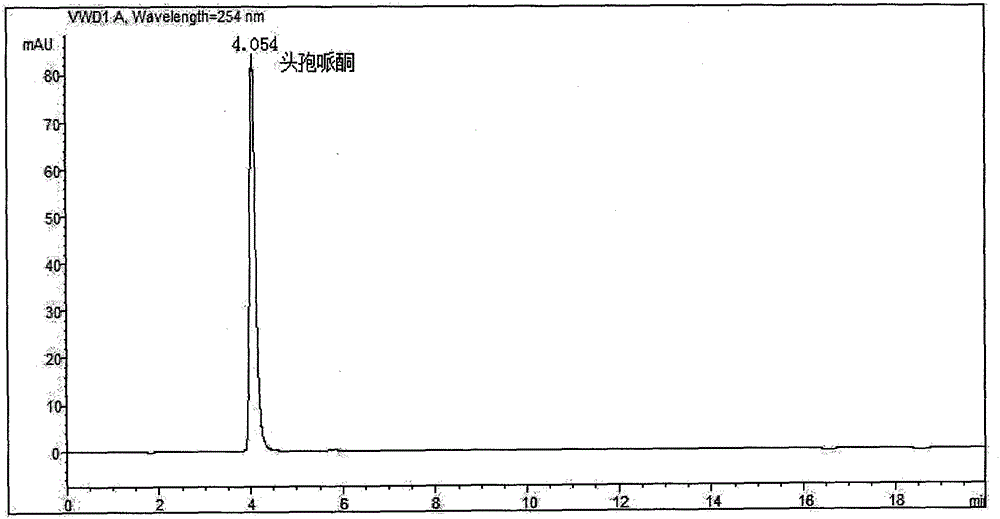
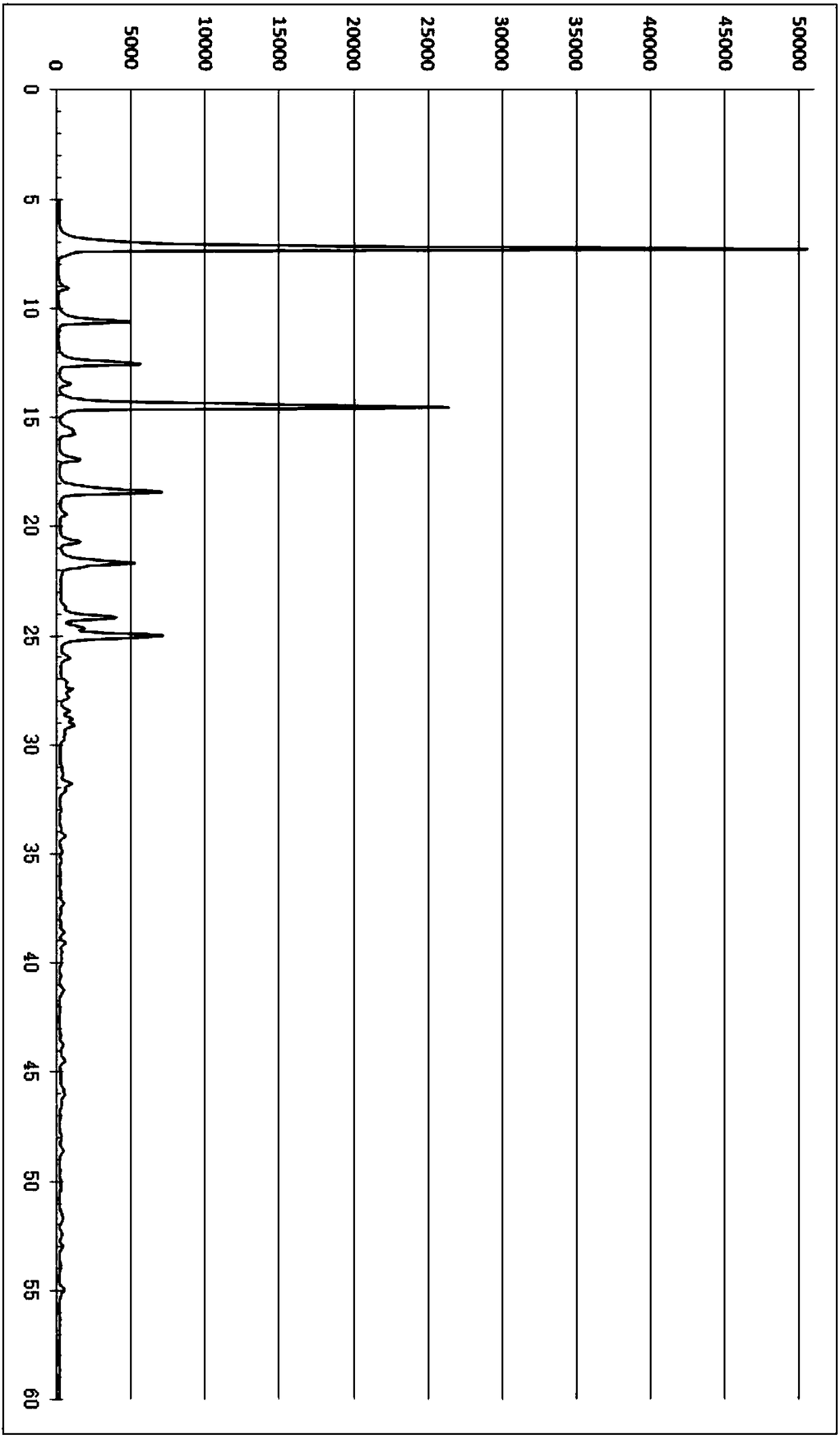
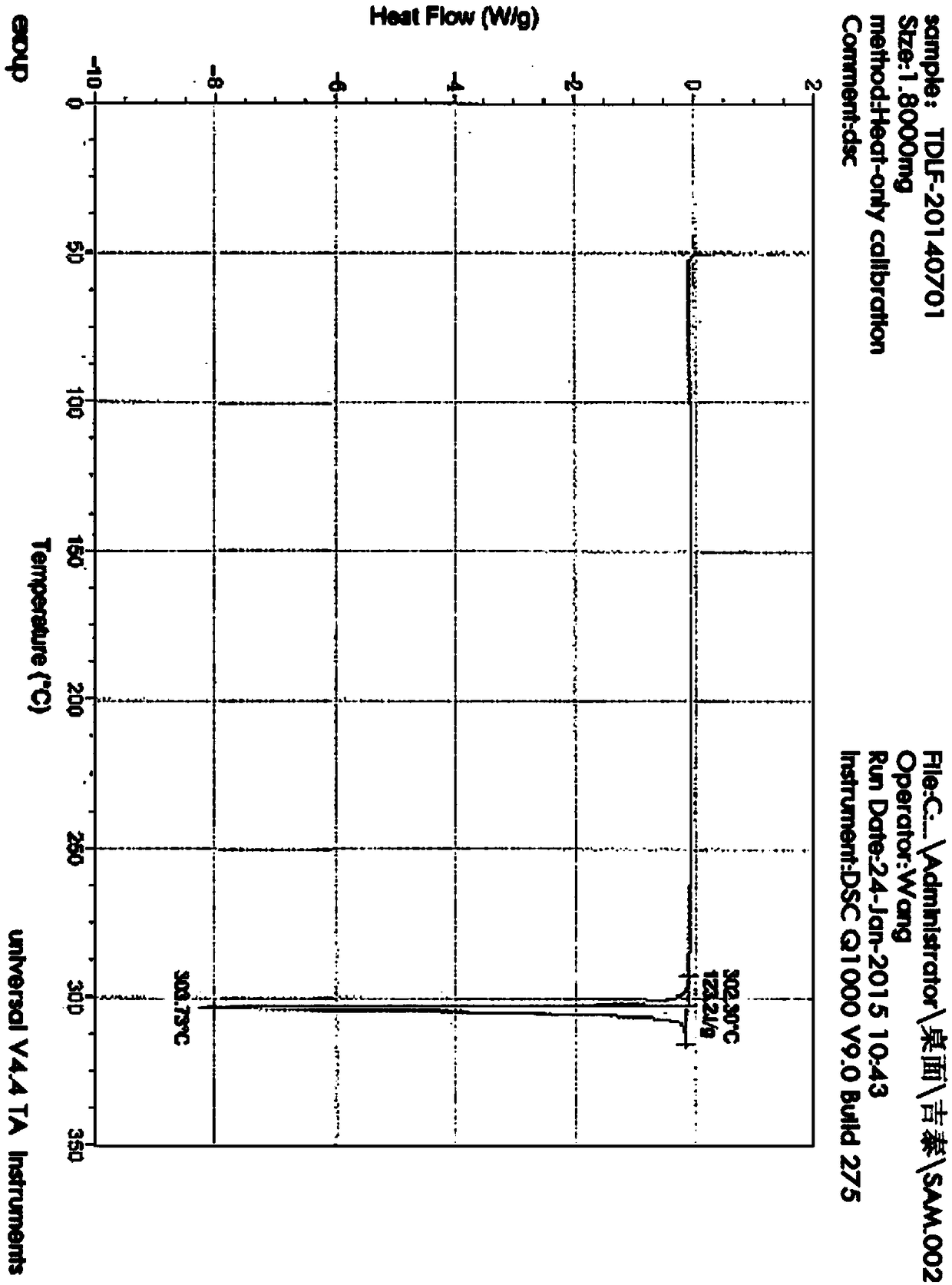
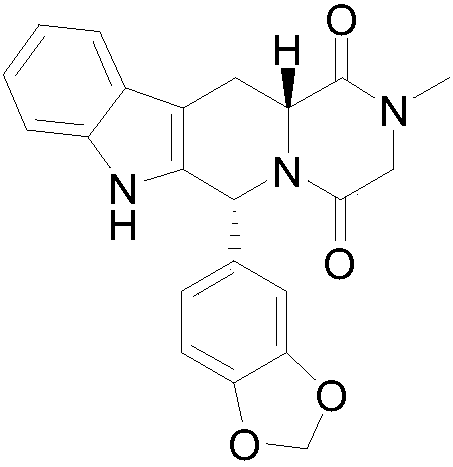
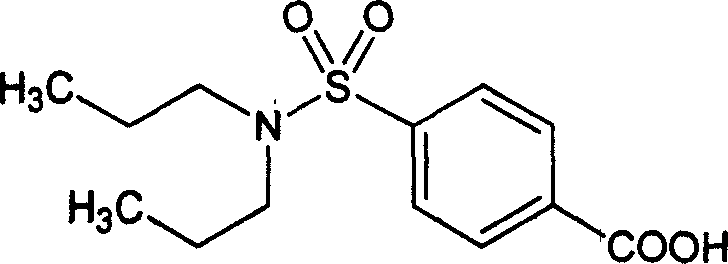
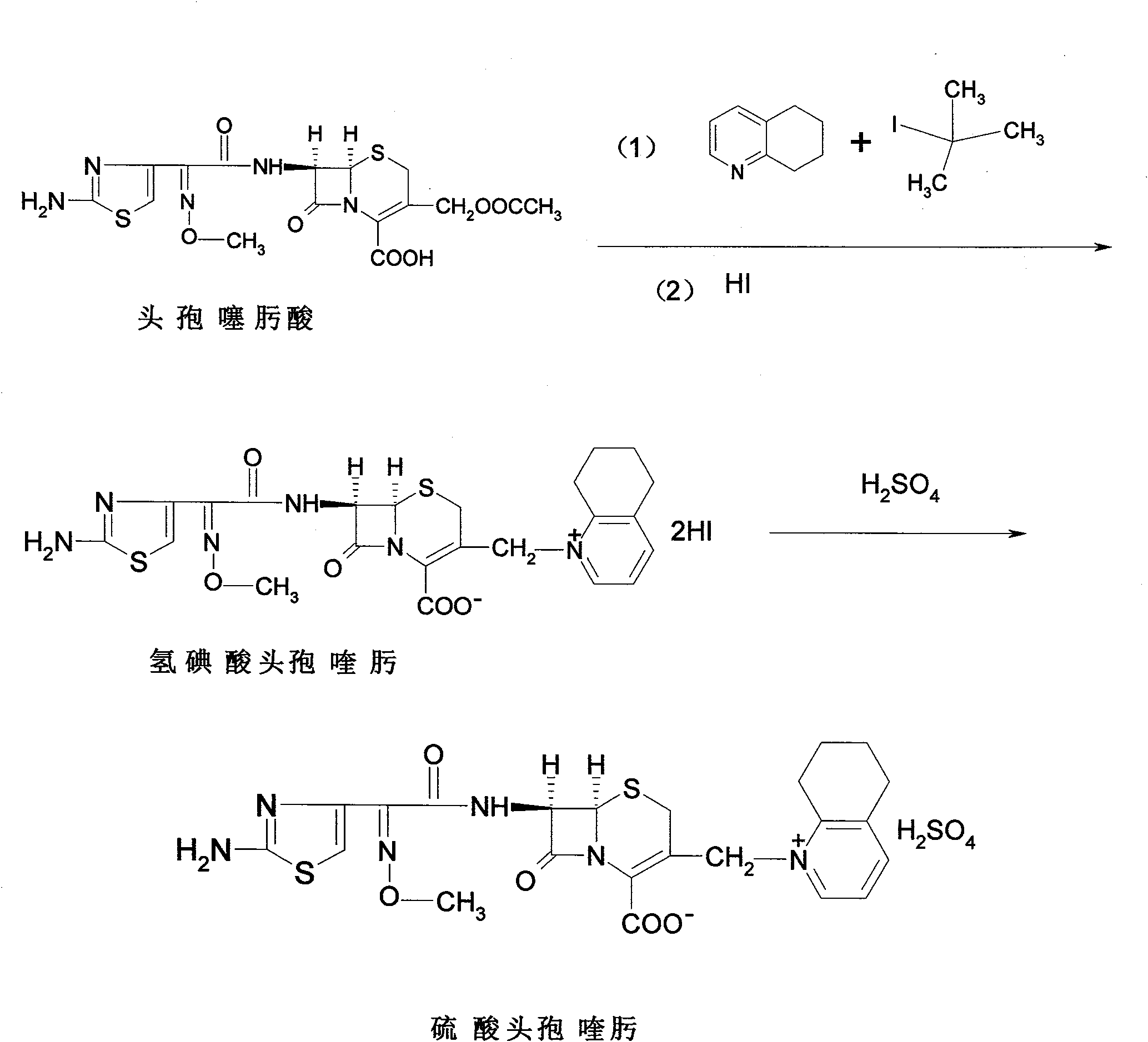
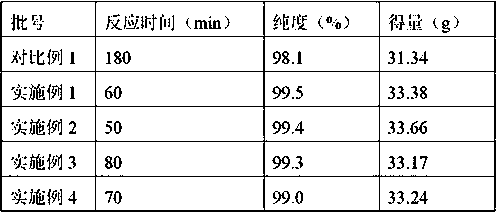
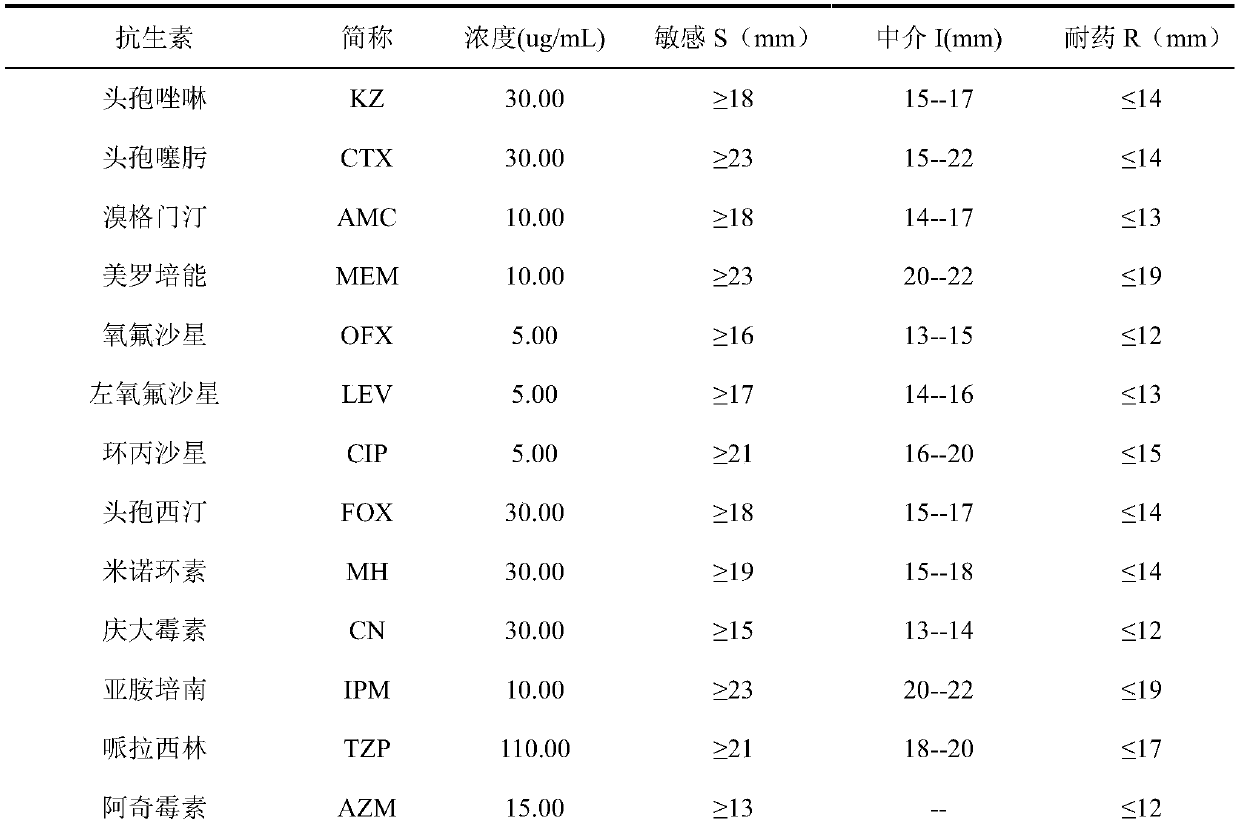
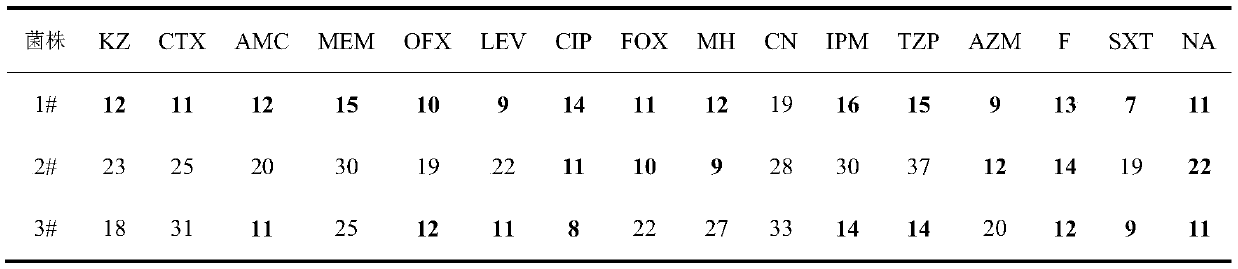
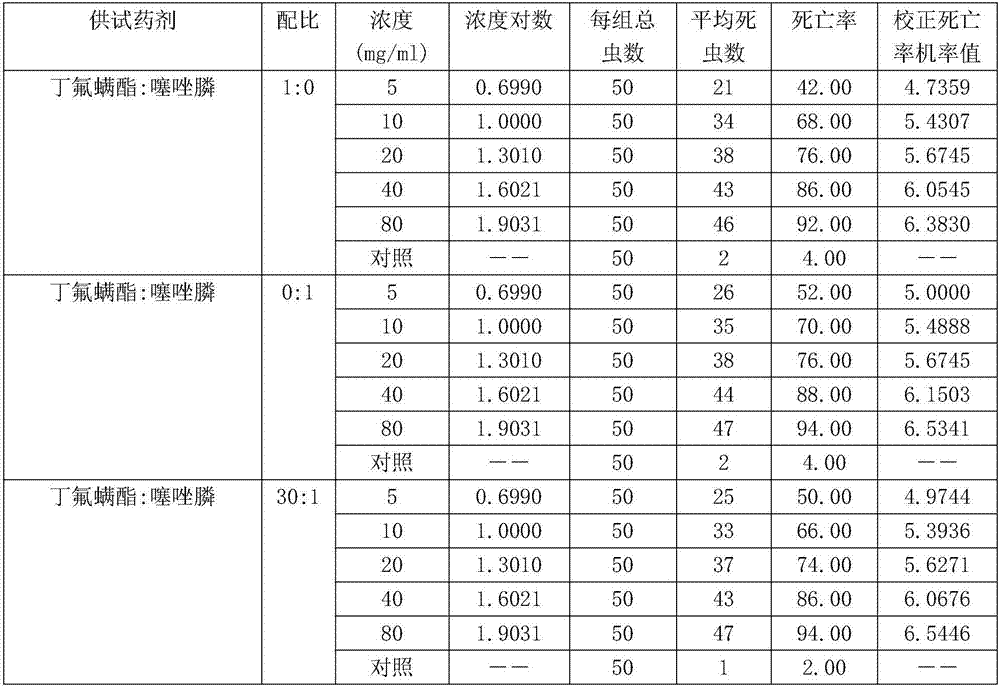
