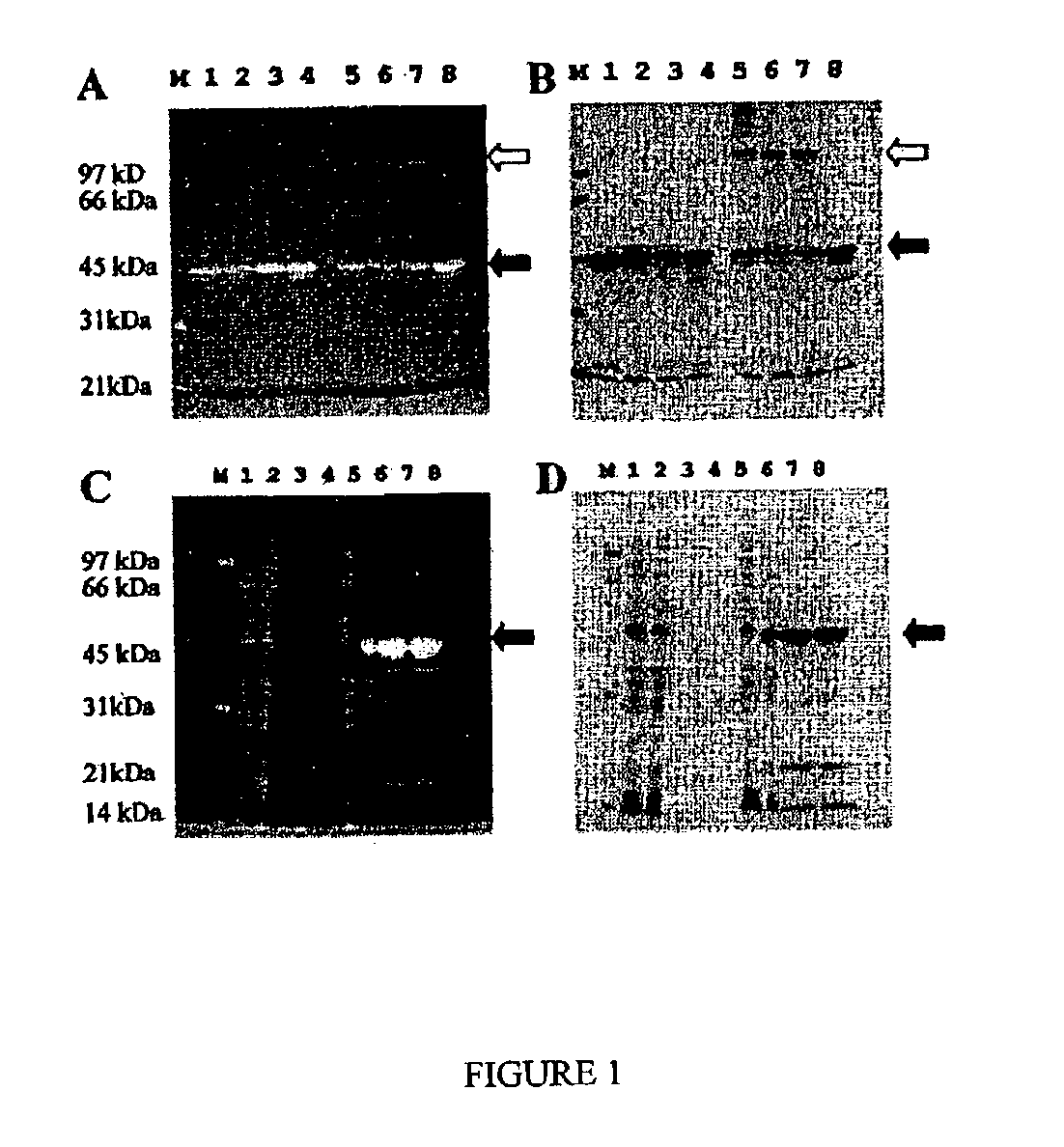
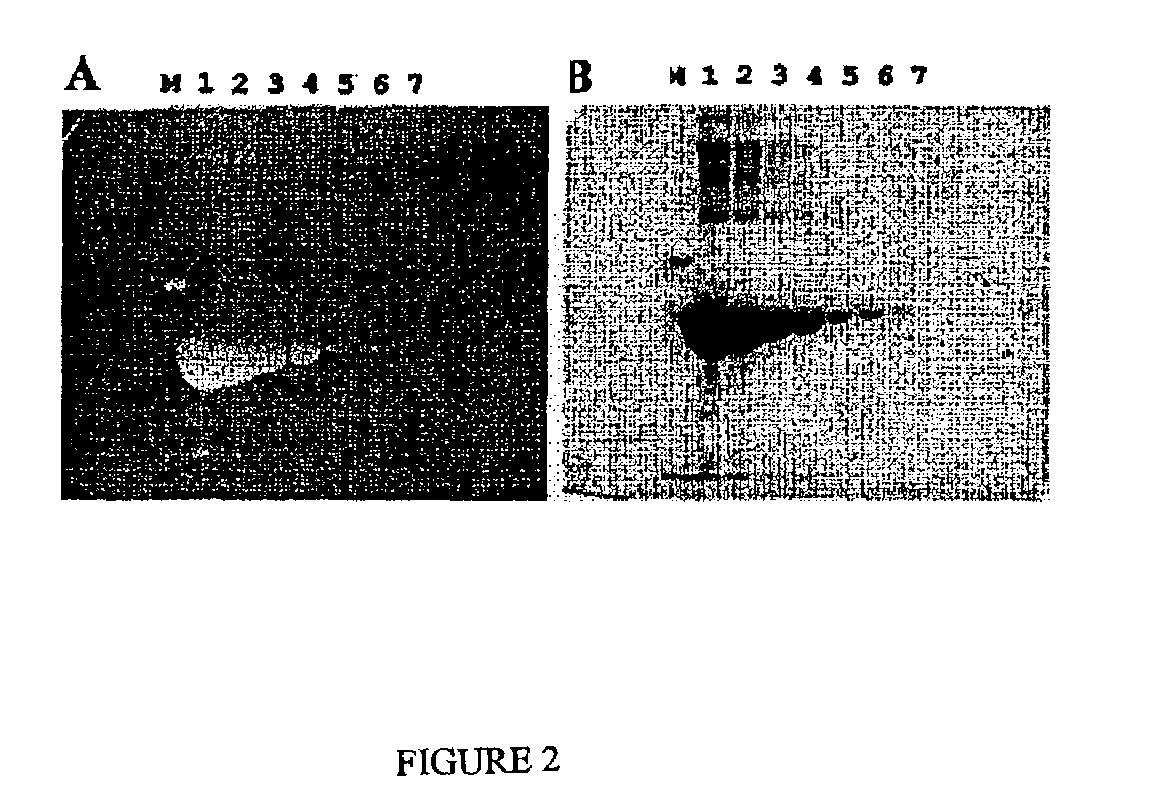
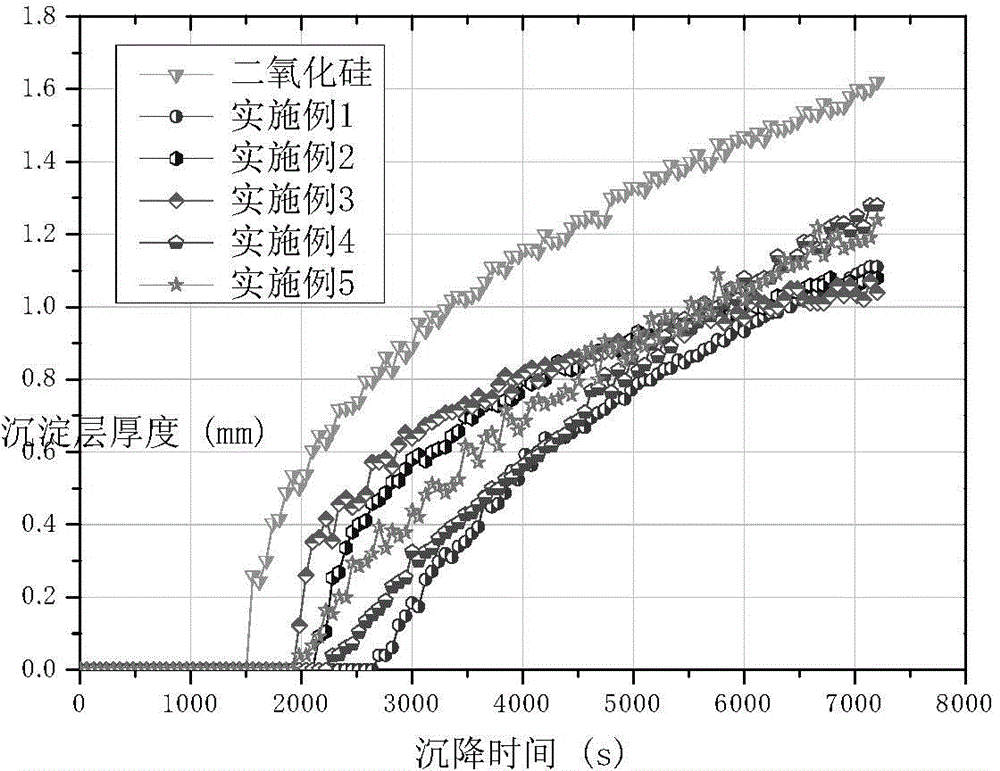
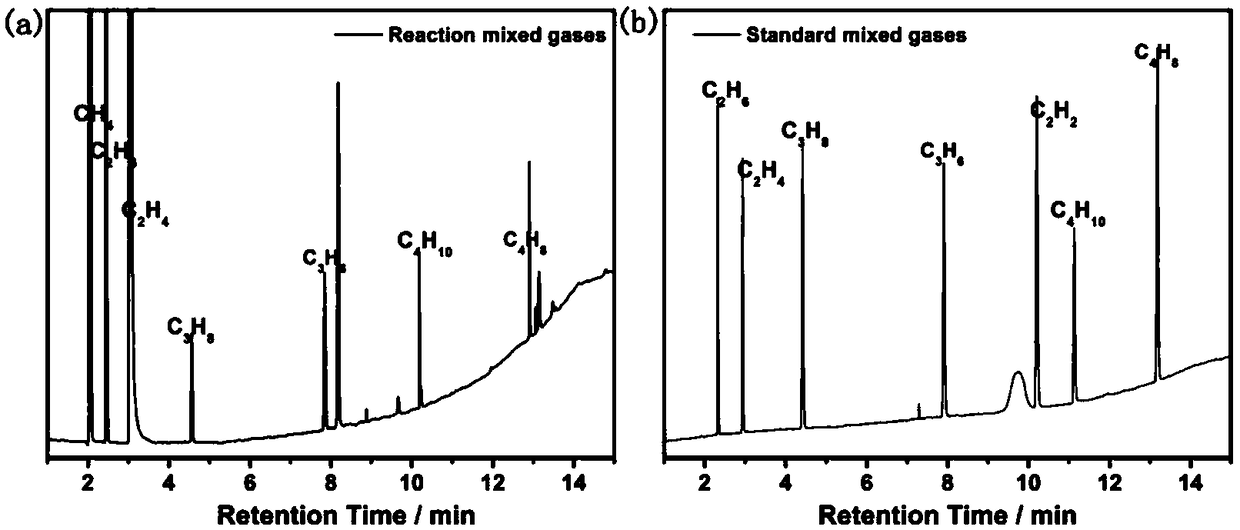
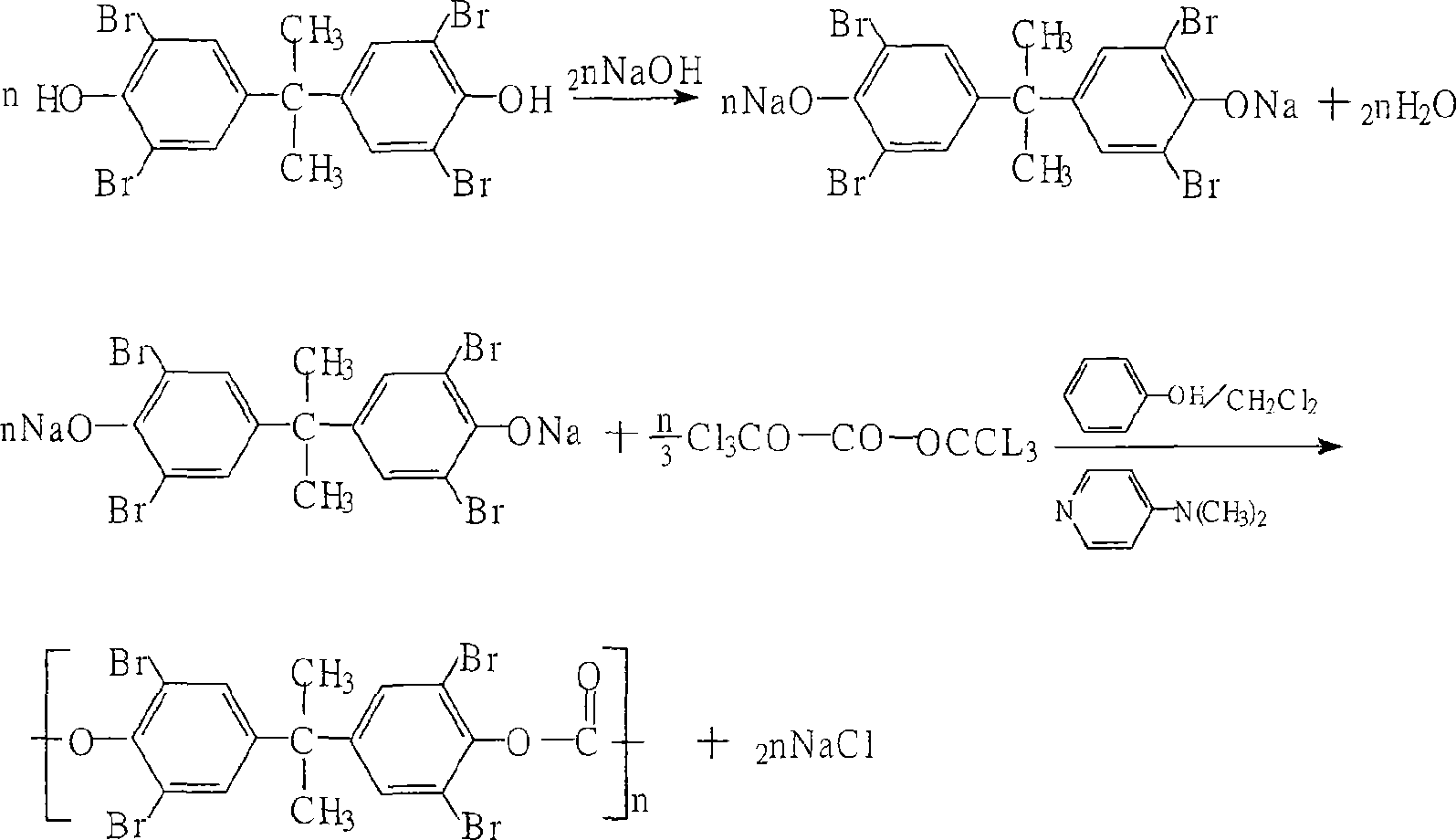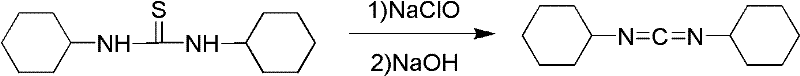Patents
Literature
448 results about "Haloalkane" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The haloalkanes (also known as halogenoalkanes or alkyl halides) are a group of chemical compounds derived from alkanes containing one or more halogens. They are a subset of the general class of halocarbons, although the distinction is not often made. Haloalkanes are widely used commercially and, consequently, are known under many chemical and commercial names. They are used as flame retardants, fire extinguishants, refrigerants, propellants, solvents, and pharmaceuticals. Subsequent to the widespread use in commerce, many halocarbons have also been shown to be serious pollutants and toxins. For example, the chlorofluorocarbons have been shown to lead to ozone depletion. Methyl bromide is a controversial fumigant. Only haloalkanes which contain chlorine, bromine, and iodine are a threat to the ozone layer, but fluorinated volatile haloalkanes in theory may have activity as greenhouse gases. Methyl iodide, a naturally occurring substance, however, does not have ozone-depleting properties and the United States Environmental Protection Agency has designated the compound a non-ozone layer depleter. For more information, see Halomethane. Haloalkane or alkyl halides are the compounds which have the general formula "RX" where R is an alkyl or substituted alkyl group and X is a halogen (F, Cl, Br, I).
