Method for preparing copper indium gallium selenide thin film battery
A technology of copper indium gallium selenide and thin-film batteries, which is applied in the manufacture of circuits, electrical components, and final products, and can solve problems such as uneven cutting line width, a large amount of residue, debris, and short-circuiting of sub-batteries
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
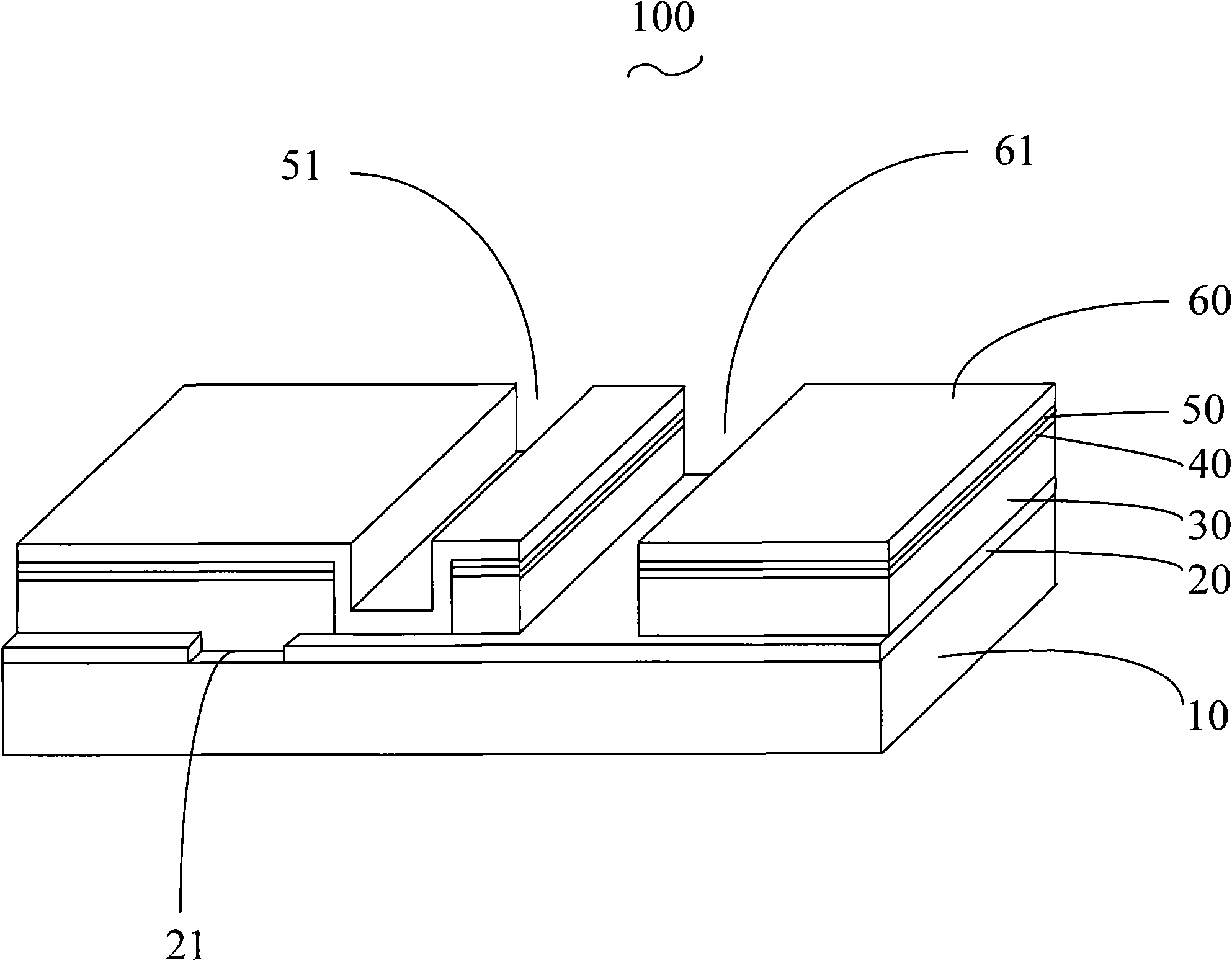
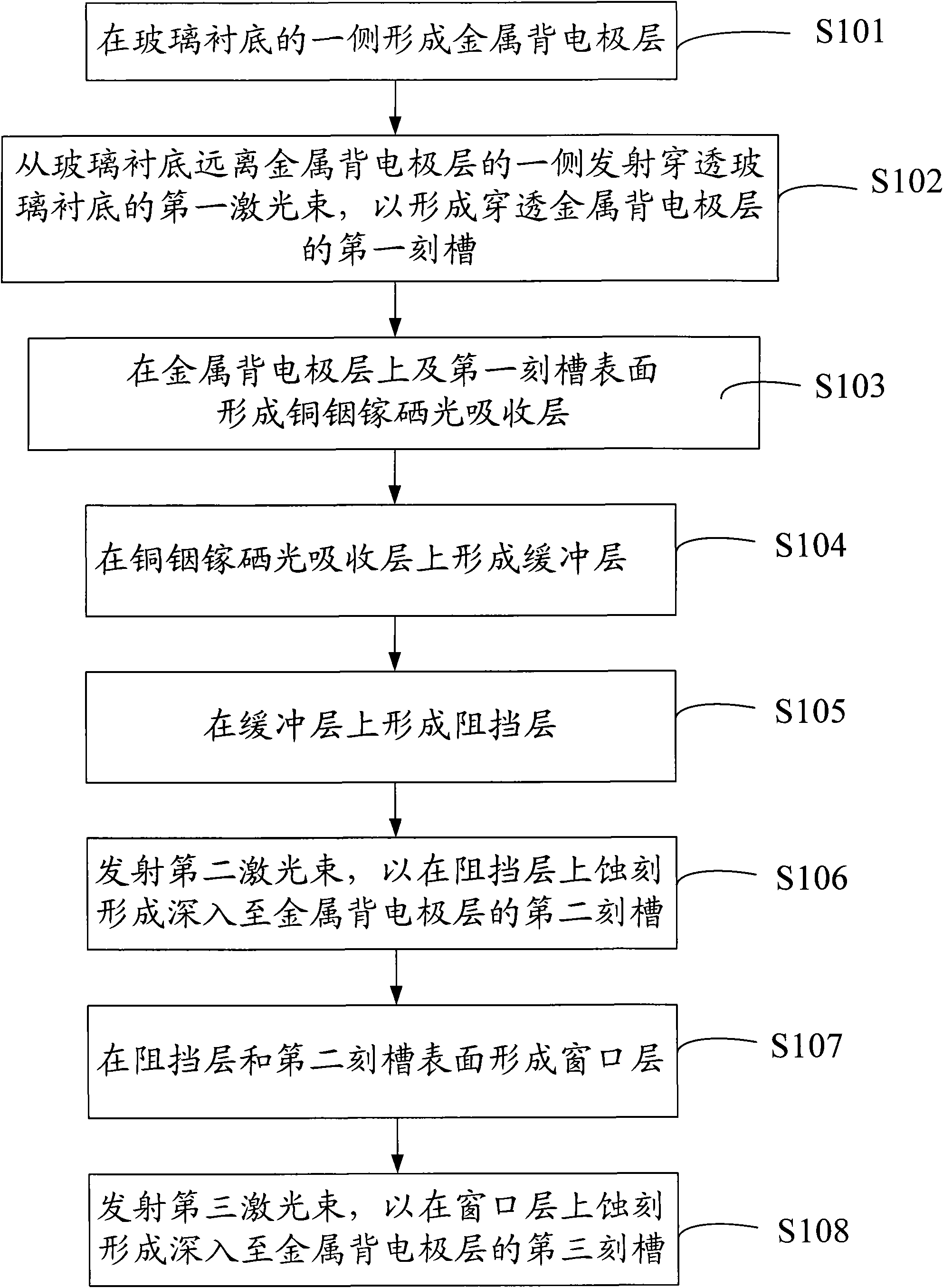
[0026] Please also refer to image 3 , the preparation method of the copper indium gallium selenide thin film battery 100 includes the following steps:
[0027] In step S101 , a flat glass substrate 10 is provided, and a metal back electrode layer 20 is formed on one side of the glass substrate 10 . Mo can be deposited on the glass substrate 10 with a thickness of about 1 μm by DC magnetron sputtering to form the metal back electrode layer 20 .
[0028] Step S102, emitting a first laser beam penetrating the glass substrate 10 from the side of the glass substrate 10 away from the metal back electrode layer 20 to form a first groove 21 penetrating the metal back electrode layer 20 to divide the cell unit, to ensure insulation between each unit. The first laser beam is preferably a pulsed laser with a wavelength range of 248-1064 nm, a scanning speed of 20-2000 mm / sec, and an adjustment frequency of 30-80 KHz. The width of the first groove 21 is not more than 60 microns. Emit...
Embodiment 1
[0037]Embodiment 1: Soda-lime glass is used as the substrate, and the thickness of the substrate is 2 mm. A molybdenum metal target is sputtered by a DC magnetron sputtering process to deposit a molybdenum metal back electrode layer with a thickness of 2 μm. A laser beam with a wavelength of 