Patents
Literature
1865 results about "Pulse frequency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
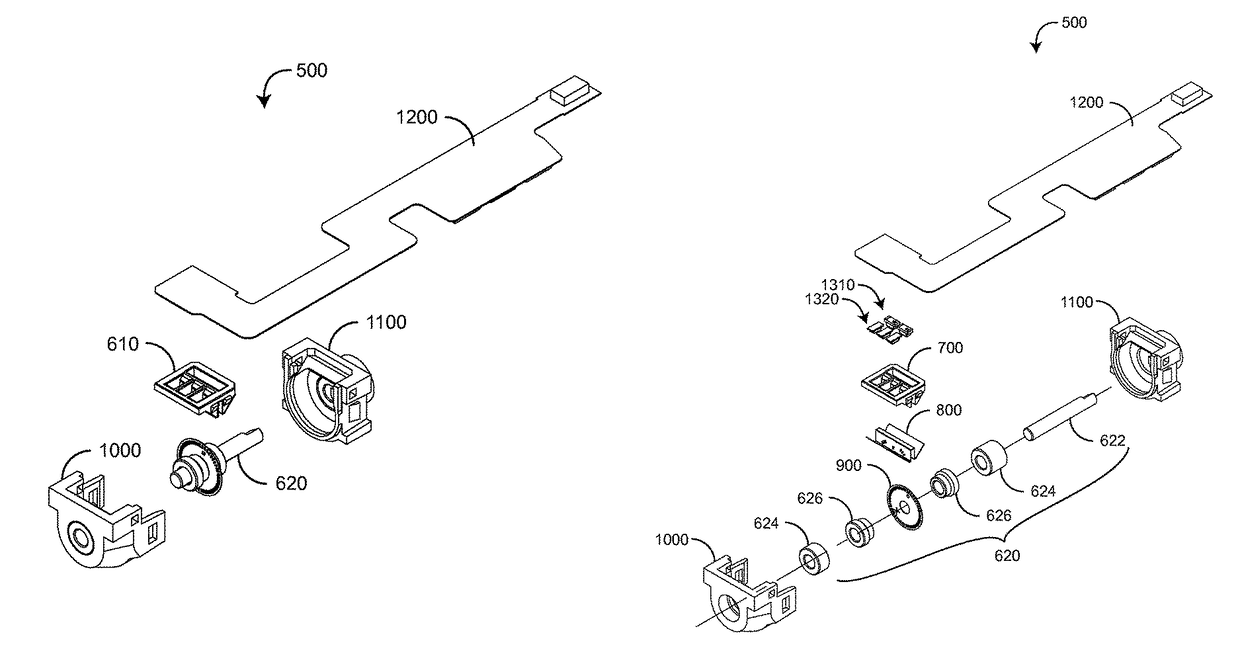
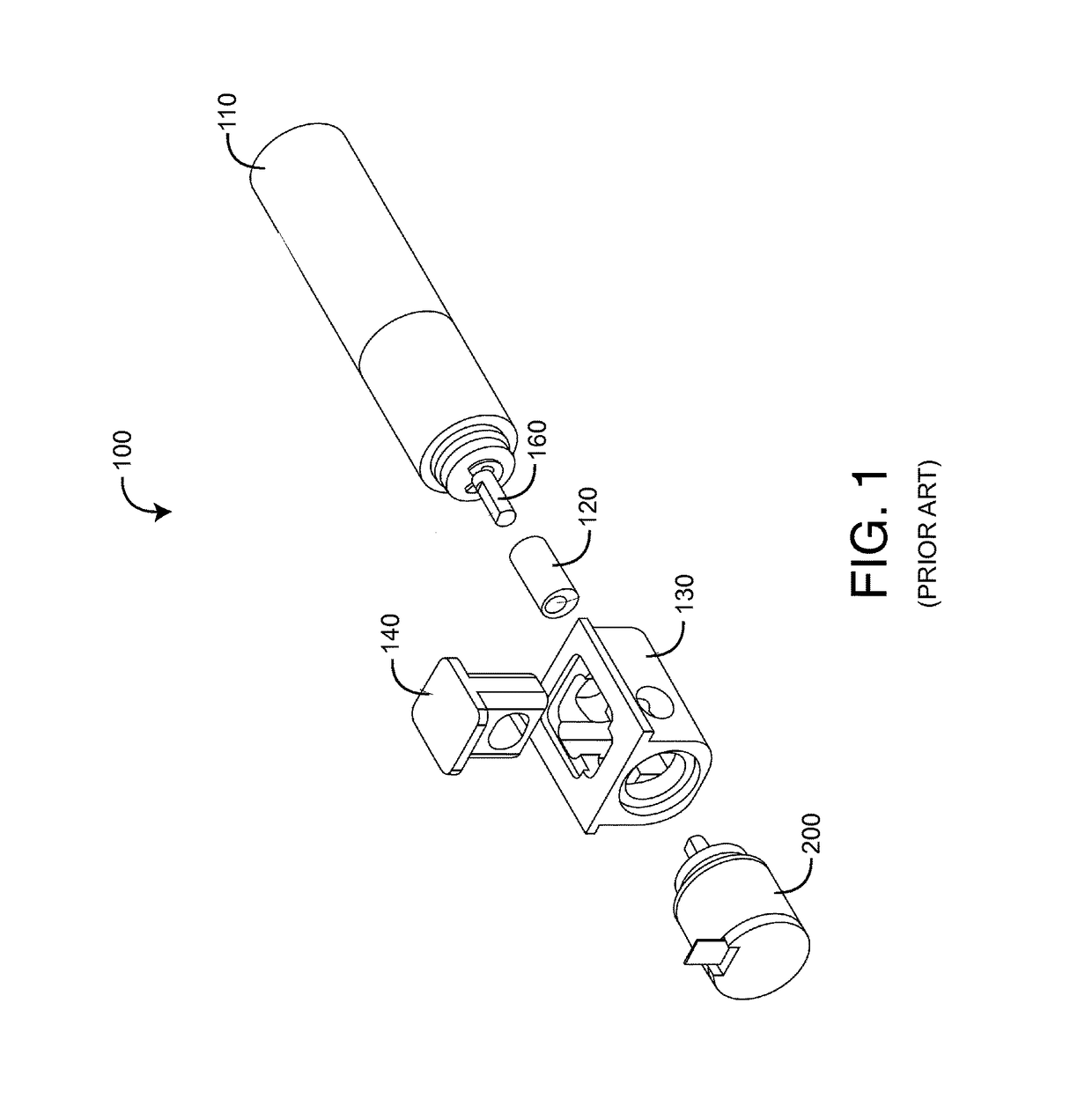
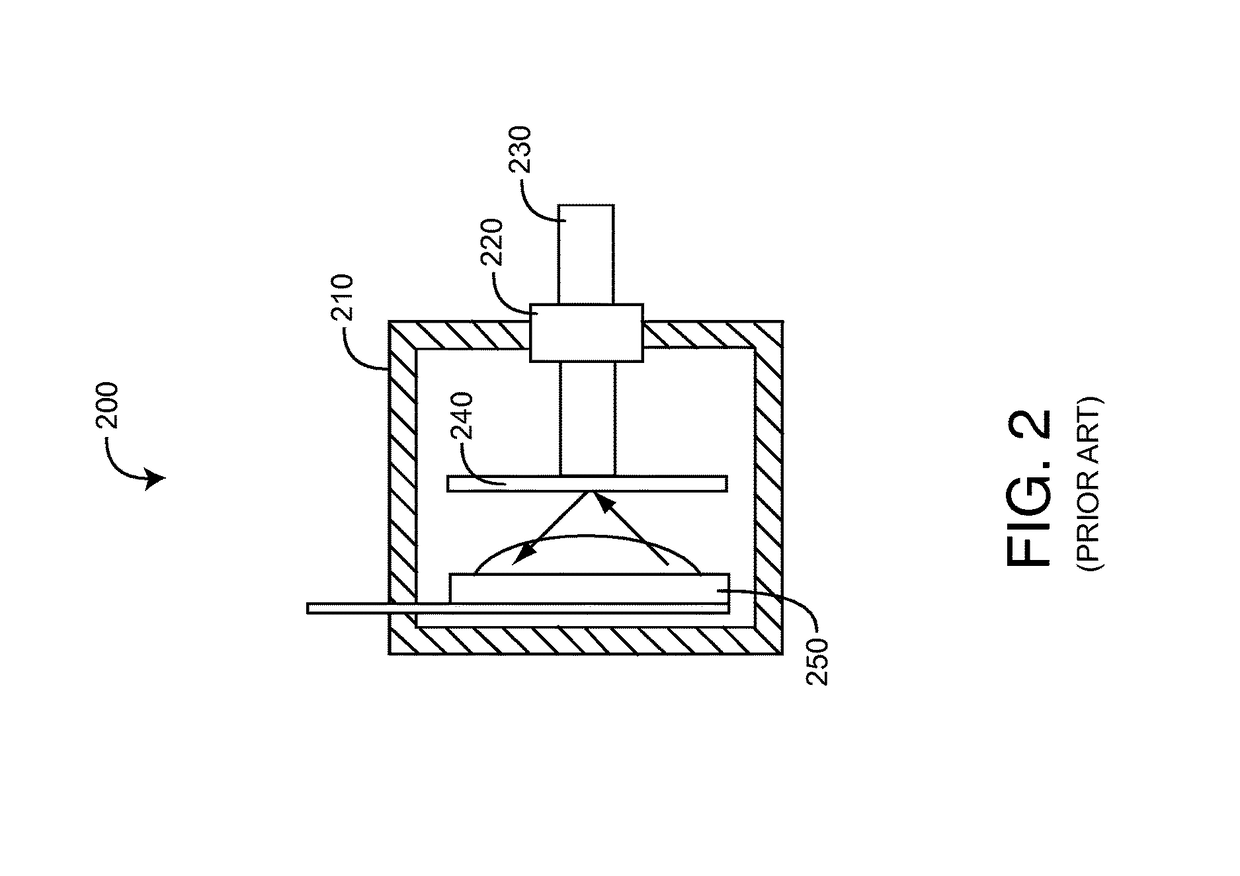
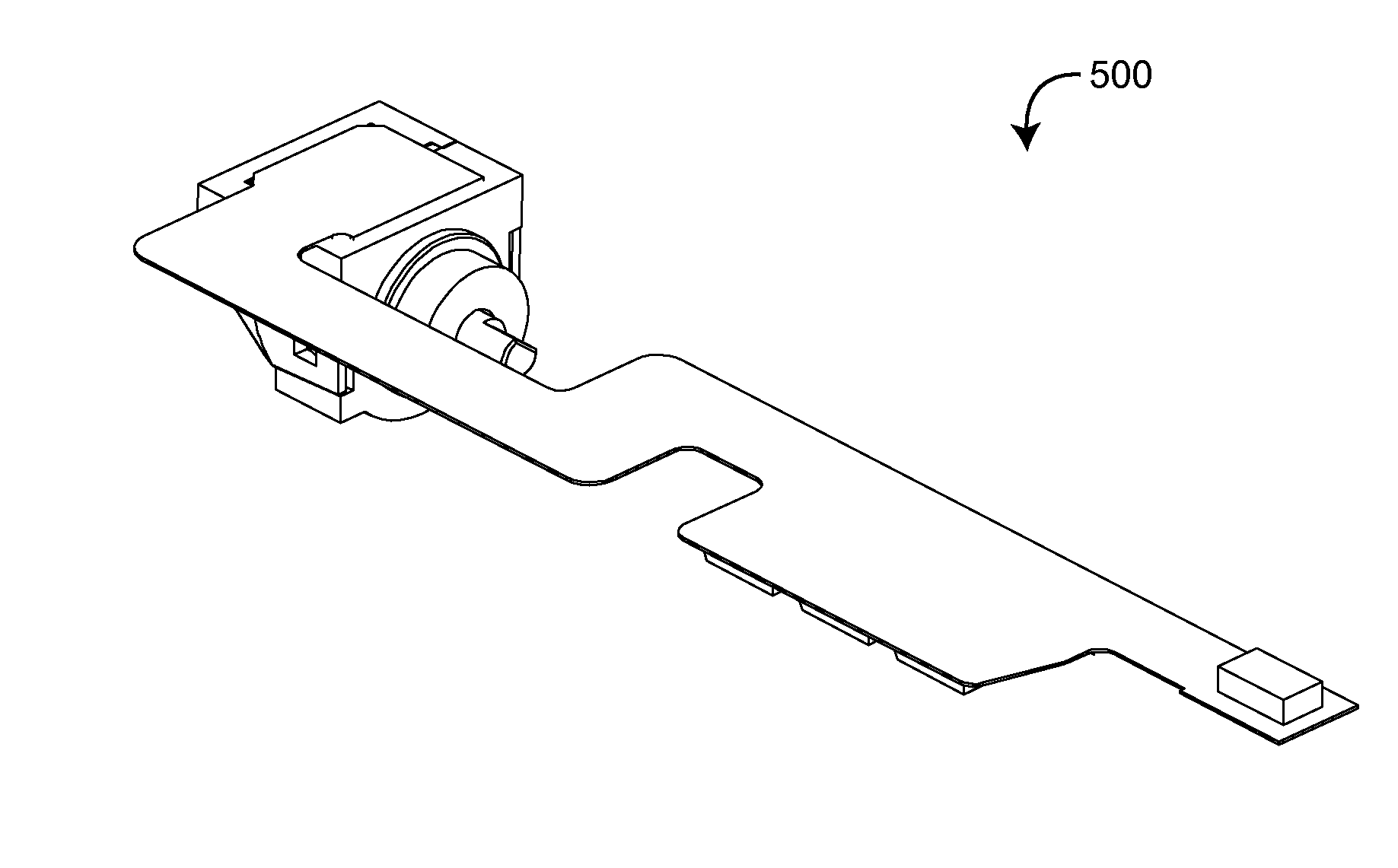
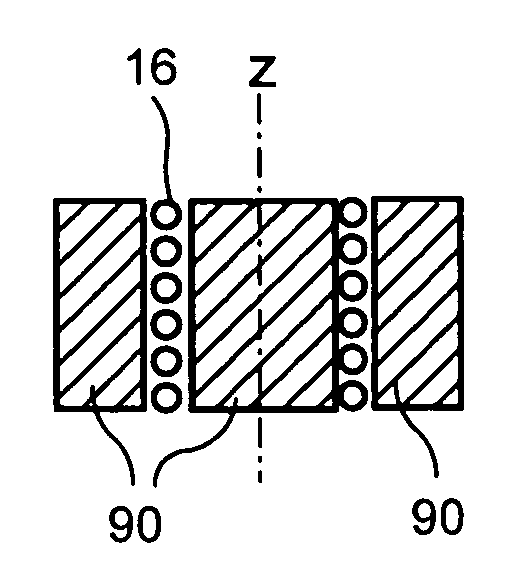
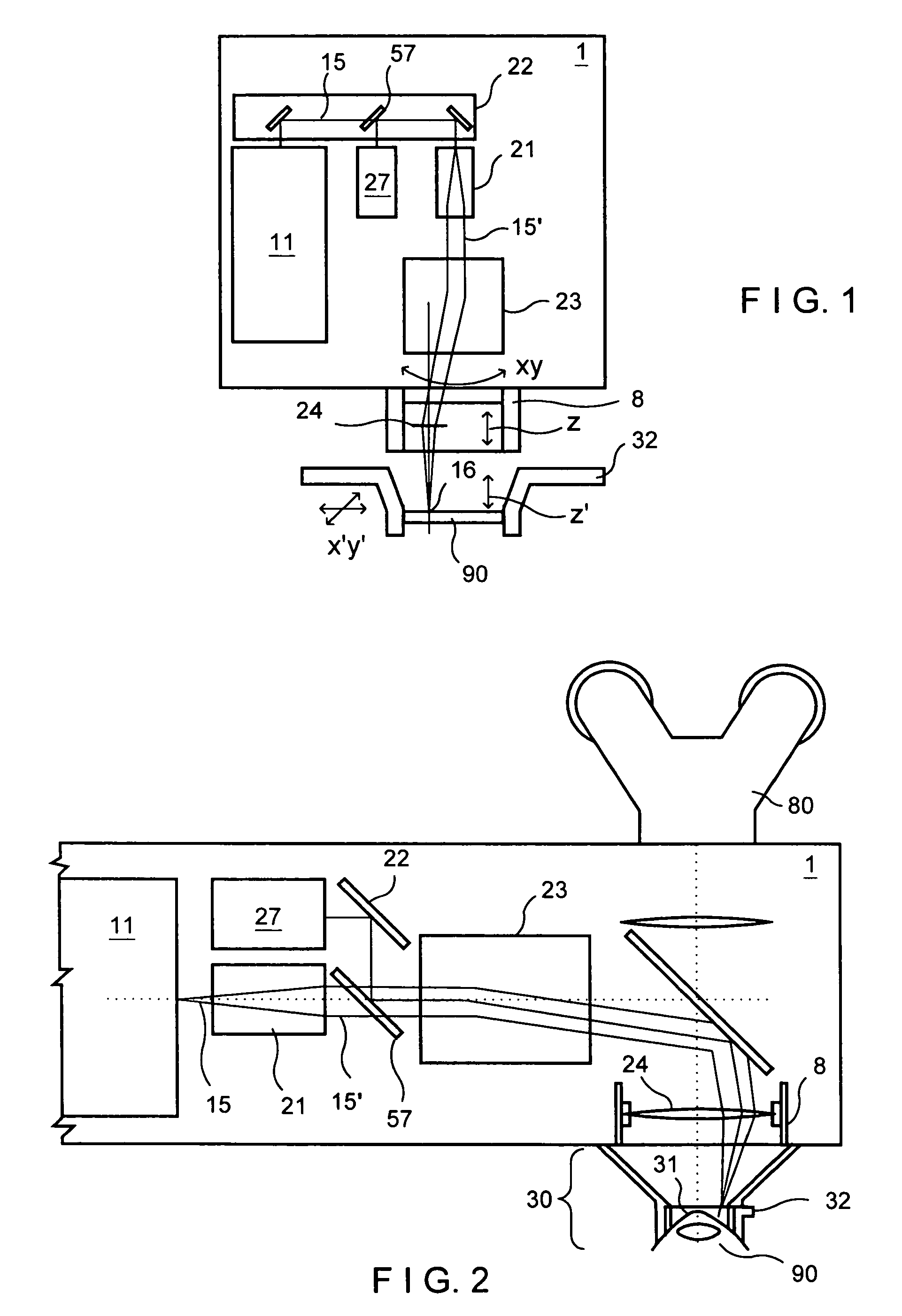
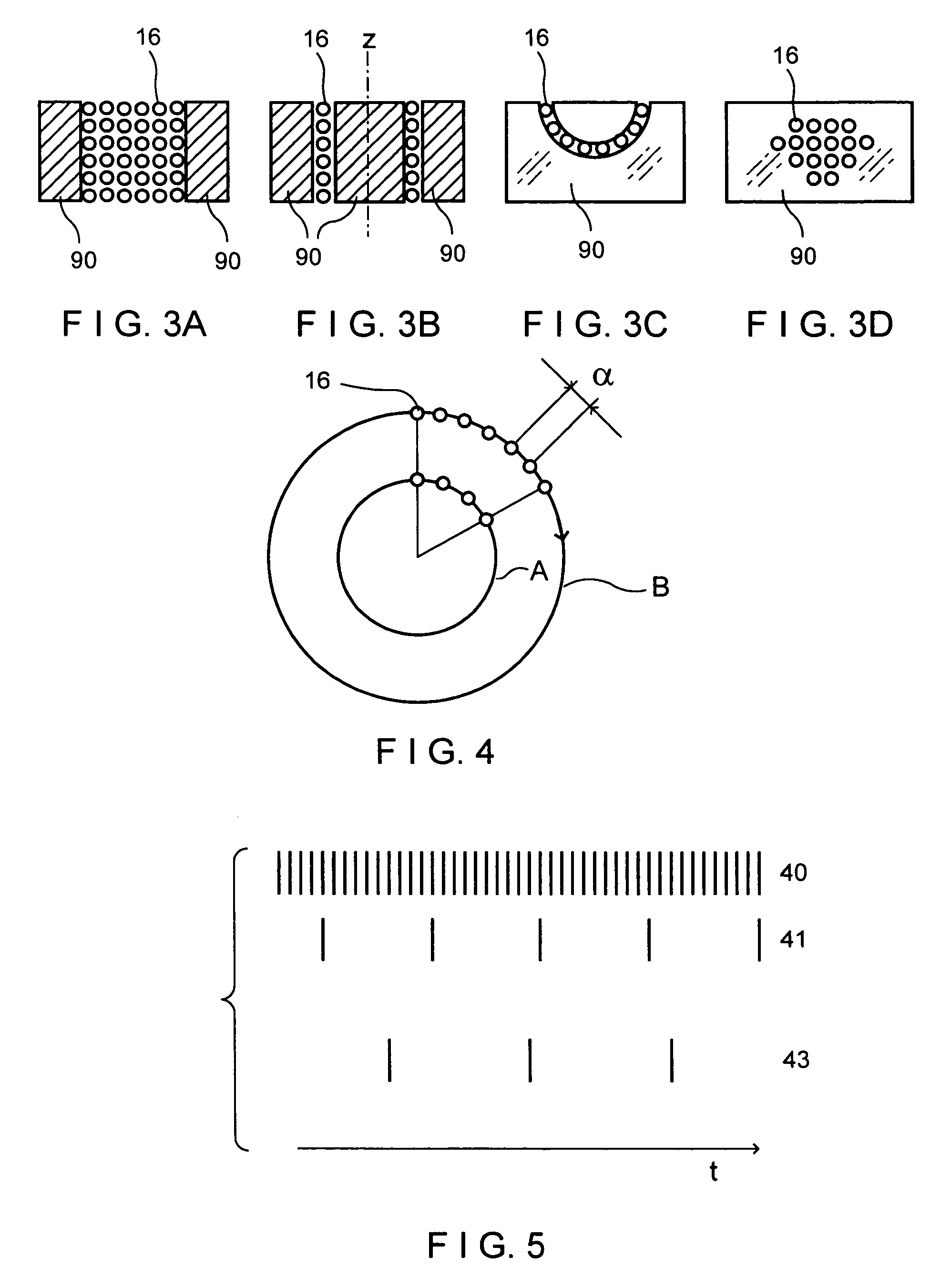
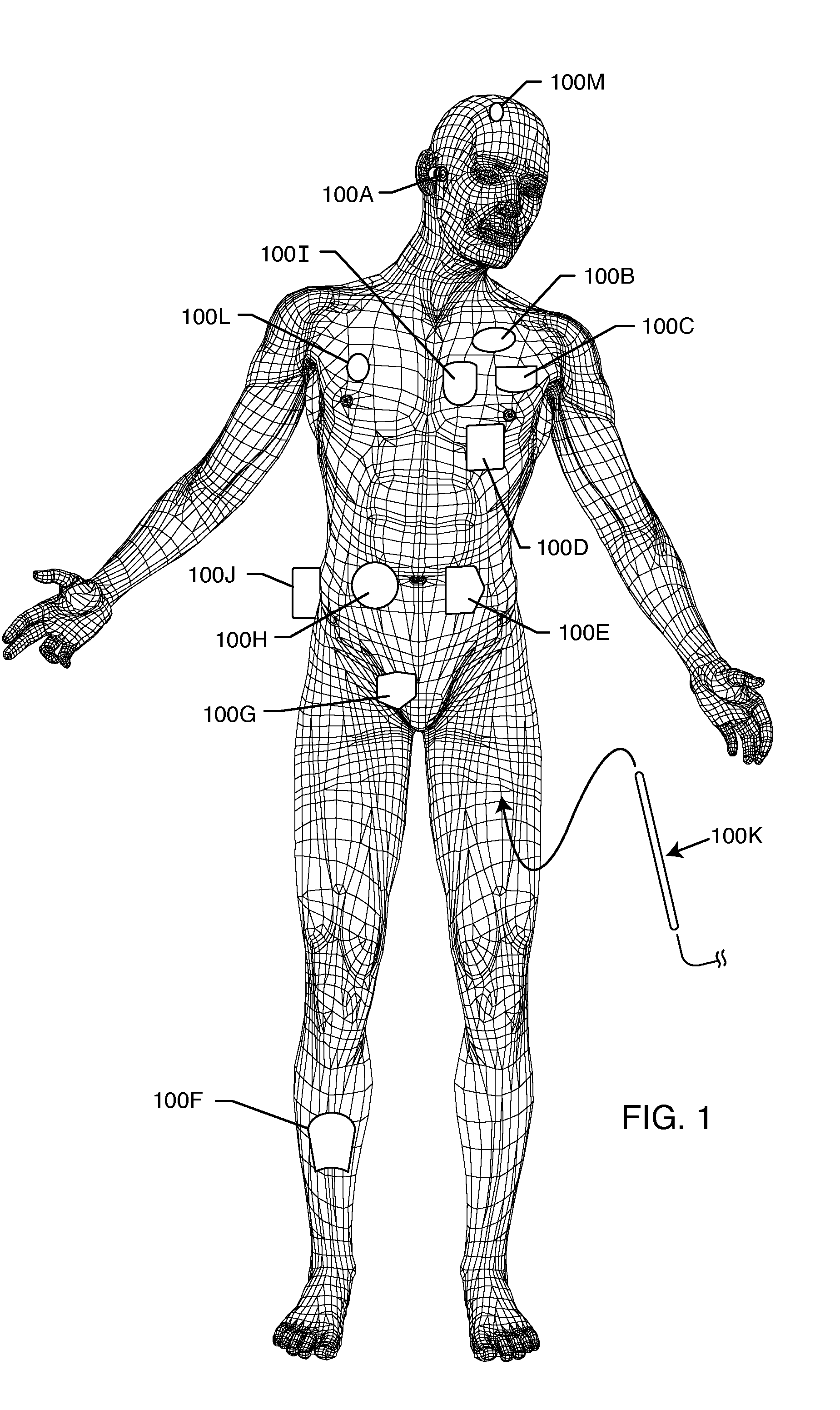
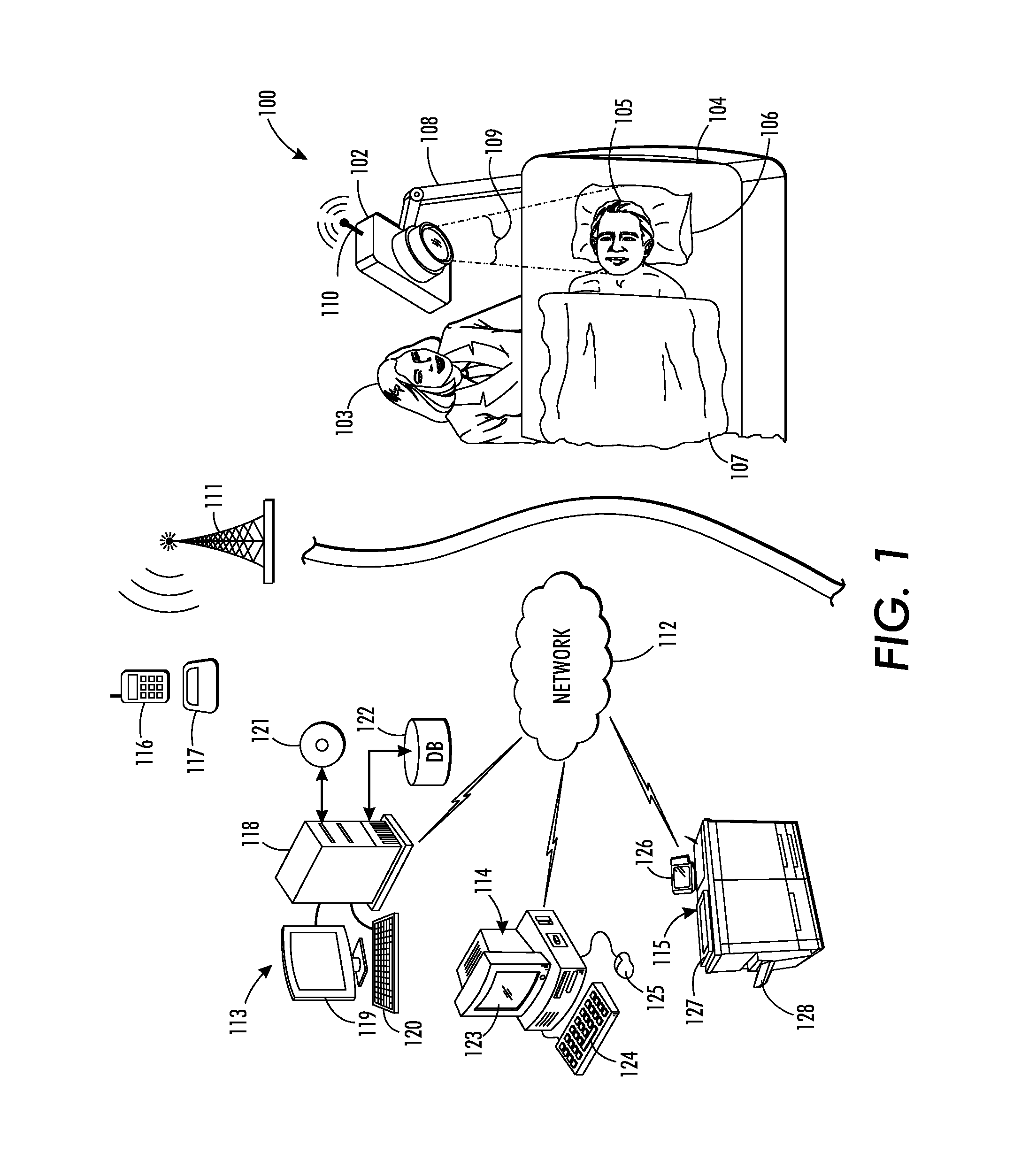
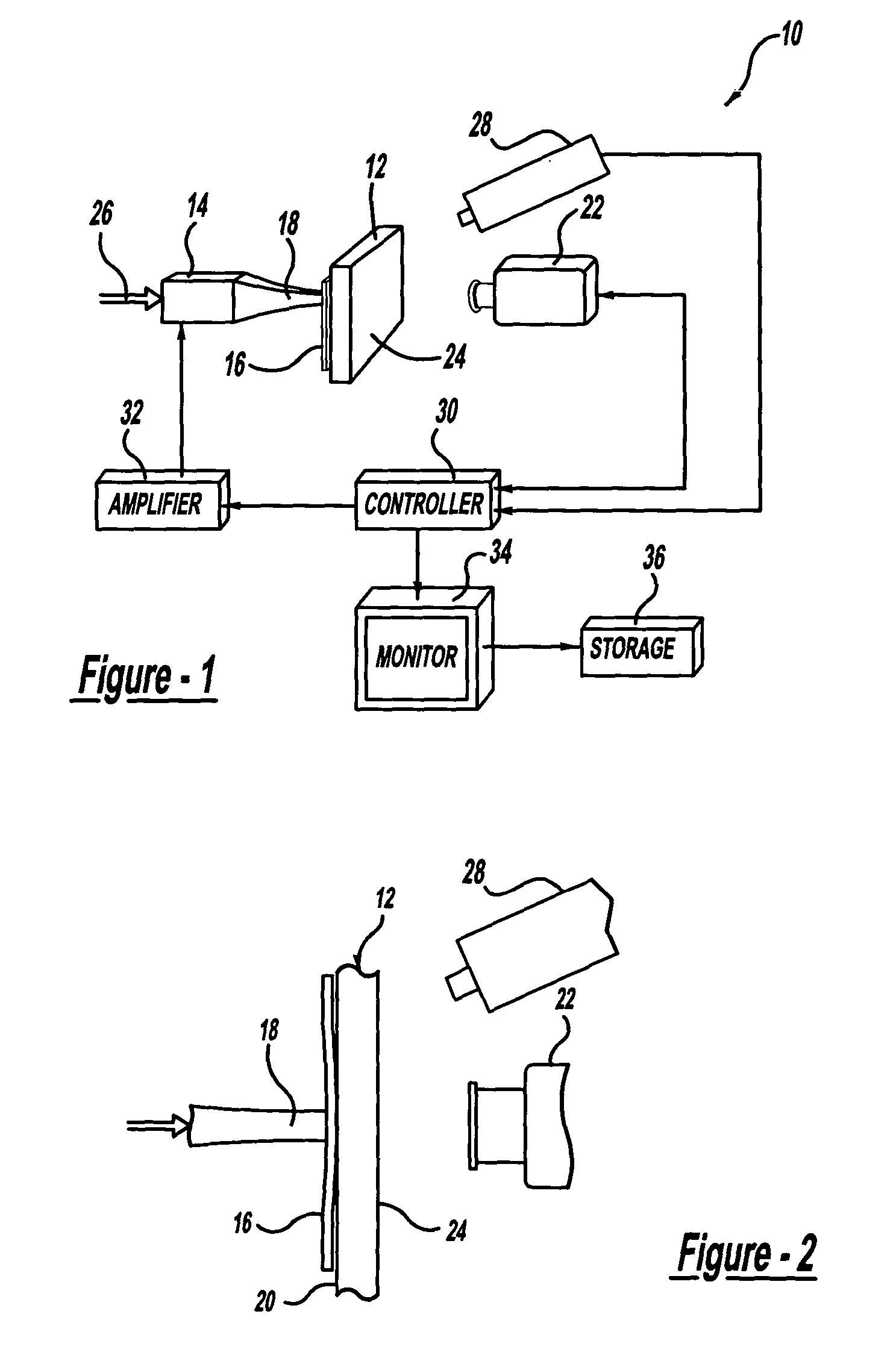
Pulser with double-bearing position encoder for non-invasive physiological monitoring
ActiveUS9891079B2Insufficient stabilityImprove stabilityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPhysiological monitoringEngineering
A double-bearing position encoder has an axle stabilized within a housing via two bearings disposed on opposite walls of the housing. The axle is in communications with a rotating cam. The cam actuates a pulser so as to generate an active pulse at a tissue site for analysis by an optical sensor. The axle rotates a slotted encoder wheel or a reflective encoder cylinder disposed within the housing so as to accurately determine the axle position and, hence, the active pulse frequency and phase.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
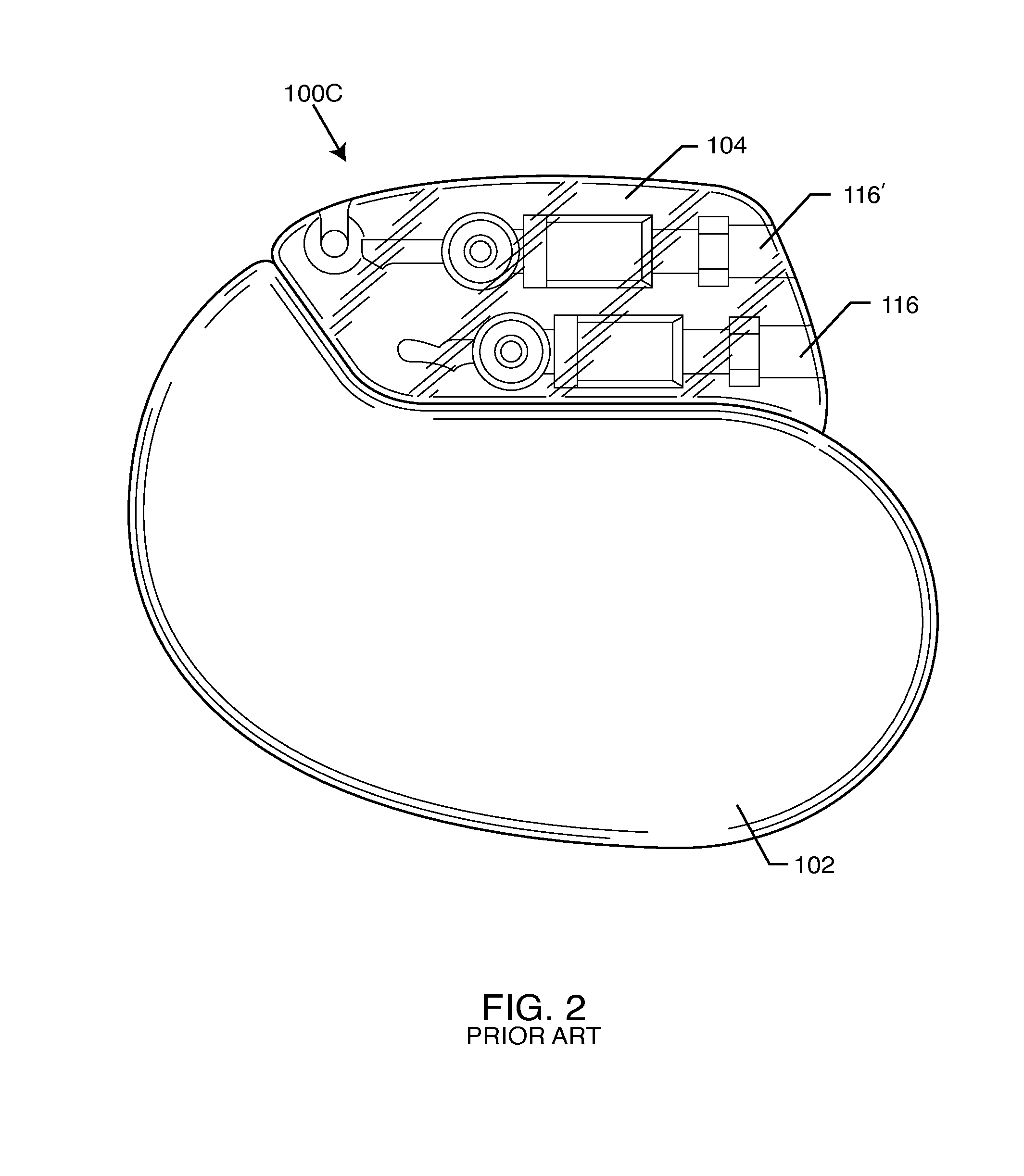
Double-bearing position encoder
ActiveUS20150045637A1Insufficient stabilityImprove stabilityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEngineeringCam
A double-bearing position encoder has an axle stabilized within a housing via two bearings disposed on opposite walls of the housing. The axle is in communications with a rotating cam. The cam actuates a pulser so as to generate an active pulse at a tissue site for analysis by an optical sensor. The axle rotates a slotted encoder wheel or a reflective encoder cylinder disposed within the housing so as to accurately determine the axle position and, hence, the active pulse frequency and phase.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
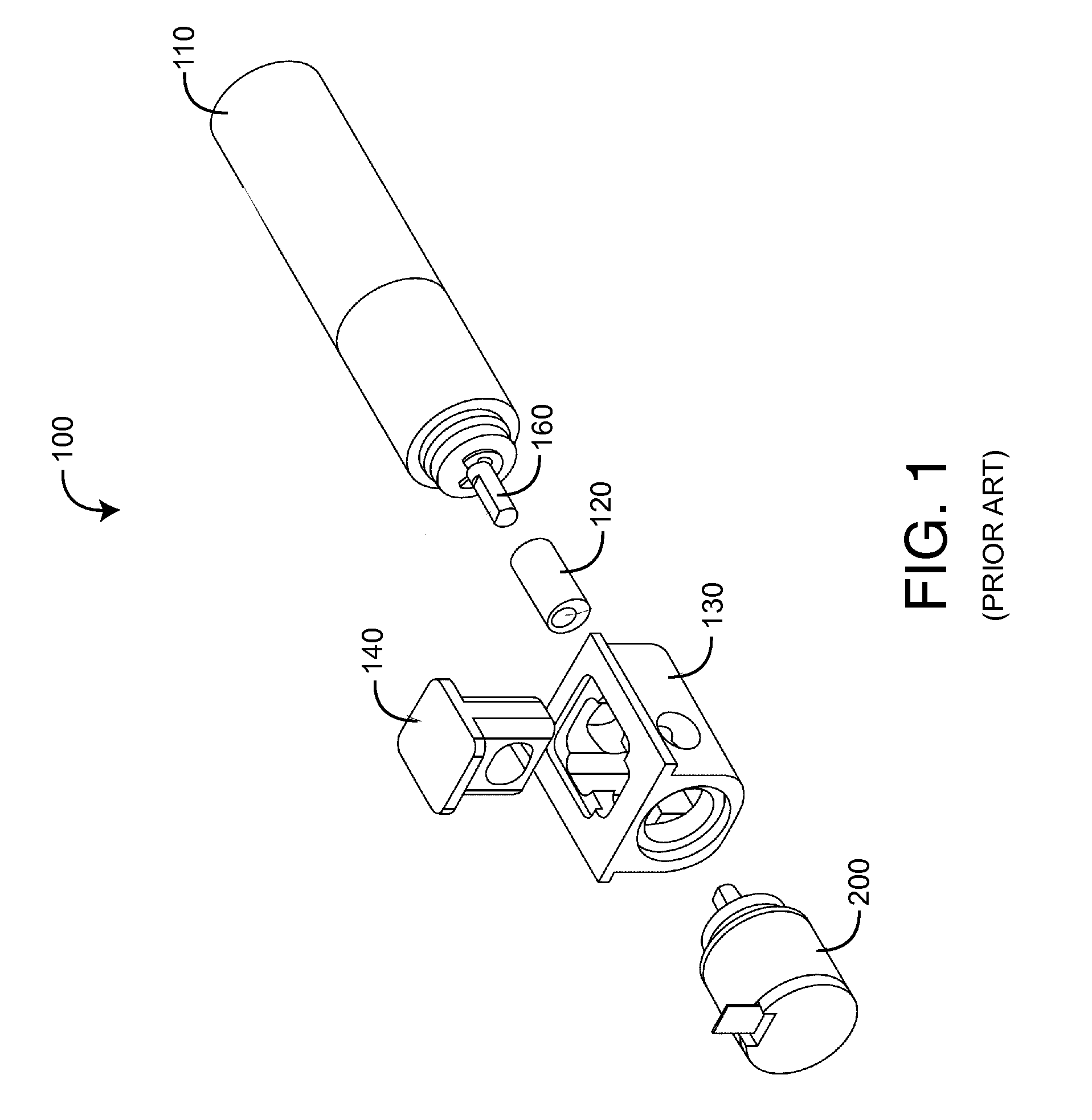
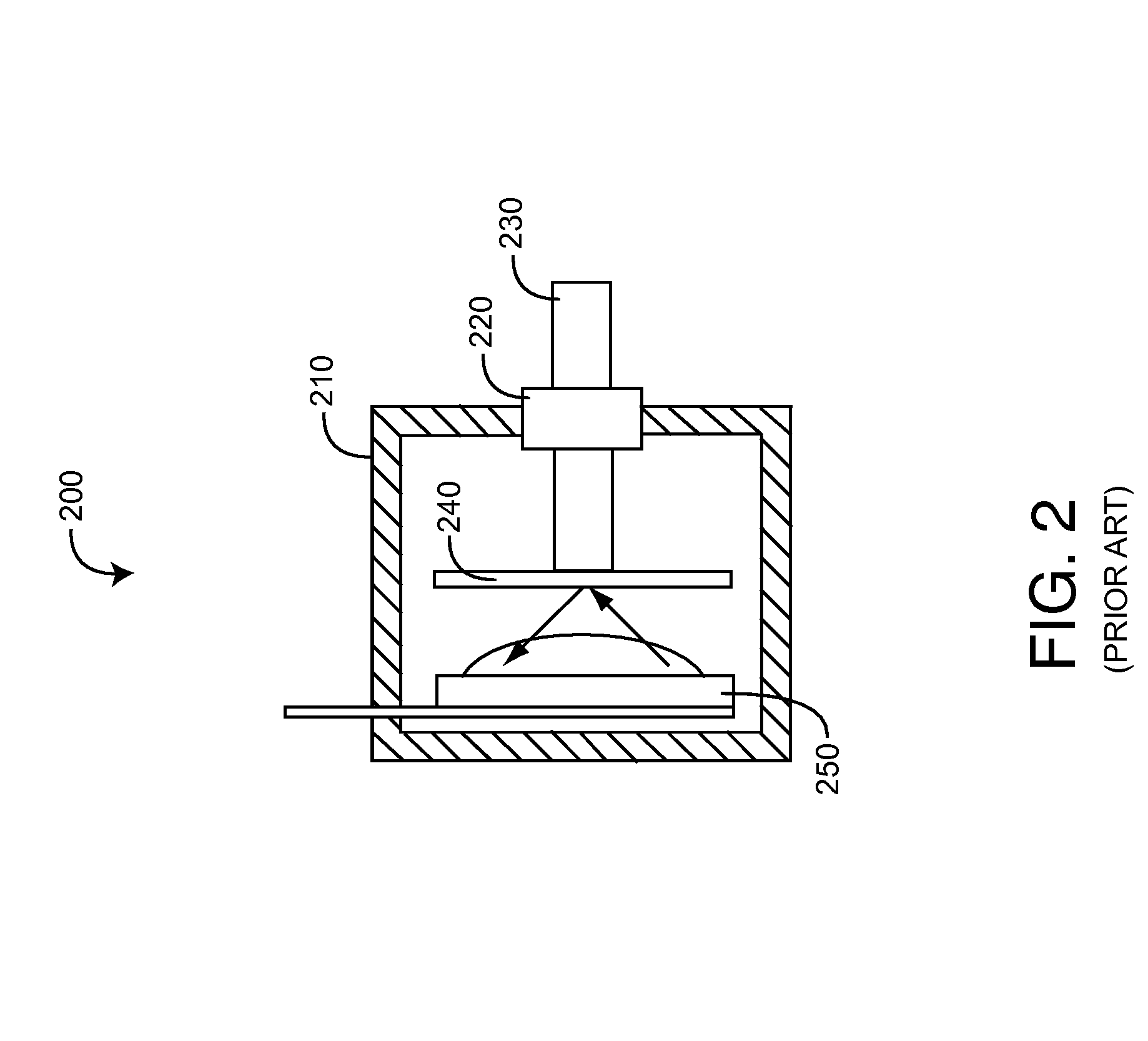
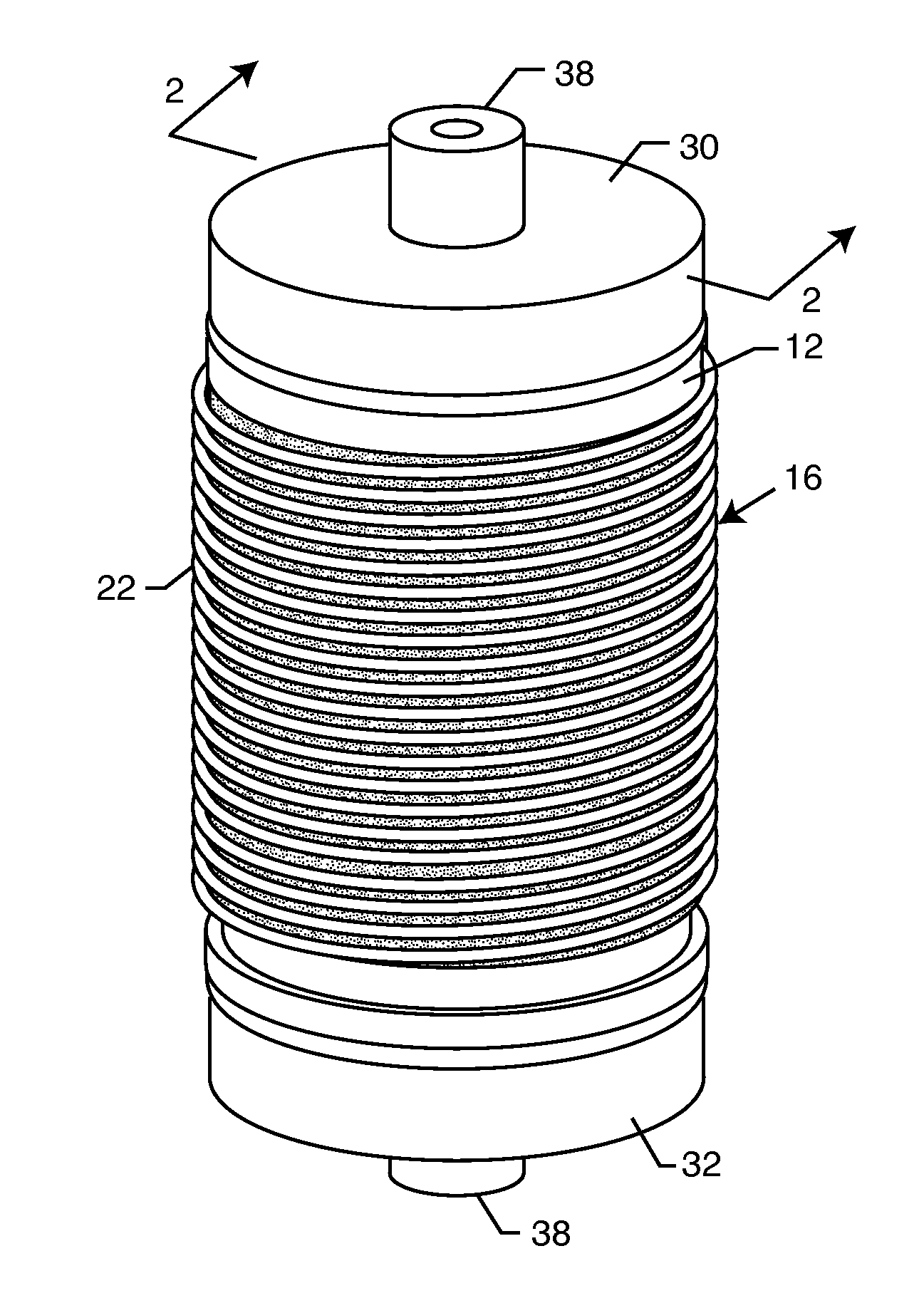
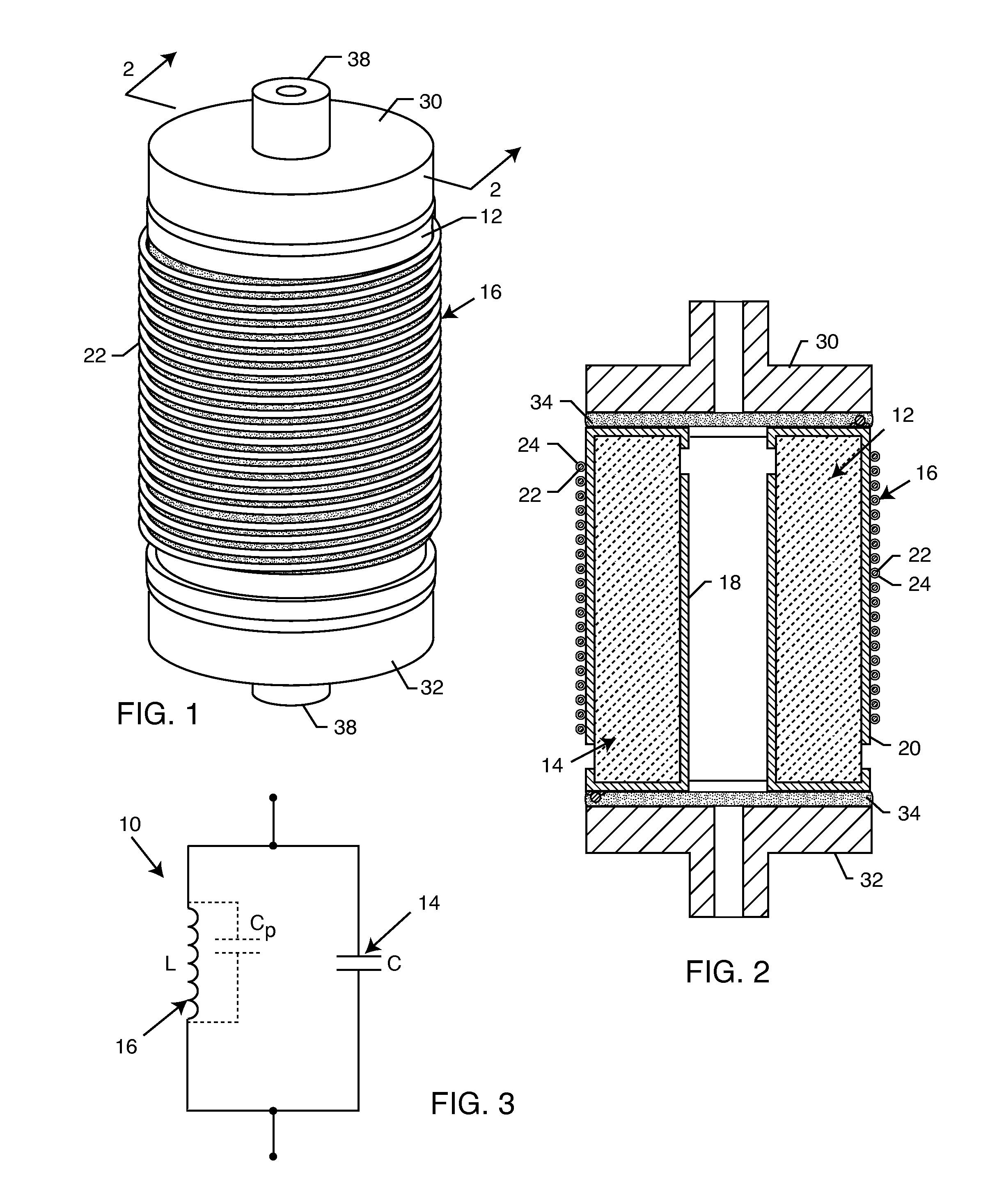
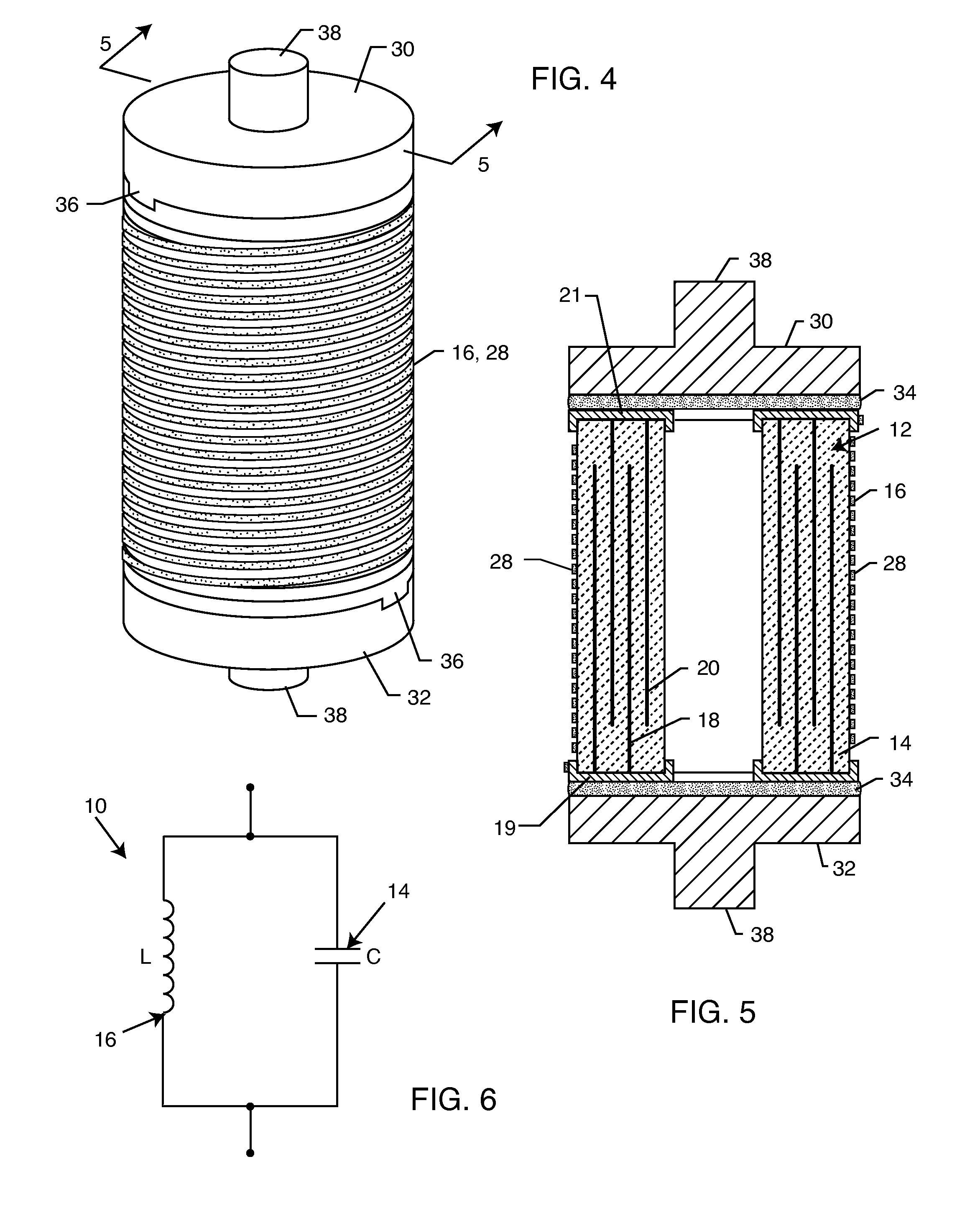
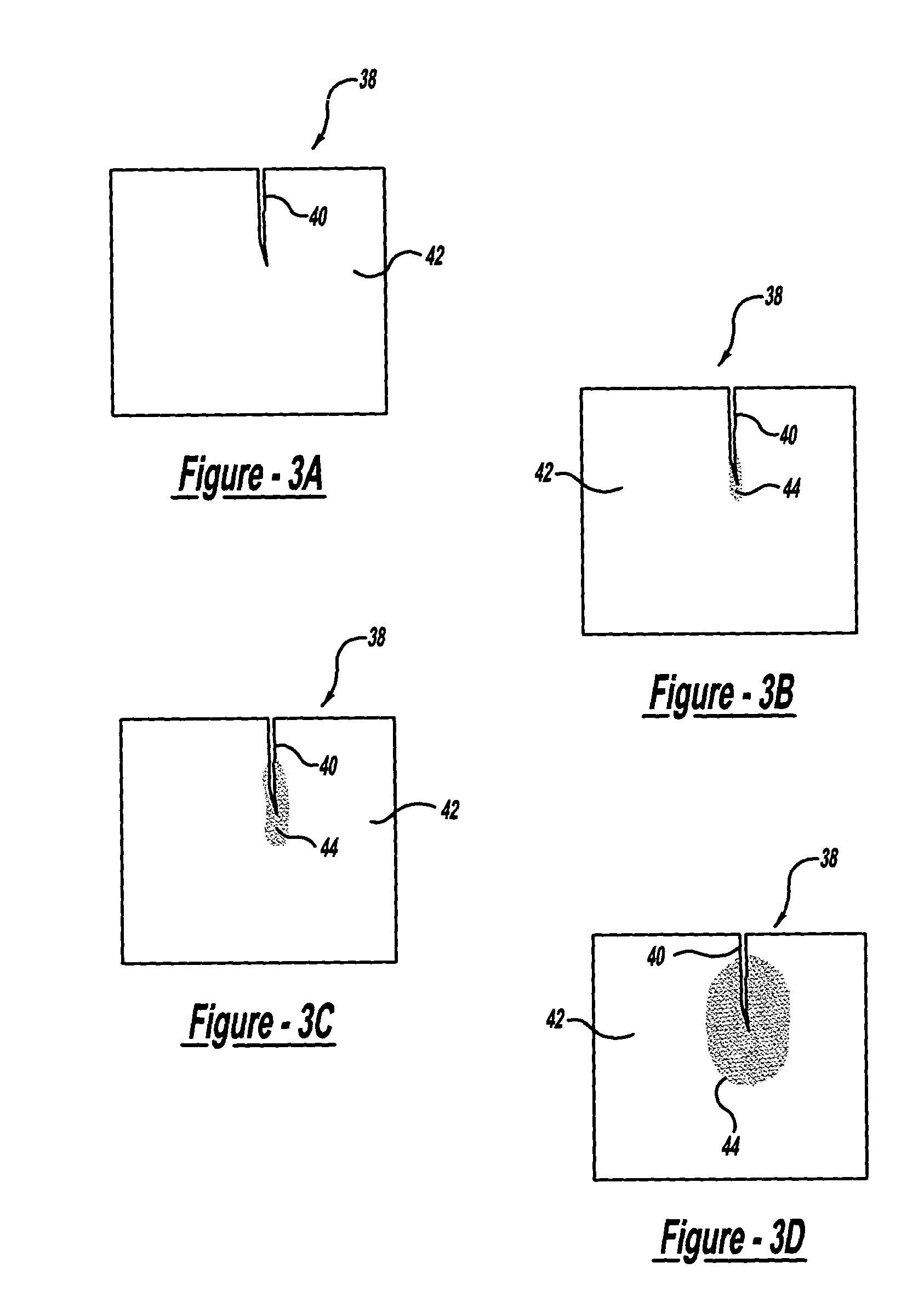
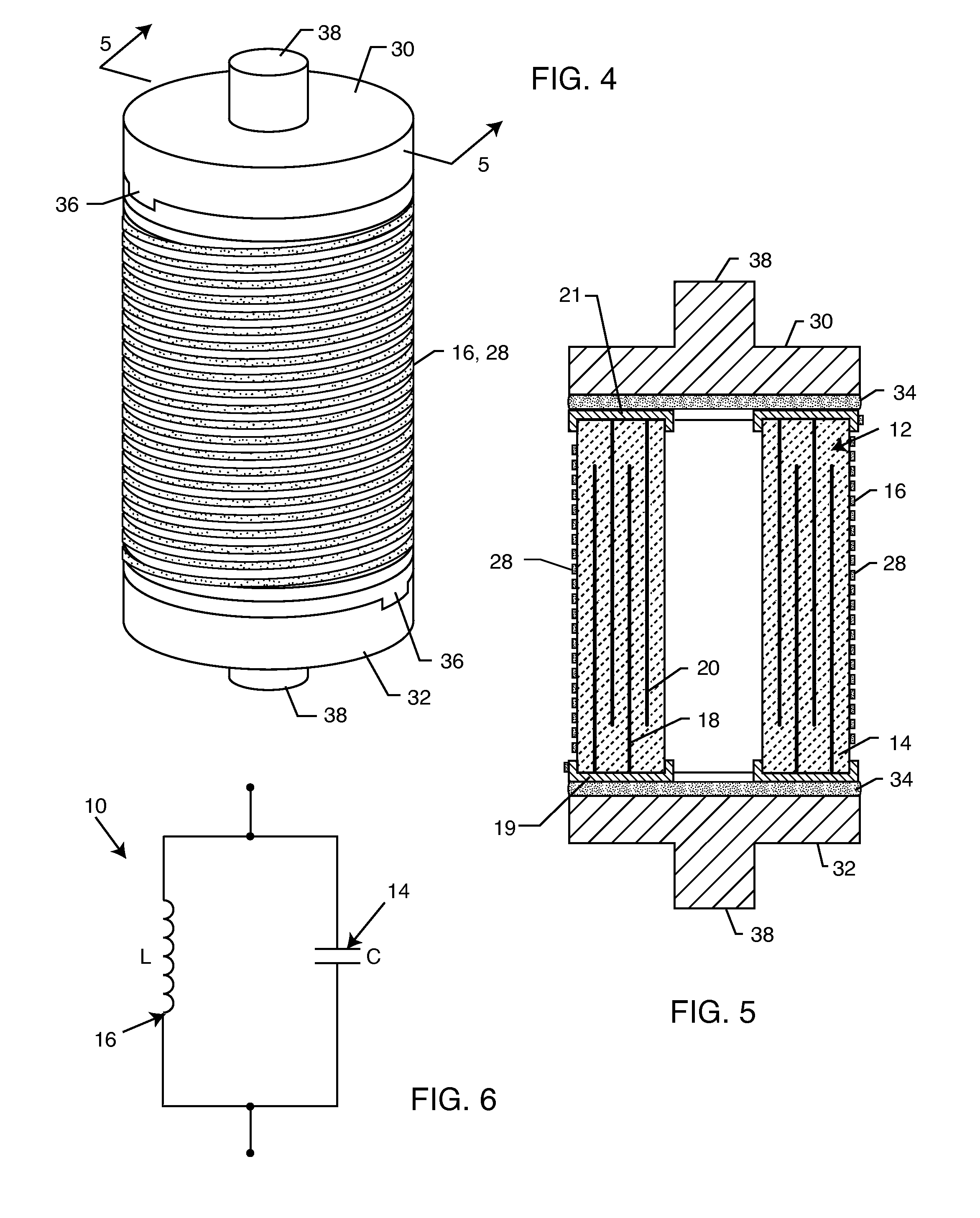
Cylindrical bandstop filters for medical lead systems
InactiveUS20080116997A1Avoid enteringMultiple-port networksAnti-noise capacitorsCapacitanceBand-stop filter
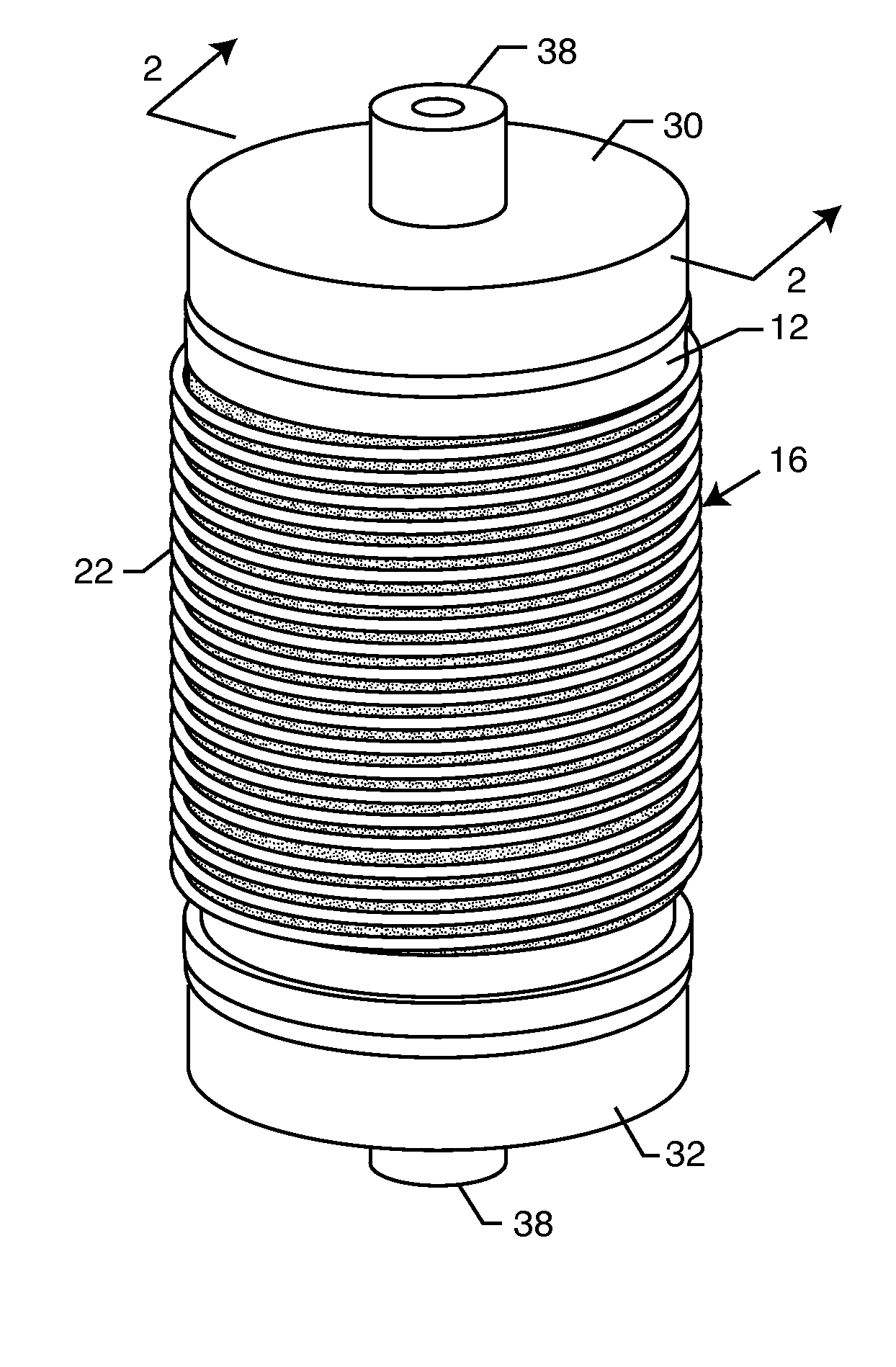
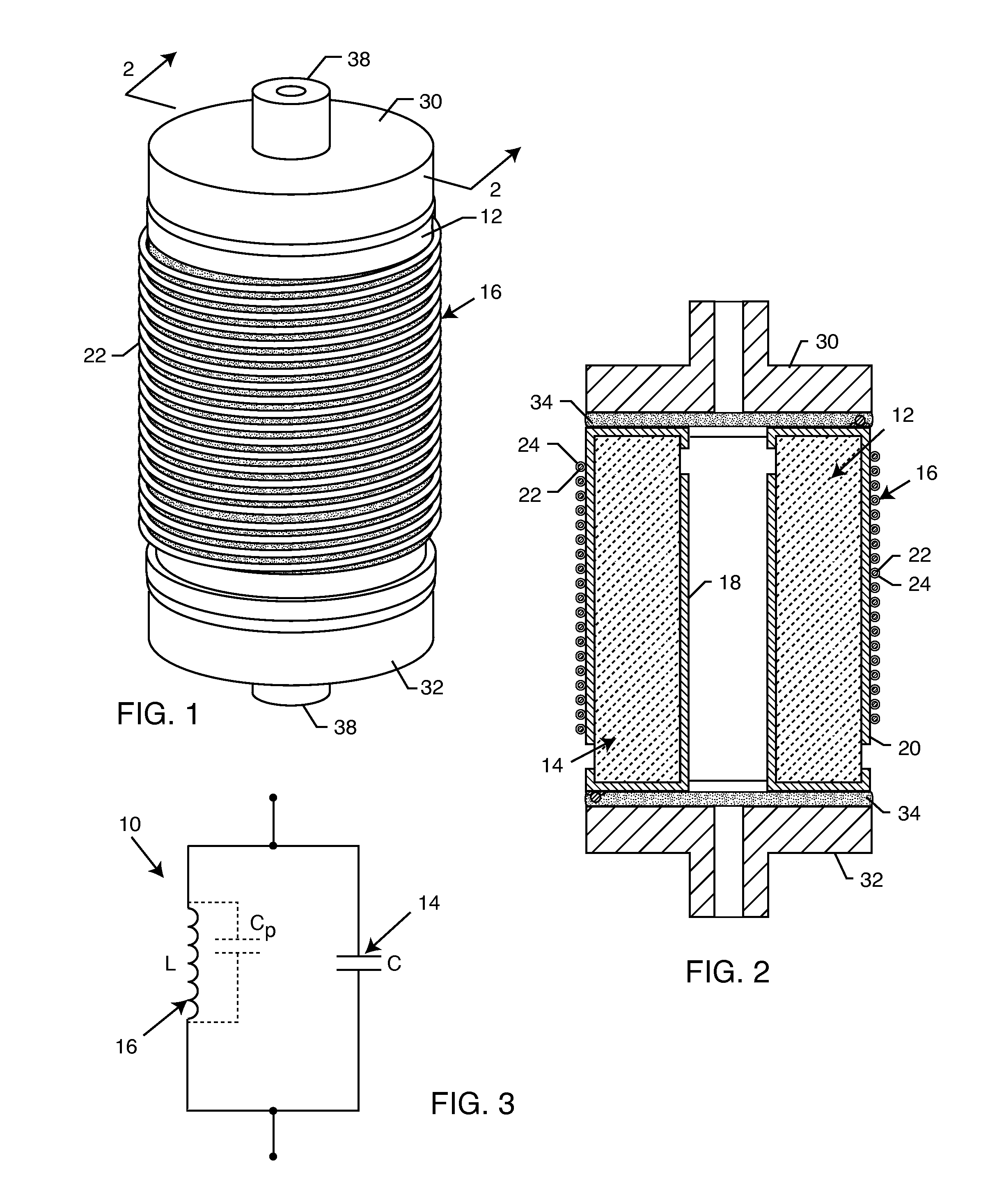
A one-piece cylindrical bandstop filter for medical lead systems incorporates parallel capacitive and inductive elements in a compact cylindrical configuration. The compact cylindrical configuration of the bandstop filter does not add significantly to the size or weight of the medical lead system. Preferably, the bandstop filters are of biocompatible materials or hermetically sealed in biocompatible containers. The parallel capacitive and inductive elements are placed in series with the medical lead system, and are selected so as to resonate at one or more selected frequencies, typically MRI pulsed frequencies.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
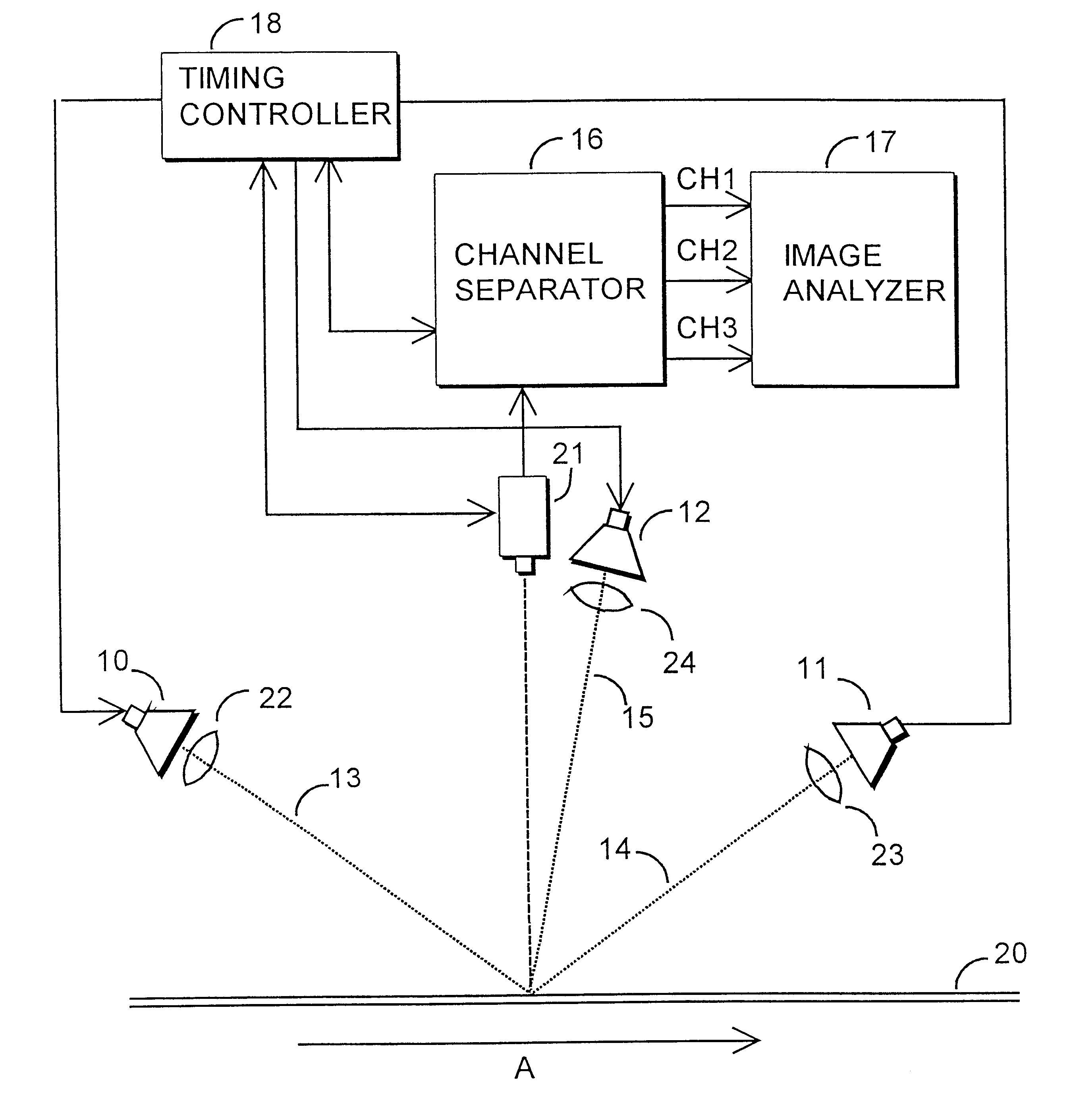
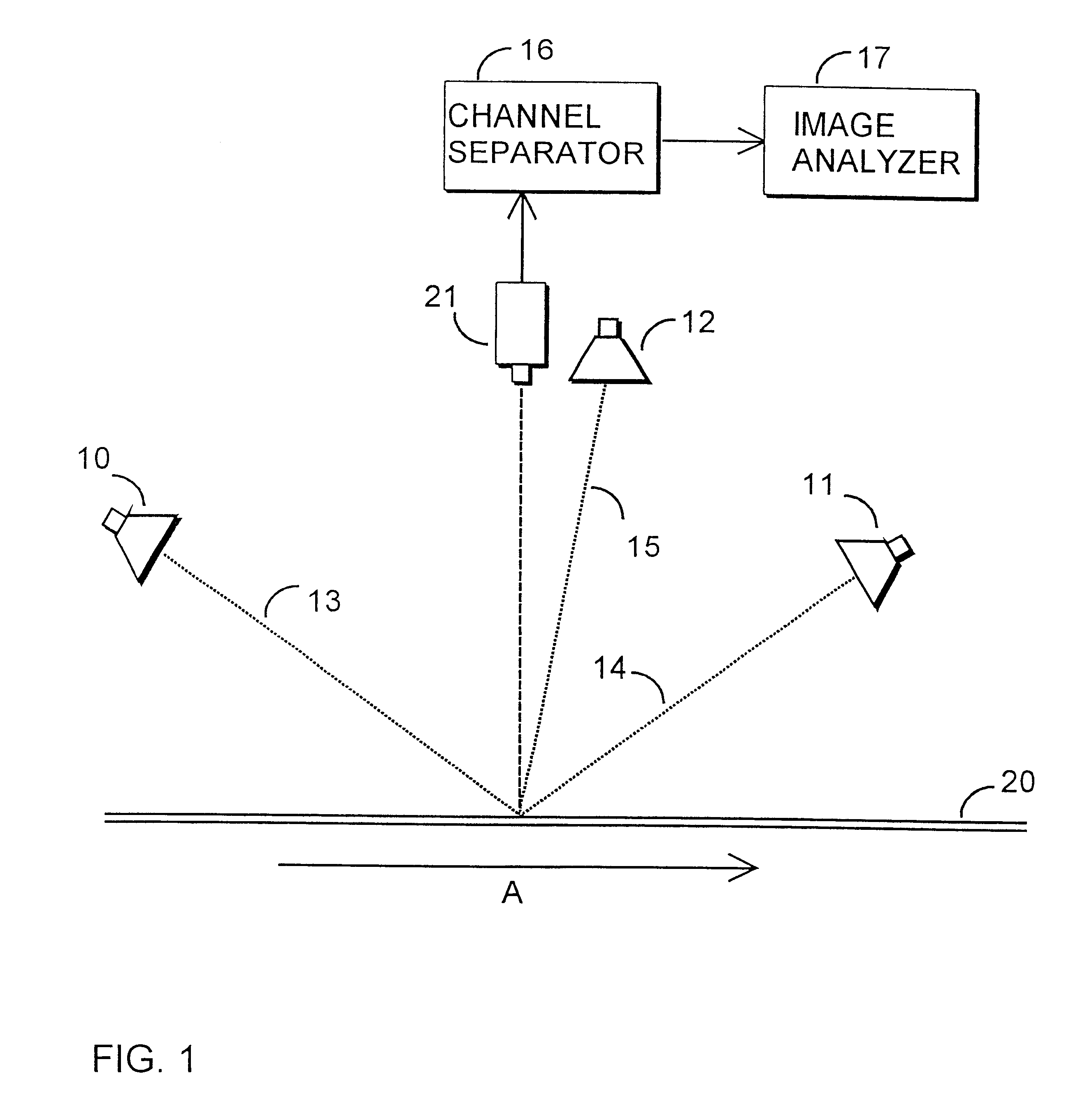
Arrangement and method for inspection of surface quality
InactiveUS6327374B1Enhances analysis of D characteristicEasy to analyzeScattering properties measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionSuperficial massLine scan
