Patents
Literature
77results about How to "High photoelectric conversion-efficiency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
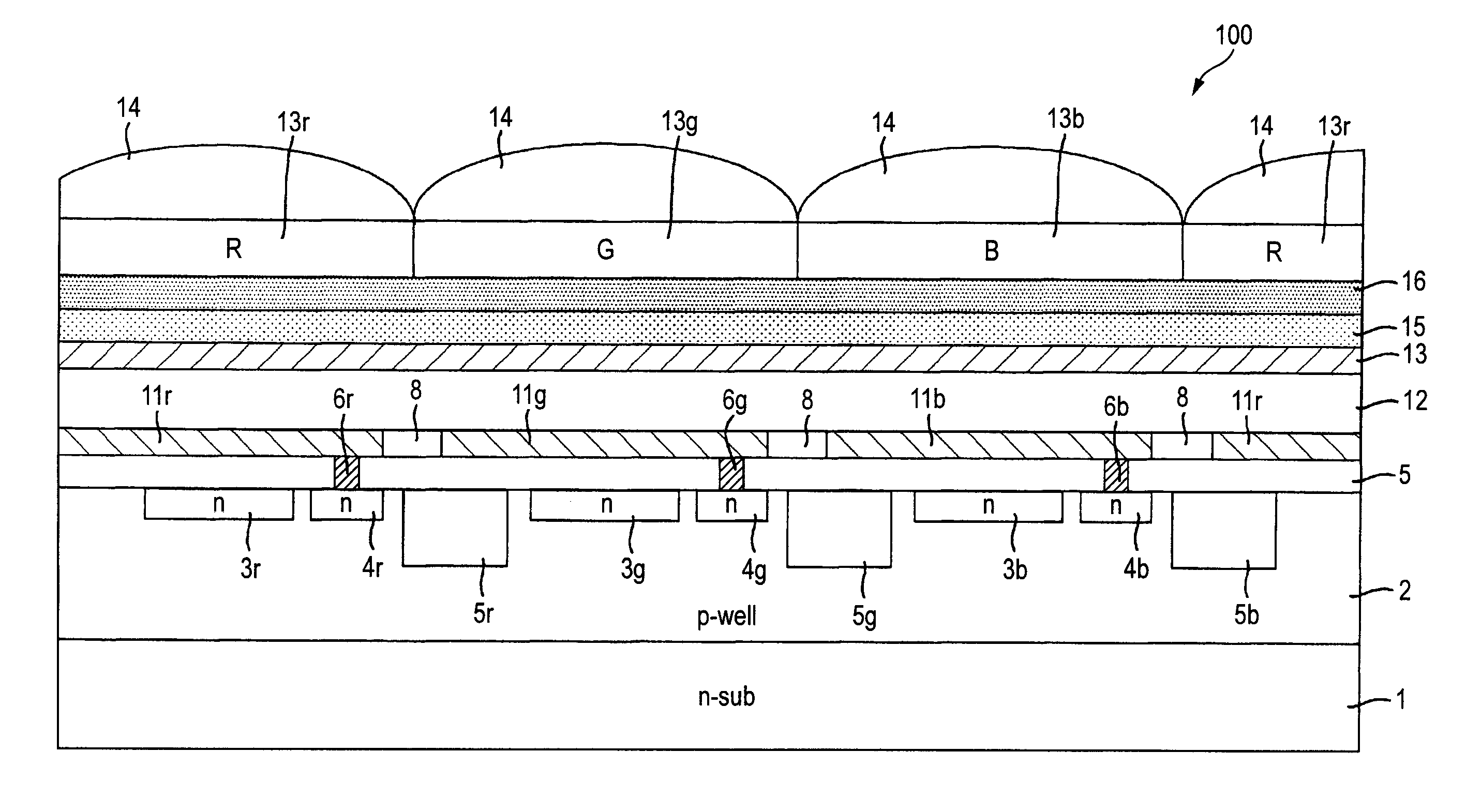
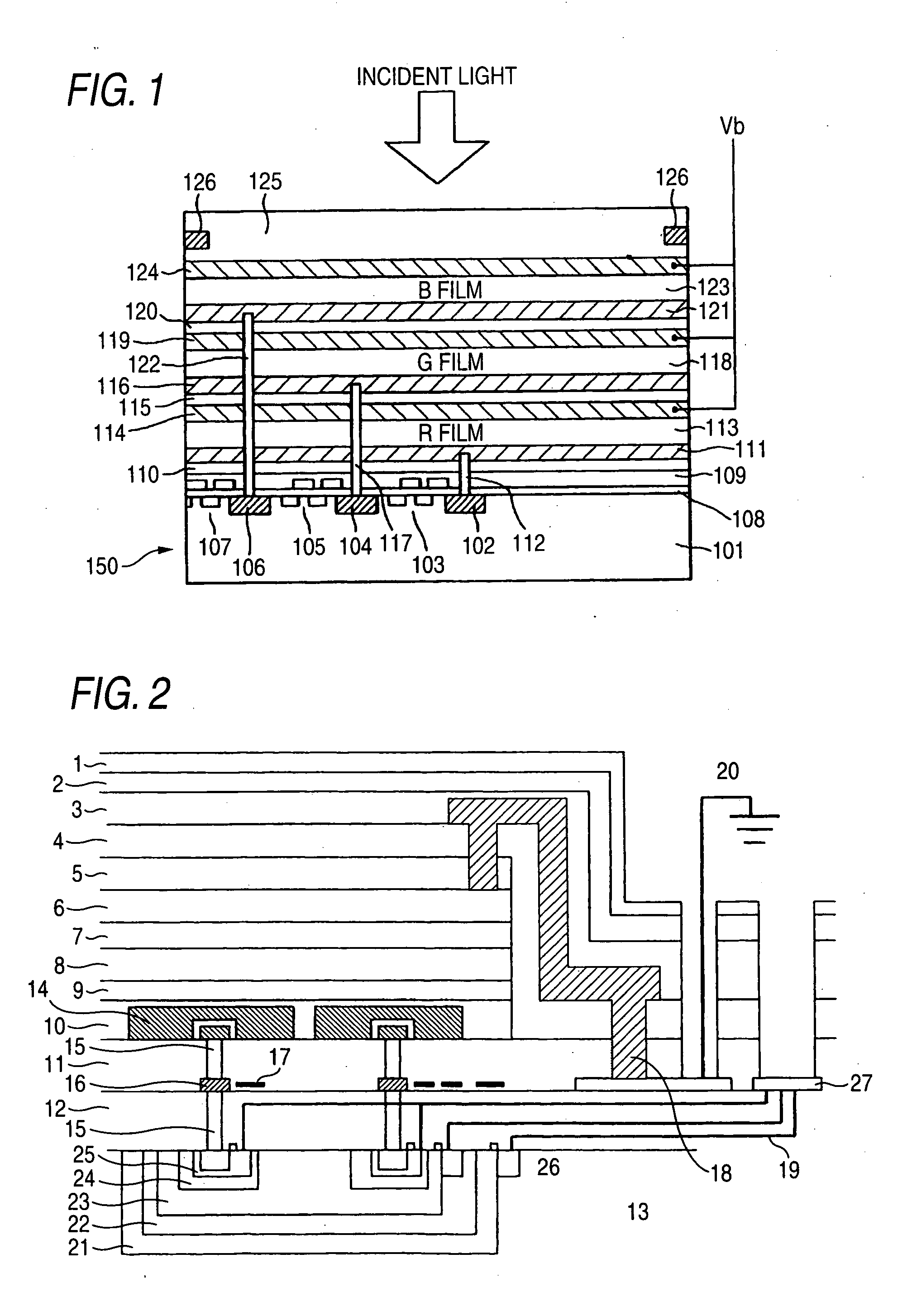
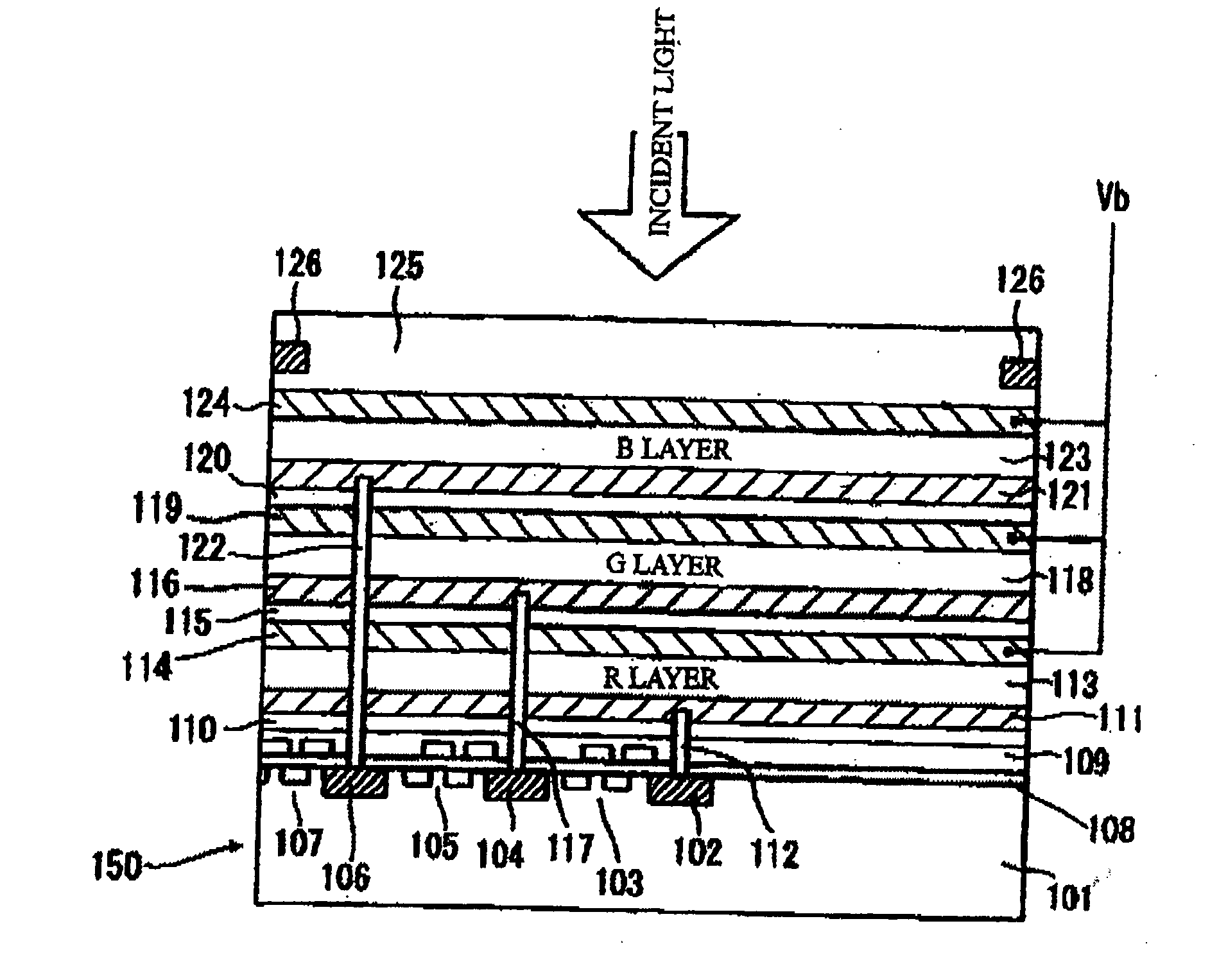
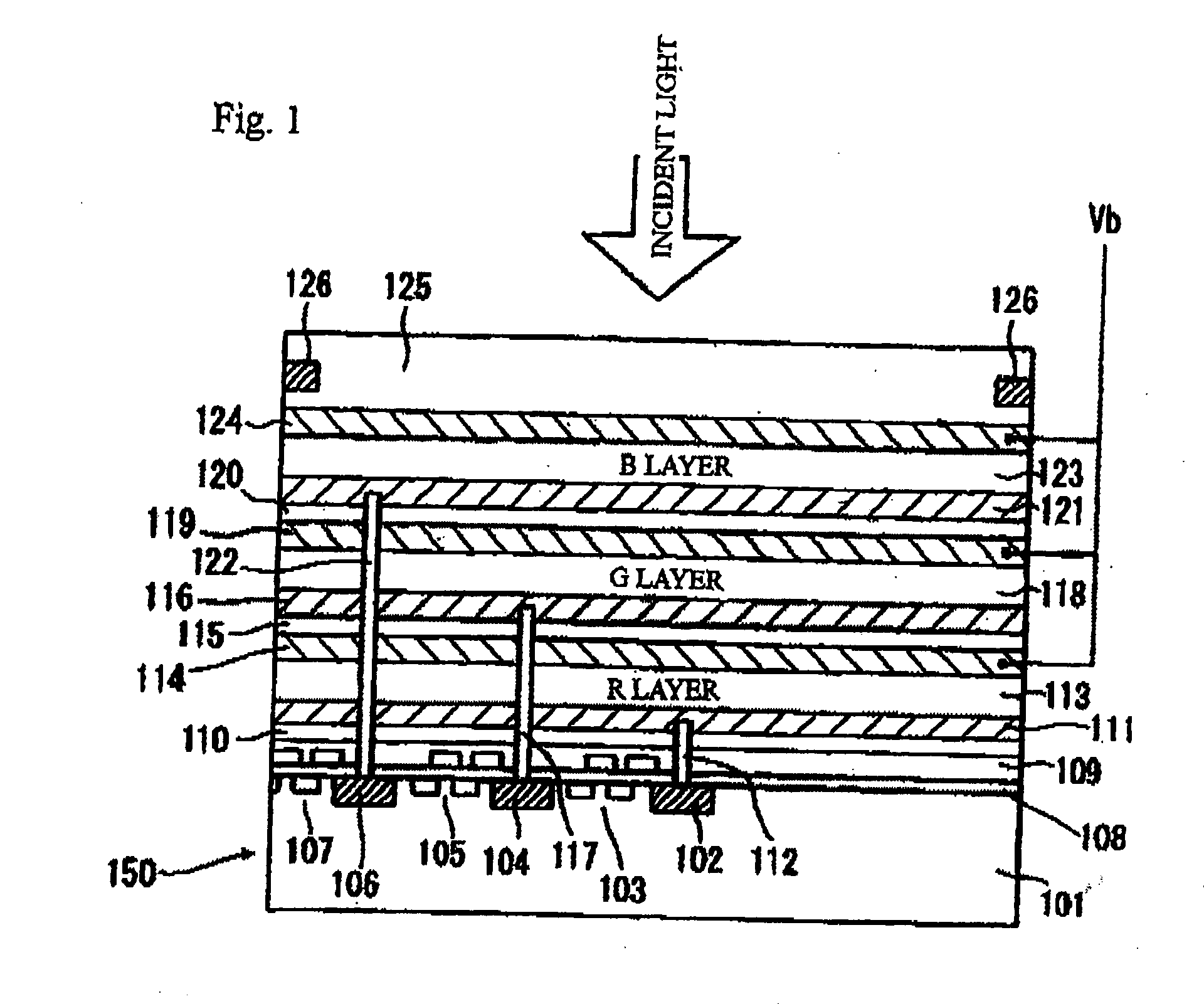
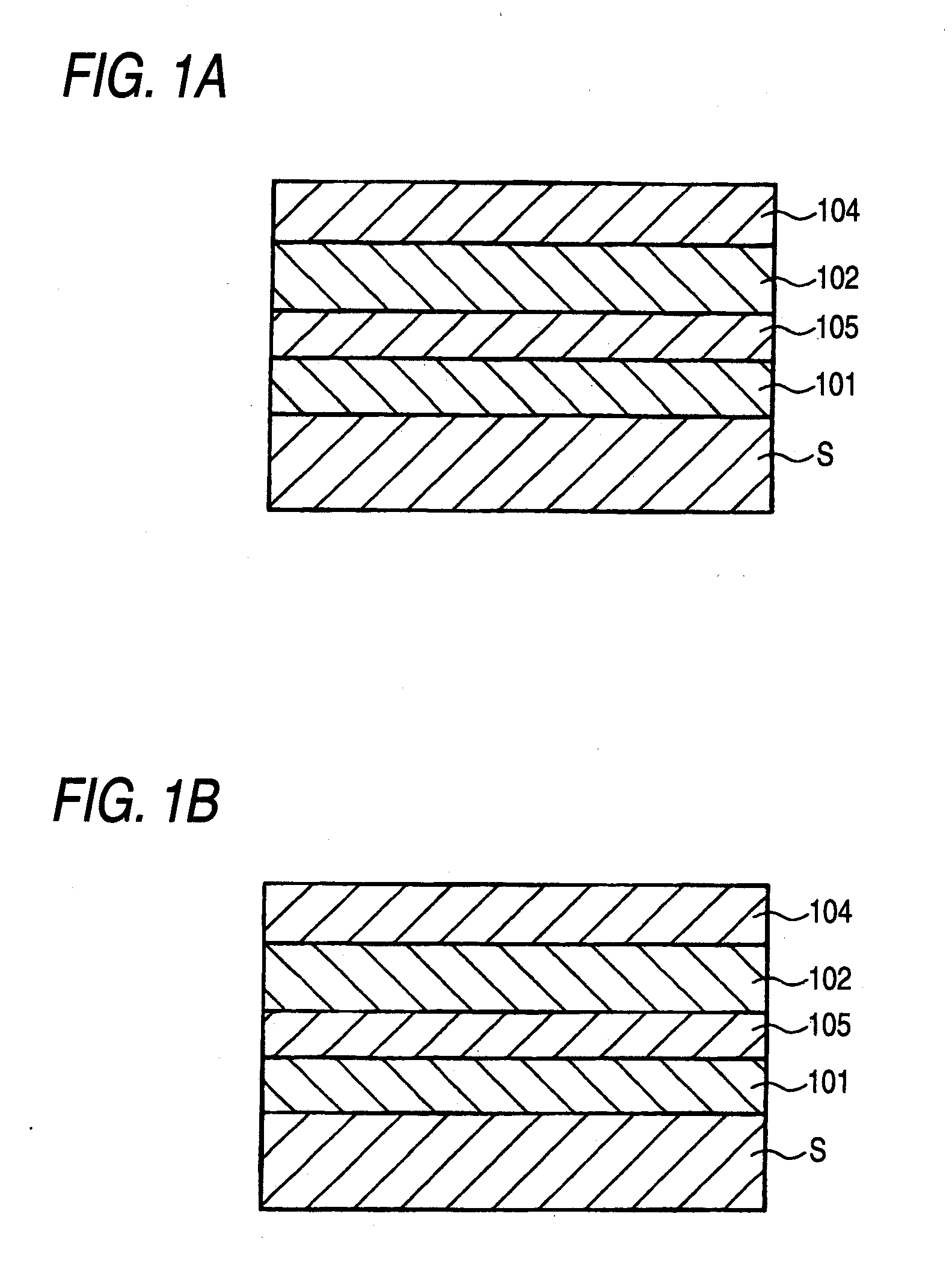
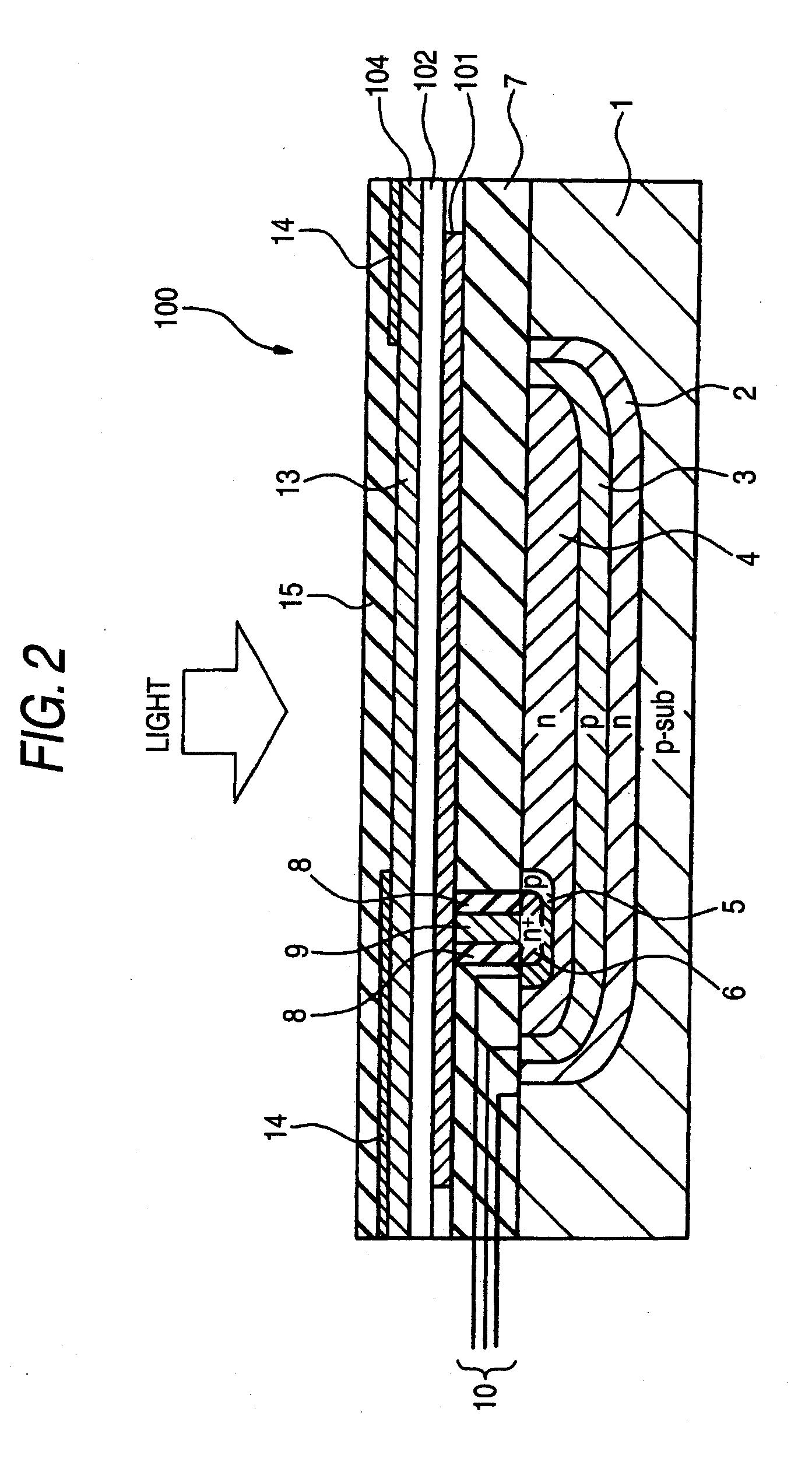
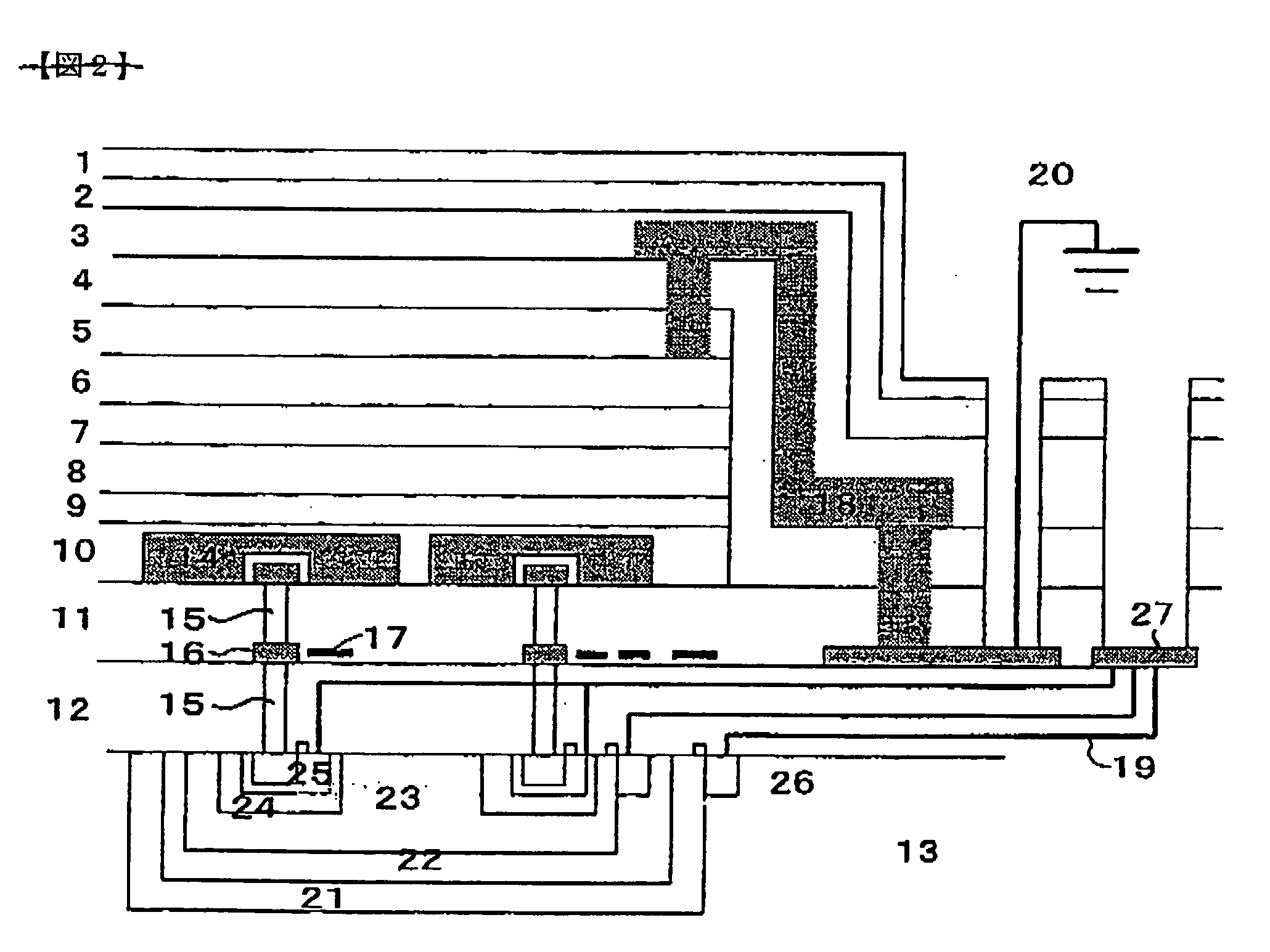
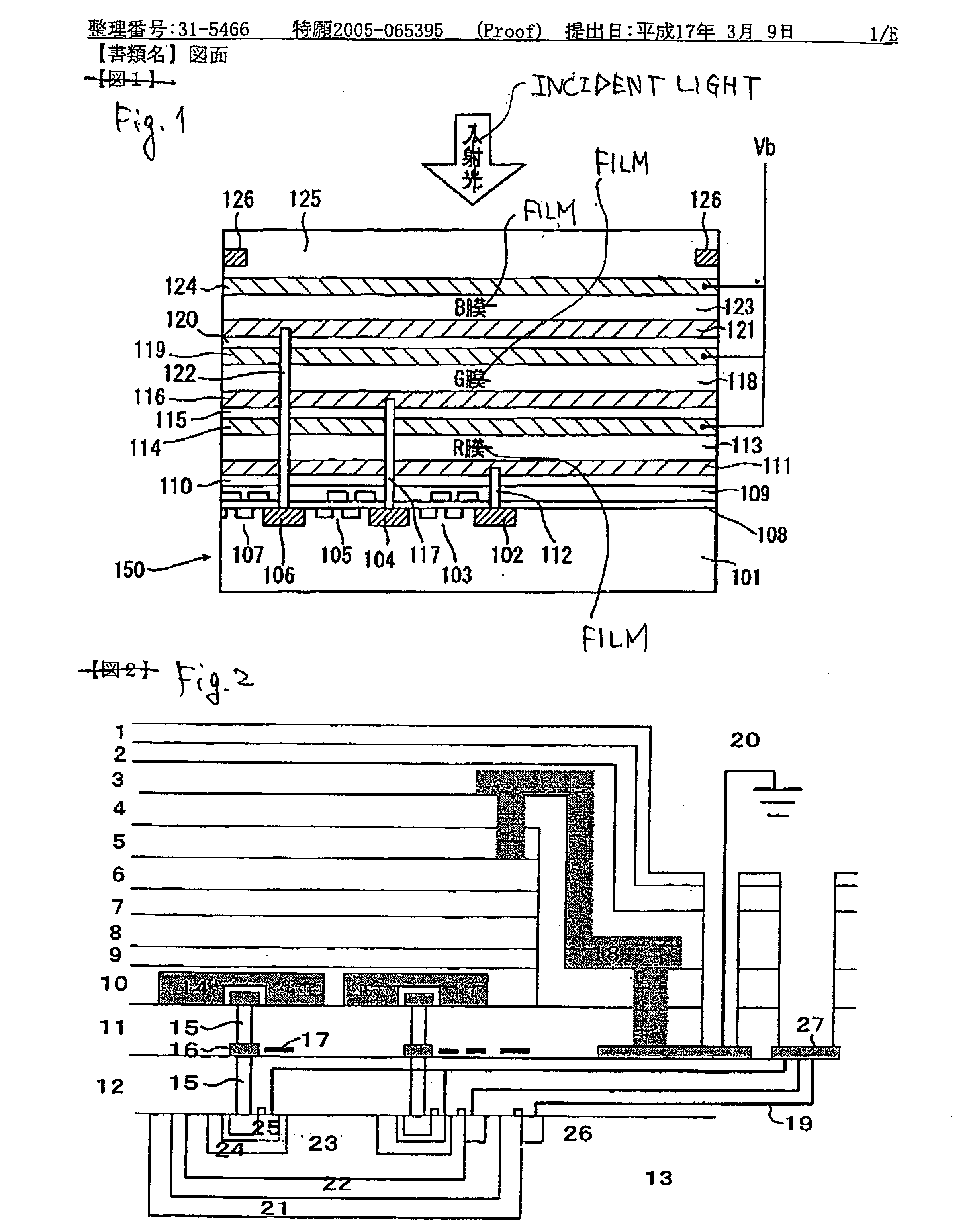
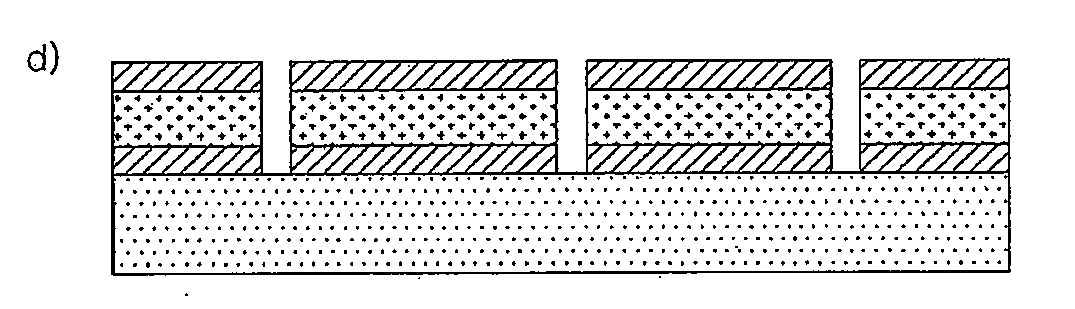
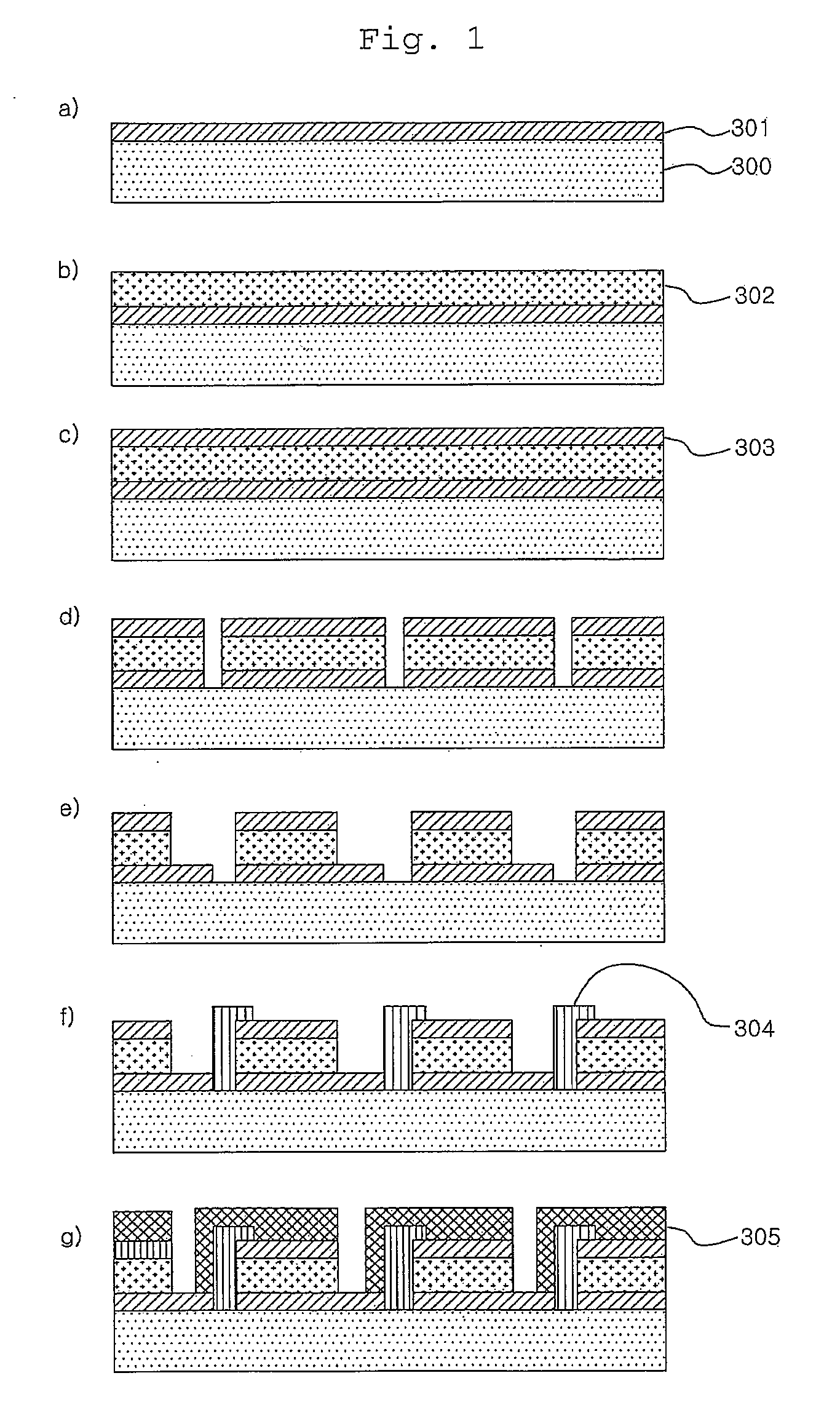
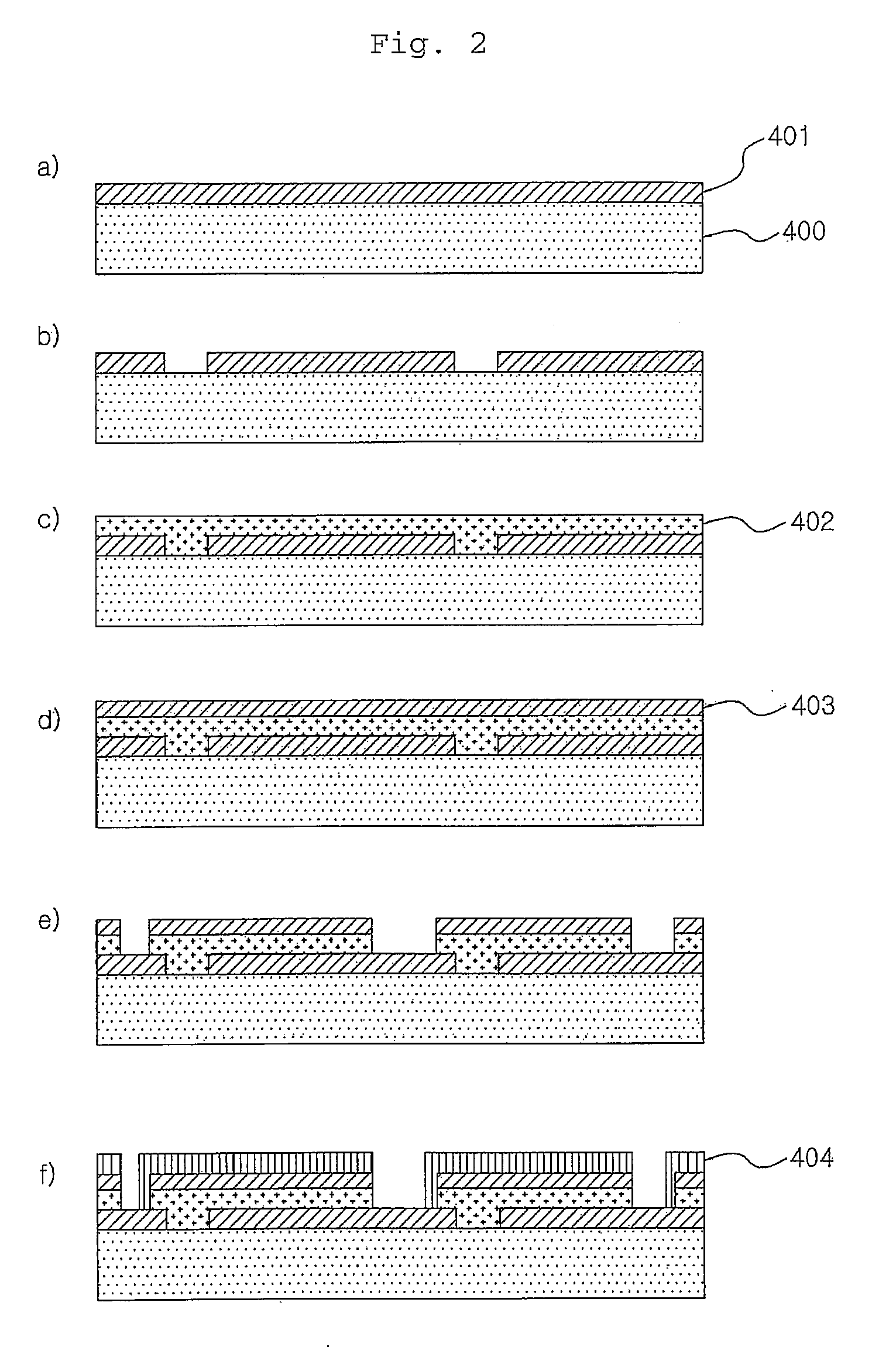
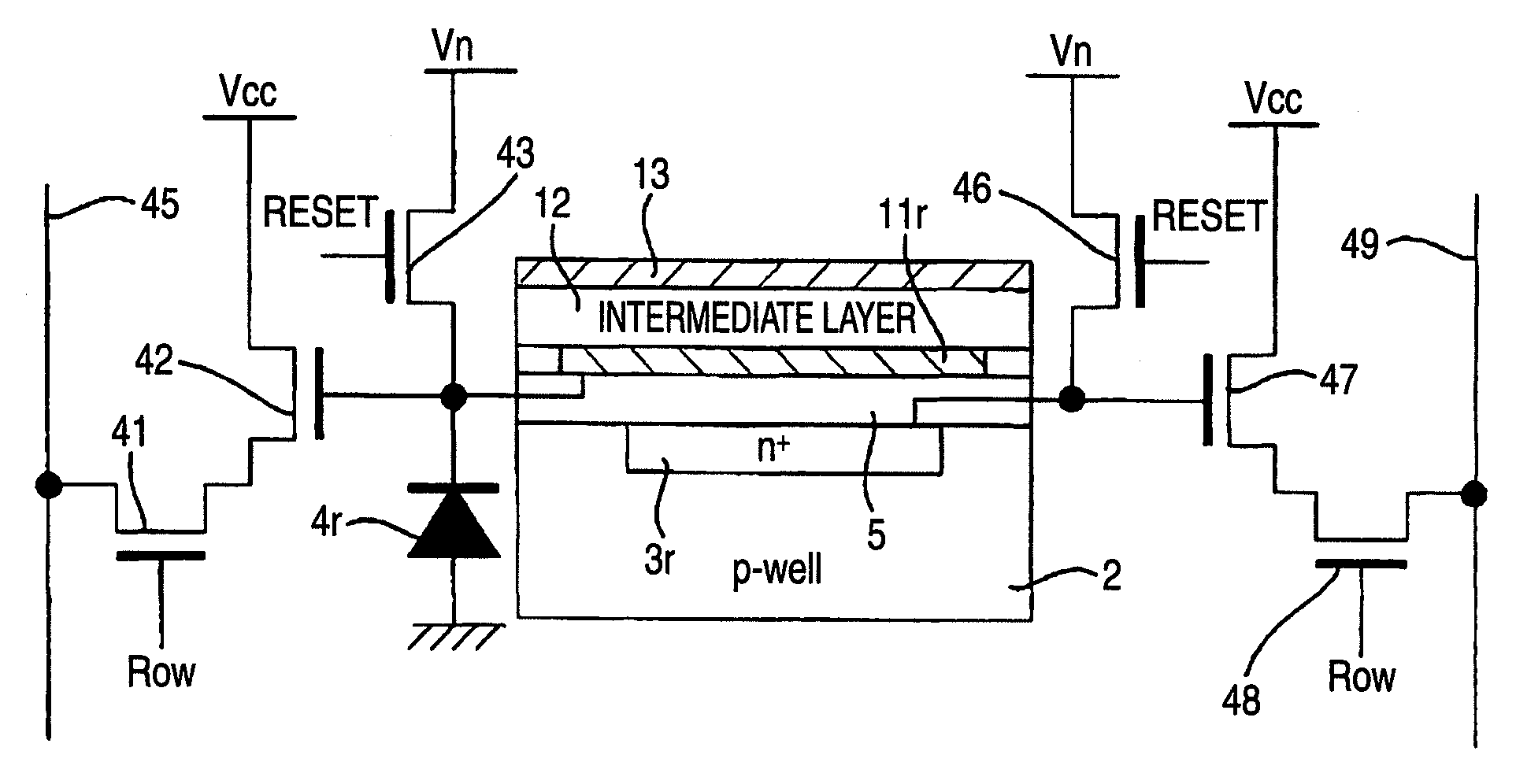
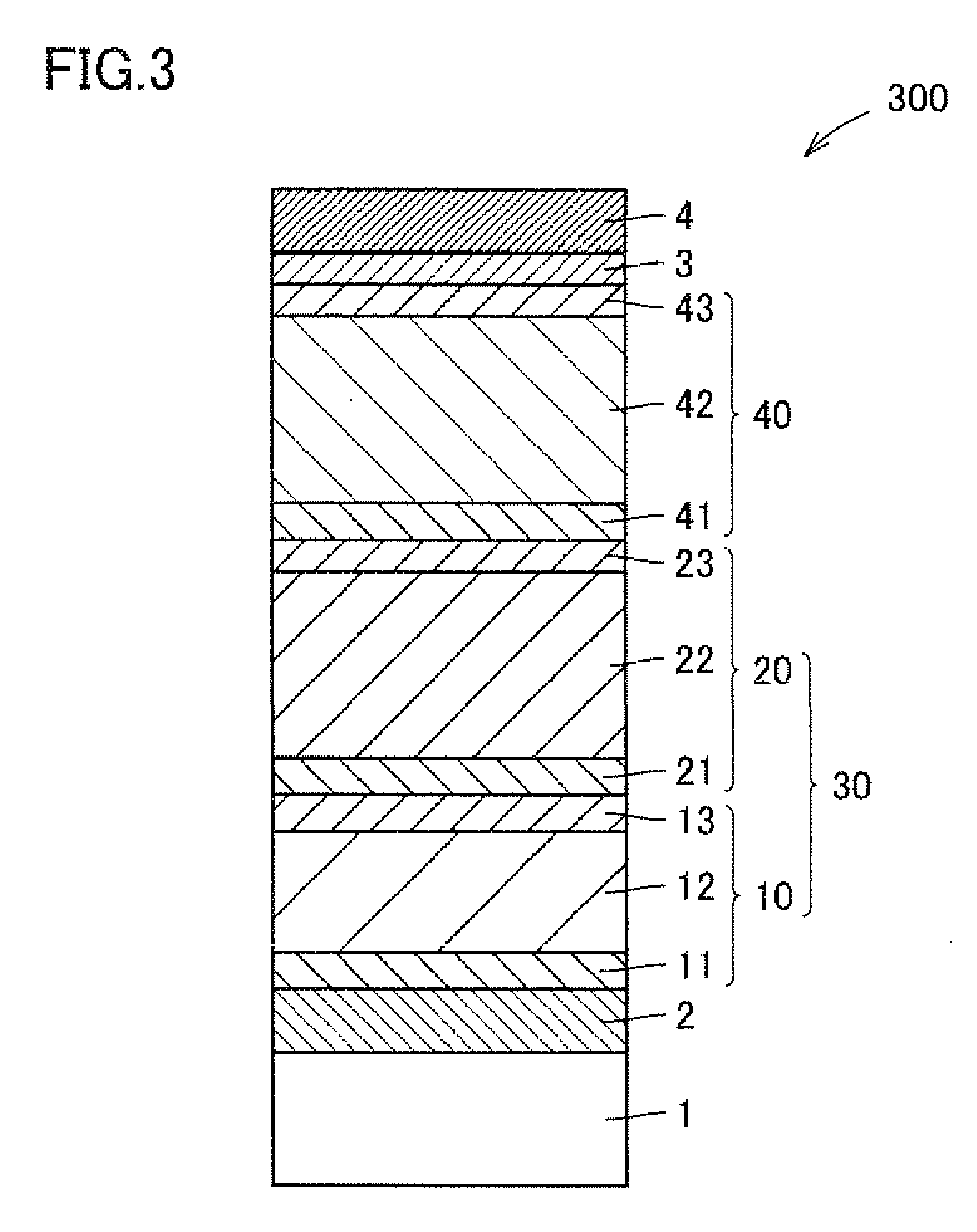
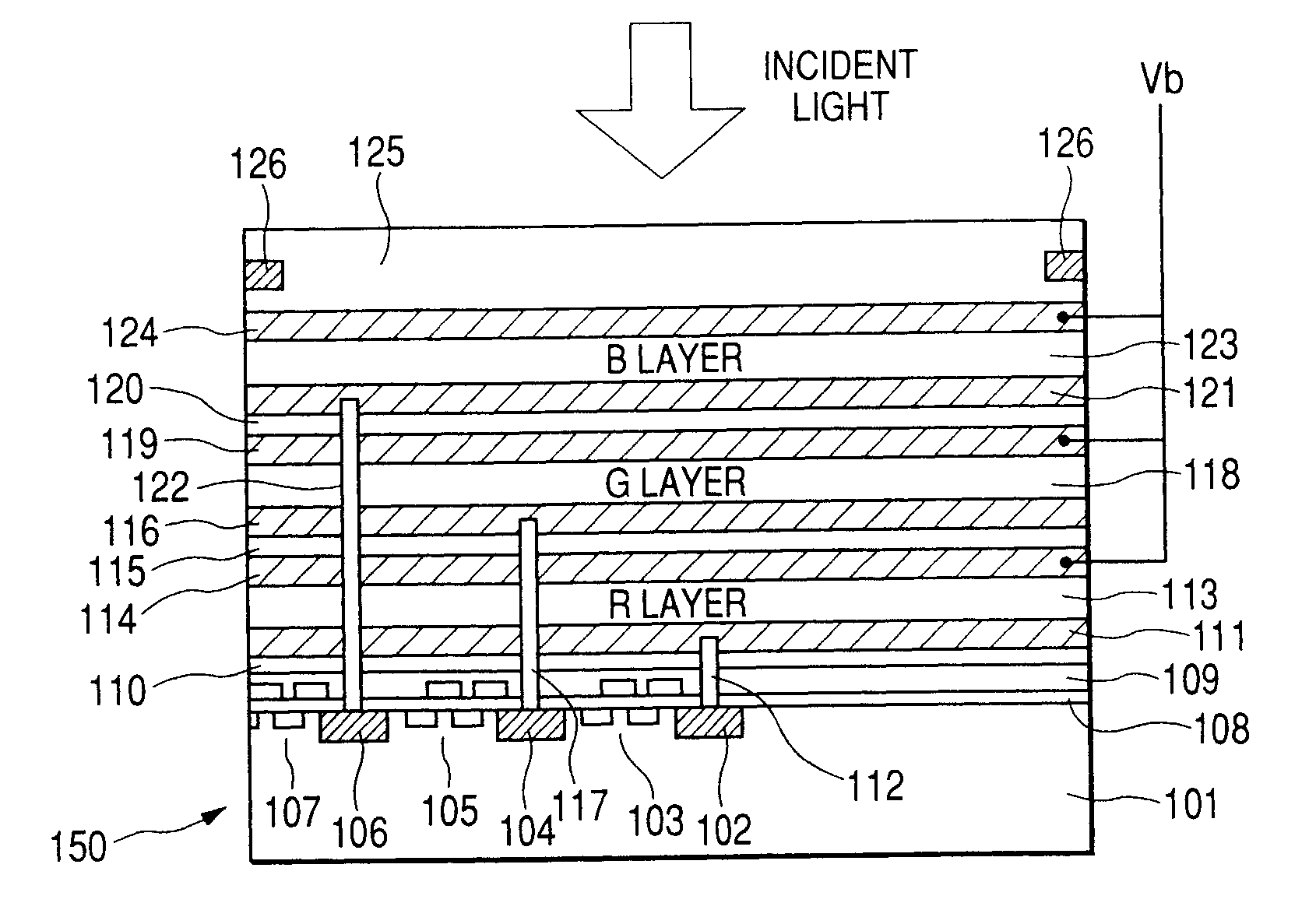
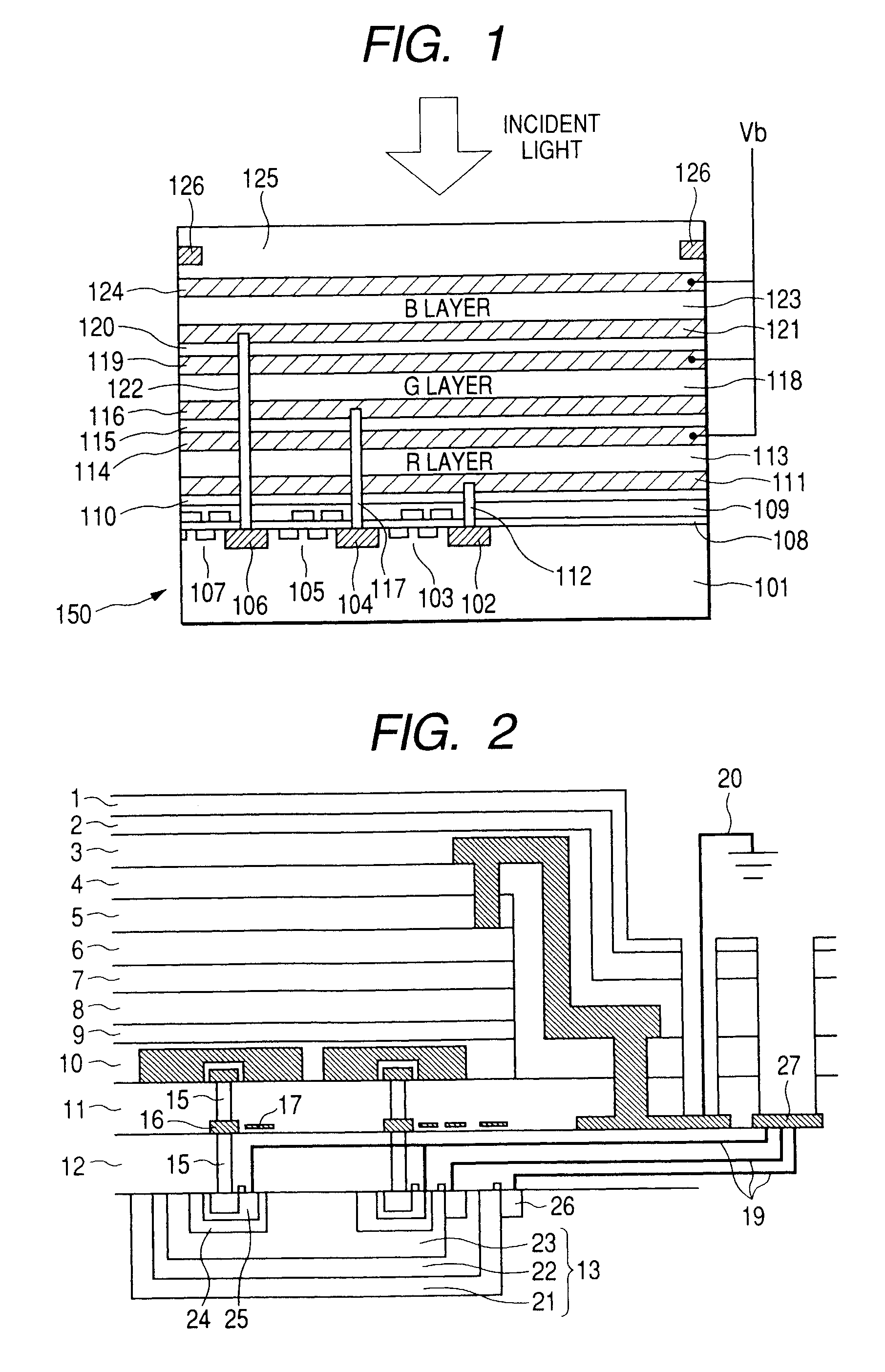
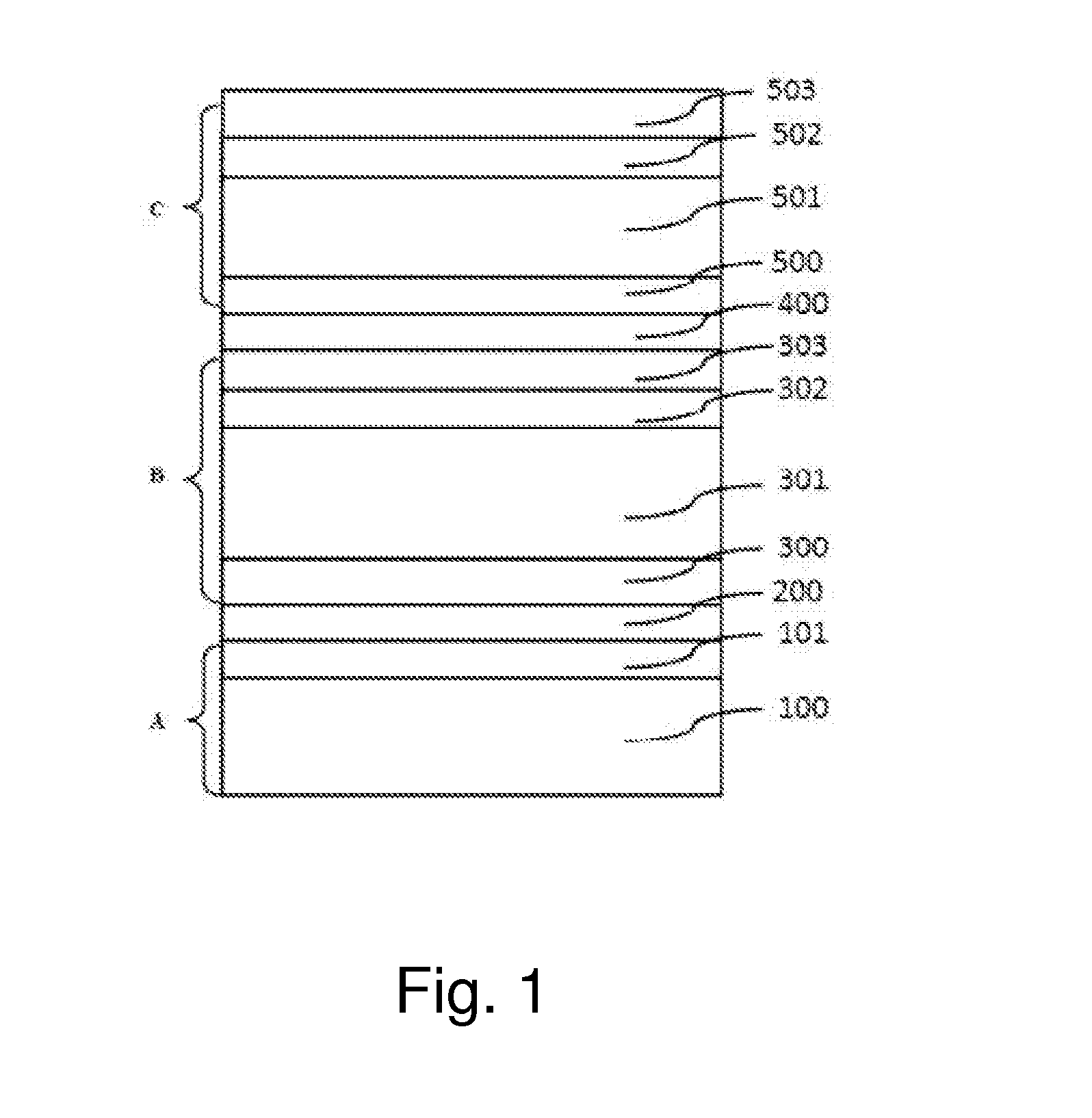
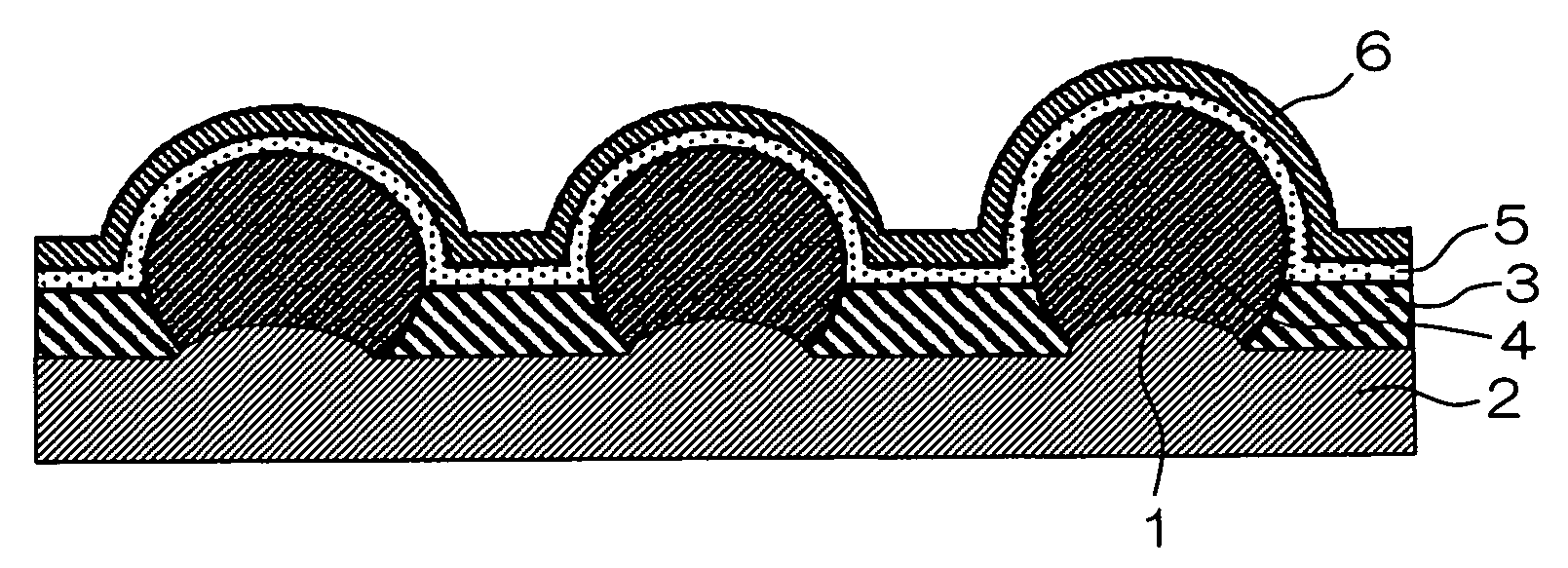
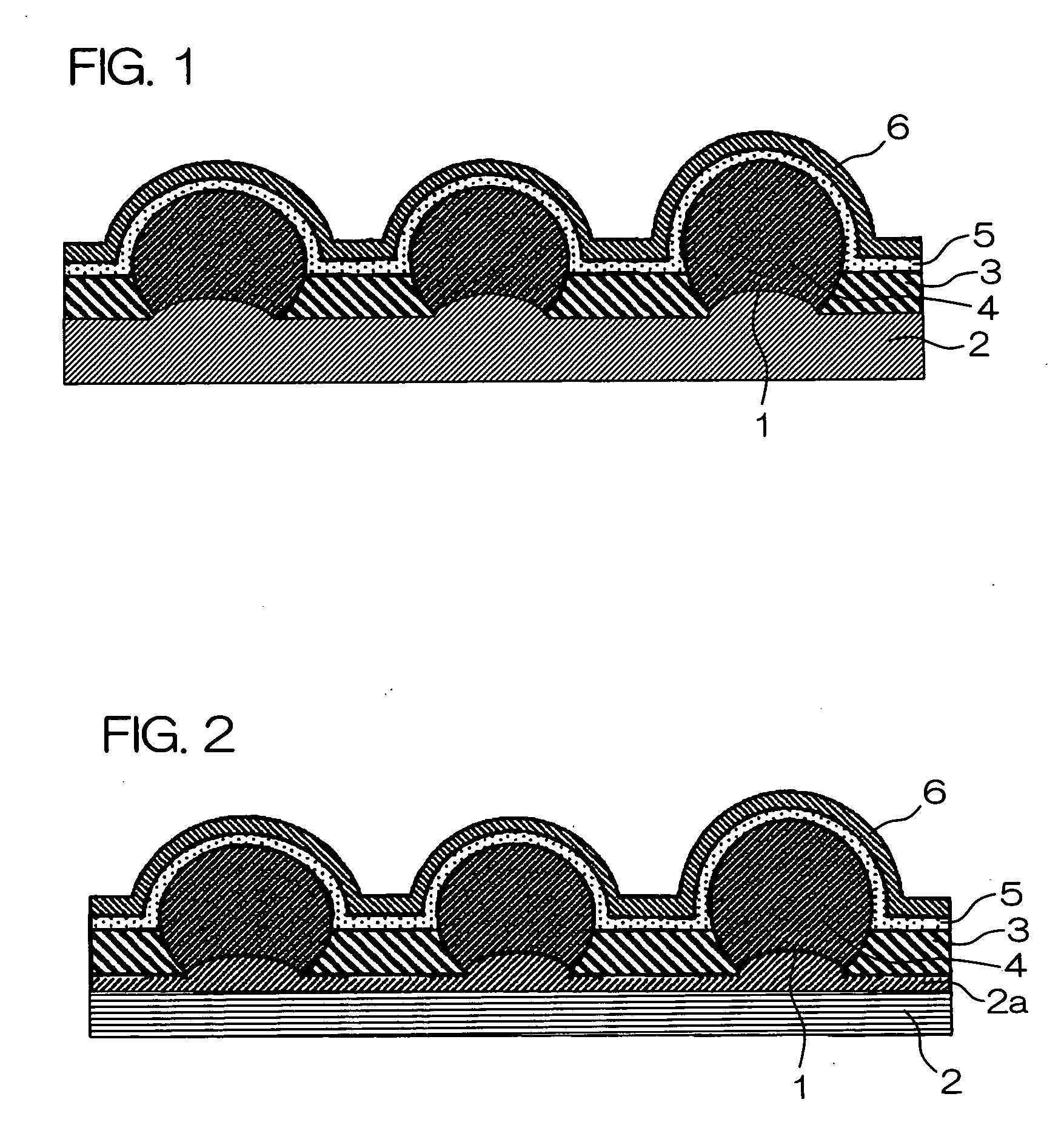
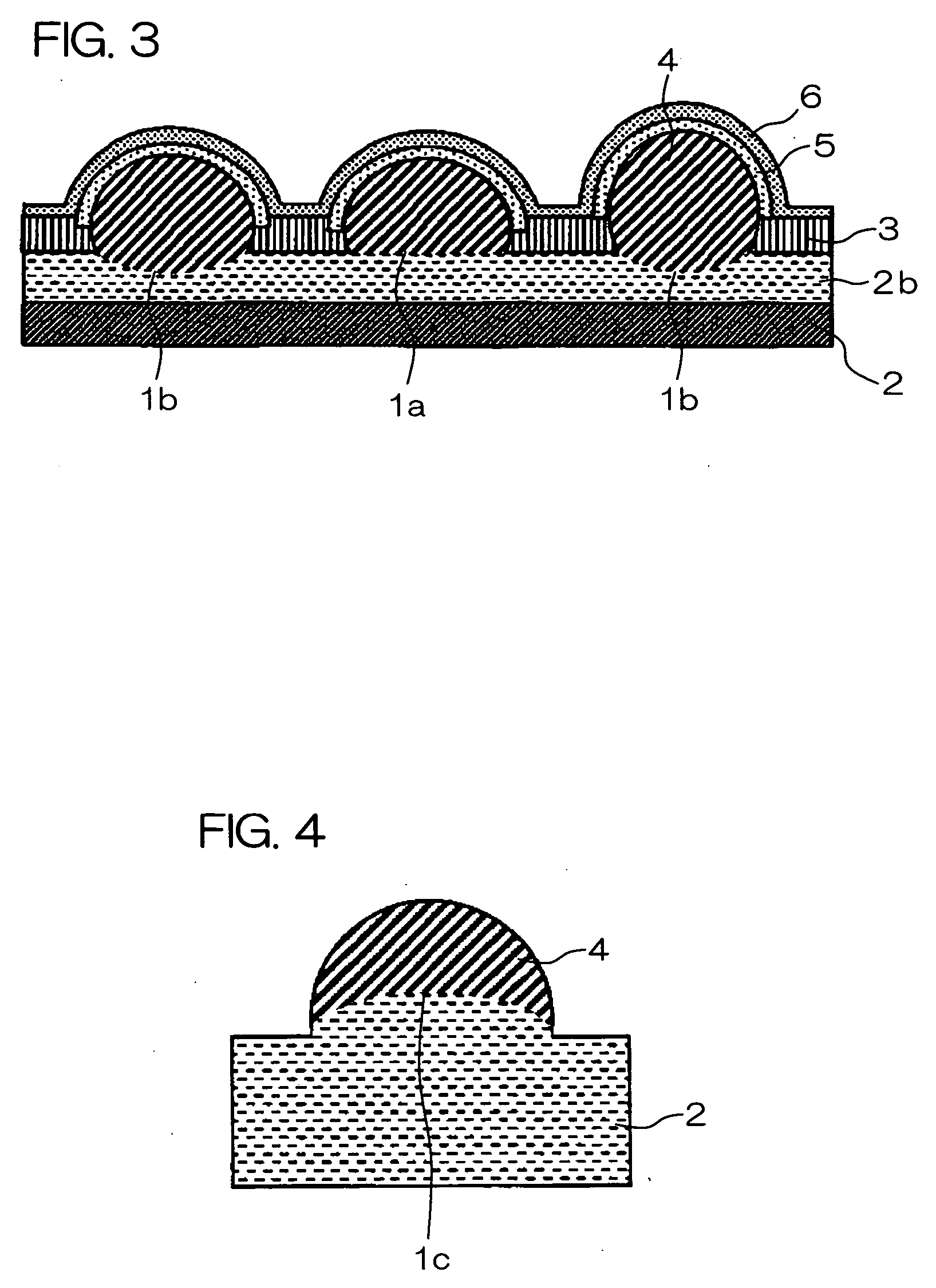
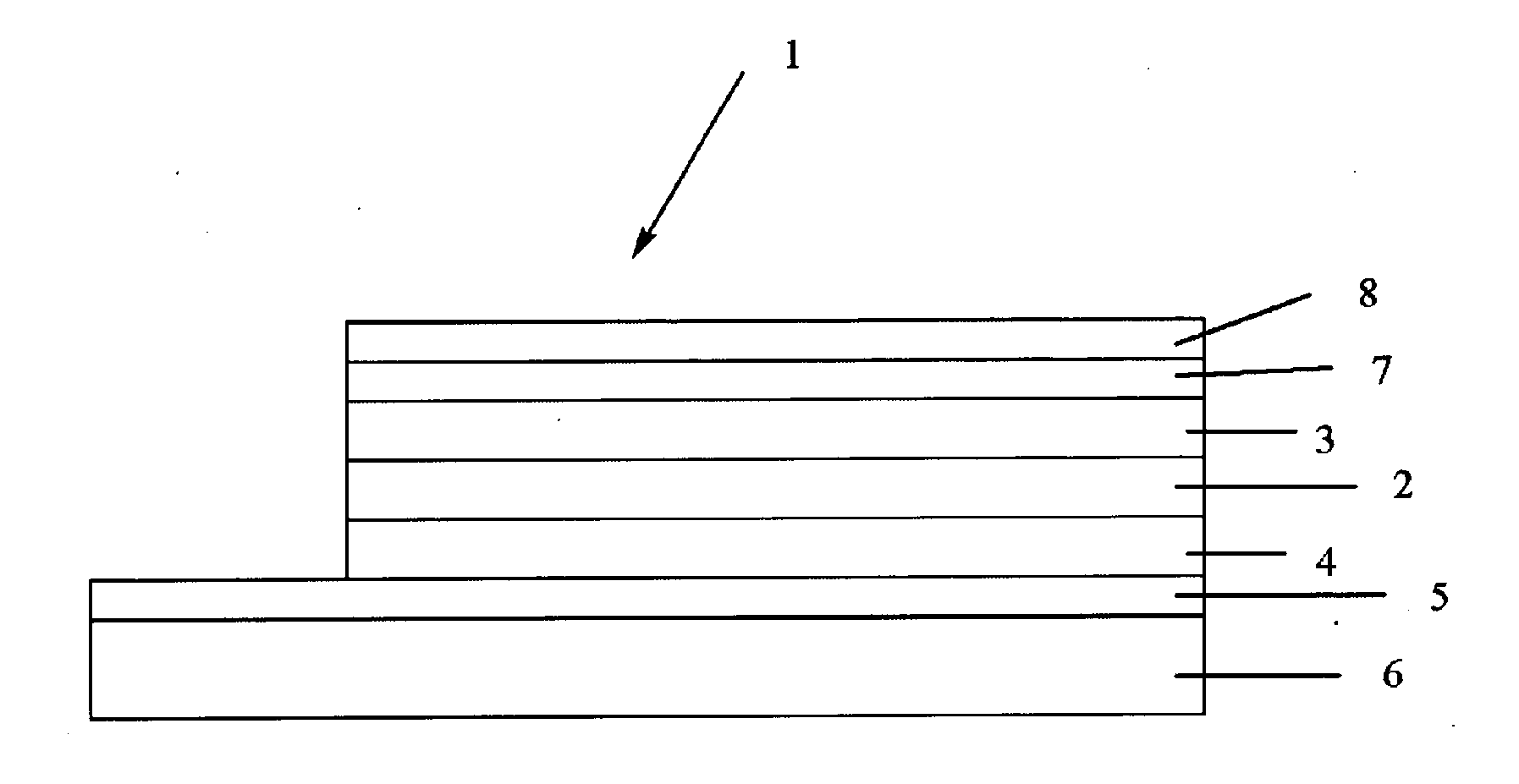
Photoelectric conversion element and solid-state imaging device
InactiveUS20080230123A1High Photoelectric Conversion EfficiencyReduce noiseMethine/polymethine dyesSolid-state devicesElectricityPhotoelectric conversion
A photoelectric conversion element comprises a first photoelectric conversion part, the first photoelectric conversion part comprising: a pair of electrodes; and a photoelectric conversion film between the pair of electrodes, wherein the photoelectric conversion film comprises an organic photoelectric conversion material having an absorption peak in an infrared region of an absorption spectrum within a combined range of a visible region and the infrared region and generating an electric charge according to light absorbed, and the first photoelectric conversion part as a whole transmits 50% or more of light in the visible region.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
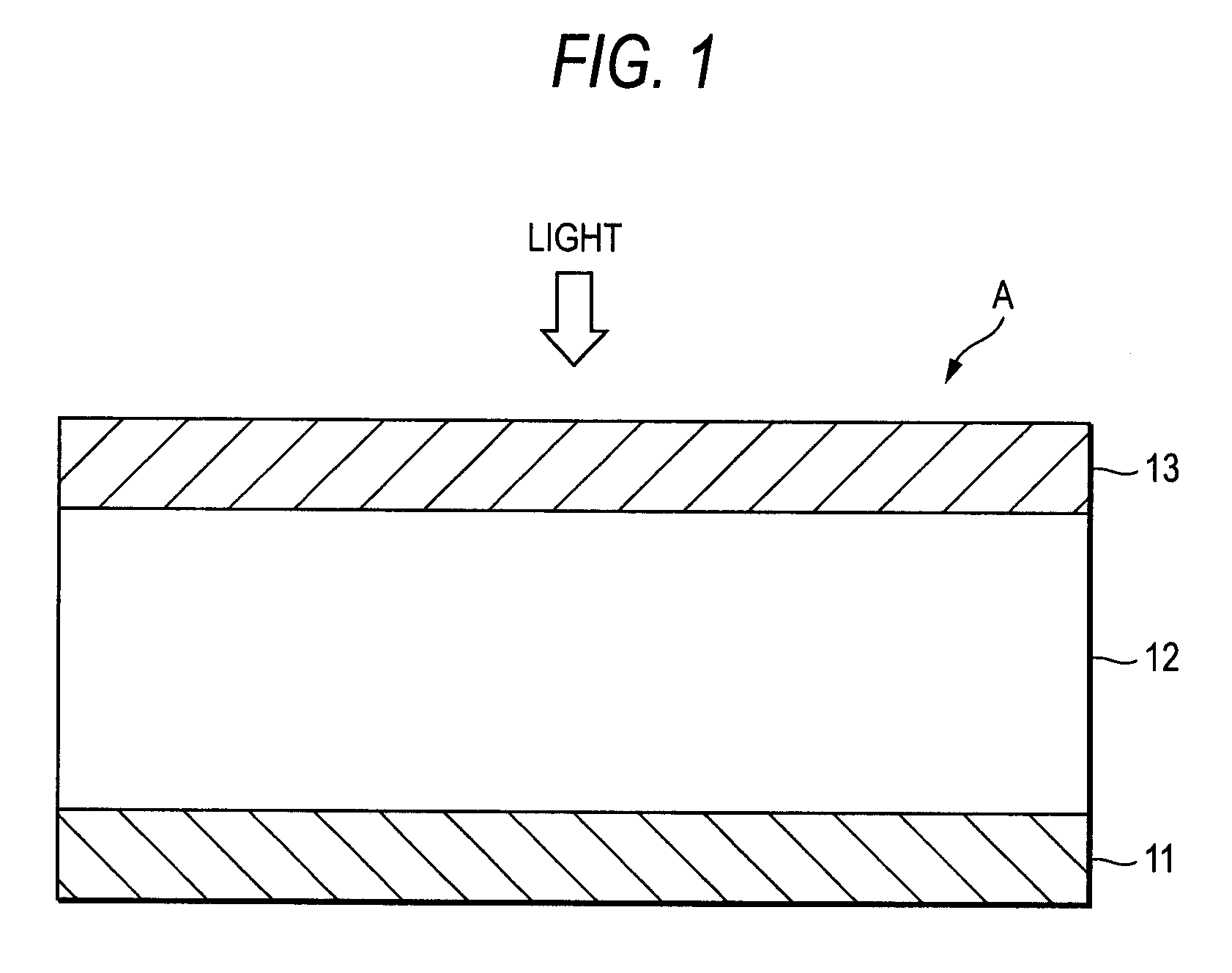
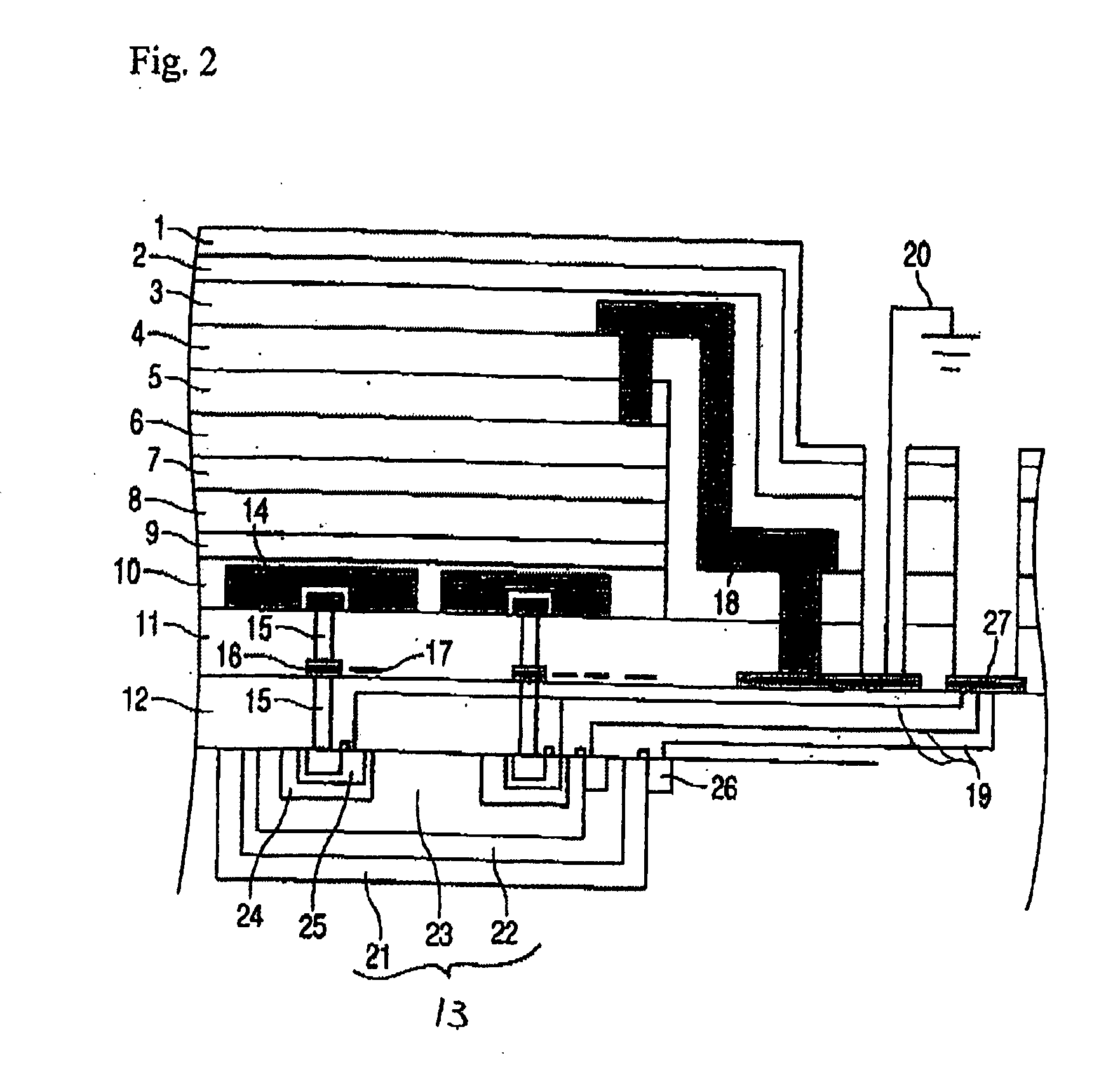
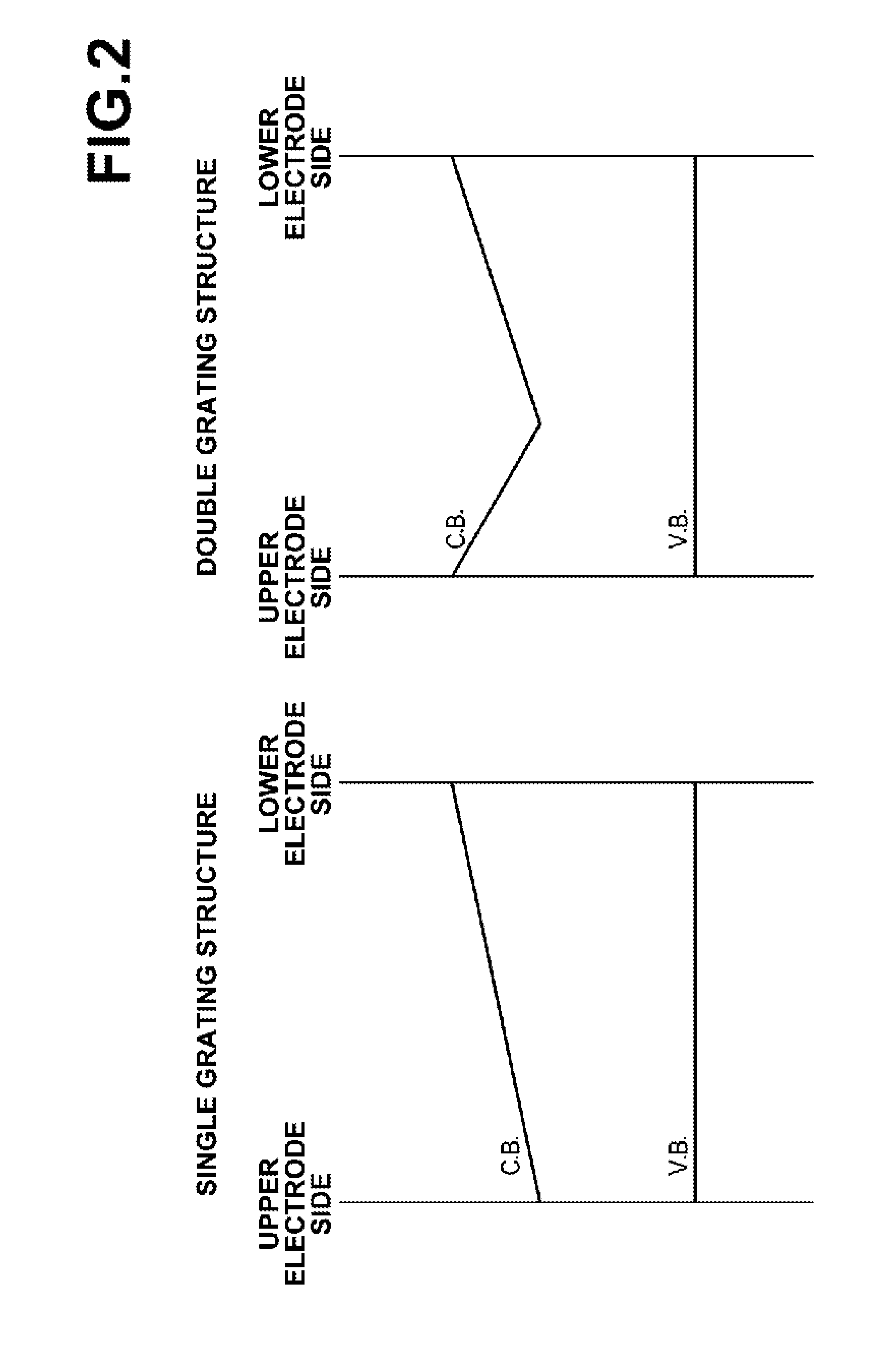
Photoelectric conversion device, image pickup device, and method for applying electric field to the same
InactiveUS20060054987A1High color reproductionIncreased durabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotoelectric conversionLength wave
A photoelectric conversion device comprises an organic photoelectric conversion film intervening between at least two electrodes, the organic photoelectric conversion film comprising a positive hole transporting photoelectric conversion film and an electron transporting photoelectric conversion film, wherein each of the positive hole transporting photoelectric conversion film and the electron transporting photoelectric conversion film has absorption in a visible range, and a difference in wavelength between longer wavelength ends of absorption of the positive hole transporting photoelectric conversion film and the electron transporting photoelectric conversion film is 50 nm or less.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