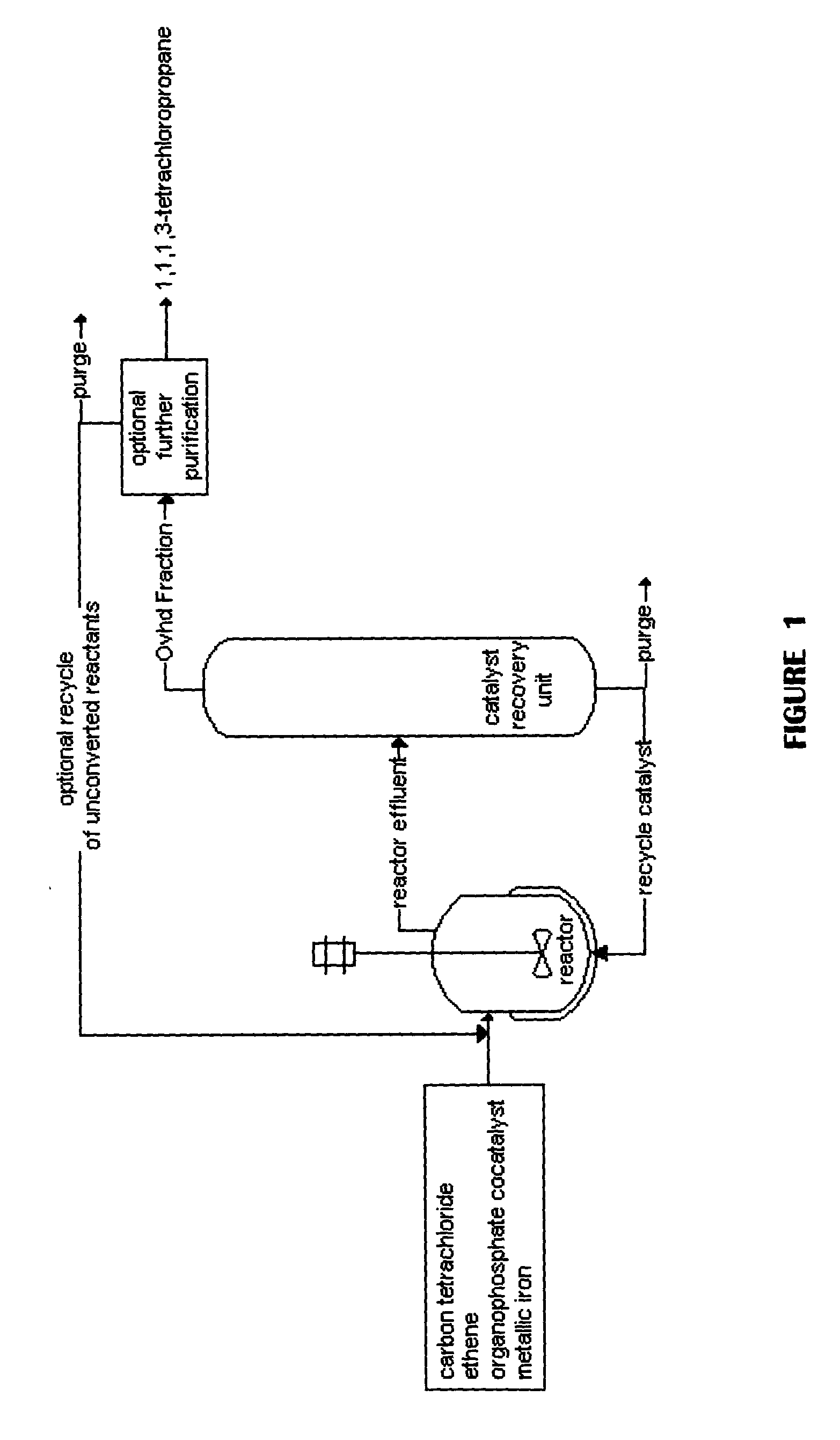
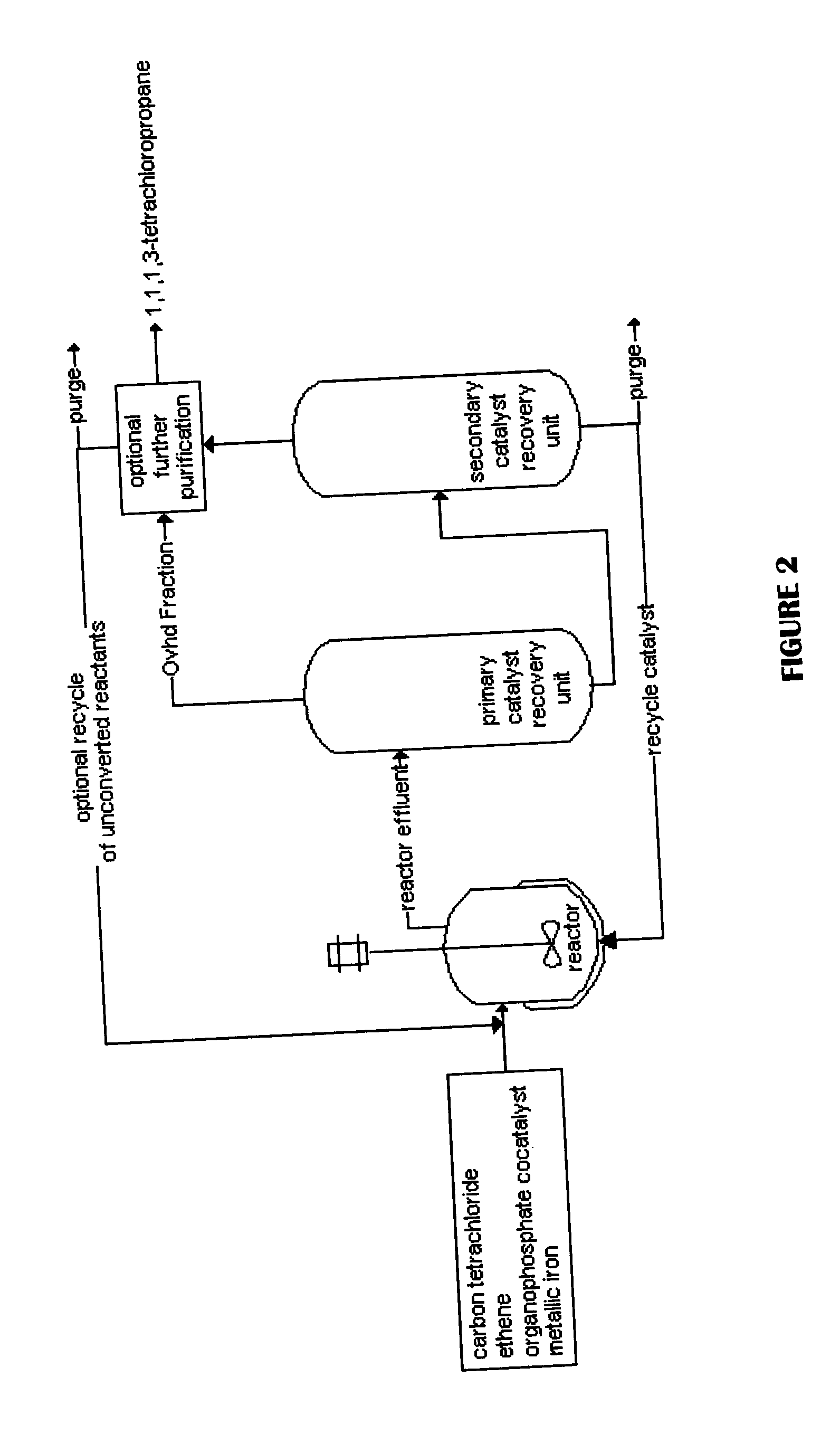
Method for producing 1,1,1,3-tetrachloropropane and other haloalkanes with iron catalyst
InactiveUS20040225166A1Efficient and economical to produceHalogenated hydrocarbon preparationTetrachlorideDistillation
A continuous process is provided for the manufacture of haloalkanes by the reaction of carbon tetrachloride with olefins in the presence of iron metal, trialkylphosphate, and ferric chloride. A fraction of the catalyst and co-catalyst are separated after the reaction and recycled. In a preferred application, the olefin is ethene, and the haloalkane product is 1,1,1,3-tetrachloropropane. Two distillation steps take place in order to enhance the production of 1,1,1,3-tetrachloropropane.
Owner:OCCIDENTAL CHEM CORP
Process for preparing halogenated alkanes
InactiveUS7094936B1High selectivityBig advantagePreparation by hydrogen halide split-offPreparation by halogen replacementAlkaneLewis acid catalysis
Methods and materials are provided for the production and purification of halogenated compounds and intermediates in the production of 1,1,1,3,3-pentafluoropropane. In a preferred embodiment, the process steps include: (1) reacting carbon tetrachloride with vinyl chloride to produce 1,1,1,3,3-pentachloropropane; (2) dehydrochlorinating the 1,1,1,3,3-pentachloropropane with a Lewis acid catalyst to produce 1,1,3,3-tetrachloropropene; (3) fluorinating the 1,1,3,3-tetrachloropropene to produce 1-chloro-3,3,3-trifluoropropene; (4) fluorinating the 1-chloro-3,3,3-trifluoropropene to produce a product mixture containing 1,1,1,3,3-pentafluoropropane; and (5) separating 1,1,1,3,3-pentafluoropropane from by-products.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
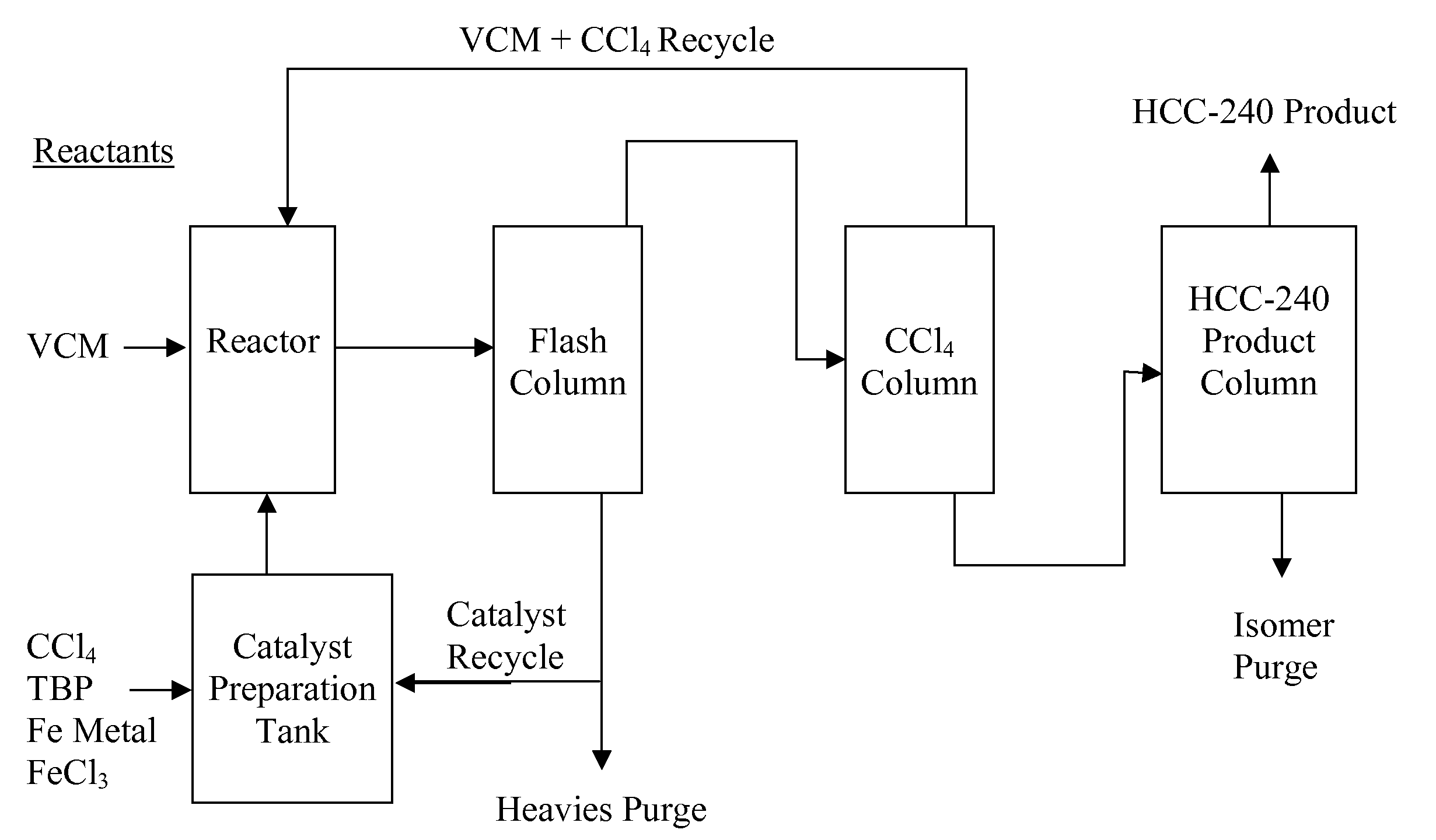
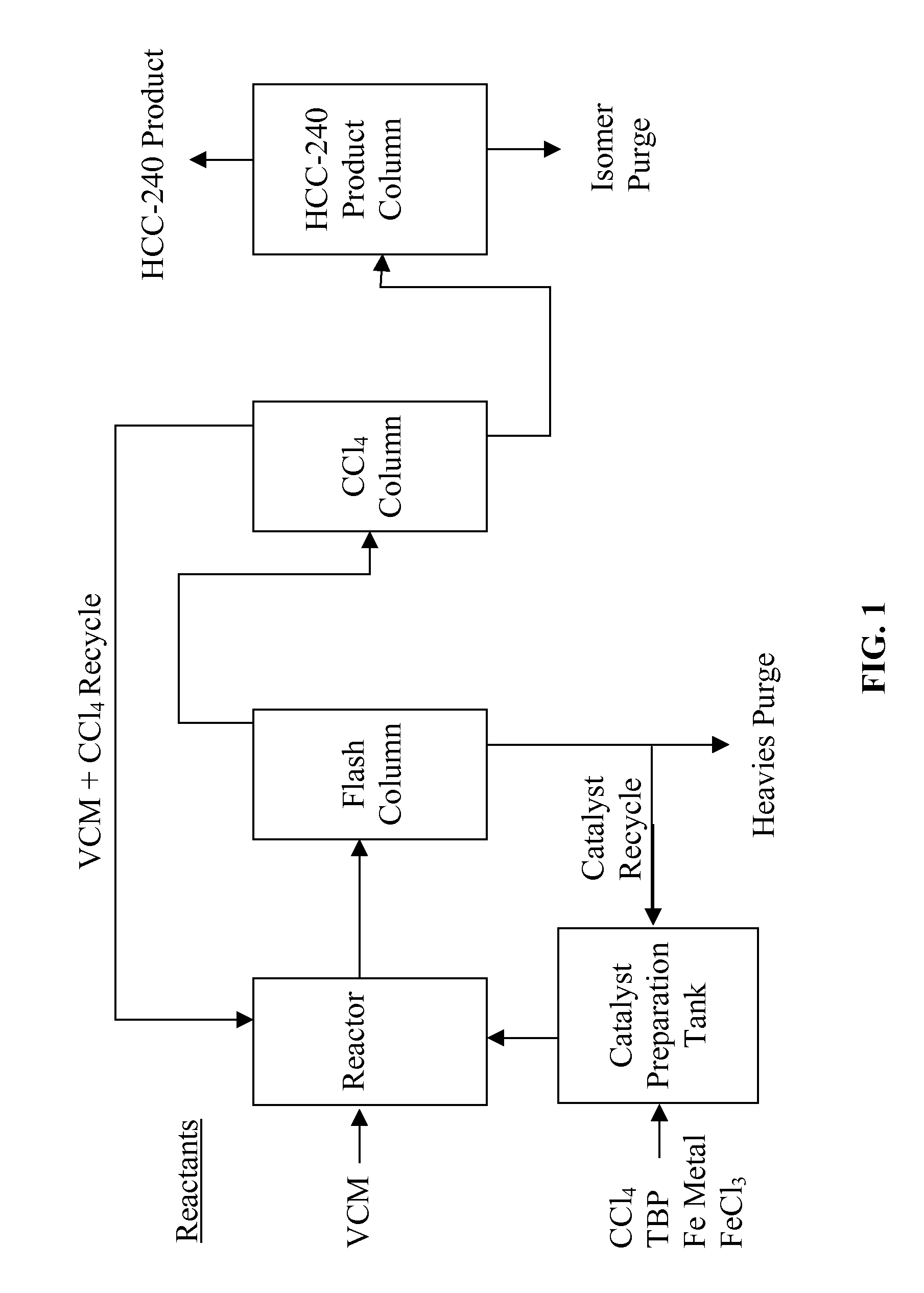
Process for the manufacture of 1,1,1,3,3-pentachloropropane
ActiveUS20080091053A1High yieldHigh selectivityPreparation by halogen halide additionHalogenated hydrocarbon separation/purificationAlkeneHaloalkane
A process for the manufacture of haloalkanes, or more particularly to a process for the manufacture of 1,1,1,3,3-pentachloropropane (HCC-240fa) and / or and / or 1,1,1,3-tetrachloropropane (HCC-250fb). The process includes (a) mixing a catalyst, co-catalyst and a haloalkane starting material under conditions suitable to produce a homogeneous mixture; (b) reacting the homogeneous mixture with a haloalkene and / or alkene starting material under conditions suitable to produce a haloalkane product stream; and (c) recovering a haloalkane product from said product stream.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
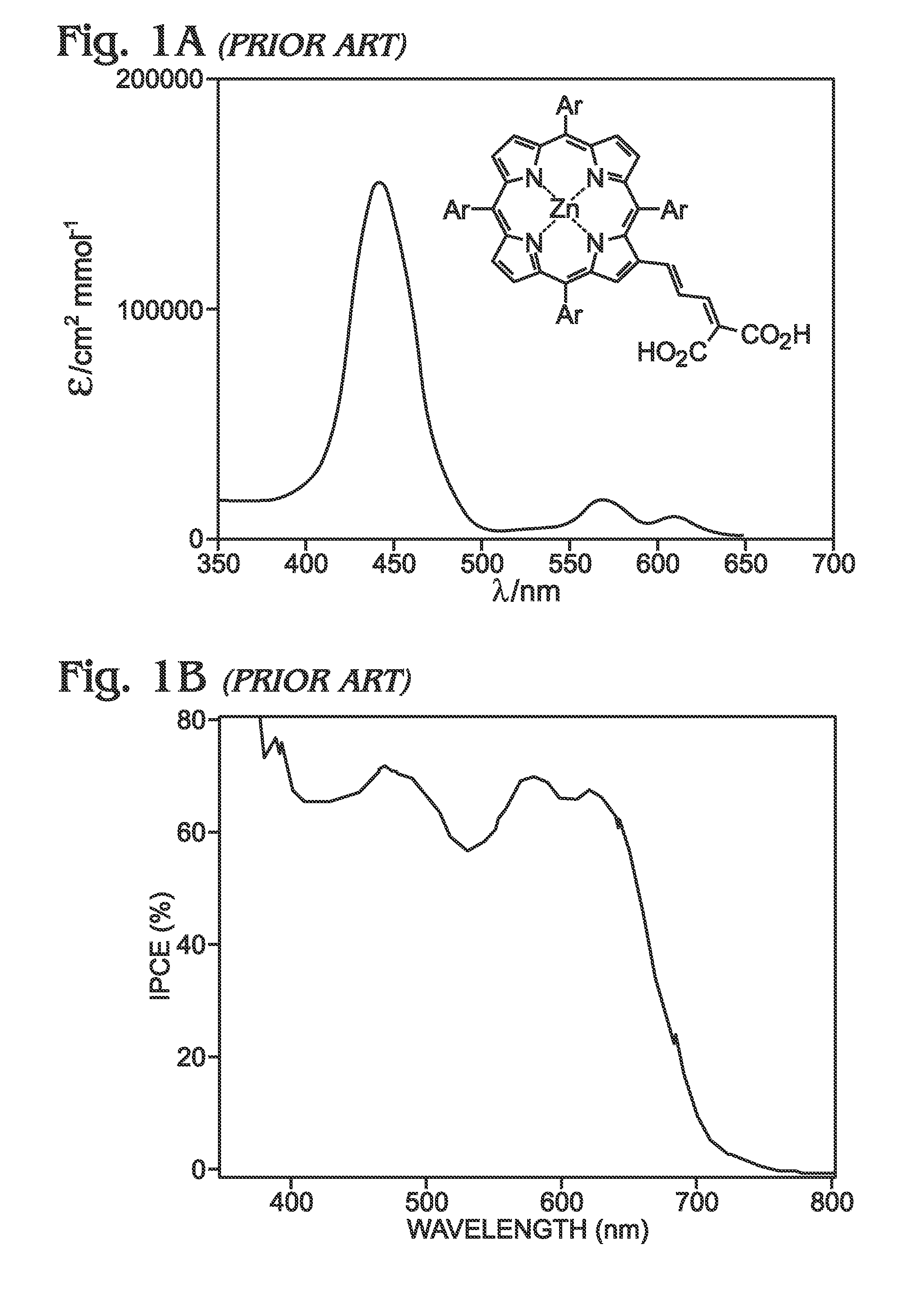
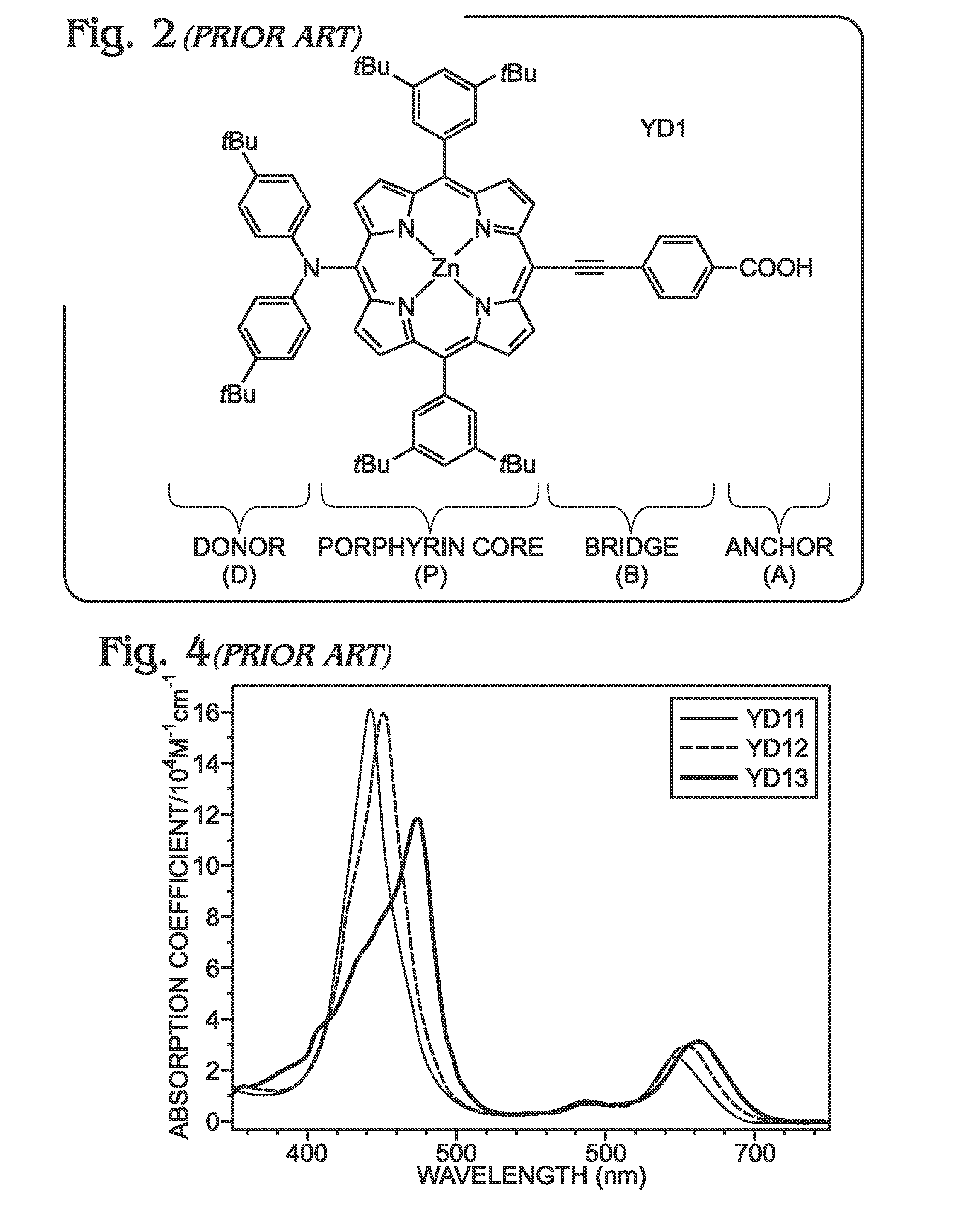
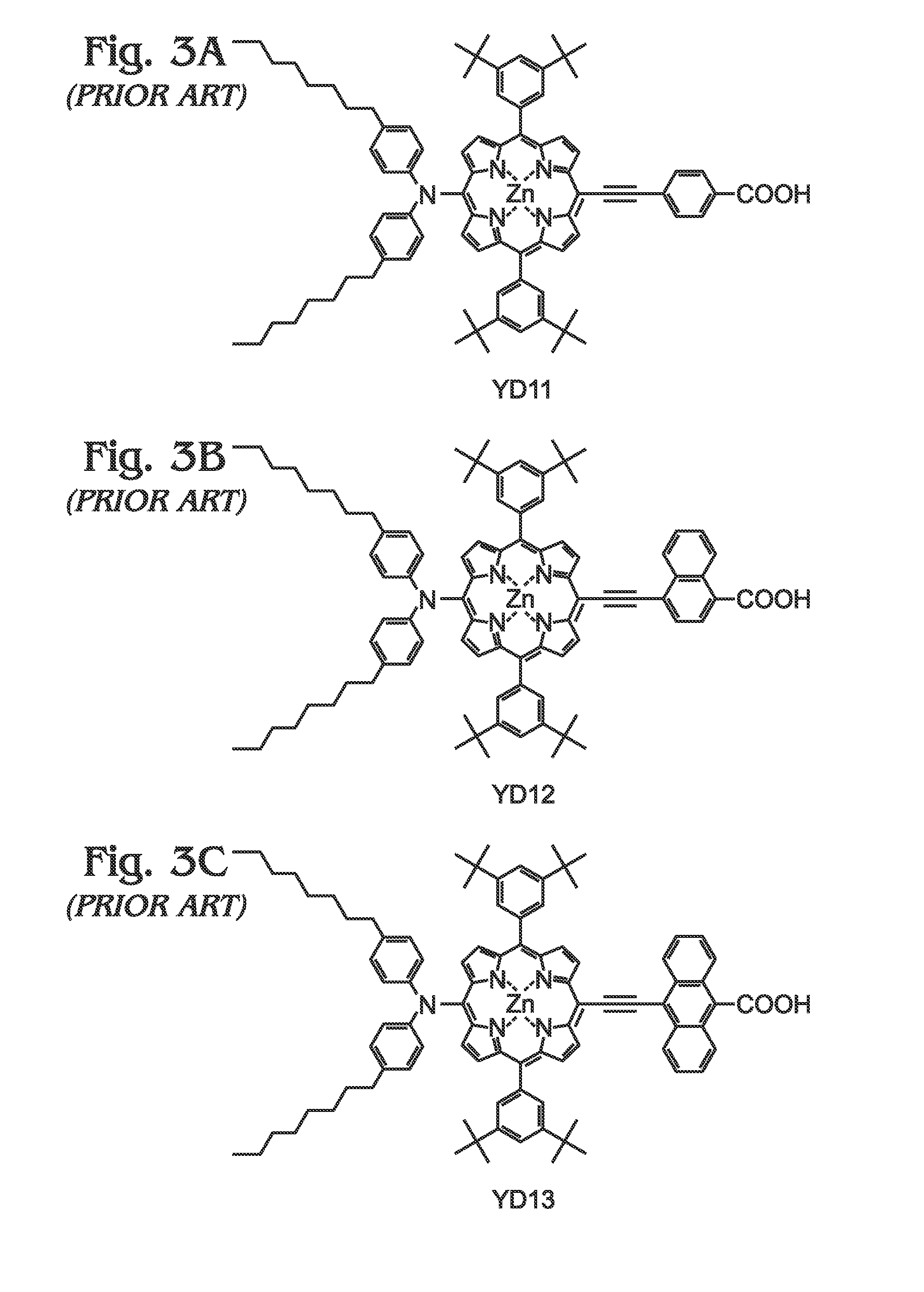
Long wavelength absorbing porphyrin photosensitizers for dye-sensitized solar cells
InactiveUS8907081B2Increase driving force (rates)Low rateFunctional group formation/introductionPhotovoltaic energy generationPhotosensitizerHydrogen