The invention relates to a method for automatic inspection of the surface 20 of a moving object, in which a region on the object's surface is illuminated from at least two different illumination directions 13-15. The object's illuminated surface region is imaged with a camera to provide image information for analysis. The light sources in the different illumination directions 13-15 are pulsed to illuminate the object's surface region at different times, the pulsing frequency being >1 kHz The object's illuminated surface region is imaged as lines with a line scan camera 21 in sync with the above pulsing. The invention also relates to an arrangement for inspecting the surface 20 of a moving object, the arrangement comprising at least two light sources 10-12 in at least two different illumination directions 13-15 for illuminating the surface region of the object under inspection; a camera for imaging the object's surface region; and an image analyzer for analyzing the image information acquired from the object's surface 20 by imaging. The light sources 10-12 illuminate the object's surface 20 from the different illumination directions 13-15 at different times, and the camera is a line scan camera 21. The arrangement further comprises a timing controller 18 for synchronous pulsing of the light sources 10-12 and the at least one line scan camera 21, the pulsing frequency of the light sources 10-12 being >1 kHz.
Owner:THERMO RADIOMETRIE +1
Method and apparatus for precision working of material
A method for precise working of material, particularly organic tissue, comprises the step of providing laser pulses with a pulse length between 50 fs and 1 ps and with a pulse frequency from 50 kHz to 1 MHz and with a wavelength between 600 and 2000 nm for acting on the material to be worked. Apparatus, in accordance with the invention, for precise working of material, particularly organic tissue comprising a pulsed laser, wherein the laser has a pulse length between 50 fs and 1 ps and with a pulse frequency of from 50 kHz to 1 MHz is also described.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Interference Classification with Minimal or Incomplete Information
ActiveUS20110188544A1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsAmplitude demodulationMonitor modeFrequency spectrum
Interference classification with minimal or incomplete information. Receivers in access points and in other network devices on a wireless digital network may be switched to a spectrum monitor mode in which they provide amplitude-versus-frequency information for a chosen part of the spectrum. This may be performed by performing a FFT or similar transform on the signals from the receiver. Receivers are calibrated with known interference sources in controlled environments to determine peaks, pulse frequency, bandwidth, and other identifying parameters of the interference source in best and worst case conditions. These calibrated values are used for matching interference signatures. Calibration is also performed using partial signatures collected over a short period in the order of microseconds. These partial signals may be used to detect interferers while scanning. Another aspect of the invention is to record the variation of noise floor in the presence of interference sources. Multiple interference sources may be detected. While data collection is performed in one or more APs, classification may be performed in theAP or on other systems associated with the network collecting and processing spectrum information from one or more APs.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Cervical wagal stimulation induced weight loss
Apparatus and methods for treating obesity using chronic cervical vagal nerve stimulation (cVNS) of the left vagus trunk are disclosed. Four men and ten women, average age 46 years (SD±10) were treated with output current typically 0.75 mA, pulse frequency 30 Hz and width 250 or 500 μs, and duty cycle of 30 s power per five minutes. Mean intake weight was 91 kg (SD±27, range 46 to 137 kg) with body mass index (BMI) 43 kg / m2 (SD±5, range 18 to 49 kg / mn2). After 6-12 months, obese patients had marked weight loss while normal weights were maintained. Decrease in BMI was consistently proportional to initial BMI. Average weight loss at one year was 7 kg (SD±3, range −6 to +24) with mean drop in BMI of 2 kg / m2 (SD±3, range −2 to +8)k. All patients denied any major dieting or exercise.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS
