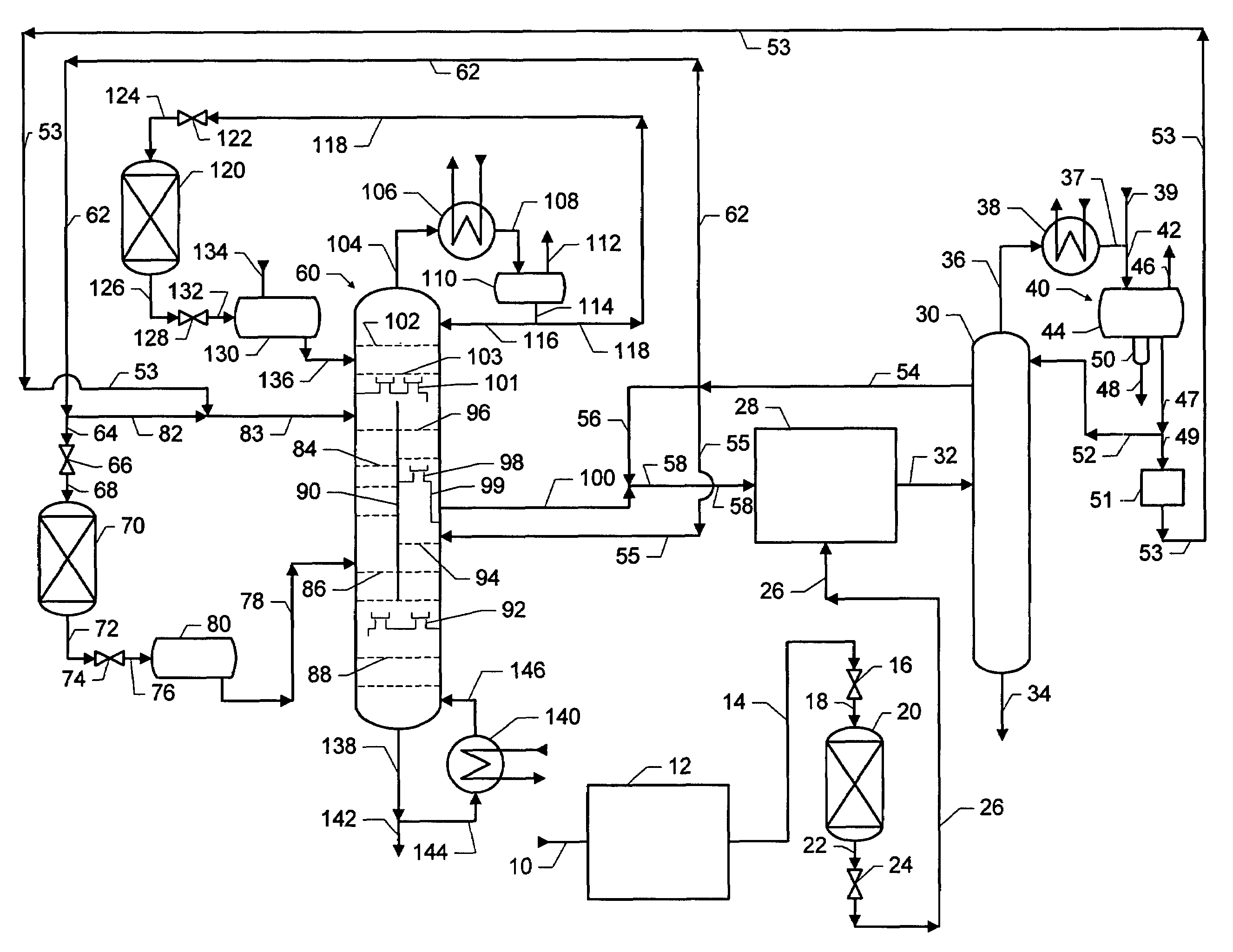
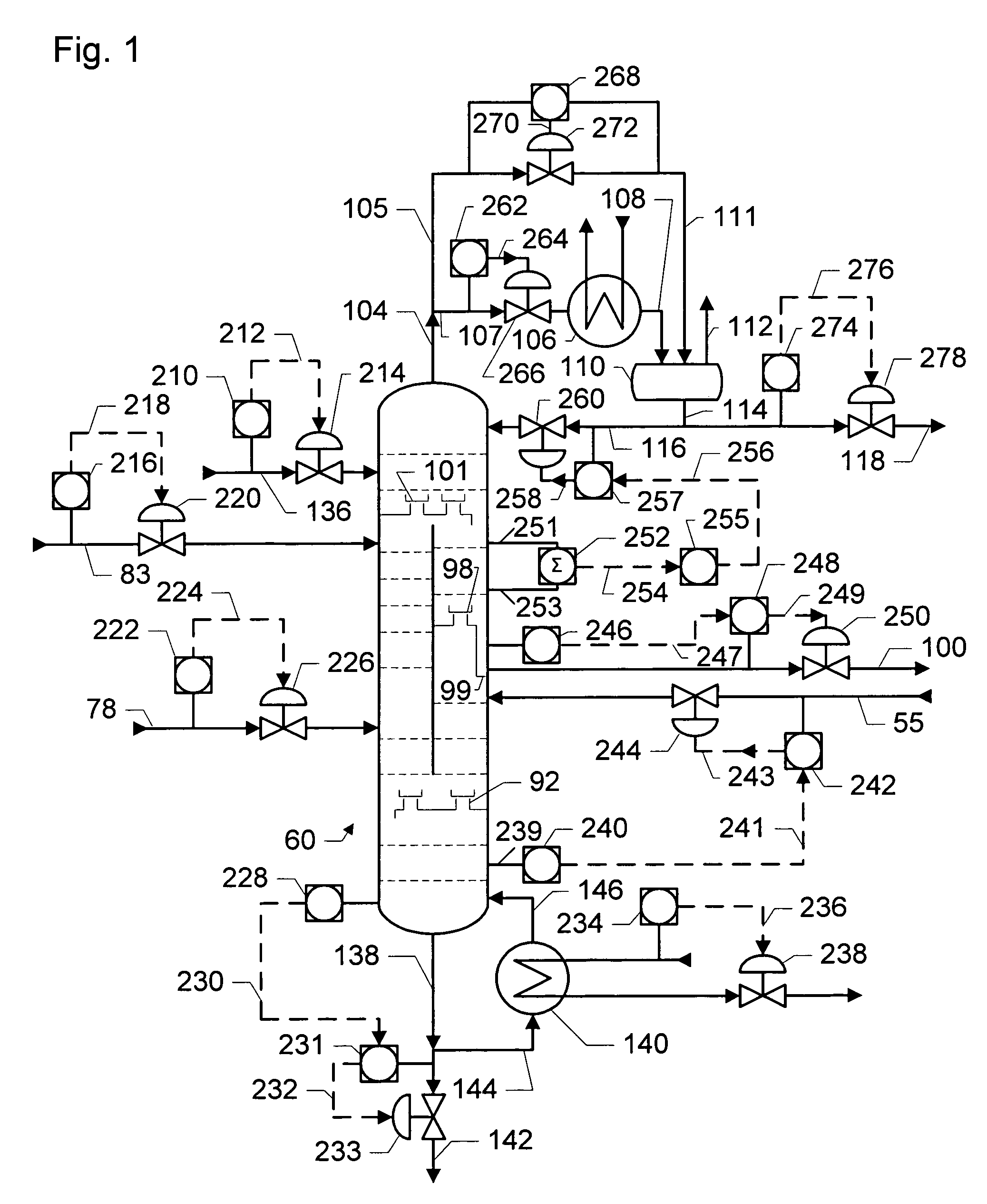
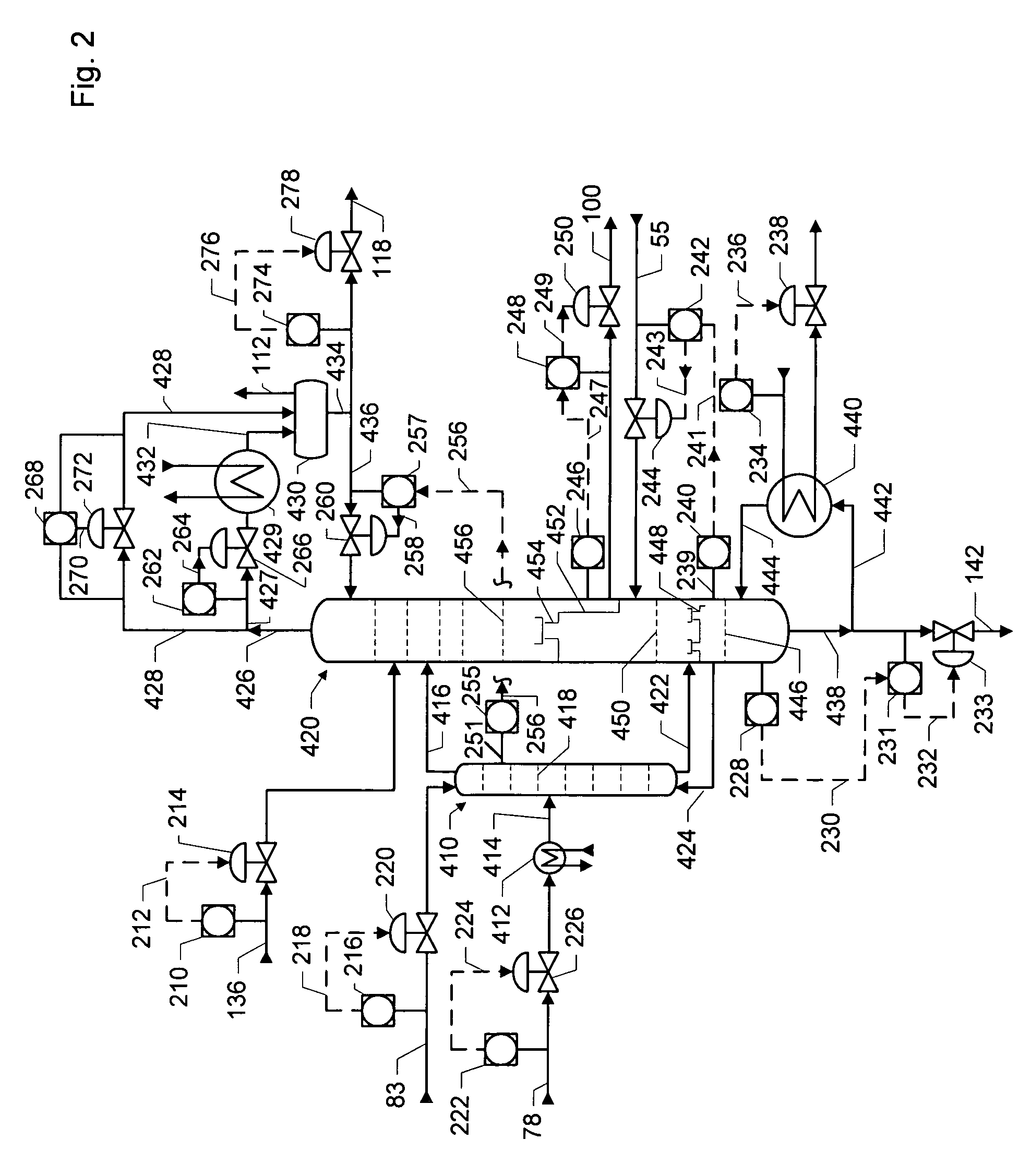
Dividing wall distillation column control apparatus
InactiveUS7267746B1Low costThermal non-catalytic crackingDistillation regulation/controlDistillationEngineering
A control apparatus and control method for controlling the separation in a dividing wall distillation column of at least two feeds into at least three products is disclosed. The apparatus uses a temperature measuring device to measure the temperature of fluid in the column, a controller, and a means for adjusting the temperature of fluid in the column. The temperature measuring device may be on either side of the dividing wall or above or below the dividing wall, and more than one such device may be used. The apparatus and method may be used in the production of alkylaromatic hydrocarbons by alkylating aromatic hydrocarbons with olefinic hydrocarbons.