A long wavelength absorbing porphyrin / metalloporphyrin molecule is provided, made up of a porphyrin macrocycle and an anchor group for attachment to a substrate. A molecular linking element is interposed between the porphyrin macrocycle and the anchor group. The porphyrin / metalloporphyrin molecule also includes an (aminophenyl)amine group, either N,N-(4-aminophenyl)amine or N-phenyl-N-(4-aminophenyl)amine, where an amino moiety of the 4-aminophenyl group is derivatized by an element such as hydrogen, haloalkanes, aromatic hydrocarbons, halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons, heteroarenes, halogenated heteroarenes, or combinations of the above-mentioned elements.
Owner:SHARP KK
Modification of polymers with basic N-groups and ion exchange groups in the lateral chain
InactiveUS20020045729A1Improve stabilityThe degree of freedom becomes largerIon-exchange process apparatusNon-metal conductorsAlkaneIon exchange
A method for lateral chain modification of aryl main chain polymers with aromatic ketones or aldehydes containing tertiary basic N-groups is described. The modification can be accomplished via addition of an aromatic carboxylic acid or an acid derivative containing a tertiary amine moiety to a metallized polymer. The tertiary amines on the modified polymer can be converted to quaternary amines with halogen alkanes. Modification of the aryl main chain polymers with aromatic groups containing sulphonic acid radicals is also described. The polymers formed can be crosslinked and prepared for use in a wide variety of membrane technologies including ion exchange, dialysis, reverse osmosis, nanofiltration.
Owner:UNIV STUTTGART
Process for the manufacture of halocarbons and selected compounds and azeotropes with HF
InactiveUS20050080302A1Preparation by hydrogen halide split-offPreparation by halogen halide additionAlkaneHalocarbon
A liquid phase process is disclosed for producing halogenated alkane adducts of the formula CAR1R2CBR3R4 (where A, B, R1, R2, R3, and R4 are as defined in the specification) which involves contacting a corresponding halogenated alkane, AB, with a corresponding olefin, CR1R2═CR3R4 in a dinitrile or cyclic carbonate ester solvent which divides the reaction mixture into two liquid phases and in the presence of a catalyst system containing (i) at least one catalyst selected from monovalent and divalent copper; and optionally (ii) a promoter selected from aromatic or aliphatic heterocyclic compounds which contain at least one carbon-nitrogen double bond in the heterocyclic ring. When hydrochlorofluorocarbons are formed, the chlorine content may be reduced by reacting the hydrochlorofluorocarbons with HF. New compounds disclosed include CF3CF2CCl2CH2CCl3, CF3CCl2CH2CH2Cl and CF3CCl2CH2CHClF. These compounds are useful as intermediates for producing hydrofluorocarbons. Azeotropes of CClF2CH2CF3 with HF and azeotropes of CF3CH2CHF2 with HF are also disclosed; as are process for producing such azeotropes. A process for purification of certain hydrofluorocarbons and / or chloro-precursors thereof from mixtures of such compounds with HF is also disclosed.