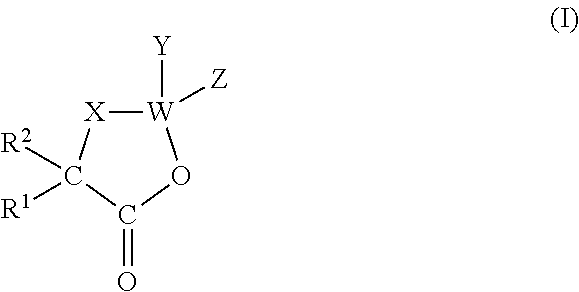Patents
Literature
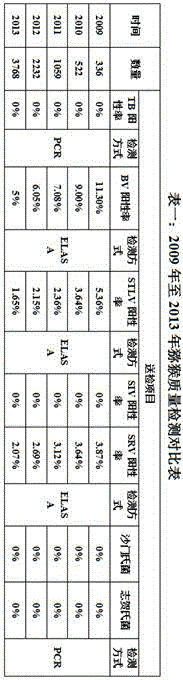
85 results about "Cefotaxime" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
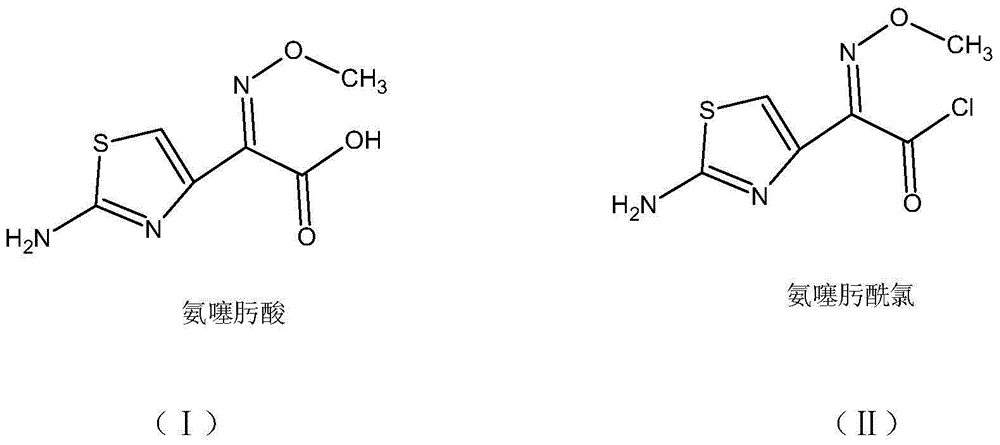
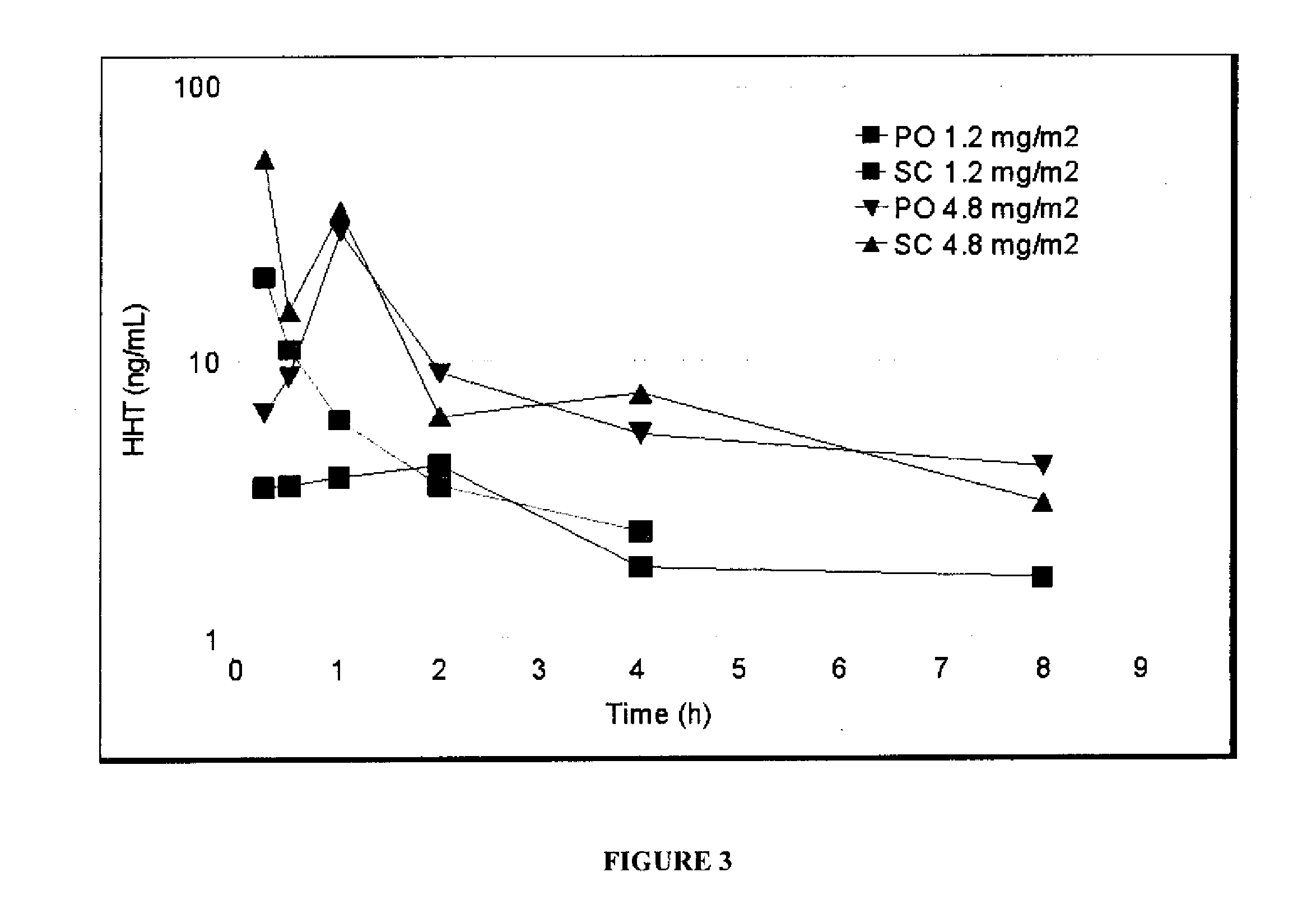
Cefotaxime is used to treat a wide variety of bacterial infections. It may also be used to prevent infection from certain surgeries.
