Method for removing antibiotics in water
A technology for antibiotics and water removal, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water pollutants, adsorbed water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve problems such as high cost and inconformity with optimal use of resources, and achieve good application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] A method for removing antibiotics in water, the specific steps are as follows:
[0031] 1) Preparation of sugarcane activated carbon:
[0032] Rinse the collected sugarcane skins with tap water, air-dry them for 2 days, put them in an oven at 70°C for 12 hours, and use a pulverizer to pulverize them to a particle size below 2cm. Wrap the weighed sugarcane husk powder with tinfoil and place it in a porcelain crucible, cover it and put it into a tubular carbonization furnace, raise it to the target temperature of 500°C at a biological rate of 10°C / min, keep it for 2 hours, and cool it down naturally After reaching room temperature the product was ground through a 50 mesh screen. Subsequently, treat it with 1200mL 1mol / L hydrochloric acid for 2 hours to remove ash such as calcium carbonate, filter it with a circulating water multi-purpose vacuum pump, wash it with deionized water to be neutral, put it in an oven at 80°C for 24 hours, and transfer it to the sample Store i...
Embodiment 2
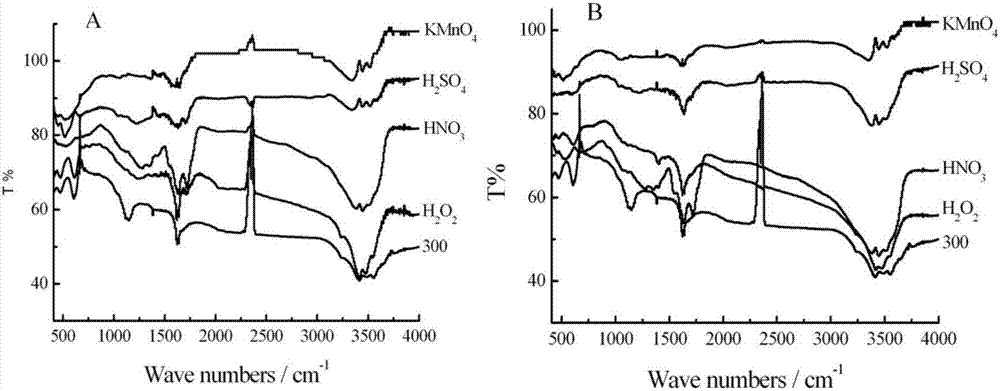
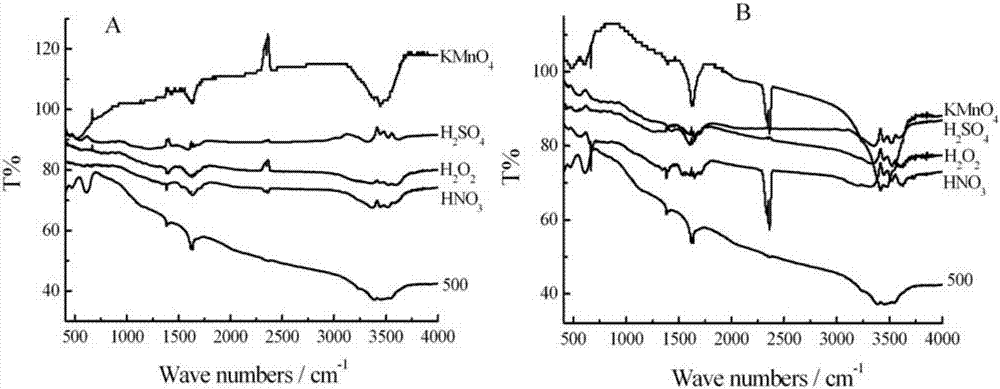
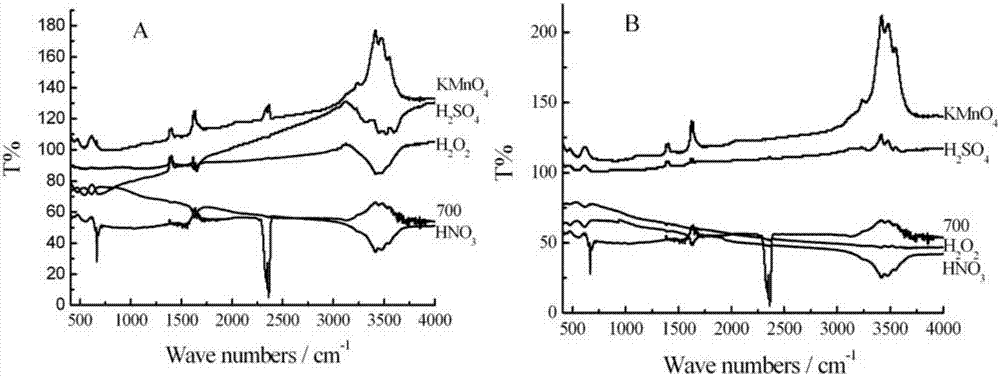
[0038] The preparation and modification method of sugarcane activated carbon are the same as in Example 1, wherein, the biochar fired at 300, 500, and 700°C is prepared with concentrated sulfuric acid, concentrated nitric acid, 30% hydrogen peroxide and 0.4mol / L potassium permanganate solution. The four oxidants were modified by impregnation and ultrasonic impregnation respectively. There were 8 modification methods in total. The biochar raw material used in each method was 11.25g, totaling 90g. Among them, the impregnation and ultrasonic impregnation methods are as follows:
[0039] Immersion modification: Put 11.25g of washed biochar into a 1000mL beaker, and add 400mL of oxidant and activated carbon into the beaker to fully contact, take out the solid after 24 hours and wash it repeatedly until neutral, then put it in an oven at 60°C Oven dry for 12 hours to constant weight.
[0040] Ultrasonic impregnation modification: put 11.25g of washed biochar into a 1000mL beaker, a...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Weigh 0.5g of biochar fired at 500°C and ultrasonically impregnated with 30% hydrogen peroxide into a 50mL colorimetric tube, add 10mL of sulfonamide antibiotics with a concentration of 20mg / L, and shake at constant temperature. , 20, 40, 60, 90, 120, and 180 min, take out and filter, and analyze the concentration of sulfonamide antibiotics in the filtrate.
[0051] Table 2 The adsorption efficiency of different antibiotics as a function of time
[0052] time Methoxazole Thiazole methyl pyrimidine Dimethylpyrimidine 5min 90.09% 42.62% 37.70% 58.43% 10min 91.07% 45.08% 39.77% 61.92% 20min 92.86% 53.01% 47.68% 70.40% 40min 93.31% 55.15% 48.99% 71.99% 60min 94.65% 61.72% 56.98% 77.76% 90min 95.21% 63.87% 58.53% 81.19% 120min 95.51% 66.43% 61.41% 82.58% 180min 96.03% 69.71% 64.24% 84.96%
[0053] The results are shown in Table 2 and Figure 4 As shown, it shows that the adsorption...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com