Patents
Literature
105results about How to "Suppress dark current" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
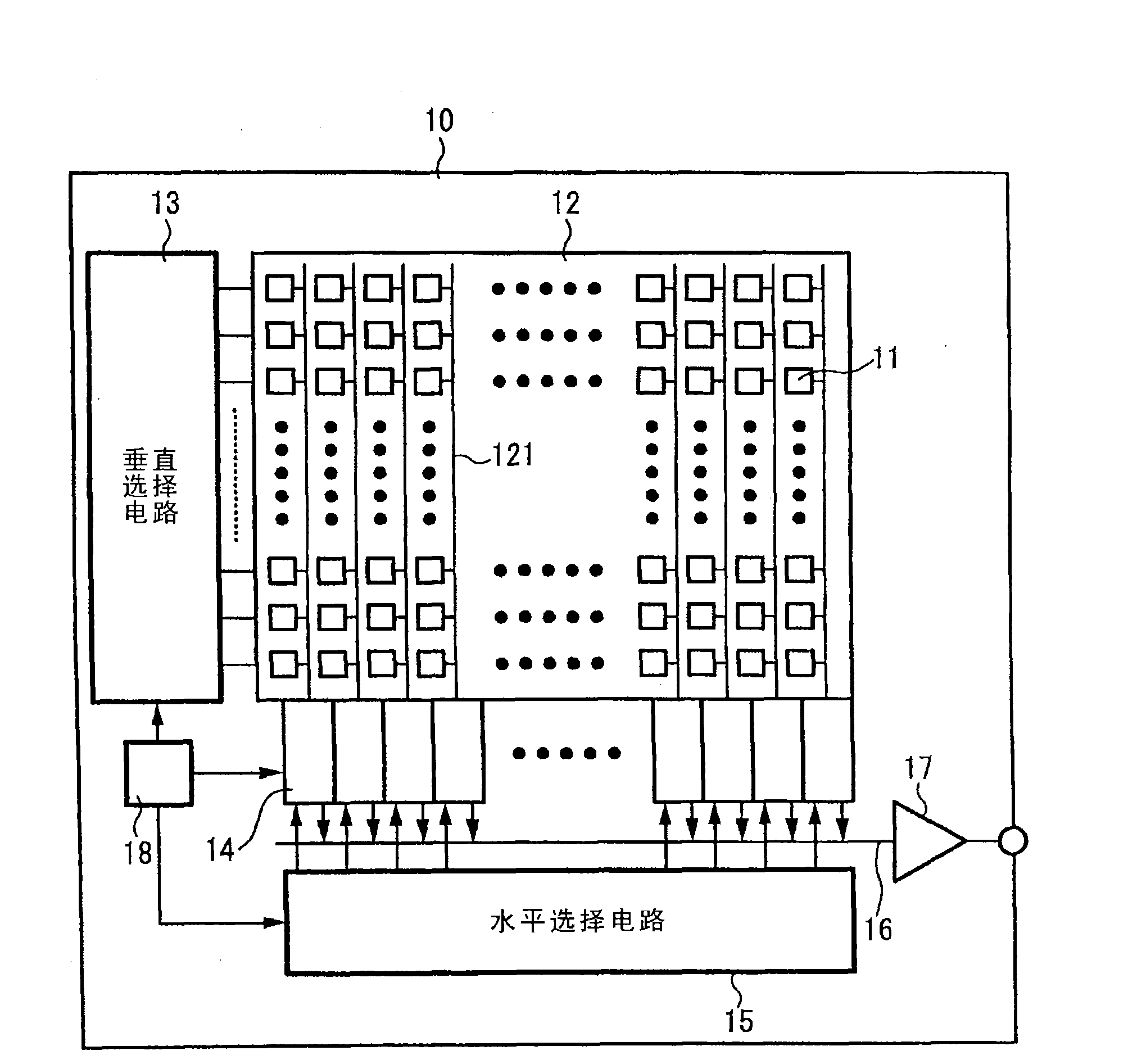
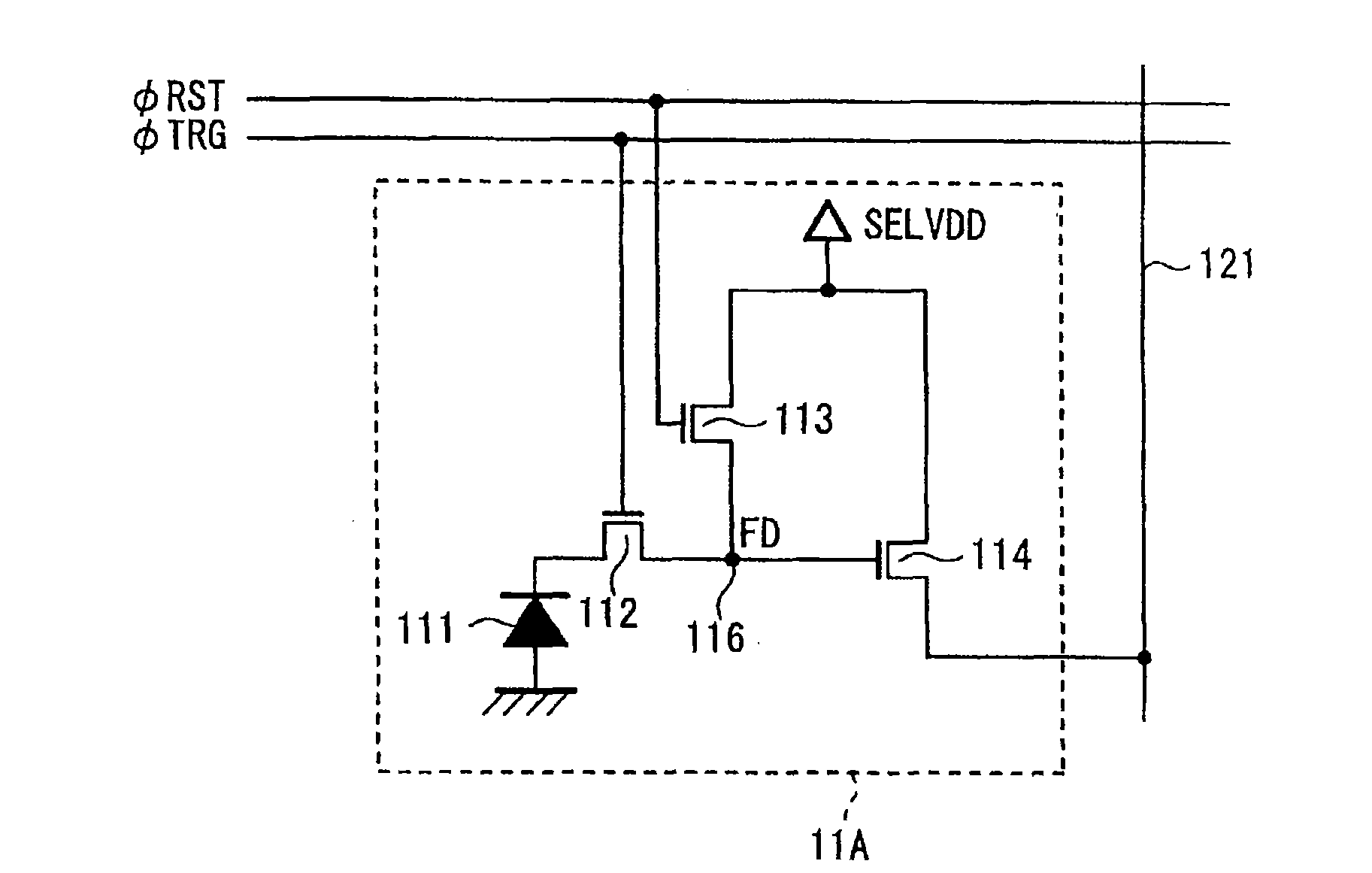
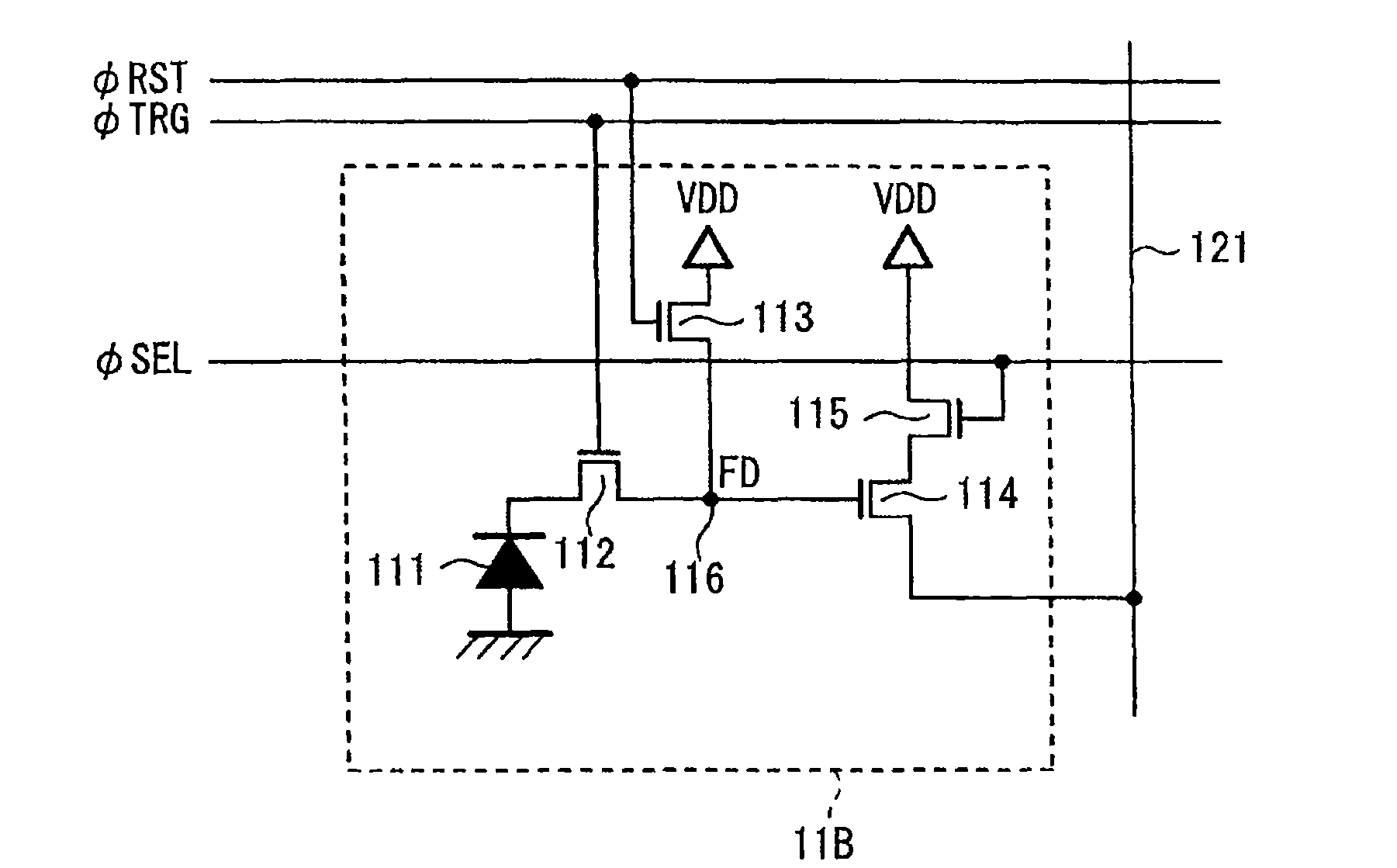
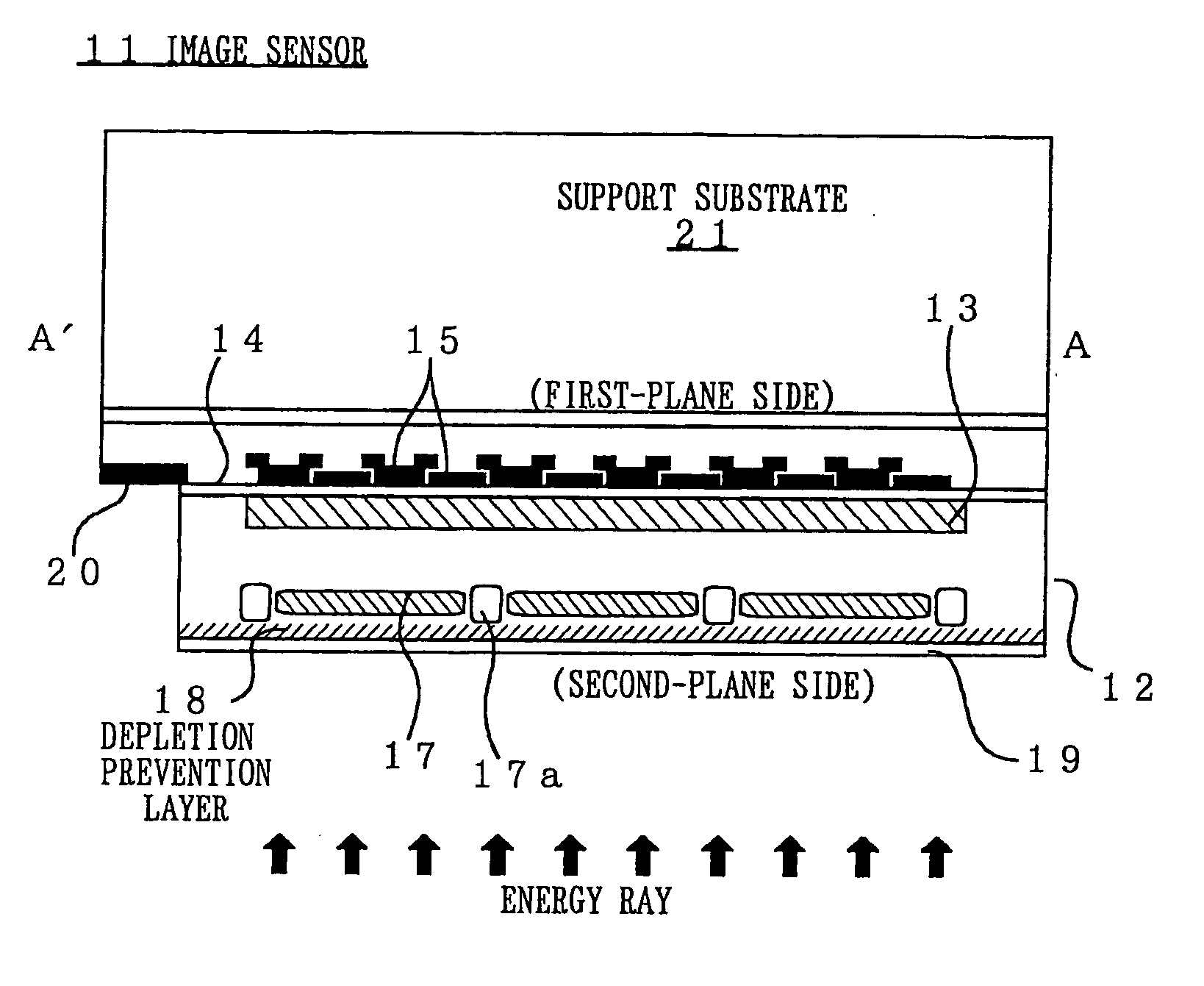
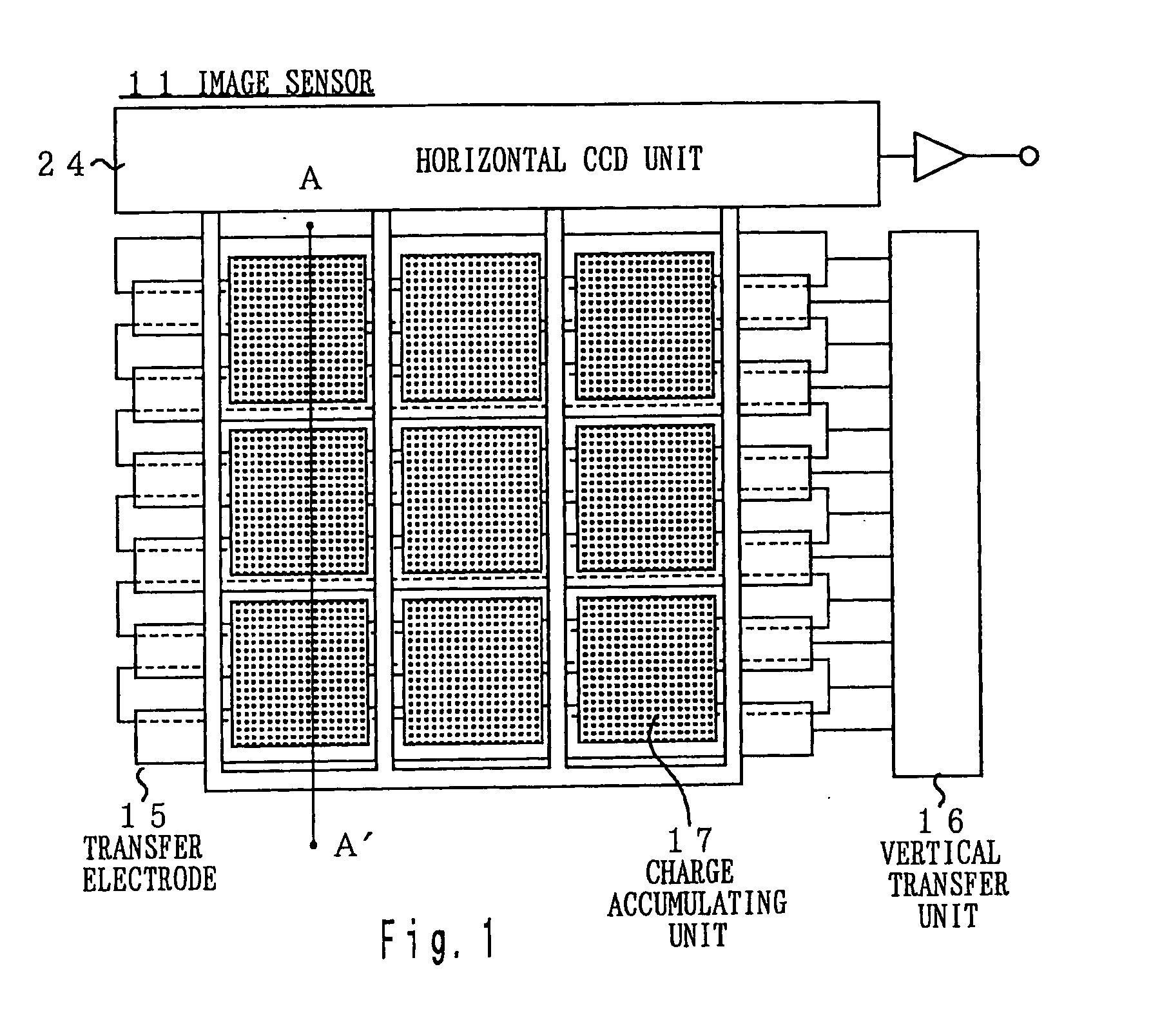
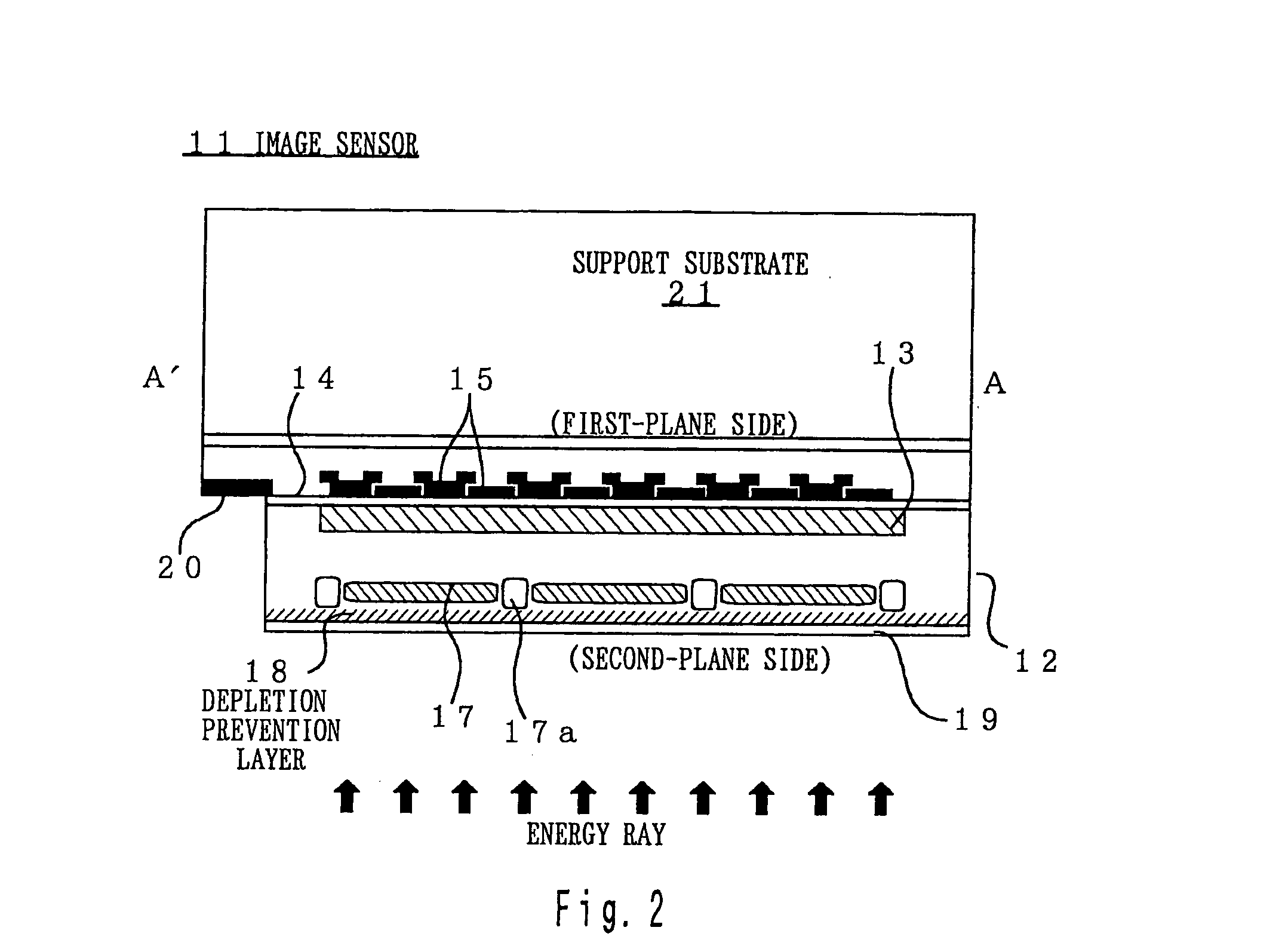
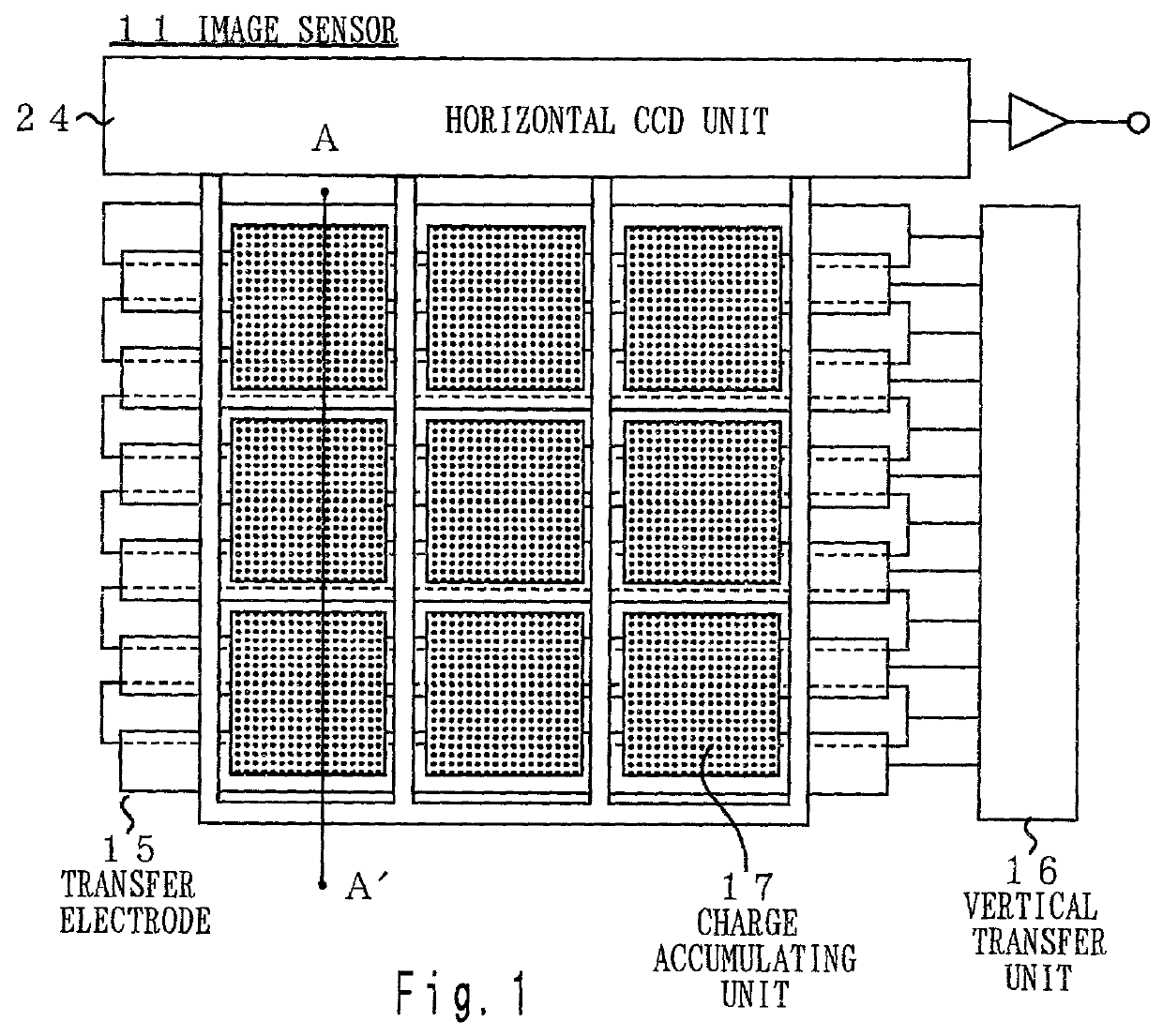
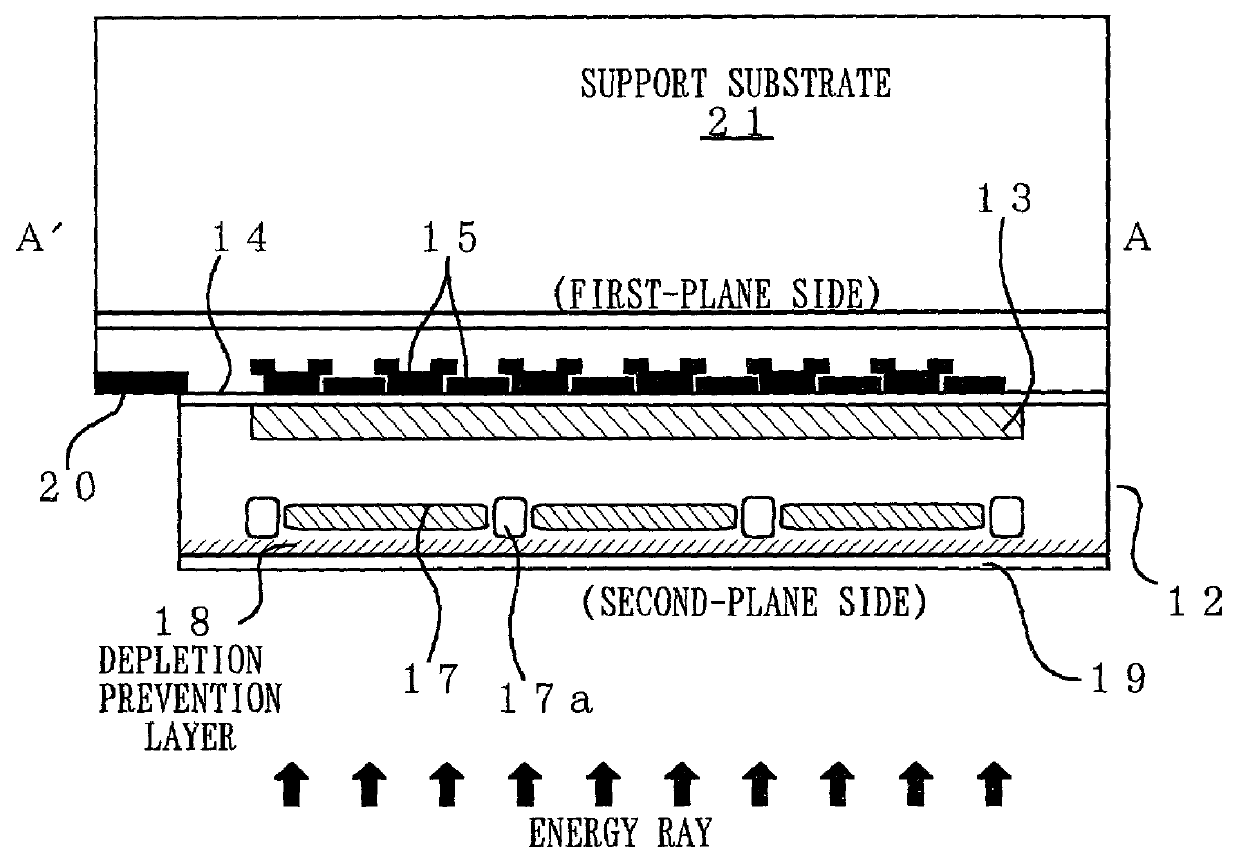
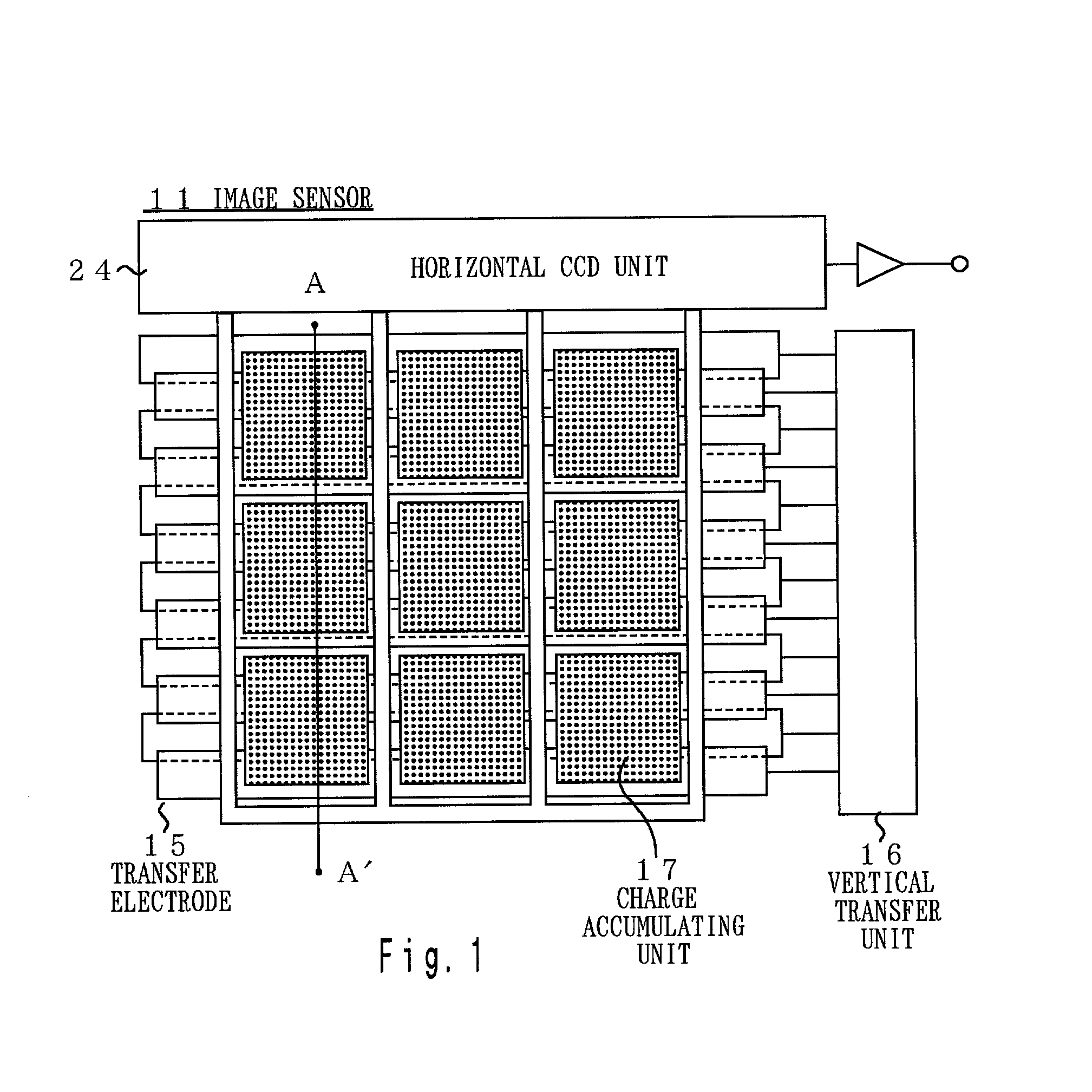
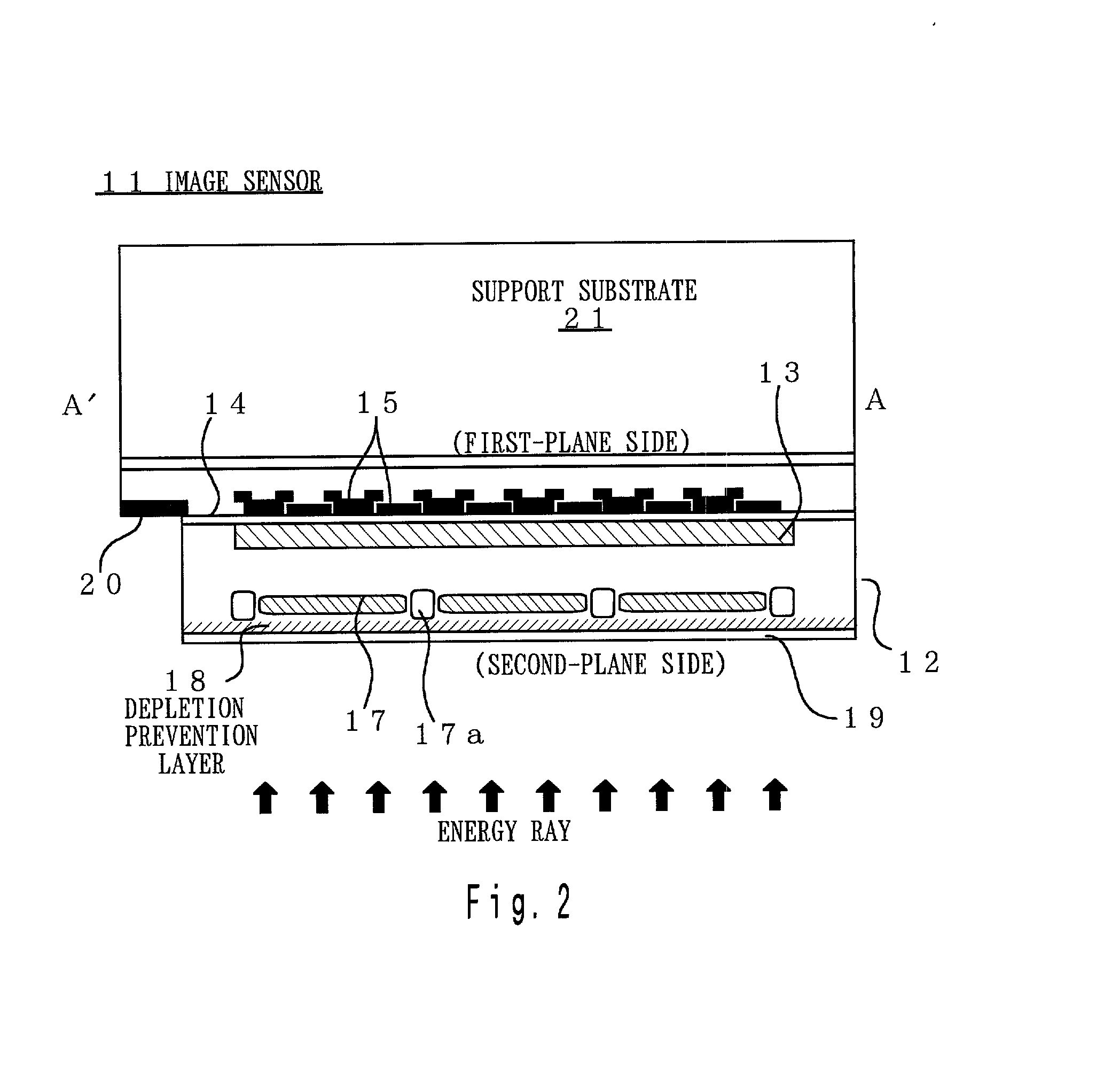
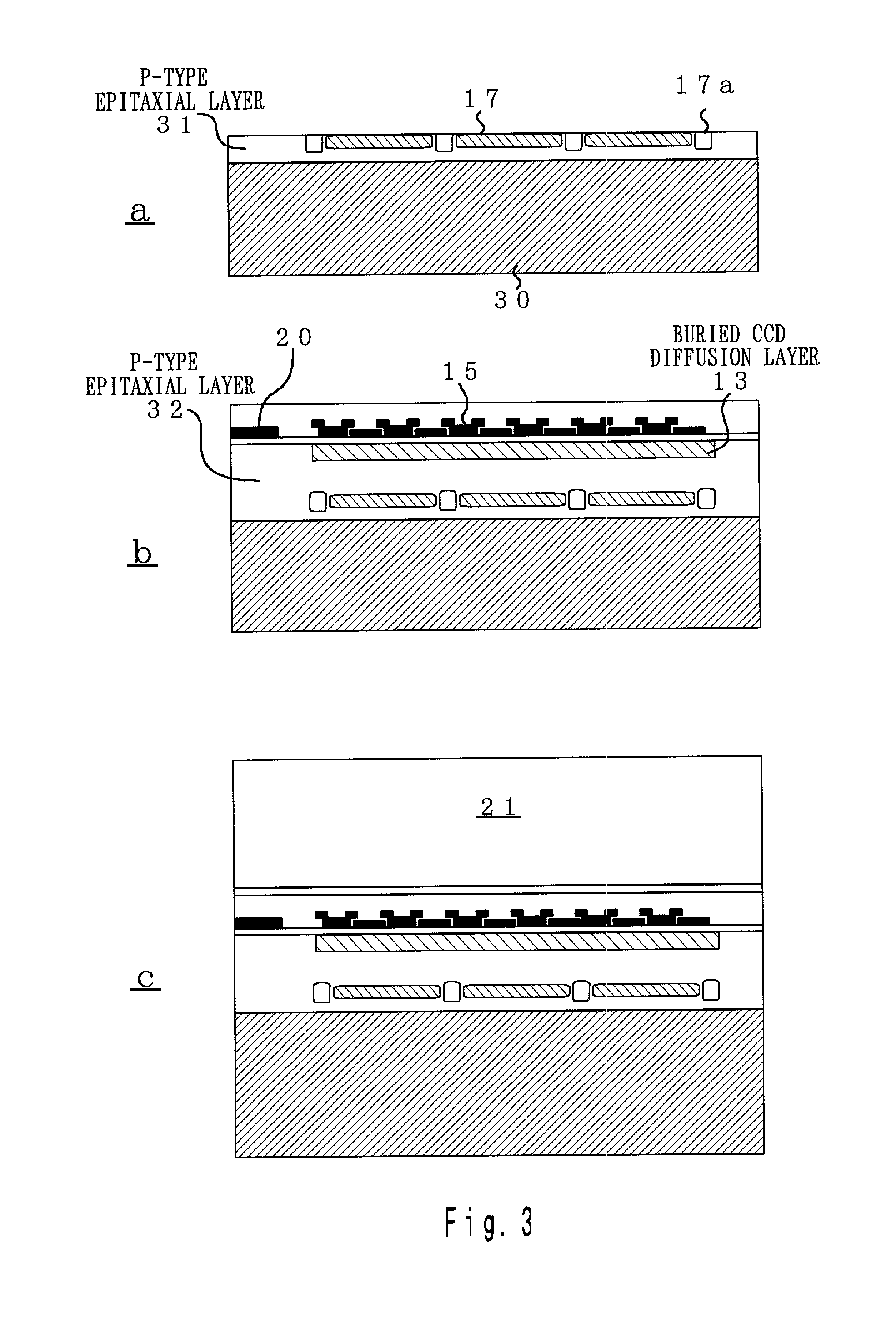
Image sensor, method of fabricating the same, and exposure apparatus, measuring device, alignment device, and aberration measuring device using the image sensor
InactiveUS20040007722A1Suppress dark currentReliable transmissionSolid-state devicesDiodeMeasurement deviceImage signal
In the present invention, a charge transfer unit is arranged on a first-plane side of a thinly-formed semiconductor base. Charge accumulating units are arranged on a second-plane side, the opposite side. A depletion prevention layer is arranged closer to the second-plane side than the charge accumulating units. The depletion prevention layer prevents a depletion region around the charge accumulating units from reaching the second plane of the semiconductor base. The depletion prevention layer can suppress surface dark current going into the charge accumulating units. Meanwhile, an energy ray incident from the second-plane side pass through the depletion prevention layer to generate signal charges in the charge accumulating units (depletion regions). The charge accumulating units collect, on a pixel-by-pixel basis, the signal charges which are to be transported to the charge transfer unit under voltage control or the like, and then are read to exterior as image signals.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Supression of dark current in a photosensor for imaging
ActiveUS20050045926A1Preventing current generationPrevent leakageSolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesGeophysicsOxide
A pixel cell having a halogen-rich region localized between an oxide isolation region and a photosensor. The halogen-rich region prevents leakage from the isolation region into the photosensor, thereby suppressing dark current in imagers.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
Image sensor, method of fabricating the same, and exposure apparatus, measuring device, alignment device, and aberration measuring device using the image sensor