Sterilizing method of spherical phaeocystis culture solution
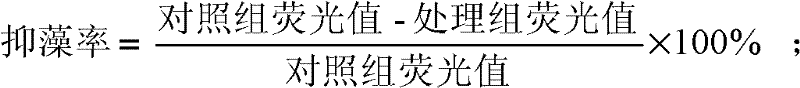
InactiveCN102391954ASimple and fast operationImprove efficiencyUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationKanamycin
The invention provides a sterilizing method of a spherical phaeocystis culture solution, and relates to a microalgae culture solution. The method comprises the following steps: centrifuging algae solution which grows to an exponential phase, and removing supernatant; carrying out gravity suspension on algae cells with an f / 2 culture medium, centrifuging, and removing supernatant, repeating twice, and carrying out gravity suspension on the algae cells with the f / 2 culture medium; adding SDS (sodium dodecyl sulfate) and antibiotics, wherein the antibiotics are clindamycin, azithromycin, gentamicin, kanamycin, streptomycin, cefotaxime, ampicillin and rifamycin; culturing under illumination, centrifuging the algae solution and removing supernatant during culturing, carrying out gravity suspension on the algae cells with the f / 2 culture medium, centrifuging and removing supernatant, removing residual SDS and the antibiotics, transferring into the f / 2 culture medium, and culturing under illumination; and selecting survival transferred algae solution which is treated with SDS and the antibiotics, and detecting whether bacteria exist or not after the transferred algae solution grows to the exponential phase. The method is convenient to operate, complex operations, such as bacterium separation and test on sensitivity to antibiotics and the like, are avoided, and long-term treatment of high-concentration antibiotics has good sterilization effect.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
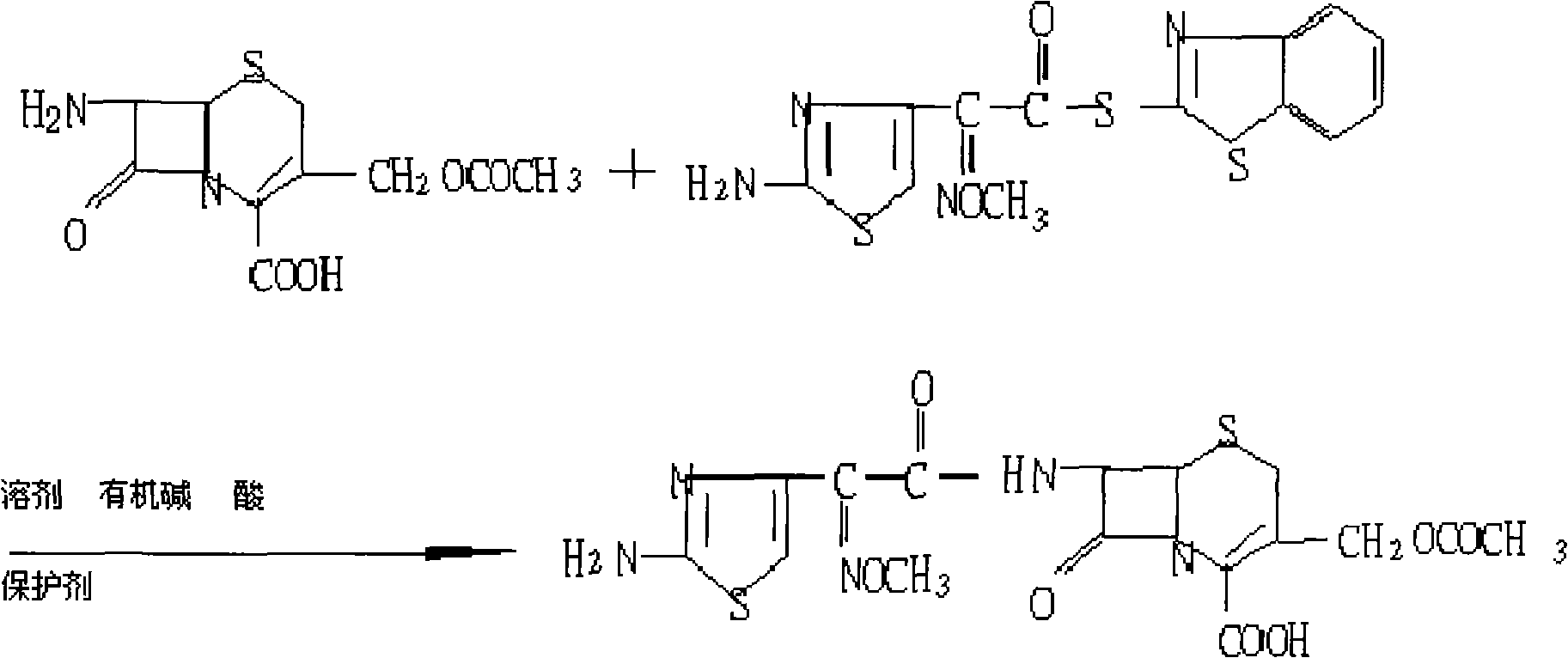
Preparation technology of cefotaxime
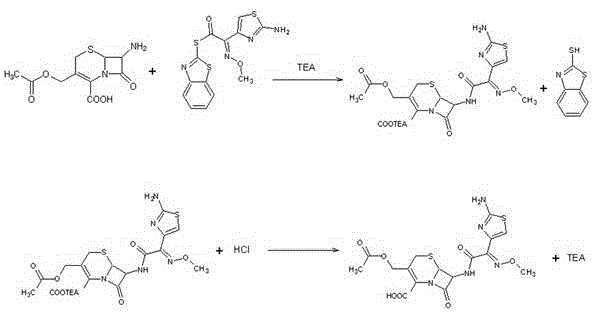
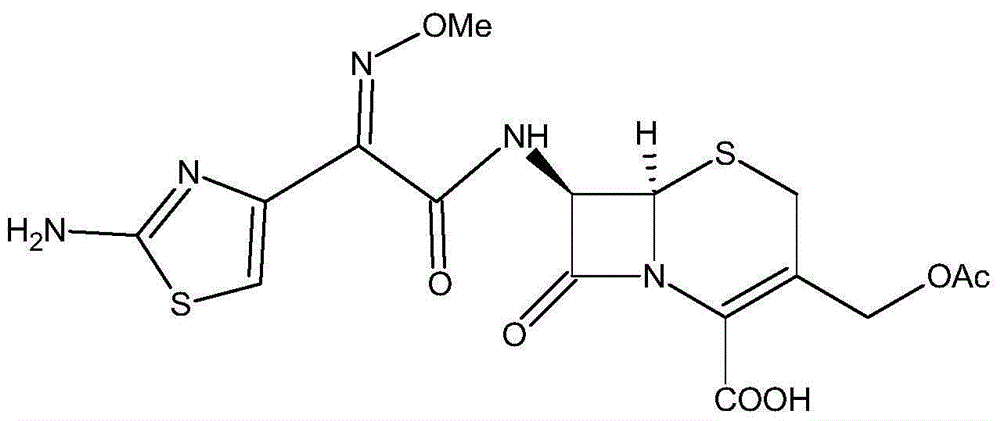
The invention relates to a preparation technology of cefotaxime, belonging to the preparation technology of medical compounds. The technology comprises the following steps: adding 7-ACA and AE-active resin reagents in solvent, and then adding an organic base and an alcohol catalyst to carry out a synthesis reaction. The preparation technology is characterized in that an acidifier is directly added for acidification after the reaction is finished so as to devitrified. The invention has simple and convenient operation, short production period, high product yield and low solvent consumption and can obtain products with uniform crystallized grains, good colors, high purity, low cost and stable quality.
Owner:REYOUNG PHARMA
Cefodizime sodium compound and method for synthesizing the same
InactiveCN101486720AEasy to operateLow costAntibacterial agentsOrganic chemistrySodium acetateAcetic acid
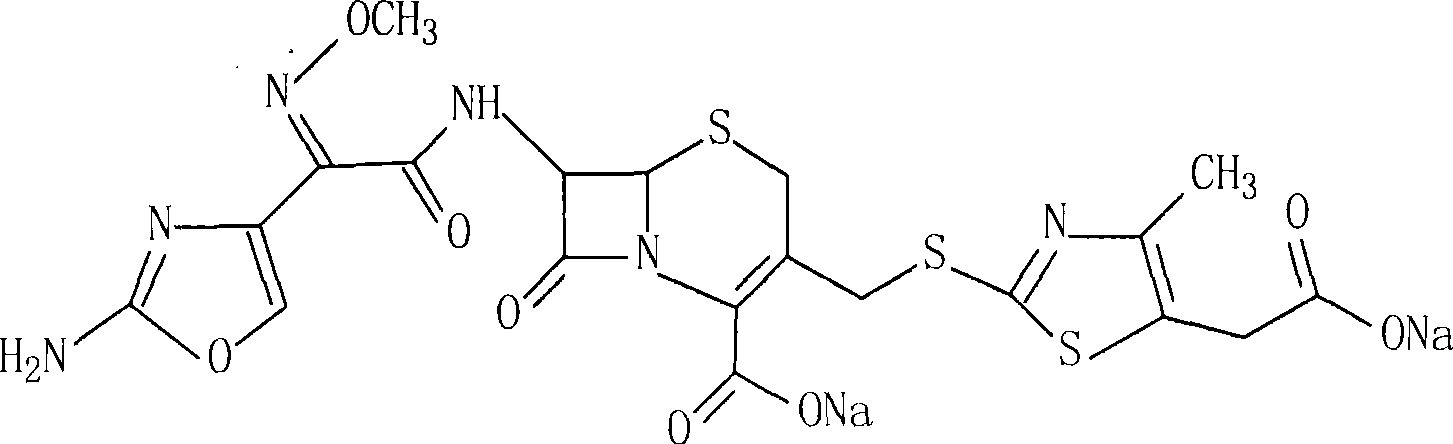
The invention relates to a cefodizime sodium compound and a synthetic method thereof; the synthetic method comprises the step that cefodizime acid reacts with sodium acetate to obtain the cefodizime sodium; the synthetic method also comprises the step that cefotaxime acid reacts with 2-sulfydryl-4-methyl-5-thiazole acetic acid in a hexahydropyridine aqueous solution to produce the cefodizime acid; and the synthetic method of the cefodizime sodium compound has the advantages of simple operation, high yield up to 80 percent and high product purity more than 99.6 percent, thus obtaining surprising technical effects.
Owner:HAINAN LINGKANG PHARMA CO LTD
Green synthetic method for cefotaxime acid
InactiveCN101550149AReduce usageRealize multiple recycling and applicationAntibacterial agentsOrganic chemistryCefotaximeOrganic base
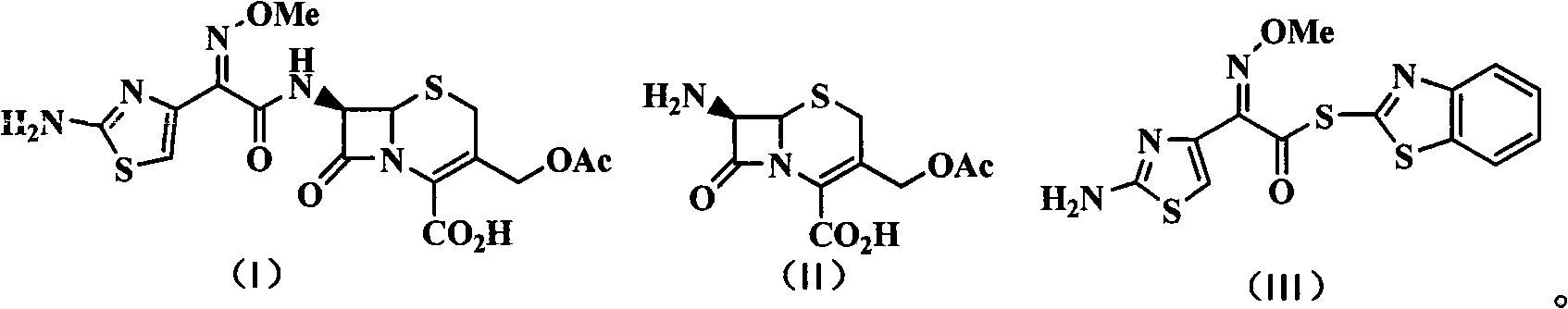
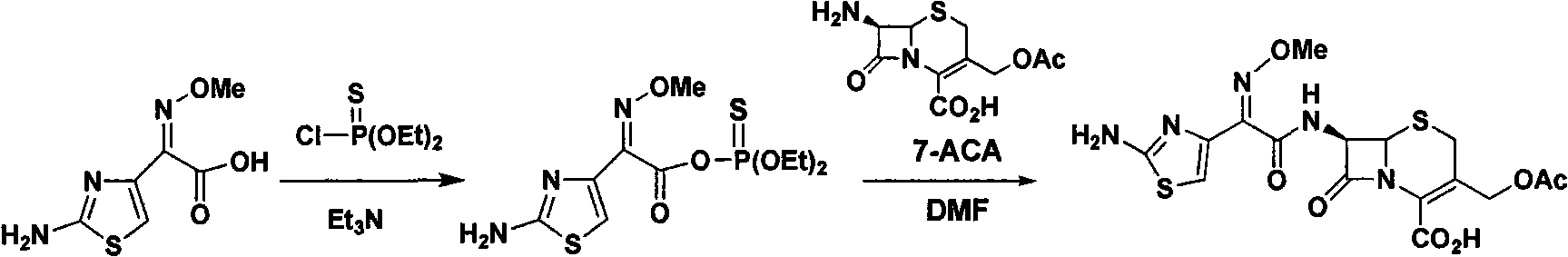
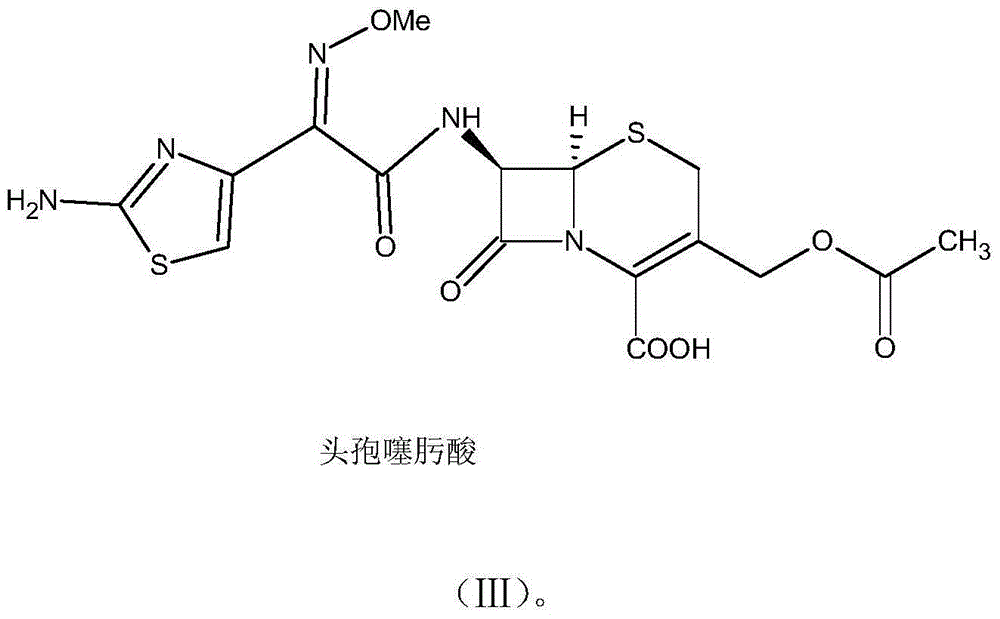
The invention discloses a green synthetic method for cefotaxime acid showed in formula (I), which comprises the following steps: adding 2-methyl tetrahydrofuran, water, 7-Aminocephalosporanic acid showed in formula (II), AE-active ester showed in formula (III) and organic base into a reaction vessel; reacting at the temperature of 0-40 degrees for 1-2 hours; adjusting system pH value to 1-3 by diluted hydrochloric acid after the reaction; precipitating solid, filtering to obtain filter cake and filtrate; and drying the filter cake to obtain cefotaxime acid. the organic base is organic amine or pyridine compound; the ratio of the 7-Aminocephalosporanic acid, the AE-active ester and the organic base is 1.0:1.0-1.8:0.01-1.5. The invention prepares cefotaxime acid in 2-methyl tetrahydrofuran which is a green solvent, avoids the using of poisonous harmful solvent such as dichloromethane; has the advantages of mild condition, good product quality, high yield and low production cost; achieves higher industrial value and potential social economic benefit.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
Preparation method for cefotaxime acid
InactiveCN105503904AImprove effectivenessLarge granularityOrganic chemistrySodium bicarbonateCefotaxime
The invention discloses a preparation method for cefotaxime acid, and belongs to the technical field of medicine. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly mixing dichloromethane with ethanol, purified water and isopropyl alcohol, and then adding 7-ACA (aminocephalosporanic acid), AE-active ester and antioxygen to obtain mixed liquor; dropwise adding triethylamine into the mixed liquor in 2 to 3 hours for a reaction, and when HPLC (high performance liquid chromatography) is adopted to detect that 7-ACA residual amount is less than 1 percent, regarding as a complete reaction; adding sodium bicarbonate aqueous solution of which the mass concentration is 1 percent to 5 percent for extraction, after reduced pressure suction filtration on an aqueous phase, adding acetone and mixing, dropwise adding hydrochloric acid of which the mass concentration is 10 percent to 25 percent under temperature of 10 to 15 DEG C until a pH (potential of hydrogen)value is 2.5 to 3.0, and cultivating crystals for 1 to 3 hours; centrifuging, spin-drying, leaching, and drying after spin-drying to obtain the cefotaxime acid. The cefotaxime acid prepared by the invention has uniform particle size distribution and stable performance; mass yield reaches more than 170 percent, and product purity can reach more than 99 percent.