Owner:THE CHEMOURS CO FC LLC
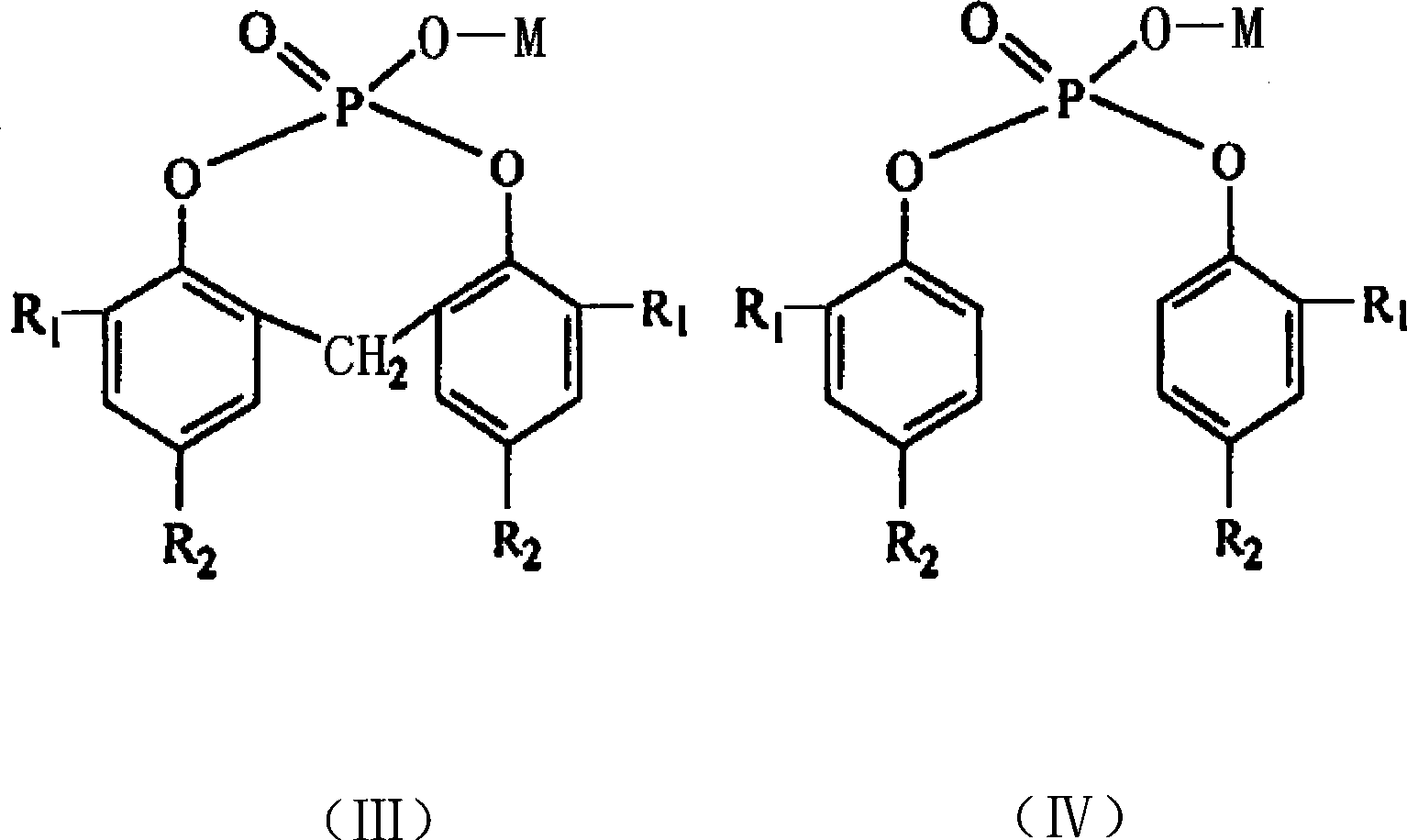
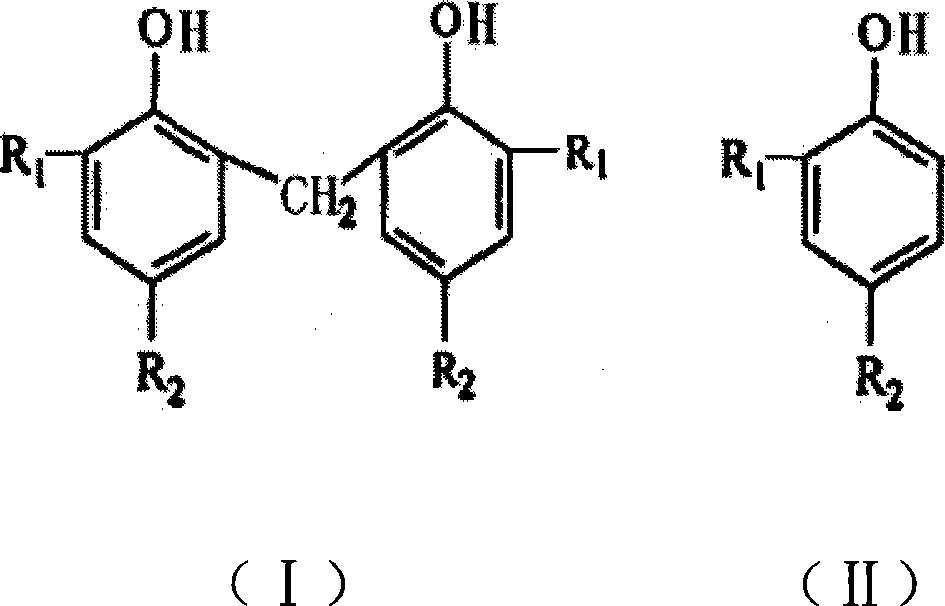
Preparation method for organic phosphate nucleating agent
The present invention relates to a method for preparing an organic compound, in particular to a method for preparing an organic phosphate nucleator, which includes the following steps: phosphorylation reaction, hydrolyzation and salification. Since the solvent for the phosphorylation reaction adopts halogenated hydrocarbon instead of benzene series compounds, which is cheap, the cost can be reduced, and since the yield of the organic phosphate synthesized with the halogenated hydrocarbon used as the solvent is higher, the yield of the final product, the organic phosphate, is greatly increased. Moreover, since the solvent does not adopt the benzene series compounds, toxicity is low, non-burning operation is safe, environment can be protected, recycling is convenient, and the diaryl-substituted organophosphate metal salt used as nucleator prepared by the method has obvious effect in the improvement of the processing property of resin.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
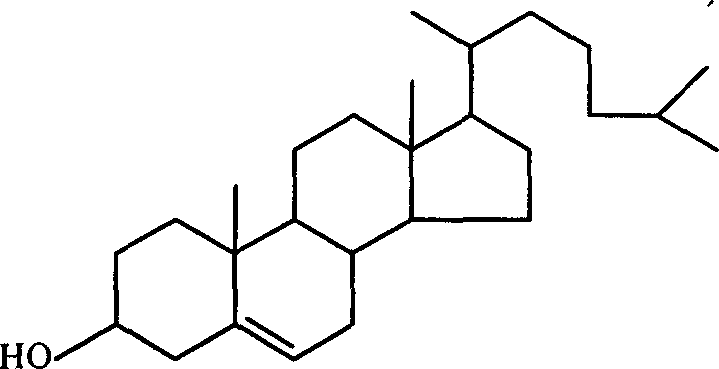
Method for separating and extracting cholesterol from lanolin
The invention discloses a method for separating and extracting cholesterol from lanolin which consists of, (1) scouring the crude product adeps lanae with surface active agent aqueous solution, (2) carrying out saponification reaction to the washed adeps lanae or lanoline in alcoholic solution, (3) extracting wool alcohols in the saponifed substance by using acetic acid ethyl ester, acetone, toluene, alkane or alkyl halide hydrocarbon as extracting agent, (4) scouring the wool alcohol hydrocarbon or haloalkane hydrocarbon solution with alcoholic solutions, removing alcoholic solution layer, removing hydrocarbon or halogenated hydrocarbons in the wool alcoholic solution through evaporation, thus obtaining grease form wool alcohols containing cholesterin, (5) selectively crystallizing the grease form wool alcohols in alcohol solvents to obtain crude cholesterin, and obtaining cholesterin crystalline body through recrystallization.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Fluorescent detection of proteins in polyacrylamide gels
ActiveUS7569130B2Laborious labelingLaborious staining stepElectrolysis componentsChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceSpectroscopyTryptophan
The mechanism of the UV light-induced reaction between the indole moiety of tryptophan and chloroform, and the structure of the modified tryptophan and polypeptides including such modified tryptophan residues. The excited indole moiety, which is formed upon UV light irradiation, emits a solvated electron which initiates a series of events that yield fluorescent derivatives that have CHO group covalently bound to the indole moiety. These derivatives are herein referred to as formyltryptophan, and are relatively stable. Similar reactions are observed when 5-hydroxytryptophan, 5-fluorotryptophan, or N-methylindolacetate are used in place of tryptophan, or when other haloalkanes, such as trichloracetic acid, trichlorethanol, trichlorethane, bromoform, and iodoactetate are used in place of chloroform. The derivatives can be used in a variety of applications in fluorescence spectroscopy, and for nuclear magnetic resonance, X-ray crystallography, infra-red spectroscopy, circular dicroism and mass spectroscopy. Additionally, the UV light-induced reaction between the indole moiety of tryptophan and haloalkanes can be used to prepare derivatives of tryptophan for chemical cross-linking studies of proteins and peptides.
Owner:UNIV TECH INT +1
Polyhydroxy lignin/silicon dioxide composite nano particle and preparation method thereof
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Fluorescent detection of proteins in polyacrylamide gels
InactiveUS20100089753A1Without laborious labeling and staining stepElectrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementSpectroscopyTryptophan
The mechanism of the UV light-induced reaction between the indole moiety of tryptophan and chloroform, and the structure of the modified tryptophan and polypeptides including such modified tryptophan residues. The excited indole moiety, which is formed upon UV light irradiation, emits a solvated electron which initiates a series of events that yield fluorescent derivatives that have CHO group covalently bound to the indole moiety. These derivatives are herein referred to as formyltryptophan, and are relatively stable. Similar reactions are observed when 5-hydroxytryptophan, 5-fluorotryptophan, or N-methylindolacetate are used in place of tryptophan, or when other haloalkanes, such as trichloracetic acid, trichlorethanol, trichlorethane, bromoform, and iodoactetate are used in place of chloroform. The derivatives can be used in a variety of applications in fluorescence spectroscopy, and for nuclear magnetic resonance, X-ray crystallography, infra-red spectroscopy, circular dicroism and mass spectroscopy. Additionally, the UV light-induced reaction between the indole moiety of tryptophan and haloalkanes can be used to prepare derivatives of tryptophan for chemical cross-linking studies of proteins and peptides.
Owner:UNIV TECH INT +1
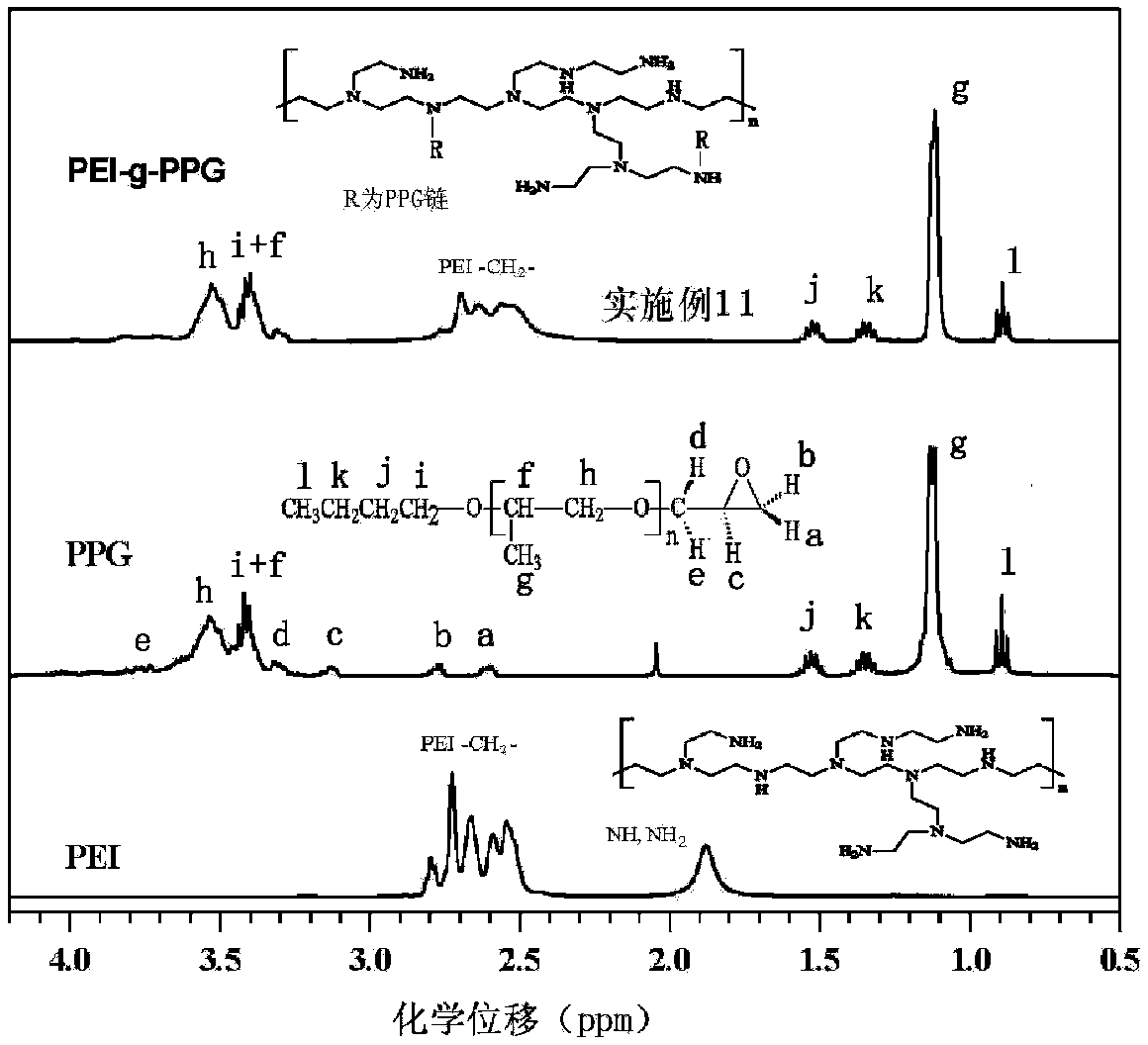
