Patents
Literature
85 results about "Cellular organization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cellular organization is the basic tool which acends from simplest to complex one. Starting from base Atom organized into molecule into organelle and here comes the Cell. Cell are combined to form tissue, tissue into organ, organ into Organ system, and finally into Living organism.
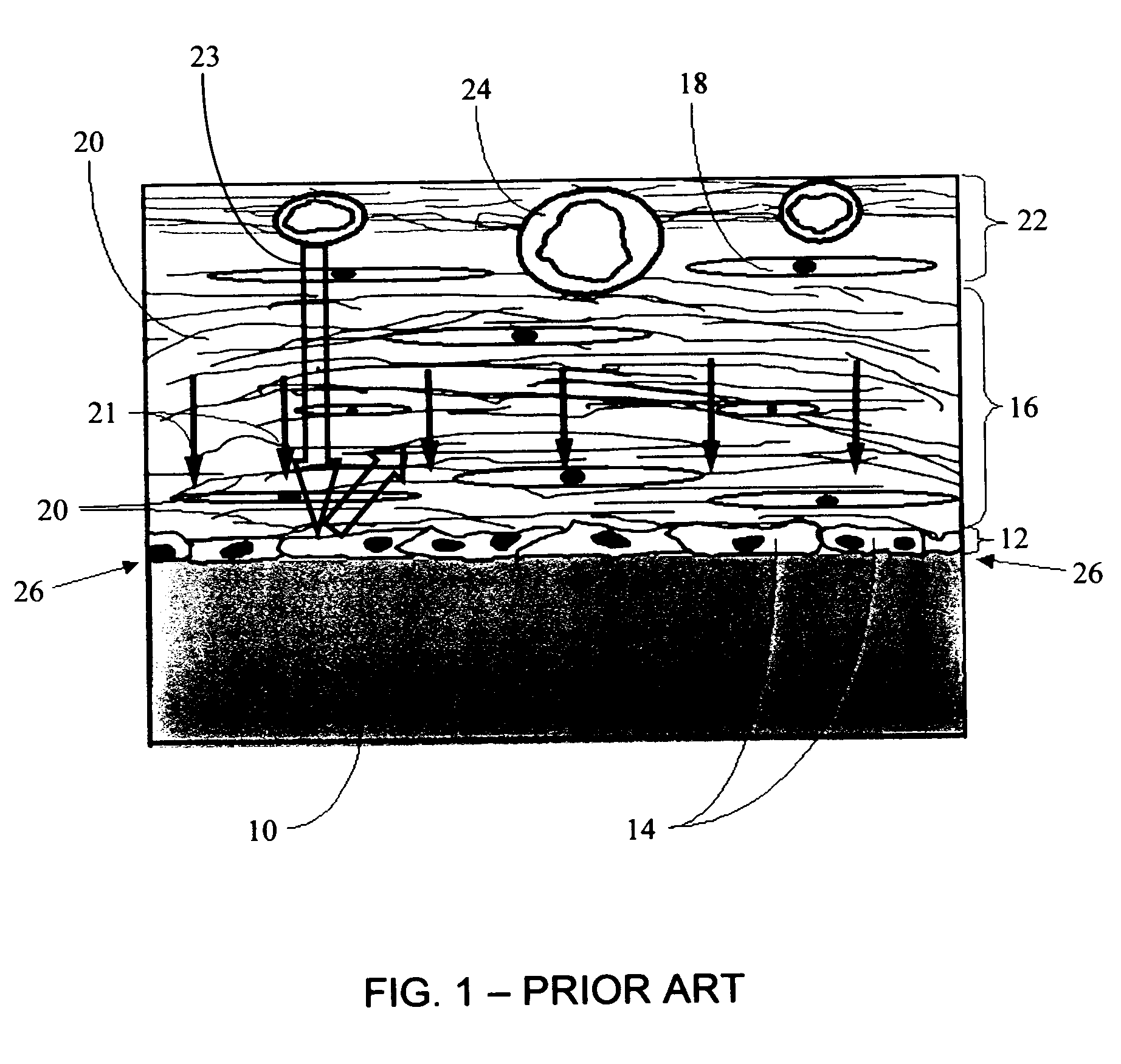
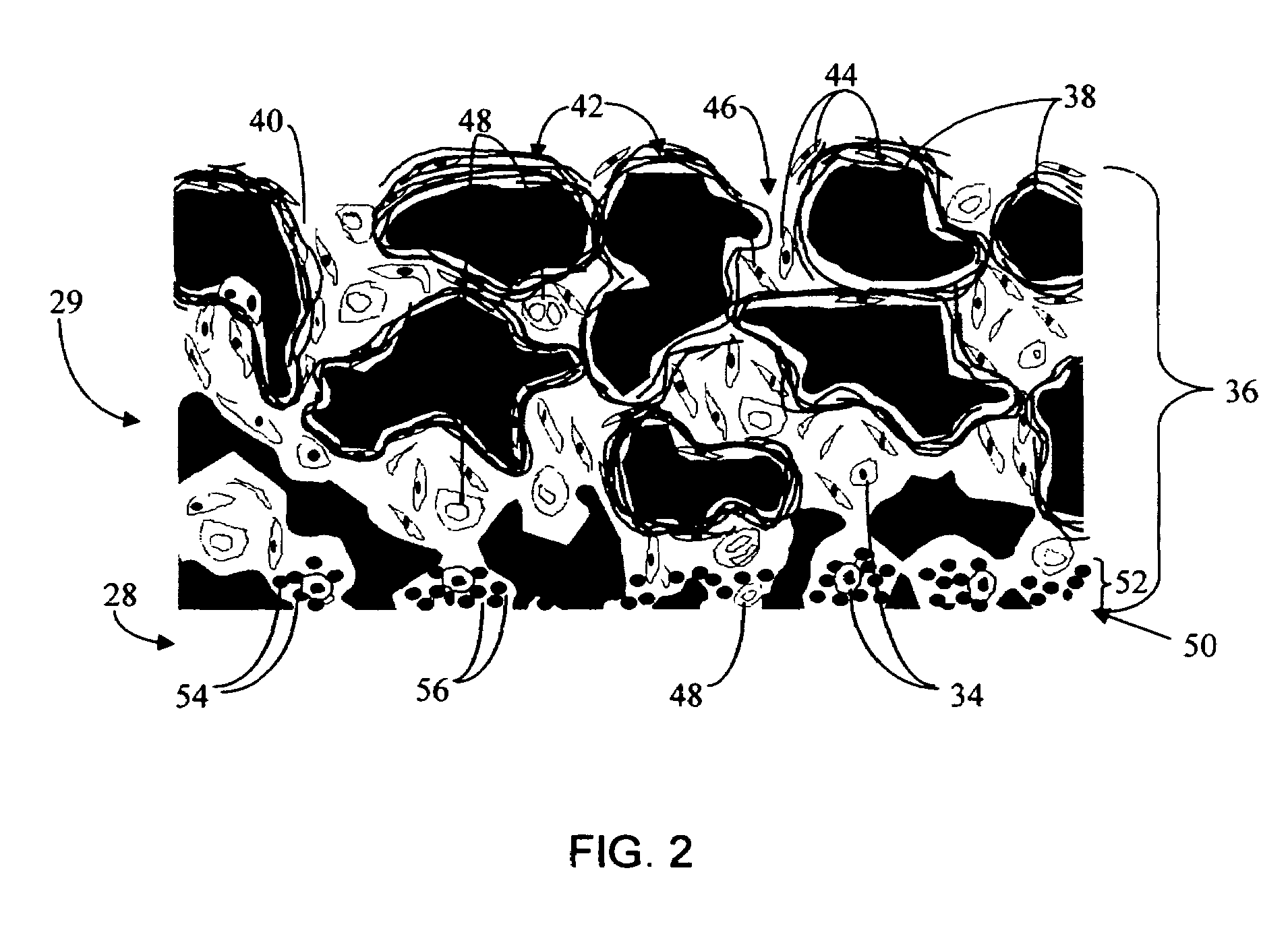
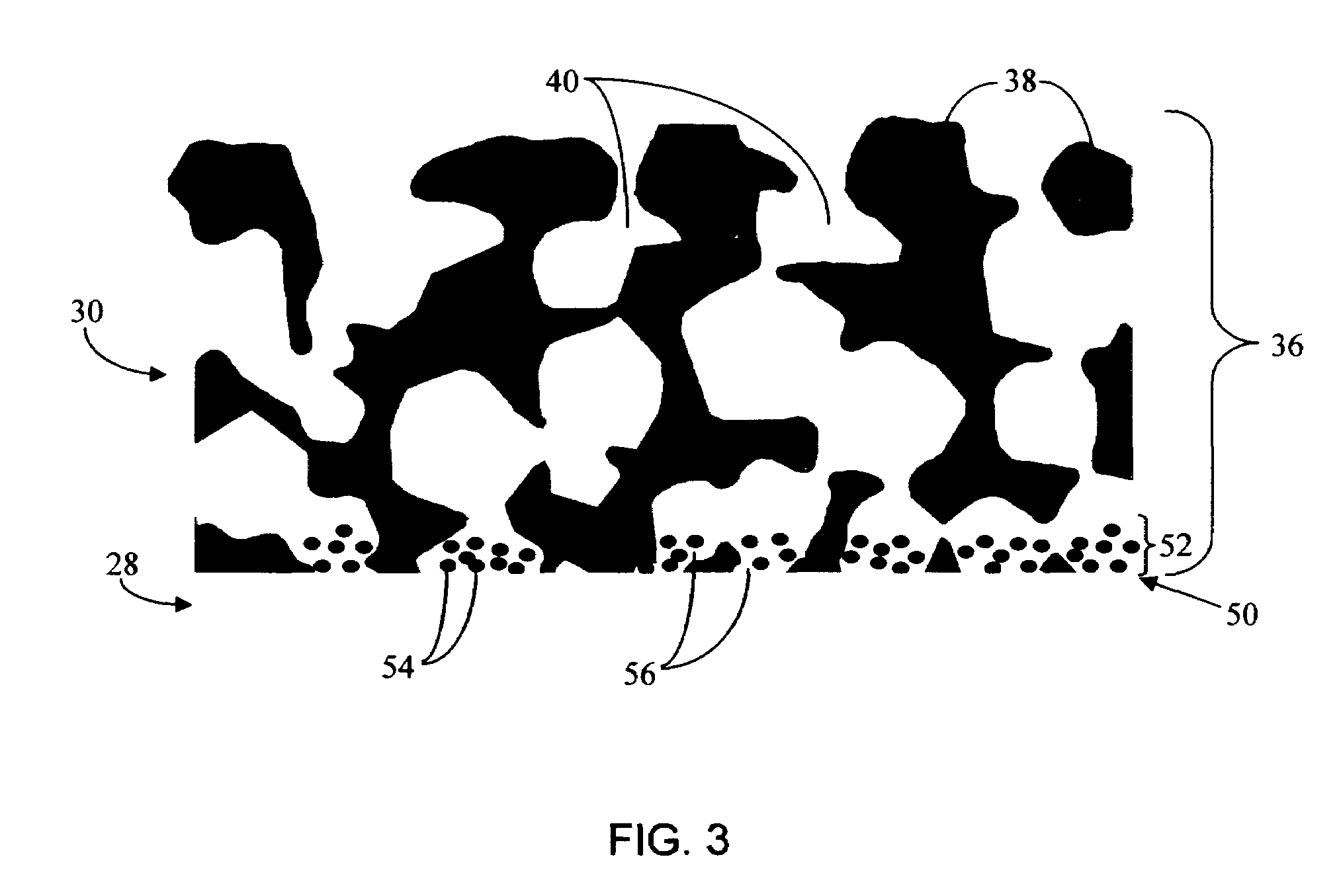
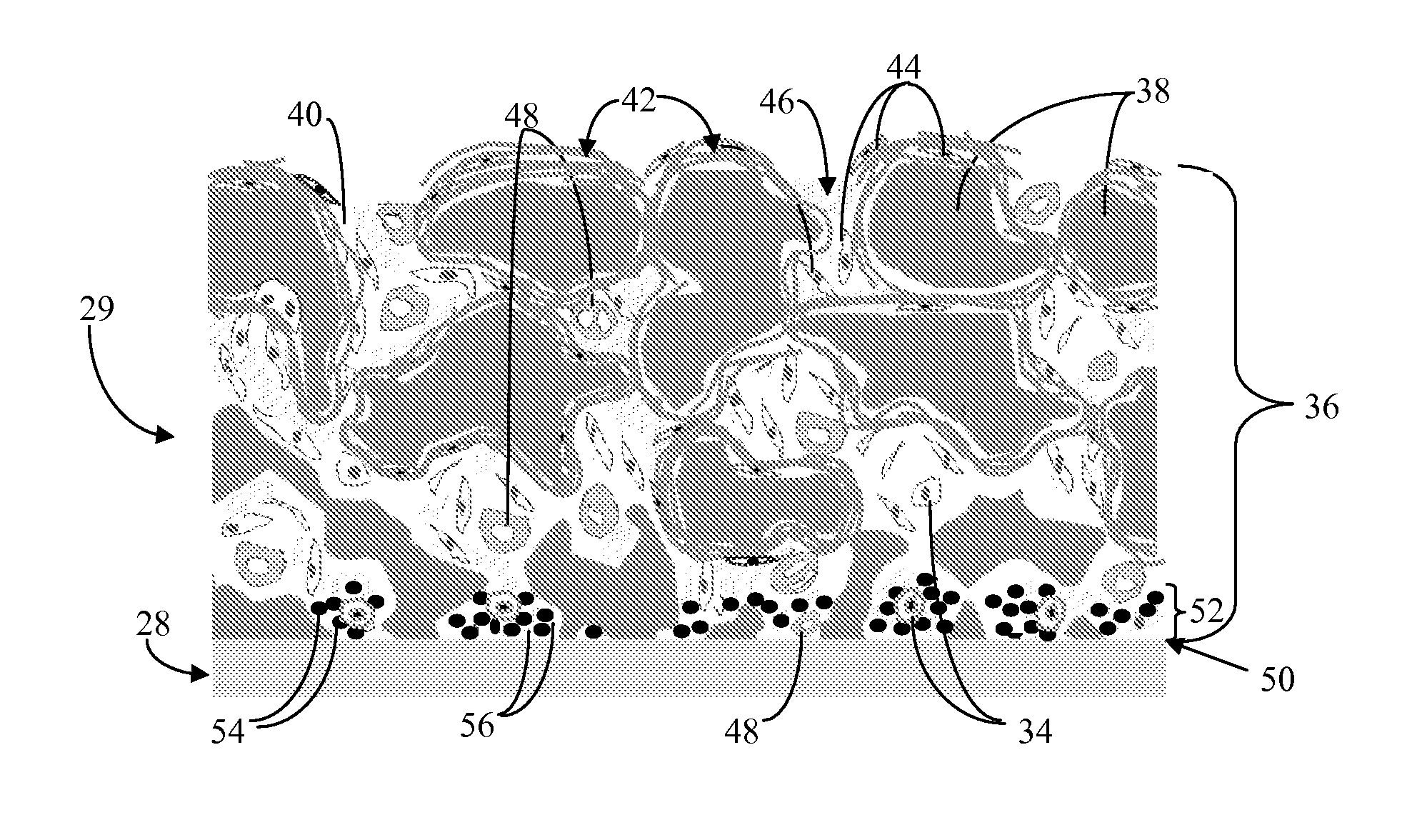
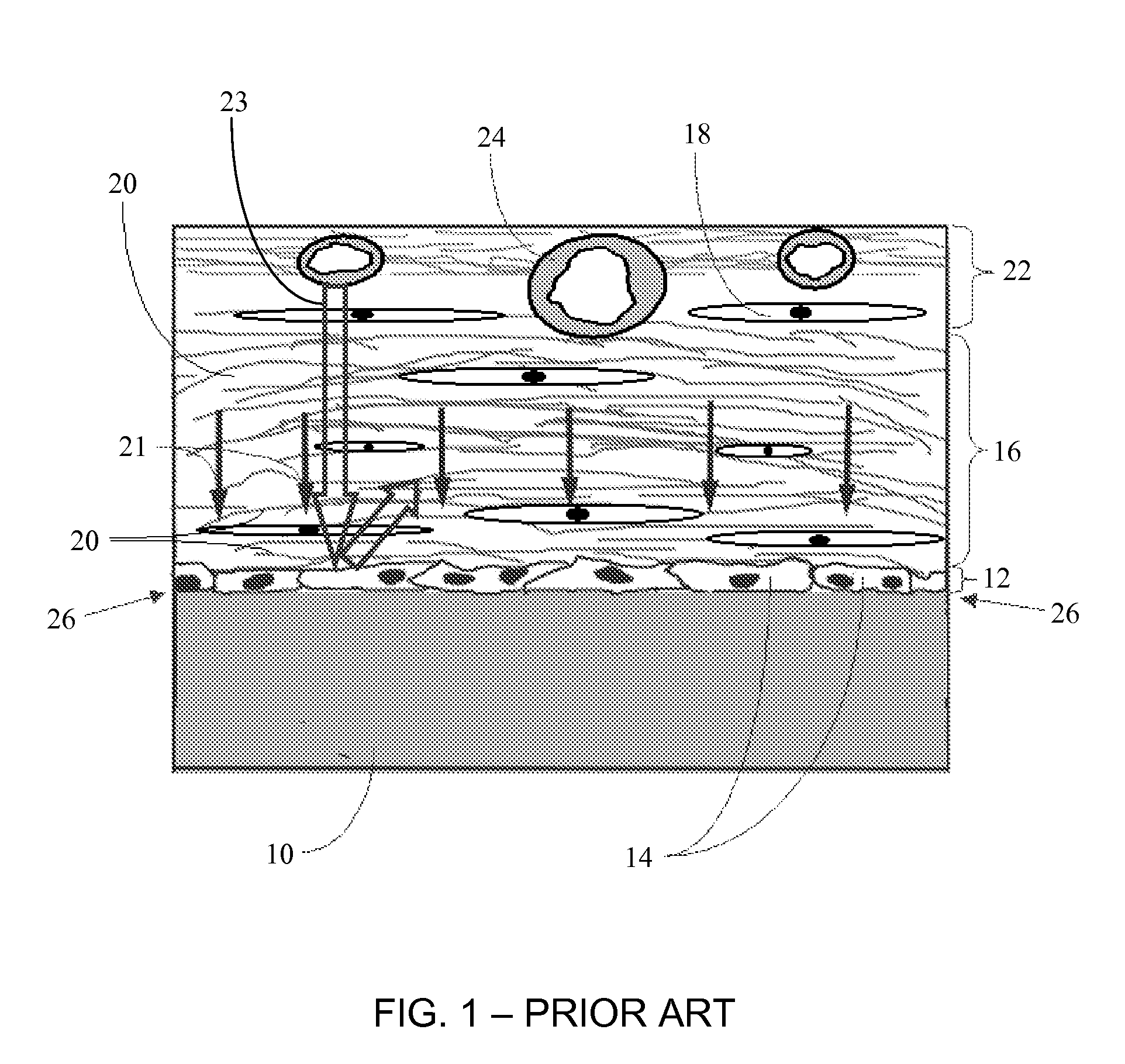
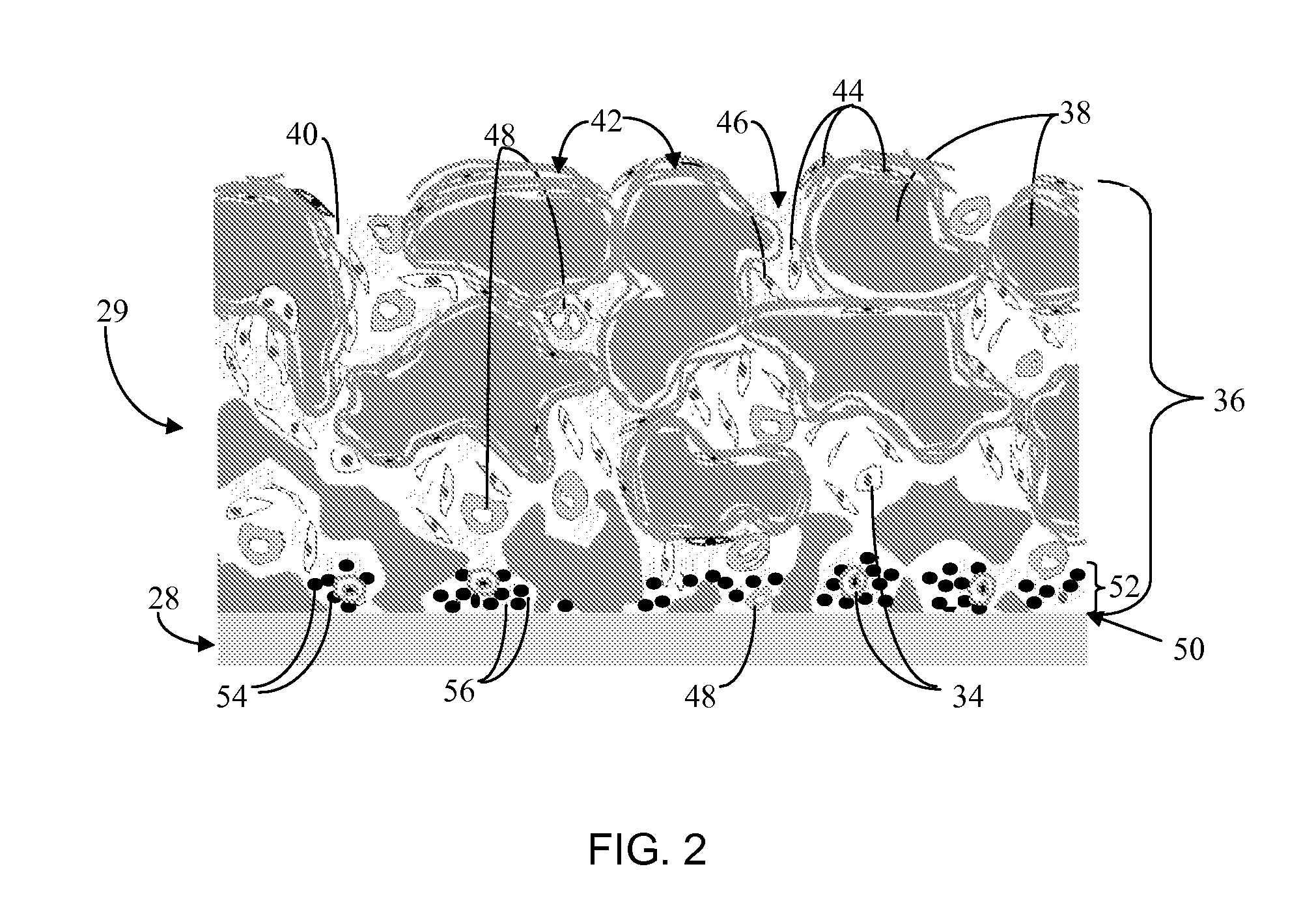
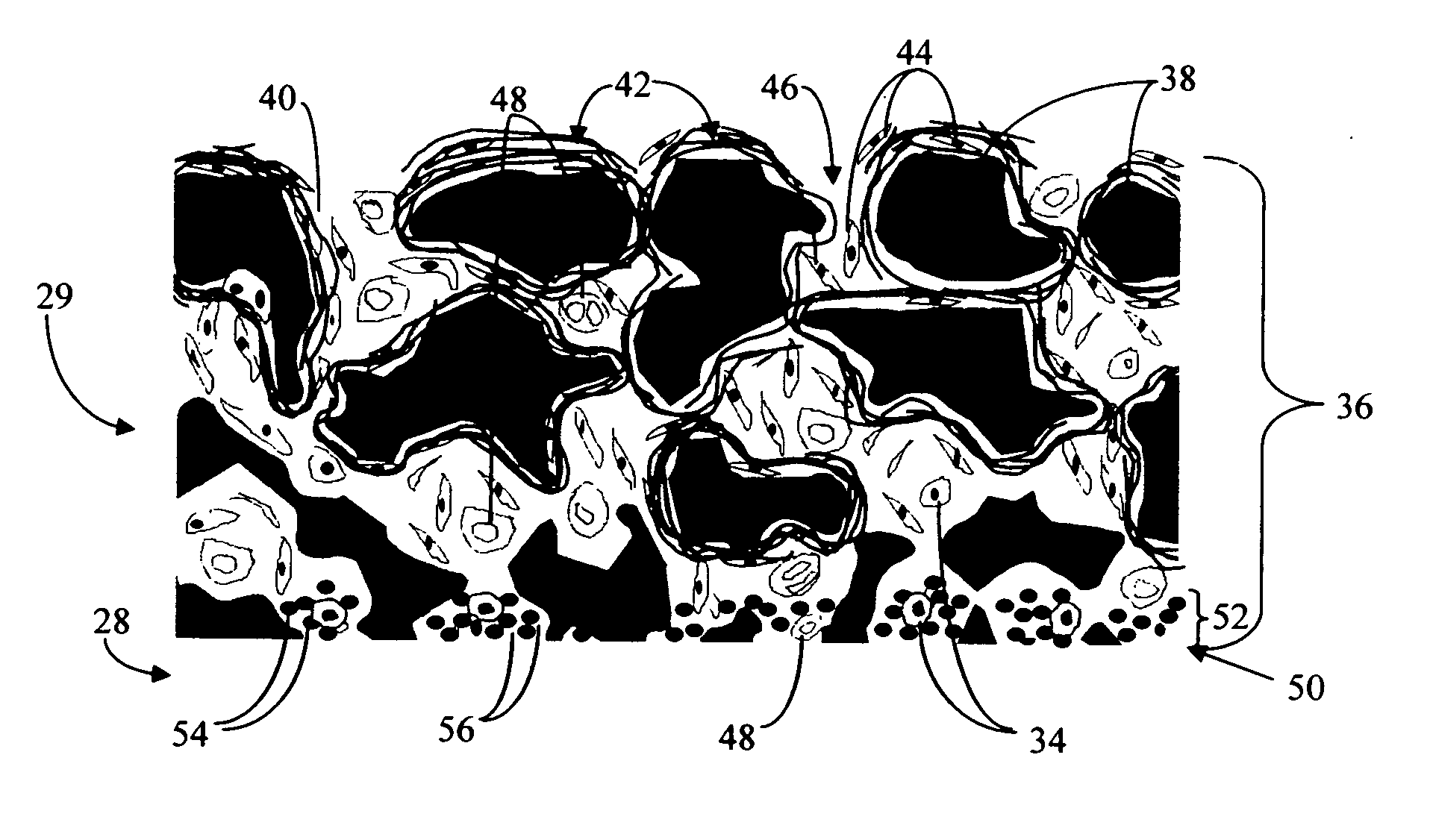
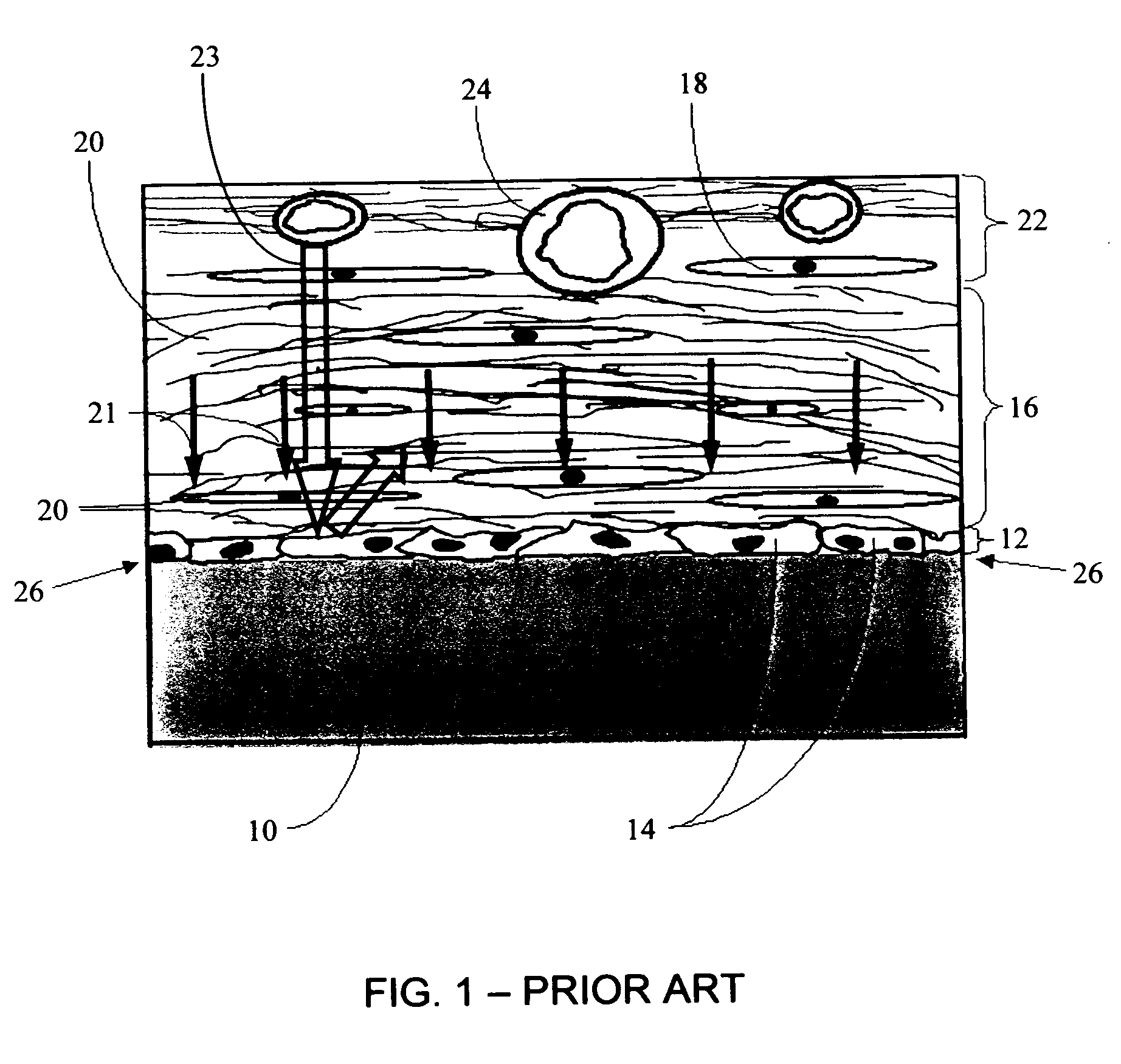
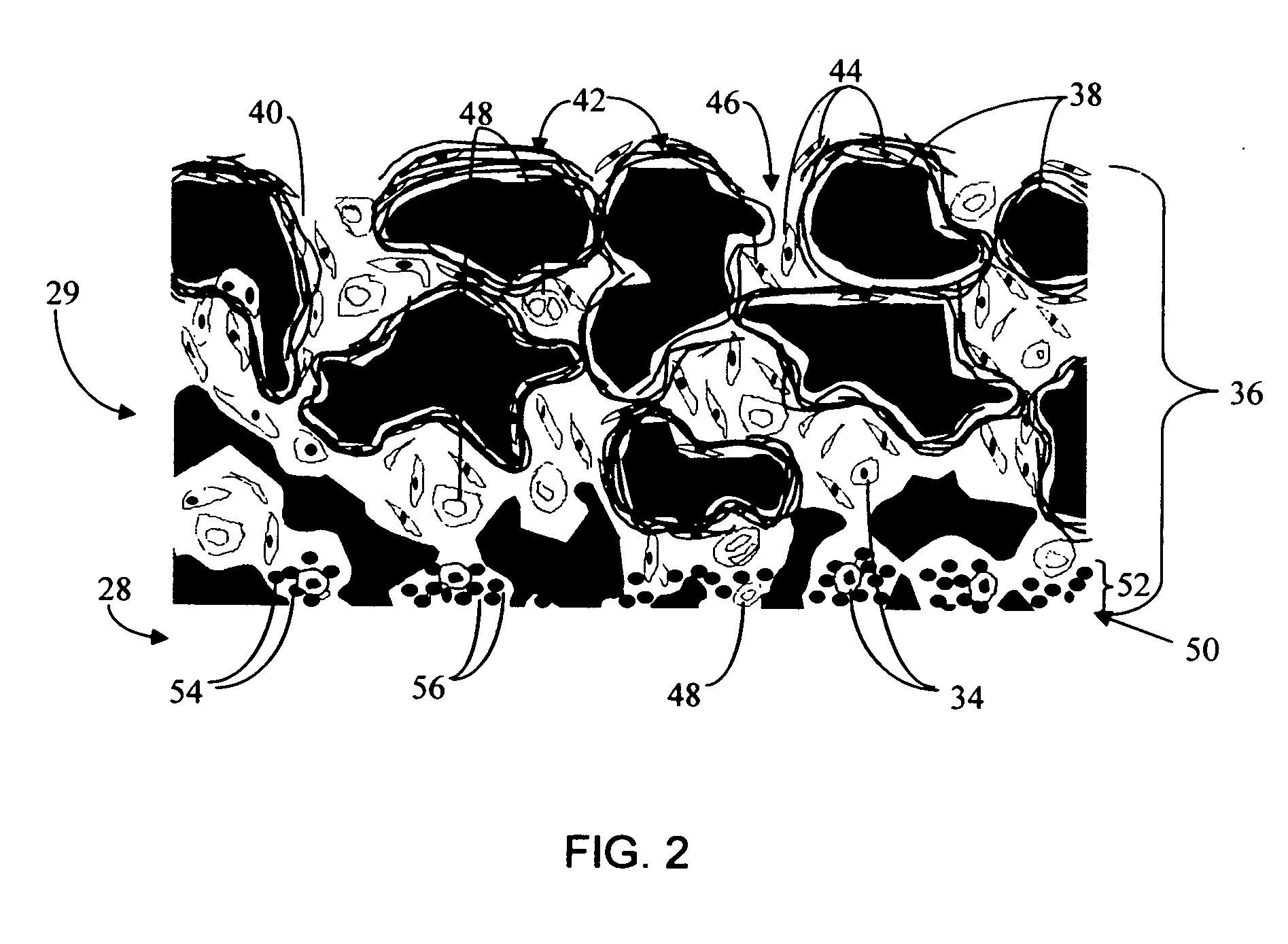
Biointerface membrane with macro-and micro-architecture
Disclosed herein are biointerface membranes including a macro-architecture and a micro-architecture co-continuous with and bonded to and / or located within at least a portion of the macro-architecture. The macro- and micro-architectures work together to manage and manipulate the high-level tissue organization and the low-level cellular organization of the foreign body response in vivo, thereby increasing neovascularization close to a device-tissue interface, interfering with barrier cell layer formation, and providing good tissue anchoring, while reducing the effects of motion artifact, and disrupting the organization and / or contracture of the FBC. The biointerface membranes of the preferred embodiments can be utilized with implantable devices such as devices for the detection of analyte concentrations in a biological sample (for example, from a body), cell transplantation devices, drug delivery devices, electrical signal delivering or measuring devices, and / or combinations thereof.
