Patents
Literature
757 results about "Cell layer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
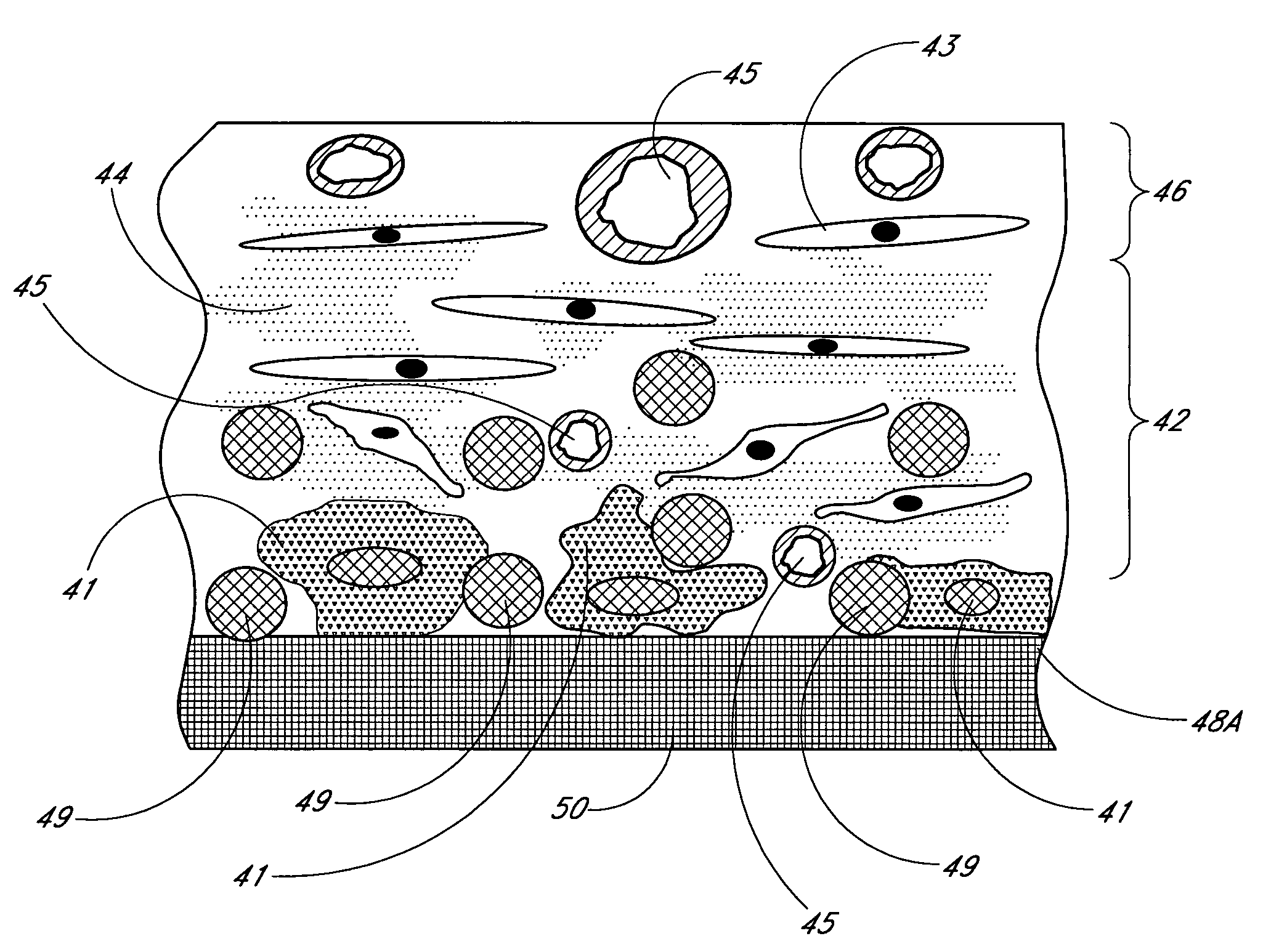
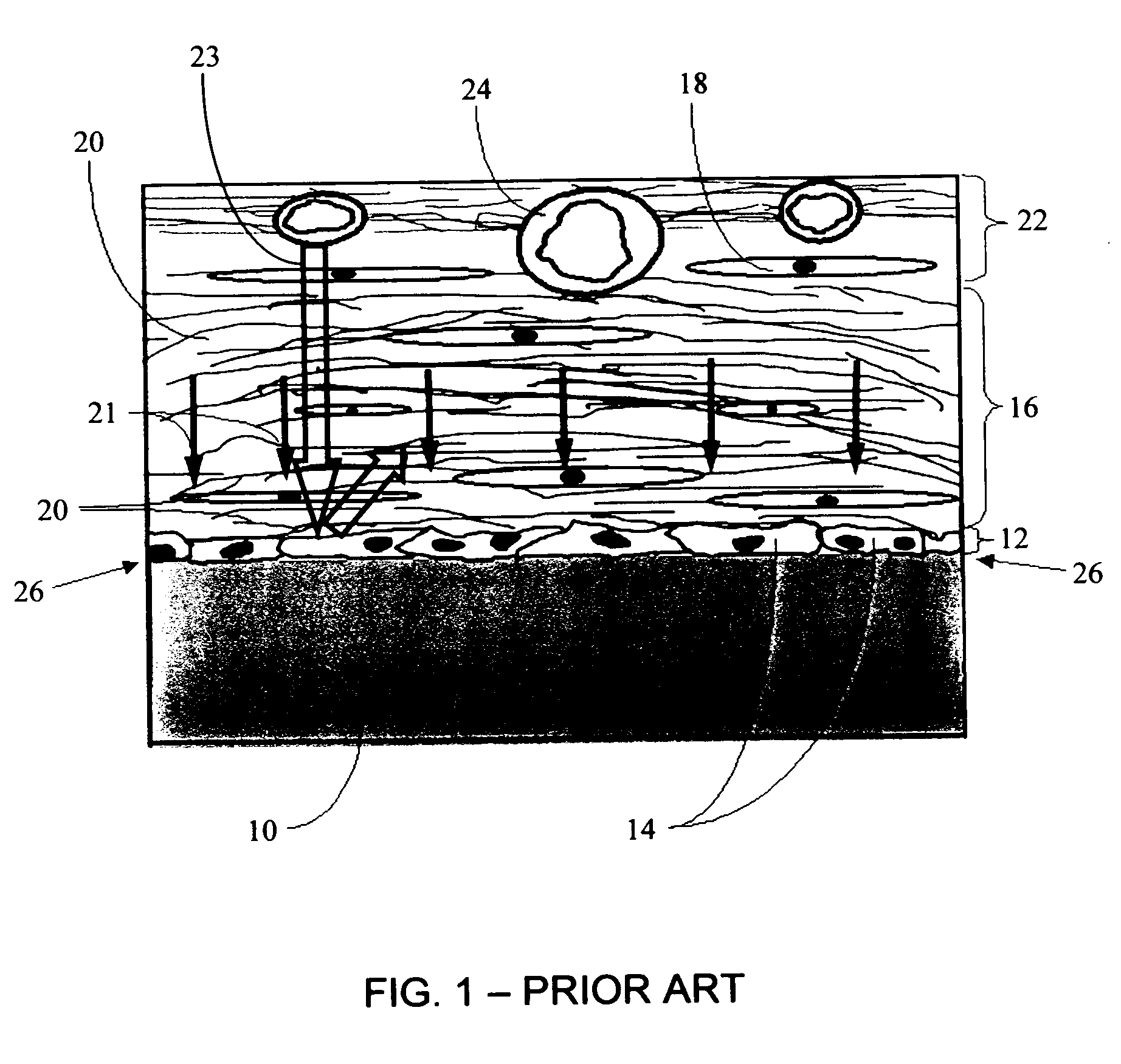
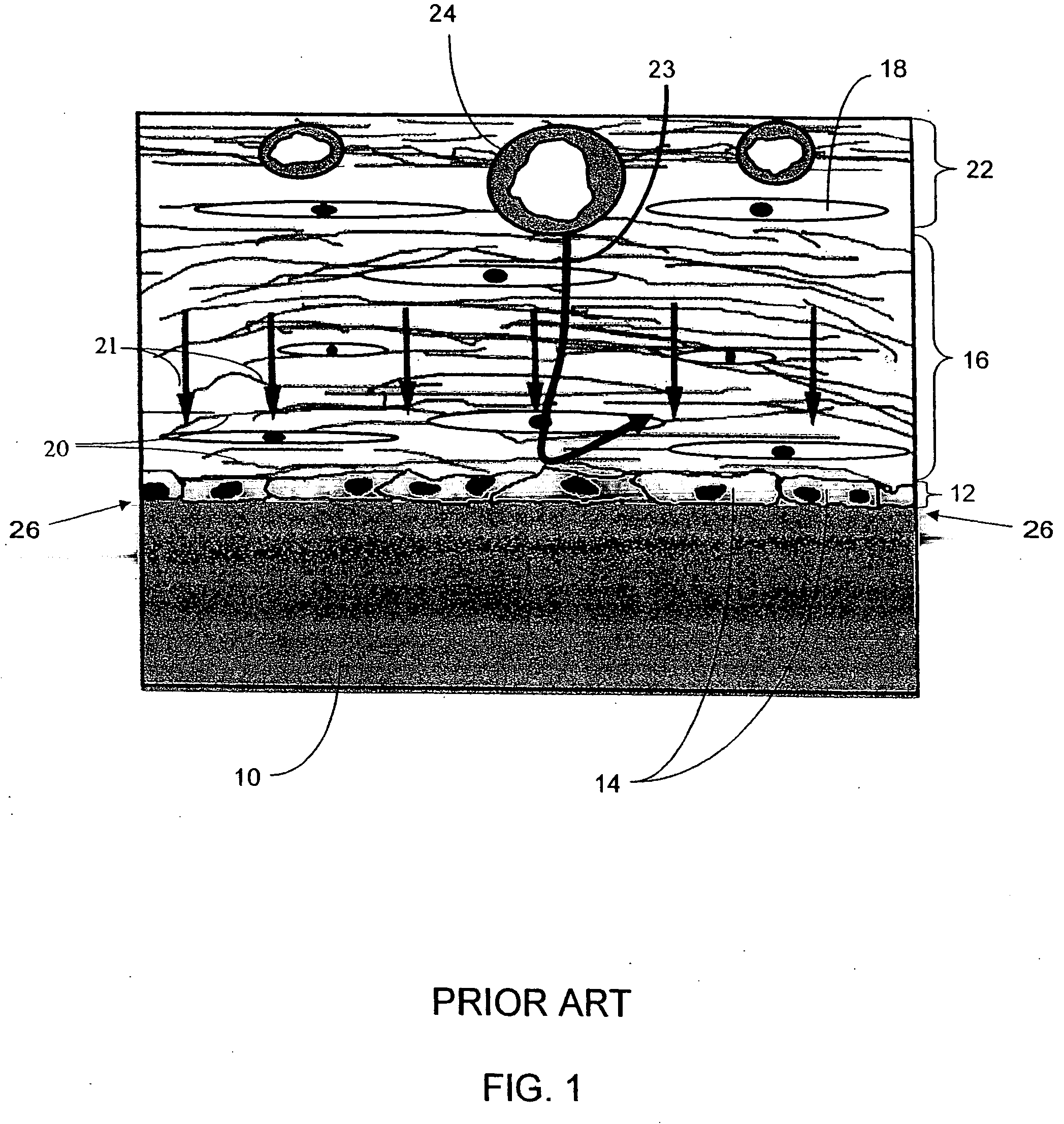
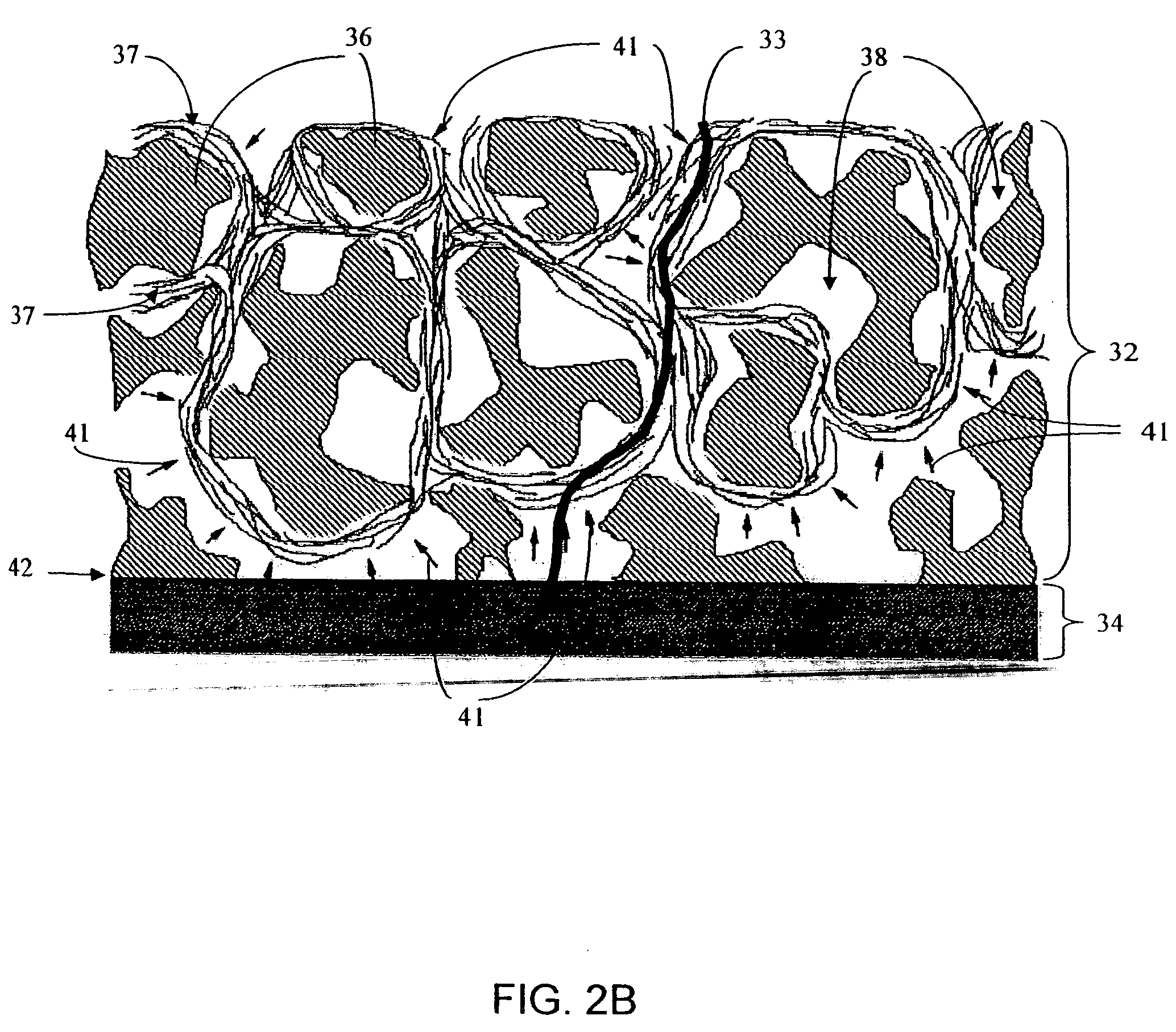
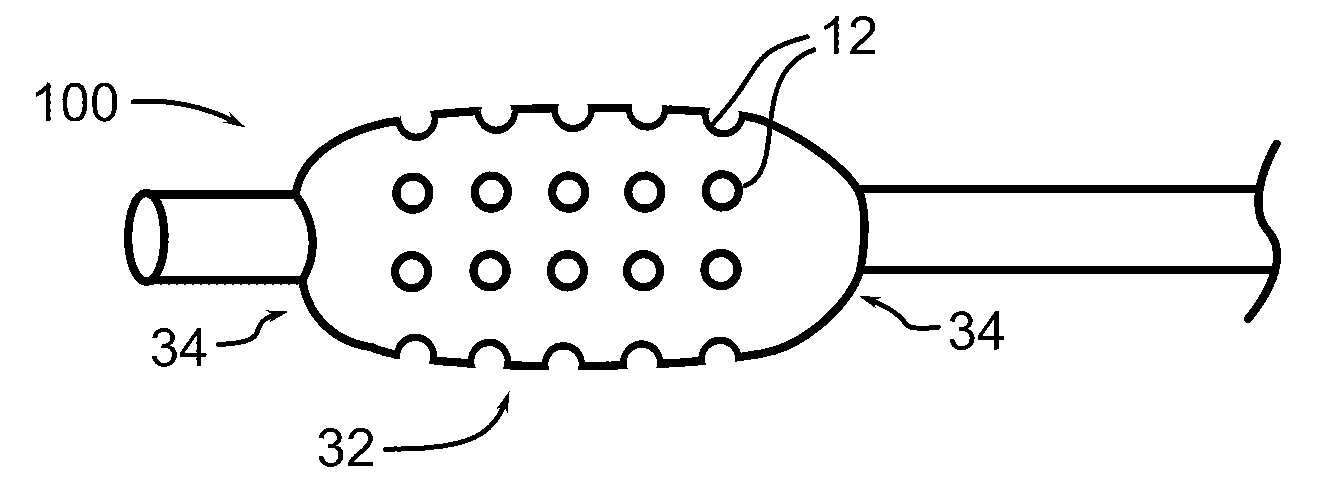
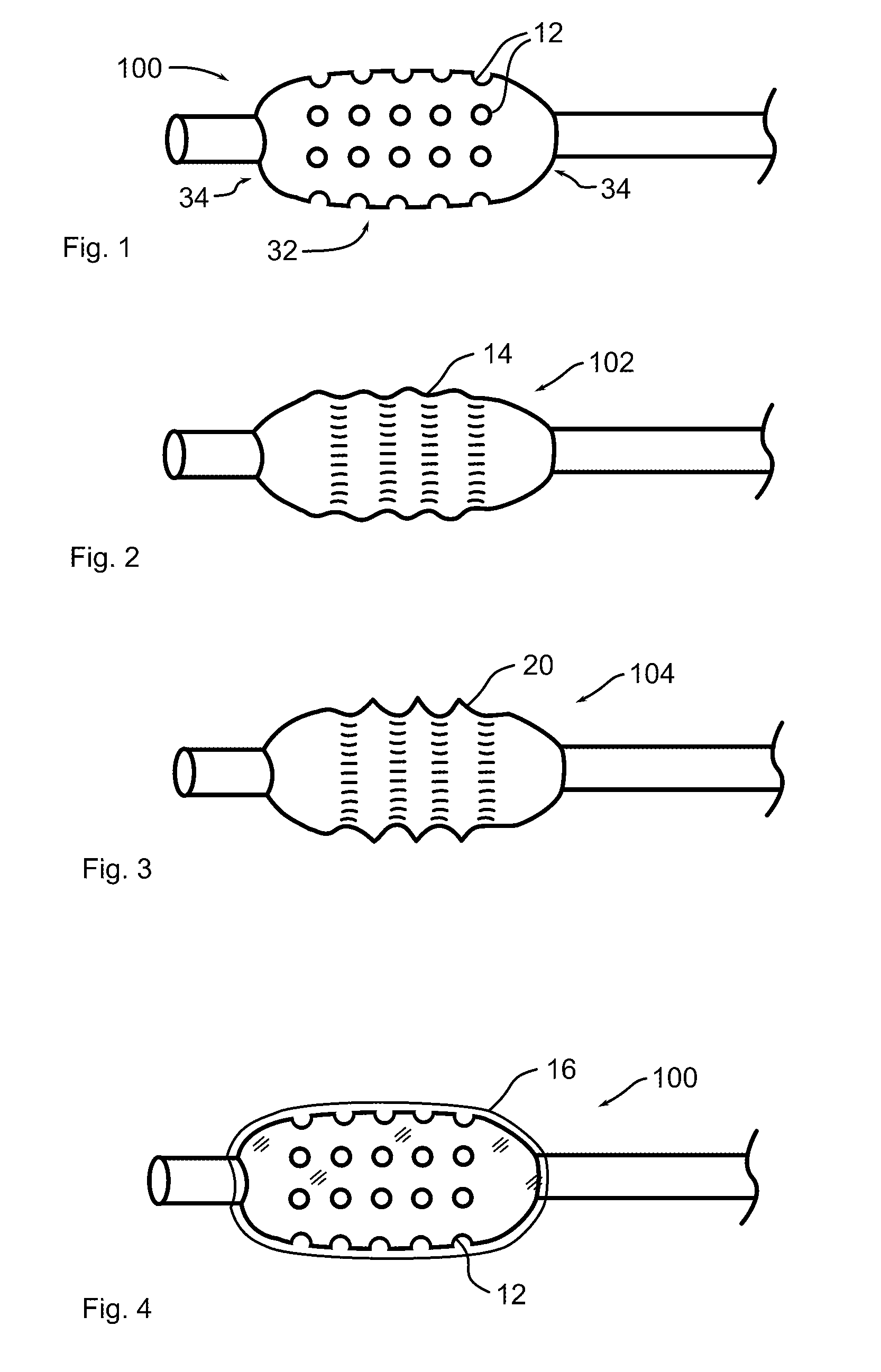
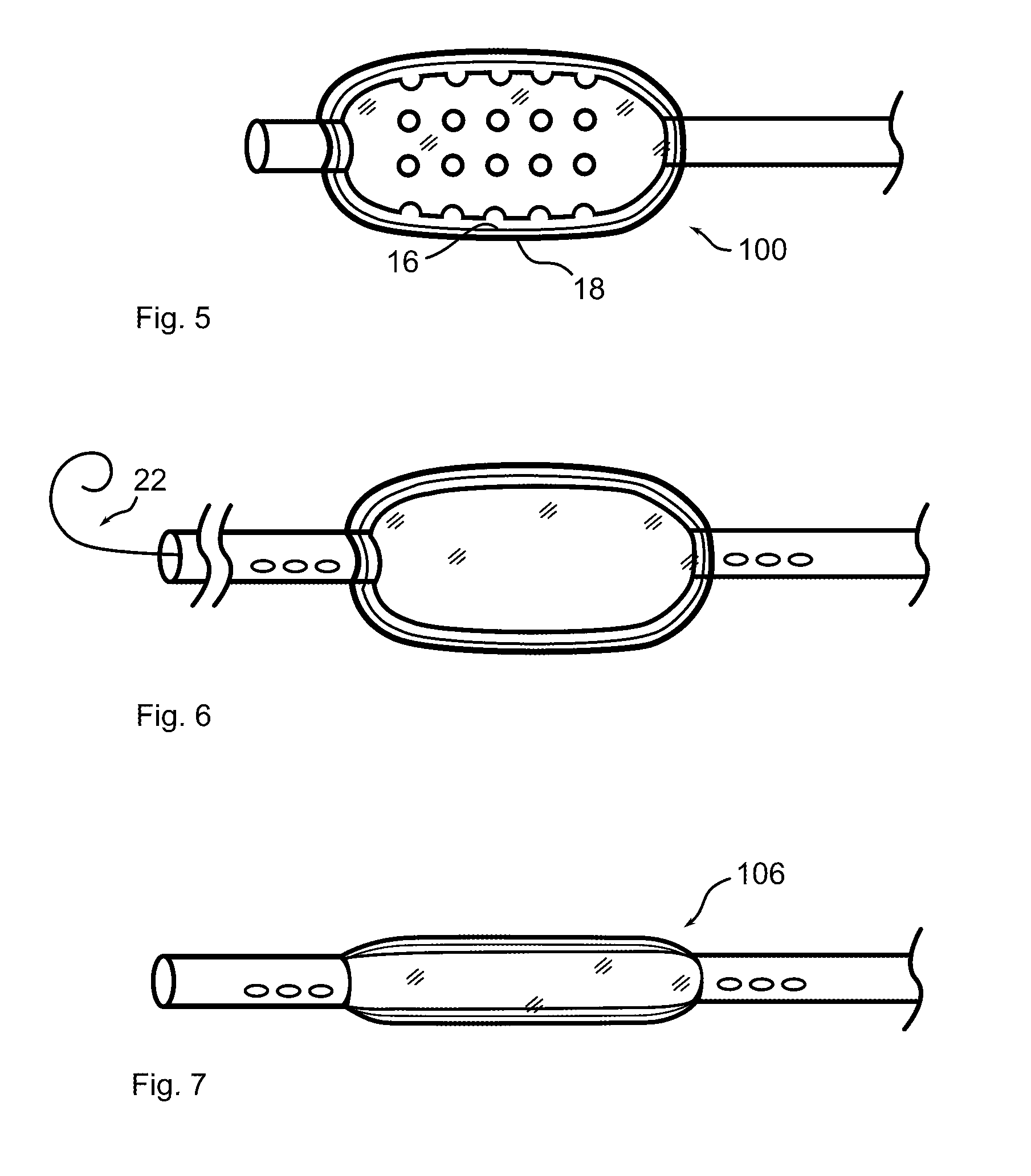
Biointerface membranes incorporating bioactive agents
InactiveUS20050031689A1Improve performancePowder deliveryAdditive manufacturing apparatusBiointerfaceActive agent
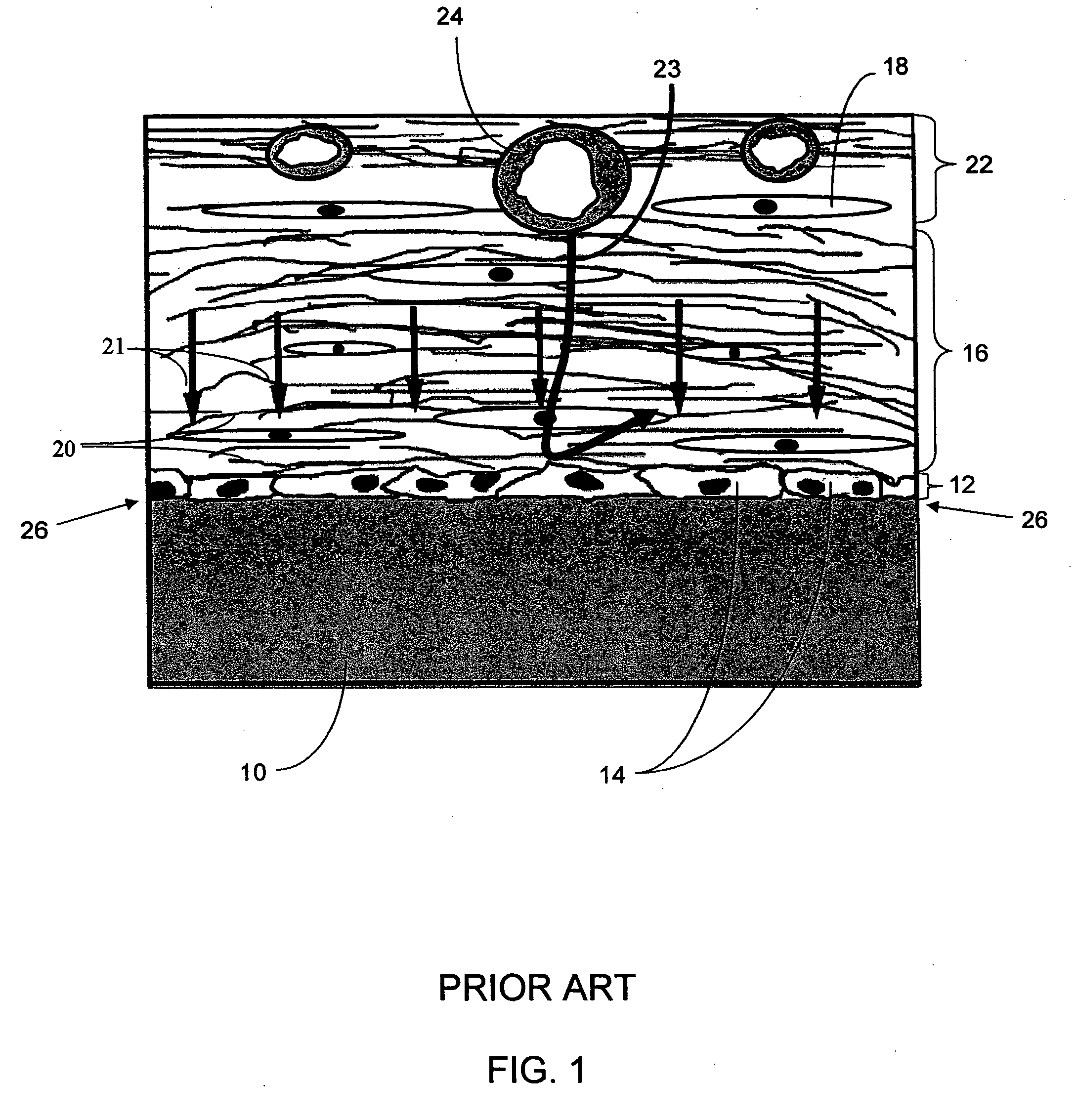
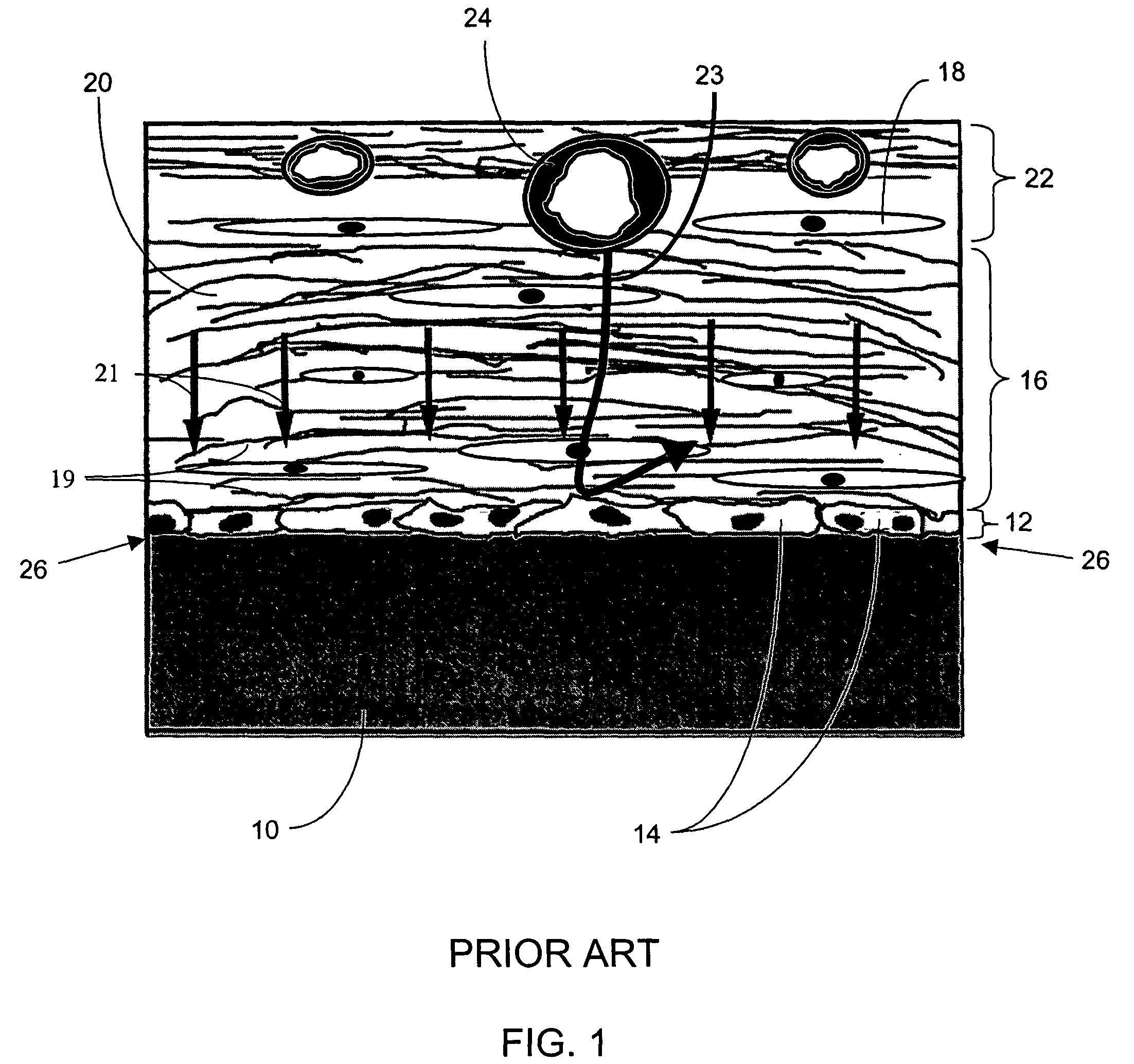
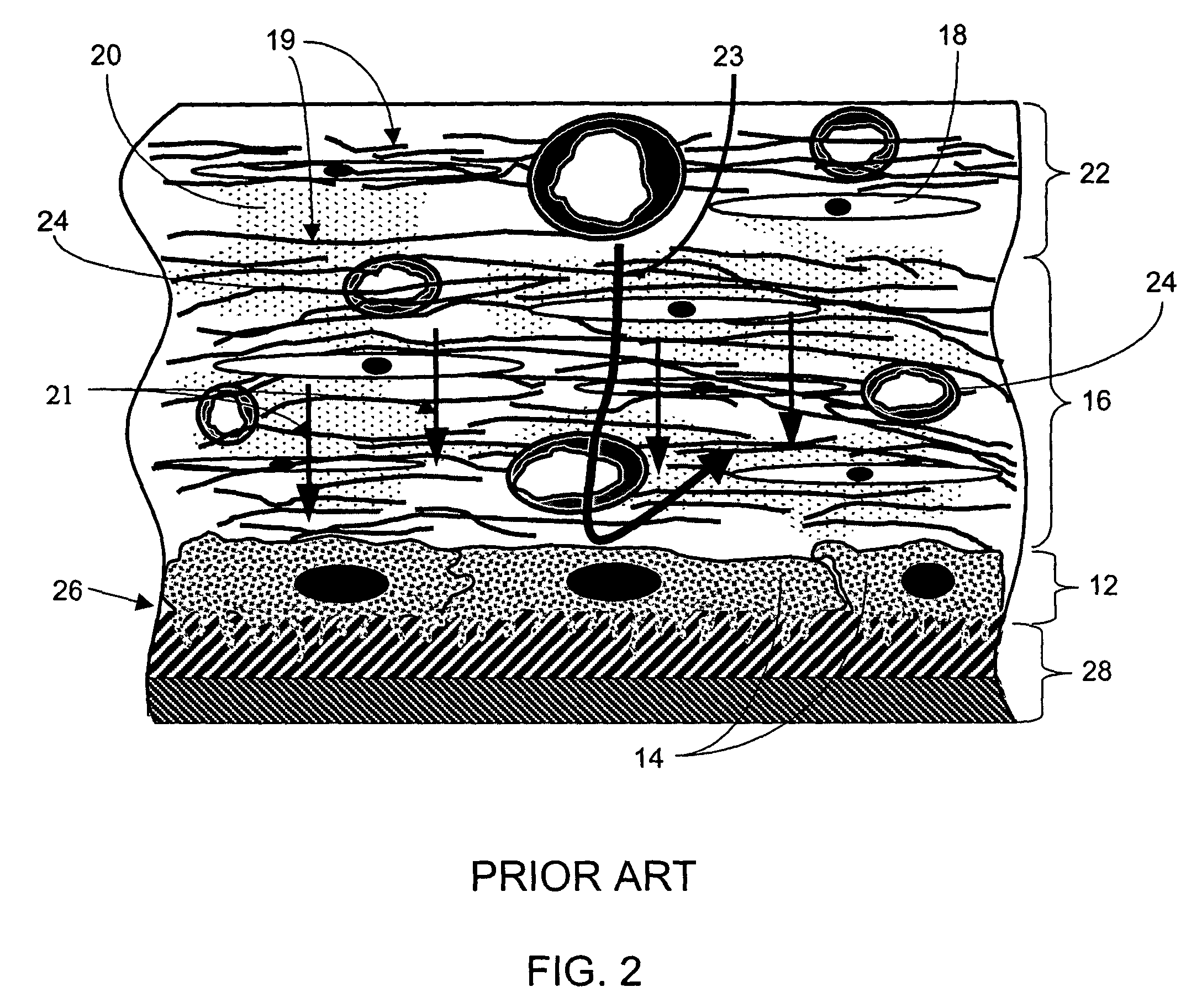
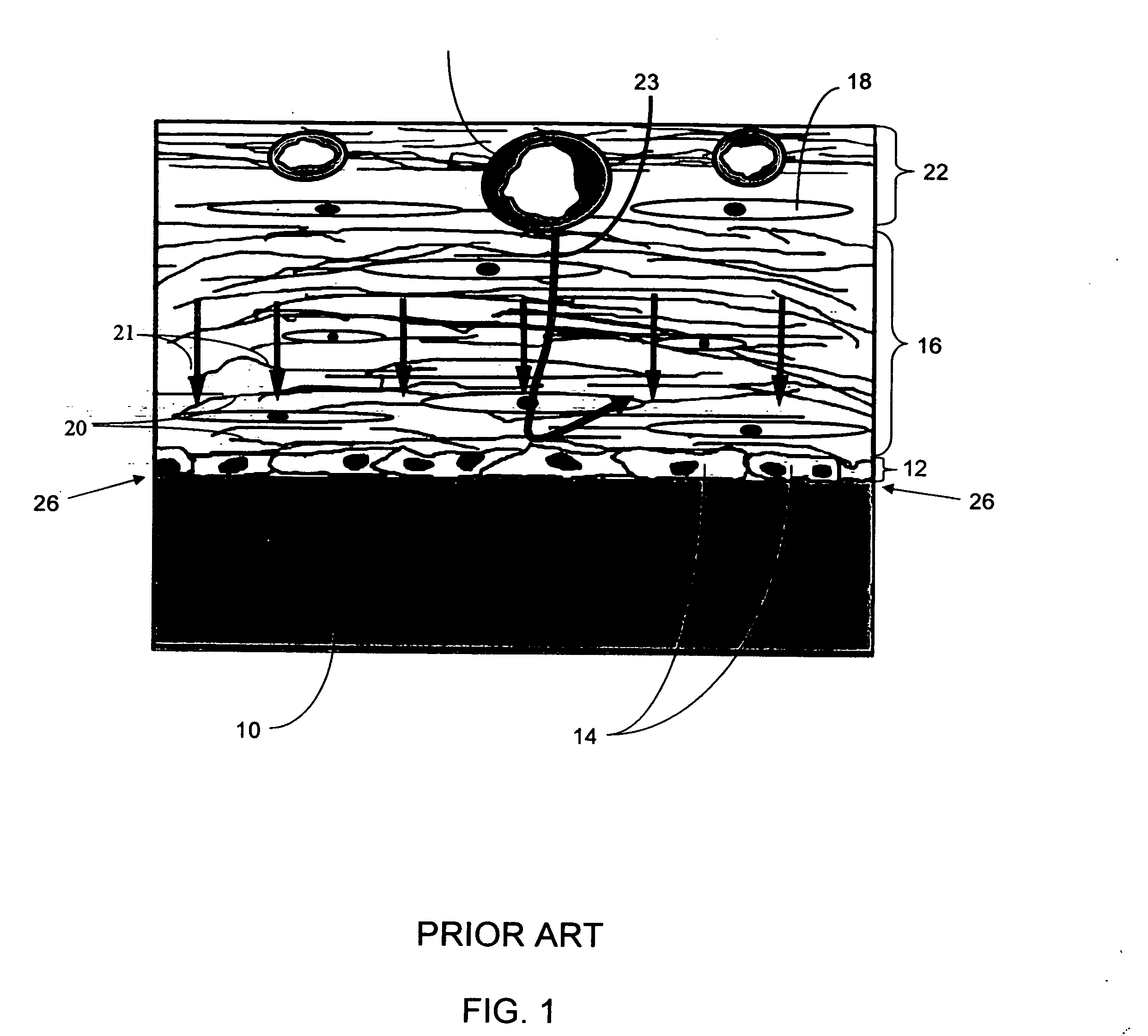
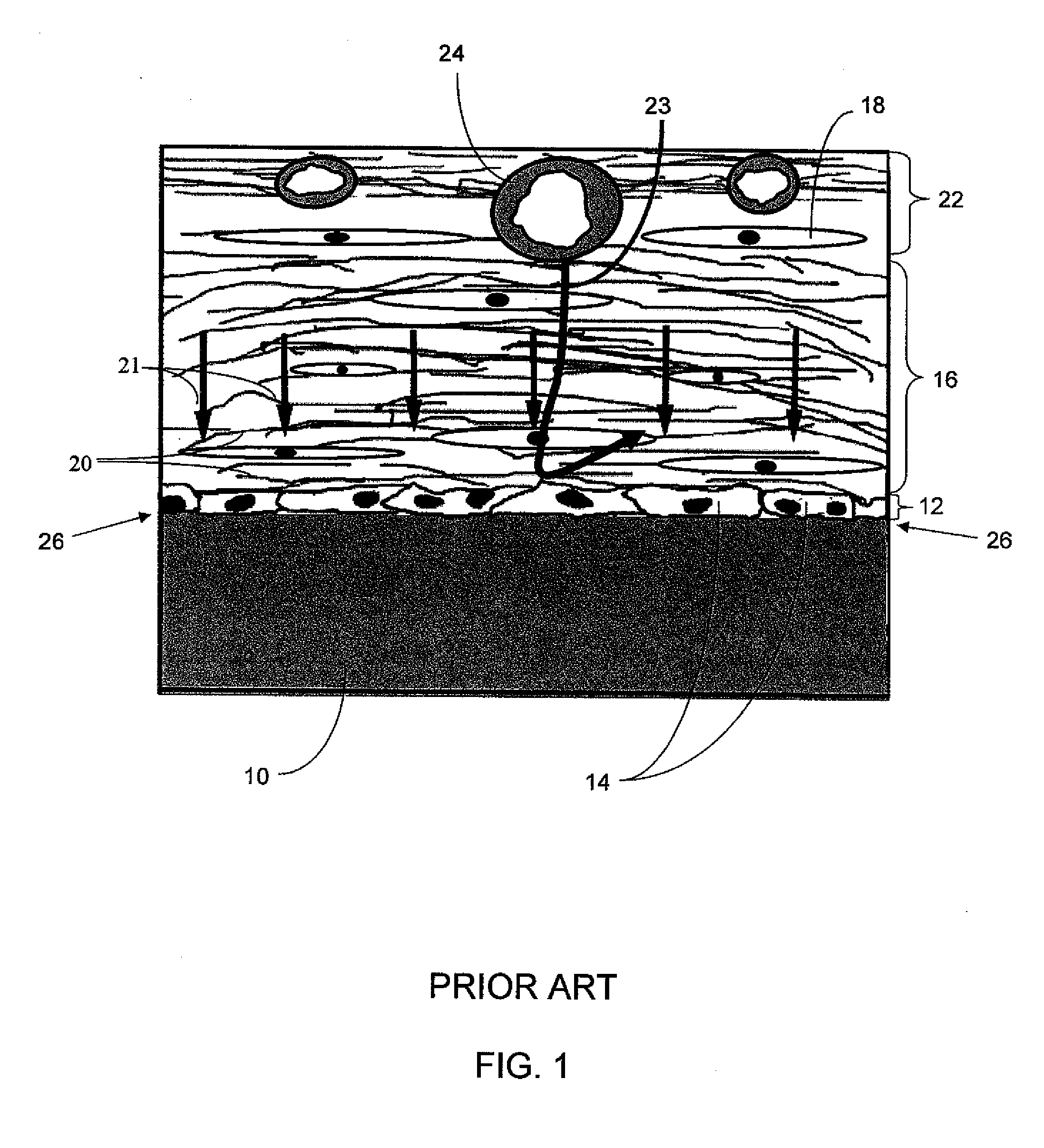