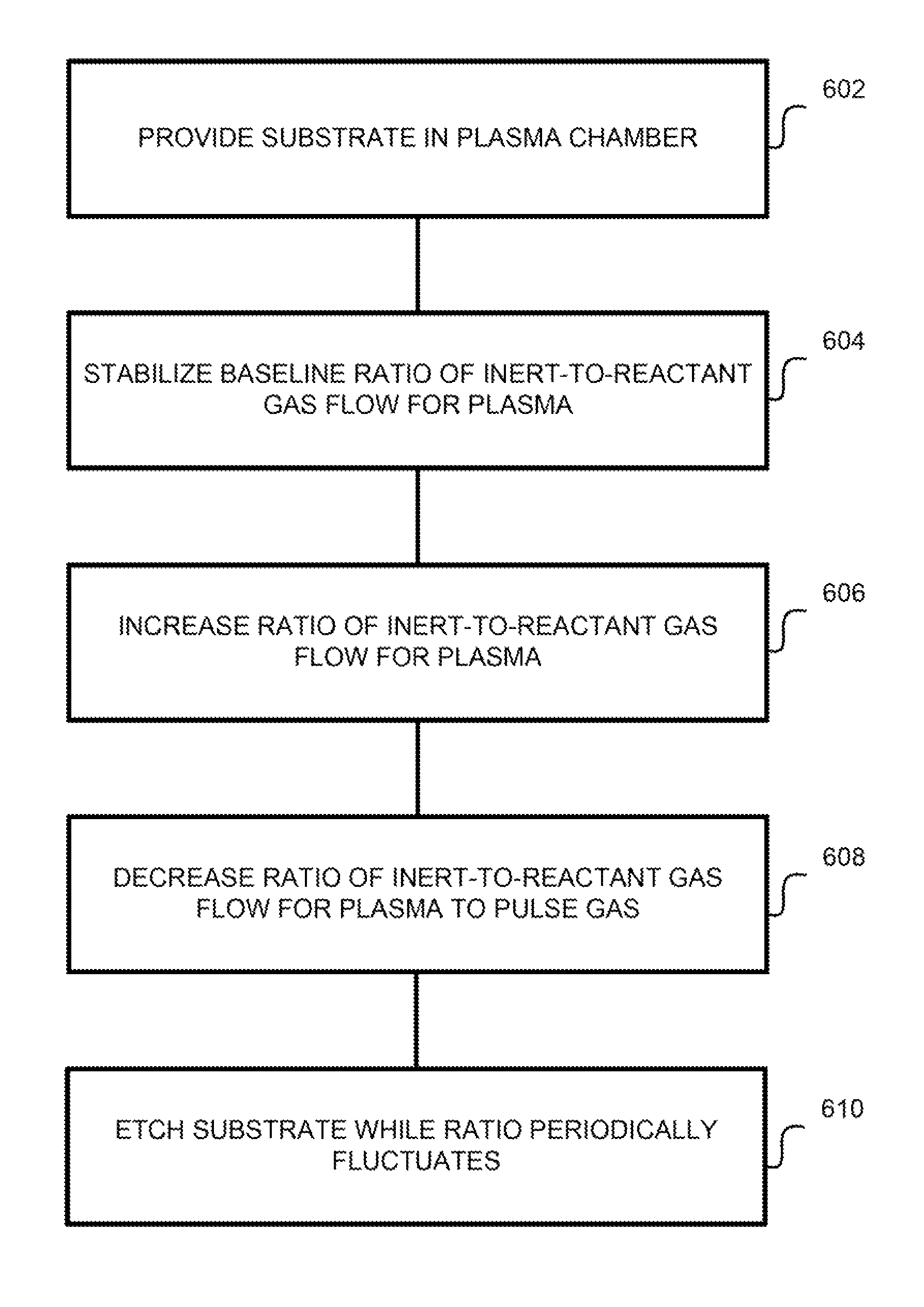
Inert-dominant pulsing in plasma processing systems
Owner:LAM RES CORP
Capacitor and inductor elements physically disposed in series whose lumped parameters are electrically connected in parallel to form a bandstop filter
One or more inductors and one or more capacitors are physically disposed relative to one another in series and are electrically connected to one another in parallel to form a bandstop filter. Chip inductors and chip capacitors having spaced apart conductive terminals are physically arranged in end-to-end abutting relation to minimize electrical potential between adjacent conductive terminals. The bandstop filter may be hermetically sealed within a biocompatible container for use with an implantable lead or electrode of a medical device. The values of the inductors and the capacitors are selected such that the bandstop filter is resonant at one or more selected frequencies, such as an MRI pulsed frequency.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
Method for extracting gas in low air permeability coal layer by pulse fracture anti-reflection
ActiveCN102155254AChange mechanical propertiesImprove breathabilityFluid removalGas removalPulse pressureDischarge rate
The invention relates to a method for extracting gas in low air permeability coal layer by pulse fracture anti-reflection, comprising the following steps: firstly using the blast-proof pulse-type coal layer high pressure water injector with adjustable frequency and pressure from the coal layer, high tunnel or low tunnel; using the pulse water effect generated by the periodical change of high pressure pulse water inside the drill hole of coal body, wherein the maximum pulse pressure is 35 MPa, the flow is about 300 L / min, and the pulse frequency is 0-1460 times / min; forcing the macroscopic fracture in the coal layer to be expanded and communicated; promoting the micro-pore fracture to be formed and extended; forming a new regeneration fracture net; providing a permeable channel of water inthe coal layer so as to achieve the effects of improving the mechanical property of the coal body, reducing the stress of the coal body in front of the working face and improving the discharge rate of the gas. Through the method, the pressure releasing range of the coal layer is enlarged, the whole pressure is adequately released, the radius of influence range of fracture can reach 10-40 m, and the air permeability of the coal body can be improved by 100-1000 times; and the method is simple, easy to operate and good in effect.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
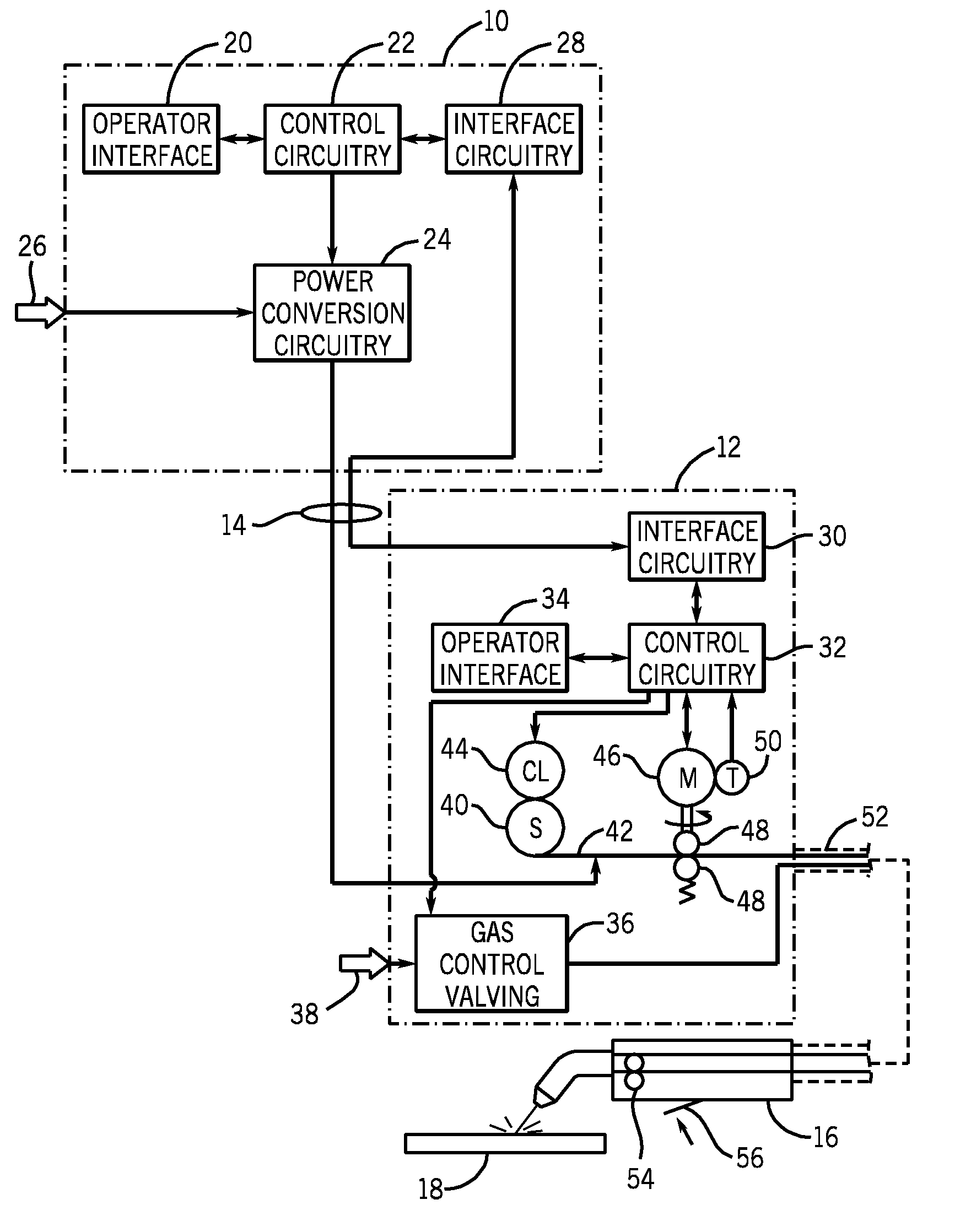
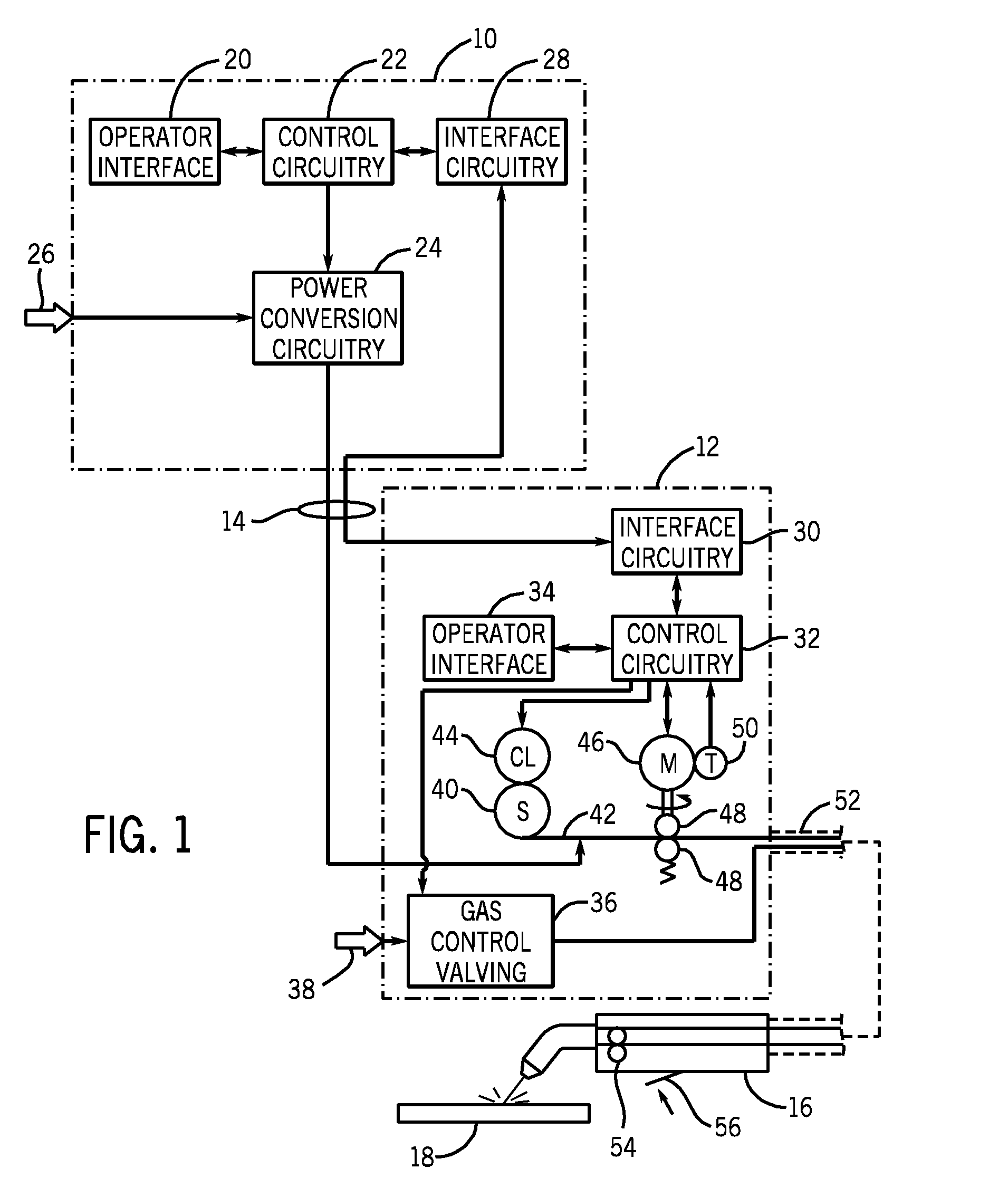
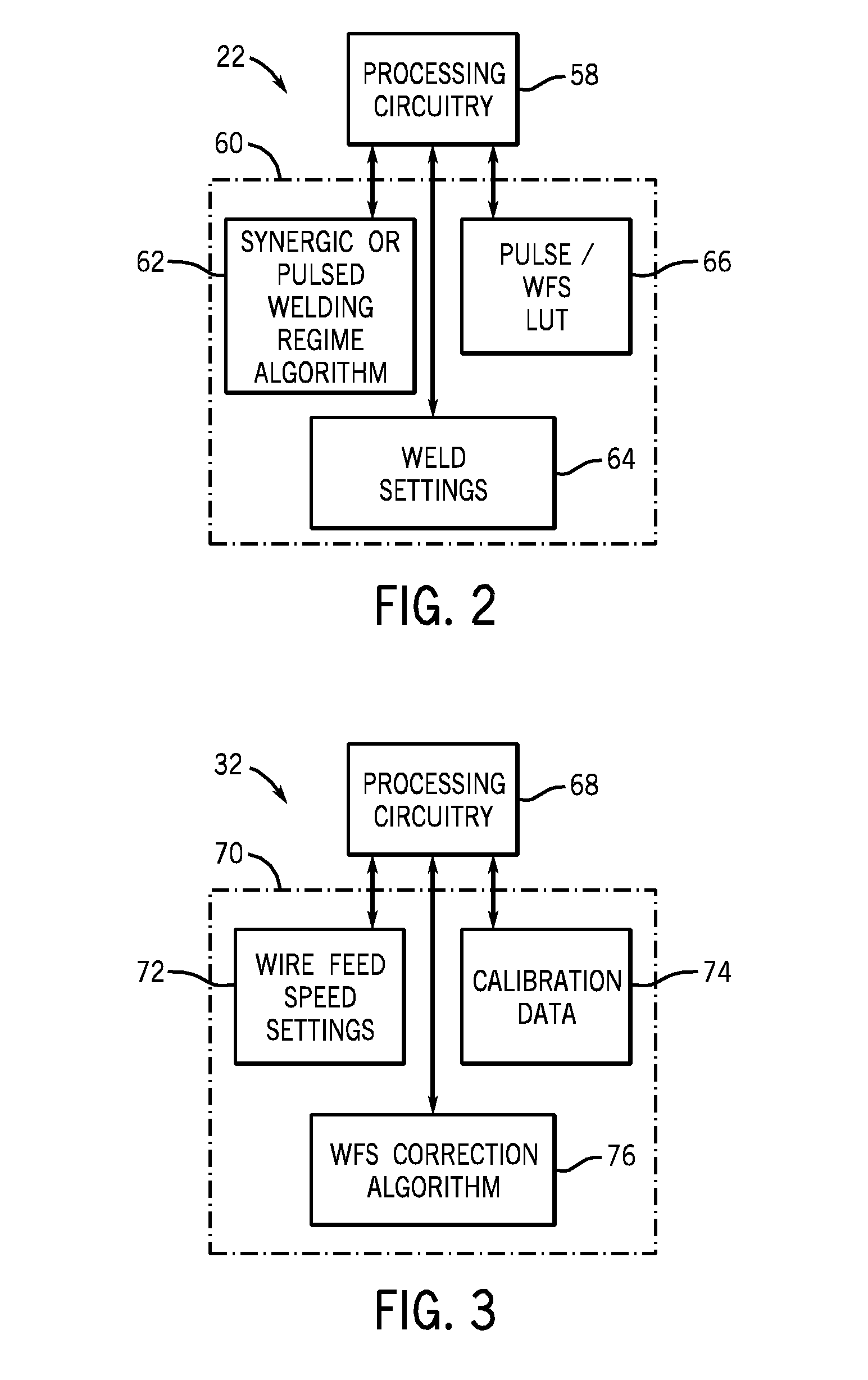
Wire feed speed referenced variable frequency pulse welding system
A pulsed waveform welding operation is implemented by reference to a commanded wire feed speed set by an operator. The wire feed speed is set on a wire feeder, and a signal representative of the commanded wire feed speed is applied to a power supply. The power supply control circuitry references a look-up table in which pulsed waveform parameters are provided based upon wire feed speed. The parameters may include multiple parameters such as pulse frequency, peak current, background current, and current ramp rates. The control circuitry commands power conversion circuitry to generate the commanded waveform as a function of the commanded wire feed speed.
