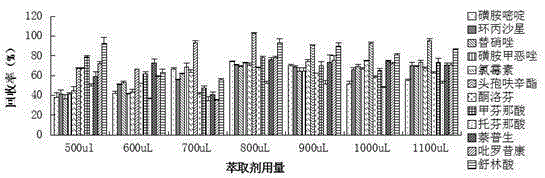
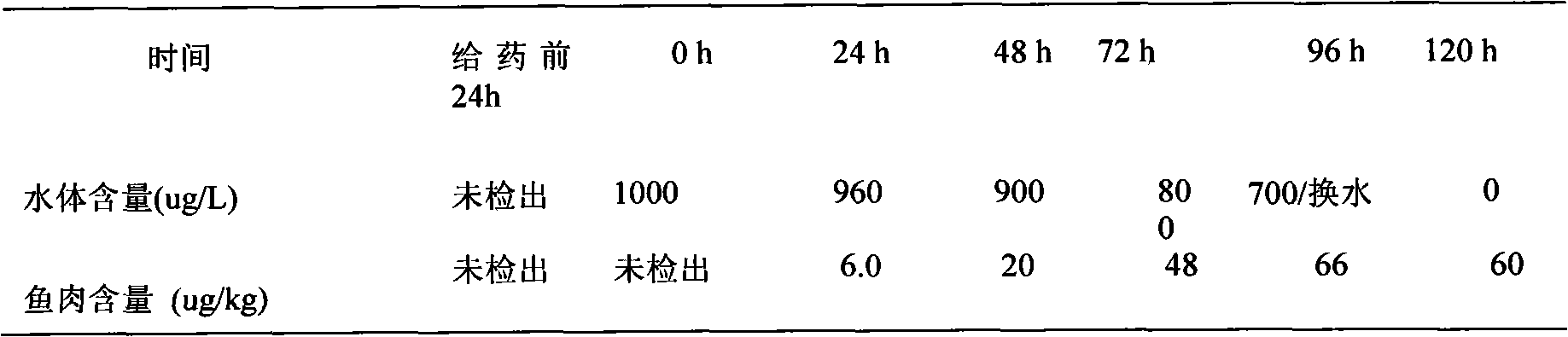
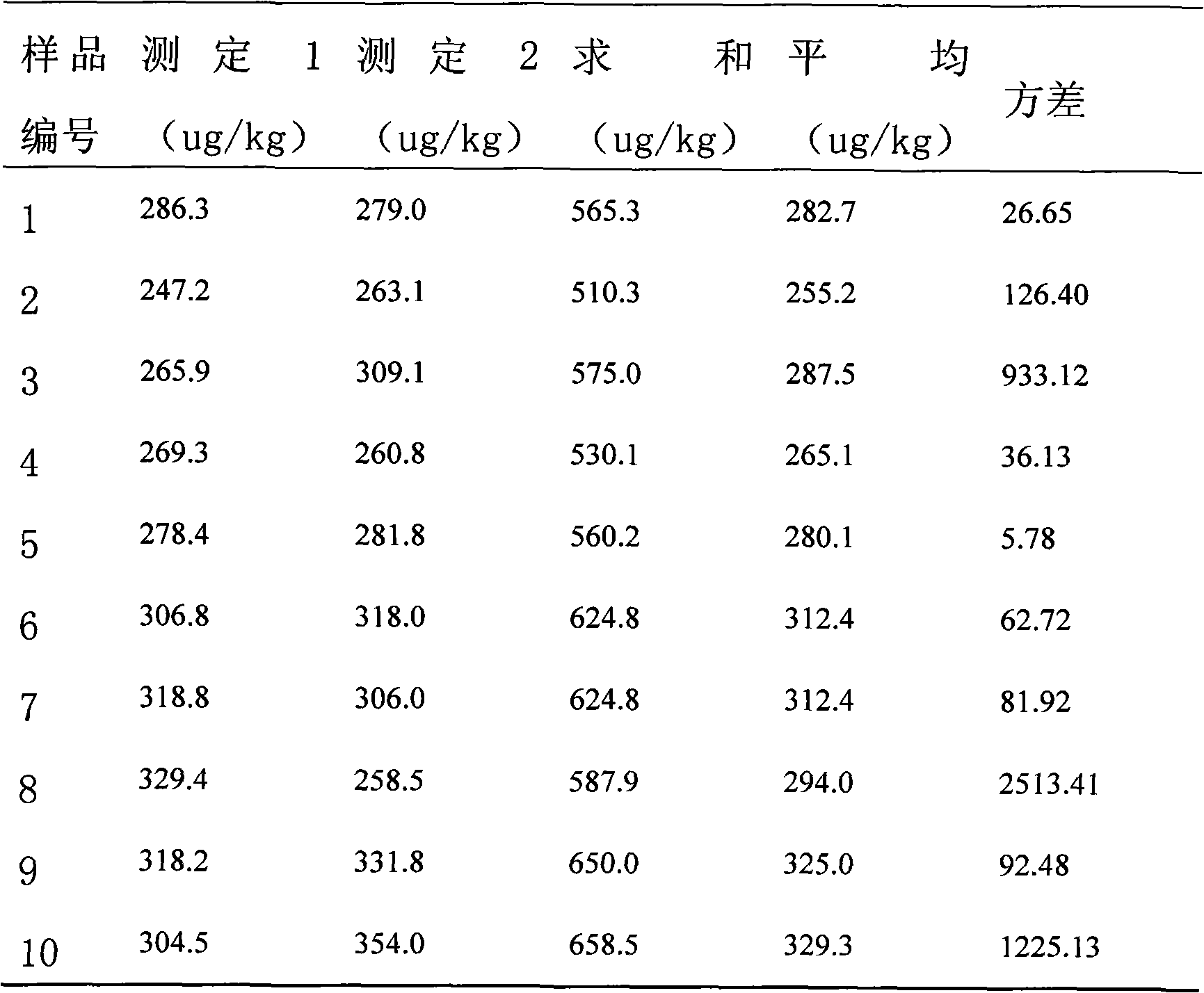
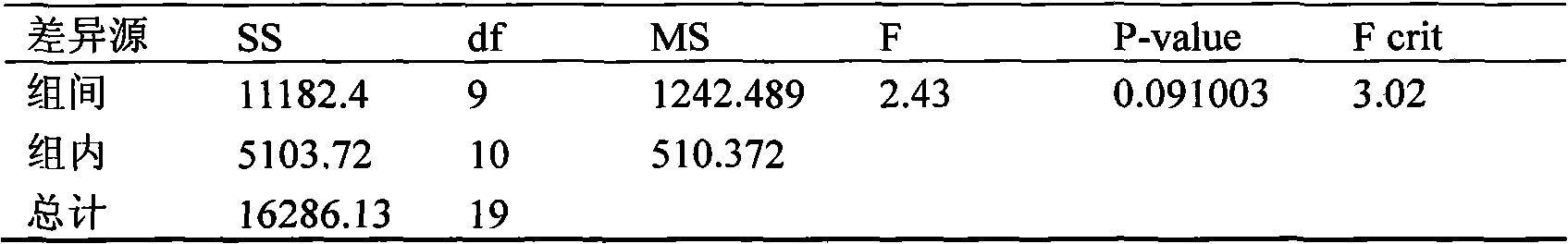
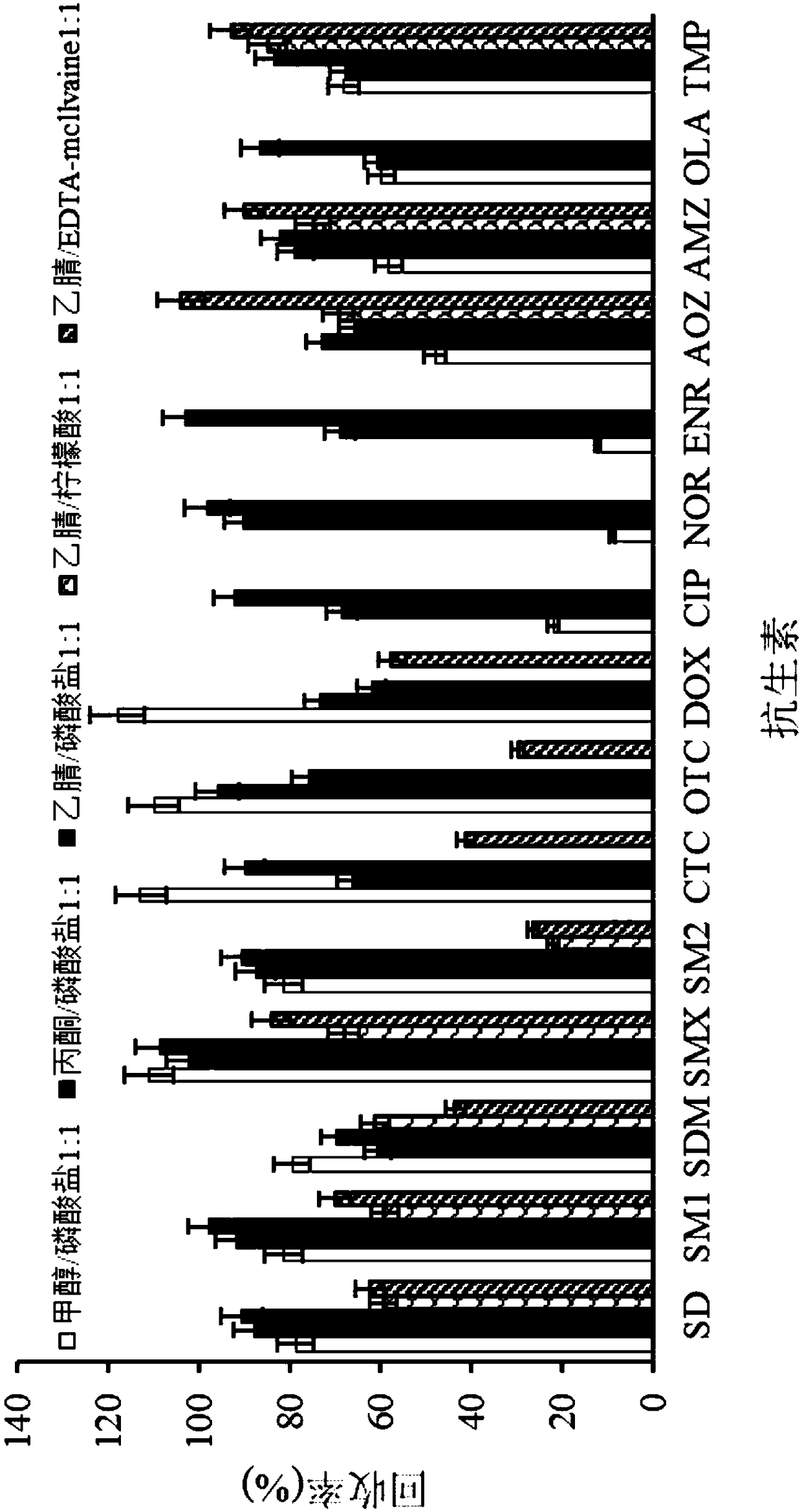
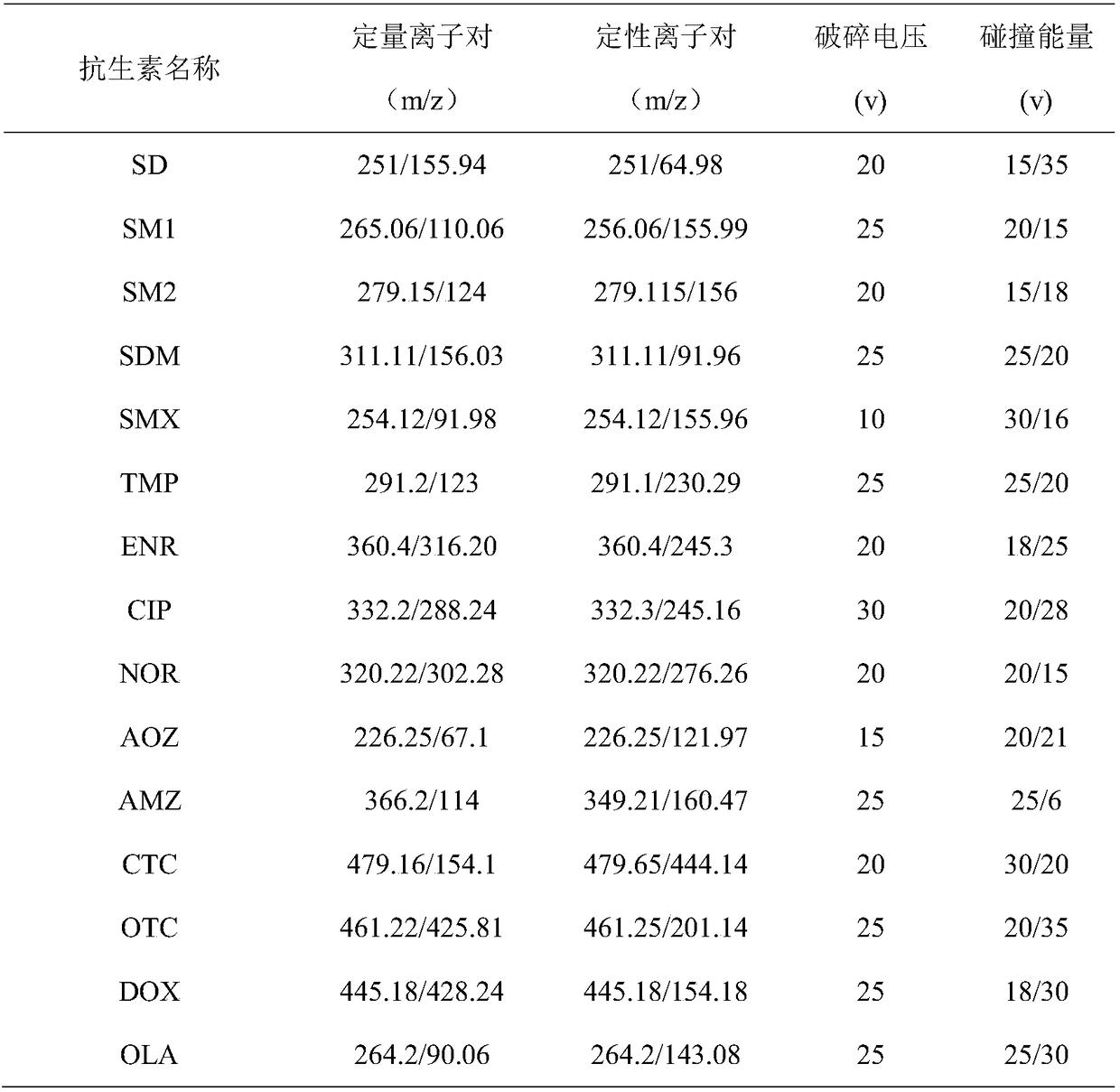
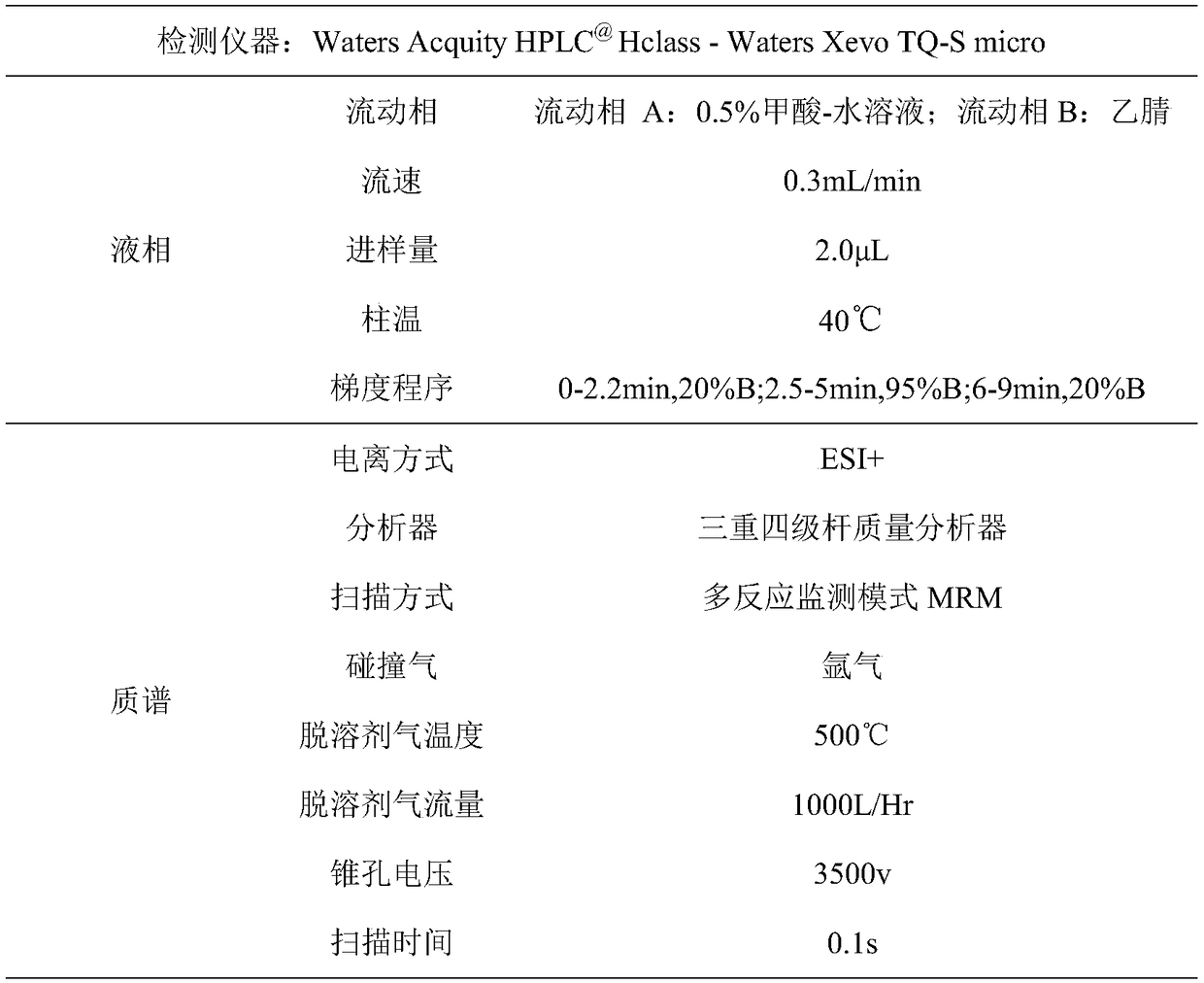
Patents
Literature
315 results about "Sulfamethoxazole" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Sulfamethoxazole (SMZ or SMX) is an antibiotic. It is used for bacterial infections such as urinary tract infections, bronchitis, and prostatitis and is effective against both gram negative and positive bacteria such as Listeria monocytogenes and E. coli.
Preparation method of Fe3O4@MnO2/active carbon magnetic compound adsorption material
InactiveCN103007882AThe synthesis method is simpleImprove stabilityOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesActivated carbonSynthetic materials
The invention relates to a preparation method of a Fe3O4@MnO2 / active carbon magnetic compound adsorption material. The material is powdery; Fe3O4@MnO2 nuclear shell magnetic grains (with the size of 50-100 nm) are loaded on the surface of active carbon in a combining manner; and the size of the grains is 200-300 meshes. On one hand, the magnetic compound adsorption material provided by the invention can adsorb trace SMZ (Sulfamethoxazole) in water on the surface of the magnetic compound adsorption material through the specific strong adsorption effect of the powdery active carbon grains; and meanwhile, the Fe3O4@MnO2 nuclear shell magnetic grains can carry out non-biological degradation on the enriched SMZ, and on the other hand, the magnetic adsorption of the Fe3O4@MnO2 nuclear shell magnetic grains on the surface and in micro-pores is utilized and the magnetic compound adsorption material can be recycled through magnetic separation. The preparation method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple synthesis method, cheap synthesis materials, good stability, good adsorption effect and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Method for removing antibiotics in water
InactiveCN106995224AGood removal effectImprove adsorption capacityOther chemical processesWater contaminantsCarbonizationAntibiotic Y
