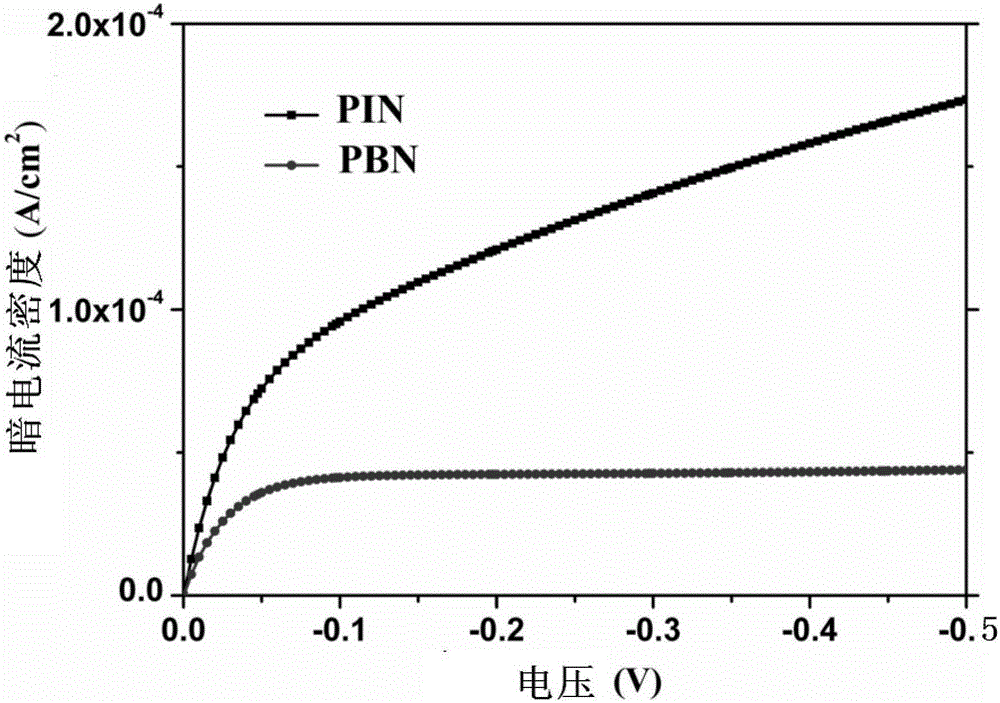
PBN-type InGaAs infrared detector
An infrared detector, n-type technology, applied in the direction of semiconductor devices, electrical components, circuits, etc., to achieve the effects of suppressing dark current generation, wide response range, and improving quantum efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0028] A PBN-type InGaAs infrared detector structure with a cutoff wavelength of 2.6 μm is: sequentially grown on an n-type InP substrate with a thickness of 1 μm and a Si doping concentration of 2×10 18 cm -3 n-type InAs 0.60 P 0.40 Buffer layer, continue to grow with a thickness of 3 μm and a Si doping concentration of 8×10 16 cm -3 In 0.82 Ga 0.18 As absorption layer, regrowth thickness is 200nm, Si doping concentration is 2×10 16 cm -3 In 0.82 al 0.18 As barrier layer, the final growth thickness is 100nm, Be doping concentration is 2×10 17 cm -3 p-type In 0.82 Ga 0.18 The As window layer forms a PBN detector structure.
[0029] The manufacturing method of the above-mentioned PBN-type InGaAs infrared detector can firstly grow Si-doped InAs on the n-type InP substrate by using the MOCVD system on the InP substrate using a two-step method. 0.60 P 0.40 The buffer layer, that is, the first step is to grow a layer of InAs with a thickness of 100nm at a temperature...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com