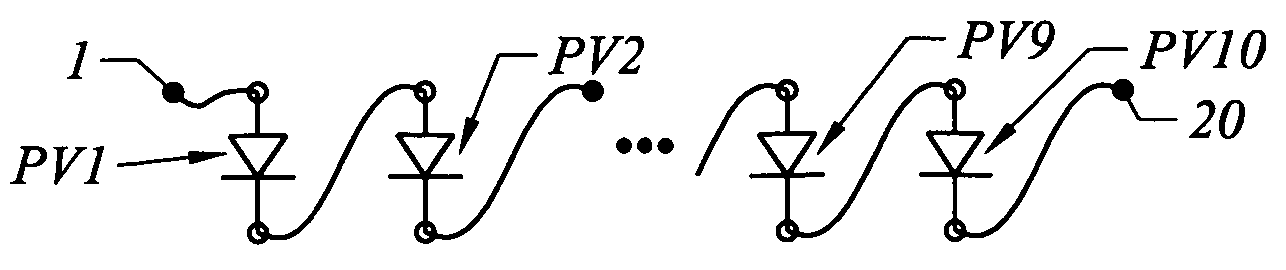Patents
Literature
833results about "Energy conversion devices" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
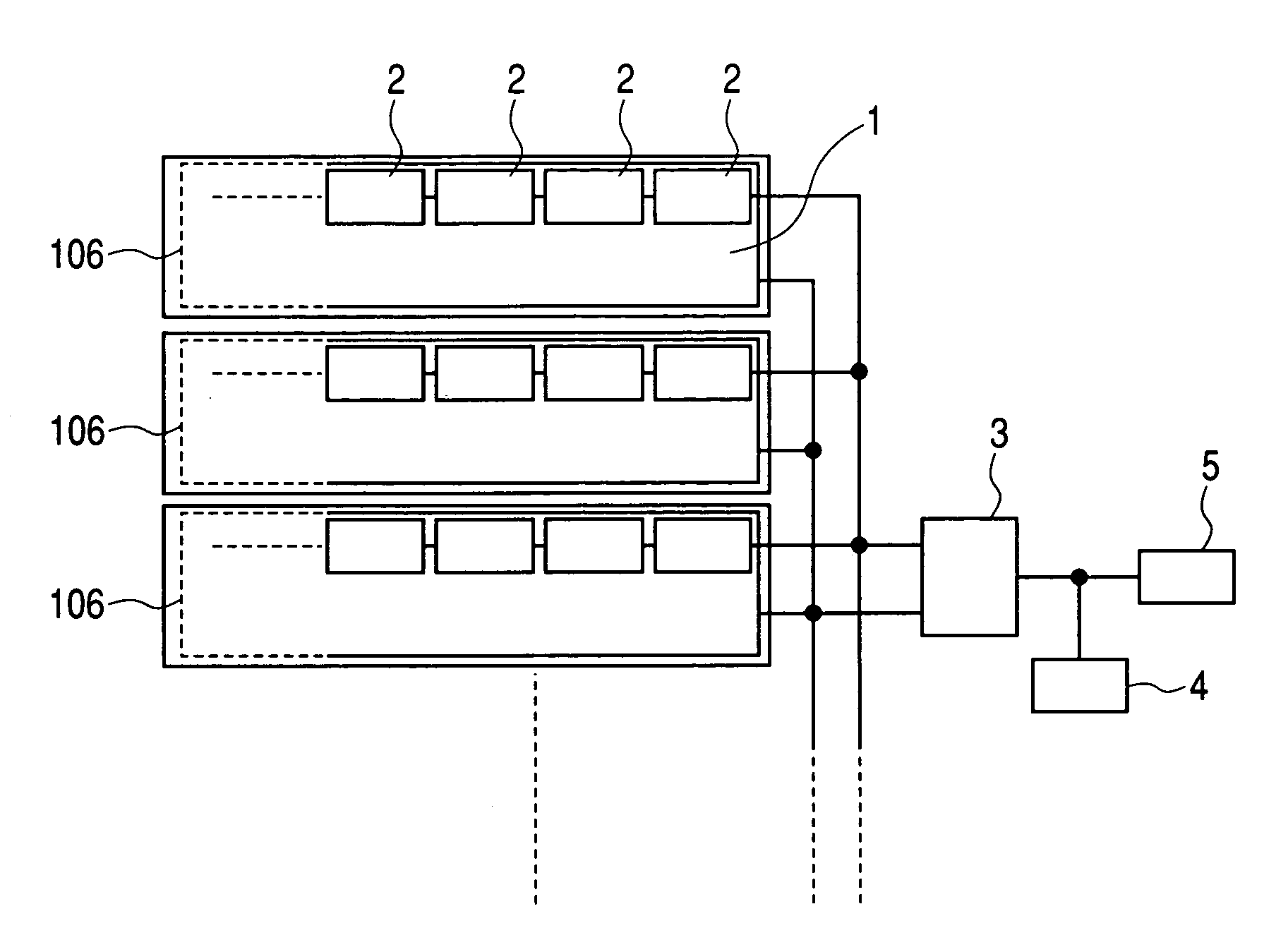
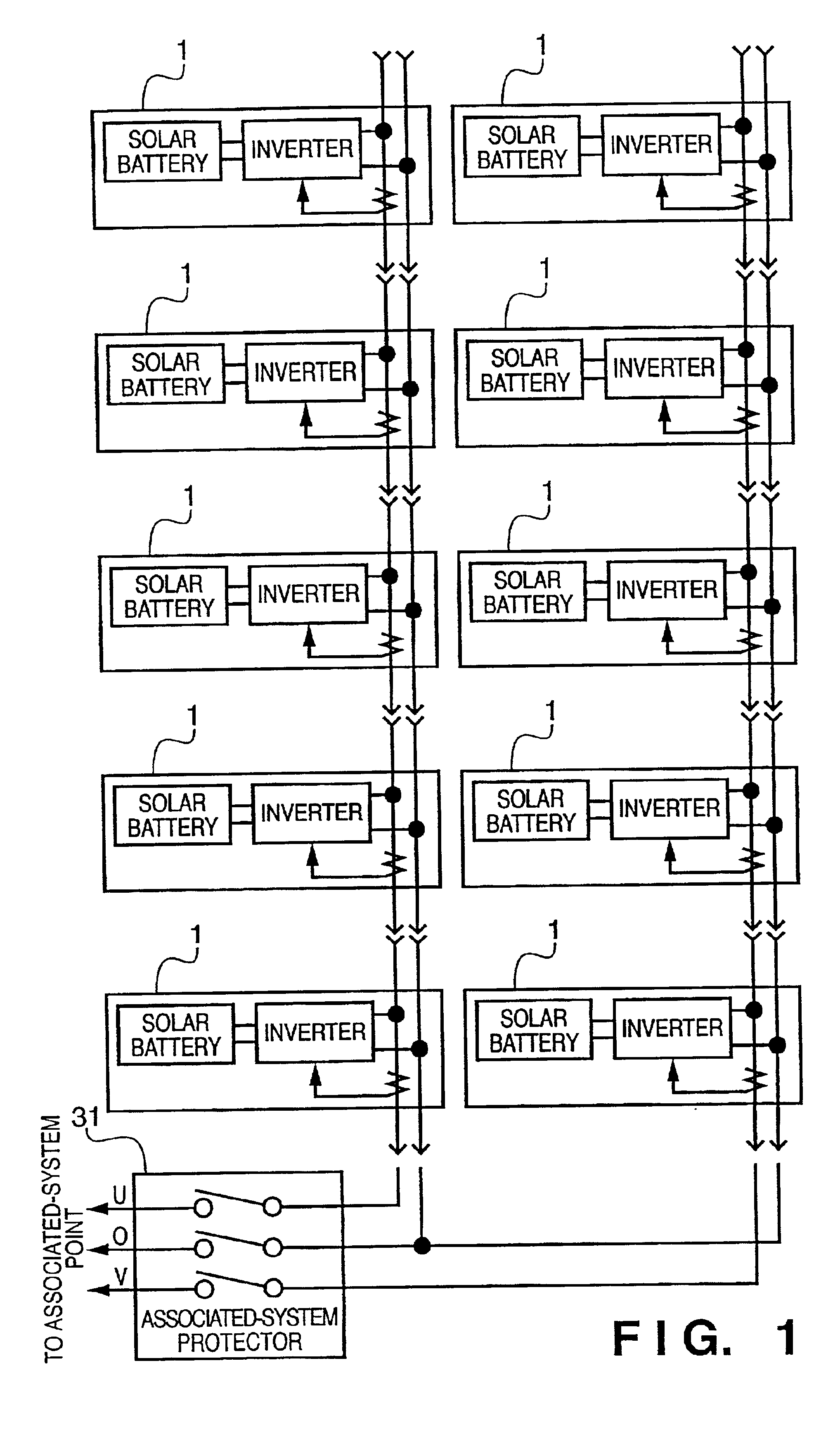
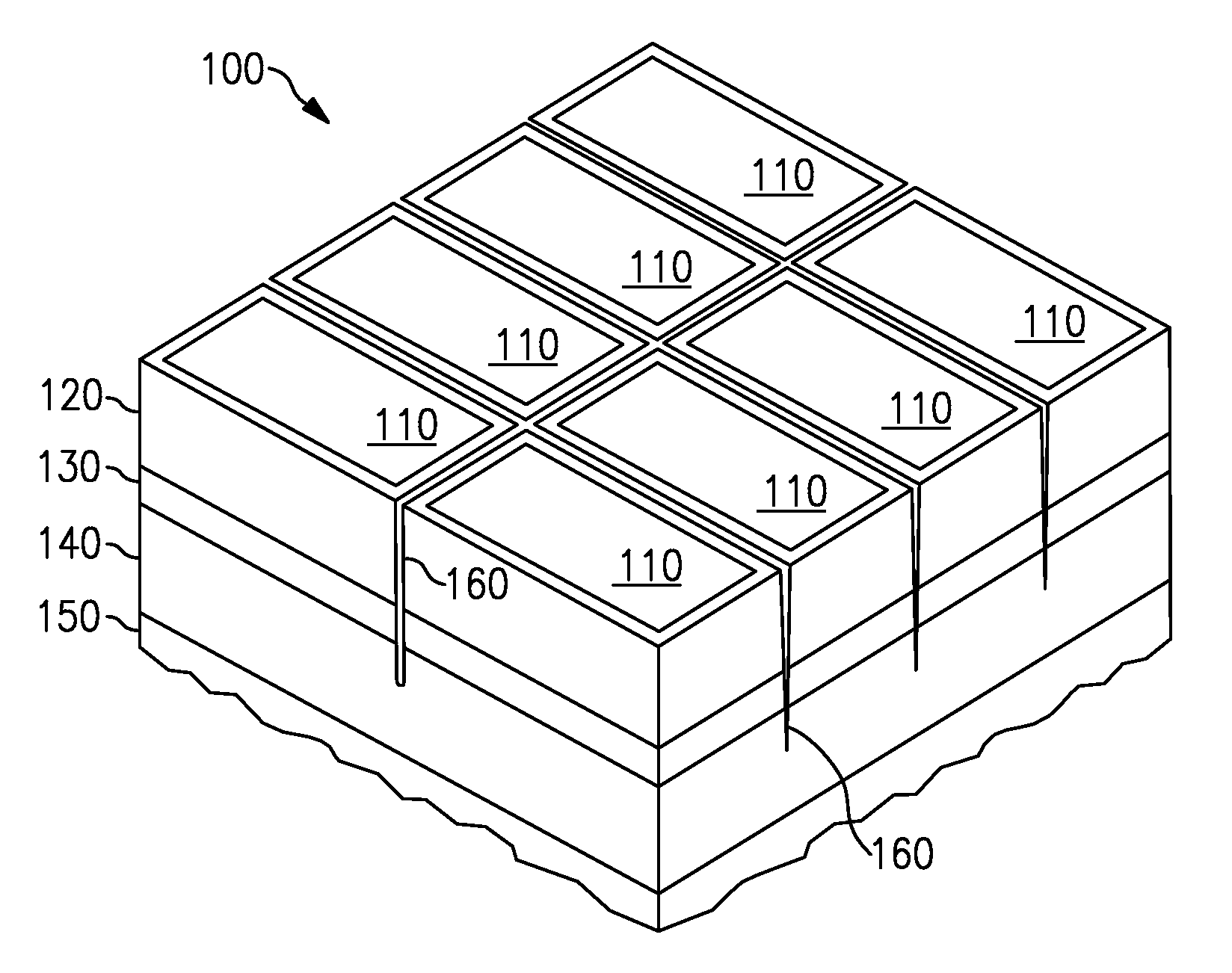
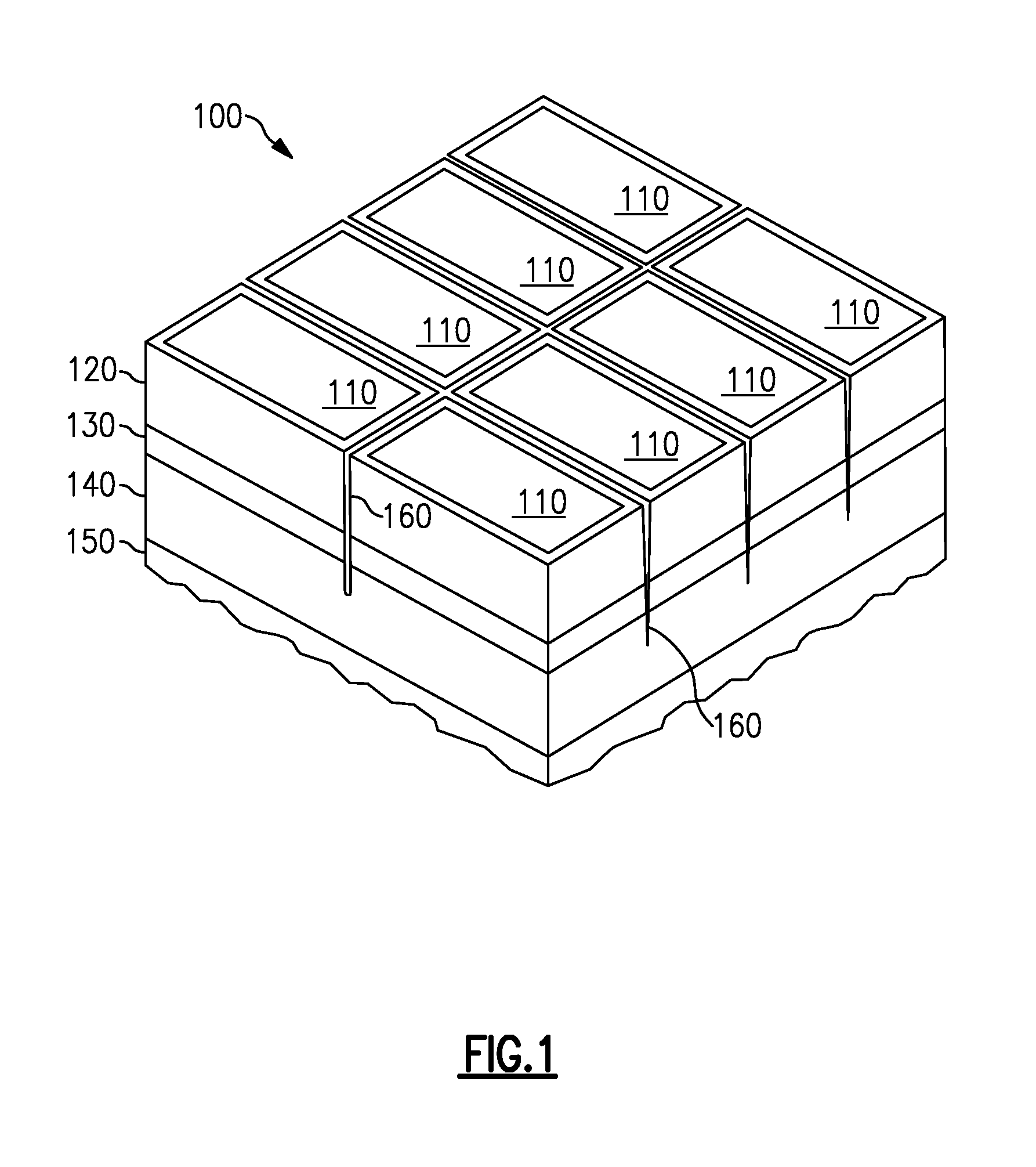
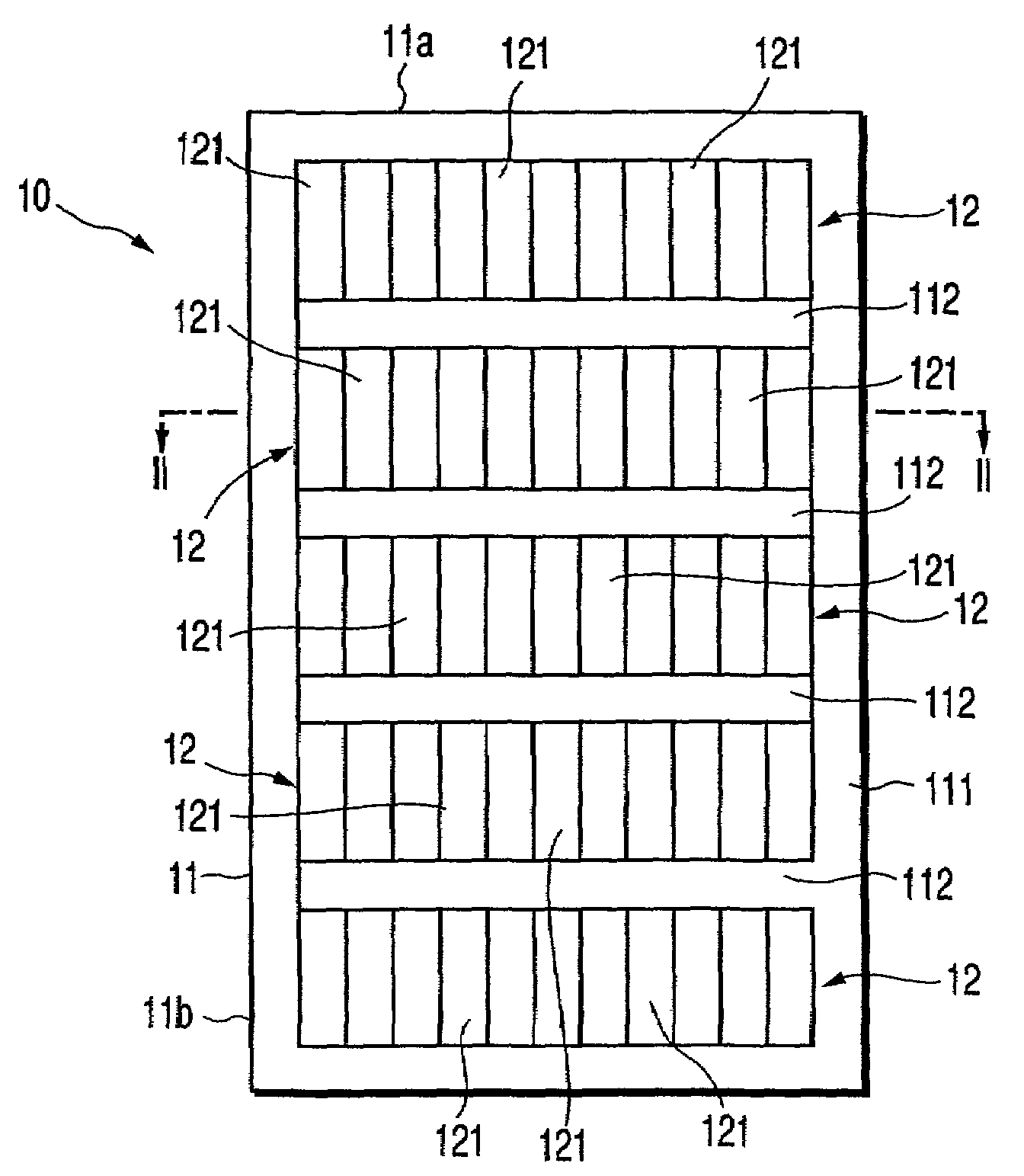
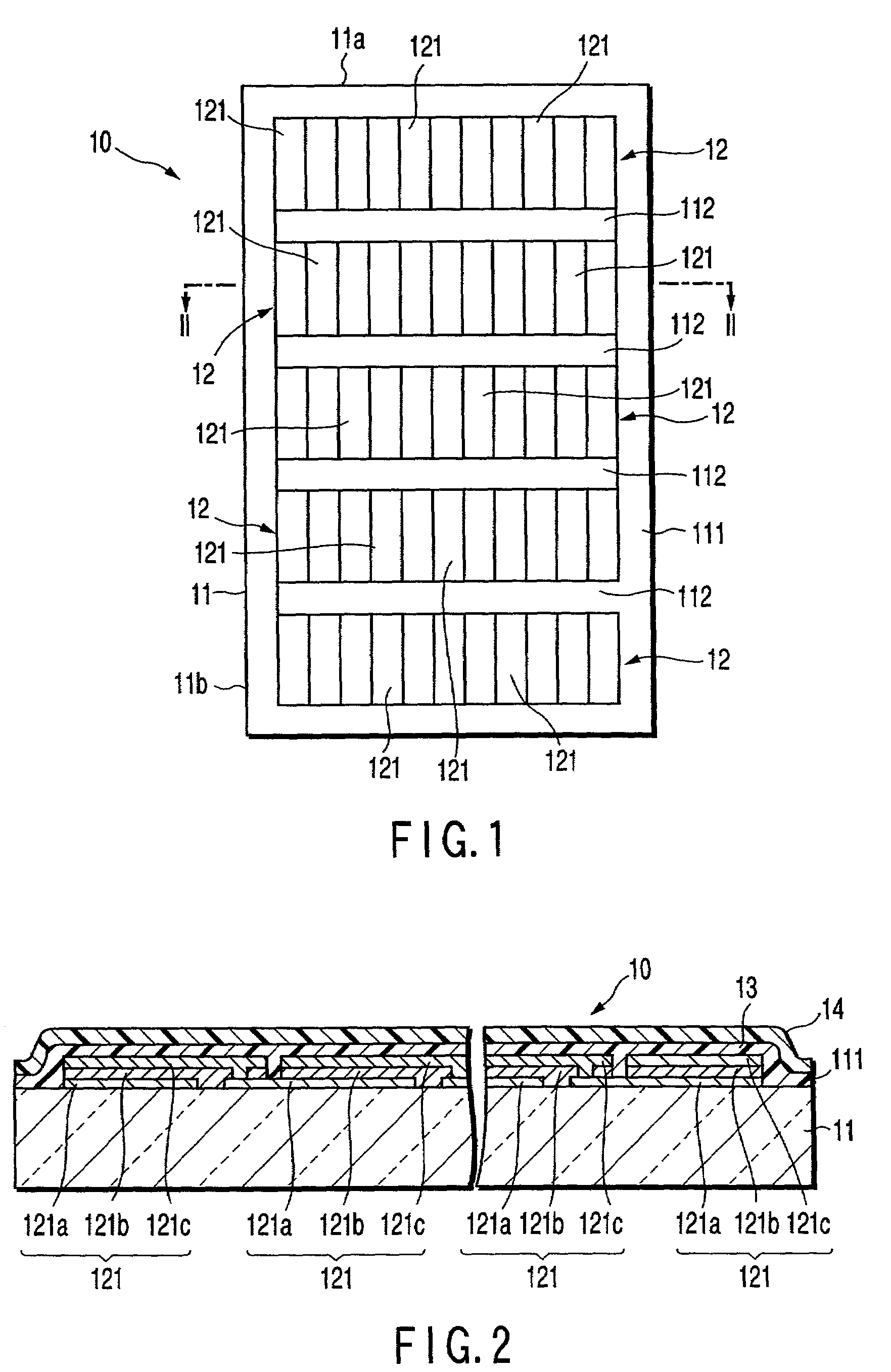
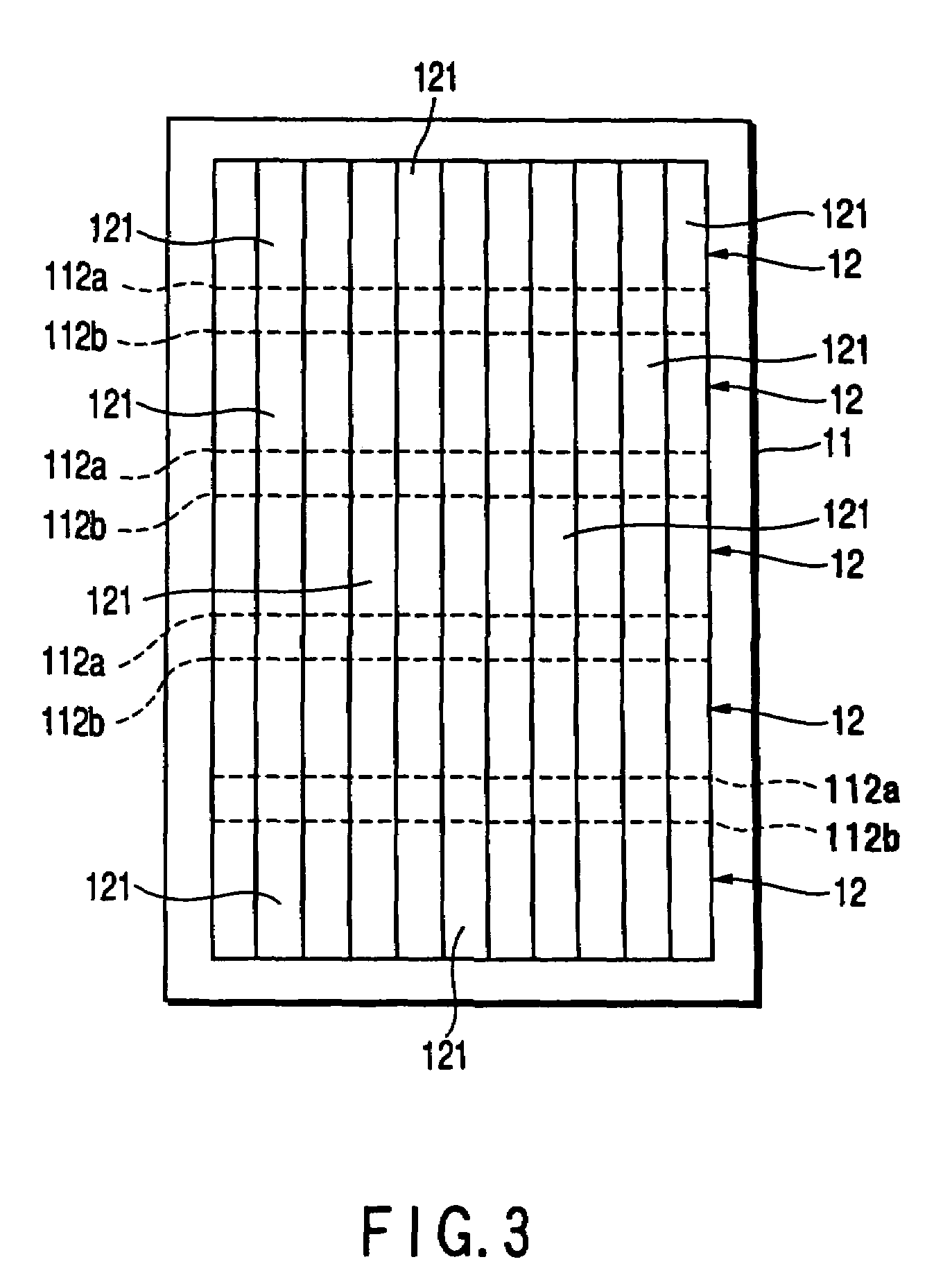
Photovoltaic power generating apparatus, method of producing same and photovoltaic power generating system
InactiveUS6966184B2Low production costReduce the impactPhotovoltaic supportsAuxillary drivesElectrical batterySolar cell
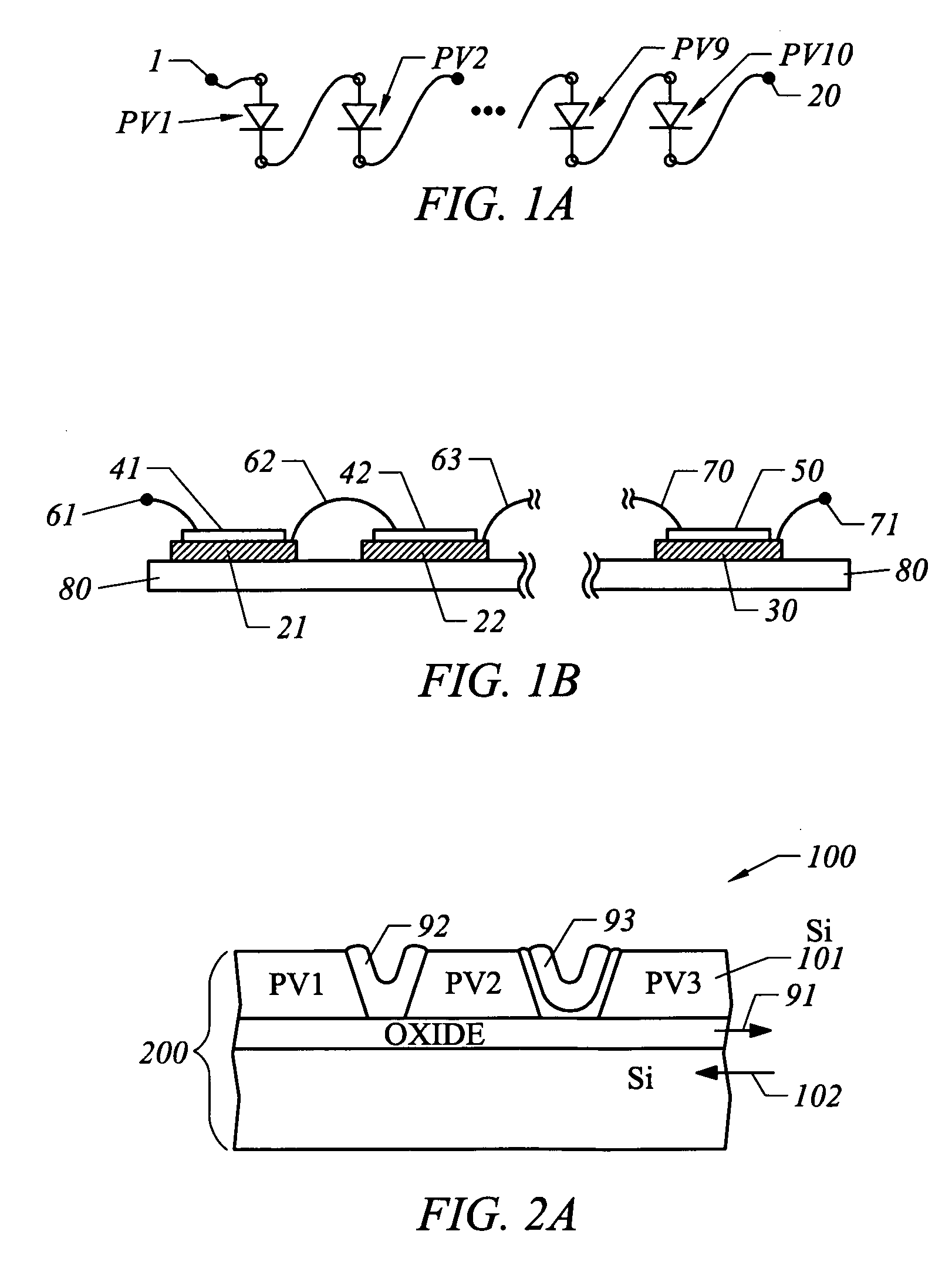
A photovoltaic power generating apparatus is provided which comprises a single solar cell element formed on a substrate and a plurality of power conversion devices individually connected to the solar cell element for converting an output of the solar cell element.