Owner:HENAN KANGDA PHARMA
Method for obtaining high-vitality superspectrum beta-lactam enzyme by directional anagenesis in vitro
InactiveCN101104858ABroad substrate spectrumIncrease productionBacteriaHydrolasesBiotechnologyCefotaxime
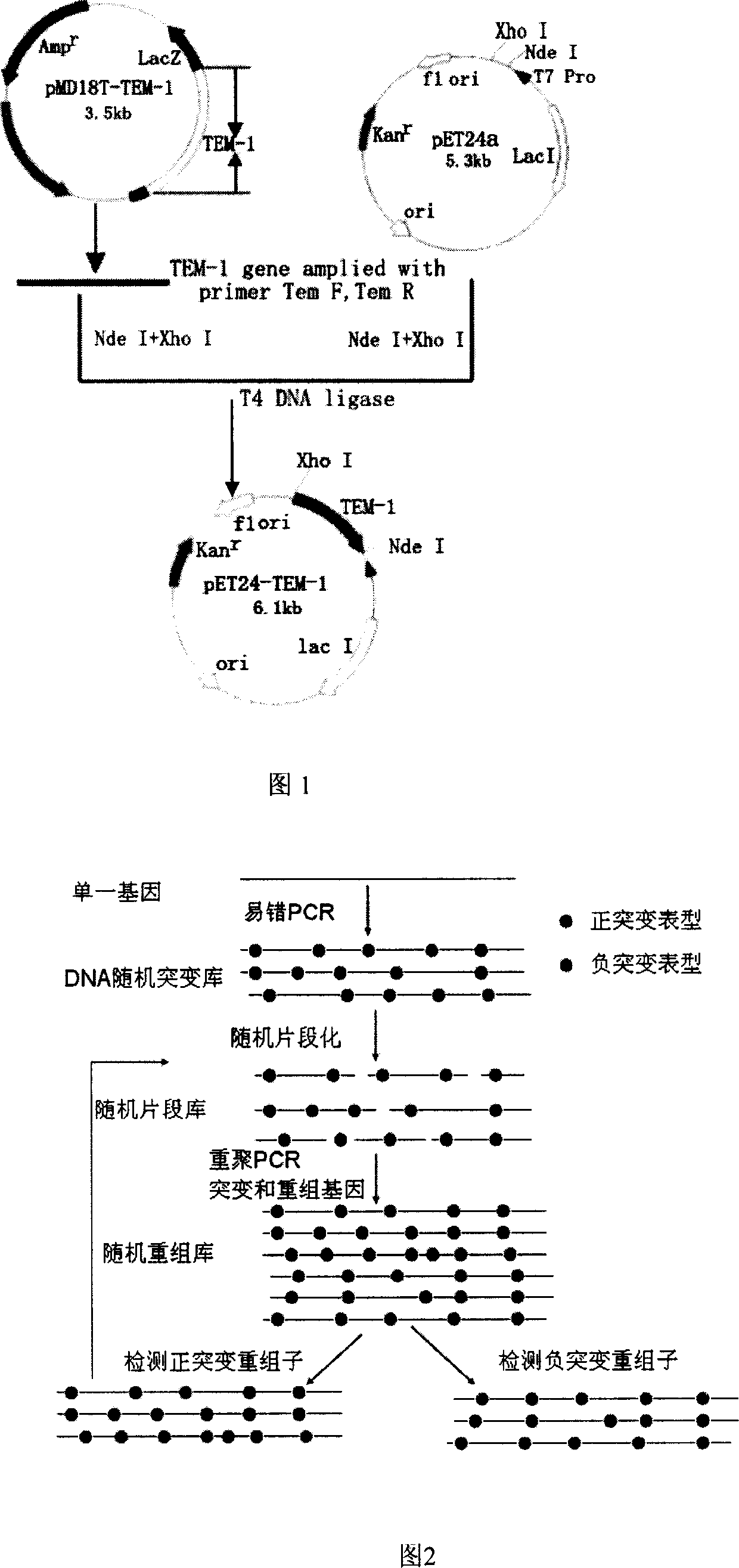
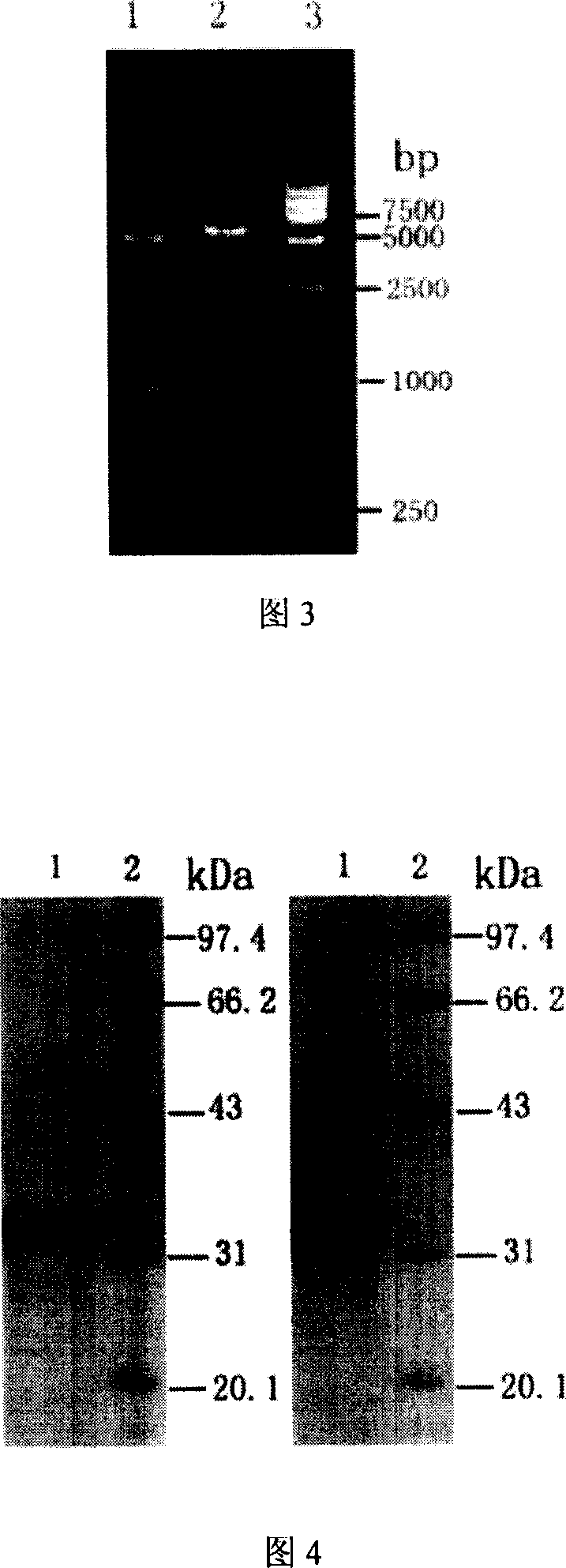
The method to prepare high active extended spectrum beta-lactamase through directed evolution in vitro of the invention belongs to medical bioengineering technical field. In particular, the invention adopts two directed evolution strategies of error-prone PCR and DNA shuffling to transform a lab strain plant which contains TEM-1 gene. The substrate spectrum enzymes of the mutated strain plant and the wild strain plant, and the activity of the substrate spectrum enzymes are compared, showing that the original substrate spectrum is enlarged because of mutation and the degradability of the third representative generation of beta-lactam antibiotics ceftazidime (CAZ) and the cefotaxime (CTX) is improved from zero to a specific activity of 43IU / mg to 78IU / mg.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
One-pot synthesis method of cefotaxime acid
InactiveCN105061470AReduce energy consumptionShorten the production cycleOrganic chemistry methodsCefotaximeOrganic solvent
The invention relates to a one-pot synthesis method of cefotaxime acid. The one-pot synthesis method mainly comprises the following steps: (1) adding 2-(2-aminothiazole-4-yl)-2-methoxyiminoacetic acid and a chlorine acylating agent into an organic solvent, and reacting to obtain an organic solution containing ammonia cefotaxine acyl chloride; (2) adding 7-ACA and a small amount of water into the organic solution containing the ammonia cefotaxine acyl chloride, dropwise adding an organic base while controlling the temperature to be minus 5-5 DEG C, continuously performing heat preservation reaction, adding water after the end of the reaction, taking water phases by layers, enabling crystals to grow, filtering, washing, and drying, so as to obtain the cefotaxime acid. According to the invention, the one-pot method is adopted, the intermediate ammonia cefotaxine acyl chloride is not separated in a solid manner, and the enriched phase of the ammonia cefotaxine acyl chloride is directly adopted to carry out next step of the reaction for synthesis of the cefotaxime acid, so that the shortening of the production period is facilitated, the production operation is simplified, the energy consumption during the intermediate drying process can be reduced, and the effect of reducing the cost to a certain degree is achieved.
Owner:山东安弘制药有限公司
Method utilizing cefotaxime acid waste-liquor to prepare 2, 2'-dithio-dibenzo thiazole
Owner:NORTH CHINA PHARMA HEBEI HUAMIN PHARMA
Breeding method for experimental macaque
ActiveCN104542475AImprove sexual functionImprove pregnancy rateAnimal feeding stuffAnimal housingCefotaximeCvd risk
The invention relates to the technical field of animal breeding, in particular to a breeding method for an experimental macaque. Main feed containing vitamin E is fed to the macaque in at least one of a suckling period, a growth period and an adult period; cefotaxime or ceftriaxone sodium or ceftazidime is added into the feed continuously for 5-7 days every 1-2 months in at least one of the growth period and the adult period; a young macaque is independently fed in the suckling period, feeding quality is further improved, the health condition of the macaque can be timely discovered and managed, the survival rate of the young macaque is improved, and the young macaque is normal in growth and development, flexible in limbs and physically strong. Moreover, the probability and the risk of bacterial dysentery infection of the macaque are reduced, and common health of the macaque and workers is ensured. A normalized experimental animal breeding standard is provided, and the breeding method is easy to popularize and use.
Owner:四川横竖生物科技股份有限公司
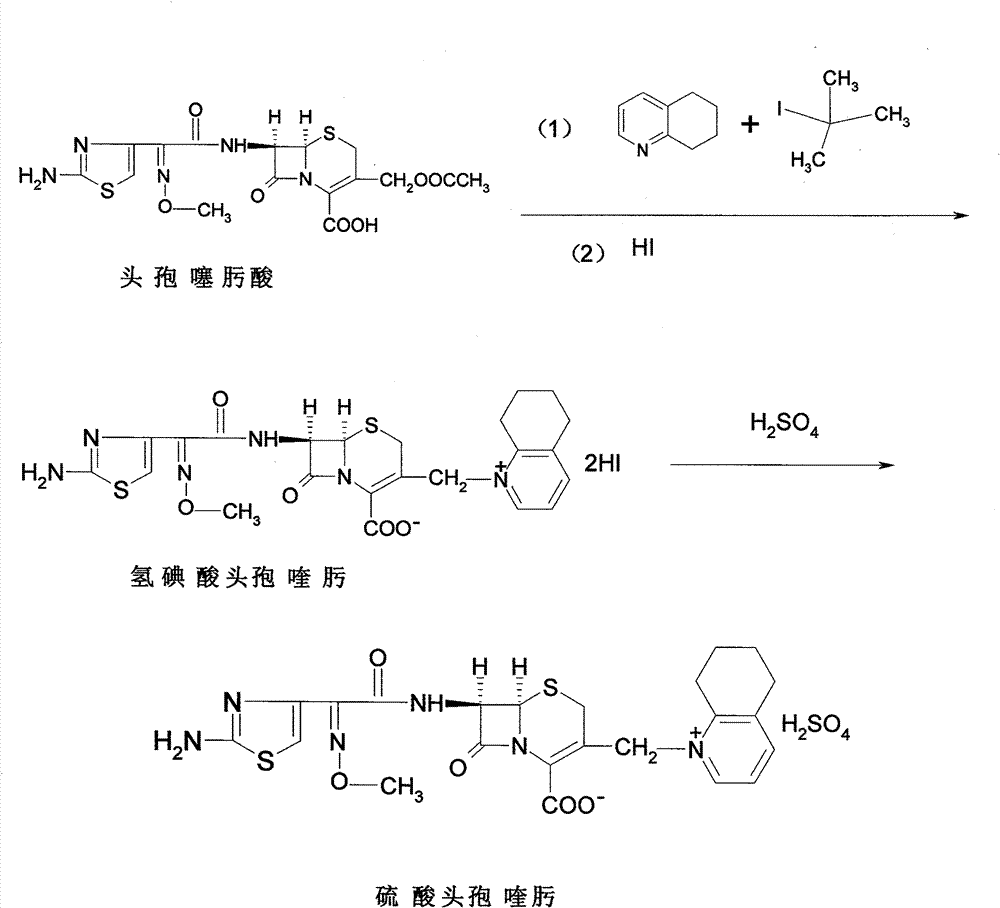
Process for preparing cefquinome sulfate
InactiveCN101307064AGood treatment effectLow toxicityAntibacterial agentsOrganic chemistryCefotaxime7-ACA
The invention discloses a method for preparing cefquinome sulfate, belonging to the cephalosporin antibiotics special for animals. The method comprises the following: A. a step of preparing 7-amino-cefquinome, during which, iodotrimethylsilane reacts with 5, 6, 7, 8-tetrahydroquinoline, and a reaction product reacts with 7-amino-cephalosporanic acid, thereby obtaining the 7-amino-cefquinome; B. a step of preparing the cefquinome sulfate, during which, the 7-amino-cefquinome reacts with AE active ester after the 7-amino-cefquinome is dissolved and is decolored by sulphuric acid, and the cefquinome sulfate is obtained after the reaction product is subject to extraction, suction filtering, leaching and drying. The method uses 7-ACA which is widely used in industry, is low in cost and is easily obtained as a raw material, without using cefotaxime acid with unstable service quality; meanwhile, the method has a mild reaction condition and simple operation, reduces the dosage of the 5, 6, 7, 8-tetrahydroquinoline which is an important intermediate, and greatly improves the product quality with the yield of 64.1 percent and the purity of 99.7 percent, thereby the method is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:崔增学
