Patents
Literature
4009 results about "Thin film solar cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
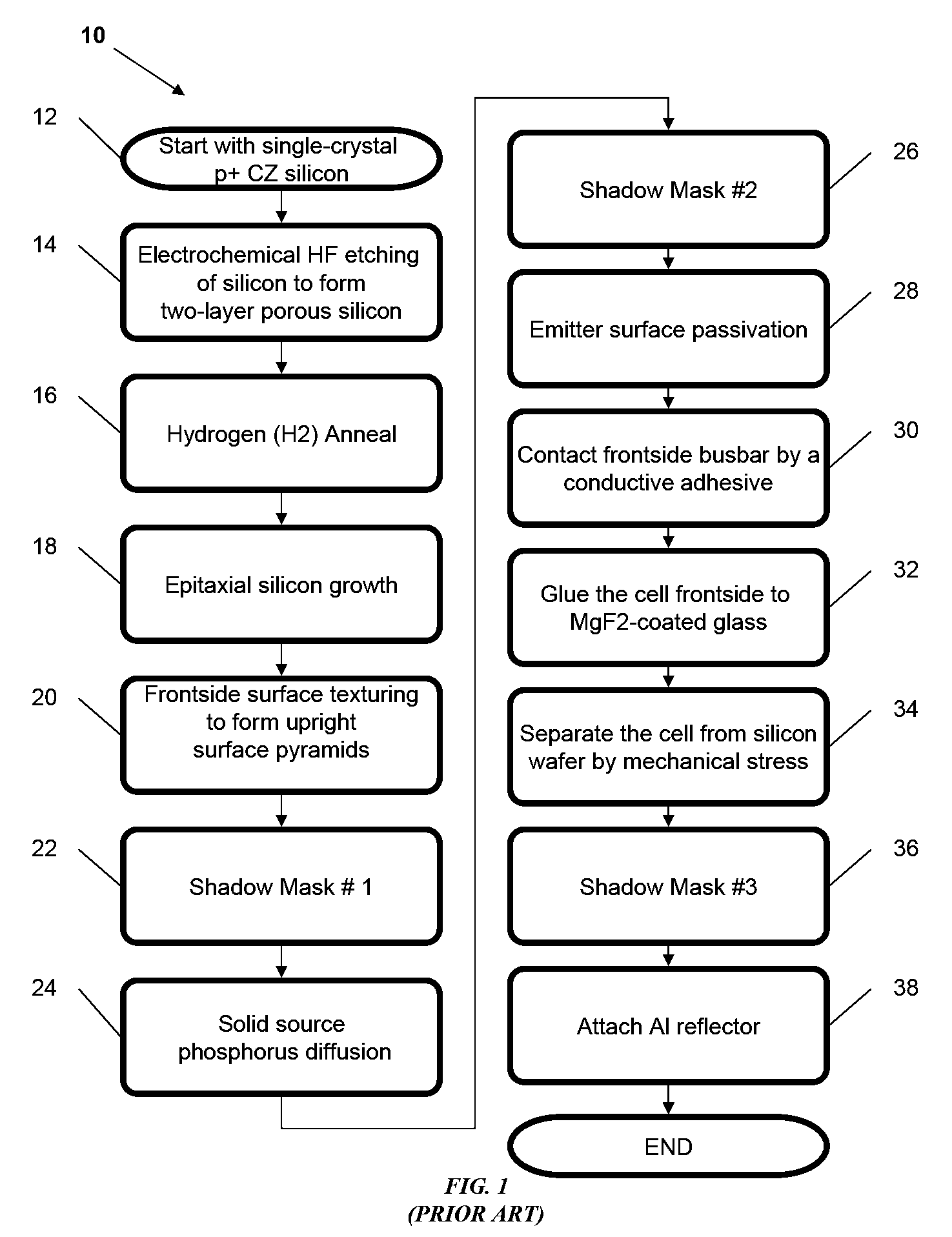
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
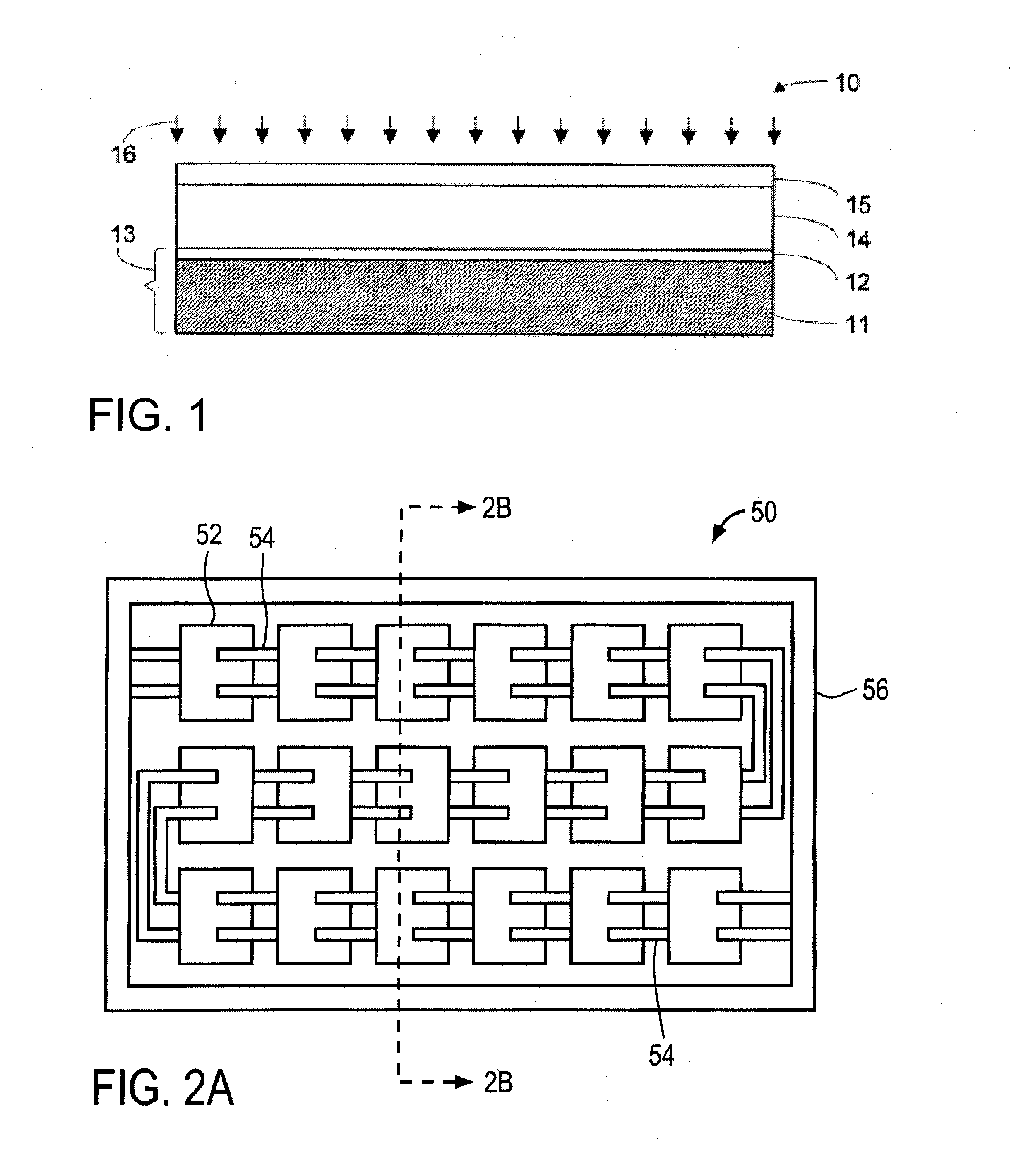
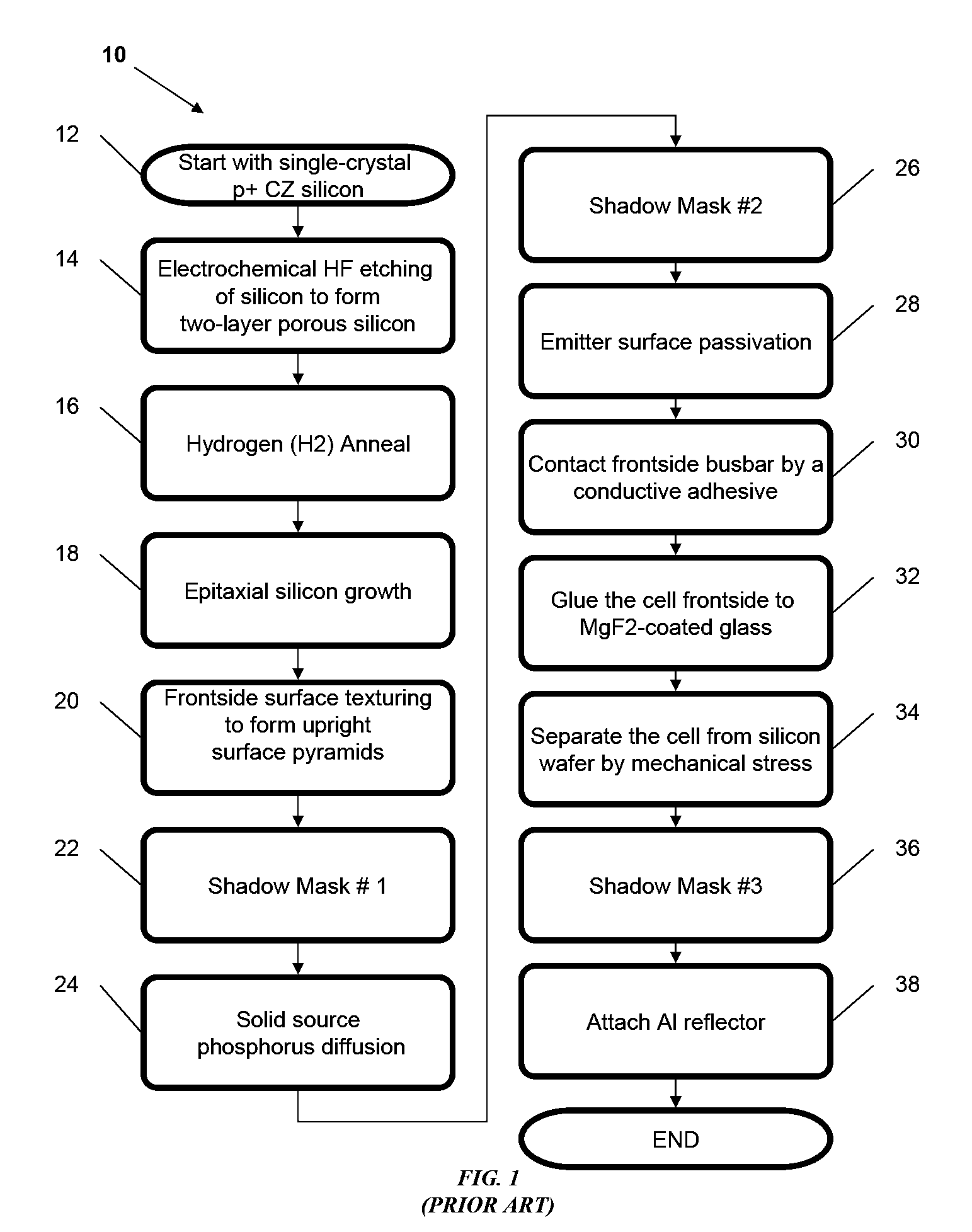
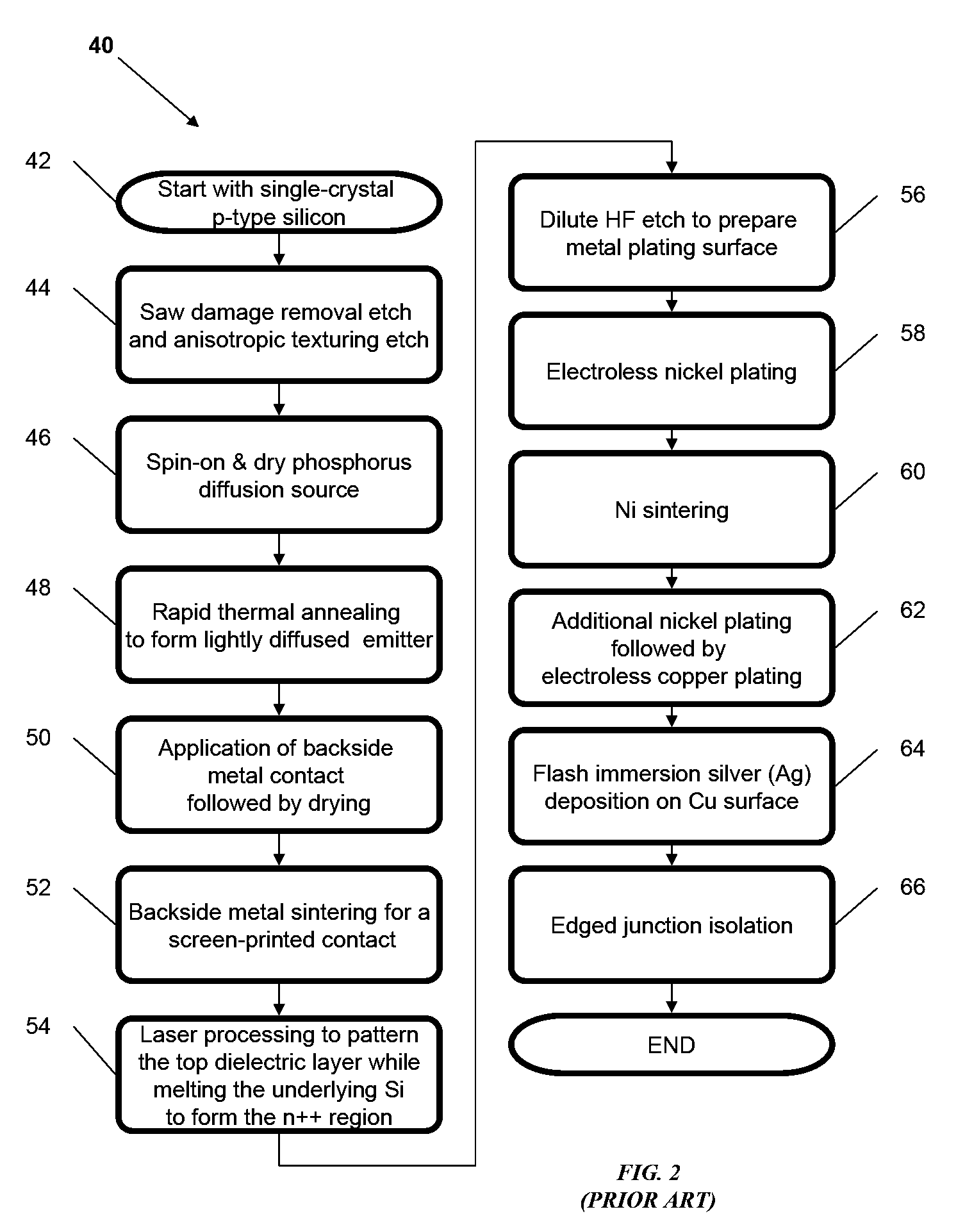
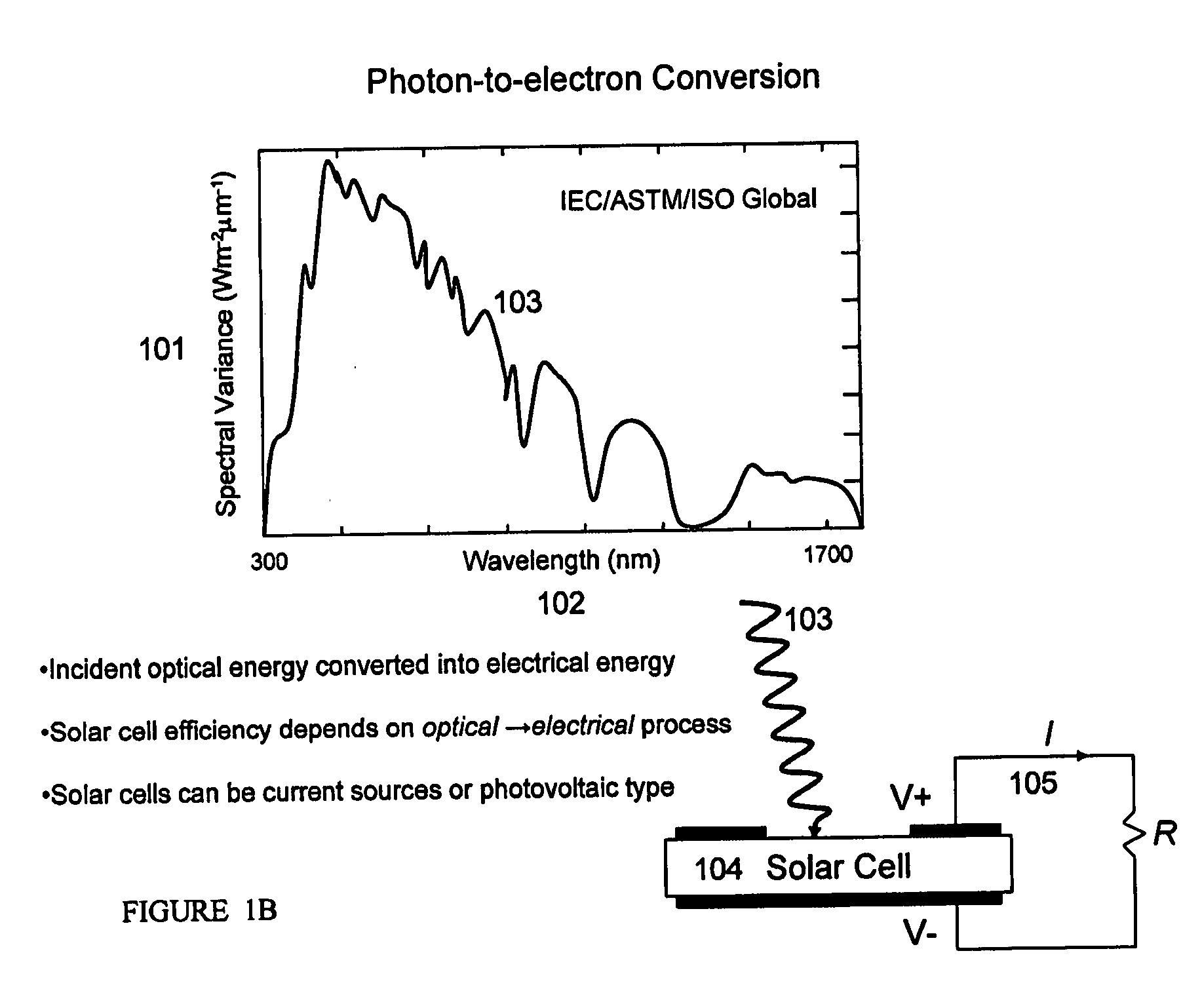
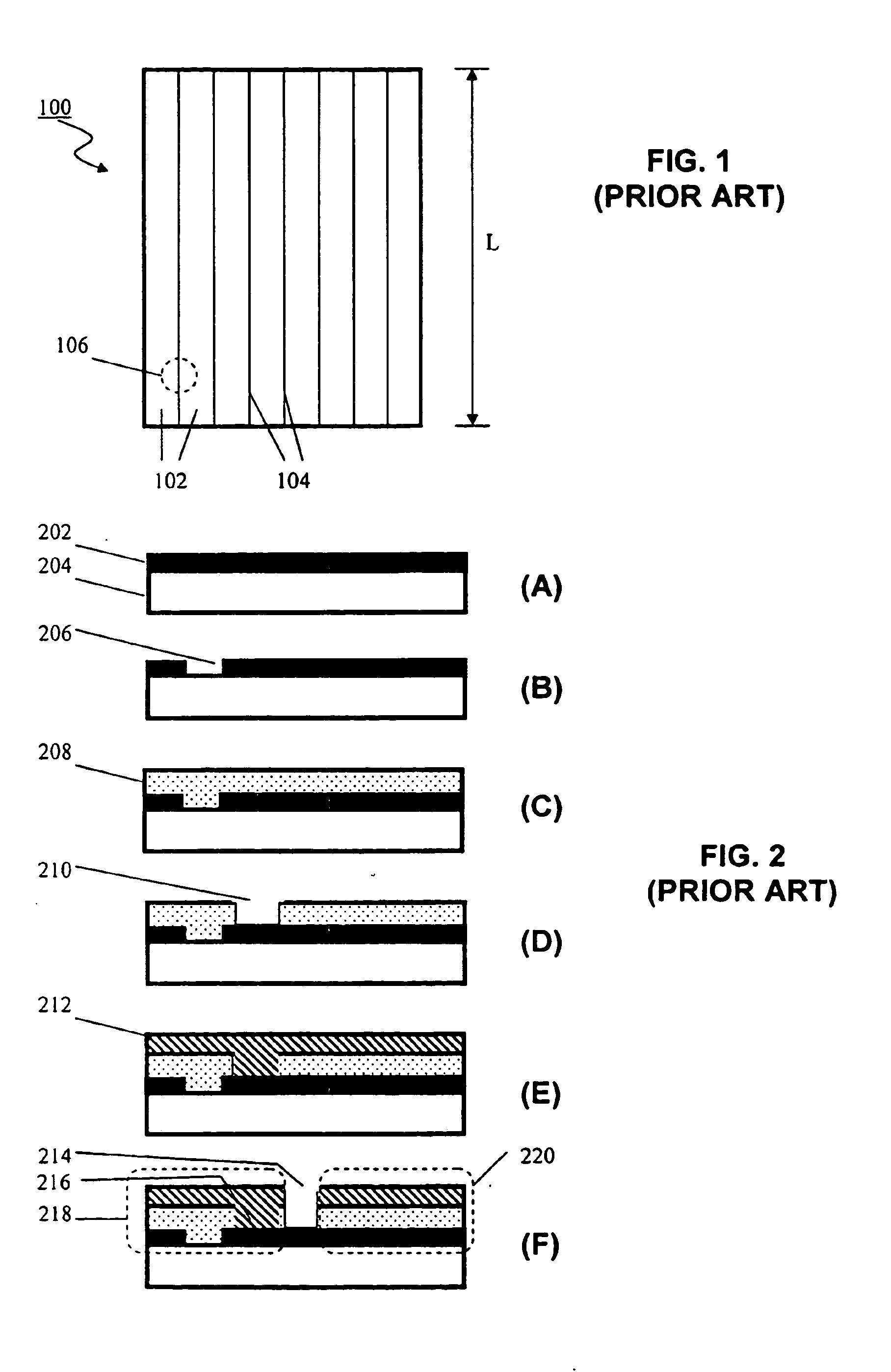
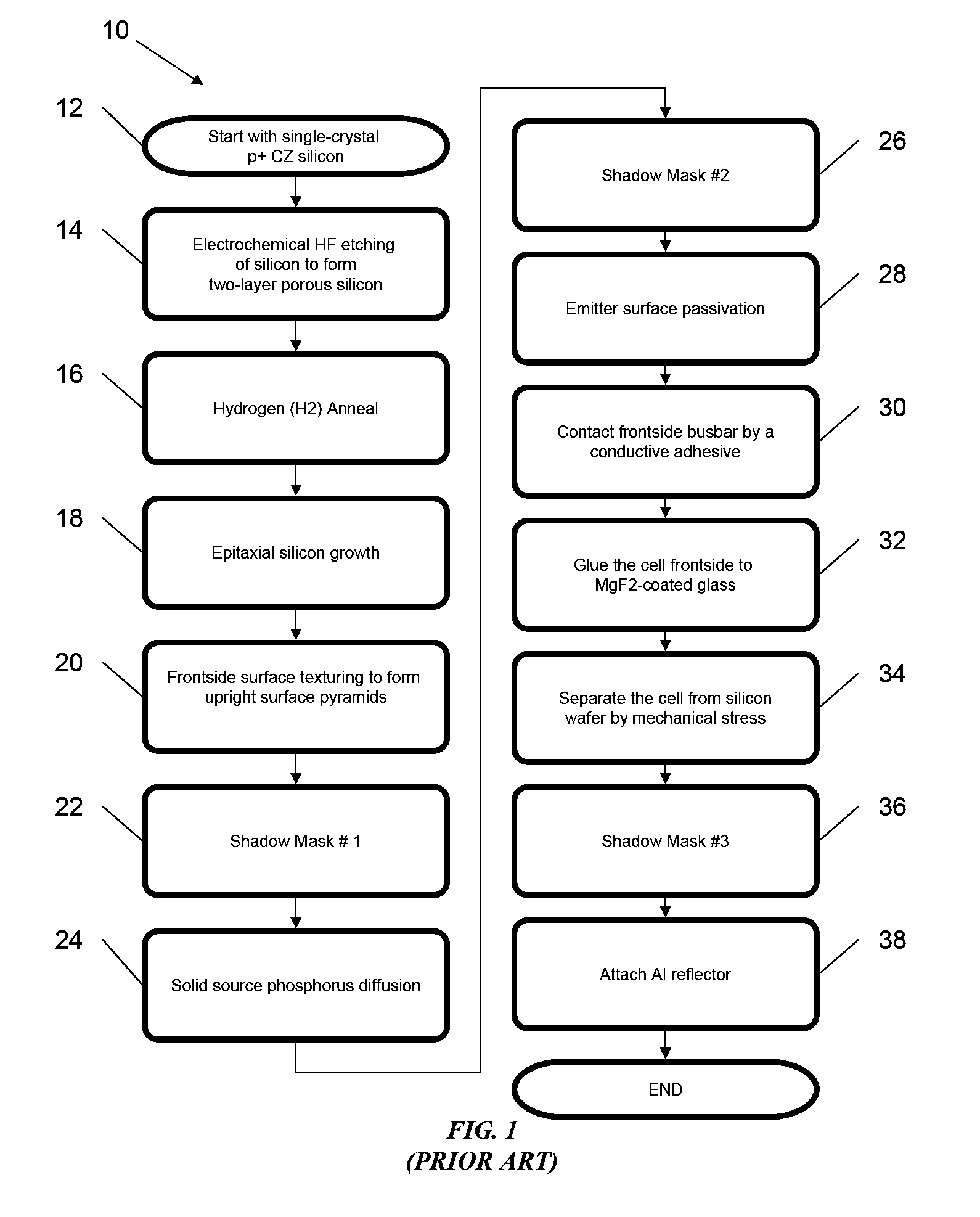
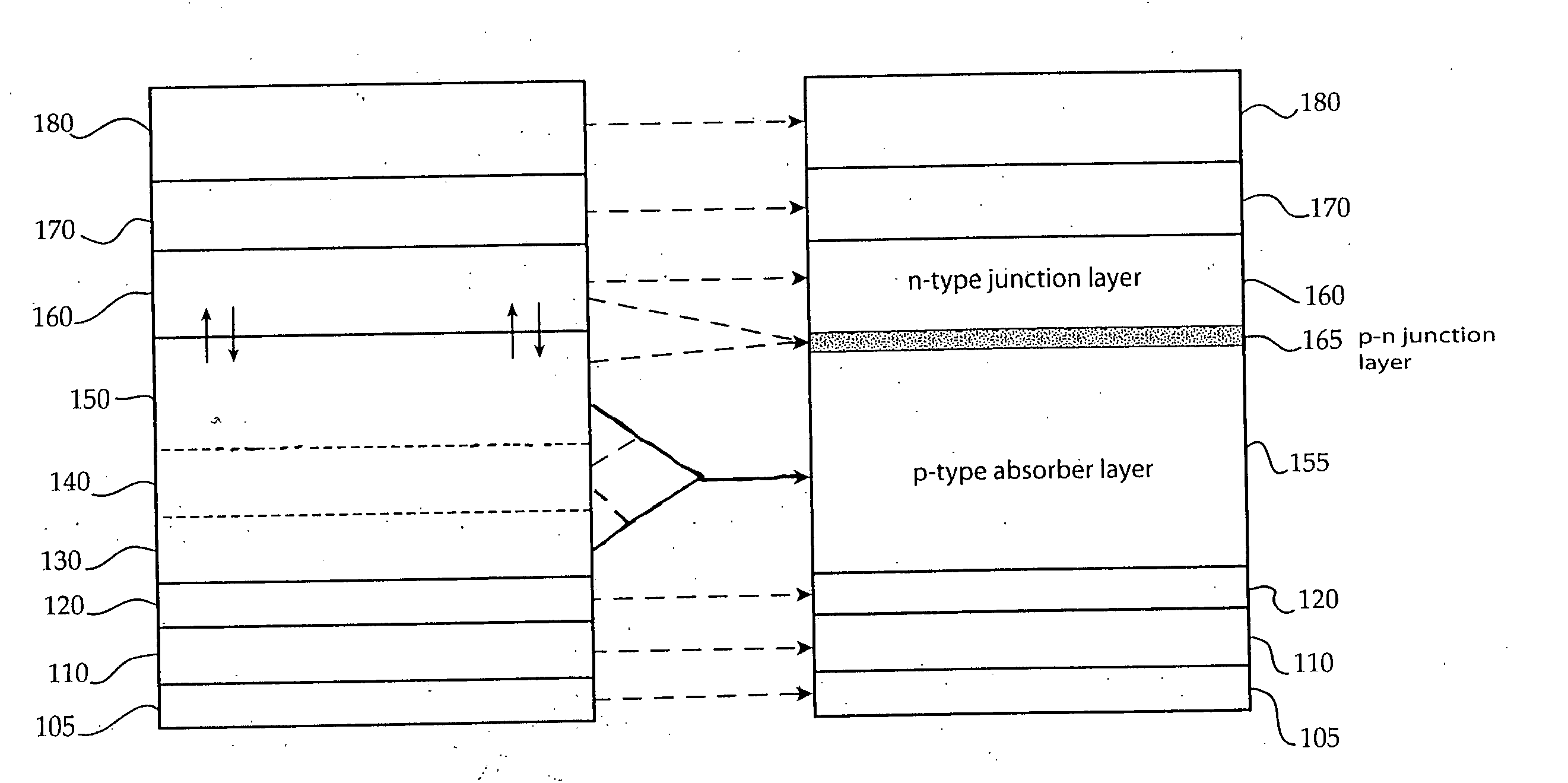
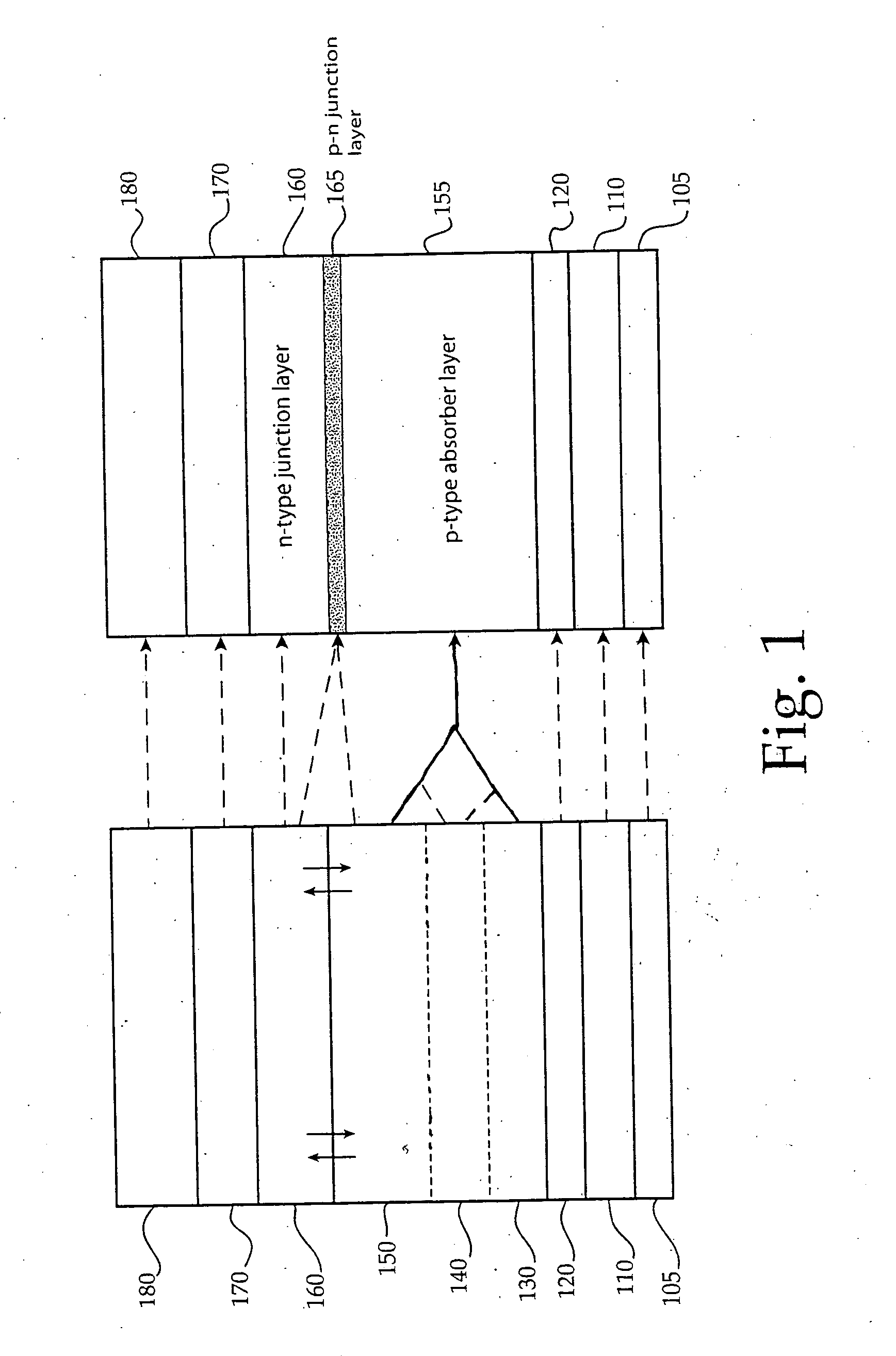
A thin-film solar cell is a second generation solar cell that is made by depositing one or more thin layers, or thin film (TF) of photovoltaic material on a substrate, such as glass, plastic or metal. Thin-film solar cells are commercially used in several technologies, including cadmium telluride (CdTe), copper indium gallium diselenide (CIGS), and amorphous thin-film silicon (a-Si, TF-Si).