InactiveUS20010054723A1Suppress dark currentReliable transmissionSolid-state devicesDiodeMeasurement deviceImage signal
In the present invention, a charge transfer unit is arranged on a first-plane side of a thinly-formed semiconductor base. Charge accumulating units are arranged on a second-plane side, the opposite side. A depletion prevention layer is arranged closer to the second-plane side than the charge accumulating units. The depletion prevention layer prevents a depletion region around the charge accumulating units from reaching the second plane of the semiconductor base. The depletion prevention layer can suppress surface dark current going into the charge accumulating units. Meanwhile, an energy ray incident from the second-plane side pass through the depletion prevention layer to generate signal charges in the charge accumulating units (depletion regions). The charge accumulating units collect, on a pixel-by-pixel basis, the signal charges which are to be transported to the charge transfer unit under voltage control or the like, and then are read to exterior as image signals.
Owner:NIKON CORP
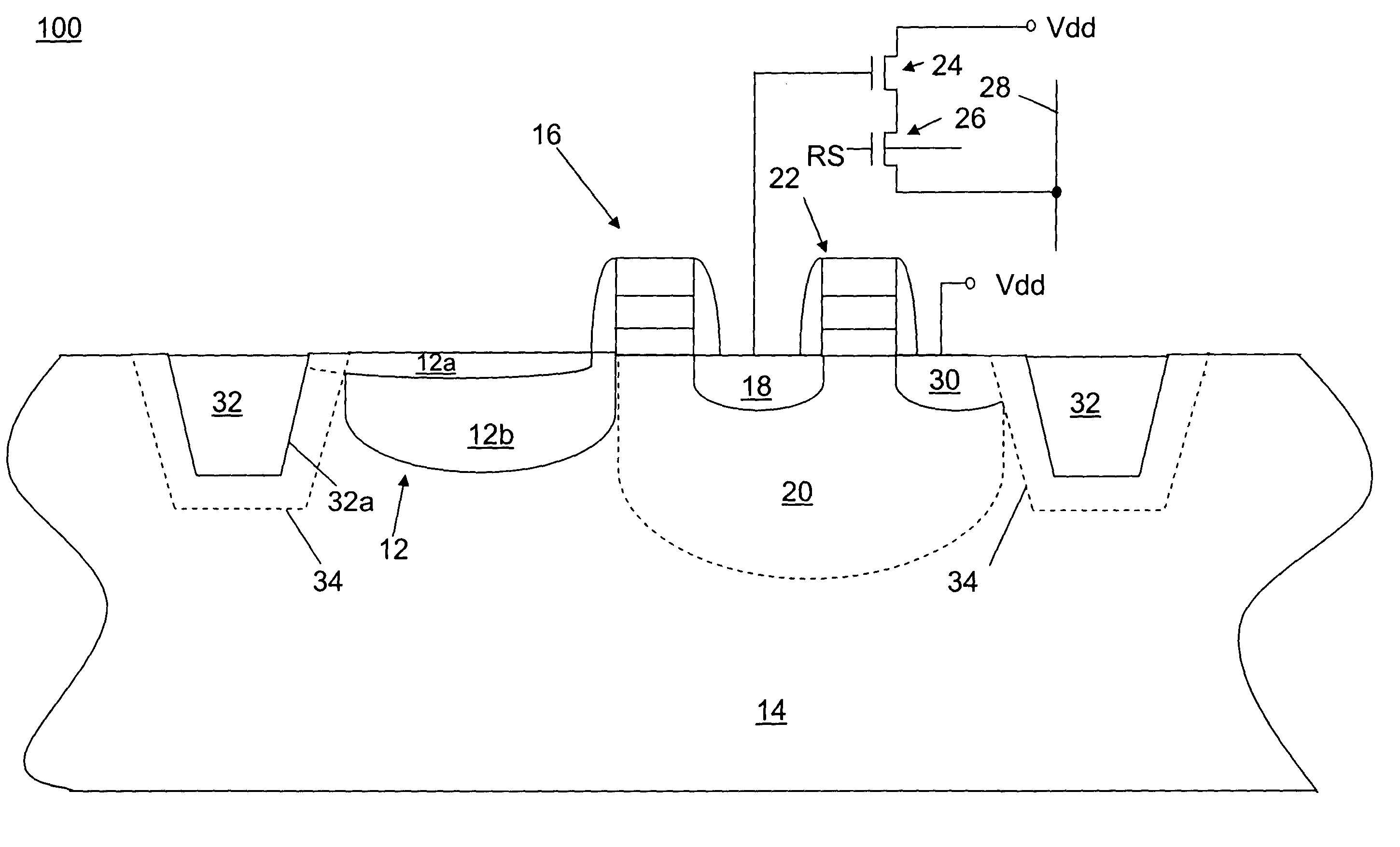
Semiconductor imaging device and fabrication process thereof
InactiveCN1905201AAccelerate emissionsAvoid excitationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFloating diffusionSemiconductor
A semiconductor imaging device, comprising: a photodetection region formed of a diffusion region of a first conductivity type and formed in an active region of a silicon substrate on a first side of a gate electrode so that its top is in contact with the silicon substrate and the inner edge portion invades under the channel region directly below the gate electrode; a shielding layer formed of a diffusion region of the second conductivity type and on the surface of the silicon substrate on the first side of the gate electrode, thereby The inner edge portion thereof is aligned with the side wall surface of the gate electrode on the first side; a floating diffusion region is formed in the active region on the second side of the gate electrode; and a channel region is formed on the second side of the gate electrode. directly below the gate electrode, wherein the channel region includes: a first channel region portion formed adjacent to the shielding layer; and a second channel region portion formed adjacent to the floating diffusion region, wherein the second The channel region portion contains impurity elements at a concentration level lower than that of the first channel region portion.
