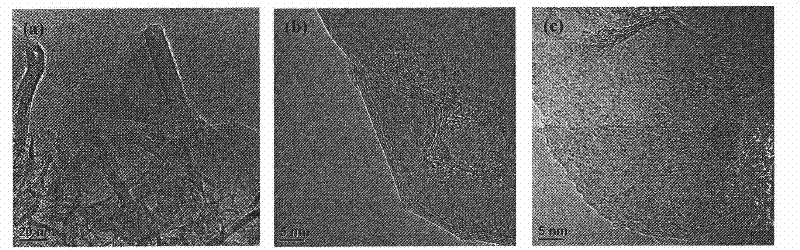
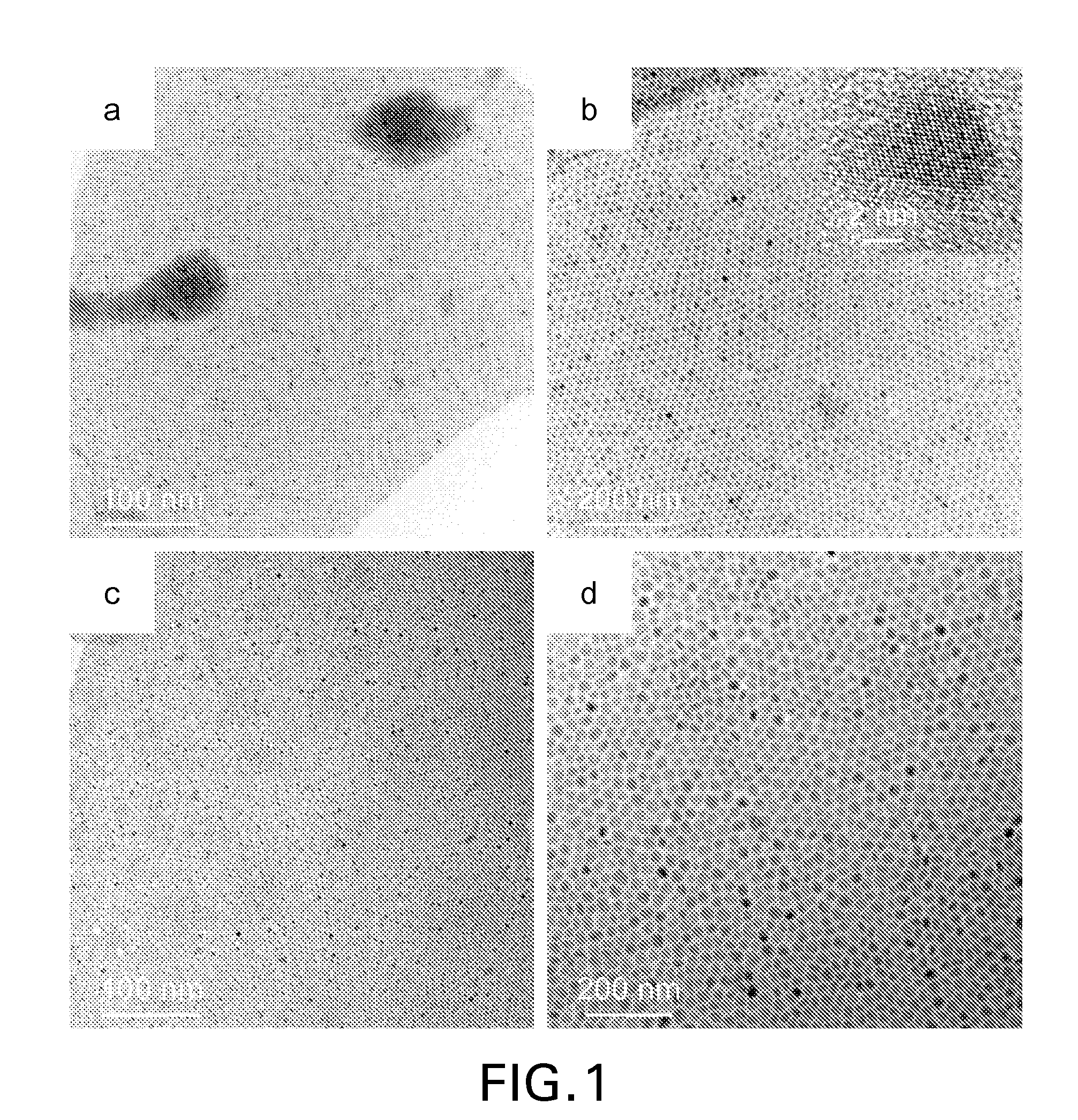
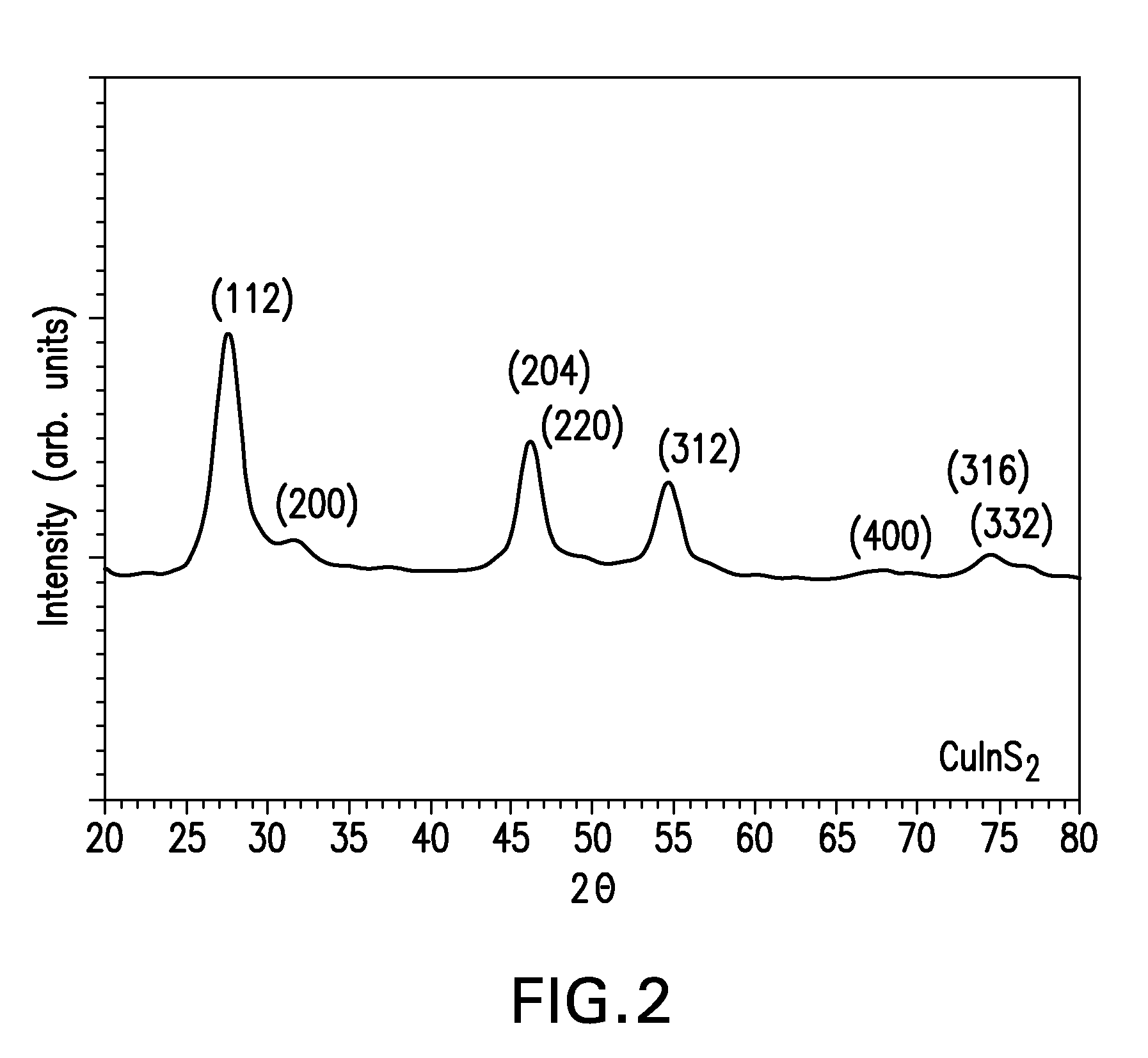
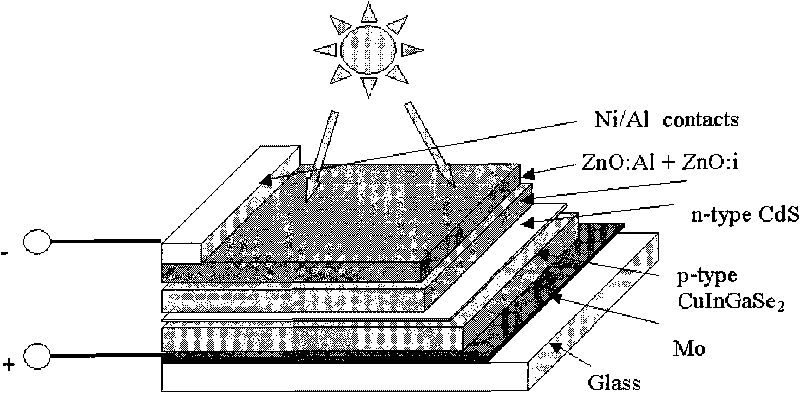
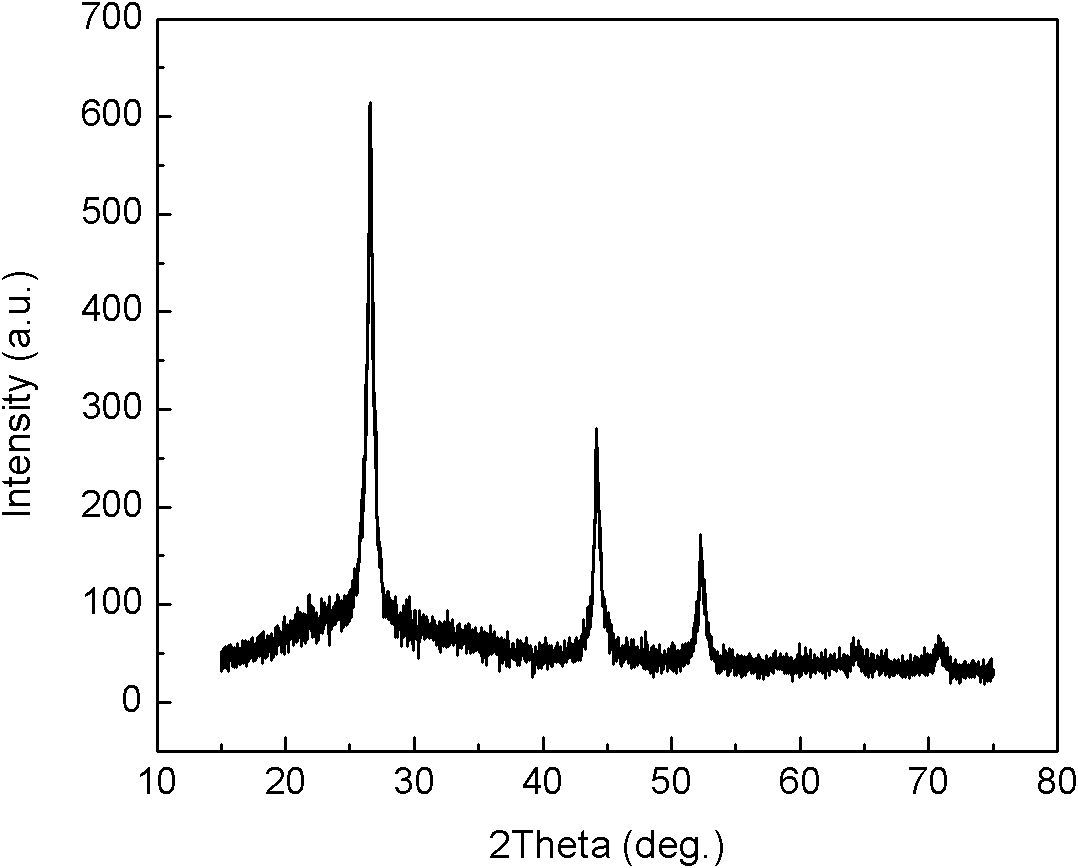
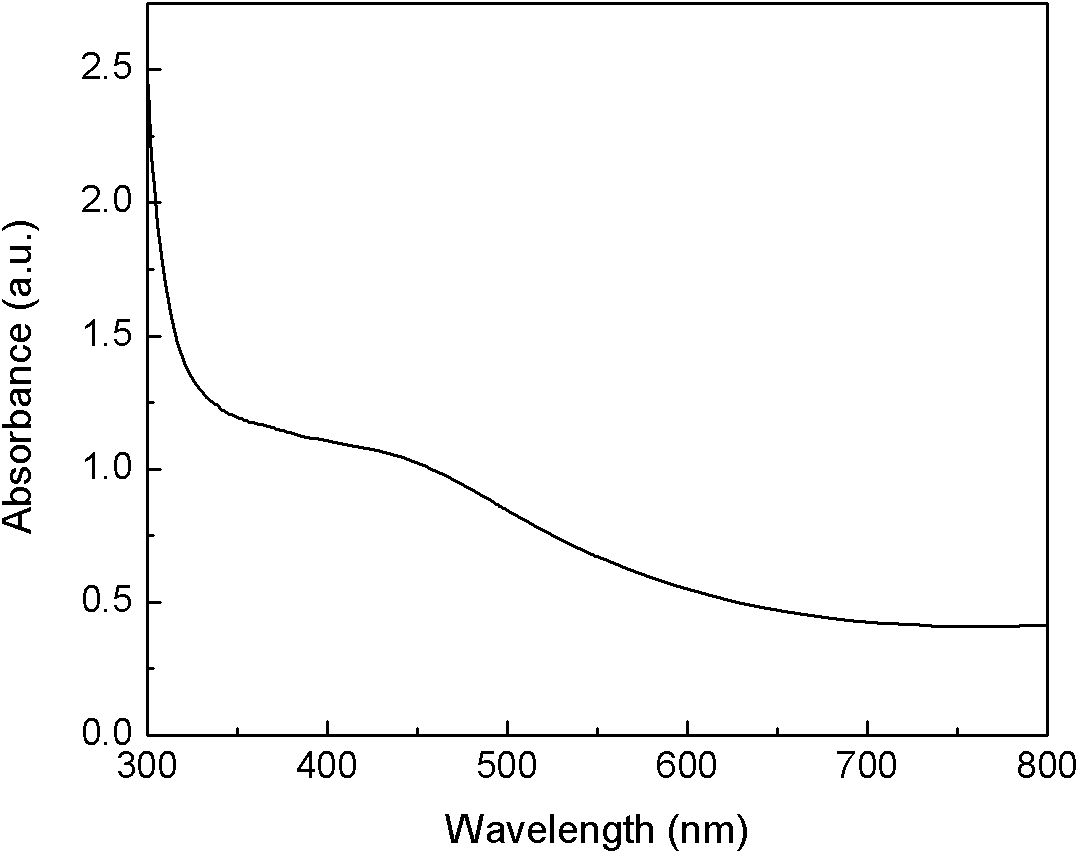
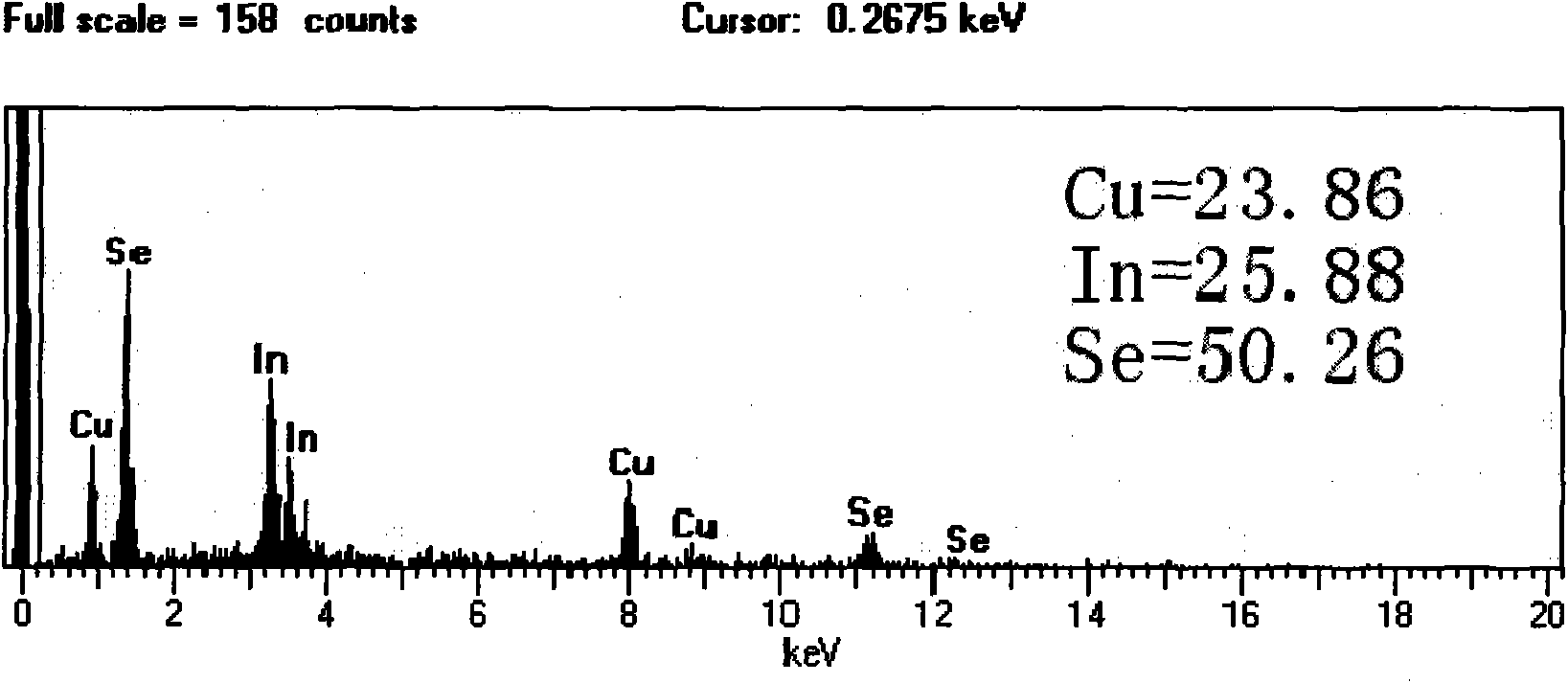
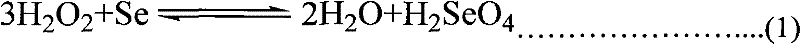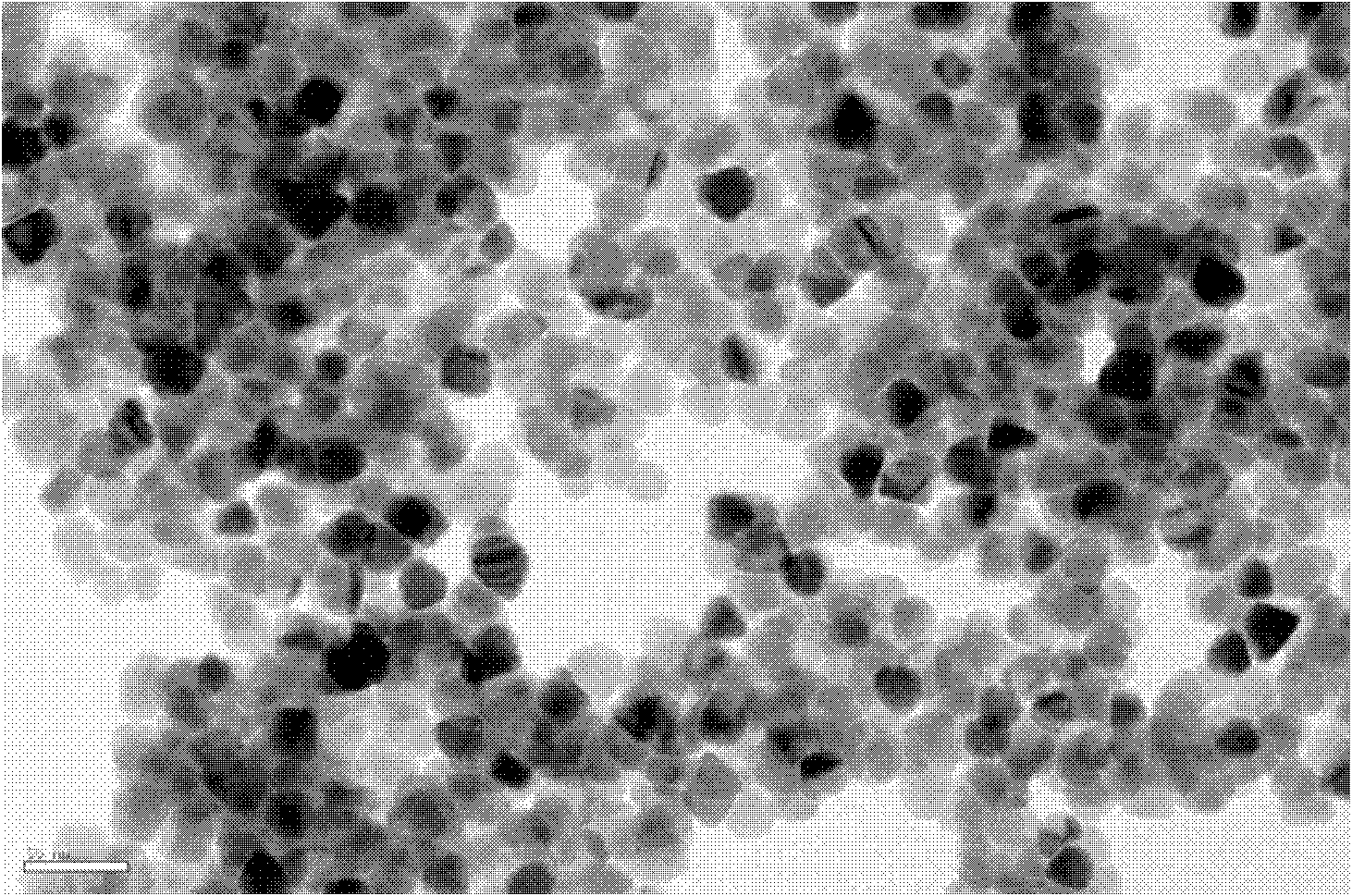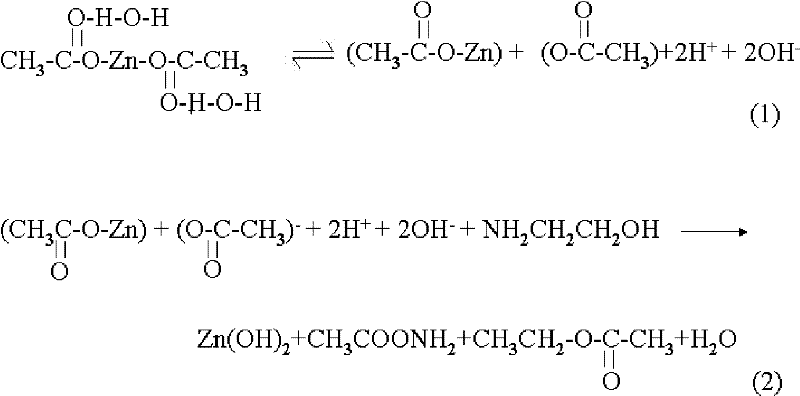Patents
Literature
244 results about "Copper indium gallium selenide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
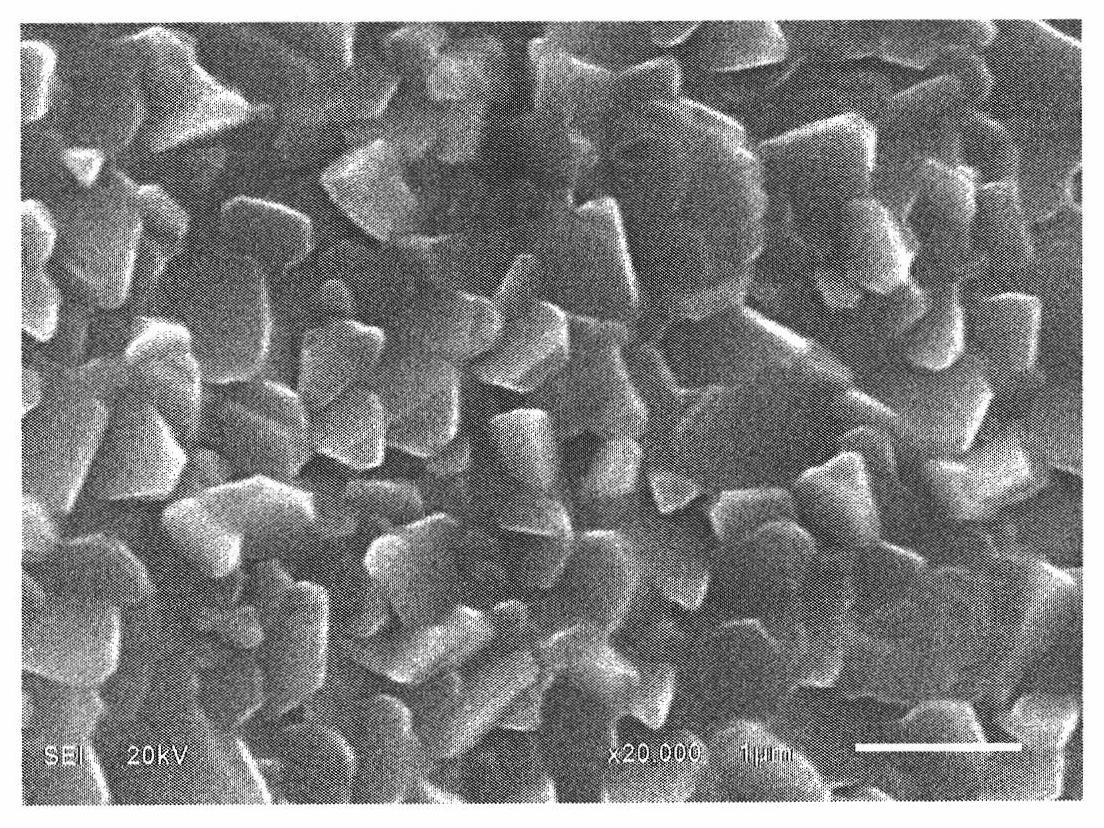
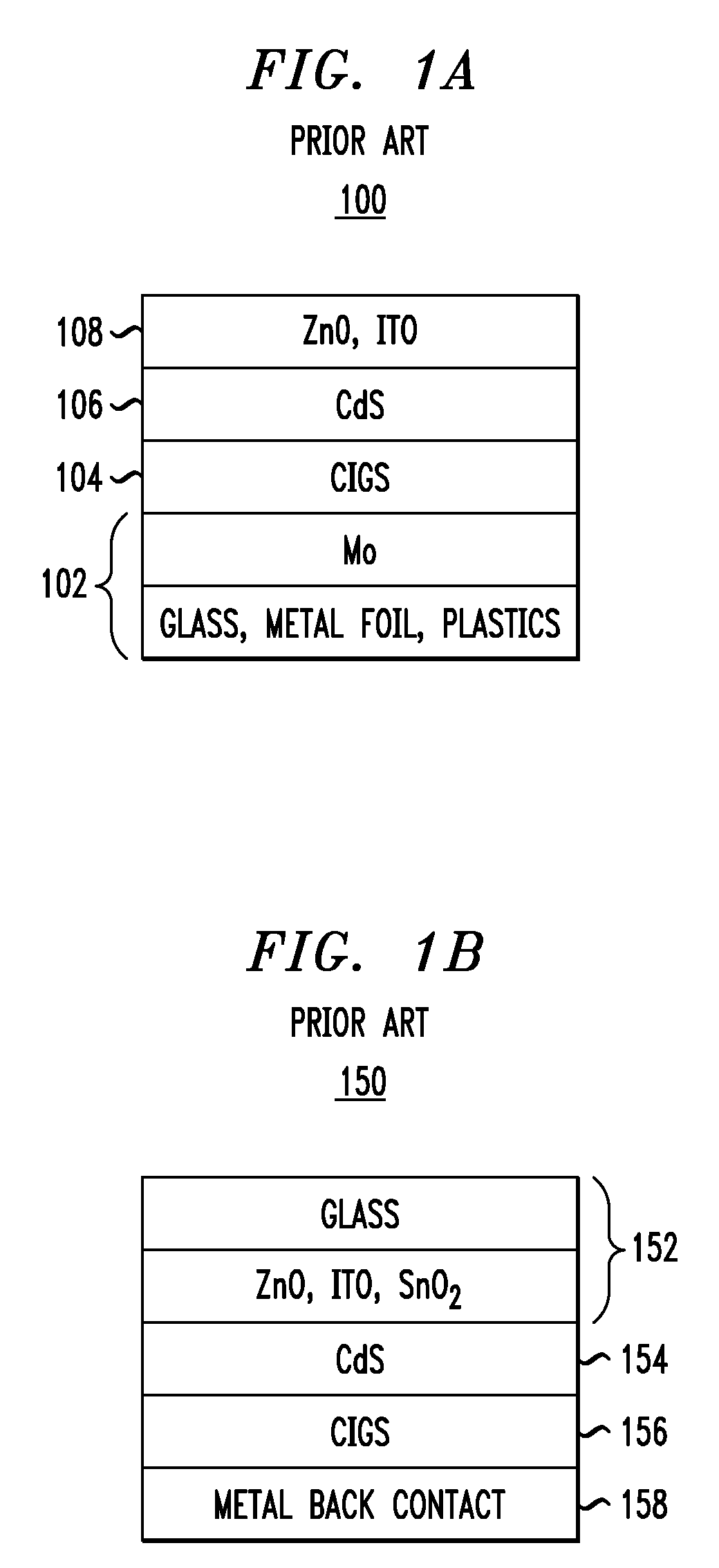
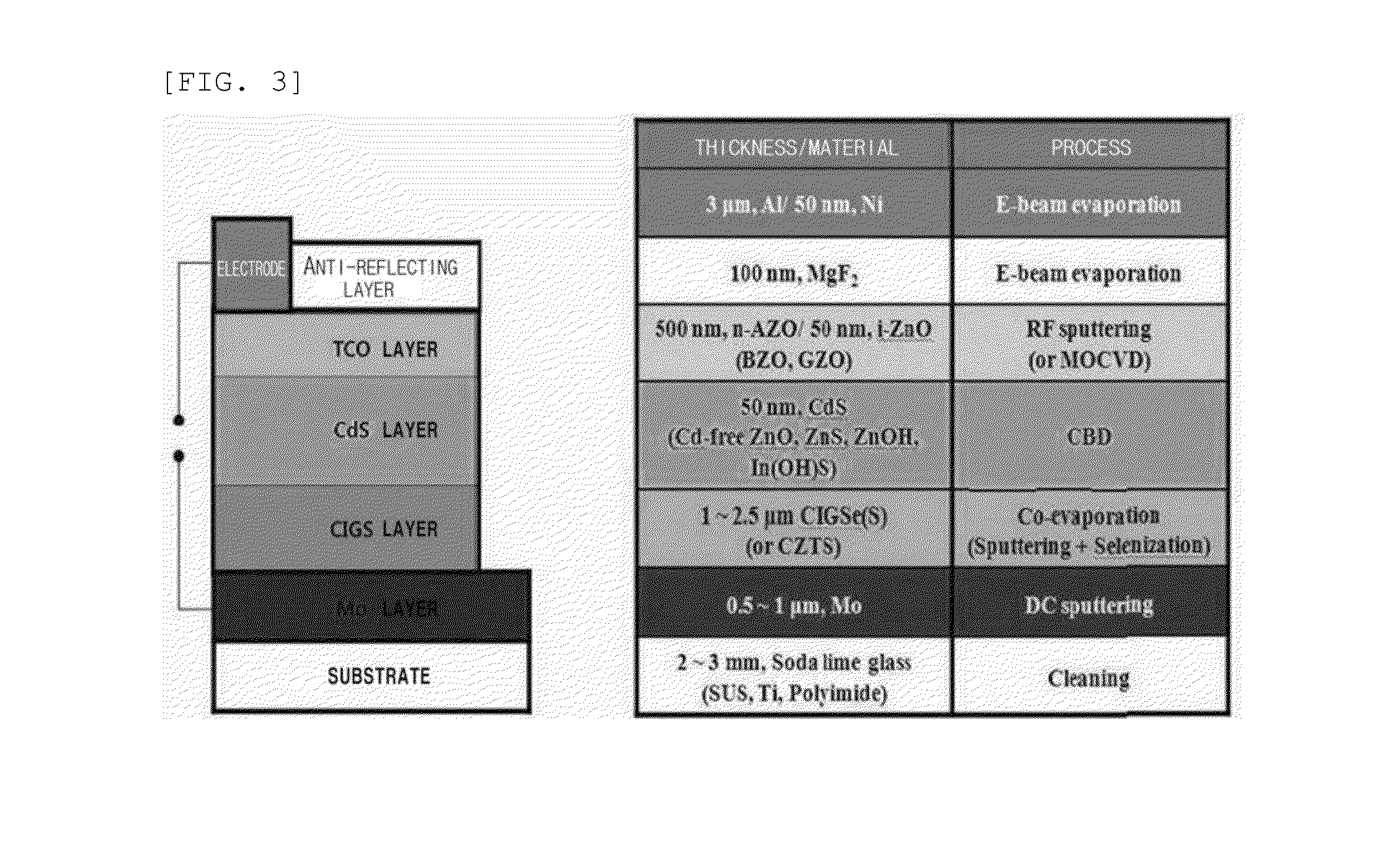
Copper indium gallium (di)selenide (CIGS) is a I-III-VI₂ semiconductor material composed of copper, indium, gallium, and selenium. The material is a solid solution of copper indium selenide (often abbreviated "CIS") and copper gallium selenide. It has a chemical formula of CuIn₍₁₋ₓ₎Ga₍ₓ₎Se₂ where the value of x can vary from 0 (pure copper indium selenide) to 1 (pure copper gallium selenide). CIGS is a tetrahedrally bonded semiconductor, with the chalcopyrite crystal structure, and a bandgap varying continuously with x from about 1.0 eV (for copper indium selenide) to about 1.7 eV (for copper gallium selenide).