Owner:ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC
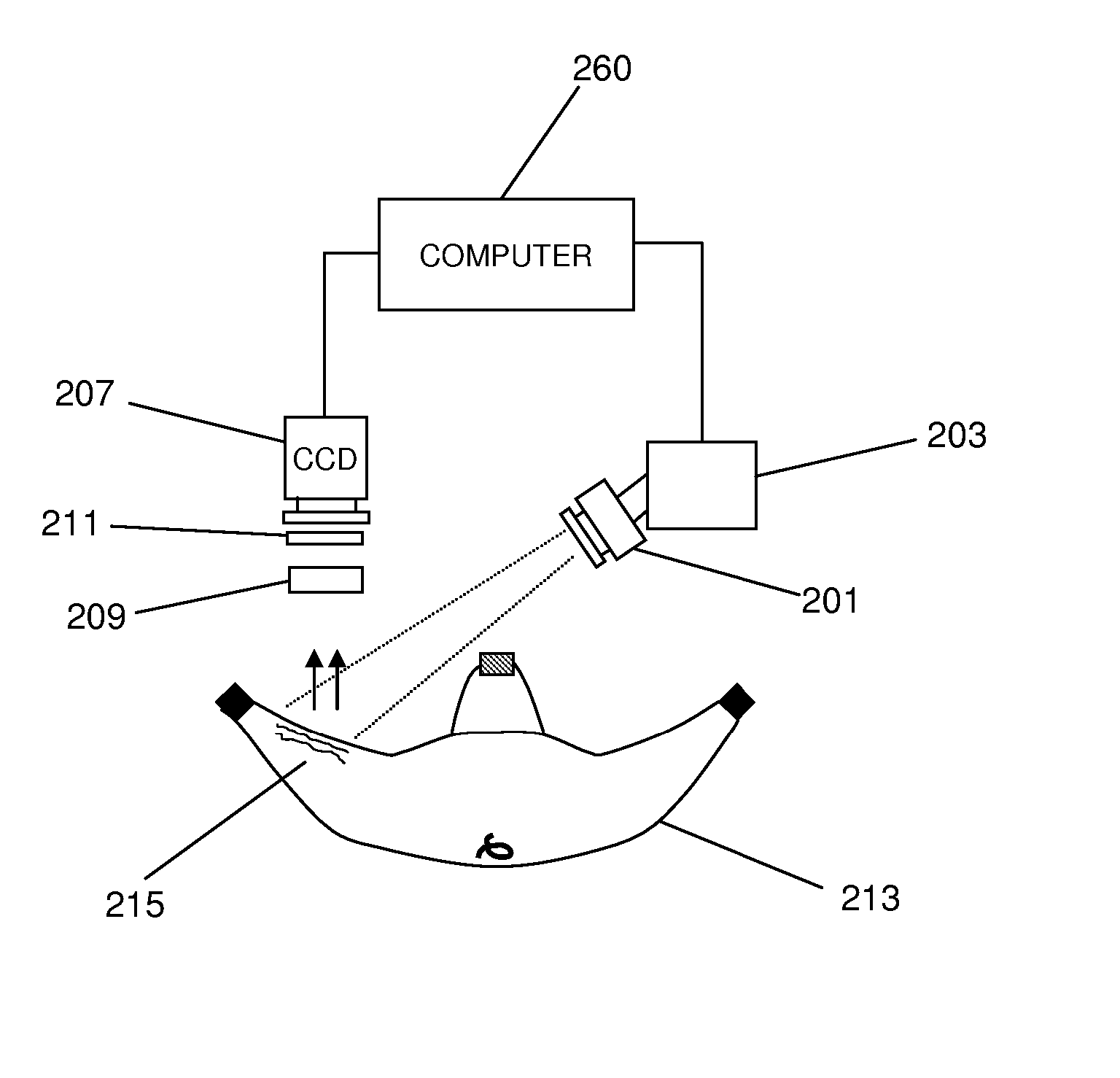
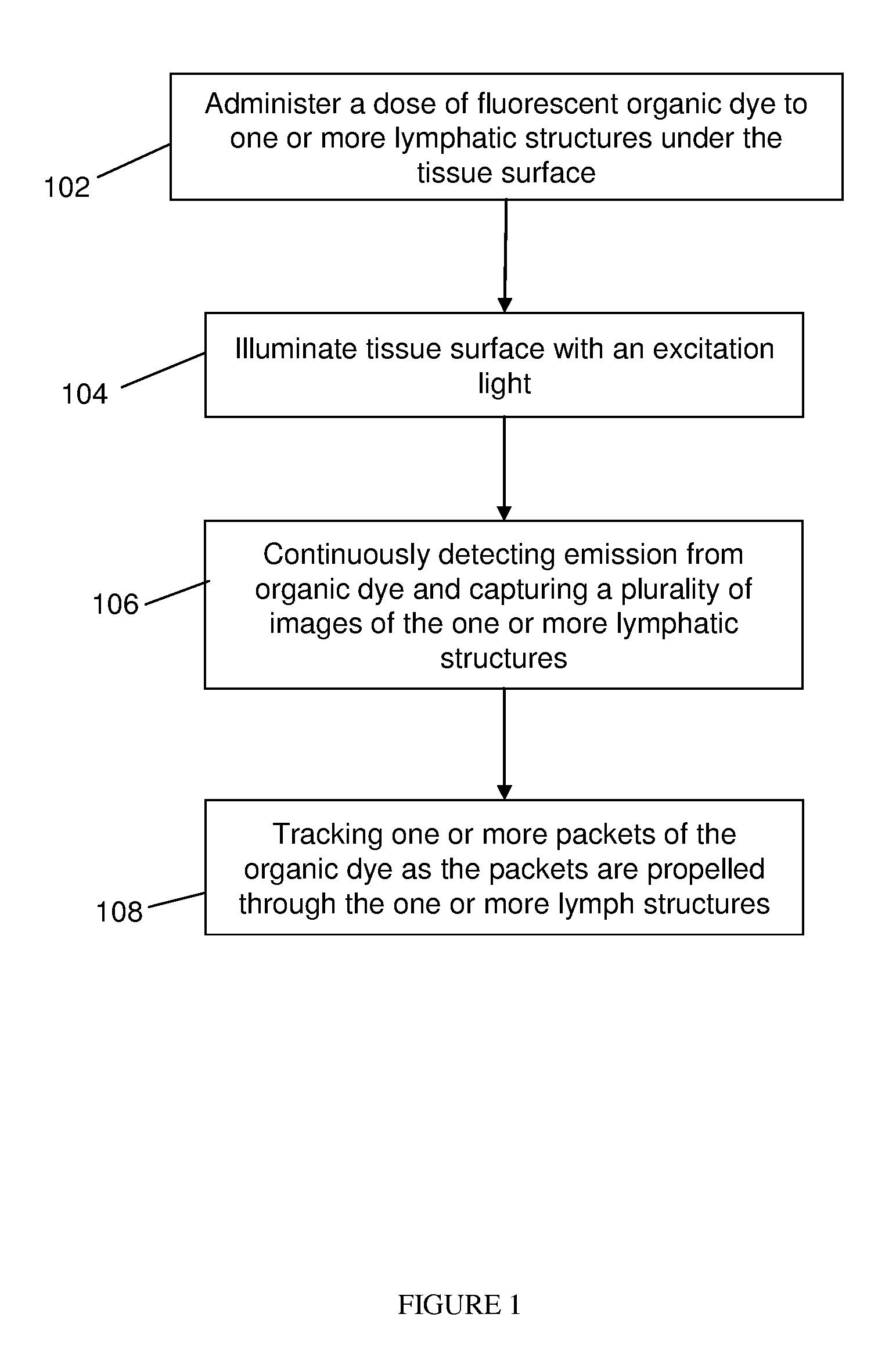
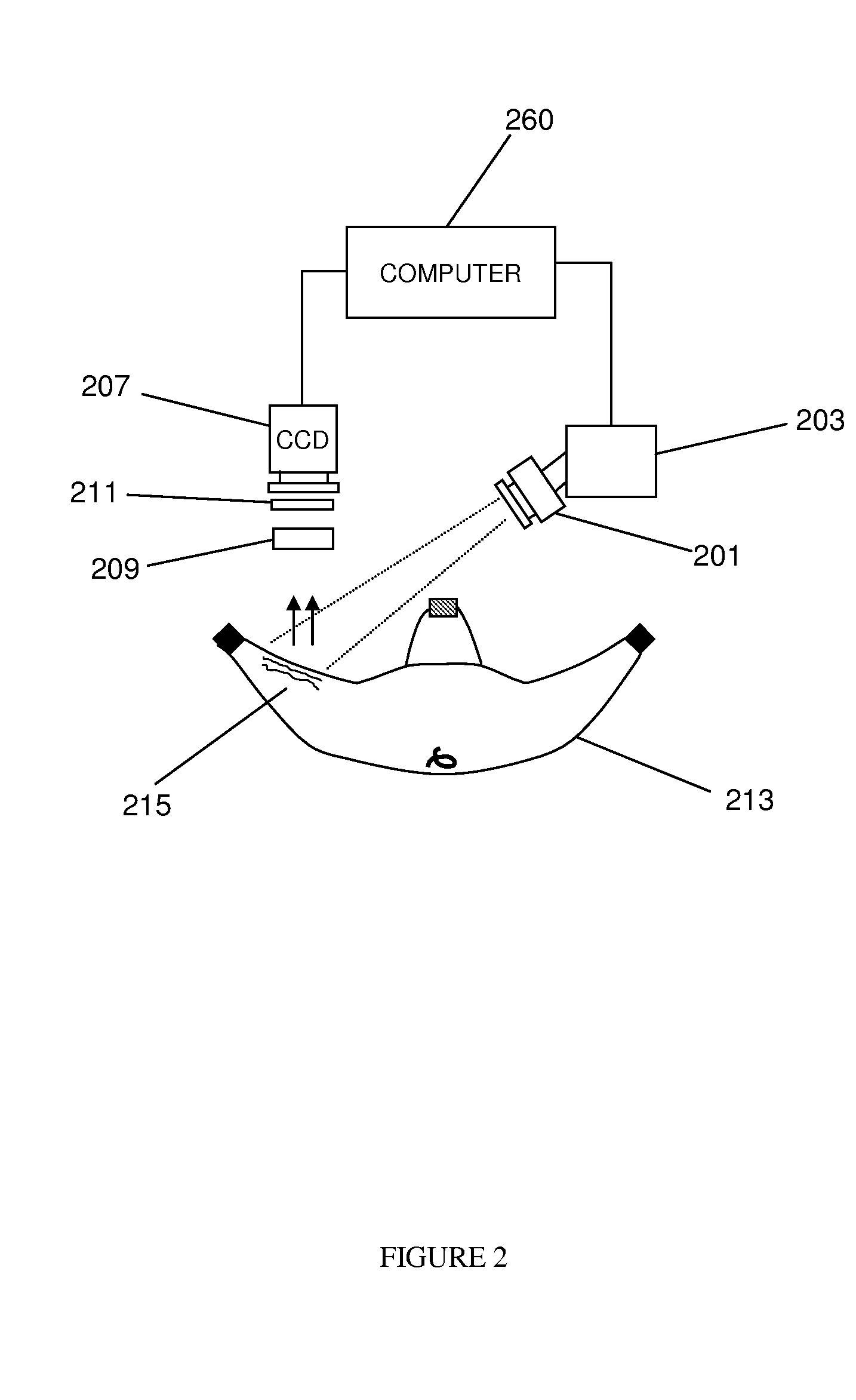
Method of measuring propulsion in lymphatic structures
InactiveUS20080064954A1Diagnostics using lightDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionOrganic dyeImaging agent
Novel methods and imaging agents for functional imaging of lymph structures are disclosed herein. Embodiments of the methods utilize highly sensitive optical imaging and fluorescent spectroscopy techniques to track or monitor packets of organic dye flowing in one or more lymphatic structures. The packets of organic dye may be tracked to provide quantitative information regarding lymph propulsion and function. In particular, lymph flow velocity and pulse frequency may be determined using the disclosed methods.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
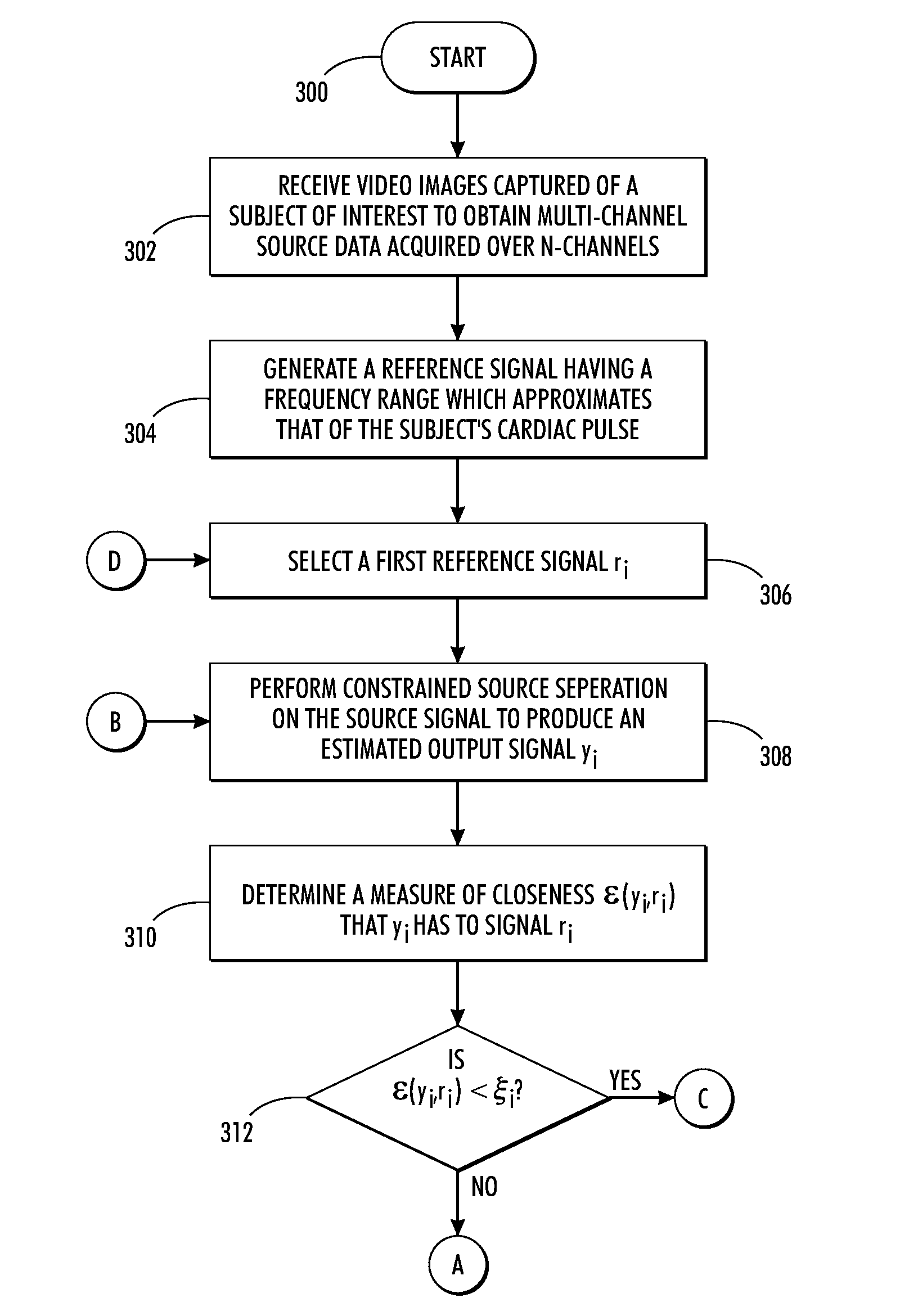
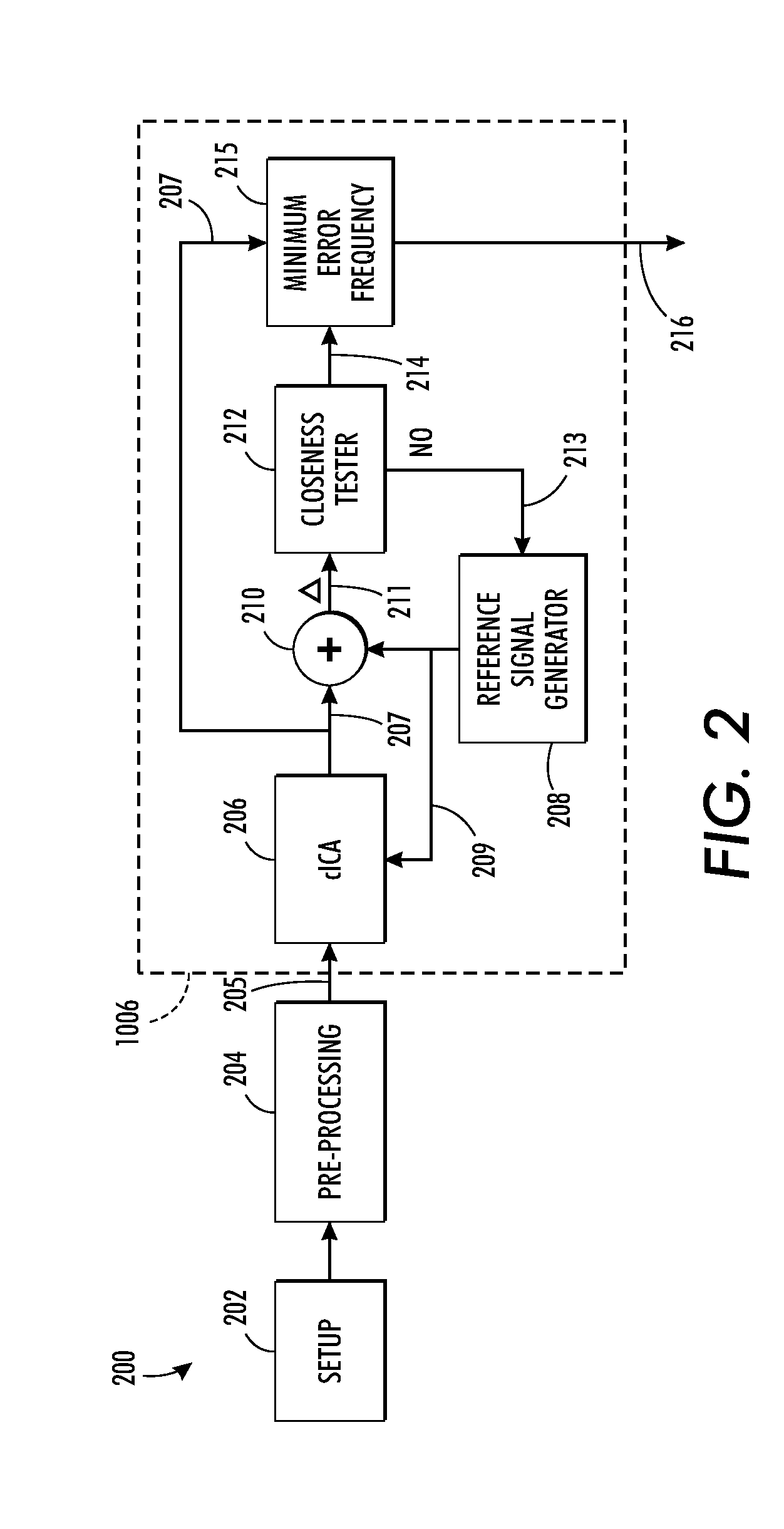
Estimating cardiac pulse recovery from multi-channel source data via constrained source separation
What is disclosed is a system and method for recovering a patient's cardiac pulse rate from a sequence of video images recording of that patient. In one embodiment, a reference signal of a particular frequency is generated at predetermined frequency intervals and a constrained source separation is performed on the source data to obtain an estimation of the source signal intended to be recovered. The reference signal is updated and constrained source separation is again performed. These operations are repeated for all frequencies of the reference signal. The frequency at which a minimum error is achieved is determined to be the subject's recovered cardiac pulse frequency. In such a manner, the source signal is extracted and recovered reliably from captured multi-channel RGB signals or multispectral signals. The teachings hereof find their uses in a variety of medical solutions including various military, security and telemedicine applications. Various embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:XEROX CORP
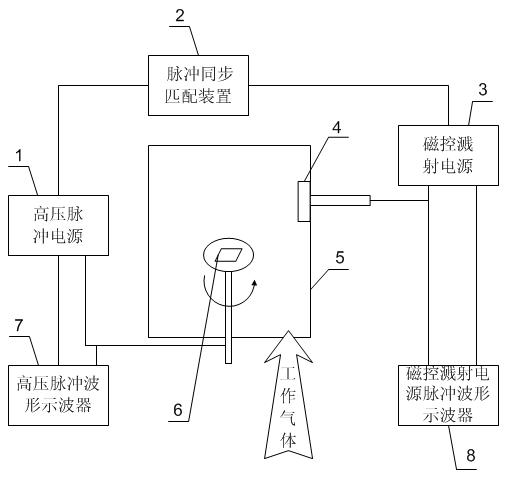
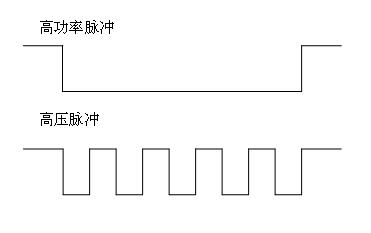
Ion implantation and deposit method of high-power composite pulse by magnetic control sputtering
ActiveCN101838795AIncrease ionization rateHigh bonding strengthVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingPhase differenceHigh pressure
The invention discloses an ion implantation and deposit method of high-power composite pulse by magnetic control sputtering, which belongs to the field of material surface treatment technology and solves the problems of large particles and low film deposit efficiency in an adopted method in which negative high voltage pulse is applied to a workpiece. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the steps of: 1. placing the workpiece on a sample platform in a vacuum chamber, connecting the workpiece with a high-voltage pulse power supply, and connecting a magnetic control sputtering target source with a magnetic control sputtering power supply; and 2. implanting and depositing: when the vacuum degree in the vacuum chamber is lower than 10-2Pa, introducing working gas until the vacuum degree in the vacuum chamber reaching 0.011-10 Pa, starting up the high-voltage pulse power supply, adjusting the voltage value of output pulse of the high-voltage pulse power supply to 0.5-100kV, adjusting the pulse frequency to 0-1000Hz, adjusting the pulse width to 0-500 microseconds, starting up the magnetic control power supply, adjusting required process parameters by direct-current luminance pre-ionization, and controlling the voltage phase difference of the two power supplies to be -1000-1000 microseconds to perform the ion implantation and deposit.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
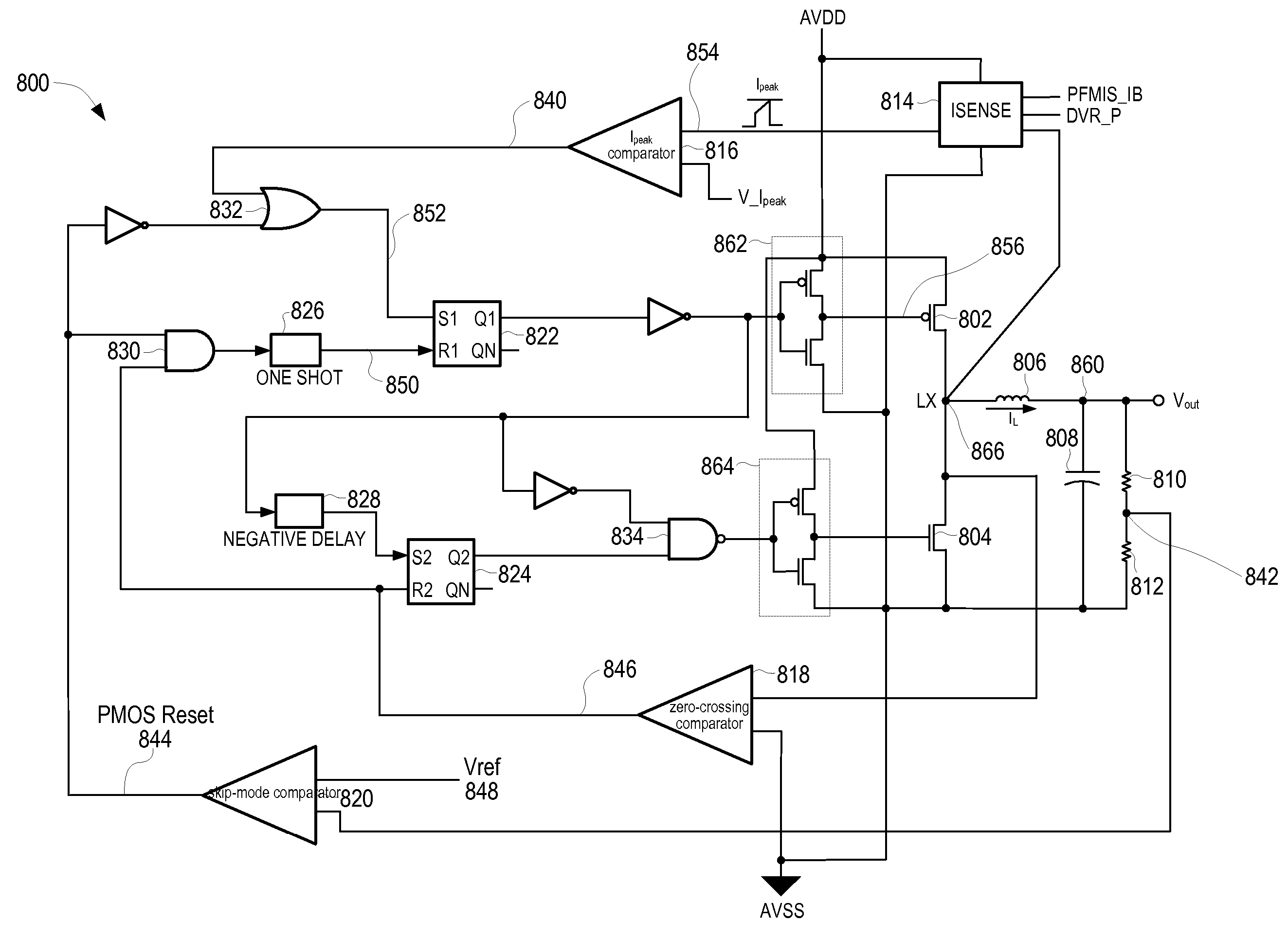
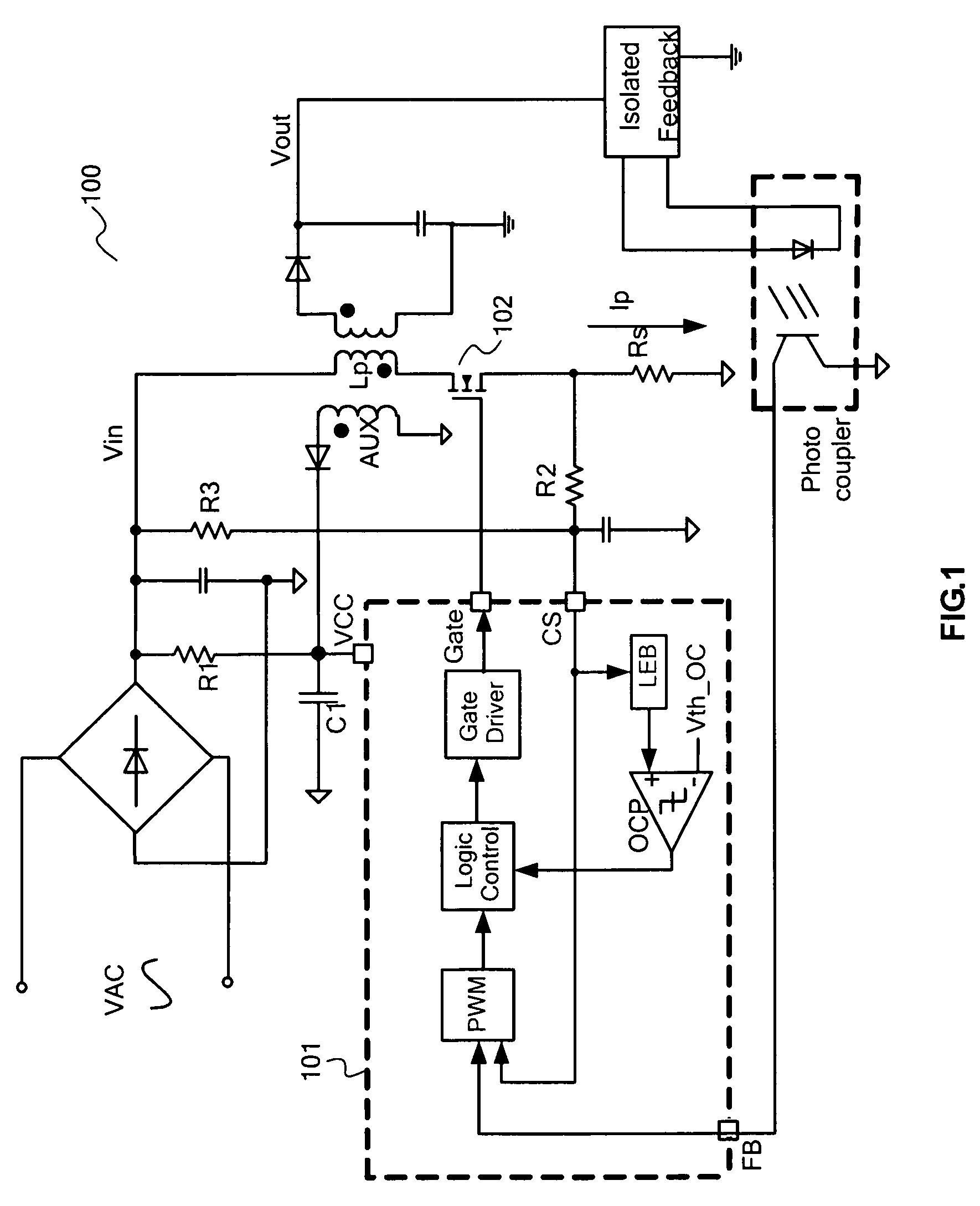
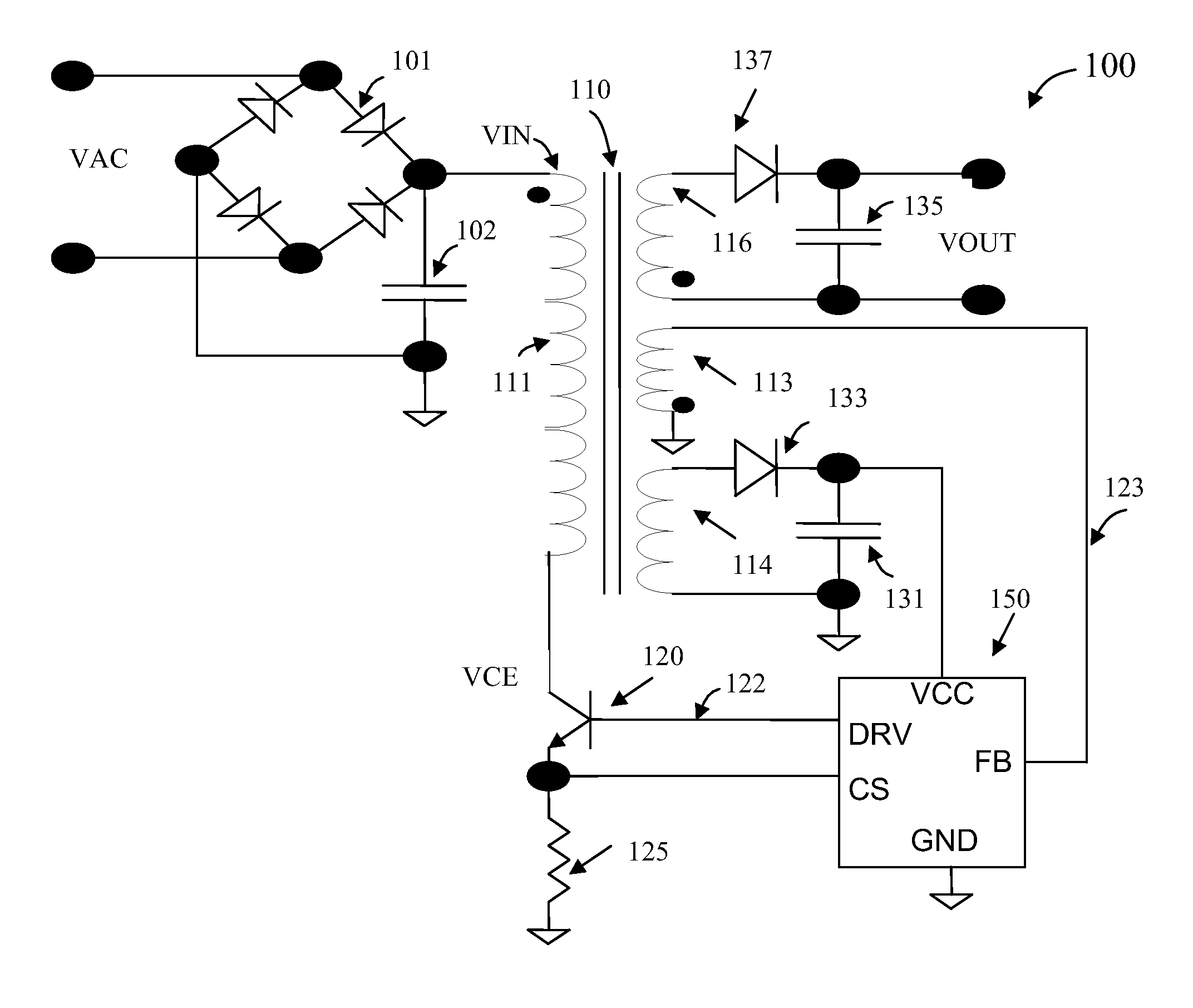
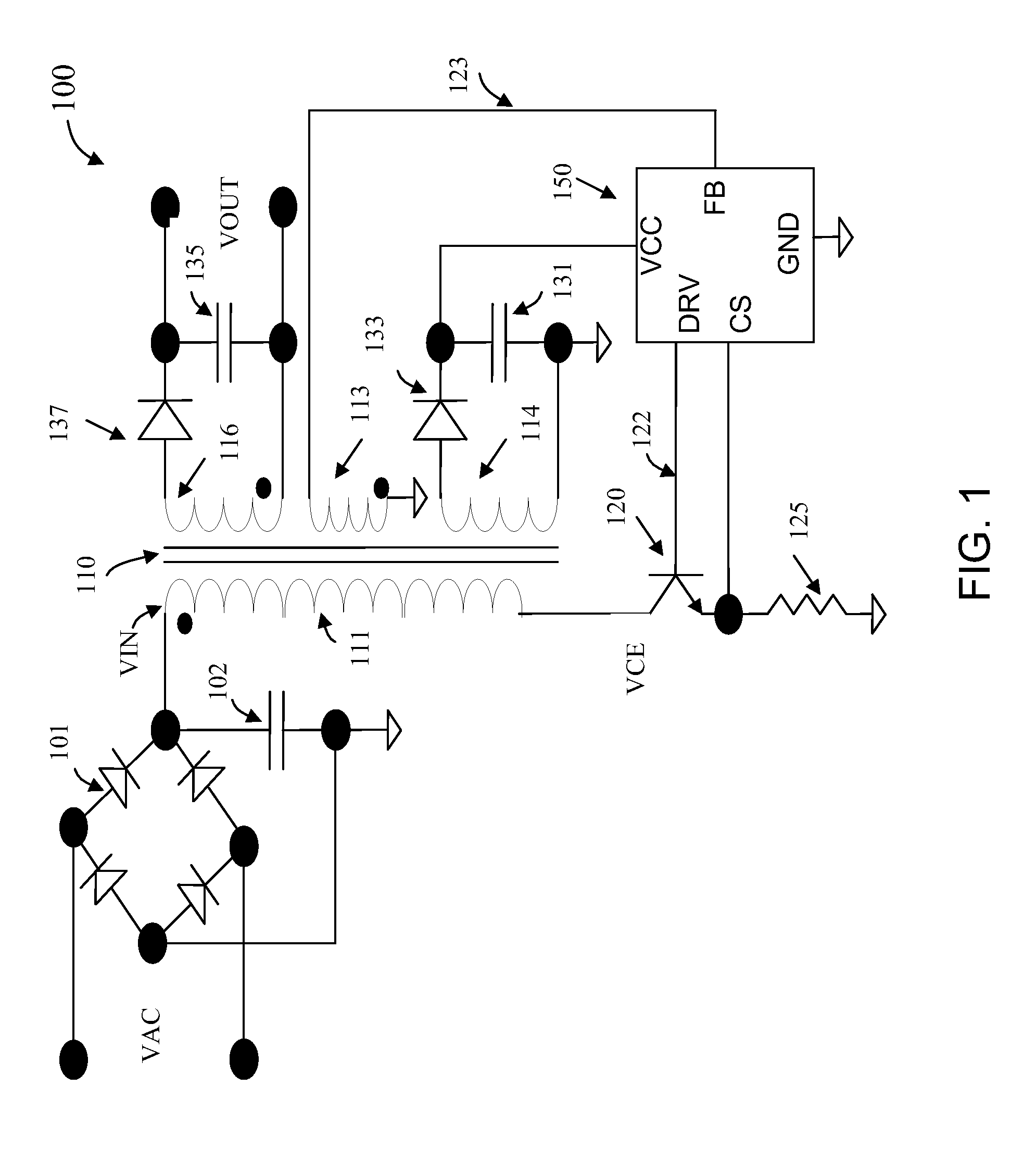
A pulse-frequency mode dc-dc converter circuit