Owner:FUJITSU SEMICON LTD
Image sensor, method of fabricating the same, and exposure apparatus, measuring device, alignment device, and aberration measuring device using the image sensor
InactiveUS20010032987A1Suppress dark currentReliable transmissionSolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesMeasurement deviceVoltage control
In the present invention, a charge transfer unit is arranged on a first-plane side of a thinly-formed semiconductor base. Charge accumulating units are arranged on a second-plane side, the opposite side. A depletion prevention layer is arranged closer to the second-plane side than the charge accumulating units. The depletion prevention layer prevents a depletion region around the charge accumulating units from reaching the second plane of the semiconductor base. The depletion prevention layer can suppress surface dark current going into the charge accumulating units. Meanwhile, an energy ray incident from the second-plane side pass through the depletion prevention layer to generate signal charges in the charge accumulating units (depletion regions). The charge accumulating units collect, on a pixel-by-pixel basis, the signal charges which are to be transported to the charge transfer unit under voltage control or the like, and then are read to exterior as image signals.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Supression of dark current in a photosensor for imaging
ActiveUS20050145902A1Suppress dark currentSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGeophysicsOxide
A pixel cell having a halogen-rich region localized between an oxide isolation region and a photosensor. The halogen-rich region prevents leakage from the isolation region into the photosensor, thereby suppressing dark current in imagers.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
Preparation method for photoanode of dye-sensitized solar cell
InactiveCN102222575ALow costThickness is easy to controlLight-sensitive devicesSolid-state devicesCrystal planeOmega
The invention discloses a preparation method for a photoanode of a dye-sensitized solar cell. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: (1) taking fluorine-doped tin oxide (FTO) conductive glass as a substrate material of a photoanode electrode, wherein the thickness of a substrate is 2 to 3mm, the visible light transmission rate of the substrate is greater than 90 percent, and the surface square resistance of the substrate is 14 to 18 omega / square; (2) sputtering a compact semiconductor layer with the thickness of about 50 to 300nm on the surface of the FTO conductive glass to serve as a baffling layer by a magnetically-controlled sputtering method; (3) mixing an alcohol solution and semiconductor granules and dispersing the mixture by using ultrasonic to obtain an electrophoretic solution; and (4) depositing the electrophoretic solution on the FTO conductive substrate with the compact semiconductor layer by an electrophoresis method in a high magnetic field of 10 to 12T. By the method, an obtained semiconductor film does not have cracks, is formed quickly and has uniform and controllable depositing thickness within a relatively large range; and a semiconductor crystal has the advantages of relatively good crystal plane orientation and the like.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
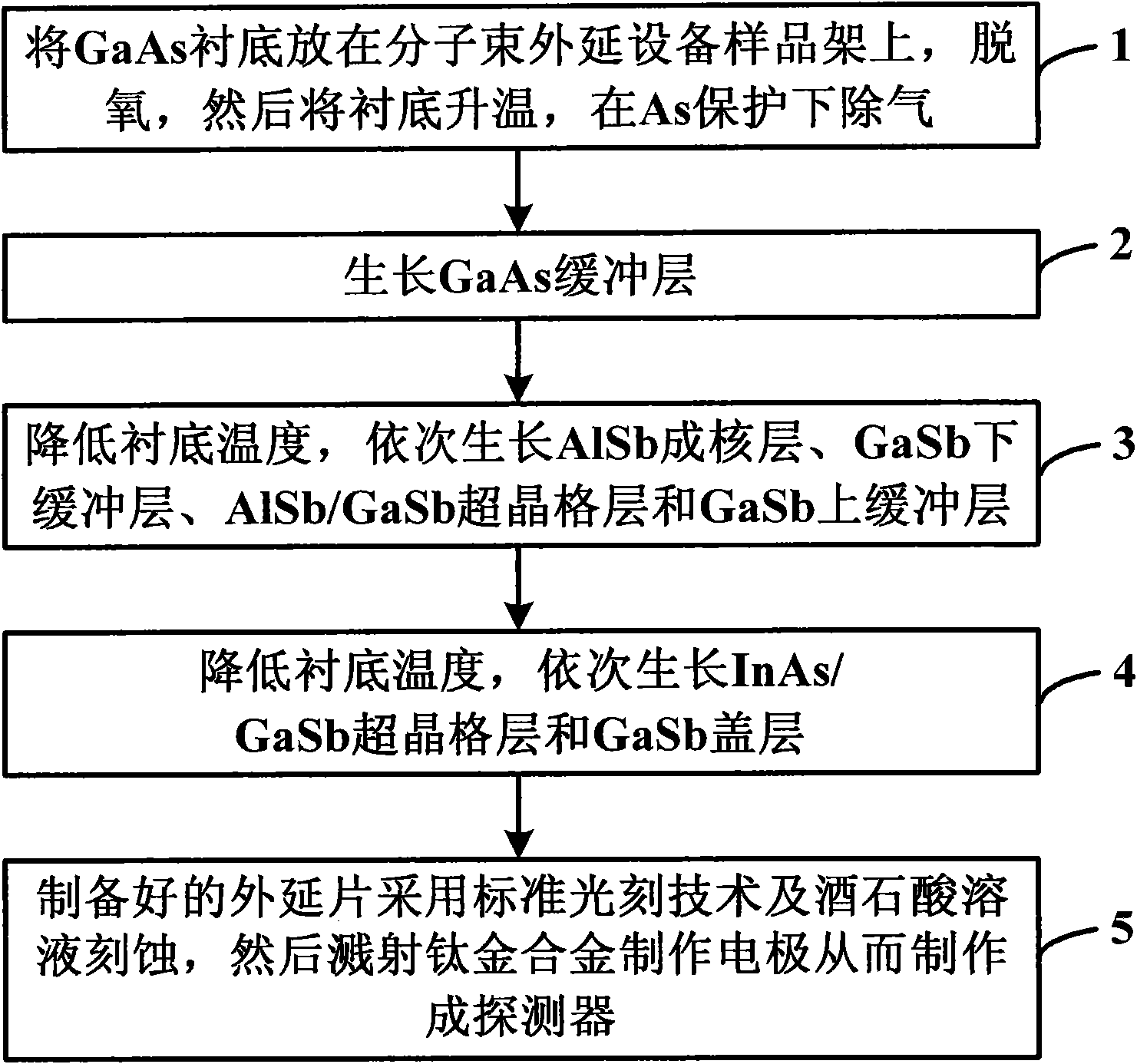
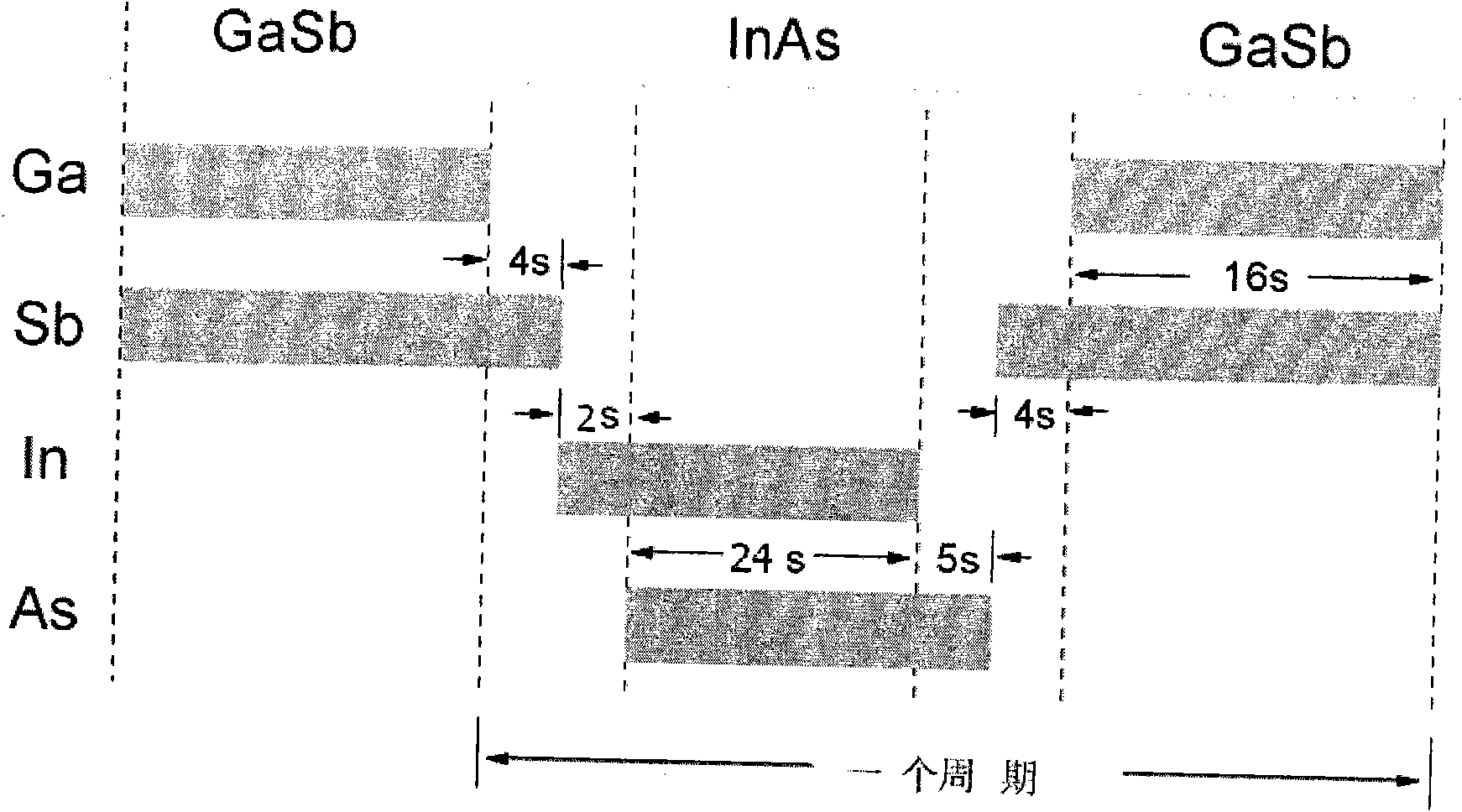
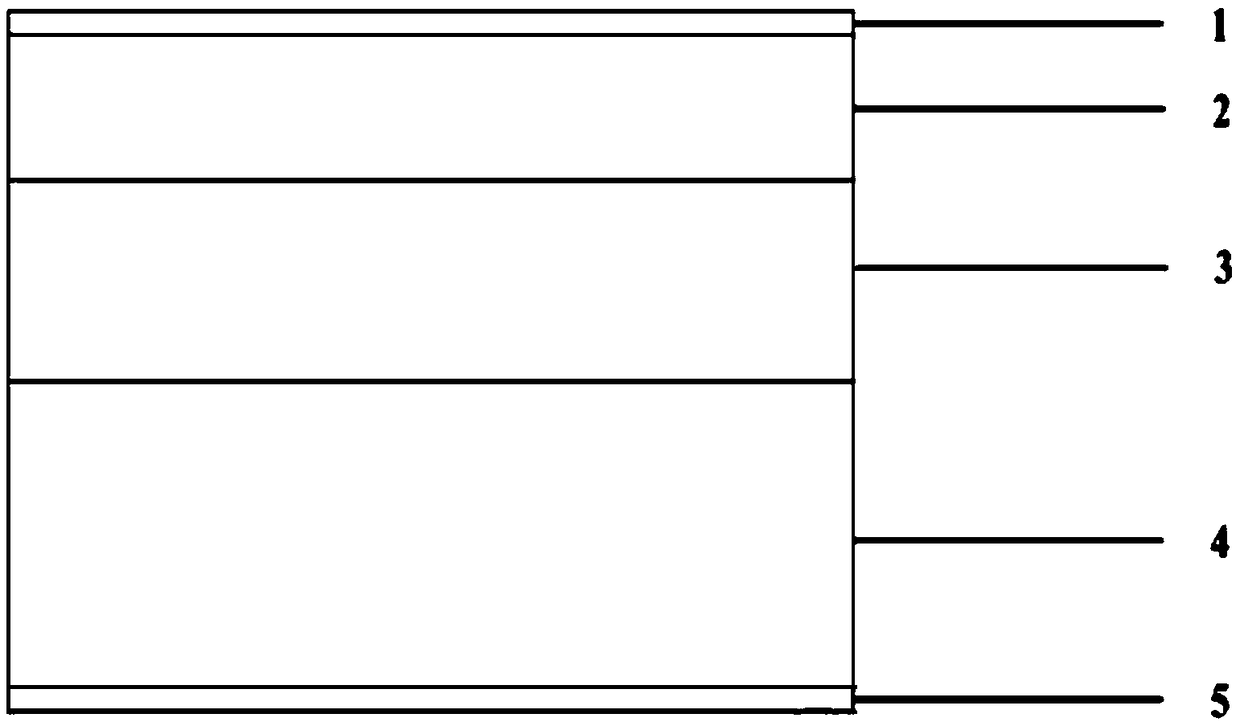
GaAs based InAs/GaSb superlattice near infrared photodetector and manufacturing method thereof
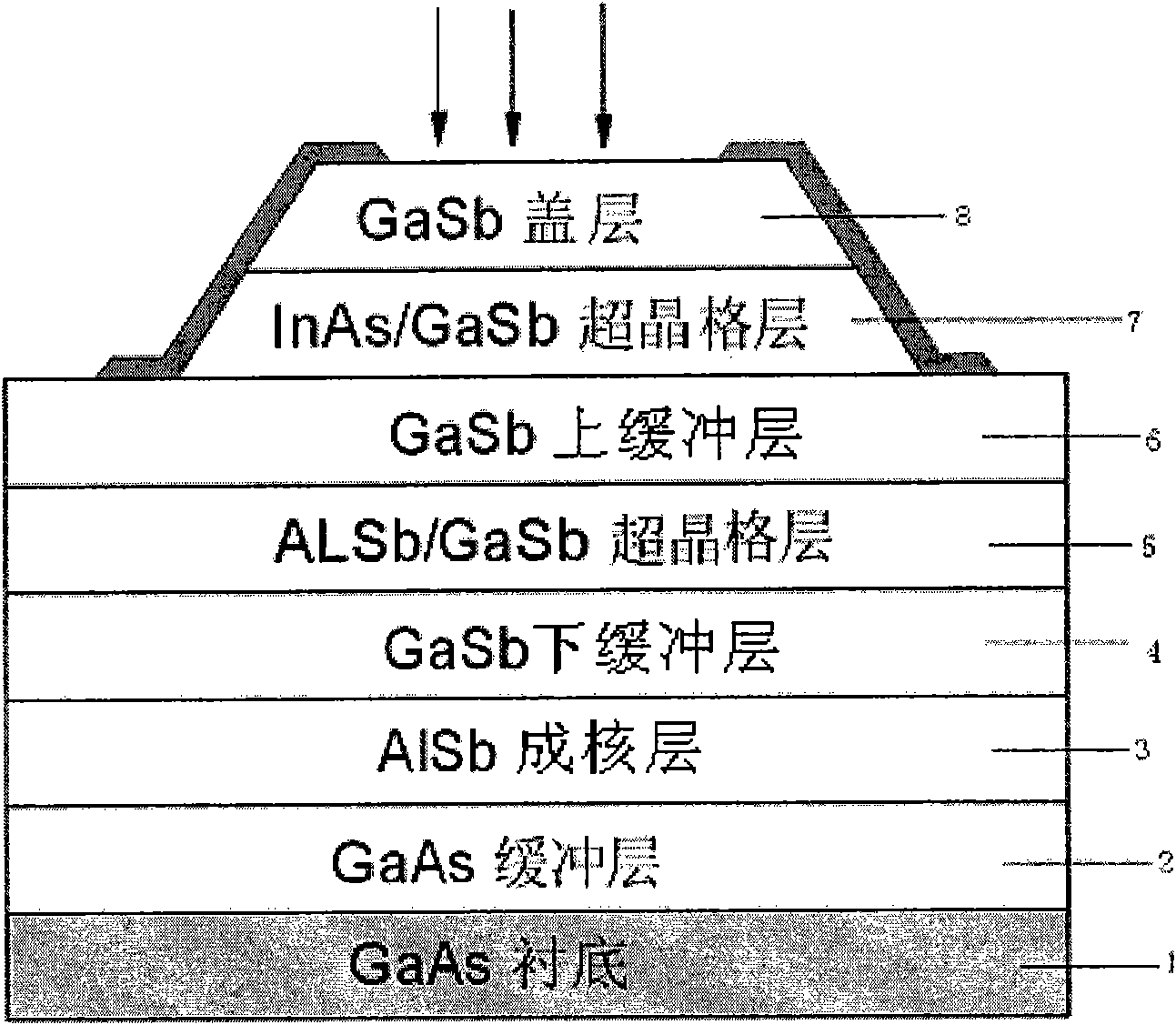
InactiveCN101576413AReduce dark currentLow costRadiation pyrometryPhotodetectorPhotovoltaic detectors