Thin-film solar cells
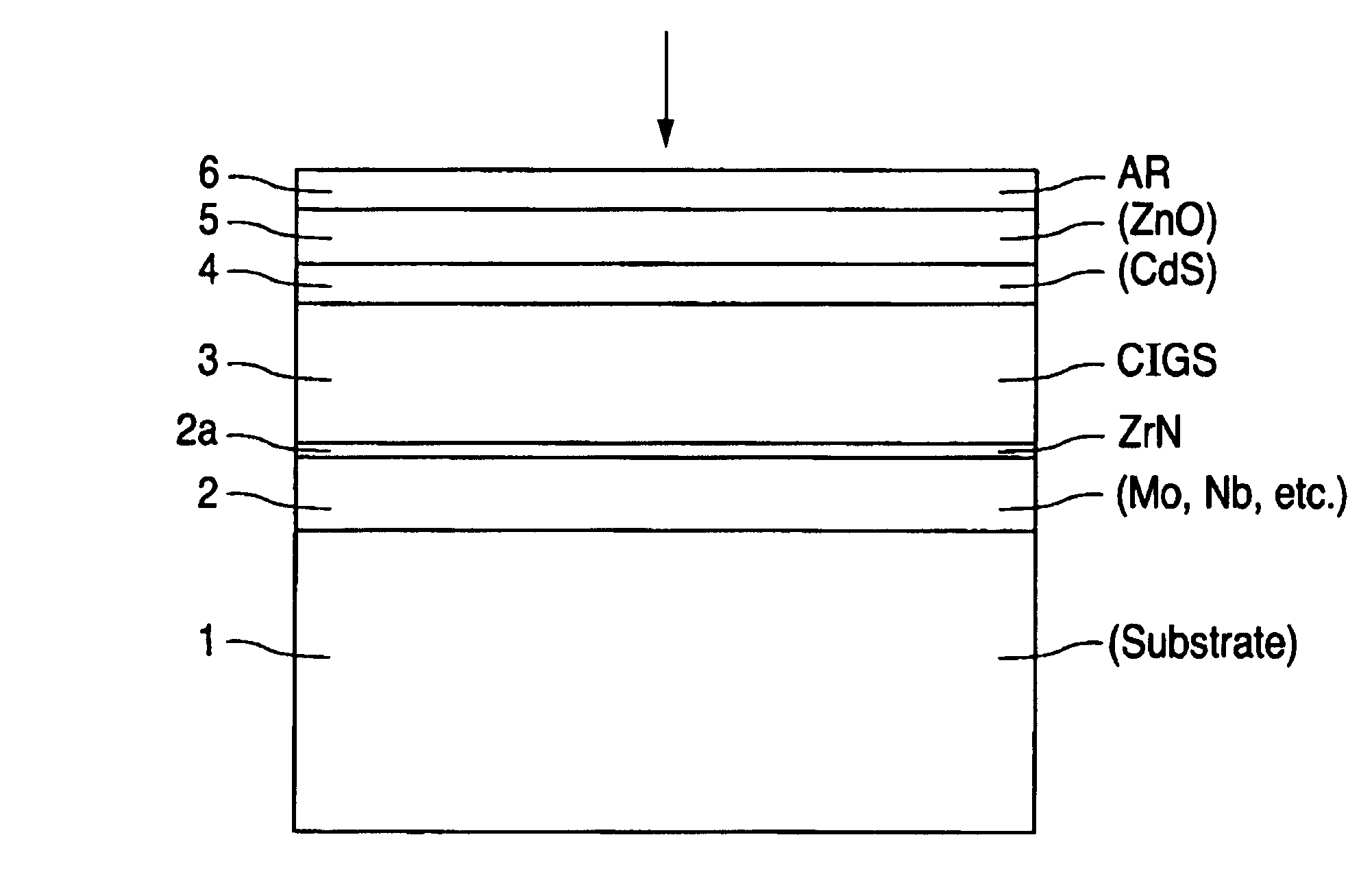
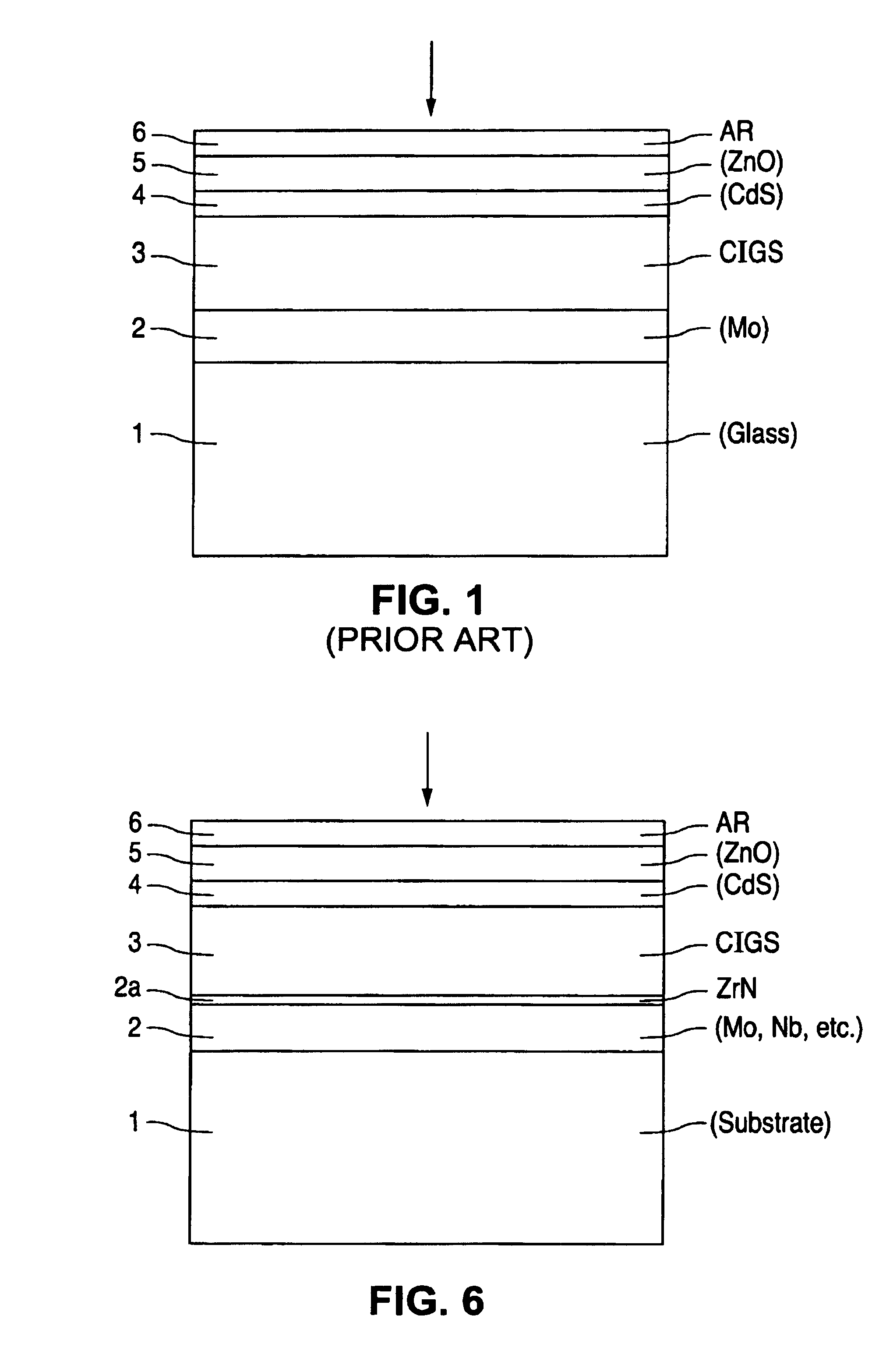
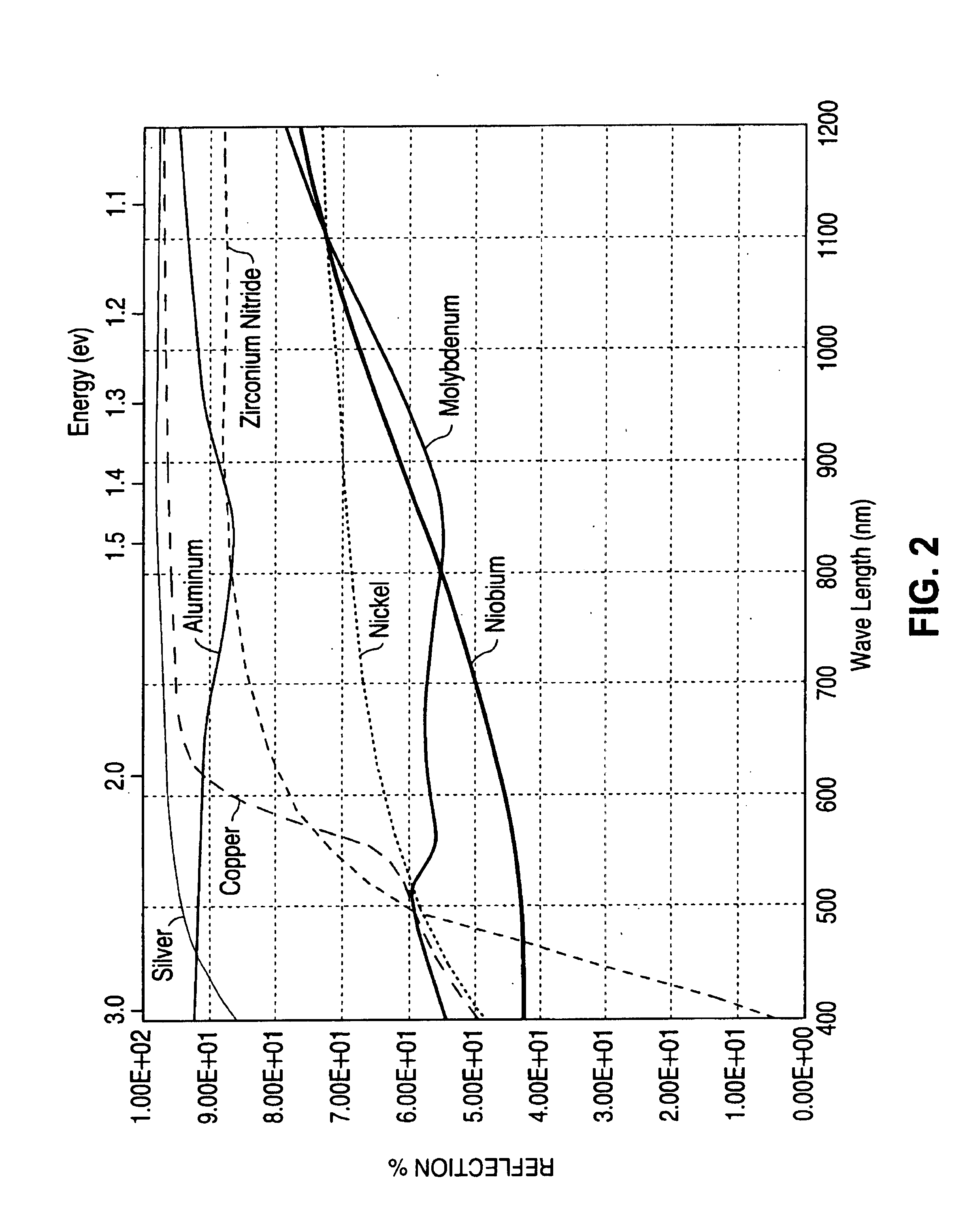
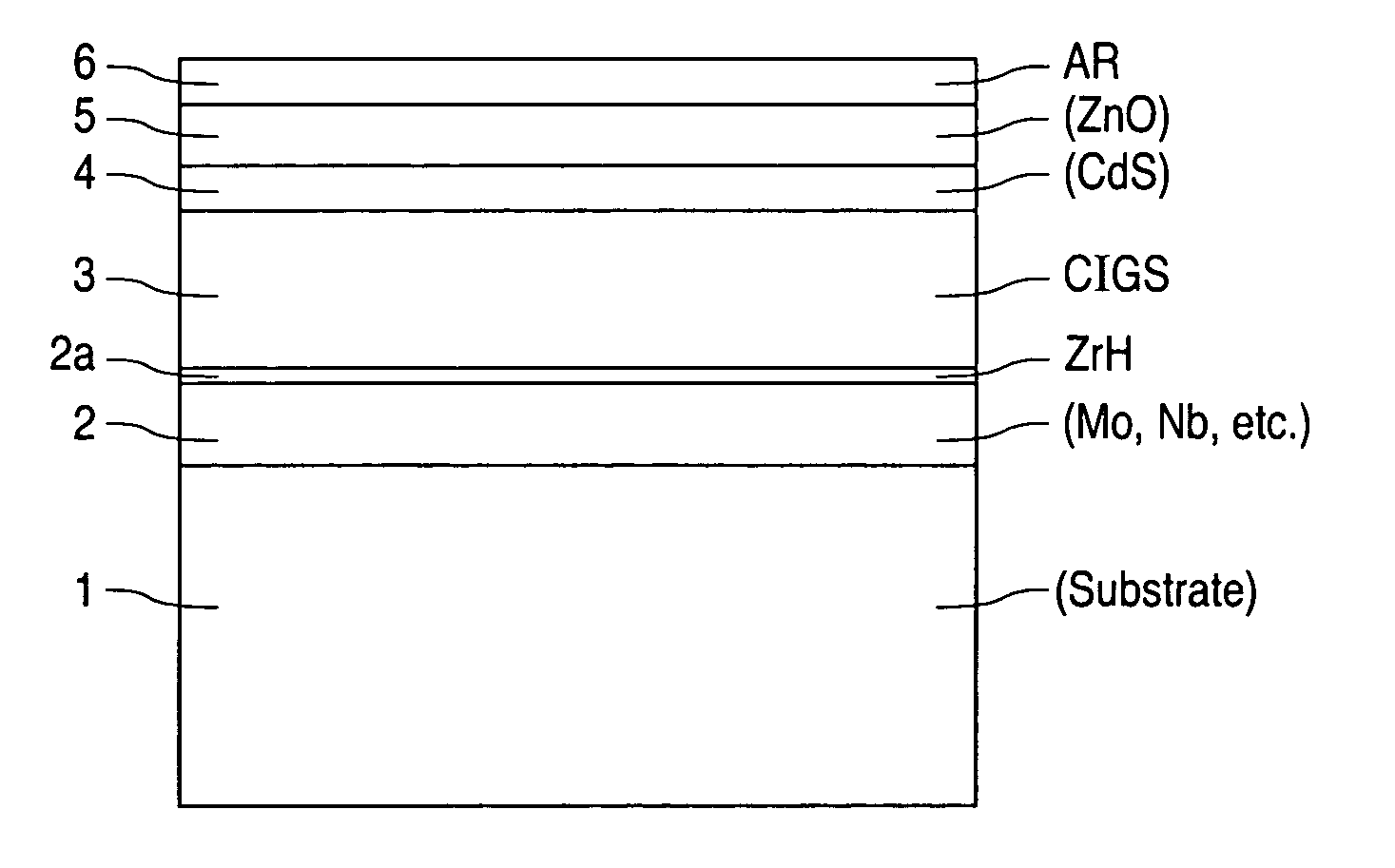
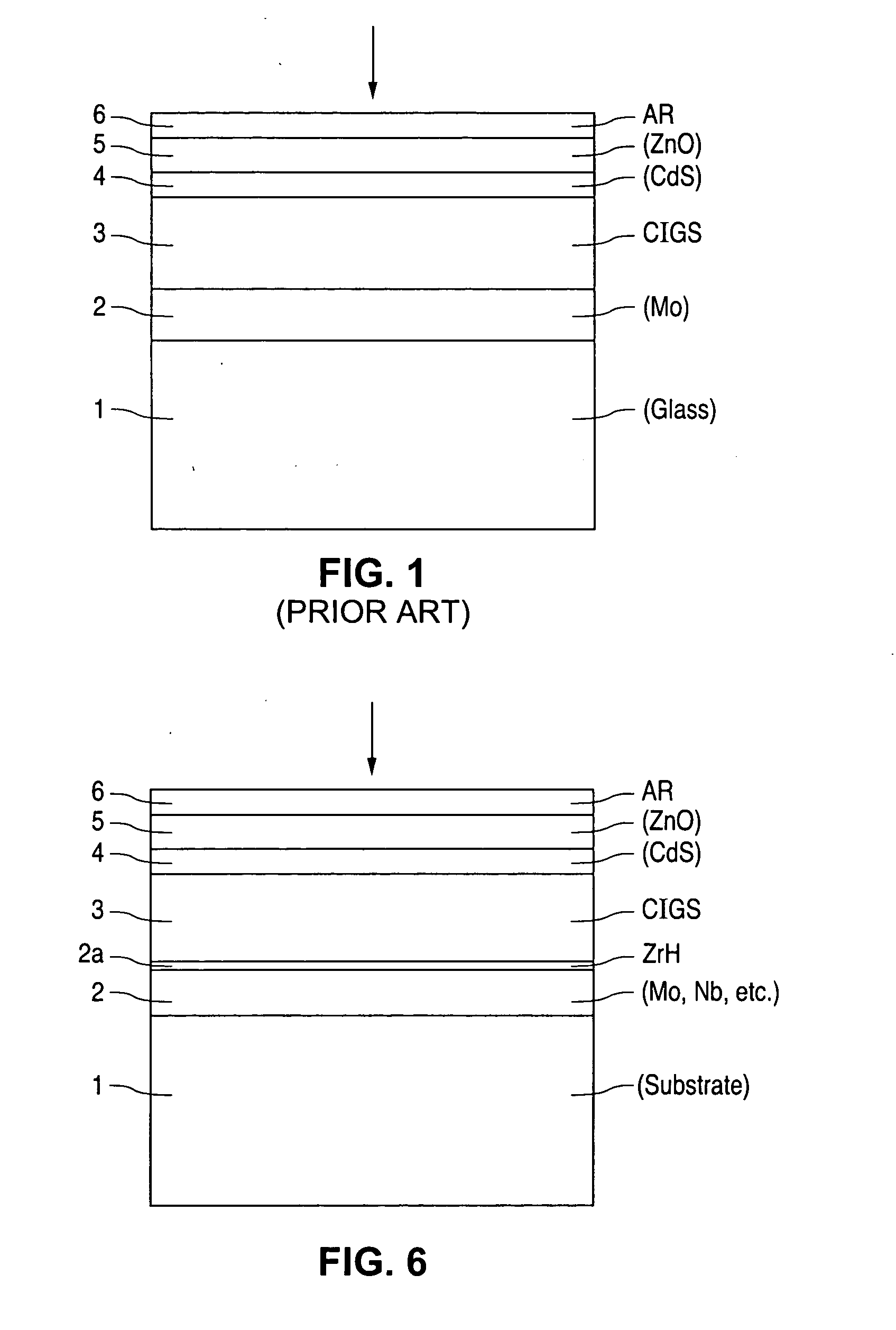
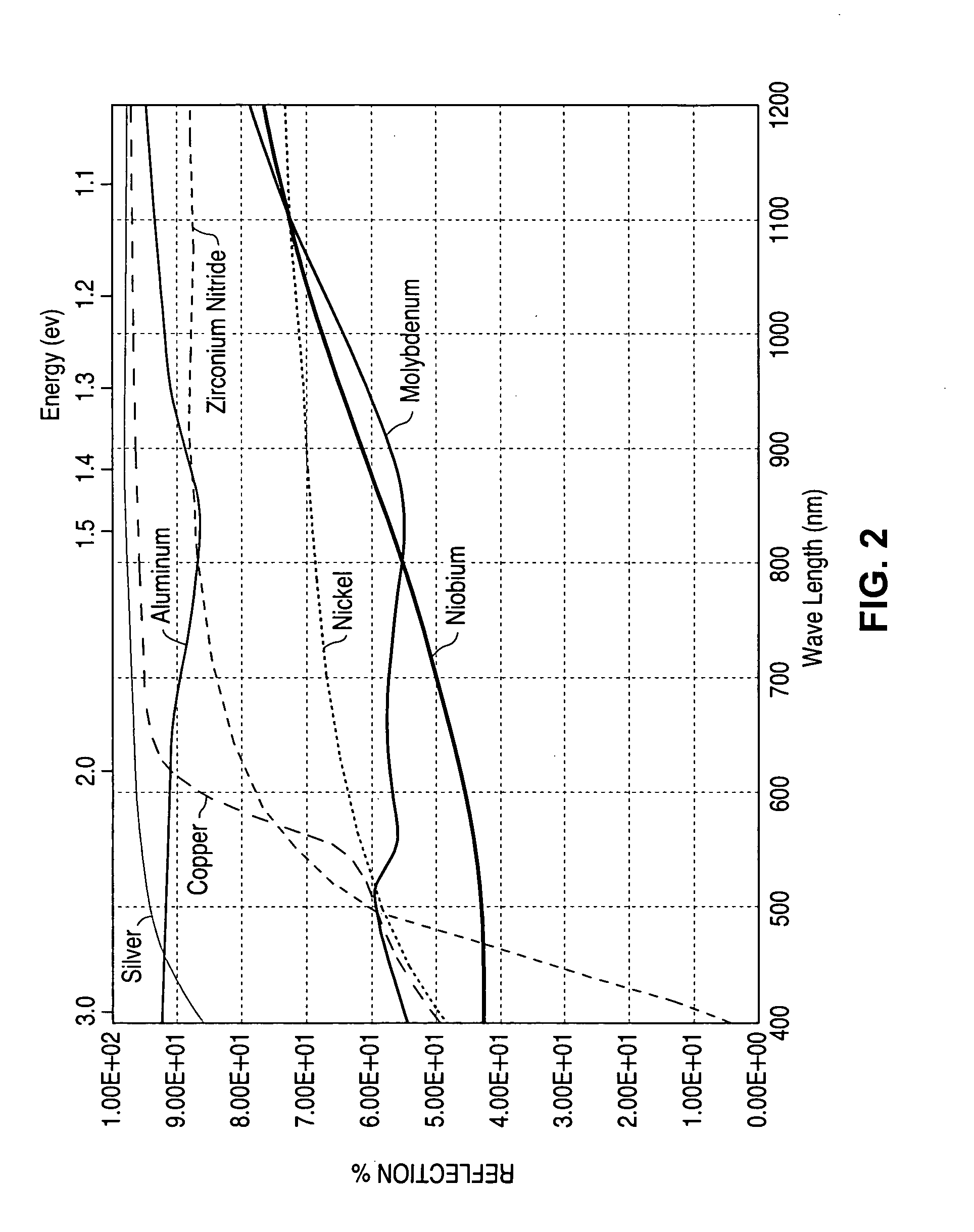
InactiveUS6974976B2Increase reflectionInhibition formationFinal product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingIndiumElectrical battery
A method of manufacturing improved thin-film solar cells entirely by sputtering includes a high efficiency back contact / reflecting multi-layer containing at least one barrier layer consisting of a transition metal nitride. A copper indium gallium diselenide (Cu(InXGa1−X)Se2) absorber layer (X ranging from 1 to approximately 0.7) is co-sputtered from specially prepared electrically conductive targets using dual cylindrical rotary magnetron technology. The band gap of the absorber layer can be graded by varying the gallium content, and by replacing the gallium partially or totally with aluminum. Alternately the absorber layer is reactively sputtered from metal alloy targets in the presence of hydrogen selenide gas. RF sputtering is used to deposit a non-cadmium containing window layer of ZnS. The top transparent electrode is reactively sputtered aluminum doped ZnO. A unique modular vacuum roll-to-roll sputtering machine is described. The machine is adapted to incorporate dual cylindrical rotary magnetron technology to manufacture the improved solar cell material in a single pass.
Owner:BEIJING APOLLO DING RONG SOLAR TECH
Manufacturing apparatus and method for large-scale production of thin-film solar cells
ActiveUS20050109392A1Cheap productionLow costPV power plantsFinal product manufactureIndiumElectrical battery
A method of manufacturing improved thin-film solar cells entirely by sputtering includes a high efficiency back contact / reflecting multi-layer containing at least one barrier layer consisting of a transition metal nitride. A copper indium gallium diselenide (Cu(InXGa1-x)Se2) absorber layer (X ranging from 1 to approximately 0.7) is co-sputtered from specially prepared electrically conductive targets using dual cylindrical rotary magnetron technology. The band gap of the absorber