Patents
Literature
859 results about "Dark current" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
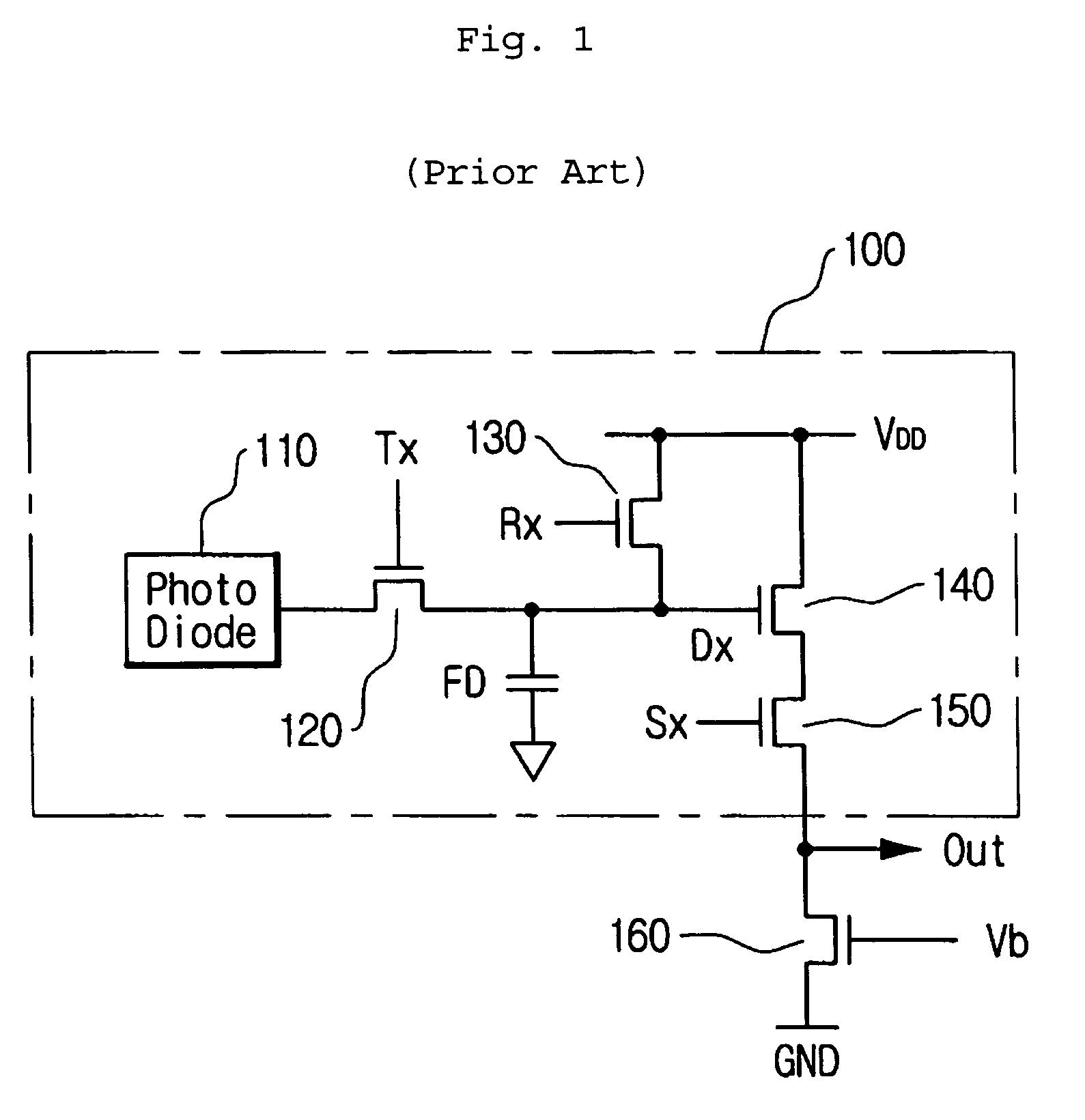
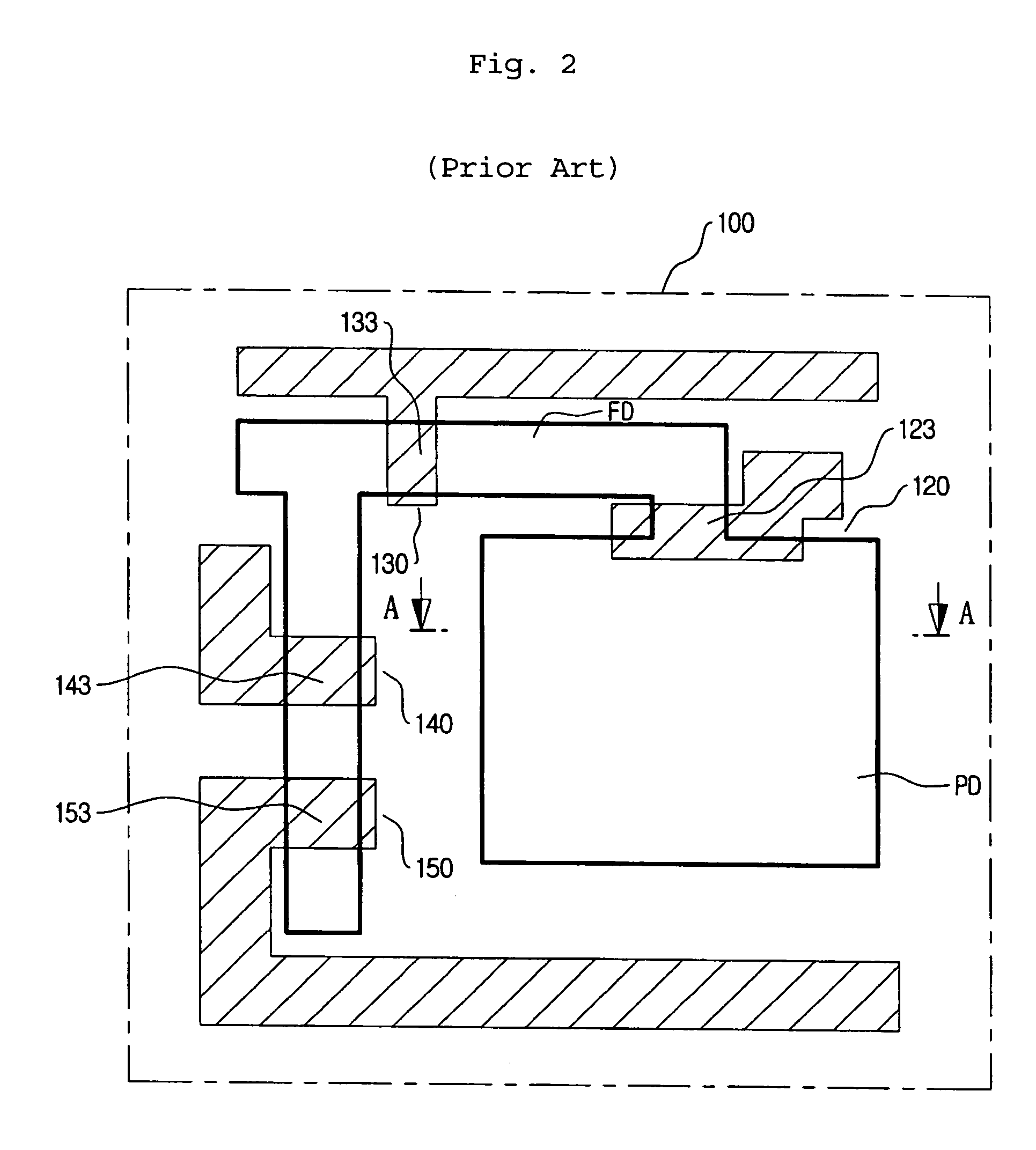
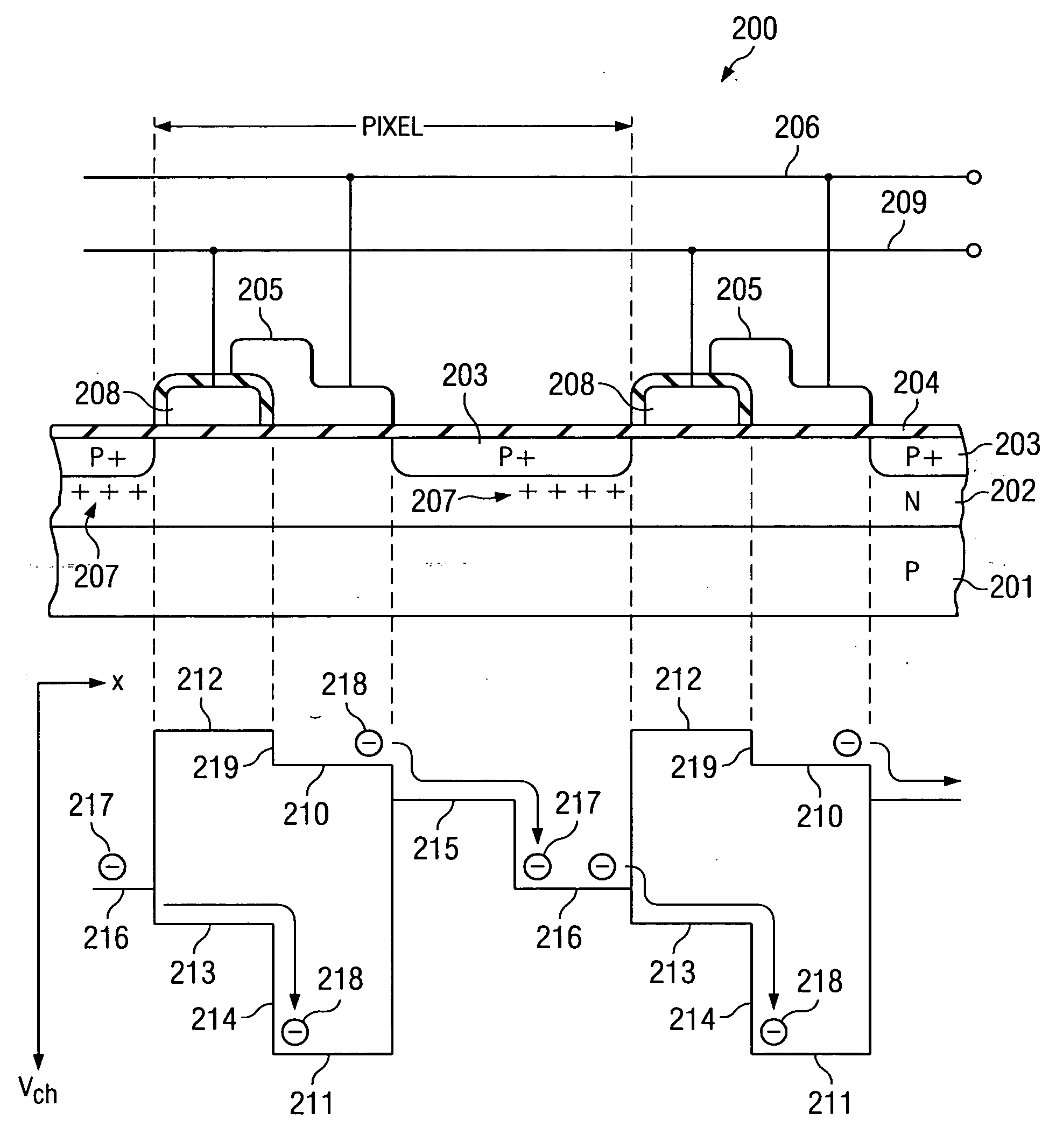
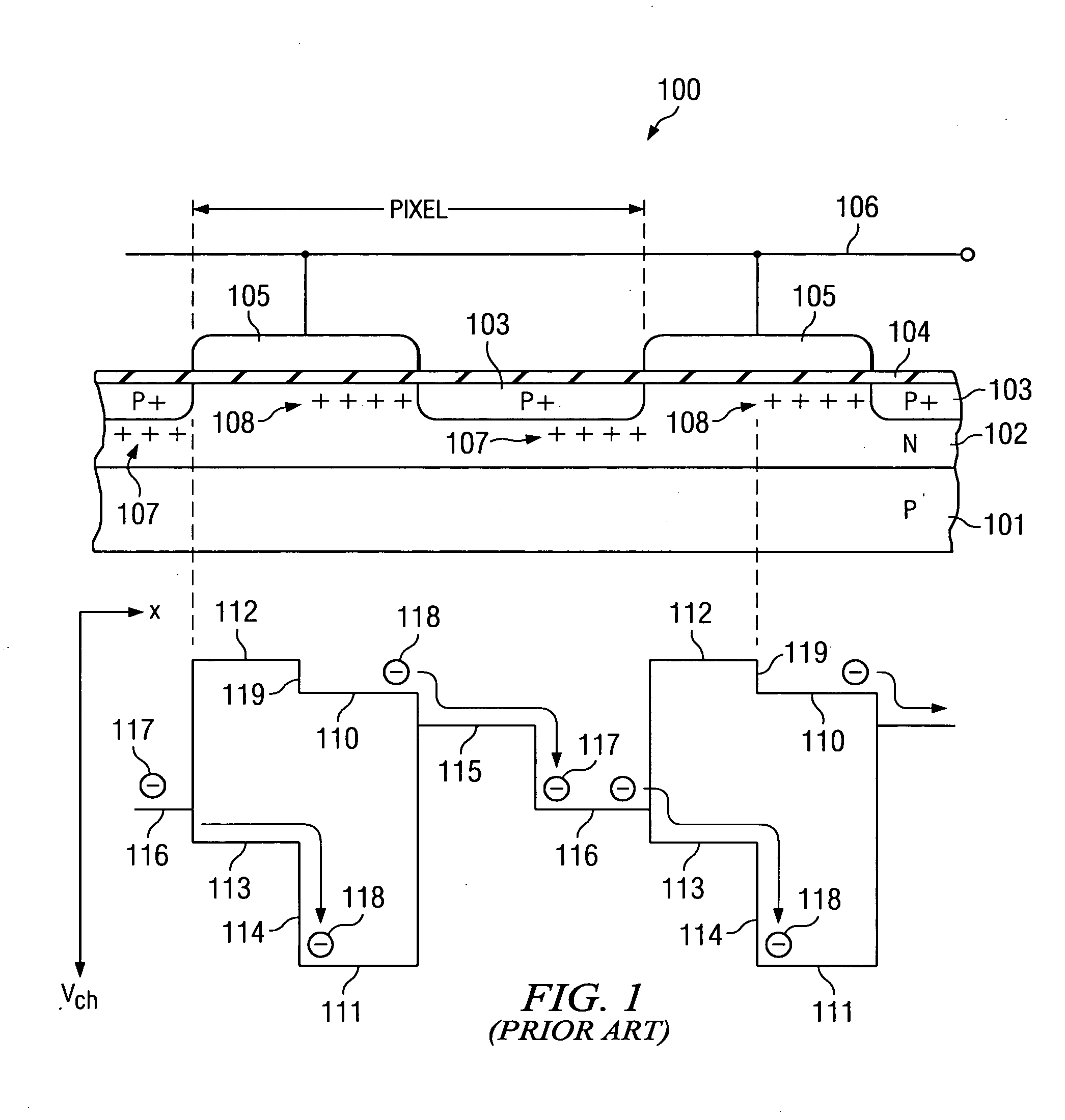
In physics and in electronic engineering, dark current is the relatively small electric current that flows through photosensitive devices such as a photomultiplier tube, photodiode, or charge-coupled device even when no photons are entering the device; it consists of the charges generated in the detector when no outside radiation is entering the detector. It is referred to as reverse bias leakage current in non-optical devices and is present in all diodes. Physically, dark current is due to the random generation of electrons and holes within the depletion region of the device.
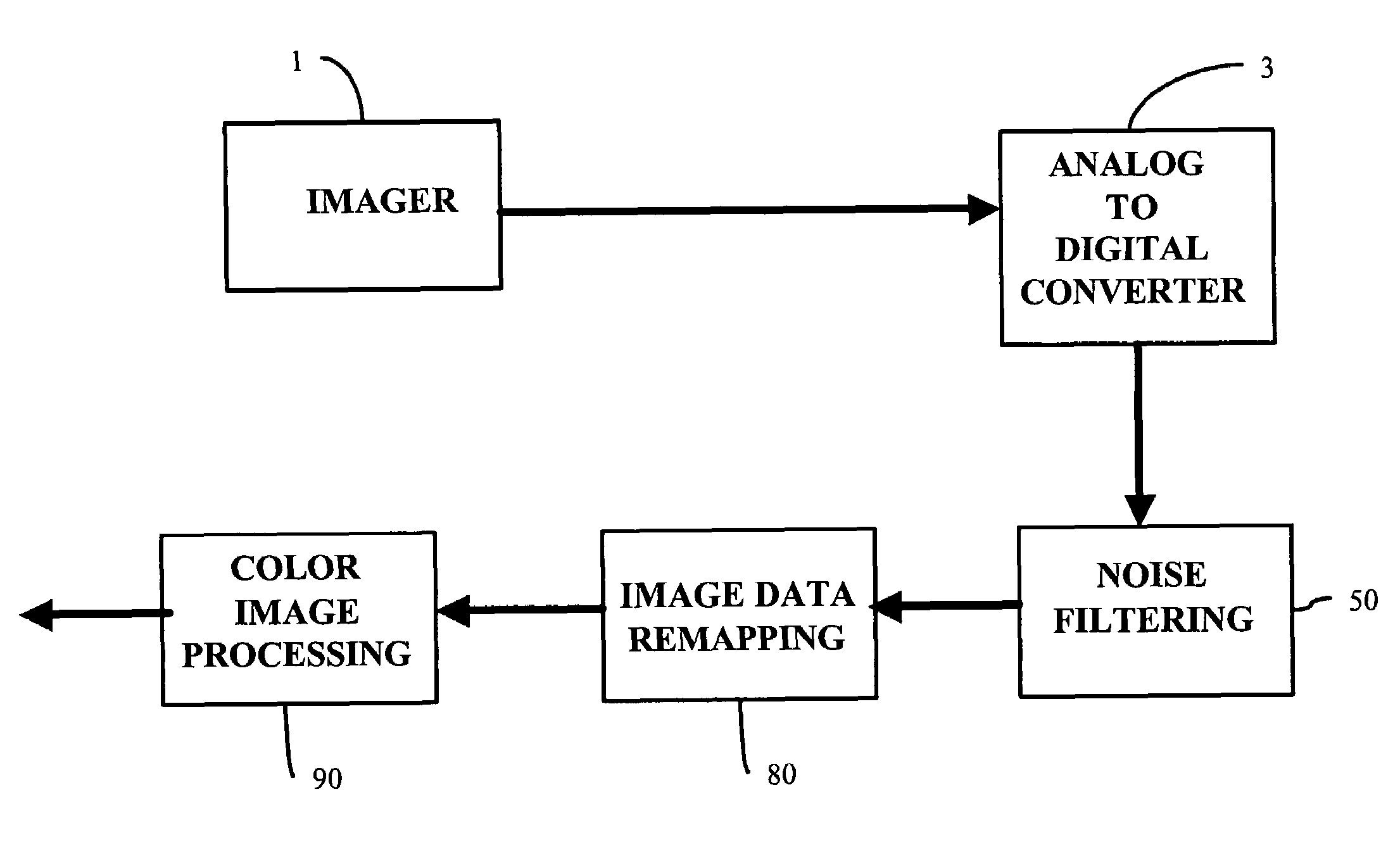
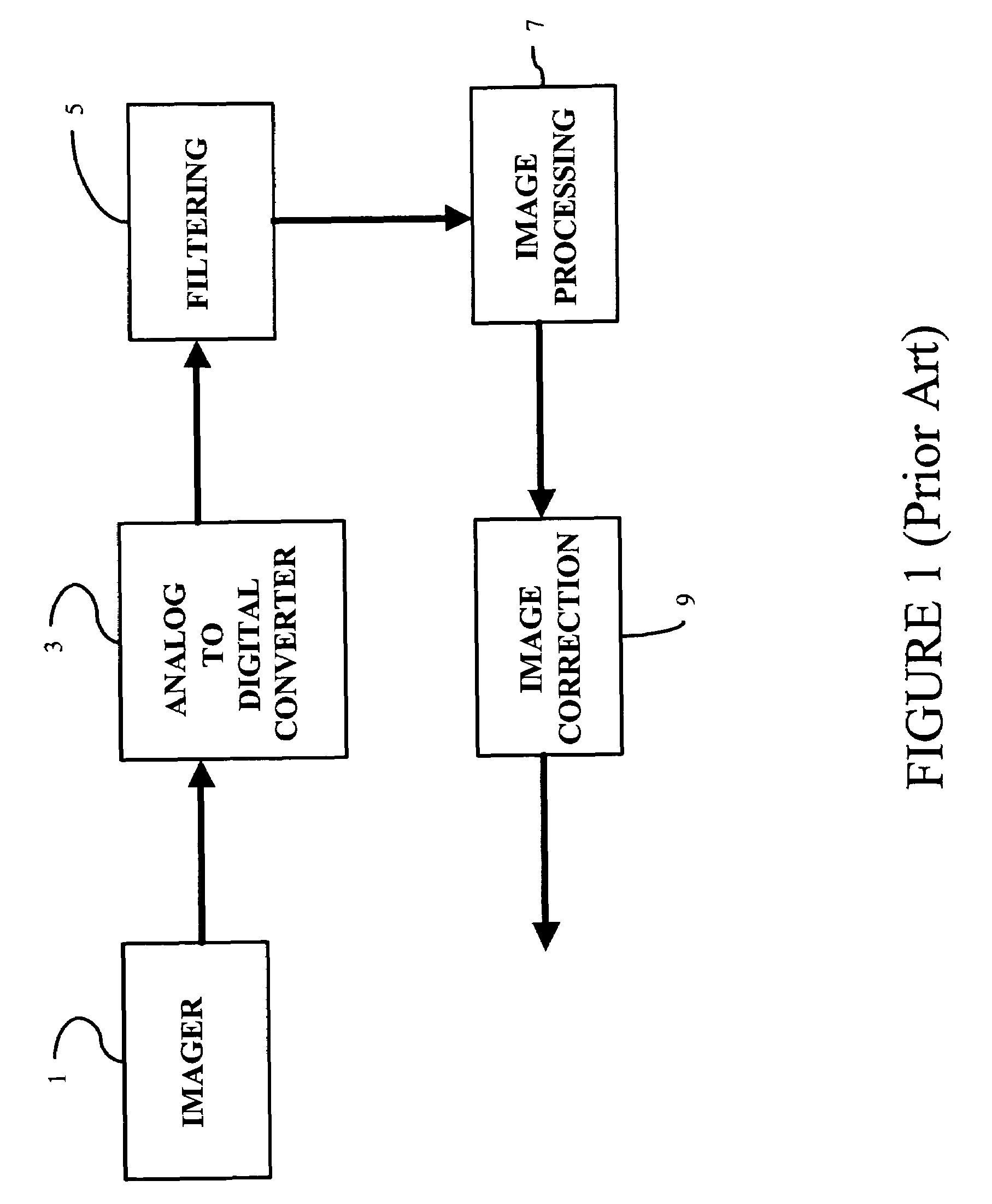
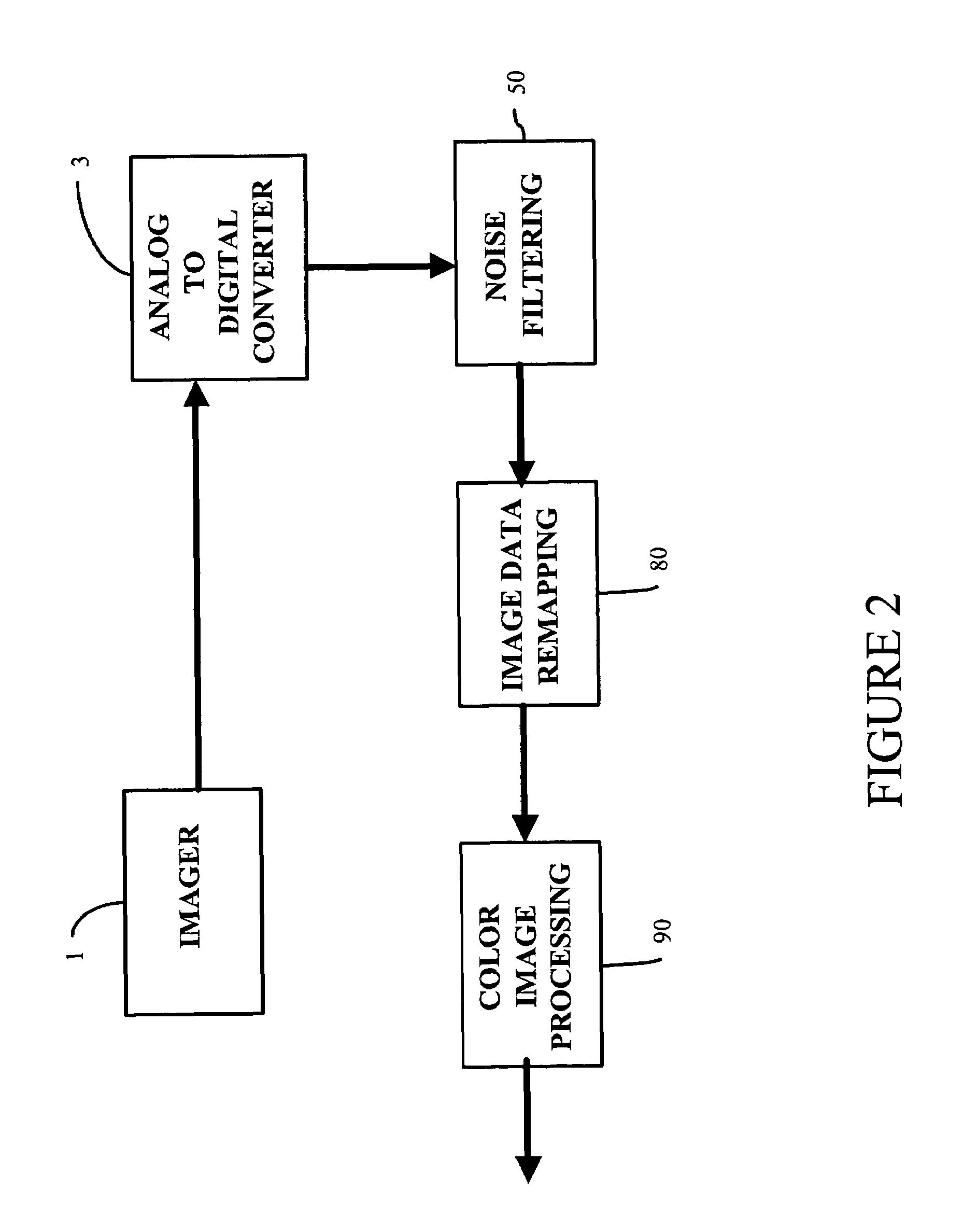
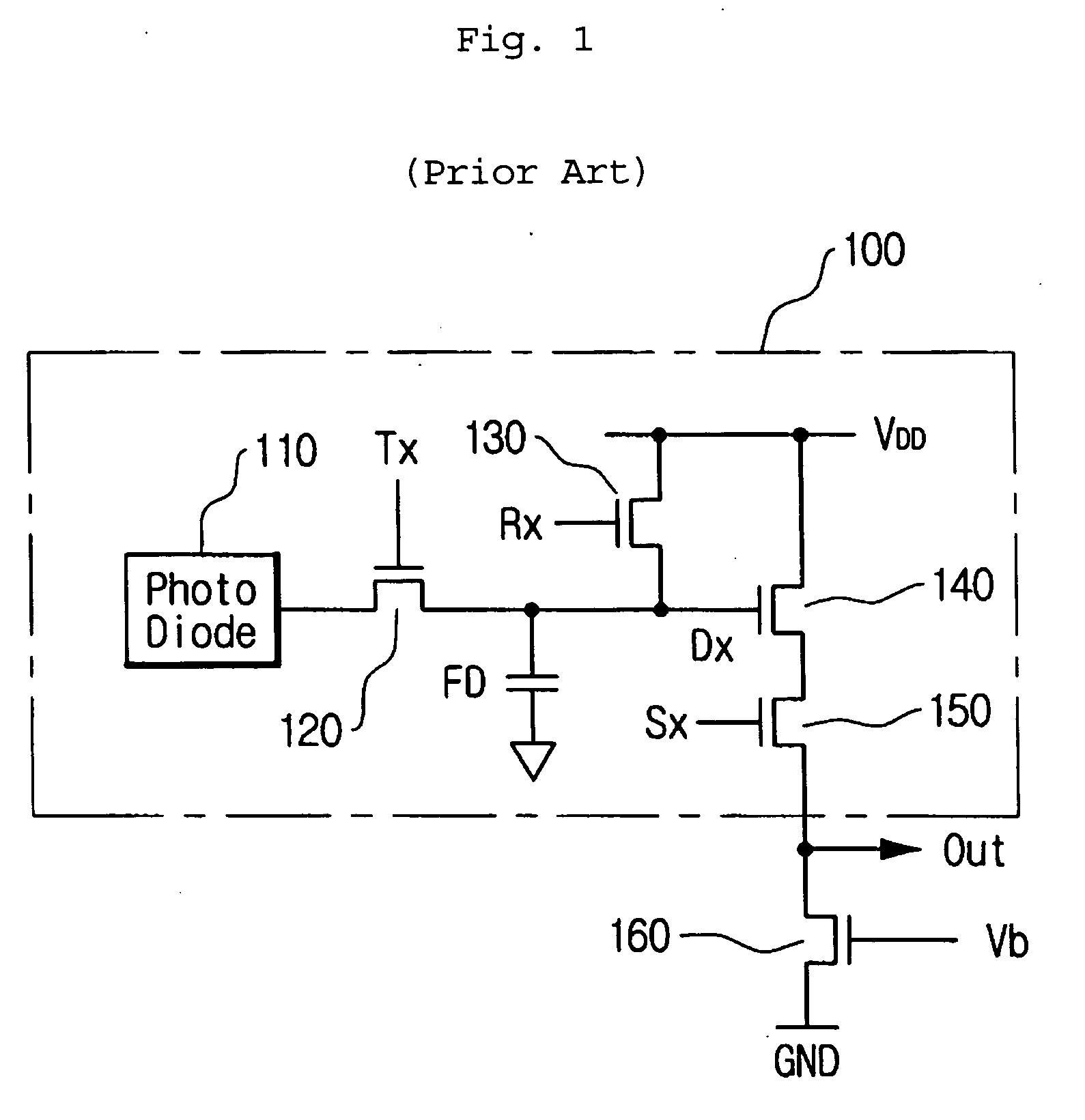
System and method for processing non-linear image data from a digital imager
ActiveUS7349574B1Avoid overcompensationEliminate the effects ofTelevision system detailsImage enhancementHueDigital image data
A system and method process non-linear image data, still or video, from a digital imager. Noise generated by analog-to-digital converters is filtered from a pixel of digital image data. Moreover, the effects of single pixel defects in the imager are eliminated by clamping a predetermined pixel of image data within the window when the value of the predetermined pixel is greater than a maximum value of the image data of neighboring pixels or less than a minimum value of the image data of neighboring pixels. Ripples in image data are reduced by eliminating the effects of single pixel defects before filtering for crosstalk caused by electrical crosstalk between sensor elements in an imager. Dark current is removed from image data generated by an imager by subtracting a fraction of a determined dark current value from all image data generated by the imager to compensate for nonlinearities in dark current across the imager. The image data is white balanced by creating a set of scalar color adjustments from determined average color values and constraining the set of scalar adjustments to plausible lighting conditions to prevent overcompensation on images having large regions of similar hue. Lastly, utilization of a fixed set of intensity levels is optimized by remapping and restreching the image data to create new luma values for each pixel.
