Patents
Literature
911results about How to "Reduce dark current" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
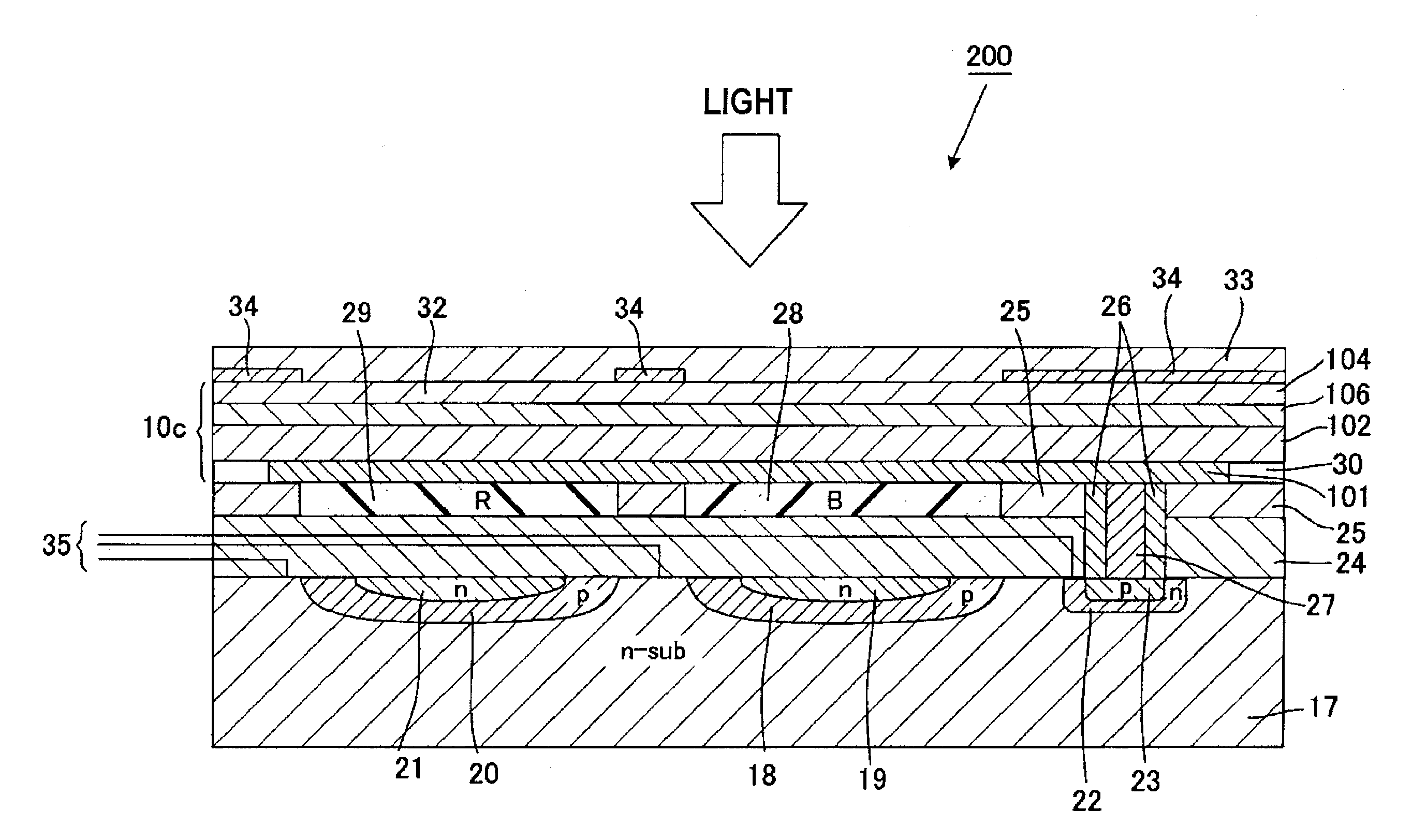
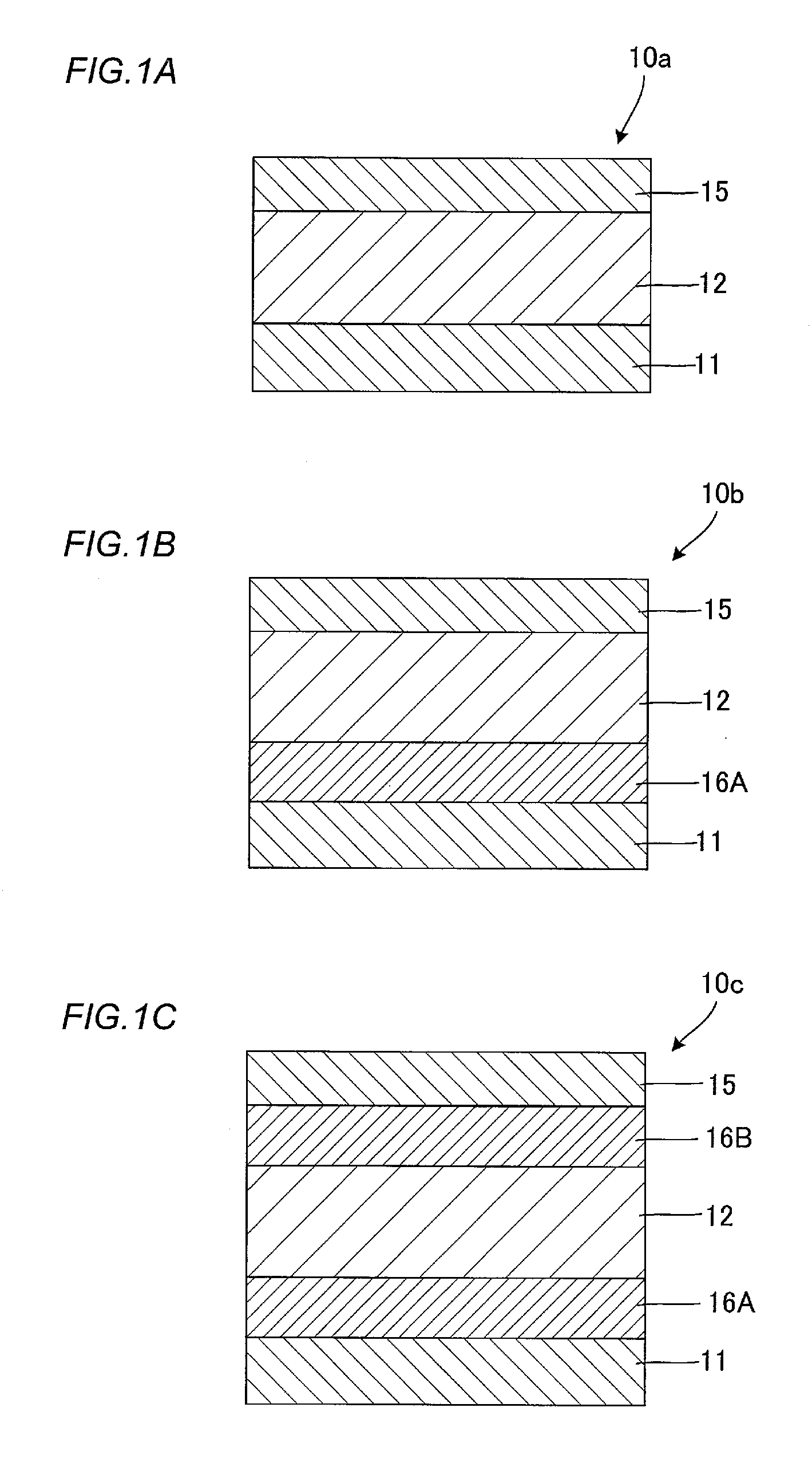
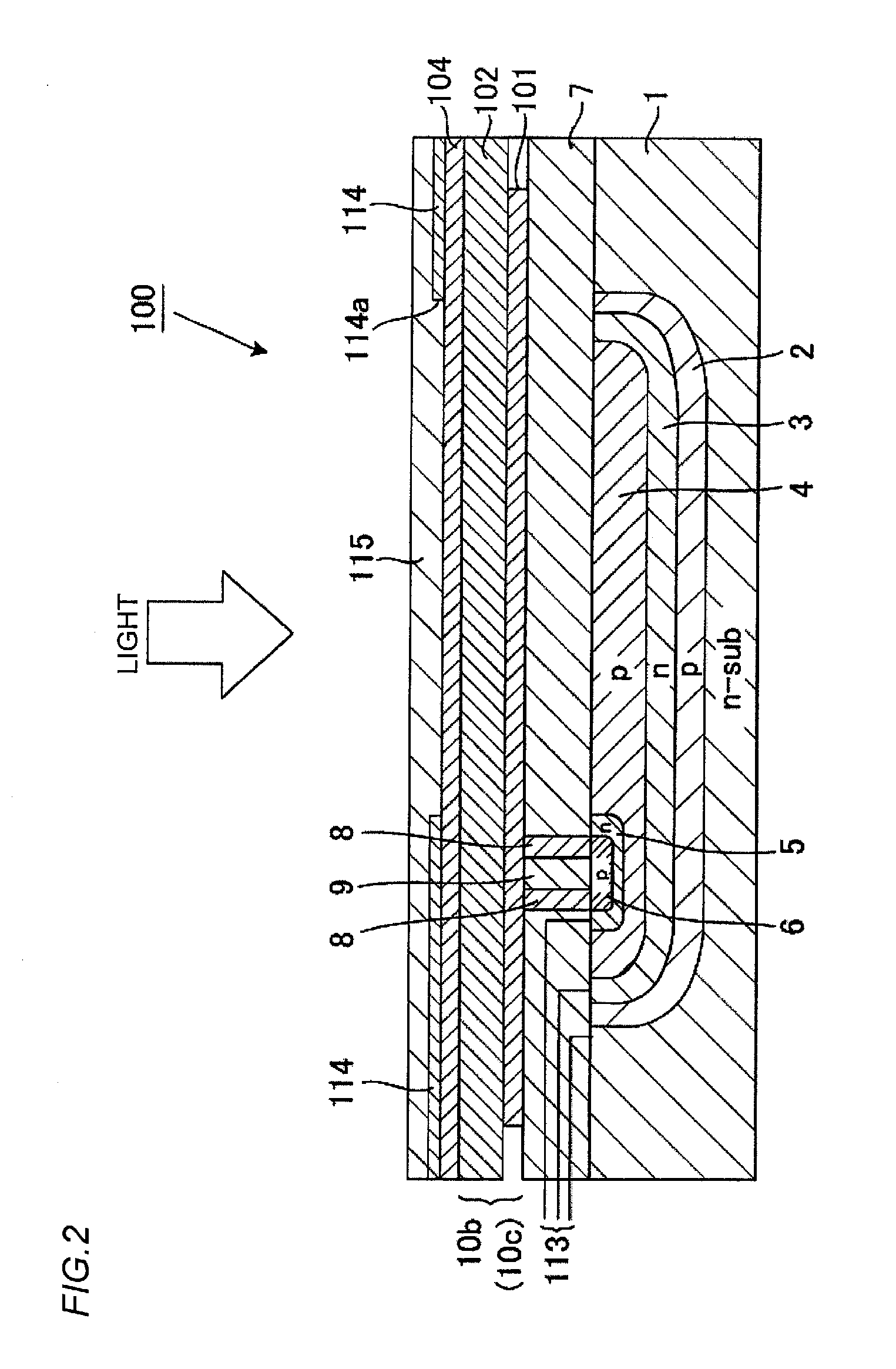
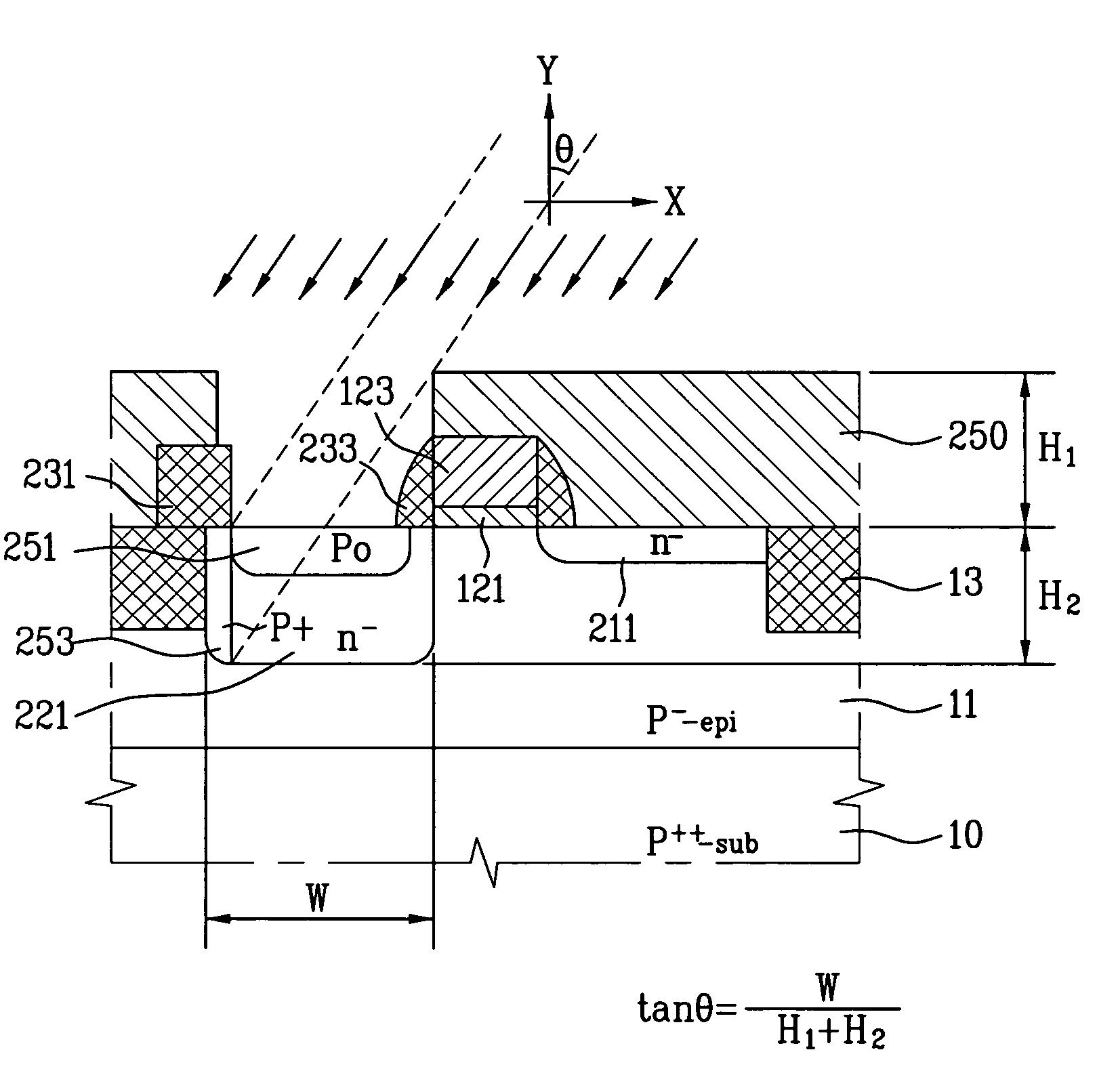
Organic photoelectric conversion element and method of producing the same, organic photodiode and image sensor using the same, organic diode and method of producing the same
InactiveUS20050217722A1Reduce dark currentHigh sensitivityNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesPhotoelectric conversionPhotodiode
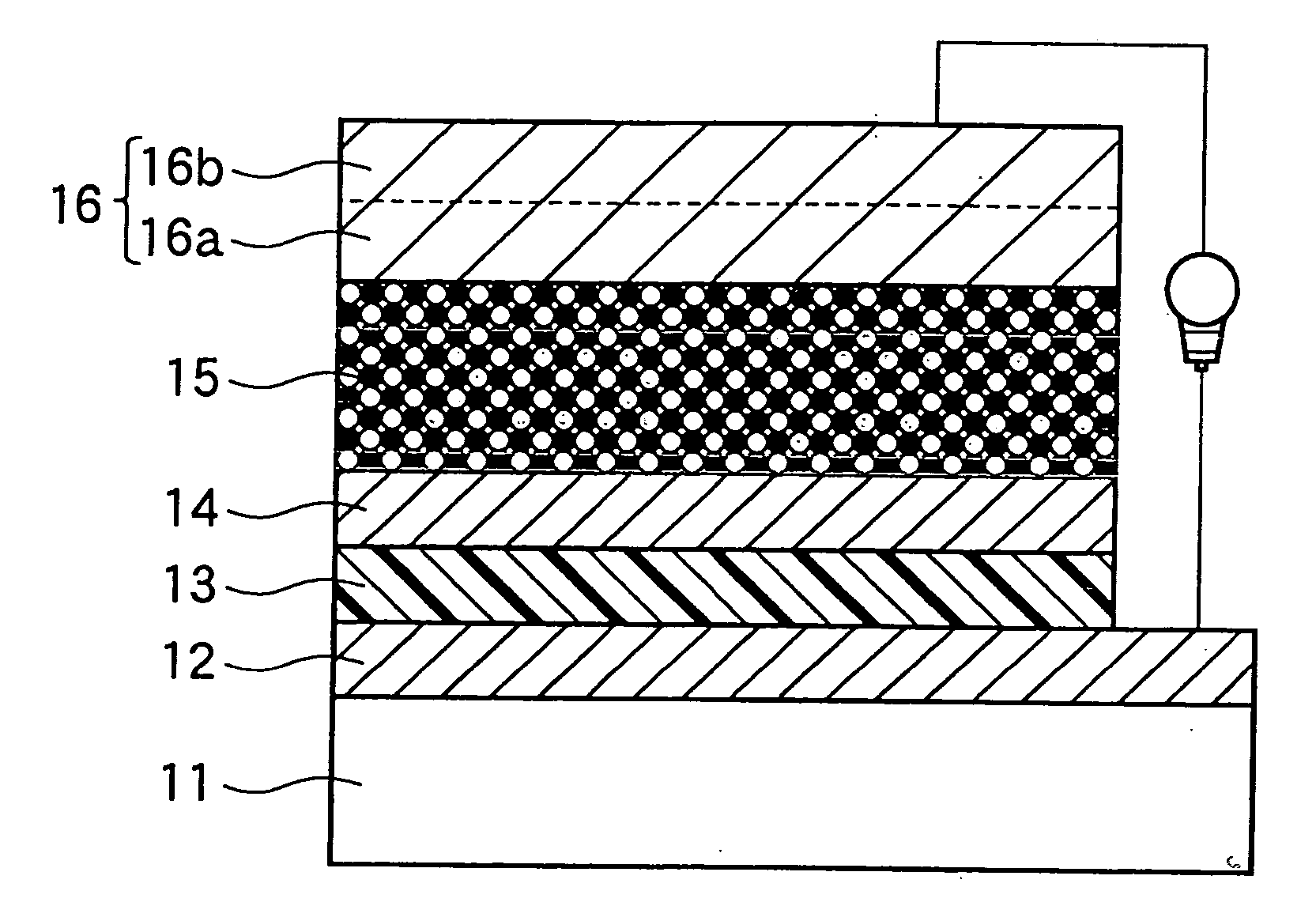
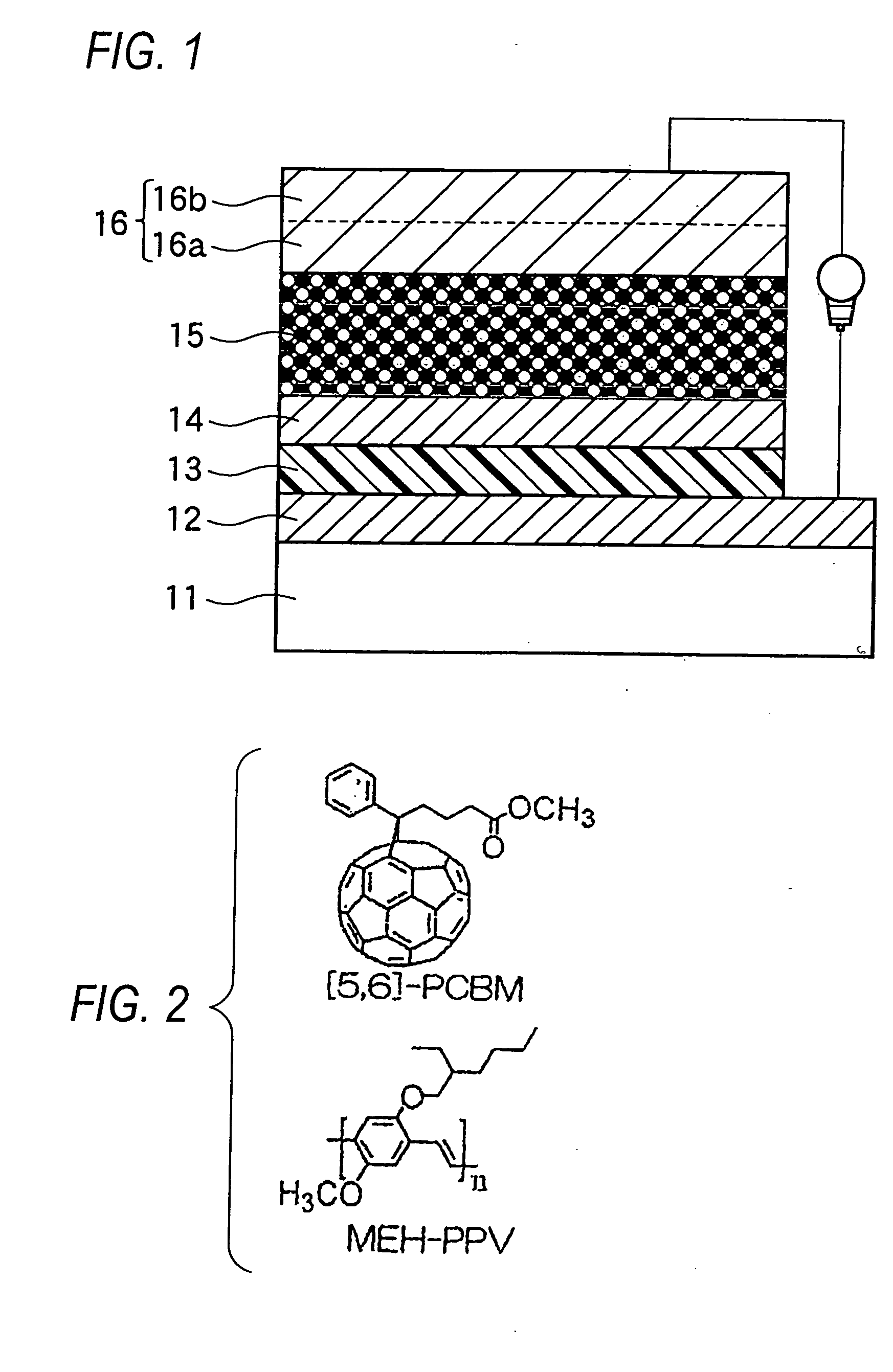
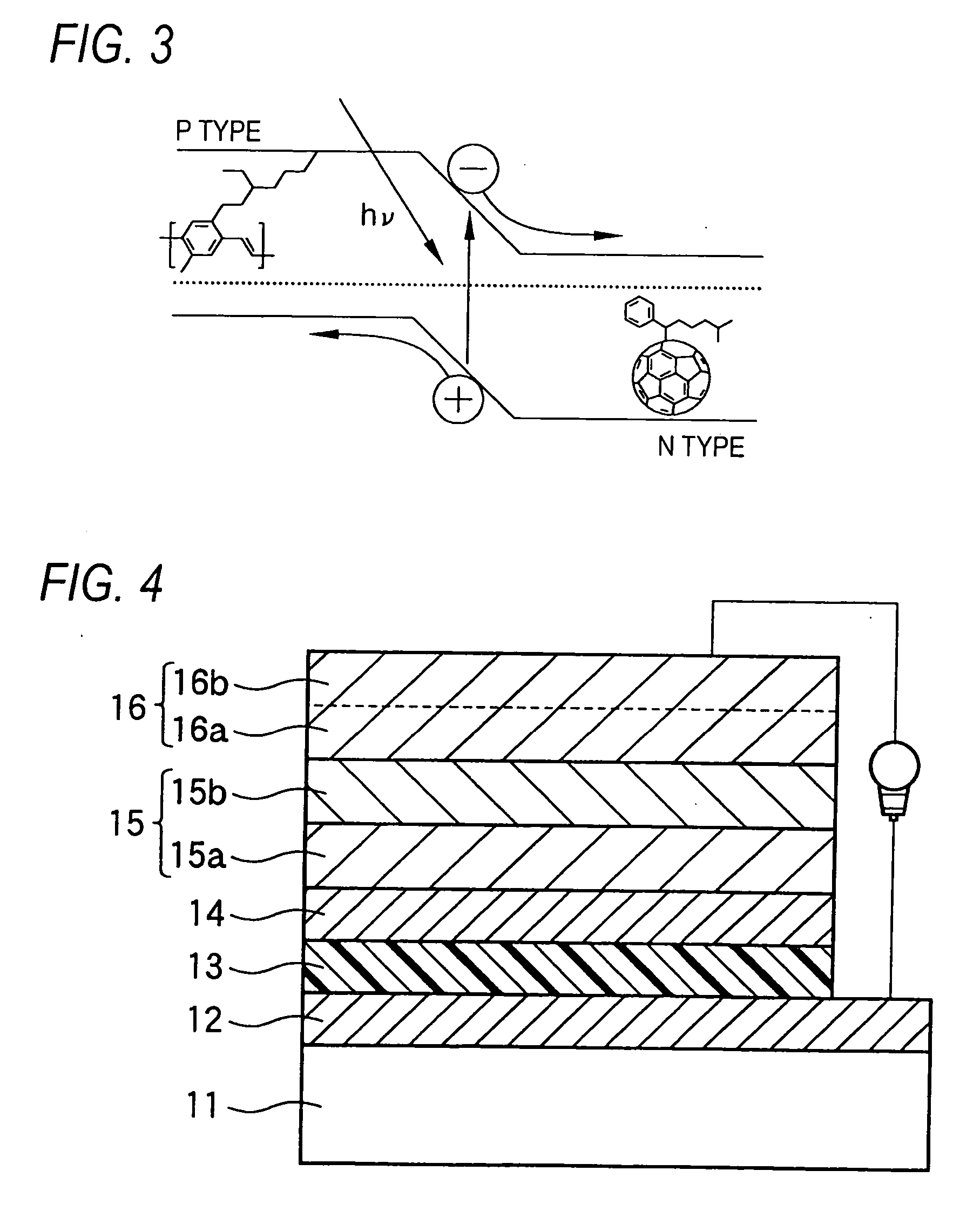
The organic photoelectric conversion element in accordance with the invention comprises at least one pair of electrodes 12 and 16, a photoelectric conversion region (layer) 15 arranged between the electrodes and containing at least an electron donating organic material and an electron accepting organic material, and a buffer layer 14 containing at least one inorganic matter and inserted between the photoelectric conversion region and at least one electrode of the above-cited pair of electrodes.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Solid-state imaging device, process of making solid state imaging device, digital still camera, digital video camera, mobile phone, and endoscope
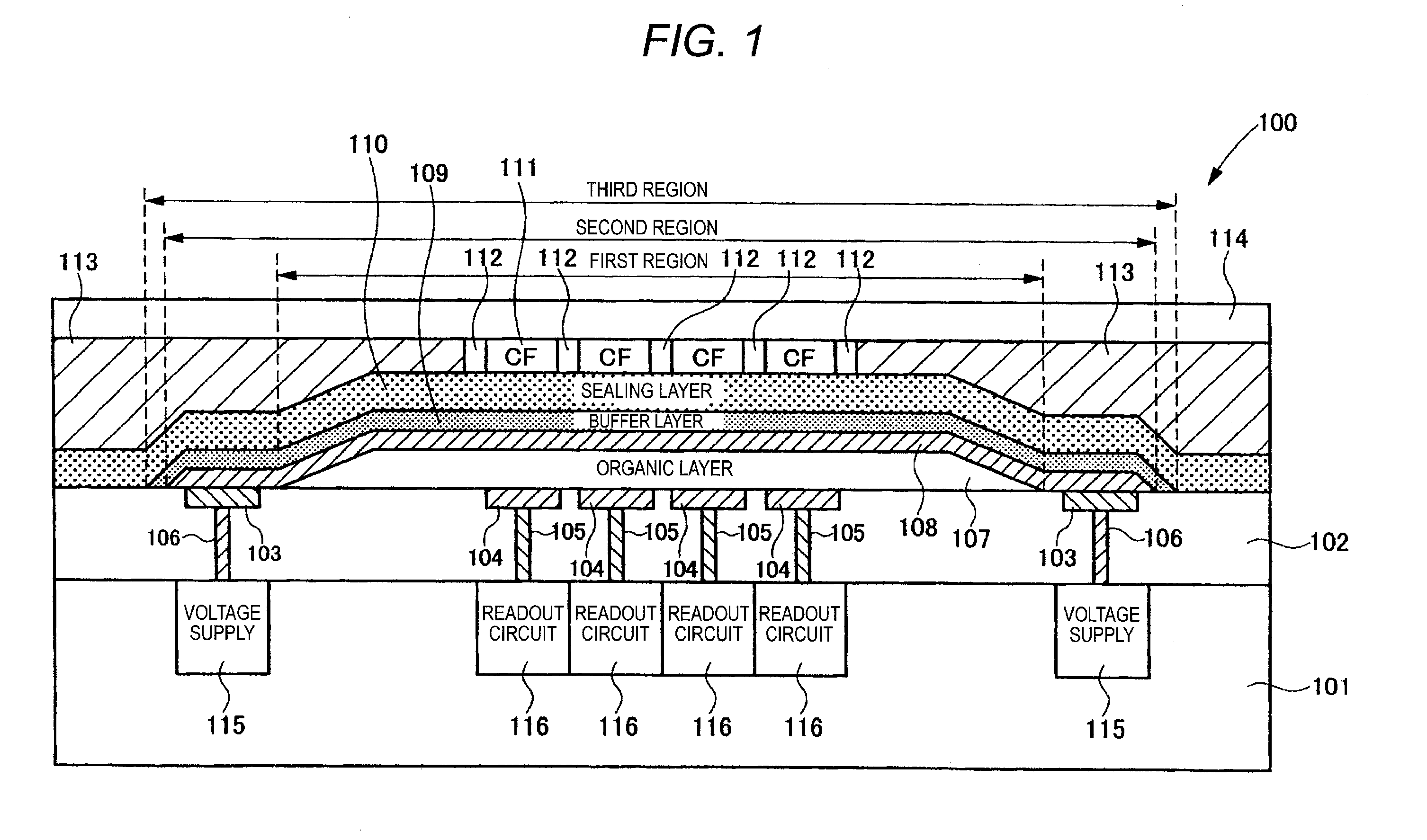
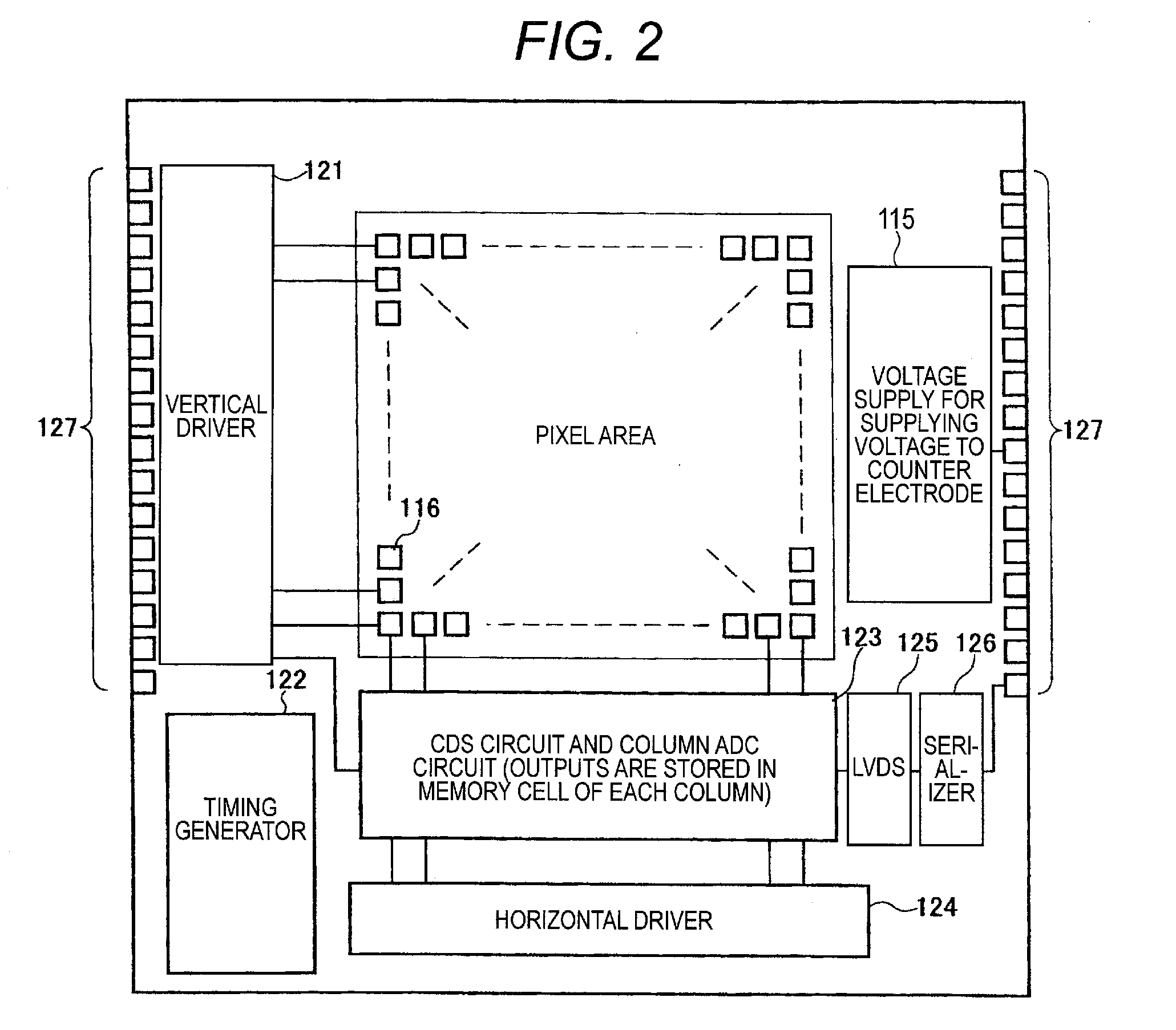
ActiveUS20110049591A1Reduce dark currentImprove signal-to-noise ratioTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesIonizationBlock layer
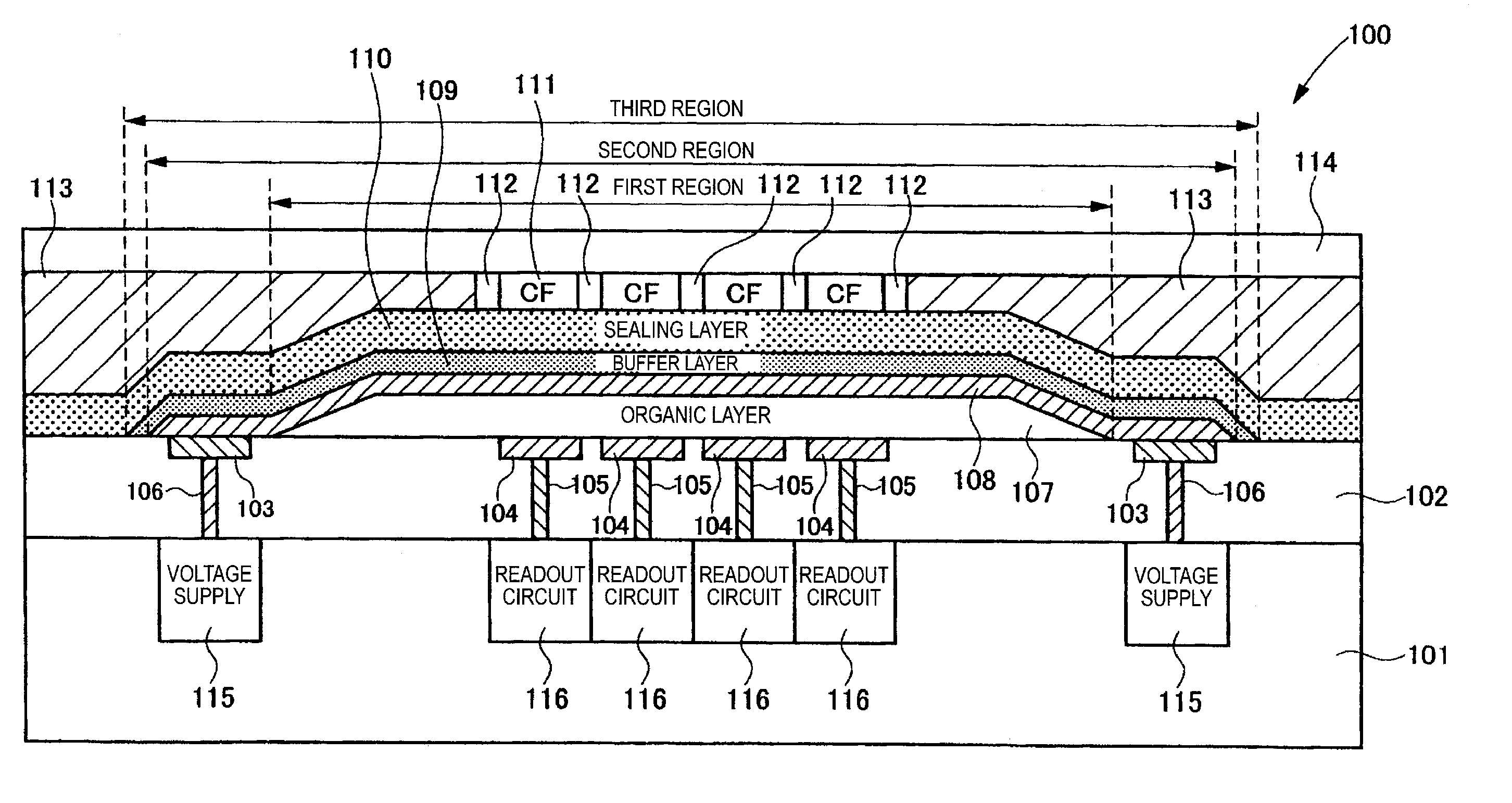
A solid-state imaging device includes an array of pixels, each pixel includes: a pixel electrode; an organic layer; a counter electrode; a sealing layer; a color filter; a readout circuit; and a light-collecting unit as defined herein, the photoelectric layer contains an organic p type semiconductor and an organic n type semiconductor, the organic layer further includes a charge blocking layer as defined herein, an ionization potential of the charge blocking layer and an electron affinity of the organic n type semiconductor in the photoelectric layer has a difference of at least 1 eV, and the sealing layer includes a first sealing sublayer formed by atomic layer deposition and a second sealing sublayer formed by physical vapor deposition and containing one of a metal oxide, a metal nitride, and a metal oxynitride.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Fluorine Passivation in CMOS Image Sensors
InactiveUS20140264507A1Reduce dark currentTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementCMOSPhotodiode
CMOS imaging sensors having fluorine-passivated structures to reduce dark current are disclosed together with methods of making thereof. The CIS comprises an array of pixels on a substrate, each pixel comprising a pinned photodiode, an isolation trench adjacent to the pinned photodiode, and a plurality of transistors. Methods of preparing a CIS comprise providing a source of fluorine (F) atoms, and annealing in the presence of the source of F atoms. After the annealing, at least one silicon-containing surface or region in the CIS comprises Si—F bonds and is fluorine passivated.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
Avalanche photo-detector with high saturation power and high gain-bandwidth product
InactiveUS20050051861A1Reduce operating voltageReducing carrier transport timeNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesLow noiseCapacitance
An avalanche photo-detector (APD) is disclosed, which can reduce device capacitance, operating voltage, carrier transport time and dark current as well as increasing response speed and output power. Thus, an avalanche photo-detector (APD) with high saturation power, high gain-bandwidth product, low noise, fast response, low dark current is achieved. The APD includes an absorption layer with graded doping for converting an incident light into carriers, an undoped multiplication layer for multiplying current by means of receiving carriers, a doped field buffer layer sandwiched between the absorption layer and the multiplication layer for concentrating an electric field in the multiplication layer when a bias voltage is applied, and an undoped drift layer sandwiched between the absorption layer and the field buffer layer for capacitance reduction.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Photoelectric conversion device, imaging device, and method for driving photoelectric conversion device