The invention discloses a GaAs based InAs / GaSb superlattice 1-3 micron band near infrared photodetector, which consists of the following components from bottom to top: a GaAs substrate, a GaAs buffer layer, an AlSb nucleating layer, a GaSb lower buffer layer, an AlSb / GaSb superlattice layer, a GaSb upper buffer layer, an InAs / GaSb superlattice layer, a GaSb cover layer and a titanium alloy electrode. The invention also discloses a method for manufacturing the GaAs based InAs / GaSb superlattice 1-3 micron band near infrared photodetector at the same time. By using the GaAs based InAs / GaSb superlattice 1-3 micron band near infrared photodetector and the method, a high-quality GaSb buffer layer is grown on the GaAs substrate, and the InAs / GaSb superlattice layer is grown on the GaSb buffer layer, thus an infrared photodetector with low dark current and low cost can be manufactured.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
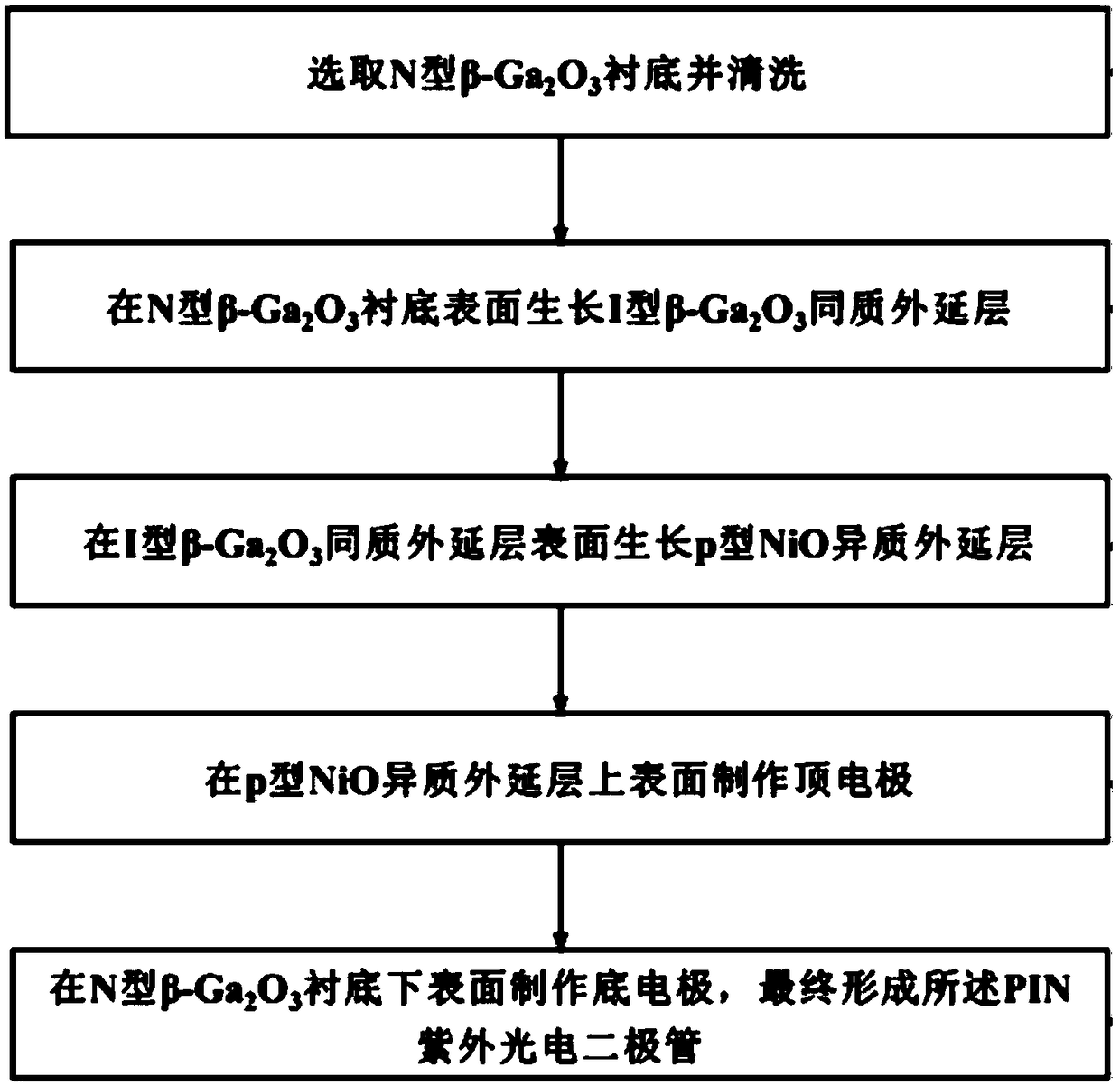
An ultraviolet photodiode based on NiO/Ga2O3 and a preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109037374AImprove the withstand voltage levelHigh light transmittanceSemiconductor devicesChemistrySingle crystal
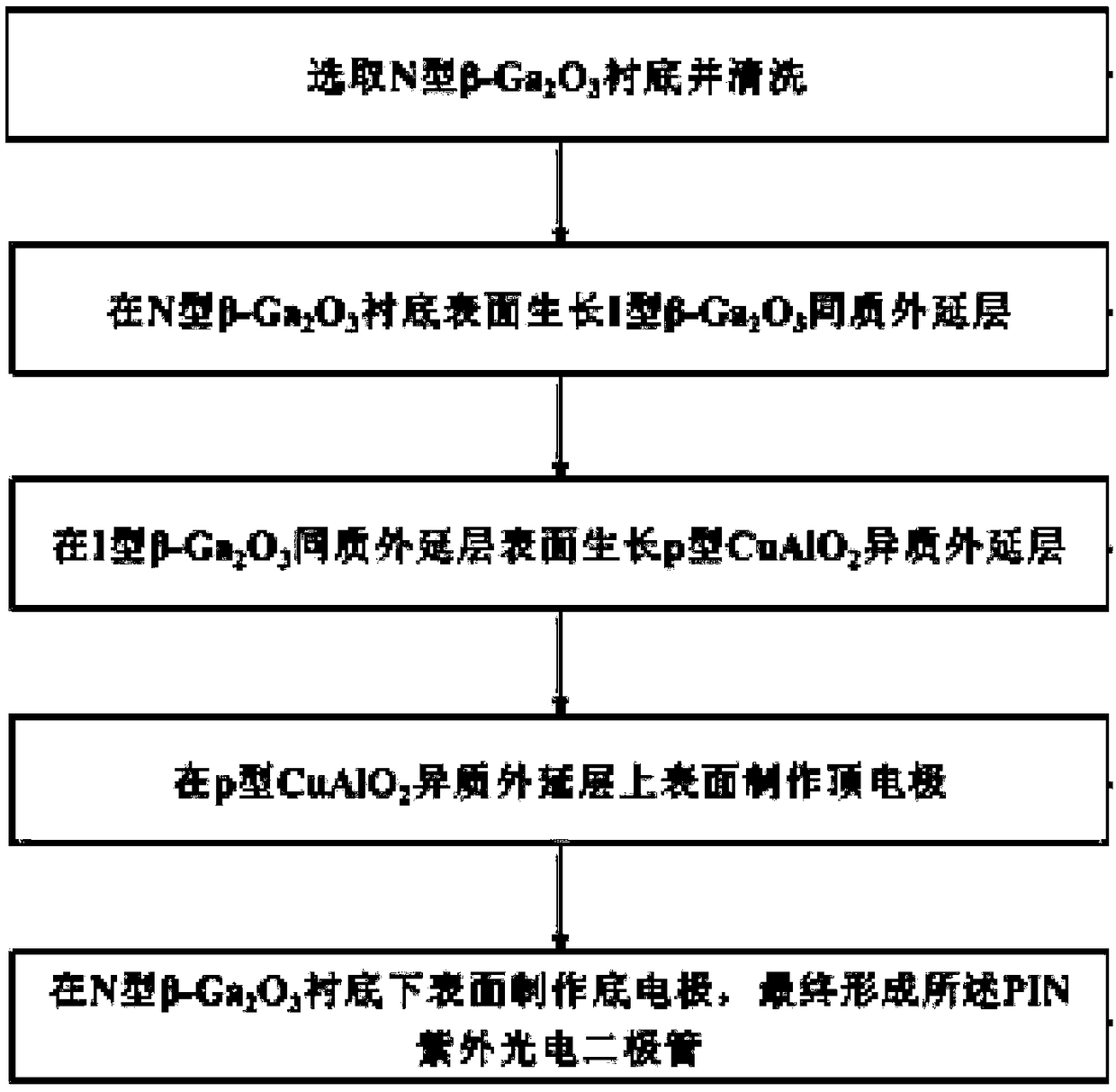
The invention discloses an ultraviolet photodiode based on NiO / Ga2O3, comprising a top electrode and a bottom electrode, wherein A P-type crystal NiO film, an I-type crystal beta-Ga2O3 film, and an N-type single crystal beta-Ga2O3 substrate are sequentially disposed between the two electrodes from the top electrode to the bottom electrode. The invention also discloses a preparation method of an ultraviolet photodiode based on NiO / Ga2O3. The invention solves the problem that the Ga2O3-based pn junction ultraviolet photodiode cannot be prepared due to the lack of p-type Ga2O3 material in the prior art.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
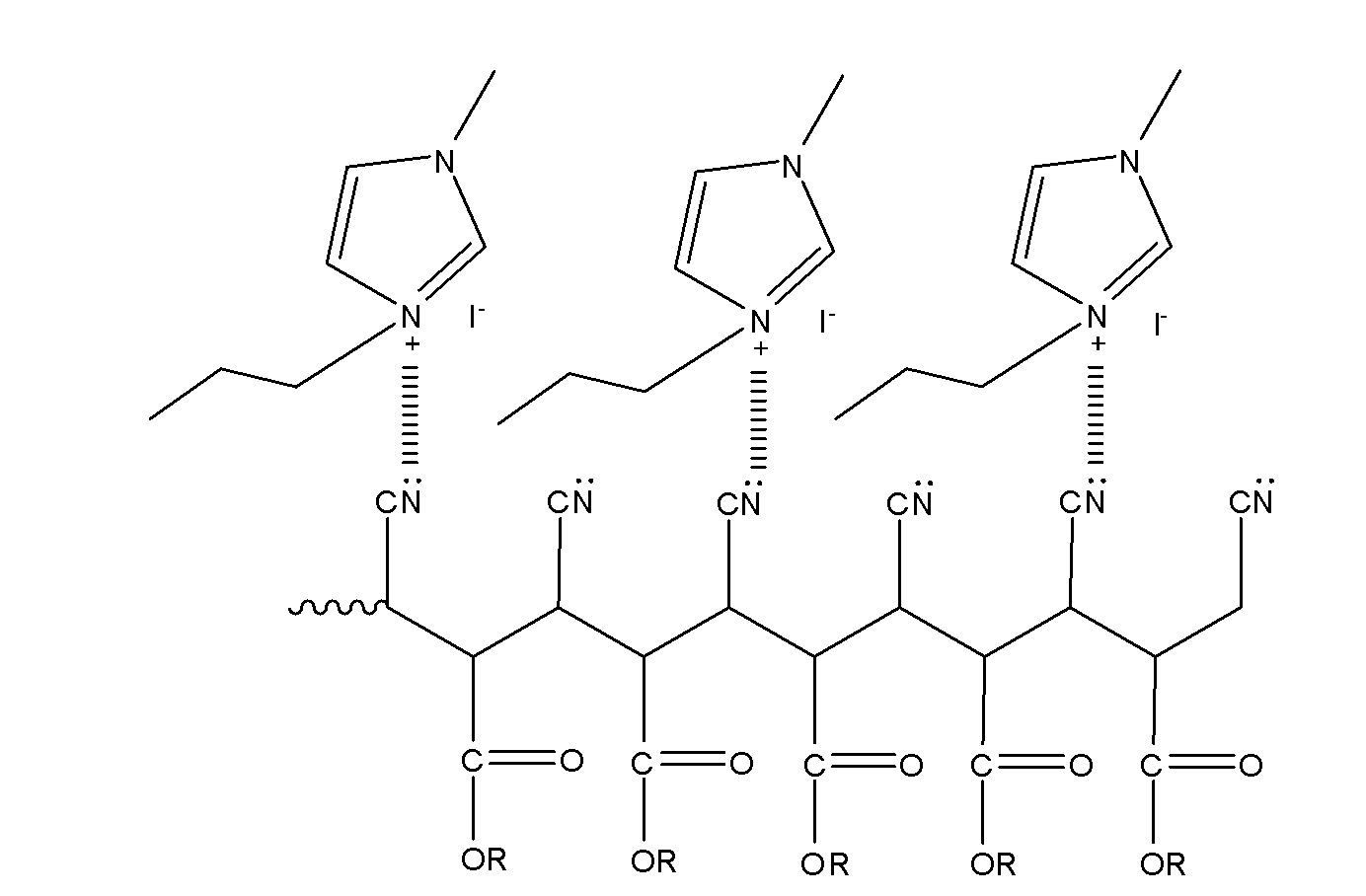
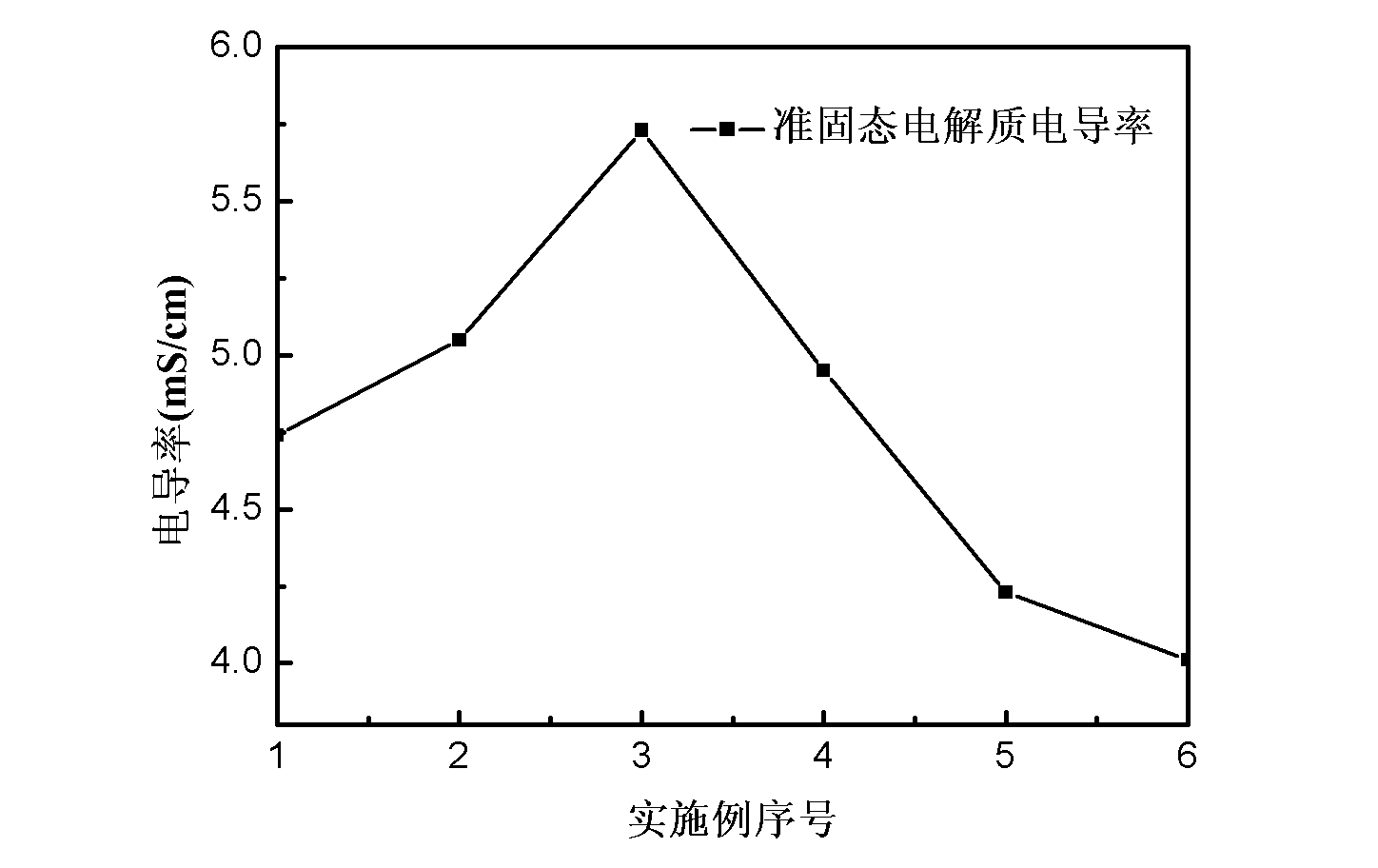
Dye-sensitized solar cell quasi-solid electrolyte and method for preparing solar cell using the same
InactiveCN102280256AImprove conductivityImprove ionic conductivityLight-sensitive devicesFinal product manufactureSolid state electrolyteIodide
A dye-sensitized solar cell quasi solid electrolyte and a method for preparing a solar cell by using same are disclosed. The dye-sensitized solar cell quasi solid electrolyte comprises, by weight, 2-30% of alpha-cyanoacrylate, 0.1-10% of an inorganic additive, 5-20% of iodide, 0.5-5% of iodine, 10-50% of plasticizer, 0.5-10% of a photoanode compounding ingredient and 10-30% of an organic solvent.The quasi solid electrolyte of the invention has good heat stability, good mechanical properties, high conductivity, a fast gel speed and low costs. The electrolyte is easy to be prepared and to realize industrialization production. A liquid electrolyte is easy to leak, difficult for packaging and possesses other problems. The above problems can be radically solved by using the quasi solid electrolyte.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
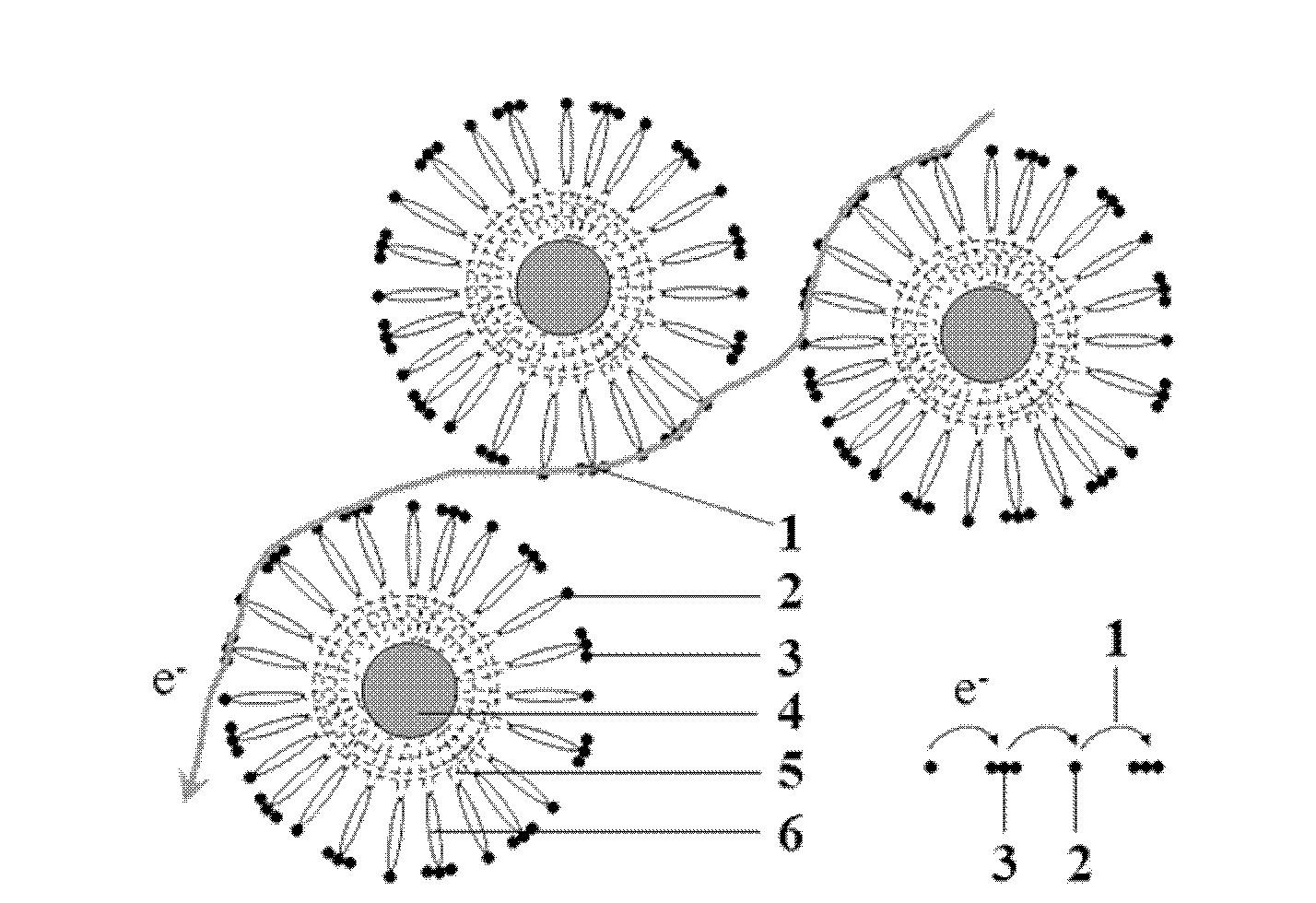
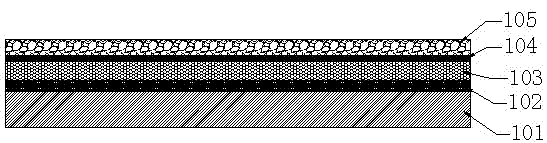
Dye-sensitized solar cell (DSSC) photo-anode and manufacturing method and application thereof
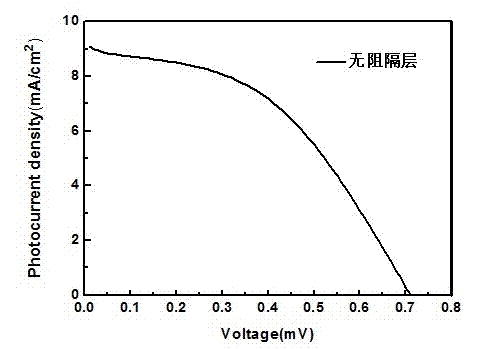
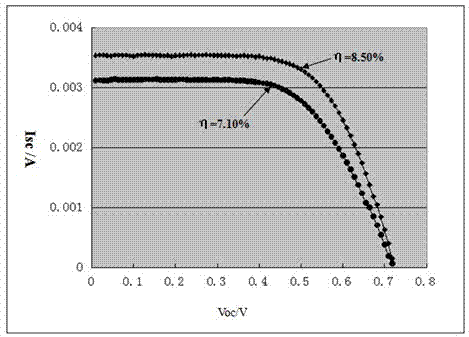
ActiveCN103794377ASuppress dark currentImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyLight-sensitive devicesPhotovoltaic energy generationOptical pathlengthDark current
The invention discloses a dye-sensitized solar cell (DSSC) photo-anode. The DSSC photo-anode is of a five-layer overlapped structure, and comprises a conductive matrix, a first compact layer, a transmission layer, a second compact layer and a scattering layer in sequence. The DSSC photo-anode adopts the five-layer overlapped structure, the compact layer is arranged between the conductive matrix and the transmission layer, dark current formed between electron, produced on the conductive matrix, and electrolyte is effectively restrained, and further the purpose of improving the photoelectric conversion efficiency of a DSSC is achieved. The scattering layer is arranged at the position of a porous membrane, an optical path and secondary absorption of sunlight are increased through a light scattering function of large grains, and therefore the secondary utilization efficiency of light is increased, and the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the DSSC is improved by about 20%.