layer can be graded by varying the gallium content, and by replacing the gallium partially or totally with aluminum. Alternately the absorber layer is reactively sputtered from metal alloy targets in the presence of hydrogen selenide gas. RF sputtering is used to deposit a non-cadmium containing window layer of ZnS. The top transparent electrode is reactively sputtered aluminum doped ZnO. A unique modular vacuum roll-to-roll sputtering machine is described. The machine is adapted to incorporate dual cylindrical rotary magnetron technology to manufacture the improved solar cell material in a single pass.
Owner:BEIJING APOLLO DING RONG SOLAR TECH
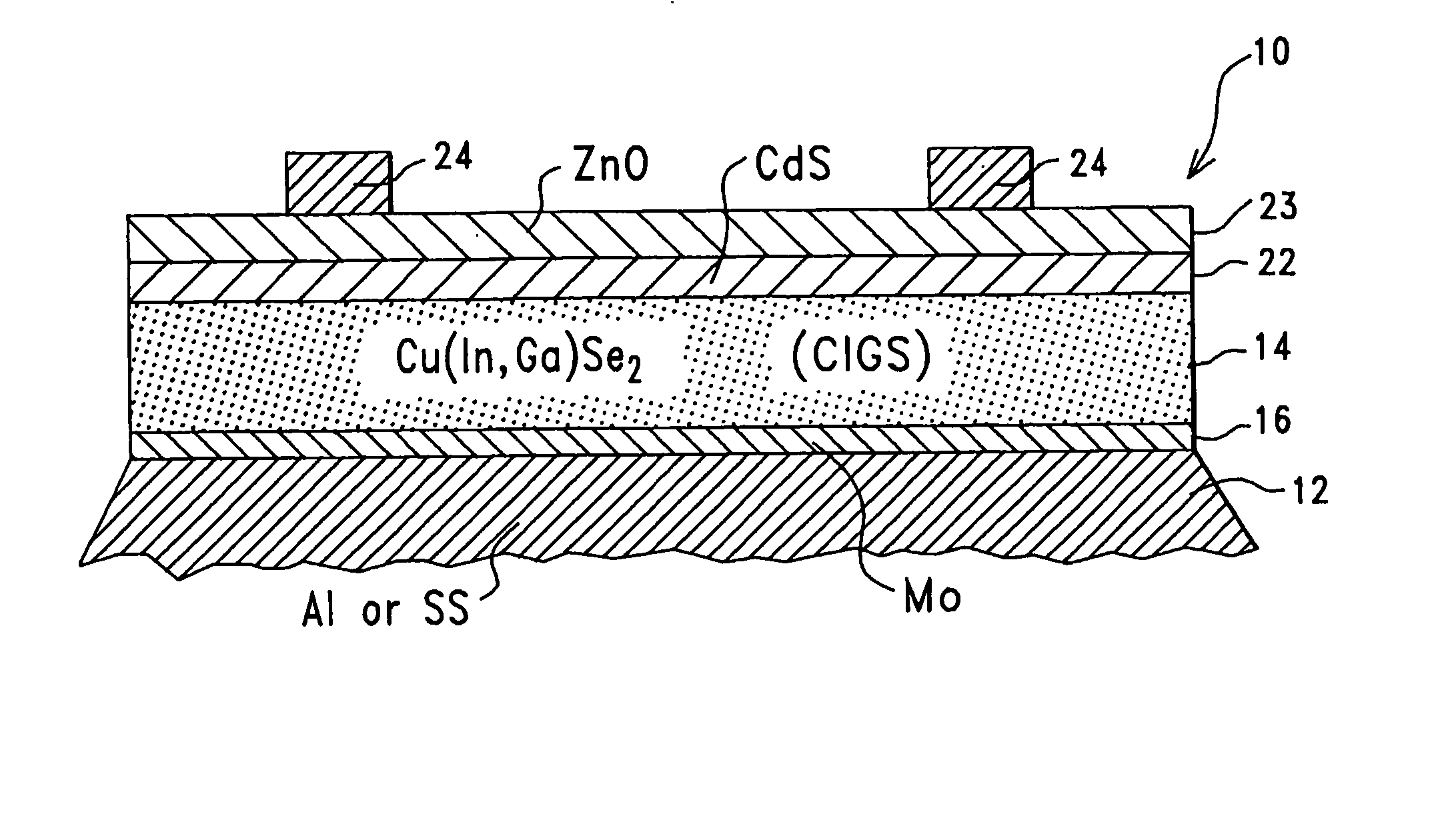
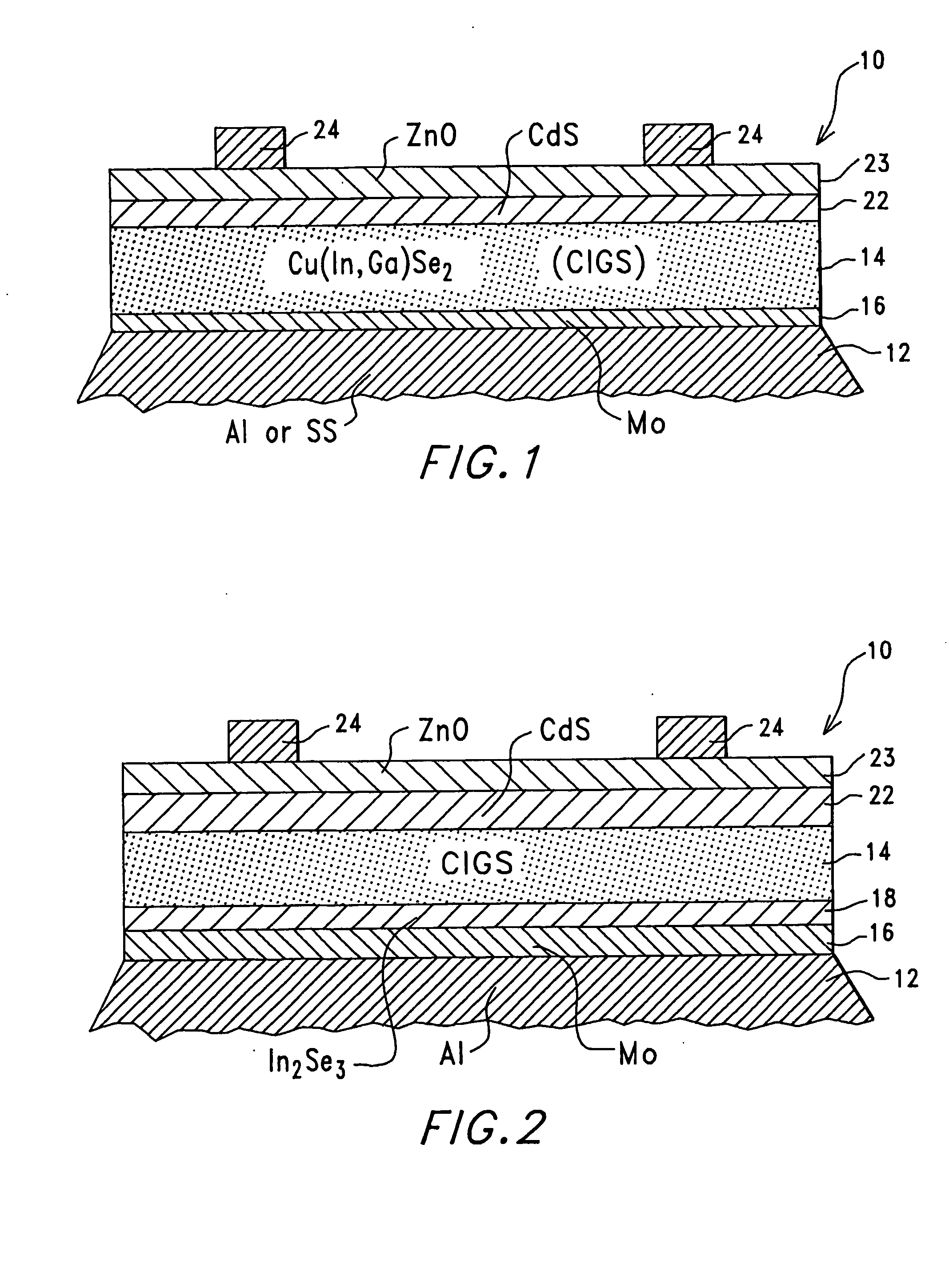
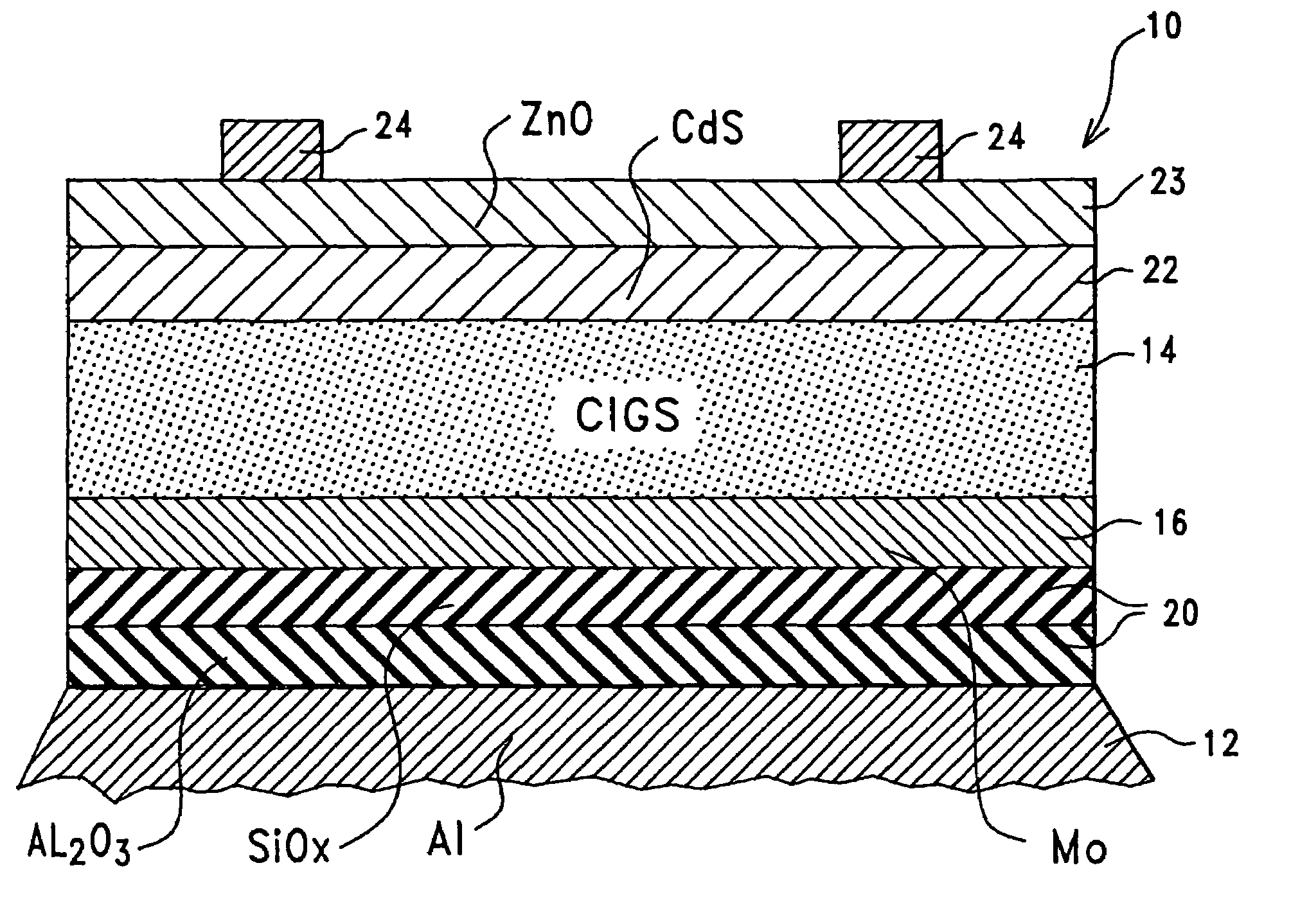
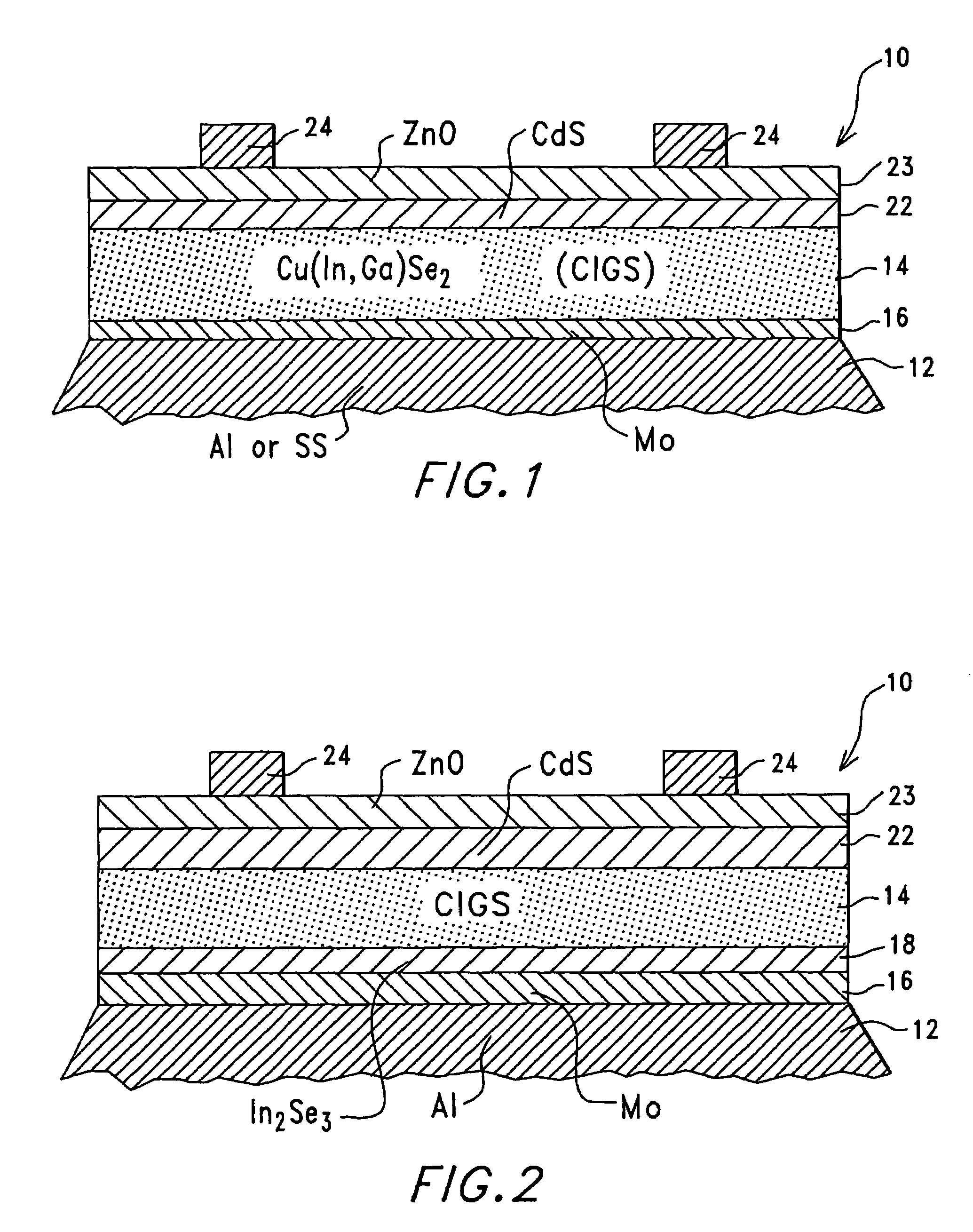
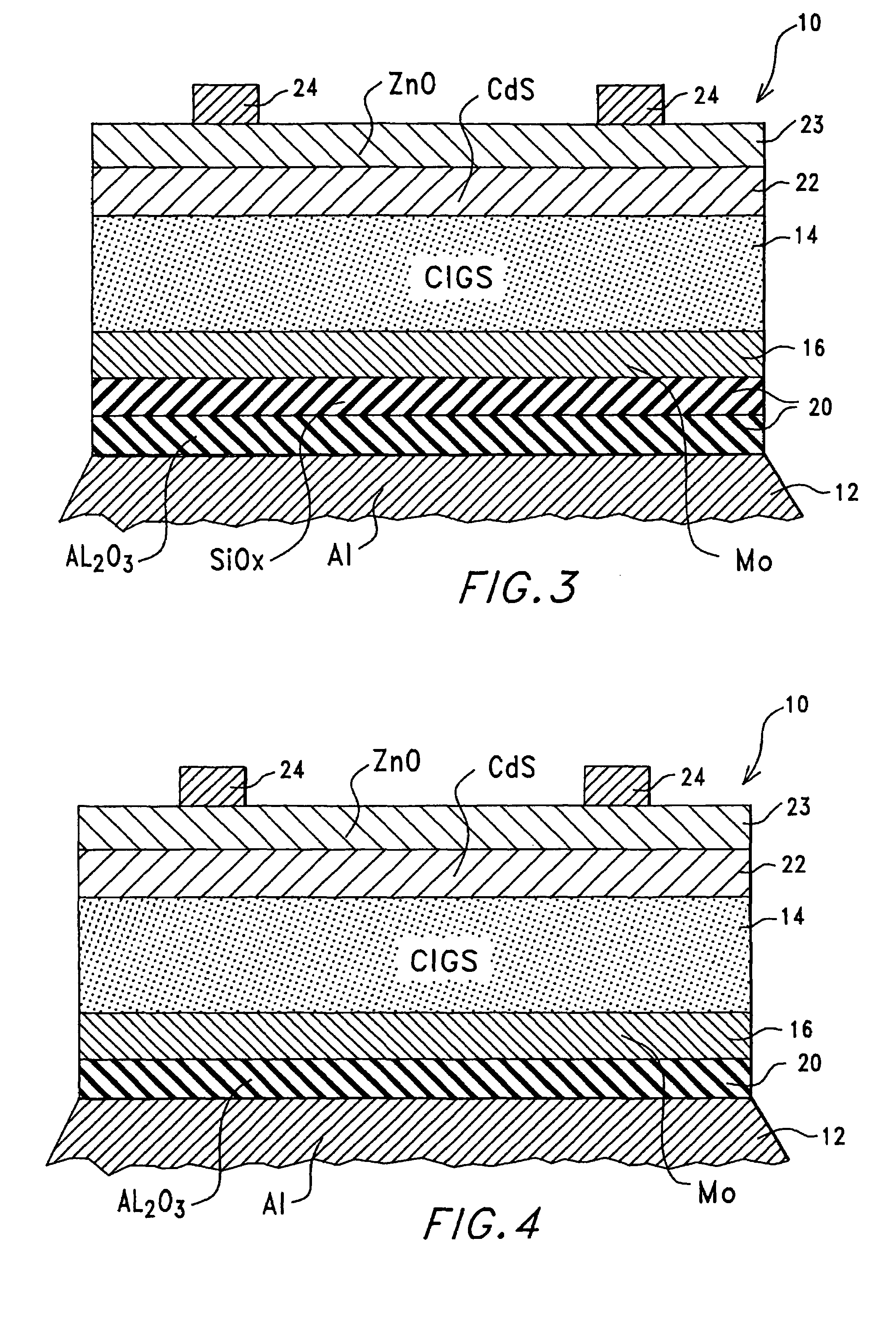
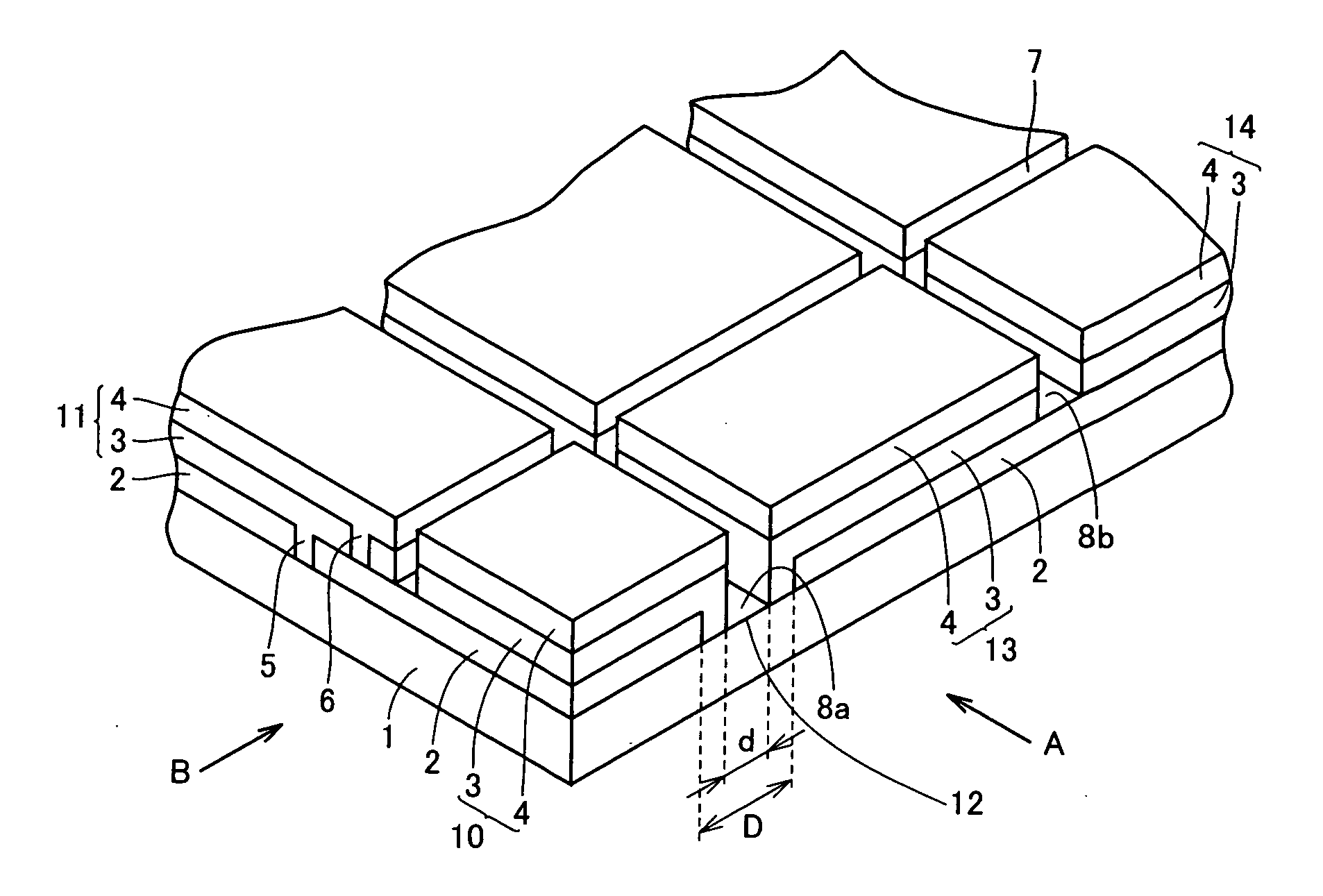
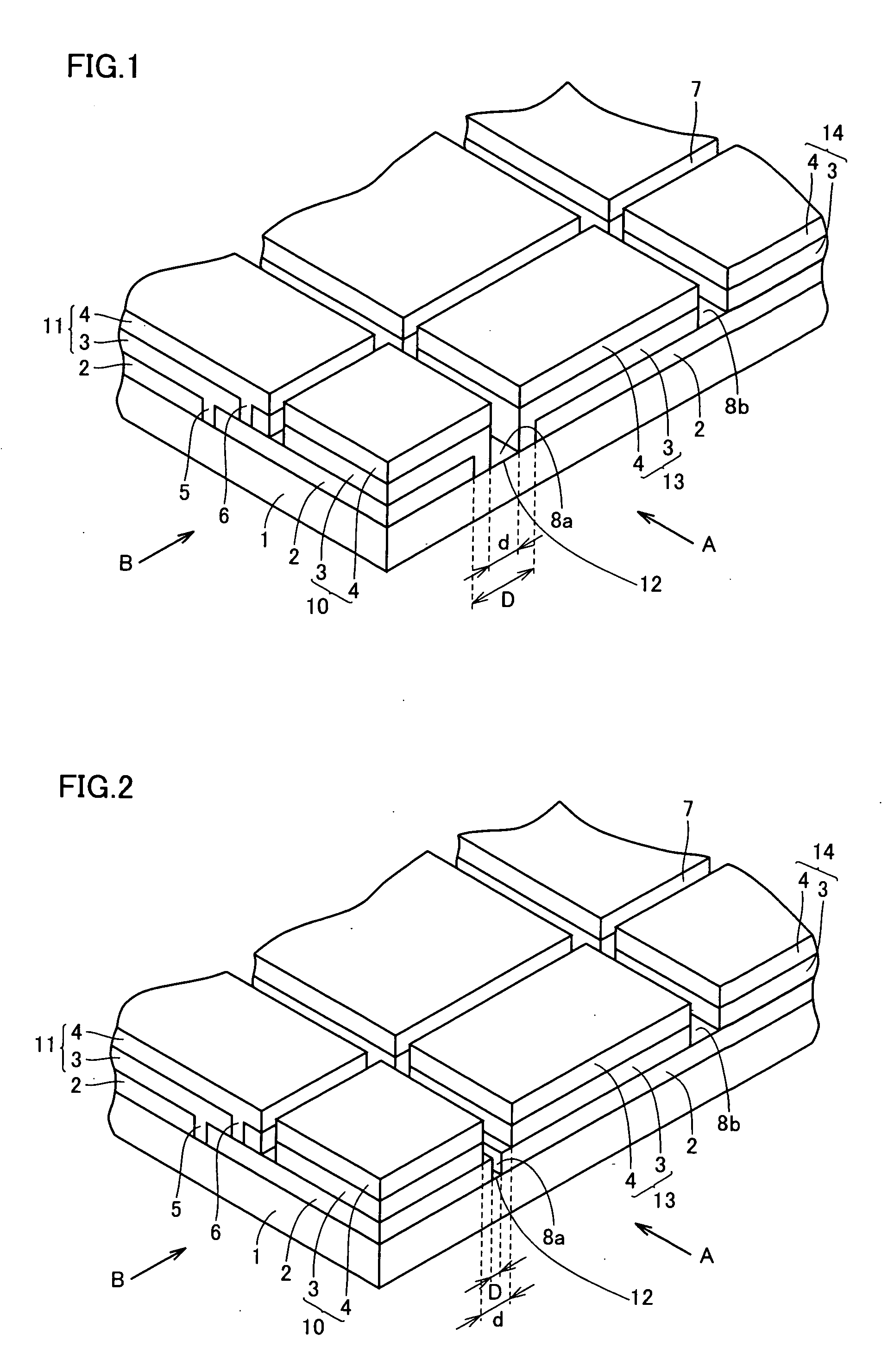
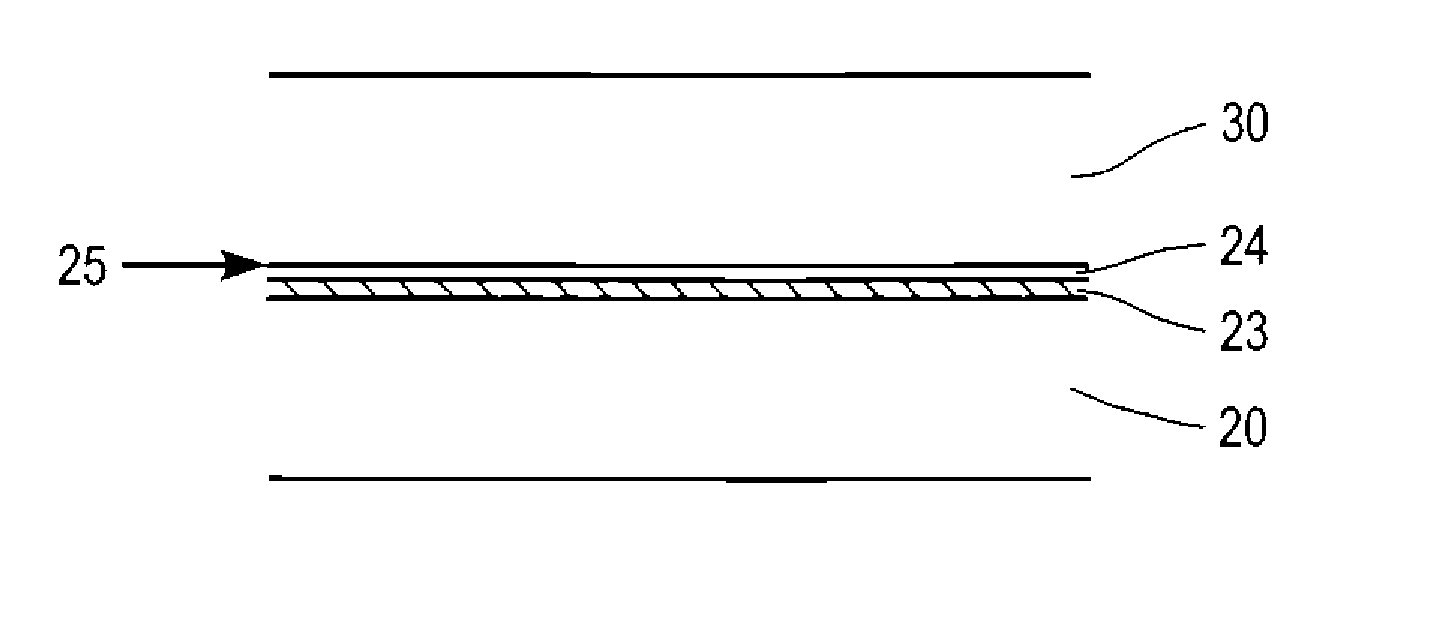
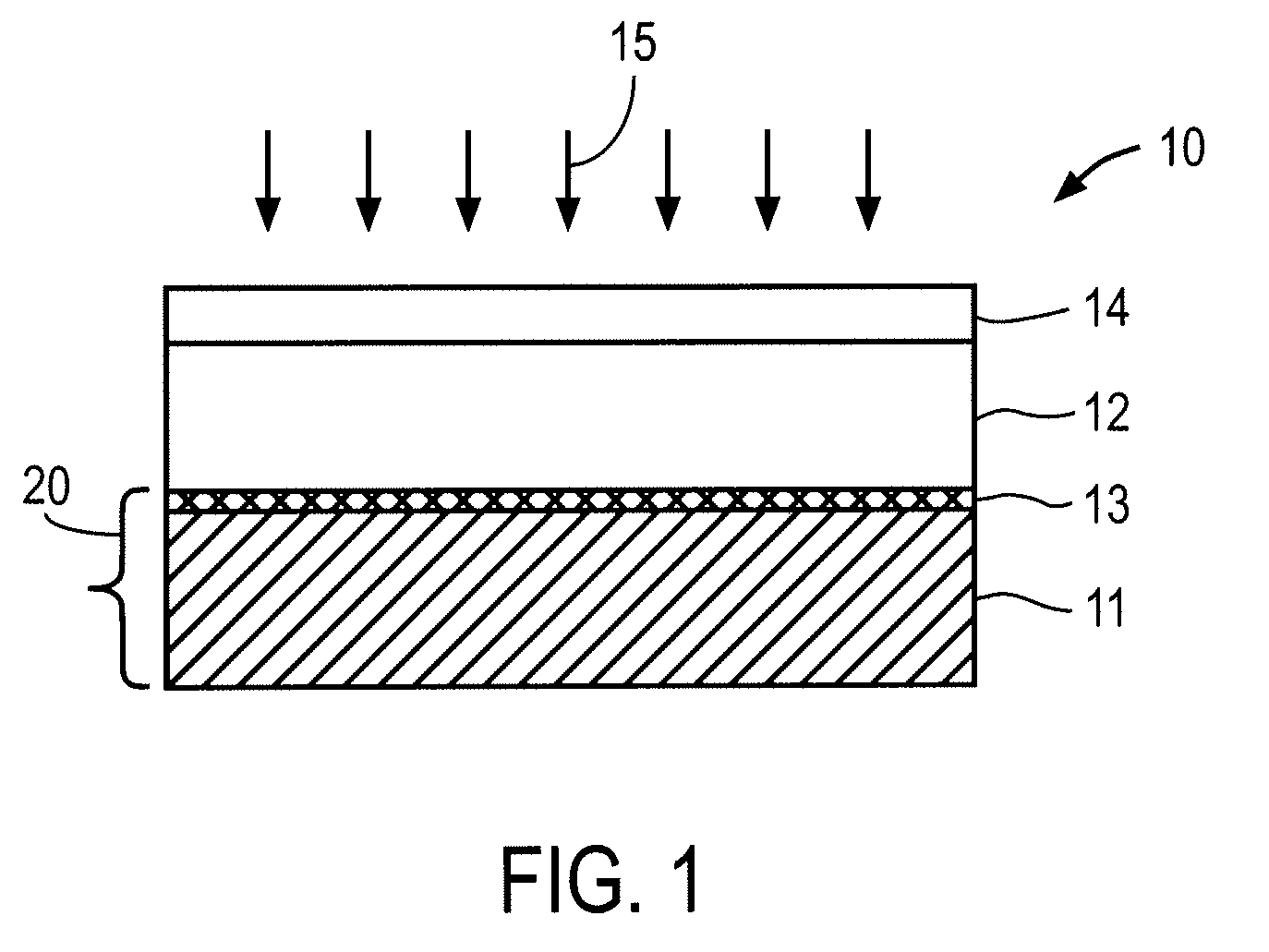
Thin-film solar cell fabricated on a flexible metallic substrate
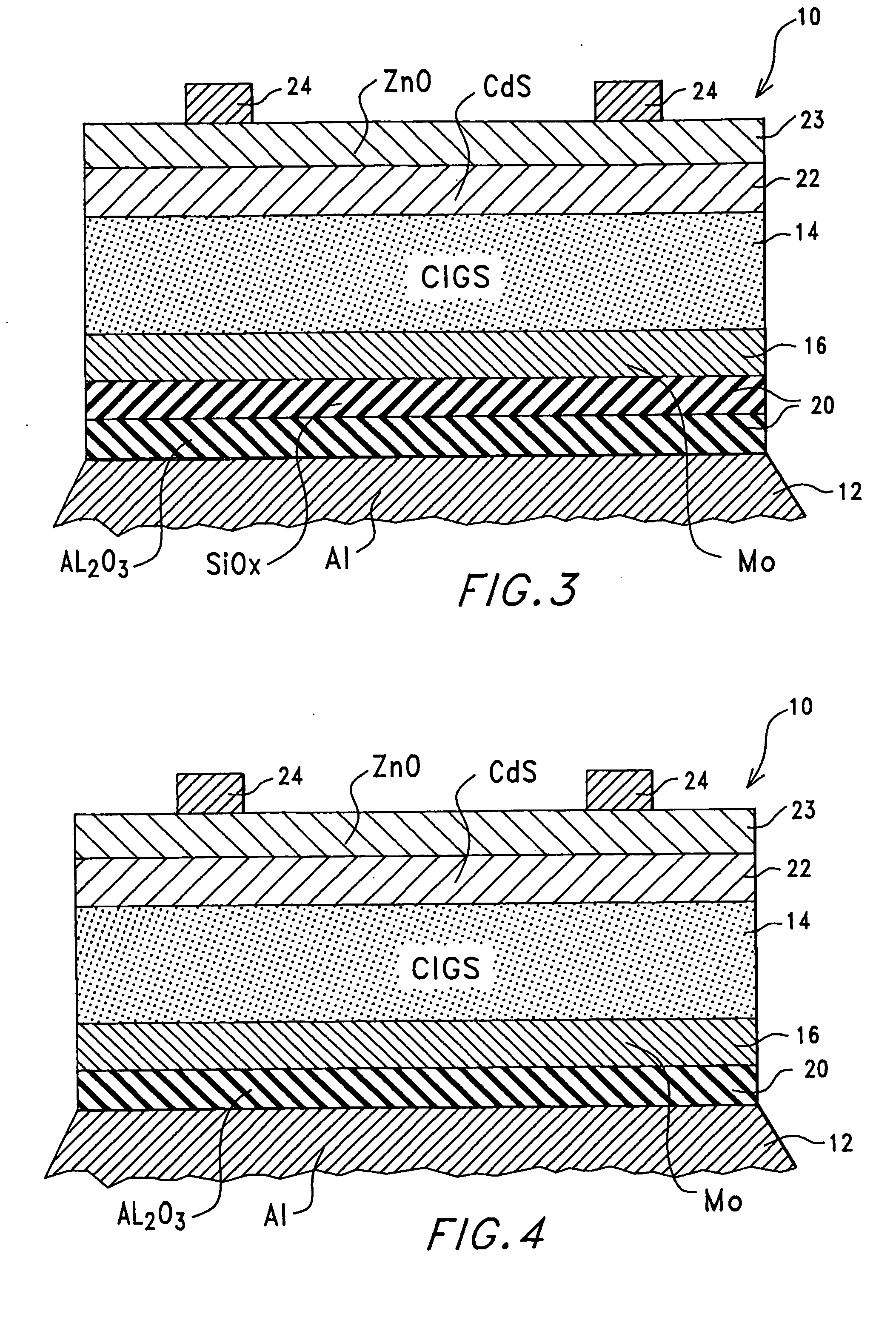
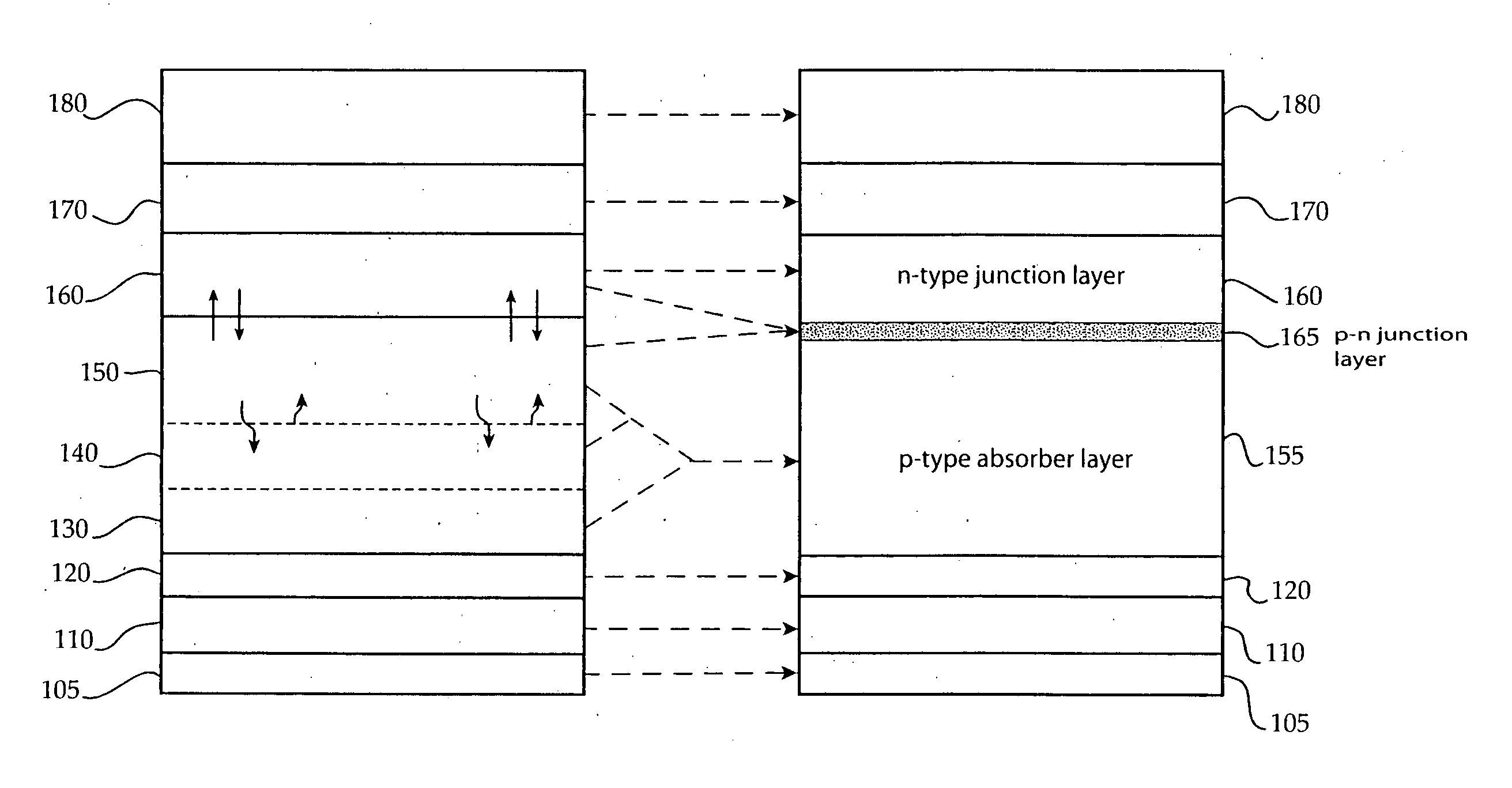
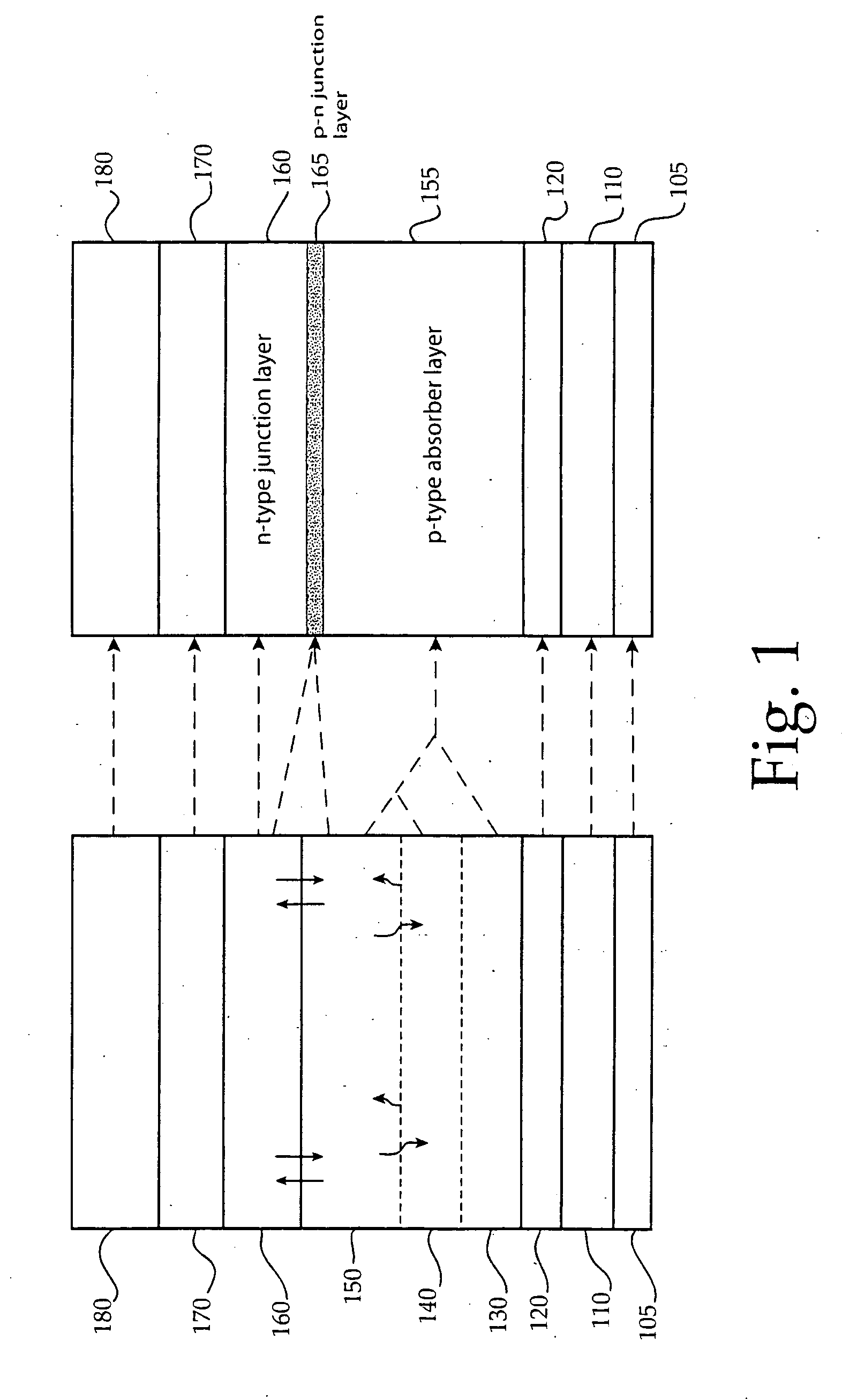
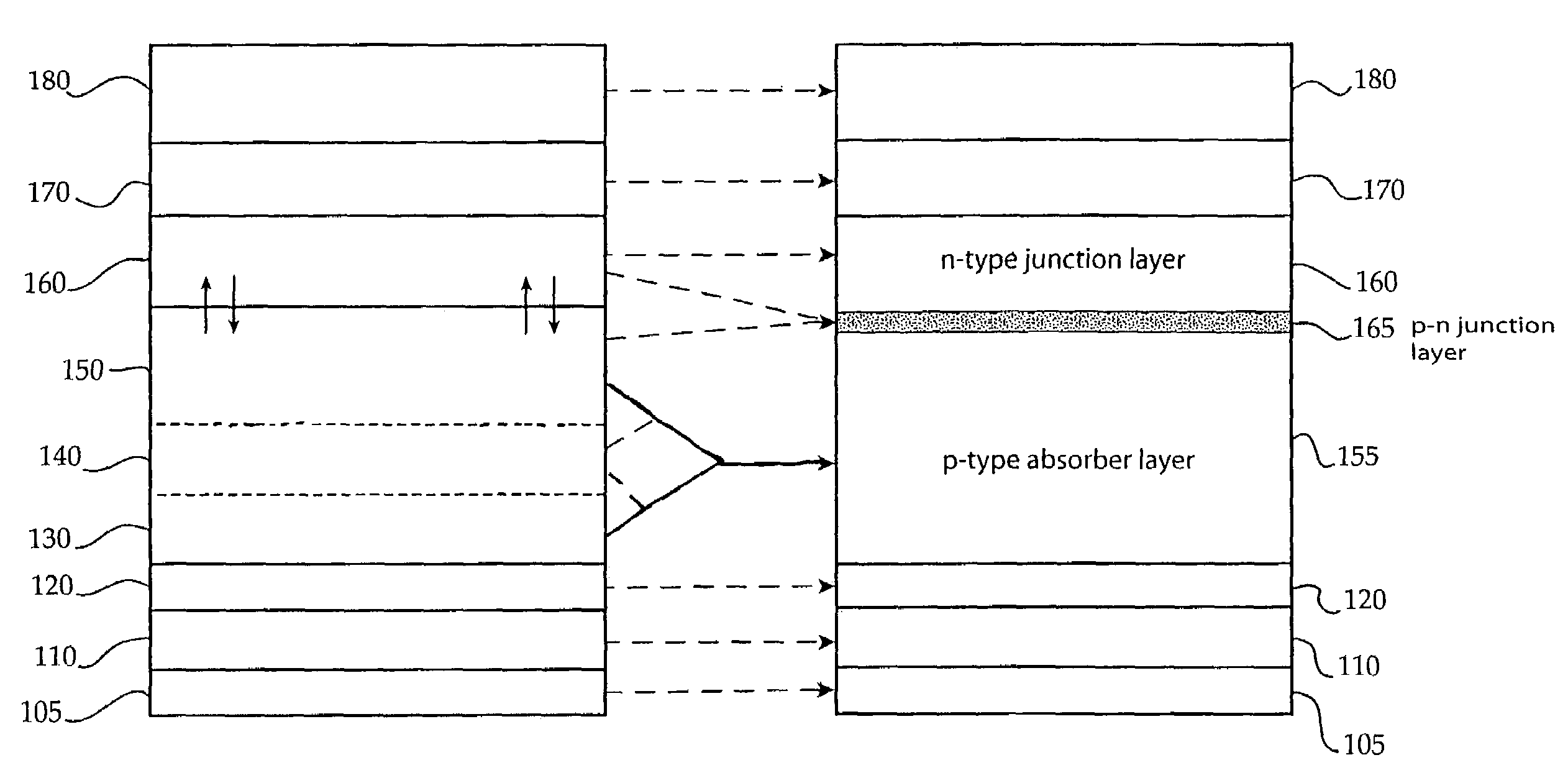
A thin-film solar cell (10) is provided. The thin-film solar cell (10) comprises a flexible metallic substrate (12) a having a first surface and a second surface. A back metal contact layer (16) is deposited on the first surface of the flexible metallic substrate (12). A semiconductor absorber layer (14) is deposited on the back metal contact. A photoactive film deposited on the semiconductor absorber layer (14) forms a heterojunction structure and a grid contact (24) deposited on the heterjunction structure. The flexible metal substrate (12) can be constructed of either aluminium or stainless steel. Furthermore, a method of constructing a solar cell is provided. The method comprises providing an aluminum substrate (12), depositing a semiconductor absorber layer (14) on the aluminum substrate (12), and insulating the aluminum substrate (12) from the semiconductor absorber layer (14) to inhibit reaction between the aluminum substrate (12) and the semiconductor absorber layer (14).