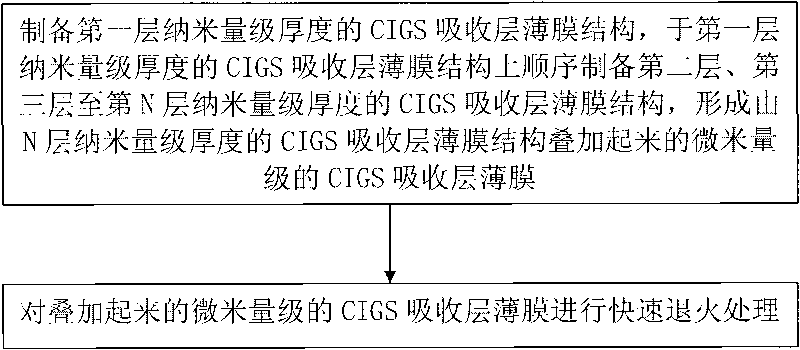
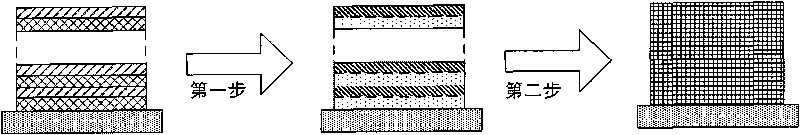
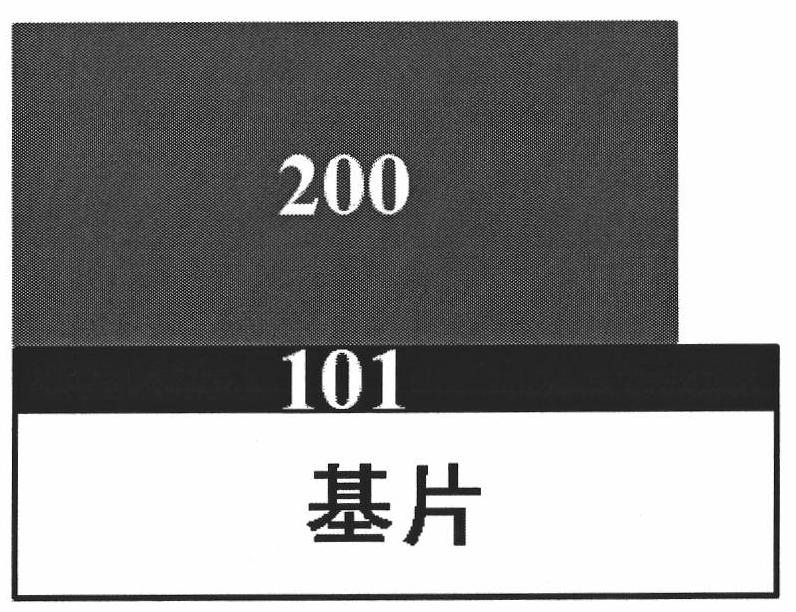
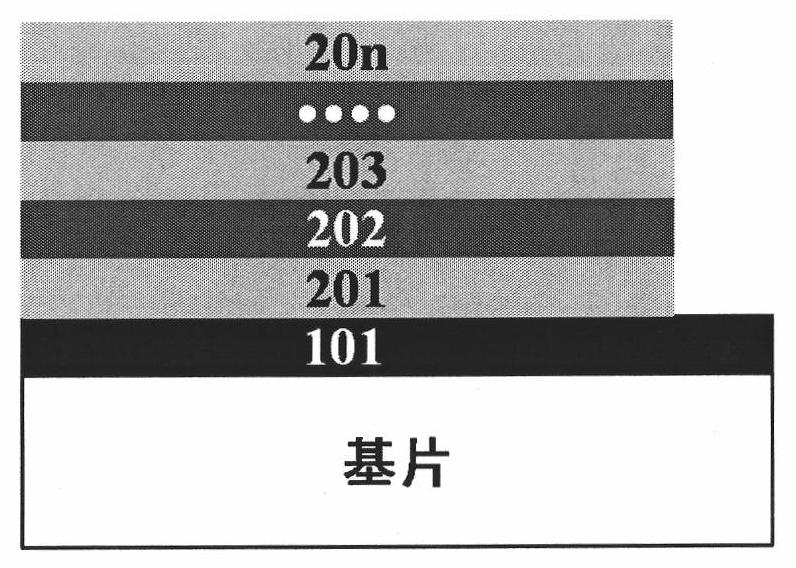
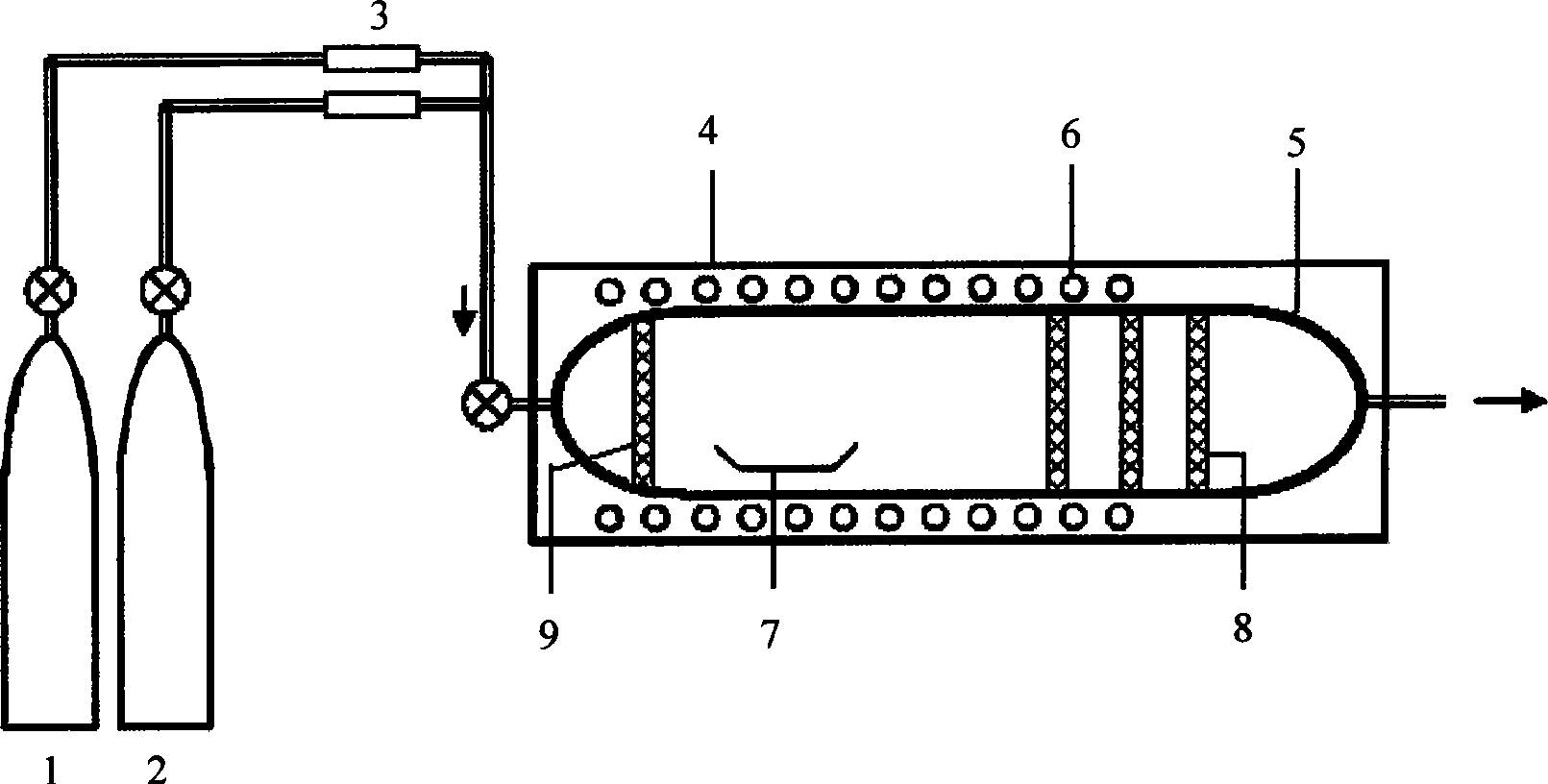
Recovery method of copper indium gallium selenide
InactiveCN102296178ASimple processReduce processing timeProcess efficiency improvementIndiumCopper indium gallium selenide
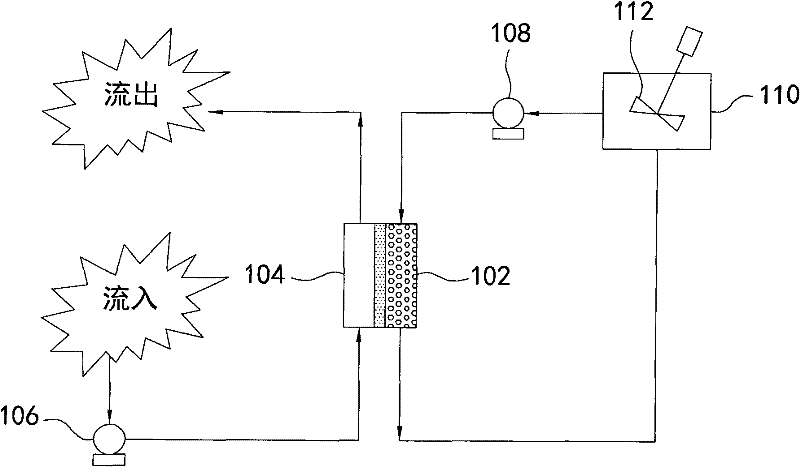
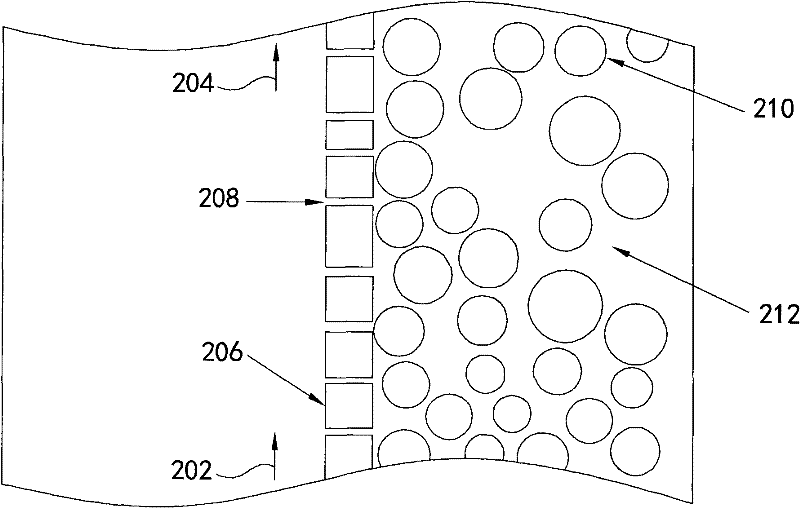
A recovery method for copper indium gallium selenide. The method includes firstly using a mixed solution of hydrochloric acid and hydrogen peroxide to dissolve the metal powder containing CIGS. After selenium is separated using hydrazine, copper is replaced by indium metal. Finally, indium and gallium are separated by a supported liquid membrane (SLM) combined with a dispersed stripping solution. The acid used in all the steps of the method is hydrochloric acid, so the copper indium gallium selenium can be separated one by one without the conversion of the solution during the operation, effectively reducing the process time and cost.
Owner:SOLAR APPLIED MATERIALS TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION
Method for preparing high-quality graphene
The invention discloses a method for preparing high-quality graphene, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: reacting active metals with low-carbon halogenated hydrocarbons or absolute ethyl alcohols in a certain time at a certain temperature so as to generate new ecological carbon; then, restructuring the new ecological carbon so as to obtain graphene; and finally, carrying out purification on the obtained graphene so as to obtain high-quality graphene. Compared with the traditional chemical stripping method for preparing graphene, the method disclosed by the invention is simple in operation and low in cost, and can prepare less-defect, good-electroconductivity and high-quality graphene. The graphene prepared by using the method disclosed by the invention can have a broad application prospect in the fields of photoelectric devices such as CIGS (copper indium gallium selenide), CdTe(cadmium telluride) and dye sensitized solar cells and the like, flat-panel displays, super capacitors, field emission materials, lithium ion batteries, and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Nanoparticles and methods of making and using
A nanoparticle composition is disclosed comprising a copper indium gallium selenide, a copper indium sulfide, or a combination thereof. Also disclosed is a layer comprising the nanoparticle composition. A photovoltaic device comprising the nanoparticle composition and / or the absorbing layer is disclosed. Also disclosed are methods for producing the nanoparticle compositions, absorbing layers, and photovoltaic devices described herein.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Copper indium gallium selenium (CIGS) solar cell, film of absorbing layer thereof, method and equipment for preparing film
InactiveCN101740660APrevent uneven distributionStop the spreadFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationIndiumCopper indium gallium selenide
Owner:北京华仁合创科技有限公司
Method for preparing light absorption layer of CIGS (copper indium gallium selenide) thin film solar cell by magnetron sputtering method
ActiveCN101768729APrevent volatilizationSolve the problem of volatilityVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSputteringCopper indium gallium selenide
The invention relates to a preparation method of a light absorption layer film of a CIGS (copper indium gallium selenide) solar cell, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: preparing a CIGS precursor thin film which has high reactivity and can be subjected to fast reaction sintering by a magnetron sputtering method on a bottom electrode through simple target sputtering and copper-enriching target and copper-lacking target sputtering simultaneously or sequentially; and then, carrying out heat treatment on the CIGS precursor thin film for fast reaction to generate a smooth, compact and uniform CIGS solar cell light absorption layer thin film with excellent photoelectric properties. The preparation method provided by the invention has the advantages of strong controllability, high thin film quality, good thin film uniformity and simple processes and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:山东中科泰阳光电科技有限公司
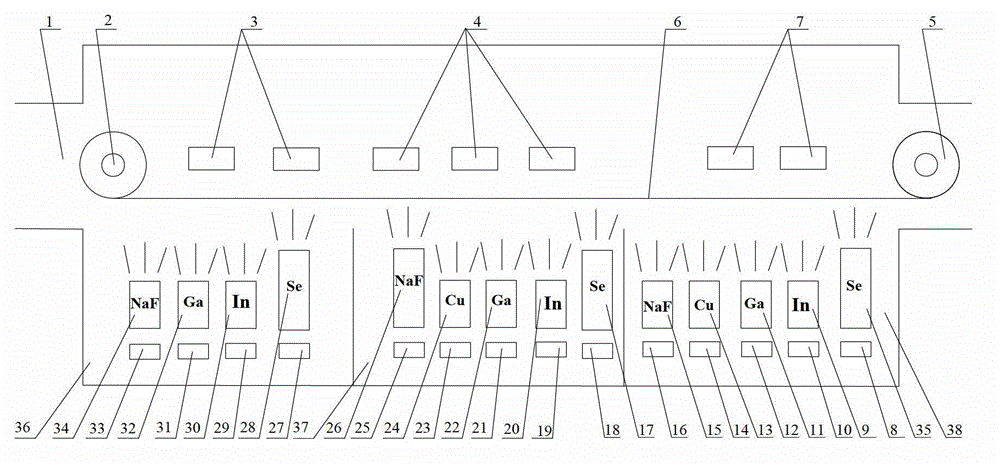
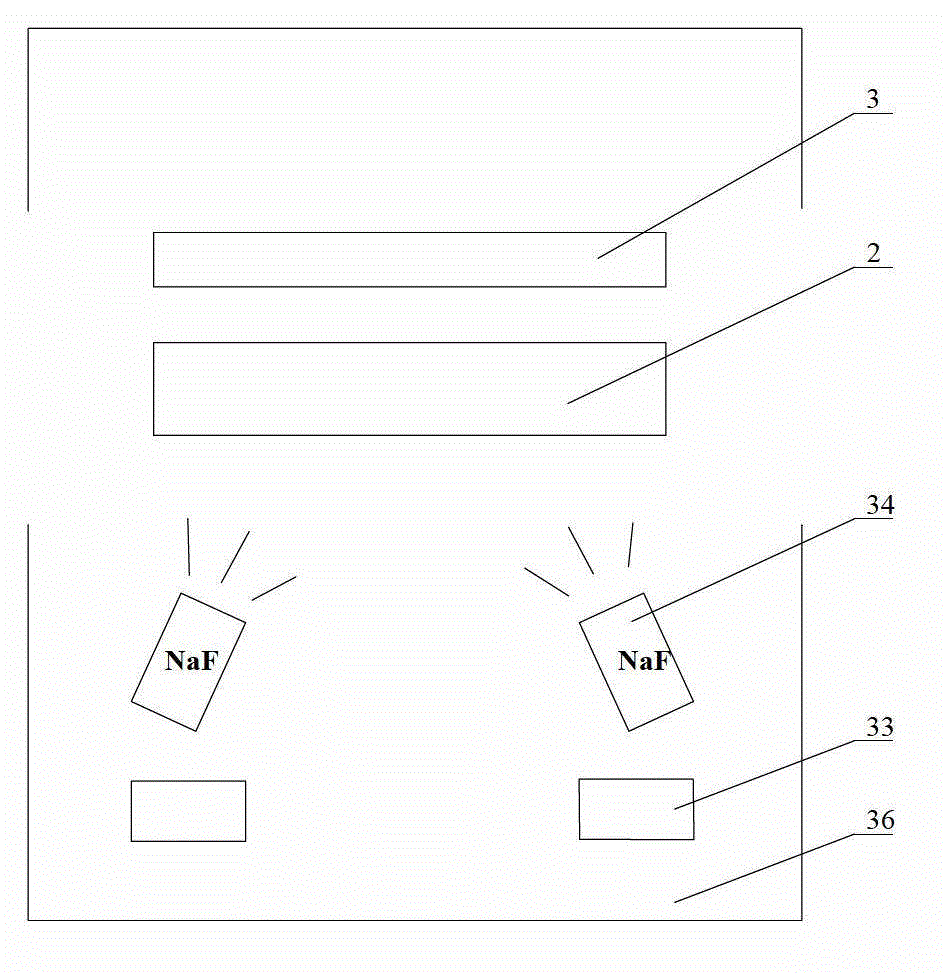
Method for manufacturing sodium-doped absorbing layer on reel-to-reel flexible polyimide (PI) substrate
ActiveCN102943241AGood adhesionIncrease the open circuit voltageFinal product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingIndiumCopper indium gallium selenide
The invention relates to a method for manufacturing a sodium-doped absorbing layer on a reel-to-reel flexible polyimide (PI) substrate. The method is characterized by comprising the steps of 1 performing preparation before work, 2 preparing Na-doped indium gallium selenide (IGS) film, 3 preparing a copper-rich copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) film; and 4 preparing the sodium-doped absorbing layer on the reel-to-reel flexible PI substrate. The method adopts a vacuum evaporation technology, keeps a distance between evaporation sources and the PI substrate to be 300-400mm and adjusts tape transporting speed of the PI substrate to enable the PI substrate to be lower than 450 DEG C, elements evaporated by the evaporation sources can be compounded on a back electrode Mo of the PI substrate well, and the Na-doped IGS film with even thickness is formed on the back electrode Mo. Due to the fact that Na atoms diffuse and enter the crystal boundary position of the IGS film to form a deep energy level defect, a foundation is laid for fully even Na doping into a large-area absorbing layer and strengthening of adhesion of the absorbing layer, and the effects of improving open-circuit voltage and electrical property of batteries are played.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP NO 18 RES INST
Preparation method for buffering layer material of copper indium gallium selenide film solar battery
InactiveCN102544237AQuality improvementControl reaction speedFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesIndiumElectrical battery
The invention discloses a preparation method for a buffering layer material of a copper indium gallium selenide film solar battery. By the method, a precursor of chemical bath reaction is prepared by using a zinc sulfate solution as a Zn<2+> source, a thiourea solution as a S<2-> source, ammonia water as a buffering agent and sodium citrate as a complexing agent; and a Zn(O,S) semiconductor film with uniform and compact grain size distribution and good adhesive force is prepared on a copper indium gallium selenide film and the common glass substrate and serves as the buffering layer of the copper indium gallium selenide film solar battery. The Zn(O,S) instead of CdS serves as the buffering layer of the copper indium gallium selenide film solar battery, so production of the copper indium gallium selenide film solar battery is environment-friendly and economic. The band gap width of the Zn(O,S) is more than that of the CdS, so more incident photons can reach an absorption layer through the buffering layer, short-circuit current of the battery is increased and photoelectric conversion efficiency of the battery is improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Method and apparatus for forming copper indium gallium chalcogenide layers
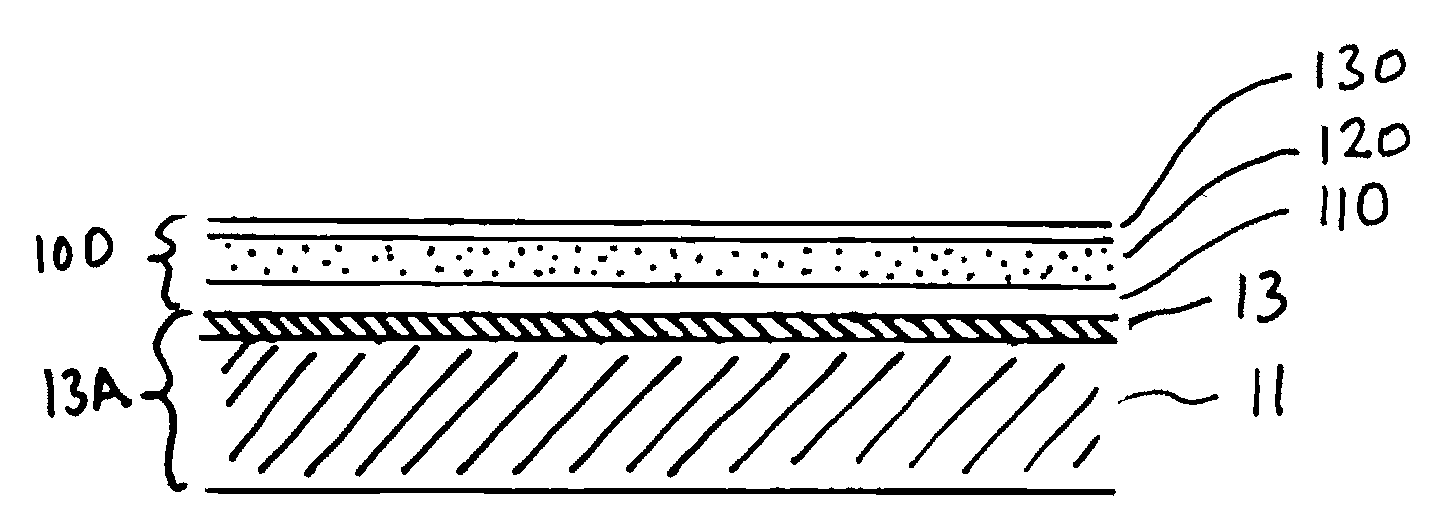
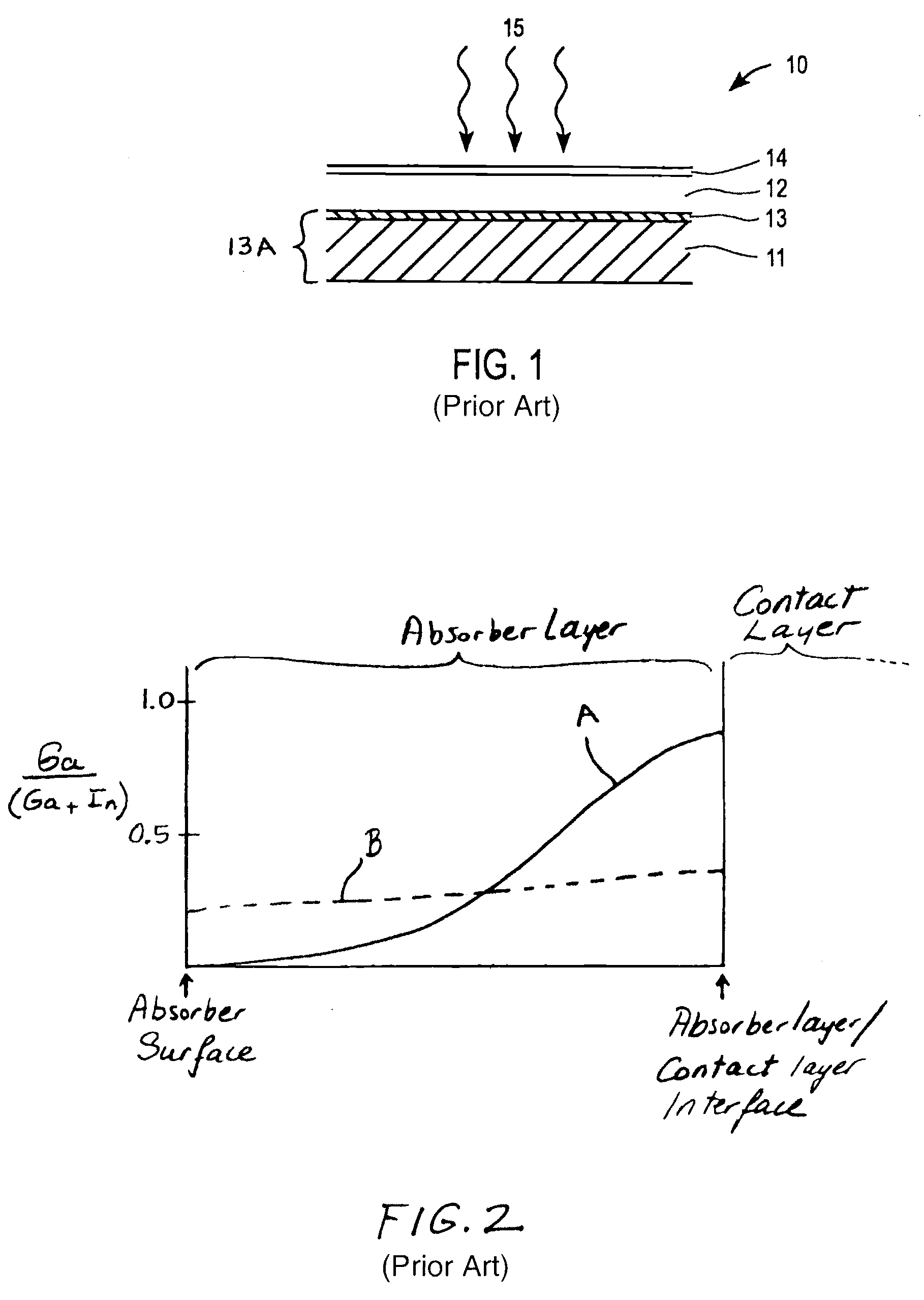
InactiveUS20090117684A1Final product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIndiumContact layer
A multilayer structure to form absorber layers for solar cells. The multilayer structure includes a base comprising a contact layer on a substrate layer, a first layer on the contact layer, and a metallic layer on the first layer. The first layer includes an indium-gallium-selenide film and the gallium to indium molar ratio of the indium-gallium-selenide film is in the range of 0 to 0.8. The metallic layer includes gallium and indium without selenium. Additional selenium is deposited onto the metallic layer before annealing the structure for forming an absorber.