Owner:KUSN INNOVATION INST OF NANJING UNIV
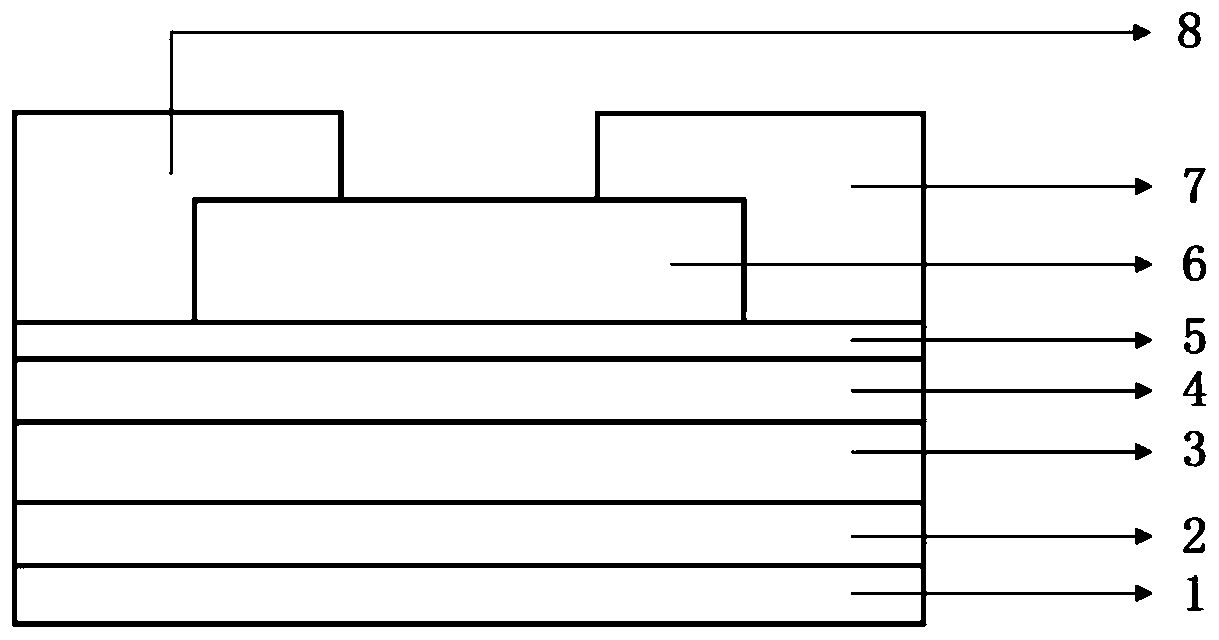
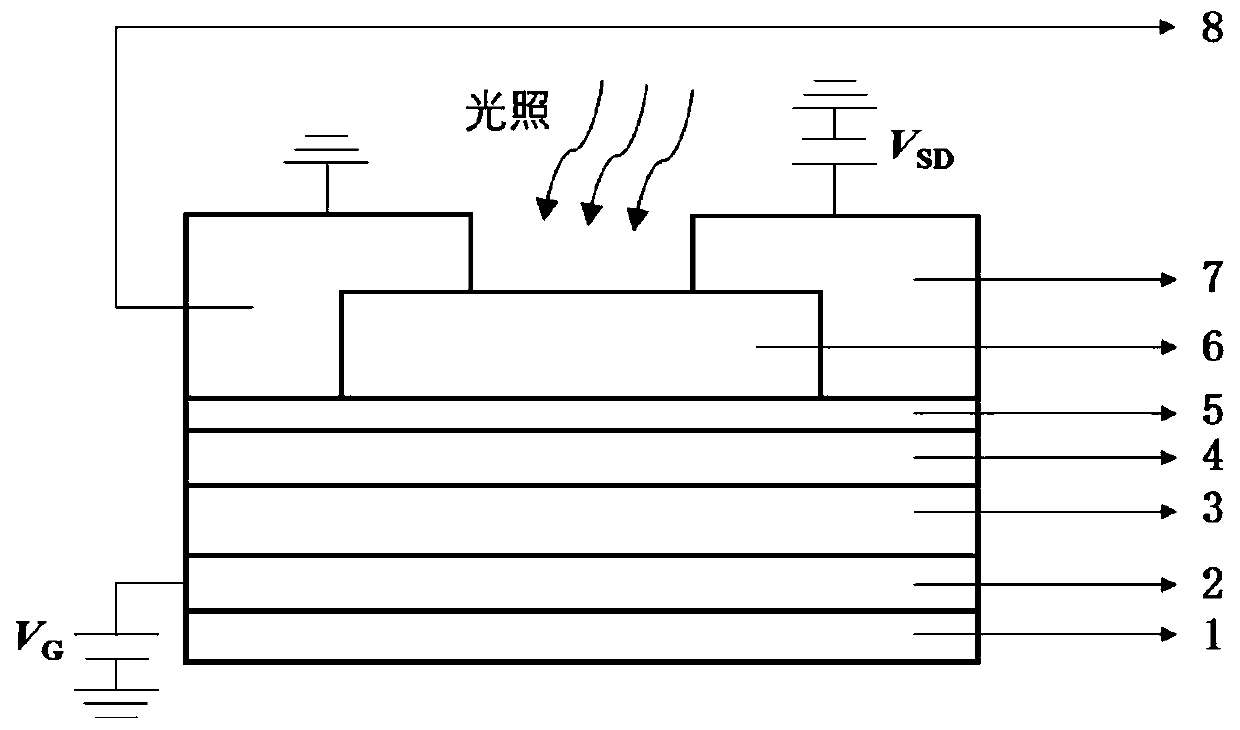
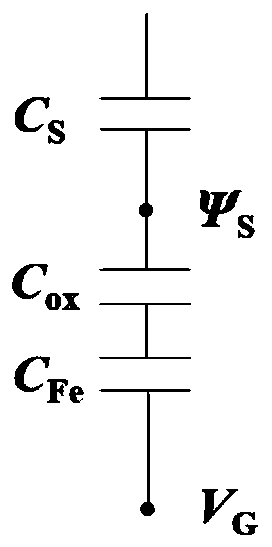
High-sensitivity negative capacitance field effect transistor photoelectric detector and preparation method
ActiveCN111312829ASuppress dark currentImprove light detection efficiencyFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesCapacitanceCapacitive effect
The invention discloses a high-sensitivity negative capacitance field effect transistor photoelectric detector and a preparation method thereof. The detector is characterized by structurally comprising a substrate, an oxide, a gate electrode, a hafnium oxide-based ferroelectric gate dielectric with a negative capacitance effect, an oxide gate dielectric, a low-dimensional semiconductor channel andmetal source and drain electrodes in sequence from bottom to top. Firstly, a gate electrode layer is prepared on a substrate through ion beam sputtering, a hafnium oxide-based ferroelectric film is grown on the electrode layer by using an atomic layer deposition method, an oxide gate dielectric is deposited after high-temperature rapid annealing, then a transition metal chalcogenide low-dimensional semiconductor is prepared on the structure, and finally metal source and drain electrodes are prepared by using an electron beam etching technology in combination with a stripping process to form the hafnium oxide-based ferroelectric film-based low-dimensional material negative capacitance field effect transistor photoelectric detection device structure. The metal-ferroelectric-oxide-semiconductor photoelectric transistor structure can realize room temperature photoelectric detection with extremely low sub-threshold swing and high performance.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
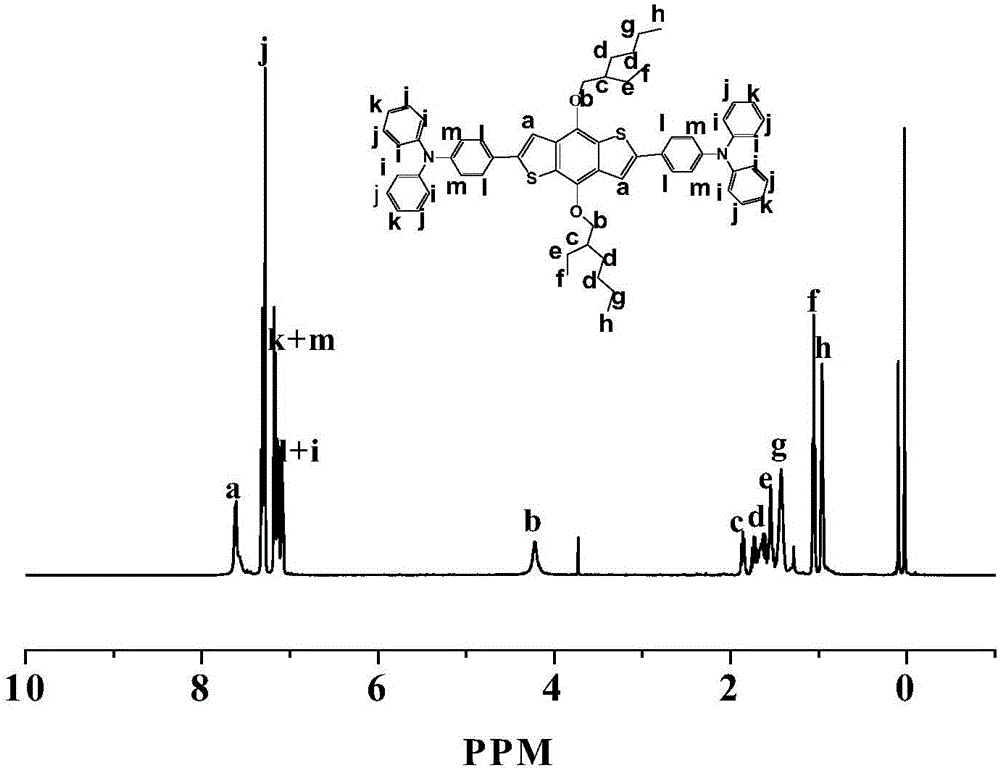
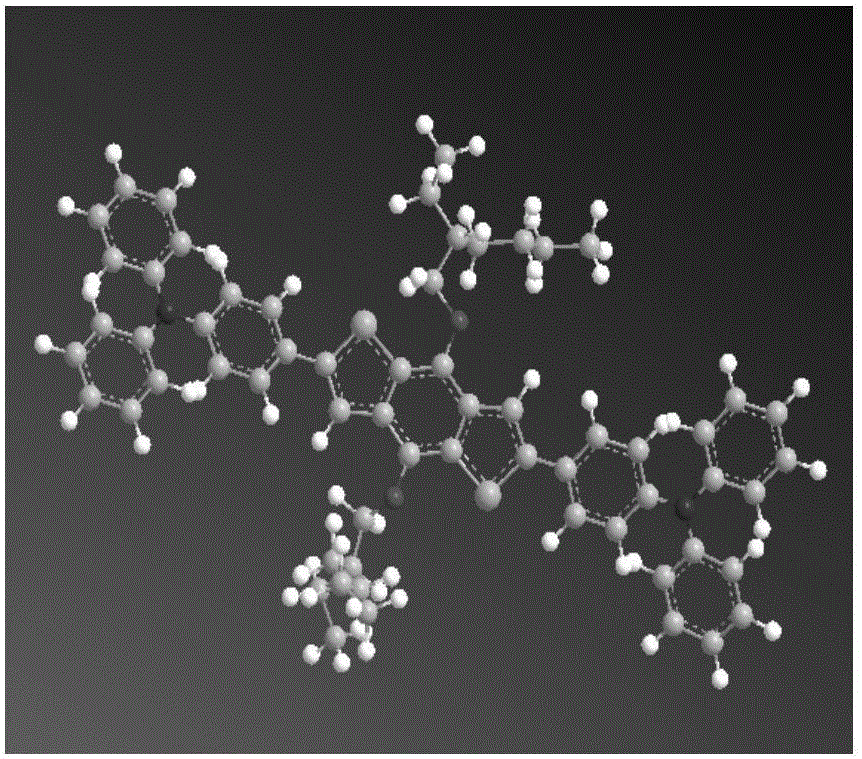
2,6-bis(triphenylamine)-4,8-bis(alkoxy)benzo[1,2-b:4,5-b']bithiophene and preparation for same
InactiveCN105968124ASimple molecular structureAchieving hole mobility coordinationOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesPerovskite solar cellElectrical battery
The invention discloses a hole transport material 2,6-bis(triphenylamine)-4,8-bis(alkoxy)benzo[1,2-b:4,5-b']bithiophene for a perovskite solar cell. The hole transport material has a simple molecular structure, a lateral group to which an aromatic functional group can be introduced, high hole mobility, high efficiency, high electrical conductivity and high dissolubility, and the perovskite solar cell prepared from the hole transport material can be matched with a perovskite energy level. The invention also discloses a preparation method for the hole transport material. The hole transport material for the perovskite solar cell is prepared by an SUZUKI reaction step from raw materials 2,6-dibromo-4,8-bis(alkoxy)benzo[1,2-b:4,5-b']dithiophene and 4-(diphenylamino)phenylboronicacid. The preparation method has the characteristics of simplicity in operation, readily available raw materials, easiness for separation and high yield.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
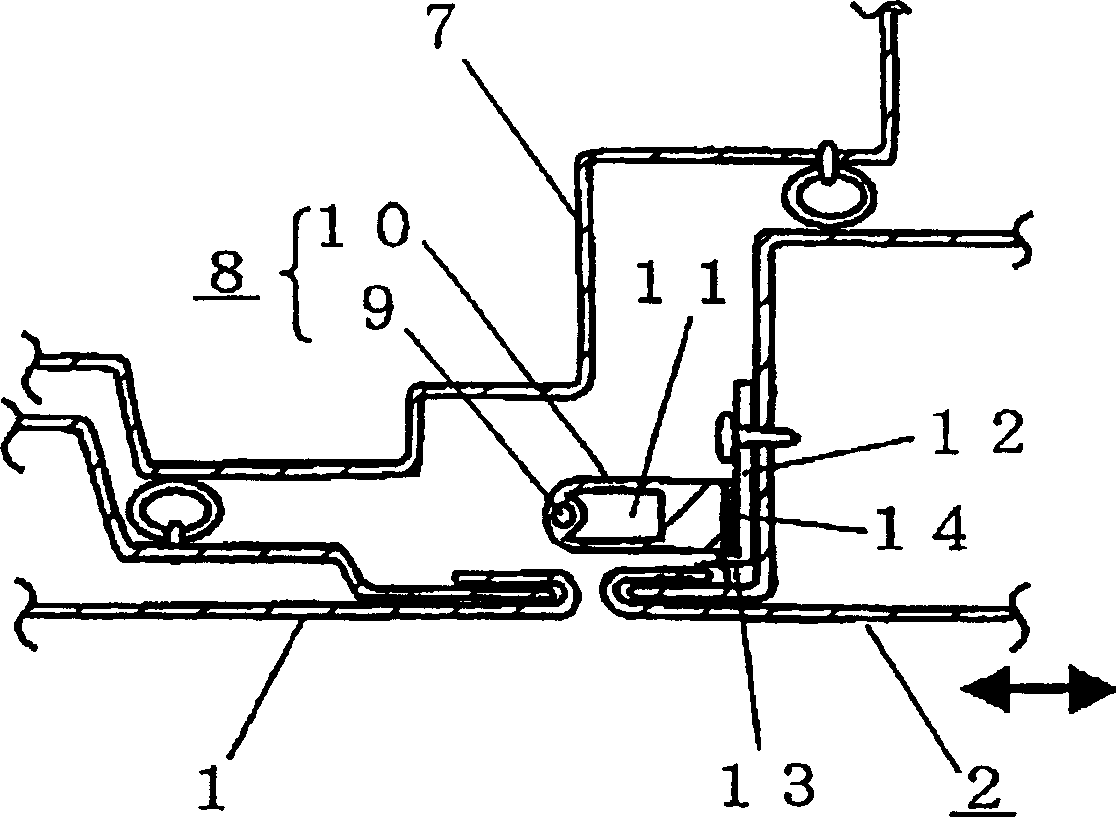
Moving device and open/close control device for moving body
There is a problem in a door such as a sliding door (2) that when the pressure sensor (3) provided on the door cannot detect the contact of an object such as a hand, even if the hand moves away to avoid being caught The door will also keep closing and moving, causing people near the door to be hit by the closing door. In a mobile device, when the object detection device (8) arranged on the door (2) detects the contact of the object or when the departure of the object that the detection device has been in contact with is detected, the driving device (20) controls the sliding door The movement direction of (2) is reversed. Even when the contact of the object cannot be detected during the closing movement of the door (2) due to the softness of the contact object and / or the slow speed of the door (2) as a moving object, the drive of the door (2) will be detected by the detection device (8) When the departure of the object is detected, the control is reversed, thereby increasing safety.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Image pickup element, method of manufacturing image pickup element, and electronic apparatus
ActiveCN104517981AImprove interface stateSuppress dark currentSolid-state devicesDiodeFixed chargeEngineering
An image pickup element includes: a semiconductor substrate including a photoelectric conversion section for each pixel; a pixel separation groove provided in the semiconductor substrate; and a fixed charge film provided on a light-receiving surface side of the semiconductor substrate, wherein the fixed charge film includes a first insulating film and a second insulating film, the first insulating film being provided contiguously from the light-receiving surface to a wall surface and a bottom surface of the pixel separation groove, and the second insulating film being provided on a part of the first insulating film, the part corresponding to at least the light-receiving surface.
Owner:SONY CORP
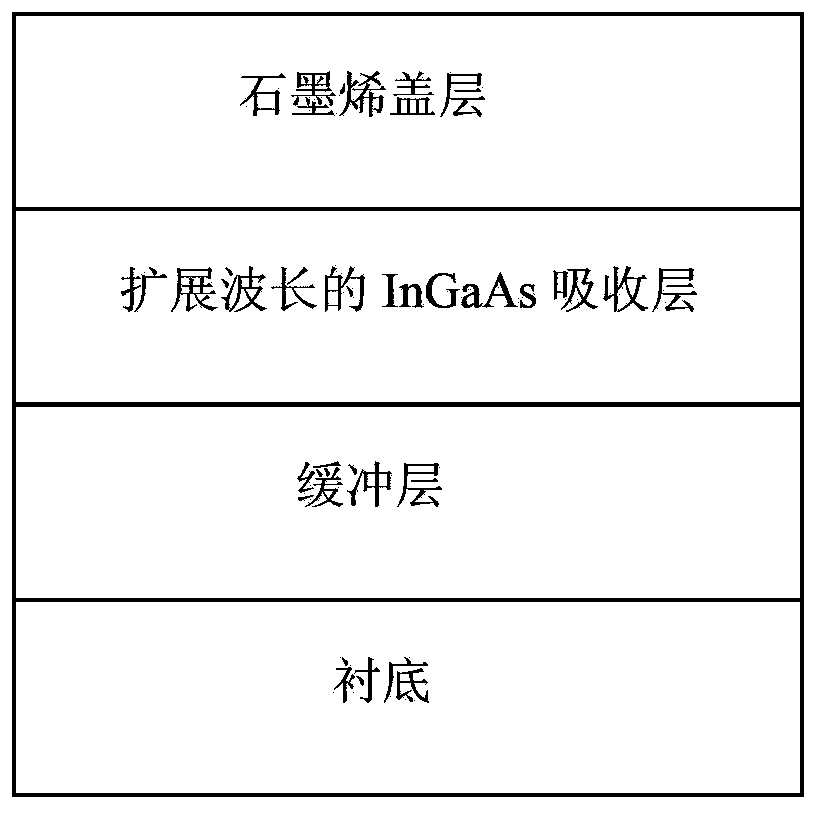
Graphene enhancement type InGaAs infrared detector
InactiveCN103383976AReduce dark currentSuppress dark currentSemiconductor devicesPower flowGas phase
The invention relates to a graphene enhancement type InGaAs infrared detector. The graphene enhancement type InGaAs infrared detector solves the technical problem that an existing infrared detector is narrow in detection range and high in dark current. According to the graphene enhancement type InGaAs infrared detector, a buffer layer, an InGaAs absorbing layer with wavelength extended and a graphene cover layer which grow sequentially on a substrate form a pin detector structure. The invention discloses a method for growing the mismatch buffer layer on the substrate in a two-step method. An InAlAs ternary system material or InAsP of an InGaAs material which is suitable for metallorganic chemical vapor deposition technology growth and convenient to control and enables forbidden bandwidth to be larger than extended wavelength is adopted and can effectively avoid mismatch dislocation and be suitable for a transparent buffer layer structure with light entering at the back. The method for utilizing graphene to serve as the cover layer of the InGaAs infrared detector to expand the detection range and reduce dark current is provided, detector performance is improved, and the graphene enhancement type InGaAs infrared detector has wide application prospect.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
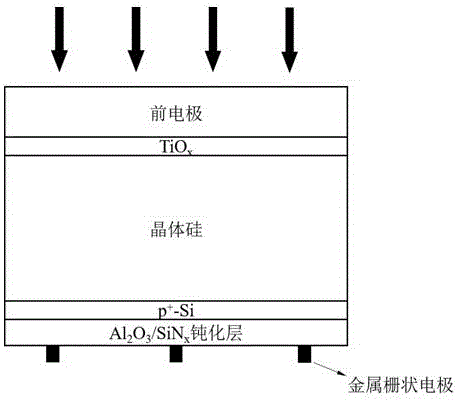
Si/TiOx heterojunction-based double-sided crystalline silicon solar cell
ActiveCN106449845AIncrease the open circuit voltageEffective passivationPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionGenerating capacity
The invention provides an Si / TiOx heterojunction-based double-sided crystalline silicon solar cell, which comprises a front electrode, a TiOx layer, a crystalline silicon absorption layer, a p-type crystalline silicon heavily doped layer, a passivation layer and a metal gate electrode, wherein the structure of the Si / TiOx heterojunction-based double-sided crystalline silicon solar cell is the front electrode, the TiOx layer, the crystalline silicon absorption layer, the p-type crystalline silicon heavily doped layer, the passivation layer and the metal gate electrode in sequence from a light facing surface; and an n-type doped TiOx and crystalline silicon are utilized by the light facing surface to form a heterojunction while a traditional crystalline silicon preparation technology based on diffusion is utilized by a back surface. The TiOx can well passivate the surface of a silicon wafer, and the TiOx and silicon form a good heterojunction, so that improvement of the open-circuit voltage and the conversion efficiency of the heterojunction cell is facilitated. Existing crystalline silicon solar cell production equipment can be fully utilized by a traditional crystalline silicon preparation technology of the back surface. The sunlight can be fully utilized by the double-sided structure; the actual generating capacity is increased; and the photovoltaic power generation cost is reduced.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
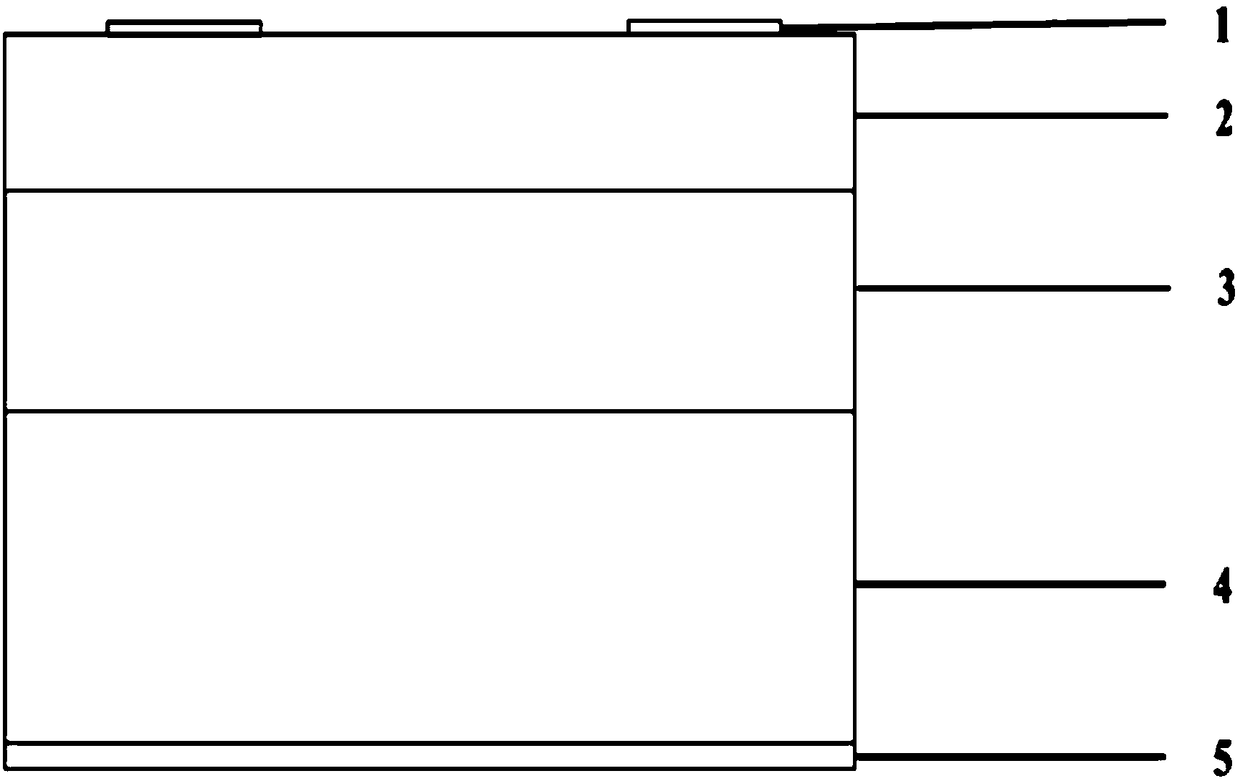
CuAlO2/Ga2O3 ultraviolet photodiode and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109148635AImprove the withstand voltage levelHigh light transmittanceSemiconductor devicesUltravioletSingle crystal
The invention discloses a CuAlO2 / Ga2O3 ultraviolet photodiode, comprising a top electrode and a bottom electrode, wherein a P-type crystal CuAlO2 film, an I-type beta-Ga2O3 film, and an N-type singlecrystal beta-Ga2O3 substrate are sequentially disposed between the two electrodes from the top electrode to the bottom electrode. The invention also discloses a preparation method of a CuAlO2 / Ga2O3 ultraviolet photoelectric diode. The invention solves the problem that the Ga2O3-based PIN ultraviolet photoelectric diode cannot be prepared due to the shortage of p-type Ga2O3 material in the prior art.
Owner:XIAN RUNWEI MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL EQUIP
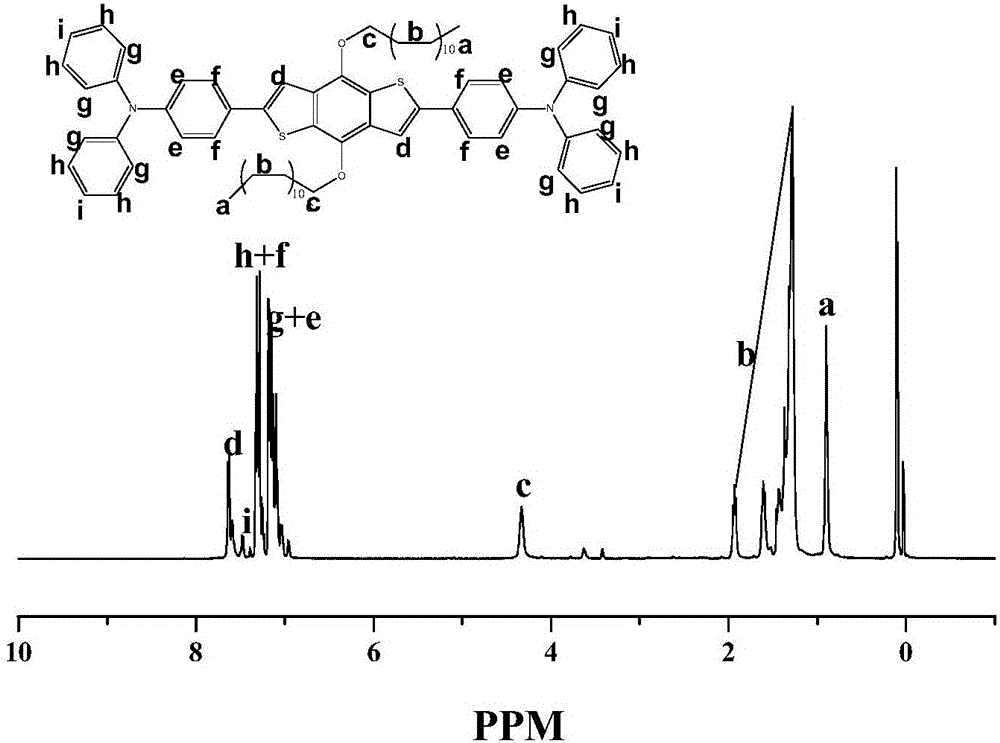
Hole transporting material for perovskite solar cell and application thereof
InactiveCN105968125ASimple molecular structureAchieving hole mobility coordinationOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesPerovskite solar cellSolubility
The invention discloses a hole transporting material 2,6-bistriphenylamine-4,8-bis(alkoxy)benzo[1,2-B:4,5-B']dithiophene for a perovskite solar cell. The hole transporting material has simple molecular structures, high hole mobility, high efficiency, high conductivity and good solubility; aromatic functional radicals can be introduced into lateral groups; the perovskite solar cell prepared from the hole transporting material can be matched with the energy level of perovskite. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the hole transporting material. The hole transporting material for the perovskite solar cell is prepared and obtained by using 2,6-dibromo-4,8-bis(alkoxy)benzo[1,2-B:4,5-B']dithiophene and 4-(Diphenylamino)phenylboronicacid as raw materials through a one-step SUZUKI reaction. The preparation method provided by the invention has the characteristics that the operation is simple, the raw materials are low-cost and easily obtained, the separation is easy, and the yield is high.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
Novel self-filtering narrow spectral response organic light detector
ActiveCN110534650AImprove controllabilityAchieve freedom of choiceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpectral responseLight filter
The invention relates to a novel self-filtering narrow spectral response organic light detector. The organic light detector sequentially comprises a substrate, a positive electrode, a P-type layer, anN-type layer and a negative electrode, the P-type layer can be further divided into a single-layer P-type layer structure and a multi-layer P-type layer structure, and in the single-layer P-type layer structure, the band gap of the P-type layer material is wider than that of the N-type layer material; in the multi-layer P-type layer structure, the band gap of at least one P-type layer material inthe P-type layer materials which are not in direct contact with the N-type layer is wider than that of the N-type layer material and / or the P-type layer material which is in direct contact with the N-type layer, and a buffer layer can be added between the positive electrode and the P-type layer and / or between the N-type layer and the negative electrode. According to the invention, a novel devicestructure and a simple preparation method are adopted, and the free selection of a detection spectrum waveband and the free adjustment of the half-peak width of a detection spectrum are achieved without a band-pass optical filter.
