Patents
Literature
115 results about "Halocarbon" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Halocarbon compounds are chemicals in which one or more carbon atoms are linked by covalent bonds with one or more halogen atoms (fluorine, chlorine, bromine or iodine – group 17) resulting in the formation of organofluorine compounds, organochlorine compounds, organobromine compounds, and organoiodine compounds. Chlorine halocarbons are the most common and are called organochlorides.
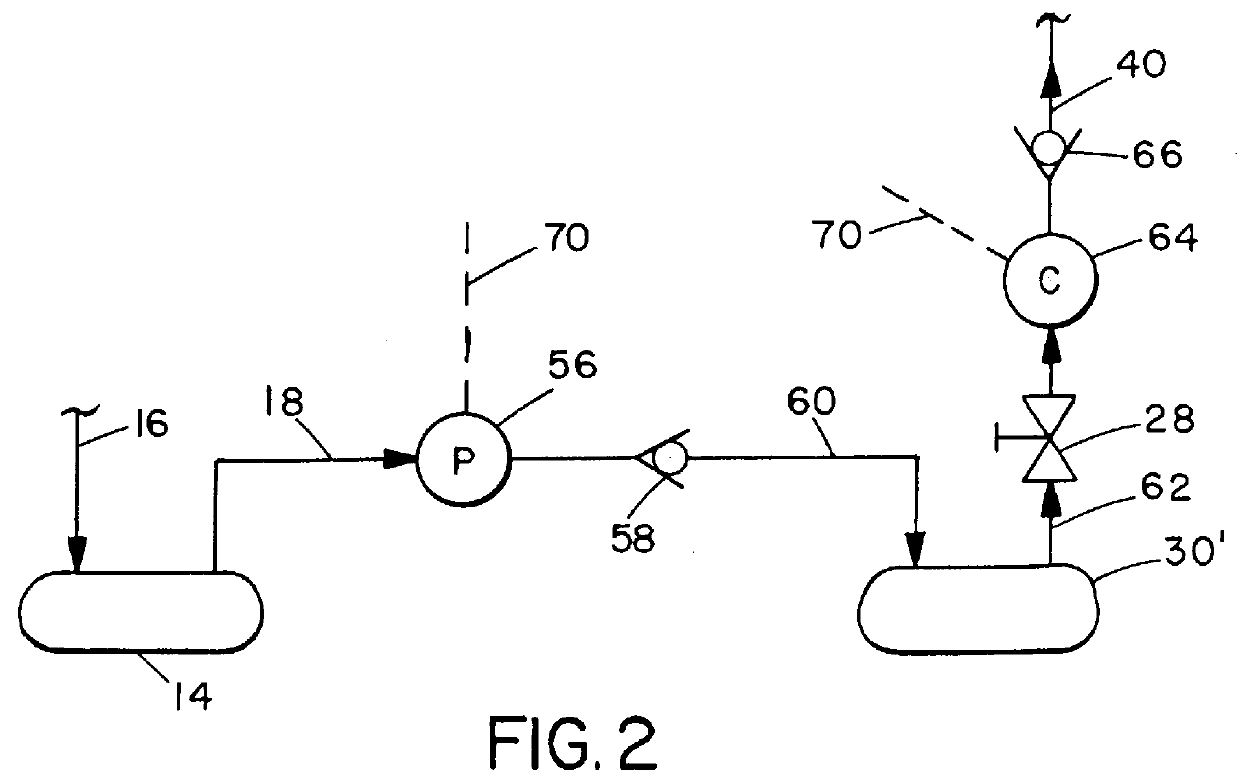
Process for removing and recovering halocarbons from effluent process streams
A process for recovery of fluorocompound gas from an effluent gas stream containing the fluorocompound gas and other gas components, in which at least one of the other gas components is removed, e.g., by oxidation or contacting of the effluent stream with a dry material such as an adsorbent or scrubber medium, to yield a first effluent gas mixture containing the fluorocompound gas. The fluorocompound gas is removed from the first effluent gas mixture and recovered as a concentrated fluorocompound gas, by a process such as cryogenic processing, membrane separation, and / or adsorption.
Owner:ADVANCED TECH MATERIALS INC
Azeotropic compositions comprising fluorinated compounds for cleaning applications
InactiveUS20070203046A1Other chemical processesDetergent mixture composition preparationAlcoholCompound (substance)
The present invention relates to compositions comprising fluorinated olefins or fluorinated ketones, and at least one alcohol, halocarbon, hydrofluorocarbon, or fluoroether and combinations thereof. In one embodiment, these compositions are azeotropic or azeotrope-like. In another emebodiment, these compositions are useful in cleaning applications as a degreasing agent or defluxing agent for removing oils and / or other residues from a surface.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Method for recovery and reuse of gas
A gas recovery and reuse / recycle method is disclosed which can readily and economically recover valuable and / or environmentally hazardous gases from a manufacturing or chemical process and then return the gas to the process for reuse, and repeat this many times without significant contamination or degradation of the gas or the produced products. All gas transport, compression and storage equipment is designed and maintained so that it is non-contaminating to the process gas. Commonly the process gas will be a Group VIII gas, preferably He, Ne, Kr or Xe, or a gas which comprises a hazard to the ambient environment or beings therein, such as a carbon oxide gas, a halocarbon gas, an acid-precursor gas, a biologically hazardous gas, or a radioactive gas.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Method for separating halocarbons
ActiveUS20100048961A1Preparation by hydrogen halide split-offPreparation by halogen halide additionHalocarbonHFO-1234yf
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
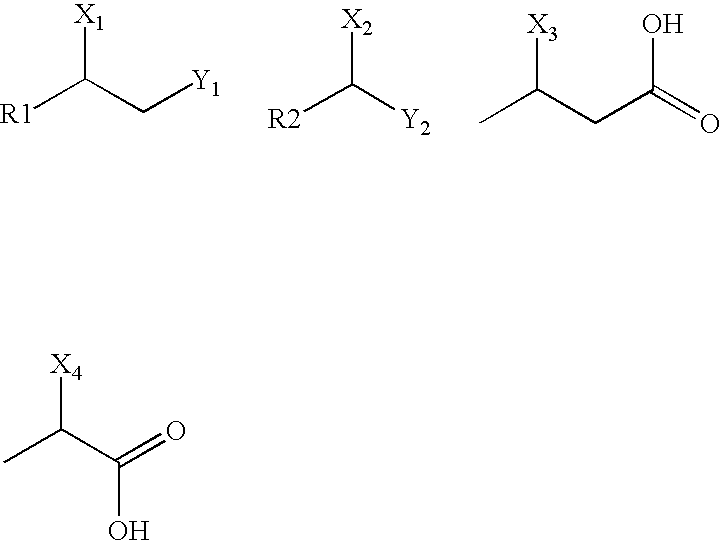
Alteration of hydrolase genes and screening of the resulting libraries for the ability to catalyze specific reactions
The present invention relates to halocarbon and halohydrocarbon chemistry, including methods of dehalogenating halocarbons and halohydrocarbons to provide, inter alia, alcohols, polyols, and epoxides. In general, the methods involve reaction pathways catalyzed by altered hydrolase enzymes that can provide stereoselective or stereospecific reaction products. The invention also includes methods of providing altered nucleic acids that encode altered dehalogenase or other hydrolase enzymes. Additionally, the invention includes various reaction formats and kits.
Owner:MAXYGEN
Azeotropic compositions comprising fluorinated compounds for cleaning applications
InactiveUS20070203045A1Other chemical processesDetergent mixture composition preparationAlcoholCompound (substance)
The present invention relates to compositions comprising fluorinated olefins or fluorinated ketones, and at least one alcohol, halocarbon, hydrofluorocarbon, or fluoroether. In one embodiment, these compositions are azeotropic or azeotrope-like. In another embodiment, these compositions are useful in cleaning applications as a degreasing agent or defluxing agent for removing oils and / or other residues from a surface.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Process for the manufacture of halocarbons and selected compounds and azeotropes with HF
InactiveUS20050080302A1Preparation by hydrogen halide split-offPreparation by halogen halide additionAlkaneHalocarbon
A liquid phase process is disclosed for producing halogenated alkane adducts of the formula CAR1R2CBR3R4 (where A, B, R1, R2, R3, and R4 are as defined in the specification) which involves contacting a corresponding halogenated alkane, AB, with a corresponding olefin, CR1R2═CR3R4 in a dinitrile or cyclic carbonate ester solvent which divides the reaction mixture into two liquid phases and in the presence of a catalyst system containing (i) at least one catalyst selected from monovalent and divalent copper; and optionally (ii) a promoter selected from aromatic or aliphatic heterocyclic compounds which contain at least one carbon-nitrogen double bond in the heterocyclic ring. When hydrochlorofluorocarbons are formed, the chlorine content may be reduced by reacting the hydrochlorofluorocarbons with HF. New compounds disclosed include CF3CF2CCl2CH2CCl3, CF3CCl2CH2CH2Cl and CF3CCl2CH2CHClF. These compounds are useful as intermediates for producing hydrofluorocarbons. Azeotropes of CClF2CH2CF3 with HF and azeotropes of CF3CH2CHF2 with HF are also disclosed; as are process for producing such azeotropes. A process for purification of certain hydrofluorocarbons and / or chloro-precursors thereof from mixtures of such compounds with HF is also disclosed.
Owner:THE CHEMOURS CO FC LLC
Azeotropic compositions comprising fluorinated compounds for cleaning applications
InactiveUS20080060687A1Other chemical processesDetergent mixture composition preparationAlcoholHalocarbon
The present invention relates to compositions comprising fluorinated olefins or fluorinated ketones, and at least one alcohol, halocarbon, hydrofluorocarbon, or fluoroether. In one embodiment, these compositions are azeotropic or azeotrope-like. In another embodiment, these compositions are useful in cleaning applications as a degreasing agent or defluxing agent for removing oils and / or other residues from a surface.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Direct conversion of HCFC 225ca/cb mixture to HFC 245cb and HFC 1234yf
ActiveUS20070096053A1Toxic reductionPreparation by dehalogenationPreparation by halogen replacementHalocarbonSelective reduction
Provided are methods for producing hydrofluorocarbons via the selective reduction of a halocarbon blend comprising 1,3-dichloro-1,1,2,2,3-pentafluoropropane.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Polyfunctional liquid urethane composition
Disclosed is a urethane-based composition of value in surface coating applications, including treatment of glass or textiles, in adhesives and in the manufacture of a stabilized latex. The composition comprises a polyfunctional liquid urethane-containing adduct wherein said adduct contains as a first functional group at least one isocyanate moiety per molecule, and a second functional group per molecule which is not an isocyanate moiety and which is not reactive towards isocyanate functionality. The second functional group can comprise ester, nitrile, halogen, halocarbon, siloxyl, silyl, alkyne or alkene, or combinations of two or more thereof.