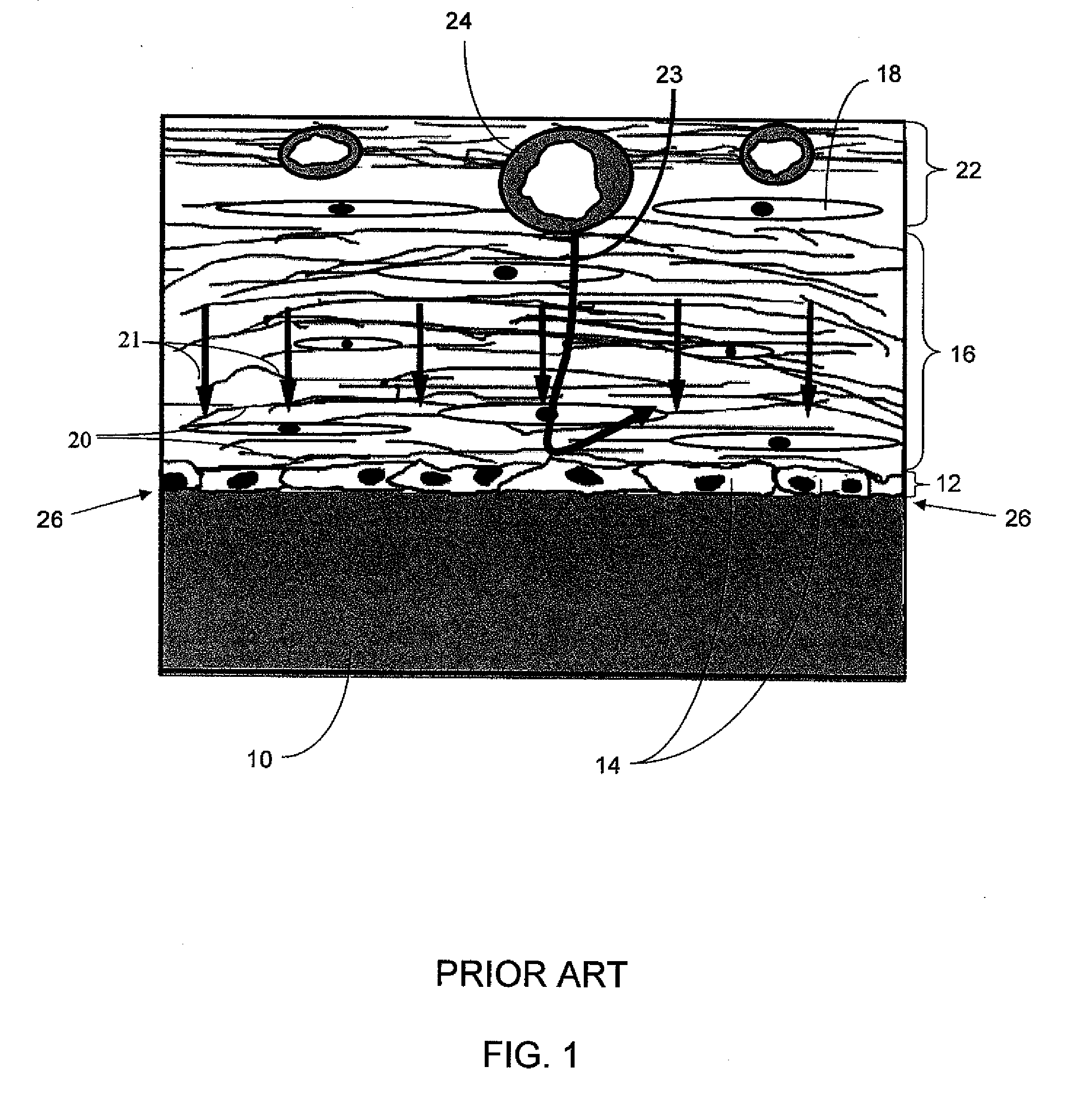
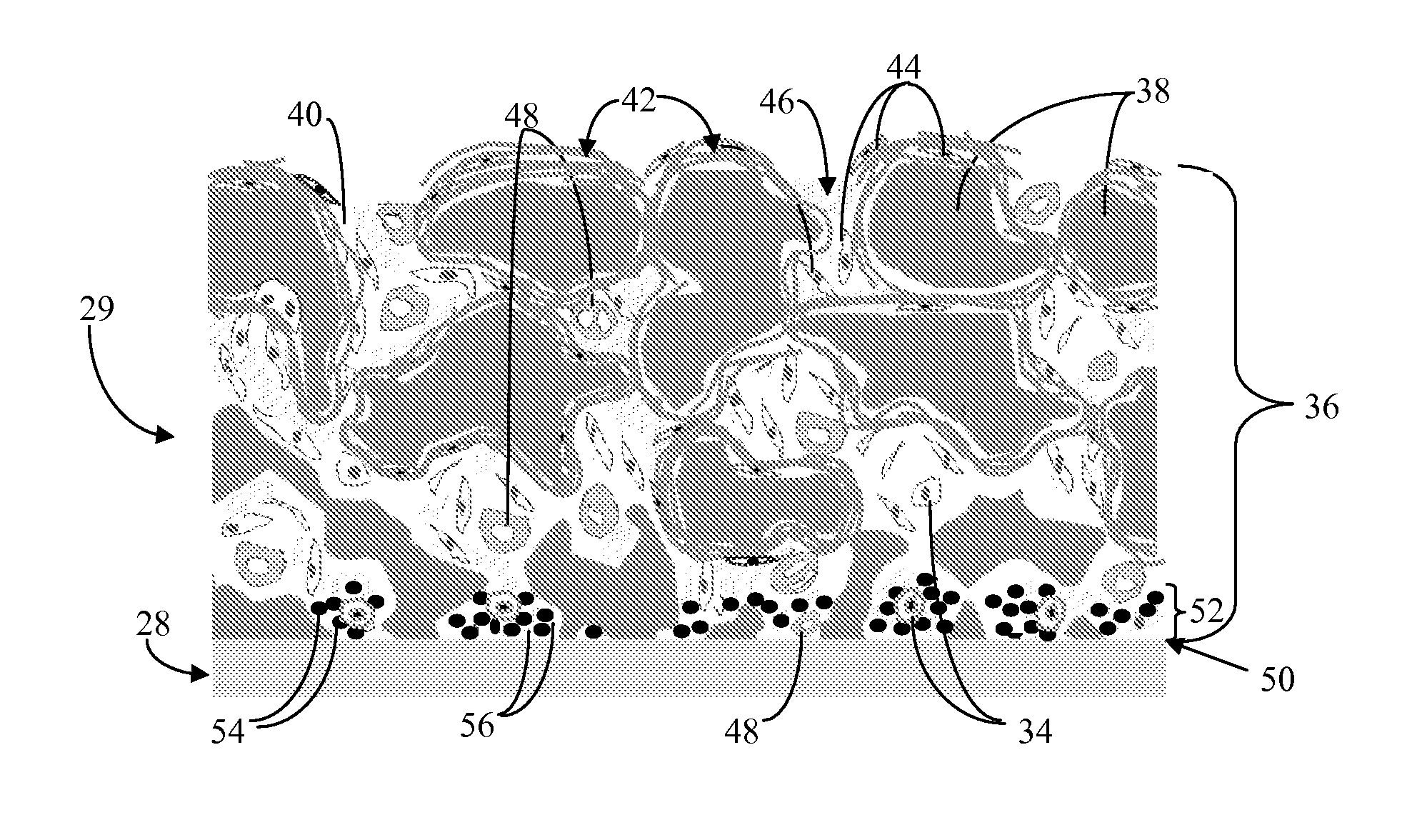
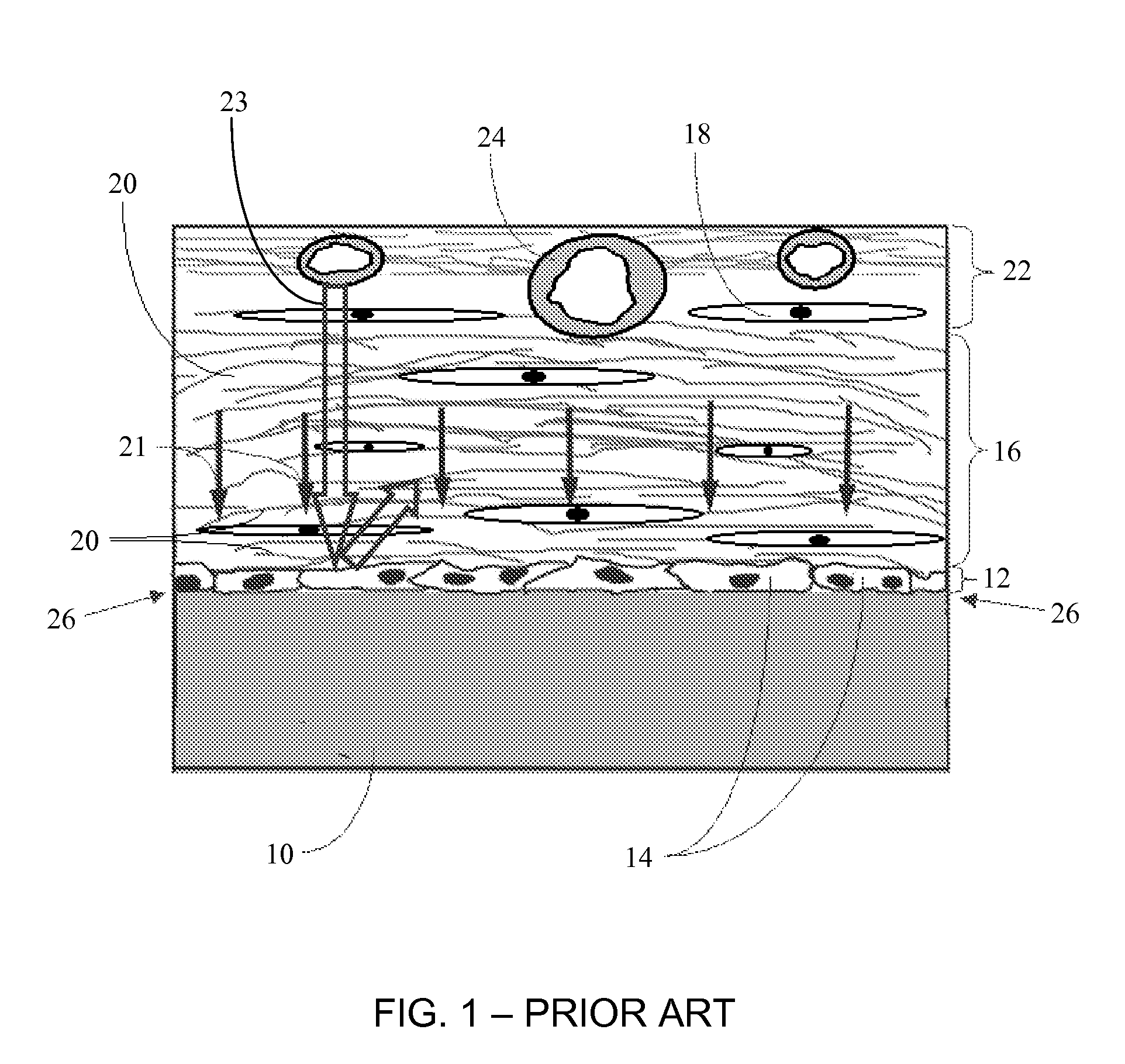
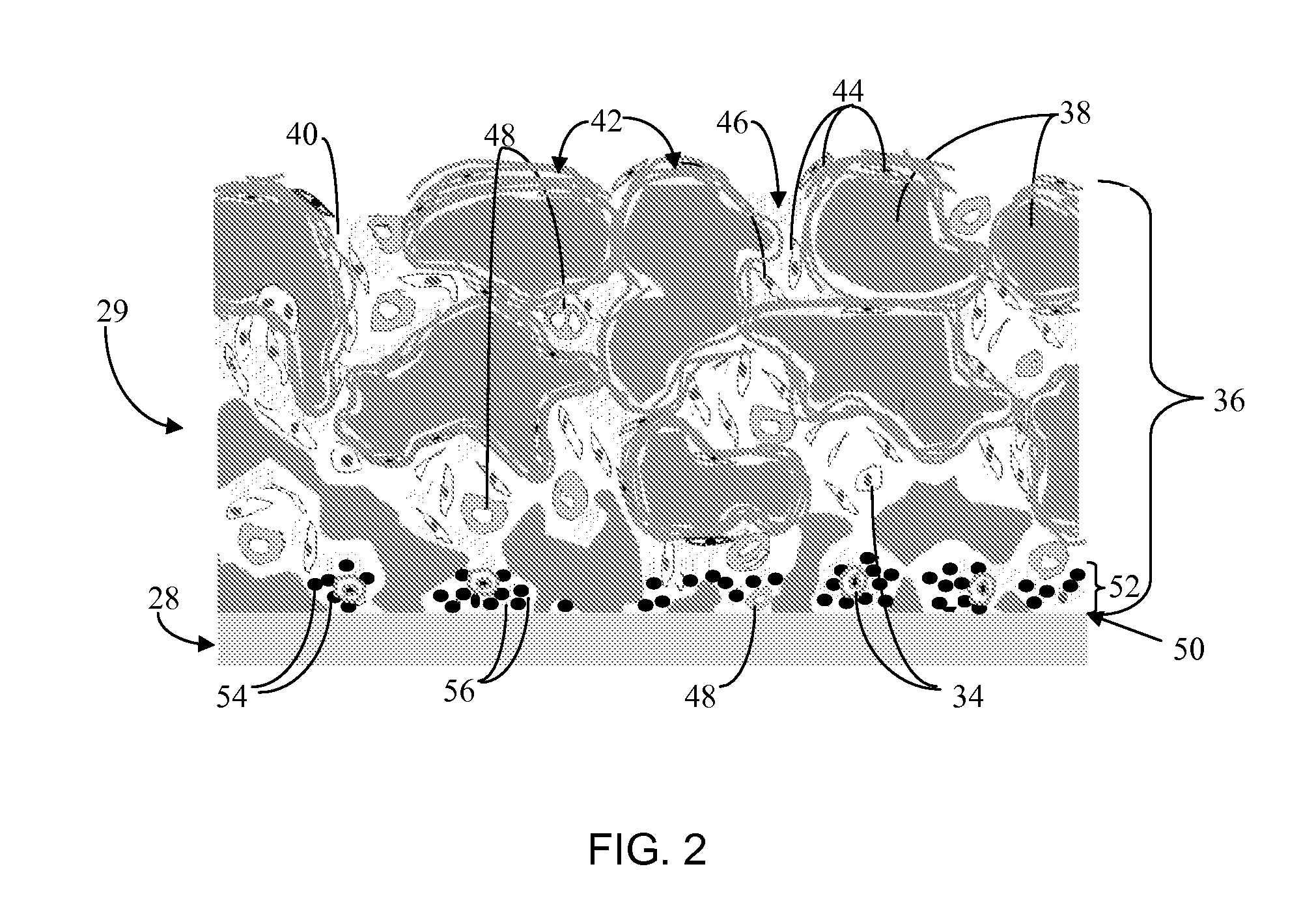
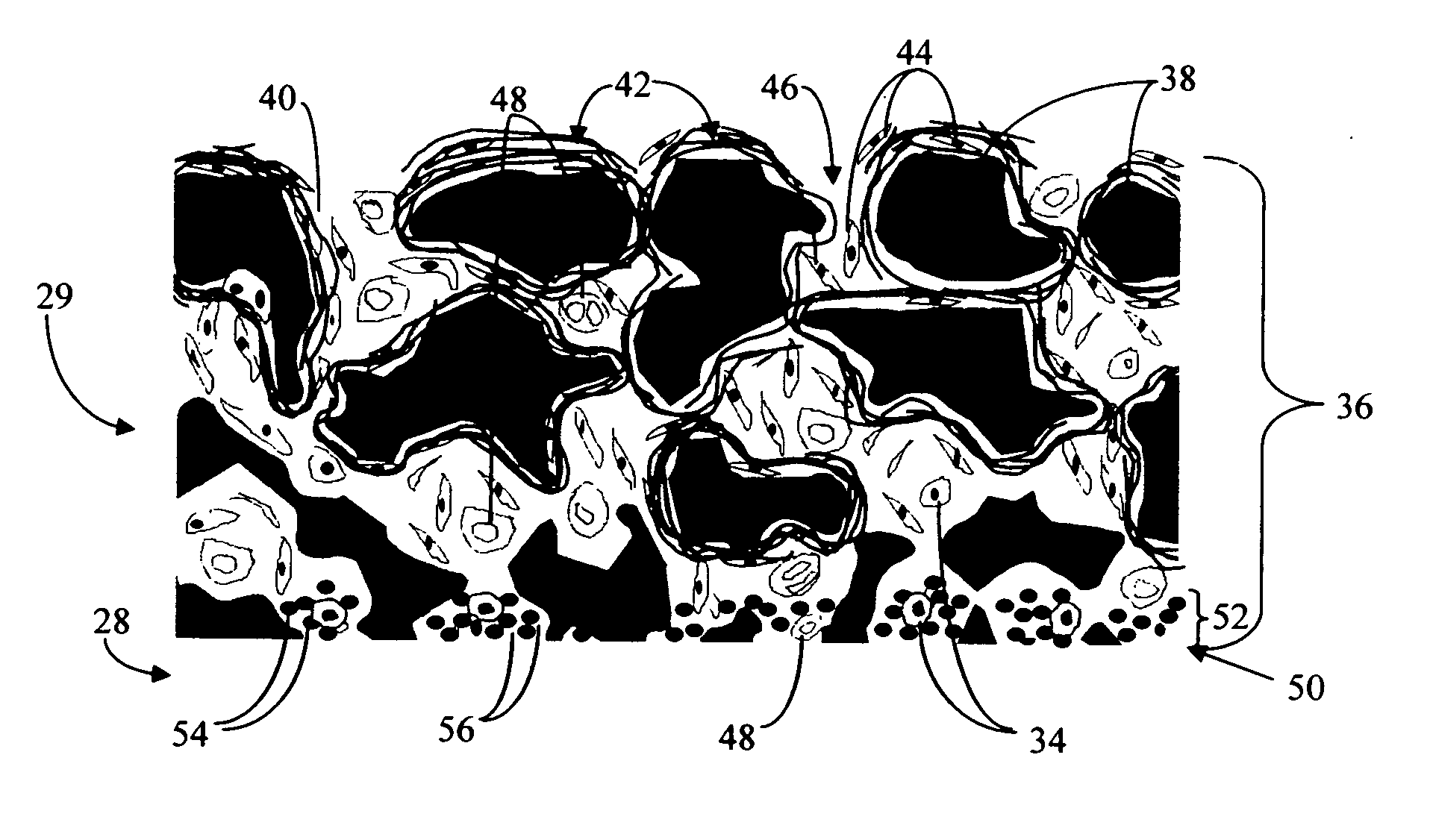
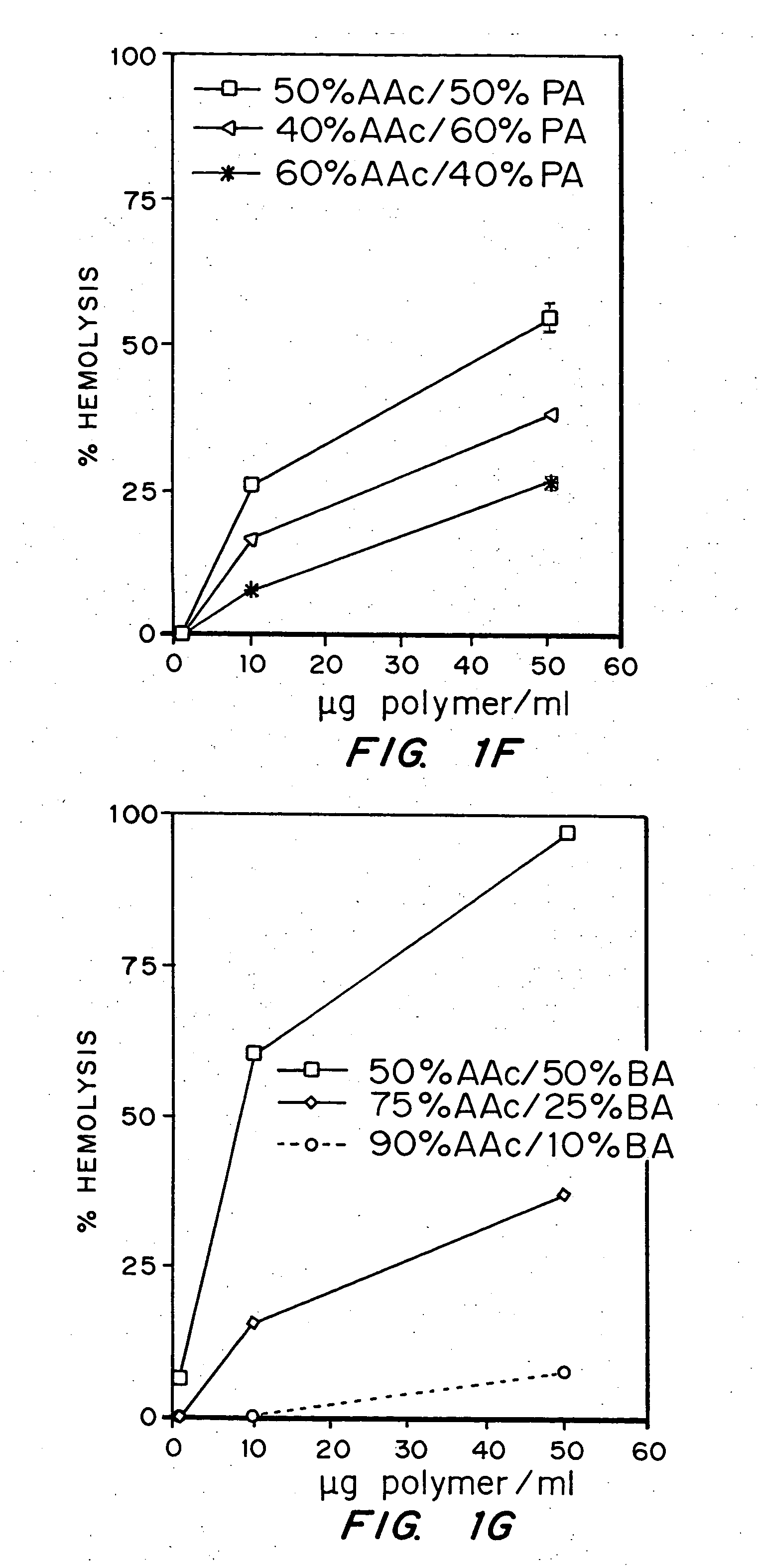
A biointerface membrane for an implantable device including a nonresorbable solid portion with a plurality of interconnected cavities therein adapted to support tissue ingrowth in vivo, and a bioactive agent incorporated into the biointerface membrane and adapted to modify the tissue response is provided. The bioactive agents can be chosen to induce vascularization and / or prevent barrier cell layer formation in vivo, and are advantageous when used with implantable devices wherein solutes are transported across the device-tissue interface.