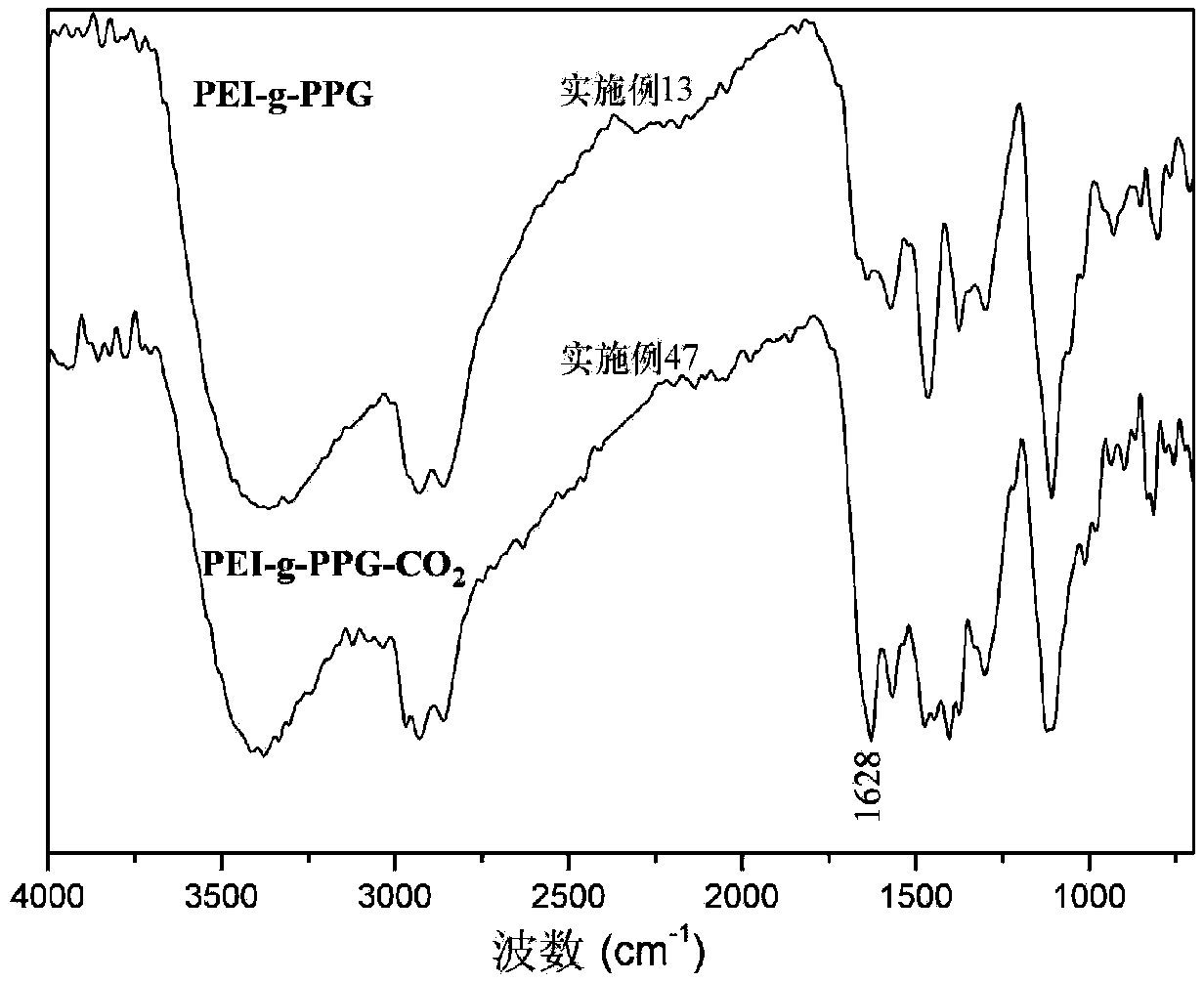
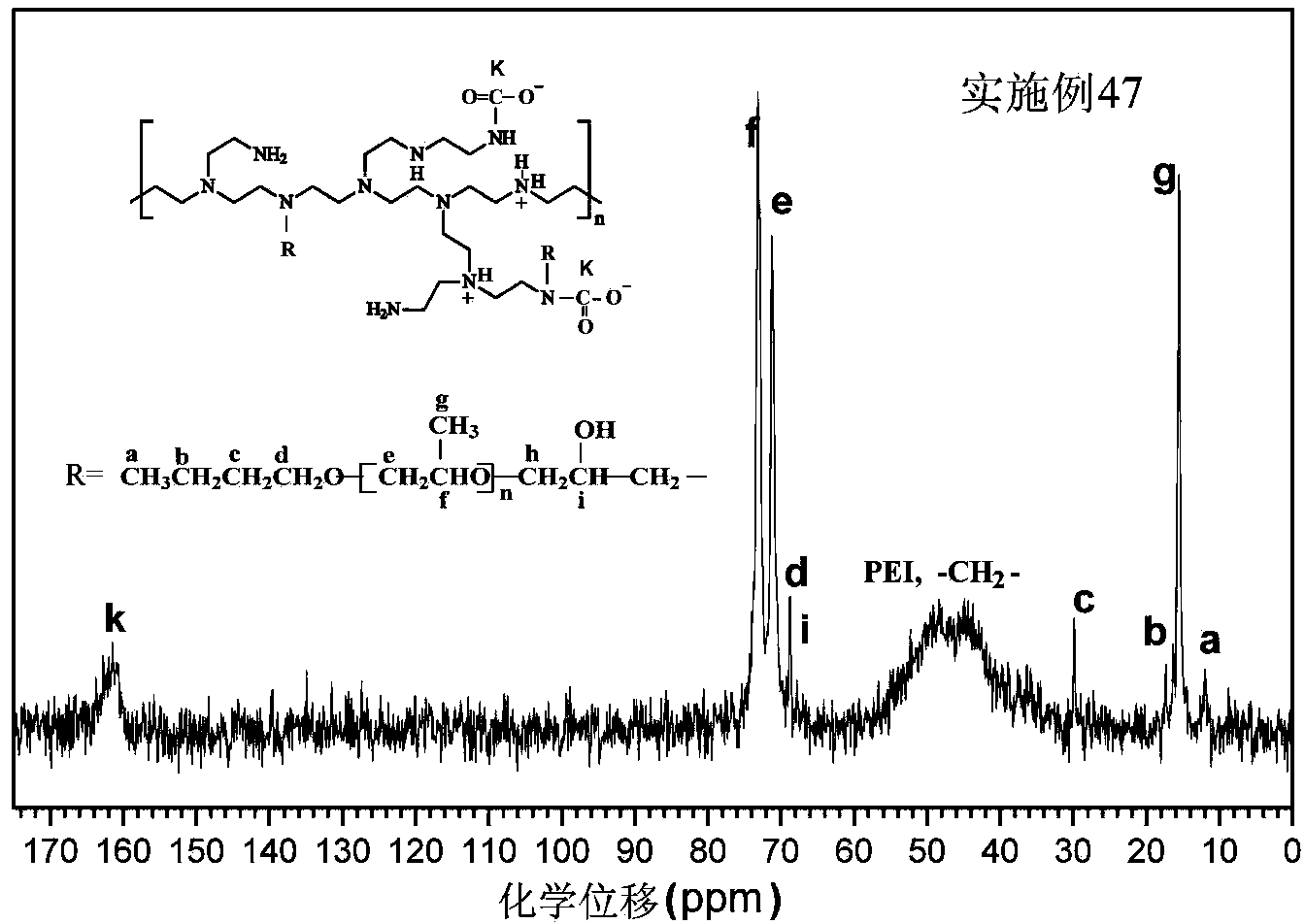
Hydrophobically-modified polyethyleneimine foaming agent capable of releasing carbon dioxide, and application thereof
The invention discloses a hydrophobically-modified polyethyleneimine foaming agent capable of releasing carbon dioxide. The hydrophobically-modified polyethyleneimine foaming agent is prepared by reacting polyethyleneimine subjected to hydrophobic modification by a glycidyl ether compound or an alkyl carboxylic compound or a halogenated alkane compound with 0-31% of distilled water at the pressure of 0.1-1 MPa in carbon dioxide at the room temperature for 1-3 days; a 5-40.4 mol% hydrophobic chain is grafted on N atoms in a polyethyleneimine molecular chain of the foaming agent, and a carbamic acid anion (-NCOO-) characteristic absorption peak or a bicarbonate (HCO3-) characteristic absorption peak exists at the range of 159-165 ppm of a C Nuclear magnetic resonance of the foaming agent, and the foaming agent can release carbon dioxide CO2 at the temperature of 50-150 to prepare a polyurethane foam material. The foaming agent provided by the invention can be uniformly dispersed in a preparation raw material of hydrophobic polyurethane foam, can solve a series of problems caused by the fact that non-modified polyethyleneimine is used as a foaming agent, and is climate-friendly.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Alkaline ionic liquid and its prepn process and application
InactiveCN1931845AEasy to separateAvoid formation of solid viscousOrganic chemistryOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsInorganic saltsIon exchange
The present invention is one kind of alkaline ionic liquid and its preparation process and application in Pd catalyzed C-C and C-N coupling reaction, and belongs to the field of new material and fine chemical technology. The alkaline ionic liquid consists of two parts, cation A+ and anion B-. The cation A+ precursor is imidazole, pyridine, etc; and the anion B- is alkaline group X- or non-alkaline group Y-. The alkaline ionic liquid is prepared through the first quaternizing with alkyl halide as the quaternizing reagent to obtain ion type halide; and the subsequent ion exchange to obtain the target alkaline ionic liquid. The alkaline ionic liquid of the present invention may act as acid-binding agent and can avoid formation of sticky inorganic salt to facilitate reuse.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Olefin polymerization catalyst as well as preparation method and application thereof
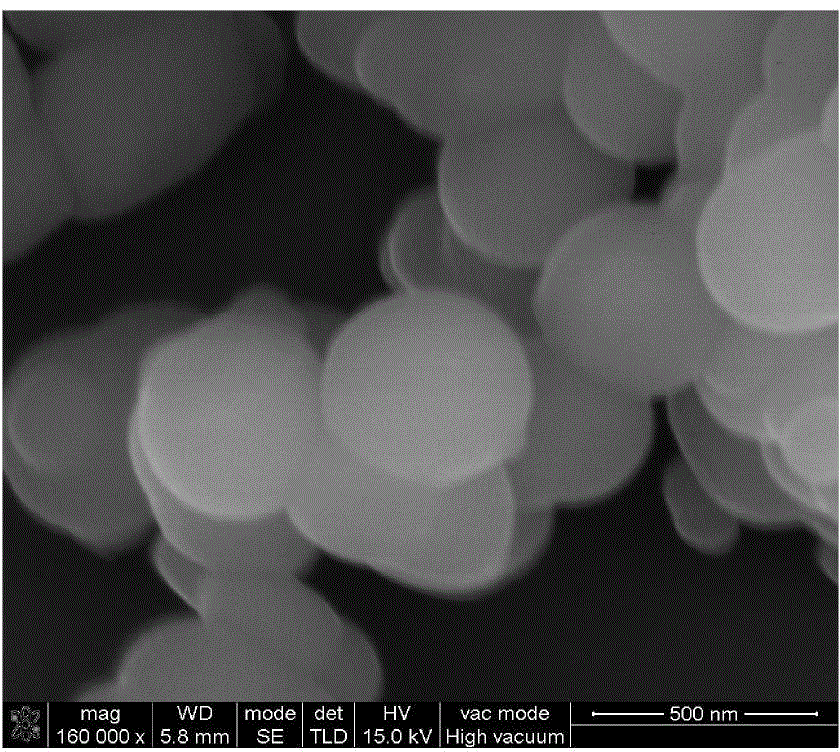
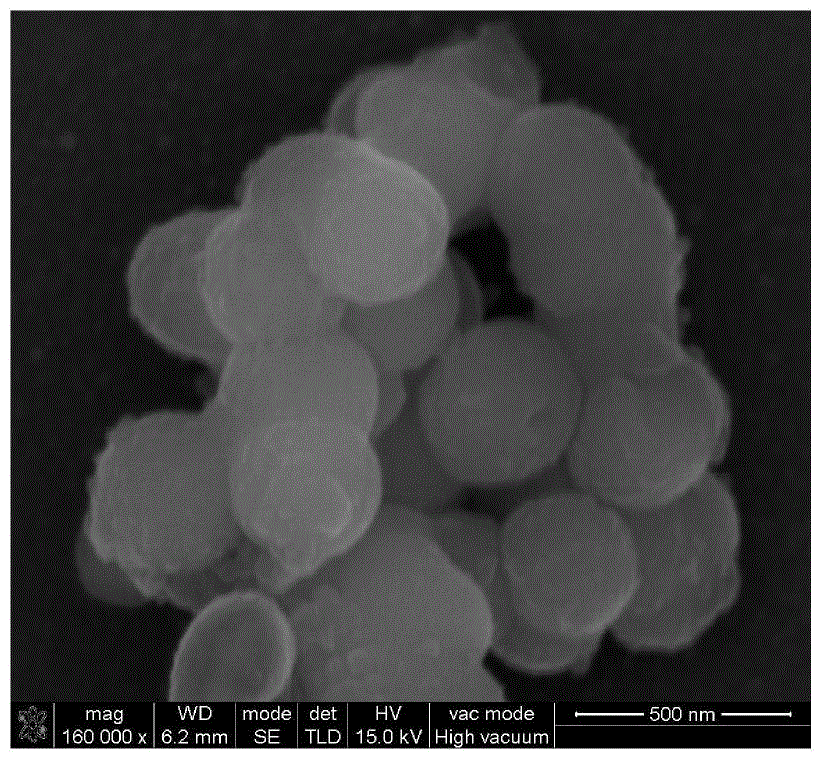
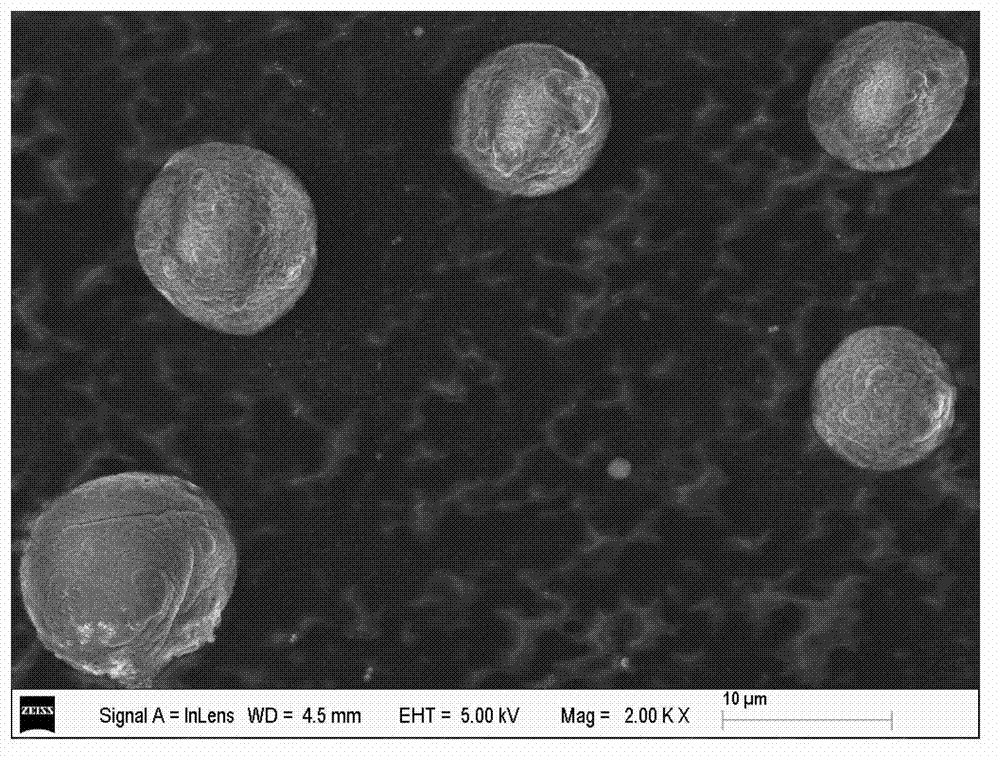
The invention relates to an olefin polymerization catalyst as well as a preparation method and application of the olefin polymerization catalyst. The olefin polymerization catalyst comprises a primary catalyst and a promoter catalyst, wherein the primary catalyst comprises magnesium halide, transition metal halide, organic alcoholate, phosphate ester compound, epoxy haloalkane compound, organo-siloxane compound and organic alcohol ether compound; and the promoter catalyst comprises one or several kinds of the combination of organoaluminum compound. The preparation method of the olefin polymerization catalyst comprises the steps as follows: dispersing the magnesium halide into an organic solvent; sequentially adding the organic alcoholate, the phosphate ester compound and the epoxy haloalkane compound; heating and agitating to dissolve; then sequentially adding the organo-siloxane compound and the organic alcohol ether compound; and dropping the transition metal halide to obtain the primary catalyst, wherein the primary catalyst and the promoter catalyst are individually stored, and combined when in use. According to the olefin polymerization catalyst provided by the invention, the primary spherical catalyst and the promoter spherical catalyst are combined when in use, thus, high catalytic activity is achieved.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD +1
Preparation method of organosilicon foam stabilizer applied to single-component polyurethane foam sealing agent
The invention discloses a preparation method of an organosilicon foam stabilizer applied to a single-component polyurethane foam sealing agent. The preparation method comprises the steps of (1) adding allyl alcohol, ethylene oxide and propylene oxide to a reaction kettle, and reacting under the action of a base catalyst at the temperature of 90-130 DEG C and pressure not more than 0.5MPa for 4-6h to obtain allyl-terminated copolymer ether; (2) reacting the polyether prepared in the step 1 with sodium at 85-120 DEG C, introducing excess haloalkane, and reacting for 4-6h to obtain methyl-terminated copolymer ether; (3) reacting octamethyl cyclotetrasiloxane, hexamethyl disiloxane and high-hydrogen-content silicone oil with hydrogen content of 1-2% in the presence of an acid ion exchanger to obtain low-hydrogen-content silicone oil with hydrogen content of 0.05-1.0%; (4) mixing the products obtained in the steps 1,2, and 3, adding a catalyst, and reacting under the condition of pressure being 0.5-2atm for 3-8h to obtain the organosilicon foam stabilizer. During foaming, the foam stabilizer has excellent dimensional stability and high foaming ratio and fluidity.