ActiveUS20070085520A1Improve efficiencyReduce dissipationEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionDc dc converterElectrical polarity
A step-down switching voltage regulator may operate in PFM mode based on peak current sense without requiring an external diode. The regulator may comprise a PMOS transistor and an NMOS transistor whose drains are coupled to a common output node and whose sources are coupled to high and low supply voltages, respectively, configured to develop a current in an inductor and generate an output voltage. A control circuit, coupled to the respective gates of the PMOS transistor and the NMOS transistor, may sense the current in the inductor (IL), sense an attenuated version of the output voltage (VFB), and sense the polarity of the voltage (VX) developed at the common output node. The control circuit may turn on the PMOS transistor when the VFB falls below a reference voltage and VX remains positive with respect to the low supply voltage, and may turn off the PMOS transistor when IL reaches a specified value or when VFB exceeds the reference voltage. The control circuit may also turn on the NMOS transistor after the PMOS transistor is turned off and VX becomes negative with respect to the low supply voltage, and may turn off the NMOS transistor when VX becomes positive with respect to the low supply voltage.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
Method and system for efficient power control with multiple modes
InactiveUS7826237B2Improve performanceImprove stabilityEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionElectricityPower mode
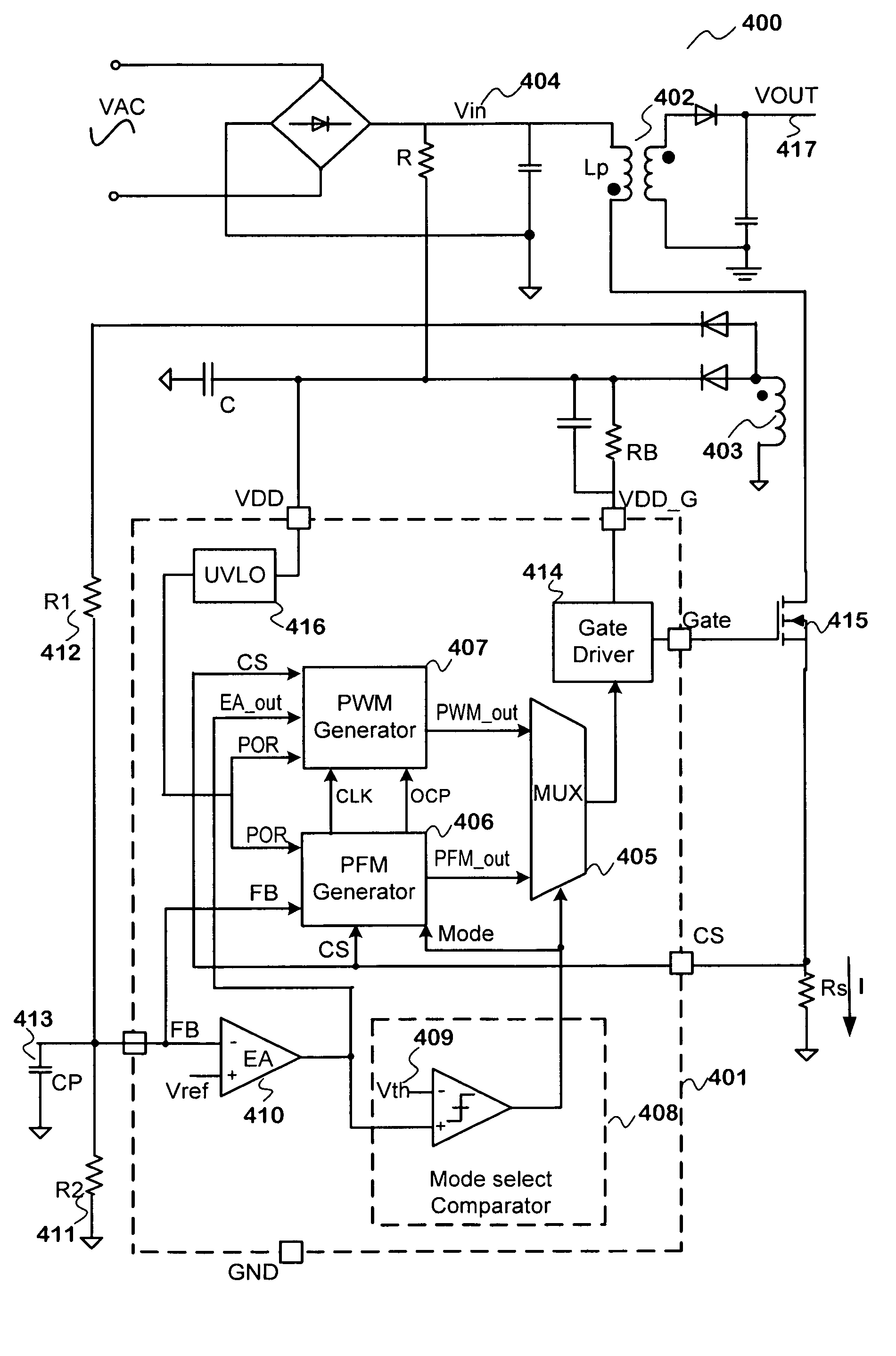
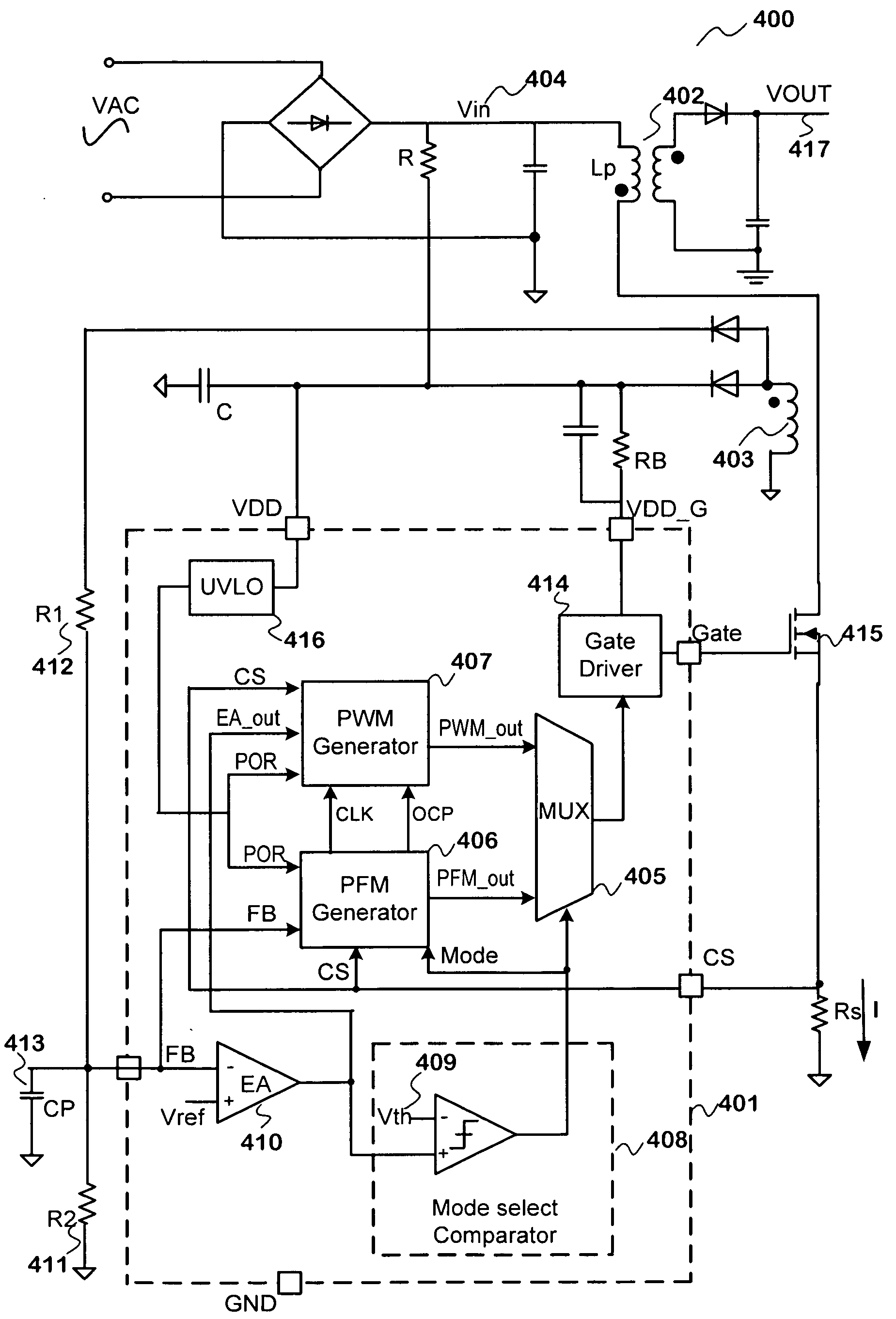
Method and system for efficient power control with multiple modes. According to an embodiment, the present invention provides a power system with selectable power modes. The power system includes a first terminal for outputting energy, and the first terminal is electrically coupled to a load. The system also includes a pulse-frequency modulation (PFM) component that is configured to adjust a pulse frequency based on the load. The system additionally includes a pulse-width modulation (PWM) component that is configured to adjust a pulse width based on the load. The system further includes a switch that is electrically coupled to the first terminal. Also, the system includes a control component, the control component being configured to provide a control signal that is capable of causing the switch to be turned on or off. The control signal is associated with an output of the PWM component and the pulse width if an output is greater than a predetermined value. The control signal is associated with an output of the PFM component and the pulse frequency if an output is lower than a predetermined value.
Owner:ON BRIGHT ELECTRONICS SHANGHAI
Method and system for efficient power control with multiple modes
InactiveUS20090206814A1Improve performanceImprove stabilityEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionEffective powerPower mode
Method and system for efficient power control with multiple modes. According to an embodiment, the present invention provides a power system with selectable power modes. The power system includes a first terminal for outputting energy, and the first terminal is electrically coupled to a load. The system also includes a pulse-frequency modulation (PFM) component that is configured to adjust a pulse frequency based on the load. The system additionally includes a pulse-width modulation (PWM) component that is configured to adjust a pulse width based on the load. The system further includes a switch that is electrically coupled to the first terminal. Also, the system includes a control component, the control component being configured to provide a control signal that is capable of causing the switch to be turned on or off. The control signal is associated with an output of the PWM component and the pulse width if an output is greater than a predetermined value. The control signal is associated with an output of the PFM component and the pulse frequency if an output is lower than a predetermined value.