The invention discloses a method for removing antibiotics in water. The method comprises the following steps: 1) pretreating collected sugarcane bark, and placing the pretreated sugarcane bark into a tubular carbonization furnace for burning to obtain sugarcane activated carbon; 2) adding a modifier into the sugarcane activated carbon for modifying; 3) removing antibiotics in water by using the modified sugarcane activated carbon. By adopting the method, the yield of biomass charcoal is about 31 percent, the yield is about 89 percent after ultrasonic impregnation modification of 30-percent hydrogen peroxide, and the produced biomass charcoal can efficiently absorb sulfonamide antibiotics in water, and has higher adsorption capacity for sulfonamide antibiotics such as sulfamethoxazole, thiazole, methylpyrimidine and dimethylpyrimidine under the adsorption condition that pH is equal to 4 and the temperature is 35 DEG C; in particular, the activated carbon has a best removing effect after being burned at the temperature of 500 DEG C and being subjected to modification with the 30-percent hydrogen peroxide and ultrasonic impregnation modification; a good way for recycling resources is provided by taking bagasse as a raw material for preparing the biomass charcoal; the biomass charcoal can absorb the antibiotics in water, and has a very good application prospect in the aspect of removal of other pollutants.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI MEP
High-efficiency bioflocculant producing bacterium, screening method thereof and application of high-efficiency bioflocculant producing bacterium to treatment of sulfamethoxazole
ActiveCN102876600AAchieve preparationPreparation to reachBacteriaWater contaminantsActivated sludgeScreening method
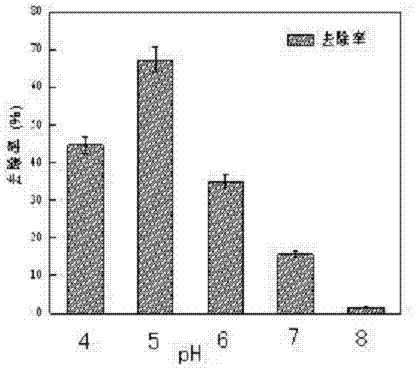
The invention discloses a high-efficiency bioflocculant producing bacterium, relates to removal of a trace amount of pollutants which are produced in the city water supply and sewage treatment processes, and solves the problems of low yield of bioflocculant, low artificial regulation performance and single treatment substrate. A screening method comprises the following steps of: domesticating activated sludge of a municipal sewage plant in the Harbin, and enriching biological bacteria, diluting and culturing by using a shake flask, performing plate streaking, separating and purifying biological bacterium species, and repeatedly performing three-area streaking for multiple times to obtain the pure bioflocculant producing bacterial strain KlebsiellaSp.. By the bacterial strain, the removal rate of a trace amount of pollutants in municipal sewage can reach 67.82 percent. By the high-efficiency bioflocculant producing bacterium, the removal rate of a trace amount of pollutants in the municipal sewage is improved, and energy consumption in production is reduced.