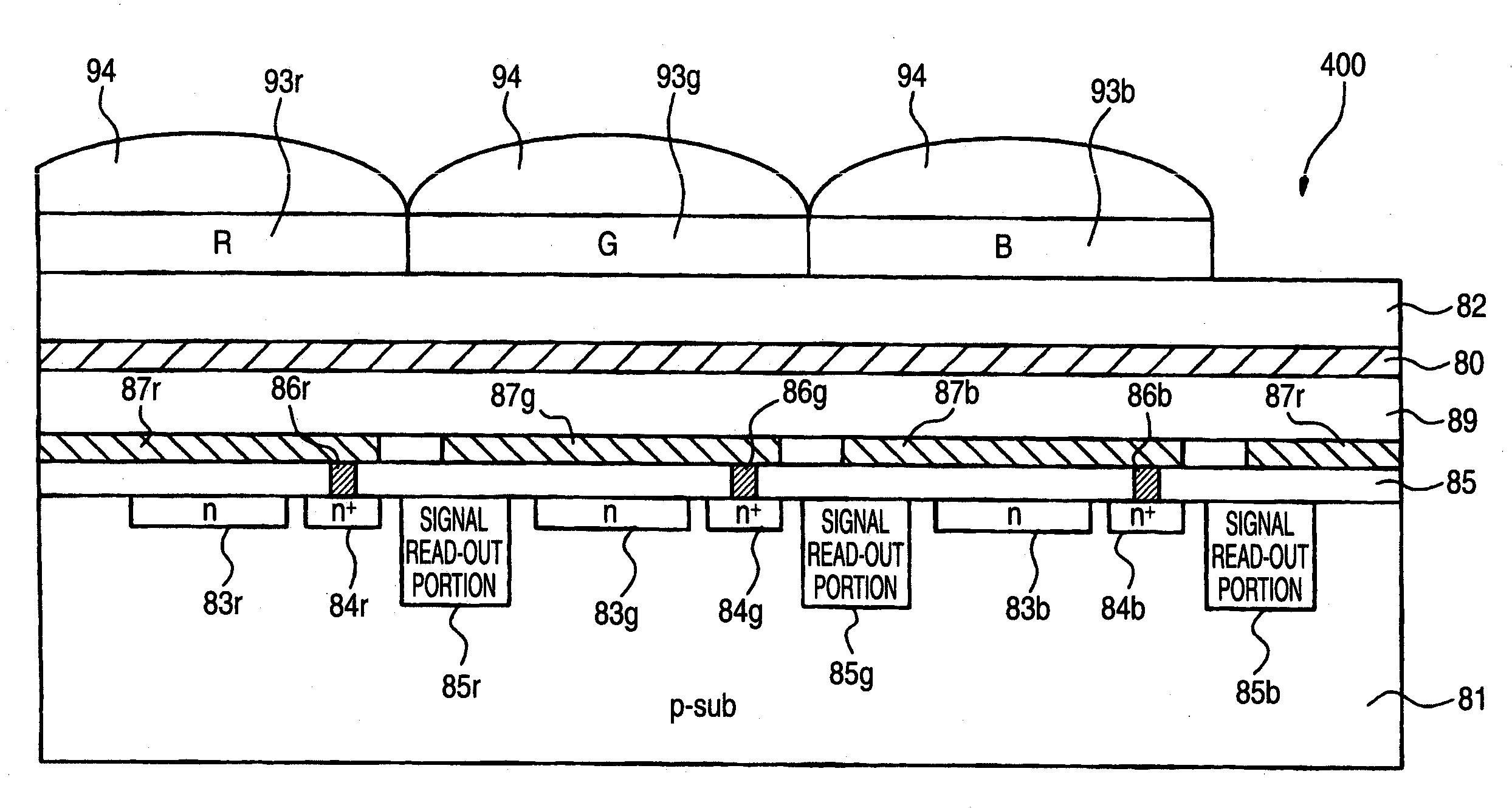
Photoelectric conversion device, imaging device, and method for driving photoelectric conversion device
InactiveUS20130087682A1High Photoelectric Conversion EfficiencyReduce dark currentMethine/polymethine dyesSolid-state devicesPhotoelectric conversionLength wave
A photoelectric conversion device includes, in the following order: a first electrode; an electron blocking layer; a photoelectric conversion layer containing a merocyanine dye; a hole blocking layer; and a transparent electrode as a second electrode, and an absorption maximum wavelength in a thin film absorption spectrum of the photoelectric conversion layer containing a merocyanine dye is within a range of from 400 to 520 nm.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
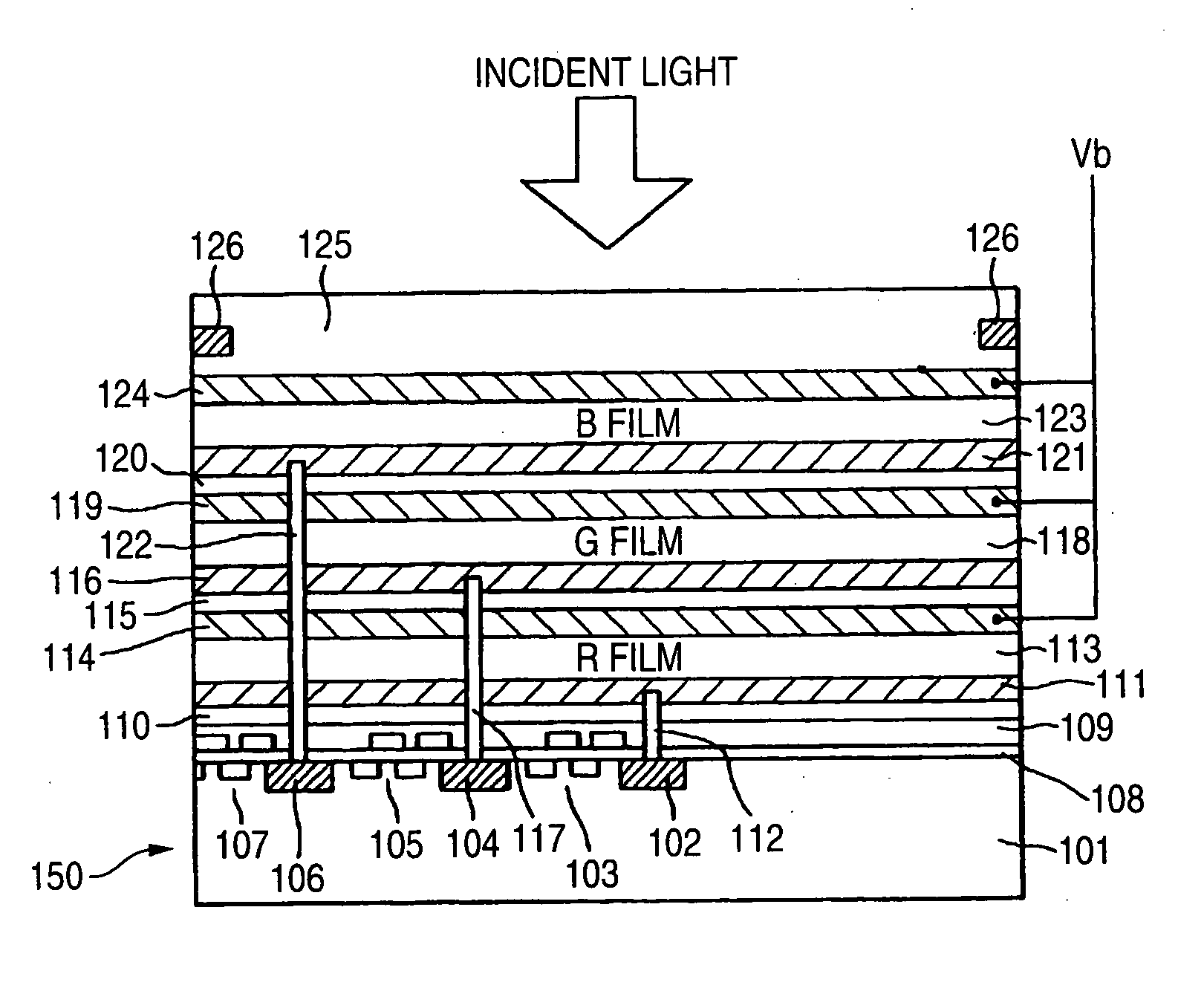
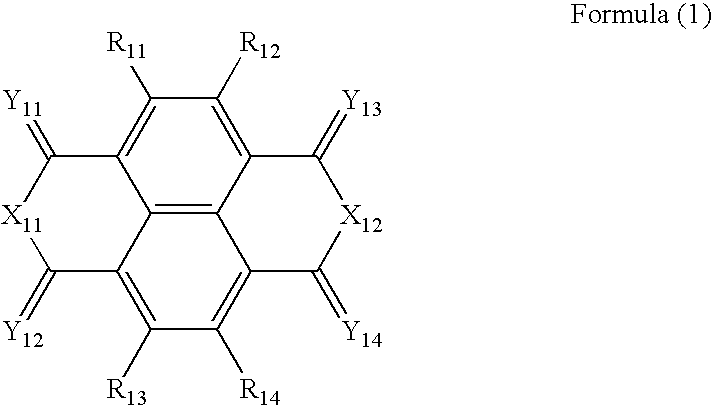
Photoelectric conversion layer, photoelectric conversion device and imaging device, and method for applying electric field thereto
InactiveUS20070052051A1High Photoelectric Conversion EfficiencyIncreased durabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogen atomPhotoelectric conversion
A photoelectric conversion layer comprising a compound represented by the following formula (1): wherein R1 to R10 each independently represents a hydrogen atom or a substituent; L represents a monovalent group or a divalent or polyvalent connecting group; m is 0 or 1; and n represents an integer of from 1 to 4.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Photoelectric conversion element and solid-state imaging device
InactiveUS20090188547A1Sufficient dark current-suppressing effectHigh Photoelectric Conversion EfficiencyPV power plantsNanoinformaticsElectrically conductiveBlock layer
A photoelectric conversion element is provided and includes: a pair of electrodes; a photoelectric conversion layer between the pair of electrodes; and a charge-blocking layer between one of the pair of the electrodes and the photoelectric conversion layer. The charge-blocking layer is capable of suppressing injection of a charge from the one of the pair of electrodes into the photoelectric conversion layer upon application of a voltage across the pair of electrodes, and the charge-blocking layer contains an insulating material and an electrically conductive material.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Image pickup device