Owner:ON BRIGHT ELECTRONICS SHANGHAI
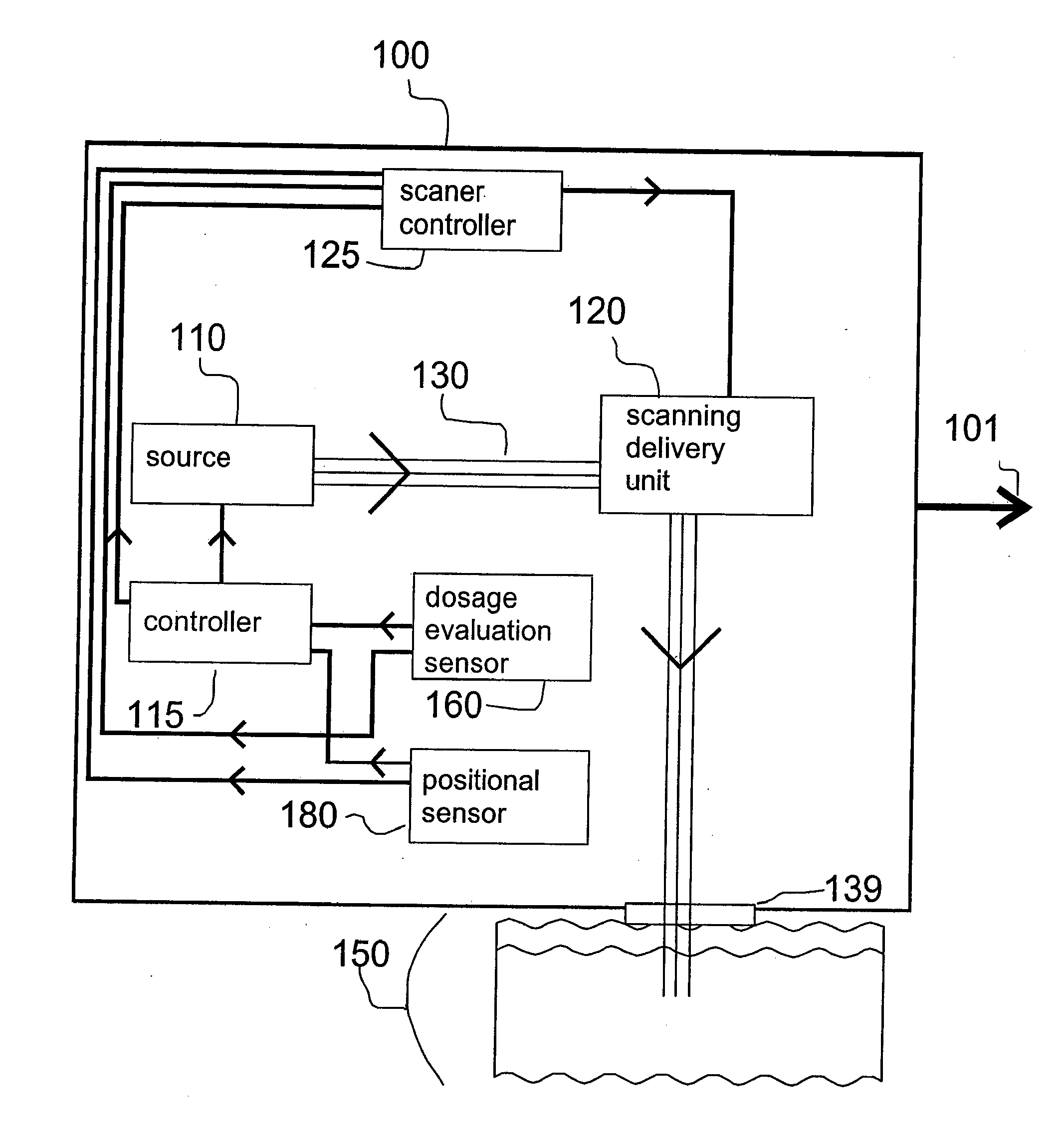
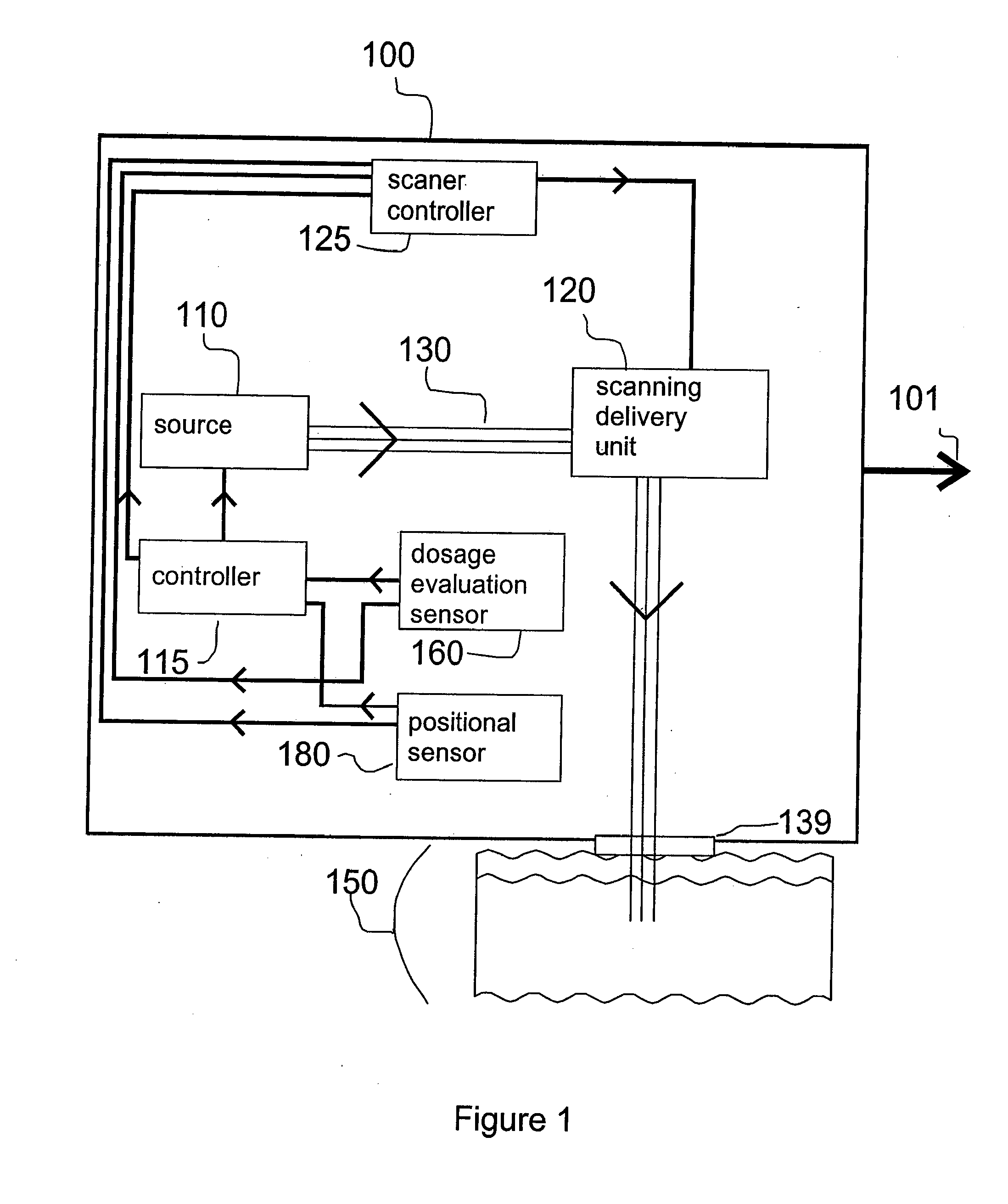
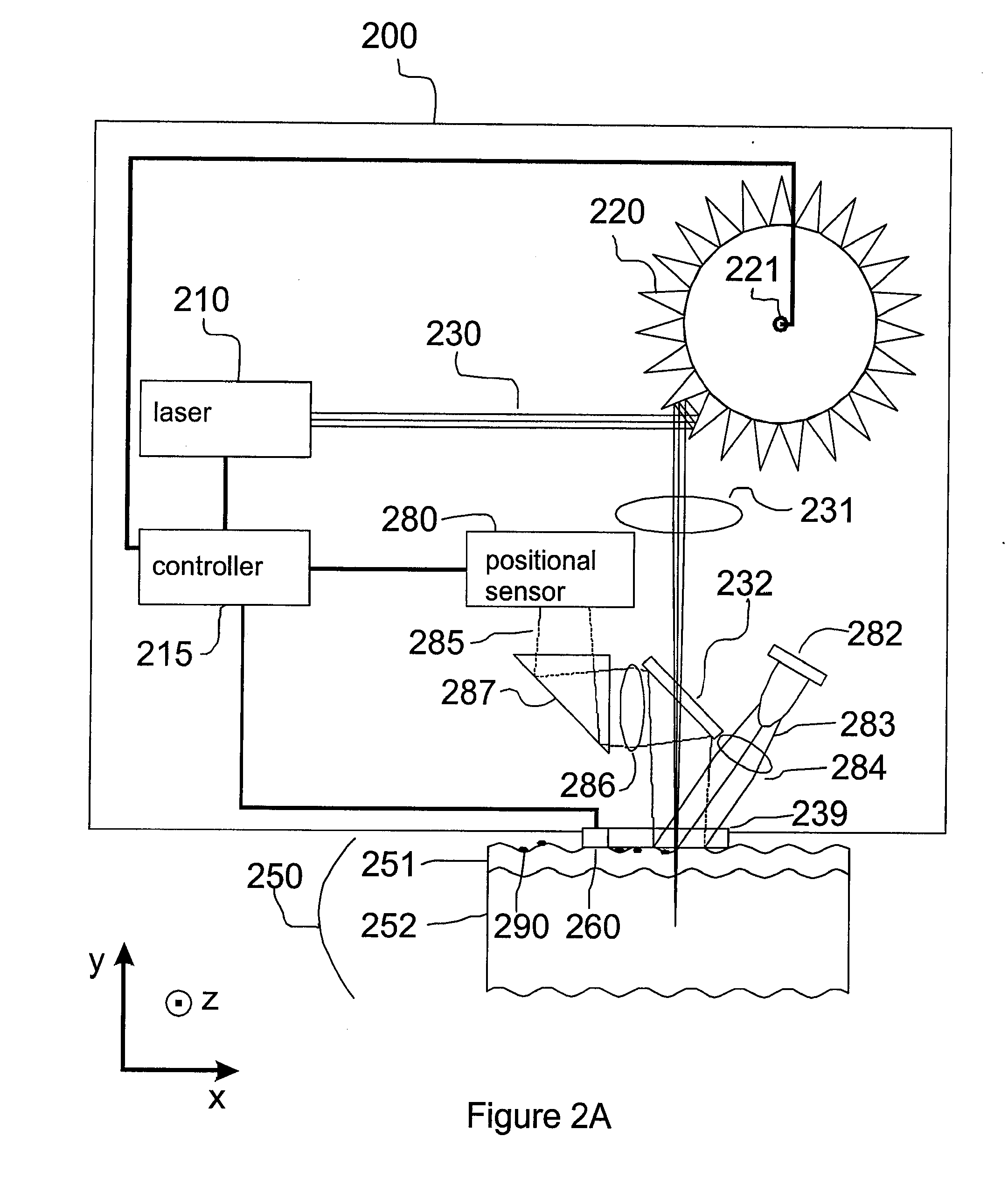
Method and Apparatus for Monitoring and Controlling Thermally Induced Tissue Treatment
InactiveUS20070093797A1Reduce treatment intensityIncrease in sizeElectrotherapyDiagnosticsEngineeringBiological activation
A method and apparatus for thermal treatment of tissue by irradiating the skin with electromagnetic energy is disclosed. Sources of electromagnetic energy include radio frequency (RF) generators, lasers, and flashlamps. The apparatus includes either a positional sensor or a dosage evaluation sensor, or both types of sensors. These sensors provide feedback to a controller. The controller may control the electromagnetic source parameters, the electromagnetic source activation, and / or the sensor measurement parameters. An additional scanning delivery unit may be operably coupled to the controller or to the sensors to provide a controlled distribution of electromagnetic energy to the target region of the skin. The use of positional measurement sensors and dosage evaluation sensors permits the controller to automatically determine the proper electromagnetic source parameters including, for example, pulse timing and pulse frequency.
Owner:RELIANT TECH INC
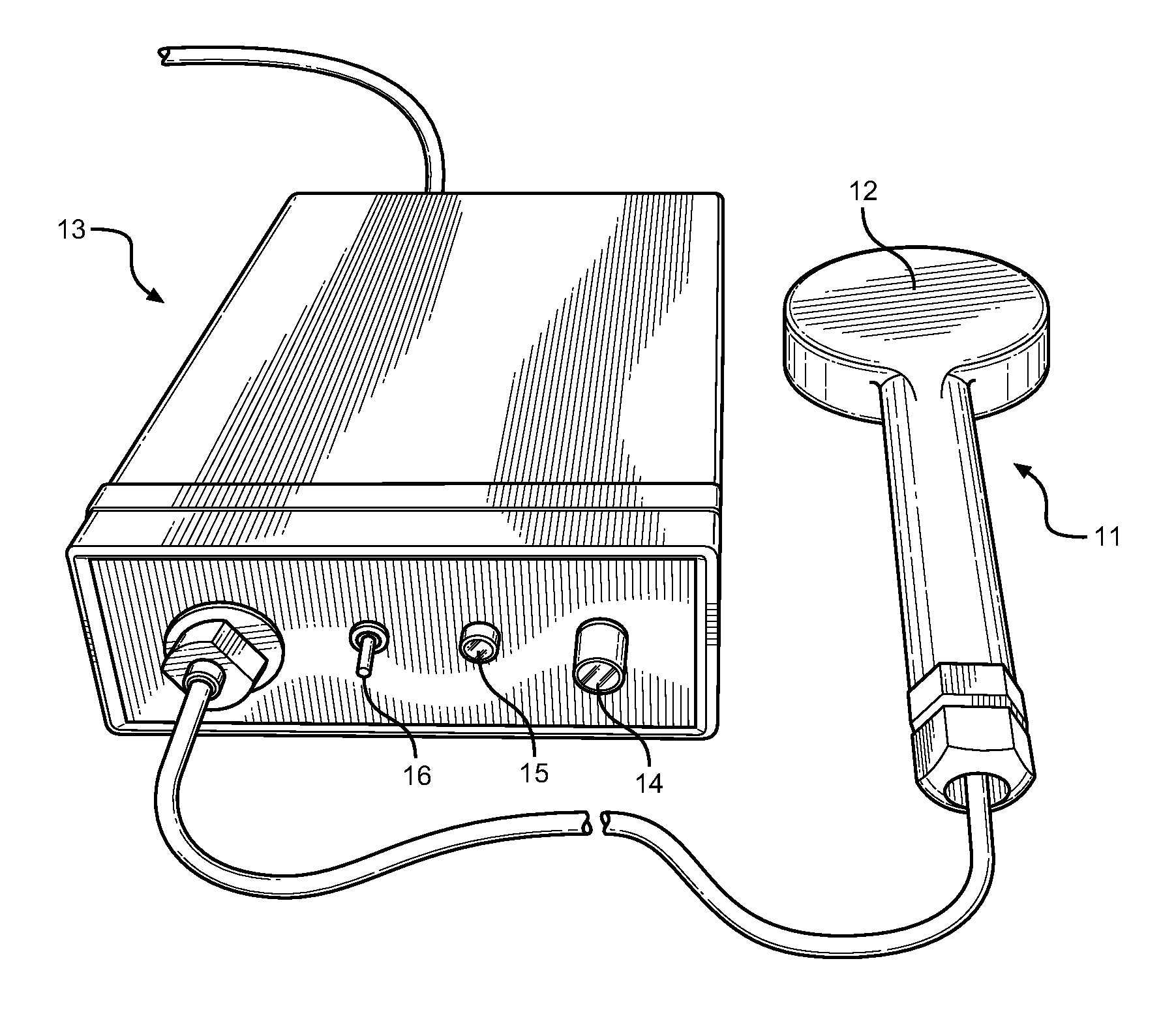
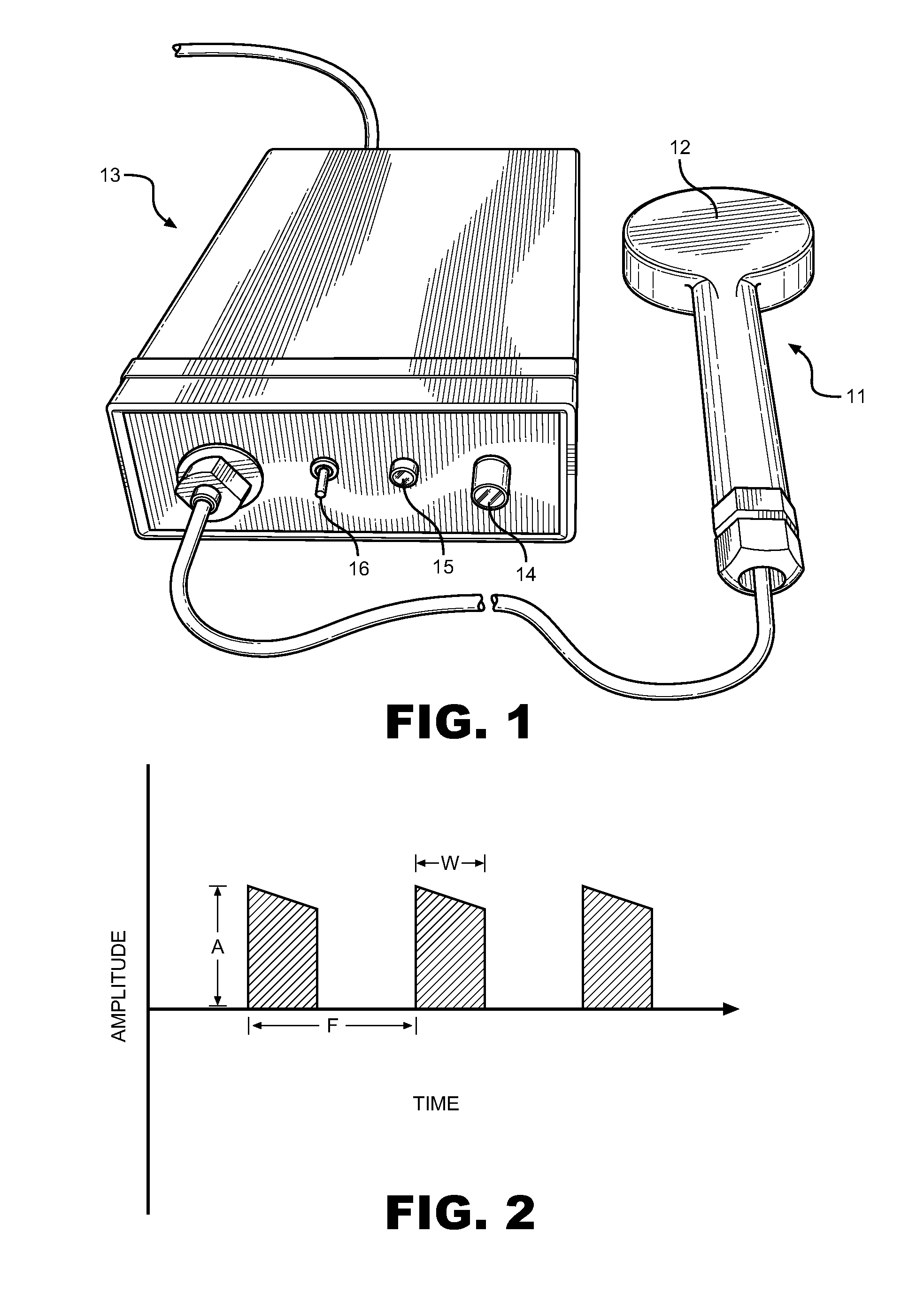
Pulsed Magnetic Therapy Device
InactiveUS20110263925A1Good for healthFunction increaseElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsDiseaseHigh energy
A device for treating diseases and chronic ailments of the human body by inducing powerful, short duration magnetic pulses in close proximity to a region of the body. The device comprises an electromagnetic coil or inductor energized by an electric circuit and a power source, pulsed between 1 and 25 pulses per second for therapeutic means and use as an alternative medical treatment. The device comprises an electric circuit that transmits pulsating current to an induction coil placed within a handheld stylus device for introducing a high energy, pulsed magnetic field to target locations on the body. The stylus is placed against the human body and introduces the pulsating magnetic field into and through body tissue, bone and the bloodstream. The stylus is completely noninvasive and provides a means to direct magnetic energy to a specific part of the body. The device is an advancement in the art, and one that provides increased magnetic energy and pulse frequency without the use of Xenon flash tubes that consume large quantities of power.
Owner:BRATTON CHARLES
Therapeutic methods using electromagnetic radiation
This invention provides methods for treating a variety of disorders using localized electromagnetic radiation directed at excitable tissues, including nerves, muscles and blood vessels. By controlling the wavelength, the wavelength bandpass, pulse duration, intensity, pulse frequency, and / or variations of those characteristics over time, and by selecting sites of exposure to electromagnetic radiation, improvements in the function of different tissues and organs can be provided. By monitoring physiological variables such as muscle tone and activity, temperature gradients, surface electromyography, blood flow and others, the practitioner can optimize a therapeutic regimen suited for the individual patient.
Owner:PHOTOMED TECH
System and method for multiple mode flexible excitation and acoustic chaos in sonic infrared imaging
ActiveUS20040089812A1Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wave generationThermal energyCamera image
A defect detection system for thermally imaging a structure that has been energized by a sound energy. The system includes a transducer that couples a sound signal into the structure, where the sound signal causes defects in the structure to heat up. In one embodiment, the sound signal has one or more frequencies that are at or near an eigen-mode of the structure. In another embodiment, an on-linear coupling material is positioned between the transducer and the structure to couple the sound energy from the transducer to the structure. A predetermined force is applied to the transducer and a pulse duration and a pulse frequency of the sound signal are selected so that the sound energy induces acoustic chaos in the structure, thus generating increased thermal energy. A thermal imaging camera images the structure when it is heated by the sound signal.
Owner:WAYNE STATE UNIV +1
Therapeutic methods using electromagnetic radiation
InactiveUS7150710B2High transparencyFunction increaseElectrotherapyPoint-like light sourceDiseaseElectromagnetic radiation
This invention provides methods for treating a variety of disorders using electromagnetic radiation directed at excitable tissues, including nerves, muscles and blood vessels. By controlling the wavelength, the wavelength bandpass, pulse duration, intensity, pulse frequency, and / or variations of those characteristics over time, and by selecting sites of exposure to electromagnetic radiation, improvements in the function of different tissues and organs can be provided. By monitoring physiological variables such as muscle tone and activity, temperature gradients, surface electromyography, blood flow and others, the practitioner can optimize a therapeutic regimen suited for the individual patient.
Owner:PHOTOMED TECH
Direct digital synthesizer for reference frequency generation
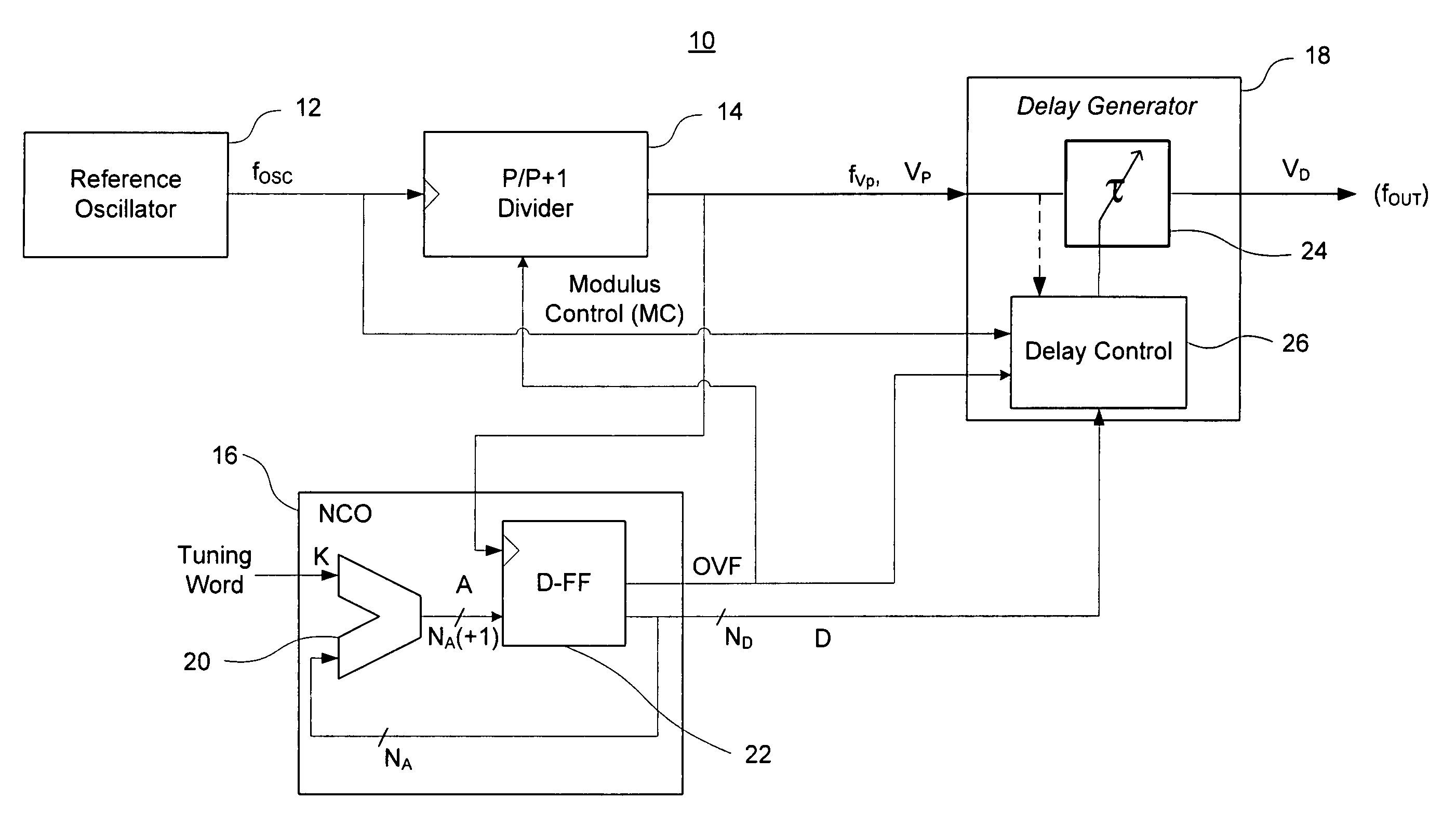
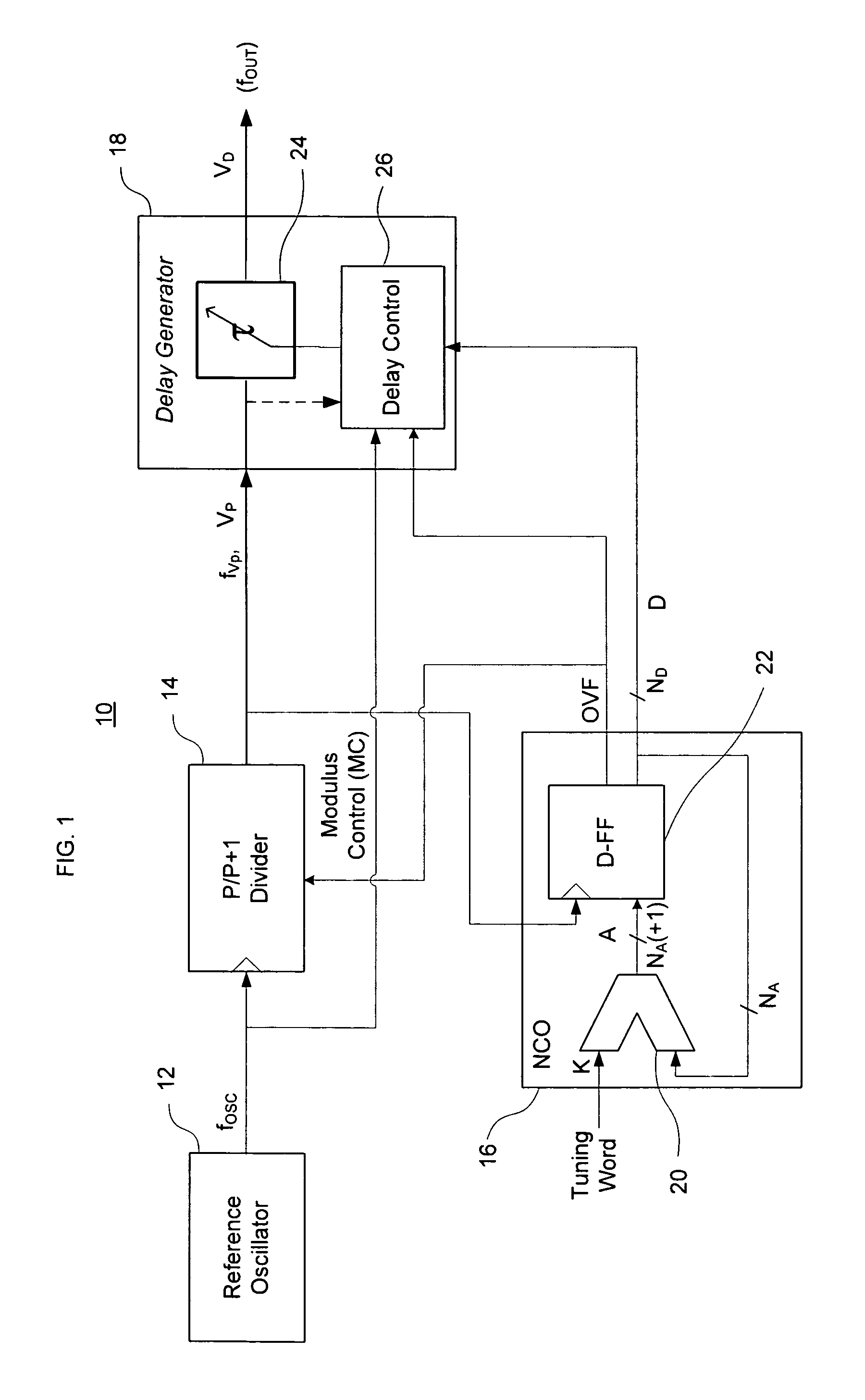
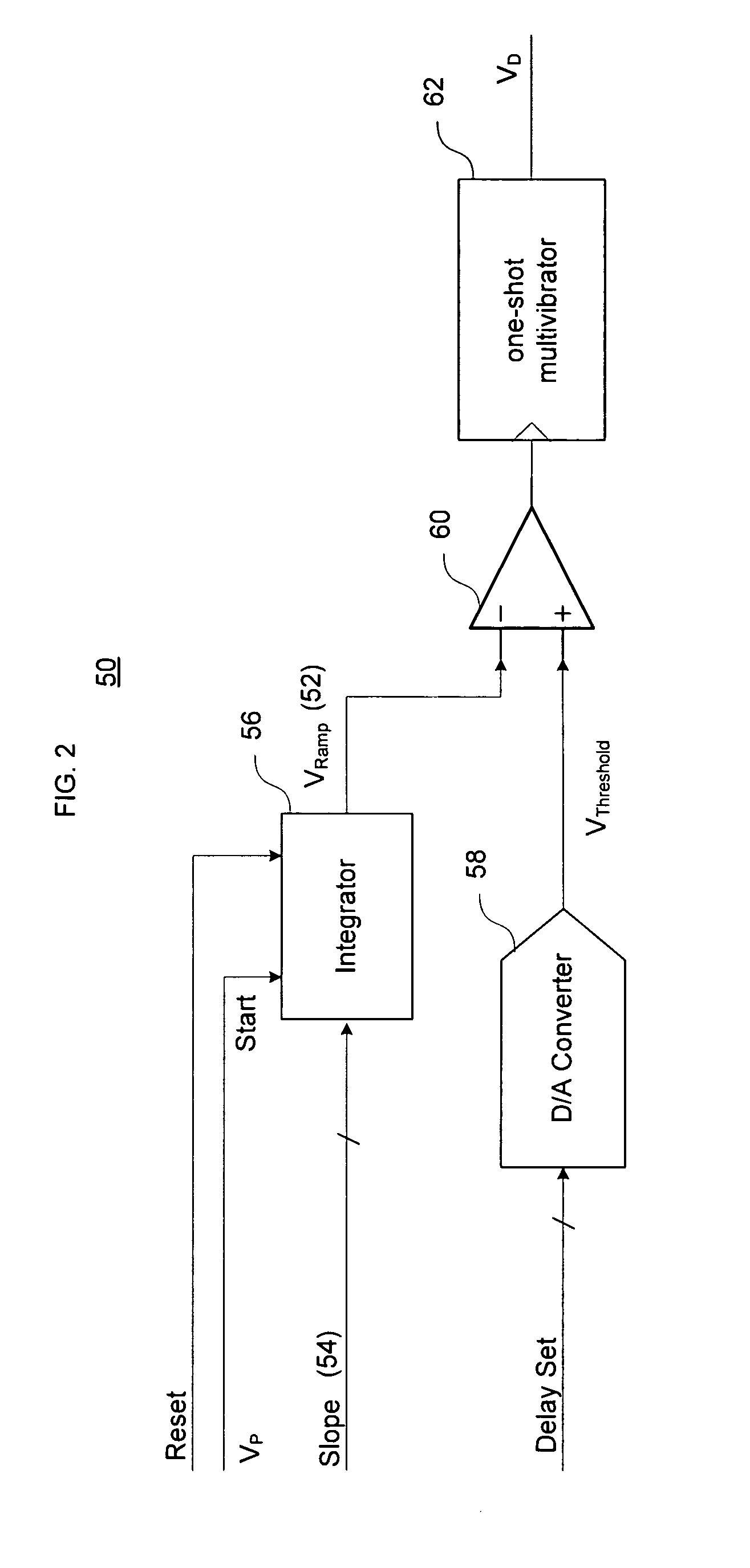
InactiveUS7724097B2Improve noiseImprove performancePulse automatic controlCounting chain pulse countersFrequency generationDigital controlled oscillator
A direct digital frequency synthesizer having a multi-modulus divider, a numerically controlled oscillator and a programmable delay generator. The multi-modulus divider receives an input clock having an input pulse frequency fosc and outputs some integer fraction of those pulses at an instantaneous frequency fVp that is some integer fraction (1 / P) of the input frequency. The multi-modulus divider selects between at least two ratios of P (1 / P or 1 / P+1) in response to a signal from the numerically controlled oscillator. The numerically controlled oscillator receives a value which is the accumulator increment (i.e. the number of divided pulse edges) required before an overflow occurs that causes the multi-modulus divider to change divider ratios in response to receiving an overflow signal. The numerically controlled oscillator also outputs both the overflow signal and a delay signal to the delay generator that further controls the frequency of the multi-modulus divider output signal (Vp) to provide an output signal (VD) with an fout that has improved phase and timing jitter performance over prior art direct digital frequency synthesizer architectures.