Owner:DEXCOM
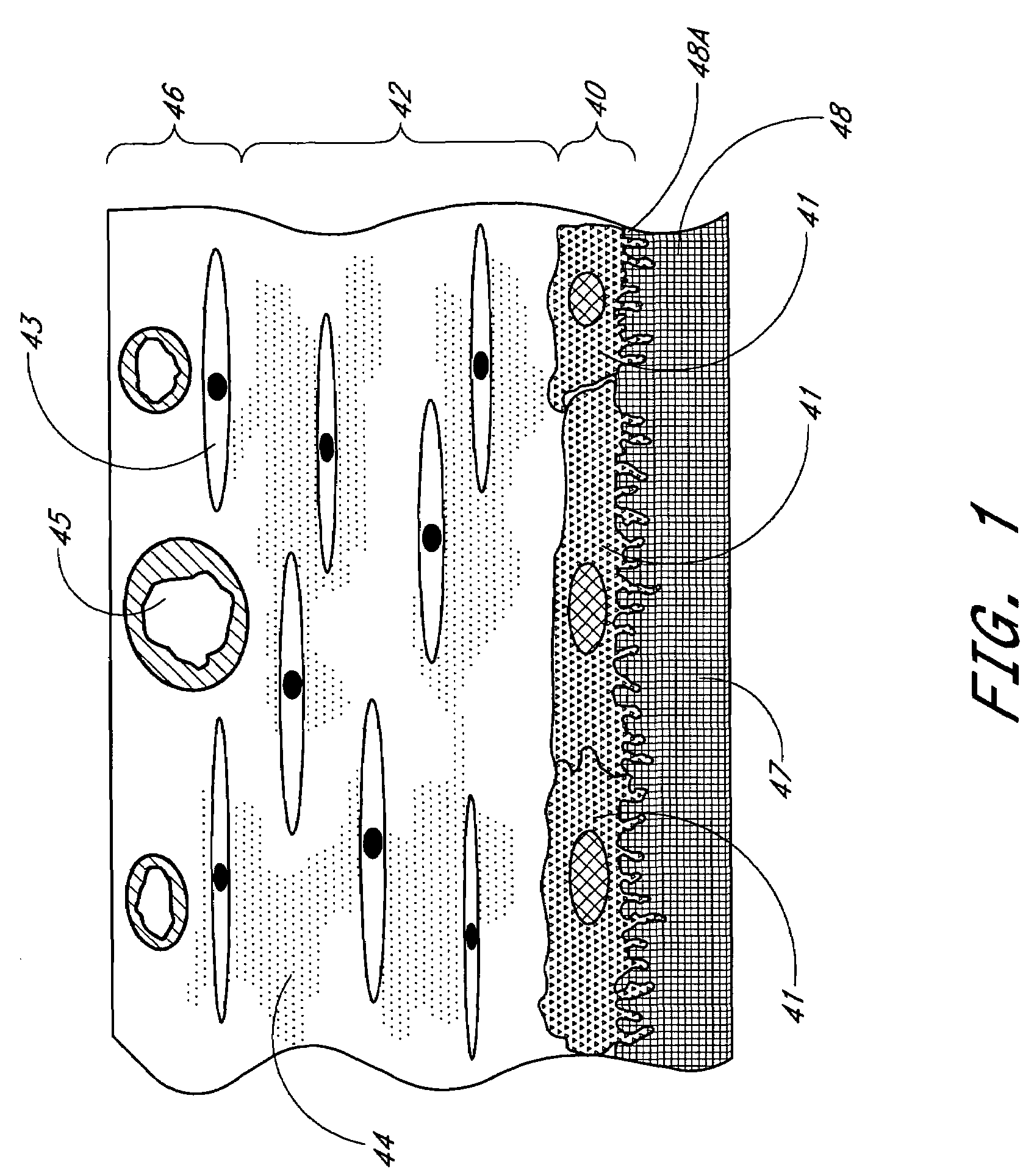
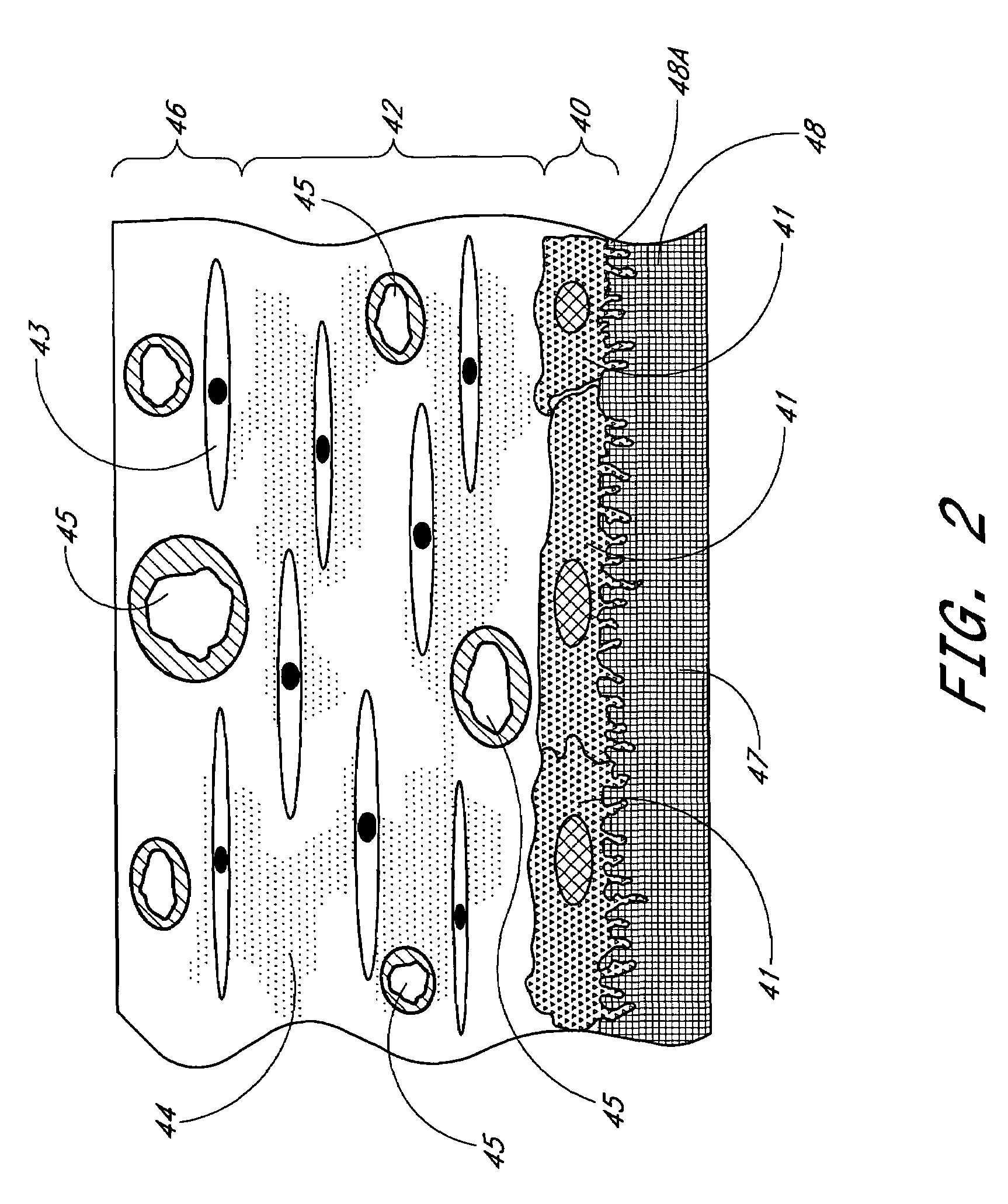
Porous membranes for use with implantable devices
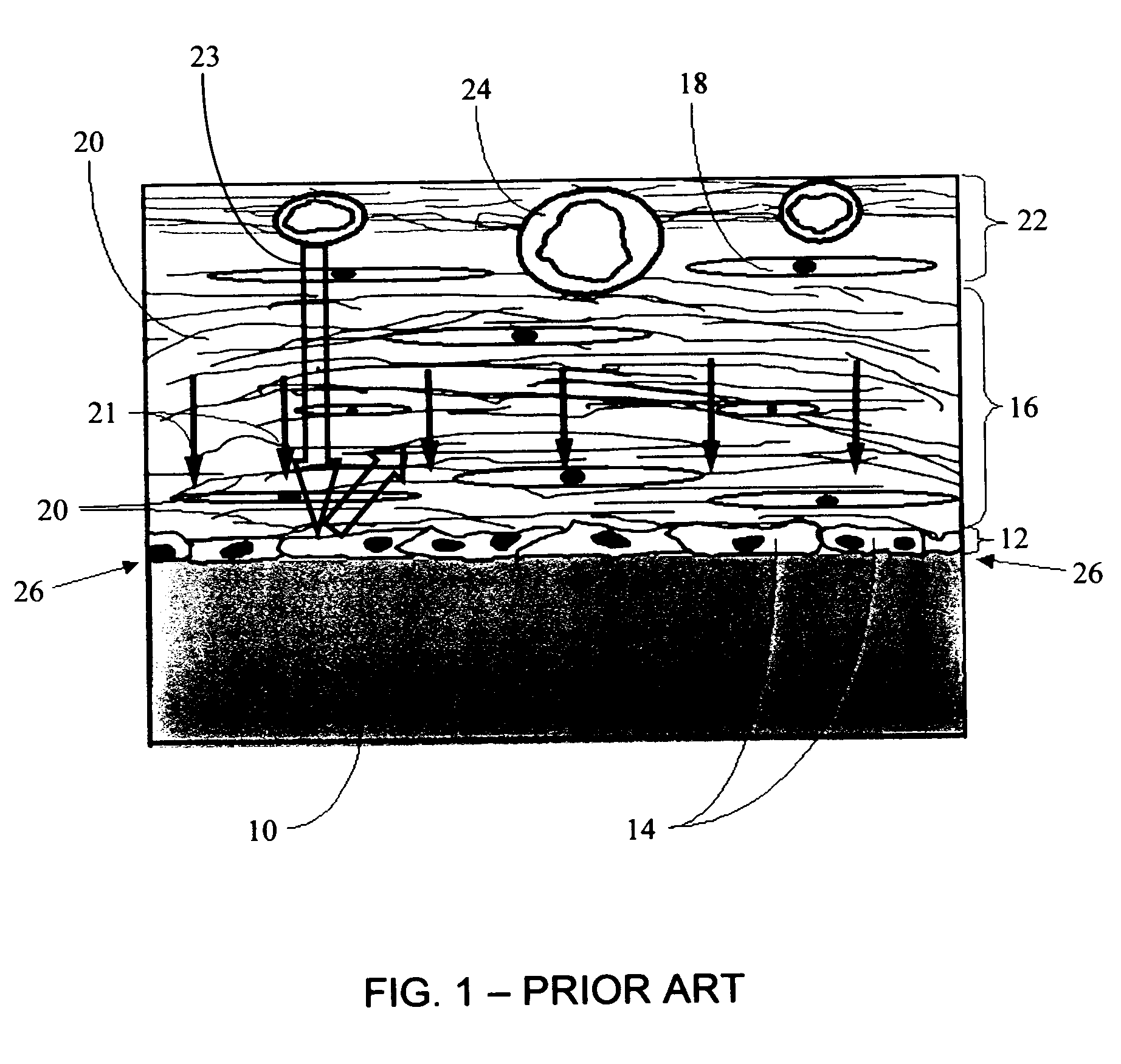
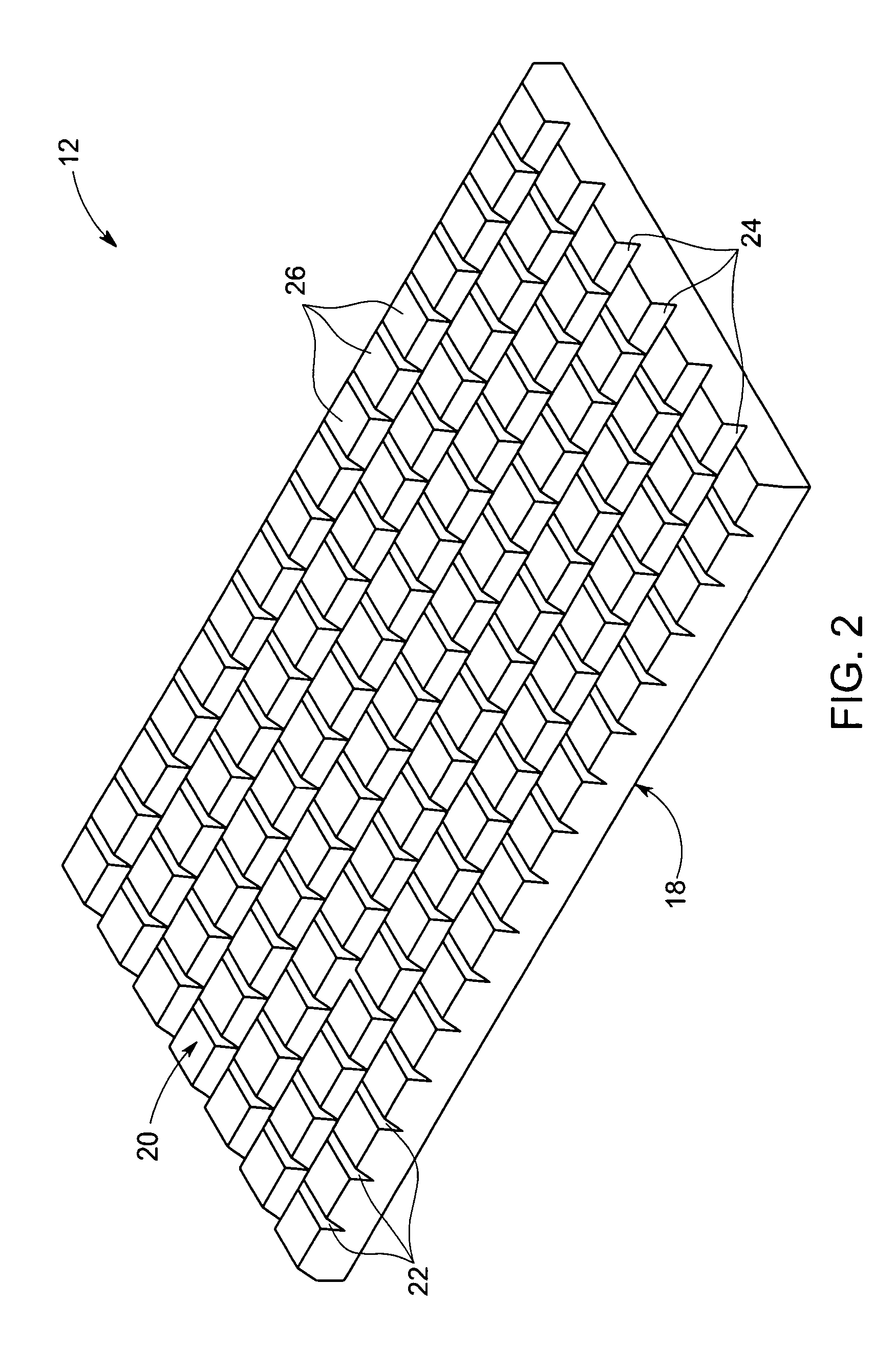
A membrane for implantation in soft tissue comprising a first domain that supports tissue ingrowth, disrupts contractile forces typically found in a foreign body response, encourages vascularity, and interferes with barrier cell layer formation, and a second domain that is resistant to cellular attachment, is impermeable to cells and cell processes, and allows the passage of analytes. The membrane allows for long-term analyte transport in vivo and is suitable for use as a biointerface for implantable analyte sensors, cell transplantation devices, drug delivery devices, and / or electrical signal delivering or measuring devices. The membrane architecture, including cavity size, depth, and interconnectivity, provide long-term robust functionality of the membrane in vivo.
Owner:DEXCOM INC
Analyte measuring device
InactiveUS20050033132A1Additive manufacturing apparatusMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalyteCell layer
An implantable analyte-measuring device including a membrane adapted to promote vascularization and / or interfere with barrier cell layer formation. The membrane includes any combination of materials, architecture, and bioactive agents that facilitate analyte transport to provide long-term in vivo performance of the implantable analyte-measuring device.