Distinguishing and determining method of entecavir chiral isomers
ActiveCN107764891AImprove separation efficiencyFast wayPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMiglitolAlkaline earth metal
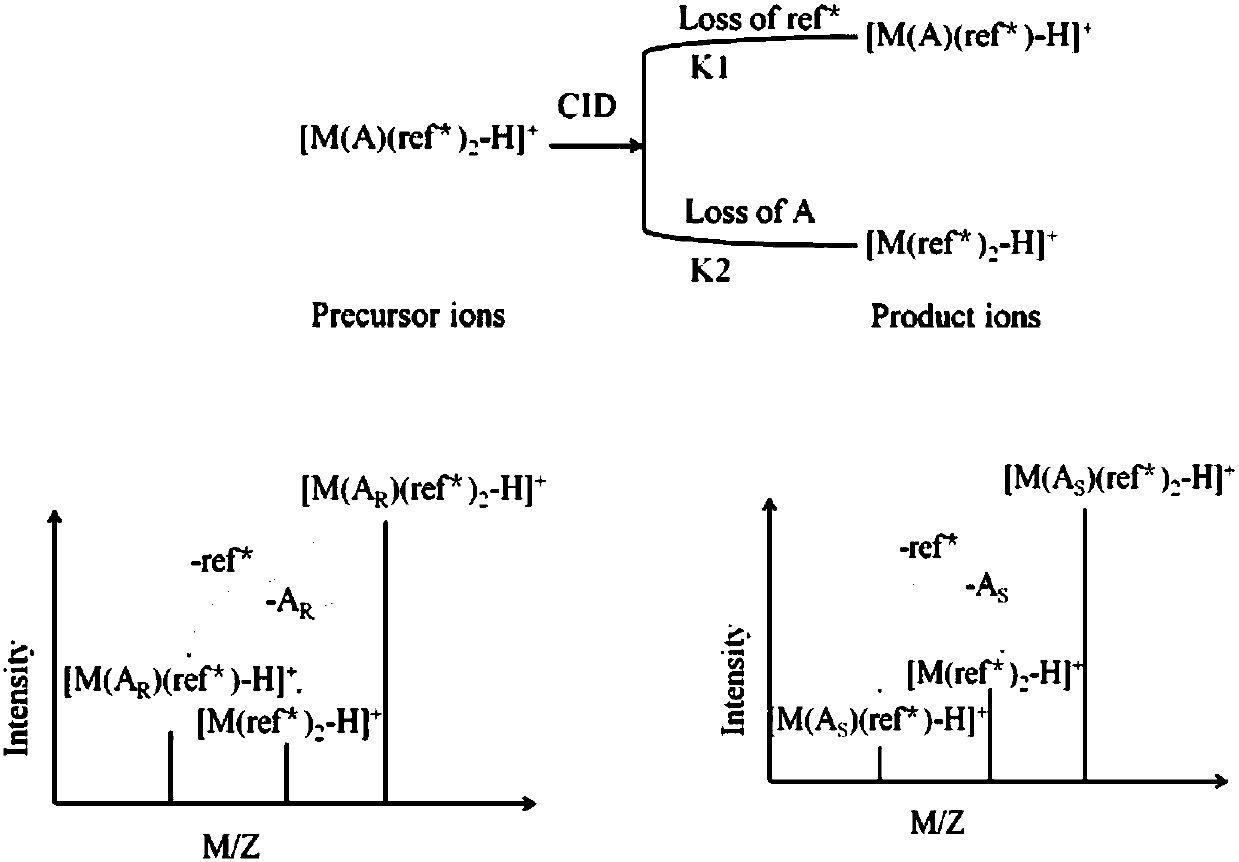
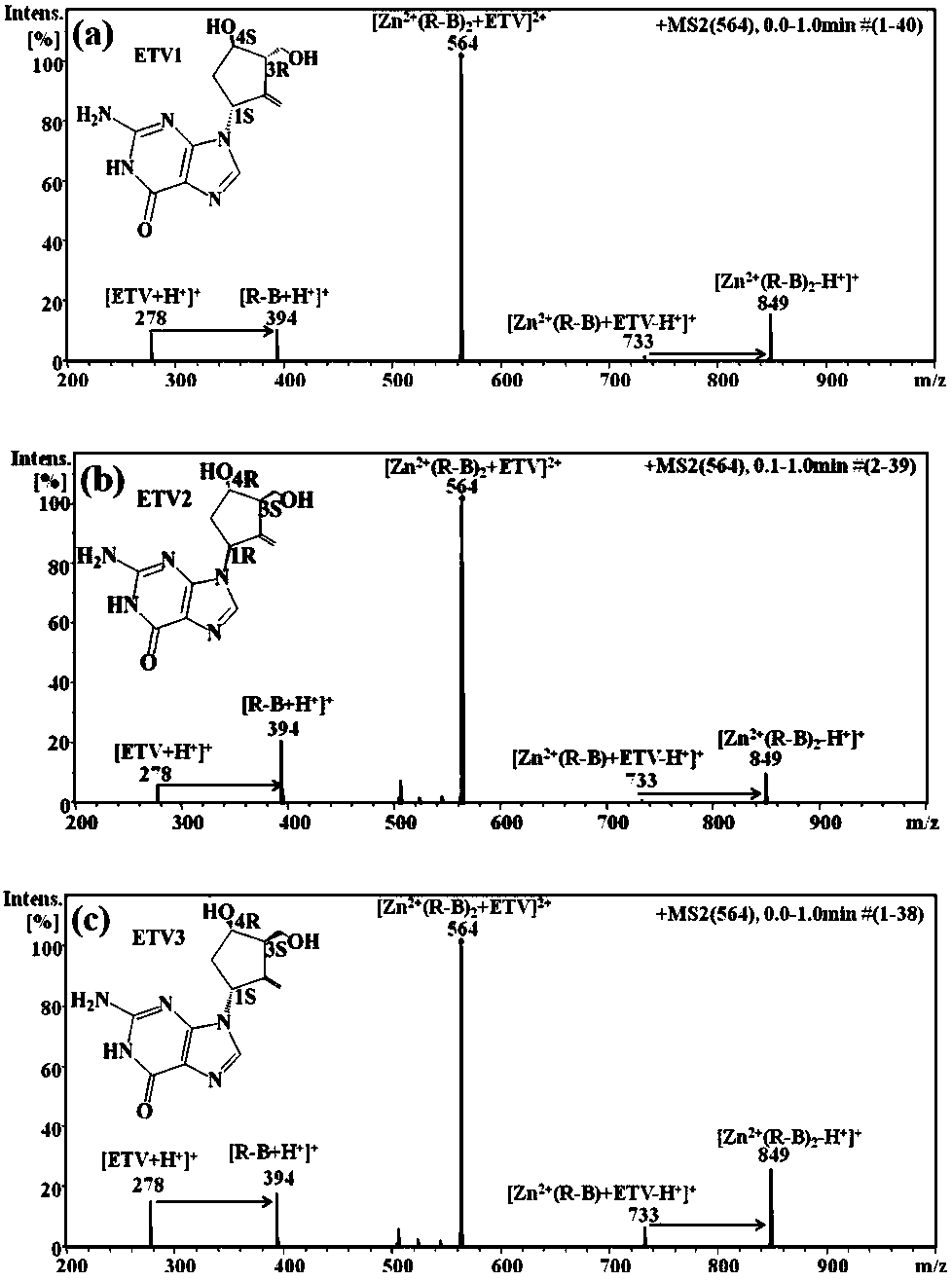
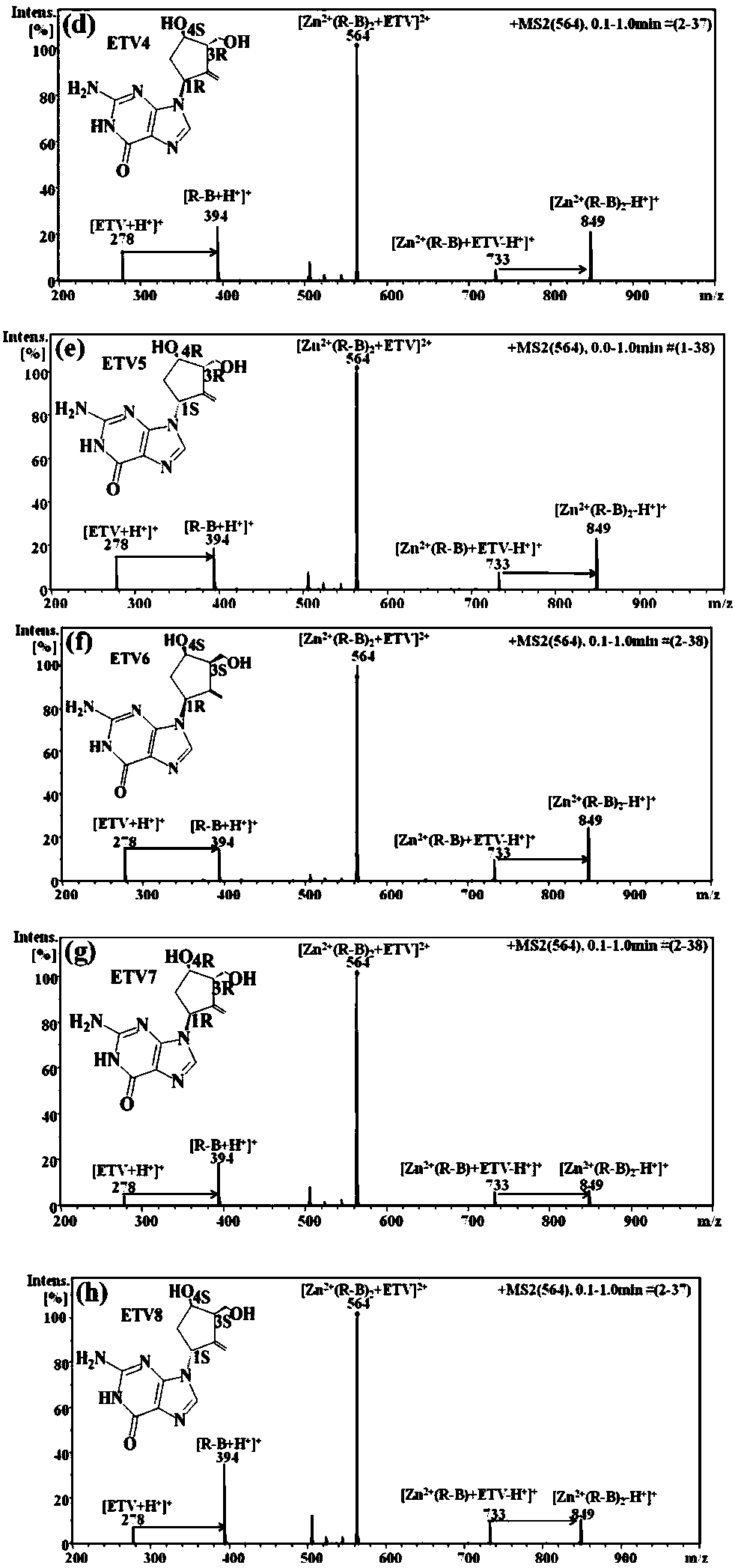
The invention discloses a distinguishing and determining method of entecavir chiral isomers. The method comprises the steps of adopting a chiral ligand, metal ions and the eight entecavir chiral isomers to form complexes with different stable forms; utilizing a mass-spectrography method for recognizing and distinguishing the complexes, wherein the chiral ligand comprises R-besifloxacin, beta-cyclodextrin, migltol or cefotaxime; the metal ions comprise alkaline-earth metals or transient state metals; the alkaline-earth metals comprise Mg and Ca; the transient state metals comprise Ni, Cu, Co, Zn and Mn. The method is fast, simple and convenient, overcomes the defects that a traditional HPLC method needs a specific chiral stationary phase, solvent gradient eluting consumed time is longer, and an enantiomeric separation degree is insufficient, and can be used for quickly distinguishing the eight entecavir chiral isomers and quantitatively determining.
Owner:HANGZHOU LEADING PHARMATECH CO LTD +1
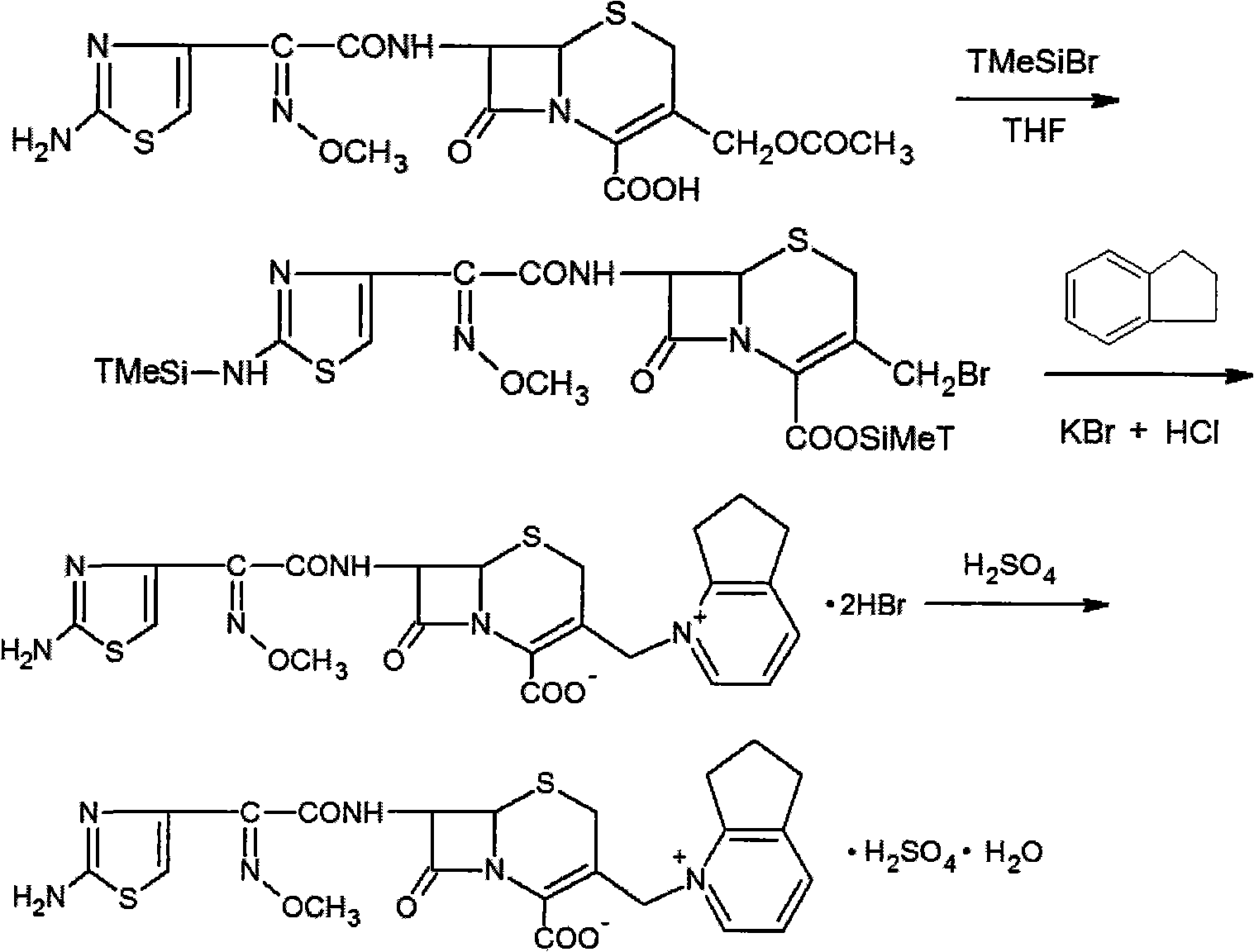
Method for preparing cefquinome sulfate
InactiveCN103275103AReduce manufacturing costMild reaction conditionsOrganic chemistryCefotaximePhosphoric acid
The invention discloses a method for preparing cefquinome sulfate. The method comprises the steps as follows: 7-aminocephalosporanic acid is taken as a raw material; a C-3 bite ester group is hydrolyzed under the action of alkali and reacts with 2-(2-Amino-4-thiazolyl)-(z)-methoxyiminoacetic, thiobenzothiazole ester, so that an intermediate A is obtained; an iodo substance 3-iodine methyl cefotaxime is obtained through the intermediate and potassium iodide under the action of phosphoric acid; the 3-iodine methyl cefotaxime reacts with 5, 6, 7, 8-tetrahydroquinoline, so that an intermediate B of cefquinome hydriodate is obtained; and finally, the intermediate B of cefquinome hydriodate reacts with sulfuric acid under the action of an alkaline anion exchange resin, so that the cefquinome sulfate is obtained. According to the method for preparing the cefquinome sulfate, the 7-aminocephalosporanic acid which is cheap and easy to obtain is taken as the raw material, so that the use of iodotrimethylsilane which is expensive and prone to decompose when contacted with light and water is avoided, and the production cost is reduced; and the reaction condition is mild, the operation is simple, the yield is high, and the cefquinome sulfate is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Multi-detection method of residual of cephalo-type drugs in milk product
ActiveCN105116063AGuaranteed SensitivityAvoid interferenceComponent separationCefotaximeRelative standard deviation
The invention belongs to the technical field of detection of residual of drugs in an animal source food, and relates to a method for determining the residual quantity of cephalo-type drugs in a milk product through a high performance liquid chromatograph. The method comprises the steps of sample pre-extraction, standard curve drafting and apparatus detection analysis, the detection method is a multi-detection method carried out by using high performance liquid chromatography, and detected drugs comprise cefoperazone, cefotaxime, ceftriaxone and cephalothin. The cefoperazone detection limit of the method is 0.26mg / Kg, the cefotaxime detection limit of the method is 0.01mg / Kg, the ceftriaxone detection limit of the method is 0.10mg / Kg, and the cephalothin detection limit of the method is 0.07mg / Kg; the method has good linear relationship in an addition concentration range of 1-50mg / kg, and the recovery rate is 90-105%; and the intra-batch relative standard deviation is not greater than 15%, and the inter-batch relative standard deviation is not greater than 20%. The method has the advantages of short analysis time, low detection limit, high precision and multi-detection, and is of great significance to accurately monitor the residual quantity of the cephalo-type drugs in milk.