InactiveUS20130087682A1High Photoelectric Conversion EfficiencyReduce dark currentMethine/polymethine dyesSolid-state devicesPhotoelectric conversionLength wave
A photoelectric conversion device includes, in the following order: a first electrode; an electron blocking layer; a photoelectric conversion layer containing a merocyanine dye; a hole blocking layer; and a transparent electrode as a second electrode, and an absorption maximum wavelength in a thin film absorption spectrum of the photoelectric conversion layer containing a merocyanine dye is within a range of from 400 to 520 nm.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
CMOS image sensor and method for fabricating the same
ActiveUS20050088556A1Reduce dark currentAvoid leakage currentTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCMOSIsolation layer
A CMOS image sensor and a method for fabricating the same is disclosed, to decrease a darkcurrent generated in the boundary between a diffusion area of a photodiode and a device isolation layer, which includes a first conductive type semiconductor substrate having an active area and a device isolation area, the active area including a photodiode and a transistor; a device isolation layer formed in the device isolation area of the semiconductor substrate; a second conductive type diffusion area formed in the photodiode of the semiconductor substrate at a predetermined interval from the device isolation layer; a gate insulating layer and a gate electrode formed in the transistor of the semiconductor substrate; and a first conductive type first diffusion area formed in the semiconductor substrate of the boundary between the second conductive type diffusion area and the device isolation layer.
Owner:III HLDG 4
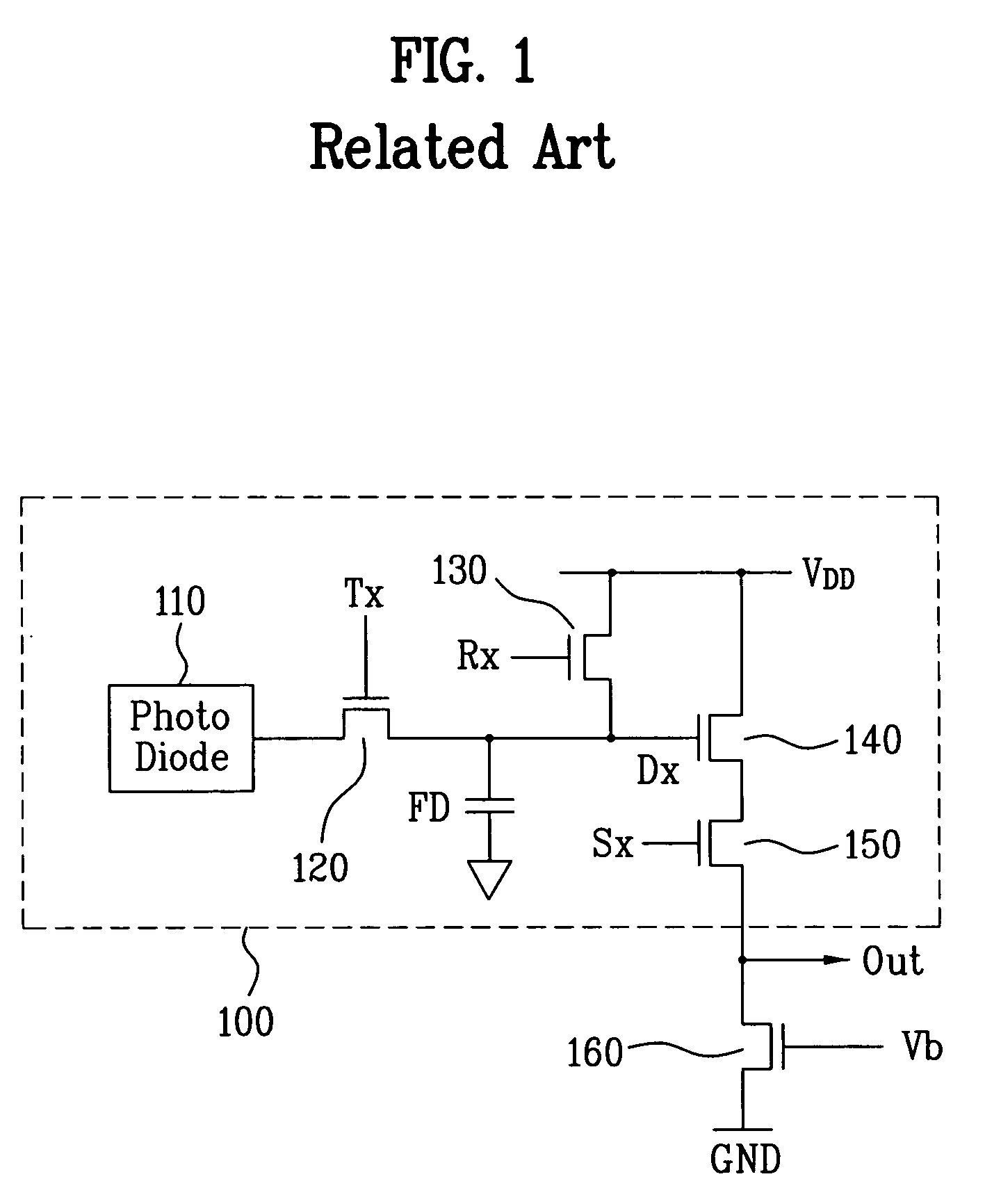
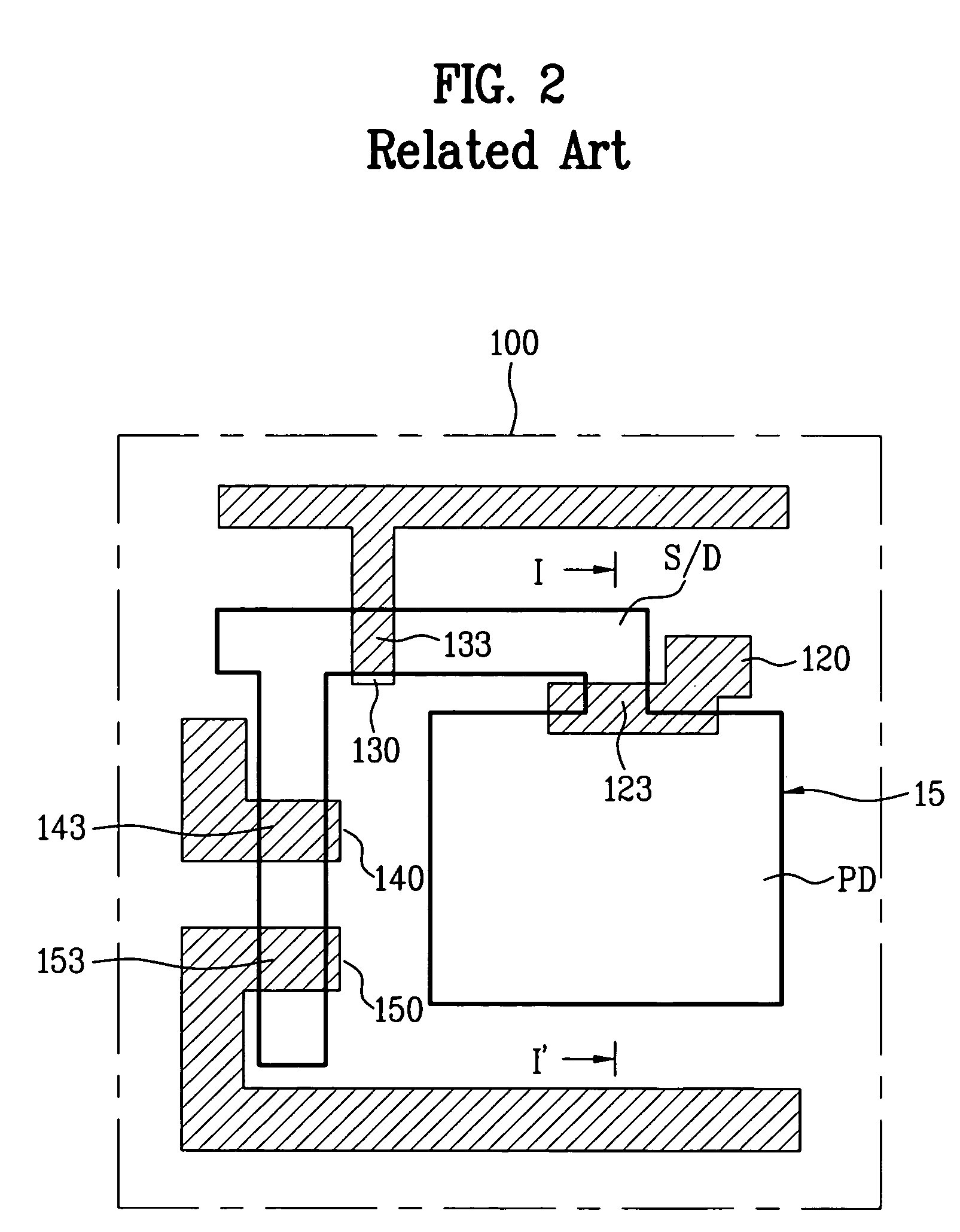
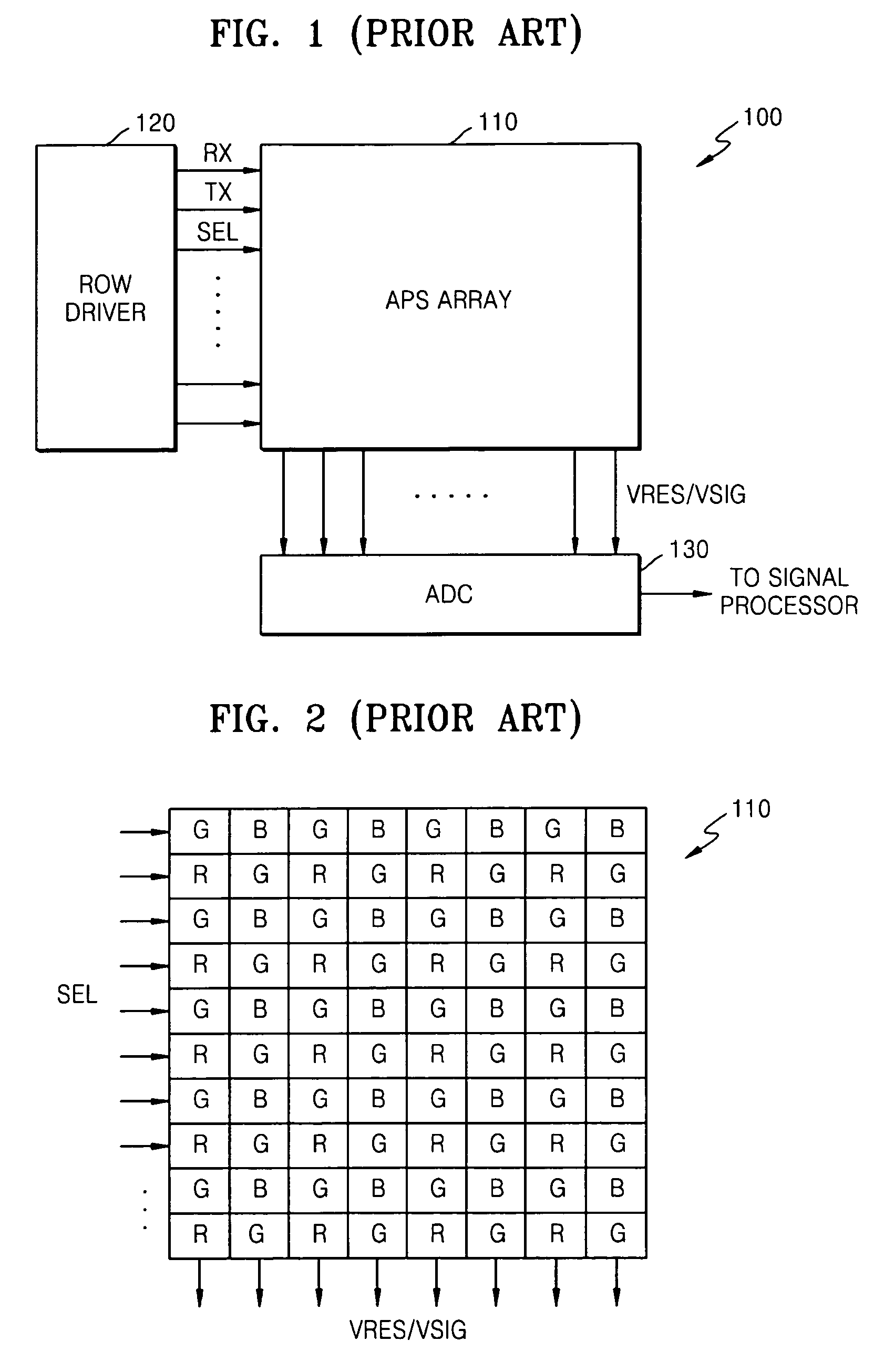
Pixel circuit with low noise in image sensor
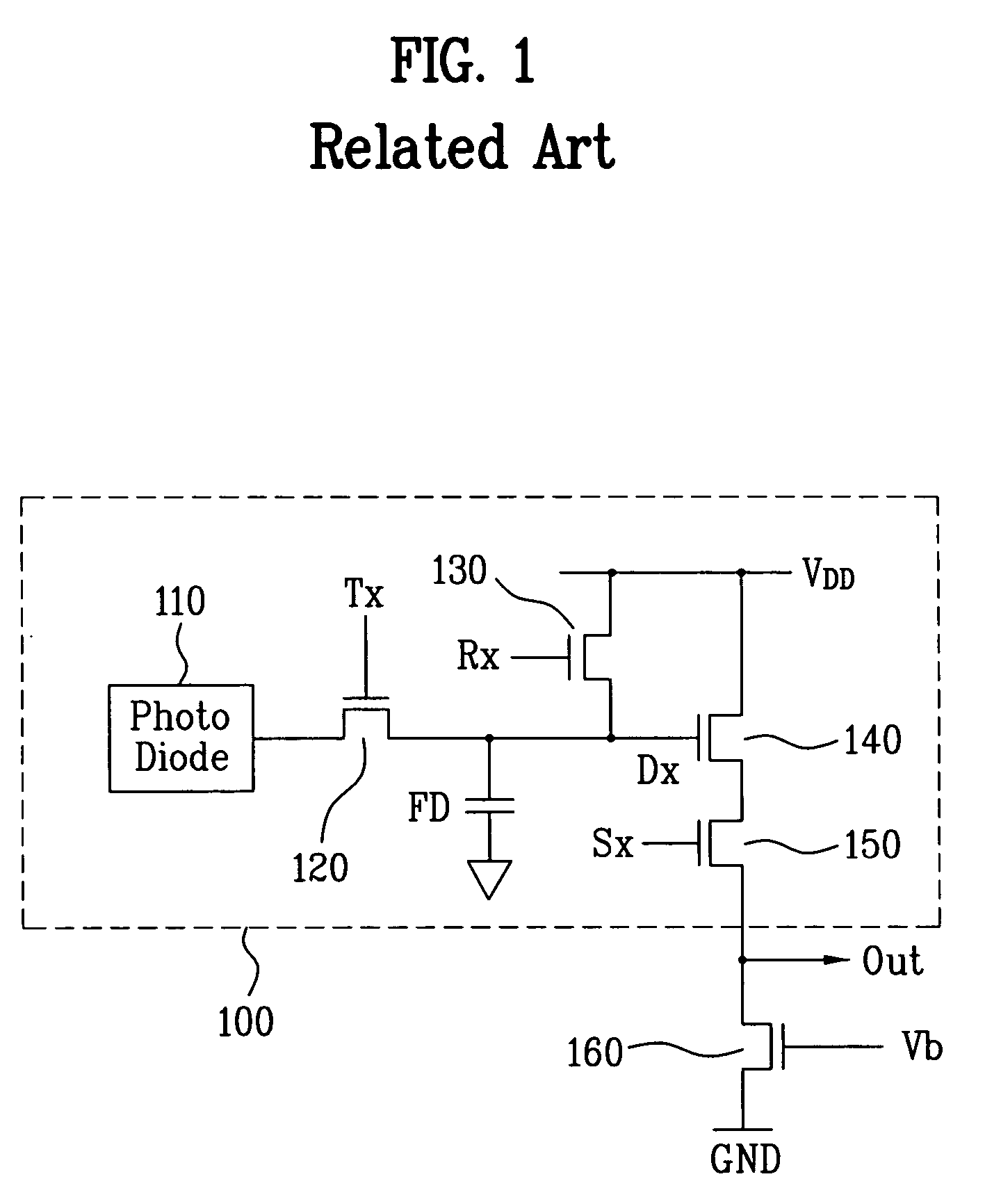
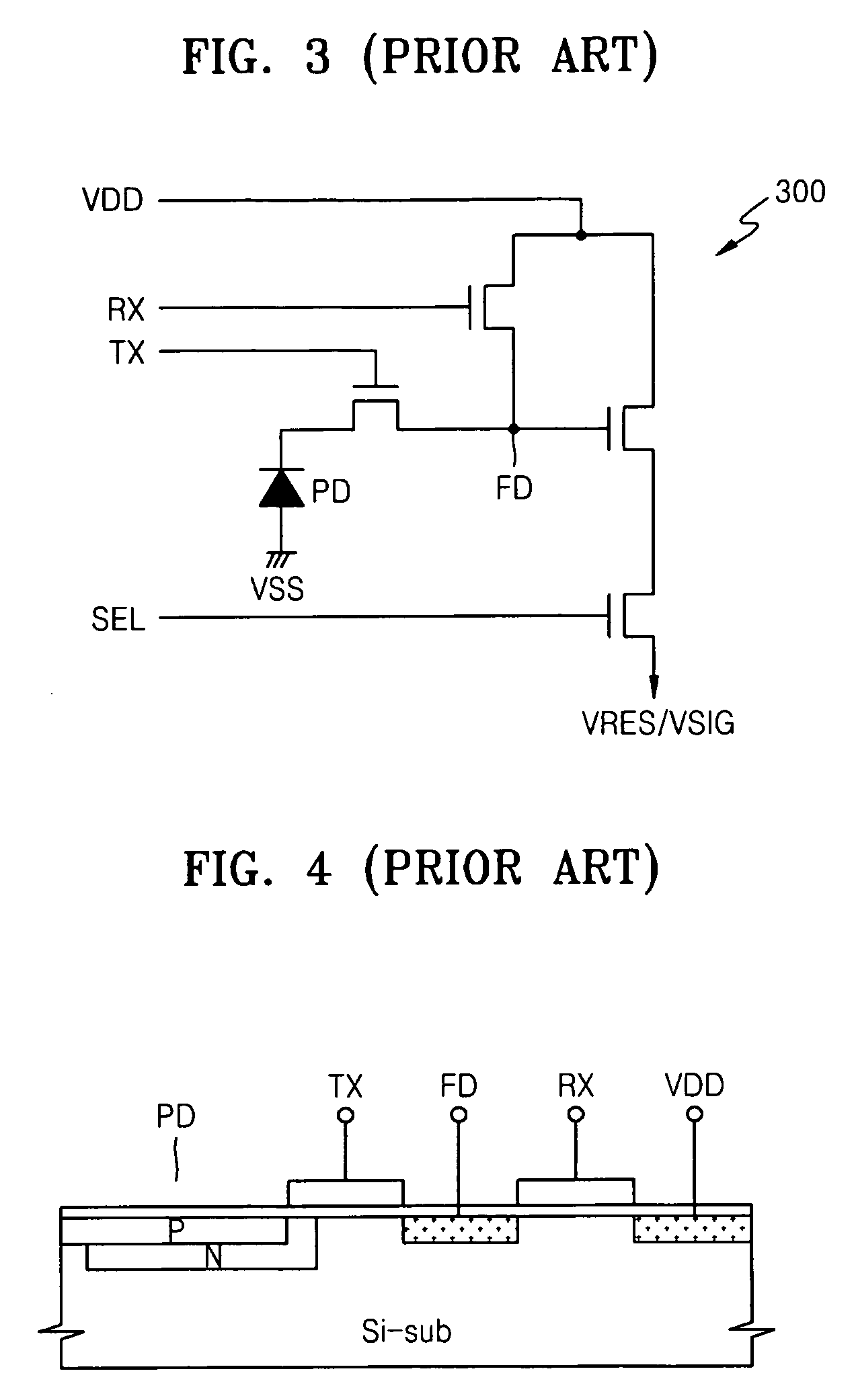
ActiveUS20060284054A1Broaden applicationReduce noiseTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsLow noiseFloating diffusion
A pixel circuit of an image sensor includes a photo-converting unit such as a photo-diode for generating charge from incident light. The pixel circuit also includes a charge storing capacitor for storing the charge generated by the photo-converting unit. The pixel circuit further includes a floating diffusion node that receives the charge from the charge storing unit after being reset. Thus, an image signal VSIG is generated after a reset signal VRES is generated from the pixel circuit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
CMOS image sensor and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20050093036A1Reduce dark currentSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSPhotodiode
CMOS image sensor and method for fabricating the same, the CMOS image sensor including a second conductive type semiconductor substrate having an active region and a device isolation region defined therein, wherein the active region has a photodiode region and a transistor region defined therein, a device isolating film in the semiconductor substrate of the device isolation region, a first conductive type impurity region in the semiconductor substrate of the photodiode region, the first conductive type impurity region being spaced a distance from the device isolation film, and a second conductive type first impurity region in the semiconductor substrate between the first conductive type impurity region and the device isolation film, thereby reducing generation of a darkcurrent at an interface between the photodiode region and a field region.