Owner:SOLOPOWER
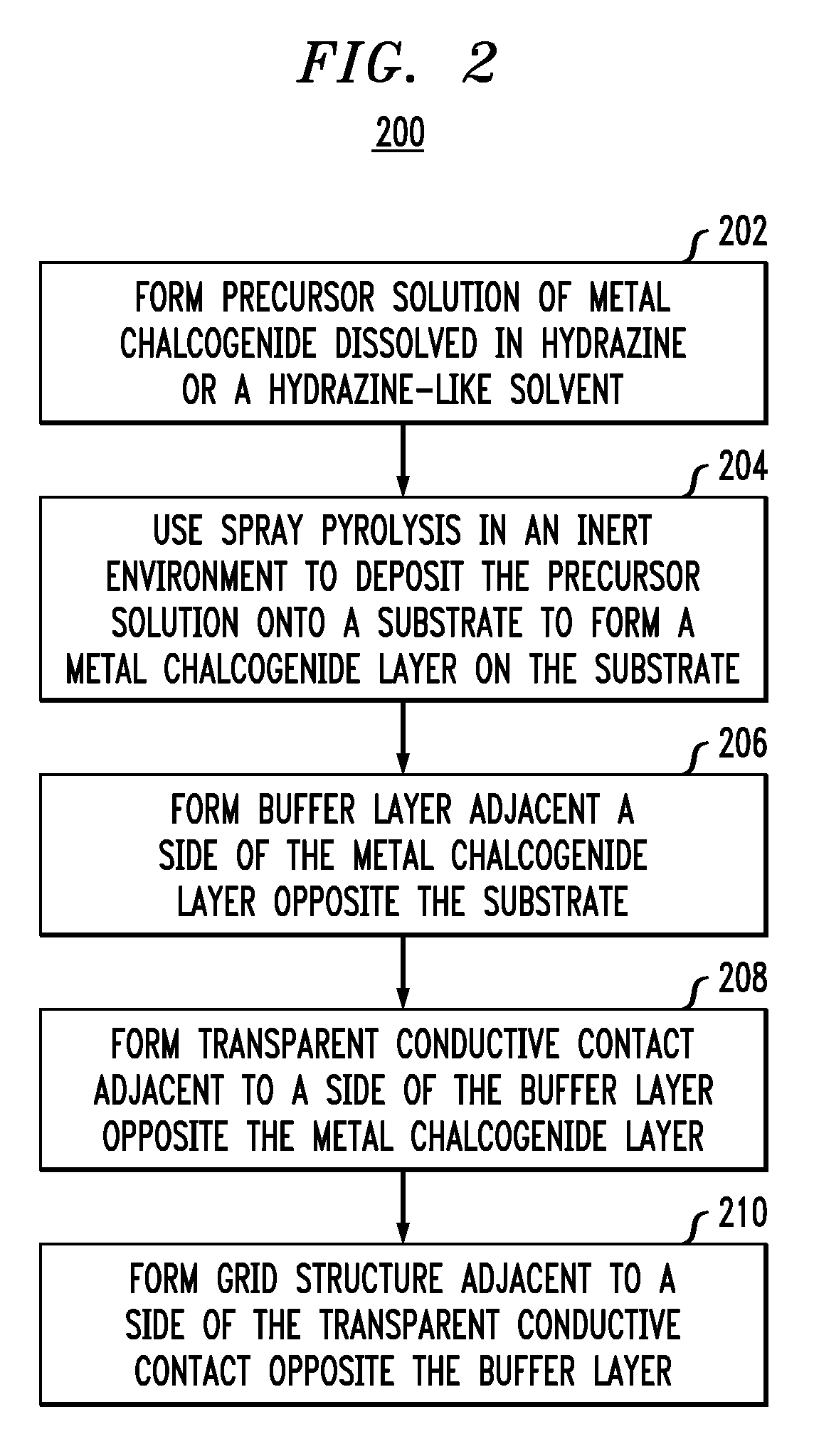
Spray pyrolysis for large-scale production of chalcopyrite absorber layer in photovoltaic devices
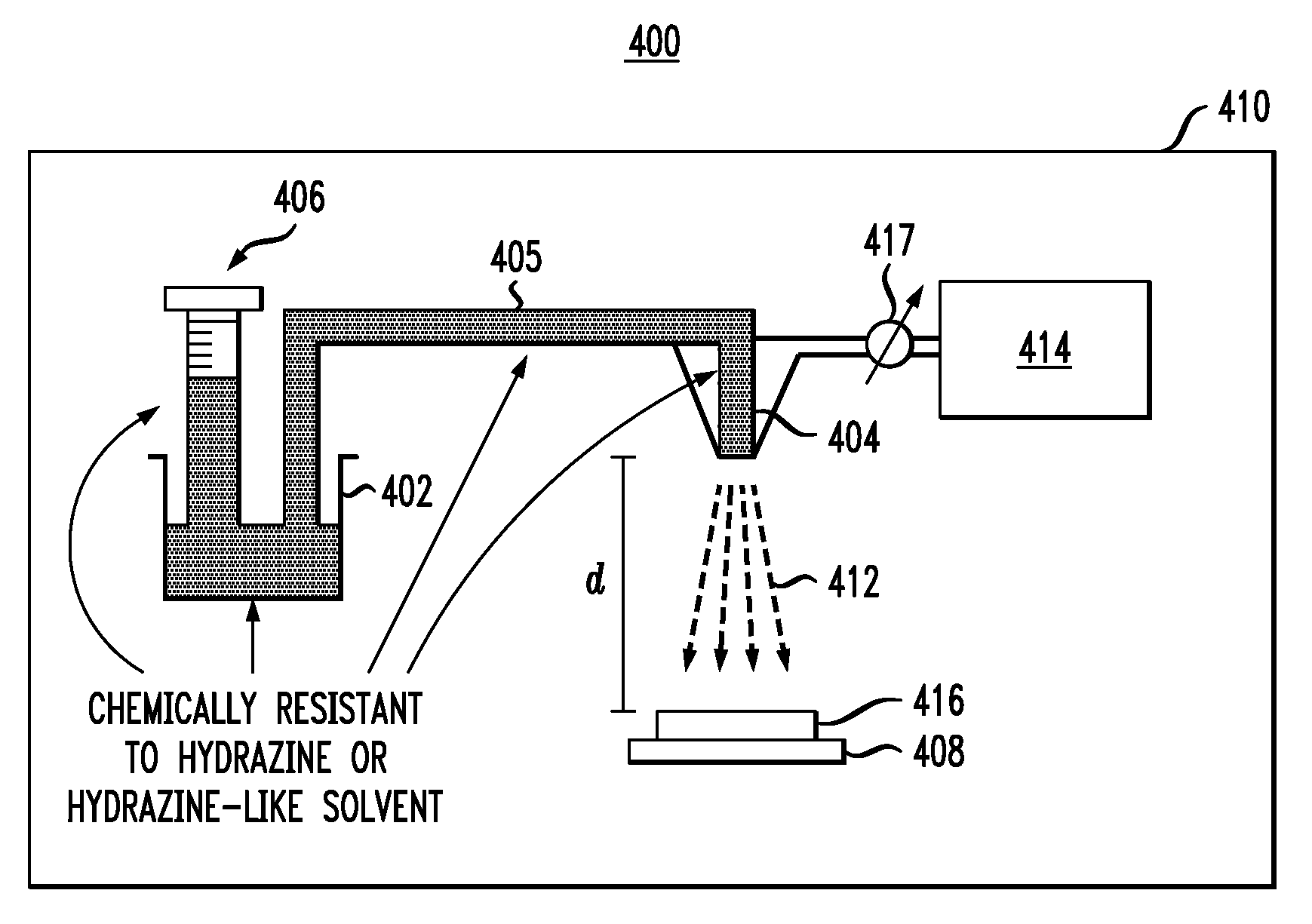
ActiveUS7838403B1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingMetal chalcogenidesSpray pyrolysis
Techniques for fabricating a photovoltaic device having a chalcopyrite absorber layer, such as a copper indium gallium selenide / sulfide (CIGSS) absorber layer, are provided. In one aspect, a method for fabricating a photovoltaic device is provided. The method includes the following steps. A precursor solution of metal chalcogenide dissolved in hydrazine or a hydrazine-like solvent is formed. Spray pyrolysis in an inert environment is used to deposit the precursor solution onto a substrate to form a metal chalcogenide layer on the substrate. A buffer layer is formed adjacent to a side of the metal chalcogenide layer opposite the substrate. A transparent conductive contact is formed adjacent to a side of the buffer layer opposite the metal chalcogenide layer.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
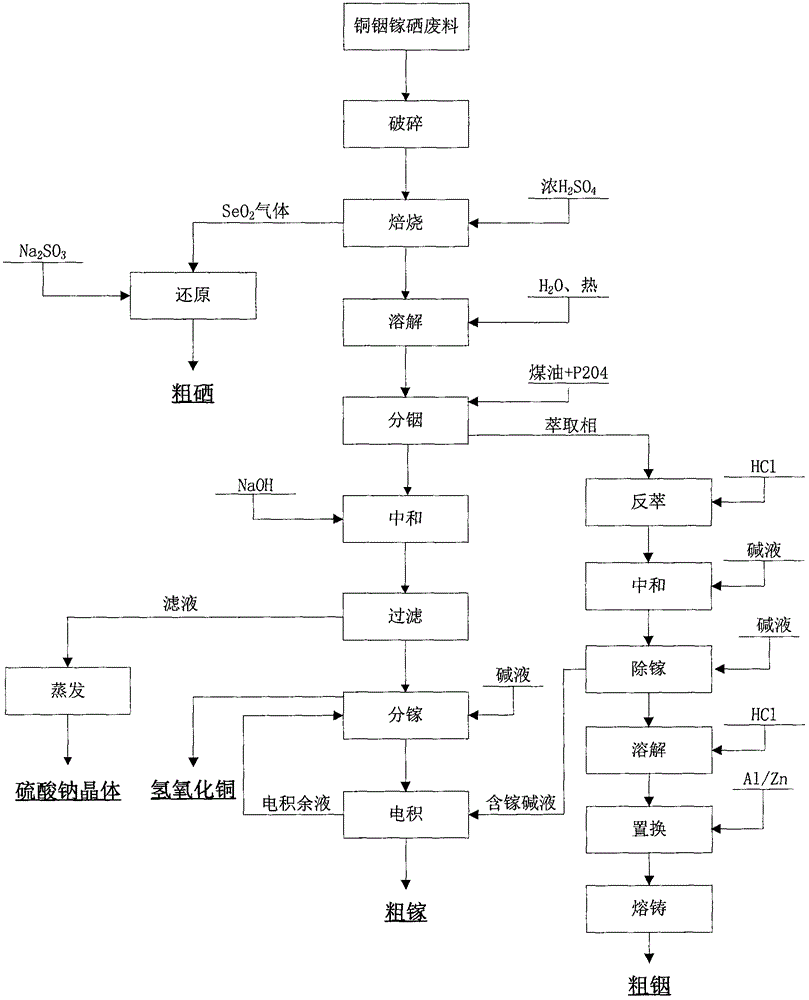
Recycling method for copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) waste
ActiveCN105886767AAchieve efficient recyclingAchieving zero emissionsProcess efficiency improvementElemental selenium/telluriumRecovery methodIndium
The invention relates to a recycling method for copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) waste. The recycling method comprises the steps that selenium in the CIGS waste is subjected to acidifying, roasting and volatilizing at first, SeO2 gas is reduced through a sodium sulfite solution, and crude selenium is obtained to achieve advance separation of the selenium, so that the problem that the selenium is always difficult to separate in the industry is solved; and then, the rest of three kinds of metal are separated, particularly, gallium-containing alkali liquor produced in the indium separation process and a gallium-containing solution obtained in the gallium separation process are combined, and electrodepositing residual liquor can be returned to the to-be-electrodeposited gallium-containing solution to be subjected to circulatory electrodepositing, so that efficient and circulatory recycling of gallium is achieved. According to the recycling scheme of the recycling method for the CIGS waste, the comprehensive recycling rate of the various materials is much higher than the existing level in the same industry; in addition, production wastewater zero discharge can be achieved in the whole recycling process, and the environment-friendly degree is high; and moreover, the whole recycling process is easy to operate, high in safety and reliability, low in cost and capable of achieving large-scale production easily and has broad application prospects.