Owner:GUANGZHOU GUANGDA INNOVATION TECH CO LTD
PNIN type InGaAs infrared detector
InactiveCN104319307AImprove photoelectric performanceInhibited transportSemiconductor devicesCharge carrierLength wave
The invention provides a PNIN type InGaAs infrared detector and belongs to the optoelectronic material and device application field. The PNIN type InGaAs infrared detector is a PNIN type detector which sequentially comprises a substrate, a buffer layer, an extended wavelength InGaAs absorption layer, an n type insert layer and a cover layer; and the thickness of the n type insert layer ranges from 50nm to 150nm, and the components of the n type insert layer are the same with the components of the extended wavelength InGaAs absorption layer. The n type insert layer which is additionally arranged on the infrared detector can suppress the transport of carriers through generating band steps, so that dark current can be lowered, and thus the photoelectric performance of the infrared detector can be improved; and requirements for InGaAs material epitaxial growth can be lowered, so that the PNIN type InGaAs infrared detector can work in a wider wavelength range. The PNIN type InGaAs infrared detector of the invention is applicable to back light entering and flip-chip package structures, and has high universality.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for manufacturing nanocrystalline thin-film device for ultraviolet detecting
InactiveCN101257065ALow costLow film forming temperatureFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesUltraviolet detectorsGas phase
The present invention discloses a manufacturing method of a nanocrystalline thin-film device for ultraviolet detecting, which includes: the soluble semi-conductor nanocrystalline material is dissolved into the solvent to obtain nanocrystalline solution; the nanocrystalline solution is on the substrate by using the spin-coating method or jet ink print method to form a homogeneous nanocrystalline thin film; the nanocrystalline thin film is proceed annealing treatment about 10-60 minutes at the temperature 100-350EDG C, then vapor plating electric pole on the nanocrystalline thin film. The method of the present invention compared with the semiconductor film ultraviolet detector of traditional gas-phase high-temperature growth can reduce the cost of the ultraviolet detecting optoelectronic device without a vacuum device, low film build temperature, simple preparation technique, and can develop the ''flexibility device''of the large size flexible device. Because nanocrystalline has super large surface area, the nanocrystalline thin-film device for ultraviolet detecting has the features of low dark current and high sensitivity, etc.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
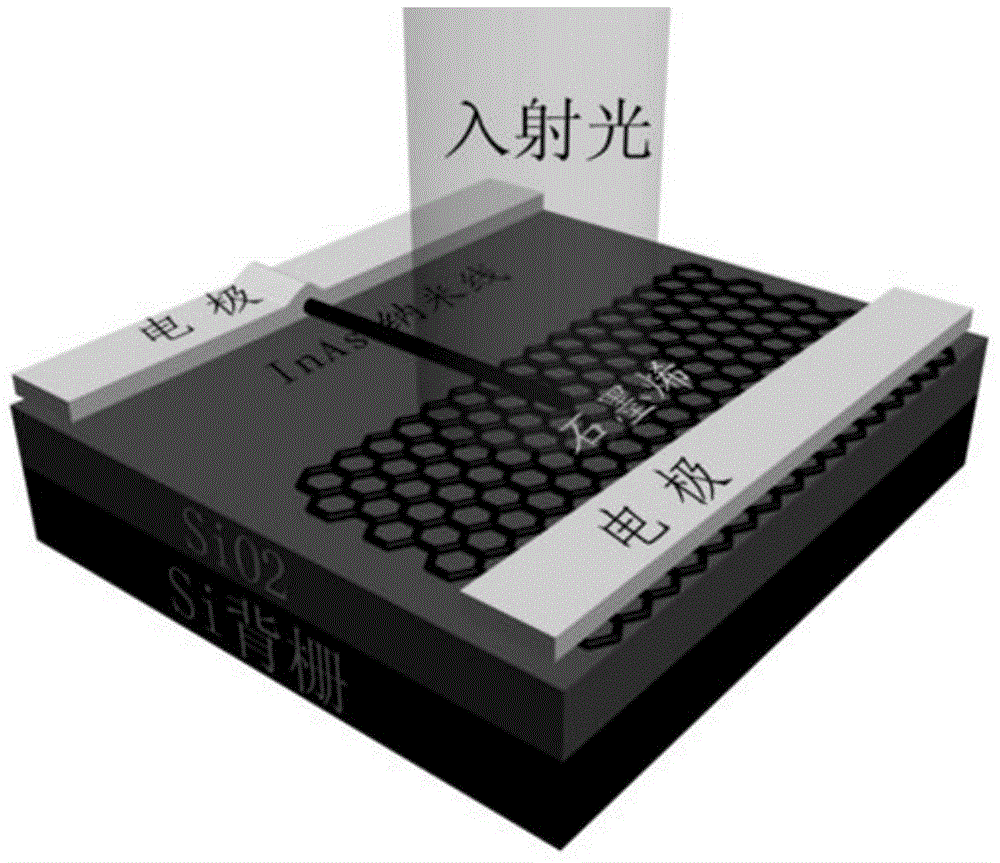
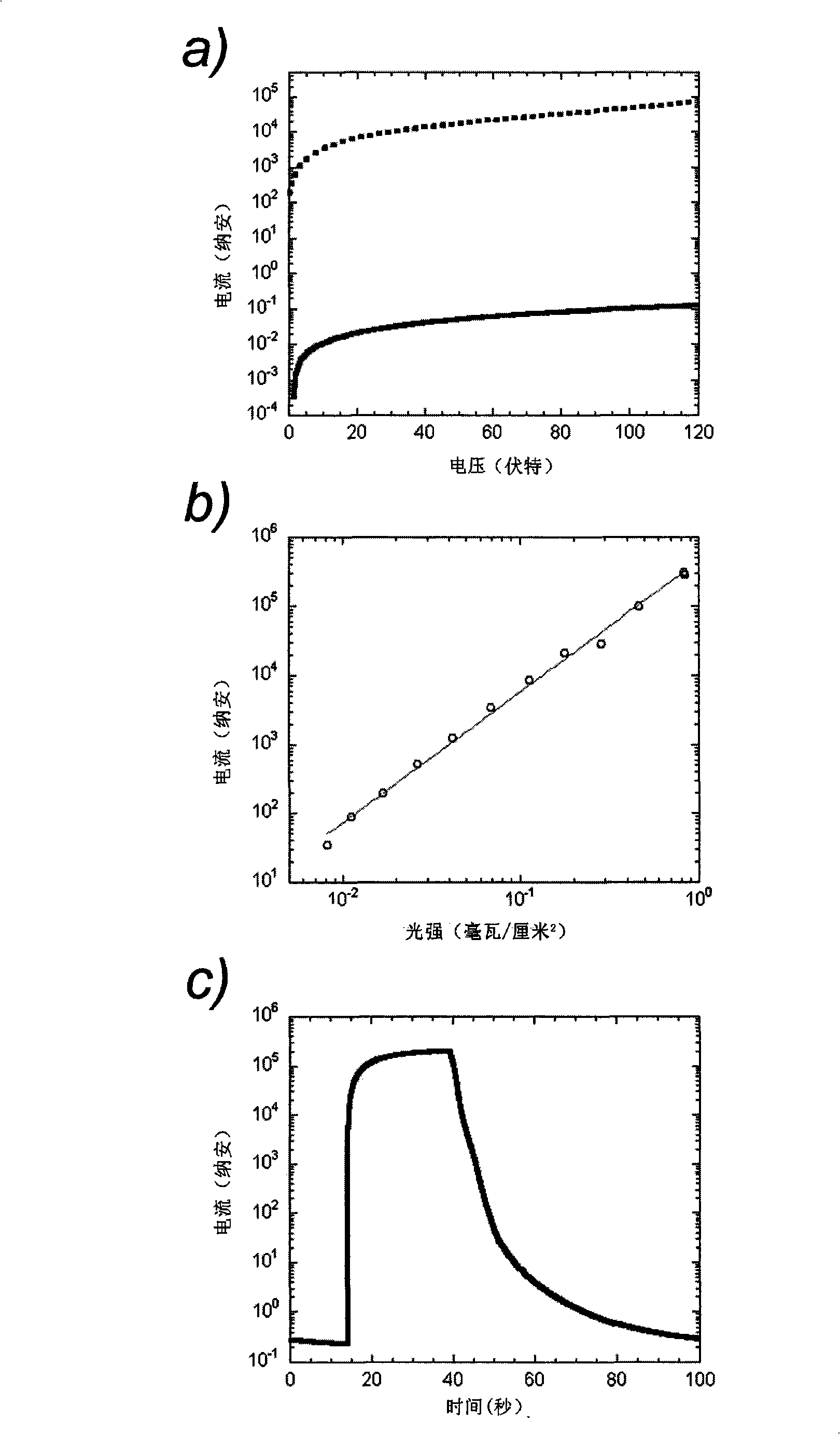
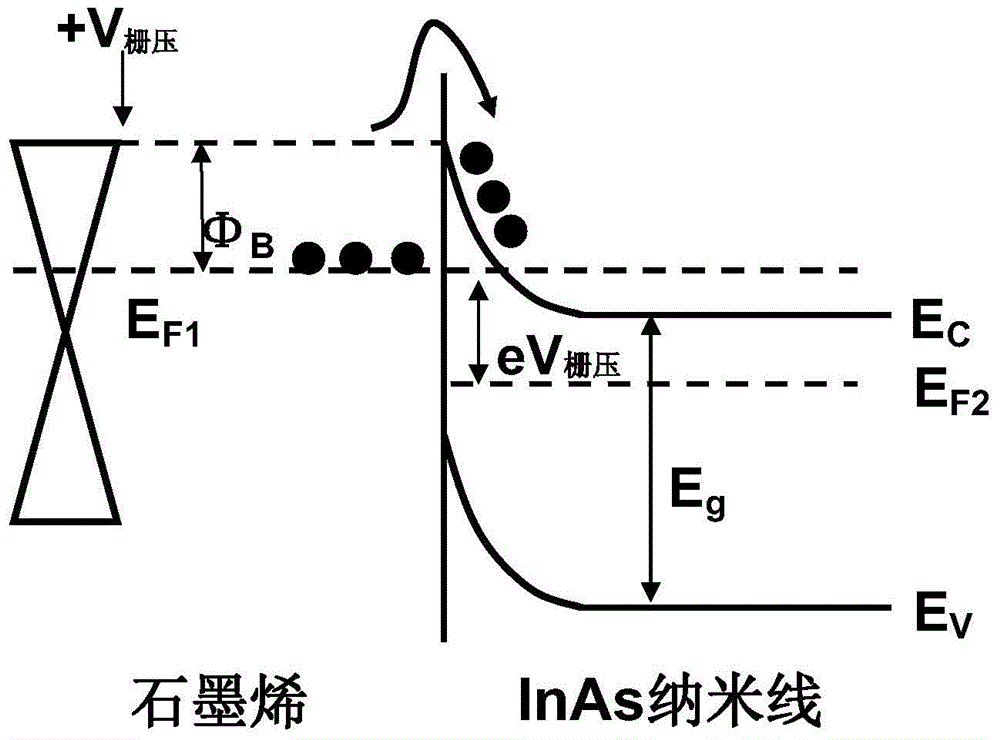
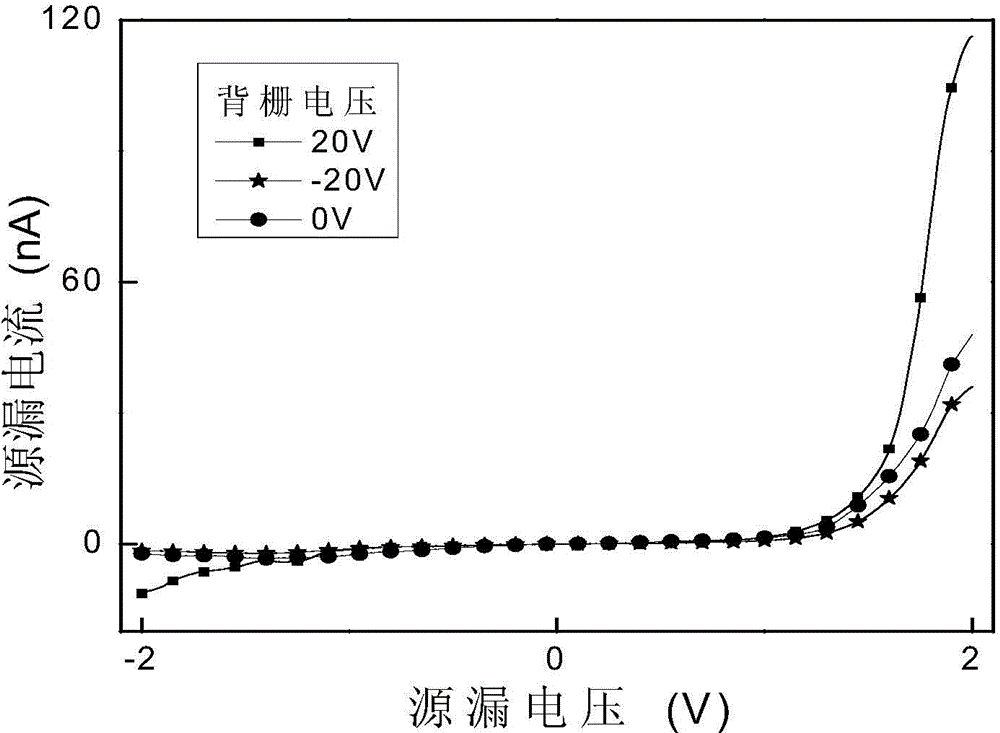
Method for increasing the switch ratio of graphene and nanowire heterojunction detector
InactiveCN104538489ASuppress dark currentHigh on/off ratioFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionSchottky barrier