Owner:COLUMBA TECH INC
CMOS image sensor and method for fabricating the same
ActiveUS7232712B2Reduce dark currentAvoid leakage currentTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCMOSIsolation layer
A CMOS image sensor and a method for fabricating the same is disclosed, to decrease a darkcurrent generated in the boundary between a diffusion area of a photodiode and a device isolation layer, which includes a first conductive type semiconductor substrate having an active area and a device isolation area, the active area including a photodiode and a transistor; a device isolation layer formed in the device isolation area of the semiconductor substrate; a second conductive type diffusion area formed in the photodiode of the semiconductor substrate at a predetermined interval from the device isolation layer; a gate insulating layer and a gate electrode formed in the transistor of the semiconductor substrate; and a first conductive type first diffusion area formed in the semiconductor substrate of the boundary between the second conductive type diffusion area and the device isolation layer.
Owner:III HLDG 4
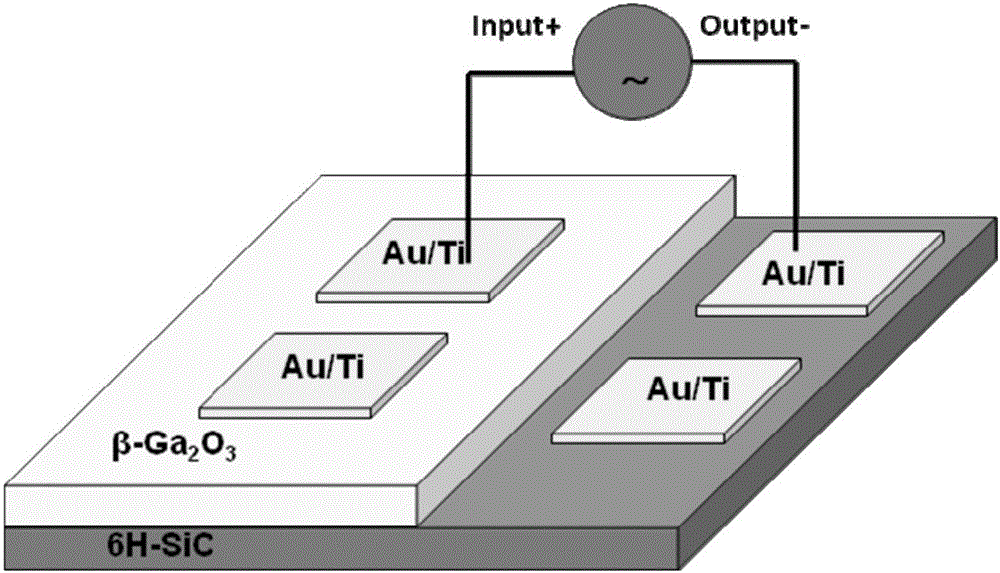
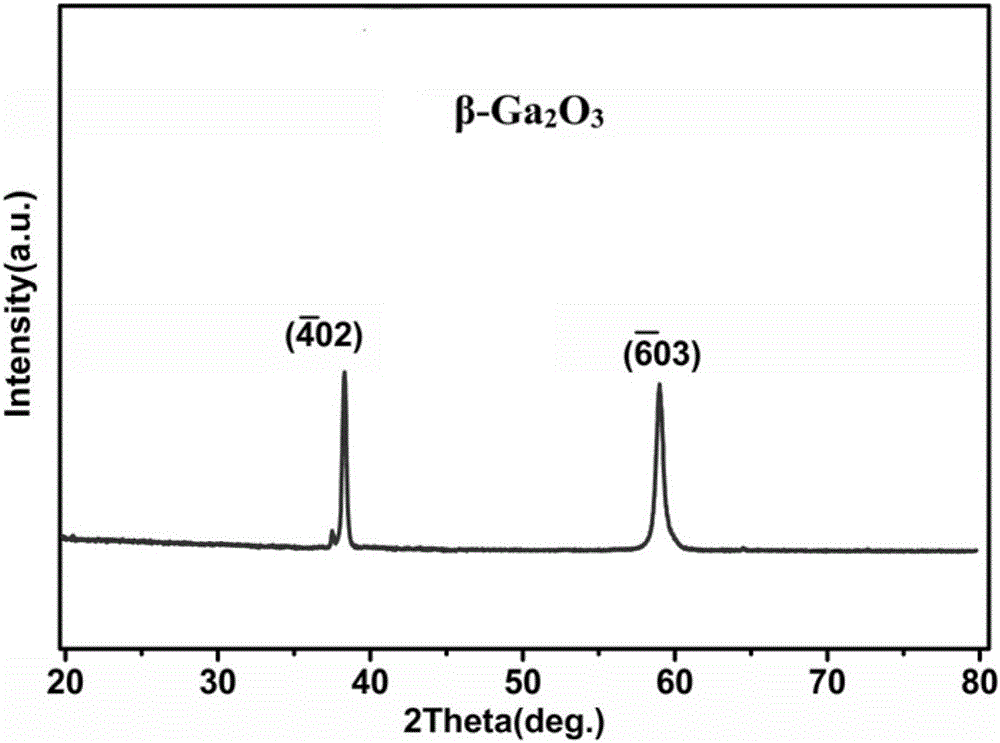
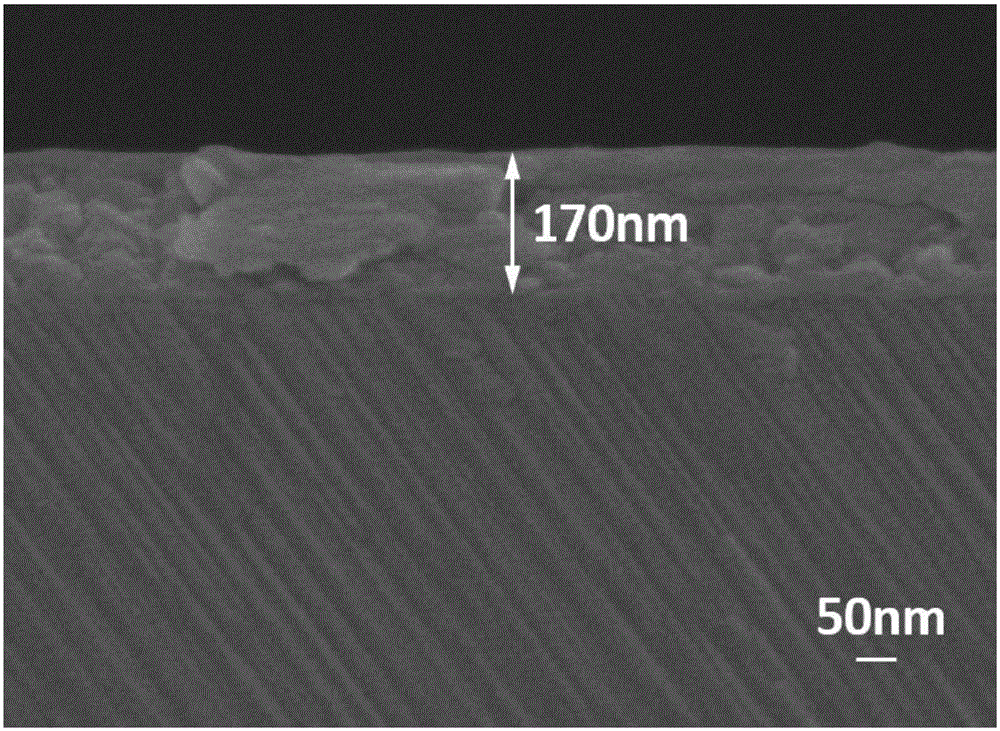
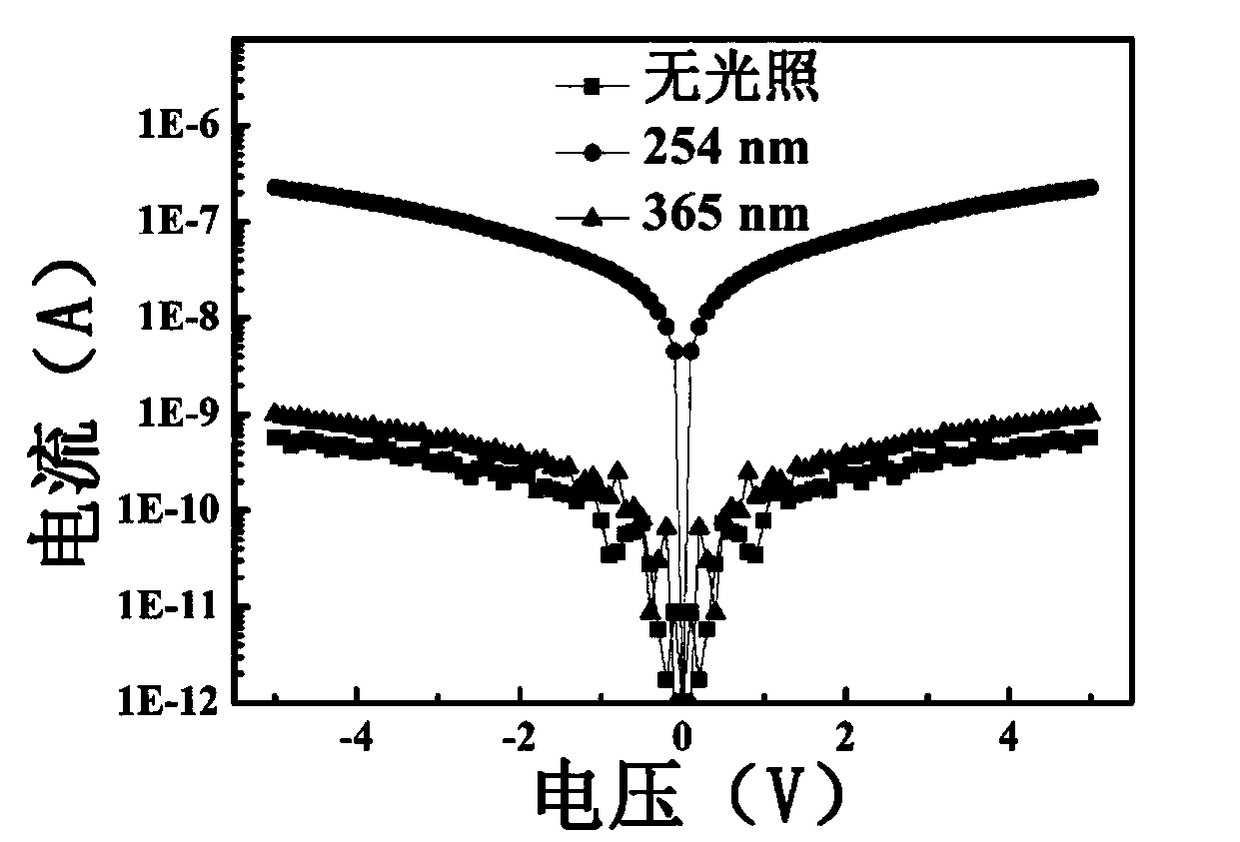
Visible-blind ultraviolet detector based on Beta-Ga2O3/SiC heterojunction thin film and fabrication method of visible-blind ultraviolet detector
ActiveCN105742398AStrong process controllabilityEasy to operateFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionUltraviolet detectors
The invention relates to an ultraviolet detector, in particular to a visible-blind ultraviolet detector based on a Beta-Ga2O3 / SiC heterojunction thin film and a fabrication method of the visible-blind ultraviolet detector. According to the fabrication method, a layer of Beta-Ga2O3 thin film is deposited on an n-type 6H-SiC substrate by a laser molecular beam epitaxial technique, and then a layer of Ti / Au thin film is deposited on the n-type 6H-SiC substrate and the Beta-Ga2O3 thin film through a mask by a radio frequency magnetron sputtering to be used as an electrode. The fabricated visible-blind ultraviolet detector has the advantages of stable performance, response sensitivity, small dark current and high potential application; and moreover, the fabrication method has the characteristics of high process controllability, simplicity in operation, high universality, restorability of repeated test and the like, and has great application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
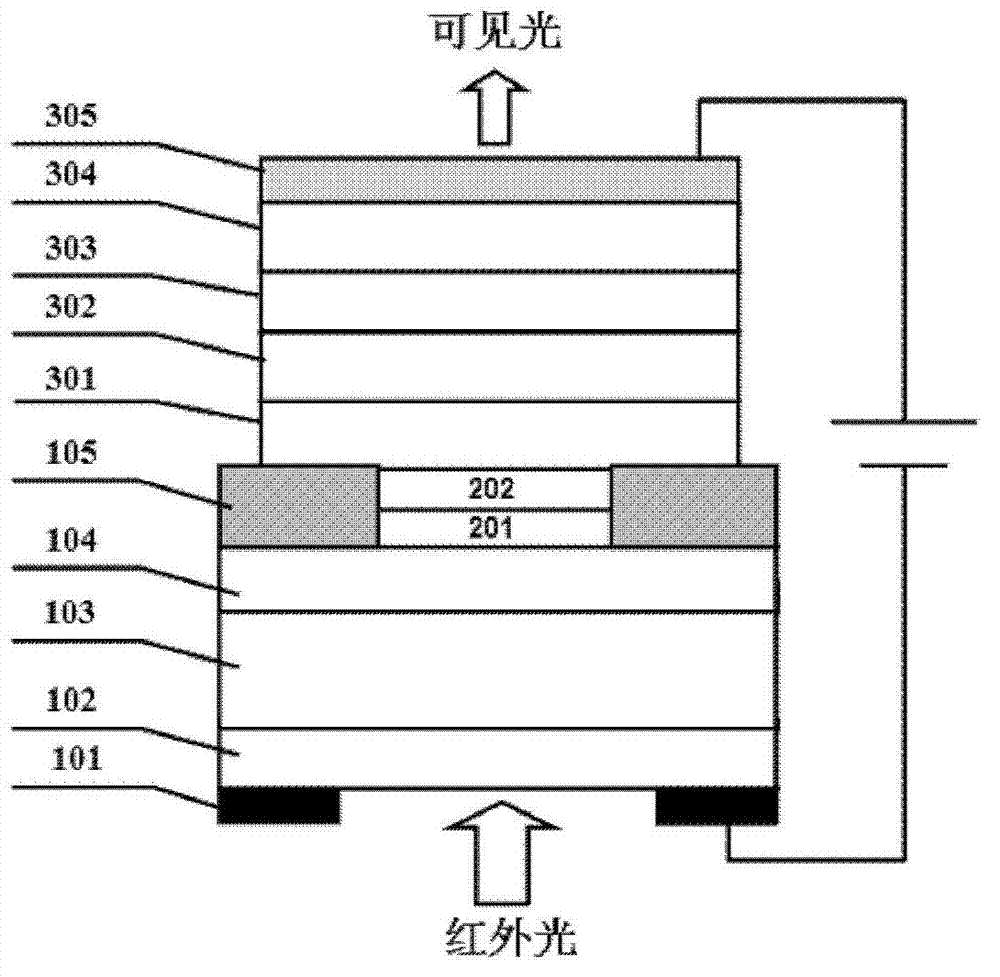
N-type injection infrared wavelength-to-visible wavelength upconversion device and manufacturing device thereof
ActiveCN103165727AImprove the detection rateInhibition imbalanceFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesNight visionLength wave
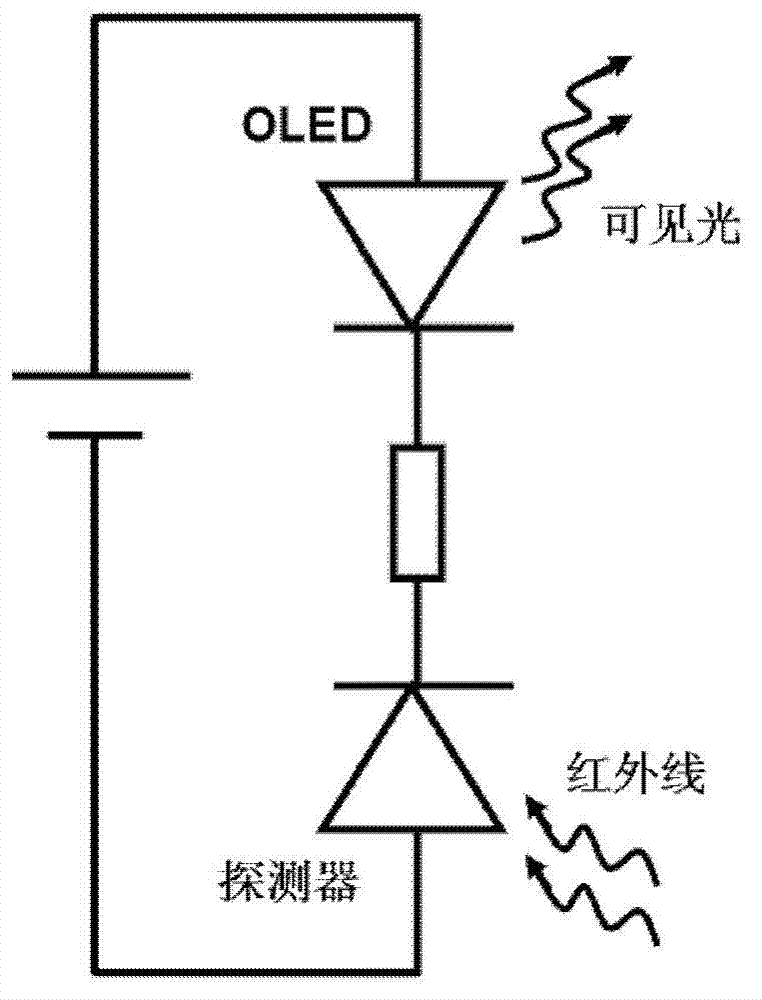
The invention discloses an N-type injection infrared wavelength-to-visible wavelength upconversion device and a manufacturing device thereof. An inverted organic light emitting diode (OLED) is epitaxially grown on an inorganic infrared detector on the lower part. According to a work principle of the device, the infrared detector unit which is reversely biased converts the input infrared signal to an electrical signal, and photoinduced electrons sequentially flow through an N-type spacing layer and a light limiting metal layer and are injected into the OLED which is biased forward, and the OLED is driven to emit visible light, so that the infrared light-to-visible light upconversion can be realized. The provided N-type injection infrared wavelength-to-visible wavelength upconversion device has the characteristics of high conversion efficiency, wide conversion wavelength range, simple manufacturing process, low cost and the like and can be used for fields of infrared night vision, medical detection, industrial fault detection and the like.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Backside illuminated image sensor with reduced dark current
ActiveUS20100006970A1Improve performanceIncreasing image sensor die sizeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantDigital imaging
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
Method for preparing titanium dioxide ultraviolet photoelectric detector
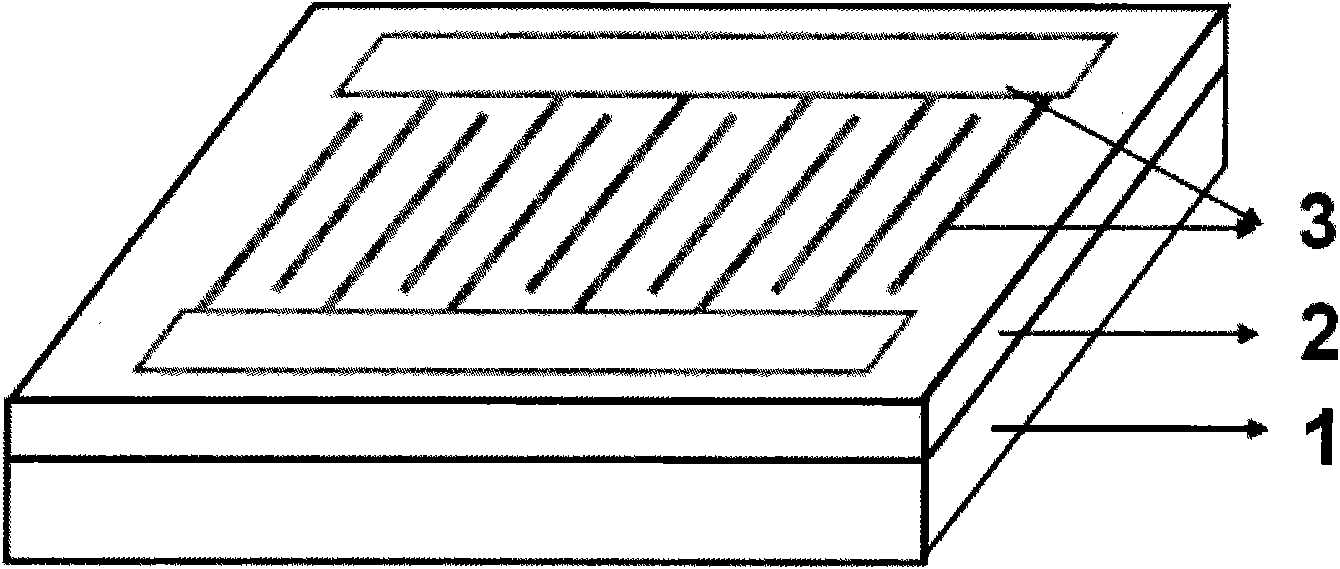
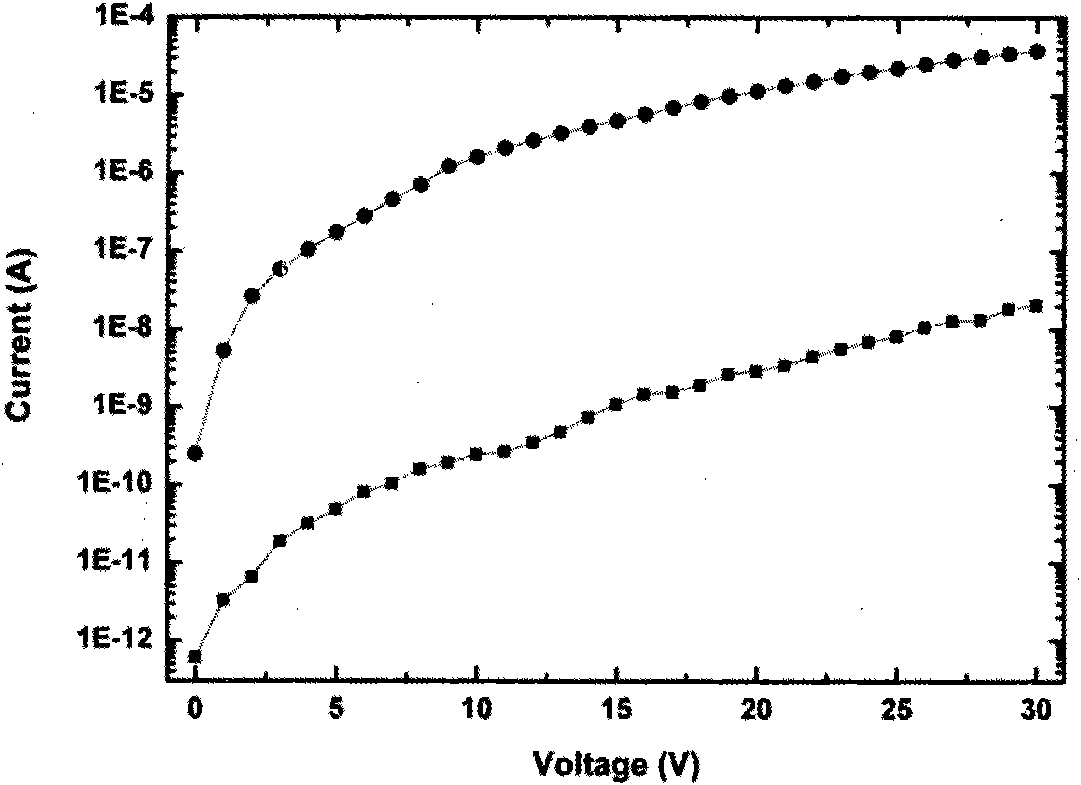
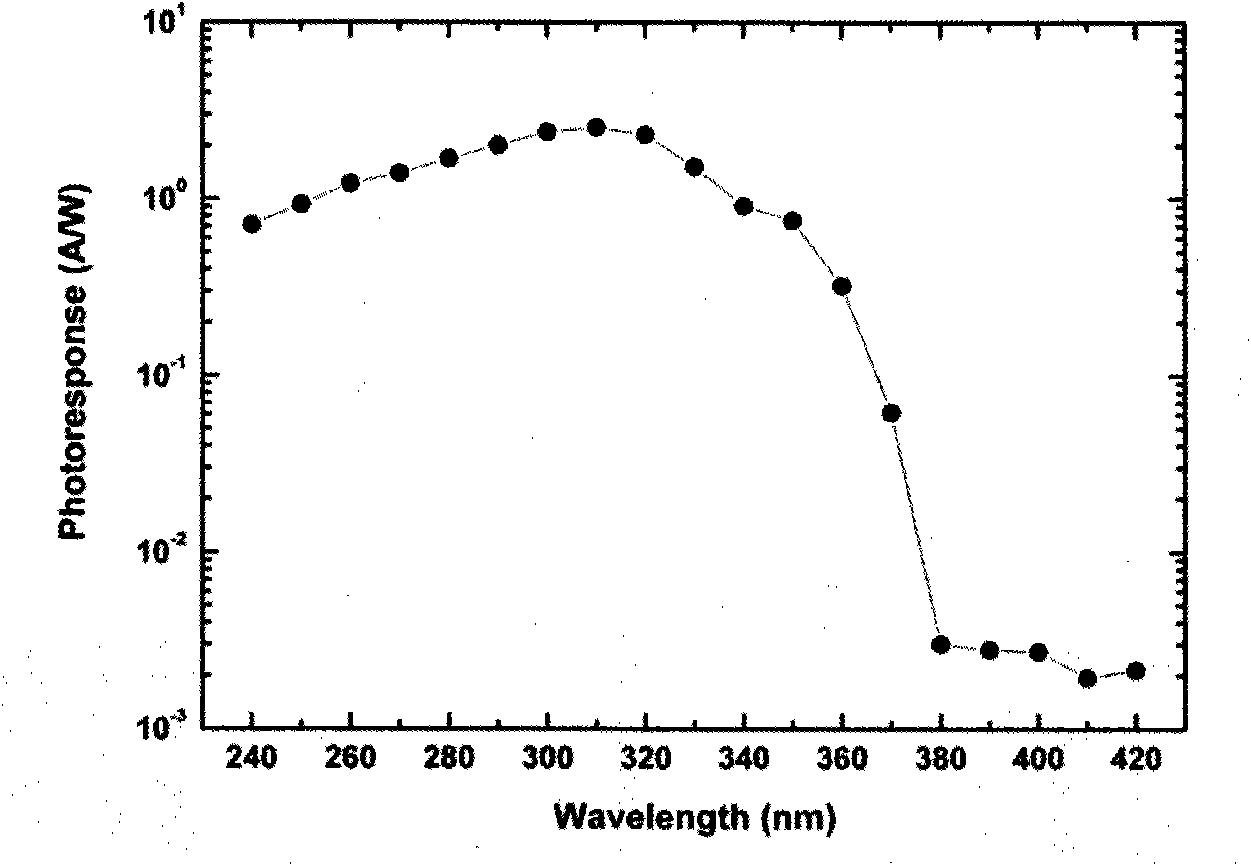
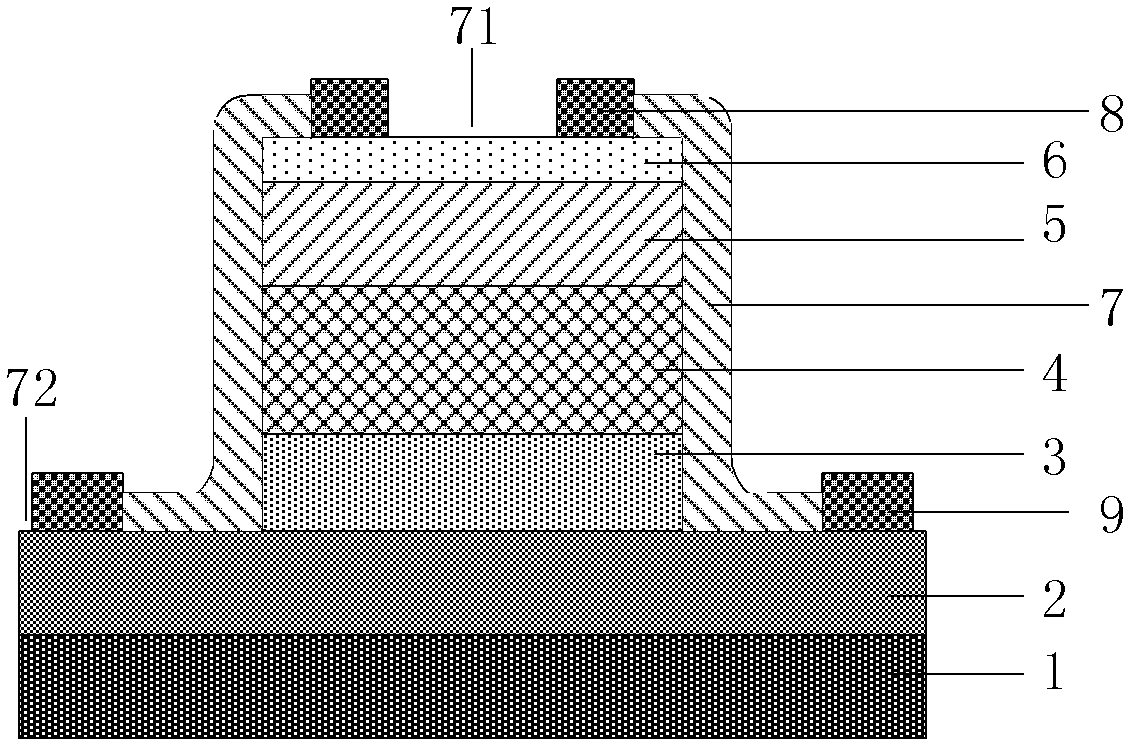
InactiveCN101820016AReduce dark currentImproved UV-Vis suppression ratioFinal product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingUltraviolet detectorsPhotovoltaic detectors