Owner:江苏哈宜环保研究院有限公司
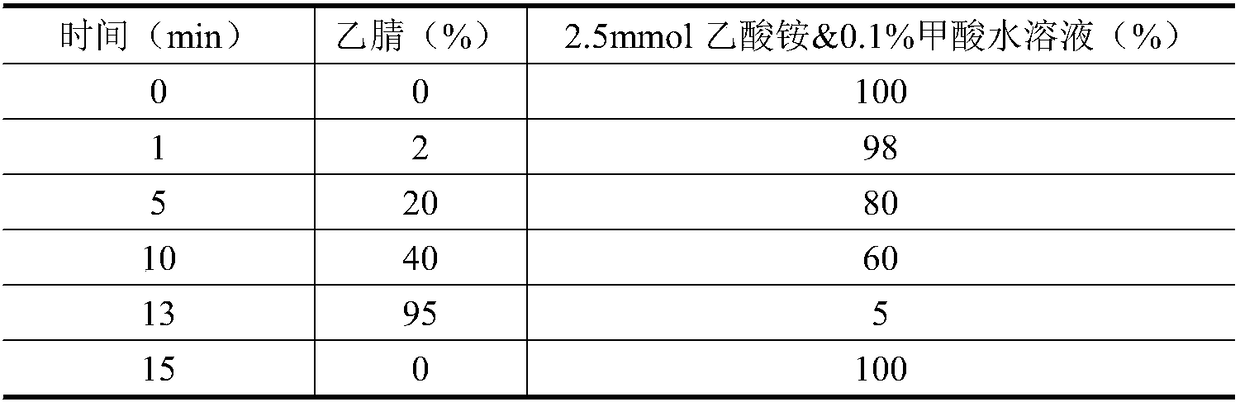
Method for determining 10 kinds of antibiotics in water environment through combination of sample pre-treatment technology and HPLC-MS
The present invention relates to a method for determining 10 kinds of antibiotics in a water environment through combination of a sample pre-treatment technology and HPLC-MS, and belongs to the field of detection of safety of trace organic contaminant residue in the water environment. The method is characterized in that a water sample is separated and enriched through combination of solid phase extraction and dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction (SPE-DLLME), and then an ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry instrument (UPLC-MS / MS) is adopted as a detection tool to directly determine the contents of 10 kinds of common antibiotics in the water environment (drinking water, tap water, river water, sewage treatment plant influent and effluent), wherein the 10 kinds of the common antibiotics respectively are sulfadiazine, sulfamethoxazole, oxytetracycline, tetracycline, doxycycline, ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, chloramphenicol, cefuroxime axetil and tinidazole. According to the present invention, the water sample pre-treatment method and the instrument detection conditions are investigated and optimized, and the optimal SPE-DLLME-UPLC-MS / MS method is established and is successfully applied for the real sample determination; and compared with the traditional method, the method of the present invention has advantages of high sensitivity, high extraction recovery rate, wide application objects, environmental protection, and the like.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
Method for measuring 12 types of remaining medicine in water environment through separation and enrichment
ActiveCN105424825ASimplified processing stepsImprove extraction efficiencyComponent separationWater dischargePretreatment method
The invention relates to a method for measuring 12 types of remaining medicine in a water environment through separation and enrichment at the same time, and belongs to the field of safety detection of a trace of organic pollutant residue in the water environment. The content of 12 types of frequently-used medicine in the water environment (drinking water, faucet water, river water and water discharged into and out of sewage treatment plants) is directly measured with an ultra performance liquid-chromatography-mass spectrometer (UPLC-MS / MS) as a detection tool after a water sample is subjected to solid phase extraction combined with ultrasonic-assisted dispersion liquid-liquid micro-extraction (UA-DLLME) separation and enrichment. The 12 types of antibiotic include ketoprofen, ciprofloxacin, tinidazole, tolfenamic acid, sulfadiazine, sulindac, naproxen, sulfamethoxazole, chloramphenicol, cefuroxime axetil, piroxicam and mefenamic acid. Inspection and optimization are conducted on a sample pretreatment method and instrument detection conditions of the water sample, and the optimal UA-DLLME method is established and is successfully applied to practical sample detection. Compared with a traditional method, the method has the advantages of being high in sensitivity, high in extraction and recycle rate, wide in suitable object, friendly to the environment, and the like.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY +1
Sulfalene oxazole molecular engram polymer producing method
InactiveCN101245121AHomogeneous block structureImprove catalytic performanceOther chemical processesSulfur drugDispersity
The invention relates to a method for preparing molecularly imprinted sulfamethoxazole polymer with ionic liquid to be a pore-forming agent. The specific steps are as follows: functional monomers and template molecules are dissolved into the ionic liquid and crosslinker and initiator are added after oscillation. Nitrogen is added to eliminate oxygen after ultrasonic degasification, the liquid is sealed by vacuum-pumping, and the polymer is then obtained by thermal initiation reaction. The molecularly imprinted polymer is obtained by the steps of elution, desiccation and grinding etc. The molecularly imprinted sulfamethoxazole polymer prepared by the invention has evenly massive structure. Compared with traditional synthetic method, the method is characterized by taking ionic liquid as the pore-forming agent which has excellent catalytic effect for polymer reaction when in the synthesis process. The synthetic polymer has the advantages of excellent dispersity, easy grinding and good molecular recognition properties, which can be used as solid phase extracting agent and packing materials for liquid phase chromatography to realize dispersion, concentration and purification of sulfonamides and resolving the defect of serious impurity interference of the existing common chromatographic detection.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Preparation method of sulfamethoxazole residue freeze-dried powder standard sample in carp muscle
The invention discloses a preparation method of sulfamethoxazole residue freeze-dried powder standard sample in carp muscle, which takes the carp as a research object to research a carp muscle material object standard sample containing sulfamethoxazole of certain concentration in a breeding mode of adding sulfamethoxazole. The key production control technology of the material object standard sample disclosed by the invention is mastered and comprises content level, evenness, stability, constant value and the like control, and the standard sample is produced and prepared in a standardization and scale mode. The standard sample is used for detection quality control and detection capability evaluation for residue of veterinary drug in animal-derived food and has an important meaning for food safety detection.
Owner:时文春
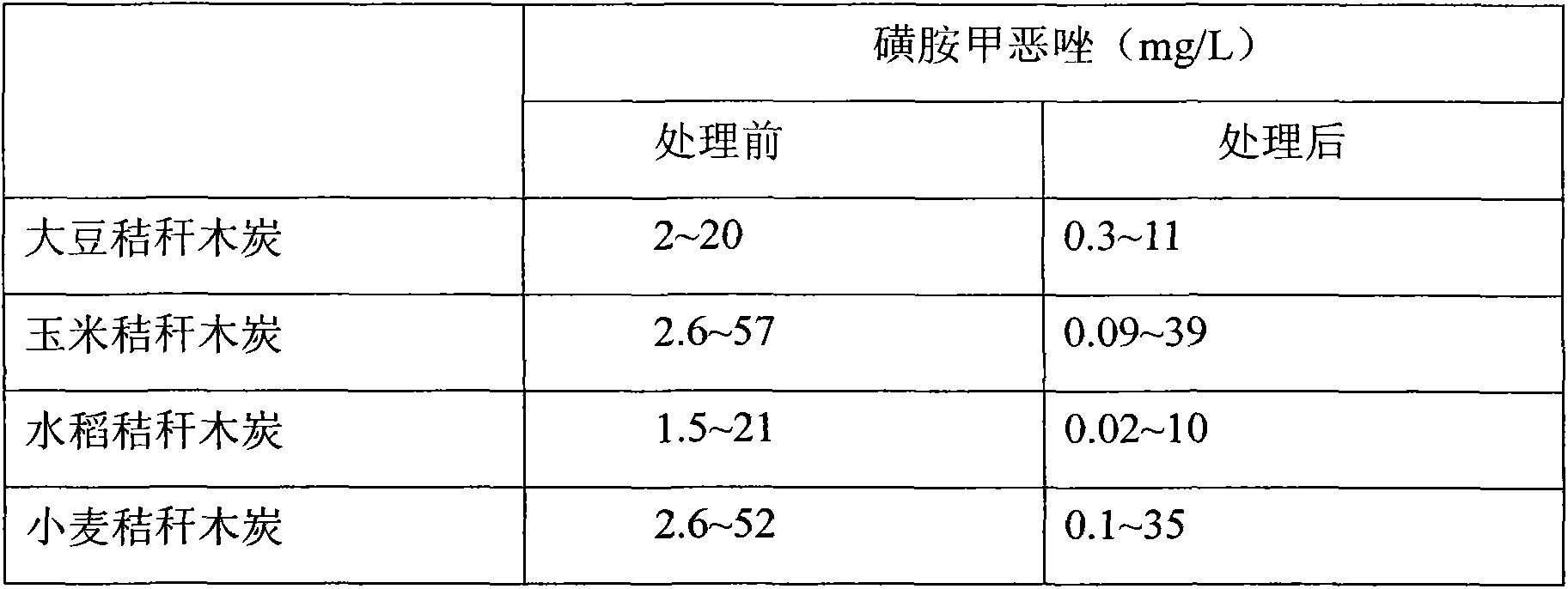
Method for removing sulfamethoxazole in water bodies with straw charcoal through adsorption and application of straw charcoal in removing sulfamethoxazole in water bodies
InactiveCN103523849AImprove adsorption capacityEfficient removalOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionAdsorption equilibriumMass ratio
The invention discloses a method for removing sulfamethoxazole in water bodies with crop straw charcoal through adsorption. The method is characterized by comprising a step of putting crop straw charcoal into water bodies containing sulfamethoxazole as an adsorbent to adsorb and remove sulfamethoxazole in the water bodies, wherein the adsorption temperature is 20-30 DEG C; the adsorption time is 72-75 hours; the pH value of solution after adsorption equilibrium is 5.8-6.0; the initial concentration of sulfamethoxazole in the water bodies is 1.5-57mg / L; the mass ratio of the crop straw charcoal to the water bodies containing sulfamethoxazole is 1:(2000-4000). Under the condition of room temperature, after adsorption for 3 days, the crop straw charcoal shows a high antibiotics adsorption removal rate. Besides, the method has the beneficial effects that the materials are simple to prepare; the method is convenient to operate; the cost is low; the raw materials are accessible; medicine pollution is effectively eliminated; the current technical gaps are filled in.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Compound sulfonamide suspensoid and its preparing process
ActiveCN1907264AEasy to takeDefinite curative effectAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsTrimethoprimSulfadiazine
Disclosed is a compound sulfonamide turbid agent which comprises the following constituents (by weight percent): sulfadiazine 8-12, sulfamethoxazole 4-8, sulfamethoxydiazine 2-6, trimethoprim 2-6, and medicinal auxiliary materials including acid-base scale modifier, suspension auxiliary agent, acidifying agent, anti-oxidant, stabilizer and purified water.
Owner:SUZHOU KEMU ANIMAL MEDICATION
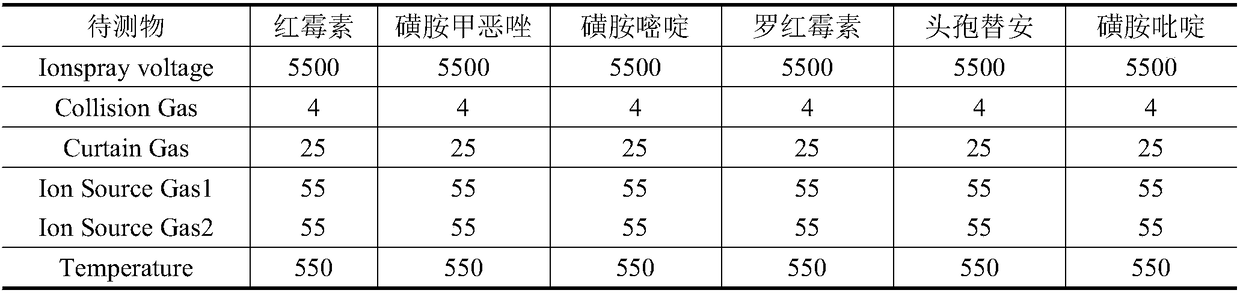
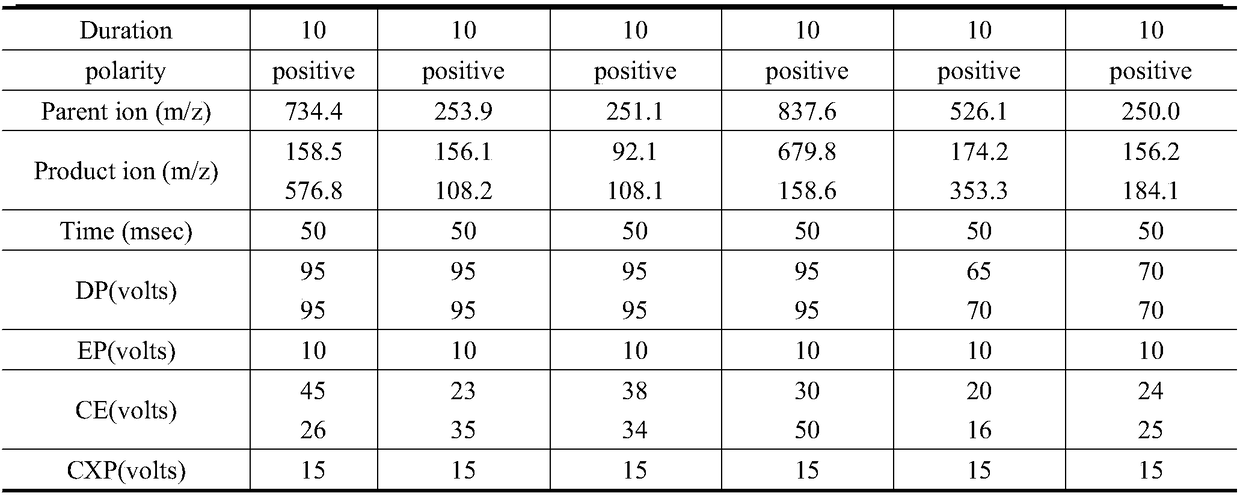
Method for detecting antibiotic in environment sample
InactiveCN108318613AEfficient enrichmentRealize detectionComponent separationNorfloxacinSurface water
The invention relates to the technical field of environment detection and is suitable for measuring erythrocin, chloramphenicol, sulfamethoxazole, sulfadiazine, roxithromycin, cefotiam, pyridazol, norfloxacin, ofloxacin, tetracycline and doxycycline in sewage, surface water and bottom mud. After being sampled, a water sample and a mud sample are pretreated and detected through ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry, and qualitative diagnosis is conducted through the characteristic ion pair (m / z) of a target compound, a standard curve is drawn accordingto the response value and the corresponding concentration, and the external standard method is used in quantification, so that the contents of various antibiotics in the sample are obtained. The method is accurate, sensitive and simple, and is suitable for measuring the contents of 11 typical antibiotics in the sewage, the surface water and the mud at the same time.