Owner:THE DOW CHEM CO
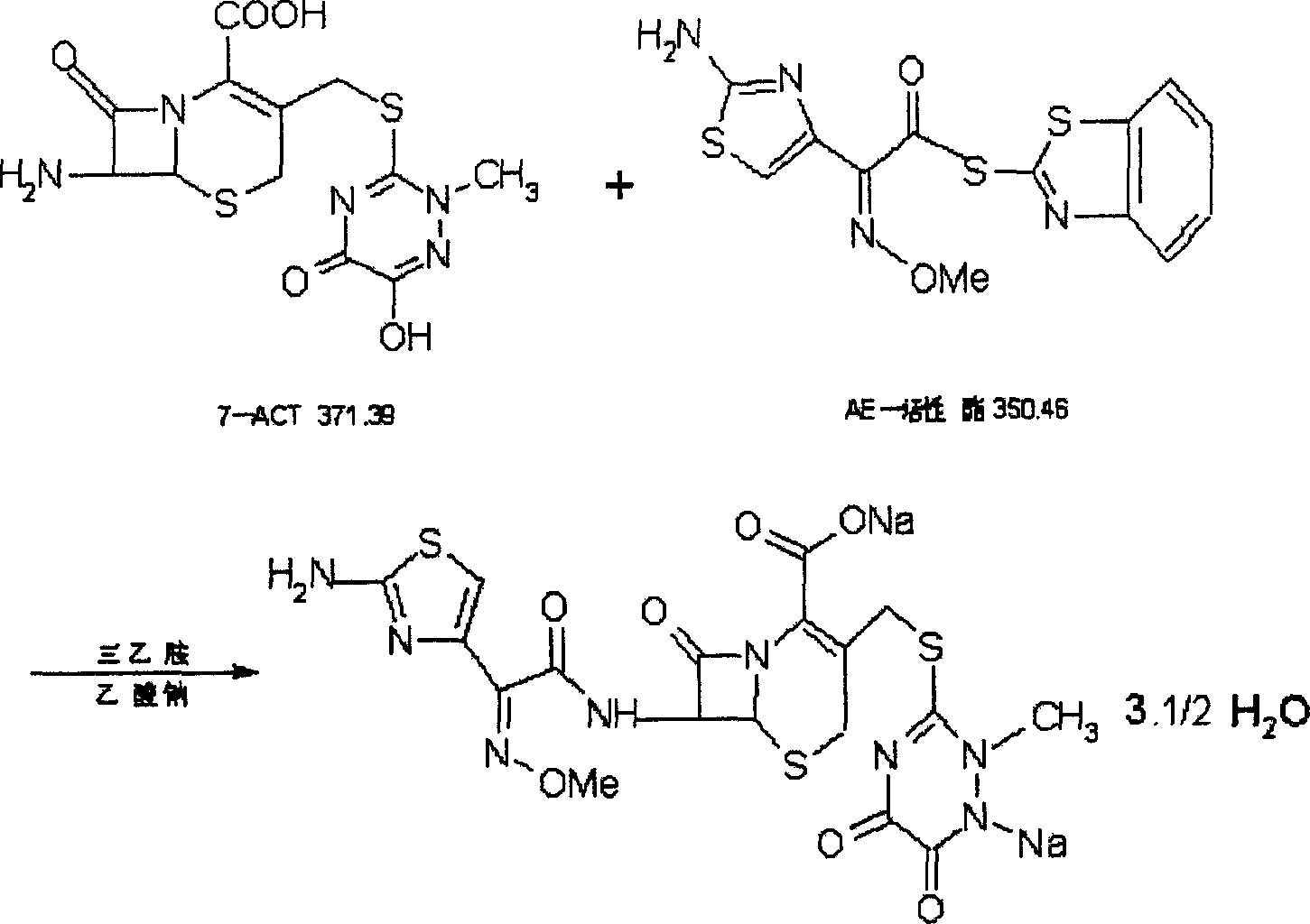
Process for preparing ceftriaxone sodium
Disclosed is a process for preparing ceftriaxone sodium belonging to compound preparation technical field. Protected by nitrogen, 7-ACT3 reacts with AE-active ester under the action of amine intermediate reactant in a solvent. Then a sodium salt forming agent is added in, and the cefotaxime sodium is obtained after reaction and seedout. The solvent is a mixed solvent composed of alkane halocarbon, ethyl acetate, or acetone and alcohol solvent and water. The solvent dosage is small, and the product yield is high.
Owner:REYOUNG PHARMA
Method for separating halocarbons
ActiveUS8252965B2Preparation by hydrogen halide split-offPreparation by halogen halide additionHalocarbonHFO-1234yf
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Halocarbon production processes, halocarbon separation processes, and halocarbon separation systems
InactiveUS20080045758A1Preparation by hydrogen halide split-offPreparation by halogen halide additionPurification methodsDistillation