Owner:CANON KK
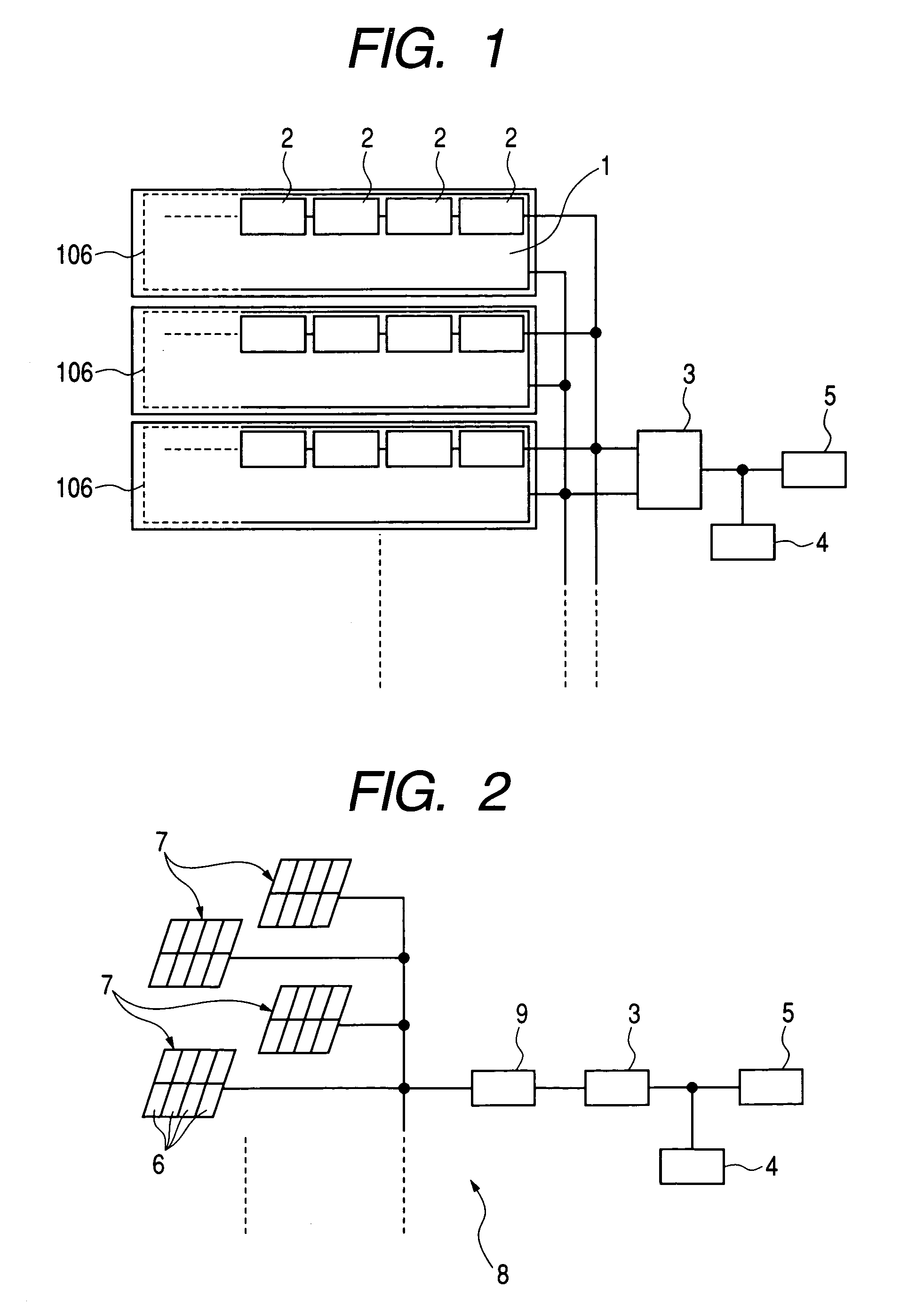
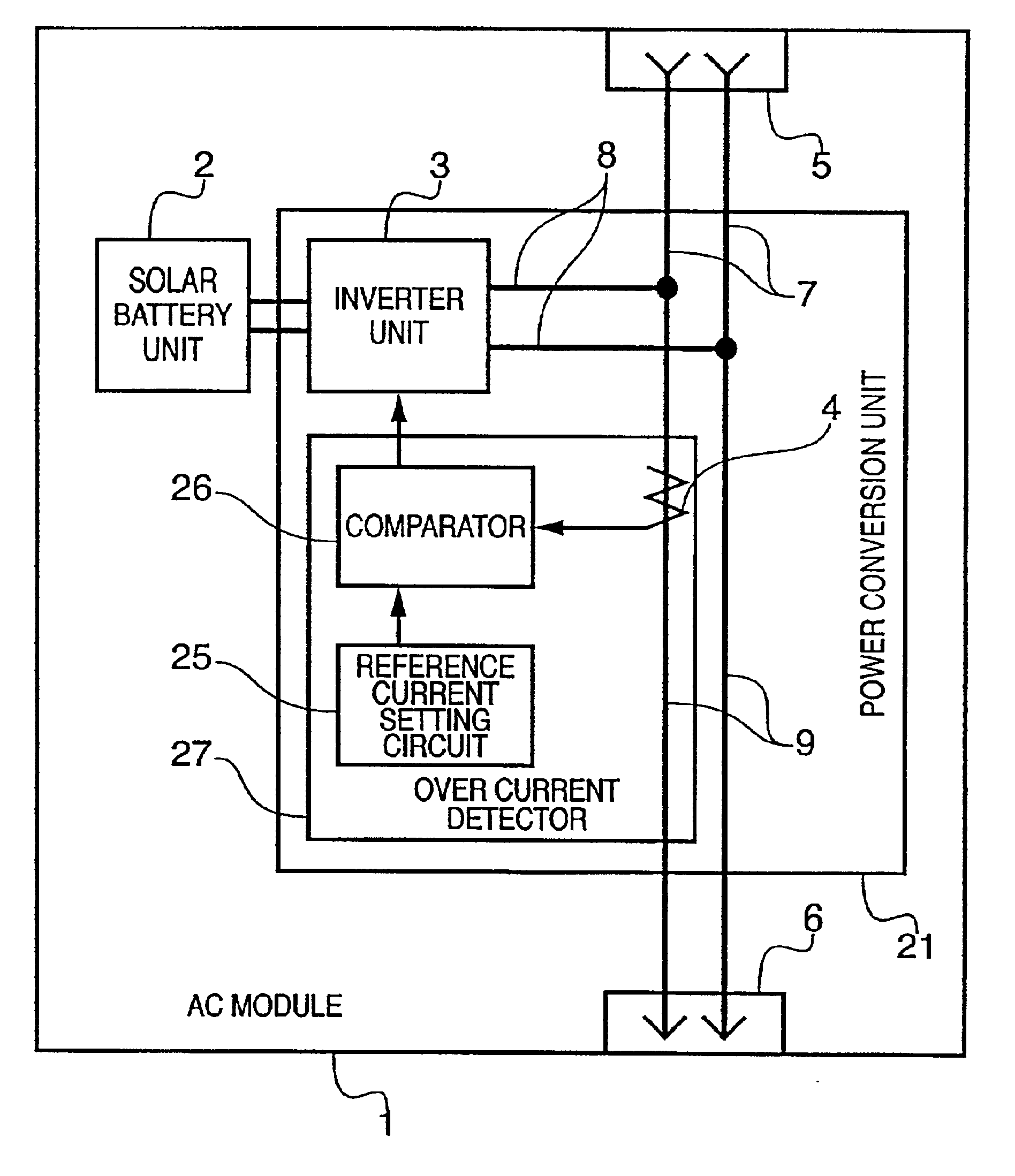
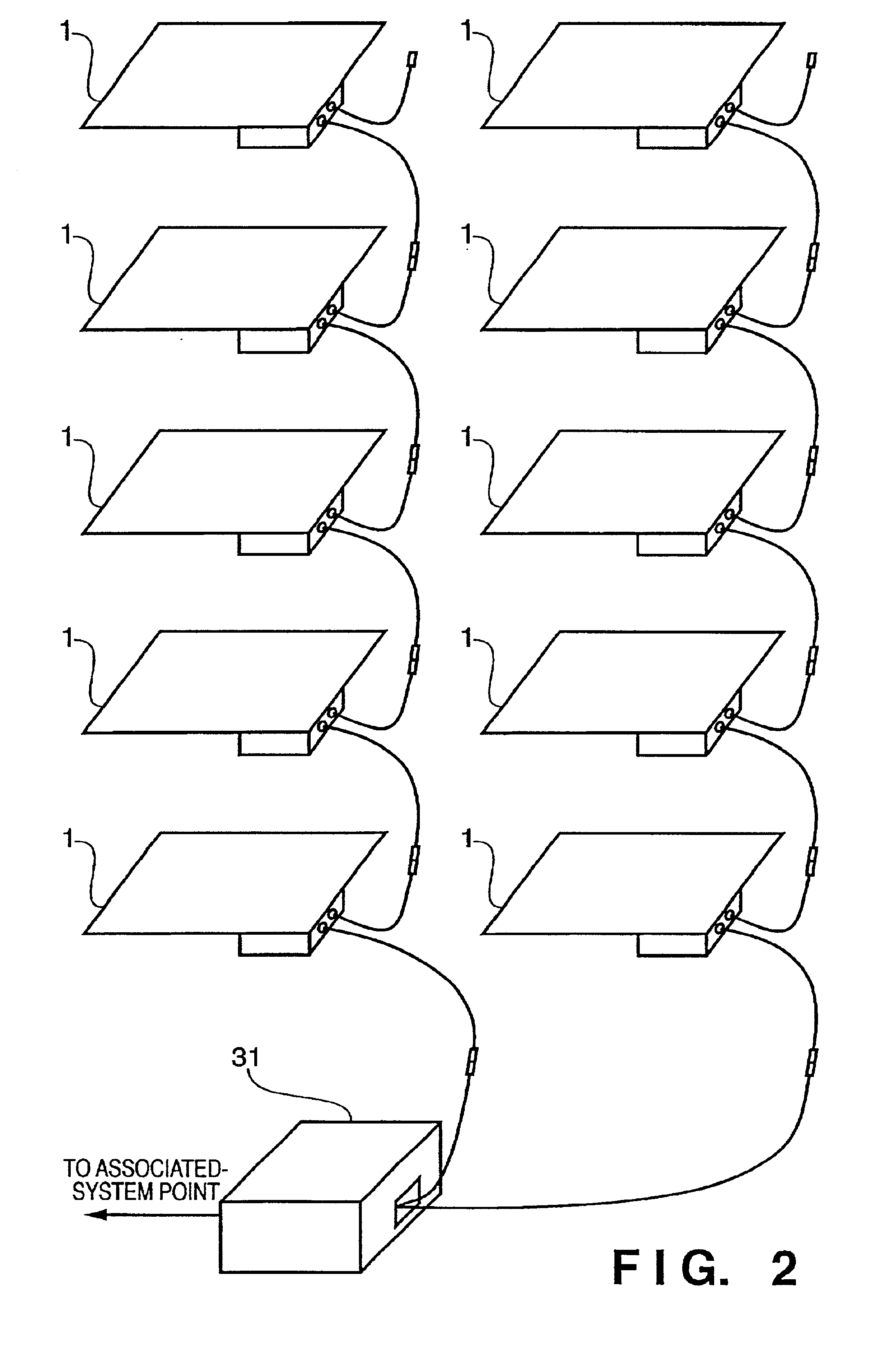
Solar battery module and power generation apparatus
InactiveUS6838611B2Prevent overcurrentBatteries circuit arrangementsPV power plantsPower inverterValue set
AC module, integrating a solar battery and an inverter, can easily be connected with other plural AC modules in parallel by way of cascade connections. However, when the number of AC modules connected is improvidently increased, the current flowing through the current path or connector of the AC module exceeds a rated current. In view of this, the current detector detects a current in the collective-power current path of the AC module, and when the detected current value exceeds a value set in the reference current setting circuit, the current detector stops the inverter.
Owner:CANON KK
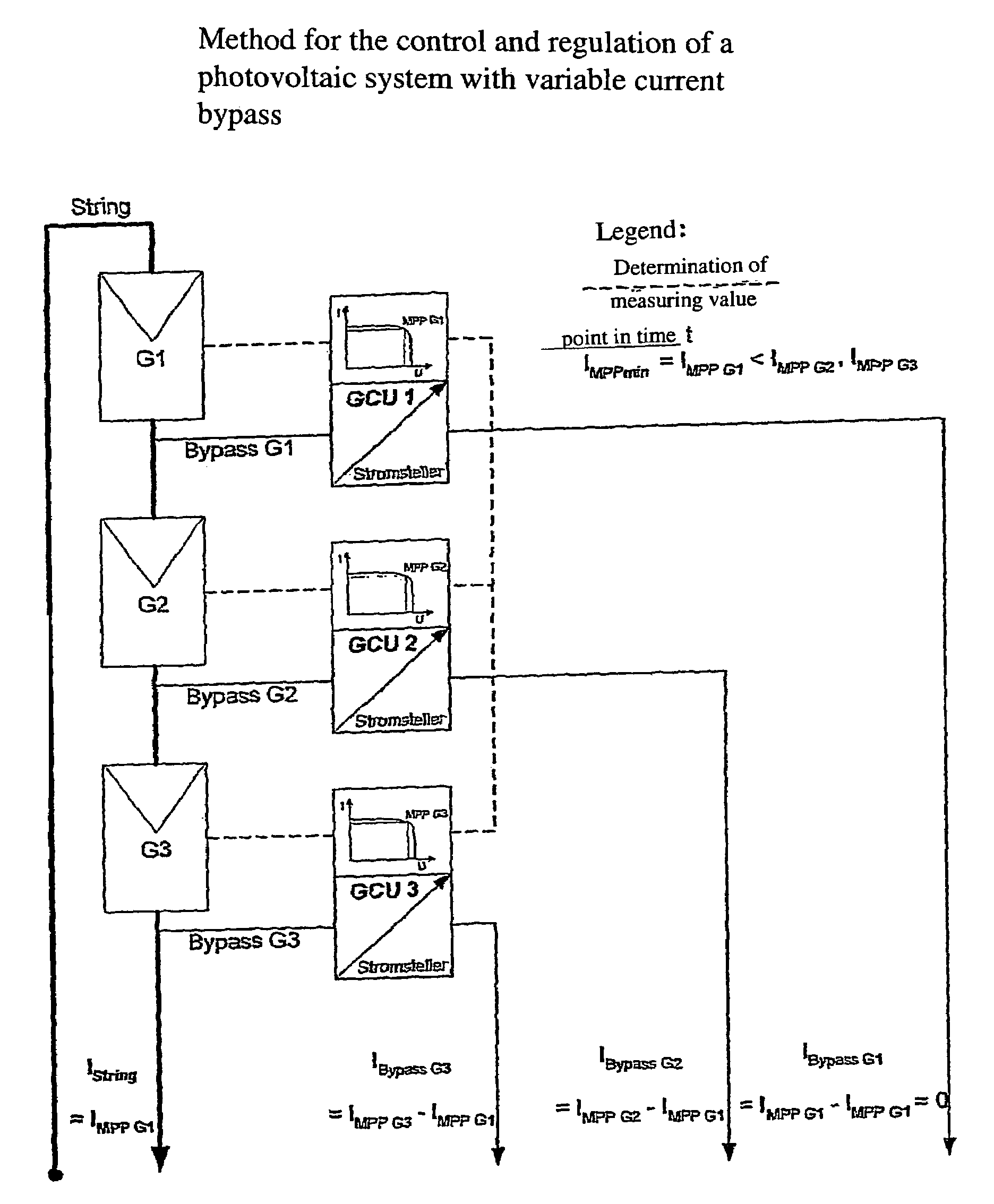
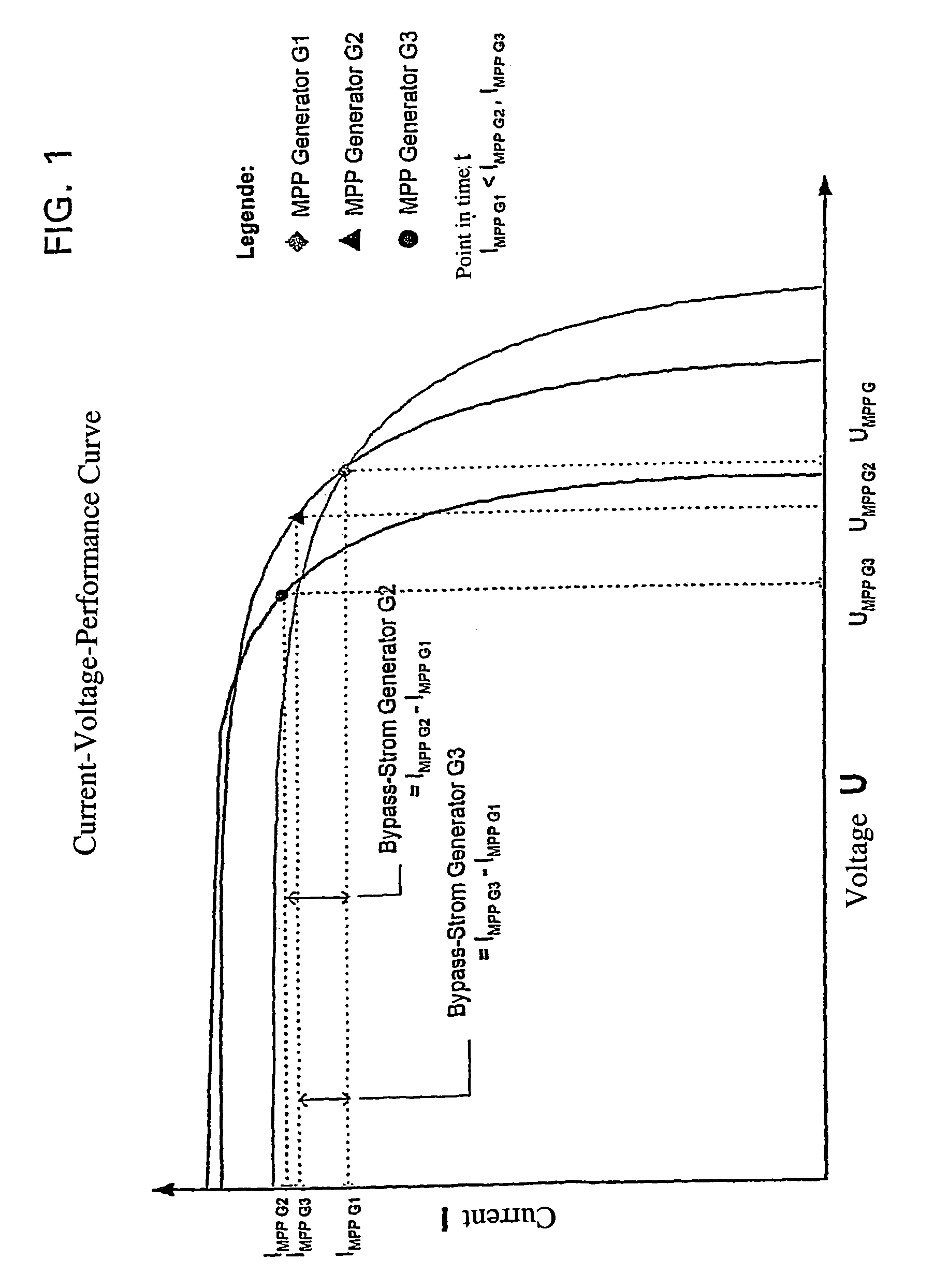
Circuit arrangement for a photovoltaic system
InactiveUS7709727B2High performance yieldImprove securityPV power plantsSolid-state devicesSolar generatorEngineering
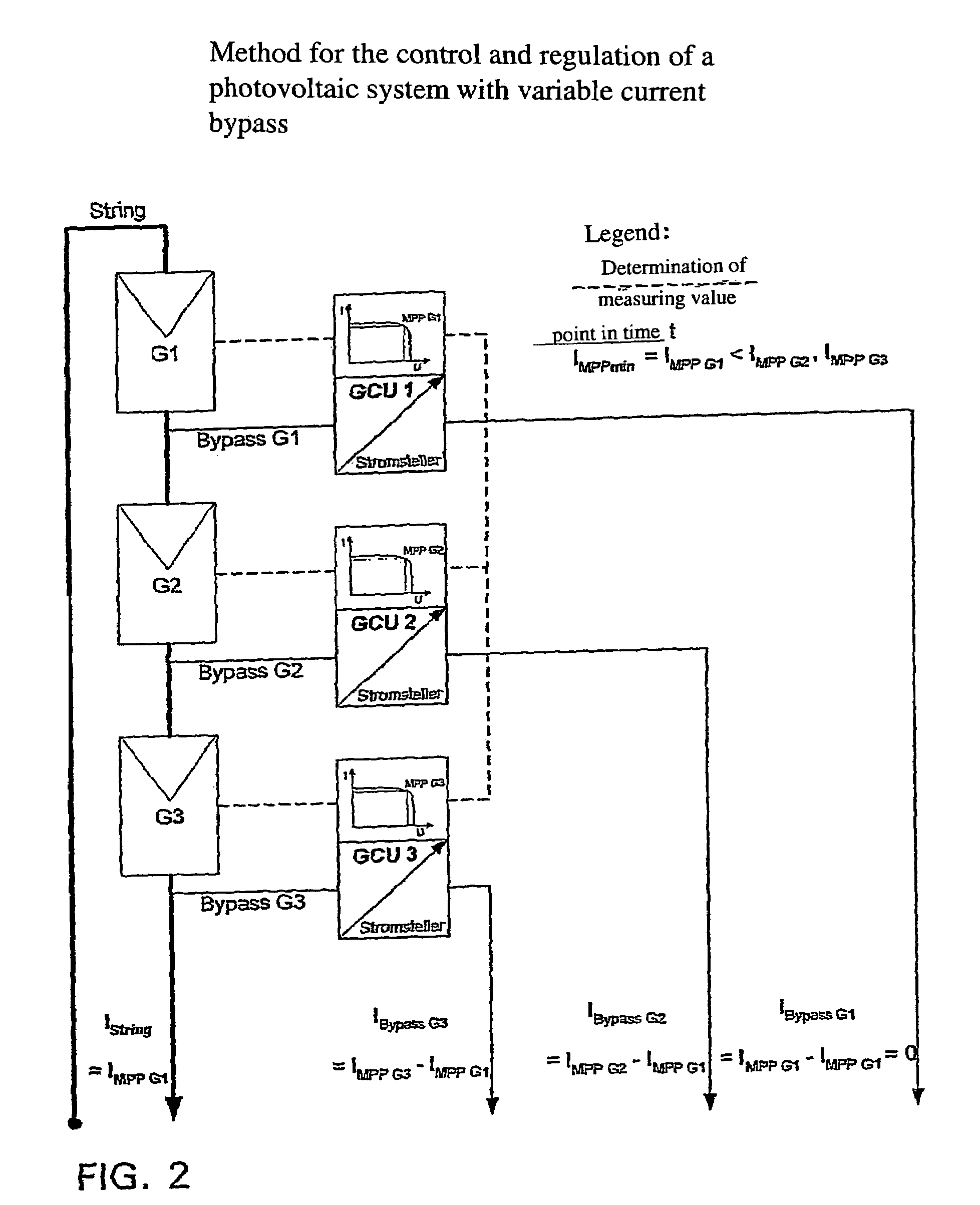
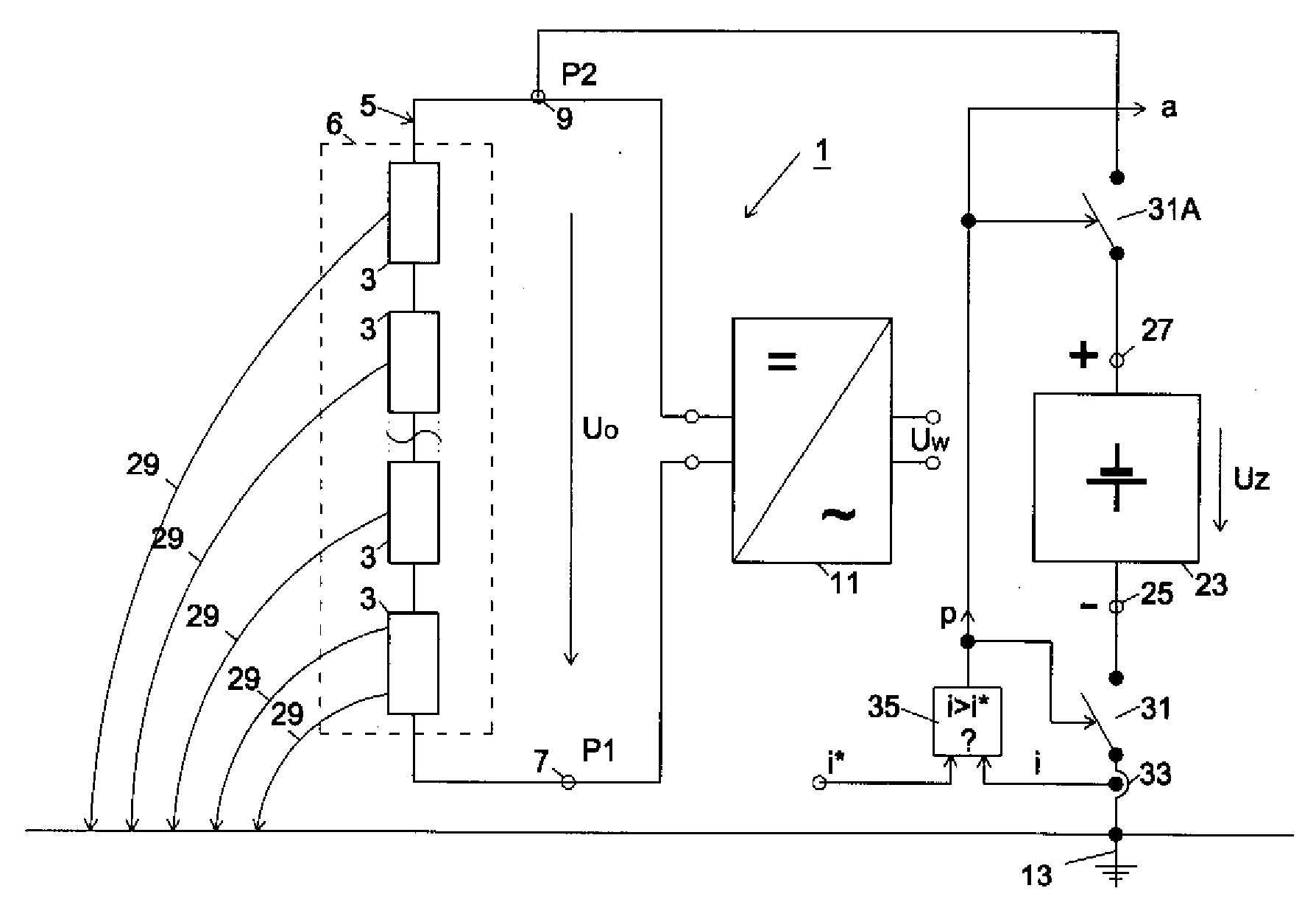
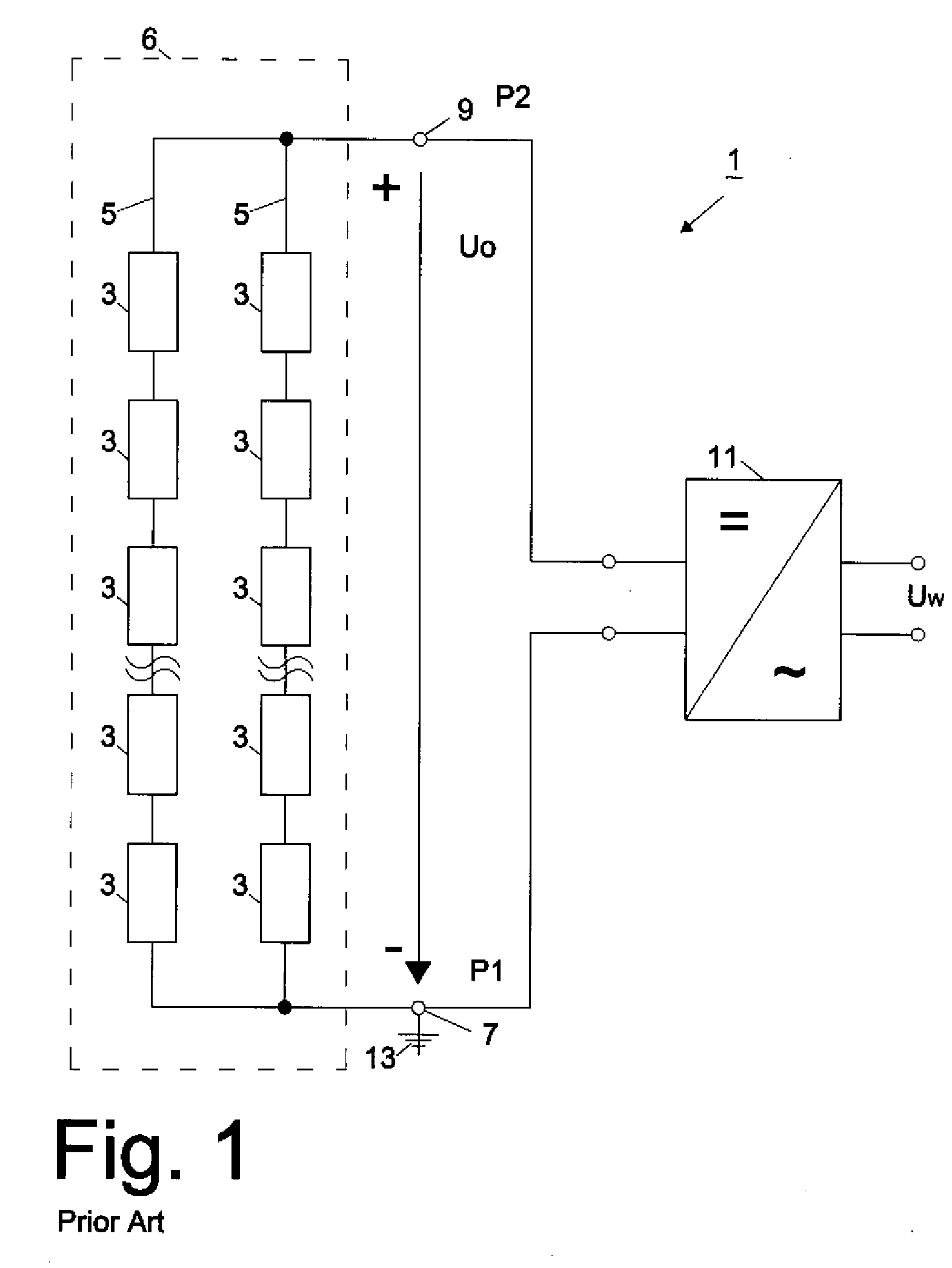
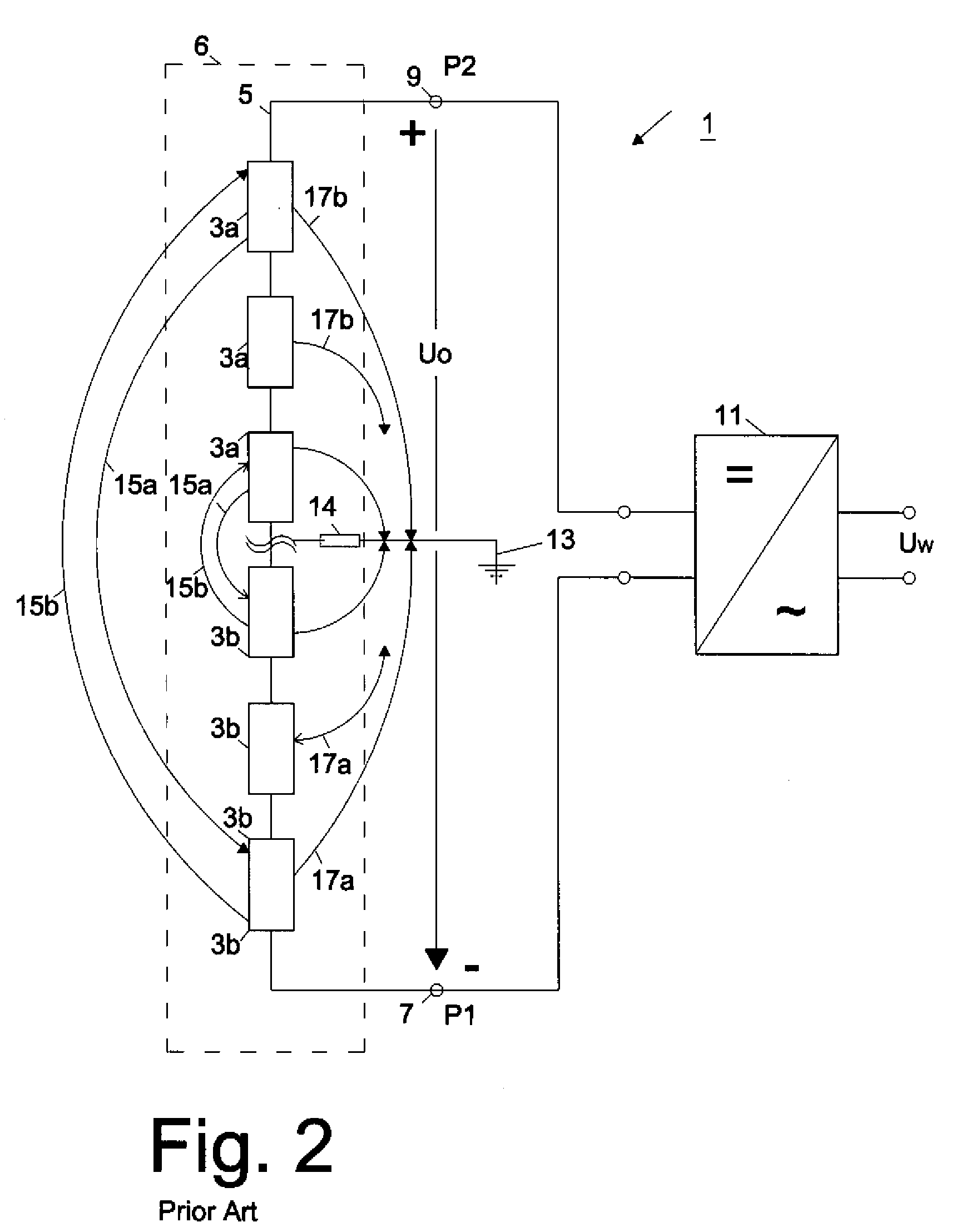
The invention relates to a circuit arrangement for controlling / regulating photovoltaic systems (10b) which comprise a plurality of solar generators (14b) connected in series or / and connected in parallel. In order to prevent power loss of solar generators, which is based on the fact that not all solar generators are operated in the MPP thereof, each solar generator is associated with a variable energy bypass (68b) that is controlled / regulated in such a manner that each solar generator (14b) is operated continuously in its respective current specific MPP.