Owner:四川国测检测技术有限公司
Method for simultaneously detecting 15 antibiotics in aquaculture sediment by combining microwave extraction-solid phase extraction pretreatment with liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry technology
InactiveCN109342632AEfficient detectionAccurate detectionComponent separationPretreatment methodTrimethoprim
The invention relates to a method for simultaneously detecting 15 antibiotics in aquaculture sediment by combining microwave extraction-solid phase extraction pretreatment with a liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) technology. The method comprises the following steps: step (1) pretreating sediment samples, adding internal standard substances sulfamethoxazole-13C6, norfloxacin-D5, penicillin G potassium salt-D5, tetracycline-D6, olaquindox-D4, amoxicillin-13C6 and trimethoprim-D3 indicating a recovery rate, adding an acetonitrile-phosphate buffer solution for microwave extraction ofextraction liquid; step (2) performing solid phase extraction, enrichment and purification on target antibiotics; and step (3) quantitatively detecting 15 antibiotics of seven types in sediment witha liquid chromatograph / mass spectrometer. The method can simultaneously detect residues of 15 antibiotics containing 8 new antibiotics in the aquaculture sediment at a time by optimizing the internalstandard substances, screening appropriate pretreatment method and optimizing detection conditions, and has the advantages of high recovery rate, high sensitivity, high stability, low detection limit,more true and reliable detection results and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACADEMY OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES
Degradation bacteria for sulfonamide antibiotics and application thereof
ActiveCN108611285APromote degradationHarm reductionFungiContaminated soil reclamationEcological environmentAntibiotic Y
The invention discloses a degradation bacteria for sulfonamide antibiotics and an application thereof, wherein the bacteria is Sakaguchia cladiensis A5 and is preserved in Guangdong Center of Microbial Culture Collection at Jan. 26th, 2018, and is assigned the accession number of GDMCC No.60319. The bacterial strain has great degradation effect on sulfonamide antibiotics such as sulfamerazine, sulfamethoxazole and the like, and can be used for degradation treatment to sulfonamide antibiotics pollution to application objects comprising wastewater, waste residue, water environment, soil and thelike, which contain the sulfonamide antibiotics. The bacterial strain can reduce damage on ecological environmental safety due to the antibiotics, is energy-saving and environment-friendly, and has extensive application prospect.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
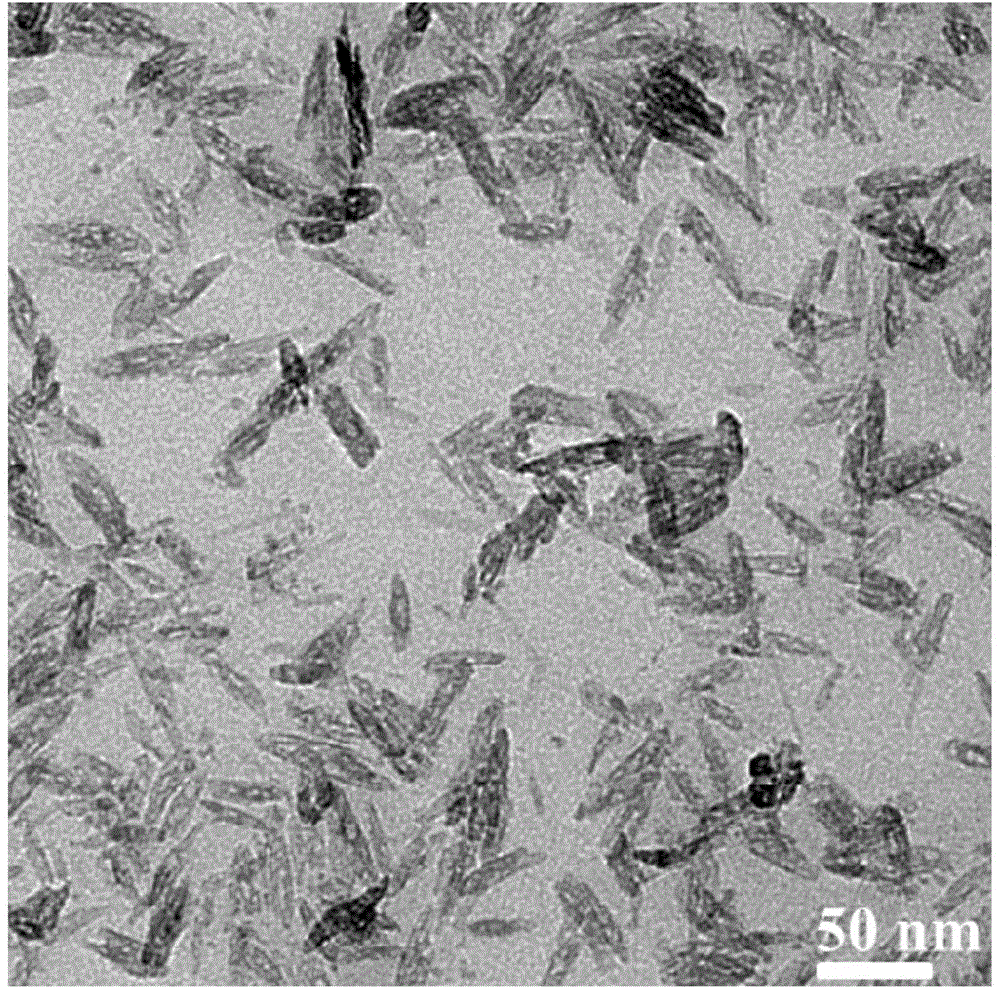
Preparation method of alpha-Fe2O3 mesoporous nanorod/nitrogen-doped graphene composite
InactiveCN104525202AEfficient deliveryReduce chance of recombinationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsNitrogenNitrogen doped graphene
The invention discloses a preparation method of an alpha-Fe2O3 mesoporous nanorod / nitrogen-doped graphene composite and relates to a preparation method of an alpha-Fe2O3 / graphene composite, aiming at solving the problem that the in-situ growth of an alpha-Fe2O3 mesoporous nanorod in nitrogen-doped graphene cannot be achieved and meanwhile the uniformity property of the alpha-Fe2O3 mesoporous nanorod cannot be guaranteed at present. The preparation method comprises the following steps: I. adding an alkali source and an inorganic iron solution to a pore forming agent water solution; II. adding graphene oxide to the mixed liquid of the step I, ultrasonically treating and stirring; and III. pouring a suspension