Owner:DEXCOM
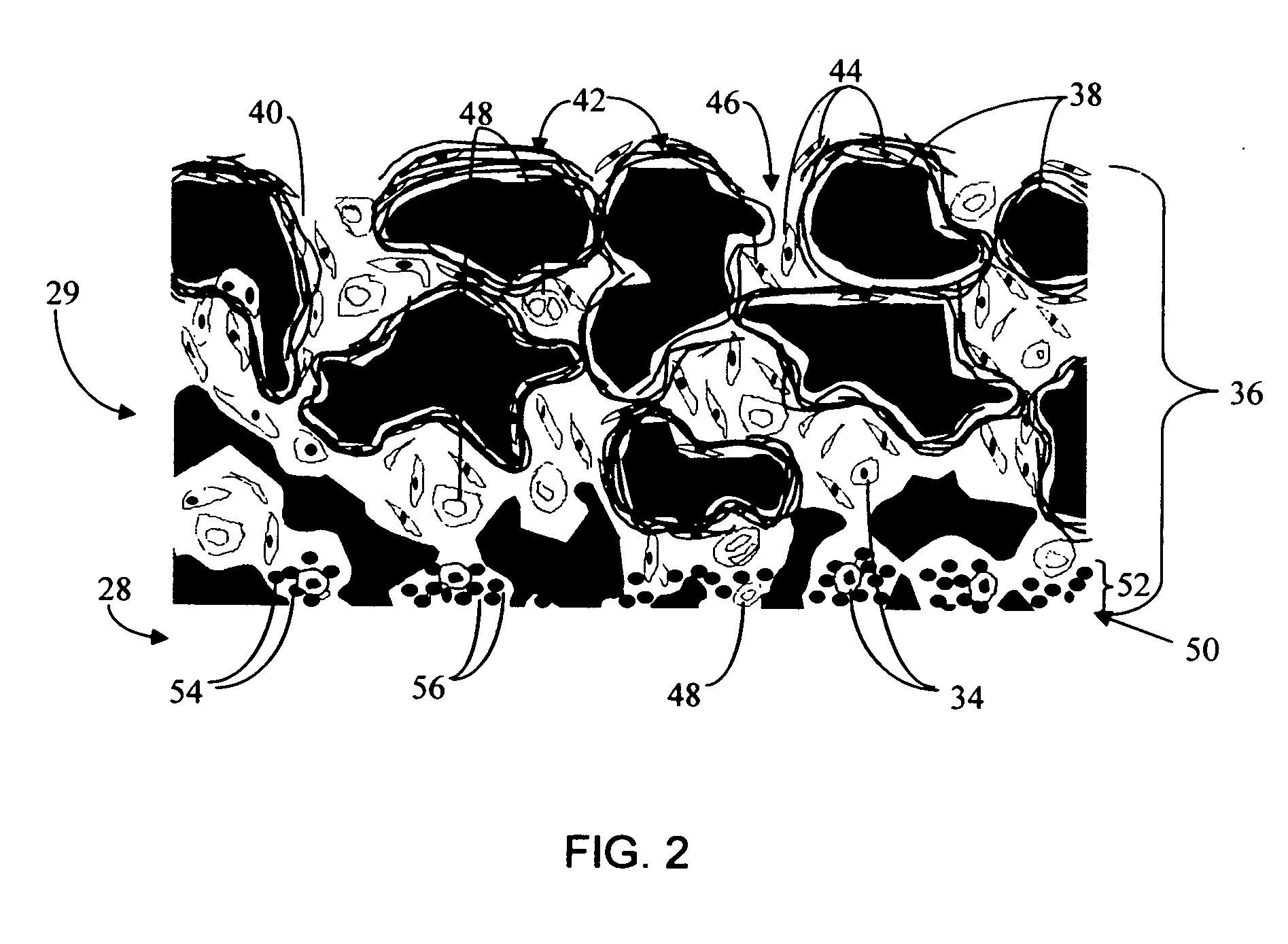
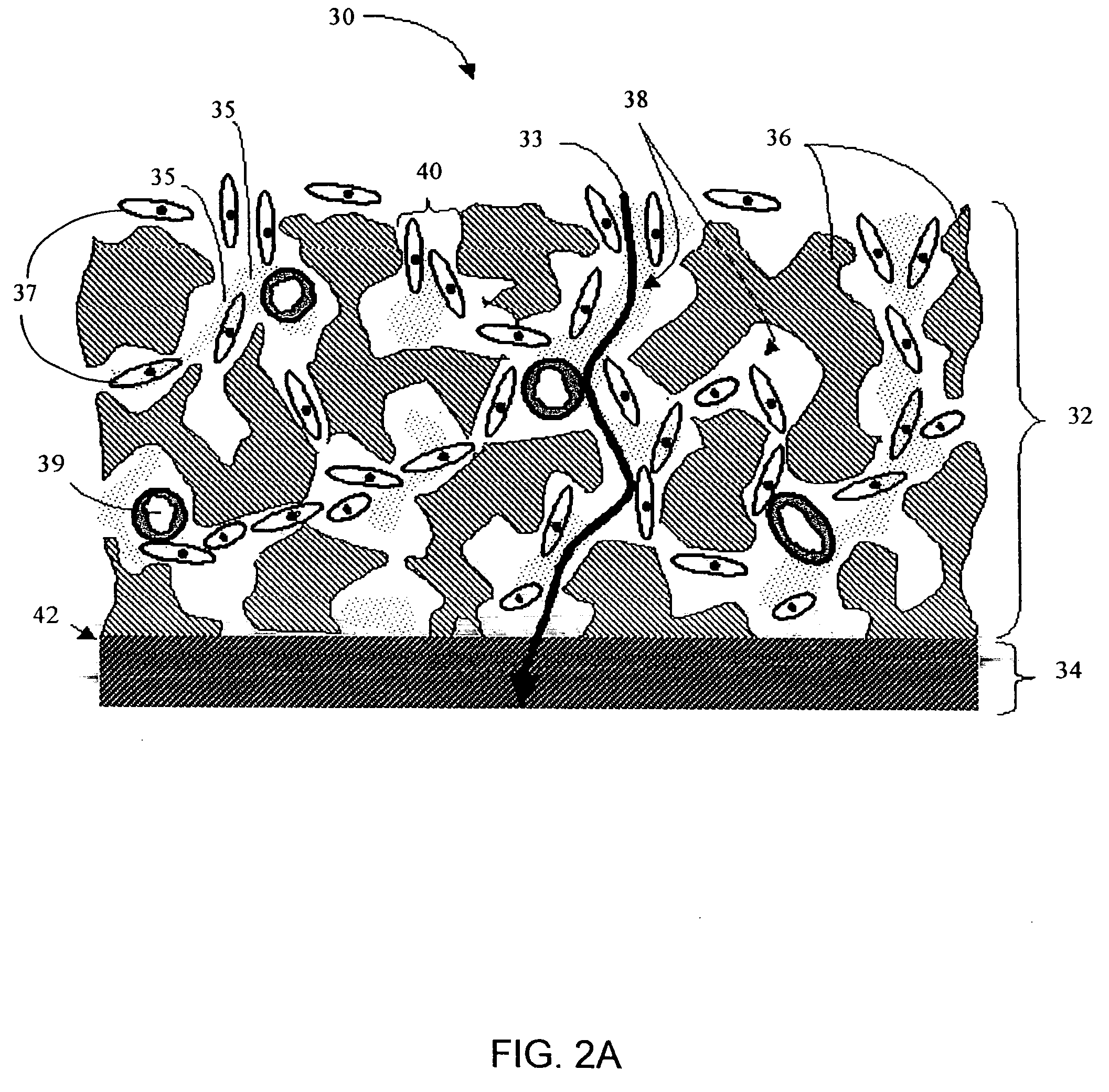
Biointerface membrane with macro-and micro-architecture
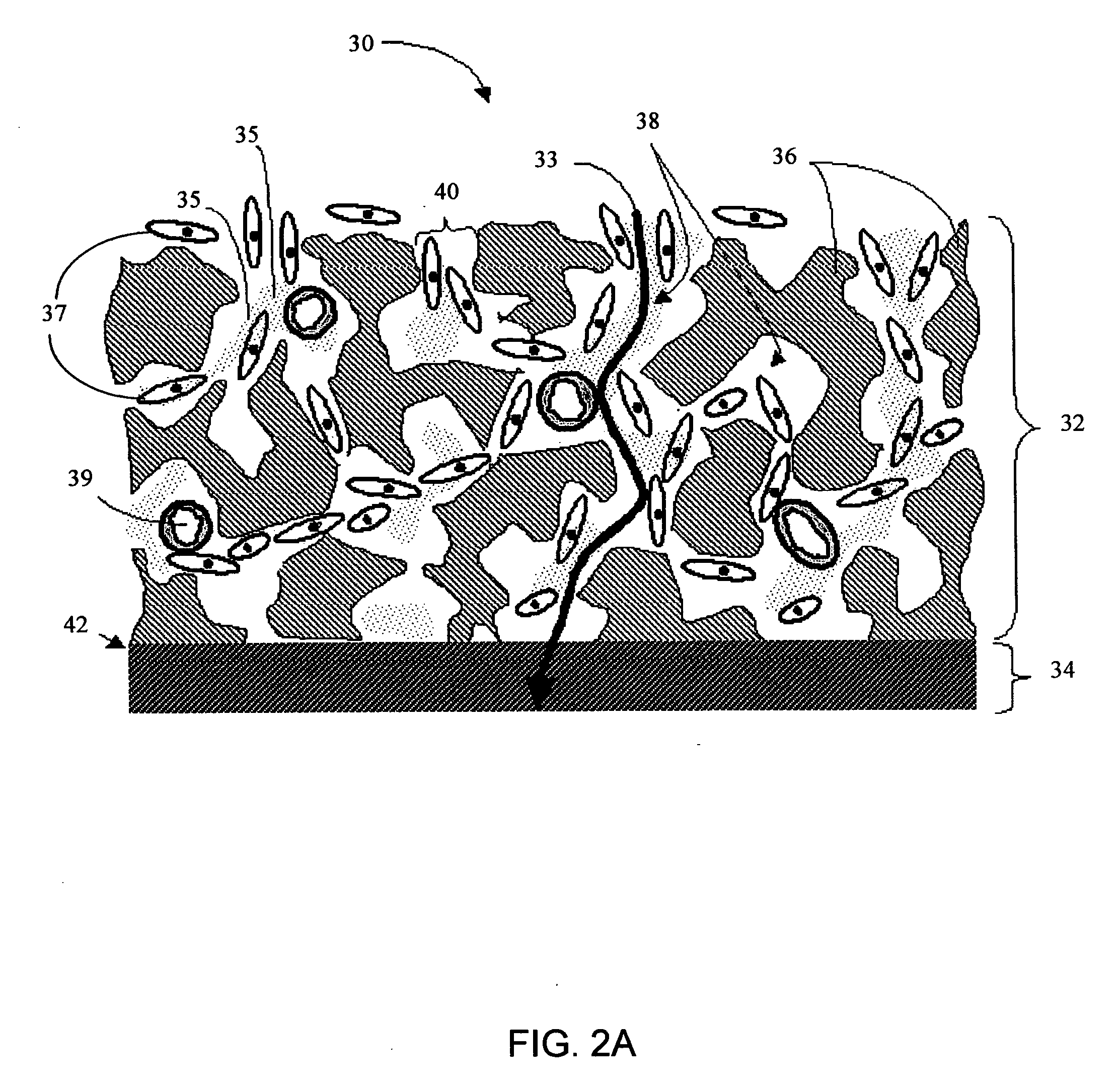
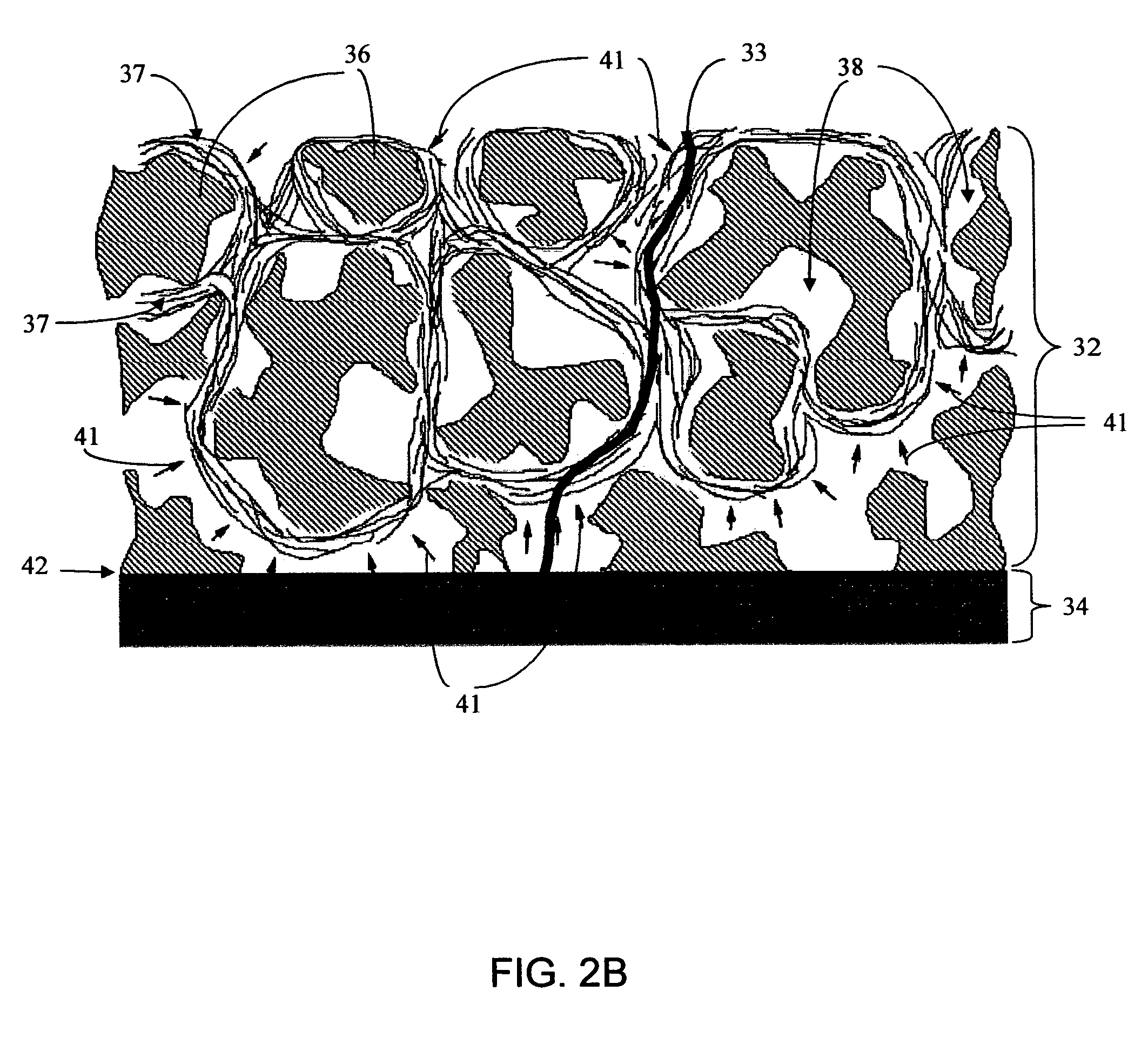
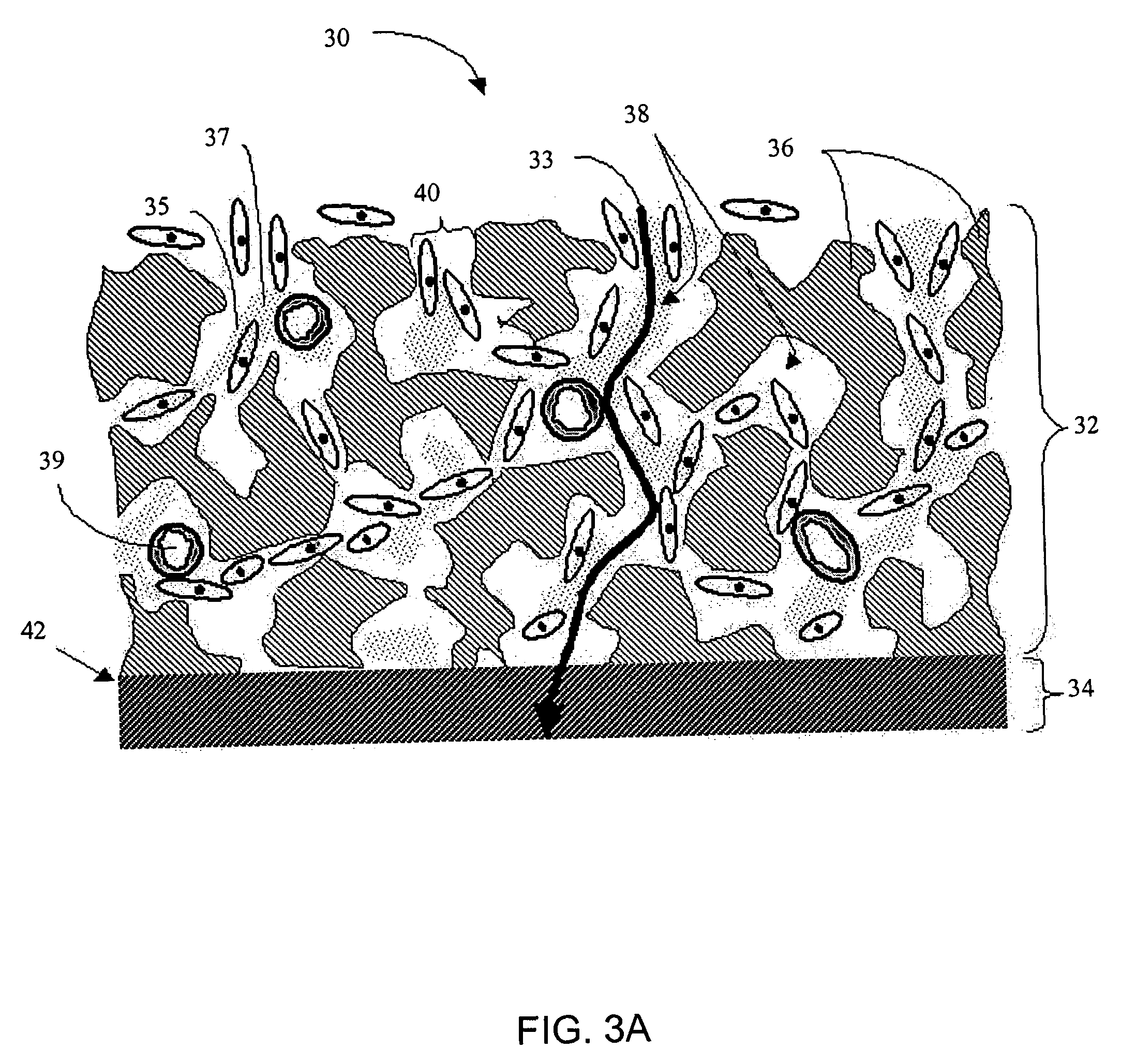
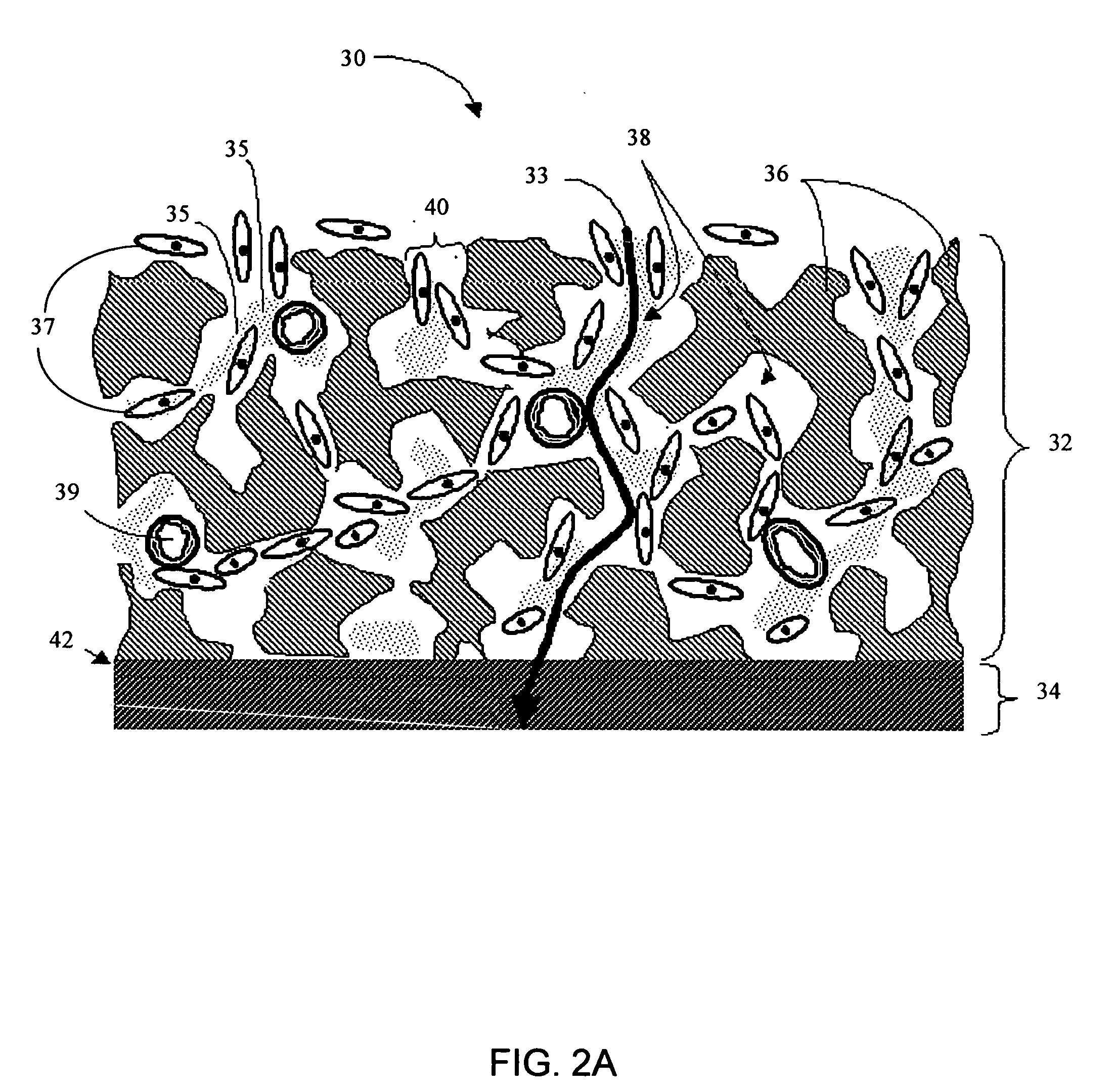
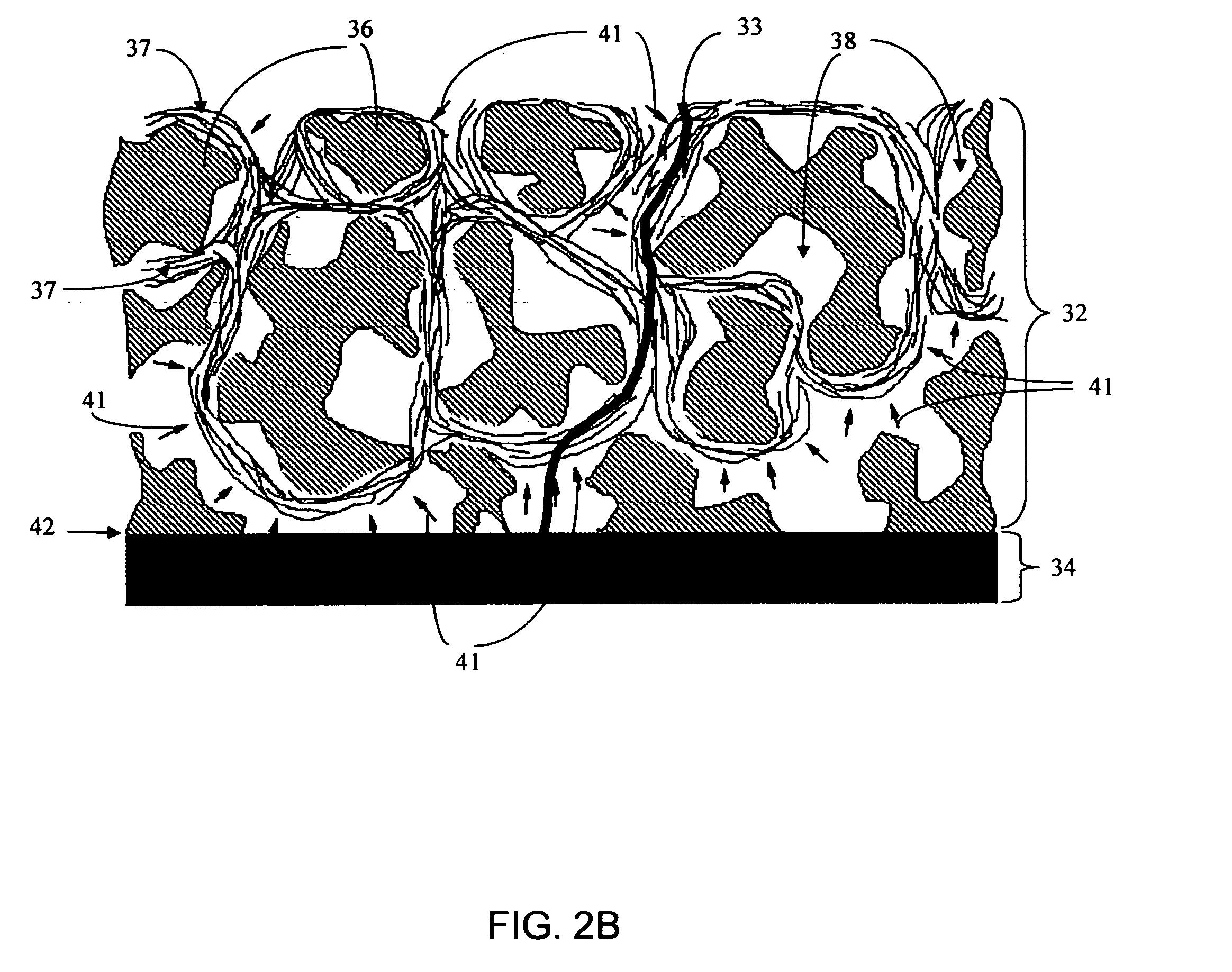
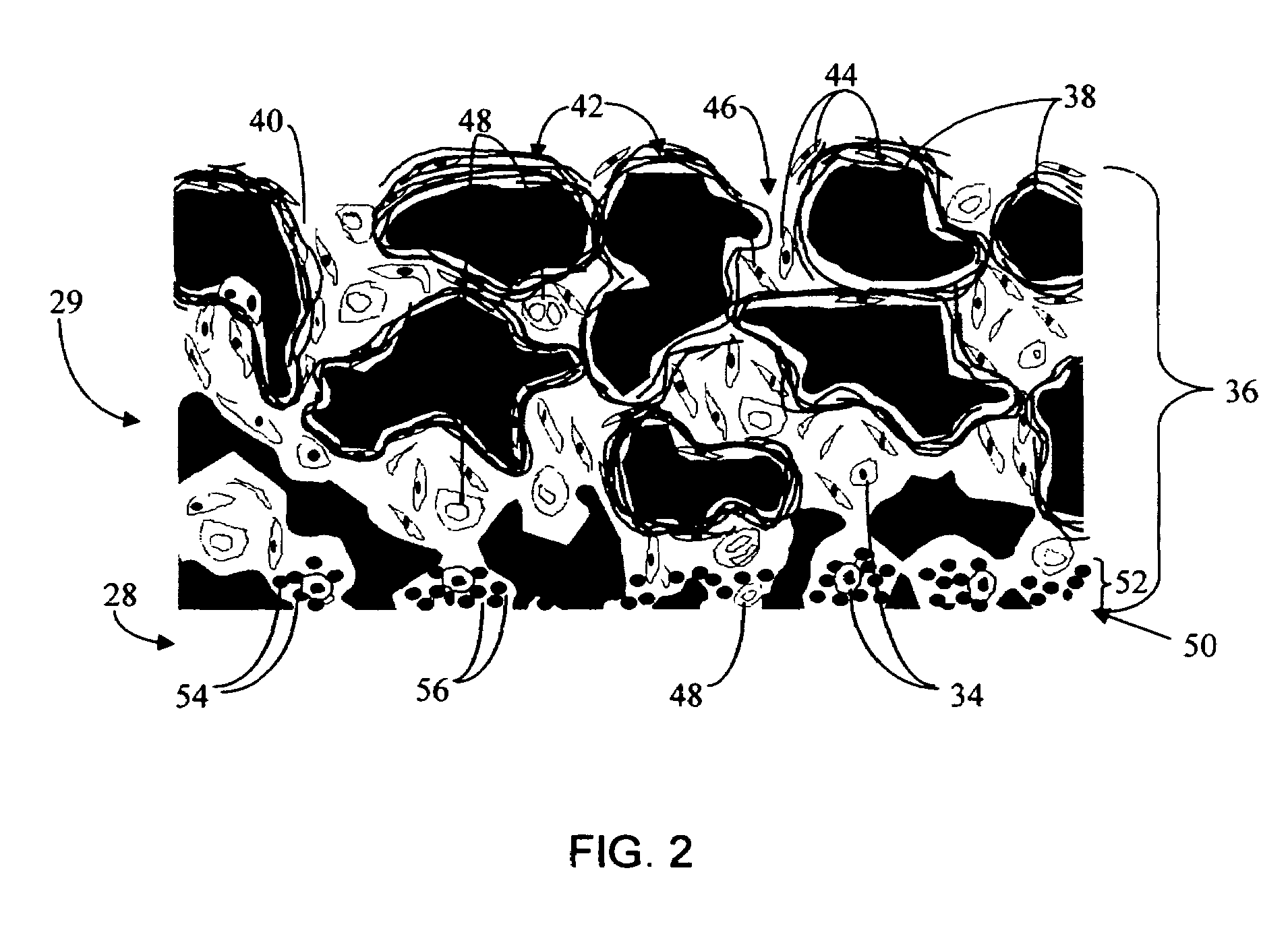
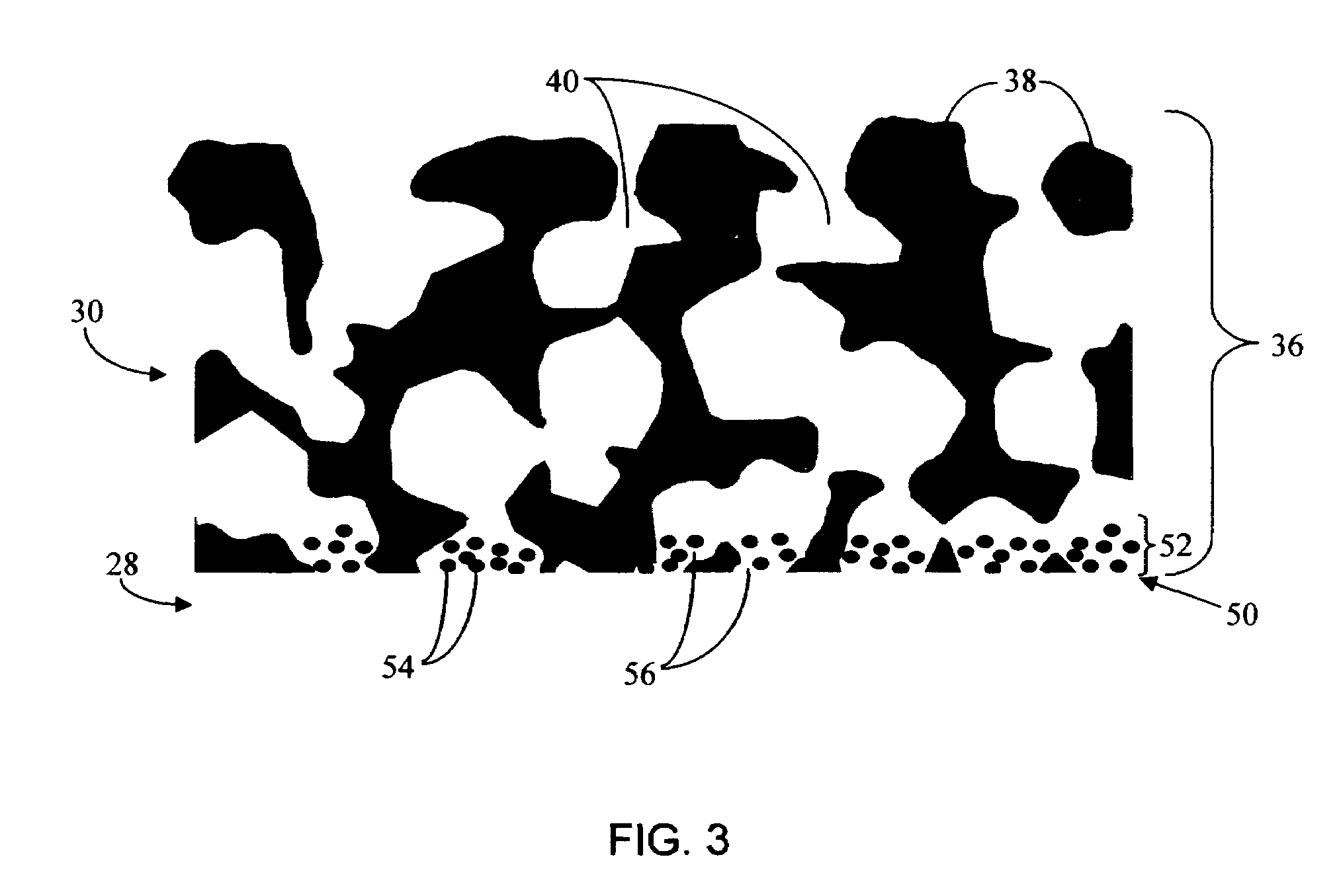
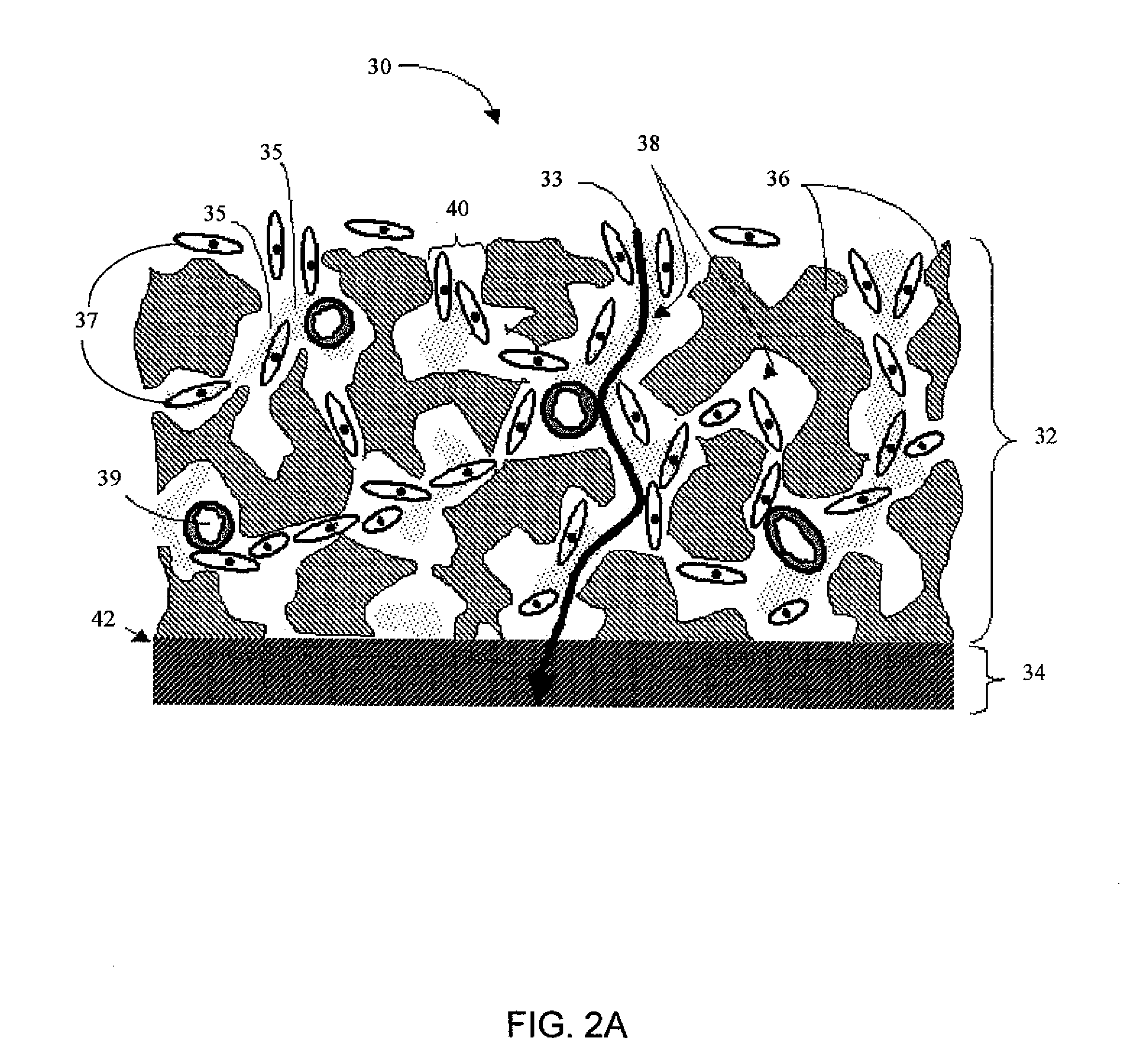
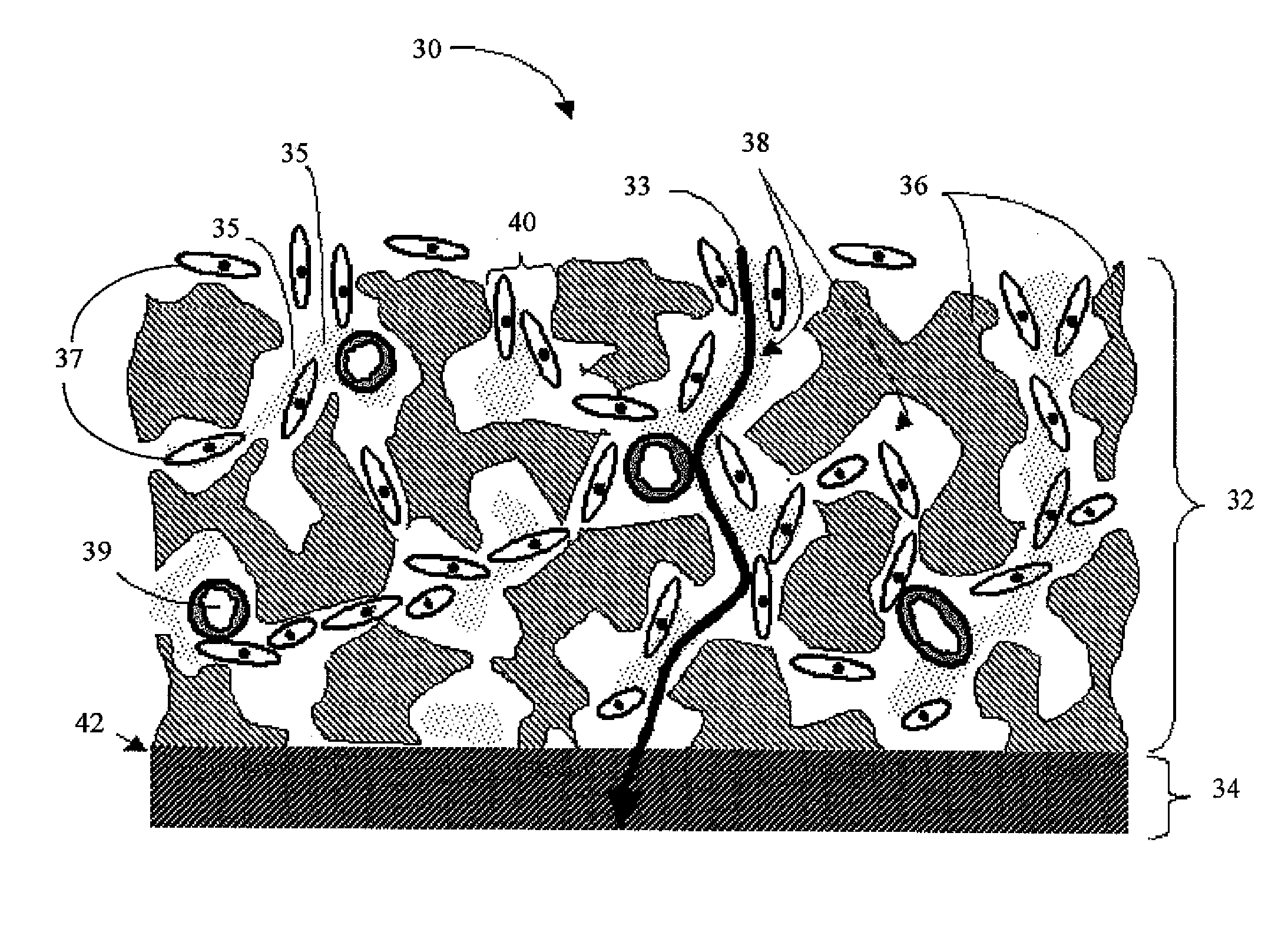
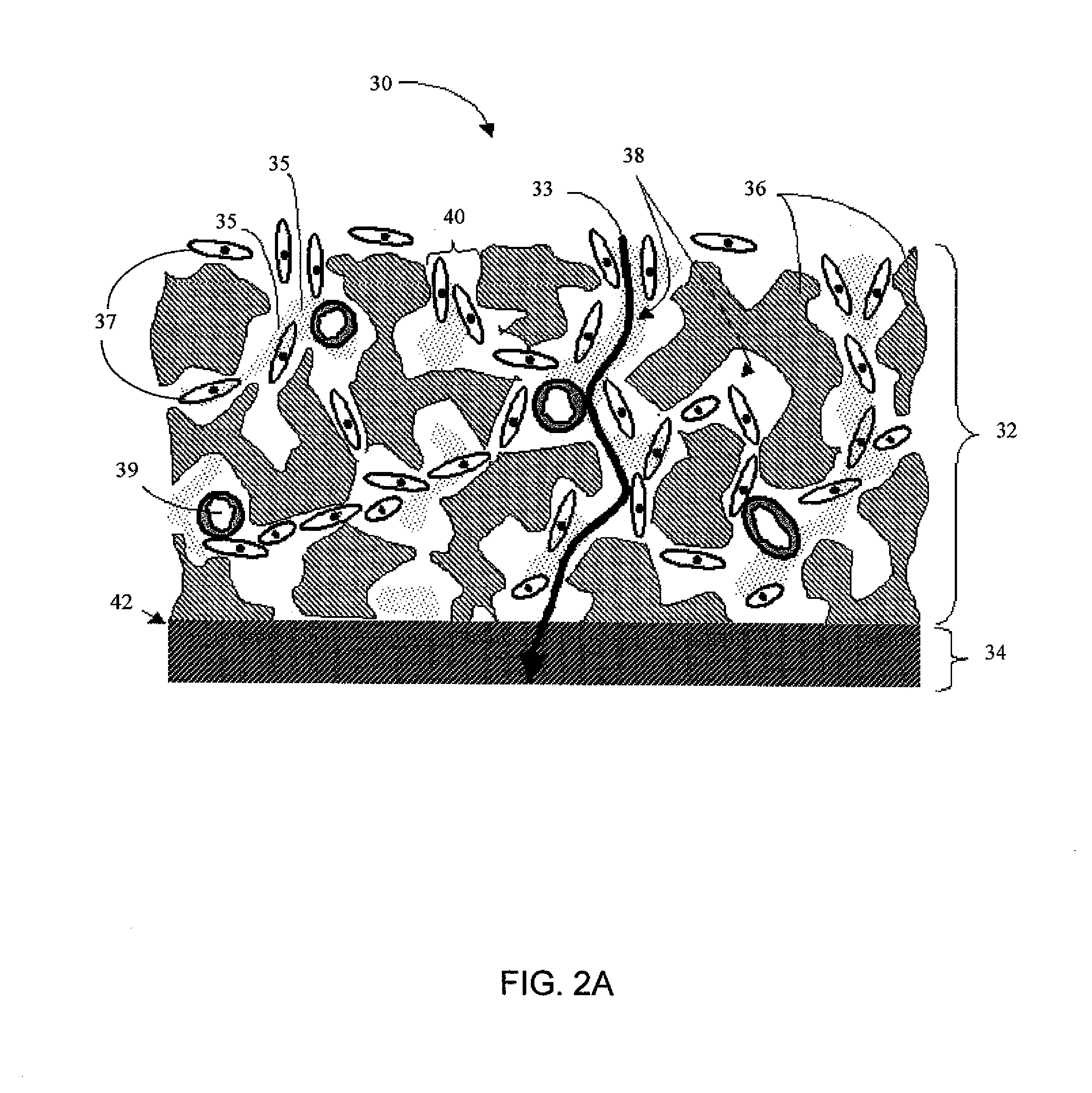
Disclosed herein are biointerface membranes including a macro-architecture and a micro-architecture co-continuous with and bonded to and / or located within at least a portion of the macro-architecture. The macro- and micro-architectures work together to manage and manipulate the high-level tissue organization and the low-level cellular organization of the foreign body response in vivo, thereby increasing neovascularization close to a device-tissue interface, interfering with barrier cell layer formation, and providing good tissue anchoring, while reducing the effects of motion artifact, and disrupting the organization and / or contracture of the FBC. The biointerface membranes of the preferred embodiments can be utilized with implantable devices such as devices for the detection of analyte concentrations in a biological sample (for example, from a body), cell transplantation devices, drug delivery devices, electrical signal delivering or measuring devices, and / or combinations thereof.
Owner:DEXCOM
Membrane for use with implantable devices
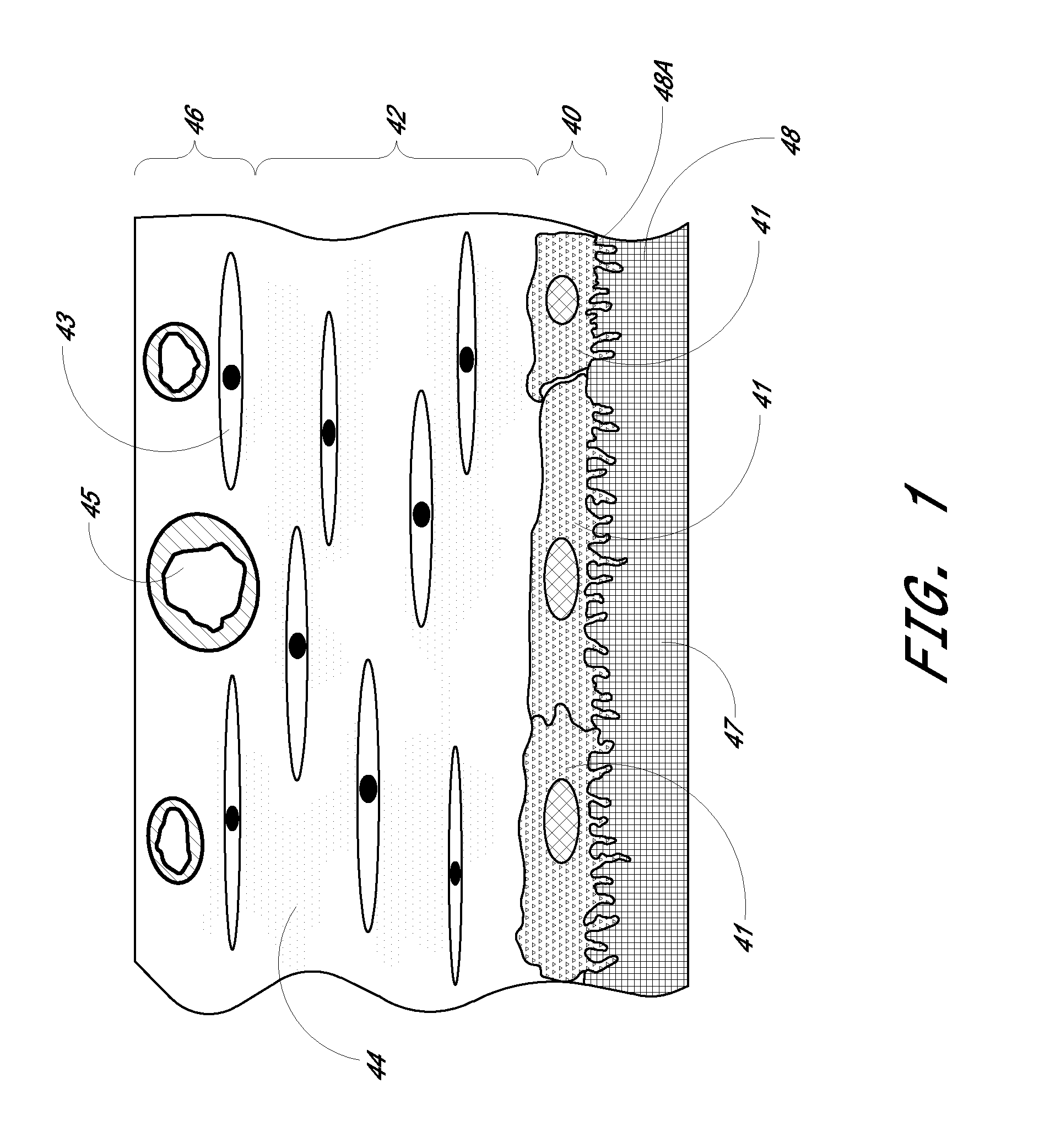
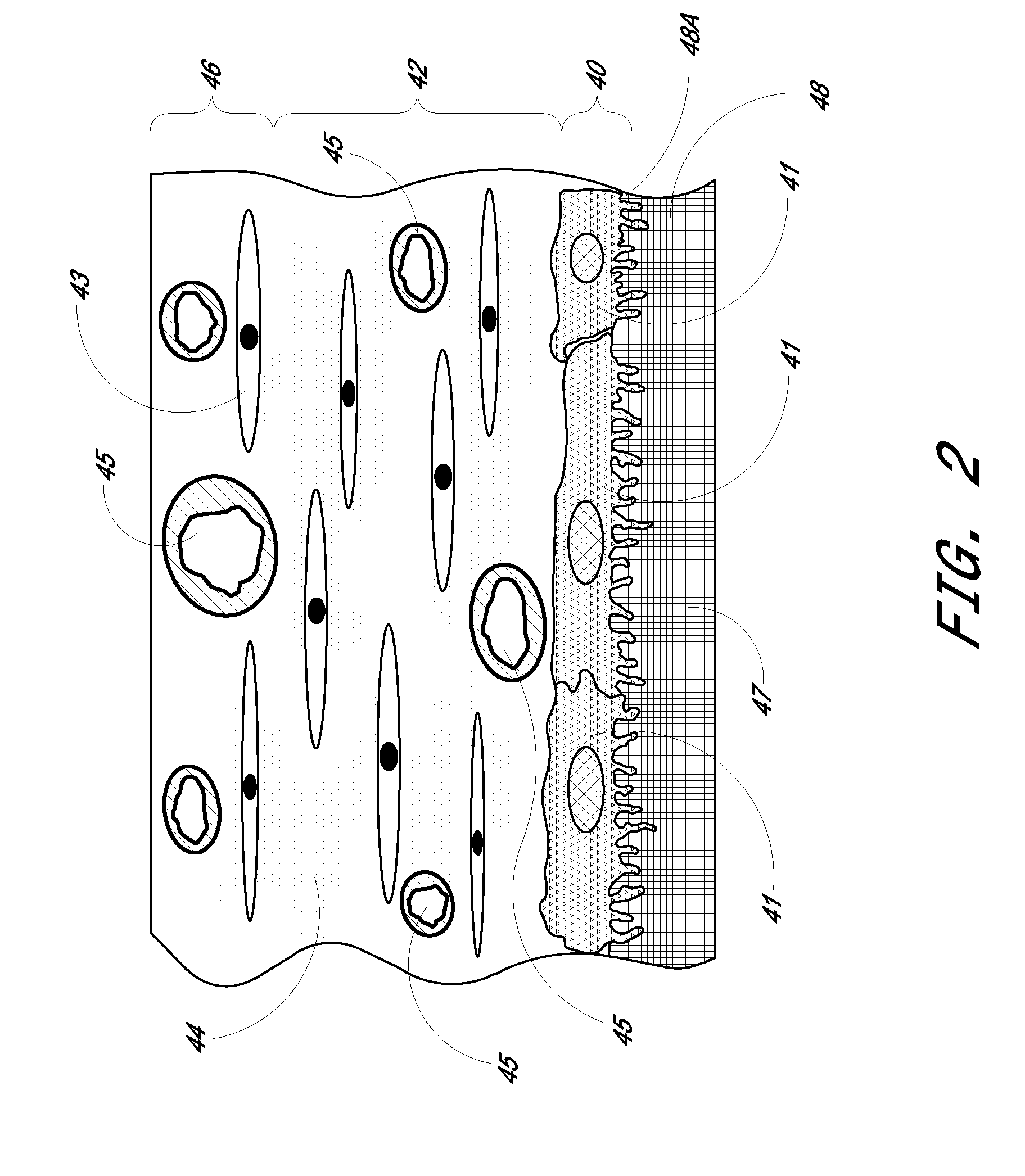
The present invention provides a biointerface membrane for use with an implantable device that interferes with the formation of a barrier cell layer including; a first domain distal to the implantable device wherein the first domain supports tissue attachment and interferes with barrier cell layer formation and a second domain proximal to the implantable device wherein the second domain is resistant to cellular attachment and is impermeable to cells. In addition, the present invention provides sensors including the biointerface membrane, implantable devices including these sensors or biointerface membranes, and methods of monitoring glucose levels in a host utilizing the analyte detection implantable device of the invention. Other implantable devices which include the biointerface membrane of the present invention, such as devices for cell transplantation, drug delivery devices, and electrical signal delivery or measuring devices are also provided.
Owner:DEXCOM
Analyte measuring device
InactiveUS20080228054A1Additive manufacturing apparatusMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalyteCell layer
An implantable analyte-measuring device including a membrane adapted to promote vascularization and / or interfere with barrier cell layer formation. The membrane includes any combination of materials, architecture, and bioactive agents that facilitate analyte transport to provide long-term in vivo performance of the implantable analyte-measuring device.
Owner:DEXCOM INC
Analyte measuring device
InactiveUS20080228051A1Additive manufacturing apparatusMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalyteCell layer