Owner:ROEHRIG RUEDIGER +1
Partially transparent photovoltaic modules
InactiveUS6858461B2Least amount of loss of photovoltaicDegree of transparencyPhotovoltaic supportsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsElectrical battery
A photovoltaic cell comprising a supporting substrate, a front contact layer on the substrate, a layer or layers of semiconductor material and a back contact layer comprising a metal, the back contact having areas without metal thereby permitting the passage of light through the cell.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Monolithic integration of non-planar solar cells
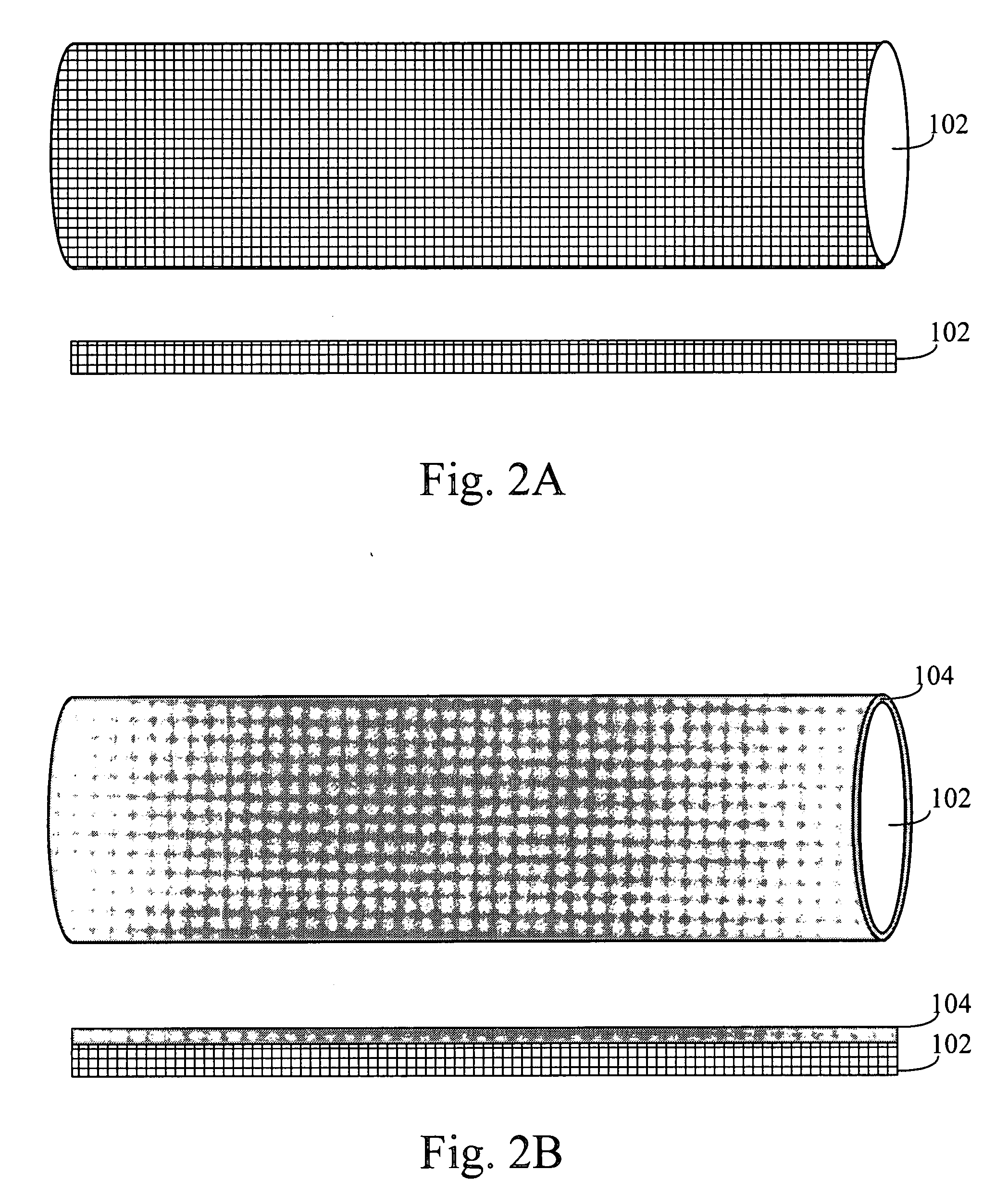
A solar cell unit comprising a substrate and a plurality of photovoltaic cells is provided. The substrate has a first end and a second end. The plurality of photovoltaic cells, which are linearly arranged on the substrate, comprises a first photovoltaic cell and a second photovoltaic cell. Each photovoltaic cell in the plurality of photovoltaic cells comprises (i) a back-electrode circumferentially disposed on the substrate, (ii) a semiconductor junction layer circumferentially disposed on the back-electrode, and, (iii) a transparent conductive layer circumferentially disposed on the semiconductor junction. The transparent conductive layer of the first photovoltaic cell in the plurality of photovoltaic cells is in serial electrical communication with the back-electrode of the second photovoltaic cell in the plurality of photovoltaic cells.
Owner:SOLYNDRA RESIDUAL TRUST
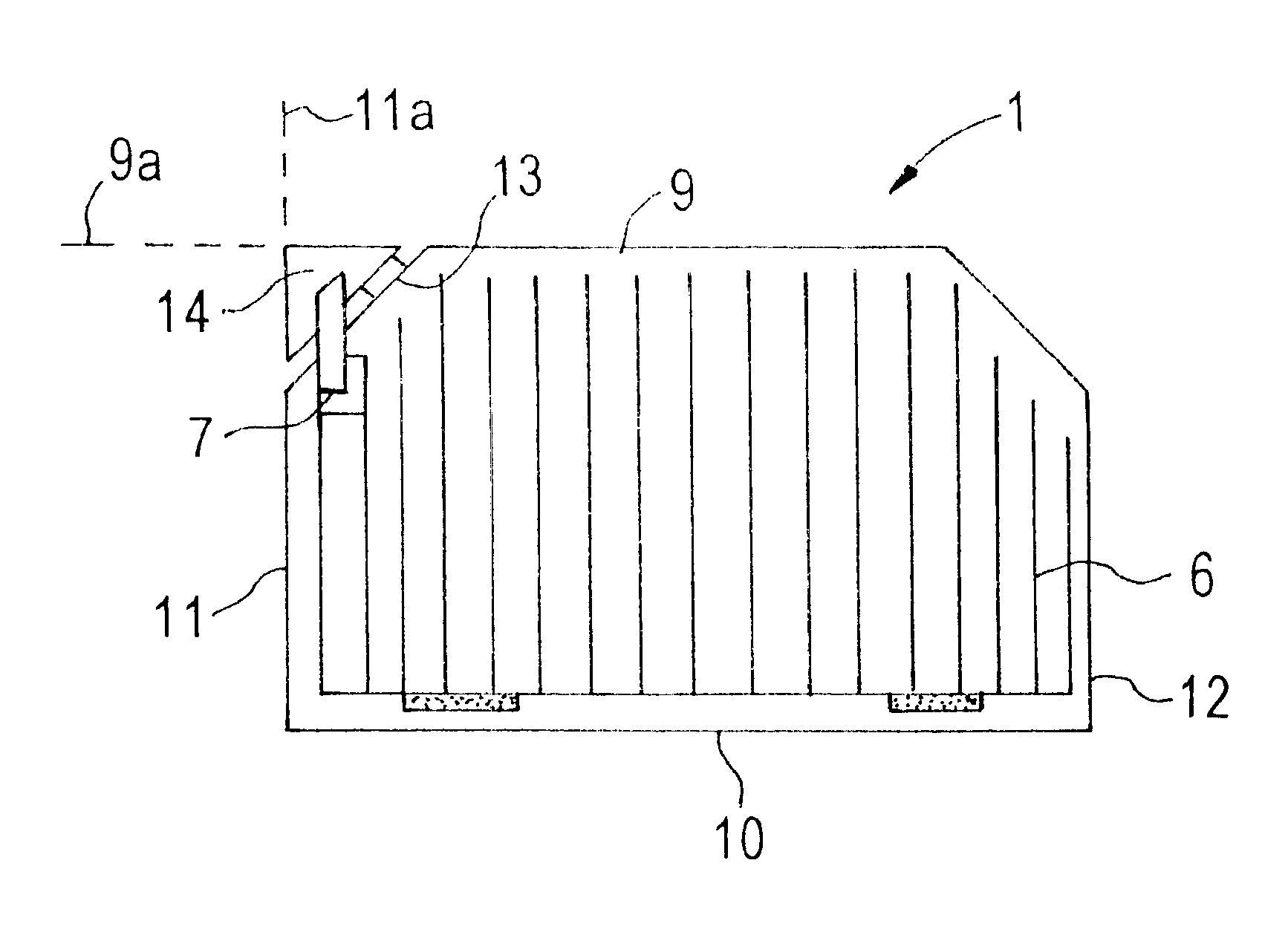
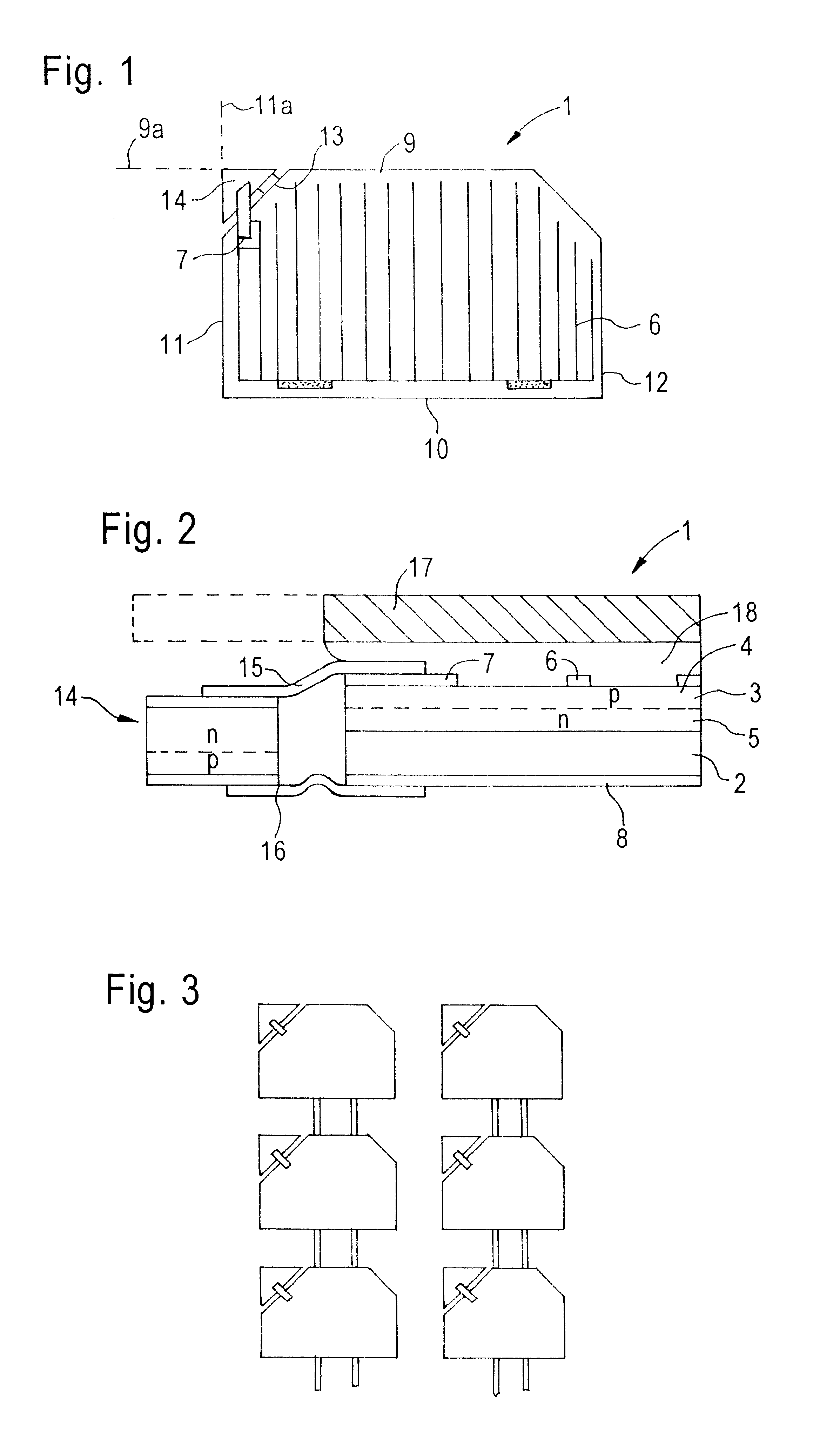
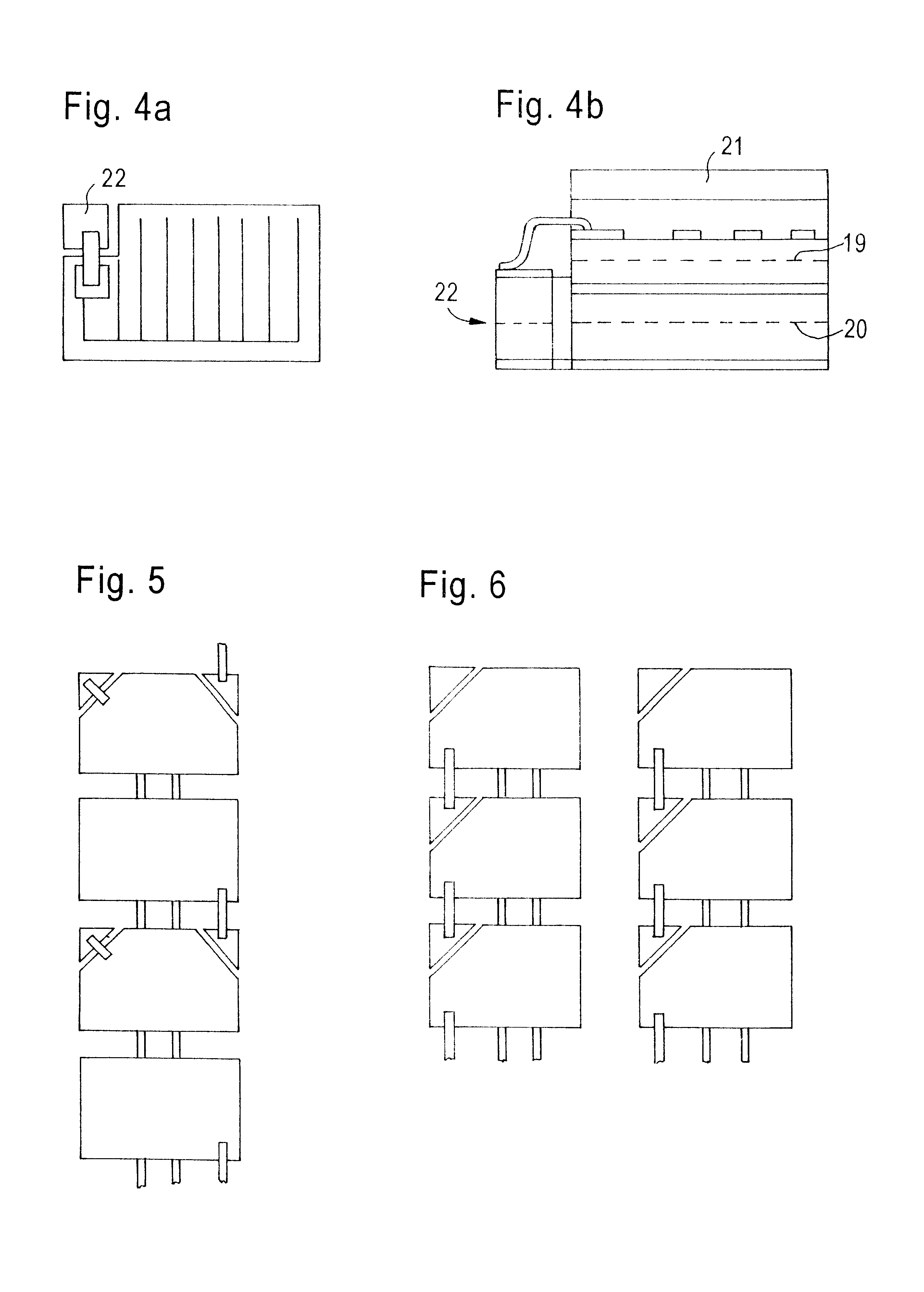
Photovoltaic system
ActiveUS20090101191A1Avoid damageEliminate dischargePV power plantsDiodePhotovoltaic generatorElectron
The photovoltaic system includes a plurality of photovoltaic modules which are connected to form a string or several strings connected in parallel, thereby forming a photovoltaic generator having a positive terminal and negative terminal. A DC constant voltage source connected to the photovoltaic generator to raise the potential of the positive terminal relative to ground potential. This reduces the flow of electrons out of the TCO layer of the modules, thereby reducing or completely eliminating cathode discharges which damage the modules.
Owner:PADCON
Connection systems and methods for solar cells
Exemplary embodiments provide an array of solar power generation devices, and method for forming the array. Each solar power generation device can be defined as a cell, a group of cells, a panel subarray, a panel from an array of panels, etc. The solar power generation device can include a controller which can address and control each solar power generation device individually. A test method and fixture is also described, which can be used to program the controller such that incorrect assembly of the array during manufacture is overcome.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
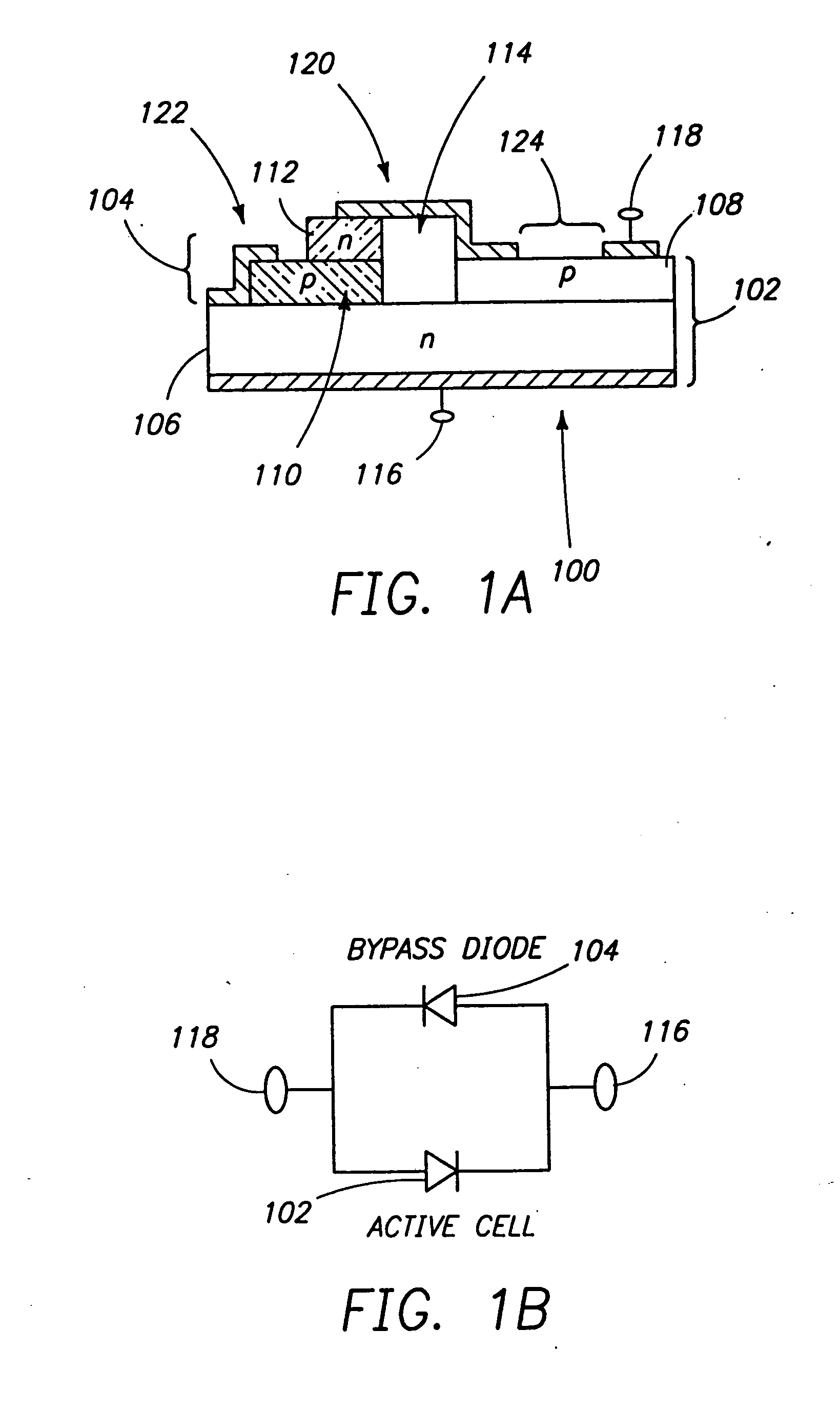
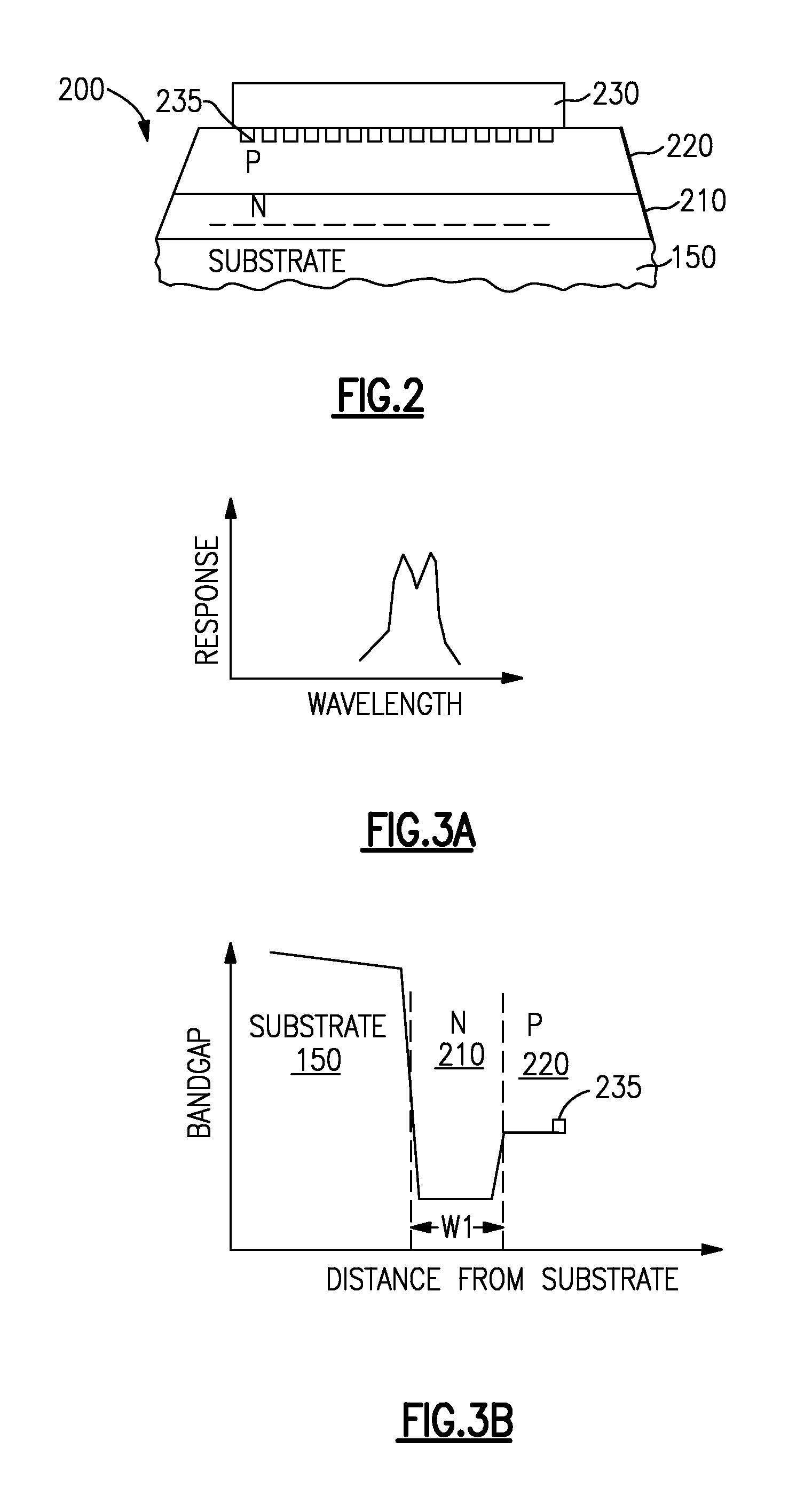
Inverted metamorphic solar cell with bypass diode
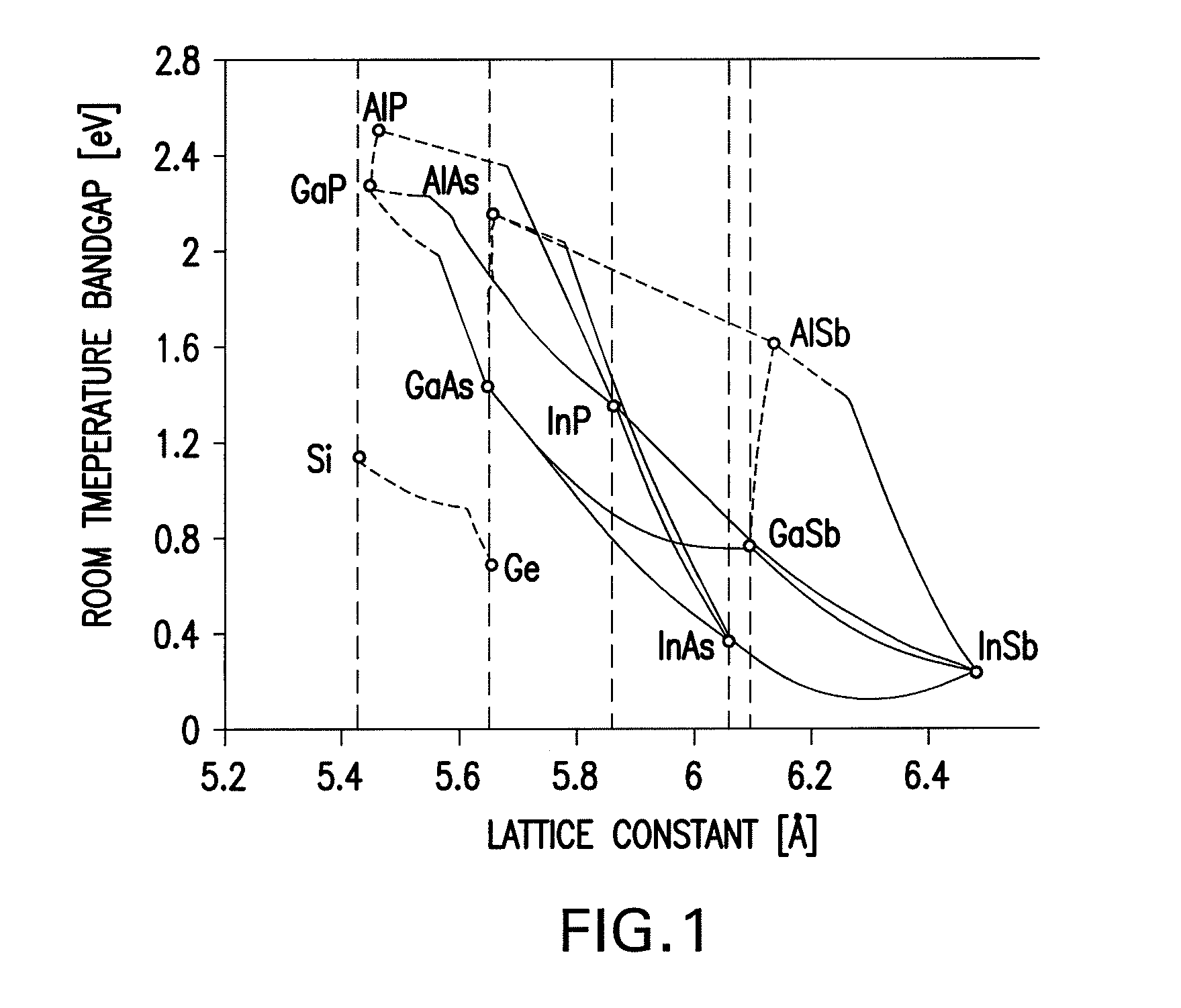
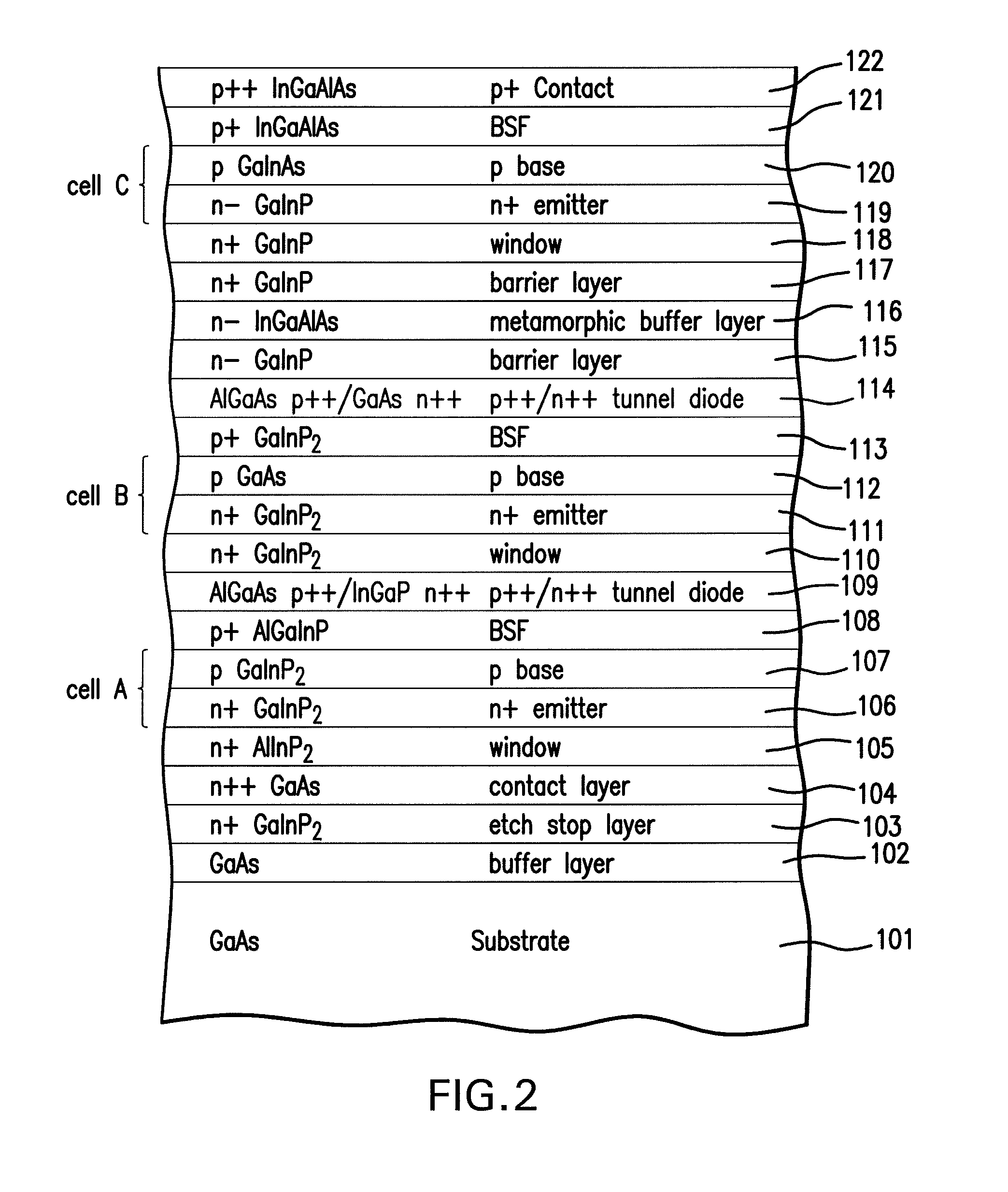
InactiveUS20080149173A1Maximize energy efficiencyFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsSemiconductor structure
A method of forming a semiconductor structure including a multijunction solar cell with an upper subcell, a middle subcell, and a lower subcell, by providing first substrate for the epitaxial growth of semiconductor material; forming a first solar subcell on said substrate having a first band gap; forming a second solar subcell over said first subcell having a second band gap smaller than said first band gap; and forming a grading interlayer over said second subcell having a third band gap larger than said second band gap; forming a third solar subcell having a fourth band gap smaller than said second band gap such that said third subcell is lattice mismatched with respect to said second subcell. A bypass diode is further provided in the semiconductor structure with a region of first polarity of the solar cell connected with a region of second polarity of the bypass diode.