obtained from the step II to a hydrothermal reaction kettle and reacting, cooling, centrifuging, washing and drying. The preparation method has the advantages that the composite functional material disclosed by the invention is high in removal rate on sulfamethoxazole, and the average grain size of the alpha-Fe2O3 mesoporous nanorod is just 4-10nm; and the preparation method is mild in reaction condition, simple in equipment, low in reagent cost, safe and non-toxic and suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Preparation and application of Nd<3-x>CoxNbO7-zincosilicate molecular sieve composite porous nanometer catalytic material
ActiveCN104646003AWater/sewage treatment by irradiationMolecular sieve catalystsElemental compositionX-ray
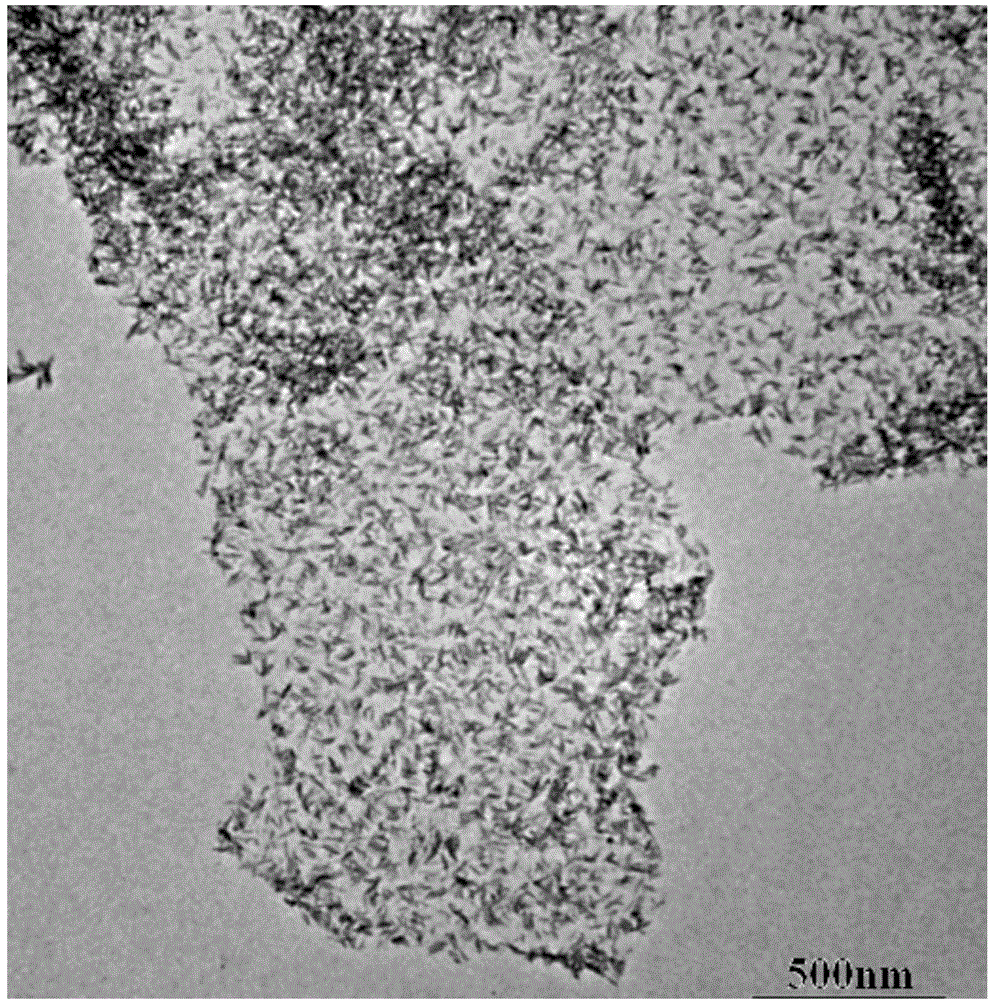
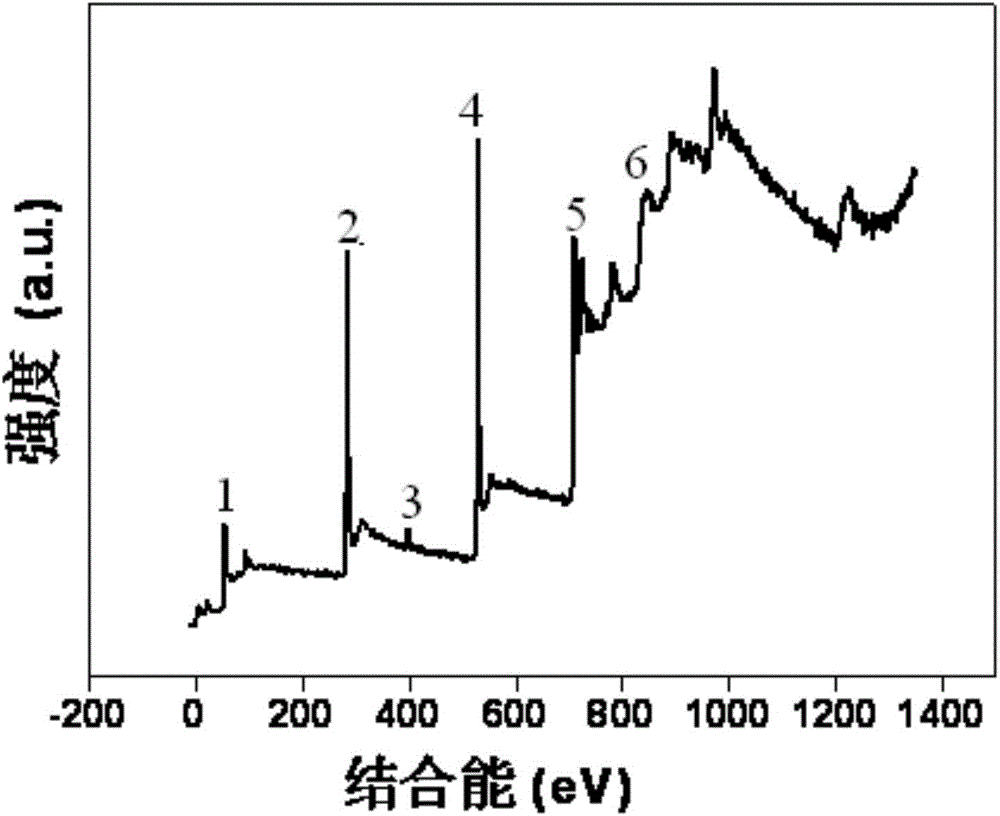
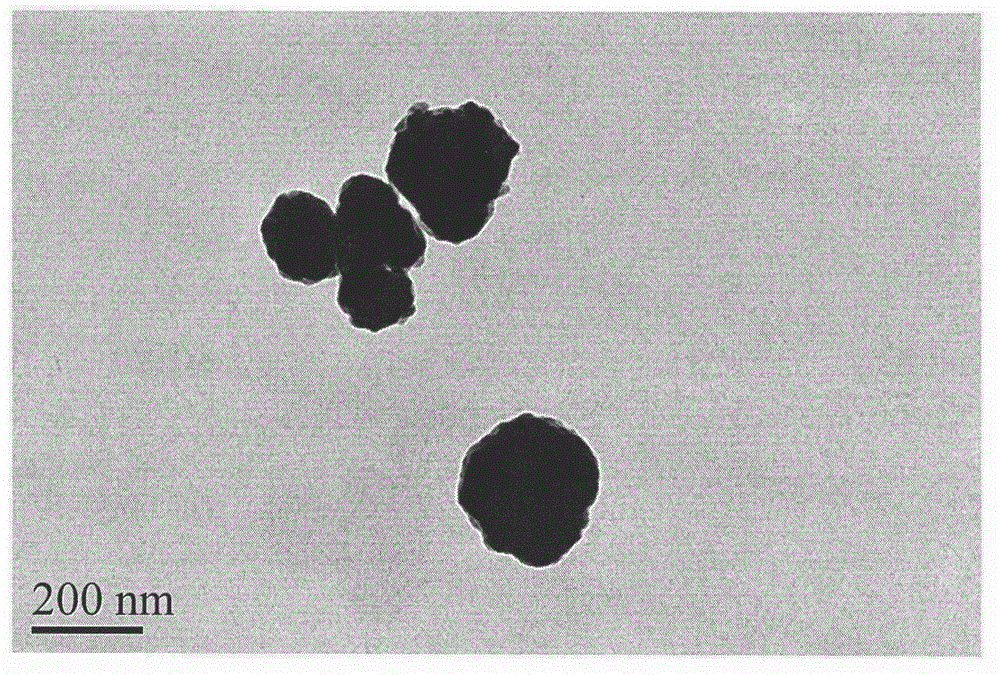
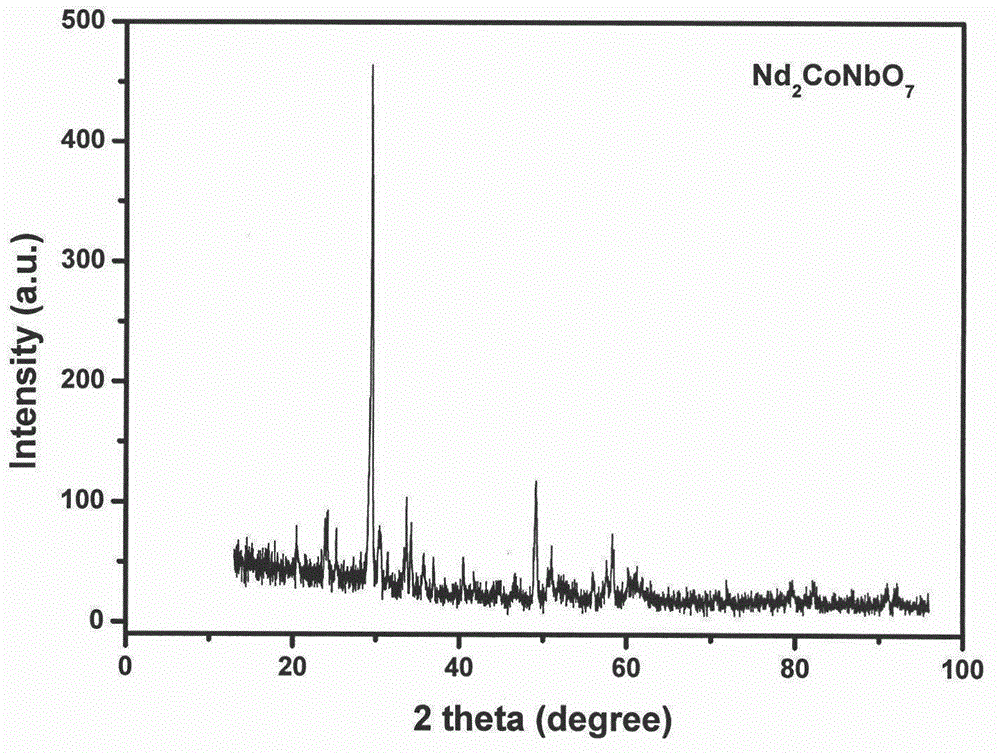
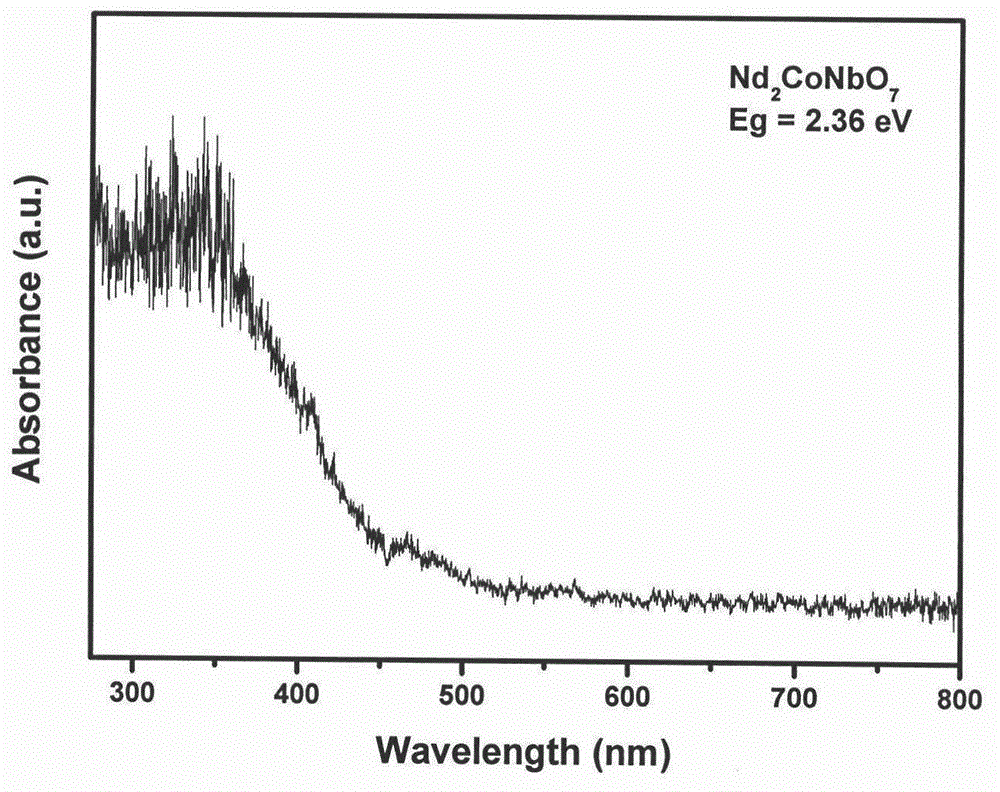
According to the invention, a powder catalytic material Nd<3-x>CoxNbO7 (x being greater than or equal to 0.5 and less than or equal to 1) is prepared by adopting a supercritical hydrosynthesis method and a chemical vapor condensation and deposition method; a composite porous nanometer catalytic material Nd<3-x>CoxNbO7 (x being greater than or equal to 0.5 and less than or equal to 1) -zincosilicate molecular sieve is prepared by adopting an impregnating and baking method; and a novel photoelectrode Nd<3-x>CoxNbO7 (x being greater than or equal to 0.5 and less than or equal to 1) is prepared. The three novel materials are represented: tissue morphology analysis is performed by a transmission electron microscopy, and results show that catalyst particles are irregular in shape, with the average particle size of 150 nm; phase analysis is performed by an X-ray diffractometer, and results show that Nd2CoNbO7 has a single phase, and relatively high crystallinity; the chemical speciation of the surface of the catalyst and the elementary composition of a microcell as well as the structural characteristics of an electronic shell are discussed by an X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy; and a characteristic absorption edge of the Nd2CoNbO7 is determined by a UV-Vis diffuse reflection spectroscopy to obtain the band gap width of the Nd2CoNbO7 which is 2.412 eV. Finally, the catalyst is used for decomposing water to produce hydrogen, and carrying out catalytic degradation on organic pollutants such as microcystic toxins, methylene blue and sulfamethoxazole in a water body under visible light. Experimental results show that the catalyst prepared according to the invention is good in catalytic effect.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
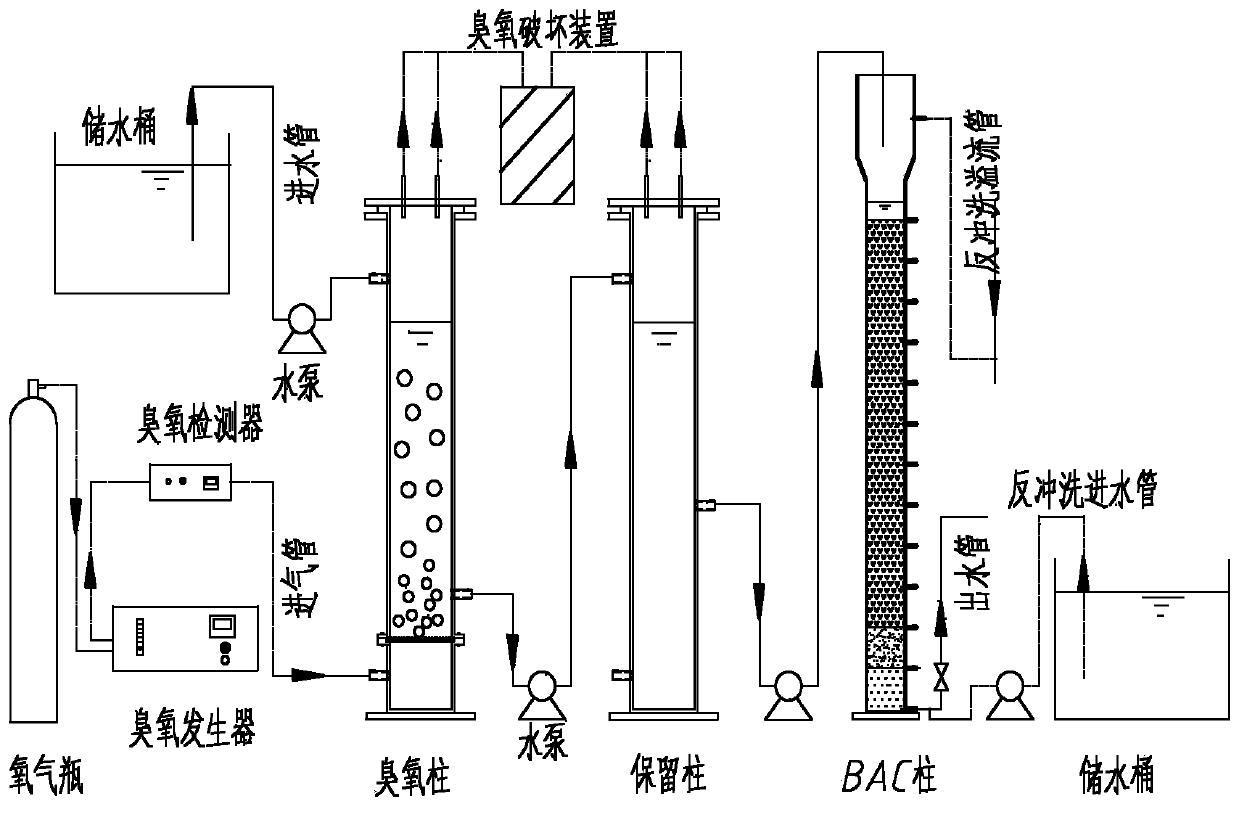
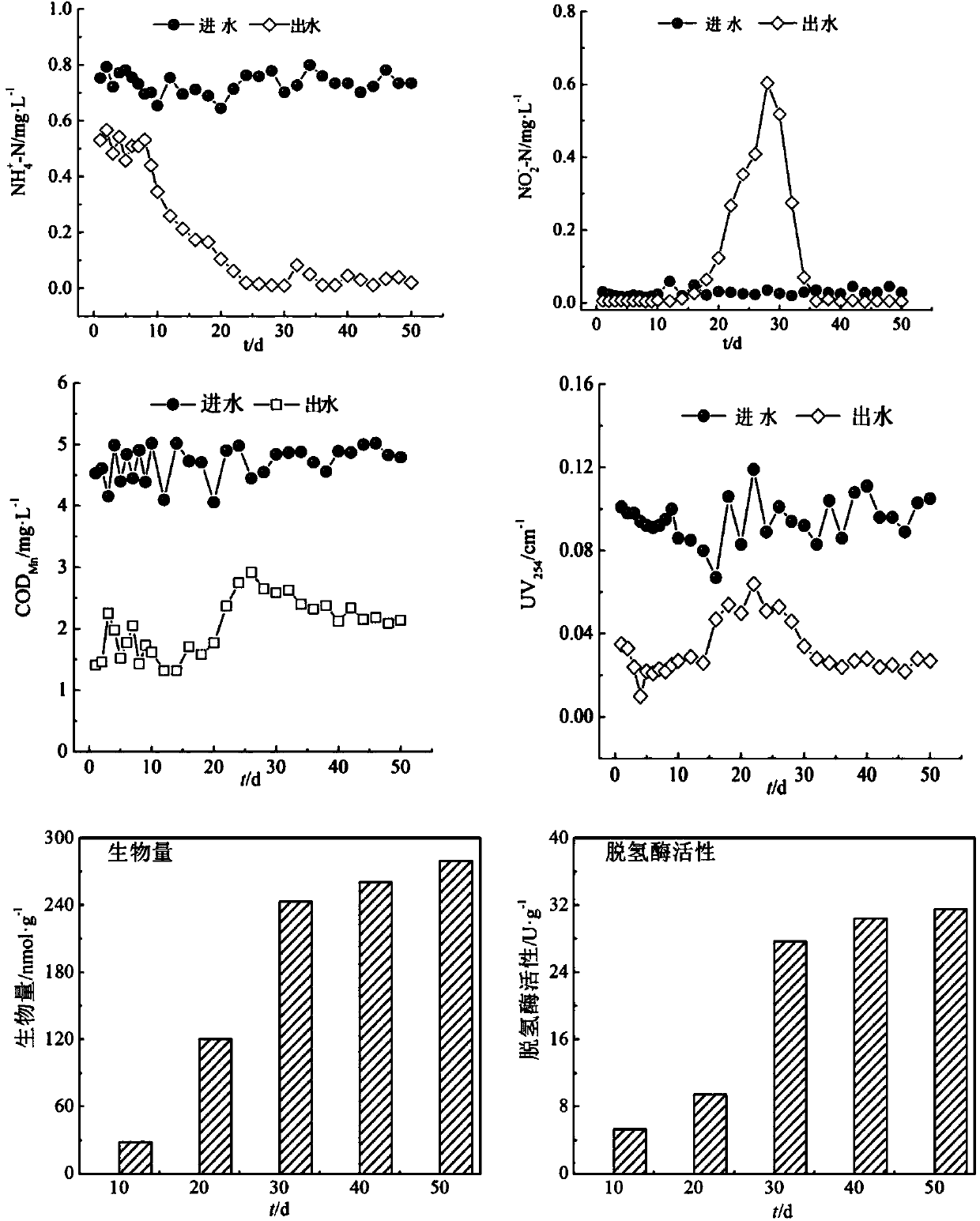
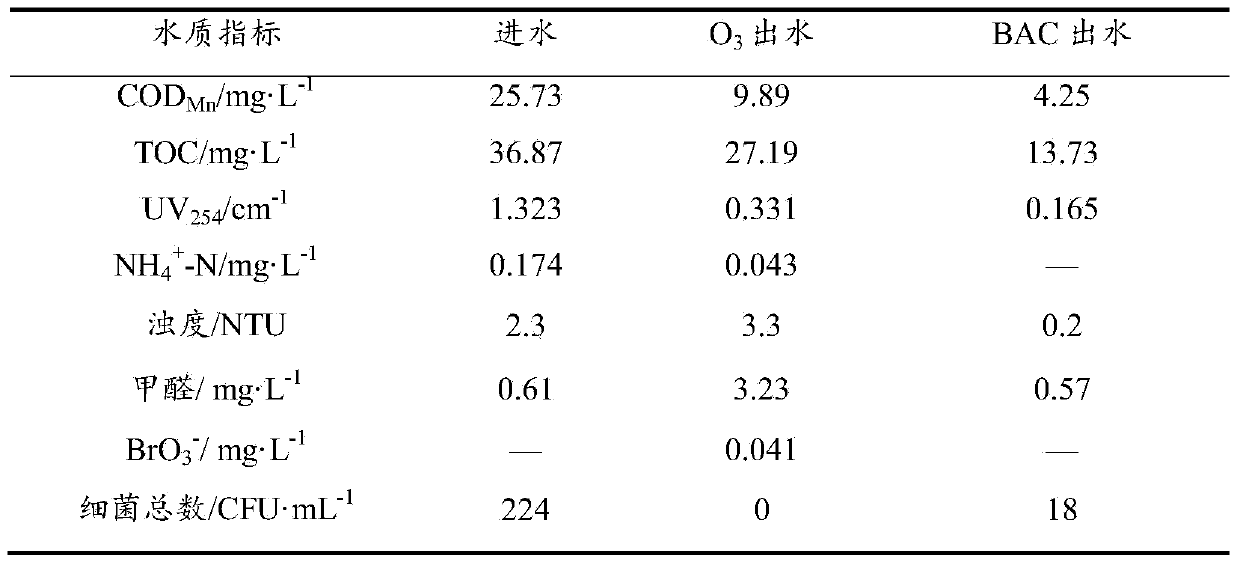
Method of removing PPCPs (Pharmaceutical and Personal Care Products) in drinking water by combination of ozone and activated charcoal
The invention discloses a method of removing PPCPs (Pharmaceutical and Personal Care Products) in drinking water by combination of ozone and activated charcoal. The method comprises the following steps: enabling ozone and aqueous liquor to be fully contacted by adopting a mode that gas and water are continuously and reversely contacted by means of ozone; then, carrying out further reaction through a retaining column, and then, enabling the obtained product to enter into a bio-activated charcoal column to be treated. The method disclosed by the invention can effectively remove PPCPs in drinking water, wherein the removal rate of carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, progesterone and progesterone reaches over 99.9% while caffeine, antipyrine, aminopyrine and sulfamethoxazole are not detected in the effluent. Compared with existing drinking water treatment technologies, the method has higher chemical safety guarantee and meanwhile has a better removal effect on conventional pollutants in domestic drinking water. The effluent can stably reach the national sanitary standard (GB5749-2006) of domestic drinking water, so that the method has huge practical value and utilization potential.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
