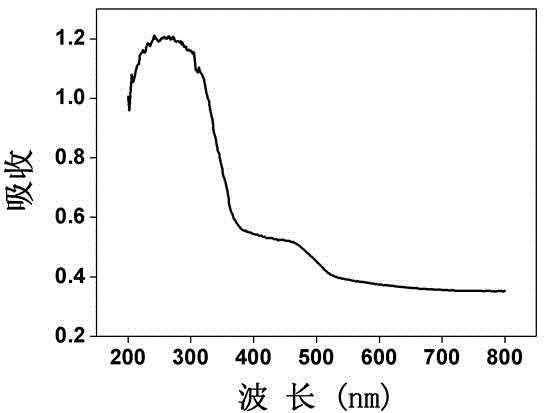
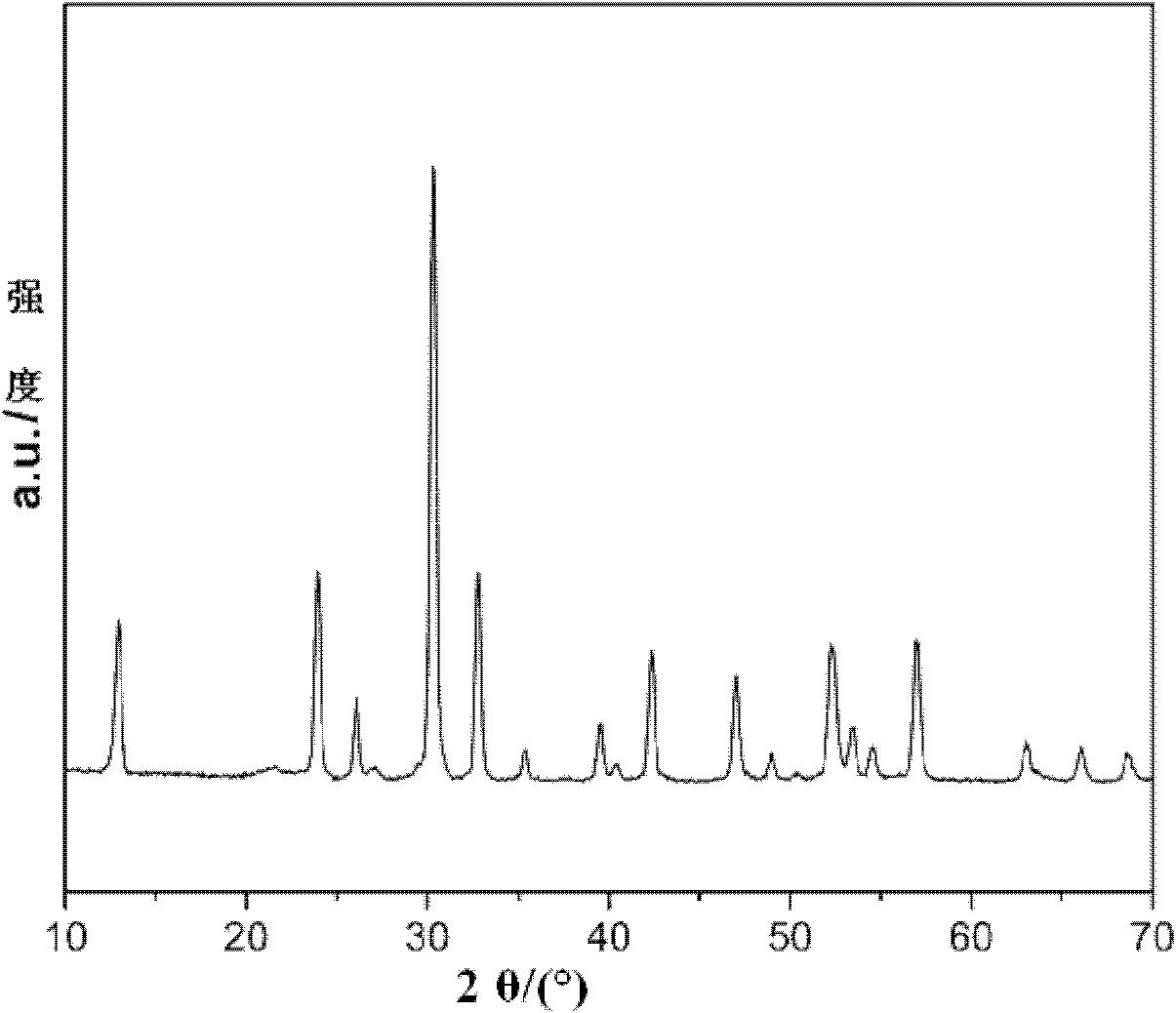
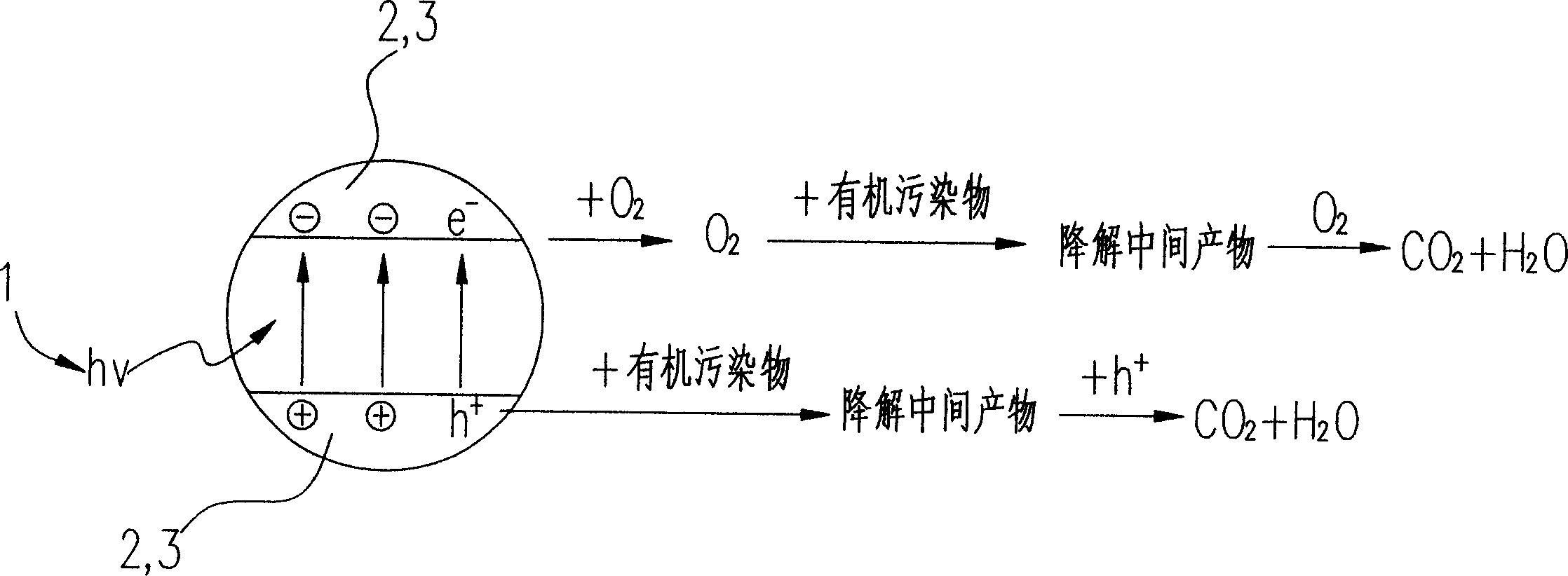
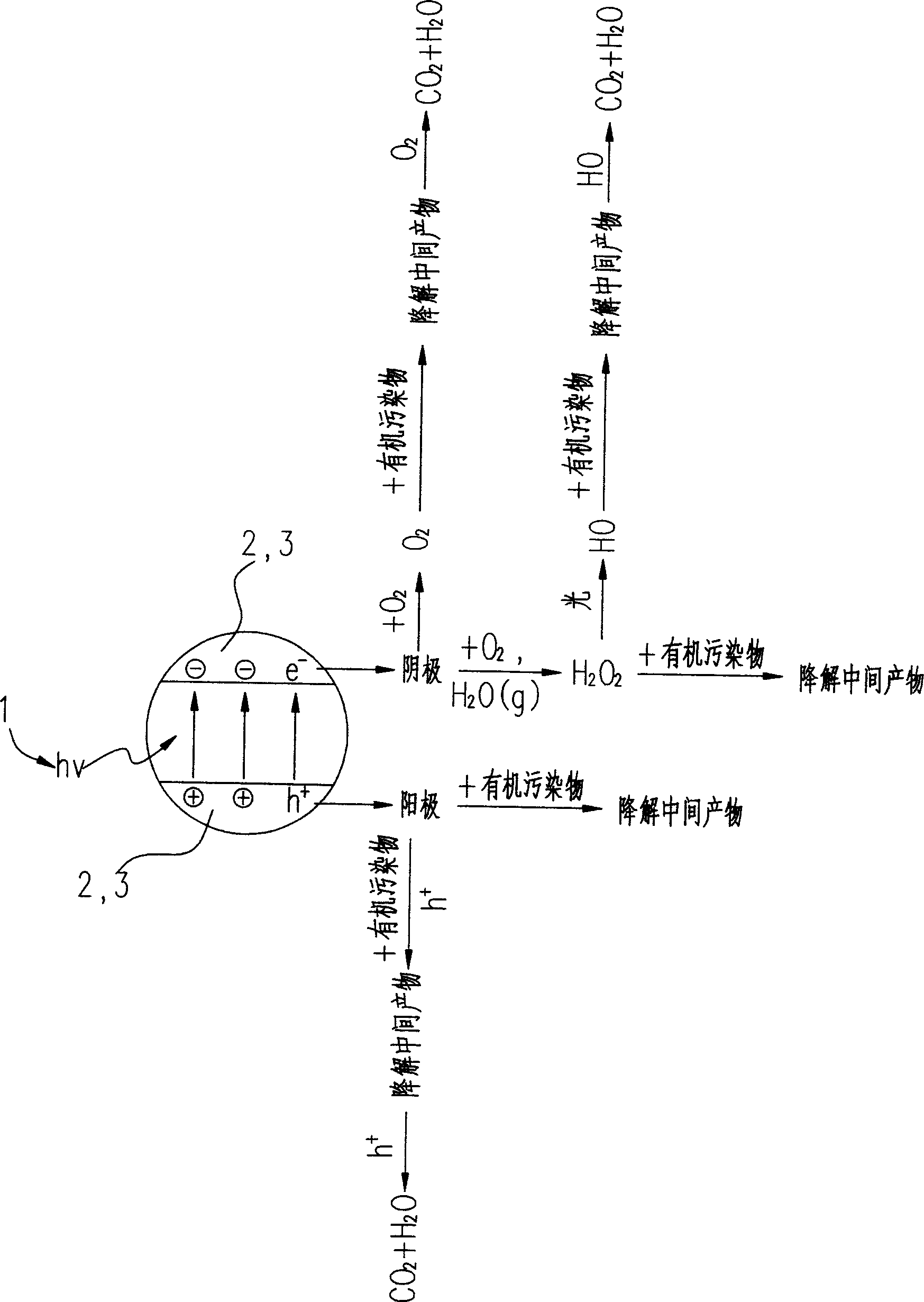
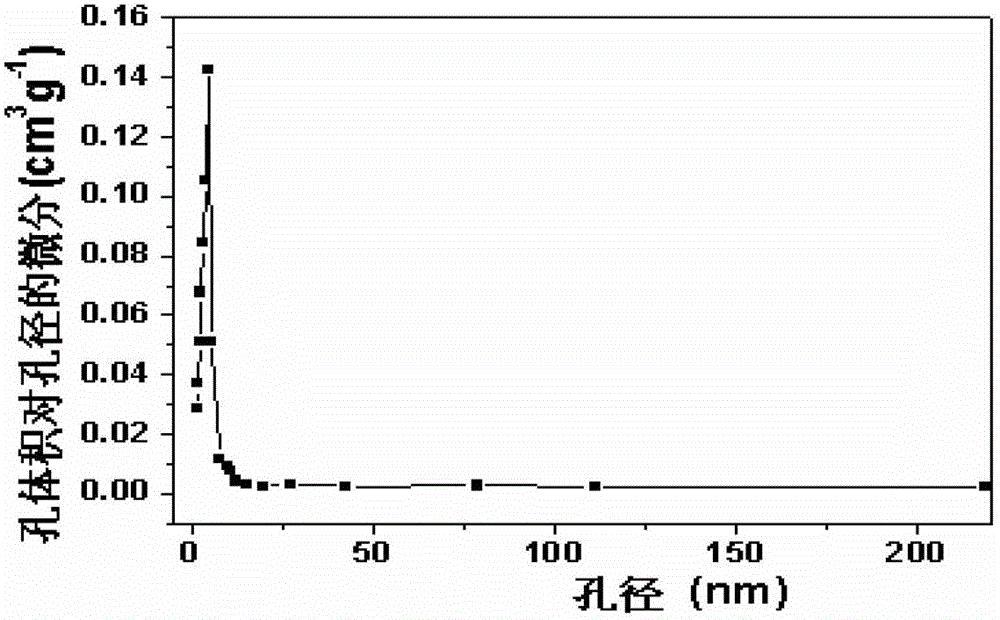
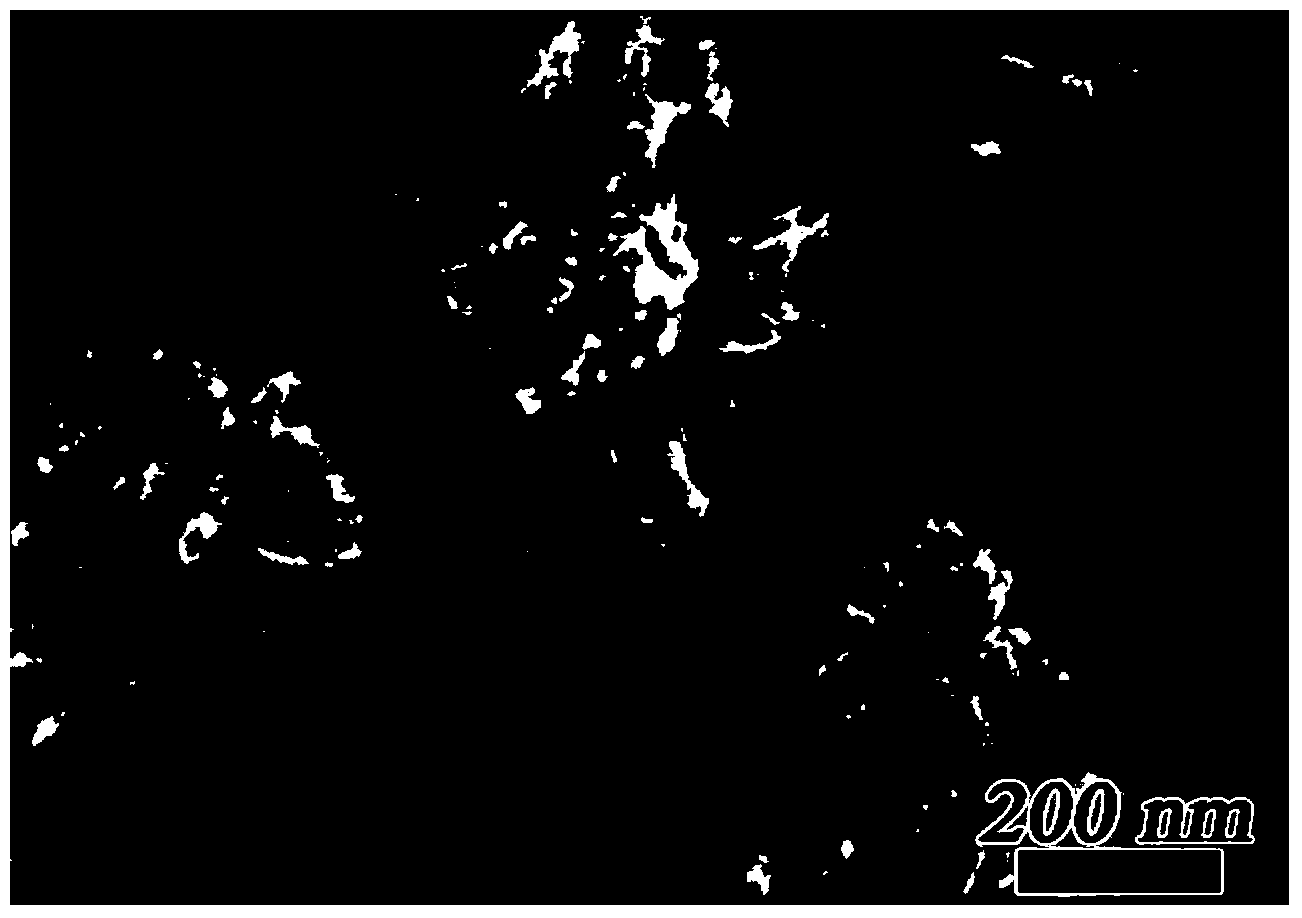
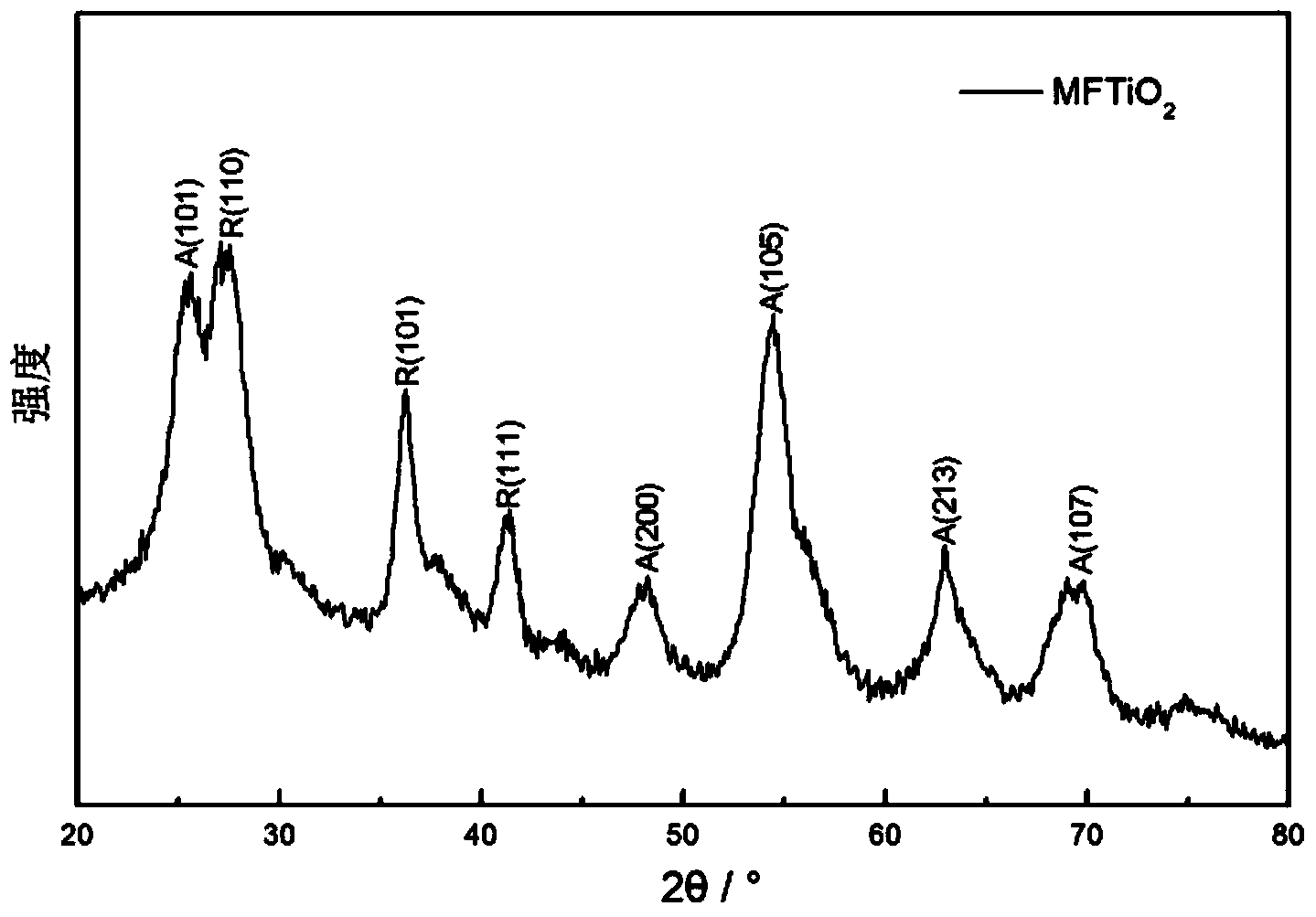
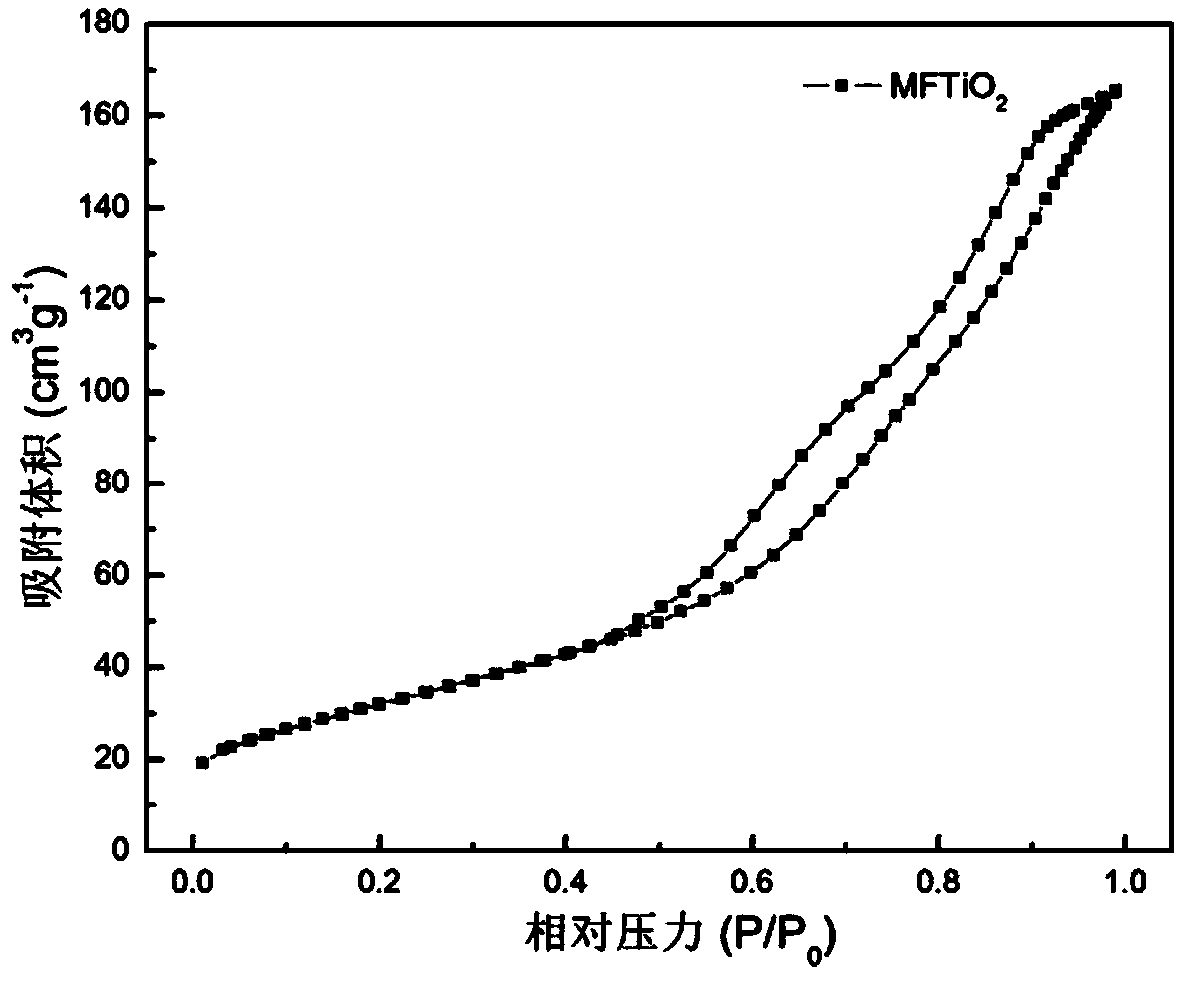
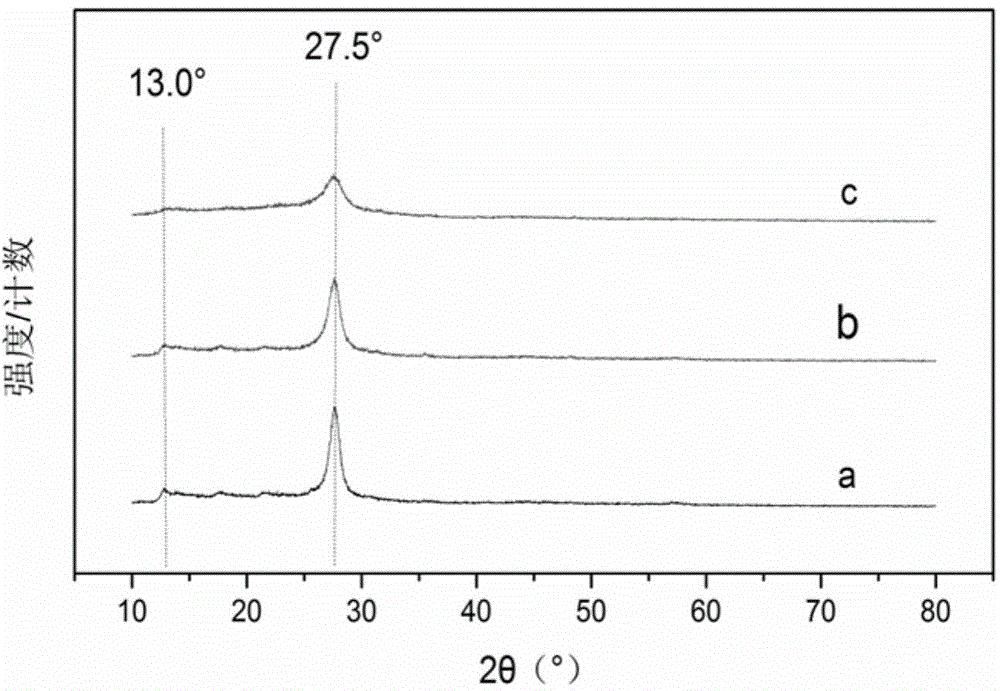
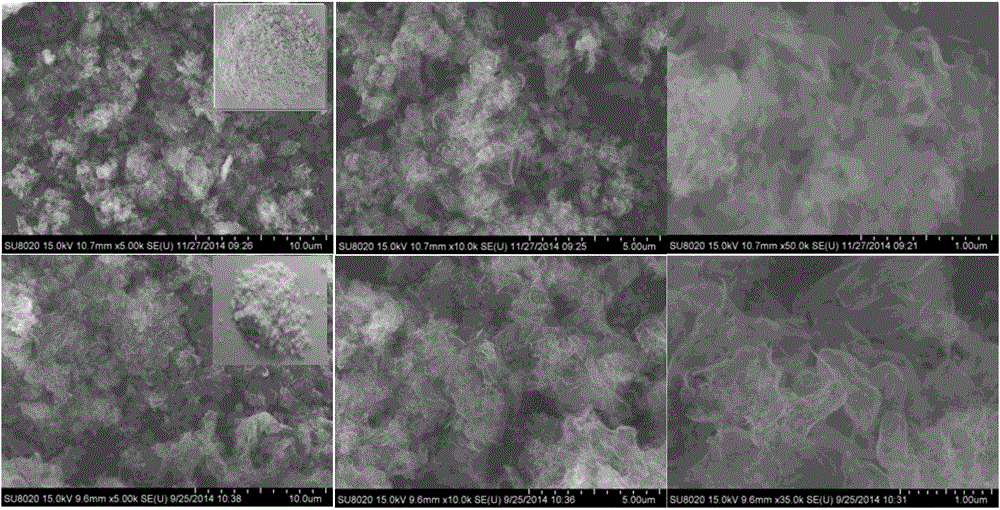
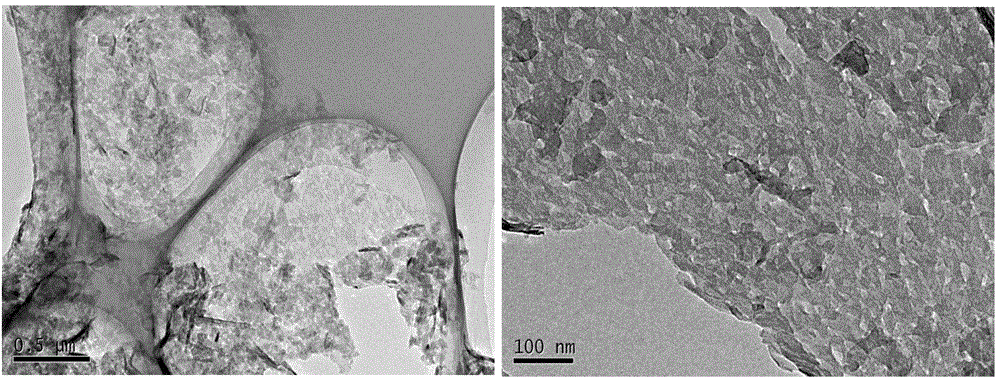
Patents
Literature
1049results about How to "Inhibitory complex" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Preparation method of visible light catalyst
InactiveCN102247877AImprove protectionImprove visible light catalytic performancePhysical/chemical process catalystsPhoto catalyticSolvent
The invention discloses a preparation method of a visible light catalyst. Compared with the prior art, the invention adopts inexpensive, non-toxic and harmless urea as the raw material, with no need for highly toxic raw materials. By controlling the calcination temperature, C3N4 can be prepared, thus being in favor of environment protection. The invention also provides a preparation method of a visible light catalyst, comprising the steps of: preparing C3N4 according to the above process; mixing the obtained C3N4 with a modifier in a solvent for reaction, drying the reaction product, thus obtaining the visible light catalyst. The modifier can be an Fe source compound, a Cu source compound, a Zn source compound, a V source compound, a W source compound, a Pt source compound, an Au source compound or a Pd source compound. The method of the invention employs an immersion method for C3N4 metal ion modification, so that metal ions can adsorb the C3N4 surface, thus inhibiting photoinduced charge recombination. Therefore, the visible light catalyst prepared by the preparation method provided in the invention has a high photo catalytic performance.