Owner:HANERGY MOBILE ENERGY HLDG GRP CO LTD
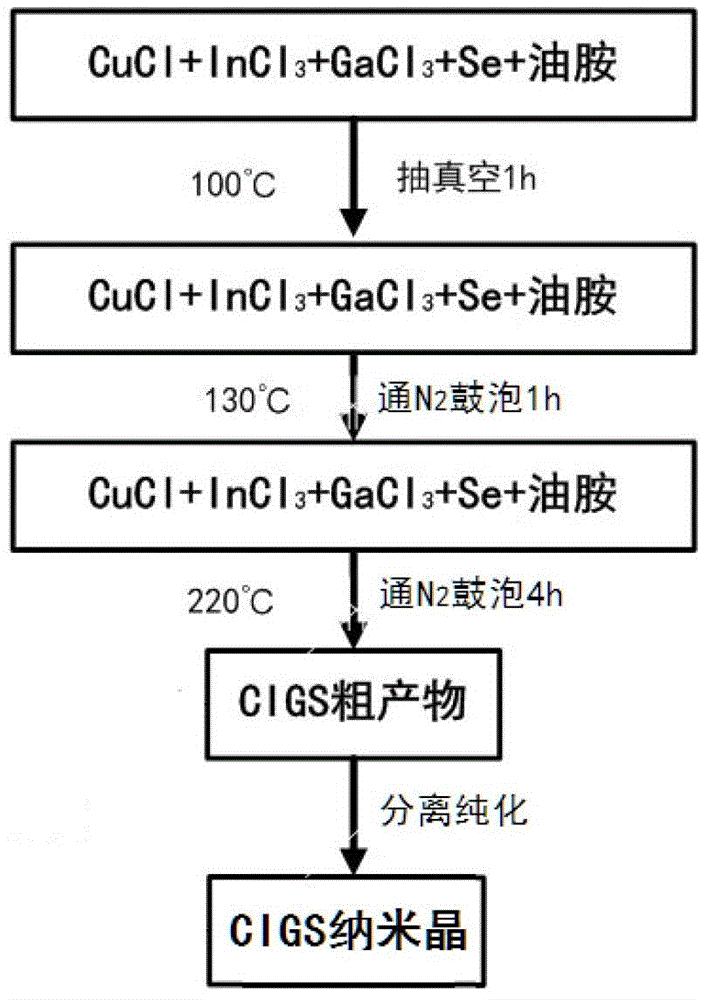
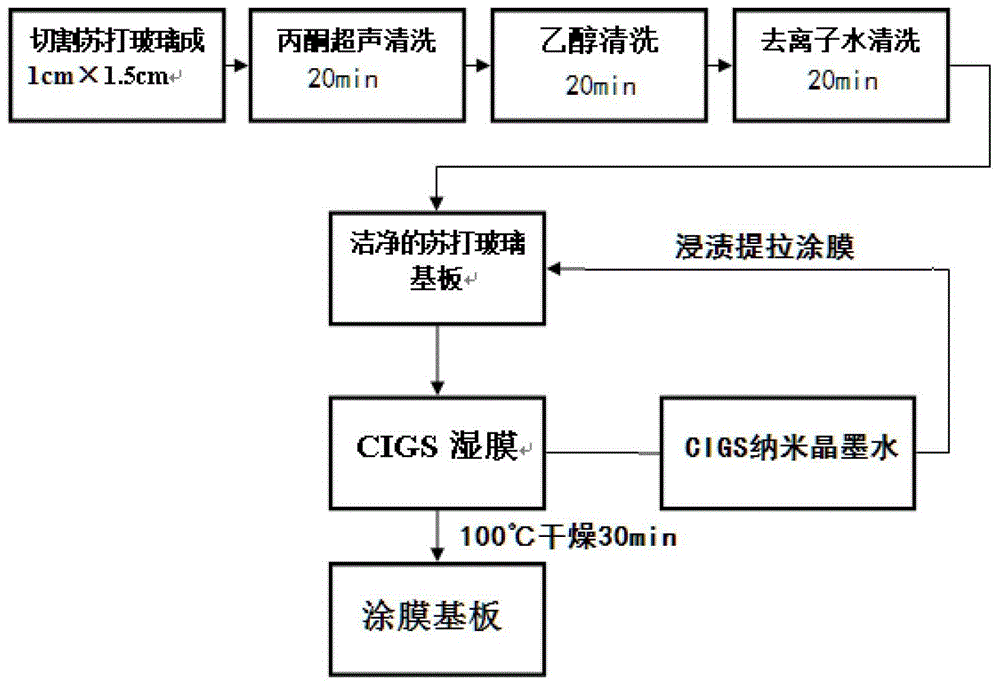
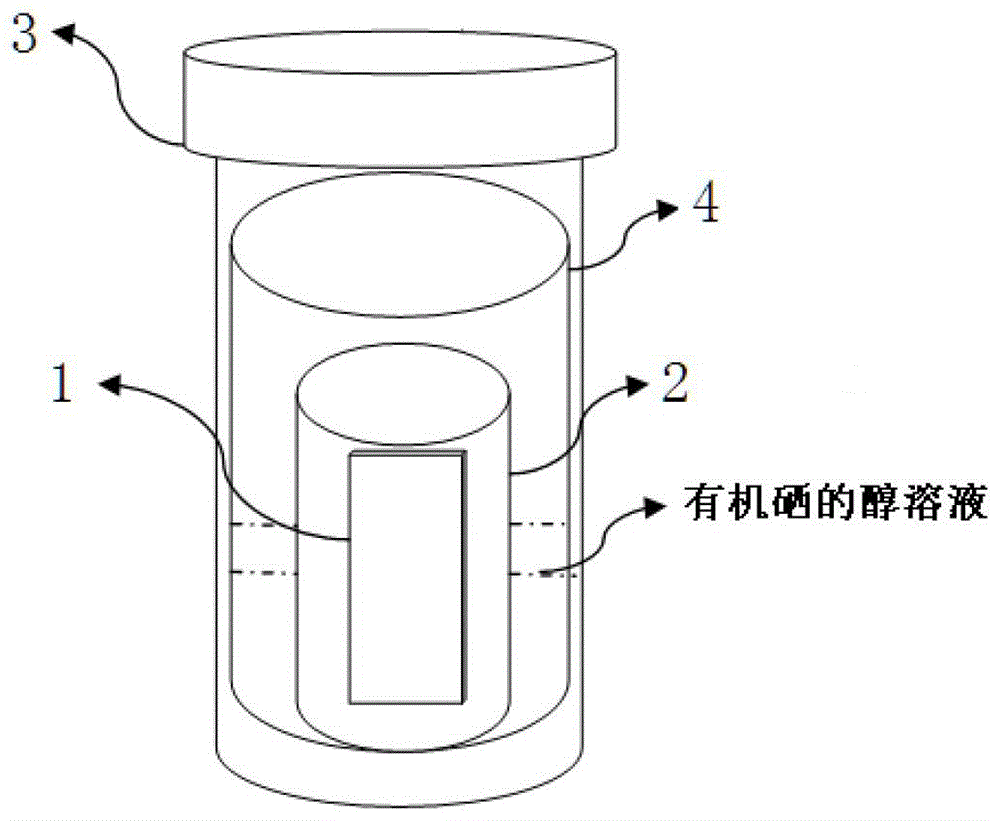
Method for preparing CIGS (copper indium gallium selenide) film through selenylation at low temperature
ActiveCN103334081ALow selenization temperatureLow toxic safetyFinal product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingCopper indium gallium selenideSolvent
The invention discloses a method for preparing a CIGS (copper indium gallium selenide) film through selenylation at low temperature. The method comprises the following steps of carrying out a reaction on a copper resource, an indium resource, a gallium resource and a selenium resource as well as alkylamine so as to obtain CIGS nanocrystalline, mixing the CIGS nanocrystalline with a solvent so as to obtain CIGS nanocrystalline ink, coating so as to obtain a coating substrate, then carrying out steam inducing low temperature selenylation: putting the coating substrate and an organic selenium alcoholic solution independently in a closed environment, heating to 100-400 DEG C, carrying out a selenylation reaction through full contact of the steam generated by the organic selenium alcoholic solution and the coating substrate, and obtaining the CIGS film. By adopting steam inducing selenylation, the method has the advantages of good selenylation effect, low toxicity and safety as well as lower selenylation temperature, and is convenient to coat the film on a low temperature enduring flexible substrate. The photoelectric conversion efficiency can be improved when obtained CIGS films are used for preparing solar energy batteries.
Owner:徐东
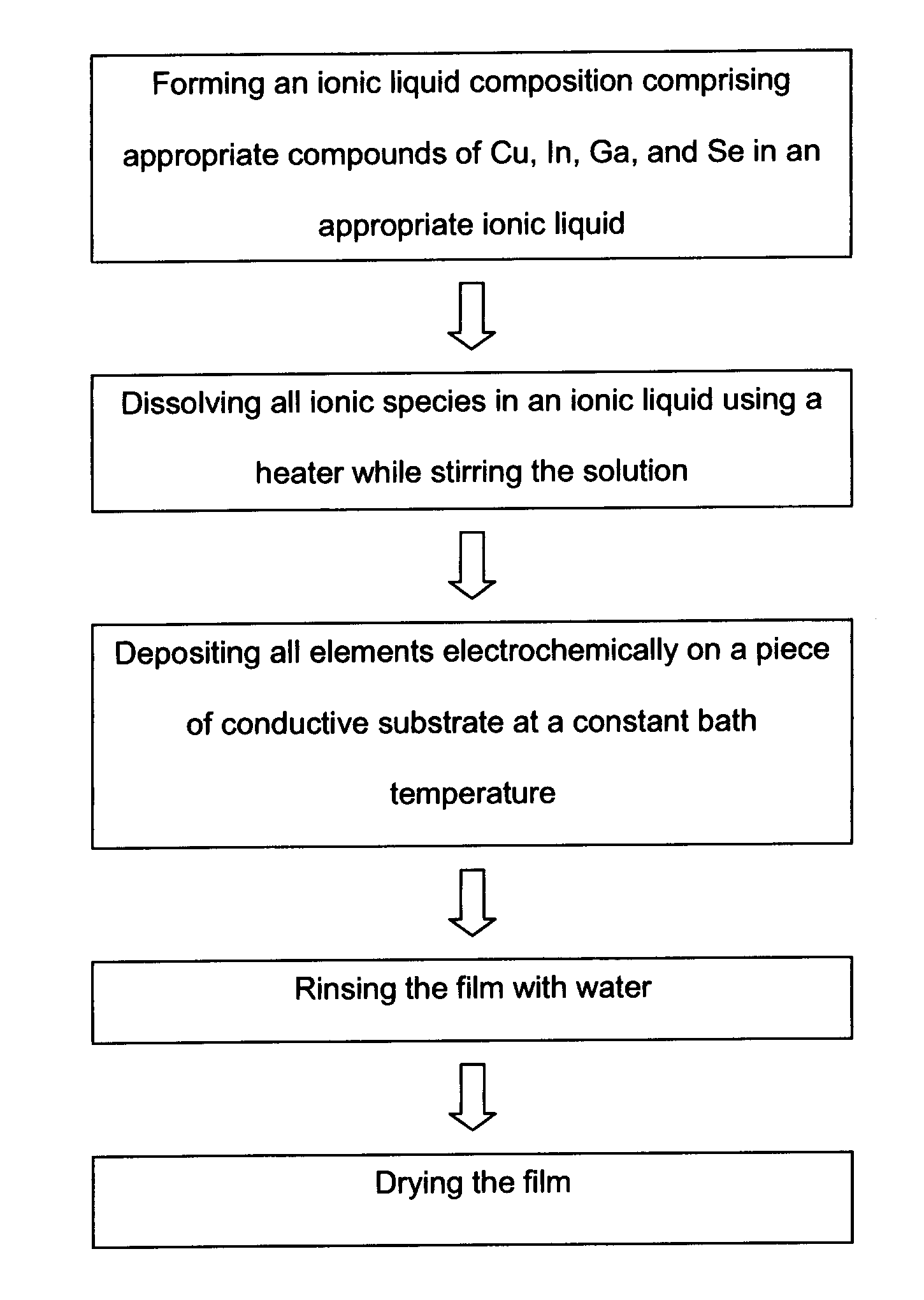
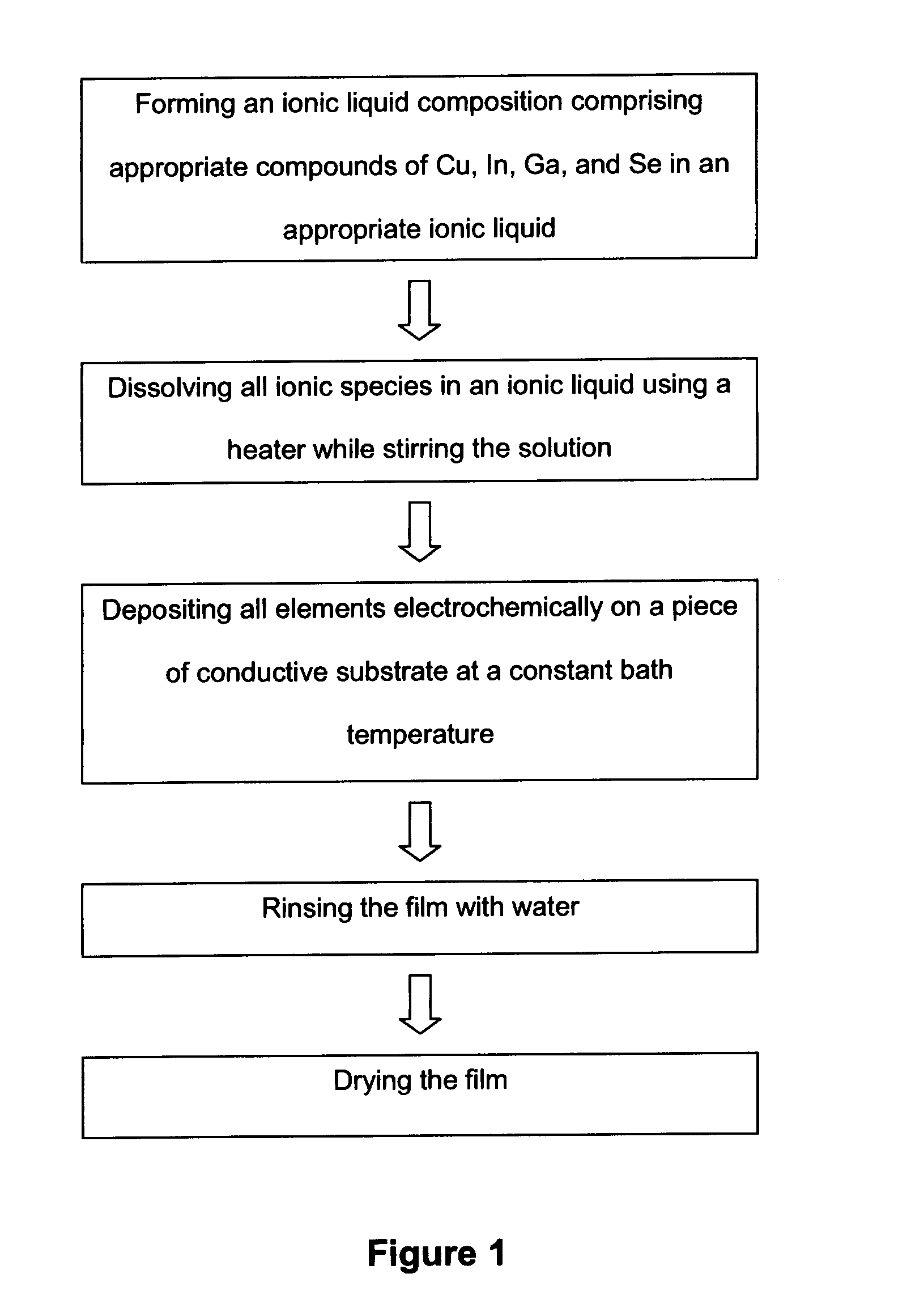
Electrochemical method of producing copper indium gallium diselenide (CIGS) solar cells
InactiveUS20120227811A1Low-cost and high-throughput productionImprove scalabilityFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesIndiumElectrochemistry
The present invention describes a method of producing a photovoltaic solar cell with stoichiometric p-type copper indium gallium diselenide (CuInxGa1-xSe2) (abbreviated CIGS) as its absorber layer and II-IV semiconductor layers as the n-type layers with electrodeposition of all these layers. The method comprises a sequence of novel procedures and electrodeposition conditions with an ionic liquid approach to overcome the technical challenges in the field for low-cost and large-area production of CIGS solar cells with the following innovative advantages over the prior art: (a) low-cost and large-area electrodeposition of CIGS in one pot with no requirement of post-deposition thermal sintering or selenization; (b) low-cost and large-area electrodeposition of n-type II-VI semiconductors for the completion of the CIGS solar cell production; and (c) low-cost and large-area deposition of a buffer layer of CdS or other compounds with a simple chemical bath method.
Owner:CHENGDU ARK ETERNITY PHOTOVOLTAIC TECH COMPANY
Method for preparing copper indium gallium selenide solar cell optical absorption layer
InactiveCN102569514AMeet the requirementsEasy to manufactureFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesIndiumNanoparticles dispersion
The invention relates to the preparation technology of film solar cell, in particular to a preparation method for a copper indium gallium selenide optical absorption layer. The preparation method comprises the steps of (1) uniformly mixing, stirring and ball-milling selenide of metal copper, indium and gallium or metal copper, indium and gallium and selenium simple substance in stoichiometric ratio, and obtaining copper indium gallium selenide nano particles, of which the particle diameter is 10-10,000nm, wherein the atom molar ratio of Cu: In: Ga: Se is (0.9-1):(0-1): (0-1):2; (2) dispersing the copper indium gallium selenide nano particles in a mixing solution formed by dispersant and film-forming agent; stirring or grinding or magnetically stirring and dispersing the particles so as to obtain CIGS (Copper Indium Gallium Selenide) precursor slurry; (3) coating a substrate with the precursor film, drying the precursor film in the air atmosphere to remove the dispersant and the film-forming agent; and obtaining precursor film; and (4) quickly warming and thermally treating the precursor film in the insert atmosphere to obtain copper indium gallium selenide solar cell optical absorption layer film finished product. The method provided by the invention simplifies the process flow, has high production efficiency and is helpful for environment friendliness and; and the method broadens the idea for large-scale industrialization of CIGS film solar cell.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
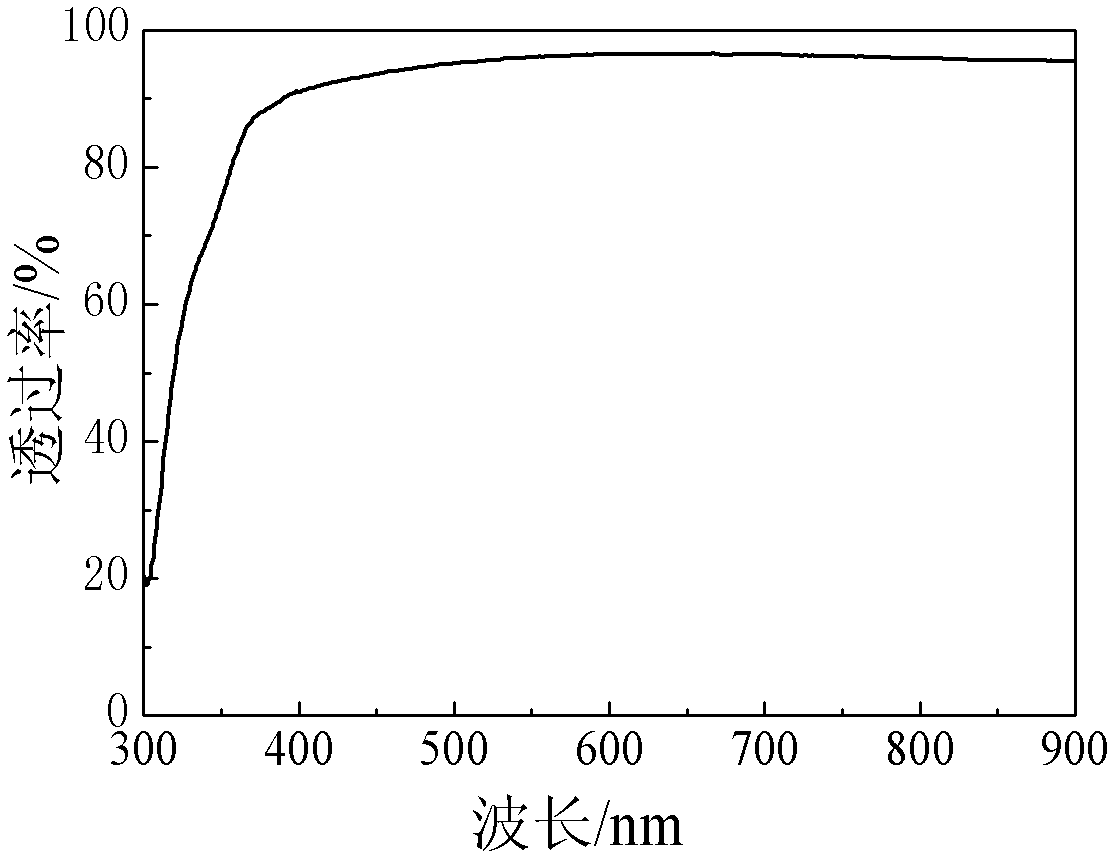
Silicate glass with high strain point and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of glass, and in particular relates to silicate glass with high strain point and application thereof. According to mass percent of oxide, the silicate glass with the high strain point comprises the following components: 56-70 percent of SiO2, 4.0-12.0 percent of Al2O3, 4.0-12.0 percent of CaO, 2.0-7.0 percent of MgO, 0-5.0 percent of SrO, 0-5.0 percent of BaO, 3.0-14.0 percent of Na2O, 0-7.0 percent of K2O, 1.5-6.0 percent of ZrO2, 0-1.0 percent of TiO2 and 0-1.0 percent of CeO2. The glass with the stain point being over 560 DEG C is high in hardness, is suitable for a CIGS (Copper Indium Gallium Selenide) film battery substrate, and is suitable to be used as a cover plate glass of medium and high-grade touch screens after chemical tempering.