Owner:SMAL CAMERA TECH
Discriminating photo counts and dark counts in an avalanche photodiode
ActiveUS20150338270A1Photometry using reference valueMaterial analysis by optical meansCarrier signalPulse height
The output of an avalanche photodiode (APD) comprises a “photocurrent” component comprising photon initiated events resulting from the interaction of photons with the APD and a “dark current” component comprising dark carrier events arising in the APD even when the APD is not exposed to light. Differences in the pulse height distributions of photon initiated events and dark carrier initiated events are used to statistically discriminate between photocurrent and dark current components of APD output.
Owner:LADARSYST INC
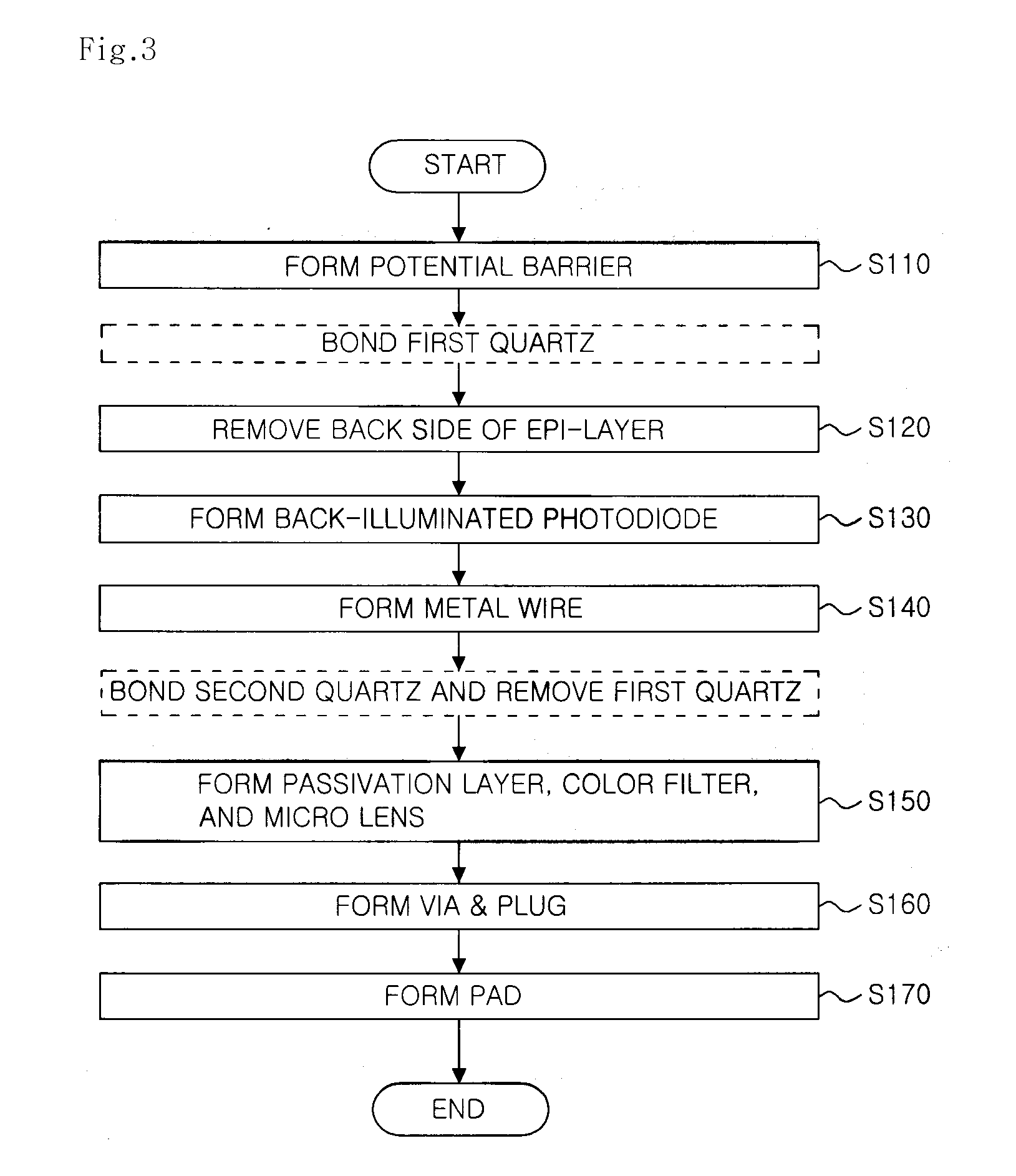
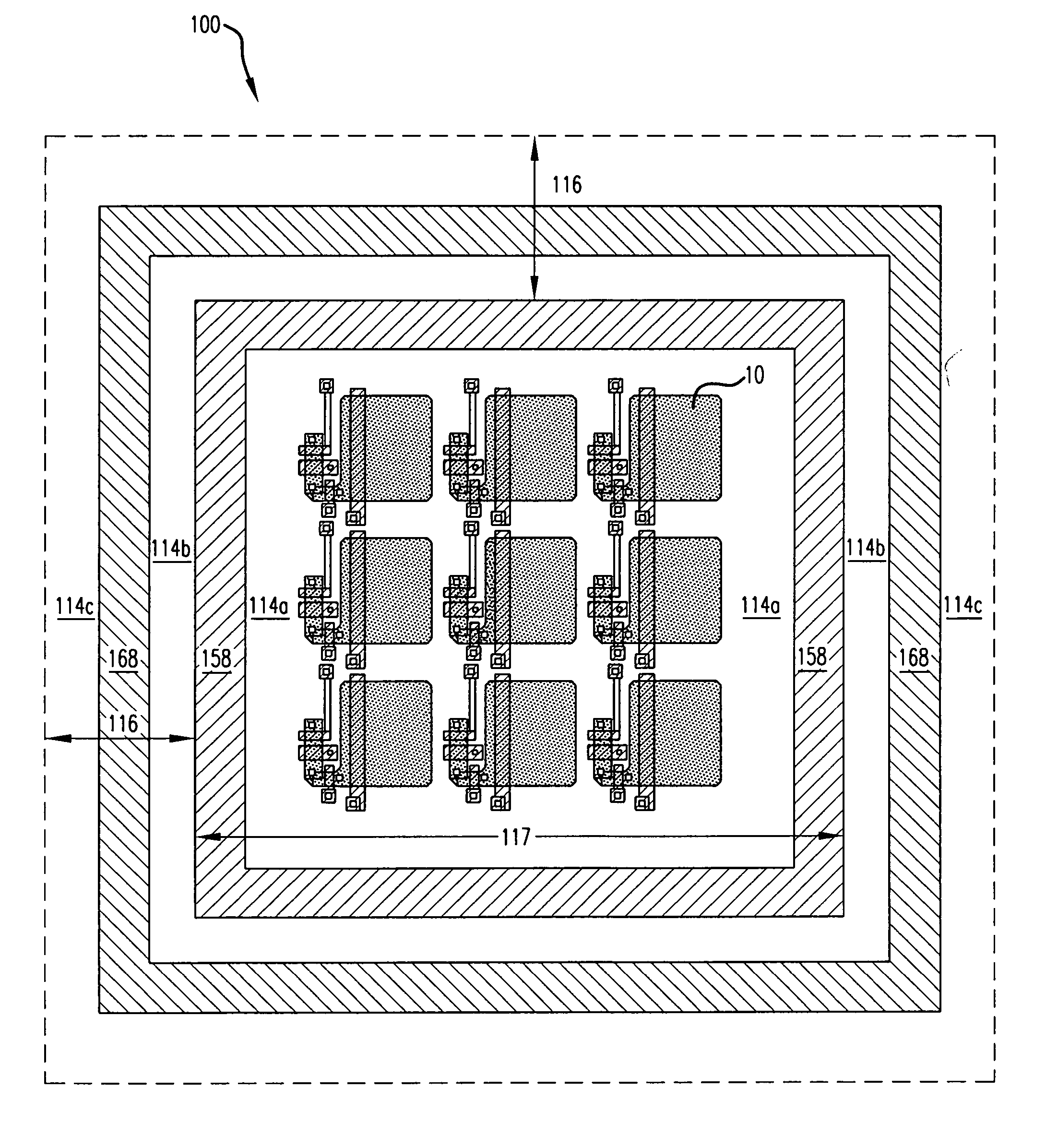
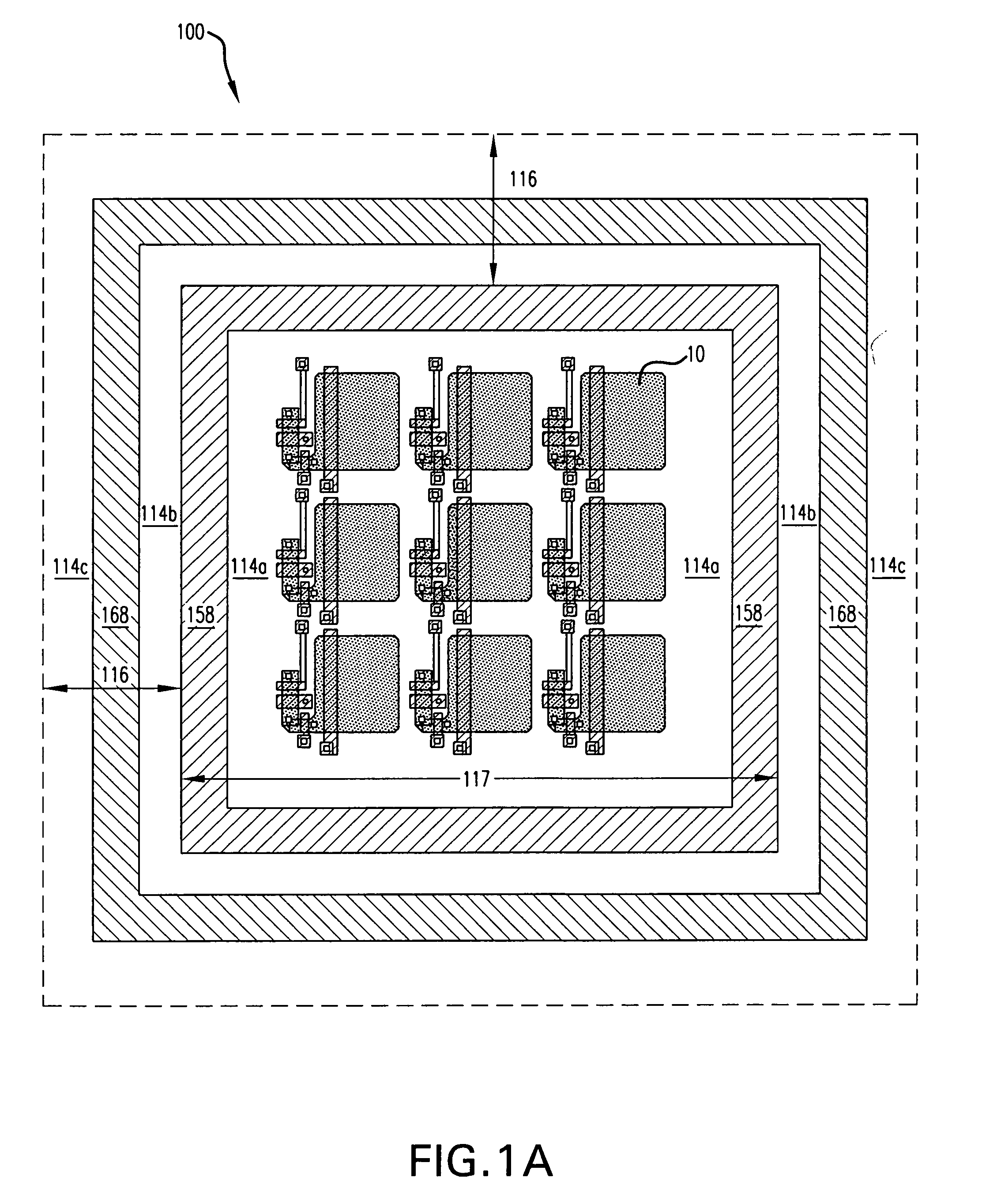
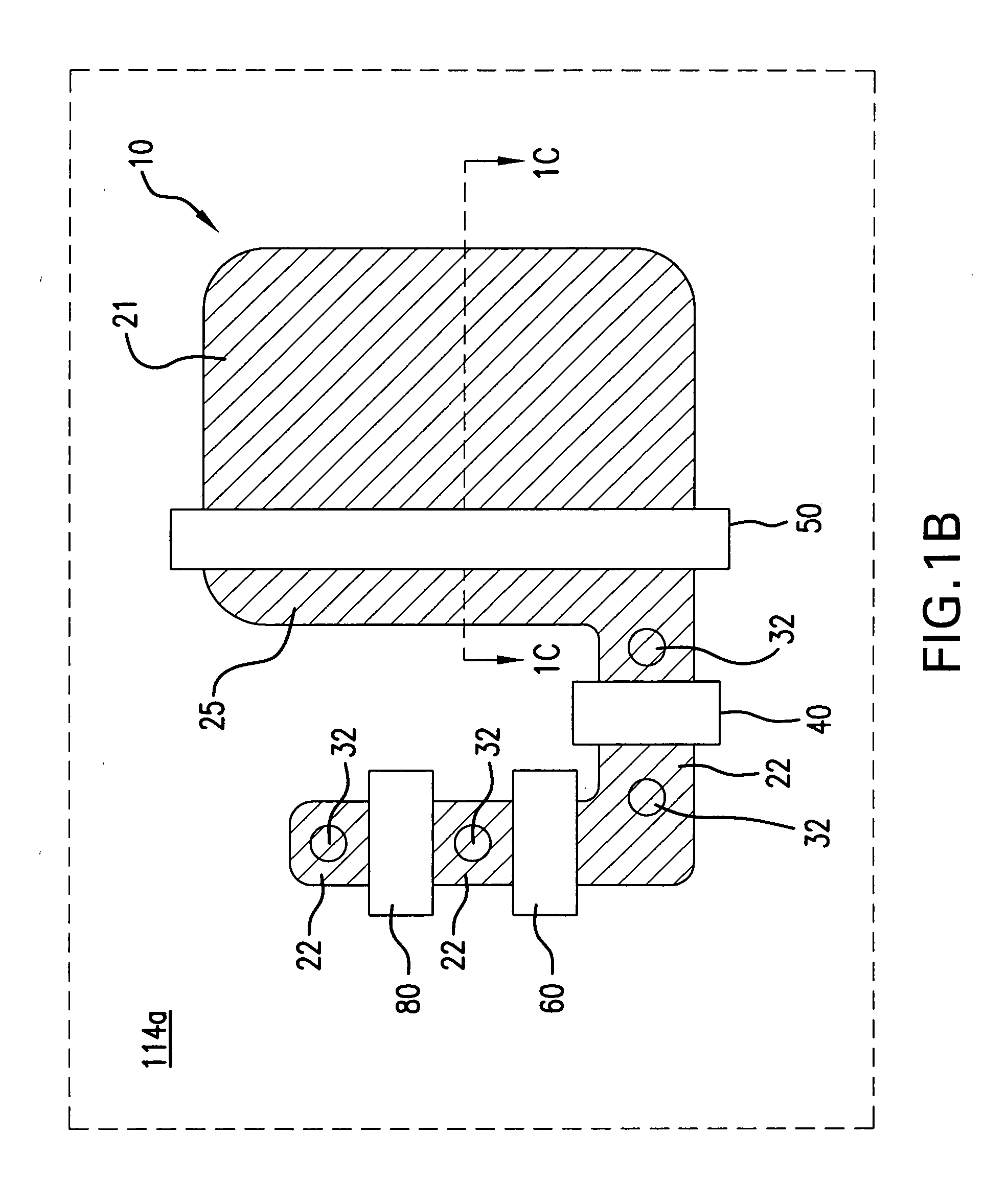
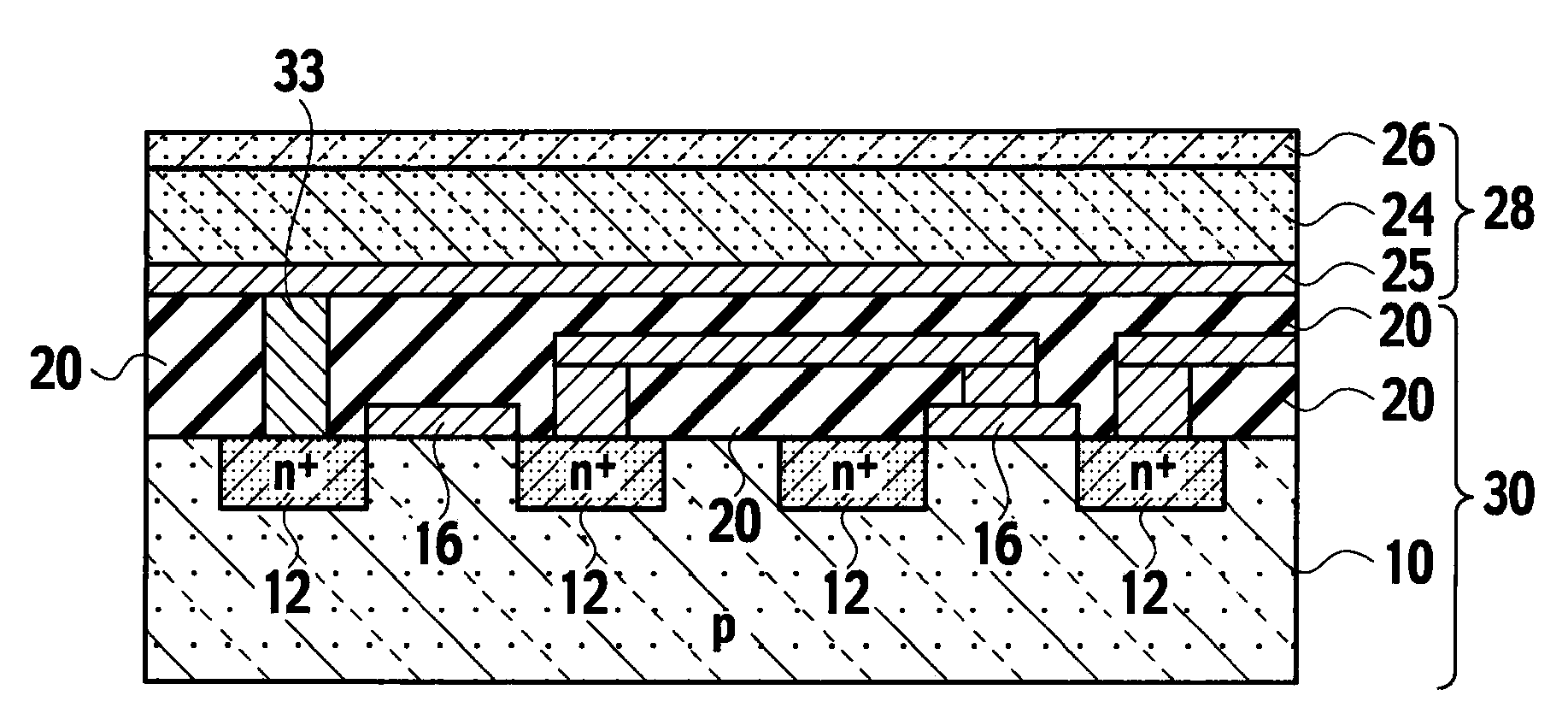
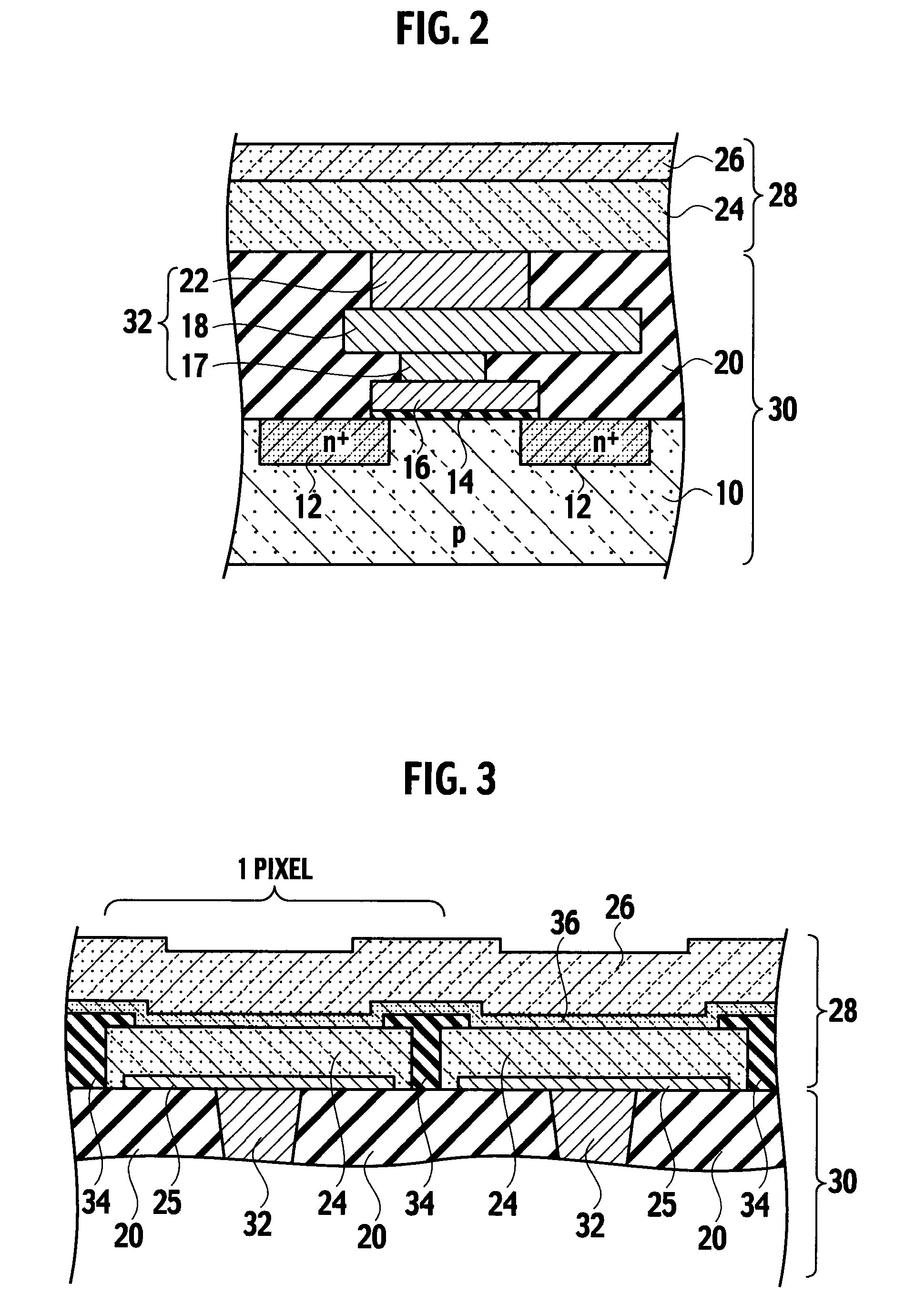
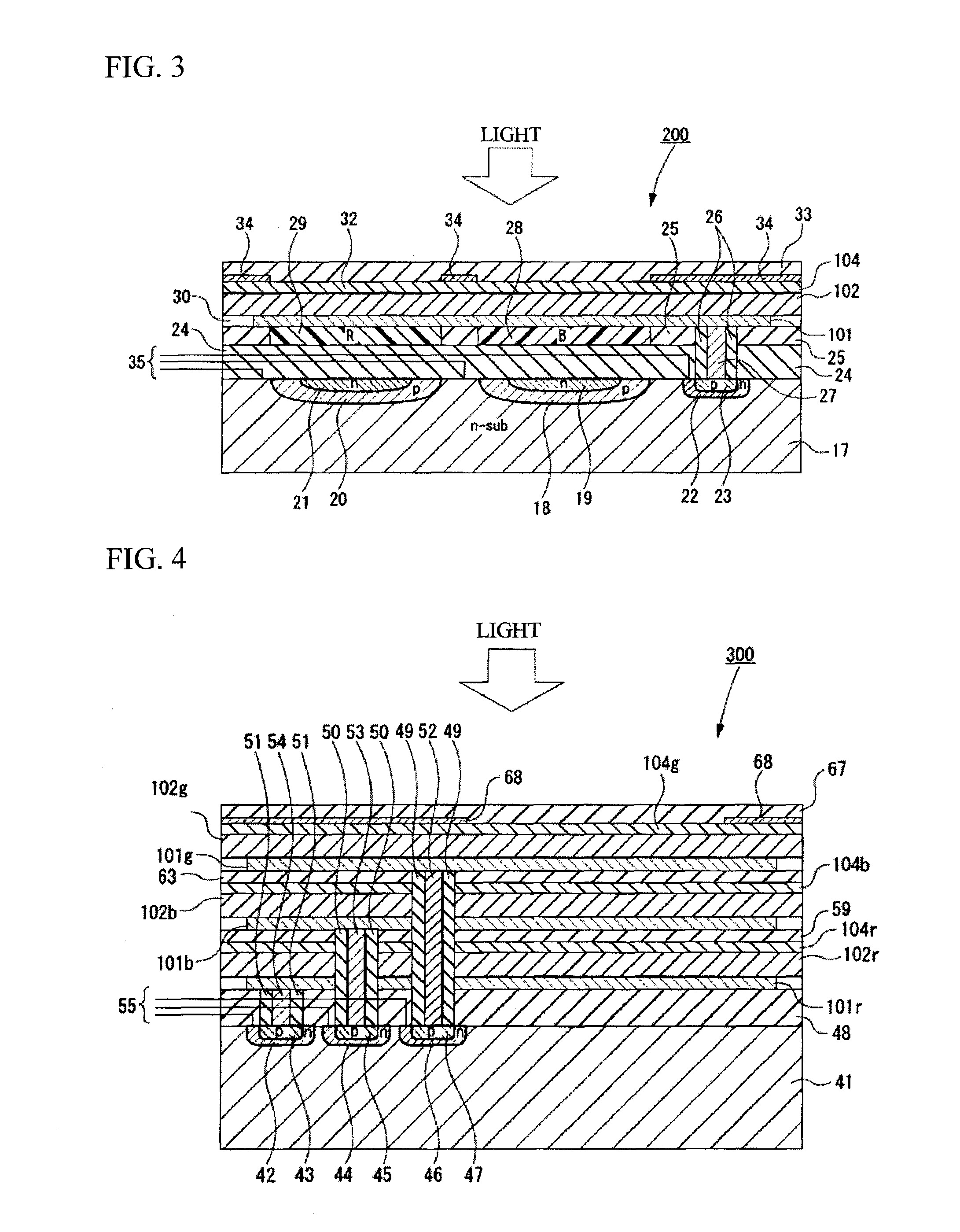
Image sensor using back-illuminated photodiode and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20090224345A1Control generationHigh sensitivitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh densityPhotodiode
An image sensor using a back-illuminated photodiode and a manufacturing method thereof are provided. According to the present invention, since a surface of the back-illuminated photodiode can be stably treated, the back-illuminated photodiode can be formed to have a low dark current, a constant sensitivity of blue light for all photodiodes, and high sensitivity. In addition, it is possible to manufacture an image sensor with high density by employing a three dimensional structure in which a photodiode and a logic circuit are separately formed on different substrates.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Image sensor for reduced dark current
ActiveUS20050133825A1Reduce dark currentImprove protectionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectronPixel array
A method and structure for reducing dark current in an image sensor includes preventing unwanted electrons from being collected in the photosensitive region of the image sensor. In one embodiment, dark current is reduced by providing a deep n-type region having an n-type peripheral sidewall formed in a p-type substrate region underlying a pixel array region to separate the pixel array region from a peripheral circuitry region of the image sensor. The method and structure also provide improved protection from blooming.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