Owner:山东世通检测评价技术服务有限公司
Refining method of tadalafil crystal form I
The invention relates to a refining method of a tadalafil crystal form I. The refining method comprises the following steps: adding a tadalafil crude product into a mixed solvent of acetic acid, methanol and water; heating, stirring and dissolving; filtering and cooling to 30 to 40 DEG C; dropwise adding water; after dropwise adding the water, cooling to 0 to 5 DEG C; stirring and crystallizing for 60min, wherein the yield of the tadalafil reaches 97 percent or more, the purity reaches 99.9 percent and the content of cefotaxime is less than 0.05 percent; centrifuging and drying to obtain the tadalafil crystal form I. The refining method provided by the invention has the advantages that the refining method is suitable for commercial production and the quality and the yield of a product areimproved (the content of biggest cefotaxime is less than 0.05 percent and the yield is 97 percent or more); the preparation method is simple and the repeatability is good.
Owner:西安吉泰医药有限公司
Compound injection with probenecid, potassium and beta-lactam antibiotic and its use
InactiveCN1853724AIncrease the total amount of drugReduce dosageAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsCefotaximePenicillin
A compound powder injection or freeze-dried powder injection is prepared from the sodium (or potassium) salt of probenecid and the beta-lactam kind of antibiotics including penicillin G, ampicillin, ancef, cefuroxime, cefotaxime and cefoxitin. It can elongate the half life of antibiotic, increase the AUC and plasma level and prevent the generation of drug-resistant bacteria.
Owner:吴晓辉
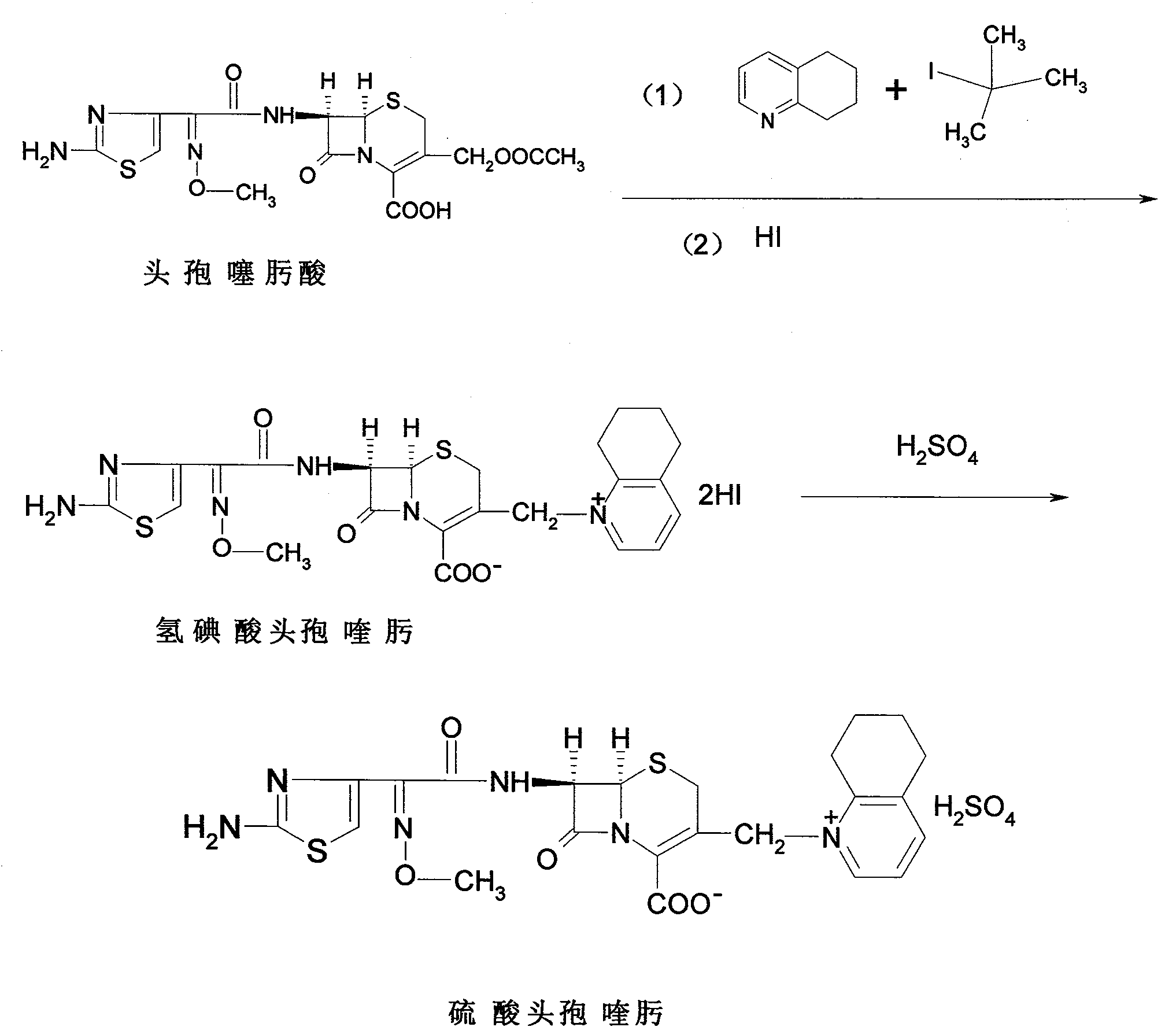
Preparation method of cefquinome sulfate
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing cefquinome sulfate and relates to a preparation method of a medicament for animals. The preparation method comprises the following steps: taking cefotaxime, 2,3-cyclohexyl pyridine and trimethyliodosilane as initial raw materials; preparing cefotaxime hydriodate from the cefotaxime; carrying out decoloring and silica column chromatography on the cefotaxime; and reacting the treated cefotaxime with sulphuric acid to prepare a cefquinome sulfate product. Compared with the prior art, the invention has the advantages of high yield of products, stable production quality and suitability for industrial production.
Owner:PU LIKE BIO ENG
Synthetic method of cefpirome sulfate
ActiveCN101284840ALow costHigh yieldAntibacterial agentsOrganic chemistryTrimethylsilyl chlorideCefotaxime
The invention relates to a synthesis method for making cefpirome sulfate. The method comprises the following steps that: cefotaxime and 2, 3-cyclopenopyridine, with the molar ratio of between 1:7 and 1:12, are mixed with trimethyl bromosilicane used as protecting agent inside organic solvent to carry out substitution reaction, thereby generating cefpirome dihydrobromide; and the salt-forming reaction of the cefpirome dihydrobromide is carried out to make cefpirome sulfate. According to the synthesis method of cefpirome sulfate provided by the technical proposal of the invention, cefotaxime and trimethyl bromosilicane are respectively used as raw material and protecting agent to make cefpirome sulfate. Because enough supply and technical maturity of cefotaxime are realized in China and trimethyl bromosilicane is more active than trimethylchlorosilane and is cheaper than trimethyliodosiliane, the synthesis method has the advantages of low cost of raw material, high yield, simple synthetic route and convenient operation.
Owner:GUANGDONG JIUMING PHARMA
ESBL Detection Kit and Method
The invention provides methods and detection kits for detecting extended spectrum β-lactamase producers (ESBLs). The kits typically comprise a carrier containing: a)at least one sugar; b) at least one antibiotic for killing Gram positive bacteria; c) at least one antifungal compound; d) a mixture of cefpodoxime and at least one additional antibiotic for killing Gram negative bacteria, and / or a mixture of cefotaxime and ceftazidime; and e) a pH indicator. The methods and kits can be used to by non-specialist health professionals to give rapid results at relatively low cost.
Owner:LEWISHAM HOSPITAL NHS TRUST THE
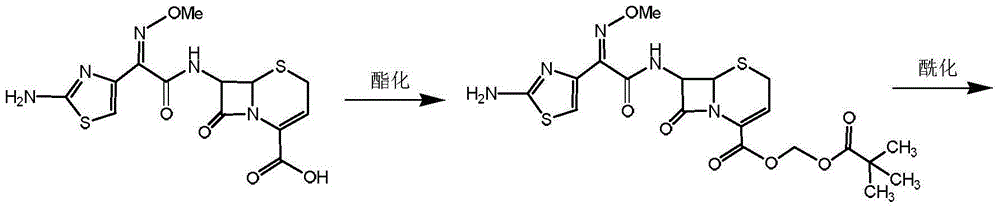
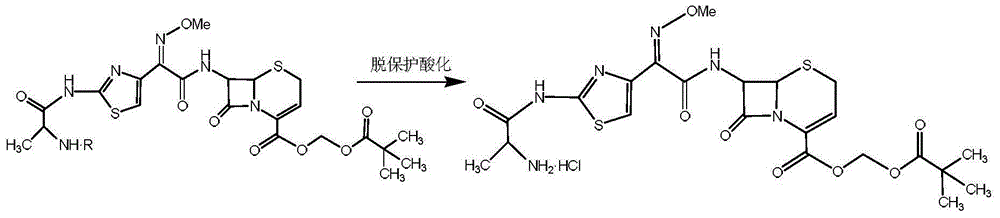
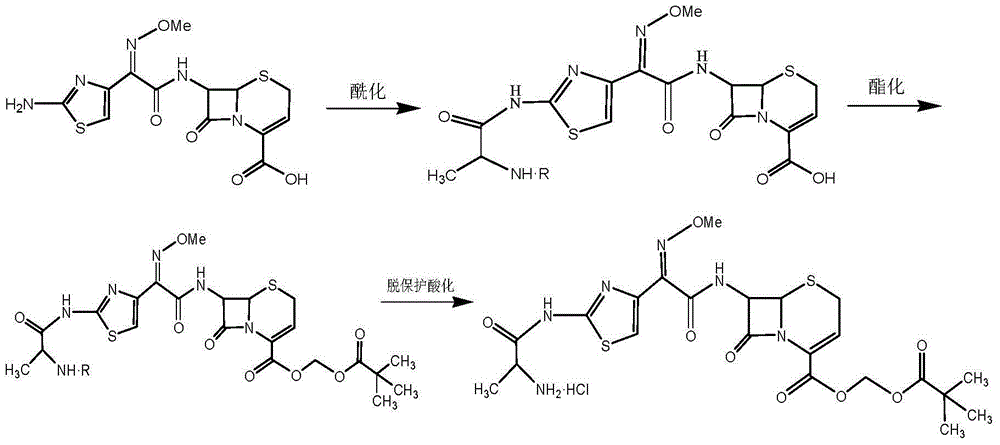
Preparation method for ceftizoxime alapivoxil, intermediates thereof and preparation method for intermediates
ActiveCN105017284ARaw materials are cheap and easy to getMild reaction conditionsOrganic chemistryCefotaximeValproic Acid
The present invention discloses a preparation method for ceftizoxime alapivoxil by using a mixture anhydrides method, intermediates 3a / 3b / 3c thereof and a preparation method for the intermediates . The method comprises: putting an ammonia cefotaxime acid ester compound in an organic solvent to react with BOC-alanine by using a mixture anhydrides method; hydrolyzing under condition of organic alcohol; generating intermediates 3a / 3b / 3c; the intermediates 3a / 3b / 3c condensation reacting with 7-ANCA in an organic solvent; generating BOC-alanyl ceftizoxime acid by esterification; the BOC-alanyl ceftizoxime acid reacting with halogenated pentanoic acid methyl ester in the presence of an acid-binding agent, to prepare BOC-alanyl ester ceftizoxime valproate; removing a BOC protection group; and after concentrating, obtaining the target compound ceftizoxime alapivoxil by crystal precipitation in the organic solvent. The preparation method for ceftizoxime alapivoxil has the advantages that raw materials are readily available, the reaction condition is mild, byproducts are fewer, purity is reliable, the yield is high, and the preparation method for ceftizoxime alapivoxil is suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG YONGNING PHARMA
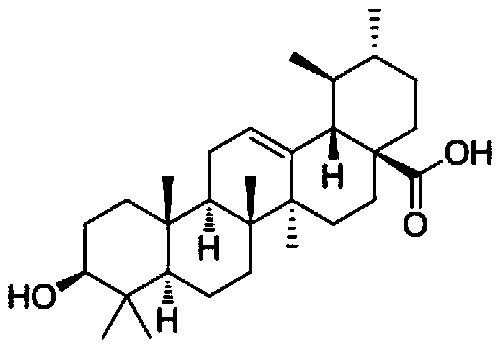
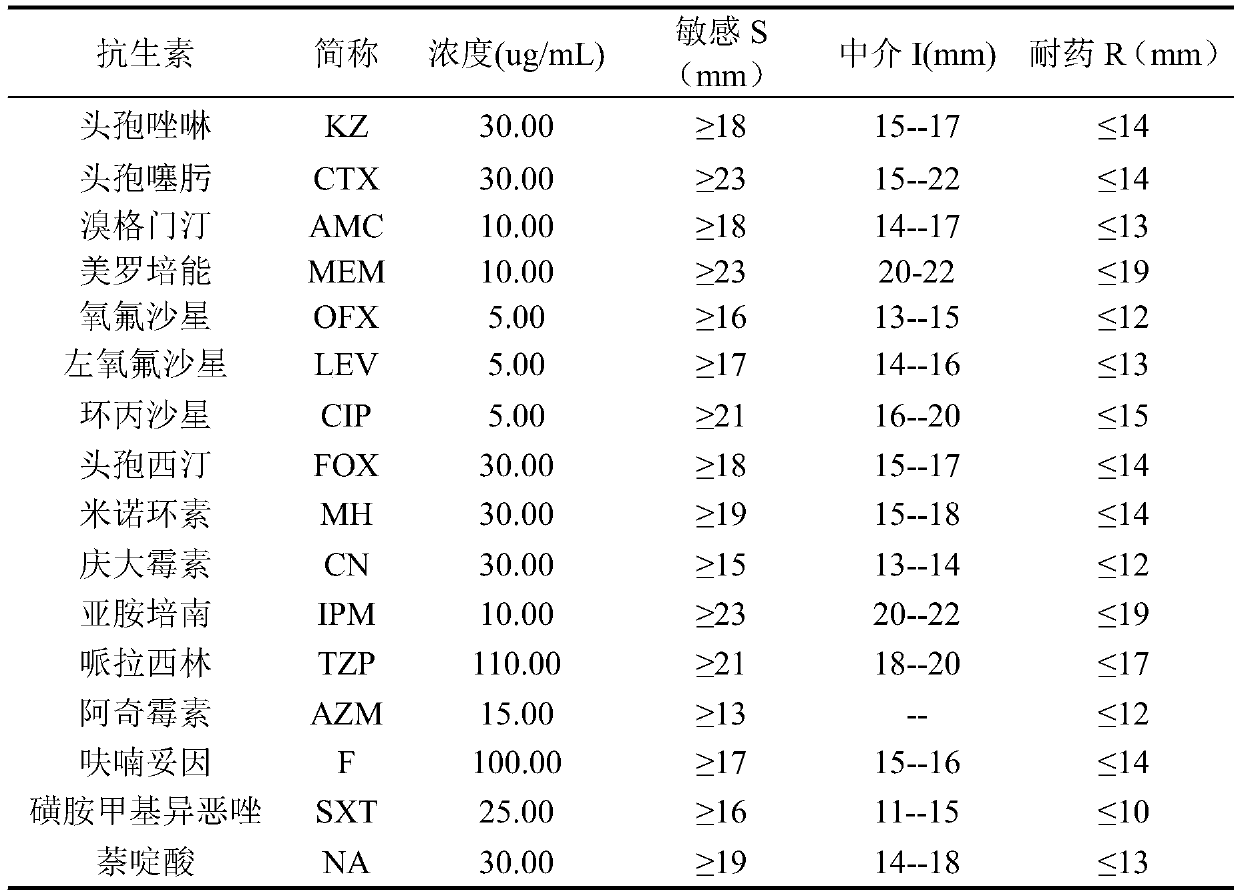
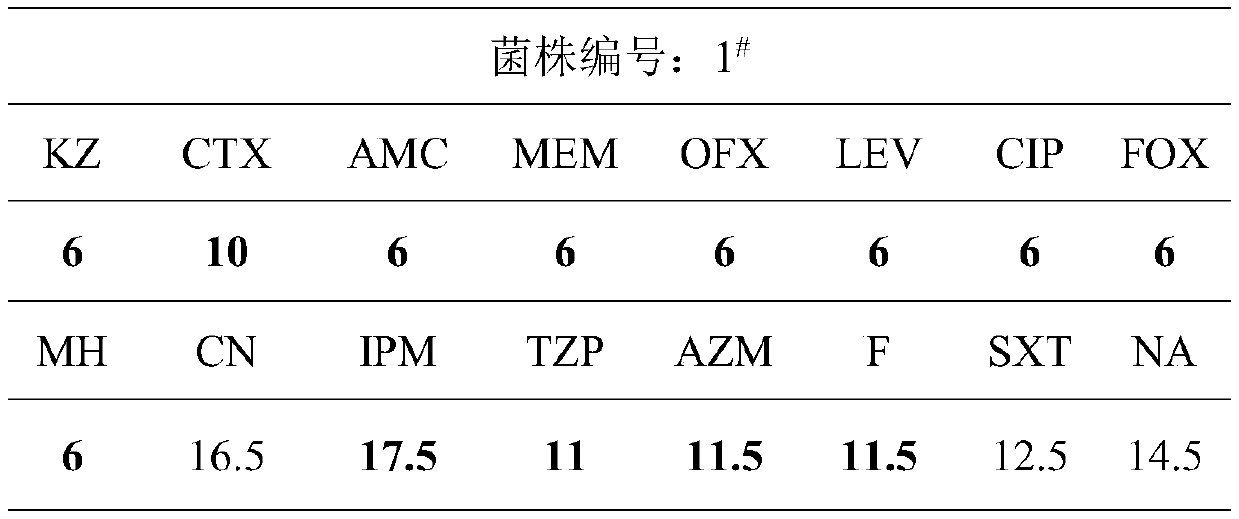
Application of ursolic acid in inhibiting growth of multi-drug-resistance enterobacter cloacae
InactiveCN110279701AMitigate or resolve drug-resistant infectionsReduce fatality rateAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsInfections problemsCase fatality rate