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY
Thin-film solar cell having hetero-junction of semiconductor and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20090194152A1Enhanced vapor depositionFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringSemiconductor
A thin-film solar cell having a hetero-junction of semiconductor and the fabrication method thereof are provided. Instead of the conventional hetero-junction of III-V semiconductor or homo-structure of IV semiconductor, the thin-film solar cell according to the present invention adopts a novel hetero-junction structure of IV semiconductor to improve the cell efficiency thereof. By adjusting the amount of layer sequences and the thickness of the hetero-junction structure, the cell efficiency of the thin-film solar cell according to the present invention is also optimized.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Methods of interconnecting thin film solar cells
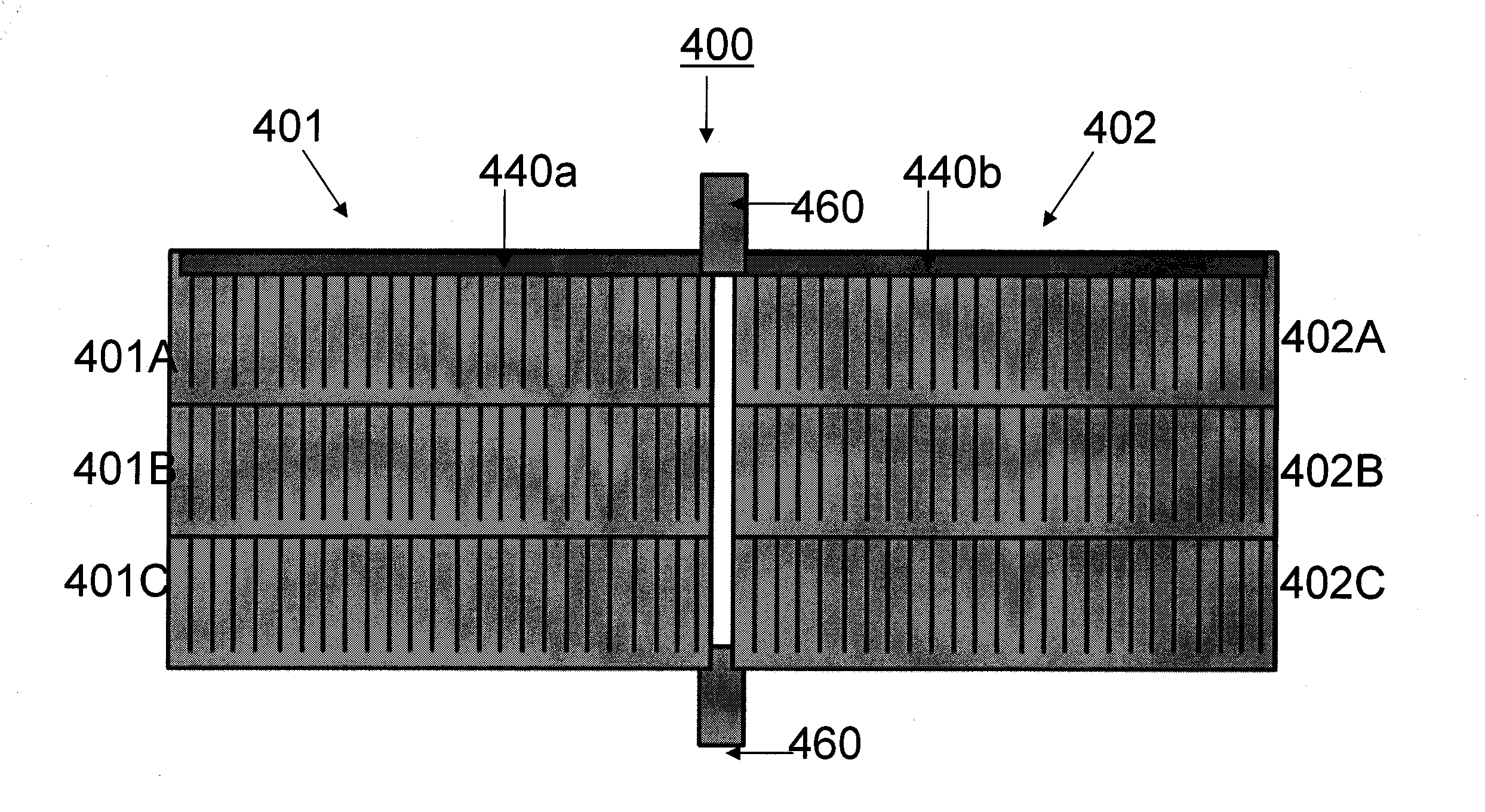
InactiveUS20120318319A1PV power plantsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical and Electronics engineeringThin film solar cell
A photovoltaic module comprises a first group of solar cells; a second group of solar cells; a first interconnection member extending across a first surface of the first group of solar cells and across a first surface of the second group of solar cells to connect the first and second groups of solar cells in parallel; and a second interconnection member extending across a second surface of the first group of solar cells and across a second surface of the second group of solar cells.
Owner:SOLOPOWER
Photovoltaic thin-film cell produced from metallic blend using high-temperature printing
The metallic components of a IB-IIIA-VIA photovoltaic cell active layer may be directly coated onto a substrate by using relatively low melting point (e.g., less than about 500° C.) metals such as indium and gallium. Specifically, CI(G)S thin-film solar cells may be fabricated by blending molten group IIIA metals with solid nanoparticles of group IB and (optionally) group IIIA metals. The molten mixture may be coated onto a substrate in the molten state, e.g., using coating techniques such as hot-dipping, hot microgravure and / or air-knife coating. After coating, the substrate may be cooled and the film annealed, e.g., in a sulfur-containing or selenium-containing atmosphere.
Owner:AERIS CAPITAL SUSTAINABLE IP
Thin-film solar cell fabricated on a flexible metallic substrate
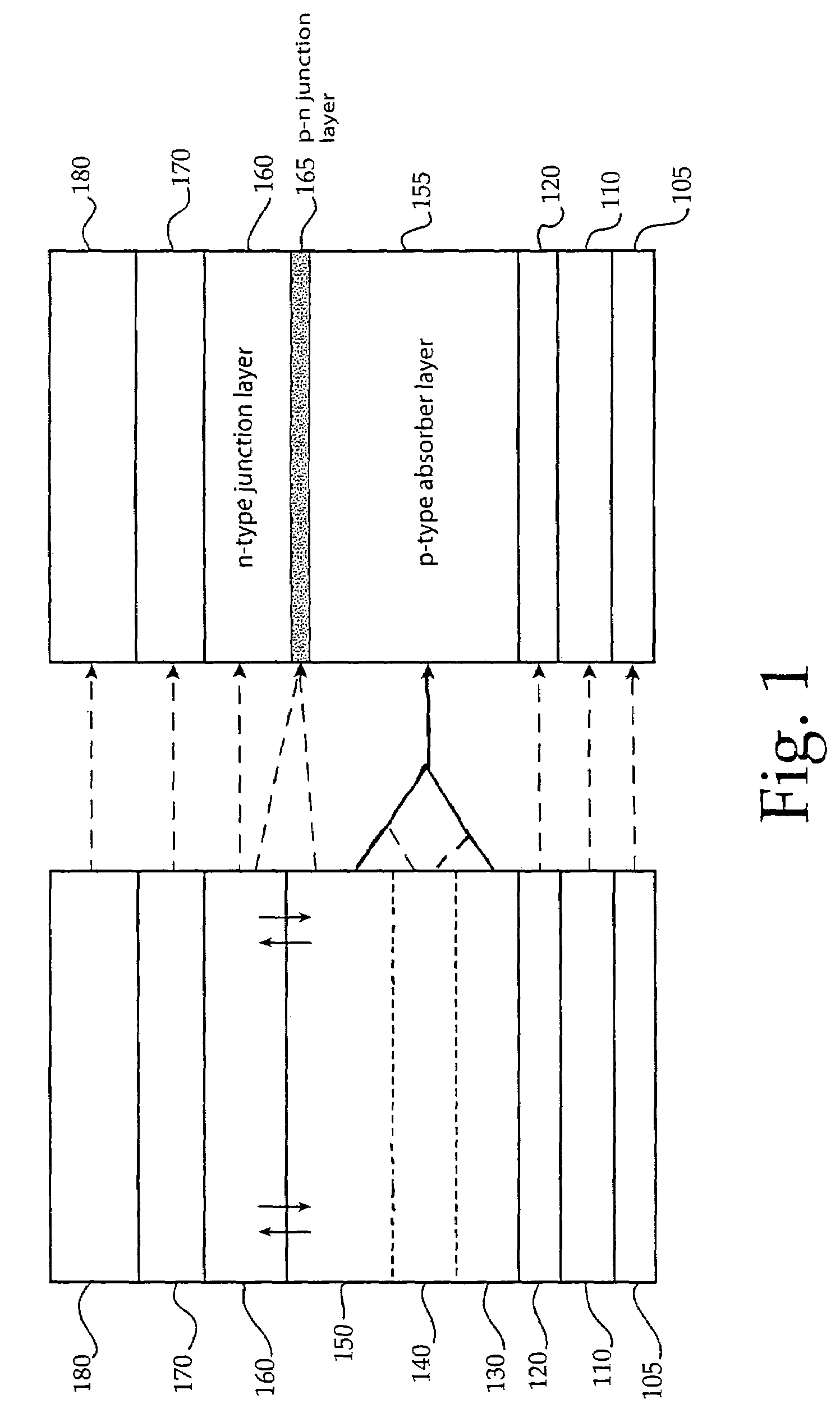
A thin-film solar cell (10) is provided. The thin-film solar cell (10) comprises a flexible metallic substrate (12) having a first surface and a second surface. A back metal contact layer (16) is deposited on the first surface of the flexible metallic substrate (12). A semiconductor absorber layer (14) is deposited on the back metal contact. A photoactive film deposited on the semiconductor absorber layer (14) forms a heterojunction structure and a grid contact (24) deposited on the heterjunction structure. The flexible metal substrate (12) can be constructed of either aluminium or stainless steel. Furthermore, a method of constructing a solar cell is provided. The method comprises providing an aluminum substrate (12), depositing a semiconductor absorber layer (14) on the aluminum substrate (12), and insulating the aluminum substrate (12) from the semiconductor absorber layer (14) to inhibit reaction between the aluminum substrate (12) and the semiconductor absorber layer (14).
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY
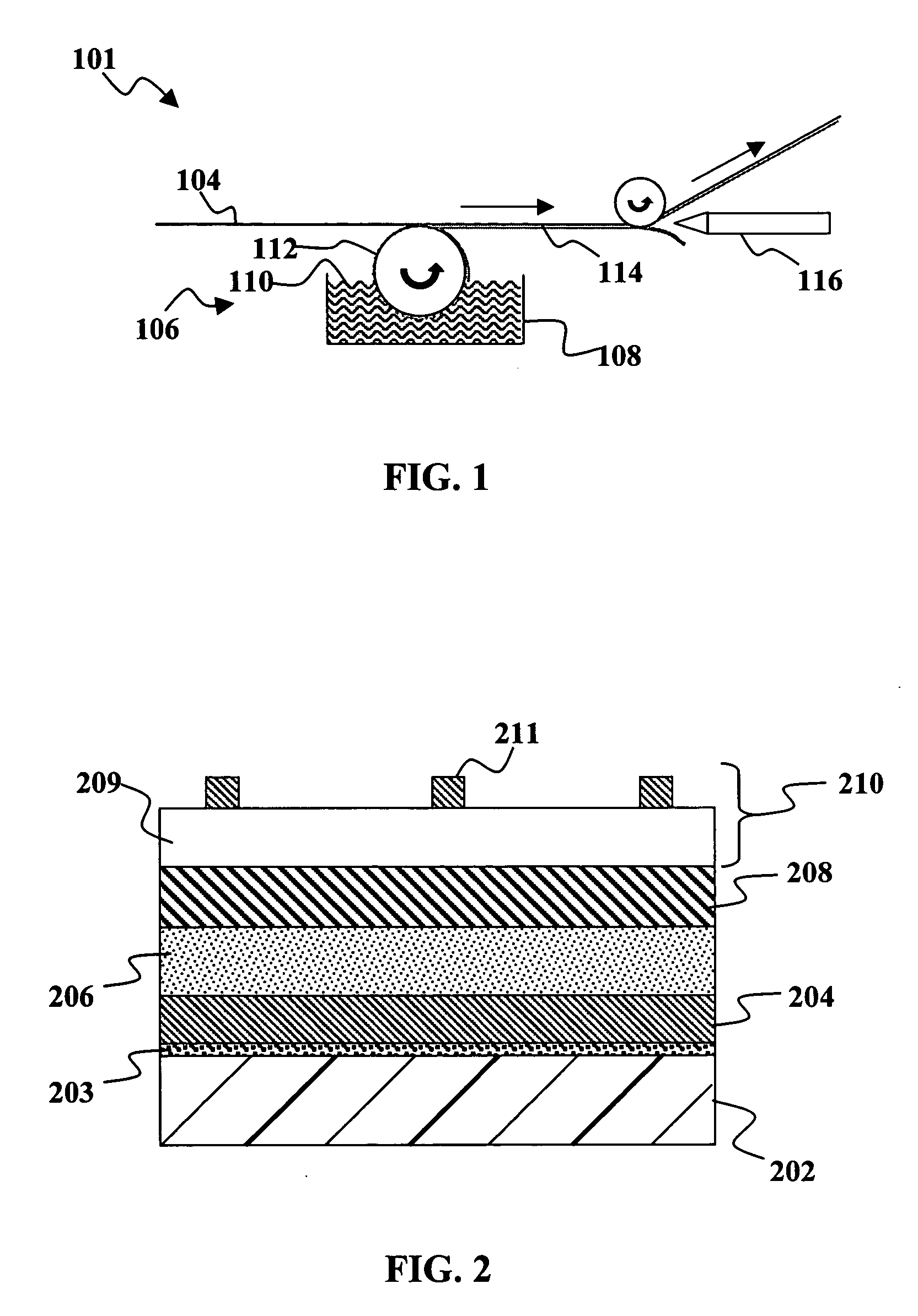
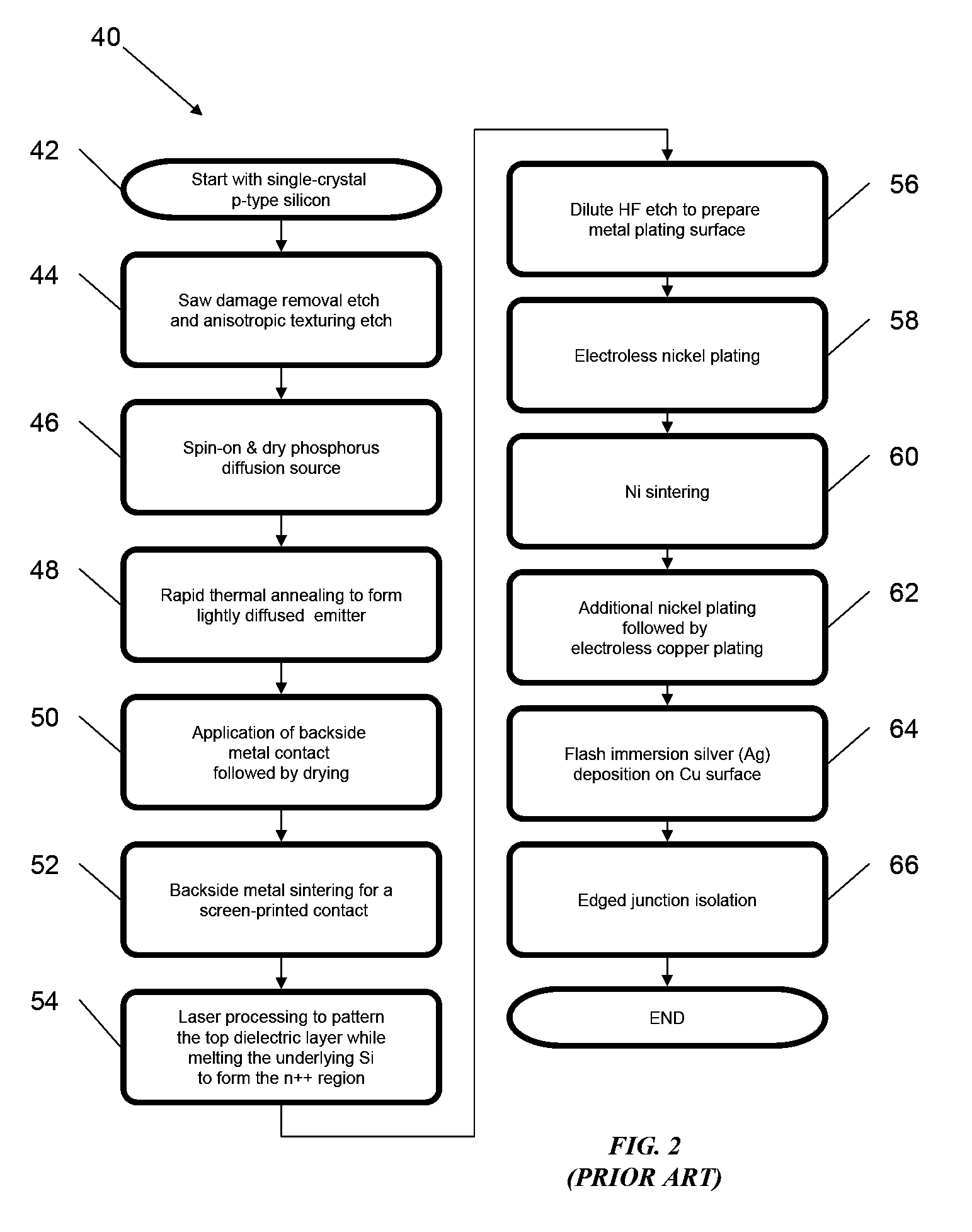
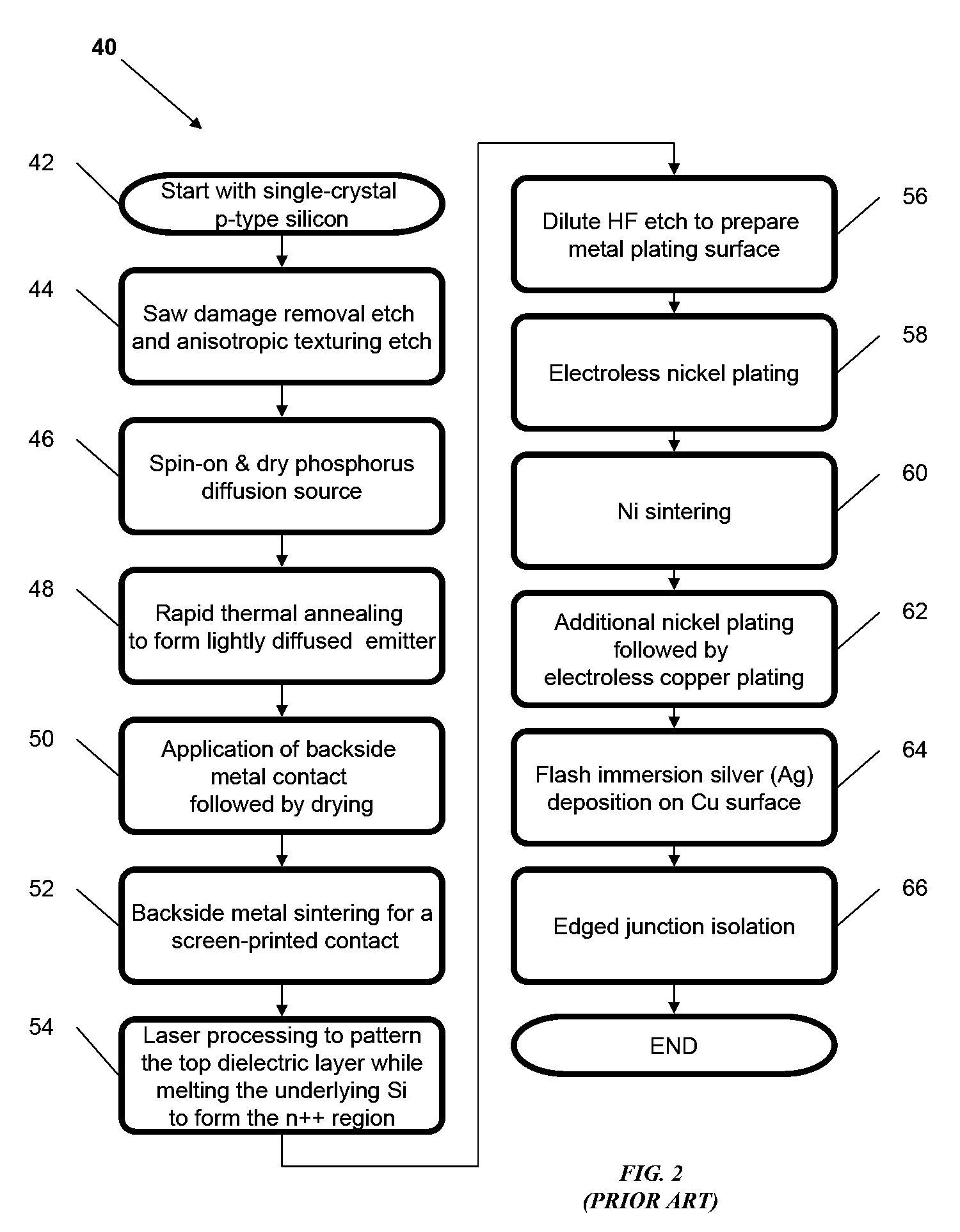
Method and apparatus for forming a thin-film solar cell using a continuous process
InactiveUS20060096537A1Prevent chemical cross-contaminationPromote recoveryFinal product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingMultiple treatmentsEngineering
The present invention relates to new methods for manufacturing photovoltaic devices and an apparatus for practicing those methods of manufacture. The present invention employs a transfer-through system for advancing work piece substrates through an integrated apparatus of multiple treatment chambers that control each of the manufacturing processes.
Owner:DAYSTAR TECHNOLOGIES
Thin film photovoltaic module manufacturing methods and structures
InactiveUS20100147364A1Reduce effective series resistance of devicePV power plantsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetallic foilAmorphous silicon solar cell
Owner:SOLOPOWER
Thin film solar cell and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20060196536A1Improve production yieldPrevent degradationPV power plantsSolid-state devicesTransparent conducting filmEngineering
A thin film solar cell includes: a transparent conductive film arranged on a translucent insulating substrate; first and second separation trenches orthogonal to each other on the translucent insulating substrate and separating the transparent conductive film; and a first opening trench parallel to the first separation trench and second opening trenches parallel to said second separation trench, orthogonal to each other on the translucent insulating substrate; wherein solar cells formed on the translucent insulating substrate are arranged at adjacent positions with said first opening trench positioned therebetween and at adjacent positions with said second opening trench positioned therebetween; pairs of said solar cells adjacent to each other with said first opening trench positioned therebetween are electrically connected, and among pairs of solar cells positioned adjacent to each other with the second opening trench in between, some are electrically connected to each other, and others are electrically insulated from each other. Method of manufacturing the thin film solar cell is also provided.
Owner:SHARP KK
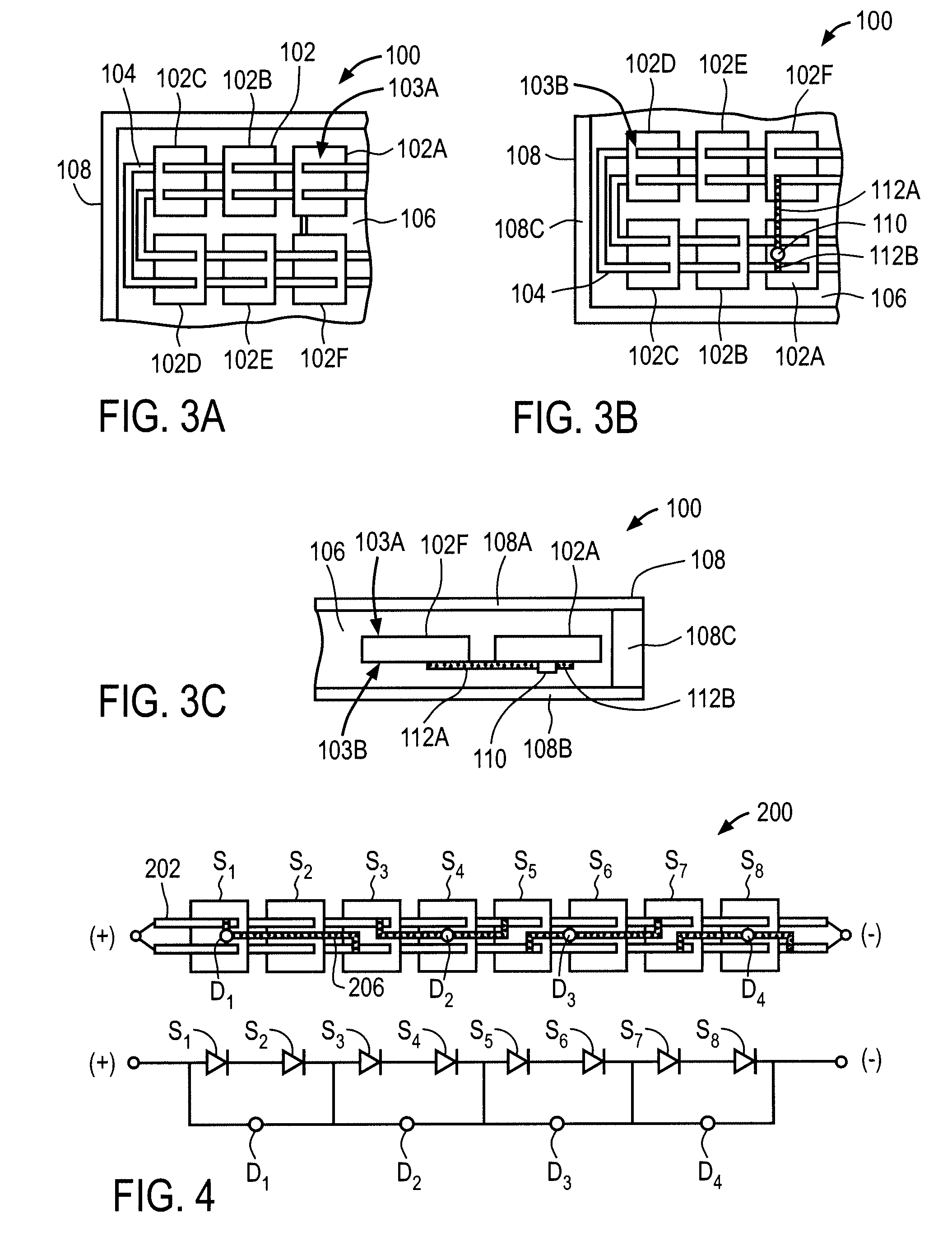
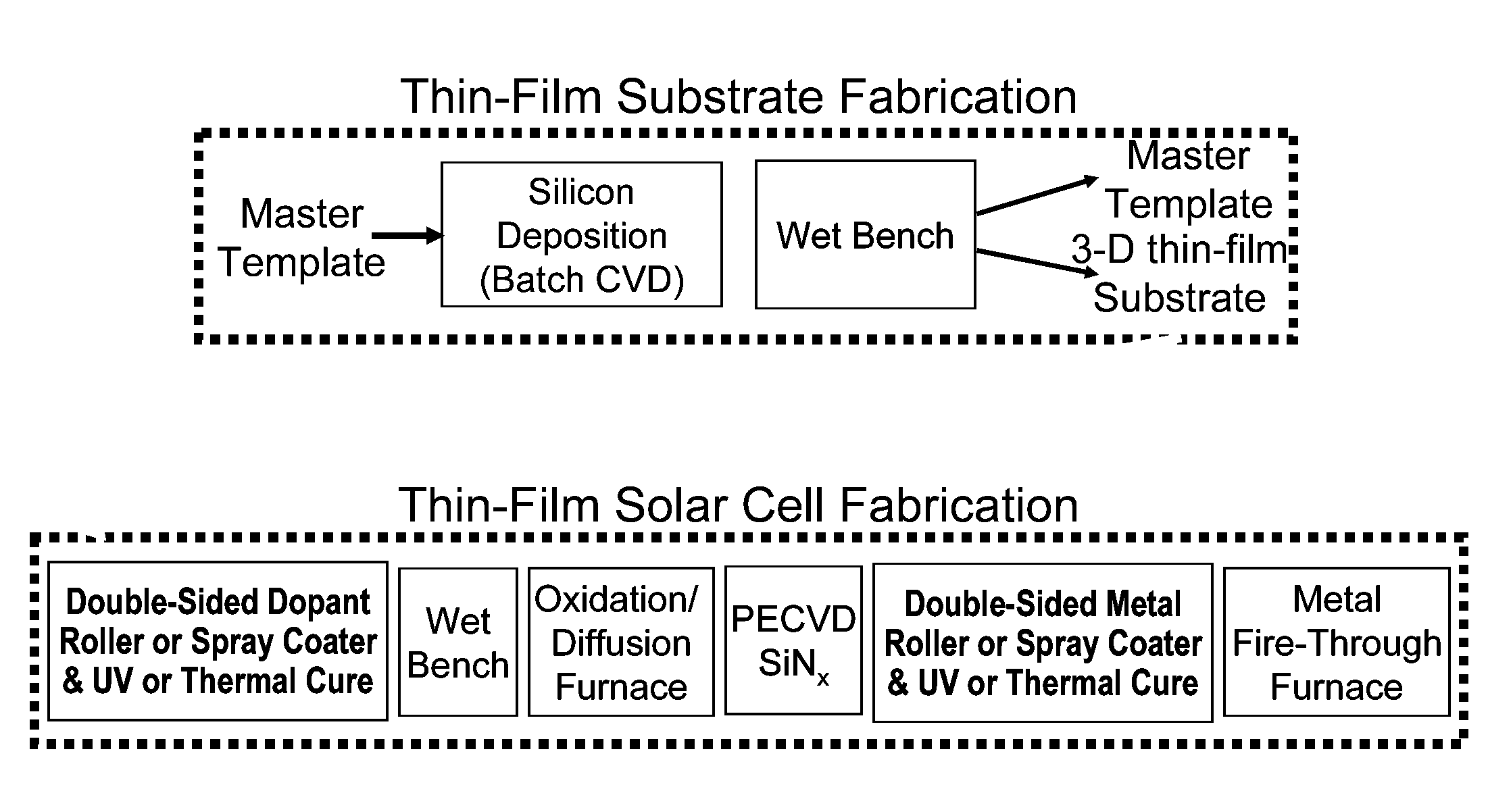
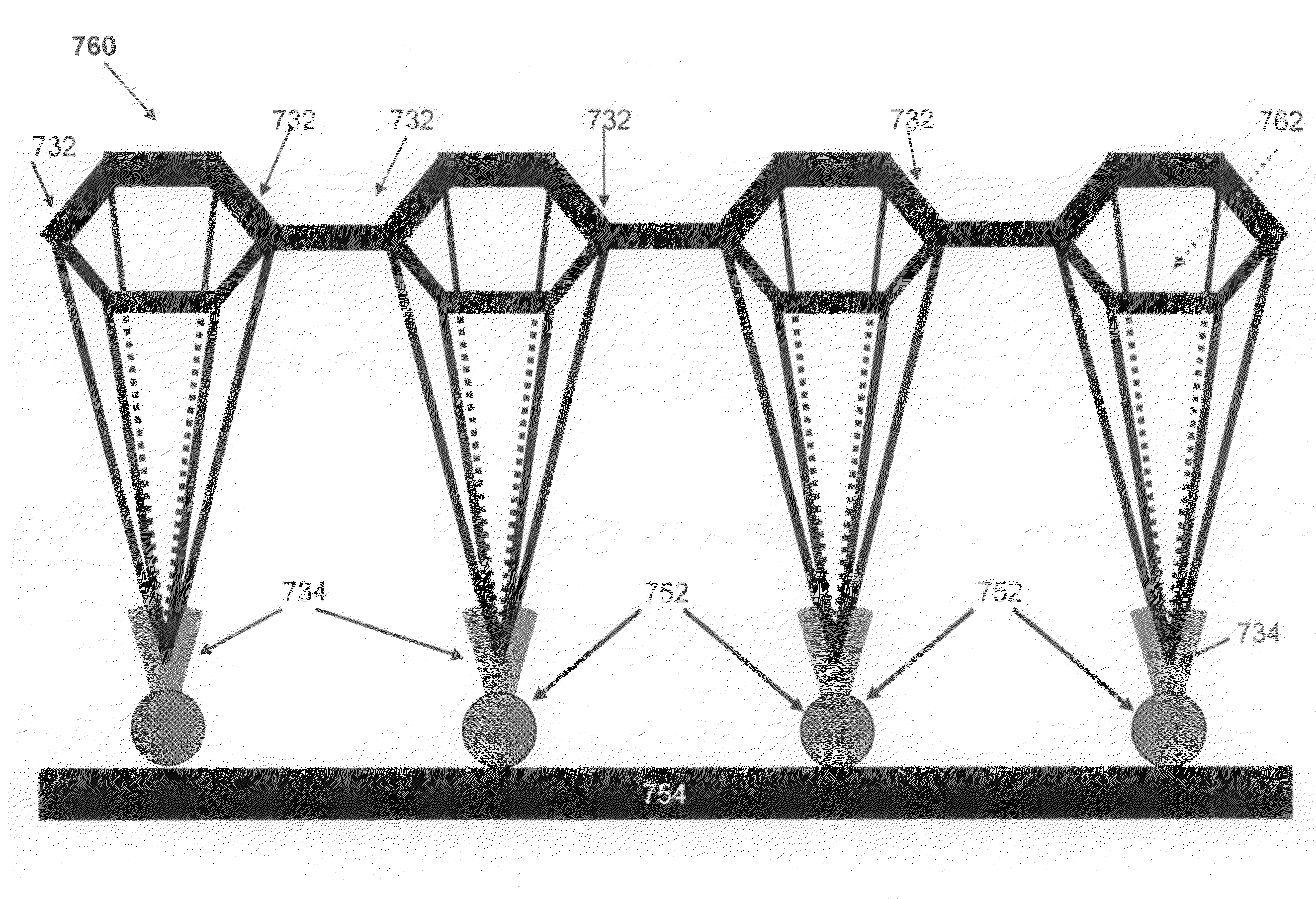
Methods for manufacturing three-dimensional thin-film solar cells
InactiveUS20080264477A1Eliminate and reduce disadvantageEliminate and reduce and problemFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationDopantThin membrane
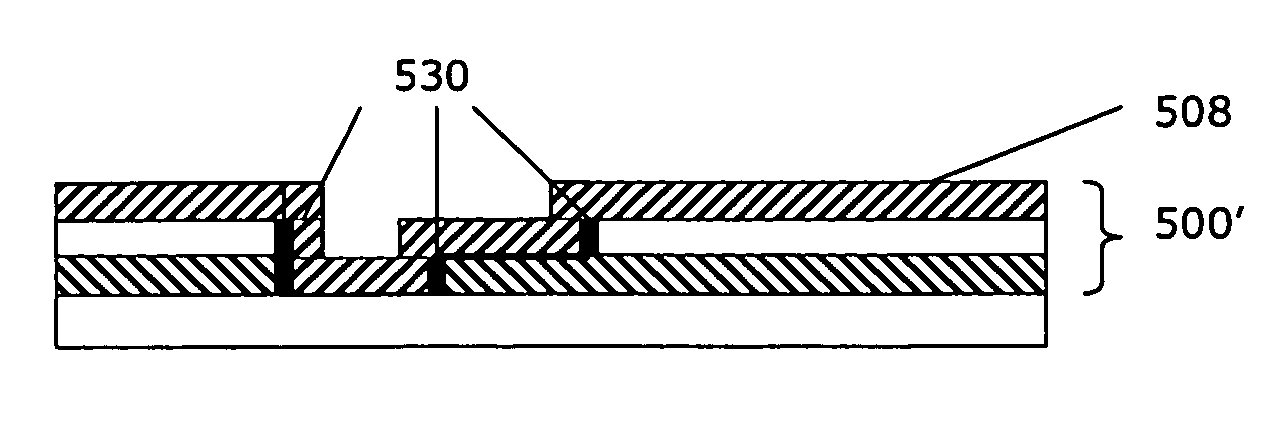
Methods for manufacturing three-dimensional thin-film solar cells 100, using a template. The template comprises a template substrate comprising a plurality of posts and a plurality of trenches between said plurality of posts. The three-dimensional thin-film solar cell substrate is formed by forming a sacrificial layer on the template, subsequently depositing a semiconductor layer, selectively etching the sacrificial layer, and releasing the semiconductor layer from the template. The resulting three-dimensional thin-film solar cell substrate may comprise a plurality of single-aperture unit cells or dual-aperture unit cells. Select portions of the three-dimensional thin-film solar cell substrate are then doped with a first dopant, while other select portions are doped with a second dopant. Next, emitter 525 and base metallization regions 532 are formed.