Halocarbon production processes are provided that can include reacting at least one C-2 halocarbon with at least one C-1 halocarbon in the presence of a phosphate to produce at least one C-3 chlorocarbon. The processes can include reacting ethylene with carbon tetrachloride in the presence of a phosphate. Halocarbon separation processes are provided that can include providing a reaction product that includes at least one saturated fluorocarbon and at least one unsaturated fluorocarbon and adding at least one hydrohalogen to produce a distillation mixture. Methods and materials are provided for the production and purification of halogenated compounds and intermediates in the production of 1,1,1,3,3-pentafluoropropane.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Perfluoropolymers
InactiveUS20070292685A1Surprising melt-extrudabilityImprove the level ofEnvelopes/bags making machinerySpecial surfacesLow dissipationHalocarbon
Perfluoropolymer made without ionic species, initiator and without halocarbon solvent polymerization medium and dispersing agent is beneficially useful in liquid contact or food contact applications, for high-speed melt extrusion wire coating, and to produce insulated wire exhibiting low dissipation factor at high signal frequencies.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Methods to separate halogentated olefins from 2-chloro-1,1,1,2-tetrafluoropropane using a solid adsorbent
InactiveUS20130085308A1Prolonged activation processSolid sorbent liquid separationHalogenated hydrocarbon separation/purificationActivated carbonSorbent
The present invention provides a method for separating halocarbons. In particular, the invention provides a method for separating halogenated olefin impurities from 2-chloro-1,1,1,2-tetrafluoropropane (HCFC-244bb) using a solid adsorbent, particularly activated carbon. More particularly the invention pertains to a method for separating 2-chloro-3,3,3-trifluoro-propene (HCFO-1233xf) from HCFC-244bb, which are useful as intermediates in the production of 2,3,3,3-tetrafluoropropene (HFO-1234yf).
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
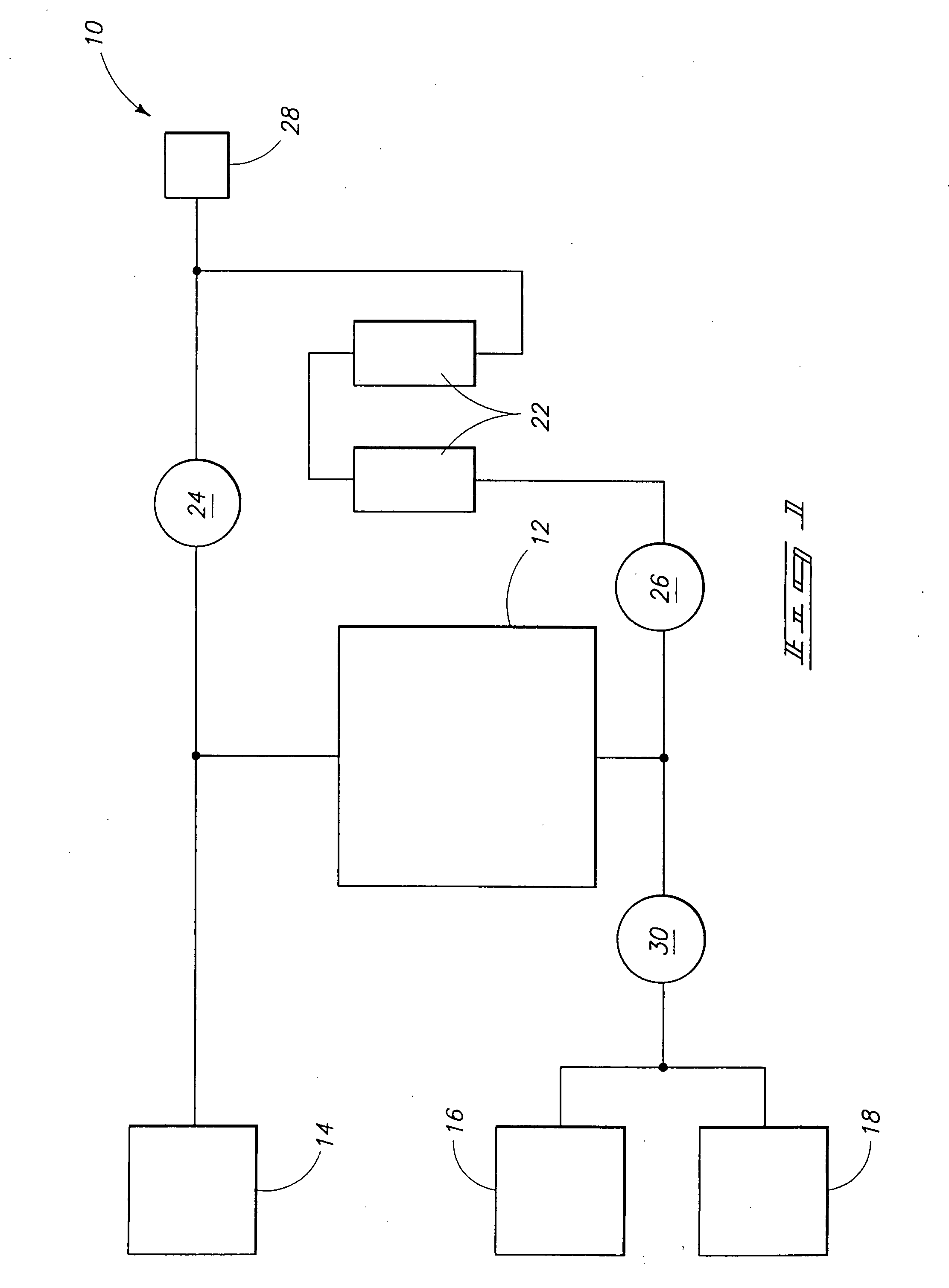
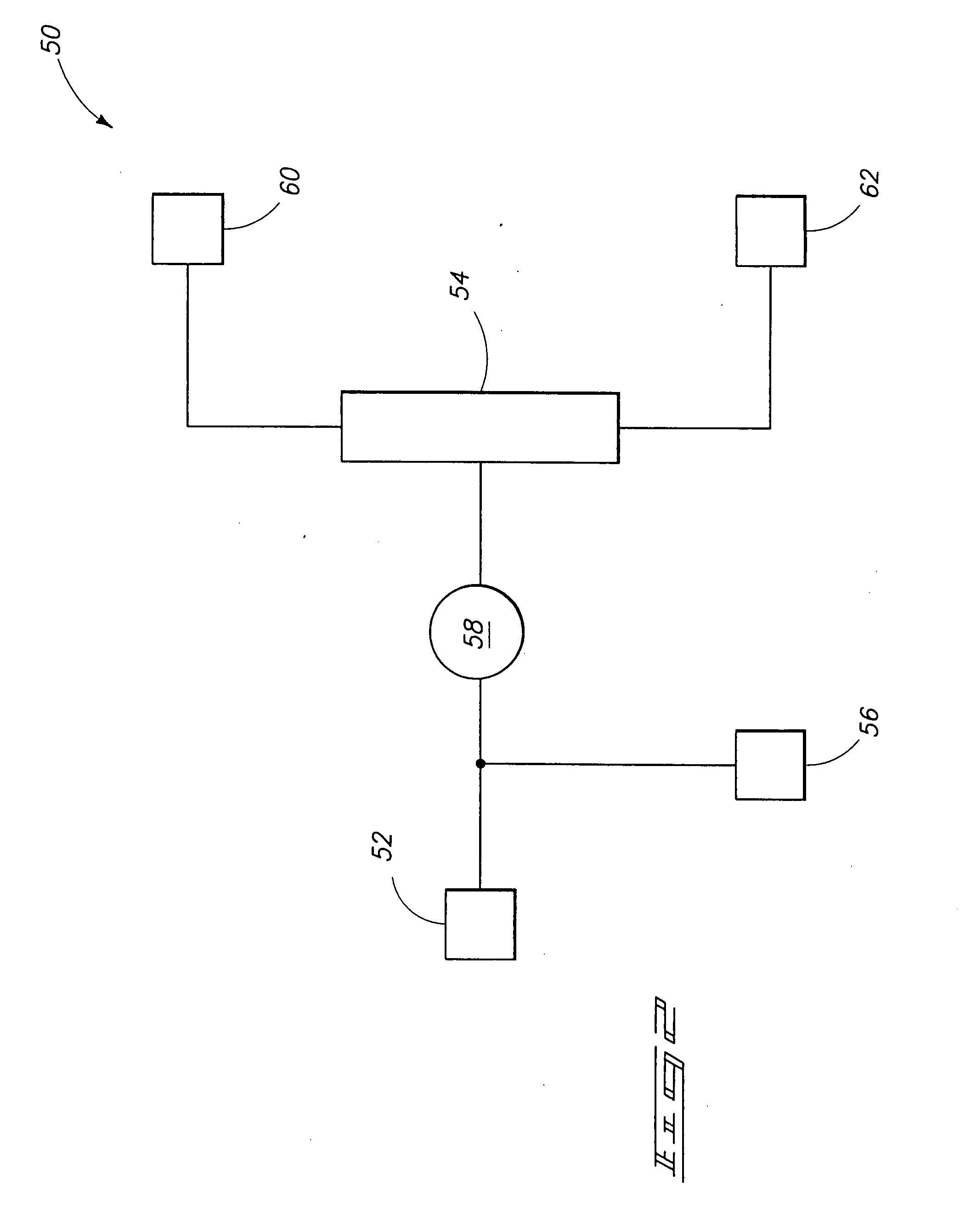
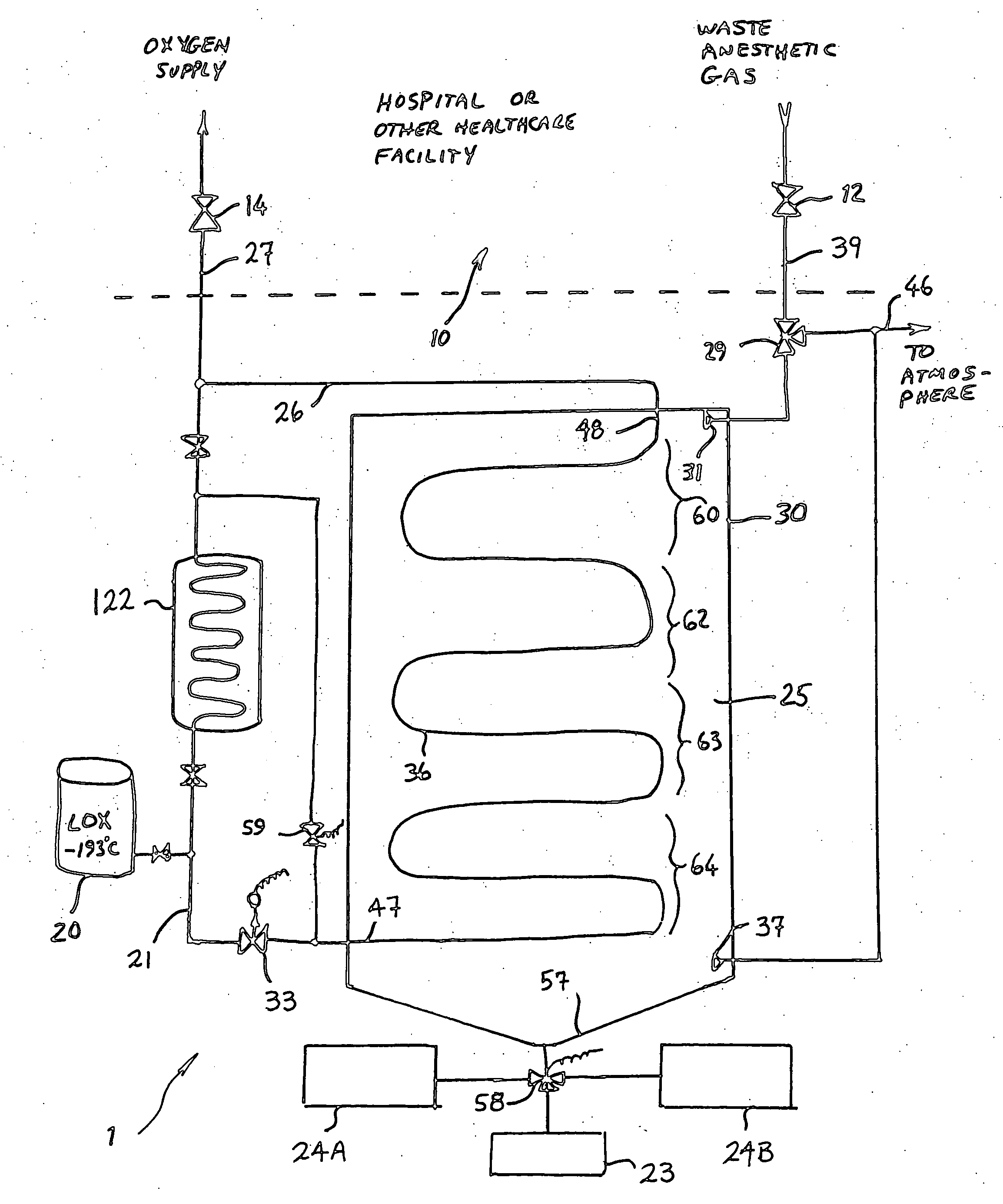
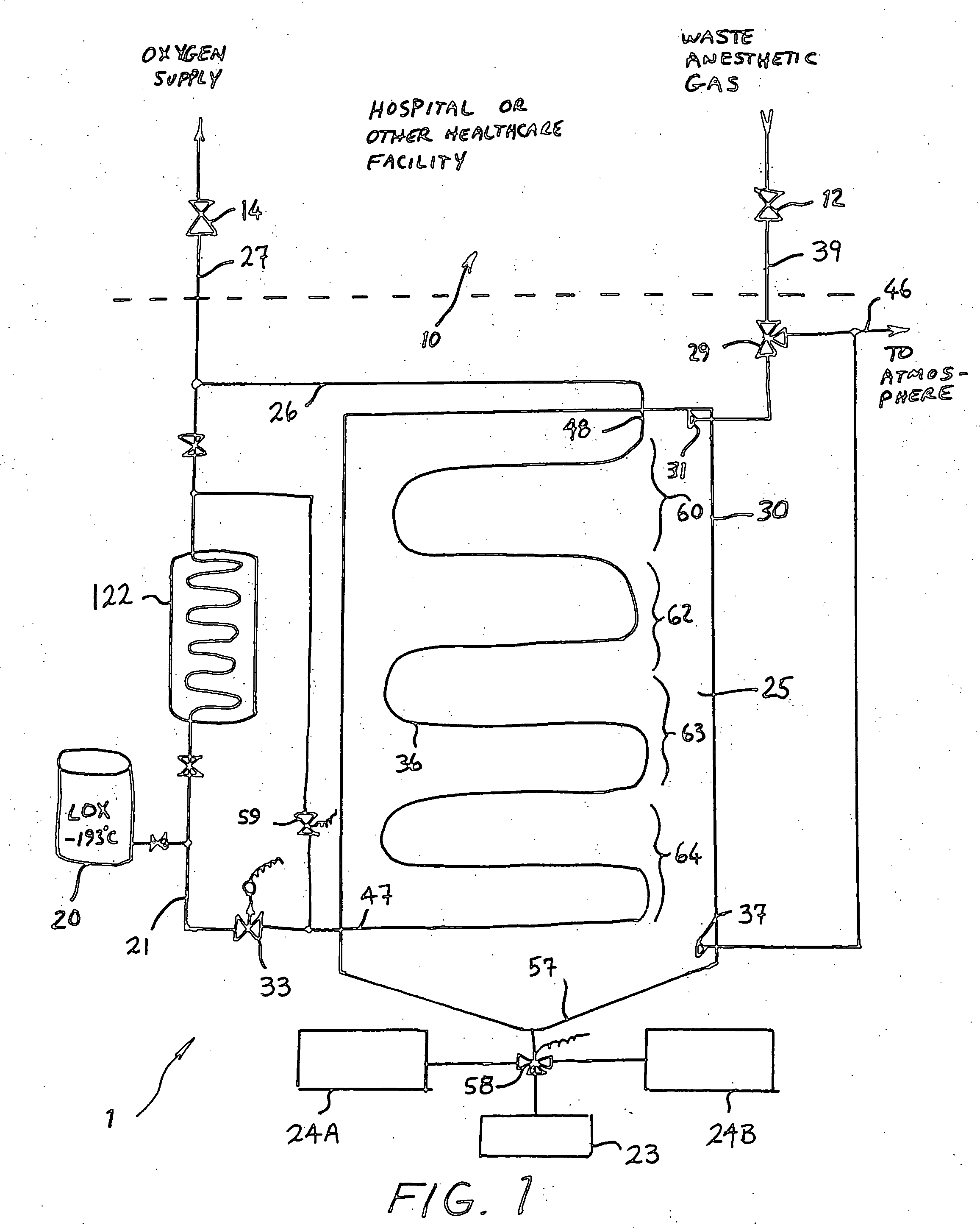
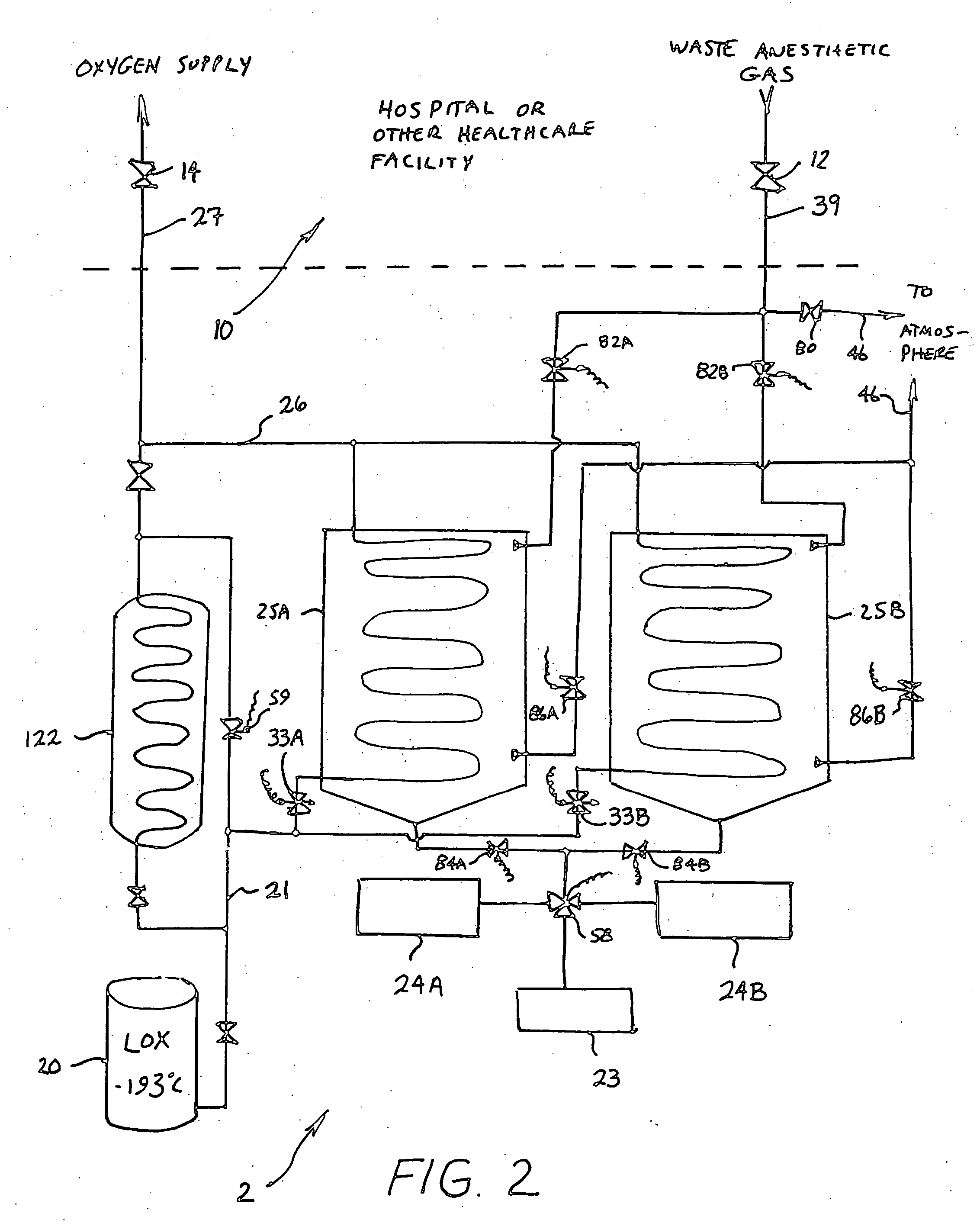
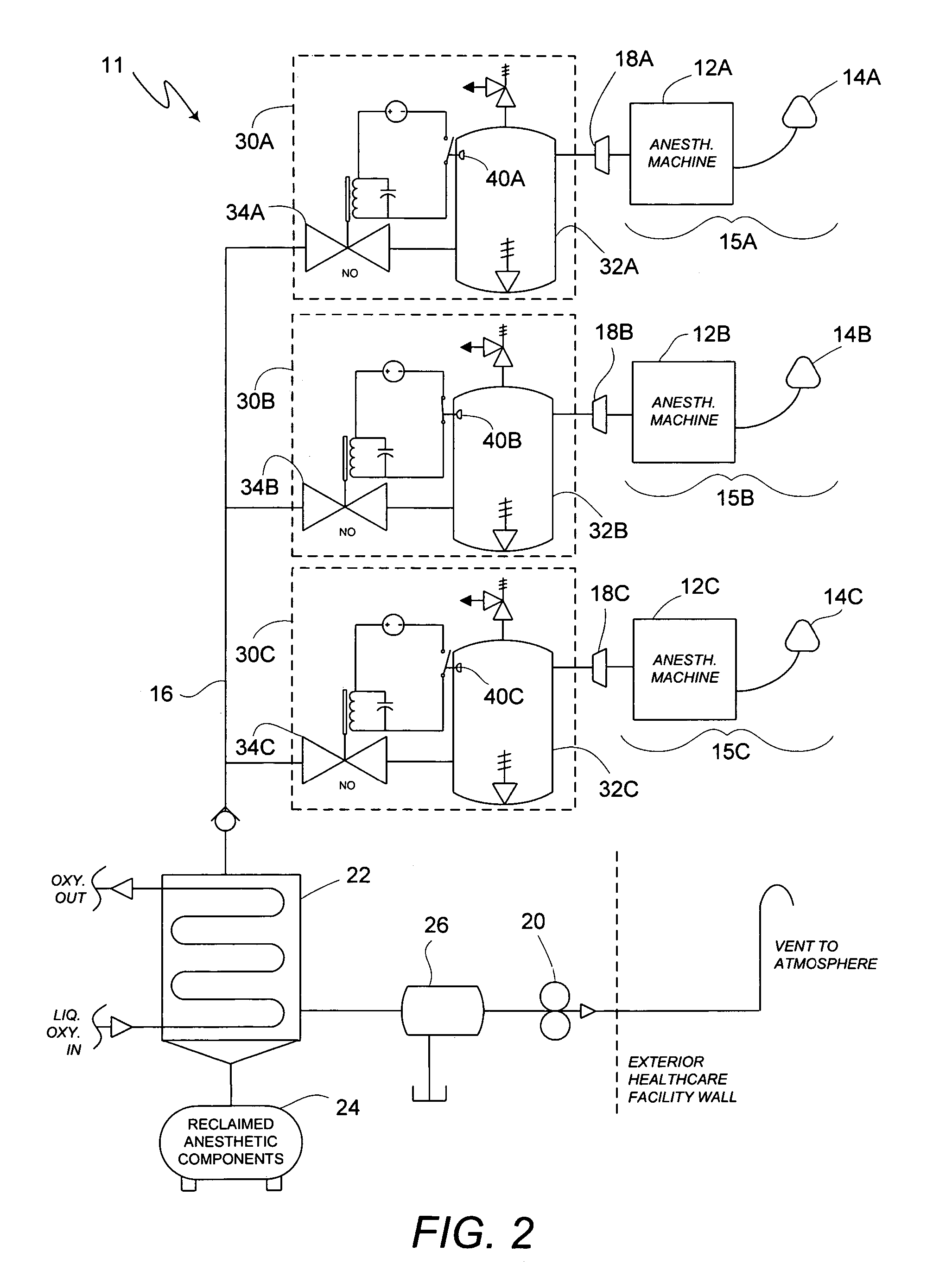
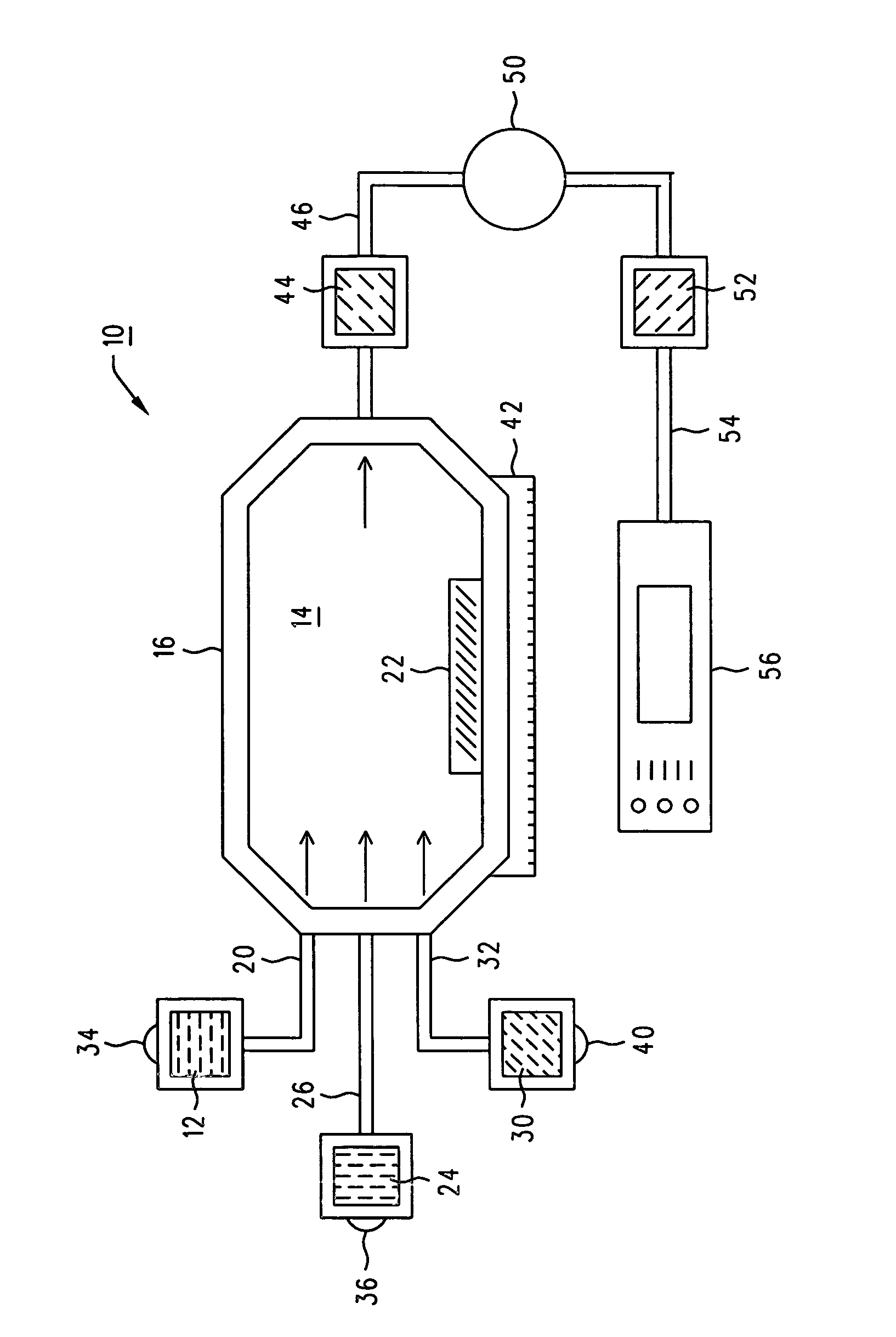
Anesthetic gas reclamation system and method