Owner:HENAN ANCAI HI-TECH
Method for preparing copper-indium-gallium-selenide (CIGS) solar photovoltaic cell
InactiveCN102386283AIncrease profitImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesVulcanizationIndium
The invention discloses a method for preparing a copper-indium-gallium-selenide (CIGS) solar photovoltaic cell. The method for preparing the photovoltaic cell comprises the following steps of: cleaning a glass substrate, sputtering a molybdenum metal, sputtering a copper-indium-gallium alloy, performing selenylation (vulcanization), depositing zinc sulfide in a chemical bath, sputtering zinc oxide and sputtering aluminum-doped zinc oxide. The method is high in utilization rate of raw materials, uniform in components of cell compounds, high in photoelectric conversion efficiency and good in repeatability.
Owner:陈群
Alkali metal doping method for preparing CIGS absorbing layer on flexible substrate
ActiveCN105720132ASimple processPrevent crystallizationFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesCu elementEvaporation
The invention relates to an alkali metal doping method for preparing a CIGS absorbing layer on a flexible substrate, and belongs to the technical field of copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) thin film solar cells. The alkali metal doping method comprises that a CIGS absorbing layer is deposited by using a co-evaporation process; and with the increase of Cu content in the absorbing layer, the thin film growth experiences a copper-poor to copper-rich process, in the copper-rich process, when Cu(In+Ga)>1 in a CIGS thin film, the evaporation of the Cu element is stopped so that the slightly copper-rich CIGS thin film can finally become copper-poor, then the In and Ga atoms are evaporated until the deposition thickness is 1 / 10-3 / 10 of the thickness of the absorbing layer, in this process, an alkali metal compound is co-evaporated, the doping amount is 0.08-0.12% of the atomic ratio with respect to the CIGS thin film, the temperature of the substrate is reduced to the room temperature, and the CIGS thin film having a thickness of 1-3 <mu>m is obtained. The invention has the advantages of having a simplified process, a high production efficiency and thin film crystal high-quality, increasing the carrier concentration of the absorbing layer, lowering the resistivity, improving the electrical properties of the thin film cell, thus improving the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the CIGS thin film solar cell and the like.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP NO 18 RES INST
Solar Cell
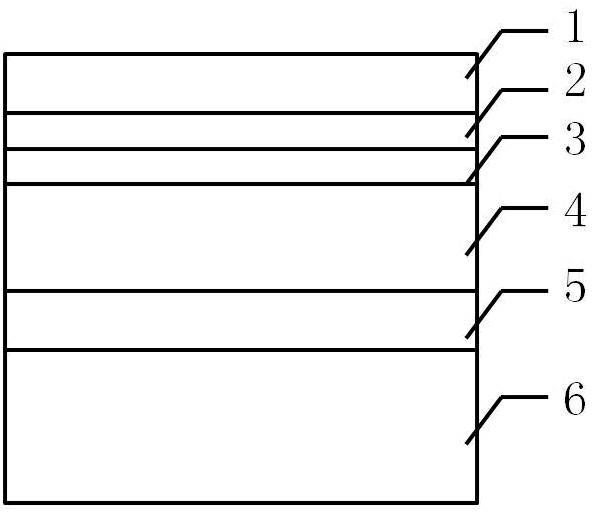
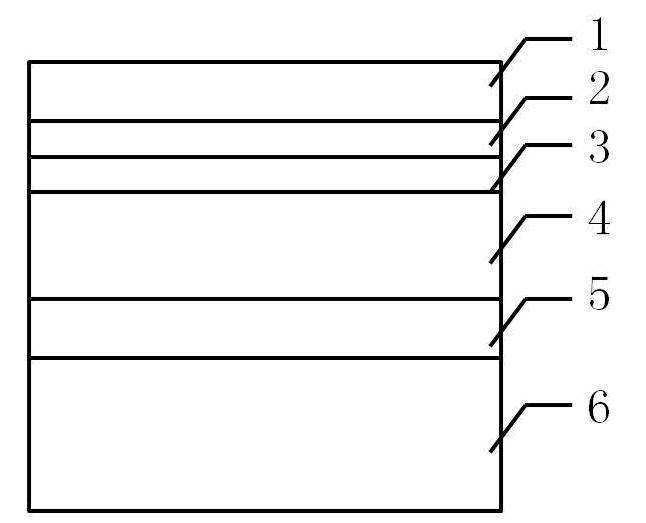
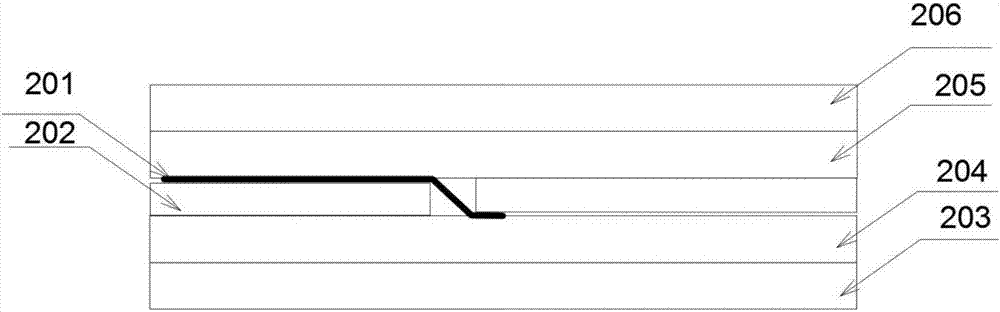
InactiveUS20090242022A1Improve reliabilityBreakage of substrate can be preventedFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorCopper indium gallium selenide
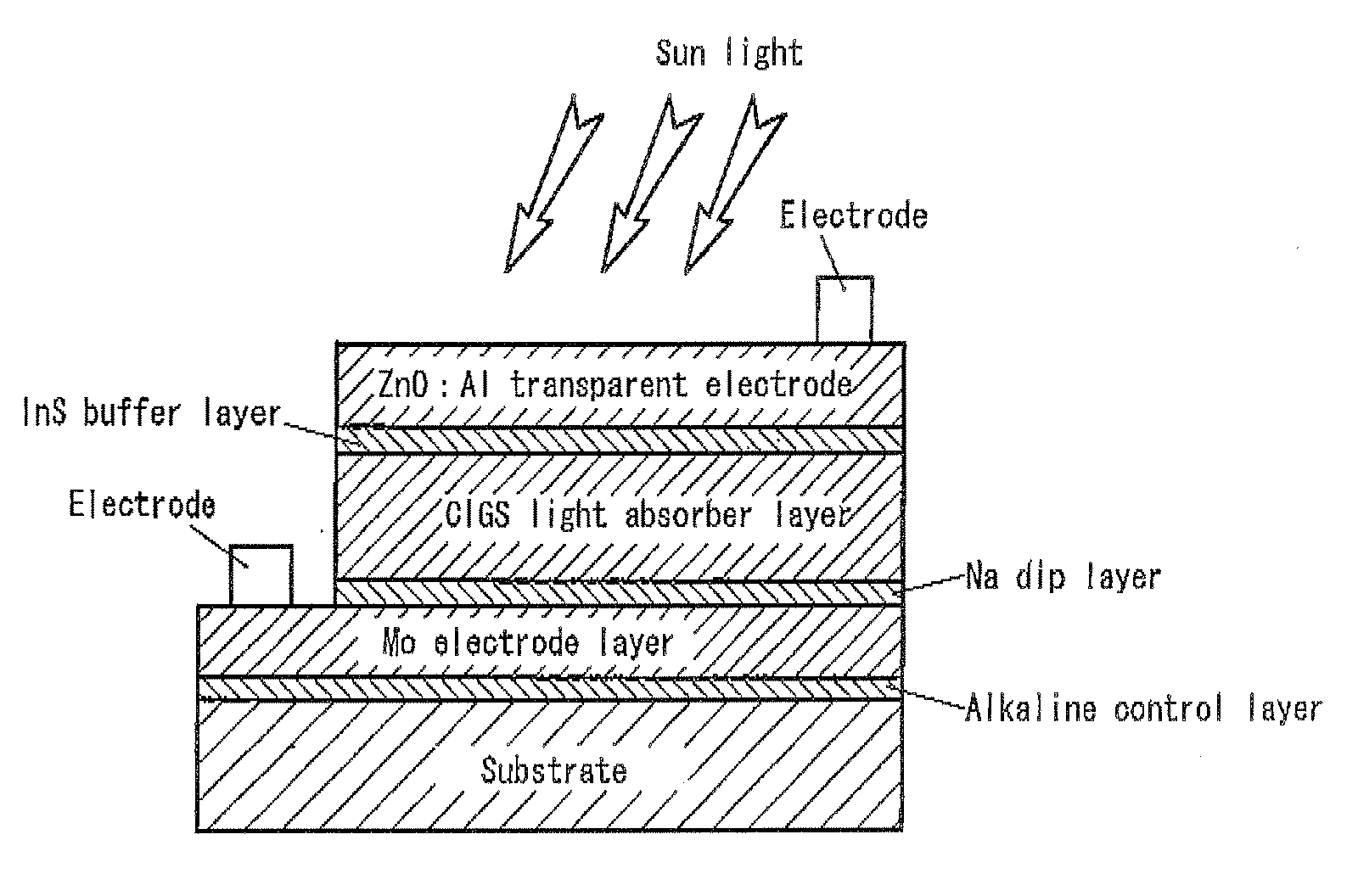
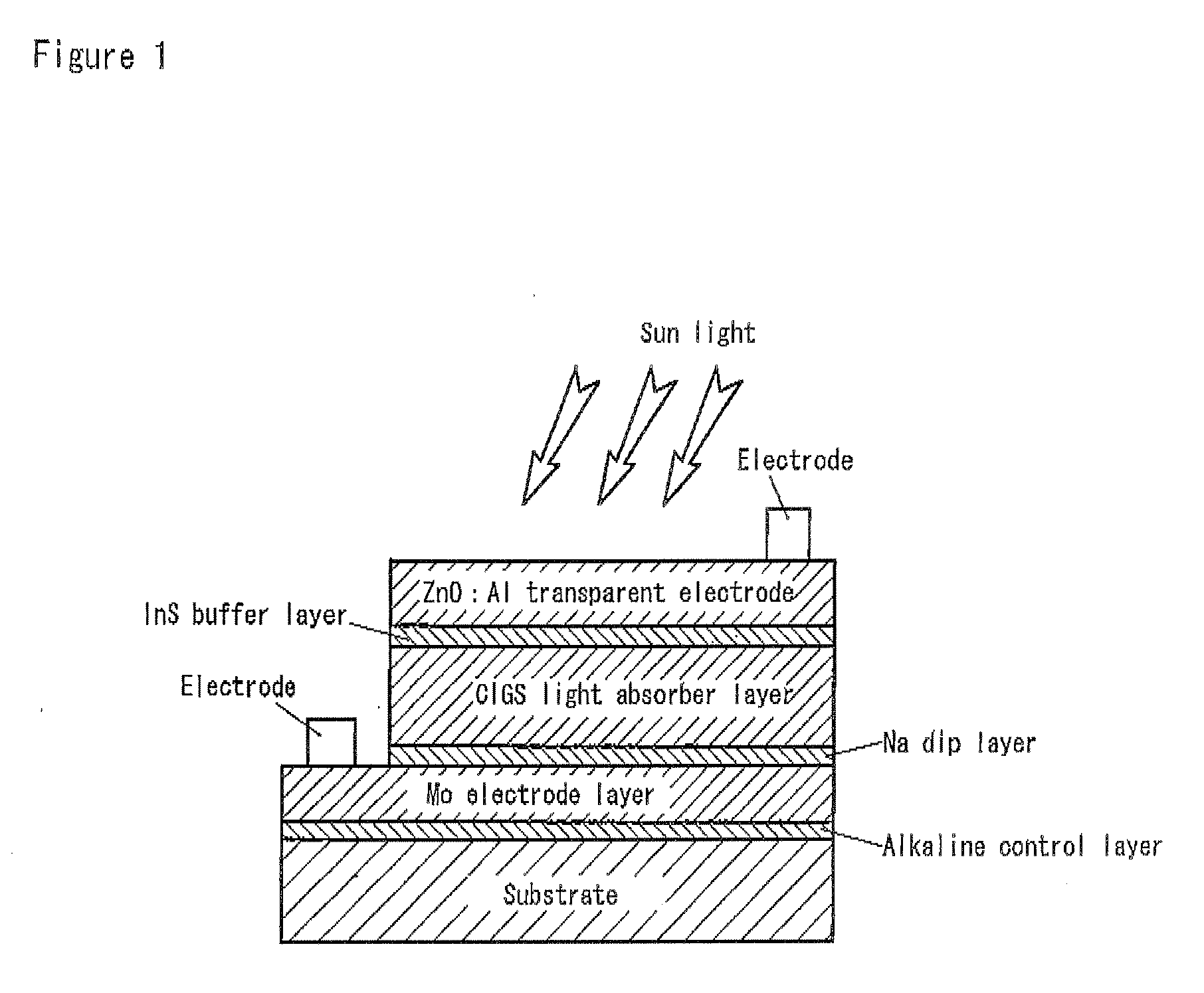
A flexible solar cell is achieved which has a high photoelectric conversion efficiency and no aged deterioration. A cell 10 (unit cell) is formed as a unit, comprising: a lower electrode layer 2 (Mo electrode layer) formed on a flexible mica sheet substrate 1 (substrate); a light absorber layer 3 (CIGS light absorber layer) which contains copper indium gallium selenide; a highly resistant buffer layer thin film 4 formed of InS, ZnS, CdS, or the like on the light absorber layer 3; and an upper electrode layer 5 (TCO) formed of ZuOAl or the like, and furthermore, a contact electrode section 6 for connecting between the upper electrode layer 5 and the lower electrode layer 2 is formed in order to connect a plurality of unit cells 10 in series. The contact electrode section 6 has a Cu / In ratio higher than that of the light absorber layer 3, and in other words, has less In contained therein to have a property of p+ (plus) type or a conductor relative to the light absorber layer 3 which is a p-type semiconductor.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Method for preparing novel conductive indium oxide target and indium oxide film
ActiveCN103205708AImprove compactnessImprove uniformityVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingIndiumElectrical battery
The invention discloses a method for preparing a novel conductive indium oxide target and an indium oxide film. A third element is added to an original binary oxide to improve the electric carrier mobility so as to further improve the light transmittance and the electrical conductivity; and the related target is prepared by the combination of casting molding and high-temperature sintering for the first time. Therefore, the uniformity and compactness of the target are improved; an abnormal electric arc in a sputtering process is greatly reduced; the service life of the target is prolonged; the utilization rate of the target is improved; the quality and the performance of the sputtering film are improved; the efficiency of a copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) solar cell is effectively improved; and the requirements of production are met.