Owner:UOP LLC
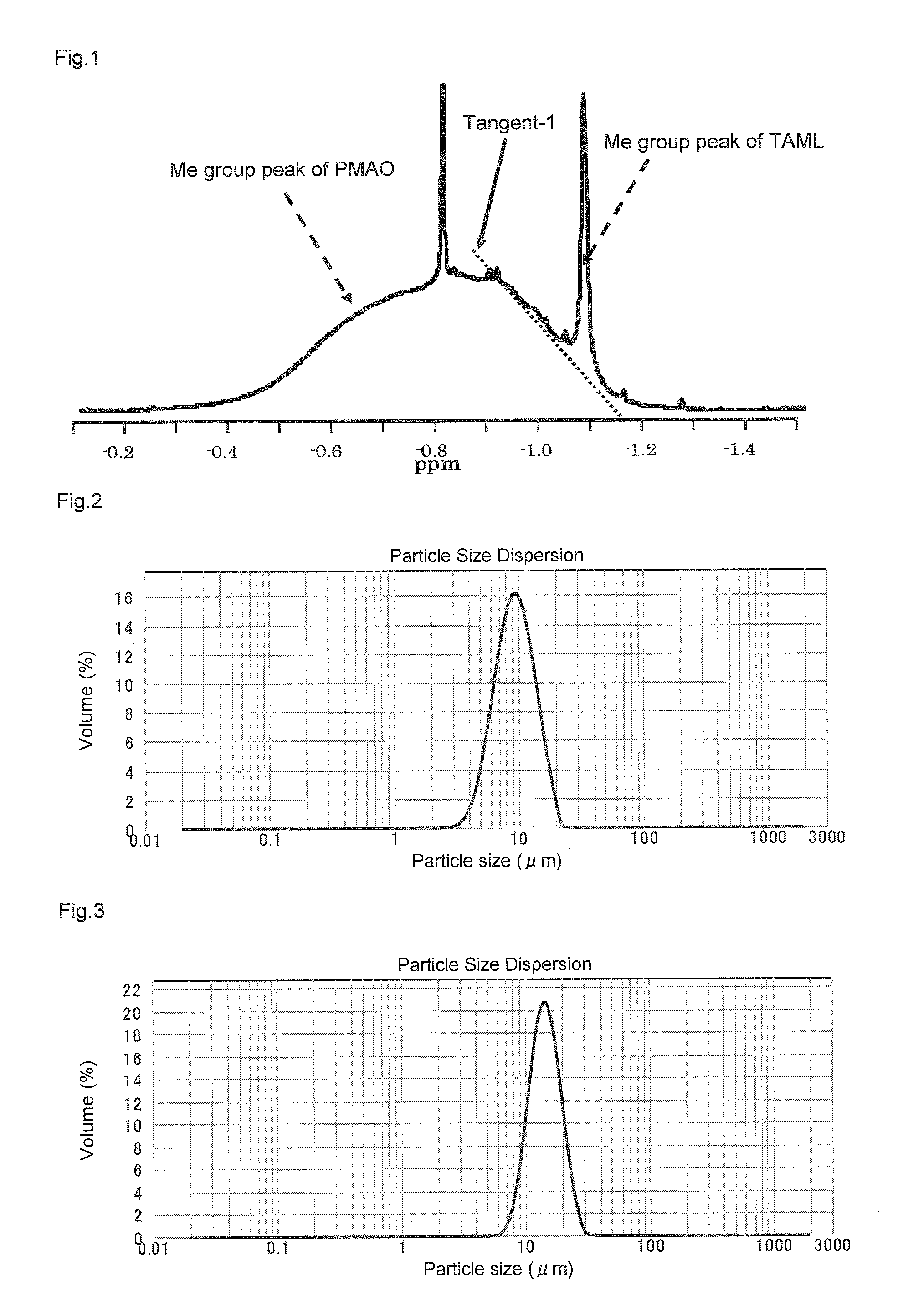
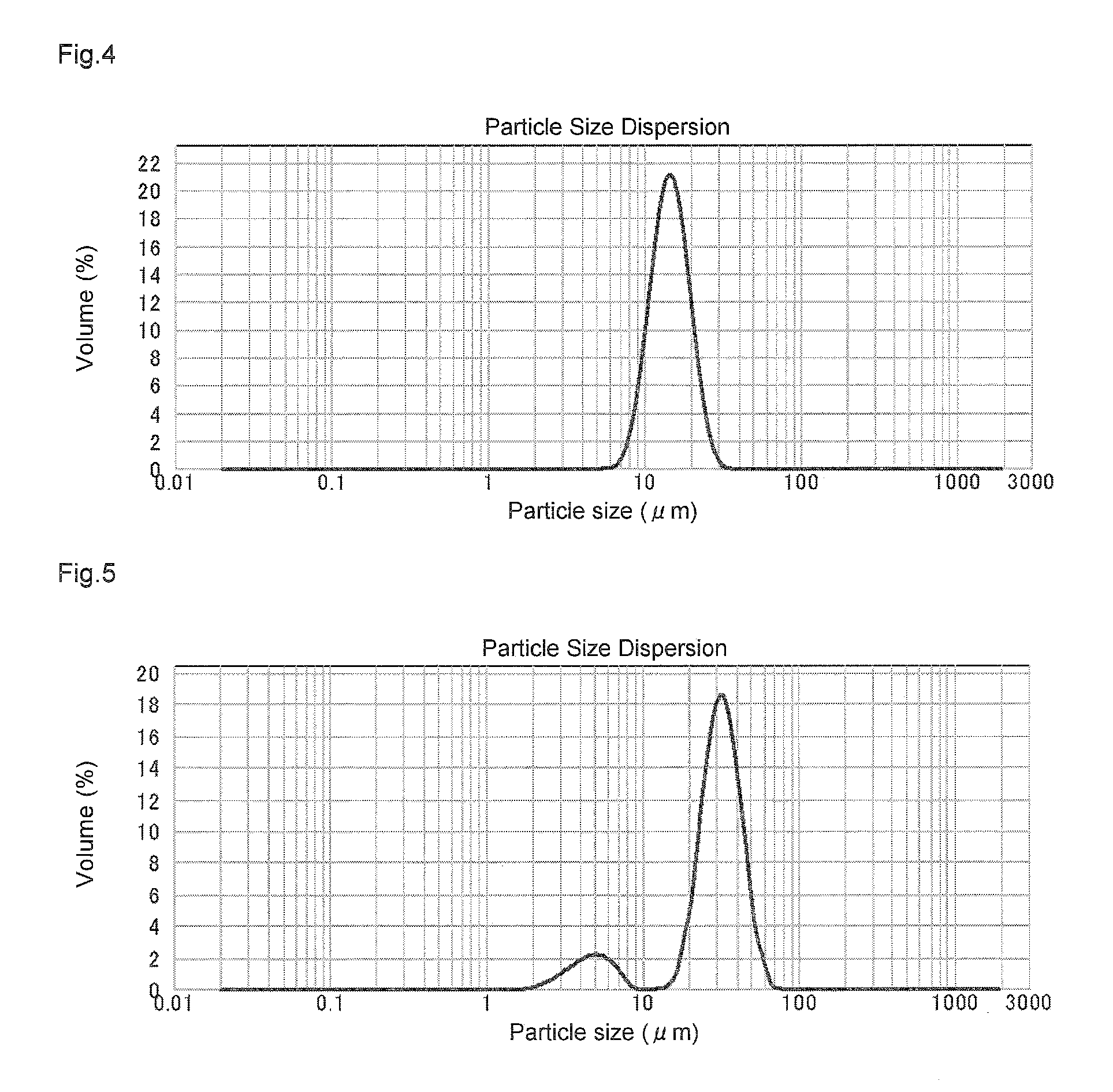
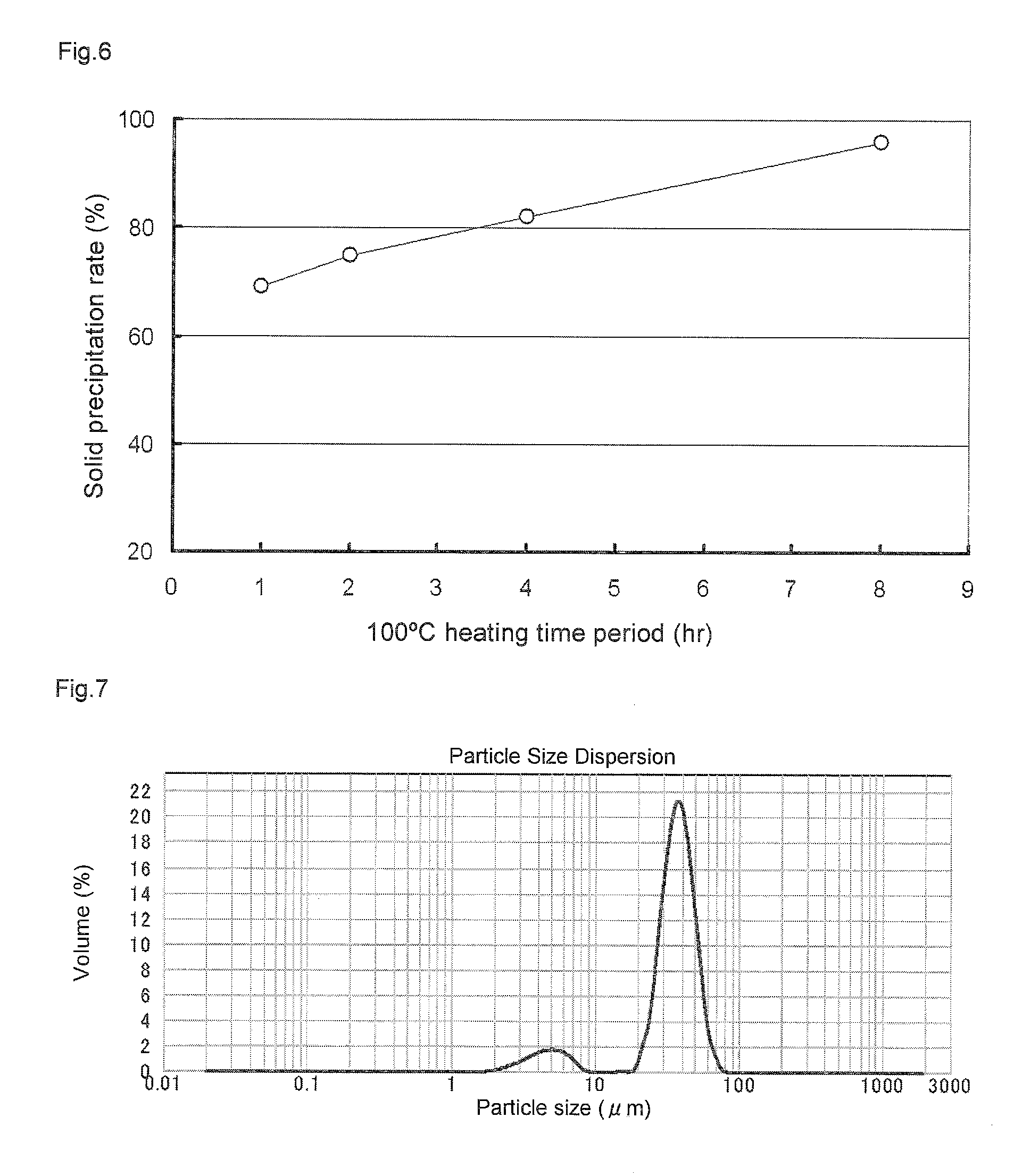
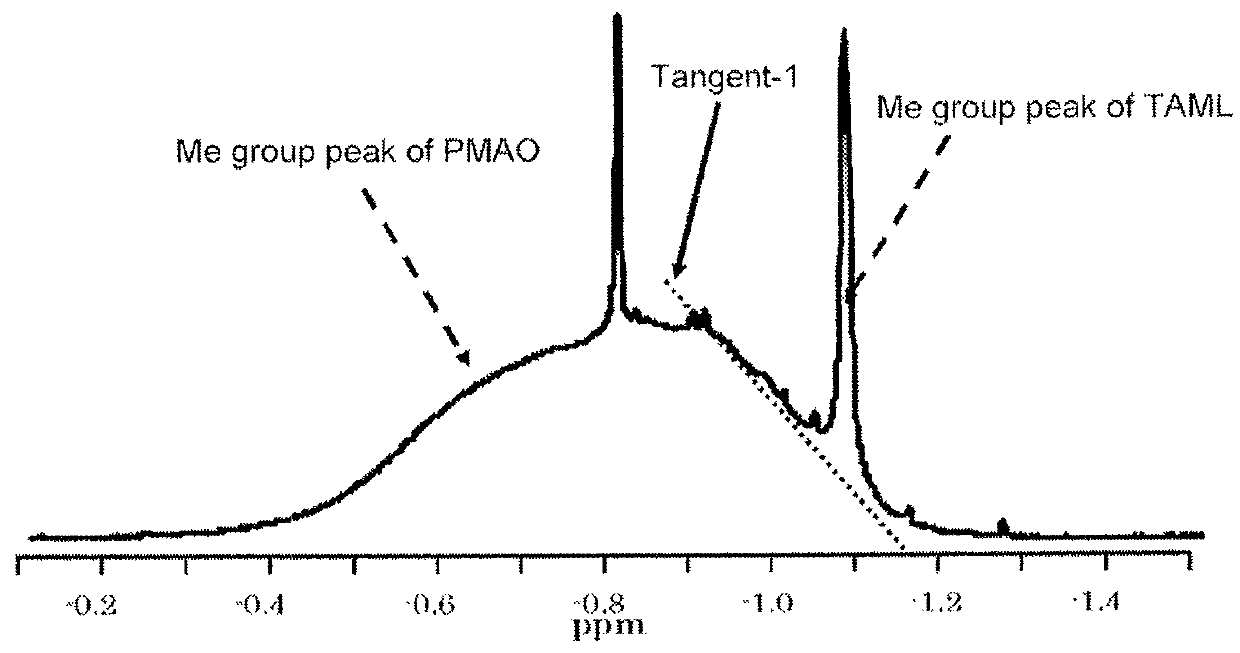
Solid polymethylaluminoxane composition and method for manufacturing same
ActiveUS8404880B2High polymerization activityReduce solubilityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationOlefin polymerizationMethyl group
Owner:TOSOH FINECHEM CORP
Method for producing aromatic hydrocarbon by adopting raw materials containing methanol
InactiveCN102199446ABoost octaneImprove conversion rateHydrocarbon from oxygen organic compoundsLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionNaphthaAromatic hydrocarbon
The invention discloses a method for producing aromatic hydrocarbon by adopting raw materials containing methanol. The raw material containing methanol comprises the methanol and Fischer-Tropsch synthesis naphtha. In the method, the raw materials containing methanol and a catalyst undergo a contact reaction under the condition of producing the aromatic hydrocarbon by using the methanol. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, the problem that great removed heat is needed to be adopted in the prior art is solved; and the method has the advantages of simple flow and simpleness and convenience for operation. By adopting the method provided by the invention and a good method for processing and utilizing Fischer-Tropsch synthesis naphtha components, aromatic hydrocarbon products are produced or the octane value of the Fischer-Tropsch synthesis naphtha components is increased to gasoline mediated components with a high octane value.