CMOS sensor with approximately equal potential photodiodes
InactiveUS20090224351A1Minimize and eliminate dark currentReduce and eliminate clock noiseTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCMOS sensorCharge detection
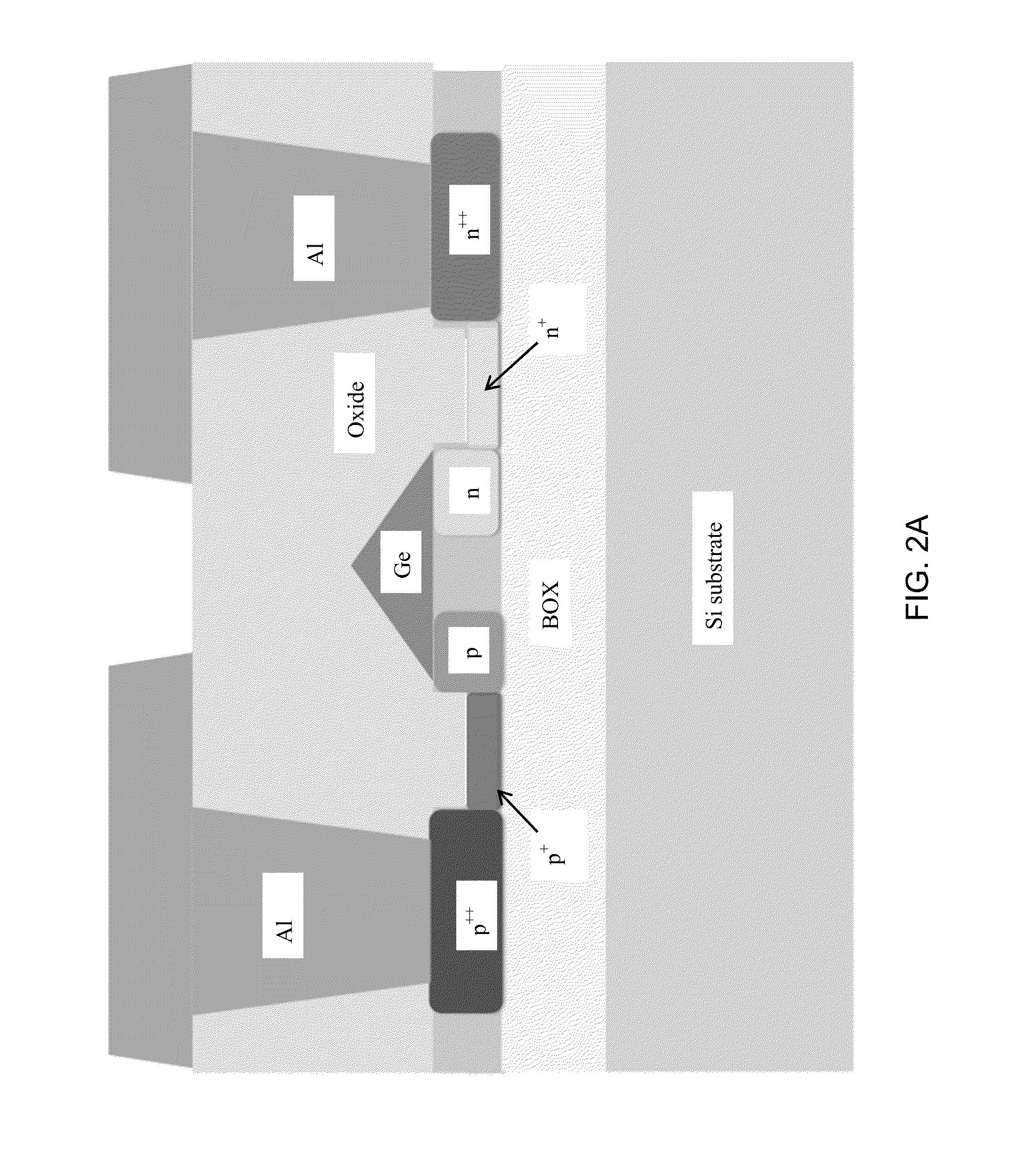
A MOS or CMOS based active pixel sensor designed for operation with zero or close to zero potential across the pixel photodiodes to minimize or eliminate dark current. In this preferred embodiment, the voltage potential across the pixel photodiode structures is maintained constant and close to zero, preferably less than 1.0 volts. This preferred embodiment enables the photodiode to be operated at a constant bias condition during the charge detection cycle. In preferred embodiments the pixel photodiodes are produced with a continuous pin or nip photodiode layer laid down over pixel electrodes of the sensor. In other preferred embodiments the pixel photodiode structures are produced beside and physically isolated from the regions where CMOS circuits are formed. In some of these preferred embodiments the isolated pixel photodiode structures are comprised of crystalline germanium deposited in cavities in a silicon substrate. This embodiment can be adapted especially for imaging at short wave infrared frequencies. Preferred embodiments are adapted for correlated double sampling.
Owner:E PHOCUS
Front-side illuminated, back-side contact double-sided pn-junction photodiode arrays
ActiveUS20080099871A1Maintain performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
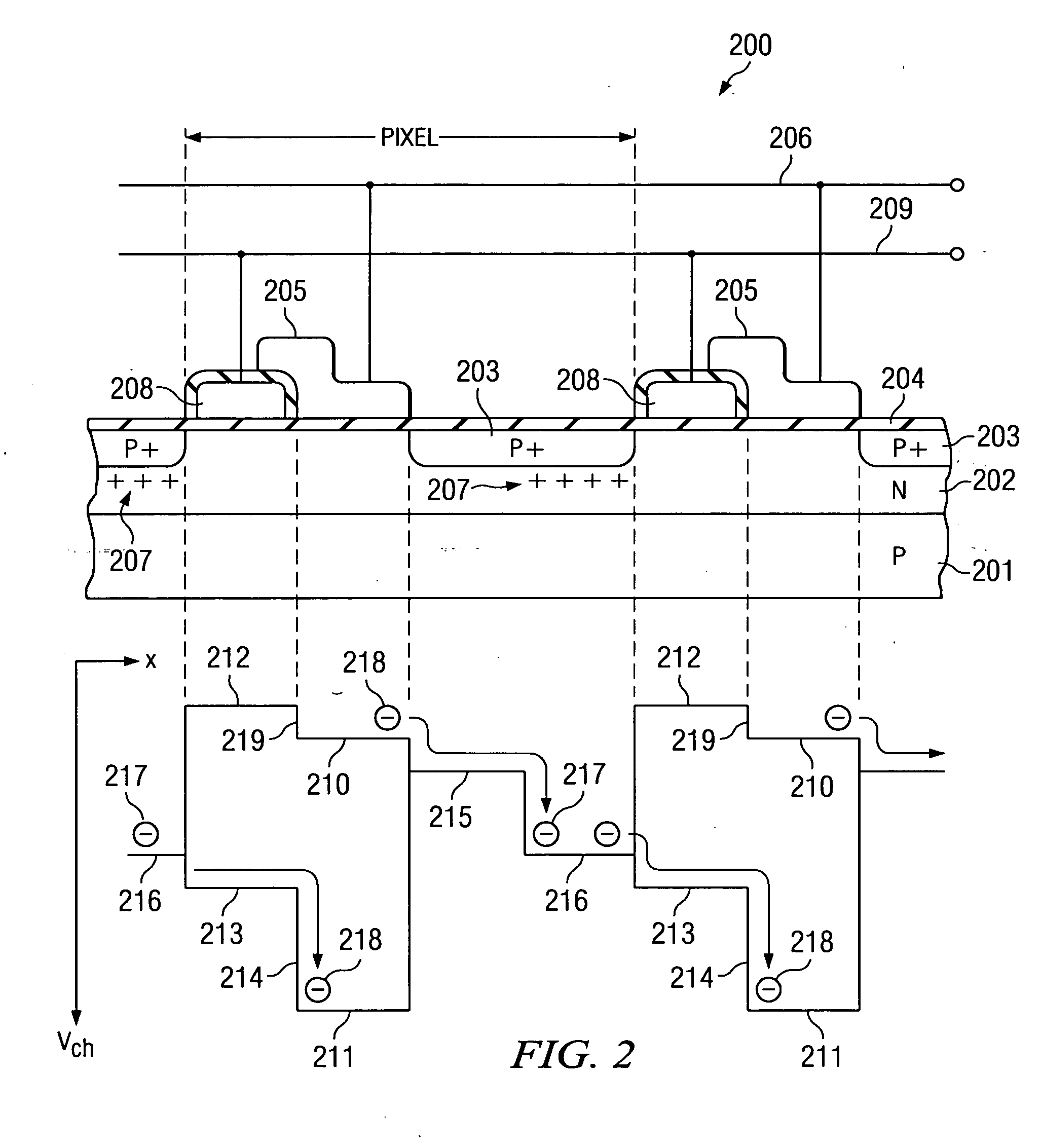
The present invention is a photodiode detector array for use in computerized tomography (CT) and non-CT applications. Specifically, the present invention is a high-density photodiode arrays, with low dark current, low capacitance, high signal to noise ratio, high speed, and low crosstalk that can be fabricated on relatively large substrate wafers. More specifically the photodiode array of the present invention is fabricated such that the PN-junctions are located on both the front side and back side surfaces of the array, and wherein the front side PN-junction is in electrical communication with the back side PN-junction. Still more specifically, the present invention is a photodiode array having PN-junctions that are electrically connected from the front to back surfaces and which can be operated in a fully depleted mode at low reverse bias.