ActiveUS20060044561A1High Photoelectric Conversion EfficiencyIncreased durabilitySolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotoelectric conversionQuinazoline
An image pickup device comprises an organic photoelectric conversion film sandwiched between at least two electrodes, wherein the organic photoelectric conversion file comprises a specific quinacridone derivative or a specific quinazoline derivative.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Method for manufacturing photoelectric conversion device
InactiveUS20100047952A1High Photoelectric Conversion EfficiencyReduce consumptionFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMonocrystalline siliconSilanes
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
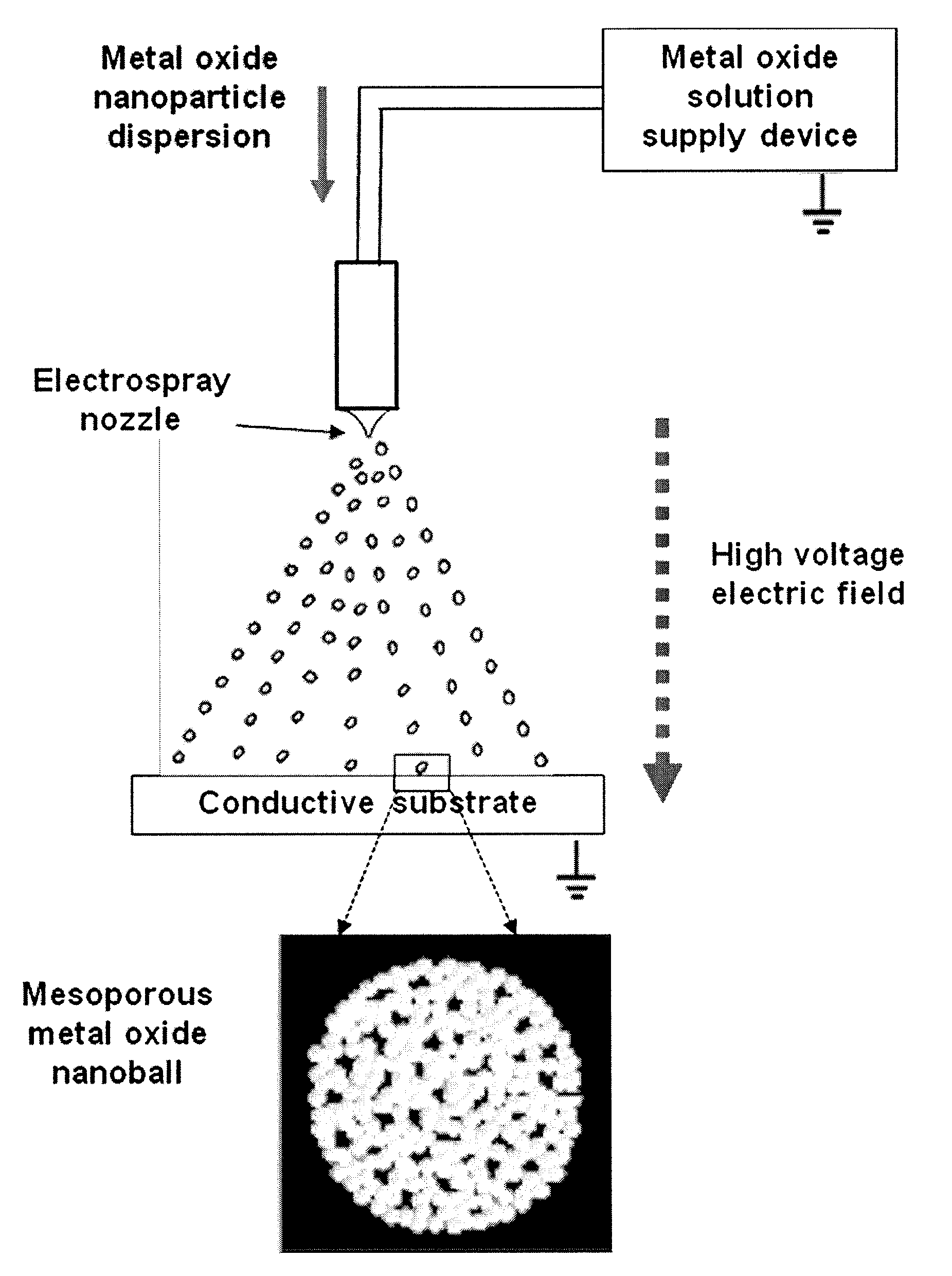
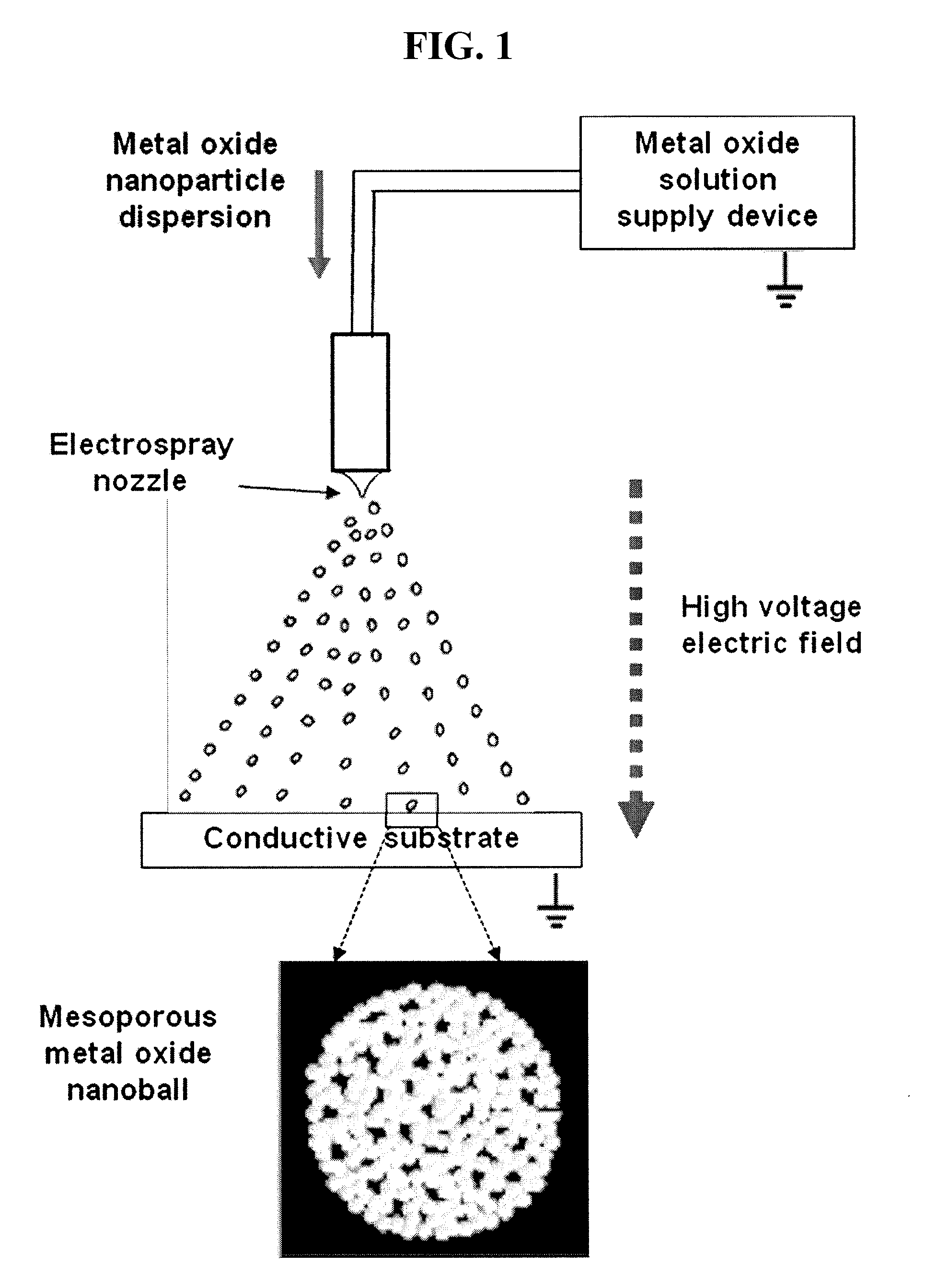
Dye-sensitized solar cell comprising metal oxide nanoball layer and preparation method thereof
ActiveUS20100084008A1Improve photoelectric conversion efficiencyImprove adsorption capacityNanotechElectrolytic capacitorsSemiconductor electrodePorosity
A dye-sensitized solar cell comprising a semiconductor electrode prepared by spraying a metal oxide nanoparticle dispersion on a conductive substrate using an electric field to form a metal oxide nanoball layer which is composed of agglomerated metal oxide nanoparticles and has a high porosity and specific surface area, exhibits improved photoelectric properties even when a gel or solid electrolyte is used.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
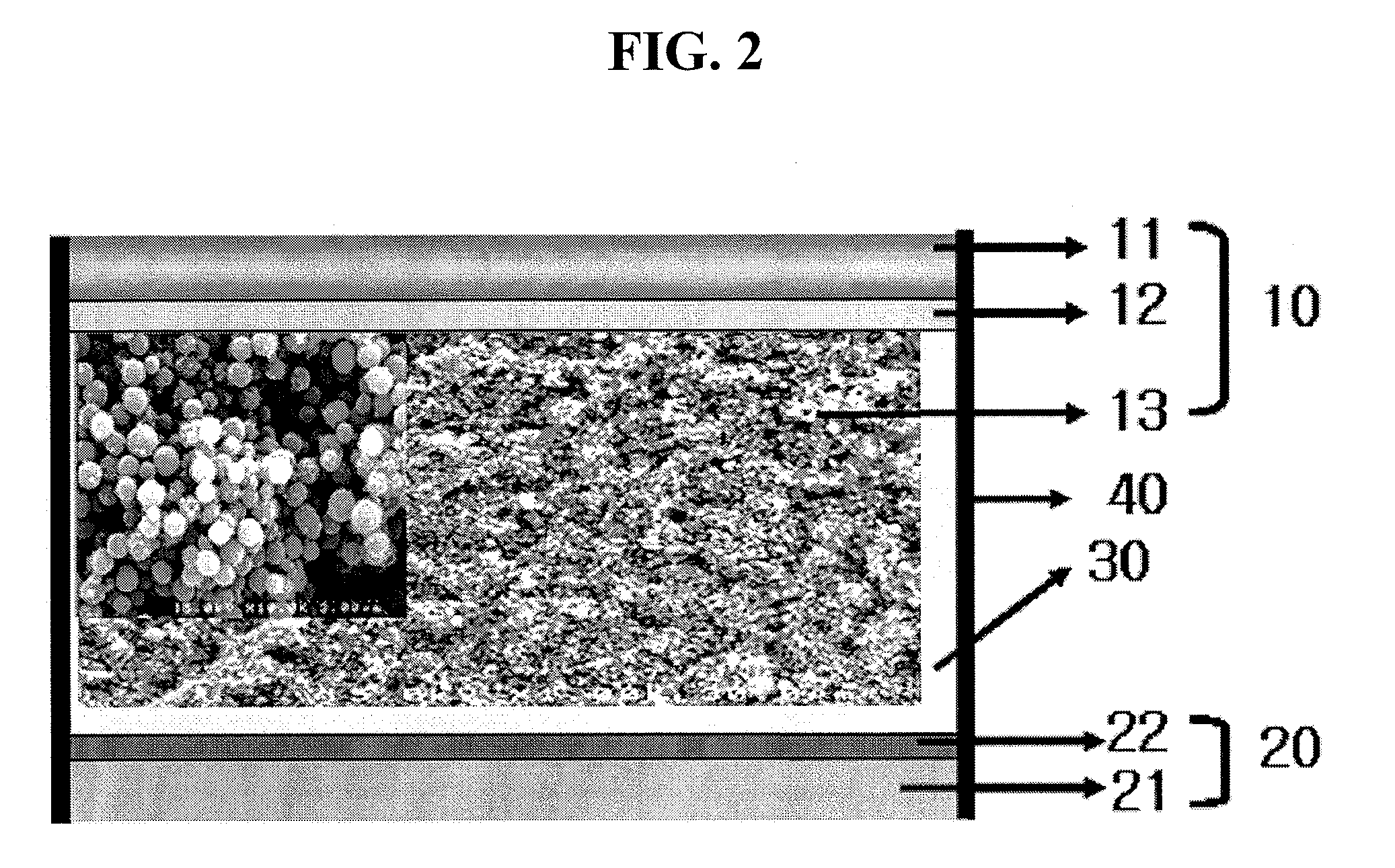
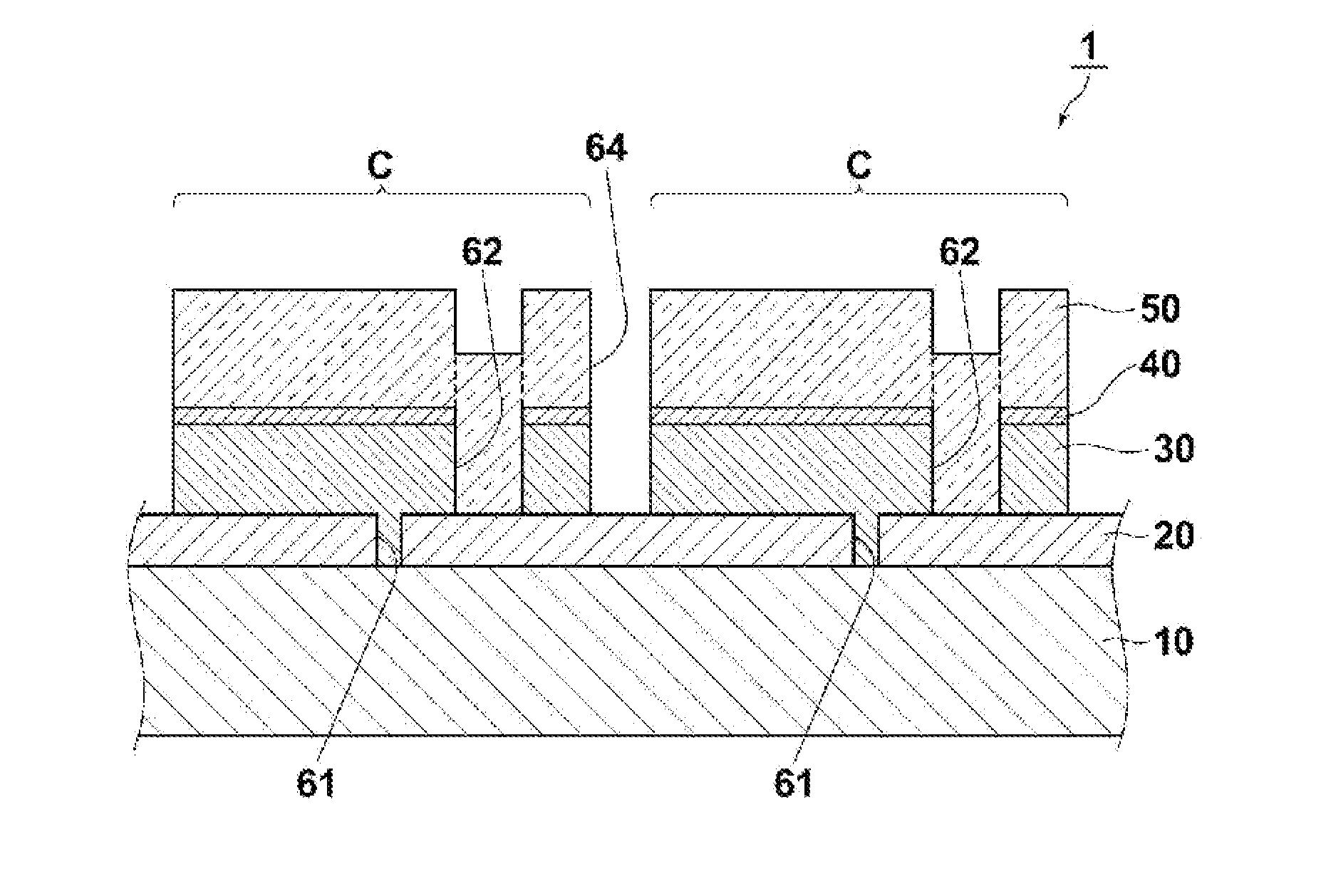
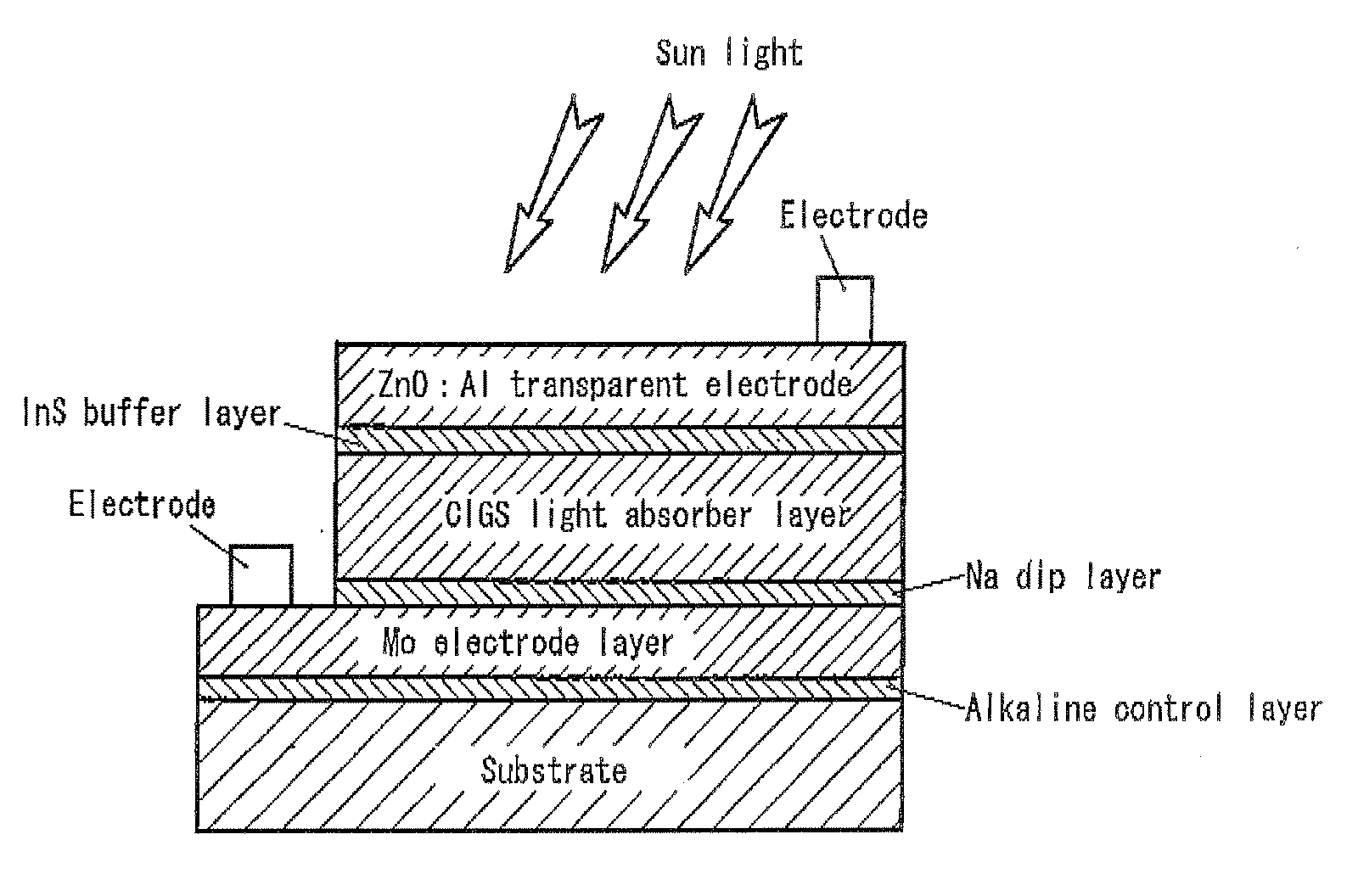
Chalcopyrite solar cell and method of manufacturing the same
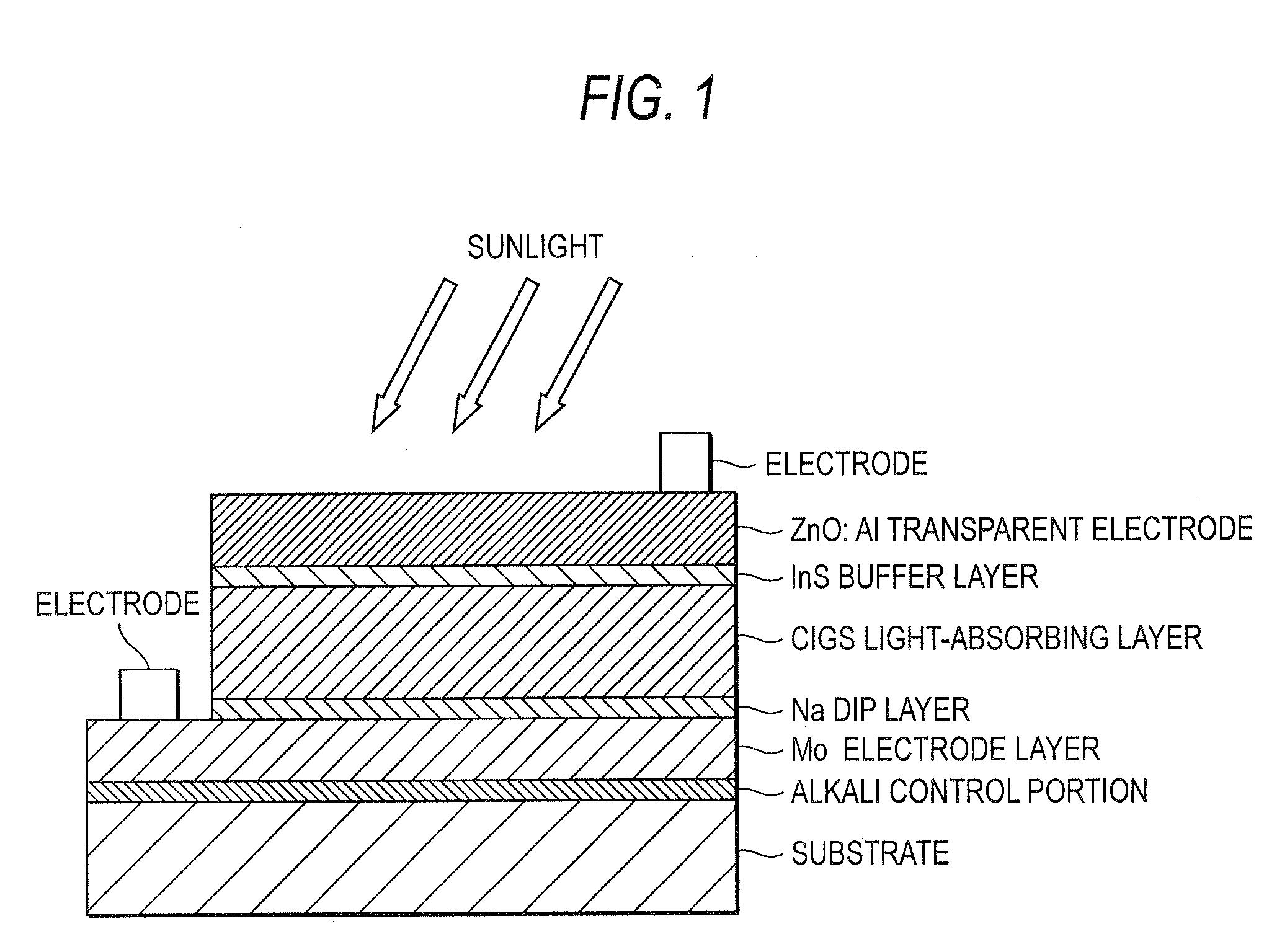
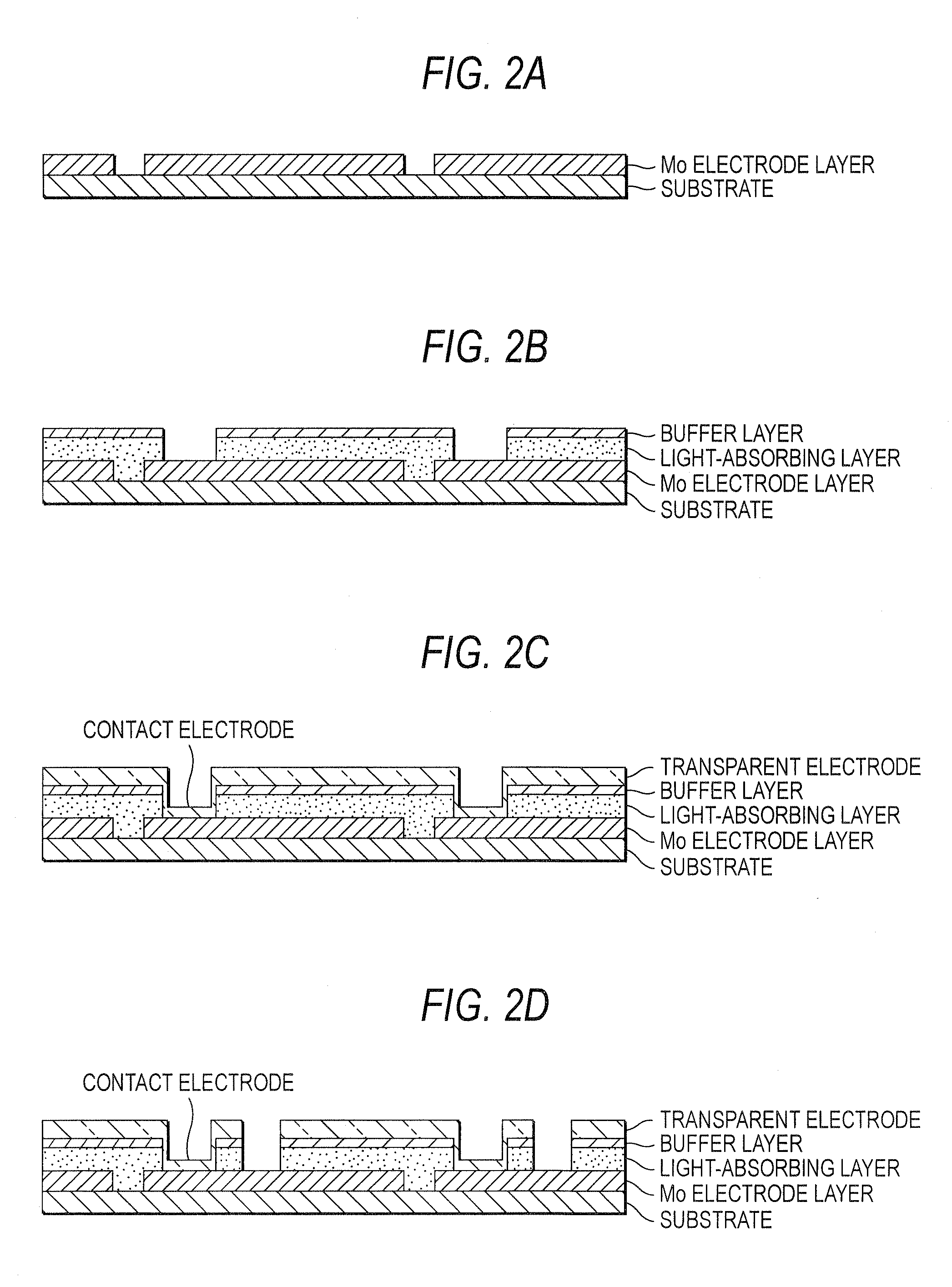
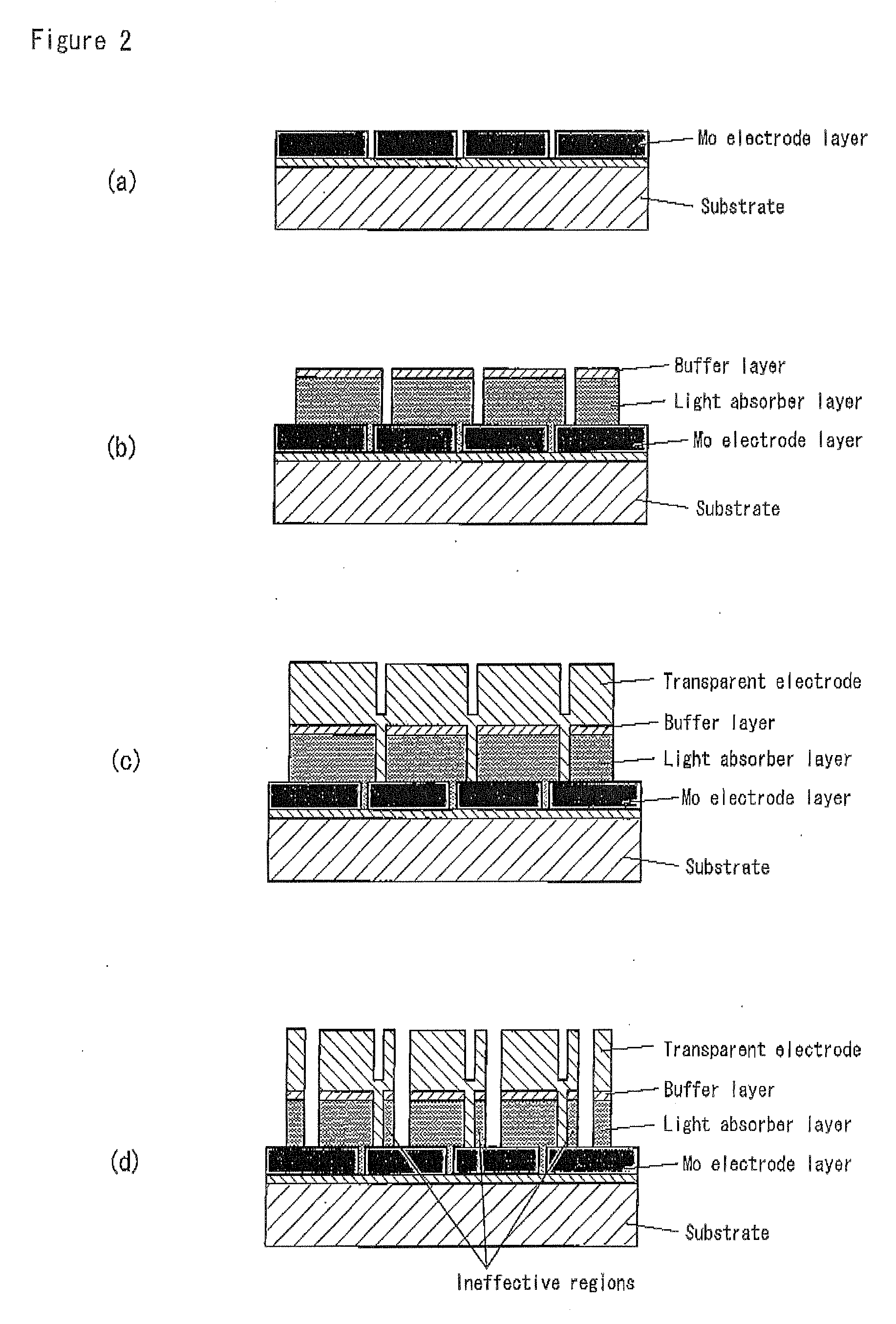
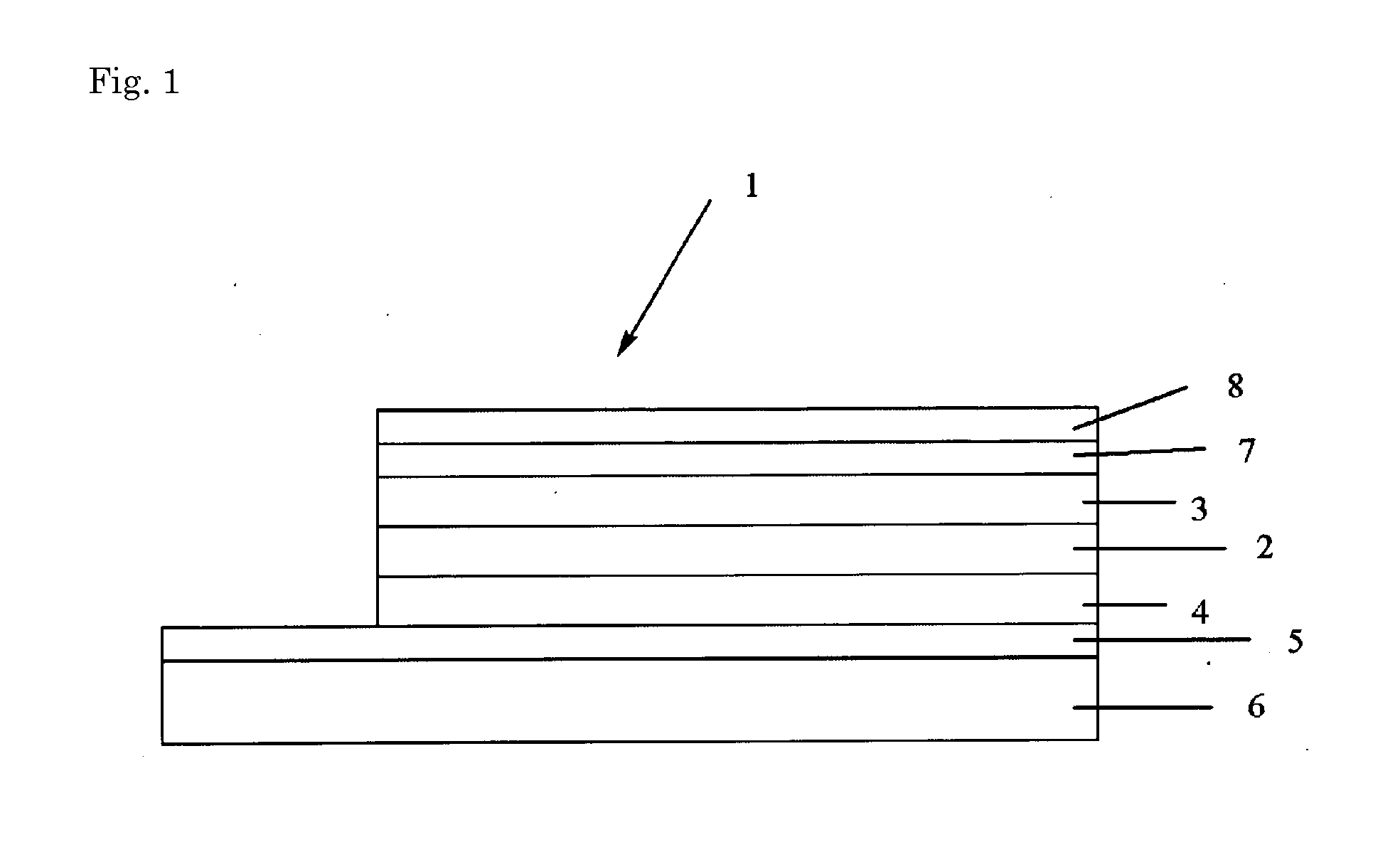
InactiveUS20080216895A1High Photoelectric Conversion EfficiencyReduce dead spaceFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh resistanceIndium
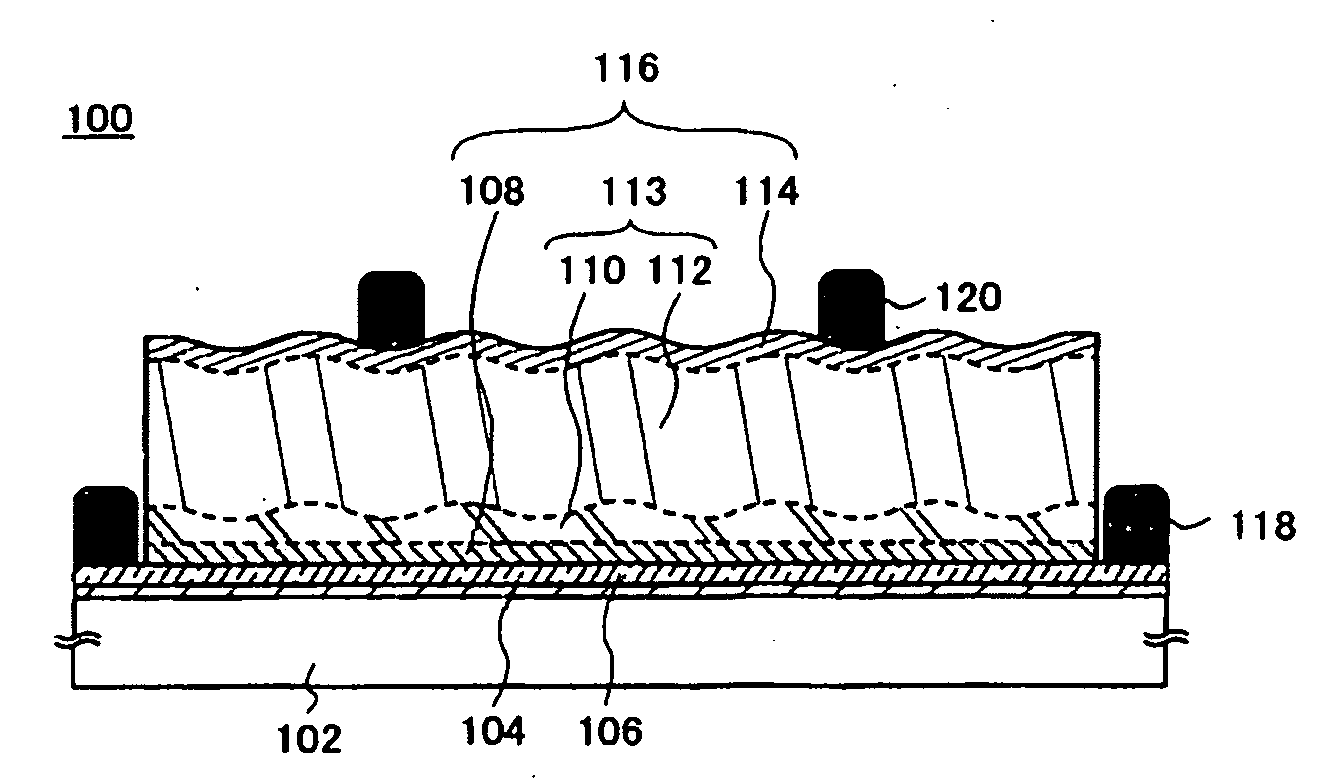
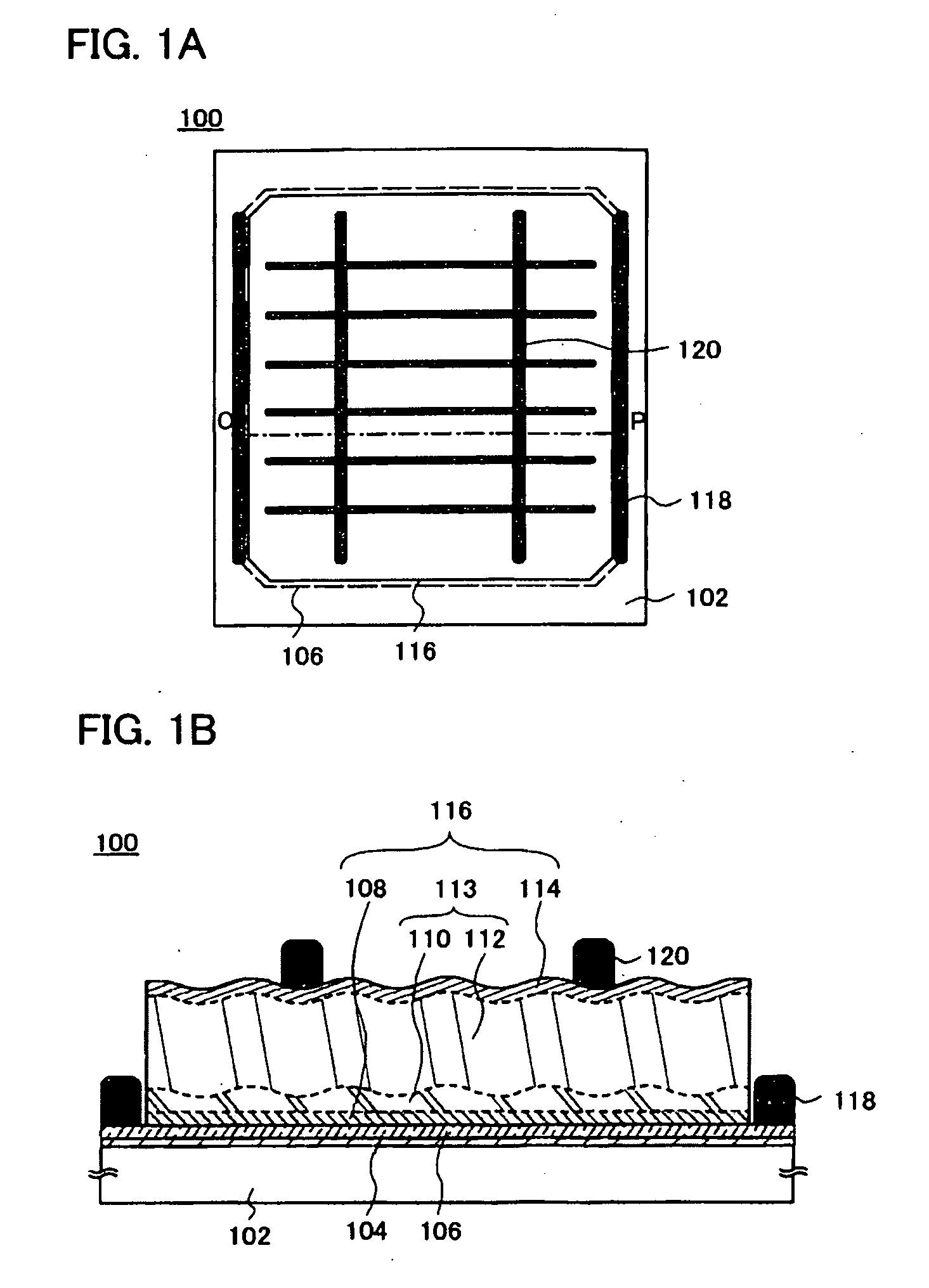
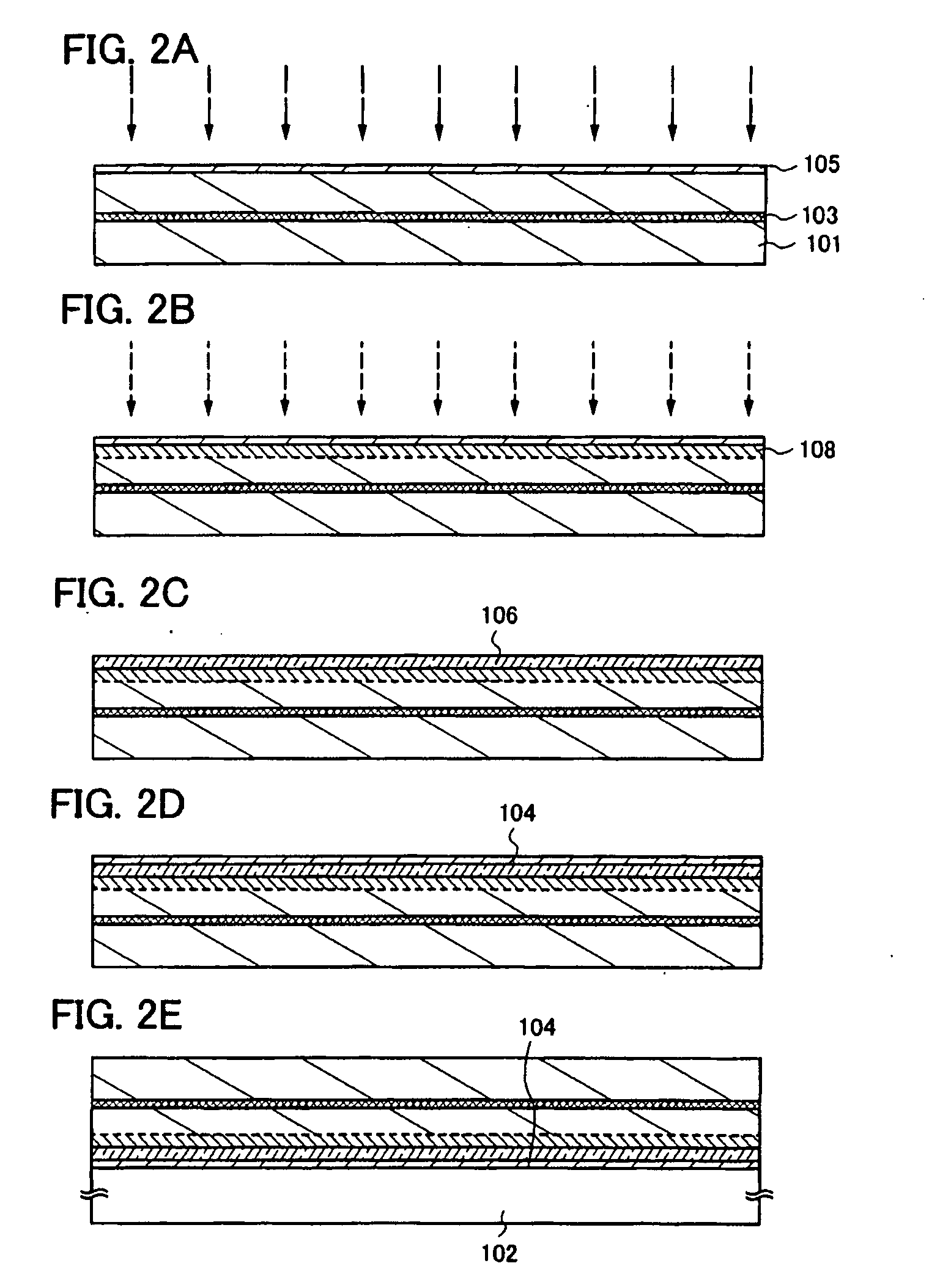
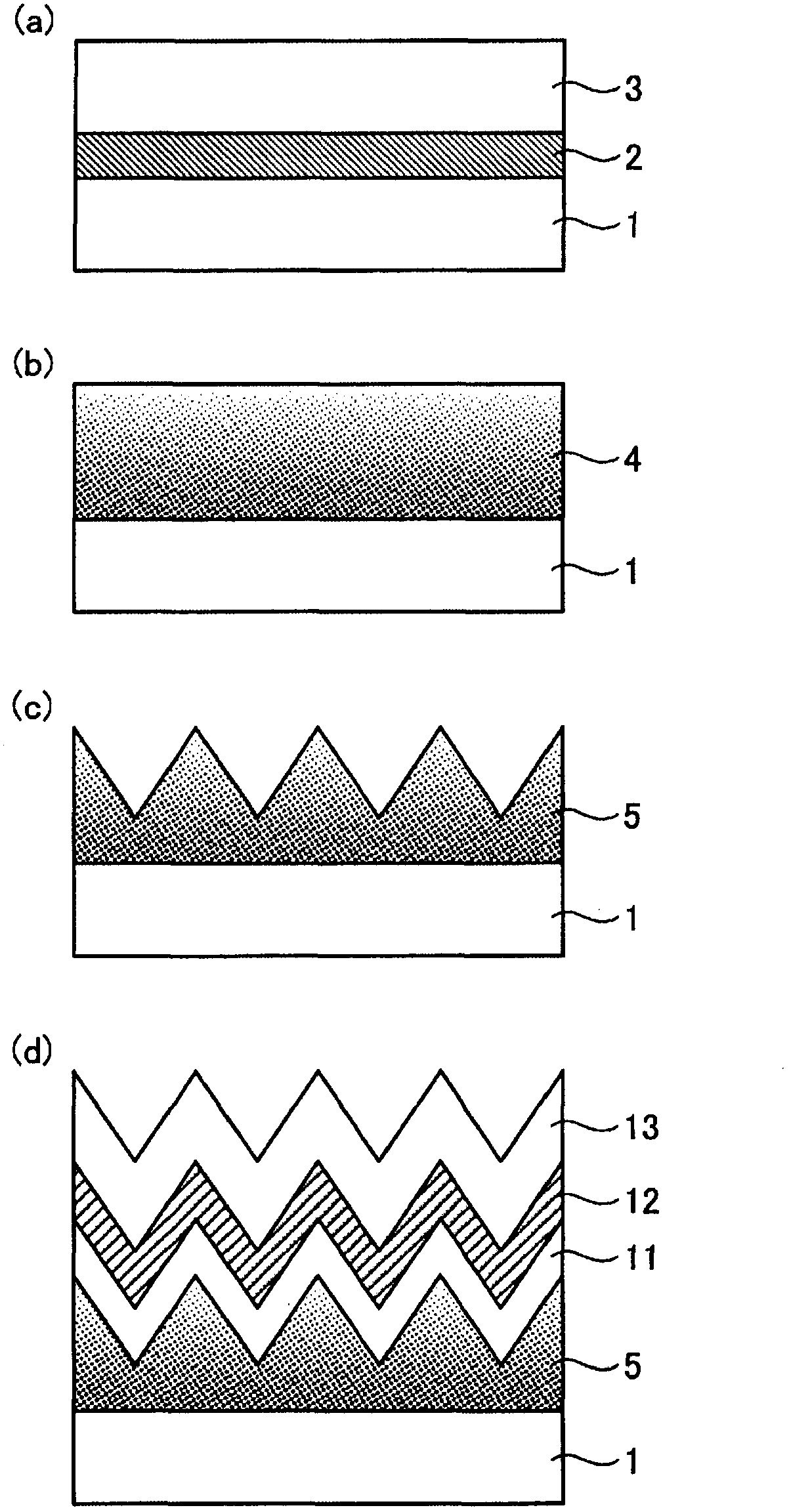