InactiveUS20060254587A1Improve energy efficiencyMinimize impactNitrous oxide captureRespiratorsGas compositionFractionation
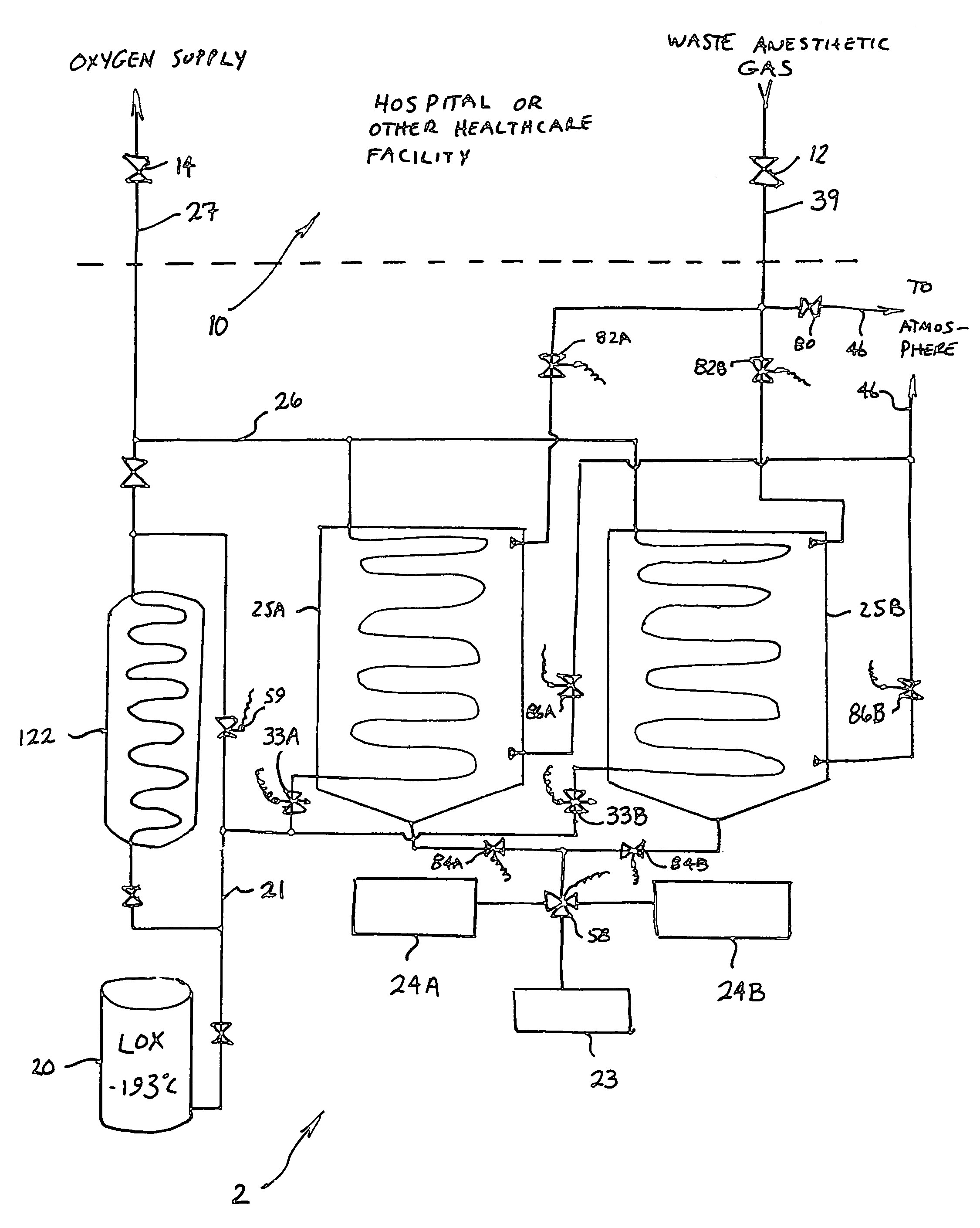
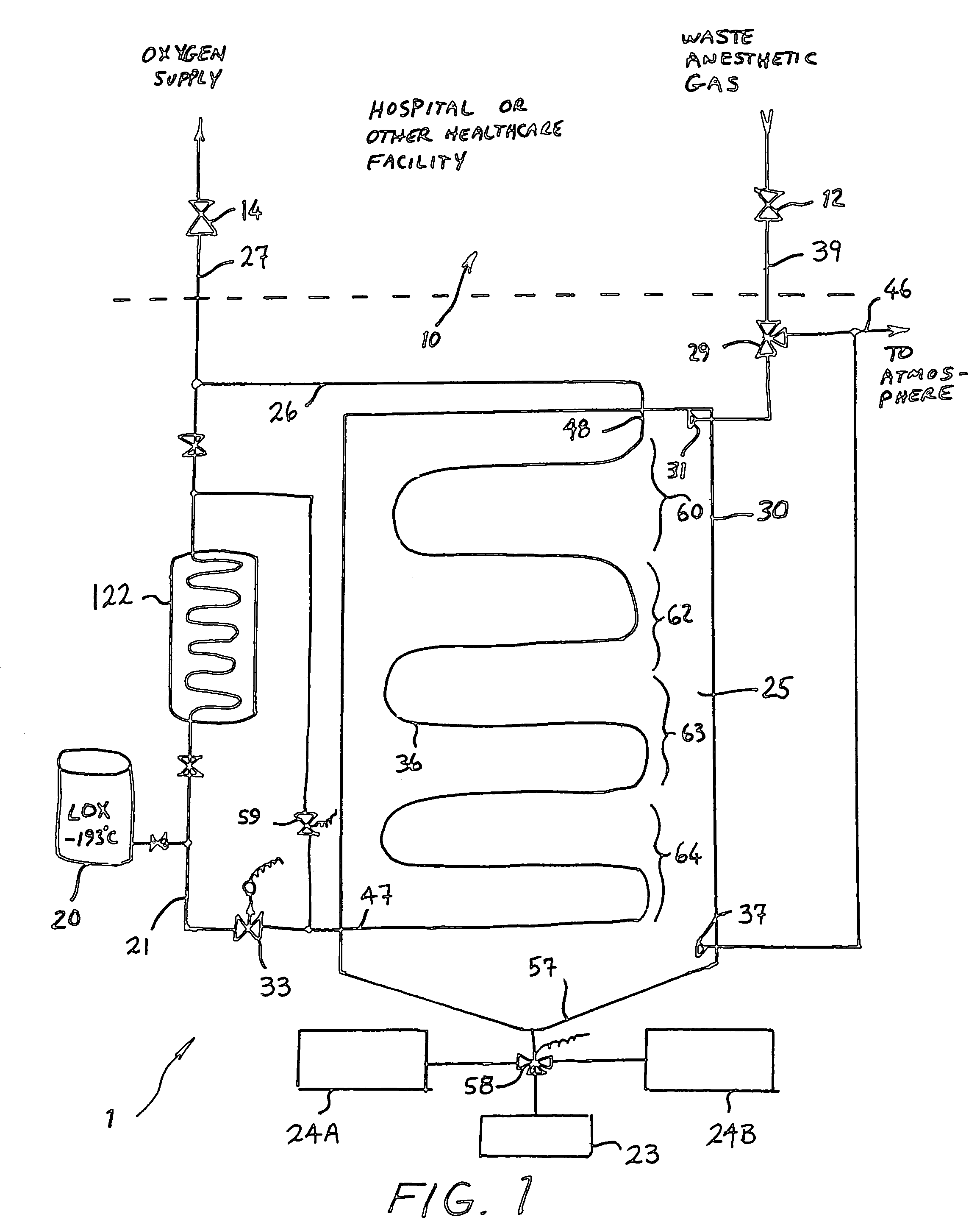
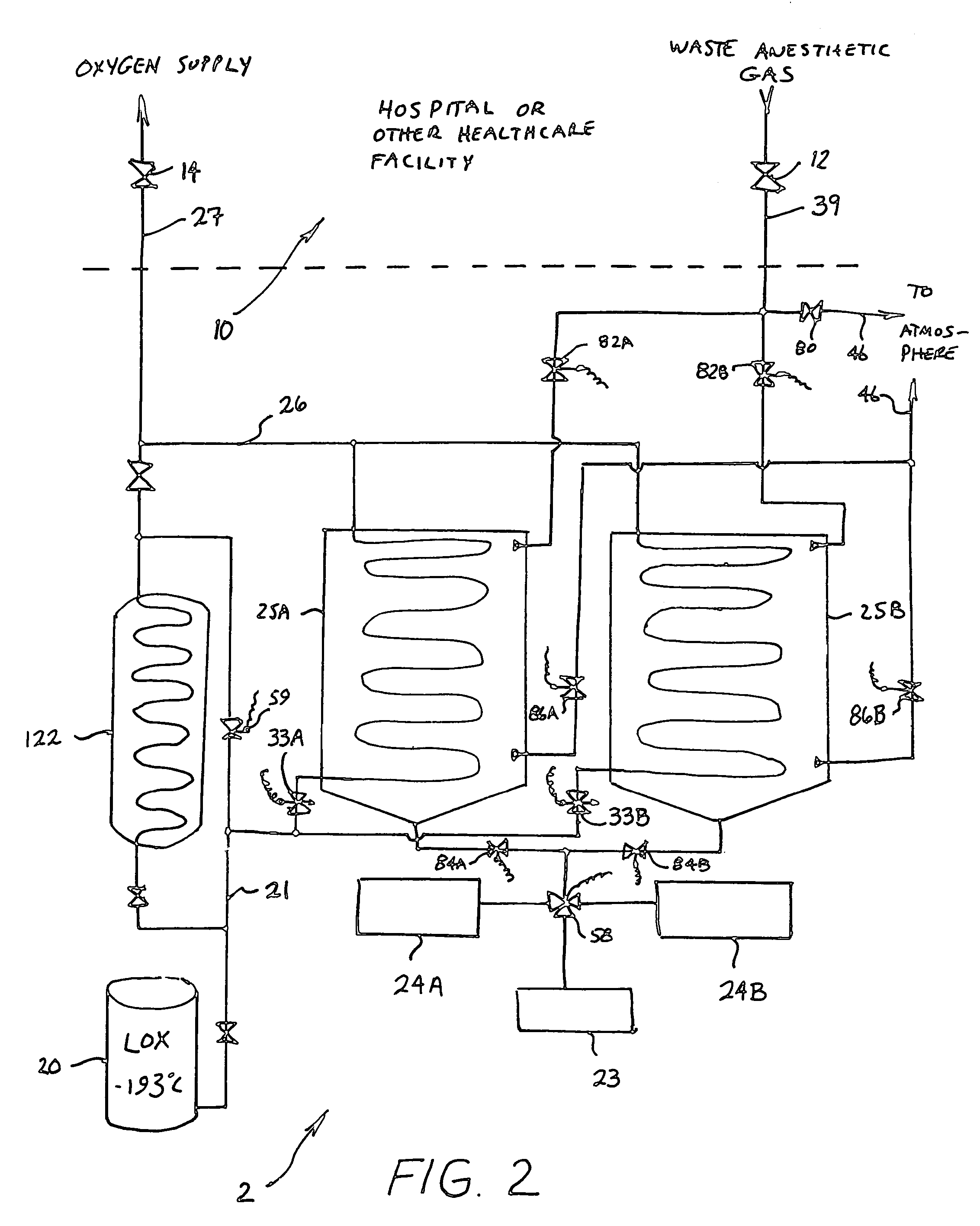
A method and system for the fractionation and removal of nitrous oxide and other volatile halocarbon gas components from waste anesthetic gases using liquid oxygen are disclosed. Liquid oxygen is warmed for use in a healthcare facility by cooling and condensing waste anesthetic gases. A cold trap / fractionator is provided wherein selective components of the waste anesthetic gas are collected as a frost on the coils of the cold trap / fractionator by desublimation / deposition and / or condensation / solidification. In a periodic batch process, the collected frost is first thawed and the melted liquids or gases are then collected at various increasing temperatures, thereby separating the nitrous oxide and other halocarbon gas components by their varying melting points. The thawed anesthetic components are collected in separate tanks based on their melting points. Warmed by the waste anesthetic gases in the cold trap / fractionator, the oxygen is supplied to the healthcare facility for its normal uses.