The invention discloses a method for preparing a titanium dioxide ultraviolet photoelectric detector, relates to a semiconductor photoelectric detection device, and provides a titanium dioxide ultraviolet photoelectric detector with low dark current and a preparation method thereof. The detector has a metal-semiconductor-metal structure, and comprises an insulating substrate, a polycrystal TiO2 film deposited on the insulating substrate by using magnetron sputtering technology and an interdigital metal electrode prepared on the TiO2 film by using magnetron sputtering or electron beam evaporation technology from the bottom to the top. The high-quality polycrystal TiO2 film is deposited by adopting optimized sputtering process parameters, and the deposited film has ideal chemical proportion and high compactness and crystallinity. The MSM structural ultraviolet detector prepared by using the film as a matrix has the advantages of high response degree, low dark current, high ultraviolet visible suppression ratio and the like. The preparation method has simple process and low cost; if the detector is manufactured on a Si-based substrate, the method can be compatible with the mature Si process; and the method is favorable for photoelectric integration and easy for industrialization.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
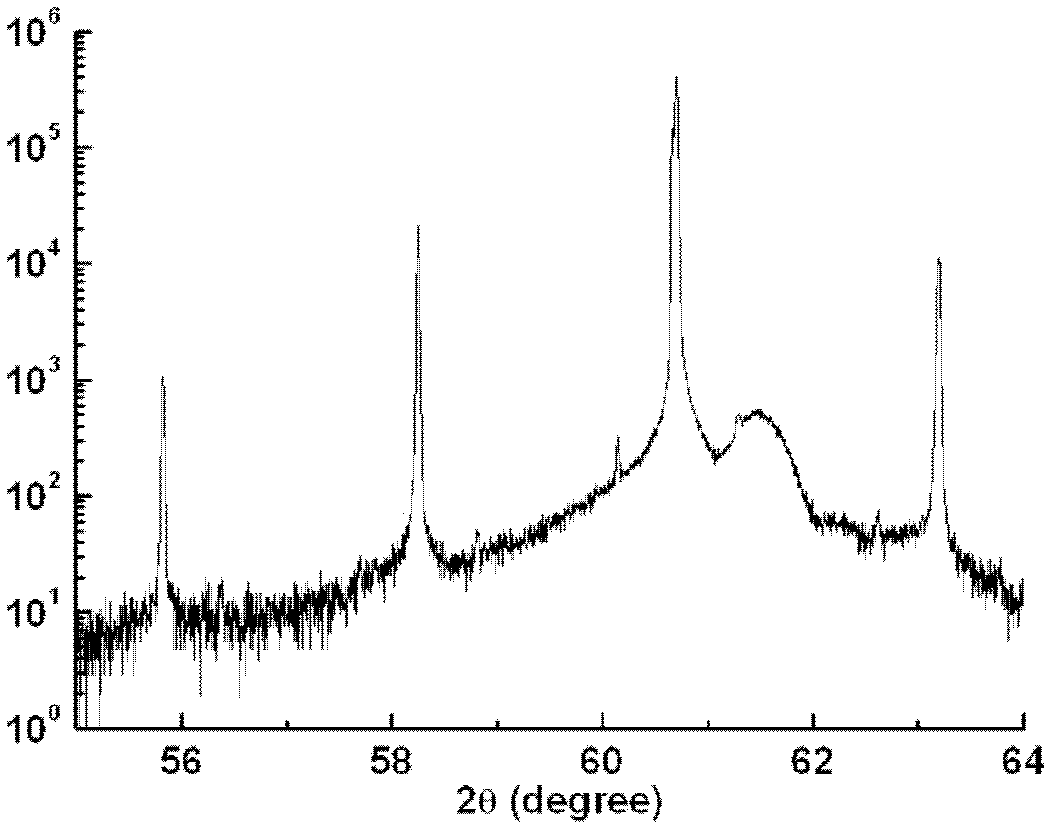
InAs/GaSb secondary category superlattice infrared detector
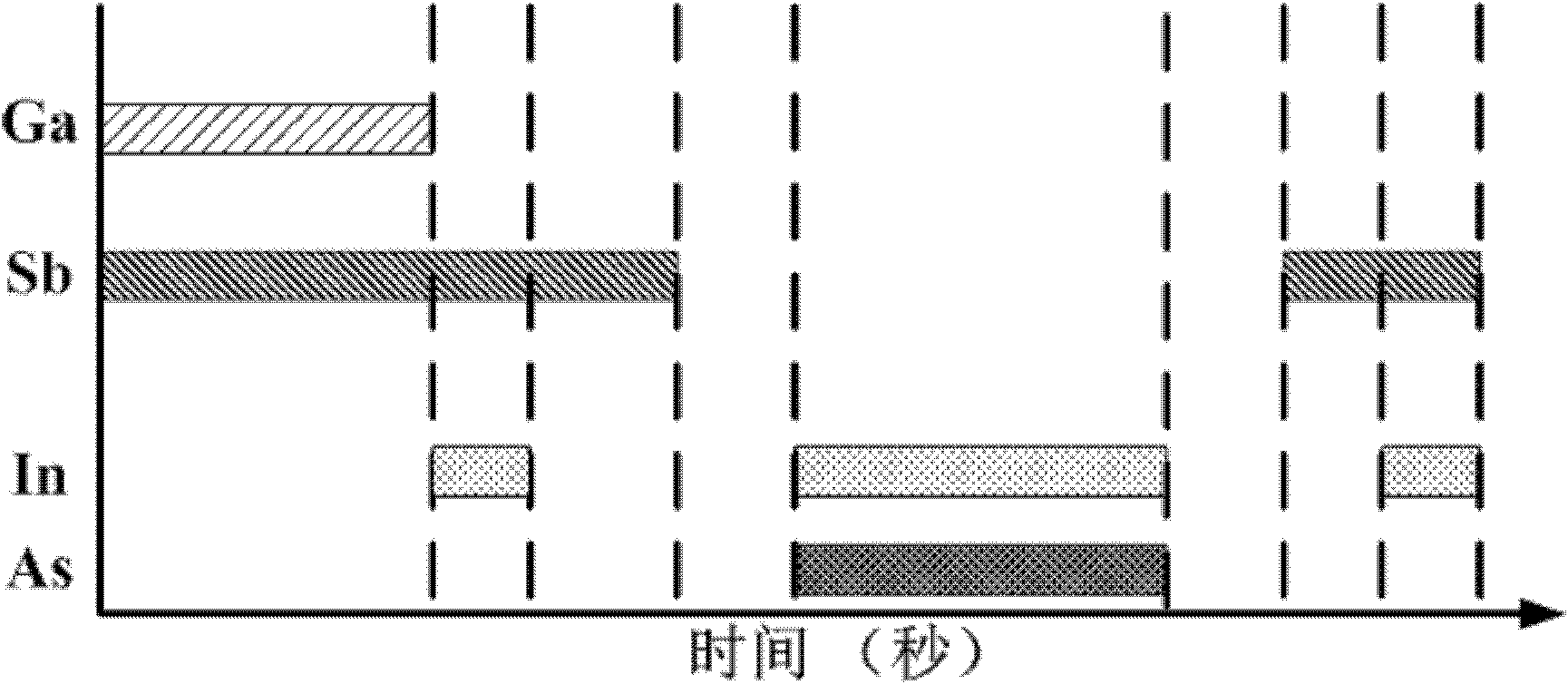
InactiveCN102569484APromote passivationReduce dark currentSemiconductor devicesOhmic contactAbsorption layer
The invention relates to an InAs / GaSb secondary category superlattice infrared detector. The infrared detector comprises: a substrate; a buffer ohmic contact layer, which is manufactured on the substrate; a first secondary category superlattice layer, which is manufactured on the buffer ohmic contact layer so as to enable table tops to be formed at two sides above the buffer ohmic contact layer; an intrinsic secondary category superlattice light absorption layer, which is manufactured on the first secondary category superlattice layer; a second secondary category superlattice layer, which is manufactured on the intrinsic secondary category superlattice light absorption layer; an ohmic contact layer, which is manufactured on the second secondary category superlattice layer; a passivation layer, which covers portions of the table tops at the two sides of the buffer ohmic contact layer, side surfaces of the first secondary category superlattice layer, the intrinsic secondary category superlattice light absorption layer, the second secondary category superlattice layer and the ohmic contact layer as well as two side surfaces on the ohmic contact layer; upper electrodes, which are manufactured at two sides of a light transmission opening; and lower electrodes, which are manufactured inside electrode windows. Specifically, the light transmission opening is arranged in the middle of the passivation layer covering the ohmic contact layer; and the electrode windows are respectively arranged on the two table tops at two sides of the passivation layer covering the buffer ohmic contact layer.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
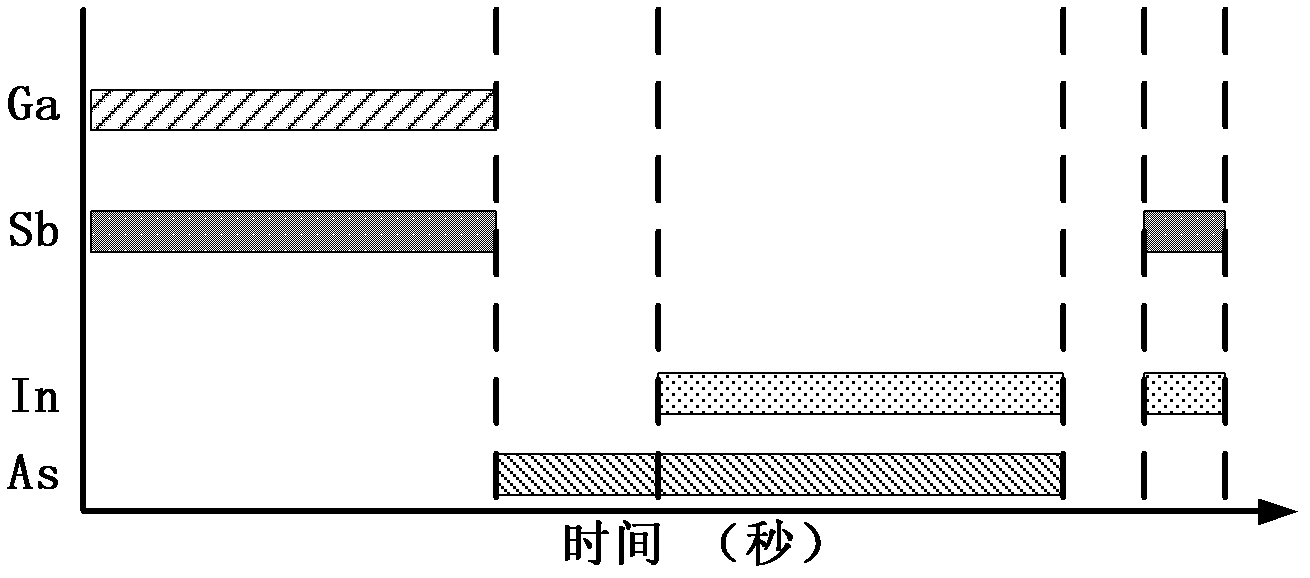
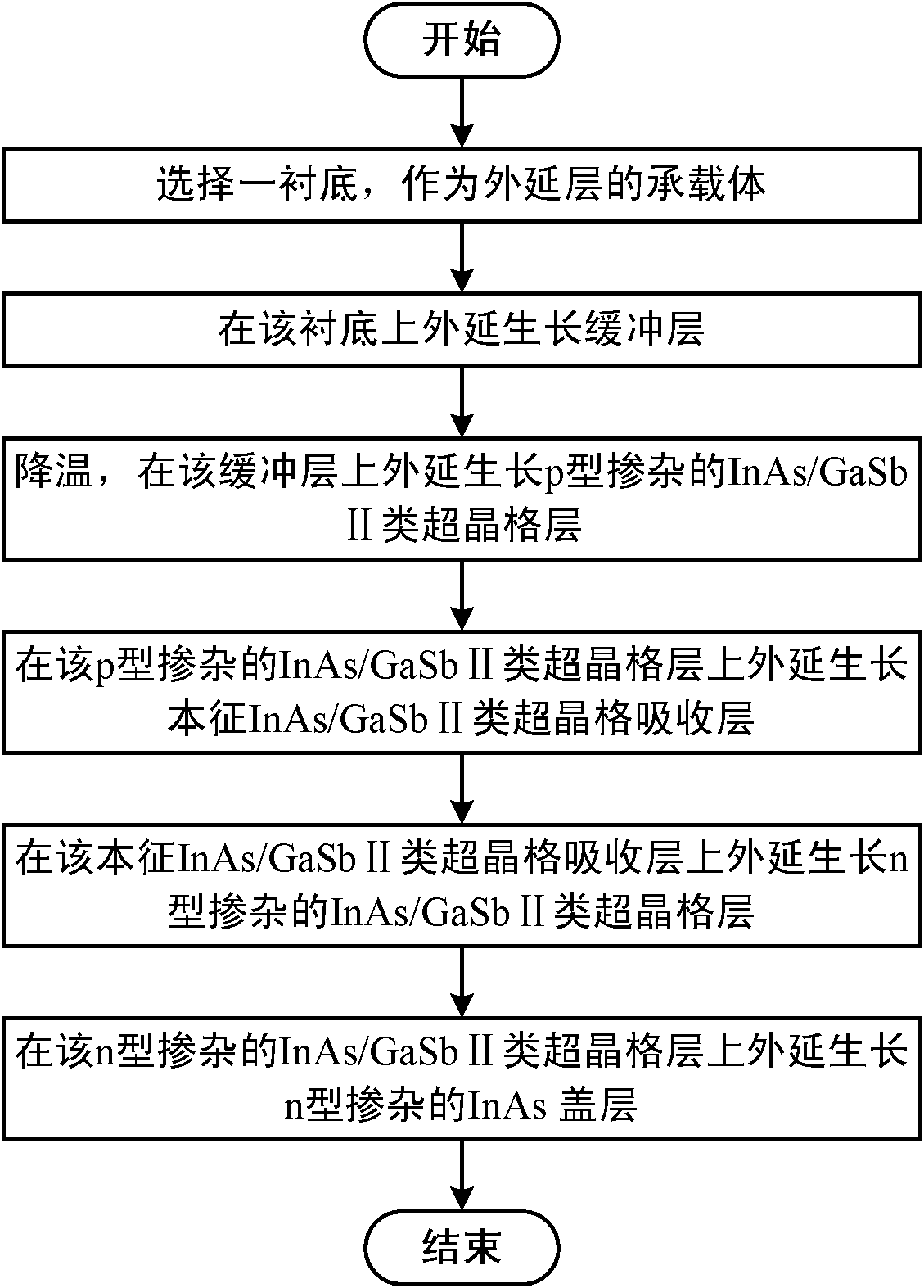
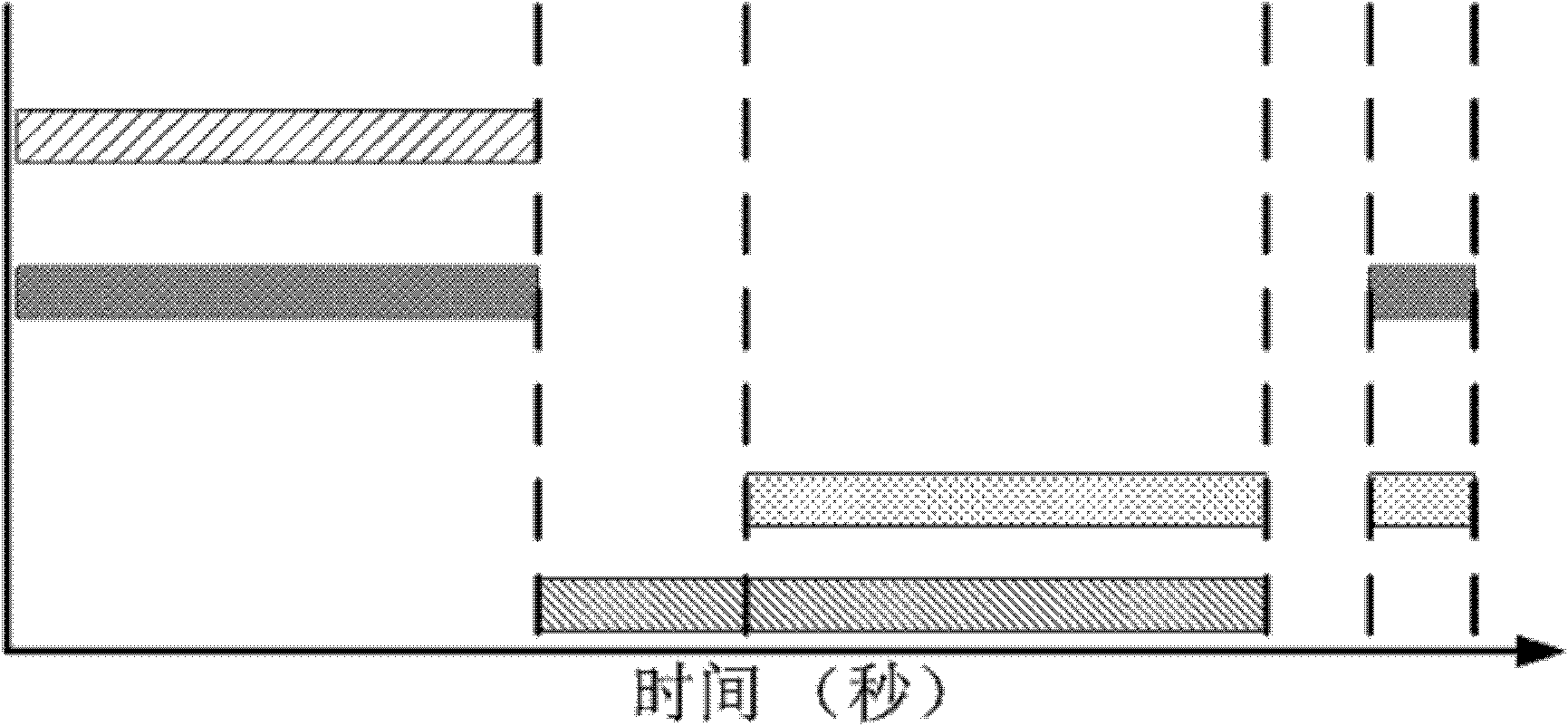
Method for epitaxially growing type-II superlattice narrow-spectrum infrared photoelectric detector material
InactiveCN102534764APromote growthImprove crystal qualityPolycrystalline material growthFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic detectorsP type doping
The invention discloses a method for epitaxially growing an InAs / GaSb type-II superlattice narrow-spectrum infrared photoelectric detector material. The method comprises the following steps of: selecting a substrate as a supporting body of an epitaxial layer; epitaxially growing a buffer layer on the substrate; cooling, and epitaxially growing a p-type doped InAs / GaSb type-II superlattice layer on the buffer layer; epitaxially growing an intrinsic InAs / GaSb type-II superlattice absorbing layer on the p-type doped InAs / GaSb type-II superlattice layer; epitaxially growing an n-type doped InAs / GaSb type-II superlattice layer on the intrinsic InAs / GaSb type-II superlattice absorbing layer; and epitaxially growing an n-type doped InAs cover layer on the n-type doped InAs / GaSb type-II superlattice layer to finish the epitaxial growth of the InAs / GaSb type-II superlattice narrow-spectrum infrared photoelectric detector material.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Pixel circuit with surface doped region between multiple transfer transistors and image sensor including the same