Owner:EMCORE SOLAR POWER
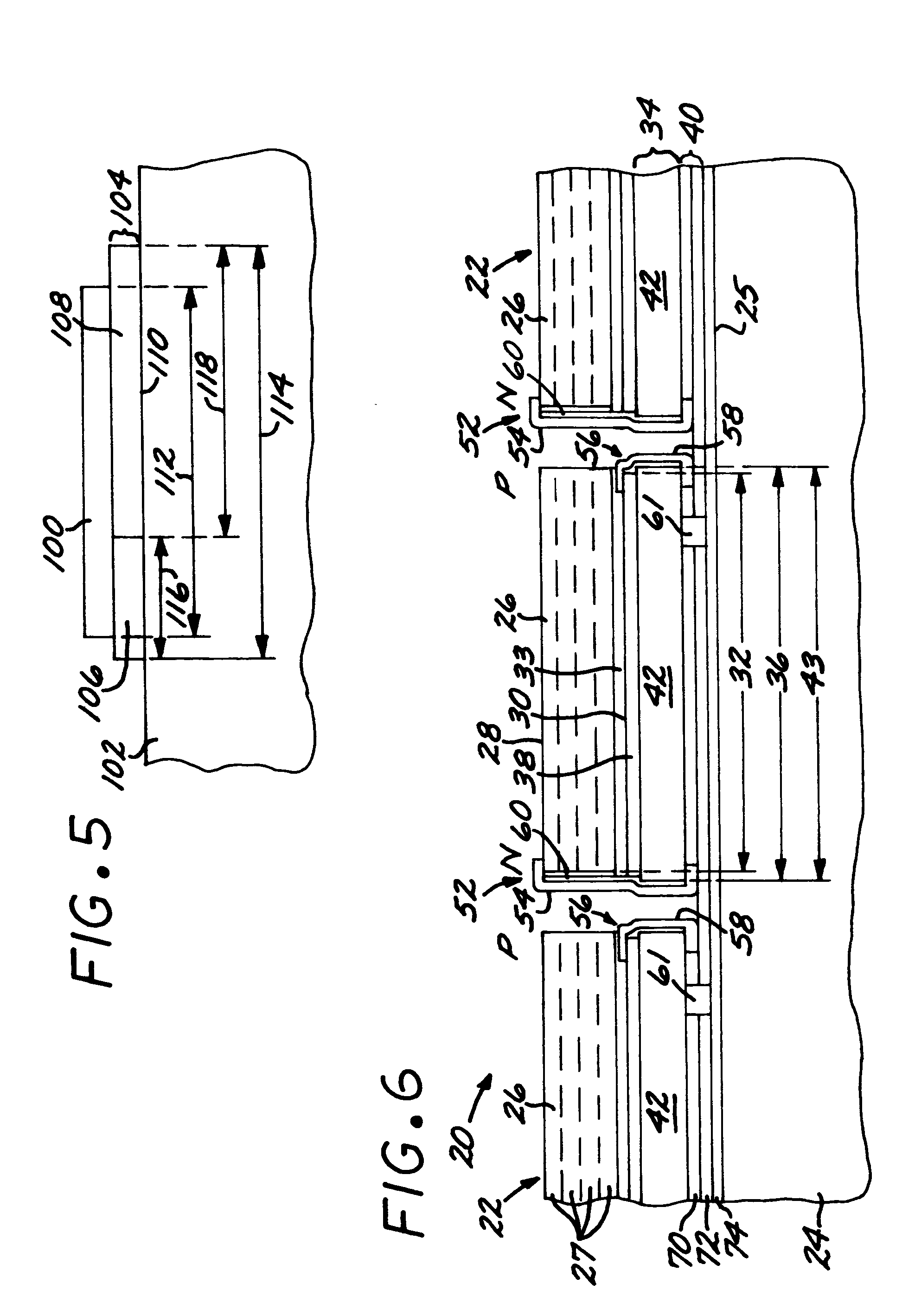
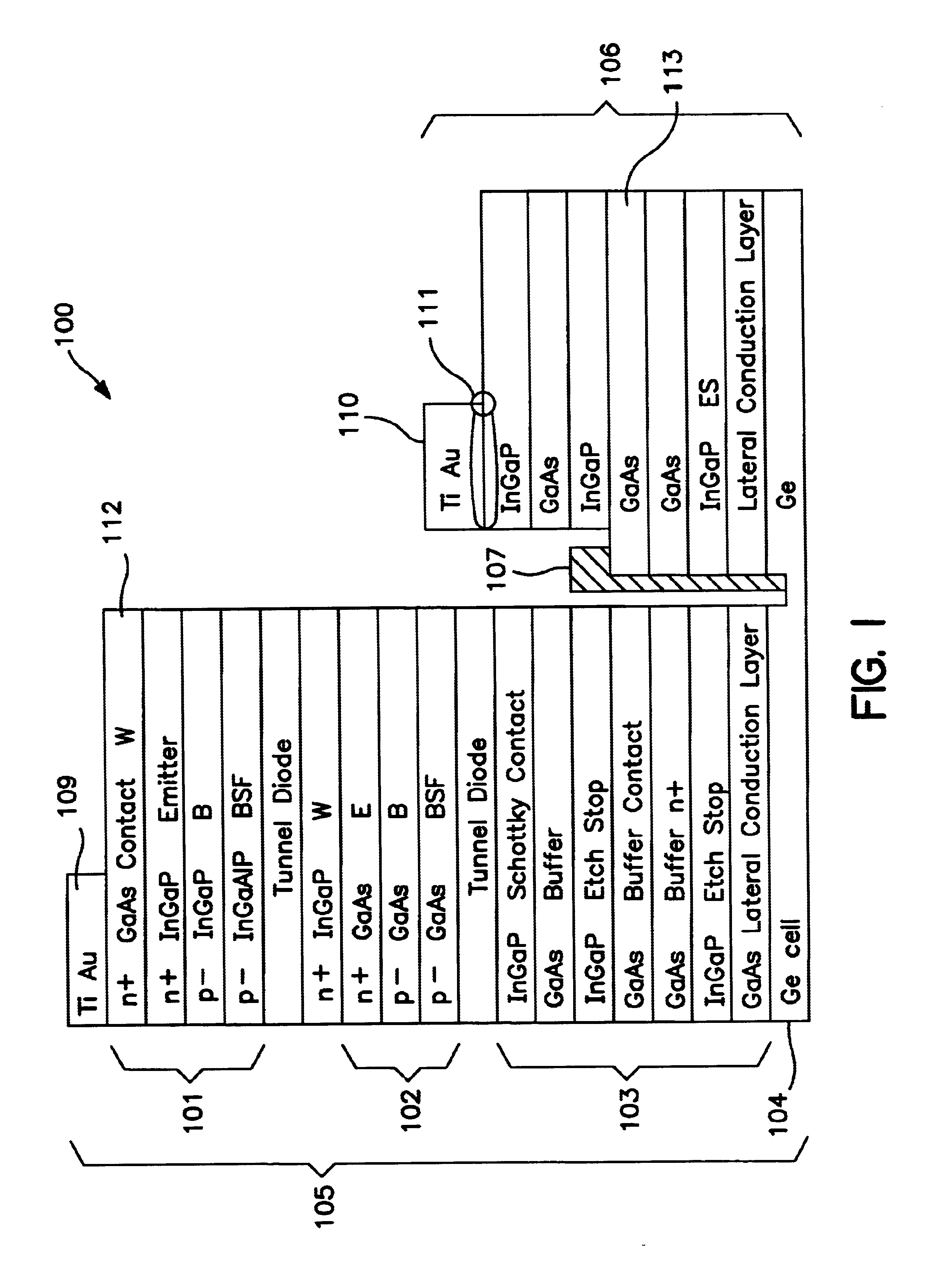
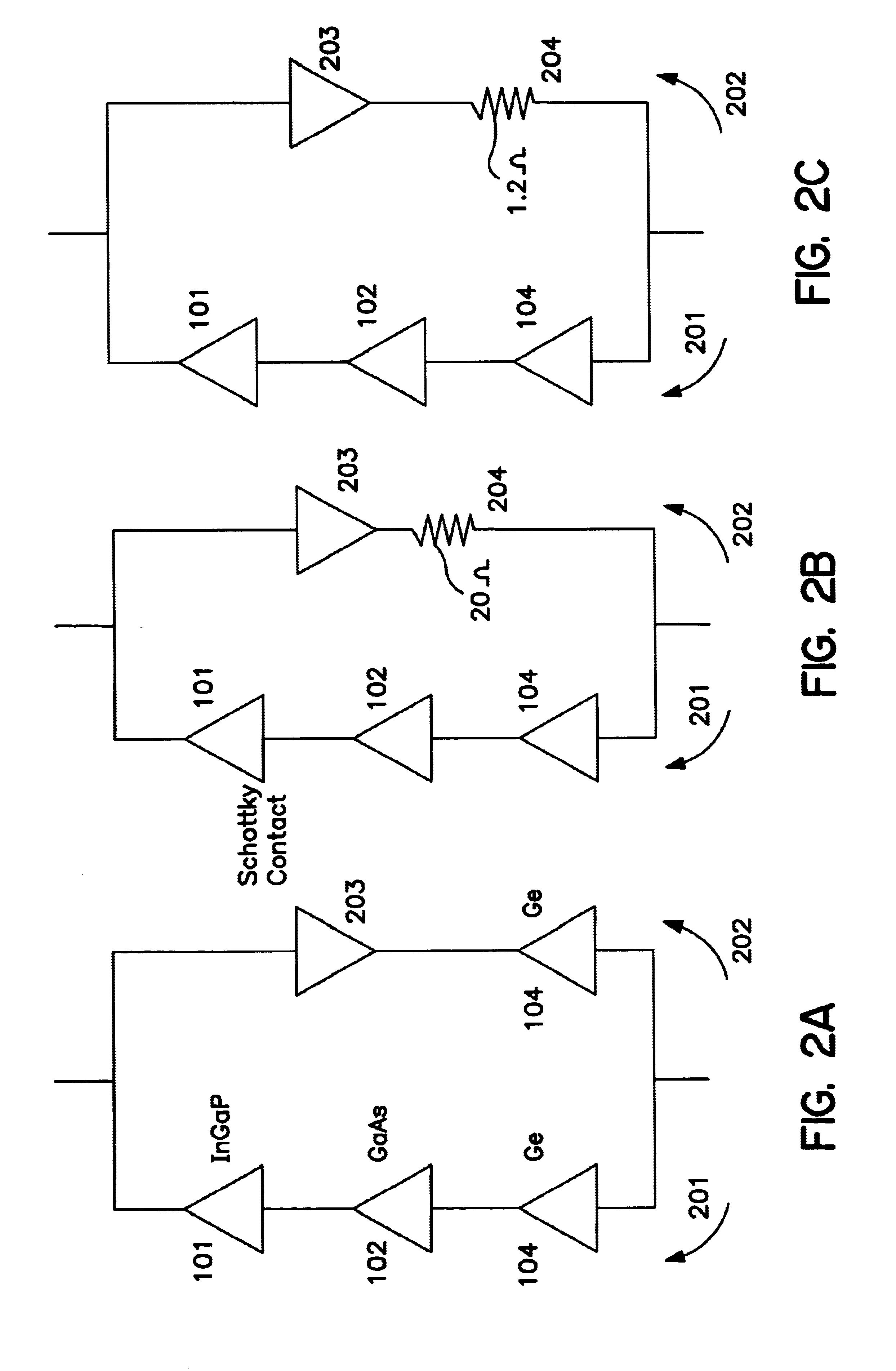
Apparatus and method for optimizing the efficiency of a bypass diode in multijunction solar cells
InactiveUS6680432B2Improve efficiencyLess voltagePV power plantsFinal product manufactureState of artMultijunction photovoltaic cell
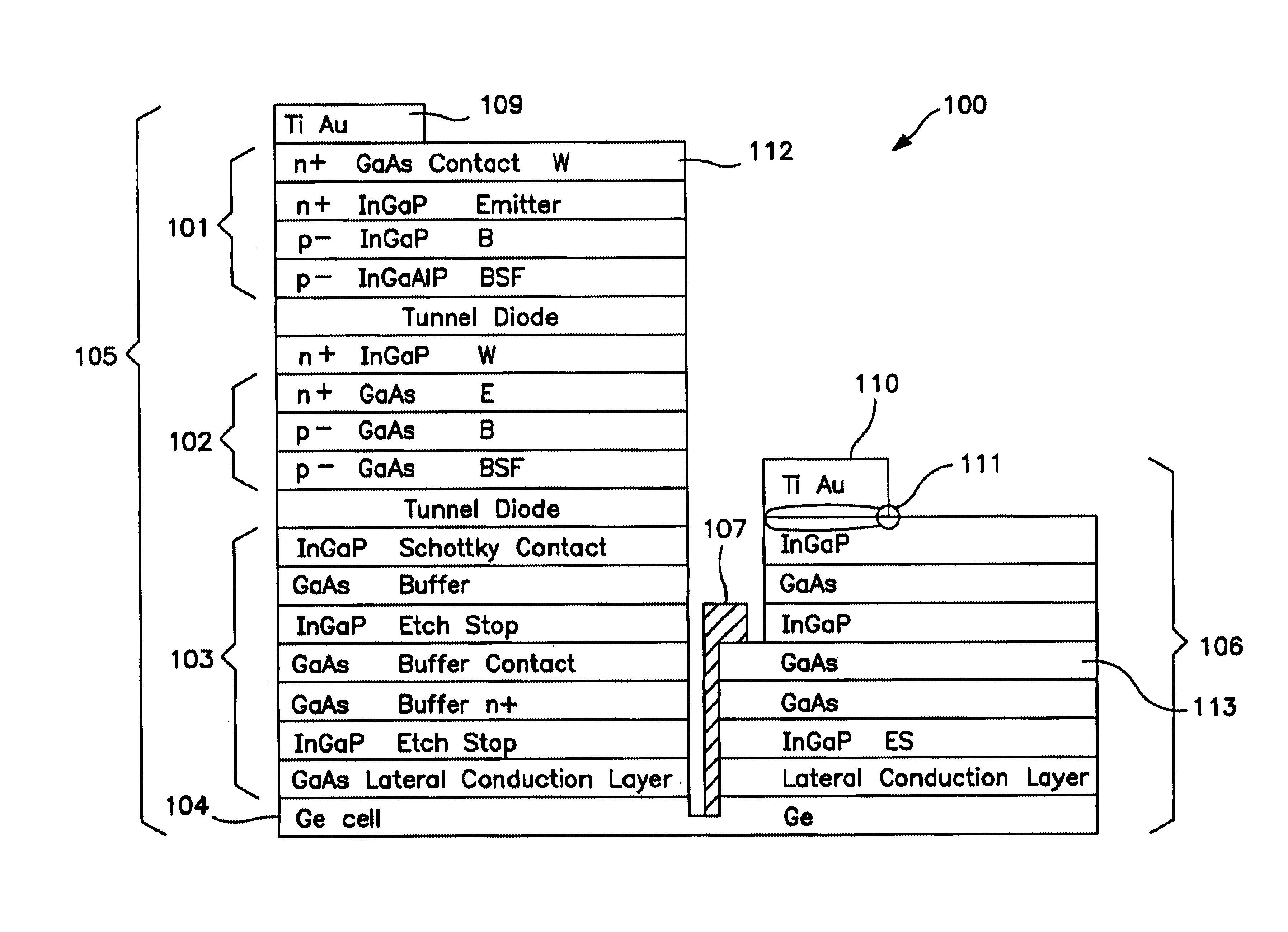
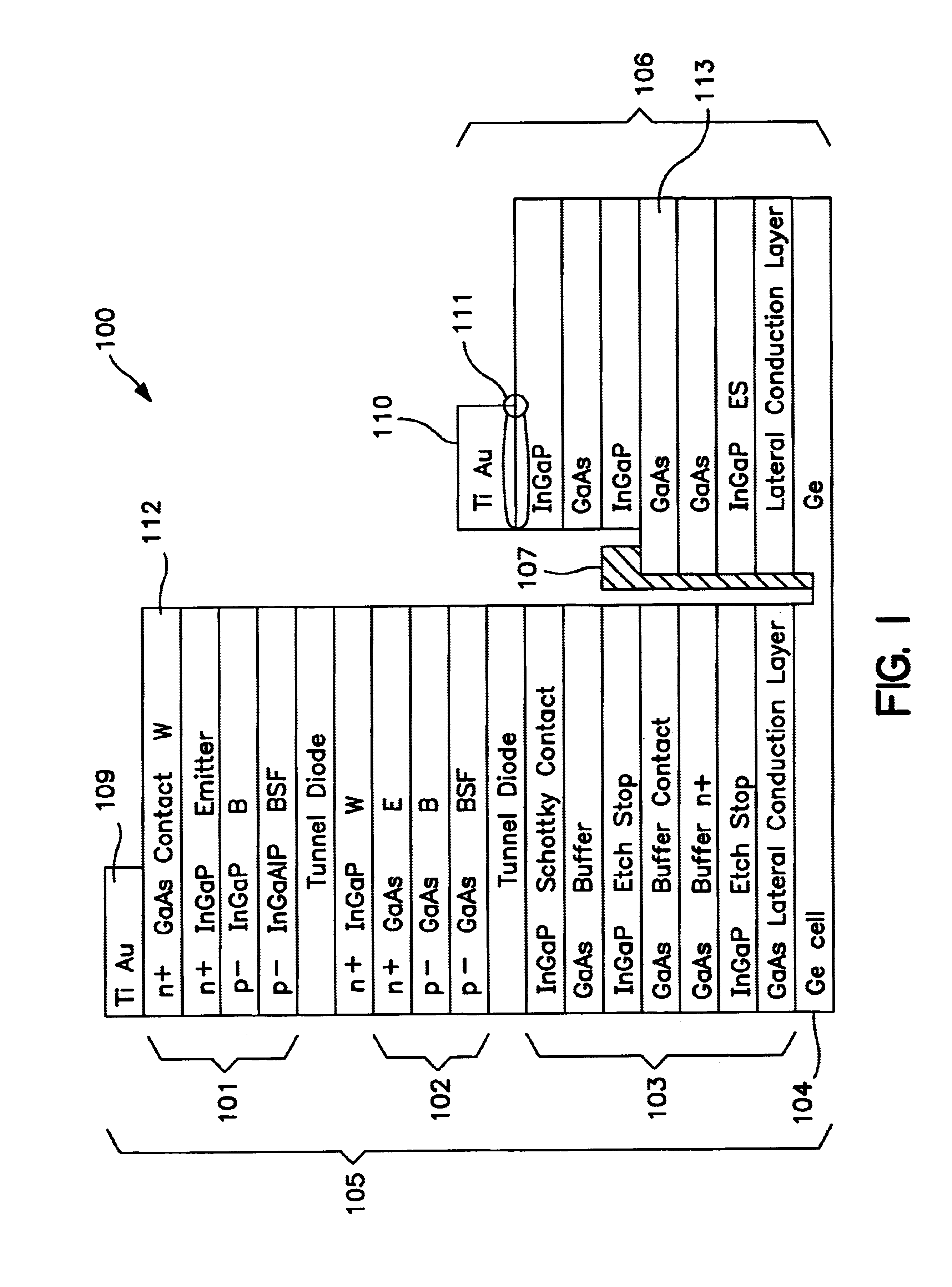
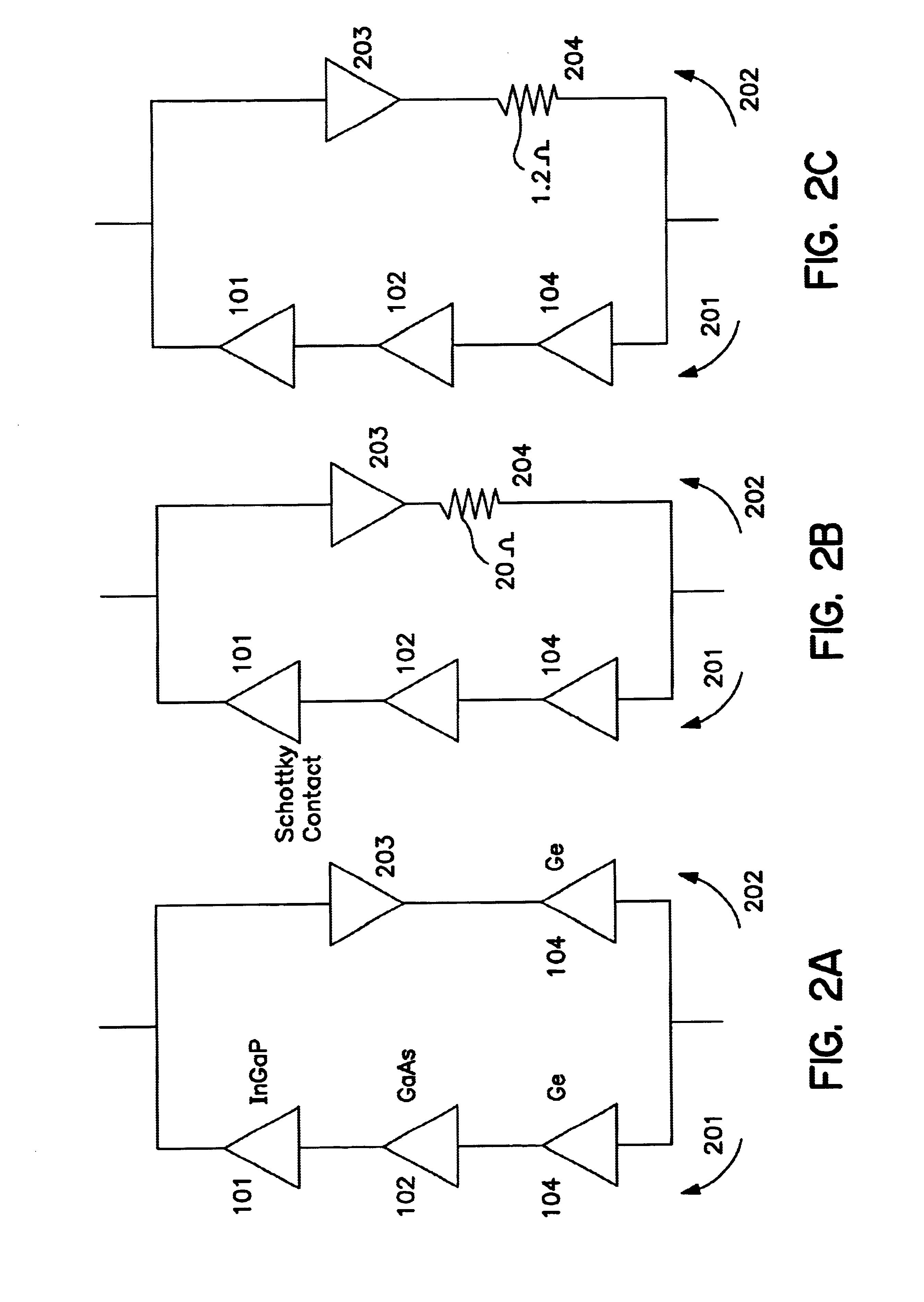
Apparatus and Method for Optimizing the Efficiency of a Bypass Diode in Solar Cells. In a preferred embodiment, a layer of TiAu is placed in an etch in a solar cell with a contact at a doped layer of GaAs. Electric current is conducted through a diode and away from the main cell by passing through the contact point at the GaAs and traversing a lateral conduction layer. These means of activating, or "turning on" the diode, and passing the current through the circuit results in greater efficiencies than in prior art devices. The diode is created during the manufacture of the other layers of the cell and does not require additional manufacturing.
Owner:SOLAERO TECH CORP
Thin-film solar array system and method for producing the same
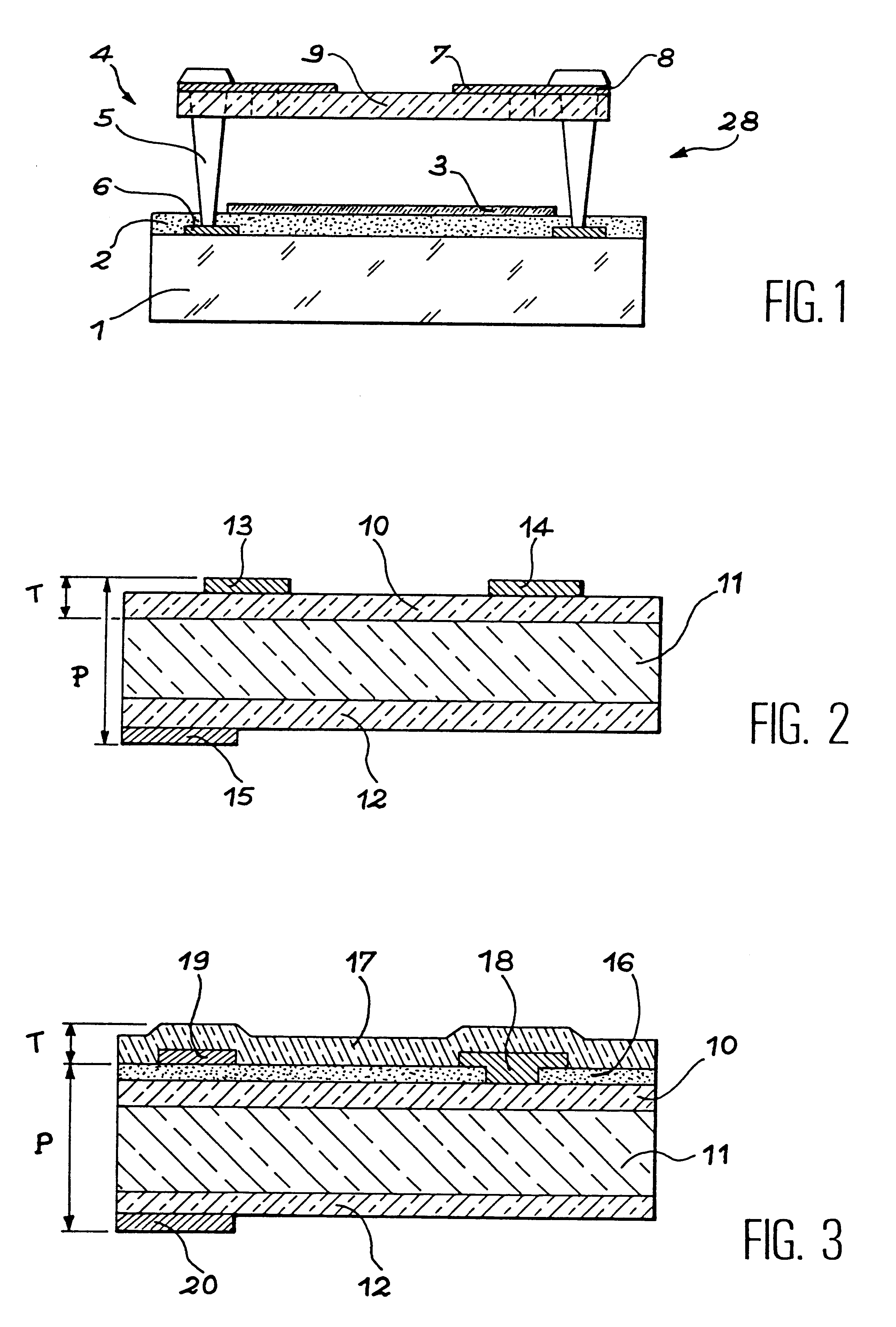
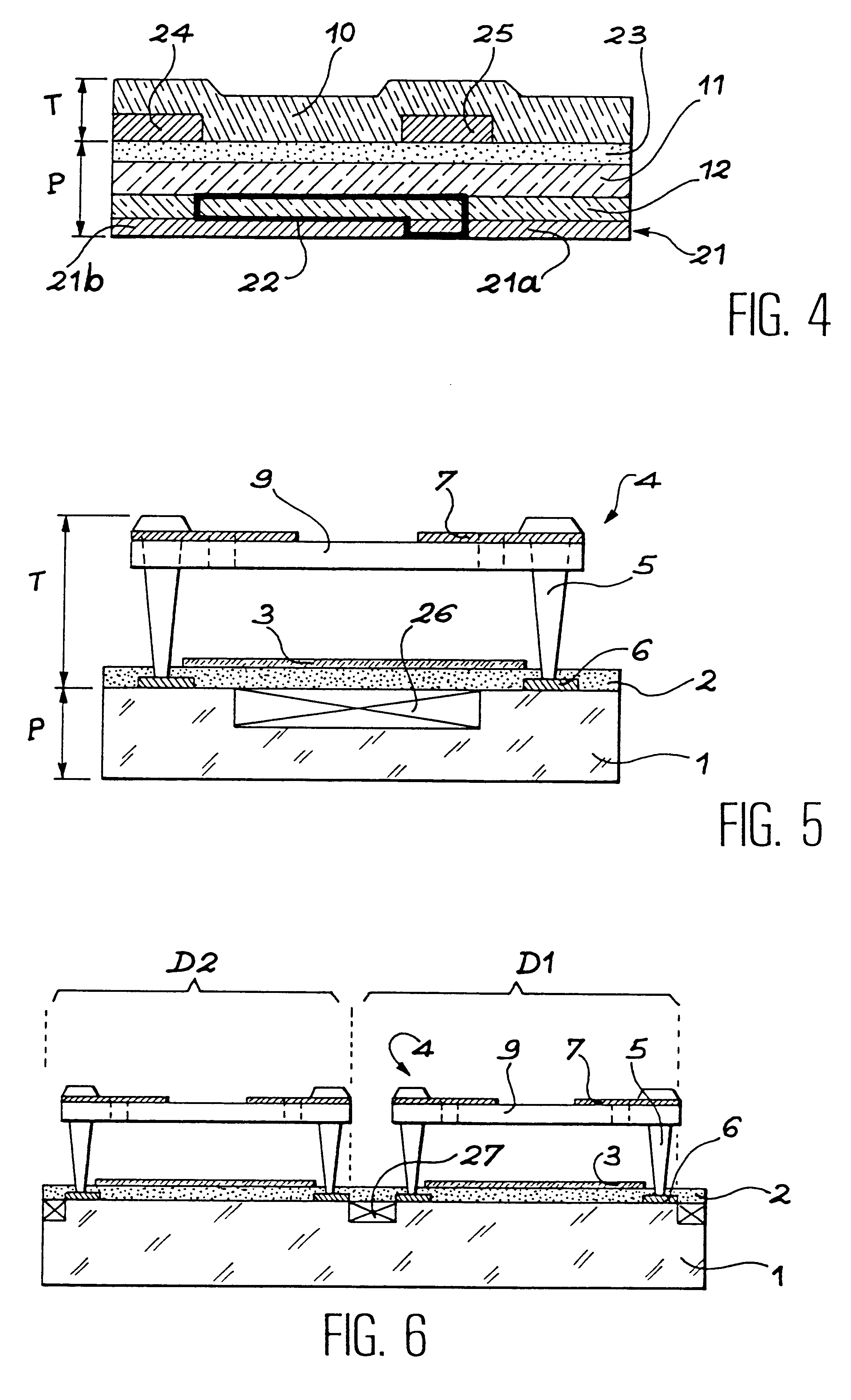
Disclosed is a thin-layer solar cell array system and a method for producing the same, having placed over a carrier substrate of plane design, a solar cell layer which is provided with at least one n-type conducting semiconductor zone (emitter) and at least one p-type conducting semiconductor zone (base) as well as a first and a second contact electrode, each of different electric polarity, which are each electrically connected to the emitter respectively to the base.The invention is distinguished by at least the first contact electrode being applied directly on the carrier substrate or separated by an electrically insulating layer, an electrically insulating layer being provided thereupon, and the solar cell layer being placed over the insulating layer, by at least one contact channel extending through the insulating layer and / or the solar cell layer in such a manner that the first contact electrode and the semiconductor layer zone of respective polarity inside the solar cell layer being electrically connectable by means of an electrically conducting material provided inside the contact channel, and by the second contact electrode like the first contact electrode being placed above or in the case of a conductive carrier layer also under the carrier layer and under the electrically insulating layer and the solar cell layer, and by at least one contact channel extending through the insulating layer and / or the solar cell layer in such a manner that the second contact electrode and the semiconductor layer zone of respective polarity inside the solar cell layer being electrically connected by means of an electrically conducting material provided inside the contact channel.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Light Emitting, Photovoltaic Or Other Electronic Apparatus and System
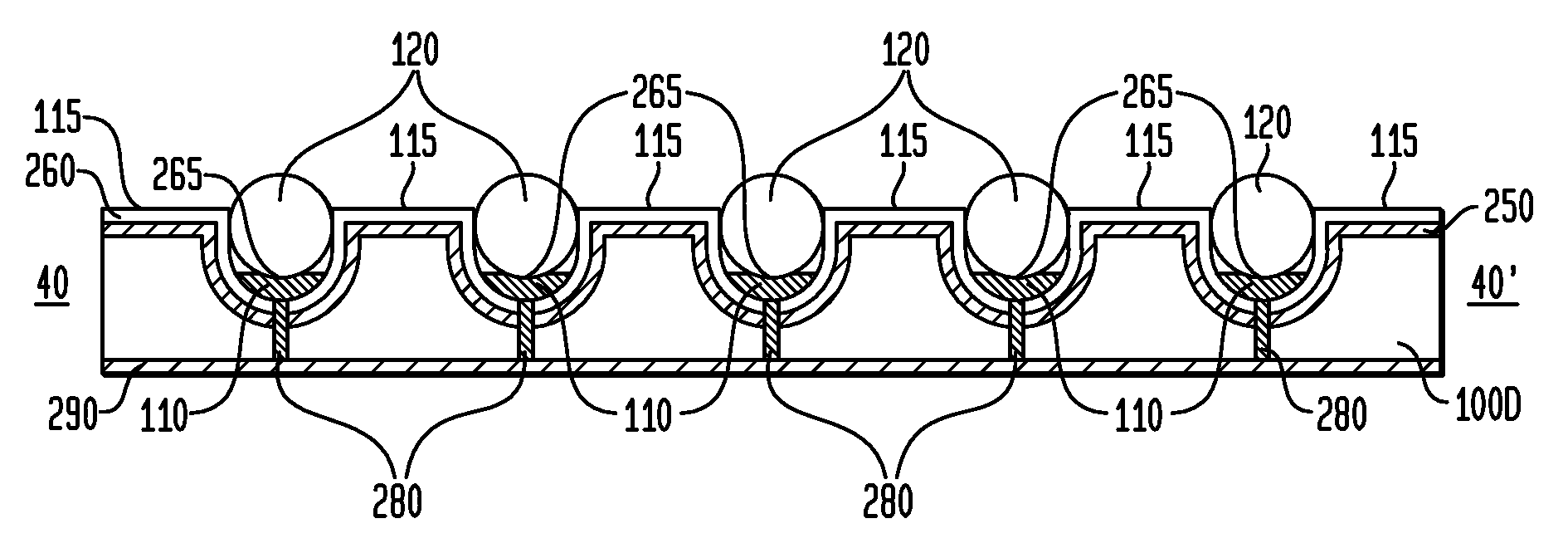
ActiveUS20100065862A1Low finished product costIncrease useMaterial nanotechnologyFinal product manufactureMean diameterElectrical conductor
The present invention provides an electronic apparatus, such as a lighting device comprised of light emitting diodes (LEDs) or a power generating apparatus comprising photovoltaic diodes, which may be created through a printing process, using a semiconductor or other substrate particle ink or suspension and using a lens particle ink or suspension. An exemplary apparatus comprises a base; at least one first conductor; a plurality of substantially spherical or optically resonant diodes coupled to the at least one first conductor; at least one second conductor coupled to the plurality of diodes; and a plurality of substantially spherical lenses suspended in a polymer attached or deposited over the diodes. The lenses and the suspending polymer have different indices of refraction. In some embodiments, the lenses and diodes have a ratio of mean diameters or lengths between about 10:1 and 2:1. The diodes may be LEDs or photovoltaic diodes, and in some embodiments, have a junction formed at least partially as a hemispherical shell or cap.