A single unit cell (herein, referred to as “a unit cell”) is formed out of a lower electrode layer (Mo electrode layer) 2 formed on a substrate 1, a light-absorbing layer (CIGS LIGHT-ABSORBING LAYER) 3 including copper, indium, gallium, and selenium, a high-resistance buffer layer thin film 4 formed of InS, ZnS, CdS, and the like on the light-absorbing layer thin film, and an upper electrode thin film (TCO) 5 formed of ZnOAl and the like. In order to connect the unit cell, a part of a contact electrode 6 connecting the upper electrode and the lower electrode is formed to overlap with a dividing line of the lower electrode 2 formed by a first scribing.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
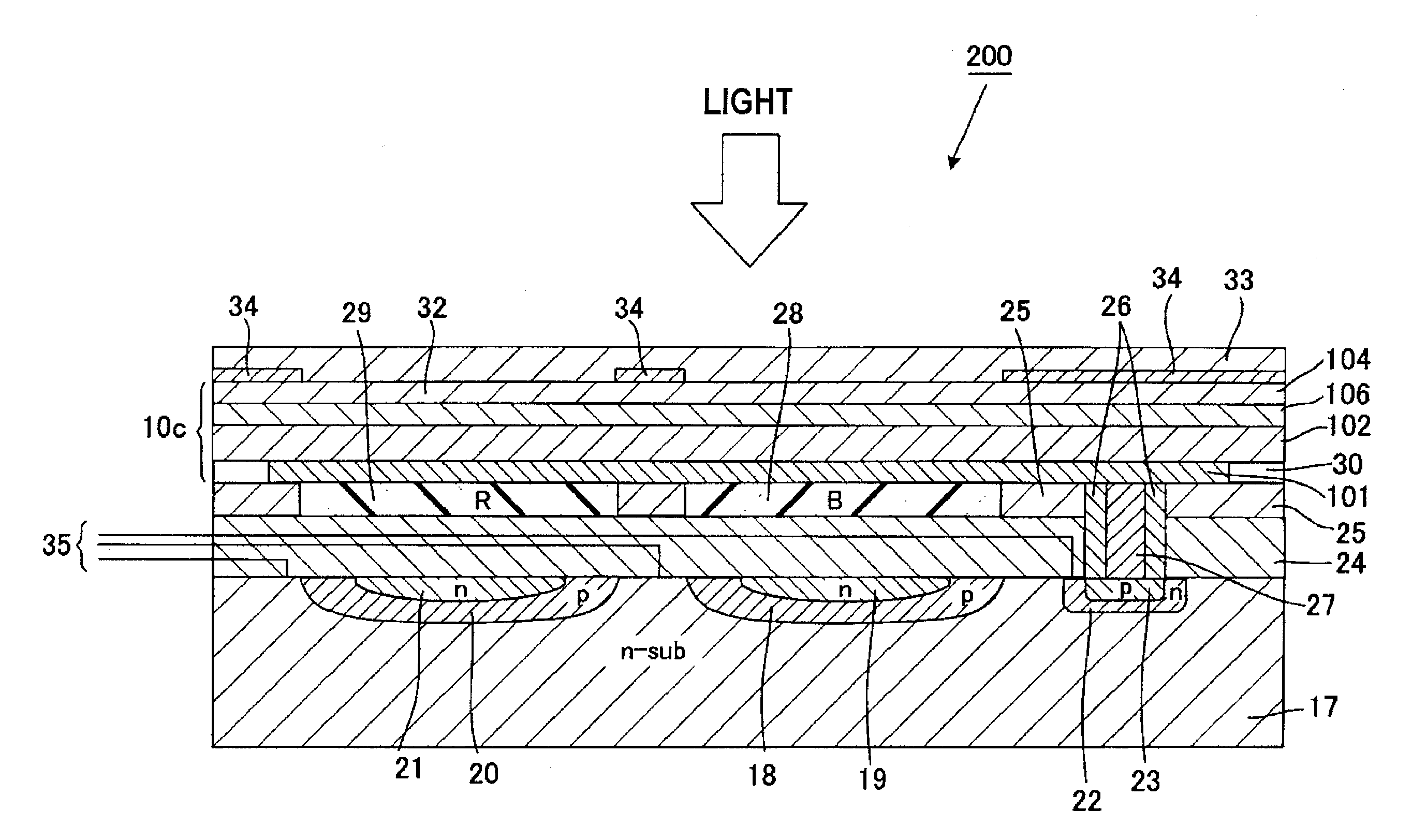
Photoelectric conversion layer, photoelectric conversion device and imaging device, and method for applying electric field thereto
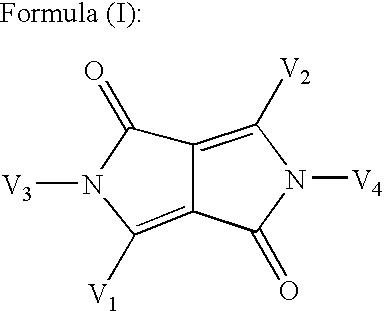
ActiveUS20060278869A1High Photoelectric Conversion EfficiencyHigh color reproductionTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesElectric fieldPhotochemistry
A photoelectric conversion layer comprising a compound represented by the following formula (I): wherein V1, V2, V3 and V4 each independently represents a hydrogen atom or a substituent.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Photoelectric conversion element and method of using the same, image sensor, and optical sensor
ActiveUS20140158859A1High Photoelectric Conversion EfficiencyLower average currentNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesGlass transition pointBlocking layer
A photoelectric conversion element includes a transparent conductive film, a conductive film, and a photoelectric conversion layer and an electron-blocking layer disposed between the transparent conductive film and the conductive film. The photoelectric conversion layer includes a condensed polycyclic hydrocarbon which contains at least 5 benzene rings, of which a total number of rings is 7 or more and which contains no carbonyl group. The electron-blocking layer includes a compound A having a residue after removal of at least one group of Ra1 to Ra9 from a compound represented by general formula (A) and having a glass transition point (Tg) of 200° C. or more. The photoelectric conversion element exhibits high photoelectric conversion efficiency and low dark current characteristics even after heating treatment, and can be manufactured with high productivity.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Thin-film type solar cell and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20100059100A1Reduce frequencyIncrease cost reducing effectPV power plantsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringSolar cell
Disclosed are a method for manufacturing a thin-film type solar cell and a thin-film type solar cell obtained thereby that uses a direct printing method and reduces the frequency of a cutting process.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Photoelectric conversion element and imaging device