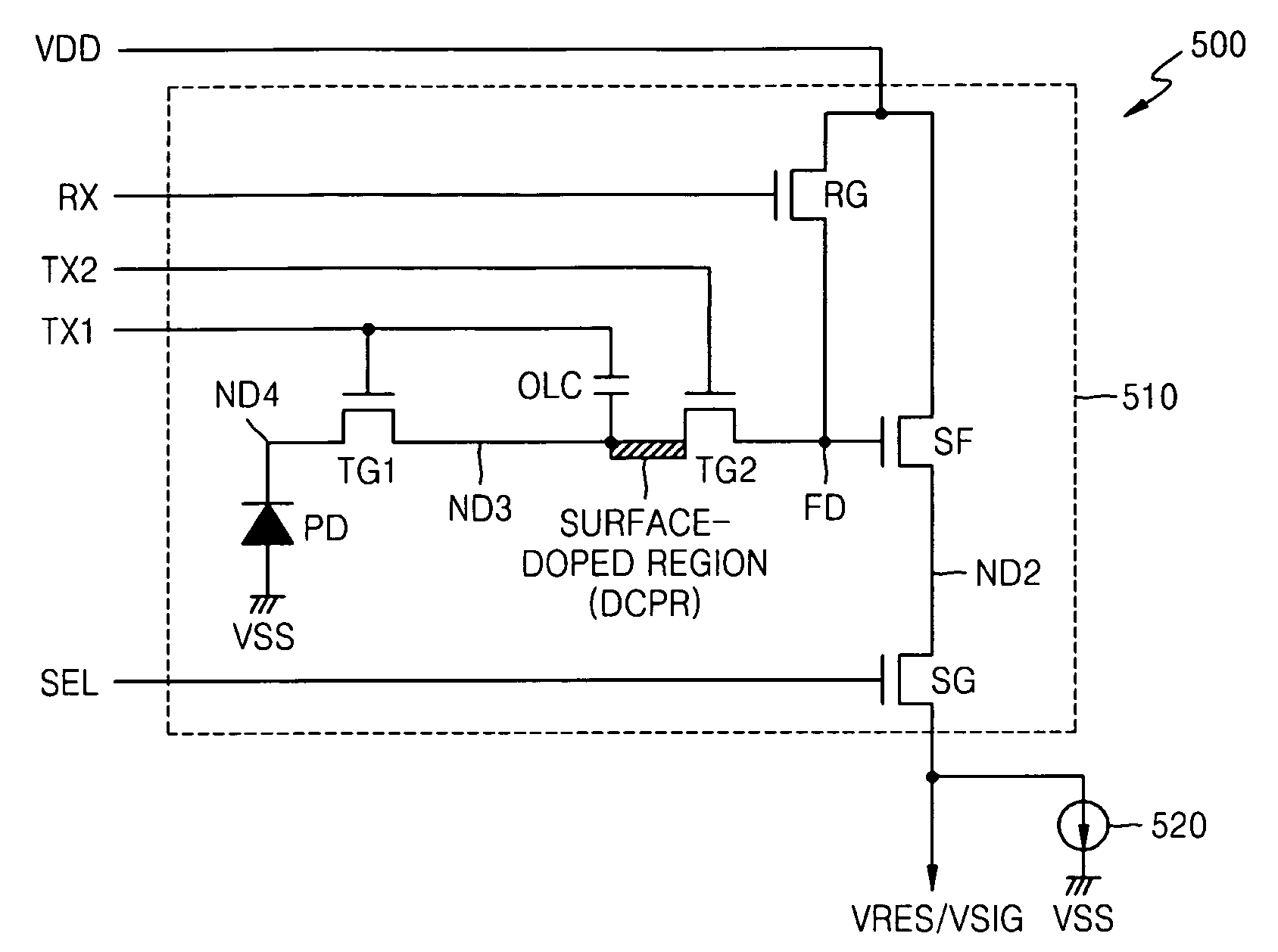
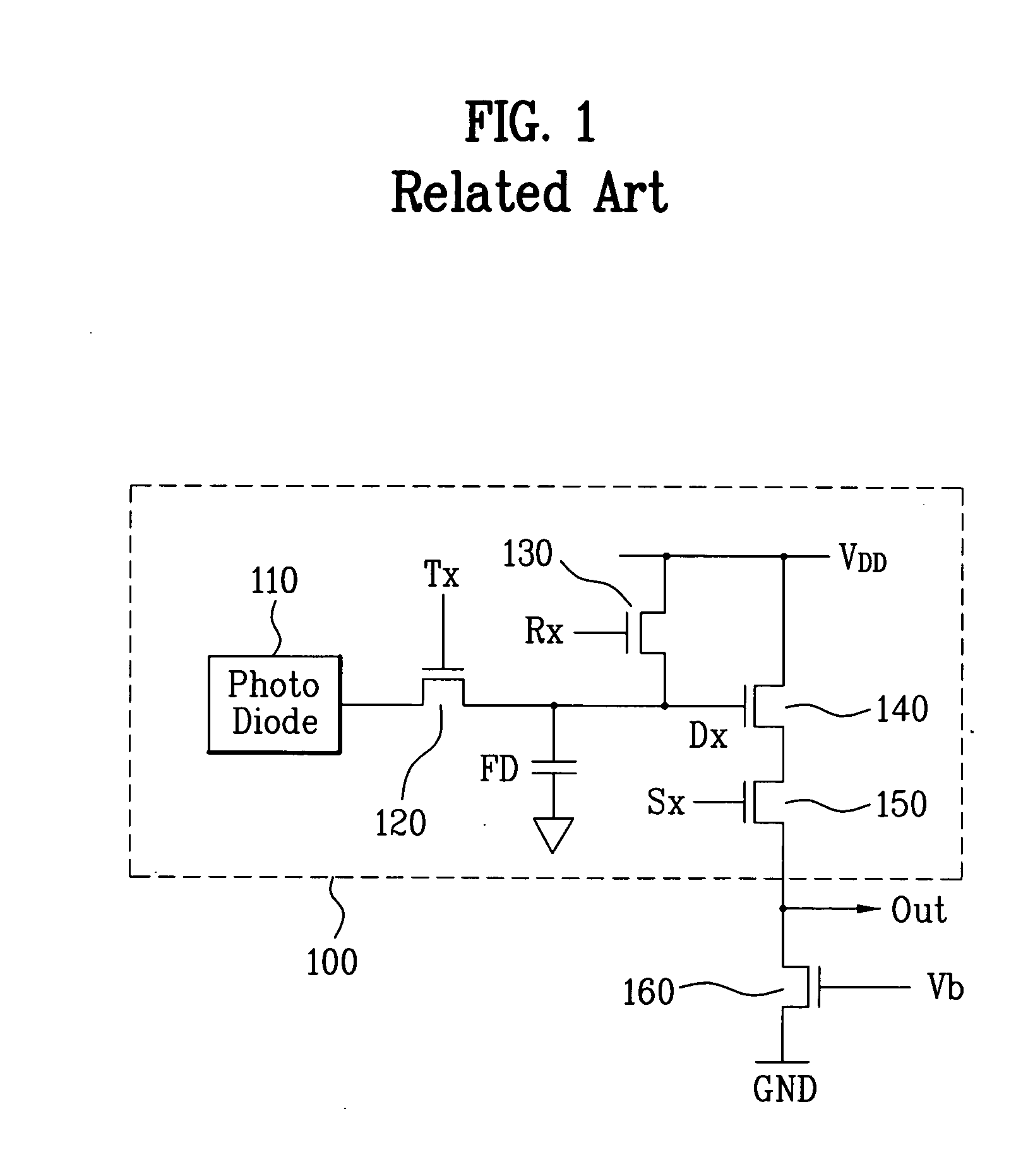
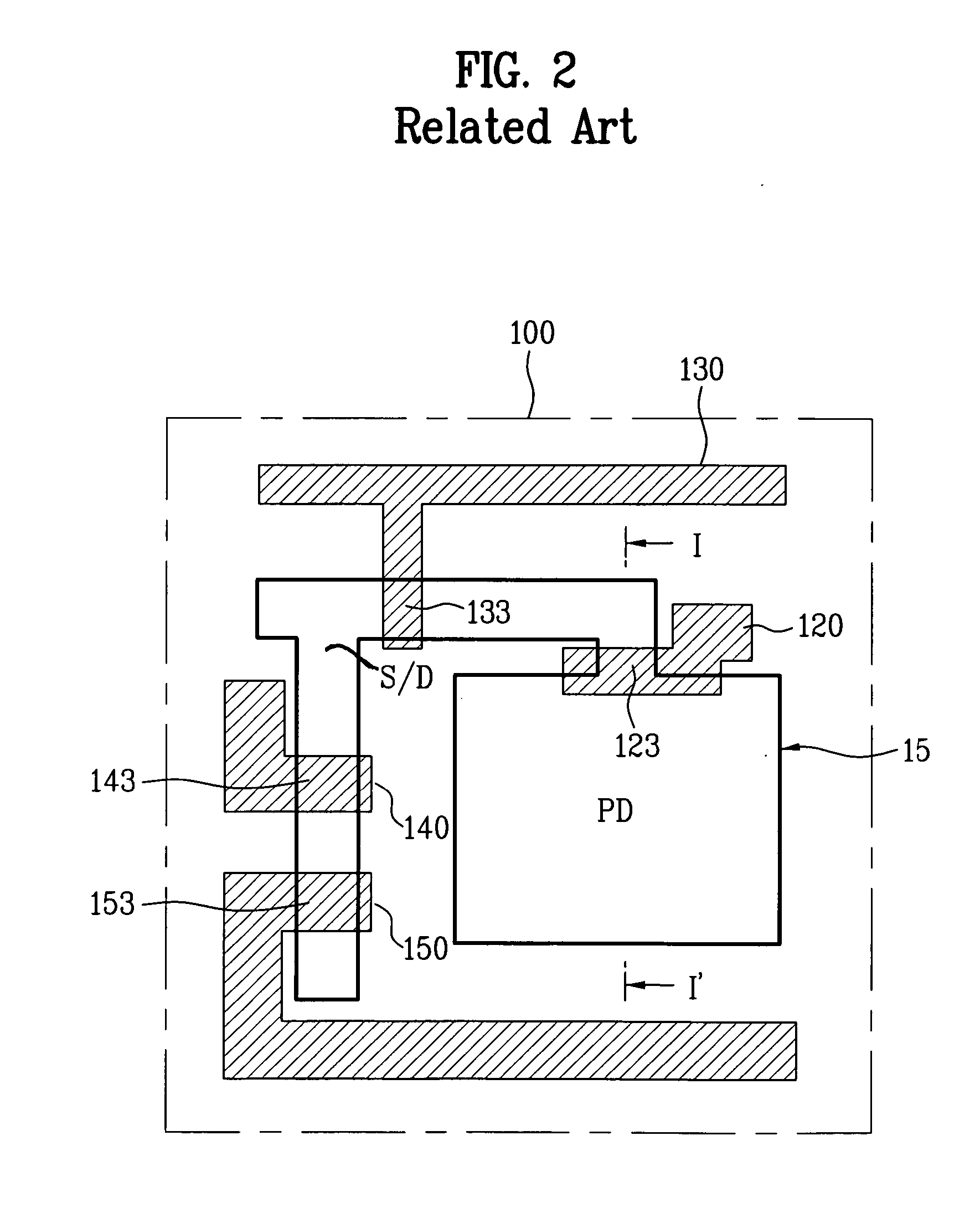
ActiveUS7414233B2Avoid dark currentReduce dark currentTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsFloating diffusionImage signal
A pixel circuit of an image sensor includes a photo-converting unit such as a photo-diode for generating charge from incident light. The pixel circuit also includes a charge storing capacitor for storing the charge generated by the photo-converting unit. The pixel circuit further includes a floating diffusion node that receives the charge from the charge storing unit after being reset. Thus, an image signal VSIG is generated after a reset signal VRES is generated from the pixel circuit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Silicon-based germanium photodetector
The present invention discloses a silicon-based germanium photodetector. The silicon-based germanium photodetector comprises an optical waveguide layer, a silicon oxide layer and a silicon substrate which are sequentially stacked from top to bottom; the optical waveguide layer includes an optical coupling region, a planar optical waveguide region and an optical output region which are distributed sequentially along the propagation direction of optical signals; a coupling grating for receiving the optical signals and guiding the optical signals to the planar optical waveguide region is formed in the coupling region; and the silicon-based germanium photodetector further comprises a germanium layer stacked on the optical output region, a silicon covering layer stacked on the germanium layer, a first electrode formed on the silicon covering layer, and a second electrode formed on the optical output region, wherein the germanium layer receives the optical signals from the optical output region and converts the optical signals into electrical signals. According to the silicon-based germanium photodetector of the invention, the silicon covering layer is adopted, so that bandwidth is greatly improved, the dark current of the device is greatly reduced, and therefore, the comprehensive performance index of the device can be improved, and the requirements of high-speed optical communication and optical interconnection systems can be better satisfied.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Manufacturing method for a solid-state image sensor
ActiveUS20100203667A1Reduce dark currentSufficient saturation loadSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIonTransducing Unit
A manufacturing method for a solid-state image sensor, the method comprises the steps of: forming a charge storage region in a photoelectric converting unit by implanting a semiconductor substrate with ions of an impurity of a first conductivity type, using a first mask; heating the semiconductor substrate at a temperature of no less than 800° C. and no more than 1200° C. through RTA (Rapid Thermal Annealing); forming a surface region of the charge storage region by implanting the semiconductor substrate with ions of an impurity of a second conductivity type, using a second a mask; heating the semiconductor substrate at a temperature of no less than 800° C. and no more than 1200° C. through RTA (Rapid Thermal Annealing); and forming an antireflection film that covers the photoelectric converting unit at a temperature of less than 800° C., after the step of forming the surface region, in this order.
Owner:CANON KK
Vehicular visible light wireless digital voice communication system
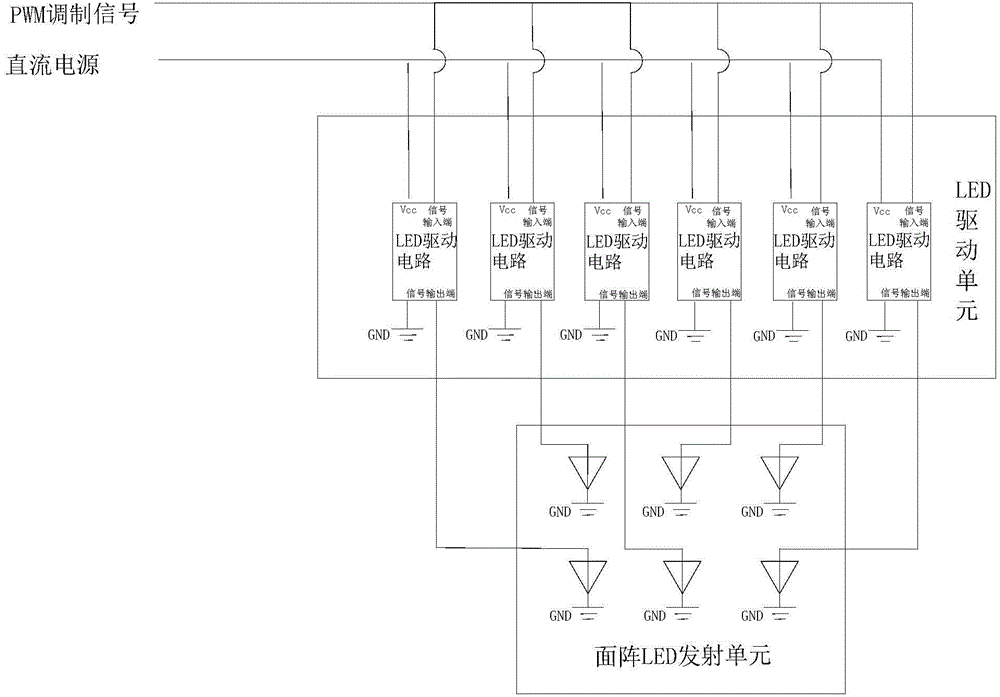
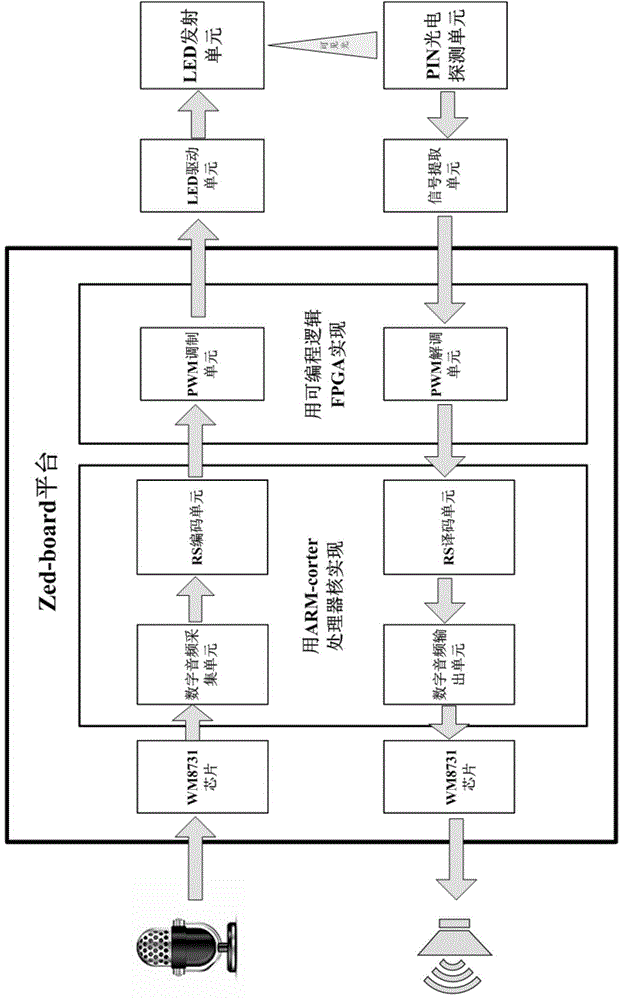
InactiveCN104485993AImplement instant voice communication technologySave spaceClose-range type systemsFrequency spectrumVoice communication
The invention discloses a vehicular visible light wireless digital voice communication system. The vehicular visible light wireless digital voice communication system comprises a sending module and a receiving module. The sending module comprises a digital audio acquisition unit, an RS coding unit, a PWM (pulse width modulation) unit, an LED (light emitting diode) drive unit and an LED transmitting unit, which are connected successively in circuit; the receiving module comprises a PIN photoelectric detection unit, a signal extraction unit, a PWM modulation unit, an RS decoding unit and a digital audio output unit, which are connected successively in circuit. The wireless digital voice communication system realizes instant voice communication between strange vehicles; an LED-based lamp is integrated with automobile lighting and communication without the need of an additional signal emission source installation space and occupation of scarce frequency spectrum resource. The voice signal transmission is high-speed and reliable, high in integration level, strong in anti-interference ability and low in cost, and bigger communication distance and more reliable communication are realized; moreover, a detector has high accuracy, high responsivity, low dark current, higher communication rate, stronger anti-interference ability and high reliability of a transmission channel.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Image sensor and method of driving transfer transistor of image sensor