Owner:赣州市创发光电科技有限公司
Method for preparing copper indium gallium selenide thin film battery
ActiveCN101980377AImprove insulation performanceNot easy to short circuitFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesIndiumCopper indium gallium selenide
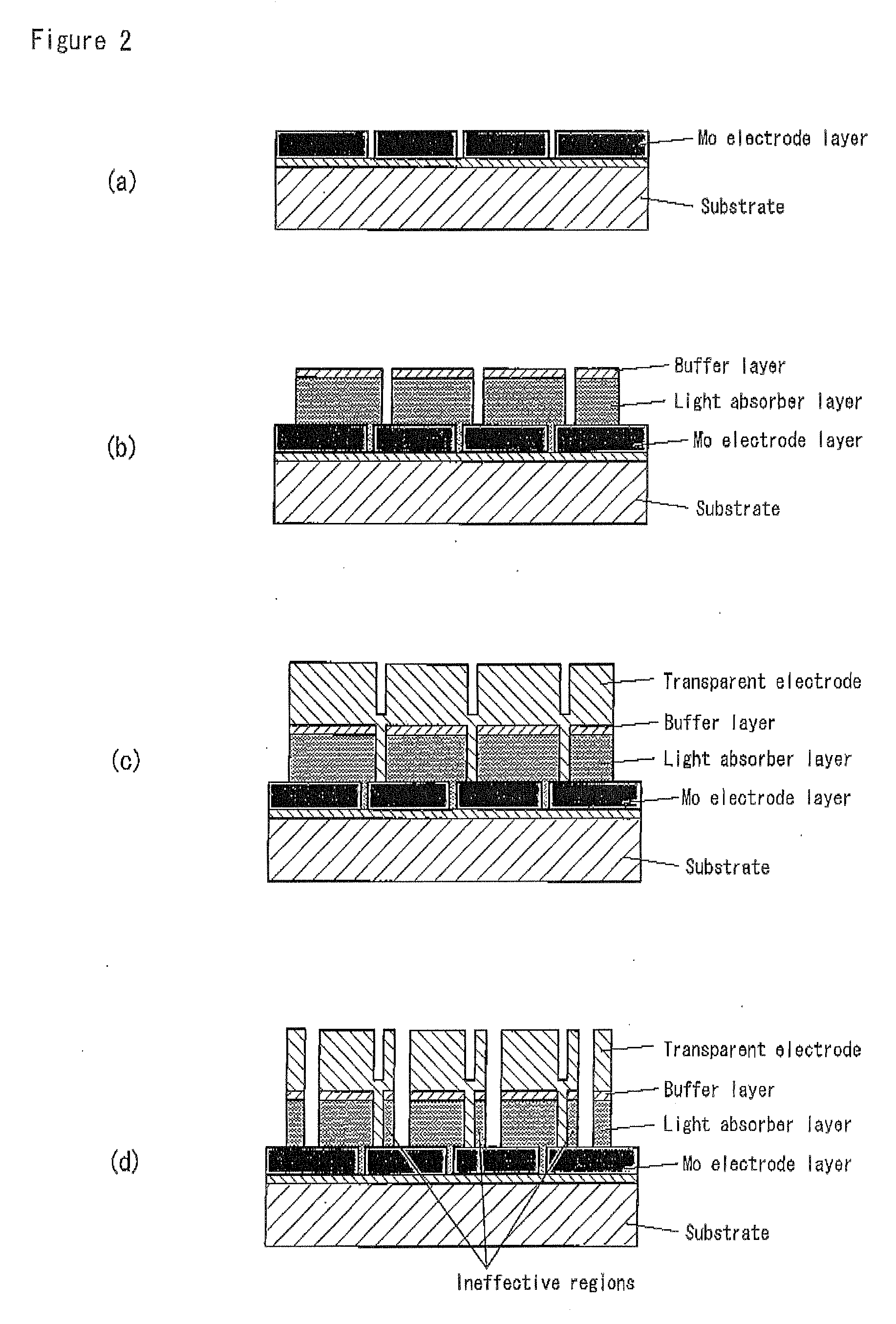
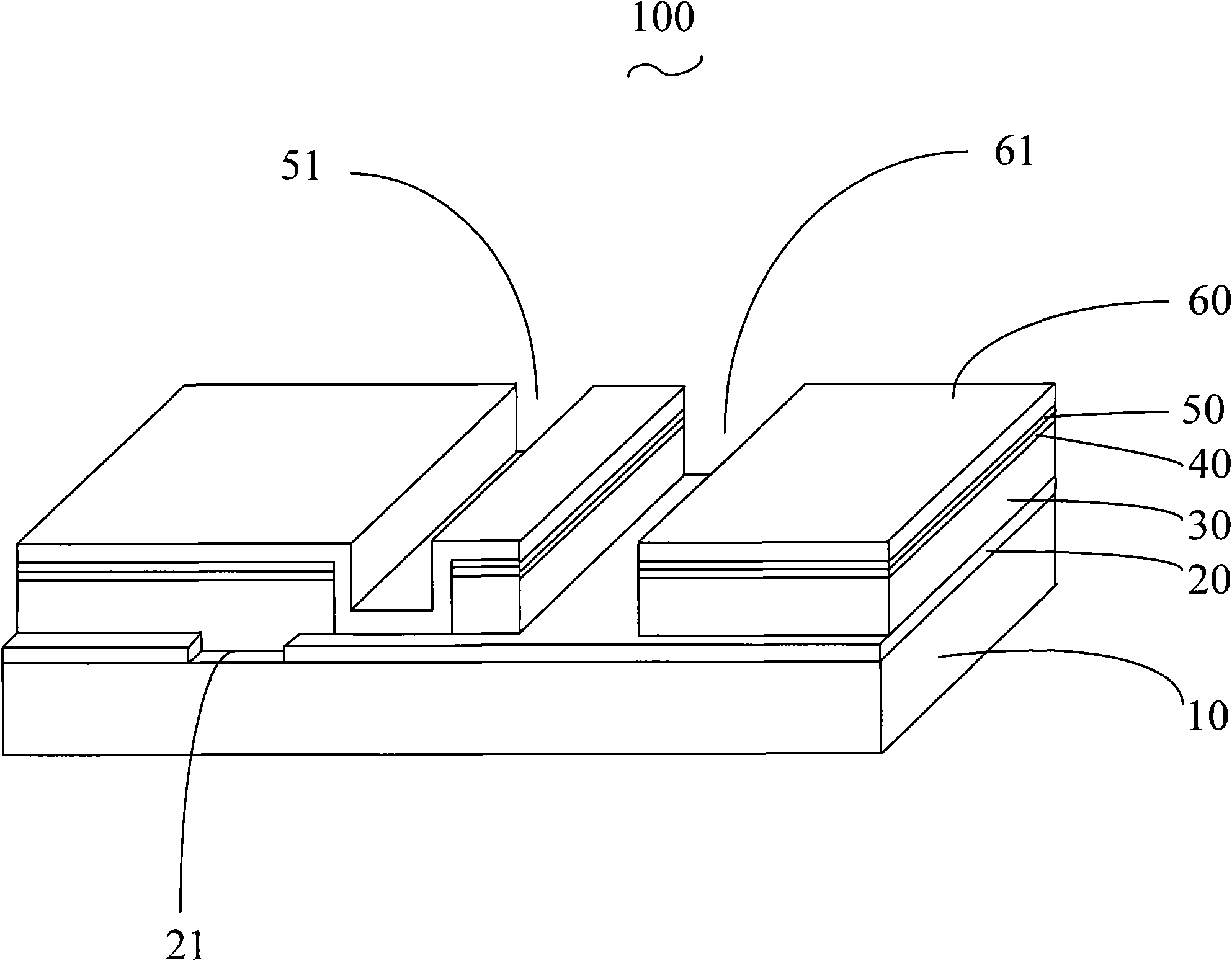
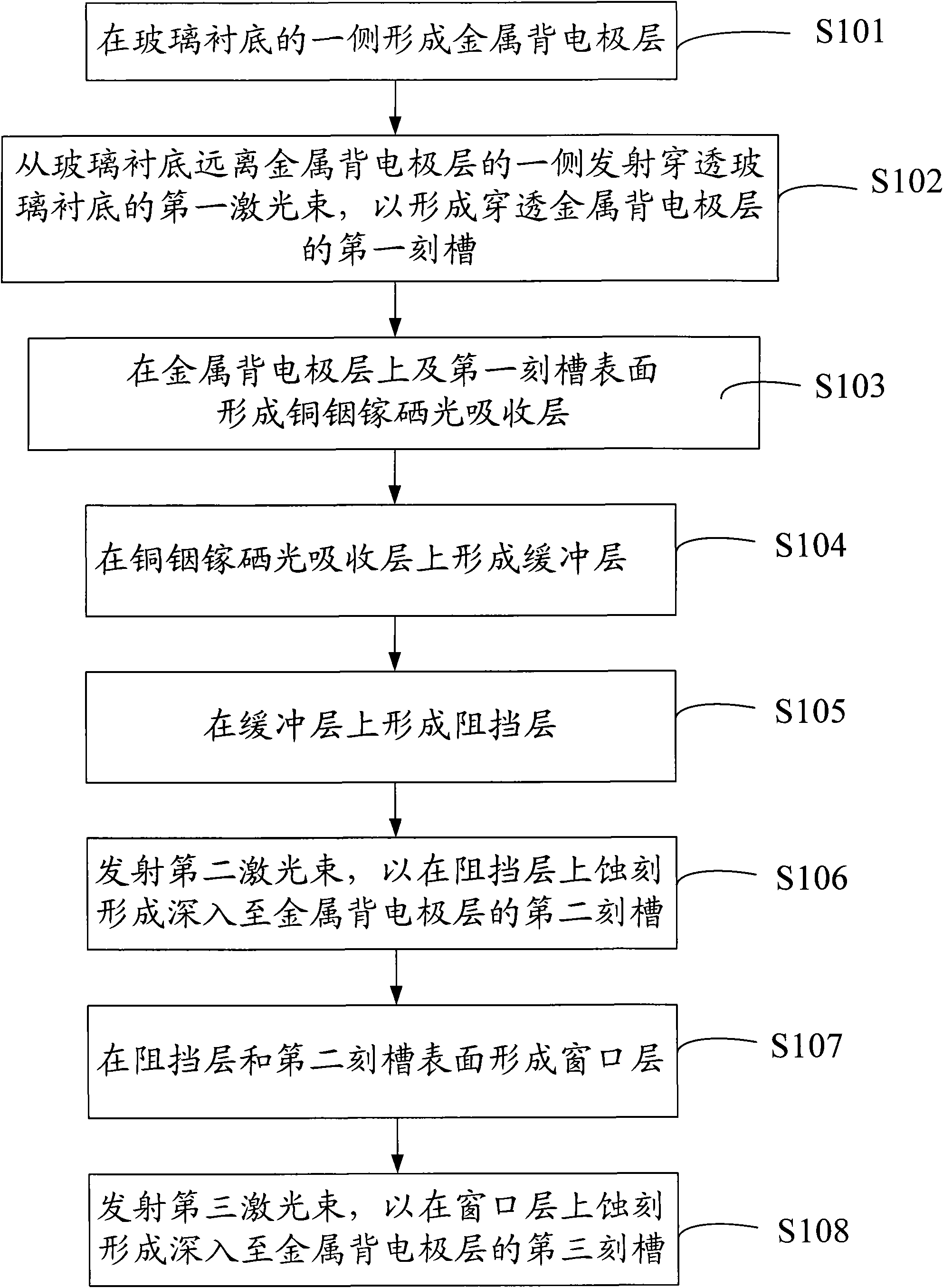
The invention discloses a method for preparing a copper indium gallium selenide thin film battery, which comprises the following steps of: forming a metal back electrode layer on one side of a glass substrate; emitting a first laser beam penetrating the glass substrate from the side of the glass substrate away from the metal back electrode layer so as to form a first groove penetrating the metal back electrode layer; forming a copper indium gallium selenide light absorbing layer on the metal back electrode layer and the surface of the first groove; forming a buffer layer on the copper indium gallium selenide light absorbing layer; forming a barrier layer on the buffer layer; emitting a second laser beam to etch the barrier layer so as to form a second groove reaching the metal back electrode layer; forming a window layer on the barrier layer and the surface of the second groove; and emitting a third laser beam to etch the window layer so as to form a third groove reaching the metal back electrode layer. The copper indium gallium selenide thin film battery prepared by the method has the advantage of low possibility of generating short circuit.
Owner:珠海中科先进科技产业有限公司
Series flexible thin film solar cell module and making method thereof
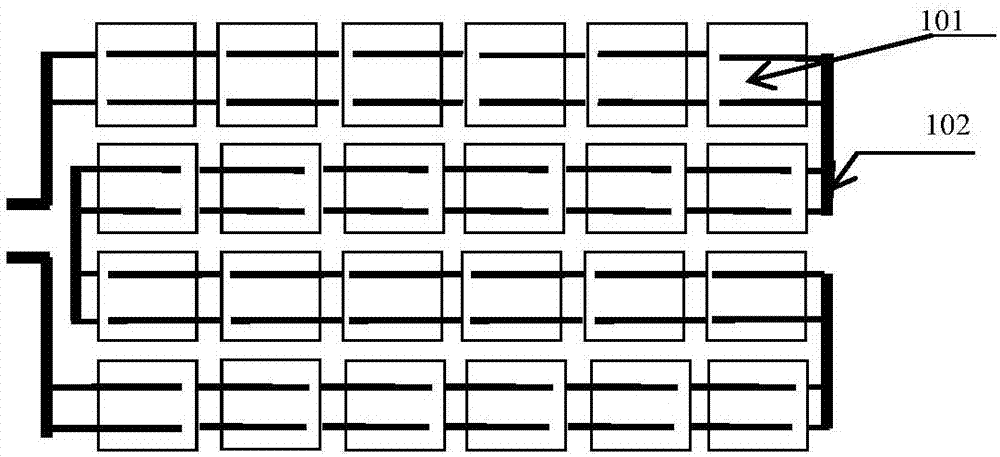
ActiveCN106898665AReduce manufacturing costThe process is simple and easy to controlFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationScreen printingMetallic materials
A series flexible thin film solar cell module and a making method thereof are disclosed. A flexible solar cell comprises at least one flexible solar cell unit. The flexible solar cell unit includes a cell substrate of a flexible metal material, a power generation thin film layer, an adhesive layer, and a water blocking layer. The power generation thin film layer has grid lines for silk-screen printing, which are subjected to conductive convergence through a bonding bus bar and connected with a metal substrate of another flexible solar cell unit to form a series structure. The invention also discloses a method for making the series flexible copper indium gallium selenide thin film solar cell. According to the invention, the process is simple to realize and free from environmental influence, is also safe and reliable, and can be used in many industries.
Owner:BEIJING SIFANG CRENERGEY OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD +1
Preparation method of copper indium selenide nanocrystalline material
InactiveCN101804971ADissolve evenly and fullyAvoid generatingSelenium/tellurium compundsIndiumSolvent
The invention relates to a preparation method of a copper indium selenide nanocrystalline material, which adopts a solvothermal method for reaction at a high temperature so as to prepare a copper indium selenide nanocrystalline material with a regular shape, a uniform size, a particle size of about 20nm and good crystallinity. Compared with the preparation of the traditional copper indium selenide film, the preparation of the copper indium selenide nanocrystalline material has the advantages of good repeatability, simple process, low environmental pollution, each control of the stoichiometric ratio of atoms and the like. Since the forbidden bandwidth of the copper indium selenide is around 1.04eV, the nanocrystalline material can be used for preparing the absorption layer of the solar cell through drip casting or film spinning, and can also be used for sensitizing titania, zinc oxide or other materials with a wide forbidden band, so as to improve the energy conversion efficiency of the solar cell.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Electroplating on roll-to-roll flexible solar cell substrates
Embodiments of the invention contemplate the formation of a low cost flexible solar cell using a novel electroplating method and apparatus to form a metal contact structure. The apparatus and methods described herein remove the need to perform one or more high temperature screen printing processes to form conductive features on the surface of a solar cell substrate. The resistance of interconnects formed in a solar cell device greatly affects the efficiency of the solar cell. Solar cell substrates that may benefit from the invention include flexible substrates may have an active region that contains organic material, single crystal silicon, multi-crystalline silicon, polycrystalline silicon, germanium, and gallium arsenide, cadmium telluride, cadmium sulfide, copper indium gallium selenide, copper indium selenide, gallilium indium phosphide, as well as heterojunction cells that are used to convert sunlight to electrical power. The flexible substrates may have a flexible base that is adapted to support the active region of the solar cell device.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
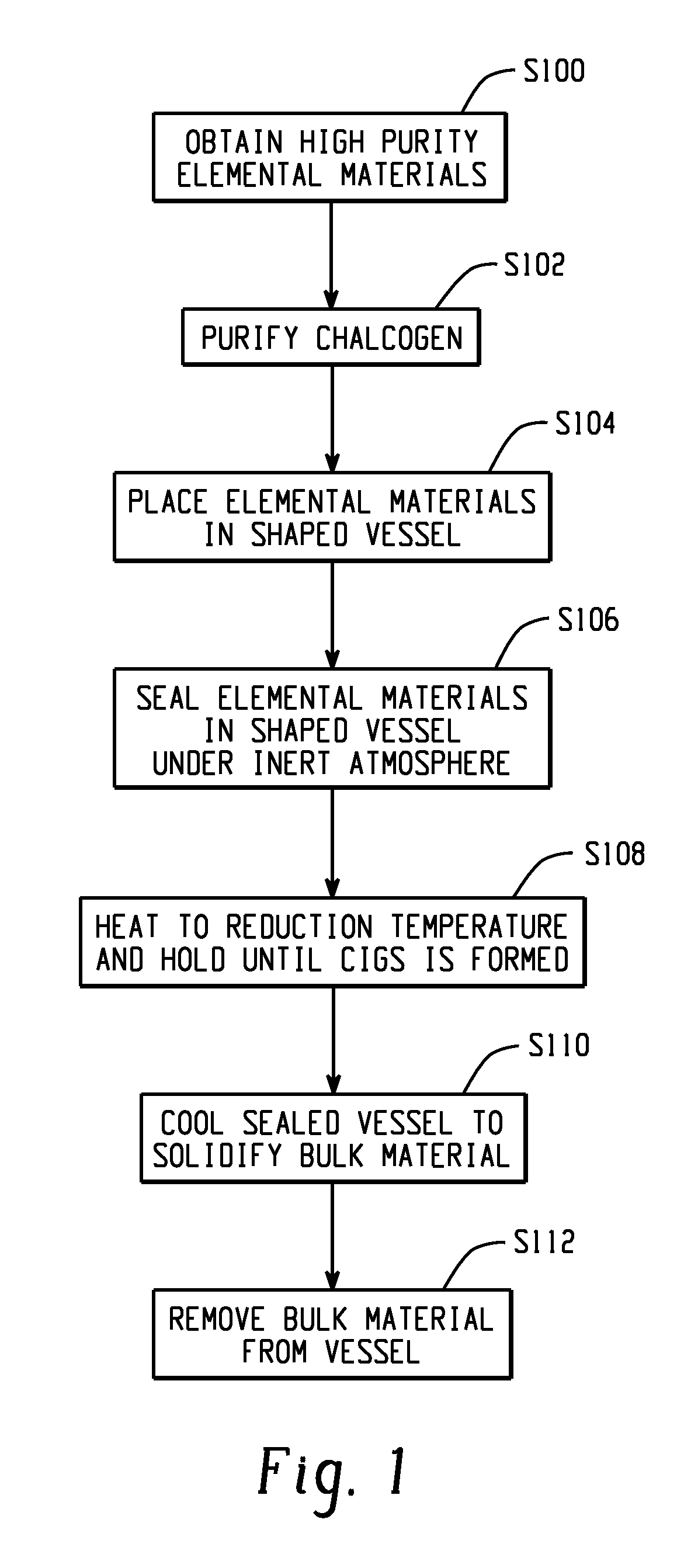
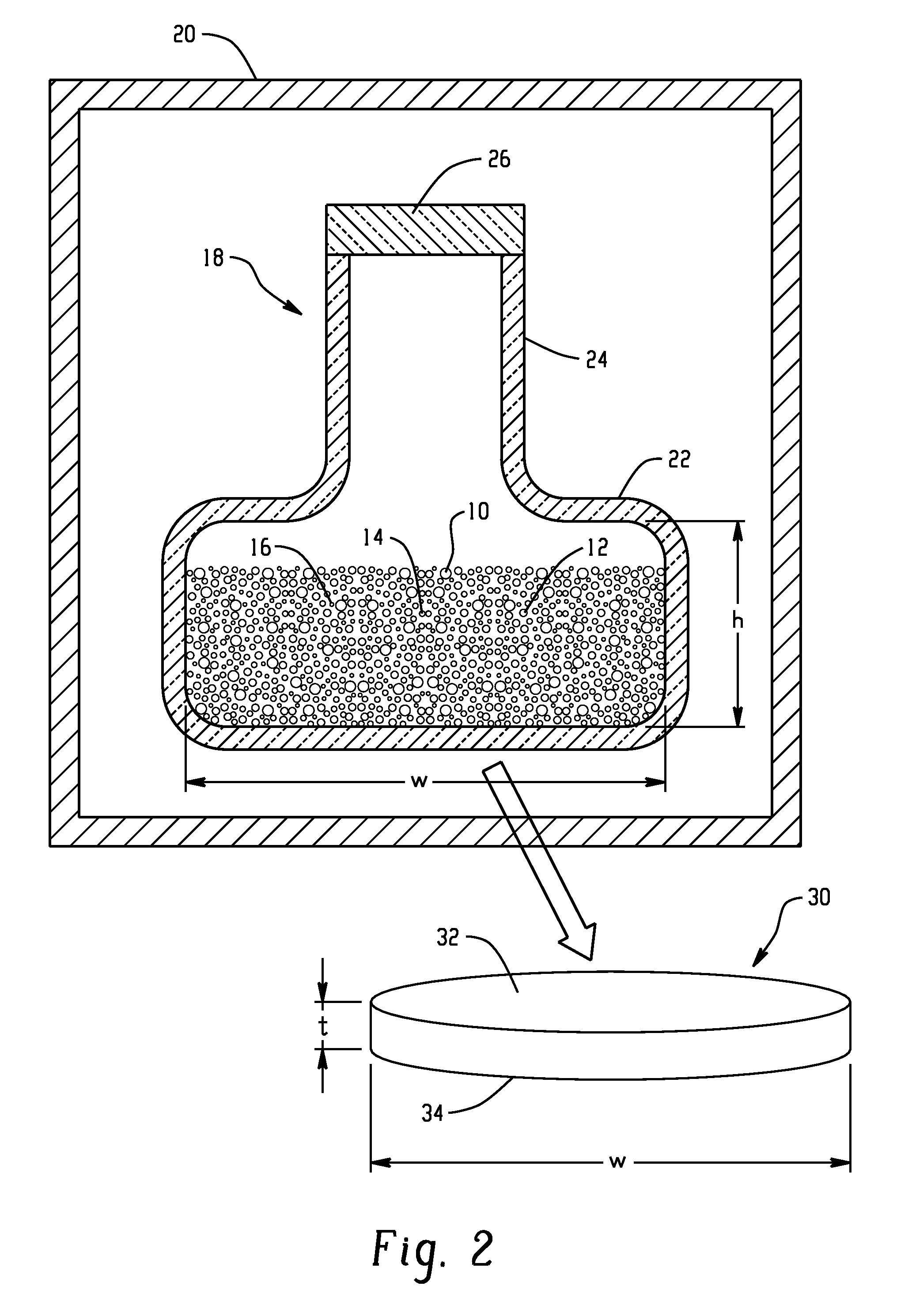
Synthesis of high-purity bulk copper indium gallium selenide materials
InactiveUS20110067997A1Efficient processIntroduce impurityCellsVacuum evaporation coatingIndiumSulfur
A method for forming a high purity, copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) bulk material is disclosed. The method includes sealing precursor materials for forming the bulk material in a reaction vessel. The precursor materials include copper, at least one chalcogen selected from selenium, sulfur, and tellurium, and at least one element from group IIIA of the periodic table, which may be selected from gallium, indium, and aluminum. The sealed reaction vessel is heated to a temperature at which the precursor materials react to form the bulk material. The bulk material is cooled in the vessel to a temperature below the solidification temperature of the bulk material and opened to release the formed bulk material. A sputtering target formed by the method can have an oxygen content of 10 ppm by weight, or less.