Owner:DEXCOM
Biointerface with macro- and micro-architecture
Owner:DEXCOM INC
Biointerface with macro-and micro-architecture
Disclosed herein are biointerface membranes including a macro-architecture and a micro-architecture co-continuous with and bonded to and / or located within at least a portion of the macro-architecture. The macro- and micro-architectures work together to manage and manipulate the high-level tissue organization and the low-level cellular organization of the foreign body response in vivo, thereby increasing neovascularization close to a device-tissue interface, interfering with barrier cell layer formation, and providing good tissue anchoring, while reducing the effects of motion artifact, and disrupting the organization and / or contracture of the FBC. The biointerface membranes of the preferred embodiments can be utilized with implantable devices such as devices for the detection of analyte concentrations in a biological sample (for example, from a body), cell transplantation devices, drug delivery devices, electrical signal delivering or measuring devices, and / or combinations thereof.
Owner:DEXCOM
Decellularized extracellular matrix of conditioned body tissues and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050013870A1Increase in sizeHigh strengthGastrointestinal cellsGenetically modified cellsCell-Extracellular MatrixECM Protein
The present invention relates generally to decellularized extracellular matrix of conditioned body tissues. The decellularized extracellular matrix contains a biological material, preferably vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), produced by the conditioned body tissue that is in an amount different than the amount of the biological material that the body tissue would produce absent the conditioning. The invention also relates to methods of making and methods of using said decellularized extracellular matrix. Specifically, the invention relates to treating defective, diseased, damaged or ischemic cells, tissues or organs in a subject by administering, injecting or implanting the decellularized extracellular matrix of the invention into a subject in need thereof. The invention is further directed to a tissue regeneration scaffold for implantation into a subject inflicted with a disease or condition that requires tissue or organ repair, regeneration and / or strengthening. Additionally, the invention is directed to a medical device, preferably a stent or an artificial heart, having a surface coated or covered with the decellularized extracellular matrix of the invention or having a component comprising the decellularized extracellular matrix of the invention for implantation into a subject, preferably a human. Methods for making the tissue regeneration scaffold and methods for manufacturing a coated or covered medical device having a component comprising decellularized extracellular matrix of conditioned body tissues are also provided.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Autogenic living scaffolds and living tissue matrices: methods and uses thereof
ActiveUS20050226856A1Preventing host rejectionThicker and strongBiocideSkin implantsTransdifferentiationOrganism
A 3-dimensional structure comprising suitable cells (or entities) and the ECM (or matrix) that has been completely produced and arranged by these cells (or entities) that promotes the differentiation, dedifferentiation and / or transdifferentiation of cells and / or formation of tissue in vitro and in vivo, while at the same time promoting cell growth, proliferation, migration, acquisition of in vivo-like morphology, or combinations thereof, and that 1. provides structural and / or nutritional support to cells, tissue, organs, or combinations thereof, termed an “Autogenic Living Scaffold” (ALS); or 2. is capable of being transformed into a more complex tissue (or matrix) or a completely different type of tissue (or matrix), termed a “Living Tissue Matrix” (LTM). Autogenic means it is self-produced. The living cells that produce the LTM or ALS, or are added to Autogenic Living Scaffolds, may be genetically engineered or otherwise modified. The matrix component of the ALS or LTM provides a structural framework for cells that guide their direction of growth, enables them to be correctly spaced, prevents overcrowding, enables cells to communicate between each other, transmit subtle biological signals, receive signals from their environment, form bonds and contacts that are required for proper functioning of all cells within a unit such as a tissue, or combinations thereof. The ALS or LTM may thus provide proper or supporting mechanical and chemical environments, signals, or stimuli to other cells, to the cells that produce the ALS, to surrounding tissue at an implantation site, to a wound, for in vitro and ex vivo generation and regeneration of cells, tissue and organs, or combinations thereof. They may also provide other cells with nutrients, growth factors, and / or other necessary or useful components. They may also take in or serve as buffers for certain substances in the environment, and have also some potential at adapting to new environments.
Owner:GENESIS TECH LTD
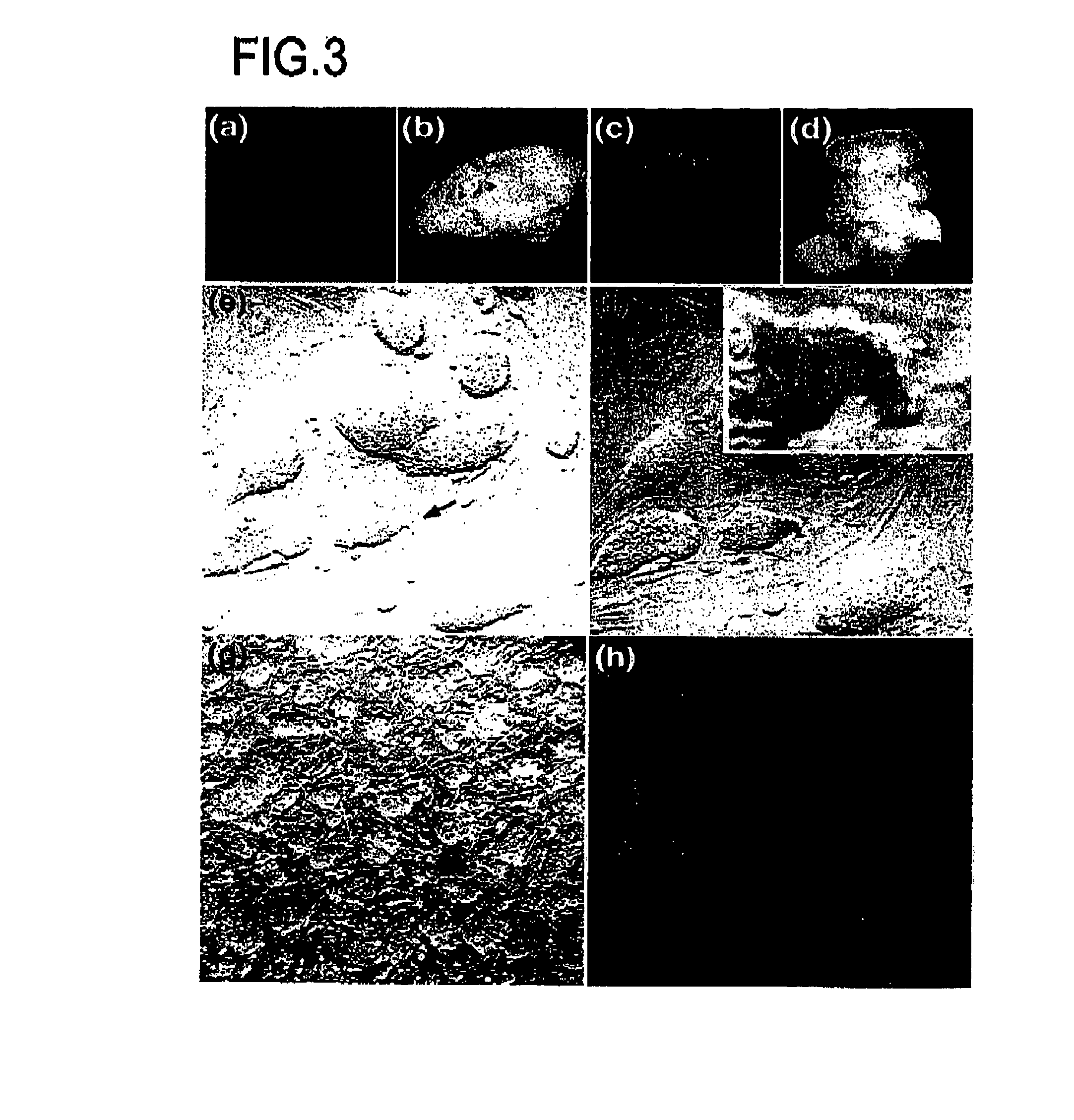
Nanotopographic Compositions and Methods for Cellular Organization in Tissue Engineered Structures
ActiveUS20080026464A1Additive manufacturing apparatusPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCell typeNanotopography
The present invention relates to tissue engineered compositions and methods comprising nanotopographic surface topography (“nanotopography”) for use in modulating the organization and / or function of multiple cell types.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
Decellularized tissue
InactiveUS20050256588A1Minimal damageGuaranteed maximum utilizationArtificial cell constructsMammal material medical ingredientsCalcificationDecellularization
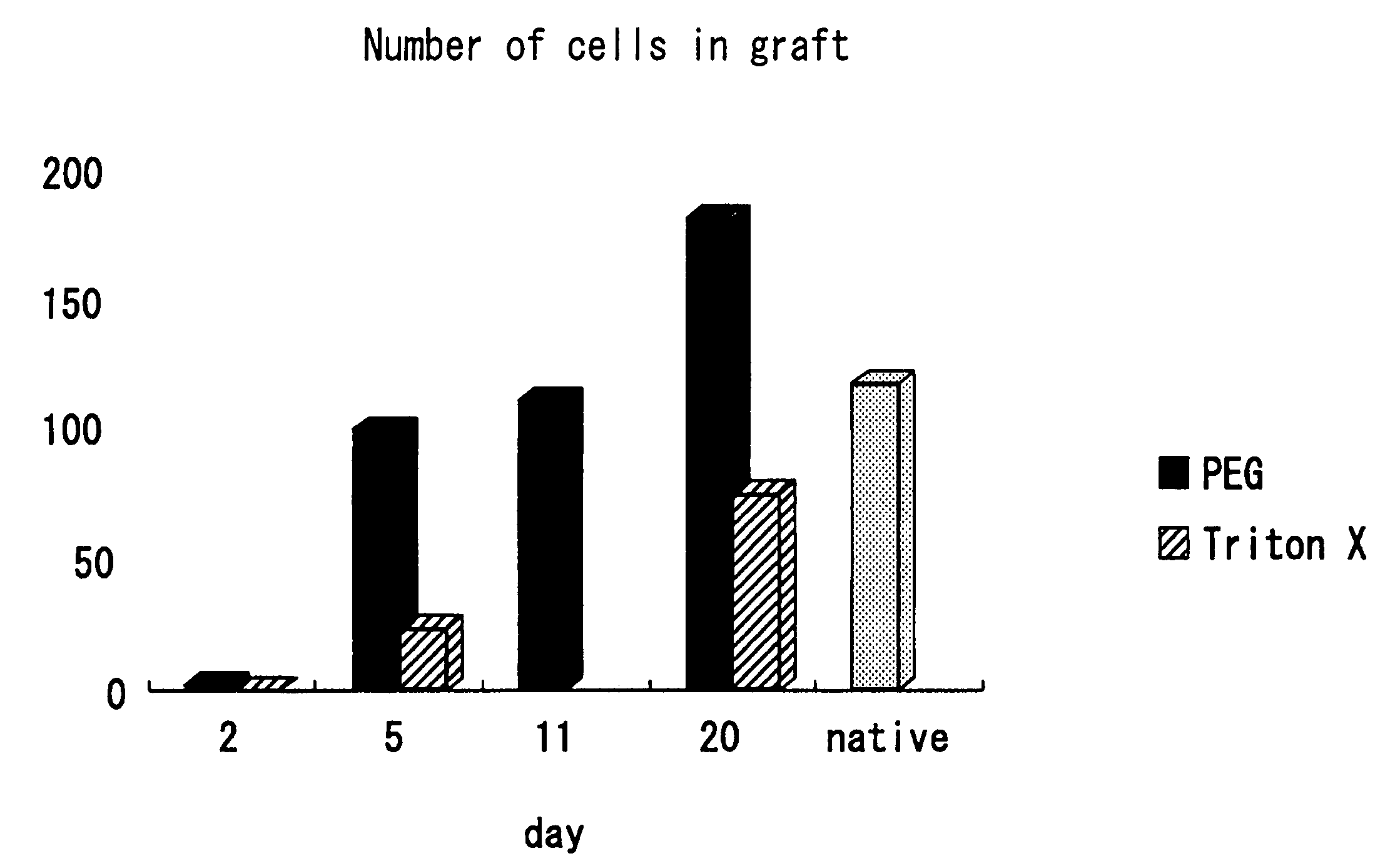
An objective of the present invention is to overcome a problem that there is an inverse relationship between the decellularization rate and the strength of tissue. This problem was solved by immersing tissue in a solution containing a non-micellar amphipathic molecule (e.g., a 1,2-epoxide polymer). Thus, the present invention provides decellularized tissue, in which the cell survival rate of the tissue is less than a level at which calcification or an immune reaction is elicited in an organism and the tissue damage rate of the tissue is suppressed to a level which permits clinical applications. Tissue prepared by the above-described treatment preferably retains a certain level of tissue strength. Further, the tissue of the present invention has an effect of performing cell replacement.
Owner:CARDIO +1
Method for facilitating the production of differentiated cell types and tissues from embryonic and adult pluripotent and multipotent cells
InactiveUS20050153443A1Improve developmentEasy to produceMammal material medical ingredientsArtificial cell constructsGerm layerCell lineage
The invention is concerned with producing differentiated cells, tissues and organs from pluripotent and mutlipotent cells. The methods of the invention are particularly useful for producing differentiated cells from pluripotent cells wherein communication between the cells of more than one embryonic germ layer or more than one organ system are required for development along a specific cell lineage. The invention methods are effected by in vivo or in vitro culturing of embryonic and developing or developed allogeneic or xenogeneic cells.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL TECH INC
Tailor-made pluripotent stem cell and use of the same
InactiveUS20080003560A1Lower Level RequirementsTransplantation rejection reaction could be significantly reducedGenetically modified cellsHybrid cell preparationEgg cellSomatic cell
An object of the present invention is to efficiently establish cells, tissues, and organs capable of serving as donors for treating diseases, without eliciting immune rejection reactions, without starting with an egg cell. This object was achieved by providing a pluripotent stem cell having a desired genome. The cell was produced by treating with a reprogramming agent, producing a fusion cell of an MHC deficient stem cell with a somatic cell, or after producing a fusion cell of a stem cell with a somatic cell, removing a gene derived from the stem cell by performing genetic manipulation with a retrovirus.
Owner:REPROCELL
Cell-free tissue replacement for tissue engineering
InactiveUS7402319B2Prevent penetrationLoss of functionPowder deliveryTissue regenerationCell freeNerve graft
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Method for preparing human body or animal accellular tissues
ActiveCN103191466AReasonable formulaReduce procurement costsTissue cultureAbsorbent padsHuman bodyCell-Extracellular Matrix
The invention discloses a method for preparing human body or animal accellular tissues. According to the method, the decellularized tissue obtained by treating human or animal tissues, such as skin, pleuroperitoneal membrane, esophagus mucous membrane, small intestine mucous membrane, pericardium, vessel, nervus, cardiac valves, bone, cartilage, muscle tendon, and the like through processes of inactivation of virus, derosination, decellularization, and the like is an acellular three-dimensional network structure tissue, and extracellular matrix components are kept. The tissue prepared by the method can be used as an implantable repair material for a human body and also can be used as a support material of tissue engineering cell culture. The skin, the pleuroperitoneal membrane, the esophagus mucous membrane, the small intestine mucous membrane, the pericardium, and the like also can be used as a wound covering material.