Owner:CHONGQING TECH & BUSINESS UNIV +1
Perovskite thin-film solar cell with three-dimensional ordered mesopore support layer
InactiveCN104409636ALarge specific surface areaGood electron transport abilityFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesWater solublePhotoelectric conversion efficiency
The invention provides a perovskite thin-film solar cell with a three-dimensional ordered mesopore support layer. The perovskite thin-film solar cell with the three-dimensional ordered mesopore support layer comprises a transparent conducting substrate, a compact layer, the three-dimensional ordered mesopore support layer, a perovskite light absorbing layer, a hole transporting layer and a counter electrode layer which are sequentially laminated to form a laminating layer, wherein the three-dimensional ordered mesopore support layer is filled with the perovskite light absorbing layer, the hole transporting layer and the counter electrode layer; the three-dimensional ordered mesopore support layer is of a three-dimensional ordered mesopore material prepared by using water-soluble colloidal crystal microspheres as a template; the aperture dimension of the three-dimensional ordered mesopore support layer depends on the dimension of the water-soluble colloidal crystal microspheres; and the perovskite light absorbing layer is prepared through materials of an ABXmY3-m type crystal structure. The perovskite thin-film solar cell has the advantages that the three-dimensional ordered mesopore support layer of which the aperture is uniform and adjustable, the specific surface area is relatively large and a good electronic transmission channel is arranged is provided and reaches high photoelectric conversion efficiency and outstanding repeatability and stability; and the preparation method has the advantages that the conditions are mild and controllable, the preparation method is simple and needs a little cost, and large-scale commercial production can be popularized.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Silver-modified carbon nitride composite photocatalytic material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104475140AGood dispersionInhibitory complexPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationOrganic dyeModified carbon
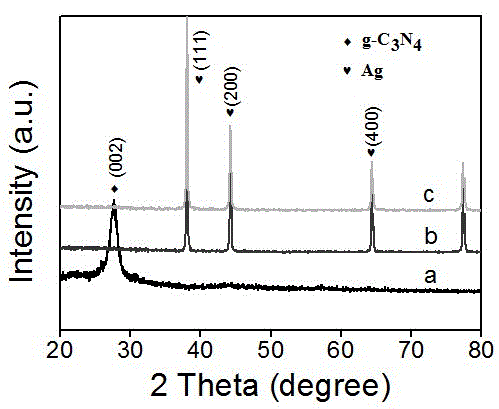
The invention relates to a silver-modified carbon nitride composite photocatalytic material and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises: dissolving dicyanodiamide or melamine in deionized water or dimethyl sulfoxide and performing ultrasonic dispersing, so as to obtain a dicyanodiamide or melamine dispersion liquid; dissolving silver nitrate in deionized water and stirring uniformly, so as to obtain a silver nitrate solution; slowly dropwise adding the silver nitrate solution into the above dicyanodiamide or melamine dispersion liquid under the condition of magnetic stirring, and continuing stirring the solution, so as to obtain a mixed precursor solution; using anhydrous ethanol and deionized water repeatedly wash the obtained mixed precursor solution for multiple times, and performing vacuum drying; and putting the obtained product in a proper crucible and covering, putting in a high-temperature furnace, and sintering for a period under the condition of nitrogen protection, so as to obtain a powdery sample. The advantages comprise that the raw material source is wide, the preparation technology is simple and practicable, and the cost is relatively low; and the prepared composite photocatalytic material has relatively good photocatalytic degradation effect on organic dye rhodamine B under irradiation of visible light.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Bismuth subcarbonate photocatalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102527420AImprove photocatalytic performanceImprove photocatalytic activityCatalyst activation/preparationMicrosphereAmmonia
The invention provides a bismuth subcarbonate photocatalyst which is a bismuth subcarbonate nanometer sheet or a microsphere formed by the bismuth subcarbonate nanometer sheet. The bismuth subcarbonate photocatalyst provided by the invention is obtained by carrying out hydrothermal reaction on a bismuth source and soluble carbonate in an aqueous solution, wherein the bismuth source is bismuth citrate or bismuth citrate ammonia. The bismuth subcarbonate photocatalyst takes the bismuth citrate or the bismuth citrate ammonia as the bismuth source, and the nanometer sheet shaped bismuth subcarbonate or the microsphere formed by the bismuth subcarbonate nanometer sheet is obtained in a hydrothermal reaction mode. The morphology obtained by the bismuth subcarbonate photocatalyst can accelerate the separation and transmission of the photoproduction electrons and holes of the bismuth subcarbonate photocatalyst so as to inhibit the composition of the electrons and holes and accelerate the diffusion and transfer of reactants and reaction products; reflection is generated between rays and a nanometer layer; and the use ratio of the light source is increased so as to improve the catalytic activity of the bismuth subcarbonate photocatalyst. An experiment result shows that the removal rate on NO by the bismuth subcarbonate photocatalyst provided by the invention is 20-50%.
Owner:铜陵博雅渡业新材料科技有限公司
Photoelectricity catalytic reactor for degrading organic contaminant and degradation method
InactiveCN1754615ANo ozone hazardLow costDispersed particle separationParticulatesElectrochemical response