ActiveUS20090085029A1High Photoelectric Conversion EfficiencyReduce dark currentSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotoelectric conversionElectron
A photoelectric conversion element is provided and includes: a conductive thin layer; an organic photoelectric conversion layer including a compound represented by formula (I); and a transparent conductive thin layer, in this order:In the formula (I), X represents O, S or N—R10; Rx and Ry each independently represents a hydrogen atom or a substituent, at least one of Rx and Ry is an electron-withdrawing group, and Rx and Ry may be connected to each other to form a ring, provided that Rx and Ry do not represent a cyano group at the same time; R7 to R10 each independently represents a hydrogen atom or a substituent, and R8 and R9 may be connected to each other to form a ring; L represents a linking group comprising a conjugated bond; and D1 represents a group of atoms.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Silicon-based thin-film photoelectric conversion device, and method and apparatus for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20100147379A1Quality improvementHigh Photoelectric Conversion EfficiencyFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPresent methodEngineering
A present method of manufacturing a silicon-based thin-film photoelectric conversion device is characterized in that a double pin structure stack body is formed by successively forming, in an identical plasma CVD film deposition chamber, a first p-type semiconductor layer, an i-type amorphous silicon-based photoelectric conversion layer, a first n-type semiconductor layer, a second p-type semiconductor layer, an i-type microcrystalline silicon-based photoelectric conversion layer, and a second n-type semiconductor layer on a transparent conductive film formed on a substrate, and the first p-type semiconductor layer, the i-type amorphous silicon-based photoelectric conversion layer and the first n-type semiconductor layer are formed under such conditions that a film deposition pressure in the plasma CVD film deposition chamber is not lower than 200 Pa and not higher than 3000 Pa and power density per unit electrode area is not lower than 0.01 W / cm2 and not higher than 0.3 W / cm2. Thus, the silicon-based thin-film photoelectric conversion device attaining excellent quality and high photoelectric conversion efficiency can be manufactured at low cost and high efficiency using a simplified manufacturing apparatus.