Owner:BEAMREACH SOLAR INC
Thermal process for creation of an in-situ junction layer in CIGS
InactiveUS7319190B2Reduce the temperatureFinal product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingJunction formationGrowth of photovoltaics
The present invention relates generally to the field of photovoltaics and more specifically to manufacturing thin-film solar cells using a thermal process. Specifically, a method is disclosed to manufacture a CIGS solar cell by an in-situ junction formation process.
Owner:DAYSTAR TECHNOLOGIES
Method for producing photovoltaic thin film module
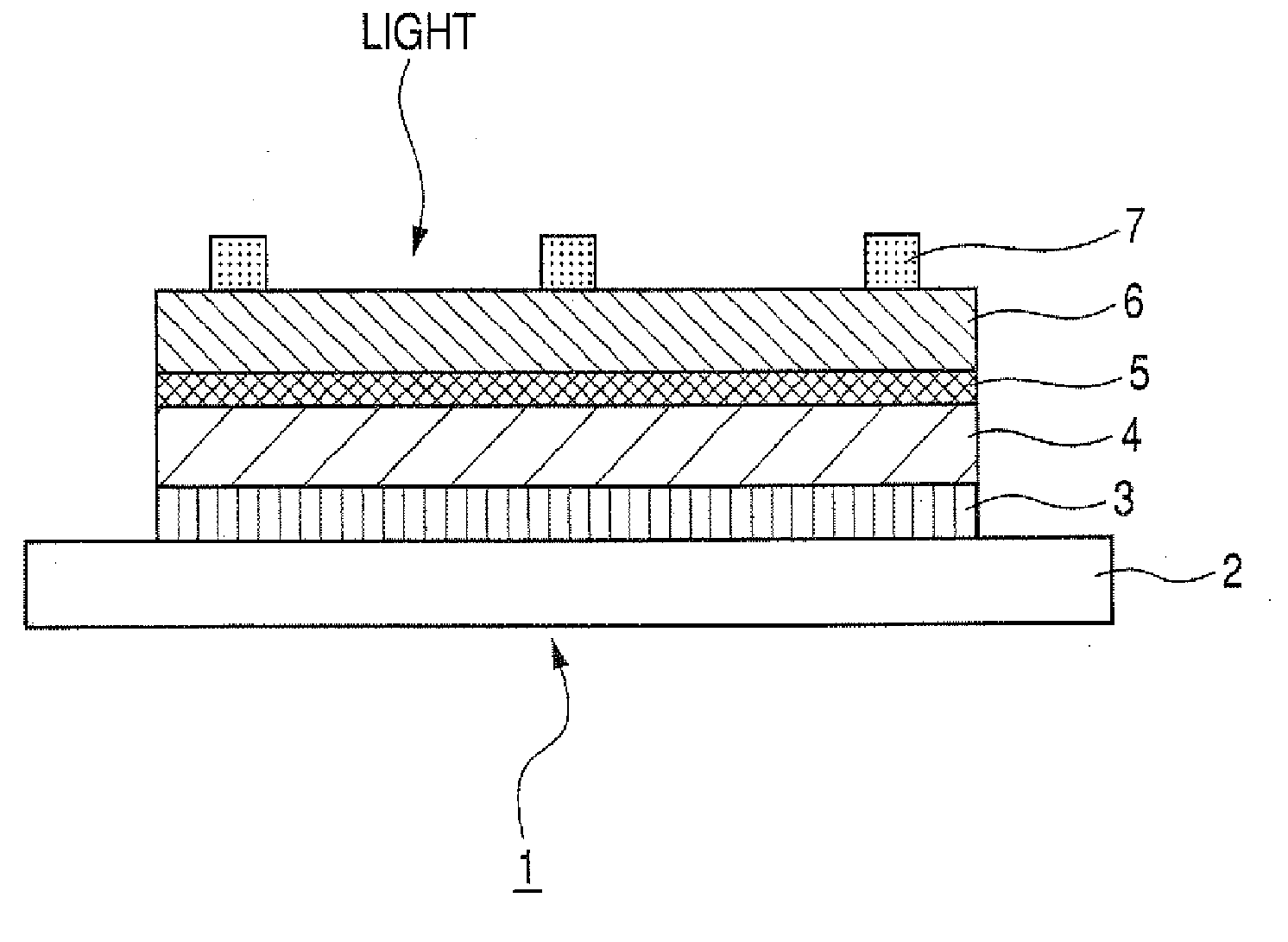
InactiveUS20030029493A1Processing duration reducedReduce energy costsLamination ancillary operationsPV power plantsElectrical batteryWater vapor
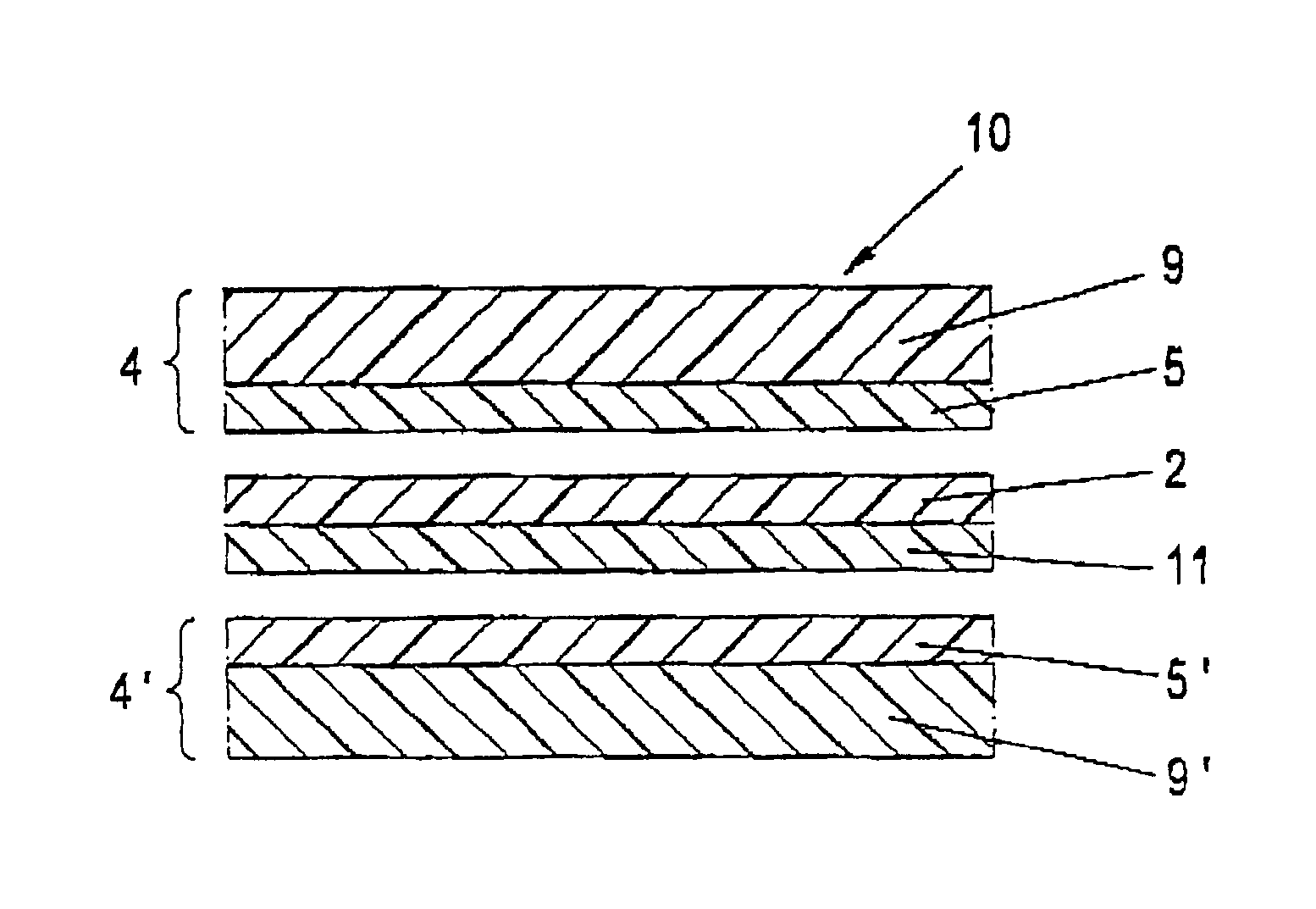
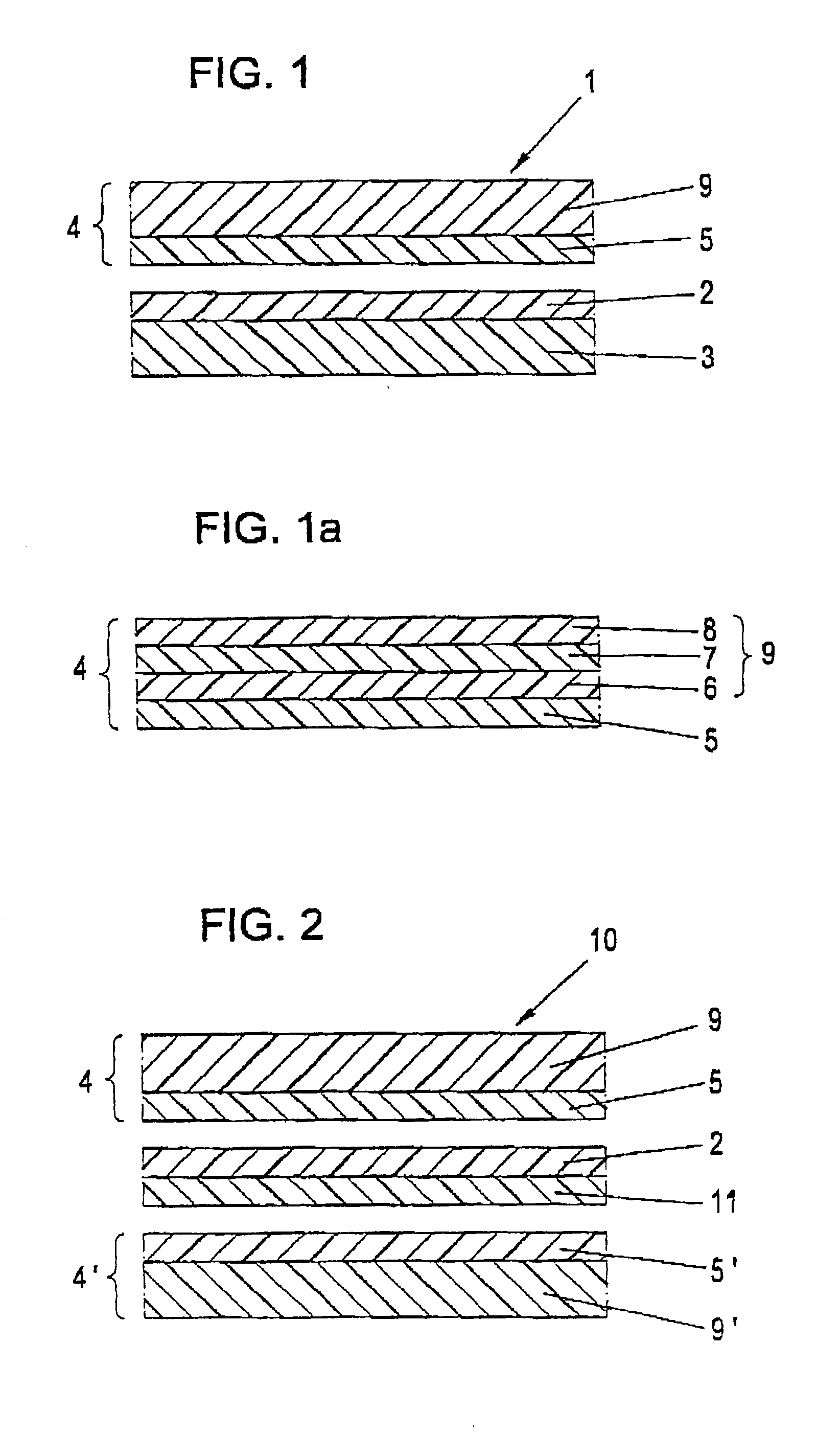
The invention relates to a method for producing a photovoltaic thin film module (1) which is provided with a thin film solar cell system (2) that is mounted on carrier materials (3) and is covered with a compound (4) on at least one side of the surface, whereby said compound consists of an encapsulating material and is provided with a sealing layer (5) on the side of the surface thereof, said side being arranged on the thin film solar cell system (2). According to a covering method, the encapsulating material (4) and the thin film solar cell system (2), together with the carrier (3), are guided along one another and are pressed under pressure and at an increased temperature in such a way that a weather-proof, photovoltaic thin film module in the form of a compound (1) is designed. According to a method that can be carried out easily, a photovoltaic thin film module that is resistant to UV light, water vapour and other effects of the weather is provided. The photovoltaic module can additionally be provided with flexible characteristics by selecting the carrier material in such a way that said material is configured in the form of plastic foils or plastic foil compounds for instance.
Owner:ISOVOLTA OSTE ISOLIERSTOFFWERKE AG
Solar module structures and assembly methods for pyramidal three-dimensional thin-film solar cells
InactiveUS20080210294A1Eliminate and reduce disadvantageEliminate and reduce and problemFinal product manufacturePV power plantsEngineeringSolar power
Solar module structures and methods for assembling solar module structures. The solar module structures comprise pyramidal three-dimensional thin-film solar cells arranged in solar module structures. The pyramidal three-dimensional thin-film solar cell comprises a pyramidal three-dimensional thin-film solar cell substrate with emitter junction regions and doped base regions. The three-dimensional thin-film solar cell further includes emitter metallization regions and base metallization regions. The three-dimensional thin-film solar cell substrate comprises a plurality of pyramid-shaped unit cells. The solar module structures may be used in solar glass applications, building façade applications, rooftop installation applications as well as for centralized solar electricity generation.
Owner:BEAMREACH SOLAR INC
Technique For Preparing Precursor Films And Compound Layers For Thin Film Solar Cell Fabrication And Apparatus Corresponding Thereto
InactiveUS20070093006A1Final product manufactureSolid-state devicesCompound (substance)Degrees of freedom
The present invention advantageously provides for, in different embodiments, improved contact layers or nucleation layers over which precursors and Group IBIIIAVIA compound thin films adhere well and form high quality layers with excellent micro-scale compositional uniformity. It also provides methods to form precursor stack layers, by wet deposition techniques such as electroplating, with large degree of freedom in terms of deposition sequence of different layers forming the stack.
Owner:SOLOPOWER
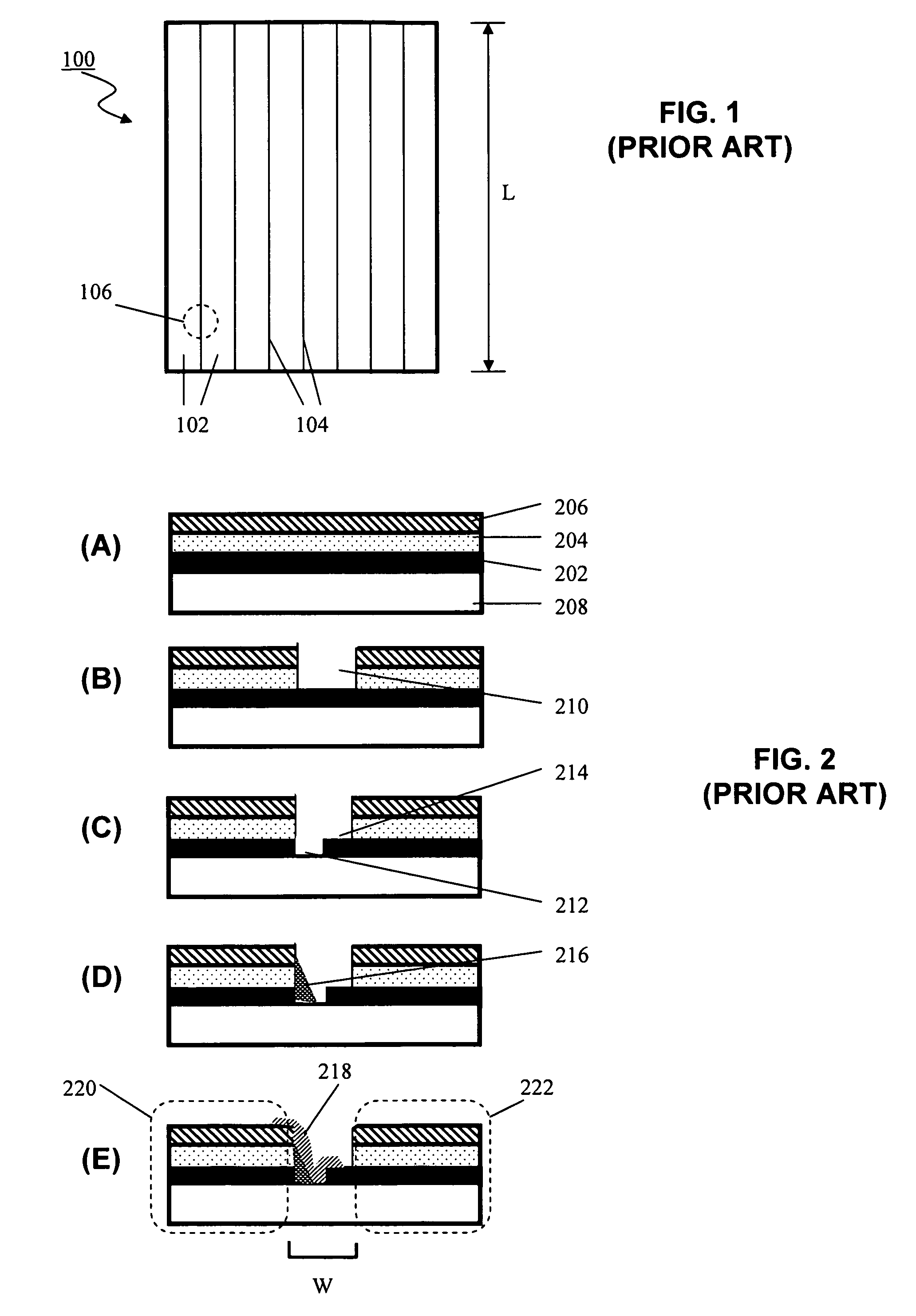
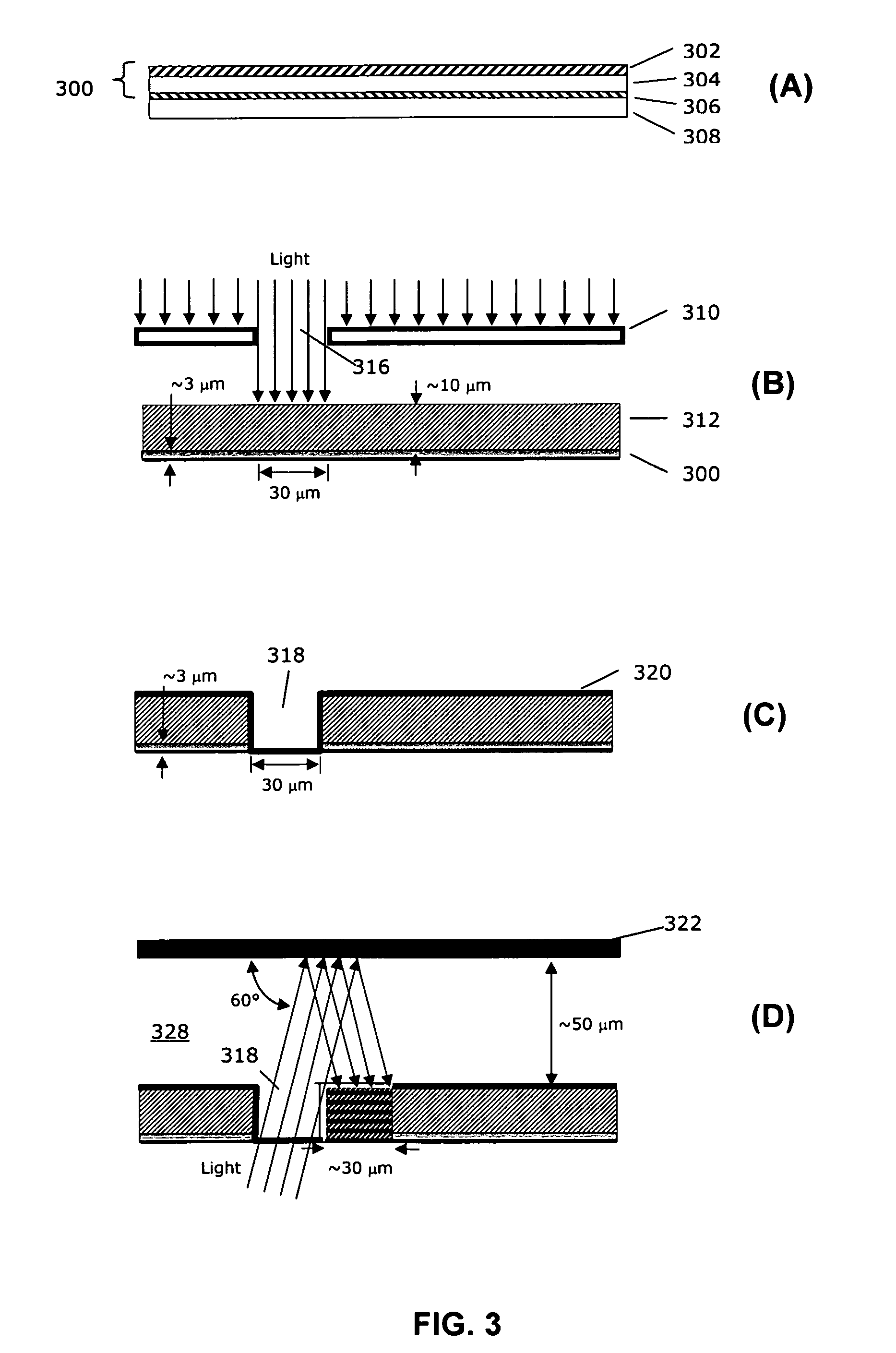
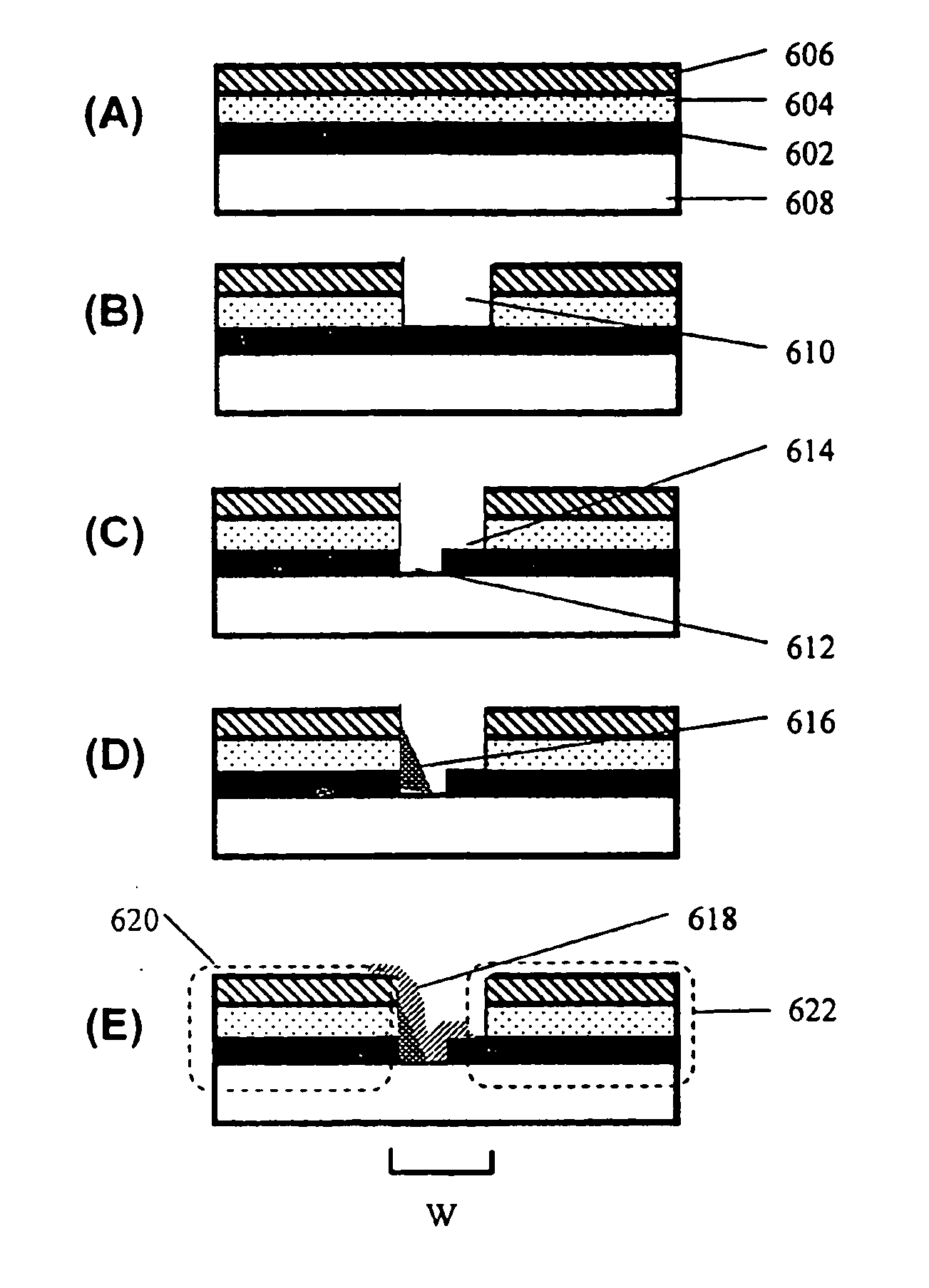
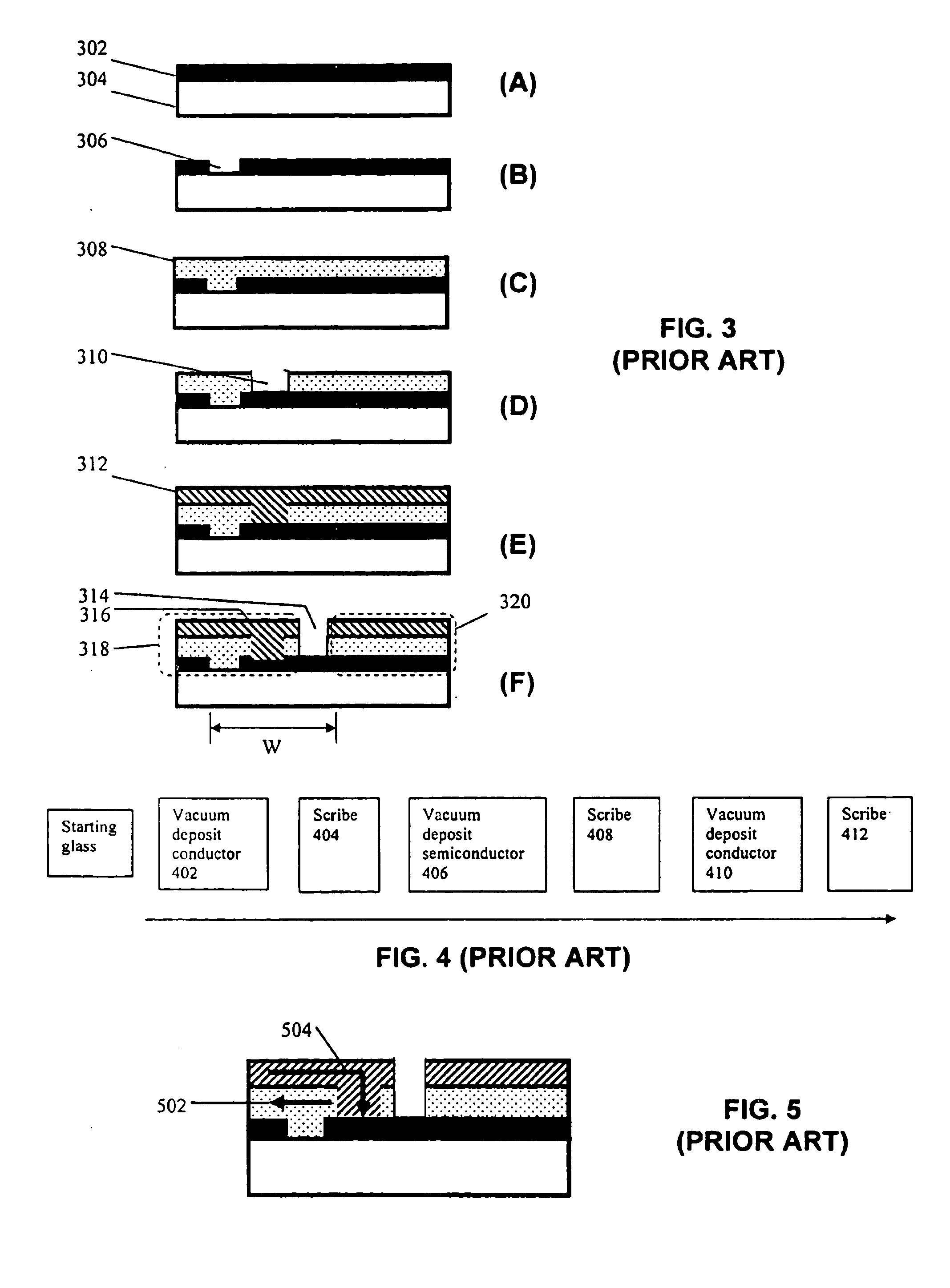
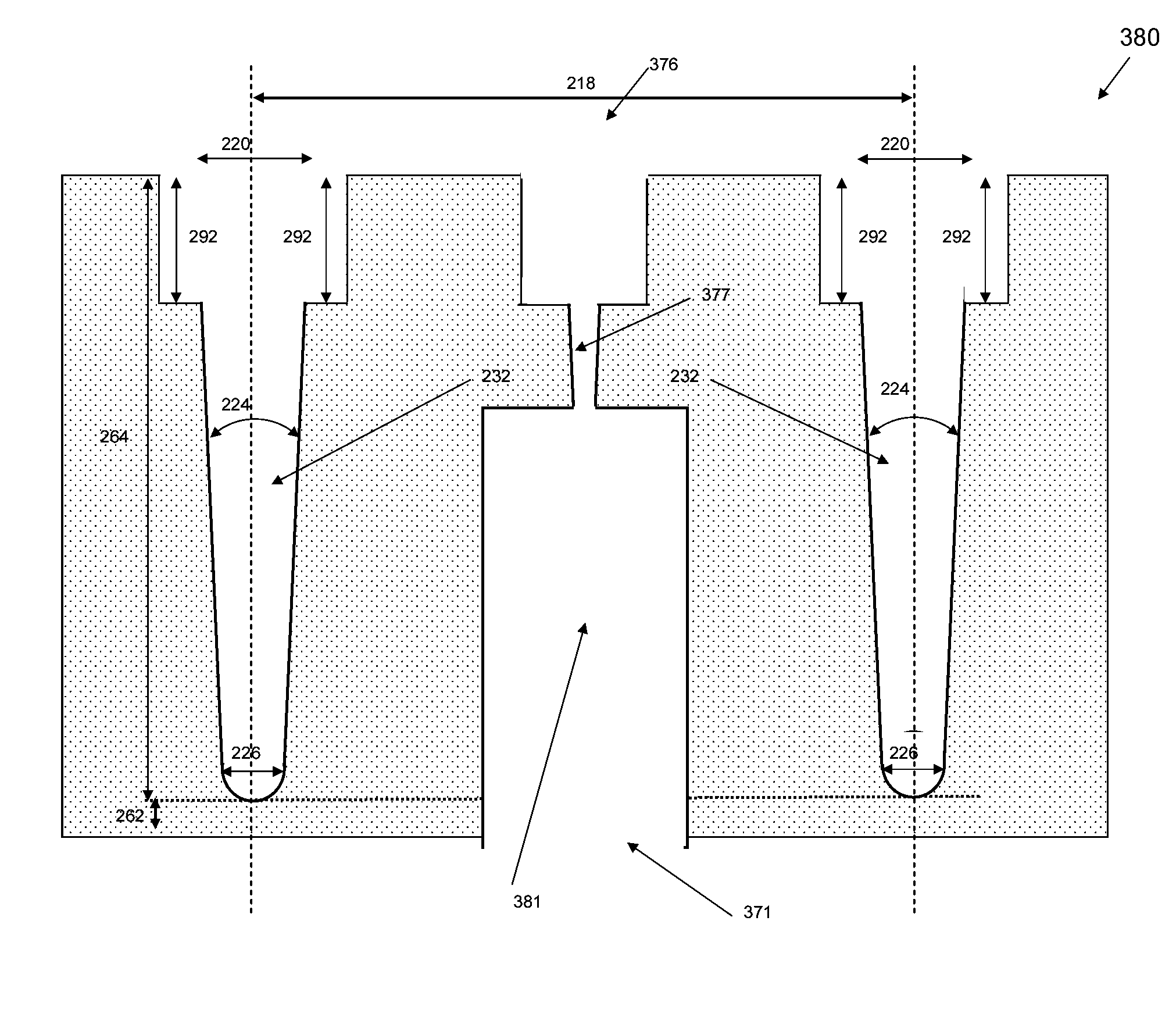
Method for making an improved thin film solar cell interconnect using etch and deposition process
InactiveUS20070238285A1Improve current transportPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringDeposition process
The present invention provides a method of forming interconnects in a photovoltaic module. According to one aspect, a method according to the invention includes processing steps that are similar to those performed in conventional integrated circuit fabrication. For example, the method can include masks and etches to form isolation grooves between cells, and additional etches to form a conductive step adjacent to the grooves that can be used to form interconnects between cells. According to another aspect the method for forming the conductive step can be self-aligned, such as by positioning a mirror above the module and exposing photoresist from underneath the substrate at an angle one or more times, and etching to expose the conductive step. According to another aspect, the process can include steps to form grid lines in the module to improve current transport in the structure.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Thin film solar cell
InactiveUS20080078444A1Good choiceImprovement factorPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesHigh energyUltraviolet
Optimal structures for high efficiency thin film silicon solar energy conversion devices and systems are disclosed. Thin film silicon active layer photoelectron conversion structures using ion implantation are disclosed. Thin film semiconductor devices optimized for exploiting the high energy and ultraviolet portion of the solar spectrum at the earths surface are also disclosed. Solar cell fabrication using high oxygen concentration single crystal silicon substrates formed using in preference the CZ method are used advantageously. Furthermore, the present invention discloses optical coatings for advantageous coupling of solar radiation into thin film solar cell devices via the use of rare-earth metal oxide (REOx), rare-earth metal oxynitride (REOxNy) and rare-earth metal oxy-phosphide (REOxPy) glasses and or crystalline material. The rare-earth metal is chosen from the group commonly known in the periodic table of elements as the lanthanide series.