An implantable analyte-measuring device including a membrane adapted to promote vascularization and / or interfere with barrier cell layer formation. The membrane includes any combination of materials, architecture, and bioactive agents that facilitate analyte transport to provide long-term in vivo performance of the implantable analyte-measuring device.
Owner:DEXCOM
Membrane for use with implantable devices
ActiveUS20100087724A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteBiointerface
The present invention provides a biointerface membrane for use with an implantable device that interferes with the formation of a barrier cell layer including; a first domain distal to the implantable device wherein the first domain supports tissue attachment and interferes with barrier cell layer formation and a second domain proximal to the implantable device wherein the second domain is resistant to cellular attachment and is impermeable to cells. In addition, the present invention provides sensors including the biointerface membrane, implantable devices including these sensors or biointerface membranes, and methods of monitoring glucose levels in a host utilizing the analyte detection implantable device of the invention. Other implantable devices which include the biointerface membrane of the present invention, such as devices for cell transplantation, drug delivery devices, and electrical signal delivery or measuring devices are also provided.
Owner:DEXCOM INC
Biointerface with macro- and micro-architecture
Owner:DEXCOM INC
Biointerface with macro-and micro-architecture
Disclosed herein are biointerface membranes including a macro-architecture and a micro-architecture co-continuous with and bonded to and / or located within at least a portion of the macro-architecture. The macro- and micro-architectures work together to manage and manipulate the high-level tissue organization and the low-level cellular organization of the foreign body response in vivo, thereby increasing neovascularization close to a device-tissue interface, interfering with barrier cell layer formation, and providing good tissue anchoring, while reducing the effects of motion artifact, and disrupting the organization and / or contracture of the FBC. The biointerface membranes of the preferred embodiments can be utilized with implantable devices such as devices for the detection of analyte concentrations in a biological sample (for example, from a body), cell transplantation devices, drug delivery devices, electrical signal delivering or measuring devices, and / or combinations thereof.
Owner:DEXCOM
Biointerface membranes incorporating bioactive agents
InactiveUS20060198864A1Improve performanceAdditive manufacturing apparatusSurgeryBiointerfaceActive agent
A biointerface membrane for an implantable device including a nonresorbable solid portion with a plurality of interconnected cavities therein adapted to support tissue ingrowth in vivo, and a bioactive agent incorporated into the biointerface membrane and adapted to modify the tissue response is provided. The bioactive agents can be chosen to induce vascularization and / or prevent barrier cell layer formation in vivo, and are advantageous when used with implantable devices wherein solutes are transported across the device-tissue interface.