Owner:UDT SENSORS +1
Sensor dark pixel offset estimation
InactiveUS20130271628A1Easy CalibrationEfficient executionTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsGainComputer science
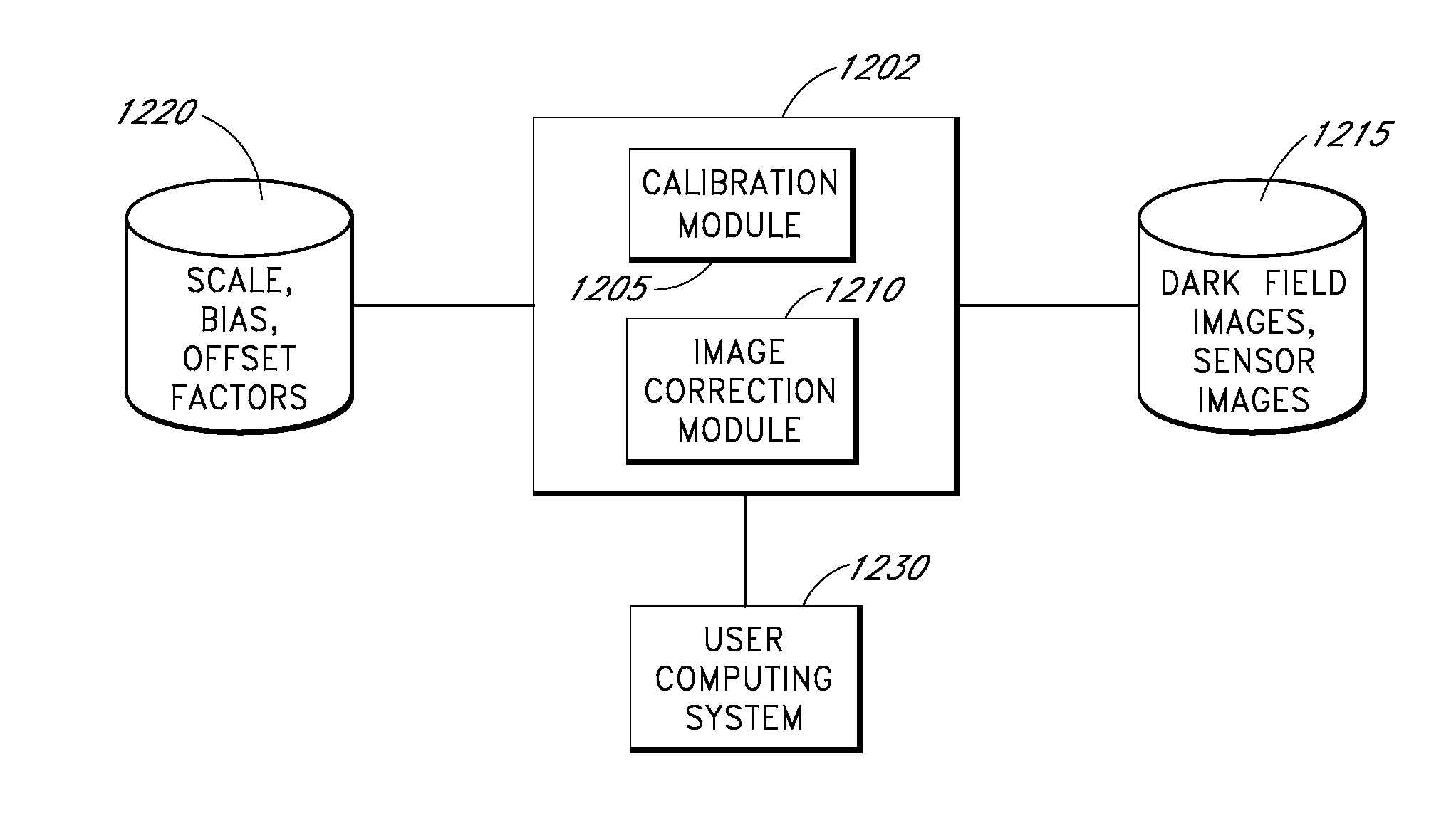
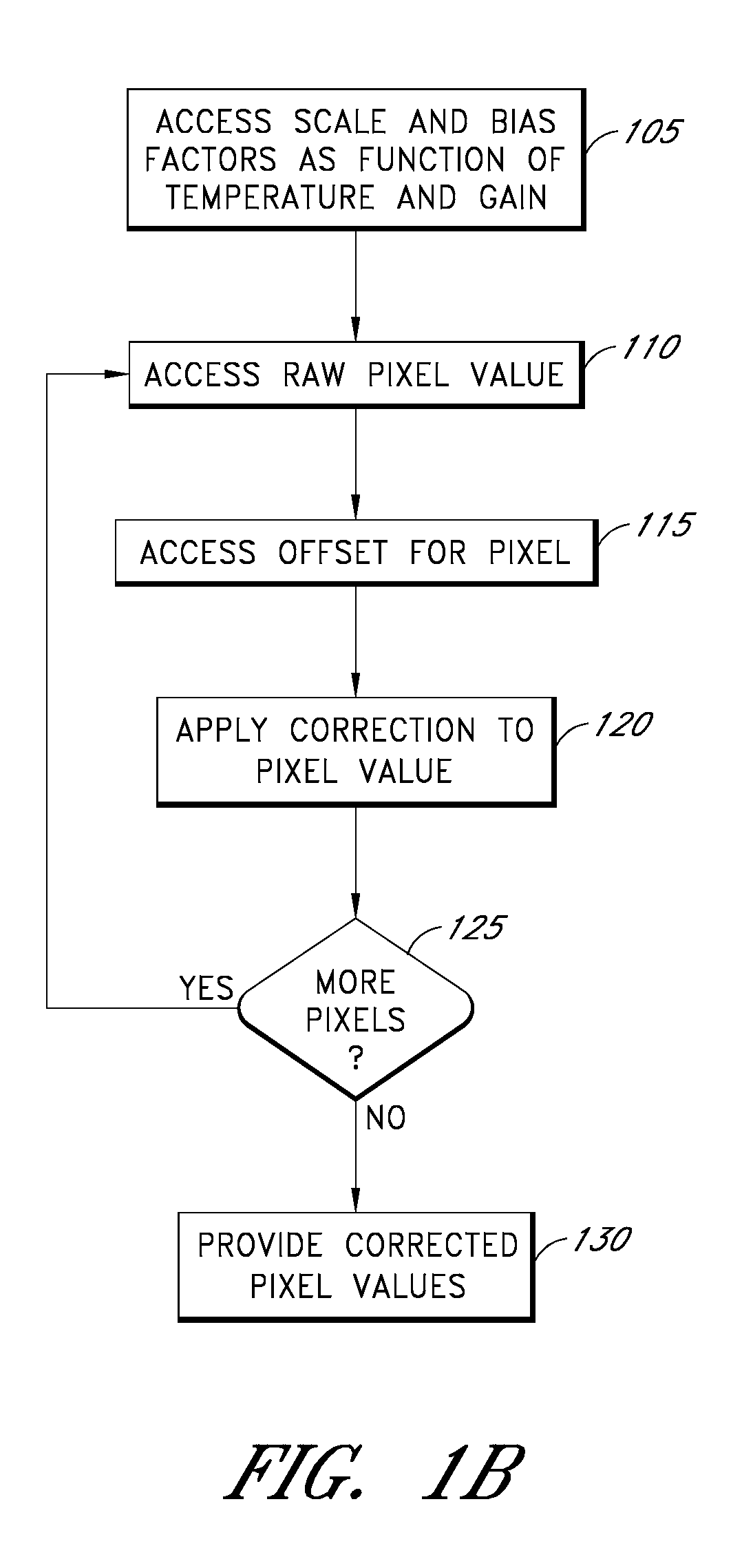
Examples of systems and methods to provide estimates of dark current for pixels of a photosensor as a function of the temperature of the sensor and the gain applied to the photosensor are described. In various implementations, the dark current estimated for each pixel can depend at least partly on a global scale factor and a global bias that depend on temperature and gain and a temperature-independent and gain-independent offset value for each pixel. The scale, bias, and offsets may be determined from multiple dark field images taken by the sensor over a range of operating temperatures. In some cases, the scale and bias can be determined using a subset of less than all the image pixels. Scale and bias derived for a particular sensor can be used in the calibration of different sensors.
Owner:PLANET LABS PBC
Solid-state image sensing device, image reading apparatus, and image forming apparatus
ActiveUS20140211273A1Solve problemsTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesImage formationEngineering
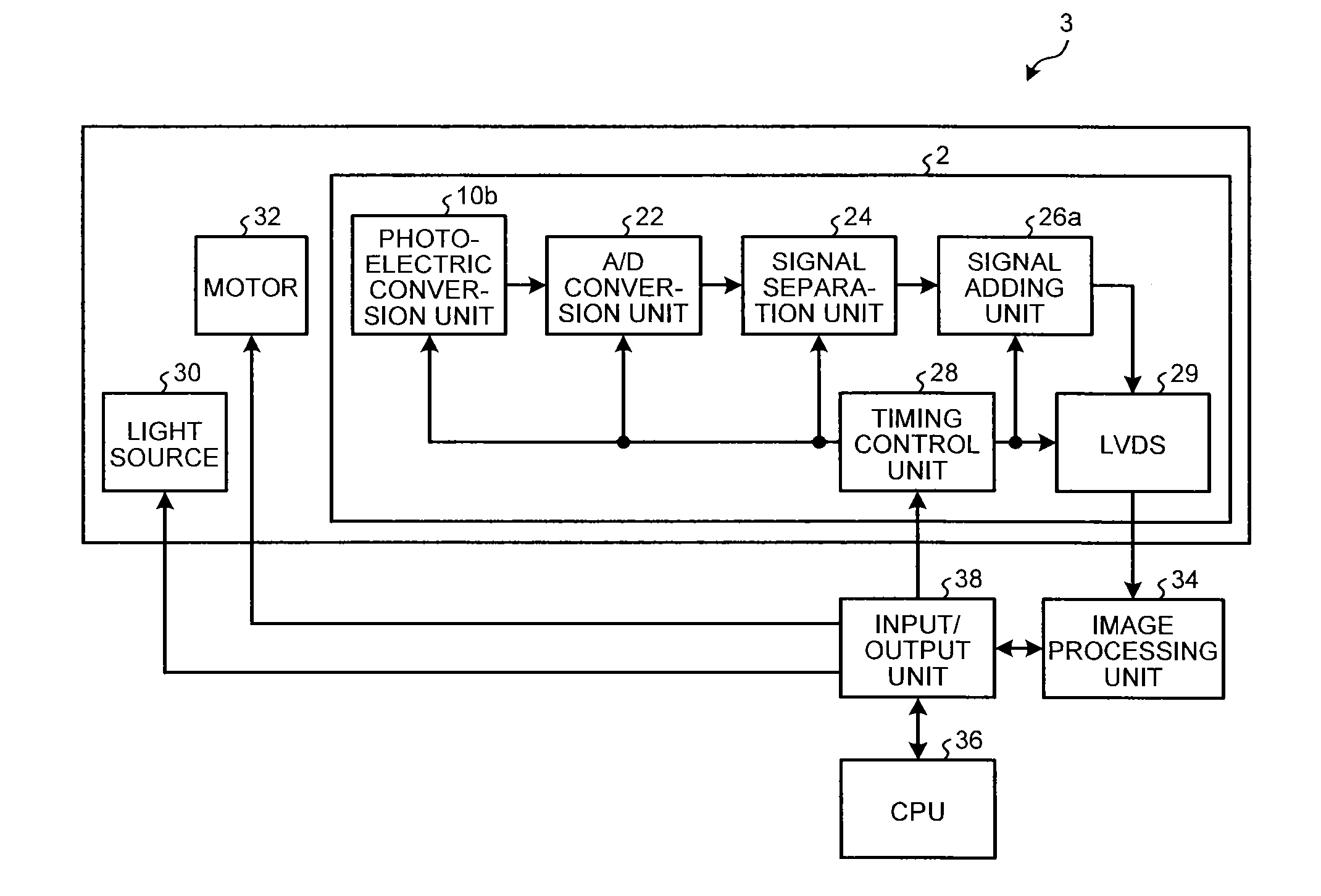
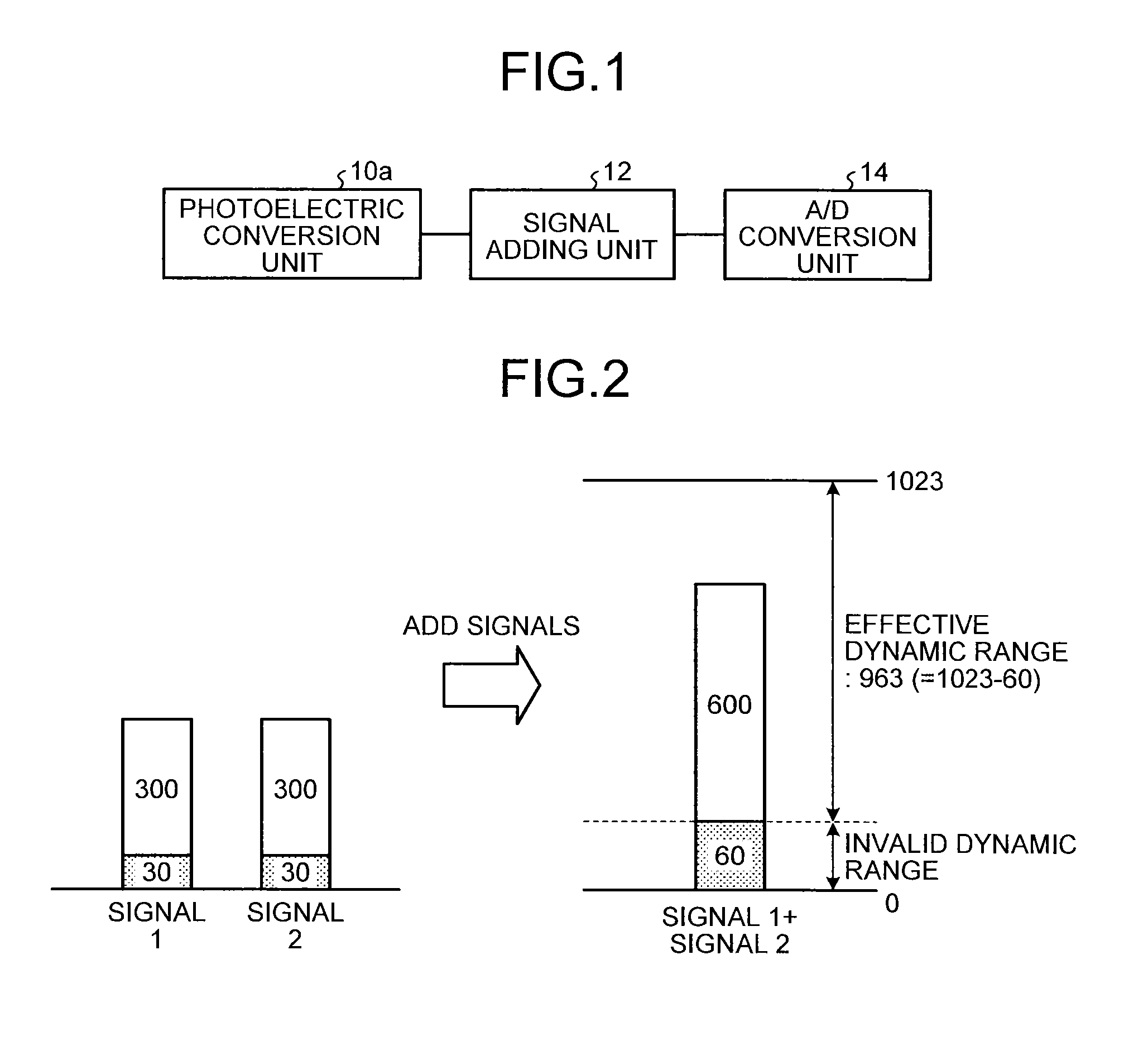
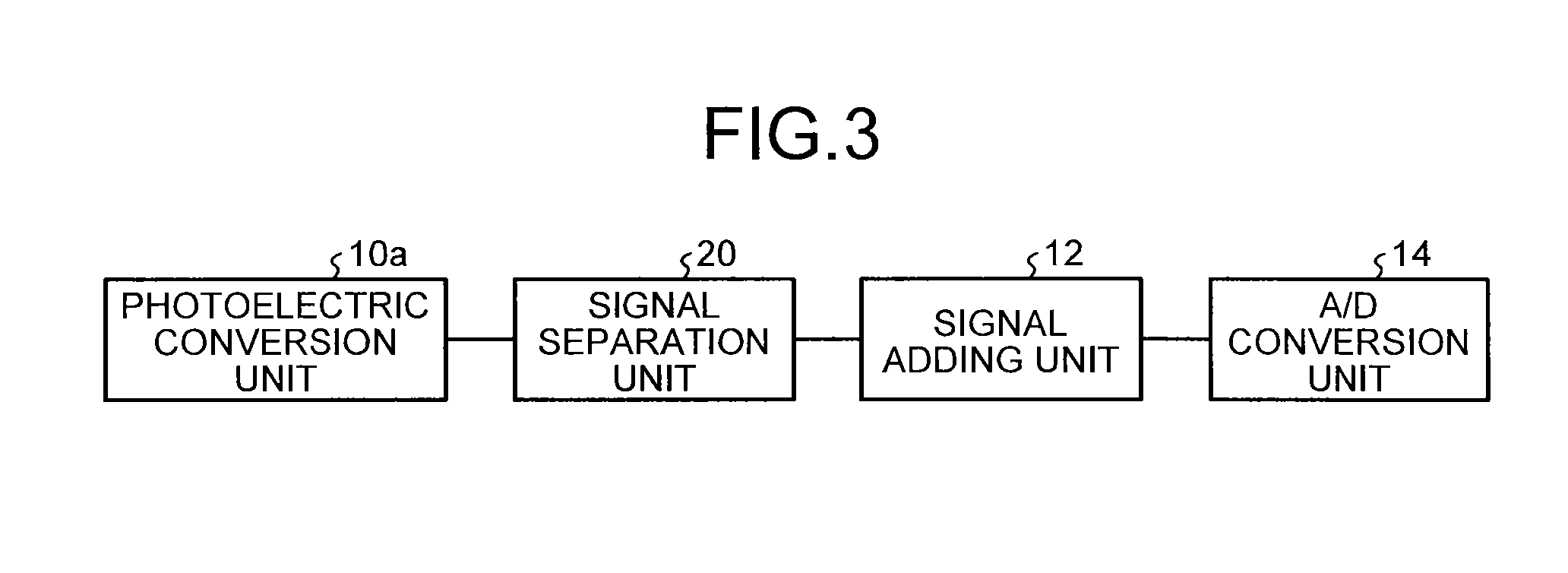
A solid-state image sensing device includes: a photoelectric conversion unit that converts light into electrical signals for respective pixels and outputs the electrical signals; a signal separation unit that separates an offset signal, which is generated due to dark current, from each of the electrical signals outputted by the photoelectric conversion unit and outputs image signals which are electrical signals converted from light for the respective pixels; and a signal adding unit that adds the image signals, which is outputted from the signal separation unit, for each group of a plurality of pixels.
Owner:RICOH KK
Solid state imaging device and fabrication method for the same
InactiveUS20100102368A1Generation of leakage can be preventedAvoid it happening againSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotoelectric conversionLength wave
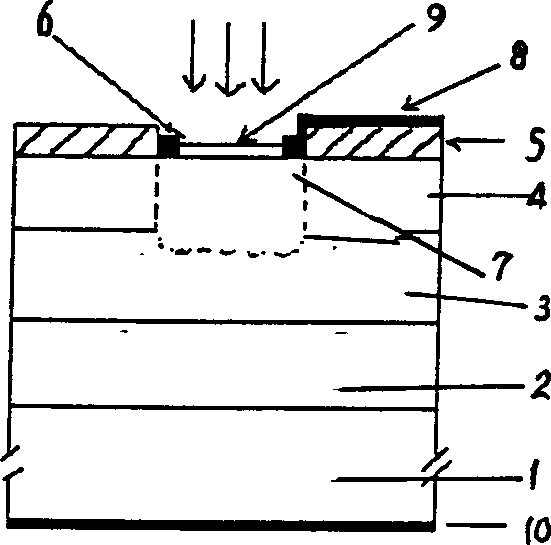
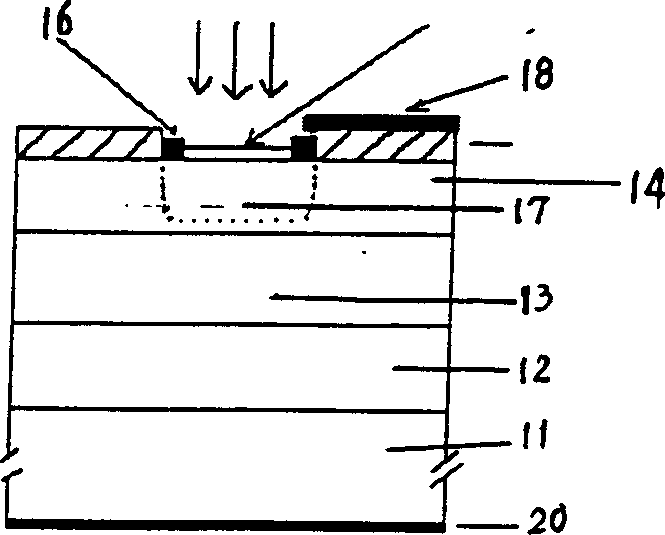
A solid state imaging device with an easy structure in which have the high sensitivity which reaches the wide wavelength region from visible light to near infrared light wavelength region, and dark current is reduced, and a fabrication method for the same, are provided.A solid state imaging device and a fabrication method for the same, the solid state imaging device comprising: a circuit unit (30) formed on a substrate; and a photoelectric conversion unit (28) including a lower electrode layer (25) placed on the circuit unit (30), a compound semiconductor thin film (24) of chalcopyrite structure which is placed on the lower electrode layer (25) and functions as an optical absorption layer, and an optical transparent electrode layer (26) placed on the compound semiconductor thin film (24), wherein the lower electrode layer (25), the compound semiconductor thin film (24), and the optical transparent electrode layer (26) are laminated one after another on the circuit unit (30).