Owner:ANESTHETIC GAS RECHAMATION LLC
Azeotropic compositions comprising fluorinated olefins for cleaning applications
The present invention relates to azeotropic or azeotrope-like compositions comprising a fluorinated olefin having the formula E- or Z-C3F7CH═CHC3F7, and at least one alcohol, halocarbon, hydrofluorocarbon, fluoroether, or alkanes and combinations thereof. In one embodiment, the one compound selected from the group consisting of alcohols, halocarbons, fluoroalkyl ethers, hydrofluorocarbons, alkanes is either methanol, ethanol, iso-propanol, n-propanol, trans-1,2-dichloroethylene, cis-1,2-dichloroethylene, n-propyl bromide, C4F9OCH3, C4F9OC2H5, HFC-43-10mee, HFC-365mfc, heptane, or combinations thereof. In another embodiment, these compositions are useful in cleaning applications as a degreasing agent or defluxing agent for removing oils and / or other residues from a surface.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
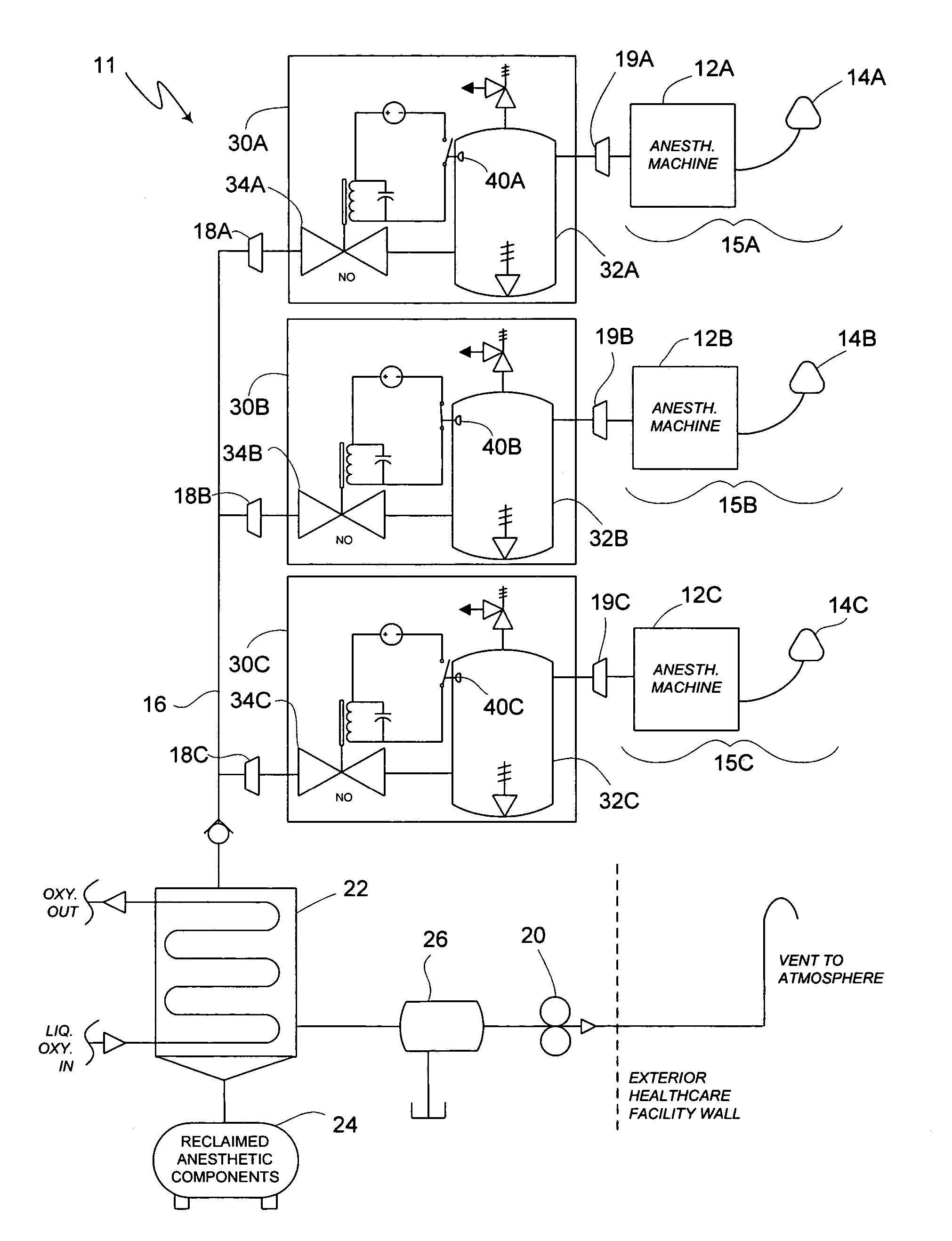
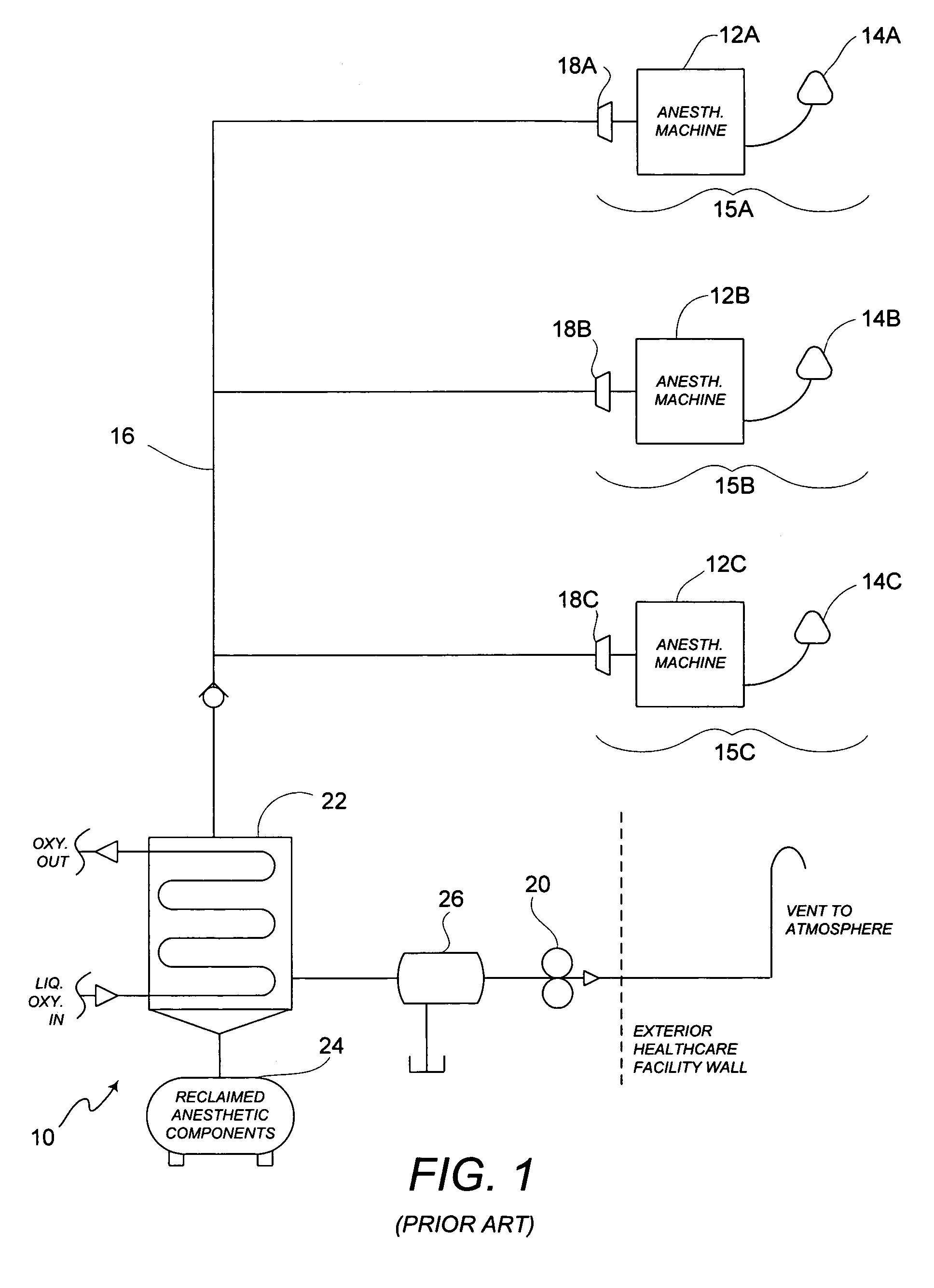
Method of low flow anesthetic gas scavenging and dynamic collection apparatus therefor
A method and system for removal of nitrous oxide and volatile halocarbon gas components from waste anesthetic gases using a low-flow scavenging or reclamation system preferably including an intelligent waste anesthetic gas collection unit fluidly coupled between each individual anesthetic machine and the waste gas evacuation manifold. Through a system including a collection chamber, a pressure detector, and a exhaust valve which is actuated based on the detected pressure in the collection chamber, the waste anesthetic gas collection unit allows flow to the waste suction manifold only in the presence of waste gas and interrupts all flow into the suction manifold when no waste gas is present.
Owner:ANESTHETIC GAS RECHAMATION LLC
Process for the manufacture of halocarbons and selected compounds and azeotropes with HF
InactiveUS6858762B2Other chemical processesPreparation by halogen halide additionAlkaneHalohydrocarbon
A liquid phase process is disclosed for producing halogenated alkane adducts of the formula CAR1R2CBR3R4 (where A, B, R1, R2, R3, and R4 are as defined in the specification) which involves contacting a corresponding halogenated alkane, AB, with a corresponding olefin, CR1R2═CR3R4 in a dinitrile or cyclic carbonate ester solvent which divides the reaction mixture into two liquid phases and in the presence of a catalyst system containing (i) at least one catalyst selected from monovalent and divalent copper; and optionally (ii) a promoter selected from aromatic or aliphatic heterocyclic compounds which contain at least one carbon-nitrogen double bond in the heterocyclic ring. When hydrochlorofluorocarbons are formed, the chlorine content may be reduced by reacting the hydrochlorofluorocarbons with HF.New compounds disclosed include CF3CF2CCl2CH2CCl3, CF3CCl2CH2CH2Cl and CF3CCl2CH2CHClF. These compounds are useful as intermediates for producing hydrofluorocarbons.Azeotropes of CClF2CH2CF3 with HF and azeotropes of CF3CH2CHF2 with HF are also disclosed; as are process for producing such azeotropes.A process for purification of certain hydrofluorocarbons and / or chloro-precursors thereof from mixtures of such compounds with HF is also disclosed.