Owner:DEXCOM INC
Enhanced transport using membrane disruptive agents
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON +1
Enhanced transport using membrane disruptive agents
InactiveUS7737108B1Prevent uptakePrevent clearanceBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsMetaboliteCell layer
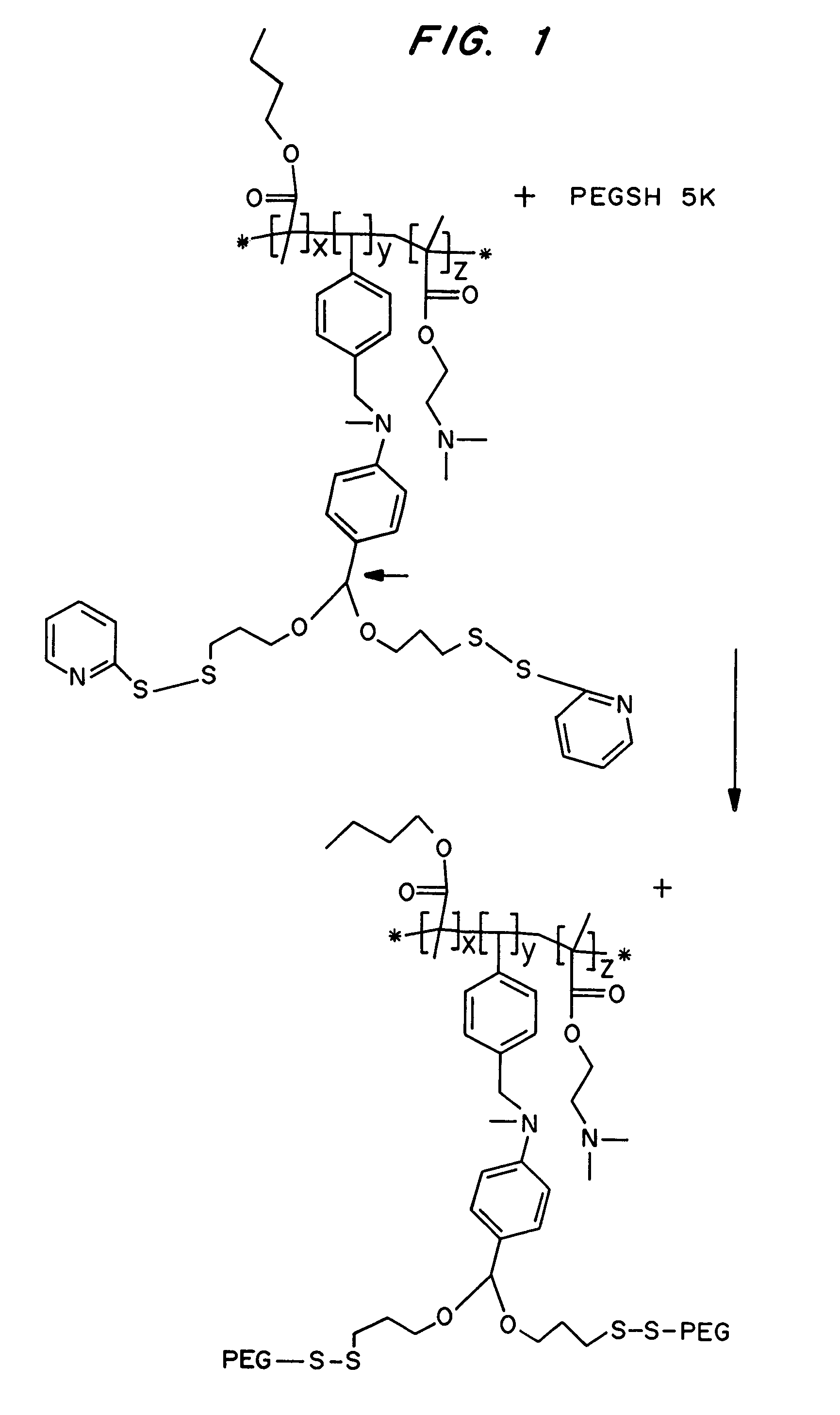
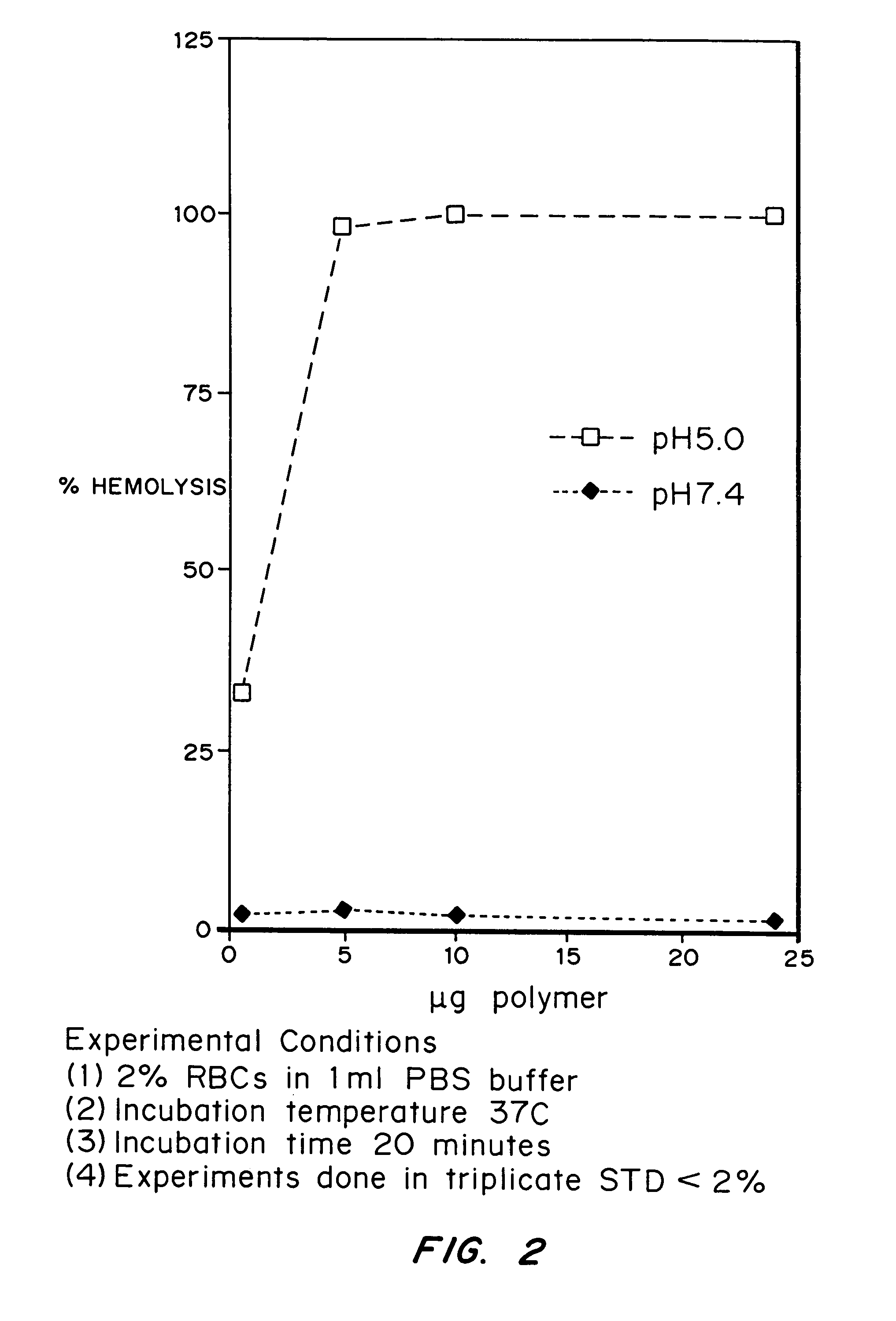
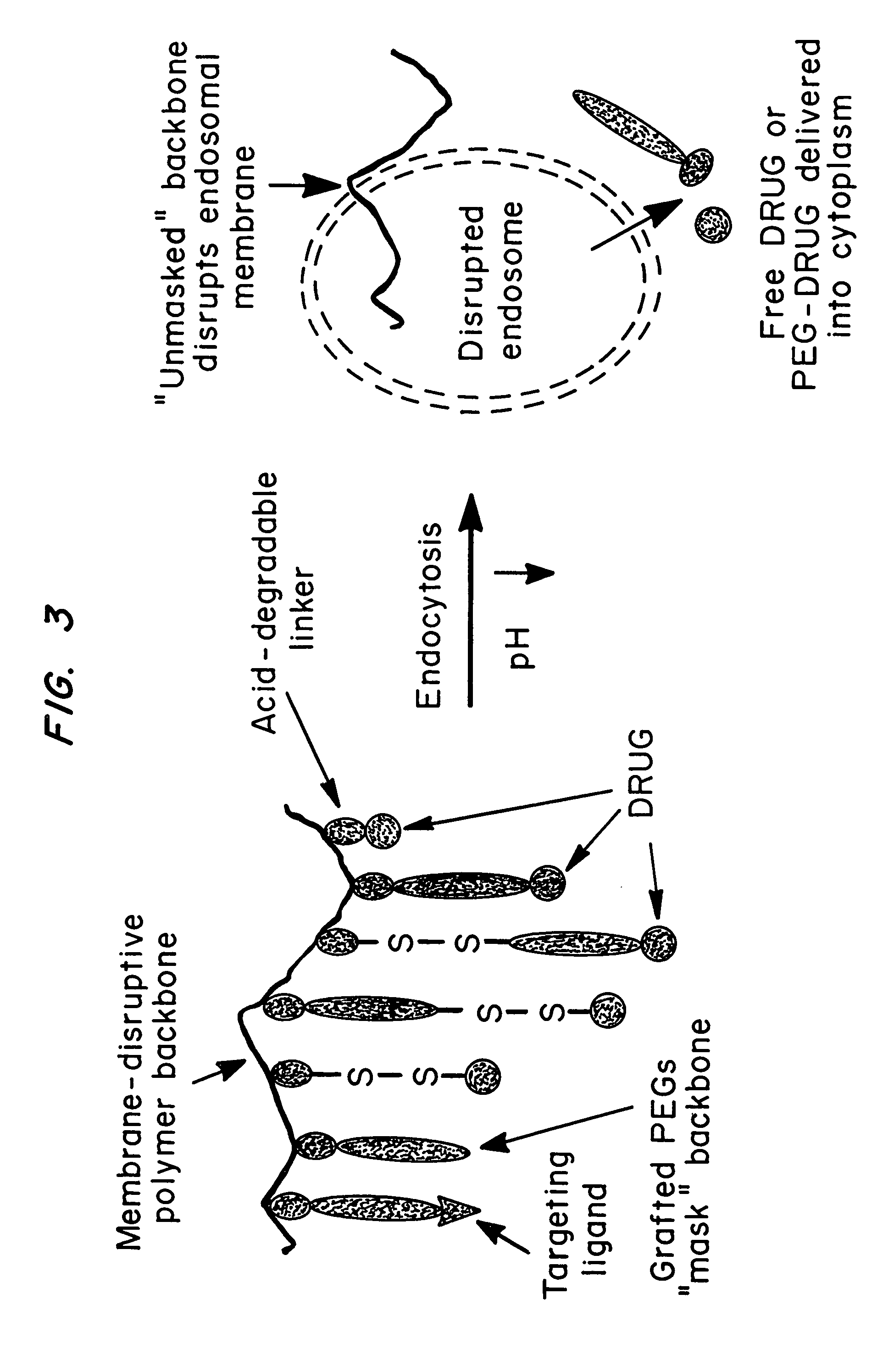
Compositions and methods for transport or release of therapeutic and diagnostic agents or metabolites or other analytes from cells, compartments within cells, or through cell layers or barriers are described. The compositions include a membrane barrier transport enhancing agent and are usually administered in combination with an enhancer and / or exposure to stimuli to effect disruption or altered permeability, transport or release. In a preferred embodiment, the compositions include compounds which disrupt endosomal membranes in response to the low pH in the endosomes but which are relatively inactive toward cell membranes (at physiologic pH, but can become active toward cell membranes if the environment is acidified below ca. pH 6.8), coupled directly or indirectly to a therapeutic or diagnostic agent. Other disruptive agents can also be used, responsive to stimuli and / or enhancers other than pH, such as light, electrical stimuli, electromagnetic stimuli, ultrasound, temperature, or combinations thereof. The compounds can be coupled by ionic, covalent or H bonds to an agent to be delivered or to a ligand which forms a complex with the agent to be delivered. Agents to be delivered can be therapeutic and / or diagnostic agents. Treatments which enhance delivery such as ultrasound, iontopheresis, and / or electrophereis can also be used with the disrupting agents.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
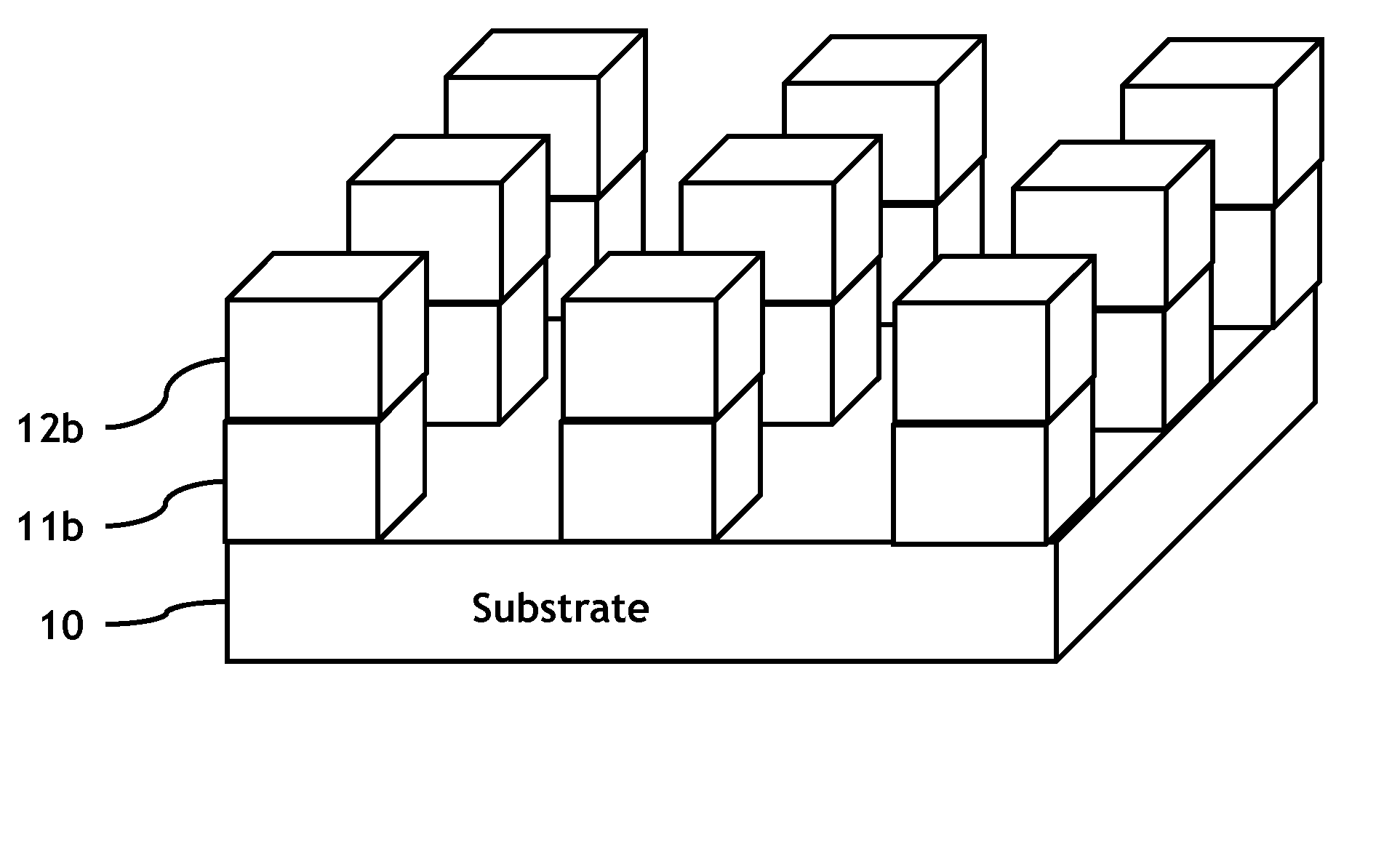
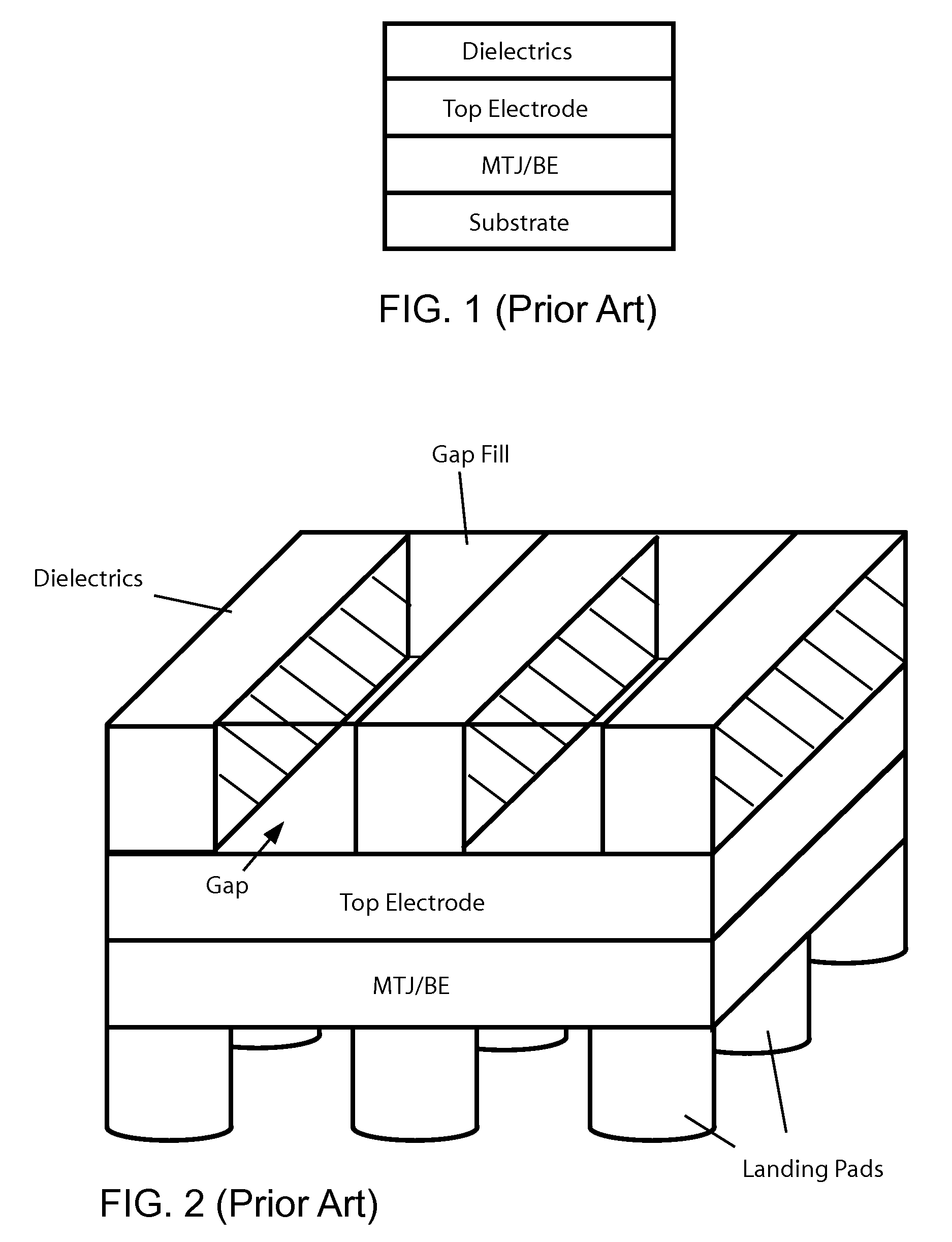
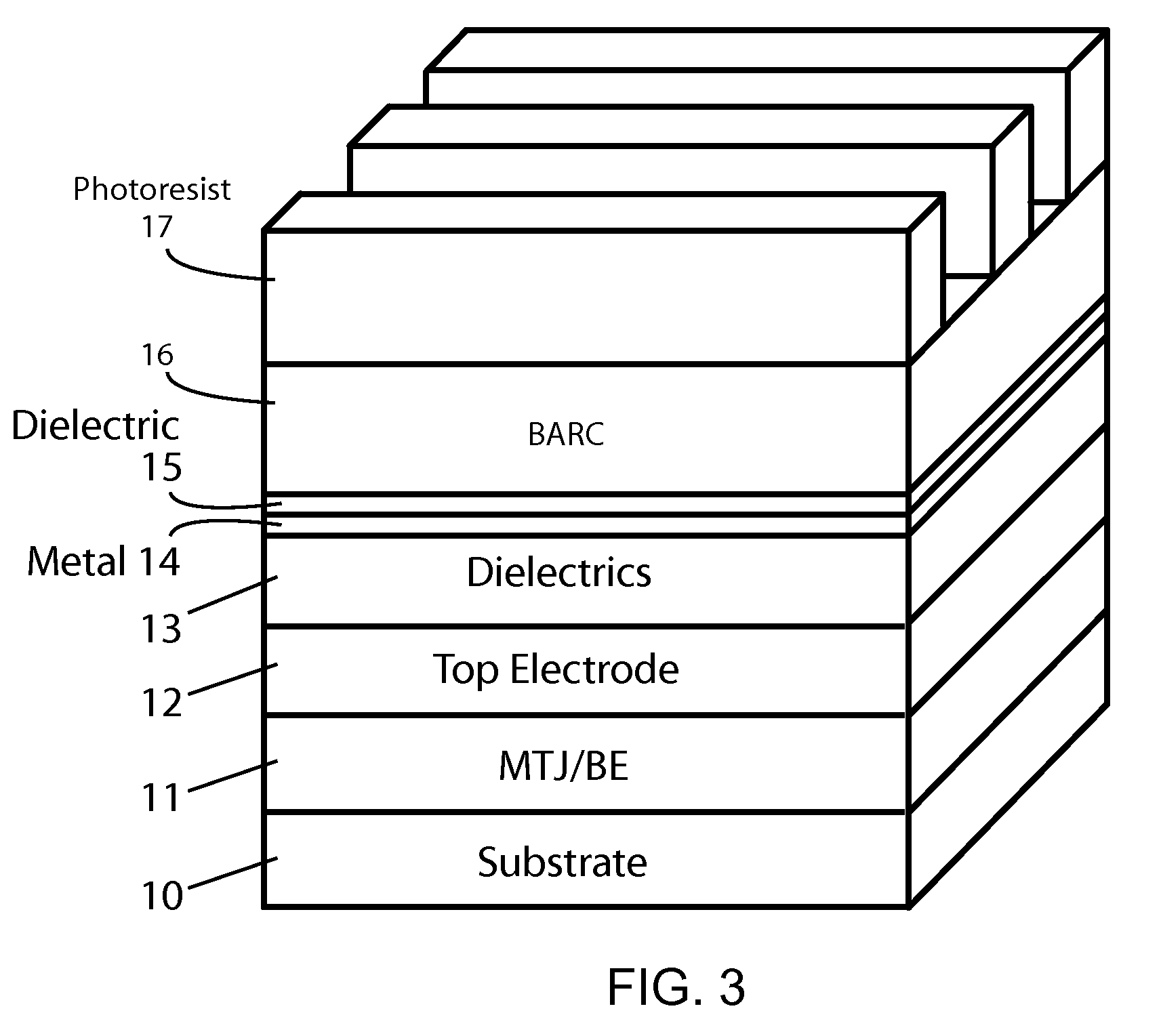
Method for manufacturing high density non-volatile magnetic memory
ActiveUS20130244344A1Reduce programming currentReduced dimensionNanomagnetismNanoinformaticsFeature DimensionLithographic artist
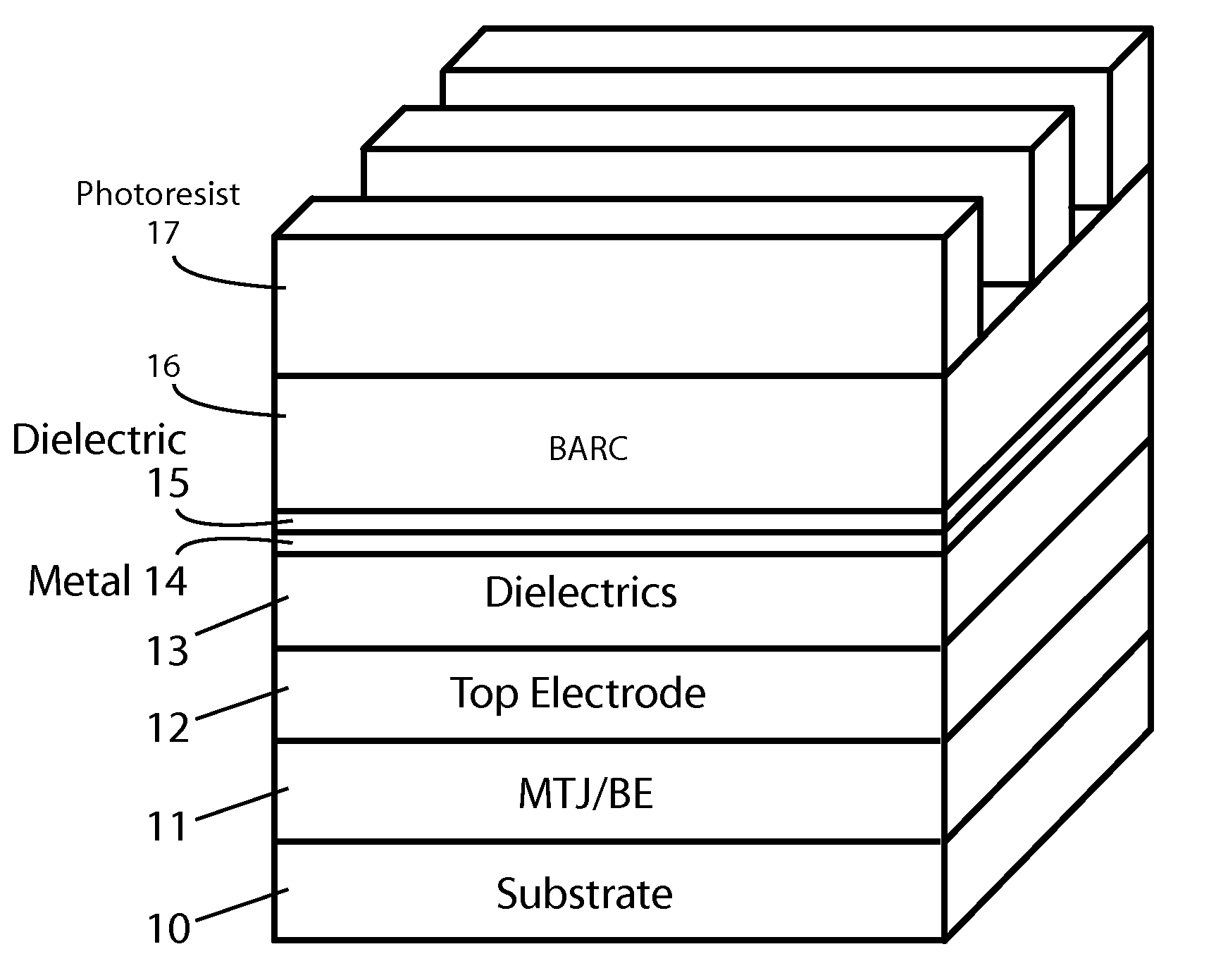
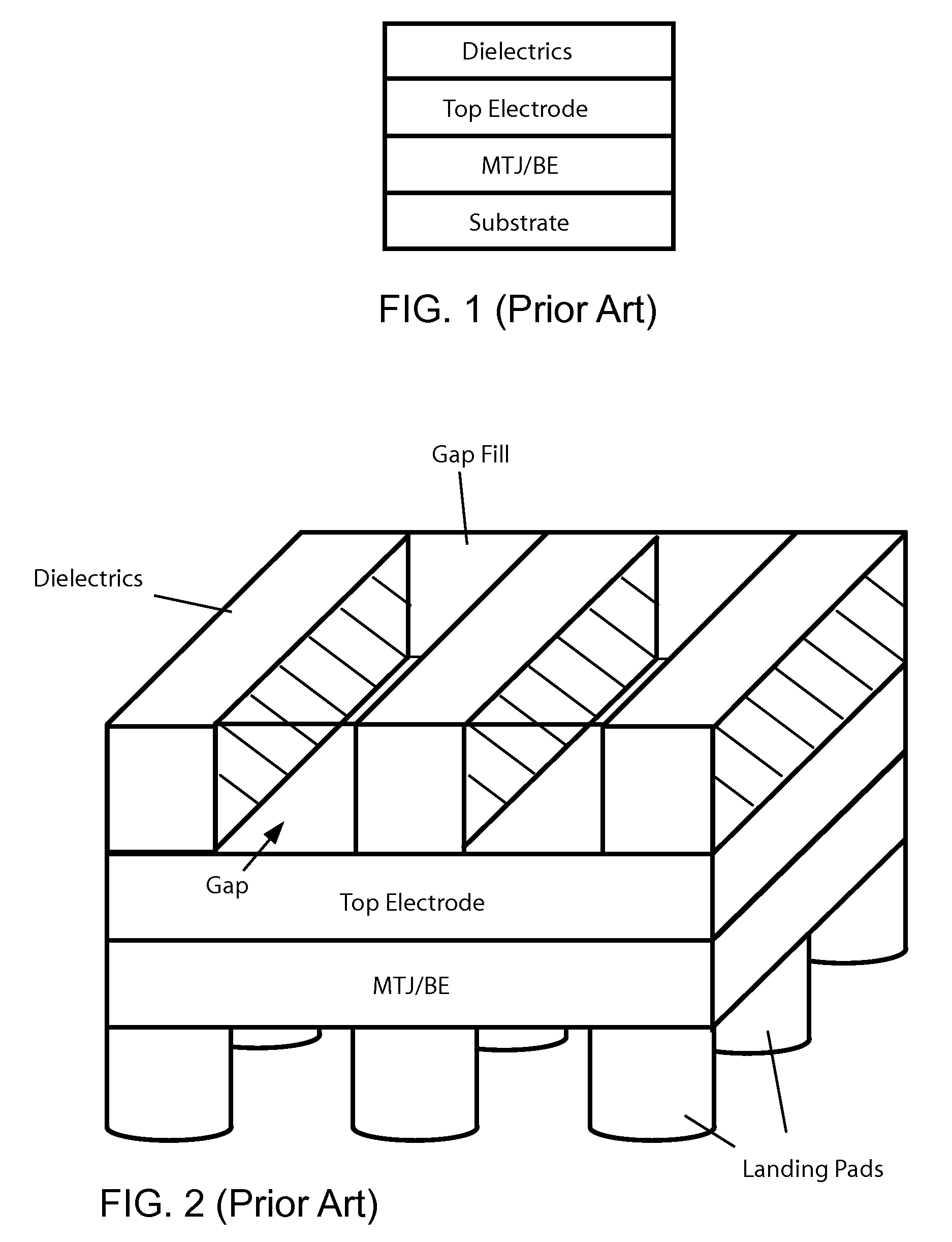
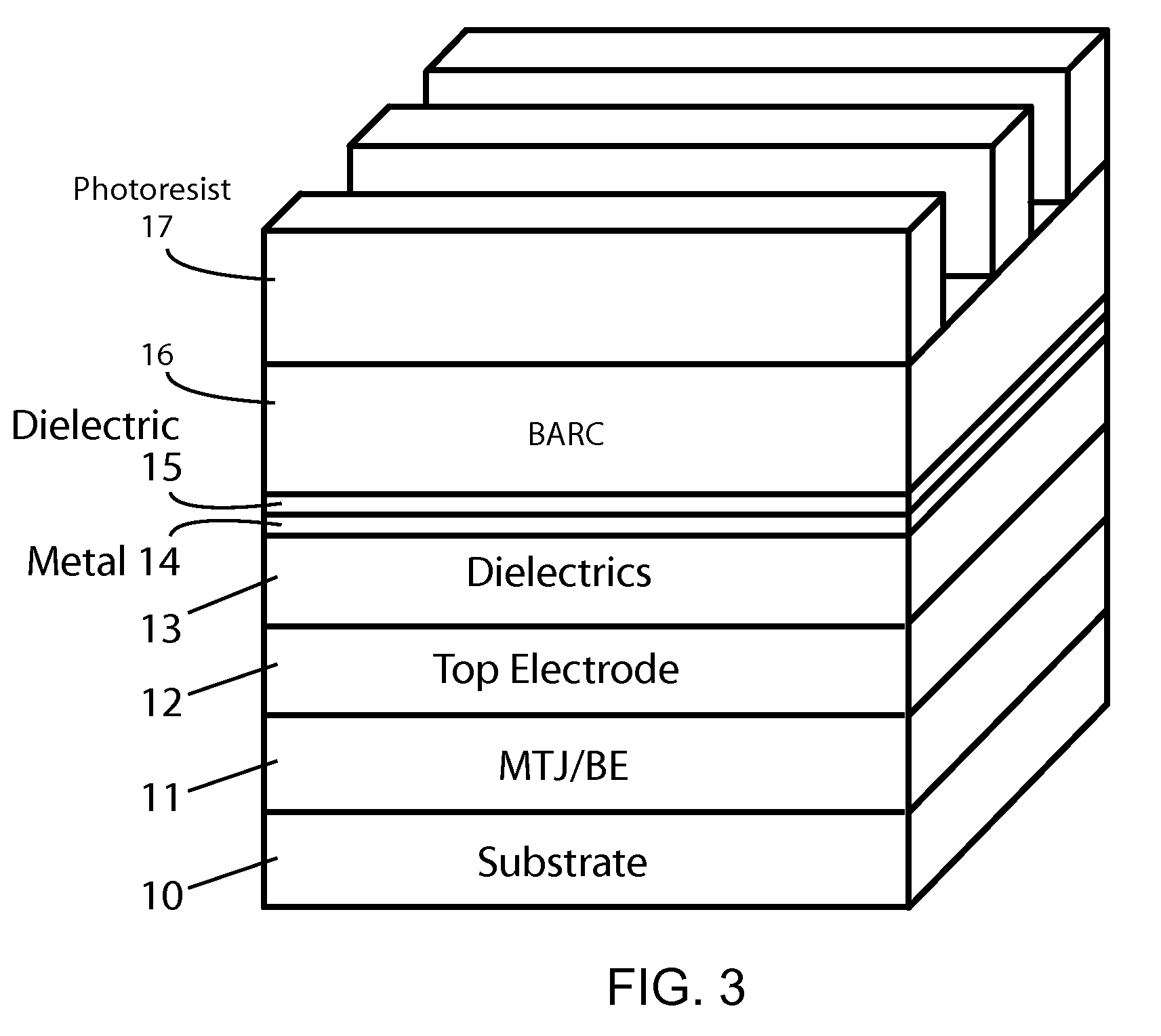
Methods of fabricating MTJ arrays using two orthogonal line patterning steps are described. Embodiments are described that use a self-aligned double patterning method for one or both orthogonal line patterning steps to achieve dense arrays of MTJs with feature dimensions one half of the minimum photo lithography feature size (F). In one set of embodiments, the materials and thicknesses of the stack of layers that provide the masking function are selected so that after the initial set of mask pads have been patterned, a sequence of etching steps progressively transfers the mask pad shape through the multiple mask layer and down through all of the MTJ cell layers to the form the complete MTJ pillars. In another set of embodiments, the MTJ / BE stack is patterned into parallel lines before the top electrode layer is deposited.