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +1
Method for manufacturing a small particle diameter product of solid polymethylaluminoxane composition
ActiveUS9340630B2Easy to optimizeHigh yieldGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsThin material handlingParticulatesDiameter product
A solid polymethylaluminoxane composition is provided having uniform particle diameter in the form of fine particles of less than 5 μm employed to polymerize olefins with high polymerization activity without silica. A method for manufacturing thereof, a polymerization catalyst, and a method for manufacturing a polyolefin are also provided. The solid polymethylaluminoxane composition: has an aluminum content within a range of 36 mass % to 43 mass %; has a mole fraction of methyl groups derived from trimethylaluminum moieties relative to the total number of mols of methyl groups of 12 mol % or less; and is particulate having a median diameter based on volume within a range of 0.1 μm to less than 5 μm. In a step of heating an aromatic hydrocarbon solution containing trimethylaluminum and the polymethylaluminoxane to cause solid polymethylaluminoxane composition to precipitate, prior to or during the heat treating step, a dry, inert gas is bubbled through.
Owner:TOSOH FINECHEM CORP
Polymer Compound And Polymer Light-Emitting Device Using The Same
ActiveUS20080138651A1High luminous intensityHigh fluorescence intensityConductive layers on insulating-supportsOrganic chemistryCompound (substance)Polystyrene
High-molecular compounds comprising repeating units represented by the general formula (1) or (2) and having number-average molecular weights of 103 to 108 in terms of polystyrene: (1) [wherein Ar1 and Ar2 are each independently a trivalent aromatic hydrocarbon group or a trivalent heterocyclic group; and X1 and X2 are each independently O, S, C(═O), S(═O), SO2, C(R1)(R2), Si(R3)(R4), N(R5), B(R6), P(R7), or P(═O)(R8), with the provisos that X1 and X2 must not be the same and that X1 and Ar2 are bonded respectively to the adjacent carbon atoms constituting the aromatic ring of Ar1, and X2 and Ar1 are bonded respectively to the adjacent carbon atoms constituting the aromatic ring of Ar2] (2) [wherein Ar3 and Ar4 are each independently a trivalent aromatic hydrocarbon group or a trivalent heterocyclic group; and X3 and X4 are each independently N, B, P, C(R9), or Si(R10), with the provisos that X3 and X4 must not be the same and that X3 and Ar4 are bonded respectively to the adjacent carbon atoms constituting the aromatic ring of Ar3, and X4 and Ar3 are bonded respectively to the adjacent carbon atoms constituting the aromatic ring of Ar4].