The invention discloses application of ursolic acid in inhibiting growth of multi-drug-resistance enterobacter cloacae. According to a good in-vitro killing function of ursolic acid upon anthropogenic multi-drug-resistance enterobacter cloacae which resists to cefazolin, cefotaxime, aupmentn, meropenem, ofloxacin, levofloxacin, ciprofloxacin, cefoxitin, minocycline, imipenem, piperacillin, azithromycin and macrodantin, growth of multi-drug-resistance enterobacter cloacae can be inhibited, the lowest sterilization concentration is 0.6mg / mL, and the lowest antibacterial concentration is 0.3mg / mL. The invention discloses an inhibition function of the ursolic acid upon the multi-drug-resistance enterobacter cloacae, and the ursolic acid is capable of effectively alleviating or solving the drug-resistance infection problem of the multi-drug-resistance enterobacter cloacae and reducing the case fatality rate, provides new ideas for inhibiting anthropogenic multi-drug-resistance enterobacter cloacae, and has great practical significances.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
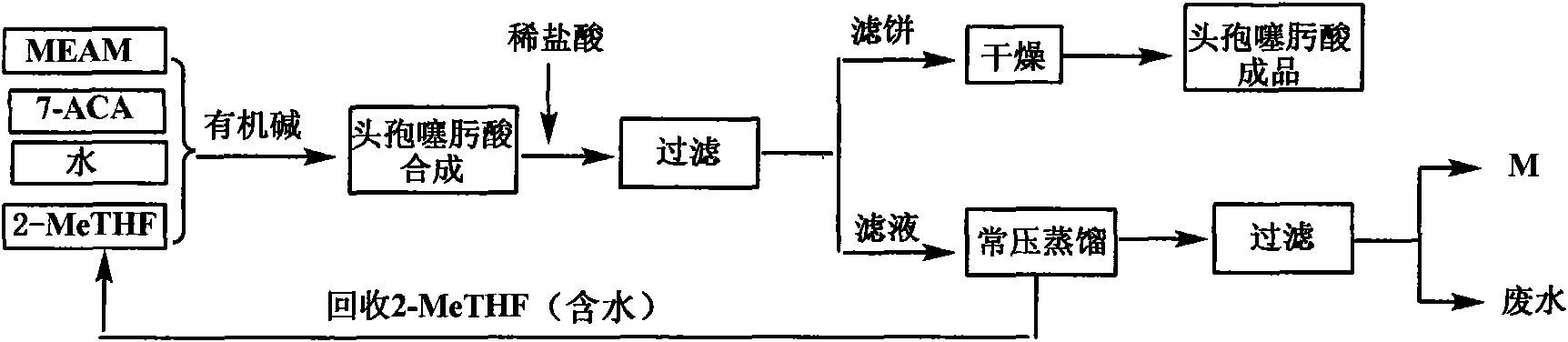
Preparation method for cefotaxime acid
The invention relates to a preparation method for cefotaxime acid, belonging to the technical field of medicines. The preparation method for the cefotaxime acid comprises the following steps: preparation of a condensed liquid: a step of adding 7-ACA and MEAM into a mixed solvent of dichloromethane, ethanol and triethylamine, and carrying out a reaction for 30 to 60 min; extraction and decolorization: a step of extracting the prepared condensed liquid with purified water and an alkali mixed solution so as to obtain an aqueous phase, and adding active carbon into the aqueous phase for decolorization; and preparation of a finished product: a step of adding monohydric alcohol after decolorization is completed, carrying out crystallization with diluted hydrochloric acid, adjusting the pH valueof a solution to 2.0 to 3.0, carrying out cooling, allowing a crystal to grow, carrying out vacuum filtering, washing an obtained material with the purified water and acetone, and carrying out dryingso as to obtain a dry cefotaxime acid product. The preparation method for the cefotaxime acid provided by the invention is scientific, reasonable, simple and practicable; and the cefotaxime acid obtained by using the preparation method provided by the invention has low impurity content and high yield.
Owner:淄博鑫泉医药技术服务有限公司
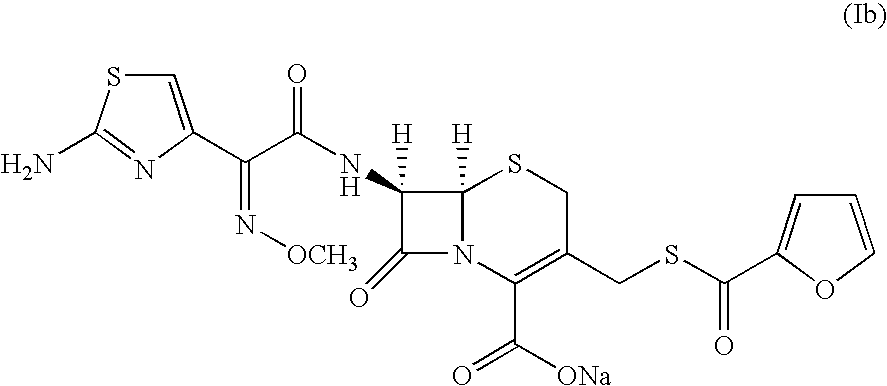
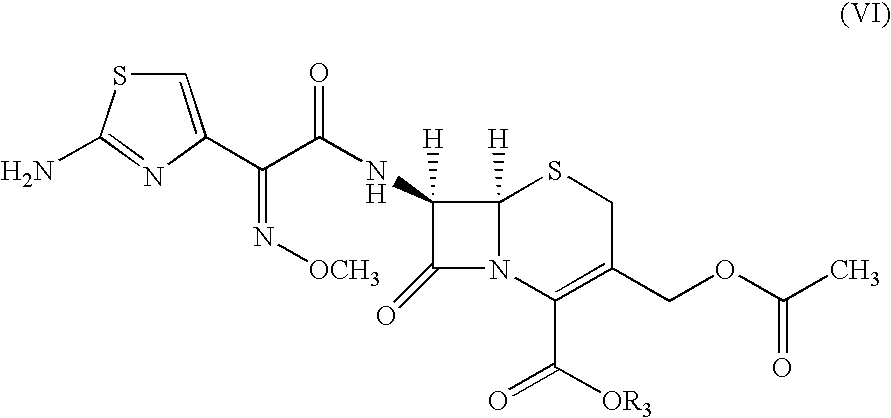
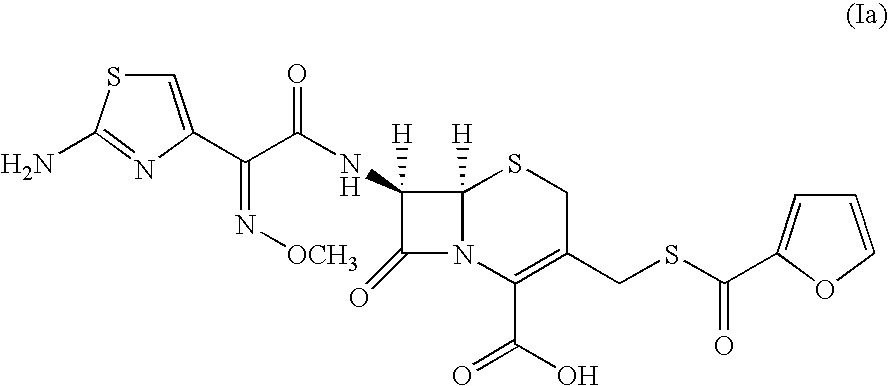
Method for preparation of ceftiofur and salts thereof
A process for preparation of ceftiofur sodium of formula (Ib)possessing high stability and having purity of more than 97% and substantially free of impurities, is disclosed. The process comprises:i) reacting cefotaxime or its salts or its esters of formula (VI)wherein R3 is hydrogen, an alkali or alkaline earth metal, or an easily hydrolysable ester, with thiofuroic acid, employed in a molar proportion of 1.5 to 3.0 moles per mole of compound (VI), in the presence of acetonitrile as solvent and in the presence of large excess of methanesulfonic acid, employed in molar proportions of 12 to 18 moles per mole of compound (VI), and at a temperature of between −5° C. to 30° C. to give after necessary neutralization of the alkali or alkaline earth metal or removal of the ester group of the 4-carboxylic acid function, wherever applicable, ceftiofur of formula (Ia), possessing high stability and having purity of more than 97% and substantially free of impurities;ii) converting the ceftiofur of formula (Ia) thus obtained to its salt with an organic amine by treating a solution of ceftiofur in a mixture of water and a water-miscible organic solvent with an organic amine, at a temperature ranging from −10° C. to 10° C.;iii) reacting of the amine salt thus obtained with a sodium metal carrier in a mixture of water and water-miscible organic solvent and in presence of sodium hydrogen sulfite to give ceftiofur sodium of formula (Ib).
Owner:LUPIN LTD
Process for preparing cephalotaxine esters
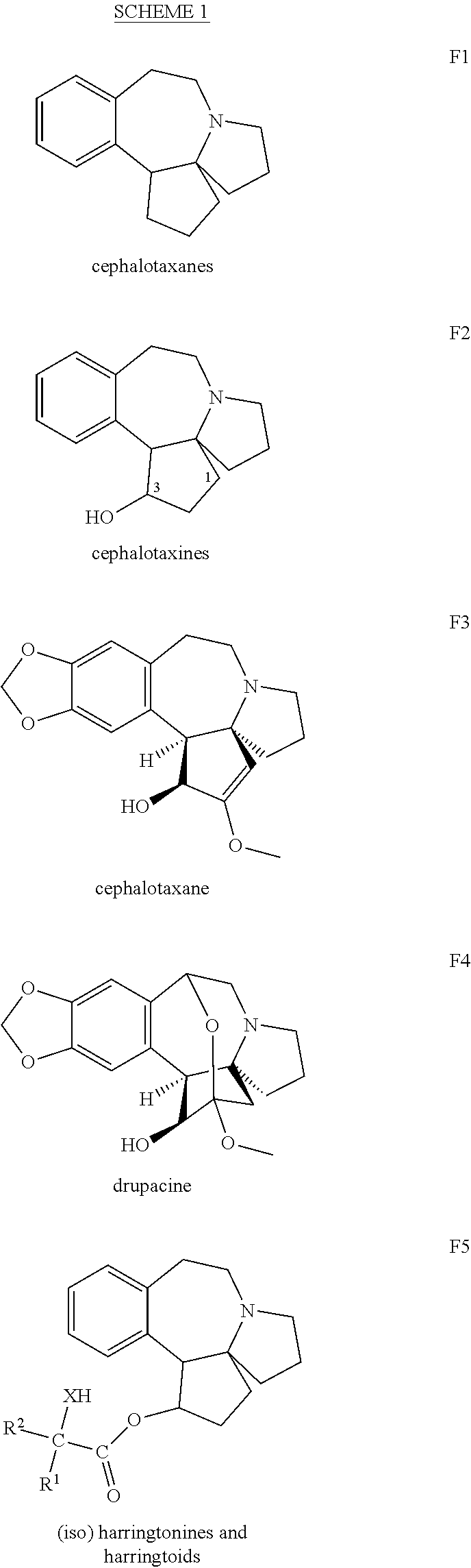
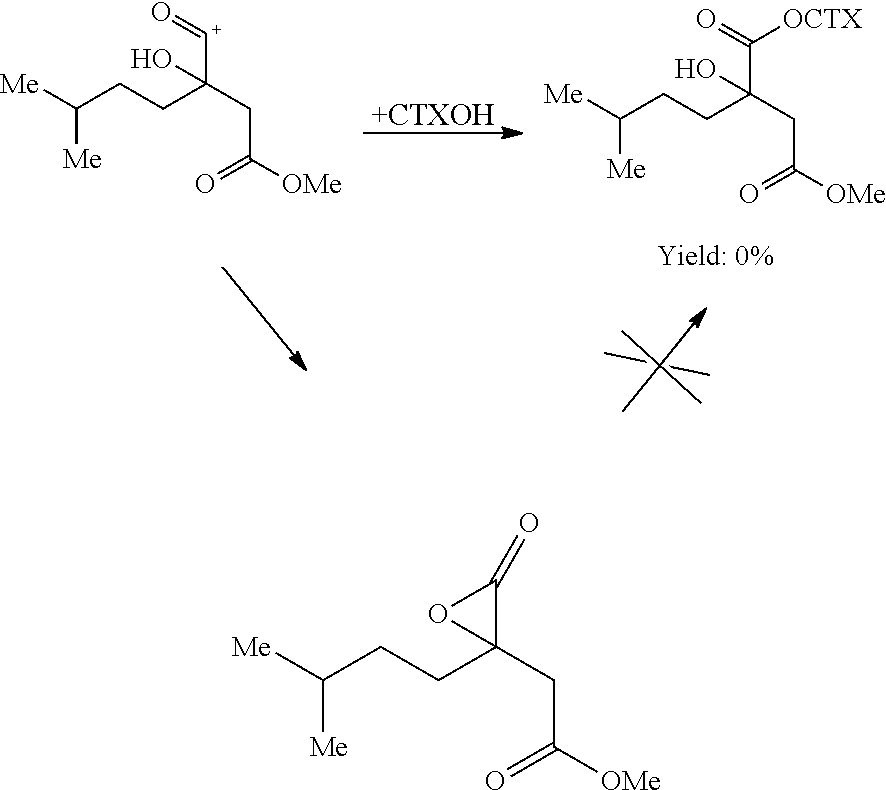
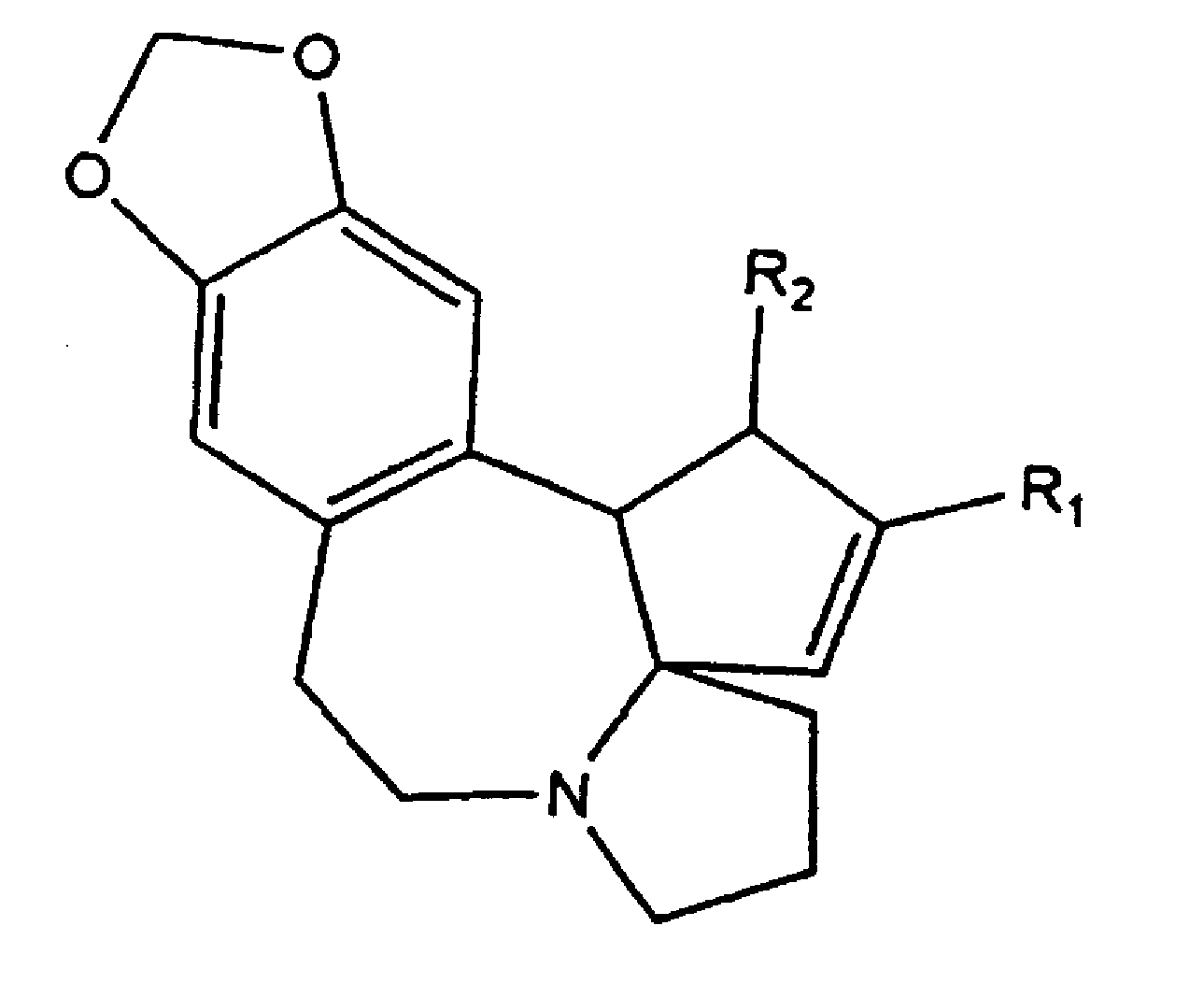
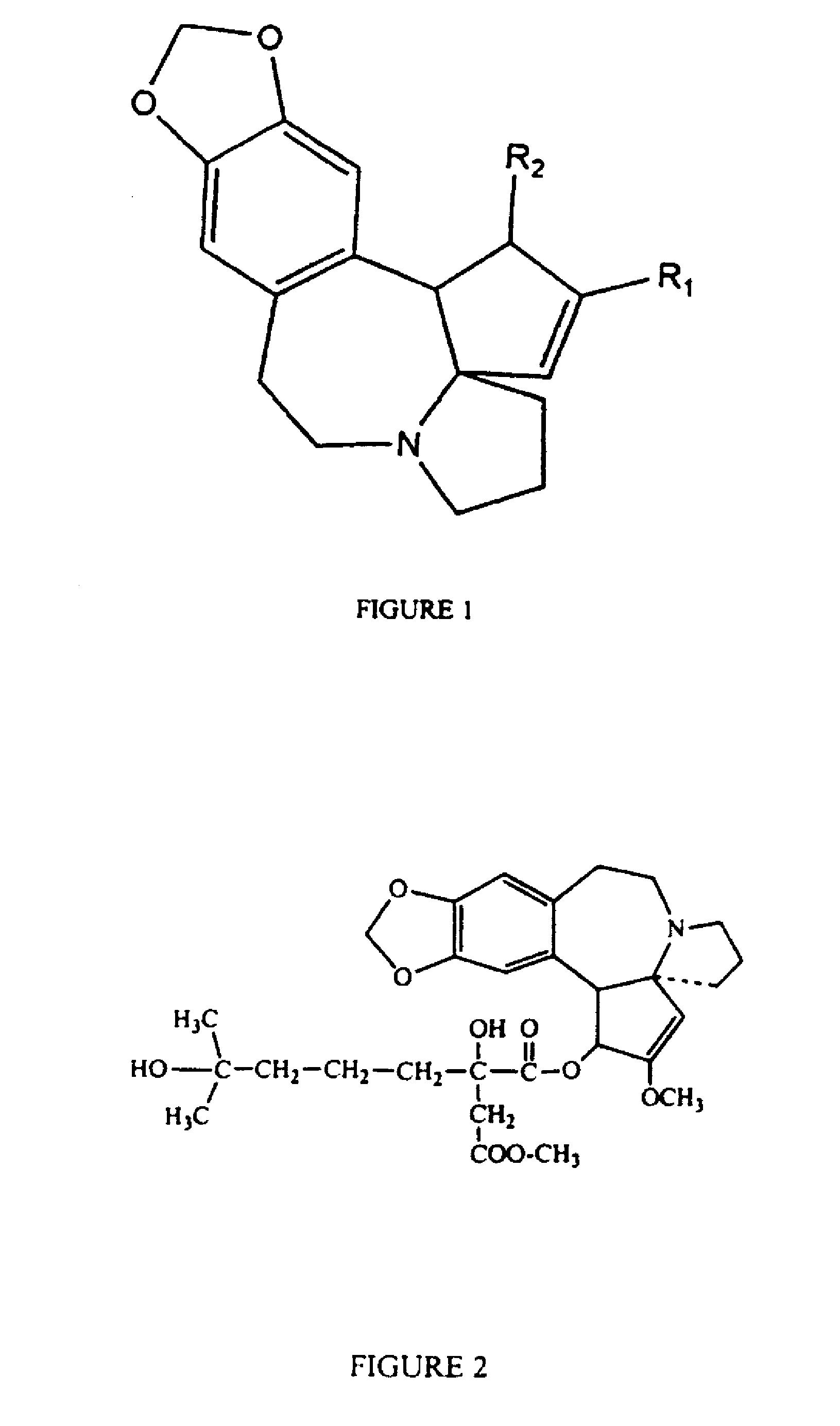
A process for preparing cephalotaxine esters corresponding to the following general formula I which comprises the cephalotaxine backbone: C(R1)(R2)(XH)COO[CTX] wherein CTX represents the cephalotaxine backbone, being optionally substituted and / or dehydrogenated, in which formula I, X is a heteroatom, preferably an oxygen, a sulfur or a nitrogen, R1 and R2, taken separately, may be alkyl, cycloalkyl, heteroalkyl, aryl, heteroaryl, heterocycloalkyl or aralkyl groups, said groups being optionally interrupted by ester functions, or groups that can form one or more rings or a heterocycle together, consisting in bringing the corresponding cephalotaxine compound, or salts, isomers or tautomeric forms thereof, which is free or which is in the form of a metal alkoxide corresponding to the following general formula CTXOM, wherein CTX represents the cephalotaxine backbone, being optionally substituted and / or dehydrogenated, in which M is a hydrogen atom or a metal atom, into contact with a heterocyclic side chain precursor having both a bifunctional protected (bidentate) and activated (acylating) form of an acid bearing a hydrogenated heteroatom, in the alpha (α) position with respect to the carboxyl group, and corresponding to the following general formula: in which case W is a carbon, sulfur, silicon or bore atom, X, R1 and R2 have respectively the same meaning as above, it being possible for R1 and R2 to form a ring or a heterocycle together, and Y and Z are alkyl or heteroalkyl radicals, or monovalent heteroatoms, which may be identical or different, in an independent manner, or may fuse so as to give a divalent heteroatom, it being possible for the X—W bond to be covalent or ionic.
Owner:ROBIN JEAN PIERRE +2
Oral Cephalotaxine Dosage Forms
The present disclosure provides oral dosage forms comprising a cephalotaxine and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier selected from protein, carbohydrate and lipid, an oral dosage form comprising cephalotaxine and a second active agent, as well as methods of treating subjects with such oral formulations.
Owner:TEVA PHARMACEUTICALS INTERNATIONAL GMBH
Preparation method of cefquinome sulfate
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing cefquinome sulfate and relates to a preparation method of a medicament for animals. The preparation method comprises the following steps: taking cefotaxime, 2,3-cyclohexyl pyridine and trimethyliodosilane as initial raw materials; preparing cefotaxime hydriodate from the cefotaxime; carrying out decoloring and silica column chromatography on the cefotaxime; and reacting the treated cefotaxime with sulphuric acid to prepare a cefquinome sulfate product. Compared with the prior art, the invention has the advantages of high yield of products, stable production quality and suitability for industrial production.
Owner:PU LIKE BIO ENG
Method for removing bacteria in chlamydomonas reinhardtii culture process through three mixed antibacterial agents