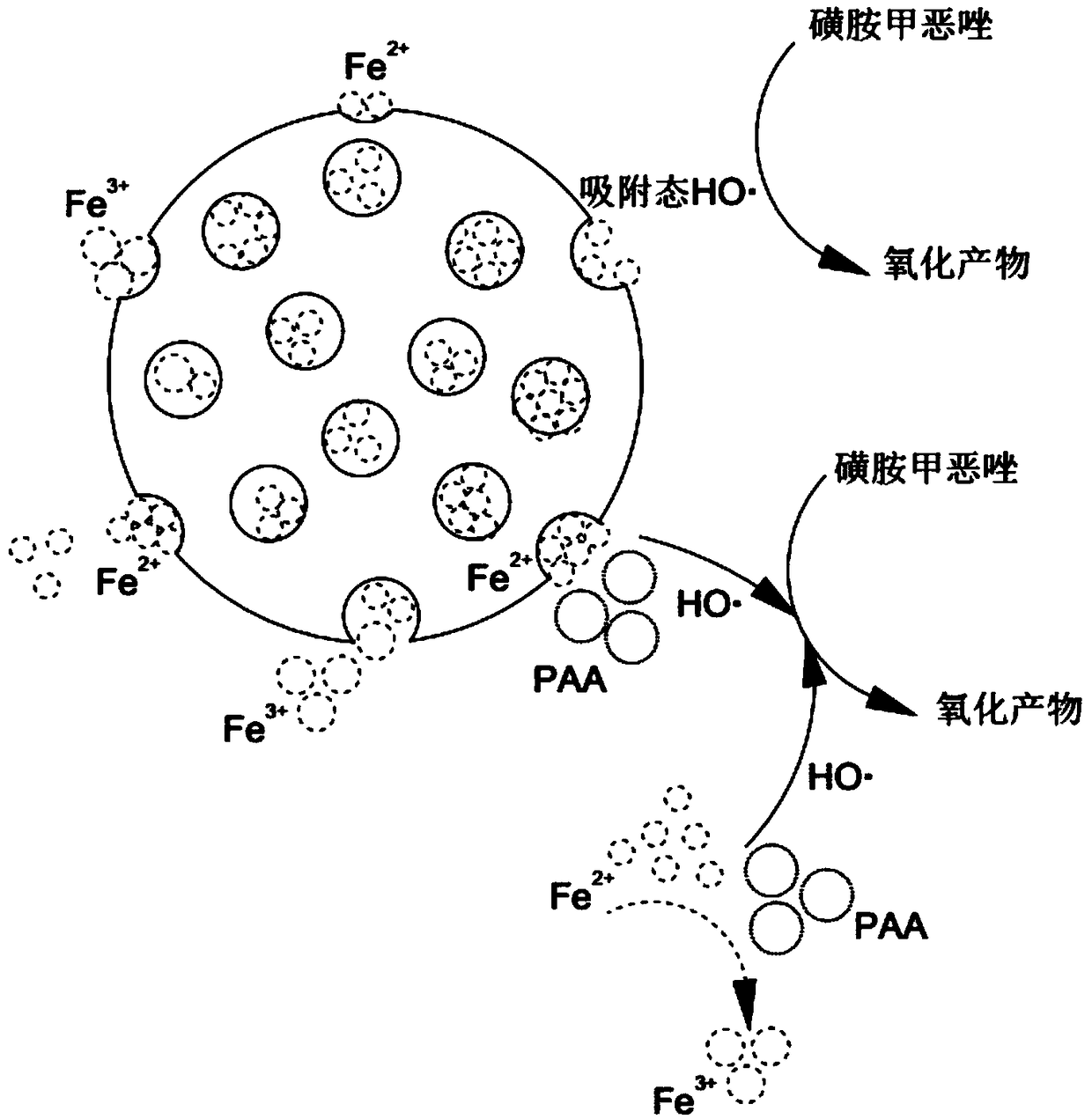
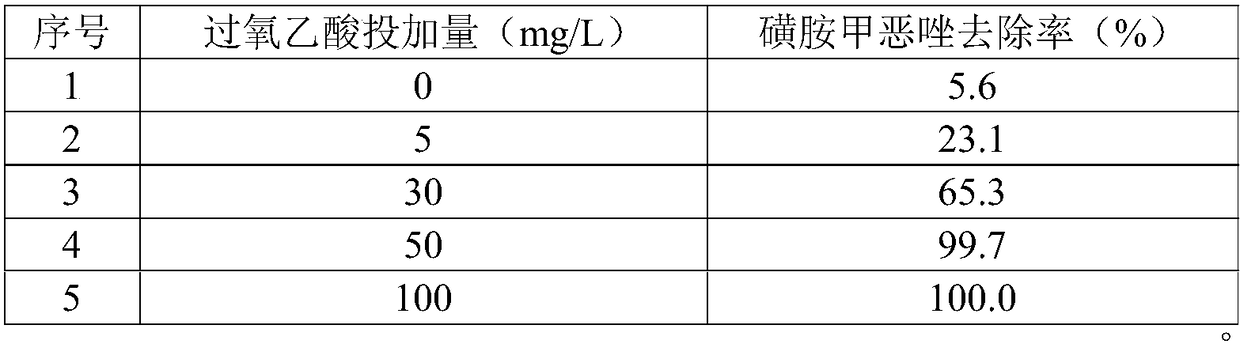
Method for removing sulfonamides in water by using modified zeolite to activate peracetic acid
ActiveCN108855083AImprove removal efficiencyLow application costWater treatment compoundsWater contaminantsSulfur drugDissolution
The invention discloses a method for removing sulfonamides in water by using modified zeolite to activate peracetic acid. The method comprises the following steps: S1, preparing a catalyst: grinding artificial zeolite into fine powder, acid pickling, washing, drying, soaking in a ferrous sulfate solution for a period of time, centrifugally separating, washing solids by using deionized water, and drying; S2, performing the oxidization reaction: adding a prepared peracetic acid solution into sulfamethoxazole waste water, adjusting initial pH of water water, adding an appropriate amount of catalyst, and performing the oxidization reaction under the normal temperature normal pressure stirring condition. The adopted catalytic material is simple in preparation, easy to store, high in activationefficiency and low in active component and low in active component dissolution rate; the activated peracetic acid system is high in oxidation performance, the treatment process also has the sterilizing function, the combination of the further treatment and disinfection treatment for the waste water can be realized, the compatibility with the modern water treatment factory process is high, the sulfamethoxazole degradation efficiency is high, the reaction condition is mild, the cost is low, and the method is suitable for the industrialized mass treatment of the waste water.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
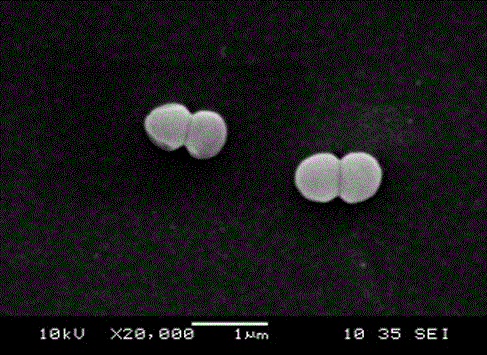
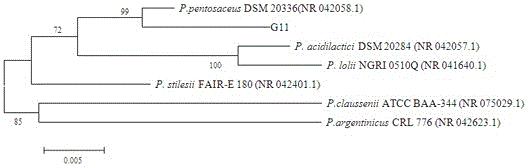
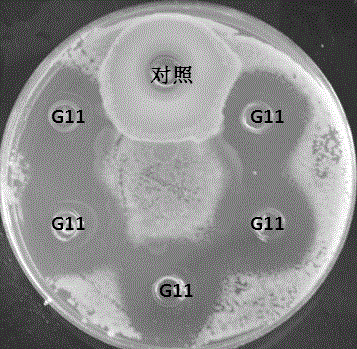
Pediococcus pentosaceus G11 strain as well as screening and applications thereof
ActiveCN106190894AToleratedHas antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsBacteriaSynechococcusAnimal mortality
The invention relates to a pediococcus pentosaceus G11 strain as well as screening and applications of the pediococcus pentosaceus G11 strain. The pediococcus pentosaceus G11 strain is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection, and is assigned with the accession number of CCTCC NO:2016248. The pediococcus pentosaceus G11 strain has tolerance to compound sulfamethoxazole and ceftazidime, has antibacterial activity for vibrio parahaemolyticus, aeromonas hydrophila, vibrio alginolyticus, staphylococcus aureus and beta streptococcus, has certain stress resistance and enzyme producing ability, is free of hemocyte solubility, and has no drug tolerance for most antibiotics; the dipping bath experiment proves that the pediococcus pentosaceus G11 strain is harmless to the host, can improve the immunity of the body, has wide application prospects, can be applied to probiotic preparations, and also can be prepared into bacterial powder which is then added into a feed as a feed additive, further, the growth of pathogenic bacteria in the bodies of the animals is inhibited, so that the death rate of animals is reduced, and the pediococcus pentosaceus G11 strain is a probiotic brain worthy of development.