Owner:上海优越生物医学科技有限公司
Nanotopographic compositions and methods for cellular organization in tissue engineered structures
ActiveUS8097456B2Additive manufacturing apparatusPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCell typeNanotopography
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
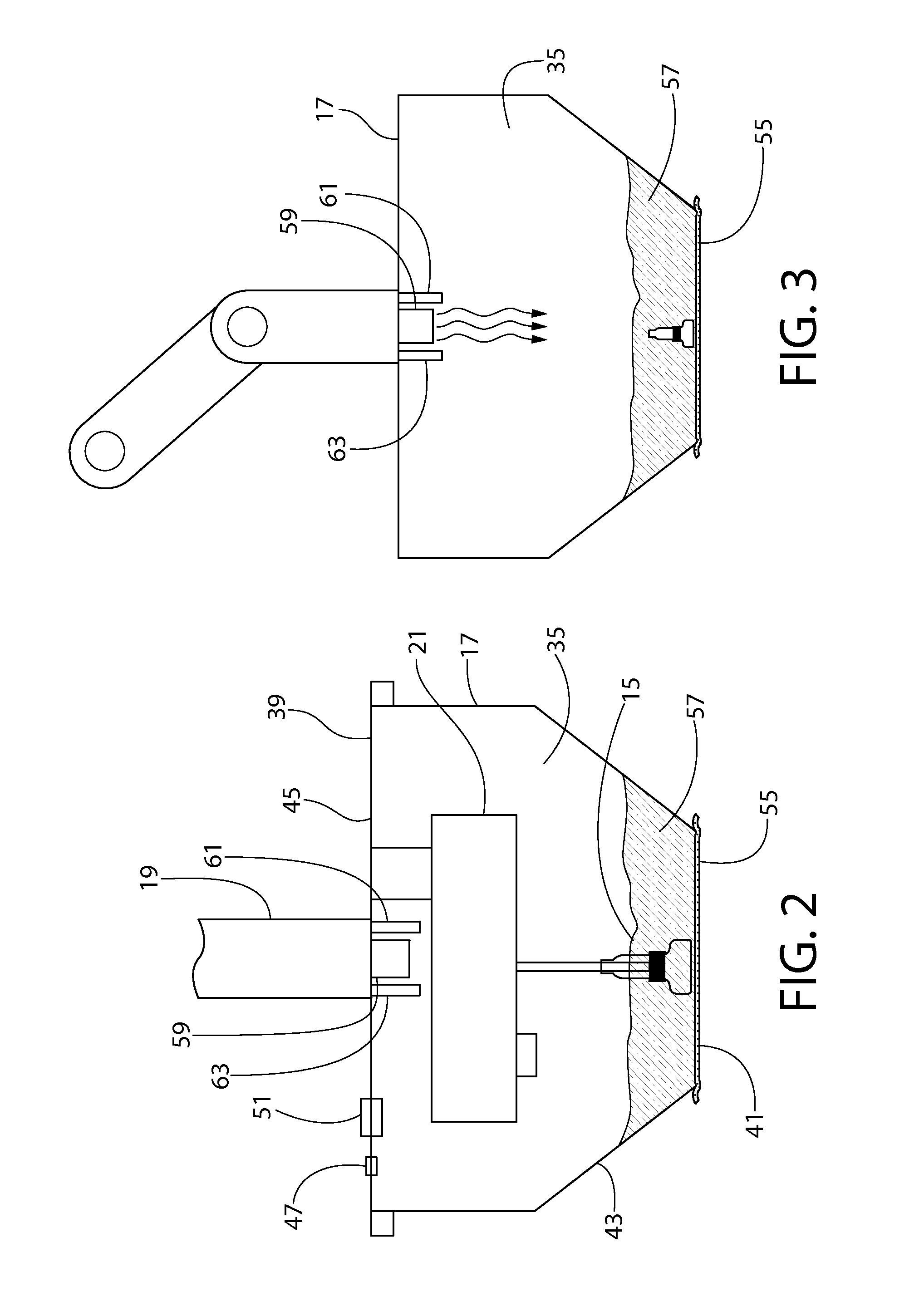
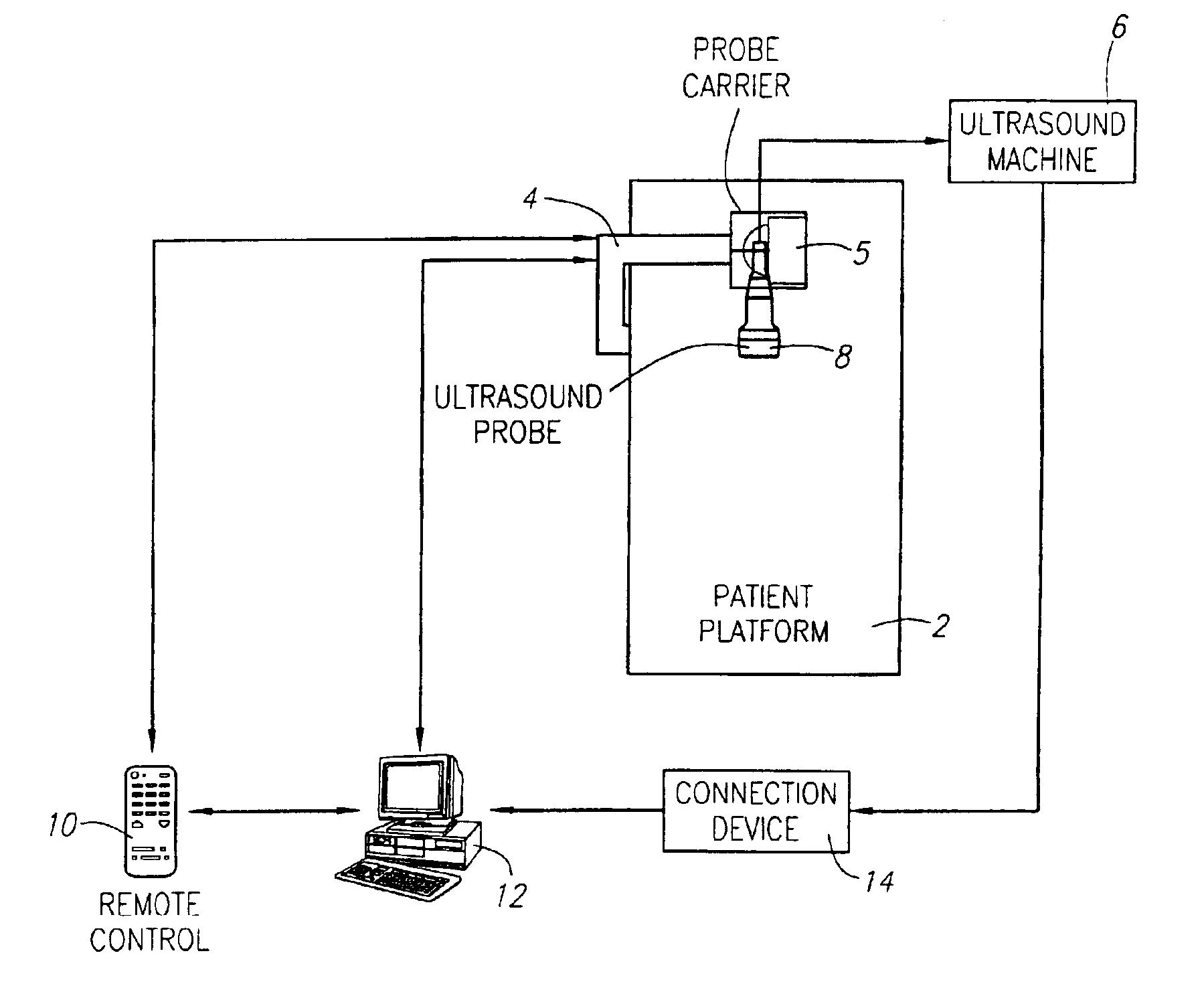
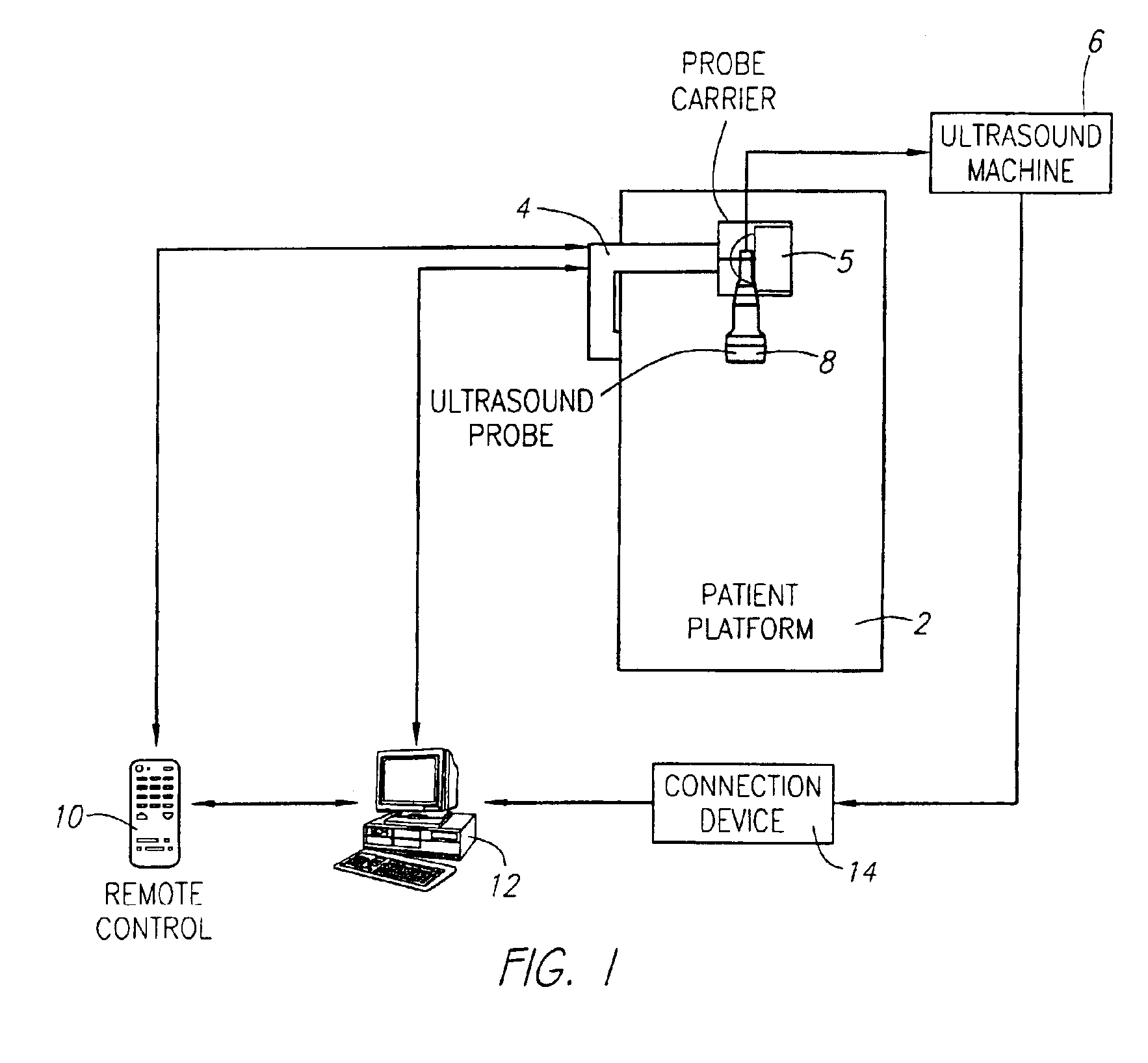
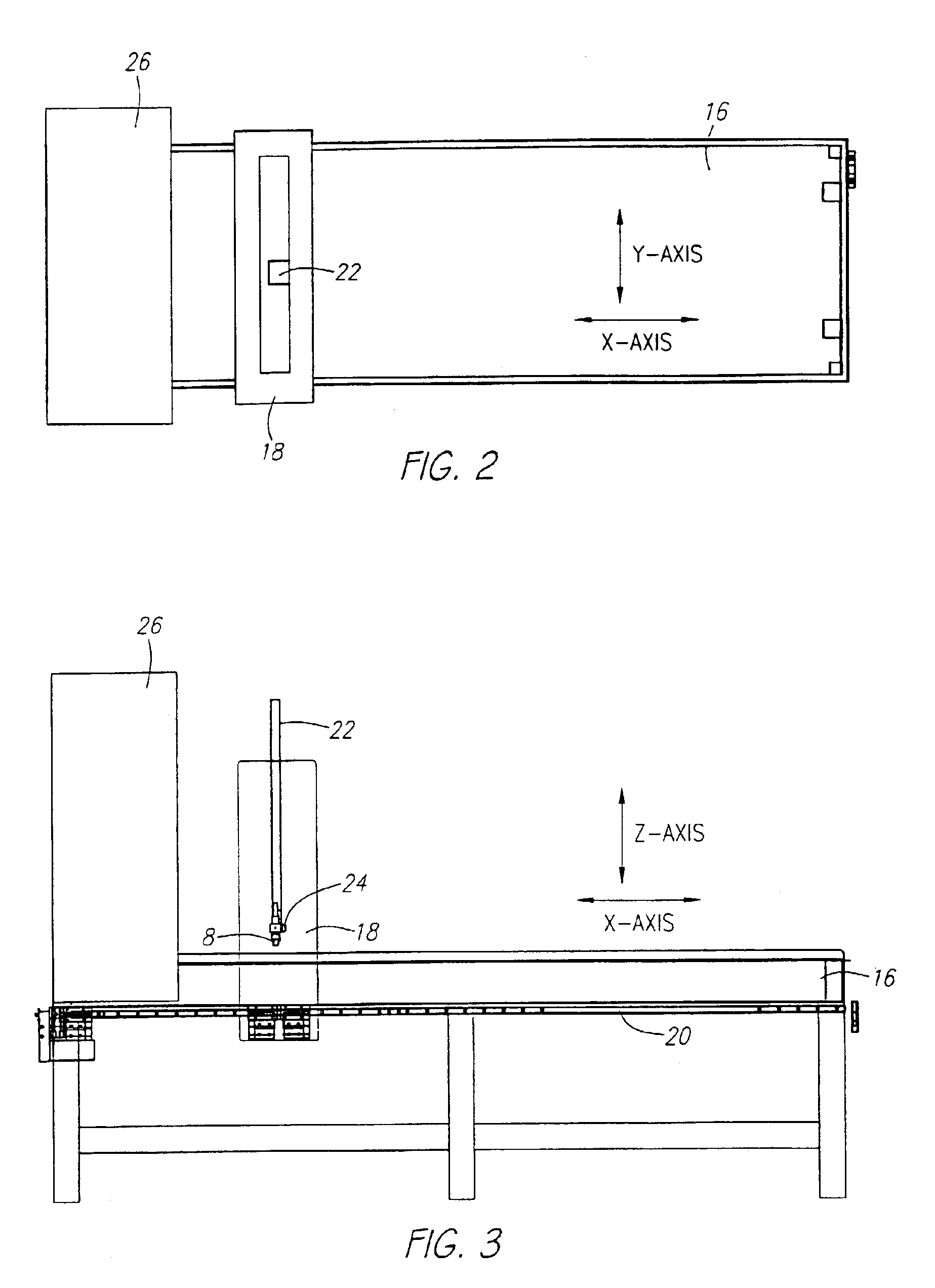
System and method for performing an ultrasound scan of cellular tissue
A system for performing an ultrasound scan of cellular tissue includes an ultrasound scanning device having an ultrasound probe, to generate cross-sectional images of the cellular tissue. A probe enclosure houses the ultrasound probe, has a bottom formed by a flexible membrane, is configured to hold an ultrasonic coupling material, and forms a pressurizable cavity adjacent the flexible membrane. An armature supports the probe enclosure and is configured to move the probe enclosure into a position where the flexible membrane is placed adjacent to and displaced by the cellular tissue. A probe positioning assembly supports the ultrasound probe within the probe enclosure and moves the ultrasound probe over the flexible membrane with a head of the ultrasound probe submerged in the ultrasonic coupling material, the ultrasound scanning device generating the cross-sectional images of the cellular tissue as the probe positioning assembly progressively moves the ultrasound probe over the flexible membrane.