Owner:UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT AS REPRESENTED BY THE ADMINISTATOR OF THE NAT AERONAUTICS & SPACE ADMINSTRATION +1
Semiconductor optoelectronic devices and methods for making semiconductor optoelectronic devices
InactiveUS20100218819A1Solar photon flux is reducingImprove device performanceFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCharge carrierSolar cell
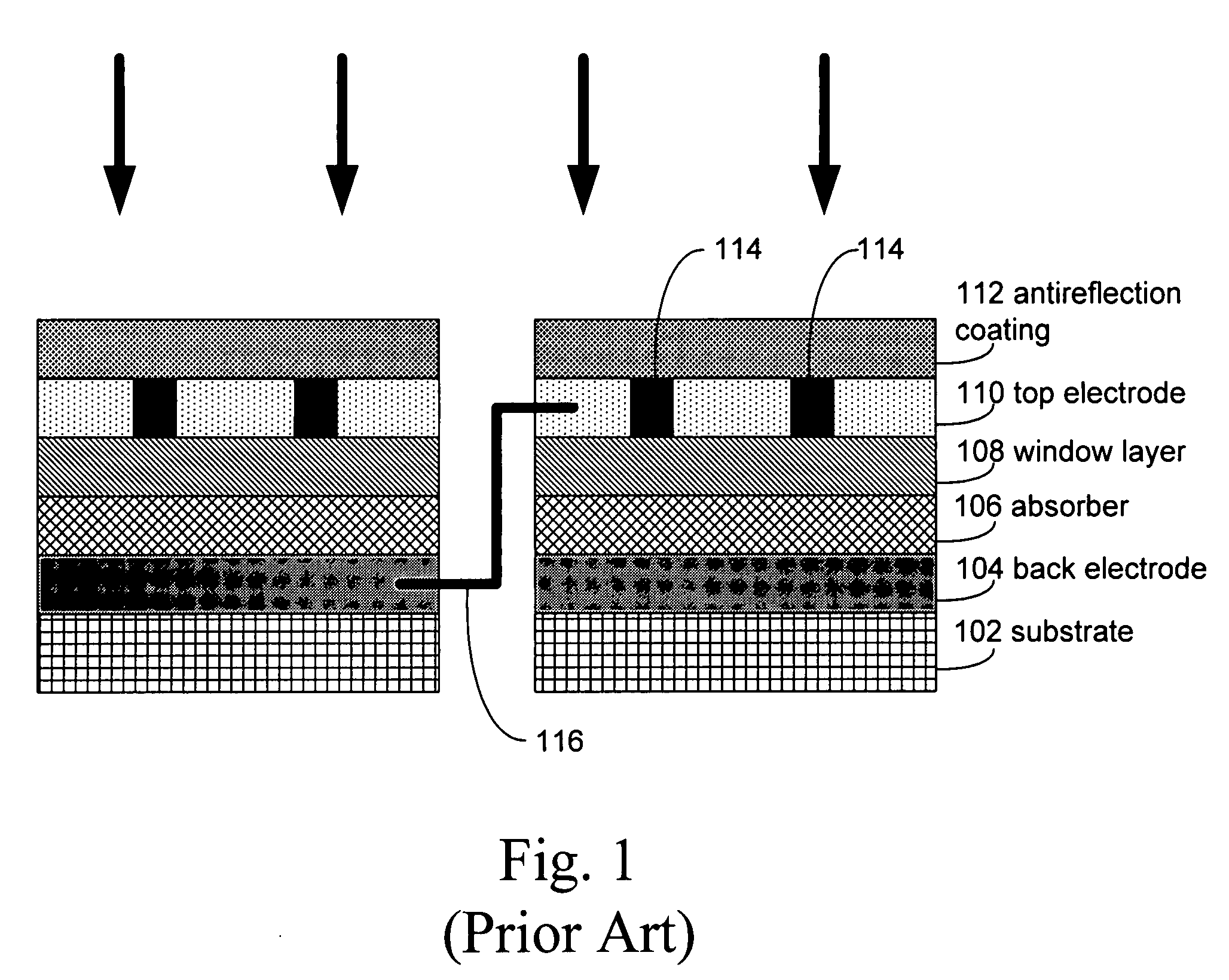
A semiconductor-based optoelectronic device such as a solar cell has an n-type layer and a p-type layer, together forming a p-n junction. Contact regions are formed on the device, with light-receiving regions between contact regions. A window layer is formed over the n-type layer or the p-type layer at the light-receiving region, the window layer promoting reduced carrier recombination at the surface of the n-type or p-type layer, and / or reflection of minority carriers in the n-type or p-type layer towards the p-n junction. The device has a window protection layer formed over the window layer, the window protection layer providing protection from degradation of the window layer during manufacture and / or operation of the device. For GaAs-based devices the window layer may be Al0.9Ga0.1As and the window protection layer may be GaAs. Additionally, an AlAs etch stop layer may be provided over the window protection layer.
Owner:THE UNIV COURT OF THE UNIV OF GLASGOW
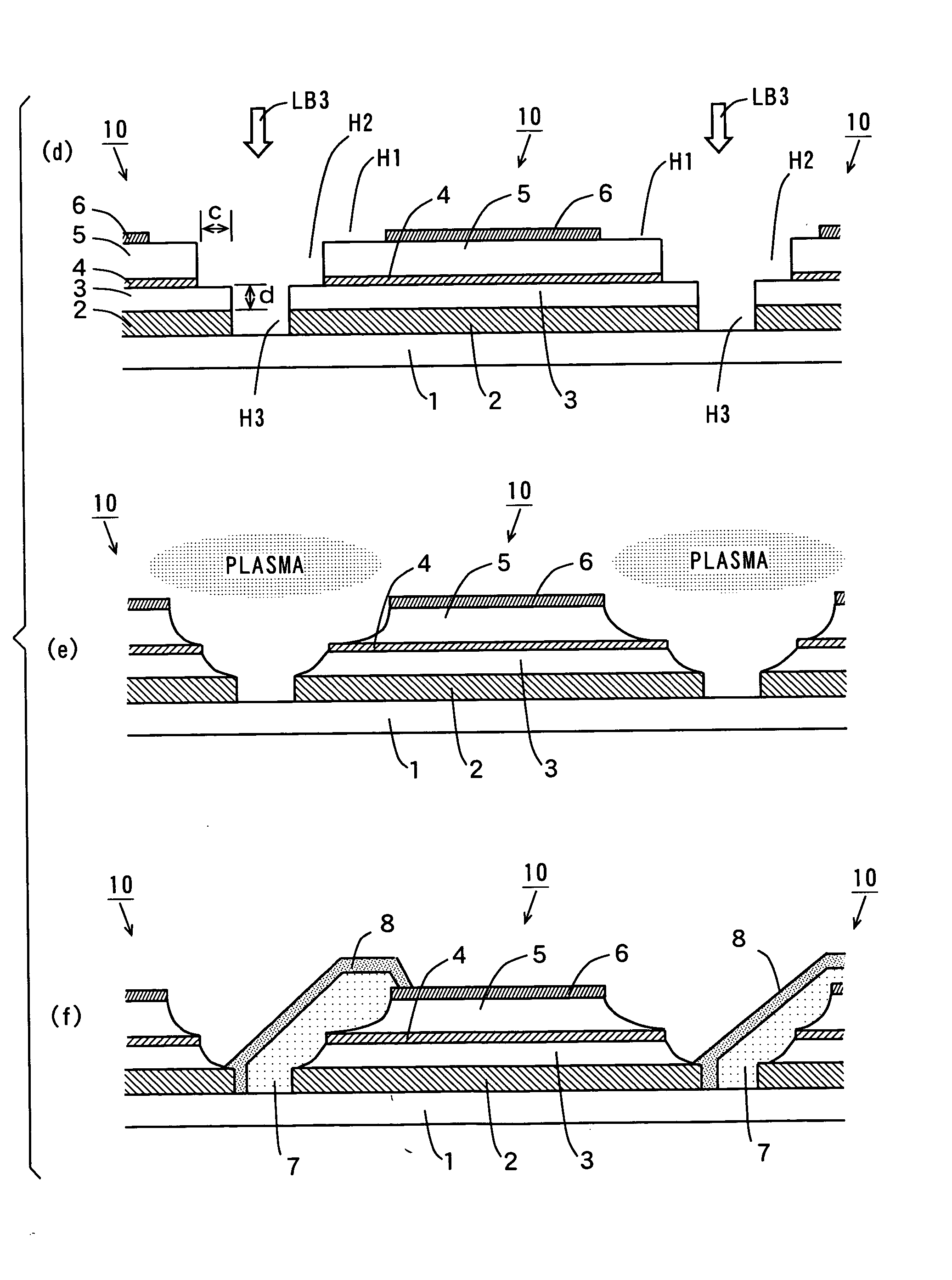
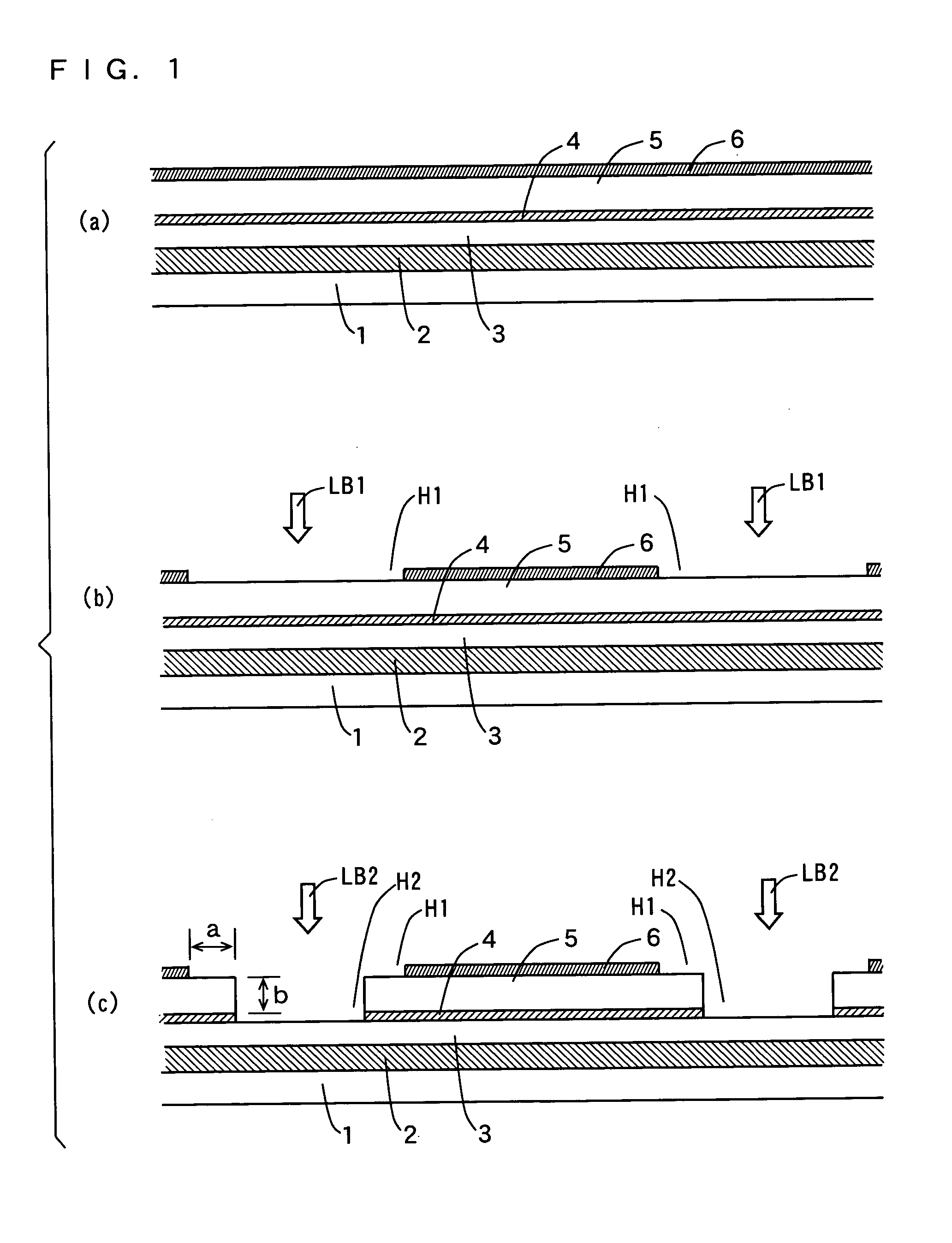
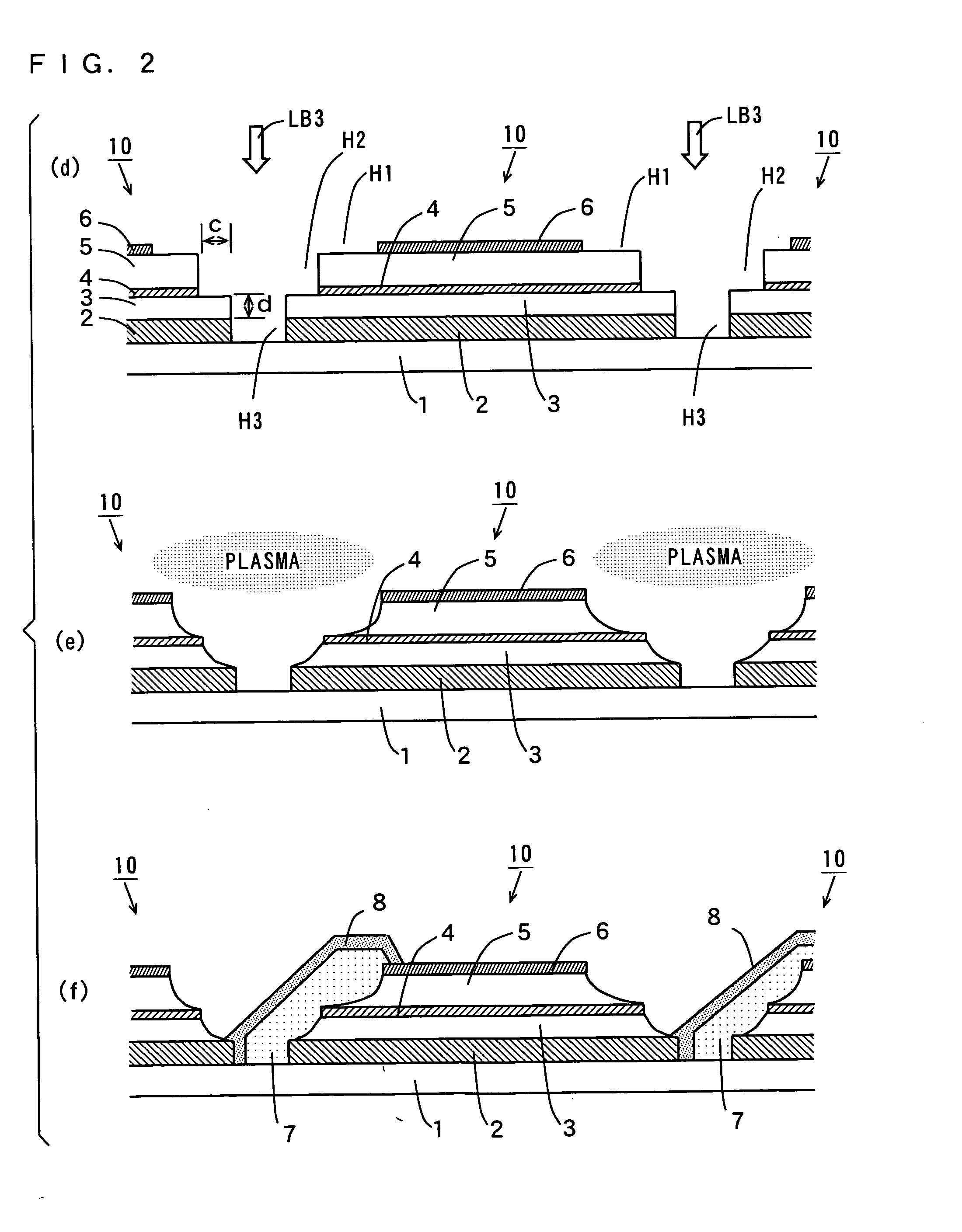
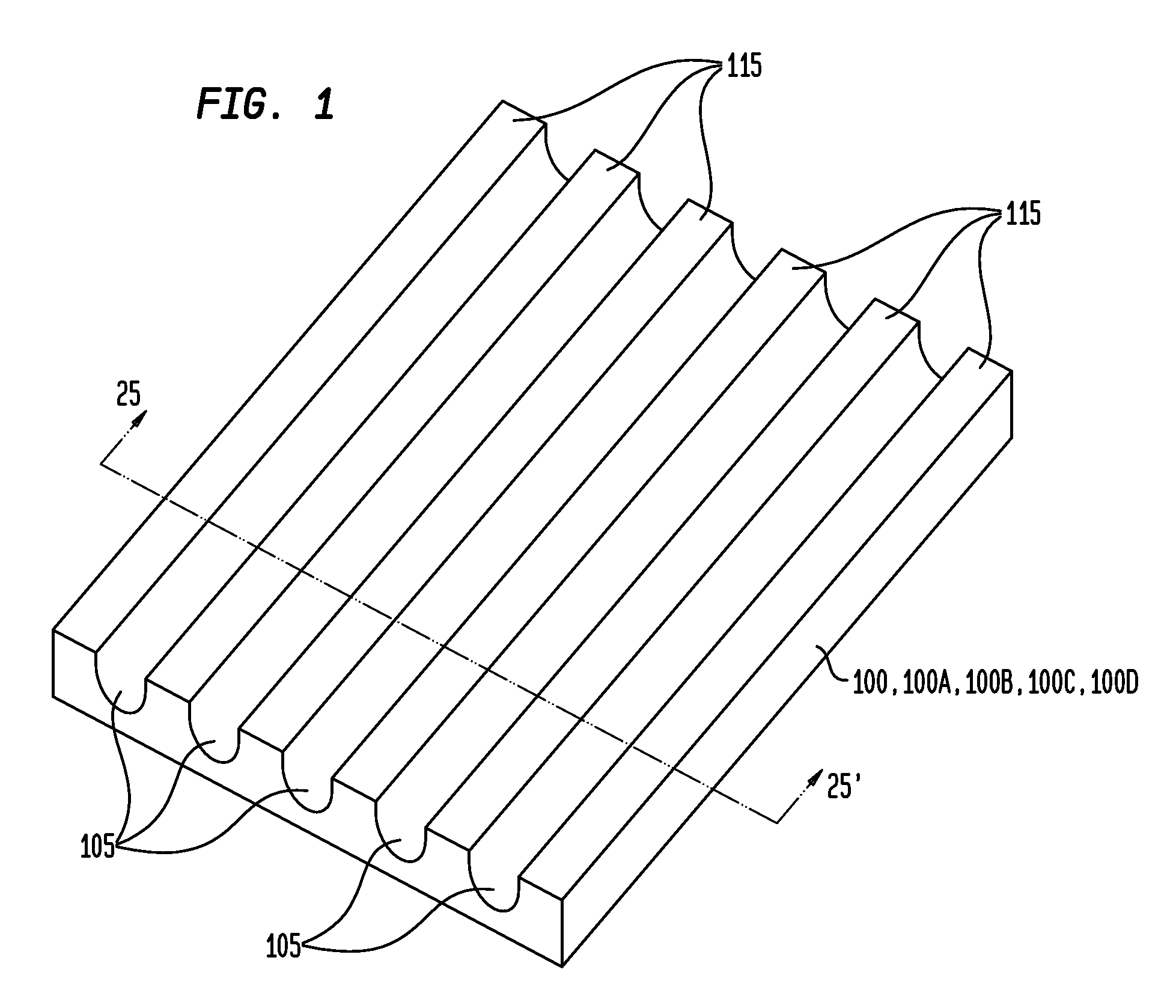
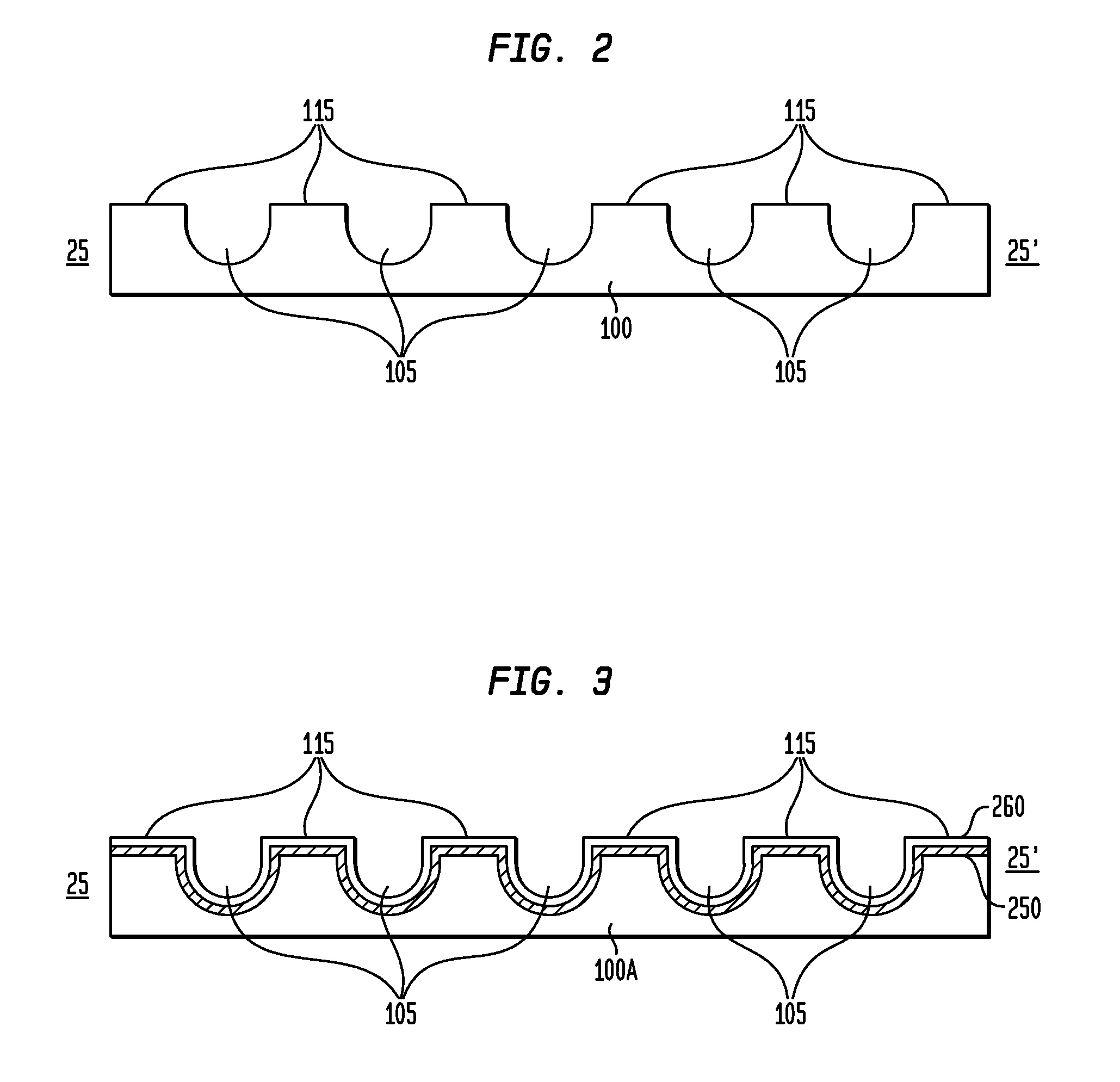
Photovoltaic cell, photovoltaic cell module, method of fabricating photovoltaic cell and method of repairing photovoltaic cell
InactiveUS20050284517A1Avoid it happening againPV power plantsSolid-state devicesEngineeringReflective layer
A plurality of first separation grooves are formed in a back electrode. Second separation grooves having a width smaller than that of the first separation grooves are formed by removing a second photovoltaic conversion layer and an intermediate reflective layer inside the first separation grooves. Third separation grooves having a width smaller than that of the second separation grooves are formed by removing a first photovoltaic conversion layer and a light reflective electrode inside the second separation grooves. Corners of the first photovoltaic conversion layer and corners of the second photovoltaic conversion layer that are exposed in the separation grooves are removed by performing plasma etching, so that the upper surfaces of side ends of the intermediate reflective layer are exposed.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Multi-junction PV module
ActiveUS8835748B2Final product manufacturePV power plantsEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
A photovoltaic device is provided which includes a plurality of junction layers. Each junction layer includes a plurality of photovoltaic cells electrically connected to one another. At least one of the junction layers is at least in part optically transmissive. The junction layers are arranged in a stack on top of each other.
Owner:SUNLIGHT PHOTONICS
Systems and methods for monolithically isled solar photovoltaic cells and modules
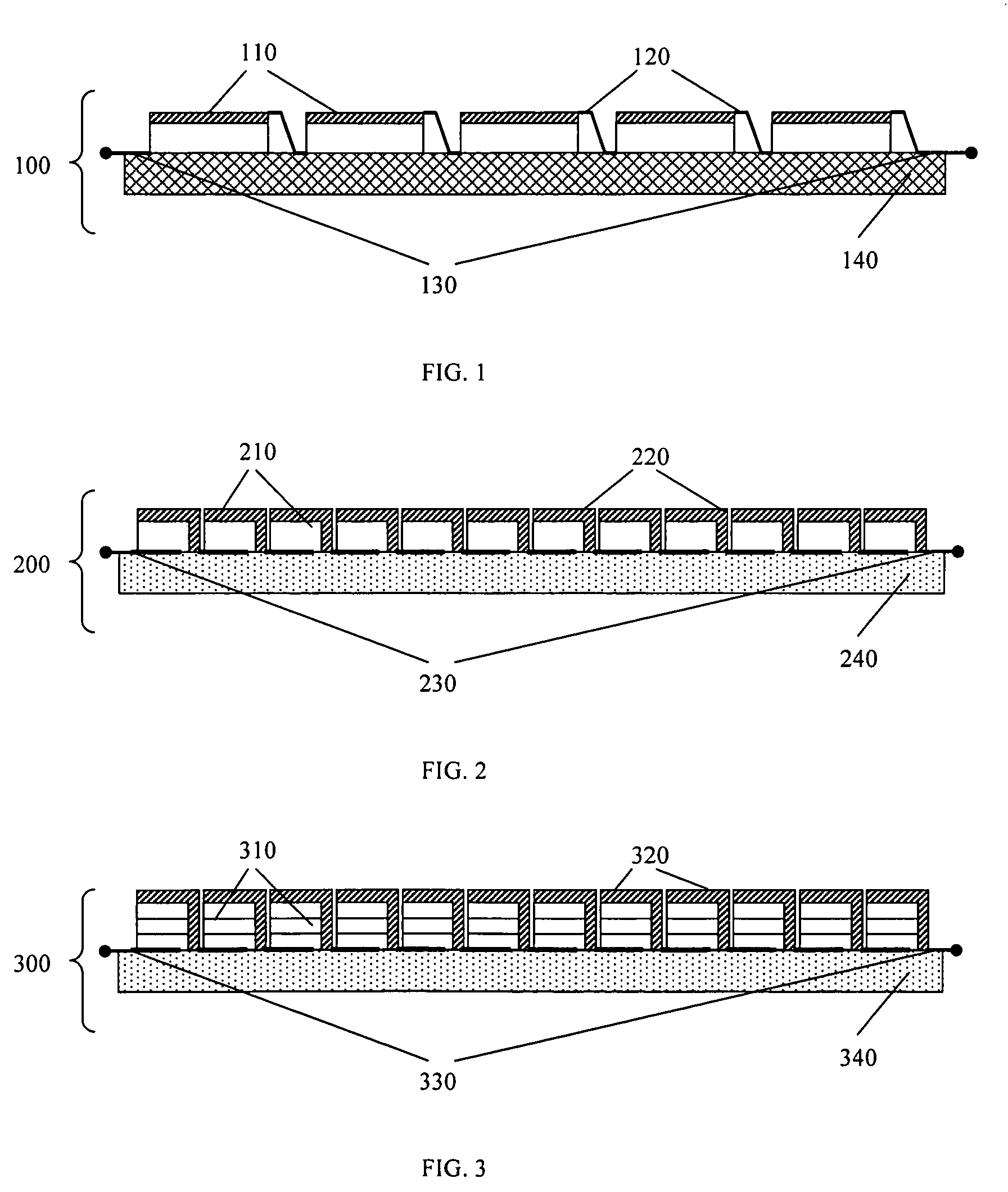
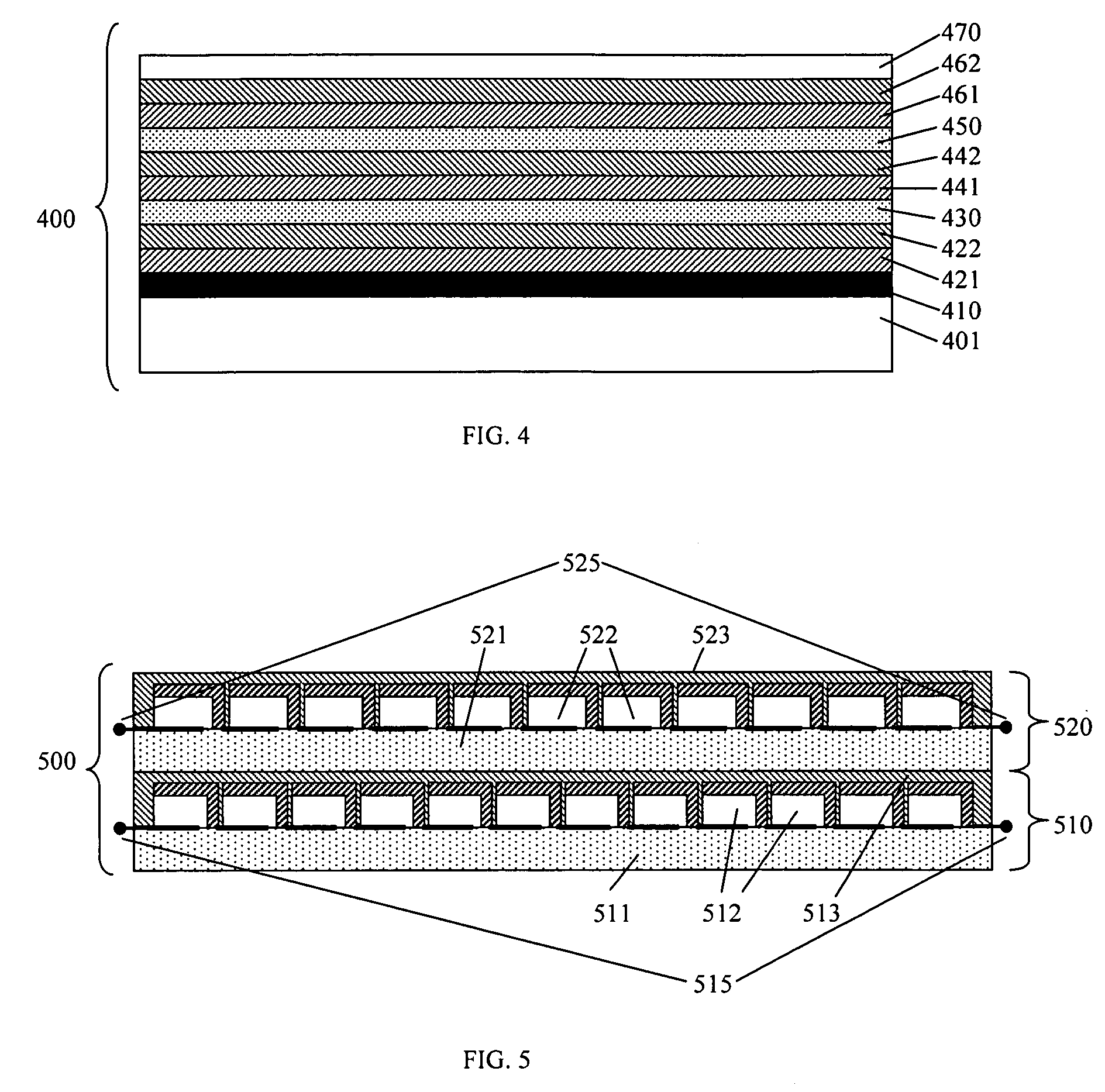
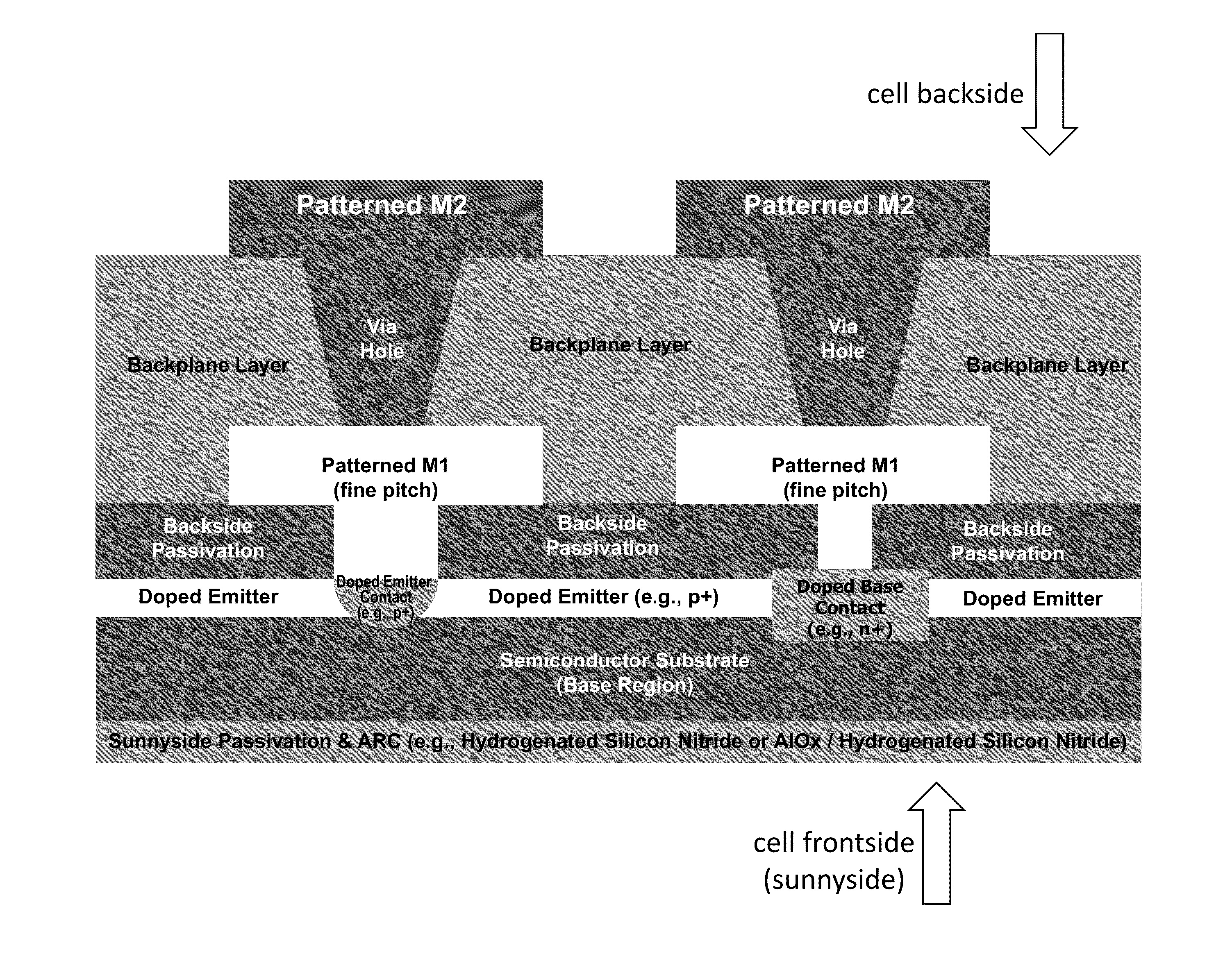
InactiveUS20140326295A1Reduce and eliminate disadvantageReduce and eliminate and problemPhotovoltaic supportsPV power plantsEngineeringBattery cell
According to one aspect of the disclosed subject matter, a monolithically isled solar cell is provided. The solar cell comprises a semiconductor layer having a light receiving frontside and a backside opposite the frontside and attached to an electrically insulating backplane. A trench isolation pattern partitions the semiconductor layer into electrically isolated isles on the electrically insulating backplane. A first metal layer having base and emitter electrodes is positioned on the semiconductor layer backside. A patterned second metal layer providing cell interconnection and connected to the first metal layer by via plugs is positioned on the backplane.