Owner:CYMATICS LAB CORP
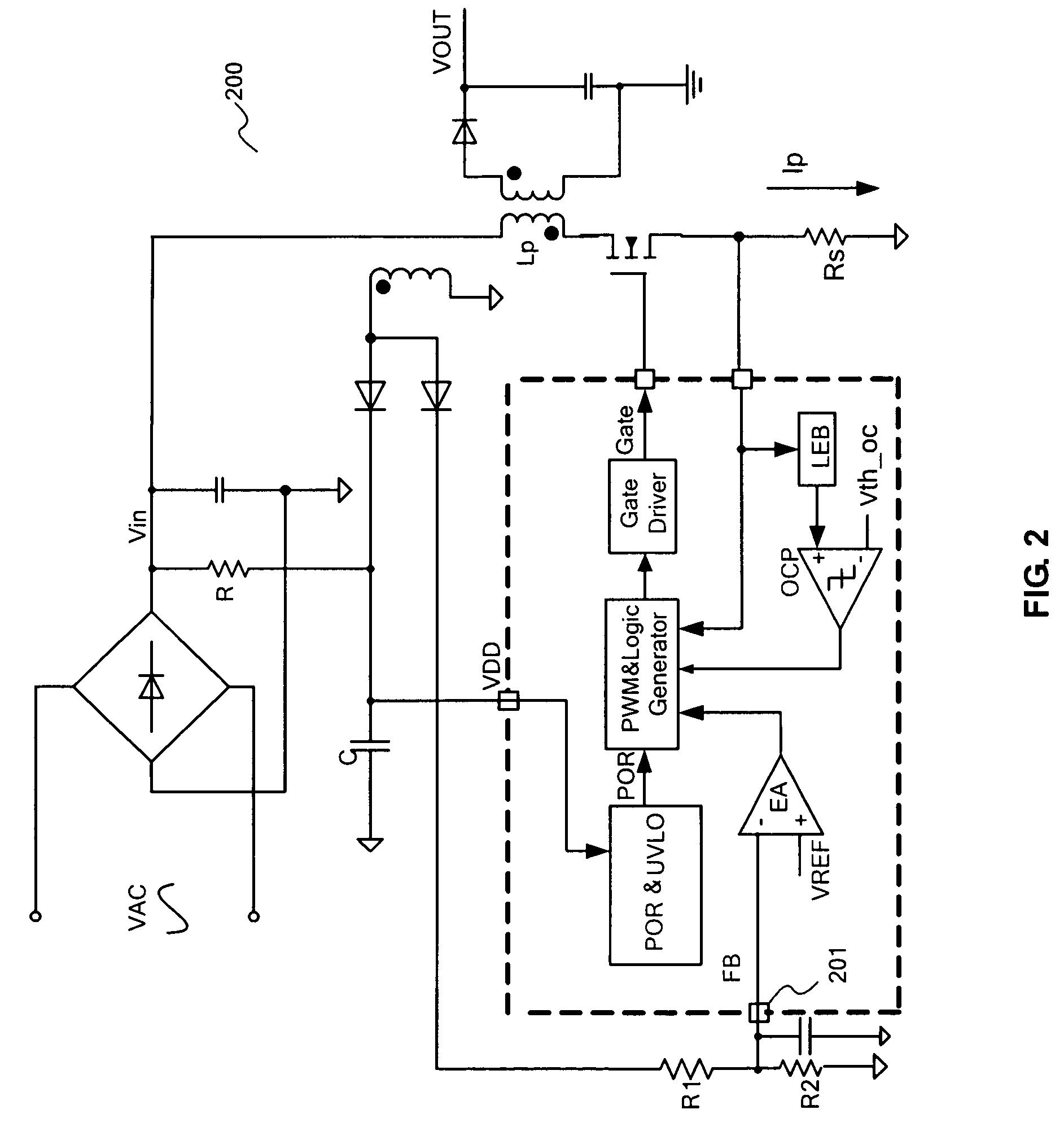
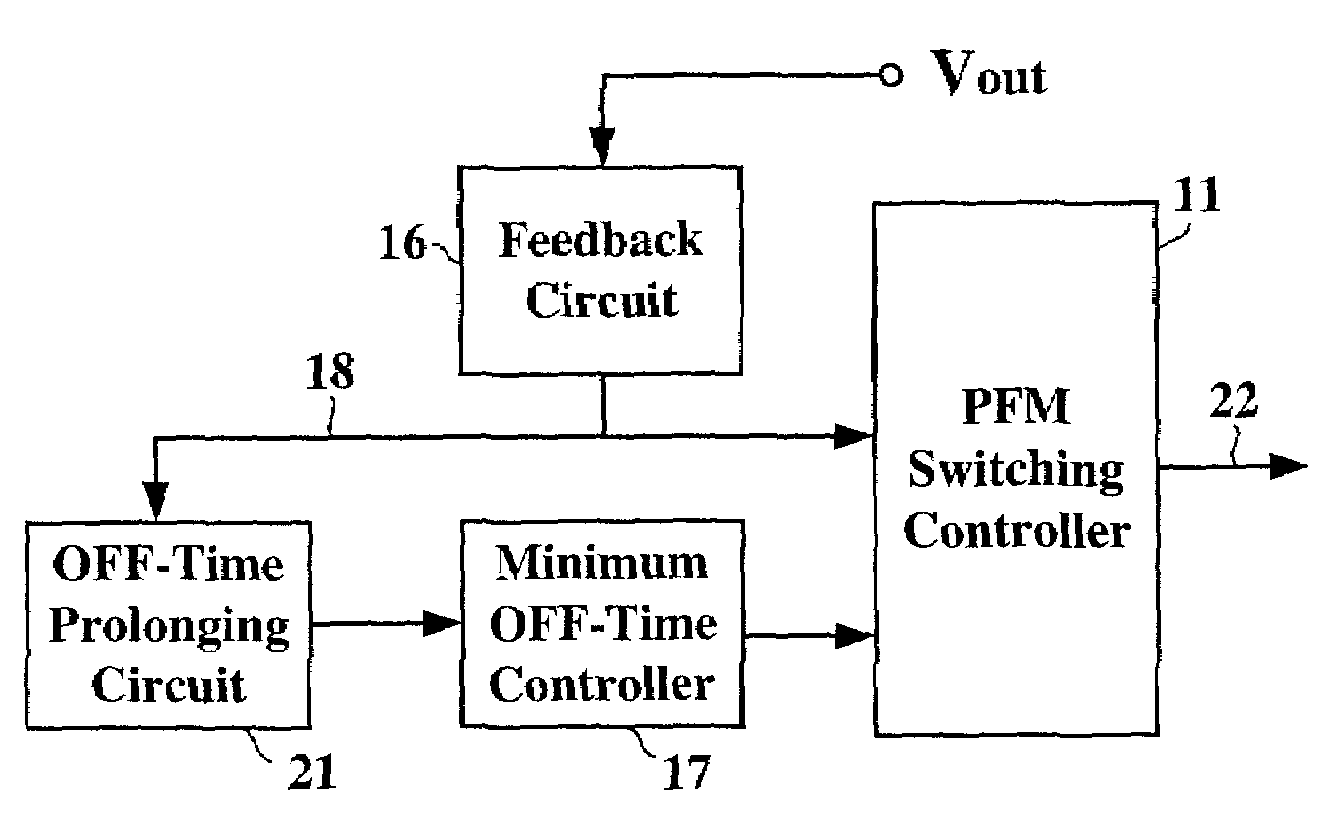
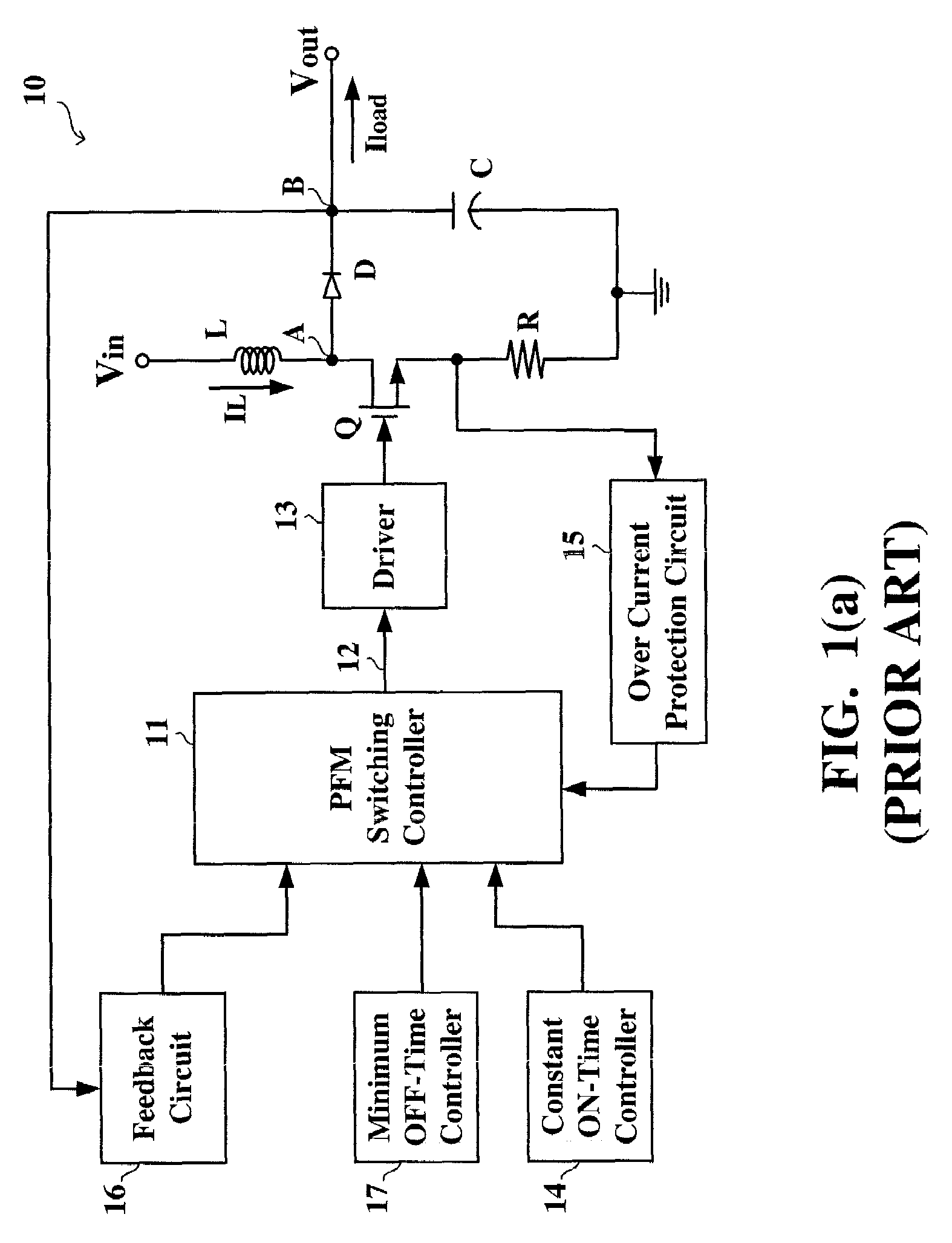
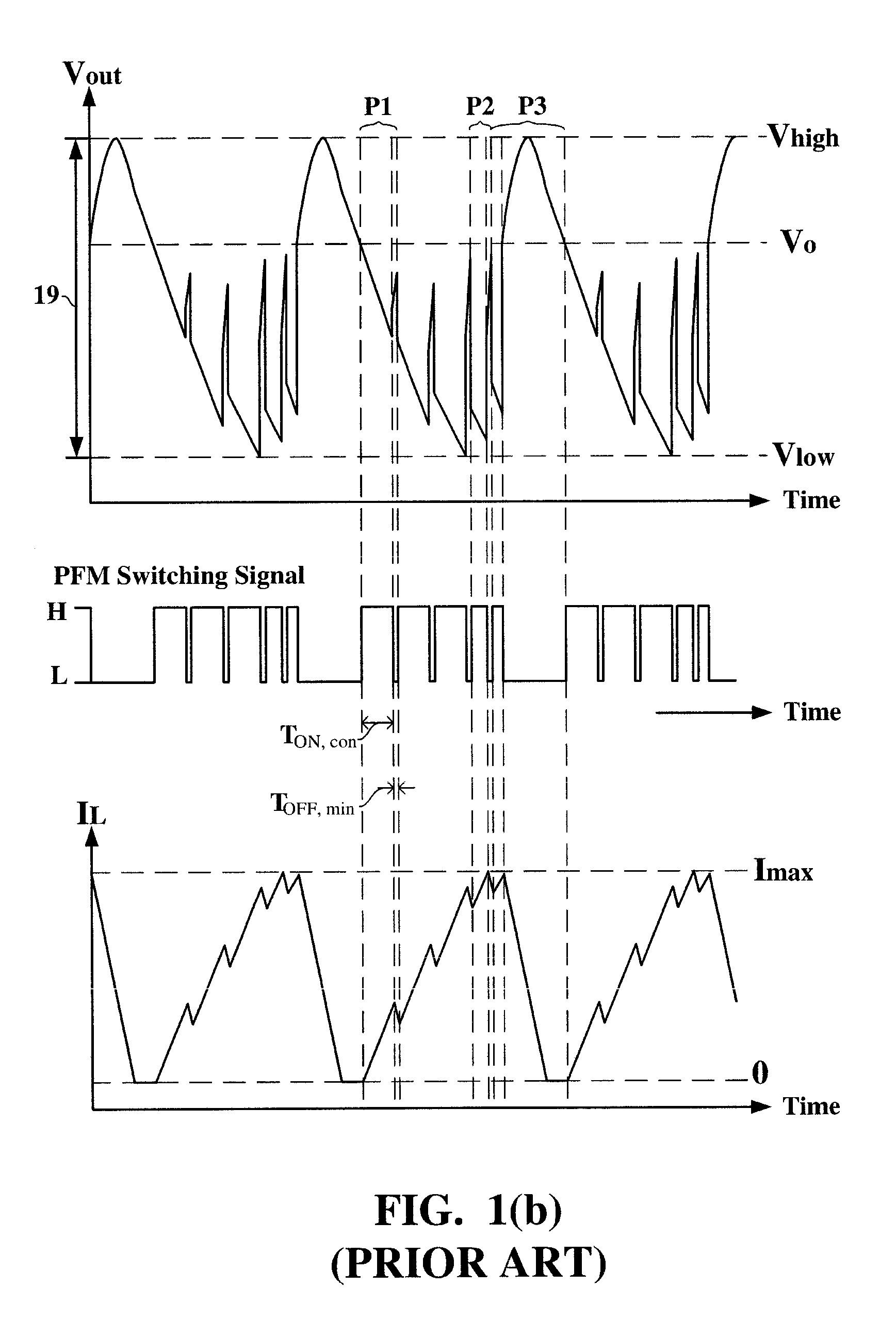
Pulse frequency modulated voltage regulator capable of prolonging a minimum off-time
ActiveUS6972548B2Reduce rippleProlonging a minimum OFF-timeElectric variable regulationPower conversion systemsTime extensionEngineering
In a pulse frequency modulated (PFM) voltage regulator, a PFM switching controller is provided to generate a PFM switching signal for converting a DC voltage source to an output voltage. A minimum OFF-time controller provides the PFM switching signal with a minimum OFF-time. In response to the output voltage, a feedback circuit generates a feedback signal. When the output voltage is lower than a predetermined target voltage, an OFF-time prolonging circuit prolongs the minimum OFF-time in response to the feedback signal. In other words, a time of delivering energy to a capacitor from an inductor may be prolonged by the OFF-time prolonging circuit. Therefore, a ripple of the output voltage is effectively reduced when the PFM voltage regulator is operated in a heavy loading condition.
Owner:GLOBAL MIXED MODE TECH
Droplet target delivery method for high pulse-rate laser-plasma extreme ultraviolet light source
InactiveUS6855943B2Radiation pyrometrySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInstabilityHigh pulse rate
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC +1
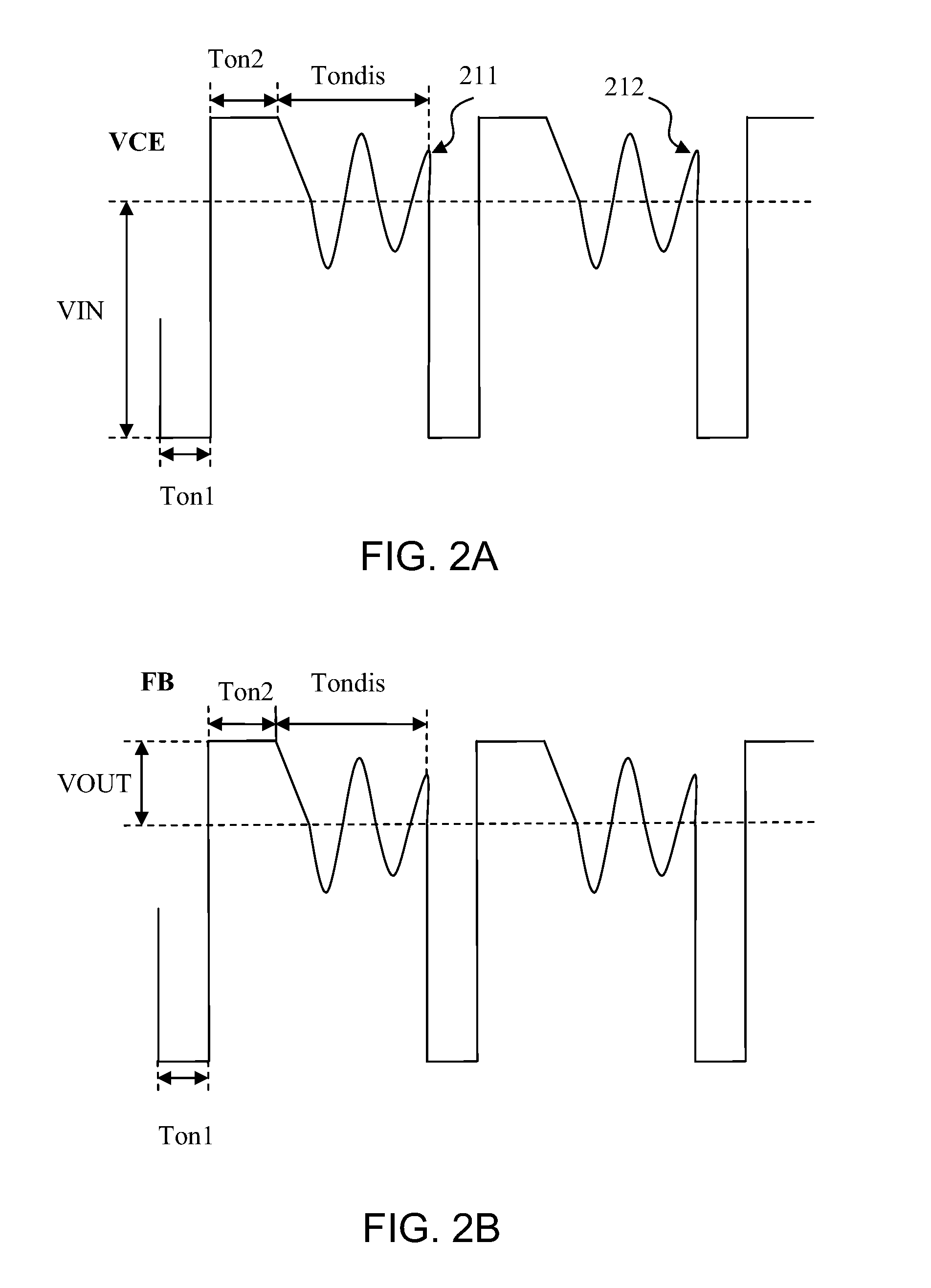
Method and system for pulse frequency modulated switching mode power supplies
ActiveUS20080310191A1Reduce conversion lossSolve the power is smallPulse generatorDc-dc conversionControl signalElectromagnetic interference
A pulse frequency modulation (PFM) controller for controlling a switching mode power supply. The controller includes an output terminal for providing a control signal to turn on and off a current in the power supply to regulate an output of the power supply. A first input terminal receives a feedback signal related to the output of the power supply, the feedback signal exhibiting a ringing waveform when the current in the power supply is turned off. The controller also includes a control circuit configured to provide the control signal in response to the feedback signal. The control signal is adapted to turn on the current in the power supply when the feedback signal is substantially at a valley of the ringing waveform of the feedback signal. In an embodiment, such a PFM controller can reduce turn-on transition loss in a power supply and provides frequency dithering to reduce electromagnetic interference.
Owner:BCD SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
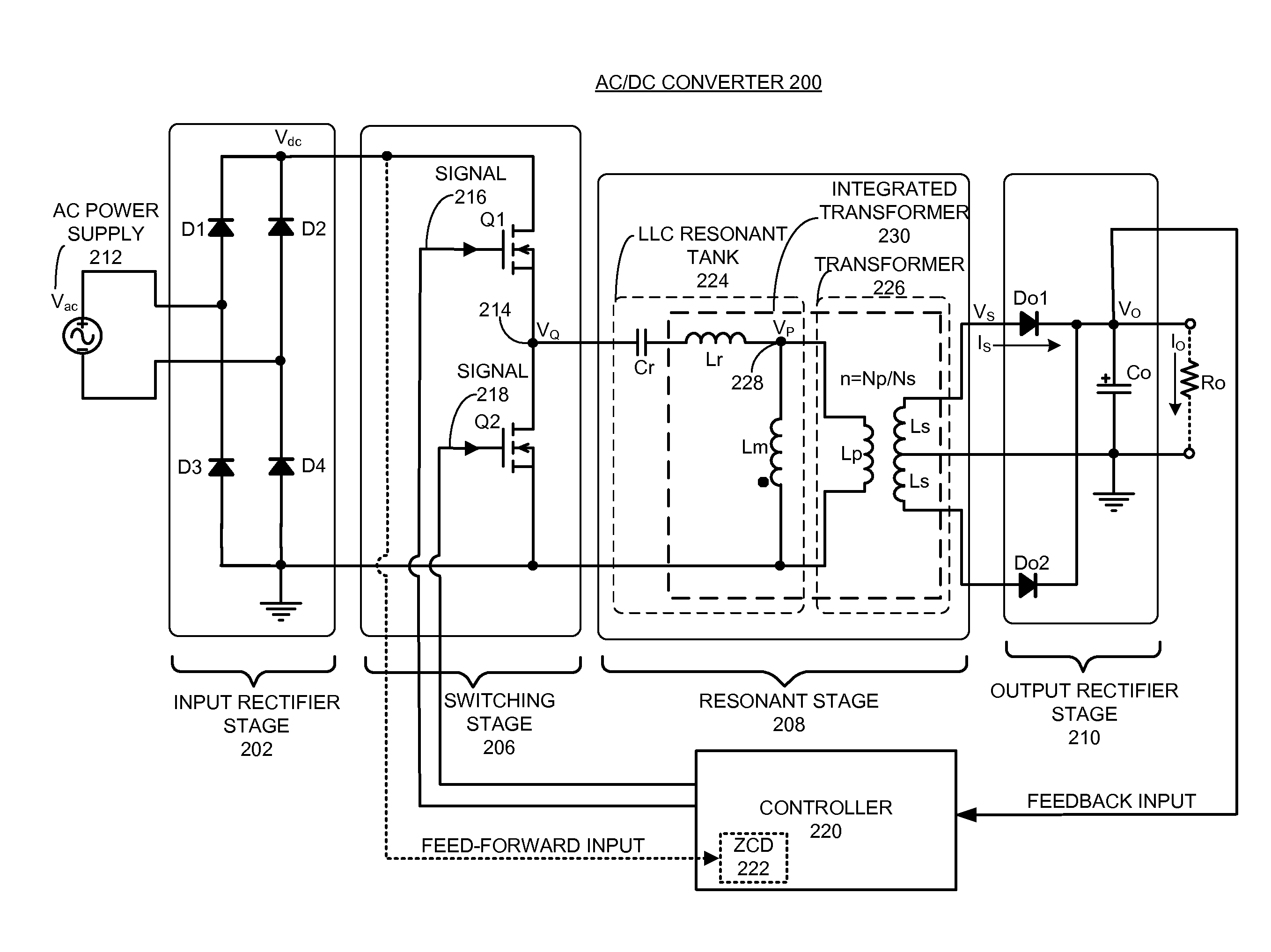
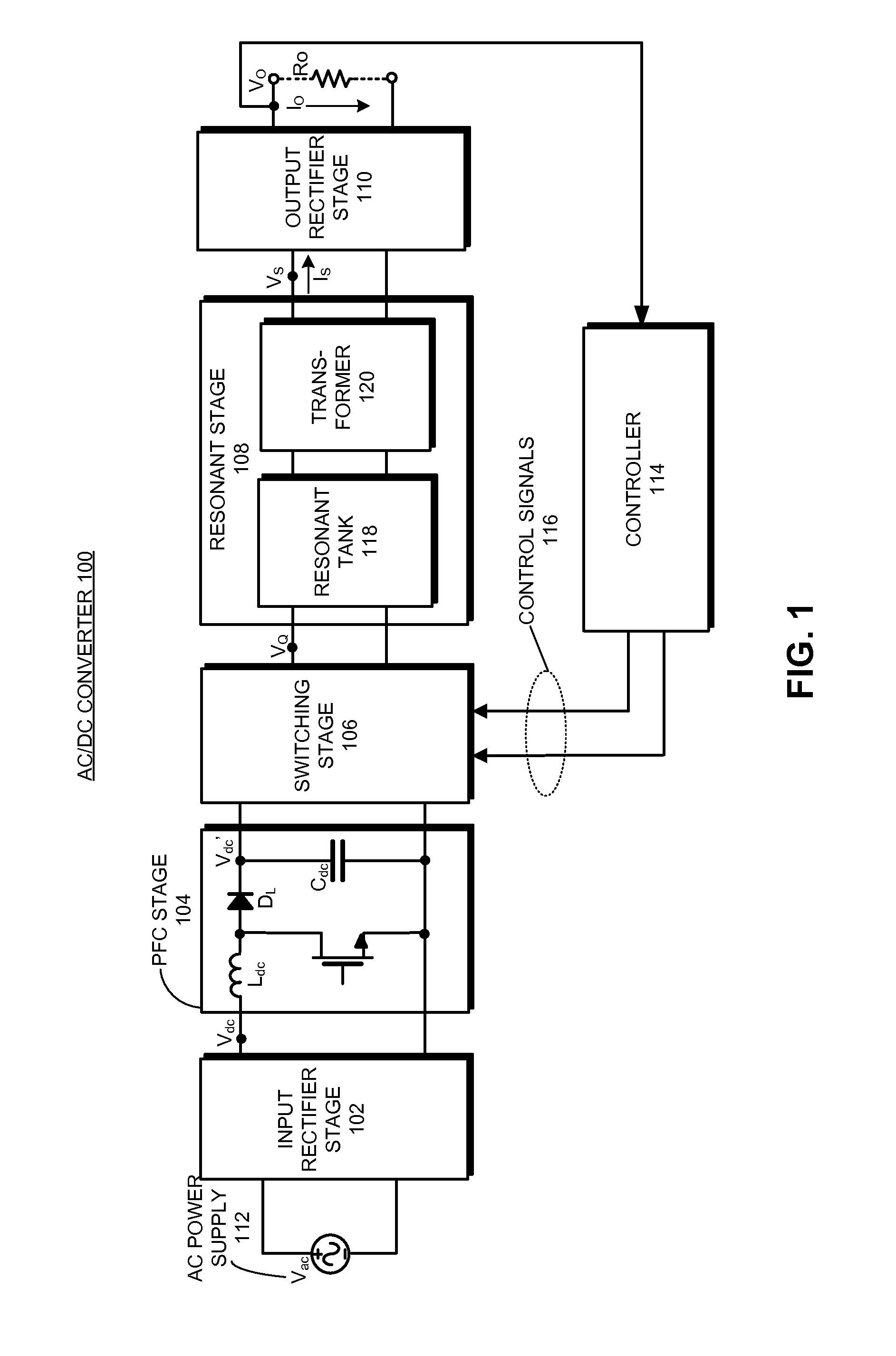
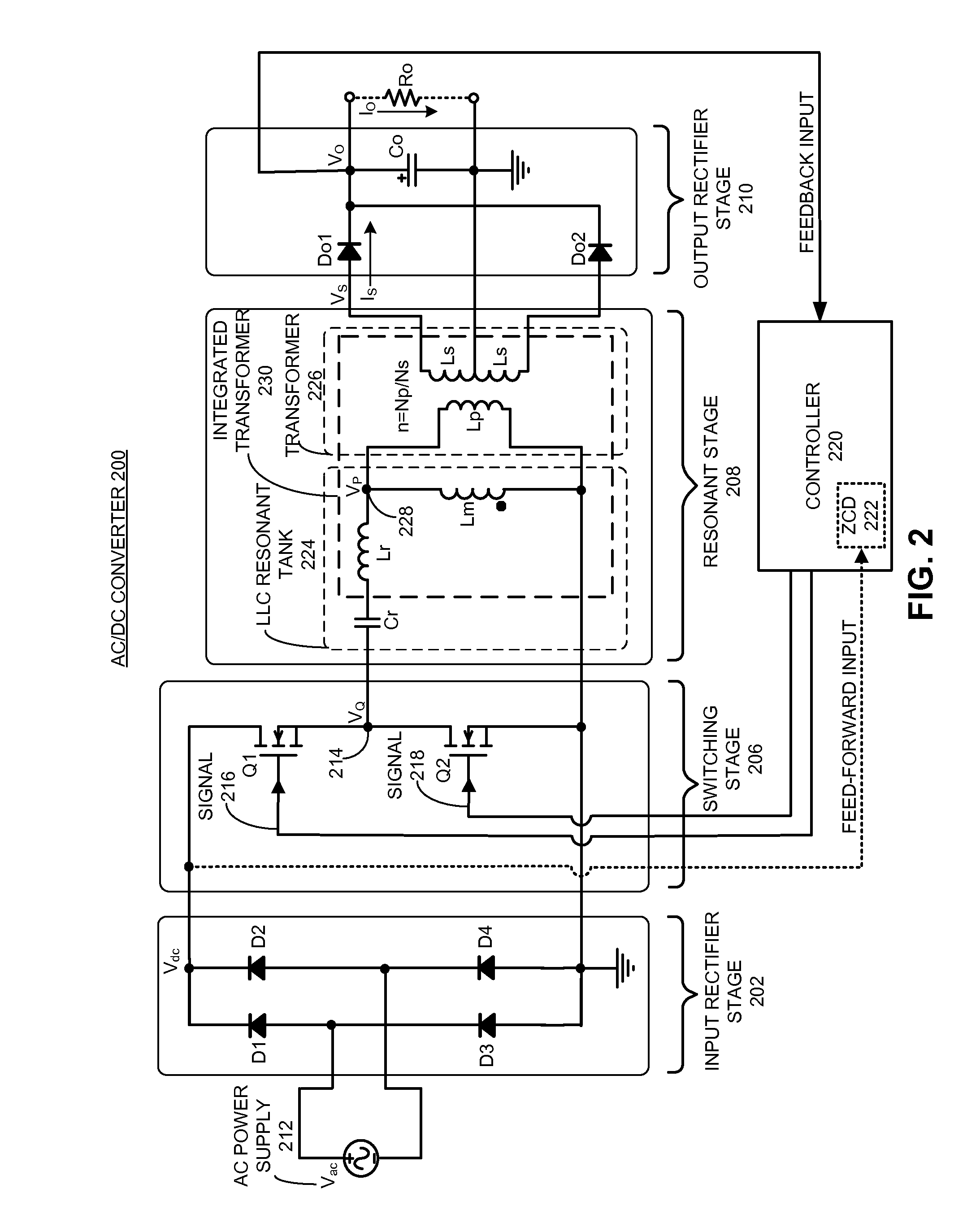
Hysteretic-mode pulse frequency modulated (hm-pfm) resonant ac to DC converter
InactiveUS20140160805A1Efficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionDirect couplingAc to dc converter
The disclosed embodiments provide an AC / DC power converter that converts an AC input voltage into a DC output voltage. This AC / DC power converter includes an input rectifier stage which rectifies an AC input voltage into a first rectified voltage. The AC / DC power converter also includes a switching resonant stage which is directly coupled to the output of the input rectifier stage. The switching resonant stage converts the rectified voltage into a first high frequency AC voltage of a first amplitude. This AC / DC power converter additionally includes a transformer which is coupled to the output of the switching resonant stage and is configured to down-convert the first high frequency AC voltage into a second high frequency AC voltage of a second amplitude. Furthermore, the AC / DC power converter includes an output rectifier stage which is coupled to the output of the transformer, wherein the output rectifier stage rectifies the second high frequency AC voltage into a DC output voltage.