Owner:IQE
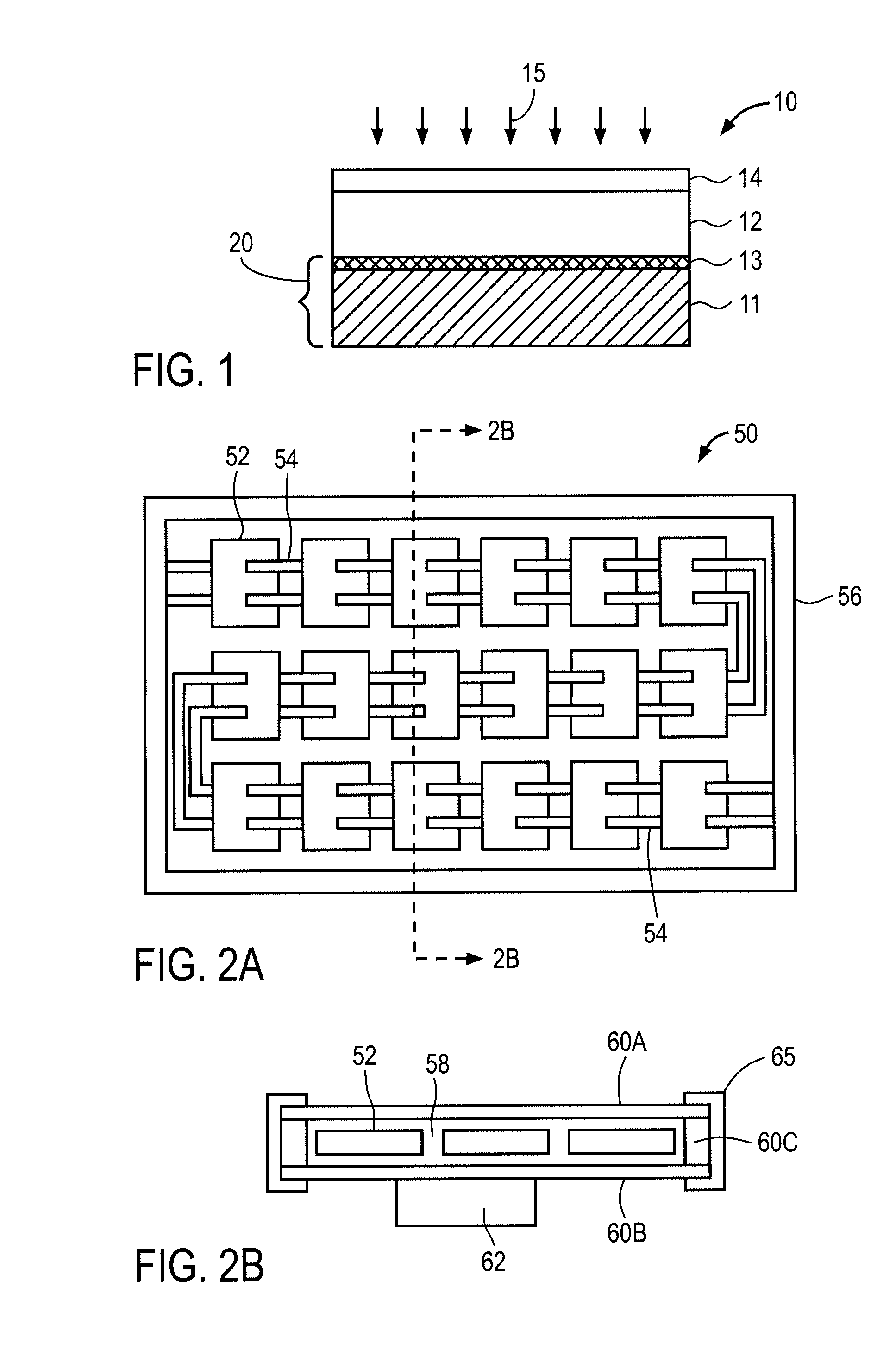
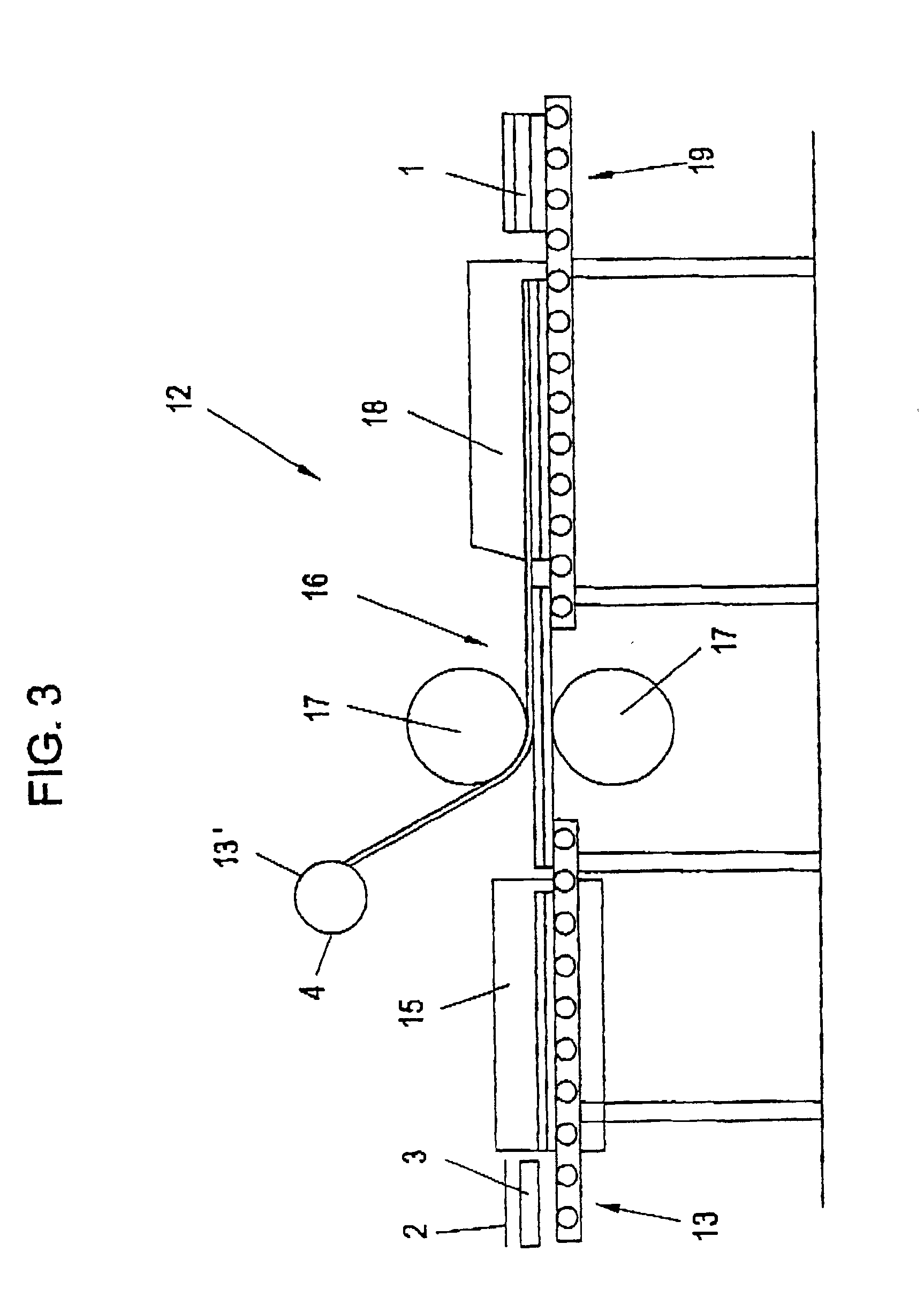
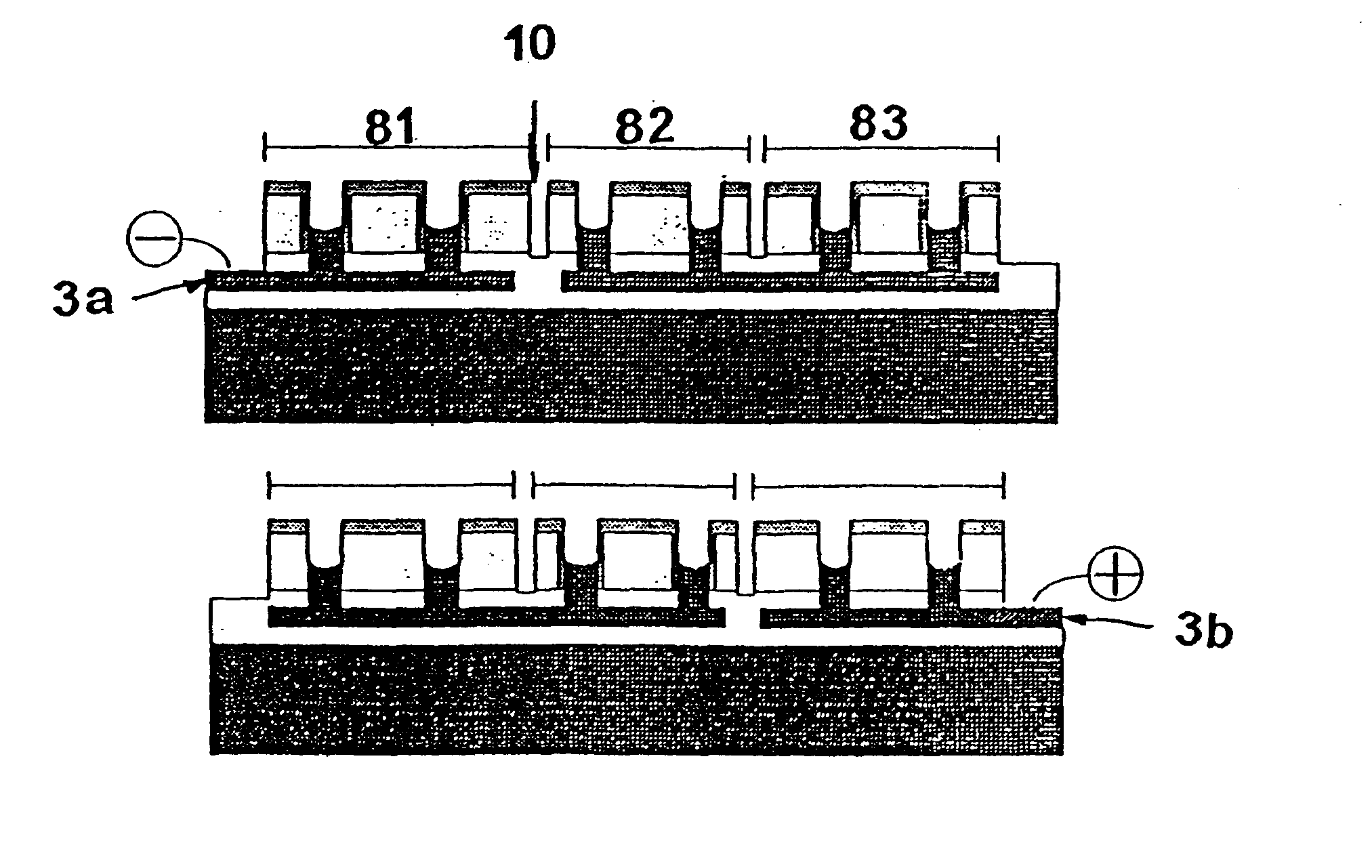
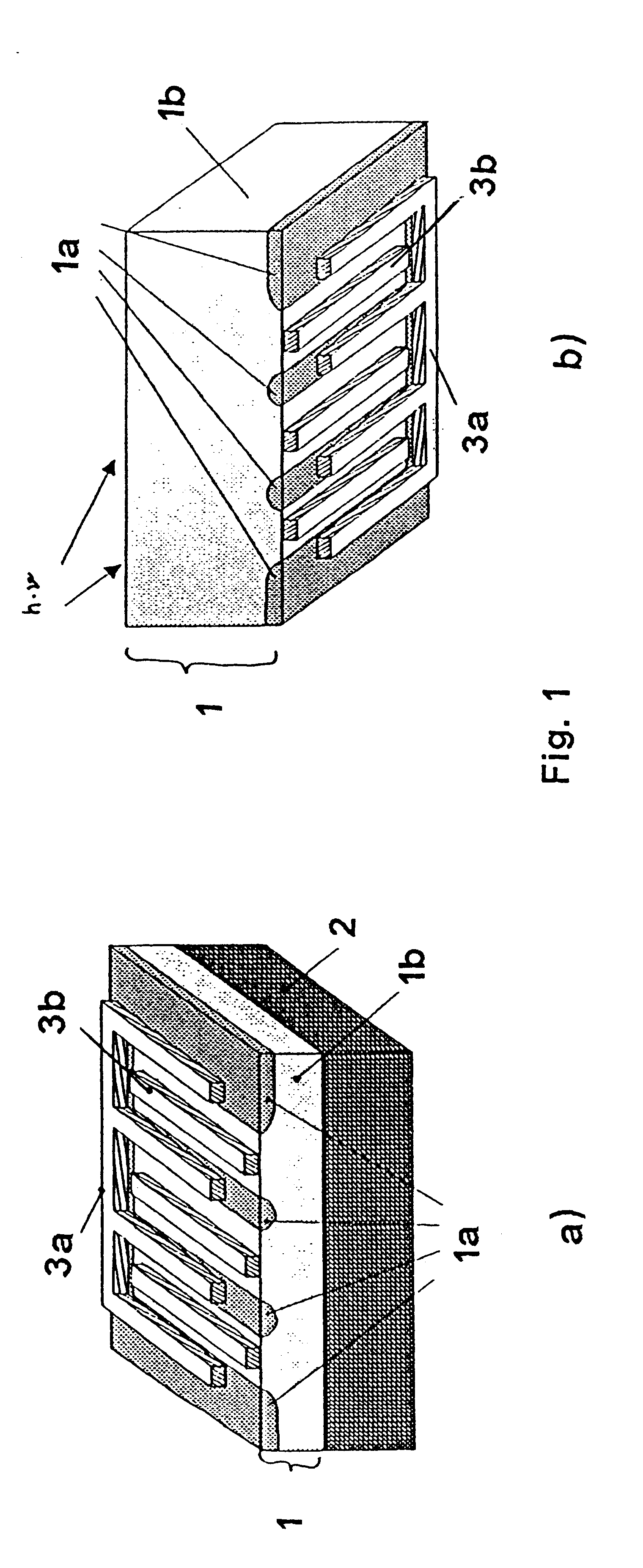
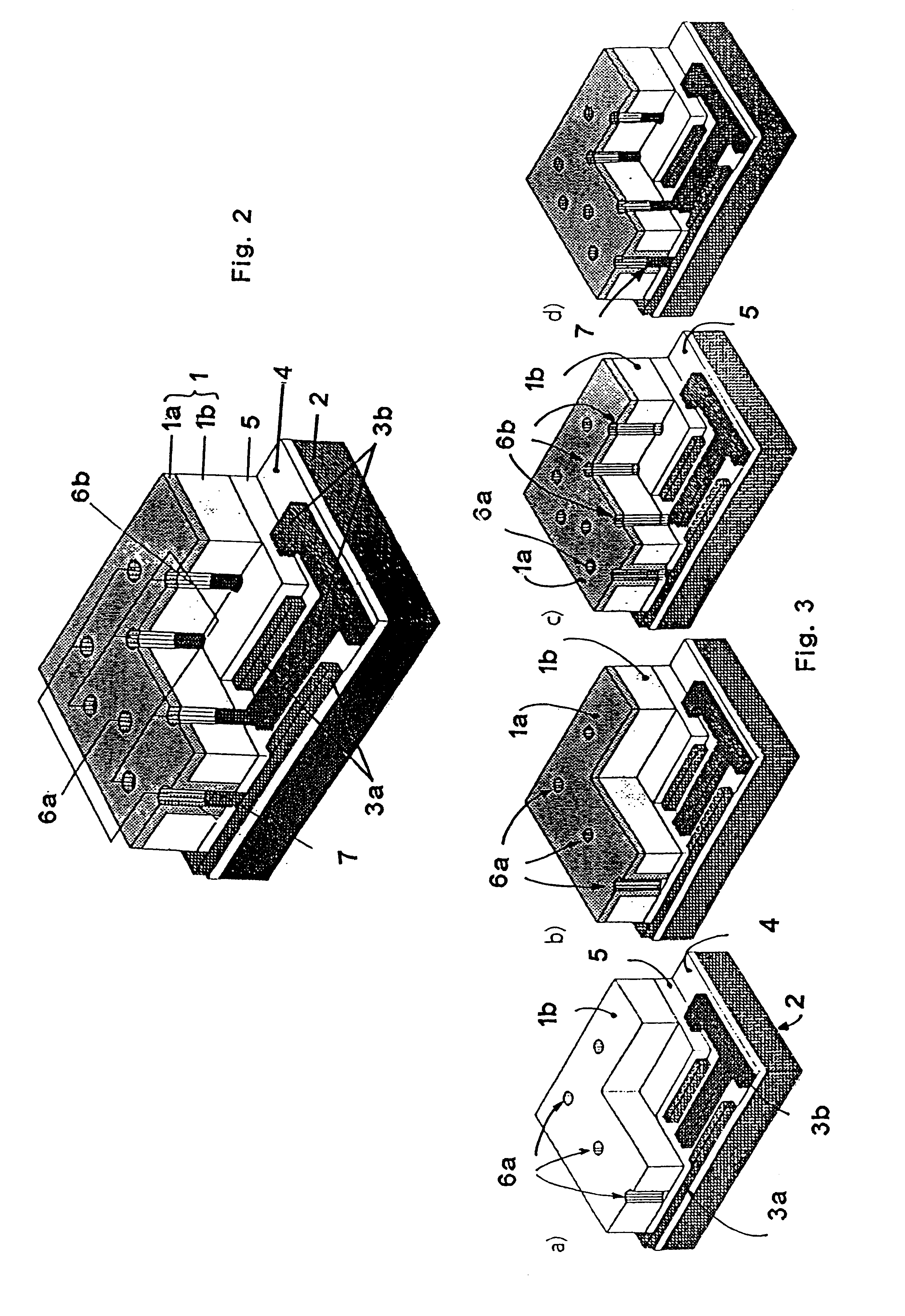
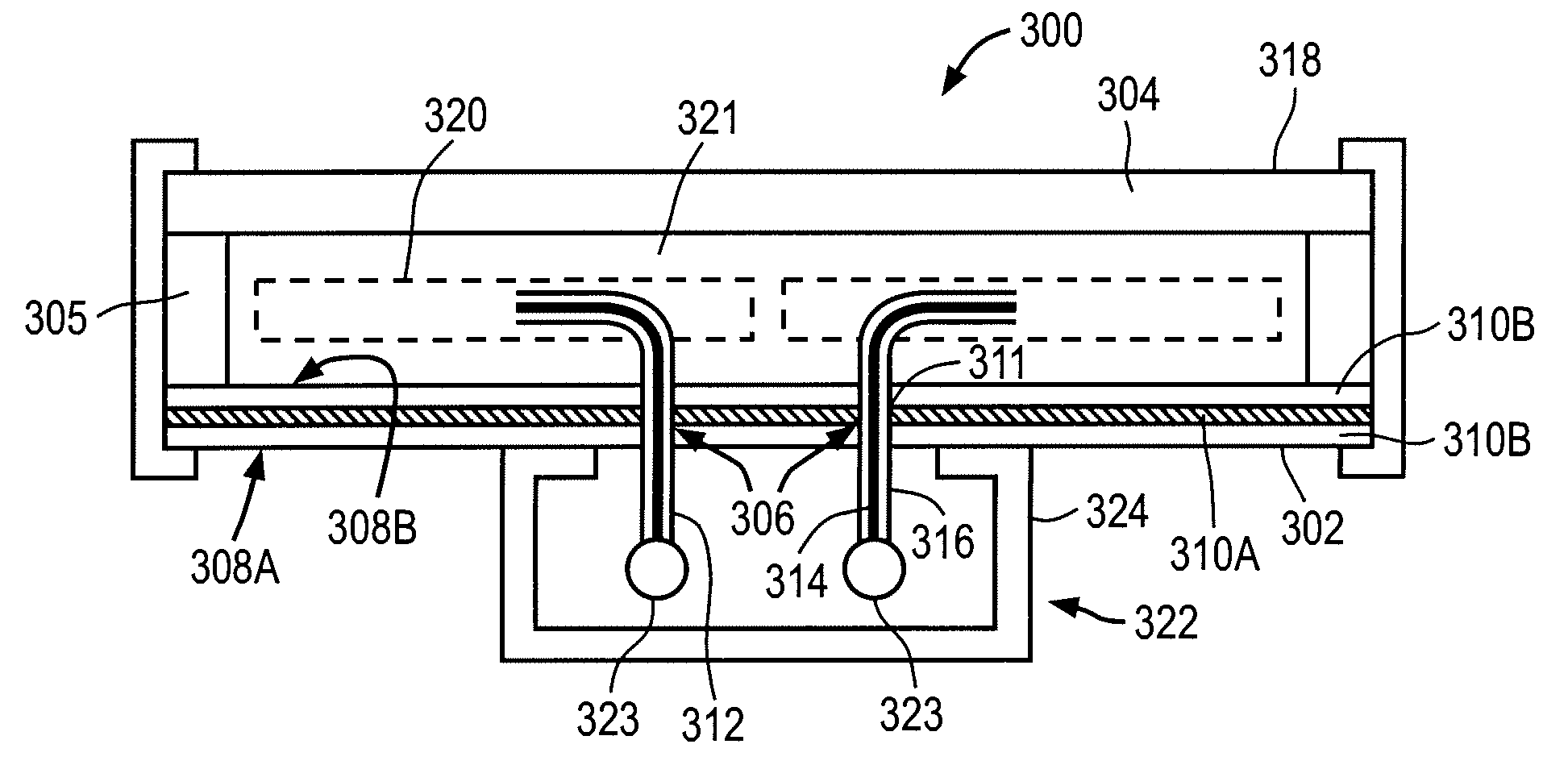
Thin-film solar array system and method for producing the same
Disclosed is a thin-layer solar cell array system and a method for producing the same, having placed over a carrier substrate of plane design, a solar cell layer which is provided with at least one n-type conducting semiconductor zone (emitter) and at least one p-type conducting semiconductor zone (base) as well as a first and a second contact electrode, each of different electric polarity, which are each electrically connected to the emitter respectively to the base.The invention is distinguished by at least the first contact electrode being applied directly on the carrier substrate or separated by an electrically insulating layer, an electrically insulating layer being provided thereupon, and the solar cell layer being placed over the insulating layer, by at least one contact channel extending through the insulating layer and / or the solar cell layer in such a manner that the first contact electrode and the semiconductor layer zone of respective polarity inside the solar cell layer being electrically connectable by means of an electrically conducting material provided inside the contact channel, and by the second contact electrode like the first contact electrode being placed above or in the case of a conductive carrier layer also under the carrier layer and under the electrically insulating layer and the solar cell layer, and by at least one contact channel extending through the insulating layer and / or the solar cell layer in such a manner that the second contact electrode and the semiconductor layer zone of respective polarity inside the solar cell layer being electrically connected by means of an electrically conducting material provided inside the contact channel.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Reliable thin film photovoltaic module structures
The inventions described herein generally relate to photovoltaic or solar module design and fabrication and, more particularly, to modules utilizing thin film solar cells. In one aspect is described a solar module and method of making the same that has a shield material that is both an electrical insulator and a moisture barrier provided at a location corresponding to at least one hole that is used to route a wiring member, such that the shield material seals the at least one hole against moisture entering into the internal space and electrically insulates the wires of the wiring member from the at least one metallic layer of the back protective sheet.
Owner:SOLOPOWER
System and method for making an improved thin film solar cell interconnect
InactiveUS20070079866A1Simple processImprove module qualityPV power plantsPhotovoltaic energy generationEngineeringActive layer
In a module of photovoltaic cells, a method of forming the module interconnects includes a single cutting process after the deposition of all active layers. This simplifies the overall process to a set of vacuum steps followed by a set of interconnect steps, and may significantly module quality and yield. According to another aspect, an interconnect forming method includes self-aligned deposition of an insulator. This simplifies the process because no alignment is required. According to another aspect, an interconnect forming method includes a scribing process that results in a much narrower interconnect which may significantly boost cell efficiency, and allow for narrower cell sizes. According to another aspect, an interconnect includes an insulator layer that greatly reduces shunt current through the active layer, which can greatly improve cell efficiency.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
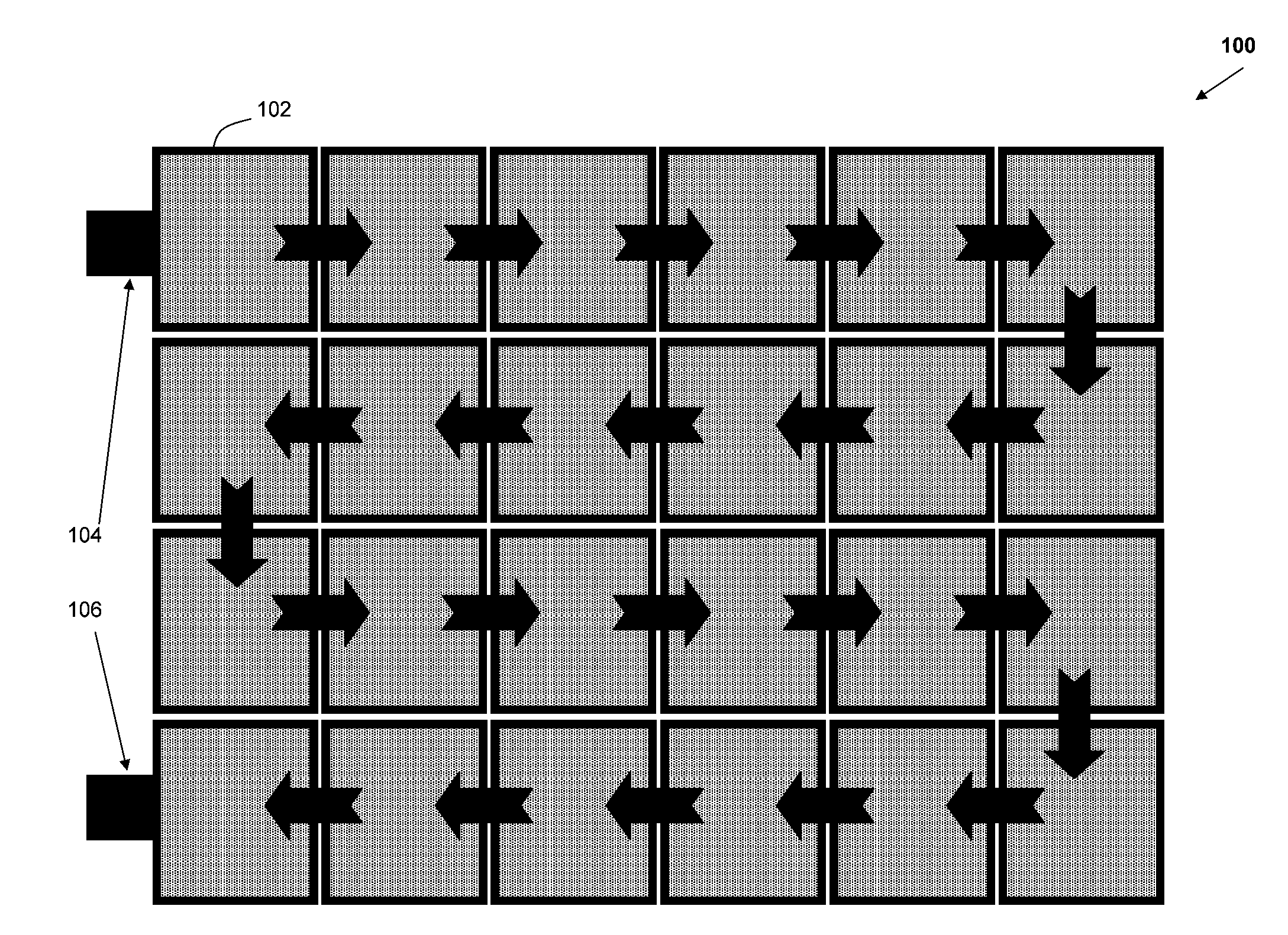
Template for three-dimensional thin-film solar cell manufacturing and methods of use
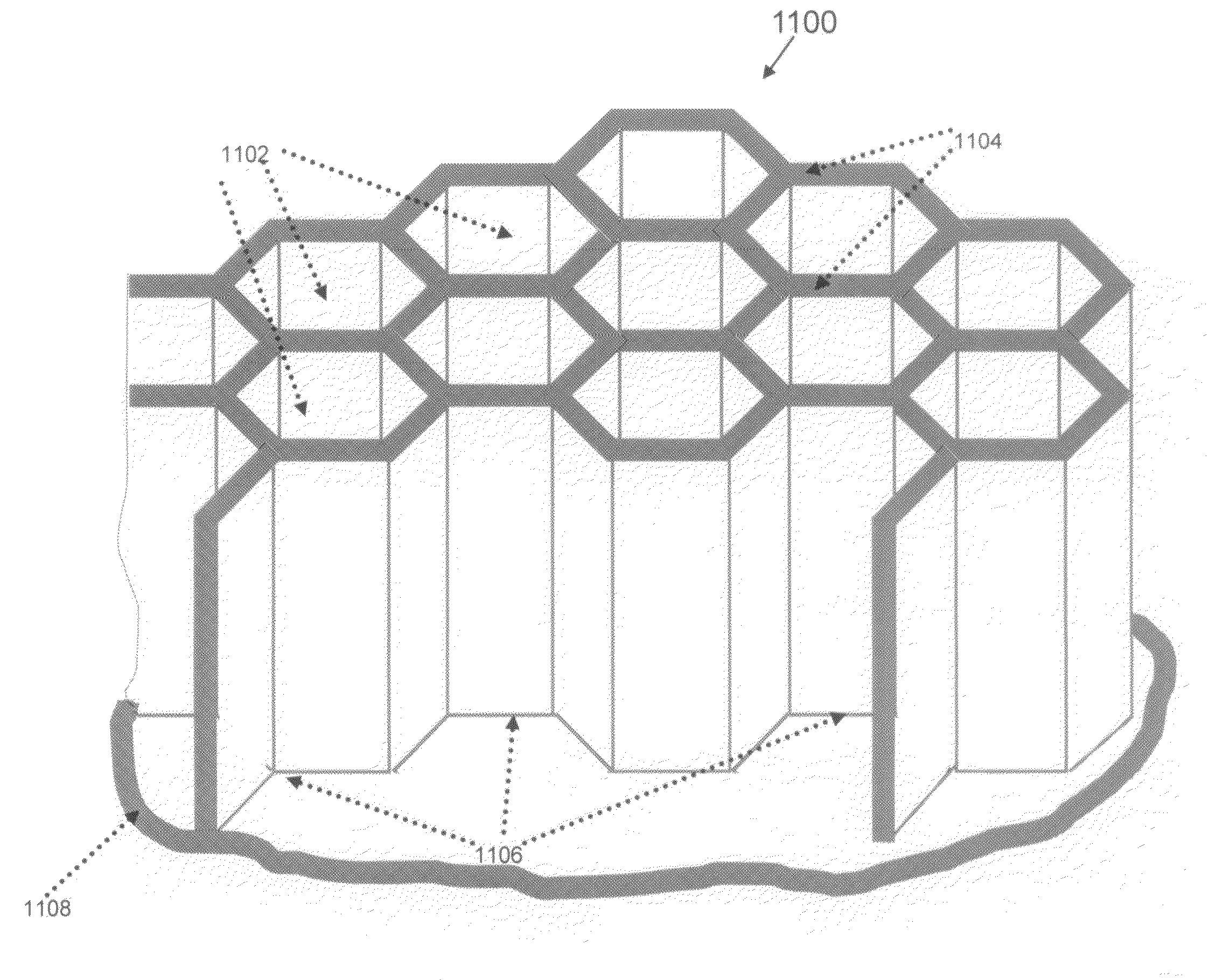
InactiveUS20080157283A1Reduce disadvantagesReduce problemsThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringSolar cell fabrication
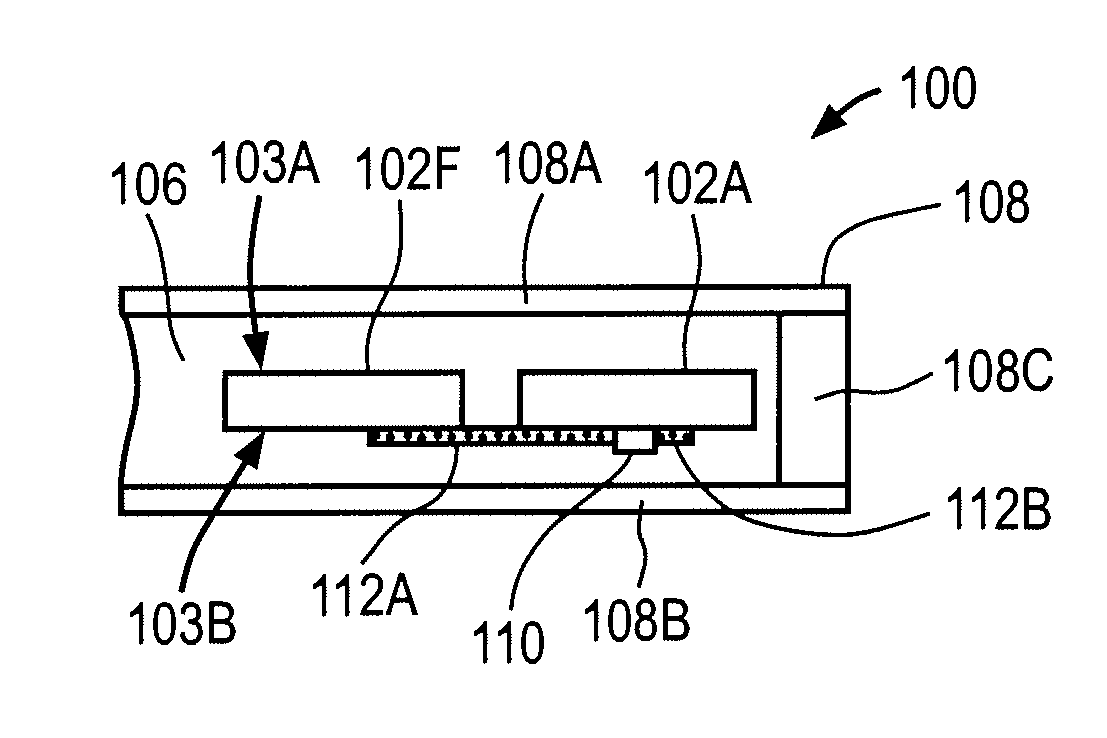
A template 100 for three-dimensional thin-film solar cell substrate formation for use in three-dimensional thin-film solar cells. The template 100 comprises a substrate which comprises a plurality of posts 102 and a plurality of trenches 104 between said plurality of posts 102. The template 100 forms an environment for three-dimensional thin-film solar cell substrate formation.