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
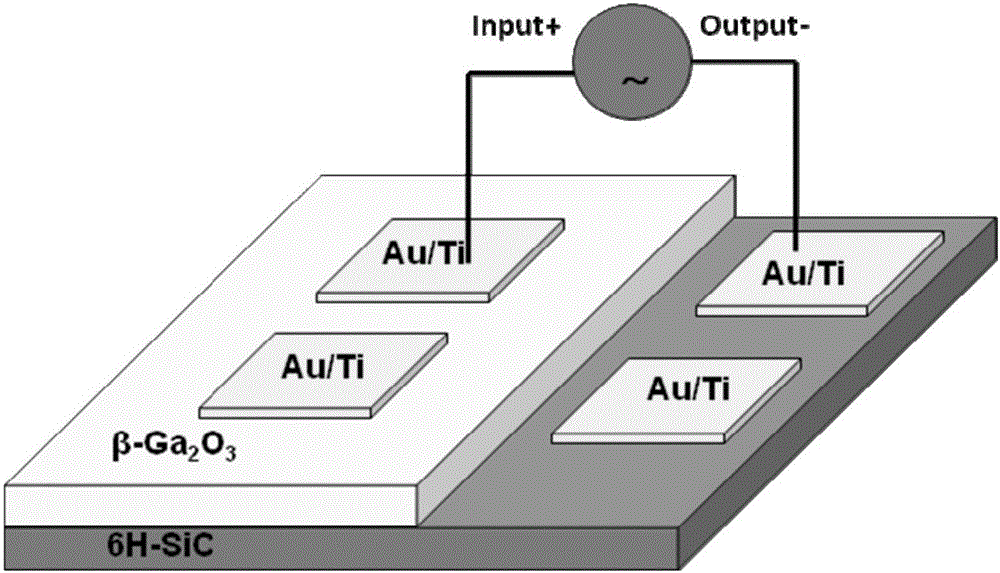
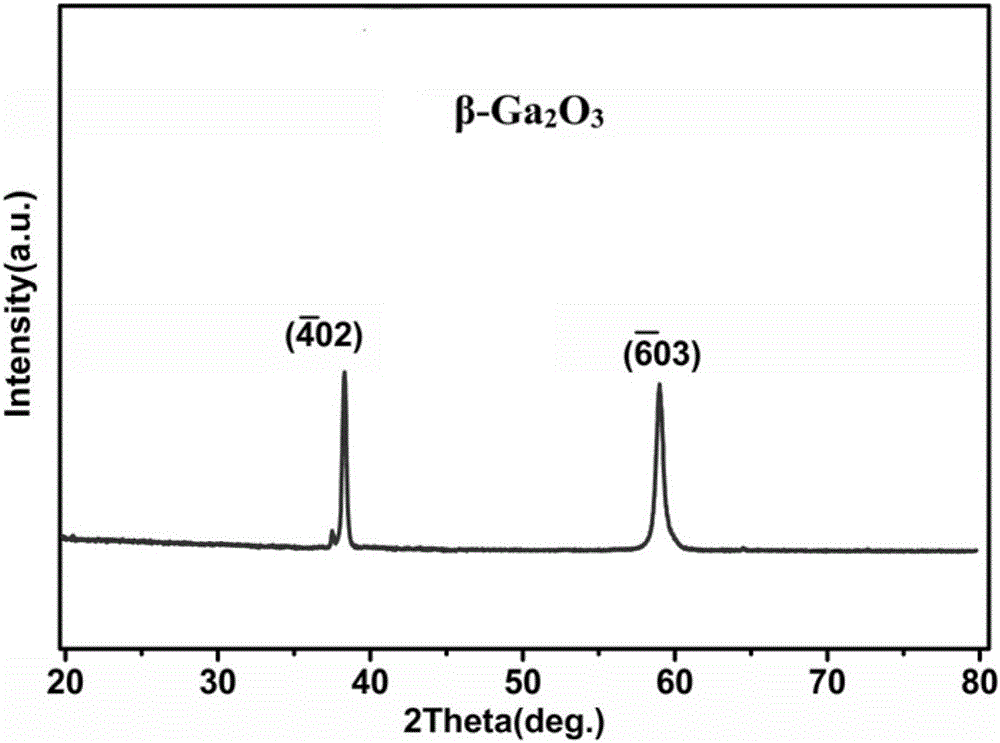
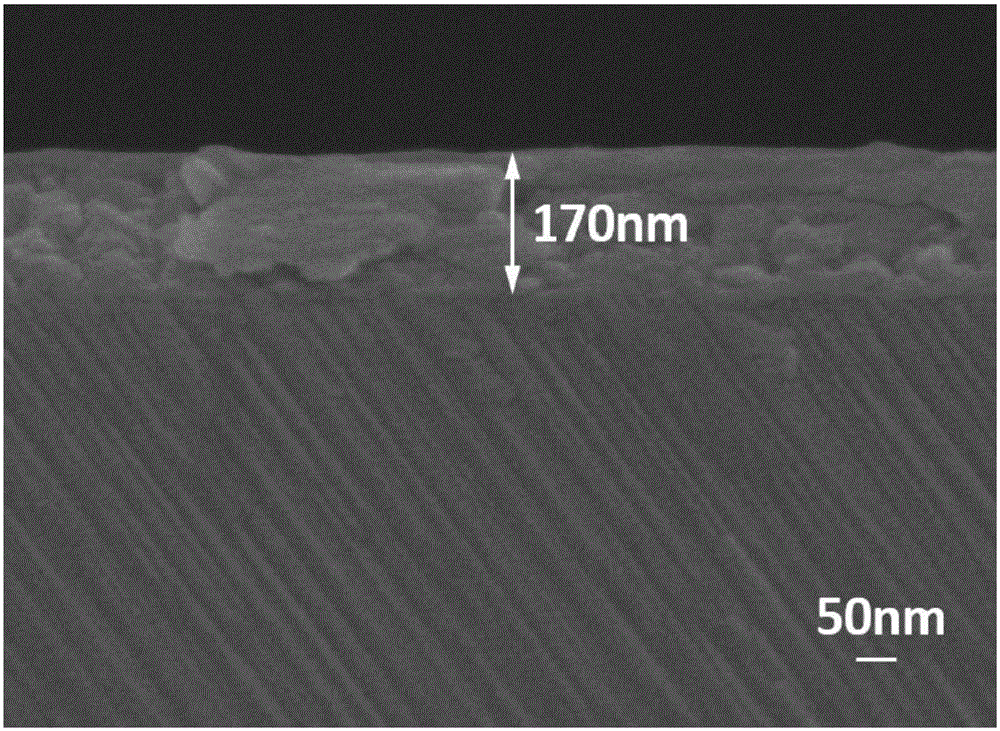
Visible-blind ultraviolet detector based on Beta-Ga2O3/SiC heterojunction thin film and fabrication method of visible-blind ultraviolet detector
ActiveCN105742398AStrong process controllabilityEasy to operateFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionUltraviolet detectors
The invention relates to an ultraviolet detector, in particular to a visible-blind ultraviolet detector based on a Beta-Ga2O3 / SiC heterojunction thin film and a fabrication method of the visible-blind ultraviolet detector. According to the fabrication method, a layer of Beta-Ga2O3 thin film is deposited on an n-type 6H-SiC substrate by a laser molecular beam epitaxial technique, and then a layer of Ti / Au thin film is deposited on the n-type 6H-SiC substrate and the Beta-Ga2O3 thin film through a mask by a radio frequency magnetron sputtering to be used as an electrode. The fabricated visible-blind ultraviolet detector has the advantages of stable performance, response sensitivity, small dark current and high potential application; and moreover, the fabrication method has the characteristics of high process controllability, simplicity in operation, high universality, restorability of repeated test and the like, and has great application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
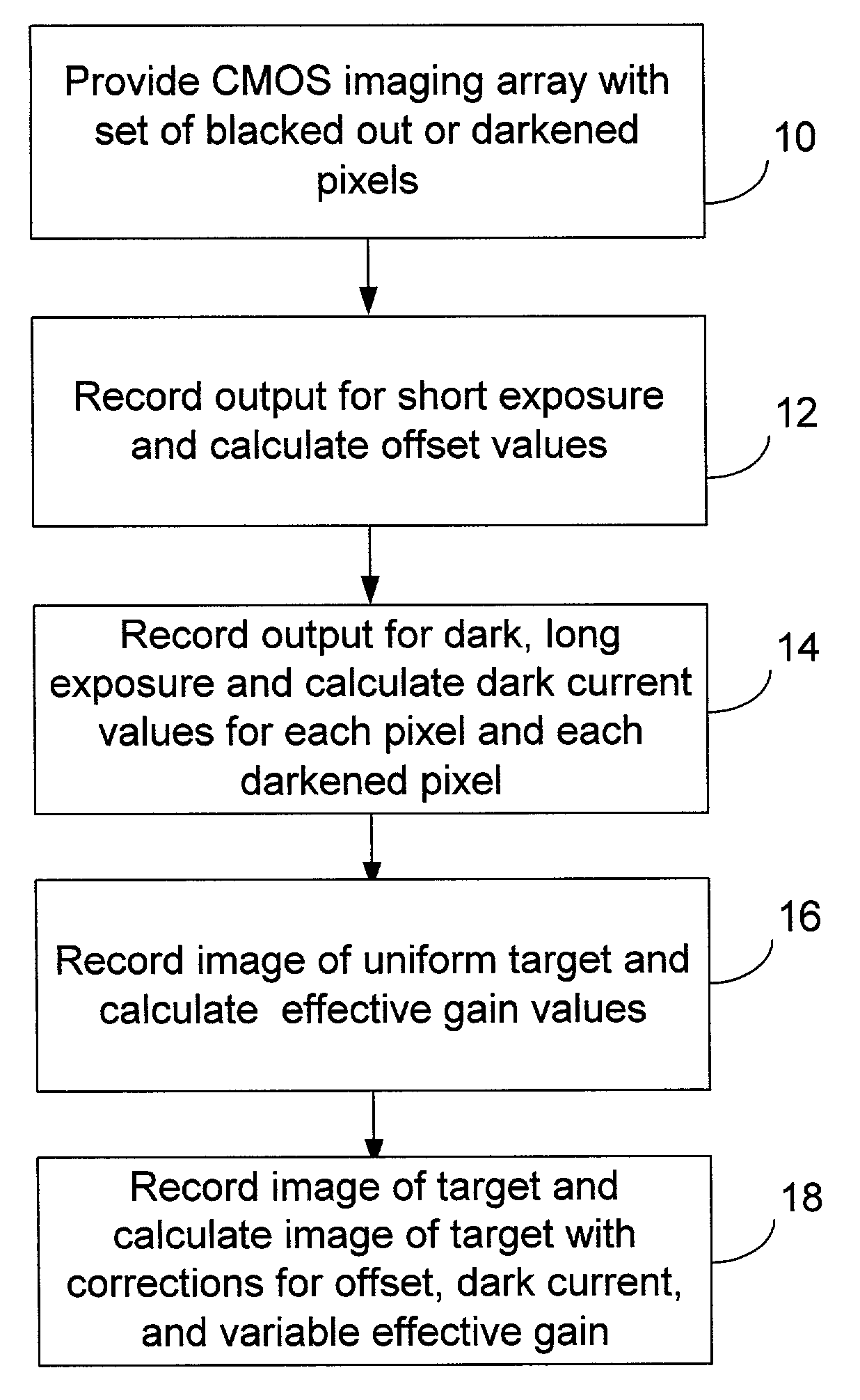
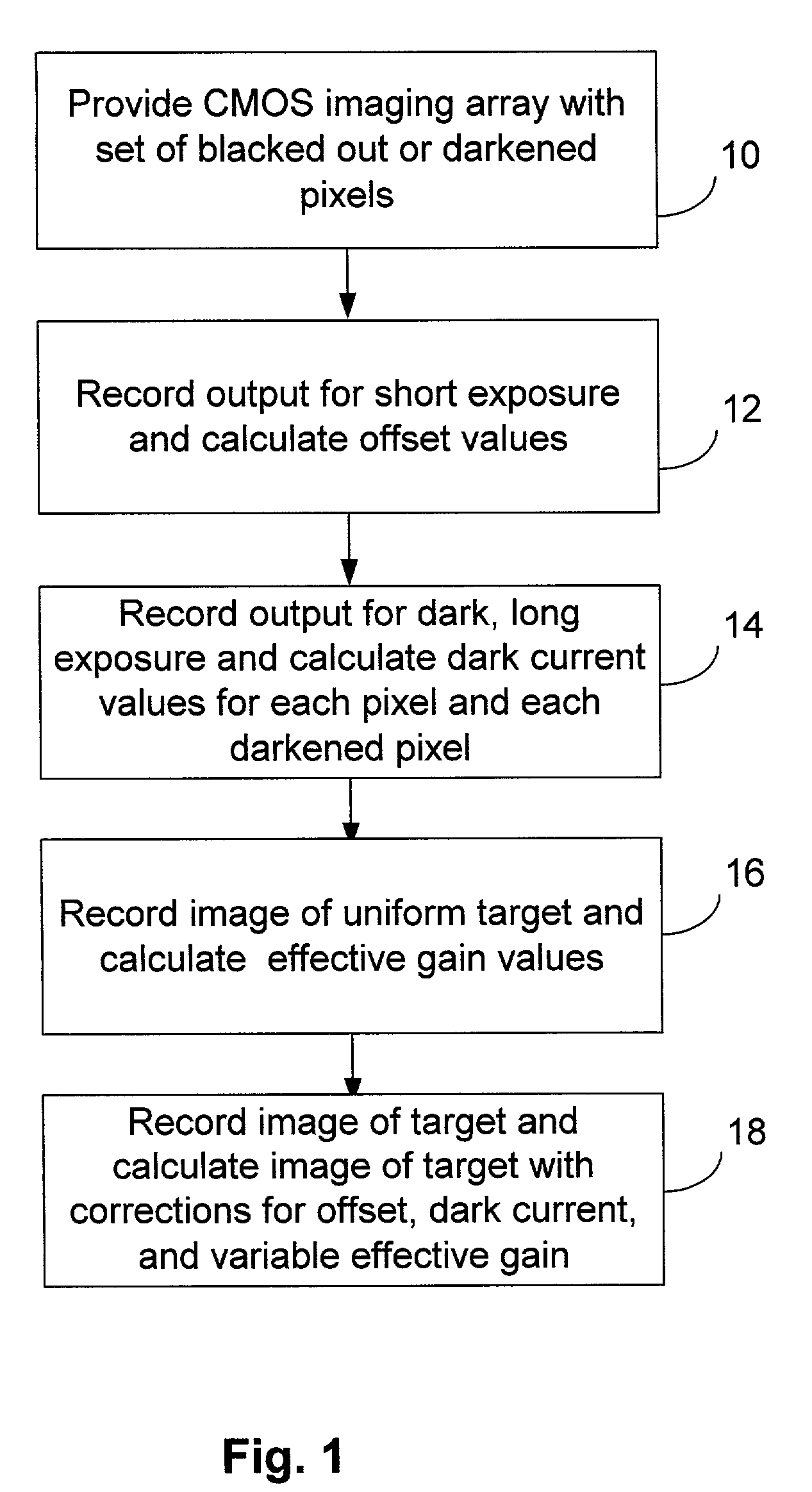
Integrated CMOS imaging array dark current monitor
A method, apparatus, and system for accounting for dark current in the output of an imaging array is presented. A dark current monitor on the monolithic semiconductor imaging array is provided. The dark current monitor may be darkened pixels of the imaging array, darkened pixels of another array, or a temperature monitor and associated circuitry necessary to calculate relative dark current from the monitored temperature.
Owner:MELA SCIENCES
Photodetector and production method thereof
ActiveUS20090001412A1Suppress dark currentWide applicationFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
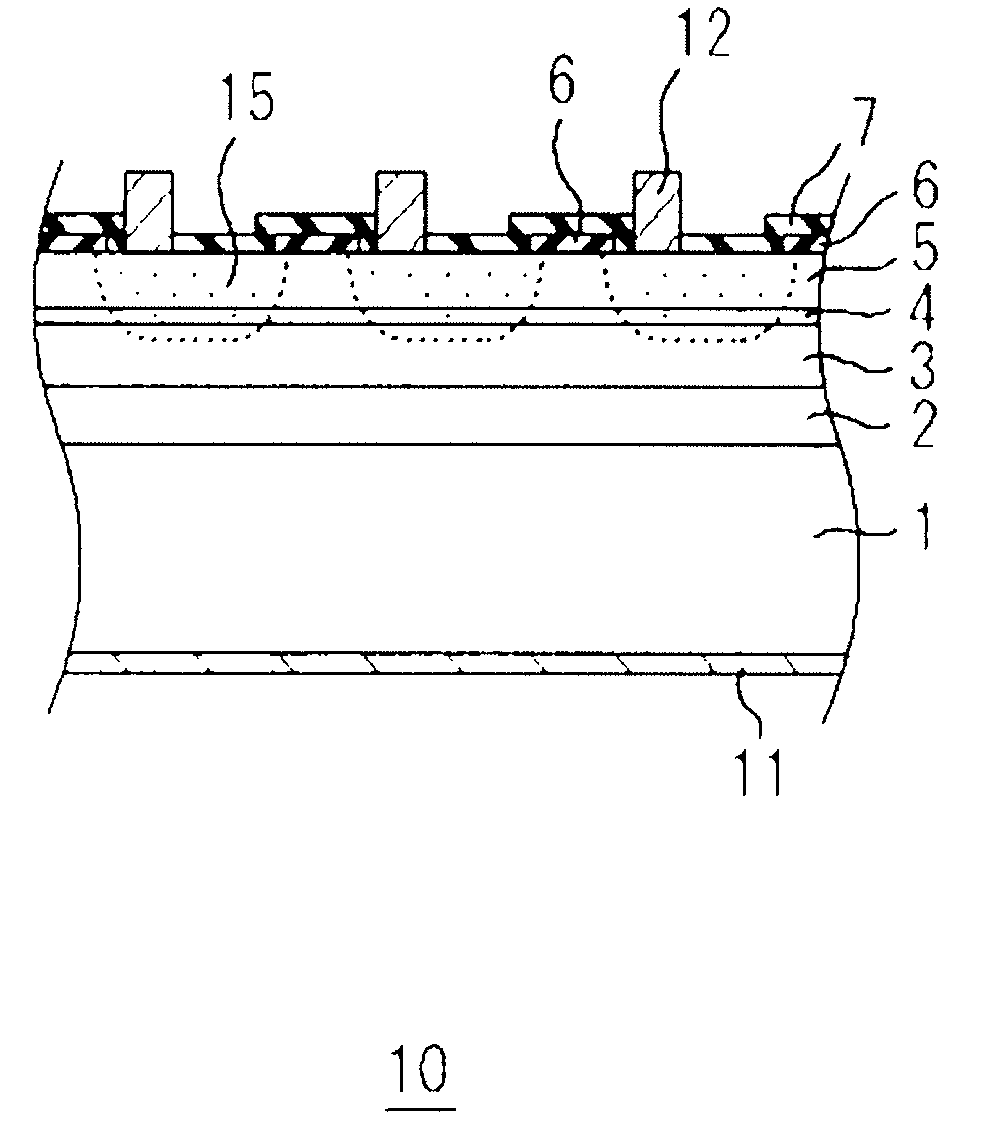
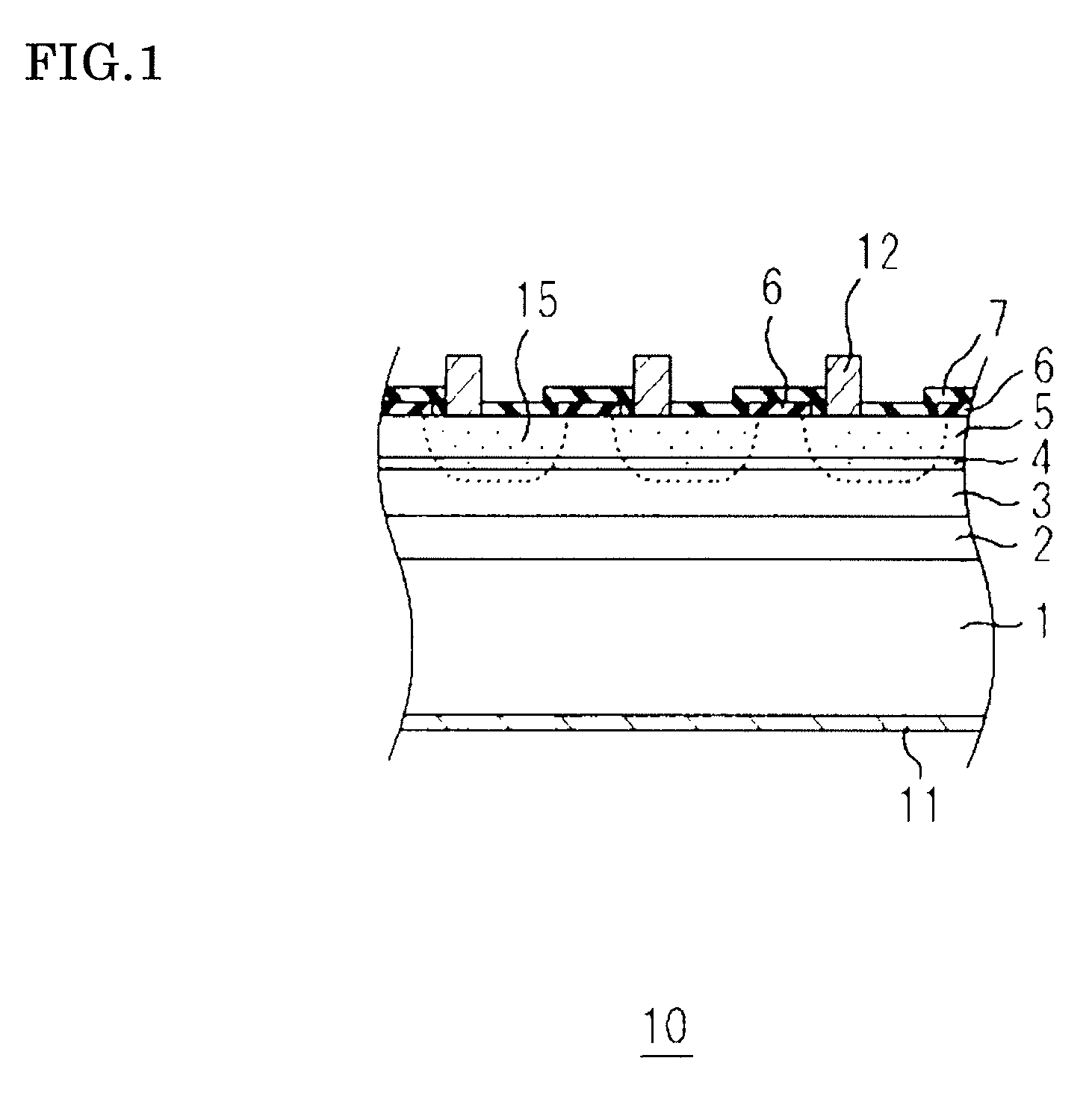
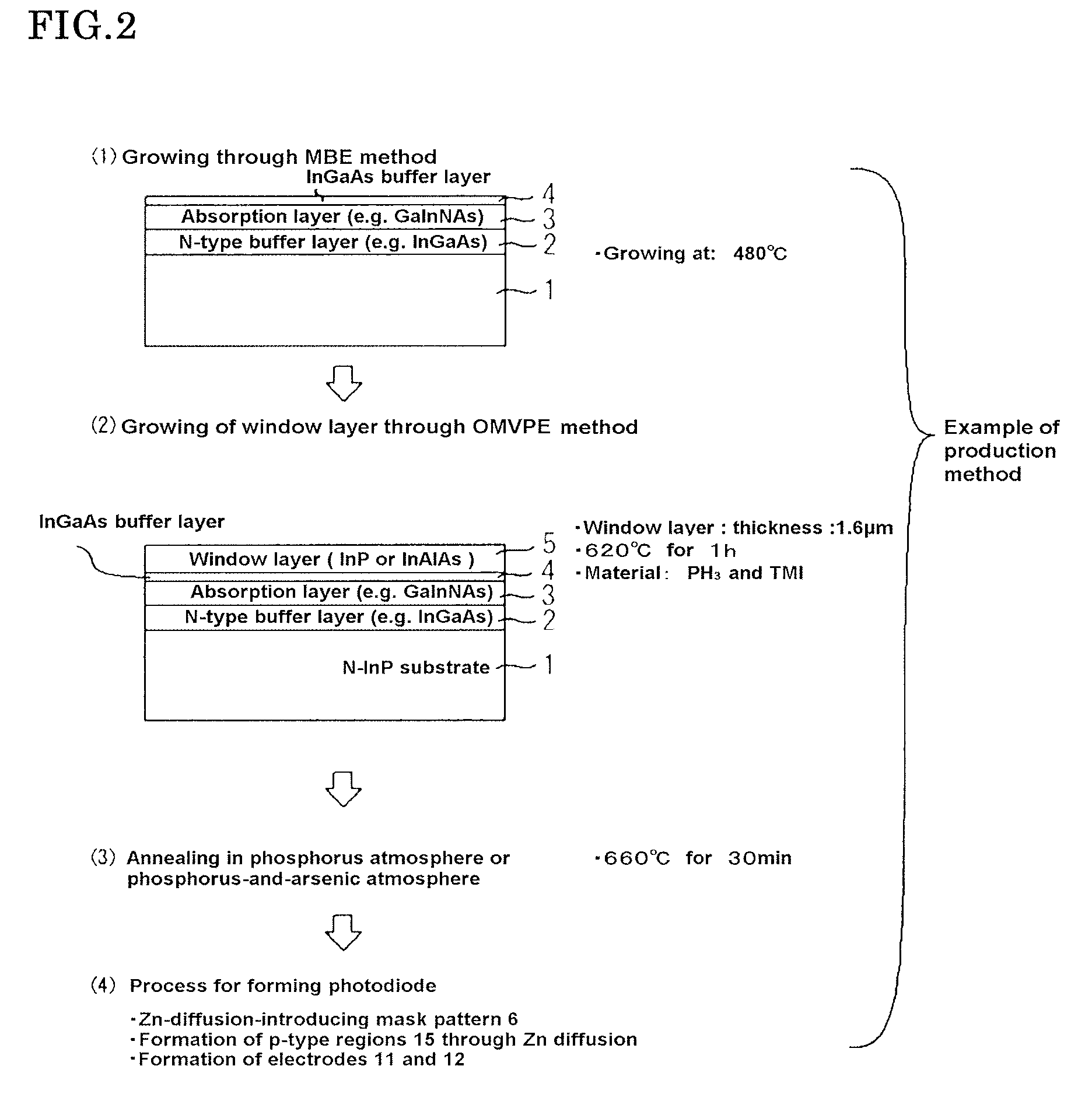
The invention offers a photodetector that has an N-containing InGaAs-based absorption layer having a sensitivity in the near-infrared region and that suppresses the dark current and a production method thereof. The photodetector is provided with an InP substrate 1, an N-containing InGaAs-based absorption layer 3 positioned above the InP substrate 1, a window layer 5 positioned above the N-containing InGaAs-based absorption layer 3, and an InGaAs buffer layer 4 positioned between the N-containing InGaAs-based absorption layer 3 and the window layer 5.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Multiband Photodetector Utilizing Unipolar and Bipolar Devices
ActiveUS20130193308A1Reduce in quantityEliminate tunnel junctionSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansPhysicsPhotodetection
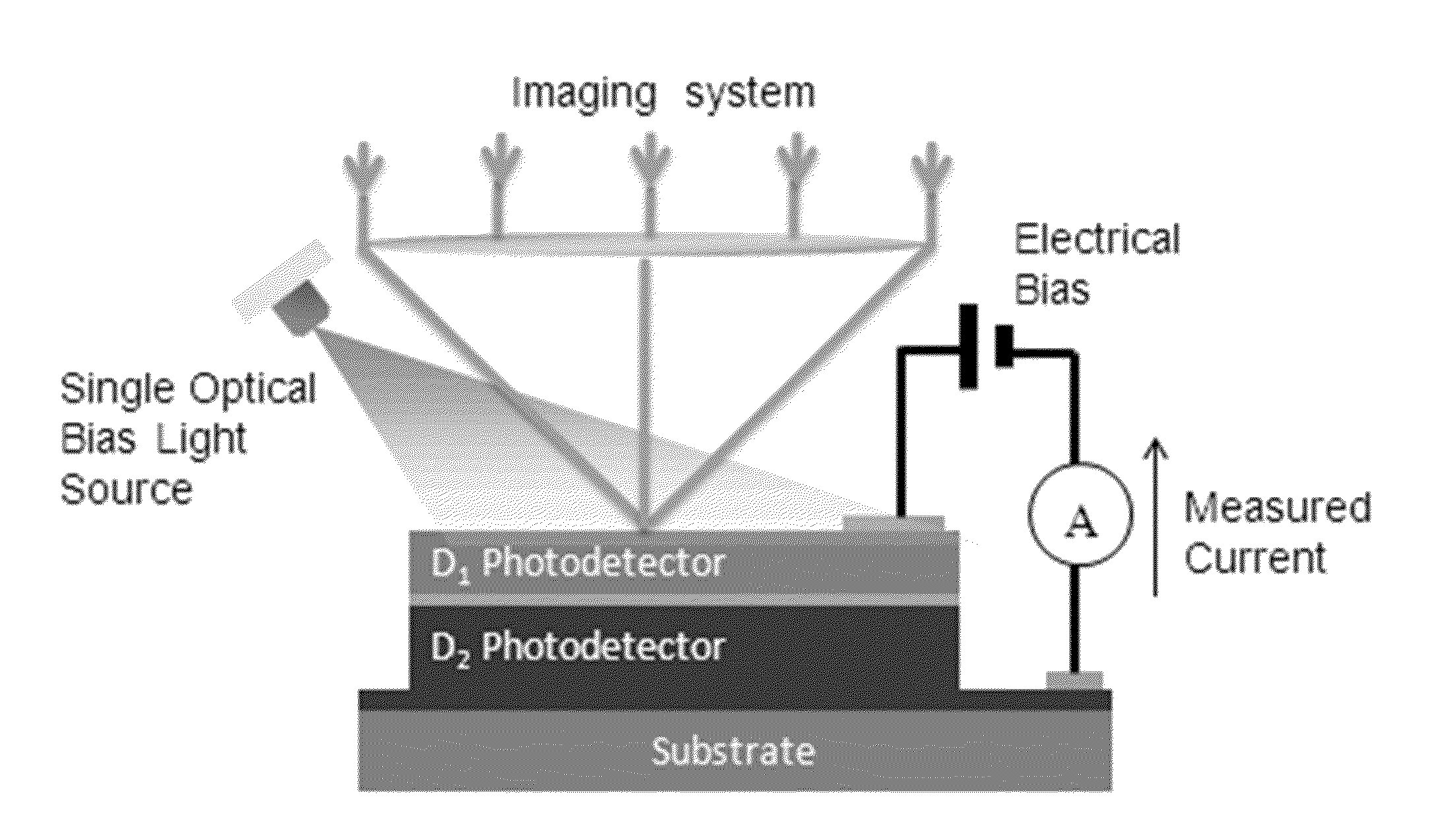
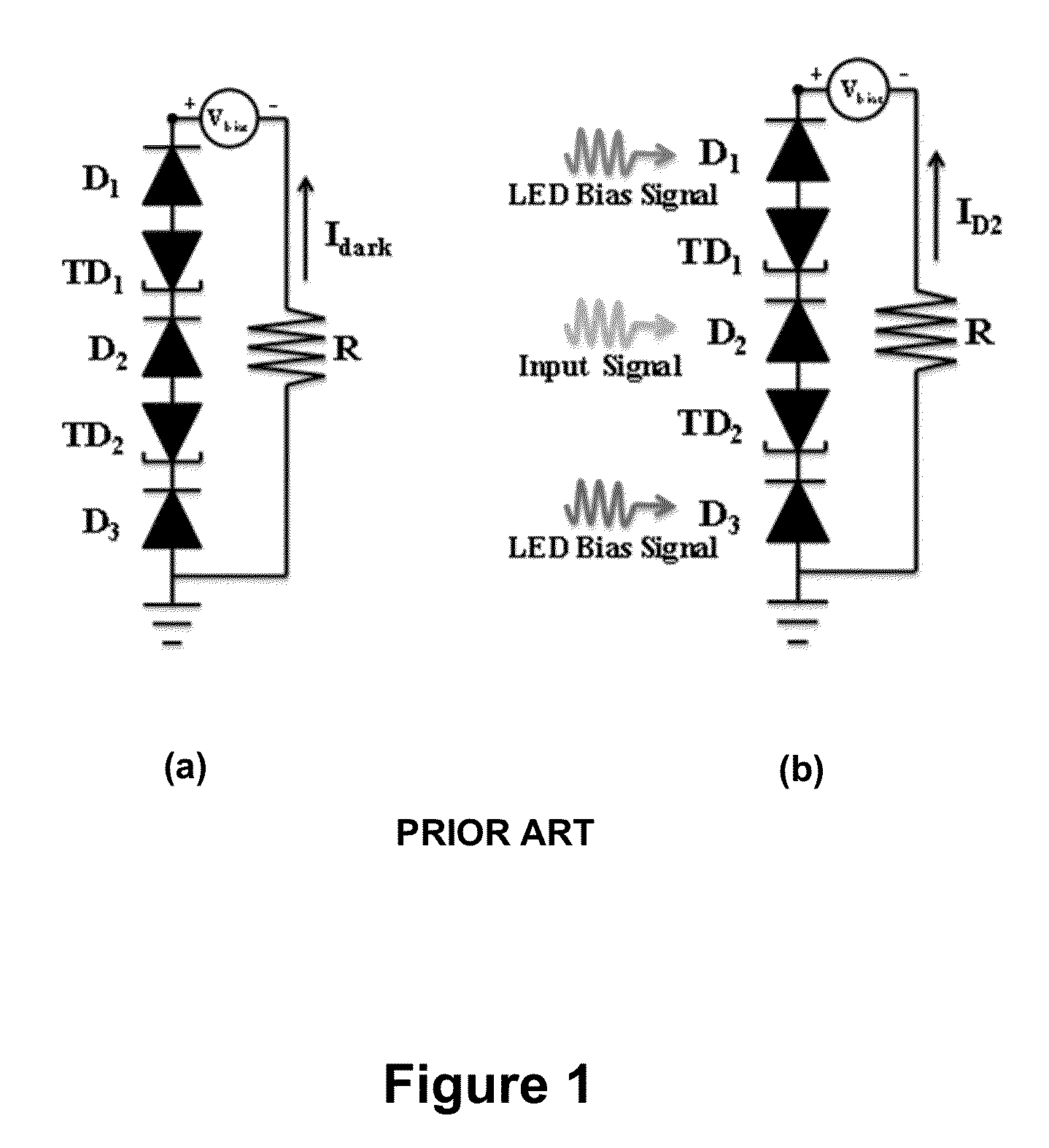
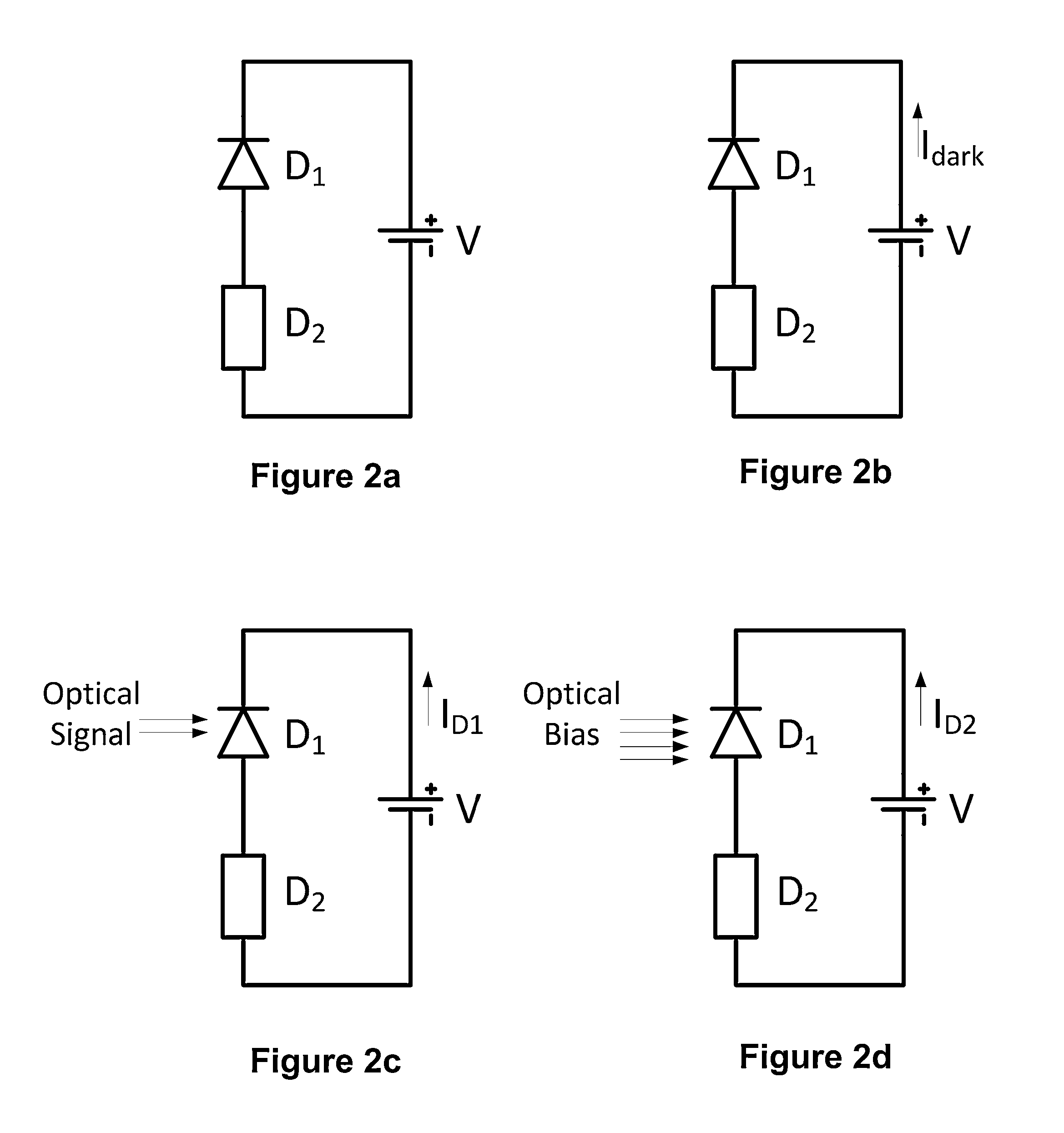
Multi-band photodetectors can be formed by series connecting unipolar and, optionally, bipolar semiconductor structures, each having different photodetection bands. Under default mode of operation, the detector with highest resistance and lowest current will be the current limiting device and will be the active photodetector. When the active photodetector is illuminated with strong light in its own detection band it will be optically biased. This active photodetector will no longer be the highest resistance device, and the next photodetector will be the active photodetector. Repeating this operation pattern, allows switching photodetection bands of the multi-band photodetector. The resistances, dark current and photocurrent of the devices should be engineered to have proper switching. Moreover, the illuminating surface, and photodetector placement should be optimized for proper light biasing. The current passing through the device will always be equal to the current of the active photodetector.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
CMOS image sensor and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS7217967B2Improve featuresTotal current dropSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSIsolation layer
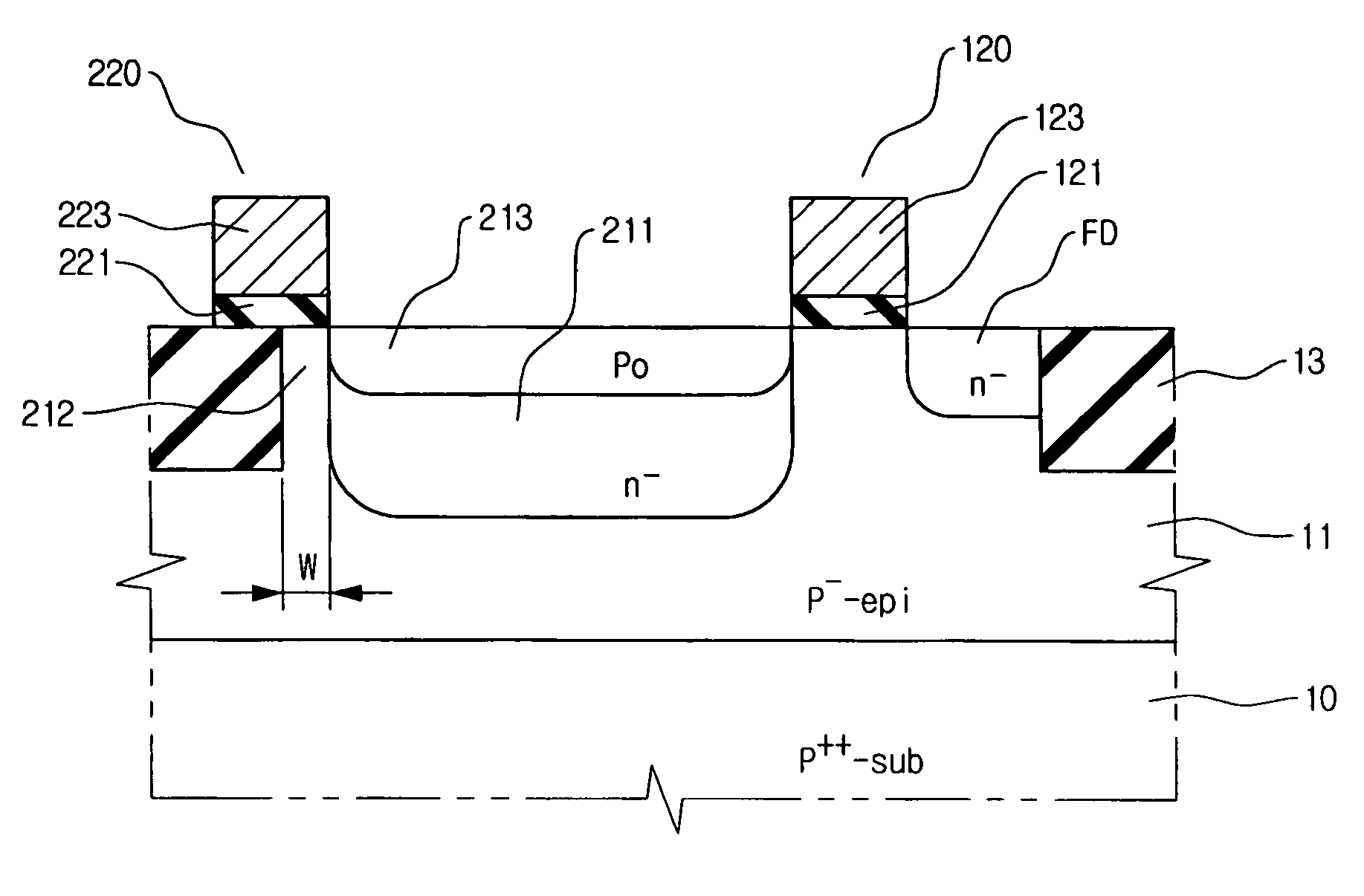