Owner:BEAMREACH SOLAR INC
Photoelectric conversion device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20060261253A1Total current dropNarrow downTelevision system detailsPhotometry using reference valueAudio power amplifierPhotoelectric conversion
It is an object to provide a photoelectric conversion device which detects light ranging from weak light to strong light. The present invention relates to a photoelectric conversion device having a photodiode having a photoelectric conversion layer, an amplifier circuit including a thin film transistor and a bias switching means, where a bias which is connected to the photodiode and the amplifier circuit is switched by the bias switching means when intensity of incident light exceeds predetermined intensity, and accordingly, light which is less than the predetermined intensity is detected by the photodiode and light which is more than the predetermined intensity is detected by the thin film transistor of the amplifier circuit. By the present invention, light ranging from weak light to strong light can be detected.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Single Junction CIGS/CIS Solar Module
InactiveUS20110259395A1Low costSimplified thin-film processPV power plantsFinal product manufactureIndiumEngineering
A high efficiency thin-film photovoltaic module is formed on a substrate. The photovoltaic module includes a plurality of stripe shaped photovoltaic cells electrically coupled to each other and physically disposed in parallel to the length one next to another across the width. Each cell includes a barrier material overlying the surface and a first electrode overlying the barrier material. Each cell further includes an absorber formed overlying the first electrode. The absorber includes a copper gallium indium diselenide compound material characterized by an energy band-gap of about 1 eV to 1.1 eV. Each cell additionally includes a buffer material overlying the absorber and a bi-layer zinc oxide material comprising a high resistivity transparent layer overlying the buffer material and a low resistivity transparent layer overlying the high resistivity transparent layer.
Owner:CM MFG
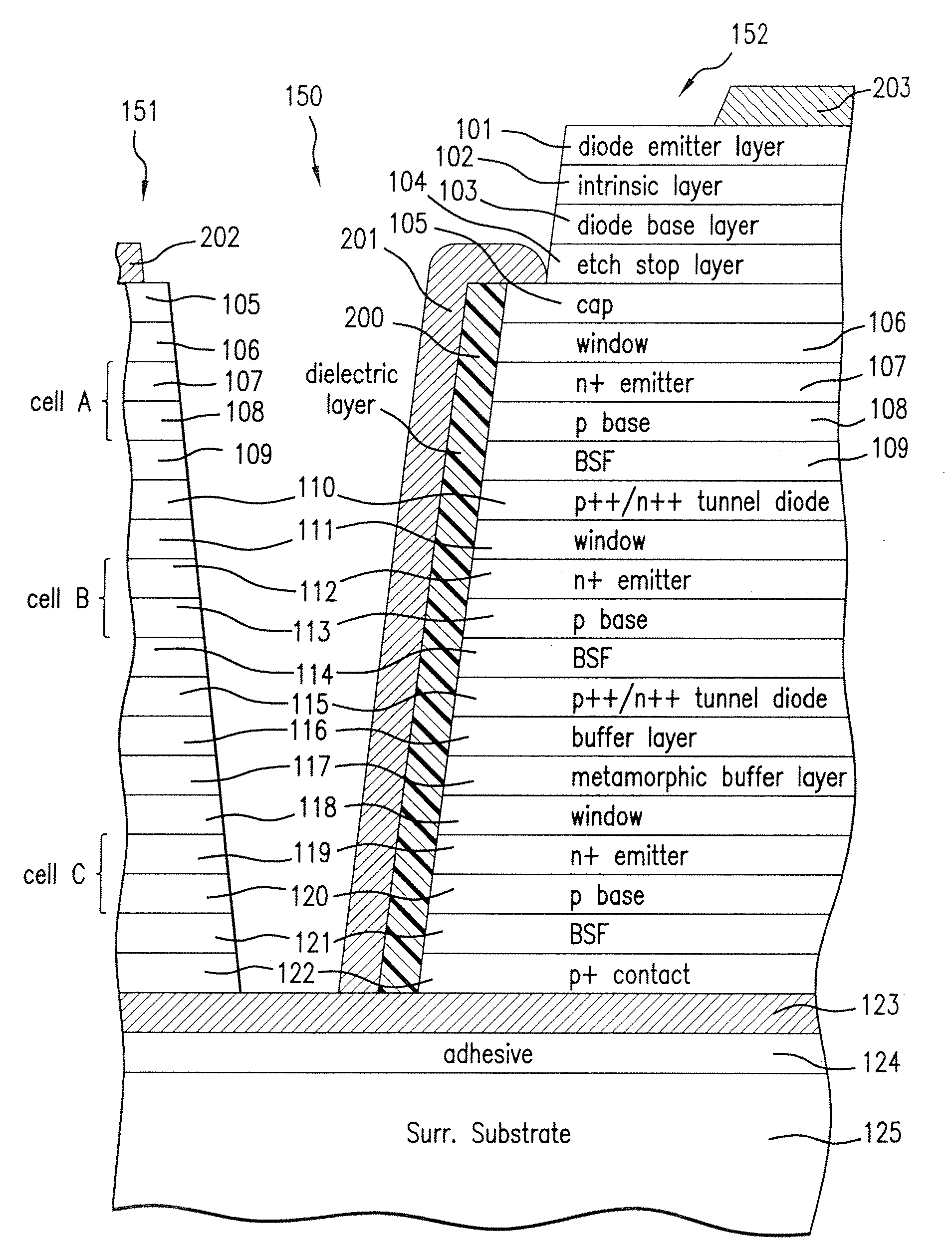
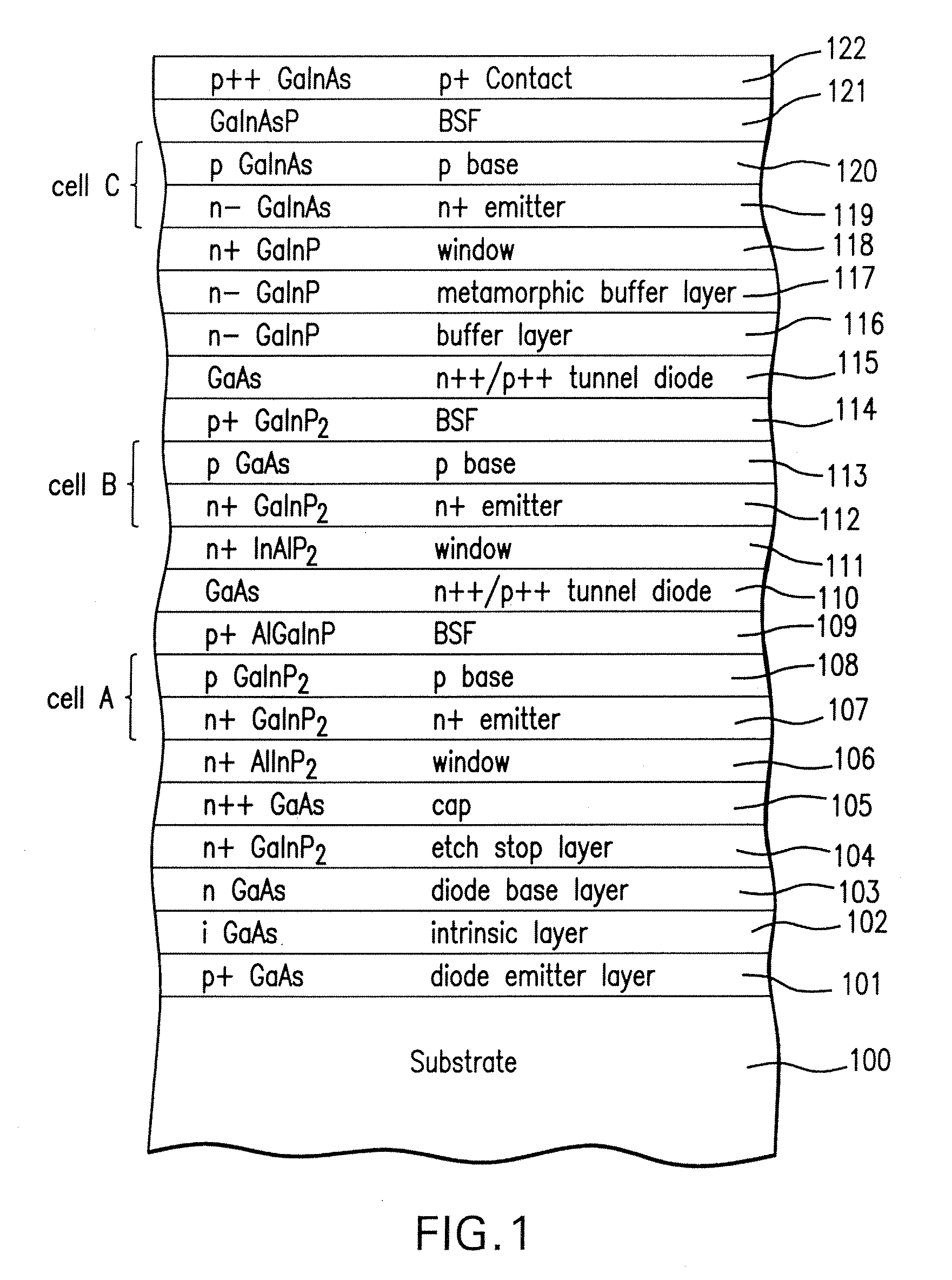
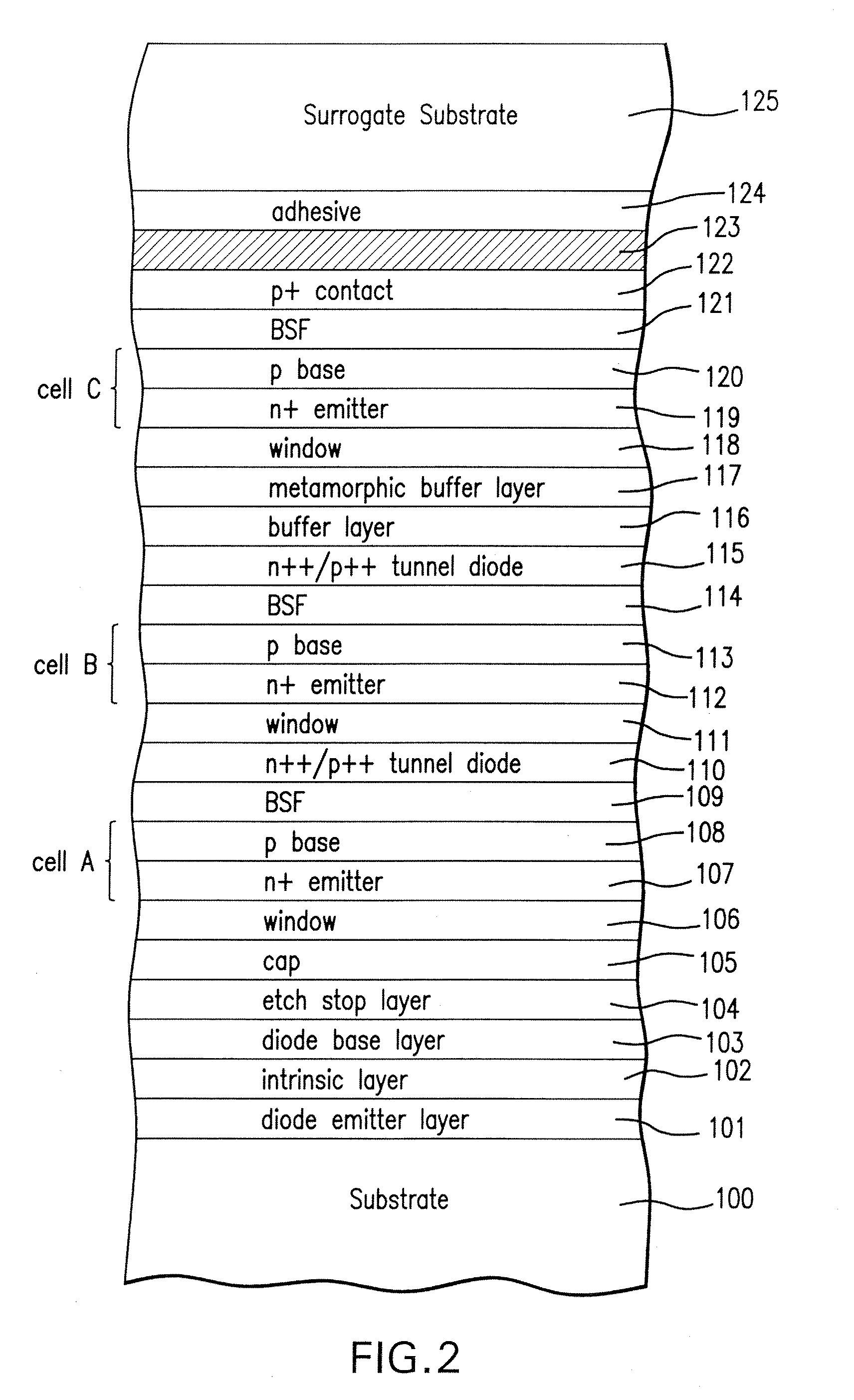
Wafer Level Interconnection of Inverted Metamorphic Multijunction Solar Cells
ActiveUS20100031994A1PV power plantsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsEngineering
A method of forming a plurality of discrete, interconnected solar cells mounted on a carrier by providing a first semiconductor substrate; depositing on the first substrate a sequence of layers of semiconductor material forming a solar cell structure; forming a metal back contact layer over the solar cell structure; mounting a carrier on top of the metal back contact; removing the first substrate; and lithographically patterning and etching the solar cell structure to form a plurality of discrete solar cells mounted on the carrier.
Owner:SOLAERO TECH CORP
Three-dimensional thin-film semiconductor substrate with through-holes and methods of manufacturing
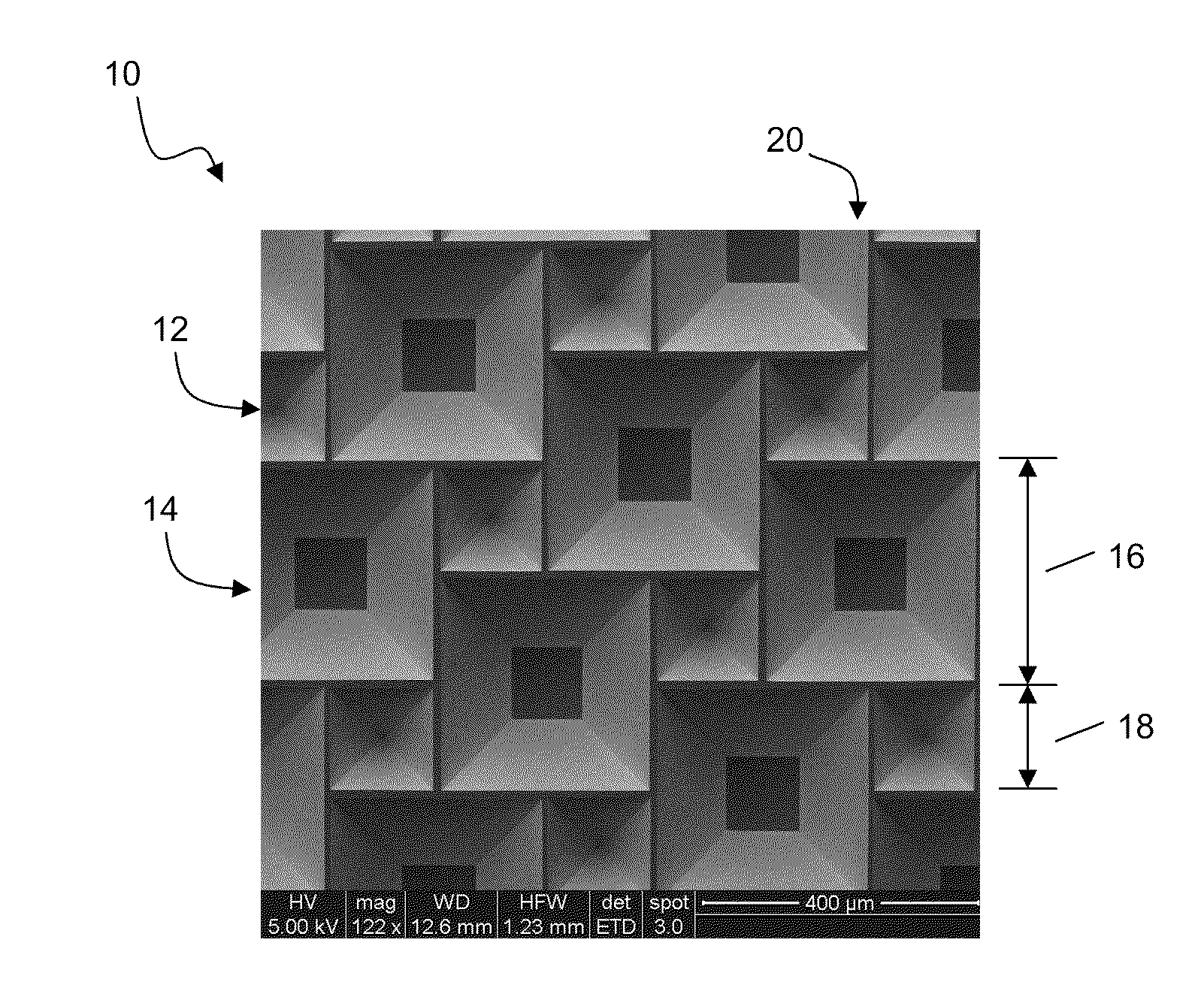
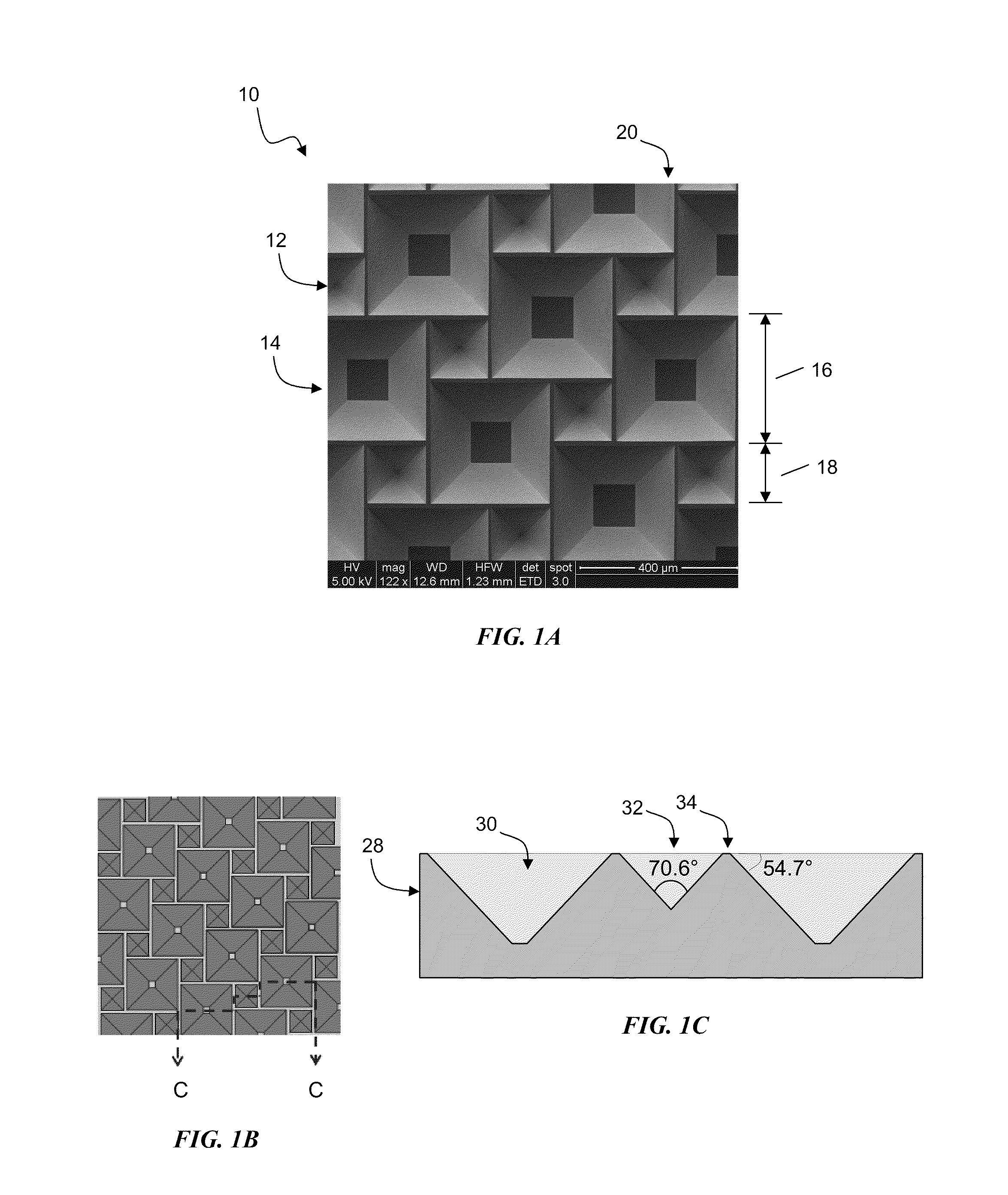
InactiveUS20100300518A1Eliminate and reduce disadvantageEliminate and reduce and problemFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptoelectronicsPorous semiconductors
A method for the fabrication of a three-dimensional thin-film semiconductor substrate with selective through-holes is provided. A porous semiconductor layer is conformally formed on a semiconductor template comprising a plurality of three-dimensional inverted pyramidal surface features defined by top surface areas aligned along a (100) crystallographic orientation plane of the semiconductor template and a plurality of inverted pyramidal cavities defined by sidewalls aligned along the (111) crystallographic orientation plane of the semiconductor template. An epitaxial semiconductor layer is conformally formed on the porous semiconductor layer. The epitaxial semiconductor layer is released from the semiconductor template. Through-holes are selectively formed in the epitaxial semiconductor layer with openings between the front and back lateral surface planes of the epitaxial semiconductor layer to form a partially transparent three-dimensional thin-film semiconductor substrate.