This invention discloses one photoelectric reactor to degrade organic pollute and one method to remove the pollute assistant with catalyze reactor, wherein, the reactor is located with conductive multi-hole materials load compound semi-conductor photo catalyze positive and negative electrodes; the optimized catalyze can be used as light source; it uses conductive solid electrolyte applied to degrade pollute with gas and liquid and to separate metal ions.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
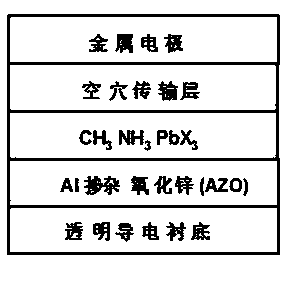
Hybrid solar cell with aluminum-doped zinc oxide nanorod as electron transfer layer
InactiveCN103474574ALarge specific surface areaGood electron transport propertiesFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesHole transport layerZinc oxide nanorod
A hybrid solar cell with an aluminum-doped zinc oxide nanorod as the electron transfer layer is composed of a transparent conducting glass substrate, the aluminum-doped zinc oxide nanorod electron transfer layer, a layered perovskite-like hybrid material CH3NH3PbX3(wherein X is Cl, or Br or I),2,2',7,7'-Tetrakis[N,N-di(4-methoxyphenyl)amino]-9,9'-spirobifluorene hole transfer layer and an Au metal back electrode layer, wherein all the parts form a laminated structure in sequence. The hybrid solar cell with the aluminum-doped zinc oxide nanorod as the electron transfer layer has the advantages that due to the fact that the aluminum-doped zinc oxide nanorod is used as the electron transfer layer in the hybrid solar cell, the specific surface area is large, electron-transport capacity is high, electron-hole combination is effectively restrained, and photoelectric conversion efficiency is high; the manufacturing method and technique are simple, reaction temperature is low, efficiency is high, raw materials are rich, cost is low, and environmental friendliness is achieved. The hybrid solar cell with the aluminum-doped zinc oxide nanorod as the electron transfer layer is suitable for industrialized large-scale production.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Preparation of nanometer composite light catalyst
InactiveCN1613555AAvoid reunionGuaranteed unchangedCatalyst activation/preparationGeneral chemistMulti pollutant
A process for preparing the nano-class composite photocatalyst includes such steps as preparing TiO2 aerogel by supercritical technique, and osmosizing metallic ions into TiO2 main body. Its advantages are high catalytic activity, wide trigger range moving from UV to visual light, and high degradability to hydrocarbon, oily sewage and more pollutants.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
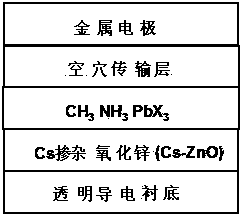
Hybrid solar cell with Cs mingling with ZnO as electron transfer layer
InactiveCN103456888AInhibitory complexImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesHole transport layerPhenyl group
Provided is a hybrid solar cell with Cs mingling with ZnO as an electron transfer layer. The hybrid solar cell with the Cs mingling with the ZnO as the electron transfer layer is composed of a transparent conductive glass substrate, a Cs mingling with ZnO nanorod electron transfer layer, layered perovskite hybrid materials CH3NH3PbX3(wherein X is C1, Br or I), a 2, 2', 7 and 7'- four [N, N - two (four - methoxy phenyl) amidogen] - 9, 9' - spirobifluorene hole transport layer and an Au metal back electrode layer which sequentially form a layered structure in a combining mode. The hybrid solar cell with the Cs mingling with the ZnO as the electron transfer layer has the advantages that the Cs mingling with the ZnO as the electron transfer layer is used in the hybrid solar cell, compared with zinc oxide, 2-3 orders of magnitude of electronic transmission capacity are improved, the recombination of electron-hole is effectively constrained, and the photoelectric conversion efficiency is high; the preparing method of the hybrid solar cell is simple in process, low in reaction temperature, high in efficiency, rich in raw material, low in cost, environmentally friendly, free of pollution, and suitable for industrial mass production.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Perovskite solar cell and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106684247AInhibitory complexImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHysteresisSpray coating
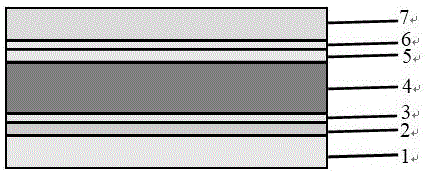
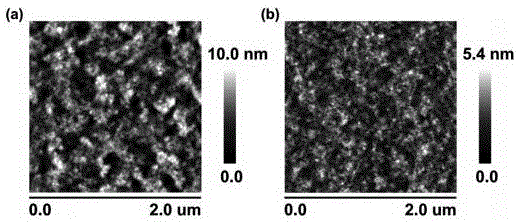
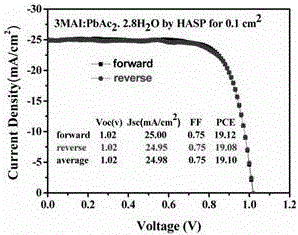
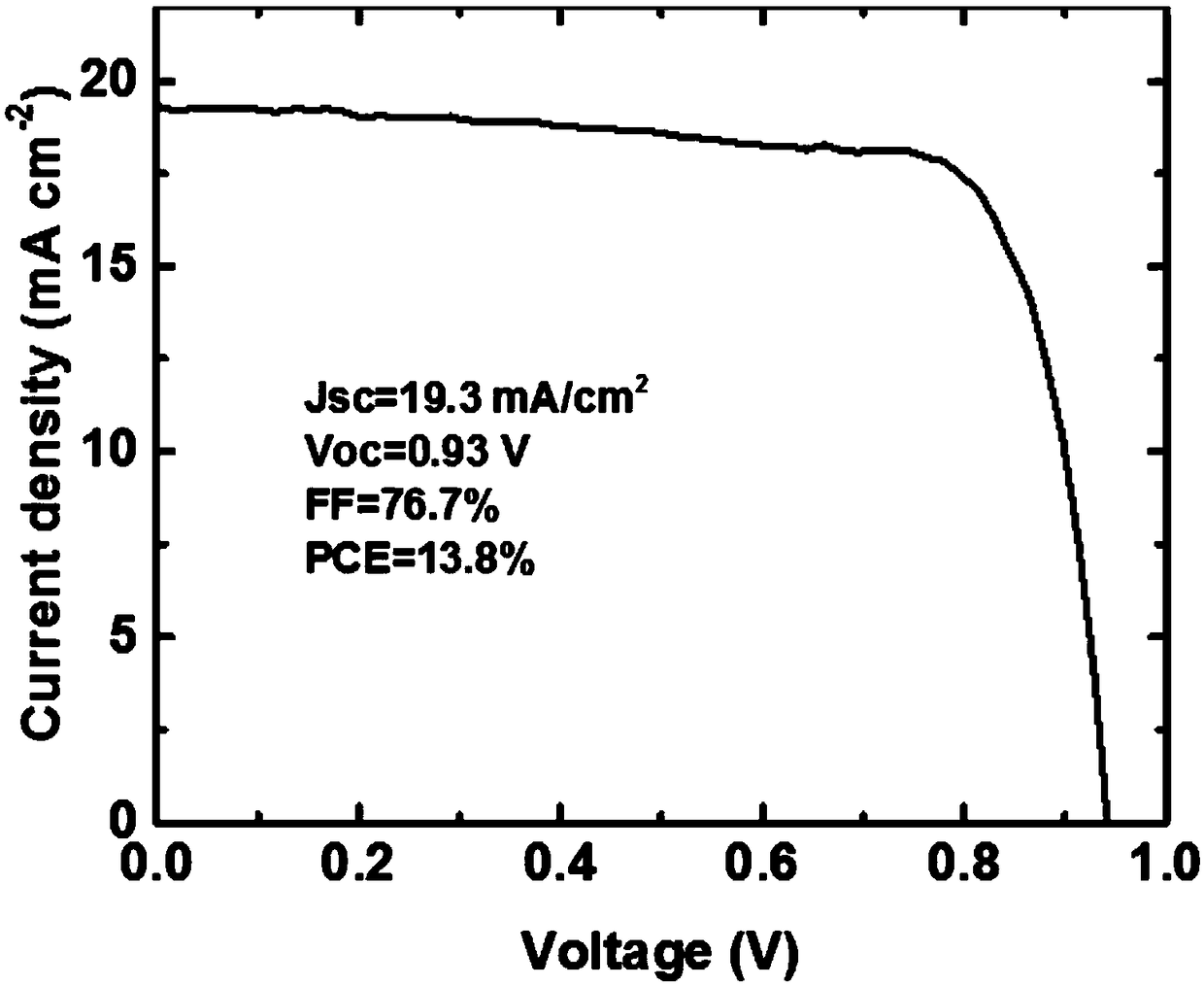
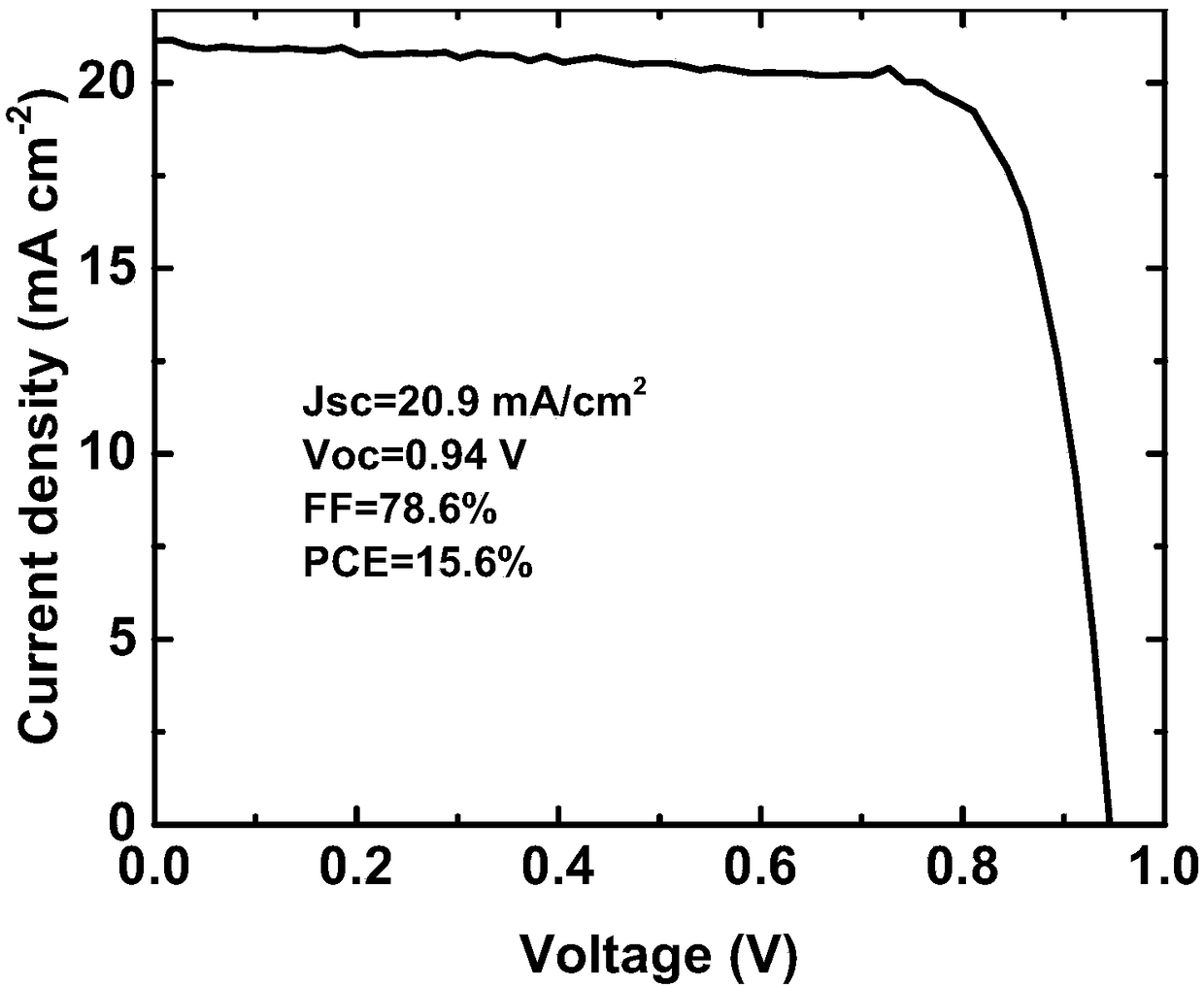
The invention discloses a perovskite solar cell and a preparation method thereof. The perovskite solar cell comprises a transparent conductive substrate, a hole transport layer, a decoration layer, a perovskite layer, an electron transport layer, a barrier layer and a metal electrode. The surfaces of PEDOT: PSS, NiOx and the hole transport layer are decorated by ionic liquid based on imidazole, atomic force microscope graphs before and after the decoration are compared, and the decorated surface appearance is more smooth, which is conducive to inhibiting the compounding of dark current. The perovskite layer is a new perovskite material 3MAI: PbAc2.xH2O (x is not smaller than 0 and is not greater than 3), and is prepared by quickly preheating a substrate and heating a perovskite precursor solution, namely instant heating assisted spray coating technology (HASP) at a low temperature (lower than 100 DEG C), which is conducive to increasing the grain size of perovskite and reducing the defects between perovskite grains so as to greatly improve the efficiency of the perovskite battery. The photoelectric conversion efficiency of the final battery device is greater than 19%, the flexible device efficiency is 10.8%, no hysteresis effect is formed, and thus the preparation method has a broad application prospect.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Graphene/titanium dioxide composite material, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108160064ASimplify the linkConducive to follow-up reactionsGas treatmentPhysical/chemical process catalystsCvd grapheneTitanium oxide