A CMOS image sensor and a manufacturing method thereof are disclosed. The gates of the transistors are formed in an active region of a unit pixel, and at the same time, a passivation layer is formed on an edge portion of the active region of a photodiode to have the same laminate structure as the gates of the transistors. Impurities for a diffusion region of the photodiode are ion-implanted into the active region for the photodiode, after the laminate structure is formed. The passivation layer prevents the edge portion from being damaged by ion implantation at the boundary or interface between the photodiode diffusion region and an isolation layer, which reduces dark current and / or leakage current of the CMOS image sensor.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
Clocked barrier virtual phase charge coupled device image sensor
InactiveUS20050029553A1Reduce generationMinimize smearTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringComputational physics
The charge coupled device includes a clocked barrier pixel architecture that has a two phase gate structure that substantially reduces clock-induced dark current.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Wide view-field three-D CT imaging method
InactiveCN1865954AScan structure is simpleCompatibleComputerised tomographsTomographyDigital RayVisual field loss
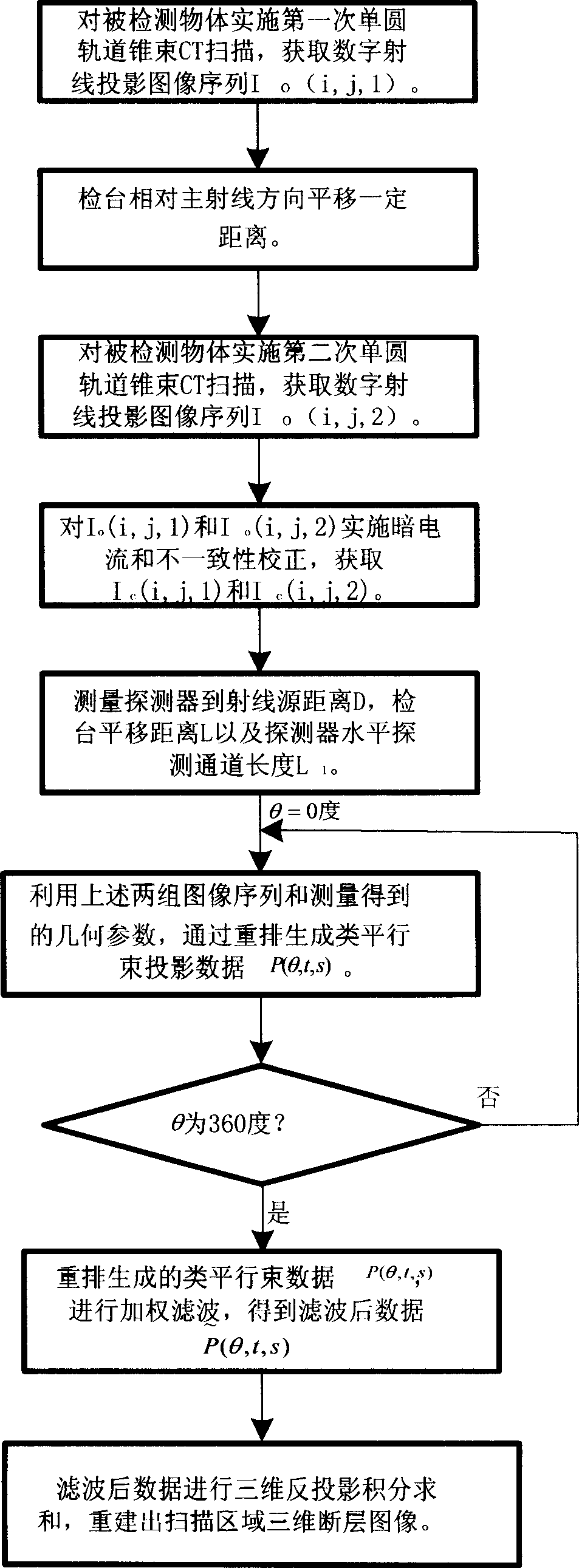
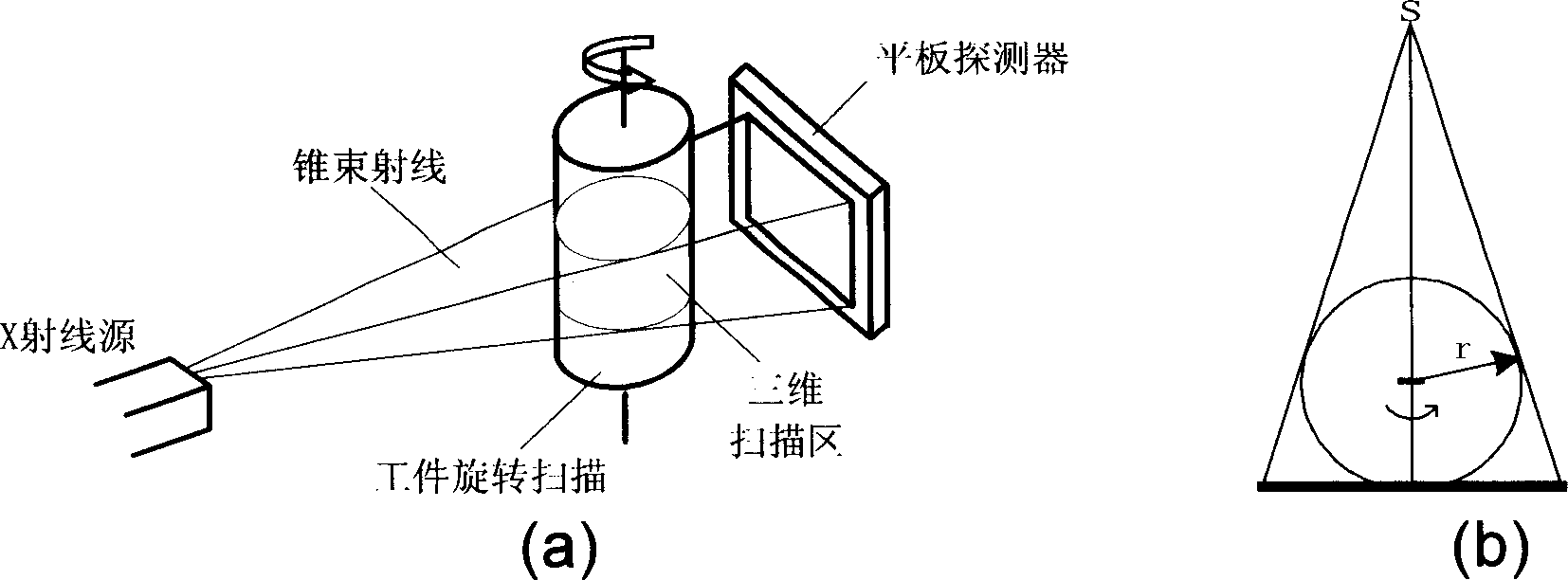
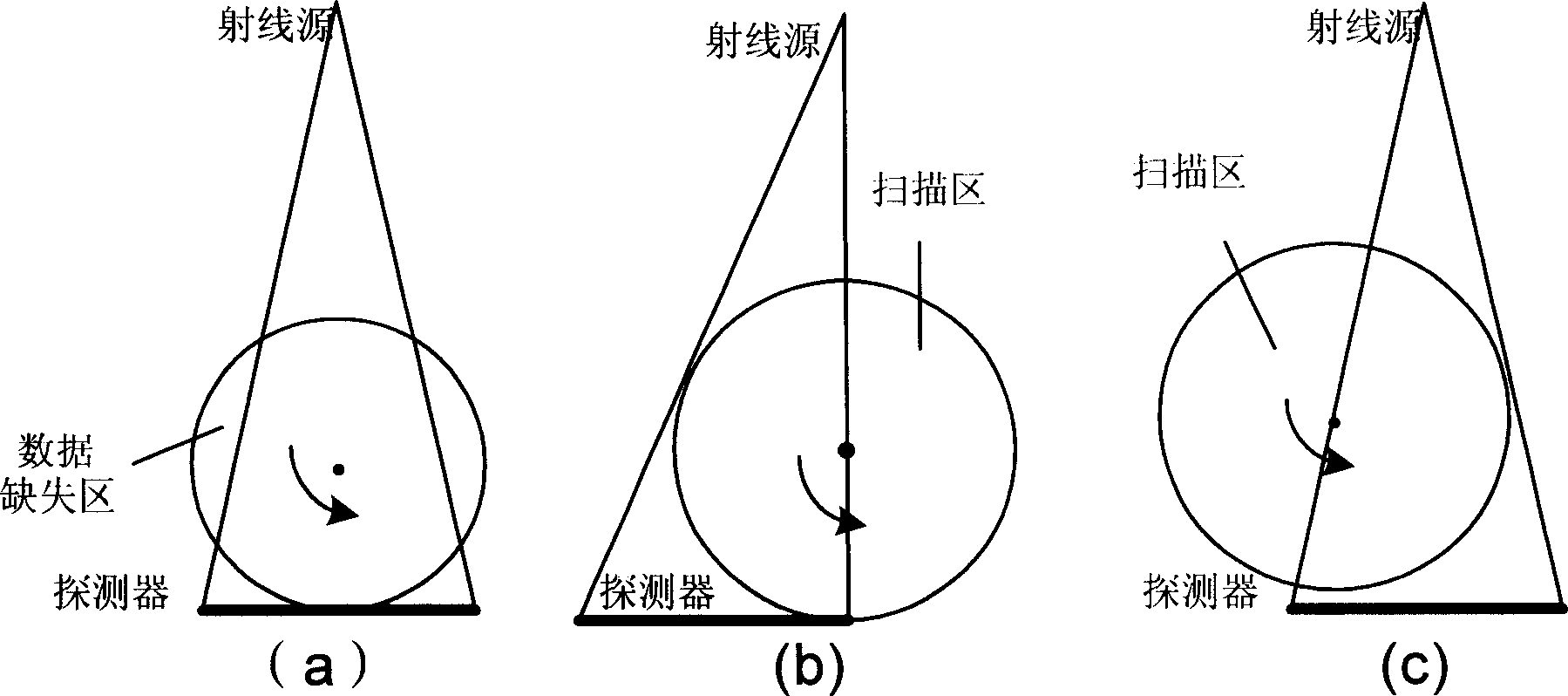
The 3D CT imaging method for large view field comprises: (1) taking first single-circular orbit cone-beam CT scanning to obtain the first digital ray projection image sequence; (2) removing the platform vertical the main ray with some distance to take the second CT scanning and obtain the second image sequence; (3) correcting former two images for dark current and inconsistency; (4) recording distance from ray source to detector, former moved distance and detector level channel number; (5) with the projection rearrangement algorithm in this invention, rearranging former two images into self-contained quasi-parallel image sequence; (6) with the quasi-parallel ray reconstructing algorithm in this invention, reconstructing the 3D CT image. This invention can enlarge the view area more than 3 times with high efficiency.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
A PIN structure TiO2 base ultraviolet detector and its making method
InactiveCN101055902AHigh external quantum efficiency and sensitivityQuick responseFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesBroadbandLight source
The invention relates to a PIN structural TiO2 base ultraviolet light detector for ultraviolet light detector and its manufacturing method. The ultraviolet light detector comprises a conductive substrate, a N-type semiconductor contact layer, an intrinsic TiO2 active layer and a P-type wide-band-gap semiconductor contact layer. The manufacturing method of the ultraviolet light detector comprises the following step: preparing the N-type semiconductor contact layer on the conductive substrate after pretreatment; preparing the intrinsic TiO2 active layer on the N-type semiconductor contact layer; carrying out a partial etching to the around part of the active layer by using a dry etching technology; preparing the P-type contact layer on the etching part of the active layer; preparing a P-type ohmic electrode on the P-type contact layer; and preparing a N-type ohmic electrode on the conductive substrate. The invention has a plurality of advantages such as high external quantum efficiency and sensitivity, rapid response speed, small dark current, small and exquisite volume, cheap cost, and long service life. The film preparation technology is convenient and maturate. The interference of light sources except the ultraviolet ligh may be prevented.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Multi-quantum-well structure used in photoelectron device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN101582478AImprove luminous efficiencyIncrease the number ofFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingQuantum efficiencyPotential well
The invention discloses a multi-quantum-well structure used in photoelectron device, wherein the thickness of a potential well layer near N type semiconductor layer is larger than that of the potential well near P type semiconductor layer. The invention also discloses a manufacturing method of the multi-quantum-well structure, including that Ga barrier layer N and InxGa potential well layer N are alternately grown on the N type semiconductor layer of the photoelectron device by adopting MOCVD technology, wherein the growth time of the InxGa1-x potential well layer N near the N type semiconductor layer is 50-200s, and the growth time of the InxGa1-x potential well layer N near the P type semiconductor layer is 0.5-1 time that of the potential well layer near the N type semiconductor layer. The multi-quantum-well structure of the invention can improve the internal quantum efficiency of the photoelectron device, improves reverse voltage and antistatic property, and reduces halfwidth of the luminous spectrum peak to improve luminous purity; and the structure can reduce dark current to improve the sensitivity of a detector when being applied in the detector.