Owner:SONOCINE INC
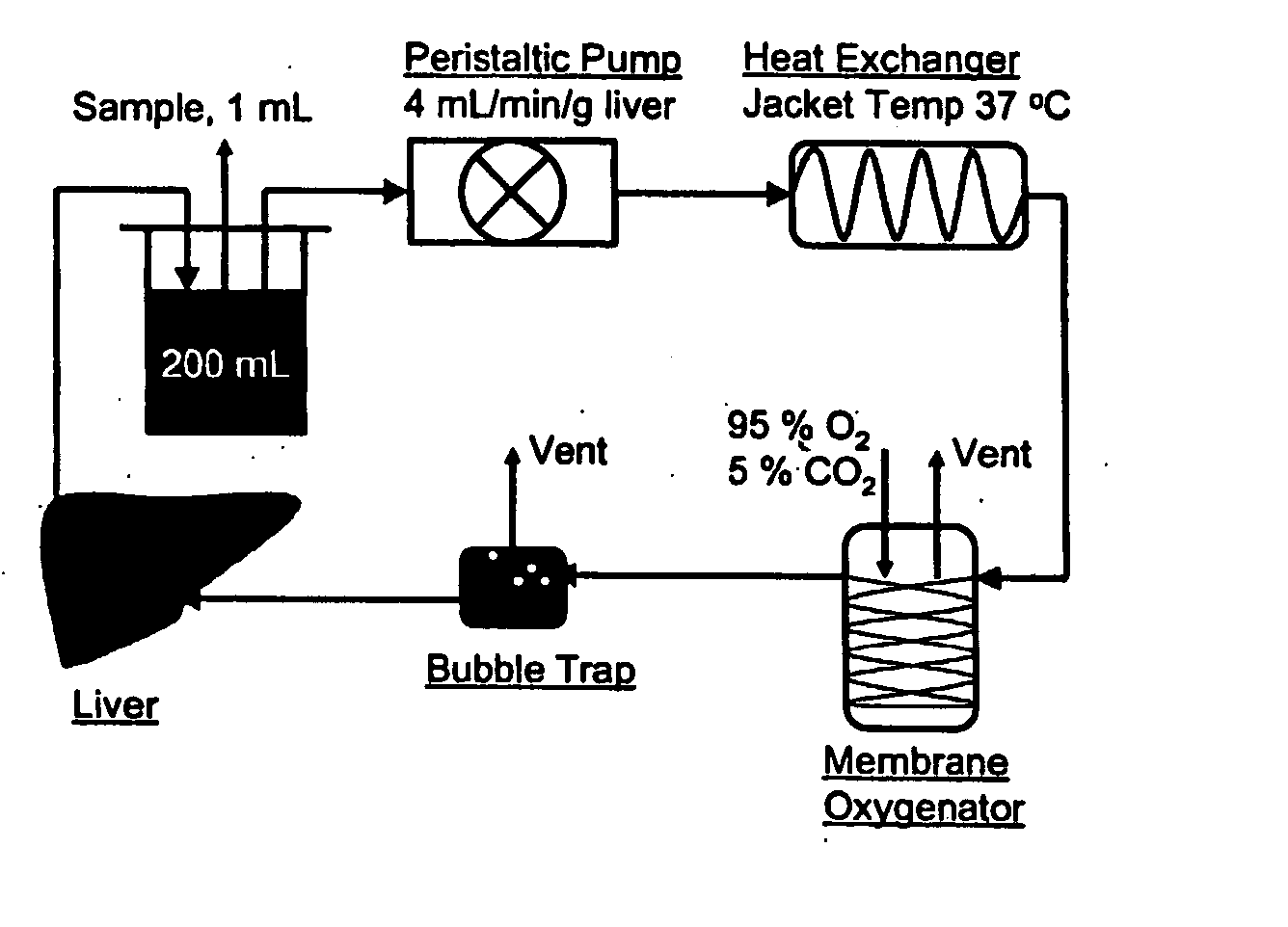
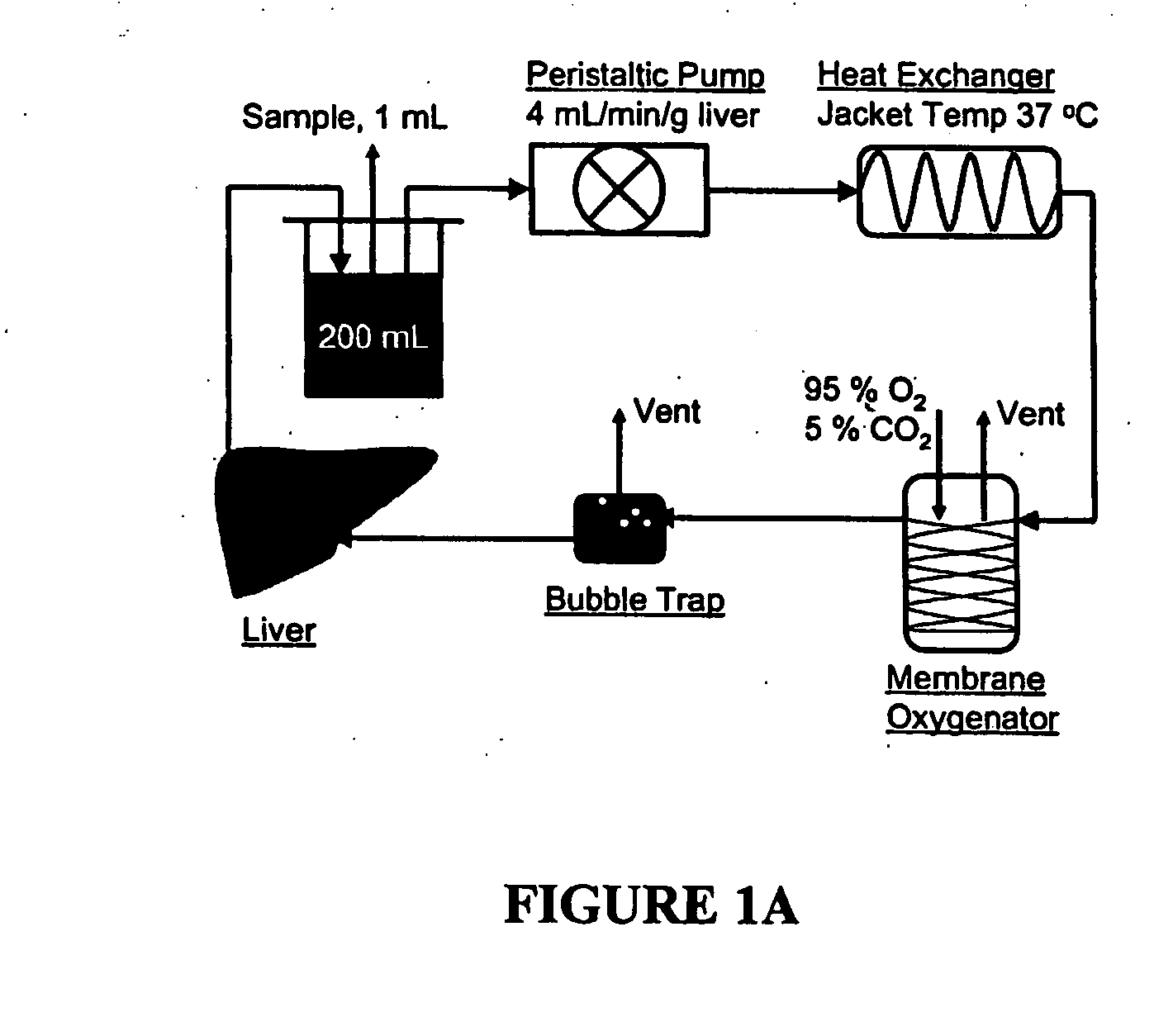
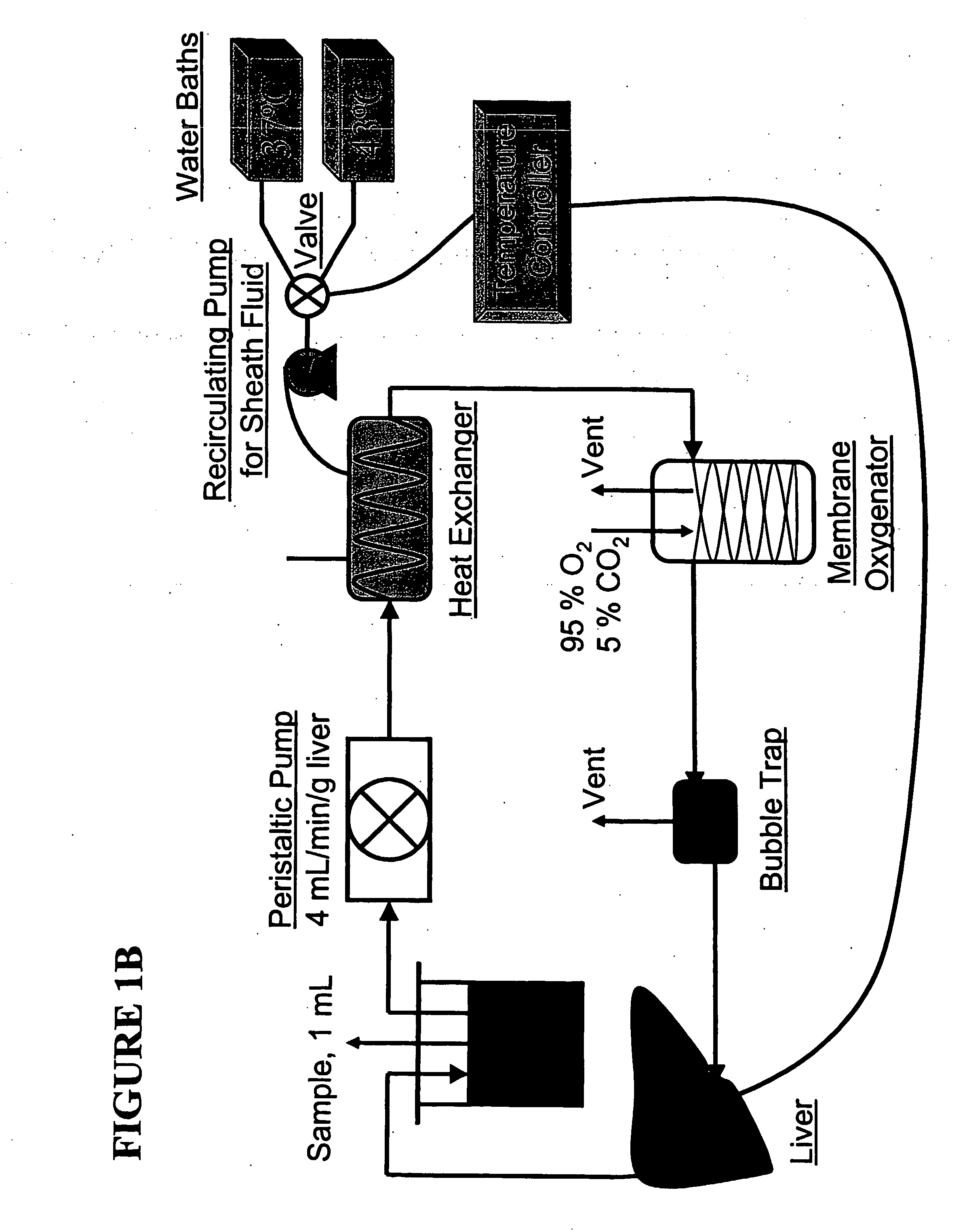
Compositions, solutions, and methods used for transplantation
InactiveUS20060166360A1Improve abilitiesIncreases pool sizeVertebrate cellsDead animal preservationLipid formationLipid storage
This invention discloses a method for reducing the intracellular lipid storage material of a cell, tissue, or organ for transplantation and features solutions, methods and kits that induce the metabolic elimination of lipid storage in a cell, tissue, or organ. In one exemplary approach, the process involves contacting a cell, tissue, or organ with a perfusate solution that include catabolic hormones and amino acids, at physiological conditions, to increase lipid export and lipid oxidation. If desired, the cell, tissue, or organ of the invention may also be heat shock preconditioned. The invention can be used to prepare, recondition, or store a cell, tissue, or organ for transplantation by increasing tolerance to ischemia-reperfusion and cold-preservation related injury.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Method for improving de-cellular system engineering valve/blood vessel stent
The invention discloses a method for linking a RGD improved acellular tissue engineering valve / intravascular stent with epoxy chloropropane. The method, by using epoxy groups of the epoxy chloropropane, cross links and fixes the functional domain RGD (YGRGDSP) polypeptide of cell adhesion and recognition receptors on an acellular tissue engineering valve / intravascular stent material; meanwhile, the chemical crosslinking function of the epoxy chloropropane can fully cross link the collagen protein which is the main component of the acellular stent material so as to achieve the purposes of anti-calcification and reducing the zymolysis speed inside the stent material, and finally proving the improved acellular tissue engineering valve / intravascular stent with better biological and mechanical properties, higher adhesion rate toward seed cell, and better property of delaying enzyme digestion and anti-calcification, therefore, the acellular tissue engineering valve / intravascular stent can actually meet the requirements of tissue engineering valves.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
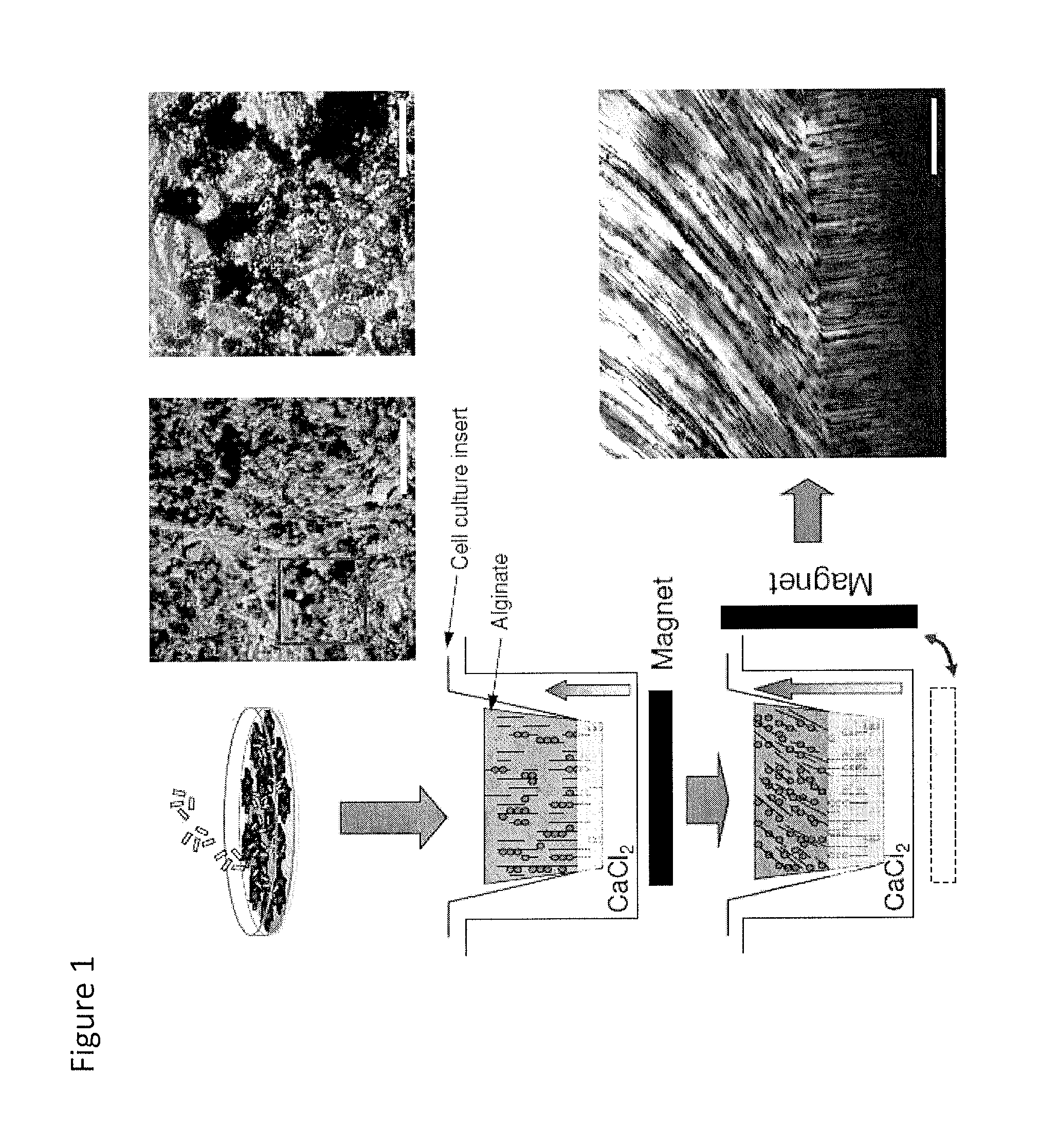
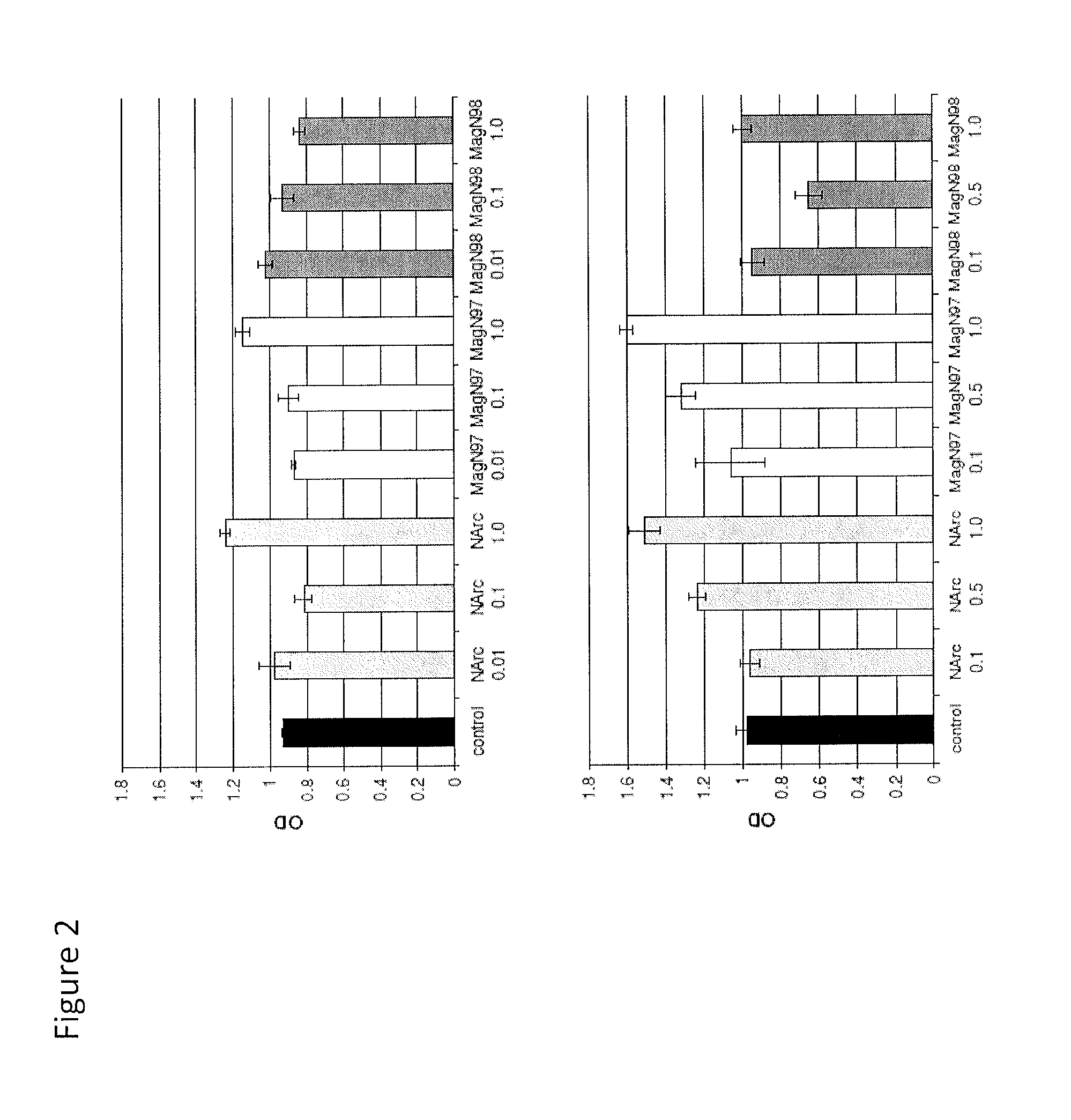
In situ tissue engineering using magnetically guided three dimensional cell patterning
Methods are provided for the three dimensional manipulation of cells, and for the formation of an organized engineered cell tissue. Also provided are the organized engineered cell tissues produced by the methods. In one method, a plurality of magnetically labeled cells are mixed with a cross-linkable hydrogel to form a cell-hydrogel mixture, the at least a portion of the plurality of magnetically labeled cells are manipulated with a magnetic field to arrange the magnetically labeled cells into a specific cellular arrangement, and the hydrogel is crosslinked to form the organized engineered cell tissue. The approach presented herein offers a means to circumvent the deficiencies in the field of regenerative medicine, and allows for the production of organized tissues in situ with specific cellular organizations that mimic the native tissue.