Owner:SHARP KK
Photoelectric conversion semiconductor layer, manufacturing method thereof, photoelectric conversion device, and solar cell
InactiveUS20120017977A1Low costHigh Photoelectric Conversion EfficiencyAnodisationFinal product manufactureEngineeringBand gap
A photoelectric conversion semiconductor layer is provided which is capable of providing a potential gradient in the thickness direction, can be manufactured at a lower cost than a layer formed by vacuum film forming, and capable of providing high photoelectric conversion efficiency. The photoelectric conversion semiconductor layer is a layer that generates a current by absorbing light and is formed of a particle layer in which a plurality of particles is disposed in plane and thickness directions. Preferably, the photoelectric conversion semiconductor layer includes, as the plurality of particles, a plurality of types of particles having different band-gaps, and the potential in the thickness direction of the layer is distributed.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
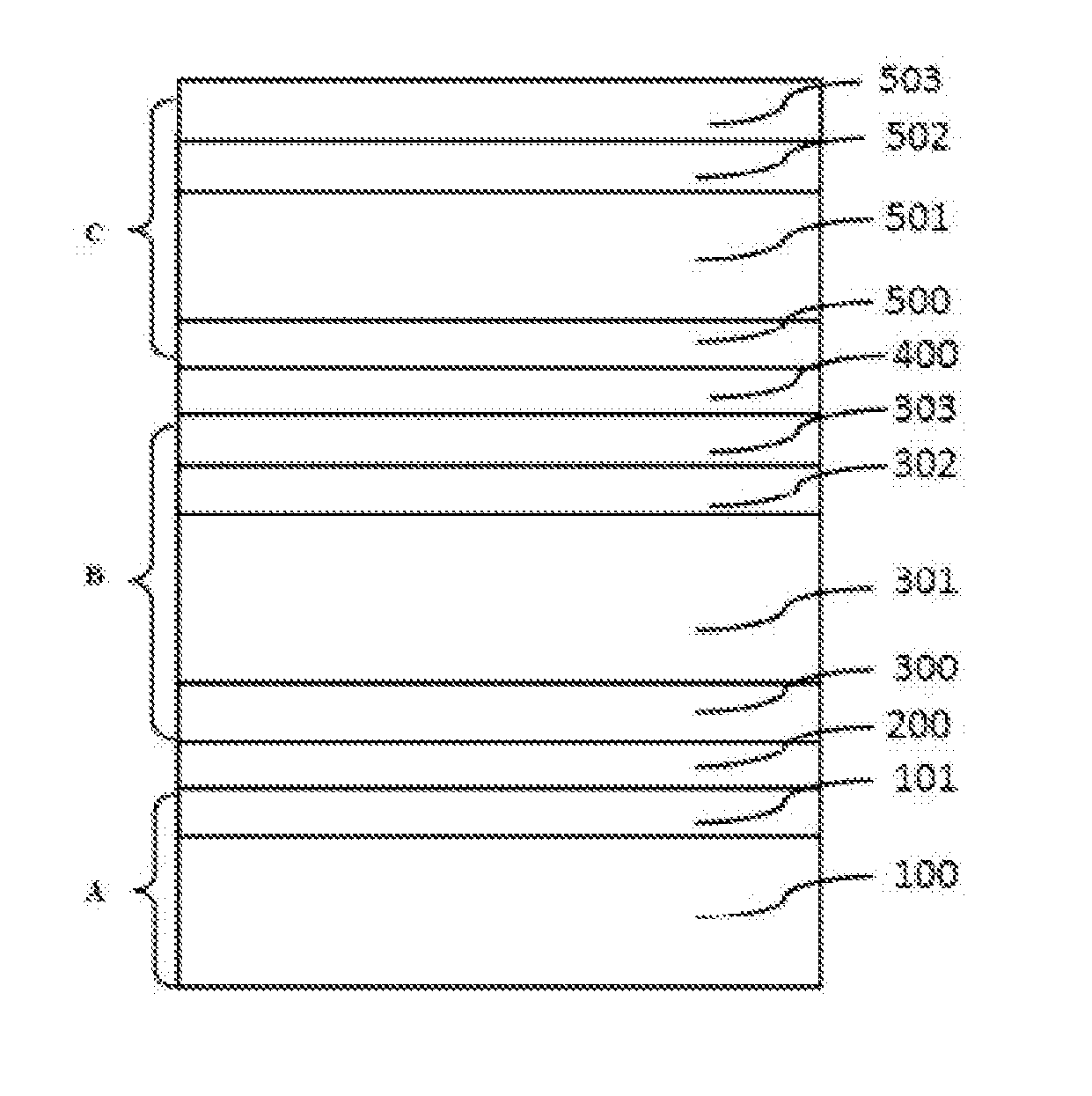
Compound semiconductor device
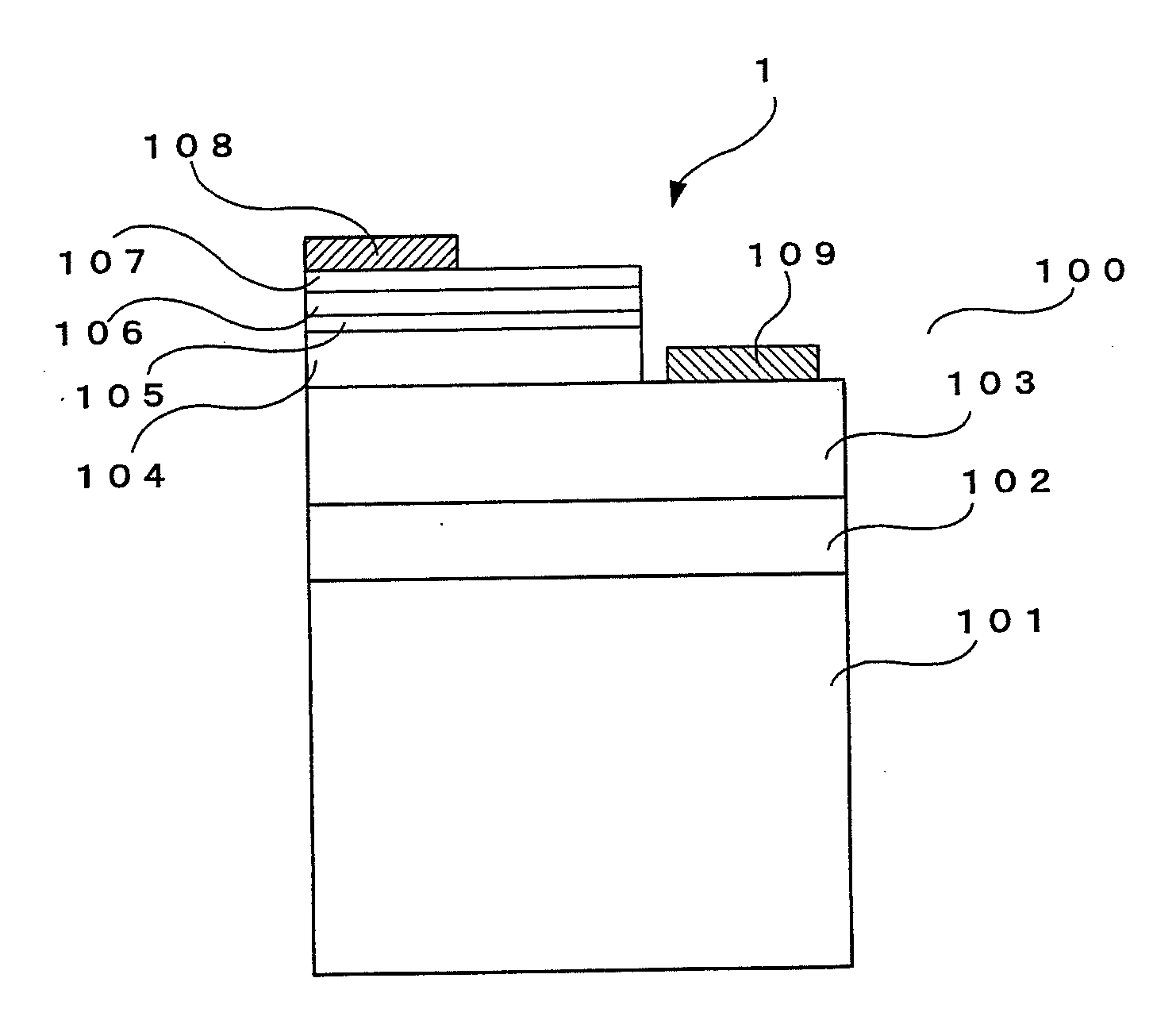
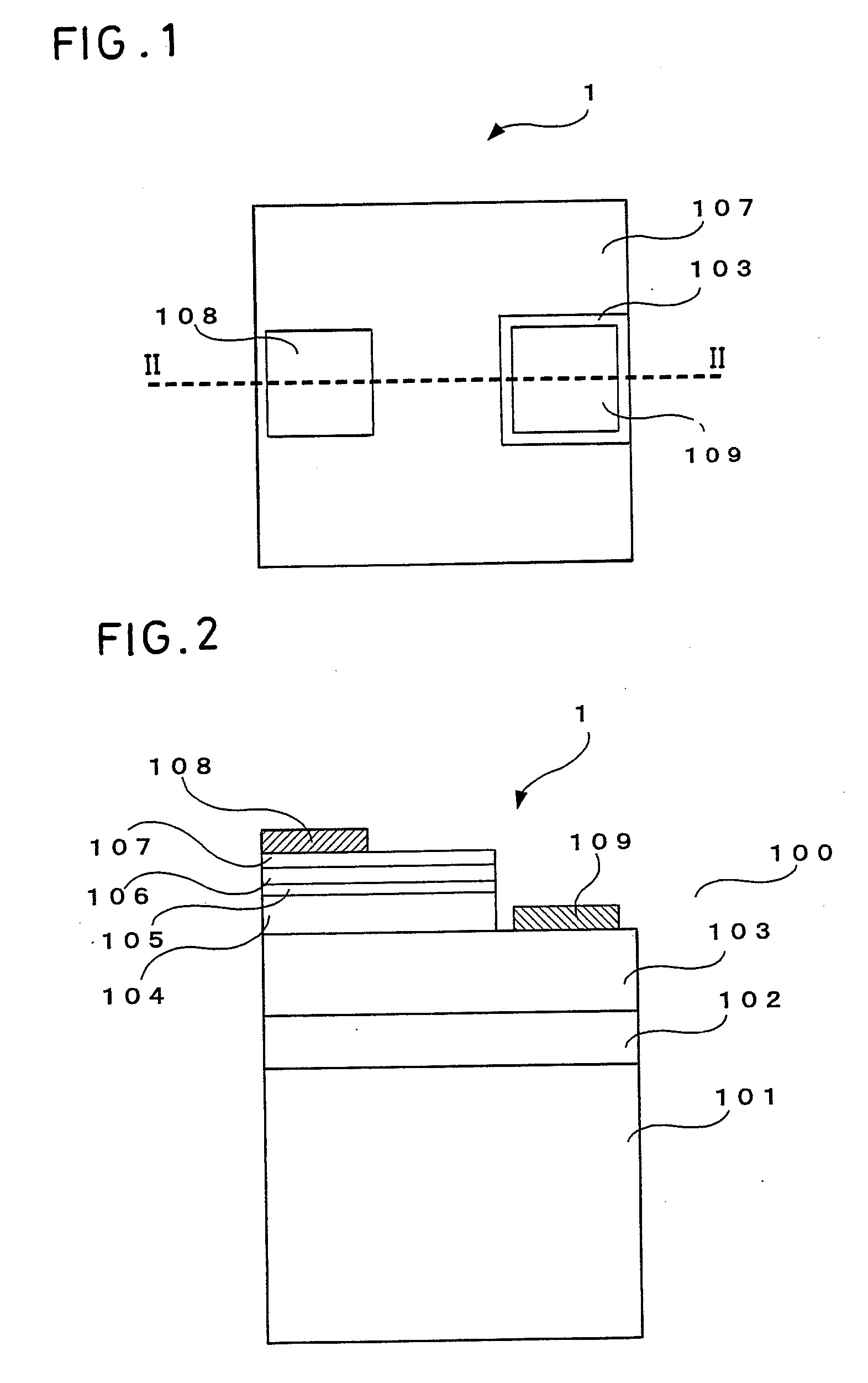
InactiveUS20090309135A1High Photoelectric Conversion EfficiencyLow flow resistanceSemiconductor devicesSingle crystalCondensed matter physics
A compound semiconductor device (1) includes a compound semiconductor having a stacked structure (100) of a hexagonal single crystal layer (101), a boron phosphide-based semiconductor layer (102) formed on a surface of the hexagonal single crystal layer and a compound semiconductor layer (103) disposed on the boron phosphide-based semiconductor layer, and electrodes (108, 109) disposed on the stacked structure, wherein the boron phosphide-based semiconductor layer is formed of a hexagonal crystal disposed on a surface formed of a (1.1.-2.0.) crystal face of the hexagonal single crystal layer.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Photoelectric conversion layer, photoelectric conversion device and imaging device, and method for applying electric field thereto
InactiveUS20060273362A1Narrow widthHigh color reproductionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogen atomSulfur
A photoelectric conversion layer comprising a compound represented by the following formula (1): wherein R11 to R14 each independently represents a hydrogen atom or a substituent; X11 and X12 each independently represents a substituted or unsubstituted carbon atom, a substituted or unsubstituted nitrogen atom, an oxygen atom, or a sulfur atom; and Y11 to Y14 each independently represents a substituted or unsubstituted carbon atom, a substituted or unsubstituted nitrogen atom, an oxygen atom, or a sulfur atom.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
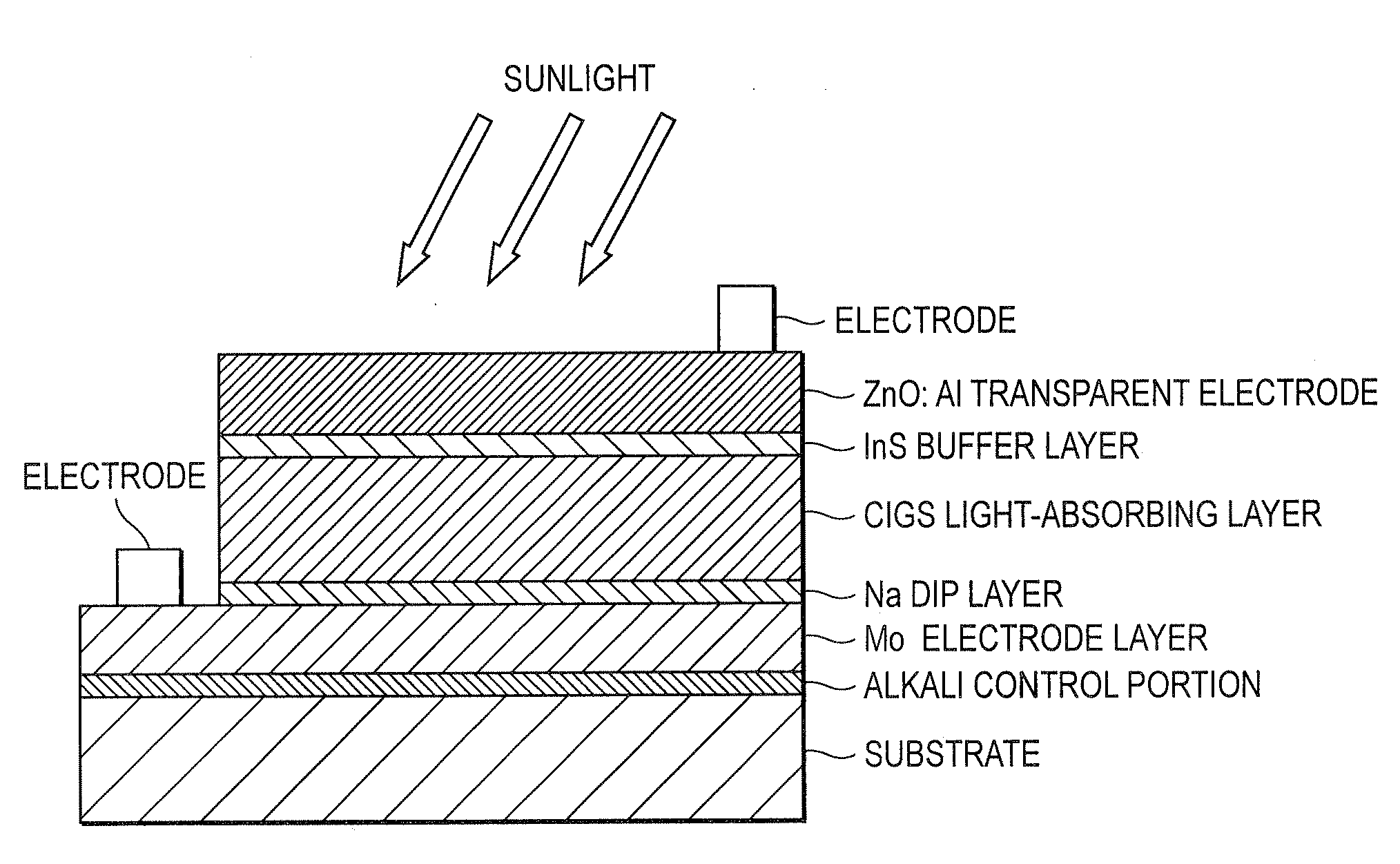
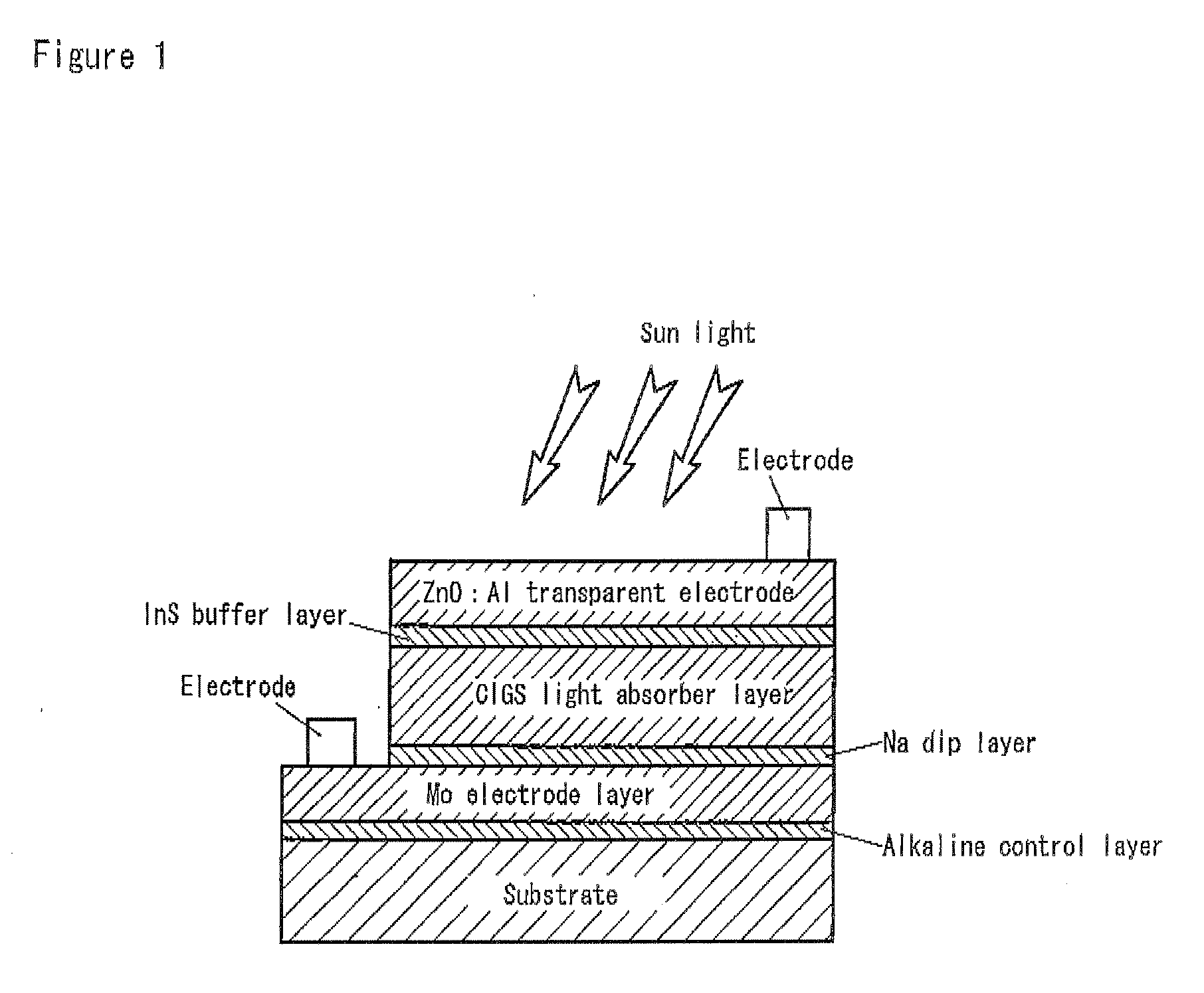
Solar Cell
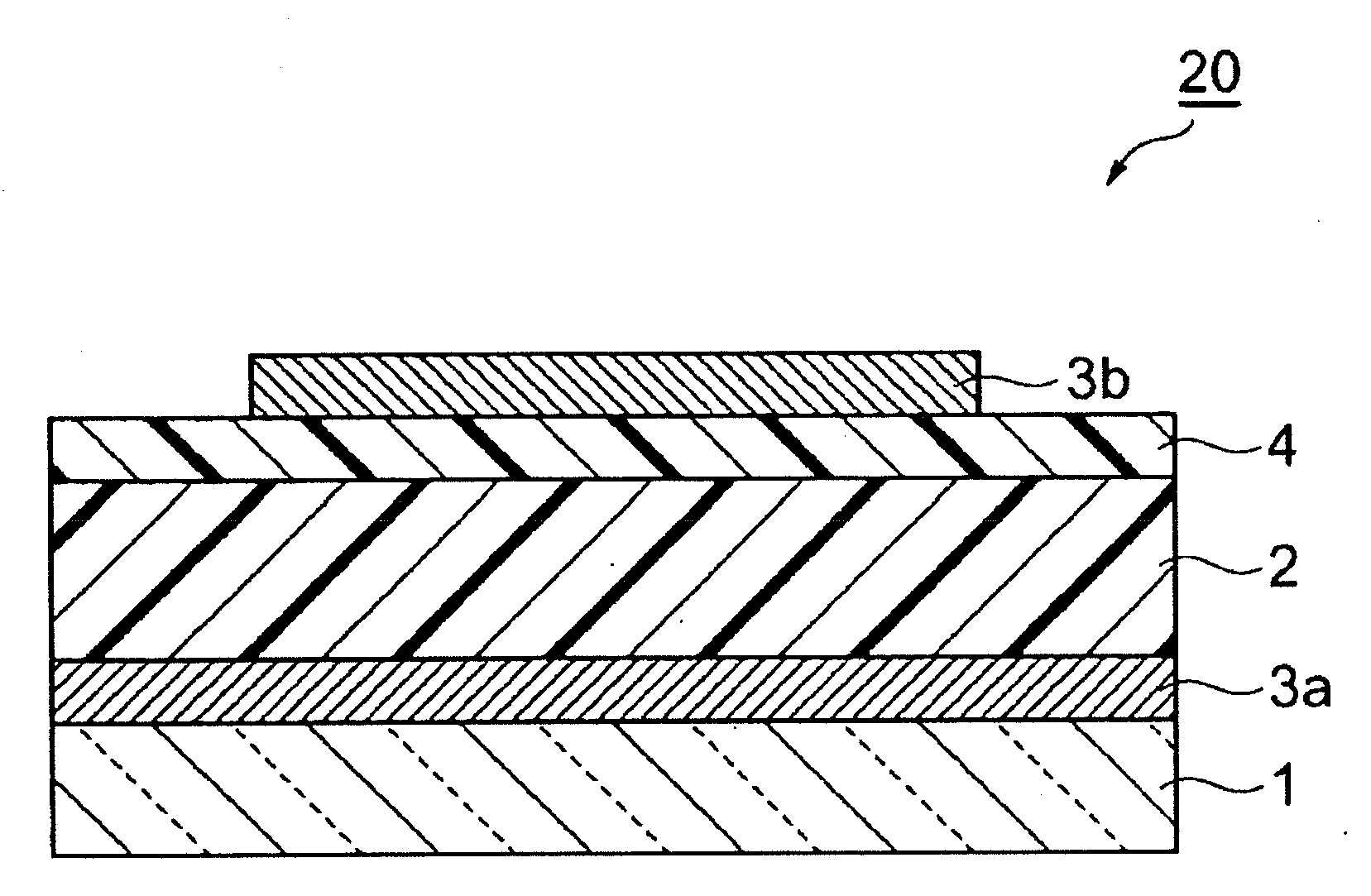
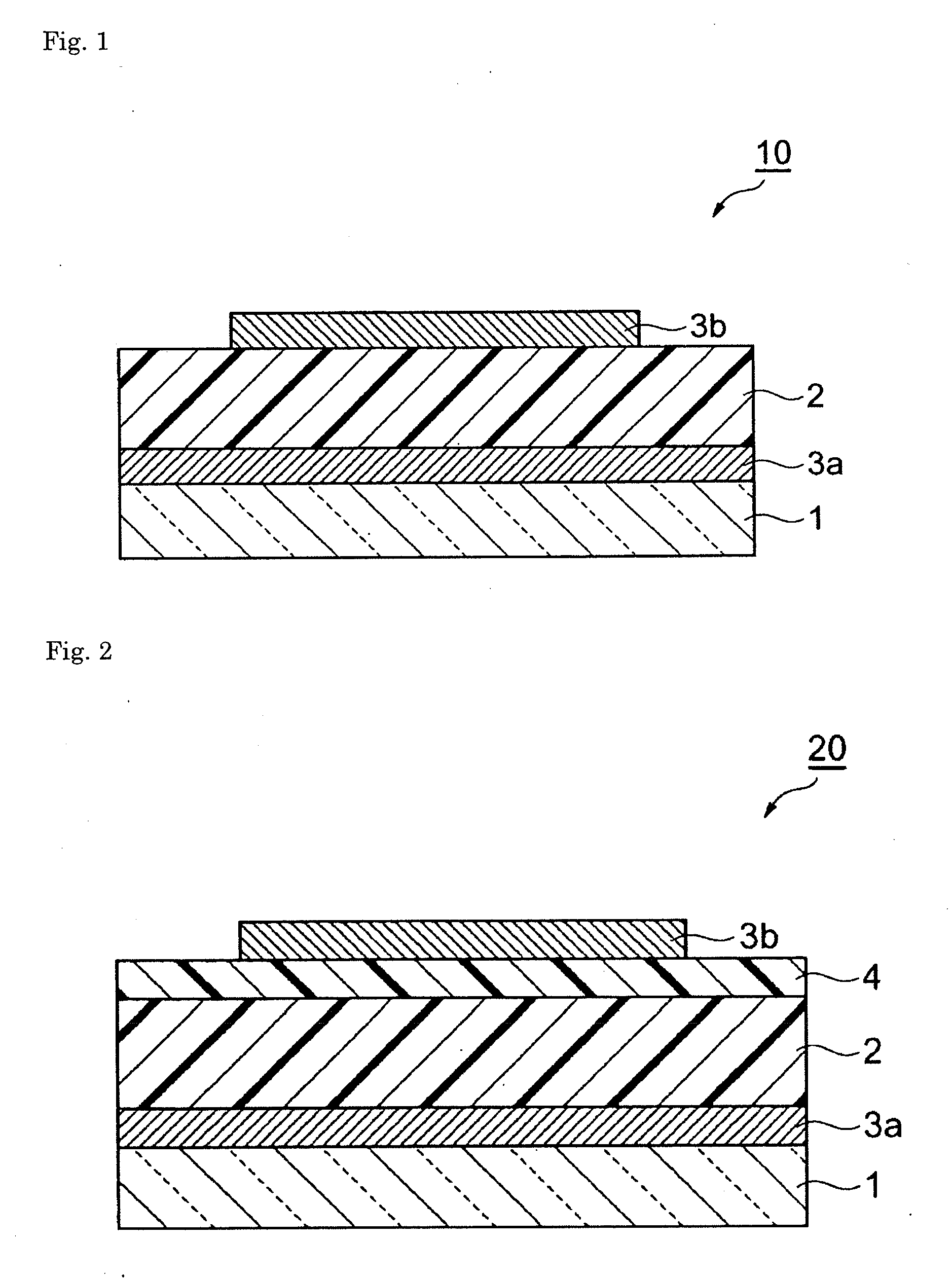
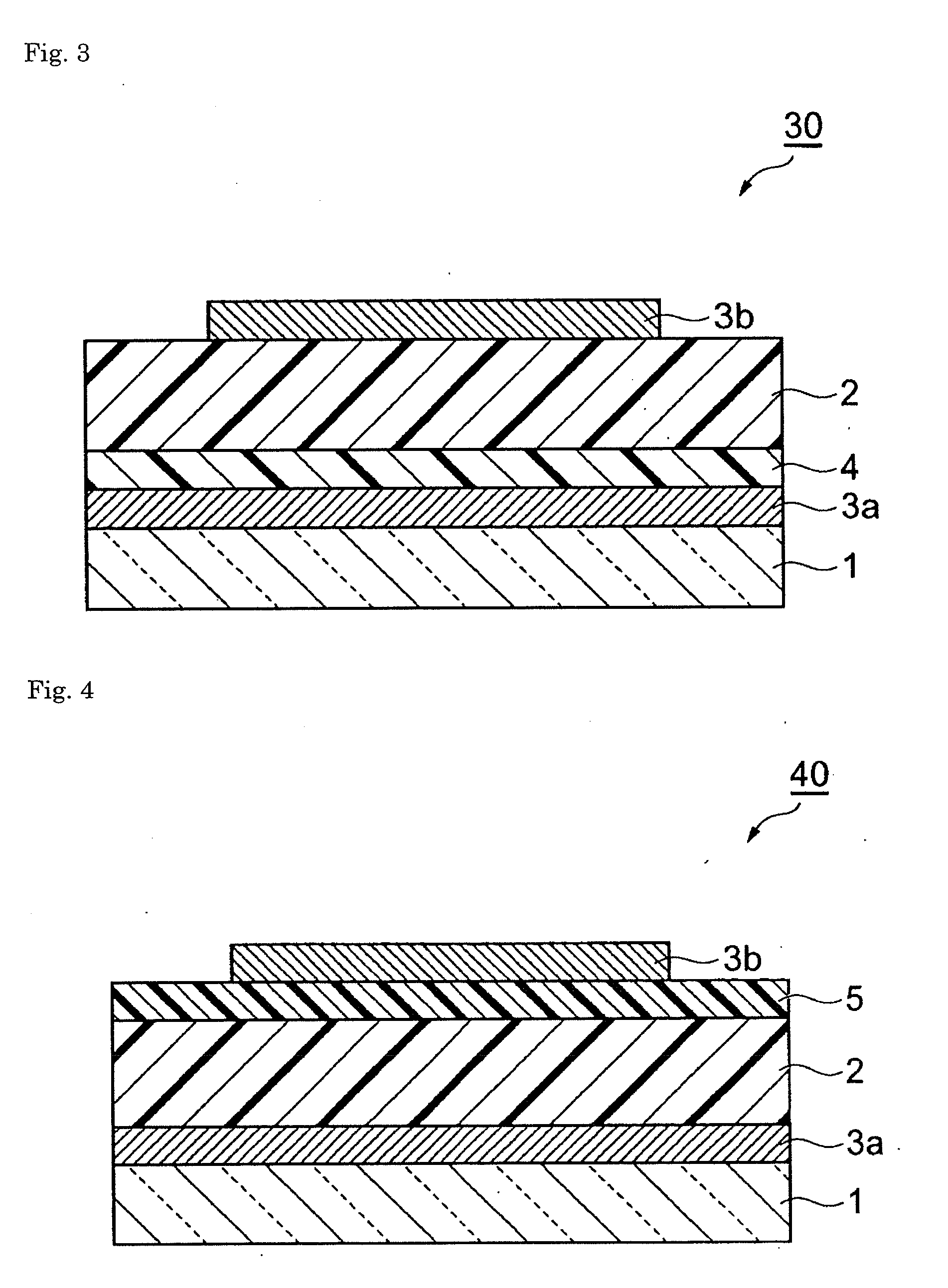
InactiveUS20090242022A1Improve reliabilityBreakage of substrate can be preventedFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorCopper indium gallium selenide
A flexible solar cell is achieved which has a high photoelectric conversion efficiency and no aged deterioration. A cell 10 (unit cell) is formed as a unit, comprising: a lower electrode layer 2 (Mo electrode layer) formed on a flexible mica sheet substrate 1 (substrate); a light absorber layer 3 (CIGS light absorber layer) which contains copper indium gallium selenide; a highly resistant buffer layer thin film 4 formed of InS, ZnS, CdS, or the like on the light absorber layer 3; and an upper electrode layer 5 (TCO) formed of ZuOAl or the like, and furthermore, a contact electrode section 6 for connecting between the upper electrode layer 5 and the lower electrode layer 2 is formed in order to connect a plurality of unit cells 10 in series. The contact electrode section 6 has a Cu / In ratio higher than that of the light absorber layer 3, and in other words, has less In contained therein to have a property of p+ (plus) type or a conductor relative to the light absorber layer 3 which is a p-type semiconductor.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Composition and organic photoelectric converter
ActiveUS20100193033A1High Photoelectric Conversion EfficiencyImprove solubilityNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesStructural unitFullerene derivatives
A composition containing a polymer having a structural unit represented by the following formula (1) and a structural unit represented by the following formula (2), and a fullerene with a carbon number of 70 or more or a fullerene derivative having a fullerene skeleton with a carbon number of 70 or more:wherein, Q, R, R1 and R2 each independently denote a hydrogen atom, and so on.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
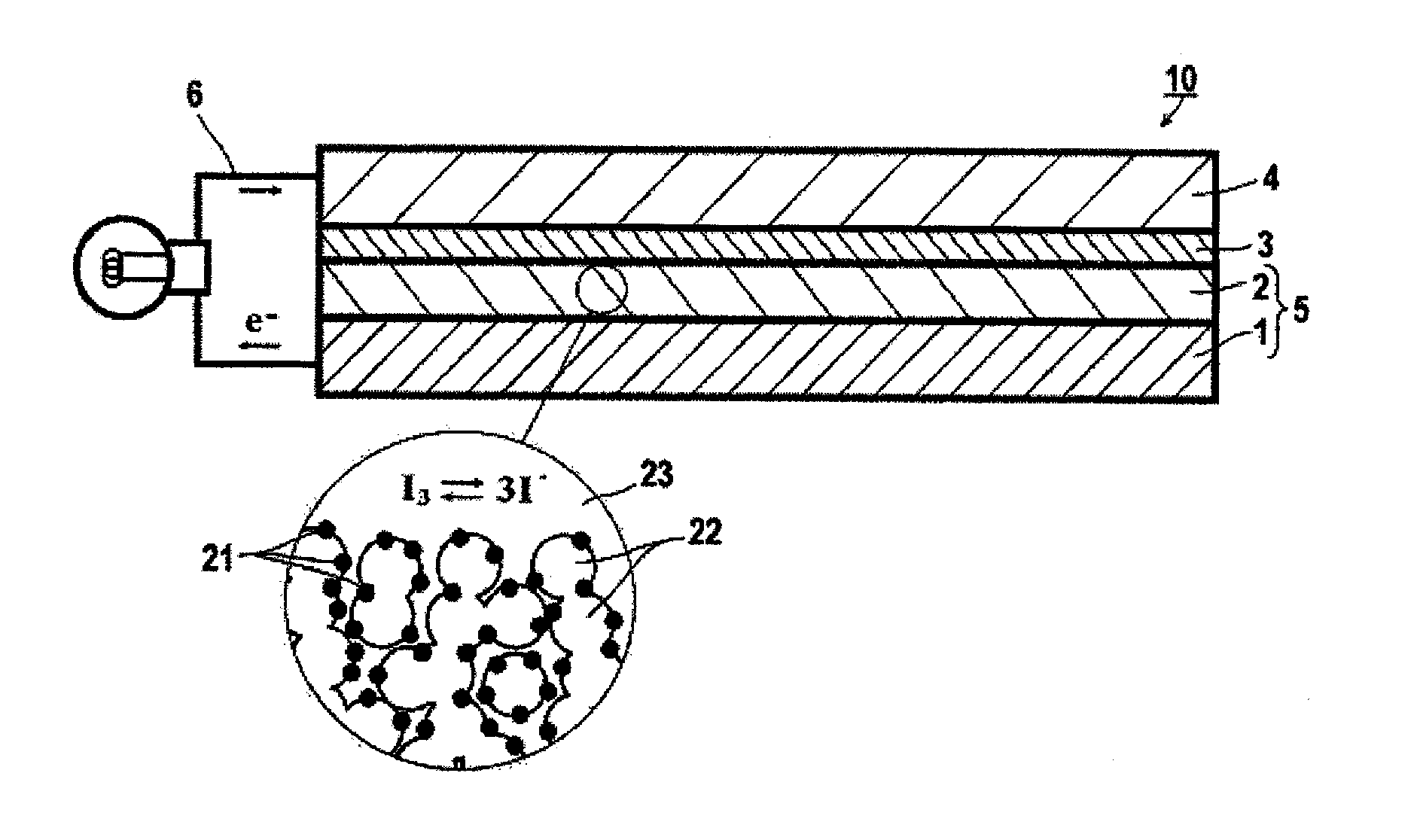
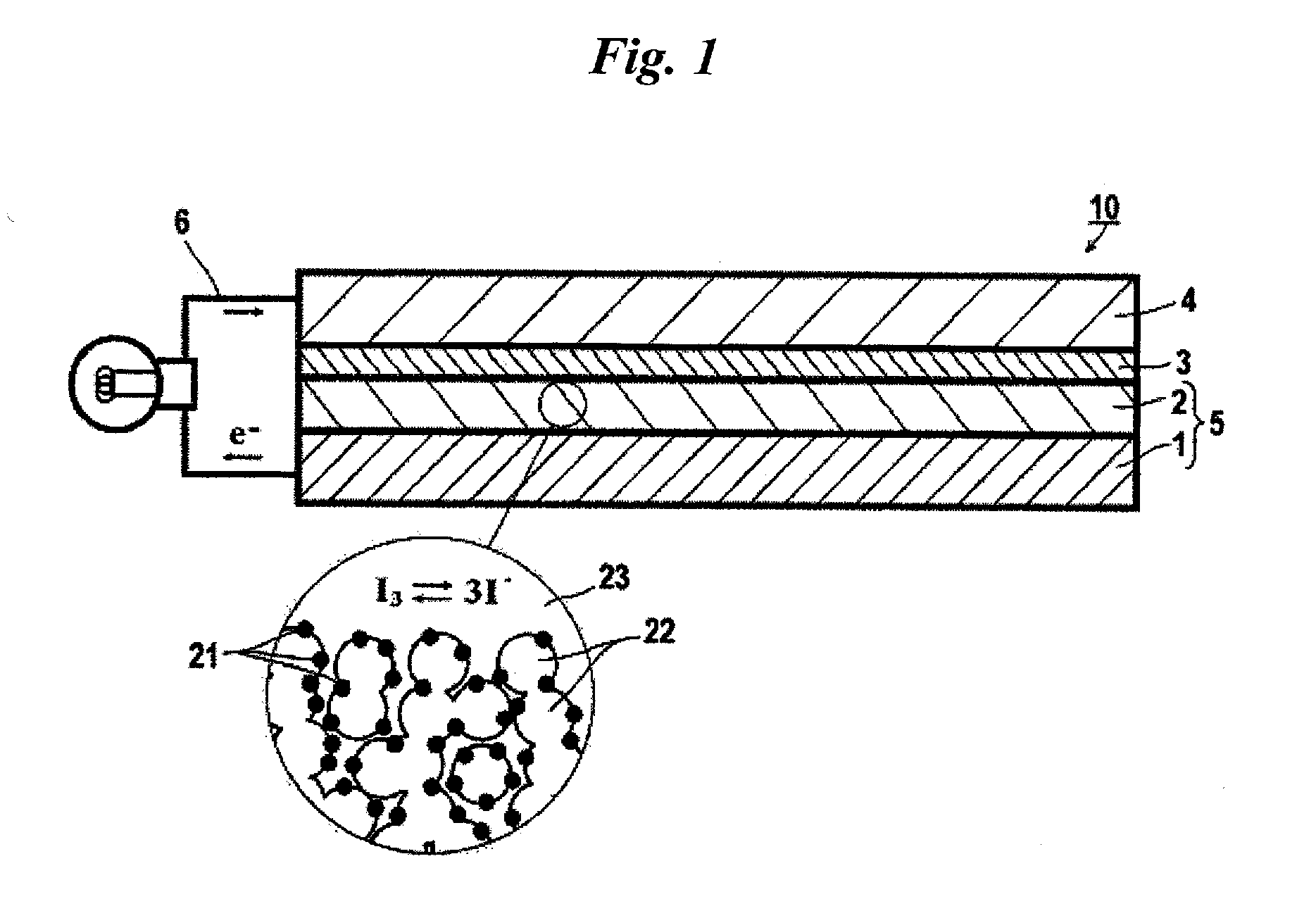
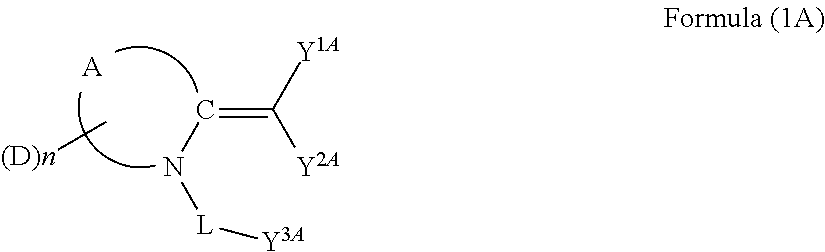
Dye, photoelectric conversion element using the same, photoelectrochemical cell, and method of producing dye
InactiveUS20110213144A1Excellent characteristicHigh Photoelectric Conversion EfficiencyMethine/polymethine dyesOrganic chemistryPhysicsPhotoelectrochemical cell