The invention discloses a method for increasing the switch ratio of a graphene and nanowire heterojunction detector. The method includes the steps that an InAs nanowire is transferred on mechanically-stripped graphene in a physical mode, and a heterojunction is formed; due to the fact that the graphene and the InAs nanowire have different work functions, a schottky barrier is formed at the contact position; the grid voltage can adjust the Fermi level of the graphene, the height of the schottky barrier can be adjusted accordingly, a built-in electric field is formed, photoproduction electron and hole pairs are separated quickly, electrons flow to the InAs nanowire, and holes flow to the graphene. Accordingly, the dark current of the graphene and nanowire heterojunction detector can be restrained effectively through the controllable advantages of the schottky barrier, and the switch ratio of the detector is increased; by means of the structure, the switch ratio of the graphene and the nanowire heterojunction detector can exceed 10<2>. The method has very great significance in increasing the switch ratio of the existing graphene and the nanowire heterojunction detector.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
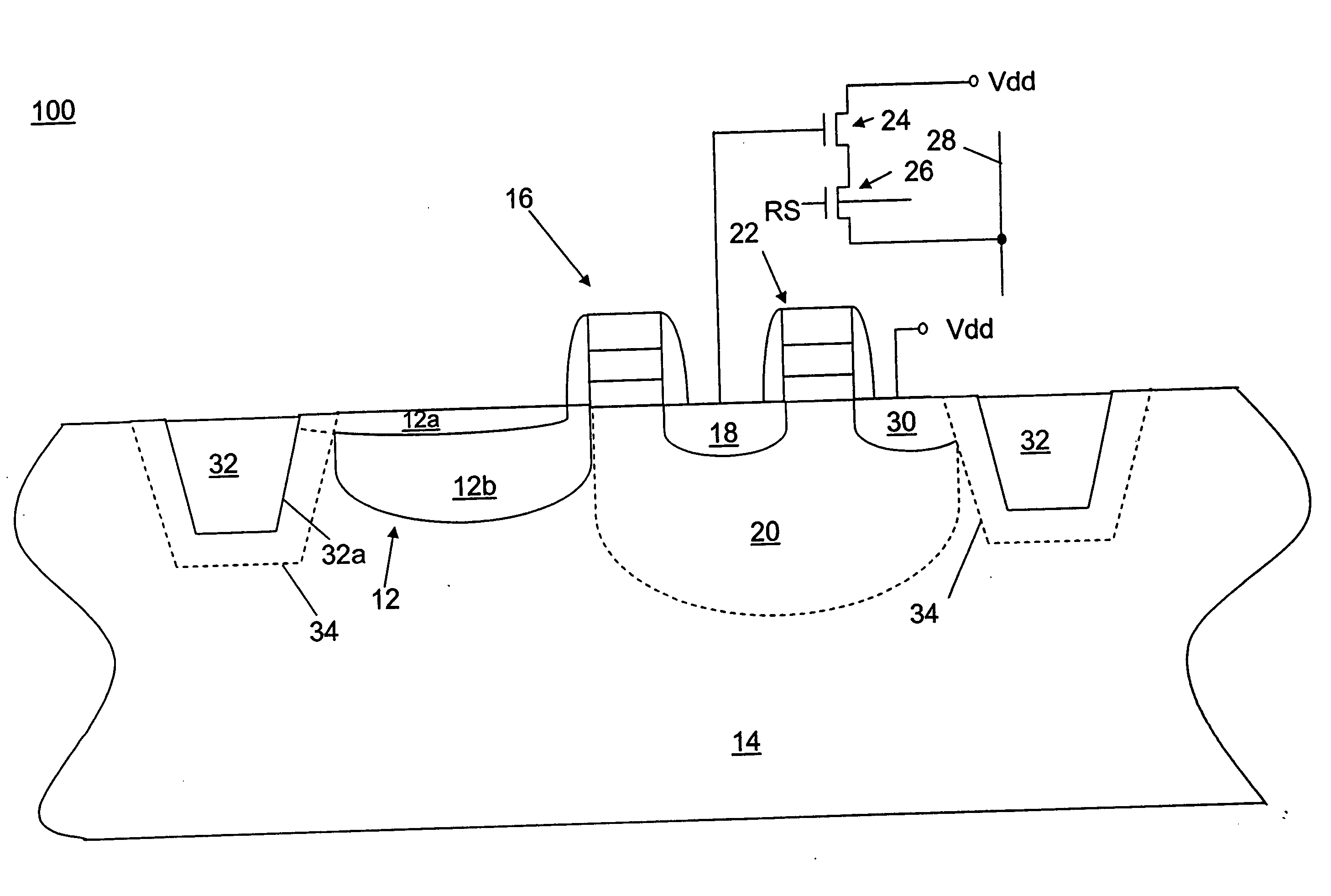
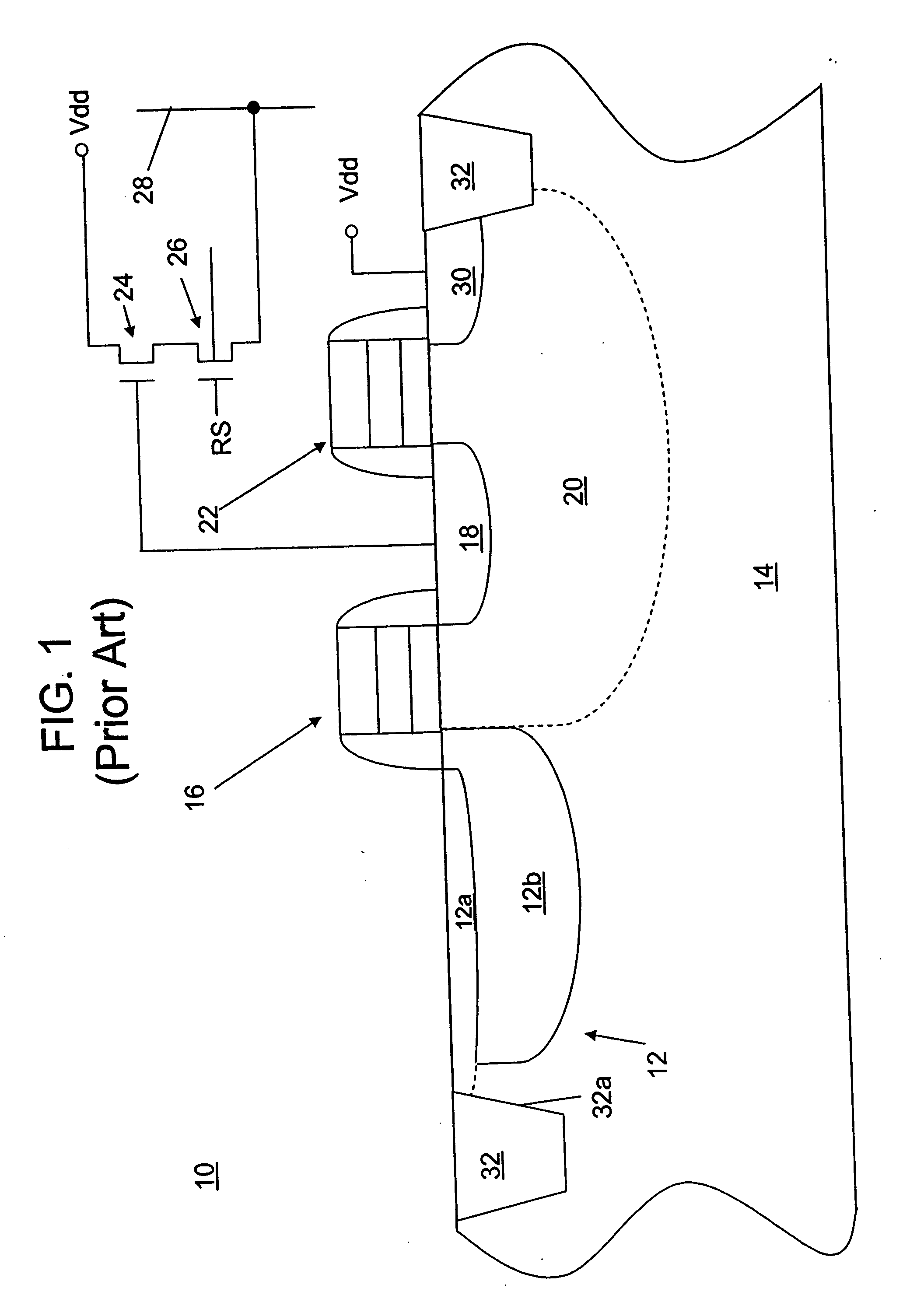
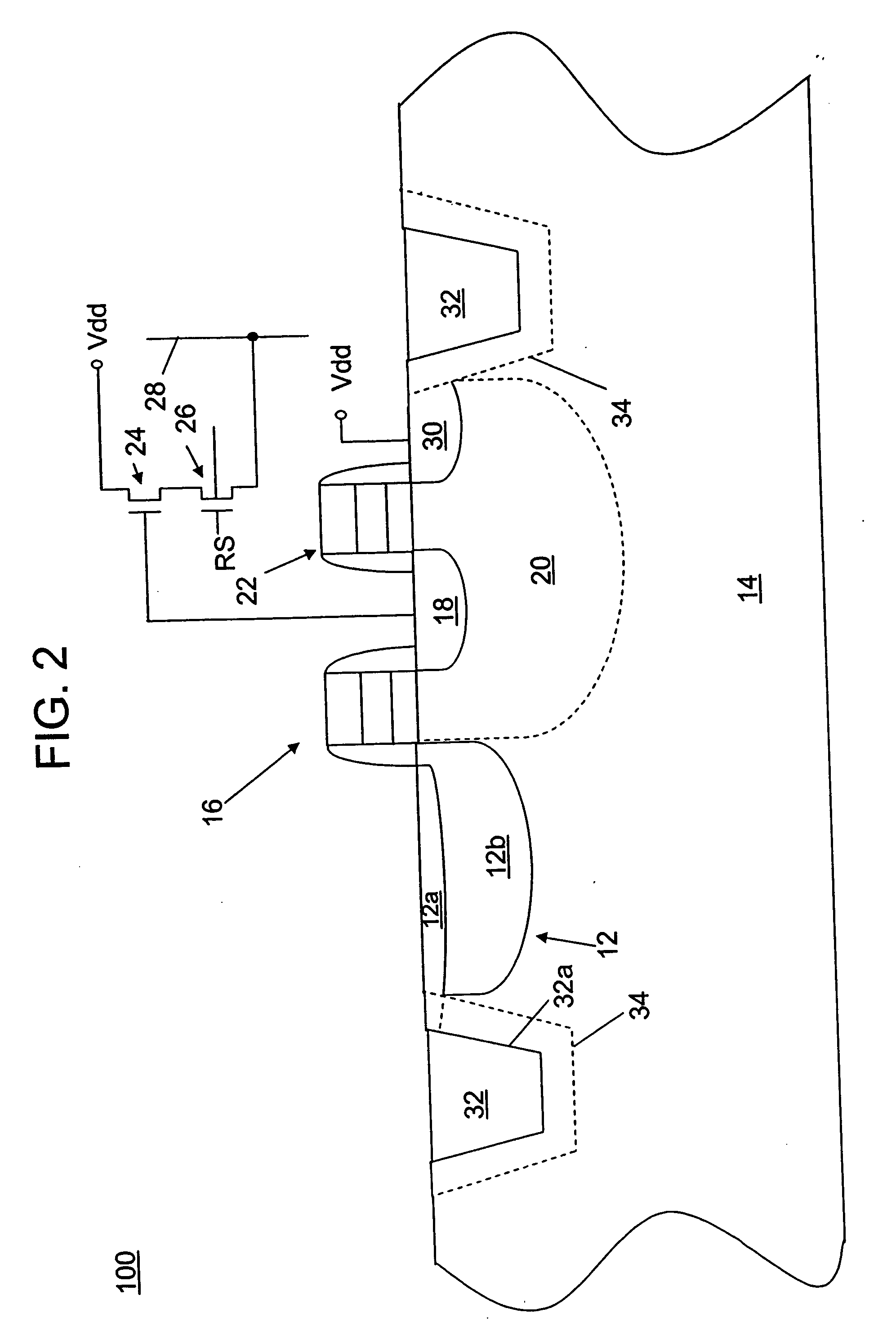
Imaging device
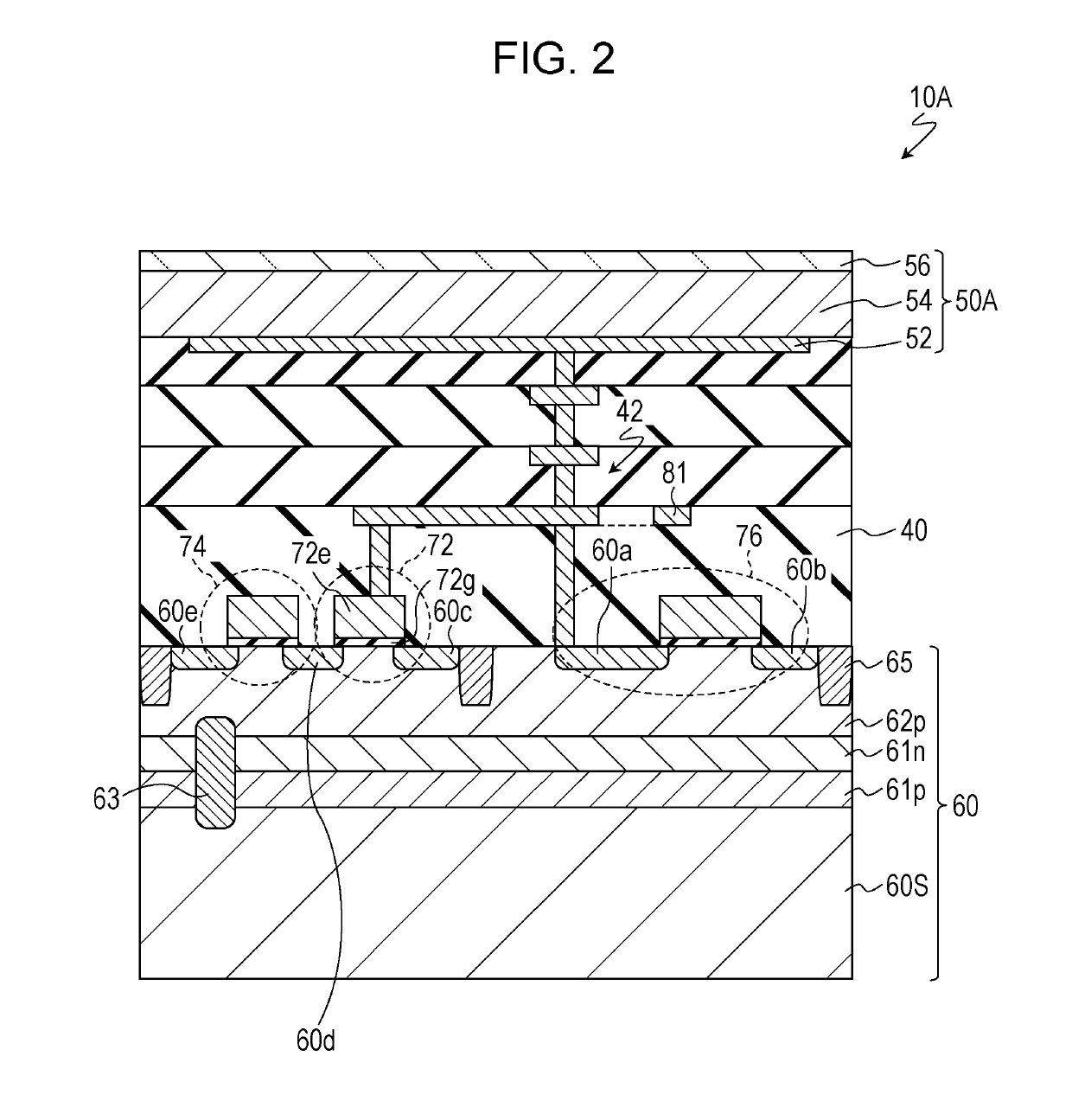
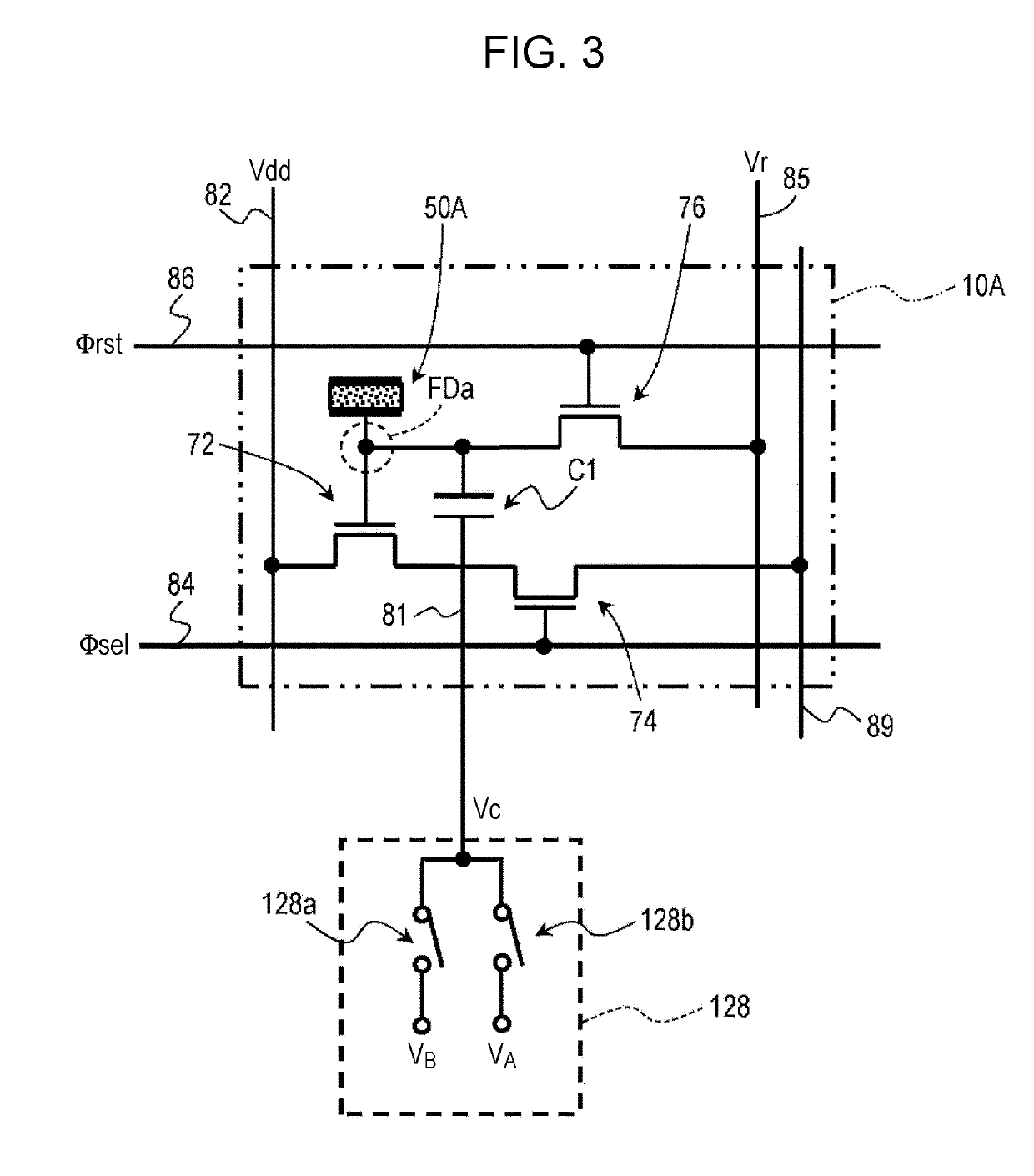
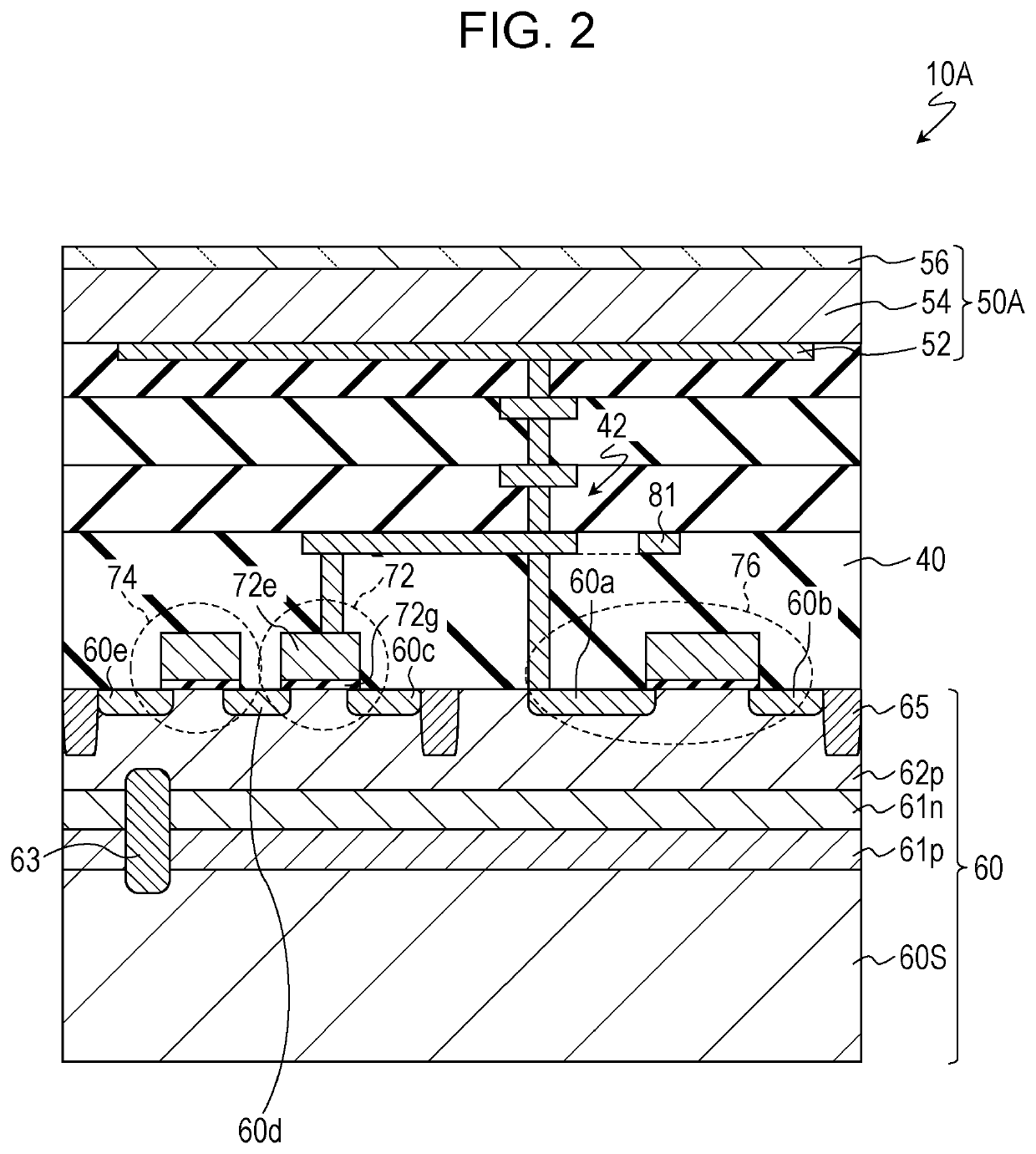
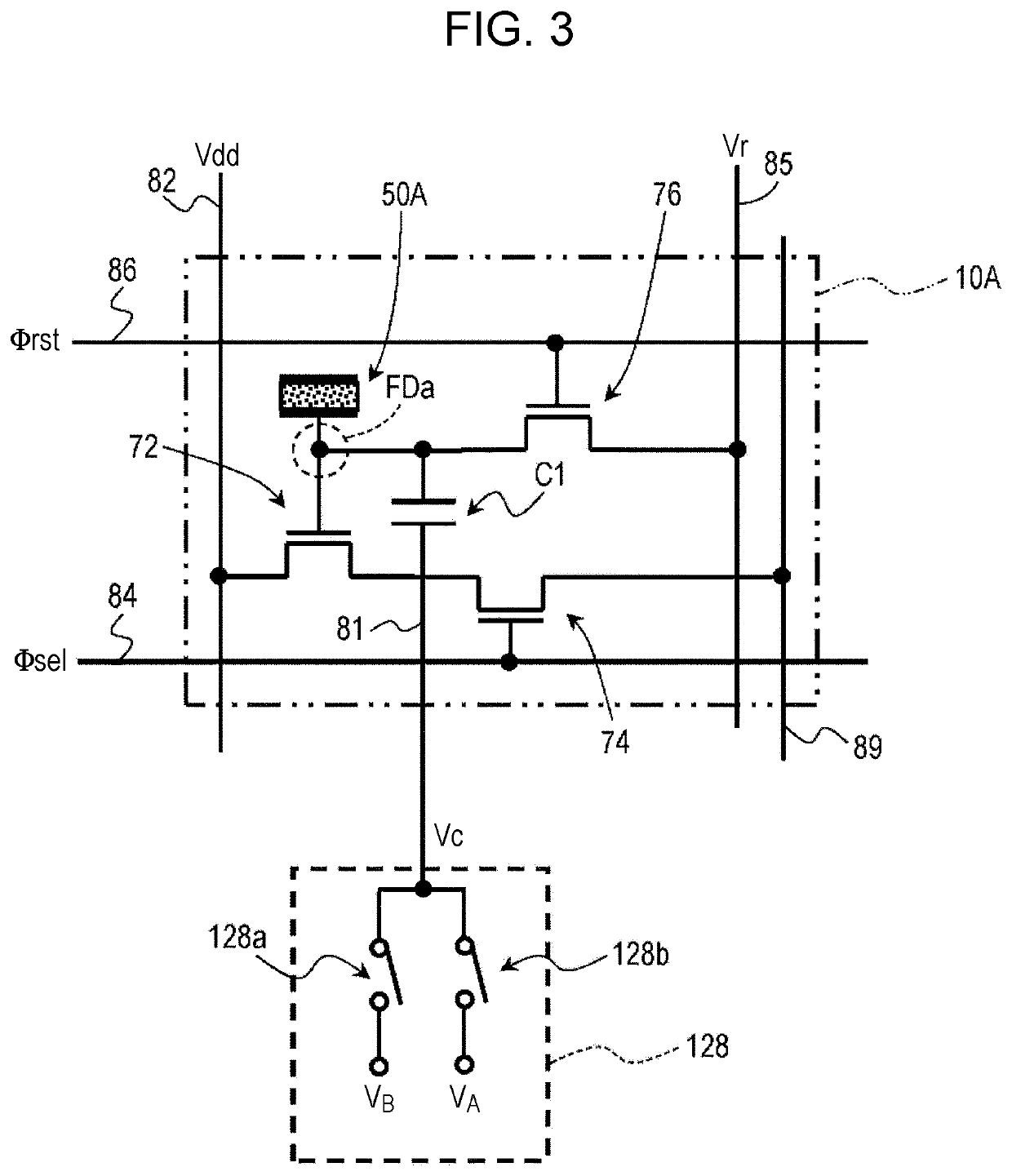
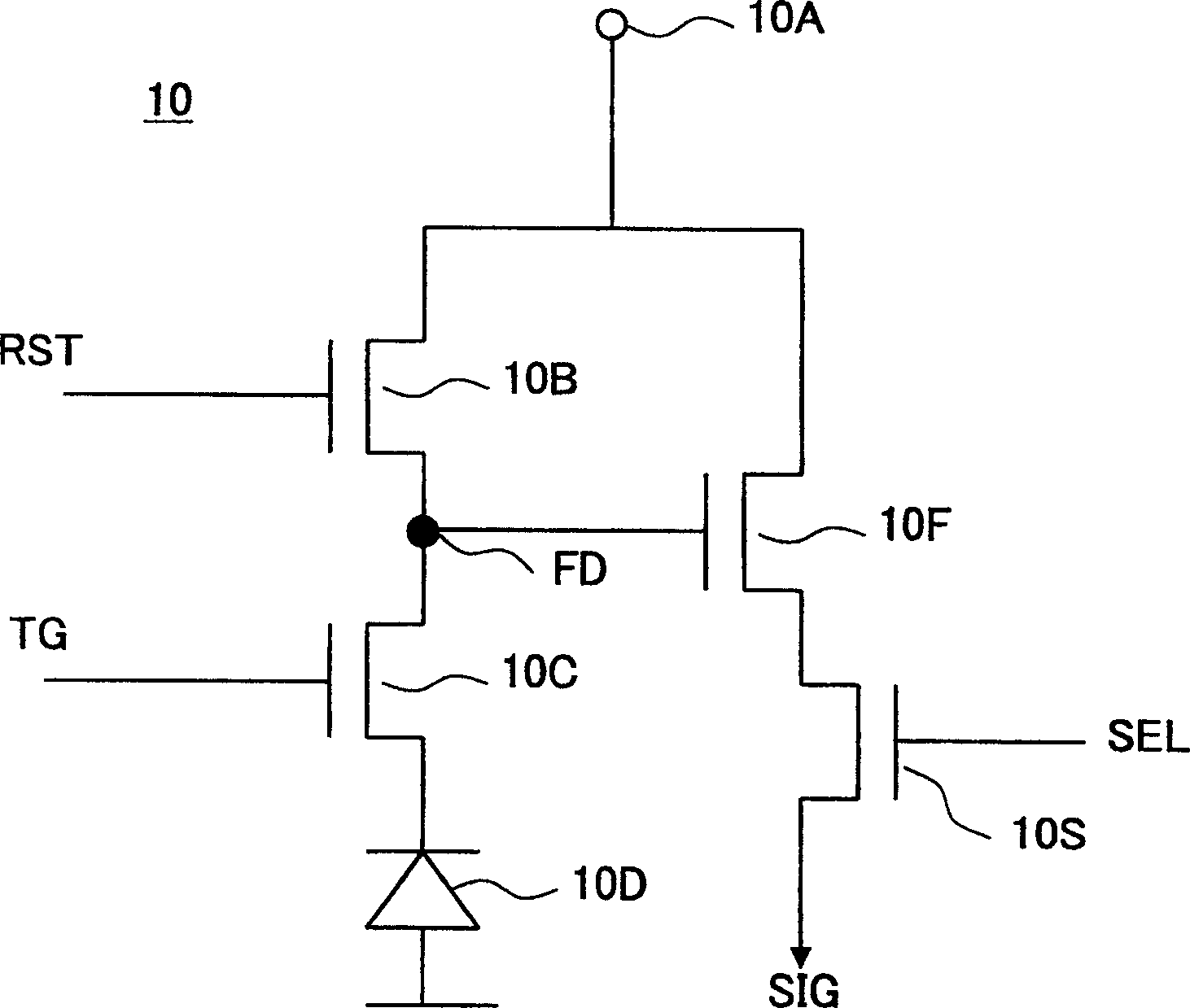
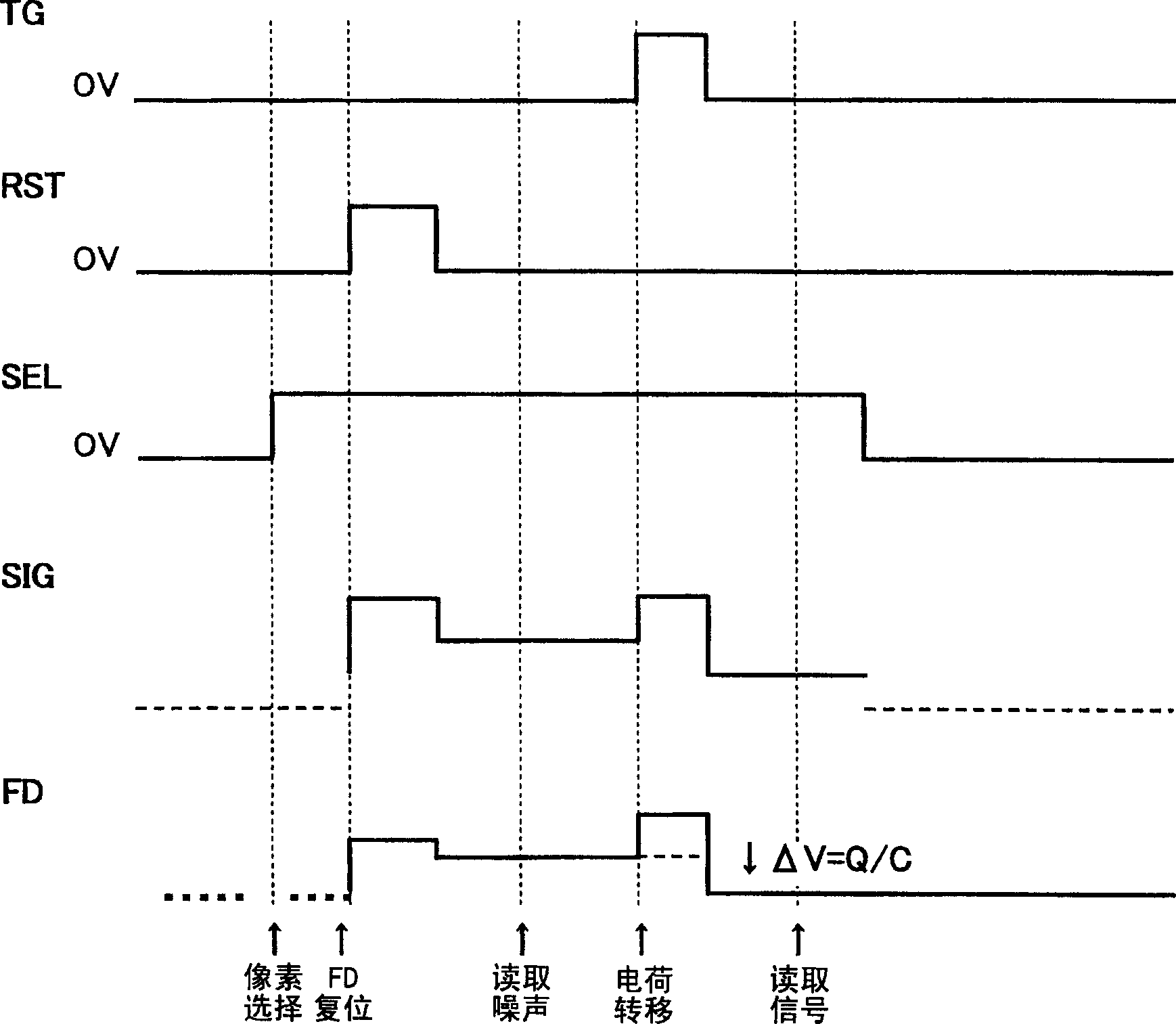
ActiveUS20190238767A1Reduce noiseTotal current dropTransistorTelevision system detailsEngineeringImaging equipment
An imaging device includes a semiconductor substrate that includes a first impurity region having n-type conductivity; a photoelectric converter that is electrically connected to the first impurity region and that converts light into charges; a capacitor that includes a first terminal and a second terminal, the first terminal being electrically connected to the first impurity region; and a voltage supply circuit electrically connected to the second terminal. The voltage supply circuit is configured to generate a first voltage and a second voltage different from the first voltage. The first impurity region accumulates positive charges generated by the photoelectric converter.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
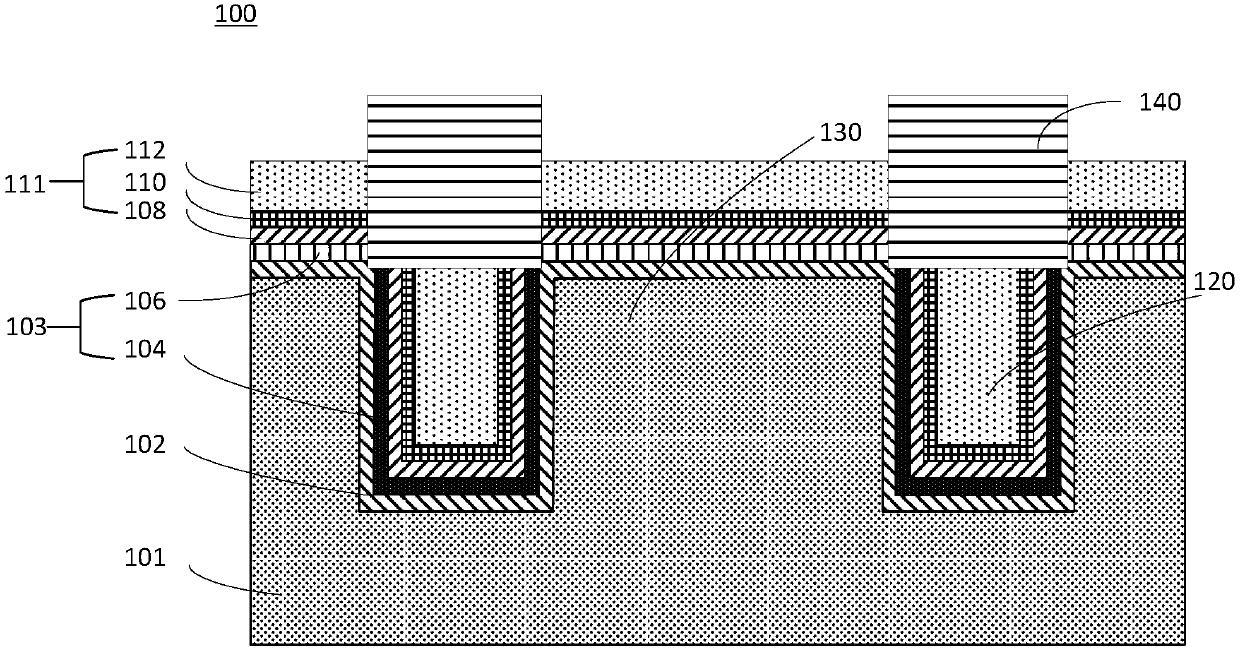
InactiveCN107749416AAdjustable barrierSuppress dark currentRadiation controlled devicesConductive materialsEngineering
The invention relates to a semiconductor device and a manufacturing method thereof. The characteristics lie in that the semiconductor device comprises a substrate, an insulating buffer layer and a barrier adjusting layer, and is characterized in that the substrate comprises trenches and a transmission region separated by the trenches; the insulating buffer layer is formed on the substrate and covers the surfaces of trenches and the transmission region; and the barrier adjusting layer is formed on the buffer layer and used for adjusting barriers at the surface of the substrate, the barrier adjusting layer comprises a first portion which is located on the buffer layer in each trench and a second portion which is located on the buffer layer in the transmission region, the first portion is formed by a conductive material, and the second portion is formed by an insulating material.