Owner:THE CHEMOURS CO FC LLC
Method for destroying halocarbon compositions using a critical solvent
InactiveUS6984768B2Improve versatilityReduce energy consumptionChemical protectionHydrogenCritical level
A method for destroying halocarbons. Halocarbon materials are reacted in a dehalogenation process wherein they are combined with a solvent in the presence of a catalyst. A hydrogen-containing solvent is preferred which functions as both a solvating agent and hydrogen donor. To augment the hydrogen donation capacity of the solvent if needed (or when non-hydrogen-containing solvents are used), a supplemental hydrogen donor composition may be employed. In operation, at least one of the temperature and pressure of the solvent is maintained near, at, or above a critical level. For example, the solvent may be in (1) a supercritical state; (2) a state where one of the temperature or pressure thereof is at or above critical; or (3) a state where at least one of the temperature and pressure thereof is near-critical. This system provides numerous benefits including improved reaction rates, efficiency, and versatility.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Sprayable powder of non-fibrillatable fluoropolymer
InactiveCN1345349APowdery paintsPigment treatment with macromolecular organic compoundsFluidized bedMicrometer
The invention provides for sprayable powder comprising friable granules of agglomerated primary particles of non-fibrillatable fluoropolymer and, optionally, at least one other component, the powder having a bulk density of at least 20g / 100cc and average particle size of 5 to 100 micrometers. The sprayable powder is preferably free of water immiscible liquid, and more preferably free of halocarbon liquid. Included among the other components are inorganic fillers, pigments, high temperature resistant polymer binders. In an other embodiment, the invention provides for a sprayable powder comprising friable granules of agglomerated primary particles of a first non-fibrillatable fluoropolymer and at least one other non-fibrillatable component. The invention further provides for a process for preparing the sprayable powder by spray drying a liquid dispersion. In a preferred embodiment, the process includes densifying the granules of agglomerated primary particles that result from spray drying. Densifying may be carried out by mechanical compaction or by contacting the granules with a heated gas to form a fluidized bed. Optional steps of communication and heat treatment may be employed to achieve a desired bulk density and particle size for specific applications.
Owner:THE CHEMOURS CO FC LLC
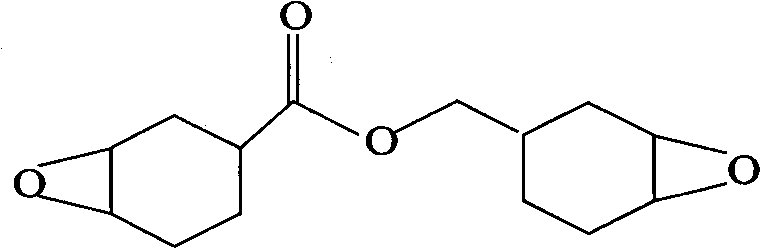
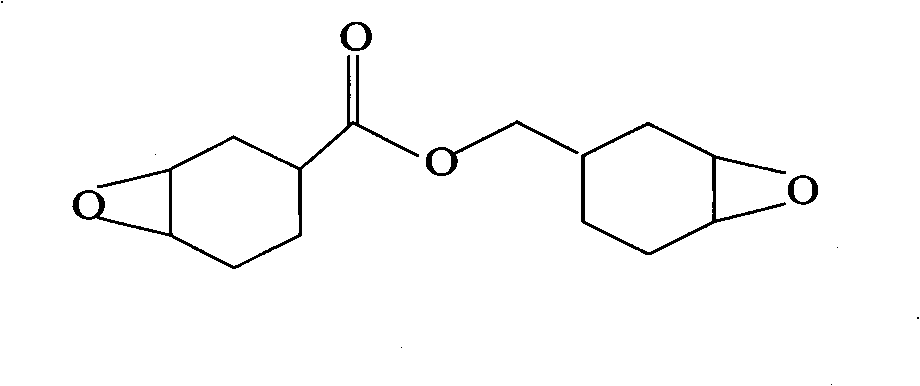
Cycloaliphatic epoxy resin and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to cycloaliphatic epoxy resin and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: taking dicycloacrylate as a raw material, hydrogen peroxide solutionas an oxidizing agent and halocarbon or halogenated hydrocarbon as a catalyst and synthesizing the cycloaliphatic epoxy resin under the action of a heteropolyacid catalyst, wherein the main reaction product of the cycloaliphatic epoxy resin, namely epoxy cyclohexane-4-carboxylic epoxycyclohexane-4-methylene ester accounts for over 90 weight percent and the epoxy equivalent weight is between 120 and 140. Each quality index of the cycloaliphatic epoxy resin of the invention is the same as that of the cycloaliphatic epoxy resin prepared by using a peroxyacetic acid as the oxidizing agent. The cycloaliphatic epoxy resin of the invention can be used as an automobile paint, a metal surface paint and an insulative substrate resin in the field of electronic and electric appliances.
Owner:AMICOGEN CHINA BIOPHARM CO LTD
Direct Conversion Of HCFC 225ca/cb Mixture To HFC 245cb And HFC 1234yf
ActiveUS20080027251A1Toxic reductionPreparation by dehalogenationPreparation by halogen replacementHalocarbonSelective reduction
Provided are methods for producing hydrofluorocarbons via the selective reduction of a halocarbon blend comprising 1,3-dichloro-1,1,2,2,3-pentafluoropropane.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Methods to separate halogentated olefins from 2-chloro-1,1,1,2-tetrafluoropropane using a solid adsorbent
InactiveUS8796493B2Solid sorbent liquid separationHalogenated hydrocarbon separation/purificationActivated carbonHalocarbon
The present invention provides a method for separating halocarbons. In particular, the invention provides a method for separating halogenated olefin impurities from 2-chloro-1,1,1,2-tetrafluoropropane (HCFC-244bb) using a solid adsorbent, particularly activated carbon. More particularly the invention pertains to a method for separating 2-chloro-3,3,3-trifluoro-propene (HCFO-1233xf) from HCFC-244bb, which are useful as intermediates in the production of 2,3,3,3-tetrafluoropropene (HFO-1234yf).
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Process for producing aromatic diaether dianhydride monomer
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing a dianhydride monomer, in particular to a method for synthesizing an aromatic HQEDA monomer. The method adopts a 3(4) substituted phthalimide to prepare HQEDA and provides novel middle steps for preparing the HQEDA. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a 3 (4) substituted-N-alkyl (aryl) phthalimide from the 3(4) substituted phthalimide through Gabriel reaction principle or by adding a salifying agent and halocarbon into an apolar aprotic solvent to react; and using the prepared 3 (4) substituted-N-alkyl (aryl) phthalimide to prepare bis imide and the bis ether anhydride. The method has the advantages that raw materials are easily available, preparation method is simple and easy to operate, and the purity and yield of the prepared 3 (4) substituted-N-alkyl (aryl) phthalimide are obviously higher than that of the prior method.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Catalyst for volatile halocarbon catalytic combustion and its preparation method and use
ActiveCN105289716ALow priceNon-toxicMolecular sieve catalystsDispersed particle separationIon exchangeHalocarbon