532nm is used to etch the molybdenum metal back electrode layer for the first time from the side of the glass surface, the frequency is 30KHz, the scanning speed is 800mm / sec, and the etching line width is 50 microns. After the etching is completed, put it into deionized water with a resistance of 18 megohm for ultrasonic vibration for 3 minutes, rinse with 80% ethanol solution, and blow dry with high-pressure nitrogen. The CIGS absorber layer was deposited with a magnetron sputtering followed by selenization process with a thickness of 0.5 μm. Deposit the CdS buffer layer with a chemical water bath method to a thickness of 0.05 μm. The ZnO ceramic target was sputtered by radio frequency ...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Embodiment 2: Soda-lime glass is used as the substrate, the thickness of the substrate is 2 mm, and the molybdenum metal target is sputtered by DC magnetron sputtering process to deposit the molybdenum metal back electrode layer with a thickness of 2 μm. A laser beam with a wavelength of 248nm is used to etch the molybdenum metal back electrode layer for the first time from the side of the glass surface, the frequency is 50KHz, the scanning speed is 900mm / sec, and the etching line width is 50 microns. After the etching is completed, put it into deionized water with a resistance of 18 megohm for ultrasonic vibration for 3 minutes, rinse with 80% ethanol solution, and blow dry with high-pressure nitrogen. The CIGS absorber layer was deposited with a magnetron sputtering followed by selenization process with a thickness of 0.5 μm. Deposit the CdS buffer layer with a chemical water bath method to a thickness of 0.05 μm. The ZnO ceramic target was sputtered by radio frequen...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com