Method for removing sulfamethoxazole in water bodies with straw charcoal through adsorption and application of straw charcoal in removing sulfamethoxazole in water bodies
A technology of sulfamethoxazole and straw charcoal, applied in the direction of adsorption water/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of air traffic safety hazards, reduced visibility near the ground, and increased PM2.5 , to achieve good economic and environmental benefits, easy operation and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
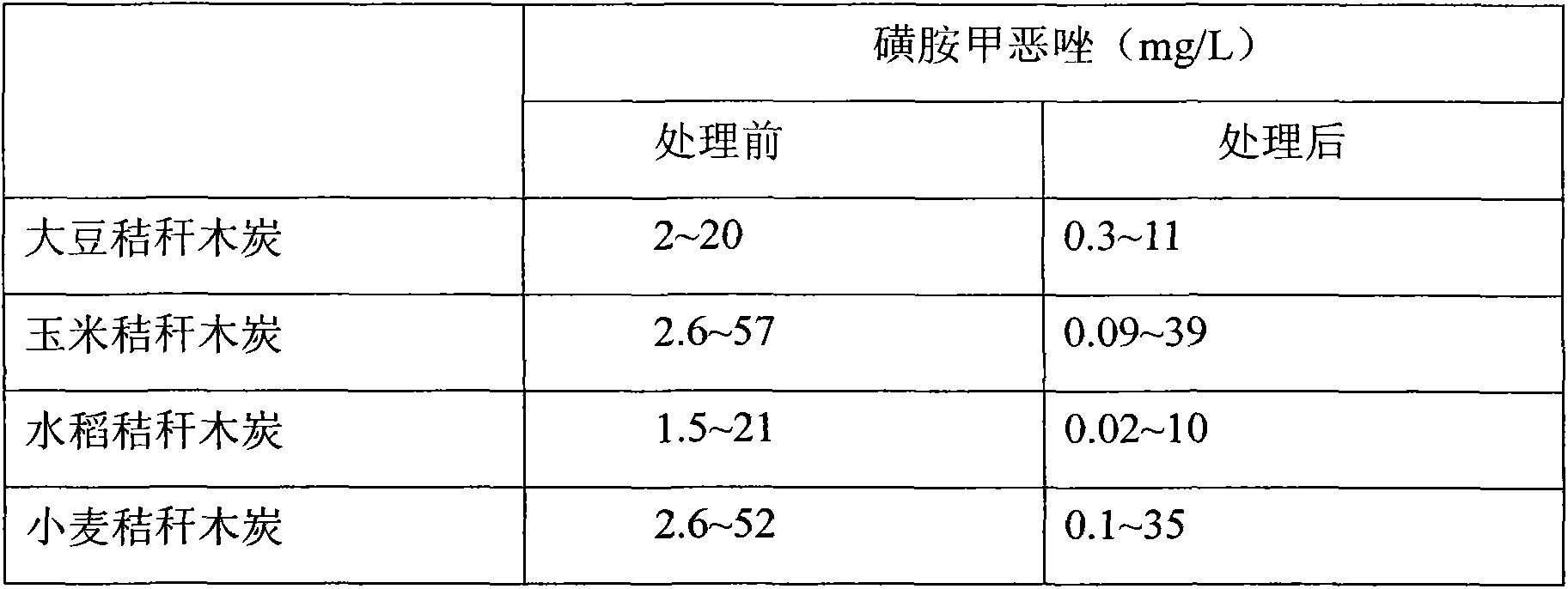
[0036] The charcoal made of soybean stalks synthesized by the above method is used as an adsorbent to treat slightly polluted water containing sulfamethoxazole. Adsorption experiments were carried out in glass vials (volume 22 mL) equipped with Teflon gaskets. Among them, the mass ratio of adsorbent to polluted water is 1:3000, the adsorption temperature is room temperature, the initial concentration of sulfamethoxazole is 2-26 mg / L, the adsorption time is 3 days, and the pH of the solution after adsorption is 5.80±0.02. The final removal rate of sulfamethoxazole is between 40% and 80%.
Embodiment 2
[0038] The charcoal made of corn stalks synthesized by the above method is used as an adsorbent to treat polluted water containing sulfamethoxazole.
[0039] The preparation of adsorbent is the same as in Example 1.
[0040] The adsorption experiment conditions are as follows: the adsorption experiment is carried out in a glass bottle (volume 22 mL) equipped with a polytetrafluoroethylene gasket. Among them, the mass ratio of adsorbent to polluted water was 1:3000, the adsorption temperature was room temperature, the initial concentration of sulfamethoxazole was 2.6-57 mg / L, the adsorption time was 3 days, and the pH of the solution after adsorption was 5.80±0.02. The final removal rate of sulfamethoxazole ranges from 40% to 97%.
Embodiment 3
[0042] The charcoal made of rice straw synthesized by the above method is used as an adsorbent to treat polluted water containing sulfamethoxazole.
[0043] The preparation of adsorbent is the same as in Example 1.
[0044] The adsorption experiment conditions are as follows: the adsorption experiment is carried out in a glass bottle (volume 22 mL) equipped with a polytetrafluoroethylene gasket. Among them, the mass ratio of adsorbent to polluted water was 1:3000, the adsorption temperature was room temperature, the initial concentration of sulfamethoxazole was 1.5-21 mg / L, the adsorption time was 3 days, and the pH of the solution after adsorption was 5.80±0.02. The final removal rate of sulfamethoxazole is between 50% and 99%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Outer diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com