The invention relates to a catalyst for volatile halocarbon catalytic combustion removal and its preparation method and use. Fe, Ni, Cu, Co, V or Mn metal oxide is used as an active ingredient, SBA-15, MCM-41 or ZSM-22 is used as a carrier, through an immersion method, an ion exchange method, a grafting method, a riveting method or a solid phase grinding method, the active ingredient is carried by the carrier, and the catalyst is used for volatile halocarbon catalytic combustion in air. Compared with the existing similar catalyst, the catalyst provided by the invention has the advantages of simple preparation processes, low price, high catalytic activity in the reaction, strong catalysis stability, complete discharge of produced CO2, H2O and halogen hydride after alkali lye absorption treatment and no secondary pollution.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES INST OF CHEM IND
Anesthetic gas reclamation system and method
InactiveUS7596965B2Improve energy efficiencyMinimize impactRespiratorsNitrous oxide captureAnesthetic AgentFractionation
A method and system for the fractionation and removal of nitrous oxide and other volatile halocarbon gas components from waste anesthetic gases using liquid oxygen are disclosed. Liquid oxygen is warmed for use in a healthcare facility by cooling and condensing waste anesthetic gases. A cold trap / fractionator is provided wherein selective components of the waste anesthetic gas are collected as a frost on the coils of the cold trap / fractionator by desublimation / deposition and / or condensation / solidification. In a periodic batch process, the collected frost is first thawed and the melted liquids or gases are then collected at various increasing temperatures, thereby separating the nitrous oxide and other halocarbon gas components by their varying melting points. The thawed anesthetic components are collected in separate tanks based on their melting points. Warmed by the waste anesthetic gases in the cold trap / fractionator, the oxygen is supplied to the healthcare facility for its normal uses.
Owner:ANESTHETIC GAS RECHAMATION LLC
METHOD, SYSTEM, AND APPARATUS FOR THE GROWTH OF ON-AXIS SiC AND SIMILAR SEMICONDUCTOR MATERIALS
ActiveUS20090025641A1Improve material qualityReduce supersaturationPolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesSemiconductor materialsGas phase
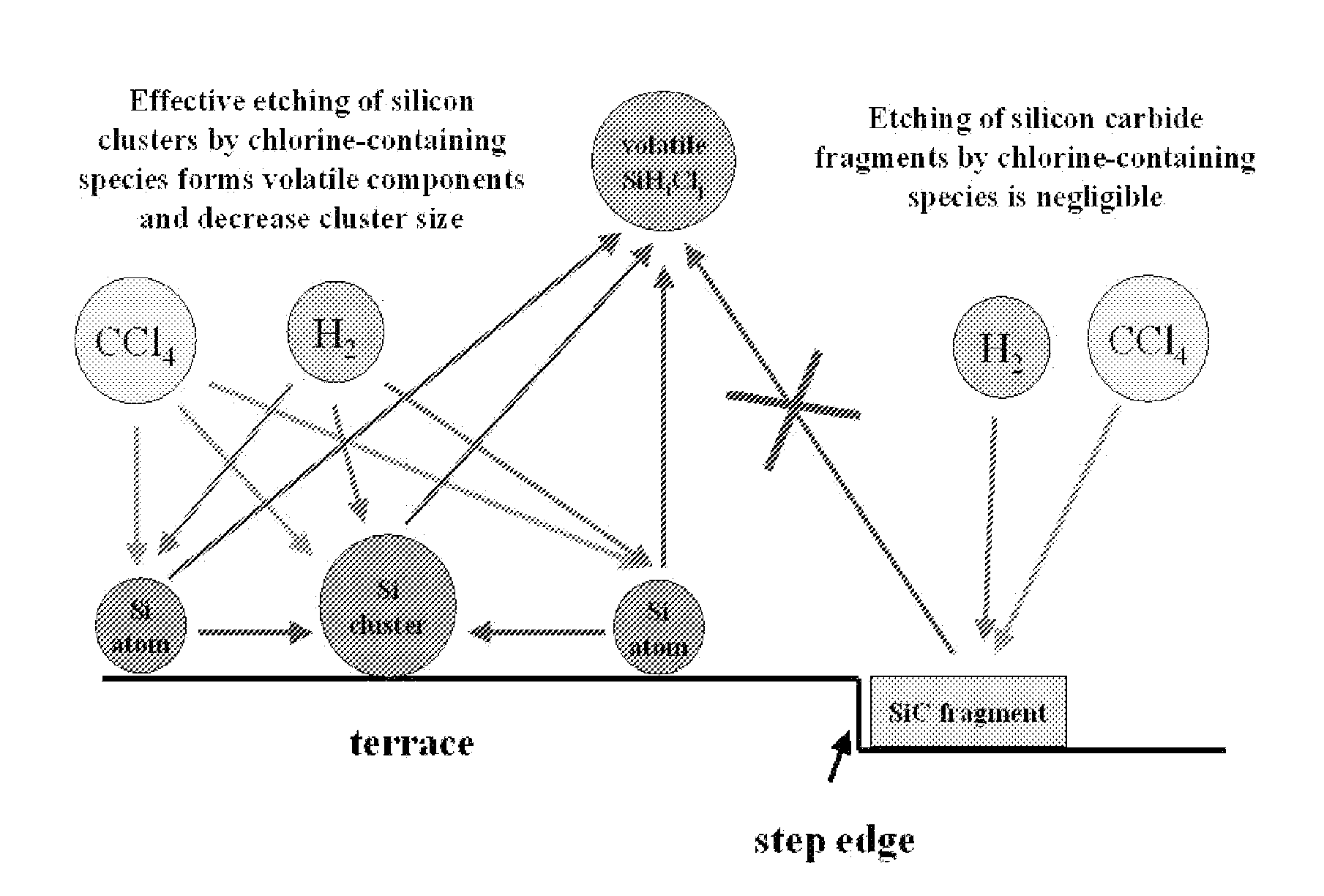
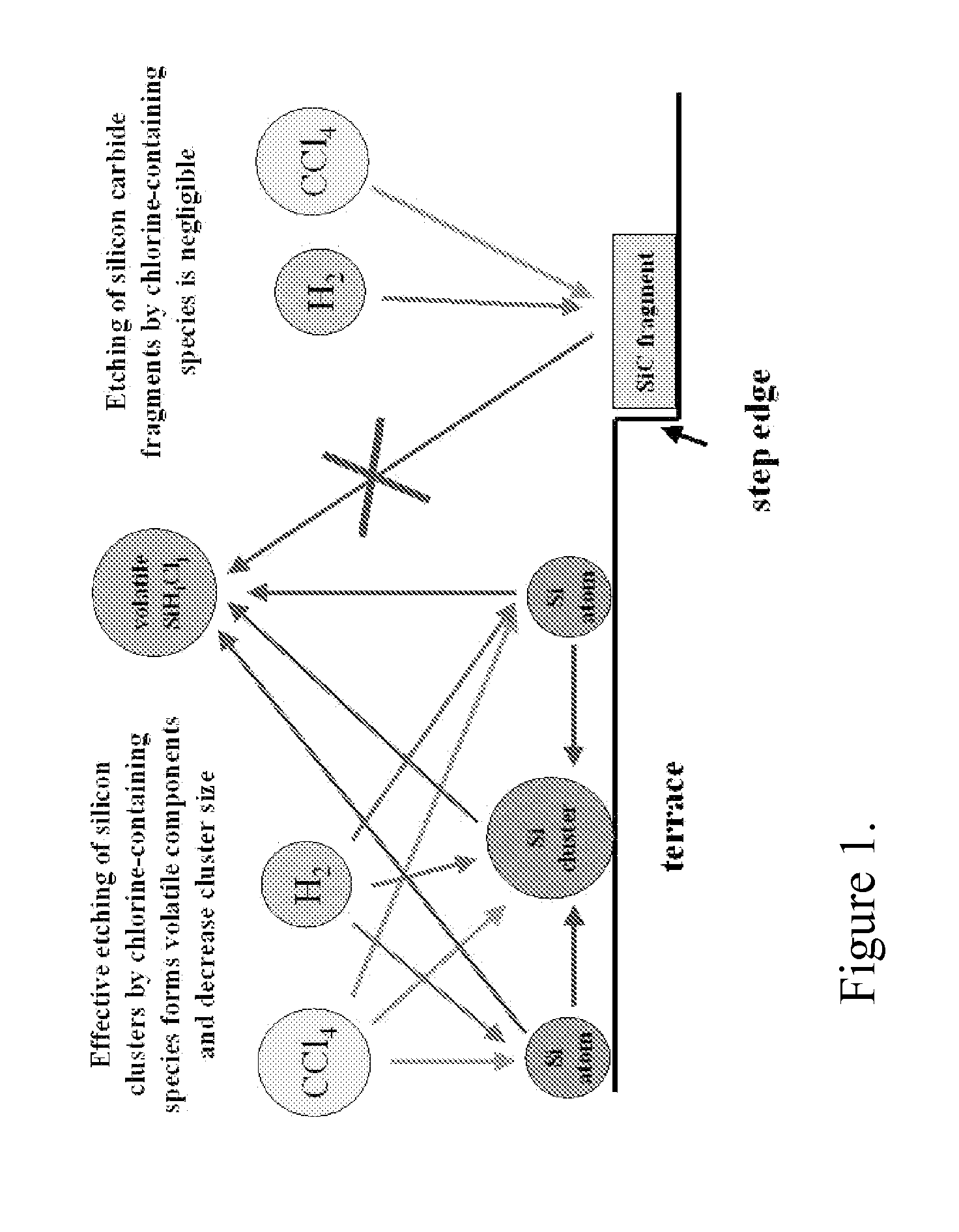
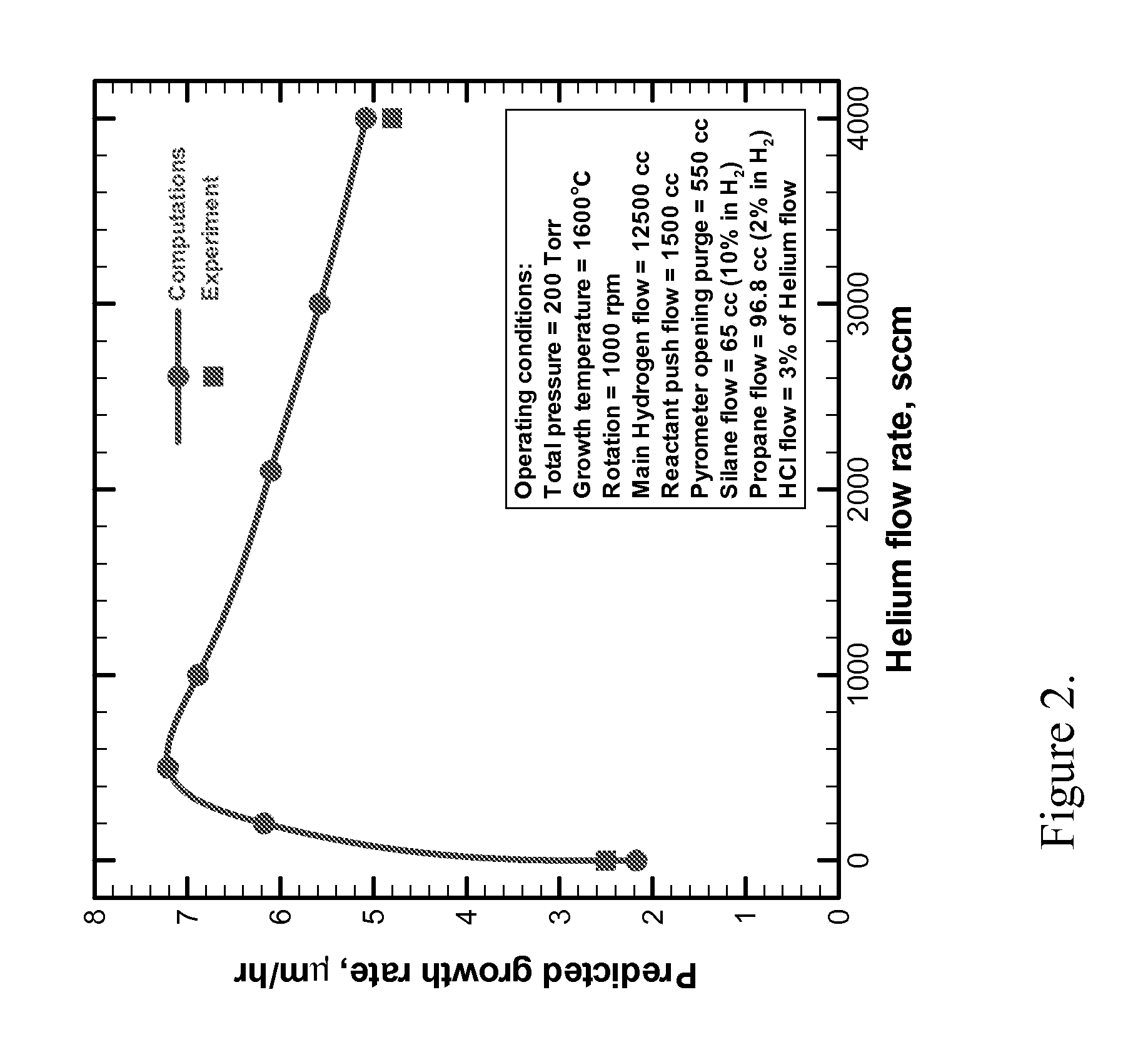
A novel approach for the growth of high-quality on-axis epitaxial silicon carbide (SiC) films and boules, using the Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) technique, is described here. The method includes a method of substrate preparation, which allows for the growth of “on-axis” SiC films, plus an approach giving the opportunity to grow silicon carbide on singular (a small-angle miscut) substrates, using halogenated carbon-containing precursors (carbon tetrachloride, CCl4, or halogenated hydrocarbons, CHCl3, CH2Cl2, or CH3Cl, or similar compounds or chemicals), or introducing other chlorine-containing species, in the gas phase, in the growth chamber. At gas mixtures greater than the critical amount, small clusters of SiC are etched, before they can become stable nuclei. The presence of chlorine and the formation of gas species allow an increased removal rate of these nuclei, in contrast to the growth without the presence of chlorine. Or, alternatively, the novel precursors introduced in the growth system reduce the effective supersaturation ratio of the Si species in the growth layer. The reduction of the supersaturation ratio reduces or eliminates the 2D (and 3C—SiC) nucleation which would occur due to the large terrace widths present on the on-axis wafers. This allows the growth of Silicon Carbide epitaxial layers on SiC substrates or composite substrates with monocrystalline layers. This can also be applied to the other semiconductors, chemicals, compounds, materials, growth methods, or devices.
Owner:WIDETRONIX
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same, dry-etching process, method for making electrical connections, and etching apparatus
InactiveUS20090102025A1Lower manufacturing requirementsReduce yieldTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsResistElectrical connection
A method for manufacturing a semiconductor device comprises dry-etching a thin film using a resist mask carrying patterns in which at least one of the width of each pattern and the space between neighboring two patterns ranges from 32 to 130 nm using a halogenated carbon-containing compound gas with the halogen being at least two members selected from the group consisting of F, I and Br. The ratio of at least one of I and Br is not more than 26% of the total amount of the halogen atoms as expressed in terms of the atomic compositional ratio to transfer the patterns onto the thin film. Such etching of a thin film avoids causing damage to the resist mask used. The resulting thin film carrying the transferred patterns is used as a mask for subjecting the underlying material to dry-etching.
Owner:PHILTECH
Porous Non-Asbestos Separator and Method of Making Same
The present invention relates to an inert, non-asbestos separator and method of making same, the separator comprising an inorganic / polymer fibrid and agglomeration composite material containing from about 5 weight percent to about 70 weight percent of organic halocarbon polymer fibers together with from about 30 wt percent to about 95 weight percent of a finely divided non-organic particulate, which non-organic particulate is firmly bound in said composite fibrids and agglomerates; a natural gum thickening agent in an amount to provide a viscosity of about 6270 to about 590 cP at 0.22 sec−1; and an inert inorganic particulate powder whereby the inert inorganic particulate remains unbound from the inorganic / polymer fibrid and agglomeration composite, the inorganic particulate powder having a mean particle size of not greater than 1.0 μm and being present in an amount to provide a ratio of polymer fiber composite to unbound inorganic particulate in a range from about 1 to 25.
Owner:IND DE NORA SPA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com