Owner:SCRIPPS HEALTH
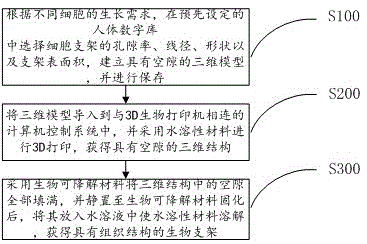
Biological scaffold manufacturing method based on 3D printing and biological scaffold
ActiveCN105617465ASimple manufacturing methodPromote growthAdditive manufacturing apparatusPharmaceutical delivery mechanismWater solublePore diameter
The invention provides a biological scaffold manufacturing method based on 3D printing and a biological scaffold. The method comprises the following steps: observing and analyzing different cell tissues; manufacturing a 3D structure capable of supporting a cell scaffold by adopting a water-soluble material; filling all inner pores of the 3D structure with a biodegradable material; and then, putting in a water solution for dissolving and removing the water-soluble material, thereby obtaining the biological scaffold composed of the biodegradable material. The pore diameters of the inner pores of the manufactured biological scaffold are different, thereby being favorable for growth of cells; and the biological scaffold manufacturing method based on 3D printing is simple and quick and is capable of meeting the manufacturing requirements.
Owner:SHENZHEN EXCELLENT TECH
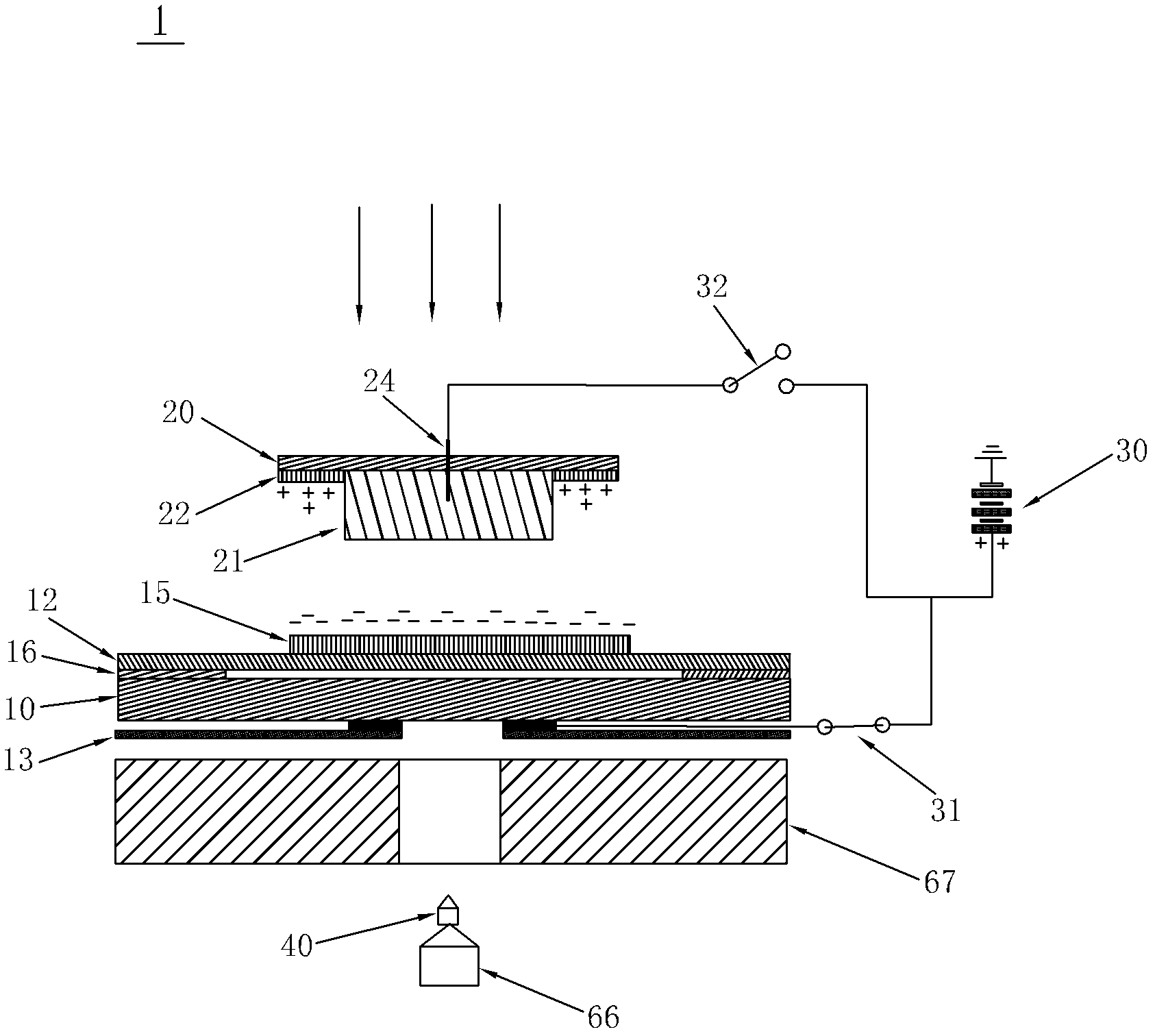
Collection device for collecting cells after laser microdissection, method and system thereof
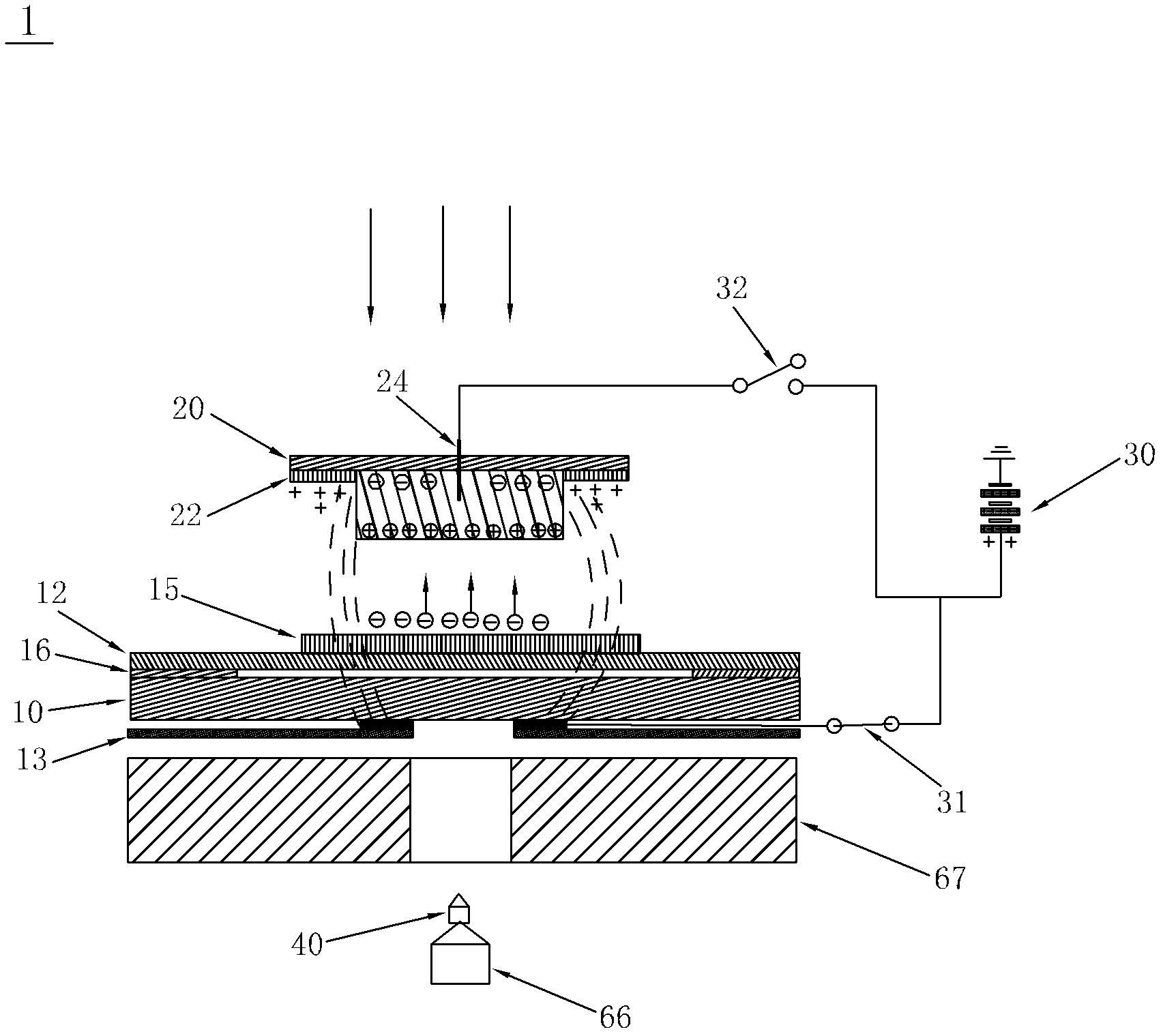
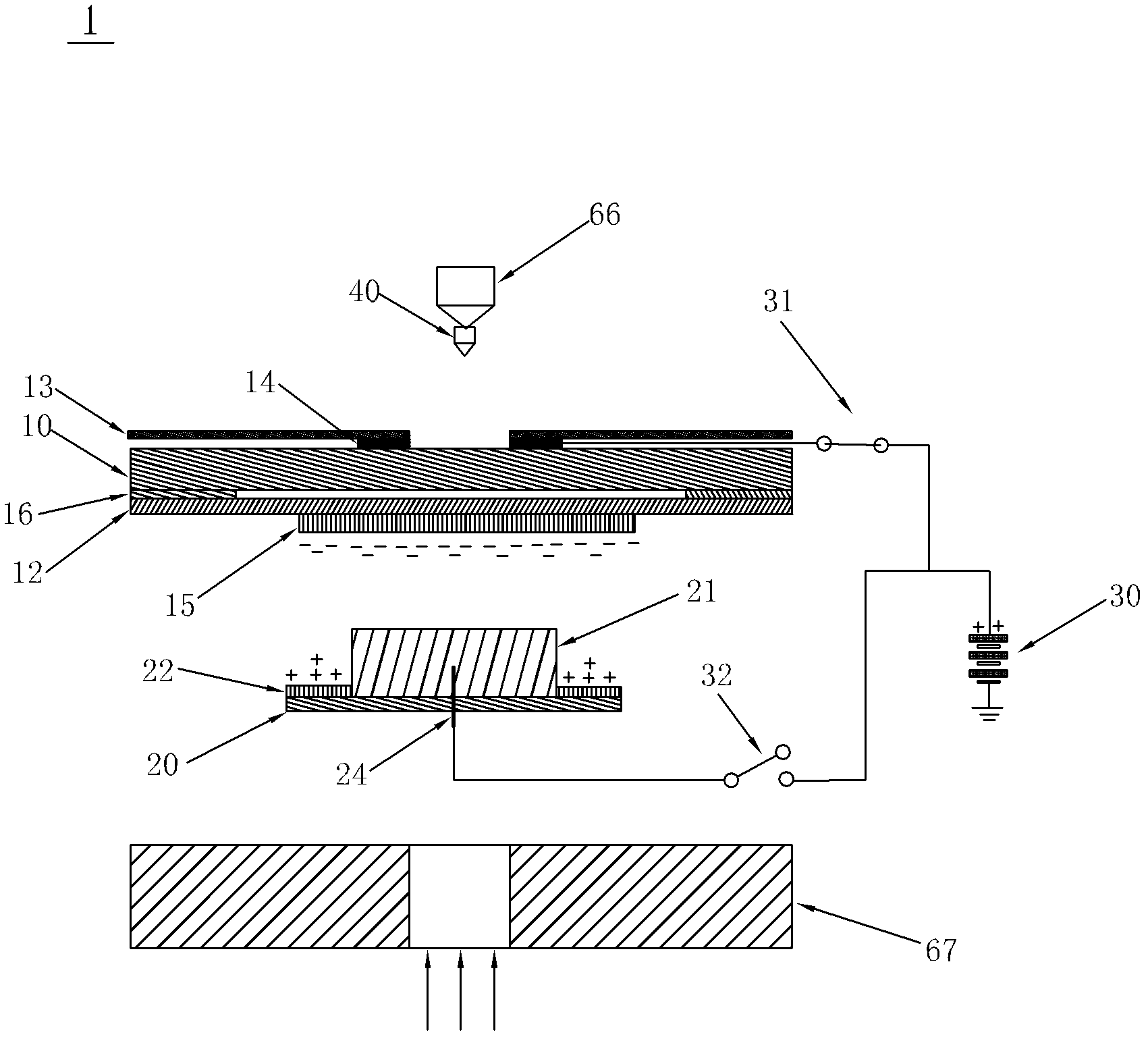
ActiveCN102628758AWill not harmImprove collection efficiencyWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationCell adhesionStatic Charges
The invention discloses a collection device for collecting cells after laser microdisssection, a method and a system thereof. The device provided by the invention comprises a sample carrier, two sides of which are respectively provided with a transparent film layer and an insulating layer, wherein the transparent film layer fits with the sample carrier and is equipped with cell tissue samples, and a first electrode is disposed between the insulating layer and the sample carrier; a sample collector which is filled with a cell adhesion material for the adhesion of cell tissues and is also provided with a light-sensitive material for photoelectric reaction after laser irradiation; and a power supply device, the positive electrode of which forms break-make stations with the first electrode through a first switch. By the above scheme, the disadvantage that the cell tissue samples during the collection process are polluted and that requirements on materials of the sample carrier and the sample collector are high, carried static charges are inconvenient to preserve and the collection efficiency is poor in the prior art is avoided. According to the cell collection device and the method thereof, functions are stable, and cell tissue samples will not be damaged.