Owner:AVALANCHE TECH
Photovoltaic concentrator for solar energy system
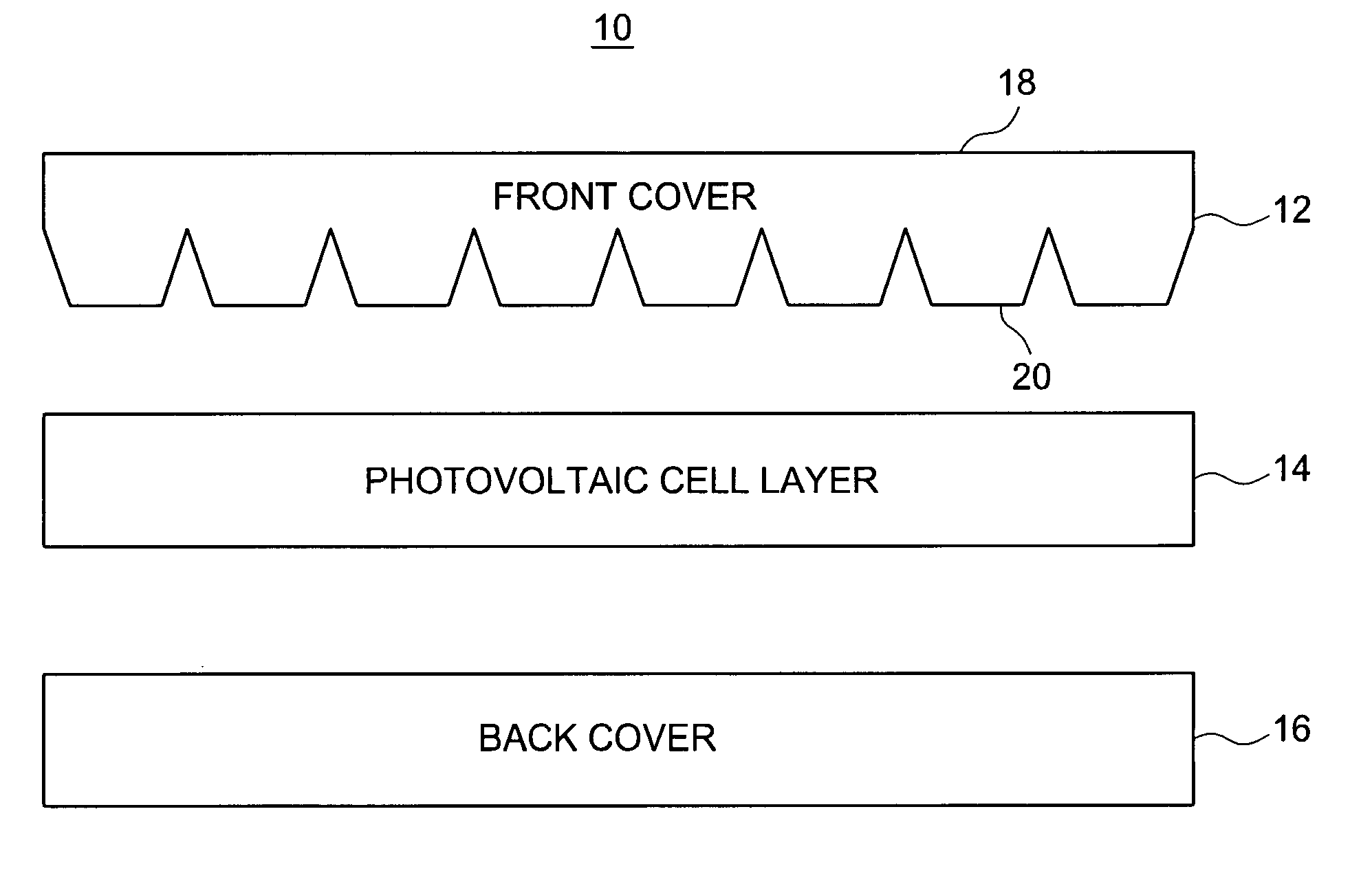
The energy conversion system includes a first optical cover having a flat surface and a patterned surface. The patterned surface is configured to receive solar energy from the flat surface, then concentrate and guide the solar energy. The system also includes a second optical cover. The system further includes providing a photovoltaic cell layer between the patterned surface of the first optical cover and the second optical cover. The photovoltaic cell layer is configured to receive the solar energy from the patterned surface and convert the solar energy into electrical energy.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Side population cells originated from human amnion and their uses
InactiveUS20050089513A1Stable supplyUseful in therapyBiocideGenetic material ingredientsDiseaseSide population
Cells which may be differentiated at least into nerve cells, which are useful for therapies of brain metabolic diseases, are disclosed. The cells are side population cell separated from human amniotic mesenchymal cell layer, in which expressions of Oct-4 gene, Sox-2 gene and Rex-1 gene are observed by RT-PCR, and which are vimentin-positive and CK19-positive in immunocytostaining.
Owner:SAKURAGAWA NORIO +1
Method of preparing cell lysate
InactiveUS7258976B2Simple preparation processStable outputSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementTransfer cellCell layer
The entire process of reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) is simplified by using oligonucleotide-immobilized microplates made of, e.g., polypropylene, to which oligonucleotides are securely immobilized and which can be subjected to thermal cycles of PCR. RT-PCR is preferably conducted in solid-phase. Capturing of mRNA and RT-PCR can be conducted in the same plates. The cDNA synthesized from the mRNA captured on the microplates can be used more than once. Further, in combination with the microplates, a filter plate is used for the preparation of cell lysates wherein target cells are placed on the filter plate, and a lysis buffer is passed through the cell layer on the filter to transfer cell lysate directly to the microplate via well-to-well communication.
Owner:RESONAC CORPORATION +1
Delivery of therapeutic and marking substance through intra lumen expansion of a delivery device
ActiveUS20090187144A1Uniform contact pressureRaise the possibilityStentsBalloon catheterCell layerBalloon catheter
A balloon catheter is formed with a plurality of depressions. The balloon is coated with a matrix incorporating a therapeutic substance, which additionally fills the depressions. When the balloon is expanded within a body lumen, the therapeutic substance may diffuse into the lumen wall, or all or a portion of the coating transfers to the lumen wall. A lattice frame may surround the balloon, applied prior to coating if the coating is to transfer, operative to maintain a more linear balloon profile during inflation, promoting more even transfer pressure. A contrast dye is incorporated into the transferred coating, enabling ready location and inspection of the treated lumen area. Projections may alternately be formed in the balloon surface, operative to urge the coating and therapeutic substance between cells, or past cell layers of the lumen, to the interior of the lumen wall. Prior to transfer, an extended inflation period, possibly including the use of perfusion ports to maintain blood supply, enables a larger initial quantity of therapeutic substance to diffuse into the body lumen, prior to transfer of the coating and withdrawal of the catheter, balloon, and frame.
Owner:JAYARAMAN SWAMINATHAN
Drug delivery systems using fc fragments
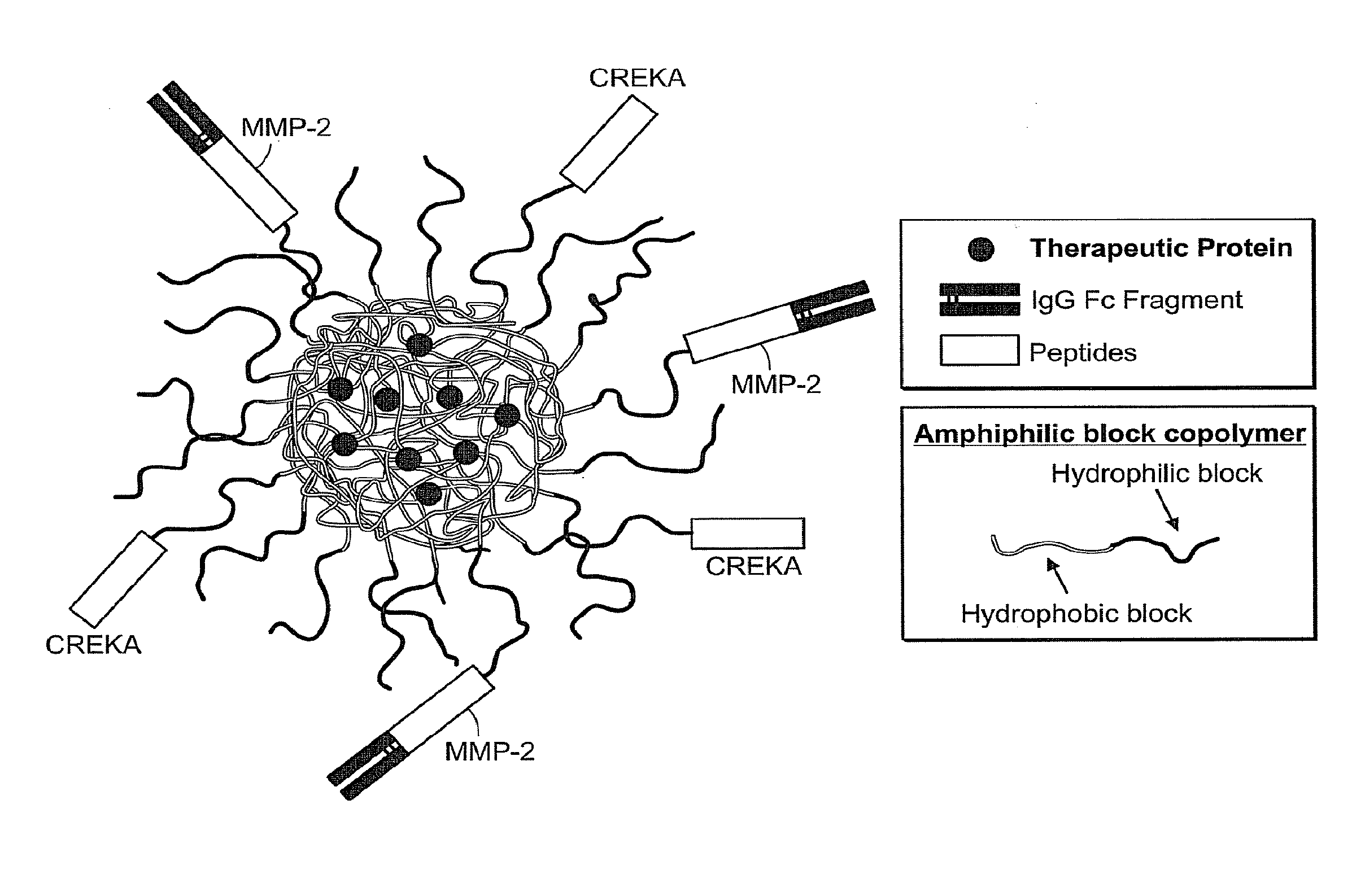
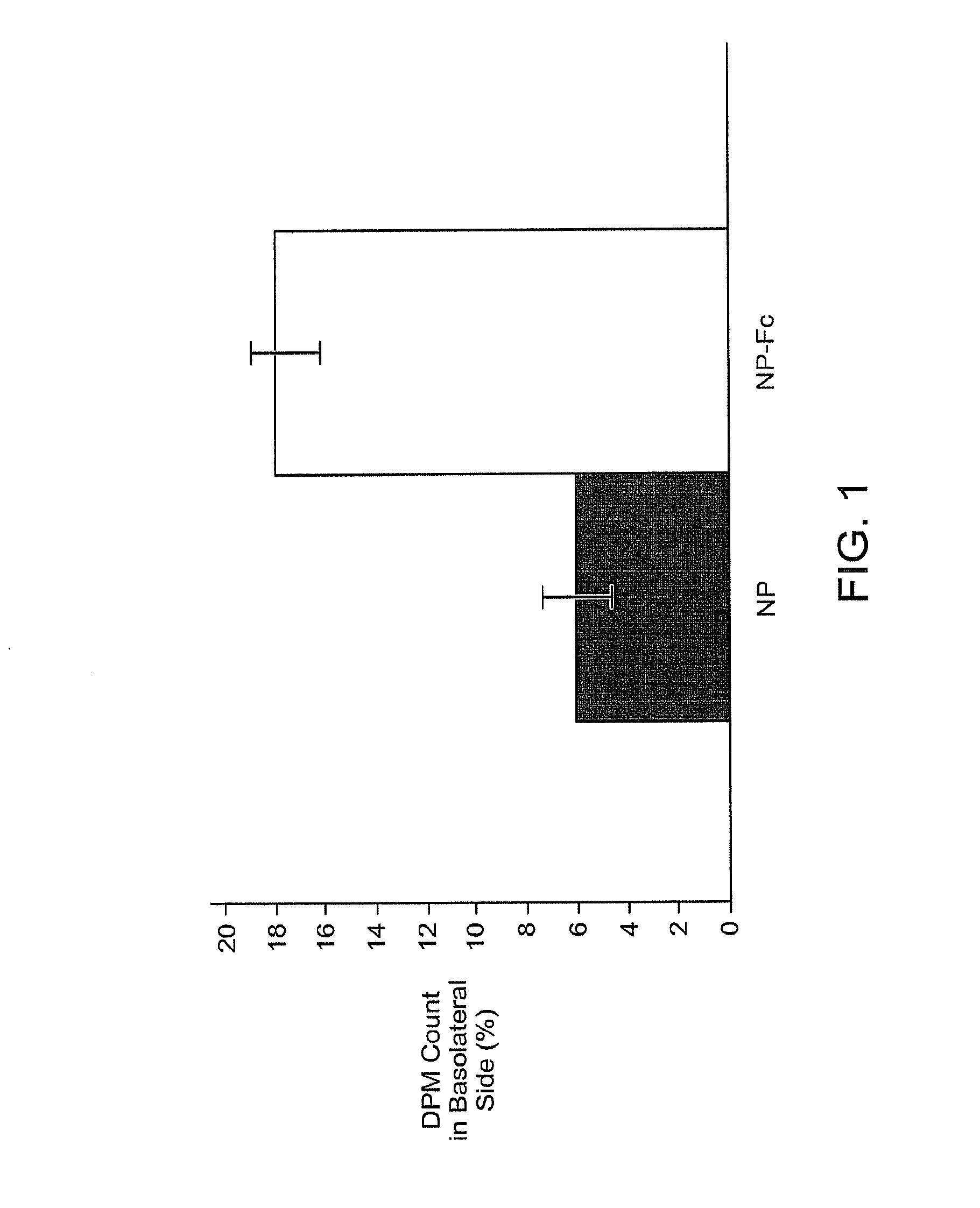
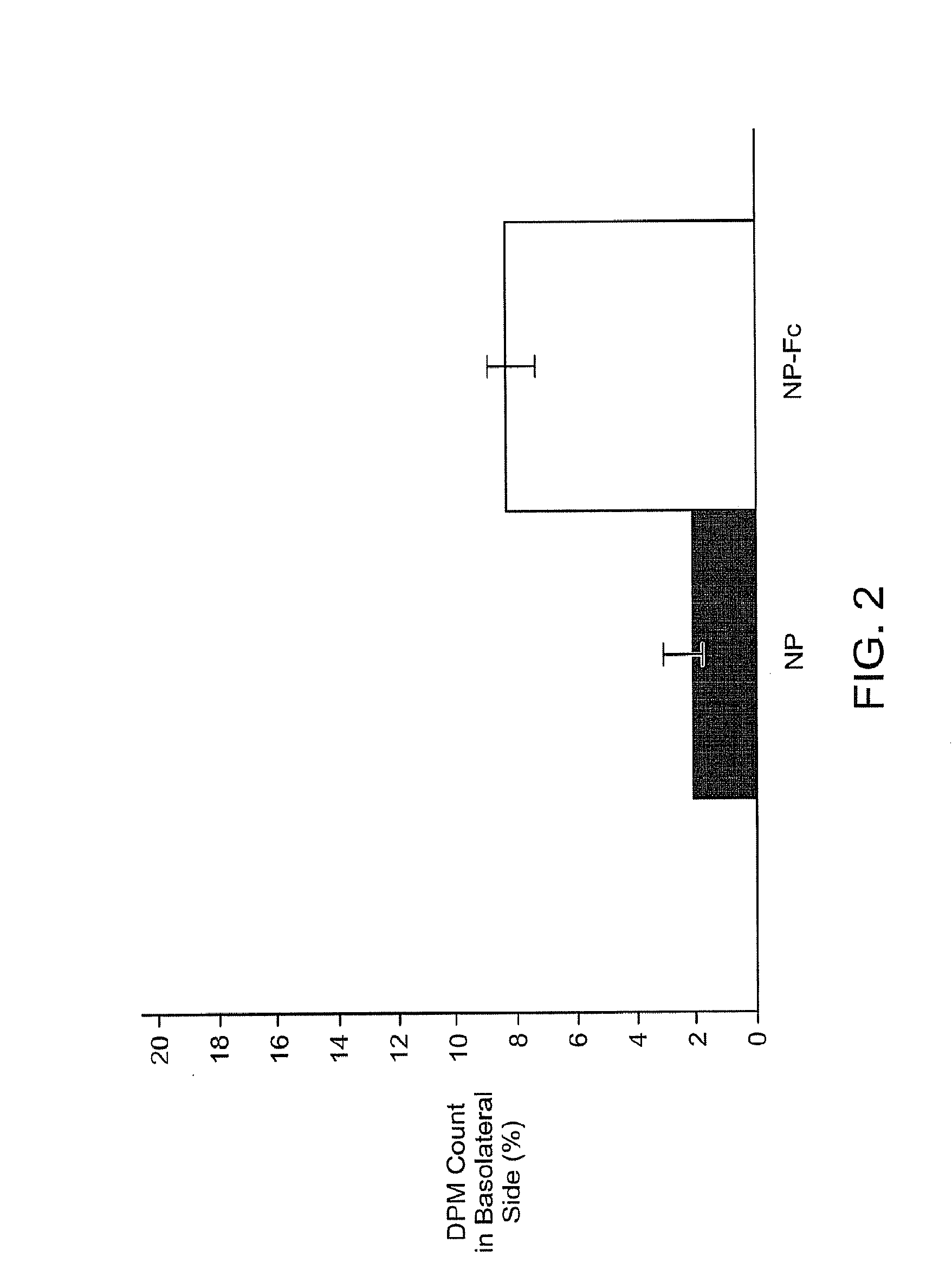
InactiveUS20100303723A1Easy to useEffectively cross epithelial cell layersPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsEpitheliumMedicine
The present invention provides drug delivery systems comprising FcRn binding partners (e.g., FcRn binding partner, Fc fragment) associated with a particle or an agent to be delivered. Inventive drug delivery systems allow for binding to the FcRn receptor and transcytosis into and / or through a cell or cell layer. Inventive systems are useful for delivering therapeutic agents across the endothelium of blood vessels or the epithelium of an organ.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC +1
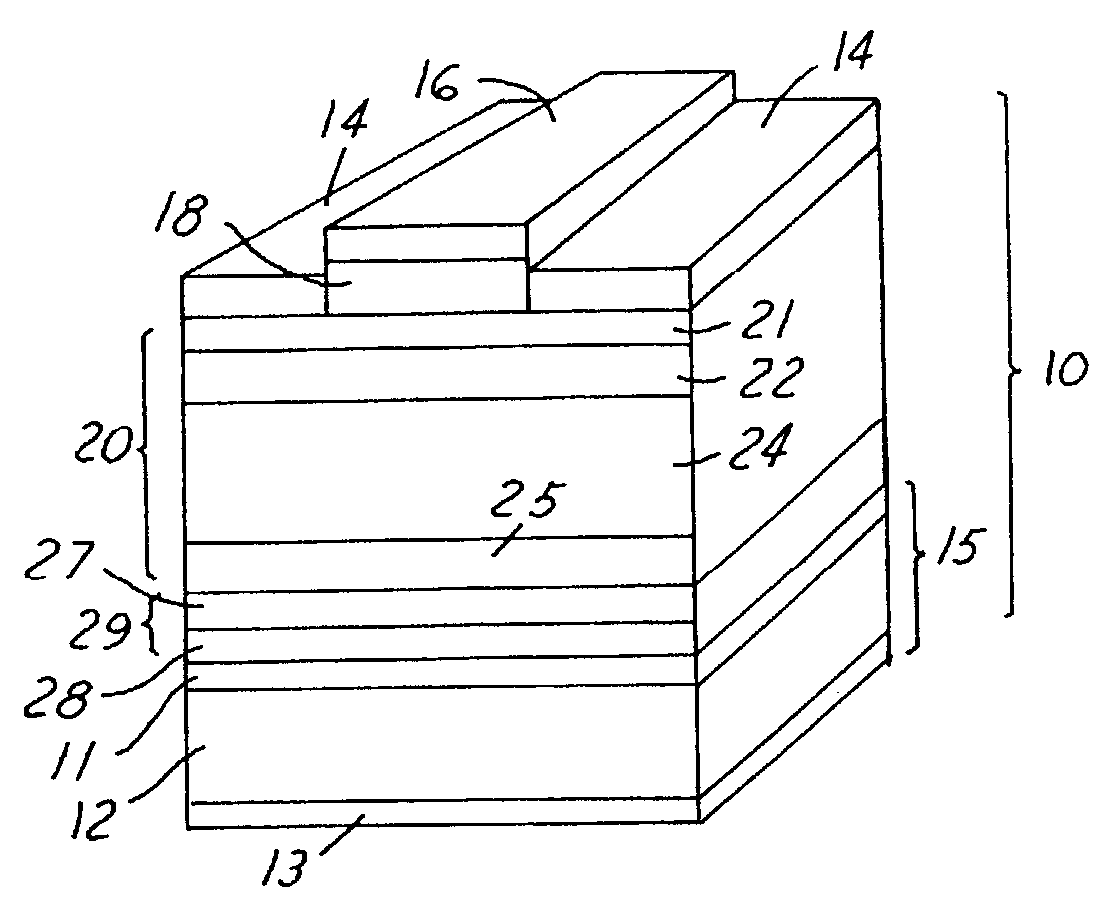
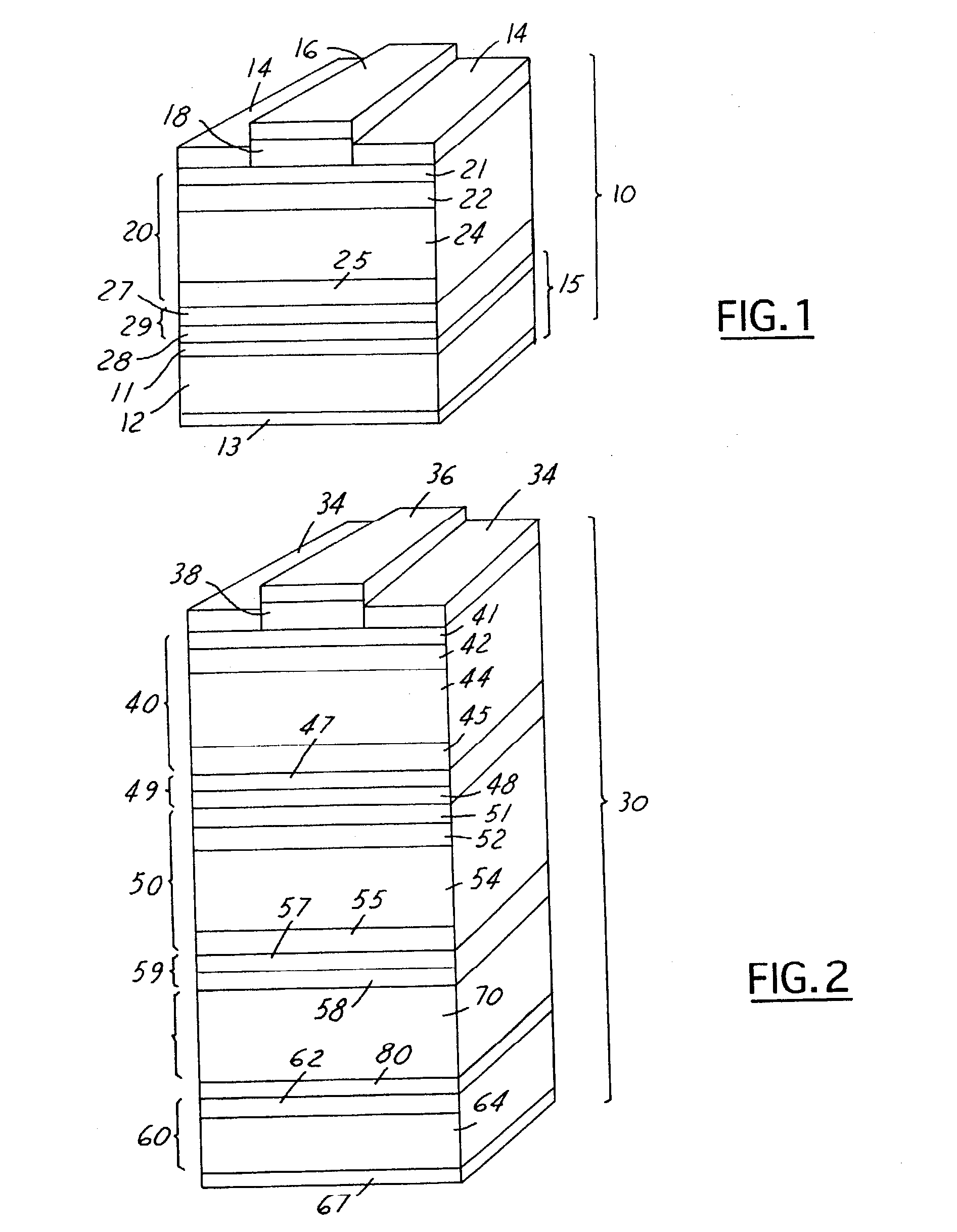
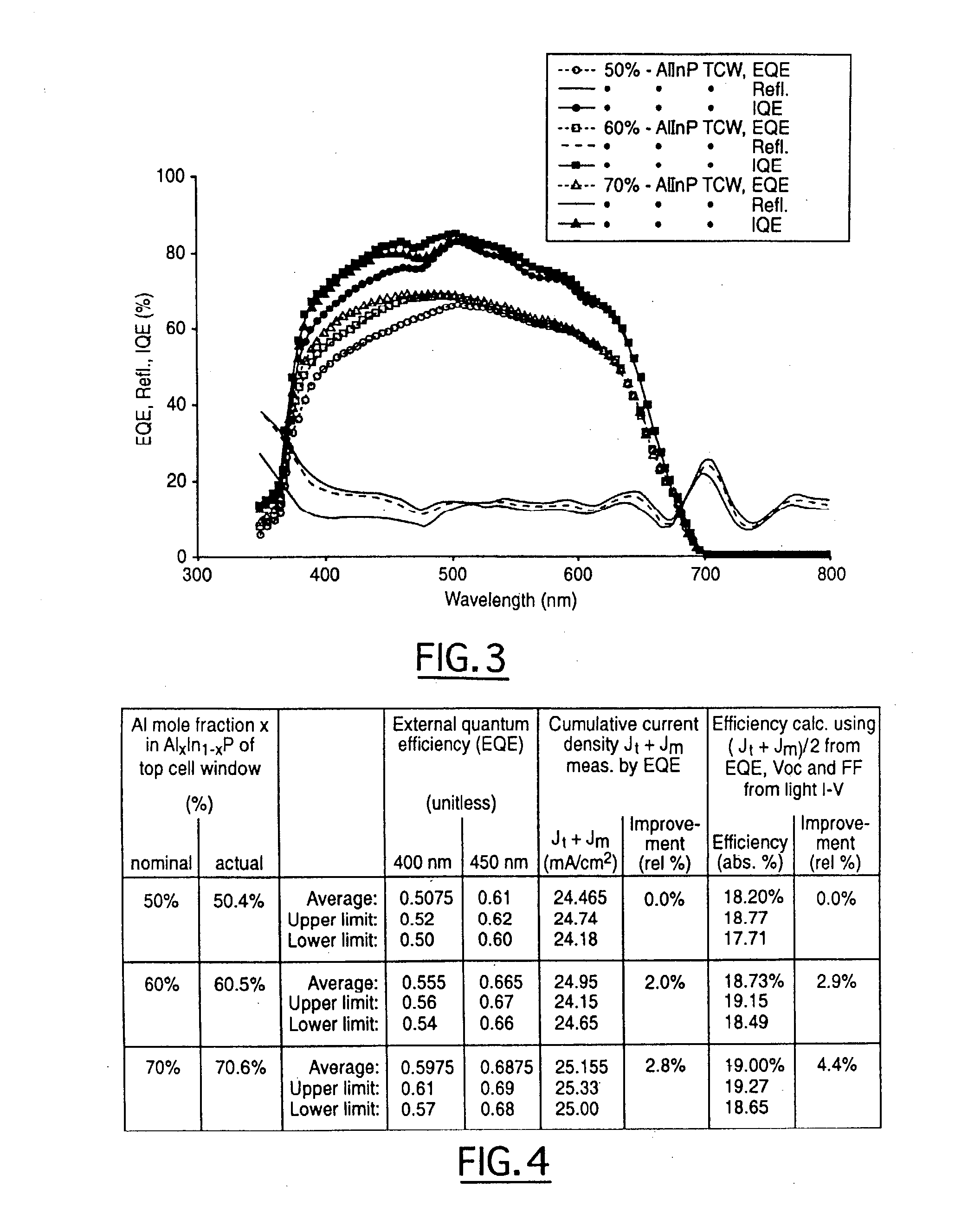
Wide-bandgap, lattice-mismatched window layer for a solar conversion device
ActiveUS7119271B2Improved surface passivationEnhanced light trapping effectPV power plantsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLattice mismatchCell layer
A photovoltaic cell or other optoelectronic device having a wide-bandgap semiconductor used in the window layer. This wider bandgap is achieved by using a semiconductor composition that is not lattice-matched to the cell layer directly beneath it and / or to the growth substrate. The wider bandgap of the window layer increases the transmission of short wavelength light into the emitter and base layers of the photovoltaic cell. This in turn increases the current generation in the photovoltaic cell. Additionally, the wider bandgap of the lattice mismatched window layer inhibits minority carrier injection and recombination in the window layer.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Human stem cells originating from human amniotic mesenchymal cell layer
InactiveUS20060281178A1Stable supplyEffective drug deliveryNervous system cellsArtificial cell constructsCell layerOsteocyte
Owner:SAKURAGAWA NORIO +1
Protective coating materials for electrochromic devices
InactiveUS6261641B1Free from mechanical damagePretreated surfacesLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingCell layerEther
Polymeric coating materials used to protect electrochromic devices from environmental and mechanical damage arc provided. The protective polymeric coating materials are physically, chemically and optically compatible with the electrochromic cell layers of electrochromic devices. The polymeric coating materials are polymers having generic polymer back-bones selected from the group of polyimides, polybenzimidazoles, polybenzothiazoles, polybenzoxazoles, poly(phenylene ethers), polyquinolines, polycarbonates, and polysulfones.