Owner:BEAMREACH SOLAR INC
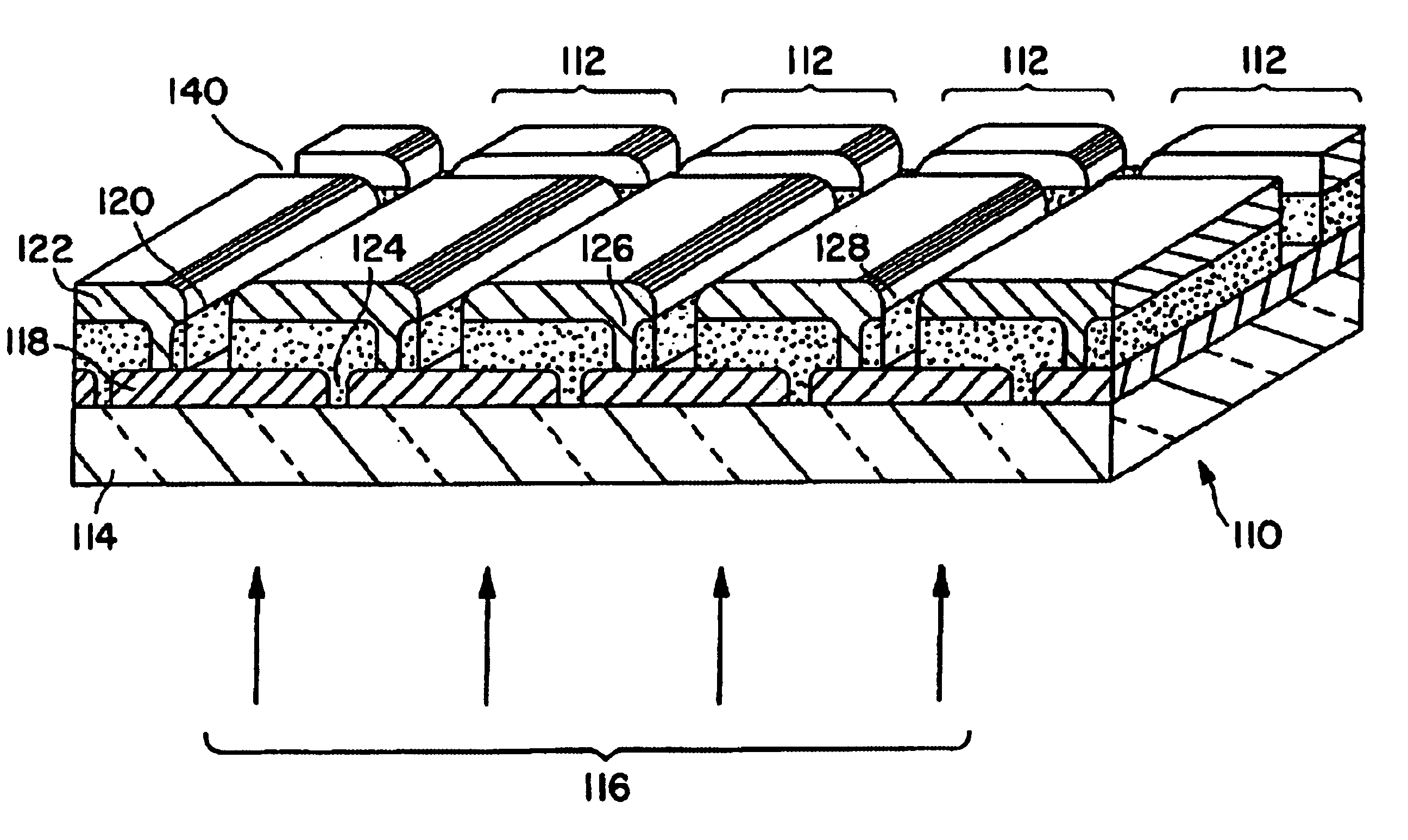
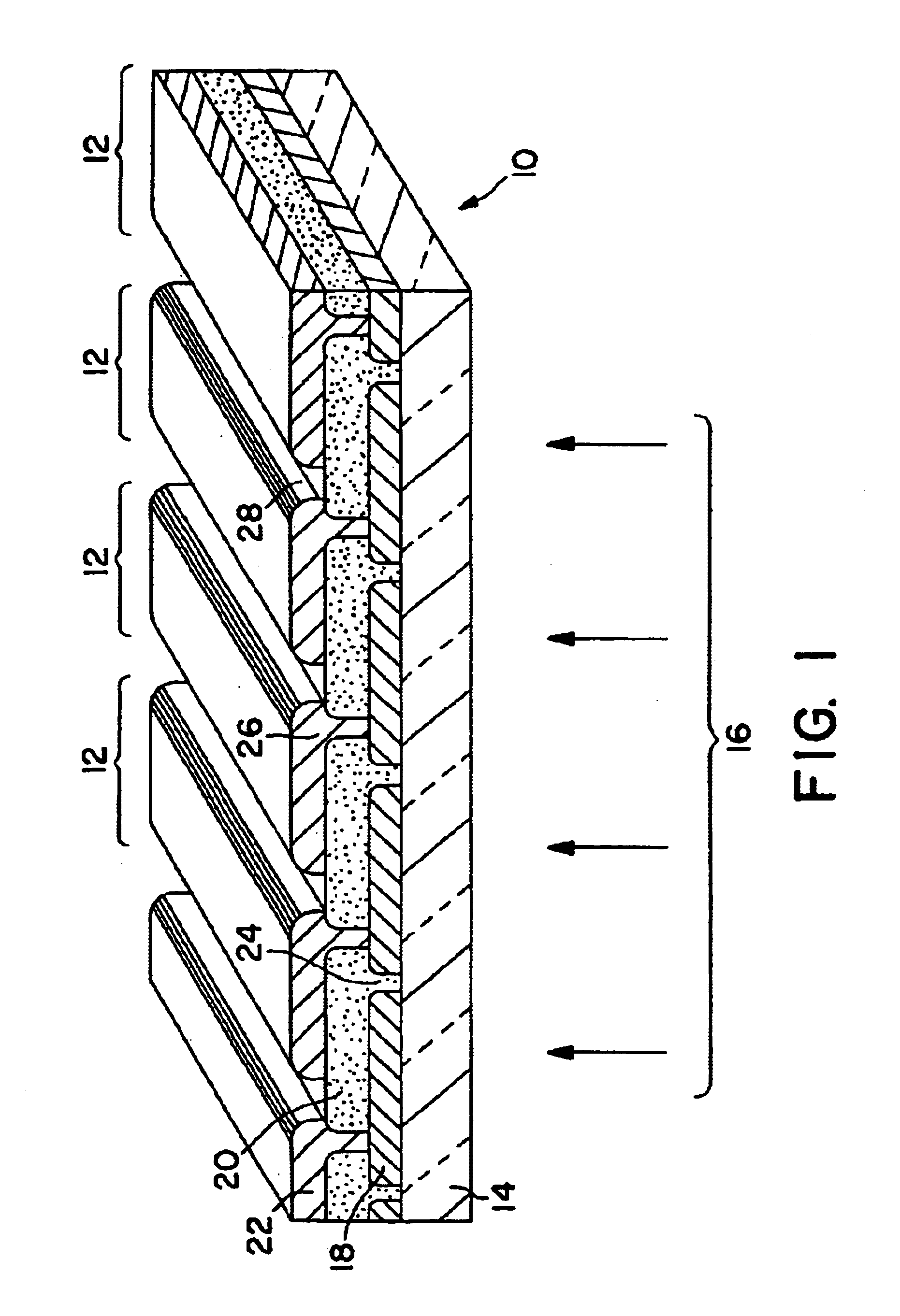
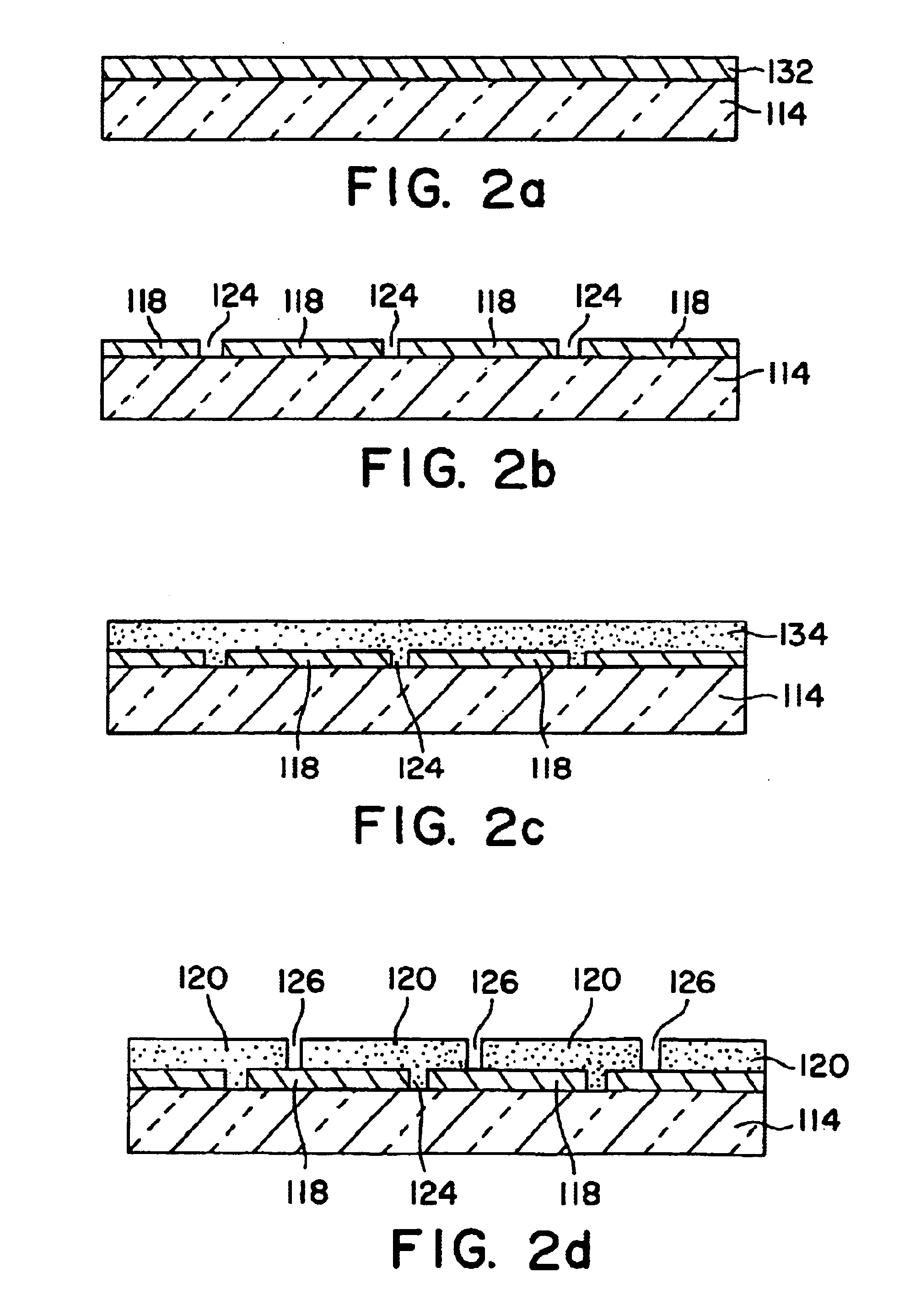
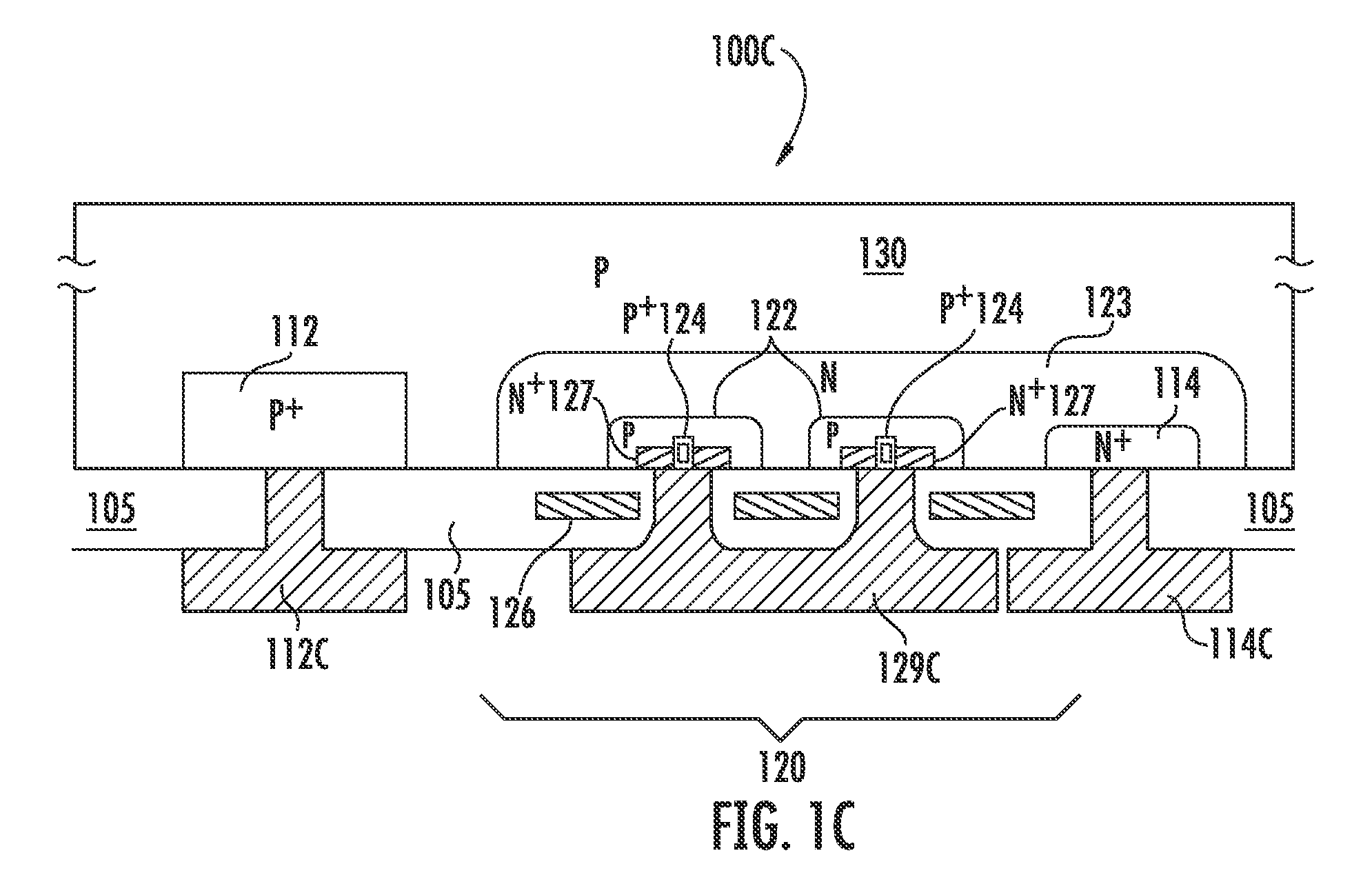
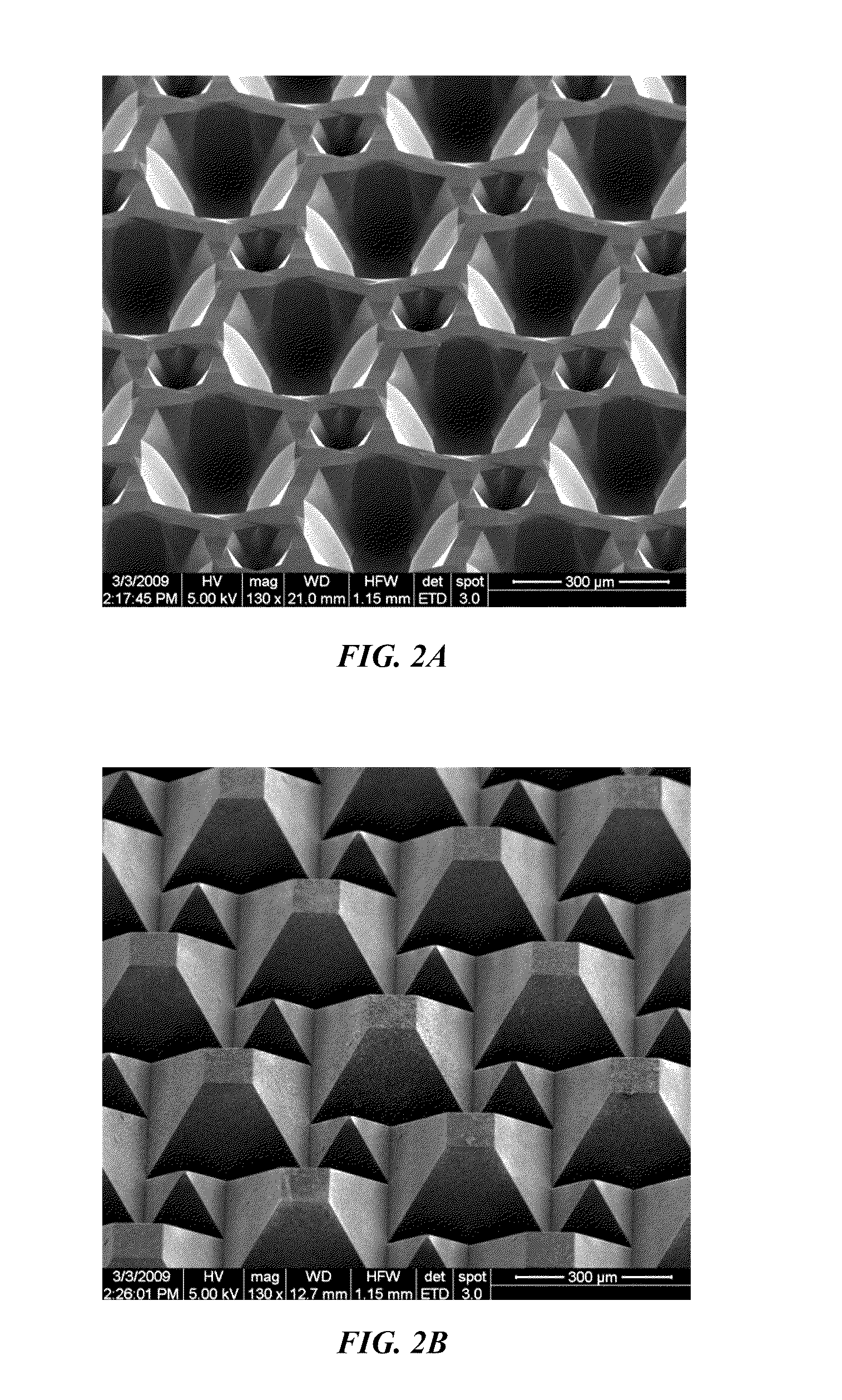
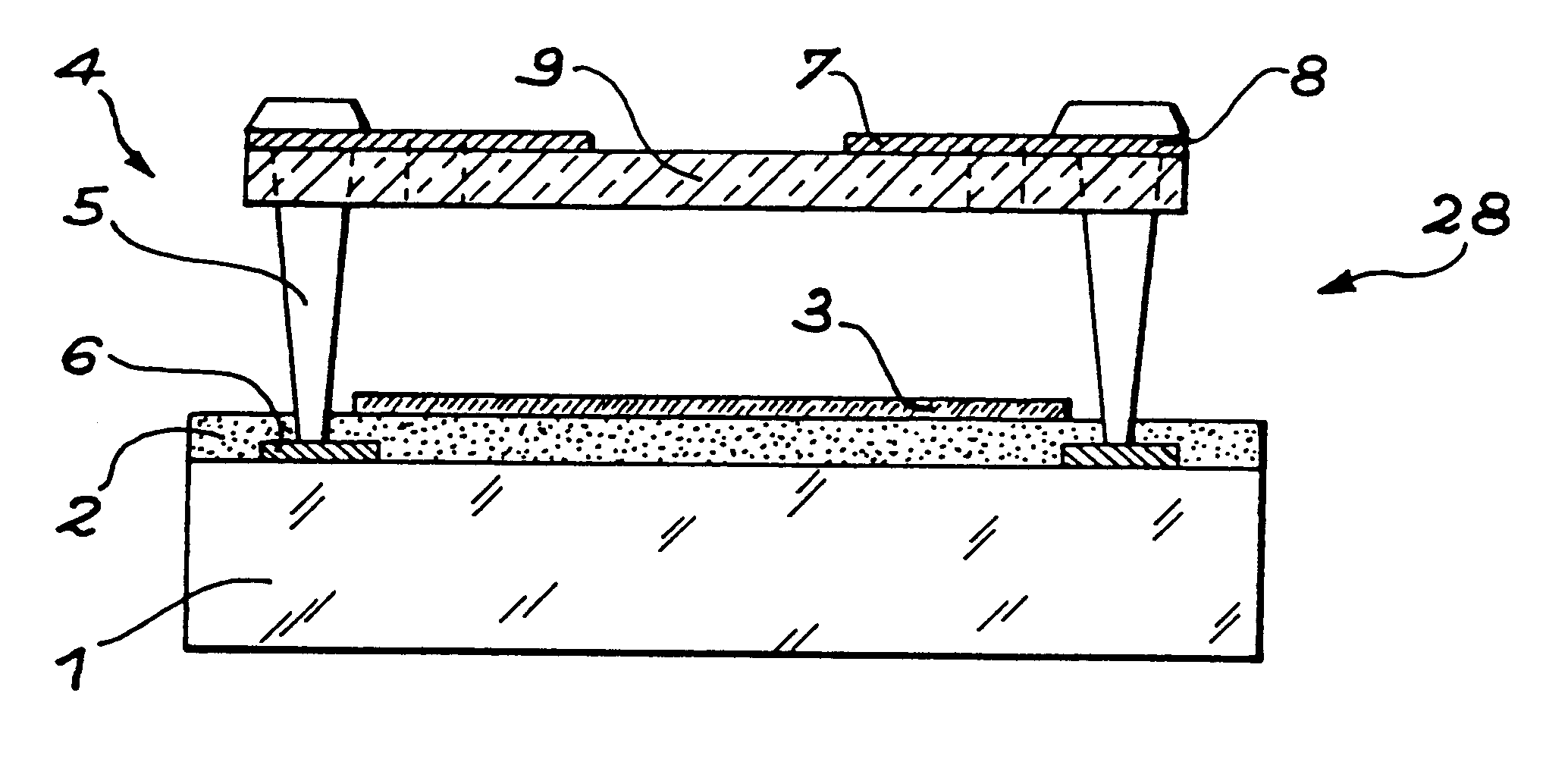
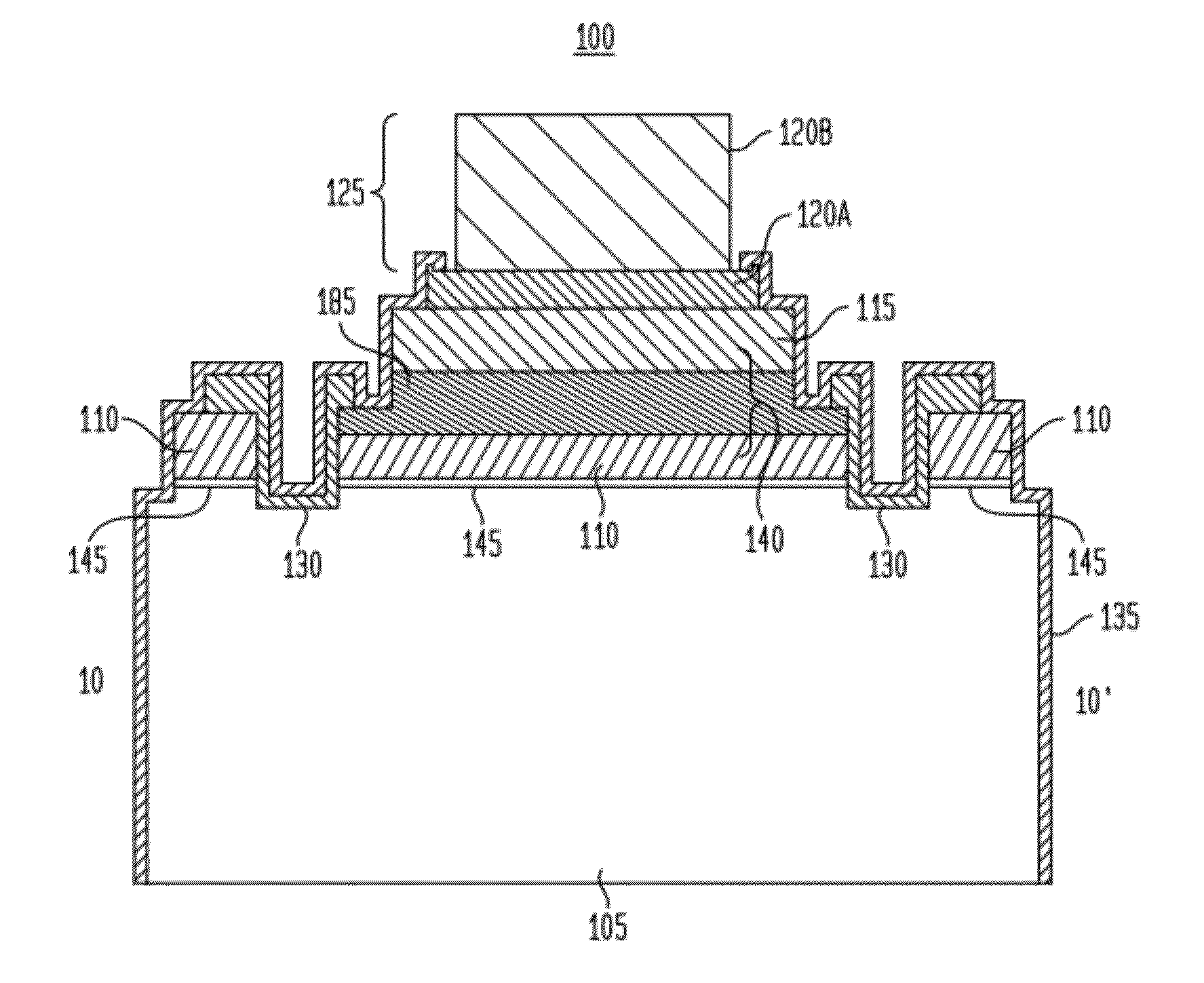
Monolithic bypass diode and photovoltaic cell with bypass diode formed in back of substrate
ActiveUS20070113884A1Minimization requirementsMinimizing failure pointDiodeEnergy conversion devicesSolar cellDiode
An apparatus and method for making a solar cell assembly. An apparatus in accordance with the present invention comprises a substrate, at least a first solar cell, coupled to a first side of the substrate, the first side of the substrate to be exposed to light such that the at least first solar cell generates a current when exposed to the light, and a bypass diode, formed on a second side of the substrate, the second side of the substrate being substantially opposite the first side of the substrate, such that the bypass diode is monolithically integrated with the at least first solar cell.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Discrete and integrated photo voltaic solar cells
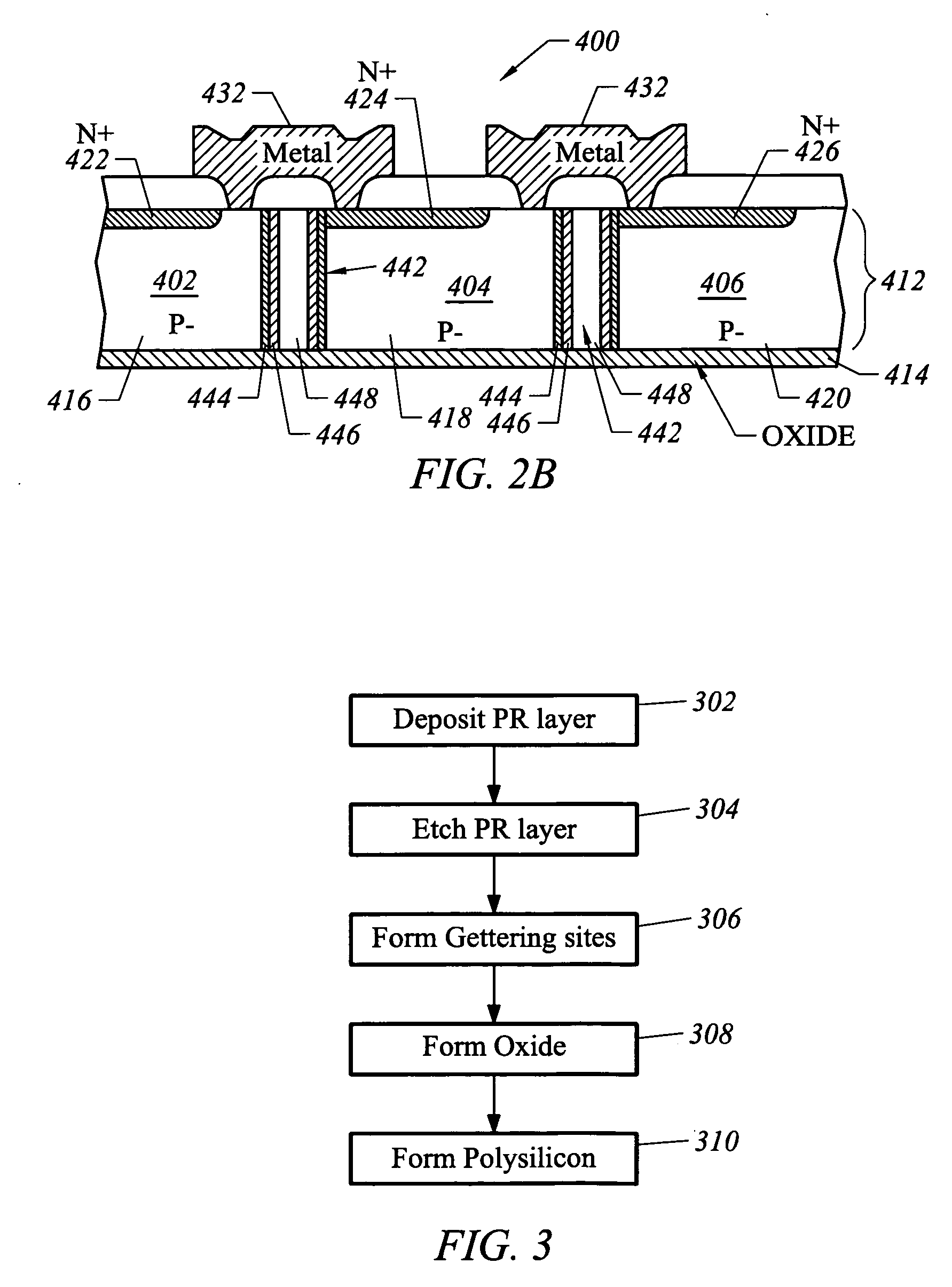
ActiveUS20050145274A1Improve efficiencyPV power plantsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIsolation layerEngineering
A photovoltaic (PV) cell device comprises a first semiconductor substrate; a second semiconductor substrate bonded to the first semiconductor substrate; an insulating layer provided between the first and second substrates to electrically isolate the first substrate from the second substrate; a plurality of PV cells defined on the first substrate, each PV cell including a n-type region and a p-type region; a plurality of vertical trenches provided in the first substrate to separated the PV cells, the vertical trenches terminating at the insulating layer; a plurality of isolation structures provided within the vertical trenches, each isolation structure including a first isolation layer including oxide and a second isolation layer including polysilicon; and an interconnect layer patterned to connect the PV cells to provide X number of PV cells in series and Y number of PV cells in parallel. The n-type regions are formed by performing ion implantation of arsenic to provide shallow junction depths for the n-type regions, so that PV cell device is optimized for sunlight.
Owner:LITTELFUSE INC
Method of Manufacturing a Light Emitting, Photovoltaic or Other Electronic Apparatus and System
ActiveUS20100068838A1Low finished product costIncrease useMaterial nanotechnologyStatic indicating devicesMean diameterElectrical conductor
The present invention provides a method of manufacturing an electronic apparatus, such as a lighting device having light emitting diodes (LEDs) or a power generating device having photovoltaic diodes. The exemplary method includes forming at least one first conductor coupled to a base; coupling a plurality of substantially spherical substrate particles to the at least one first conductor; converting the substrate particles into a plurality of substantially spherical diodes; forming at least one second conductor coupled to the substantially spherical diodes; and depositing or attaching a plurality of substantially spherical lenses suspended in a first polymer. The lenses and the suspending polymer have different indices of refraction. In some embodiments, the lenses and diodes have a ratio of mean diameters or lengths between about 10:1 and 2:1. In various embodiments, the forming, coupling and converting steps are performed by or through a printing process.
Owner:NTHDEGREE TECH WORLDWIDE +1
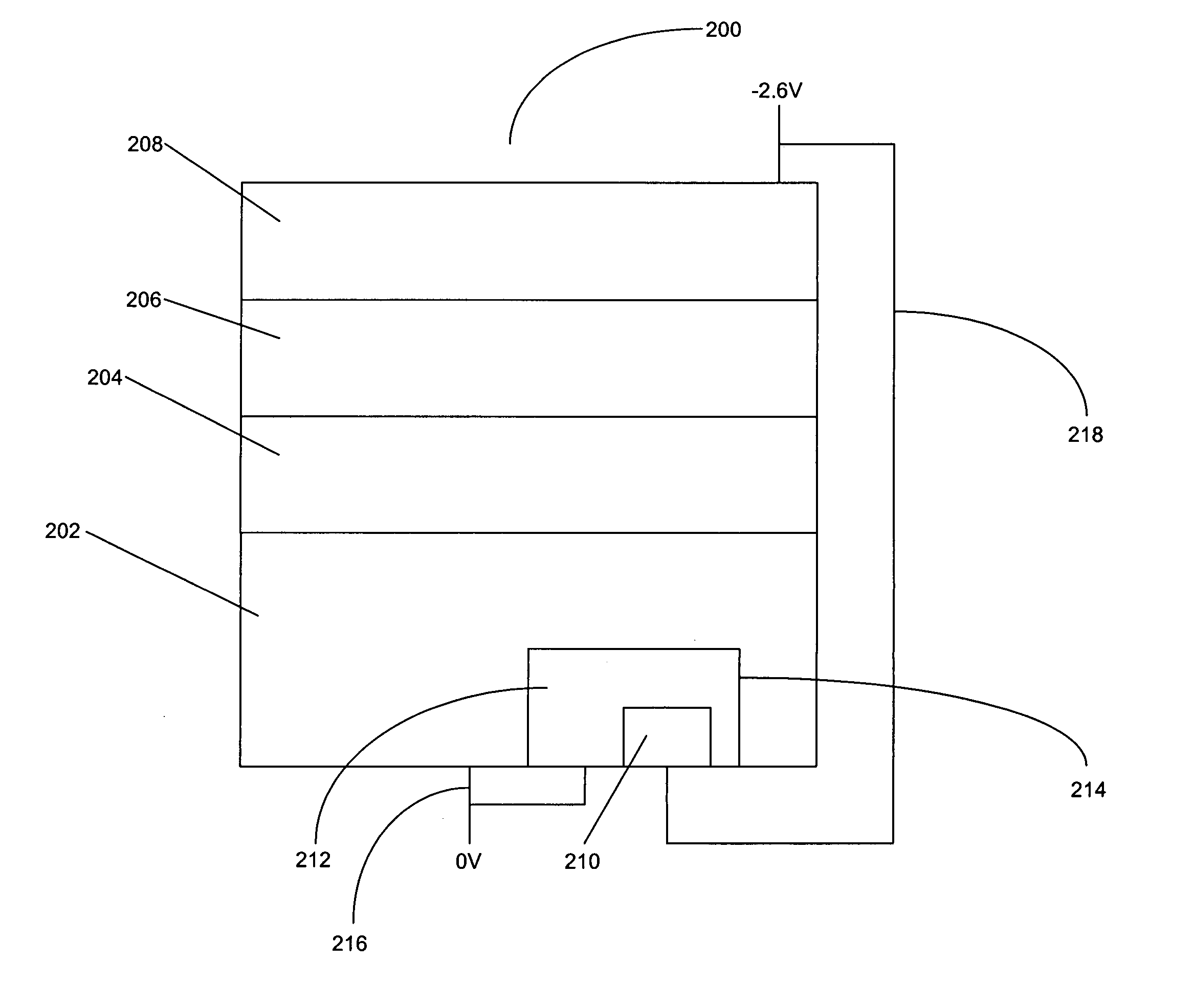
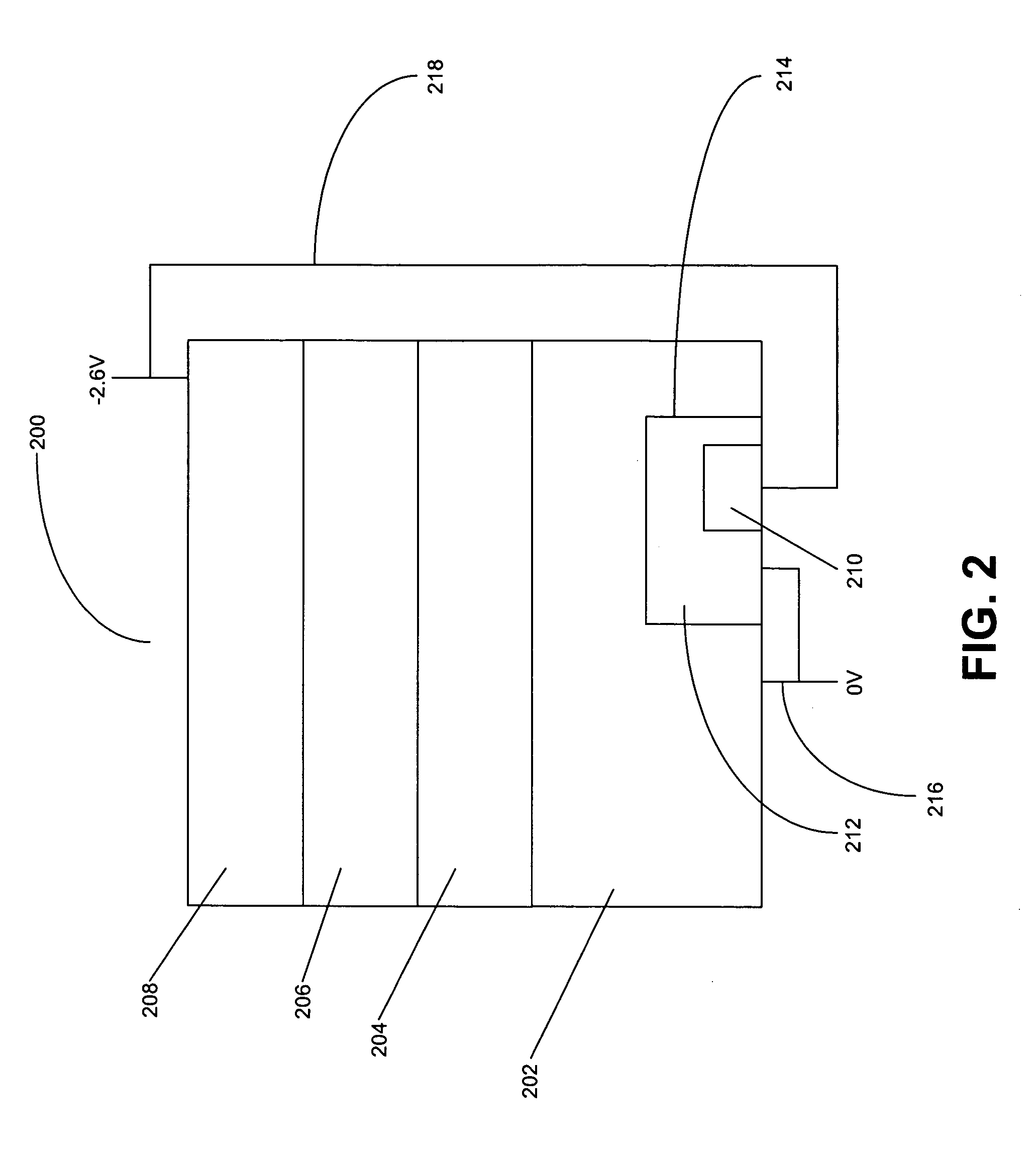
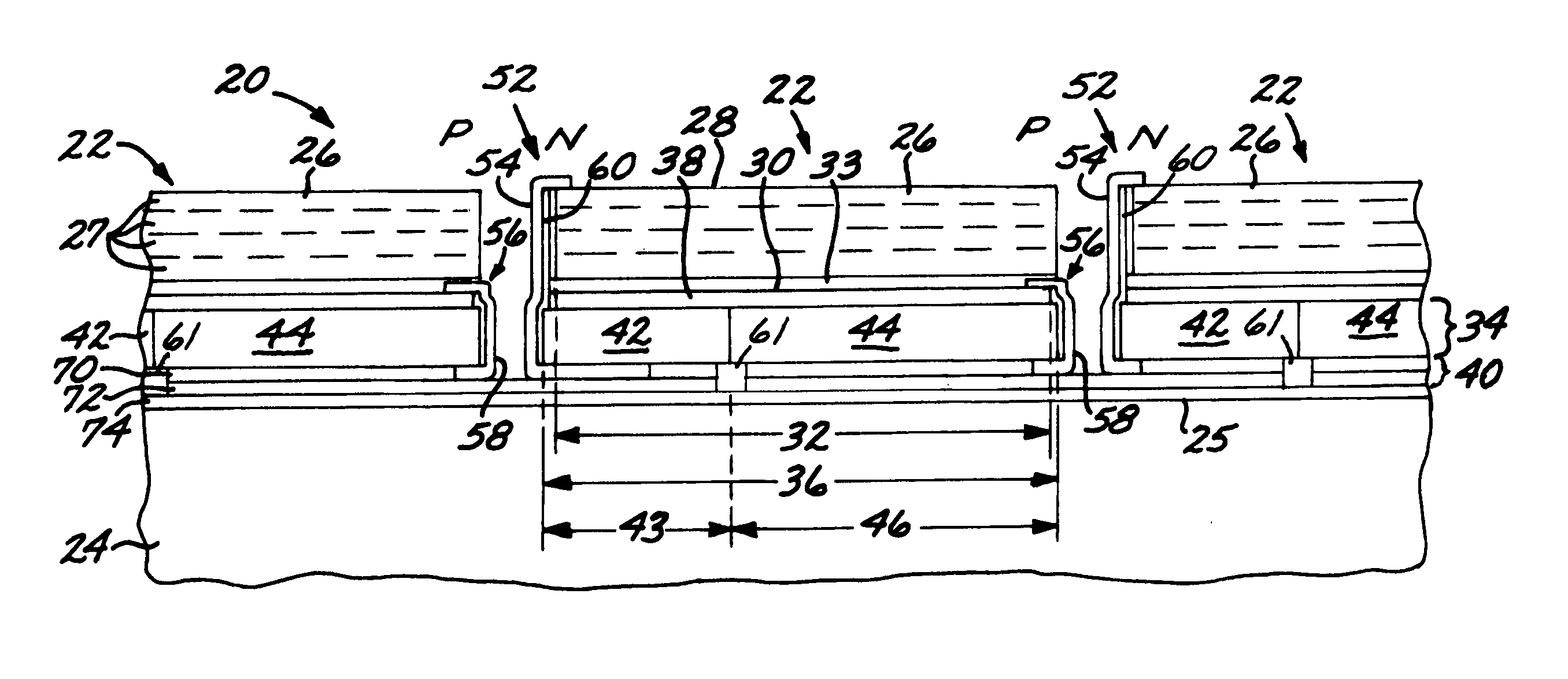
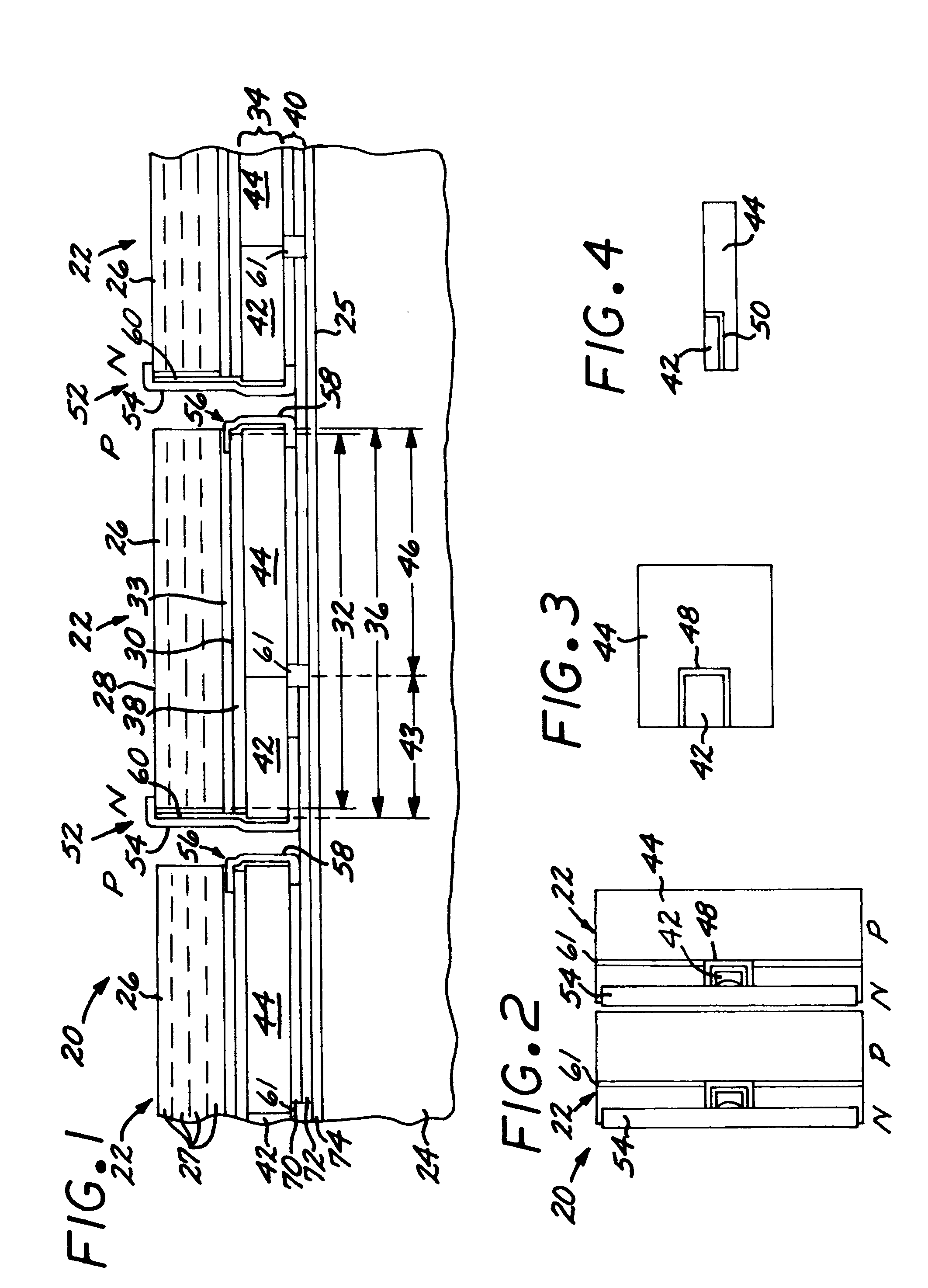
Solar cell structure with integrated discrete by-pass diode
A solar cell structure has a solar cell unit structure including a heat sink, and a solar cell having a front side, a back side, and a solar-cell projected area coverage on the heat sink. The solar cell has an active semiconductor structure that produces a voltage between the front side and the back side when the front side is illuminated. An intermediate structure is disposed between and joined to the back side of the solar cell and to the heat sink. The intermediate structure has an intermediate-structure projected area coverage on the heat sink and includes a by-pass diode having a diode projected area coverage on the heat sink. The diode projected area coverage on the heat sink may be substantially the same as the intermediate-structure projected coverage on the heat sink. Alternatively, the diode projected area coverage on the heat sink maybe less than the solar-cell projected area coverage on the heat sink, and the intermediate structure further includes a substrate coplanar with the by-pass diode.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
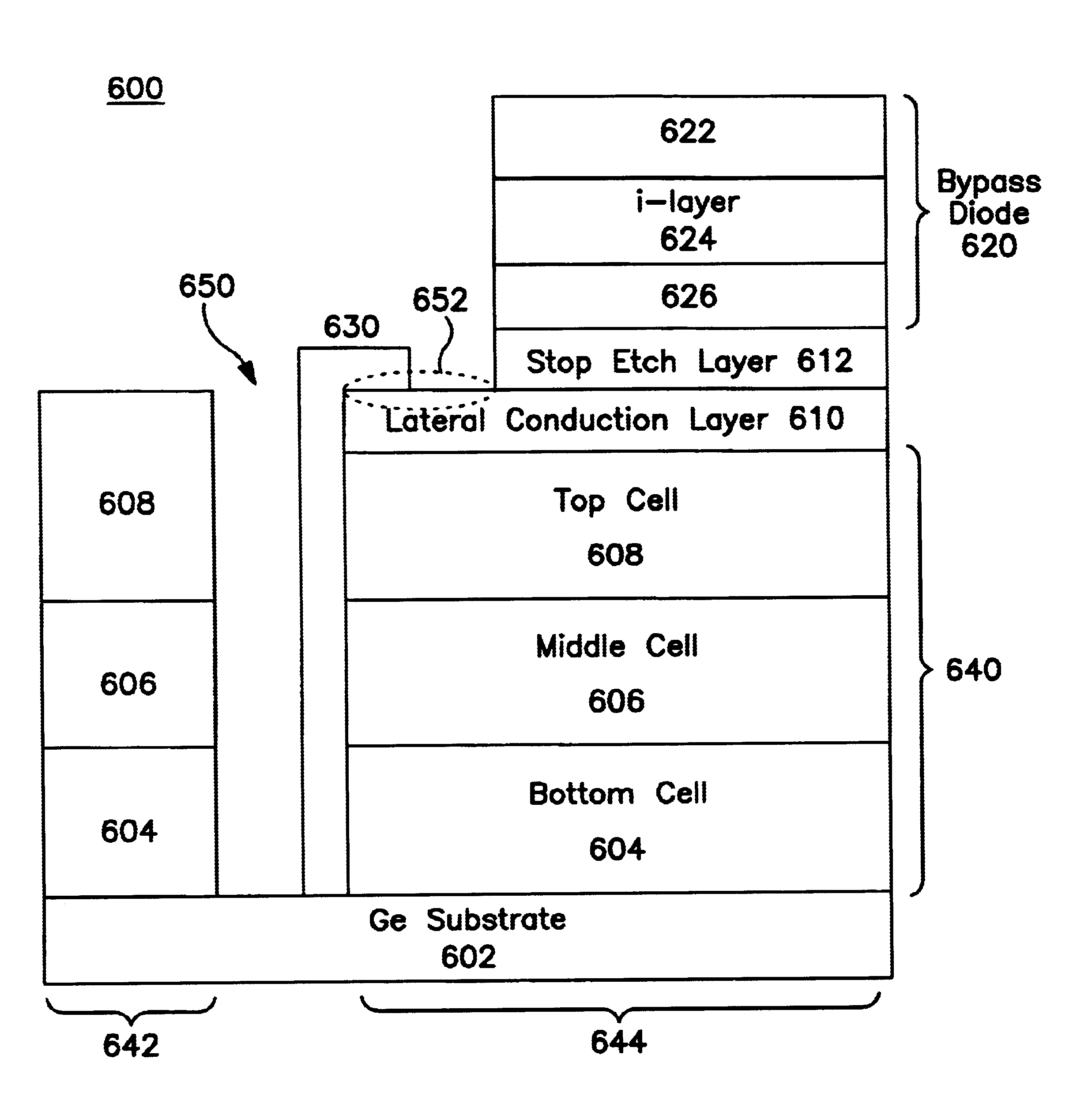
Apparatus and method for integral bypass diode in solar cells
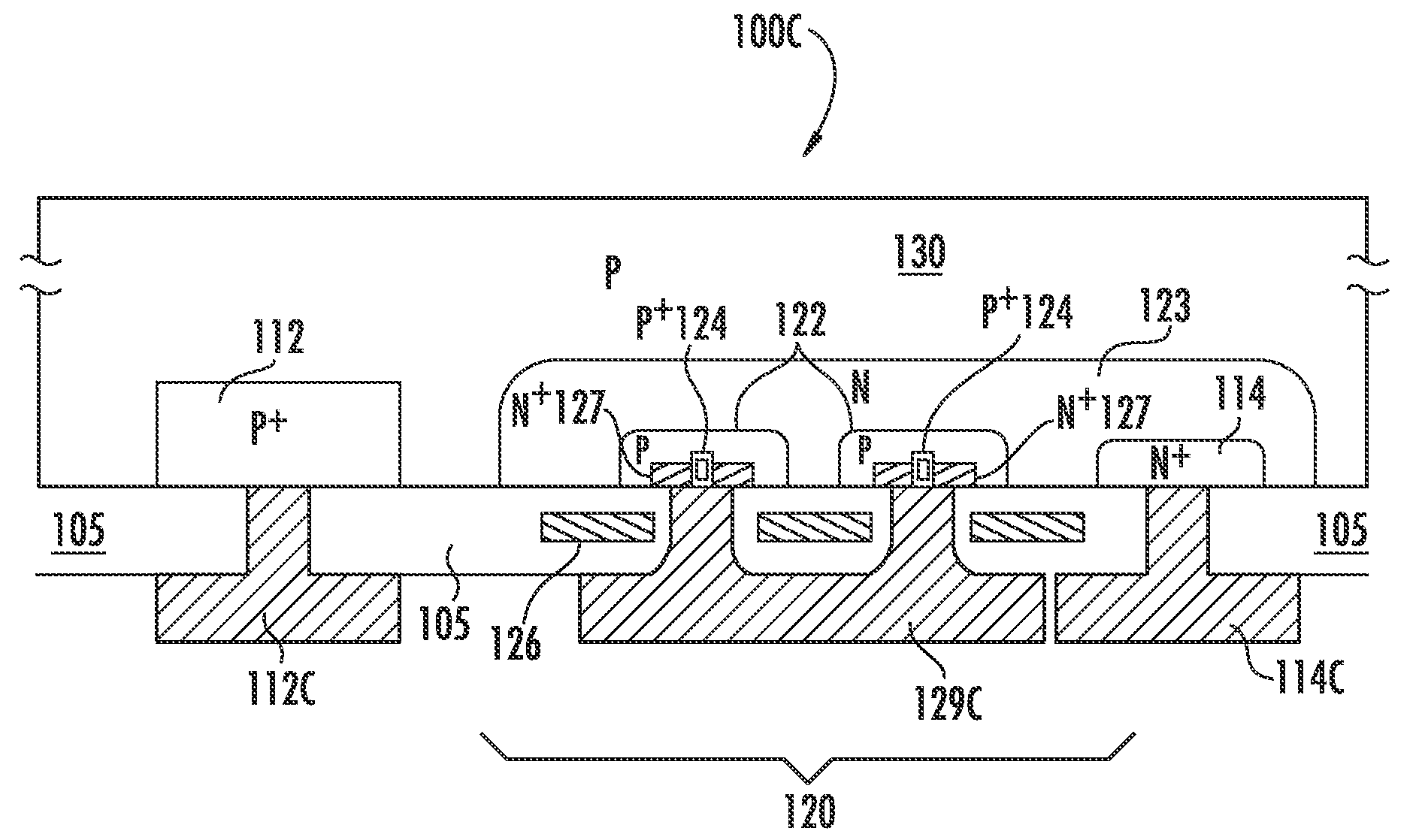
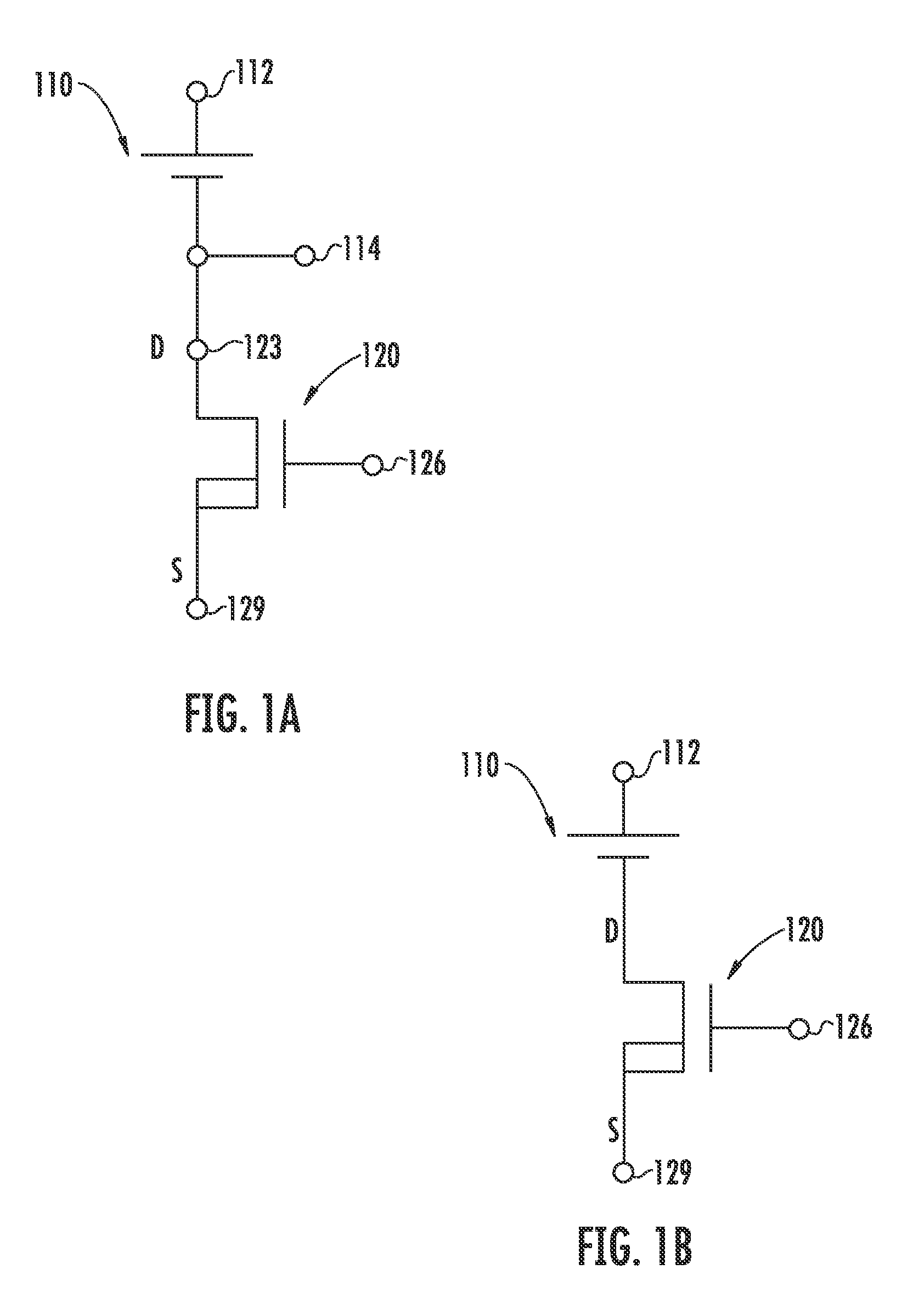
InactiveUS6864414B2Improve performancePV power plantsFinal product manufactureEngineeringReverse bias