Owner:MOTIC CHINA GRP CO LTD
Method for inducing in vitro directed differentiation of stem cells through non-contact coculture
InactiveCN102102090AEasy to separateEasy to operateNervous system cellsArtificial cell constructsDamages tissueDirected differentiation
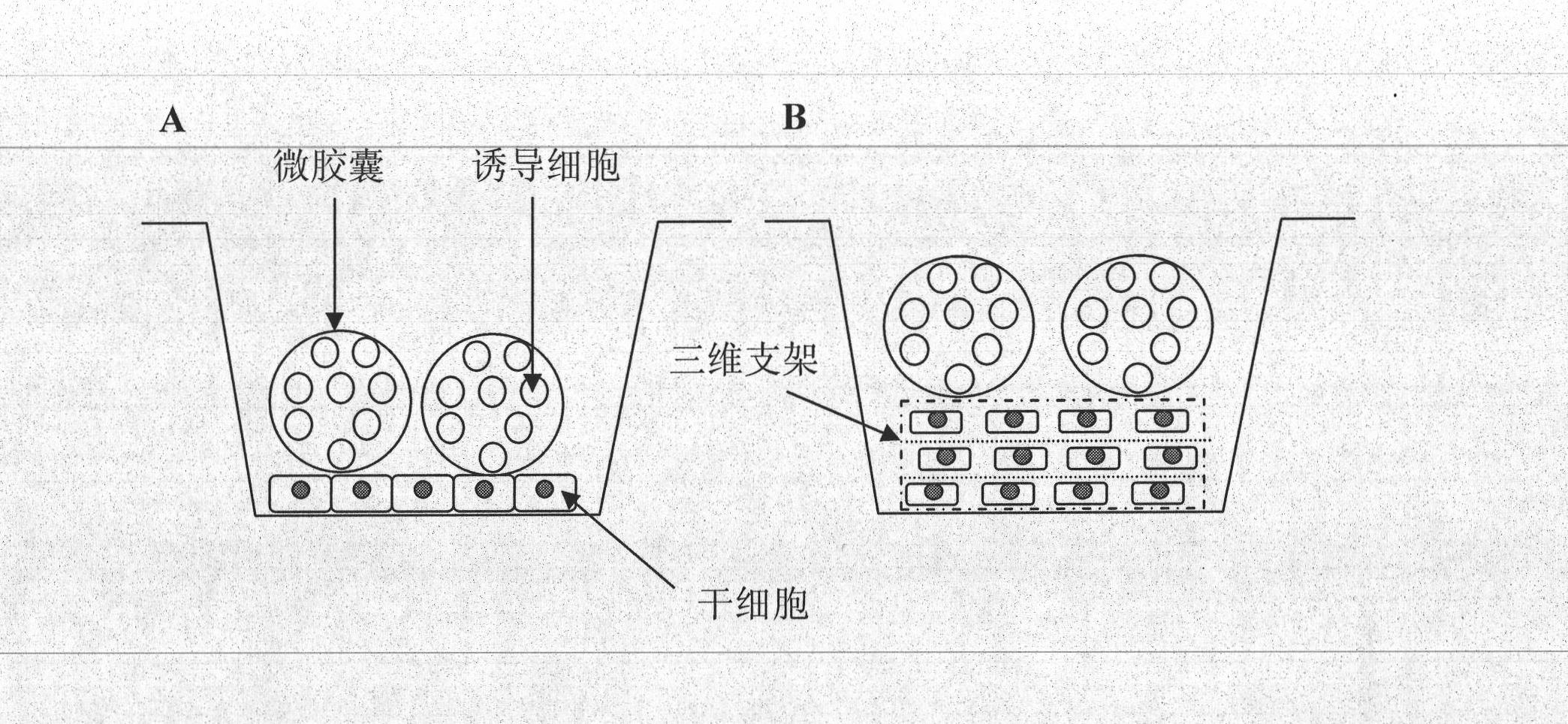
The invention relates to the field of stem cell and tissue engineering, and discloses a method for inducing in vitro directed differentiation of stem cells through non-contact coculture. The method comprises the following steps of: embedding inducing cells with function of inducing differentiation in biological microcapsules; and coculturing the microcapsules and the stem cells, so that the stem cells are subjected to directed induction and differentiation through the directed induction function of the inducing cells in the microcapsules. The method is easy to operate; and one or more kinds of dioecious and heterogeneous inducing cells are allowed to be used for promoting the in vitro directed differentiation of the stem cells, namely microcapsule films can make inducing factors secreted by the inducing cells permeate the microcapsules to act on the external stem cells, and the inducing cells and the stem cells can be subjected to imunoisolation and do not contact each other directly to facilitate the separation and harvest of different cells. By the method, in vitro directed induction and differentiation of the stem cells can be realized under the condition of conventional static culture, an effective induction method can be provided for dynamically inducing directed differentiation of the stem cells to form three-dimensional tissues in a biological reactor, and the method has important significance for clinical therapeutic research of damaged tissues.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Automatic medical cell separation device
ActiveCN102220224AShorten Nutrient Free TimeEasy to storeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiochemical engineeringQuality control
The invention belongs to the technical field of cell separation, and particularly discloses an automatic medical cell separation device which comprises a separation tube. The separation tube is internally provided with a transmission rod, the transmission rod is provided with a structure which can extrude and crush or smash a medical cell, the top end of the transmission rod is connected with a driving motor, and an outlet is arranged on the bottom part of the separation tube and is provided with a plug cover. By the medical cell separation device, a large cell tissue can be conveniently and easily extruded and crushed or smashed into cell particles, the operation process of cell separation of the separation device and an operation can be simultaneously carried out in an operating room, nonnutritive time after the medical cell separation can be effectively shortened, pollution opportunities and harms of the cell can be reduced, and the quality control of the cell treatment can be convenient; simultaneously, the storage and transportation of samples are greatly convenient, the standard operation can be carried out, and the repeatability of a research can be increased; and automation control and personalized customization can be carried out according to different tissue cells, so that the use is simple and convenient.
Owner:GUANGZHOU YIDAI PHARMA
Method for preparing an animal decellularized tissue matrix material and a decellularized tissue matrix material prepared thereby
ActiveUS20160199540A1Good flexibilityAvoid damageUnknown materialsTissue regenerationAntigenCell-Extracellular Matrix
A method for manufacturing an animal acellular tissue matrix material and a tissue matrix material manufactured by the same. The tissue matrix material manufactured by the method retains an original basic scaffold structure of a tissue extracellular matrix, with an antigen causing immunological rejection in a human body being effectively removed from the animal tissue. An animal dermal matrix manufactured by the method retains the biological integrity of a natural dermal tissue matrix and can be used for restoration and repair of lesion and missing tissues.
Owner:BEIJING RUIJIAN GAOKE BIOTECH
Cellular entity maturation and transportation systems
A device for transporting at least one cellular entity during culture or maturation, the device comprising a substrate having one or more wells, said one or more wells being adapted to hold a cellular entity in a fluid, lid means for preventing entry or exit of the cellular entity from the one or more wells and fluid transport means connecting the one or more wells to enable flow of fluid or diffusion of chemical species. The apparatus alternatively or in addition comprise a module for transporting a payload at a controlled temperature, the module comprising an outer housing, an outer thermally insulating region, an inner thermally insulating region, and a heat sinking region located between the inner and outer thermally insulating regions, the inner thermally insulating region defining a cavity for receiving a payload, and heating means.
Owner:ROBIO SYST
Artificial nerve graft constructed based on chip-type acellularized scaffold and preparation method of artificial nerve graft
ActiveCN106730034AAvoid the disadvantages that if the strength is too small, it will easily remain, and if the strength is too high, it will be crushedImproved cell loading capacityTissue regenerationProsthesisAdhesiveSpinal cord
The invention relates to an artificial nerve graft constructed based on a chip-type acellularized scaffold and a preparation method of the artificial nerve graft, belonging to the field of tissue engineering. According to the artificial nerve graft and the preparation method, heterogeneous animal medulla spinalis, skeletal muscle or tendon acellularized tissue slices are adopted as a bracket, genipin is adopted for crosslinking cytokines, autologous ecto mesenchymal stem cells are planted on the bracket, and fibrous protein is taken as an adhesive for constructing the artificial nerve graft, so that the repairing of the nervous tissue is promoted. The artificial nerve graft and the preparation method have the advantages that the preparation cost is low, the period is short, the preparation raw materials are easily available, and the preparation is simple and is easy to operate. The constructed artificial nerve graft has low immunogenicity, contains a large number of autologous stem cells and cell factors, and is beneficial for adjusting the nerve injury microenvironment, and promoting the nerve regeneration and myelinogenesis. The artificial nerve graft can be used for preparing peripheral nerve and medulla spinalis defect, and has the broad application prospect.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Ultrasonic cellular tissue screening system
InactiveUS6932768B2Rapid sequential displayCharacteristic is differentOrgan movement/changes detectionNanosensorsSonificationCoupling
A system for screening cellular tissue, in particular breast tissue. The system comprises an ultrasound probe that is capable of generating image data representing images of cellular tissue, one or more sensors to determine the probe's location, an image viewer, a pad, which is ultrasonically conductive and placed over the patient's nipple, and a fabric covering is placed over the breast tissue to be scanned. The pad has different ultrasonic characteristics than the cellular tissue to be scanned. The fabric covering includes an ultrasonic coupling agent and is used to hold the breast tissue in place. The fabric of the covering and the coupling agent transmit ultrasonic energy with minimal interference. The ultrasound probe is scanned over the tissue, and the one or more sensors are employed to determine the probe's location. The images representing the scanned tissue are displayed by a viewer which is capable of providing a rapid sequential display of the images.
Owner:SONOCINE INC
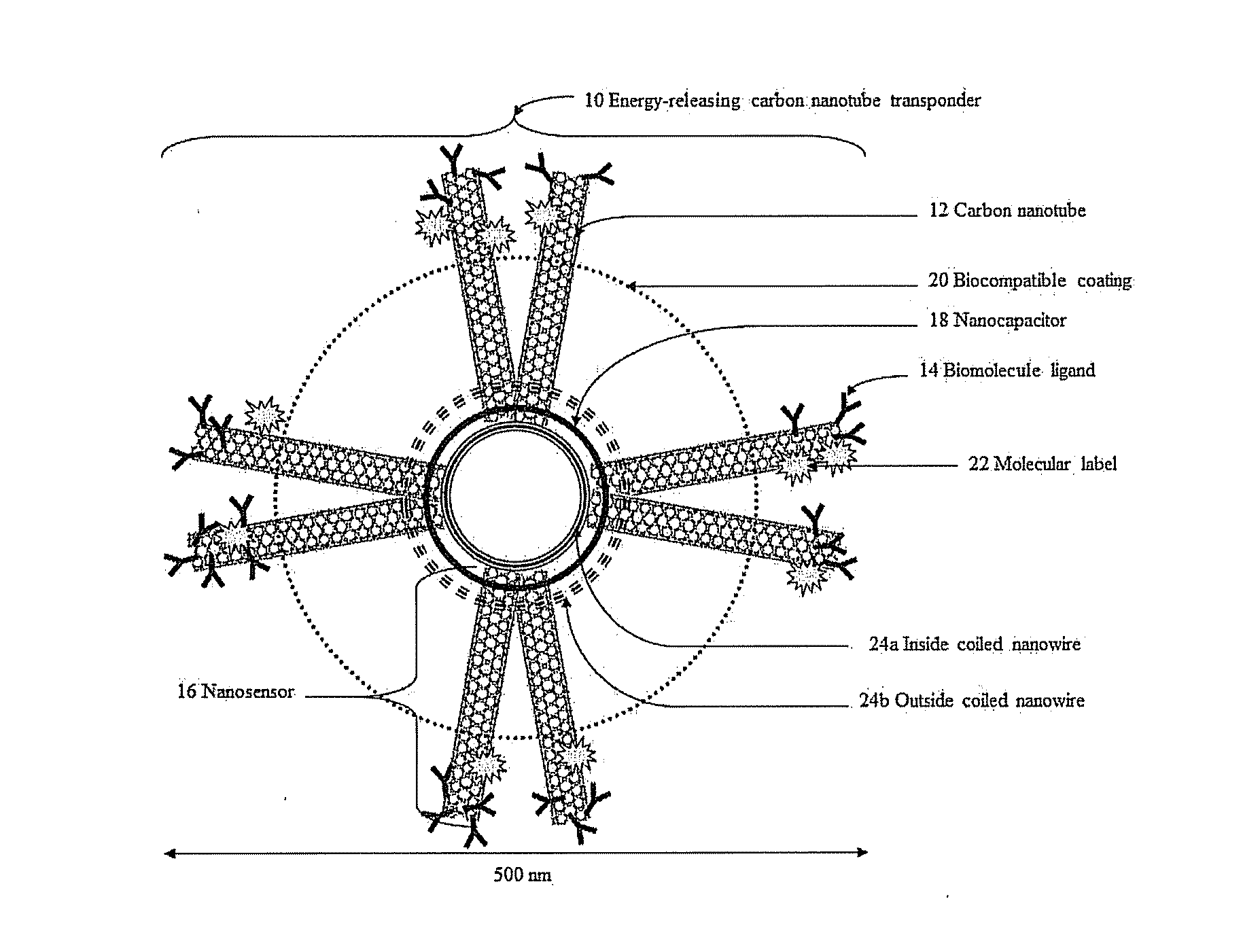
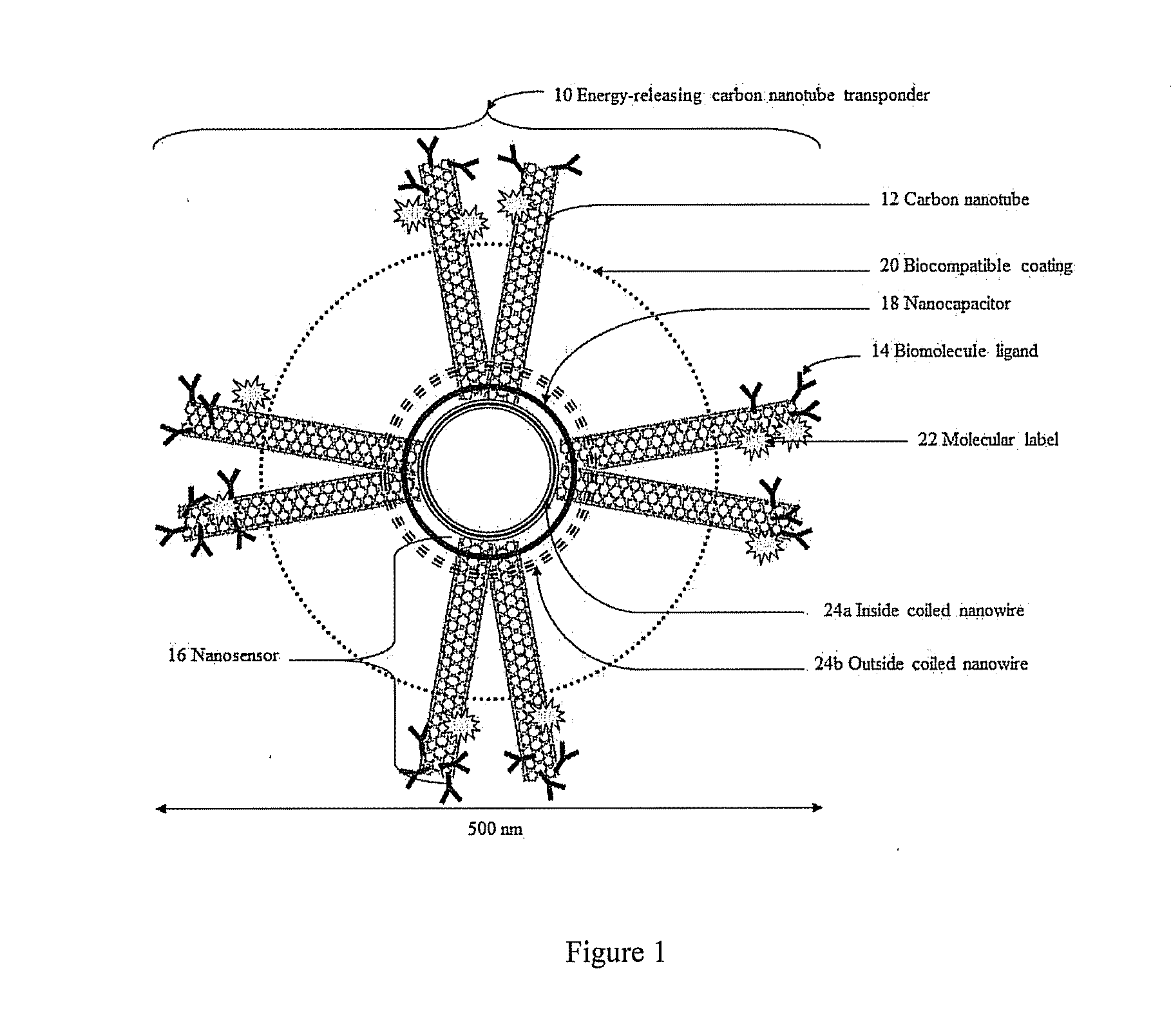
Energy-releasing carbon nanotube transponder and method of using same
An energy-releasing carbon nanotube transponder comprising a nanocapacitor connected to at least one carbon nanotube and method of using same are described. An adjustable amount of electric energy is stored within the nanocapacitor so that the energy-releasing carbon nanotube transponder delivers either a biologically destructive or a biologically non-destructive electrical charge to target cells in response to biological, chemical or electrical stimuli.An optional biocompatible coating onto the outer surface of the carbon nanotube transponder improves cellular targeting, cellular binding or body tolerance towards the carbon nanotube transponder. Optionally, a molecular label attached to at least one carbon nanotube allows for in vivo tracking of the carbon nanotube transponder.The targeted release of electric energy from the carbon nanotube transponder can, for example, destroy cancer cells in cancer patients, or control the flux of electric wave within a cellular tissue to treat cardiac and / or epileptic patients.
