Sensor dark pixel offset estimation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
Overview
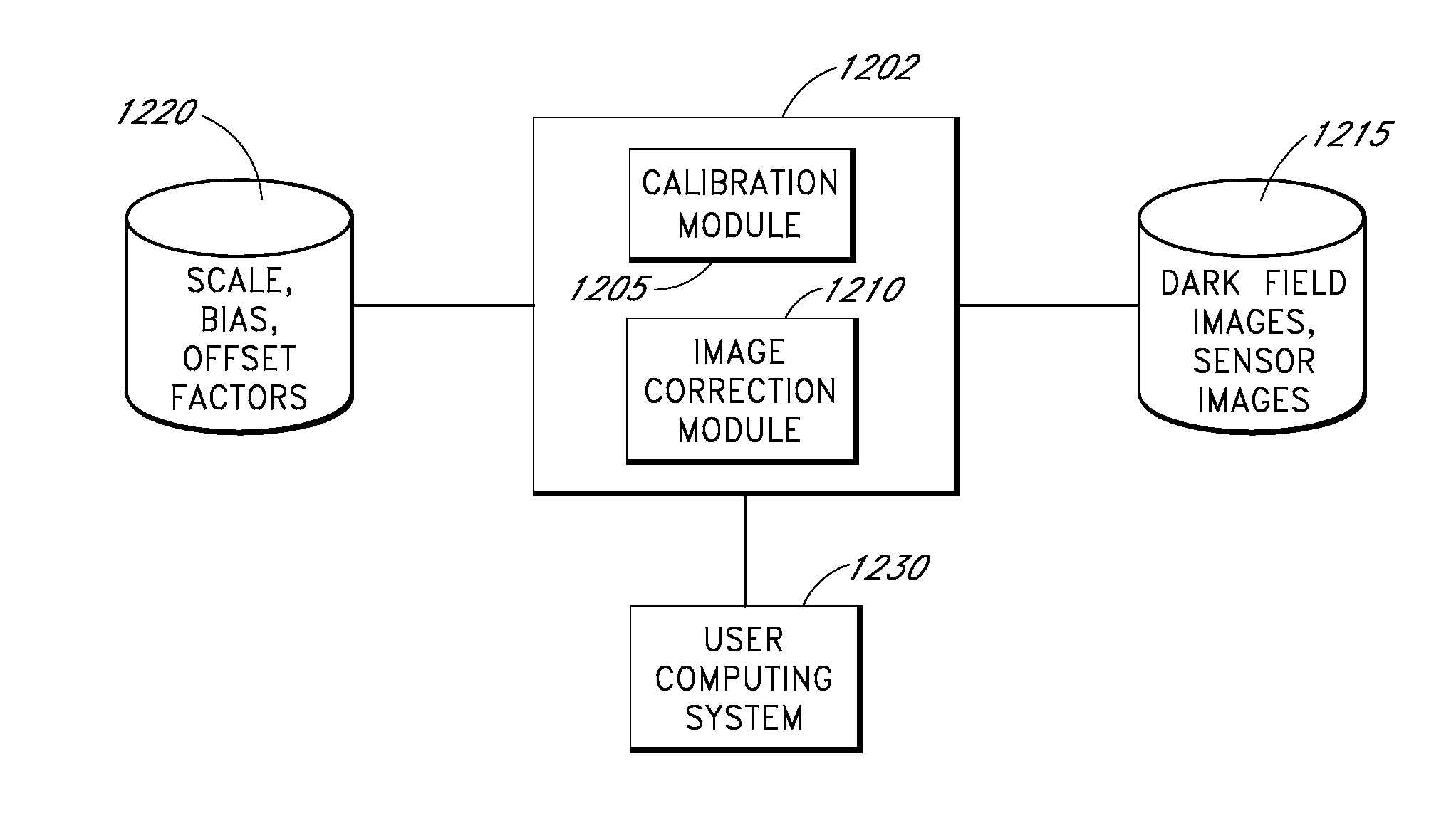
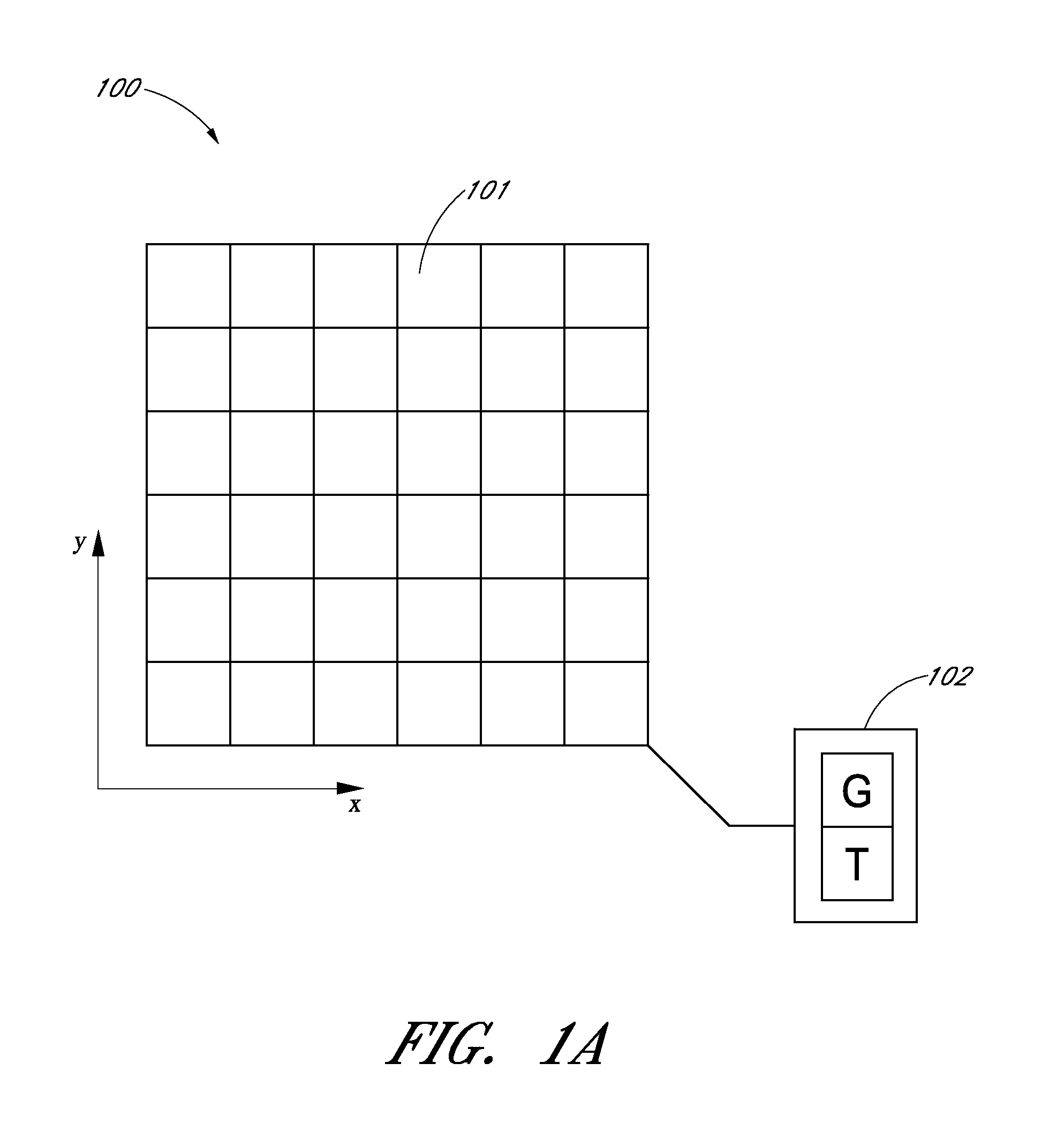
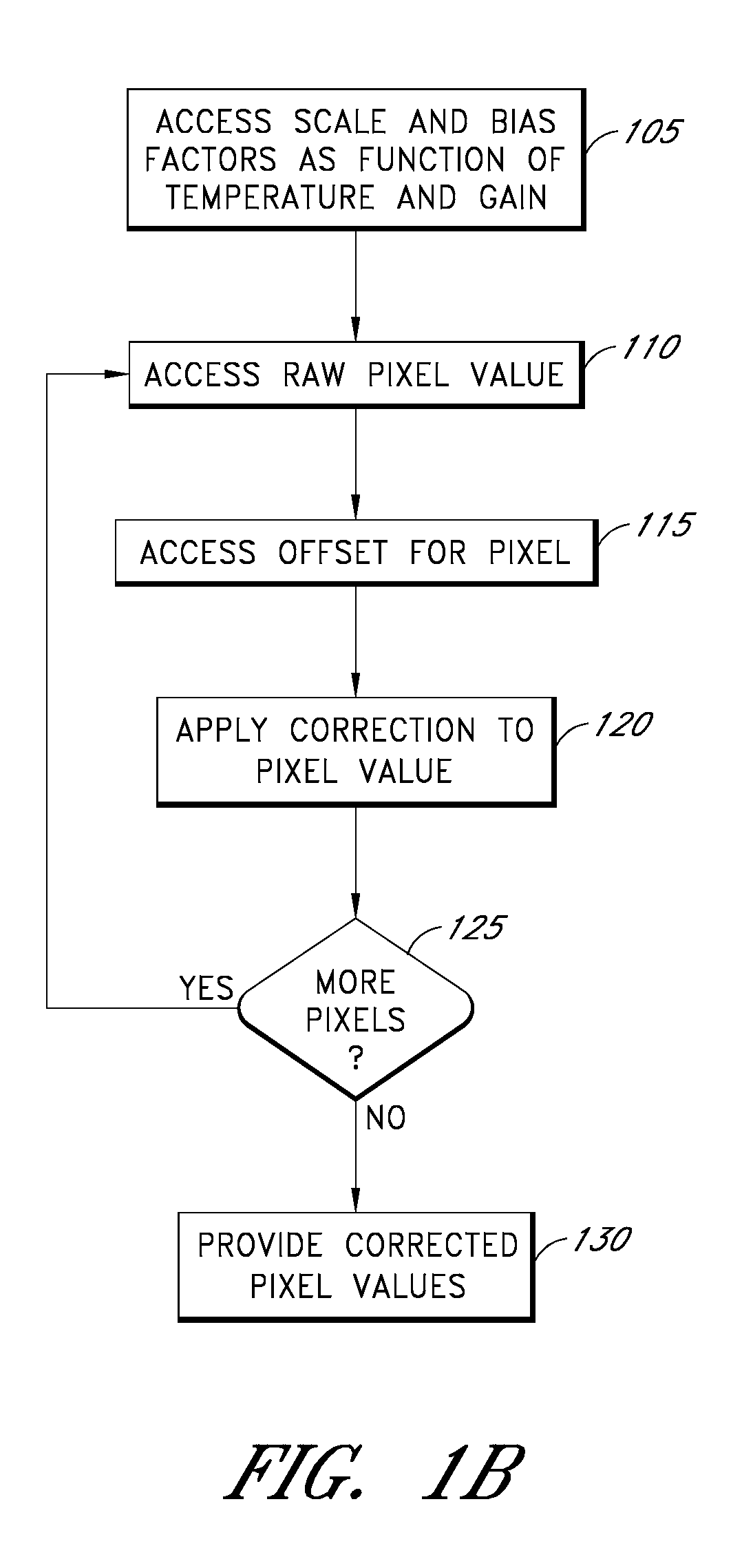
[0030]As discussed, dark current can depend, among other factors, on the temperature of the sensor (and / or the gain applied to the sensor). Some implementations of an imaging device may include a temperature controller configured to adjust or control the temperature of the sensor. Because the sensor is kept at a controlled temperature, the dark current need not be corrected for variations in temperature of the sensor. However, temperature controllers often use significant amounts of power, and thus may not be used in certain implementations such as low-power implementations, satellite implementations, and so forth. In some of these implementations, the temperature of the sensor may vary during operation, and it may be desirable to correct for temperature-dependent effects of the dark current. Thus, a temperature sensor can be used to measure the temperature of the sensor. The disclosure herein provides examples of systems and methods for correcting for temperature-dependent ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com