Owner:宁波安芯美半导体有限公司
CMOS image sensor and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050064620A1Easy to limitAvoid damageSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSIsolation layer
A CMOS image sensor and a manufacturing method thereof are disclosed. The gates of the transistors are formed in an active region of a unit pixel, and at the same time, a passivation layer is formed on an edge portion of the active region of a photodiode to have the same laminate structure as the gates of the transistors. Impurities for a diffusion region of the photodiode are ion-implanted into the active region for the photodiode, after the laminate structure is formed. The passivation layer prevents the edge portion from being damaged by ion implantation at the boundary or interface between the photodiode diffusion region and an isolation layer, which reduces dark current and / or leakage current of the CMOS image sensor.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
Testing method and testing device of avalanche photodiode
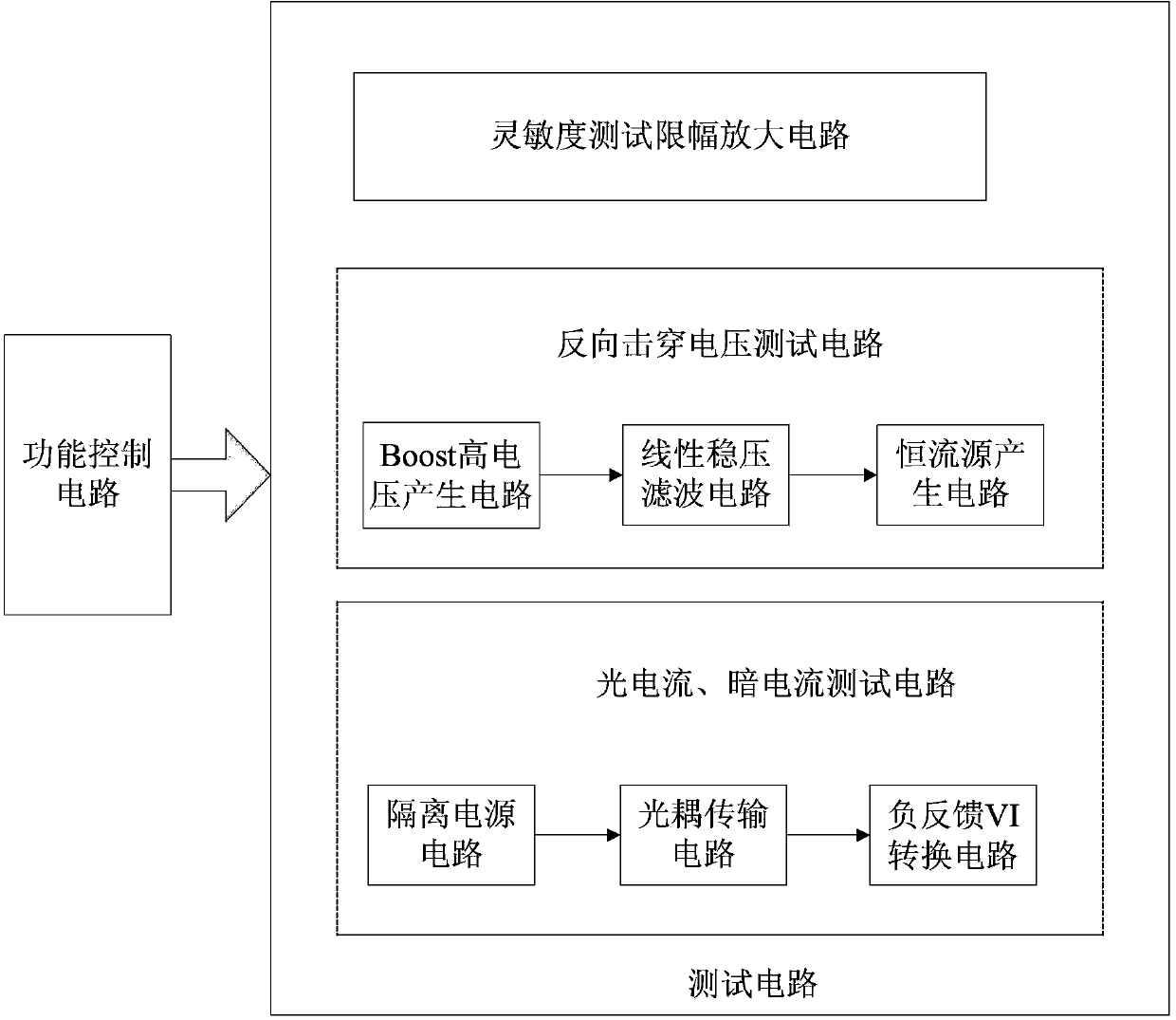
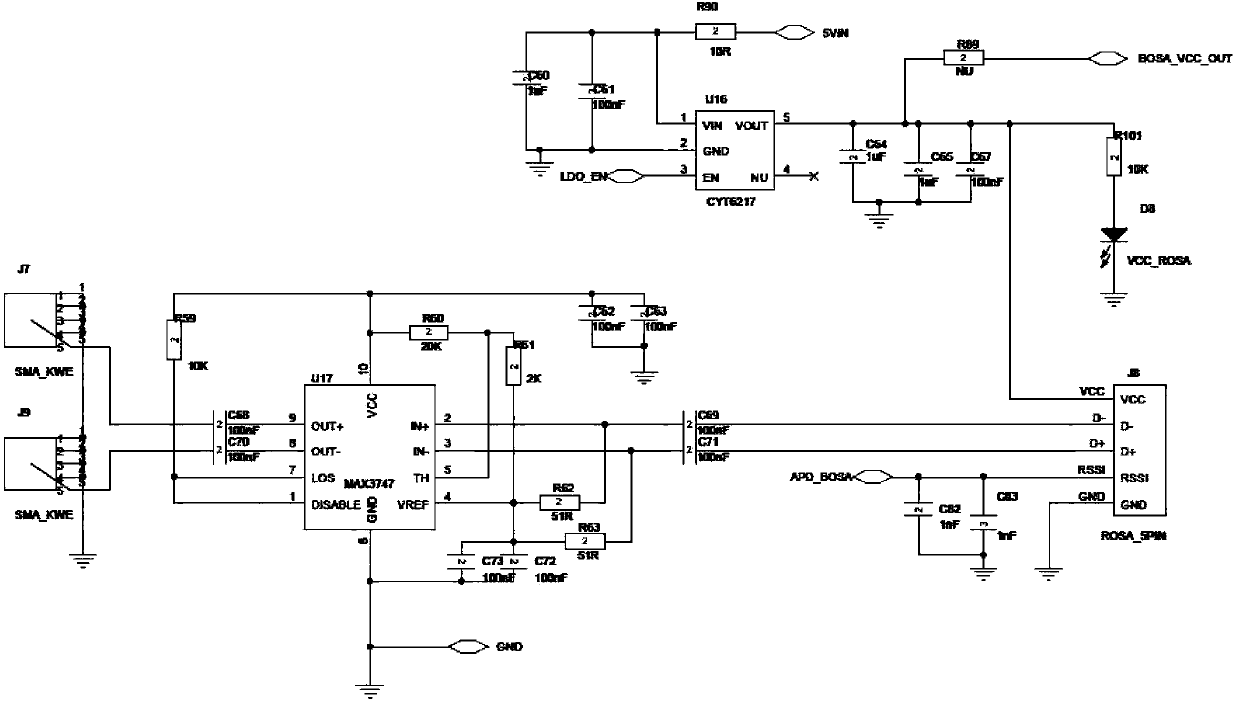
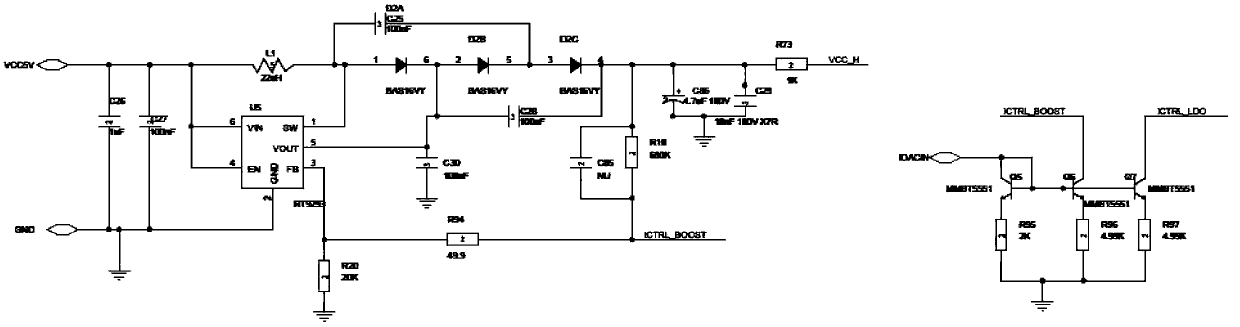
ActiveCN103389451AReduce the impactHigh measurement accuracyIndividual semiconductor device testingCurrent voltageEngineering
The invention discloses a testing method of an avalanche photodiode, which is characterized by comprising the following steps that (1), a function control circuit and a testing circuit are arranged on a circuit mainboard, and the function control circuit tests the avalanche photodiode through controlling the testing circuit; (2), a sensitivity testing amplitude limiting amplification circuit, a reverse breakdown voltage testing circuit and a light current and dark current testing circuit are arranged in the testing circuit in Step (1); and (3), a Boost high voltage generation circuit, a linear voltage stabilization filter circuit, a constant current source generation circuit, a feedback type IV (current-voltage) conversion circuit, an isolated power supply circuit and an optocoupler transmission circuit which are connected sequentially are arranged in the testing circuits in Step (2). The invention further discloses a testing device of the avalanche photodiode, which implements the method.
Owner:GUANGDONG RUIGU OPTICAL NETWORK COMM CO LTD
Front-side illuminated, back-side contact double-sided PN-junction photodiode arrays
ActiveUS7656001B2Maintain performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceDetector array
The present invention is a photodiode detector array for use in computerized tomography (CT) and non-CT applications. Specifically, the present invention is a high-density photodiode arrays, with low dark current, low capacitance, high signal to noise ratio, high speed, and low crosstalk that can be fabricated on relatively large substrate wafers. More specifically the photodiode array of the present invention is fabricated such that the PN-junctions are located on both the front side and back side surfaces of the array, and wherein the front side PN-junction is in electrical communication with the back side PN-junction. Still more specifically, the present invention is a photodiode array having PN-junctions that are electrically connected from the front to back surfaces and which can be operated in a fully depleted mode at low reverse bias.
Owner:UDT SENSORS +1
Germanium metal-contact-free near-IR photodetector
A Ge-on-Si photodetector constructed without doping or contacting Germanium by metal is described. Despite the simplified fabrication process, the device has responsivity of 1.24 A / W, corresponding to 99.2% quantum efficiency. Dark current is 40 nA at −4 V reverse bias. 3-dB bandwidth is 30 GHz.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
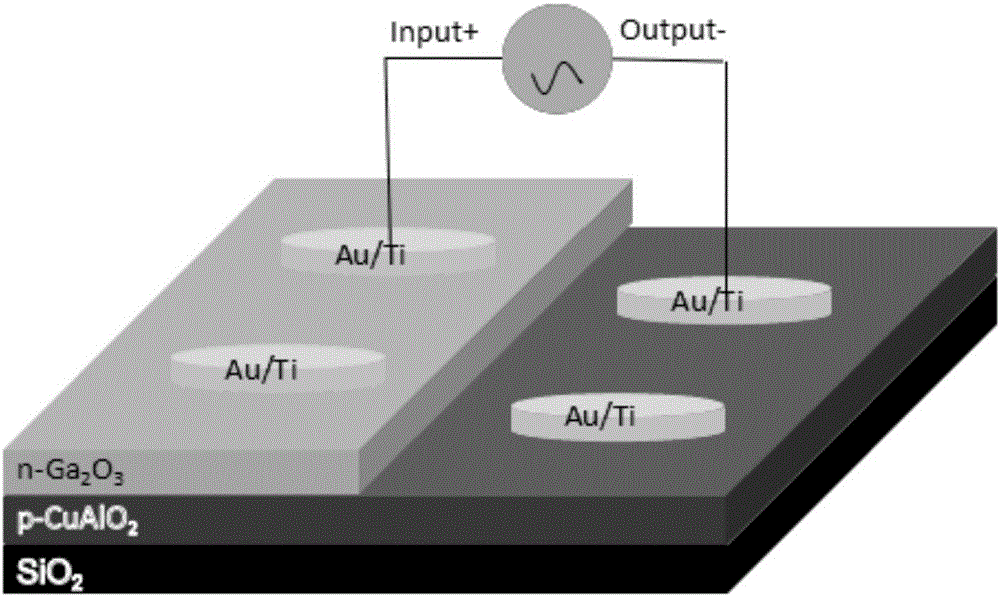
Preparation method of solar blind type ultraviolet detector based on Ga2O3/CuAlO2 heterojunction
ActiveCN106449889AImprove photoelectric propertiesHigh rectification ratioFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionUltraviolet detectors
The invention relates to a preparation method of a solar blind type ultraviolet detector based on Ga2O3 / CuAlO2 heterojunction. The method is characterized in that a layer of p-CuAlO2 thin film is deposited on a quartz (SiO2) substrate through a radio frequency magnetron sputtering technology; then, a layer of n-Ga2O3 thin film is deposited on the p-CuAlO2 thin film by using a mask plate through the radio frequency magnetron sputtering technology; the area of the n-Ga2O3 thin film is half of the area of the p-CuAlO2 thin film; finally, a layer of Ti / Au thin film is deposited on the p-CuAlO2 and n-Ga2O3 thin films by the radio frequency magnetron sputtering technology and is used as an electrode. The preparation method has the advantages that the prepared solar blind type ultraviolet detector has stable performance, sensitive response, small dark current and wide application range; in addition, the preparation method has the characteristics of high process controllability, simple operation, good universality, recoverability during repeated test and the like; great application prospects are realized.
Owner:北京镓创科技有限公司
Image pickup apparatus, image processing method, and computer program
The present invention discloses an image pickup apparatus and an imaging processing method. The image pickup apparatus includes an image pickup device including a plurality of imaging planes each having different dark current characteristics, and an image processing unit for receiving a signal from the image pickup device and performing an image generating process. The image processing unit calculates a dark current estimated to be generated in each of the plurality of imaging planes, independently for each imaging plane, and performs a dark current eliminating process on the basis of a dark current value calculated for each imaging plane.
Owner:SONY CORP
Avalanche photo-diode based on AlInAsSb body material as multiplication region and preparation method therefor
InactiveCN107170847AReduce noiseHigh Gain-Bandwidth ProductSemiconductor devicesHigh bandwidthOhmic contact
The invention provides an avalanche photodiode based on AlInAsSb body material as the multiplication region, comprising: a substrate; a buffer layer epitaxially on the substrate; an N-type ohmic contact layer epitaxially on the buffer layer and having a cross section of "" Convex" shape, its lower half is consistent with the shape of the substrate, and its upper half is cylindrical; the avalanche multiplication layer is epitaxial on the upper surface of the upper half of the N-type ohmic contact layer, composed of AlxIn1‑xAsySb1‑y Bulk material preparation, the doping concentration is less than 1016cm-3, the value range of x is: 0≤x≤1, the value range of y is: 0.08≤y≤1; the P-type charge layer is epitaxial on the avalanche multiplication layer ; The light absorbing layer is epitaxial on the P-type charge layer; and the P-type ohmic contact layer is epitaxially on the light absorbing layer. The avalanche photodiode has the advantages of low noise and high gain-bandwidth product, and at the same time effectively reduces the dark current, which not only meets the requirement of high sensitivity of the photodetector, but also realizes the design of energy band engineering and broadens its application range.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Photoelectric conversion element, production method thereof, photosensor, imaging device and their driving method
ActiveUS8847141B2Reduce dark currentReducing range of increaseGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsFinal product manufactureEngineeringPhotoelectric conversion
To provide a photoelectric conversion element capable of functioning as a photoelectric conversion element when a compound having a specific structure is applied to the photoelectric conversion element, causing the element to exhibit a low dark current, and reducing the range of increase in the dark current even when the element is heat-treated, and an imaging device equipped with such a photoelectric conversion element. A photoelectric conversion element having a photoelectric conversion film which is sandwiched between a transparent electrically conductive film and an electrically conductive film and contains a photoelectric conversion layer and an electron blocking layer, wherein the electron blocking layer contains a compound having, as a substituent, a substituted amino group containing three or more ring structures.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
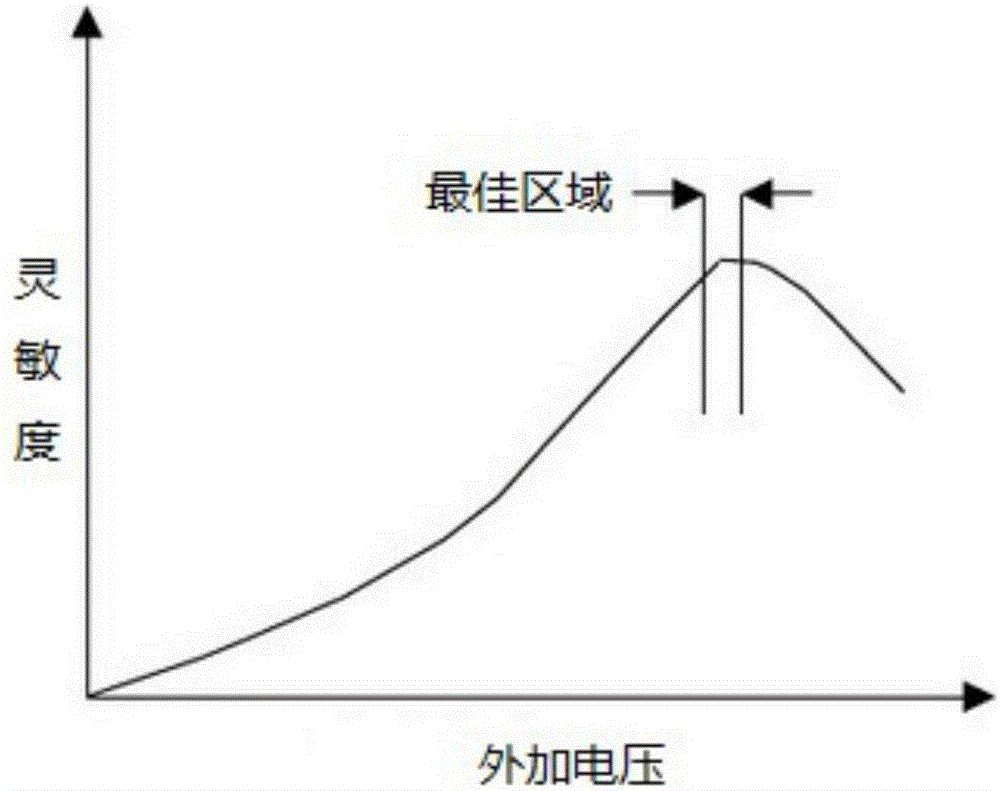
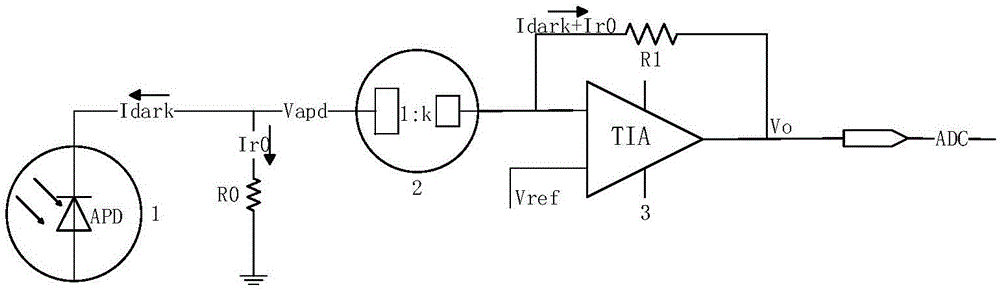
Method for calculating APD breakdown voltage and circuit thereof
ActiveCN106841970AImprove production yieldShorten the timeDiode testingAudio power amplifierOptical Module
The present invention provides a method for calculating APD breakdown voltage and a circuit thereof. The method comprises the following steps: 1, adding reserve voltage Vapd on an APD in a condition without light; 2, dark current (Idark) generated by the APD flows into a trans-resistance amplifier (3) after passing through a current mirror (2); 3, reversely calculating the dark current (Idark) through output voltage (Vo) of the trans-resistance amplifier (3); and 4, determining whether the dark current (Idark) of the APD is equal to 10 [Mu]A or not, if the dark current (Idark) of the APD is equal to 10 [Mu]A, allowing the APD at present to be the breakdown voltage of the APD, or else, repeatedly setting the Vapd, and returning back to the step 3. The method for calculating APD breakdown voltage and the circuit thereof can accurately find the Vbr of the APD so as to find reasonable reverse direction work voltage Vapd, are good in precision, efficiency and consistence, improve the yield rate of an optical module, improve production efficiency and reduce production cost.