Owner:RUSH UNIV MEDICAL CENT
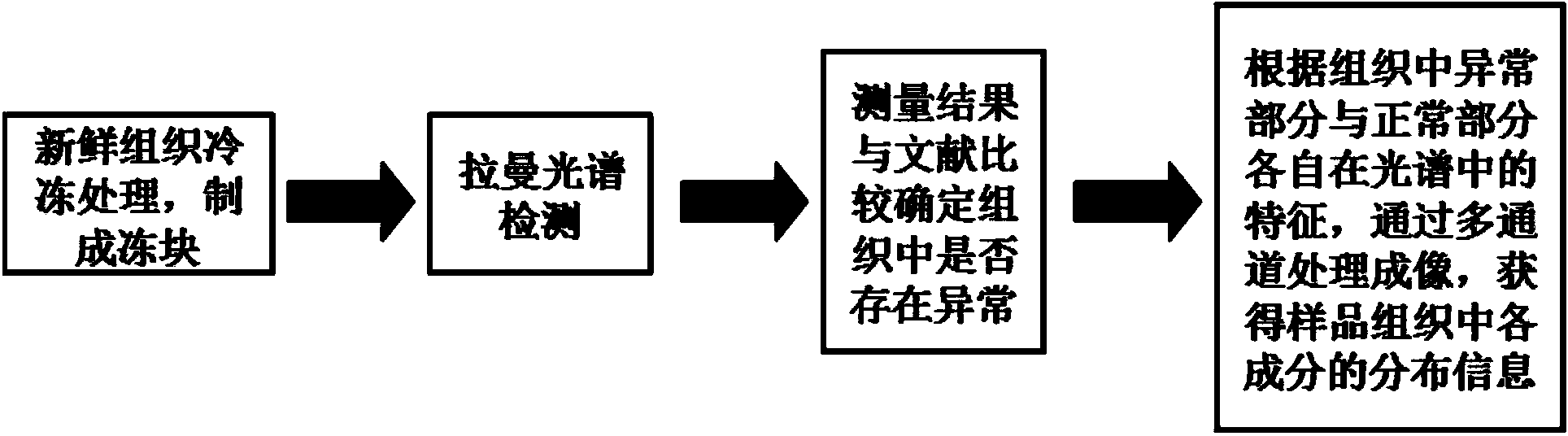
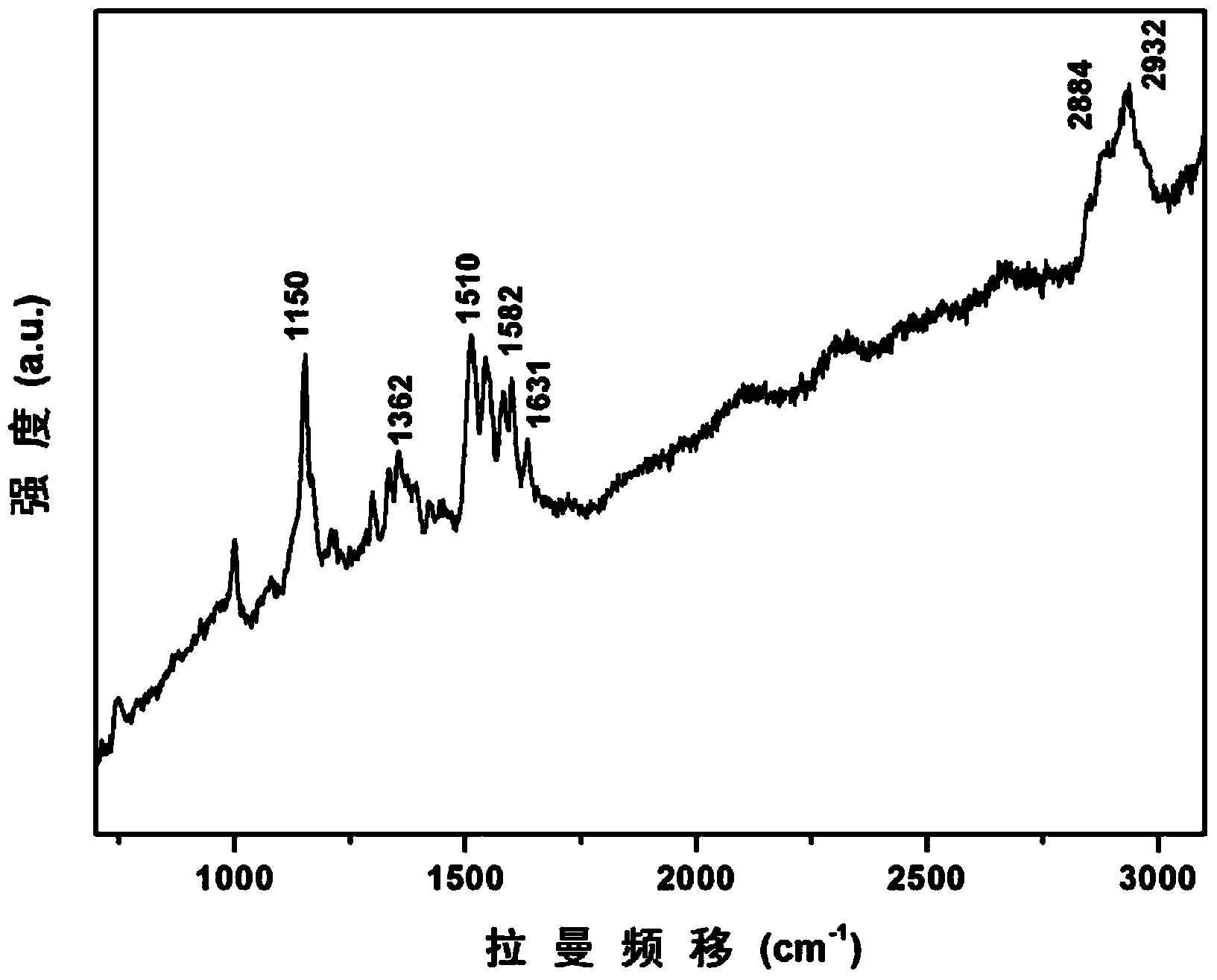
Cell tissue resonance Raman spectroscopy scanning imaging method
InactiveCN104111247ARapid Qualitative DetectionEasy to operatePreparing sample for investigationRaman scatteringResonance Raman spectroscopyFluorescence
The invention discloses a cell tissue resonance Raman spectroscopy scanning imaging method which comprises the following step of: carrying out (1) freezing treatment and (2) sample preparation and scanning imaging on a cell tissue. The cell tissue resonance Raman spectroscopy scanning imaging method is easy and fast to operate, can fast carry out qualitative detection on a tissue sample, effectively enhances the Raman detection sensitivity, inhibits the fluorescence disturbance, enhances the Raman signal intensity, ensures the spectroscopy imaging quality, shortens the detection time and visually shows the distribution of characteristic components of the tissue sample in a clear image mode.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Natural extract-containing plant growth accelerator
InactiveCN104082355AImprove qualityIncrease resistanceBiocidePlant growth regulatorsGrowth plantNutrition
The invention provides a natural extract-containing plant growth accelerator. The natural extract containing plant growth accelerator is prepared form natural extracts, a growth promoter, water and the like in a mixing manner; all nutrient substances contained in the natural extracts are used for substituting all kinds of chemical substances or chemical fertilizers which are added artificially, and the novel plant growth accelerator for promoting the plant growth is formed through research trials and screening according to the characteristics of growth characteristics, genetic genes and in-vivo cell tissue structures of arbor plants. The natural extract-containing plant growth accelerator has the advantages of rich nutrition, no poison, no harm, capacity of protecting the environment, and improving the plant quality and the like, can effectively improve the arbor resistance and the poor growth performance, and can increase the economic benefit.
Owner:YIBIN YUNCHEN ARBOR GARDEN
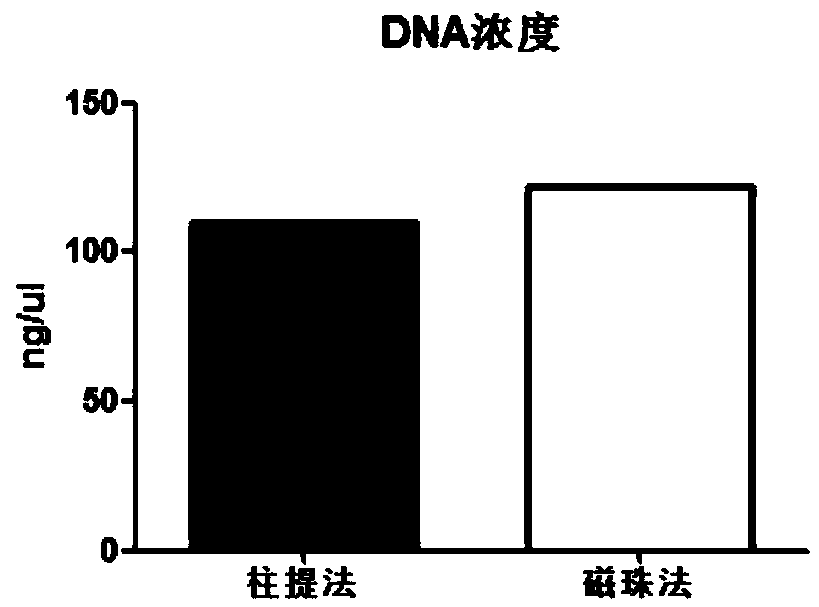
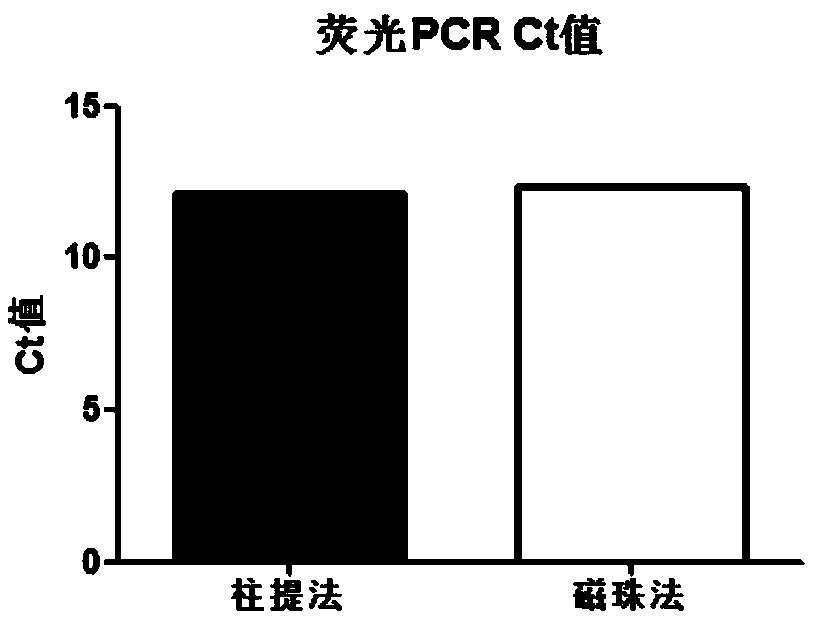
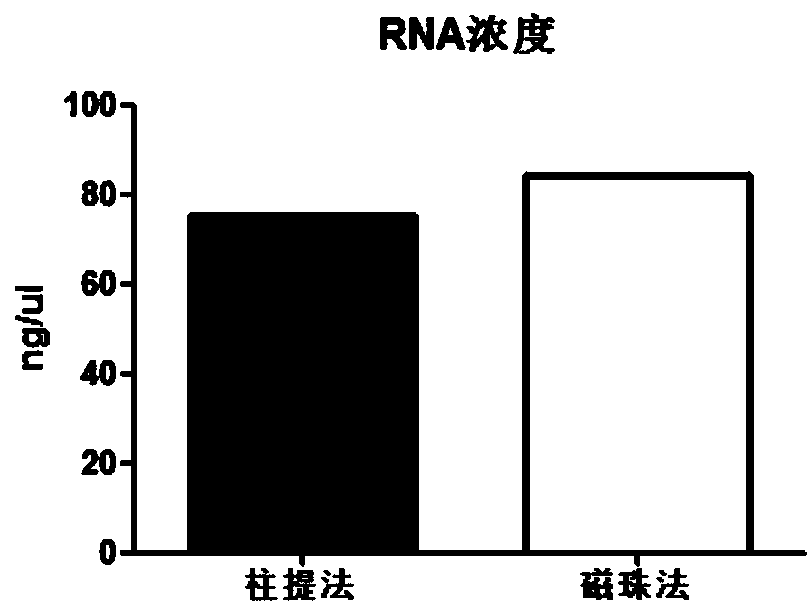
Automatic extraction method for nucleic acid in FFPE ((Formalin-Fixed and Parrffin-Embedded) sample
PendingCN108841920AAchieve separationImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementRNA extractionMagnetic bead
The invention discloses an automatic extraction method for nucleic acid in an FFPE (Formalin-Fixed and Parrffin-Embedded) sample. When DNA or RNA of FFPE is independently extracted, cell tissue can beconfined in a certain space range by magnetic beads through a magnetic separation device, the consequence that tissue is sucked off along with a dewaxing agent or other solution can be effectively avoided, and furthermore the DNA or RNA of FFPE can be extracted; in co-extraction of the DNA or RNA of FFPE, the tissue is dewaxed and rehydrated along with the magnetic beads, lysate RTL is added, andthen RNA can be released into the solution. A centrifugal tube is placed in the magnetic separation device, digestion lysate with the RNA is transferred into a new centrifugal tube by using a liquidtransferring device, and then RNA extraction can be carried out; lysate DTL is continuously put into the magnetic beads into which the cell tissue is adsorbed in the original centrifugal tube, then the DNA can be released into the solution, and DNA extraction can be carried out.
Owner:AMOY DIAGNOSTICS CO LTD
Tailor-made multifunctional stem cells and utilization thereof
InactiveUS20050084968A1Lower Level RequirementsTransplantation rejection reaction could be significantly reducedHybrid cell preparationDrug compositionsEgg cellSomatic cell
An object of the present invention is to efficiently establish cells, tissues, and organs capable of serving as donors for treating diseases, without eliciting immune rejection reactions, without starting with an egg cell. This object was achieved by providing a pluripotent stem cell having a desired genome. The cell was produced by treating with a reprogramming agent, producing a fusion cell of an MHC deficient stem cell with a somatic cell, or after producing a fusion cell of a stem cell with a somatic cell, removing a gene derived from the stem cell by performing genetic manipulation with a retrovirus.
Owner:REPROCELL
3D printing method for cell tissue by using bio-ink
The invention discloses a 3D printing method for MC (methyl cellulose) based hydrogel bio-ink. MC hydrogel is the best matrix to obtain regenerative medicine application cell slices. However, a preparation method of the MC hydrogel currently only allows obtain geometric shapes with standardization and simplicity (namely, geometric shapes of container generated by the hydrogel). By use of the MC hydrogel, corresponding cell plate engineering and 3D printing of complicated shapes of biological tissues and organs can be realized through the 3D printing method. The stability and the rheological property of the method is suitable for an application of biological plate engineering under 37 DEG C. The cells are embedded in the MC based hydrogel, the cell viability is detected to be larger than 90%; the bio-imprinting survival rate of C2C12 cells embedded into the MC based hydrogel is higher than 80% by use of optimized printing parameters.
Owner:INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS JIANGXI ACADEMY OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com