The invention relates to a graphene / titanium dioxide composite material, a preparation method and application thereof. The graphene / titanium dioxide composite material comprises: graphene and titaniumdioxide particles closely attached to the graphene sheet. According to the invention, graphene and titanium dioxide are selected for compounding to obtain an efficient photocatalyst with the excellent properties of graphene and titanium oxide simultaneously.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
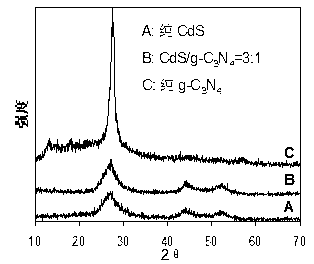
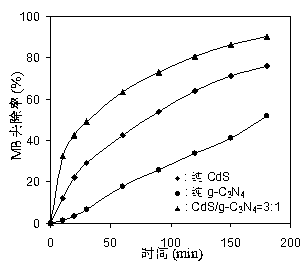
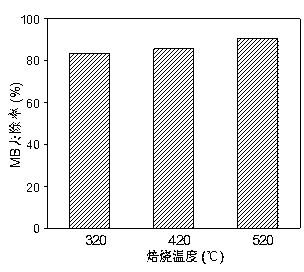
CdS/g-C3N4 composite visible light catalyst, preparation method and application
InactiveCN103191766AReduce the chance of being oxidized by photocorrosionImprove stabilityPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationMethyl violetPtru catalyst
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of a cadmium sulfide / graphite like carbon nitride (CdS / g-C3N4) composite visible light catalyst. The preparation method of the catalyst is a chemical precipitation method which is performed in an alkaline environment, wherein g-C3N4 is taken as a matrix, and CdCl2 and Na2S are taken as raw materials. The weight ratio of CdS to g-C3N4 in CdS / g-C3N4 is (1:2)-(5:1), and when the composite visible light catalyst is used for visible light catalysis treatment of methylene blue and methyl violet solutions, a better degradation effect can be obtained; and furthermore, the catalyst can still keep higher catalytic activity after being reused for five times. The composite visible light catalyst disclosed by the invention has important significance for development of the visible light catalyst, and also has good application prospects in treatment of dye wastewater.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
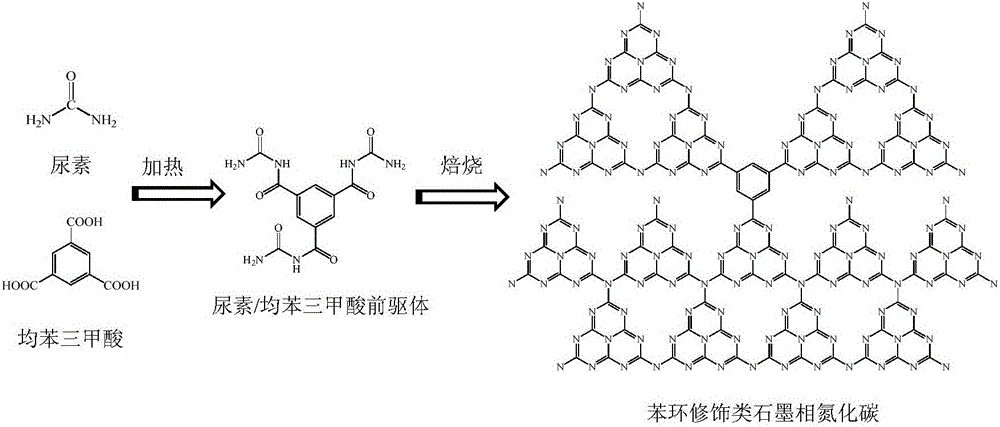
Phenyl ring modified graphite-like carbon nitride photocatalyst, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106238086AEfficient separationVisible light response range is widePhysical/chemical process catalystsHydrogen productionBenzoic acidBenzaldehyde
The invention belongs to the technical fields of material preparation and photocatalysis, and discloses a phenyl ring modified graphite-like carbon nitride photocatalyst, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: 1, dissolving nitrogen-containing organic micro-molecules and a phenyl ring-containing compound in a solvent, and evaporating the obtained solution until the solution is dry in order to obtain a mixed precursor; and 2, roasting the mixed precursor to obtain the phenyl ring modified graphite-like carbon nitride photocatalyst, wherein the nitrogen-containing organic micro-molecules are one or more of urea and melamine; and the phenyl ring-containing compound is one or more of trimesic acid, phenol, benzoic acid and benzaldehyde. The electron structure of the photocatalyst is changed by phenyl ring modification, so the pi electron delocalization of graphite-like carbon nitride is excited, the absorption of visible lights is improved, compounding of photon-generated carriers is inhibited, and the photocatalytic hydrogen production performance is improved. The method has the advantages of simple preparation, no expensive device and good practical application prospect.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
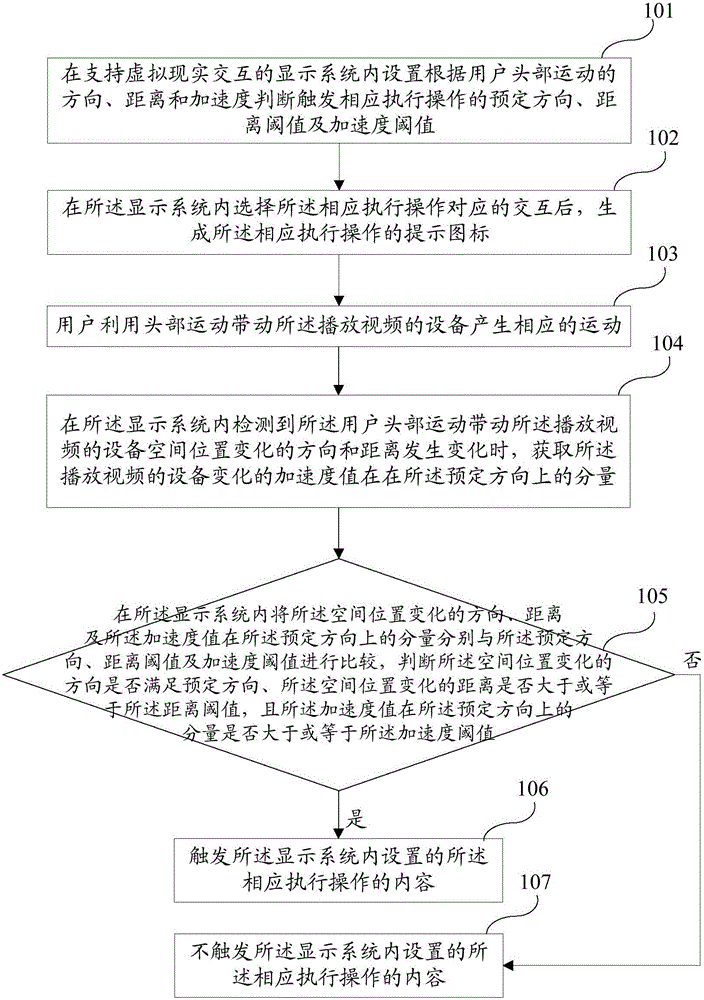
Method and system for controlling virtual reality interaction according to head motion of user
InactiveCN106200899AAvoid complexityImprove user experienceInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingVirtual realityDistance threshold
The invention discloses a method for controlling virtual reality interaction according to the head motion of a user. The method comprises the following steps of setting preset direction and distance threshold values and acceleration values for judging and triggering the corresponding execution operation according to the direction, distance and acceleration of the head motion of the user in a display system supporting the virtual reality interaction; and triggering the content of the corresponding execution operation set in the display system when the conditions that the space position change direction and distance of video playing equipment change, the space position change direction meets the preset direction, the space position change distance is greater than or equal to the distance threshold value, and the component of the acceleration value in the preset direction is greater than or equal to the acceleration threshold value are detected in the display system. The method provided by the invention has the advantage that the control of the virtual reality interaction according to the head motion of the user is realized.
Owner:北京奇思信息技术有限公司
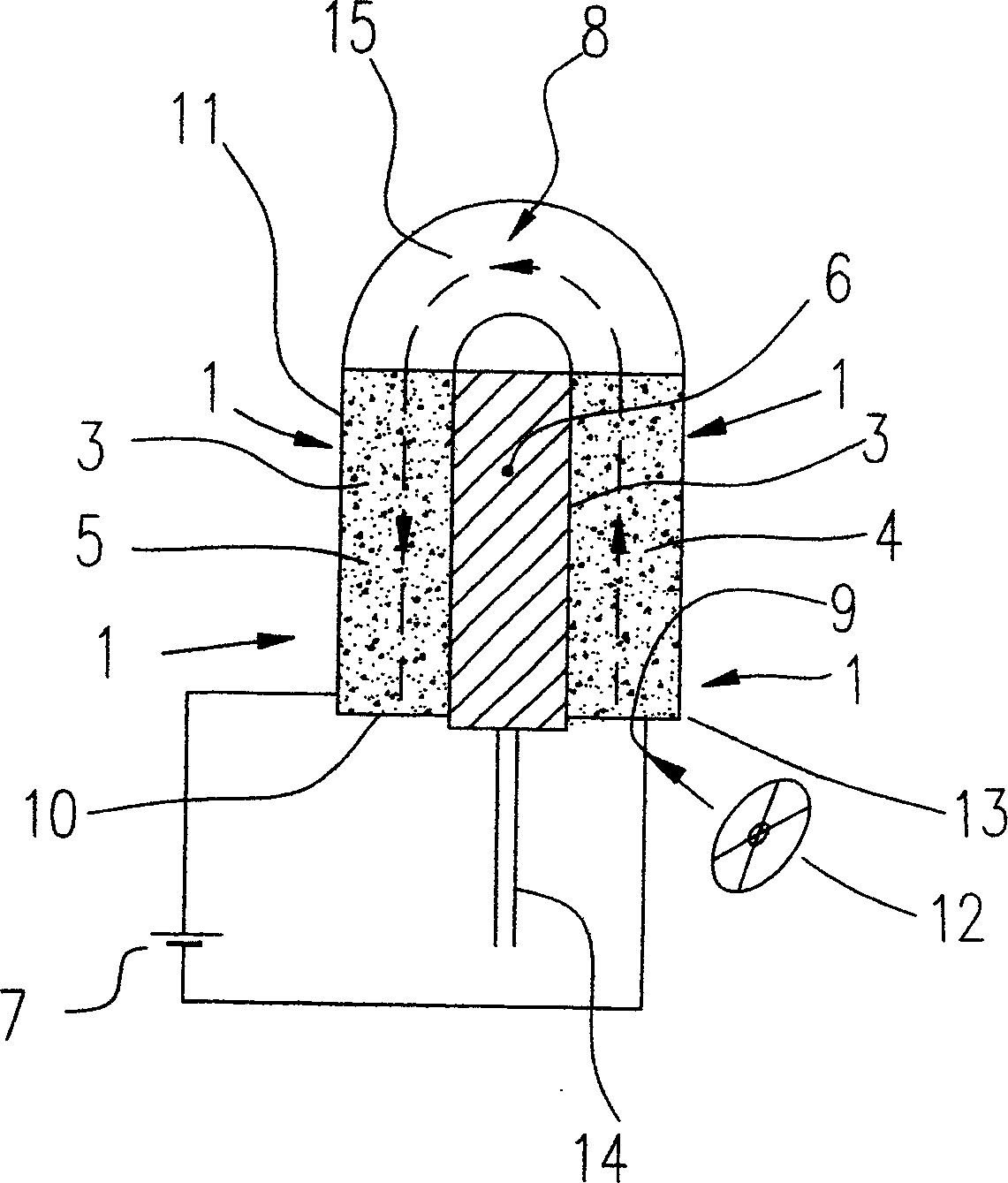
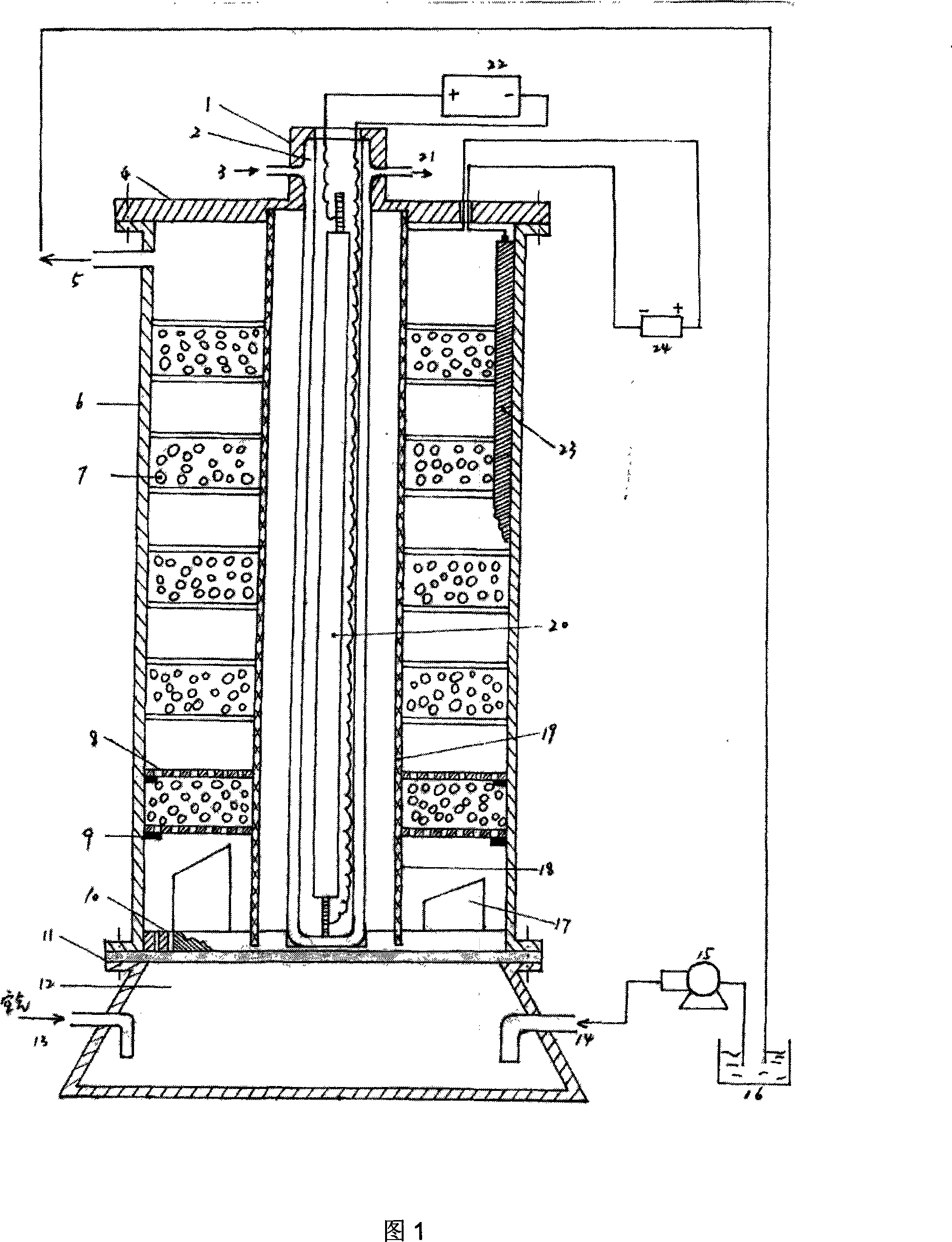
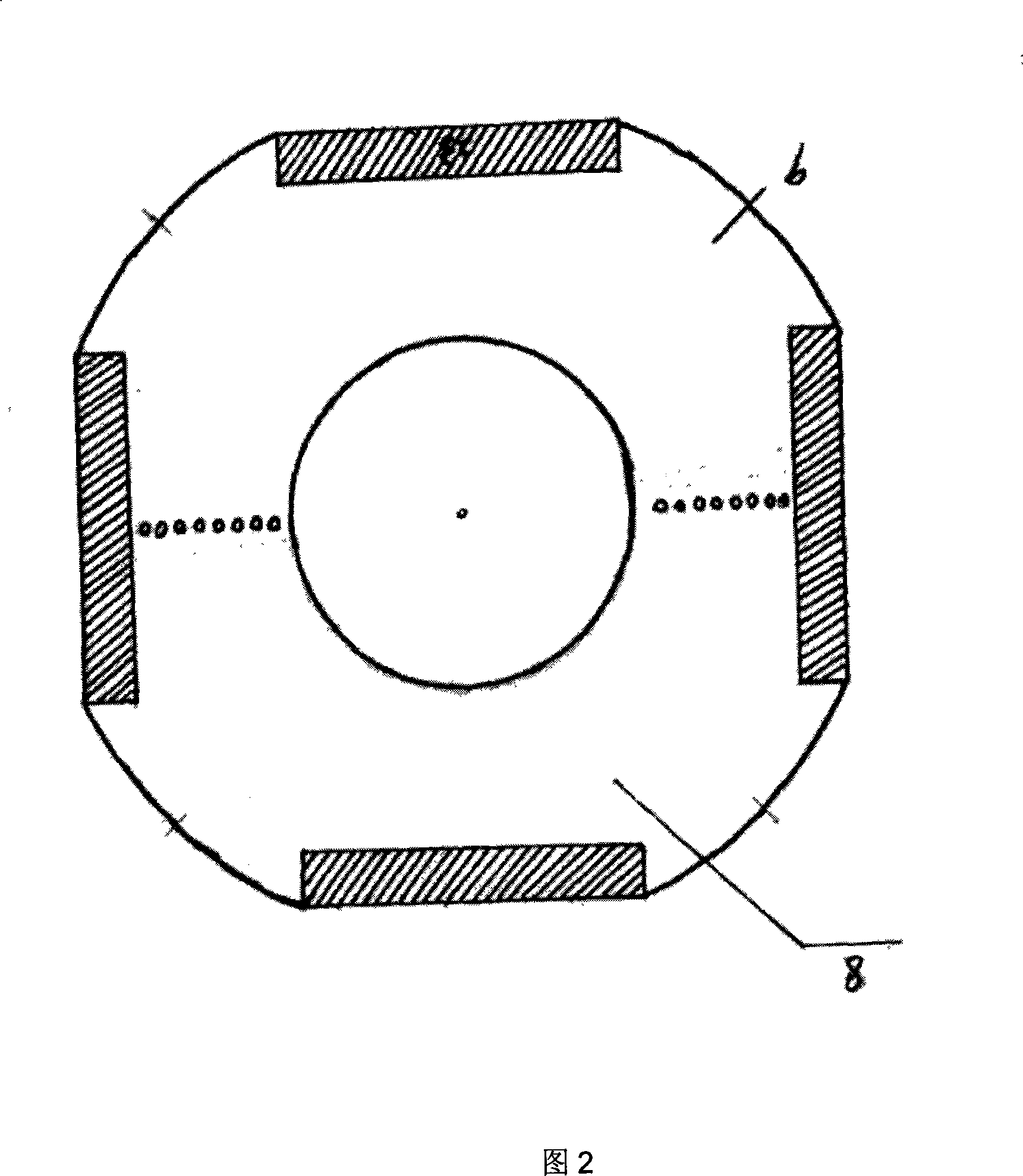
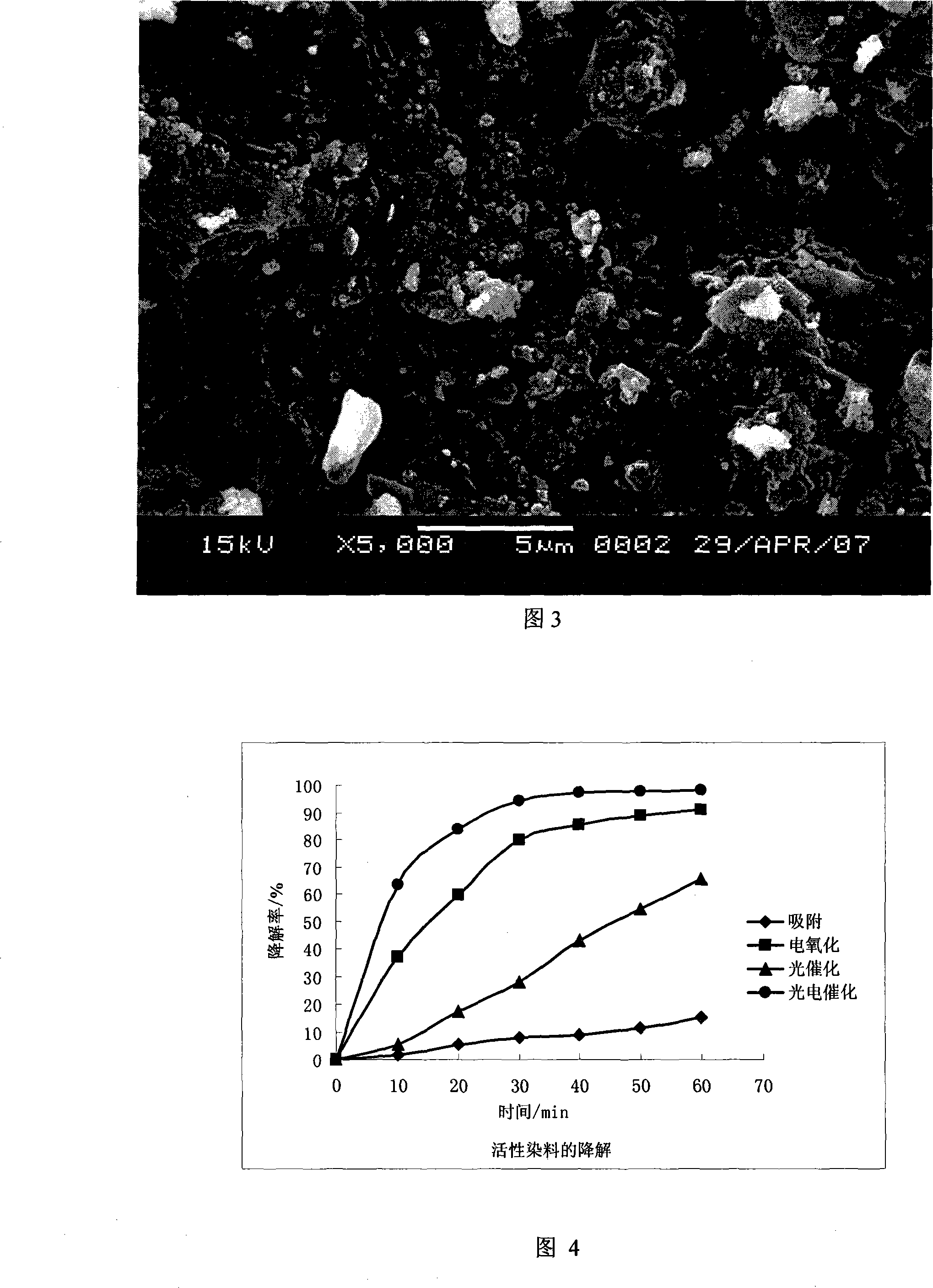
Fixed bed inhomogeneous three dimensional electrode photo electrocatalysis reactor