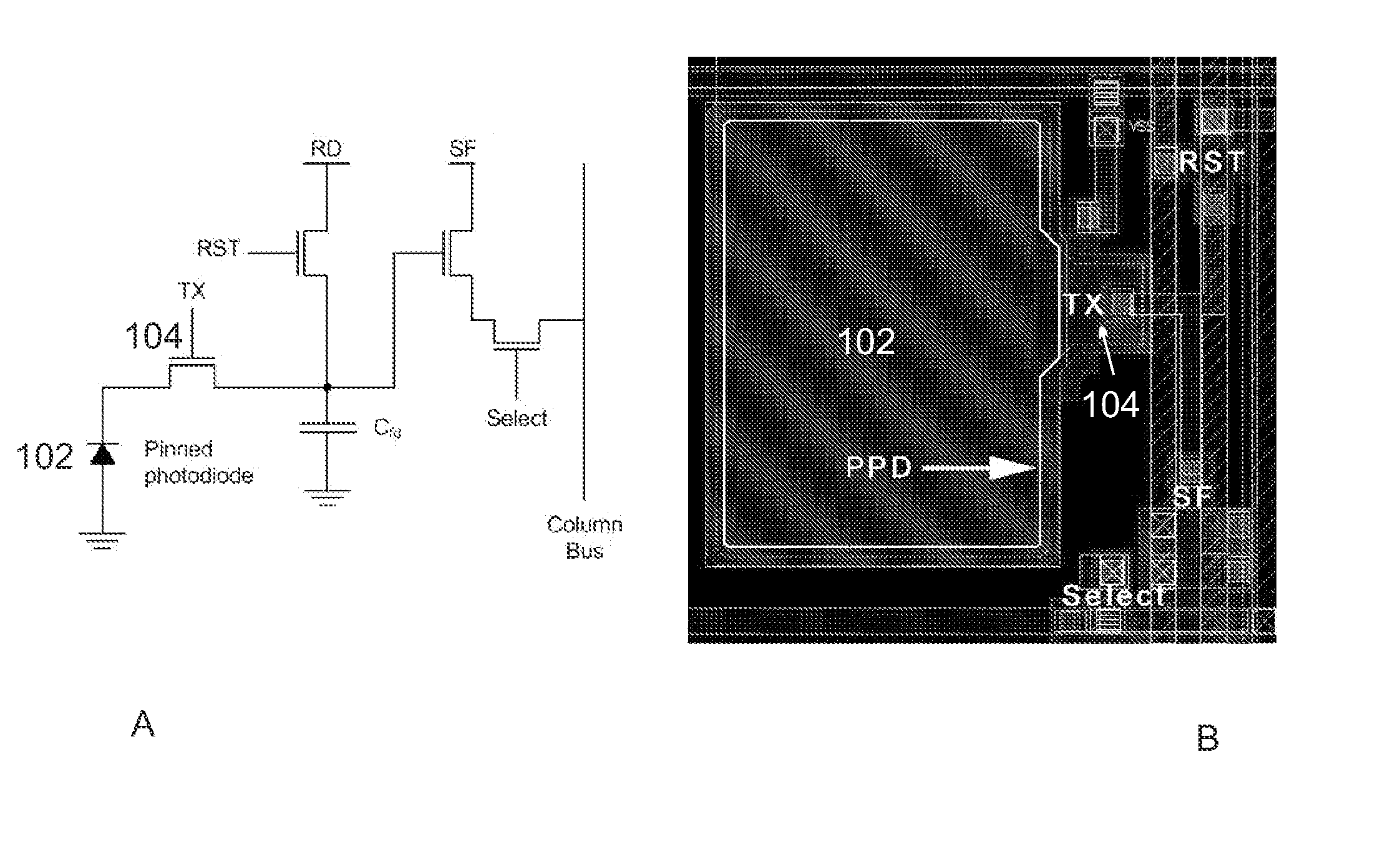
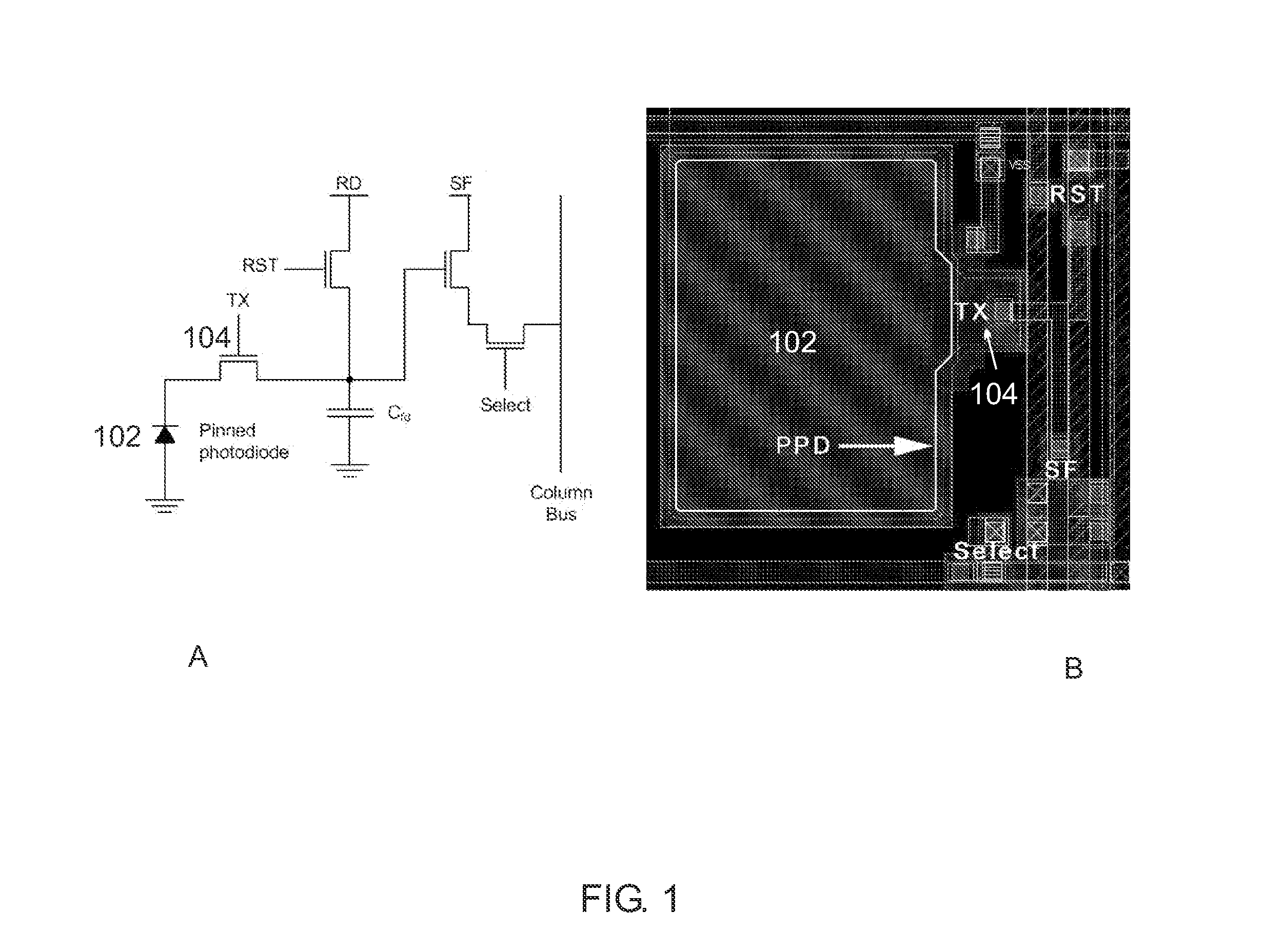
ActiveUS20070145239A1Reduce noiseReduce dark currentTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsEngineeringFloating diffusion
Provided is a 4-transistor CMOS image in which a driving condition or a pixel structure is changed so that a transfer transistor in a pixel operates in a pinch-off condition during reset and transfer operations in order to reduce dark current and fixed-pattern noise caused by a change in an operation condition of the transfer transistor and inter-pixel characteristic discrepancy. The image sensor includes a photosensitive pixel including a transfer transistor for transferring photon-induced charges created in a photodiode; and a voltage control unit for controlling a turn-on voltage applied to a gate of the transfer transistor to be lower than a floating diffusion node voltage plus the threshold voltage of the transfer transistor during a partial or entire section of a turn-on section of the transfer transistor such that the transfer transistor operates in a pseudo pinch-off mode.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
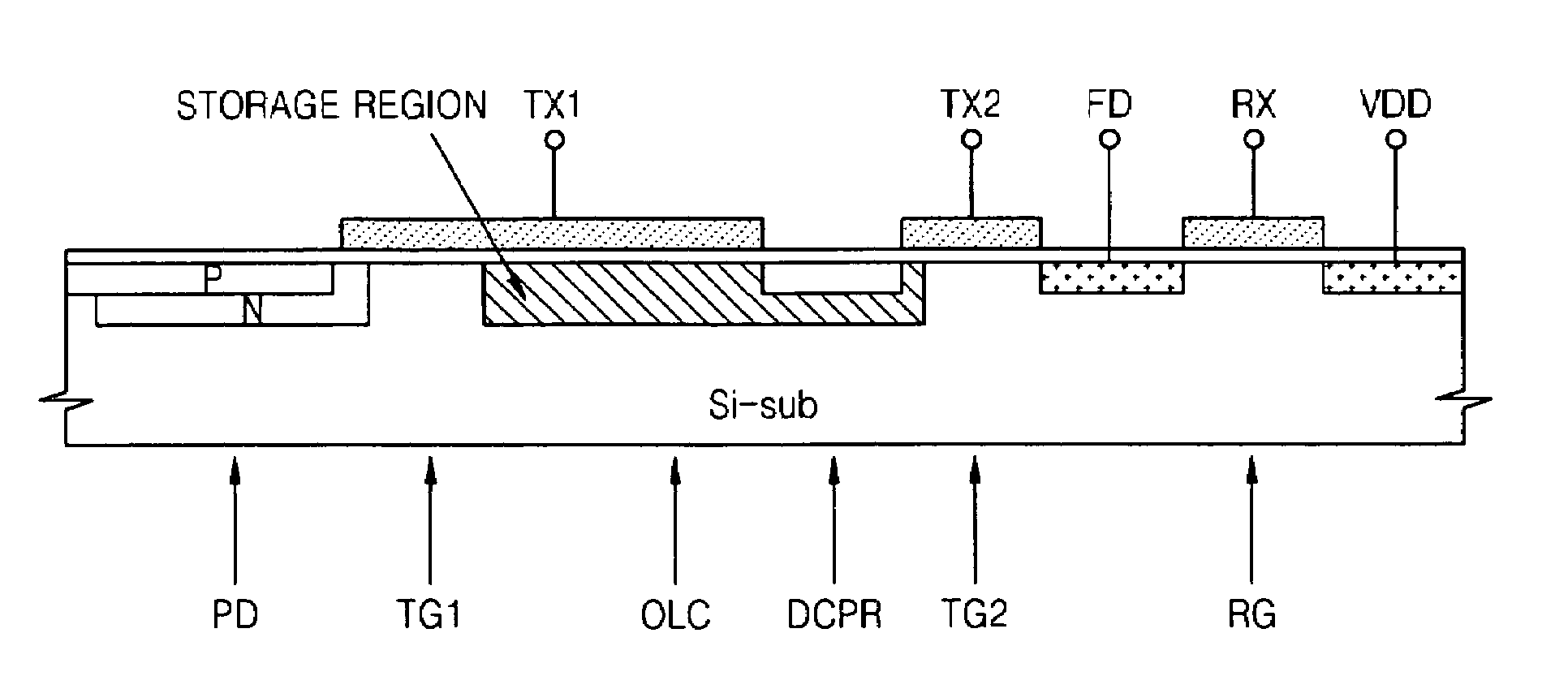
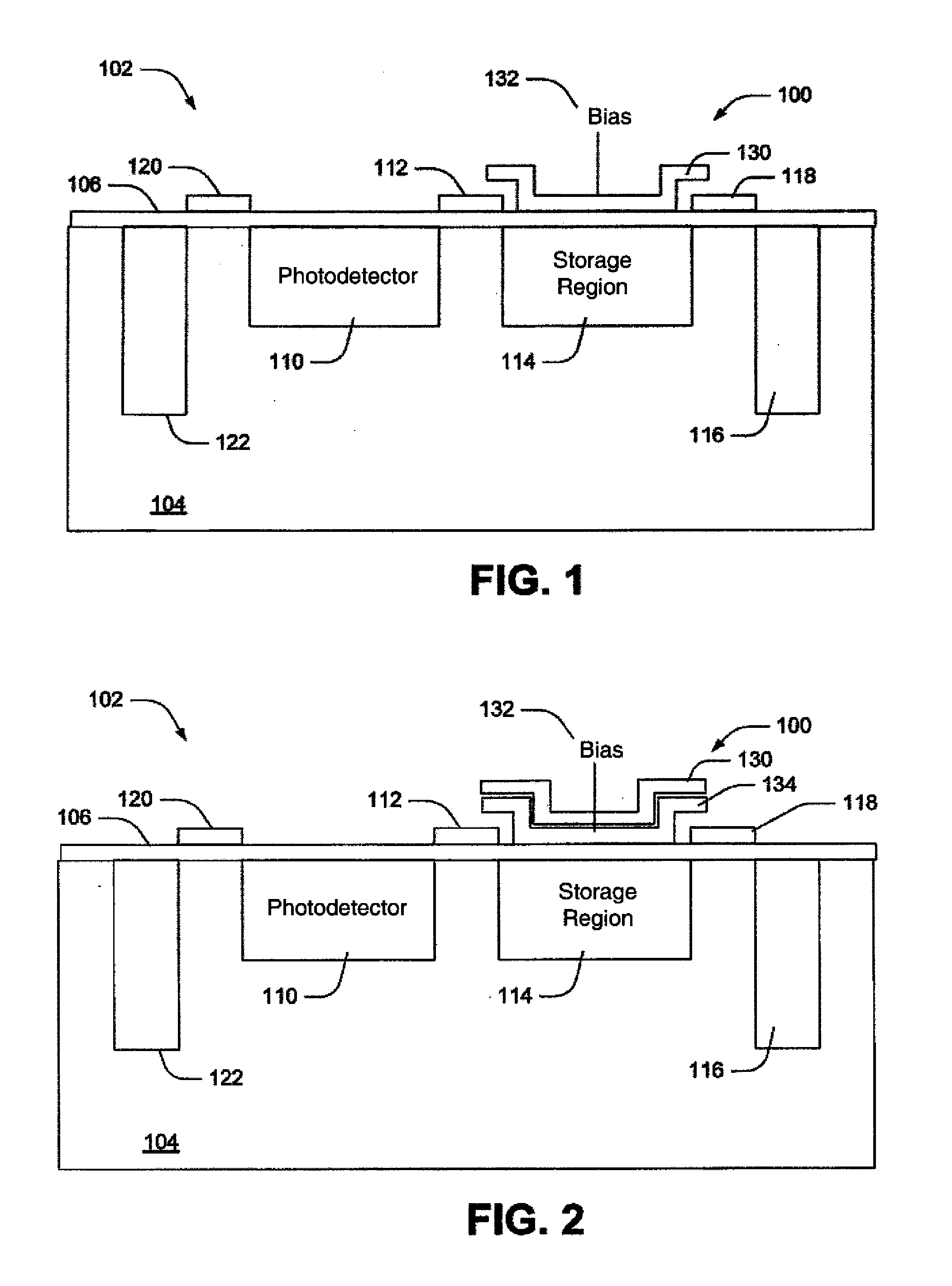
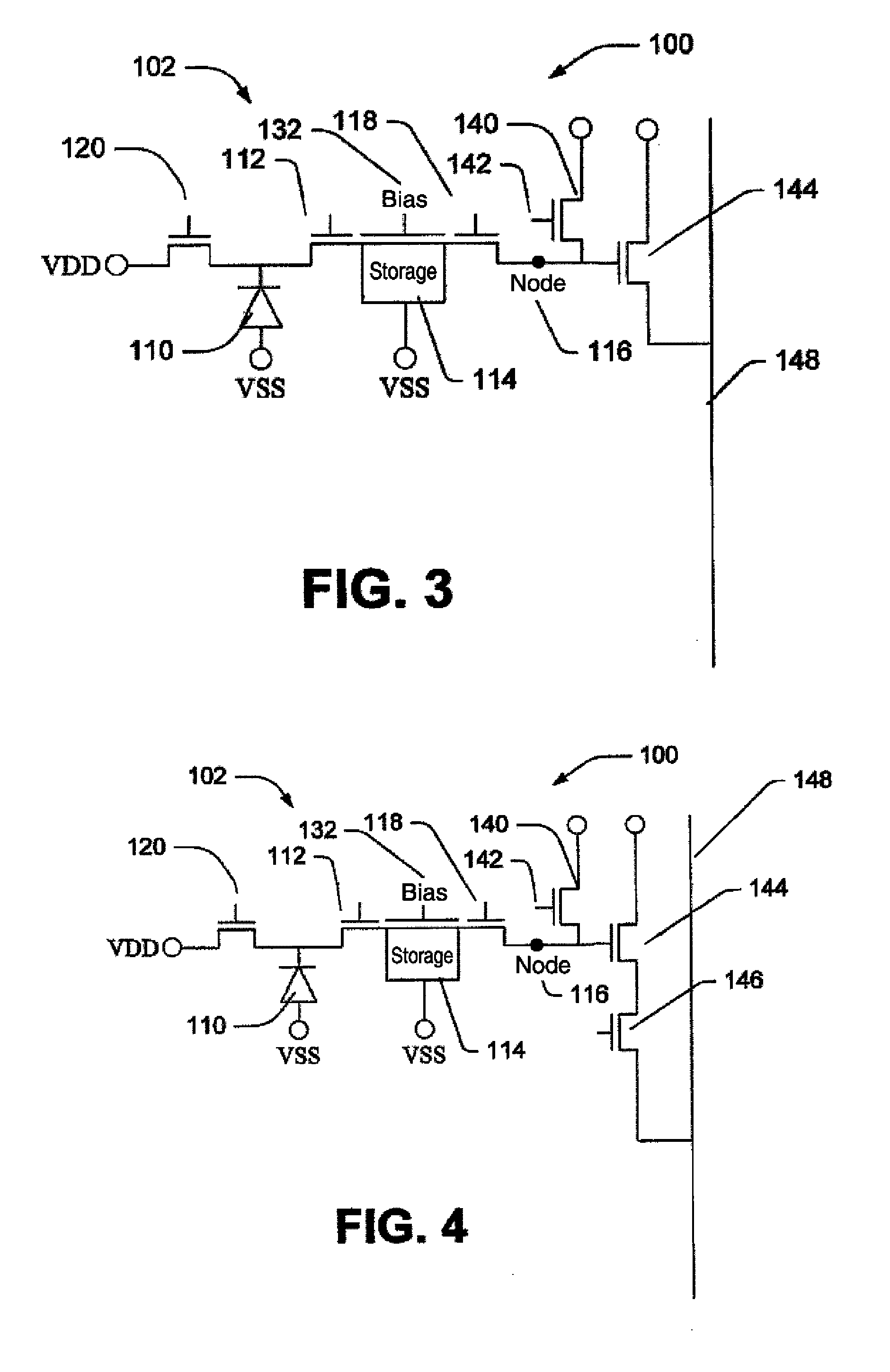
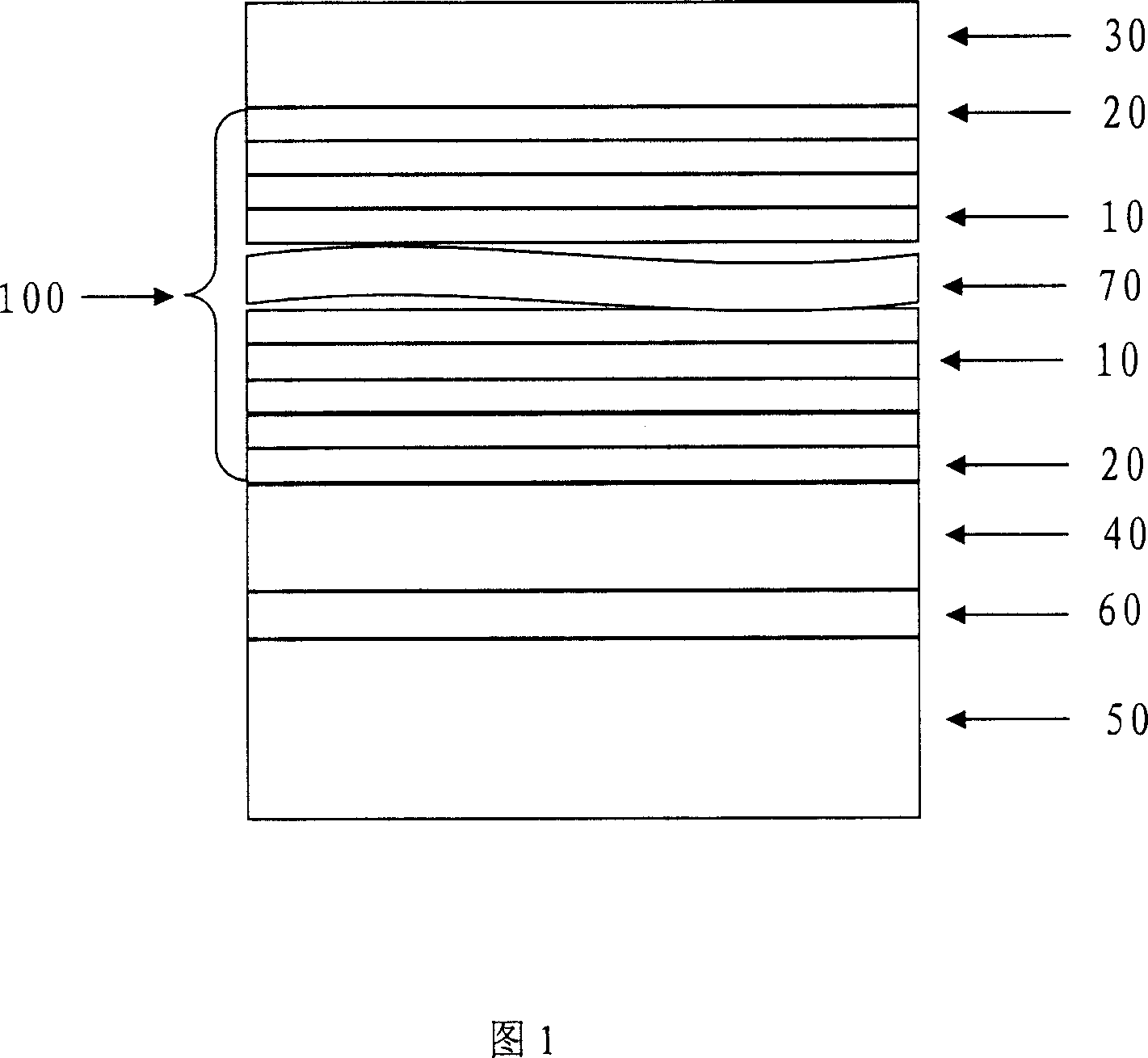
Image sensor and method to reduce dark current of CMOS image sensor
InactiveUS20090219418A1Reduce dark currentTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsCMOSPhotovoltaic detectors
An image sensor includes one or more photodetectors for collecting charge in response to incident light and a storage region adjacent each photodetector. A transfer mechanism transfers charge from each photodetector to a respective storage region. A conductive layer or a polysilicon layer is situated over each storage region. A bias voltage terminal is connected to each conductive layer or polysilicon layer for receiving a bias voltage to bias the conductive layer or polysilicon layer to a predetermined voltage level.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
InGaN series broad band solar battery comprising multiple quanta structure
InactiveCN1929153AReduce dark currentAchieving Energy Conversion EfficiencyPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesUnderlayBroadband
This invention relates to InGaN wide spectrum solar battery with several well structures, which comprises one underlay, one transit layer, P shape InGaN layer, several quanton well structure layer, n shaoe InGaN layer, wherein, the structure layer is composed of two different InGaN alloy materials with one of thin band InxwGa1-xwN alloy to form quanton well and with second of wide gap InxbGa1-xbN alloy. The battery uses InGaN alloy materials quanton well structure to process solar energy battery absorptive area.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
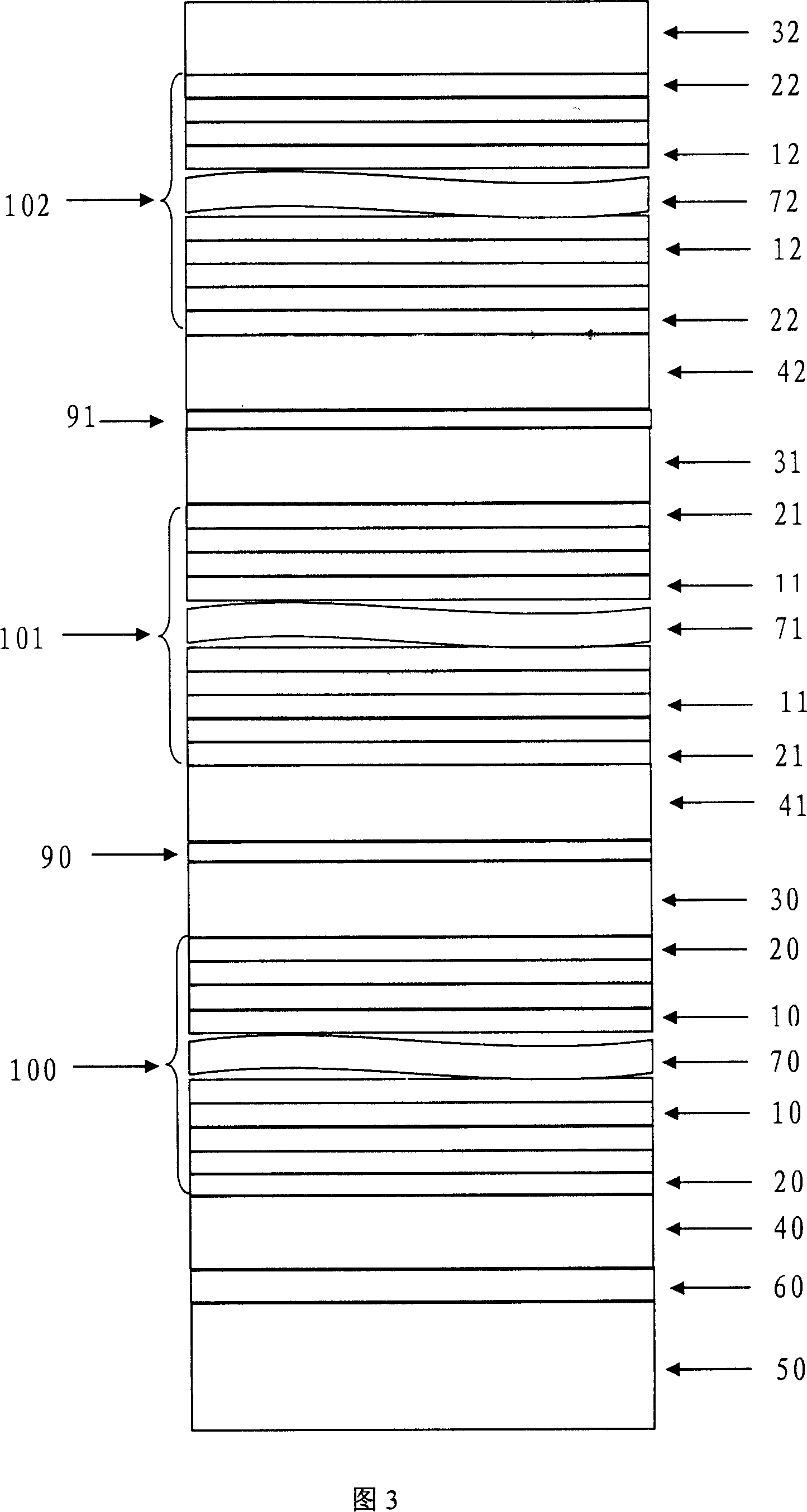
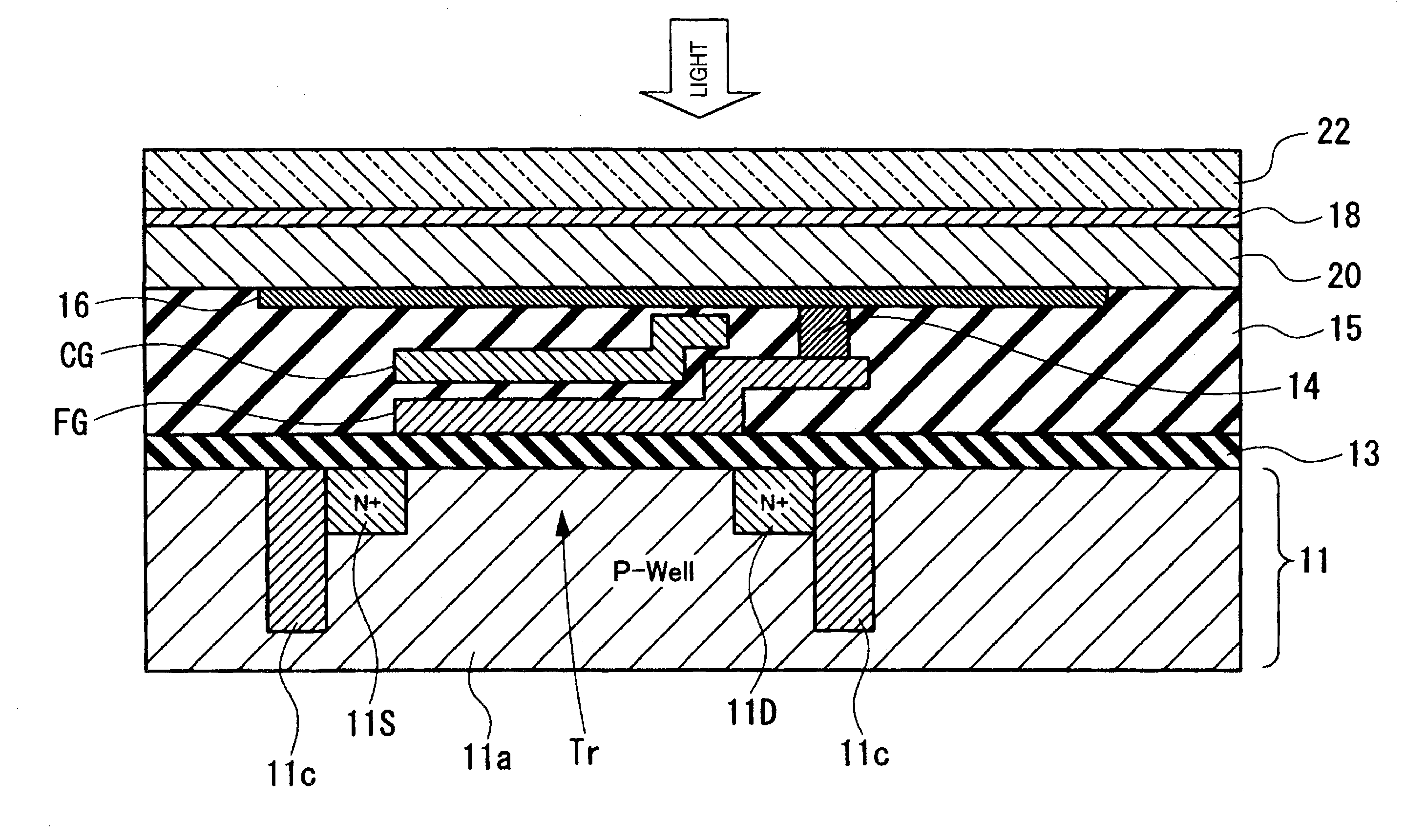
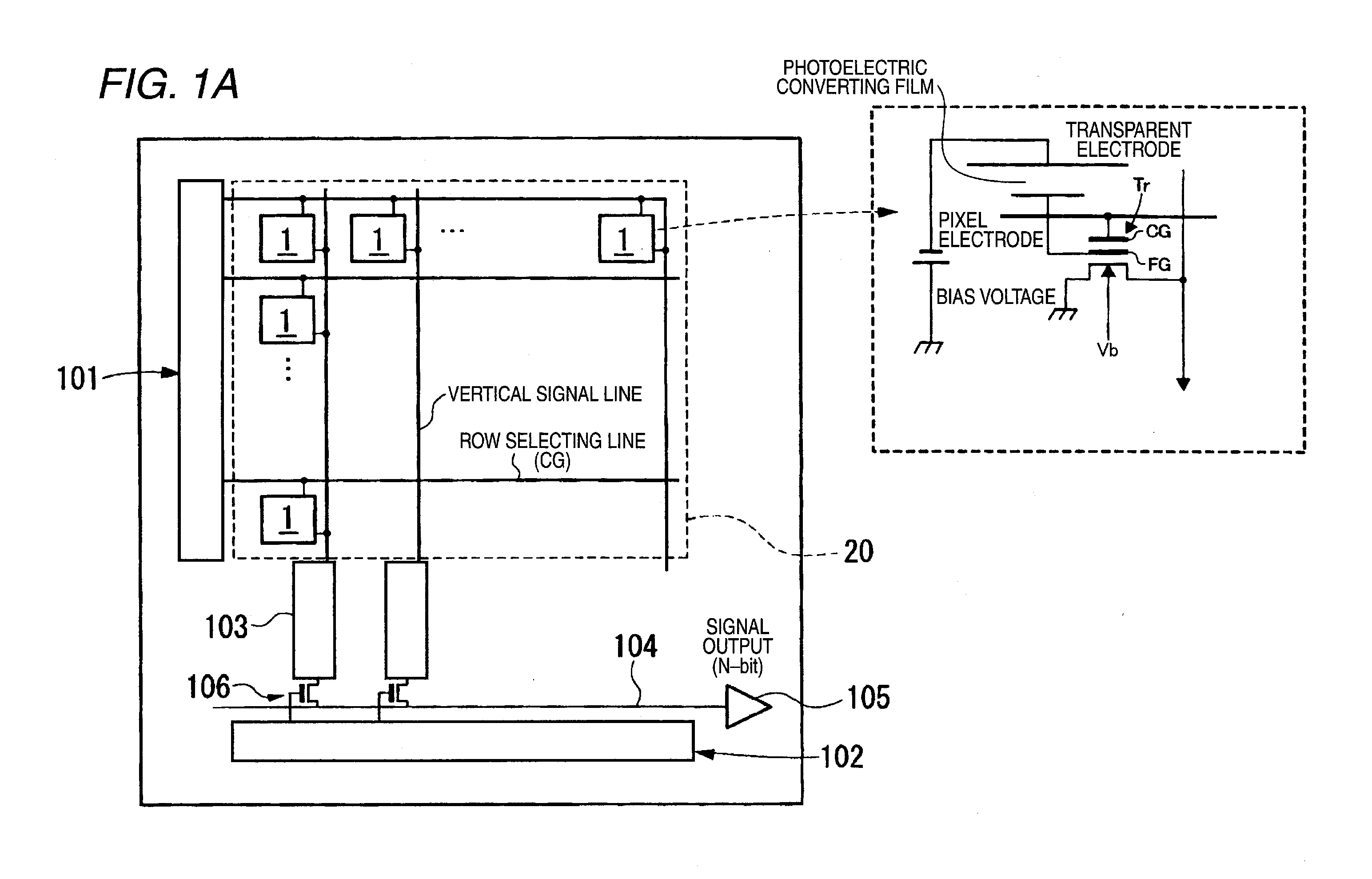
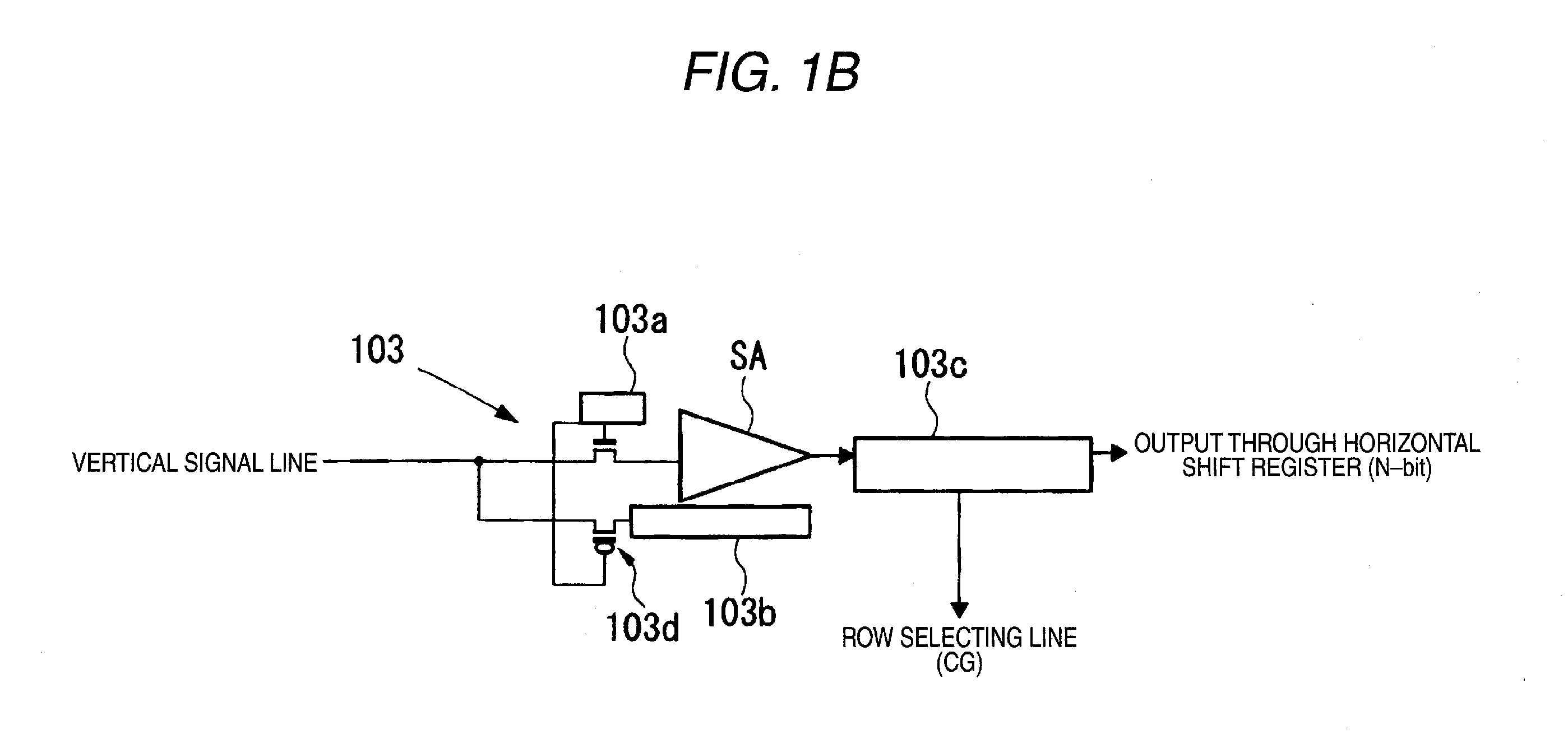
Imaging device, method of driving imaging device and imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20100053386A1Avoid desensitizationImprove finenessTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsEngineeringDrain current
An imaging device includes: a semiconductor substrate; a photoelectric converting film that is forms on the semiconductor substrate and that generates charges corresponding to an incident light; a plurality of pixel portions that receive the charges from the photoelectric converting film, a floating gate that is electrically connected to the photoelectric converting film; and a transistor that fluctuates a threshold voltage so as to start to increase a drain current when an electric potential of the floating gate changes.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Ultraviolet light detector with titanium dioxide nanotube array serving as matrix and preparation method thereof
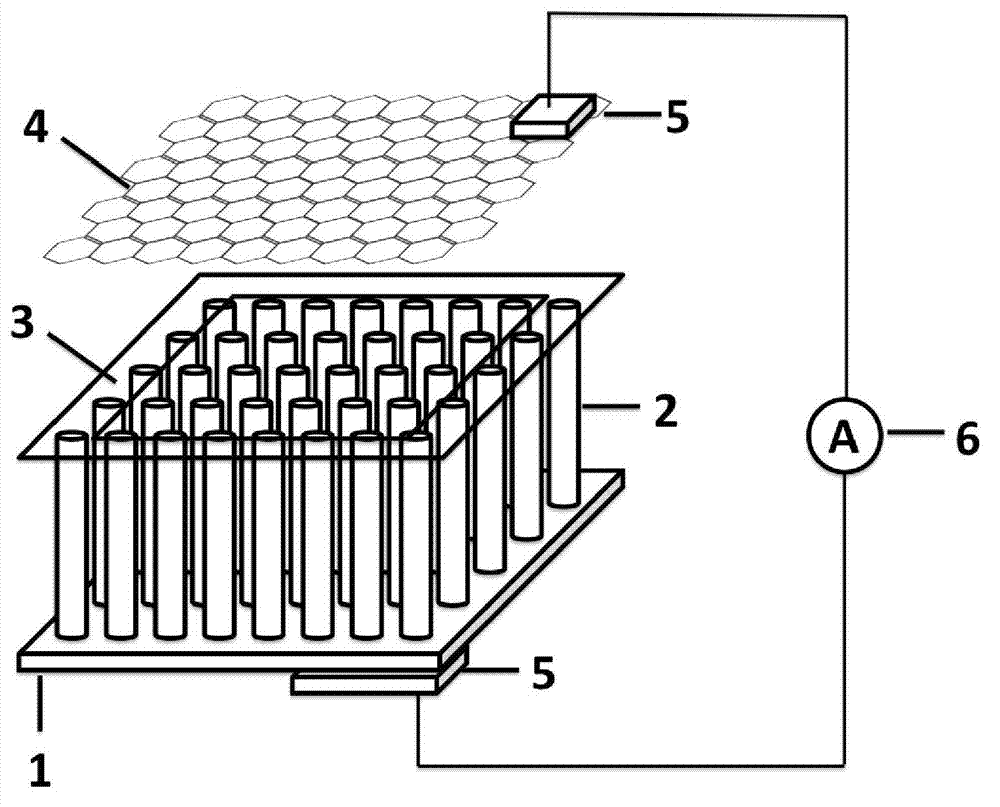
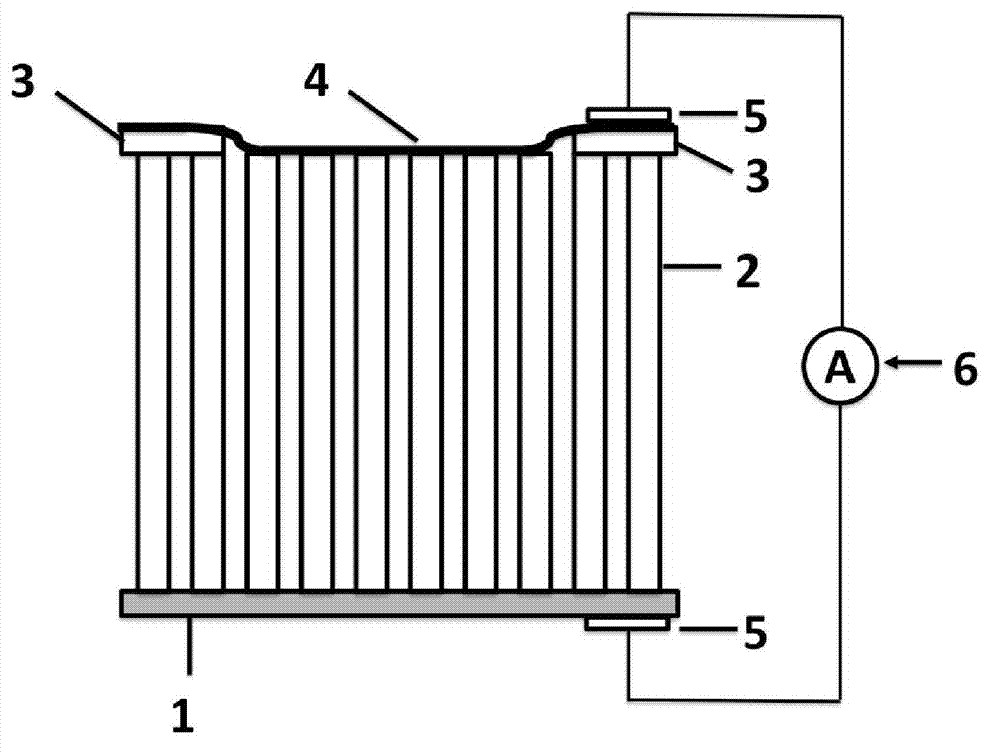
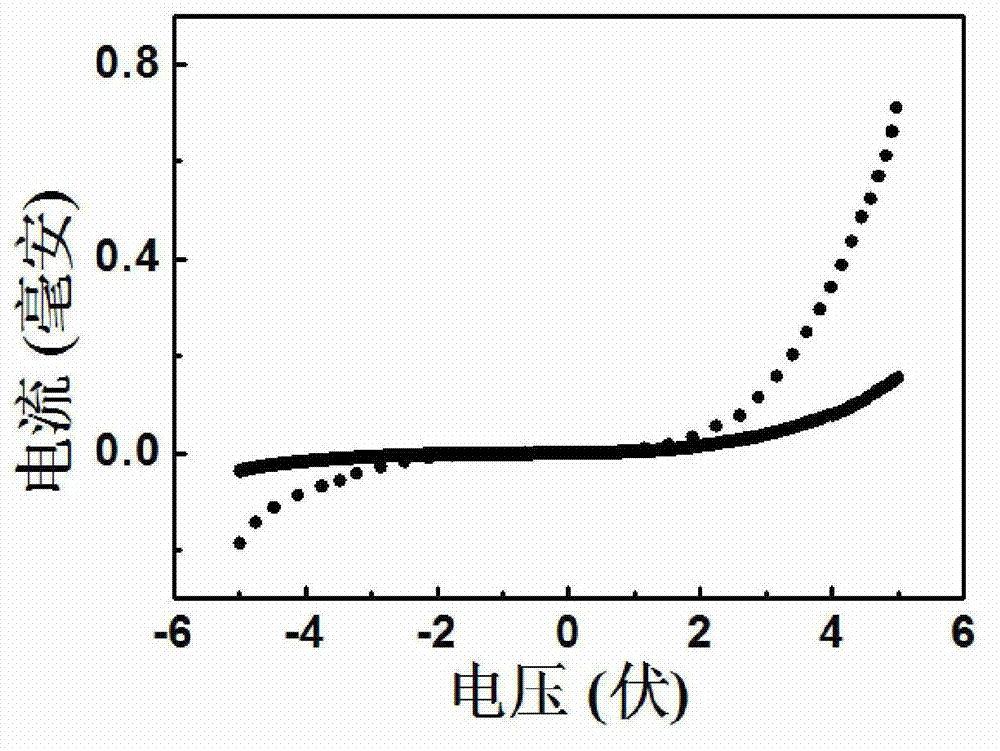
InactiveCN102856423AImprove responsivenessReduce dark currentFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesCvd grapheneOxygen vacancy