Owner:苏州思德新材料科技有限公司
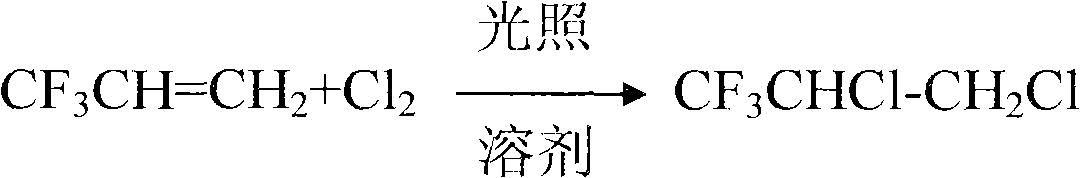
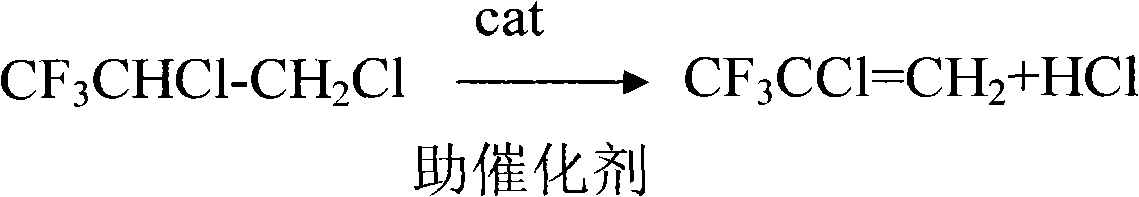
Method for preparing 2,3,3,3-tetrafluoropropylene
The invention relates to a method for preparing 2,3,3,3-tetrafluoropropylene, which comprises the following steps: 1, performing the addition reaction of 3,3,3-trifluoropropylene (CF3CH=CH2) (I) serving as a raw material and chlorine at -10 to 100 DEG C under the irradiation of a ultraviolet lamp in alkyl halide to prepare 3,3,3-trifluoro-1,2-dichloropropane (CF3CHClCH2Cl)(II); 2, performing the dehydrochlorination reaction of the compound of the formula (II) at 0 to 150 DEG C in the presence of an alkali metal hydroxide serving as a catalyst and a high molecular polyether or macromolecular ether serving as a cocatalyst to form CF3CCl=CH2 (III); 3, performing the addition reaction of the compound of the formula (III) and HF to form CF3CClFCH3 (IV) in the presence of a catalyst consisting of SnCl4, TiCl4 and fluosulfonic acid, wherein a polymerization inhibitor is aprotic inert compound, the reaction temperature is 5 to 100 DEG C and the pressure is 0.2 to 1.0MPa; and 4, performing thedehydrochlorination reaction of the compound (IV) at 0 to 100 DEG C and under 0 to 0.5MPa in the presence of an alkali metal catalyst and an organic amine halide serving as a phase transfer catalyst to obtain FO-1234yf.
Owner:衢州环新氟材料有限公司
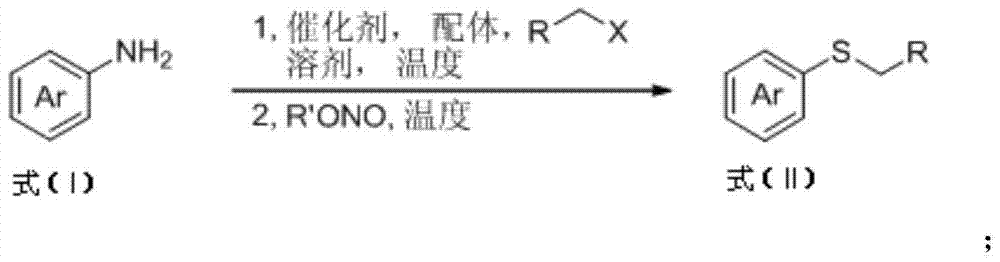
Aryl alkyl thioether compounds and synthesis method thereof
ActiveCN103787802AAchieve conversionLow costMercapto/sulfide group formation/introductionSugar derivativesVulcanizationSynthesis methods
The invention discloses aryl alkyl thioether compounds and a synthesis method thereof. The synthesis method comprises the steps: in a reaction solvent, with an arylamine derivative and halogenated hydrocarbon as reaction raw materials, and Na2S2O3 as a vulcanization reagent, in the presence of a copper reagent catalyst, and reacting to obtain the aryl alkyl thioether compounds. According to the synthesis method disclosed by the invention, raw materials are easy to obtain and low in price, the reaction operation is simple, the reaction conditions are mild, the yield is higher, the tolerance of a functional group is excellent, later-phase modification of compounds of medicines, sugars, amino acids and the like is successfully realized, and an efficient method for constructing a carbon-sulfur bond is provided for researches of medicinal chemistry and biology orthogonal chemistry.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Self-assembled calixarene nucleating agent and application thereof in polylactic resin composition
InactiveCN102020784AIncrease the nucleation rateThere is no problem of degradationAlkaneStructural formula
The invention relates to a self-assembled calixarene nucleating agent and an application thereof in a polylactic resin composition. The self-assembled calixarene nucleating agent is a supermolecular nucleating agent self-assembled by the below A and B, wherein A is calixarene and derivatives thereof expressed by structural formula A while B consists of one or more organic micromolecular compounds as follows: C1-C30 alkane, C1-C30 halogenated alkane, C1-C30 alcohol, C1-C30 nitrile, a 5-6 membered heterocyclic compound, substituted 5-6 membered heterocyclic compound (substituent can be hydroxyl, aldehyde group and alkyl), benzene, naphthalene, substituted benzene and substituted naphthalene. The invention has the advantages of simple production process, relative low cost and great nucleating speed, thereby overcoming the low crystallization rate of polylactic resin and reducing the processing and forming period.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing mesophase pitch through catalytic cracking oil slurry hydrogenation reduction and co-carbonization
ActiveCN105238431ALow mesophase contentHigh content of mesophaseWorking-up pitch/asphalt/bitumen by chemical meansCarbonizationSlurry
The invention provides a preparation method of petroleum base mesophase pitch with even high mesophase content. The FCC oil slurry of naphthenic crude oil or intermediate base crude oil serves as the raw material, under the action of a catalyst, haloalkane is mixed with the raw material, the temperature is increased to range from 280 DEG C to 350 DEG C, the pressure ranges from 0 MPa to 2 MPa, reaction is conducted for 5-20 h, and modified oil is obtained. Distillate oil, obtained at the temperature higher than 400 DEG C, of the modified oil is taken, the distillate oil is mixed with a co-carbonization agent, the temperature ranges from 360 DEG C to 480 DEG C, the reaction pressure ranges from 4 MPa to 10 MPa, reaction is conducted for 2-10 h, and the high-quality mesophase pitch is obtained. According to the preparation method of the petroleum base mesophase pitch with the even high mesophase content, preparation technology is simple and easy to operate, the anisotropic structure of the prepared mesophase pitch is uniform, the mesophase content is high and larger than 96 percent, the softening point is low, the temperature ranges from 240 DEG C to 260 DGE C, and the spinnability is good.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
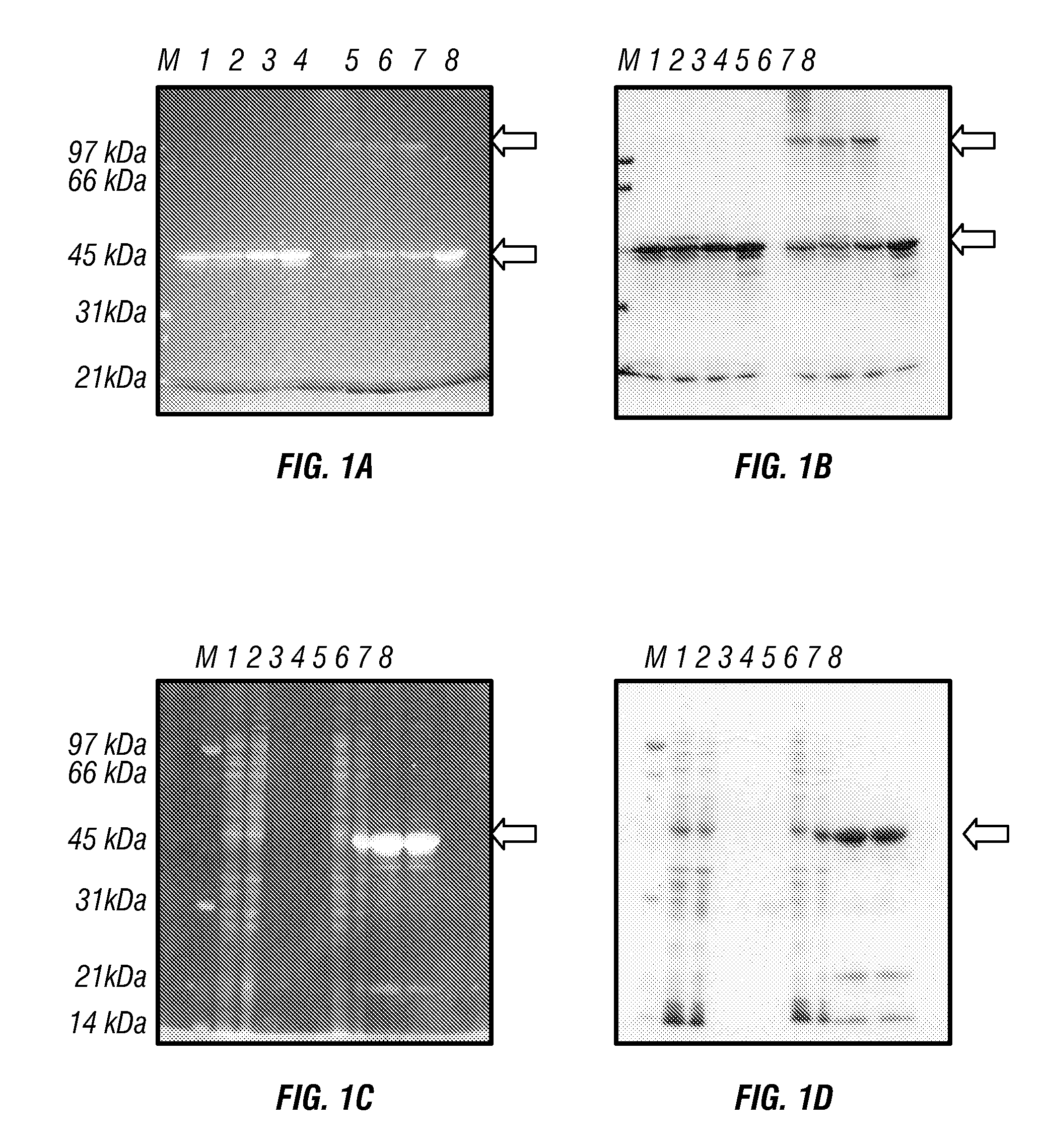
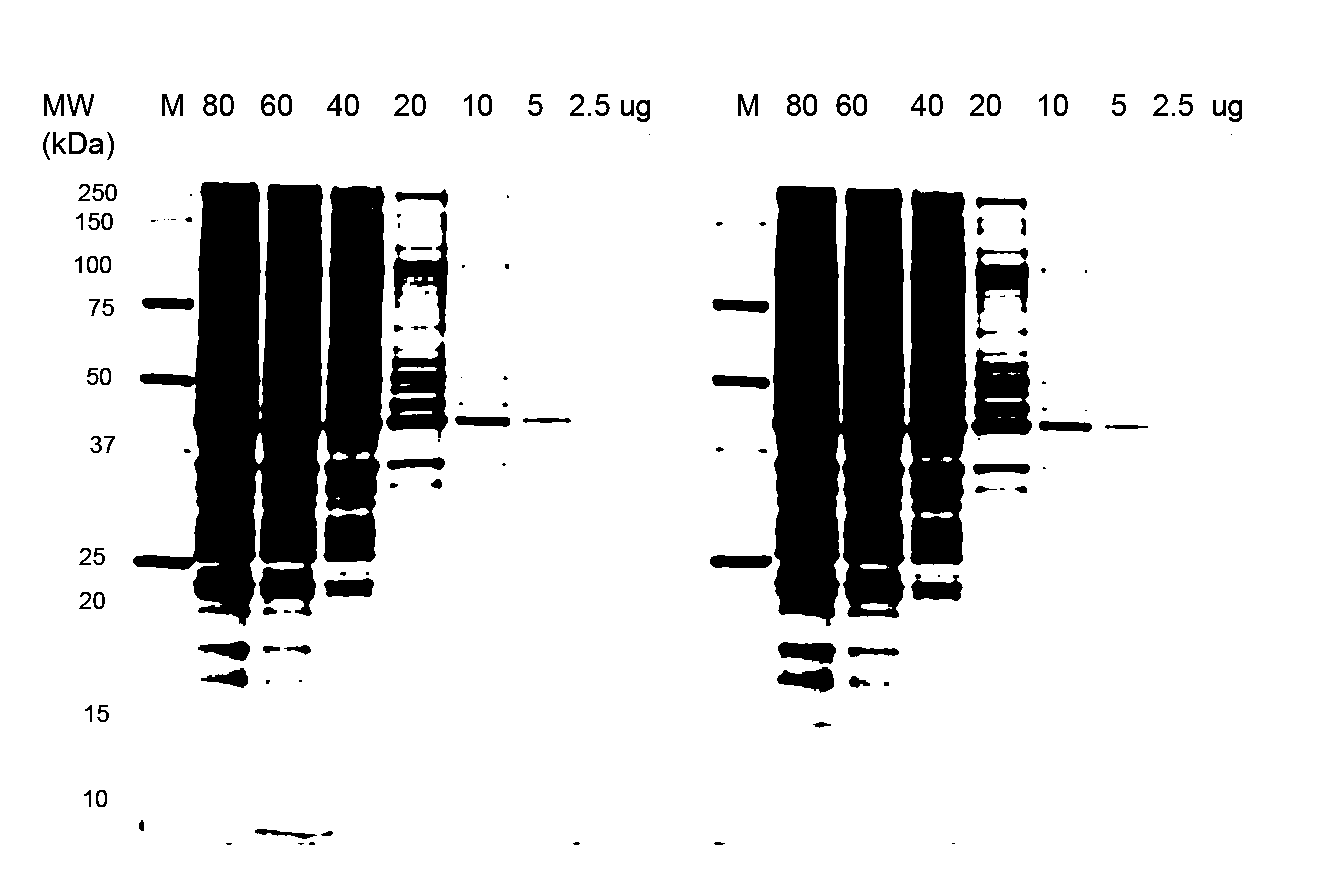
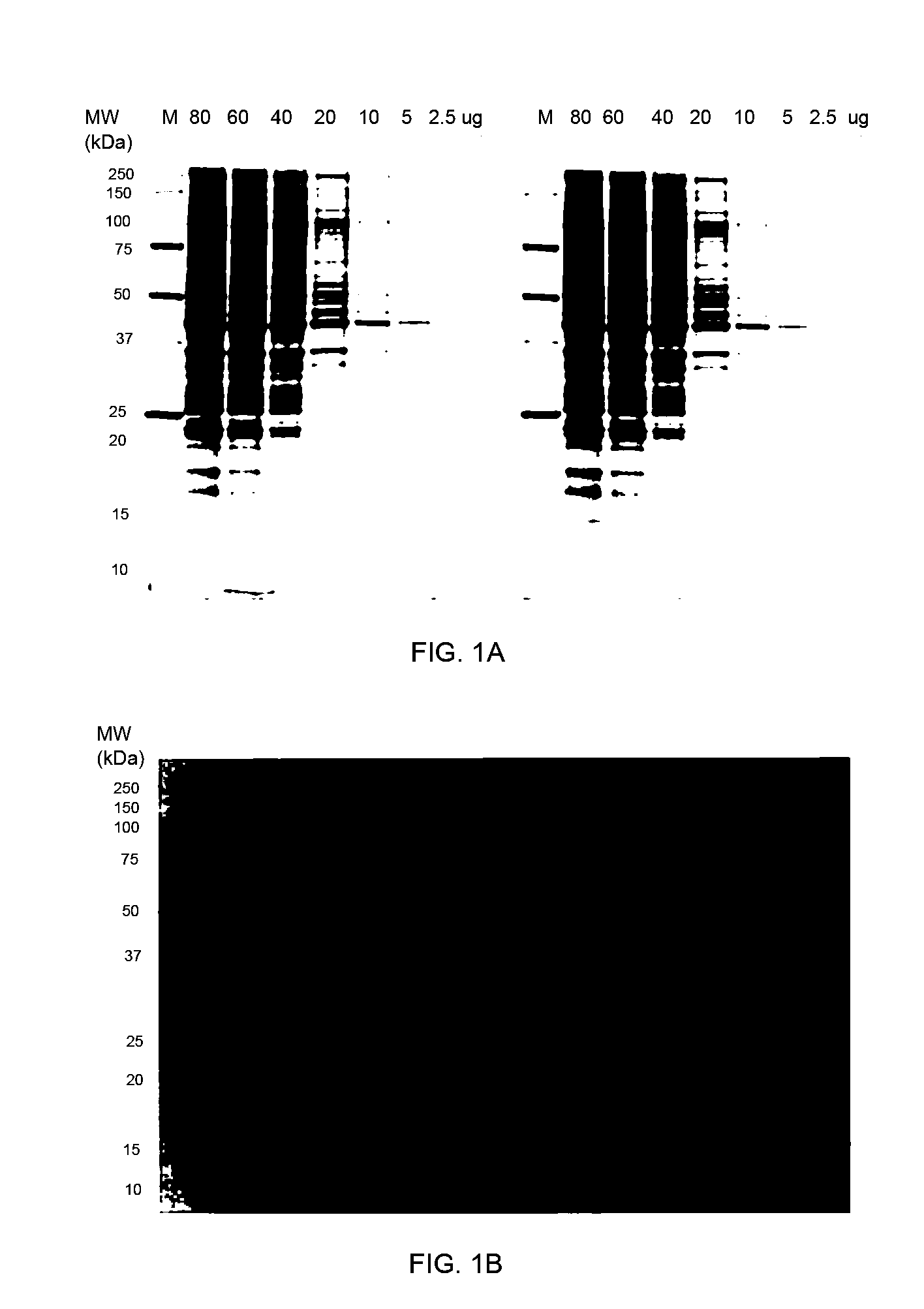
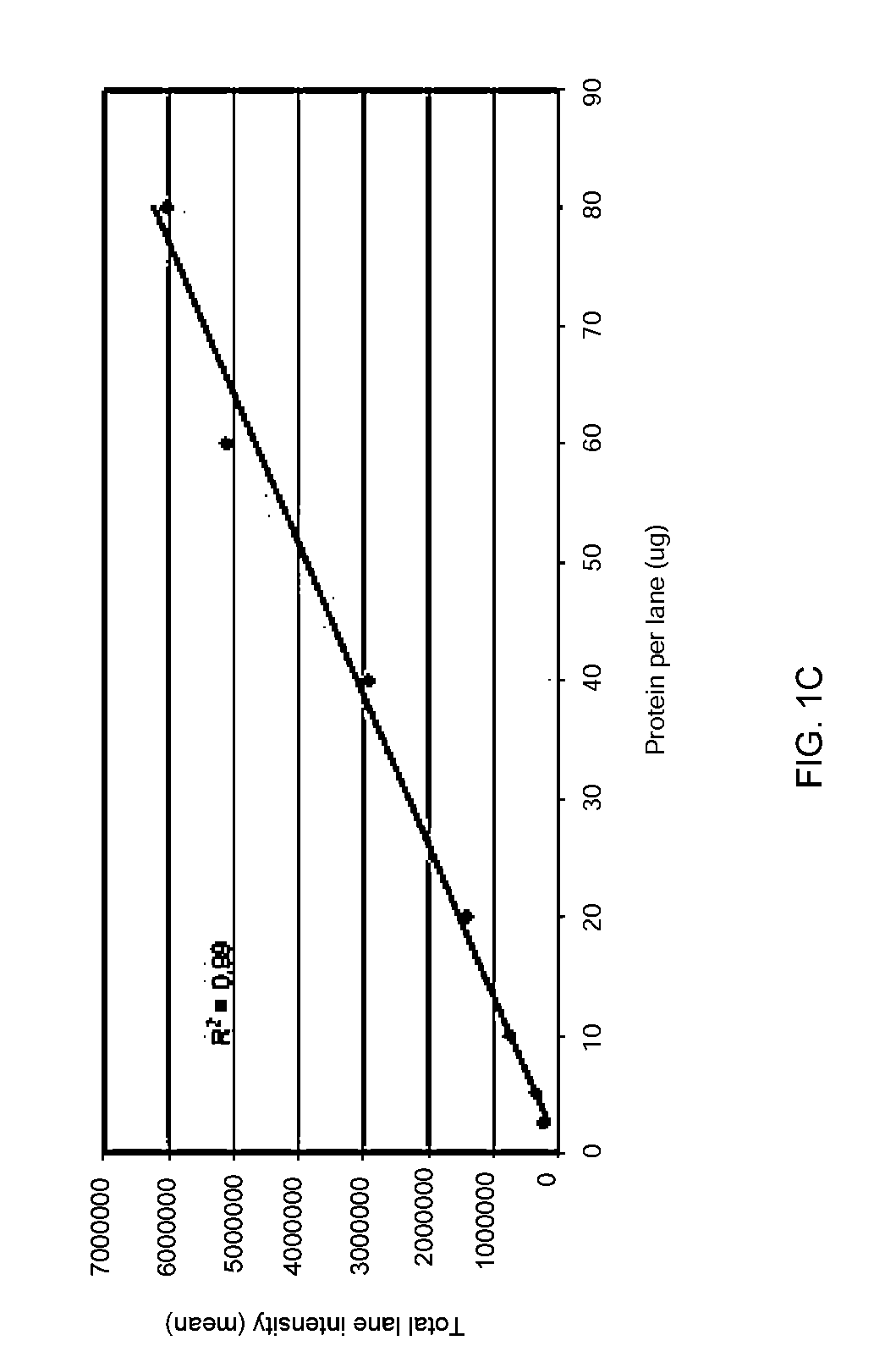
Stain-free protein quantification and normalization