Owner:CHENGDU SUPERXON COMM TECH CO LTD
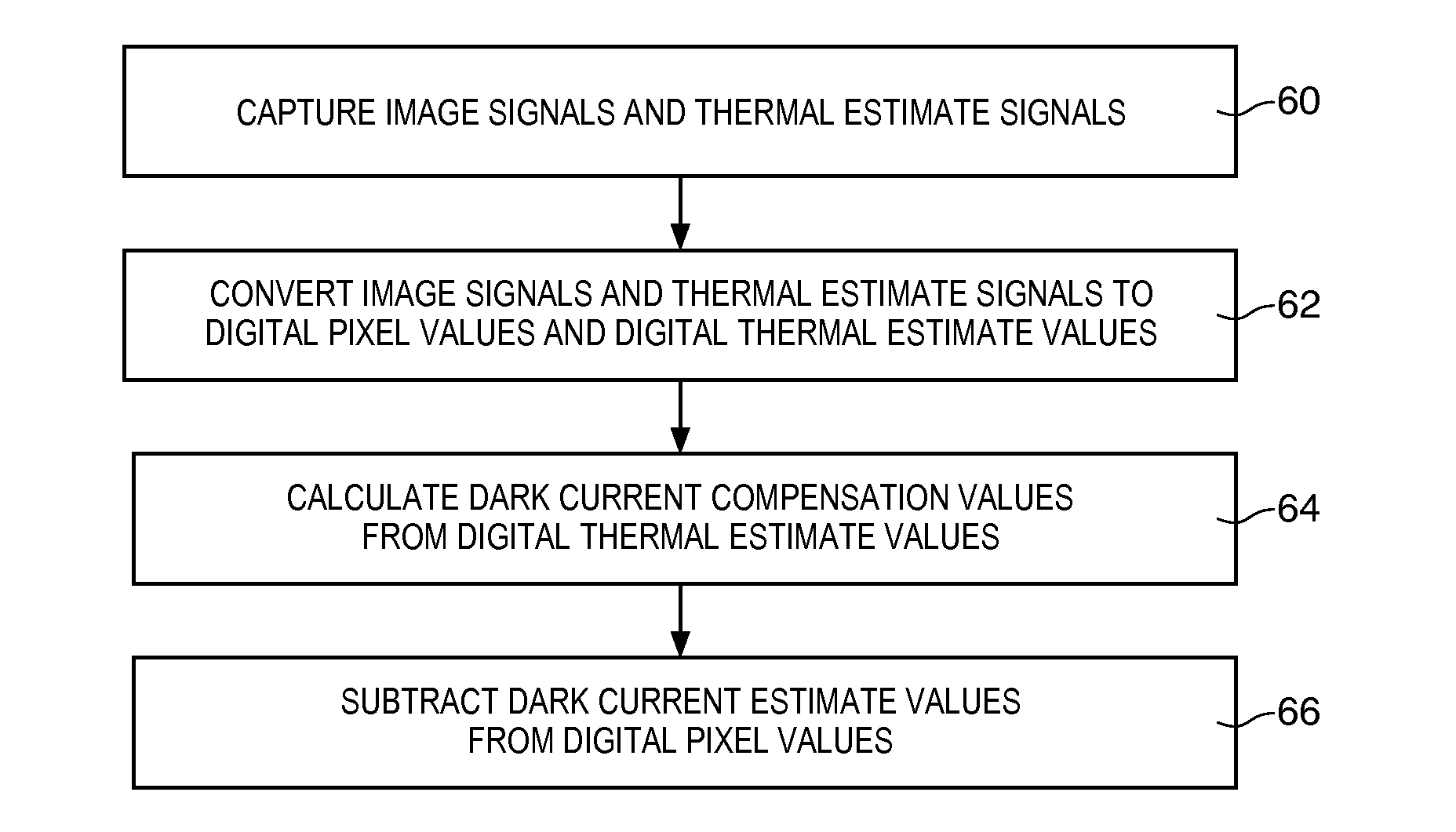
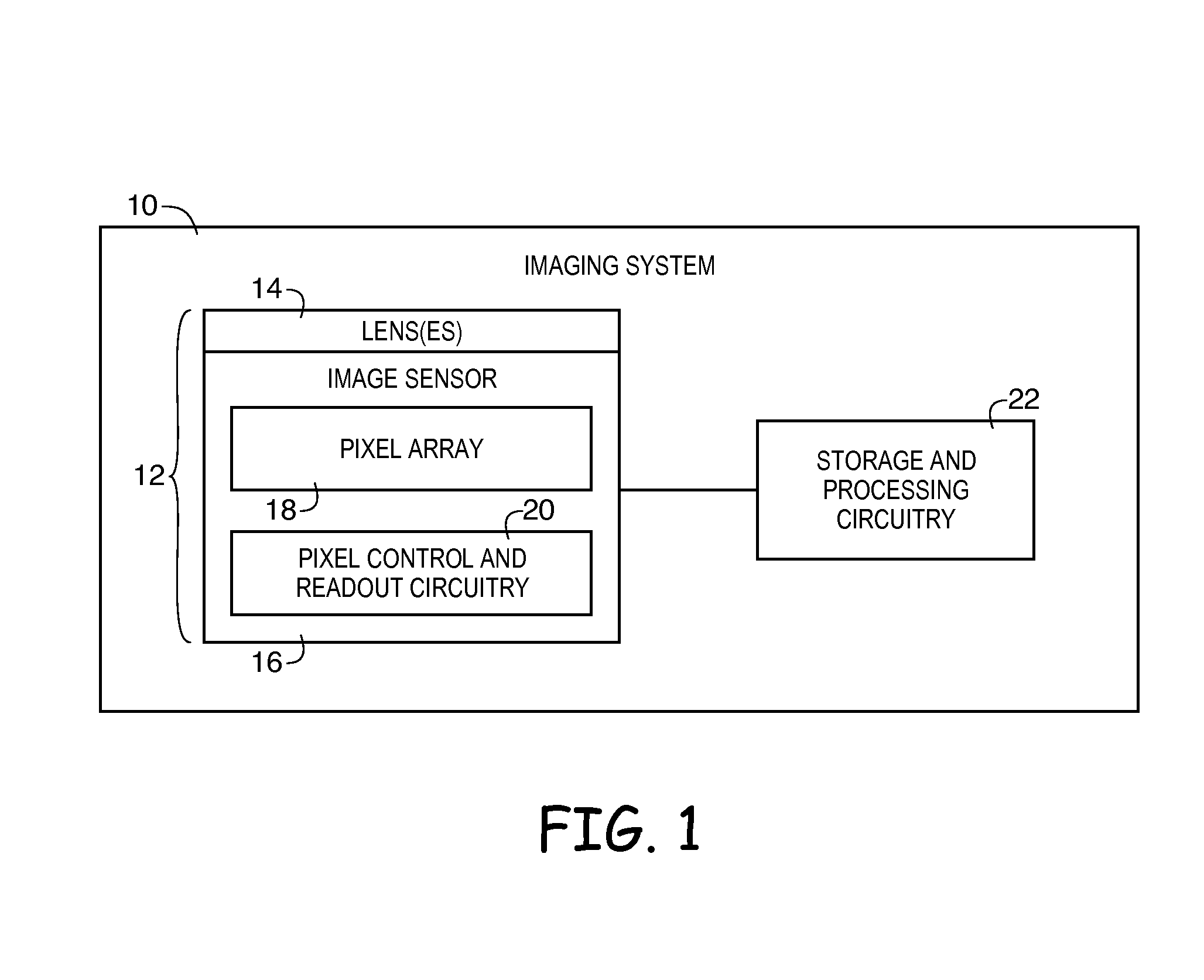
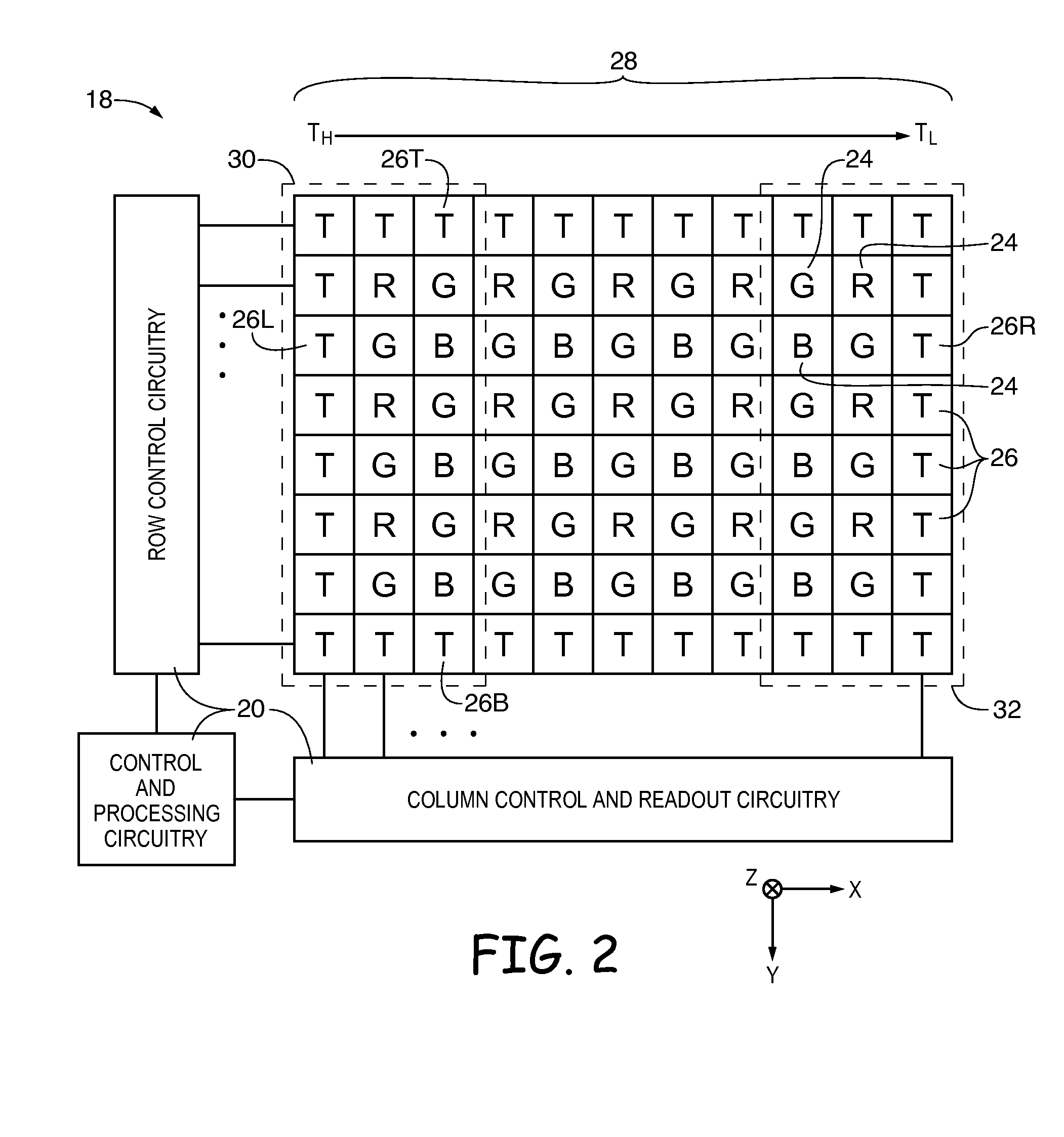
Systems and methods for pixel-level dark current compensation in image sensors
ActiveUS20160173794A1Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsPixel basedDark current
An imaging system may include processing circuitry, a lens, and an array of pixels including image sensor pixels and temperature sensor pixels. The image sensor pixels may generate image pixel values in response to image light received through the lens. The temperature sensor pixels may generate thermal estimate signals based on the temperature of the pixel array. The image sensor pixels and temperature sensor pixels may generate dark current. As the temperature of the pixel array increases, the image sensor pixels and temperatures sensor pixels may generate increased dark current. Temperature sensor pixels may generate more dark current than image sensor pixels. Dark current generated by the temperature sensor pixels may be used to generate dark current compensation values that may compensate for the dark current generated by the image sensor pixels.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
InGaAs/InP PIN photo electric detector and its manufacturing technology
InactiveCN1414642AStable growth conditionsEasy to controlFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesManufacturing technologySignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
A InGaAs / InP PIN photoelectric detector relating to a semiconductor component has the structure of double hetergeneous material in four layer of i-In0.53 Ga 0.47As photosensitive layer / i-InP buffer layer / N+-Inp substrate. There is P+ zinc diffusion layer which is close to i-In 0.53 Ga0.47 As photosensitive layer but not reach the photosensitive layer at the top layer. It is prepared by the following steps, growing a passivation film of aluminium oxide on the epitaxial sheet and carrying out open-type zinc diffusion by using zinc as a diffusion source, depositing high quality film of aluminiumoxide on InP material by directly using evapouration to reduce dark current, and raising the signal to noise ratio. The film obtained can be used in passivation film of InP material.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
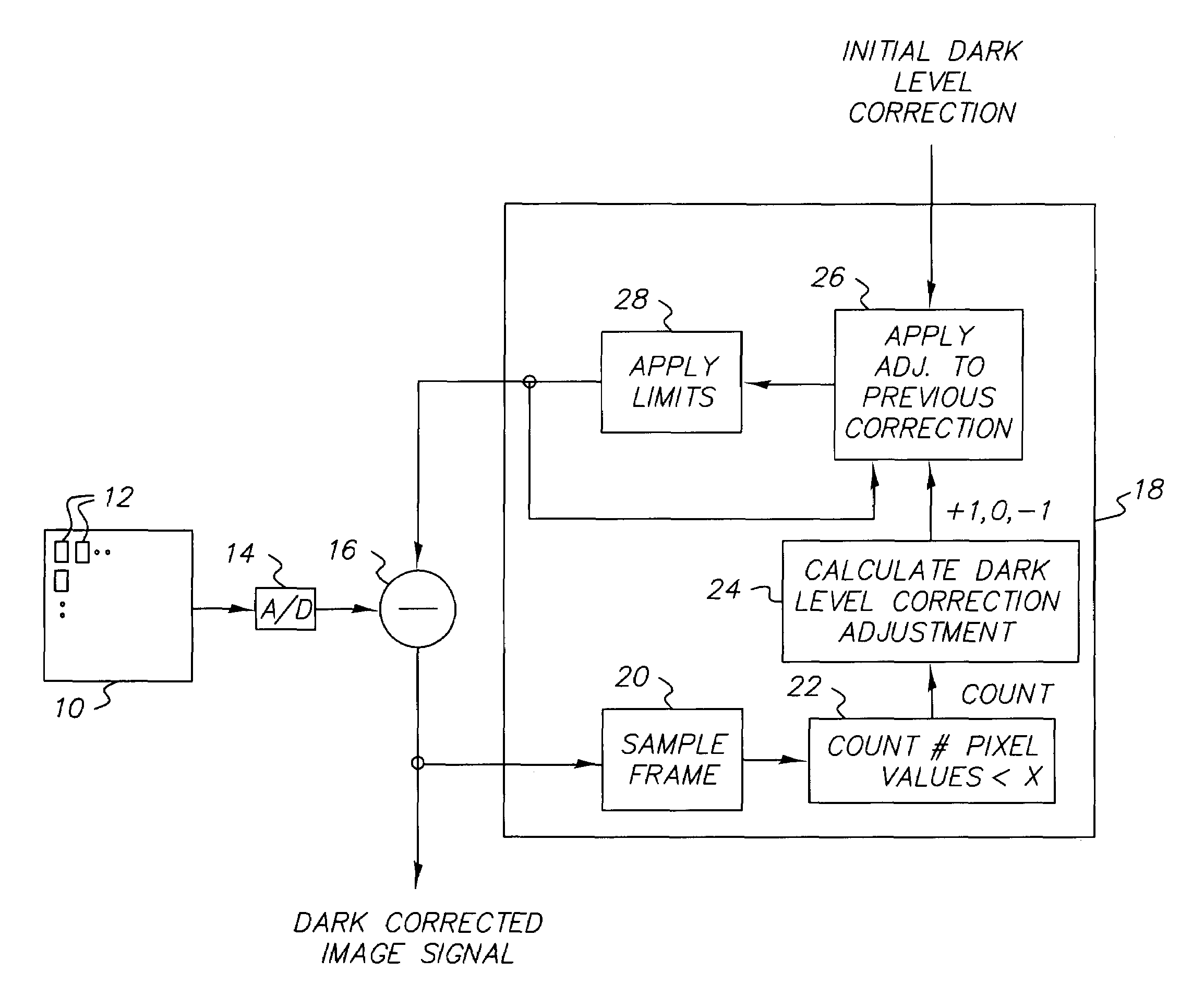
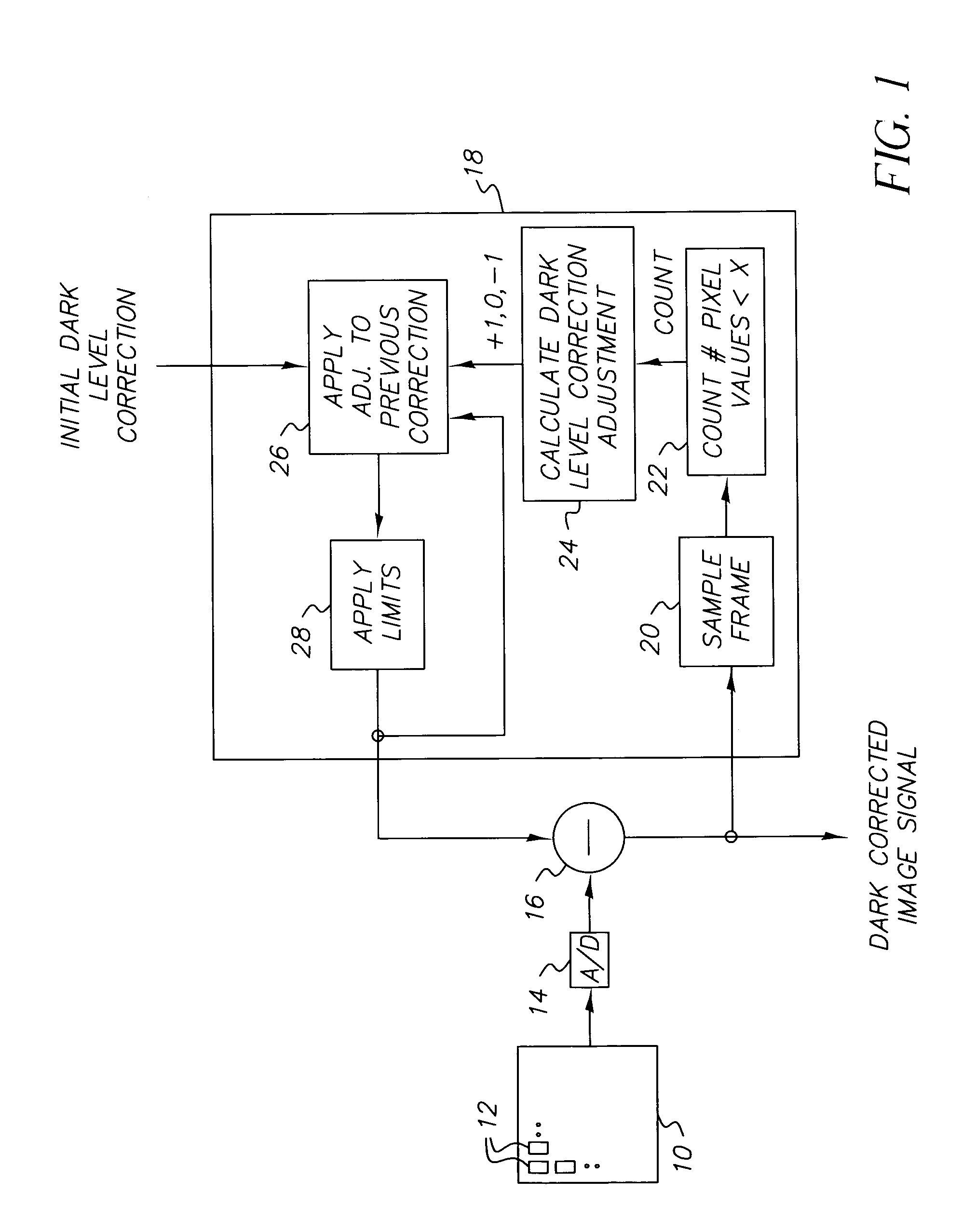
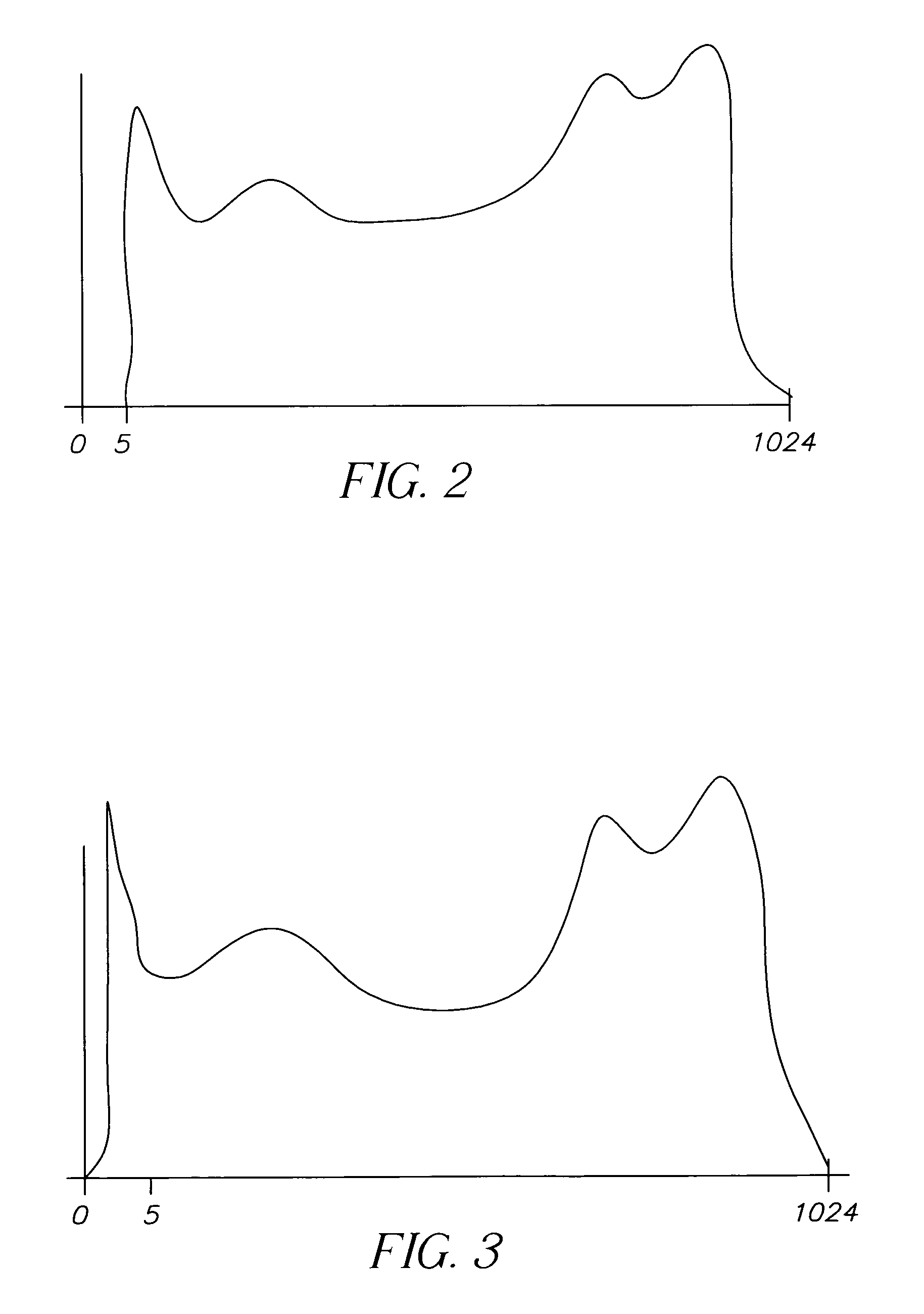
Apparatus and method of correcting for dark current in a solid state image sensor
ActiveUS7064785B2Reduce the impactImprove image qualityTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsControl systemDigital image
Apparatus and method of correcting for dark current in a solid state image sensor, include capturing an image with the image sensor to produce a digital image having pixel values; correcting the pixel values with a dark level correction value; employing a control system to adjust the dark level correction value to drive the number of pixels having values lower than a predetermined value chosen to represent dark scene content to a predetermined range.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com