Owner:SUNLIGHT PHOTONICS +1
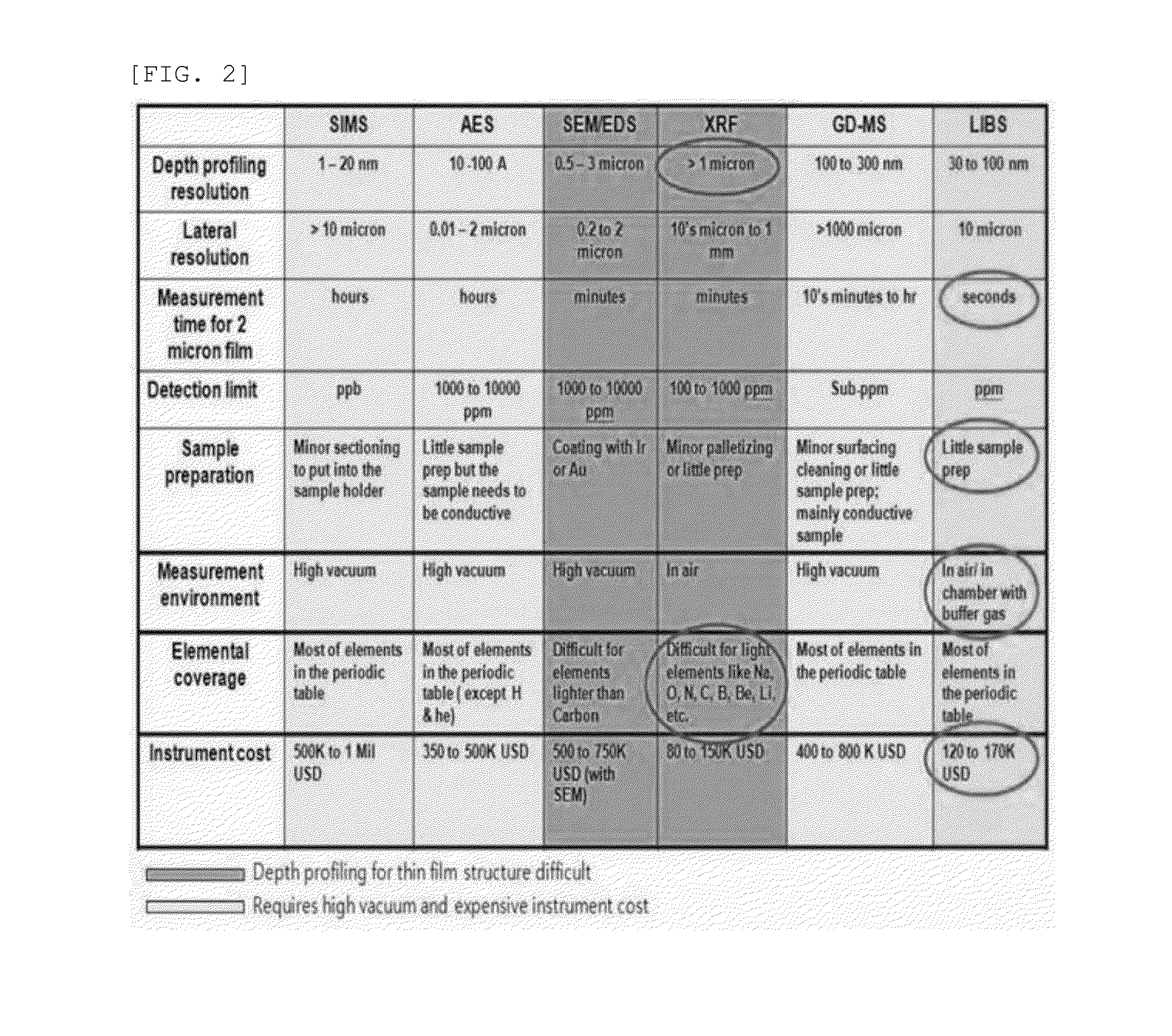
Quantitative analyzing method of CIGS film using a laser induced breakdown spectroscopy
ActiveUS20140336971A1Radiation pyrometryTesting/calibration apparatusCurve fittingCopper indium gallium selenide
Disclosed herein is a quantitative analyzing method of a copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) film, the method including: obtaining spectra by irradiating a laser on the plurality of CIGS films having different component compositions, selecting a first spectral line and a second spectral line among the spectra of target elements to be analyzed and obtaining a correlation plot between a measured intensity of the first spectral line and a measured intensity of the second spectral line, correcting the measured intensity of the first spectral line and the measured intensity of the second spectral line using results obtained by curve fitting the correlation plot, obtaining a linear calibration curve using the corrected intensity of the first spectral line and the corrected intensity of the second spectral line; and comparing the linear calibration curve with LIBS analysis of a target sample to be analyzed.
Owner:GWANGJU INST OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing novel conductive indium tin oxide material and film thereof
InactiveCN103510047ALower resistanceHigh light transmittanceVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingIndiumPolyethylene glycol
The invention aims at providing a method for preparing a novel conductive indium tin oxide material and a film of the material. In the process that a novel indium tin oxide film is prepared, an indium tin oxide film with high light transmittance and a titanium element is initially used, and the design of a multi-layer film structure of a sandwich shape is formed with the combination of a silver or silver alloy film in the middle layer is utilized, so that the resistance of the film is greatly reduced under appropriate thickness control, the high visible light transmittance of the film is maintained, the applicability of the indium tin oxide film in a film photo battery such as a touch control screen and a CIGS (Copper Indium Gallium Selenide) is improved, and the production requirements are met. As the film is applicable to low-temperature (less than 150 DEG C) film plating, the film can be applied to a glass base material or a flexible PET (Polyethylene Glycol Terephthalate) base material, and the application range is widened. The resistance can be reduced to be less than 5*10<-5>omega cm, and the light transmittance can reach more than 90%.
Owner:YANCHUANG APPLIED MATERIALS GANZHOU CO LTD
Cadmium-free copper indium gallium selenide thin film solar cell and preparation method of zinc sulfide buffer layer film thereof
InactiveCN102270699AImprove crystal qualityImprove uniformityFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesZinc Acetate DihydrateMaterials science
A method for preparing a cadmium-free copper indium gallium selenide thin film solar cell, comprising the following steps: step 1, forming a back electrode and a copper indium gallium selenide light absorption layer on a substrate in sequence to form a sample; step 2, adding zinc acetate dihydrate Dissolve in absolute ethanol, add a stabilizer, and heat to form a sol; step 3, immerse the sample in the sol for 5 to 10 seconds, and then lift the sample from the sol; step 4, put the sample Dry at 100-200° C. for 30 minutes to form a zinc oxide film on the surface of the sample; Step 5, put the sample into a selenization chamber and perform annealing treatment under an atmosphere of hydrogen sulfide to convert the zinc oxide film into a zinc sulfide buffer layer film; And step six, sequentially forming a barrier layer and a window layer on the zinc sulfide buffer layer film. Due to the high temperature in the annealing process of the above preparation method, the crystalline quality of the thin film can be improved. The invention also provides a preparation method of the zinc sulfide buffer layer film.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for electrodepositing copper indium diselenide or copper indium gallium selenide film by special pulsing power source
The invention particularly discloses a method for electrodepositing a copper indium diselenide or copper indium gallium selenide film by a special pulsing power source. The method comprises the following steps: in electrolytic solution containing copper, indium, selenium ions or copper, indium, gallium and selenium ions, a preformed film is prepared through electrodepositing on a cathode substrate by adopting bell-shaped wave adjusted square-wave pulse; and then, the preformed film is annealed under vacuum, nitrogen or argon having a solid selenide source to generate the copper indium diselenide or copper indium gallium selenide film finally, wherein, parameters of pulse electrodepositing are as follows: pulse frequency is between 26 and 400kHz, duty factor is between 1 and 100 percent; the mode of electrodepositing is pulse constant potential or pulse constant current, the range of the pulse potential is between 0.5 and 4V, the range of the pulse current is between 0.5 and 3mA, and the deposit time is between 10 and 120min. The method has high frequency and high strength of burst pulse polarization; the method leads ions requiring depositing to perform resonance through adjusting frequency in large scale to effectively deposit the ions; and the method can less deposit current, and realize deposit of elements with more negative potential of a standard electrode without adverse phenomena of liberation of hydrogen.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
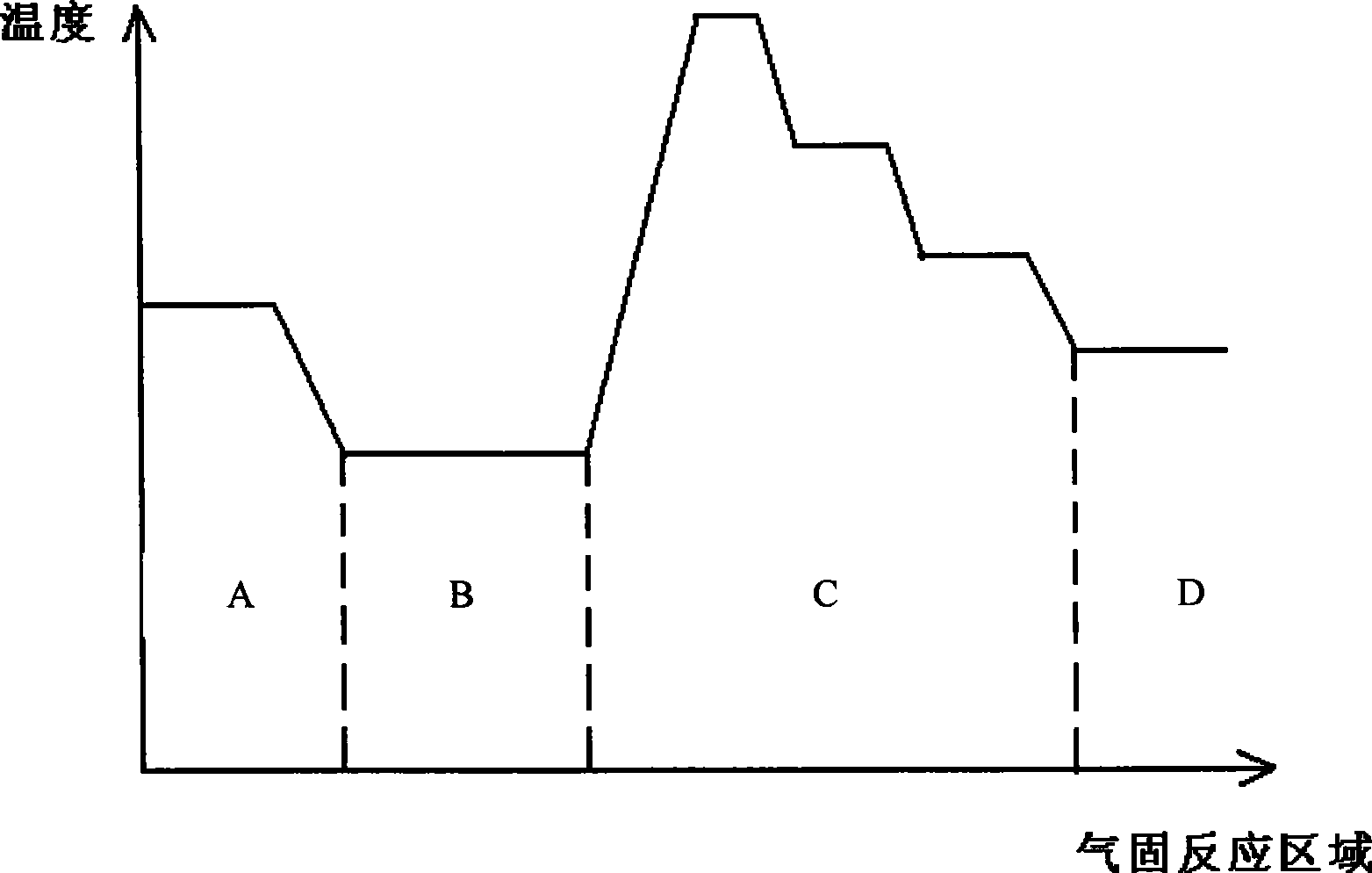
Preparation of yellow copper CIG selenide or sulfide semiconductor thin film material
The invention discloses a method for preparing a chalcopyrite-type copper indium gallium selenide or sulfide semiconductor film material and relates to a semiconductor film material. The invention provides a method for preparing the chalcopyrite-type copper indium gallium selenide or sulfide semiconductor film material. A Cu metal prefabricated layer, a In metal prefabricated layer and a Ga metal prefabricated layer are deposited on a soda lime glass Mo substrate by stages through a vacuum magnetron sputtering, heating evaporation or chemical water bath electrodeposition method; N2 and H2 or Ar and H2 are mixed to obtain mixed gas; the mixed gas is introduced to a gas-solid reaction chamber; the reaction chamber is divided into two regions; a solid selenium(sulphur) sublimation region ensures that H2 / N2 (or H2 / Ar) gas and selenium(sulphur) steam are mixed; a hot wire catalytic gas-solid reaction region ensures that H2 and the selenium(sulphur) steam react to generate gaseous H2Se / Se(or H2S / S) mixed atmosphere; and the mixed atmosphere and the Cu metal prefabricated layer, the In metal prefabricated layer and the Ga metal prefabricated layer have thermal selenizing reaction and / or vulcanizing reaction.
Owner:泉州创辉光伏太阳能有限公司
Copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) three-dimensional nano structure array prepared by self-assembled electrodeposition-free mode based on solution method
InactiveCN103824898AFast growthGood removal effectAnodisationMaterial nanotechnologyIndiumNano structuring
Provided is a method for preparing a copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) three-dimensional nano structure array in a self-assembled electrodeposition-free mode. A porous alumina template with the back sputtered with molybdenum and the periphery provided with aluminum supports serves as a CIGS growth substrate which is immersed into copper ions, indium ions, gallium ions and selenide ions mixed liquor serving as copper indium gallium selenide growth-promoting medium to enable copper, indium, gallium and selenide to grow on the CIGS growth substrate in a self-assembled mode, and CIGS materials with three-dimensional nano structures can be obtained after annealing is performed. Therefore, preparation methods of nano structure CIGS are enriched, and material support for researching preparation of high-efficiency, large-area, low-power-consumption and low-cost nano solar cells and p-n node devices is provided. The preparation method is simple relatively, no expensive vacuum equipment is needed, and the preparation method has no special requirements for the surrounding and is applicable to popularization in the industry.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
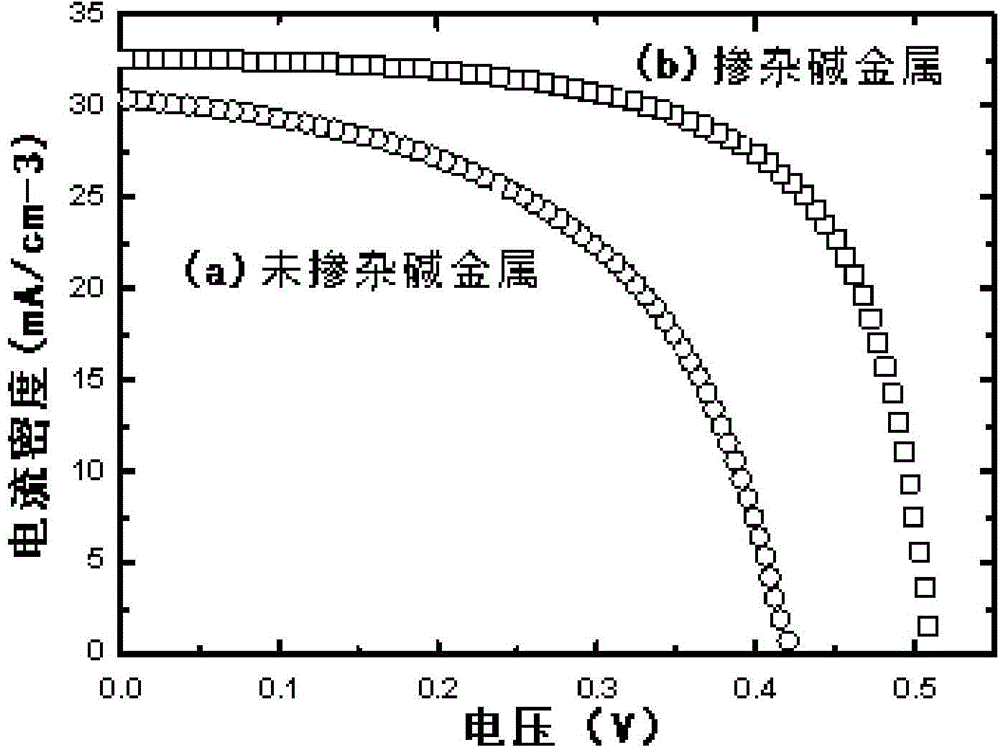
Sodium-potassium co-doping technology for preparing high-efficiency copper indium gallium selenide solar cell
InactiveCN105632903AImprove performanceFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPotassium ionsCopper indium gallium selenide
The invention relates to a sodium-potassium co-doping technology for preparing a high-efficiency copper indium gallium selenide solar cell. The copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS for short) thin film solar cell becomes a solar cell technique with the most development potential due to various advantages. During the preparation process of the CIGS solar cell, the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the cell can be improved by doping of alkali metal ions. The patent proposes a novel technology, sodium ions and potassium ions are co-doped in a CIGS absorption layer, and thus, the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the CIGS solar cell is further improved. The patent also proposes four technical schemes to achieve co-doping of the sodium ions and the potassium ions, and the four technical schemes are suitable for different CIGS absorption layer deposition technologies.
Owner:SUZHOU RUISHENG SOLAR ENERGY TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com