Owner:JDS UNIPHASE CORP
Corneal endothelium-like sheet and method of constructing the same
It is our intention to provide a transplantation material applicable to the treatment of various diseases that require corneal endothelium transplantation. Corneal endothelial cells are collected, proliferated and then sown on amnion and cultured. Thus, a corneal endothelium-like sheet, which has a cell layer made up of the corneal endothelium-origin cells formed on the amnion, can be obtained.
Owner:ARBLAST
Method for manufacturing high density non-volatile magnetic memory
ActiveUS8802451B2Total current dropReduced dimensionNanomagnetismNanoinformaticsFeature DimensionHigh density
Methods of fabricating MTJ arrays using two orthogonal line patterning steps are described. Embodiments are described that use a self-aligned double patterning method for one or both orthogonal line patterning steps to achieve dense arrays of MTJs with feature dimensions one half of the minimum photo lithography feature size (F). In one set of embodiments, the materials and thicknesses of the stack of layers that provide the masking function are selected so that after the initial set of mask pads have been patterned, a sequence of etching steps progressively transfers the mask pad shape through the multiple mask layer and down through all of the MTJ cell layers to the form the complete MTJ pillars. In another set of embodiments, the MTJ / BE stack is patterned into parallel lines before the top electrode layer is deposited.
Owner:AVALANCHE TECH
Device and method for controlled electroporation and molecular delivery into cells and tissue
InactiveUS20050170510A1Accurate measurementAccurate voltage controlGenetically modified cellsArtificial cell constructsCell layerElectroporation
In biology and biotechnology, electroporation is an important technique for introducing entities (DNA, RNAi, peptides, proteins, antibodies, genes, small molecules, nanoparticles, etc.) into cells. Applications range widely from genetic engineering to regenerative medicine to drug delivery. It has been demonstrated that the electrical currents flowing through cells can be used to monitor and control the process of electroporation for biological and artificial cells. In this application, a device and system are disclosed which allow precise monitoring and controlling electroporation of cells and cell layers, with examples shown using adherent cells grown on porous membranes.
Owner:HUANG YONG +2
Aminion-origin medical material and method of preparing the same
InactiveUS20060153928A1Easy to handleImprove adhesionMammal material medical ingredientsAbsorbent padsCell layerMembrane configuration
It is intended to provide an amnion-origin medical material which can be easily handled and fully sterilized and, moreover, favorably acts as a base material for forming a cell layer thereon. This material is prepared by: (i) removing the epithelial layer from the amnion while remaining at at leaset a part of the base membrane thereof; and (ii) drying it under such conditions that the remaining base membrane can sustain a structure allowing the adhesion and proliferation of cells thereon in using.
Owner:ARBLAST USA +1
Compositions and processes for format flexible, roll-to-roll manufacturing of electrophoretic displays
InactiveUS6873452B2High yieldImprove throughputSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementCell layerDisplay device
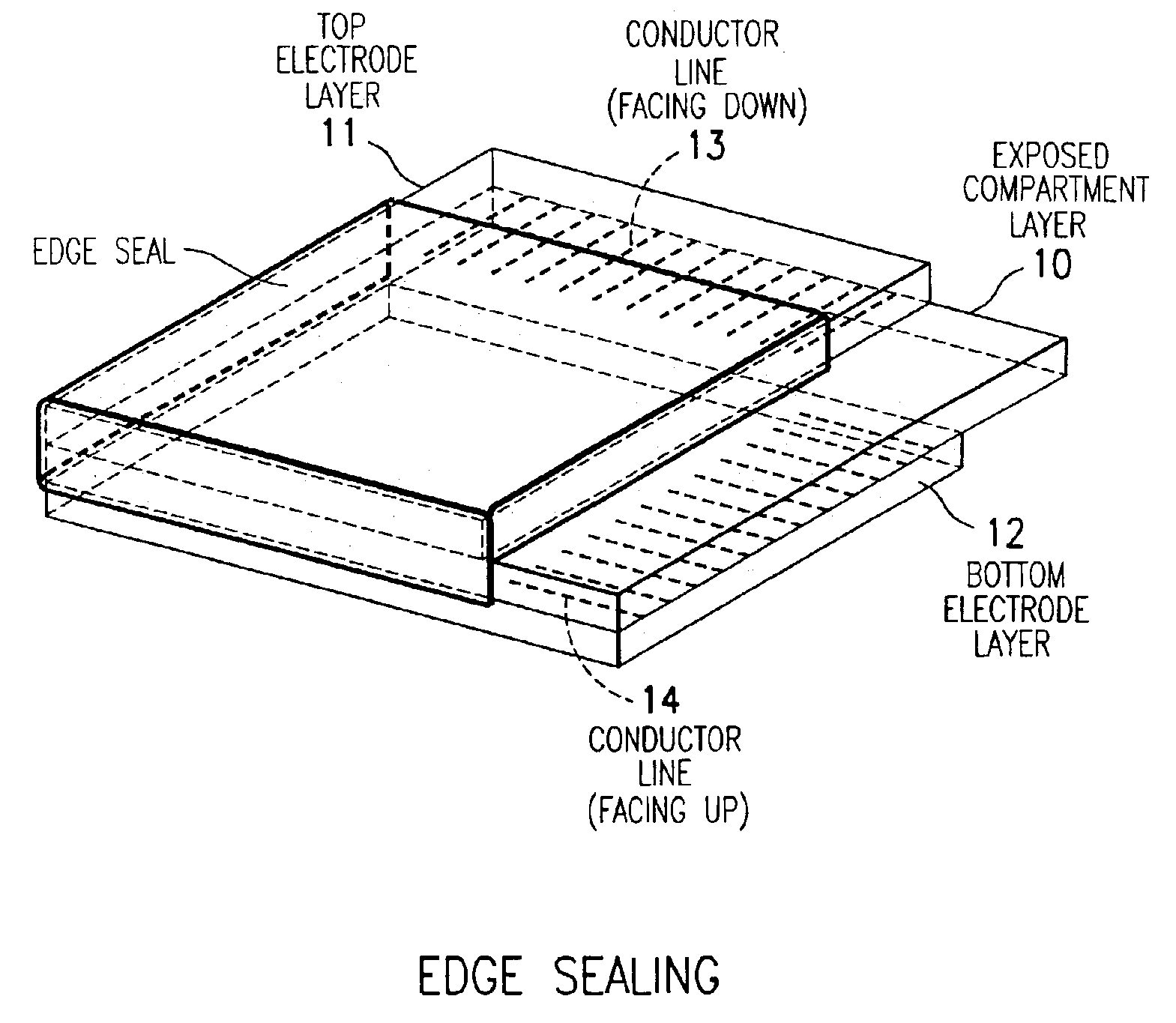
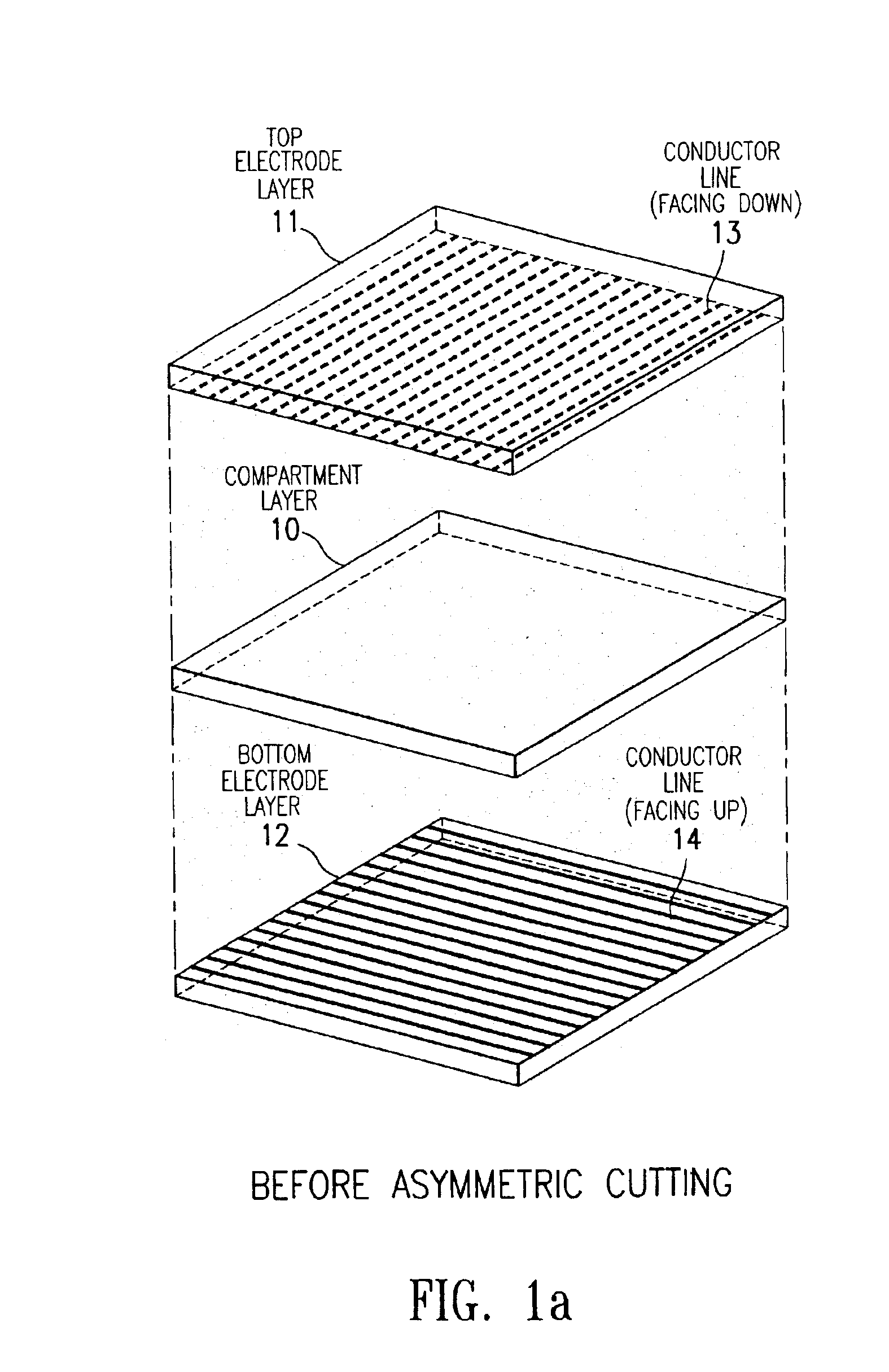
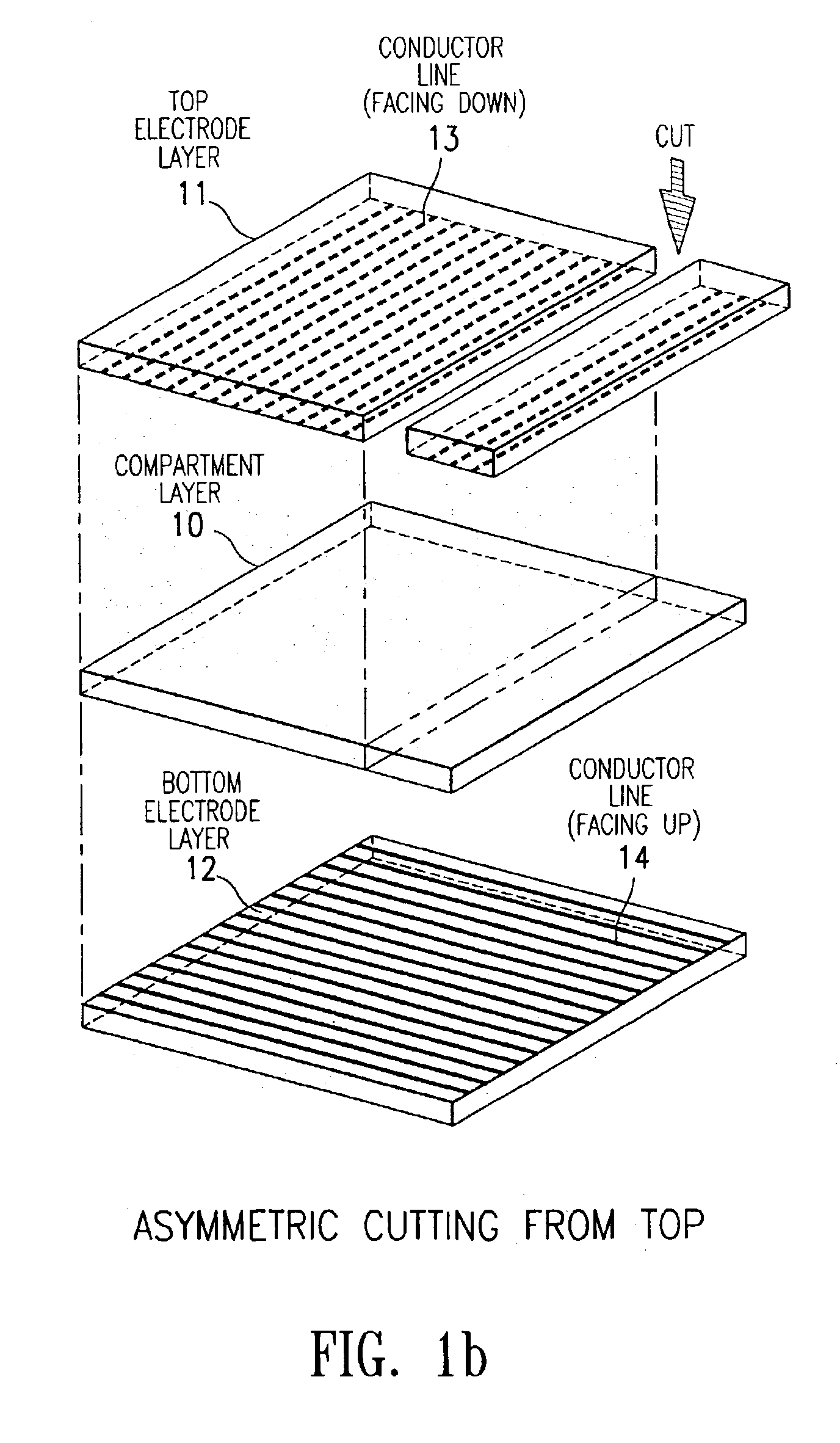
The present invention is directed to a process which comprises removing and stripping off part of the display panel in order to expose and connect the conductor lines on an electrode plate to a driver circuitry. More specifically the process involves (1) preparing a display panel having filled display cells sandwiched between a first and a second substrate layers, preferably by a roll-to-roll process; (2) removing part of a first substrate by asymmetrical cutting by, for example, a die, diamond, knife or laser cutting method to expose the layers underneath (which may include adhesive layer, primer layer, display cell layer and in the case of a display prepared by the microcup technology, the microcup layer and the sealing layer); and (3) stripping off the exposed layers by a stripping solvent or solution. After stripping, the conductor lines on the second substrate are exposed and ready for connection to the driver circuitry.
Owner:E INK CALIFORNIA
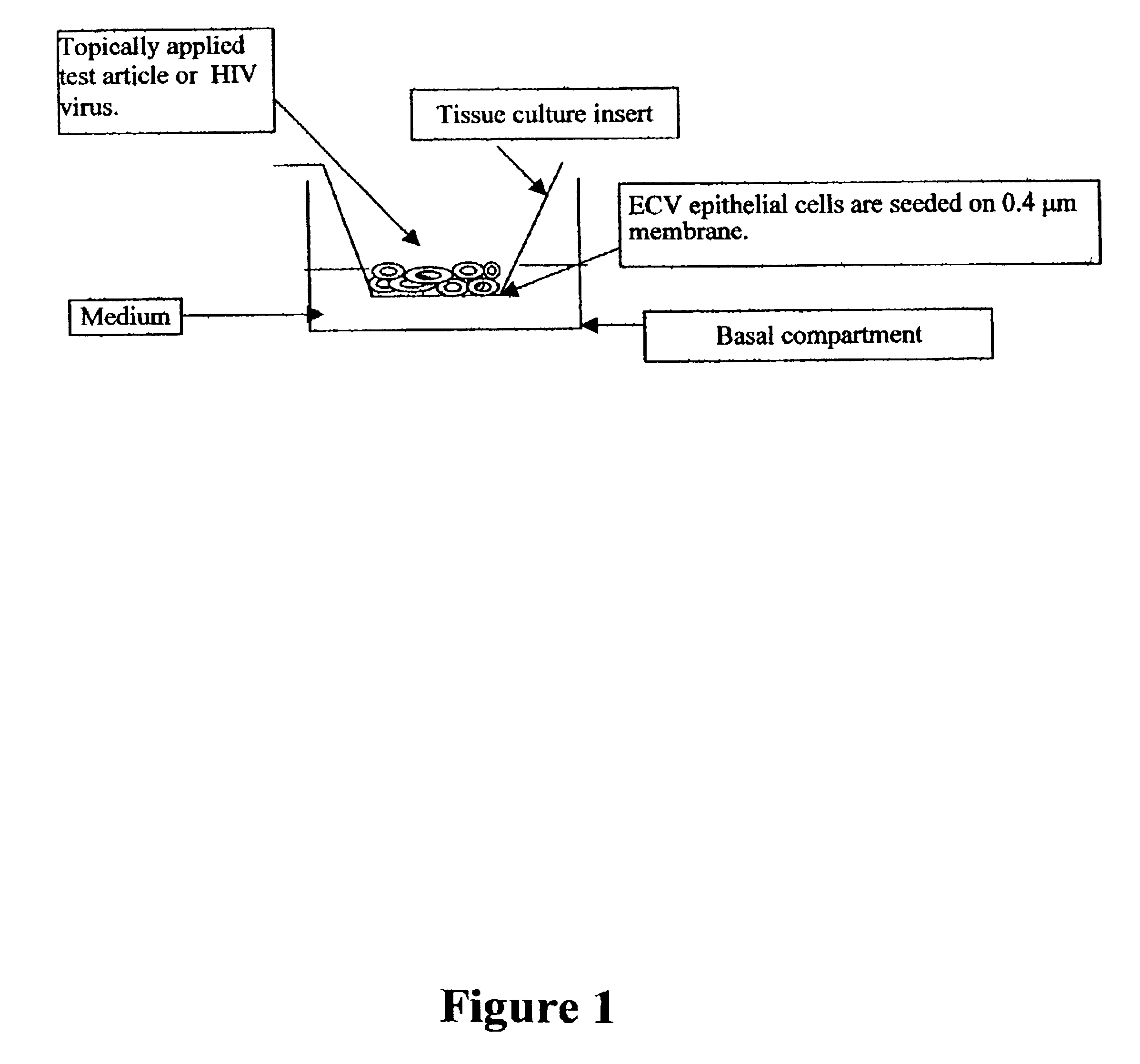
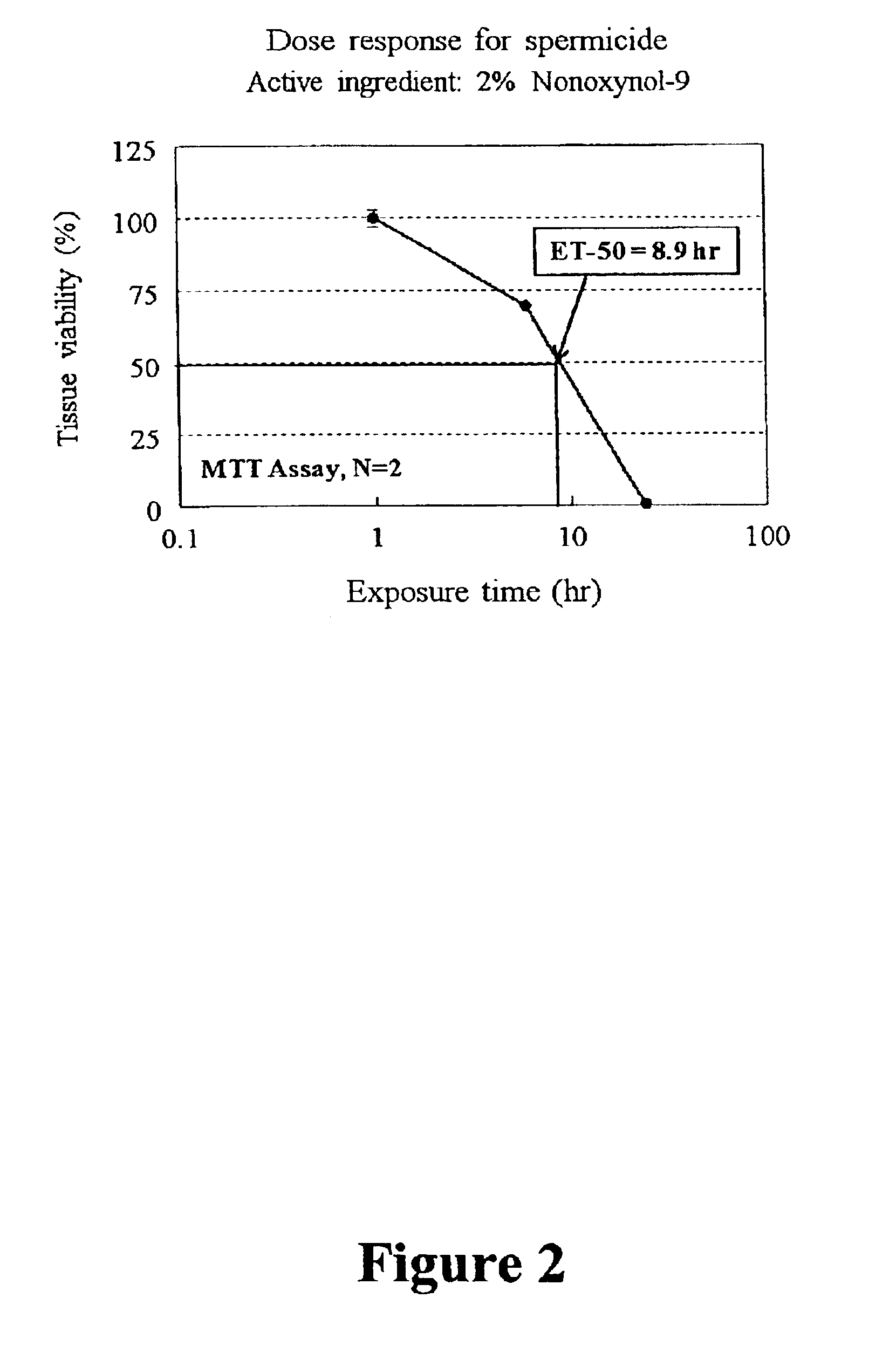
Three dimensional vaginal tissue model containing immune cells
InactiveUS6943021B2Improve survivabilityInduced proliferationBiocideEpidermal cells/skin cellsSerum free mediaAir liquid interface
Disclosed is a cervico-vaginal tissue equivalent comprised of vaginal epithelial cells and immune cells, cultured at the air-liquid interface. The tissue equivalent is capable of being infected with a sexually transmitted pathogen such as a virus (e.g., HIV), a bacteria, a helminthic parasite, or a fungus. The tissue equivalent is also capable of undergoing an allergic-type reaction or an irritant-type reaction. The tissue equivalent is characterized as having nucleated basal layer cells and nucleated suprabasal layer cells, and further as having cell layers external to the suprabasal layer progressively increasing in glycogen content and progressively decreasing in nuclei content. Immune cells of the tissue equivalent are primarily located in the basal and suprabasal layers. Also disclosed are methods for producing the tissue equivalent. The methods involve providing vaginal epithelial cells and immune cells, seeding the cells onto a porous support, and co culturing the seeded cells at the air-liquid interface under conditions appropriate for differentiation. One such method disclosed is for generation of the tissue equivalent in serum free medium. Specific cells from which the tissue equivalent is generated, and also specific preferred components of the medium in which the tissue equivalent is generated are provided. Also disclosed is a cervico-vaginal tissue equivalent produced by the methods disclosed herein.
Owner:MATTEK CORP
Enhanced transport using membrane disruptive agents
Compositions and methods for transport or release of therapeutic and diagnostic agents or metabolites or other analytes from cells, compartments within cells, or through cell layers or barriers are described. The compositions include a membrane barrier transport enhancing agent and are usually administered in combination with an enhancer and / or exposure to stimuli to effect disruption or altered permeability, transport or release. In a preferred embodiment, the compositions include compounds which disrupt endosomal membranes in response to the low pH in the endosomes but which are relatively inactive toward cell membranes, coupled directly or indirectly to a therapeutic or diagnostic agent. Other disruptive agents can also be used, responsive to stimuli and / or enhancers other than pH, such as light, electrical stimuli, electromagnetic stimuli, ultrasound, temperature, or combinations thereof. The compounds can be coupled by ionic, covalent or H bonds to an agent to be delivered or to a ligand which forms a complex with the agent to be delivered. Agents to be delivered can be therapeutic and / or diagnostic agents. Treatments which enhance delivery such as ultrasound, iontopheresis, and / or electrophereis can also be used with the disrupting agents.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON +1
Systems and methods for electrosurgical removal of the stratum corneum
InactiveUS7758537B1Good lookingEnhanced regrowthElectrotherapySurgical instruments for heatingThermal energyWrinkle skin
The present invention provides systems, apparatus and methods for removing the outer layer, or stratum corneum, of a patient's skin. In one aspect of the invention, a method includes positioning an active electrode adjacent to or near a target site on a patient's outer skin, and applying a sufficient high frequency voltage to the active electrode to remove the stratum corneum without removing the entire epidermis layer. In this manner, the present invention removes dead and / or damaged skin cells on the surface of the skin which improves the overall appearance of the skin. In addition, this process helps to stimulate the bodies own rejuvenation process. In some embodiments, this rejuvenation process occurs by the actual removal of the stratum corneum, which accelerates the regrowth of new cell layers in the skin. In other embodiments, thermal energy is applied to the underlying epidermis and / or dermis to stimulate the growth of new collagen. In both of these embodiments, the skin appears healthier and, in some cases, small wrinkles are removed or reduced.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com