Owner:HUAIAN IMAGING DEVICE MFGR CORP
PBN-type InGaAs infrared detector
InactiveCN105185846ADifficulty spreadingSuppress dark currentSemiconductor devicesSi dopedBlocking layer
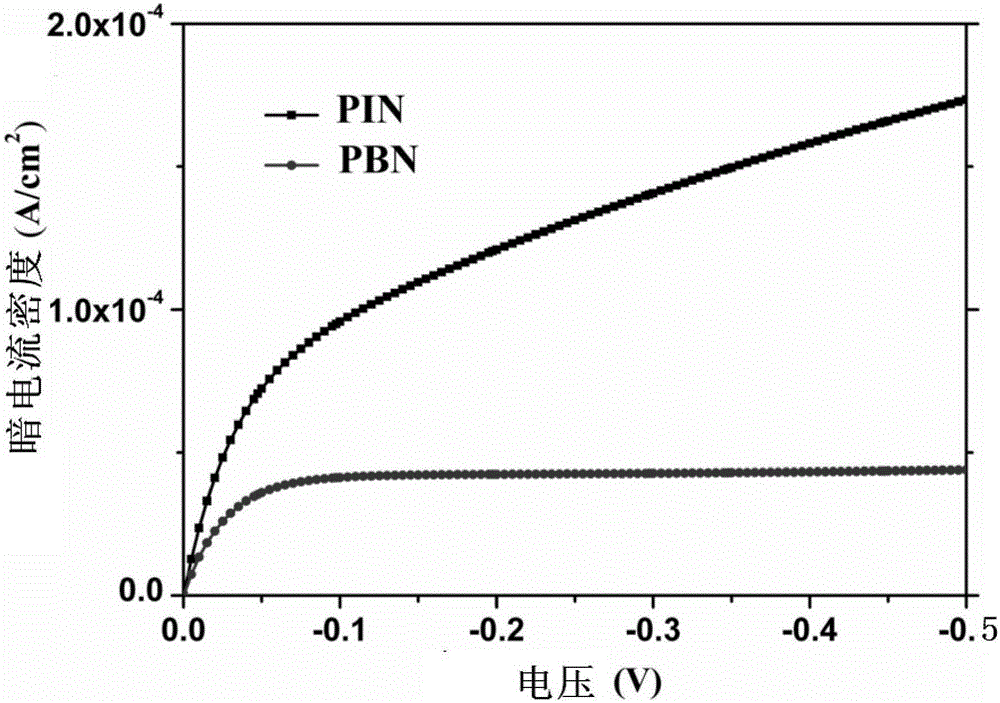
The invention discloses a PBN-type InGaAs infrared detector, and belongs to the technical field of optoelectronic materials and devices. The invention solves a technical problem that an InGaAs detector has more dark currents in the prior art, thereby further enlarging the response range of the InGaAs detector. The detector consists of a window layer, a blocking layer, an absorption layer, a buffering layer and a substrate, wherein the window layer, the blocking layer, the absorption layer, the buffering layer and the substrate are sequentially arranged from the top to the bottom. The blocking layer is made of an Si-doped InAlAs material or Si-doped InAsP material which is larger in energy gap than the absorption layer and the window layer and is matched with the absorption layer in crystal lattice. The thickness of the blocking layer is from 100 nm to 300 nm. The detector can prevent the generation of the dark currents well, is high in quantum efficiency, is low in surface recombination, is wider in response range, and can be used for remote detection.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
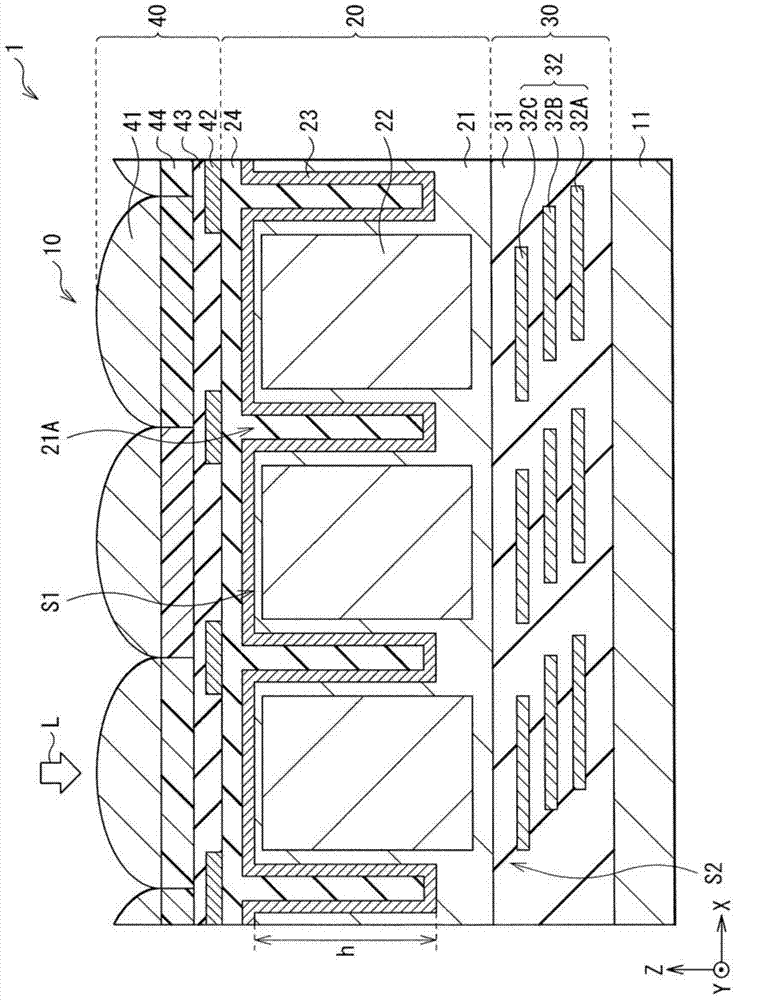
Back-illuminated CMOS image sensor and manufacturing method thereof
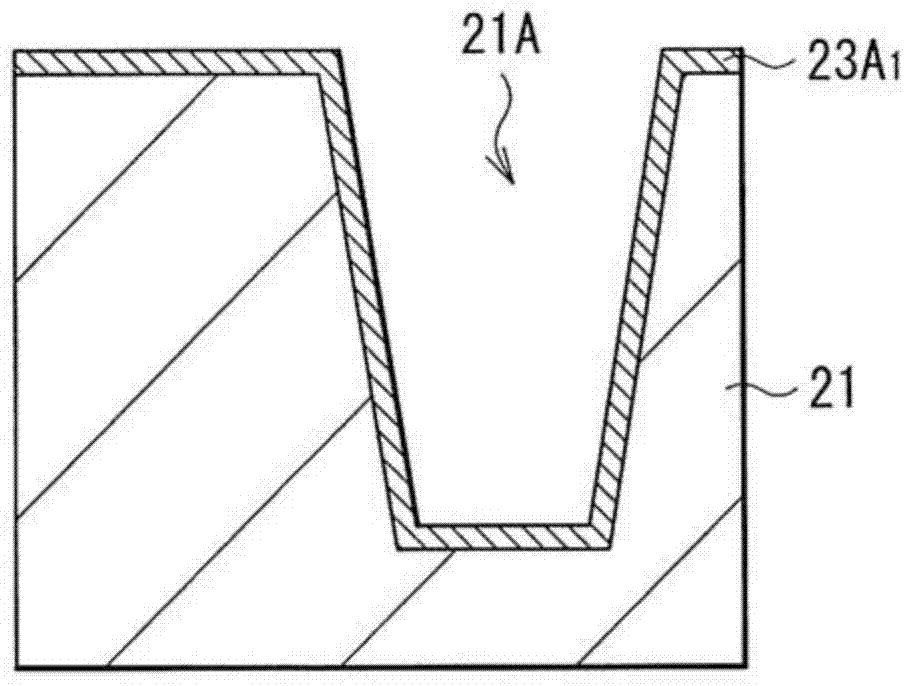
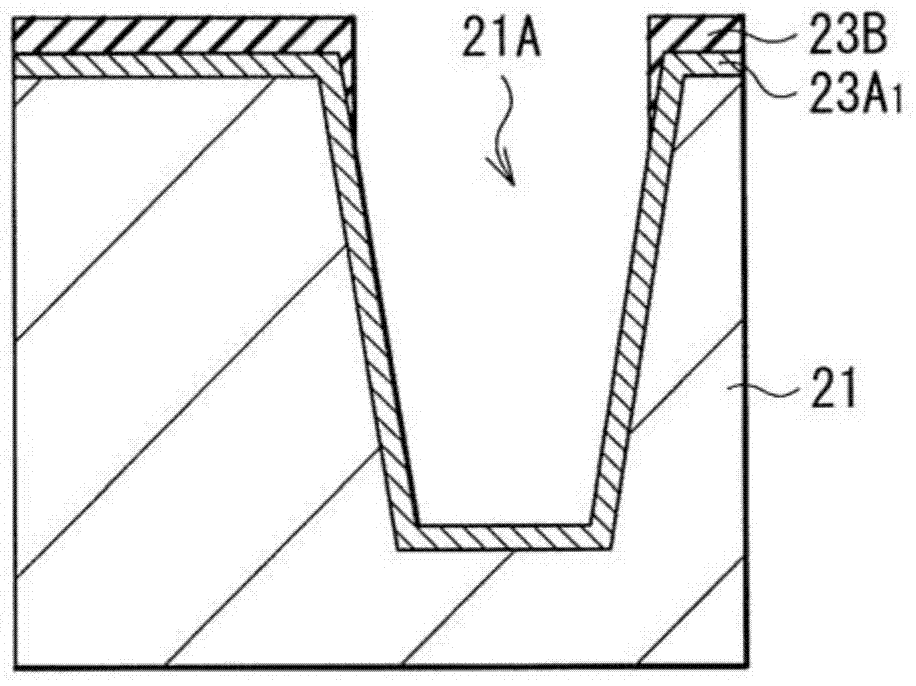
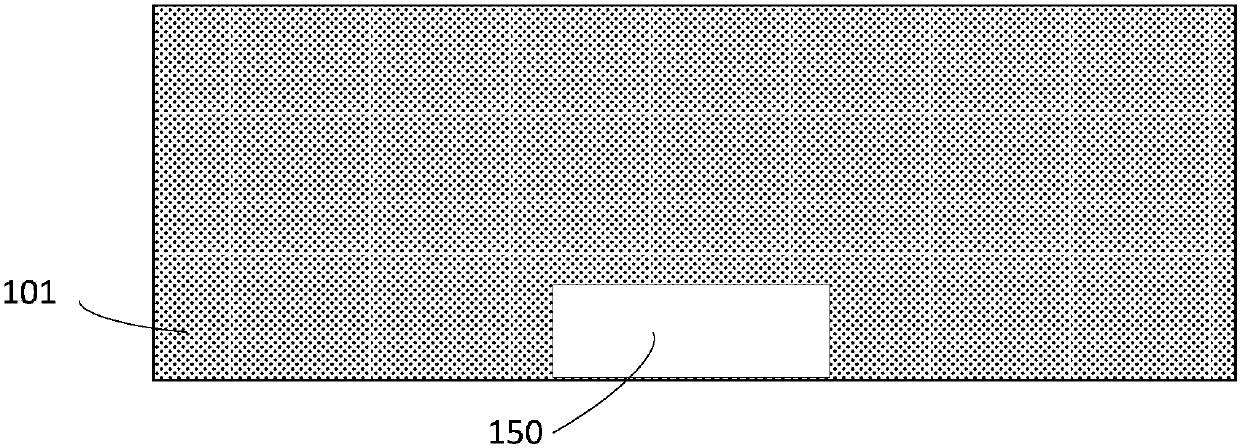
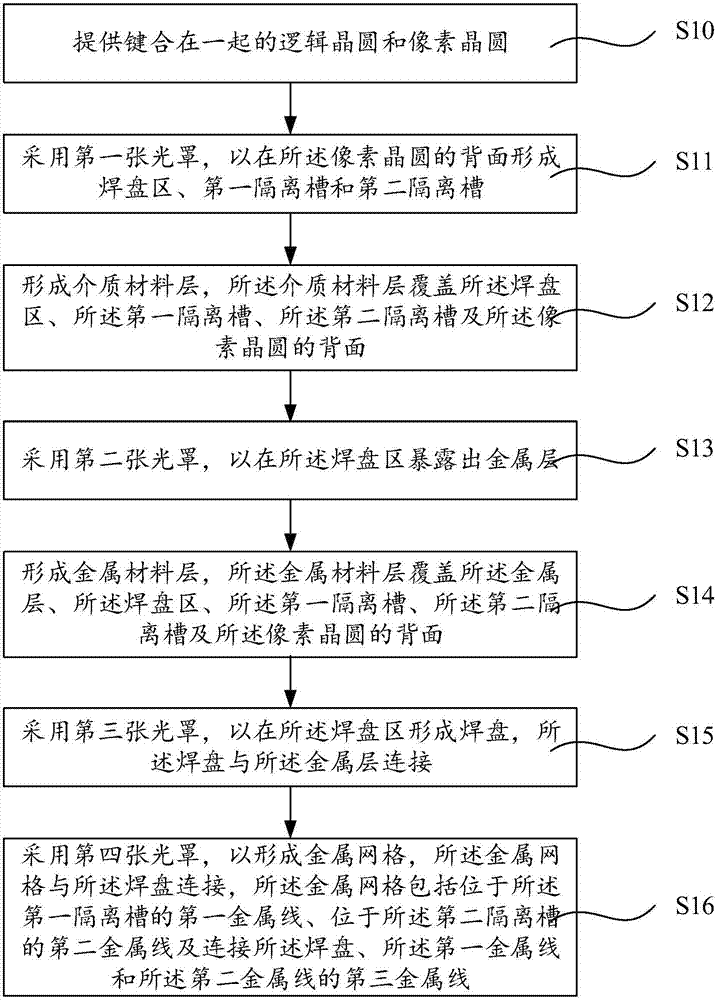
The invention provides a back-illuminated CMOS image sensor and a manufacturing method thereof. The structure such as a bonding pad can be formed through the application of four photomasks, so that the application of the photomasks is reduced; and furthermore, a formed metal gridding is connected with the bonding pad, and comprises a first metal wire positioned in a first isolation groove, a second metal wire positioned in a second isolation groove, and a third metal wire for connecting the bonding pad, the first metal wire and the second metal wire, so that incident light can be preferably limited through the metal gridding, the appearance of crosstalk is avoided, and the quality of the back-illuminated CMOS image sensor is improved. Further, negative pressure is applied onto the bonding pad, so that the negative pressure is also applied onto the metal gridding connected with the bonding pad, namely the negative pressure is applied on a first isolation structure formed in the first isolation groove and a second isolation structure formed in the second isolation groove, and the generation of noisy points and dark current can be inhibited through the negative pressure applied onto the first isolation structure and the second isolation structure.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Image pickup element and image pickup device
ActiveCN104377215ASuppress thermal noiseSuppress dark currentSolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesChalcopyritePhotoelectric conversion
An image pickup element includes: a photoelectric conversion film provided on a semiconductor substrate and including a chalcopyrite-based compound; an insulating film provided on a light incident surface side of the photoelectric conversion film; and a conductive film provided on the insulating film.
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
Solid-state imaging device and camera
ActiveCN102938408AReduce capacitanceImprove conversion efficiencyTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesImpurity diffusionPhotoelectric conversion
A solid-state imaging device and a camera are provided. The solid-state imaging device includes: pixels arrayed; a photoelectric conversion element in each of the pixels; a read transistor for reading electric charges photoelectrically-converted in the photoelectric conversion elements to a floating diffusion portion; a shallow trench element isolation region bordering the floating diffusion portion; and an impurity diffusion isolation region for element isolation regions other than the shallow trench element isolation region.
Owner:SONY GRP CORP
Imaging device
ActiveUS11233958B2Reduce noiseTotal current dropTransistorTelevision system detailsTerminal voltageHemt circuits
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![2,6-bis(triphenylamine)-4,8-bis(alkoxy)benzo[1,2-b:4,5-b']bithiophene and preparation for same 2,6-bis(triphenylamine)-4,8-bis(alkoxy)benzo[1,2-b:4,5-b']bithiophene and preparation for same](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/b7ba0c82-b6f5-4a27-816b-e9ff2f23e578/HDA0000988576790000011.PNG)
![2,6-bis(triphenylamine)-4,8-bis(alkoxy)benzo[1,2-b:4,5-b']bithiophene and preparation for same 2,6-bis(triphenylamine)-4,8-bis(alkoxy)benzo[1,2-b:4,5-b']bithiophene and preparation for same](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/b7ba0c82-b6f5-4a27-816b-e9ff2f23e578/HDA0000988576790000012.PNG)
![2,6-bis(triphenylamine)-4,8-bis(alkoxy)benzo[1,2-b:4,5-b']bithiophene and preparation for same 2,6-bis(triphenylamine)-4,8-bis(alkoxy)benzo[1,2-b:4,5-b']bithiophene and preparation for same](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/b7ba0c82-b6f5-4a27-816b-e9ff2f23e578/HDA0000988576790000021.PNG)