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Nanoparticles with controlled architecture and method thereof
The present invention provides polymer nanoparticles with a controlled architecture of nano-necklace, nano-cylinder, nano-ellipsoid, or nano-sphere. The polymer nanoparticle comprises a core polymerized from multiple-vinyl-substituted aromatic hydrocarbons, a shell polymerized from alkyl-substituted styrene, and a polystyrene layer between the core and the shell. The present invention also provides a method of preparing the polymer nanoparticles and a rubber article such as a tire manufactured from a formulation comprising the polymer nanoparticles.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
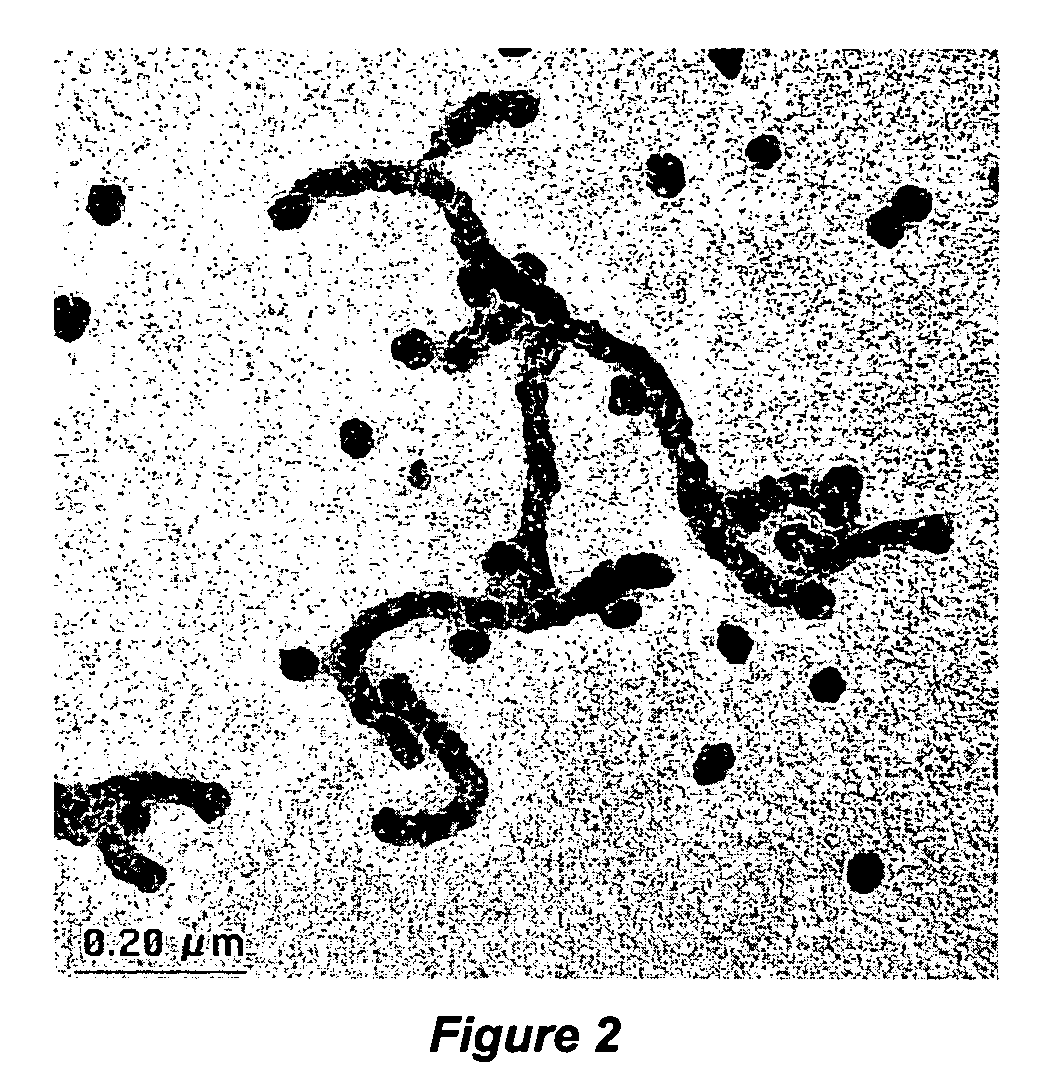
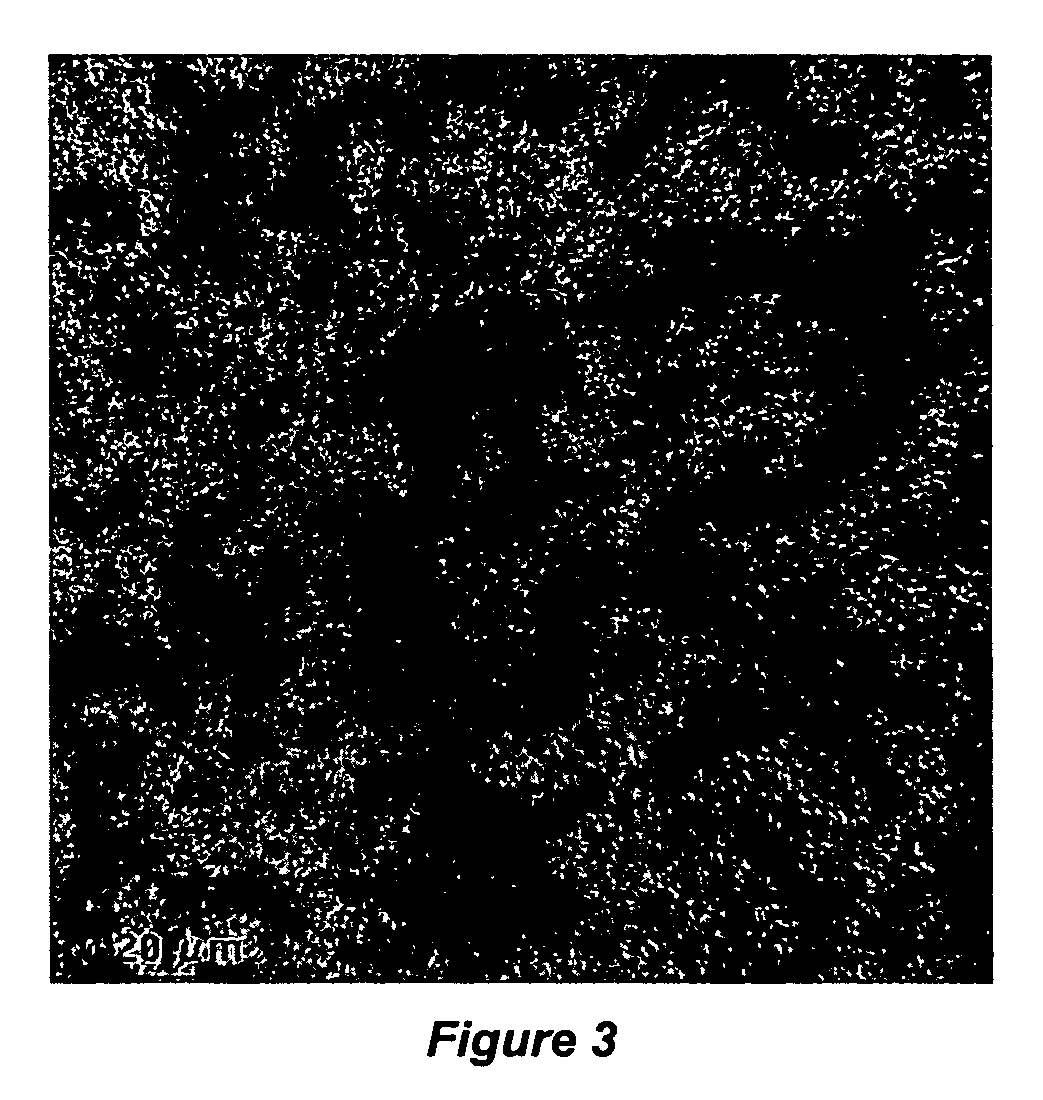
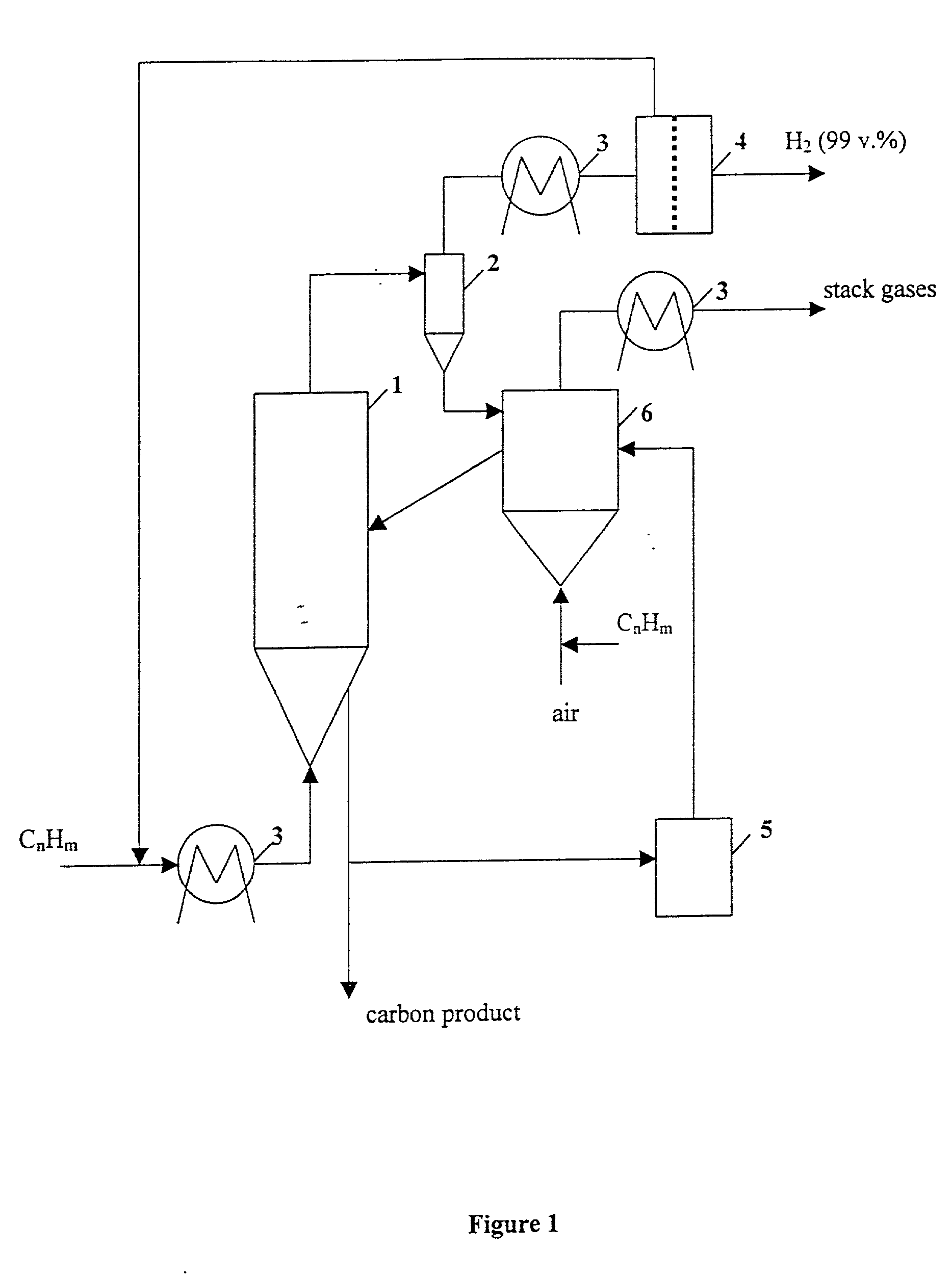
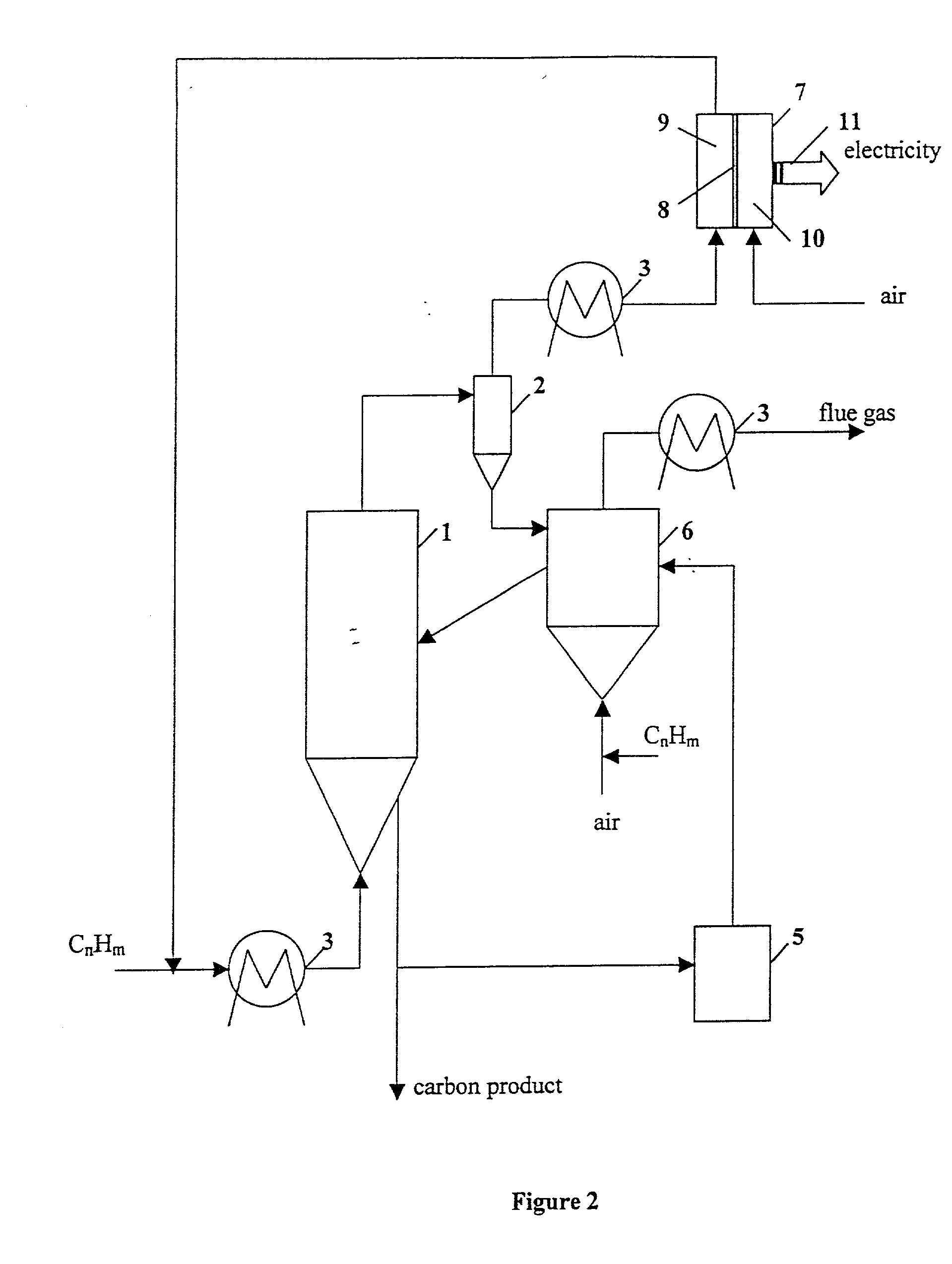
Thermocatalytic process for CO2-free production of hydrogen and carbon from hydrocarbons
InactiveUS20020007594A1Pigmenting treatmentPressurized chemical processDecompositionBiological activation
This invention relates to a novel process for sustainable CO2-free production of hydrogen and carbon by thermocatalytic decomposition (or dissociation, pyrolysis, cracking) of hydrocarbon fuels over carbon-based catalysts in the absence of air and / or water. The process is applicable to any hydrocarbon fuel, including sulfurous fuels. Combination of a catalytic reactor with a gas separation unit allows to produce high purity hydrogen (at least, 99.0 v %) completely free of carbon oxides. In a preferred embodiment, sustainable continuous production of hydrogen and carbon is achieved by both internal and external activation of carbon catalysts. Internal activation of carbon catalyst is accomplished by recycling of hydrogen-depleted gas containing unsaturated and aromatic hydrocarbons back to the reactor. External activation can be achieved via surface gasification of carbon catalysts by hot combustion gases during catalyst heating. The process can conveniently be integrated with any type of fuel cell.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC +1