InactiveCN101224401ALow costGive full play to the efficiency of synergistic catalytic oxidationEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by oxidationHigh concentrationFixed bed
The invention relates to a continuous cycle multilayer interval type fixed bed non- homogeneous phase three-dimensional electrode photoelectric catalytic reactor, which includes a reactor shell body, a titanium network anode, a porous graphite cathode, a double layer U-shaped silica tube and an illuminant UV lamp arranged in the silica tube, wherein, a photoelectric catalytic reaction chamber is formed between the graphite cathode and the titanium network anode, a multilayer compartment type fixed bed three-dimensional particle electrode is arranged in the chamber, and the three-dimensional particle electrode material is made by coating nanometer TiO2 on the active carbon particles; a circulating device composed of a fluid reservoir and a pump is arranged between a fluid inlet and a fluid outlet of the reaction chamber. The invention wonderfully integrates the three-dimensional electrode and the photocatalytic technology; the multilayer interval type fixed bed is beneficial to the mass transfer effect and can improve the degradation rate of the system. The invention is highly efficient and rapid and is suitable for the treatment of dyeing waste water that has high concentration and is difficult to degrade. The device has no secondary pollution and more than one reaction device can be connected in series for use, which is mobile and flexible.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
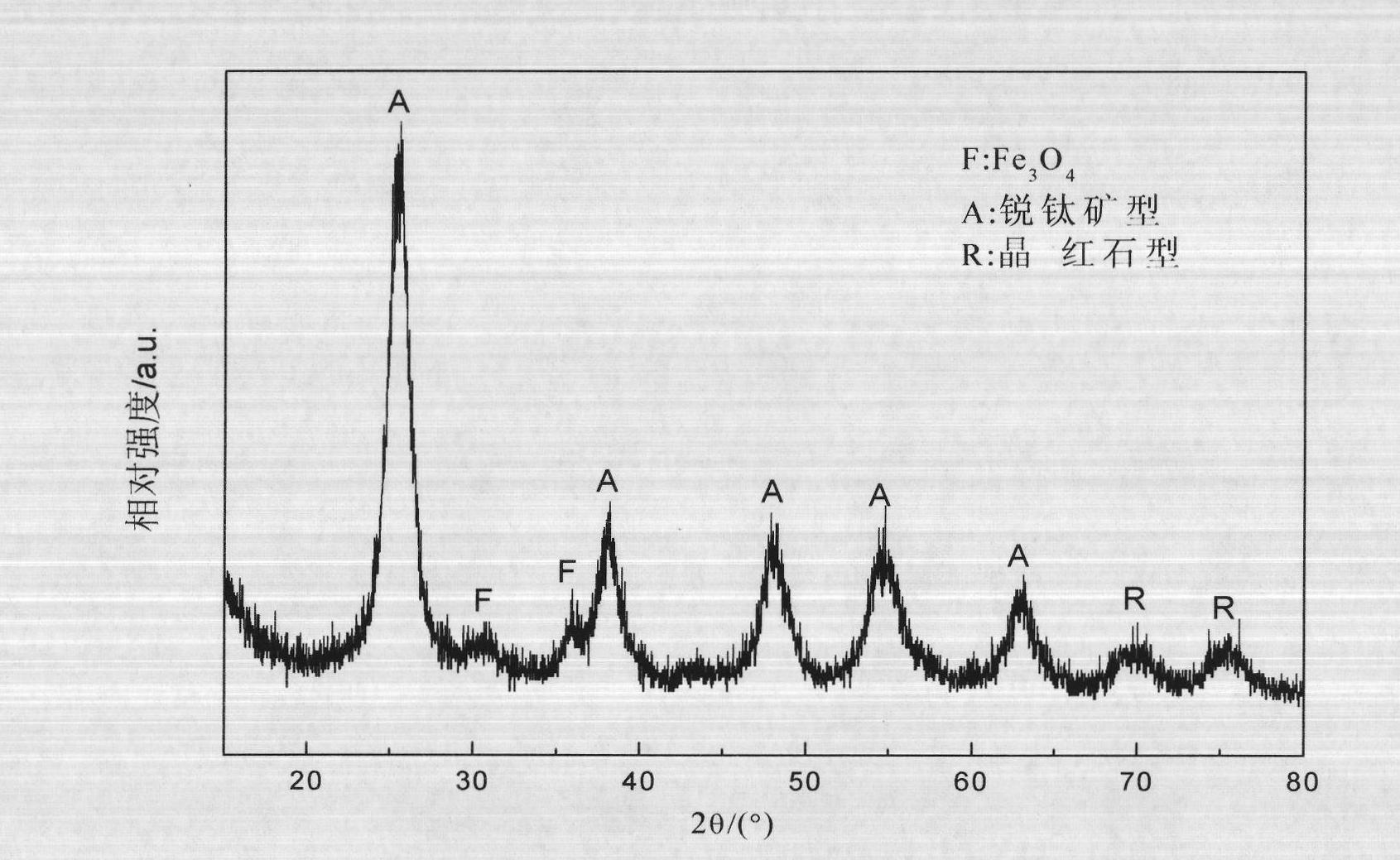
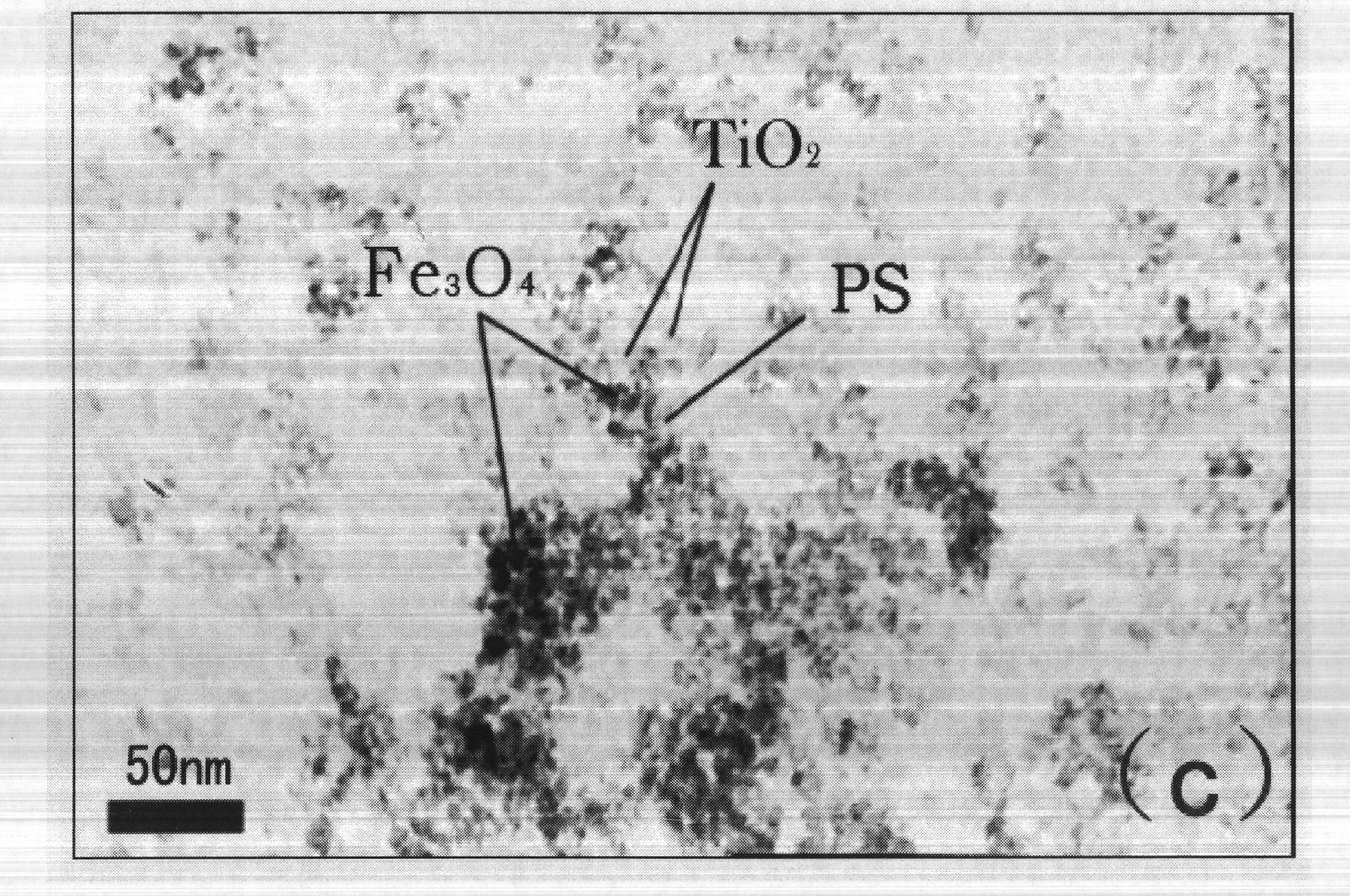
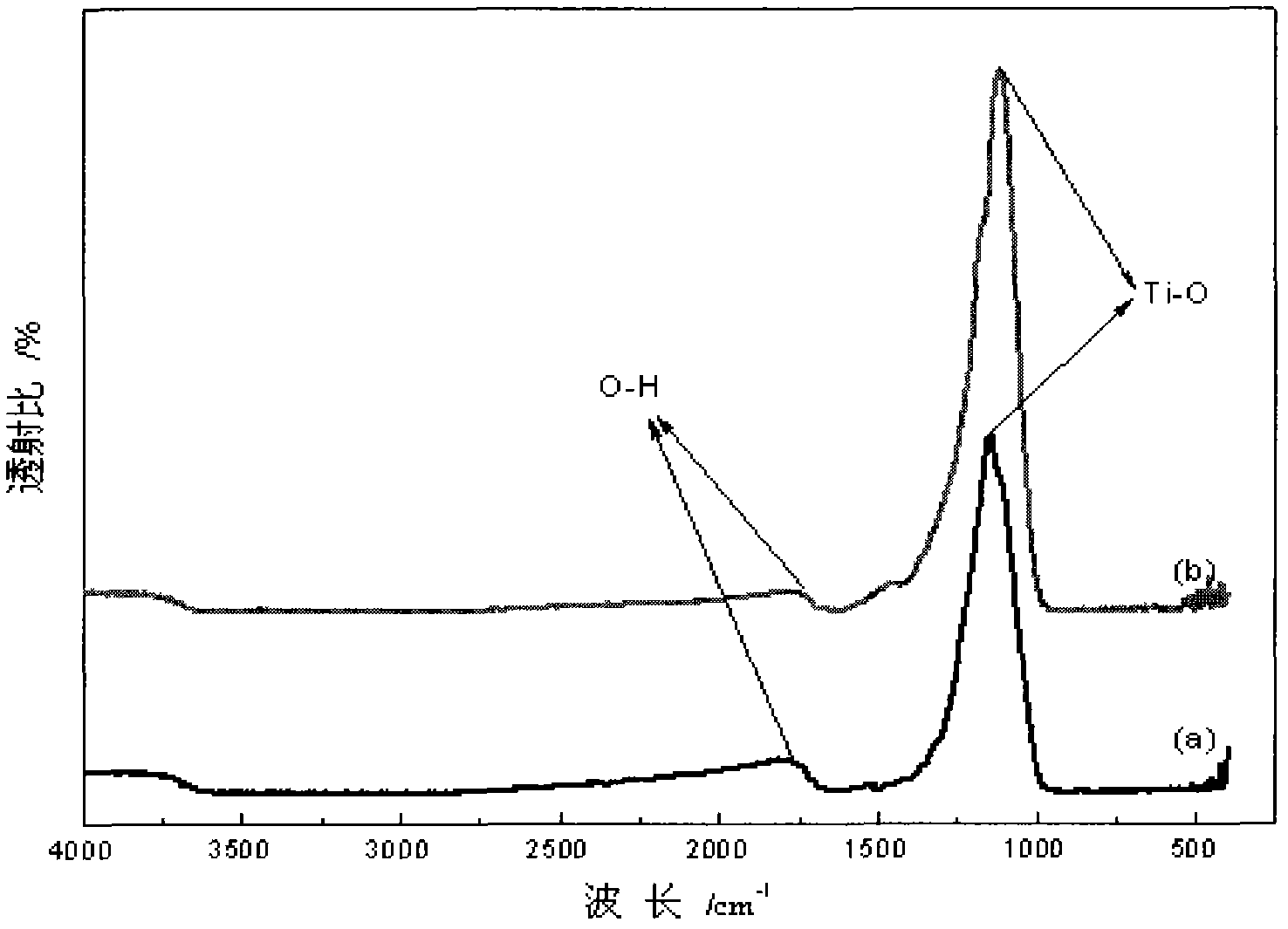
Method for preparing TiO2/PS/Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticle photocatalyst
InactiveCN102580783ANot corrosiveNo secondary pollutionWater/sewage treatment by irradiationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsWater bathsPolystyrene bead
The invention relates to a method for preparing a TiO2 / PS / Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticle photocatalyst, comprising the following steps of: (1) preparing oleic acid modified Fe3O4 nanoparticles; (2) preparing an aqueous-phase magnetic fluid; (3) preparing styrene miniemulsion; (4) preparing magnetic polystyrene beads PS / Fe3O; and (5) preparing the magnetic photocatalyst TiO2 / PS / Fe3O4, which specifically comprises the following steps of: mixing absolute ethyl alcohol with tetra-n-butyl titanate, and performing magnetic stirring to form a solution A; adding the magnetic polystyrene beads PS / Fe3O to de-ionized water and performing ultrasonic treatment to form a solution B; under magnetic stirring, adding the solution A to the solution B, thereby obtaining sol after 30-40 min, wherein TiO2 covers the PS / Fe3O at the moment; after condensing and refluxing the sol in a water bath, filtering the sol to obtain the TiO2 / PS / Fe3O4, washing the TiO2 / PS / Fe3O4 by using ethanol, filtering, washing by using distilled water and filtering, thus obtaining a solid; and drying the solid until the weight thereof is constant, thereby obtaining the magnetic photocatalyst TiO2 / PS / Fe3O4 with the polystyrene PS as an isolating layer, the Fe3O4 as a magnetic core and the TiO2 as a shell. The product obtained by using the method is low in energy consumption, high in catalytic activity and recyclable.
Owner:LANZHOU JIAOTONG UNIV
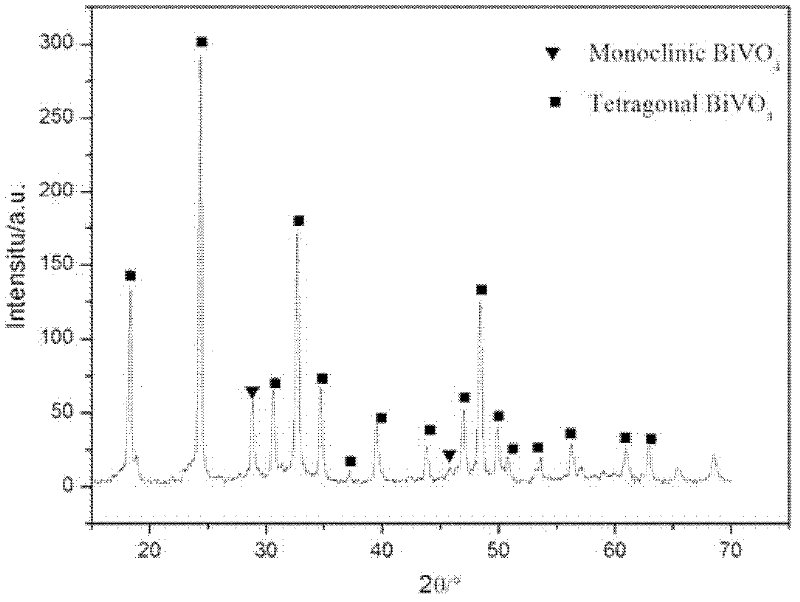
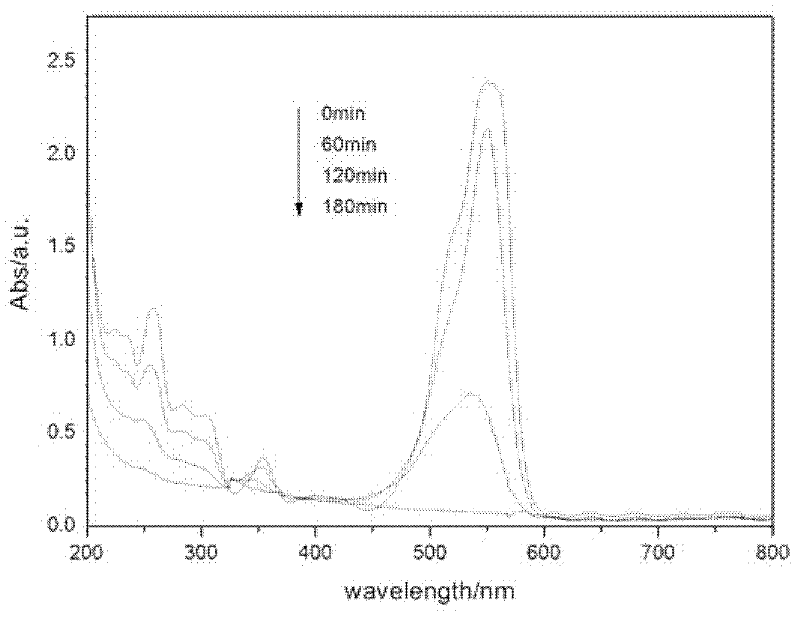
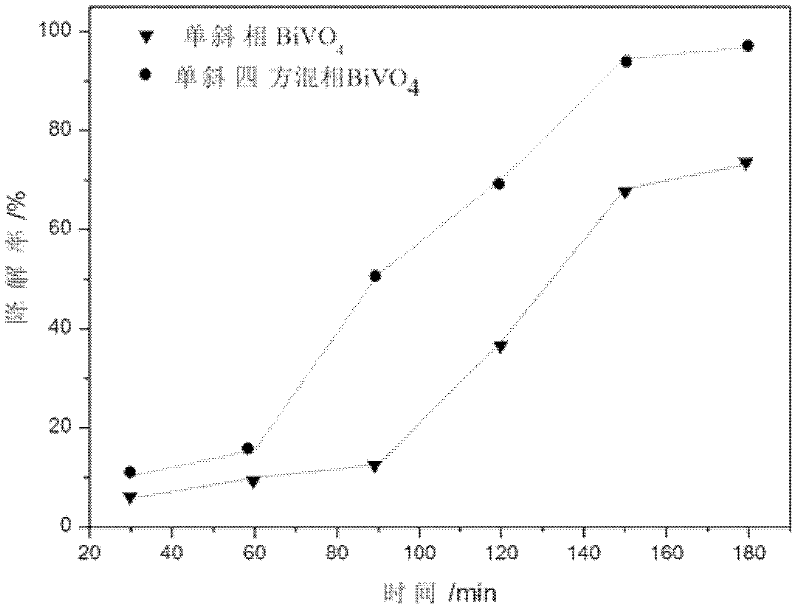
Method for synthesizing monoclinic phase and tetragonal phase mixed high-catalytic-activity bismuth vanadate powder by microwave hydrothermal process
InactiveCN102249305AUniform particle size distributionIncrease the diffusion lengthVanadium compoundsMicrowaveBismuth vanadate
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing monoclinic phase and tetragonal phase blended high-catalytic-activity bismuth vanadate powder by a microwave hydrothermal process, and the method comprises: separately dissolving bismuth nitrate pentahydrate used as a bismuth source and ammonium metavanadate used as a vanadium source in a HNO3 solution and a NaOH solution with a molar ratio of Bi to V being 1:1, adding an appropriate amount of sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate used as a template agent and NaOH used as a mineralizing agent, and controlling the pH value at 4.6-8.0, microwave hydrothermal reaction temperature at 160-220 DEG C and heat-insulation time at 60-120 minutes to synthesize the monoclinic phase and tetragonal phase blended BiVO4 powder. By adopting the microwave hydrothermal synthesis technique in the invention, high-photocatalytic-activity BiVO4 powder is quickly synthesized. The method as a novel environmentally-friendly rapid synthesis process combines the unique heating characteristics of microwave and the advantages of a hydrothermal method, the process is simple and easy to control, the preparation period is short, the energy is saved, and the resulting powder has uniform particle size distribution and very wide application prospects.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation method and application of ZnO-doped TiO2 composite hollow sphere
InactiveCN101905153ALow costNo pollution in the processWater/sewage treatment by irradiationEnergy based wastewater treatmentSpectral responsePhoton