The invention discloses an ultraviolet light detector with a titanium dioxide nanotube array serving as a matrix and a preparation method thereof. The ultraviolet light detector comprises a titanium sheet substrate (1), the titanium dioxide nanotube array (2), an insulating layer (3) and a graphene film (4) sequentially from bottom to top, extraction electrodes (5) are arranged on the lower surface of the titanium sheet substrate (1) and the upper surface of the graphene film (4) respectively and are connected with a current measurer (6). The titanium dioxide nanotube array is prepared on the titanium sheet substrate by an anodizing method, oxygen vacancy of the array prepared by the method is less, and mismatch of stoichiometric ratio is avoided. Therefore, titanium dioxide is good in crystalline structure after annealing to lead to high response, low dark current and high ultraviolet-to-visible rejection ratio.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
InAlGaN/GaN PIN photoelectric detector without strain
InactiveCN101188256ASimple structureImprove quantum efficiencySemiconductor devicesPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
An unstrained InAlGaN / GaN PIN photodetector relates to a photodetector, in particular to an InAlGaN / GaN PIN photodetector which can convert light signals into electrical signals. The invention provides an unstrained InAlGaN / GaN PIN photodetector. The invention is provided with sapphire (Al2O3) substrates, a GaN buffer layer, a n-GaN layer, an i-InAlGaN photosensitive layer, a p-InAlN layer and a p-GaN top layer. The GaN buffer layer, the n-GaN layer, the i-InAlGaN photosensitive layer and the p-GaN top layer are orderly arranged on the sapphire (Al2O3) substrates from lower to top. A p-electrode is arranged on the p-GaN top layer, and a n-electrode is arranged on the n-GaN layer.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Two-stage table-top InGaAs/InP avalanche photodiode and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107768462AReduce fringe electric fieldSuppresses edge breakdownSemiconductor devicesCharge layerContact layer
The invention belongs to the fields of photoelectric detection and image sensors, and in order to inhibit fringe field and reduce device dark current while guaranteeing a high field in the central area of the device, reference basis is provided for industrial application. The invention discloses a two-stage table-top InGaAs / InP avalanche photodiode and a preparation method thereof. The structure comprises an N<+>-InP substrate, an N-InP buffer layer, an N<->-InGaAs In0.53Ga0.47As absorbed layer, an N-InGaAsP In(1-x)GaxAsyP(1-y) component gradient layer, an N-InP charge layer, an i-InP multiplying layer, a P-InP field buffer layer and a P<+>-InP contact layer, wherein the P-InP field buffer layer forms a shallow table-top through etching, the N-InP buffer layer forms a deep table-top through etching, and constant impact ionization of photon-generated carriers inside the multiplying layer causes avalanche multiplication. The avalanche photodiode is mainly applied to the design occasionsof photoelectric detection and photoelectric sensors.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
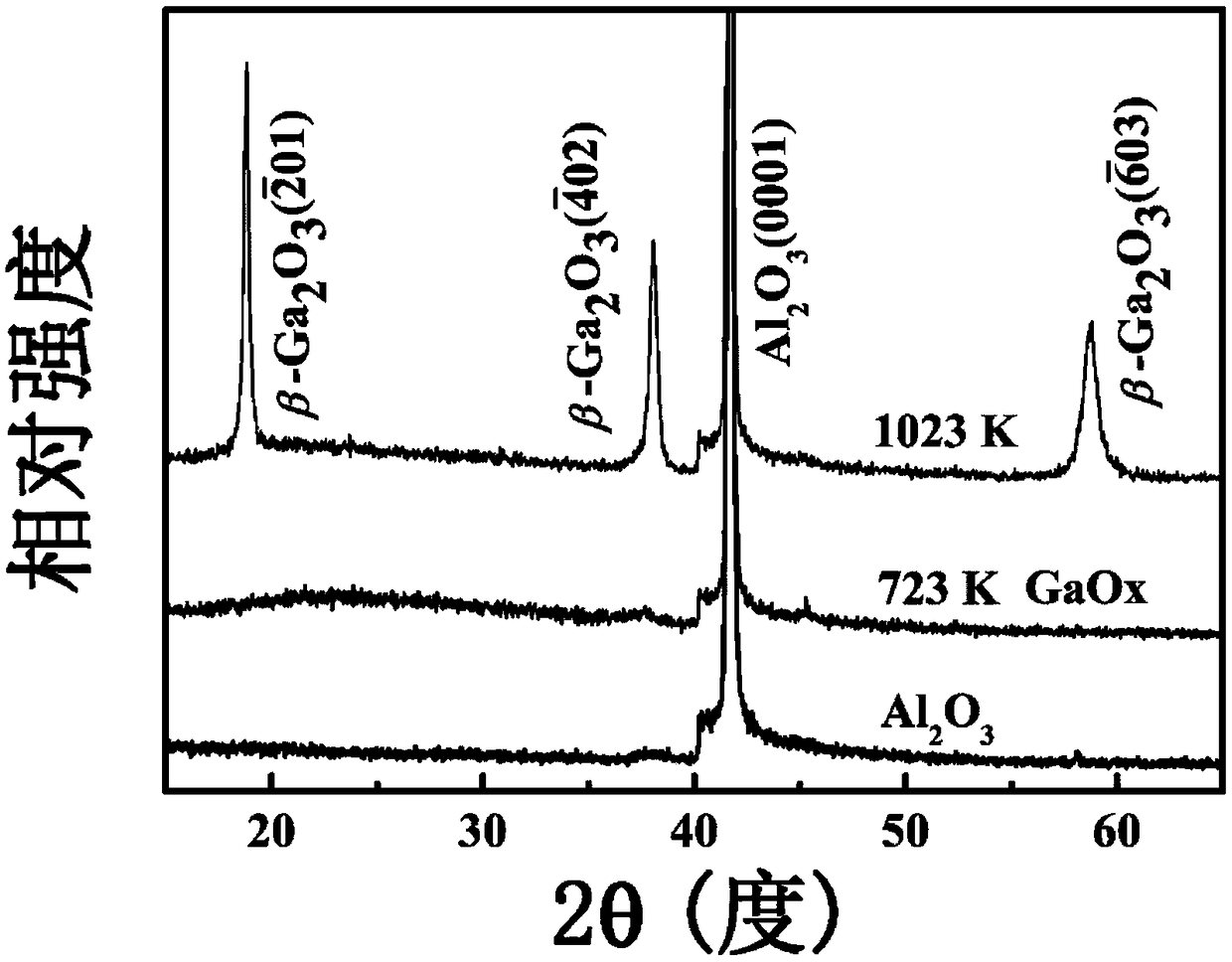
Solar blind ultraviolet photoelectric detector based on amorphous gallium oxide film and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108666395AUniform textureLow growth temperatureFinal product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingManufacturing technologyRadio frequency magnetron sputtering
The invention discloses a solar blind ultraviolet photoelectric detector based on an amorphous gallium oxide film and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of photoelectricdetectors. The method comprises the steps that the crystal face (0001) Al2O3 is adopted as a substrate, and the substrate is cleaned; then, the cleaned substrate is fed into a settling chamber, a radio frequency magnetic control sputtering technology is applied to the substrate to grow a gallium oxide film; finally, a hollow interdigital mask plate is used for shielding on the amorphous gallium oxide film, a direct current magnetic control sputtering method is adopted for sputtering an interdigital metal electrode on the interdigital mask plate to obtain the solar blind ultraviolet photoelectric detector, the structure is an MSM type sandwiched structure, and the Al2O3 substrate, the amorphous gallium oxide film material and the Ti / Au interdigital metal electrode are arranged from bottom to top. The manufacturing technology is simple, the repeatability is good, dark current is small, the stability is high, the response speed is high, the ultraviolet visible restrain ratio is high, andthe detector conforms to the energy-saving and emission-reducing theory, is suitable for large-scale production, and has the wide development prospect.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