Catalyst for preparing aromatic hydrocarbon through methanol conversion as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102416342AHigh yieldHigh activityMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon from oxygen organic compoundsLiquid productGas phase
The invention discloses a catalyst for preparing aromatic hydrocarbon through methanol conversion. The catalyst comprises a component A and components B, wherein the mass ratio of component A to components B is 0.25-4; the component A is a modified zeolite molecular sieve and comprises 80-99wt% of molecular sieves and 1-20wt% of molecular sieve modifiers; the components B are oxide loaded metallic elements and halogen and comprise 85-95wt% of oxide, 0.5-10wt% of total metallic elements and 0.1-5wt% of halogen; and the component A and the components B are formed through squashing or extruding after being mixed uniformly. The catalyst has the following characteristics that: (1) the total recovery of benzene, toluene and xylene is higher and selectivity is high; (2) the raw material treatment capacity is large; (3) the non-aromatic hydrocarbon liquid product can serve as the solvent oil or gasoline component; (4) C4 hydrocarbon and non-aromatic hydrocarbon liquid phase products in the gas phase product can circularly enter into the catalyst bed layer, thus not only balancing the reaction heat but also improving the total recovery of the aromatic hydrocarbon; and (5) the catalyst has high activity and long life.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
Method for preparing propylene and aromatic hydrocarbon by virtue of conversion of methanol
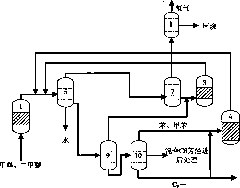
ActiveCN102190546AHigh yieldHydrocarbon from oxygen organic compoundsEthylene productionLiquid productGas phase
The invention relates to a method for preparing propylene and aromatic hydrocarbon by virtue of conversion of methanol, and the method is mainly used for solving the problem that the methanol is just converted into propylene and the aromatic hydrocarbon can not be co-produced in the prior art. The method comprises the following steps: 1) converting above 80% of methanol into