Disclosed herein are methods of protein quantification and normalization using haloalkylated tryptophan fluorescence. Complex protein samples, i.e., samples that each contain 1,000 or more distinct proteins, from diverse sources that do not have common protein profiles are treated with a halo-substituted organic compound (i.e. haloalkane) that reacts with tryptophan residues to form fluorescent products. Irradiation of the samples with ultraviolet light and the detection and quantification of the resultant fluorescent emissions from all proteins in each sample are then used to obtain comparative values for total protein content among the various samples. The values thus obtained are found to be valid indications of comparative total protein content, despite the fact that the tryptophan levels vary widely among the various proteins in any single sample and the samples, due to the diversity of their origins, tend to differ among themselves in the identities and relative amounts of the proteins that they contain. Protein samples are also normalized to correct for differences in sample dilution, sample loading, and protein transfer inconsistencies, by using stain-free detection of total protein in each of the samples, or detection of subsamples within each sample.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Method for preparing tetrabromo-bisphenol A polycarbonate
The invention relates to a method for preparing molecular tetrabromobisphenol-A polycarbonate. Its character shows as follow: a. it dissolves the tetrabromobisphenol-A and inhibitor in the natrium hydroxydatum, filtering. Then, it dissolves triphosgene in the halogenated alkane, filtring. b. it adds the filtered triphosgene solution to the filtered tetrabromobisphenol-A and inhibitor solution, and then it adds natrium hydroxydatum at room temperature under normal pressure, and maintains the system to be pH9-12, then it stirs the solution for 0.5-1 hours. c. it adds 10%-20% of the natrium hydroxydatum at room temperature under normal pressure, and maintains the system to be pH8-10, then it stirs the solution for 0.5-1 hours. d. it regulates the solution with acid to be neutral and takes out from the organic layer, then it washes the material with deionized water and adds fatty alcohol to precipitate white powder, then it achieves the molecular weight range of 150,000 ~ 250,000 molecular of tetrabromobisphenol-A polycarbonate through filtration and drying.
Owner:TAIZHOU UNIV
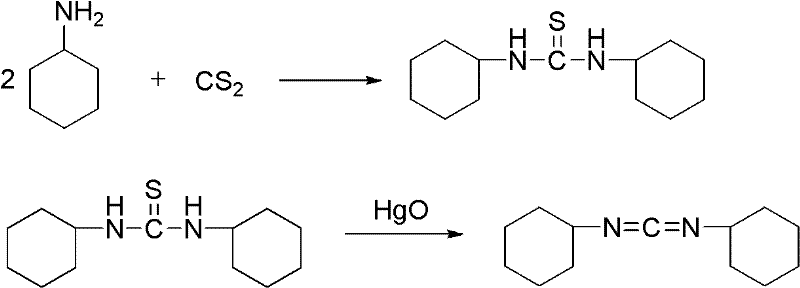
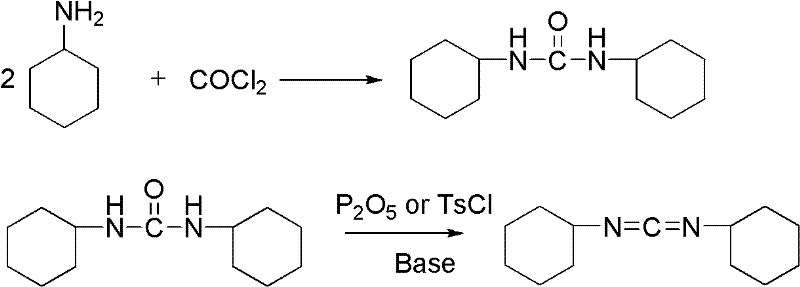
Method for synthesizing dicyclohexylcarbodiimide compound
InactiveCN102408355AEliminate security concernsEliminate pollutionOrganic chemistryChlorobenzeneNitrobenzene
The invention discloses a synthetic method of a dicyclohexylcarbodiimide compound. The method comprises the following steps: taking dicyclohexylurea and di(trichloromethyl) carbonate as a raw material, fully reacting in an organic solvent A at the temperature of 20-110 DEG C, cooling to the room temperature after finishing the reaction, adding triethylamine and neutralizing to pH value of 7-8, post-treating a reaction solution to prepare the dicyclohexylcarbodiimide compound; wherein the organic solvent A is C1-C5 haloalkanes, C3-C8 fatty ester, ketones, ethers, benzene, toluene, xylene, chlorobenzene, nitrobenzene, cyclohexane or nitromethane. The method basically eliminates the problems of big hidden trouble of traditional technical safety and serious three wastes pollution. The method for synthesizing dicyclohexylcarbodiimide compound has the advantages of safety, reliability, simple process, less three wastes, small energy consumption, high overall yield, low cost and excellent product quality, and is suitable for industrialization production and has good economic benefit.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
Preparation and application method of polyionic liquid solid acid catalyst
ActiveCN107297222AImprove conversion rateHigh yieldOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsHydrocarbon from saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbon additionCross-linkStrong acids
The invention discloses preparation and an application method of a polyionic liquid solid acid catalyst, and relates to a polyionic liquid solid acid catalyst for preparing diphenylethane via alkylation reaction of ortho xylene and styrene, and a preparation method of the polyionic liquid solid acid catalyst. The catalyst has a higher alkylation conversion rate, diphenylethane yield and reusability at high temperature and atmospheric pressure. The polyionic liquid catalyst is prepared by performing a hydrothermal reaction of a vinyl imidazole monomer, N,N-methylene bisacrylamide cross-linking agent, an initiator and a dispersant to form a precursor porous polymer, and adding the obtained precursor porous polymer into haloalkane and strong acid for reaction.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Preparation method of trimethylaluminium
InactiveCN105175440AHigh yieldHigh purityGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsEvaporationMethyl group
The invention relates to a preparation method of trimethylaluminium. The method comprises steps as follows: (1) magnalium and haloalkane have a contact reaction in the presence of an ether solvent and in the inert atmosphere to produce a trimethylaluminium ether complex; (2) the trimethylaluminium ether complex and an amine and / or phosphine compound with the high boiling point have a contact reaction to produce a trimethylaluminium amine complex and / or a trimethylaluminium phosphine complex; (3) the complexes obtained in Step (2) are decomposed. With the adoption of the preparation method, the yield and the purity of the trimethylaluminium can be significantly increased, the yield of the trimethylaluminium can be higher than 80%, the purity can be 99.9999%, besides, a reaction kettle used in the method can be used as an evaporation kettle, the technology and equipment are simplified, the reaction process is easy to control, the prepared product can be separated from raw materials and byproducts more easily, the method is very applicable to industrial production, in addition, the byproducts can be used for synthesizing aluminum sulfate, and almost no waste is produced.