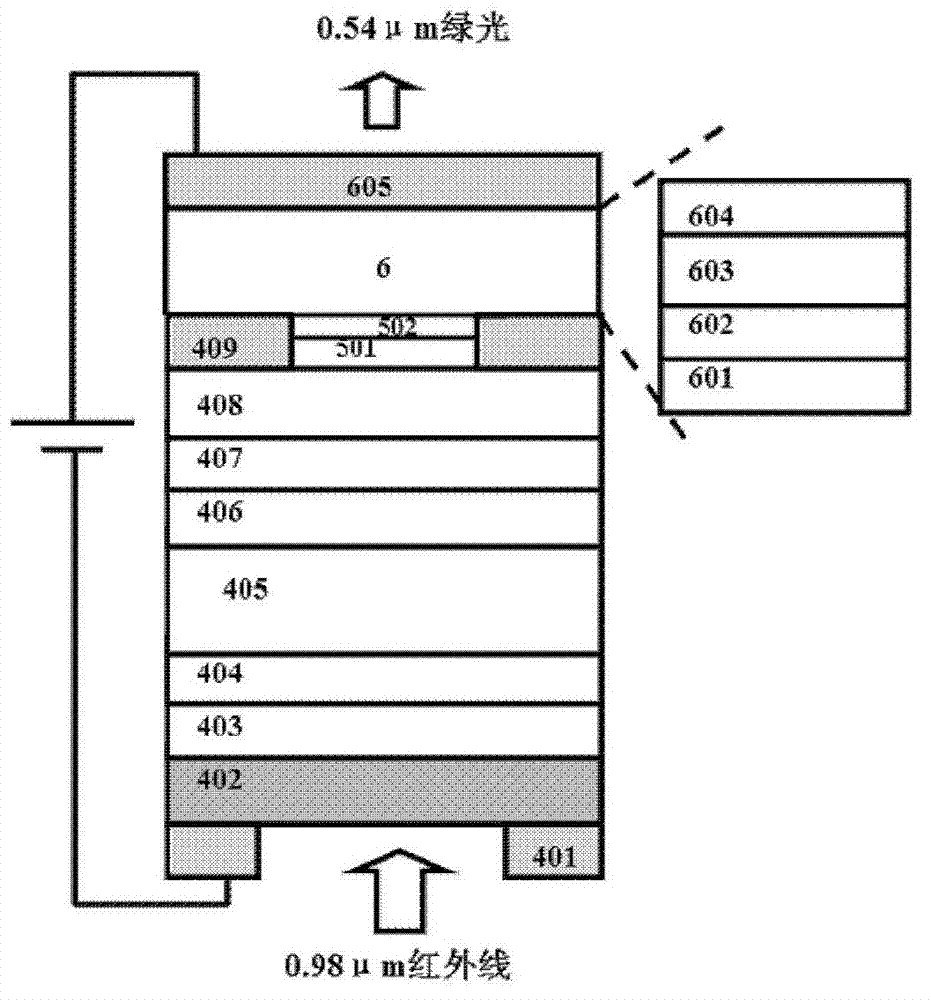
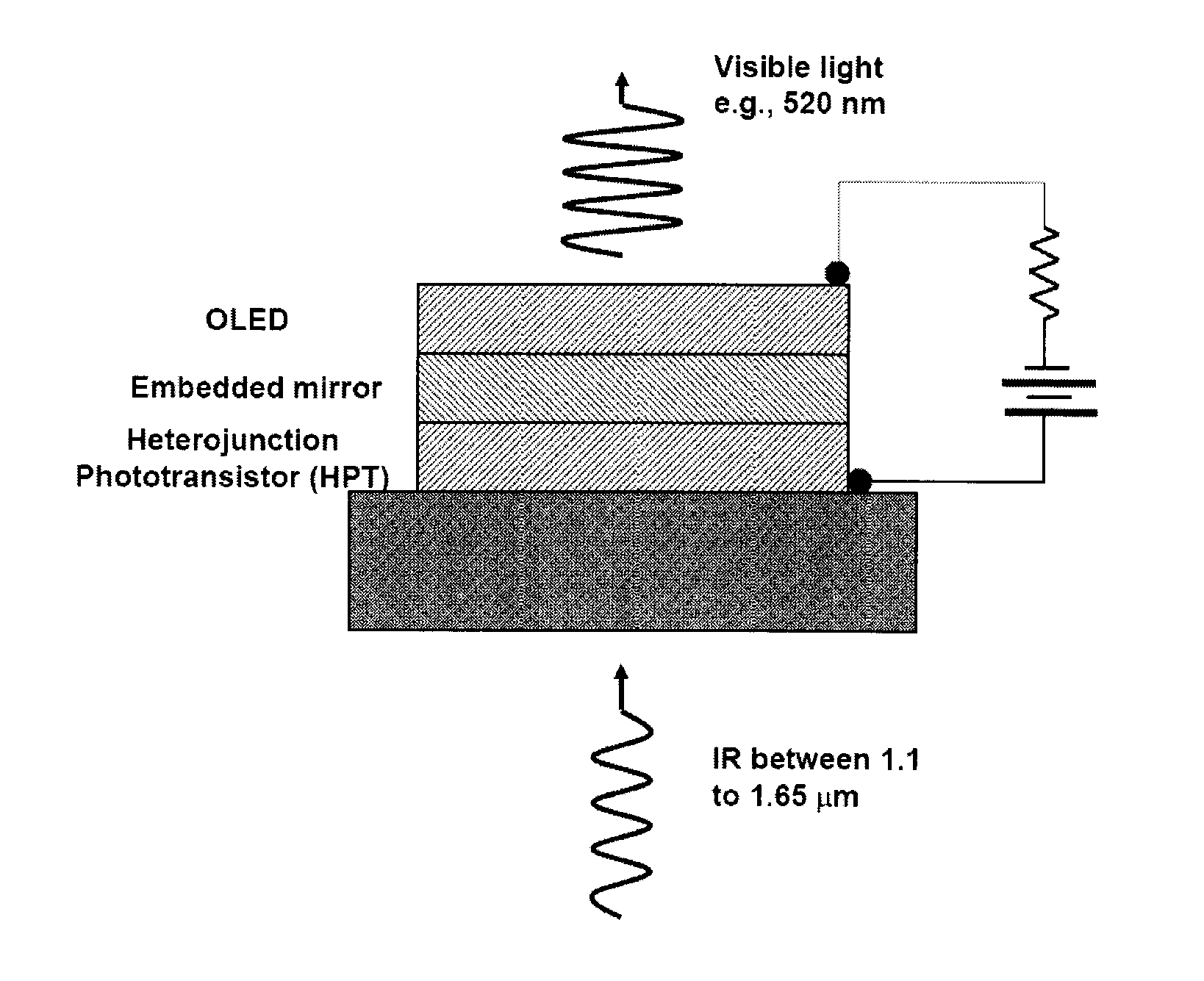
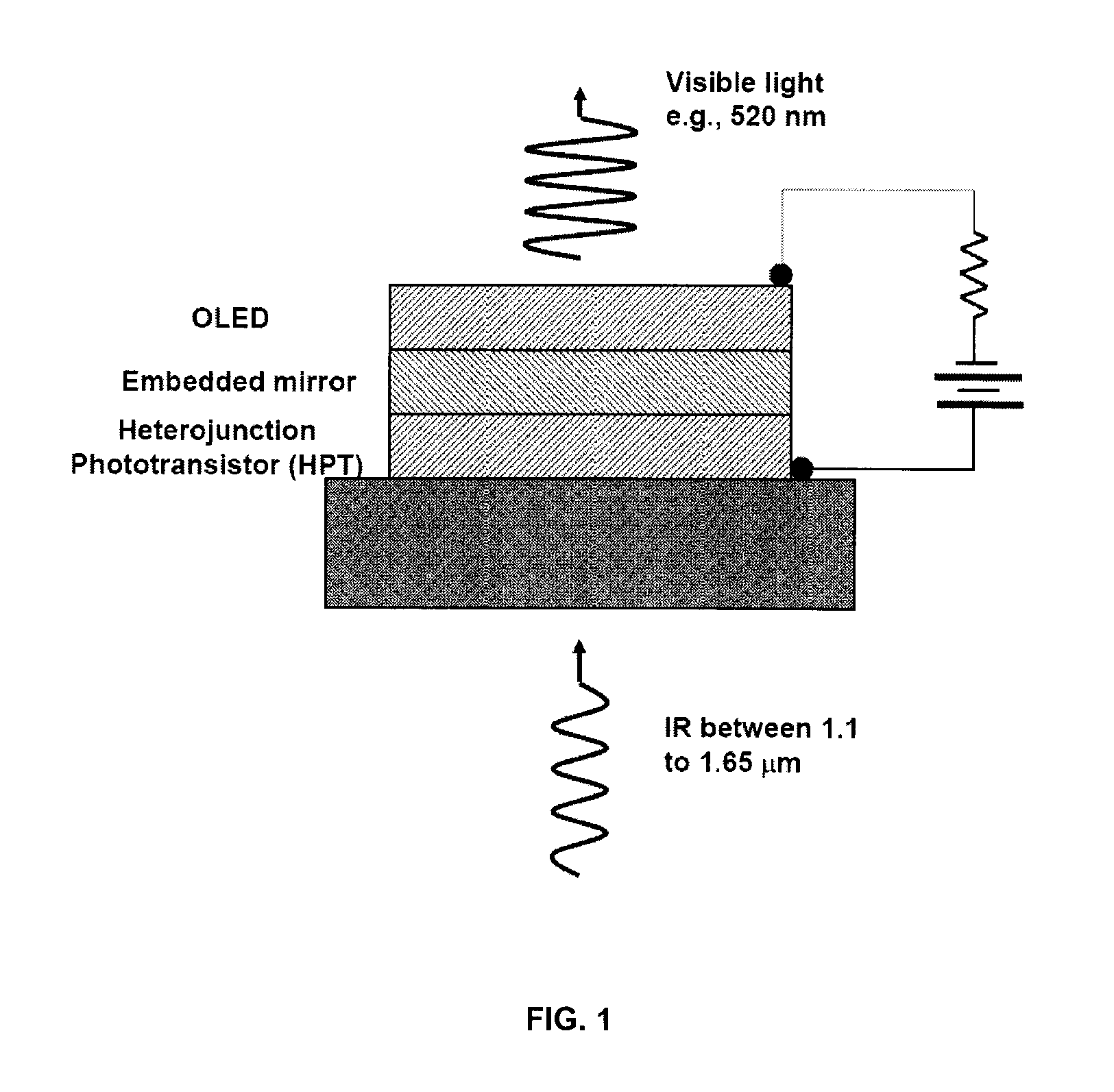
Organic/inorganic hybrid optical amplifier with wavelength conversion
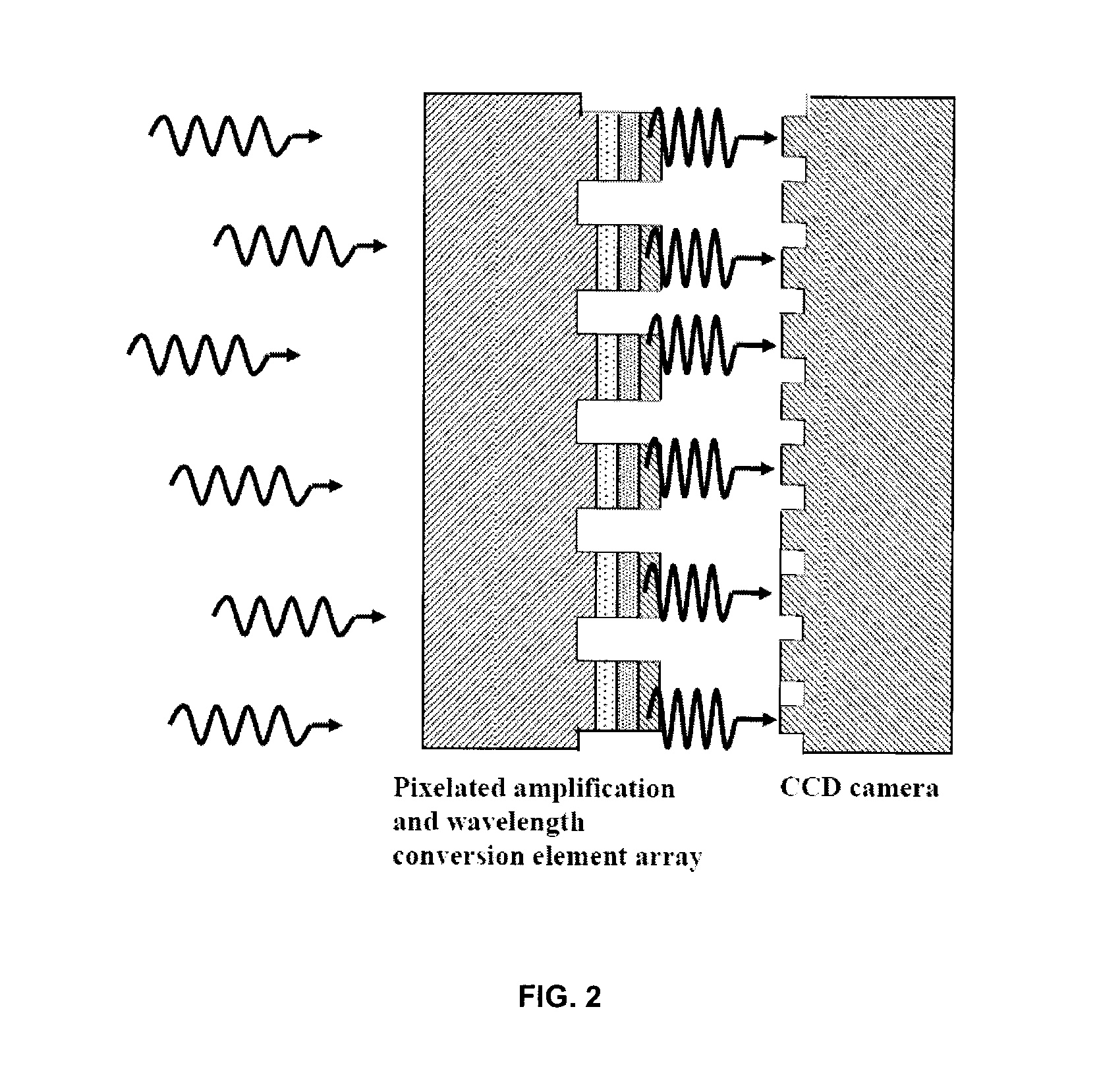
ActiveUS20130215496A1Improve absorption efficiencyImprove emission efficiencyLaser detailsSolid-state devicesMetallic electrodePhotodetector
A device and related fabrication method is provided for an organic / inorganic hybrid optical amplifier with a function of converting infrared light to visible light. The hybrid device integrates an inorganic heterojunction phototransistor (HPT), an embedded metal electrode mirror with a dual function as an optical mirror and charge injection electrode, and an organic light emitting diode (OLED). This integrated optical amplifier is capable of amplifying the incoming light and producing light emission with a power greater than that of the incoming signal. In the second aspect of the invention, the optical amplifier is capable of detecting an incoming infrared electromagnetic wave and converting the wave back to a visible light wave. The optical device has dual functions of optical power amplification and photon energy up-conversion. The optical amplifier device consists of an InGaAs / InP based HPT structure as photodetector, gold-coated metals as embedded mirror and a top-emission OLED. New optical up-conversion imaging devices are also provided that include focal-point array of the organic / inorganic hybrid optical amplifier devices in pixelated formats. The up-conversion imaging devices have a fast response time to enable gated operation for practical applications such as night vision, active surveillance, semiconductor wafer inspection and eye-safe infrared imaging. More importantly, the up-conversion imaging devices would be particularly useful for detecting ultra-low intensity infrared scenes.
Owner:BAN DAYAN +2
Method for synthetizing high-stability metal halide perovskite/lead sulfide heterostructure nanocrystals
ActiveCN105602560AImprove stabilityImprove efficiencyNanotechnologyLuminescent compositionsSynthesis methodsSolvent
The invention discloses a method for synthetizing high-stability metal halide perovskite / lead sulfide heterostructure nanocrystals. The method comprises the following steps: firstly mixing lead halide with reactive solvent oleic acid, organic amine with long alkyl chains and octadecene in the presence of an inert gas so as to completely dissolve lead halide; then heating a mixed solution to 160-200 DEG C, rapidly injecting a caesium precursor, and reacting to generate CsPbX3; cooling to room temperature, then sequentially injecting a sulphur precursor and a lead precursor, and stirring for reaction, thereby finally obtaining the CsPbX3 / PbS heterostructure nanocrystals. The synthetized CsPbX3 / PbS heterostructure nanocrystals are uniform in appearance; the synthesis method is simple; due to epitaxial growth of lead sulfide, the perovskite performance stability is improved, and the CsPbX3 / PbS heterostructure nanocrystals are enhanced in light-emitting efficiency and are beneficial to later-stage photoelectric device assembly.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
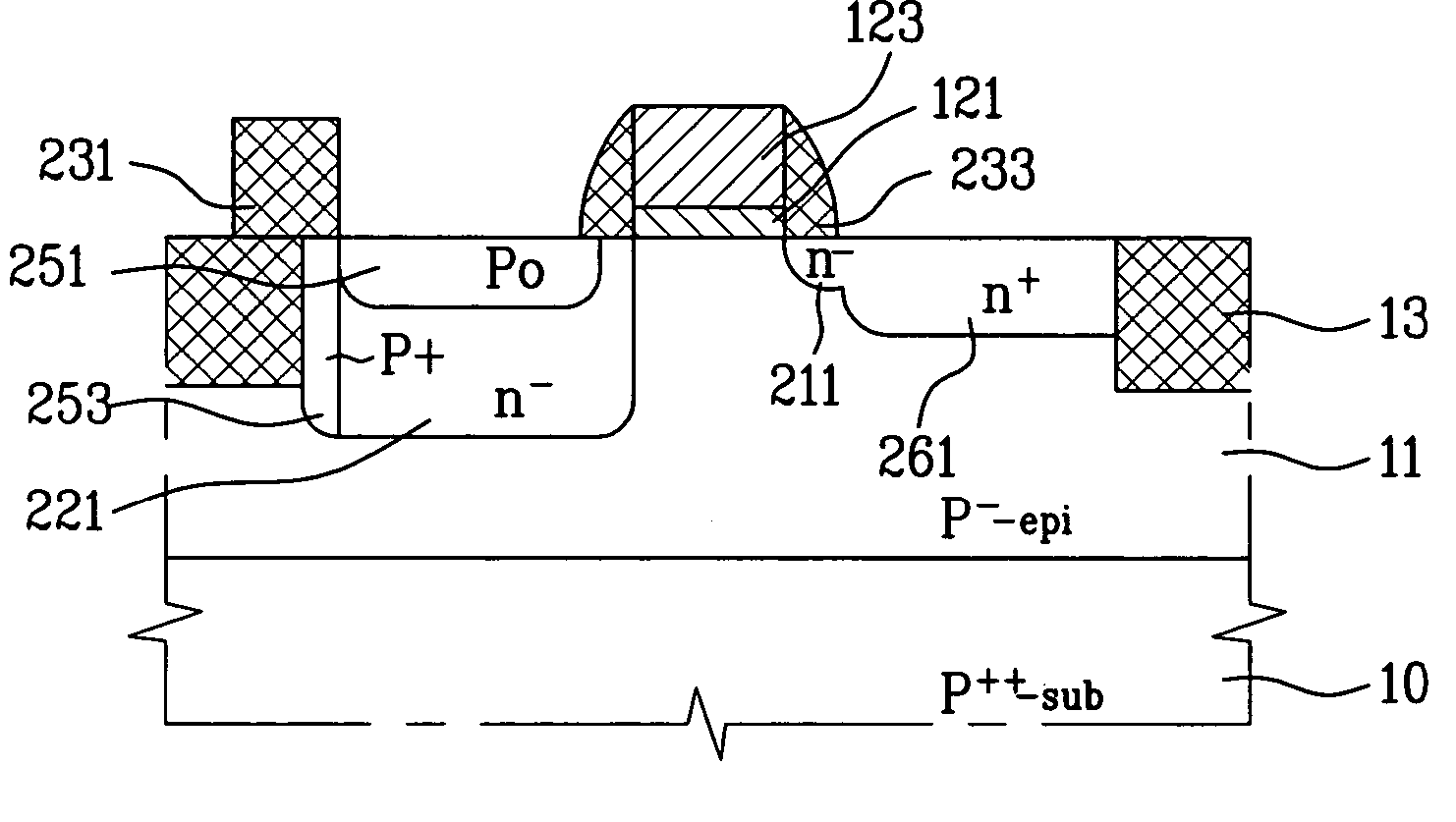
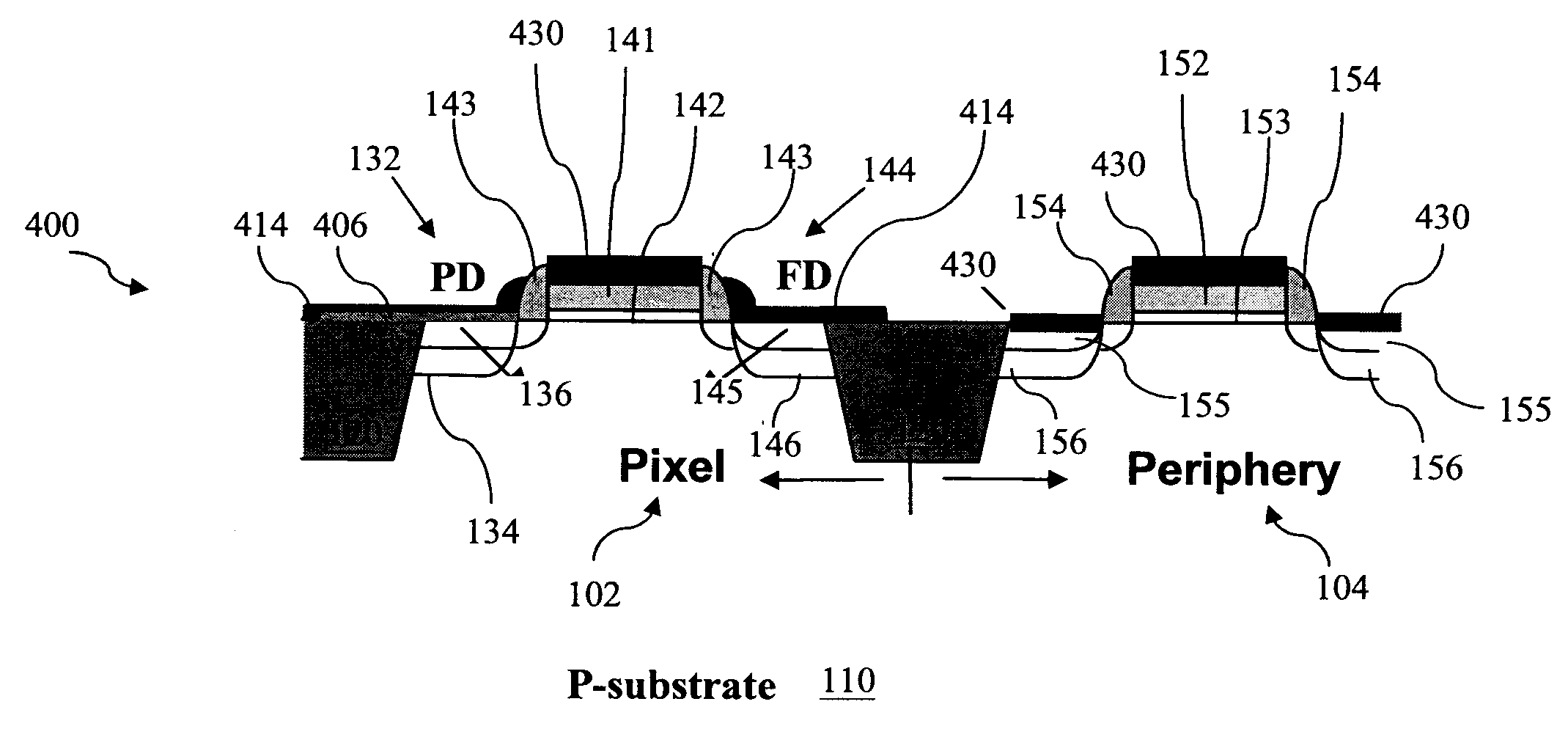
Method and structure to reduce dark current in image sensors
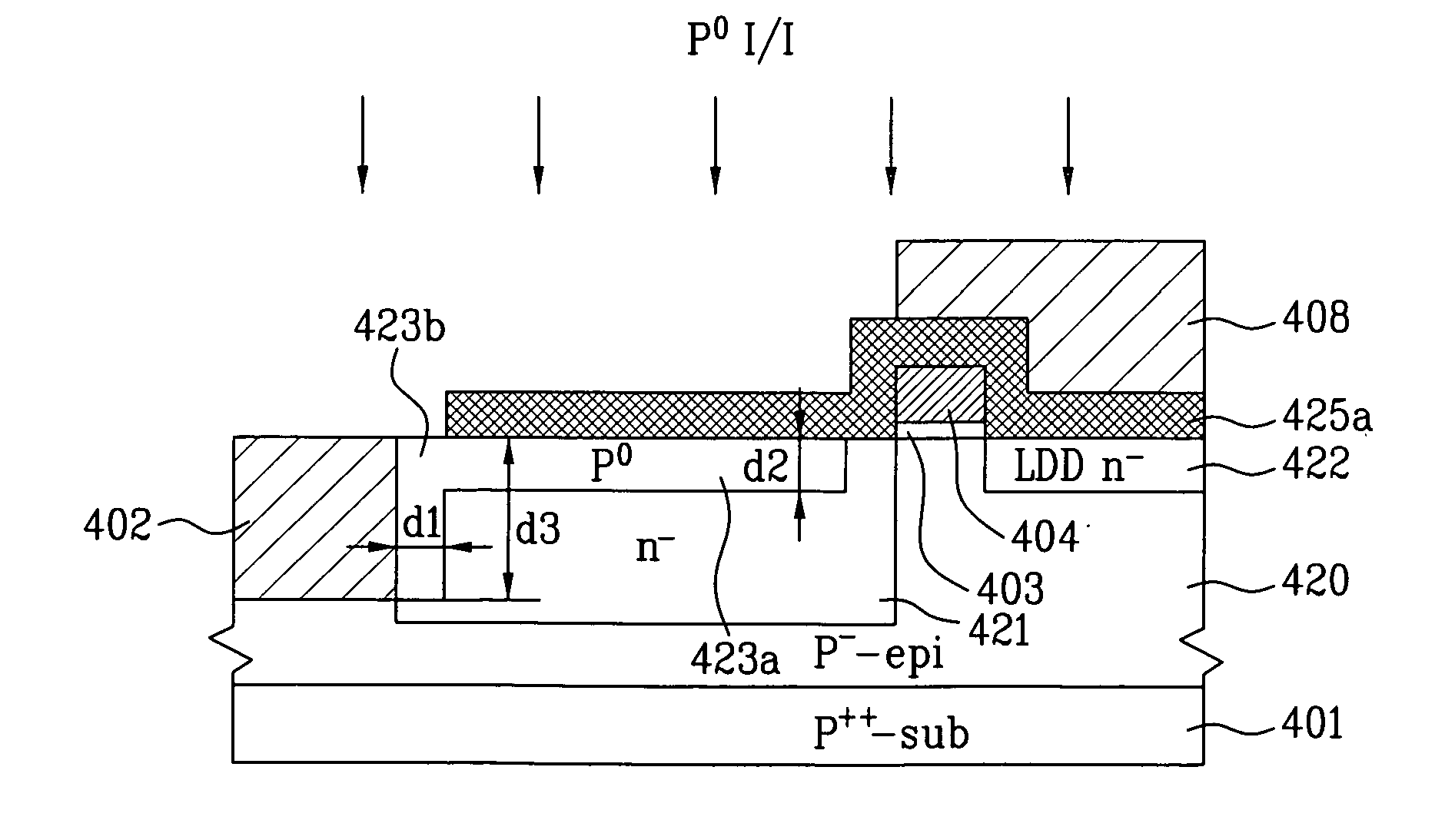
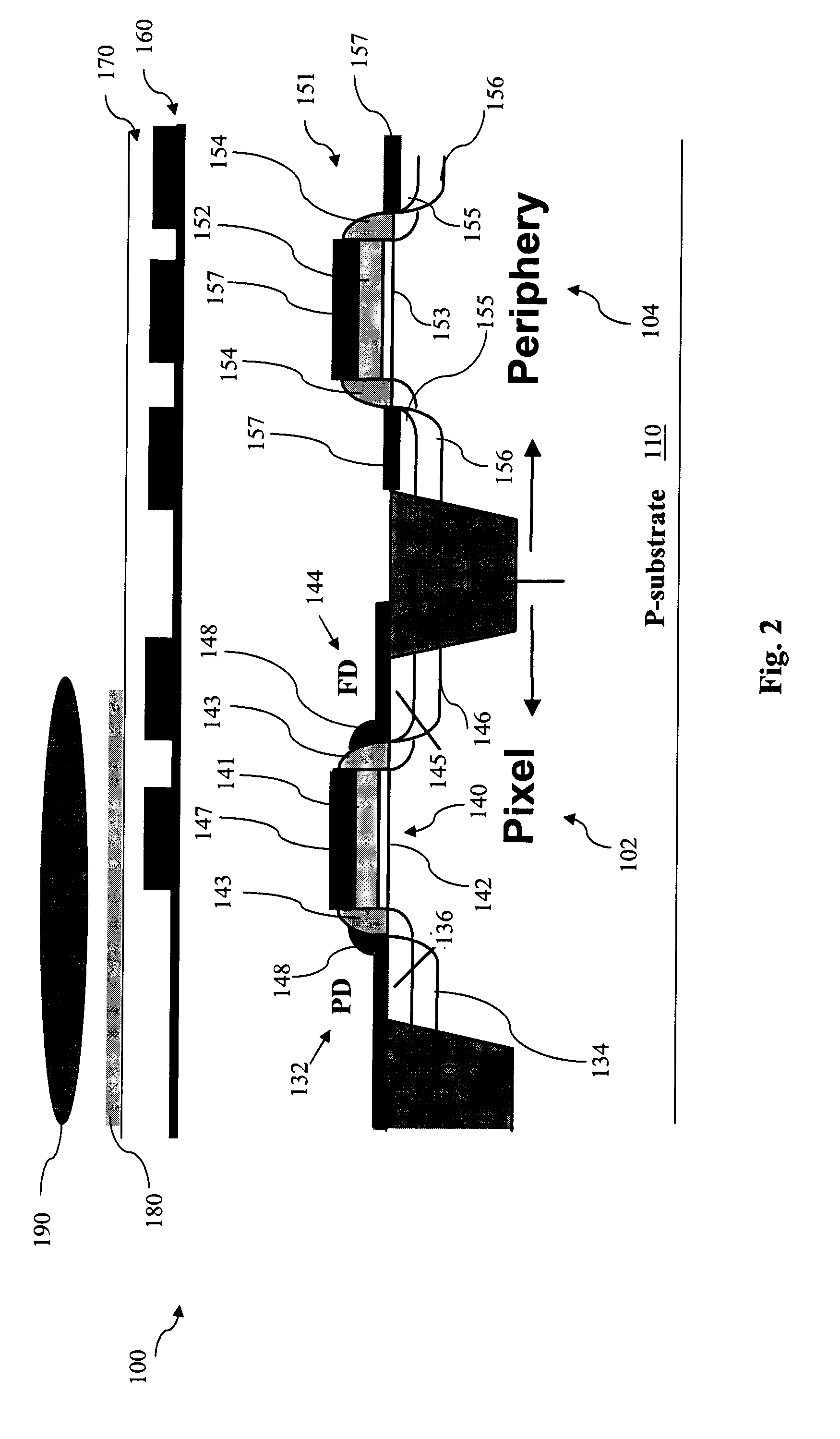
InactiveUS20080179640A1Reduce dark currentSimple and cost-effectiveSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLight sensingDielectric layer
A method to fabricate an image sensor includes providing a semiconductor substrate having a pixel region and a periphery region, forming a light sensing element on the pixel region, and forming at least one transistor in the pixel region and at least one transistor in the periphery region. The step of forming the at least one transistor in the pixel region and periphery region includes forming a gate electrode in the pixel region and periphery region, depositing a dielectric layer over the pixel region and periphery region, partially etching the dielectric layer to form sidewall spacers on the gate electrode and leaving a portion of the dielectric layer overlying the pixel region, and forming source / drain (S / D) regions by ion implantation.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com