Owner:SHANTOU UNIV
Preparation method of ionic liquid functionalized metal organic framework- molecularly imprinted composite material
InactiveCN110420627AReduce usagePlay a protective effectOther chemical processesWater contaminantsFunctional monomerSorbent
The invention discloses a preparation method of an ionic liquid functionalized metal organic framework-molecularly imprinted composite material, belonging to the technical fields of analytical chemistry and pollutant analysis and detection. The key points of the preparation method are as follows: UIO-66 and / or UIO-66-NH2 are taken as carriers in pure water solvent, 1-allyl-3-vinyl imidazole bromide is taken as a functional monomer, sulfamethoxazole is taken as a template molecule, and a molecularly imprinted polymer is prepared through N, N'-methylene bisacrylamide crosslinking and azodiisobutyronitrile thermal initiation polymerization under nitrogen protection. The molecularly imprinted polymer prepared by the method has a large specific surface area, a plurality of adsorption binding sites, and three-dimensional holes which are highly matched with the template molecule sulfamethoxazole, can be used as a solid phase extraction adsorbent to separate and enrich trace sulfamethoxazole in the environment, and has wide commercial application prospects.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
Liquid phase chromatographic method for simultaneously measuring compound sulfamethoxazole and metabolite thereof
InactiveCN1908654ASave human effortSave moneyComponent separationPreparing sample for investigationMetaboliteIcebox
The liquid phase chromatogram method for detect both compound sulfathiazole and its metabolite comprises: using the mixed liquid with HCl and 3:1 CH2Cl2 / acetone as the extractant to extract target with less impurity; after adding the extractant, keeping for some time in 4Deg icebox to modify protein fully and reduce loss and improve recovery yield; drying the solvent with N2, filtering, and detecting. This invention is simple, fast and very sensitive, and has wide application.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Method for removing sulfamethoxazole from water through adsorption of KOH-activated coal-based active carbon
InactiveCN102923810ALarge adsorption capacityImprove adsorption capacityCarbon compoundsOther chemical processesActivated carbonTreatment effect
The invention discloses a method for removing sulfamethoxazole out of water through adsorption of KOH-activated coal-based active carbon. The method comprises the following steps of preparing KOH-activated coal-based active carbon by taking KOH as an activating agent and anthracite as a carbon source, putting an adsorbing agent into water containing sulfamethoxazole, and adsorbing and removing sulfamethoxazole in the water. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the adsorption performance of the KOH-activated coal-based active carbon serving as an activating agent is remarkably better than that of commercial active carbon, and the KOH-activated coal-based active carbon is used for removing the sulfamethoxazole from the micropolluted water; the adsorption capacity is large, the adsorption speed is high, the treatment effect is remarkable, and the economical and environmental benefits are excellent.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Medicament for preventing and treating livestock and poultry blast disease
InactiveCN101249202AEasy to solveGood treatment effectTetracycline active ingredientsAntiviralsDiseaseBird flu
The invention discloses a medicine for preventing and treating livestock blast diseases, which is made from Melastoma dodecandrum, dandelion, Herba Lobeliae Chinensis, honeysuckle, radix isatidis, rhizoma anemarrhenae, Bupleurum, pomegranate rind, plantain, cornu saigae Tataricae, terramycin, sulfamethoxazole compound, and chloromycetin. The medicine has the efficacies of clearing heat, purging fire, sterilizing, detoxifying, dissipating swollen symptom as well as lump, stopping blooding as well as relieving diarrhea, inducing diuresis for treating stranguria, calming liver-wind, treating diarrhea with astringents, evacuating and reducing fever, producing fluid as well as moisturizing dryness, and removing heat from the blood as well as relieving sore throat. The medicine has better effects of preventing and treating the blast diseases of a plurality of domestic animals and fowls such as pigs, chickens, ducks, gooses, etc., and further has certain curative effects on the blast diseases of cattle, sheep and dogs and the diseases such as bird flu, aftosa, etc.
Owner:陈月明
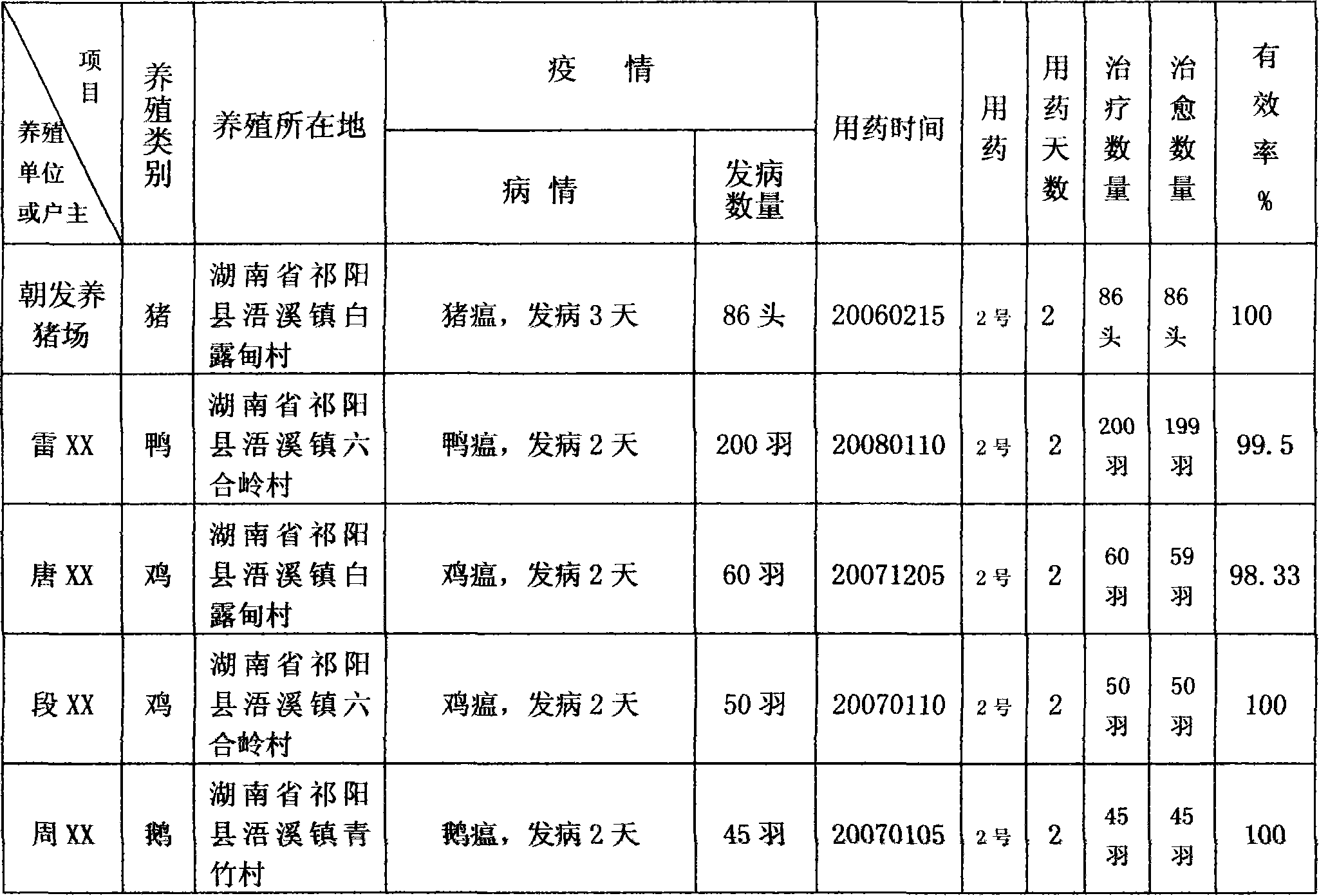
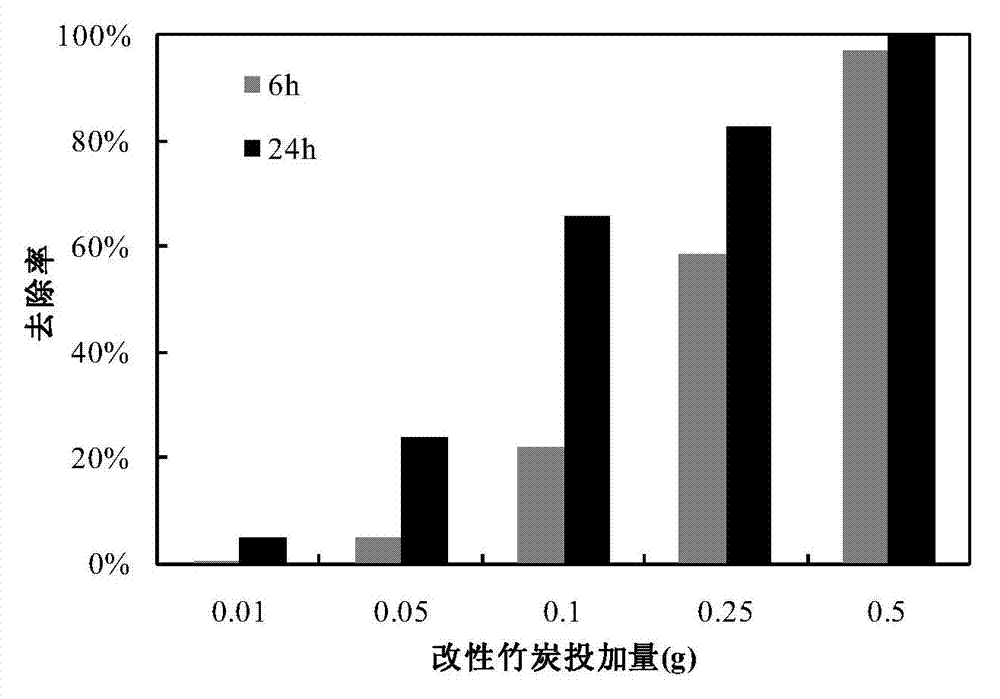
Method for removing sulfamethoxazole in water body by using modified bamboo charcoal
InactiveCN104261504AHigh porosityLow priceOther chemical processesWater contaminantsState of artSorbent
The invention belongs to the technical field of water treatment, and relates to a method for removing sulfamethoxazole in a water body by using modified bamboo charcoal, which comprises the following steps: sequentially carrying out pulverization, ultrasonic treatment, impregnation-process iron oxide loading and freeze-drying on bamboo charcoal to obtain modified bamboo charcoal, and adsorbing and removing sulfamethoxazole in the water body by using the modified bamboo charcoal as a filler or adsorbent. Compared with the prior art, the ultrasonic / impregnation-process iron oxide loading greatly enhances the antibiotic removal capacity of the bamboo charcoal. The adsorbent is high in adsorbability and easy to prepare; and the method is convenient to operate and low in price. The method is applicable to a sulfamethoxazole wastewater treatment technique, and has favorable economic and environmental benefits.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Medicament for treating dysentery
The invention discloses a drug for curing dysentery, which is produced by uniformly mixing the active pharmaceutical ingredients with the parts by weight: 625 of oxytetracycline, 625 of chloramphenicol, 1000 of sulfamethoxazole, 500 of furazolidone, 200 of methylbenzylamine pyrimidine, 50 of extractum belladonnae, 2500 of sodium bicarbonate and 25 of prednisone acetate to produce into powder, tablet or capsule and other formulation. The drug for curing dysentery has the advantages that the effective rate for curing the dysentery is 100%, the cure rate is 99.99%, and the sufferer can be recovered between 24 to 48 hours; in addition, the drug also has the advantages of fast therapeutic effect, short treatment cycle and low treatment cost.