Owner:JIANGXI JIAYIN PHOTOELECTRIC MATERIAL
Photocatalytic halohydrocarbon dehalogenation conversion method
InactiveCN109438156AHigh economic valueAvoid it happening againPhysical/chemical process catalystsHydrocarbon from halogen organic compoundsHalohydrocarbonAlkyne
The invention provides a photocatalytic halohydrocarbon dehalogenation conversion method which comprises the following steps: adding a photocatalyst quantum dot / rod into a solvent to obtain a solutionA; adding halohydrocarbon and an electronic sacrificial body into the solution A to obtain a solution B; utilizing a light source to irradiate the solution B and catalyzing the solution B to performhalohydrocarbon dehalogenation conversion. According to the photocatalytic halohydrocarbon dehalogenation conversion method disclosed by the invention, a nano quantum dot and a nano quantum rod are applied to dehalogenation conversion reaction of alkyl halide, alkenyl halide and alkyne halide for the first time; the reaction conditions are moderate, visible light is utilized as driving energy, a product is hydrocarbon compound, and the whole process has the advantages of environmental protection, conciseness and high efficiency. In addition, higher hydrocarbon of carbon chain growth can be generated after dehalogenation reaction, so that the method has potential application in preparation of higher hydrocarbon. According to the method disclosed by the invention, halohydrocarbon dehalogenation conversion and deuteration marking processes are jointly performed; hydrocarbon deuteration marking can be finished when a halohydrocarbon dehalogenation process is finished. The invention furtherprovides a method for performing deuteration marking on hydrocarbon.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
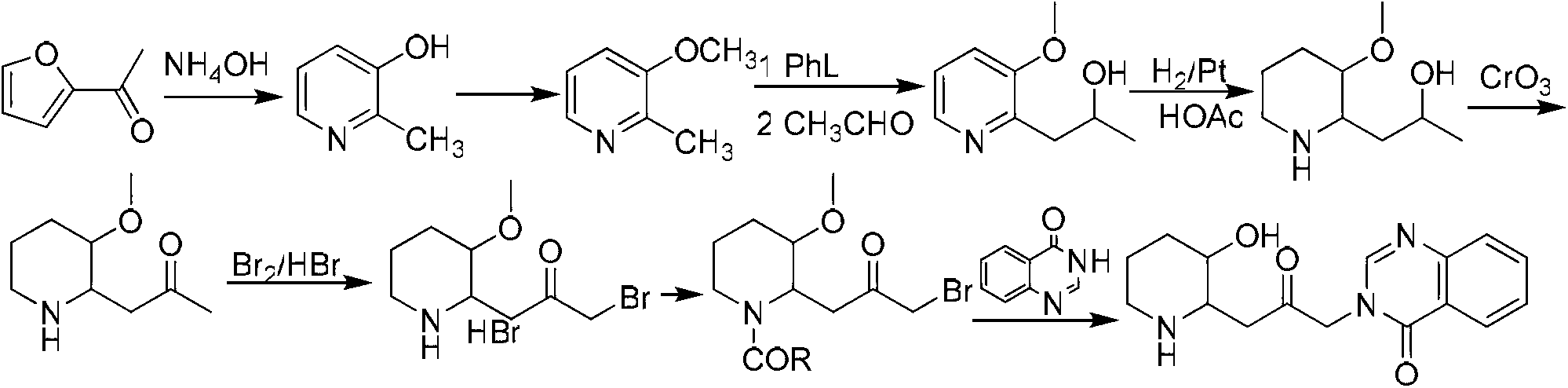
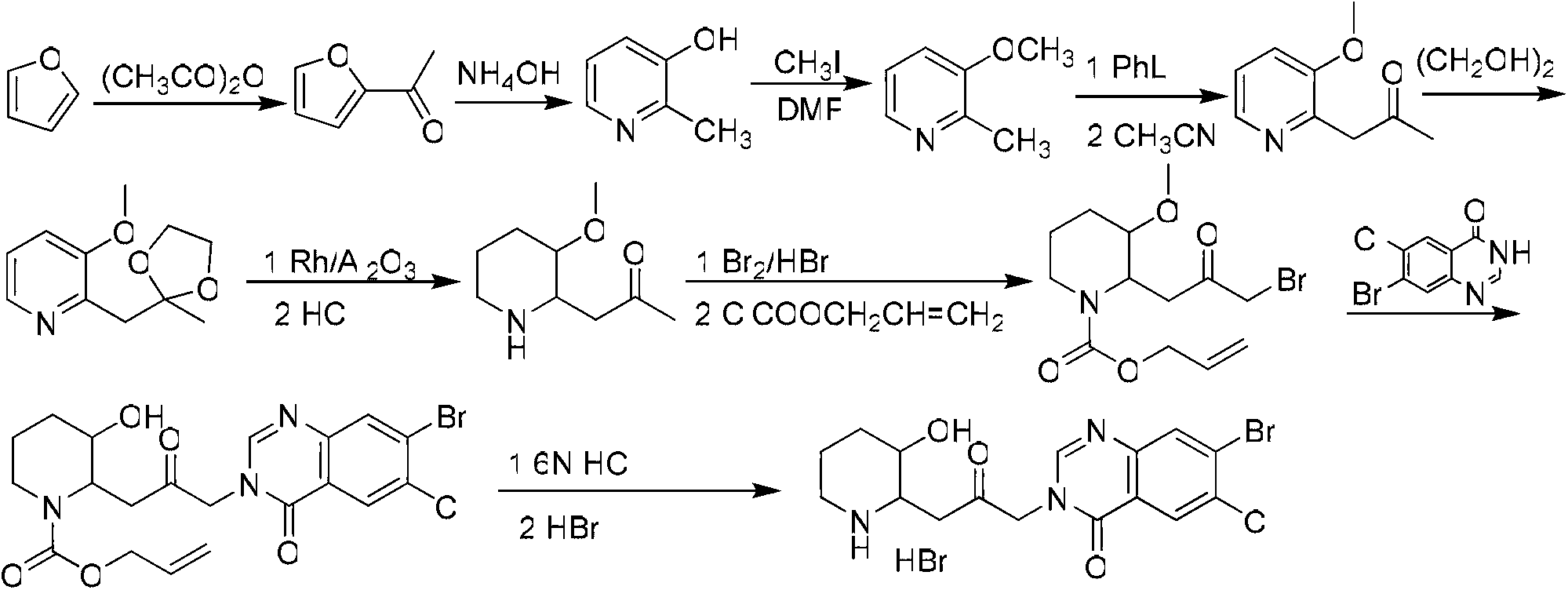
Method for preparing halofuginone hydrobromide
The invention discloses a method for preparing halofuginone hydrobromide, which comprises the following steps: by using N-benzyl-3-piperidone or hydrochloride thereof, organic or inorganic base, halide of alkali metal and beta, gamma-dihaloalkene or allyl haloalkane as initial raw materials, performing Steven rearrangement reaction to obtain an intermediate VIII; performing Von Braun reaction on the intermediate VIII to obtain an intermediate VII; performing reduction reaction on the intermediate VII to obtain an intermediate VI; obtaining an intermediate V after reaction of the intermediate VI and NBS (N-bromosuccinimide); obtaining an intermediate IV after the reaction of the intermediate V and a compound 7-bromine-6-chlorine-4(3H) quinazolinone; performing deprotection on the intermediate IV to obtain an intermediate III; performing backflow processing on the intermediate III in ethanol to obtain an intermediate II; and obtaining the halofuginone hydrobromide after the salt forming reaction of intermediate II. The invention develops an efficient and simple method for synthesizing the halofuginone hydrobromide. The total yield can reach over 50 percent, cost is greatly reduced and the product has high purity.
Owner:CHONGQING WEIPENG PHARMA
Method for preparing low-water-content solid methyl disulfonic acid through taking methylene chloride as raw material
The invention provides a method for preparing low-water-content solid methyl disulfonic acid through taking methylene chloride as a raw material. The method comprises the following steps of the processes of sulfonating, barium treating, acidifying, dewatering and the like, and mainly comprises the steps that an aqueous methyl disulfonic acid system which is obtained after acidifying is mainly subjected to reduced pressure distillation, when the water content of the system is 8-10% and the temperature is between 50-100 DEG C, an organic solvent and a dehydrating agent are dripped, after reacting for 2-4 hours, the mixture is cooled to the room temperature, filtrated and washed, and thus, the solid methyl disulfonic acid with the water content being lower than 0.50% is obtained, wherein the organic solvent is selected from one of haloalkanes, ethers and alkanes or is the mixture of the haloalkanes, the ethers and the alkanes arbitrarily, and the use amount of the organic solvent is 1-5 times of the quantity of methyl disulfonic acid; and the dehydrating agent is thionyl chloride, and the molar ratio of thionyl chloride to the water content of methyl disulfonic acid is (1.0-2.5):1. The drying method is simple and ingenious, the drying and dehydrating time is shortened, the production cost is lowered, and the method has great practicable value and industrial economic benefit.
Owner:LIANHE CHEM TECH +1
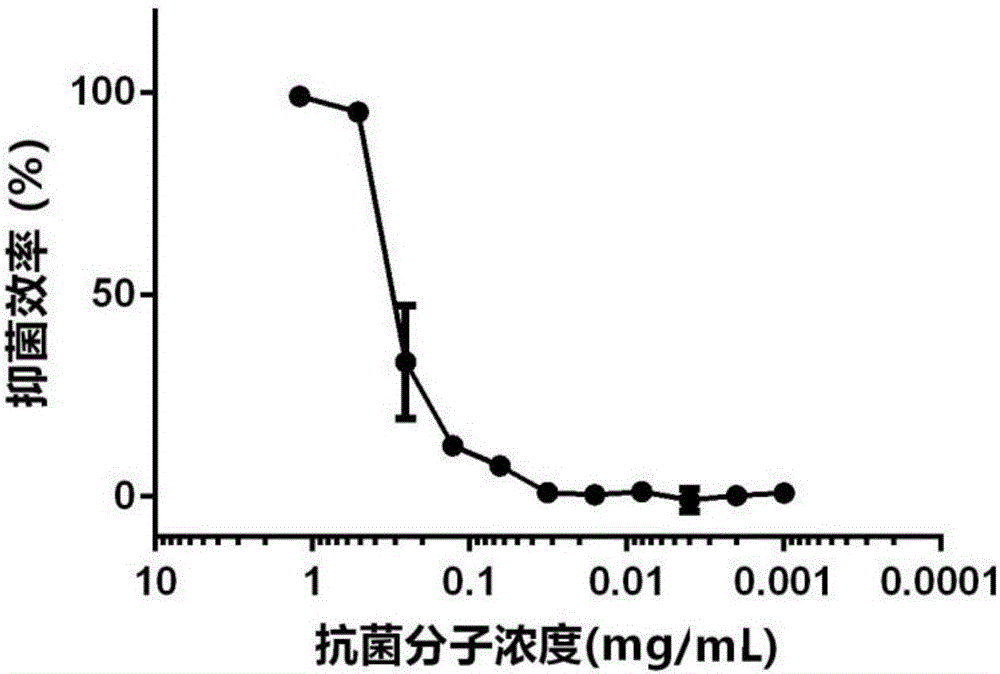
High polymer quaternary ammonium salt antibacterial agent preparation method and application
ActiveCN106146835AImprove antibacterial propertiesImprove hydrophilicityBiocideDisinfectantsEnvironmental resistancePolymer science
The invention provides a high polymer quaternary ammonium salt antibacterial agent preparation method and application, and belongs to the technical field of antibacterial agents. The antibacterial agent is prepared by conducting a quaterization reaction on large molecular weight polyethyleneimine (b-PEI) and short-chain haloalkane. The high polymer quaternary ammonium salt antibacterial agent prepared through the method has an efficient, lasting and broad-spectrum antibacterial property, has the advantages of being high in safety, simple in preparation process and the like, can serve as an antibacterial additive and has a potential commercial application prospect in the fields of medical treatment, sanitation and environmental protection.
Owner:成都康钧生物科技有限公司
Siliceous aromatic ether and aryne polymer and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a siliceous aromatic ether and aryne polymer and a preparation method thereof. The polymer is structurally characterized by comprising silicon atoms, aryne groups and an aromatic ether structure on a main chain. The siliceous aromatic ether and aryne polymer is polymerized from diacetylene-benzene or a dyhydroxy aromatic compound and dichlorosilane by Grignard reaction under an inert atmosphere. The preparation method of the polymer comprises the following steps of: firstly reacting haloalkane with magnesium powder to produce an alkyl magnesium halide Grignard reagent; and then reacting with the dyhydroxy aromatic compound to obtain an alkyl magnesium halide Grignard reagent of the dyhydroxy aromatic compound or reacting with diacetylene-benzene to obtain an alkyl magnesium halide Grignard reagent of diacetylene-benzene; and finally reacting with dichlorosilane to obtain the siliceous aromatic ether and aryne polymer. The invention has the advantages of simple process, short reaction time, easily controlled process condition and simple subsequent processing and is convenient to operate; in addition. The product of the method is stable at room temperature and easy to store, the condensate of the polymer has excellent heat-resisting stability and mechanical property and is a high-performance thermosetting resin with good heat-resisting property.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
High-valent metal fluorination catalyst and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109999788AIncrease temperatureHigh catalytic activityPreparation by halogen replacementMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsChemical synthesisAlkane
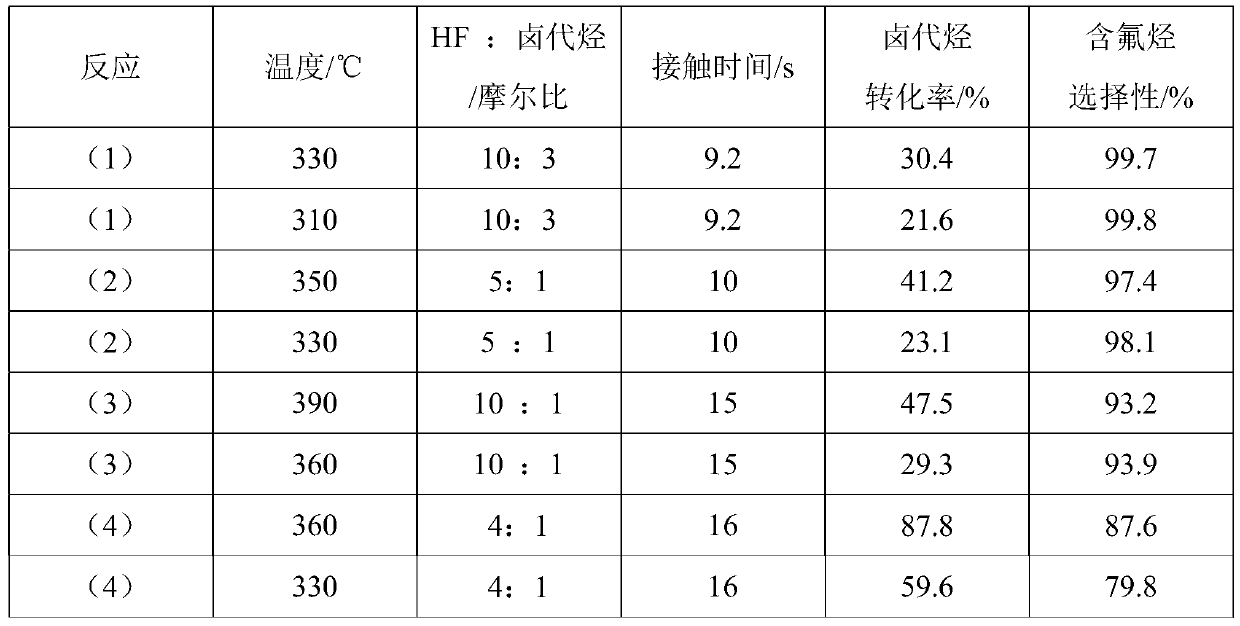
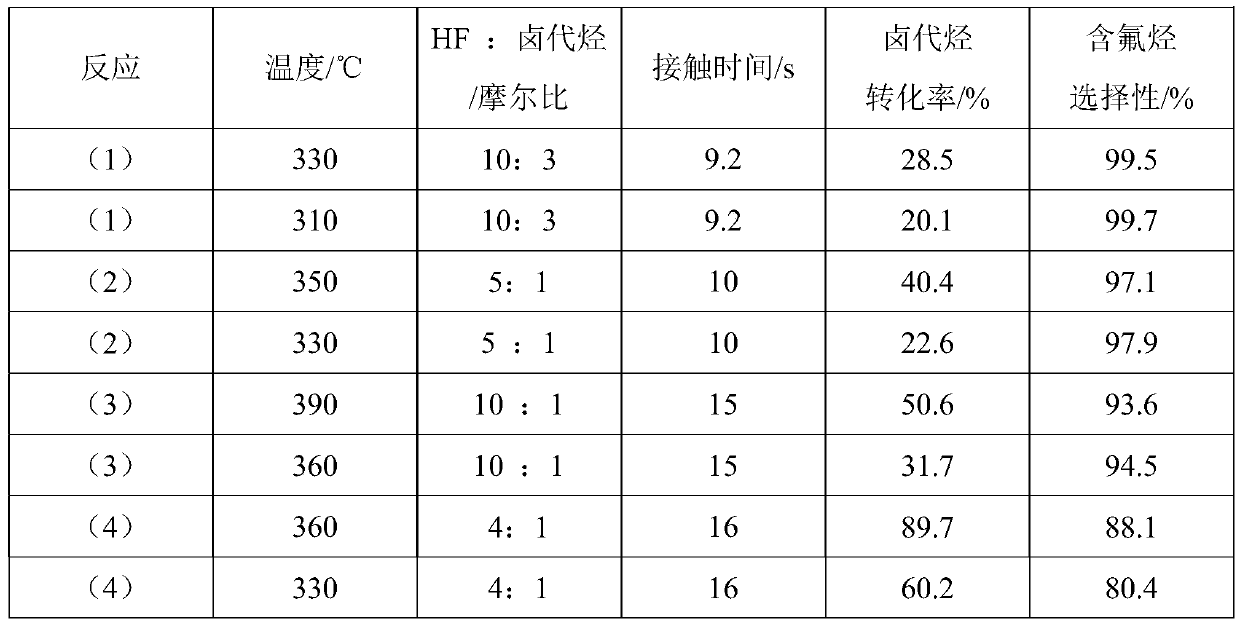
The invention discloses 'a high-valent metal fluorination catalyst and a preparation method and application thereof', and belongs to the field of chemical synthesis. The high-valent metal fluorinationcatalyst is composed of high-valent metal ions and auxiliary agents, wherein the mass percentages of high-valent metal ions and auxiliary agents are 70%-100% and 0-30% in sequence. A 'fluorine storage material' is introduced in an oxidation stage to convert low-valent metal ions into high-valent metal ions. The high-valent metal fluorination catalyst has high use temperature, high catalytic activity and long service life, and is mainly used for preparing a fluorine-containing alkane through a fluorine-chlorine exchange reaction of gas-phase catalytic halogenated alkane and hydrogen fluoride under high temperature or preparing a fluorine-containing olefin through a fluorine-chlorine exchange reaction of gas-phase catalytic halogenated olefin and hydrogen fluoride under high temperature.
Owner:泉州宇极新材料科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com