Owner:APPLE INC
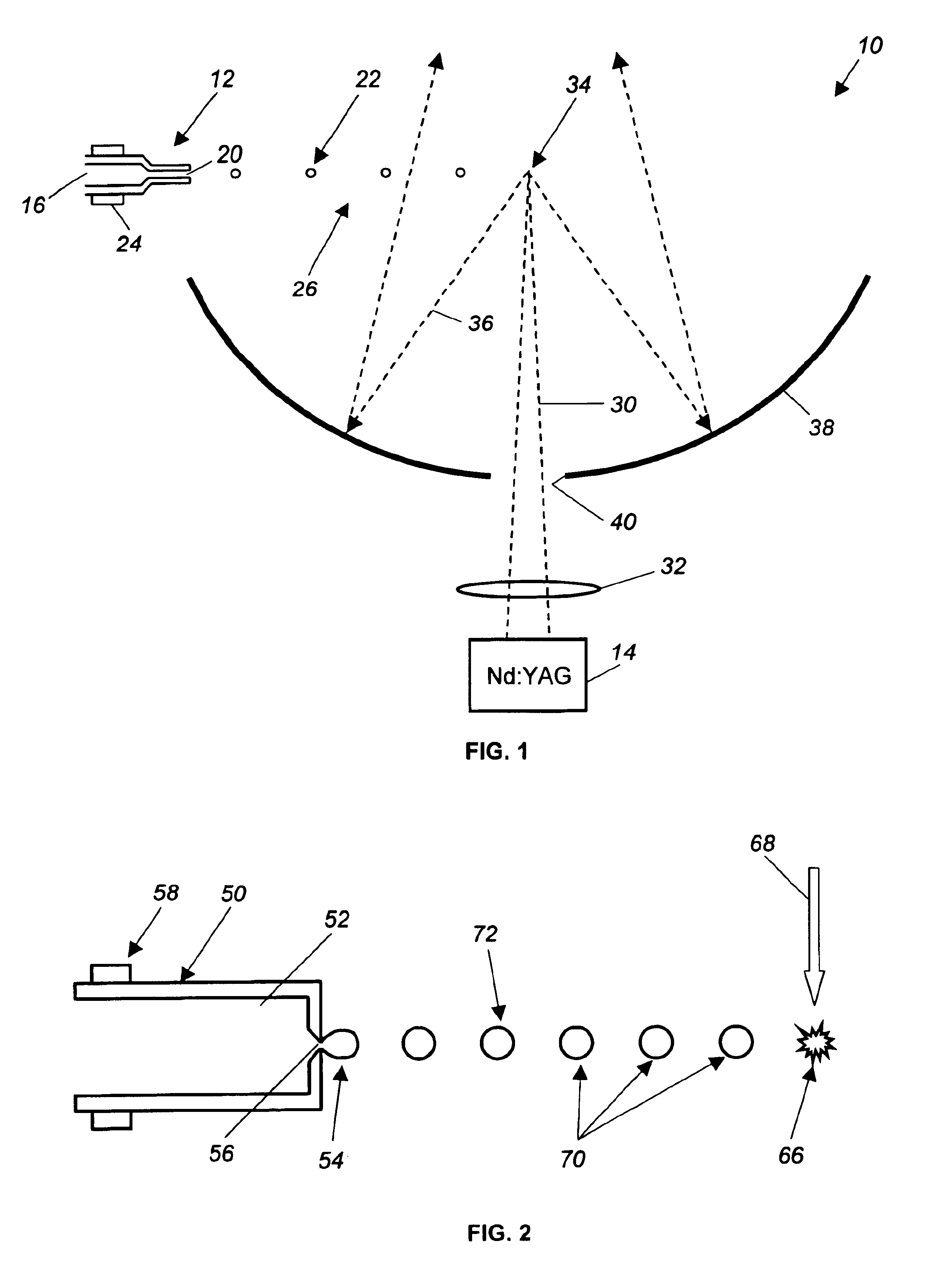
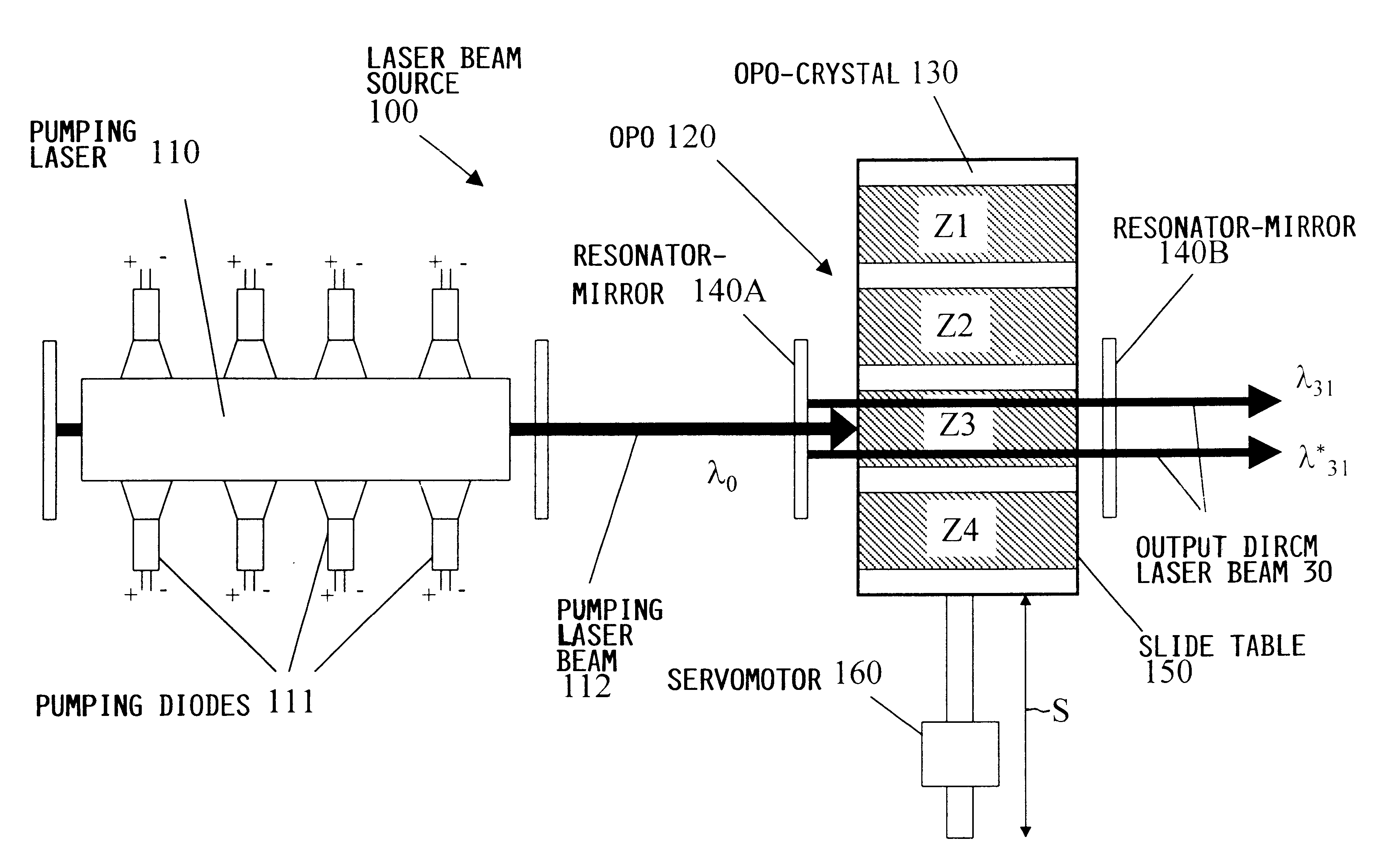
Laser beam source for a directional infrared countermeasures (DIRCM) weapon system
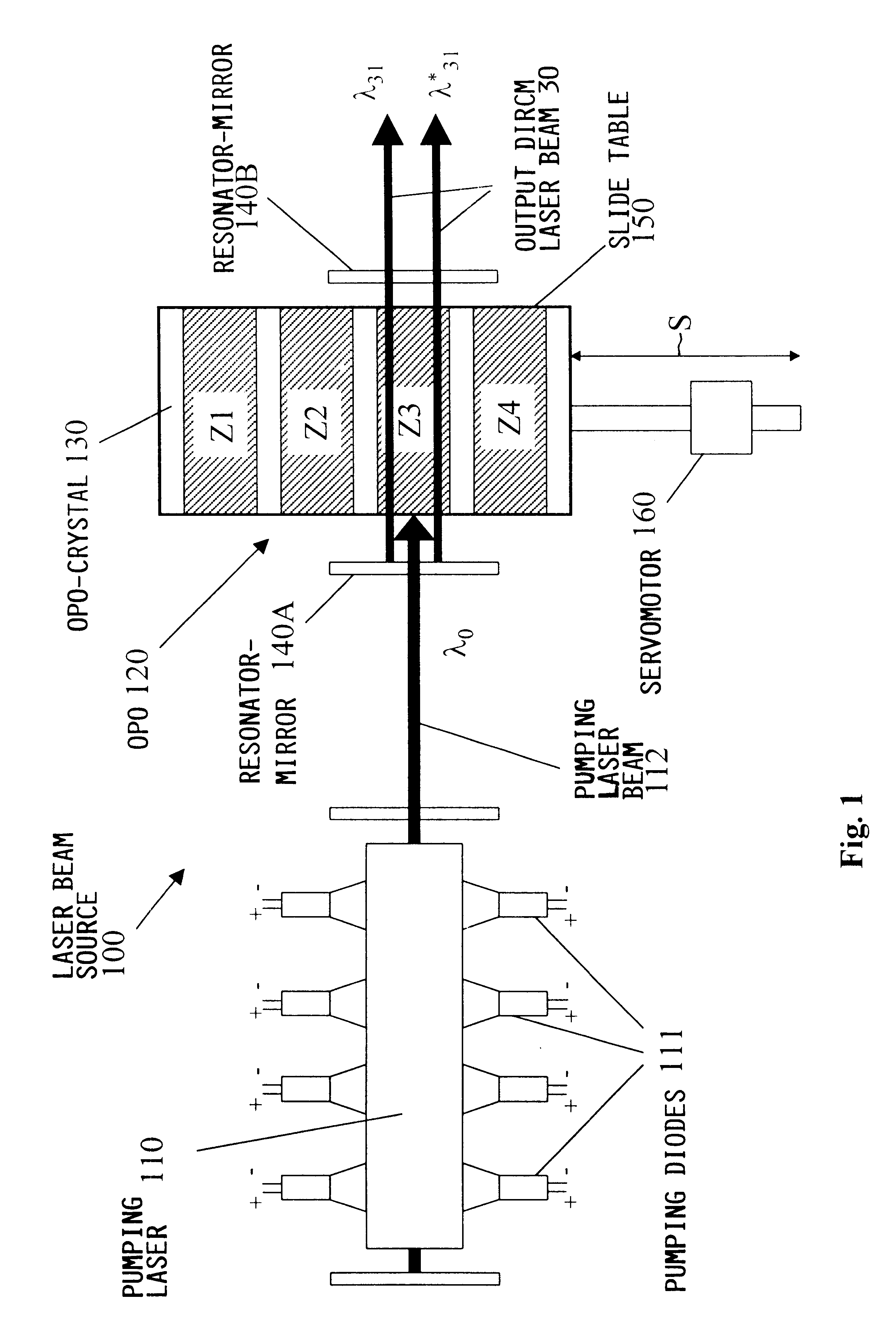
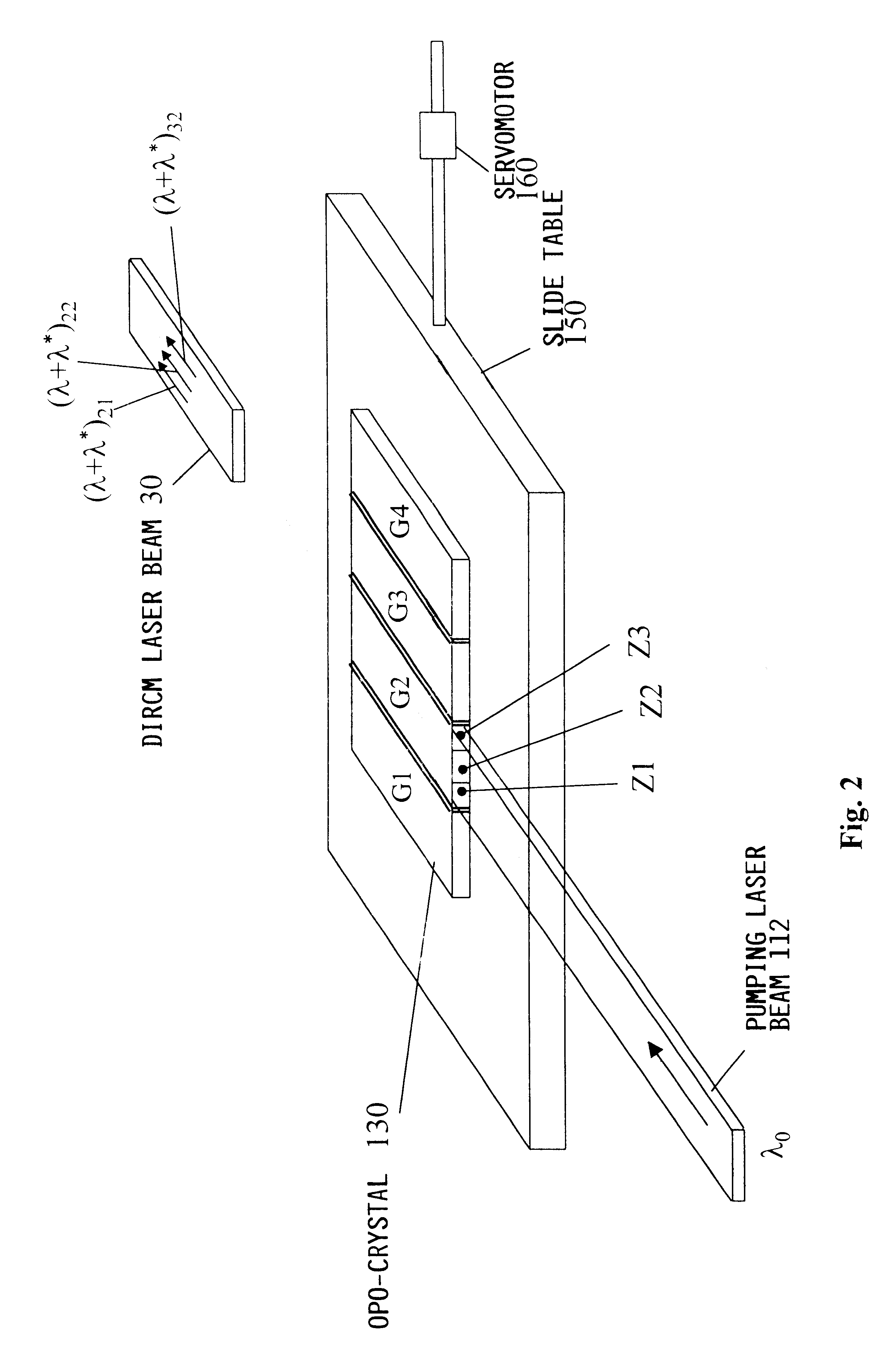
A laser beam source and an operating method thereof is provided for a directional infrared countermeasures (DIRCM) weapon system for defensively countering guided missiles having infrared seeking heads, by directing an infrared laser beam at the guided missile so as to disorient, saturate, or irreversibly destroy the IR detectors and circuitry arranged in the target seeking head. The power, pulse frequency and spectral composition of the laser beam is adjustable and selectable as required to adapt to any particular defensive engagement. To achieve this, the laser beam source comprises an Nd:YAG pumping laser and an optical parametric oscillator including an oscillator crystal arranged in a resonator cavity. The crystal includes a plurality of different periodically polarized crystal zones having different lattice constants. The adjacent zones can be grouped together into selectable crystal zone groups. The beam cross-section of the pumping laser beam corresponds to the cross-section of a single crystal zone or of a crystal zone group encompassing plural zones. The crystal is arranged on a slide table that is slidably displaceable by a servomotor, to move a selected crystal zone or group into the path of the pumping laser beam. Thereby the wavelength components and the relative intensities thereof of the output laser beam can easily be selectively adjusted.
Owner:EADS DEUT GMBH
Cylindrical bandstop filters for medical lead systems
InactiveUS7853325B2Avoid enteringMultiple-port networksAnti-noise capacitorsCapacitanceBand-stop filter
A one-piece cylindrical bandstop filter for medical lead systems incorporates parallel capacitive and inductive elements in a compact cylindrical configuration. The compact cylindrical configuration of the bandstop filter does not add significantly to the size or weight of the medical lead system. Preferably, the bandstop filters are of biocompatible materials or hermetically sealed in biocompatible containers. The parallel capacitive and inductive elements are placed in series with the medical lead system, and are selected so as to resonate at one or more selected frequencies, typically MRI pulsed frequencies.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
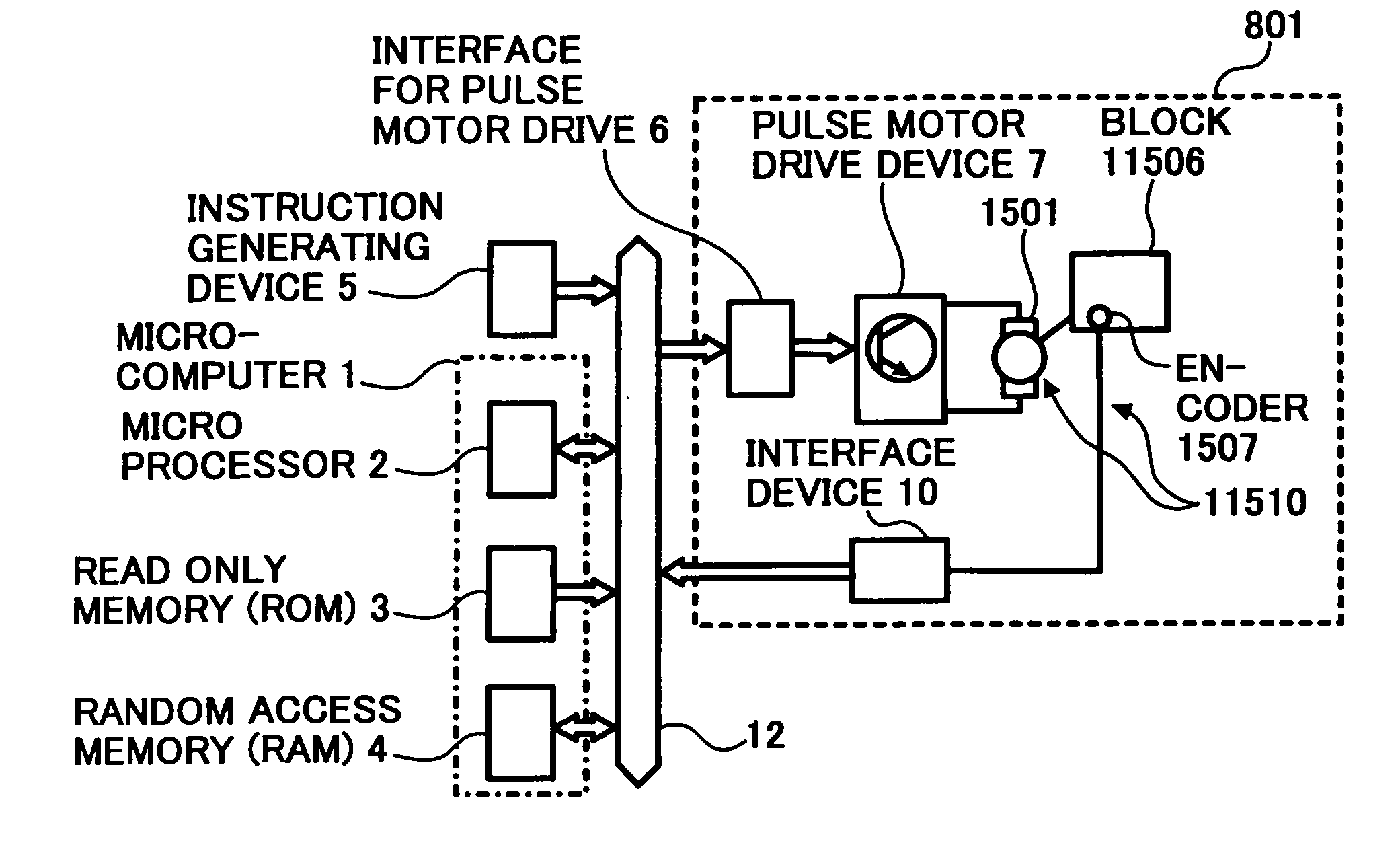
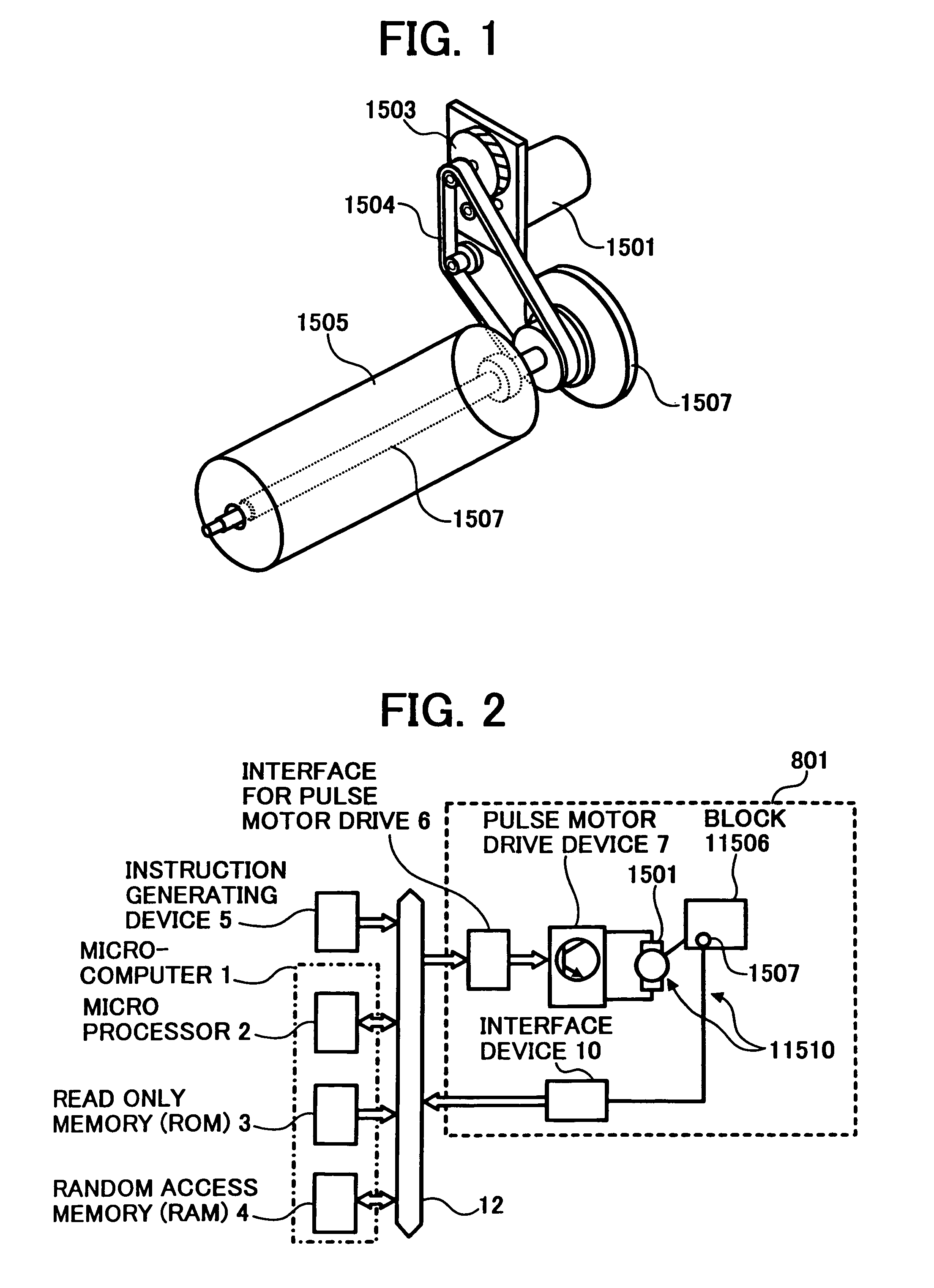
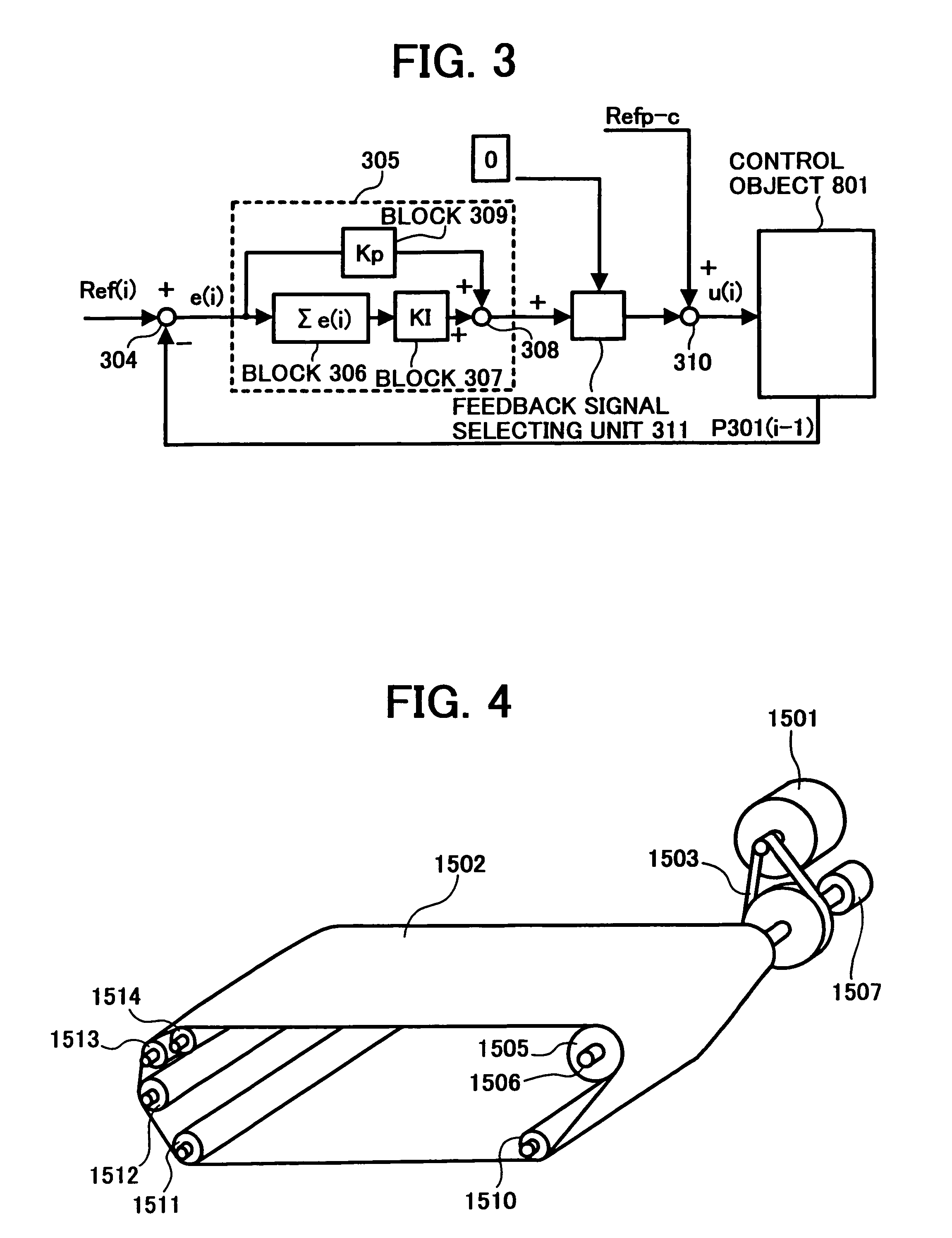
Drive control method, drive control device, belt apparatus, image forming apparatus, image reading apparatus, computer product
InactiveUS20050099153A1Smooth rotationGuaranteed uniform velocityAC motor controlDC motor speed/torque controlAngular velocityAngular displacement
Driving of a pulse motor is controlled in such a manner that a rotating body driven by the pulse motor rotates at a uniform angular velocity. Angular displacement of the rotating body is detected, a difference between a detection value of the angular displacement and a target value of angular displacement set in advance is calculated, and a drive pulse frequency of a drive pulse signal to be used for driving the pulse motor is calculated based on the difference and a reference drive pulse frequency. Whether the difference is added to the reference drive pulse can be selected.
Owner:RICOH KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com