Owner:BEAMREACH SOLAR INC
Template for pyramidal three-dimensional thin-film solar cell manufacturing and methods of use
InactiveUS20090107545A1Reduce disadvantagesReduce problemsFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringSolar cell fabrication
A template 120 for pyramidal three-dimensional thin-film solar cell substrate formation for use in pyramidal three-dimensional thin-film solar cells. The template 120 comprises a substrate which comprises a plurality of pyramid trenches 122 between a plurality of posts 123. The template 120 forms an environment for pyramidal three-dimensional thin-film solar cell substrate formation.
Owner:BEAMREACH SOLAR INC
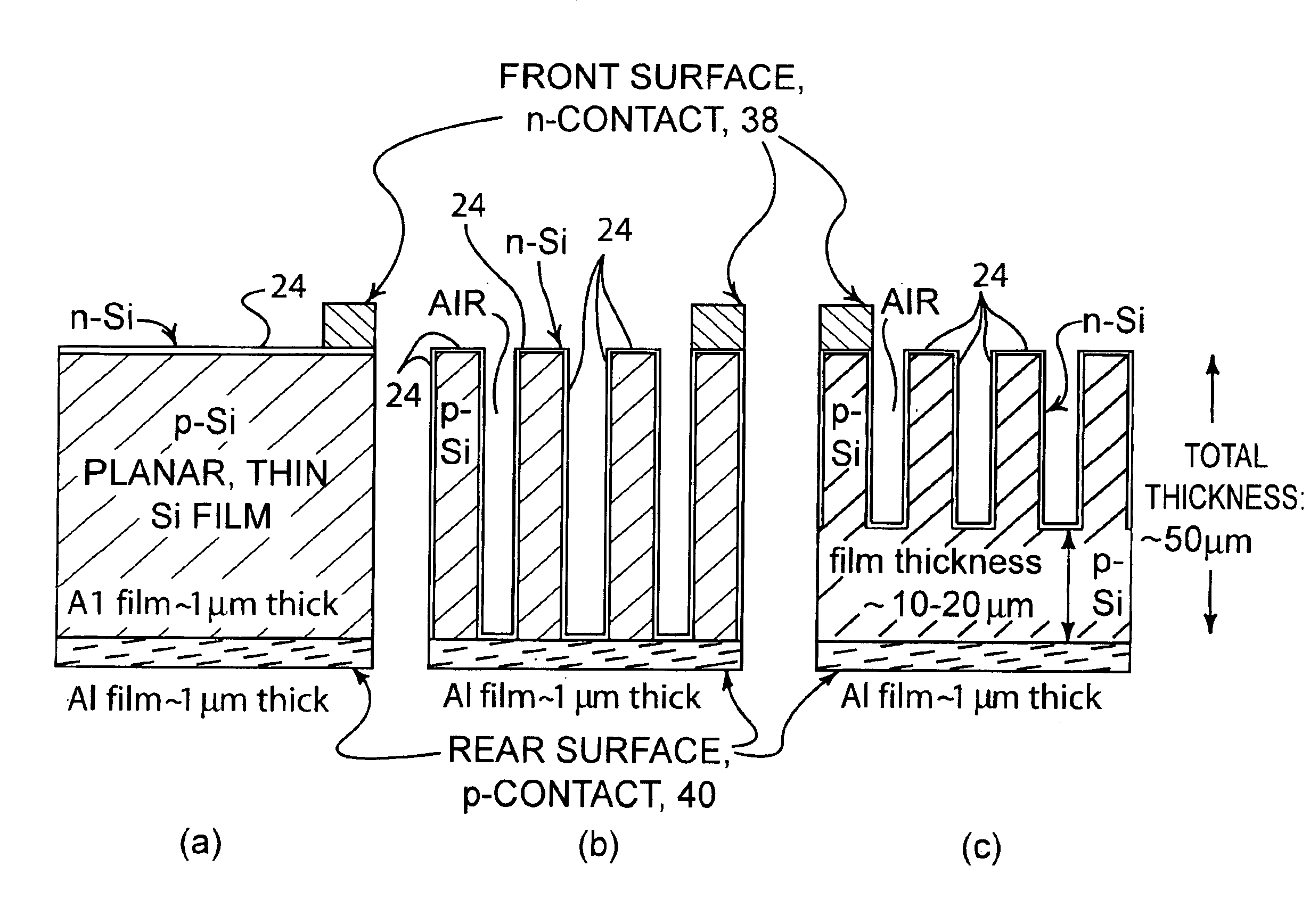
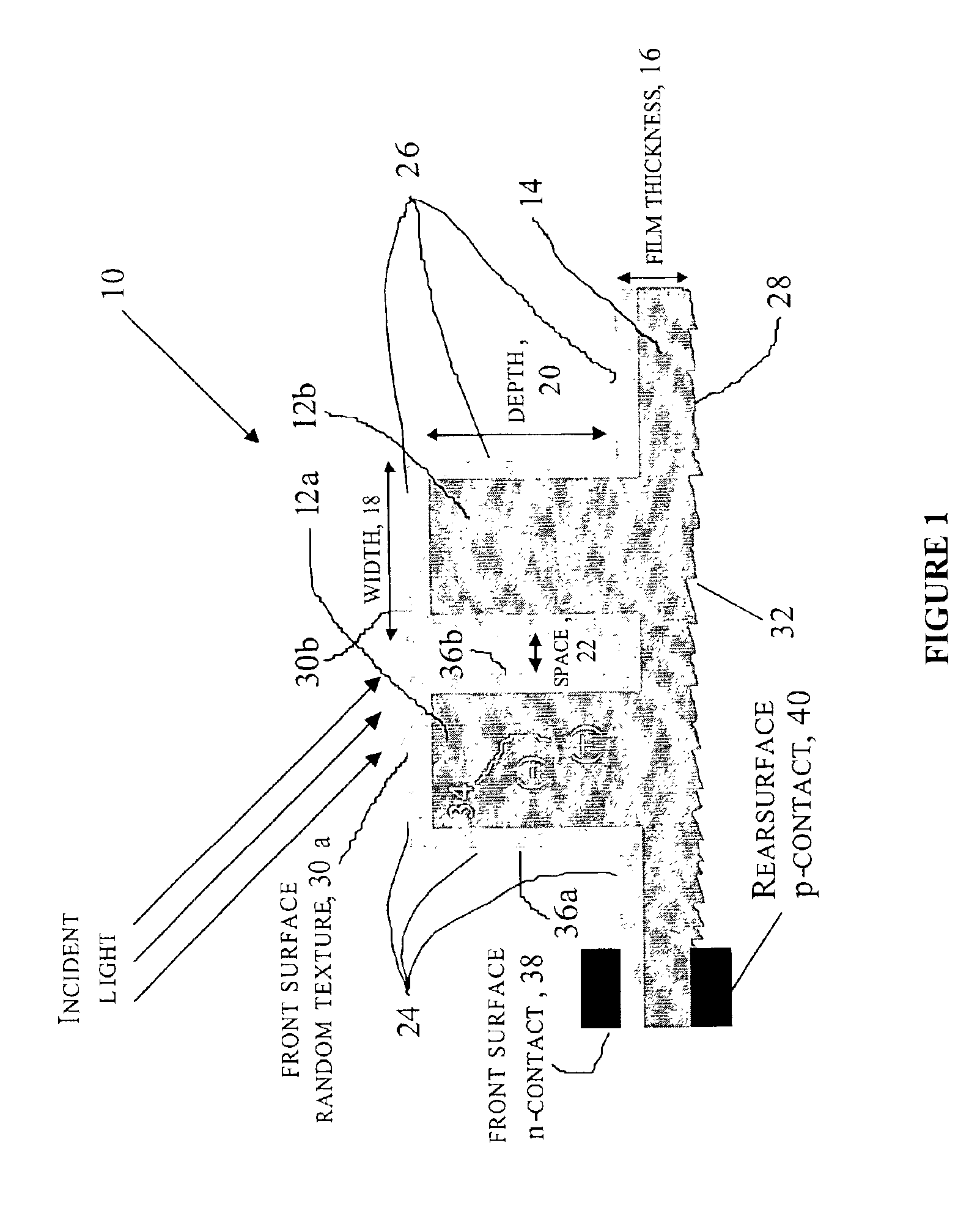
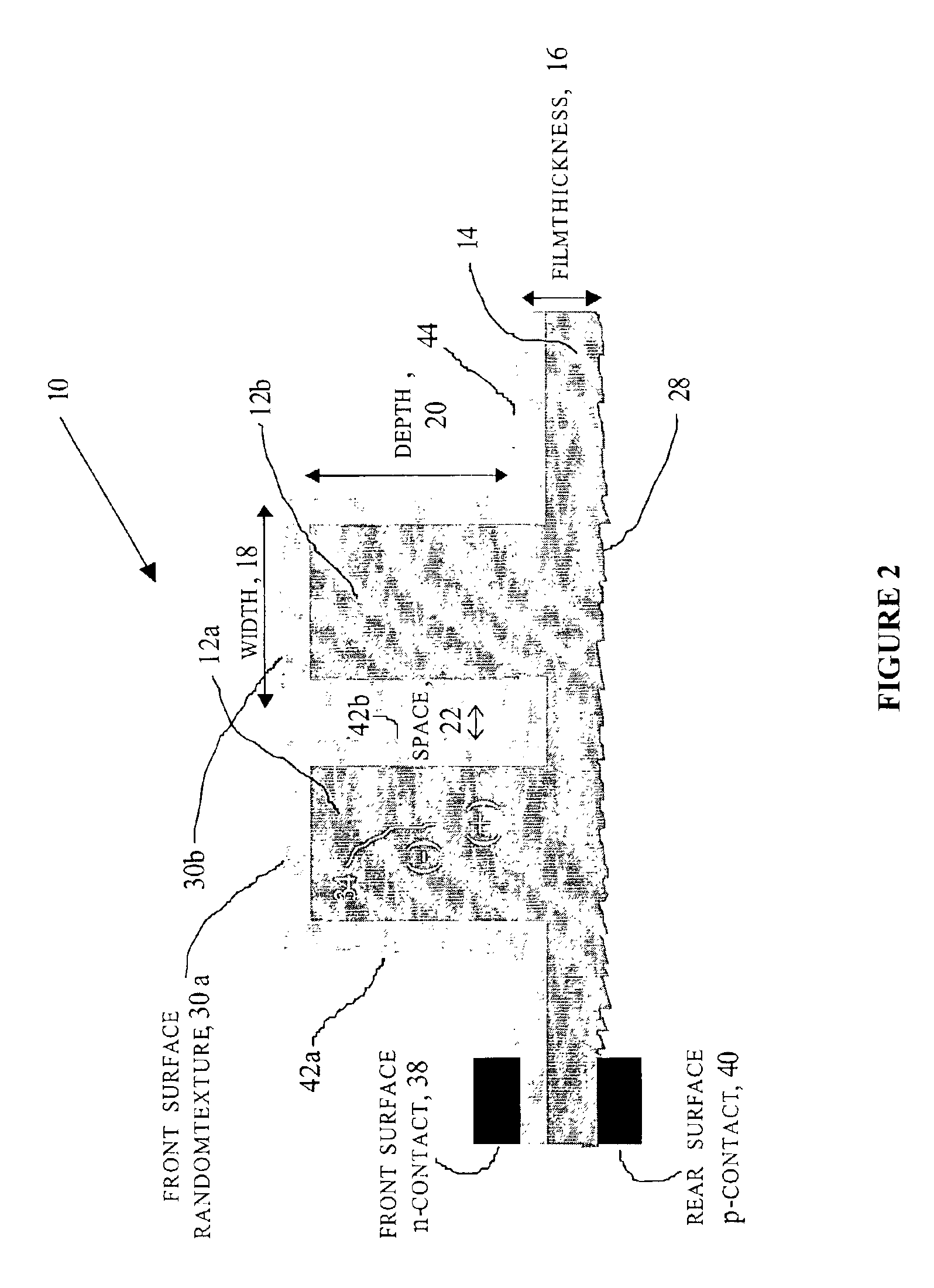
Method of making an enhanced optical absorption and radiation tolerance in thin-film solar cells and photodetectors
InactiveUS7109517B2Promote absorptionImprove toleranceFinal product manufacturePhotoelectric discharge tubesDiffraction orderPhotodetector
Subwavelength random and periodic microscopic structures are used to enhance light absorption and tolerance for ionizing radiation damage of thin film and photodetectors. Diffractive front surface microscopic structures scatter light into oblique propagating higher diffraction orders that are effectively trapped within the volume of the photovoltaic material. For subwavelength periodic microscopic structures etched through the majority of the material, enhanced absorption is due to waveguide effect perpendicular to the surface thereof. Enhanced radiation tolerance of the structures of the present invention is due to closely spaced, vertical sidewall junctions that capture a majority of deeply generated electron-hole pairs before they are lost to recombination. The separation of these vertical sidewall junctions is much smaller than the minority carrier diffusion lengths even after radiation-induced degradation. The effective light trapping of the structures of the invention compensates for the significant removal of photovoltaic material and substantially reduces the weight thereof for space applications.
Owner:ZAIDI SALEEM H
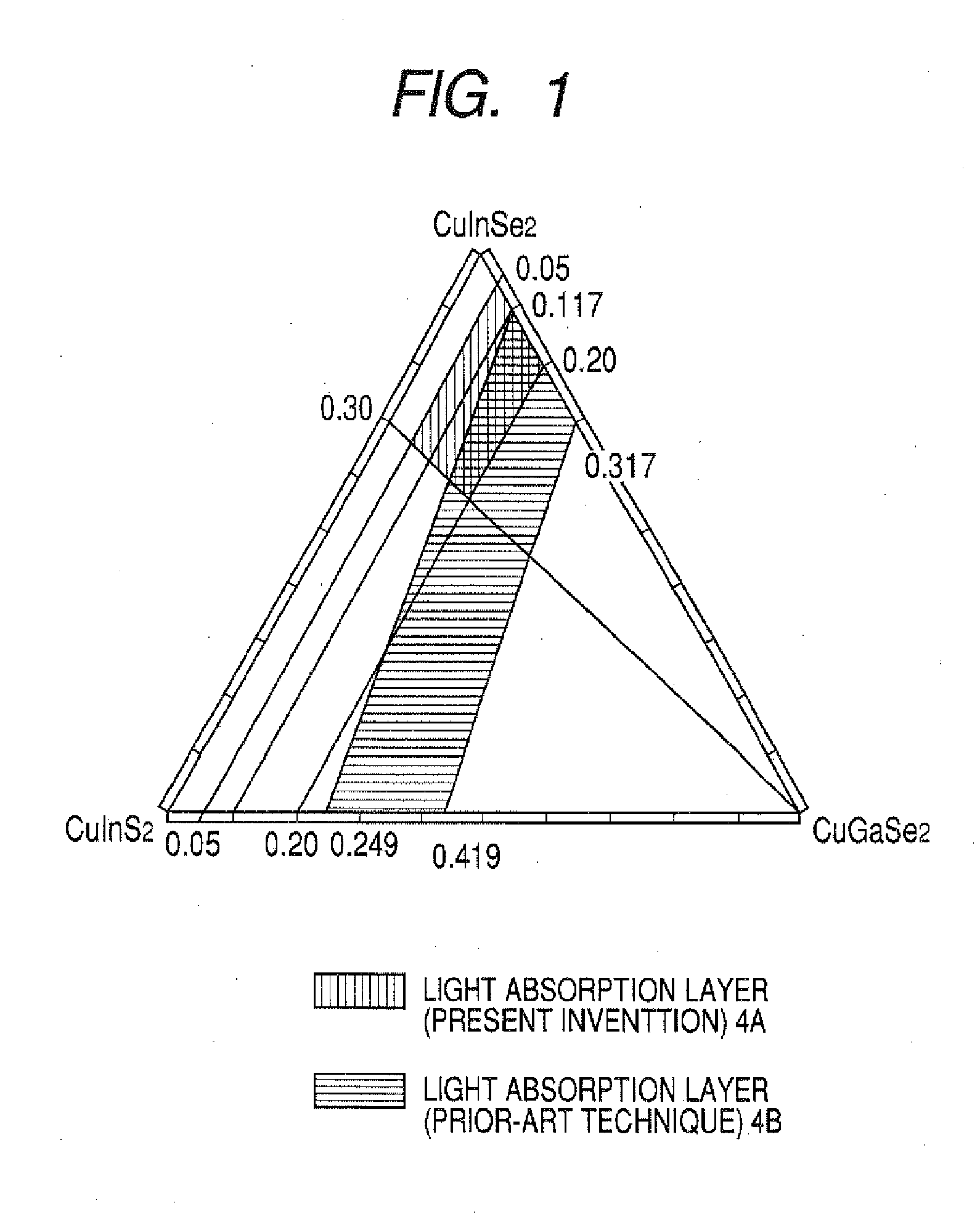
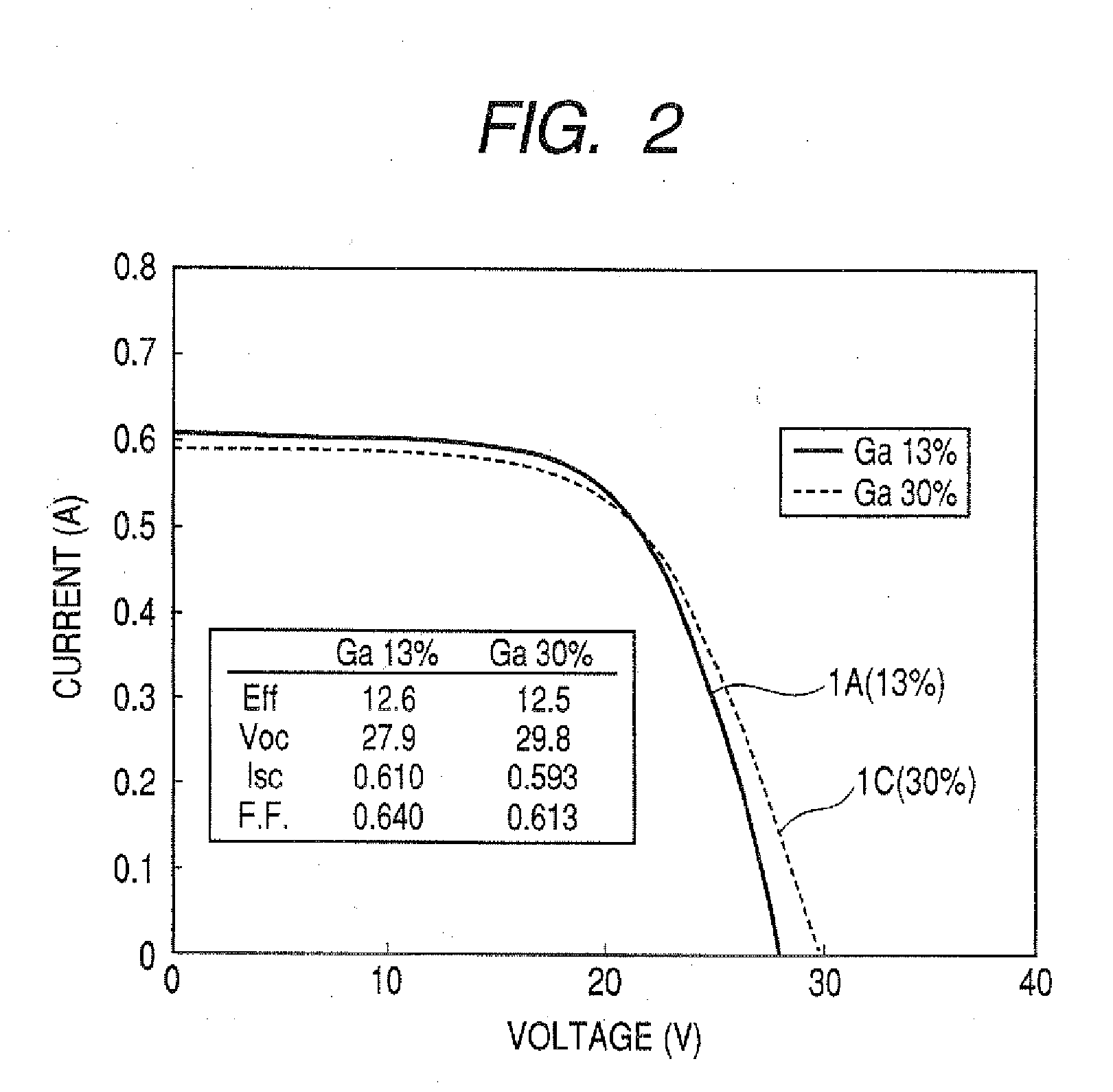
Cis Compound Semiconductor Thin-Film Solar Cell and Method of Forming Light Absorption Layer of the Solar Cell
InactiveUS20070289624A1Improve conversion efficiencyImprove productivityFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationProduction rateAbsorption layer
Film formation is conducted at a low temperature to improve conversion efficiency and productivity and to enable a wider choice of substrate materials to be used. The invention relates to the light absorption layer of a CIS compound semiconductor thin-film solar cell and to a method of forming the layer. The light absorption layer comprises a compound represented by Cux(In1-yGay)(Se1-zSz)2 and having a chalcopyrite type structure, the proportions of the components satisfying 0.86≦x≦0.98, 0.05≦y≦0.25, 0≦z≦0.3, x=αT+β, α=0.015y−0.00025, and β=−7.9y+1.105, provided that T (° C.) is anneal temperature and the allowable range for x is ±0.02. The layer is formed by the selenization method at a low temperature (about 500≦T≦550). As the substrate is used a soda-lime glass having a low melting point.
Owner:SHOWA SHELL SEKIYU KK
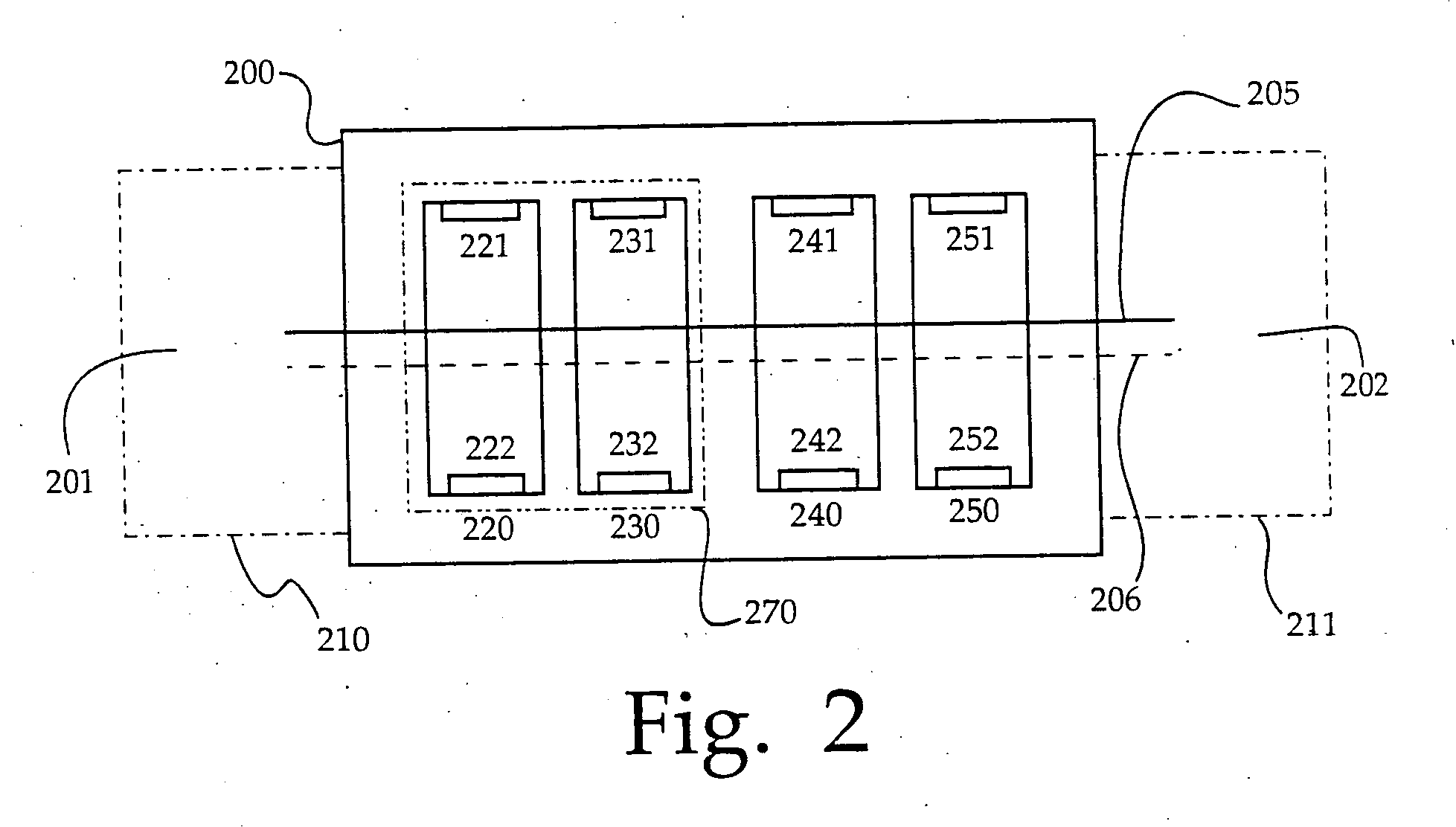
Solar module structures and assembly methods for three-dimensional thin-film solar cells
ActiveUS20090301549A1Eliminate and reduce disadvantageEliminate and reduce and problemPV power plantsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringThin film solar cell
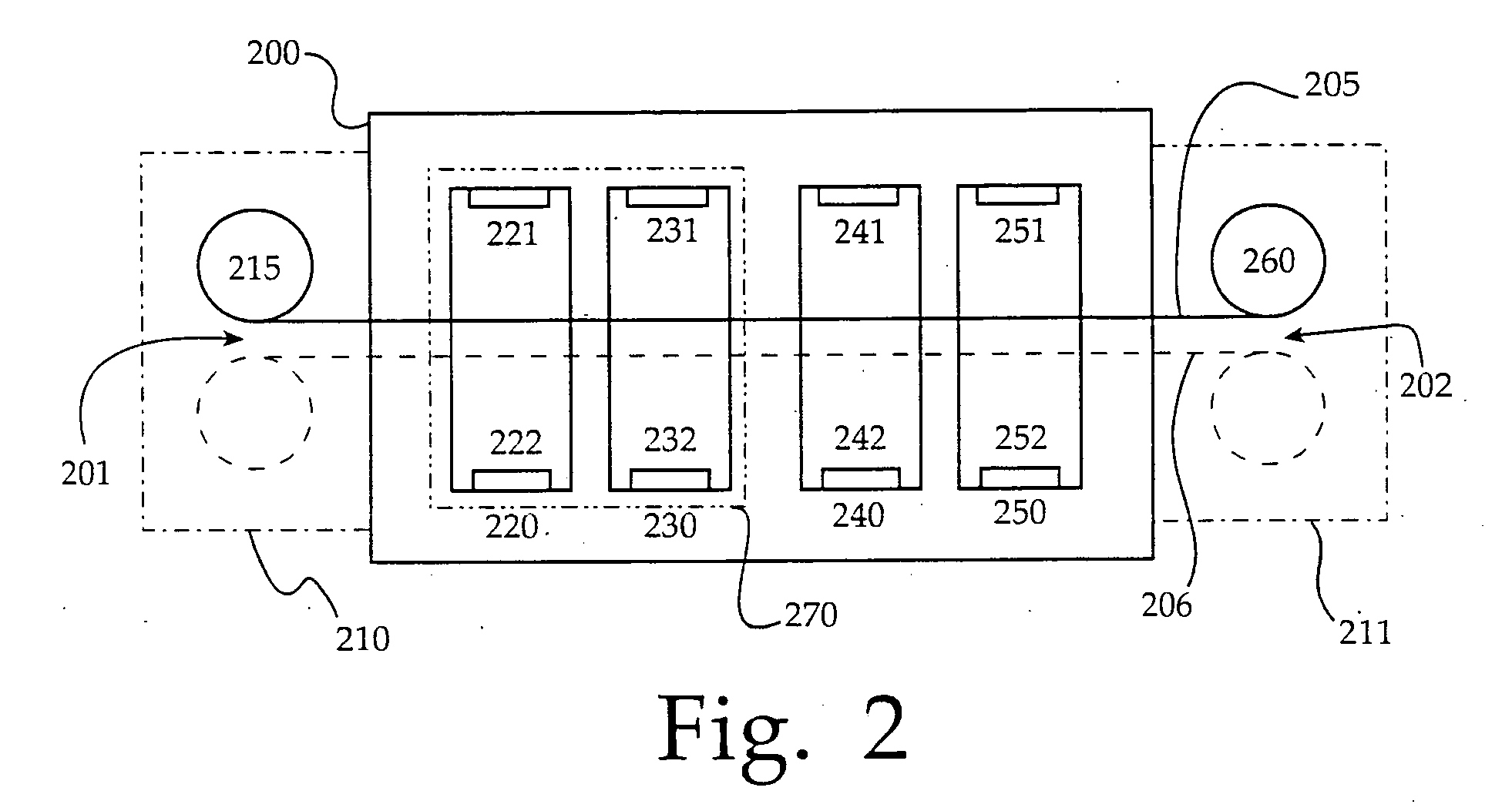
Solar module structures 210 and 270 and methods for assembling solar module structures. The solar module structures 210 and 270 comprise three-dimensional thin-film solar cells 110 arranged in solar module structures 210 and 270. The three-dimensional thin-film solar cell comprises a three-dimensional thin-film solar cell substrate (124 and 122, respectively) with emitter junction regions 1352 and doped base regions 1360. The three-dimensional thin-film solar cell further includes emitter metallization regions and base metallization regions. The 3-D TFSC substrate comprises a plurality of single-aperture or dual-aperture unit cells. The solar module structures 270 using three-dimensional thin-film solar cells comprising three-dimensional thin-film solar cell substrates with a plurality of dual-aperture unit cells may be used in solar glass applications. The solar module structures 210 using three-dimensional thin-film solar cells comprising three-dimensional thin-film solar cell substrates with a plurality of single-aperture unit cells may be used in building façade and rooftop installation applications as well as for centralized solar electricity generation.
Owner:BEAMREACH SOLAR INC
Method for Forming Light Absorption Layer of Cis Type Thin-Film Solar Cell
InactiveUS20080110495A1Good conditionSmooth circulationFinal product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingSulfurEngineering
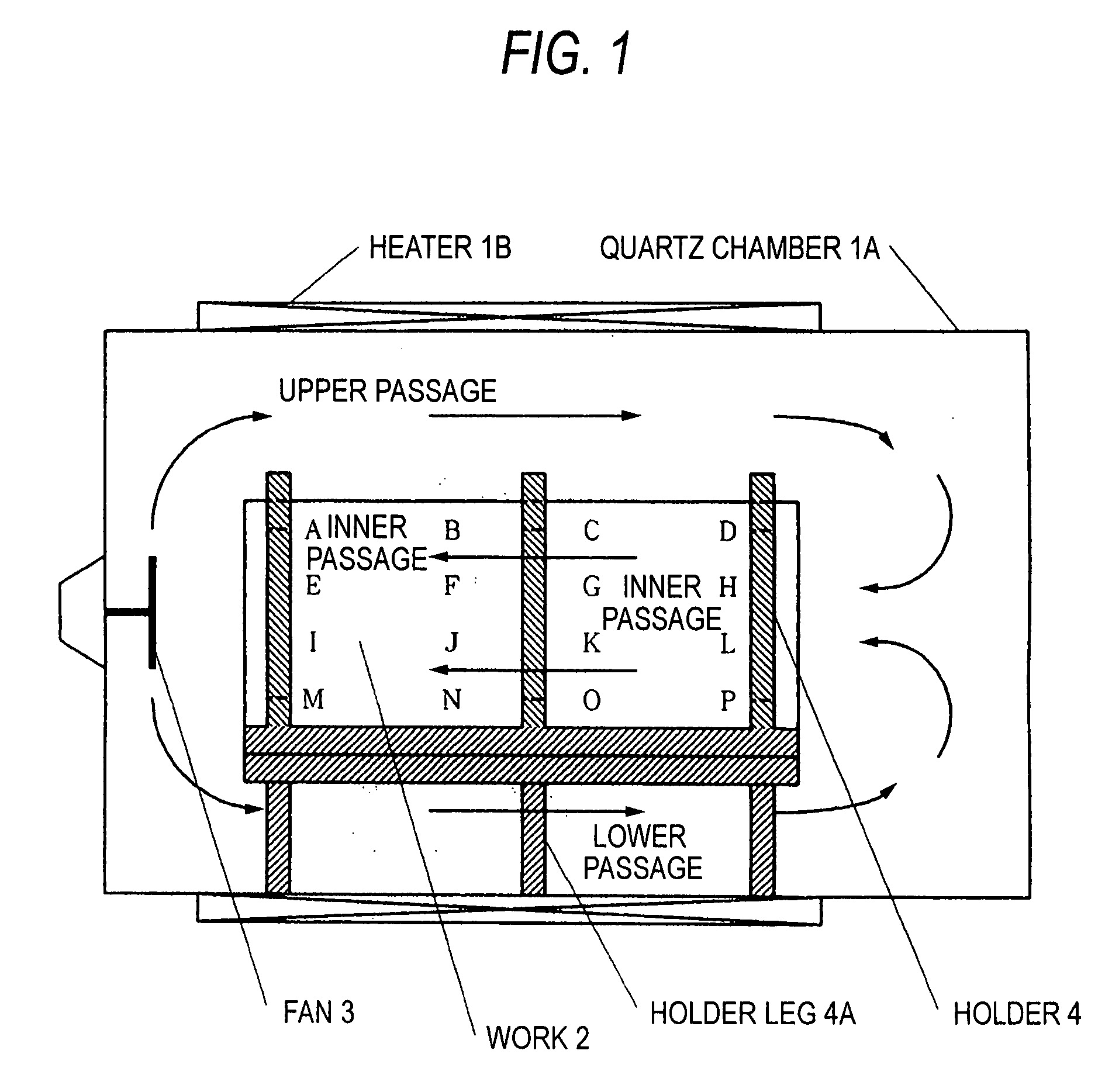
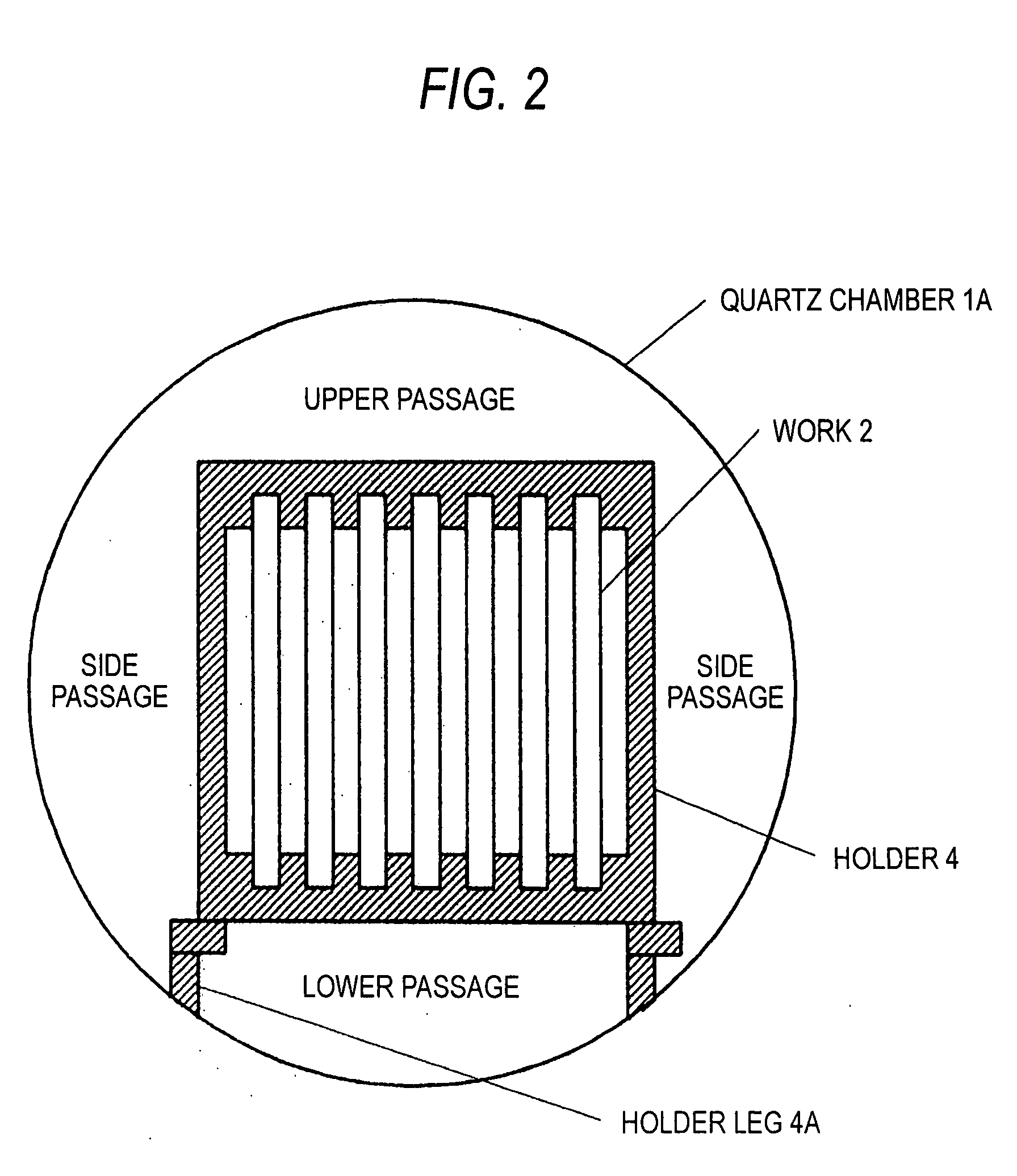
A simple device is used to make the temperature in an apparatus even and improve the state of being in contact with reactant gases, selenium, and sulfur.A fan 3 as a device for atmosphere homogenization is disposed in an apparatus, and the work is disposed in the manner which enables a reactant gas to circulate smoothly. Namely, flat platy works 2 are disposed apart from each other at a certain distance parallel to the direction of the major axis of the apparatus while keeping the plates vertical so that the apparatus has passages within the group of works and has gas passages over and under the works and on both sides thereof. Thus, each work is apt to come into contact with the reactant gases in the apparatus and the temperature in the apparatus is even. The state of being in contact with the reactant gases, selenium, and sulfur is improved.