dimethyl ether by virtue of pre-reaction; 2) feeding the generated diamethyl ether and residual methanol into a device for producing propylene from the methanol for reaction so as to obtain a material flow I which mainly comprises the propylene, ethylene and C4, C5, C6 and over-C6 hydrocarbons; 3) after the material flow I is separated, returning the ethylene back to the device for producing the propylene from the methanol for cycling reaction, and feeding C4 and C5 hydrocarbons into an aromatizing device for reaction so as to obtain a material flow II containing aromatic hydrocarbon; and 4) cooling the material flow II, separating a gas-phase product low-carbon hydrocarbons from a liquid-phase product, and separating the liquid product from the material flow I so as to obtain C6 and over-C6 hydrocarbons, mixing, extracting and separating so as to obtain the aromatic hydrocarbon and non-aromatic hydrocarbon. By using the technical scheme, the problem is well solved; and the method can be used in industrialproduction for preparing the ethylene and the aromatic hydrocarbon by virtue of conversion of methanol.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for preparing aromatic hydrocarbons by methanol-containing raw materials
InactiveCN102199069AHigh yieldAvoid inactivationHydrocarbon from oxygen organic compoundsAromatic hydrocarbonChemistry
A method for preparing aromatic hydrocarbons by methanol-containing raw materials. The methanol-containing raw materials comprise methanol and distilled gasoline. The method comprises that the methanol-containing raw materials and catalysts undergo a reaction under conditions of preparing aromatic hydrocarbons by methanol. The method provided by the invention solves the problems that in the prior arts, heat in a reactor is removed through an intermediate cooler and a multitubular reactor is utilized for heat removal or cold product gas is transmitted back to a raw material inlet to remove heat or a diluting material is added to control reaction heat. The method has the advantages of simple processes, and simple and convenient operation.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com