A dye, having a structure represented by formula (1A):wherein A represents a group of atoms necessary for forming a ring together with the carbon-nitrogen bond; at least one of Y1A and Y2A represents an acidic group, in which when they each represent an acidic group, they may be the same as or different from each other, or when only one of them represents an acidic group, the other represents an electron-withdrawing group; D represents a group to give a dye; n represents an integer of 1 or greater; L represents a single bond or a divalent linking group; and Y3A represents an acidic group.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
High-concentration multi-junction solar cell and method for fabricating same
InactiveUS20140090700A1High Photoelectric Conversion EfficiencyGreat series resistanceFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh concentrationFill factor
A high-concentration multi-junction solar cell and method for fabricating same is provided. The high-concentration multi-junction solar cell comprises a top cell, an intermediate cell, a bottom cell and two tunneling junctions connecting the top cell and intermediate cell and the intermediate cell and bottom cell. The emitter layers of the top and intermediate cells both employ the graded doping concentrations and have high open circuit voltage and short circuit current. The top cell emitter layer is over several hundred nanometers thicker than that of the traditional multi-junction cell so as to decrease the whole series resistance of the multi-junction cell, improve the fill factor, and gain higher photoelectric conversion efficiency.
Owner:XIAMEN SANAN OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
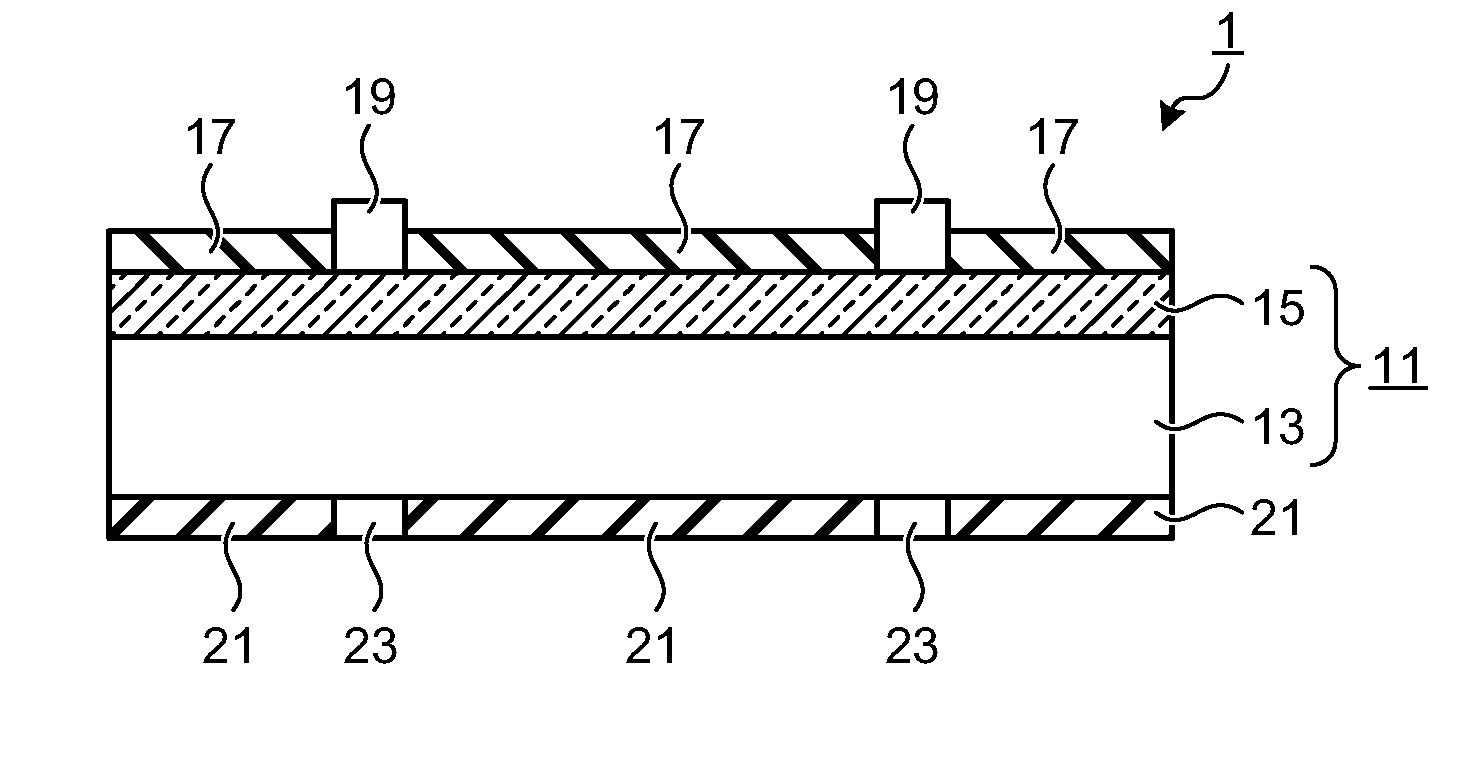
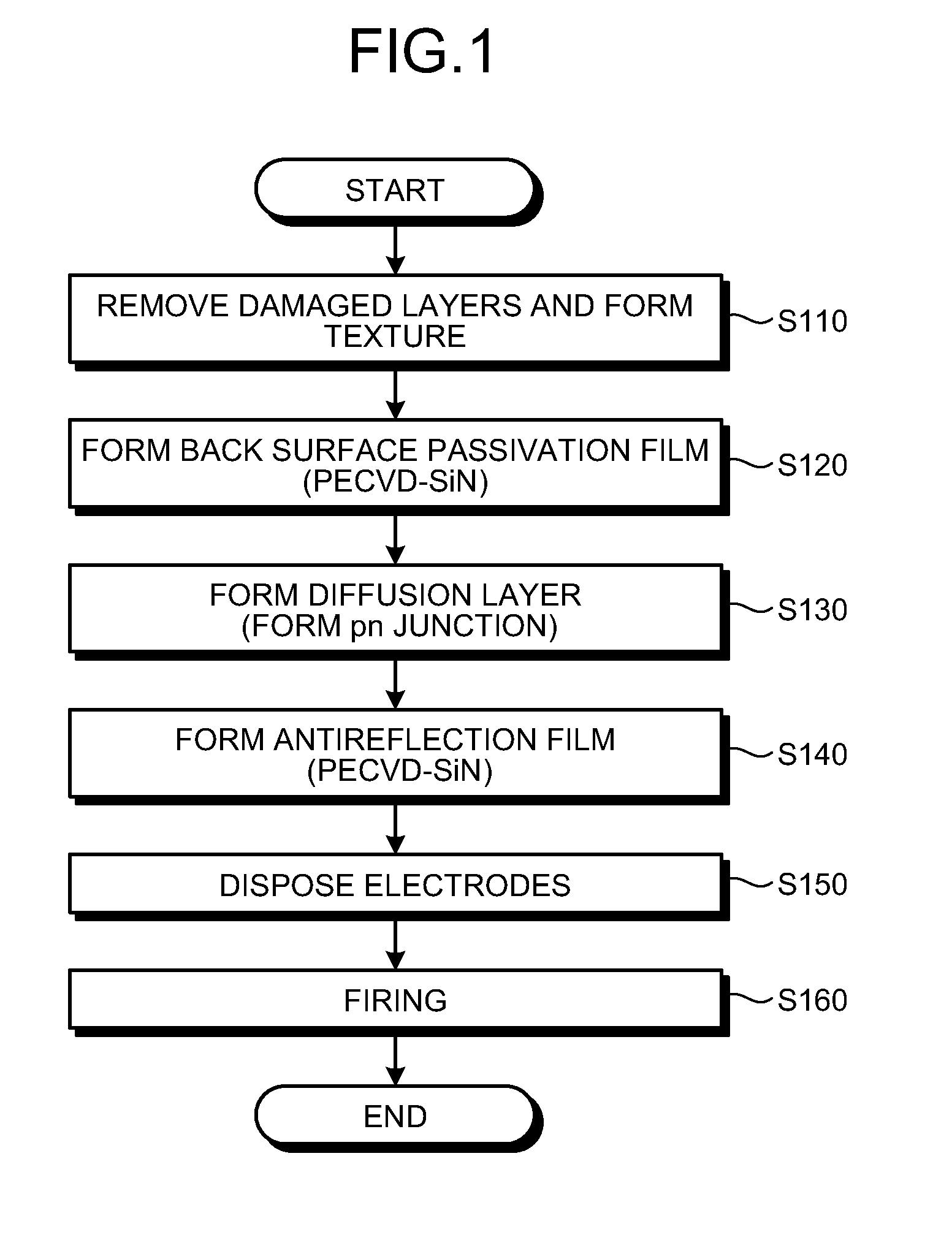
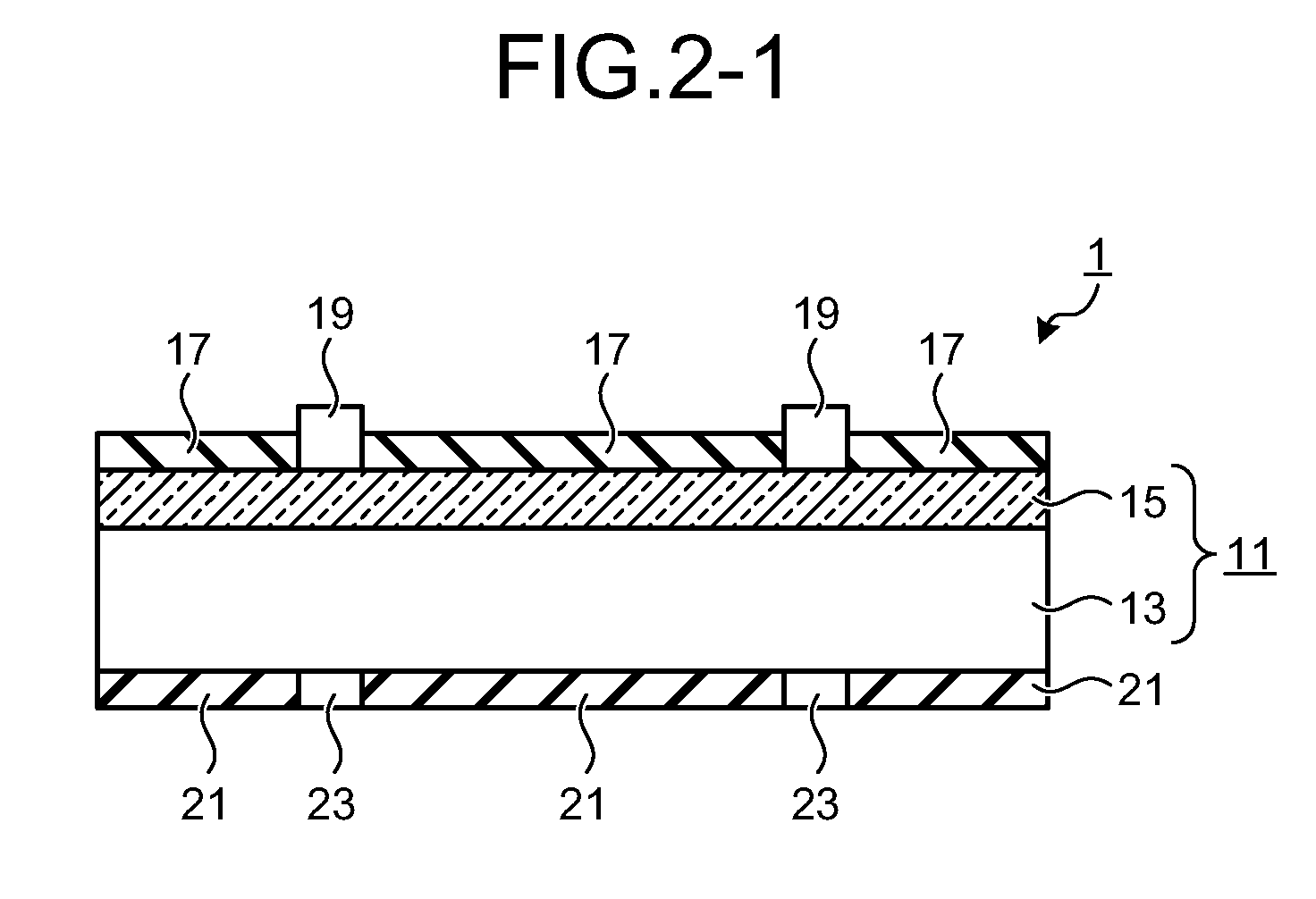
Method for manufacturing solar battery cell
InactiveUS20110237016A1High Photoelectric Conversion EfficiencyImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptoelectronicsP–n junction
A method includes: a first step of forming a passivation film on a first surface of a crystalline silicon substrate of a first conductive type; a second step of diffusing an element of a second conductive type into a second surface of the crystalline silicon substrate by thermal diffusion to form a diffusion layer, whereby a pn junction is formed; a third step of forming an antireflection film on the diffusion layer; a fourth step of disposing a first electrode paste on the second surface of the crystalline silicon substrate; a fifth step of disposing a second electrode paste on the passivation film; and a sixth step of firing the first electrode paste and the second electrode paste to form electrodes.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Photoelectric conversion device and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20060118898A1High Photoelectric Conversion EfficiencyImprove power generation efficiencyFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationPhotoelectric conversionCrystalline semiconductor
Disclosed is a photoelectric conversion device in which a plurality of p-type crystal semiconductor particles 4 are joined to one main surface of a conductive substrate 2. A boron concentration in a junction of a lower part of each of the p-type crystal semiconductor particles 4 with the conductive substrate 2 is higher than a boron concentration in a portion, other than the junction, of the p-type crystal semiconductor particle 4. The junction is a p+ layer having a high impurity concentration. The p+ layer allows p-type carriers to be collected, thereby making it possible to improve a BFS effect.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Photoelectric conversion element
InactiveUS20110114185A1High Photoelectric Conversion EfficiencyImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyOrganic chemistryElectrolytic capacitorsOrganic layerPhotoelectric conversion
A photoelectric conversion element comprising a first electrode, a second electrode, a functional layer arranged between the first electrode and the second electrode, and a porous semiconductor material arranged between the first electrode and the functional layer. The functional layer contains a polymer compound having an aromatic amine residue, and a dye is adsorbed on the porous semiconductor material. The photoelectric conversion element may additionally have a dense layer between the first electrode and the functional layer, and a dye may be absorbed on a part of the functional-layer-side surface of the dense layer. The photoelectric conversion element may additionally have an organic layer between the functional layer and the second electrode.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Photoelectric Conversion Devices
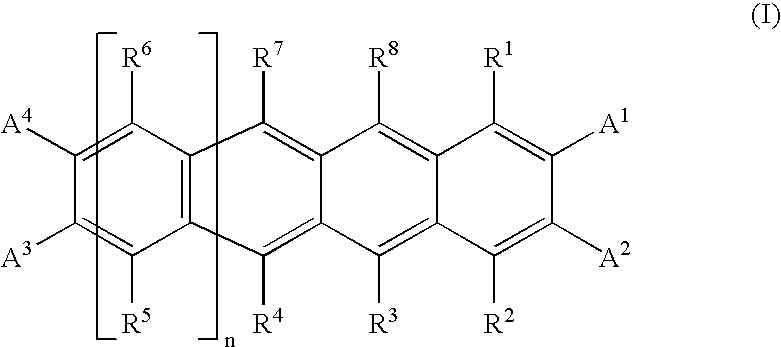
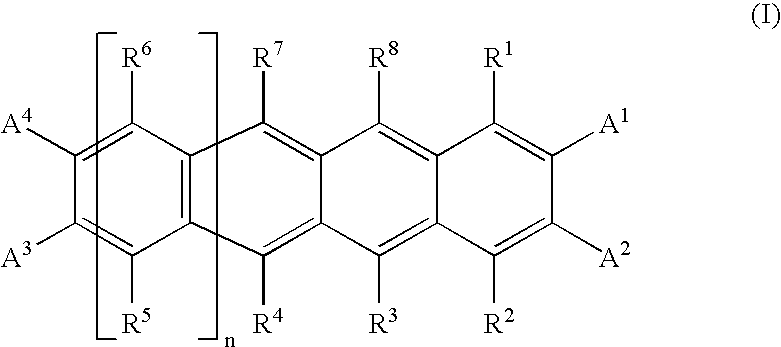
InactiveUS20080264487A1Improve workabilityIncrease productivityOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationHydrogen atomHalogen
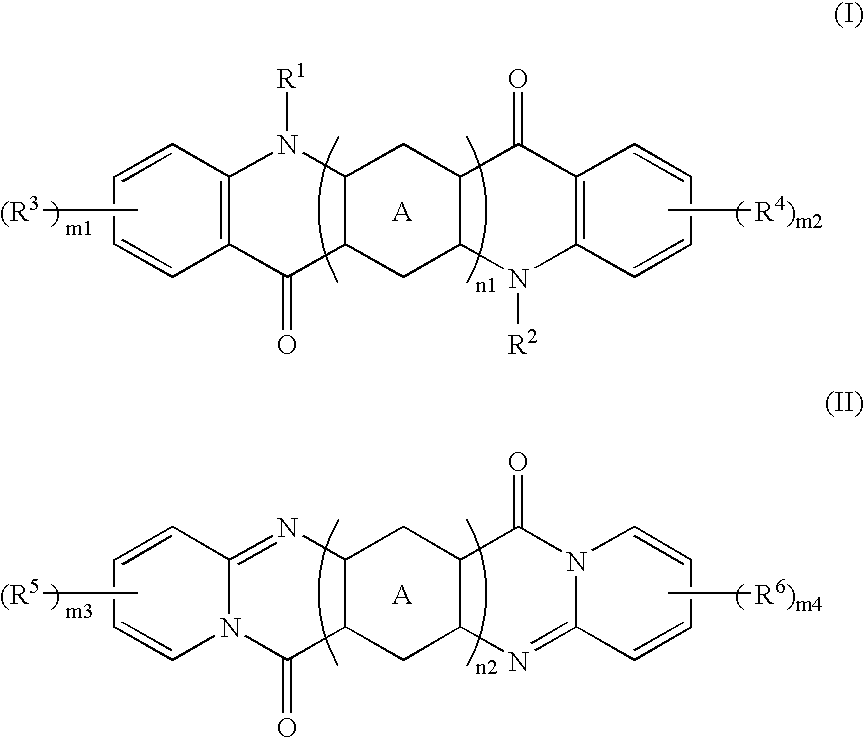
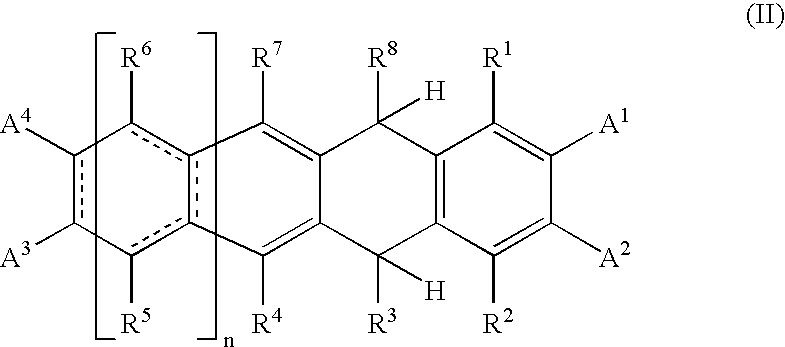
Materials for photoelectric conversion devices, consisting of polyacene derivatives represented by general formula (I) below; and photoelectric conversion devices made by using the materials. The materials for photoelectric conversion devices have excellent workability and productivity, exhibit low toxicity, are easily flexibilized, and have high photoelectric conversion efficiencies.In the formula, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, R8, A1, A2, A3, and A4 are independent from each other, either the same or different, and each represents a hydrogen atom, a halogen atom, an optionally substituted hydrocarbon group having 1 to 40 carbon atoms, or the like. n is an integer of 1 or more.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +1