The invention discloses a preparation method of a ZnO-doped TiO2 hollow sphere composite photocatalyst, comprising the following steps of: preparing Zn<2+> doped carbon / titanium dioxide nuclear-shell particles by adopting a template method and a hydrolytic cladding method, and then calcinating the nuclear-shell particles to obtain the ZnO-doped TiO2 nano hollow sphere composite photocatalyst. The photocatalyst can be used for catalyzing and degrading cationic dyes under ultraviolet or solar visible light. By utilizing low-cost titanium sources, zinc sources and carbon spheres for preparing the ZnO-doped TiO2 nano hollow sphere composite photocatalyst, the preparation method has the advantages of low cost of raw materials, simple process, short preparation period, less energy consumption and belongs to green synthetic technologies. After TiO2 hollow spheres are doped and compounded by utilizing ZnO, absorption spectrums generate red shift by utilizing the interface coupling effect of the TiO2 hollow spheres and the ZnO so that the spectral response range of the photocatalyst is broadened, and the utilization rate of solar energy is improved; and meanwhile, the method can also inhibit the compounding of photon-generated carriers and improve the activity of the photocatalyst by utilizing the high conductivity of ZnO particles.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Platinum supported nitrogen-doped molybdenum disulfide photocatalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105618098AGood hydrogen production capacityAnd stable hydrogen production capacityHydrogen productionHydrogen/synthetic gas productionElectrochemistryHydrogen production
The invention provides a platinum supported nitrogen-doped molybdenum disulfide photocatalyst and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: with sodium molybdate and thioacetamide as raw materials, preparing molybdenum disulfide nanoplates via a hydrothermal method; performing thermal treatment on the molybdenum disulfide nanoplates in an ammonia atmosphere to obtain nitrogen-doped molybdenum disulfide nanoplates; and finally, loading precious metal platinum on the nitrogen-doped molybdenum disulfide nanoplates via a photo reduction method to obtain the platinum supported nitrogen-doped molybdenum disulfide photocatalyst. With the platinum supported nitrogen-doped molybdenum disulfide photocatalyst, molybdenum disulfide is taken as a photocatalyst to produce hydrogen from water by visible light catalytic decomposition for the first time. The platinum supported nitrogen-doped molybdenum disulfide photocatalyst has excellent visible light catalytic hydrogen production capability and excellent stability. The preparation method is simple to operate, the photocatalyst is good in repeatability, and the application of molybdenum disulfide in the aspects of photocatalysis and electrochemistry is expanded.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
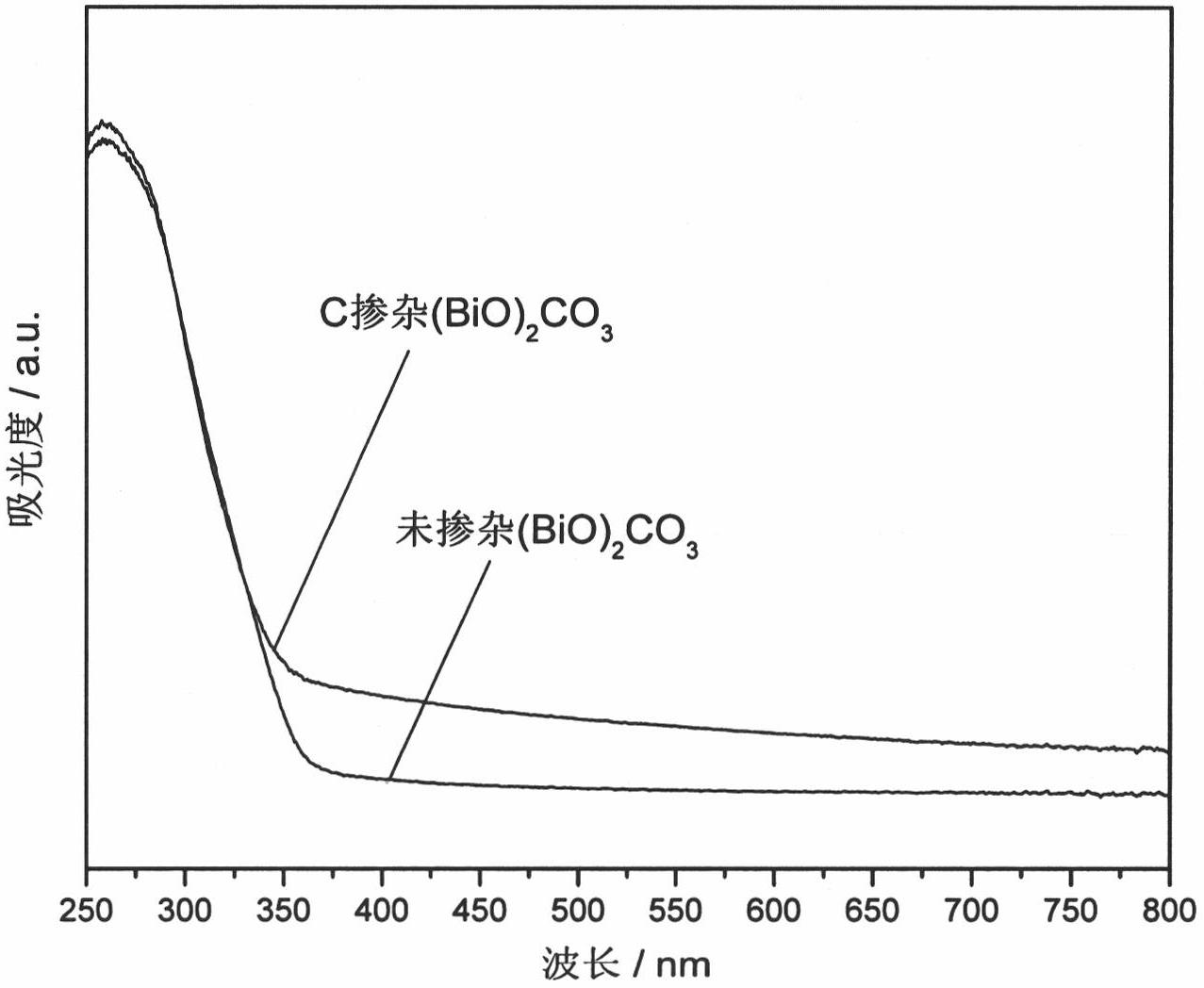
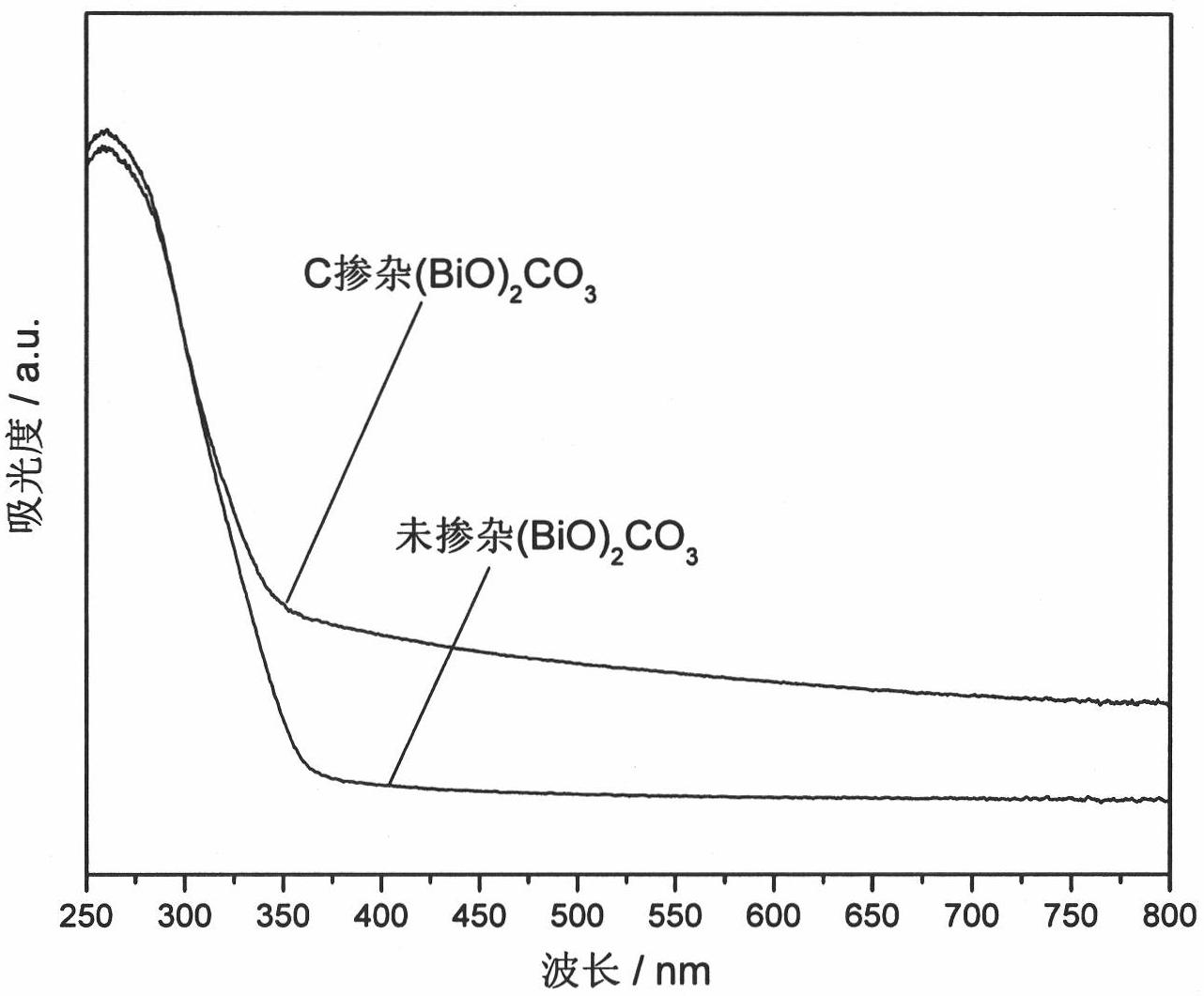
Preparation method of nanosheet self-assembled C-doped (BiO)2CO3 microsphere visible light catalyst
ActiveCN102671683AReduce defectsEasy to separatePhysical/chemical process catalystsDispersed particle separationMicrosphereHigh pressure
The invention discloses a preparation method of a nanosheet self-assembled C-doped (BiO)2CO3 microsphere visible light catalyst, which comprises the following steps: (1) dissolving a bismuth-containing precursor, a soluble carbonate and a doping carbon source in a water solution, stirring for 30 minutes, transferring the obtained mixed solution into a high-pressure hydrothermal kettle, and carrying out hydrothermal reaction at 120-250 DEG C for 3-100 hours; and (2) after the hydrothermal reaction finishes, cooling, filtering out the precipitate, respectively washing the precipitate with deionized water and ethanol, and drying to obtain the nanosheet self-assembled C-doped (BiO)2CO3 microspheres. According to the C-doped (BiO)2CO3 prepared by the method disclosed by the invention, the doping C element reduces the energy gap of (BiO)2CO3, and the (BiO)2CO3 has visible light catalytic activity. The experimental result proves that the NO removal rate of the bismuthyl carbonate photocatalyst disclosed by the invention is 30-45%, which indicates that the bismuthyl carbonate photocatalyst has high visible light catalytic activity.
Owner:江苏碧峰环保科技有限公司
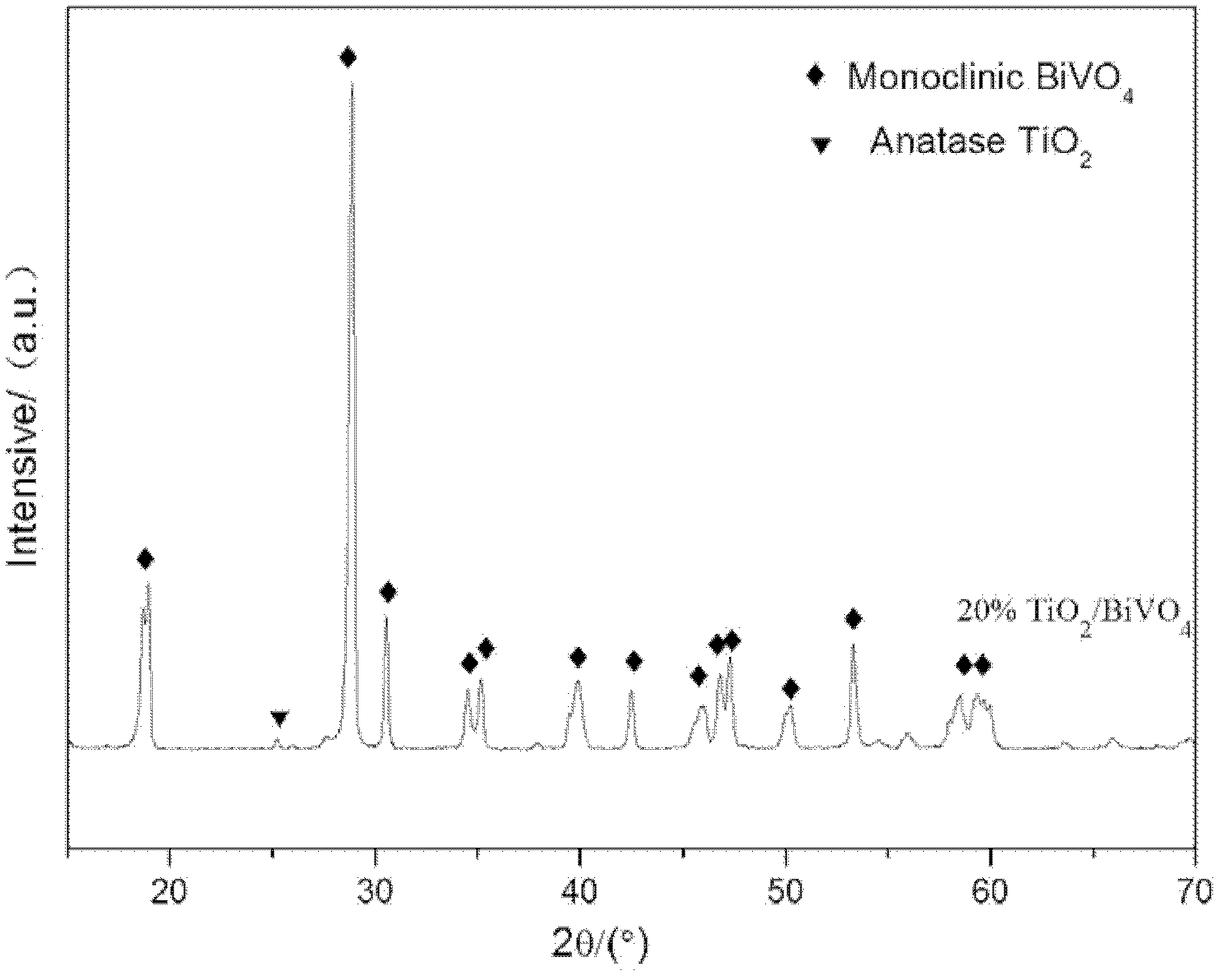
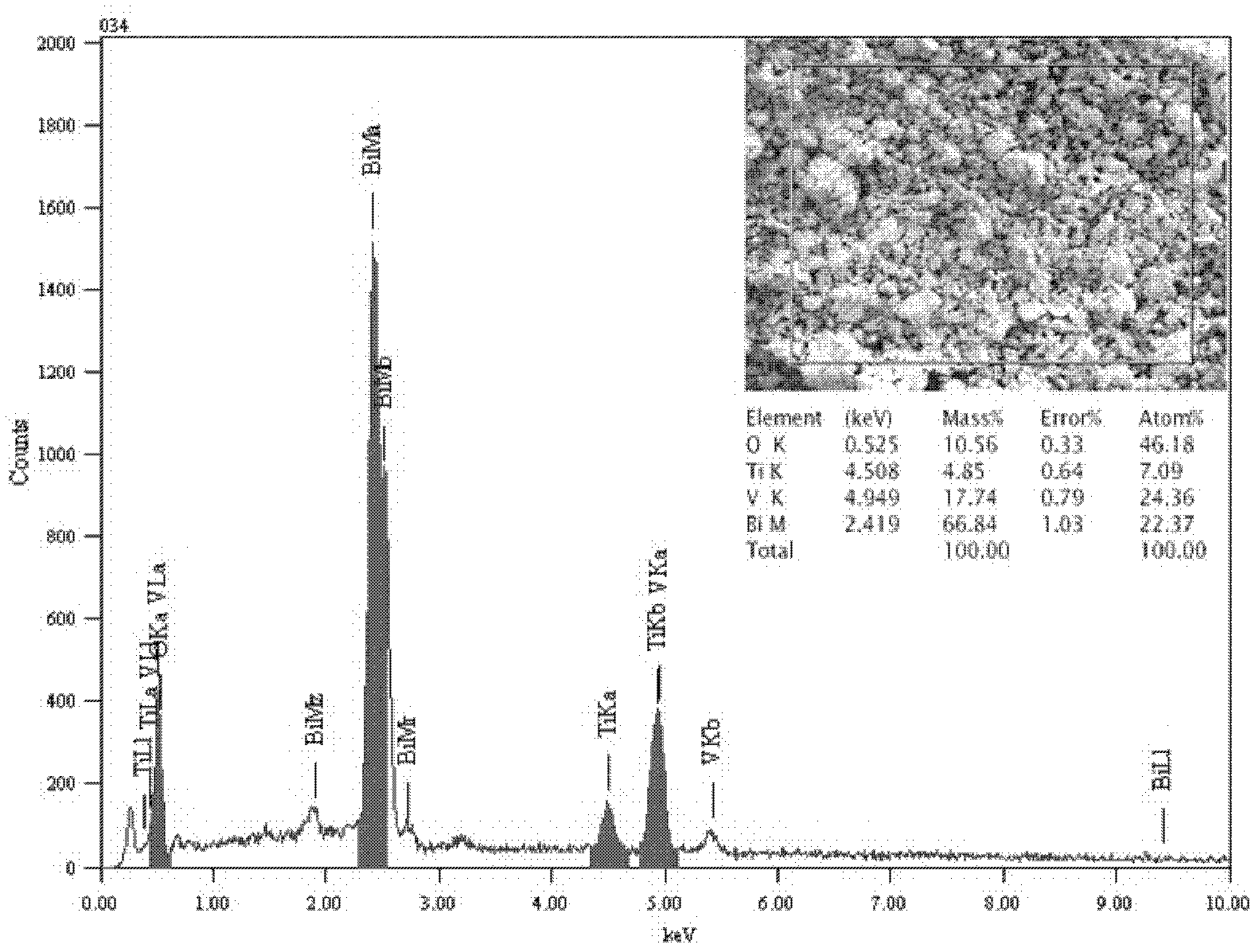
Method for preparing TiO2/BiVO4 composite photocatalyst by MH method
ActiveCN102580721AImprove photocatalytic performanceInhibitory complexWater/sewage treatment by irradiationCatalyst activation/preparationHydrothermal synthesisSalt solution
The invention discloses a method for preparing TiO2 / BiVO4 composite photocatalyst by a MH (microwave-hydrothermal) method. The method comprises the steps as follows: Bi(NO3)3 5H2O and (NH4)2TiF6 are resolved in HNO3 to form mother salt solution A, NH4VO3 is resolved in NaOH solution to form mother salt solution B, the mother salt solution A and the mother salt solution B are mixed uniformly to form precursor solution, the precursor solution is placed in a microwave hydrothermal reaction kettle for microwave hydrothermal reaction and is cooled after the reaction is over, and yellow sediment in the reaction kettle is taken out and is washed and dried. According to the invention, TiO2 / BiVO4 powder is synthesized quickly through a microwave-hydrothermal synthesis technology, and the photocatalysis performance of the powder is better because TiO2 particles are carried on the surface of BiVO4 to serve as an electron acceptor, and then compounding of a photon-generated carrier is inhibited, further the photocatalysis efficiency of pure-phase BiVO4 powder can be improved.