Owner:SHOWA SHELL SEKIYU KK
Preparation method for haze-adjustable flexible transparent conductive film
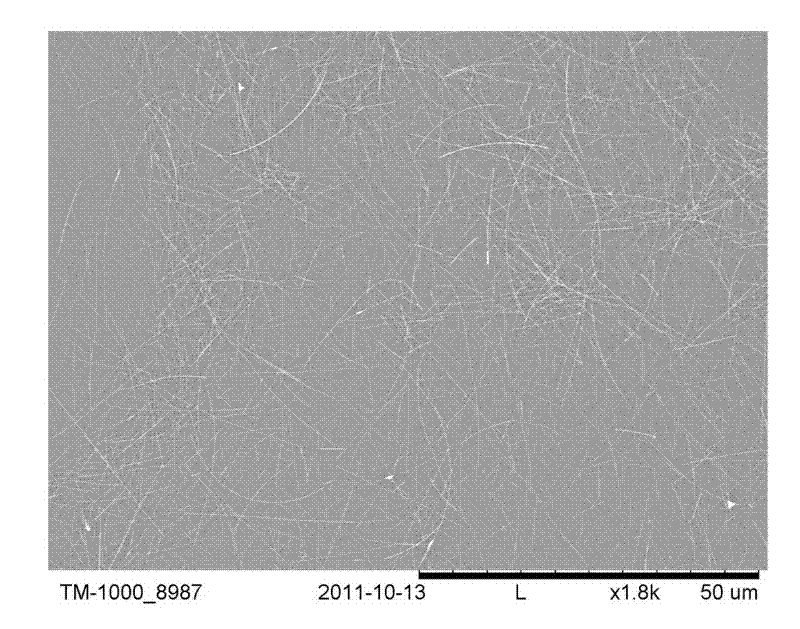
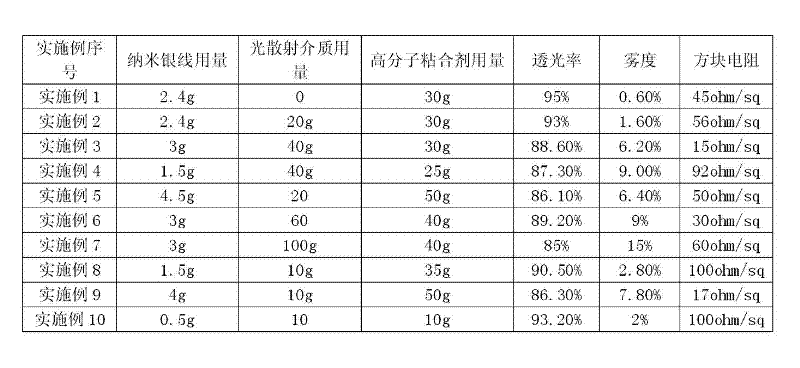
ActiveCN102527621AHigh Diffuse Light Scattering CapabilityInksCoatingsOrganic solventOptical transmittance
The invention provides a preparation method for a haze-adjustable flexible transparent conductive film. The transparent electrode is a nanometer silver line ink which is composed of a light scattering medium, a nanometer silver line and a high molecular bonder and an organic solvent and is coated on a flexible substrate material; after the ink is baked, a transparent nanometer silver line conductive network is formed on the flexible substrate, and the nanometer silver line conductive network is embedded with the light scattering medium at the same time, so that the flexible transparent conductive film is formed; the haze adjustment of the transparent electrode can be realized finally according to the difference of the parameters such as the type as well as the concentration, the size and the like of the light scattering medium; and the transparent electrode is obtained by coating of the nanometer silver line ink, so that the adjusting of the haze can be realized while good conductivity and high light transmittance are remained. The prepared product not only can be applied to the field of a touch screen and a display panel and the like which require lower haze, but also can satisfy requirement for higher haze of the transparent electrode in the field of a film solar cell panel. Meanwhile, a one-step film forming process is simple and is suitable for roll-to-roll printing.
Owner:JIANGSU NANOWELL ADVANCED MATERIALS SCI&TECH
Thermal process for creation of an in-situ junction layer in CIGS
InactiveUS20060102230A1Reduce the temperatureFinal product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingJunction formationEngineering
The present invention relates generally to the field of photovoltaics and more specifically to manufacturing thin-film solar cells using a thermal process. Specifically, a method is disclosed to manufacture a CIGS solar cell by an in-situ junction formation process.
Owner:DAYSTAR TECHNOLOGIES
Vertical production of photovoltaic devices
InactiveUS20060219547A1Final product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingElectrical batteryEngineering
The present invention provides a photovoltaic thin-film solar cell produced by a providing a vertically oriented pallet based substrate to a series of reaction chambers where layers can be sequentially formed on the pallet.
Owner:DAYSTAR TECHNOLOGIES
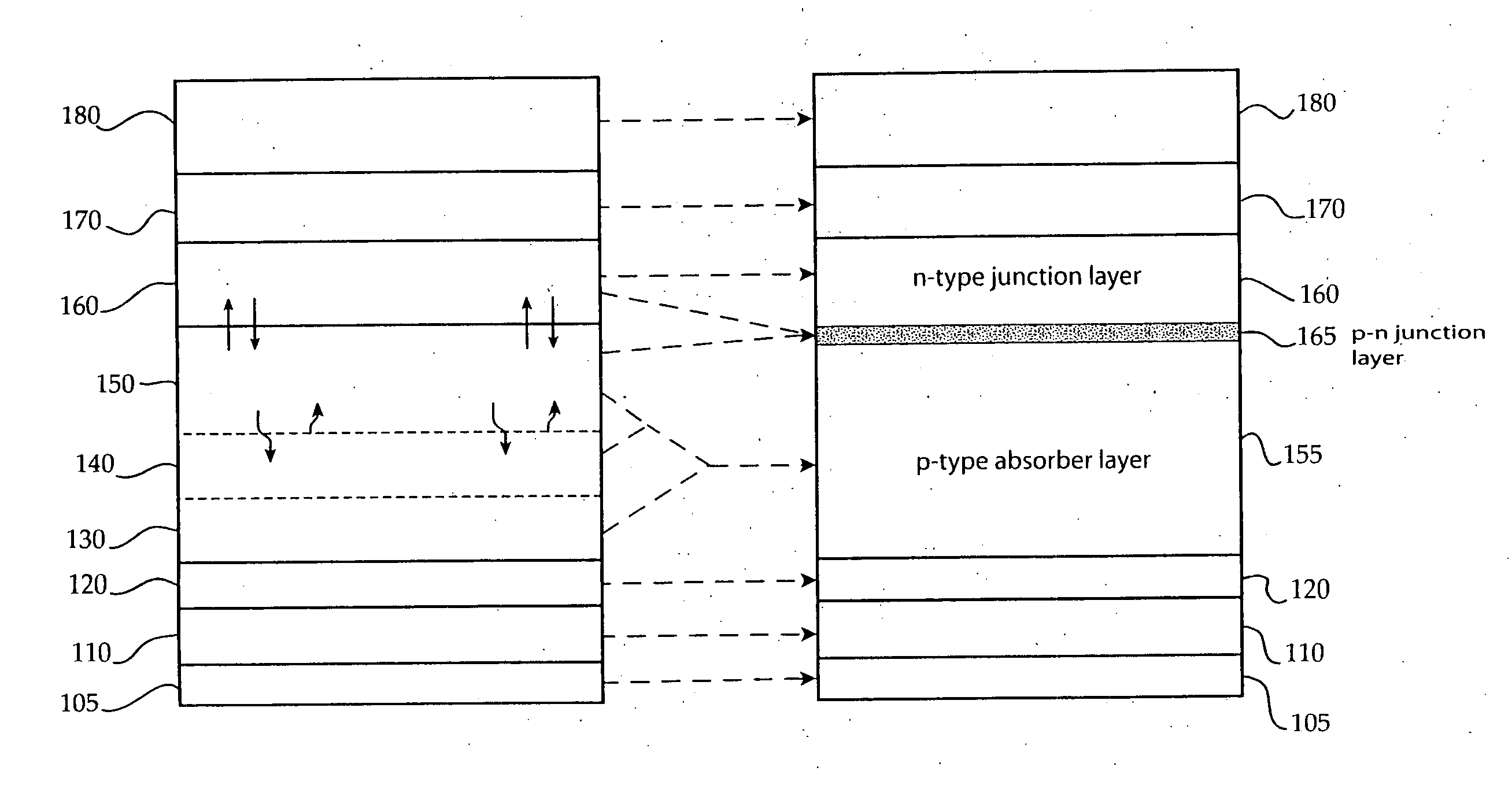
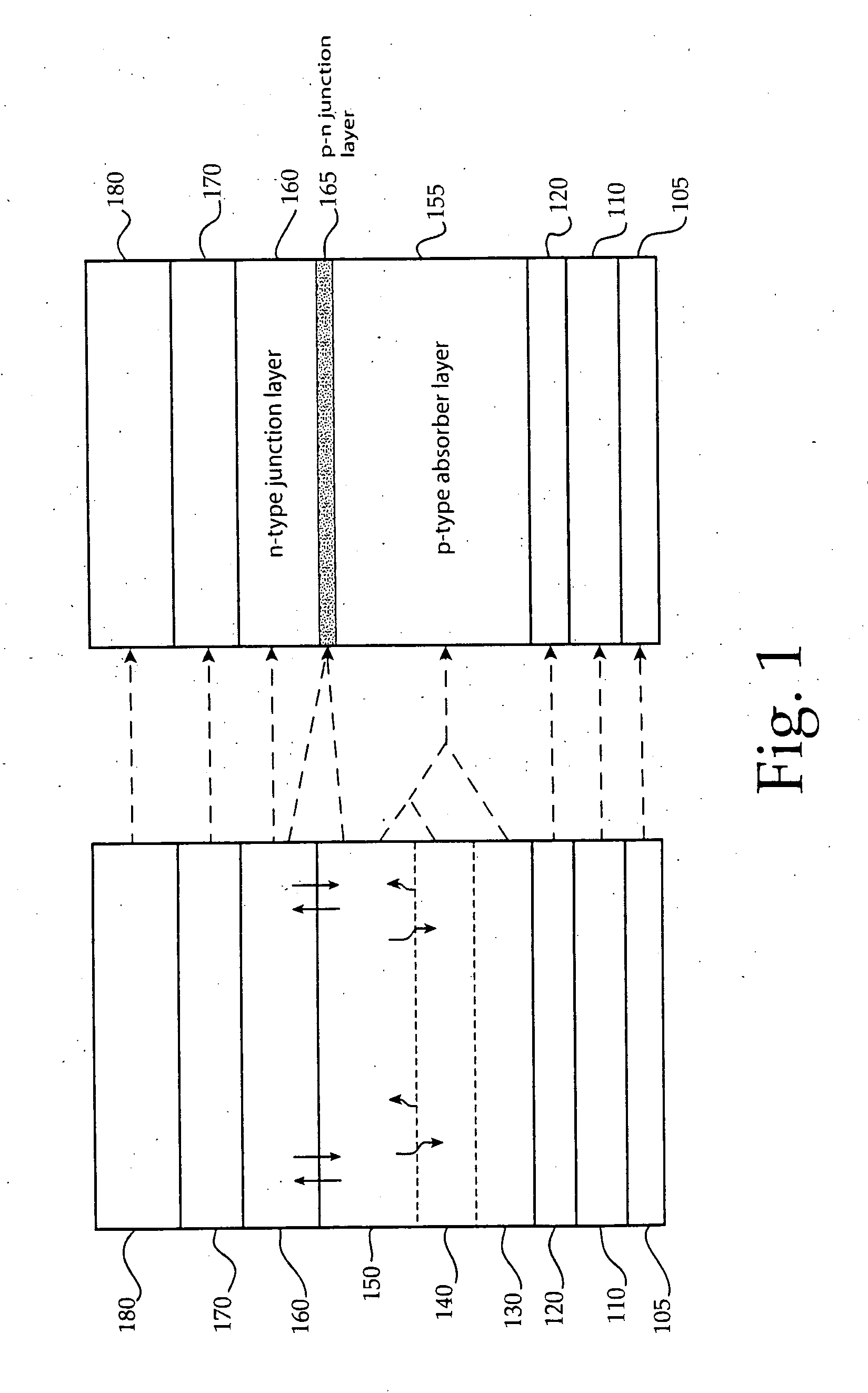
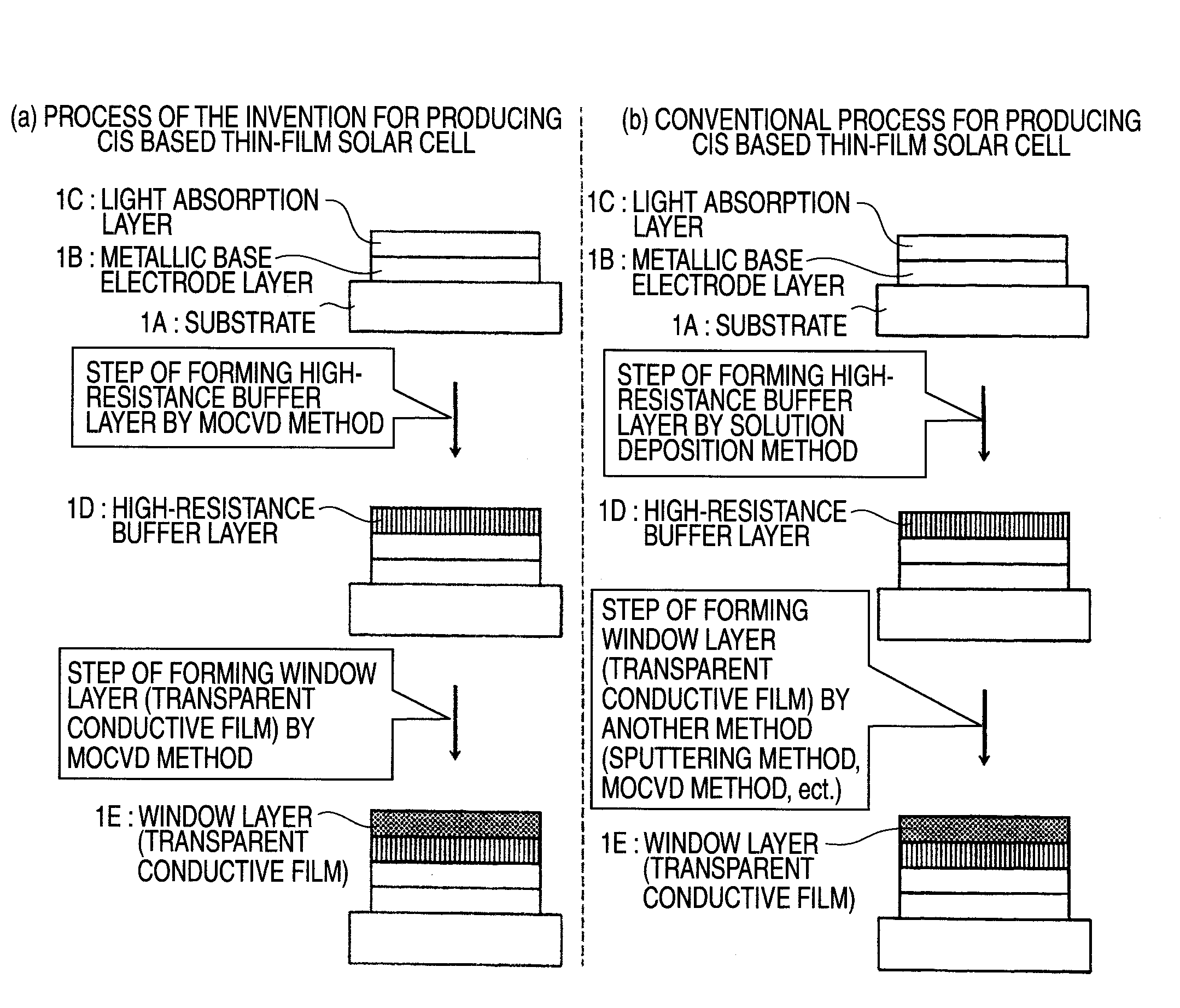
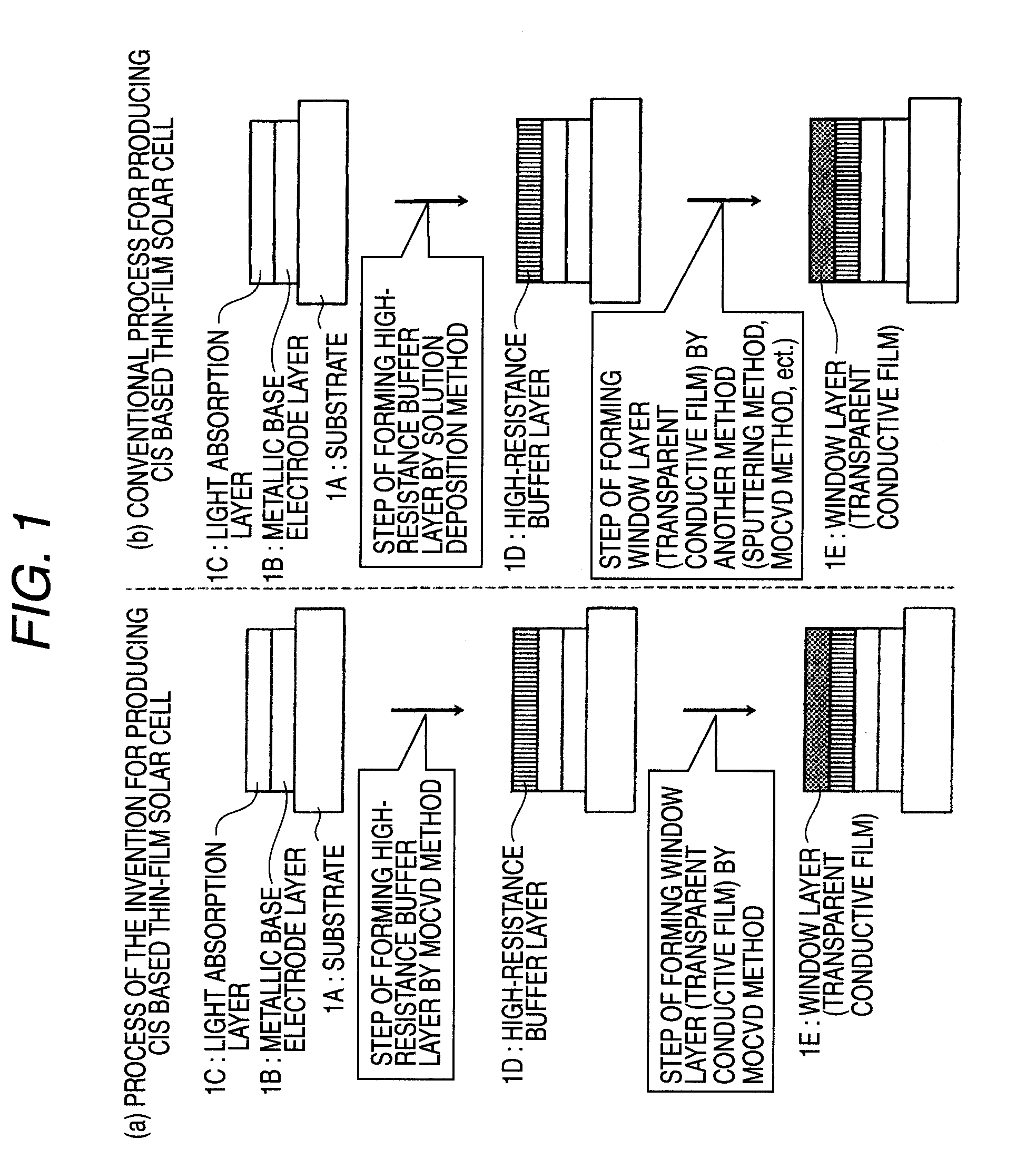
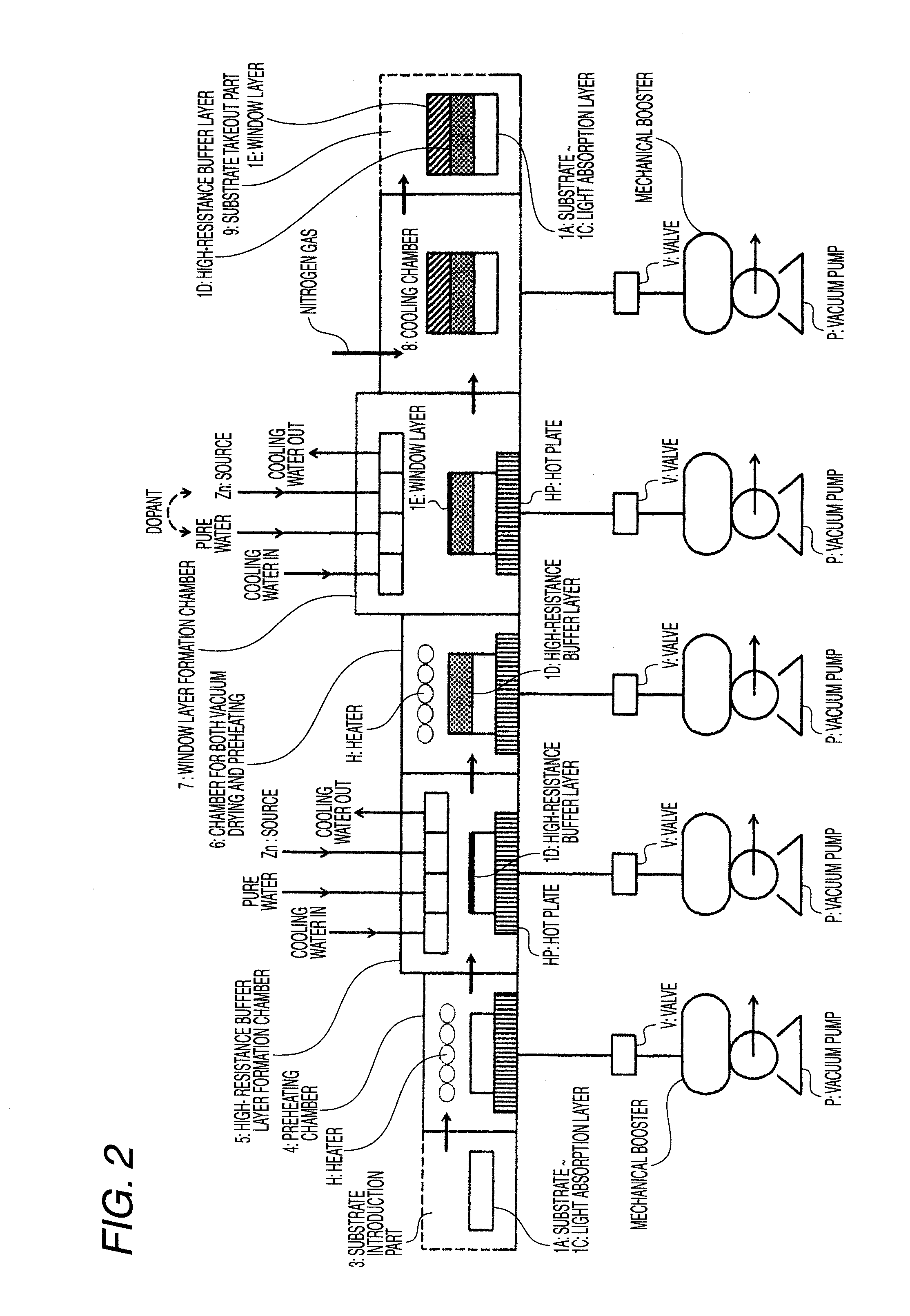
Method of Successive High-Resistance Buffer Layer/Window Layer (Transparent Conductive Film) Formation for CIS Based Thin-Film Solar Cell and Apparatus for Successive Film Formation for Practicing the Method of Successive Film Formation
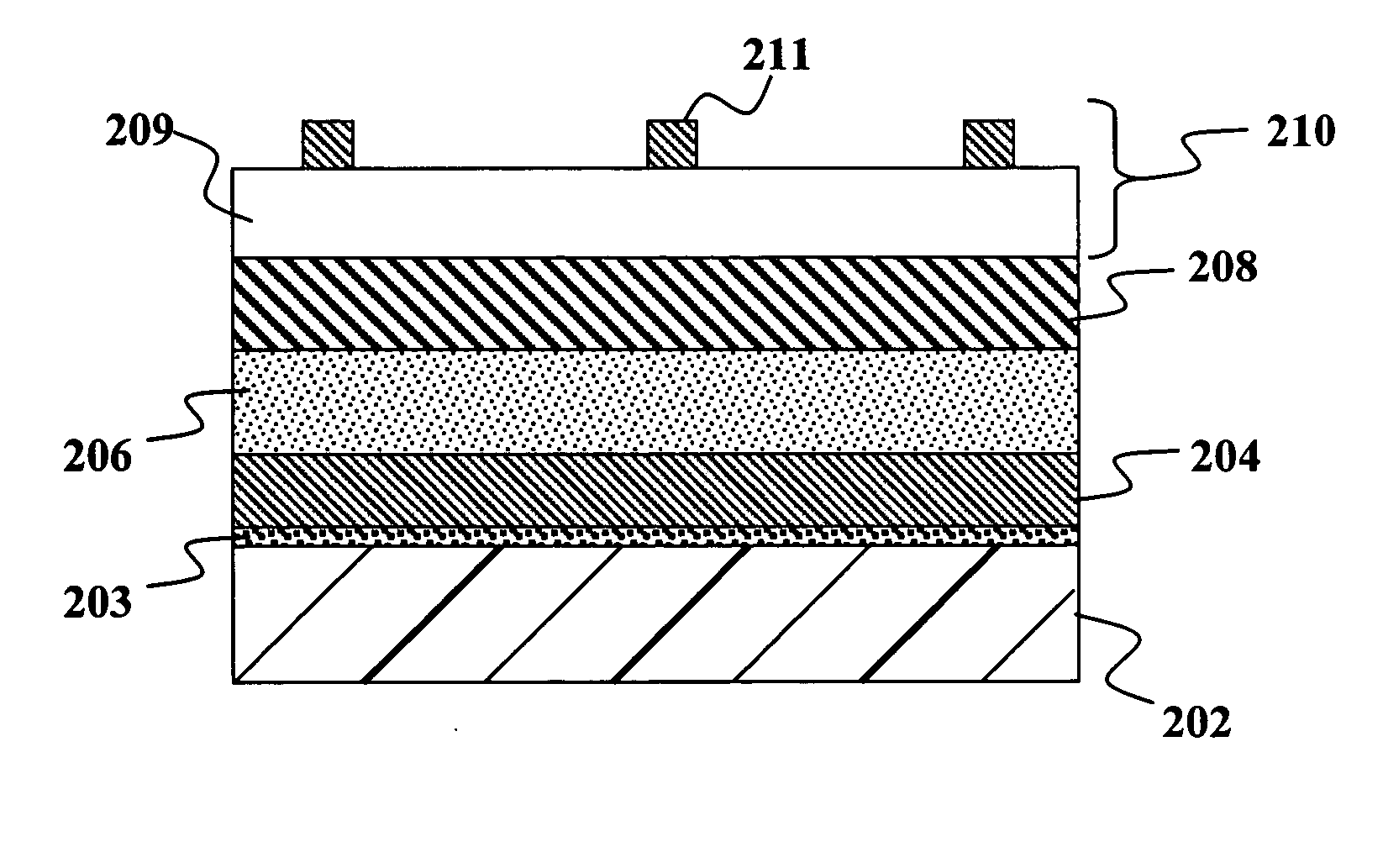
ActiveUS20090087940A1Reduction in raw-material costLow cost of treatmentFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh resistanceWork in process
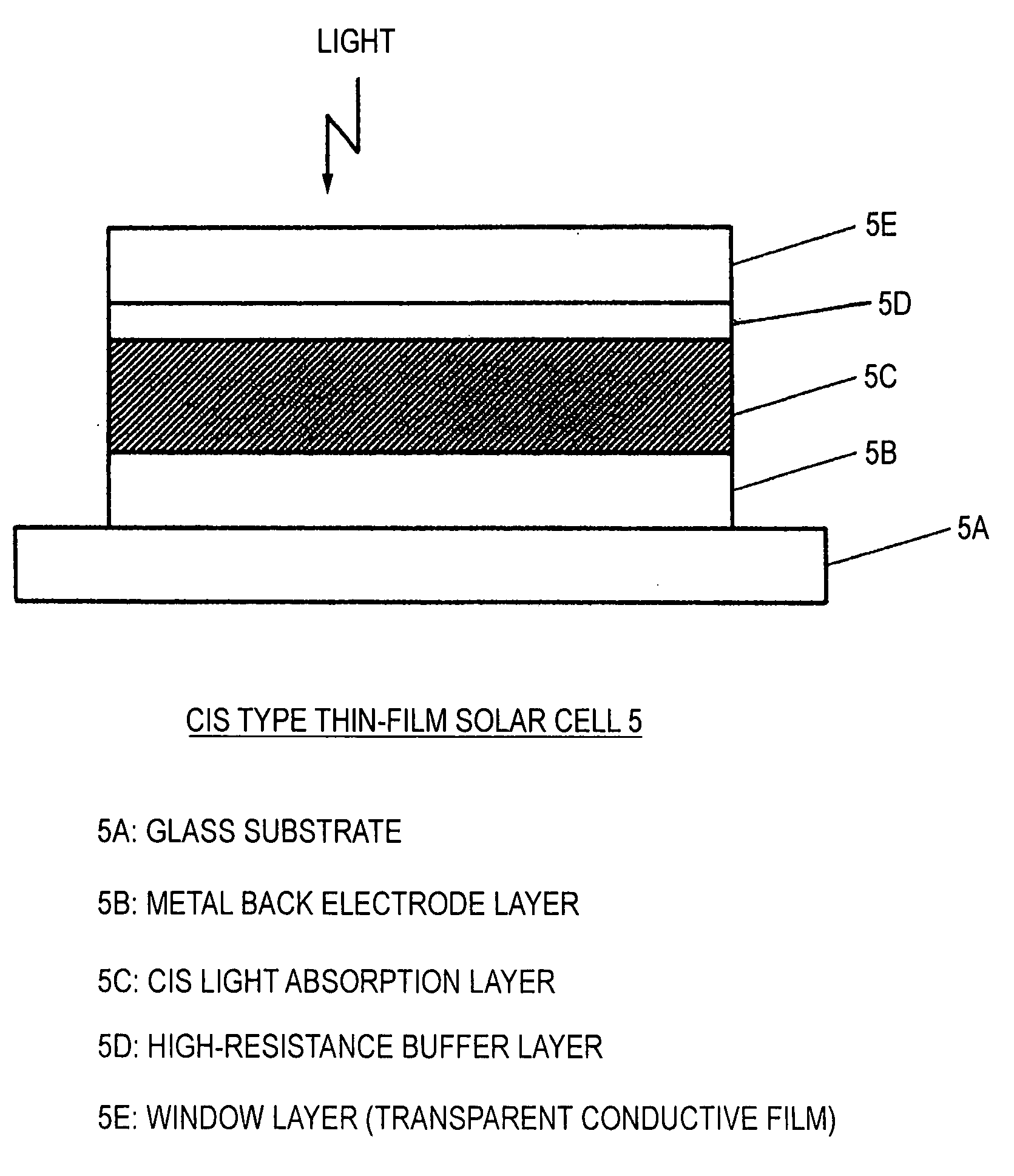
A high-resistance buffer layer and a window layer (transparent conductive film) are successively formed by the MOCVD method to obtain the same output characteristics as in conventional film deposition by the solution deposition method and to simplify a film deposition method and apparatus. Thus, the cost of raw materials and the cost of waste treatments are reduced to attain a considerable reduction in production cost.After a metallic base electrode layer 1B and a light absorption layer 1C are formed in this order on a glass substrate 1A, a high-resistance buffer layer 1D and a window layer 1E are successively formed in this order in a multi layer arrangement on the light absorption layer 1C of the resultant semifinished solar cell substrate by the MOCVD method. Consequently, a film deposition method and apparatus are simplified and the cost of raw materials and the cost of waste treatments can be reduced.
Owner:SOLAR FRONTIER
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com