Preparation method of two-dimensional nano-flake photocatalyst
InactiveCN105642331AEasy to prepareFast preparation methodPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationManganeseCarbon nitride
The invention belongs to the technical field of nano functional materials and green energy and discloses a preparation method of a two-dimensional nano-flake photocatalyst which is not doped with precious metal and is low in cost, simple to prepare and high in photocatalytic activity. The prepared two-dimensional nano-flake photocatalyst is manganese-doped titanium dioxide in-situ composite carbon nitride two-dimensional nanocomposite Mn-TiO2 / g-C3N4 and has good photocatalytic activity.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Solar cell
InactiveUS20090145477A1High Photoelectric Conversion EfficiencyNanotechnologyPhotovoltaic energy generationNanowireEnergy absorption
There is provided a solar cell including: a substrate; and an energy absorption structure formed on the substrate, the energy absorption structure including a metal layer, a semiconductor layer and an insulator formed therebetween, wherein at least one of the metal layer, the semiconductor layer and the insulator is formed of a plurality of nanowire structures. The solar cell has the energy absorption structure formed of a nanowire MIS junction structure to ensure high photoelectric conversion efficiency. Further, the solar cell does not require an epitaxial growth, thereby free from drawbacks of an epitaxial layer such as crystal defects.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Preparing method for binary metal co-doping photocatalyst
InactiveCN105618105AEasy to prepareFast preparation methodMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsCarbon nitrideManganese
The invention discloses a preparing method for a photocatalyst free of precious metal doping, low in cost, easy to prepare and high in photocatalytic activity, and belongs to the technical field of novel nanometer functional materials and green energy.The binary metal co-doping photocatalyst prepared through the method is an iron-manganese co-doping titanium dioxide nanosheet in-situ synthesis carbon nitride two-dimensional nanocomposite FeMn-TiO2 / g-C3N4, and has good photocatalytic activity.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Semiconductor laser device
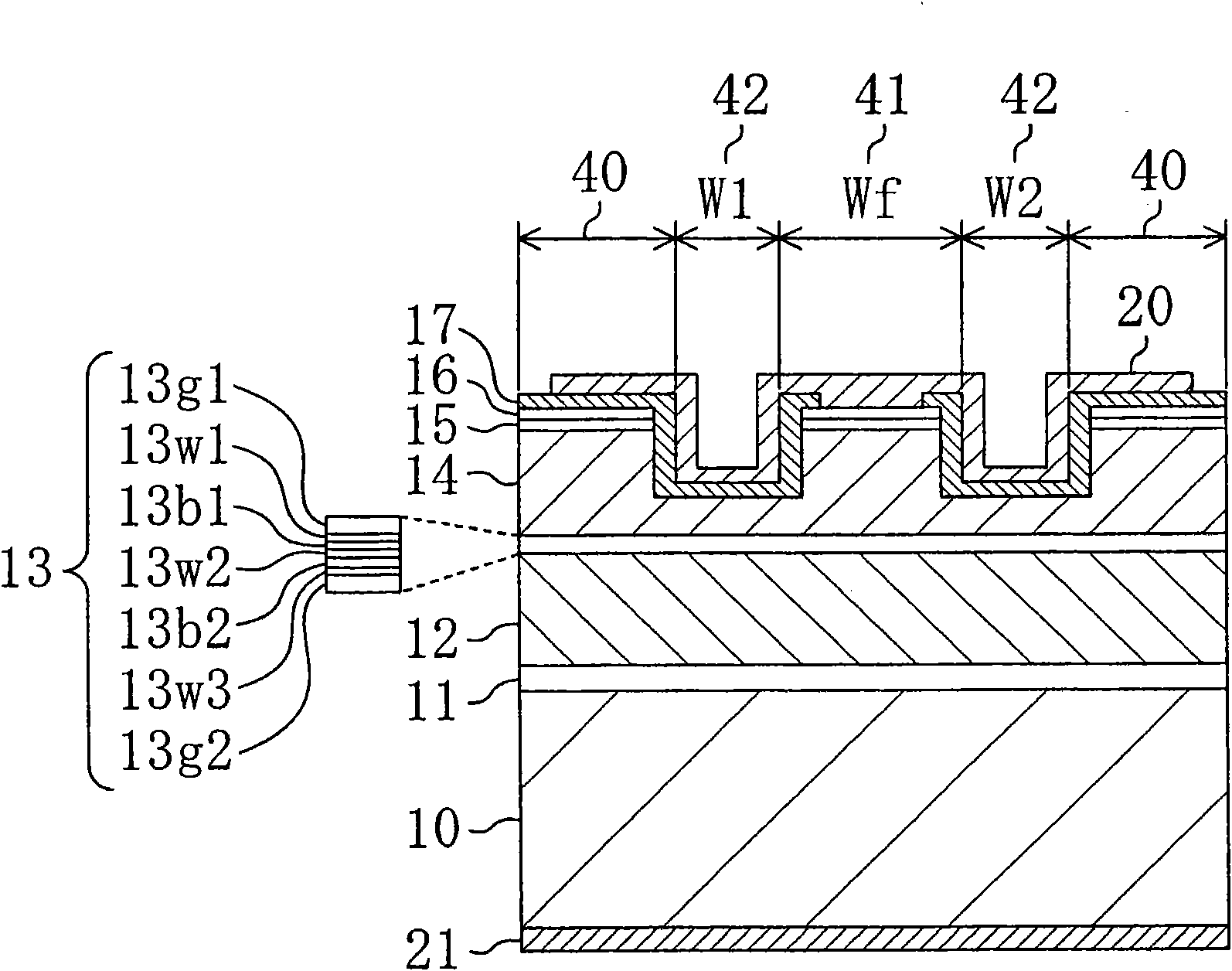
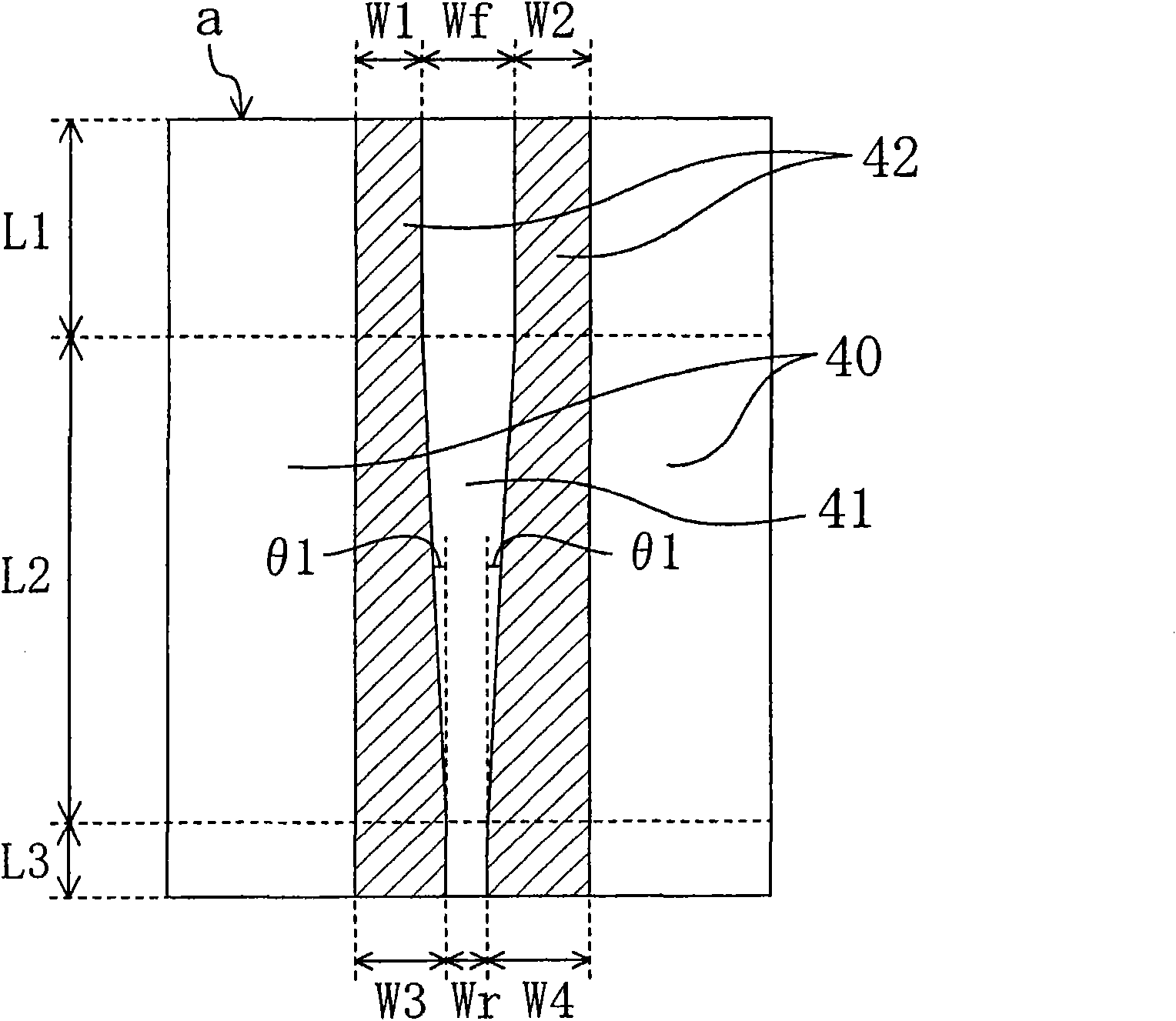
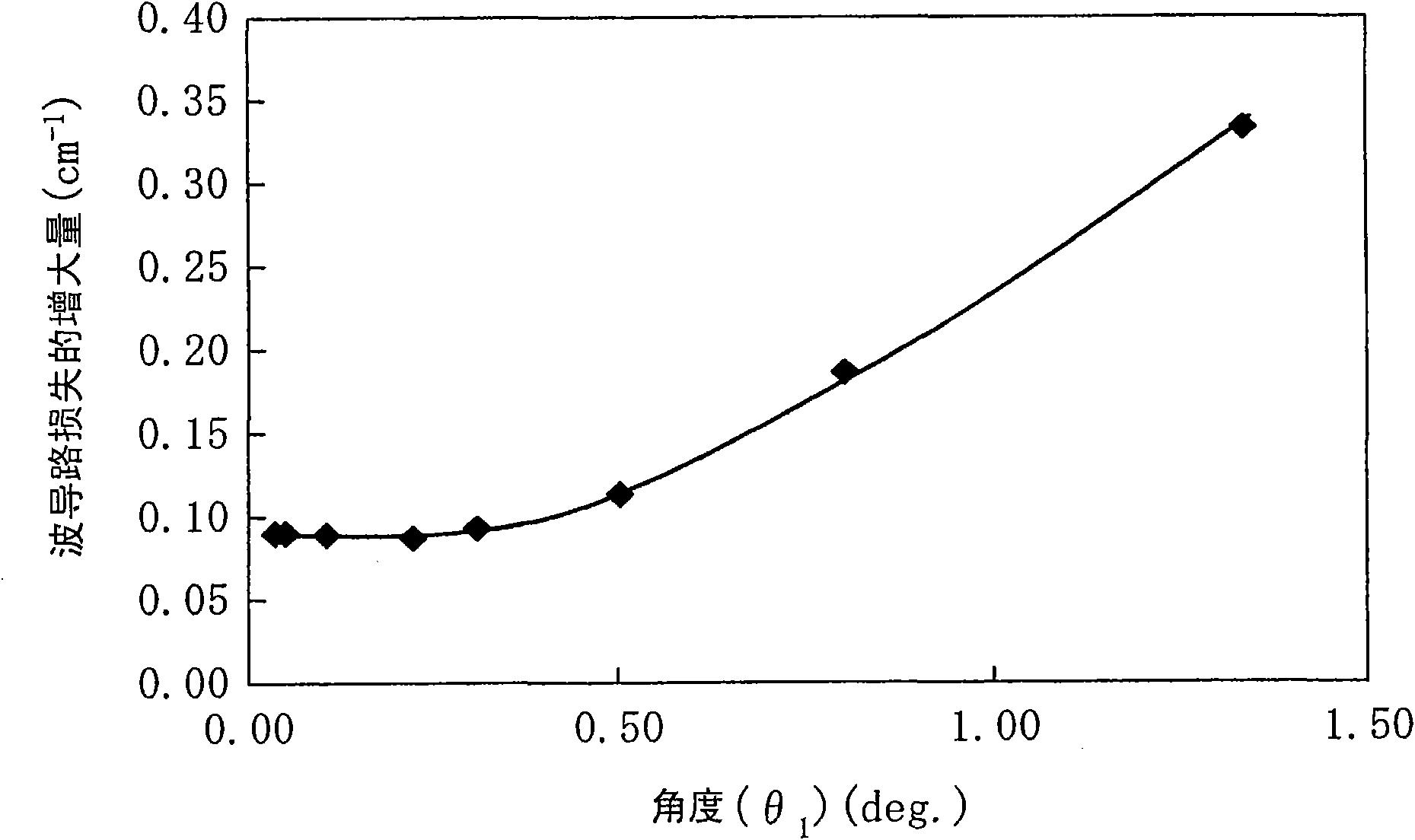
ActiveCN101599617AGood temperature characteristicsHigh polarization ratioOptical wave guidanceLaser optical resonator constructionEngineeringActive layer
The invention provides a semiconductor laser device with good temperature characteristic, high polarization rate and high refraction light output. A semiconductor laser device includes an n-type clad layer, an active layer, and a p-type clad layer having a ridge and wing regions. The wing regions are provided with a first trench present on one side of the ridge and a second trench provided on the other side thereof being interposed therebetween. A reflectivity Rf at a front end face of a resonator, a reflectivity Rr at a rear end face of the resonator, a minimum value W1 of a width of the first trench in a region adjacent to the front end face, a minimum value W2 of a width of the second trench in the region adjacent to the front end face, a width W3 of the first trench at the rear end face, and a width W4 of the second trench at the rear end face satisfy Rf<Rr, W1<W3, and W2<W4. A width Wf of the ridge at the front end face, and a width Wr of the ridge at the rear end face satisfy Wf>Wr. The ridge includes a region where a width decreases with distance from the front end side toward the rear end side.
Owner:PANASONIC SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
Transparent electrode substrate, method for producing same, photoelectric conversion device, method for producing same, and photoelectric conversion module
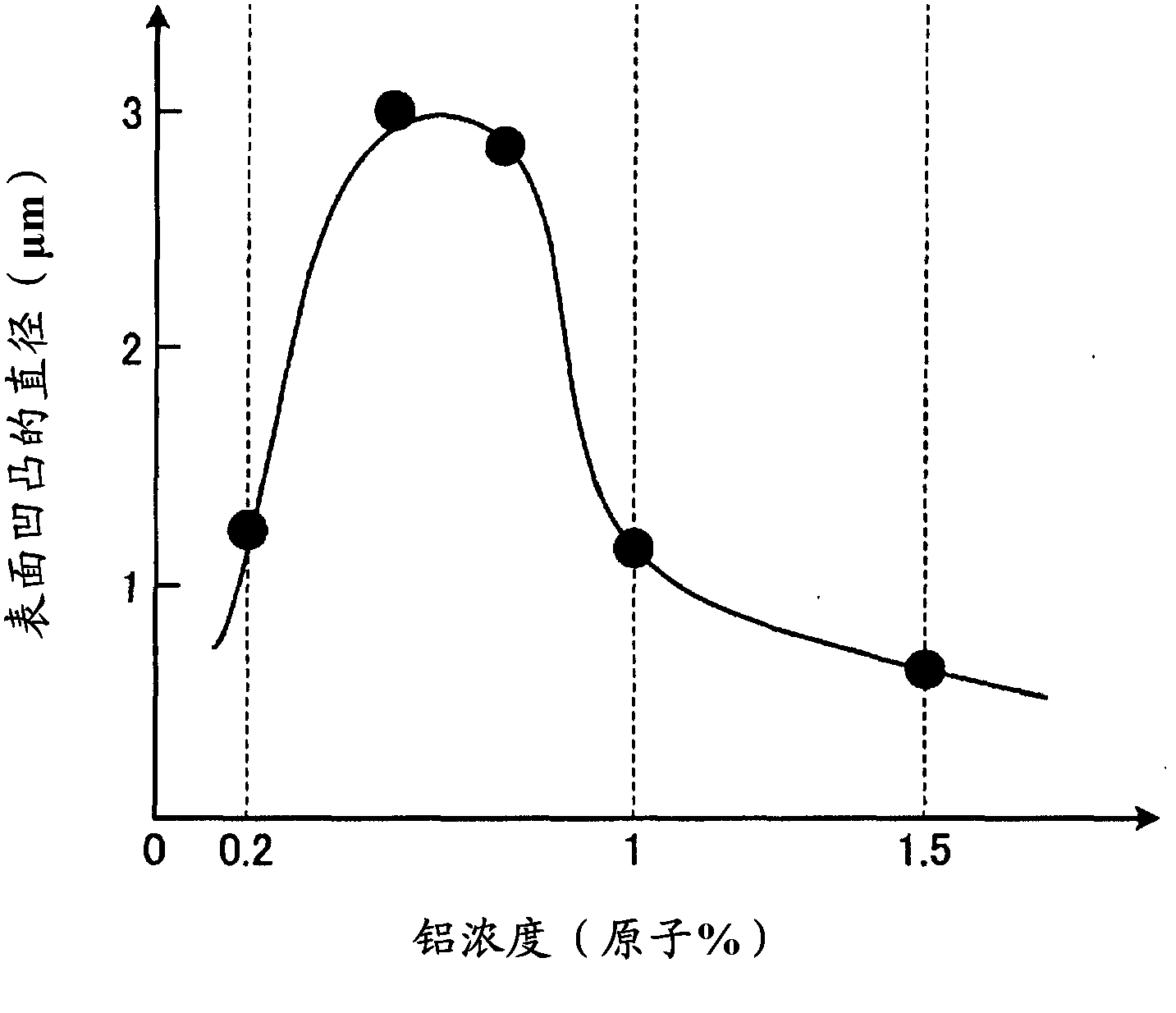
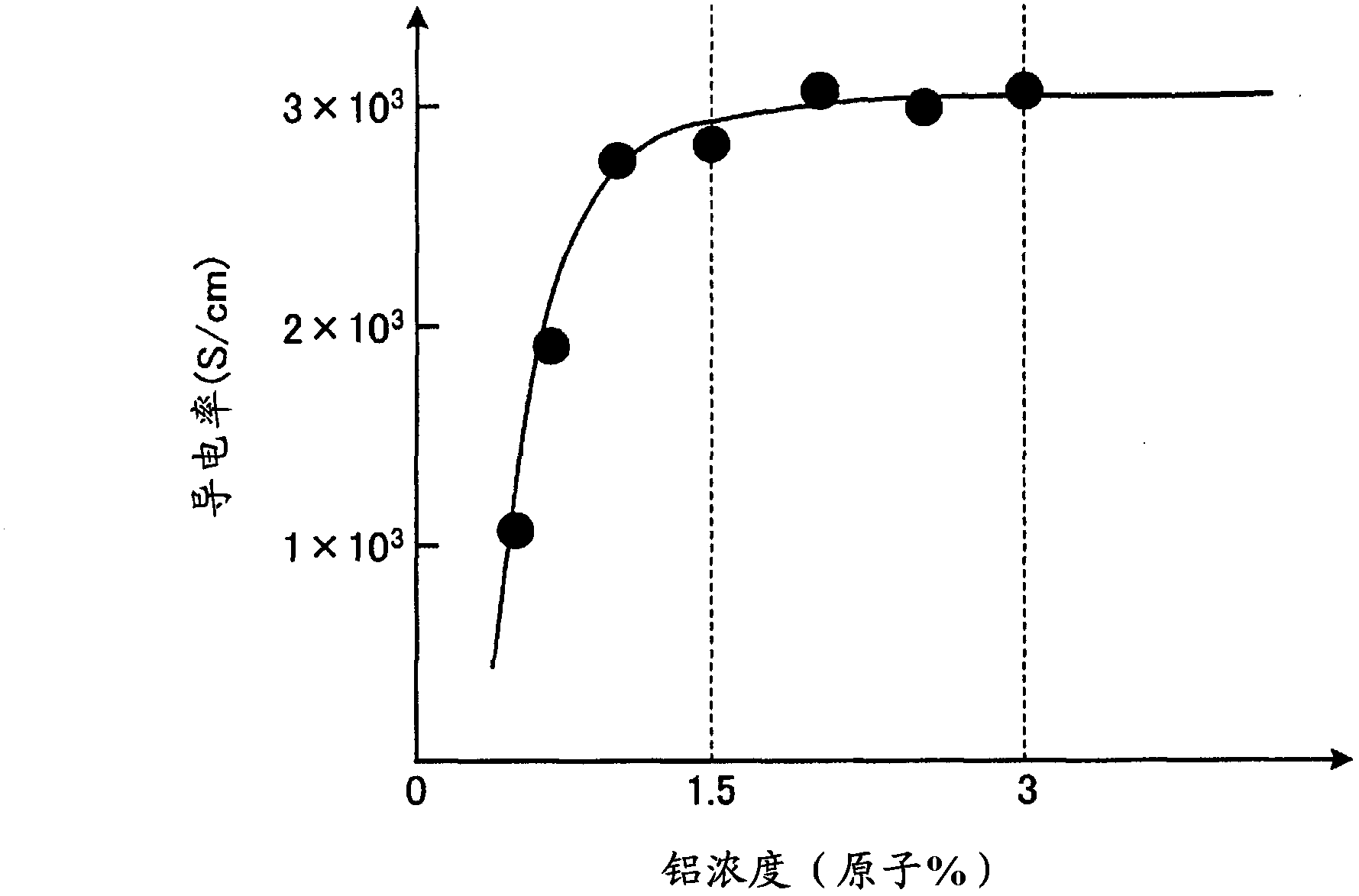
InactiveCN103339688AImprove light scattering performanceImprove conductivityConductive layers on insulating-supportsPhotovoltaic energy generationDopantPhotoelectric conversion
A transparent electrode substrate in which a transparent electrode formed from a zinc oxide-based thin film is formed on a translucent insulating substrate, the zinc oxide-based thin film containing zinc oxide as the main component and at least one type of dopant element. The zinc oxide-based thin film has an uneven surface and a dopant element concentration gradient in which the concentration of the dopant element continuously decreases from the side of the translucent insulating substrate to the surface of the zinc oxide-based thin film. The concentration of the dopant element in the zinc oxide-based thin film is 1.5 atom % to 3 atom % in a region from the translucent insulating substrate to 50 nm inward in the thickness direction and is 0.2 atom % to 1 atom % in a region from the surface of the zinc oxide-based thin film to 300 nm inward in the thickness direction.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com