Owner:南通润能机械有限公司
Sandwiched Zr-MOFs (Metal-organic Frameworks)/graphene composite photocatalyst as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104190470AImprove photocatalytic efficiencyInhibitory complexOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsMetal-organic frameworkAromatic alcohol
The invention provides a sandwiched Zr-MOFs (Metal-organic Frameworks) / graphene composite photocatalyst as well as a preparation method and an application of the photocatalyst. The composite photocatalyst is a material with a sandwich-like structure, formed by a zirconium-containing metal-organic framework compound Zr-BDC-NH2 and graphene through compounding, wherein the graphene is 0.5-5.0% in mass fraction, the modified oxidized graphene is used as a graphene precursor, and a non-covalent self-assembly in-situ solvent thermal method is adopted for preparation; compared with the Zr-MOFs which is not loaded with graphene, the sandwiched Zr-MOFs / graphene composite photocatalyst has the photocatalytic performance improved remarkably, and can transform aromatic alcohol organic matters into the corresponding aromatic aldehyde substances in a high-selectivity manner under the excitation of visible light with 420-800 nanometers, the selectivity is 100% and the primary conversion rate can reach 70%. The non-covalent self-assembly in-situ solvent thermal method is simple and is easy to operate, and the prepared sandwiched Zr-MOFs / graphene composite photocatalyst has excellent capability of selectively oxidizing aromatic alcohol substances under a photocatalytic condition, and has important promotion significance on clean and high-efficiency industrial production of fine chemicals.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Low-concentration copper-doped titanium dioxide nanotube photocatalyst and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102240550AClear shapeImprove photocatalytic activityWater/sewage treatment by irradiationCatalyst activation/preparationElectrolytic agentTio2 nanotube
The invention relates to the field of titanium dioxide photocatalysis, in particular to researches in application of a titanium dioxide nanotube modified through metal doping to the field of photocatalysis. The invention provides a simple and feasible preparation method of a copper-doped TiO2 nanotube catalyst. According to the preparation method provided by the invention, low-concentration copper is effectively doped into a titanium dioxide nanotube array through adoption of a constant-voltage electrodeposition method; and the copper inside the titanium dioxide nanotube exists in the form of copper oxide; the copper-doped TiO2 nanotube catalyst has a good photocatalytic activity under ultraviolet light and sunlight; and the composition of electron hole pairs contained in titanium dioxide is effectively inhibited through copper doping, and therefore the photocatalytic property of the titanium dioxide nanotube is enhanced. The preparation method of the photocatalyst is a constant-voltage electrochemical deposition method, in which copper sulfate is taken as electrolyte, and a preparation process is simple; and in addition, the prepared copperdoped TiO2 nanotube catalyst has a stable property and can be used repeatedly.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Preparation method of ordered mesoporous titania/silver photocatalyst
InactiveCN102744059AImprove photocatalytic activityGood dispersionMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsWastewaterMunicipal sewage
The invention discloses a preparation method of ordered mesoporous titania / silver photocatalyst, relating to a preparation method of titania / silver and aiming to solve the technical problems of small specific surface area, poor orderliness and low photocatalytic activity of mesoporous titania / silver photocatalyst prepared by prior arts. The preparation method comprises the steps of silver solution preparation, titanium precursor preparation, titania / silver gel preparation, and heat treatment. The inventive photocatalyst has specific surface area of 120-160 m<2> / g, has the advantages of uniform mesopores and high catalytic activity; can be applied to photocatalysis field, and water treatment field of lake, ocean, municipal sewage and industrial sewage.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIV
Method for removing pollutant from water
InactiveCN1962474AFast responseShorten the timeWater/sewage treatment with mechanical oscillationsWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationPollutantEnvironmental chemistry
The invention discloses a water disposing method to remove pollution, which comprises the following steps: (1) detecting pollution content; adding water purification agent with quality rate at 1-10: 1 corresponding to pollution; (2) irradiating the disposed flow through ultrasonic reactor with inflow frequency of at 10KHz-10MHz and acoustic intensity at 0.1W-12W for 1-30min; (3) sedimenting; filtering; draining. The water purification agent is ferrate or ferrate composite agent, which improves removing rate of organic pollution effectively.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Flower-shaped mesoporous titanium dioxide material and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104016405AEasy to makeLow reaction temperatureMaterial nanotechnologyPhysical/chemical process catalystsHigh ratePhotocatalytic water splitting
The invention discloses a flower-shaped mesoporous titanium dioxide material and a preparation method and application thereof. The material is prepared by the following method: 1) adding a template agent into a diluent, adding concentrated hydrochloric acid, and stirring evenly; 2) adding a titanium source into the solution, and stirring; 3) placing the solution in the conditions of the relative humidity above 60% at the temperature of 40-80 DEG C for 12h-24h, crystallizing at 80-90 DEG C for 6-12h; and 4) refluxing a sample to remove a surface active agent, and drying to obtain the flower-shaped mesoporous titanium dioxide. According to the method, high-temperature calcinations is not needed, the reaction synthesis temperature is lower than 100 DEG C, and the obtained flower-shaped mesoporous titanium dioxide material has the advantages of good monodispersity, high specific surface area and controllable crystalline phase and the like. The flower-shaped mesoporous titanium dioxide material can be used for negative electrode materials of a lithium ion battery, has high charge and discharge specific capacity, stable cycle performance, excellent high rate performance and very good photocatalytic activity, and can be used in the fields of degradation of organic pollutants, photocatalytic water splitting for hydrogen production, dye-sensitized solar cells and the like.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Polypyrrole-TiO2 magnetically supported photocatalytic composite material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103464213AImprove magnetic propertiesImprove stabilityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsSpectral responsePolypyrrole
The invention discloses a polypyrrole-TiO2 magnetically supported photocatalytic composite material and a preparation method thereof, belongs to the field of magnetically supported photocatalytic material technology, and relates to a ferrite magnetically supported photocatalytic composite material. The polypyrrole-TiO2 magnetically supported photocatalytic composite material comprises a magnetic substrate and a photocatalyst; the magnetic substrate is obtained by subjecting ferrite to surface organic modification with a silane coupling agent, and the photocatalyst is prepared by subjecting TiO2 to surface photosensitization with polypyrrole; and the polypyrrole-TiO2 magnetically supported photocatalytic composite material is of a multi-layer core-shell structure comprising ferrite, the silane coupling agent, TiO2 and polypyrrole from inside to outside. The polypyrrole-TiO2 magnetically supported photocatalytic composite material is capable of increasing magnetic property and acid stability of ferrite; inhibiting recombination of TiO2 carriers; enlarging spectral response range of TiO2; and improving utilization ratio of sunlight.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Perovskite solar cell with high fill factor and method for preparing perovskite solar cell
ActiveCN109360889AImprove efficiencyImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesPhysicsFill factor
The invention discloses a perovskite solar cell with a high fill factor and a method for preparing the perovskite solar cell. The perovskite solar cell is sequentially provided with a transparent conductive substrate, a hole transport layer, a perovskite thin film, an interface passivation layer, an electron transport layer and a cathode from bottom to top. The interface passivation layer is madefrom alkali metal halide or alkaline earth metal halide on the perovskite thin film by means of evaporation, and the thickness of the interface passivation layer ranges from 1 nm to 5 nm; the electrontransport layer is a C<60> thin film formed on the interface passivation layer by means of evaporation, and the thickness of the C<60> thin film ranges from 10 nm to 20 nm; the cathode is a metal thin film formed on the electron transport layer by means of evaporation, and the thickness of the metal thin film ranges from 50 nm to 120 nm; the perovskite thin film is made from methylamine lead halide or formamidine lead halide; conductive thin films are arranged on the transparent conductive substrate. The perovskite solar cell and the method have the advantages that the shortcoming of incapability of preparing large-area solar cell devices by the aid of existing spin-coating technologies can be overcome by the aid of the perovskite solar cell and the method; the interface passivation layeris prepared by the aid of processes for carrying out evaporation on the alkali metal halide or the alkaline earth halide, accordingly, current carrier recombination at interfaces of perovskite lightabsorption layers and the electron transport layer can be reduced, the efficiency of the perovskite solar cell can be improved, and mass production of large-area cells further can be implemented.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for preparing visible light photocatalyst Bi2O3/TiO
InactiveCN101745377AImprove quantum efficiencyEasy to operateCatalyst activation/preparationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsCompound semiconductorVisible spectrum
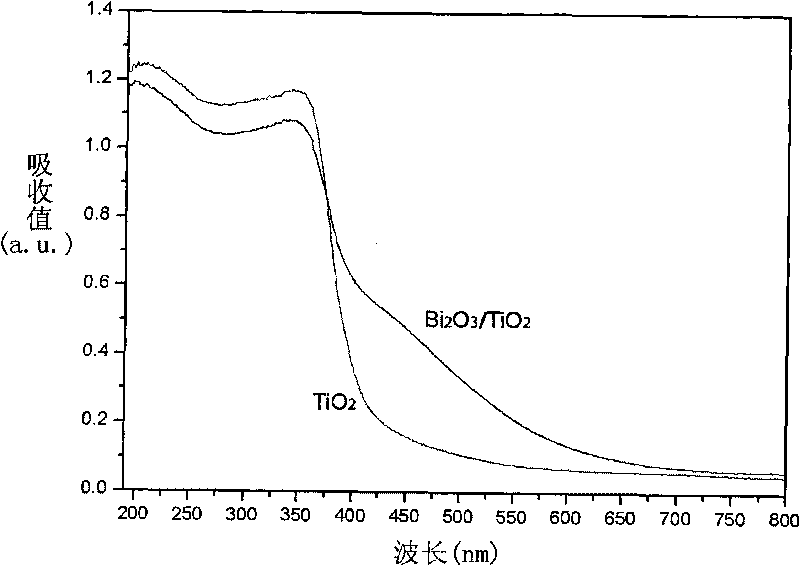
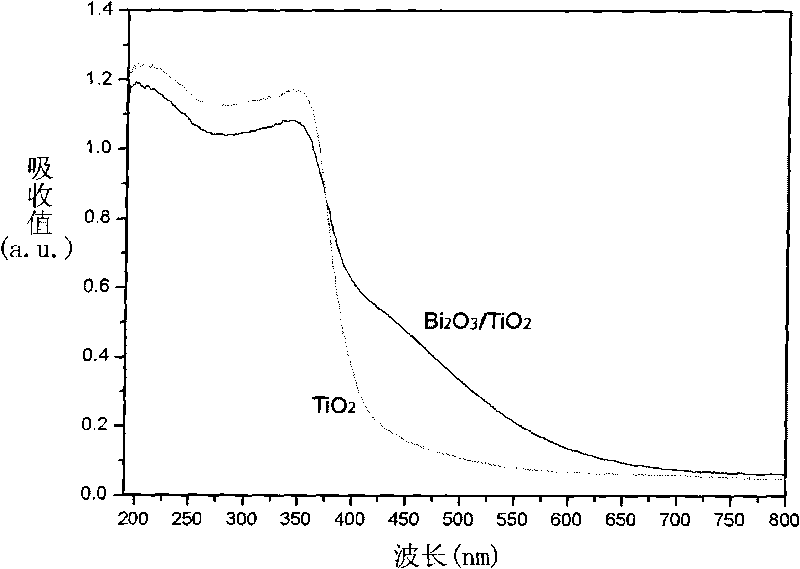
The invention relates to a method for preparing visible light photocatalyst Bi2O3 / TiO2, comprising the following steps: (1) adding cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide to anhydrous ethanol, and ultrasonically dissolving the cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide to the anhydrous ethanol to form transparent solution A; (2) adding tetrabutyl titanate to the solution A, and ultrasonically dissolving the tetrabutyl titanate to the solution A to form light yellow transparent solution B; (3) heating the solution B to 75-85 DEG C, adding bismuth nitrate pentahydrate to the solution B, and ultrasonically dispersing the bismuth nitrate pentahydrate to the solution B to form light yellow sol; (4) standing the light yellow sol at 25-45 DEG C to form light yellow gel; (5) aging the light yellow gel at 80-100 DEG C to form light yellow particles; and (6) heating light yellow particles from the room temperature to 450-550 DEG C, calcining the light yellow particles for 5-8h, and cooling the calcined light yellow particles to room temperature naturally to obtain compound semiconductor with visible light catalytic activity. The method for preparing the visible light photocatalyst of Bi2O3 / TiO inhibits the combination of the light induced electrons and the hole, improves the quantum efficiency of the photocatalytic reaction and the utilization of solar energy, is easy to operate, has low cost and lays a foundation for the light catalytic technology to be practical. The photocatalyst Bi2O3 / TiO2 has high visible light catalytic performance.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for preparing B-doped g-C3N4 photocatalyst through nonmetal liquid-phase doping
InactiveCN104549500AGood thermal stabilityGood chemical stabilityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsEnergy inputSemiconductor materialsNew energy
The invention discloses a method for preparing a B-doped g-C3N4 photocatalyst through nonmetal liquid-phase doping, and belongs to the technical field of hydrogen production through photocatalytic materials. According to the prepared organic polymer semiconductor material g-C3N4 photocatalyst, cheap chemical material urea is taken as a reactant source, sodium tetraphenylborate is taken as a doping source, PEI (polyethyleneimine) is taken as a surface charge modifier, and the B-doped g-C3N4 photocatalyst is successively prepared with a pyrolysis and polymerization method easy to operate. The nonmetal liquid-phase doping modified g-C3N4 photocatalyst has novel organization structure appearance, good response of visible light with wavelength larger than 420 nm and good photocatalytic hydrogen generation property, and promotes solar energy conversion into new energy under the photocatalysis action at a low cost; the provided preparation method has the advantages of cheap raw materials, simple and convenient technology and the like and has an important research value and a wide industrialized application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
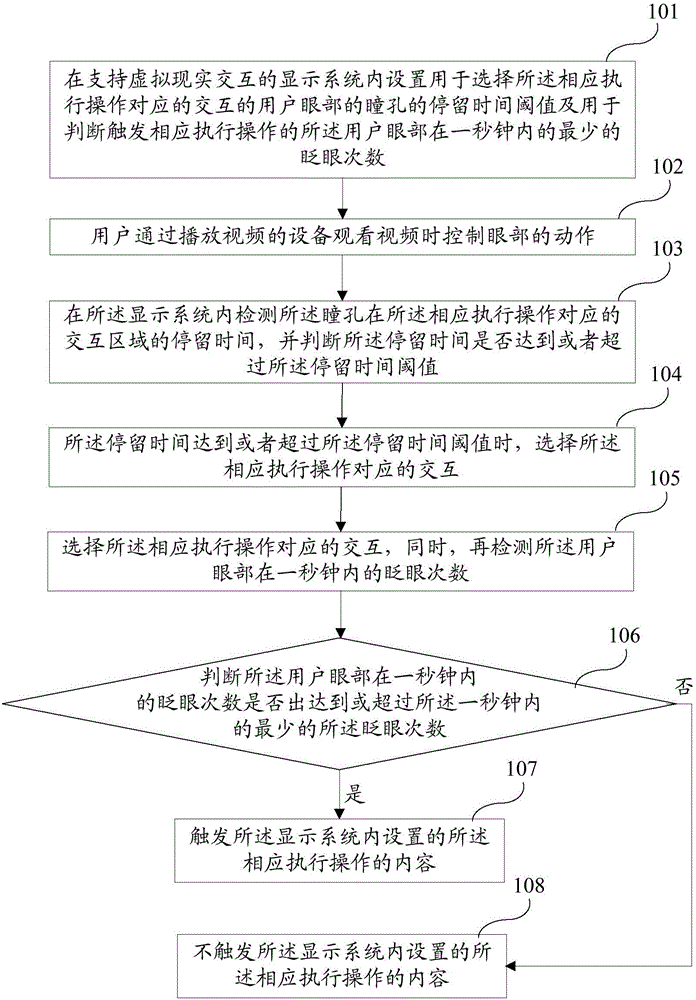
Method for controlling virtual reality interaction according to use eye actions
InactiveCN106095111AInhibitory complexImprove experienceInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingBlink frequencyRetention time
The invention discloses a method for controlling virtual reality interaction according to use eye actions. The method comprises the steps that a residence time threshold value, for selecting interaction corresponding to a corresponding execution operation, of the pupils of the user eyes and the least blinking frequency, for judging and triggering the corresponding execution operation, of the user eyes within one second are set in a display system supporting virtual reality interaction; the retention time of the pupil in the interaction area corresponding to the corresponding execution operation is detected in the display system, and when the retention time reaches or exceeds the retention time threshold value, interaction corresponding to the corresponding execution operation is selected; the blinking frequency of the user eyes within one second is detected, and when the blinking frequency of the user eyes within one second reaches or exceeds the least blinking frequency within one second, content, arranged in the display system, of the corresponding execution operation is triggered. According to the method, control of the user eye actions over virtual reality interaction is achieved.
Owner:北京奇思信息技术有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com