Owner:刘廷剑
Filtering medium for removing antibiotic-sulfamethoxazole in drinking water, filtering element and preparation method of filtering medium for removing antibiotic-sulfamethoxazole in drinking water
InactiveCN105289550AHigh removal rateEliminate damageOther chemical processesWater contaminantsMolecular sieveActivated carbon
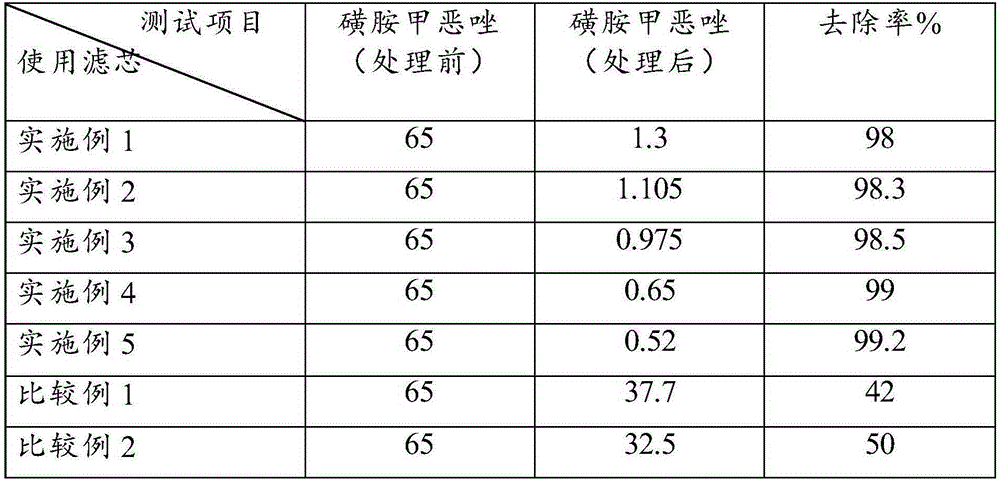
The invention provides a preparation method of a filtering medium for removing an antibiotic-sulfamethoxazole in drinking water. The method comprises the following steps: (a) mixing ultra high molecular weight polyethylene powder, activated carbon powder, micron molecular sieve powder, nanometer molecular sieve powder and a foaming hole agent to obtain a mixture, wherein the weight ratio of the ultra high molecular weight polyethylene powder to the activated carbon powder to the micron molecular sieve powder to the nanometer molecular sieve powder to the foaming hole agent is (200-300) to (100-200) to (50-100) to (50-100) to (50-100); and (b) putting the mixture obtained in (a) into a mold, pressing, sintering, and cooling, wherein the pressing pressure is 0.4-1MPa, the sintering temperature is 200-240 DEG C, the sintering time is 90-150min, and the cooling temperature is 40-60DEG C. In the invention, the filtering medium prepared by a synergistic effect of the raw materials and matching with special sintering temperature, pressure and cooling temperature has high removal rate for the antibiotic-sulfamethoxazole in the drinking water. The method is simple, and proved by tests, the filtering medium has a removal rate up to 98.0% and above for the antibiotic-sulfamethoxazole in the drinking water.
Owner:广州市康水科技有限责任公司
Preparation method of cerium dioxide nanosphere-carbon nitride composite visible light catalyst
InactiveCN110560130AImprove photocatalytic activityInhibitory complexMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsCerium(IV) oxideCarbon nitride
The invention discloses a preparation method of a cerium dioxide nanosphere-carbon nitride composite visible light catalyst, relates to a preparation method of a carbon nitride composite visible lightcatalyst, and aims to solve the problem that photogenerated electrons and holes of the existing carbon nitride are easy to compound. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: (1), preparing carbon nitride; (2), preparing cerium dioxide hollow nanospheres, to be more specific, 1, preparing silicon dioxide powder; 2, preparing silicon dioxide slurry; 3, preparing mixed slurry; 4, preparing cerium dioxide @ silicon dioxide nanospheres; and 5, performing alkali etching to obtain cerium dioxide hollow nanospheres; and (3), compounding to obtain the cerium dioxide nanosphere-carbon nitride composite visible light catalyst. The preparation method has the advantages that 1, the compounding of the photo-induced electrons and the holes is effectively inhibited, and the photocatalyticactivity of the catalyst is improved; and 2, the degradation rate of sulfamethoxazole antibiotics is greatly improved; the method is mainly used for preparing the cerium dioxide nanosphere-carbon nitride composite visible light catalyst.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for analyzing and determining four sulfonamide antibiotics in water sample
The invention belongs to the field of antibiotic detection, and relates to a method for analyzing and determining four sulfonamide antibiotics in a water sample. A negative pressure suction filtrationmembrane solid phase extraction technology is utilized, and a metal organic framework material NH2-MIL-101(FE) membrane solid phase extraction-high performance liquid chromatography method is adoptedto determine four antibiotics such as sulfadiazine, sulfamethazine, sulfachloropyridazine and sulfamethoxazole in an environmental water sample. The method is simple, convenient, rapid and sensitiveto operate, and has the advantages of low detection limit, accuracy and good reproducibility; and moreover, the raw materials are cheap and easy to obtain, the material preparation process is simple,the reaction conditions are mild, the application environment is friendly, and the market prospect is wide.
Owner:QINGDAO TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
Medicinal composition and injecta for curing avian toxoplasmosis, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101816663ARelieve complicationsAvoid secondary infectionOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical product form changeAntioxidantSulfamonomethoxine
The invention relates to a medicinal composition and injecta for curing avian toxoplasmosis, and a preparation method thereof. The medicinal composition comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 18 to 36 percent of sulfamonomethoxine, 16 to 65 percent of sulfamethoxazole, 7 to 18 percent of trimethoprim, 4 to 14 percent of pyrimethamine and 6 to 16 percent of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicament. The injecta comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 5 to 10 percent of sulfamonomethoxine, 4 to 20 percent of sulfamethoxazole, 2 to 5 percent of trimethoprim, 1 to 3 percent of pyrimethamine, 1.5 to 4 percent of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicament, 5 to 10 percent of polyethyleneglycol-400, 10 to 30 percent of propylene glycol, 30 to 60 percent of alpha-pyrrolidone, 0.1 to 0.2 percent of antioxidant, 0.01 to 0.02 percent of metal complexing agent and the balance of water for injection. Sulfamonomethoxine, sulfamethoxazole, trimethoprim and pyrimethamine are jointly applied and a long-acting preparation is prepared by adopting composite solvent, so that the medicinal composition and the injecta can prevent the secondary infection of other pathogen at the same time of destroying and expelling toxoplasma so as to relieve different symptoms and complicating diseases caused by the toxoplasma.
Owner:HENAN HUITONGTIANXIA ANIMAL MEDICINE
Whelk treating medicine composition and its preparation method
InactiveCN1557326AEasy to useQuick resultsOrganic active ingredientsAerosol deliveryDexamethasoneSide effect
The acne treating medicine composition consists of Ethinylestradiol, compound sulfamethoxazole, promethazine, chlorpheniramine, dexamethasone, isotretinoin, chloromycetin, vitamin E and vanishing cream. The present invention can heal acne radically according to the pathogenesis, has unique acne healing effect, and has the functions of eliminating scar, nourishing skin, beautifying, etc. when used regularly. The present invention has fast effect and no toxic side effect.
Owner:陈开明
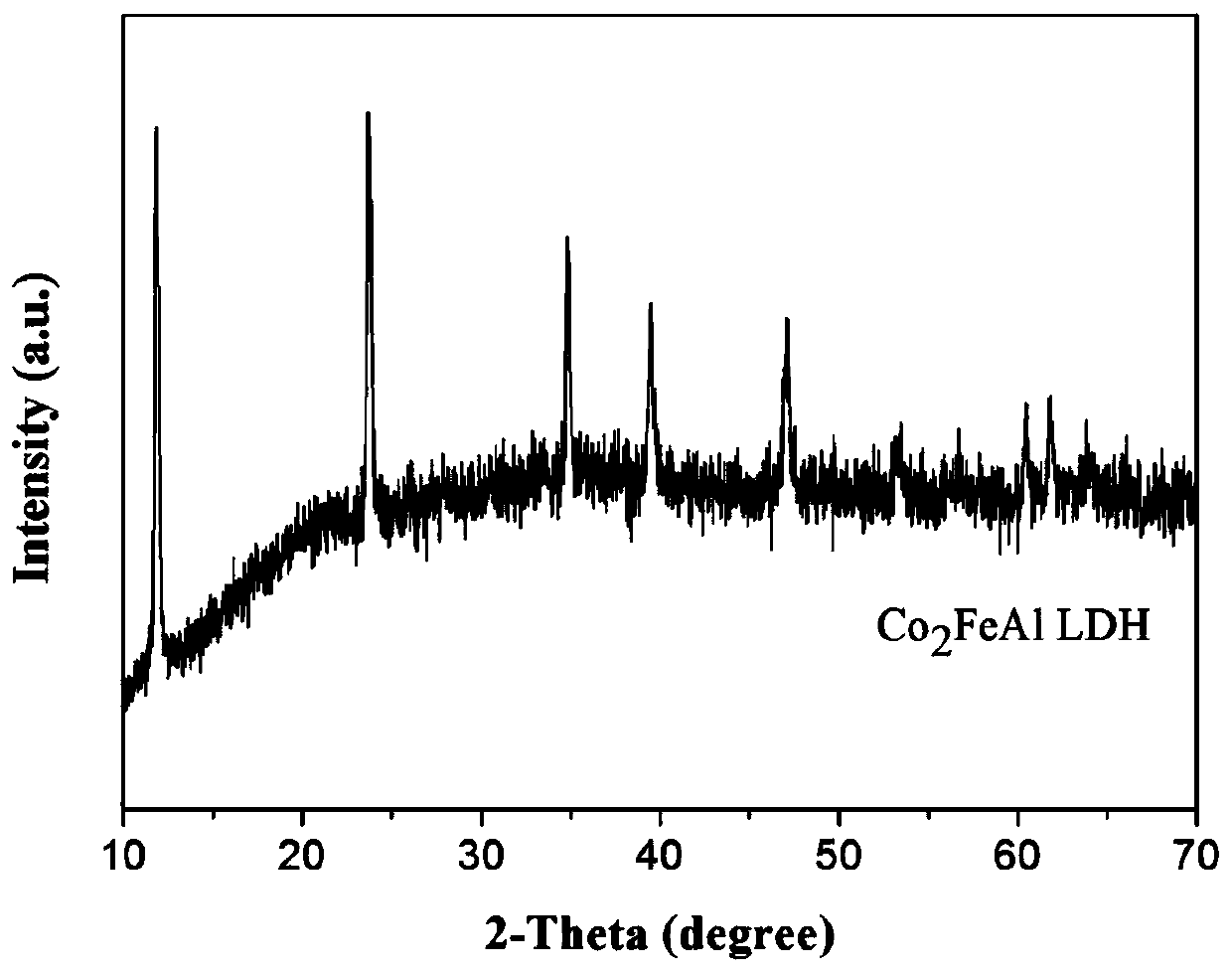
Co2FeAl-LDH, preparation method of Co2FeAl-LDH and method for degrading pollutants
ActiveCN110801839APromote degradationEasy to degradeWater contaminantsHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsSulfate radicalsPtru catalyst
The invention provides Co2FeAl-LDH, a preparation method thereof and a method for degrading pollutants, and the method for the Co2FeAl-LDH comprises the following steps: dissolving nitrate of cobalt,nitrate of iron, nitrate of aluminum and urea in water to obtain a uniform solution; and reacting the uniform solution for 22 to 26 hours at the temperature of between 105 and 115 DEG C to obtain theCo2FeAl-LDH nanosheet. The Co2FeAl-LDH prepared by co-precipitating the nitrate of cobalt, nitrate of iron and nitrate of aluminum by using the urea can be used as a catalyst. By means of the synergistic effect of cobalt and iron on strongly oxidative sulfate radicals which are generated by activation of peroxymonosulfate and the carrier effect of aluminum, pollutants such as sulfamethoxazole, ciprofloxacin and tetracycline in sewage are rapidly catalyzed and degraded. The process is simple. The Co2FeAl-LDH is a heterogeneous catalyst, is easy to recycle, and has the advantages of favorable stability and favorable reusability.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Sulfonamide antibiotic synergistically degraded bacteria and application thereof
ActiveCN111518715AEfficient removalNo accumulationBacteriaWater contaminantsBiotechnologyMethyl palmoxirate
The invention provides a sulfonamide antibiotic synergistically degraded bacteria and an application thereof. The sulfonamide antibiotic synergistically degraded bacteria comprise arthrobacterium P27and nocardioides N27, wherein the arthrobacterium P27 is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on December 03, 2019, and the preservation number is CGMCC No. 19070; andthe nocardioides N27 is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on December 03, 2019, and the preservation is CGMCC NO. 19071. According to the technical scheme, compounding of the two strains of bacteria can synergistically complete degradation of sulfamethoxazole and an azacyclo product 3-amino-5-methylisoxazole; and in addition, the strain P27 can degrade one side of benzene rings of various sulfonamide antibiotics, the degradation substrate spectrum is wide, and a new idea and a new strain resource are provided for deep removal of the sulfonamide antibiotics.
Owner:HARBIN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SHENZHEN (INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY INNOVATION HARBIN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SHENZHEN)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com