A solar cell having a multijunction solar cell structure with a bypass diode is disclosed. The bypass diode provides a reverse bias protection for the multijunction solar cell structure. In one embodiment, the multifunction solar cell structure includes a substrate, a bottom cell, a middle cell, a top cell, a bypass diode, a lateral conduction layer, and a shunt. The lateral conduction layer is deposited over the top cell. The bypass diode is deposited over the lateral conduction layer. One side of the shunt is connected to the substrate and another side of the shunt is connected to the lateral conduction layer. In another embodiment, the bypass diode contains an i-layer to enhance the diode performance.
Owner:SOLAERO TECH CORP
Photodetector with surface plasmon resonance
ActiveUS20130228887A1Reduce thicknessEasy to solveSolid-state devicesDiodePhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
Methods and structures for providing single-color or multi-color photo-detectors leveraging plasmon resonance for performance benefits. In one example, a radiation detector includes a semiconductor absorber layer having a first electrical conductivity type and an energy bandgap responsive to radiation in a first spectral region, a semiconductor collector layer coupled to the absorber layer and having a second electrical conductivity type, and a plasmonic resonator coupled to the collector layer and having a periodic structure including a plurality of features arranged in a regularly repeating pattern.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Device for the detection of multispectral infrared/visible radiation
A device for the detection of multi-spectral infrared and visible radiation using a bolometric detector having at least one active layer and two control electrodes for the detection of both infrared and visible radiation, and also using at least one photodetector having at least two active layers and two control electrodes for detecting solely visible radiation. The device is uncooled, and the two detectors are superimposed and combined with one-another for forming the same sensitive element.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
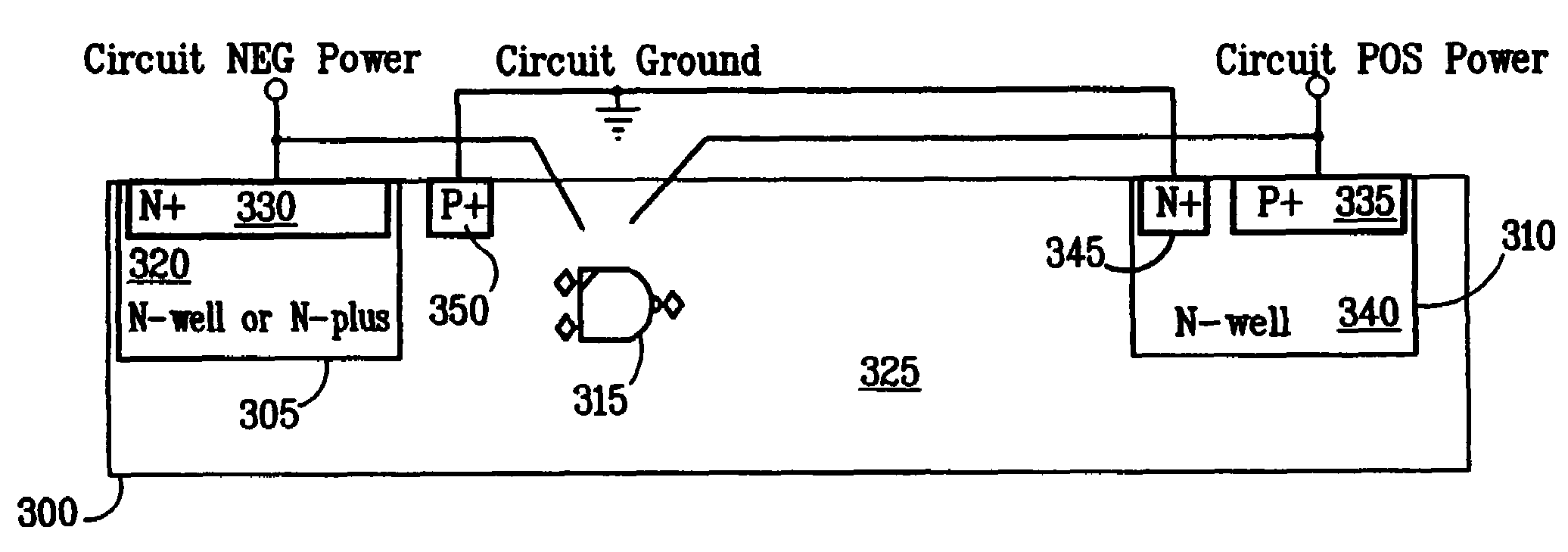
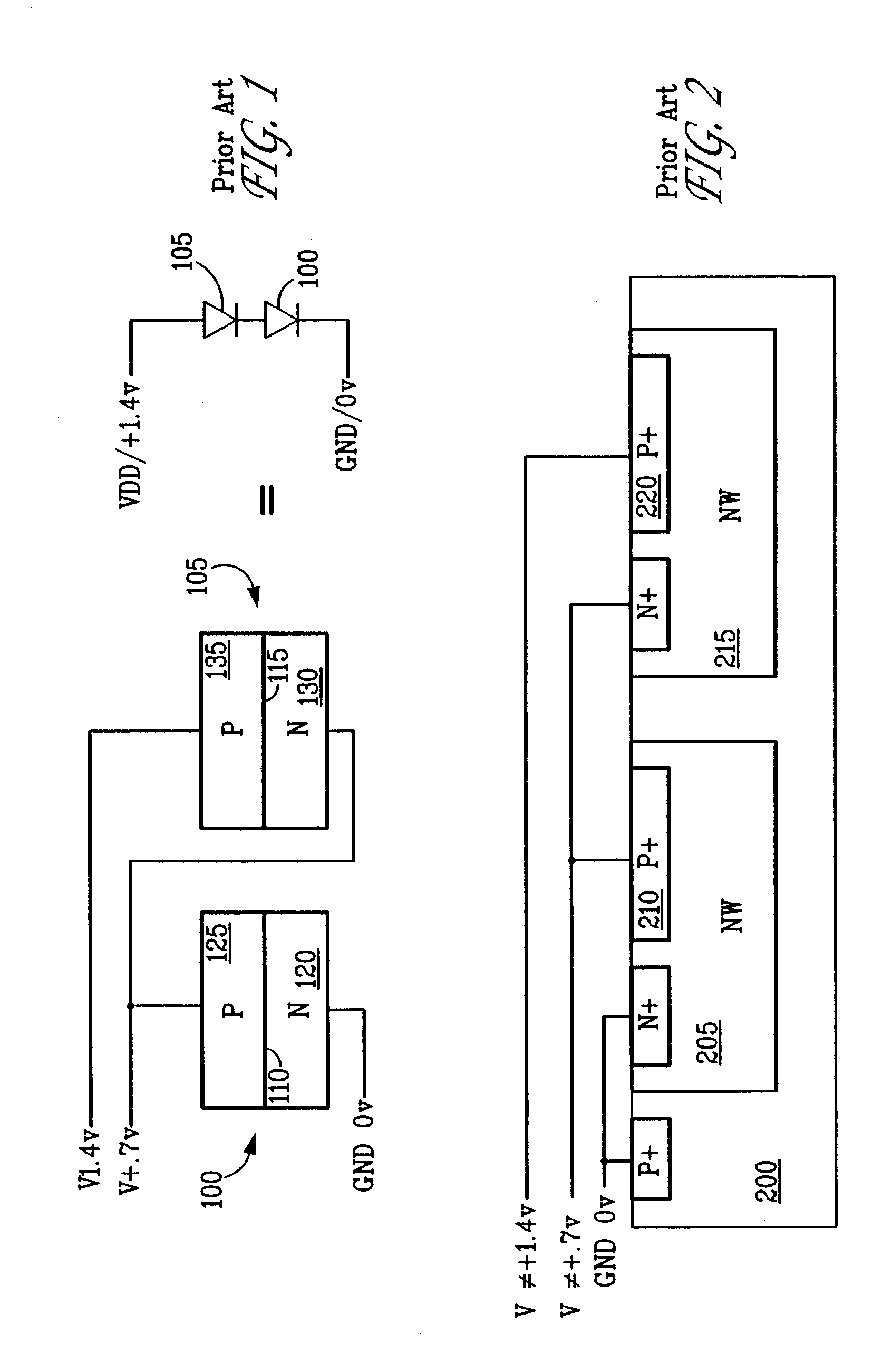
Method and apparatus for powering circuitry with on-chip solar cells within a common substrate
A system and method for providing power to a light-powered transponder. In order to create a sufficient voltage differential, two different photovoltaic elements are used. The photovoltaic elements generate voltages of different polarities. Because the photovoltaic elements are used independently to generate voltages with different polarities, the present system can achieve a desired voltage differential despite the inherent difficulties presented by the use of a standard CMOS process.
Owner:PHARMASEQ INC
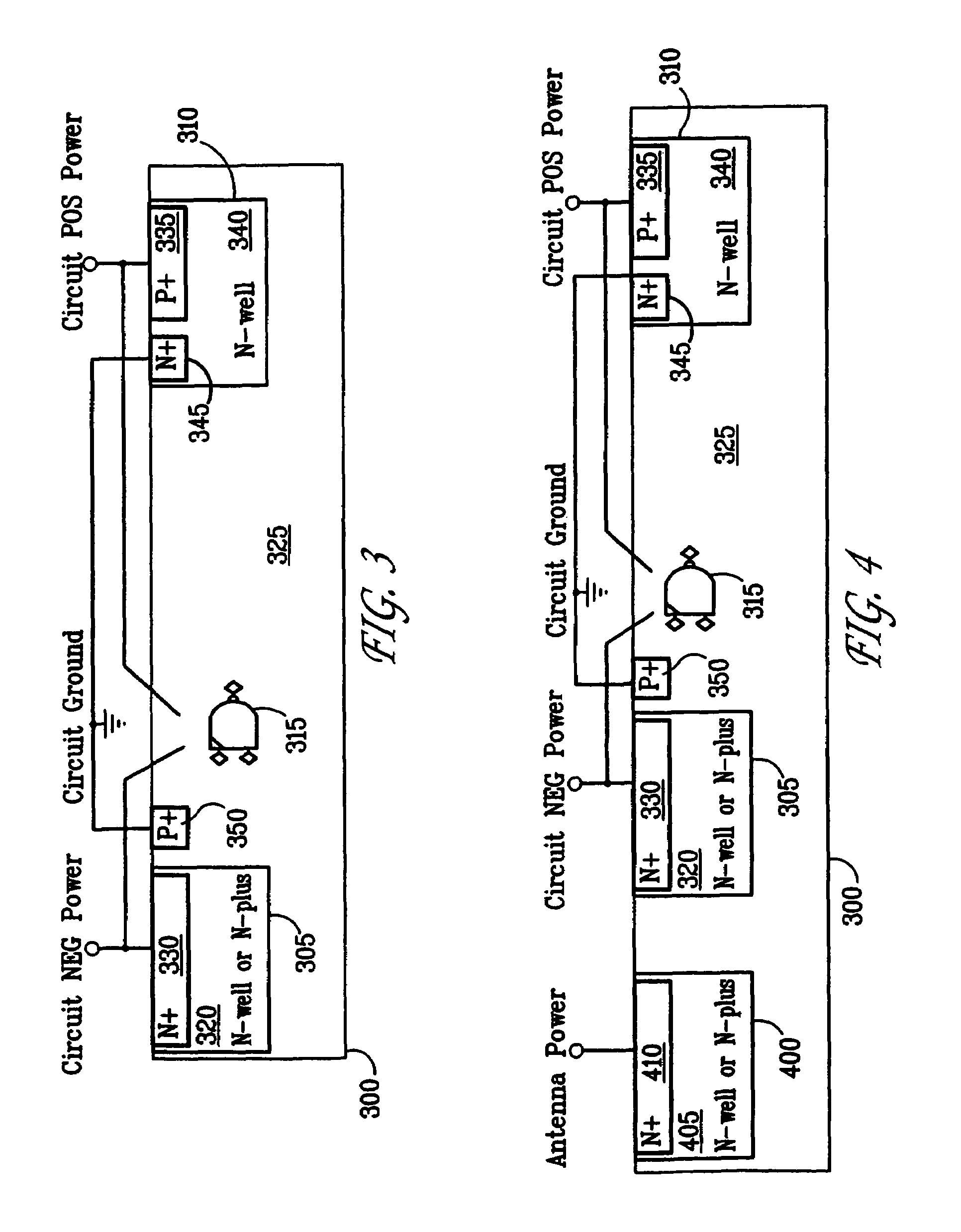
Solar cell arrangements
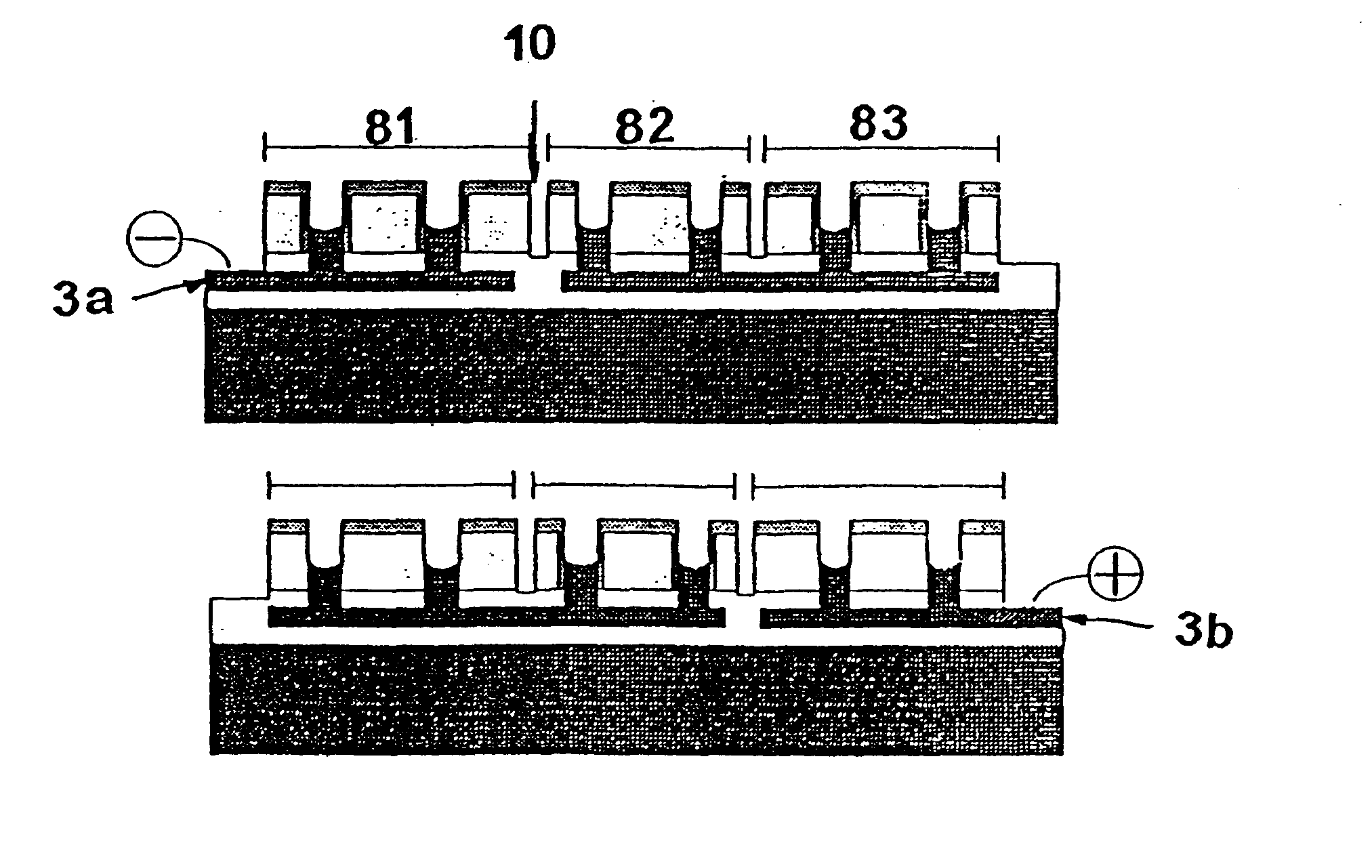
InactiveUS6563289B1Increase the areaEasy to integrateBatteries circuit arrangementsDiodeElectricityEngineering
In a solar cell arrangement, a generally rectangular solar cell has mutually orthogonal sides in plan view and a third oblique side to them which adjoins them. A protection diode is located in the region bounded by the third side and projections of the first and second sides. The protection diode is electrically connected to the solar cell. Use of the invention enables protection to be provided individual solar cells of a solar cell array without a significant loss in the area occupied by the light sensitive solar cell surfaces.
Owner:E2V TECH (UK) LTD
Thin-film solar cell module of see-through type
InactiveUS7098395B2PV power plantsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringThin film solar cell
A thin-film solar cell module of a see-through structure has a plurality of integrated thin-film solar cell segments, each having a rectangular surface, provided on at least a portion of a surface region of a light-transmitting substrate having a rectangular surface and are spaced apart from each other. Adjacent solar cell segments are spaced apart at substantially regular intervals, with their long sides extending parallel to each other. Those portions of the substrate, which lie between the solar cell segments, are exposed, defining light-transmitting windows. A transparent sealing resin fills the gaps between the adjacent solar cell segments.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Method of Manufacturing a Light Emitting, Power Generating or Other Electronic Apparatus
An exemplary printable composition of a liquid or gel suspension of diodes comprises a plurality of diodes, a first solvent and / or a viscosity modifier. An exemplary method of fabricating an electronic device comprises: depositing one or more first conductors; and depositing a plurality of diodes suspended in a mixture of a first solvent and a viscosity modifier. Various exemplary diodes have a lateral dimension between about 10 to 50 microns and about 5 to 25 microns in height. Other embodiments may also include a plurality of substantially chemically inert particles having a range of sizes between about 10 to about 50 microns.
Owner:NTHDEGREE TECH WORLDWIDE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com