InactiveCN108485982ASolve pollutionImprove survival rateUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesAmpicillinCefotaxime
A method for removing bacteria of chlamydomonas reinhardtii through kresoxim-methyl, ampicillin and cefotaxime mixed antibacterial agents comprises the following steps: inoculating mixed and pollutedchlamydomonas through a TAP solid culture medium flat plate, and culturing; preparing a mixed antibacterial agent flat plate which is a TAP solid culture medium in which kresoxim-methyl, ampicillin and cefotaxime are added, and waiting for later use; transferring and marking the mixed and polluted chlamydomonas which is cultured on the TAP solid culture medium to the antibacterial agent mixed TAPsolid culture medium flat plate for culturing; and transferring and marking the antibacterial chlamydomonas from the antibacterial flat plate to a common TAP solid culture medium flat plate to cultureagain. According to the method, kresoxim-methyl, ampicillin and cefotaxime are used in match to effectively remove the bacteria and fungus pollution in the chlamydomonas culture process; the method has the characteristics of being high in wide popularization scope, efficient, and low in toxicity, and is extremely high in value of popularization and application in storing of precious chlamydomonasand accuracy improving of following experiments.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Synthesis method of cefotaxime acid
The invention provides a synthesis method of cefotaxime acid. The synthesis method of cefotaxime acid includes the following steps that 1, 7-aminocephalosporanic acid and benzothiazole active ester are added into a mixed solvent composed of aqueous dichloromethane and a cosolvent, and the mixture is stirred to be uniform to obtain a mixed solution; 2, purified water and trimethylamine are added into the mixed solution obtained in step 1, and then acylation reaction is conducted for 50-80 minutes to obtain a reaction solution; 3, water is adopted to conduct extraction on the reaction solution,hydrochloric acid is added into extraction liquid to adjust pH to be 2.5-3.0, and after crystallization, filtration and drying, cefotaxime acid is obtained. According to the method of using quantitative water and aqueous dichloromethane with the water content of 0.1-0.2% for synthesizing cefotaxime acid, aqueous dichloromethane with the water content of 0.1-0.2% is adopted, therefore, the recoverydifficulty of dichloromethane is reduced, the purpose of energy saving is achieved, and cefotaxime acid with high purity is obtained.
Owner:NORTH CHINA PHARMA COMPANY
Application of citral in inhibiting growth of multi-drug resistant enterobacter cloacae
ActiveCN110279679AAvoid drug resistanceMitigate or resolve drug-resistant infectionsAntibacterial agentsAldehyde active ingredientsNalidixic acidCefotaxime
The invention discloses an application of citral in inhibiting growth of multi-drug resistant enterobacter cloacae. The citral can inhibit growth of multi-drug resistant enterobacter cloacae as the citral has relatively good in vitro killing action to multi-drug resistant enterobacter cloacae resisting cefazolin, cefotaxime, augmentin, meropenem, ofloxacin, levofloxacin, ciprofloxacin, cefoxitin, minocyline, imipenem, piperacillin, azithromycin, macrodantin, sulfamethoxazole and nalidixic acid. The minimum bactericidal concentration is 1.6 mg / mL and the minimal inhibitory concentration is 1.0 mg / mL. The invention provides inhibiting action of citral to multi-drug resistant enterobacter cloacae and the citral has wide application value in the field of medicine.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Nematicidal composition containing cyflumetofen
ActiveCN106973937AImprove the effect of prevention and controlIncrease productionBiocideDead animal preservationCefotaximeChemical composition
The invention relates to a nematicidal composition containing cyflumetofen. The composition comprises an active ingredient A which is cyflumetofen and an active ingredient B which can be one of fosthiazate and cefotaxime. The weight ratio of cyflumetofen and fosthiazate is (20-1): (1-20); the weight ratio of cyflumetofen and cefotaxime is (30-1): (1-30); and the sum of the content of the active ingredients is 0.5-80% by weight of the composition. The composition can be prepared into agriculturally allowable missible oil, wettable powder, water dispersible granules, a microemulsion, a suspending agent, an emulsion in water and granules, and the effect of preventing and treating underground nematodes is not simply overlaid of the effects of the active ingredients. Compared with a single preparation, the composition has a remarkable nematicidal synergic effect, the dosage is reduced, the pesticidal residues are reduced, the service life of the pesticide is prolonged, generation of drug resistance of injurious insects is delayed, the composition is good in safety to crops and the output and quality are improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG ZHENGE BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD +1
Method for establishing agrobacterium-mediated high-efficient transformation system of Lanzhou lily
InactiveCN101748146AOvercoming the defects that are difficult to apply to the genetic transformation of grassesIncrease Vc contentVector-based foreign material introductionKanamycinCefotaxime
The invention discloses a method for establishing an agrobacterium-mediated high-efficient transformation system of Lanzhou lily, which comprises the steps of cutting scales of tissue culturing seedlings, carrying out dark culture on a differentiation culture medium for 2 days, and being used as a receptor material; inoculating a donor strain onto an LB liquid culture medium with kanamycin, streptomycin and rifampicin, collecting bacterial liquid, centrifugalizing, tossing away supernatant liquid, using liquid MS for dissolving the sediment and diluting till the concentration that OD600 is 0.4-0.6, adding into the liquid Ms, adding the receptor material for infection, placing the scales after the infection on filter paper for drying by absorption, inoculating onto the differentiation culture medium containing 20mg / L AS and 200mg / L cefotaxime for carrying out the dark culture for 3d, then inoculating onto the differentiation culture medium containing 2mg / L representative hygromycin, and carrying out the dark culture at 26 DEG C till the outgrowth of resistant shoots; and further screening and culturing the resistant shoots, carrying out rooting culture when 4-5 leaves are grown, and then transplanting. The method opens up a new way for culturing good rice varieties.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com